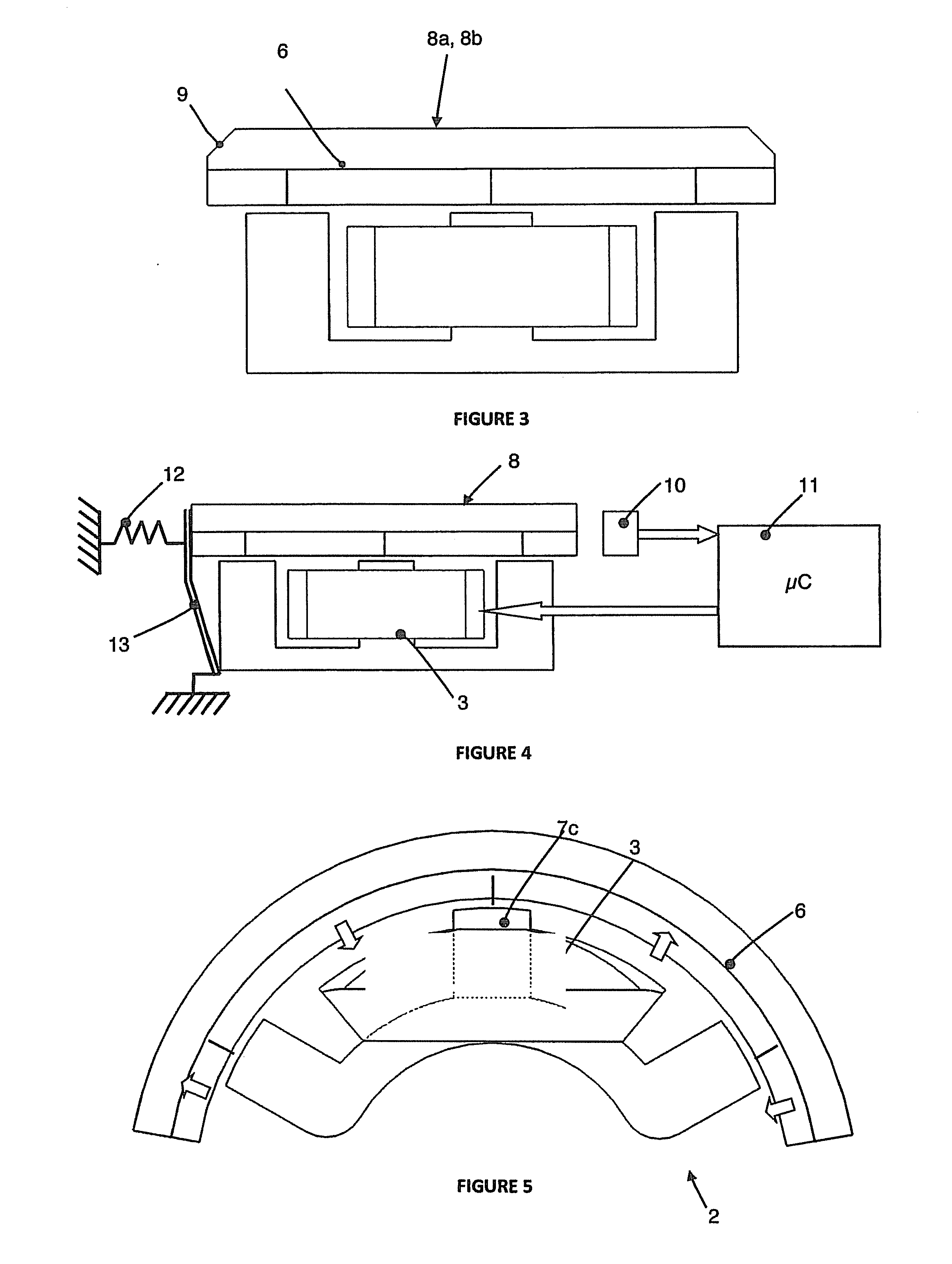
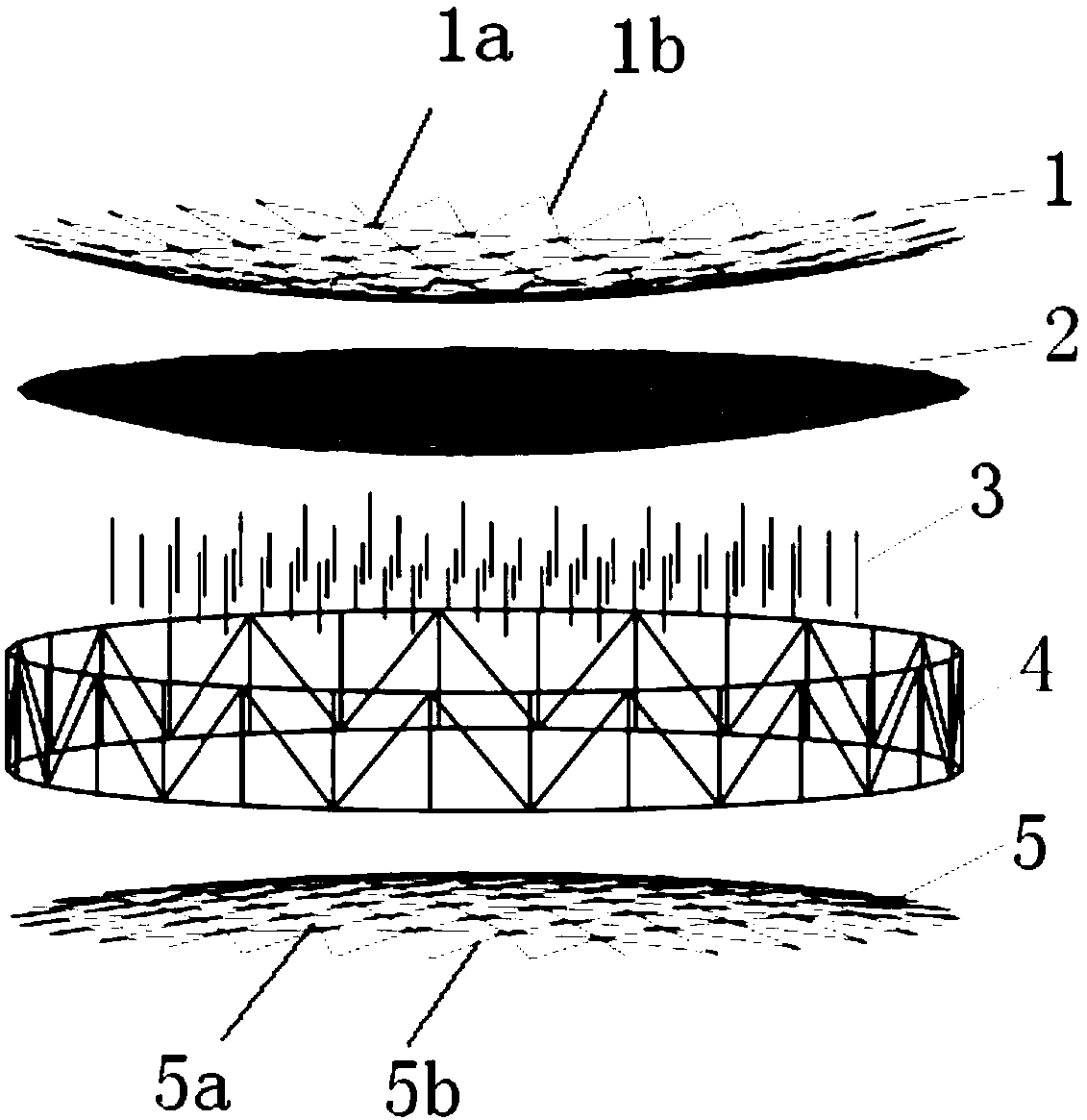
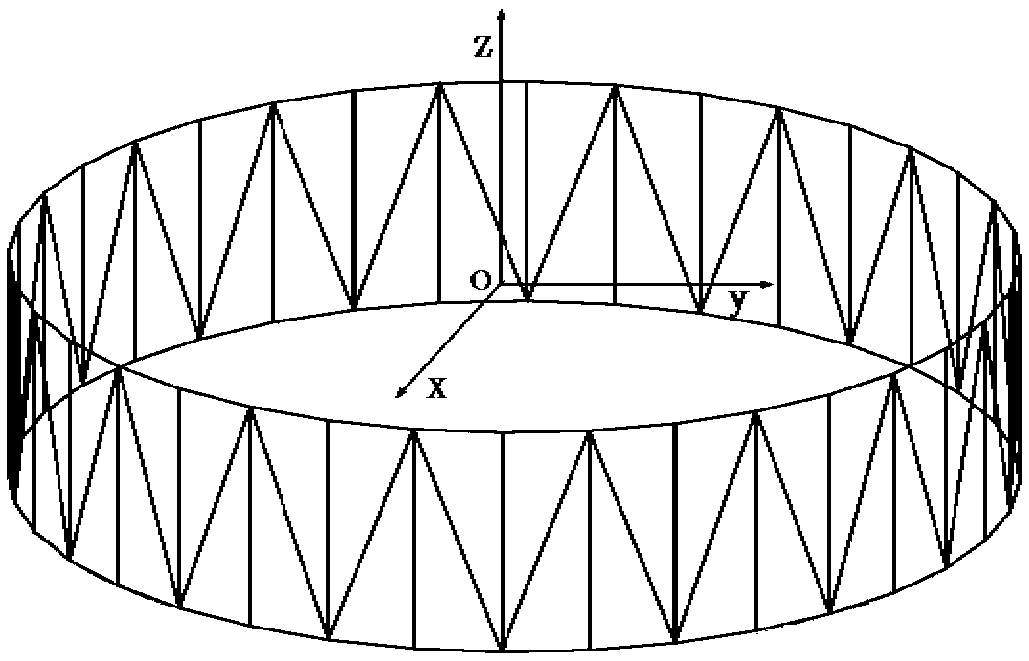
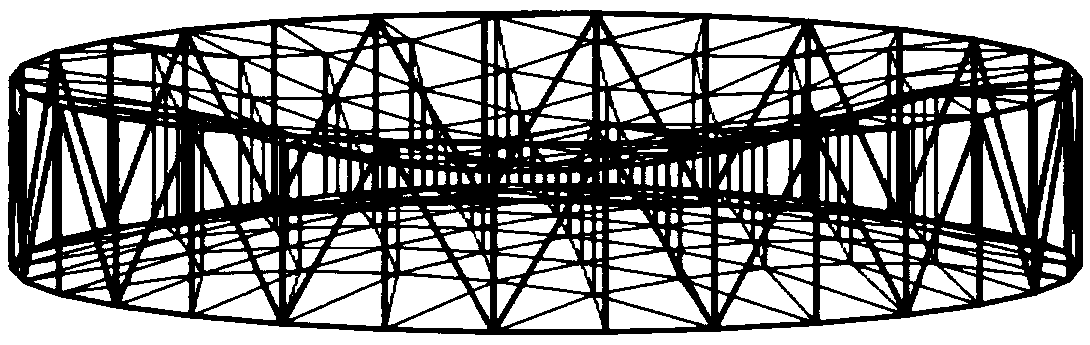
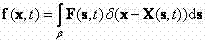Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
53 results about "Force density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In fluid mechanics, the force density is the negative gradient of pressure. It has the physical dimensions of force per unit volume. Force density is a vector field representing the flux density of the hydrostatic force within the bulk of a fluid. Force density is represented by the symbol f , and given by the following equation, where P is the pressure: 𝐟=-∇P. The net force on a differential volume element dV of the fluid is: d𝐅=𝐟dV Force density acts in different ways which is caused by the boundary conditions.
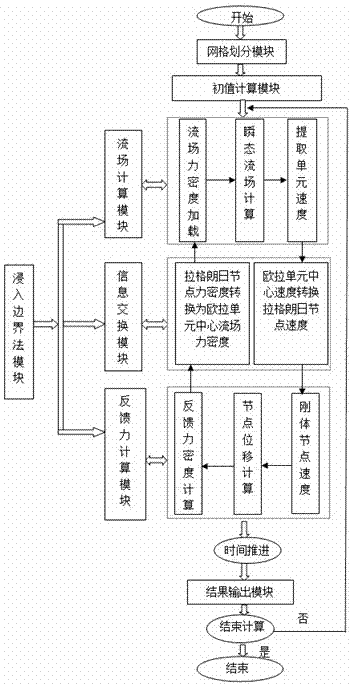
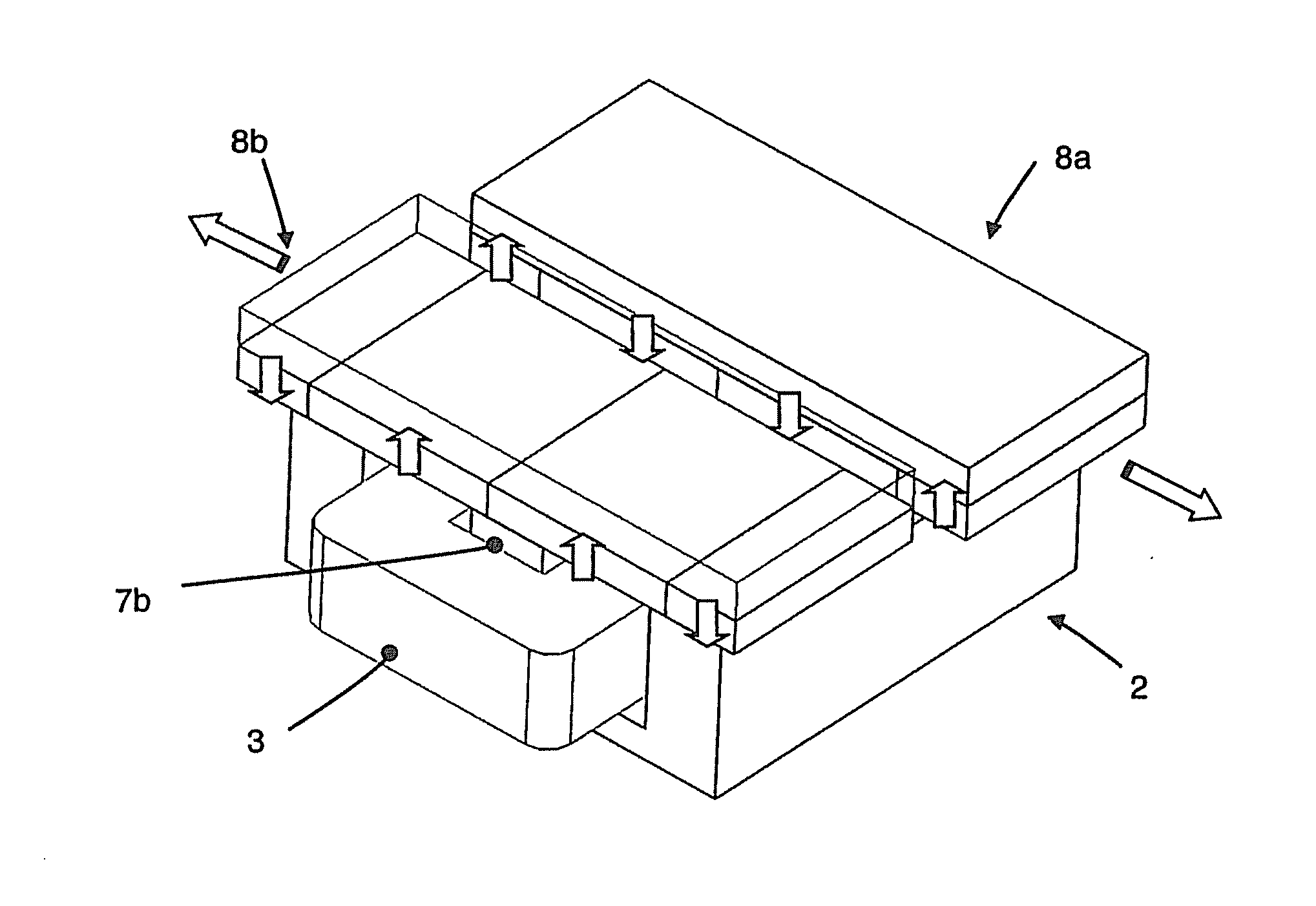
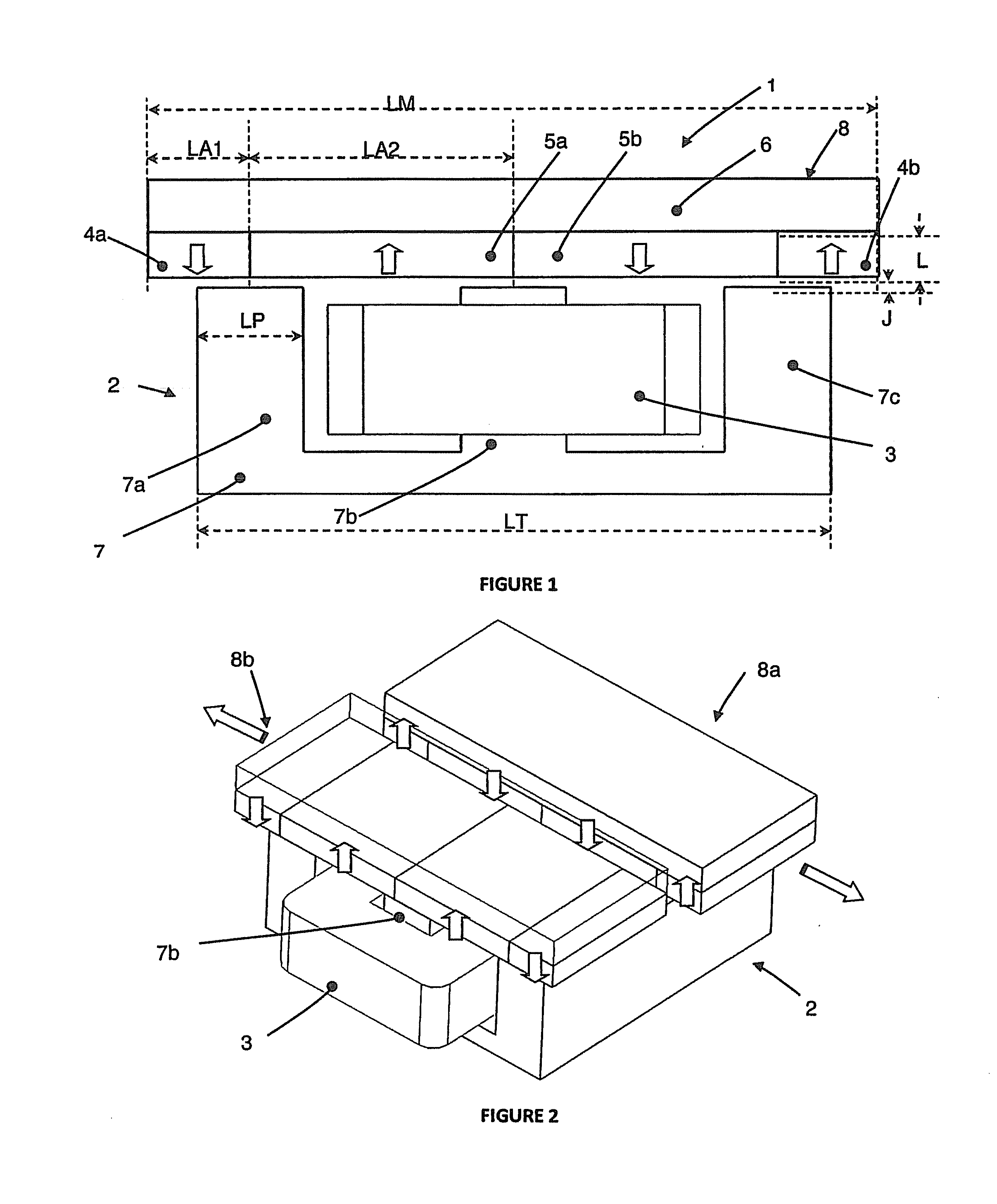
Immersing boundary flow field calculation method based on fluid/solid interface consistency
ActiveCN103970989AReduce usageSave computing resourcesSpecial data processing applicationsCouplingComputer module
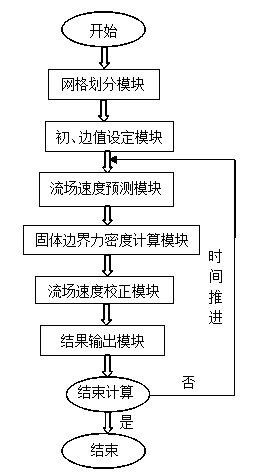
The invention relates to an immersing boundary flow field calculation method based on fluid / solid interface consistency and belongs to the technical field of computational fluid mechanics and liquid / solid coupling simulation. The method comprises the steps that A, a grid division module is called, and two grids including a flow field region and a solid boundary region are adopted; B, a flow field calculation model is called, and a predicted value of the flow field region is obtained; C, a solid boundary force density calculation model is called, and the density of force acting on a solid boundary is obtained; D, a flow field velocity