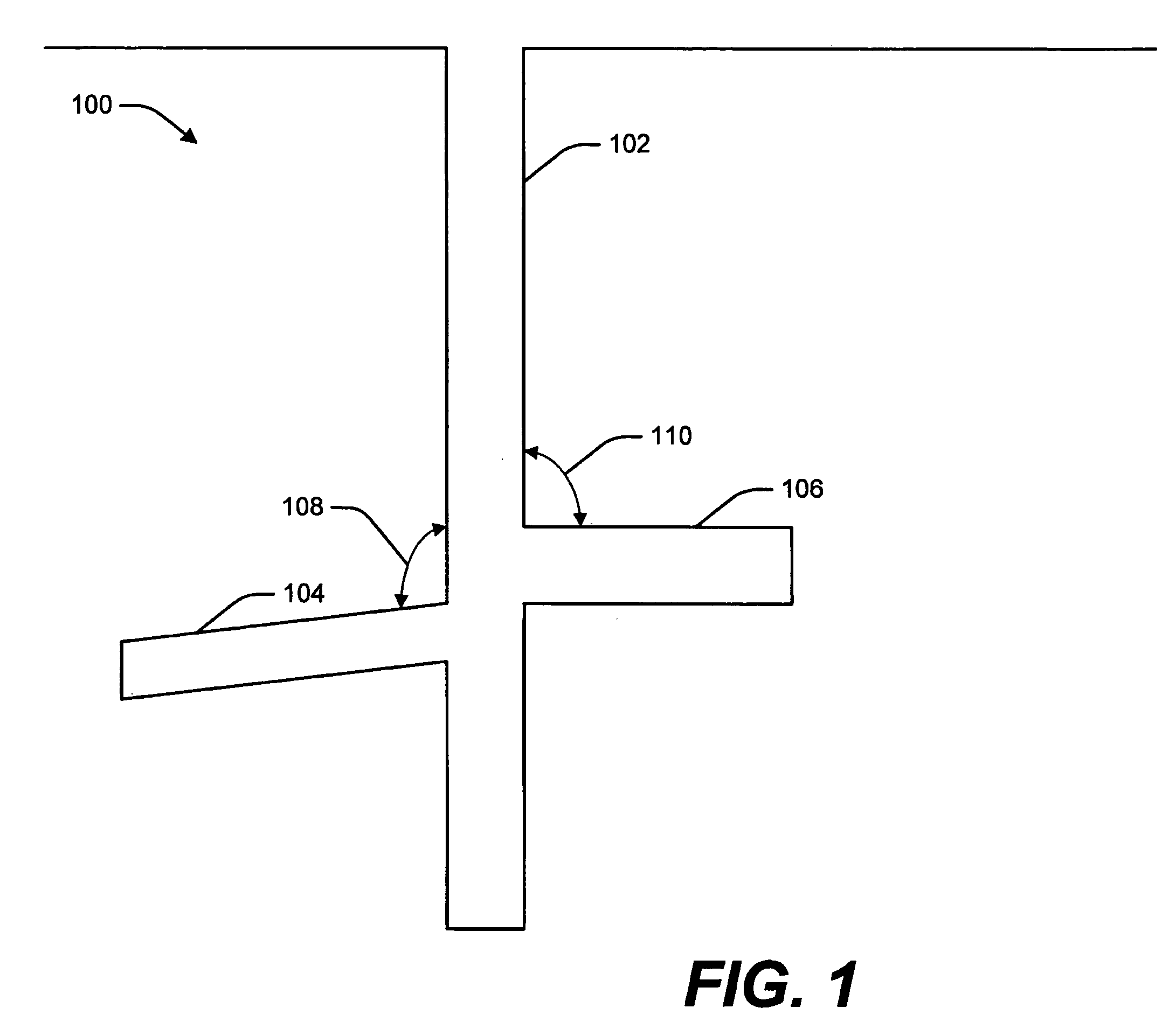
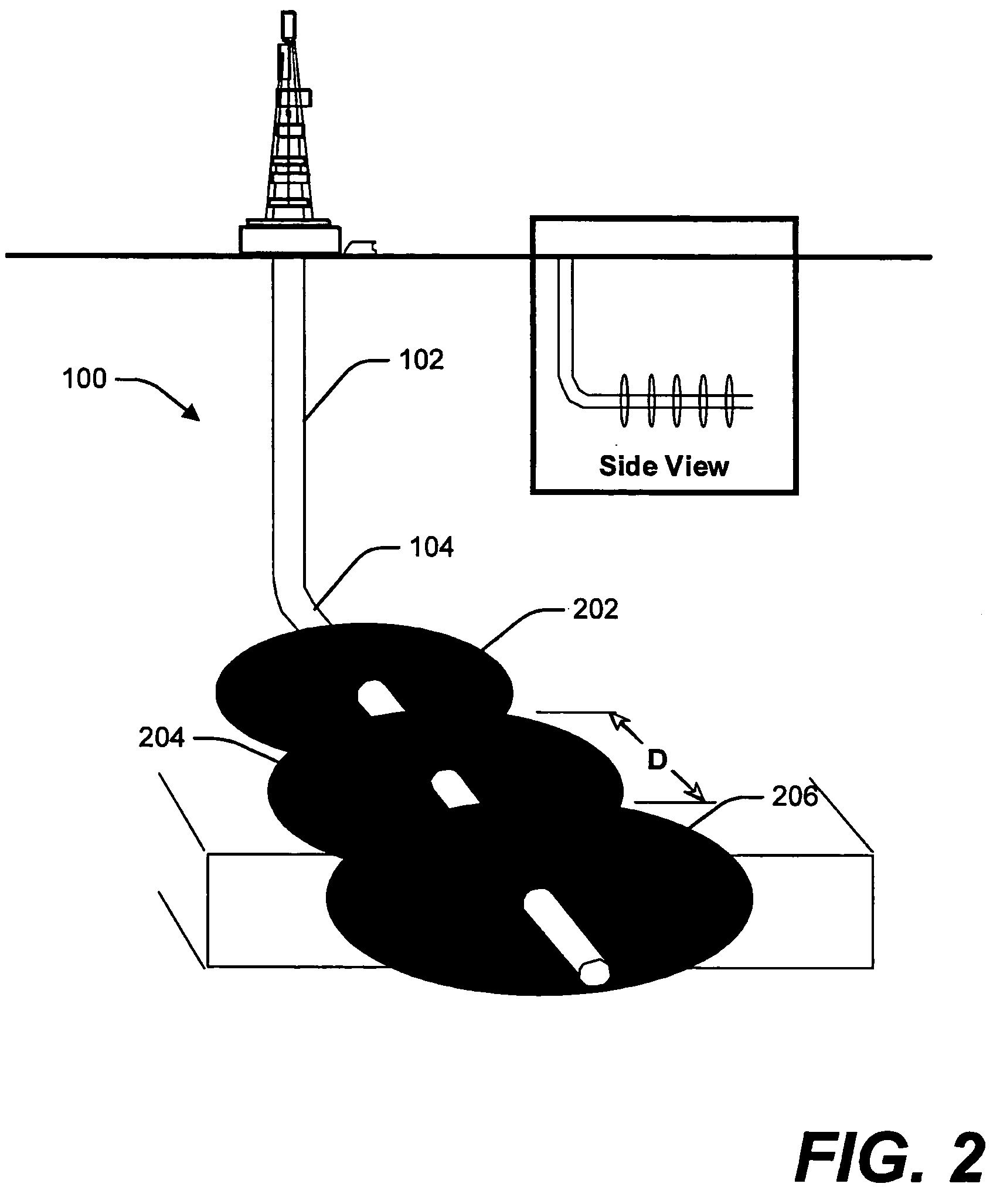
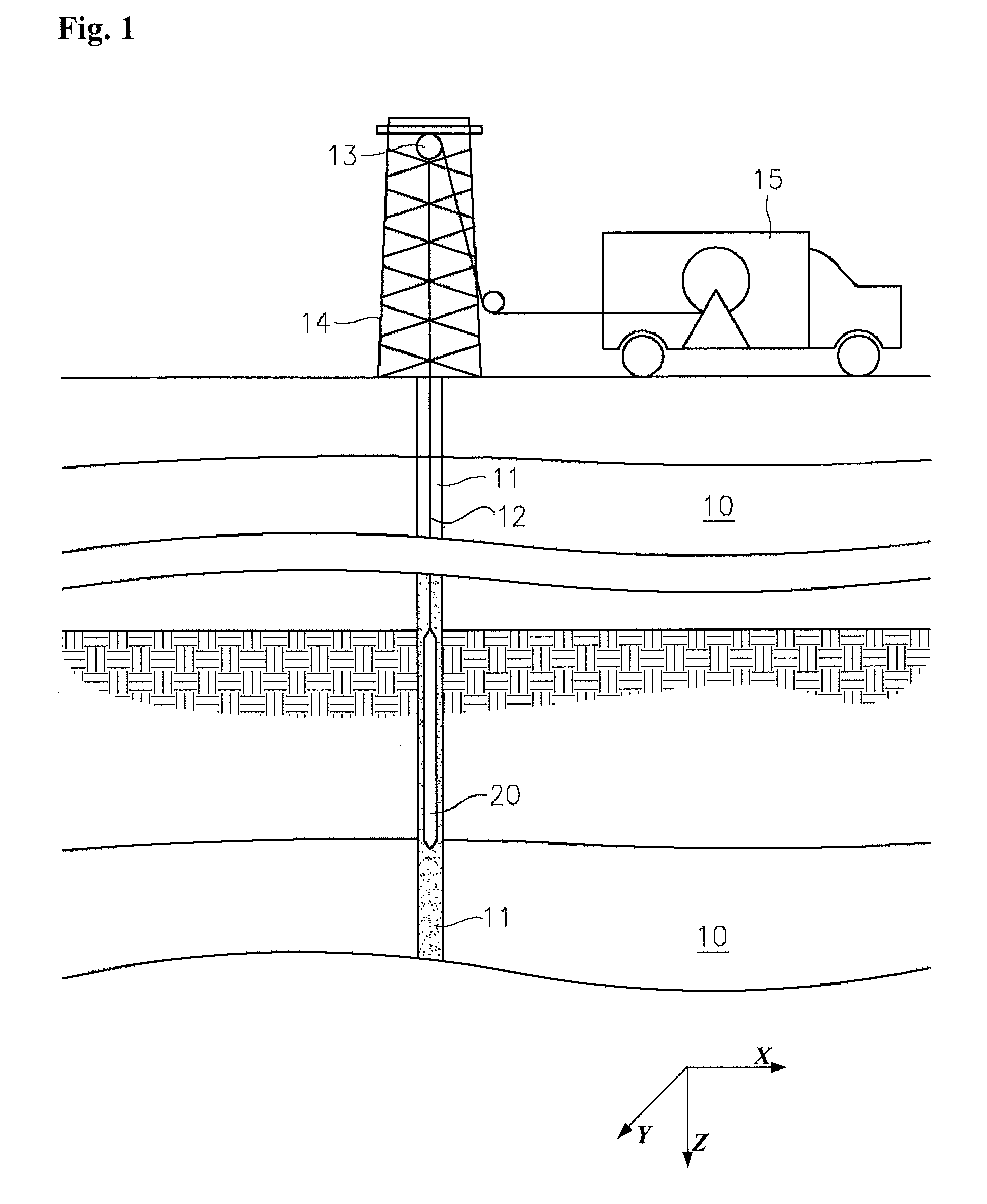
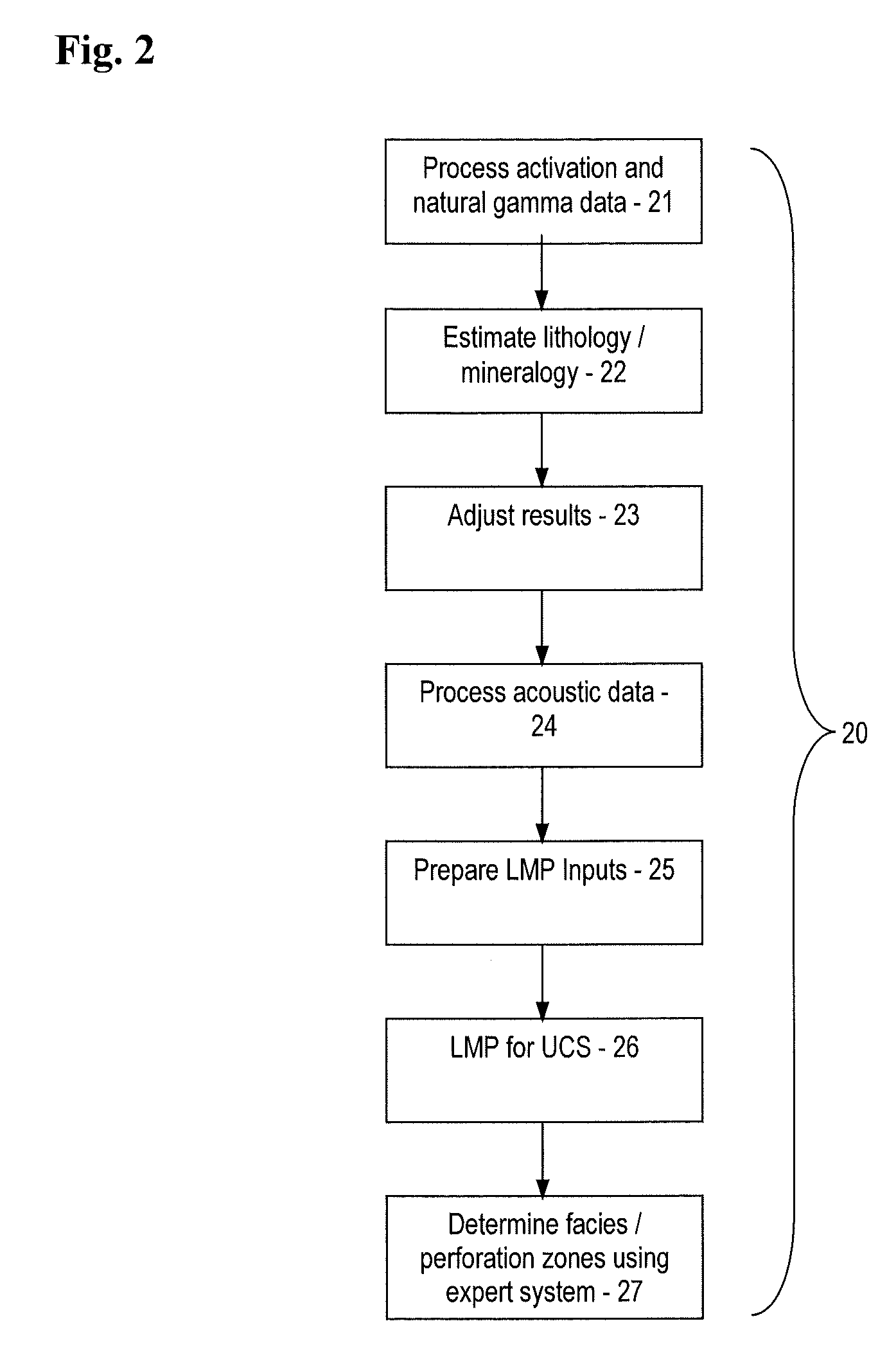
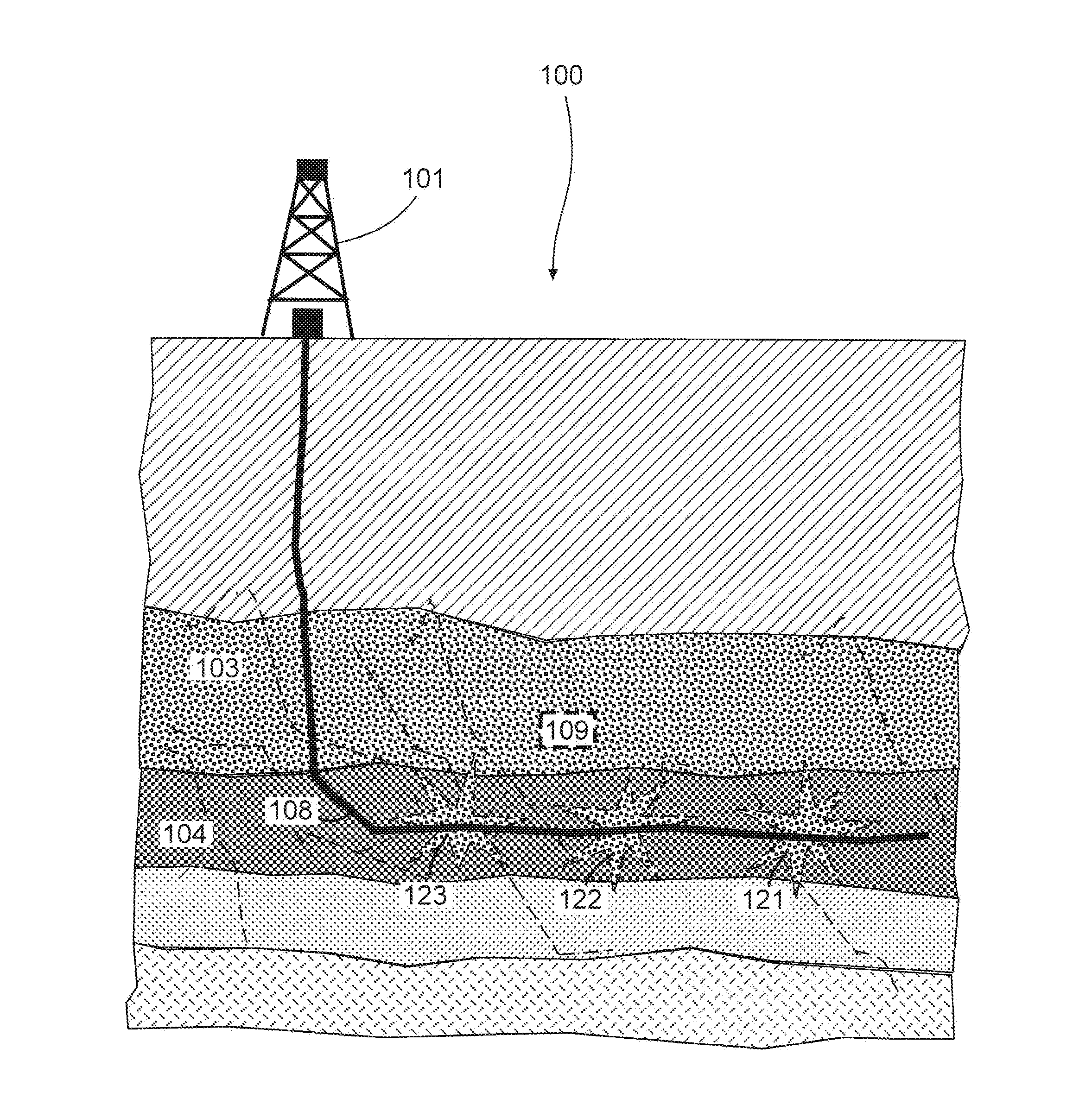
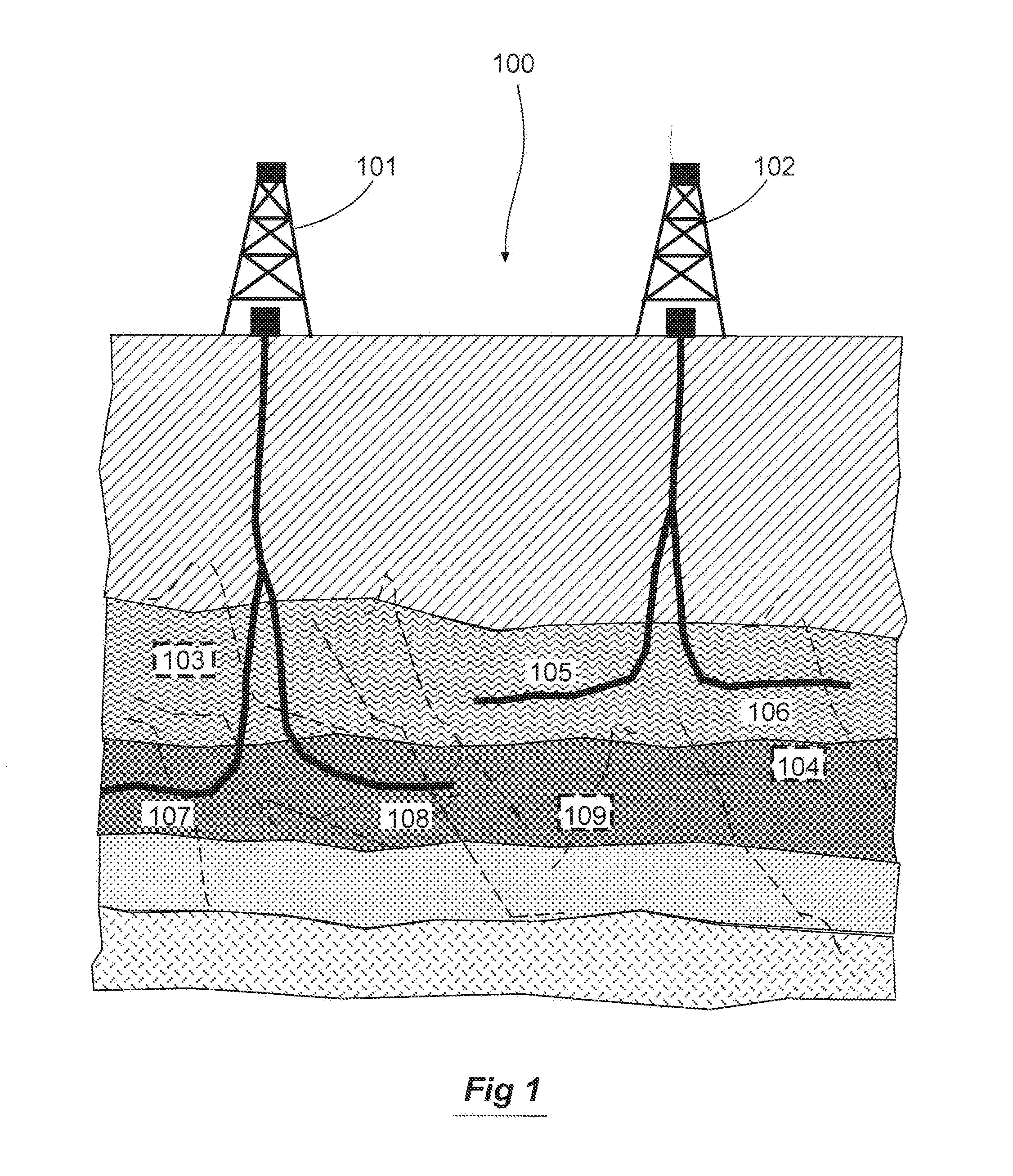
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
374 results about "Geomechanics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Geomechanics (from the Greek prefix geo- meaning "earth"; and "mechanics") involves the study of the mechanics of soil and rock.
