Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
320 results about "Planar motor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
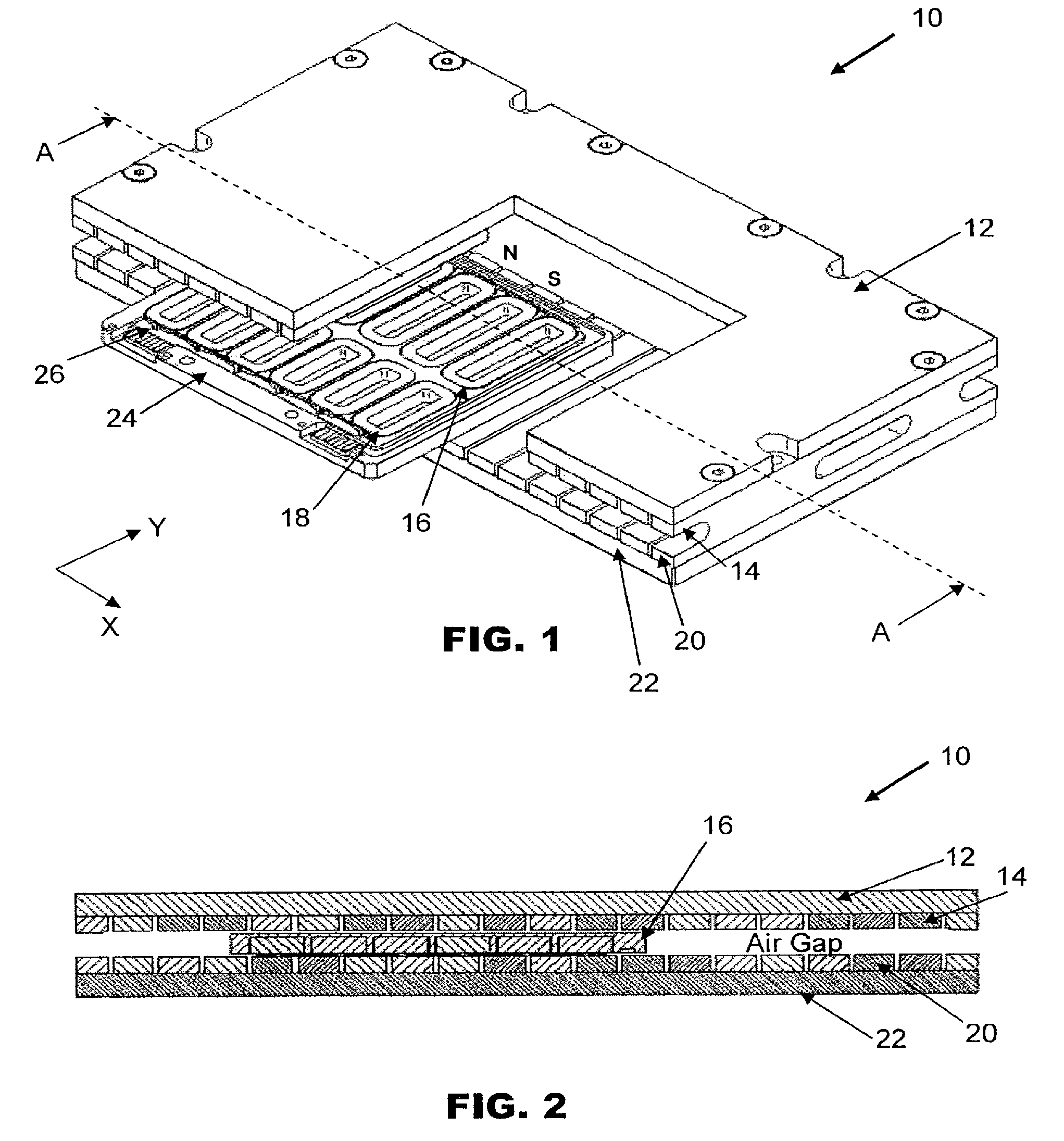
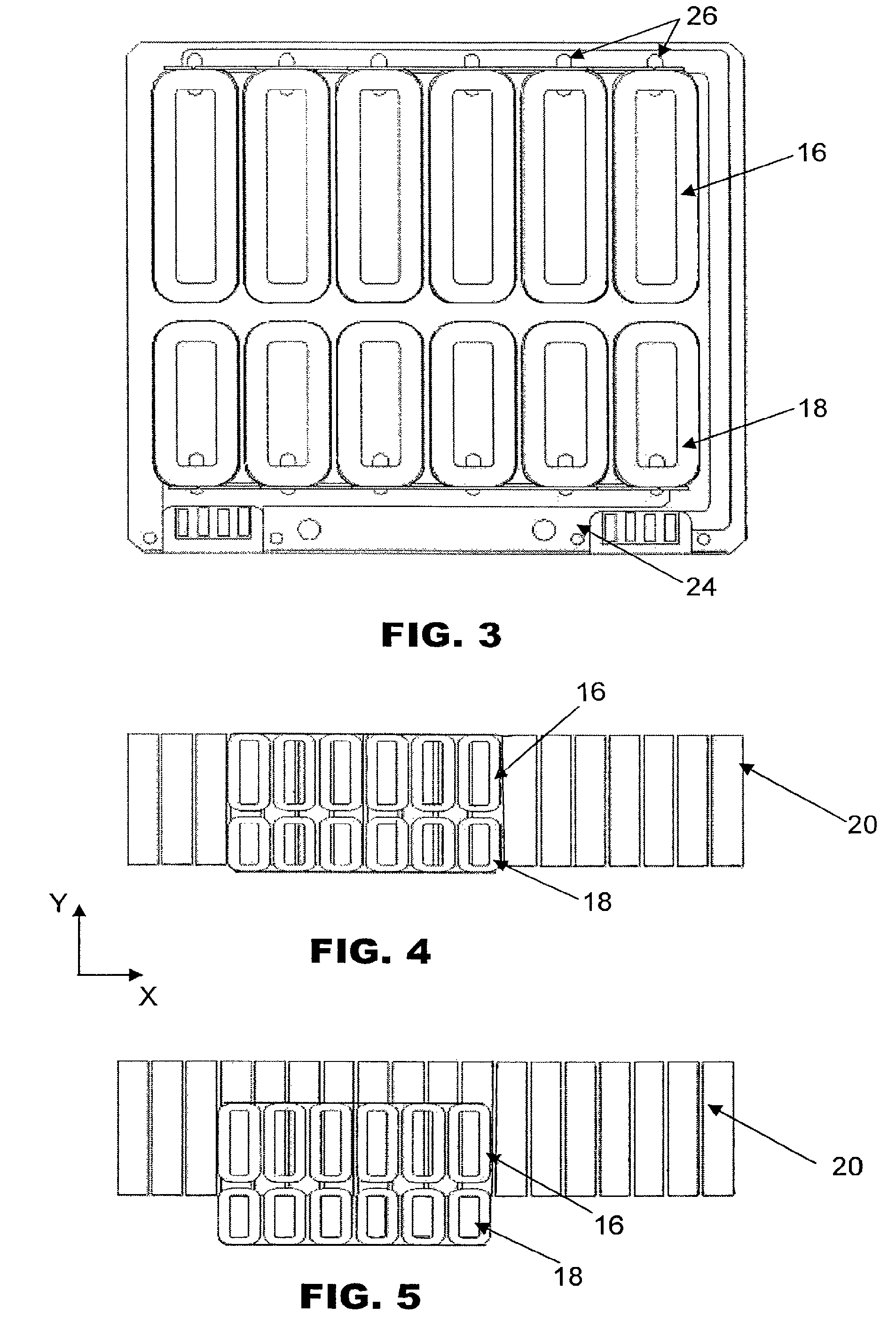
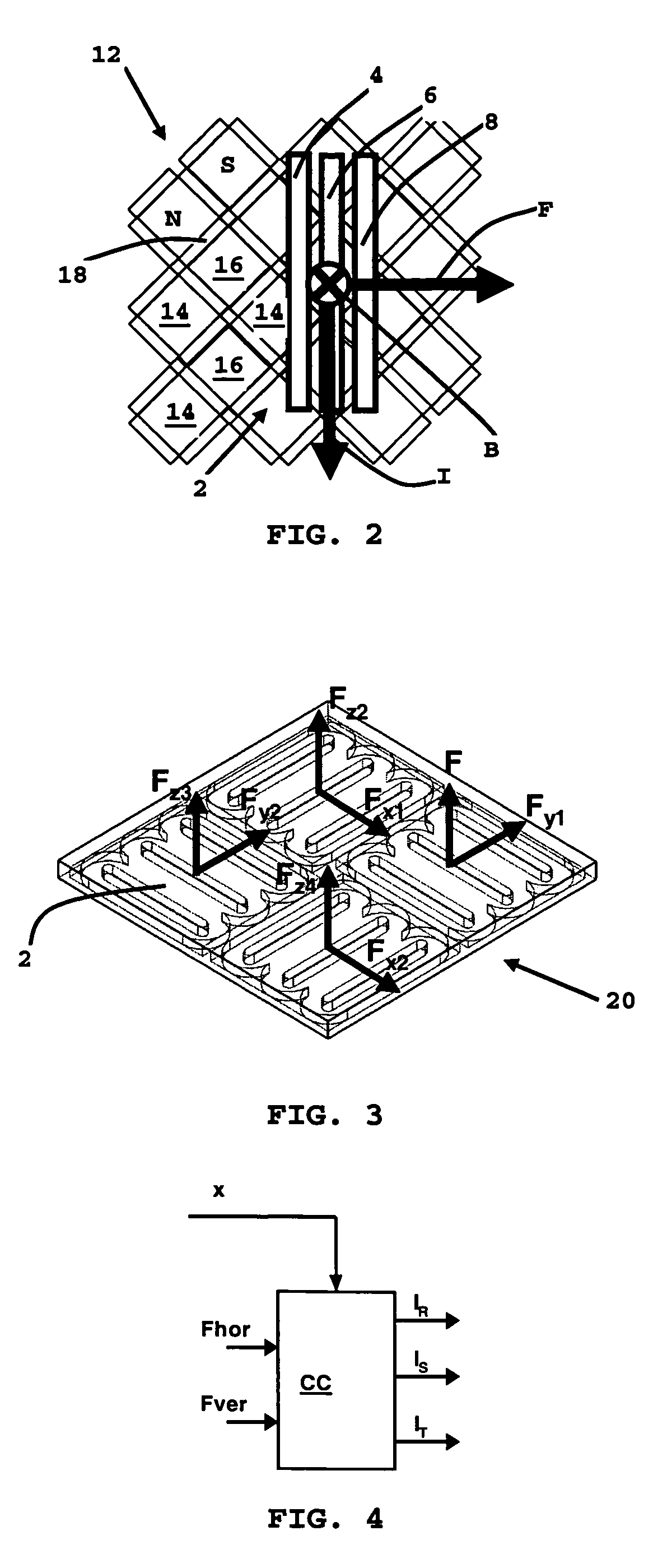
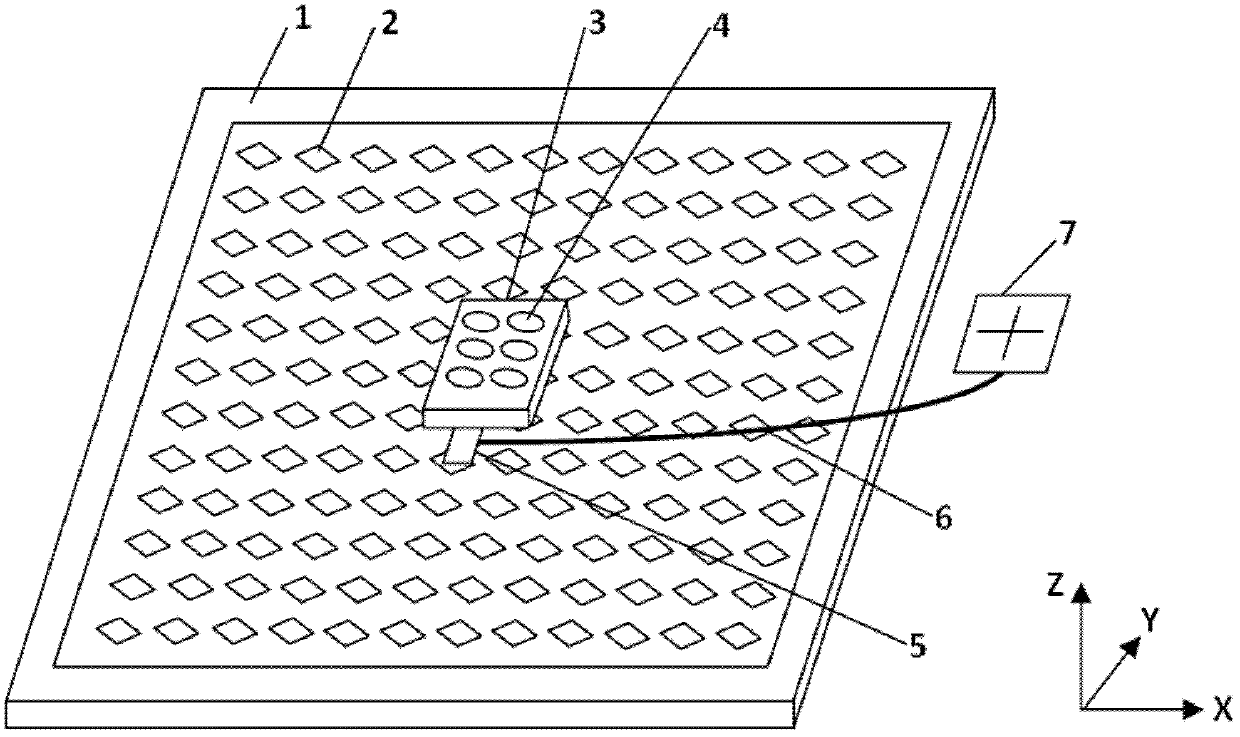
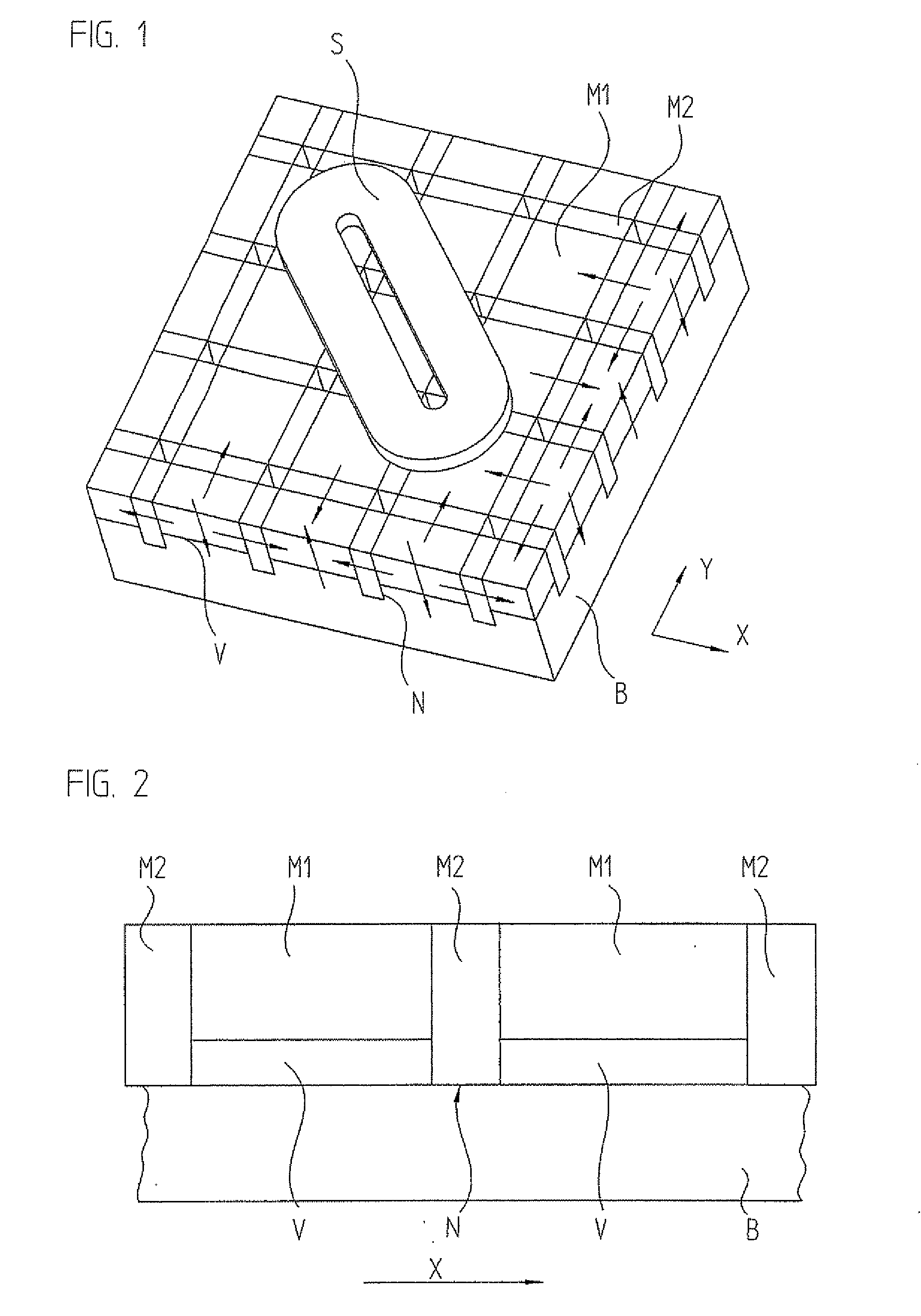
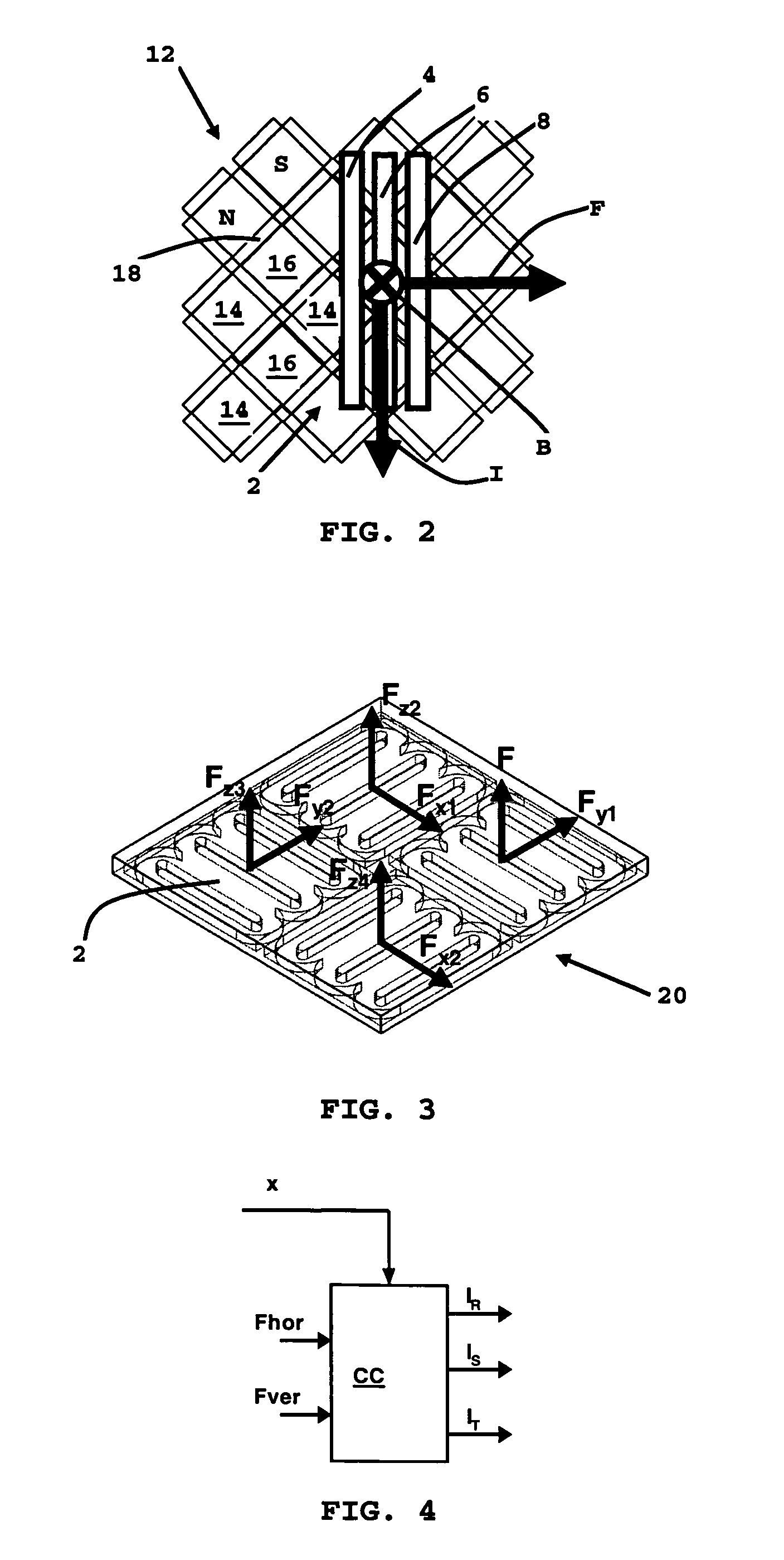
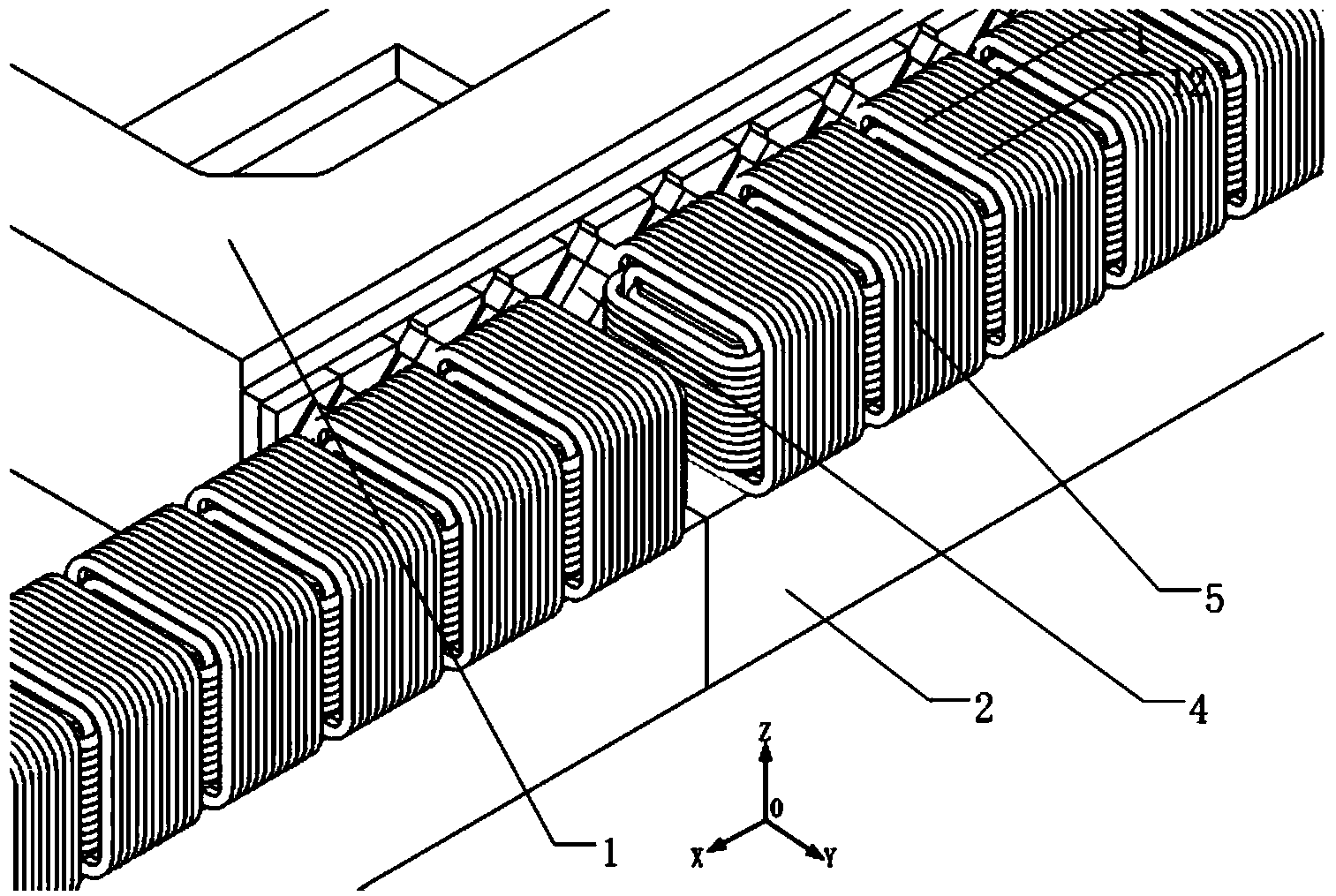
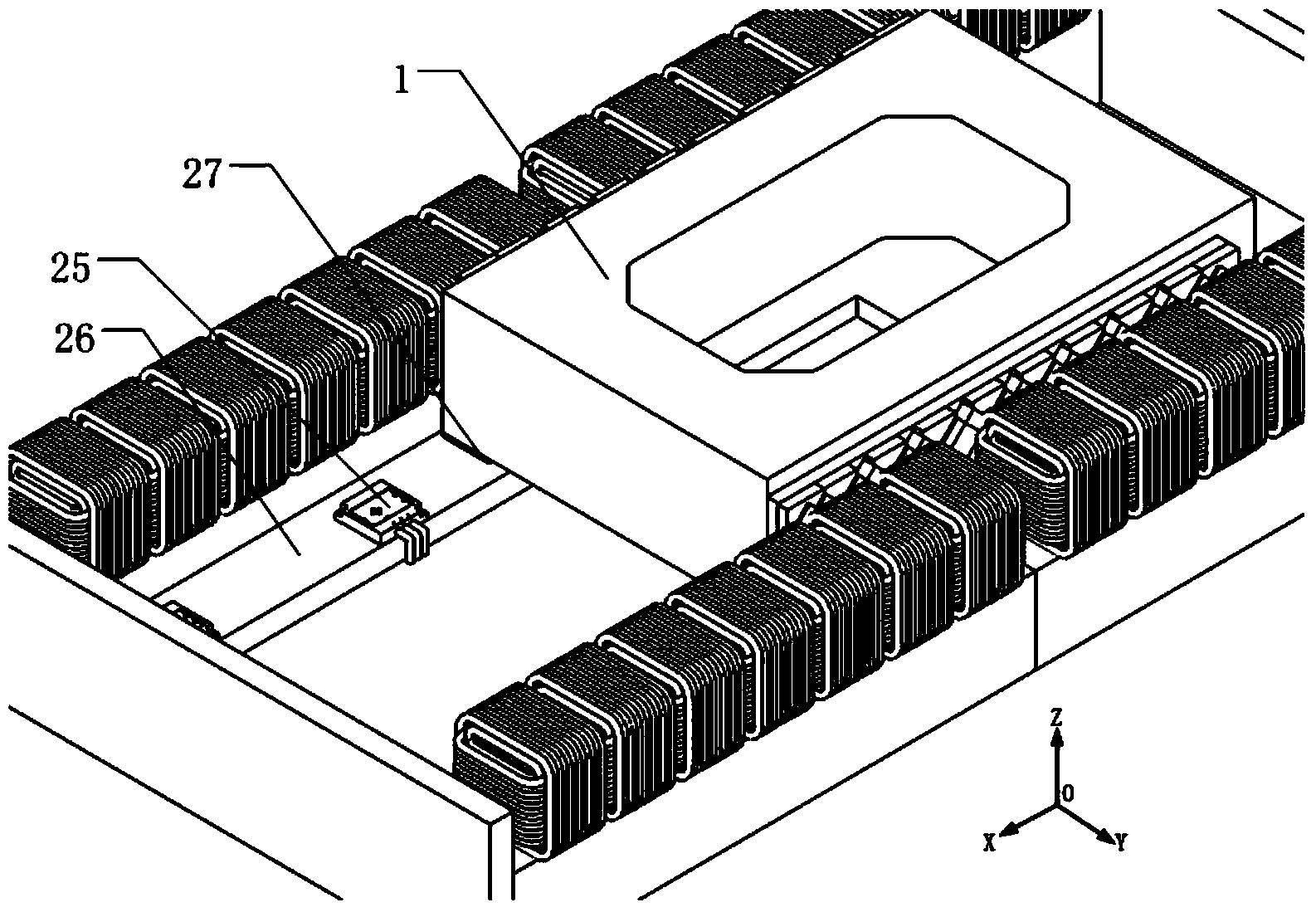
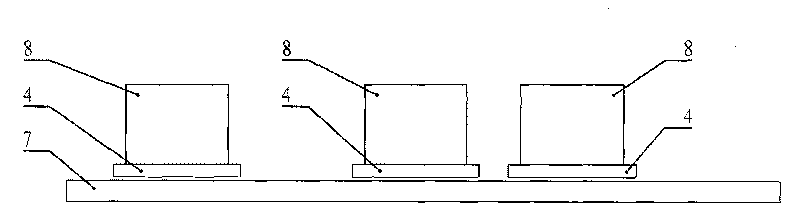
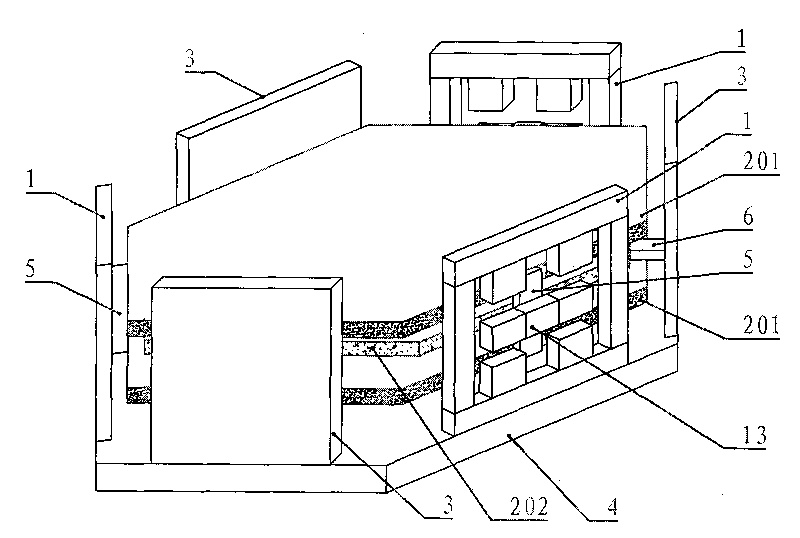
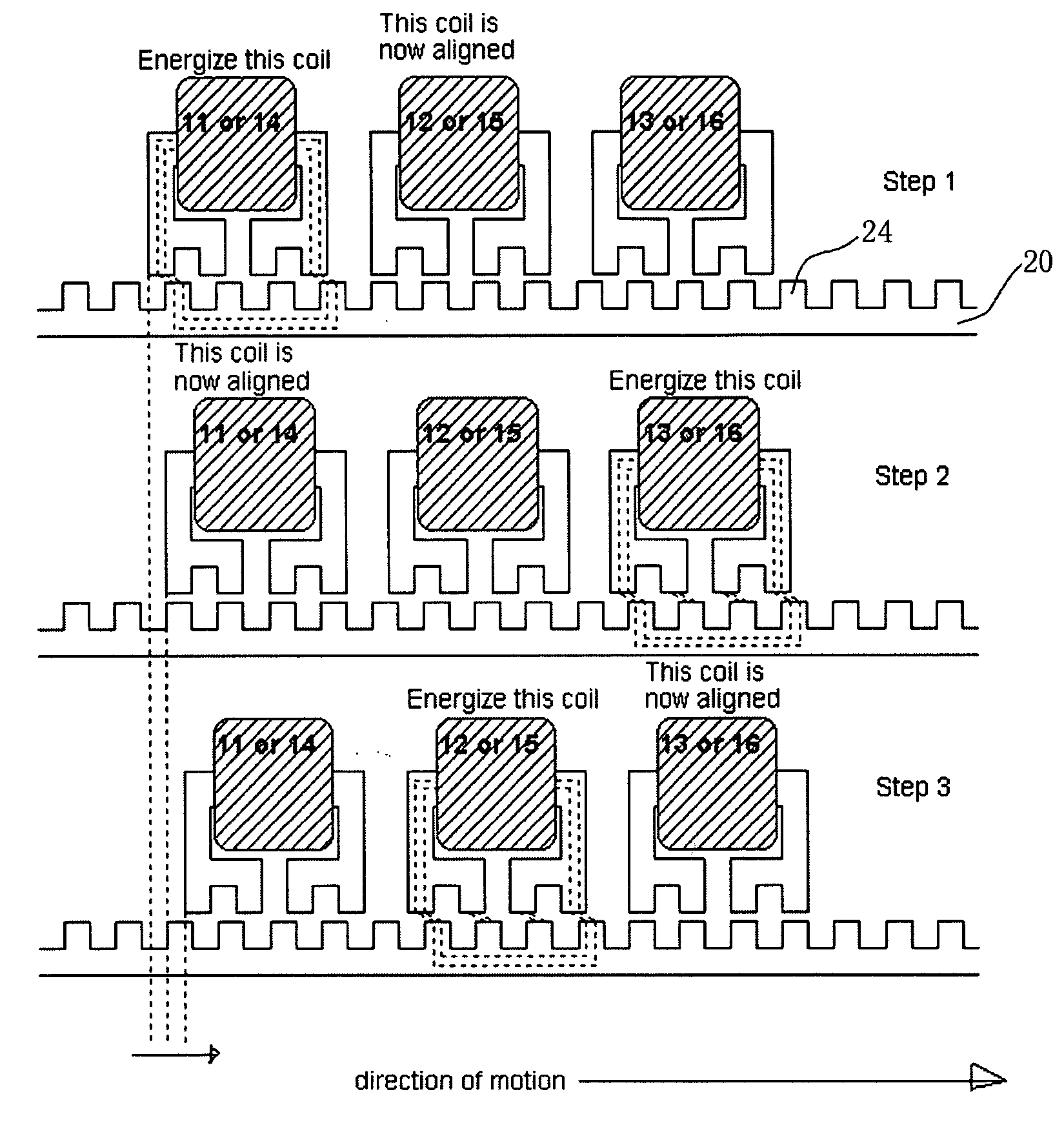
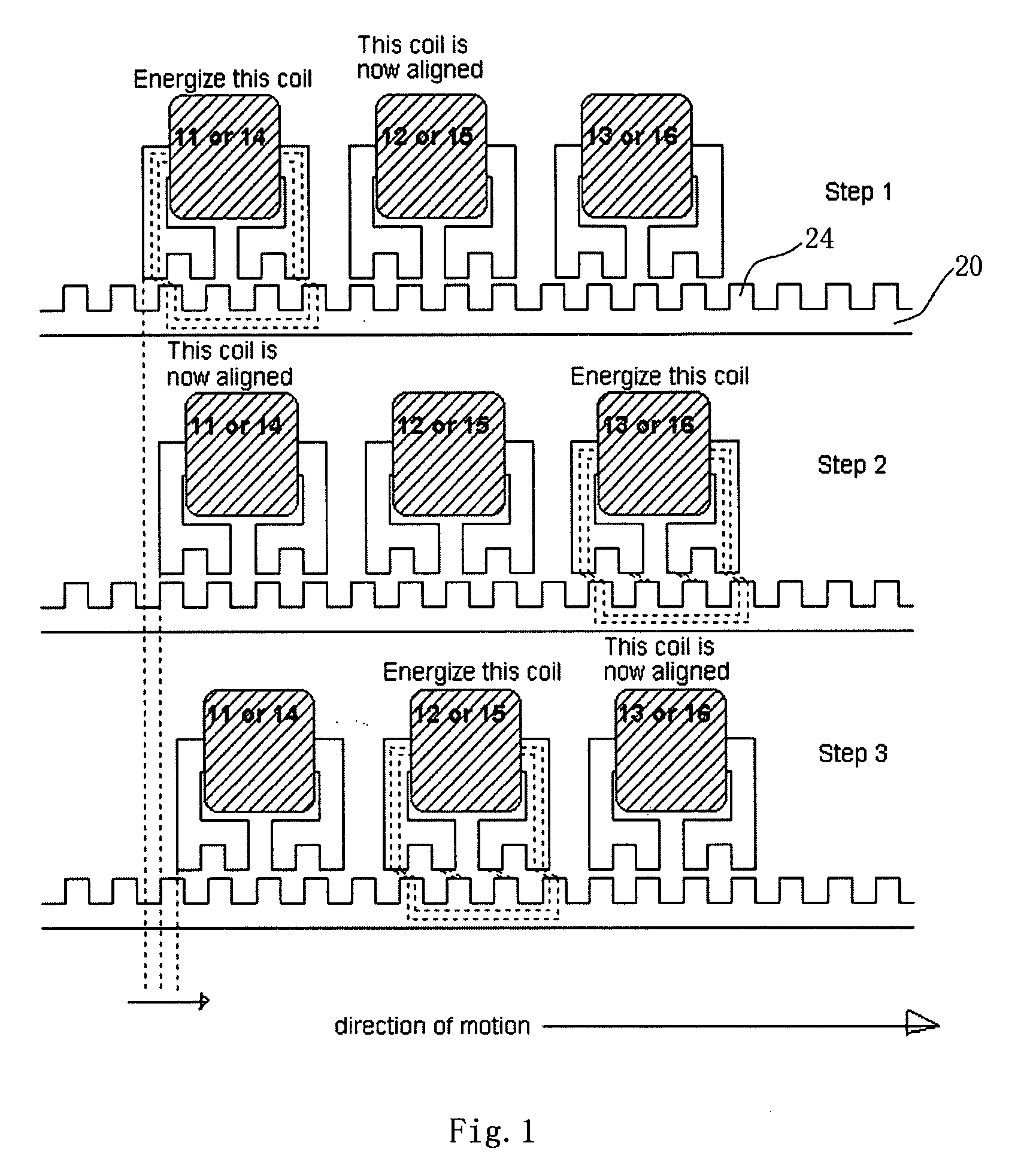
A Sawyer motor or planar motor is a type of linear electric motor with a forcer capable of moving in two dimensions, riding on a stator which is a large flat—or nearly flat—plate. Sawyer motors have been used in positioning stages and pen plotters.