correction module is called, a correction value of the flow field region is obtained, and the flow field velocity is updated; E, a result output module is called, the force acting on the solid boundary and flow field information are output to a file and are read and displayed on a backstage; F, whether calculation is ended is judged. According to the method, use of the dynamic mesh technique is avoided, and a large number of computing resources are saved; the defects that when a traditional immersing boundary method is used, an interpolation algorithm is complex in the velocity solving process in a near wall region, and the intensity of the acting force on the solid boundary can not be calculated easily are overcome.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Linear hybrid brushless servo motor
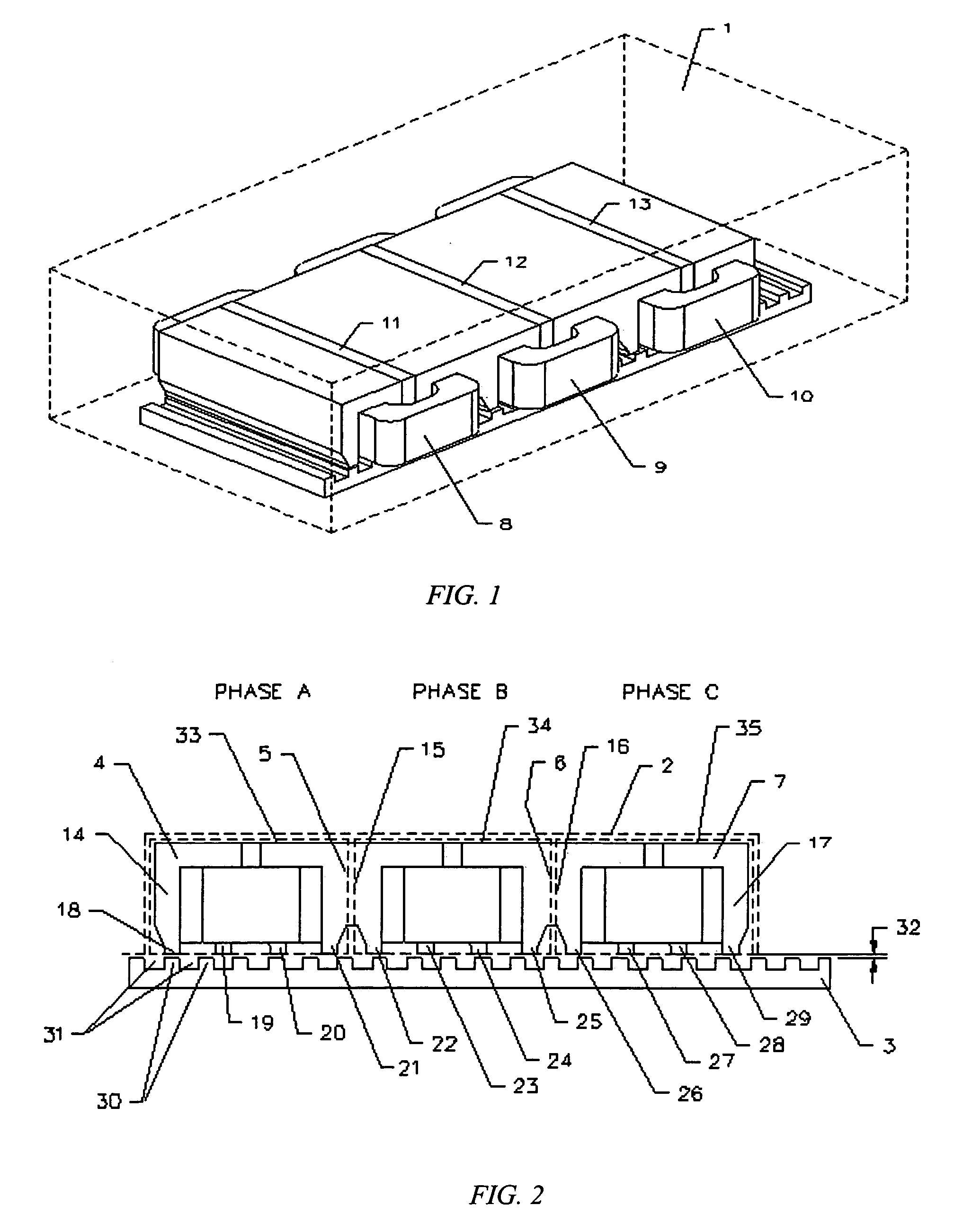
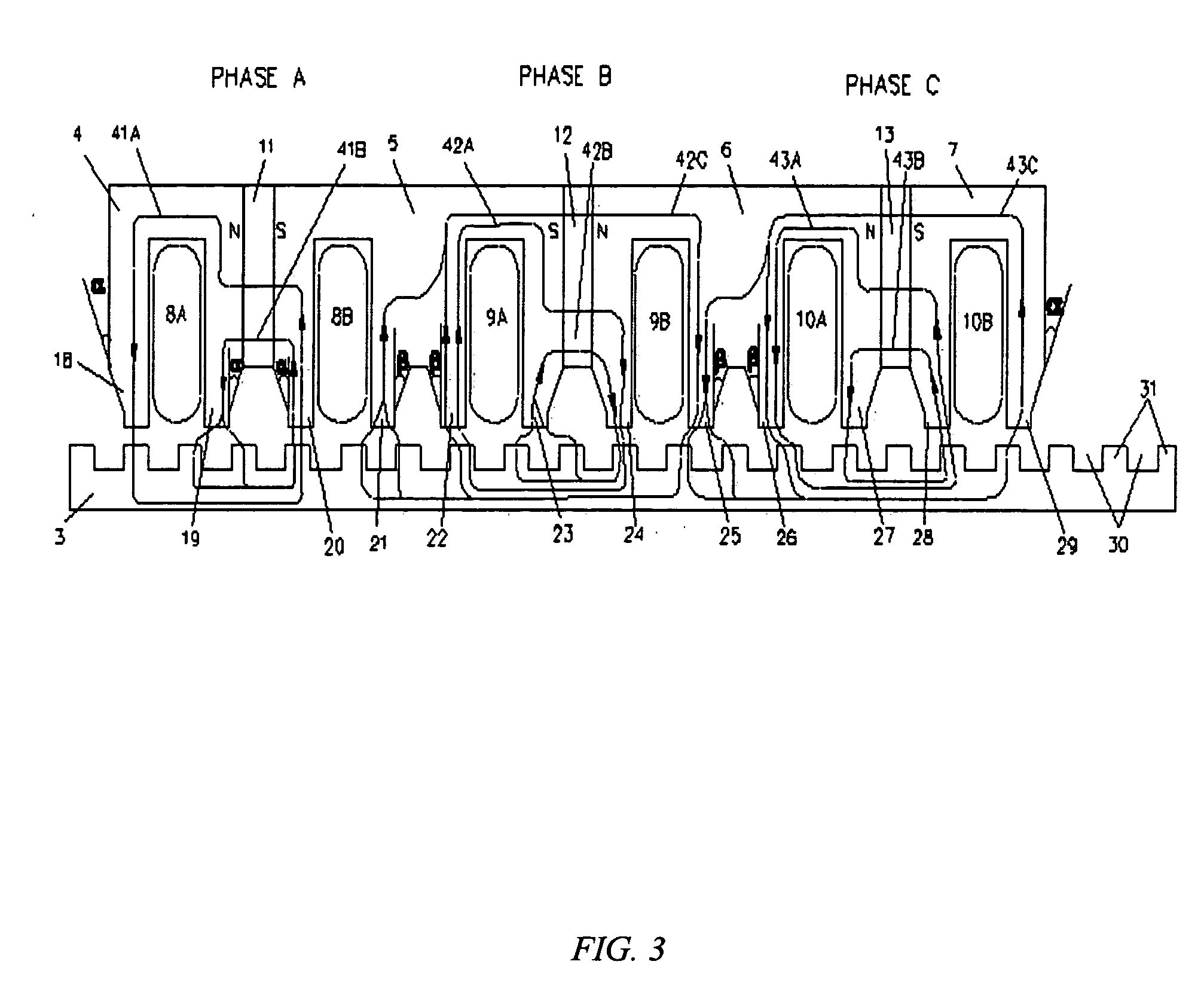
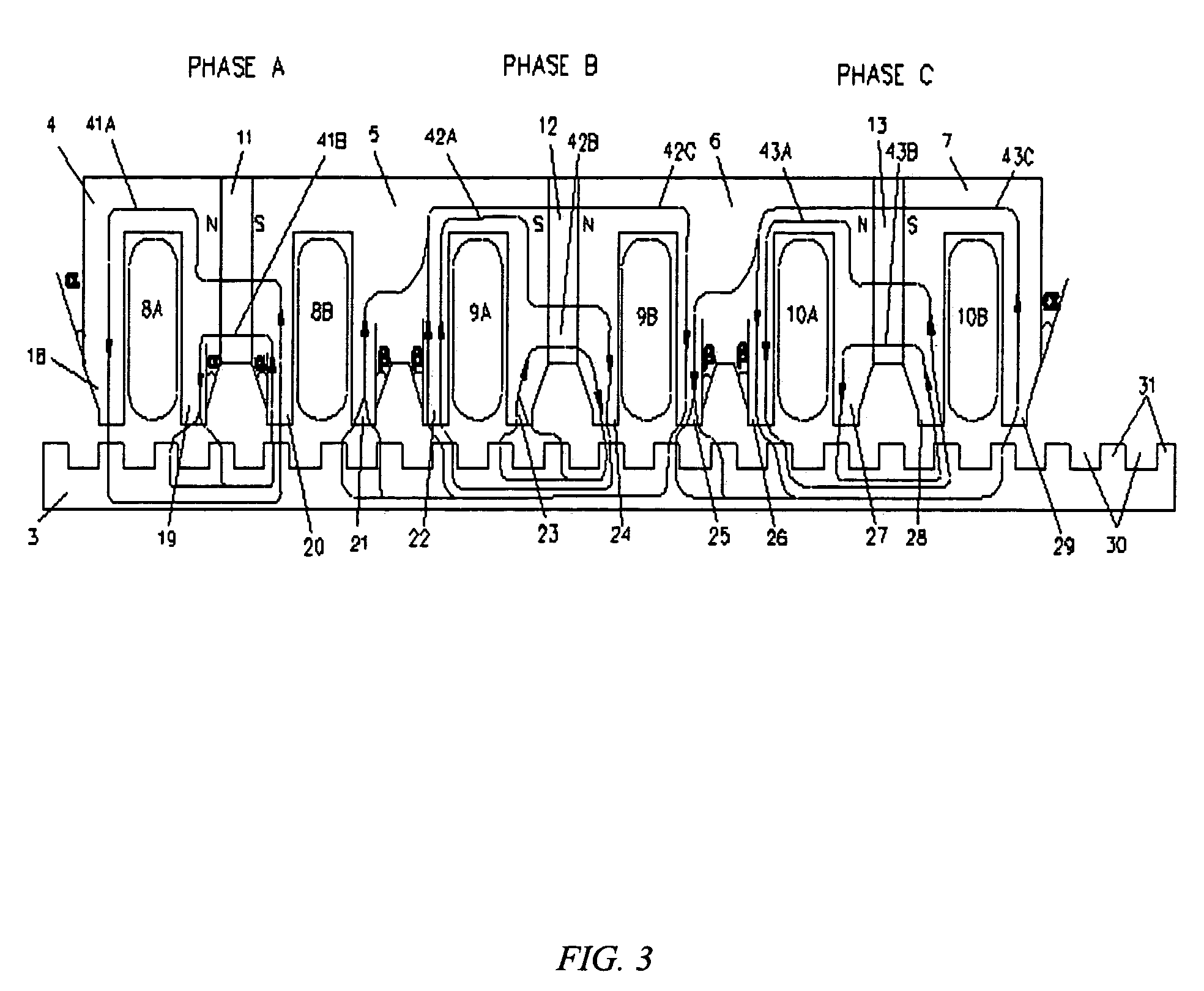
ActiveUS20060131967A1Improve performanceReduce manufacturing costPropulsion systemsElectromagnetic couplingElectric machine
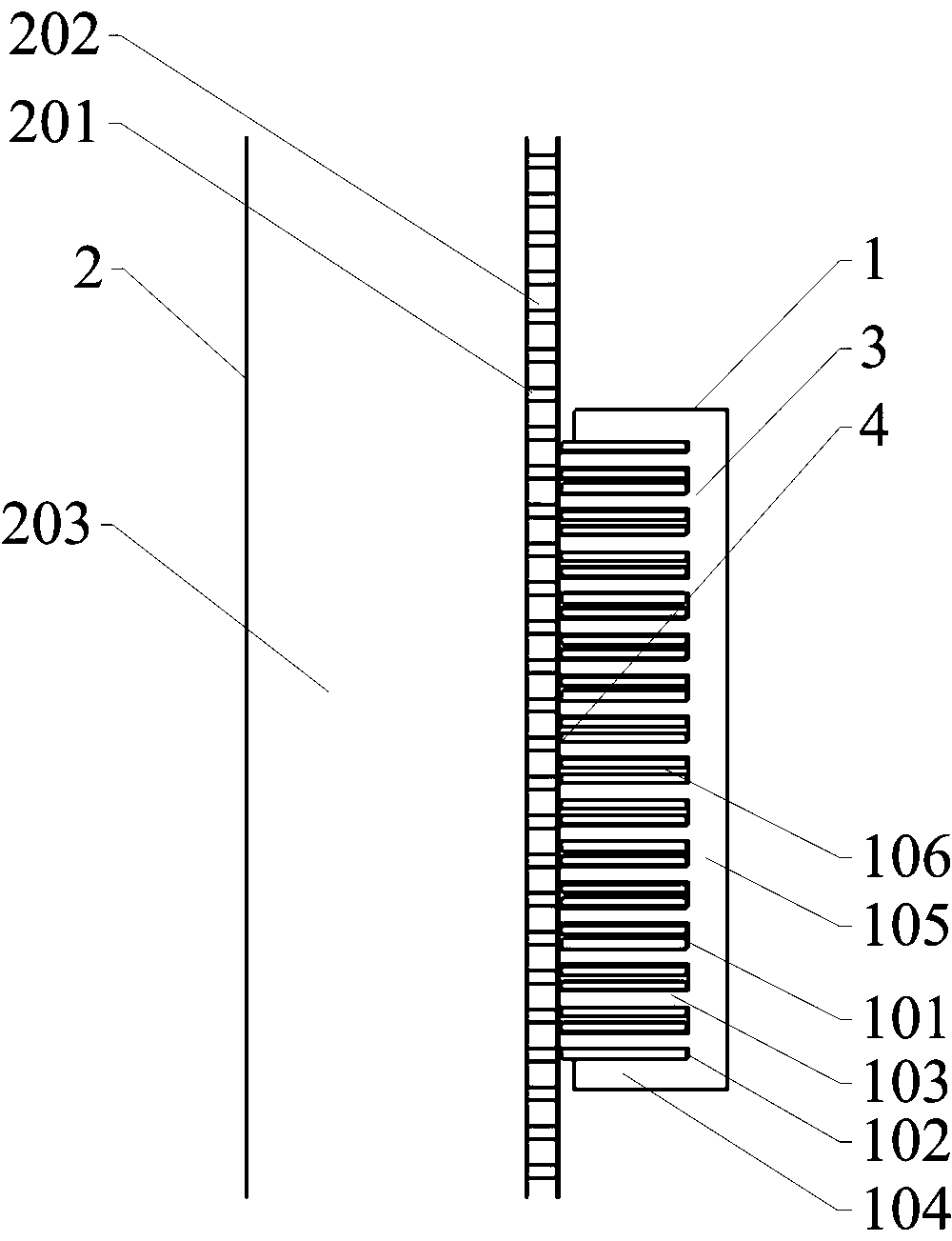
An improved linear hybrid brushless servo motor is disclosed. The motor comprises a forcer and a platen. The forcer has a plurality of stacks, permanent magnets, and coils which form a three-phase motor. The platen has a low cost ferromagnetic steel plate. The stacks, permanent magnets and phase coils of the forcer are specially designed to have the optimal electromagnetic coupling between the forcer and platen to achieve a high force density servomotor. In one embodiment, two E-shaped stacks are used to physically couple two phases to substantially minimize the unexpected cogging force and force ripple. Three other forcer configurations which achieve a three-phase, highly cost effective and high force density linear hybrid brushless servo motor are also disclosed.