Staged and/or patterned heating during in situ thermal processing of a hydrocarbon containing formation
A method for treating a hydrocarbon containing formation is described. The method for treating a hydrocarbon containing formation may include heating a first volume of the formation using a first set of heaters. A second volume of the formation may be heated using a second set of heaters. The first volume may be spaced apart from the second volume by a third volume of the formation. The first volume, second volume, and / or third volume may be sized, shaped, and / or located to inhibit deformation of subsurface equipment caused by geomechanical motion of the formation during heating.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
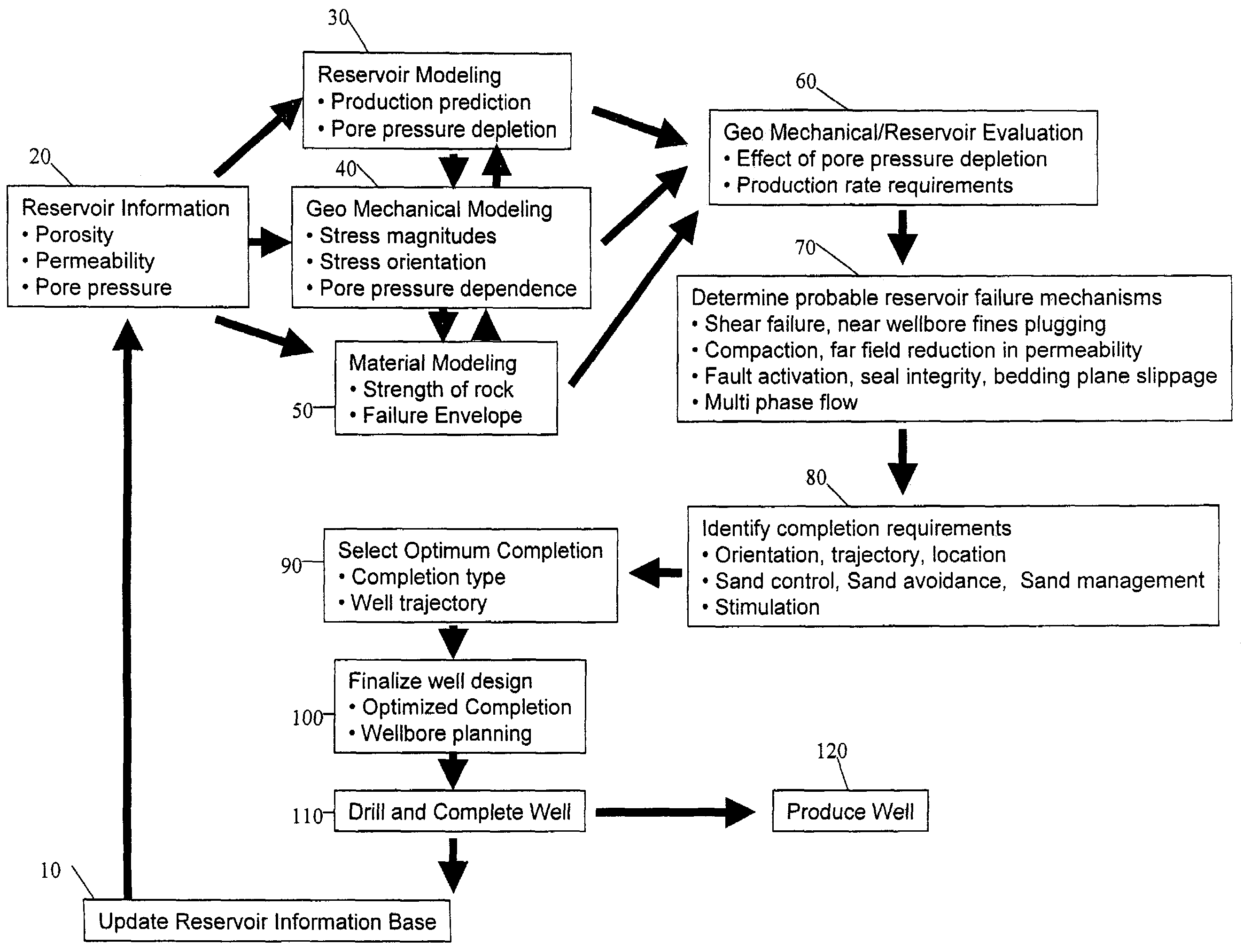
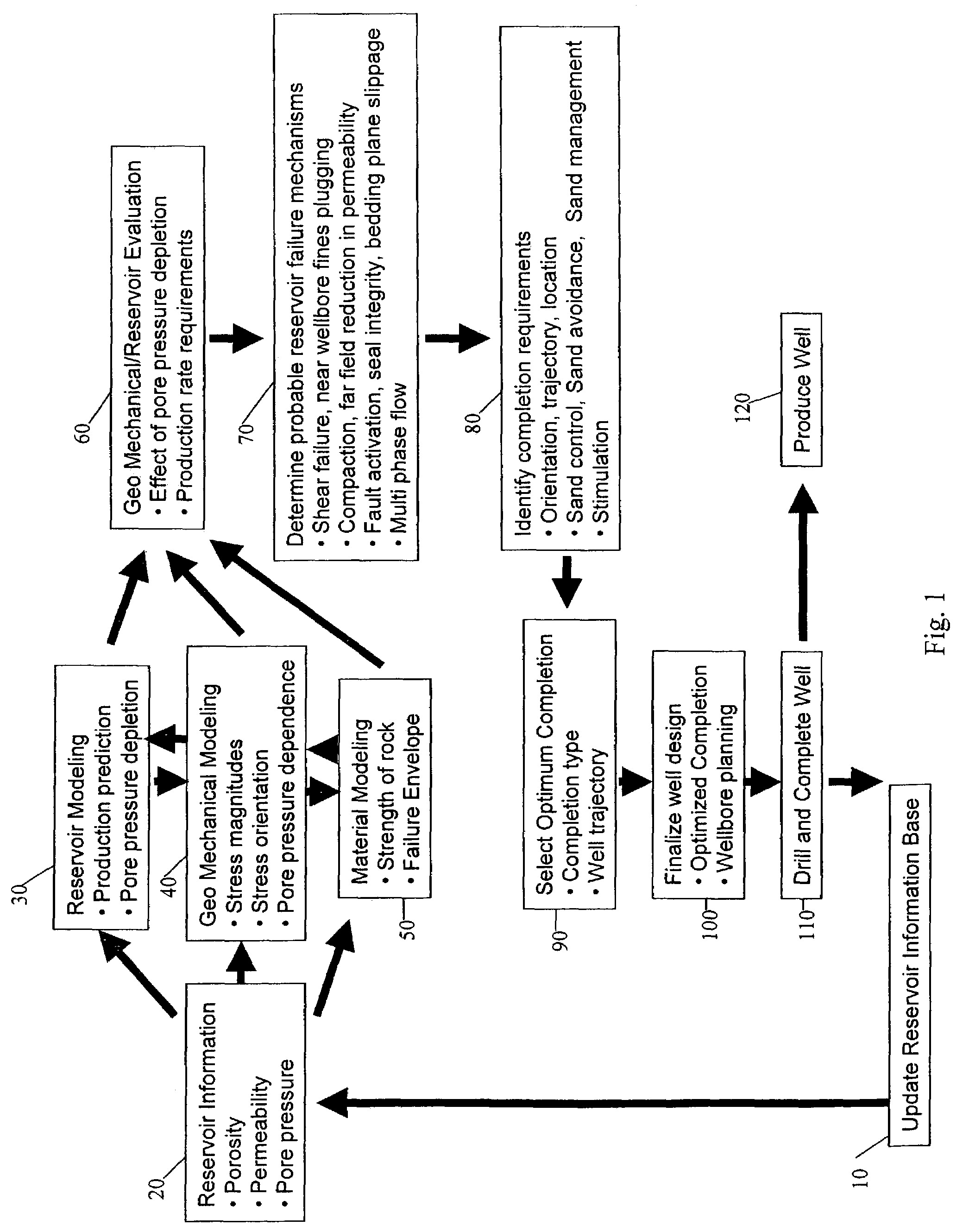
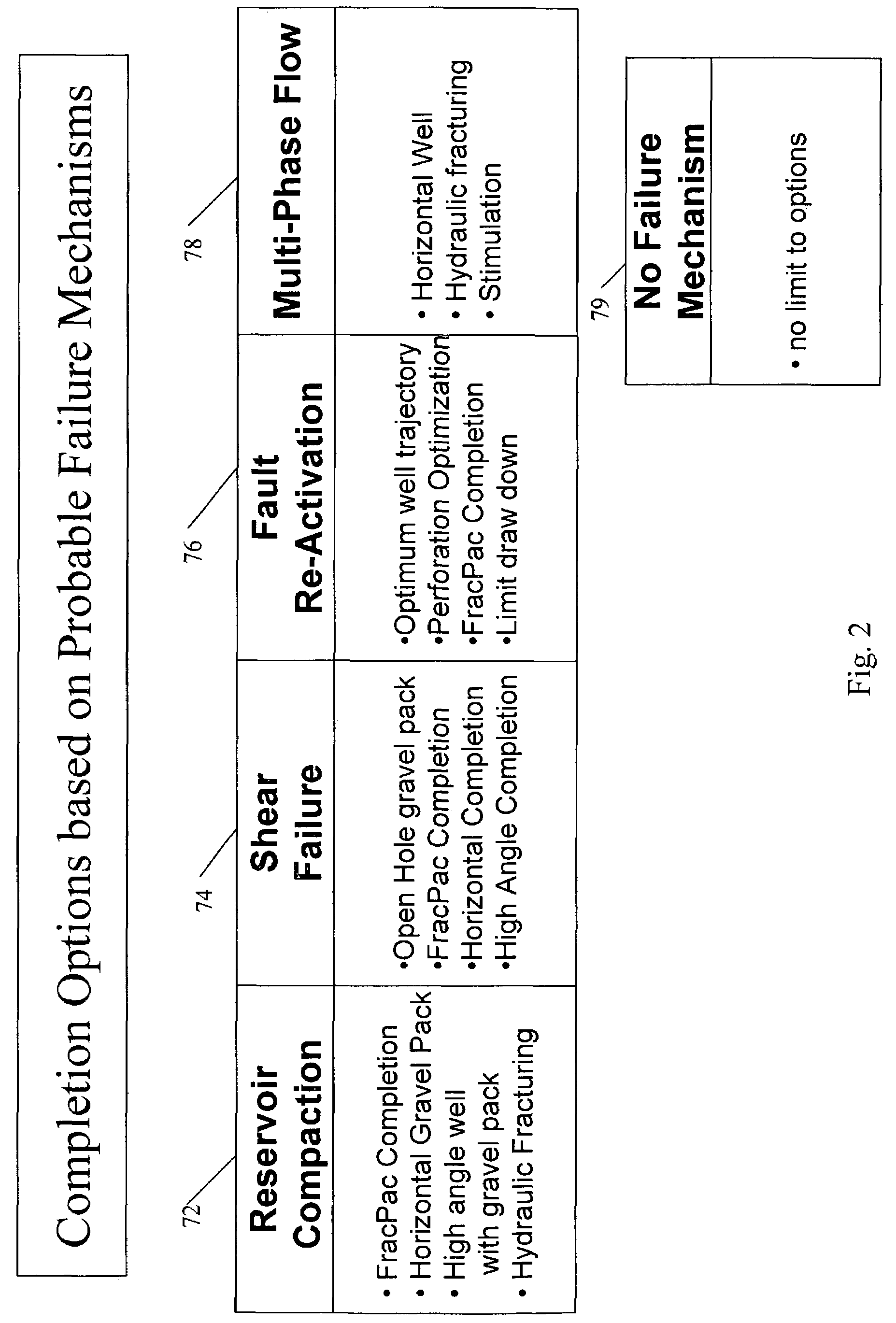
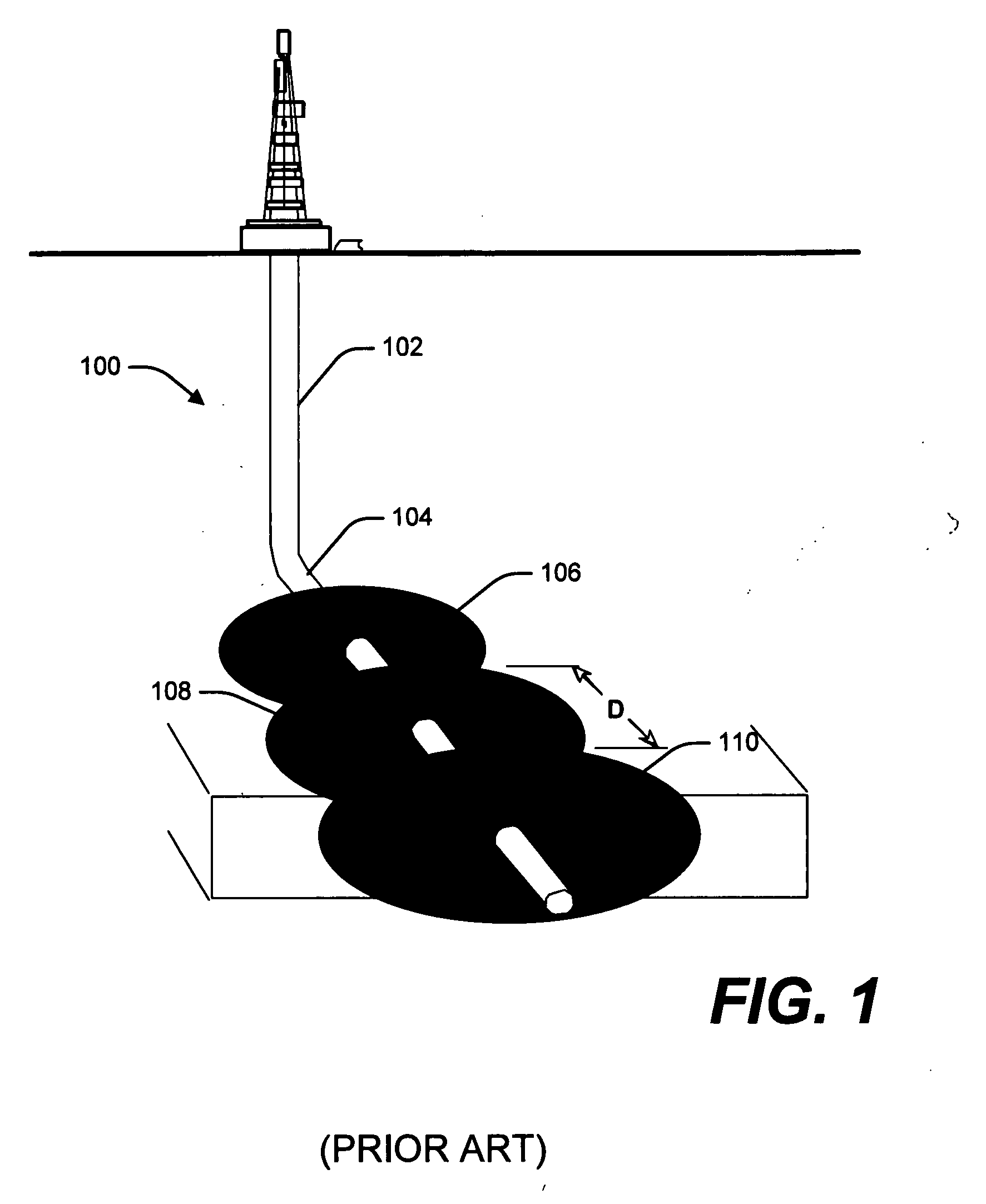
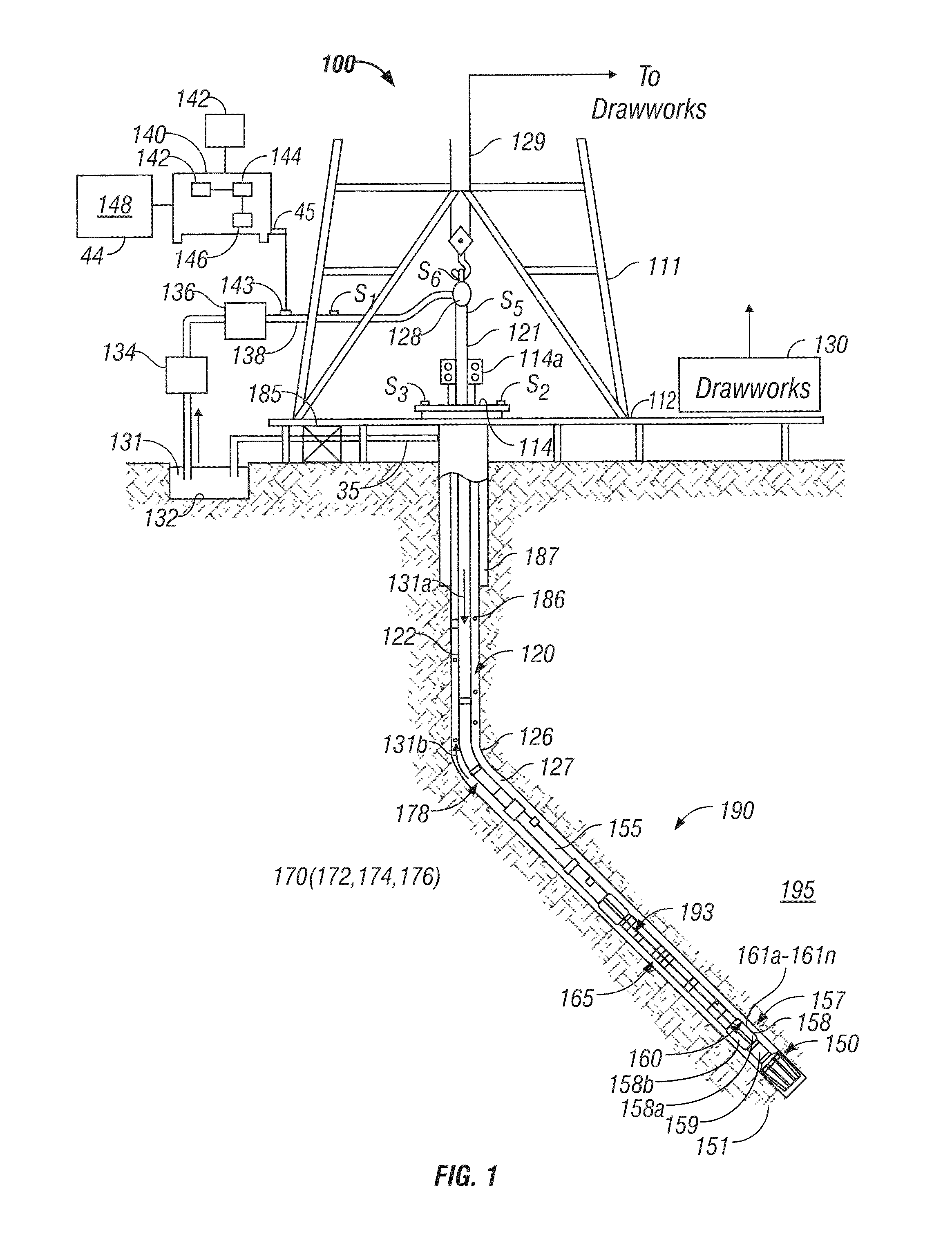
System and process for optimal selection of hydrocarbon well completion type and design
ActiveUS7181380B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyUltimate tensile strengthFailure mechanism
A process to determine optimal completion type and design prior to drilling of a hydrocarbon producing well utilizing information from hydrocarbon recovery modeling such as reservoir, geo-mechanical, and material modeling over the production life of the well. An embodiment of the process includes obtaining information regarding pore pressure depletion, stress magnitudes and orientations, and strength of rock formation from hydrocarbon recovery modeling to determine optimum well completion design including the selection of a completion type, trajectory, and location. Additionally, the process may also consider probable failure mechanisms and identified completion requirements, and their corresponding effect on completion options.