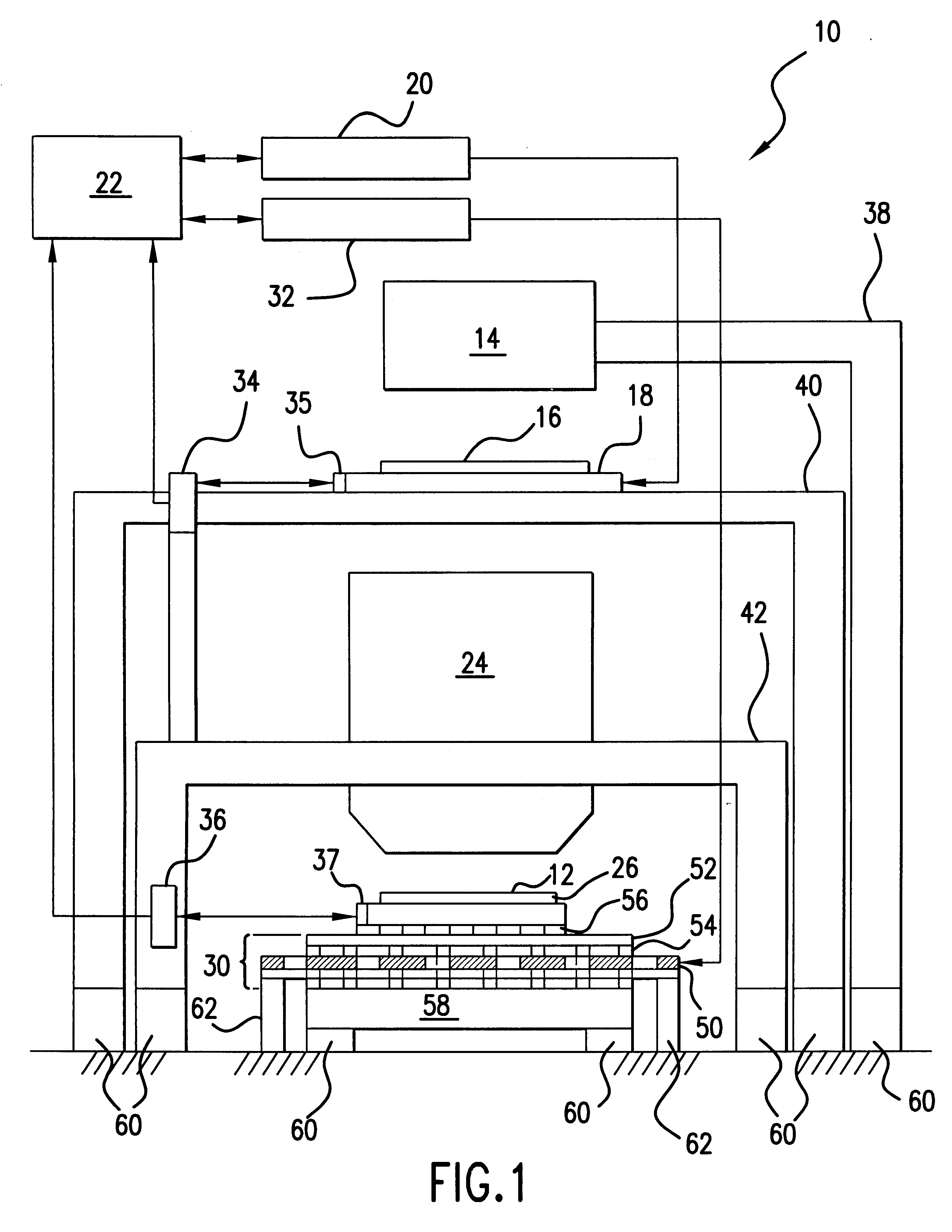
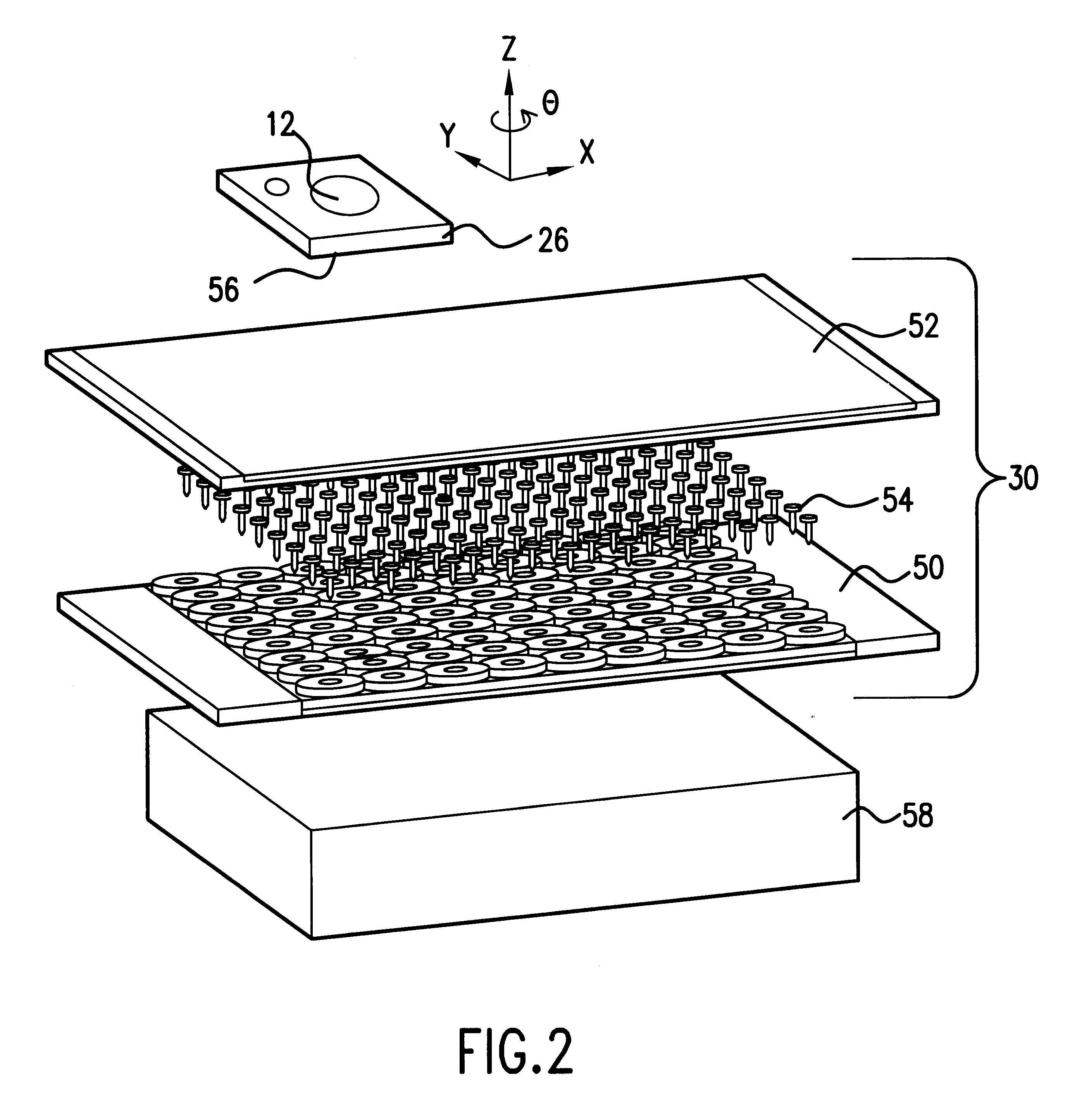
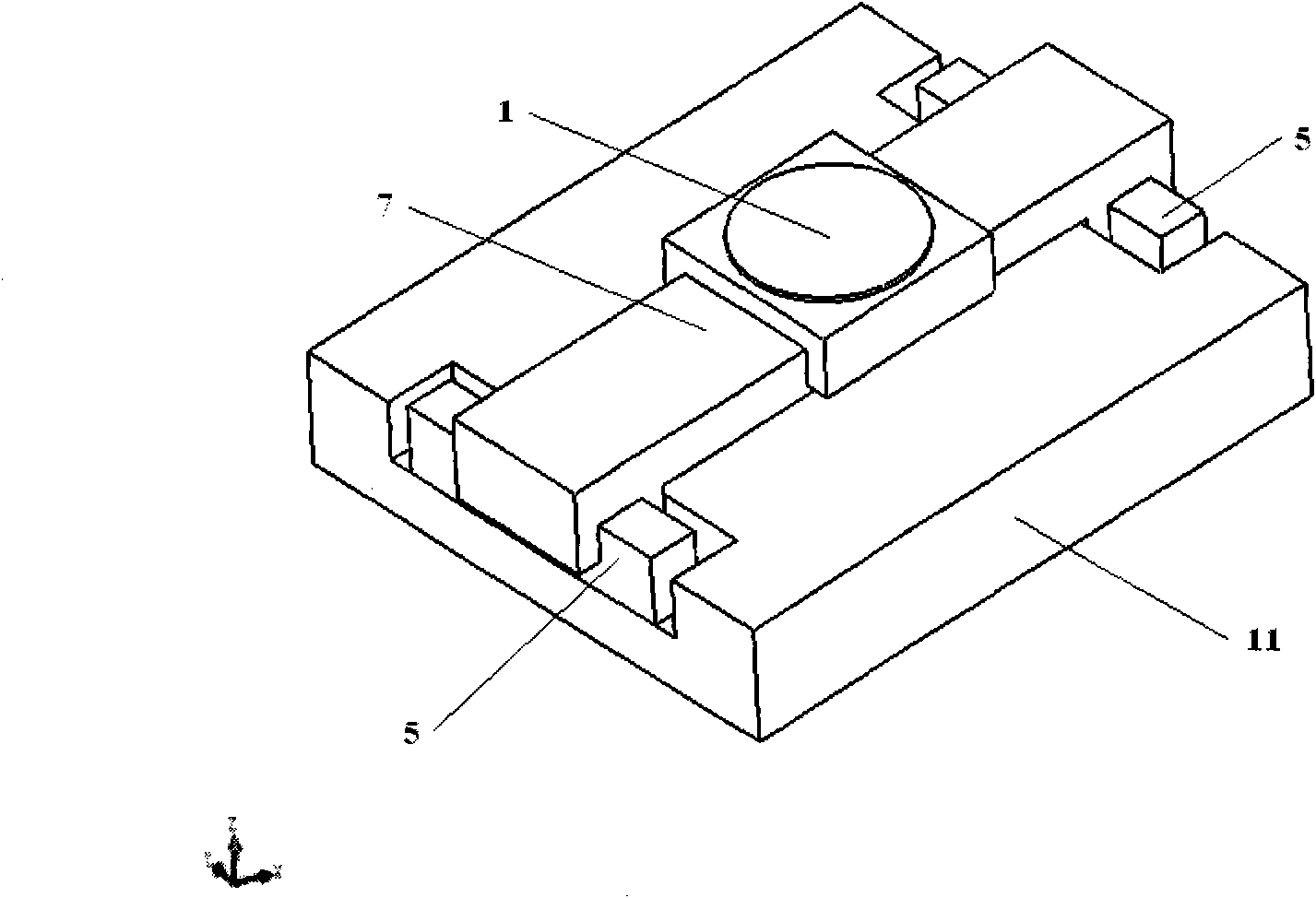
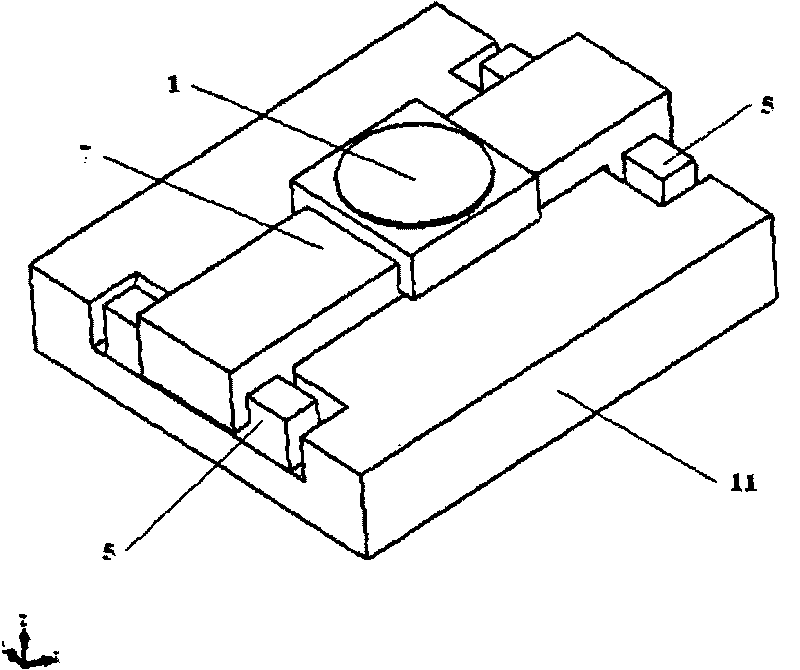
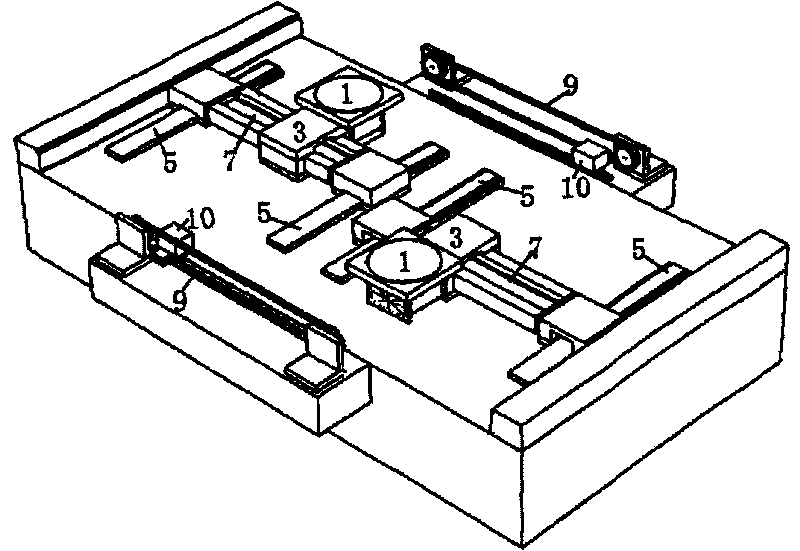
Stage device
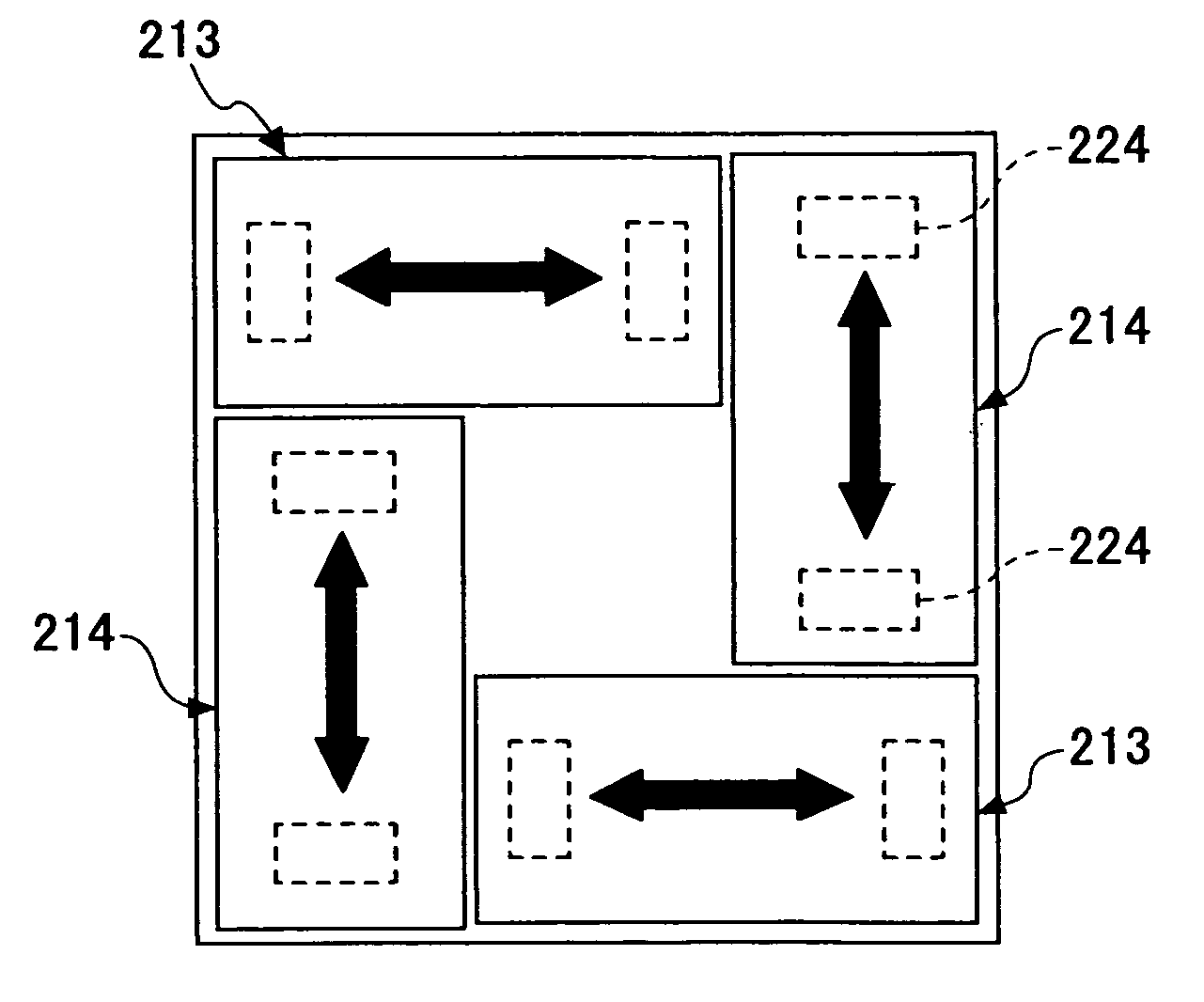
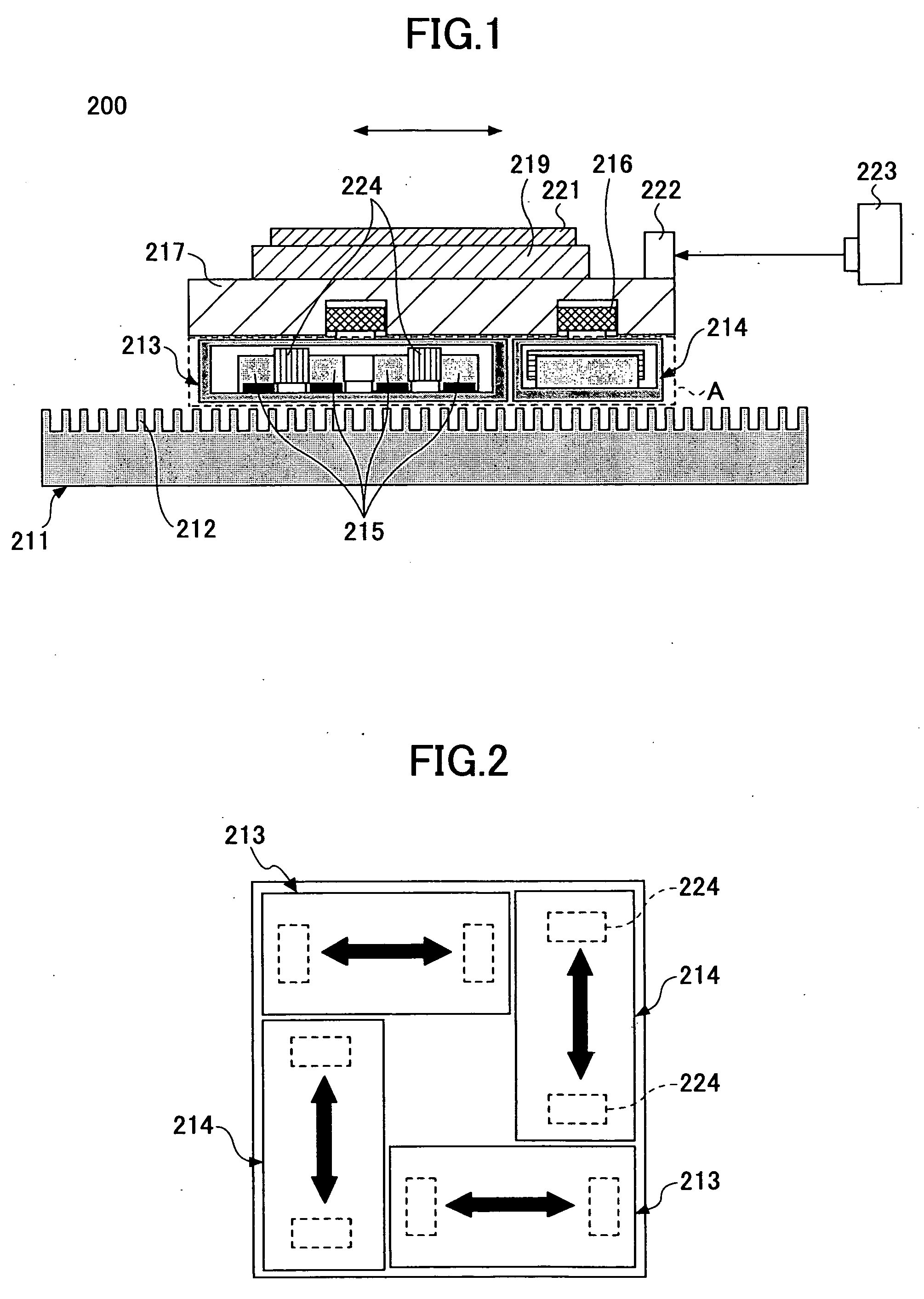
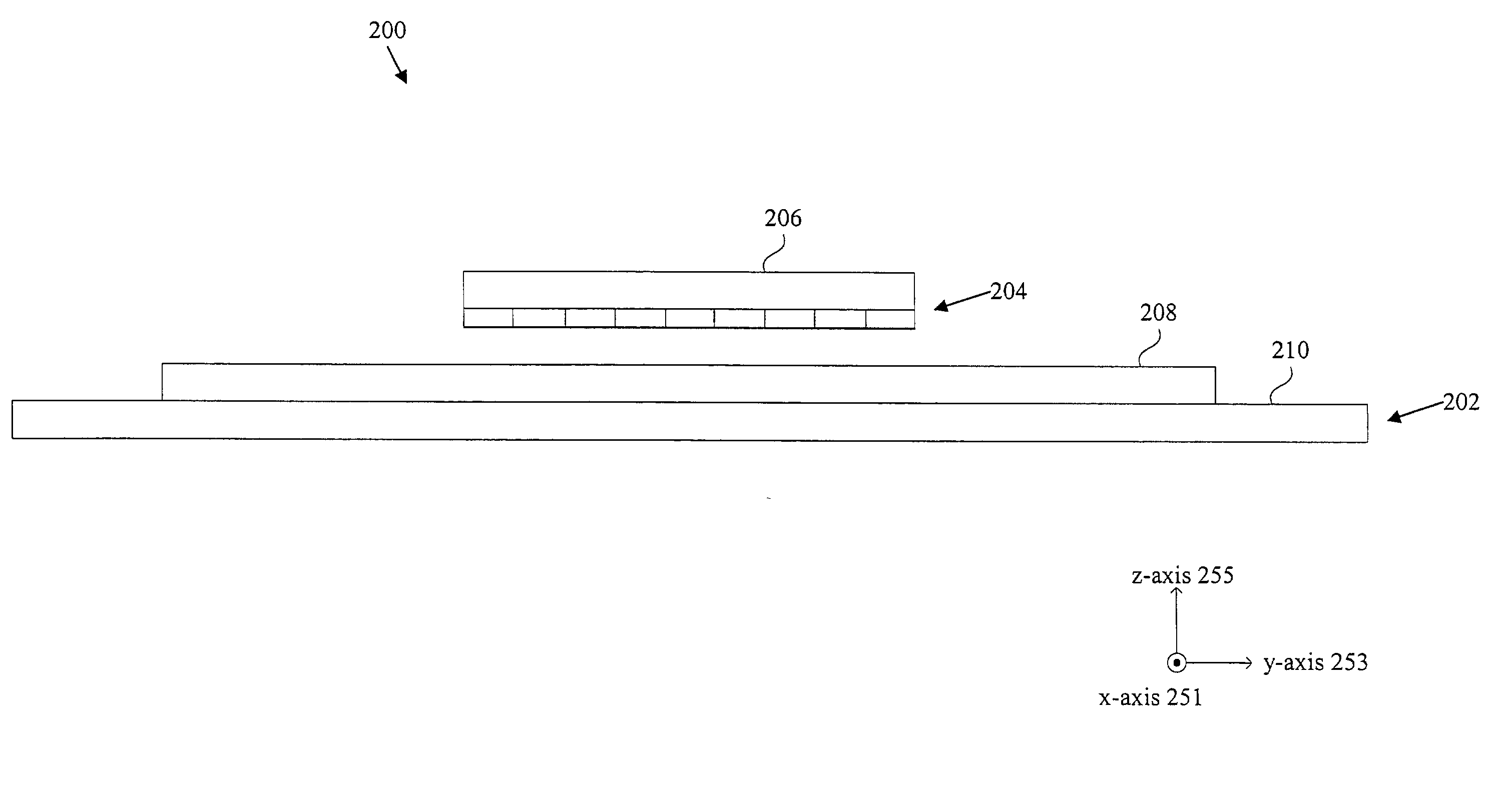
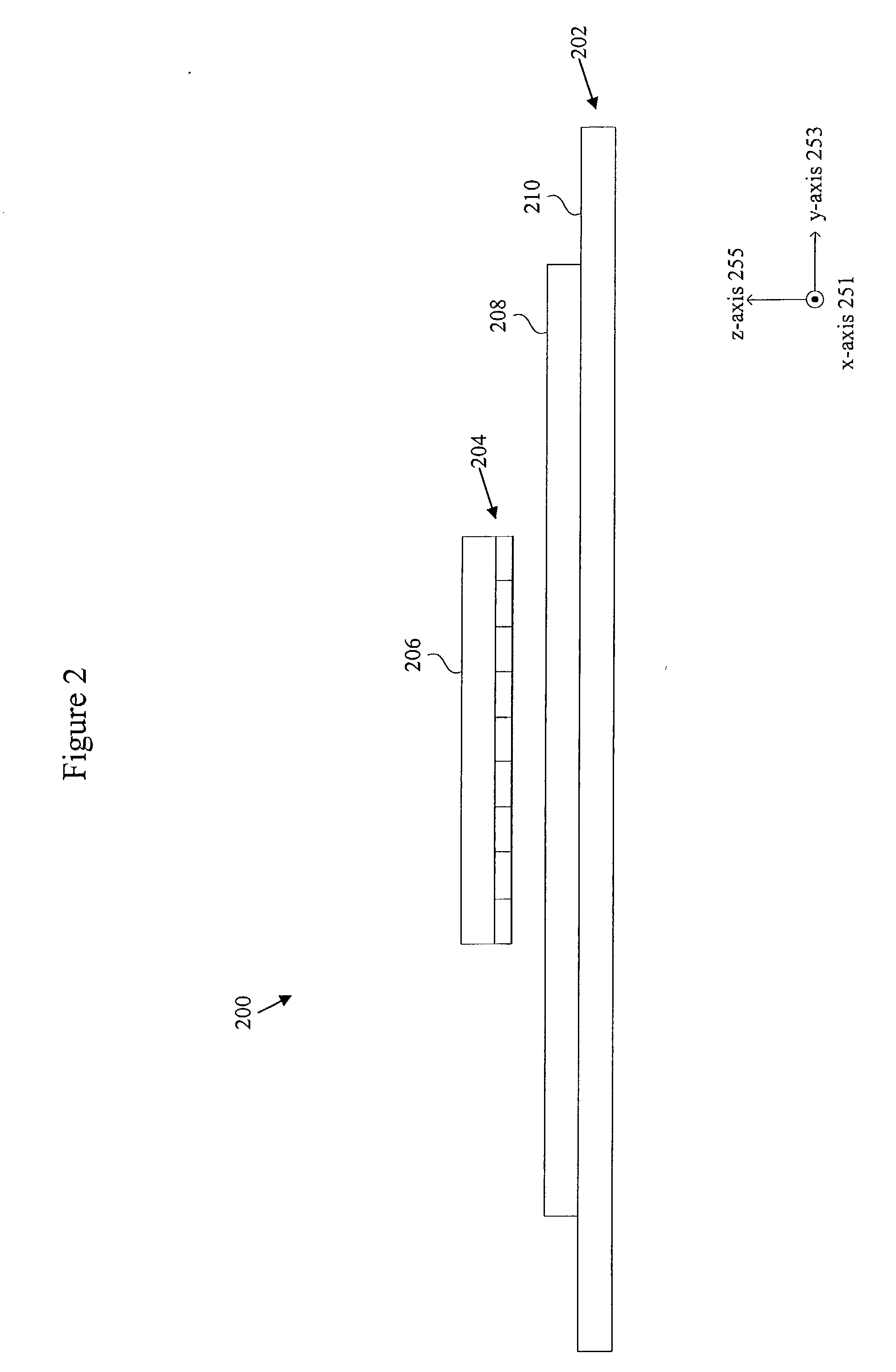
InactiveUS20070035267A1Improve accuracyReduce weightPrecision positioning equipmentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingScale unitPlanar motor
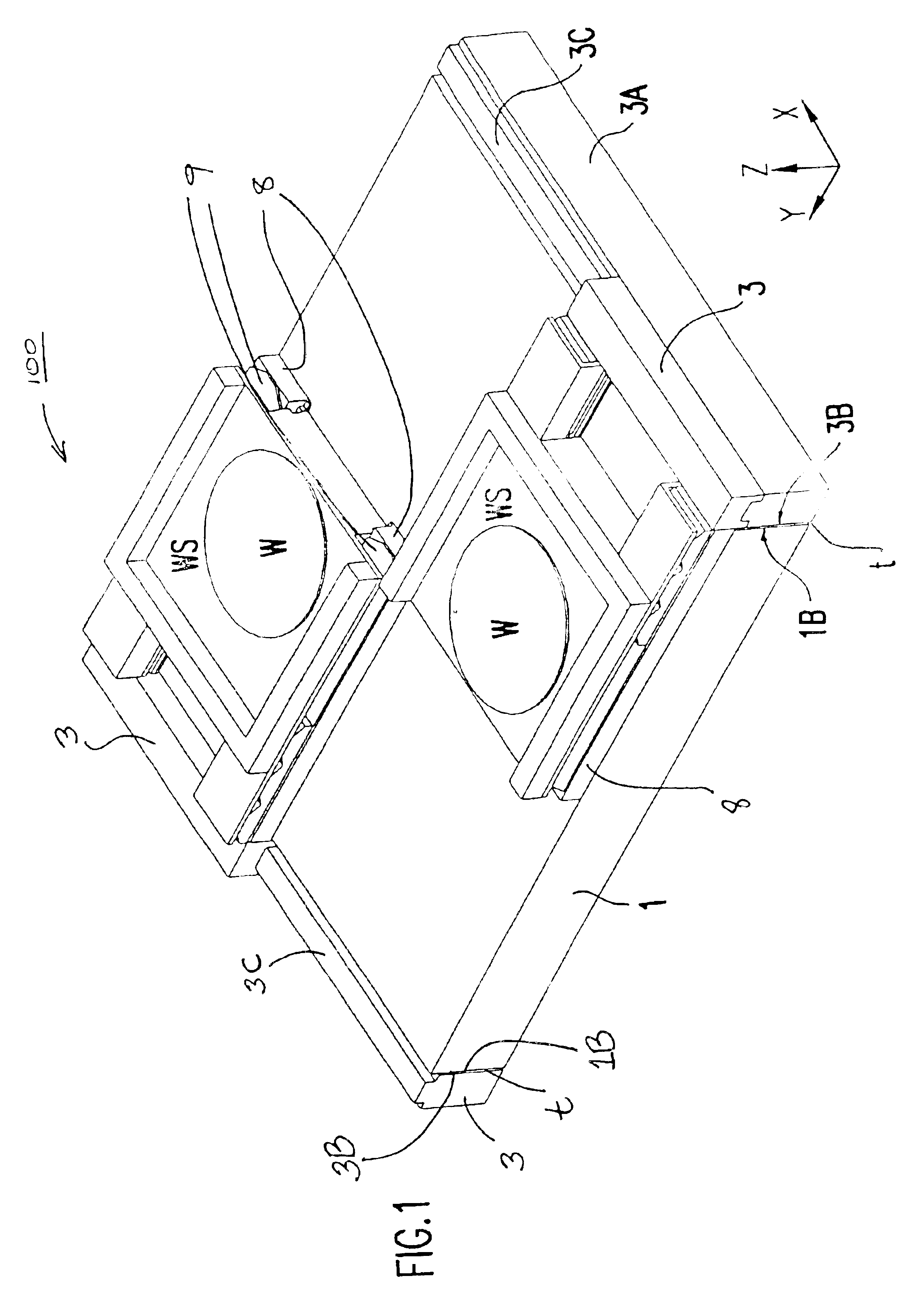
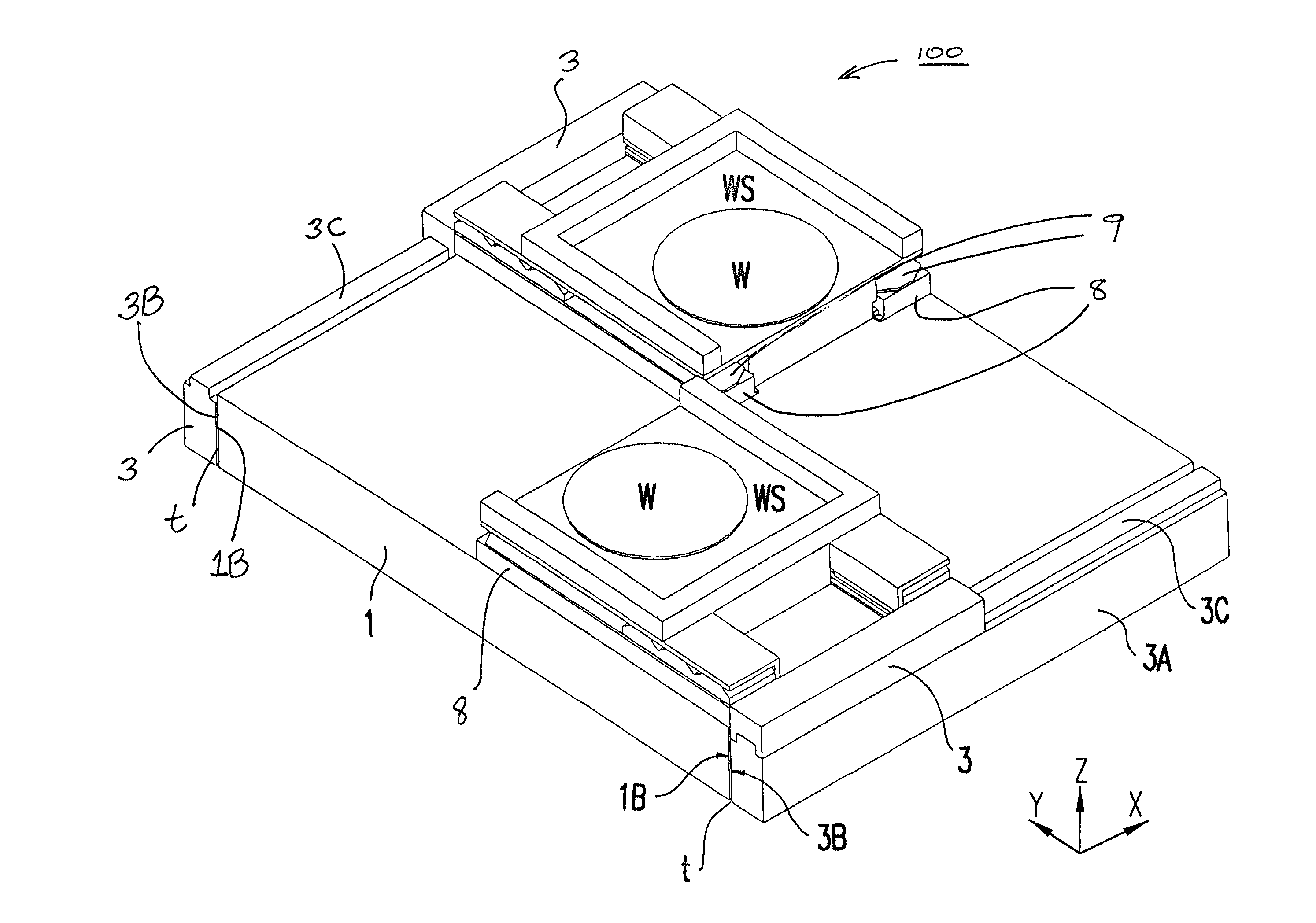
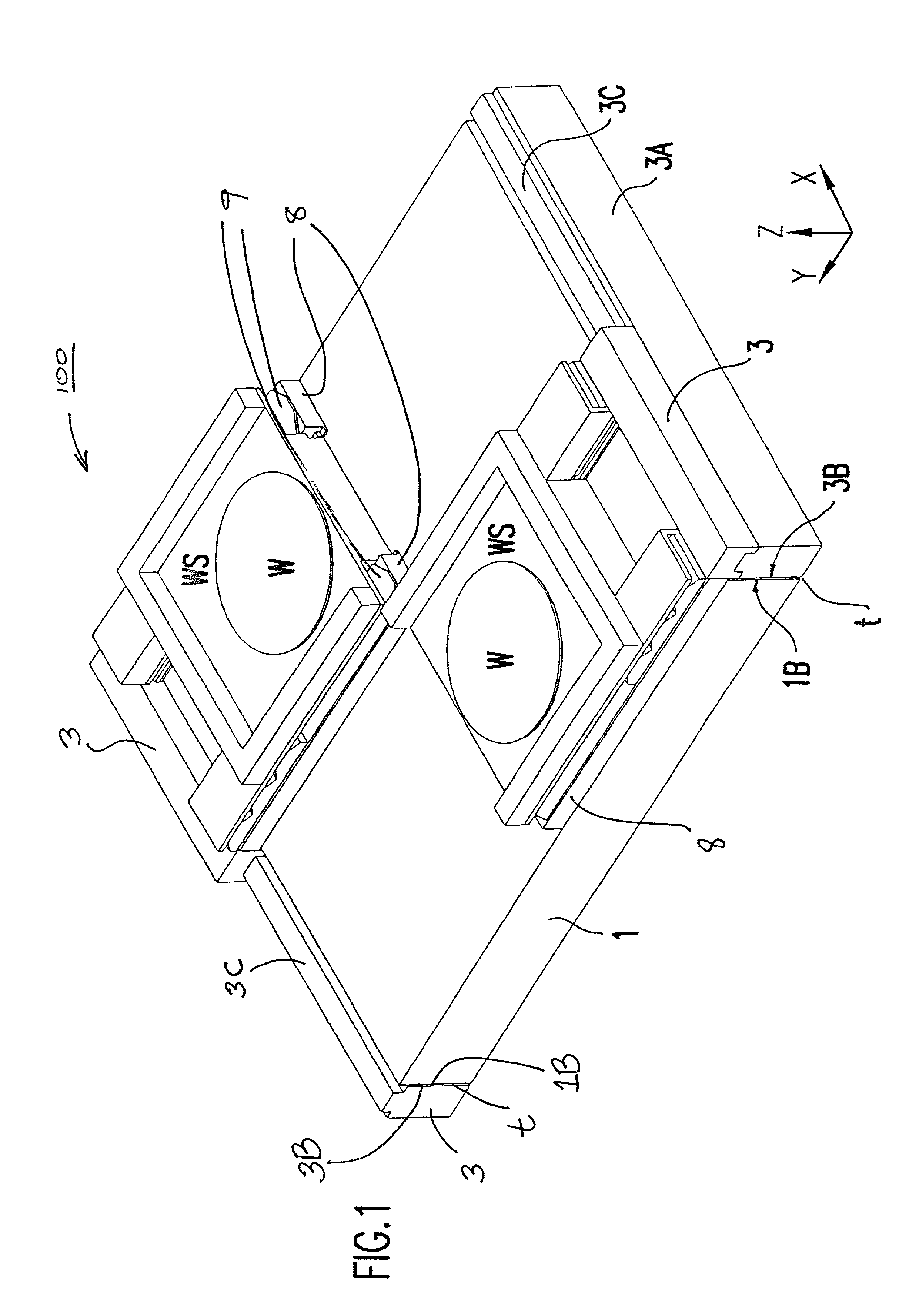
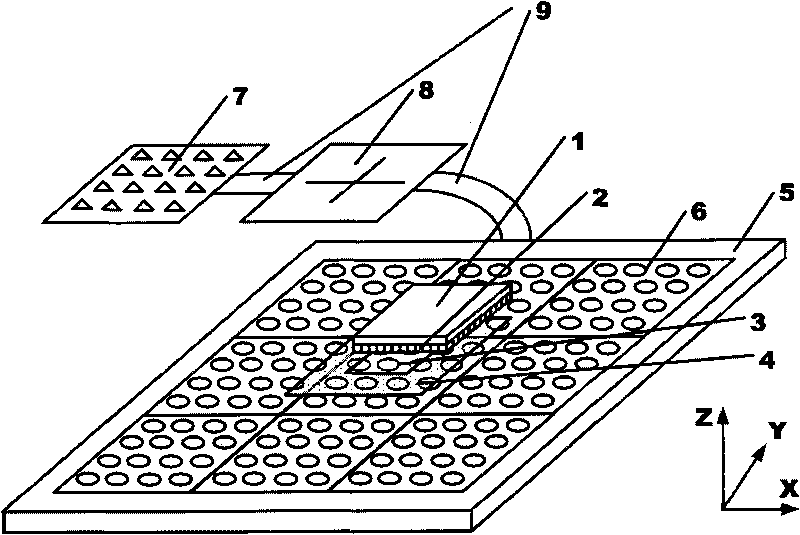
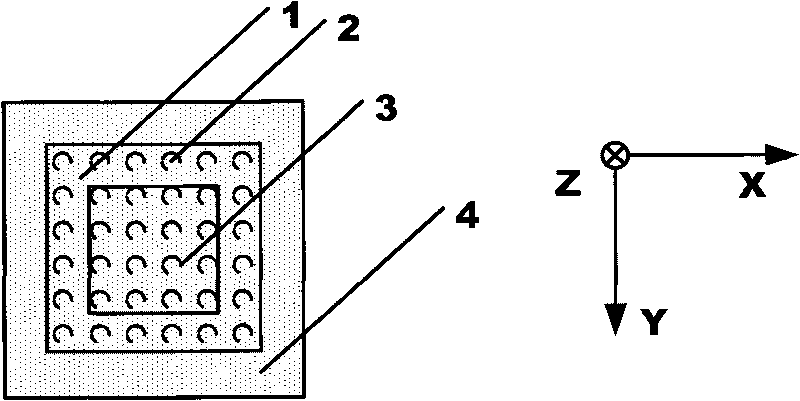
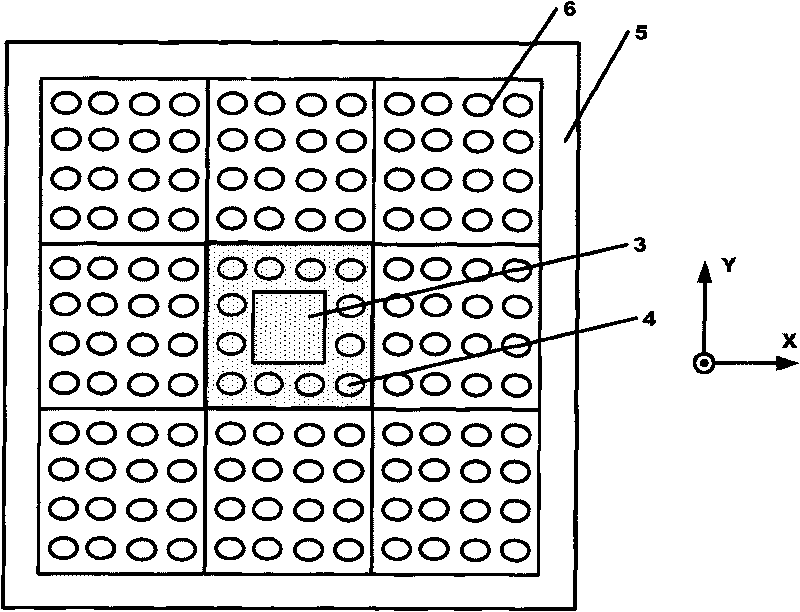