Owner:BALDOR ELECTRIC COMPANY
High force hydraulic actuator
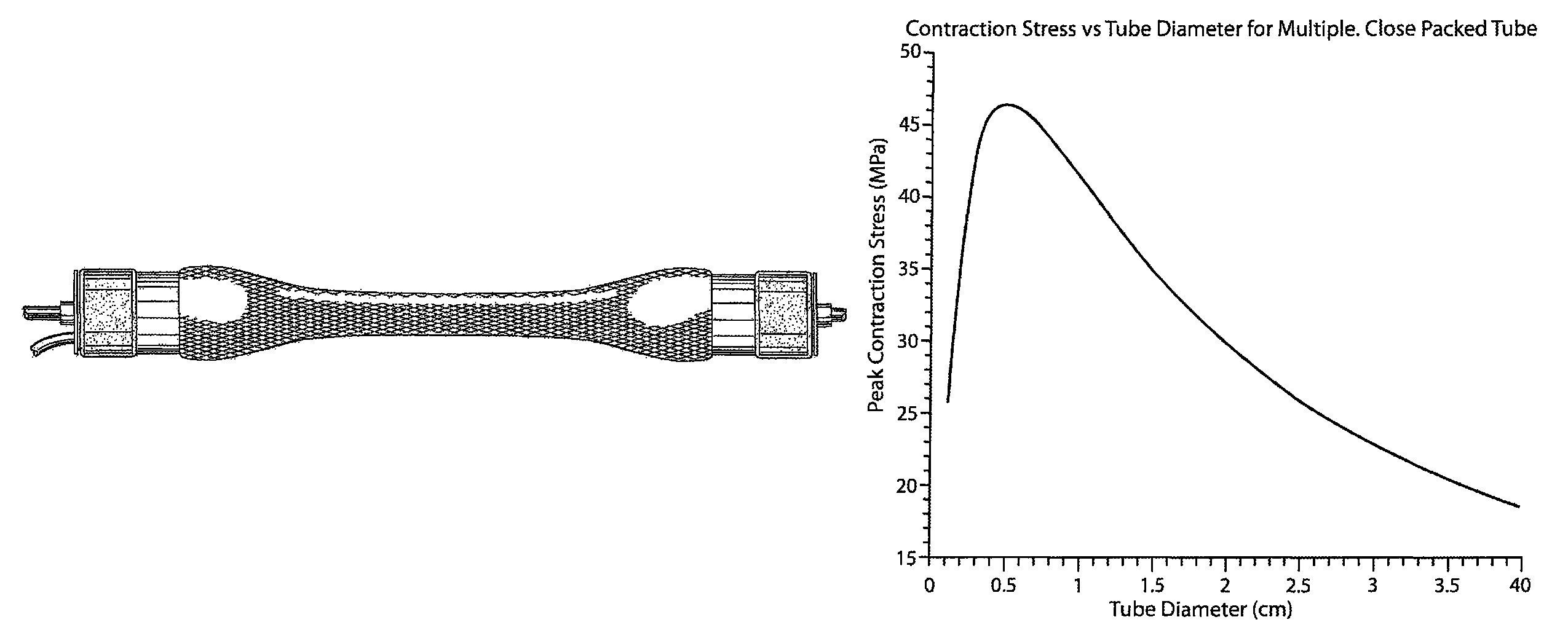
An actuator has a plurality of artificial muscle style hydraulic actuator elements forming a bundle with a bundle force density. Each artificial muscle style hydraulic actuator element has a first diameter. The bundle force density is at least two times greater than the force density of any single one of the artificial muscle style hydraulic elements if that single one artificial muscle style hydraulic actuator element had a second diameter. In illustrative embodiments, the second diameter is at least five times greater than the first diameter.
Owner:VECNA TECHNOLOGIES
Immersed boundary force feedback method based on right body and fluid coupling effect prediction
InactiveCN103778326AReduce usageSave computing resourcesSpecial data processing applicationsTransient stateFluid coupling
The invention relates to an immersed boundary force feedback method based on right body and fluid coupling effect prediction, and belongs to the technical field of the computational fluid mechanics and fluid-solid coupling simulation of the computational fluid mechanics. The method includes the steps that 1, grids are called for dividing modules, and two sets of grids including a fluid field region and a rigid body region are adopted; 2, an initial value calculation module is called to obtain initial value conditions calculated with a stable fluid field of the fluid field region serving as a fluid field transient state ; 3, an immersed boundary method module is called, a whole physical system composed of rigid bodies and fluid fields advances in time, and the following three sub-modules of the fluid field calculation module, the information exchange module and the feedback force calculation module are set in the immersed boundary method module; 4, a result output module is called, force exerted on the rigid bodies and fluid field information are output to a file to be read and displayed by a background; 5 whether calculation ends or not is judged. According to the method, the moving-grid technology is prevented from being used, and therefore a large number of calculation resources are saved; the defects that deformation energy of the rigid bodies is zero, and the acting force density of solid bodies cannot be calculated easily are overcome.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
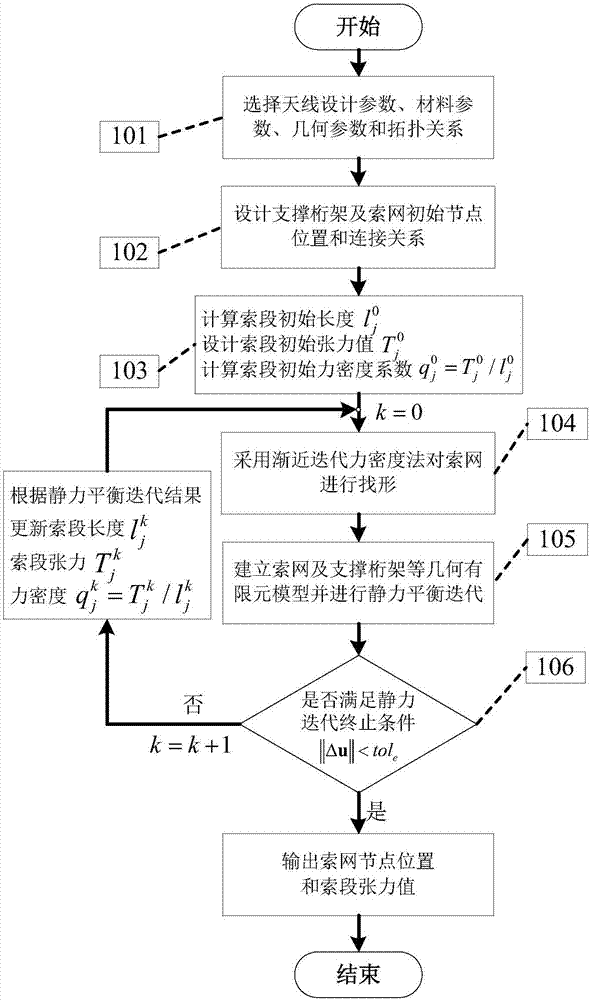
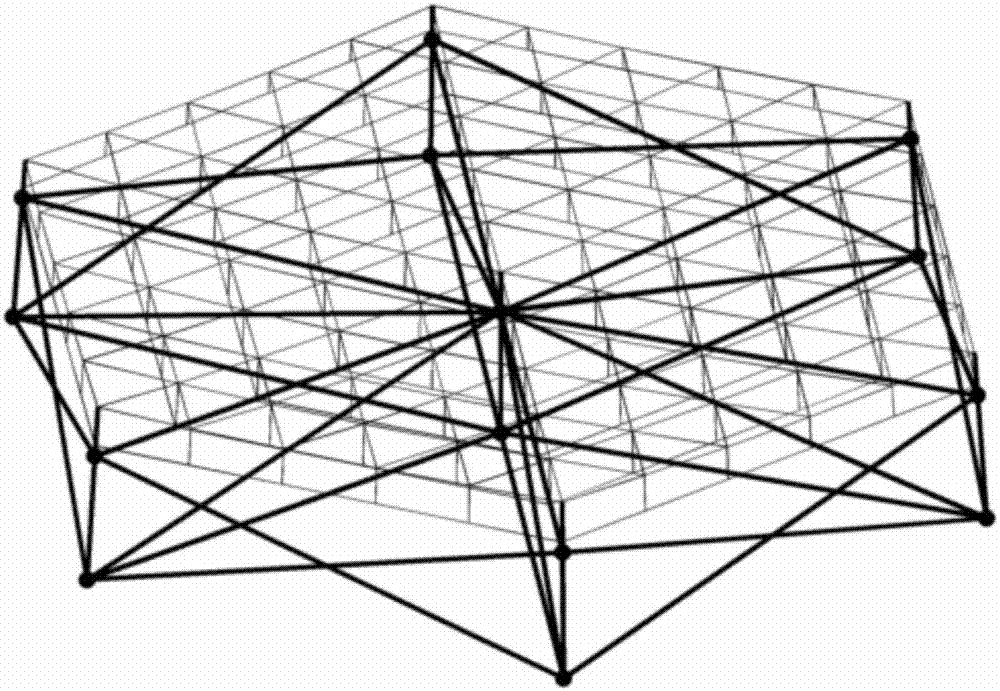
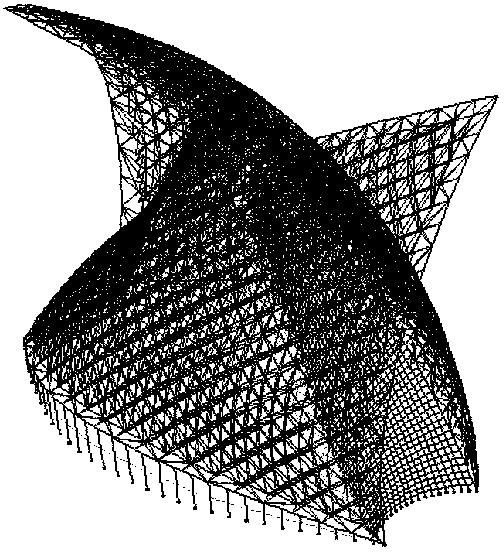
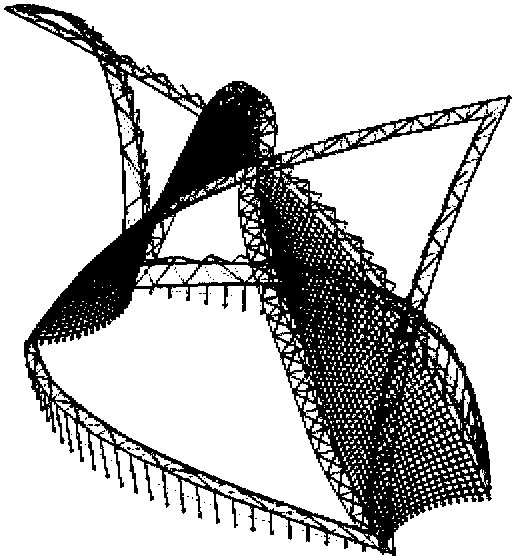
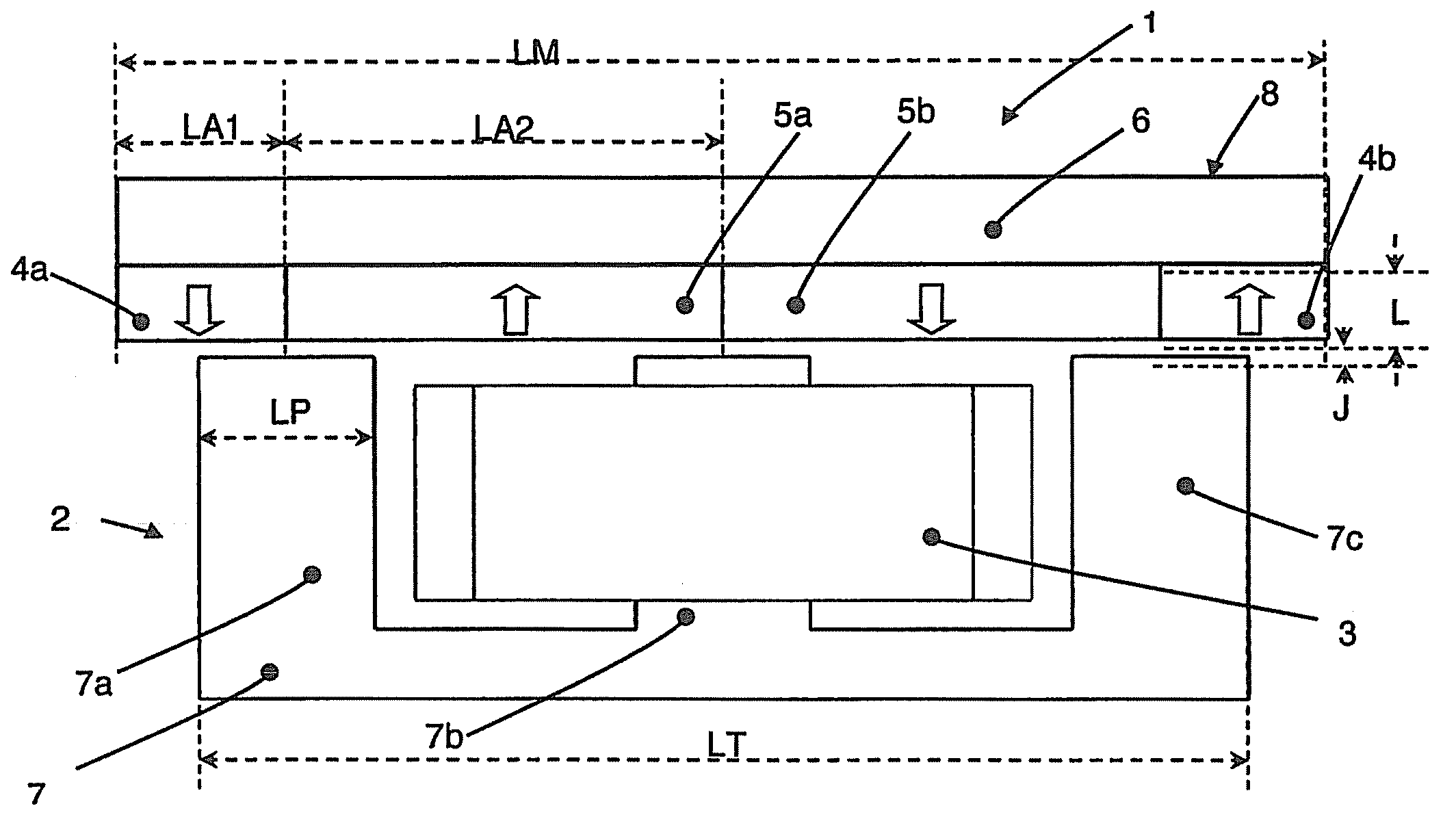
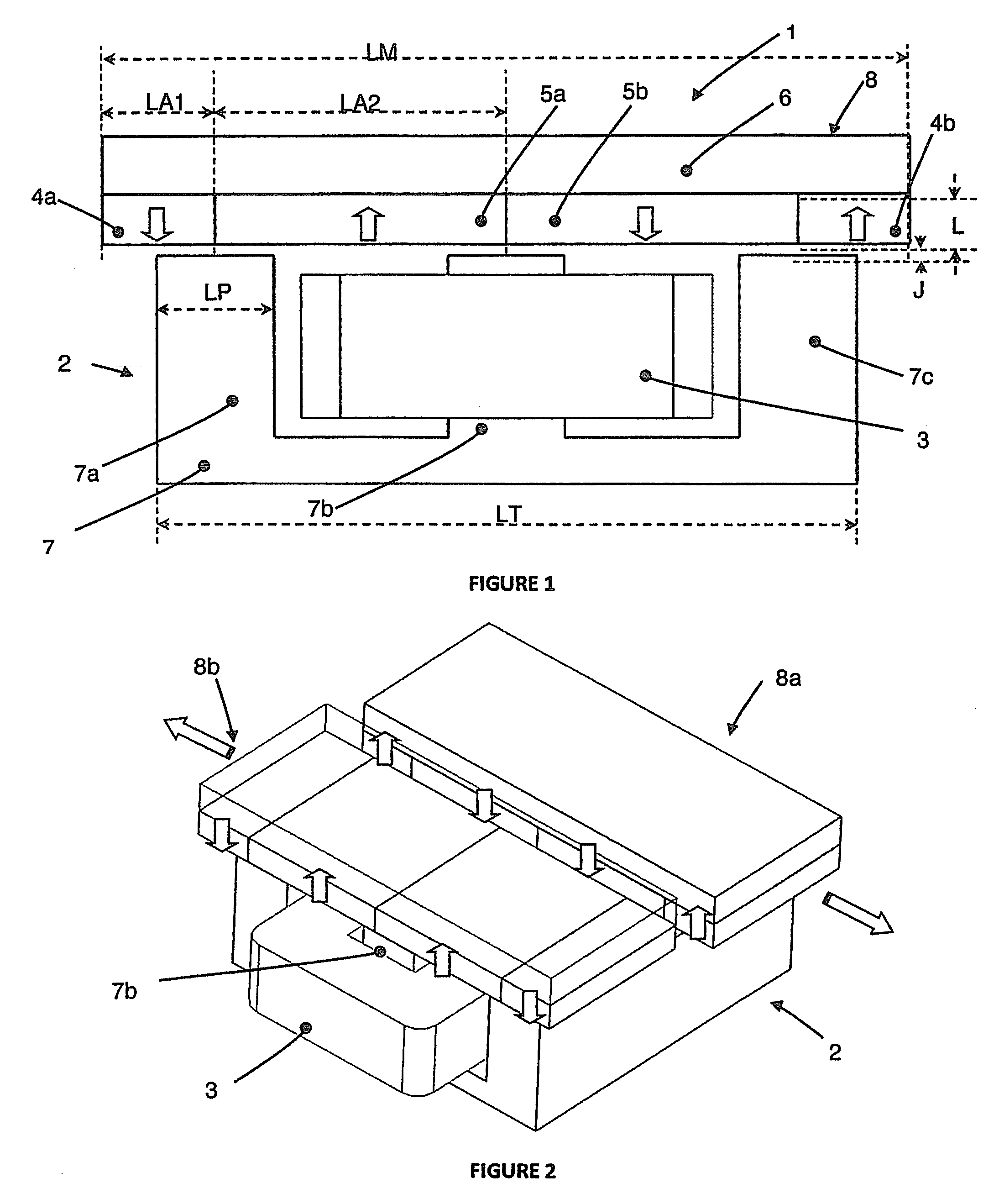
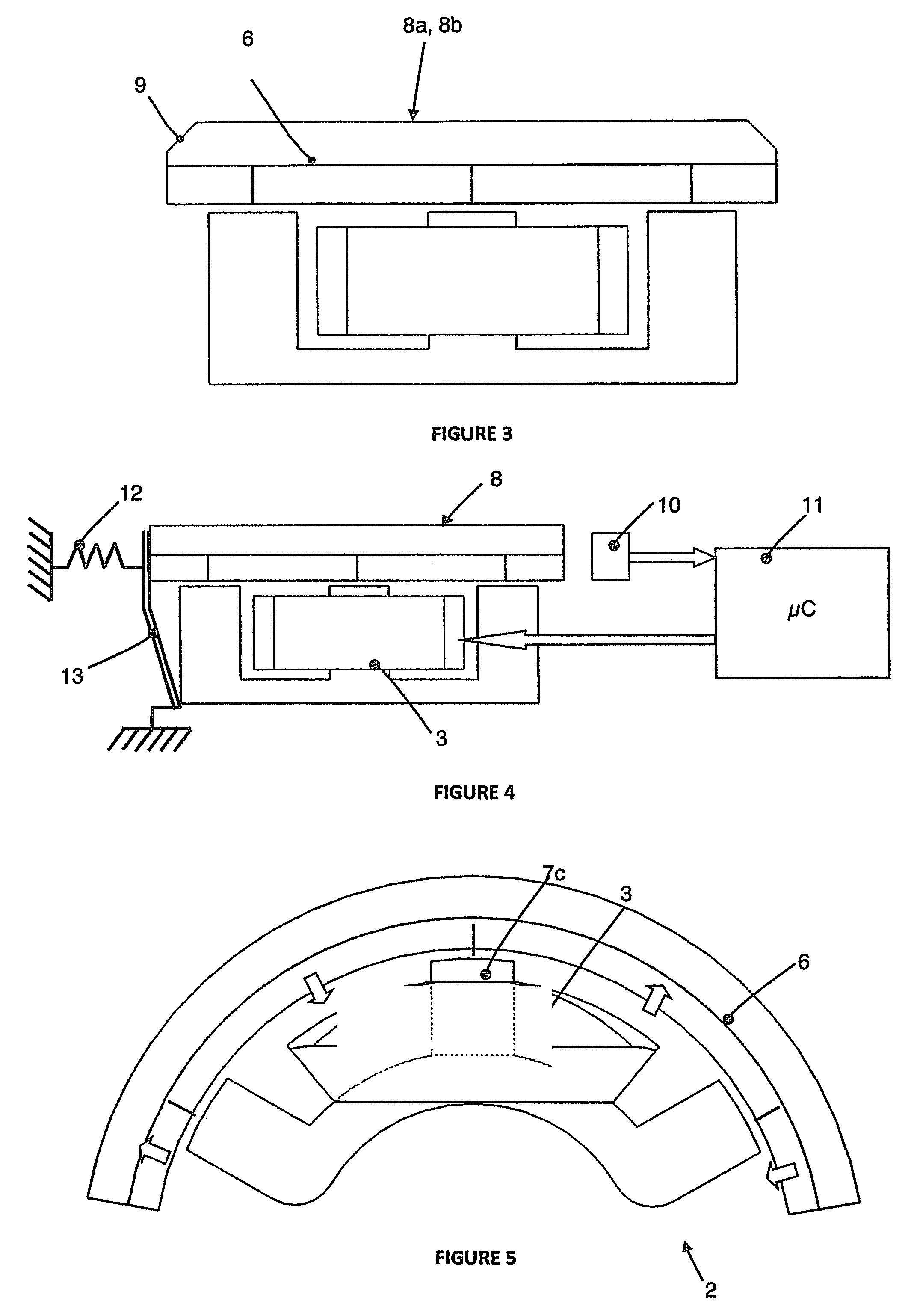
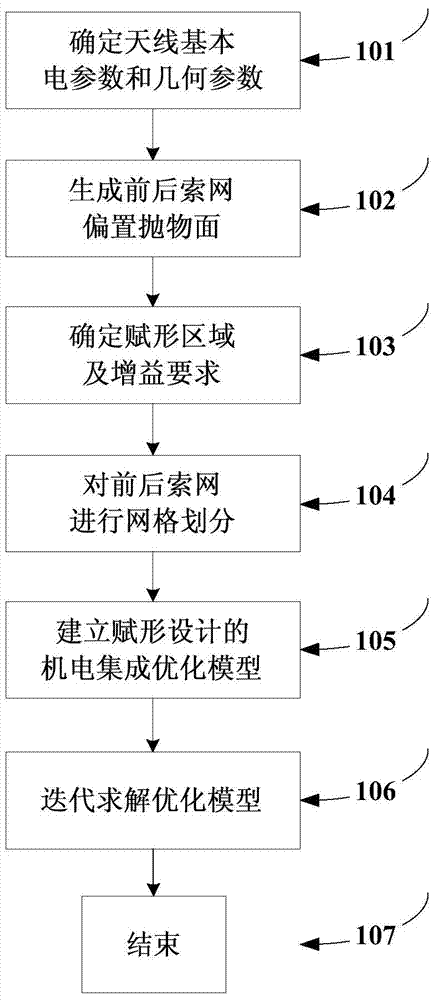
Isogeometric form-finding method for space truss cable-net antenna
ActiveCN106934147AImprove surface accuracySimple form-finding methodDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelCable net
The invention discloses an isogeometric form-finding method for a space truss cable-net antenna. The method is capable of performing form finding on the truss cable-net antenna simply and effectively while improving accuracy. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a support truss and current node coordinates of a cable net based on a topological relation of the antenna according to set design parameters of the antenna; according to a set tension value of a cable section and the current node coordinates of the cable net, calculating an initial length of the cable section, obtaining a current force density coefficient of the cable section, and performing form-finding analysis on the cable net by adopting an asymptotic iterative force density method based on the initial force density coefficient of the cable section on the basis of not considering truss deformation; performing static balance iteration on finite element models of the truss and the cable net; and judging whether the antenna satisfies a static balance error or not, thereby finishing form finding of the truss cable net.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