Owner:GEOMECHANICS INT +1
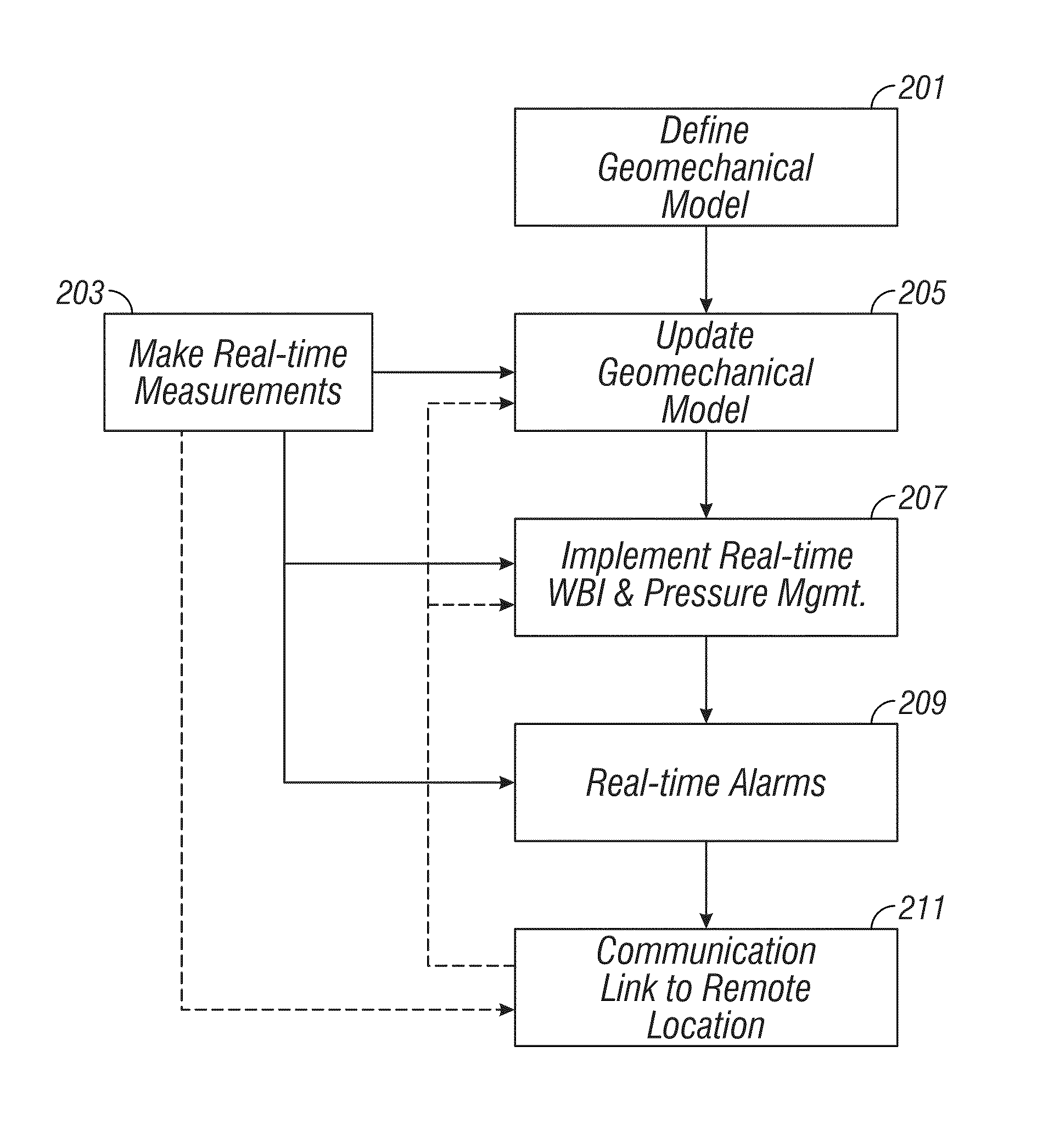
System and methods for real-time wellbore stability service
ActiveUS20110153296A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingEnvironmental geologyGeomechanics
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
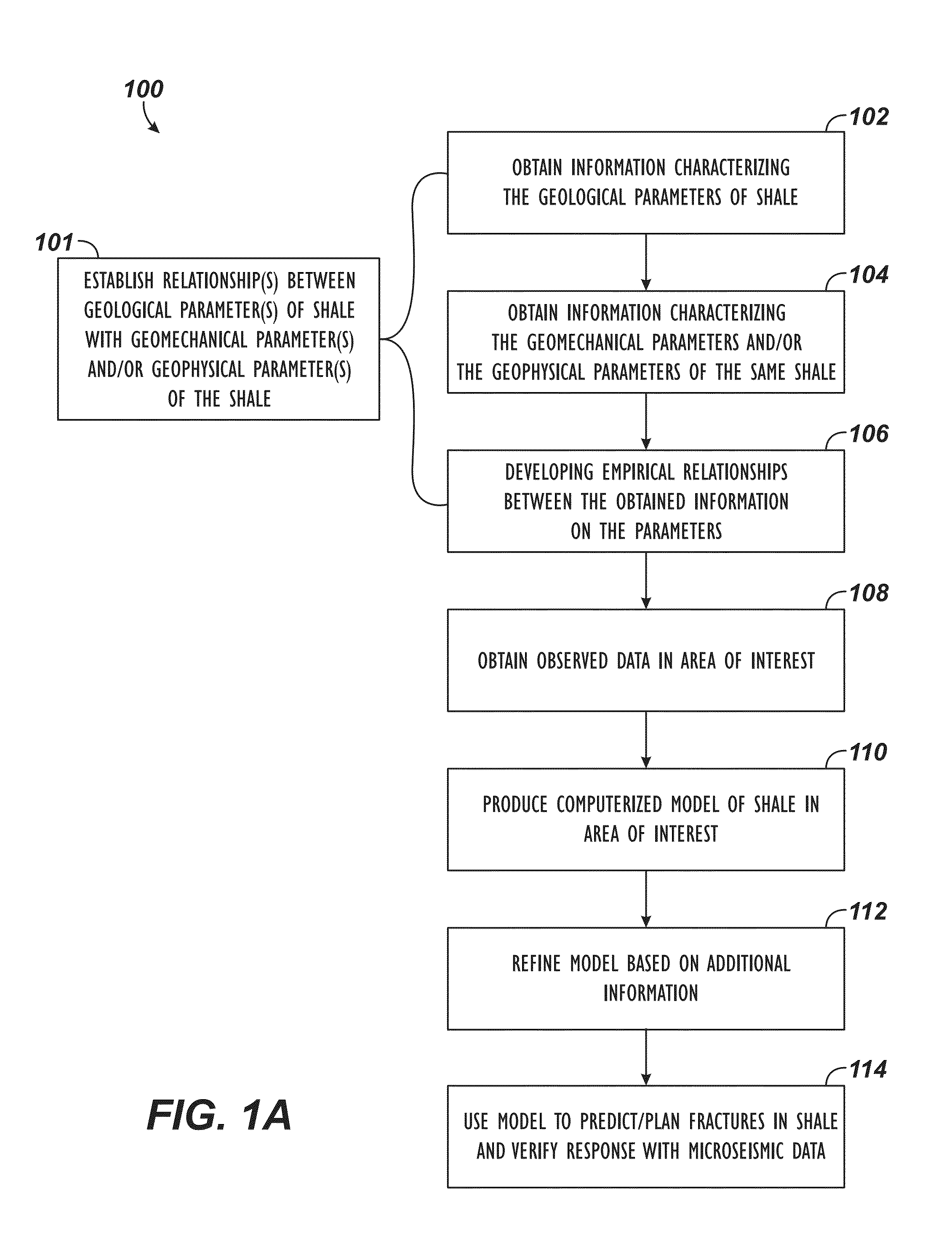
Model Predicting Fracturing of Shale
ActiveUS20130238304A1Promote recoveryMinimizes probabilityGeomodellingDesign optimisation/simulationWell loggingHydraulic fracturing
A model for predicting fracturing in shale can minimize surface disruption, protect groundwater, maximize efficiency of hydraulic fracturing, and manage fluids used in unconventional gas development. The model provides a more comprehensive understanding of the geological, geophysical, and geomechanical properties of shales and imbeds these properties in geomechanical computer simulations to predict both the reservoir performance from the fracturing, and the associated microseismic events generated by fracturing. Since the geological and geophysical properties can be estimated from surface seismic, well logs, and geologic concepts with regional context; the performance of the fracturing can be predicted and optimized. Since the microseismic events can be predicted with the model, the simulations can be verified and the model can be updated to be consistent with the observed microseismic.
Owner:ION GEOPHYSICAL CORP
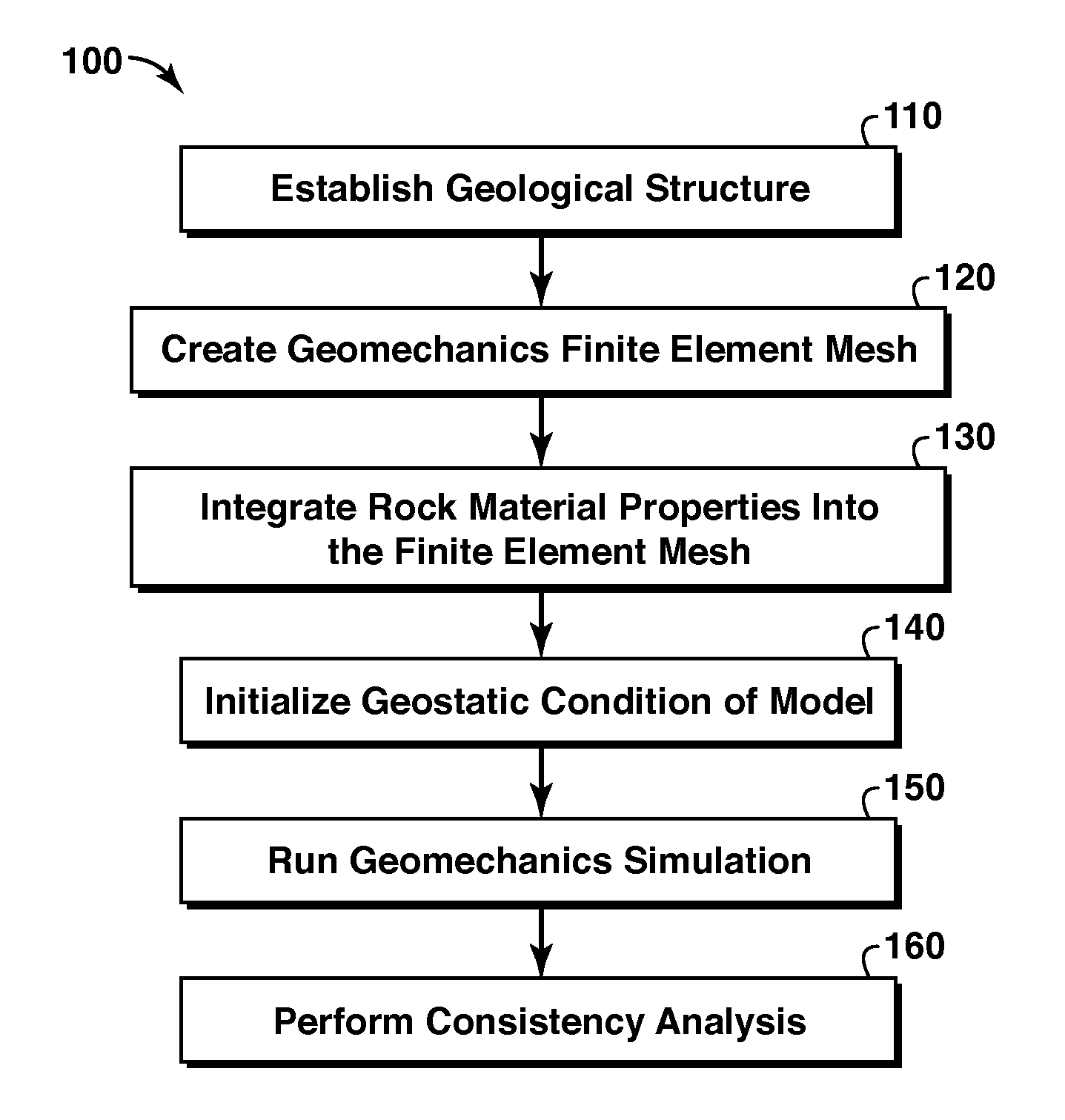
Method For Multi-Scale Geomechanical Model Analysis By Computer Simulation
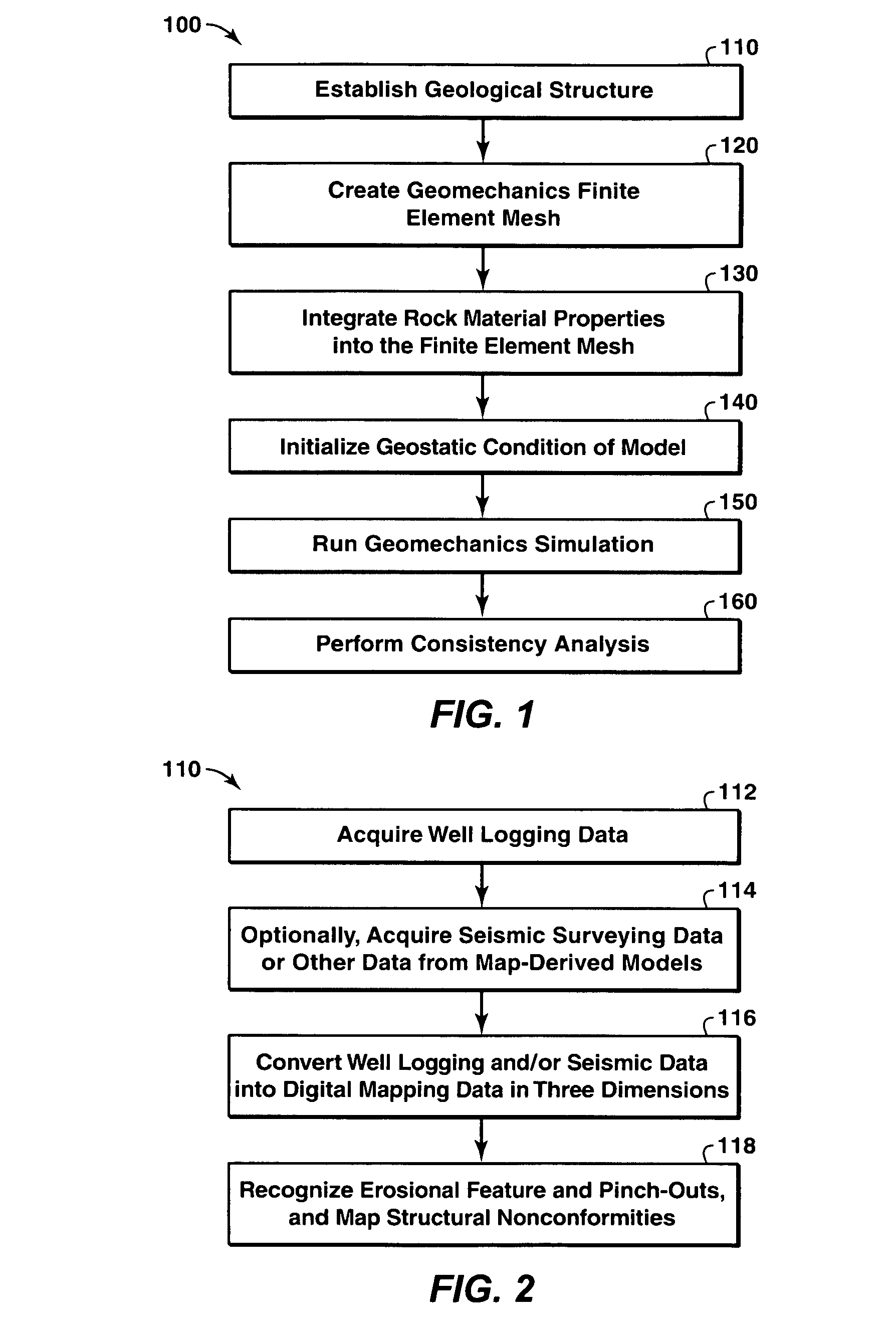
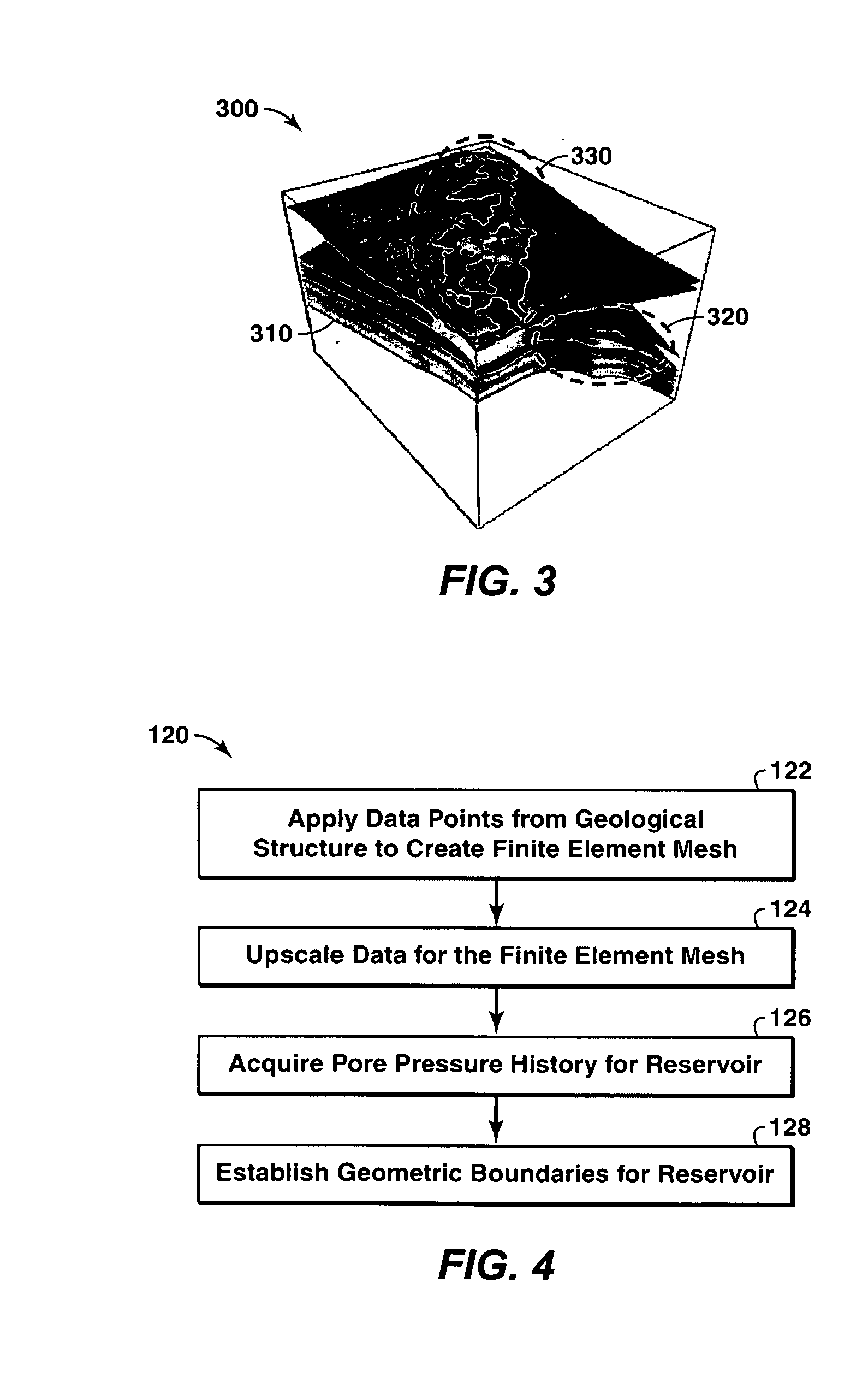
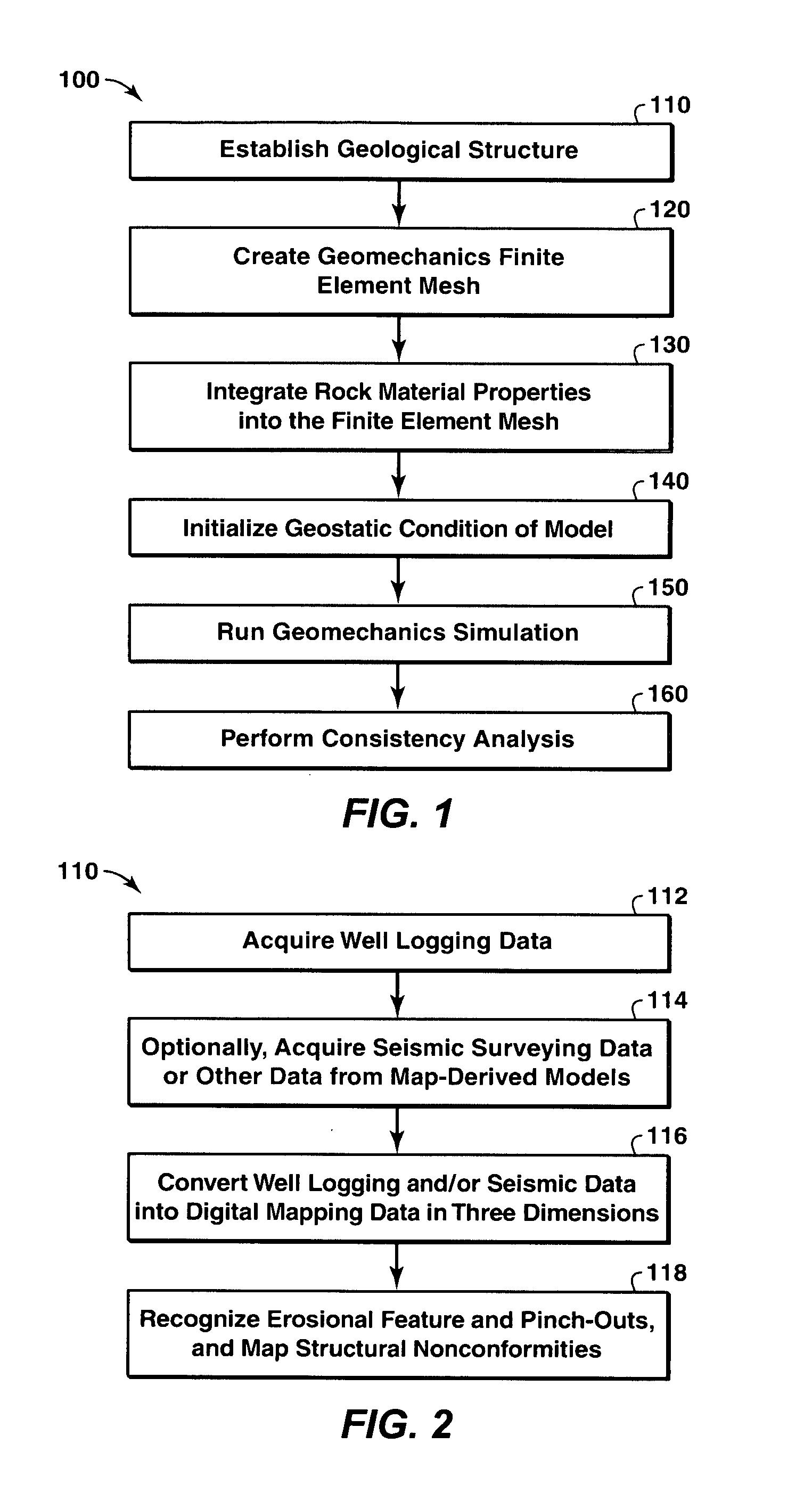
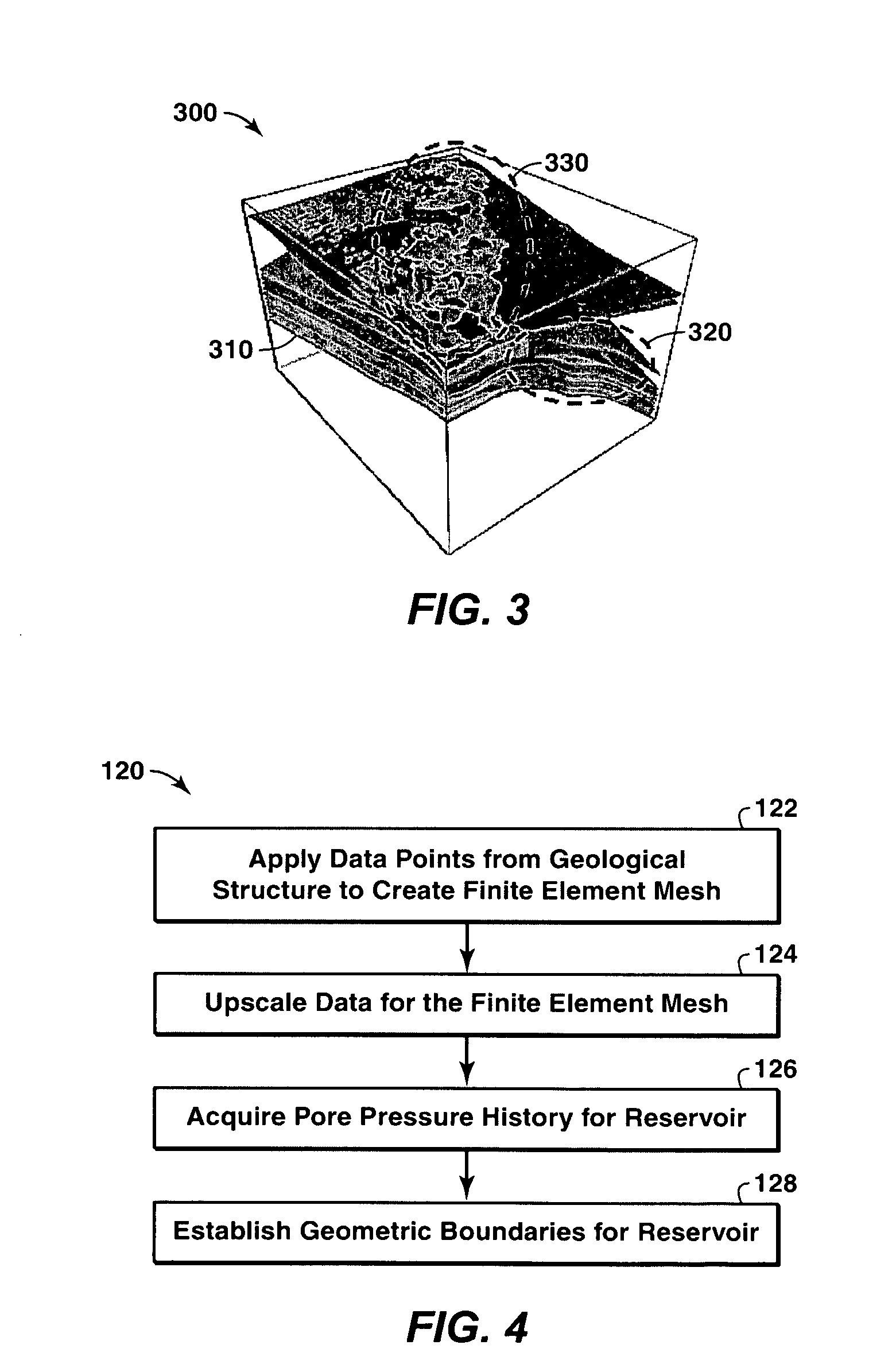
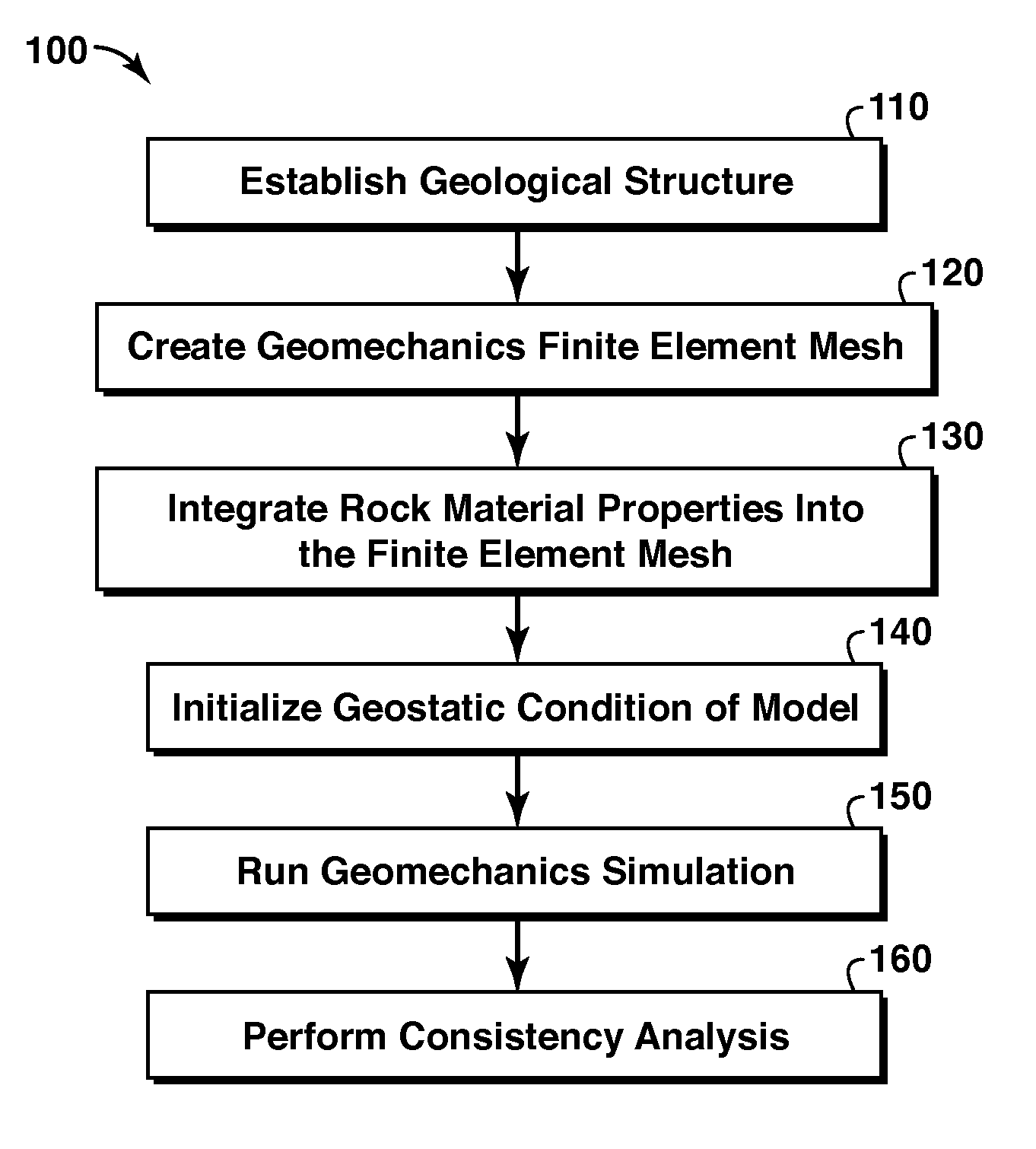
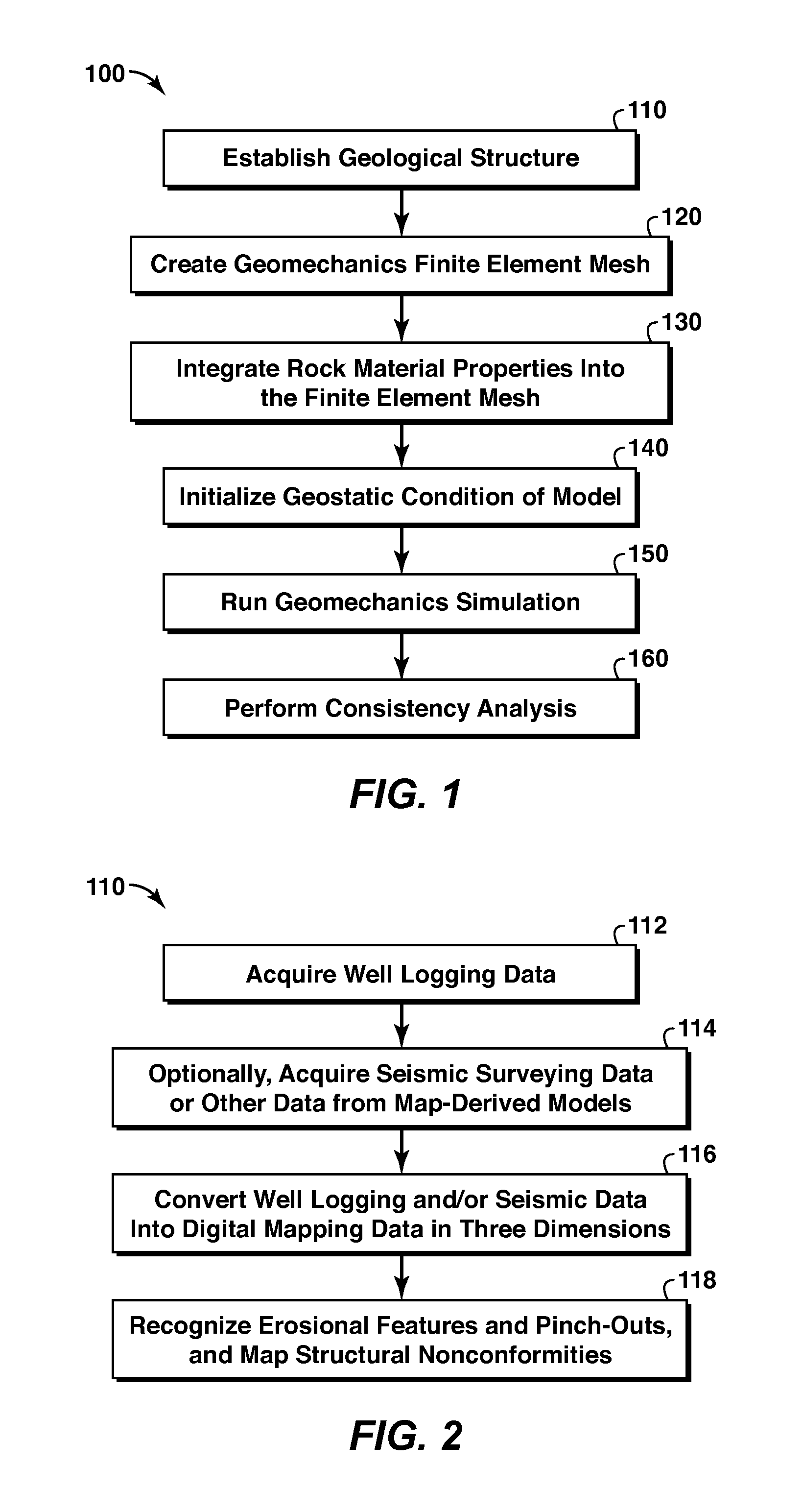
