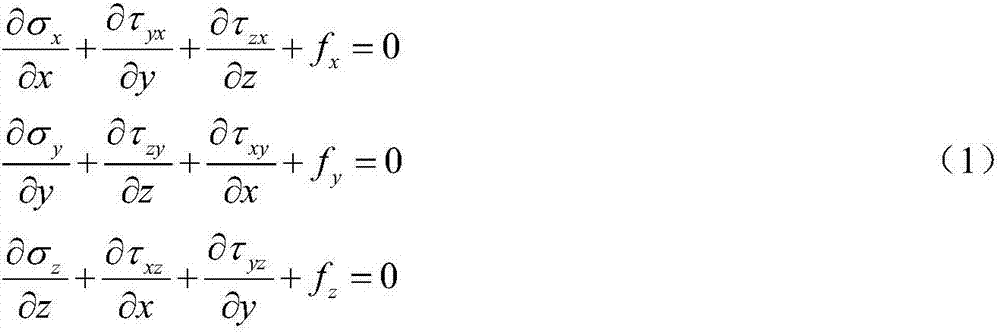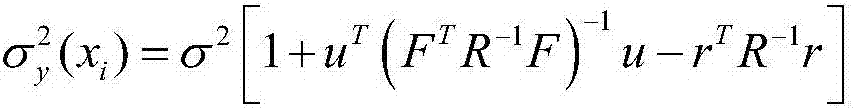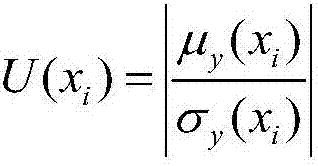Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
209 results about "Extended finite element method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The extended finite element method (XFEM), is a numerical technique based on the generalized finite element method (GFEM) and the partition of unity method (PUM). It extends the classical finite element method (FEM) approach by enriching the solution space for solutions to differential equations with discontinuous functions.
Finite element methods and systems
ActiveUS20150120261A1Address limitationsComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationMulticore architectureCpu architecture
The computational efficiency of Finite Element Methods (FEM) on parallel architectures is typically severely limited by sparse iterative solvers. Standard iterative solvers are based on sequential steps of global algebraic operations, which limit their parallel efficiency, and prior art techniques exploit sophisticated programming techniques tailored to specific CPU architectures to improve performance. The inventors present a FEM Multigrid Gaussian Belief Propagation (FMGaBP) technique that eliminates global algebraic operations and sparse data-structures based upon reformulating the variational FEM into a probabilistic inference problem based upon graphical models. Further, the inventors present new formulations for FMGaBP, which further enhance its computation and communication complexities where the parallel features of FMGaBP are leveraged to multicore architectures.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
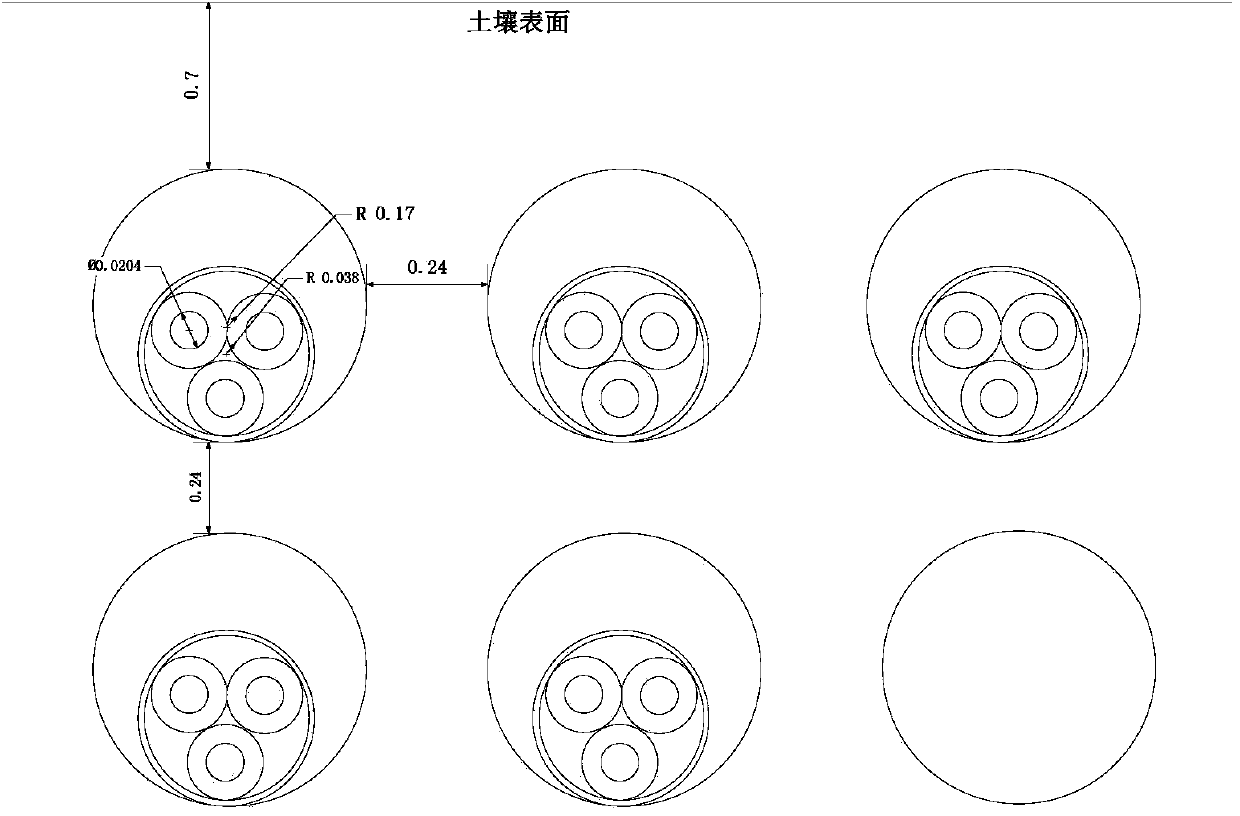
Transformer electromagnetic vibration noise calculating method based on finite element method
InactiveCN105095609AEasy data transferCalculations are reliableSpecial data processing applicationsTransformerEngineering
The invention discloses a transformer electromagnetic vibration noise calculating method based on the finite element method. The transformer electromagnetic vibration noise calculating method comprises the steps of 1, establishing a structured grid model and an acoustics grid model according to a three-dimensional geometrical model of a transformer; 2, conducting transient electromagnetic simulation on the structured grid model to obtain transient electromagnetic force waves borne by each phase winding and an iron core; 3, conducting FFT on the transient electromagnetic force waves borne by each phase winding and the iron core to obtain the frequency domain distribution of electromagnetic force borne by each phase winding and the iron core; 4, conducting harmonic response analysis on the structured grid model to obtain the vibration displacement data of nodes on the surfaces of the windings and the iron core; 5, conducting sound field calculation on the acoustics grid model to obtain the radiation noise distribution of the transformer. According to the transformer electromagnetic vibration noise calculating method, all noise influence factors are considered, and calculation results are accurate and reliable. The transformer electromagnetic vibration noise calculating method can be used for winding short circuit vibration deformation analysis and the like and can also provide method and basis for motor noise analysis.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Variable Discretization Method For Flow Simulation On Complex Geological Models
ActiveUS20130231907A1GeomodellingComputation using non-denominational number representationCapillary pressureExtended finite element method
A variable discretization method for general multiphase flow simulation in a producing hydrocarbon reservoir. For subsurface regions for which a regular or Voronoi computational mesh is suitable, a finite difference / finite volume method (“FDM”) is used to discretize numerical solution of the differential equations governing fluid flow (101). For subsurface regions with more complex geometries, a finite element method (“FEM”) is used. The invention combines FDM and FEM in a single computational framework (102). Mathematical coupling at interfaces between different discretization regions is accomplished by decomposing individual phase velocity into an averaged component and a correction term. The averaged velocity component may be determined from pressure and averaged capillary pressure and other properties based on the discretization method employed, while the velocity correction term may be computed using a multipoint flux approximation type method, which may be reduced to two-point flux approximation for simple grid and permeability fields.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
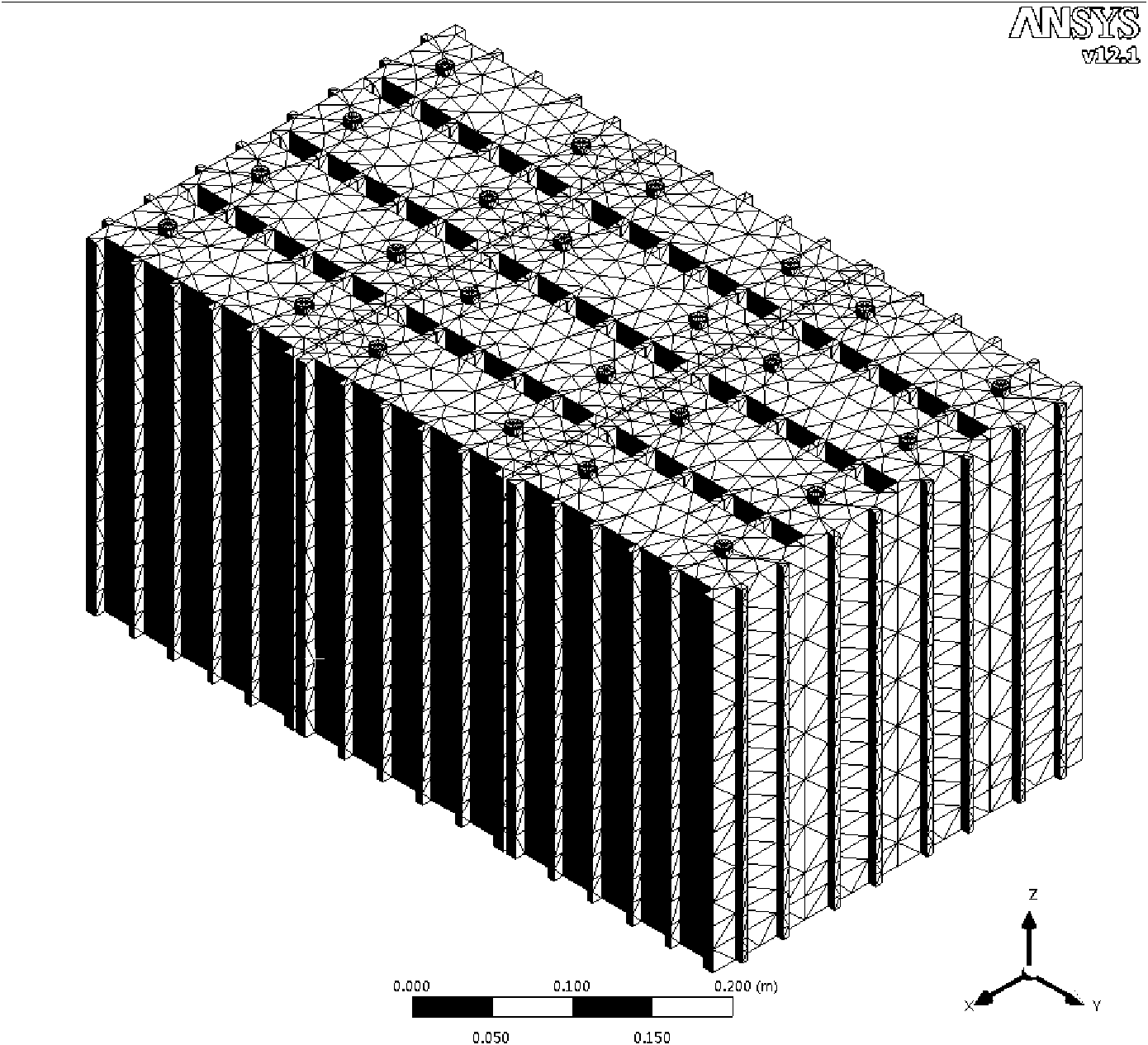
Finite element method-based storage battery thermal management analysis and optimization method
InactiveCN102034006AGreat adaptabilityGreat ability to solveSpecial data processing applicationsExtended finite element methodField analysis
The invention discloses a finite element method-based storage battery thermal management analysis and optimization method. The finite element method-based storage battery thermal management analysis and optimization method comprises the following steps of: acquiring parameters of a plurality of batteries and a battery pack respectively and establishing three-dimensional models of the plurality of batteries and the battery pack; performing the meshing of a definite element on the three-dimensional models of the plurality of batteries and then performing thermal field analysis after the meshing to acquire temperature field analytical results of the plurality of batteries; performing fluid mechanics meshing on the three-dimensional models of fluid in the battery pack and then after the meshing, using temperature field analytical results of the plurality of batteries as constraint conditions of the plurality of batteries in the fluid grid models in the battery pack; performing fluid mechanics calculation on the constrained grid models to acquire flow field analytical results of the storage batteries; judging whether the flow field analytical results accord with preset conditions or not; and if the flow field analytical results do not accord with the preset conditions, optimizing the design scheme of the battery pack and establishing the models again. The finite element method-based storage battery thermal management analysis and optimization method is not limited to mathematic analysis capacity, has higher adaptability and solving capacity, does not need entity models, is economic and quick in the analytical process, and has higher degree of freedom and flexibility.