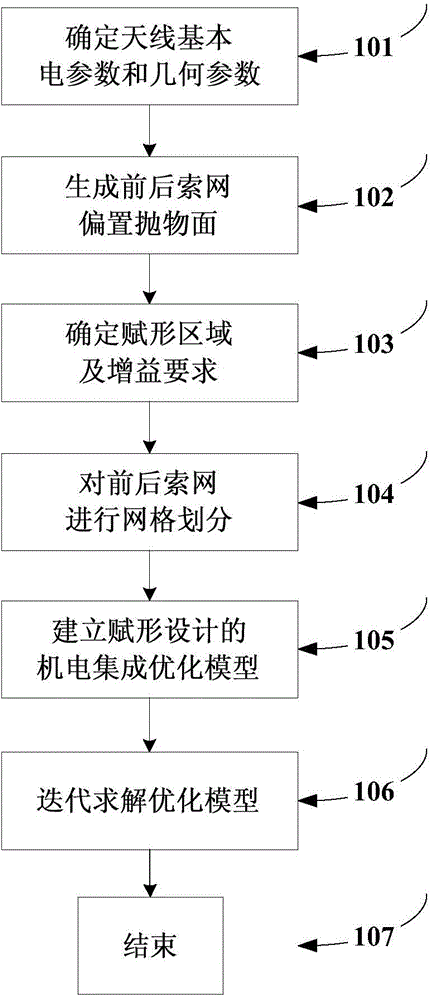
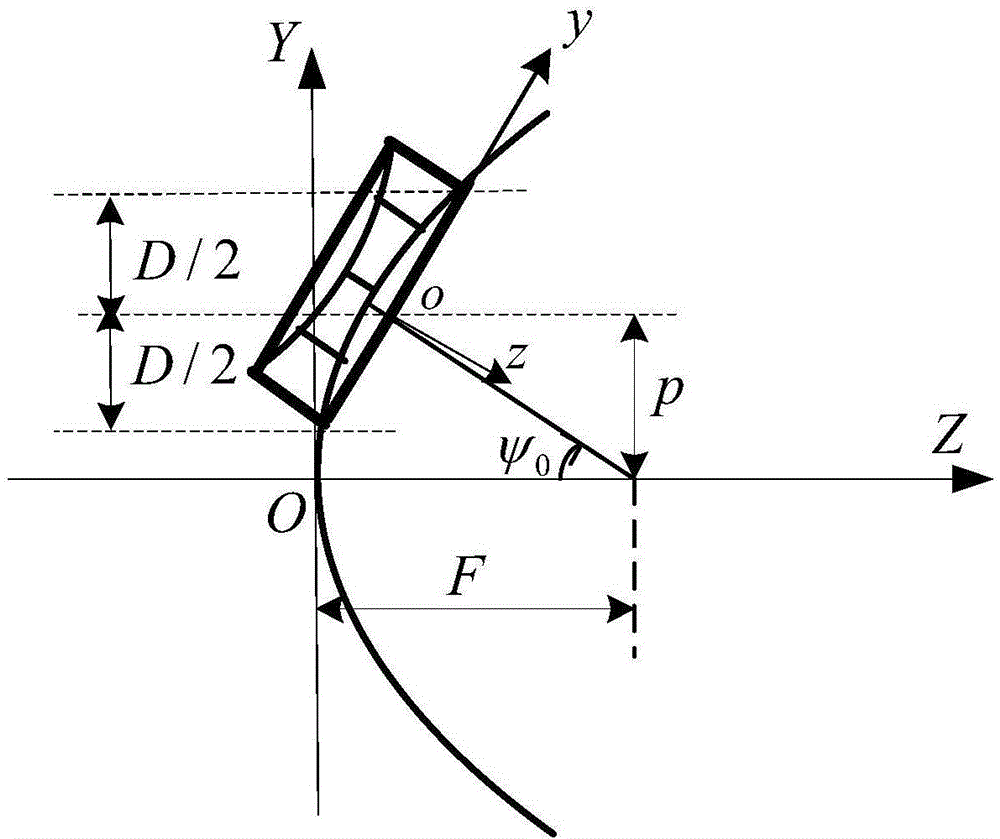
Electromechanical-integration-based shaped beam design method for satellite-borne mesh antenna
InactiveCN104794262AImproves tension uniformityRealize electromechanical integration designSpecial data processing applicationsElectricityShaped beam
The invention discloses an electromechanical-integration-based shaped beam design method for a satellite-borne mesh antenna. In the method, firstly, an electromechanical-integration-based shaped design optimization model for the mesh antenna is built, the force density of a cable net serves as the design variable of the optimization model directly, and under the condition that the cable net is in a tensioned and balanced state without loose cables, the method aims to achieve the targets of enabling the electrical performance of a far field to meet the shaping requirement as far as possible and making the tension of the cable net uniform as far as possible; then, iterative solving is performed on the optimization model till the optimal comprehensive target of the electrical performance and the tension uniformity is achieved, and shaped beam design of the mesh antenna is completed.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
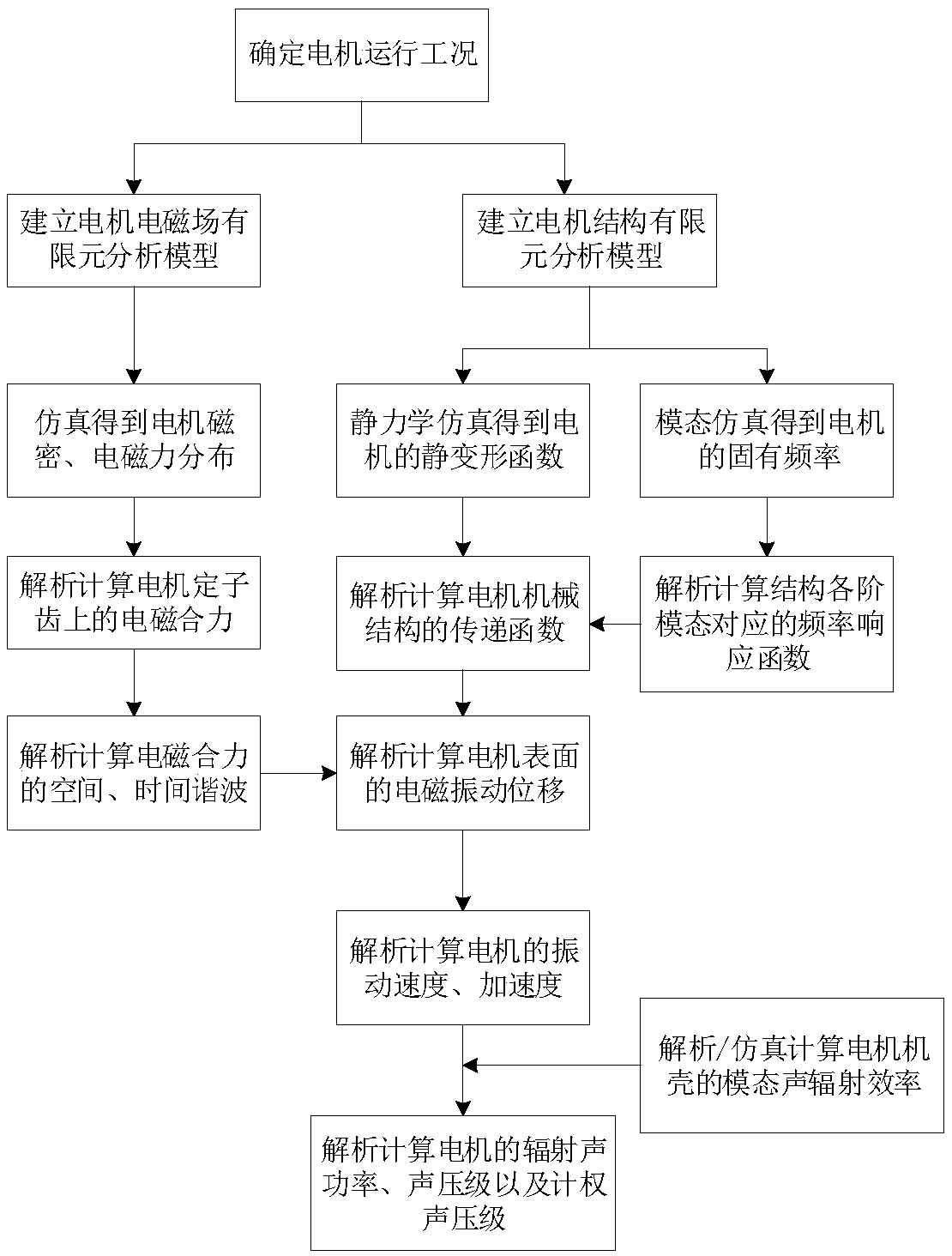
A calculation method of electromagnetic vibration noise of electric machine
ActiveCN109214125AHigh precisionImprove computing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAuditory radiationFrequency response
The invention discloses a method for calculating the electromagnetic vibration noise of a motor, which comprises the following steps: calculating the distribution of the electromagnetic force densityof the motor according to the operation condition of the motor, and calculating the static deformation and the natural frequency of the motor respectively; according to the distribution of the electromagnetic force density, the electromagnetic resultant force on the stator teeth of the motor is calculated, and the time-space harmonic of the electromagnetic resultant force is calculated. The frequency response function of the motor structure corresponding to each vibration mode is calculated according to the natural frequencies of each vibration mode corresponding to each spatial order of the electromagnetic force, and the transfer function of the motor mechanical structure is calculated according to the static deformation function and the frequency response function. The vibration displacement of the motor surface is calculated according to the time-space harmonics and the transfer function. The modal acoustic radiation efficiency of the motor housing is obtained, and the electromagnetic vibration noise of the motor is calculated according to the modal acoustic radiation efficiency and vibration displacement. In the process of analyzing the vibration and noise of the motor, the invention ensures that the calculation accuracy meets the precision requirement, and reduces the calculation amount to avoid consuming a large amount of calculation resources.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Linear hybrid brushless servo motor
ActiveUS7230355B2Improve performanceReduce manufacturing costPropulsion systemsElectromagnetic couplingElectric machine
An improved linear hybrid brushless servo motor is disclosed. The motor comprises a forcer and a platen. The forcer has a plurality of stacks, permanent magnets, and coils which form a three-phase motor. The platen has a low cost ferromagnetic steel plate. The stacks, permanent magnets and phase coils of the forcer are specially designed to have the optimal electromagnetic coupling between the forcer and platen to achieve a high force density servomotor. In one embodiment, two E-shaped stacks are used to physically couple two phases to substantially minimize the unexpected cogging force and force ripple. Three other forcer configurations which achieve a three-phase, highly cost effective and high force density linear hybrid brushless servo motor are also disclosed.
