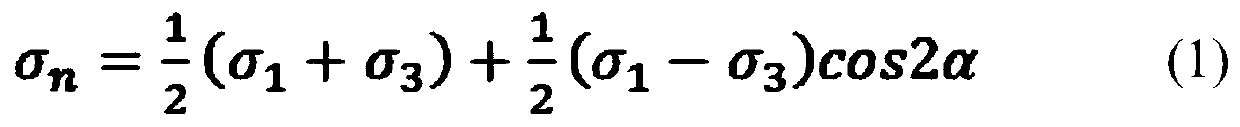Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
103 results about "Differential stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Differential stress is the difference between the greatest and the least compressive stress experienced by an object. For both the geological and civil engineering convention σ₁ is the greatest compressive stress and σ₃ is the weakest, σD=σ₁-σ₃. In other engineering fields and in physics, σ₃ is the greatest compressive stress and σ₁ is the weakest, so σD=σ₃-σ₁. These conventions originated because geologists and civil engineers (especially soil mechanicians) are often concerned with failure in compression, while many other engineers are concerned with failure in tension.
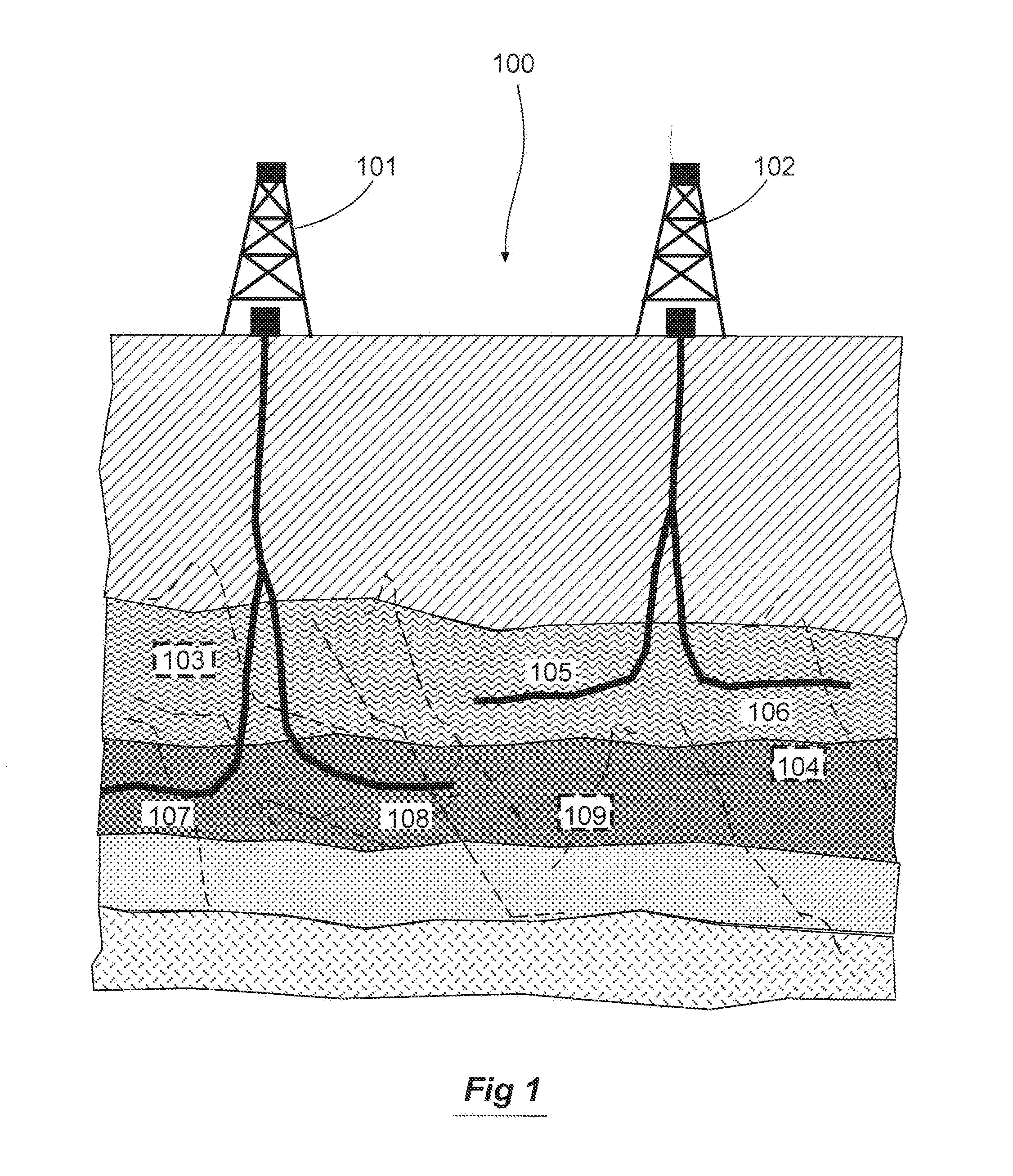
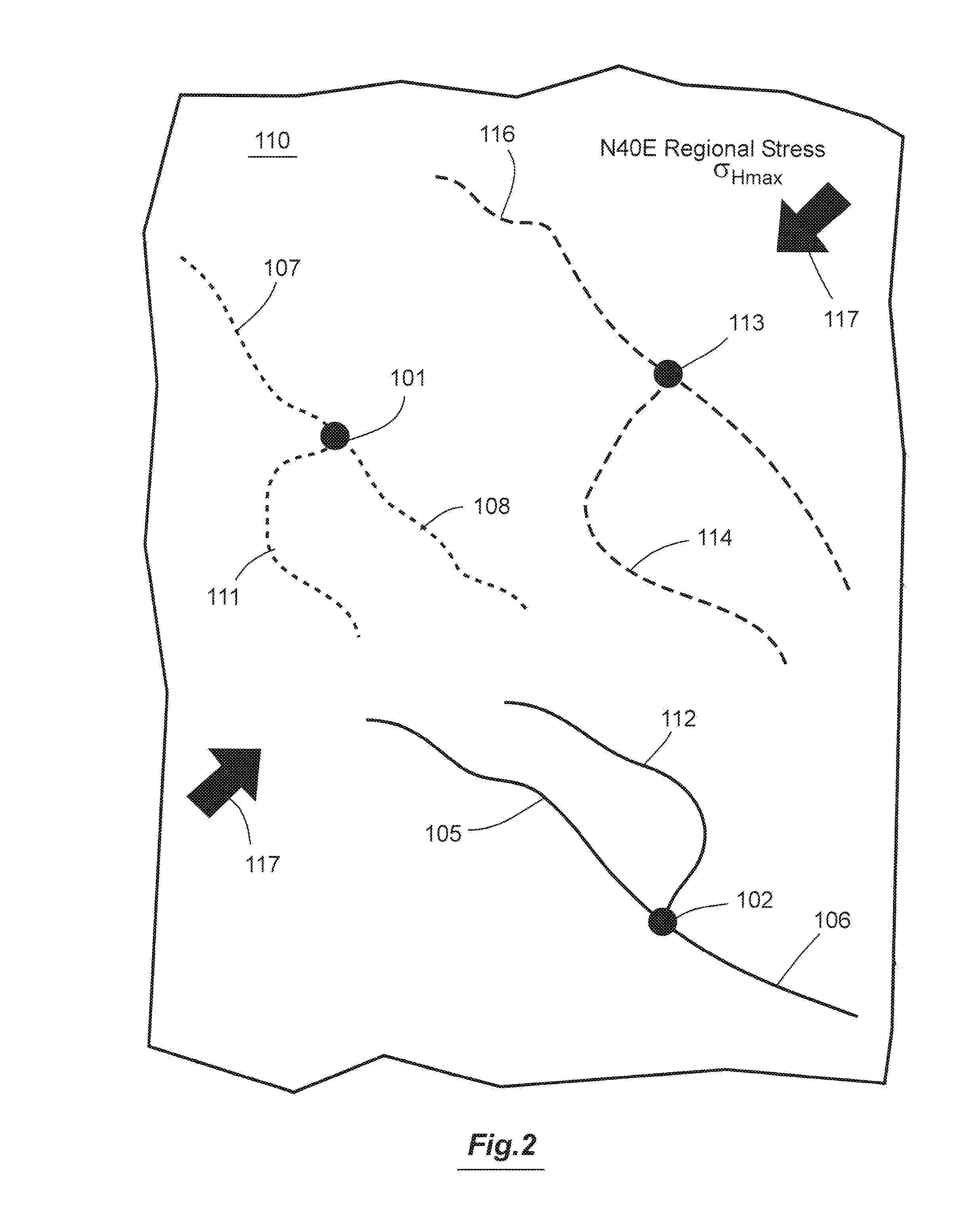
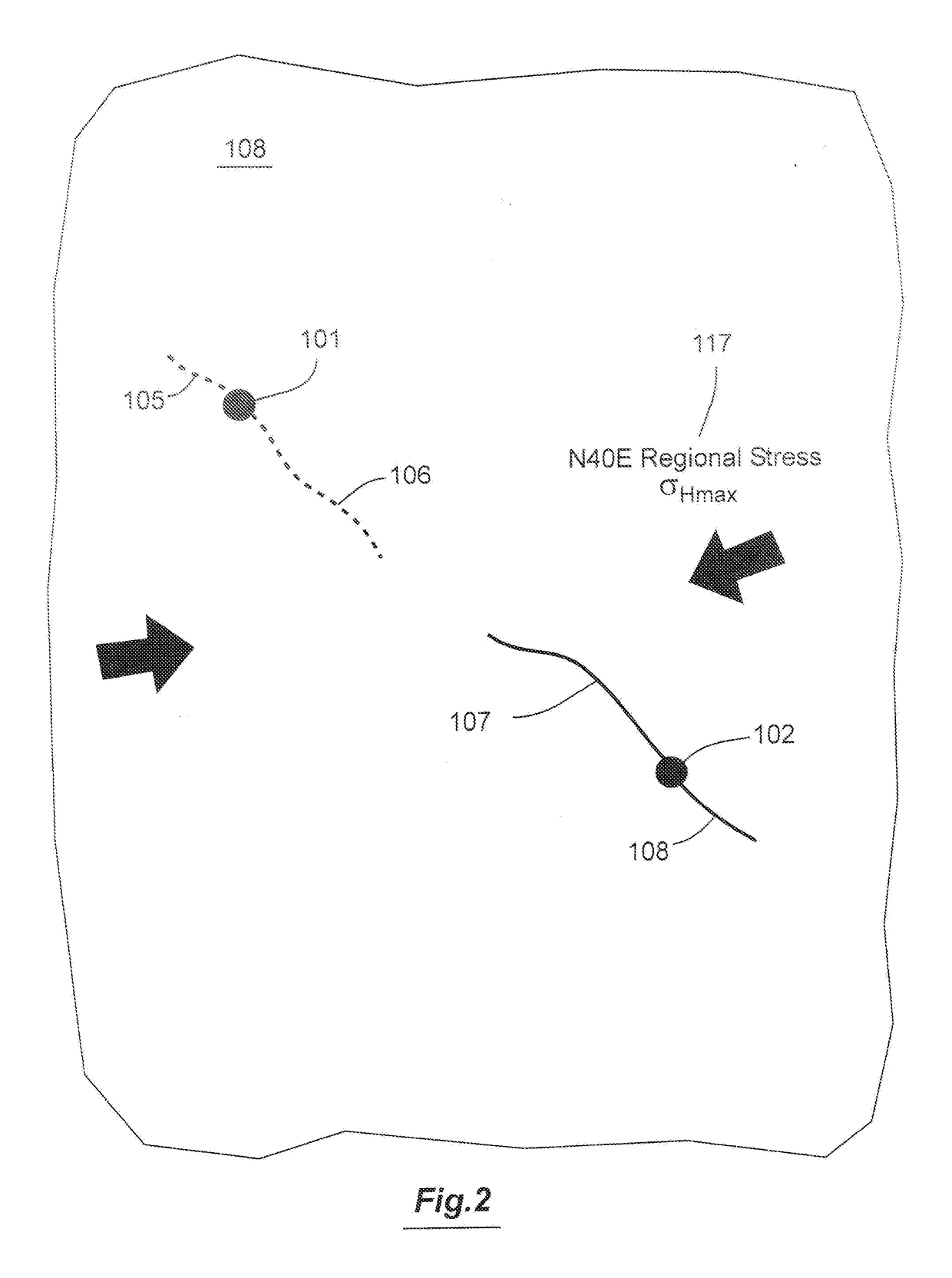
Method For Modeling Stimulated Reservoir Properties Resulting From Hydraulic Fracturing In Naturally Fractured Reservoirs
InactiveUS20170145793A1Increase productionLow costFluid removalDesign optimisation/simulationPrincipal stressHydraulic fracturing
A method for optimizing hydraulic fracturing simulates the geomechanical interaction between regional stress and natural fractures in a reservoir. An equivalent fracture model is created from data on the natural fracture density, regional stress and geomechanical properties of the reservoir, so that points in the reservoir are assigned a fracture length and fracture orientation. The horizontal differential stress and maximum principal stress direction at points in the reservoir are then estimated by meshless particle-based geomechanical simulation using the equivalent fracture model as an input. The meshless particle-based geomechanical simulator uses the derived initial geomechanical condition to simulate the sequence of hydraulic fracturing and derive the resulting strain and J integral that can be used to estimate the asymmetric half fracture lengths and initial propped permeability needed by hydraulic fracturing design and reservoir simulation software to optimize wellbore and completion stage positions.
Owner:FRACGEO LLC
System For Hydraulic Fracturing Design And Optimization In Naturally Fractured Reservoirs
InactiveUS20170051598A1Increase productionHigh productFluid removalDesign optimisation/simulationPrincipal stressHydraulic fracturing
A method for optimizing hydraulic fracturing and refracturing simulates the geomechanical interaction between regional stress and natural fractures in a reservoir. An equivalent fracture model is created from data on the natural fracture density, regional stress and elastic properties of the reservoir, so that points in the reservoir are assigned a fracture length and fracture orientation. The horizontal differential stress and maximum principal stress direction at points in the reservoir are then estimated by meshless particle-based geomechanical simulation using the equivalent fracture model as an input. Regions in the reservoir having low differential stress based on the simulation can then be selected for initial hydraulic fracturing. Regions in the reservoir having high differential stress based on the simulation can then be selected for refracturing.