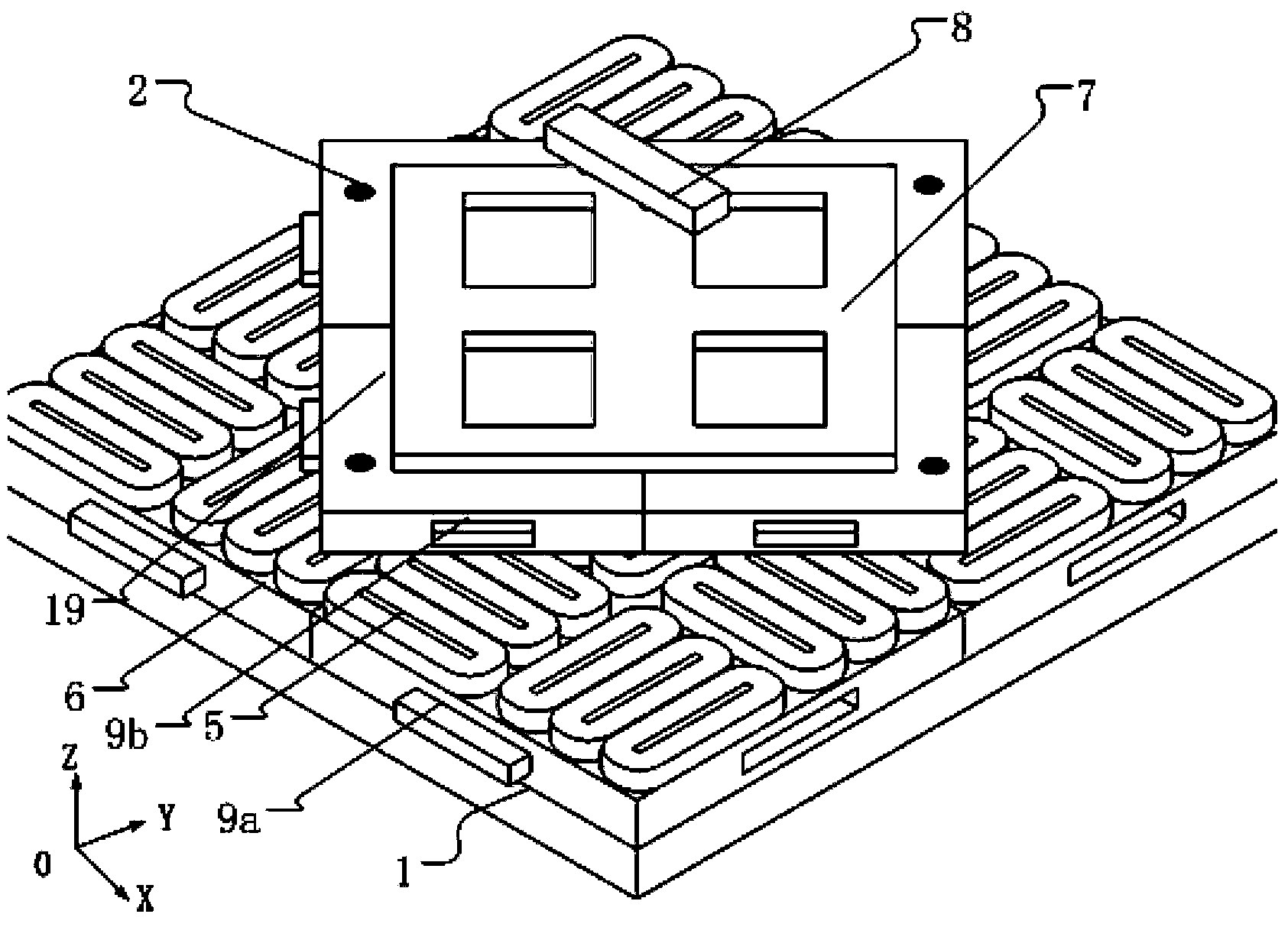
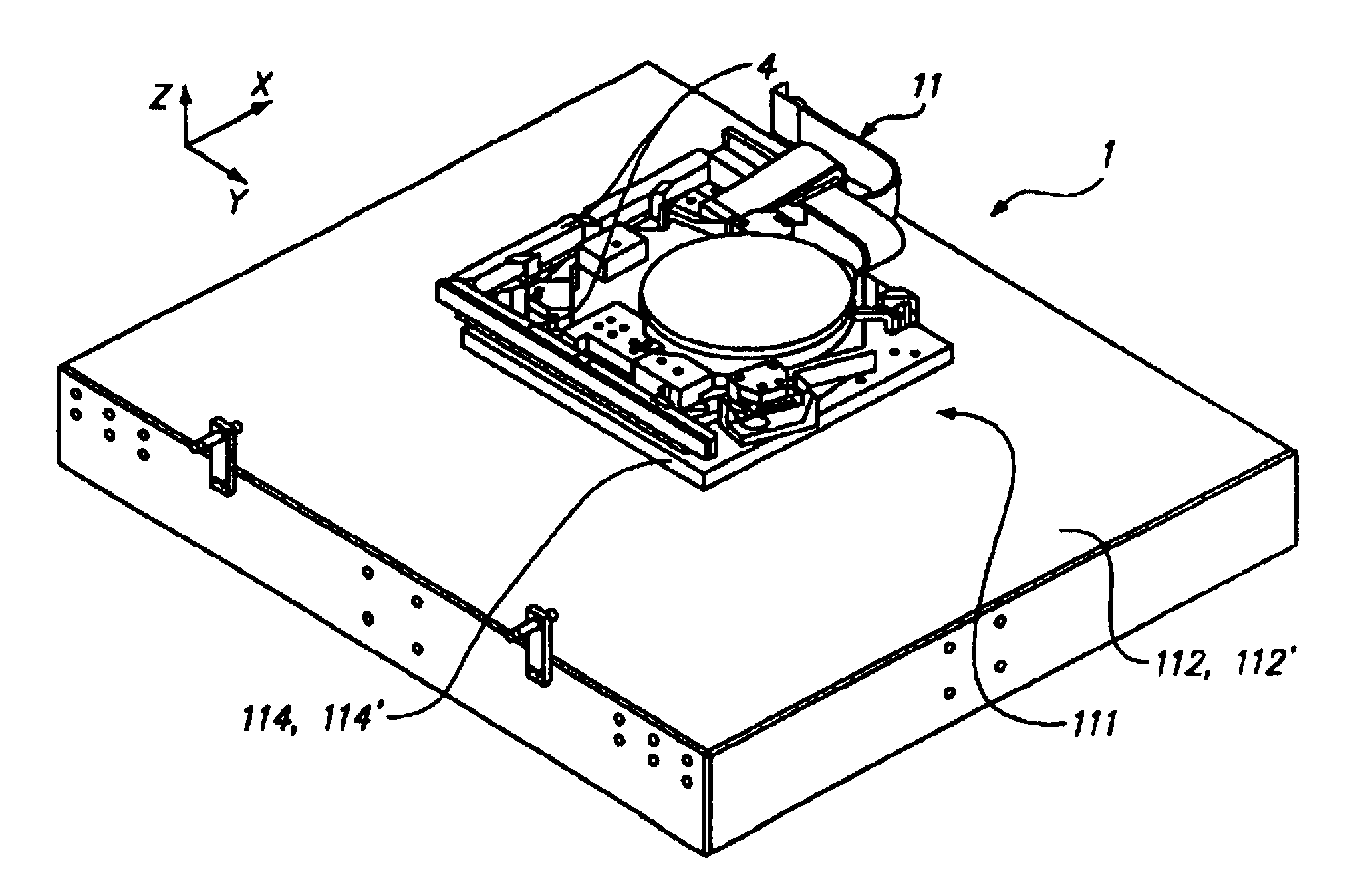
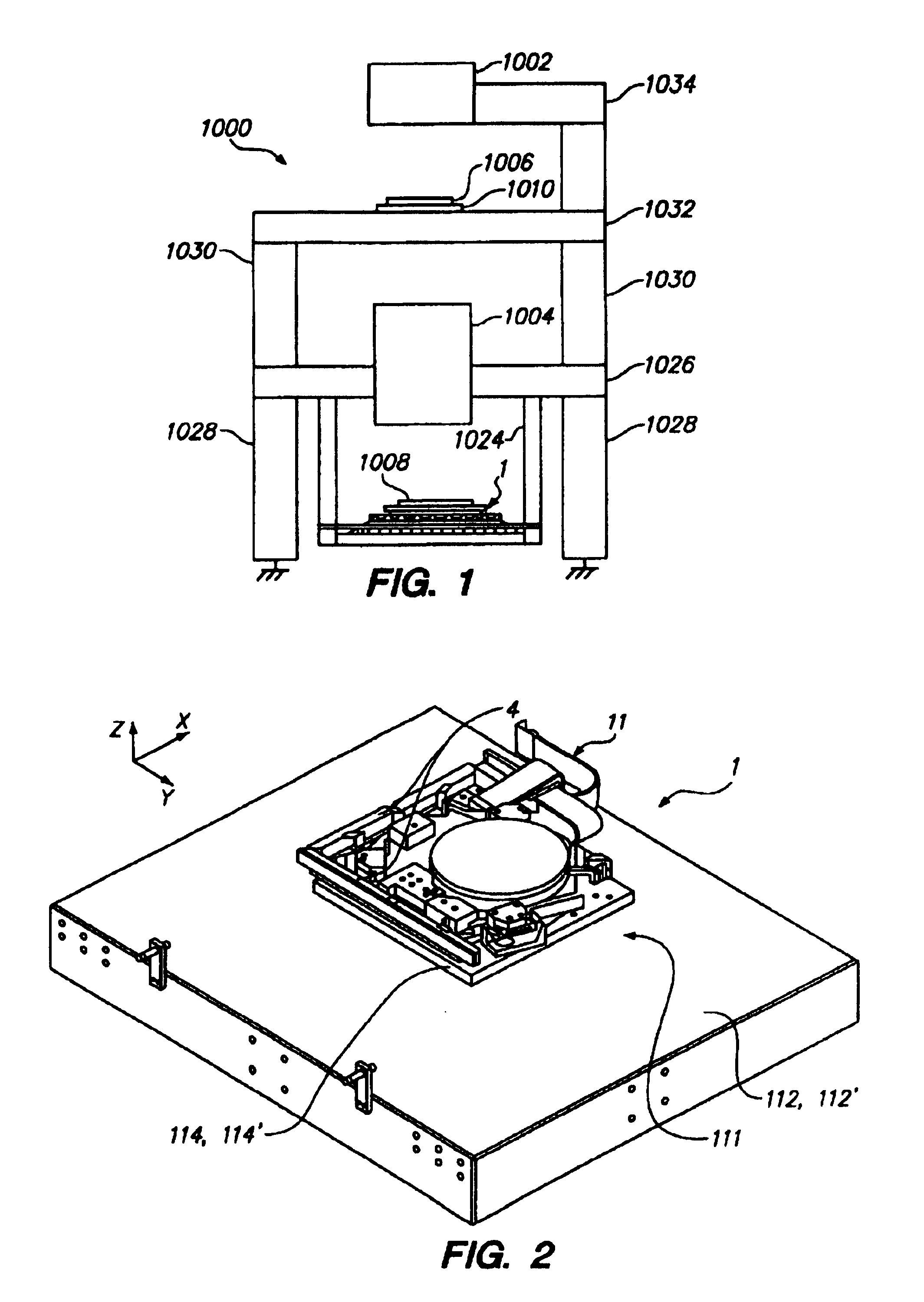
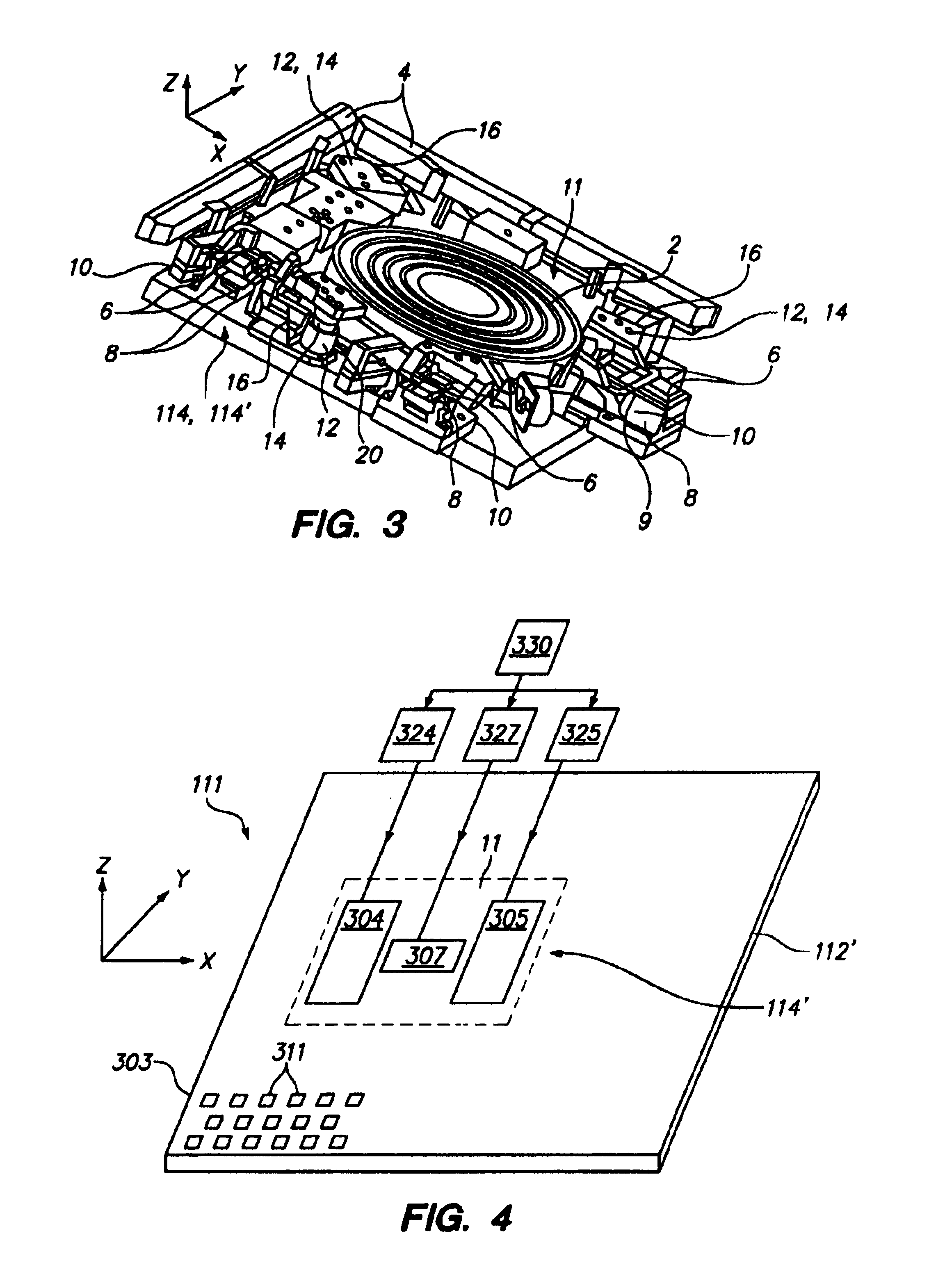
This invention relates to a stage device which is moved with high accuracy in an X-Y direction and a rotating direction using a planar motor. The invention is aimed at reducing the size of the stage device and at performing accurately measurement of a position of the stage to the base. The stage device comprises a scale unit having a scale part on the entire plane of the base, and three two-dimensional angle sensors disposed on a bottom surface of a movable stage part. The scale unit and the two-dimensional angle sensors form a surface encode. A position of the movable stage part is measured by the surface encoder.