Owner:BALDOR ELECTRIC COMPANY
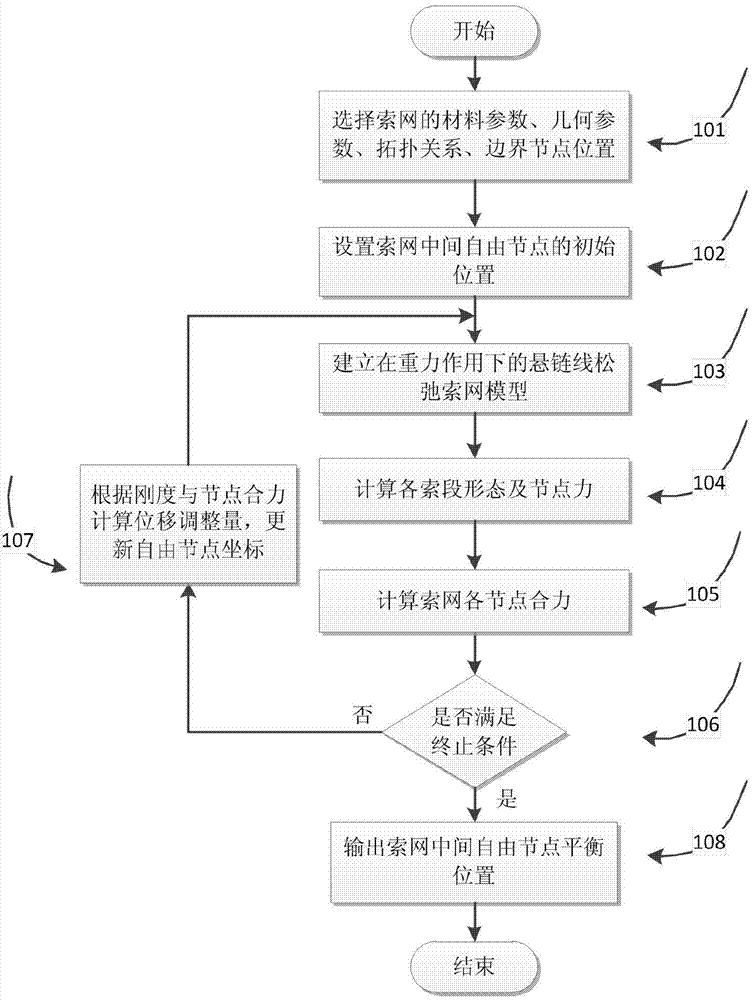
Loose cable net form-finding method based on catenary element
InactiveCN104504284AImplementing form-finding analysisSpecial data processing applicationsCable netEngineering
The invention provides a loose cable net form-finding method based on a catenary element. The loose cable net form-finding method mainly includes the steps: selecting material parameters D, geometrical parameters S, topological structures and boundary node positions Pfix of a cable net; setting an initial position Pfree of a middle free node of the cable net; building a catenary loose cable net model under the action of gravity; calculating cable segment forms and node force in a cable net system; analyzing resultant force of nodes of the cable net; judging whether resultant force of an optional node meets requirements or not, and outputting results if the resultant force meets the requirements; continuing to set the initial position Pfree of the middle free node of the cable net if not; finally, outputting the balance position of the middle free node of the cable net. Form-finding analysis for the loose cable net is realized by a nonlinear finite element method, the results are matched with a force density method, stiffness information of the loose cable net in any configuration is acquired, dynamic performances of the loose cable net can be further analyzed, or the loose cable net is combined with other finite elements (such as rods, beams, plates and shells) to realize modeling, and kinetic analysis of complicated structures is performed.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
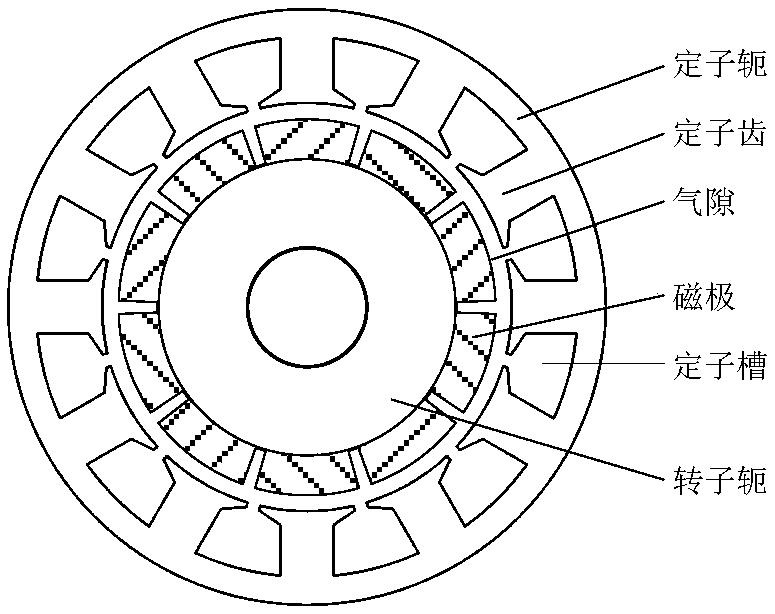
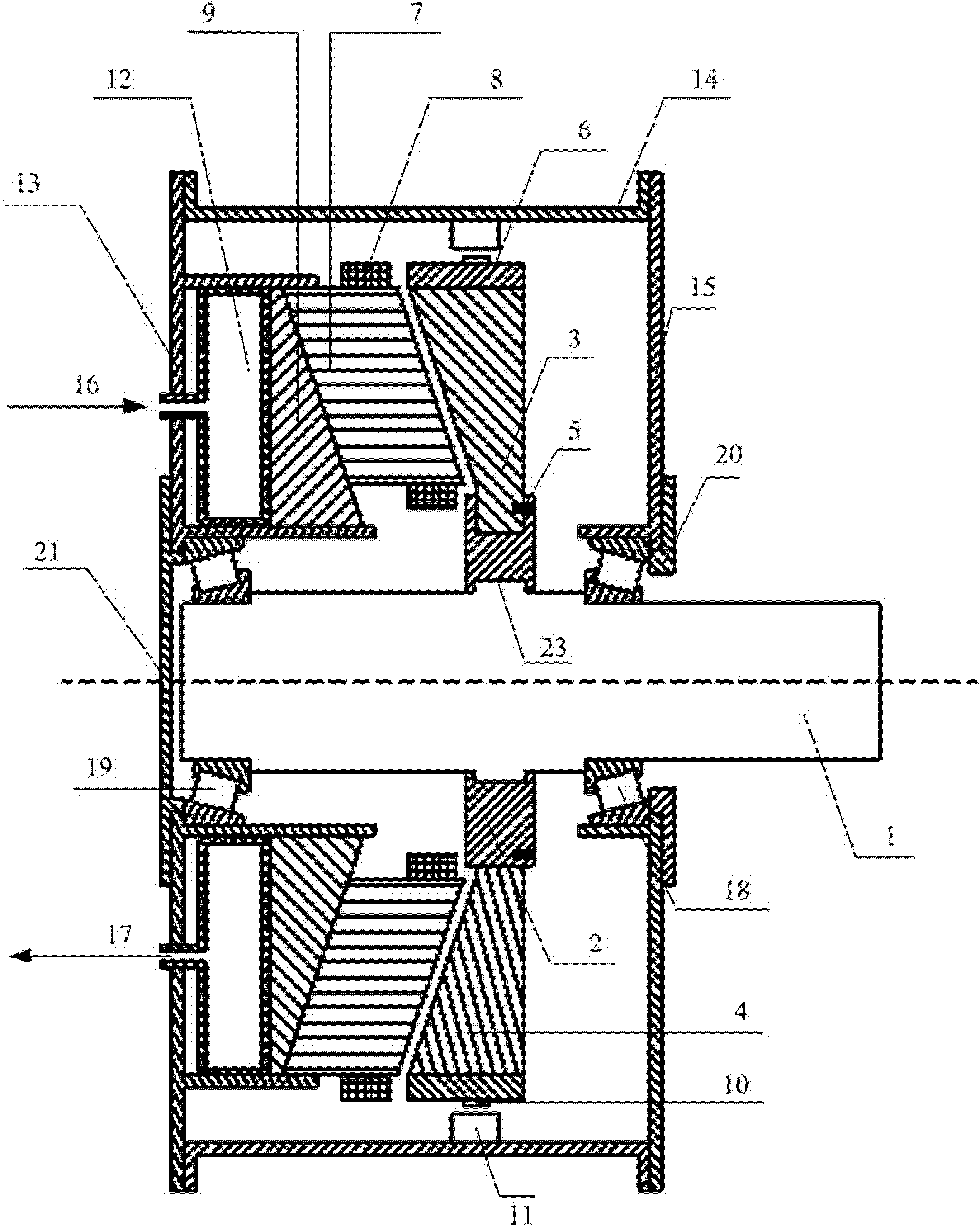
Magnetism-gathering disc type permanent magnet torque motor with fluid cooling function
InactiveCN102185392AImprove utilization efficiencyImprove power densityMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsTorque motorConductor Coil
The invention discloses a magnetism-gathering disc type permanent magnet torque motor with fluid cooling function, comprising a stator core, an armature winding, a rotor core, a permanent magnet and a motor rotor shaft; each motor stator consists of the stator core and the armature winding; the stator core can carry out the winding along the circumferential direction after stamping notches by equal-width silicon steel sheets; and adjacent silicon steel sheets offset by a certain distance along the axial direction so that the section of the stator core in the direction vertical to the rotatingdirection of the motor is a parallelogram. A motor rotor forms a magnetism-gathering structure by the rotor core and a permanent magnet; when the motor is designed as a single-stator single-rotor structure; the sections of the rotor core and the permanent magnet in the direction vertical to the rotating direction of the motor are respectively a right-angled trapezium; and a conical air clearance is formed between the rotor core and the stator core as well as the permanent magnet and the stator core. The disc type permanent magnet torque motor has the advantages that the effective area of the air clearances is enlarged, the force density of the motor is high, cooling liquid flowing chambers are arranged between the motor stators and at the external sides of the motor stators at two sides, so that the heat dissipation of the motor is ensured.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Double-permanent-magnet lateral magnetic flux linear permanent magnet motor
InactiveCN105356720ACompact structureEasy to assemblePropulsion systemsElectric machinePermanent magnet motor
