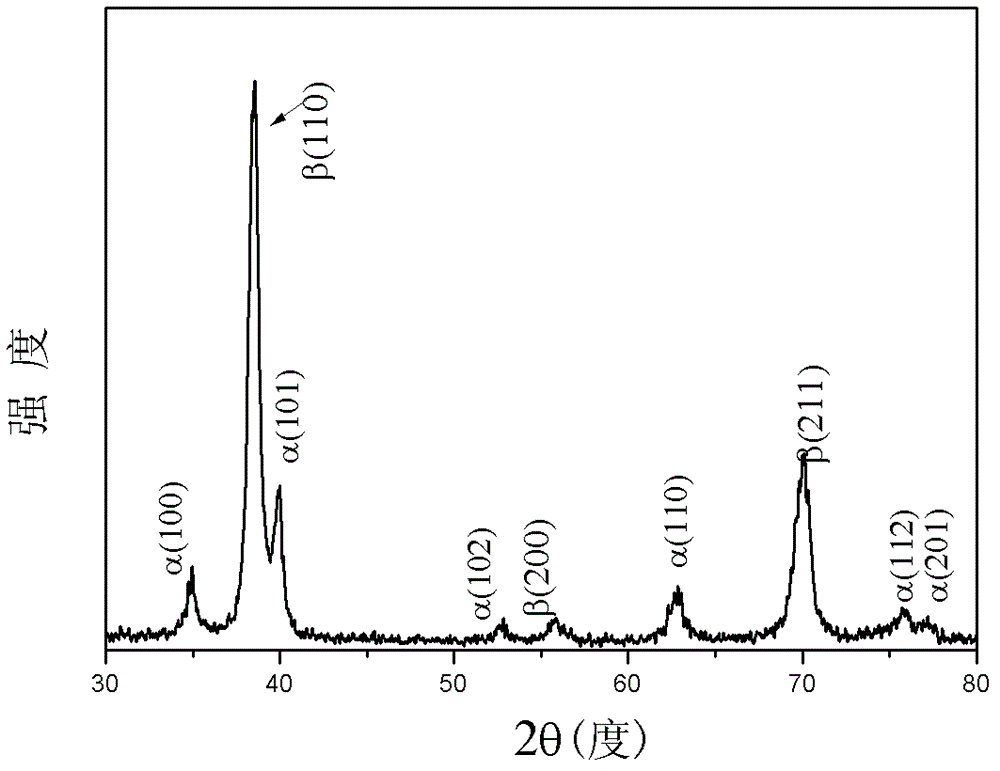
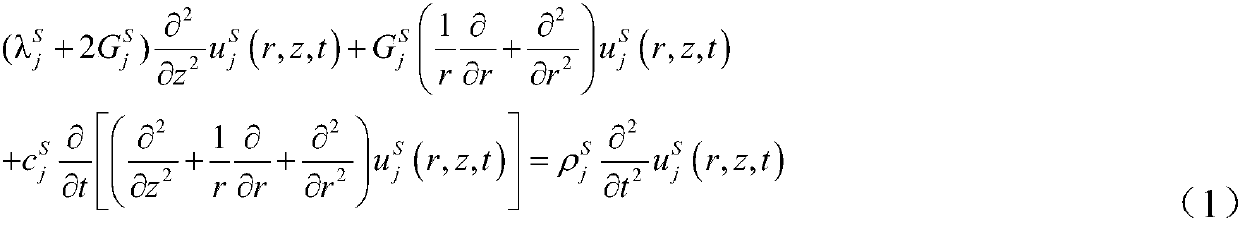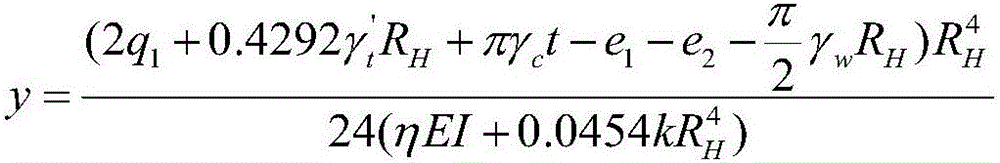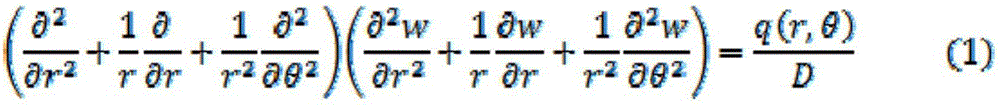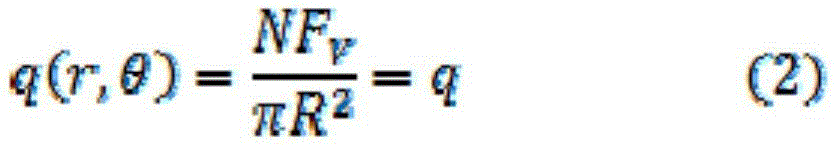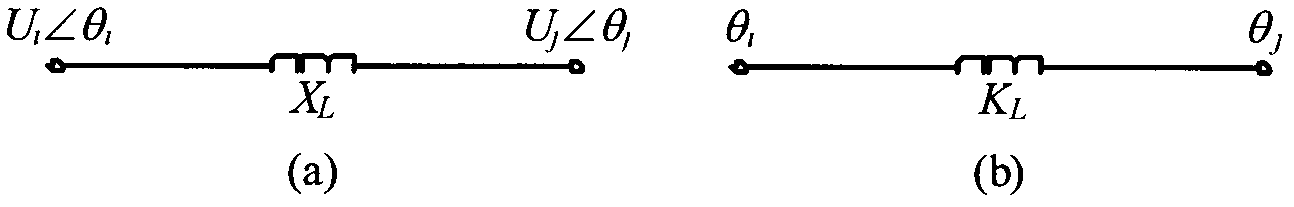Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
126 results about "Linear elasticity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Linear elasticity is a mathematical model of how solid objects deform and become internally stressed due to prescribed loading conditions. It is a simplification of the more general nonlinear theory of elasticity and a branch of continuum mechanics.
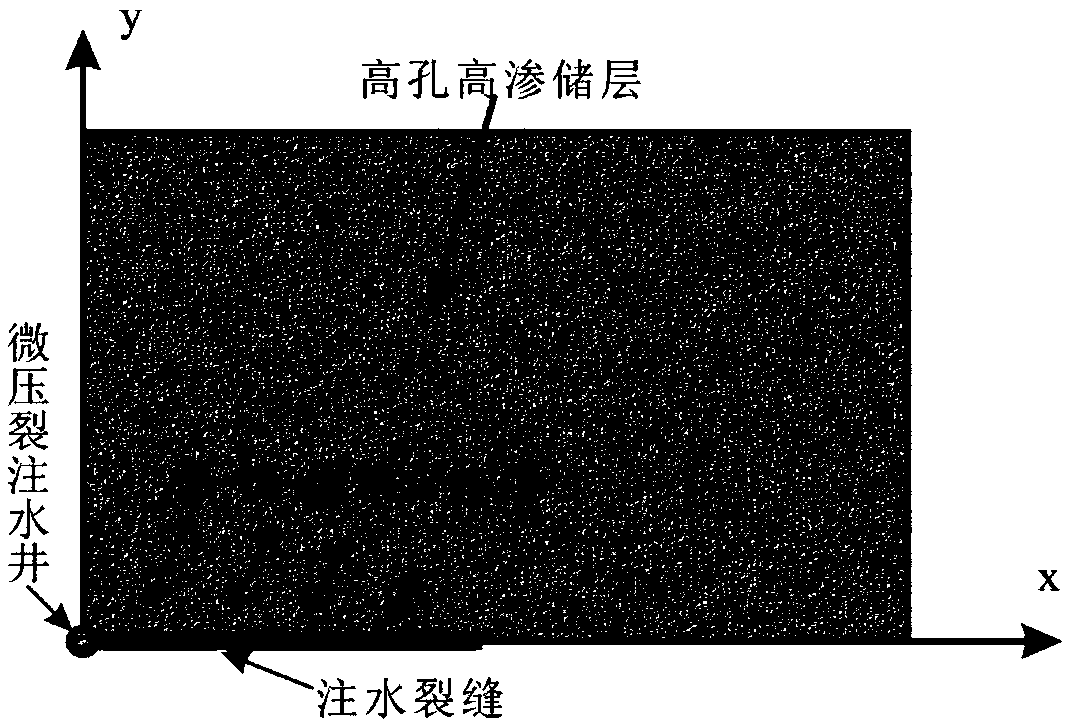
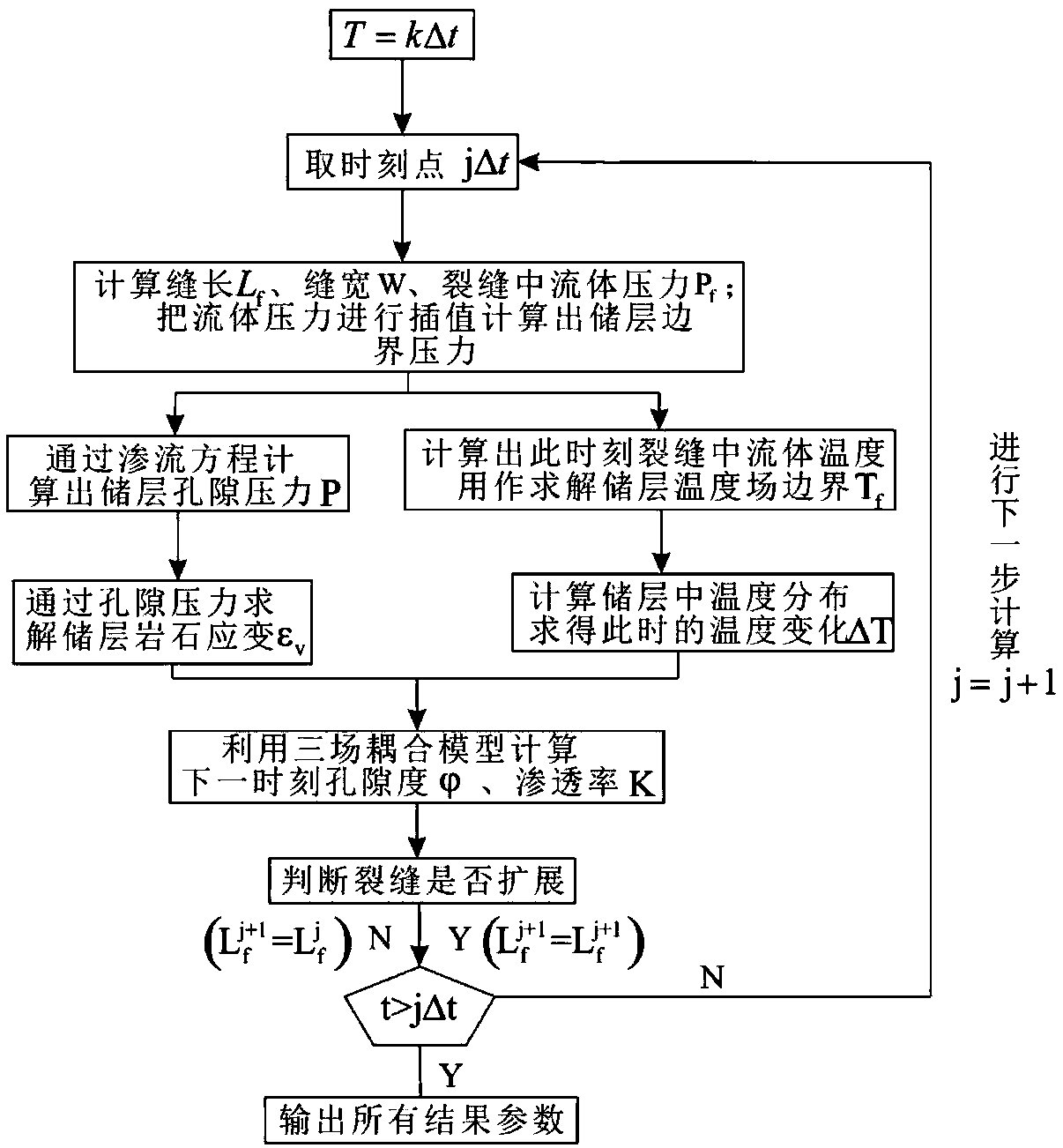
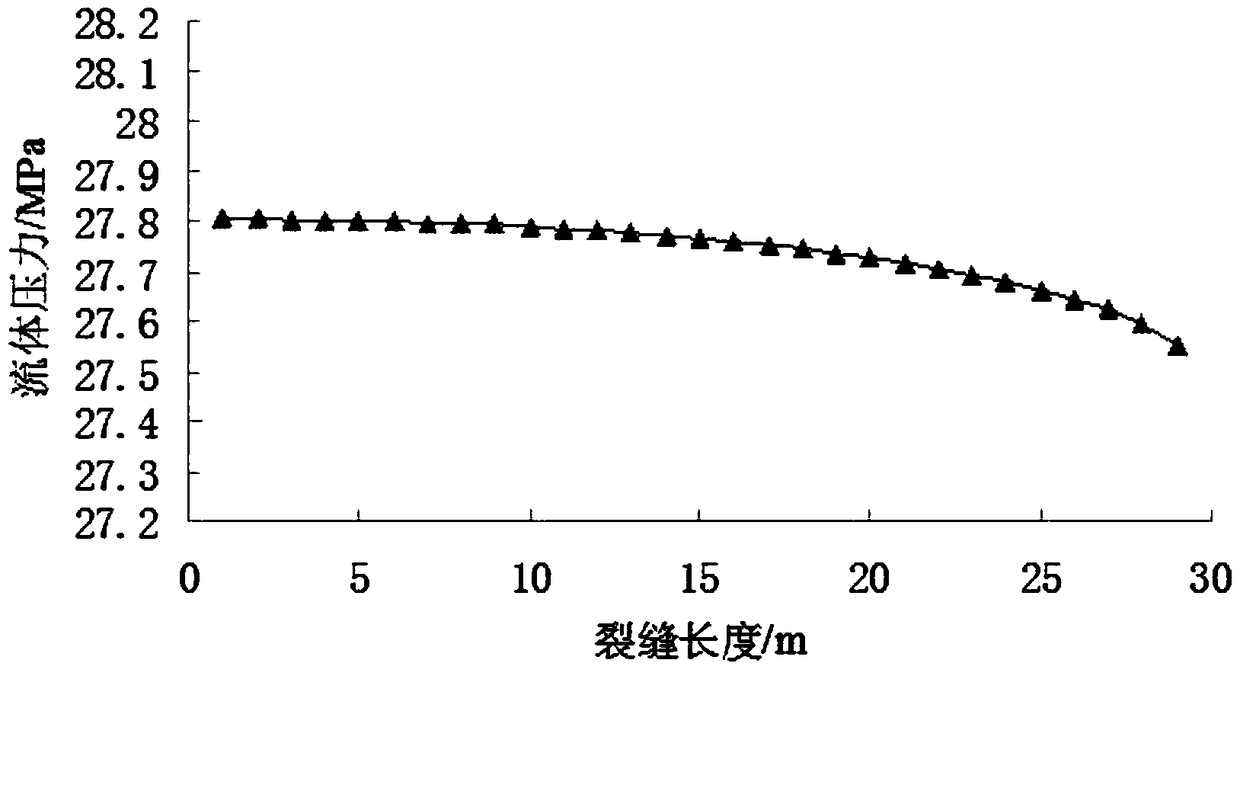
Method for simulating offshore oilfield micro fracturing injection increase crack propagation on basis of fluid-solid-heat coupling theory
ActiveCN108830020AInjection speed is smallReliable Analytical Research MethodsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPorosityFiltration
The invention discloses a method for simulating offshore oilfield micro fracturing injection increase crack propagation on the basis of fluid-solid-heat coupling theory. The method comprises the following steps that geological characteristic parameters are obtained on the basis of offshore micro fracturing well geological data; a hydraulic crack propagation model is built, and fluid pressure and filter loss in a crack are obtained; on the basis of a reservoir matrix model, dynamically changing pore pressure in a reservoir is worked out; on the basis of elastic mechanics and permeation fluid mechanics, a pore elastic deformation relation between fluid and rock is built, that is to say, a fluid-solid coupling model is built, and by means of the calculated pore pressure, rock strain caused bythe fluid can be obtained; a heat effect relation between the temperature and the rock is built, a strain, porosity, permeability and temperature fluid-solid-heat coupling model is built, the permeability and porosity after coupling change are obtained, the pore pressure after three-field coupling change is obtained, the changed pore pressure reacts on a Darcy filtration model, and the crack extension dynamic of the next moment is obtained. According to construction and geological parameters, the dynamic extension situation of the hydraulic crack and real-time change situation of the reservoir parameters in the offshore micro fracturing well long-term injection increase process can be predicted according to the construction and geological parameters.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
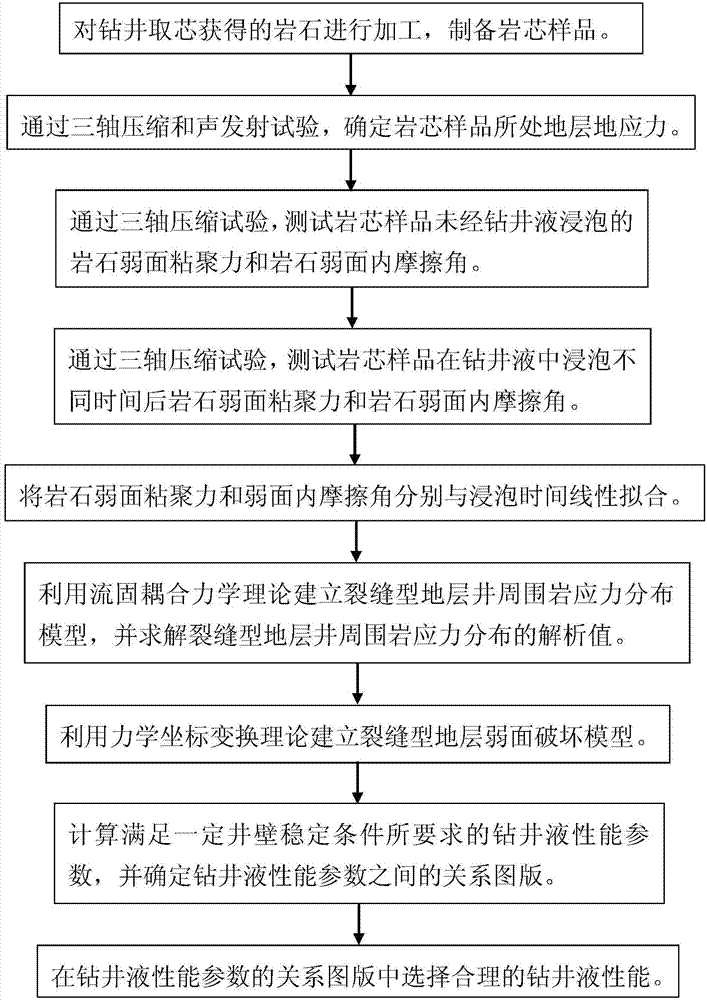
Design method for property parameters of anti-collapse drilling fluid for fractured formations
ActiveCN104778303AAchieving Stability RequirementsApp performance is stableSpecial data processing applicationsStress distributionAcoustic emission
The invention discloses a design method for property parameters of anti-collapse drilling fluid for fractured formations. According to sequence, the design method includes the following steps: core samples are prepared; four of the core samples are chosen for a triaxial compression test and an acoustic emission test, and the crustal stress of a formation owning the core samples is determined; two of the core samples are chosen for the triaxial compression test, and the cohesion and internal friction angle of the weak planes of the rocks are tested; eight of the core samples are chosen to be put into the drilling fluid, the triaxial compression test is carried out after the core samples are soaked for different times, and the cohesion and internal friction angle of the weak planes of the rocks are tested; the cohesion and internal friction angle of the weak planes of the rocks are respectively linearly fitted to soaking times; the fluid-solid coupling theory is utilized to create a fractured formation well surrounding rock stress distribution model; the elastic mechanics coordinate transformation theory is utilized to create a fractured formation weak plane destruction model; a relation chart between the property parameters of the drilling fluid is determined. The design method disclosed by the invention can quantitatively optimize the key property parameters of the drilling fluid according the requirement of a site for well wall stability.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Load measurement-based residual stress detection method
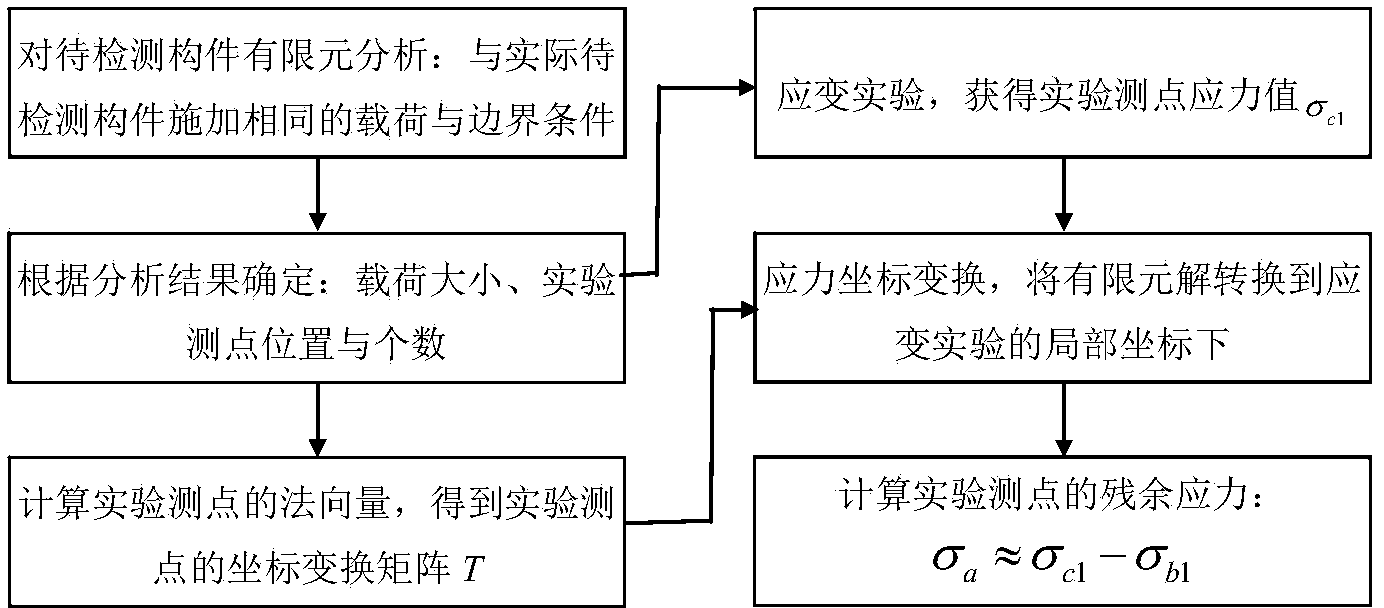
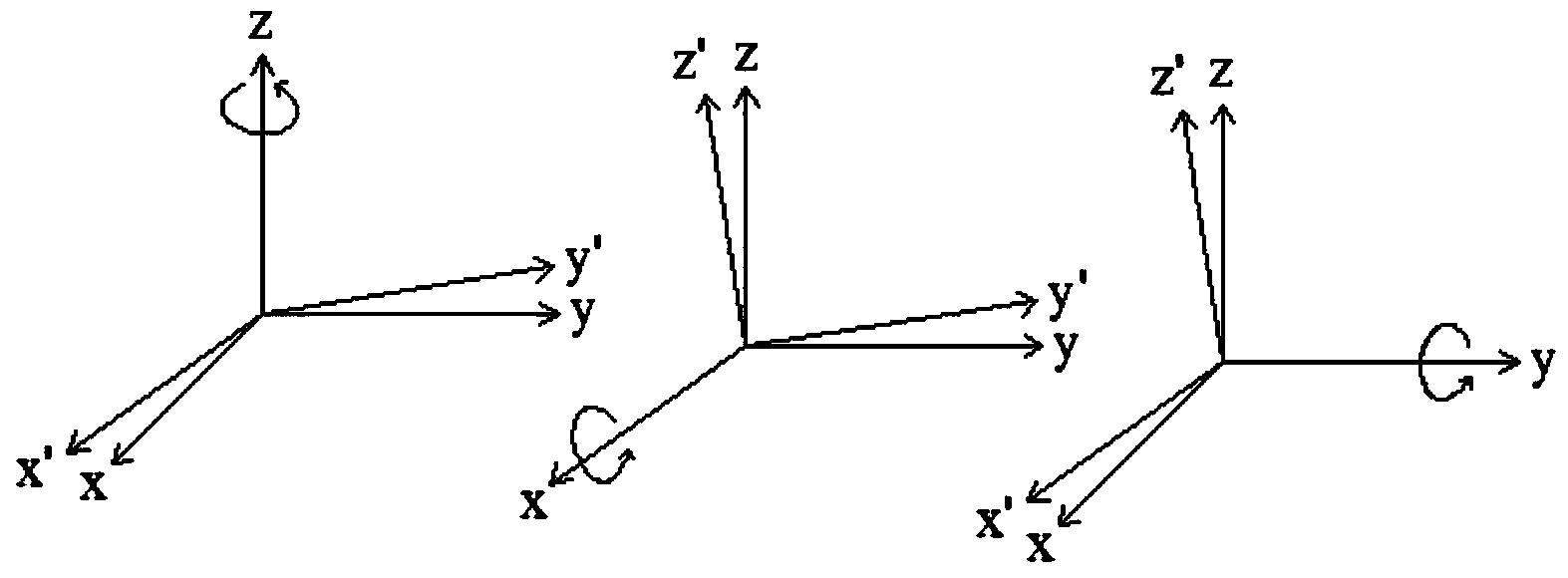
ActiveCN104142265AAddressing the disadvantages of damageForce measurementStrength propertiesExtended finite element methodMixed finite element method