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD +1
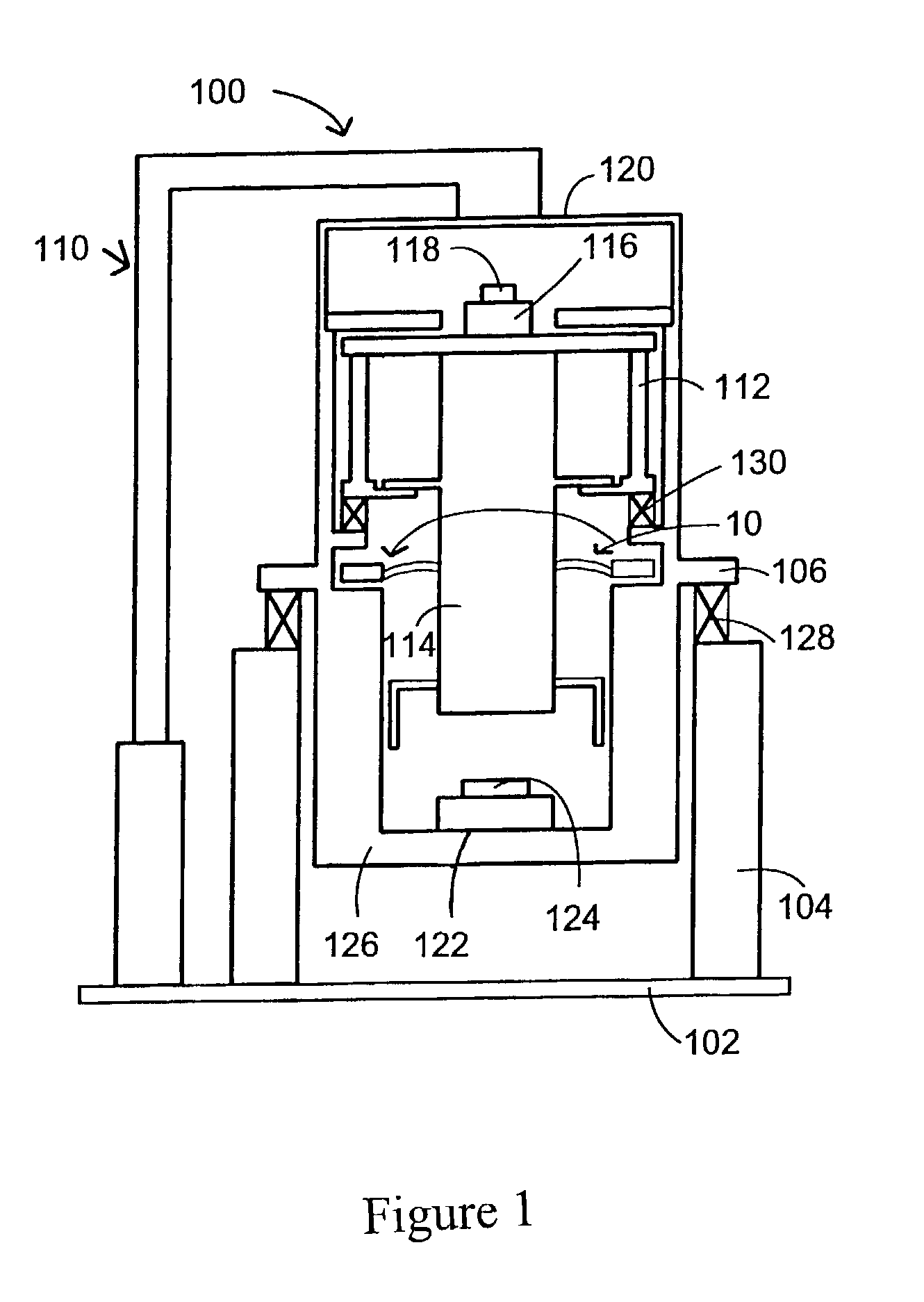
Reaction force isolation system for a planar motor
InactiveUS6252234B1Multiple dynamo-motor startersNon-rotating vibration suppressionPlanar motorEngineering
The present invention provides a structure for isolating the reaction forces generated by a planar motor. Specifically, the fixed portion of the reaction motor, which is subject to reaction forces, is structurally isolated from the rest of the system in which the planar motor is deployed. In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, the fixed portion of the planar motor is separated from the rest of the system and coupled to ground. The rest of the system is isolated from ground by deploying vibration isolation means. Alternatively or in addition, the fixed portion of the planar motor may be structured to move (e.g., on bearings) in the presence of reaction forces, so as to absorb the reaction forces with its inertia. In a further embodiment of the present invention, the fixed portion of the planar motor and the article to be moved are supported by the same frame, with the fixed portion of the planar motor movable on bearings.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Stage device
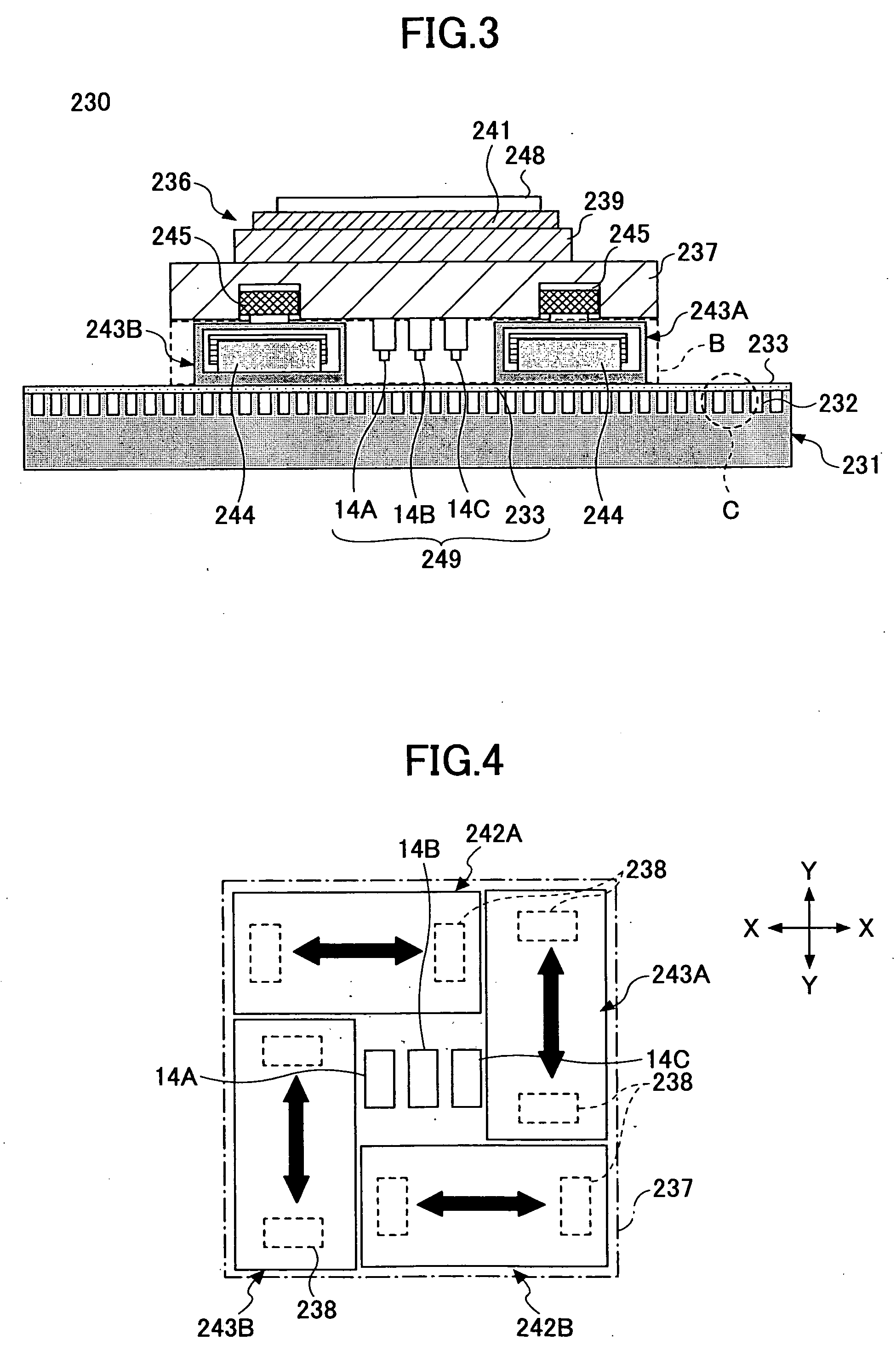
InactiveUS7257902B2Improve accuracyReduce weightPrecision positioning equipmentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingScale unitPlanar motor
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD +1
Silicon slice platform multi-platform exchange system adopting magnetic levitation planar motor
ActiveCN101609265AQuick responseHigh speedPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusProduction rateImage resolution
The invention relates to a silicon slice platform multi-platform exchange system adopting a magnetic levitation planar motor, which is mainly used in a lithography machine system. The silicon slice platform multi-platform exchange system comprises a base platform, a silicon slice platform group and a silicon slice platform driving device, wherein, the silicon slice platform group comprises a plurality of silicon slice platforms which have the same structure and are respectively worked in pretreatment working positions or exposure working positions, the silicon slice platform driving device adopts the magnetic levitation planar motor, a stator of the magnetic levitation planar motor is arranged at the top of the base platform, and rotors of the planar motor are arranged at the bottom of the silicon slice platform. The invention discloses a specific example of one silicon slice platform multi-platform exchange system adopting the moving coil type permanent magnet magnetic levitation planar motor. In the example, the stator of the planar motor adopts a novel planar permanent magnet array, wherein, the magnetizing directions of adjacent permanent magnets mutually form an angle of 45 degrees. The silicon slice platform multi-platform exchange system realizes multi-platform exchange and progressive scanning motion on a plane and improves the productivity, the overlay accuracy and the resolution of the lithography machine by using the planar motor to directly drive the silicon slice platforms.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Silicon wafer stage double-stage exchange system by adopting air-floatation planar motor
ActiveCN101694560AQuick responseHigh speedPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusProduction rateImage resolution
The invention relates to a silicon wafer stage double-stage exchange system by adopting an air-floatation planar motor, mainly applied to a photoetching machine system. The silicon wafer stage double-stage exchange system comprises a drill base as well as a silicon wafer stage and a silicon wafer stage driving device having the same structure and respectively working on a preprocessing station and an exposure station. The silicon wafer stage driving device consists of a planar motor and an air-floatation structure, wherein the planar motor adopts a permanent magnetic planar motor, a stepping planar motor, an induction-type planar motor or a switch reluctance planar motor, and consists of a stator and two rotors, wherein the stator is arranged on the top of the drill base, and the rotors are arranged at the bottom of the silicon wafer stage; and the air-floatation structure is formed by a plurality of air-floatation bearings arranged at the bottom of the silicon wafer stage. The system realizes double-stage exchange and stepping scanning motion on the plane by directly driving the silicon wafer stage with the planar motor, thereby improving the productivity, alignment precision and resolution of the photoetching machine.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
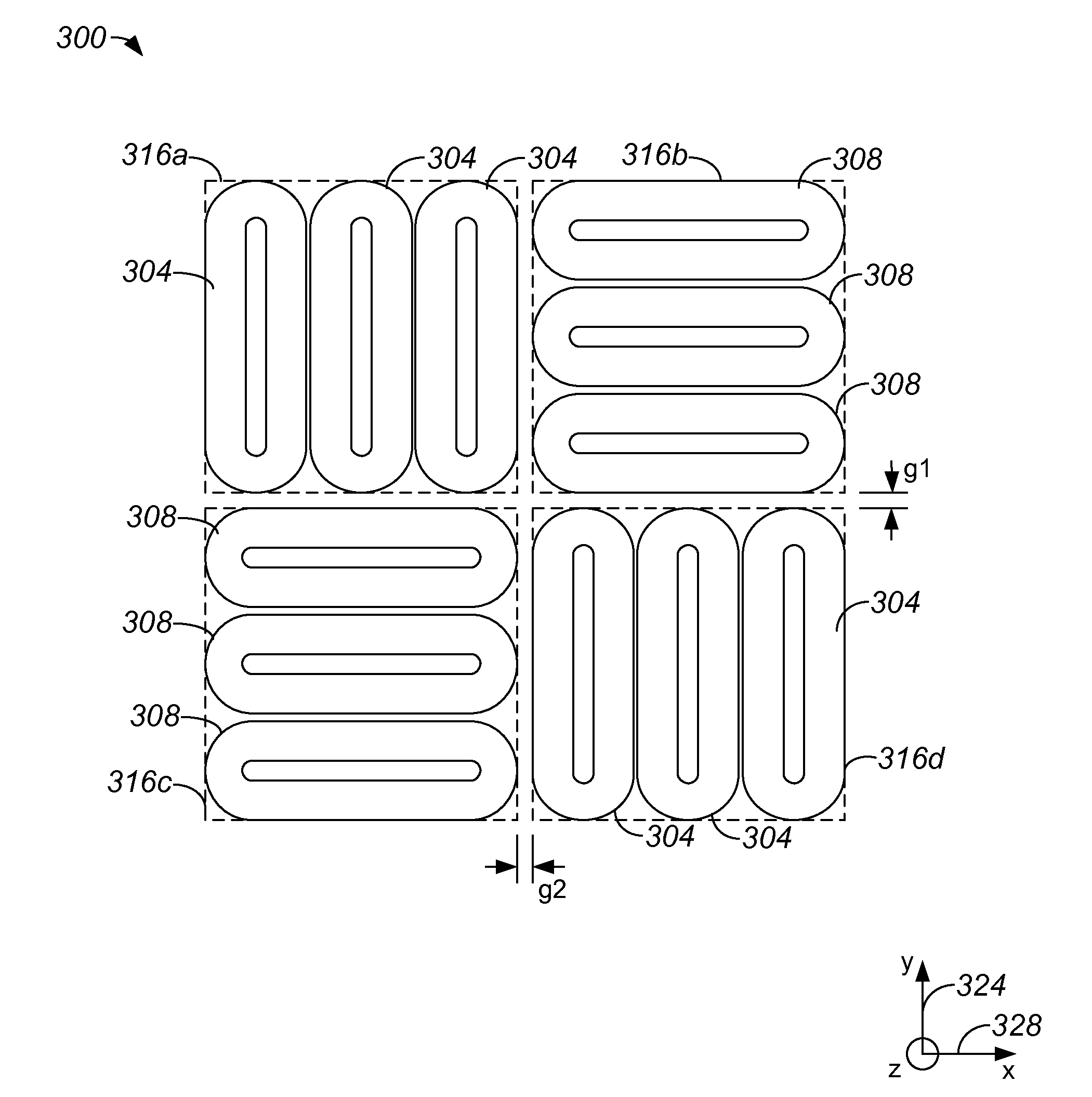
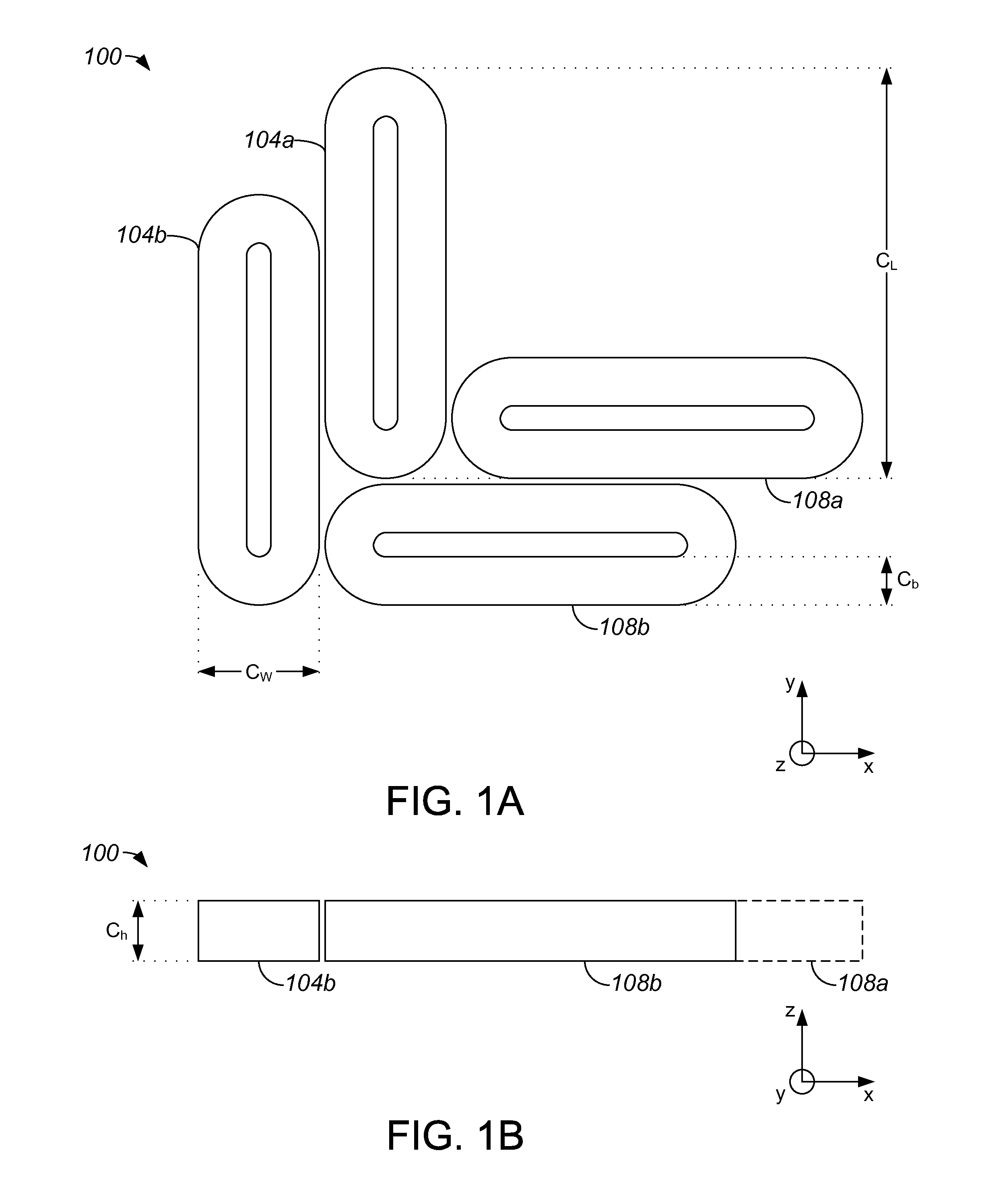
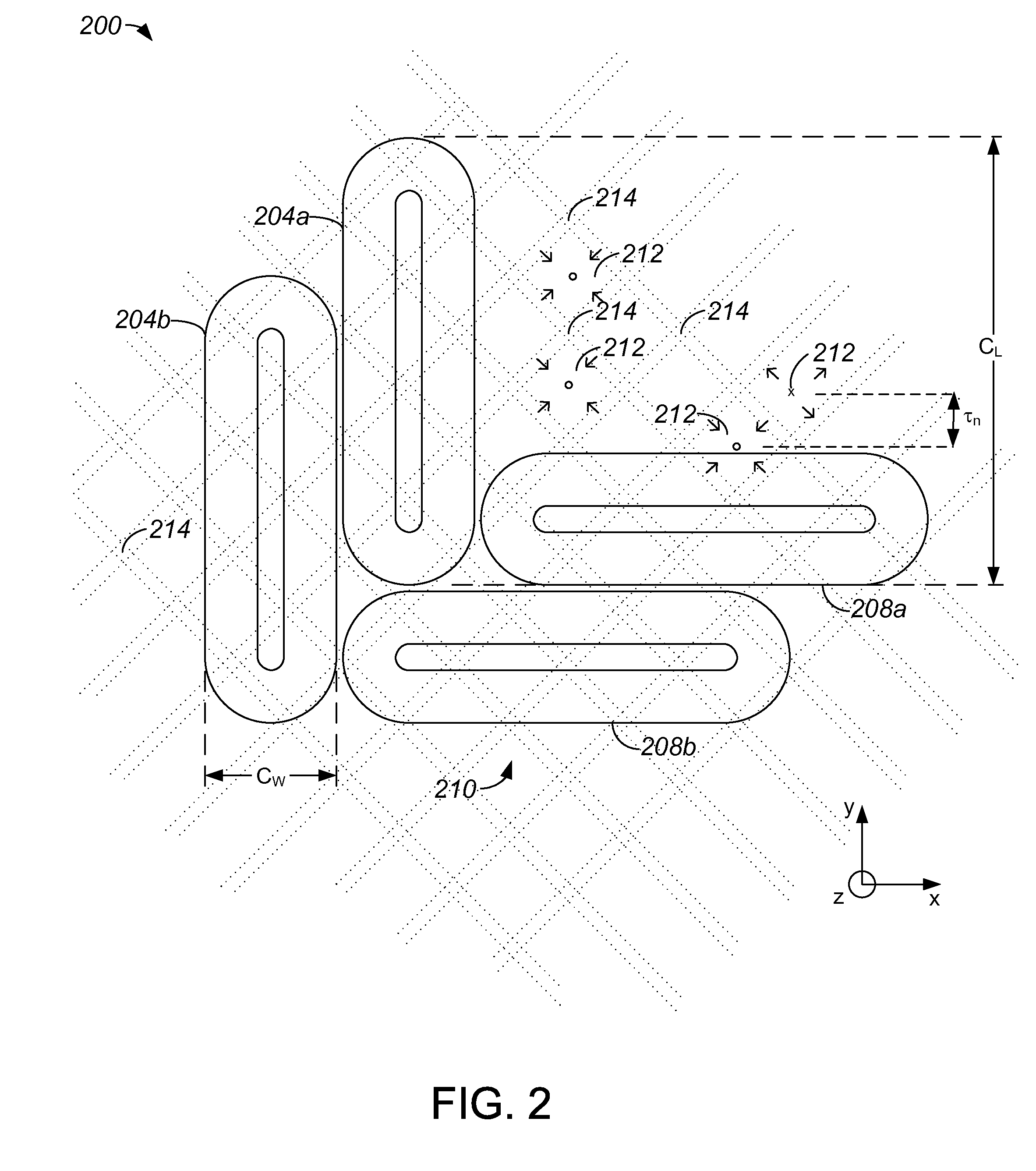
Coil Variations for an Oval Coil Planar Motor
Methods and apparatus for providing an efficient oval coil planar motor are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, an electromagnetic actuator includes at least a first coil group, at least a second coil group, and a magnet array. The first coil group includes at least a first coil that is of an elongated toroidal shape. The first coil has a first coil length and a first coil width that is approximately equal to a multiple of three times the first coil width. The second coil group includes at least a second coil that is of an elongated toroidal shape. The second coil has a second coil width and a second coil length that is approximately equal to a multiple of three times the second coil width. The second coil group is approximately adjacent to the first coil group. The magnet array is configured to cooperate with the first and second coil groups, and includes a plurality of magnets. The magnets have an associated magnet pitch, and the first coil width and the second coil width are a function of the magnet pitch.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Methods and apparatus for initializing a planar motor
InactiveUS20040007920A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlCoil arrayPlanar motor
Methods and apparatus are provided for initializing a planar motor. A magnet array floating above a coil array may reside in one of a definite number of positions upon the introduction of current into the coil array. Torque characteristics of the magnet array are acquired when driving the magnet array with no phase offsets. Phase offsets for driving the magnet array with substantially no yaw can then be determined by analyzing the torque characteristics.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Following stage planar motor
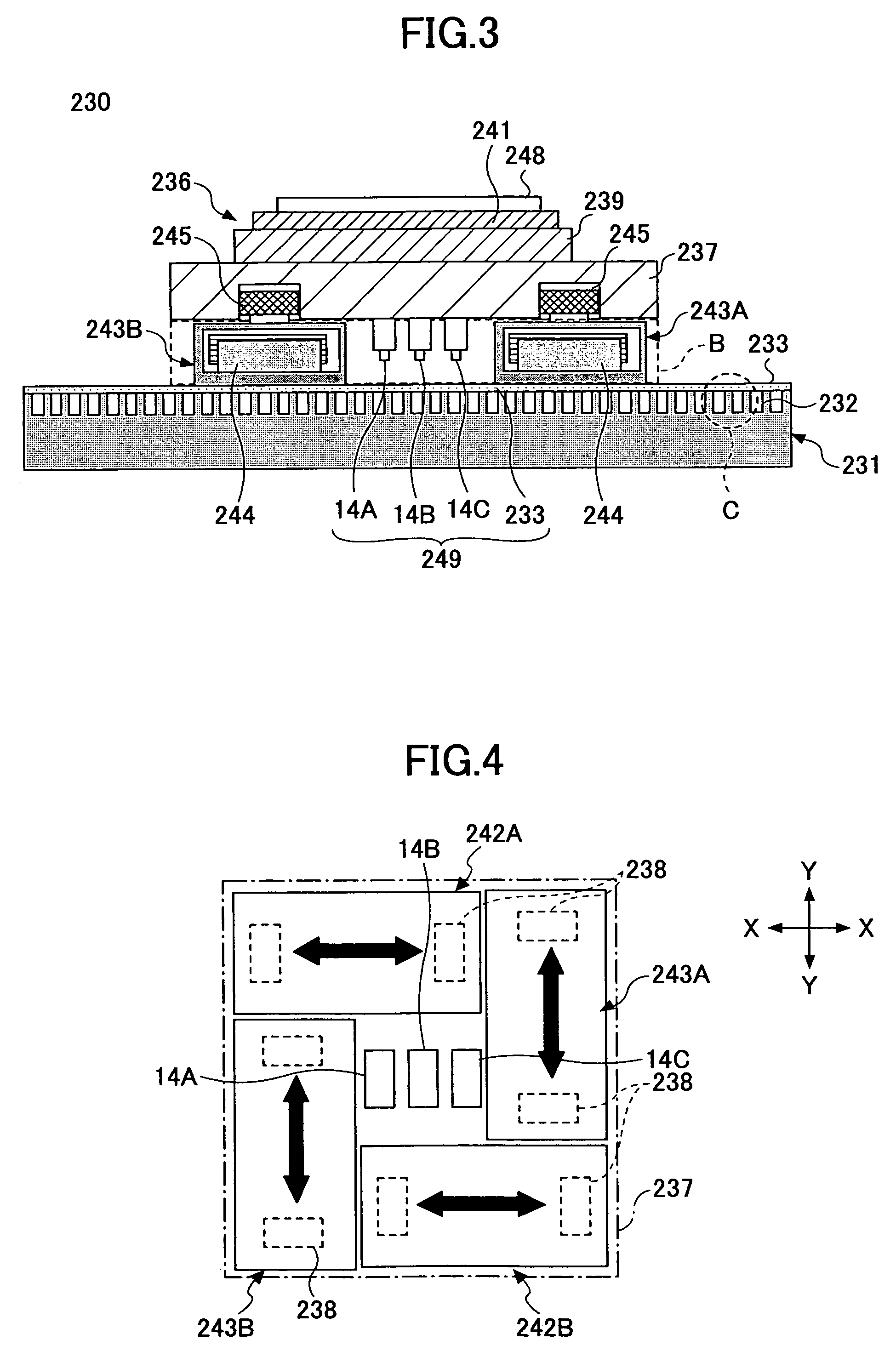
InactiveUS6927505B2Large range of motionFunction increaseMagnetic circuitSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoil arrayPlanar motor
In electric motor assemblies, separating the x and y coils may achieve significant advantages. An advantageous design includes pairs of interacting magnet array / coil arrays. Separated coil arrays are provided, with a coil array on an arm connected to a following stage, and another coil array on a stage base (the stage being one to which is attached magnet arrays). Positioning devices, moving magnet motor assemblies, moving coil motor assemblies, and methods of driving a stage are provided. By differential driving and creation of torques about the x and y axes, a stage may be driven in six independent degrees of freedom.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Following stage planar motor
InactiveUS20030111912A1Magnetic circuitSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoil arrayDegrees of freedom
In electric motor assemblies, separating the x and y coils may achieve significant advantages. An advantageous design includes pairs of interacting magnet array / coil arrays. Separated coil arrays are provided, with a coil array on an arm connected to a following stage, and another coil array on a stage base (the stage being one to which is attached magnet arrays). Positioning devices, moving magnet motor assemblies, moving coil motor assemblies, and methods of driving a stage are provided. By differential driving and creation of torques about the x and y axes, a stage may be driven in six independent degrees of freedom.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Dual-axis planar motor providing force constant and thermal stability
ActiveUS7808133B1Reducing thermal driftMinimize changesMagnetic circuitPropulsion systemsForce constantPlanar motor
A motor is provided comprising a magnet assembly having two rows of magnets arranged along a first axis, which are separated by a gap for generating magnetic flux lines between the rows of magnets. The motor further comprises a coil bracket which is located within the gap between the two rows of magnets. The coil bracket includes a first set of coils arranged along the first axis that are operative to drive movement of the coil bracket relative to the magnet assembly along the first axis. A second set of coils arranged along the first axis are operative to drive movement of the coil bracket relative to the magnet assembly along a second axis which is orthogonal to the first axis between a first end position and a second end position along the second axis. The first set of coils is fully located within the flux lines generated by the magnet assembly at both the first and second end positions of the coil bracket and the second set of coils is located at least partially outside the flux lines generated by the magnet assembly at the second end position of the coil bracket.