The invention discloses a double-permanent-magnet lateral magnetic flux linear permanent magnet motor, and the motor comprises a primary mechanism and a secondary mechanism. The primary mechanism comprises a plurality of primary units in the same structure, and each primary unit comprises a magnetic conduction part and an armature winding. The magnetic conduction part is provided with three projection parts: a main magnetic tooth and auxiliary magnetic teeth located at two sides of the main magnetic tooth. The armature winding is wound around the periphery of the main magnetic tooth. The secondary mechanism comprises a permanent magnet fixing plate and a permanent magnet matrix, wherein the permanent magnet matrix comprises a plurality of permanent magnets which are arranged in parallel. The two rows of permanent magnets are sequentially fixed at two sides of the permanent magnet fixing plate in a one-one corresponding manner. There are gaps between the magnetic conduction part and the permanent magnets. The motor can achieve a purpose that one iron core lamination is corresponding to two parallel magnetic flux loops of one armature winding, is simple in structure, is short in each magnetic loop, is higher in force density, and is smaller in output force fluctuation. The shorter magnetic loop can reduce the eddy-current loss of the motor, improves the efficiency of the motor, and improves the utilization rate of the permanent magnets.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Tape muscle
InactiveUS20120228991A1Increase clamping forceLow costProgramme-controlled manipulatorElectrostatic generators/motorsTape speedComputer module
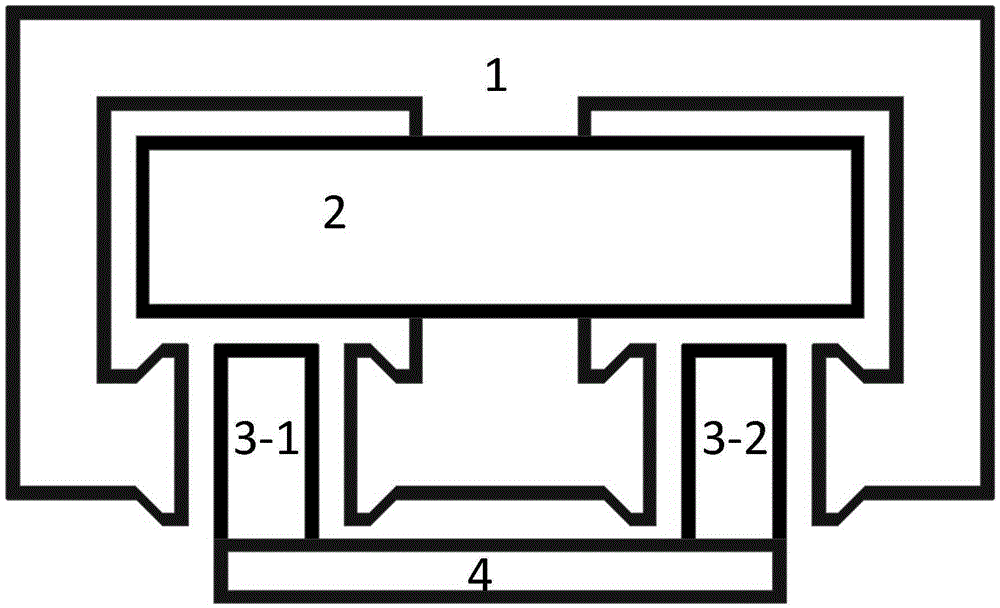
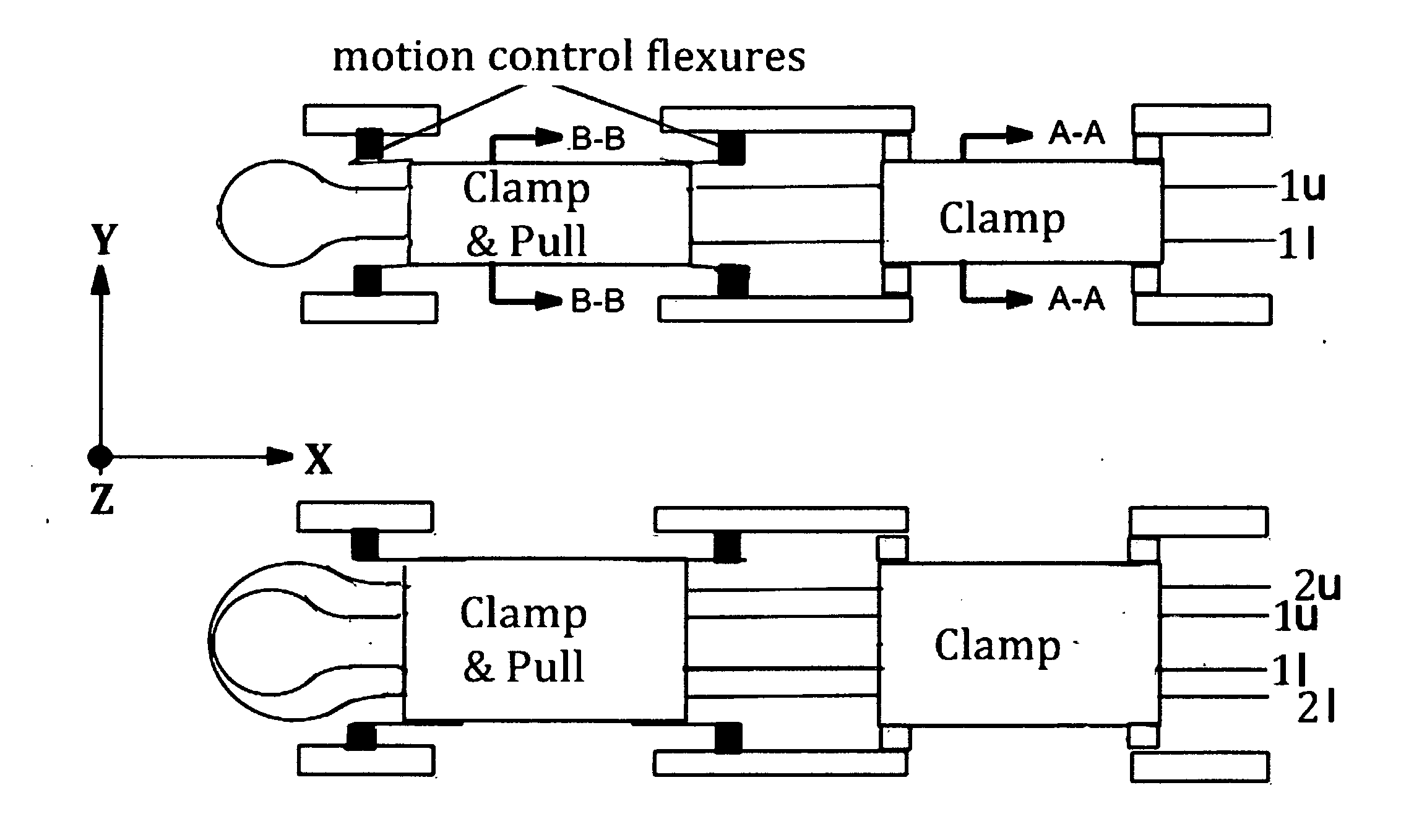
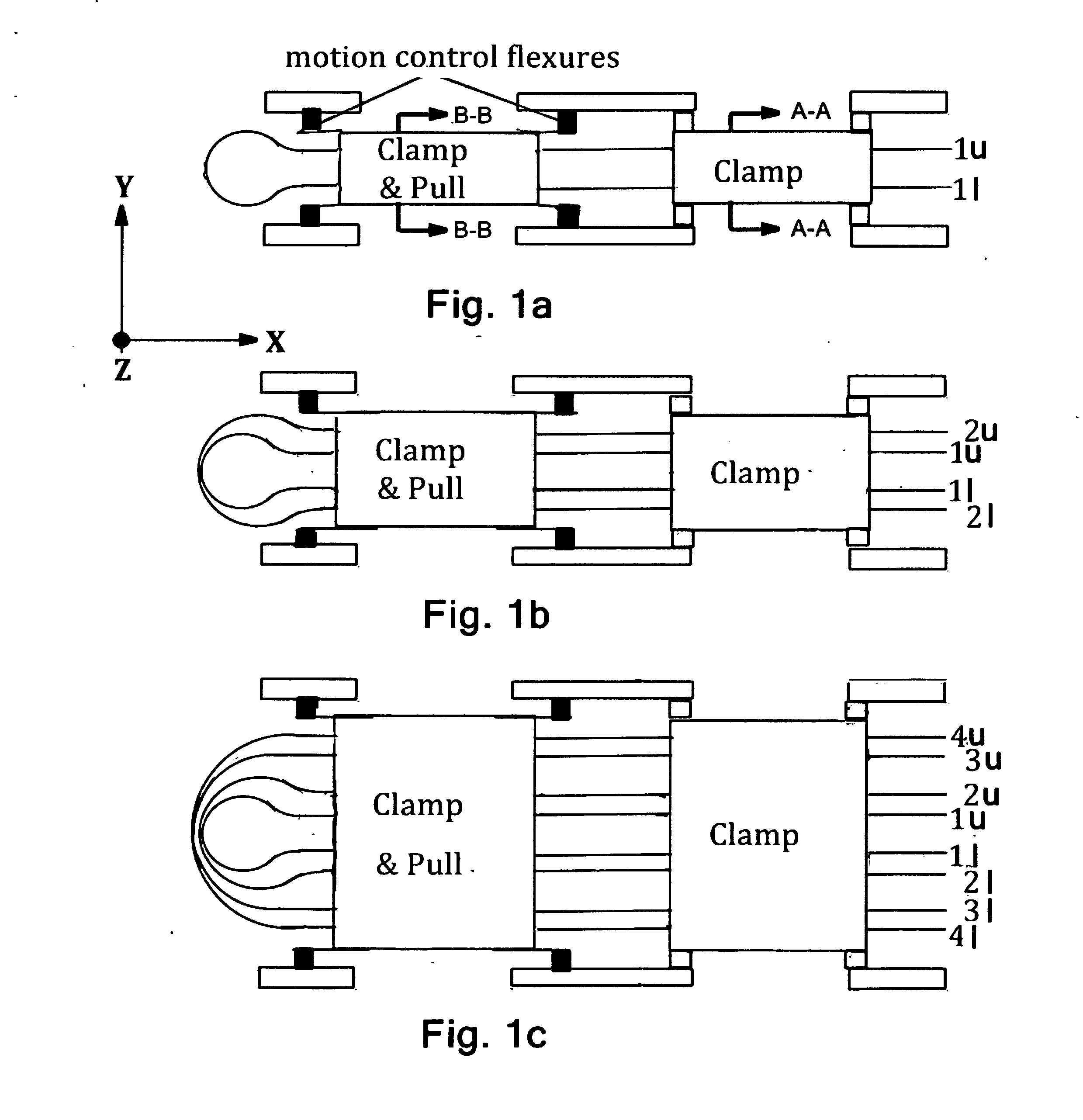
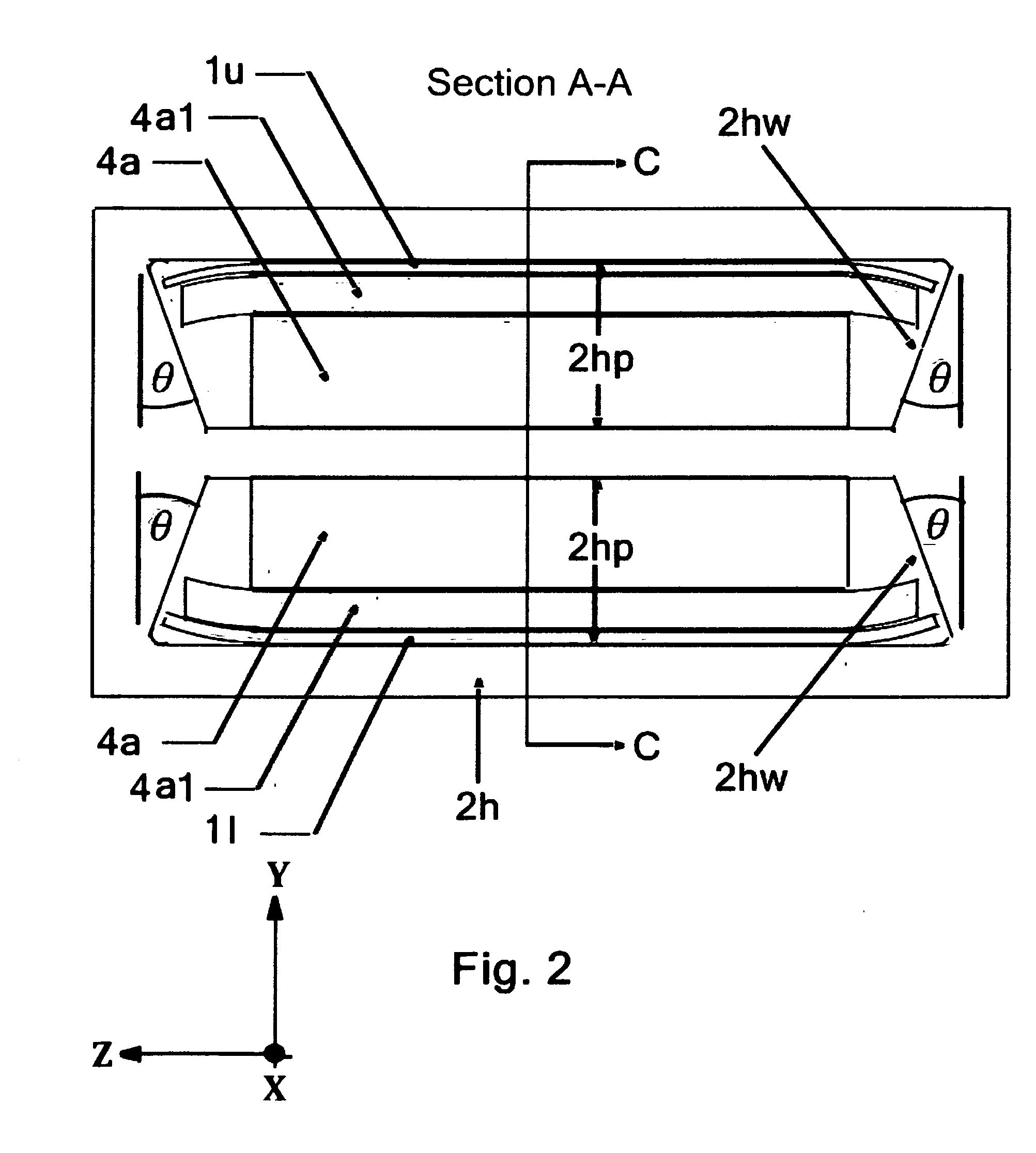
A Tape Muscle is described where multiple tape loops are independently driven by synchronized grasp and pull actions from a tandem of Clamp, Clamp & Drive modules. Each tape loop is elastically bent, with its open ends threaded through individual passageways in both modules. Tape loops are nested inside each other with all tape open ends on the same side. Each loop moves its open ends in equal, opposite directions, while the loop position remains fixed. Tape movements do not interfere with each other. The open ends of each loop attach to a shared appendage, which is pulled back and forth using tensile forces. Drive and hold forces use small angle flexure bending mechanical advantage and high force density electrostatic induction methods. Tape speed results from high frequency clock speed and novel hand-off methods. Governing equations, design details and performance estimates are provided.
Owner:VRANISH JOHN M
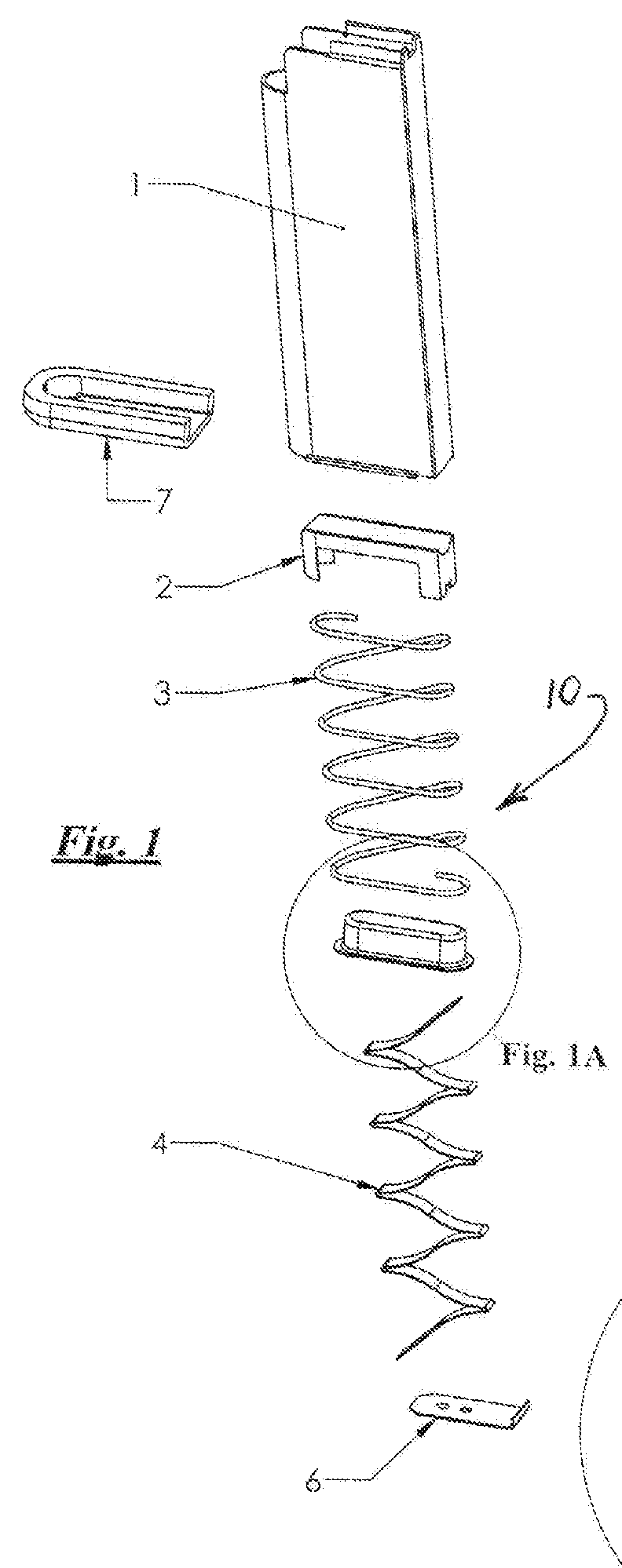
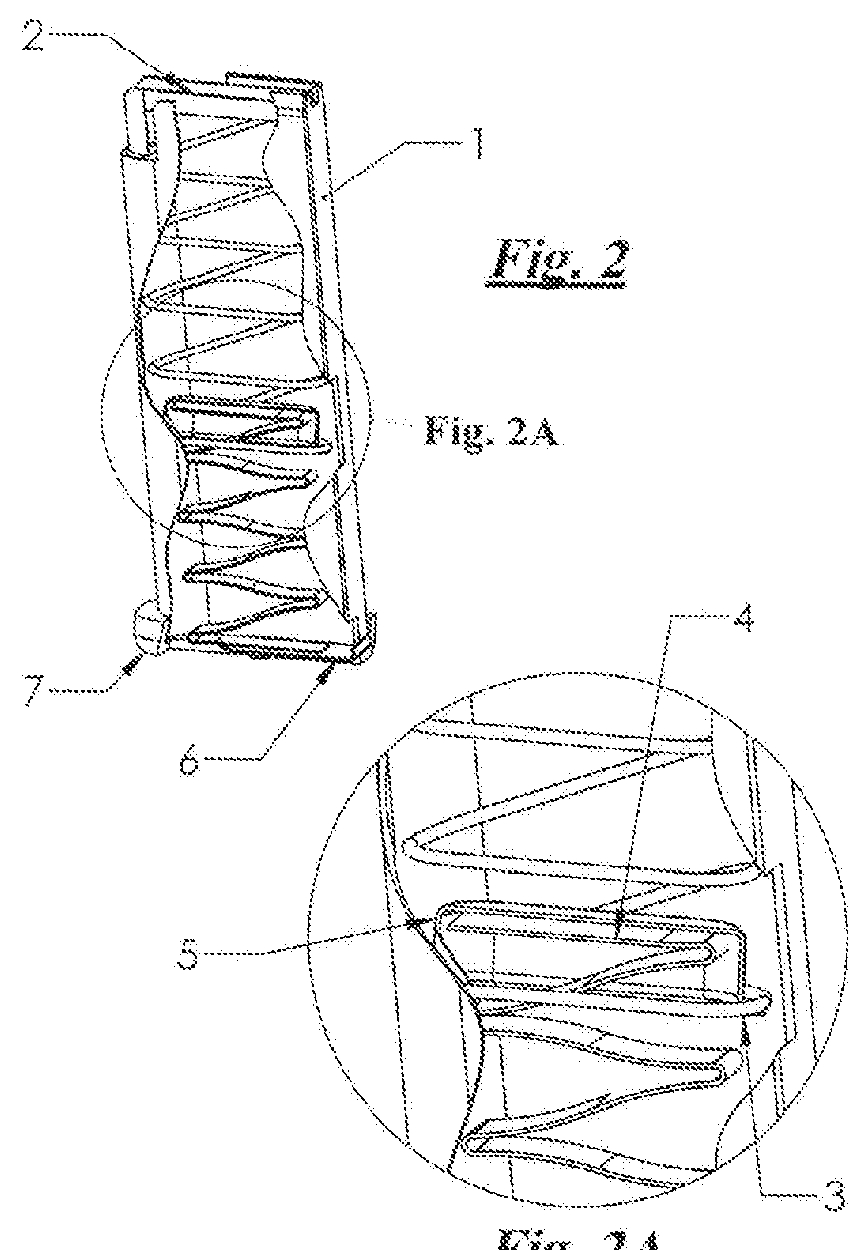
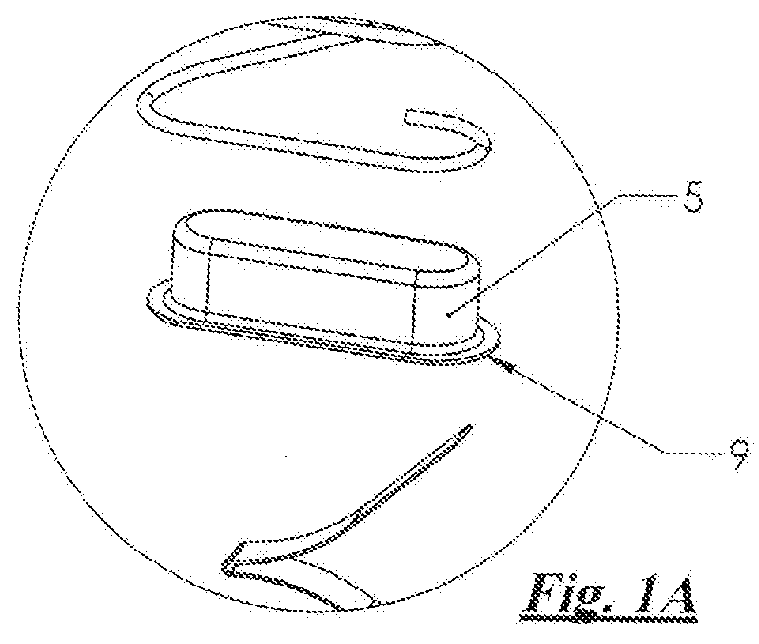
Compact firearm spring arrangement
A compact firearm spring arrangement within a firearm magazine utilizes two or more springs connected in a linear arrangement by a connecting cup that allows one spring to compress within the other, thereby resulting in a free length spring system having a reduced height when fully compressed. At least one of the springs is a wire spring coiled in an oblong shape and one of the springs is a flat spring for providing increased force density for operation of the firearm. The reduced height of the spring arrangement when fully compressed, and increased force density from the flat spring(s), allows for additional bullet storage space within a magazine of standard size or, alternatively, a more compact system within a magazine that provides an equal amount of bullet storage space while reducing the friction of operation of the firearm.