The invention belongs to the technical field of detection and discloses a load measurement-based residual stress detection method. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a computer geometric model of a to-be-detected member, applying restrictions to the model by a finite element method, performing linear elasticity finite element static analysis after a load is applied to a loading point, reading stress value sigma'<b1> of an experimental measuring point, and adjusting the position of the loading point or increasing the load so as to enable the maximum value of the component of the stress value sigma'<b1> to be larger than 0.1MPa if the maximum value of the component of the stress value sigma'<b1> is less than 0.1MPa; applying restrictions and a load same as those of the computer geometric model to the to-be-detected member, and performing a strain experiment to obtain a stress value sigma<c1> of the experimental measuring point; and transforming the sigma'<b1> under local coordinates of the experimental measuring point to obtain sigma<b1>, and subtracting sigma<b1> from sigma<c1> to obtain residual stress value sigma<a1> of the member at the experimental measuring point. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the surface of the member is not damaged in the detection process, and the problem that a member is damaged due to a conventional mechanical residual stress method is solved. In addition, the method is convenient, simple and flexible to apply.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TIANCHONG VEHICLE LAMP GROUP
Joint shearing whole-process damage constitutive model for determining a yield point based on a stress difference
ActiveCN109885980AWell formedThe physical meaning of the parameter is clearSpecial data processing applicationsBreakage probabilityThin layer
The invention discloses a joint shearing whole-process damage constitutive model for determining a yield point based on a stress difference. The method comprises the steps that S1, setting a joint thin-layer microscopic unit body to be loaded and then enters a linear elasticity stage, the joint thin-layer microscopic unit body is an isotropic continuous medium, the microscopic unit body is instantaneously completed when being converted from a lossless state to a lossy state, and the process is irreversible; S2, defining an external load threshold F * based on a Weibull distribution function toobtain a damage probability density function of the mesoscopic unit body; S3, based on a rheological model mechanical element, simulating the load condition of a mesoscopic unit body by adopting thecombination of a spring and a friction plate to obtain a statistical damage constitutive model of the joints under the shearing action; S4, determining an external load threshold F * according to twoparts, namely damage and non-damage, of the rock and soil material after being subjected to load damage, and obtaining a damage evolution model and a joint shear deformation damage constitutive modelof the joint in the shear deformation process; S5, determining parameters m, u0 and us of the joint shear deformation damage constitutive model; and S6, verifying the correctness of the constitutive model.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
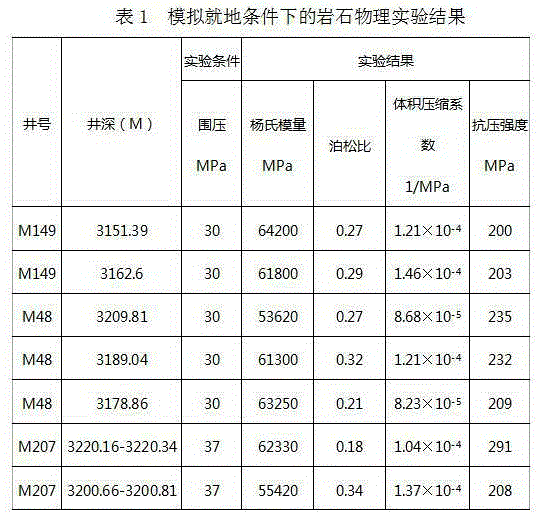
Method for measuring static elasticity modulus of porous metal material
InactiveCN102998181AAccurate measurementGood repeatabilityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMechanical solid deformation measurementsMicrometerMetallic materials
The invention discloses a method for measuring static elasticity modulus of a porous metal material. The method comprises the following steps of: measuring the flexibility of a simply supported beam span in different loads by utilizing a simply supported beam four-point bending testing device and adopting static step-by-step loading; subsequently establishing a relationship curve between the flexibility in the span and the loads, and calculating according to a curve slope in equations so as to obtain a single time measurement value of the static elasticity modulus of the porous metal material; and measuring for multiple times within a linear elasticity range, and taking the average value so as to obtain the static elasticity modulus of the porous metal material. The method not only has the advantages of measurement result accuracy, good repeatability, high reliability, simple equipment, low testing cost, simpleness in sample preparation and the like, but also can realize repeated loading (unloading) and multiple measurements within the linear elasticity range; the method can be carried out on a conventional material mechanics pure bending testing table, no strain gages are necessary to be adhered, and only a dialgauge (micrometer gauge) is additionally arranged; and the method is simple and easy to operate and is applicable to popularization and application.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF ENG SCI +1