Owner:上海奕洁汽车科技有限公司
Multi-support shafting finite element method with bearing stiffness coupling nonlinearity considered
ActiveCN103530468AImprove computing efficiencyAccurate and efficient calculationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALElement model
The invention relates to a multi-support shafting finite element method with bearing stiffness coupling nonlinearity considered. The method comprises the steps of (1) establishing a local coordinate system of each bearing and obtaining a six-freedom-degree bearing stiffness matrix of each bearing under the corresponding local coordinate systems through calculating by means of the difference method with a corresponding bearing load calculation formula; (2) dividing a shaft into different shaft sections according to the difference of diameters, establishing nodes at the positions of bearing section starting positions, the bearing installation position and load action positions, then establishing finite element models of the shaft between the nodes, and obtaining a stiffness matrix of the whole shaft; (3) establishing a global coordinate system of a shafting, establishing another node at the bearing installation position to be used for simulating a fixed end, integrating the bearing stiffness matrix onto the installation node and the corresponding fixed end node on the shaft to obtain the overall stiffness matrix of the shafting, and establishing the stiffness equation of the shafting; (4) restraining the freedom degrees in six directions of the fixed end node, restraining the freedom degree, of rotating around the axis, of the node at the position of origin of the global coordinate system of the shafting, reducing the stiffness equation of the shafting according to restraining conditions, and solving the reduced stiffness equation of the shafting with the Newton-Raphson method in an iterative mode to obtain the displacement and load of each node.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
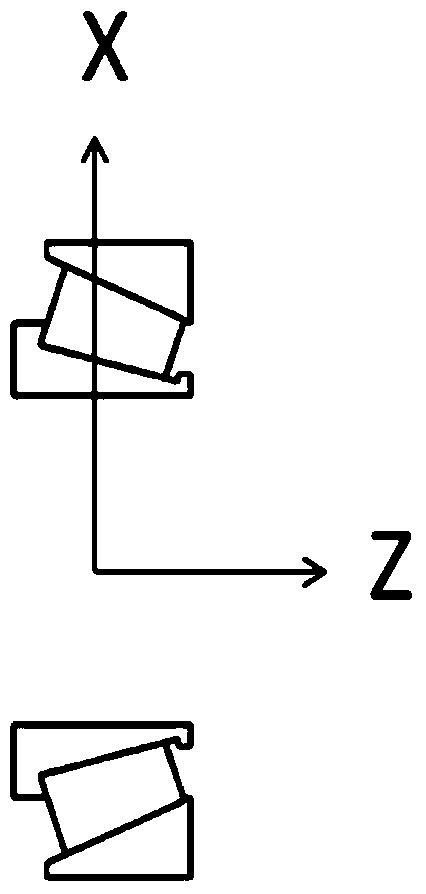
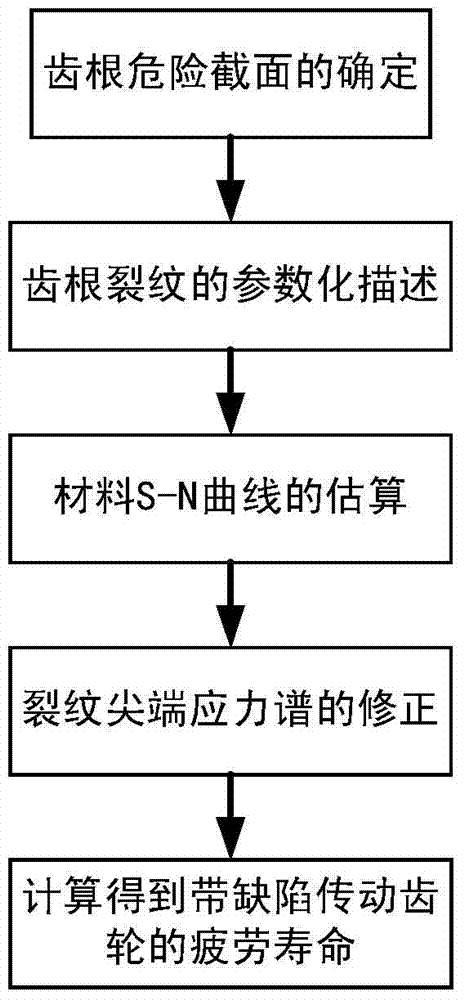
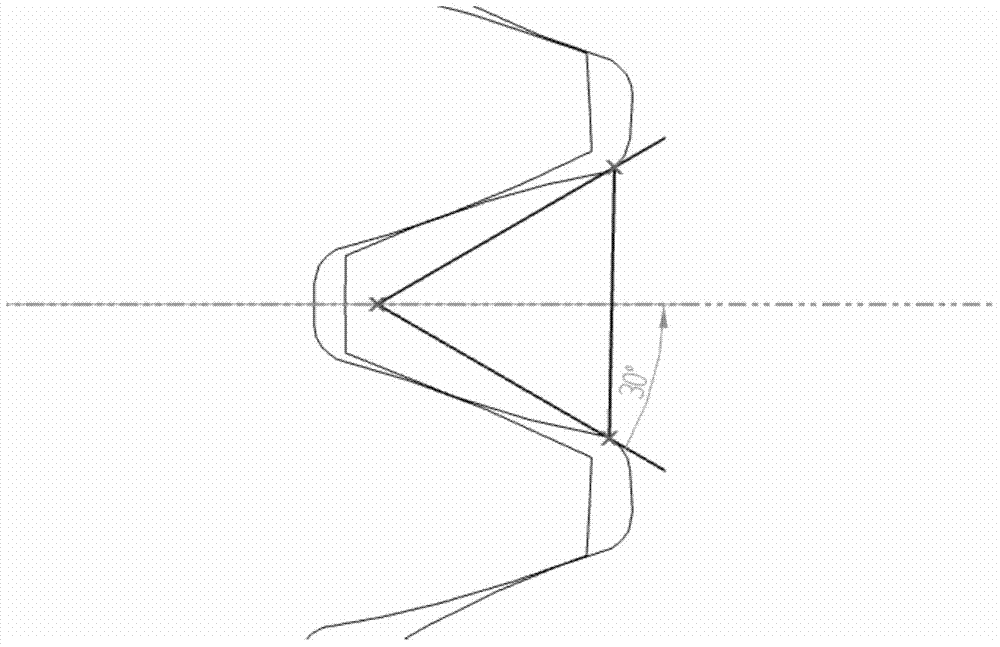
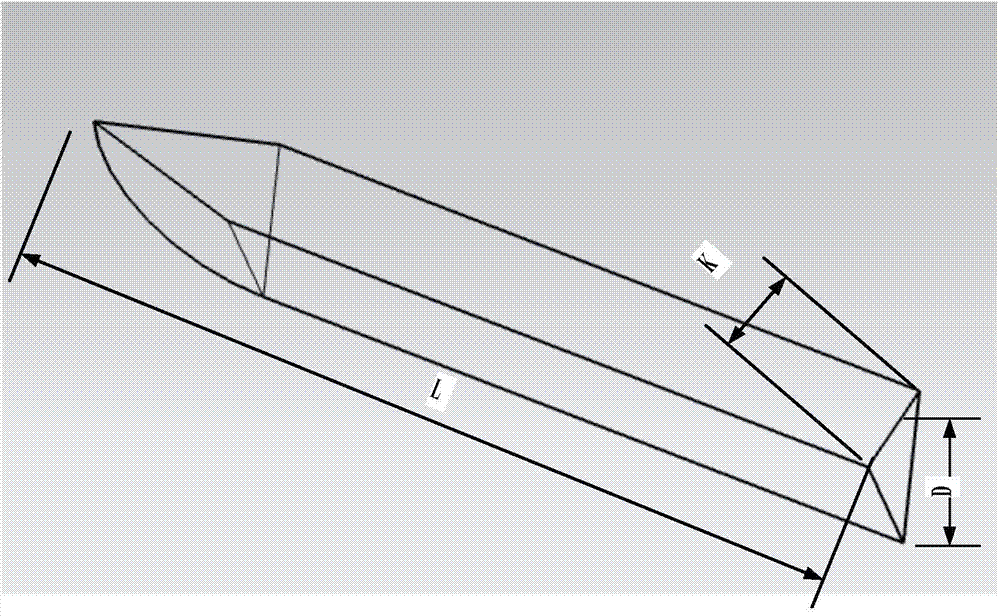
Transmission gear fatigue life assessment method based on defect modeling
InactiveCN103616179AImprove fatigue analysis efficiencyReduce fatigue life analysis complexityMachine gearing/transmission testingFatigue damageEstimation methods
The invention discloses a transmission gear fatigue life assessment method based on defect modeling. The method includes the following steps that (1), crack occurrence rules and reasonable crack forms are analyzed, and the method for introducing cracks into a gear model is researched; (2), material fatigue characteristic parameters are obtained through test data fitting or a numerical value estimation method; (3), a stress spectrum under the condition of working situations of a gear containing the cracks is calculated by using a finite element method, and the stress spectrum is corrected according to obtaining conditions of the material fatigue characteristic parameters; (4), fatigue life under the condition of working situations of a gear containing the cracks is calculated by using the reasonable fatigue damage accumulation theory. The fatigue life assessment method based on defect modeling is provided for the transmission gear, and an effective detection basis is provided for the remanufacturing process of a gear recycled part.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Contact analysis method in three-dimensional mechanical finite element model analysis
ActiveCN107515982ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelExtended finite element method
The invention belongs to the technical field of mechanical analysis and numerical solution of a three-dimensional structure and relates to a contact analysis method in three-dimensional mechanical finite element model analysis. The method comprises the steps of firstly modeling a target electron device structure; introducing a displacement boundary condition or a stress boundary condition to establish a corresponding geometric structure model; generating a contact relation between parts according to a mutual relation between the parts; then subdividing the established geometric structure model by use of a tetrahedral mesh; generating a joint surface mesh according to a surface mesh in a simulated area contact surface; and finally establishing a finite element general intrinsic equation of a target electron device in consideration of a contact problem by use of a finite element method, solving the equation to obtain a characteristic value and a characteristic vector, and post-processing to obtain a vibration modal frequency and a vibration model. Therefore, the contact analysis in modal analysis is realized and a high-precision numerical calculation result is obtained.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Hydraulic fracture simulation with an extended finite element method
A computer-implemented method includes defining respective positions of a first set of nodes and a second set of nodes in an enrichment region, and performing a coupled pore fluid diffusion and stress analysis on the enrichment region at the first set of nodes. It is then determined whether the second set of nodes is activated—representing a fracture—as a result of the analysis, and the results are visually output to a user.