Owner:CORSO STEVEN
Cable section tension variance optimization-based design method for cable net structure of deployable satellite-borne antenna
InactiveCN107256288AImprove structural performanceTension variance is smallDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCable netIterative method
The invention discloses a cable section tension variance optimization-based design method for a cable net structure of a deployable satellite-borne antenna. The cable net structure of the deployable satellite-borne antenna consists of a front cable net surface, a back cable net surface and a longitudinal pull cable; when the cable net structure is designed, all cable net surface nodes fall on a paraboloid through a force density iterative method; meanwhile, boundary nodes of the front and back cable net surfaces are subjected to boundary cable section and annular truss reconnection by taking a regular hexagon in the cable net structure as an effective reflective surface, and serve as basic mesh configuration of the cable net structure of the deployable satellite-borne antenna; and then, by taking cable section tension of the front and back cable net surfaces and tension of the longitudinal pull cable as design variables, taking a cable section tension variance of the front and back cable net surfaces as a target function and taking boundary node fixation as a constraint condition, the cable net structure of the deployable satellite-borne antenna is designed. According to the method, excellent structure layout of the deployable satellite-borne antenna is realized, so that the stability and reliability of the deployable satellite-borne antenna can be remarkably improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Primary permanent magnet linear motor actuator
InactiveCN109787448AReduce the effect of temperature riseImprove power densityMagnetic circuit stationary partsCooling/ventillation arrangementPrimary permanentDrive shaft
The invention discloses a primary permanent magnet linear motor actuator. The primary permanent magnet linear motor actuator comprises a driving shaft, a secondary mover convex tooth block, a secondary mover channel block, primary stator iron cores, an armature winding and a permanent magnet body, wherein a secondary mover of a primary permanent magnet linear motor is arranged on a driving shaft and consists of the secondary mover convex tooth block and the secondary mover channel block arranged in the axial direction of the driving shaft at intervals; four primary stators of the primary permanent magnet linear motor are separately and symmetrically arranged on the outer side of the driving shaft; each of the primary stator comprises two primary stator iron cores; each of the primary stator iron cores is provided with a plurality of stator channels; each of the stator channel comprises a large stator channel and a small stator channel; and the large stator channels and the small statorchannels are arranged at intervals. Through creative proposal of a four-sided tubular structure, the pushing force density and the power density of the actuator can be improved, so that the driving shaft of the actuator has a simple structure and is high in robustness; and through arrangement of a built-in water cooling pipeline, the heating effect is reduced.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Novel magnet-gathering type transverse flux permanent magnet linear motor
InactiveCN103795204ASimple structureHigh stator space utilizationMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsFault toleranceTransverse flux
The invention discloses a novel magnet-gathering type transverse flux permanent magnet linear motor which comprises stators and a rotor. The rotor is rectangular and is composed of two salient pole iron cores and a connecting board. The two salient pole iron cores are fixed to the two ends of the connecting board respectively and respectively provided with a groove. The groove of each salient pole iron core is provided with a permanent magnet and a winding. Multiple strip-shaped air grooves with equal intervals are evenly formed inside each stator. The salient pole iron cores at the two ends of the rotor are arranged in the two stators respectively. According to the novel magnet-gathering type transverse flux permanent magnet linear motor, a primary level and a secondary level are respectively of a salient pole structure, the independence between phases is good, and the high force density and fault tolerance are integrated; the use rate of stator space is high; the fault tolerance capacity is strong and operation reliability is high; fluctuation of the locating force and the pushing force is small and the control characteristic is flexible; the permanent magnets are placed in the primary-level rotor iron cores, so that the temperature is easy to control, the permanent magnet use amount is small, and the motor can be applied to the field with the high requirement for reliable operation of a system.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Force density finite element mixing method used for rope-pole-beam mixed system form-finding
InactiveCN103399981AFulfil requirementsSpecial data processing applicationsSupporting systemStructure analysis
The invention discloses a force density finite element mixing method used for rope-pole-beam mixed system form-finding. The method comprises the steps of (1) precisely defining a building structural model as combination of a flexible rope-pole system and a supporting system, (2) defining the force density of components of the flexible rope-pole system, (3) 'killing' the supporting system of the structural model, (4) carrying out the form-finding with the force density method to obtain the shape of the rope-pole system and internal force distribution which coincide with the mechanics principle, (5) 'activating' the supporting system of the structural model, and (6) carrying out linear finite element analysis to obtain the balanced internal force state of the supporting system at the original position of the model. The force density finite element mixing method used for the rope-pole-beam mixed system form-finding is applied to a mixed building structure comprising double-curved-surface cable nets, the ideal shape of a flexible cable net structure and the internal force distribution which coincide with the mechanical equilibrium condition are obtained, the internal force distribution of the supporting system under drawing geometry is also obtained, requirements of architects are met, and basic conditions are provided for follow-up structure analysis.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGLEI CIVIL ENG TECH +1
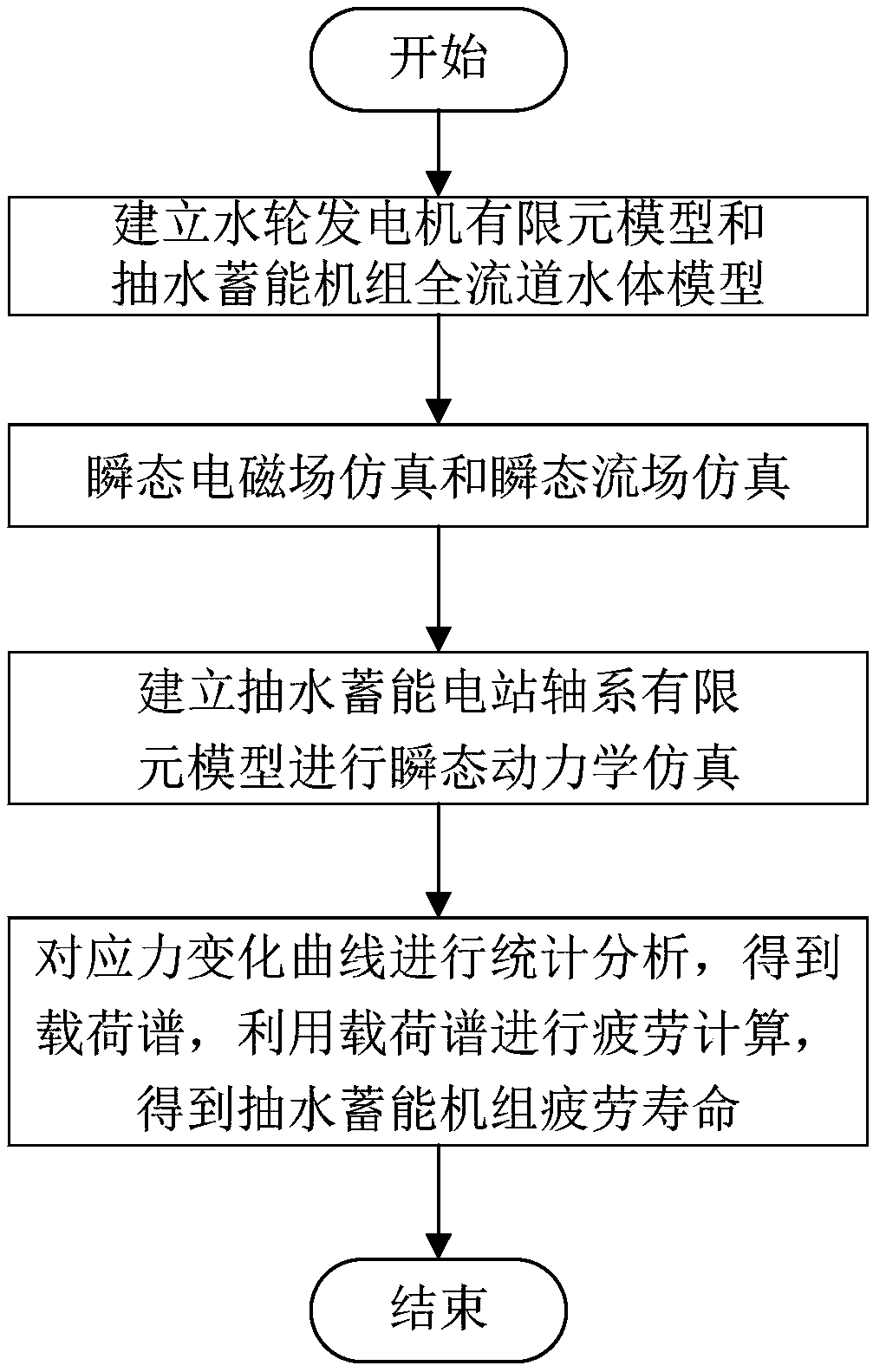
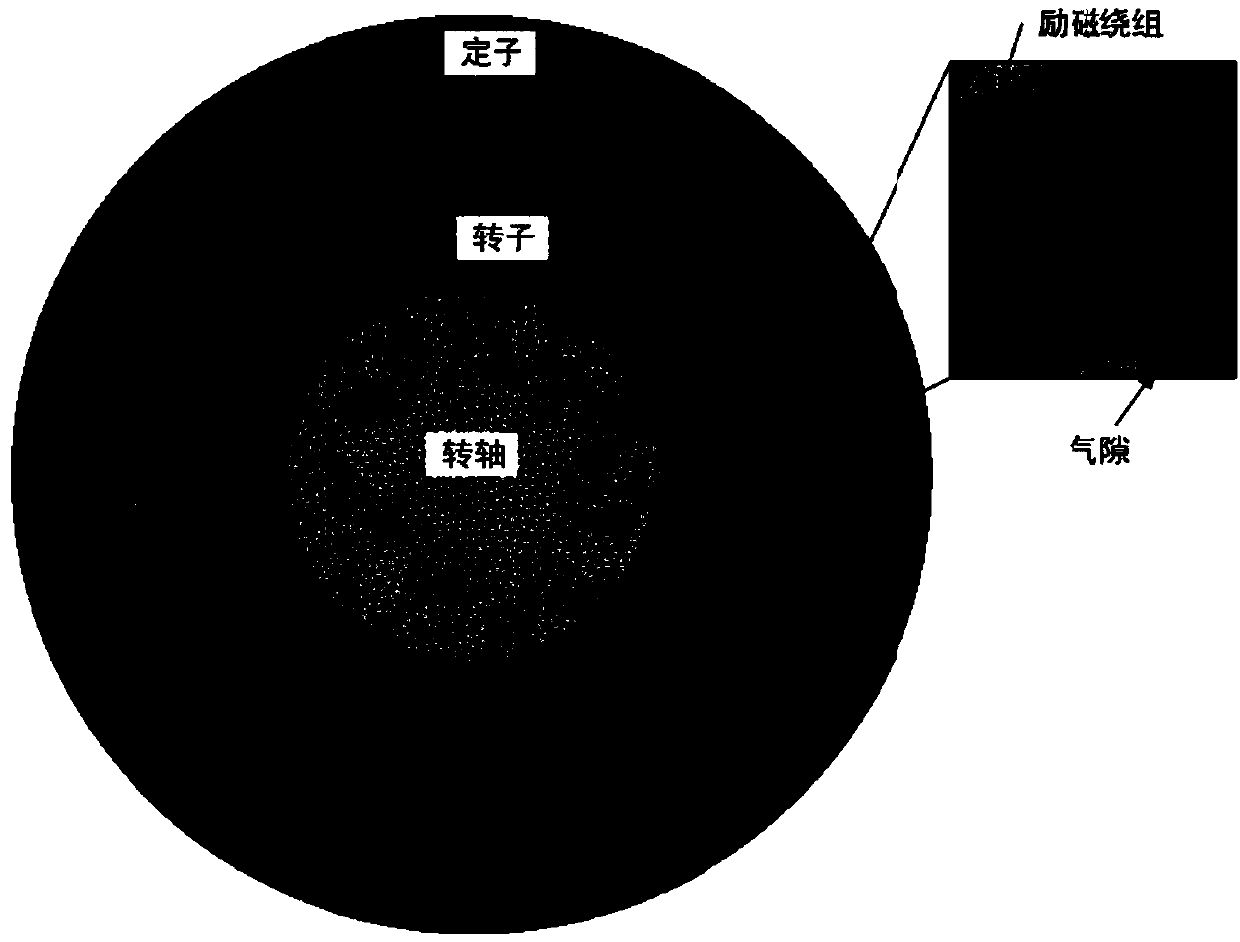
A life analysis method of pumped storage unit based on hydro-mechanical coupling model
ActiveCN109033488AHigh precisionClose to life analysis resultsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelStatistical analysis
The invention discloses a life analysis method of a pumped storage unit based on a hydro-mechanical coupling model, which includes establishing finite element model of a hydro-generator and a water body model of whole flow channel of a pumped storage unit, simulating transient electromagnetic field and transient flow field respectively, obtaining electromagnetic field distribution and electromagnetic force density between stator and rotor air gap of hydro-generator, pressure distribution and velocity distribution in flow field of whole flow channel; transforming the electromagnetic field distribution and electromagnetic force density between stator and rotor air gap, the pressure distribution and velocity distribution in the whole flow field into transient excitation. The transient excitation is applied to the finite element model of pumped storage power station shafting, and the transient dynamics simulation is carried out to obtain the stress-strain nephogram and stress-strain curveof shafting. The fatigue life of the pumped storage unit is calculated by using the load spectrum which is obtained from the statistical analysis of the stress curve. The invention obtains the life analysis result with higher precision and closer to the engineering practice.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Double-face double-magnetic-circuit transverse flux linear permanent magnet motor
InactiveCN105356721ASimple structureEasy to assembleMagnetic circuitPropulsion systemsTransverse fluxPermanent magnet motor
The invention discloses a double-face double-magnetic-circuit transverse flux linear permanent magnet motor. The motor comprises a primary part, a second part and air gaps; and the primary part is composed of a plurality of primary units having the same structure, each primary unit is composed of a magnetic conducting material and a coil winding, and the magnetic conducting material can be formed through lamination of silicon steel sheets or be composed of a composite magnetic conducting material in a forging and stamping manner. The primary units are successively arranged on an operation direction, the number of the primary units is an integer times of the motor phase number, and windings in the same-phase primary units are mutually connected in parallel or in series. The secondary part is composed of a plurality of secondary units having the same structure, each secondary unit comprises a magnetic conducting plate and two permanent magnets, the secondary units are arranged on the two sides of the primary units in a paired symmetrical manner to form a double-face structure, and two parallel magnetic circuits are formed between the primary units and the secondary units on the two sides of the primary units. The double-face double-magnetic-circuit transverse flux linear permanent magnet motor has the advantages of the short magnetic circuits, less loss and large force density, the double-face double-magnetic-circuit transverse flux linear permanent magnet motor can be taken as a motor and also can be taken as a generator, and the double-face double-magnetic-circuit transverse flux linear permanent magnet motor has a wide application prospect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method and apparatus for magnetic separation of particles
InactiveUS7258799B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic field gradientMagnetic separation
A magnetic circuit is shaped to generate an essentially uniform magnetic field parallel across the length of a container, and an essentially uniform magnetic field gradient along the length of the container as well. The dot product of the magnetic field and magnetic field gradient, known as the relative force density, is substantially uniform over the entire container, thereby causing particles to uniformly separate throughout the container.