Owner:ASM ASSEMBLY AUTOMATION LTD
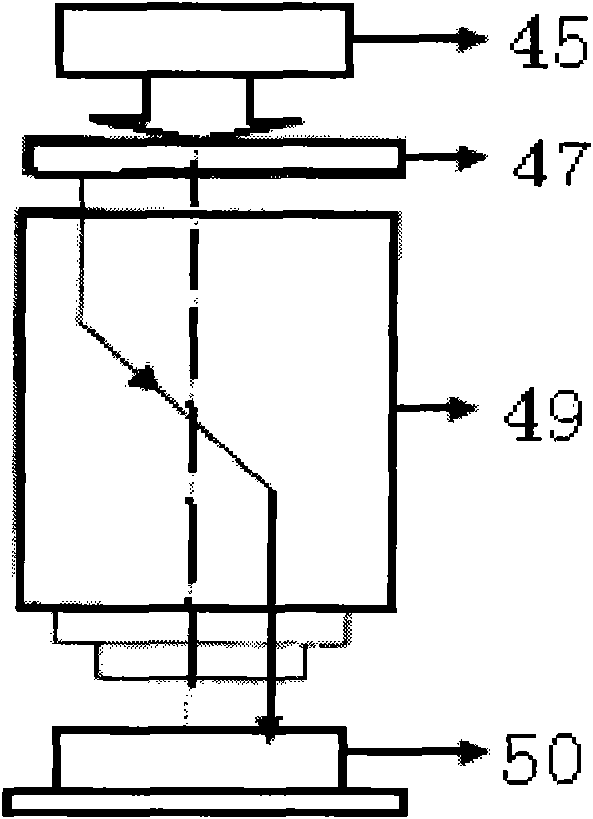
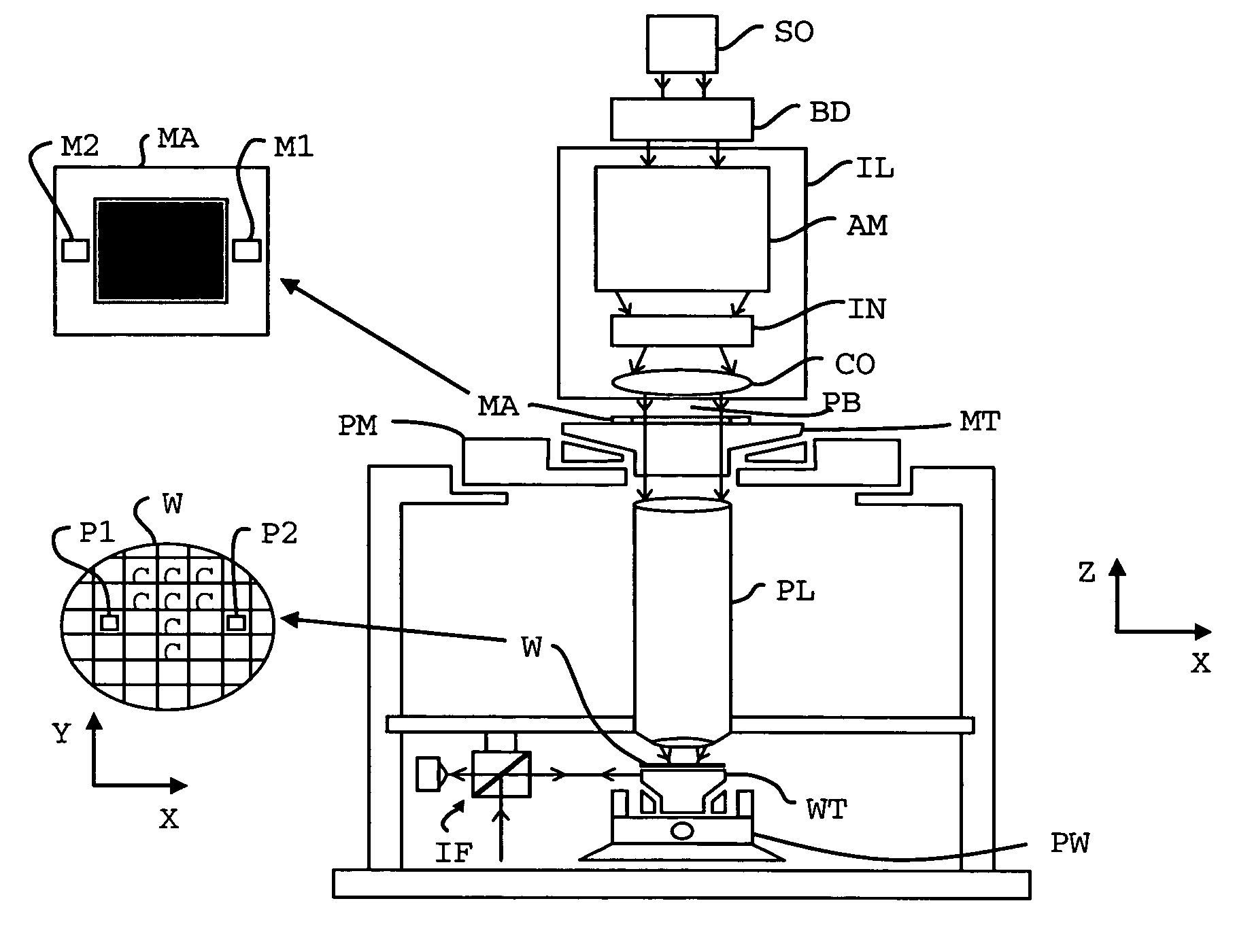
Planar motor initialization method, planar motor, lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
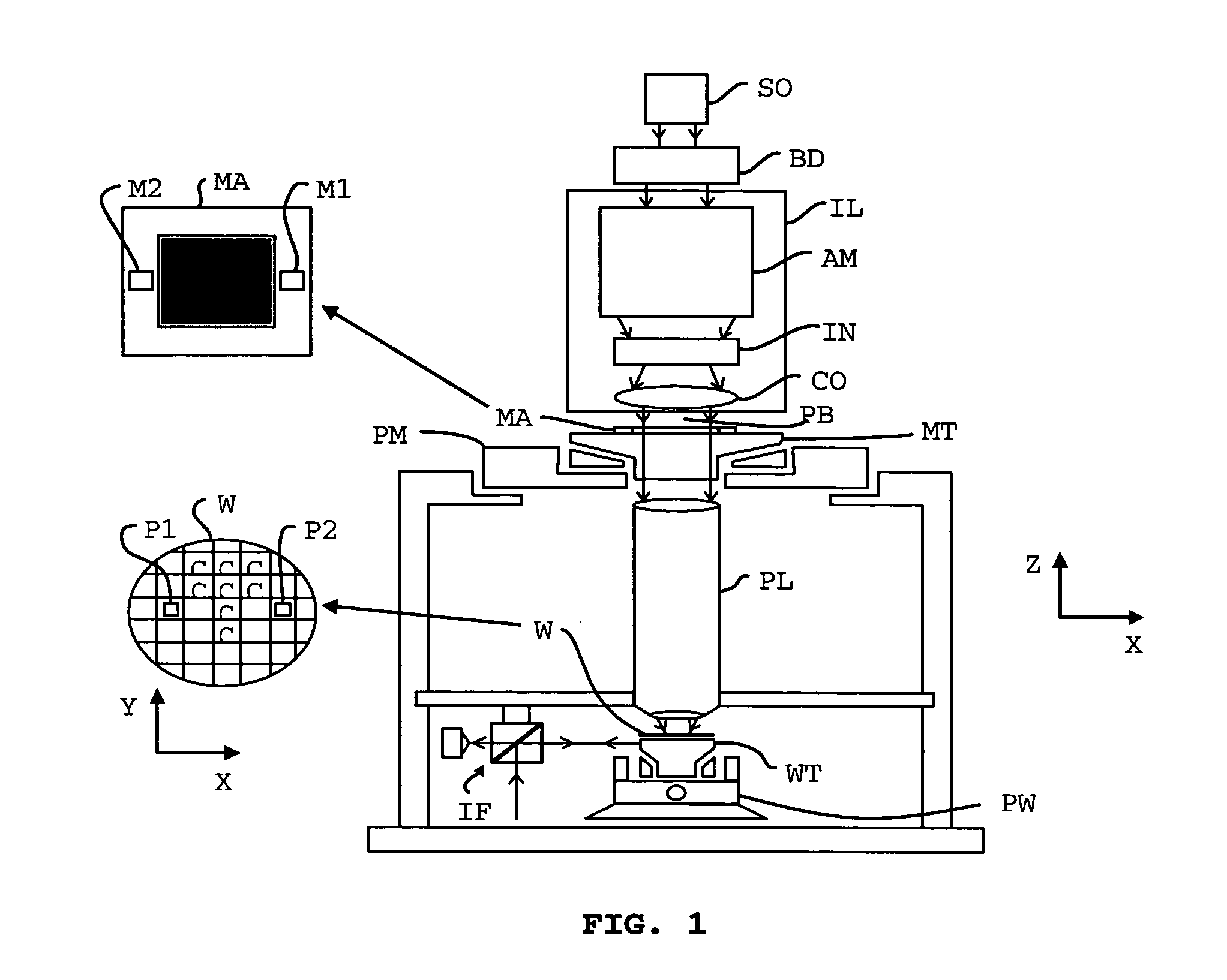
ActiveUS7205741B2Avoid damageSignificant valueDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlEngineeringPlanar motor
A planar motor is controlled by supplying a three-phase alternating current to a coil assembly. Each phase is supplied to one of three coils. The coils are positioned in a magnetic field generated by a magnet plate having alternating magnet poles at its surface for generating an alternating magnetic field. In operation, the phase of each current flowing through each coil determines the direction of a force generated due to the current in the magnetic field. For correct operation, the phase angle of each current is to be adapted to the local direction of the magnetic field by determining a commutation-offset angle. The commutation-offset angle is determined by generating a force in an unknown direction and varying the commutation-angle, and determining when the generated force is directed perpendicular to the magnet plate, while ensuring that the generated force does not exceed a horizontal friction force. By determining a maximum compression of end stops of the coil assembly, or determining a maximum pressure, it may be determined when the generated force is directed perpendicular to the magnet plate.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Methods and apparatus for initializing a planar motor
InactiveUS6777896B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlCoil arrayPlanar motor
Methods and apparatus are provided for initializing a planar motor. A magnet array floating above a coil array may reside in one of a definite number of positions upon the introduction of current into the coil array. Torque characteristics of the magnet array are acquired when driving the magnet array with no phase offsets. Phase offsets for driving the magnet array with substantially no yaw can then be determined by analyzing the torque characteristics.
Owner:NIKON CORP
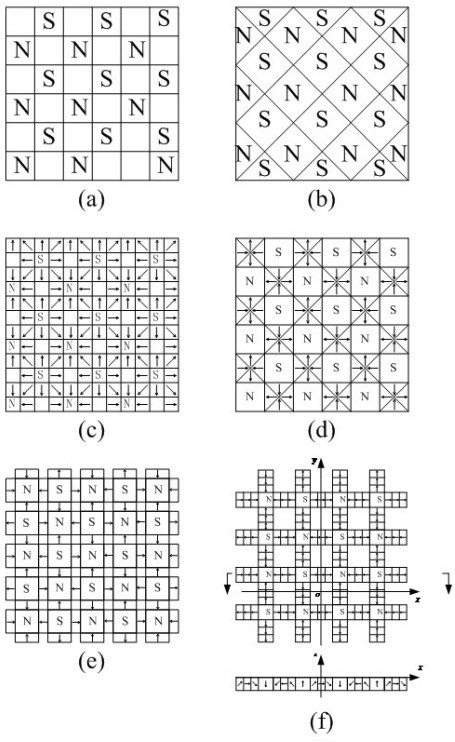
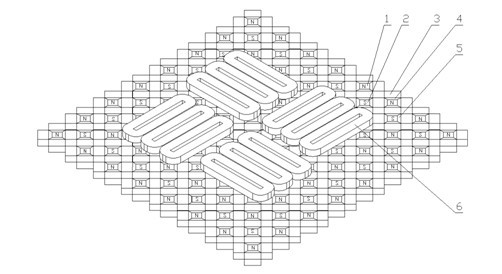
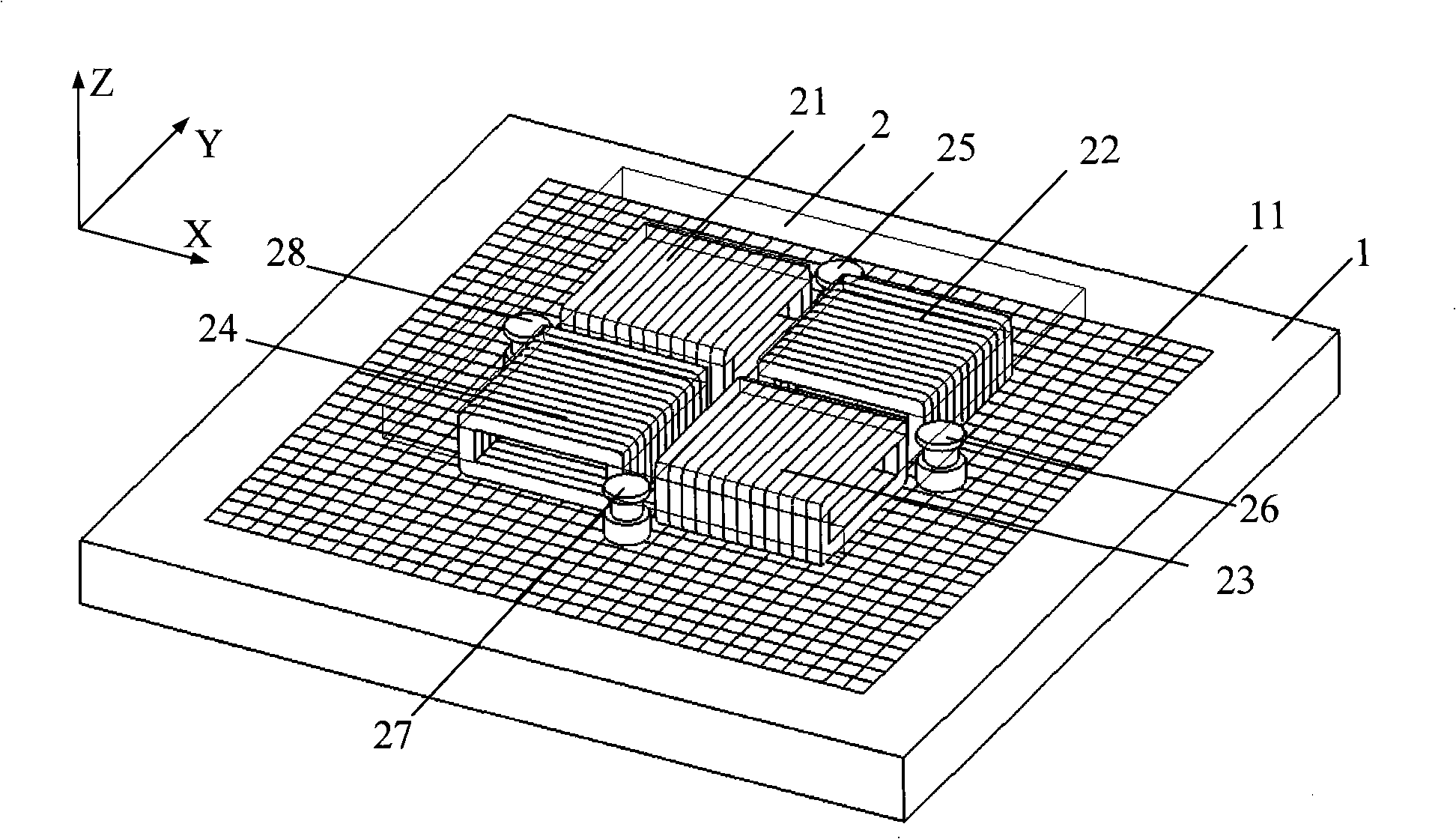
Permanent-magnet synchronous magnetic suspension planar motor
InactiveCN102097982AImprove efficiencyHigh precisionMagnetic holding devicesElectric machineMagnetization
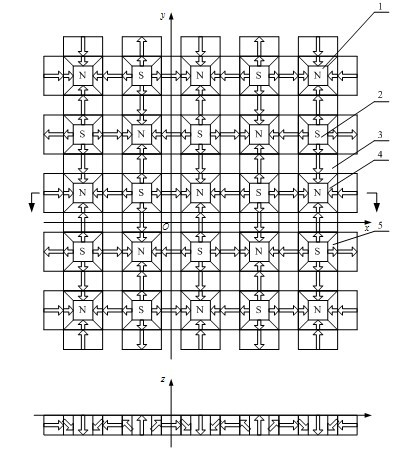
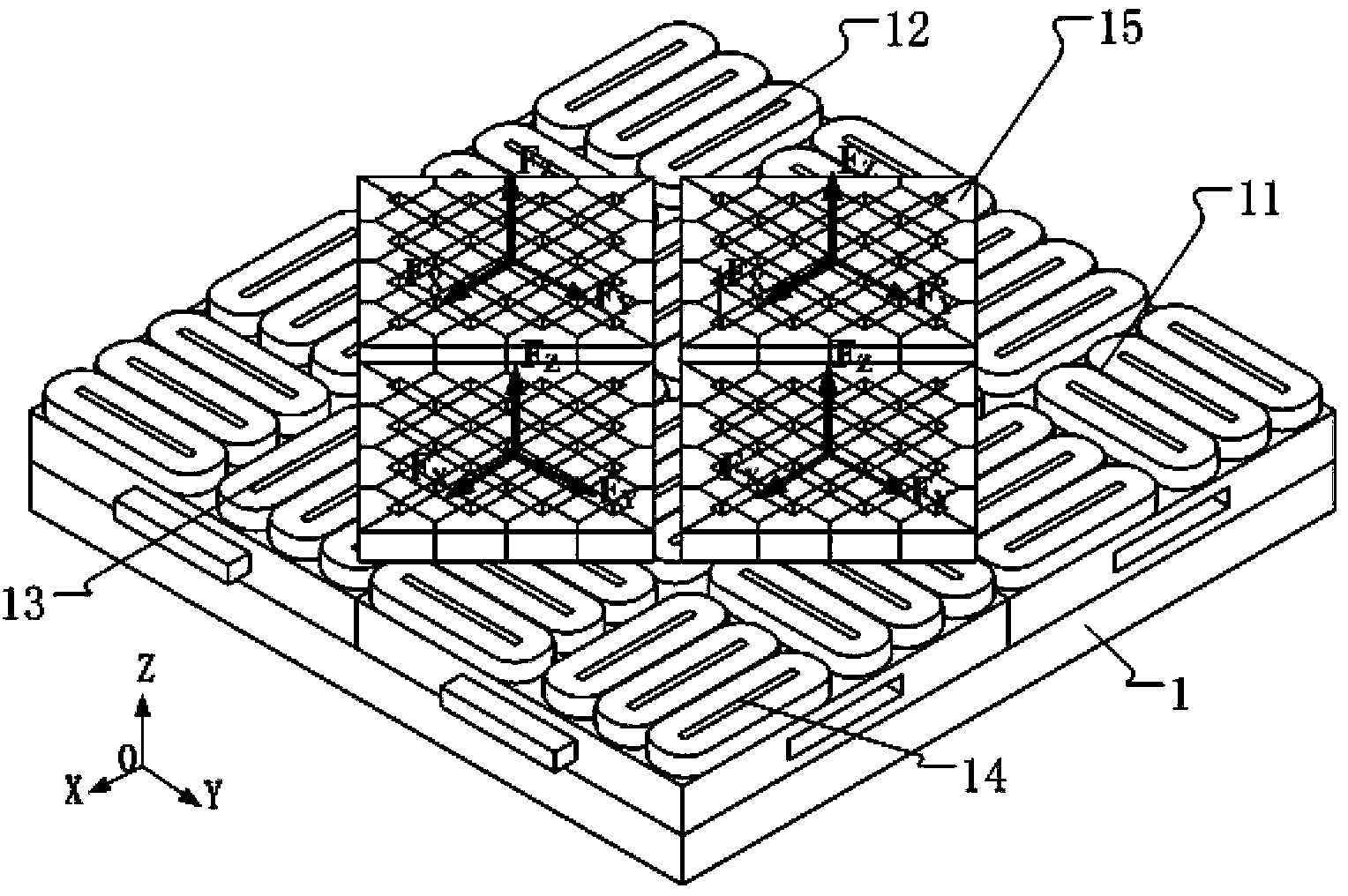
The invention provides a permanent-magnet synchronous magnetic suspension planar motor, which comprises a rotor and a stator, wherein the stator employs a specific two-dimensional permanent magnet array; a first main permanent magnet and a second main permanent magnet in the two-dimensional permanent magnet array are staggered along an X direction and an Y direction to form a planar array; four second secondary permanent magnets are arranged at the periphery of the first main permanent magnet; four third secondary permanent magnets are arranged at the periphery of the second main permanent magnet; a first secondary permanent magnet is arranged between the second secondary permanent magnets and the third secondary permanent magnets; and the side surfaces of each permanent magnet and the side surfaces of adjacent permanent magnets thereof are jointed with each other; all the included angles between the magnetization directions of any two adjacent permanent magnets in the two-dimensionalpermanent magnet array are 45 DEG. By the specific two-dimensional permanent magnet array, the magnetic field intensity of the motor is high, the sinusoidal characteristic is good, and the deficiencyof the existing permanent-magnet synchronous magnetic suspension planar motor that high precision, high response and high efficiency cannot be taken into account together is compensated. The permanent-magnet synchronous magnetic suspension planar motor provided by the invention is a planar motor with better performance.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
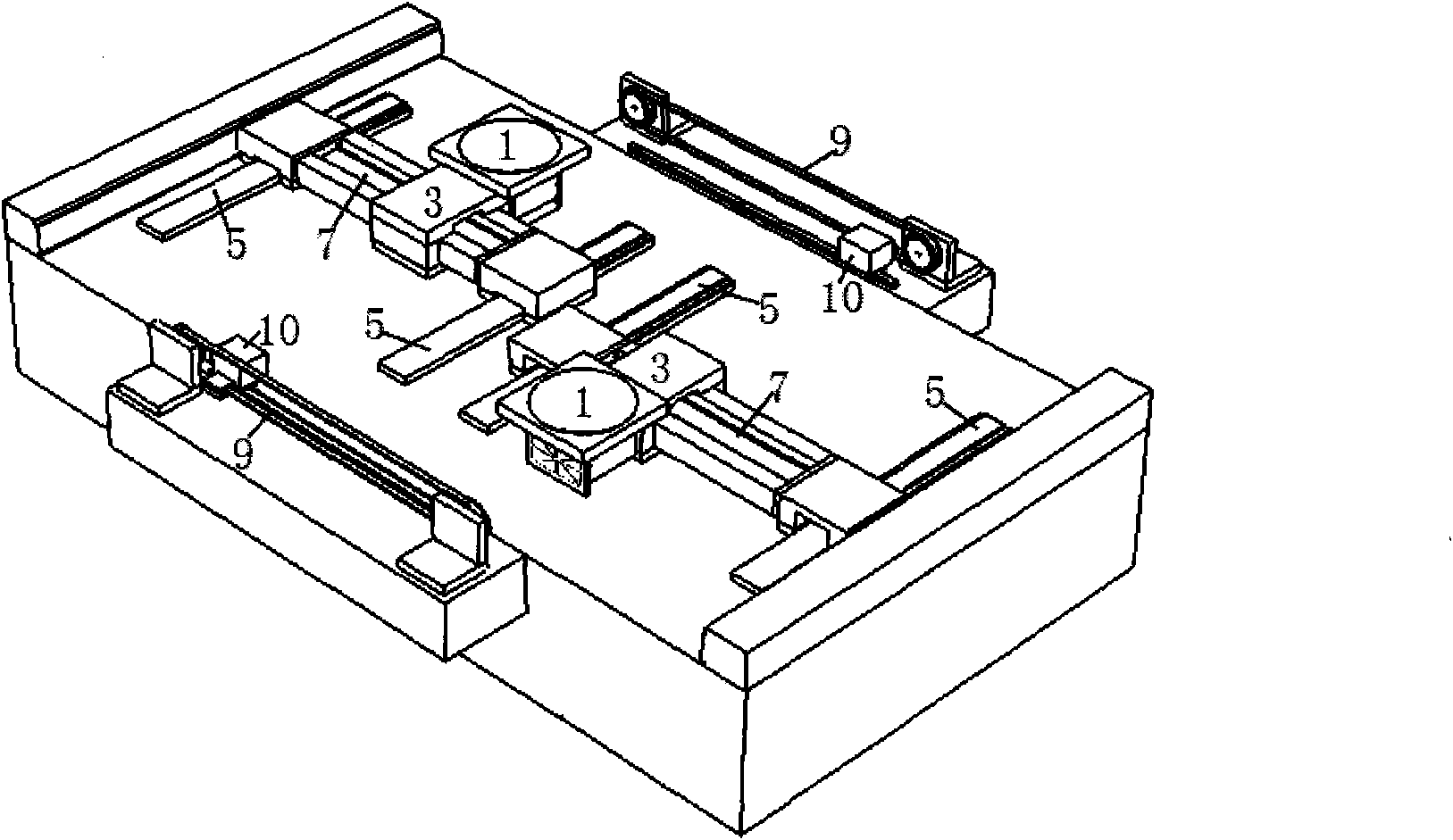
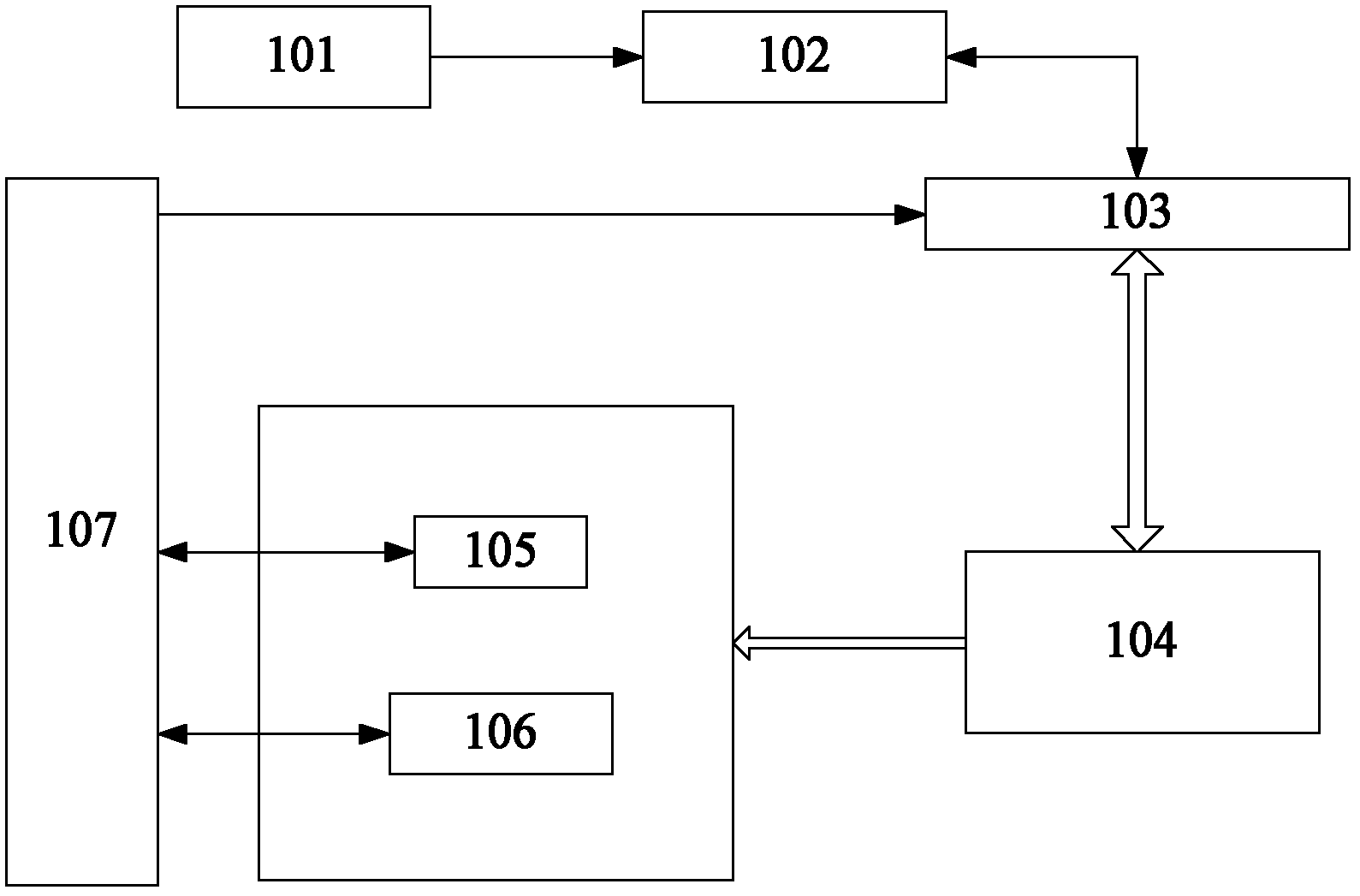