Geometric multigrid on incomplete linear octrees for simulating deformable animated characters
A method and system for simulation of deformation of elastic materials are disclosed herein. A matrix-free geometric multigrid method utilizing a direct coarse grid discretization is presented for the solution of linear systems resulting from an octree discretization of the equations of corotational linear elasticity. The diagonal component of the stiffness matrix needed for the multigrid smoother is calculated without generating the stiffness matrix. The use of an incomplete linear octree data structure supports the efficient simulation of objects with complicated boundaries. Furthermore, the method is robust to large deformations, making it suitable for character skinning applications in computer animation.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Major diameter pile longitudinal vibration analysis method in axisymmetric radial inhomogeneous medium soil
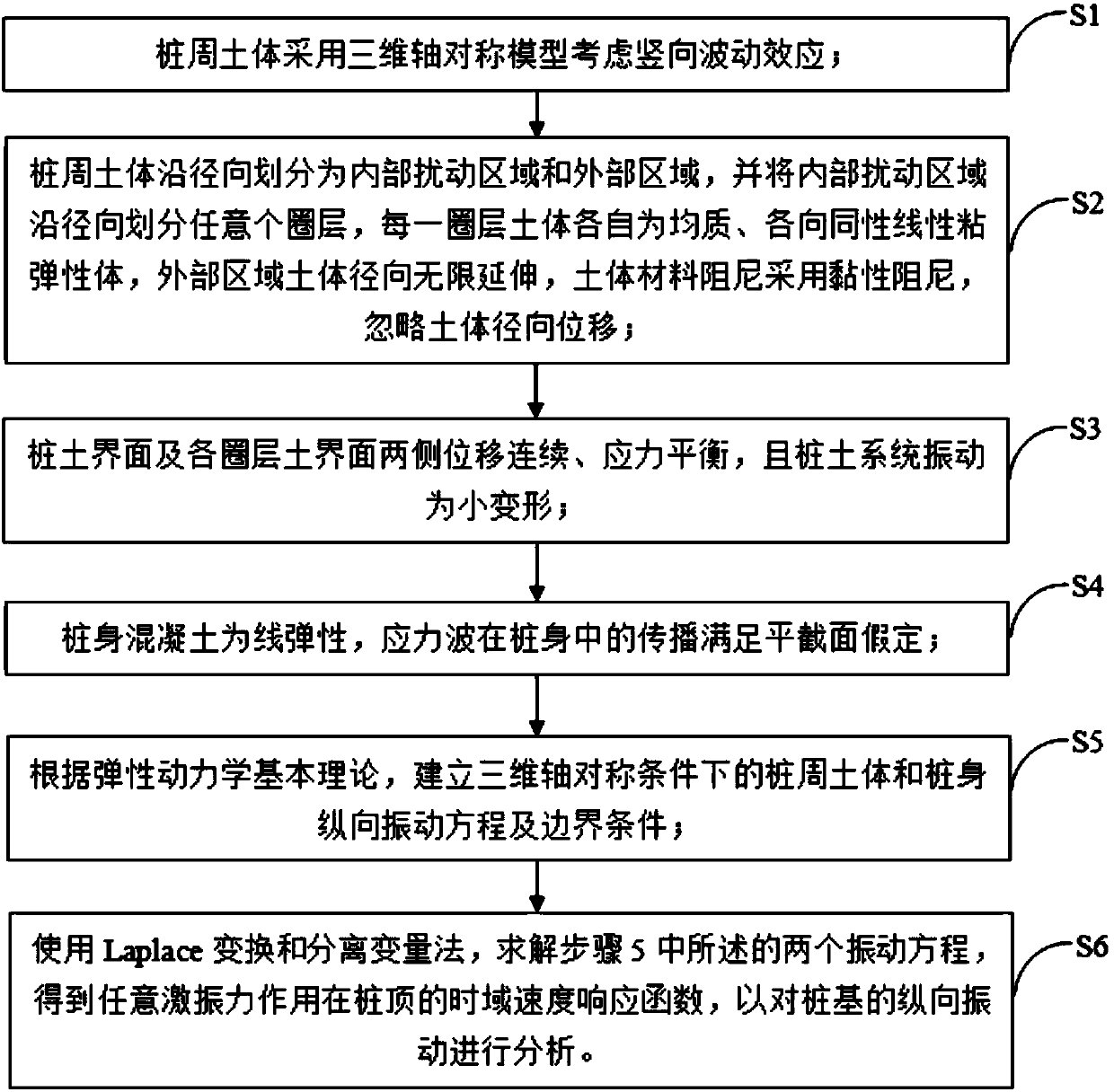
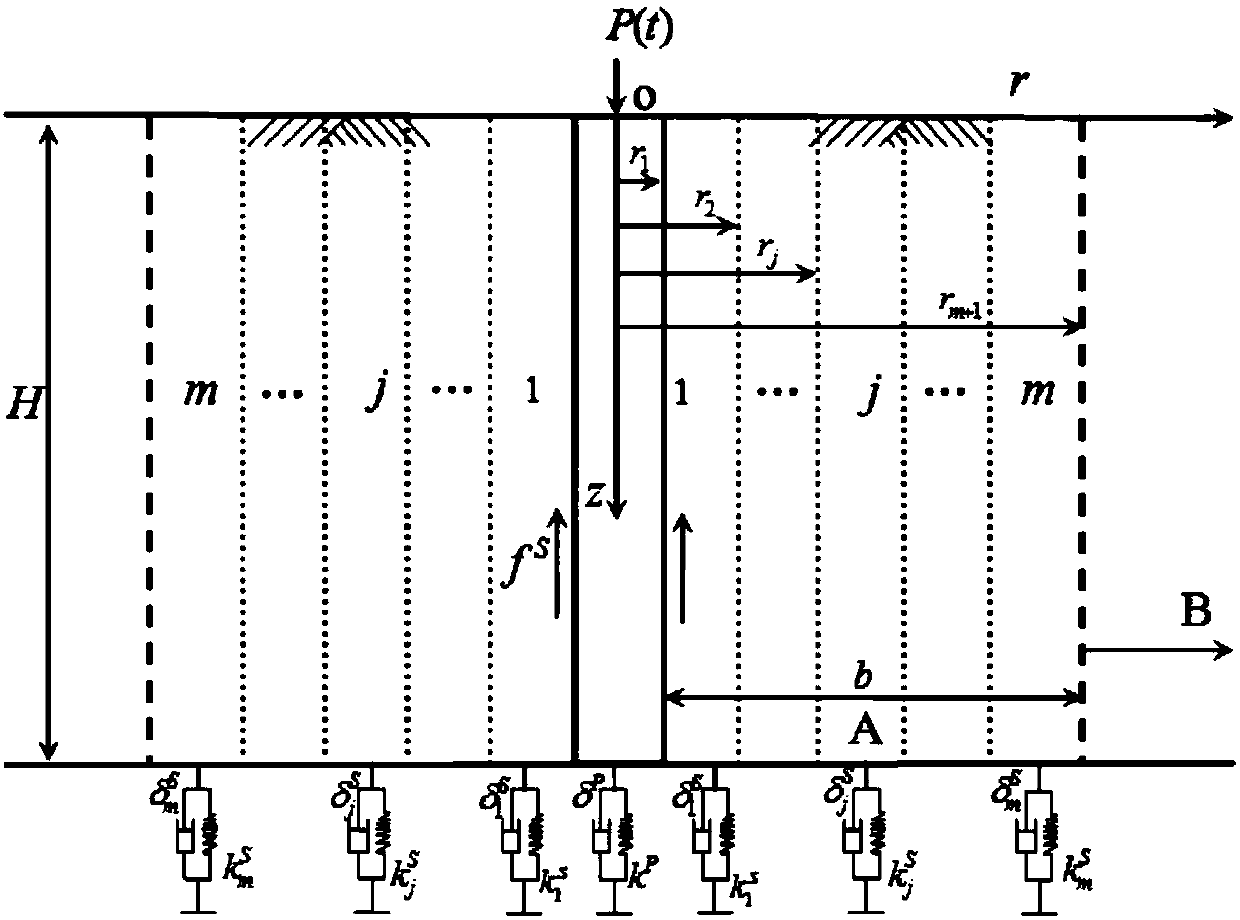
The invention provides a major diameter pile longitudinal vibration analysis method in axisymmetric radial inhomogeneous medium soil. The method comprises the following steps that soil body around pile adopts a three-dimensional axisymmetric model to consider a vertical fluctuation effect; the soil body around pile is divided into an internal disturbance area and an external area, the internal disturbance area is divided into random layers, each layer of the soil body is a respective homogeneous isotropy linear viscoelastic body, the soil body of the outer area infinitely extends in the axialdirection, and soil body material damping adopts viscous damping; constant displacement and balanced stress are achieved on pile-soil interfaces and two sides of each layer of soil interface and pile-soil interfaces, and pile-soil system vibration is small in deformation; pile body concretes are linear elasticity, and stress wave propagation in the pile body meets plane cross-section assumption; asoil body around pile and pile body longitudinal vibration function is constructed under the condition of constructing three-dimensional axial symmetry; Laplace conversion and a variable separation method are used for solving the vibration function, and a time domain speed responding function that any exciting force is applied to a pile top. The method is closer to a realistic model and can provide theoretical guidance and reference for pile foundation dynamic detection.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Static microrelay based on bistable compliant mechanism
InactiveCN101834097ASolve the main technical problems of practical applicationAchieve closureElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysCompliant mechanismAnti jamming
The invention relates to a static microrelay based on a bistable compliant mechanism, belonging to static relays used in a micro-electro mechanical system (MEMS). Bistable fully-compliant beams of the static microrelay adopt two compliant beams, wherein one end of the left compliant beam is fixed on a left insulated anchor point, and the other end of the left compliant beam is fixed on a member; one end of the right compliant beam is fixed on a right insulated anchor point, and the other end of the right compliant beam is also fixed on the member; under the voltage drive, a movable comb tooth drives the bistable fully-compliant beams to transversely move and rapidly overturn to a second stable position; a movable contact is in bridging connection with a left fixed contact and a right fixed contact which are fixed on a lower insulated anchor point so as to switch a circuit on; and the relay is rapidly skipped to return to a first stable position when an aelotropic driving voltage is applied. The static microrelay substitutes a traditional linear elasticity structure by adopting the bistable compliant mechanism so as to improve the response speed and the stable holding capacity and has the characteristics of simple mechanism, short-distance drive, low energy consumption and strong anti-jamming capacity.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Shape memory type high-elasticity activity nano-fiber stent and application thereof
InactiveCN105536055AImprove hydrophilicityConducive to loadPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationBiomechanicsHigh activity