A method of predicting earth stresses in response to changes in a hydrocarbon-bearing reservoir within a geomechanical system includes establishing physical boundaries for the geomechanical system, acquiring logging data from wells drilled, and acquiring seismic data for one or more rock layers. The well and seismic data are automatically converted into a three-dimensional digital representation of one or more rock layers within the geomechanical system, thereby creating data points defining a three-dimensional geological structure. The method also includes (a) applying the data points from the geological structure to derive a finite element-based geomechanical model, and (b) initializing a geostatic condition in the geomechanical model, and then running a geomechanics simulation in order to determine changes in earth stresses associated with changes in pore pressure or other reservoir characteristics within the one or more rock layers.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Method For Predicting Well Reliability By Computer Simulation
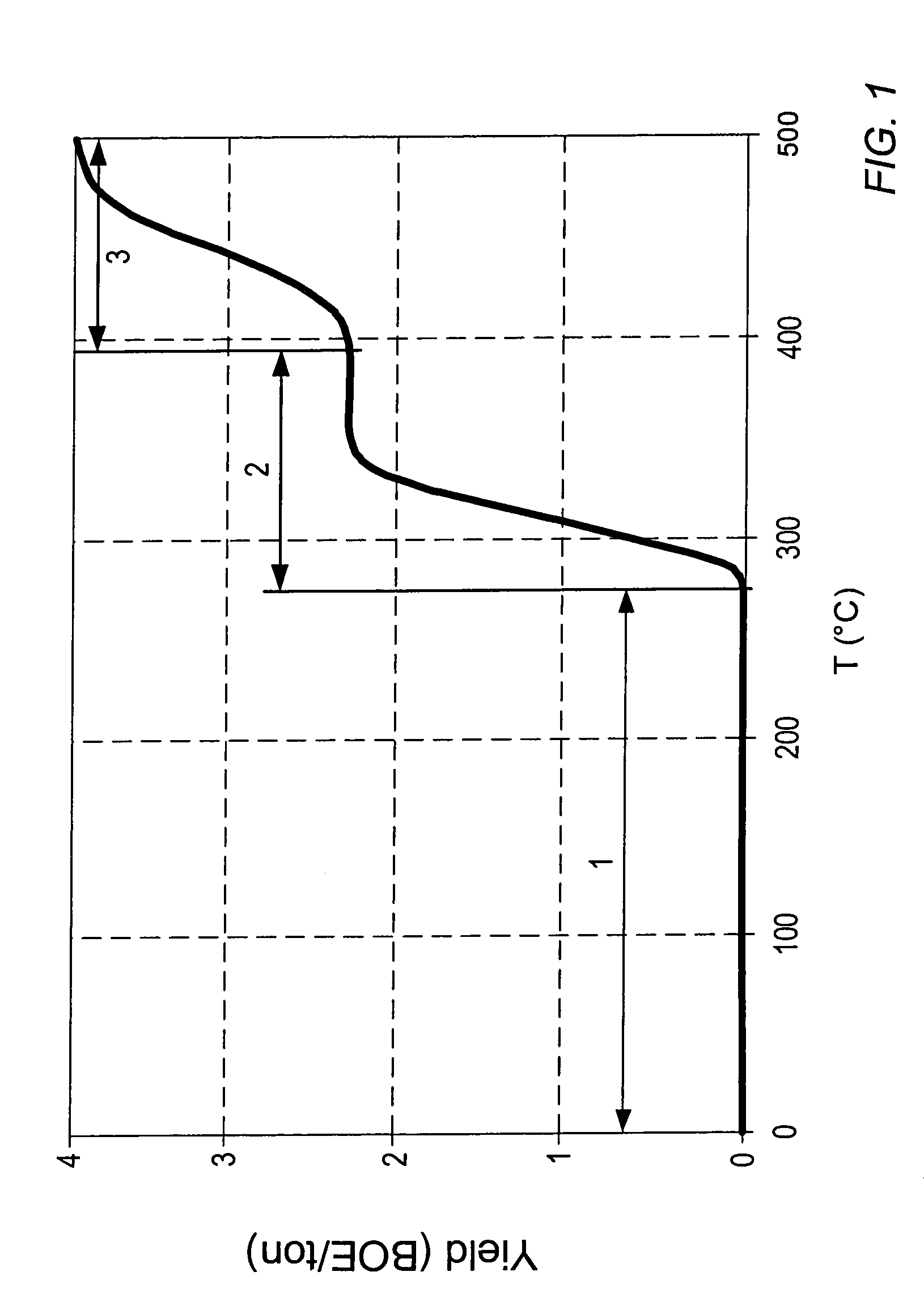
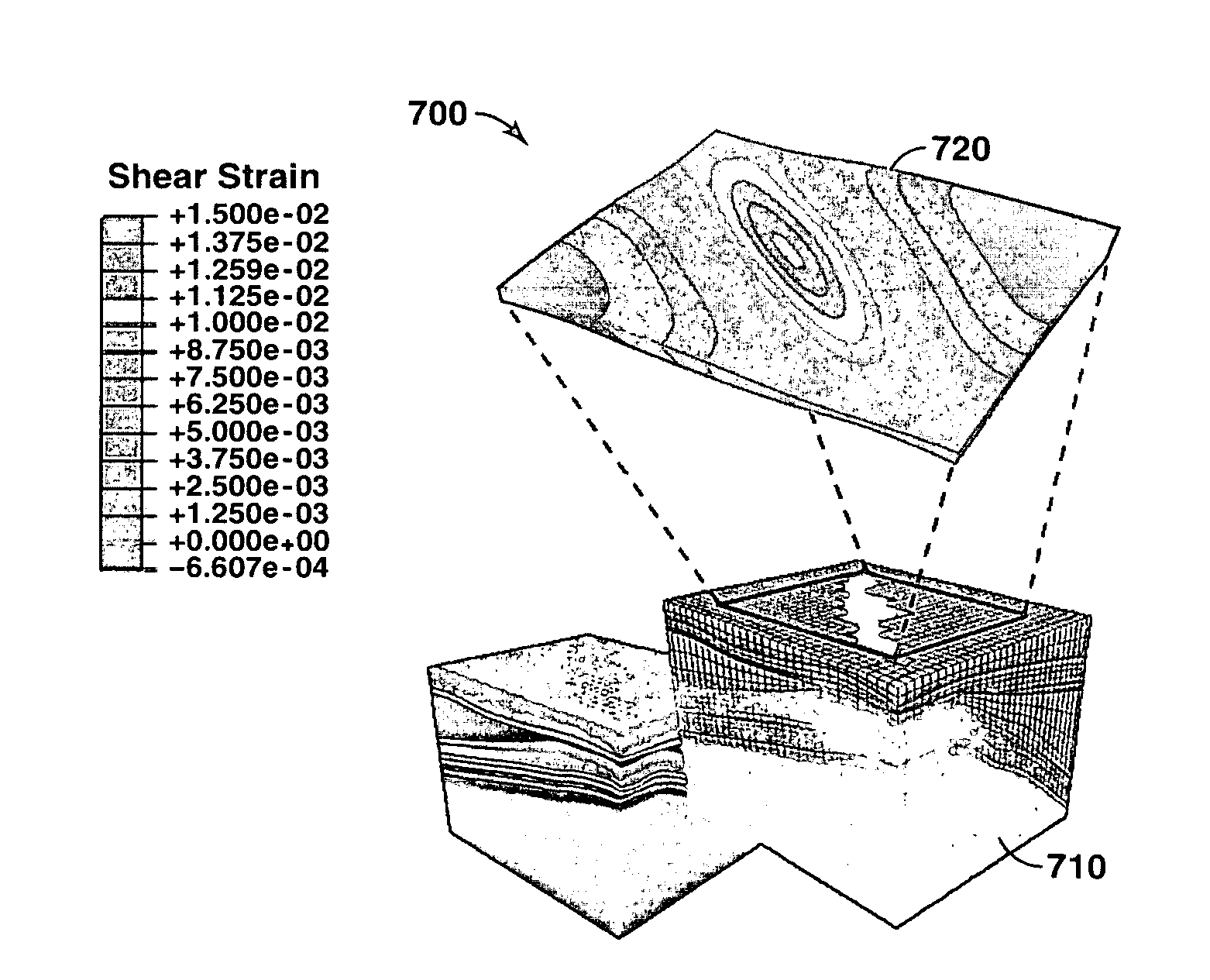
Methods of predicting earth stresses in response to pore pressure changes in a hydrocarbon-bearing reservoir within a geomechanical system, include establishing physical boundaries for the geomechanical system and acquiring reservoir characteristics. Geomechanical simulations simulate the effects of changes in reservoir characteristics on stress in rock formations within the physical boundaries to determine the rock formation strength at selected nodes in the reservoir. The strength of the rock formations at the nodes is represented by an effective strain (εeff), which includes a compaction strain (εc) and out-of-plane shear strains (γ1-3, Y2-3) at a nodal point. The methods further include determining an effective strain criteria (εeffcr) from a history of well failures in the physical boundaries. The effective strain (εeffcr) at a selected nodal point is compared with the effective strain criteria (εeffcr) to determine if the effective strain (εeff) exceeds the effective strain criteria (εeffcr).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