Owner:FRACGEO LLC
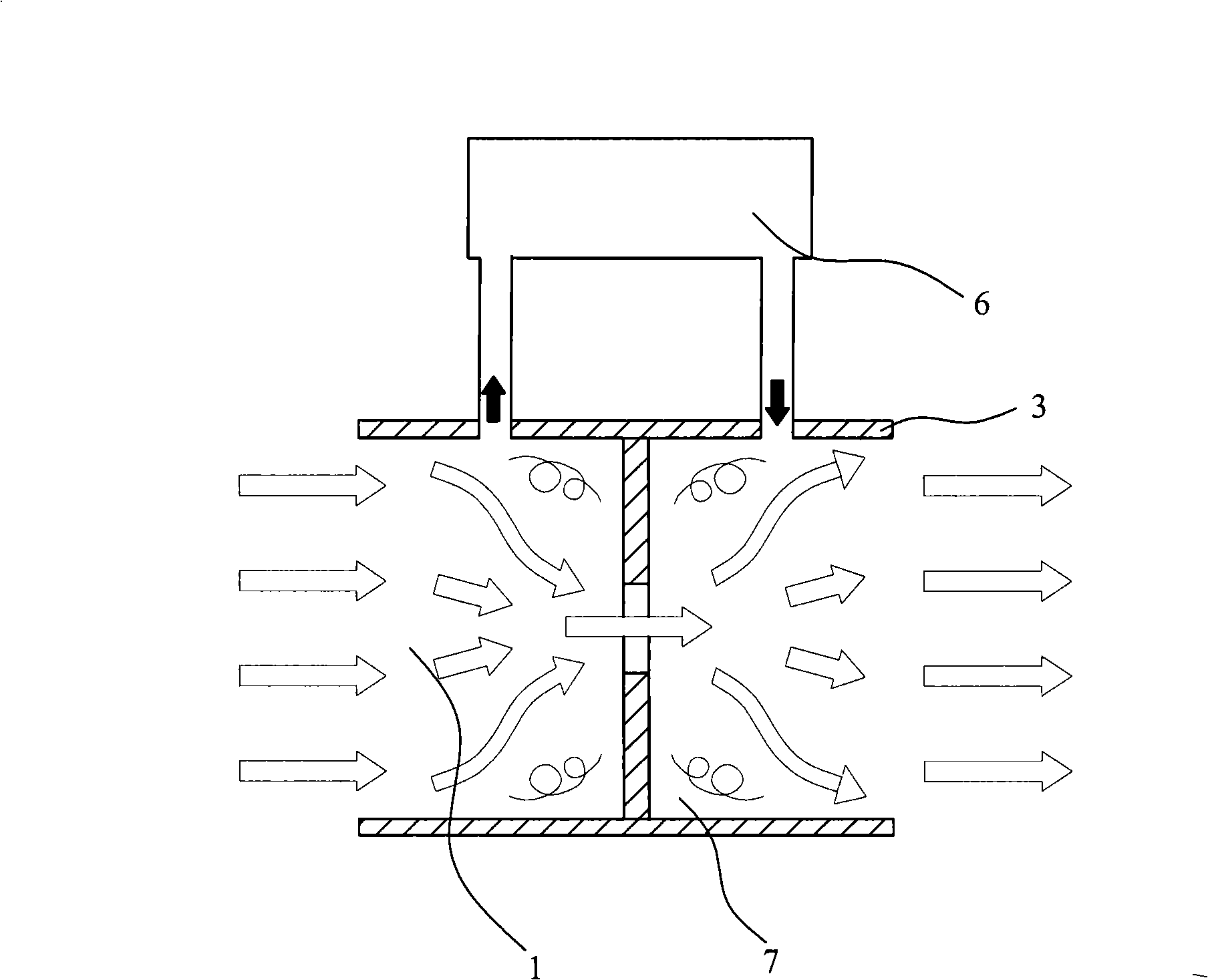
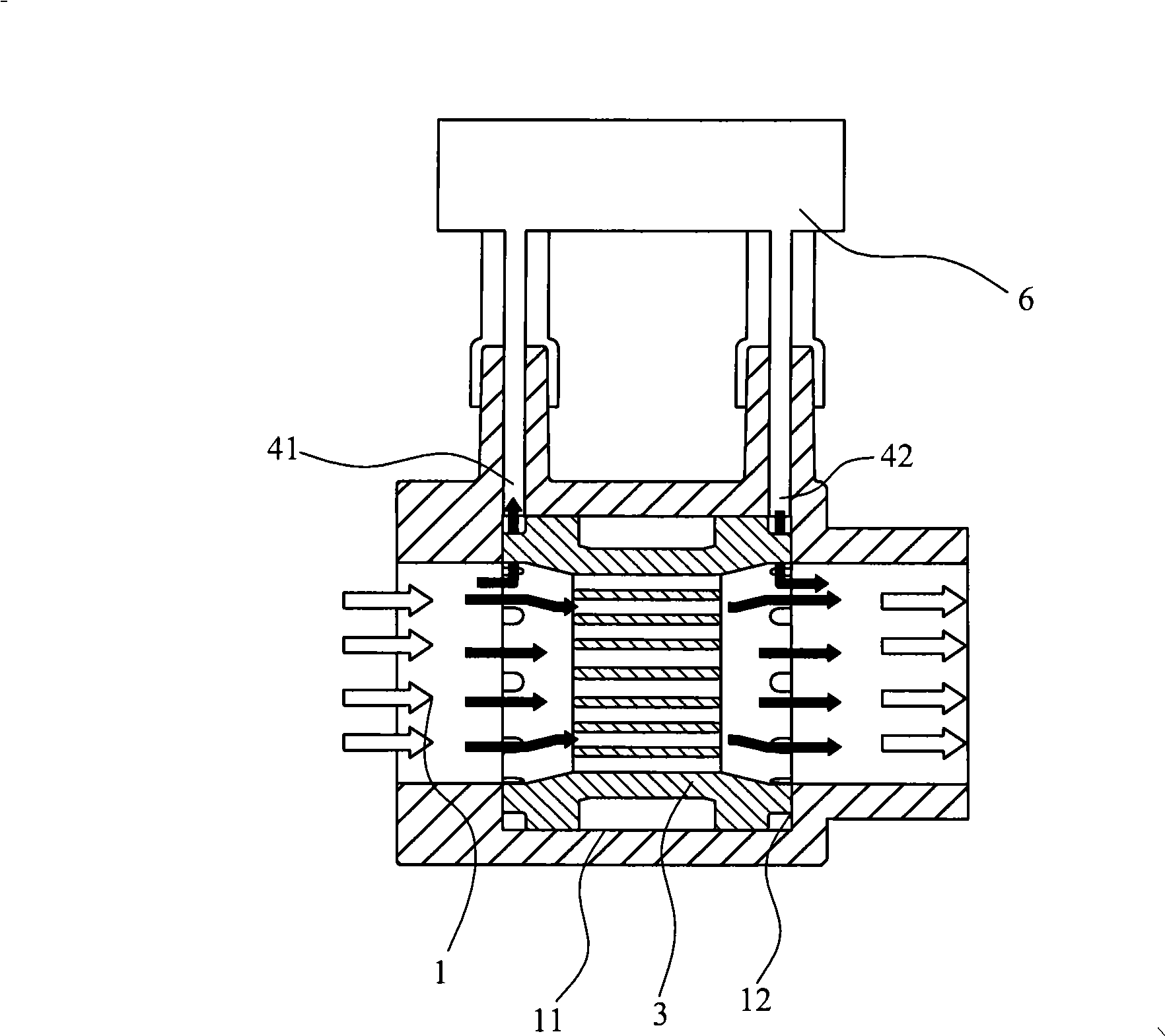
Breathing machine and its low differential pressure type flow quantity detection mechanism
InactiveCN101311683AReduced work of breathingAccurate measurementRespiratorsVolume/mass flow by differential pressureDifferential pressureEngineering
The invention relates to a low differential stress flow detection mechanism, comprising a main gas path (1), a throttling gear (3), a first sampling port (41), a second sampling port (42) and a metering device (6); wherein, the throttling gear (3) is arranged in the main gas path (1); the first sampling port (41) and the second sampling port (42) are positioned in the main gas path (1) and are respectively arranged at the front end and the back end of the throttling device (3); the gauging device (6) is connected with the first sampling port (41) and the second sampling port (42); the throttling gear (3) is provided with a plurality of concentric orifices (32) which are uniformly distributed around a central axis. The mechanism also relates to a ventilator which adopts the flow detection mechanism.
Owner:BEIJING AEONMED
Integrated Anisotropic Rock Physics Model
ActiveUS20080086287A1Computation using non-denominational number representationGeological measurementsStress inducedWell logging
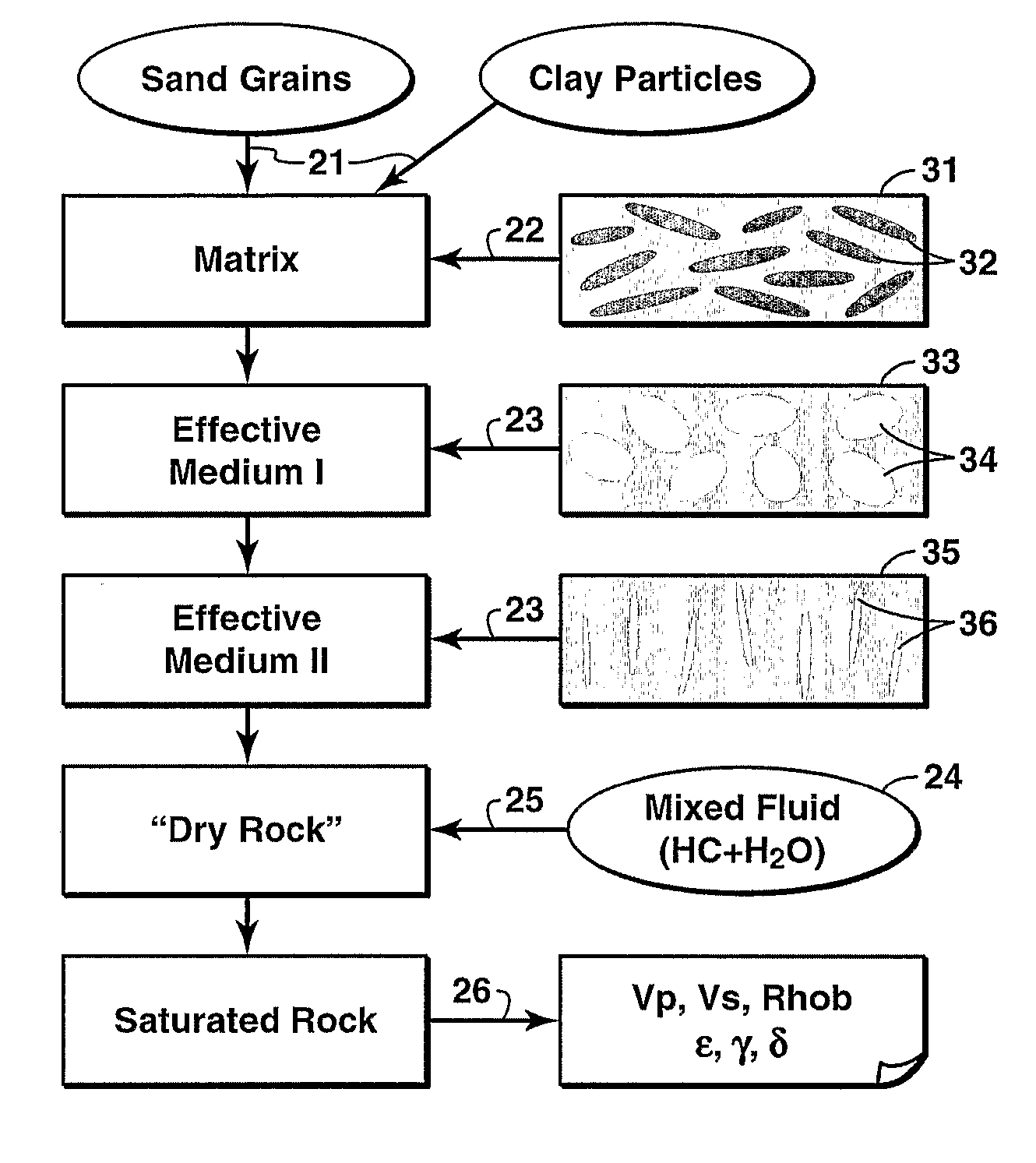
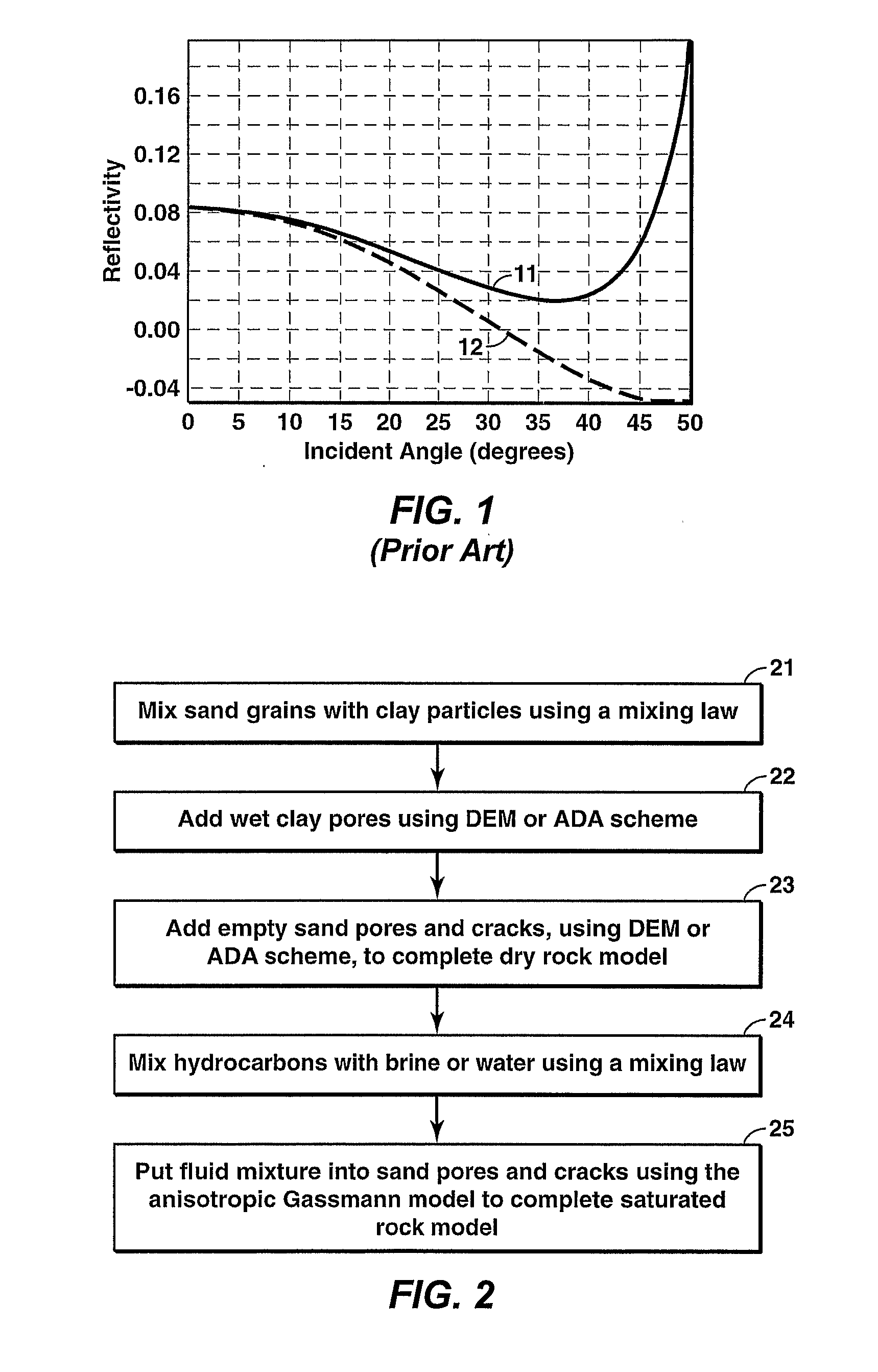
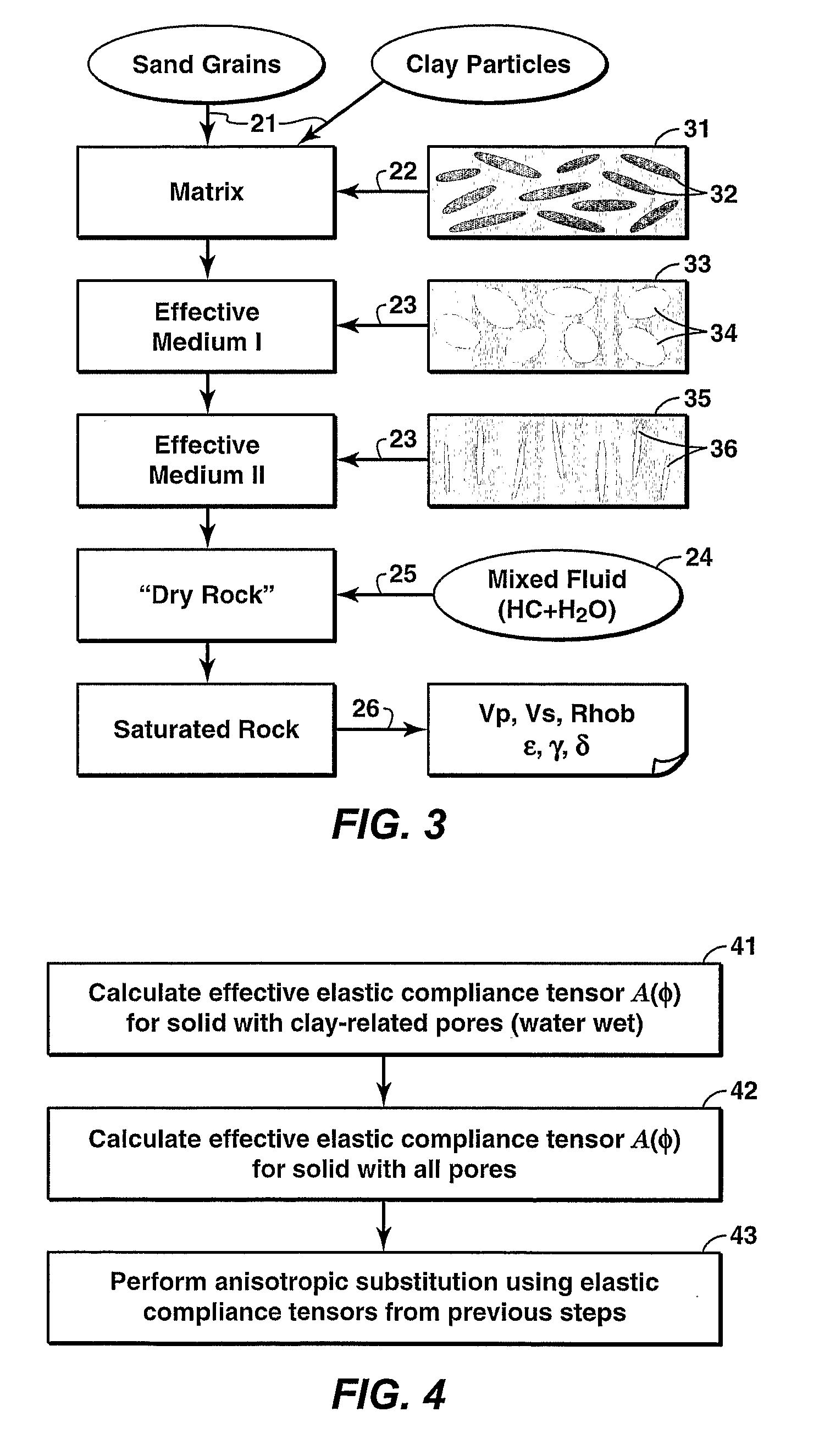
Method for constructing an integrated rock physics model that simulates both shale anisotropy and stress-induced anisotropy of clastic rocks. In the model, the total pore volume is divided into three parts according to the estimated shale volume and effective stress: (1) clay-related pores, (2) sand-related pores, and (3) microcracks (mainly in the sand component). The pore space is then partitioned into the clay-related and sand-related pores using a scheme first disclosed by Xu and White in 1995. The model simulates shale anisotropy via the preferred orientation of clay-related pores and stress-induced anisotropy via the preferred orientation of microcracks, which is controlled by the differential stresses. Laboratory measurements or well logs are needed to establish a relationship between crack density and the effective stress.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
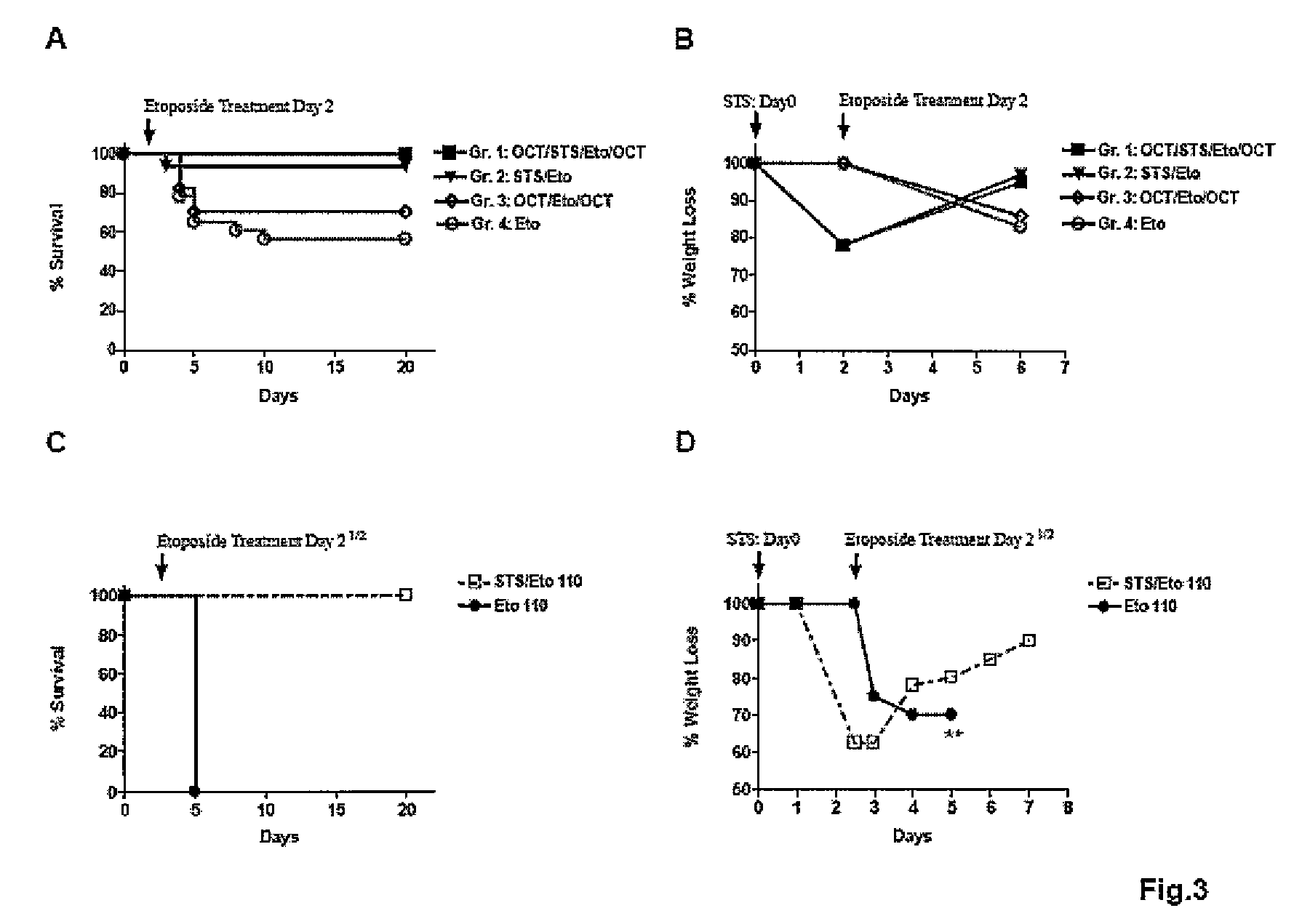
Induction of differential stress resistance and uses thereof
ActiveUS8211700B2Improve efficiencyImprove the immunityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGlucose intakeSide effect
This invention relates to methods of inducing differential stress resistance in a subject with cancer by starving the subject for a short term, administering a cell growth inhibitor to the subject, or reducing the caloric or glucose intake by the subject. The induced differential stress resistance results in improved resistance to cytotoxicity in normal cells, which, in turn, reduces cytotoxic side-effects due to chemotherapy, as well as improved effectiveness of chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
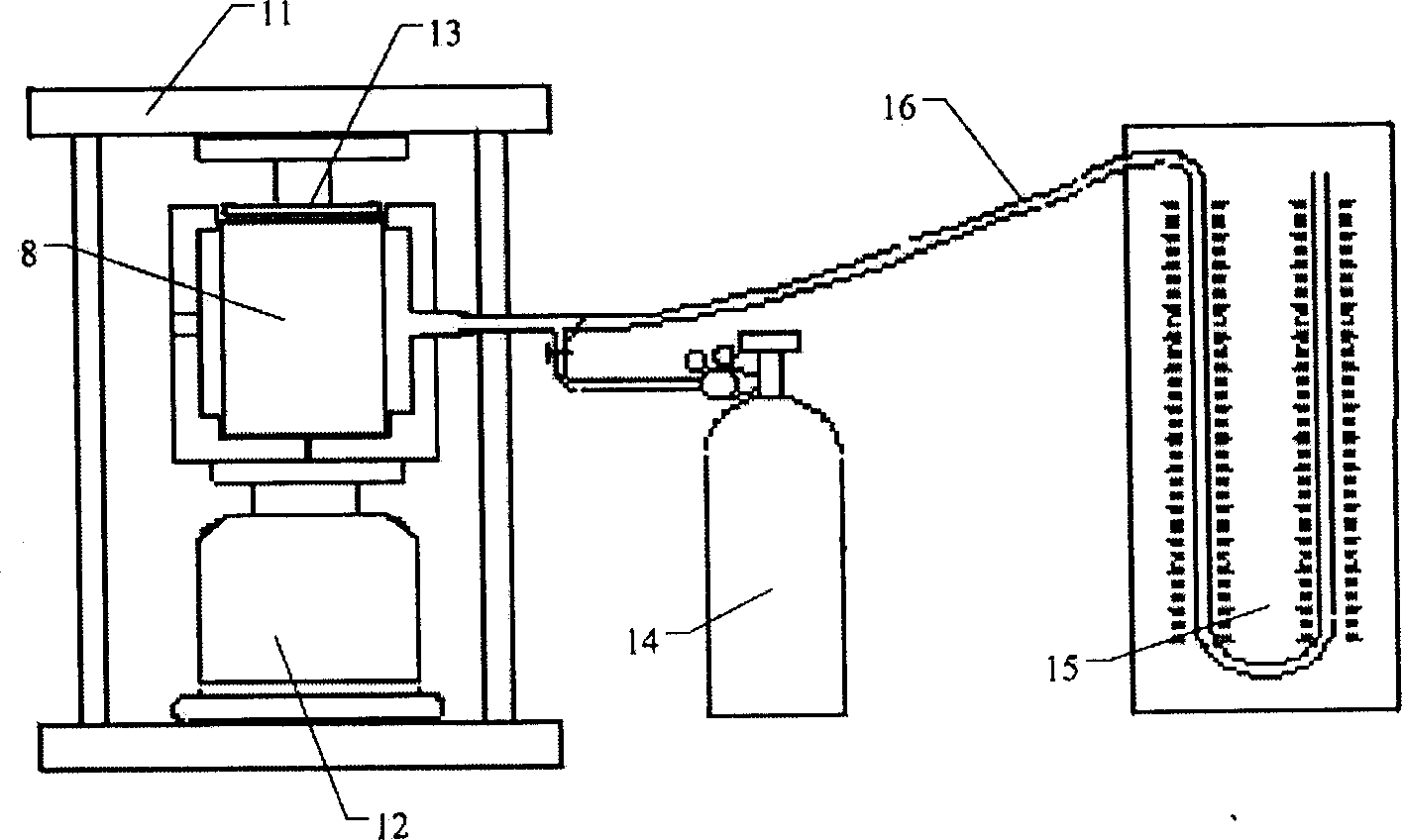
Detecting instrument for concrete gas seepage coefficient under single-shaft-pressure stress and detecting method
InactiveCN1815175ASolve the test problem of permeability coefficientSolve test problemsSurface/boundary effectMaterial testing goodsTest sampleTester device
Said invention refers to concrete gaseous permeability coefficient uniaxial compressive stress tester and testing method belonging to concrete material viability detection technique field. It contains dying, dying sample room, supporting frame, lifting jack, pressurizing plate, compressed gas tank, and pressure gauge etc, wherein dying consisting of dying cover board and dying bottom case, dying sample room located in dying bottom case, dying cover board and dying bottom case respectively set with outgoing gas chamber, intake chamber in turn connected with inlet valve, compressed gas, and pressure gauge, lifting jack and pressurizing respectively located at two ends of test sample, one side of dying bottom case set leakage check groove. In testing, tested sample is located in dying sample room, pressing in wedge, screwing dying, checking leak tightness, starting up lifting jack, applying compressive stress in test sample, opening compressed gas tank valve, keeping tested sample equilibration time being 10-20 minute, each tested sample repeating testing gas permeation time by more than 3-5 times, changing test pressure and repeat testing, to obtain tested sample permeability coefficient average value, taking 3-5 tested sample permeability coefficient average value as test value of said group tested sample. Said invention has easy and simple to handle, reliable test result, assembly type unit, and convenient for carrying.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Integrated anisotropic rock physics model
ActiveUS7676349B2Computation using non-denominational number representationGeological measurementsStress inducedWell logging