The invention discloses a shape memory type high-elasticity activity nano-fiber stent and application thereof. The shape memory type high-elasticity activity nano-fiber stent is manufactured by introducing biological activity components (laminin, heparin, CD34+, VEGF and the like) into degradable linear elasticity polyester PCT with a shape memory effect through an electrostatic spinning technology; the molecular weight of the linear elasticity polyester PCT is 50000-400000, and the percentage composition of functionality caprolactone monomers, containing side cyclic ether substitutes, in a copolyester is 5-50%. The shape memory type high-elasticity activity nano-fiber stent is a high-activity nano-fiber stent with human body biomechanics elasticity, is a three-dimensional degradable tissue engineering stent which can provide an ideal biomechanics environment and an ideal biological activity microenvironment for cell growth, and is expected to be widely applied to regeneration and repair of elastic human body tissue such as blood vessels, cardiac muscles, nerves, skin, tendon, heart and the like.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
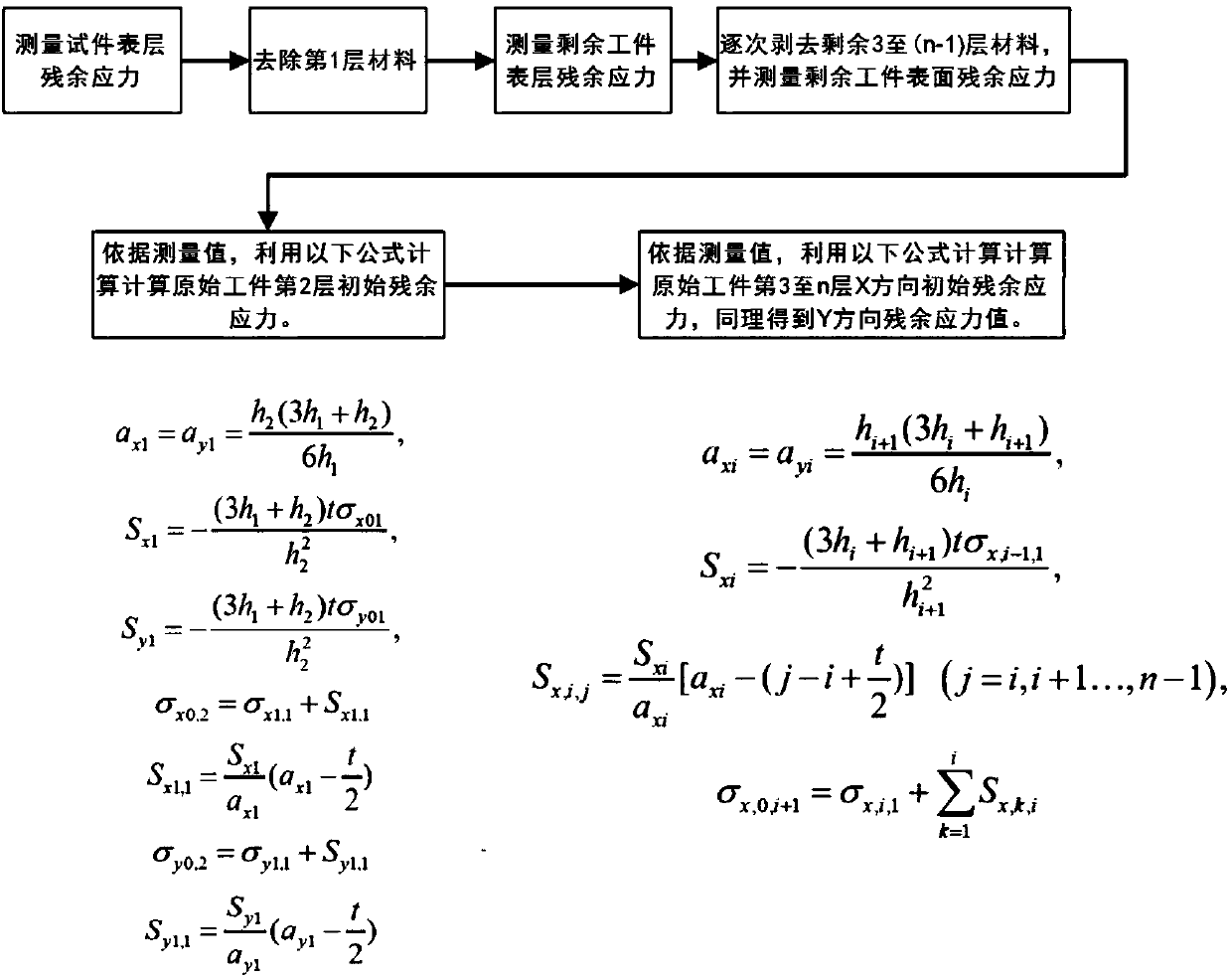
Correcting method for layer-peeling-method residual stress measurement value based on plate and shell theory
InactiveCN107729605AImprove correction accuracySimple procedureGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationShell theoryCalculation methods
The invention provides a correcting method for a layer-peeling-method residual stress measurement value based on the plate and shell theory. For increasing the measurement accuracy of the residual stress inside a material of the layer peeling method, based on the elastic mechanics and the plate and shell theory, a calculating method for releasing of the residual stress inside the material in the material removing process is deduced, and therefore the conversion relationship between surface residual stress peeled layer by layer and initial residual stress of a layer is established; under the condition that all kinds of surface residual stress after layer peeling are known, the initial residual stress of the layer can be reversely calculated and obtained.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Parallel type flexible wrist mechanism
ActiveCN109048987ARealize proactive adjustmentSolution to short lifeProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsClosed loopEngineering
The invention relates to a parallel type flexible wrist mechanism. The parallel type flexible wrist mechanism comprises a fixed platform, a moving platform and three branched chains between the fixedplatform and the moving platform. The fixed platform comprises an upper sub-platform, a lower sub-platform and three sets of guide rails fixedly connected between the two sub-platforms. The upper sub-platform and the lower sub-platform are parallel to each other and the central axes of the upper sub-platform and the lower sub-platform coincide. The three sets of guide rails are distributed in an axial symmetry mode about the central axis of the upper sub-platform. The three branched chains are identical in structure, include linear elasticity bodies, sliding blocks, middle rod pieces and motion pairs, and are correspondingly connected with the fixed platform and the moving platform to form a spatial parallel closed-loop mechanism. The sliding blocks are mounted on the guide rails between the two fixed sub-platforms, and can only move along the guide rails. The linear elastic bodies are installed between the sliding blocks and the fixed platform. The three branched chains of the parallel mechanism are matched with each other to realize the error compensation of a position or an angle of an end effector.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
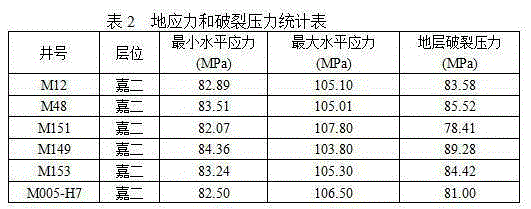
Method for predicting formation fracturing pressure by utilizing imaging logging information
ActiveCN105243210ABurst pressure is not easyPrediction is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsMechanical modelsHydraulic fracturing
The present invention discloses a method for predicting a formation fracturing pressure by utilizing imaging logging information. The method comprises the following steps of: a, determining a crustal stress direction of a research block by utilizing the imaging logging information; b, according to the crustal stress direction, determining a boundary of a finite element simulation geometric model; c, establishing a finite element simulation mechanical model by adopting a linear elastic mechanics theory so as to obtain the maximum horizontal stress and the minimum horizontal stress of a formation of each well point in the research block; and d, according to a Haimson formula, carrying out calculation to obtain the formation fracturing pressure of each well point. By using the method, the technical difficult problems of higher expenditure, difficulty in implementation in the deep formation and difficulty in measuring the formation fracturing pressure of a hydraulic fracturing measurement method in the prior art are solved; and relative to array acoustic logging, a brand new method for predicting the fracturing pressure by utilizing the imaging logging information is provided.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Near-beta titanium alloy with low elastic modulus and high strength and preparation method of near-beta titanium alloy