Owner:DEXTER MAGNETIC TECH
High-speed repetitive pulse type radial flow trace gas supply valve
ActiveCN105840904AOpen quicklySmall structure sizeOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMiniaturizationProduct gas
The invention discloses a high-speed repetitive pulse type radial flow trace gas supply valve which comprises a valve body, a driving part and an executing component. The driving part and the executing component are arranged on the valve body and used for controlling switching of the work states of a radial valve opening. The driving part comprises an induction driving coil and a pulse driving circuit, the induction driving coil is located on the valve opening and arranged opposite to a reed. The executing component is the reed in a flat truncated conical shell shape. The inner edge of the reed is fixed, and the outside of the reed can be deformed in the axial direction. Due to the fact that the mass of the reed is small, the valve can be fast opened under the action of the repelling force of induction vortex. Compared with a common flat plate type structure, when identical deformation is generated on the outer edge, elastic potential energy stored by the truncated-conical-shell-shaped structure of the reed is larger, and therefore quick closing can be achieved. The induction driving coil is designed to be of a flat truncated conical spiral structure and arranged opposite to the reed, and therefore the electromagnetic force density in the reed can be effectively improved. By means of the combination manner of the driving part and the executing component, the overall structural size and mass of the valve body are greatly reduced, and miniaturization and weight reduction of the structure are facilitated.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
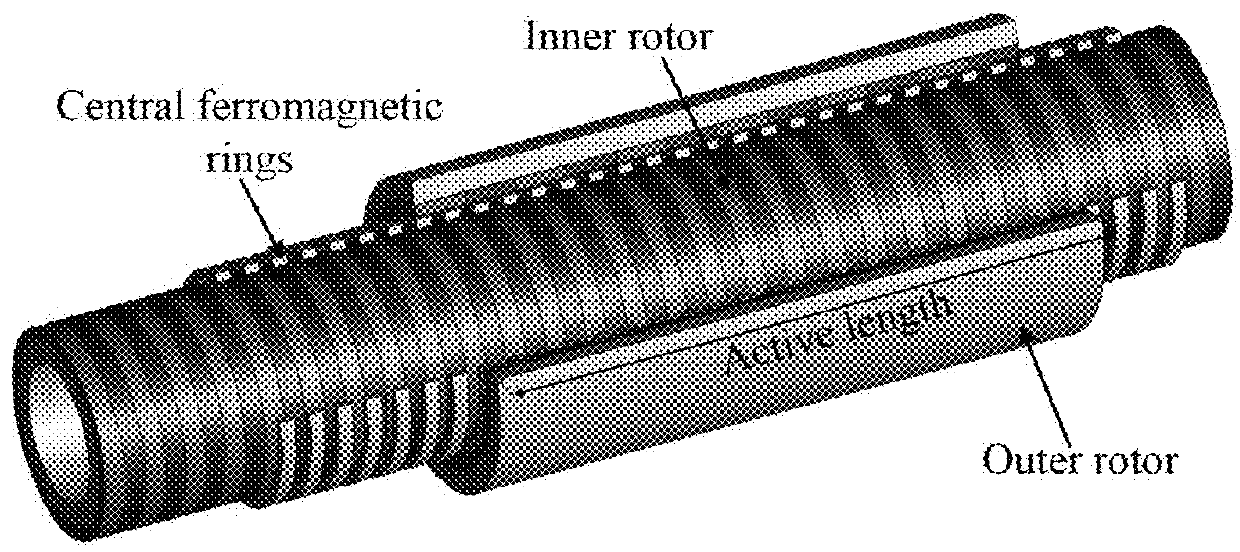
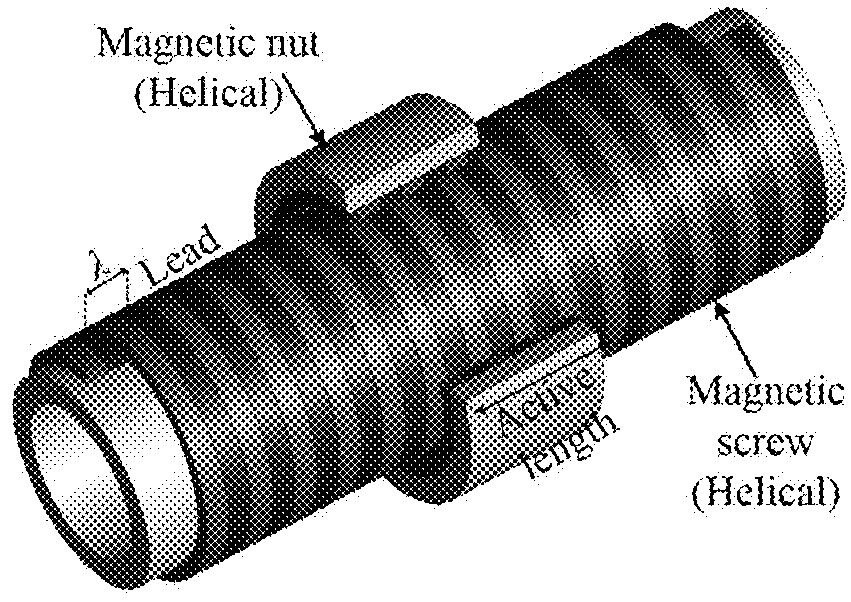
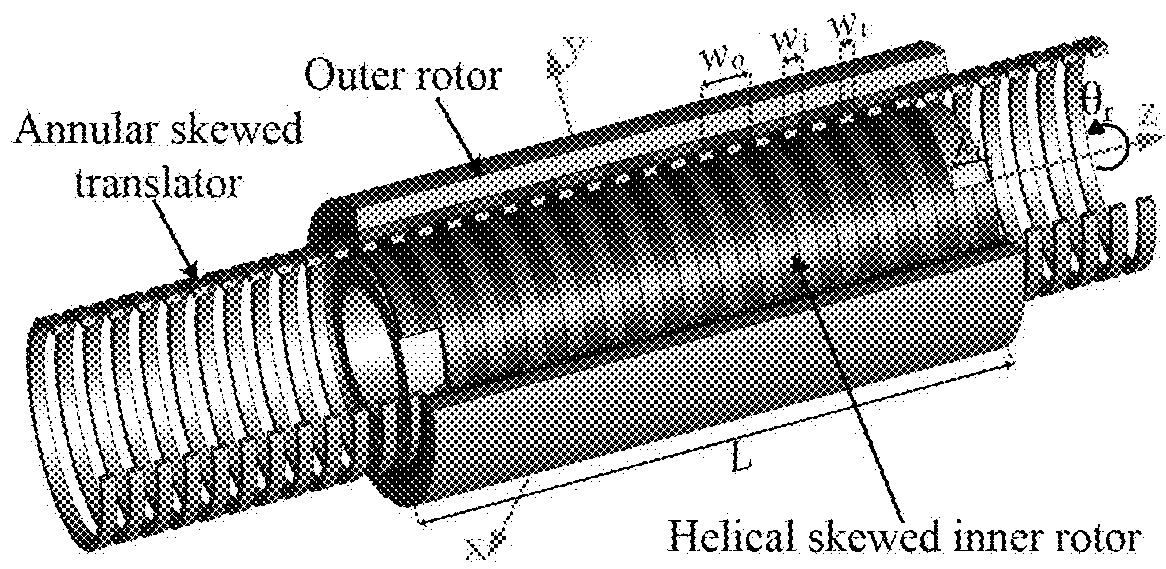
Magnetically geared lead screw
In some embodiments, the invention comprises a new type of high force density magnetically geared lead screw. It is shown that by using a helical inner and an annularly skewed ring translator a rotational motion can be converted into a magnetically geared translational motion. The advantage of the new design is that all of the magnets are continuously utilized to create the magnetically geared translational force.
Owner:BIRD JONATHAN Z +1
Composite current driving high pushing force density nine phase plane motor and driver thereof
InactiveCN101394123AReduce volumeReduce weightElectric motor controlPropulsion systemsRange of motionEngineering
A recombination current driving high thrust density nine-phrase planar motor and a driver thereof relate to a recombination current driven high thrust density nine-phrase planar motor and a driver thereof, and belongs to the motor field. Permanent magnets are distributed in a plane matrix type and an armature coil is fixedly arranged on a plane-shaped armature magnet core. The armature coil is divided into nine groups, the coils of each group are connected in series and form nine phrase armature windings, and the nine phrase armature windings are connected in a star-shape manner. When the motor works, all that is required is to connect the nine phrase armature windings to nine driving current signal output ends of the invention, and each driving current is a combined current of an X direction current and a Y direction current. The motor of the invention has the advantages of small size, light weight, simple insulation among winding phrases, large output force in unit volume, quick dynamic response, small positioning force and large rotor motion range. The invention can be applied in the motor which needs two dimensional motions and the controlling field thereof.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
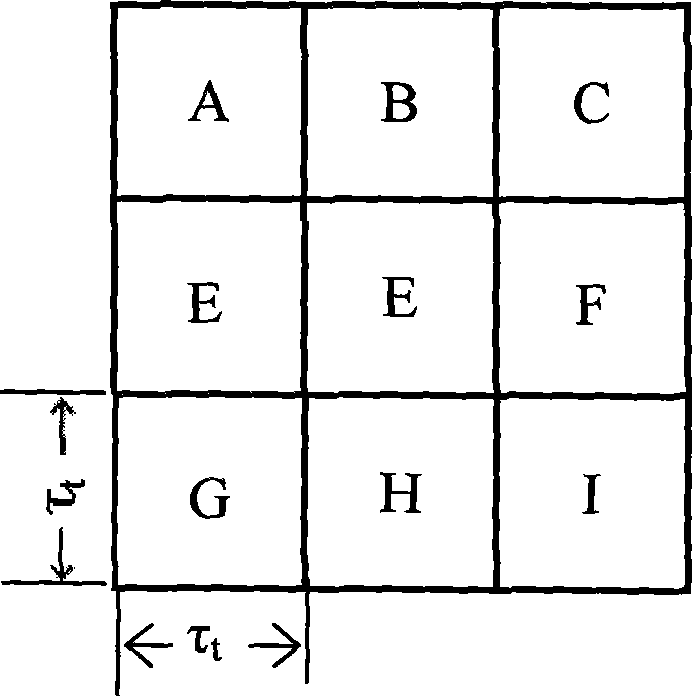
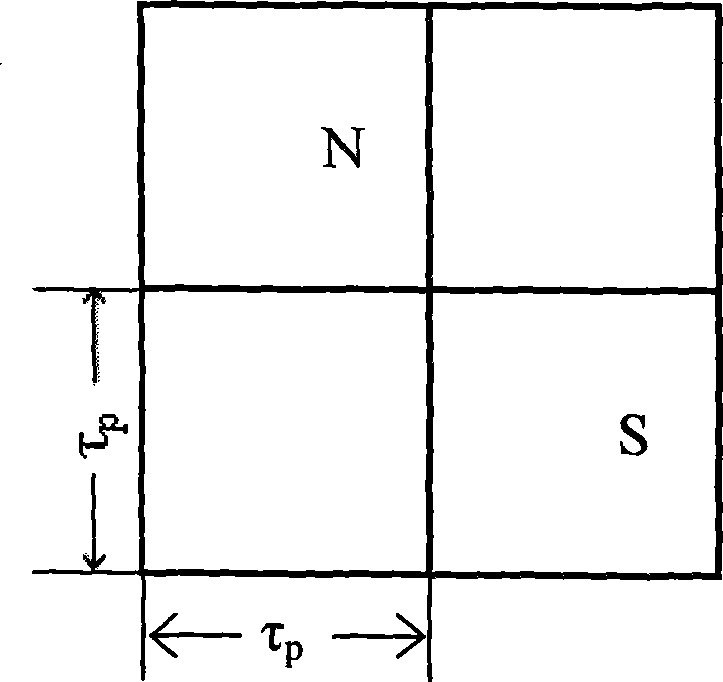
Electromagnetic actuator having improved force density and use therof for an electric razor
ActiveUS20140150265A1High strengthImprove actuator performanceMechanical energy handlingMetal working apparatusMagnetizationRelative motion
An electromagnetic actuator includes a stator unit having N poles having the width LP, and at least one coil surrounding one of the poles, wherein N≦3, and a magnetic portion, which is movable, relative to the stator unit, in a direction of relative movement and over a course of travel C, and including N+1 magnetized areas, the magnetizations of which are perpendicular to the relative movement direction and in alternate directions. The magnetic portion includes a yoke for closing off the magnetic fluxes passing through the magnetized areas, the course of travel C of the magnetic portion being less than or equal to the width LP of each pole, and the thickness of the magnetized areas perpendicular to the direction of movement being less than the course of travel C of the magnetic portion.
Owner:MOVING MAGNET TECH
A method and a device for determining a cable net structure of an annular mesh reflector
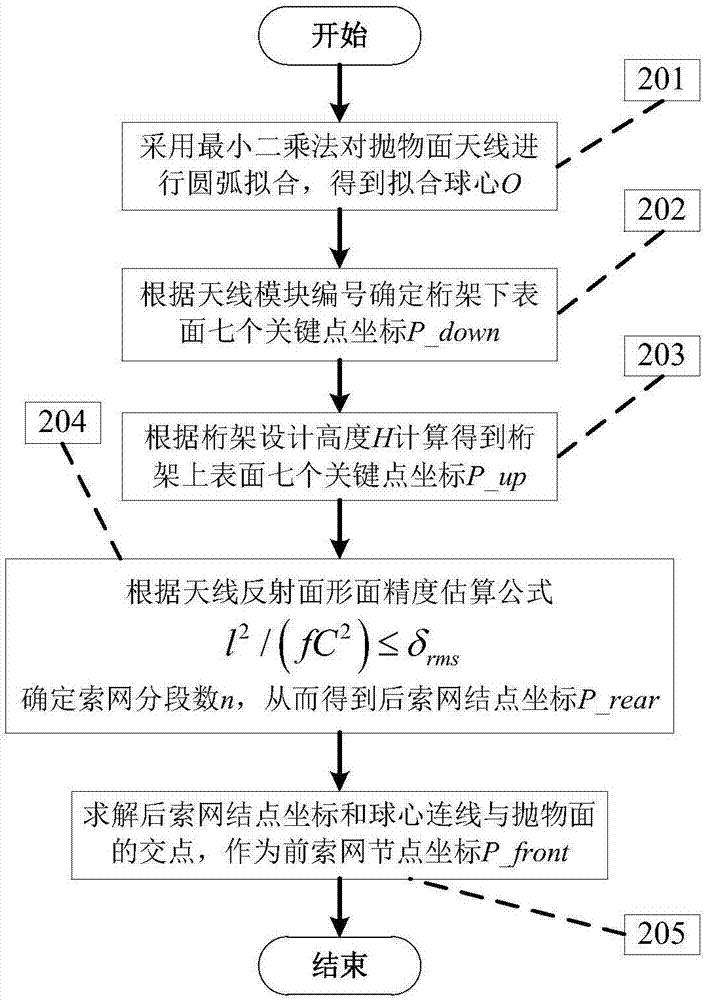
ActiveCN109101747AAvoid losing balanceGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsVertical barElectricity
The invention provides a method and a device for determining the cable net structure of an annular mesh reflector, belonging to the technical field of spacecraft structure design. The method comprises: in accordance with that structural parameter of the reflector, the structural parameters of the front tension net and the tension of each tension rope in the corresponding tension matrix being determined, according to the three-dimensional position coordinates of each first node, determining the XOY plane coordinates of each second node forming the rear tension net, determining the force densityof each second rope segment according to the force density of each first rope segment, and determining the three-dimensional position coordinates of each second node forming the rear tension surfaceaccording to the plane coordinates of each second node, the force density of each second rope segment, and the tension of each tension rope; according to the three-dimensional position coordinates ofthe first node and the three-dimensional position coordinates of the second node, the length of each tension rope being determined to determine the entire cable network structure. The invention effectively solves the possible problems of the post-tensioned net rope when the length of the truss vertical bar is low, and obtains a stable and reliable cable net structure which meets the electric performance requirements.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Low-speed high-thrust-density double-layer fractional slot winding cylindrical linear motor
InactiveCN108683319AReduce cogging forceSuppression of thrust fluctuationsPropulsion systemsWindings conductor shape/form/constructionPrimary ToothLow speed
The invention provides a low-speed high-thrust-density double-layer fractional slot winding cylindrical linear motor which belongs to the technical field of a linear motor. The low-speed high-thrust-density double-layer fractional slot winding cylindrical linear motor comprises a motor primary stage, a motor secondary stage, a primary iron core, an air gap, a primary wire duct, a primary half wireduct, primary teeth, primary edge teeth, a primary yoke, a cake-shaped winding, a permanent magnet, a magnet guiding ring, etc. A double-layer factional slot winding structure is utilized. A motor polar distance is reduced, and working frequency is effectively increased, thereby improving motor efficiency, and realizing a certain speed adjusting range of the motor. The width of an edge trough isset to one half of that of a normal primary trough, and the thickness of the primary edge trough is smaller than that of the primary tooth. Furthermore the effective length of the motor primary pole is equal with (n+1 / 2)*tau, and a remarkable inhibition effect is performed on motor thrust force fluctuation. A motor fixing force is reduced so that higher stability and higher reliability are realized in motor operation. The low-speed high-thrust-density double-layer fractional slot winding cylindrical linear motor has advantages of simple structure, relatively low cost, high efficiency, relatively large speed adjusting range, high thrust force density, high operation stability, high operation reliability, etc. The low-speed high-thrust-density double-layer fractional slot winding cylindricallinear motor is suitable for a low-speed large-thrust-force occasion.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
High-speed repetitive pulse type radial flow trace gas supply valve
ActiveCN105840904BOpen quicklySmall structure sizeOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMiniaturizationEngineering
The invention discloses a high-speed repetitive pulse type radial flow trace gas supply valve which comprises a valve body, a driving part and an executing component. The driving part and the executing component are arranged on the valve body and used for controlling switching of the work states of a radial valve opening. The driving part comprises an induction driving coil and a pulse driving circuit, the induction driving coil is located on the valve opening and arranged opposite to a reed. The executing component is the reed in a flat truncated conical shell shape. The inner edge of the reed is fixed, and the outside of the reed can be deformed in the axial direction. Due to the fact that the mass of the reed is small, the valve can be fast opened under the action of the repelling force of induction vortex. Compared with a common flat plate type structure, when identical deformation is generated on the outer edge, elastic potential energy stored by the truncated-conical-shell-shaped structure of the reed is larger, and therefore quick closing can be achieved. The induction driving coil is designed to be of a flat truncated conical spiral structure and arranged opposite to the reed, and therefore the electromagnetic force density in the reed can be effectively improved. By means of the combination manner of the driving part and the executing component, the overall structural size and mass of the valve body are greatly reduced, and miniaturization and weight reduction of the structure are facilitated.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Transverse flux reluctance type low-speed large-torque direct drive synchronous motor
InactiveCN108258866AIncrease diameter sizeIncrease the number of coresMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous motorsTransverse fluxLow speed
The force density of the transverse flux reluctance type low-speed large-torque direct drive synchronous motor is 3-5 times that of the existing radial flux motor. The motor consists of a stator and arotor iron core, a stator and a rotor base body, a phase winding and the like. The stator and the rotor iron core are manufactured by adopting silicon steel sheet punching, rotor iron core punching,cambered surface lamination and argon arc welding to form a stator and a rotor iron core. The stator base body and the rotor base body are axially divided into an m-phase segment, and the pole logarithm of each phase segment is p. The m-phase annular winding is directly wound on the channel of each phase of the stator base, and 2p stator cores are installed in each window segment, distributed circumferentially around the motor axis; 2p rotors are installed in the window hole of each phase of the rotor base, distributed in a circumferential array around the axis of the motor. Each phase rotor core is radially aligned, and each phase stator core is radially offset from each other by a 1 / m pole pitch angle. Under the same rated power, the invention realizes the multi-pole logarithmic design of the motor by reducing the thickness of stator and rotor core and increasing the number of stator cores.
Owner:王新
Electromagnetic actuator having improved force density and use thereof for an electric razor
ActiveUS9276454B2High strengthMechanical energy handlingMetal working apparatusMagnetizationMagnetic flux
An electromagnetic actuator includes a stator unit having N poles having the width LP, and at least one coil surrounding one of the poles, wherein N≦3, and a magnetic portion, which is movable, relative to the stator unit, in a direction of relative movement and over a course of travel C, and including N+1 magnetized areas, the magnetizations of which are perpendicular to the relative movement direction and in alternate directions. The magnetic portion includes a yoke for closing off the magnetic fluxes passing through the magnetized areas, the course of travel C of the magnetic portion being less than or equal to the width LP of each pole, and the thickness of the magnetized areas perpendicular to the direction of movement being less than the course of travel C of the magnetic portion.
Owner:MOVING MAGNET TECH
A Mechatronic Spaceborne Mesh Antenna Shaped Beam Design Method Based on Electromechanical Integration
InactiveCN104794262BImproves tension uniformityRealize electromechanical integration designSpecial data processing applicationsAntenna designElectricity
The invention discloses an electromechanical-integration-based shaped beam design method for a satellite-borne mesh antenna. In the method, firstly, an electromechanical-integration-based shaped design optimization model for the mesh antenna is built, the force density of a cable net serves as the design variable of the optimization model directly, and under the condition that the cable net is in a tensioned and balanced state without loose cables, the method aims to achieve the targets of enabling the electrical performance of a far field to meet the shaping requirement as far as possible and making the tension of the cable net uniform as far as possible; then, iterative solving is performed on the optimization model till the optimal comprehensive target of the electrical performance and the tension uniformity is achieved, and shaped beam design of the mesh antenna is completed.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com