Method for constructing an integrated rock physics model that simulates both shale anisotropy and stress-induced anisotropy of clastic rocks. In the model, the total pore volume is divided into three parts according to the estimated shale volume and effective stress: (1) clay-related pores, (2) sand-related pores, and (3) microcracks (mainly in the sand component). The pore space is then partitioned into the clay-related and sand-related pores using a scheme first disclosed by Xu and White in 1995. The model simulates shale anisotropy via the preferred orientation of clay-related pores and stress-induced anisotropy via the preferred orientation of microcracks, which is controlled by the differential stresses. Laboratory measurements or well logs are needed to establish a relationship between crack density and the effective stress.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
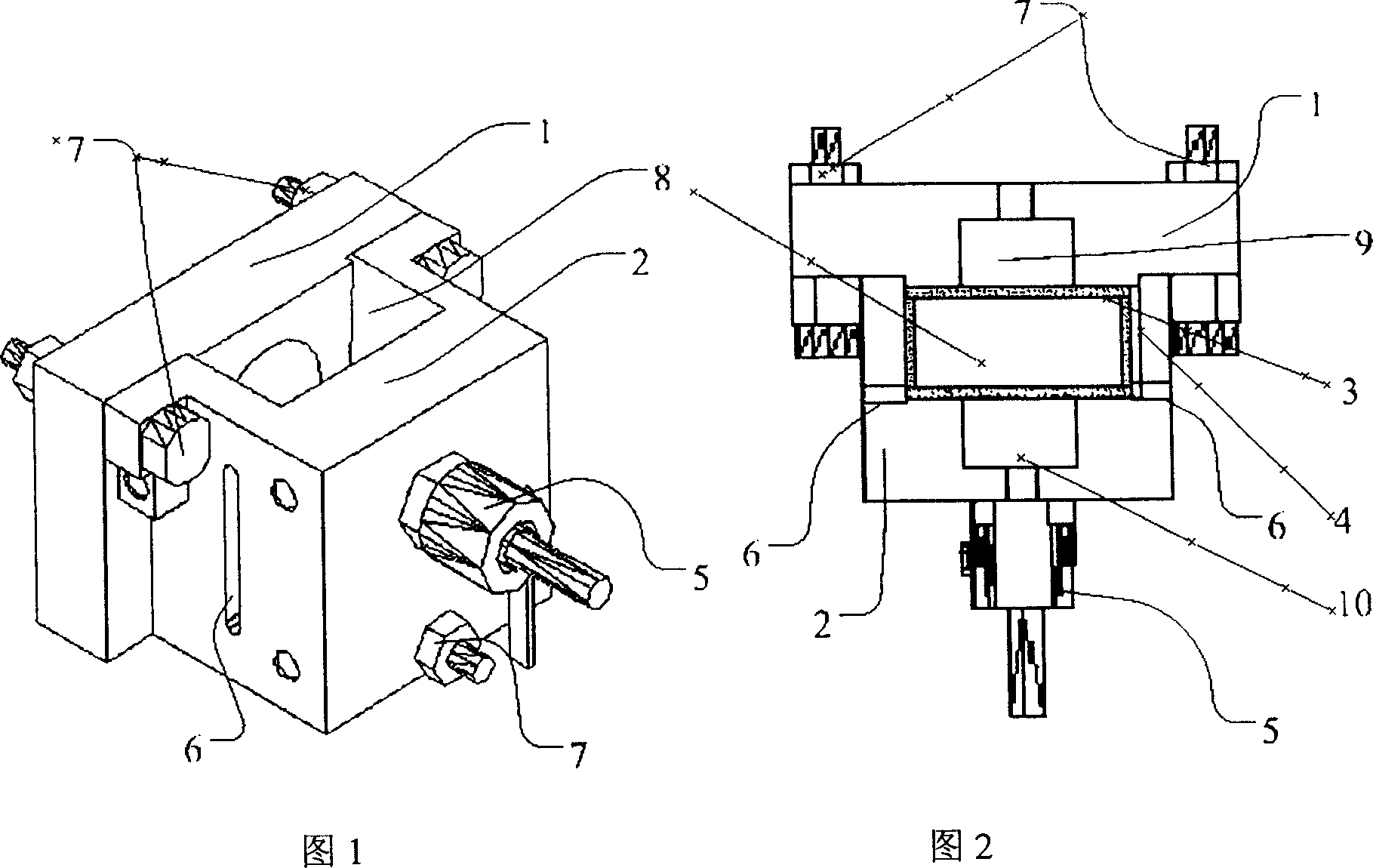
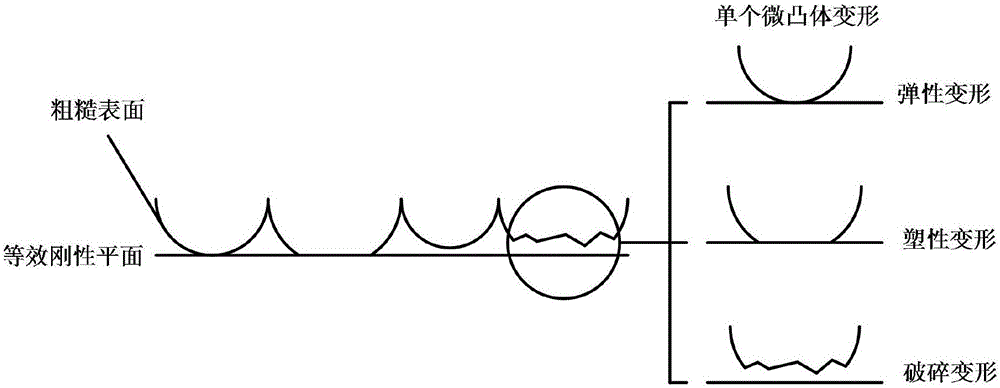
Machine tool-base joint surface contact stiffness calculation method in consideration of concrete asperity fracture
ActiveCN106768741AThe contact stiffness is obtainedImprove working precisionElasticity measurementContact pressureTheory model
The invention discloses a machine tool-base joint surface contact stiffness calculation method in consideration of concrete asperity fracture. According to the method, a fracture phenomenon is thought to be generated when the asperity on the surface of the concrete suffers from large load, the originally-fractured asperity load is shouldered by other un-fractured asperities, fracture of an asperity continues to happen, and so on and so forth, a balance state is achieved. Firstly, according to a uniaxial pressure stress-strain curve of a corresponding concrete mark, the relationship between the concrete critical fracture stress and a critical fracture area of a single asperity is built, a critical deformation area value of the single asperity is acquired, and based on a fractal theory, the bearing forces of the concrete asperity in elasticity, plasticity and fracture deformation stages are solved respectively. A finite element method is adopted to extract the contact pressure of a sample joint surface under different pretightening forces, the concrete-steel joint surface contact stiffness is acquired and calculated on the basis, simulation analysis is carried out by using ANSYS, and an experiment is designed to verify a theoretical model.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
System for predicting induced seismicity potential resulting from injection of fluids in naturally fractured reservoirs
ActiveUS20170132339A1Fast outputFluid removalDesign optimisation/simulationSoil scienceInduced seismicity
A method for minimizing the risk of induced seismicity from injection of fluids into a naturally fractured reservoir uses a meshless particle-based simulation to quantify the heterogeneity in energy storage within the reservoir. In particular, this methodology creates an equivalent fracture model from data on the natural fracture density, regional stress, pore pressure and elastic properties of the reservoir, in which points in the reservoir have a fracture length and fracture orientation. A meshless particle-based method is then employed to simulate the geomechanical interaction between regional stress and natural fractures to estimate the stress anisotropy and strain (e.g., differential stress and shear strain). The induced seismicity potential is then calculated at points in the reservoir based on the estimated stress anisotropy and strain. A zone for injection of fluids into the reservoir can be selected by identifying a large area of the reservoir having low induced seismicity potential.
Owner:FRACGEO LLC
Control system of electric execution mechanism
The invention relates to a control system of an electric execution mechanism. The control system comprises a main control and remote control board, an analog control board, a valve position detection board, a torque detection board and a bus control board, and is characterized in that the main control and remote control board processes valve position information, torque information, a remote switching value, an analog value and a bus instruction signal inside and outside the electric execution mechanism; a circuit of the valve position detection board is a hall increment encoder or a magneto-electric absolute encoder; and the torque detection board is a double-channel electronic circuit detection board or a double-channel constant-elasticity differential stress technology detection board. A double-channel constant-elasticity differential stress technology is used for measuring torque of the electric execution mechanism without being influenced by voltage fluctuation and frequency fluctuation of a power grid; and by the technical scheme, the control system, which does not produce drift and does not damage a valve rod, of the electric execution mechanism is provided.