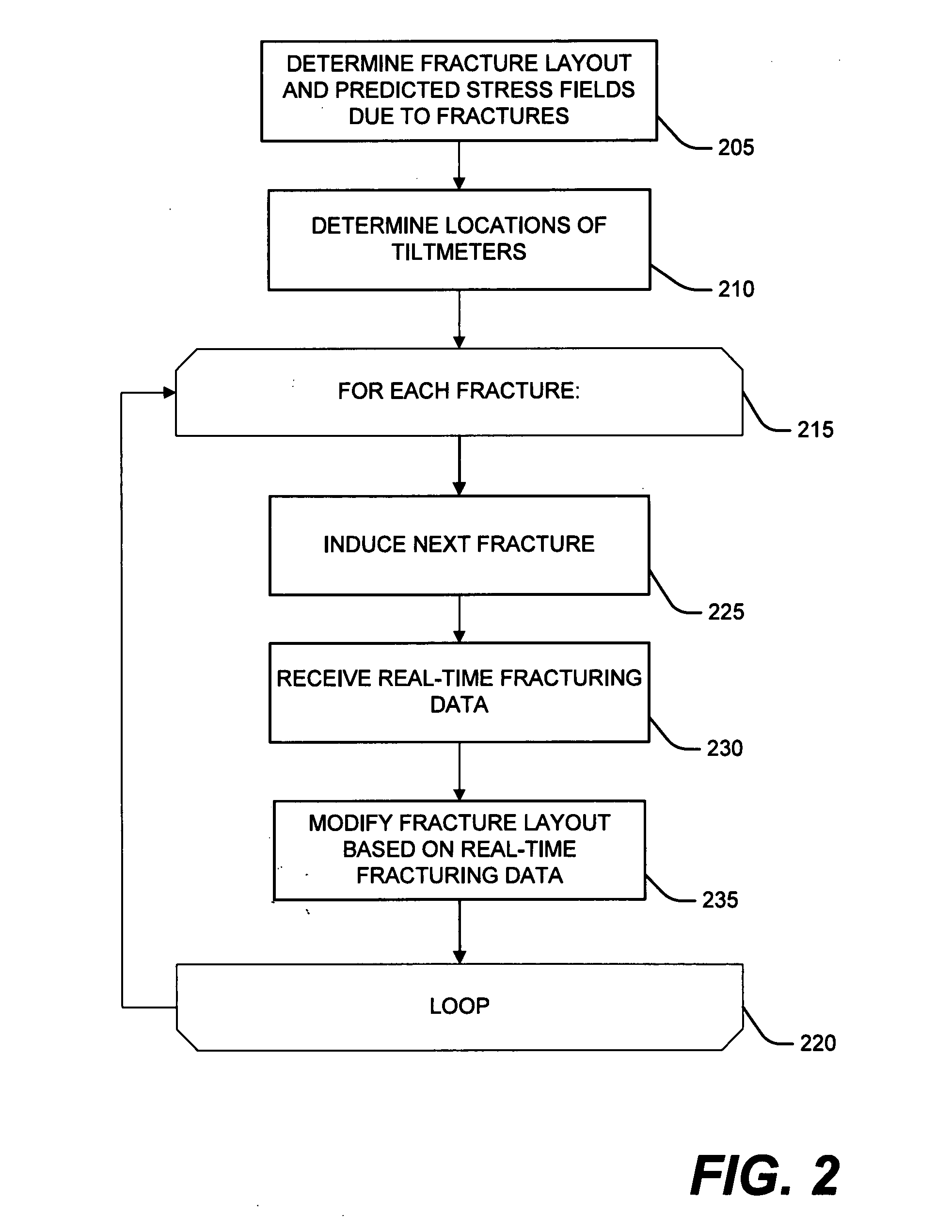
Methods for geomechanical fracture modeling
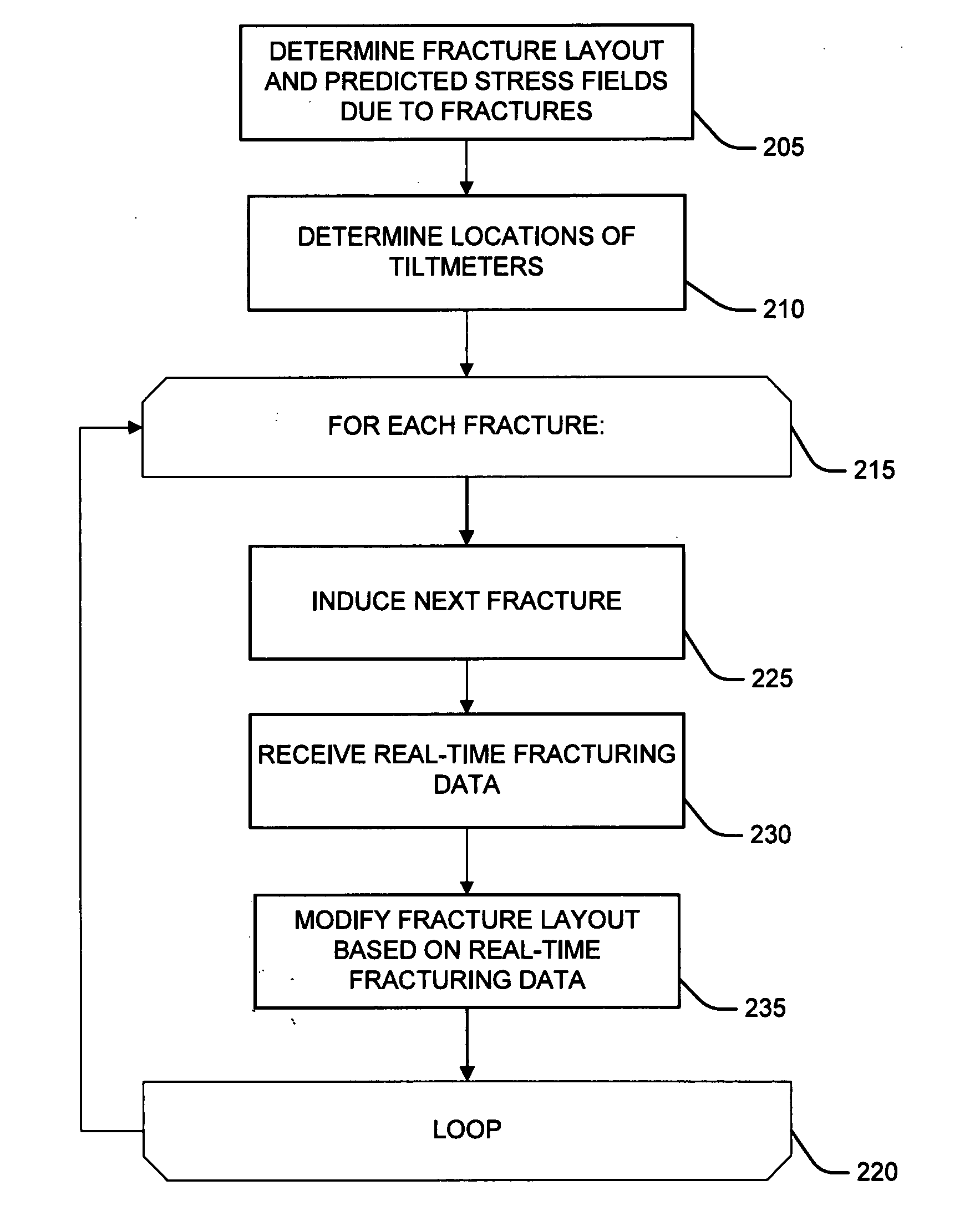
The present invention relates generally to methods for designing and optimizing the number, placement, and size of fractures in a subterranean formation and more particularly to methods that account for stress interference from other fractures when designing and optimizing the number, placement, and size of fractures in the subterranean formation. The present invention optimizes the number, placement and size of fractures in a subterranean formation. The present invention determines one or more geomechanical stresses induced by each fracture based on the dimensions and location of each fracture, including surface deformations caused by each fracture. The present invention determines a maximum number of fractures and a predicted stress field based on the geomechanical stresses induced by each of the fractures.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
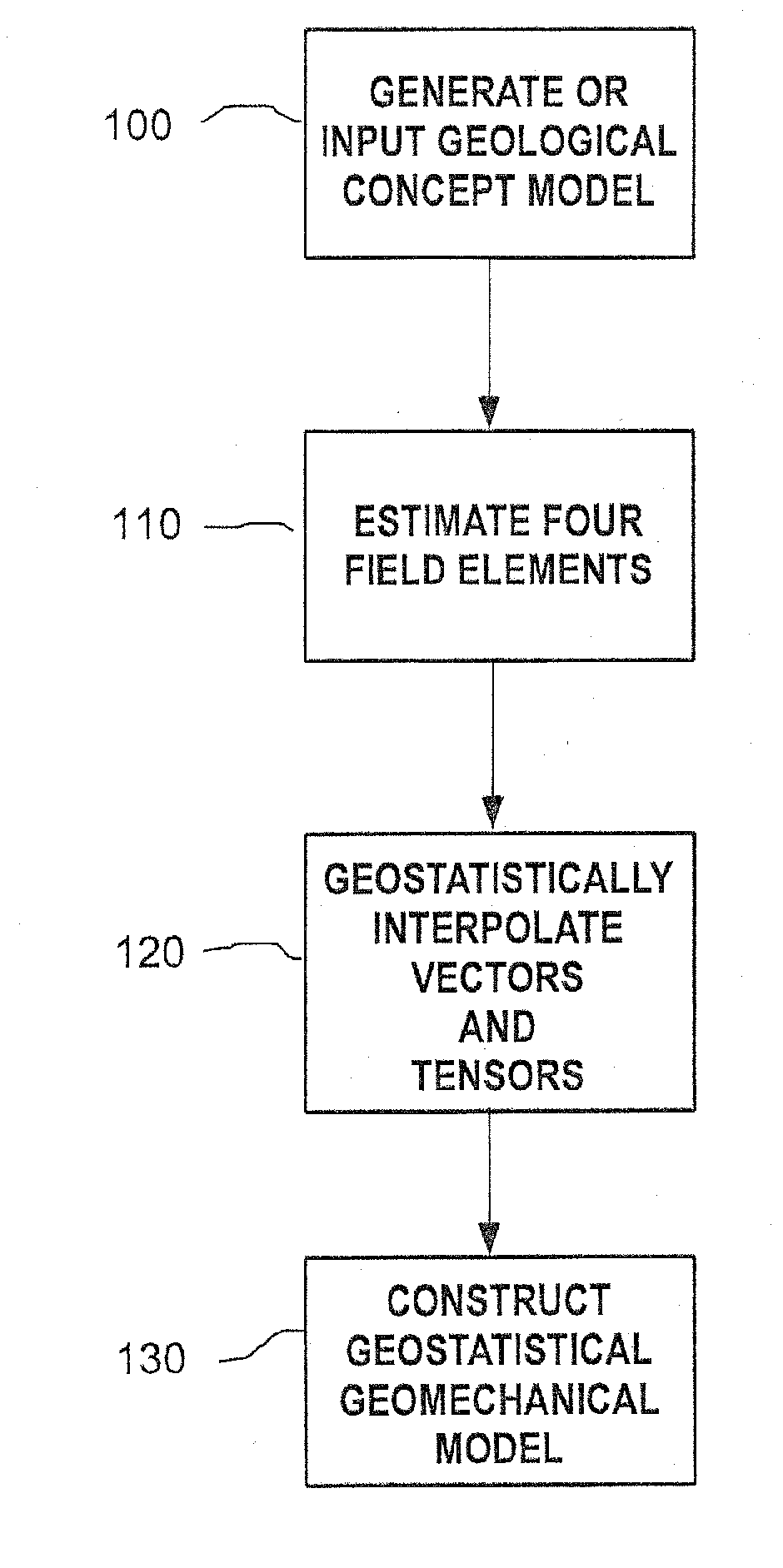
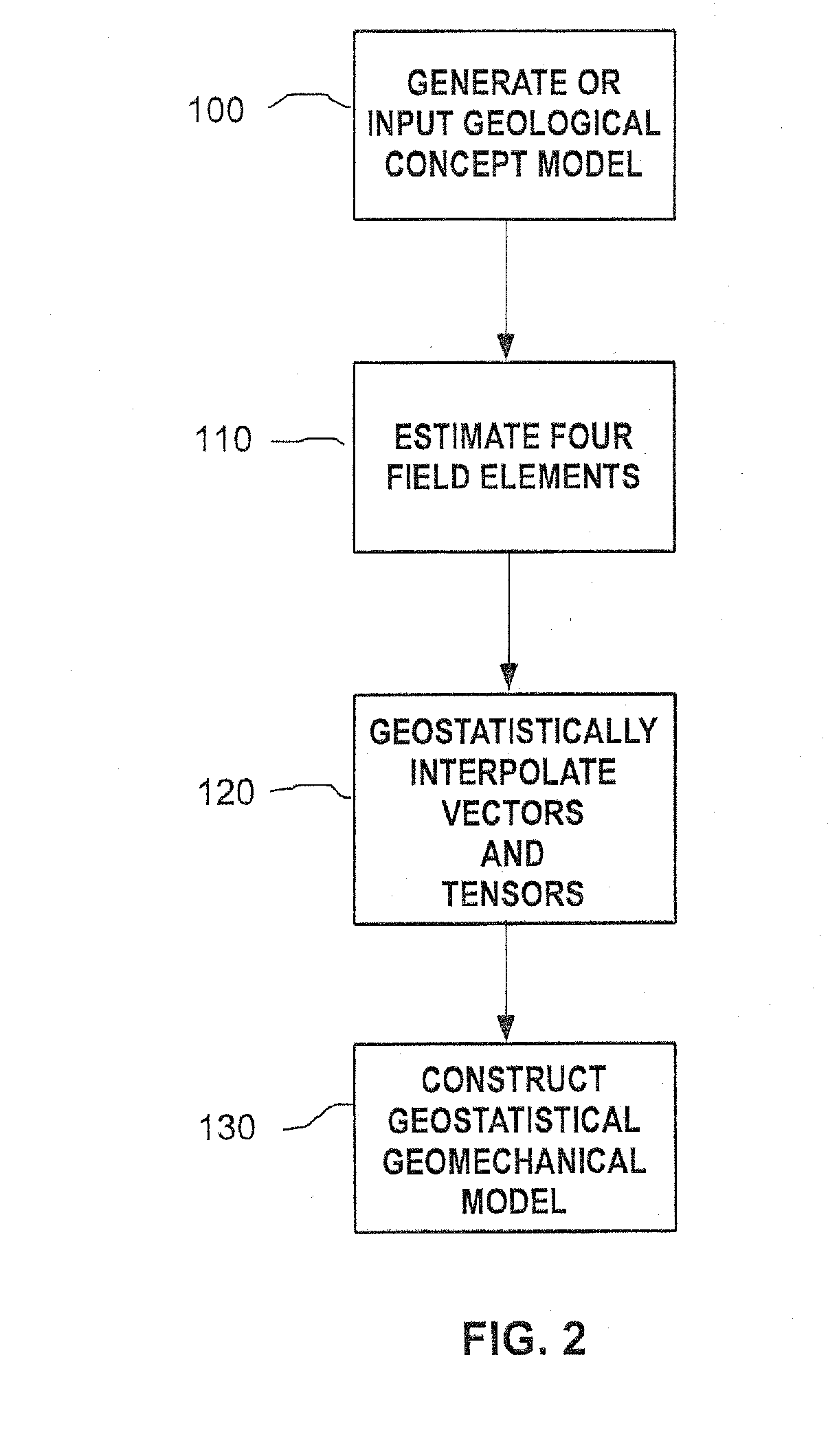
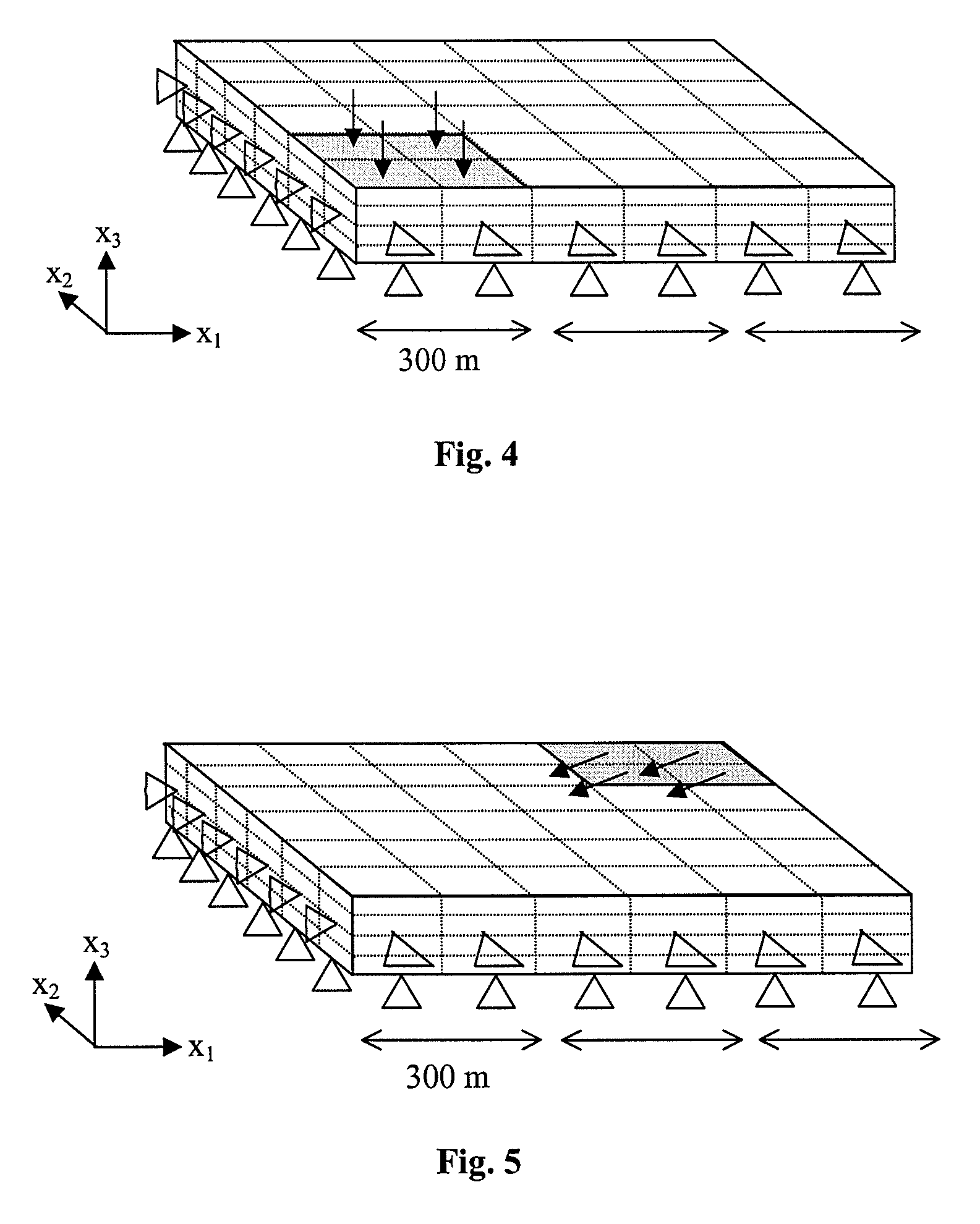
Methods and systems for constructing and using a subterranean geomechanics model spanning local to zonal scale in complex geological environments
ActiveUS20100121623A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingGeomodellingSoil scienceSubsurface geology
In an exemplary embodiment, a method and system is disclosed for developing a subterranean geomechanics model of a complex geological environment. The method can include estimating a pore pressure field, a stress field, a geomechanics property field, and a geological structure field from a geological concept model; geostatistically interpolating vectors and tensors from the estimated fields; and combining the results from the estimated fields and the geostatistically interpolated vectors and tensors to derive a geostatistical geomechanical model of the geological environment.