InactiveCN103060609AImproved cold working propertiesLow work hardening rateMedical equipmentNonlinear deformation
The invention provides a Ti-Nb-Mo-Sn near-beta titanium alloy with low elastic modulus and high strength. The alloy comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 15-35% of niobium, 1-8% of molybdenum, 1-8% of stannum and 0-1.2% of titanium dioxide powder. The Ti-Nb-Mo-Sn near-beta titanium alloy with low elastic modulus and high strength has the beneficial effects that the systemic alloy has good cold machining performance and a low machining cementation index and can coldly deform in a large scale by using cold machining processes such as cold rolling, cold wire drawing and the like; the systemic alloy has the characteristic of nonlinear deformation after being thermally machined or coldly machined and has large restorable elastic strain, low initial modulus and average modulus and high strength; the systemic alloy has low elastic modulus, high yield strength and breaking strength and high linear elasticity after being smelted, thermally machined or coldly machined and thermally treated; and the systemic alloy can be used for preparing medical equipment, physical training equipment and industrial equipment, and can be used for biomedical applications such as artificial bones, bone joints, implanted tooth roots, bony plates and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Deep sea steel catenary vertical pipe touchdown point power response analyzing method
InactiveCN103902754AAdd nonlinear stiffness modelImprove suction capacitySpecial data processing applicationsSuction forceEngineering
The invention relates to a deep sea steel catenary vertical pipe touchdown point power response analyzing method. The method includes: simulating a steel catenary vertical pipe a large-deflection camber beam model, using the movement of a floating platform as the top end boundary condition of the vertical pipe, using a P-y curve method to numerically simulate the mutual effect, including linear elasticity rigidity when a seabed does not deform, the suction force effect when the vertical pipe leaves the seabed and nonlinear rigidity in a reciprocation effect, of the steel catenary vertical pipe and the seabed, building the mutual effect model of the steel catenary vertical pipe and the seabed, combining the mutual effect model with the movement equation of the floating platform and the simulating module of the steel catenary vertical pipe, and applying the combined model to the steel catenary vertical pipe touchdown point power response analyzing. The method has the advantages the existing methods simulating the seabed into a linear elastic spring or a rigid seabed are modified, the mutual effect of the steel catenary vertical pipe and the seabed can be accurately simulated, and calculation precision of steel catenary vertical pipe touchdown point power response analyzing is increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
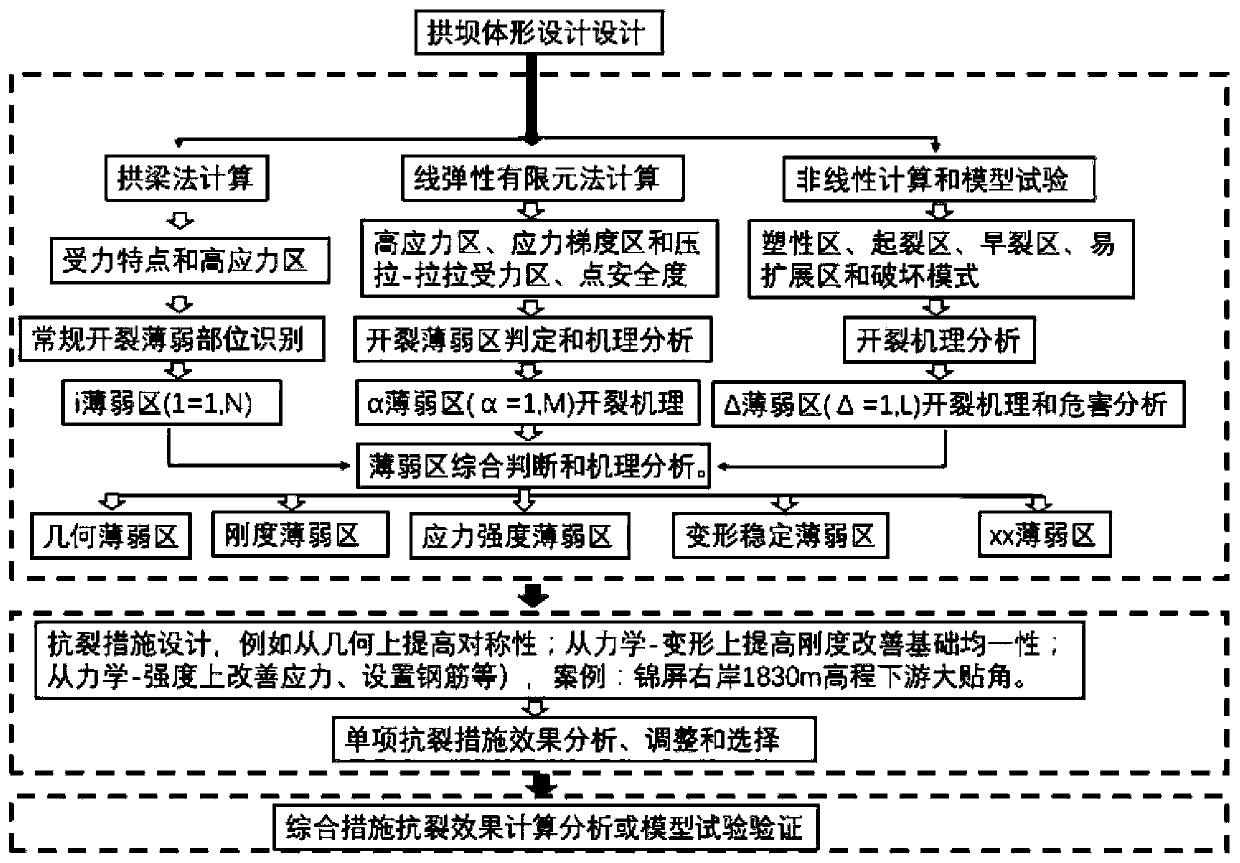
Complex foundation extra-high arch dam overall crack resistance design method
InactiveCN110263355AFind the crack-resistantPinpoint the weak linkGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationBody shapeCrack resistance
The invention discloses a complex foundation extra-high arch dam overall crack resistance design method, relates to the technical field of hydropower station arch dam design, and provides the complex foundation extra-high arch dam overall crack resistance design method. The method comprises the following steps that A, arch dam body shape design is conducted; B, the arch dam is analyzed by adopting an arch beam method, a linear elasticity finite element method, a nonlinear finite element method and a geomechanical model test method; numerical calculation and physical test results are comprehensively compared, and arch dam deformation, stress characteristics and the overall damage process are analyzed, judged and grasped, so that crack initiation points, crack weak links and reinforcement key objects and parts of arch dam damage are found out; the comprehensive influence of various factors influencing arch dam cracking on arch dam cracking is systematically analyzed; C, arch dam anti-cracking measures are designed in a targeted manner according to different cracking mechanisms of the anti-cracking weak area and the controllable cracking influence factors of the anti-cracking weak area; and D, the effect of the anti-cracking measure is evaluated by adopting a three-dimensional finite element equal numerical analysis method.