Owner:ZHUZHOU SOUTHERN GENERAL ELECTRIC CO LTD
Use of contacts to create differential stresses on devices
InactiveUS20120074501A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField-effect transistorIntegrated circuit
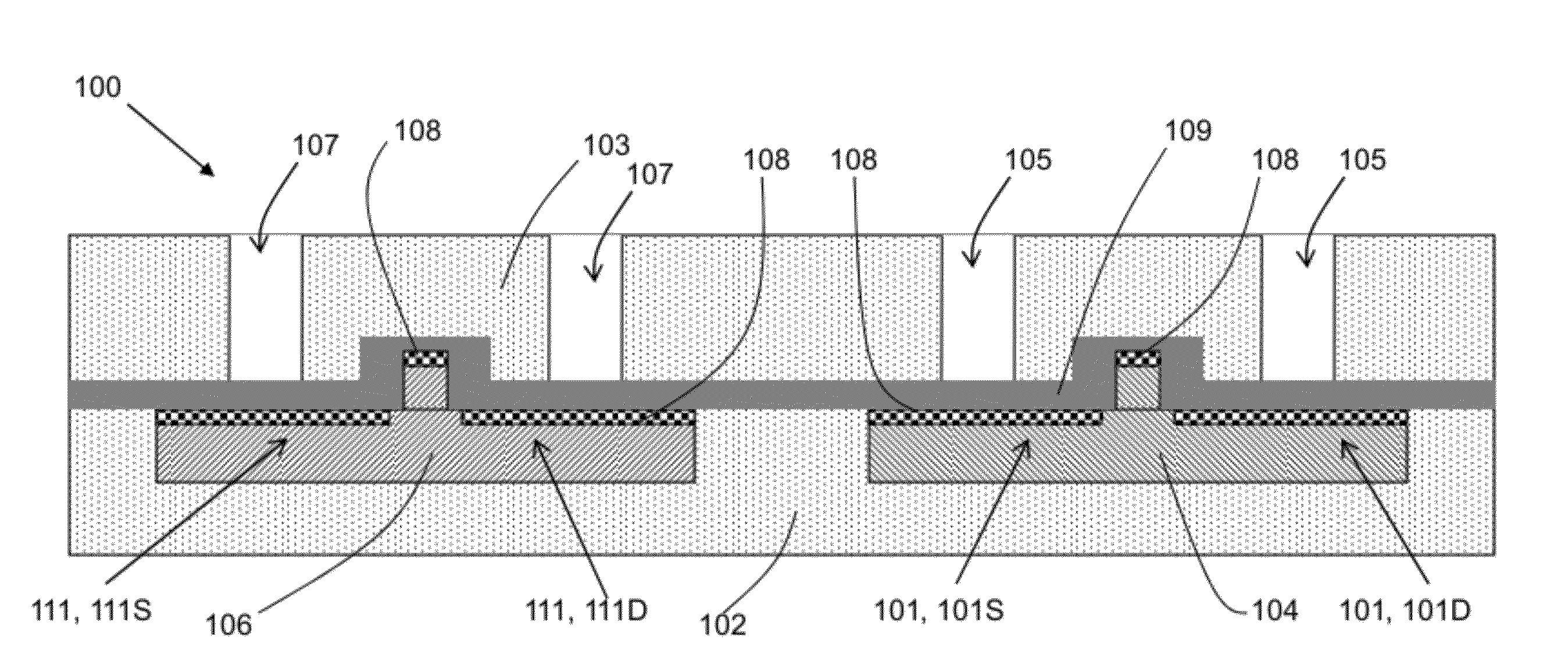
Disclosed herein are various methods and structures using contacts to create differential stresses on devices in an integrated circuit (IC) chip. An IC chip is disclosed having a p-type field effect transistor (PFET) and an n-type field effect transistor (NFET), a PFET contact to a source / drain region of the PFET and an NFET contact to a source / drain region of the NFET. In a first embodiment, a silicon germanium (SiGe) layer is included only under the PFET contact, between the PFET contact and the source / drain region of the PFET. In a second embodiment, either the PFET contact extends into the source / drain region of the PFET or the NFET contact extends into the source / drain region of the NFET.
Owner:ALSEPHINA INNOVATIONS INC
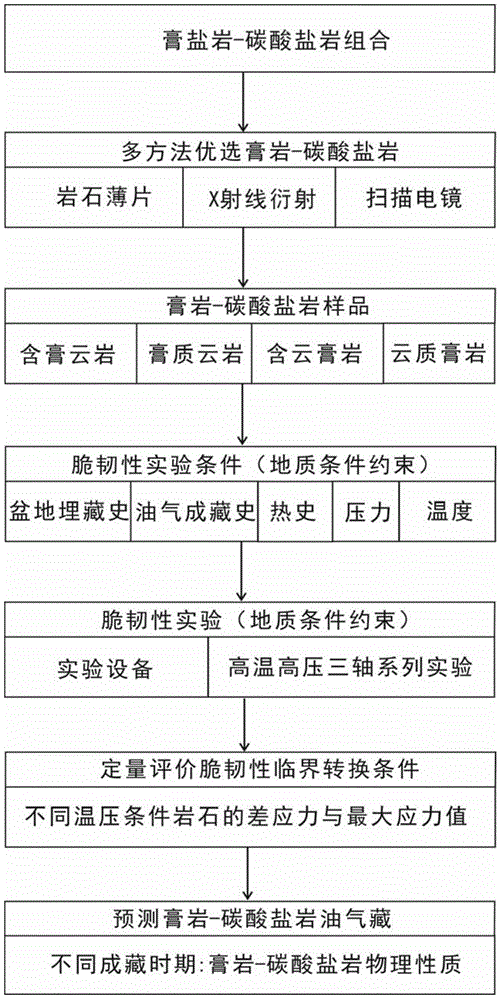
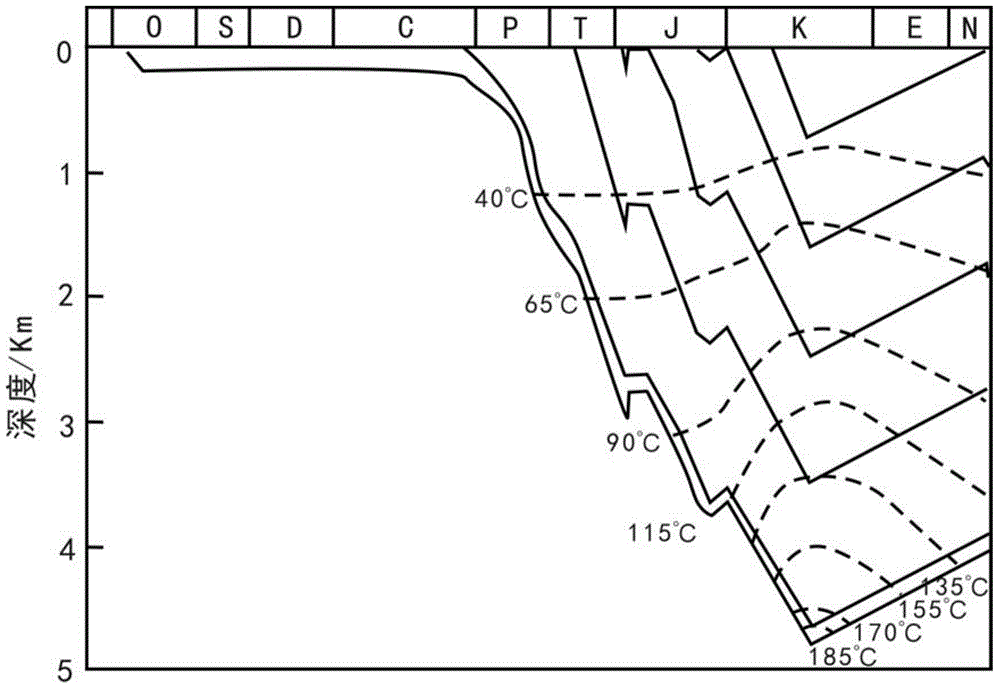
Method for quantitatively determining brittle-ductile critical condition of gypsum rock-carbonatite
ActiveCN105116129ACrisp implementationRealize quantitative evaluationEarth material testingEntrapmentDolomite
The invention provides a method for quantitatively determining the brittle-ductile critical condition of gypsum rock-carbonatite. The method comprises the steps that the gypsum rock-carbonatite is adopted as a sample, and the sample comprises the lithological characters of gypsum containing dolomite, gypseous dolomite, dolomite-quality gypsum rock and dolomite containing gypsum rock; temperature and pressure of a critical construction period of petroleum entrapment evolution according to the history of structural evolution of a basin where the gypsum rock-carbonatite is located, and are adopted as temperature and pressure of experimental simulation; the maximum differential stress value and the maximum inflection point stress point of the sample are measured under simulation temperature and pressure respectively; the critical position of conversion of the brittleness and tenacity of the sample is quantitatively evaluated according to the maximum differential stress value and the maximum inflection point stress point of the sample, and the brittle-ductile critical condition of the gypsum rock-carbonatite is quantitatively determined. According to the method, the brittle-ductile critical condition of the gypsum rock-carbonatite can be accurately evaluated, and a basis is provided for accurately evaluating and predicting petroleum entrapment of the gypsum rock-carbonatite.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Simulating hydraulic fracturing geometry propagation using a differential stress and pattern-based model
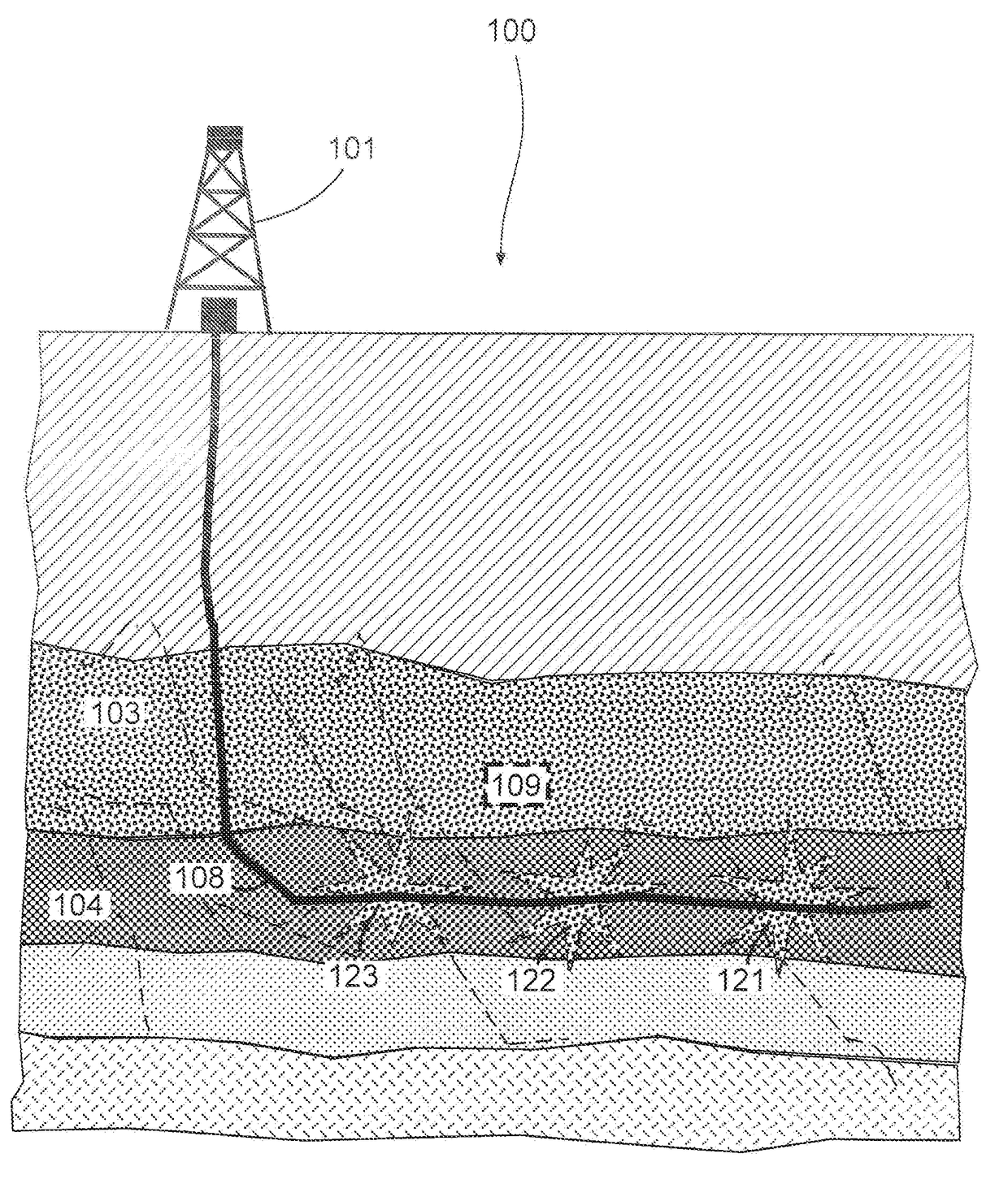
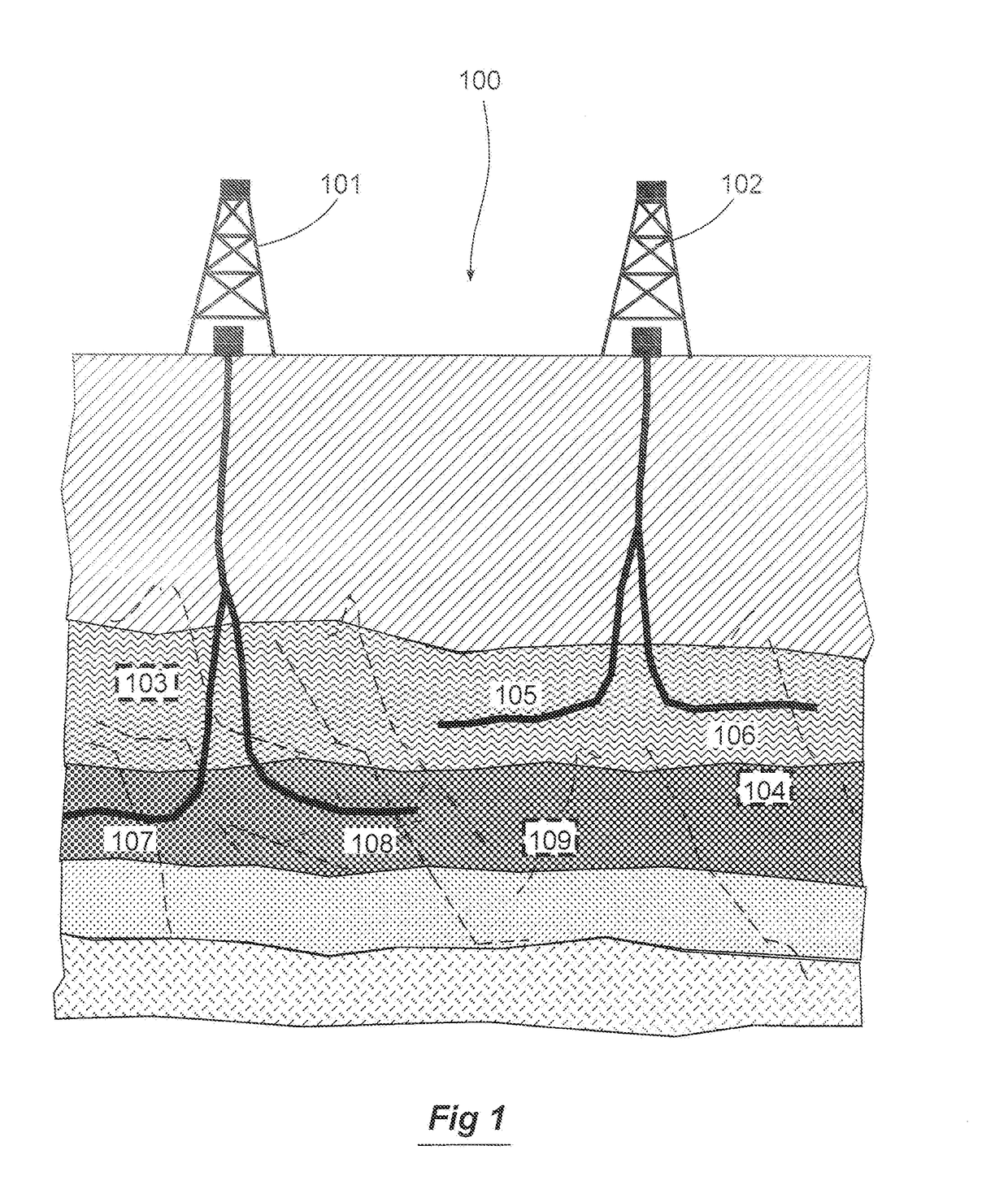
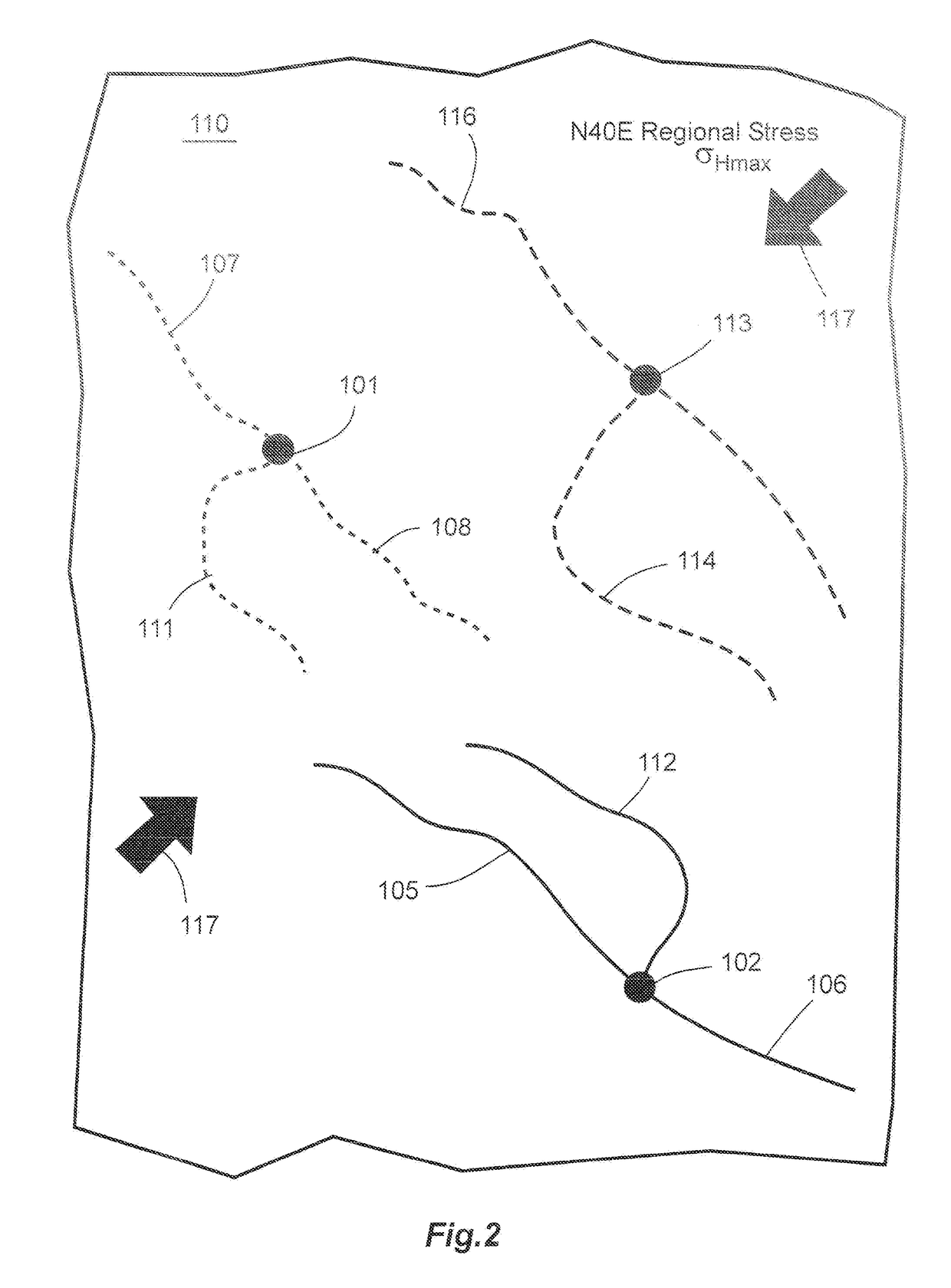
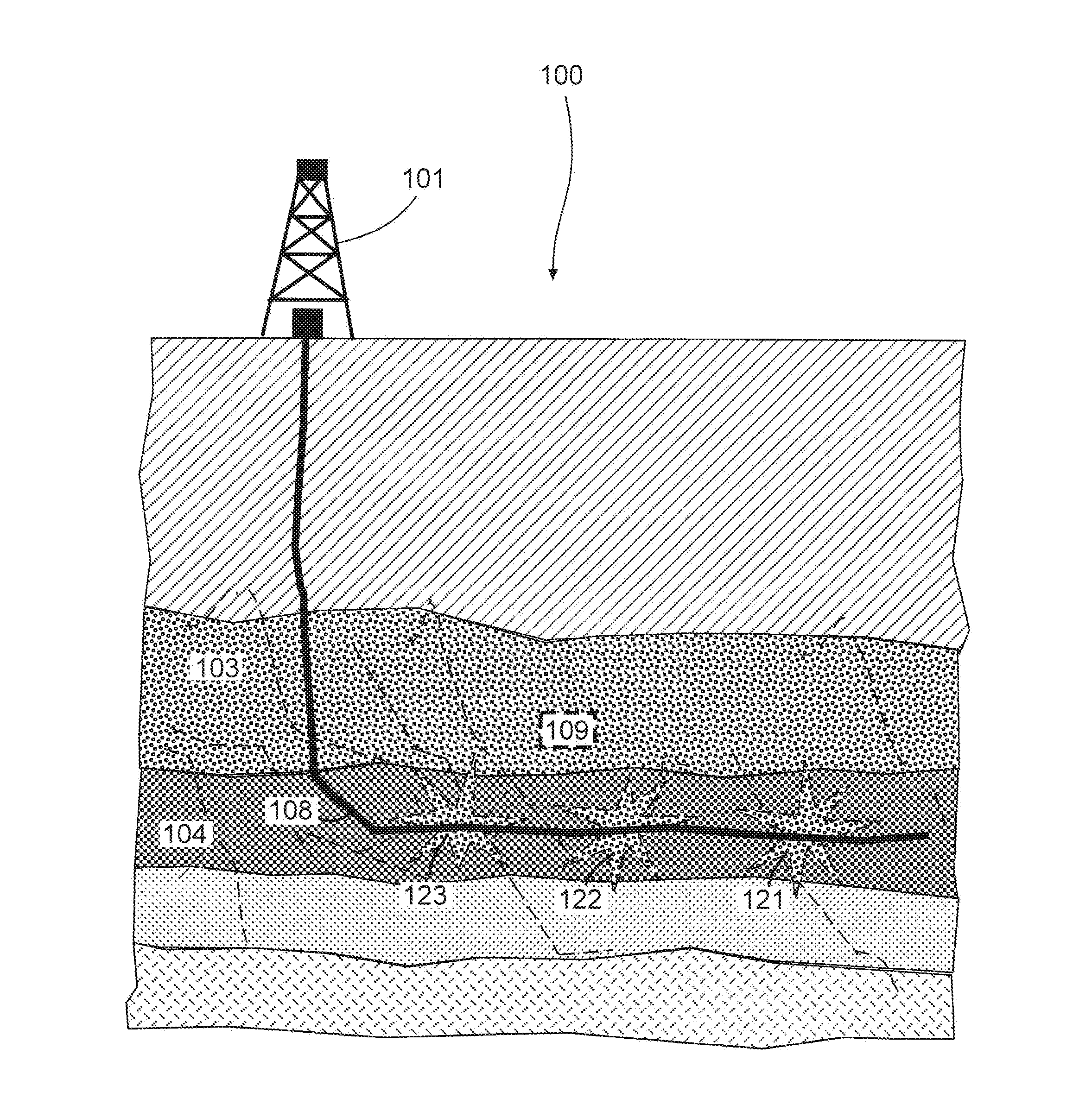
The disclosure presents a technique to generate a fracture model using a differential stress map and model inputs. The technique simulates the fracture model using fracture fronts, initiated at perforations of a perforation stage of a hydraulic fracturing (HF) wellbore. Each fracture front is evaluated using a propagation step of a fracture model process. Using the relative differential stress states, a fracture pattern is composited to the fracture model. At each propagation step, the total energy available from the simulated fluid being pumped into the wellbore location is reduced by the amount necessary to generate the computed fractures. Once the remaining energy is reduced to a level where no further fractures can be created, or if a map boundary is encountered, the fracture model process terminates. The generated fracture model can be communicated to update HF job plans, wellbore placements, and other uses of the fracture model.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS
Method for measuring differential stress by using rock core
InactiveCN109630098AEasy to useAccurate calculationSurveyData processing applicationsRock coreStress measurement
The invention relates to the technical field of ground stress measurement, in particular to a method for measuring the differential stress by using a rock core. The method for measuring the differential stress by using the rock core comprises the steps that radial deformation of the rock core is measured first, development and distribution characteristics of micro-cracks in the rock core are evaluated, the accumulated width of the micro-cracks at different radial directions is counted and determined, and finally, the Shmax-Shmin true measured value is obtained. By measuring the widths of the micro-cracks of the rock core, when the radial deformation of the rock core is calculated, the widths of the micro-cracks are added, so that the calculation of the radial deformation of the rock core is more accurate, errors are reduced, it is ensured that the final data can be normally used under various conditions, and then the elastic deformation measurement of the rock core can be widely used.
Owner:INST OF GEOMECHANICS
Induction of differential stress resistance and uses thereof
ActiveUS20080242638A1Improve efficiencyImprove the immunityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGlucose intakeSide effect
This invention relates to methods of inducing differential stress resistance in a subject with cancer by starving the subject for a short term, administering a cell growth inhibitor to the subject, or reducing the caloric or glucose intake by the subject. The induced differential stress resistance results in improved resistance to cytotoxicity in normal cells, which, in turn, reduces cytotoxic side-effects due to chemotherapy, as well as improved effectiveness of chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Method for measuring two-dimensional stress at weld joint by using Barkhausen effect and detection instrument
InactiveCN112945427AAchieve bi-directional stress detectionForce measurement by measuring magnetic property varationApparatus for force/torque/work measurementTangential stressNoise
The invention discloses a method for measuring two-dimensional stress at a weld joint by using a Barkhausen effect and a detection instrument. A ferrite magnetic core and a magnetic core of a Barkhausen measuring probe are directly contacted with the surface of the weld joint of the test piece, so that the X-direction tangential stress and the Y-direction axial stress of the weld joint of the test piece are calibrated; the Barkhausen measuring probe is used for collecting excitation signals and detecting Barkhausen signals, stress signal amplitude waveforms are obtained, and signal amplitude noise is obtained according to the waveforms; a Barkhausen noise signal amplitude is extracted from a signal detected by the Barkhausen measuring probe, the Barkhausen noise signal amplitude continuously changes along with the tension and pressure stress values to form a tension and pressure fitting curve, and the tension and pressure fitting curve serves as a calibration result of the relation between the Barkhausen noise signal amplitude and the continuous tension and pressure stress; and finally, a Barkhausen noise signal, the residual stress sigma1 in the vertical direction, the residual stress sigma2 in the parallel direction and the quantitative relation of the included angle theta between the main stress direction and the magnetic field direction are obtained, and the two-dimensional residual stress of the welding area is directly detected.
