Method for measuring two-dimensional stress at weld joint by using Barkhausen effect and detection instrument
A technology of stress detection and stress, which is applied in the direction of measuring force, measuring the change of material magnetic properties caused by applied stress, force/torque/power measuring instrument, etc., and can solve the problem that the two-dimensional residual stress cannot be realized.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
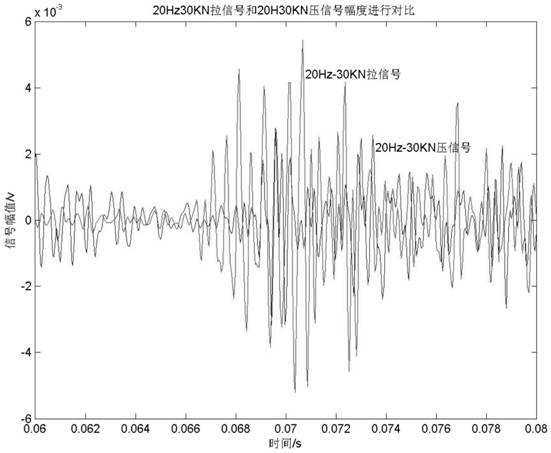
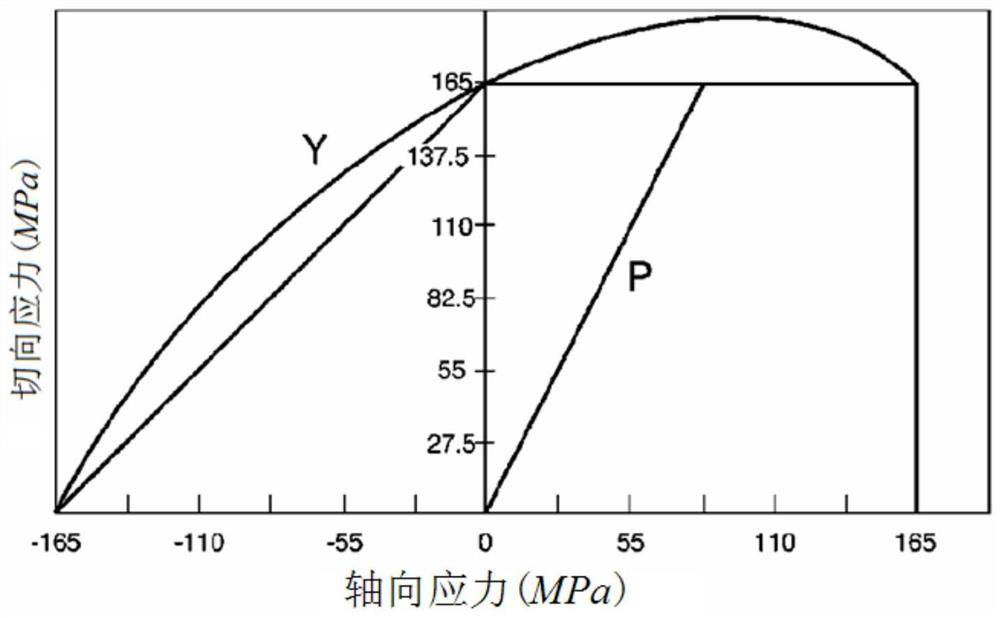
[0032] Such as figure 1 As shown, a detection method for measuring the two-dimensional stress at the weld using the Barkhausen effect described in this embodiment, wherein, the weld of the ferromagnetic material member, the weld and the stress on both sides of the weld are not only parallel The stress in the direction of the weld also has the stress perpendicular to the direction of the weld, which is called bidirectional stress, biaxial stress, or two-dimensional stress. In other words, the internal stress of ferromagnetic material components is generally two-dimensional stress, but at some point the stress in a certain direction can be ignored and considered as uniaxial stress or one-dimensional stress. For example, when the sample is stretched by a tensile testing machine, it can be considered that there is only tensile stress in the direction parallel to the tensile force inside the sample, and the stress in the direction perpendicular to the tensile force can be ignored. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com