Owner:POWERCHINA CHENGDU ENG
Elastic-plastic buckling bearing capacity calculation method
InactiveCN110287637AThe calculation method is reasonableThe calculation method is feasibleGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsElastic analysisElastic plastic
The invention discloses an elastic-plastic buckling bearing capacity calculation method which comprises the following steps: S1, carrying out linear elasticity analysis on a truss structure under a stress load condition, and determining the most unfavorable rod piece of the truss structure under the load condition; S2, calculating and acquiring the linear elastic buckling bearing capacity and the elastic-plastic buckling bearing capacity of the most unfavorable rod piece of the truss structure; S3, calculating the elastic-plastic buckling bearing capacity of the truss structure according to the elastic-plastic buckling bearing capacity of the most unfavorable rod piece of the truss structure; S4, respectively calculating the elastic-plastic buckling bearing capacity of the truss structure by adopting a characteristic value buckling analysis method and a riks analysis method in finite element software Abaqus, comparing and analyzing the obtained elastic-plastic buckling bearing capacity result of the truss structure and the calculated elastic-plastic buckling bearing capacity result of the truss structure so as to verify the correctness and feasibility of the elastic-plastic buckling bearing capacity of the truss structure.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for calculating triangular resistance loads of shield tunnel model structure
InactiveCN105787193ASafe and reliable structural designAccurate Structural Internal ForceGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsCorrelation coefficientEngineering
The invention discloses a method for calculating triangular resistance loads of a shield tunnel model structure.The method comprises the steps that S1, due to the fact that a pipe sheet structure calculating model belongs to a small-deformation linear elasticity problem, resistance displacement y at the horizontal diameter position of a tunnel ring can be regarded as superposition of horizontal deformation caused by loads except for triangular deformation and horizontal deformation caused by the triangular resistance loads, y is set to be equal to U(q1, qG, e1, e2, g, qw)-U(ky), all the parameter are substituted into the formula, and a correlation coefficient determined by back arch soil pressure qG is 0.3145; S2, based on correct arc-shaped back arch soil pressure derivation, the coefficient 0.3145 is substituted to the formula, and the set resistance displacement (see the formula in the description) at the horizontal diameter position of the tunnel ring can be obtained.Based on correct arc-shaped back arch soil pressure, the precise triangular resistance displacement calculating formula is derived, a basis is provided for correct calculation of the internal force of the shield tunnel model structure, and the technical problem that an existing triangular resistance displacement calculating formula does not conform to the tunnel back arch soil pressure shape is solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI URBAN CONSTR DESIGN RES INST GRP CO LTD
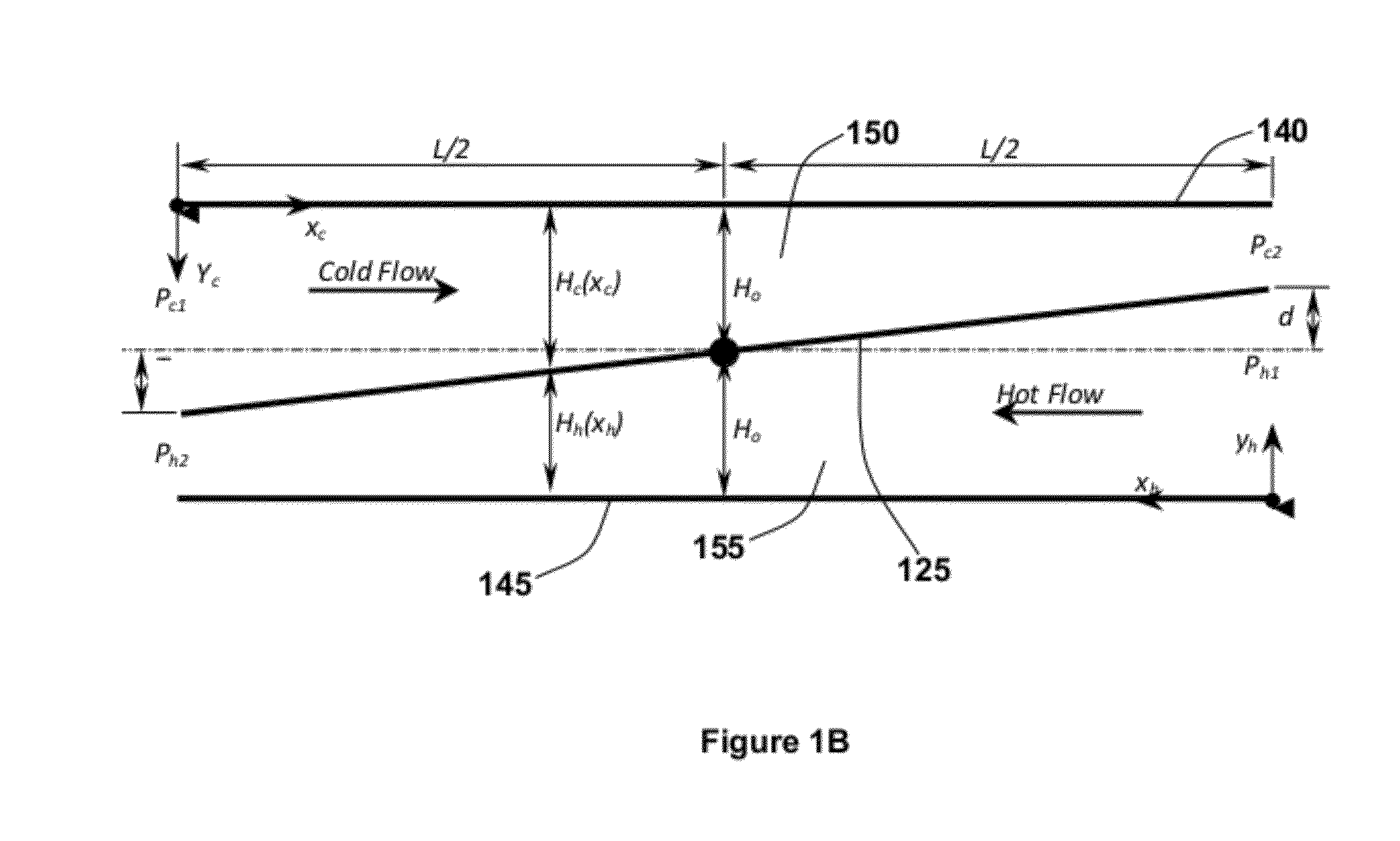
Cooling augmentation using microchannels with rotatable separating plates
InactiveUS20120168128A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringEnergy equation
A DL-microchannel cooling device with rotatable separating plate is disclosed. The separating plate is supported via anti-leaking flexible seals. The only allowable motion for that plate is the rotational motion about a pivot rod. The rod is taken to be aligned along the microchannel center line normal to its sides boundaries. The device can be configured as a flexible microheat exchanger and a heated DL-flexible microchannel device. The theory of linear elasticity applied to flexible seals supporting the separating plate is used to relate the moment of the pressure forces on that plate to its rotational angle. The energy equations for both fluids flows are solved numerically and analytically under special conditions. As such, the effectiveness of the flexible microheat exchanger and other performance indicators for flexible microheat exchanger and heated DL-flexible microchannel devices are calculated. The advantages of the proposed device in cooling attributes over the performance of the DL-rigid microchannel device is examined.
Owner:KAMBIX INNOVATIONS
Method for determining support radius and tool quantity of full face rock tunnel boring machine cutter head
ActiveCN106354916AReduce warpageReduce vibrationGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsThrust bearingRock tunnel
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
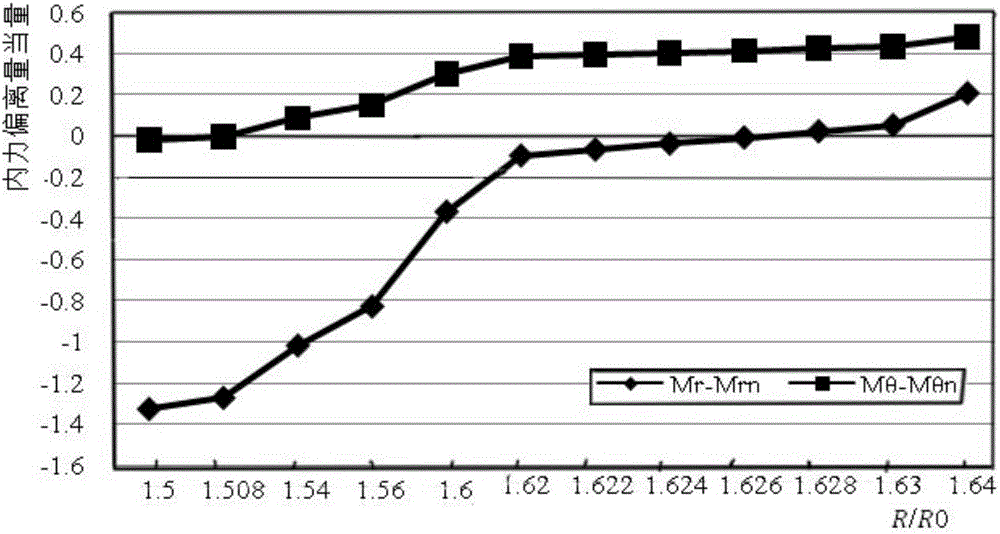
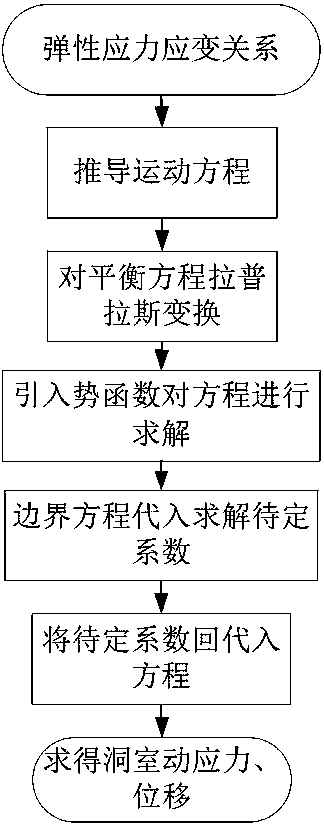
Method for calculating dynamic stress of circular cavern under directional blasting loads
InactiveCN108197402AComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsGoverning equationElastance
The invention relates to a method for calculating dynamic stress of a circular cavern under directional blasting loads. The method includes the following steps of simplifying a cylindrical cavern intoa plane strain problem, establishing a polar coordinate system, and establishing a relationship between the strain and stress of the circular cavern according to a classical elastic mechanics theory;re-deriving a motion equation to enable the loads to change along with theta; introducing a displacement potential function to solve a governing equation, and obtaining the relationship among the potential function and the dynamic stress and displacement; using boundary conditions for solving undetermined coefficients, and substituting the undetermined coefficients into a dynamic stress equationto determine the dynamic stress of the circular cavern under the directional blasting loads.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
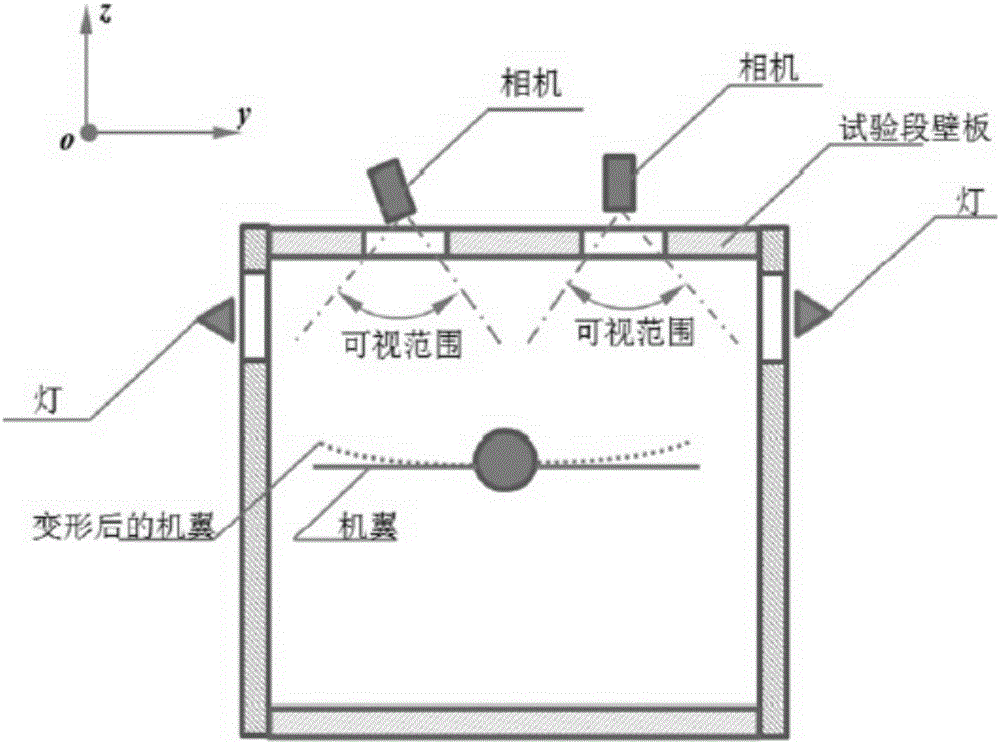
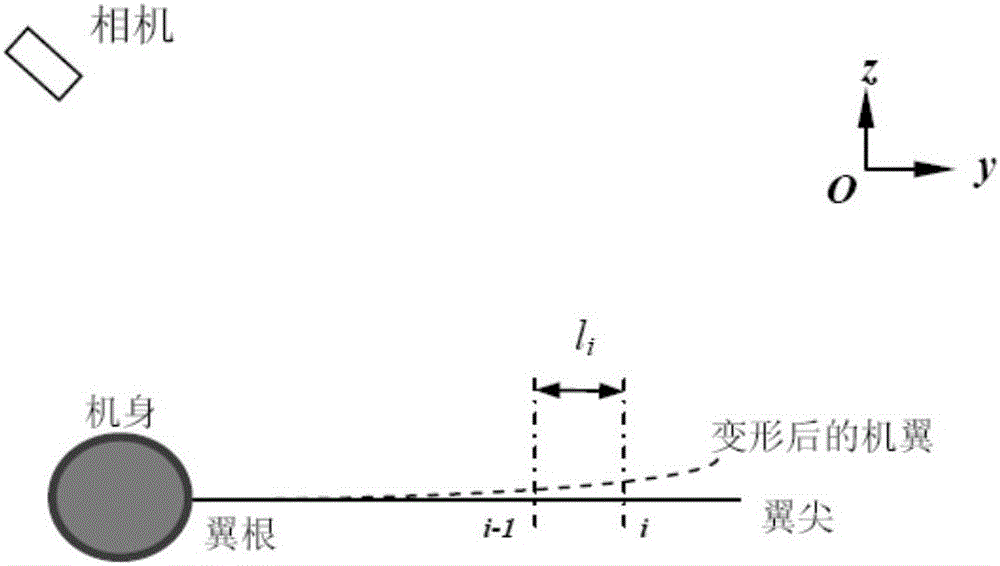
Monocular video high precision measuring method for wing wind tunnel test model elastic deformation
ActiveCN106323587AGuaranteed accuracyReduce hardware costsAerodynamic testingObservational errorMeasurement device
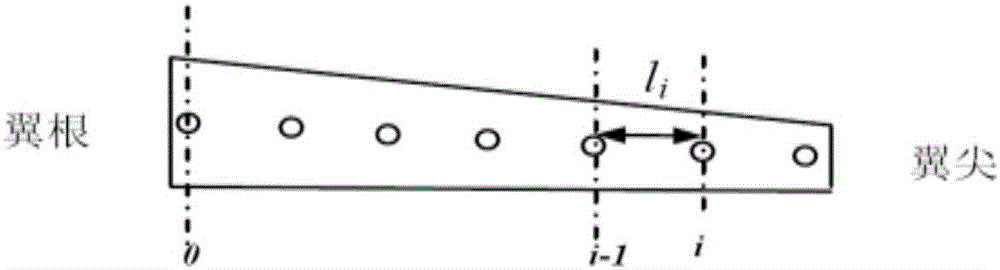
The invention discloses a monocular video high precision measuring method for wing wind tunnel test model elastic deformation. Based on a fact that relative deformation of two adjacent cross sections of a wing wind tunnel test model is small linear elasticity deformation, coordinate figures of corners and deformation mark points Y of all cross sections are orderly calculated from a wing root according to a superposition principle; a conventional monocular video measuring method is adopted, the coordinate figures of the deformation mark points Y are brought in a collinearity equation, and deformation data of the mark points on all the cross sections can be orderly obtained. Via the monocular video high precision measuring method, monocular video measurement errors of wing wind tunnel test model elastic deformation can be greatly reduced, only one camera needs to be used, multi-view video measurement precision can be obtained, hardware cost of a measurement device can be lowered, tedious homonymous point matching work of multi-view video measurement can be prevented, the monocular video high precision measuring method is particularly suitable for an environment where camera installation positions are limited, and the monocular video high precision measuring method has great engineering application prospects.