Owner:思特尔智能检测系统(苏州)有限公司
Low permeable sandy conglomerate stratum pressure prediction method and apparatus thereof
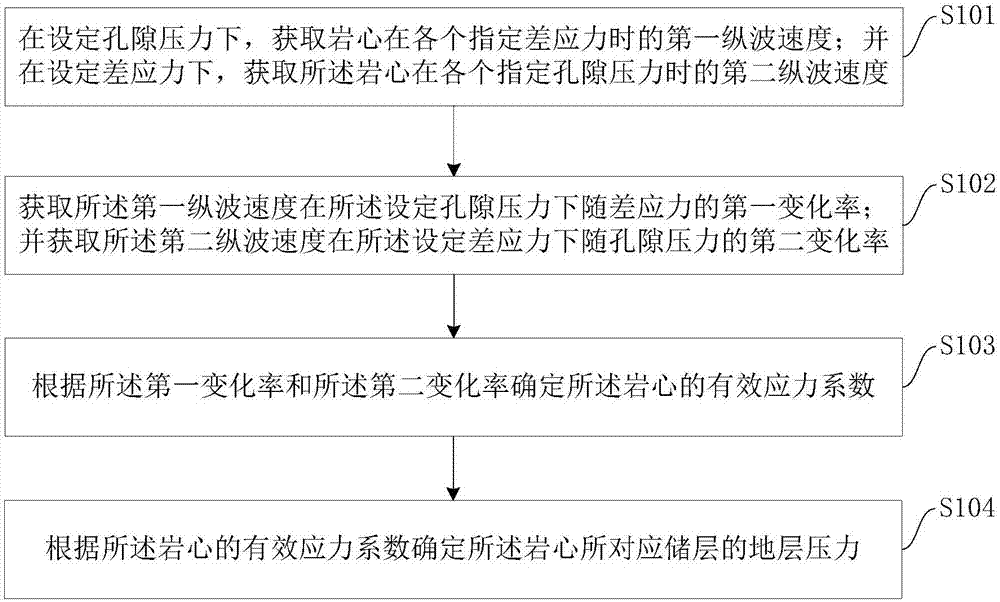
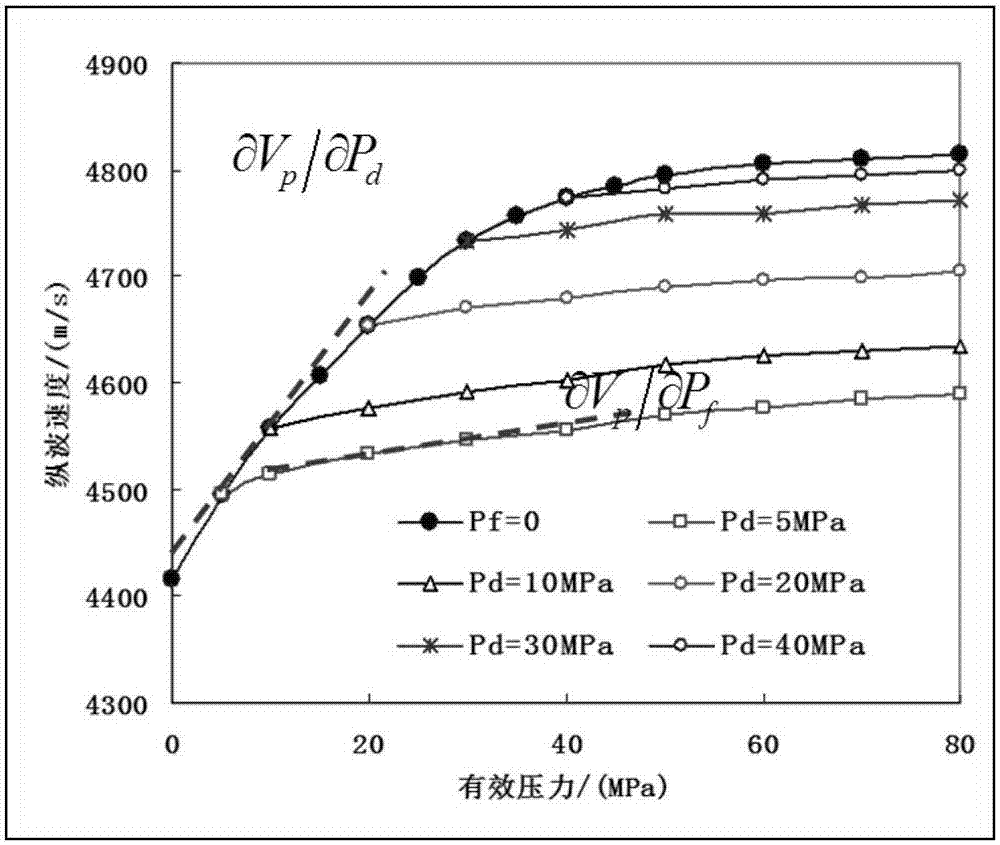
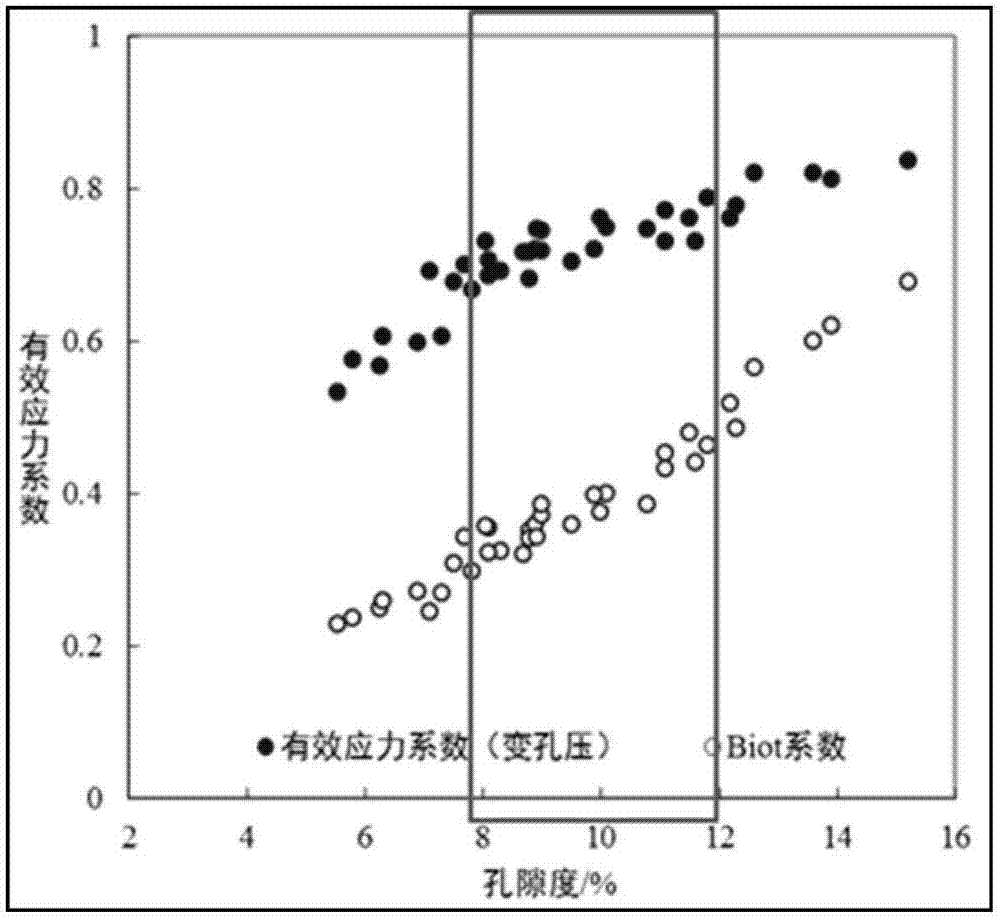
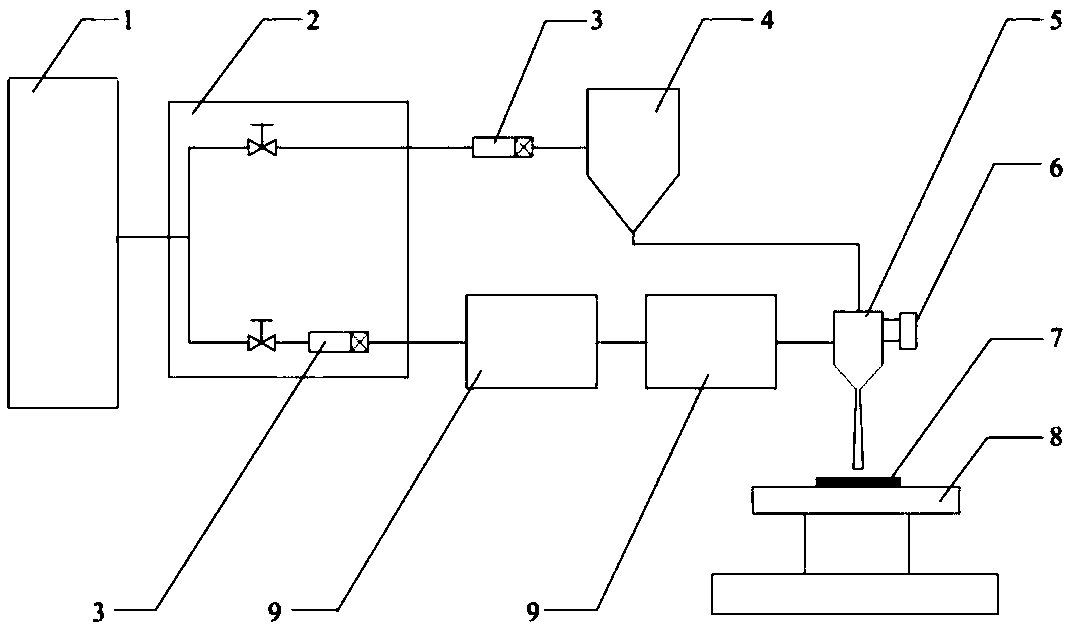
An embodiment of the invention provides a low permeable sandy conglomerate stratum pressure prediction method and an apparatus thereof. The method comprises the following steps of under set pore pressure, acquiring a first longitudinal wave speed of a rock core under each assigned differential stress; under a set differential stress, acquiring a second longitudinal wave speed of the rock core under each assigned pore pressure; acquiring a first rate of change of the first longitudinal wave speed along with the differential stress under the set pore pressure; acquiring a second rate of change of the second longitudinal wave speed along with the pore pressure under the set differential stress; according to the first rate of change and the second rate of change, determining an effective stress coefficient of the rock core; and according to the effective stress coefficient of the rock core, determining stratum pressure of a reservoir stratum corresponding to the rock core. In the embodiment of the invention, low permeable sandy conglomerate stratum pressure prediction accuracy can be increased.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for preparing amorphous alloy bulk material
InactiveCN108914024AReduce dependenceGrow fastHeat inorganic powder coatingParticle accelerationStressed state
The invention provides a method for preparing an amorphous alloy bulk material. The preparation method adopts amorphous alloy powder as a raw material, and the characteristics of viscosity decrease and gradual softening of amorphous alloy with the increase of the temperature and the characteristic of superplasticity of the amorphous alloy in a supercooled liquid region are combined with the characteristics of rapid particle acceleration, low heating temperature, small heat influences, difficult oxidation and microstructure change, small thermal stress and final compressive stress state in thecold spraying process and the optimization control of process parameters to achieve high-speed bumping deposition of the particles layer by layer in order to form the he bulk material; and the impactof the subsequent particles has a compacting and densifying effect on formed deposits in a range of sizes of several particle thicknesses. The method has the technical advantages of simple process, short production cycle, low processing cost, strong adaptability, and unlimited size of the material.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Model for simulating stress state of concrete and test method
ActiveCN111024480AAchieve stiffnessAchieve strengthPreparing sample for investigationStrength propertiesStress ratioEngineering
The invention discloses a model for simulating the stress state of concrete and a test method, and belongs to the field of concrete structure simulation tests. According to the model, corresponding stress distribution is generated on a wet joint interface of the model through a method of generating eccentric tension prestress through eccentric arrangement of prestressed twisted steel, a convex cross section is adopted so that pressure stress can be more easily concentrated on the top face of a web and tensile stress can be more easily concentrated on the bottom face of a flange plate, and therefore, a large-numerical-value tensile-compressive-stress ratio can be generated through a small-size model, and the tensile-compressive-stress states of various large bridges and buildings can be simulated. The stress distribution mode and the stress magnitude of the model section can be accurately controlled by adjusting the size of the model section, the prestress tensioning force and the position of the prestress twisted steel relative to the neutral axis section, and then the tension and compression stress state of the actual prefabricated assembled bridge wet joint construction stage issimulated. The model and the test method can be used for researching the rigidity, strength and stress mechanism of a precast concrete wet joint.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for improving anti-wear/anti-fatigue performance of carburized gear by utilizing comprehensive means
ActiveCN111041409AImprove reliabilityExtended service lifeSolid state diffusion coatingGear teethGear wheelPeening
The invention discloses a method for improving anti-wear / anti-fatigue performance of a carburized gear by utilizing comprehensive means, and belongs to a surface strengthening treatment technology. The method specifically comprises the following steps of laser shock peening-grinding-shot blasting. According to the method, a laser impact peening, grinding and shot blasting combined strengthening treatment process is adopted, the process compensates for the defect of a single process, and also exerts the respective advantages, the surface hardness and residual compressive stress of the aero-engine transmission gear are effectively improved, the anti-wear performance and the anti-fatigue performance of the carburized gear are improved, and the requirements of industrial application are met.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Use of contacts to create differential stresses on devices
InactiveUS8460981B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringField-effect transistor
Disclosed herein are various methods and structures using contacts to create differential stresses on devices in an integrated circuit (IC) chip. An IC chip is disclosed having a p-type field effect transistor (PFET) and an n-type field effect transistor (NFET), a PFET contact to a source / drain region of the PFET and an NFET contact to a source / drain region of the NFET. In a first embodiment, a silicon germanium (SiGe) layer is included only under the PFET contact, between the PFET contact and the source / drain region of the PFET. In a second embodiment, either the PFET contact extends into the source / drain region of the PFET or the NFET contact extends into the source / drain region of the NFET.