Owner:DASSAULT SYSTEMES SIMULIA CORP
Finite element method for predicting progressive failure of composite laminates under low-speed impact
ActiveCN106503292AAccurately Predict Progressive Damage FailureAccurate predictionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsLow speedElement model
The invention relates to damage prediction for composite materials and is aimed at providing a finite element method for predicting progressive failure of composite laminates under low-speed impact. The method comprises following processes: a low-speed impact finite element model containing a hammer, composite laminates and support plates is established; a composite material elastoplasticity damage constitutive model is established; the elastoplasticity damage constitutive model is realized on the basis of ABAQUS-VUMAT user dynamic material subprogram module and by means of the backward Euler algorithm; the low-speed impact is calculated to further obtain impact force, displacement, speed and acceleration. According to the method, the ABAQUS-VUMAT user subprogram is adopted to numerically realize the elastoplasticity damage constitutive model combining plasticity and damage, wherein the model simultaneously considers the influence of plasticity and material performance degeneration; the method can accurately predict progressive damage failure of composite materials having plasticity characteristics under low-speed impact.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
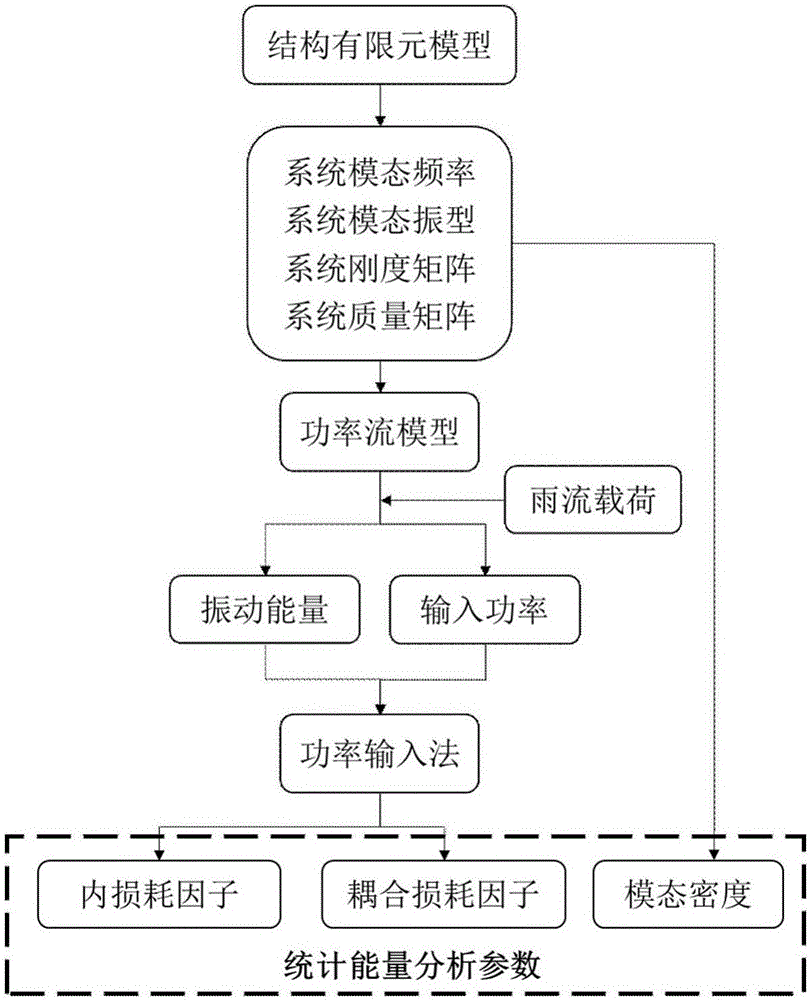
Statistical energy analysis parameter acquisition method based on finite element method and power input method
ActiveCN106844906AOvercome limitationsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelStatistical analysis
The invention provides a statistical energy analysis parameter acquisition method based on a finite element method and a power input method. A finite element model of a structure is established according to a geometric model of the structure, boundary conditions are applied, the finite element model of the structure is subjected to mode analysis, a mode of a system and a rigidity matrix and a mass matrix of a subsystem are obtained, vibration energy of the subsystem and input power of the system are obtained through a power flow model, and statistical energy analysis parameters are obtained through calculation through the power input method. The finite element method and the power input method are combined to obtain the statistical energy analysis parameters of the structure, the calculated rigidity matrix, mass matrix, mode shape and inherent frequency are obtained through the finite element method, the input power and the vibration energy are obtained through calculation through the power flow model, and the input power and the vibration energy are substituted into the power input method for calculation to obtain the statistical energy analysis parameters. According to the method, statistical energy analysis can be carried out aiming at the problem of strong coupling between structures, the limitation about weak coupling assumption between the structures in existing statistical energy analysis is solved, and the method can be popularized to complex structures.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Numerical simualtion of structural behaviors using a meshfree-enriched finite element method
ActiveUS20120226482A1Simple designAvoid oscillationComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationExtended finite element methodSmoothed finite element method
System, method and software product for numerically simulating structural behaviors of an engineering product in compressible and near-incomprssible region is disclosed. Meshfree enriched finite element method (ME-FEM) is used for such numerical simulation. ME-FEM requires an engineering product be represented by a FEM model comprising a plurality of finite elements. Finite elements used in the ME-FEM are generally low-order finite elements. Each of the finite elements in the FEM model is enriched by at least one meshfree enriched (ME) node located within the element's domain. Each ME node has additional degrees-of-freedom for the element it belongs independent from those of the corner nodes. A displacement based first-order convex meshfree approximation is applied to the ME node. The convex meshfree approximation has Knonecker-delta property at the element's boundary. The gradient matrix of ME-FEM element satisfies integration constraint. ME-FEM interpolation is an element-wise meshfree interpolation that is discrete divergence-free at the incompressible limit.