Owner:INST OF HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS OF CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
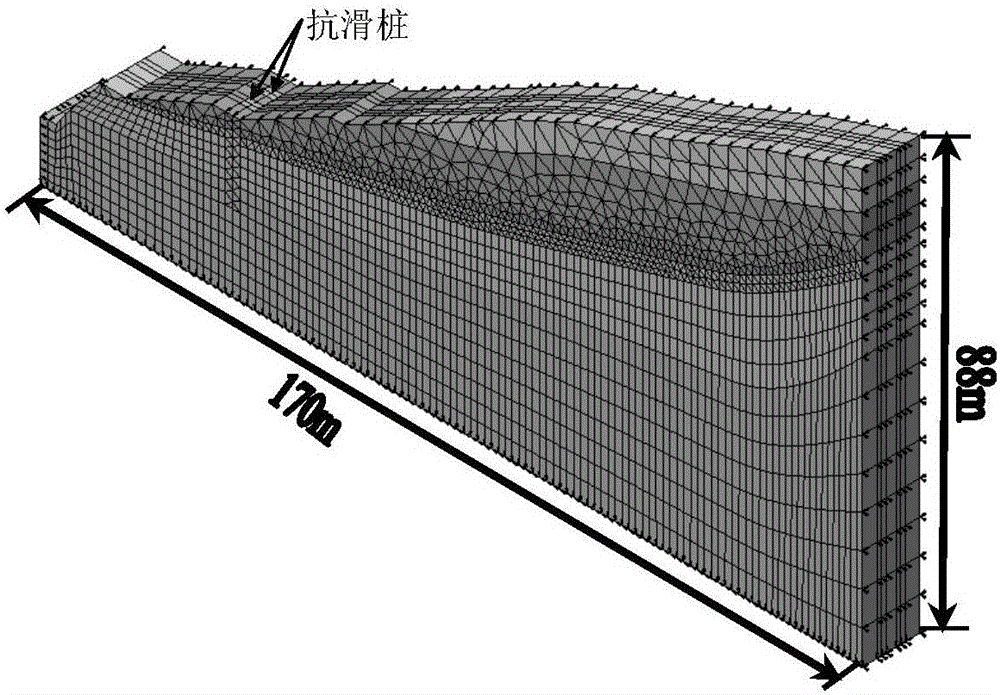
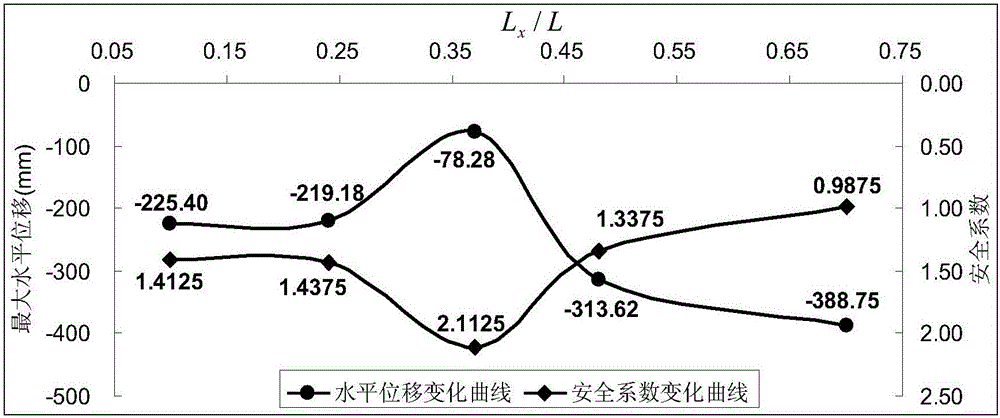
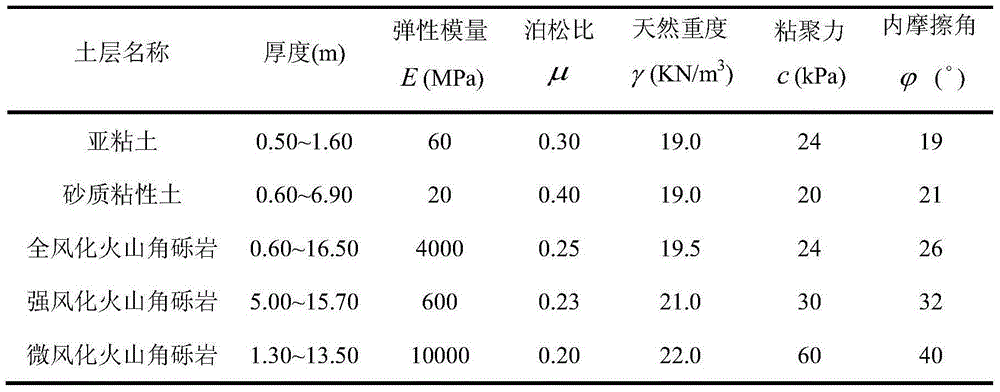
Three-dimensional side slope model establishing method for study on anti-slide pile position
The present invention discloses a three-dimensional side slope model establishing method for study on an anti-slide pile position. The method comprises: arranging two anti-slide piles symmetrically; arranging a row of prestressed anchor cables in the top center of each anti-slide pile; arranging four rows of anchor cables on a middle-layer slide surface, wherein a short edge is a force-receiving surface; implanting a two-dimensional massless and zero-thickness beam unit coupled with the entity anti-slide pile, and arranging three-dimensional Goodman contact units between the pile and soil and on a weak layer and a potential slide surface layer, wherein the anti-slide pile adopts C25 concrete; and adopting a mole-coulomb constitutive model when establishing an entity side slope and the entity anti-slide pile, and simulating both a one-dimensional truss and an implantable truss by using a linear elasticity constitutive model. The beneficial effects of the present invention are that the three-dimensional side slope model establishing method for study on the anti-slide pile position is provided and the best burying point of the anti-slide piles in a real project is obtained by combination of mathematical modeling and reality.