Owner:ALSEPHINA INNOVATIONS INC
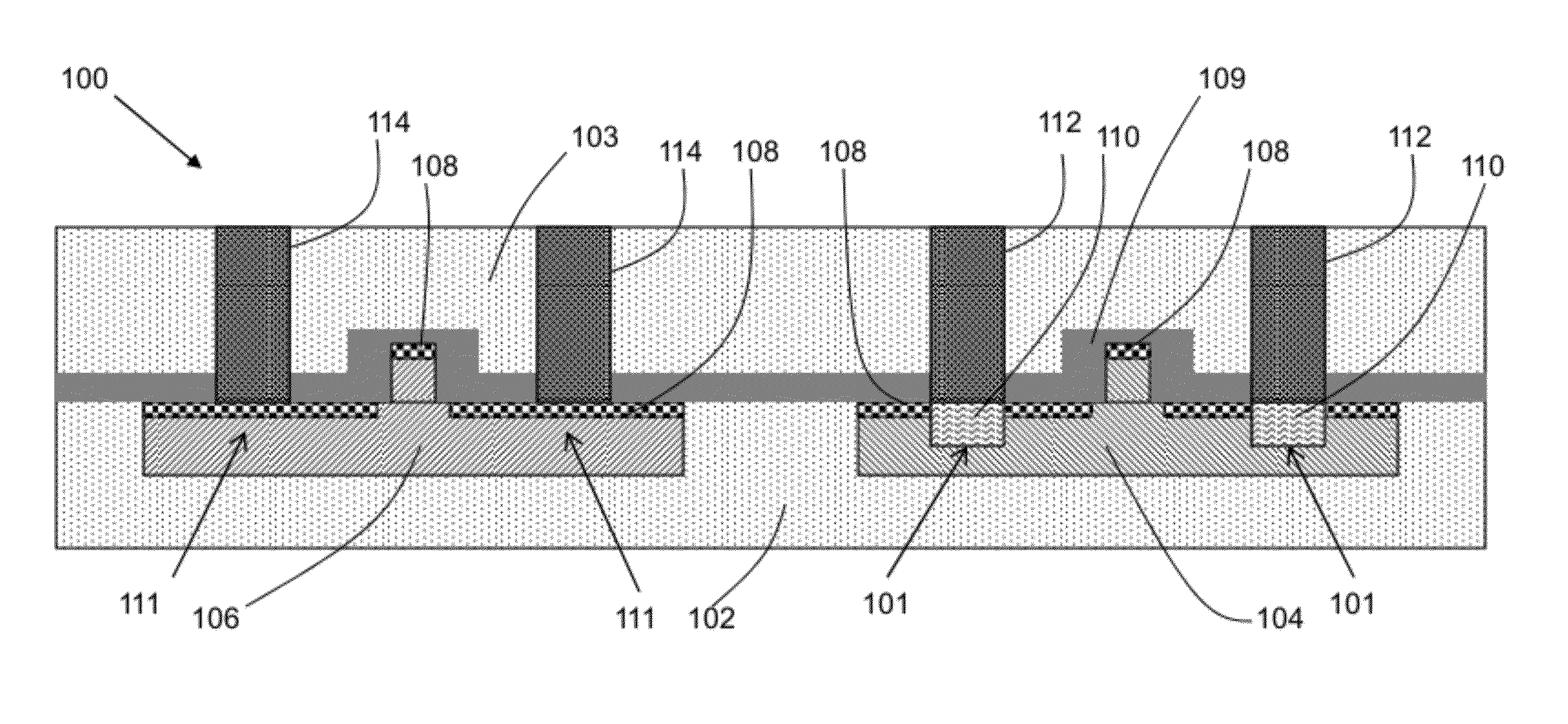
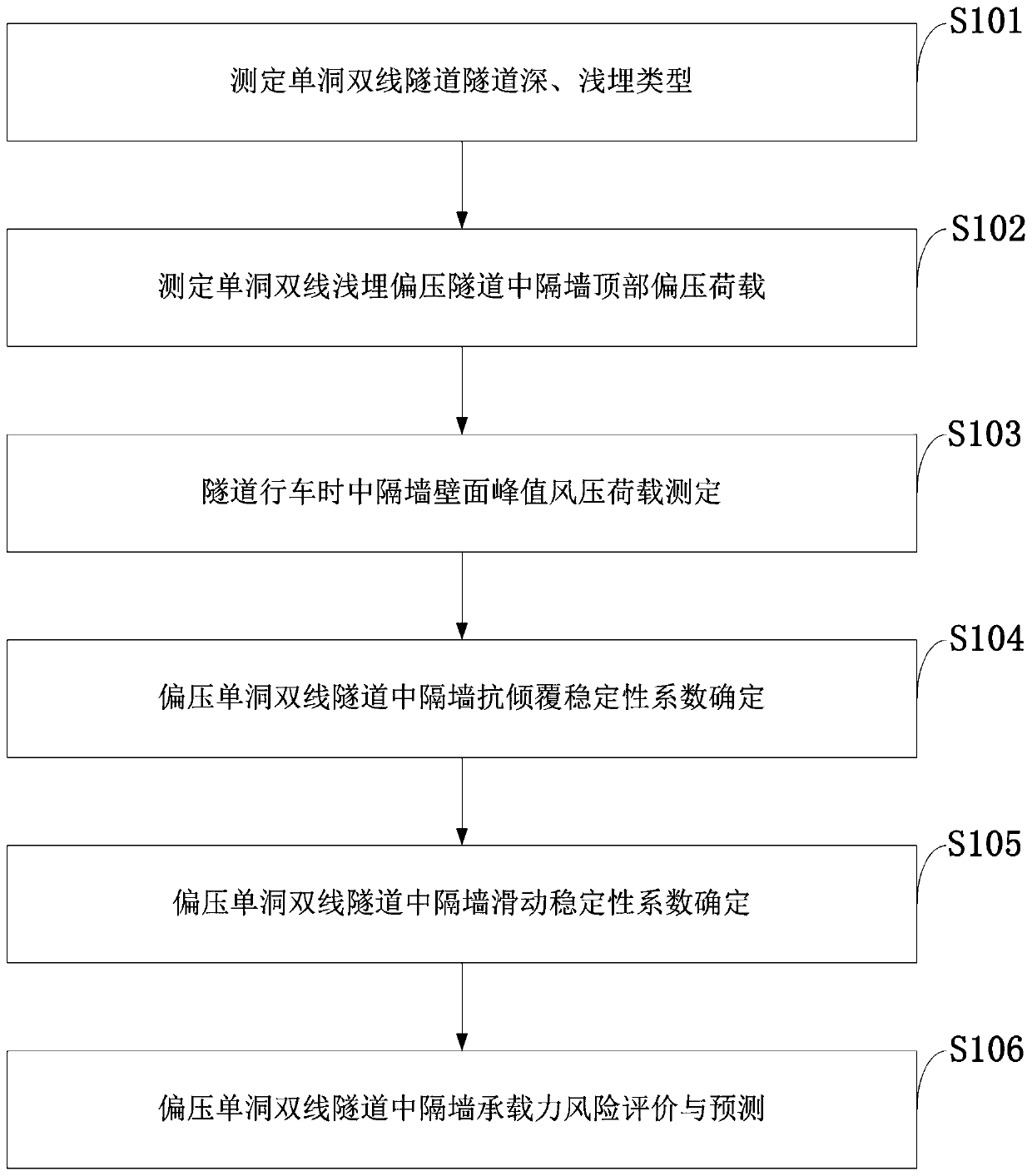
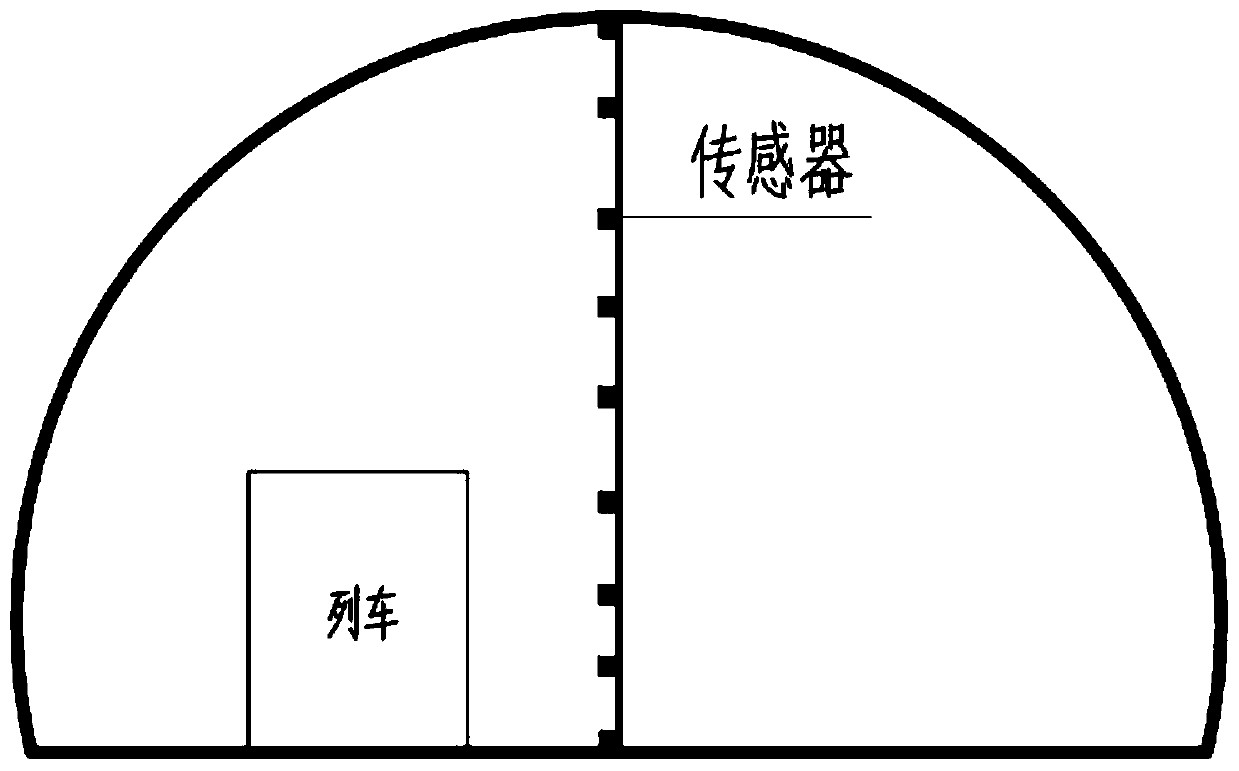
Method for measuring stability of partition wall in shallow-buried single-hole double-line bias tunnel
ActiveCN111189660ARealize the stability checkClear stability criteriaStructural/machines measurementStability coefficientStability criterion
The invention belongs to the technical field of tunnel engineering. The invention discloses a method for measuring the stability of a partition wall in a shallow-buried single-hole double-line bias tunnel. An instability evaluation method and checking calculation criteria for the partition wall in the single-hole double-line bias tunnel are established according to the change rule of surrounding rock bias stress transmitted by an upper lining on the partition wall and the composite effect of wind pressure generated in the tunnel driving process on the partition wall of the operating tunnel, and stability checking calculation of the bias partition wall is achieved; bias stress borne by surrounding rock on the upper portion of the single-hole partition wall and horizontal bias stress and vertical stress borne by the partition wall are combined, and then distribution and action modes of pneumatic wind pressure on the partition wall are considered in an overlapped mode; a composite stability determination method is derived and established based on bias voltage and wind pressure, and a K value stability coefficient is proposed for determining the stability of the partition wall. The method provided by the invention has a clear stability criterion, provides a basis for single-hole double-line bias tunnel evaluation and prevention and control, and has the characteristics of simplicity, convenience and practicability.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY 19TH BUREAU GRP FIFTH ENG CO LTD +1
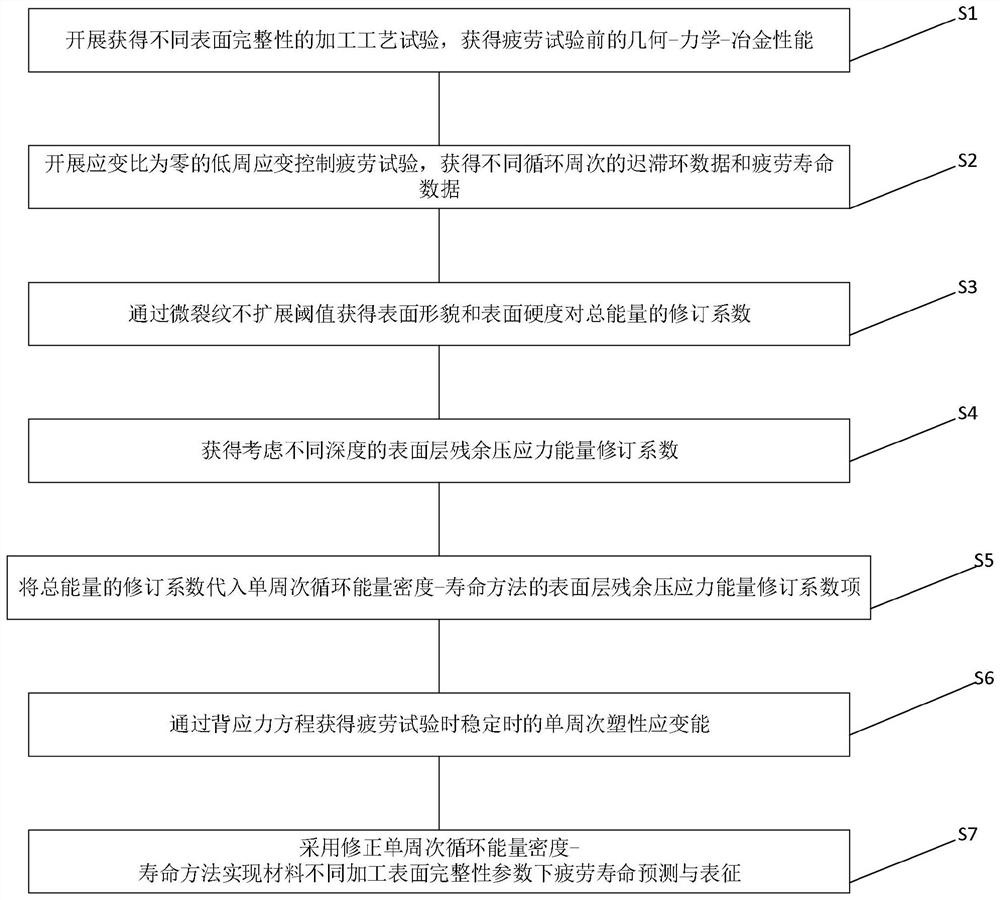
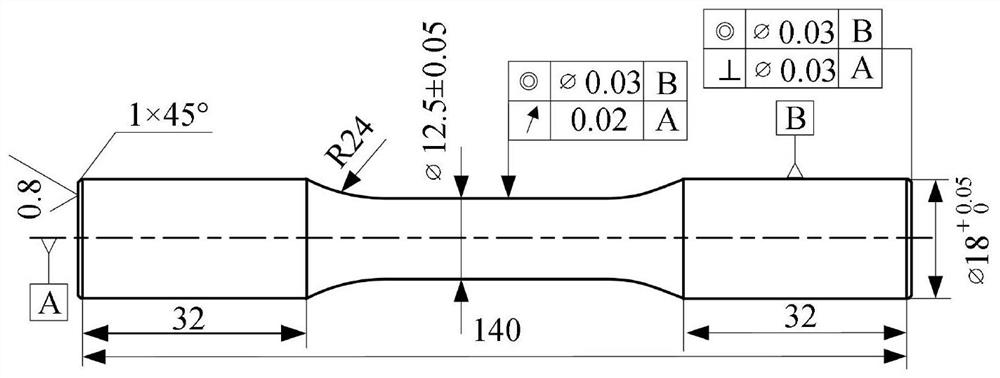
Method for predicting fatigue life by energy method considering machined surface integrity
InactiveCN113252479AImproved characterization methodsSolid theoretical foundationMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesCrazingMachined surface
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
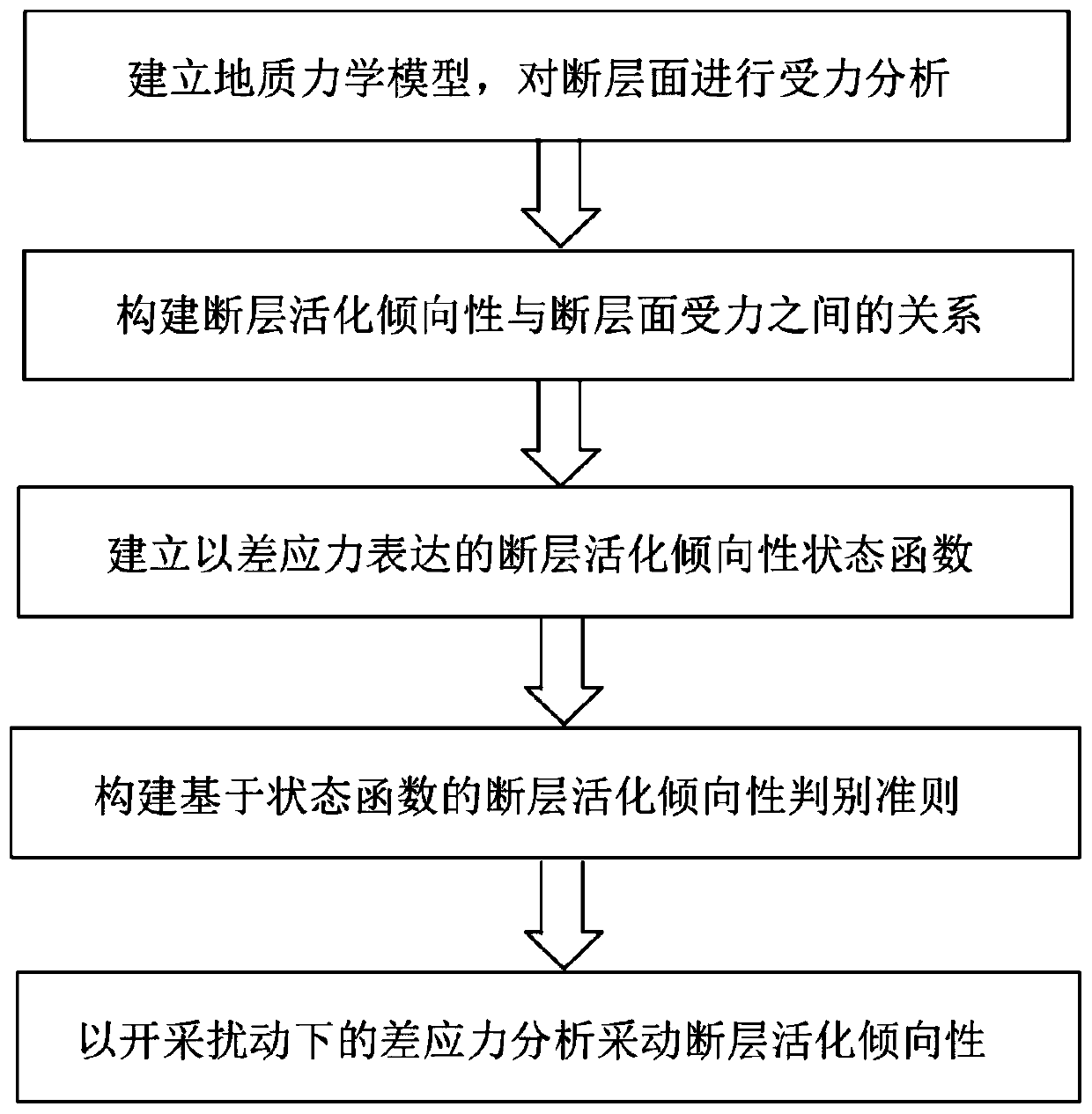
Mining fault activation tendency discrimination method based on differential stress
The invention discloses a mining fault activation tendency discrimination method based on differential stress, and the method comprises the following steps: building a standard two-dimensional fault activation analysis geomechanical model, and analyzing the relation among the normal stress, shear stress, maximum principal stress and minimum principal stress of a fault surface according to the built model; establishing the relationship between the fault activation tendency and the fault surface normal stress, shear stress and fault surface friction strength; constructing a fault activation tendency state function expressed by differential stress; establishing a fault activation tendency discrimination criterion based on a state function; analyzing the activation tendency of the mining faultaccording to the surrounding rock stress redistribution rule under mining disturbance, and analyzing the activation stability of the mining fault. According to the mining fault activation tendency discrimination method based on the differential stress, the influences of fault characters, the ground stress state of the regional environment, the mining stress and the like are considered, and the mining fault stability analysis and evaluation method is more comprehensive and scientific.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
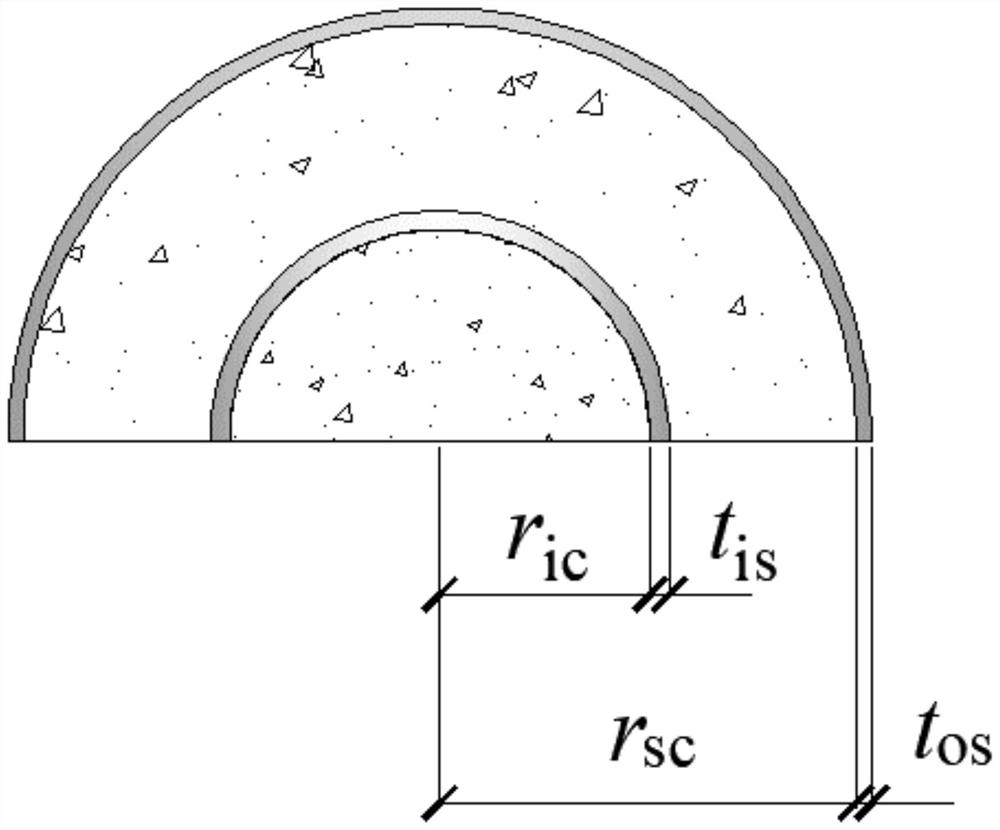