Owner:ANSYS
Finite element method for on-line board temperature calculation in course of hot rolling
InactiveCN101221416AImprove calculation accuracyTotal factory controlAdaptive controlTime domainElement model
A finite element method for on-line calculation of slab band temperature during hot rolling belongs to the rolling technical field, and comprises the following steps that: (1) the establishment of a finite element model: unit division of the cross section of a rolling piece is carried out to set up a finite element analysis model; unit node numbering is carried out to calculate nodal coordinate; (2) the determination of parameters during calculation: the data needed during calculation includes initial information, rolling parameters, thermal physical property parameters of material, unit division information, control parameters and heat exchange coefficient; (3) the establishment of finite element solving equations set: through combining spatial domain finite element discretization and time domain finite difference, the solving linear equations set of temperature field finite element is set up; (4) pass rolling starting temperature is calculated; (5) on-line application is carried out. The invention has the advantages that: the invention can obtain high temperature calculation precision and the detailed information of slab band temperature distribution during entire hot rolling, thereby providing set parameters and optimized parameters for the rolling process; meanwhile, with strong practicality, the invention reduces calculation time and improves calculation efficiency; moreover, the invention is suitable for online application and optimization.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
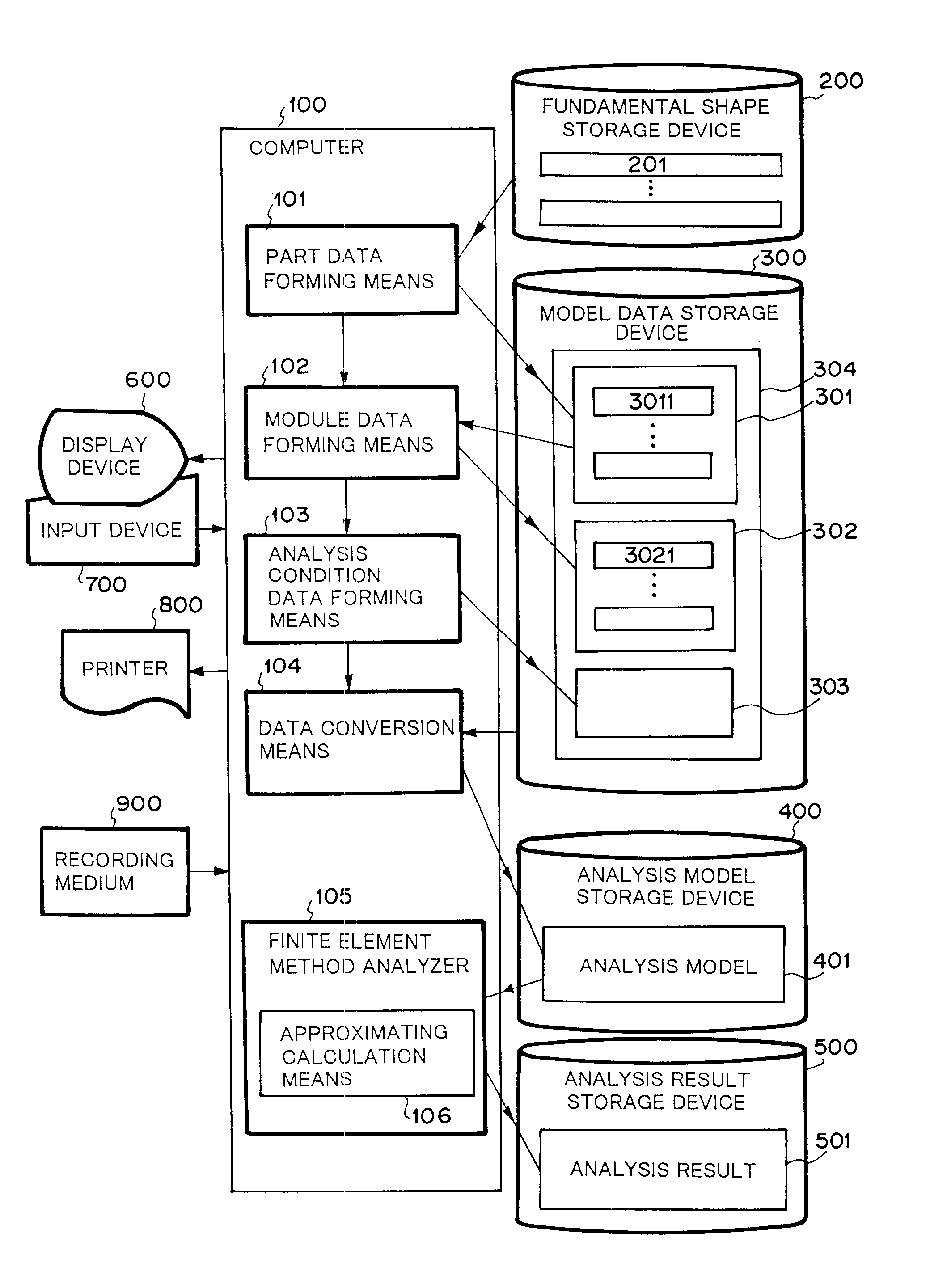
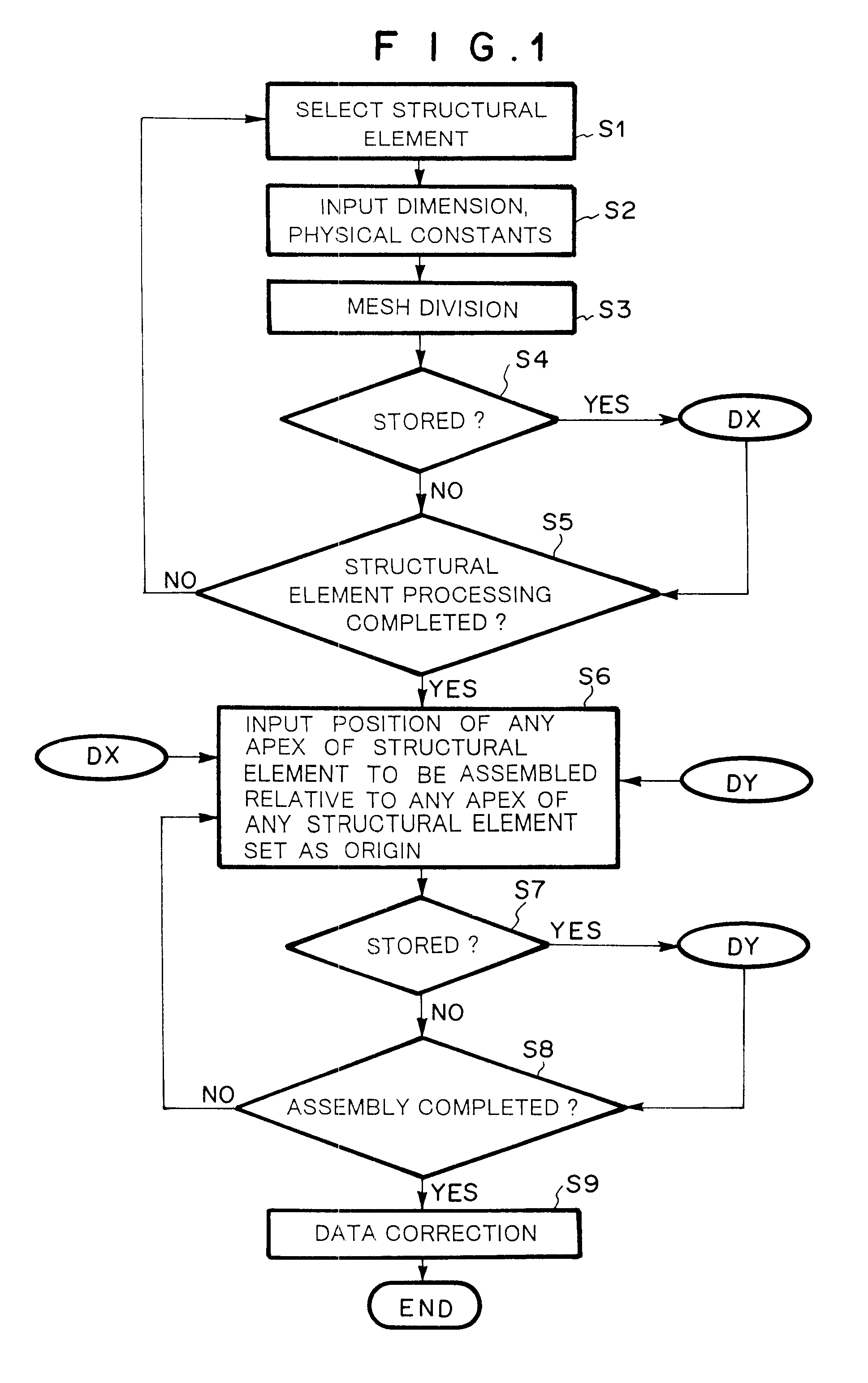
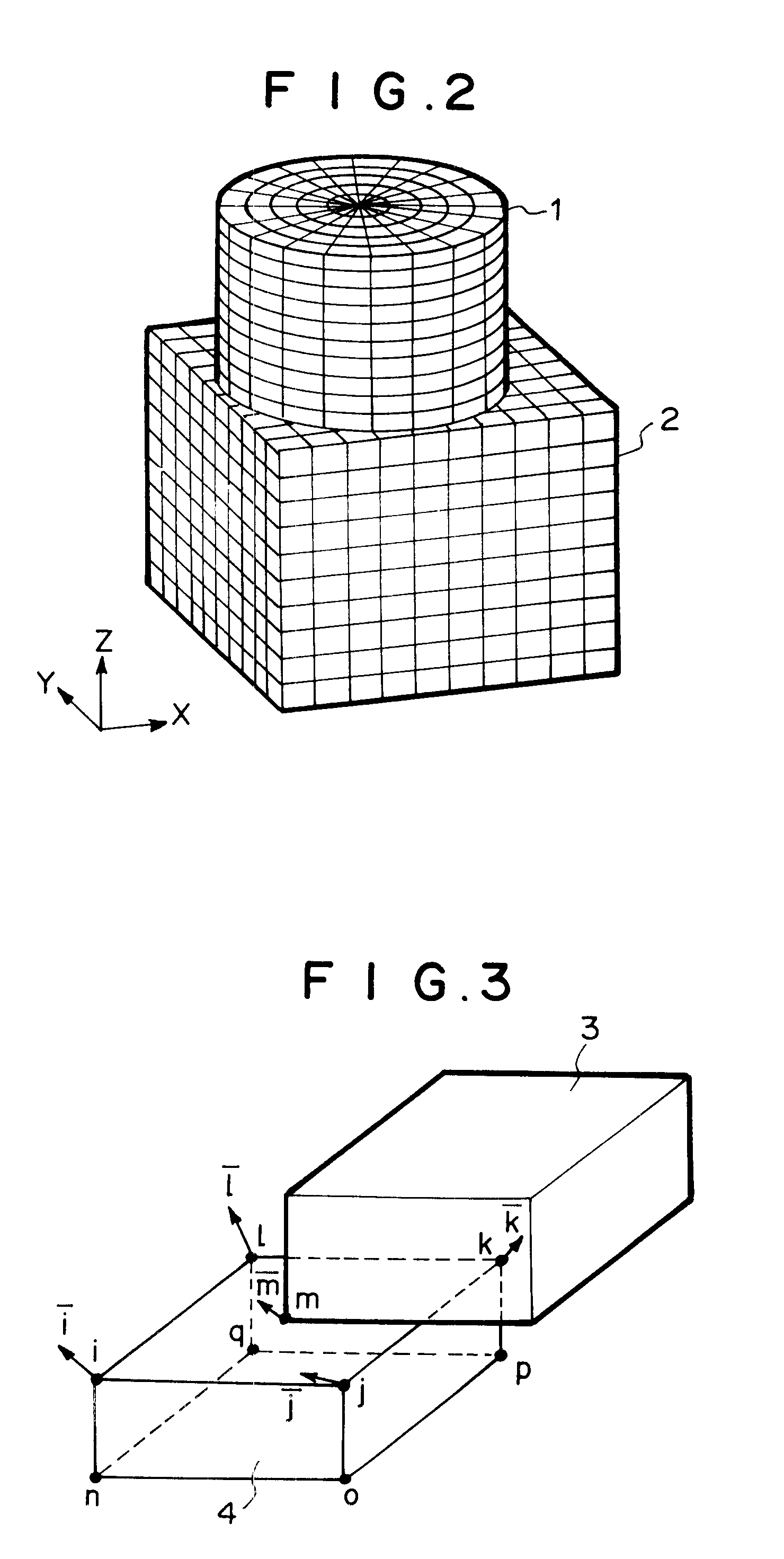
Method, apparatus and computer program product for forming data to be analyzed by finite element method and calculation method based on finite element method
InactiveUS6618694B1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationAnalysis dataMixed finite element method
A user uses part data forming means 101 and module data forming means 102 to input the actual dimension, physical constants and mesh dividing number for fundamental shapes which are registered in advance, thereby forming parts, and then indicates the relative position between the parts to form the entire shape of an assembly of plural parts without paying attention to coincidence or non-coincidence of nodal points. Data converting means 104 divides the shape of each part thus assembled according to the indicated mesh divisional number to generate element data and nodal point data. Further, it generates a constraint equation for connecting nodal points which are non-connected between neighboring parts, and forms an analysis model 401. A finite element method analyzer 105 uses approximate calculation means 106 to approximate a non-connected nodal point displacement from a nodal point displacement of neighboring structural elements on the basis of the constraint equation.