Owner:YOWAREN ELAN
Methods for geomechanical fracture modeling
The present invention relates generally to methods for designing and optimizing the number, placement, and size of fractures in a subterranean formation and more particularly to methods that account for stress interference from other fractures when designing and optimizing the number, placement, and size of fractures in the subterranean formation. The present invention optimizes the number, placement and size of fractures in a subterranean formation. The present invention determinines one or more geomechanical stresses induced by each fracture based on the dimensions and location of each fracture. The present invention determinines a maximum number of fractures and a predicted stress field based on the geomechanical stresses induced by each of the fractures
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Method For Modeling Deformation In Subsurface Strata
ActiveUS20110166843A1Minimize prospectElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyElement analysisMechanical property
A method for modeling deformation in subsurface strata, including defining physical boundaries for a geomechanical system. The method also includes acquiring one or more mechanical properties of the subsurface strata within the physical boundaries, and acquiring one or more thermal properties of the subsurface strata within the physical boundaries. The method also includes creating a computer-implemented finite element analysis program representing the geomechanical system and defining a plurality of nodes representing points in space, with each node being populated with at least one of each of the mechanical properties and the thermal properties. The program solves for in situ stress at selected nodes within the mesh.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Method For Modeling Stimulated Reservoir Properties Resulting From Hydraulic Fracturing In Naturally Fractured Reservoirs
InactiveUS20170145793A1Increase productionLow costFluid removalDesign optimisation/simulationPrincipal stressHydraulic fracturing
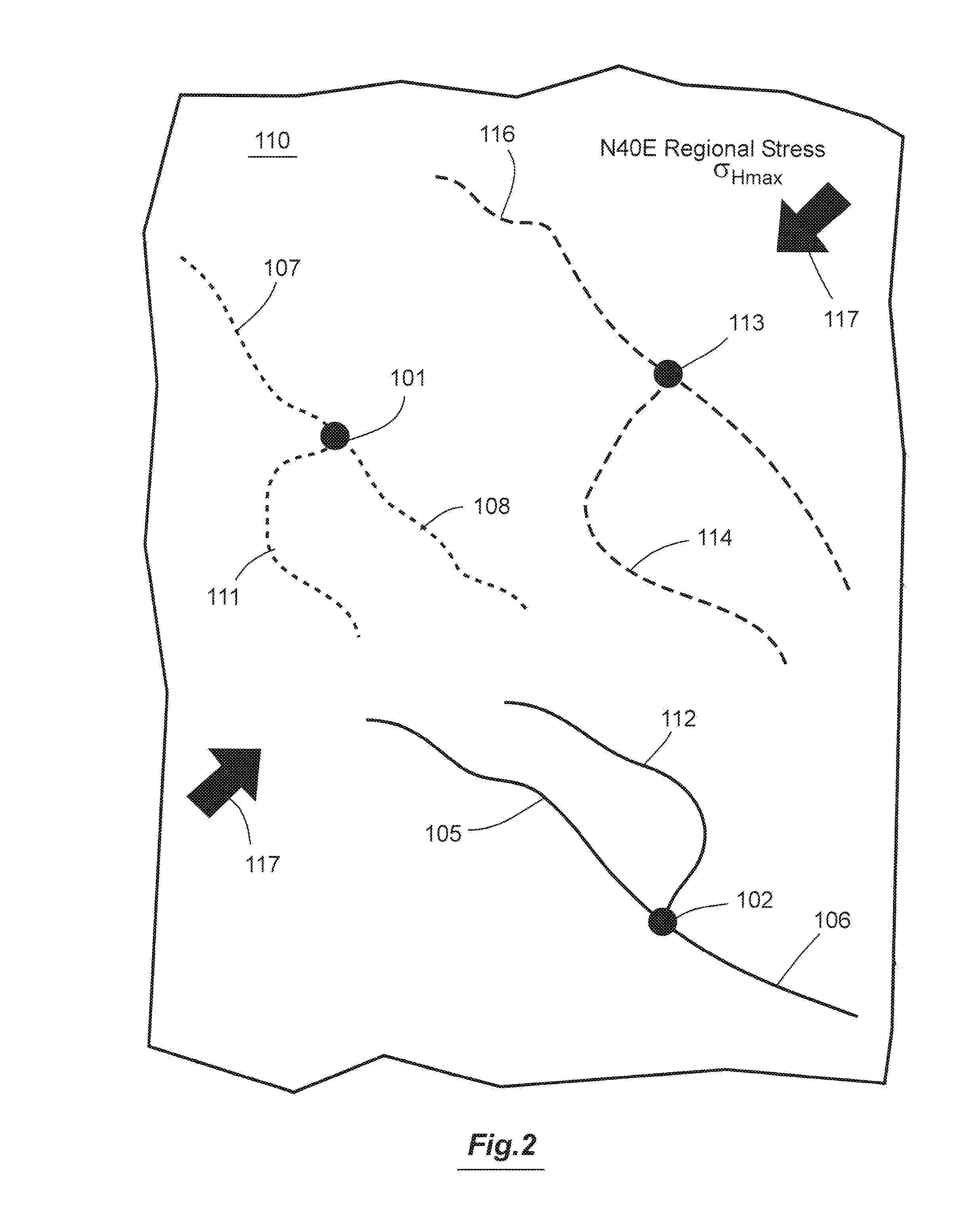
A method for optimizing hydraulic fracturing simulates the geomechanical interaction between regional stress and natural fractures in a reservoir. An equivalent fracture model is created from data on the natural fracture density, regional stress and geomechanical properties of the reservoir, so that points in the reservoir are assigned a fracture length and fracture orientation. The horizontal differential stress and maximum principal stress direction at points in the reservoir are then estimated by meshless particle-based geomechanical simulation using the equivalent fracture model as an input. The meshless particle-based geomechanical simulator uses the derived initial geomechanical condition to simulate the sequence of hydraulic fracturing and derive the resulting strain and J integral that can be used to estimate the asymmetric half fracture lengths and initial propped permeability needed by hydraulic fracturing design and reservoir simulation software to optimize wellbore and completion stage positions.
Owner:FRACGEO LLC
Method of constructing a geomechanical model of an underground zone intended to be coupled with a reservoir model
InactiveUS20050234690A1MoreEasy to predictElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingComputation using non-denominational number representationModel methodDiscretization
Method of constructing a geomechanical model of an underground zone intended to be coupled with a reservoir model allowing simulation of fluid flows in the zone, from a geological model of the zone discretized by a fine grid. Basically, geomechanical properties are associated with the various cells of the geological model on the basis of experimental data, the underground zone is discretized by a geomechanical grid with larger cells than the geological grid, and a scale change is applied to the geomechanical data included in the geological model in order to define equivalent geomechanical properties at the scale of the geomechanical grid of the zone. Application: improvement in the quality of coupled simulations between geomechanical and reservoir models.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Method for petrophysical evaluation of shale gas reservoirs
A method for evaluating an earth formation from a well bore, that includes: collecting at least one of geochemical data, petrophysical data and geomechanical data from a wellbore; and identifying depositional facies of the earth surrounding the wellbore. A computer program product and a system are provided.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
System For Hydraulic Fracturing Design And Optimization In Naturally Fractured Reservoirs
InactiveUS20170051598A1Increase productionHigh productFluid removalDesign optimisation/simulationPrincipal stressHydraulic fracturing
A method for optimizing hydraulic fracturing and refracturing simulates the geomechanical interaction between regional stress and natural fractures in a reservoir. An equivalent fracture model is created from data on the natural fracture density, regional stress and elastic properties of the reservoir, so that points in the reservoir are assigned a fracture length and fracture orientation. The horizontal differential stress and maximum principal stress direction at points in the reservoir are then estimated by meshless particle-based geomechanical simulation using the equivalent fracture model as an input. Regions in the reservoir having low differential stress based on the simulation can then be selected for initial hydraulic fracturing. Regions in the reservoir having high differential stress based on the simulation can then be selected for refracturing.
Owner:FRACGEO LLC
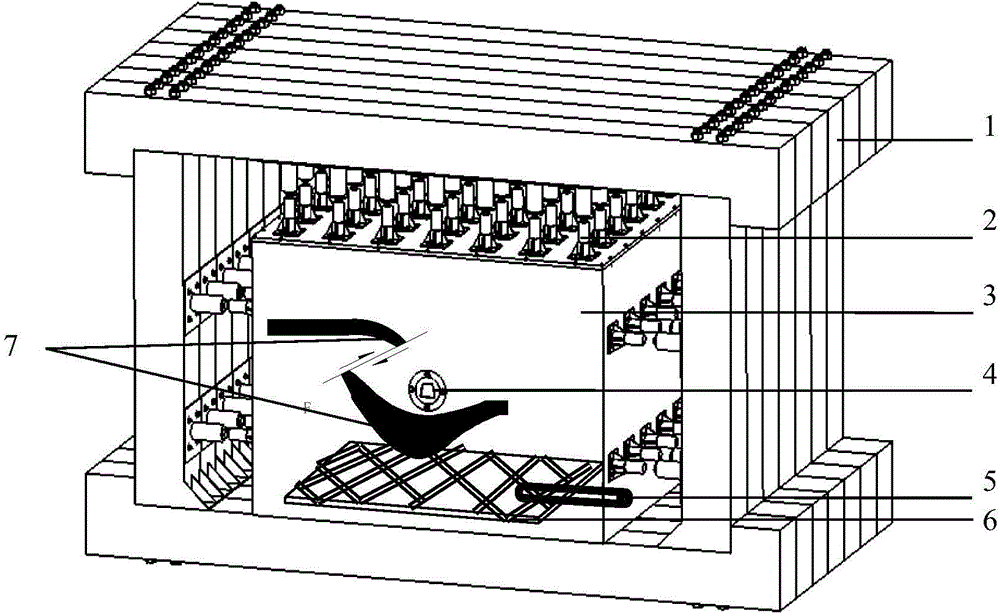
Geomechanics test platform for water invasion regularity of mine
InactiveCN101576458AMonitor changes in real timeMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesPore water pressureData acquisition
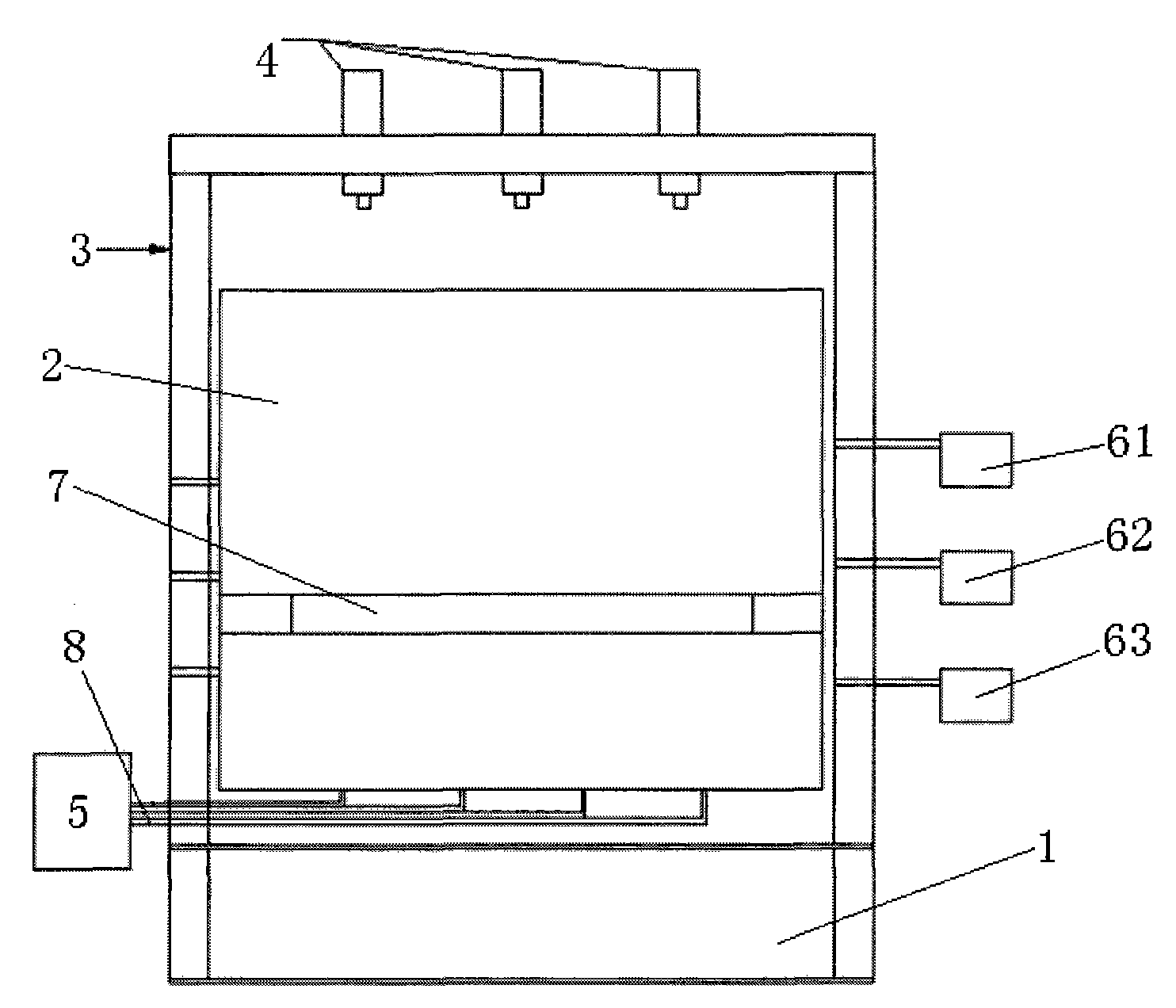
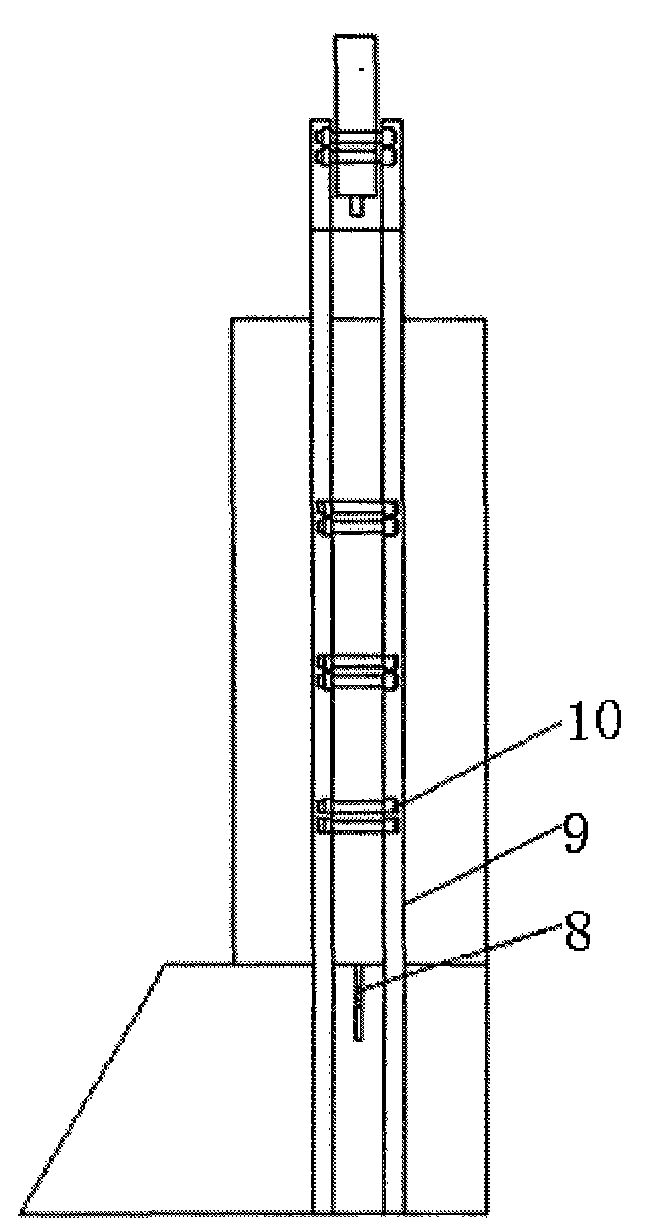
The invention discloses a geomechanics test platform for the water invasion regularity of a mine, which comprises a base, a box body, a reaction frame, a pressurized jack, a hydraulic control system and a data acquisition system and the like. When simulating the water invasion of the mine, test material is paved in the box body according to a calculated similarity ratio; an electrode, a stress sensor and a pore water pressure sensor are paved on a coal seam bottom plate by layers; and a data cable is led out from a pore preserved on a side surface. By filling water into the paved test material through the bottom plate of the box body, when the water in an aquifer is saturated, a pore preserved for coal mining in the front of the box body is opened for excavation, simultaneously, the hydraulic control system continue to fill water according to the pre-calculated water pressure, and the data acquisition system is started to record the test data until water invasion occurs at the bottom plate, and then excavation is stopped and the test is ended. The system structure is simple, can effectively simulate the water invasion regularity of the mine, and solves the problems that the indoor test can not simulate the role of seepage and erosion of confined water.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Method For Predicting Time-Lapse Seismic Timeshifts By Computer Simulation
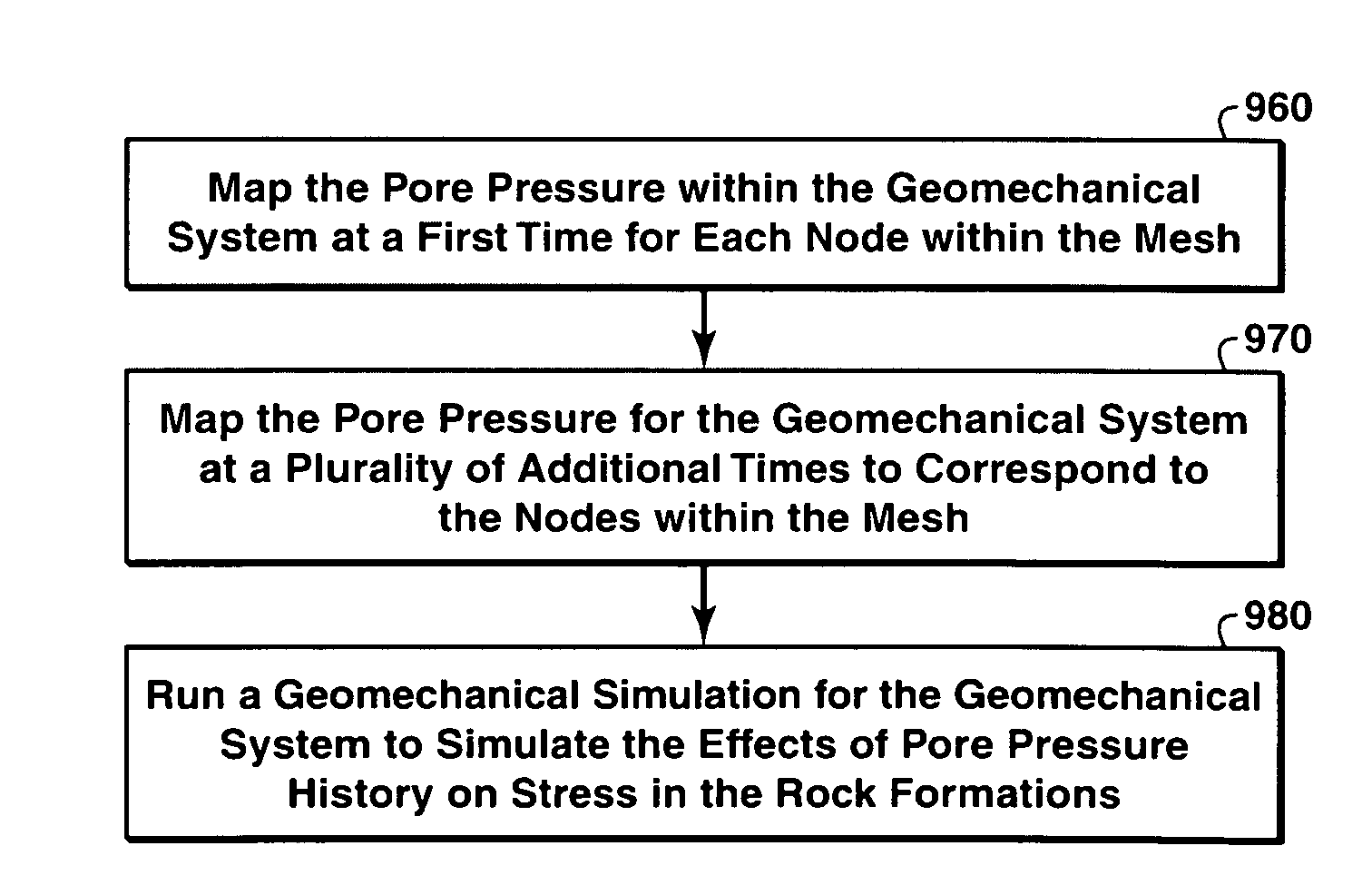
A method for predicting time-lapse seismic timeshifts in a three-dimensional geomechanical system including defining physical boundaries for the geomechanical system. In addition, one or more reservoir characteristics such as pore pressure and / or temperature history are acquired from multiple wells within the physical boundaries. The method also includes determining whether a formation in the geomechanical system is in an elastic regime or a plastic regime. The method also includes obtaining first and second seismic data sets for the geomechanical system, taken at first and second times. The method also includes running a geomechanical simulation to simulate the effects of changes in pore pressure or other reservoir characteristic on time-lapse seismic timeshifts in the formation.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
System and Method for Stress Field Based Wellbore Steering
ActiveUS20090065252A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyMechanical engineeringTime data
A system and method for the geomechanical steering of the orientation of a wellbore is disclosed. In one embodiment, any available a priori data regarding the stress characteristics of a region of interest are used to develop a preliminary stress model for the region. A geosteered drilling operation is thereafter commenced, with the trajectory being steered in a direction relative to the stress model of the region. While drilling, real-time data is obtained from conventional down-hole instrumentation. The real-time data is used to refine the stress model for the region, such that the trajectory can be guided on an ongoing basis to achieve an optimal relationship with the measured stress characteristics of the region.