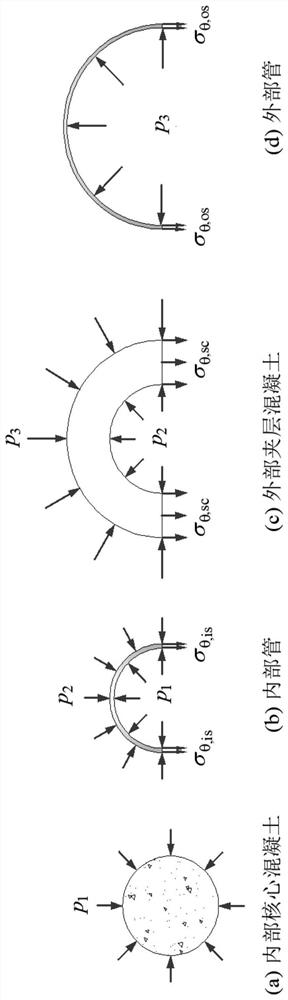
Method and system for calculating extrusion stress of isotropic double-pipe concrete column
The invention provides a method and system for calculating extrusion stress of an isotropic double-pipe concrete column, and the method comprises the steps: 1, obtaining calculation parameters of a double-pipe concrete column, including the Poisson's ratio and elastic modulus of internal core concrete and external interlayer concrete, and the Poisson's ratio, elastic modulus, inner diameter and wall thickness of an internal pipe and an external pipe; 2, establishing an extrusion stress relationship among all parts of the double-pipe concrete column; 3, substituting calculation parameters into the step 2 to obtain the extrusion stress between the parts; 4, based on the calculation parameters and the result obtained through solving in the step 3, obtaining the annular and radial strain of the inner core concrete, the annular stress and the annular strain of the inner pipe, the radial and annular stress of the outer interlayer concrete changing along the thickness and the radial and annular strain of the outer interlayer concrete changing along the thickness, the circumferential strain of the inner side and the outer side of the outer interlayer concrete and the circumferential stress and the circumferential strain of the outer pipe.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method of cutting a laminate glass article
InactiveUS20180312422A1Relieve pressureGlass forming apparatusGlass/slag layered productsCutting glassDifferential stress
A method of cutting a laminate glass article is disclosed. The method comprises heating at least a portion of a laminate glass article to a reheat temperature. The laminate glass article has a core layer and a first cladding layer and is in stress characterized by a thermally-induced differential stress between the core layer and first cladding layer. The laminate glass article having been set at a setting temperature and the reheat temperature is lower than the setting temperature. The heating of the laminate glass article reduces the thermally-induced differential stress between the core layer and first cladding layer. The method may further comprise scoring the laminate glass article in the heated portion to create a score in the laminate glass article along a cutting line and bending the laminate glass article at the score to cut the glass.
Owner:CORNING INC
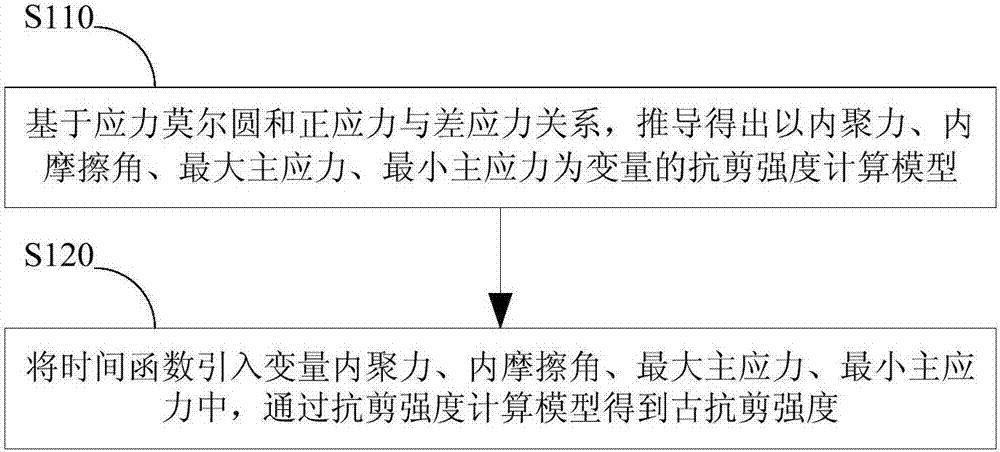
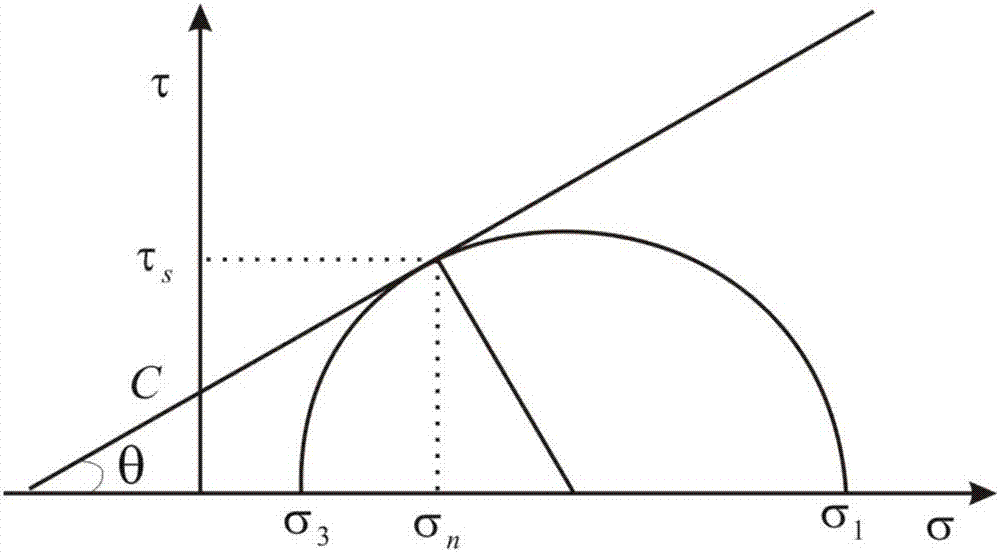
Method for determining ancient shear strength of shale
The invention discloses a method for determining the ancient shear strength of shale. The method comprises: a step of establishing a shear strength calculating model, which takes cohesive force, internal friction angle, maximum principal stress and minimum principal stress as variables, by performing derivation, based on a relation of stress Mohr's circle and direct stress and differential stress; and a step of calculating the ancient shear strength by introducing a time function into variables of cohesive force, internal friction angle, maximum principal stress and minimum principal stress through the shear strength calculating model. The method allows the ancient shear strength of shale to be determined.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
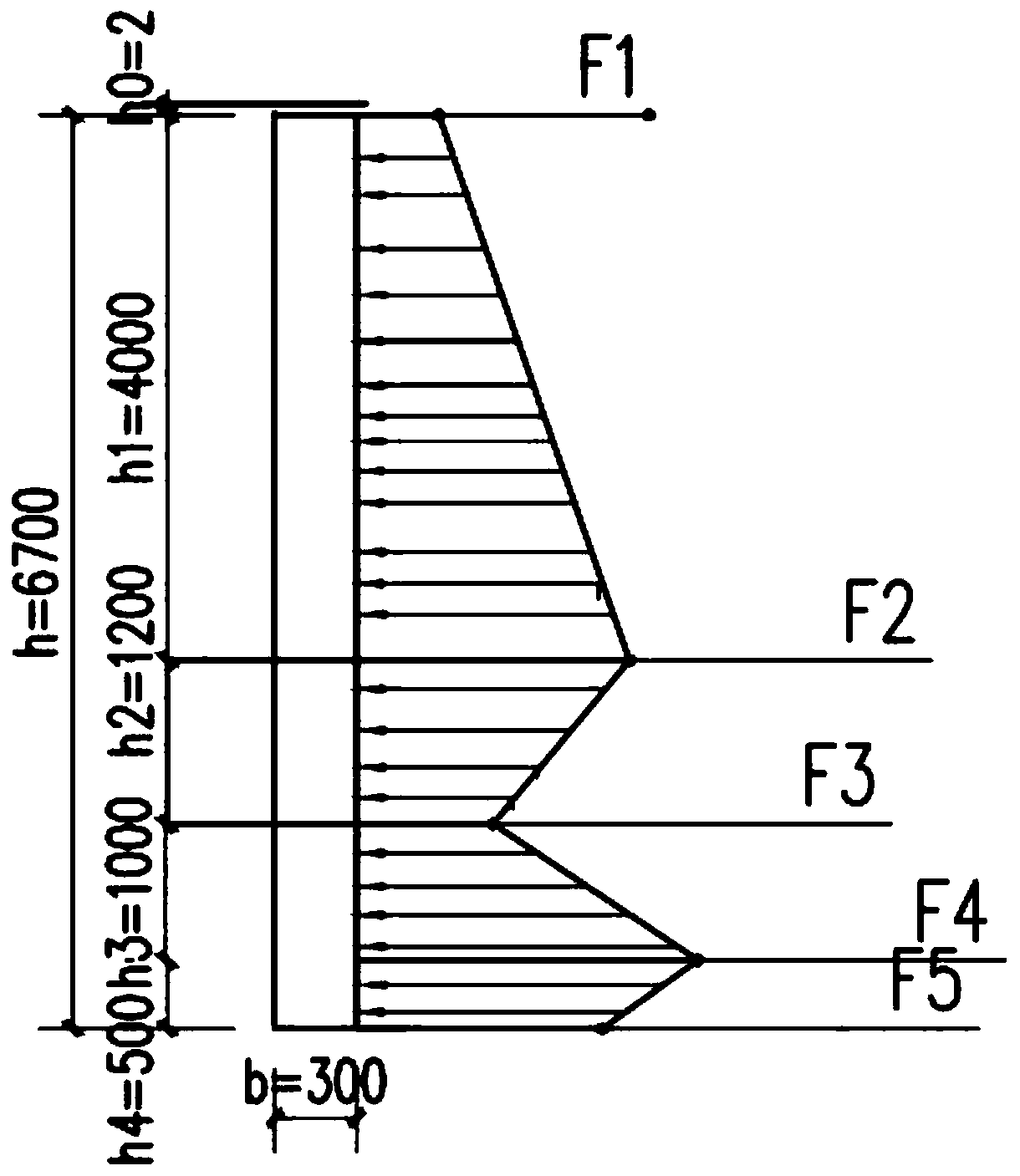
Dynamic engineering response measuring and calculating method for reinforced concrete sheet-pile wall in collapse rockfall geological disasters
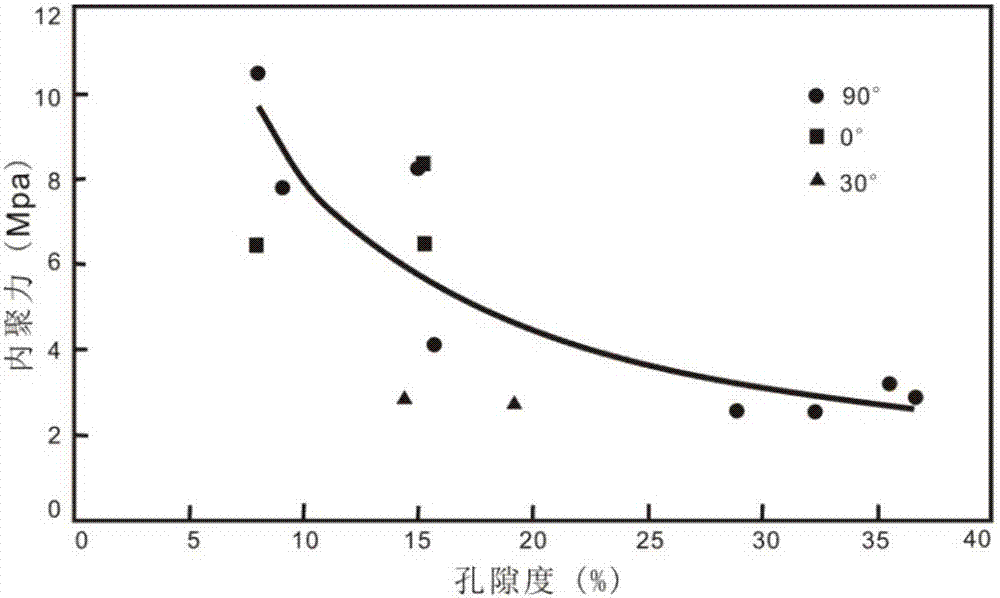
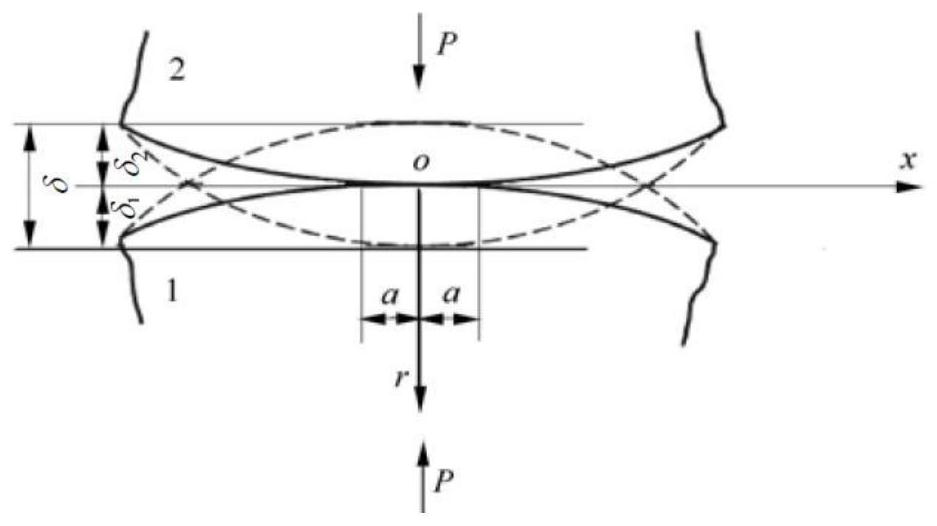
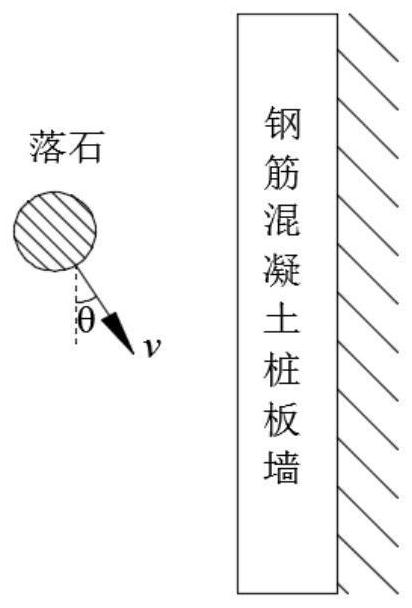
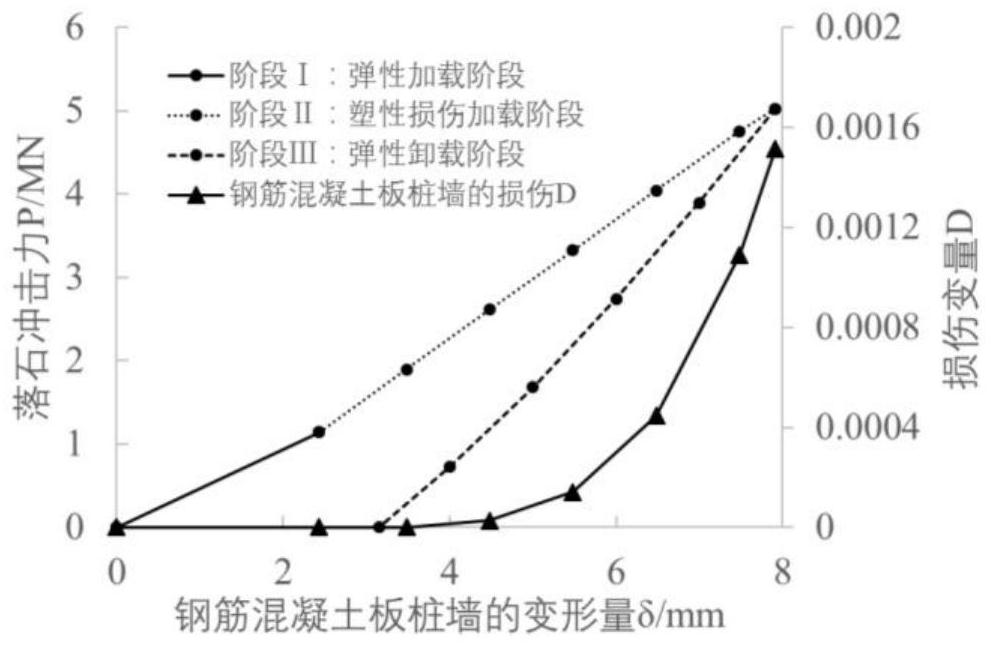