Owner:NEC CORP
Metal fatigue crack full-life estimation method based on damage mechanics non-probabilistic interval analysis model
InactiveCN106096073AMake up for and perfect limitationsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisEstimation methods
The invention discloses a metal fatigue crack full-life estimation method based on a damage mechanics non-probabilistic interval analysis model. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, selecting a damage evolution equation from a damage mechanics model to establish a finite element analysis formation which structurally comprises damage information, and inquiring a fatigue test manual to fit to obtain a parameter in the damage evolution equation; then, combining with a damage mechanics finite element method with an interval finite element method to regard an initial damage degree and a damage parameter as interval uncertainty variables to represent fatigue life dispersivity; further, establishing the finite element analysis model of the structure, giving an initial critical element damage degree increment, constantly carrying out iteration increase on the damage degrees of all elements, judging that the element is damaged through the damage degree of each element, and endowing with intensity and rigidity attributes; and finally, when crack expansion achieves critical crack length, judging that the structure is damaged, and calculating to obtain a fatigue life range via a damage evolution equation variant and an interval vertex propagation analysis method. By use of the metal fatigue crack full-life estimation method, the life of the fatigue crack can be more elaborately estimated.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Cable group cable core transient temperature calculation method based on finite element method
InactiveCN103793558AImprove telemetry capabilitiesSolve agingSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical resistance and conductanceExtended finite element method
The invention provides a cable group cable core transient temperature calculation method based on a finite element method. The method includes the steps of firstly, checking the cable group laying condition, secondly, measuring relevant parameters of cables, thirdly, building a model for a cable group according to measured data, fourthly, dividing the cable model, fifthly, reading currents and determining alternating current resistance and thermal loads, sixthly, conducting simultaneous solution on all division units, and seventhly, repeatedly executing the fifth step and the sixth step, and repeatedly conducting iteration to get a cable core transient temperature. The cable group cable core transient temperature calculation method plays a significant role in solving the problem of cable core temperature when multiple cables are used at the same time under a complex laying condition, real-time temperature of cable cores can be accurately calculated, and judgment of the real-time operating state of cables can be facilitated.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
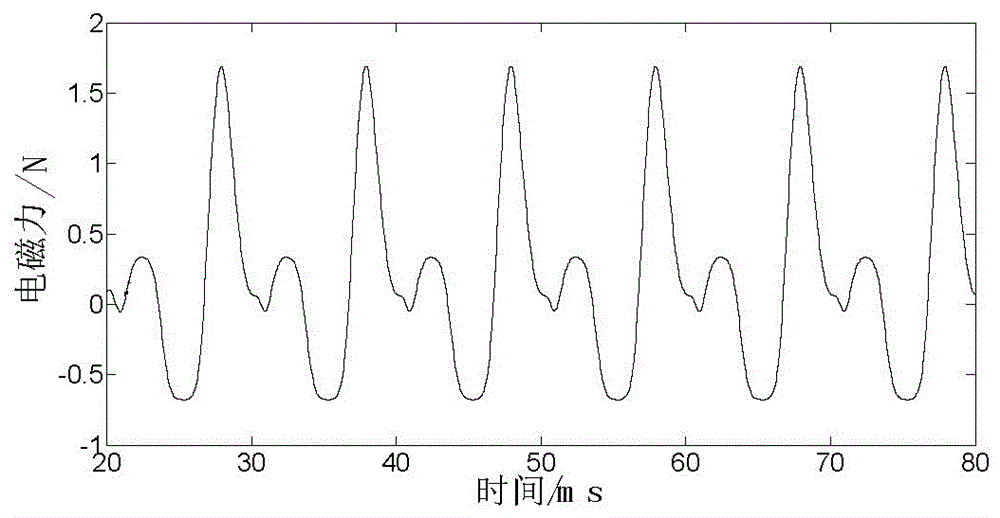
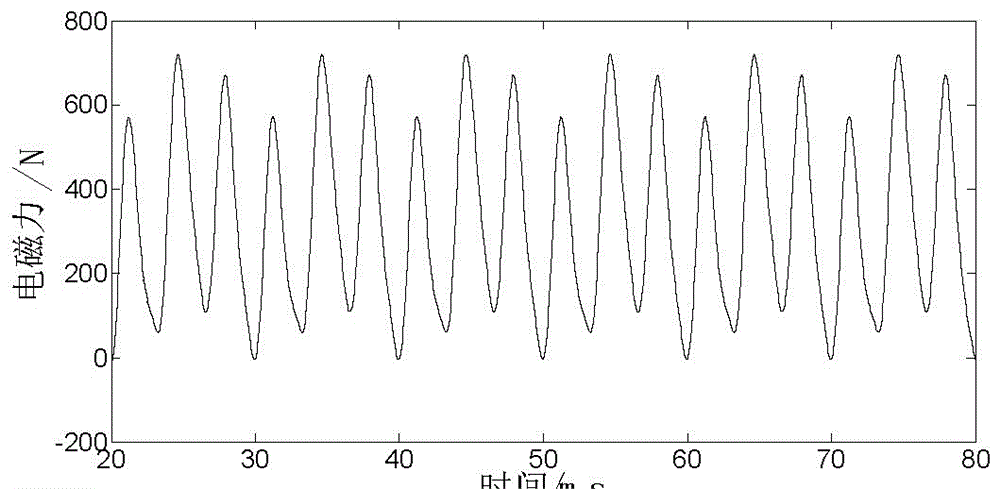
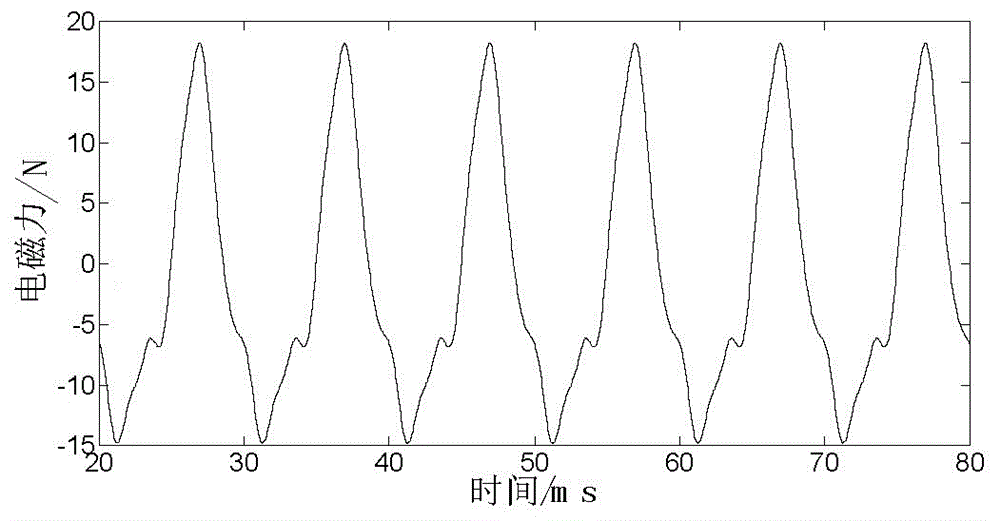
Method for computing electromagnetic force of transformer iron core based on finite element method
InactiveCN106570218ACalculation method directlyCalculation method is simpleDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTransformerLow voltage
The invention discloses a method for computing electromagnetic force of a transformer iron core based on a finite element method. The method comprises the steps that structural parameters of a winding, the iron core and a fuel tank of a transformer are collected, and then a three-dimensional geometric grid model of the transformer is established; the three-dimensional geometric grid model is input into software, sinusoidal currents with a phase different of 120 DEG are applied to the cross section of the three-phase low voltage winding respectively, and Dirichlet boundary conditions are applied to the outer side of the structural grid model; and an instant electromagnetic field is solved by a virtual displacement method, magnetic field energy is computed, a virtual work method is used to compute instant electromagnetic force borne by the transformer iron core and the winding, FFT is conducted to the instant electromagnetic force, and frequency domain distribution of the electromagnetic force of the iron core can be obtained. The computation method disclosed by the invention is direct and convenient; electromagnetic vibration and force bearing situations of the transformer iron core can be analyzed from the perspective of energy; each influential factor on force bearing of the iron core is considered comprehensively; and computation results are accurate and reliable.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Sensitivity analysis based dynamic construction control method for one-time tension of stay cables
ActiveCN107025342AAvoid multiple redistributionsImprove structural stabilityGeometric CADData processing applicationsCompletion timeCable stayed
The invention discloses a sensitivity analysis based dynamic construction control method for one-time tension of stay cables. The method comprises the following steps: a cable-stayed bridge completion time model is established with finite element software, the model is calculated with a finite element method, and tension import value of each stay cable is obtained; uncontrollable external factors are subjected to sensitivity analysis according to the established cable-stayed bridge completion time model; the sensitivity of each stay cable is determined through analysis according to the established cable-stayed bridge completion time model; multiple tension sequence schemes and corresponding tension force are predetermined according to stay cable sensitivity analysis results, the different tension sequence schemes are calculated with the finite element method, and the optimal tension sequence scheme is selected; construction is performed according to the optimal tension sequence scheme obtained through calculation, the tension force of each stray cable and a result about sensitivity analysis of the uncontrollable external factors. With adoption of the sensitivity analysis based dynamic construction control method for one-time tension of the stay cables, the stay cable construction process is simplified.