Owner:GEOMECHANICS INT +1
System and methods for real-time wellbore stability service
ActiveUS8818779B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingEnvironmental geologyGeomechanics
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method of constructing a geomechanical model of an underground zone intended to be coupled with a reservoir model
InactiveUS7603265B2MoreEasy to predictElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingComputation using non-denominational number representationMesh gridGeomechanics
A method of the invention provides improvement in the quality of coupled simulations between geomechanical and reservoir models by constructing a geomechanical model of an underground zone intended to be coupled with a reservoir model allowing simulation of fluid flows in the zone, from a geological model of the zone discretized by a fine grid. Geomechanical properties are associated with the various cells of the geological model on the basis of experimental data, the underground zone is discretized by a geomechanical grid with larger cells than the geological grid, and a scale change is applied to the geomechanical data included in the geological model in order to define equivalent geomechanical properties at the scale of the geomechanical grid of the zone.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
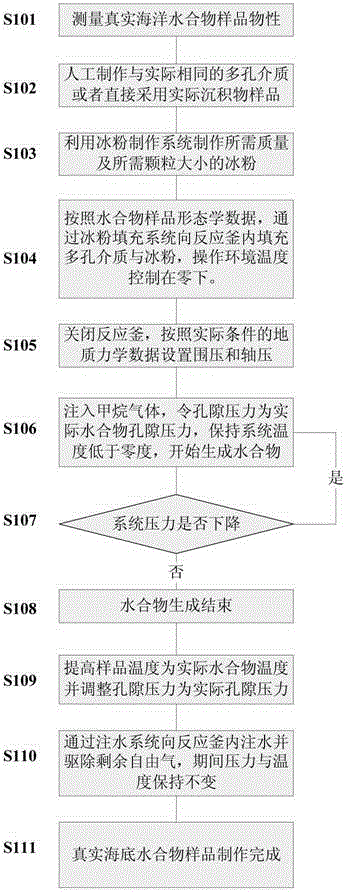
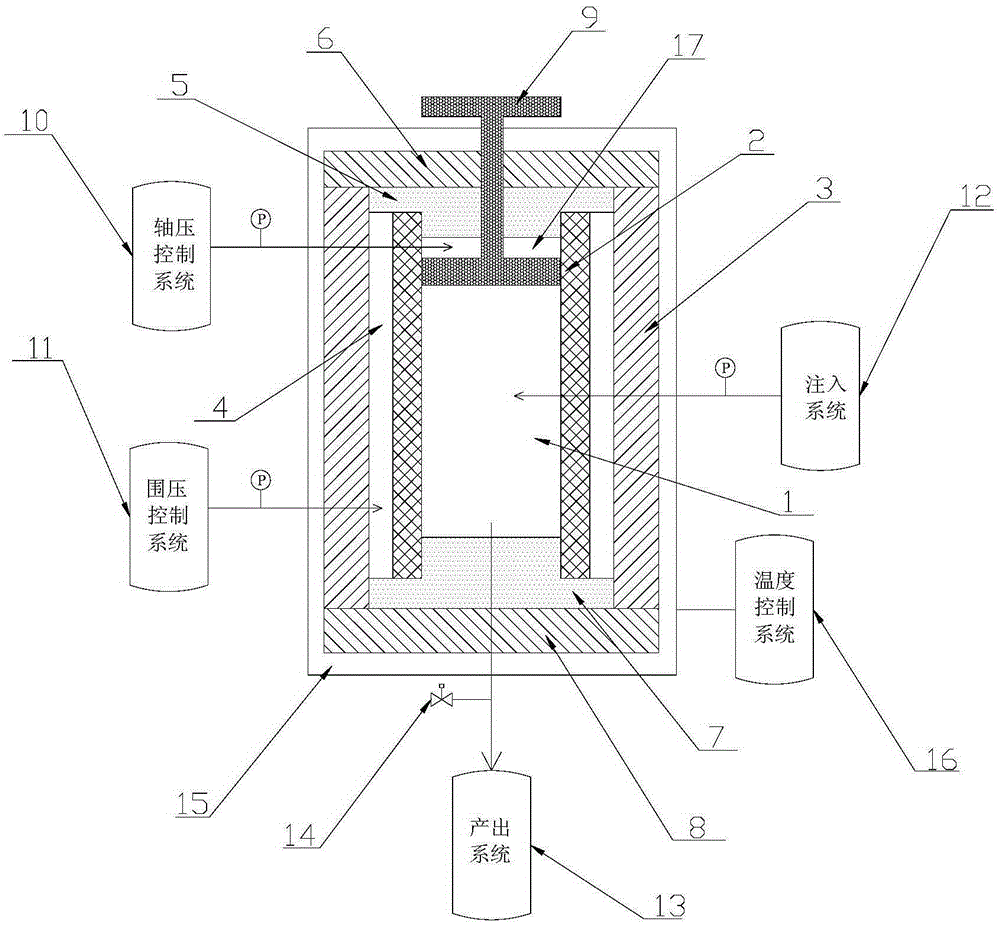
Experiment device and method for synthesizing marine natural gas hydrate sample
ActiveCN105259003AEconomic gainEfficiently obtainedPreparing sample for investigationOcean bottomPrill
The invention discloses an experiment device for synthesizing a marine natural gas hydrate sample. The device comprises a reaction kettle, an axial compression piston, a kettle outer jacket, an injection system, an axial compression control system, a confining pressure control system and an output system. The invention further discloses an experiment method adopting the experiment device for synthesizing the marine natural gas hydrate sample. The method comprises the steps that firstly, ice powder particles are manufactured, then, the ice powder particles and dried porous medium particles are mixed and placed into the high-pressure reaction kettle in the subzero low-temperature environment so as to simulate seabed geomechanical properties, then, methane is injected to generate a hydrate, ice is directly converted into the hydrate, and finally free gas inside the reaction kettle is removed through the liquid injection system. According to the experiment device and method, true marine natural gas hydrate samples which are hard to obtain on various geological conditions and various occurrence form conditions can be economically, efficiently and accurately obtained, the research on the hydrate is closer to the reality, and the experiment basis is provided for research of natural gas hydrate exploitation.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Combining geomechanical velocity modeling and tomographic update for velocity model building
InactiveUS20090303834A1Well formedSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsGeomechanicsEnvironmental geology
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
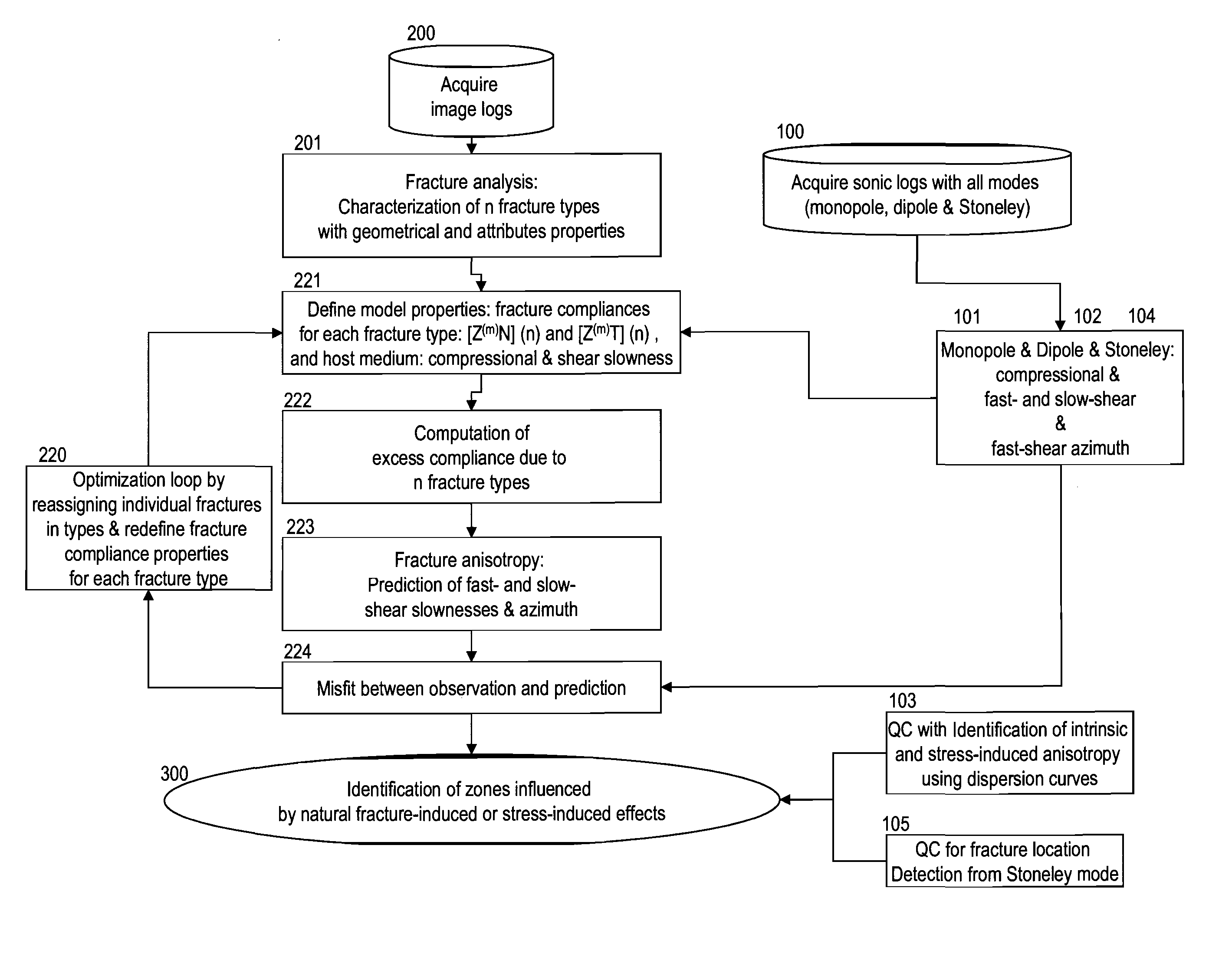
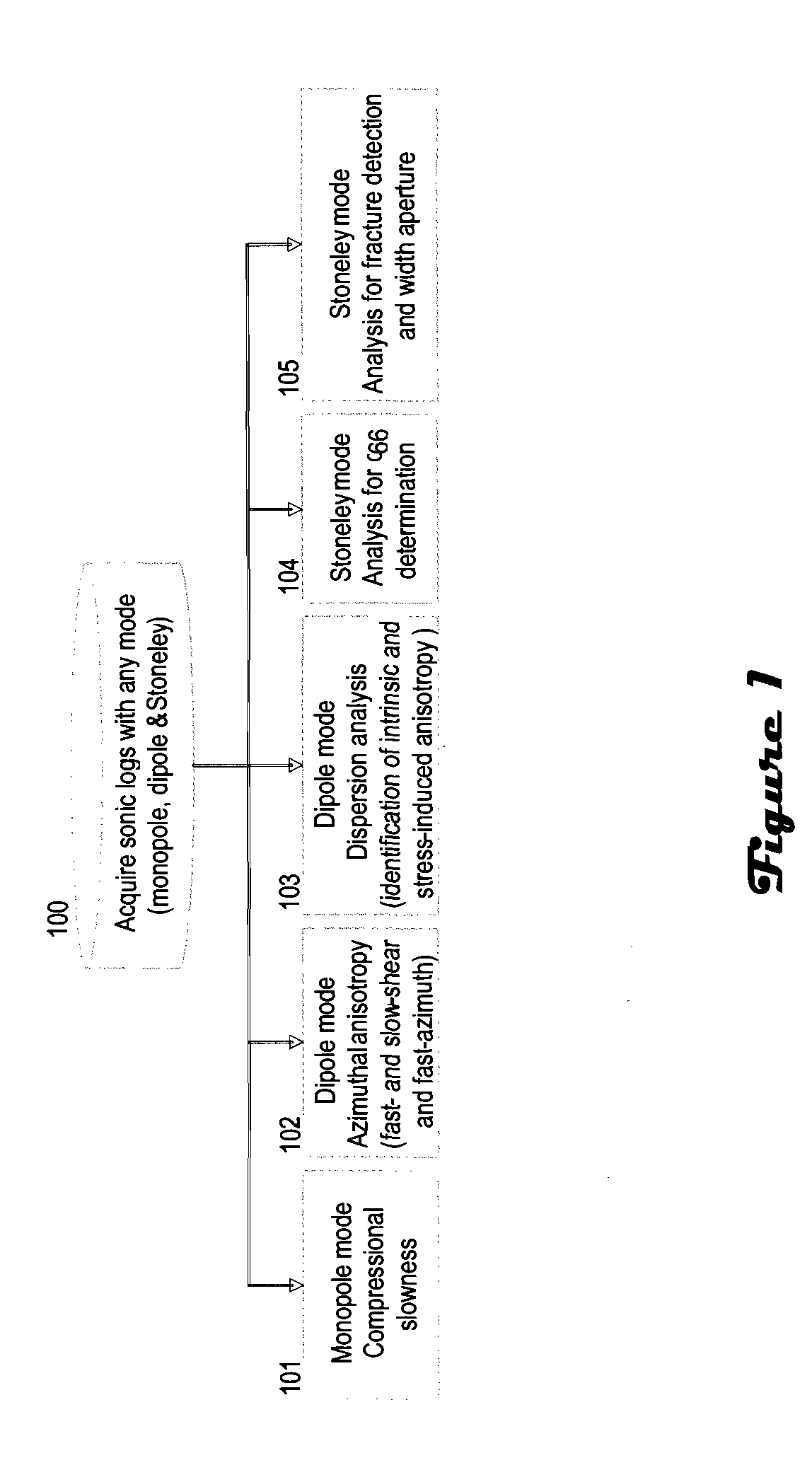
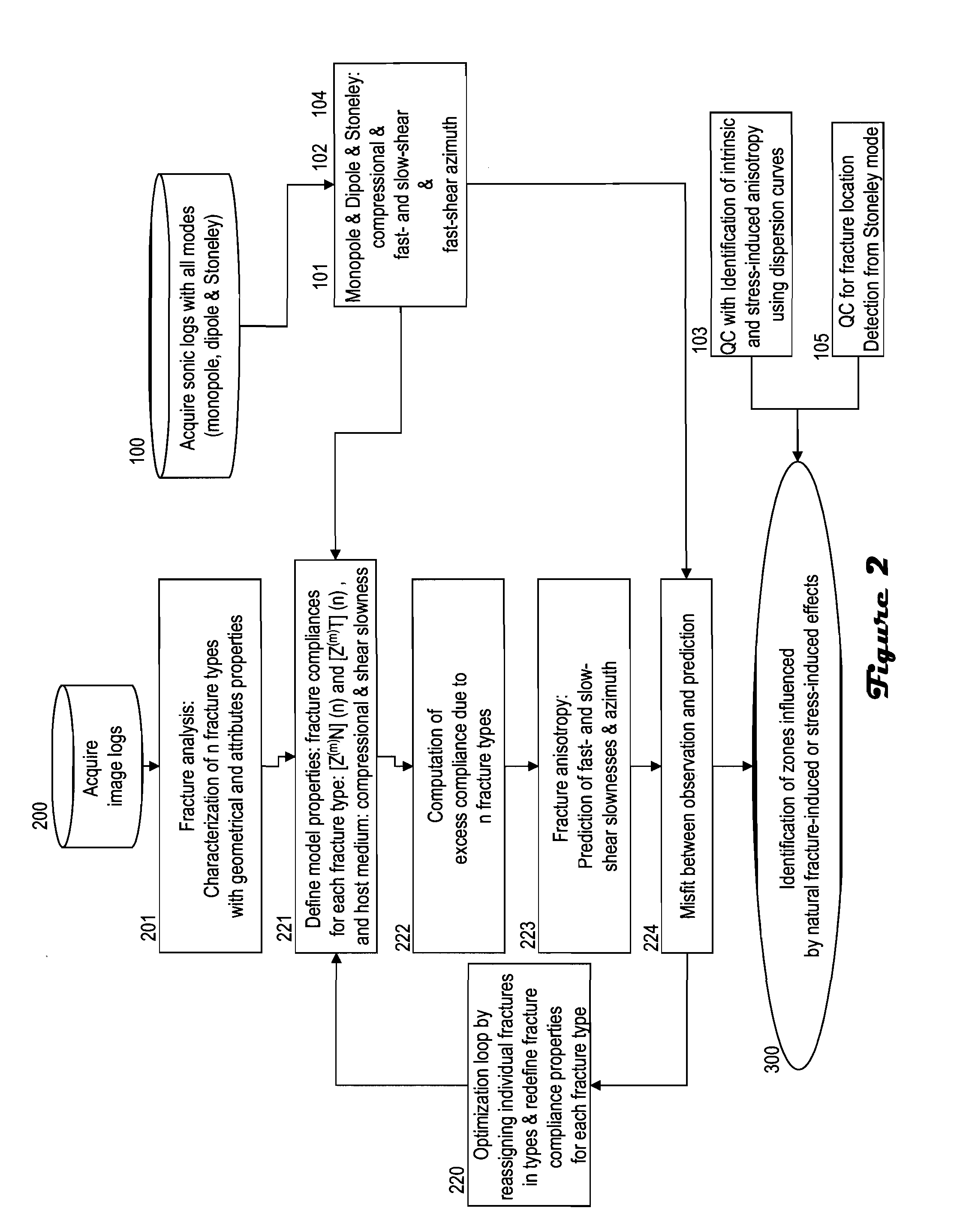
Discriminating natural fracture- and stress-induced sonic anisotropy using a combination of image and sonic logs
Fracture- and stress-induced sonic anisotropy is distinguished using a combination of image and sonic logs. Borehole image and sonic logs are acquired via known techniques. Analysis of sonic data from monopole P- and S-waves, monopole Stoneley and cross-dipole shear sonic data in an anisotropic formation are used to estimate at least one compressional and two shear moduli, and the dipole fast shear direction. Fracture analysis of image logs enables determination of fracture types and geometrical properties. Geological and geomechanical analysis from image logs provide a priori discrimination of natural fractures and stress-induced fractures. A forward quantitative model of natural fracture- and stress-induced sonic anisotropy based on the knowledge of fracture properties interpreted from image logs allows the computation of the fast-shear azimuth and the difference in slowness between the fast- and slow-shear. The misfit between predicted and observed sonic measurements (i.e. fast-shear azimuth and slownesses) is then optimized in order to discriminate depth zones with an elastic medium as being influenced by the presence of open natural fractures, closed natural fractures and fractures induced by non-equal principal stress effects.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
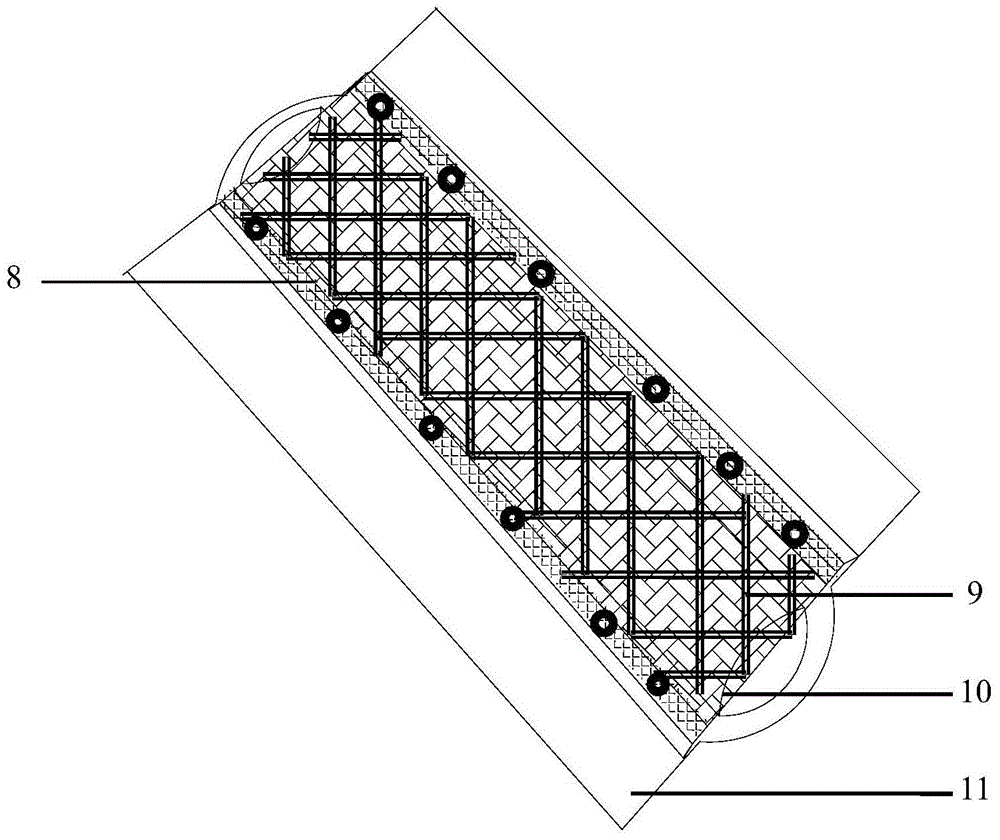
Coal and gas outburst similarity simulation test method based on geological mechanical model test
The invention provides a novel coal and gas outburst similarity simulation test method based on a geological mechanical model test by referring a coal and gas outburst simulation test device and a geotechnical engineering multifunctional test device on the basis of the similar material simulation test concept and the technical concept of the geological mechanical model test. A large-sized three-dimensional coal and gas outburst simulation test device is designed and mainly comprises a reaction frame (1), a hydraulic load (2), a test box body (3), a roadway excavation device (4), a sealing and gas face inflating device (6) and the like. Gas is introduced into a test model of the test box body by establishing a geological structure coal test model (7), so that the geological mechanical model test and the coal and gas outburst similarity simulation test can be reasonably combined, the coal, rock, gas and complex geological structure are integrated, the coal and gas outburst mechanism under variable conditions of the complex geological structure and the coal seam gas reservoir can be explored, and a novel thought is provided for researching the coal and gas outburst mechanism.