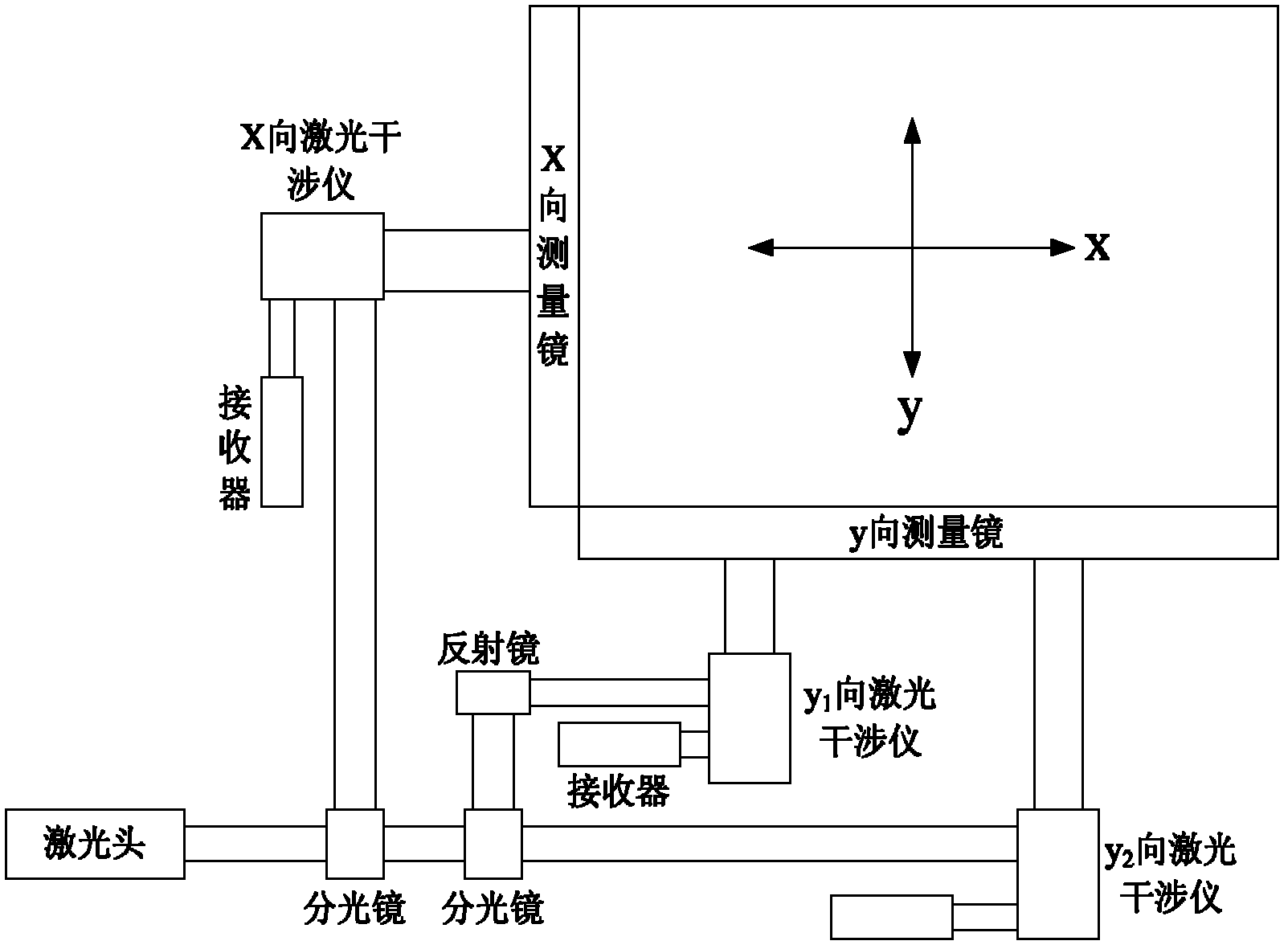
Long-stroke high-speed dual-drive nano positioning system
InactiveCN102629122AImprove real-time performanceImprove response speedNumerical controlGratingSmall range
The invention discloses a long-stroke high-speed dual-drive nano positioning system, which comprises a motion track instruction system (101), a master control computer (102), a PMAC motion control board (103), a servo motion control system (104), a positioning platform and a measurement control system (107), wherein the positioning platform comprises a macro motion platform (105) and a micro motion platform (106); triaxial measurement and triaxial control are taken into consideration in the nano positioning system so that precision control for X, Y1 and Y2 can be implemented, the positioning platform adopts a motion mode of 'long-stroke linear motor + short-stroke planar motor' and adopts master / slave control as motion control mode, the short-stroke planar motor is the target of master control, and feedback is measured by a laser interferometer to accomplish high-precision motion within a small range; and the long-stroke linear motor serves as a slave control system for the short-stroke motor, and feedback is measured by a grating scale to accomplish long-stroke high-speed gross motion. The response speed and real-time performances of the system are dramatically improved by means of motion decoupling for the planar motor and introduction of the PMAC motion control board.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rotor displacement measurement device and method for planar motor
ActiveCN102607388AHigh precisionLow costPhotomechanical apparatusUsing electrical meansSignal processing circuitsMeasurement device
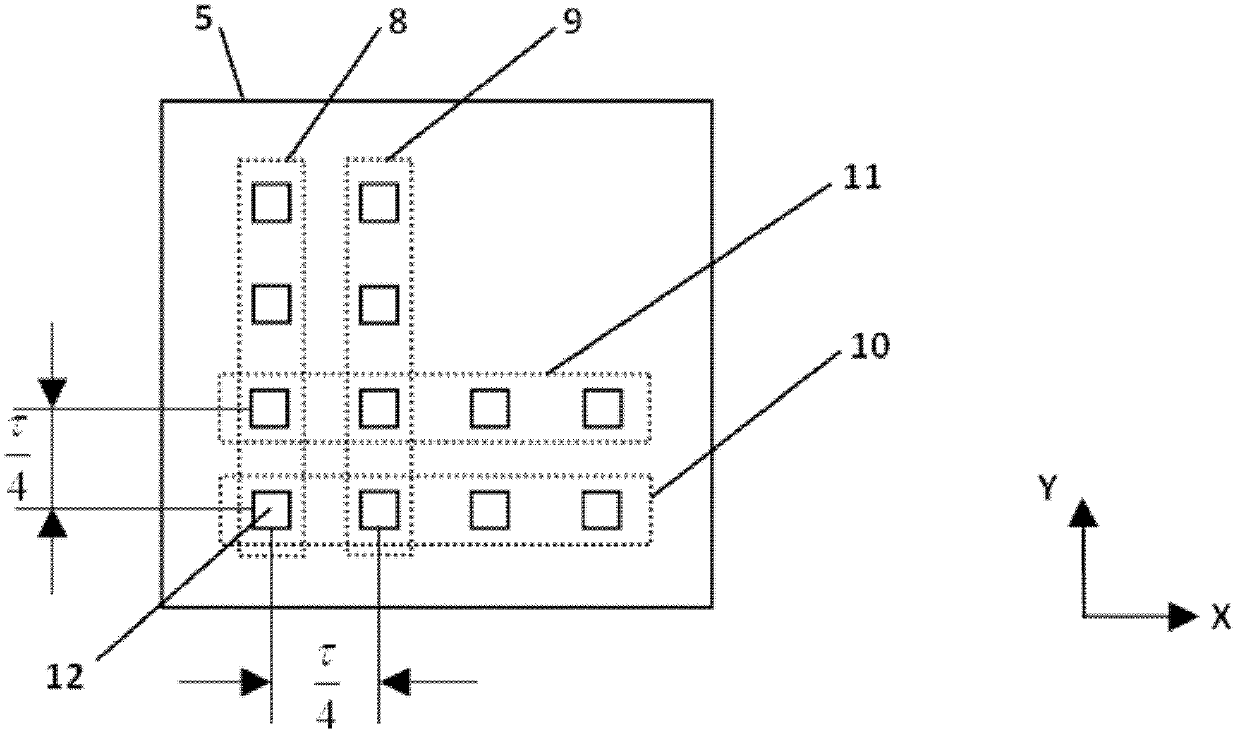
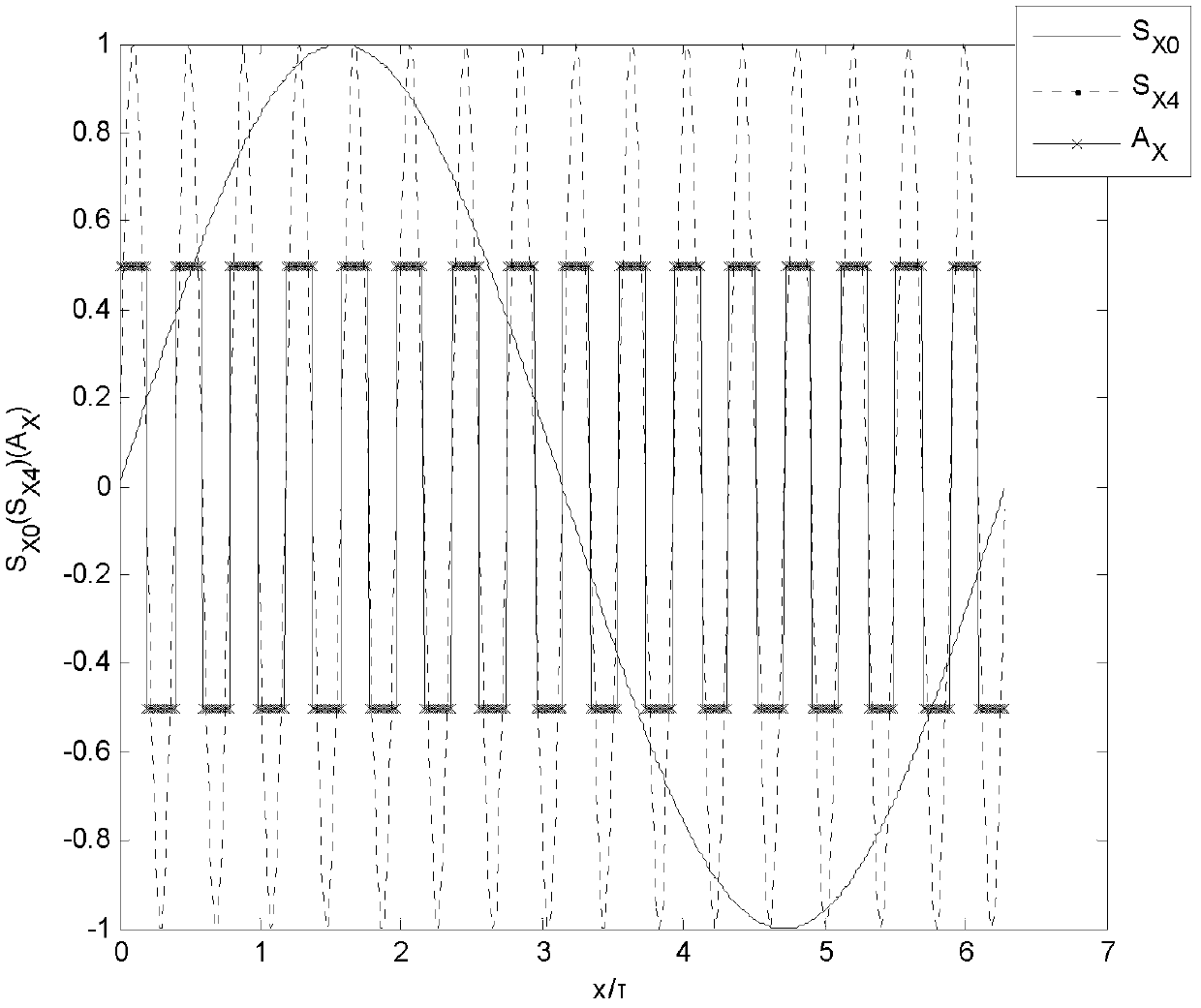
The invention provides a rotor displacement measurement device and method for a planer motor. According to the method, two sets of magnetic flux density sensors are respectively and uniformly distributed in a field pole polar distance tau in two mutually perpendicular moving directions of a sine magnetic field area formed by a stator magnetic steel array on the planer motor, sampled signals of the four sets of sensors are subjected to frequency multiplication operation by a signal processing circuit respectively to obtain four subdivided signals, zero crossing points of the four subdivided signals are detected to generate two orthogonal pulse signals, pulses of the two orthogonal pulse signals are counted respectively and the phase differences of the two orthogonal pulse signals are detected respectively. According to the invention, based on the magnetic field information of the planar motor, the magnetic field space tau is subdivided to realize the long-travel high-accuracy rotor displacement of the planar motor. Through adoption of the device and method disclosed by the invention, the problems caused by the requirements of long travel and high accuracy that calculation methods are complicated or hardware is inconvenient to install and the total cost of a measurement device is high can be solved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Planar motor
ActiveUS20080290741A1Easy to produceEasy to installMagnetic circuitPropulsion systemsElectric machineMagnetization
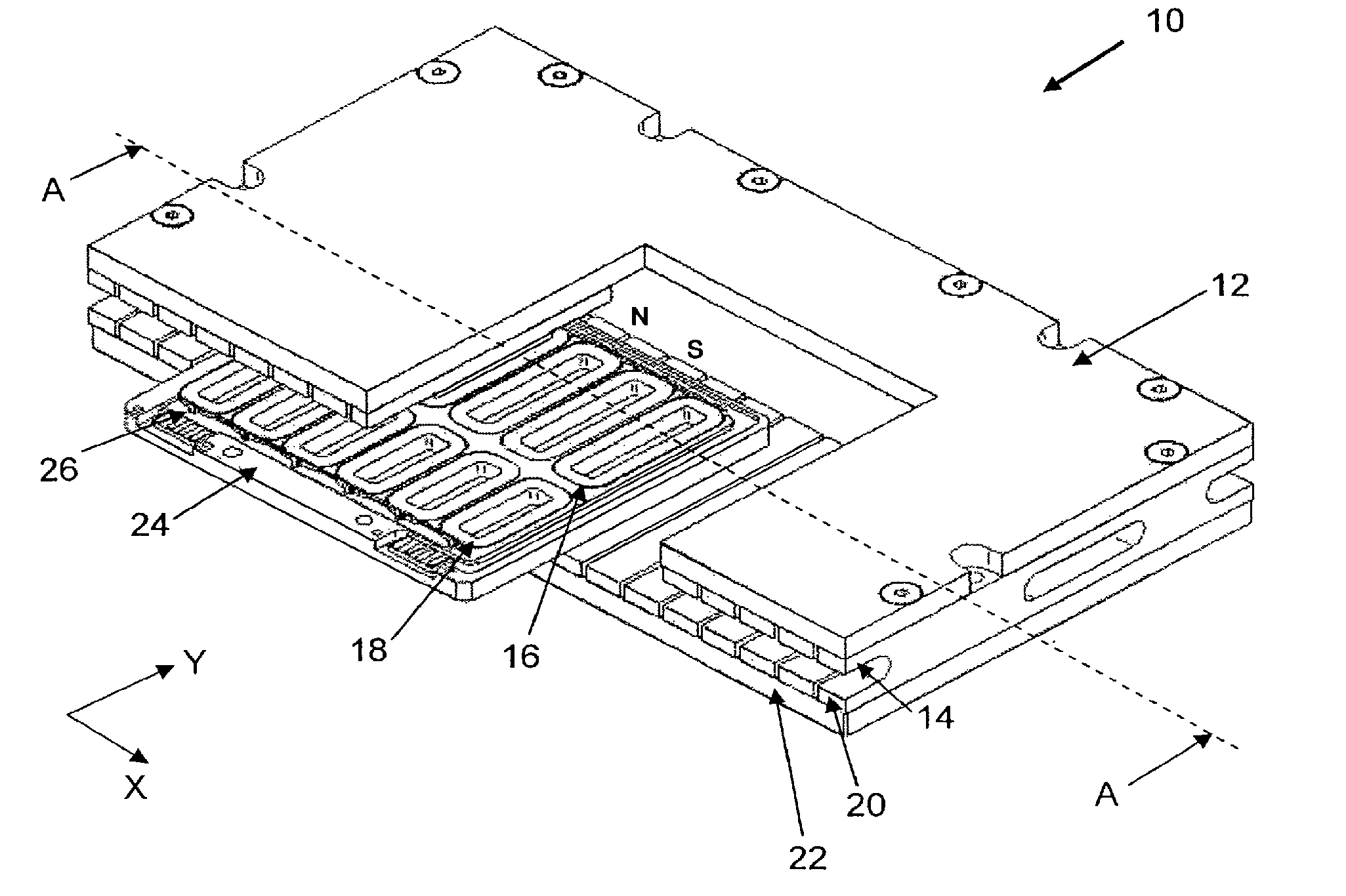
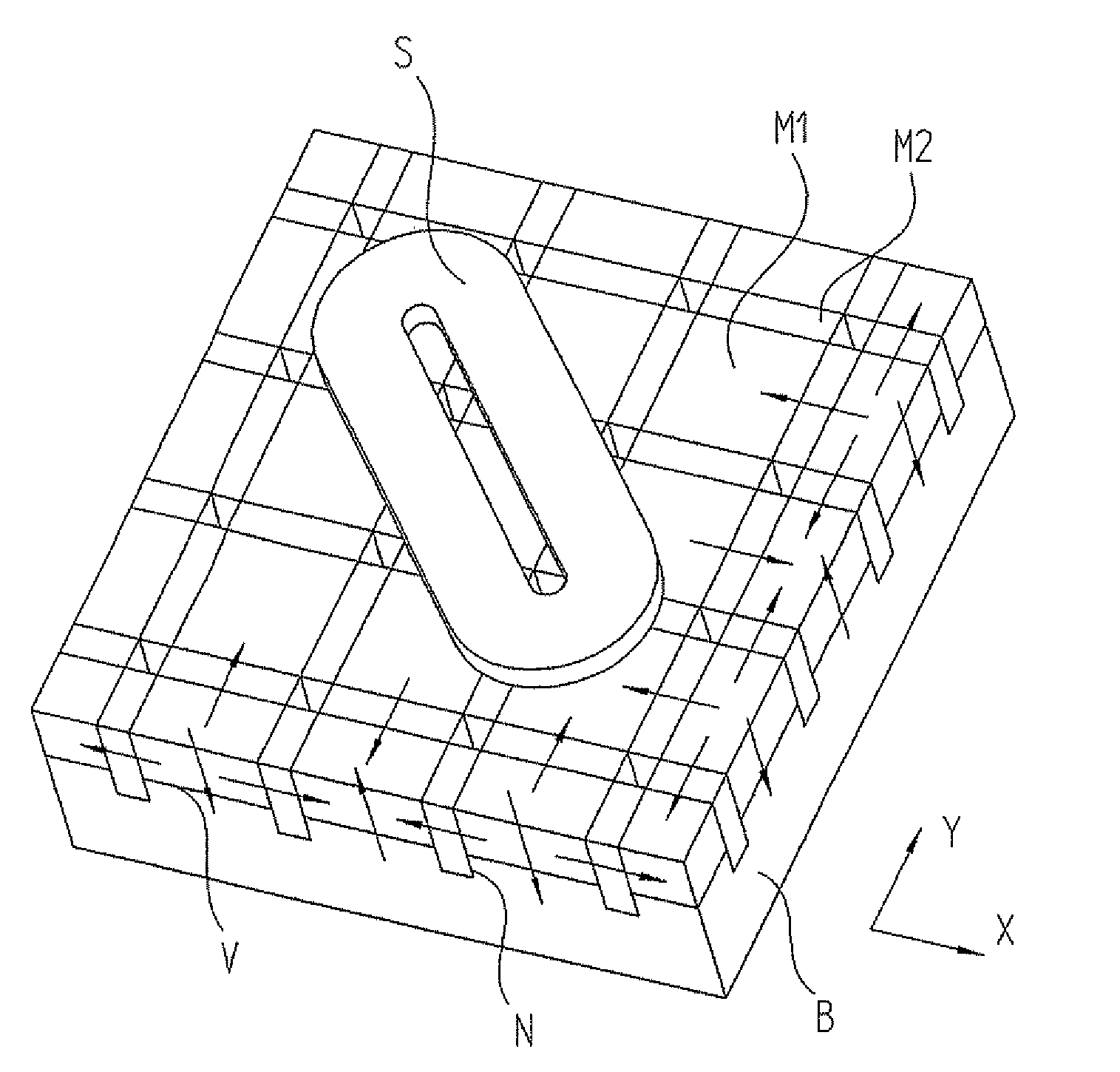
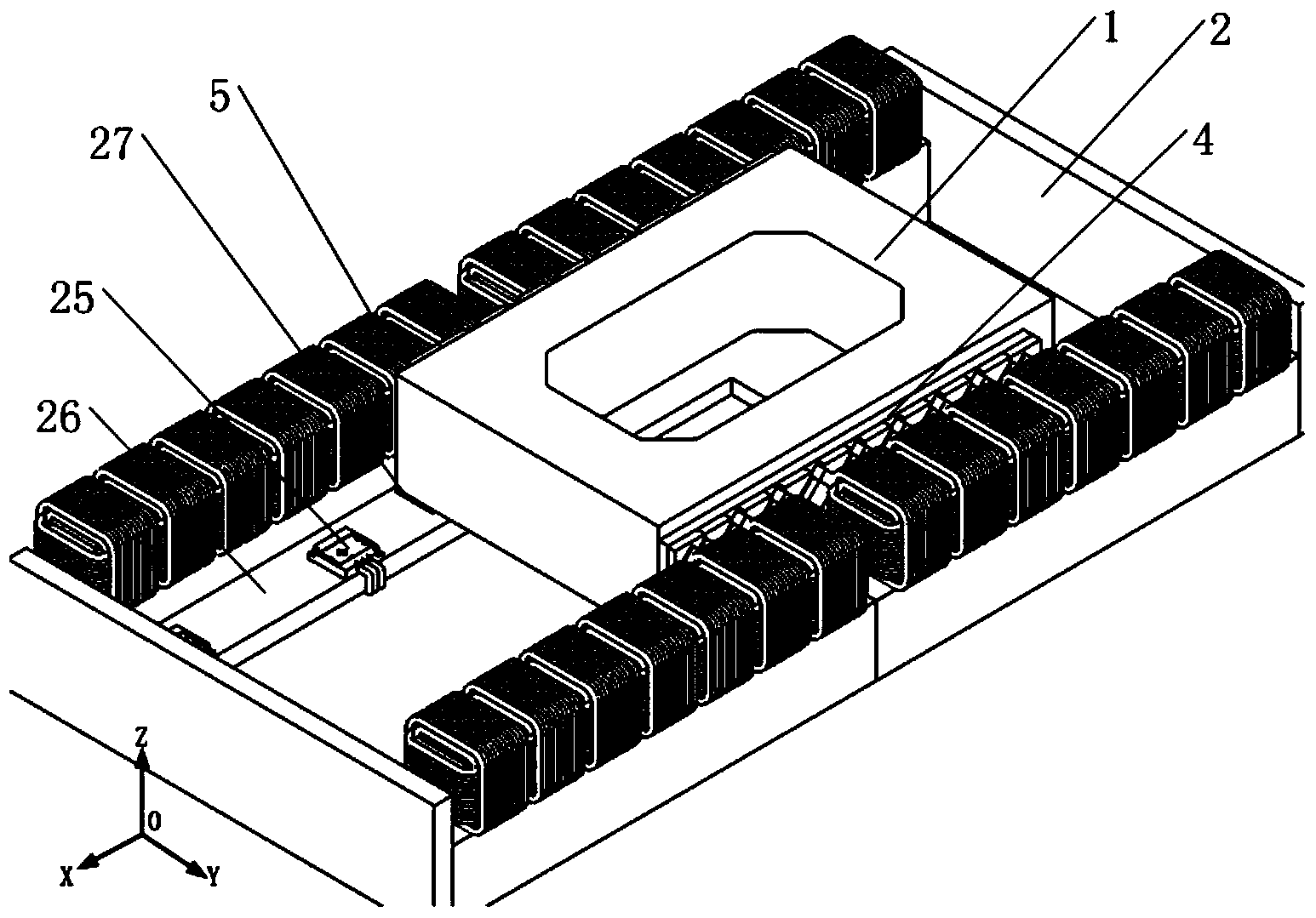
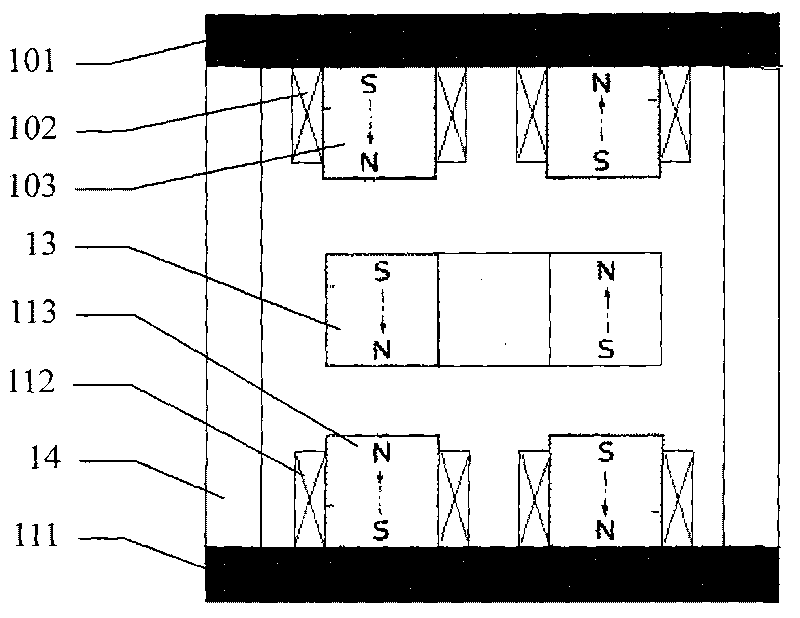
A planar motor includes a flat base element arranged in a plane, and substantially cuboidal first magnets arranged on the base element whose magnetization is perpendicular to the plane and which are arranged at evenly spaced intervals and with alternating polarity in a first direction and in a second direction. The planar motor also includes substantially cuboidal second magnets whose magnetization is parallel to the plane and which are disposed with alternating polarity in the first direction and second direction between the first magnets, so that each first magnet is surrounded by four second magnets. The first magnets are disposed on protrusions of the base element.