Owner:NO 1 CONSTR ENG CO LTD OF CHINA CONSTR THIRD ENG BUREAU CO LTD +1
Shale hydraulic fracture propagation prediction method
ActiveCN108468538AGuaranteed accuracyHigh precisionFluid removalDesign optimisation/simulationFracture mechanicsStrain energy
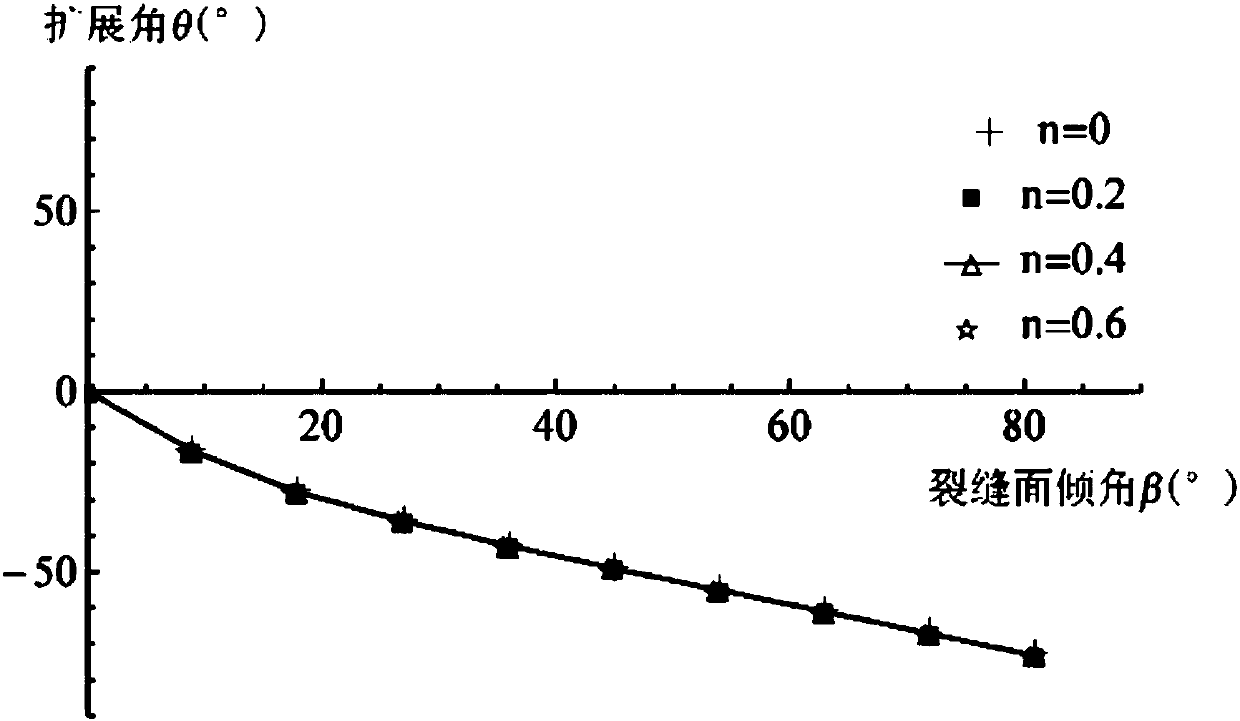
The invention relates to the field of rock fracture prediction, in particular to a shale hydraulic fracture propagation prediction method. The method comprises the steps that 1, the normal direction,tangential stress and effect stress of an inclined fracture under the action of the external stress and water pressure are calculated; 2, a strain energy density function is obtained according to thetype of the fracture; 3, a strain energy density factor is obtained according to the strain energy density function; 4, the propagation direction and propagation angle of the fracture are judged according to a strain energy density criterion; 5, influences of stratification, natural fractures and the like on the propagation direction of hydraulic fractures are obtained through numerical simulation, so that fracture propagation under the effect of shale hydraulic pressure is predicted. The prediction method is based on fracture mechanics, a hydraulic condition factor is introduced, and the influences of different stratification directions on the propagation direction of the shale hydraulic fractures are obtained by researching the relation between the fracture propagation direction and themagnitude of the hydraulic pressure and utilizing an extended finite element method, so that accurate prediction of hydraulic fracture propagation is achieved, and higher prediction accuracy is obtained.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
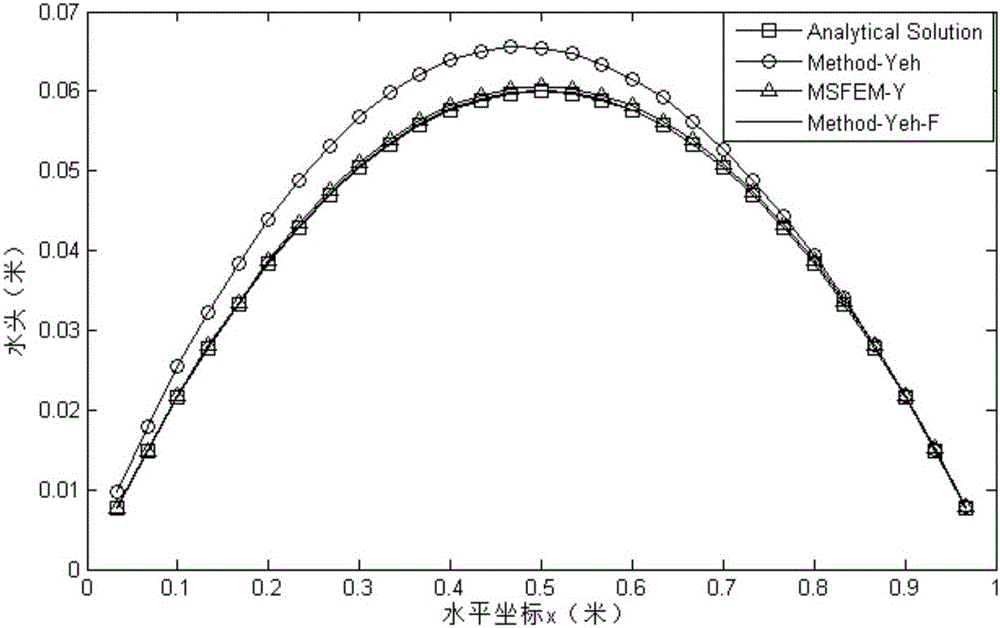
Yeh-multi-scale finite element method for simulating water flow Darcy velocity of porous medium
ActiveCN106202746AGuaranteed continuityEfficient solutionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALElement model
The invention discloses a Yeh-multi-scale finite element method for simulating water flow Darcy velocity of a porous medium, comprising the steps of: performing variation on the problem which needs resolution by a Galerkin method; subdividing a research area into coarse grid cells and subdividing all the coarse grid cells into fine grid units; resolving a degradation elliptic equation on each coarse grid cell to construct a basis function; resolving variational form by applying the basis function to obtain a total rigidity matrix; obtaining a right-hand term according to the source sink term and the boundary condition of the research area; performing simultaneous operation to obtain a waterhead equation set; resolving the equation set by an effective numerical method to obtain the node waterhead of the research area; and resolving a Darcy equation directly in the research area by combining a Galerkin finite element model of Yeh and applying the constructed basis function and the waterhead value of the research area to obtain continuous Darcy permeating velocity on the coarse-scale node, and linearly expressing the fine-scale Darcy permeating velocity by the basis function. Compared with the prior art, the method has similar precision and higher efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
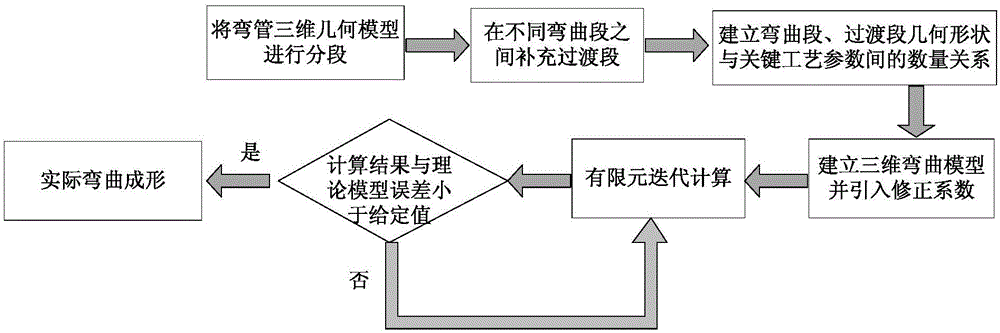
3D free bending forming technology optimization method for complex metal components
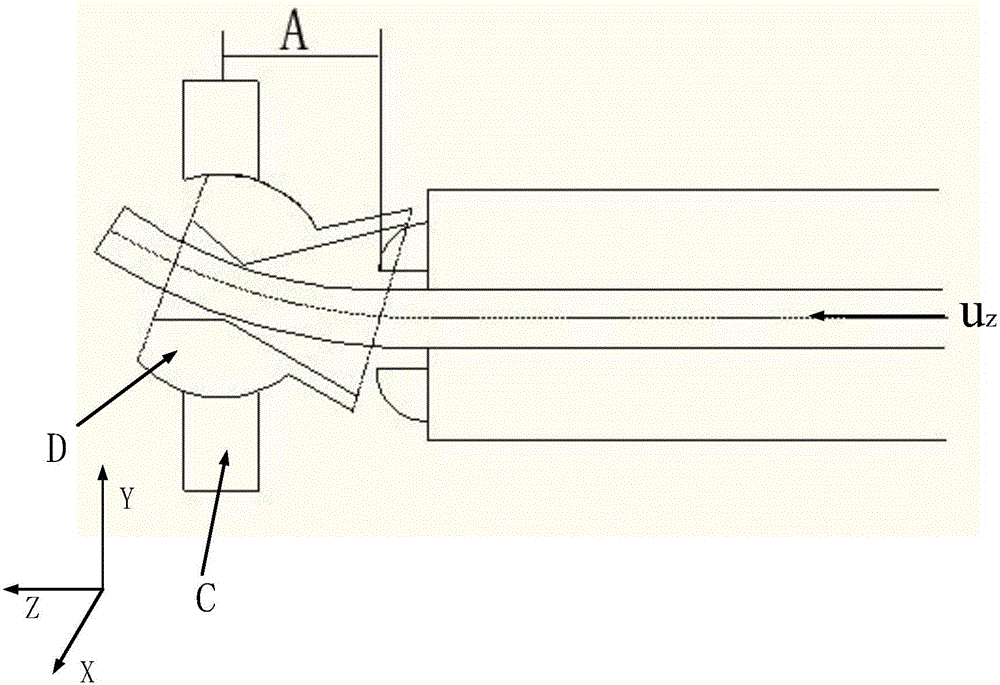
ActiveCN106270059AChange bend radius in real timeAchieve bendingSpherical bearingExtended finite element method
The invention discloses a 3D free bending forming technology optimization method for complex metal components. The method includes the steps that quantitative relations between geometrical shape parameters of a straight section, a transition section and a bent section and movement velocity u of a spherical bearing within the X / Y plane, pipe Z-axis feed-in velocity v, movement time t and a distance A between the center of a bending mold and the front end of a guiding mechanism are established; a finite element method is adopted for establishing a 3D bending model, and a correction factor k is introduced into the quantitative relations; the quantitative relations with the introduced correction factor k are adopted as bending technology parameters, bent pipe finite element repeated iterative computation is started, computation results are imported into geometry software to be processed, and the dimension difference between the computation results and the established 3D bending model is obtained through comparison; based on an established dimension error criterion, whether the correction factor k is modified, and iteration is performed again is determined; when the error is smaller than a set value, iteration is ended; final technology parameters are transmitted to equipment to execute actual bending forming.