Owner:ANHUI AODE MINING MACHINERY & EQUIP LTD
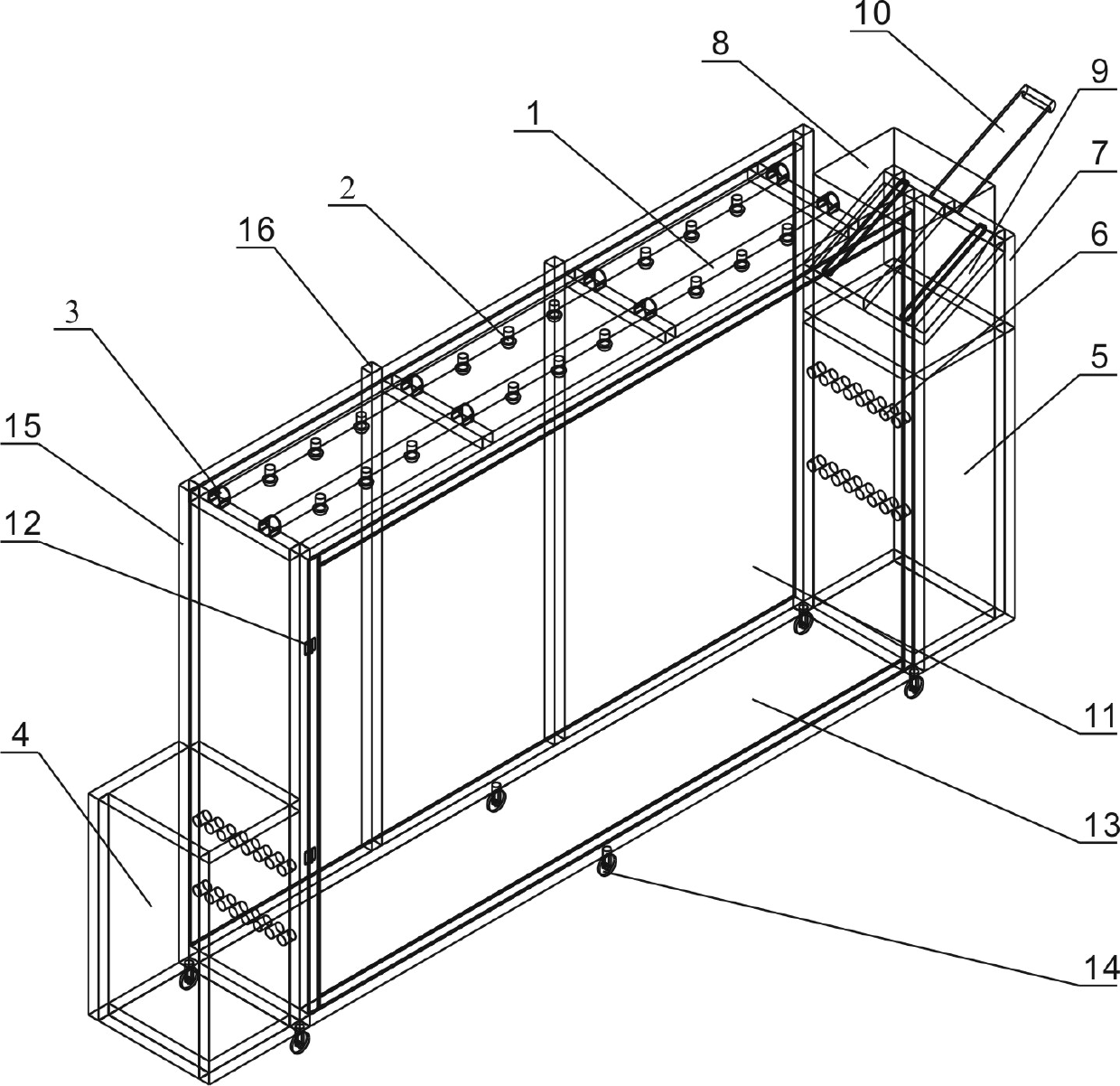
Multi-operating mode frame type portable landslide testing device for geomechanical model
ActiveCN102681028AReduce sizeOvercome the cycleEarth material testingGeological measurementsLandslideEngineering
A multi-operating mode frame type portable landslide testing device for a geomechanical model belongs to the field of geological hazard model test. The testing device comprises a frame-beam-type testing bed, a rainfall simulator, a water level regulator and a self-weight horizontal loading mechanism, wherein the frame-beam-type testing bed mainly comprises a cuboid framework, a front panel, a rear panel and a base plate; the rainfall simulator is arranged at the top of the frame-beam-type testing bed and comprises a plurality of spraying pipes and nozzles on the spraying pipes and is used for simulating rainfall in the frame-beam-type testing bed; the water level regulator comprises a left-side trough and a right-side trough respectively formed on the left and the right sides of the frame-beam-type testing bed, and a plurality of drainage holes are respectively formed on the right panel of the left-side trough and the left panel of the right-side trough and used for changing the water levels of water level simulation libraries in the left-side trough and the right-side trough; and the self-weight horizontal loading mechanism is arranged above the right-side trough and used for bearing weights, so as to exert horizontal load to the landslide model in the frame-beam-type testing bed.
Owner:中部知光技术转移有限公司
Three-qimension geomechanics model exporiment system
InactiveCN1793828AScale upMeet the requirements of model tests of different scalesInvestigating material hardnessControl systemMechanical models
A test system of 3D geologic mechanical model is composed of box testing device formed by connecting box cast steel component, angle element and chassis together through high strength bolts; hydraulic loading control system formed by variable ¿C load loading plate with thin jack at top, hydraulic loading control table and oil separator. It features that said loading plate is connected on left and right internal walls of box testing device through thin jack and said loading control table is connected to jack through oil separator and oil pipe.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
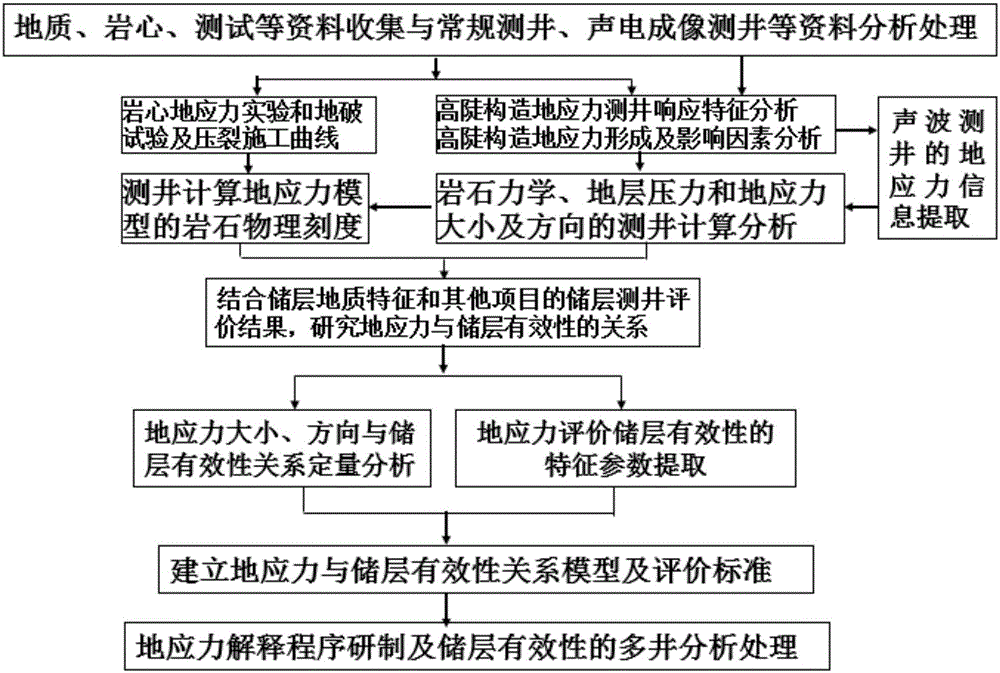
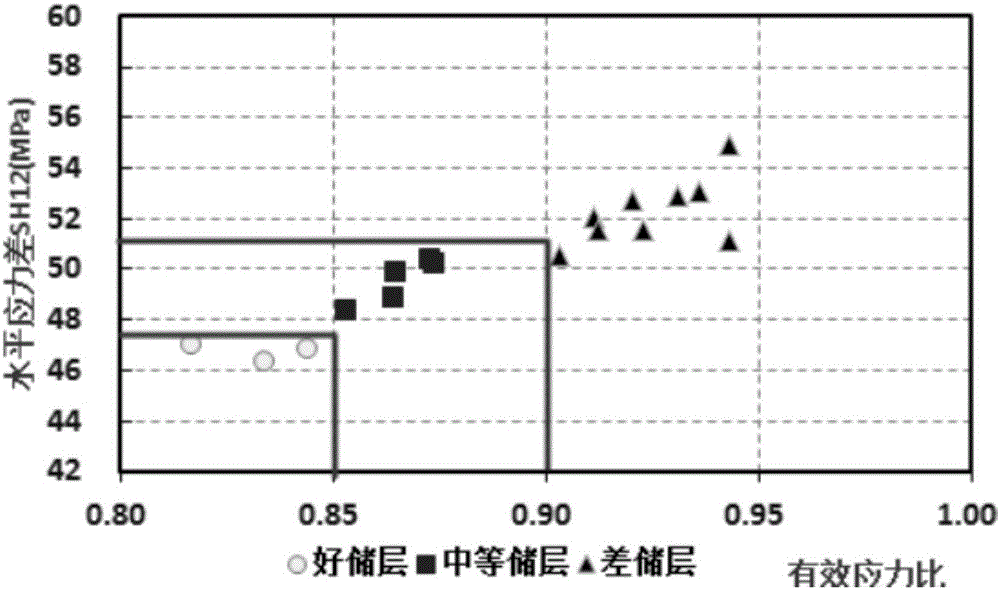
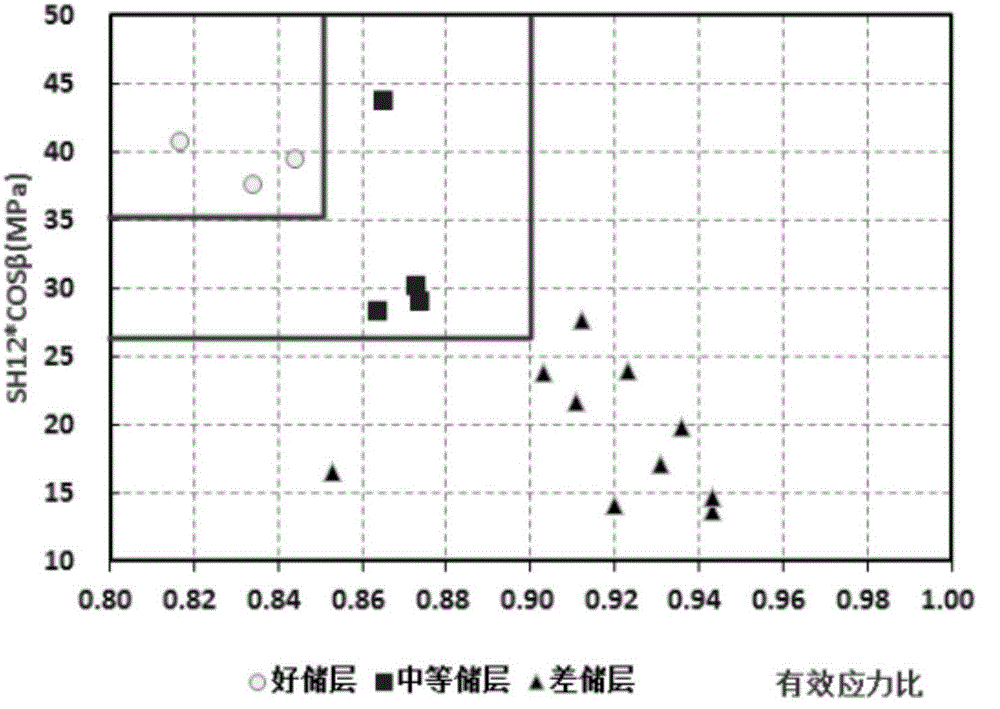
Logging GeoMechanics Identify Reservoir (LogGMIR) method
The invention provides a Logging GeoMechanics Identify Reservoir (LogGMIR) method. Starting from the perspective of rock mechanics, the method researches the relation between crustal stress and reservoir validity, establishes a reservoir effectiveness evaluation standard and recognizes high-quality reservoirs, forms a set of method and technology applicable to high and steep structure crustal stress calculation and reservoir recognition, establishes a calculation method for the crustal stress of mountain front high and steep stratums and a mechanical standard for evaluating the reservoir effectiveness, provides a brand-new technological support for logging evaluation on the deep fractured sandstone reservoir effectiveness in a work area and provides a reliable geological mechanics basis for formation testing, acidification, crushing and other layer selection processes.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Softrock-like material and preparation method
InactiveCN101614629ALight weightLittle elasticityPreparing sample for investigationEarth material testingFilling materialsSlurry
The invention discloses a softrock-like material and a preparation method thereof. The softrock-like material is composed of filler, aggregate, cementitious materials, additives and water in certain proportion. The preparation method comprises the steps of: 1. weighing the raw materials; 2. loading and stirring: adding water in a stirrer, causing the barrel wall of the stirrer to be smooth, then starting the stirrer, and adding the filler, aggregate, cementitious materials and additives sequentially followed by continuous stirring; 3. adding water and stirring: adding water during stirring, setting the speed of the stirrer at high and continuing stirring; 4. shaking and forming: discharging the materials, pouring the slurry into a pre-manufactured die, vibrating with a vibrating rod, causing the slurry to be even, removing foam and finally scraping the surface of the model to be level; and 5. maintaining in a baking house: sending the manufactured die into the baking house for maintenance. The material has the characteristics of low volume-weight, low compression strength and elastic modulus, stable property, easy processing, low cost and no toxicity, and is suitable for geomechanics research on softrock exploration and stability of softrock underground gas storage cavity.
Owner:INST OF ROCK & SOIL MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Model predicting fracturing of shale
InactiveUS9152745B2Promote recoveryMinimizes probabilityGeomodellingDesign optimisation/simulationWell loggingHydraulic fracturing
A model for predicting fracturing in shale can minimize surface disruption, protect groundwater, maximize efficiency of hydraulic fracturing, and manage fluids used in unconventional gas development. The model provides a more comprehensive understanding of the geological, geophysical, and geomechanical properties of shales and imbeds these properties in geomechanical computer simulations to predict both the reservoir performance from the fracturing, and the associated microseismic events generated by fracturing. Since the geological and geophysical properties can be estimated from surface seismic, well logs, and geologic concepts with regional context; the performance of the fracturing can be predicted and optimized. Since the microseismic events can be predicted with the model, the simulations can be verified and the model can be updated to be consistent with the observed microseismic.
Owner:ION GEOPHYSICAL CORP
Miniature TBM (Tunnel Boring Machine) excavation system for tunnel excavation in physical simulation test
InactiveCN103364218AImprove excavation efficiencyImprove accuracyStructural/machines measurementTunnelsEngineeringRock tunnel
The invention relates to a miniature TBM (Tunnel Boring Machine) excavation system for tunnel excavation in a physical simulation test and belongs to the technical field of geotechnical engineering. The system comprises a cutter head, a protective shield, a gripper, a transmission shaft, a pulling jack, a guide rail, a motor, a base and the like; one end of the pulling jack is fixed to a support rack; a piston at the other end of the pulling jack is used for pulling the base and the motor to move forwards or backwards together; the motor is used for driving the transmission shaft to rotate to push the cutter head to move forwards to cut tunnel face rock mass; jacks on two sides of the gripper can push gripper arms to exert specified pressure to wall rock. The system can accurately simulate the rock breaking process of the cutter head, takes the interaction between the wall rock and the gripper, the interaction between the tunnel face and cutter head and the interaction between the wall rock and the protective shield into consideration, can be applied for simulating a shield TBM to excavate a soft rock tunnel, a subway or the like in a common geomechnical model test and can also be applied for simulating excavation of a TBM for a deep-lying hard rock tunnel to study the relationship between rock-machine interaction and rock burst.
Owner:INST OF ROCK & SOIL MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
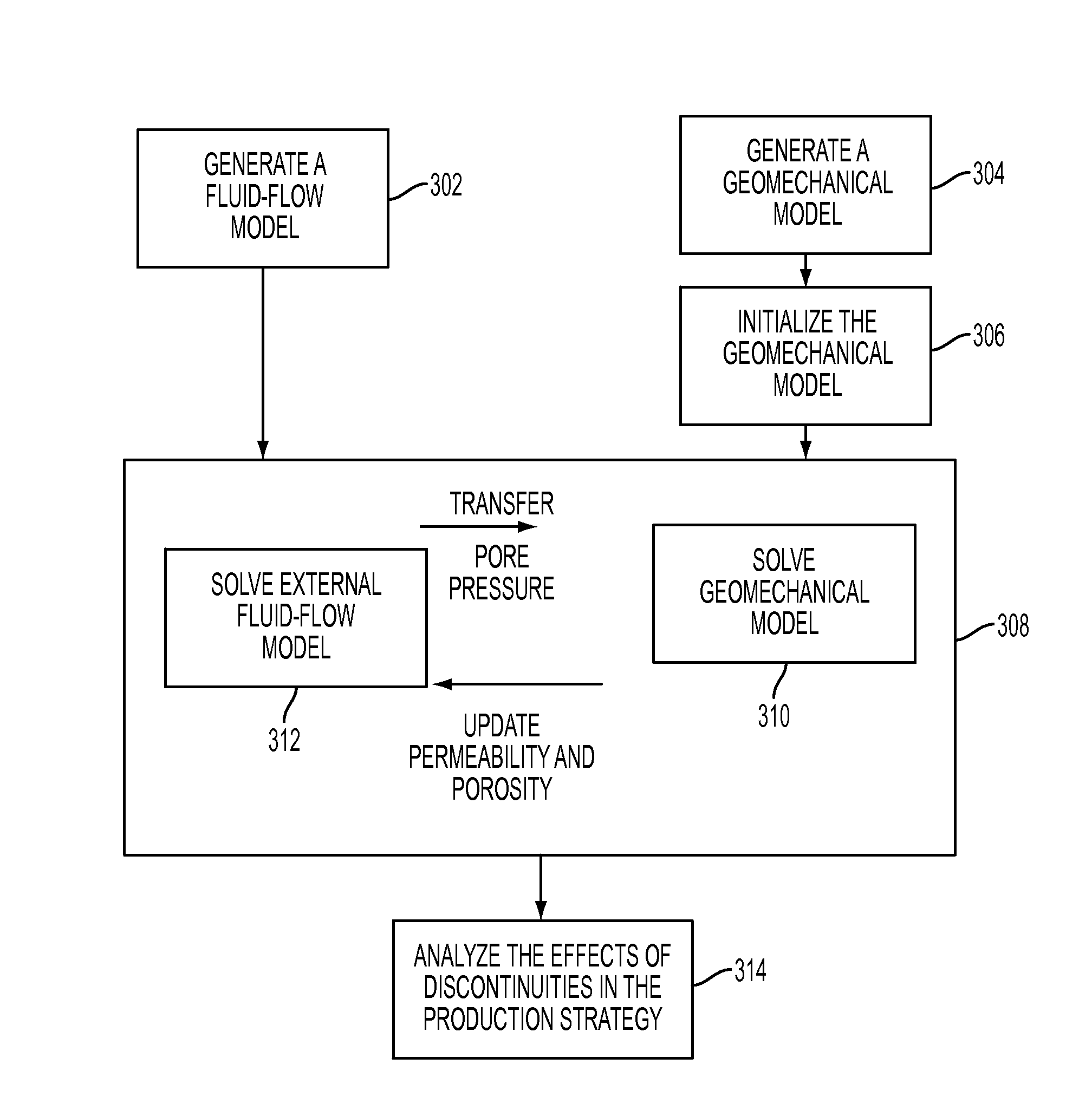
Method to assess the impact of existing fractures and faults for reservoir management
Assessing the impact of existing fractures and faults for reservoir management, in one aspect, may comprise employing a numerical mesh to generate a geomechanical model, the numerical mesh representing a geological reservoir and its surrounding regions, the numerical mesh comprising delimitation associated with regions and layering of geology without constraining the numerical mesh to explicitly represent a fault or fracture, initializing the geomechanical model to define initial stress-strain compatible with measured stress in well locations associated with the geological reservoir, generating a fluid-flow model employing the numerical mesh, solving for a coupled solution of the fluid-flow model and the geomechanical model, and employing the solved fluid-flow model and the geomechanical model to assess the impact.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com