Owner:ETEL SA
Gas-magnet mixing suspended planar motor with easily expanded horizontal stroke
InactiveCN101527484ASimple mechanical structureReduce processing difficultySynchronous machinesMagnetic holding devicesClassical mechanicsMagnetic poles
The invention relates to a gas-magnet mixing suspended planar motor with easily expanded horizontal stroke, comprising a stator basal body arranged along a horizontal XY plane and a mover basal body suspended on the stator basal body and is parallel with the stator basal body. Two degrees of freedom Halbach permanent magnet arrays with wavelengths along the axis X and the axis Y directions are embedded on the surface of the stator basal body; each pair of magnetic poles of the two degrees of freedom Halbach permanent magnet arrays are formed by arraying first magnet to sixth magnet according to a four* four matrix; four corners of the lower surface of the mover basal body are respectively provided with a first thrust winding, a second thrust winding, a third thrust winding and a fourth thrust winding, wherein the wavelength direction of the first thrust winding and the third thrust winding are in the axis X direction; the wavelength direction of the second thrust winding and the fourth thrust winding are in the axis Y direction; four sides of the lower surface of the mover basal body are respectively provided with a first aerostatic bearing air-cushion, a second aerostatic bearing air-cushion, a third aerostatic bearing air-cushion and a fourth aerostatic bearing air-cushion.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
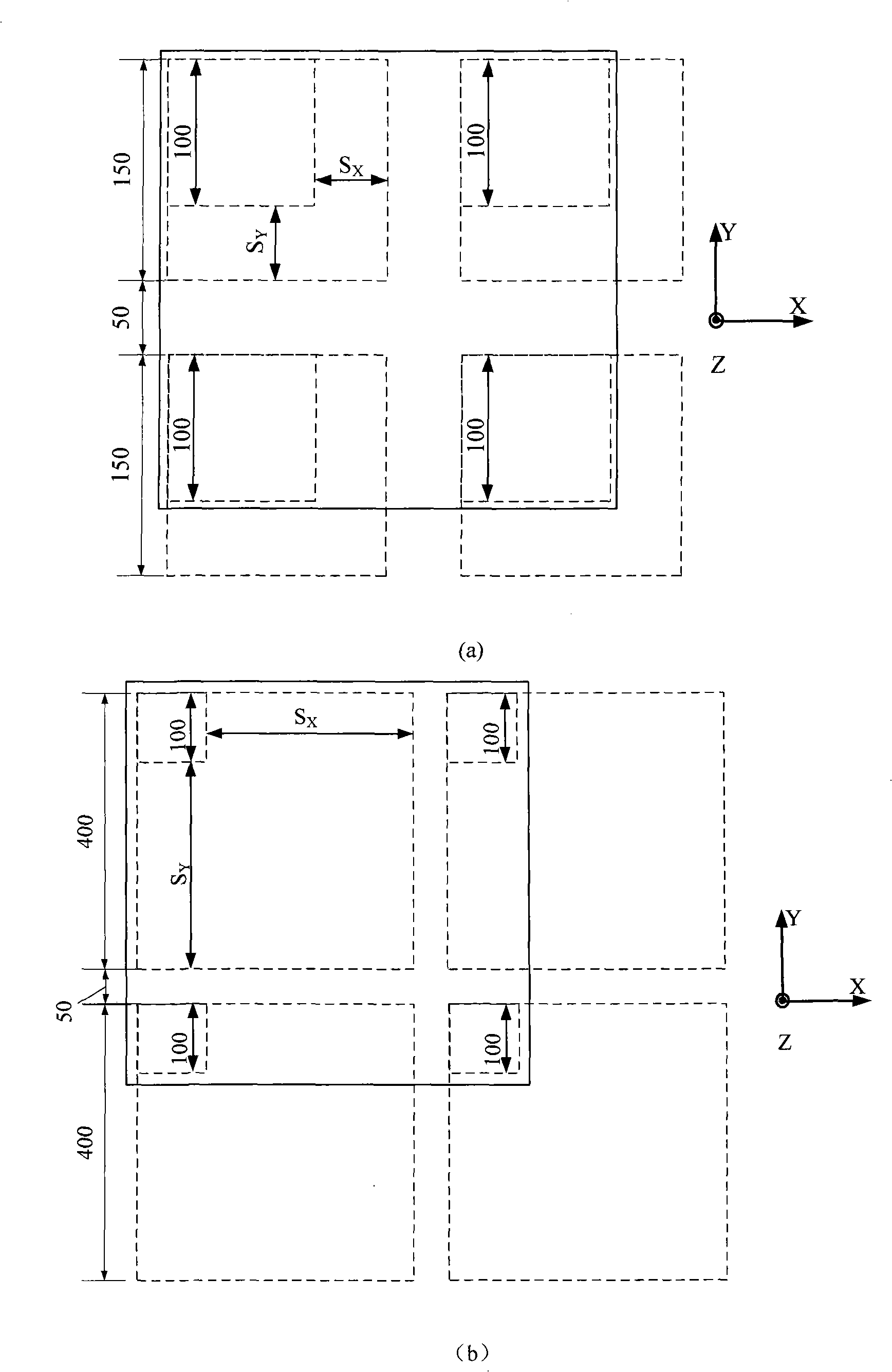
Magnet unit, magnet array, magnetic levitation planar motor and lithographic device using magnetic levitation planar motor
ActiveCN103208867AUnilateral magnetic densityReduce magnetic leakagePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusElectric machinePlanar motor
The invention discloses a cross magnet unit which comprises a first magnet and a second magnet unit surrounding the first magnet. The first magnet is an N-pole magnet or an S-pole magnet. The magnetization direction of the first magnet is the Z-xis direction. The second magnet unit comprises four groups of magnet combinations with identical structure. The four groups of magnet combinations are respectively located in the X-axis direction and the Y-axis direction. The magnetization direction of the magnet combinations points at the N-pole magnet or is far away from the S-pole magnet. Each group of magnet combinations comprise at least two prism magnets, pyramid magnets or pyramid frustum magnets. A magnet array, a magnetic levitation planar motor and a lithographic device using the magnetic levitation planar motor are further disclosed.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Planar motor
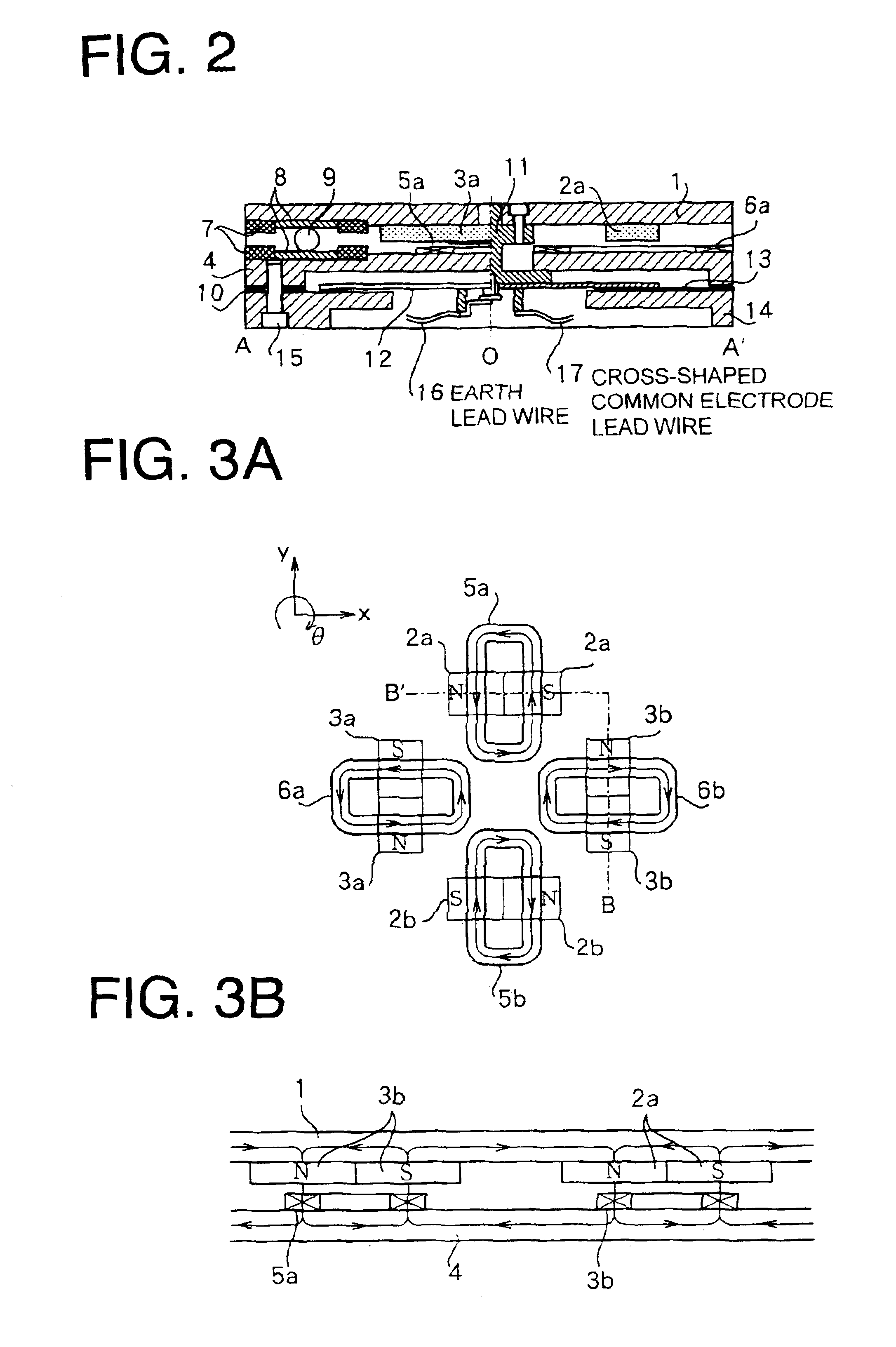
InactiveUS6949845B2Reduce designReduce vibrationMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlCapacitanceElectric machine
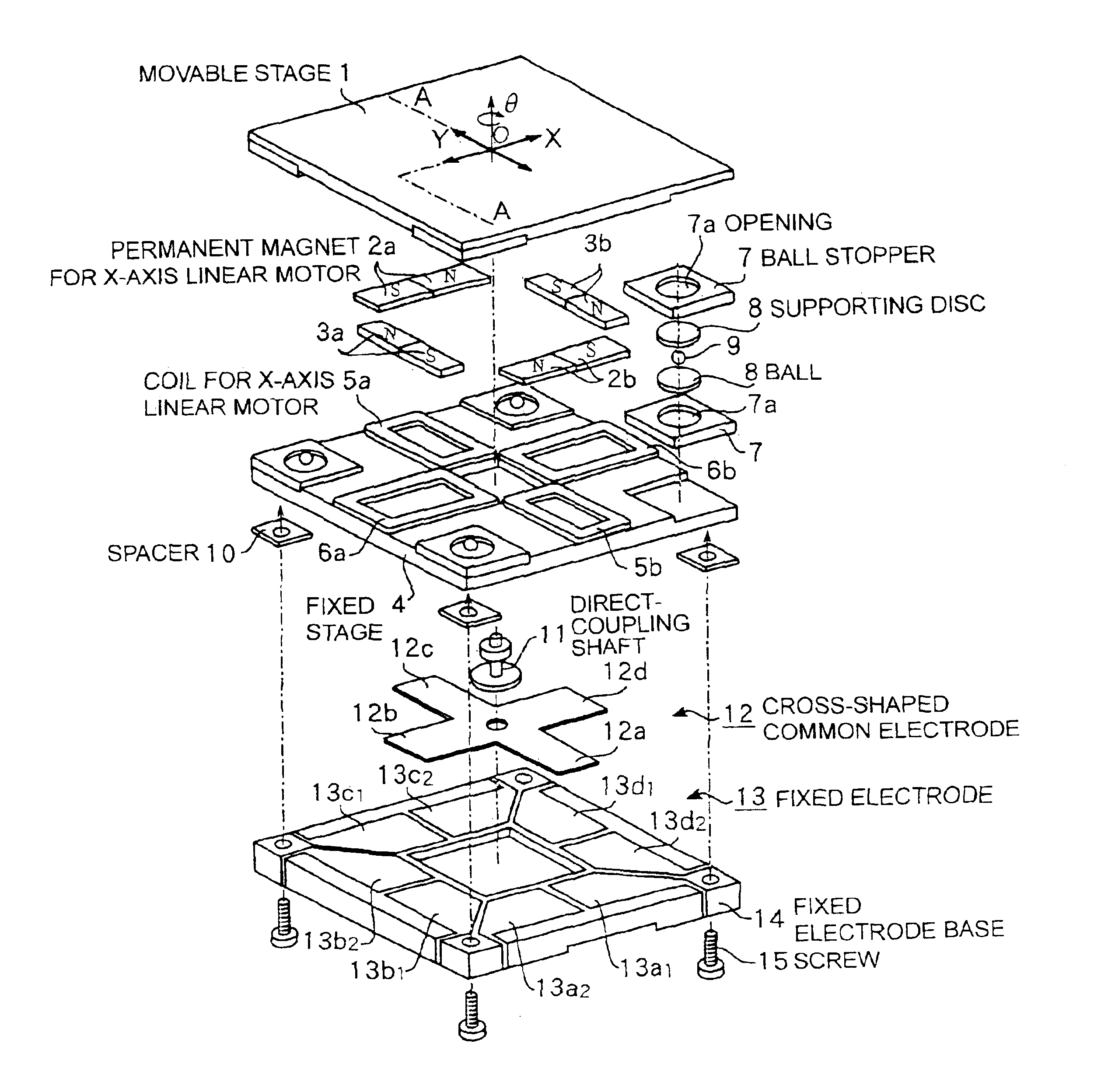
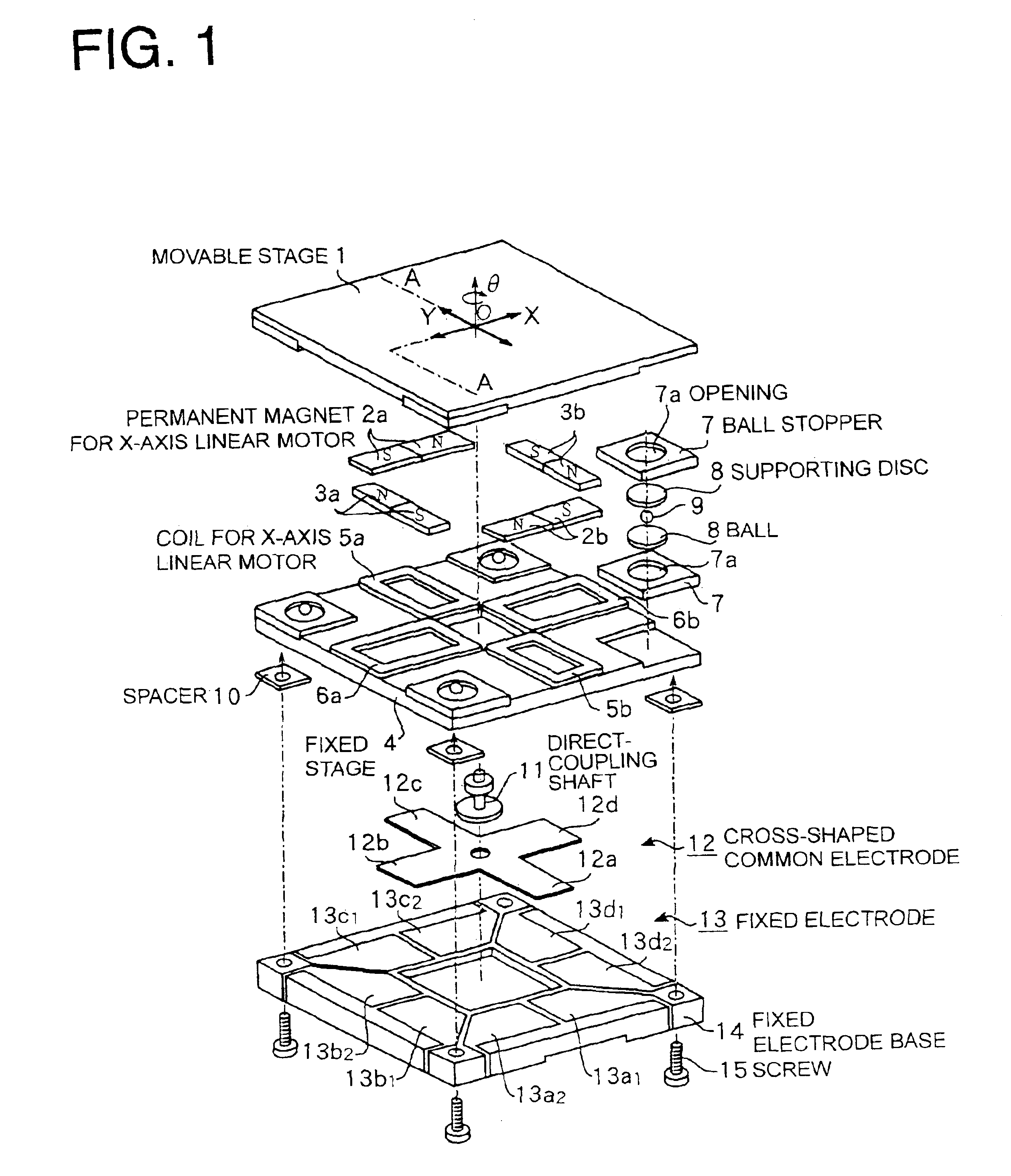
A planar motor permits a thinner design, controlled vibration, and highly accurate positioning by disposing X-axis and Y-axis coreless type linear motors on the same plane without using an expensive linear guide and by incorporating high-accuracy capacitance displacement sensors in X and Y directions. Two pairs of permanent magnets are disposed such that they are respectively orthogonalized with respect to two axes that are orthogonalized with each other on a movable stage and that they generate magnetic fluxes in a direction perpendicular to a surface of the movable stage. Furthermore, the permanent magnets of one pair are disposed symmetrically to each other about one of the two axes, while those of the other pair are disposed symmetrically to each other about the other axis. Two pairs of coils are provided such that they oppose and match the two pairs of permanent magnets. A cross-shaped common electrode is installed to the movable stage and disposed such that it opposes a fixed electrode composed of two electrodes disposed on a fixed electrode base. Displacements of the movable stage can be determined from changes in capacitance of capacitors formed by the cross-shaped common electrode and the fixed electrodes.
Owner:CHIBA PRECISION
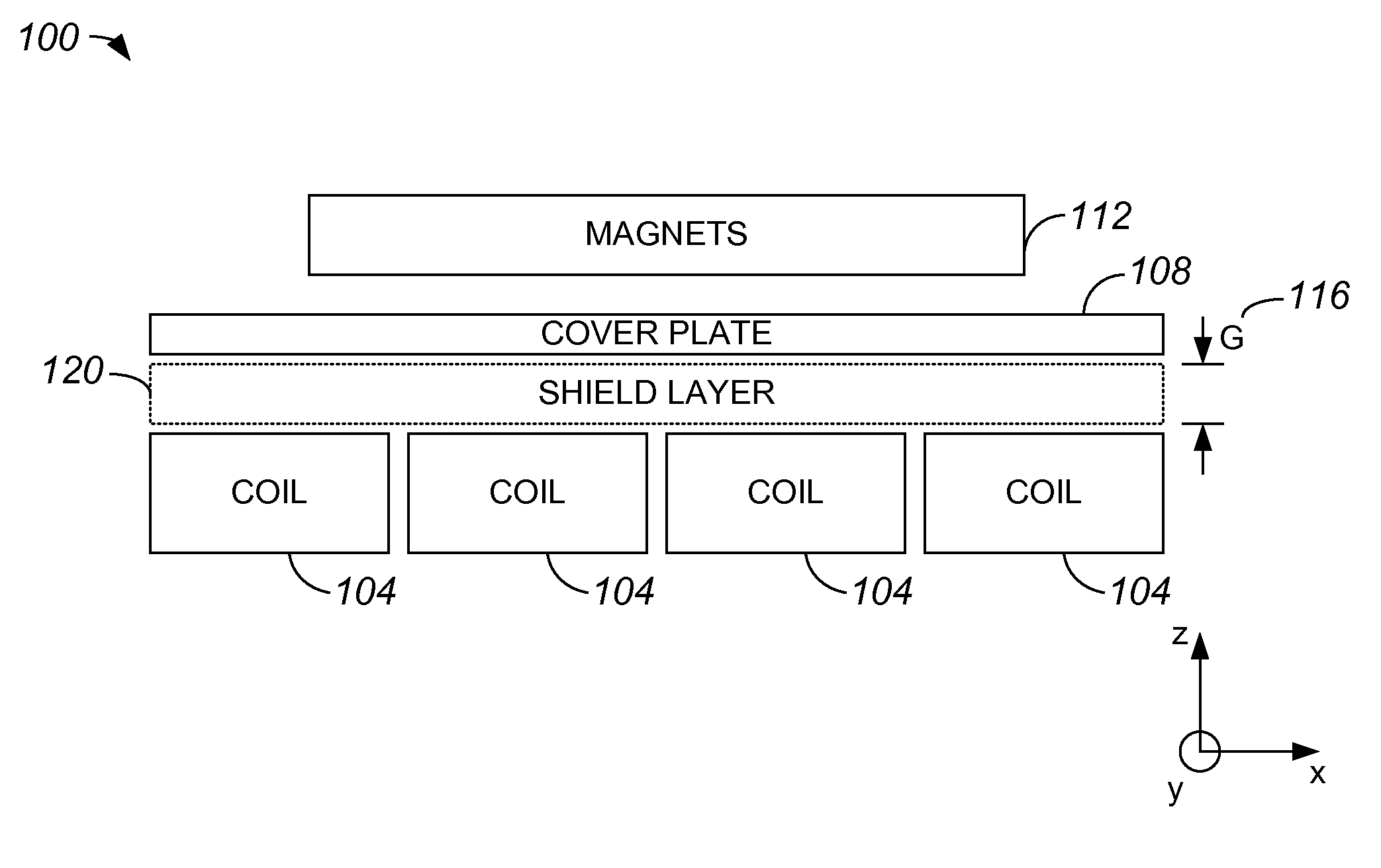
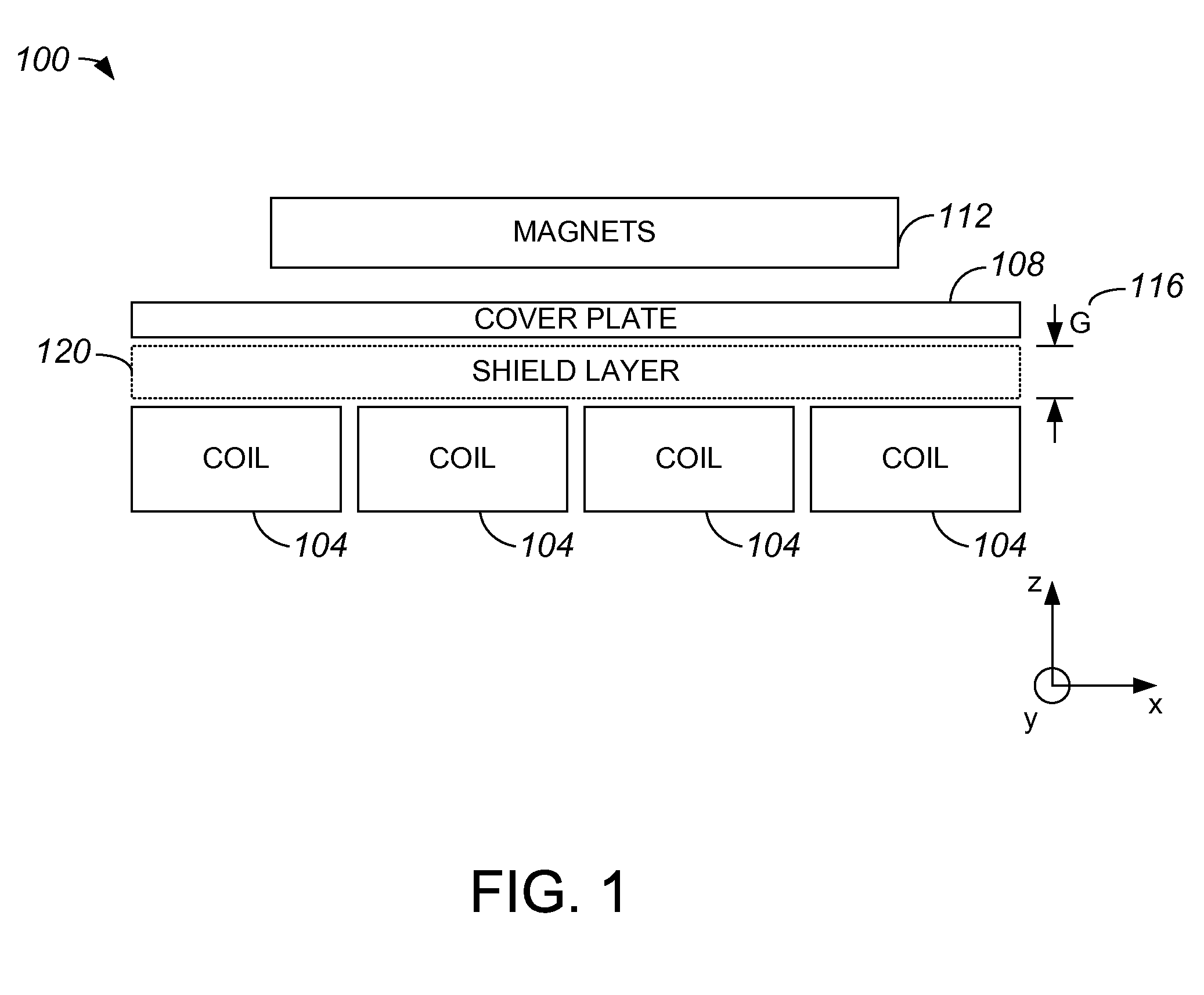
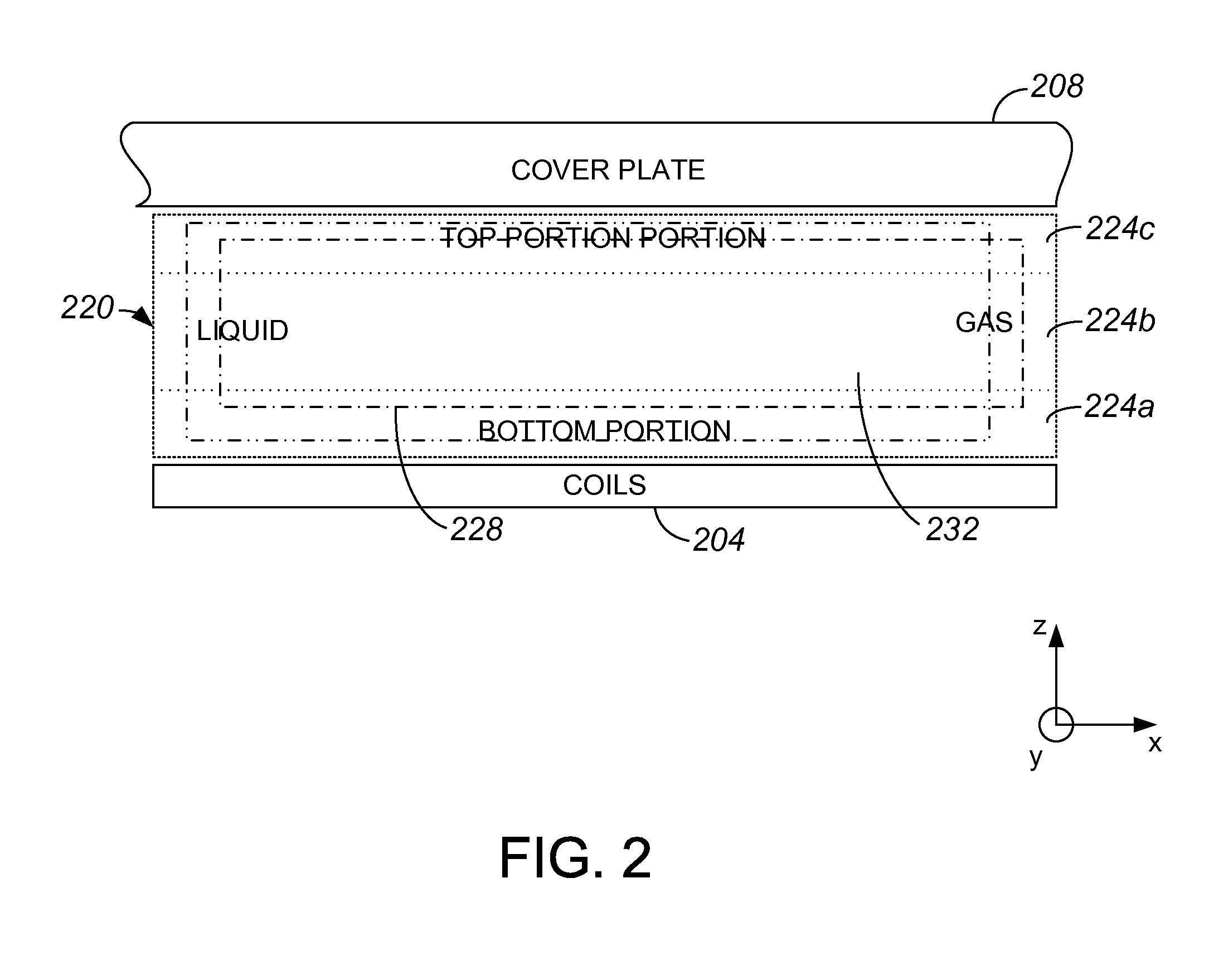
Shield layer plus refrigerated backside cooling for planar motors
InactiveUS20100156198A1Excessive heatingLess heatMagnetic circuitPhotomechanical apparatusPlanar motorElectric motor
Owner:NIKON CORP
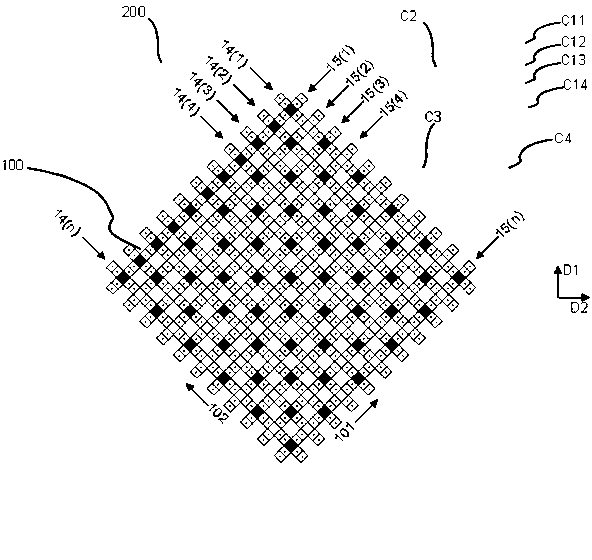
Power driving distribution method of moving iron type planar motor coil array
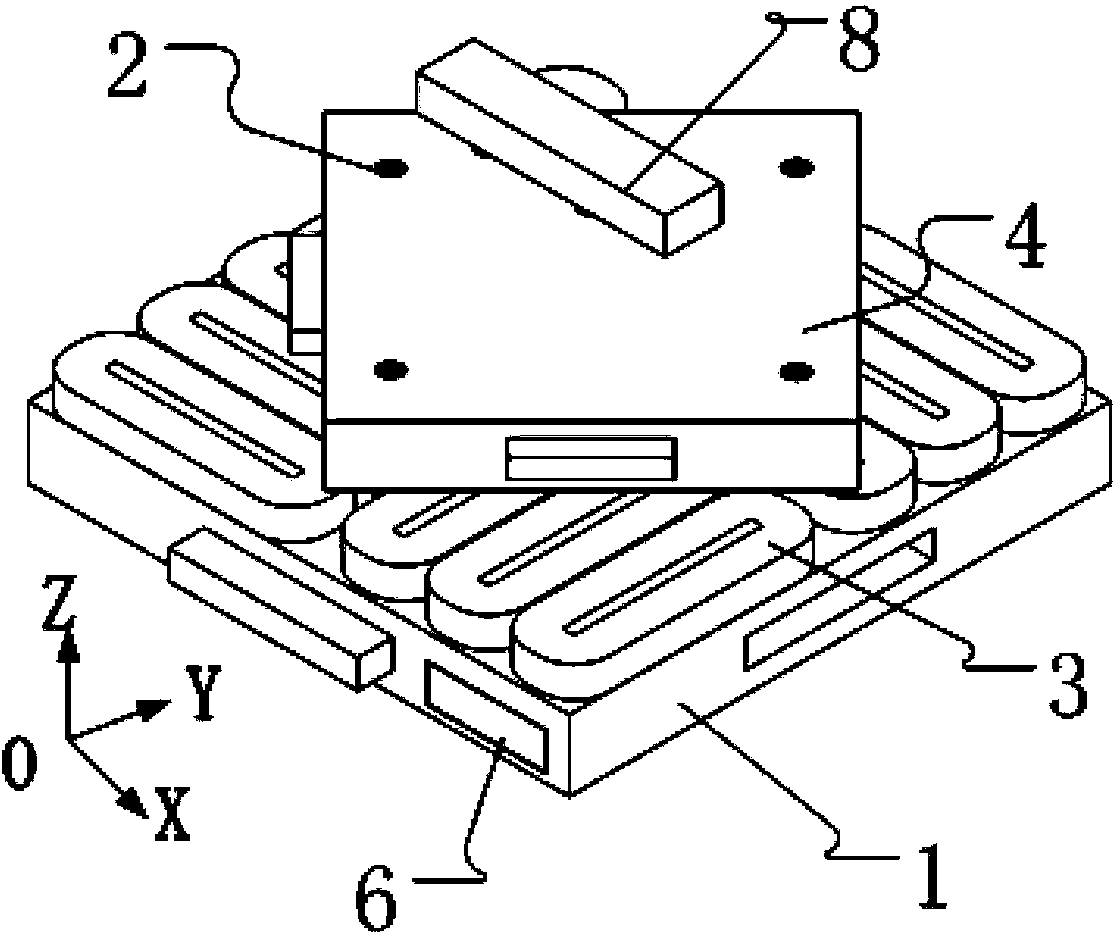
ActiveCN101707472AReduce in quantityRealize large stroke movementElectric motor controlMagnetic holding devicesCoil arrayDistribution method
The invention relates to a power driving distribution method of a moving iron type planar motor coil array. The method comprises the following steps: dividing a square stator coil array of the moving iron type planar motor into n*n dividing areas, dividing each dividing area into a work state area and a transitional state area, and determining the total quantity of power drivers according to the quantity of coils in each dividing area, and forming a driver array; and connecting the driver array with the stator coil array by switch equipment, and guaranteeing that each driver is connected with the coil at a corresponding position in each dividing area by the switch equipment. According to the position of a rotor magnetic steel array, the power driving distribution method determines the range of action of the coil array, uses the limitation of the transitional state area to control the on-off and the current of the coils, and realizes large-stroke planar vector movement of a rotor. The power driving distribution method can solve the problems of complex structure and extremely high total cost of the driver equipment, resulting from excessive quantity of the drivers due to excessive quantity of the stator coils.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Modularization moving-iron type six-freedom-degree maglev motion platform
ActiveCN103441708AReduce in quantityReduce complexityPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusCarrying capacityComputer module
The invention discloses a modularization moving-iron type six-freedom-degree maglev motion platform and is mainly applied to semiconductor lithography equipment. The motion platform comprises a pedestal, at least one maglev planar motor module and a somatosensory controller. Each maglev planar motor module is composed of a maglev planar motor rotor and a maglev planar motor stator so that a micro moving workbench can rotate in an X direction, in a Y direction and around a Z axis. Compared to the prior art, the motion platform provided by the invention has the following advantages: coils are optimized and the coils with different specifications can be adaptive to a certain thrust range so that combination can be carried out according to different carrying capacity requirements; and the provided motion platform also has the advantages of simple structure, high-efficient integration, saved production cost and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Planar motor initialization method, planar motro, lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20050285550A1Force generatedImprove accuracyAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlThree-phasePlanar motor
A planar motor is controlled by supplying a three-phase alternating current to a coil assembly. Each phase is supplied to one of three coils. The coils are positioned in a magnetic field generated by a magnet plate having alternating magnet poles at its surface for generating an alternating magnetic field. In operation, the phase of each current flowing through each coil determines the direction of a force generated due to the current in the magnetic field. For correct operation, the phase angle of each current is to be adapted to the local direction of the magnetic field by determining a commutation-offset angle. The commutation-offset angle is determined by generating a force in an unknown direction and varying the commutation-angle, and determining when the generated force is directed perpendicular to the magnet plate, while ensuring that the generated force does not exceed a horizontal friction force. By determining a maximum compression of end stops of the coil assembly, or determining a maximum pressure, it may be determined when the generated force is directed perpendicular to the magnet plate.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
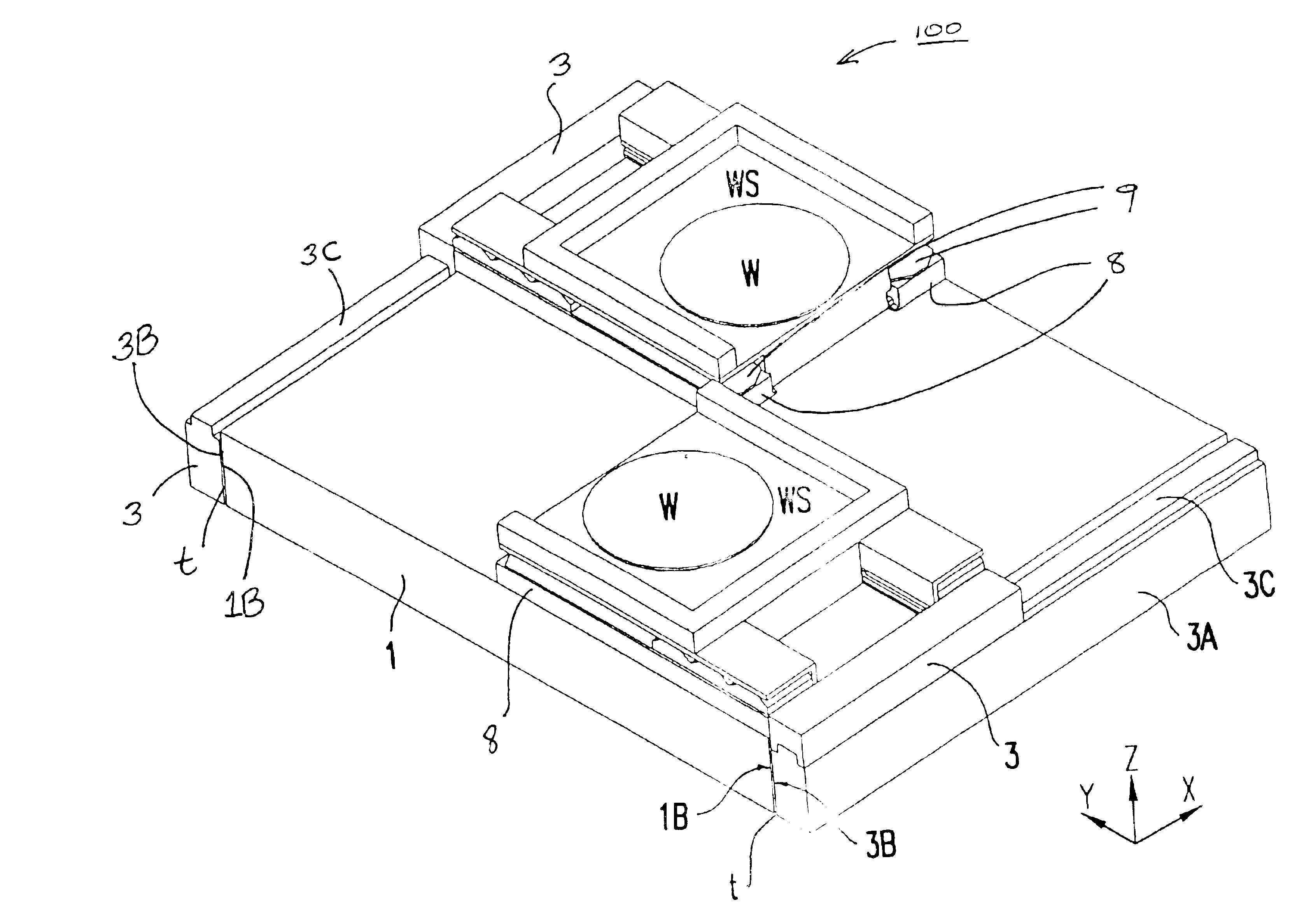