Owner:固航科技(常州)有限公司
Load measurement-based residual stress detection method
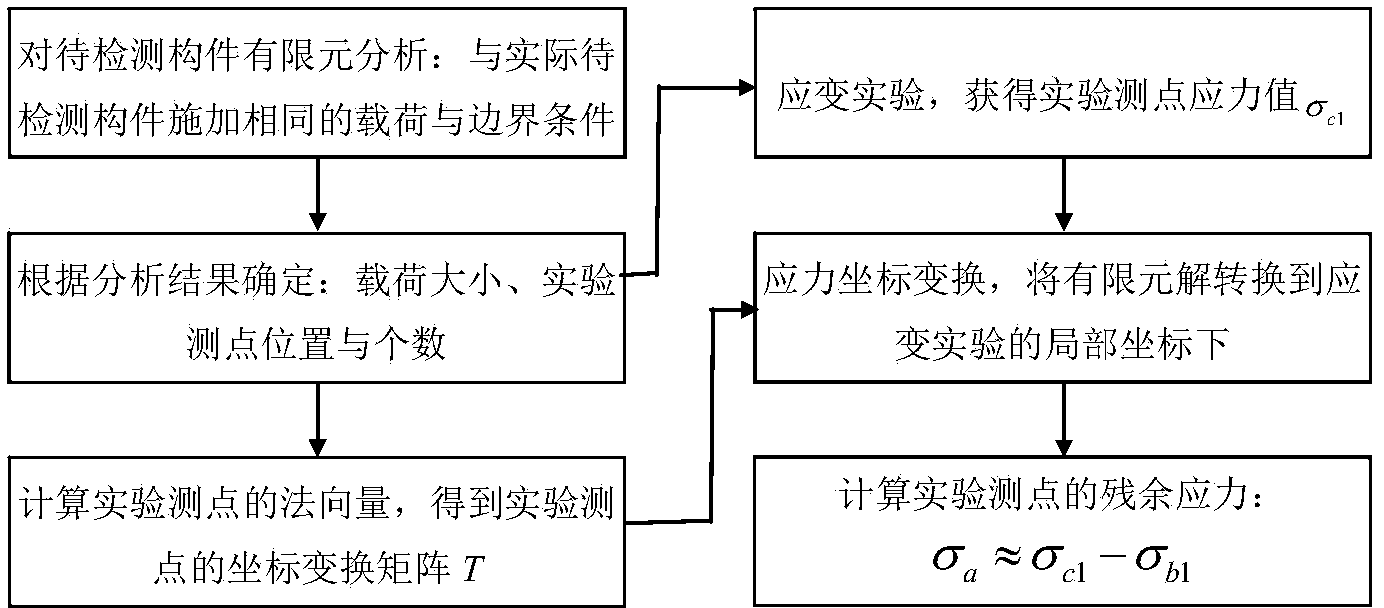
ActiveCN104142265AAddressing the disadvantages of damageForce measurementStrength propertiesExtended finite element methodMixed finite element method
The invention belongs to the technical field of detection and discloses a load measurement-based residual stress detection method. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a computer geometric model of a to-be-detected member, applying restrictions to the model by a finite element method, performing linear elasticity finite element static analysis after a load is applied to a loading point, reading stress value sigma'<b1> of an experimental measuring point, and adjusting the position of the loading point or increasing the load so as to enable the maximum value of the component of the stress value sigma'<b1> to be larger than 0.1MPa if the maximum value of the component of the stress value sigma'<b1> is less than 0.1MPa; applying restrictions and a load same as those of the computer geometric model to the to-be-detected member, and performing a strain experiment to obtain a stress value sigma<c1> of the experimental measuring point; and transforming the sigma'<b1> under local coordinates of the experimental measuring point to obtain sigma<b1>, and subtracting sigma<b1> from sigma<c1> to obtain residual stress value sigma<a1> of the member at the experimental measuring point. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the surface of the member is not damaged in the detection process, and the problem that a member is damaged due to a conventional mechanical residual stress method is solved. In addition, the method is convenient, simple and flexible to apply.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TIANCHONG VEHICLE LAMP GROUP
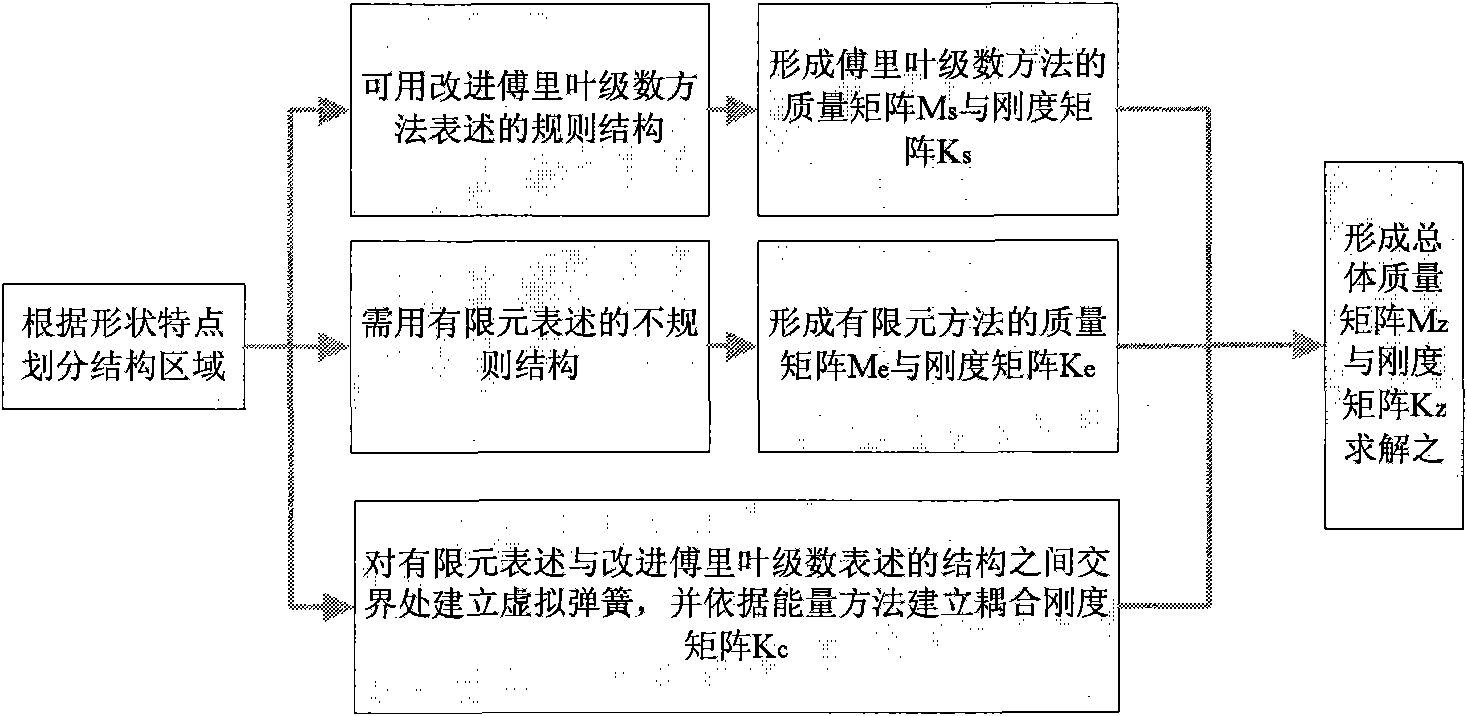
Structural vibration analysis method based on finite element method and generalized Fourier series method
InactiveCN101887474AFast convergenceSave resourcesSpecial data processing applicationsEnergy variationExtended finite element method
The invention aims at providing a structural vibration analysis method based on a finite element method and a generalized Fourier series method, which comprises the following steps of: dividing a structure region to be subjected to vibration analysis to respectively and correspondingly form a finite element expression region and a generalized Fourier series expression region; dividing the finite element grids of the finite element expression region to form a corresponding quality stiffness matrix, and selecting a corresponding assumption displacement form according to the characteristics of the generalized Fourier series expression region to form a quality stiffness matrix; subsequently, establishing a virtual spring between the two regions, and converting the potential energy of the virtual spring into an overall coupling stiffness matrix by using an energy variation method; then, arranging the formed quality stiffness matrices according to displacement to form an overall structure quality stiffness matrix; and solving linear equations to obtain an unknown coefficient in corresponding node displacement and series expansion. When applied to a large complex structure, the method not only can obtain precision higher than the finite element method, but also can save a large amount of calculation cost.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Random thermal homogenizing analysis method of two-phase composite material
ActiveCN105044146ASolving Numerical Modeling ProblemsMaterial heat developmentHeat fluxElement analysis
The invention discloses a random thermal homogenizing analysis method of a two-phase composite material. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a corresponding microscopic homogenization model of a two-phase composite material composed of a matrix and particles, constructing constitutive equations, and calculating the thermal boundary values of the heterogeneous material; (2) determining and analyzing to obtain one RVE from the two-phase composite material, and determining the effective constitutive relationships among the effective heat conduction coefficient, the volumetric average temperature gradient and the volumetric average heat flux, wherein the volumetric average temperature gradient and the volumetric average heat flux are obtained from RVE; (3) applying boundary conditions on RVE, and at the same time carrying out finite element analysis and calculation to obtain the value of effective heat conduction coefficient of the RVE numerical model; (4) establishing a random homogenizing model to obtain the macroscopic effective quantity of the composite material. In the provided method, a finite element method and Matlab software are used to solve the problem of complicated RVE numerical modeling, the influences of parameter randomness of components of the composite material under three boundary conditions on the macroscopic thermal physical properties are taken into account comprehensively, and thus the provided method has an application value, a certain academic value, and theoretical significance.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
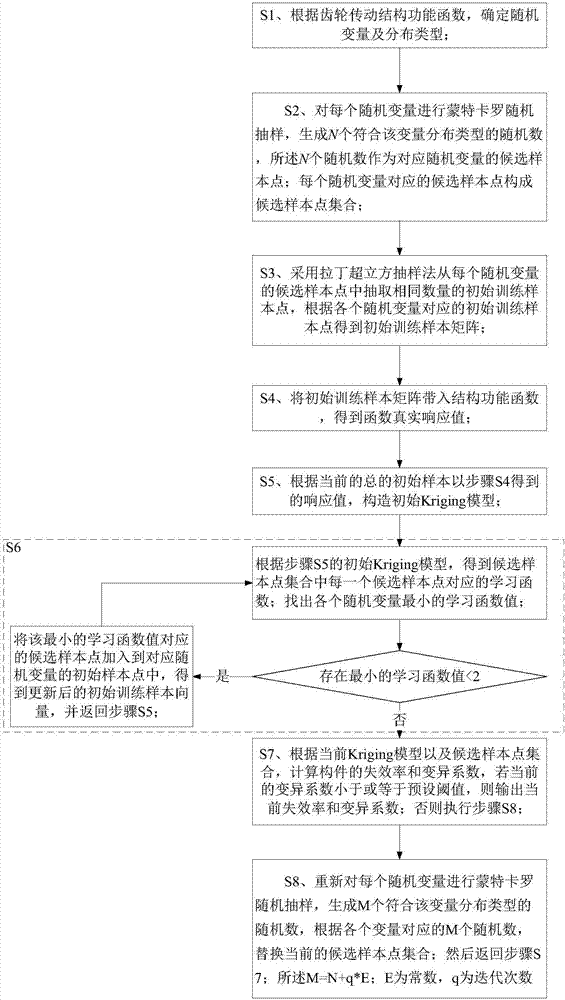
Gear drive reliability assessment method based on Kriging model
InactiveCN107273609AReduce the number of trialsSmall amount of calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsStructural reliabilityGear drive
The invention discloses a gear drive reliability assessment method based on a Kriging model and is applied to the field of reliability assessment. According to the gear drive reliability assessment method, the Kriging model is established firstly according to an initial sample, then whether variable coefficients meet the requirements or not is judged according to the established Kriging model, new variable coefficients are recalculated in a sample point adding mode. The stress calculation quantity based on a finite element method in a traditional method is greatly decreased. The gear drive reliability assessment method adopts a Monte Carlo method to calculate the structural reliability, and meanwhile combines with a learning function to obtain a high-precision agent model with fewer sample points, and accordingly testing times are decreased.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Simulation method for gas static pressure main shaft dynamic predication
ActiveCN102880765APrediction of dynamic characteristics is accurateNo omissionsSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelExtended finite element method
The invention relates to a simulation method for gas static pressure main shaft dynamic predication, and the method can be used for solving the problems of modeling difficulty, and difficulty in predicating the dynamic characteristics of the main shaft at the design stage due to low precision of a traditional method in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of: partitioning a gas static pressure main shaft bearing gas film into finite element grids by utilizing a finite element method and a gas static pressure theory, and calculating to obtain the pressure distribution data We of a gas static pressure main shaft; establishing a finite element model, corresponding to the finite element grids, of a main shaft body; converting the pressure distribution data We of the finite element main shaft into equivalent spring stiffness values and assigning the equivalent spring stiffness values to nodes corresponding to the finite element grids of the gas film; and establishing a finite element model of the gas static pressure main shaft, and calculating the dynamic characteristics of the gas static pressure main shaft according to the established finite element model. The method is mainly used for predicating the dynamic characteristics of the gas static pressure main shaft.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