ActiveCN112818532AClimate change adaptationDesign optimisation/simulationReinforced concreteRockfall
The invention discloses a dynamic engineering response measuring and calculating method for a reinforced concrete sheet-pile wall in collapse rockfall geological disasters. The dynamic response of the reinforced concrete sheet-pile wall in the collapse rockfall geological disaster is obtained by obtaining the contact pressure considering material damage, the relation between the maximum contact pressure stress and contact deformation in the collapse rockfall geological disaster and obtaining the impact force of rockfall on the reinforced concrete sheet-pile wall in the collapse rockfall geological disaster. Geological practice examples show that the dynamic mechanical behavior of the reinforced concrete sheet-pile wall under the impact of falling rocks can be well described, high-value reference can be provided for engineering design, and the method has very good application prospects.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Rigid auxiliary system for concrete uniaxial compression test
PendingCN112284884AImprove securityRigid enoughMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesUniaxial compressionArchitectural engineering
The invention discloses a rigid auxiliary system for a concrete uniaxial compression test; the rigid auxiliary system is composed of four sets of rigid auxiliary devices, and the four sets of rigid auxiliary devices are symmetrically distributed on the periphery of concrete test pieces, namely the four corners of a lower pressing plate of a press machine. Each set of rigid auxiliary device comprises a force transmission steel pipe, a belleville spring, a connecting plate, a guide steel column and a bolt. The device supports high-strength concrete test pieces of different sizes, has high applicability and operability, can adjust the rigidity of the auxiliary system according to the rigidity of the concrete test pieces, and can adjust the height of the rigid auxiliary system according to theconcrete test pieces of different sizes; the device can basically cover the uniaxial compressive stress-strain test work of existing concrete test pieces.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
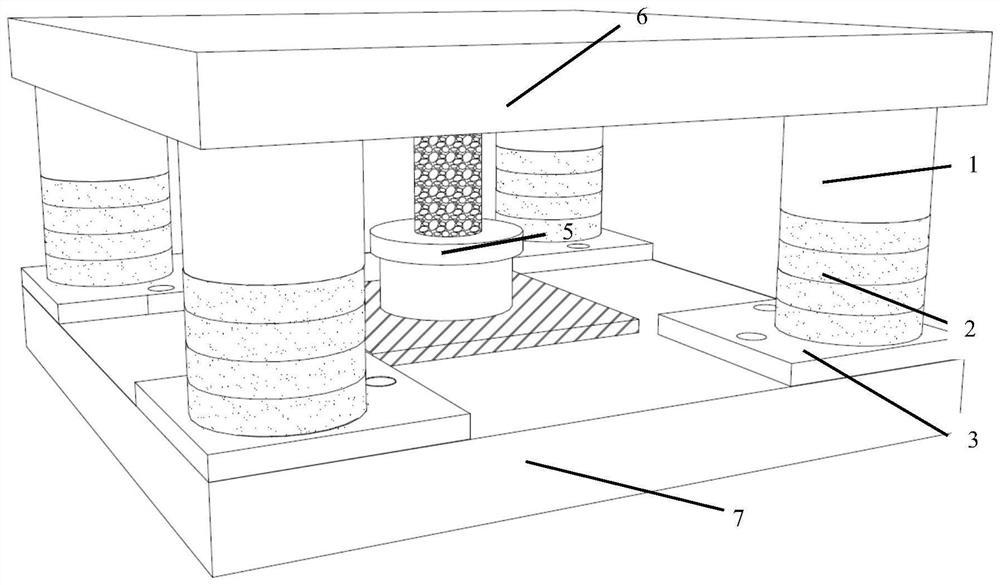
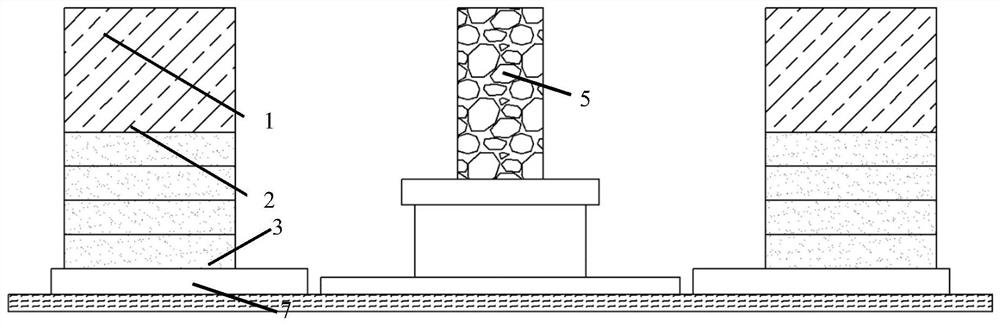
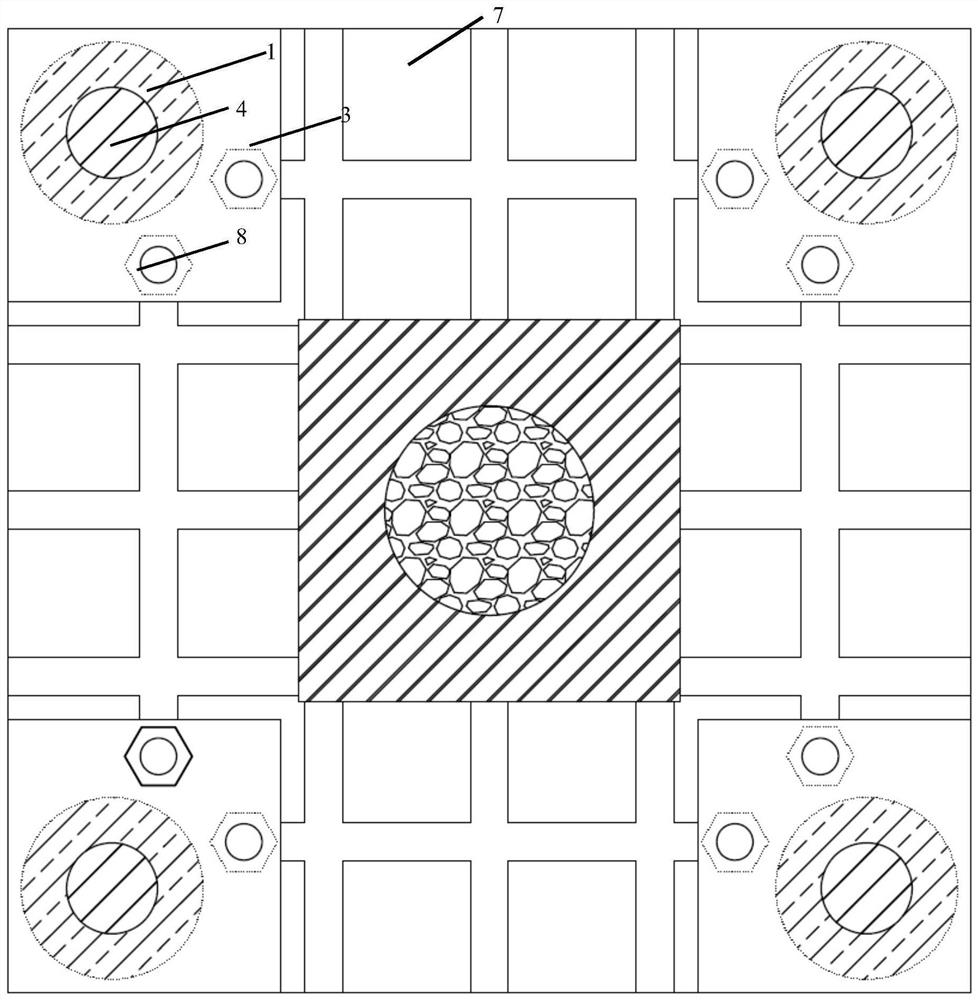
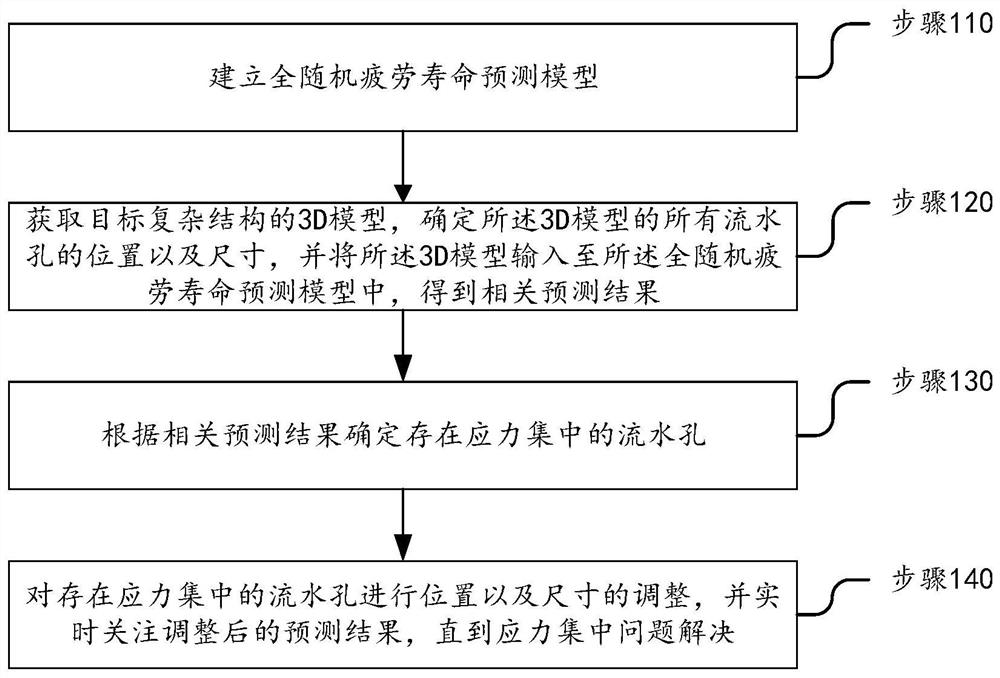
Method for prolonging fatigue life of complex structure of crude oil transfer barge
ActiveCN112906269AImprove fatigue lifeImprove fatigue strengthGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationStructural fatigueMechanics
The invention provides a method for prolonging the fatigue life of a complex structure of a crude oil transfer barge. The method comprises the following steps: step 110, establishing a full-random fatigue life prediction model; 120, collecting a 3D model of a target complex structure, determining positions and sizes of all drain holes of the 3D model, and inputting the 3D model into the full-random fatigue life prediction model to obtain a related prediction result; 130, determining drain holes with stress concentration according to related prediction results; and step 140, adjusting the position and the size of the drain hole with stress concentration, and paying attention to the adjusted prediction result in real time until the stress concentration problem is solved. According to the method, stress concentration can be effectively reduced by adjusting the position of the drain hole in the structural design. Meanwhile, residual compressive stress is further formed by using a laser shock peening method, and the fatigue life of a complex structure is prolonged.
Owner:COSCO SHIPPING SHIPYARD (NANGTONG) CO LTD +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com