Multi-stage exchange system and exchange method for multi-station silicon wafer stage
ActiveCN102681363ALow costReduce the use of areaPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusEngineeringHigh productivity
The invention discloses a multi-stage exchange system and a multi-stage exchange method for a multi-station silicon wafer stage. The multi-stage exchange system comprises a measurement station, an exposure station and a process treatment station, wherein the process treatment station, the measurement station and the exposure station are all positioned in an air floatation plane or a magnetic suspension plane on the upper surface of a base stage; and a wafer carrying stage is arranged on the upper surface of the base stage through an air floatation bearing or magnetic suspension, carries a silicon wafer and is driven by a linear motor or a planar motor to finish exchange of all stations. By adding the process treatment station, the process treatment of two adjacent exposure procedures can be realized in a photo-etching machine, and an exposure procedure and a process treatment procedure can be concurrently finished in the same photo-etching machine, so continuous exposure is realized in the same photo-etching machine, and requirements for improving productivity and accuracy and reducing cost and using area in a dual-exposure technology or even a multi-exposure technology are met.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Wafer positioner with planar motor and mag-lev fine stage
InactiveUSRE41232E1Magnetic circuitSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThree degrees of freedomPlanar motor
A positioning stage assembly having a coarse stage which includes a planar motor driveable in at least two degrees of freedom, and a fine stage positioned on the coarse stage which is driveable in at least three degrees of freedom with respect to the coarse stage. More preferably, the fine stage is driveable in six degrees of freedom and includes variable reluctance actuators for positioning in three degrees of freedom.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Coarse-fine motion integrated magnetic-levitation mask platform system
ActiveCN103454864APhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusProduction rateCoil array
The invention relates to a coarse-fine motion integrated magnetic-levitation mask platform system mainly applied to a photoetching machine. The system comprises a mask platform, a drive motor and a stander, wherein the drive motor is a moving-iron type magnetic-levitation planar motor, and permanent magnet arrays of the drive motor are connected with the mask platform, so that an active cell part of the mask platform system is formed; coil arrays of the drive motor are connected with the stander to form a stator part of the mask platform system. According to the coarse-fine motion integrated magnetic-levitation mask platform system, due to the drive motor, the six-degree-of-freedom movement of the mask platform system can be realized, and a planar grating ruler is taken as a measurement sensor of the mask platform system to carry out feedback measurement on the mask platform; the volume of the mask platform is reduced, meanwhile, the speed, the accelerated speed and the control bandwidth of the mask platform are improved, requirements of high moving accuracy and positioning accuracy are met, and then the production rate, the alignment precision and the resolution of the photoetching machine are improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Long-travel high-accuracy multiple-degree-of-freedom planar motor
The invention relates to a long-travel high-accuracy multiple-degree-of-freedom planar motor which belongs to the field of motors. The planar motor solves the problems that the traditional planar motors have the defects of limited travel of rotors, complex control, low positioning accuracy and the like. The planar motor comprises a stator of the long-travel planar motor, i rotors of the long-travel planar motor, i short-travel planar motors and i sets of magnetic levitation supporting device, wherein one short-travel planar motor and one magnetic levitation supporting device are fixed on each rotor of the long-travel planar motor; each magnetic levitation supporting device comprises m magnetic levitation support mechanisms, and the m magnetic levitation support mechanisms are evenly distributed to the periphery of the stator of the short-travel planar motor; the stator of the short-travel planar motor is fixedly connected with the rotor of the long-travel planar motor and stators of the m magnetic levitation support mechanisms, and all rotors of the m magnetic levitation support mechanisms are fixedly connected with a rotor of the short-travel planar motor; i is an integer greater than 0, and m is an integer greater than 1.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
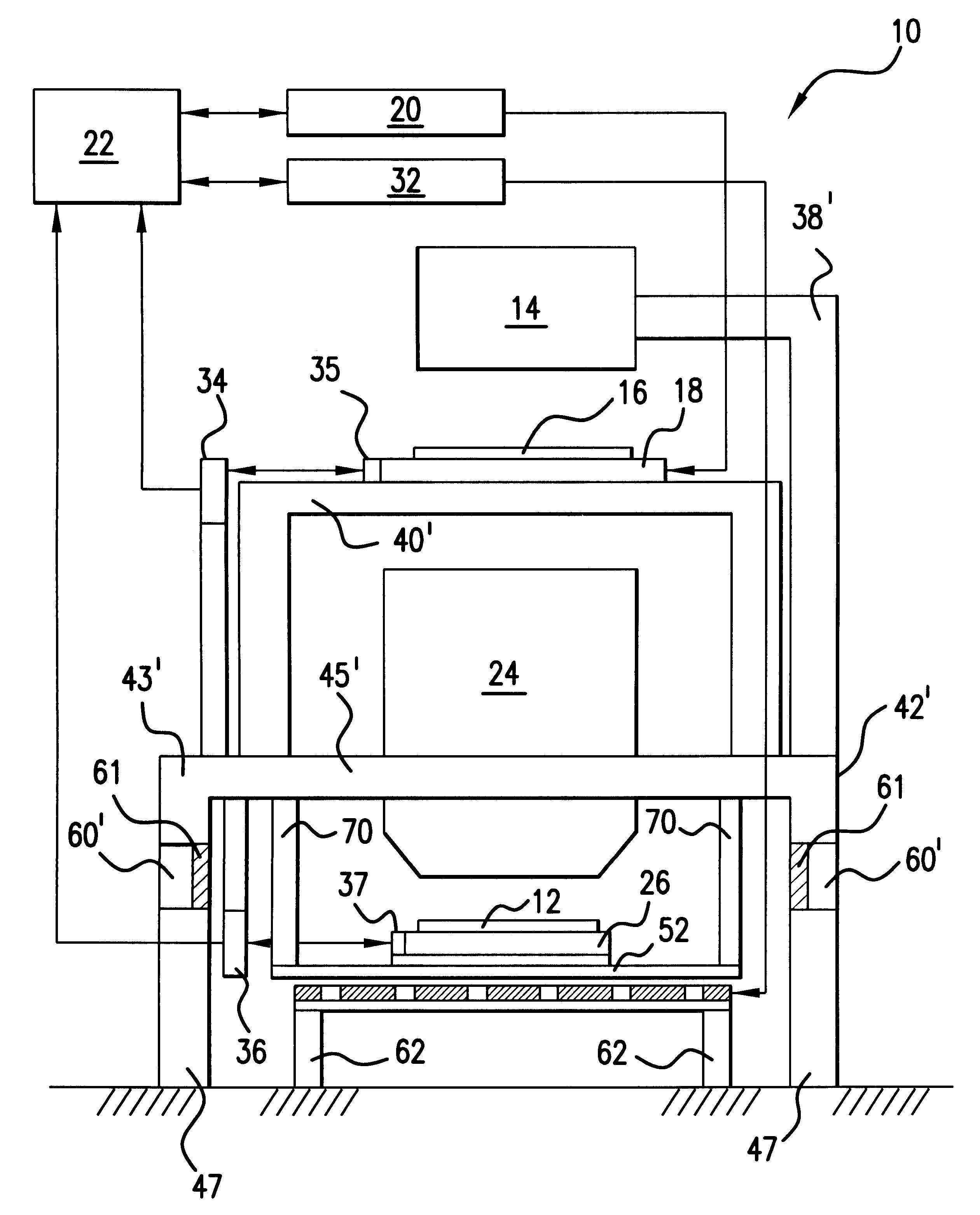
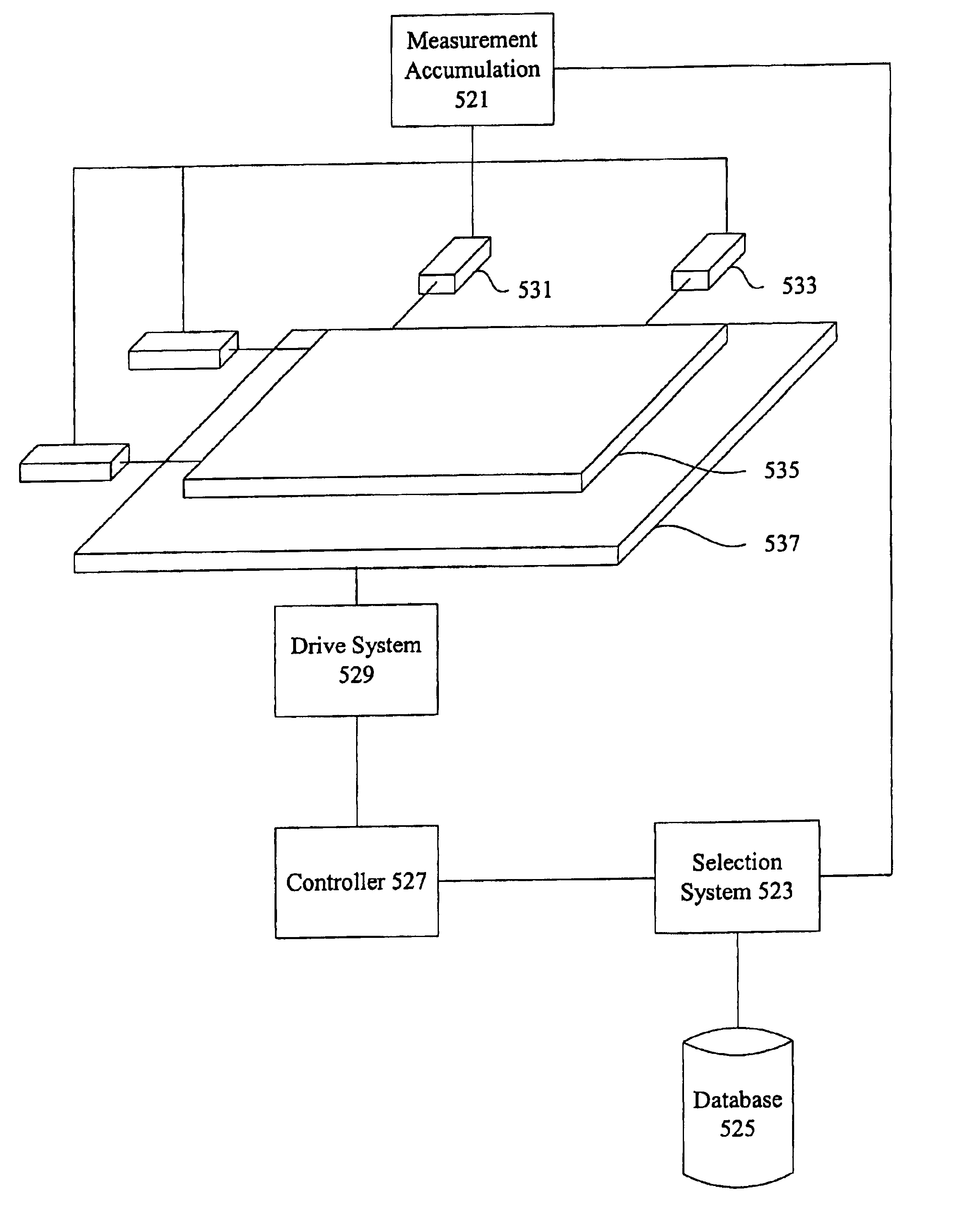
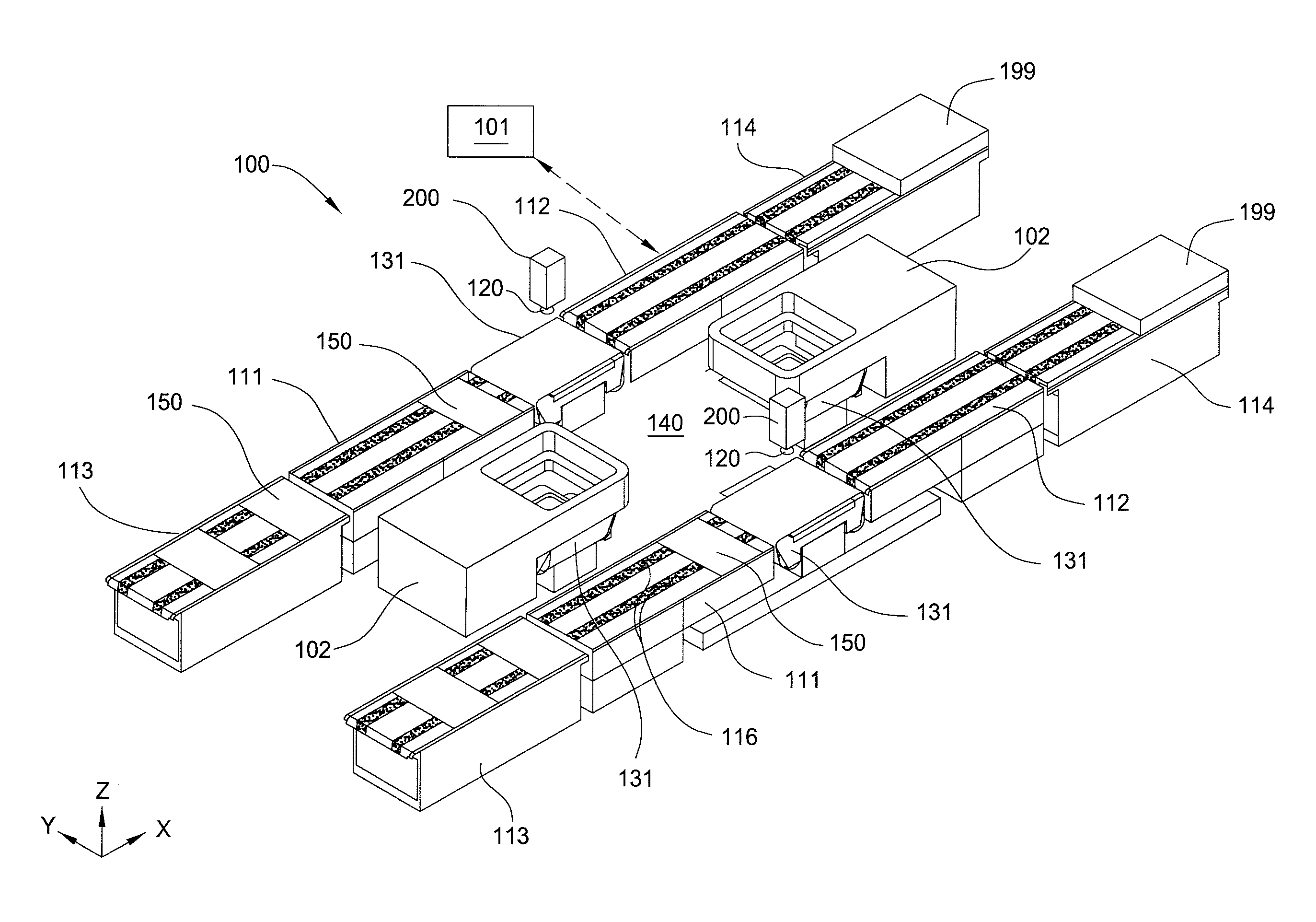
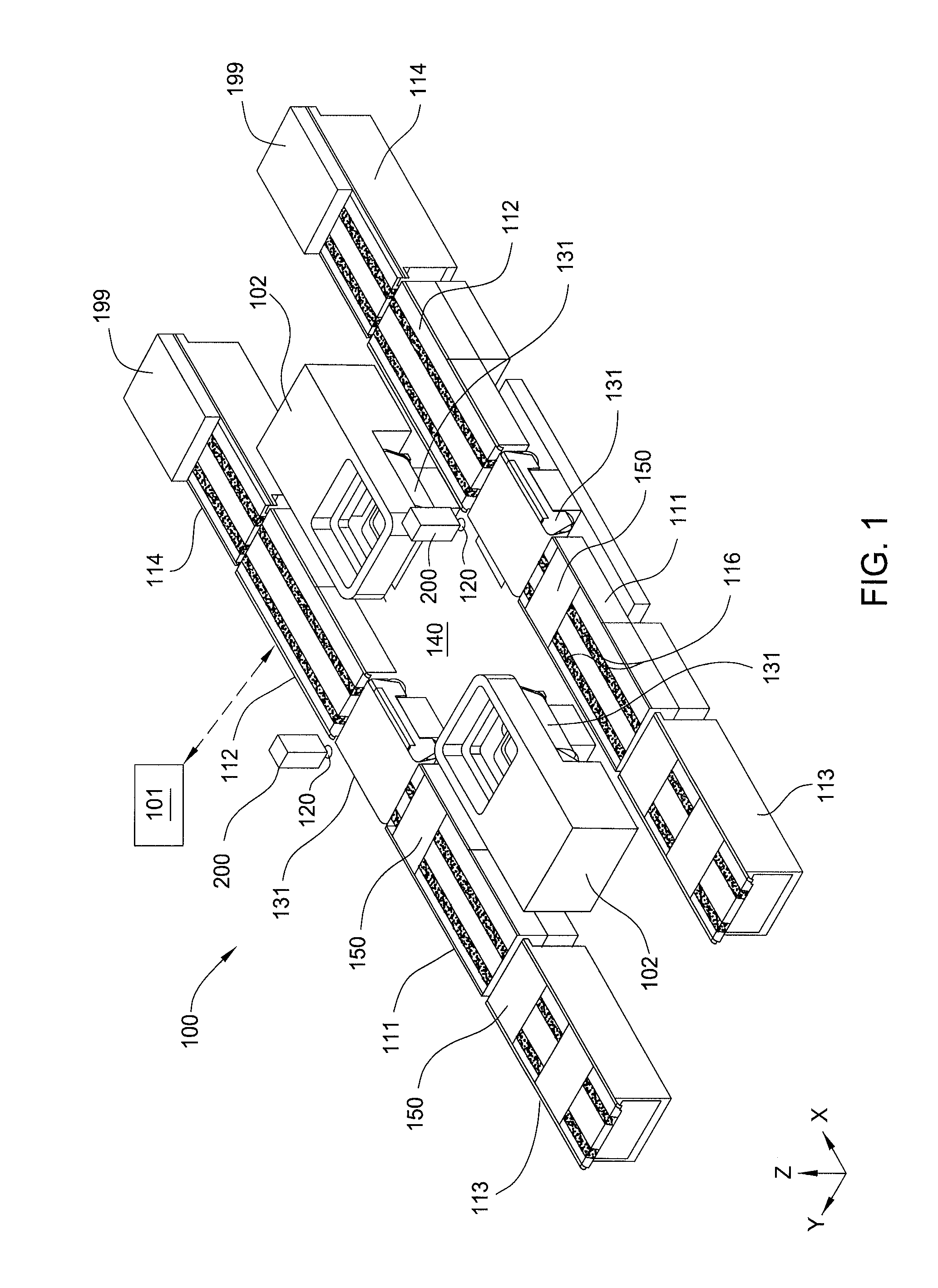
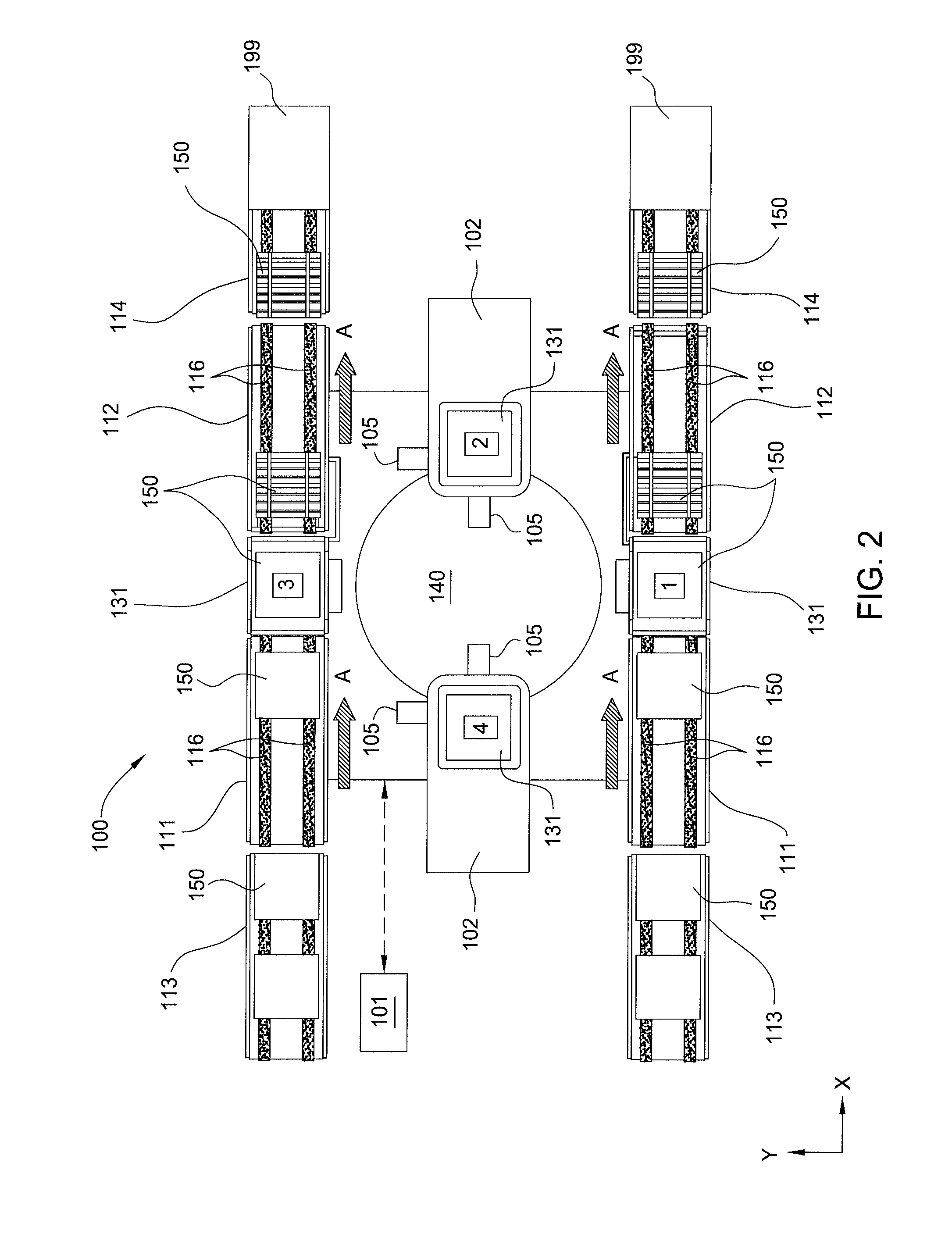
Substrate processing system
InactiveUS20120109355A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingControl using feedbackScreen printingMaterial removal
Embodiments of the present invention provide an apparatus and method for processing substrates in a processing system that has an increased system throughput, improved system uptime, and improved device yield performance, while maintaining a repeatable and accurate substrate processing. The system may include multiple processing nests laterally positionable by use of a planar motor via multiple planar movers controlled by a system controller. A substrate supported by each processing nest may be angularly positionable by a rotary actuator. The system may be used in screen printing, ink jet printing, thermal processing, device testing, and material removal processes, among others.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Two-dimensional variable reluctance planar motor
InactiveUS20050248217A1Easy to useBig gapMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlBrickPlanar motor
A kind of 2-D variable reluctance planar motor comprises: a stator base combined by a plurality of laminated steel bricks; a moving platform consisting of two rows of spaced coil-shoes; traditional sliding supports to hold said platform above said stator base; two electronic rulers for scaling the real position of the platform; traditional supporting means for holding the platform at a distance above the stator base; computer and software for generating motion command signal to PWM generator; PWM current generator for energizing the coils of the moving platform; when a reference data (the final position of the platform) is input into the computer, the computer will give command to the platform and make it moving; once the moving platform is set in motion, the electronic rules continuously detect and transfer the location data of said platform to the computer; the computer continuously compares the data sent by said rules with reference data and gives command to the platform until said two kinds of data are equal. The planar motor of this invention uses no magnets, no constant air-gap and no accurately manufactured component. The working accuracy can easily reach 0.001 mm and the cost is very low.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Magnetic-suspension planar feed motion device
InactiveCN102176649APrecise feed movementImprove stabilityMagnetic holding devicesGratingThree-phase
The invention discloses a magnetic-suspension planar feed motion device, which is characterized in that a planar motor is adopted to drive; a stator platform is provided with a square raised head array stator which is formed by silicon sheets evenly; a Y-direction movable platform is provided with two sets of mutually orthorhombic three-phase exciting winding rotors; magnetic-suspension sliding sleeves in two directions are used for supporting a rotor platform respectively; the magnetic-suspension sliding sleeves are arranged on cylindrical guides in the X and Y directions; coil currents in the magnetic-suspension sliding sleeves are controlled to suspend the rotor platform, thus improving the stability and the efficiency of planar motion; excitation voltages are exerted on the three-phase exciting winding rotors by regulation to generate electromagnetic driving power so as to control the planar motion direction of the rotor platform; and grating sensors in two motion directions are utilized to detect motion positions so as to realize accurate planar feed motion. The magnetic-suspension planar feed motion device can be applied to special equipment for manufacturing photoelectrons,micro-electronics and the like, and has wide market prospects.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com