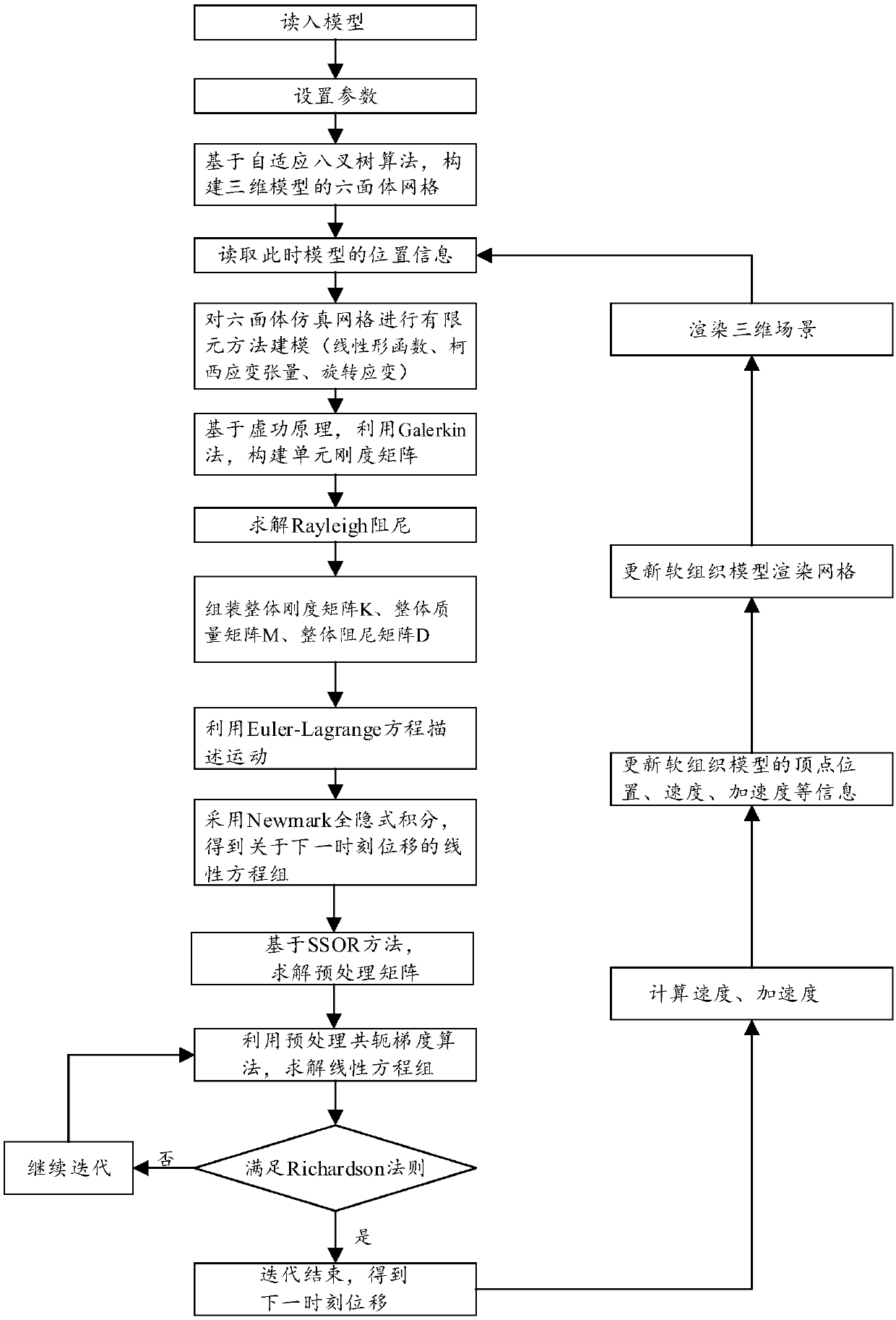
Soft tissue deformation method based on finite element model of octree mesh
InactiveCN108694290AImprove real-time performanceSmall amount of calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALElement model
The invention provides a soft tissue deformation method based on a finite element model of an octree mesh. The method comprises: drawing a three-dimensional model of soft tissue, constructing a plurality of uniform hexahedral meshes based on the AABB method, and generating an octree mesh based on the mesh generation algorithm of an octree based on the hexahedral mesh, modeling the hexahedron meshby the finite element method, solving the deformation process of the soft tissue, assembling the element stiffness matrixes on adjacent element nodes into the total stiffness matrix of the discrete domain, solving the dynamic equilibrium differential equation for each matrix by time integral under dynamic equilibrium, to obtain the displacement of the nodes with time, and displaying the stress deformation of the soft tissue by the rendering of the displacement of the nodes. The method realistically simulates the process of tension deformation of the soft tissue epidermis of any shape in virtual surgery, has high real-time performance, reduces the calculation amount, and solves the problem that the number of finite element meshes is complicated and the soft tissue deformation process cannotbe simulated in real time.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
An electrical tomography image reconstruction method based on a convolutional neural network
ActiveCN109598768AOptimizing Numerical Computation ResultsHigh precisionReconstruction from projectionImage generationExtended finite element methodReconstruction method
The invention relates to an electrical tomography image reconstruction method based on a convolutional neural network. The method comprises the following steps: solving a positive problem of electrical tomography by adopting a finite element method; Designing a convolutional neural network structure to enable the convolutional neural network structure to be suitable for an electrical tomography image reconstruction process; Determining a loss function; Updating the network parameters by adopting a small-batch gradient descent strategy, and synthesizing the parameters obtained by each round ofiteration by using a moving average model to determine a final parameter updating value; After the iteration is finished, obtaining a convolutional neural network of which the connection weight and the threshold are determined; When the image is reconstructed, taking the actually measured boundary measurement value as a trained convolutional neural network input layer neuron, wherein the output ofthe output layer neuron is the value of each pixel point in the image.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Wind power master control cabinet heat management analysis and optimization method based on finite element method
ActiveCN103699744AGreat adaptabilityGreat ability to solveSpecial data processing applicationsElectricityHeat management
The invention discloses a wind power master control cabinet heat management analysis and optimization method based on a finite element method. The wind power master control cabinet heat management analysis and optimization method includes the steps of from a cabinet-top arrangement diagram, acquiring attributes of materials of a wind power master control cabinet and parameters of a circuit breaker and a relay inside the wind power master control cabinet; performing initial geometric modeling on the circuit breaker and the relay to obtain a three-dimensional model; subjecting the three-dimensional model to finite element meshing to obtain a finite element mesh model; acquiring design parameters of a heater and a fan; establishing a three-dimensional model for the wind power master control cabinet and fluid inside; performing hydro-mechanical meshing to obtain a flow field mesh model; restraining the flow field mesh model; determining physical parameters of the fluid in the flow field; calculating the temperature field and flow field of the flow field mesh model to obtain flow field analysis results; judging whether or not the flow field analysis results for the wind power master control cabinet meet industrial standards; if yes, ending; if not, optimizing a design scheme. The precise calculation results can be obtained with no need of building a solid model.
Owner:GUODIAN NANJING AUTOMATION
Finite element method based aircraft cabin door seal load computing method
ActiveCN105260505ATroubleshoot moment calculationsEasy to useSpecial data processing applicationsStress conditionsExtended finite element method
The invention relates to a finite element method based aircraft cabin door seal load computing method. The sealing strip stress condition is simplified to be a plane strain state; modeling, loading and definition contact are performed on a sealing strip, a support and a cabin door, so as to resolve the stress for compression of the sealing strip per unit length, and the sealing strip is between the support and the cabin door; a revolute pair is defined at a hinge of the cabin door and rotation angular displacement is restrained, and pressure equivalent to the sealing compression force of per unit length is applied on the cabin door at the sealing position, so as to obtain bending moment of the hinge, namely, the cabin door seal load. The method solves the problem of moment computation caused by sealing in automatic closing and opening of the aircraft cabin door, provides design basis for design of an automatic closing and opening mechanism of the cabin door, and is initiative at home.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF LAUNCH VEHICLE TECH
Method for calculating quenching medium heat exchange coefficient by combining finite element method with inverse heat conduction method
ActiveCN102521439AGuaranteed credibilityGuaranteed accuracySpecial data processing applicationsCooling curveElement model
The invention discloses a method for calculating a quenching medium heat exchange coefficient by combining a finite element method with an inverse heat conduction method, which relates to a method for calculating a quenching medium heat exchange coefficient. The method comprises the following steps of: using a probe body, testing by an experiment to obtain the cooling curve of an internal point of the body, establishing a finite element model of the probe body, simulating a temperature field, and verifying the one-dimensional property of a problem; establishing a one-dimensional heat conduction micro equation and a sensitive coefficient equation under a coordinate system, and solving the heat-flow density value of the surface of the body surface by using the inverse heat conduction method; and verifying the measured temperature of the internal point of the probe in comparison to a calculated value, namely the heat exchange coefficient of the quenching medium calculated according to the Newton heat exchange law, so that the solution accuracy is ensured. The method is used for calculating the heat exchange coefficient of quenching medium.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com