Owner:XUCHANG UNIV
Deformation analysis method of expanded-base uplift pile group considering reinforcement effect
InactiveCN111460547ALarge uplift displacement reduction rateImproved pull-out load bearing propertiesGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationClassical mechanicsShearing deformation
The invention discloses a deformation analysis method of an expanded-base uplift pile group considering a reinforcement effect. The analysis method comprises the following steps: based on an elastic mechanics theory, a pile foundation load transfer principle and a thin-wall concentric cylinder shear deformation model, deducing a deformation nonlinear analytical solution expression of the expanded-base uplift pile group considering a reinforcement effect, and giving out specific calculation steps. The accuracy and effectiveness of the method are proved by comparing the calculation result of theanalytical solution with the suite of the measured data and the finite element simulation result. Calculation results show that the influence of the soil body performance, the pile end expanding bodyand the pile length on the deformation of the reinforced effect expanded-base uplift pile group is remarkable. Along with the increase of the elasticity modulus of the soil body, the increase of thepile end expanding body and the increase of the pile length, the uplift displacement reduction rate of the pile group is increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Nonlinear aeroelasticity dynamic response analysis method based on structure reduced-order model
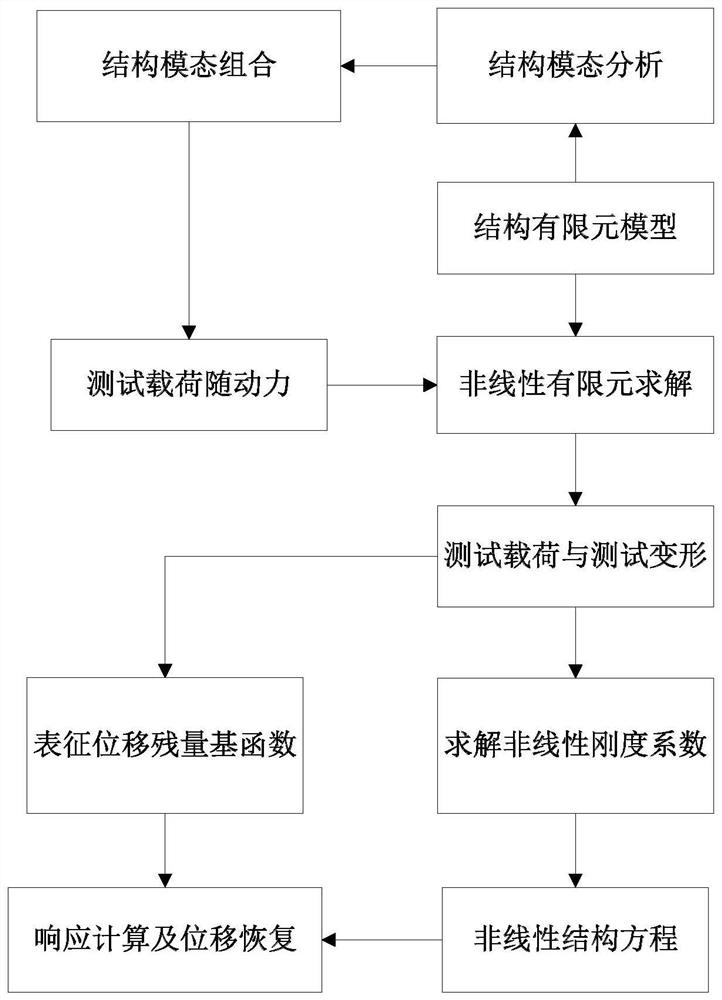
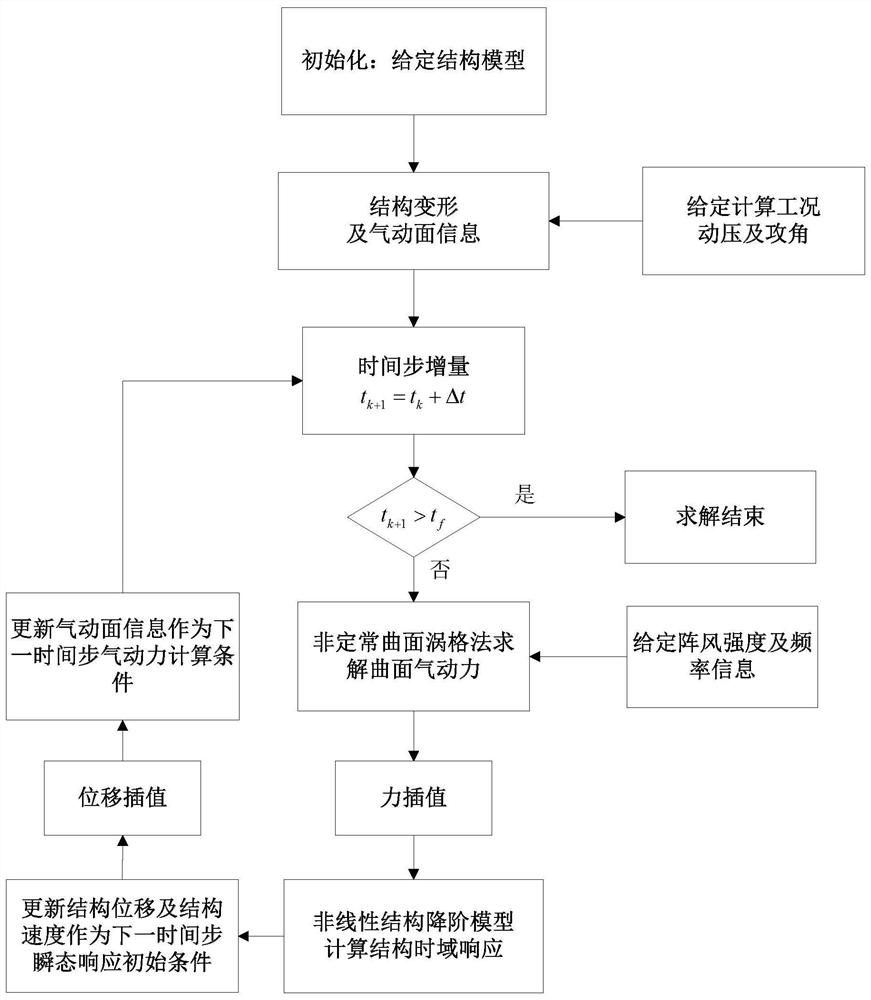
ActiveCN112580241AReduce consumptionImprove computing efficiencyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationStructural deformationStructural dynamics
The invention belongs to the field of structural dynamics and aeroelastic mechanics analysis, and particularly relates to a nonlinear aeroelastic dynamic response analysis method based on a structuralreduced-order model. The method includes: solving a structural nonlinear stiffness coefficient in a given form by adopting a method for carrying out regression analysis on an input test load and corresponding structural deformation, constructing a large-deformation structural kinetic equation by utilizing the nonlinear stiffness coefficient, and on the basis, constructing the test load by utilizing a mode of multiplying a proportionality coefficient by a mode combination; accurately recovering the spanwise displacement of the wing by constructing a displacement residual basis function; and finally, constructing a geometric nonlinear aeroelastic gust response solving process in combination with a kinetic equation given by the structure reduced-order model and an unsteady curved surface vortex lattice method. The method gives consideration to the solving precision, the calculation efficiency and the applicability of a complex model, and can be applied to the analysis and calculation ofthe geometrical nonlinear aeroelastic gust response of aerospace aircrafts.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
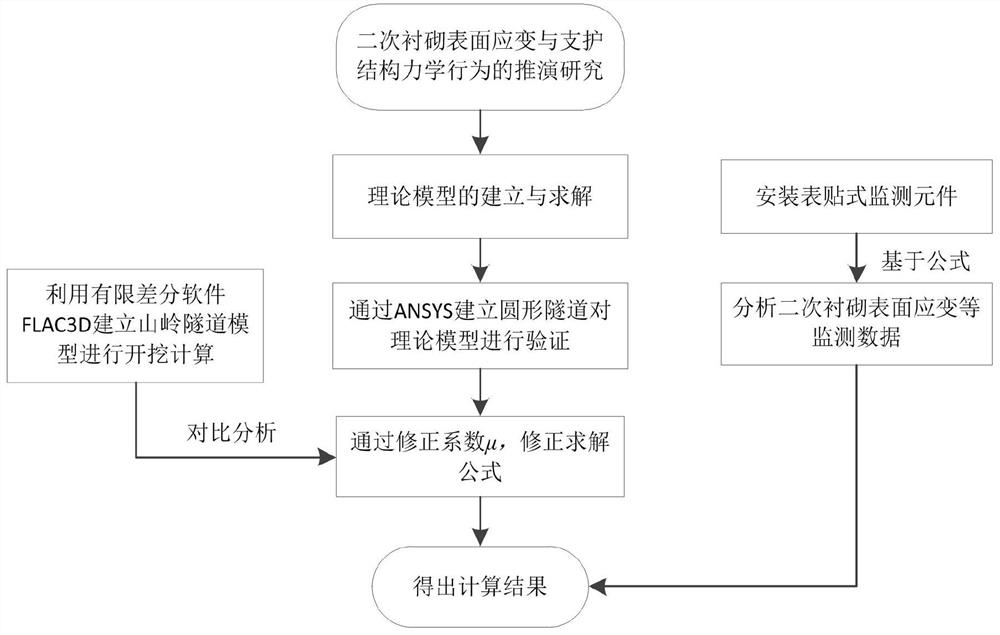
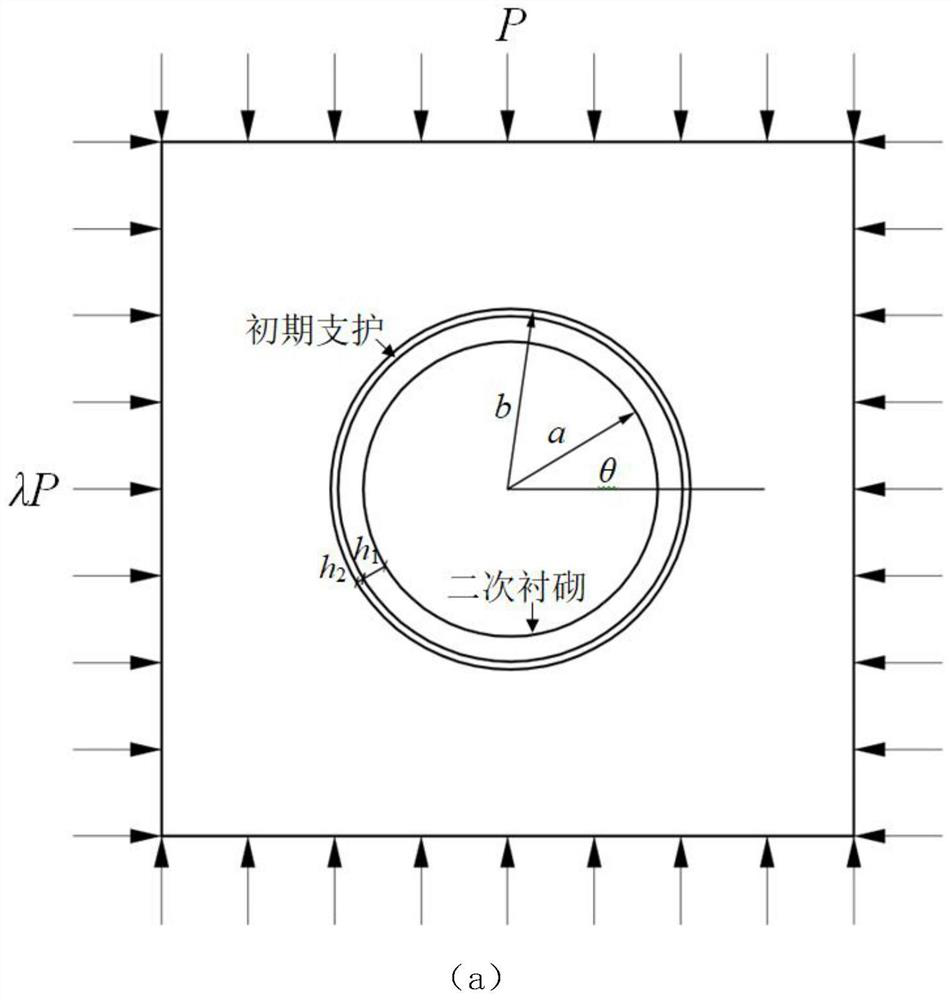
Tunnel mechanical behavior analysis method based on tunnel secondary lining surface strain
The invention discloses a tunnel mechanical behavior analysis method based on tunnel secondary lining surface strain. The method uses a homogeneous ring tunnel model in an elastic mechanics theory, utilizes the secondary lining surface strain at the positions of a tunnel vault, a tunnel shoulder, a tunnel haunch and a tunnel springing, a stress equation set of a simplified double-layer circular ring is deduced based on a geometric equation, a compatibility equation and a stress balance equation, and an MATLAB solving program is written to obtain a stress value inside the double-layer circular ring, and therefore the axial force and the bending moment of the tunnel secondary lining are derived. Finite element software ANSYS is utilized to establish an entity unit load-structure model of the tunnel, numerical calculation under elastic constitutive is carried out, and a structure correction coefficient is determined through comparison with actual engineering. The problems that a traditional sensor is high in loss rate in the long-term operation process of a tunnel, and tunnel full-life mechanical detection cannot be carried out are solved. The method is of great significance in reflecting the long-term mechanical properties of the tunnel by using the secondary lining surface strain and giving full play to the advantages of the fiber grating sensor.
Owner:四川藏区高速公路有限责任公司 +1
Method for predicting fractured reservoir stress evolution based on fractured continuum model
ActiveCN110750930AReliable referenceReliable GuidanceDesign optimisation/simulationPhysical modelClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a method for predicting fractured reservoir stress evolution based on a fractured continuum model, and the method comprises the following steps: building a simulated physical model based on geological parameters, construction parameters, boundary conditions and initial conditions, and determining basic parameters; establishing a natural fracture random distribution model, and calculating permeability of grids corresponding to natural fractures; establishing a stress balance equation and a continuity equation based on elastic mechanics, a finite element method and a seepage theory, and substituting the permeability into the stress balance equation and the continuity equation; and establishing a non-planar hydraulic fracture, a discrete stress balance equation and a continuous seepage equation based on a finite element method to obtain a discrete form of the discrete equation and the continuous equation, and calculating the distribution state of reservoir stress corresponding to each age limit. According to the method, stress prediction can be carried out in the later period of fractured reservoir development, a reliable guiding effect is provided for repeatedfracturing design and infilled well design, and development of oil and gas development theoretical research can be promoted.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Wide-temperature-range high-strength linear-elasticity metallic nano material and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a wide-temperature-range high-strength linear-elasticity metallic nano material and a preparation method and application thereof. The metallic nano material is a wire material, wherein the metallic nano material is composed of, in total, an element Ti and an element Ni with the atomic ratio of Ti to Ni being (0.8:1)-(0.9:1), and the sum of atomic percentages of the Ti and Ni is 100%; and the metallic nano material is a martensite NiTi nano material composed of NiTi nanocrystals which are uniformly distributed, and the martensite NiTi nanocrystals are formed by martensite variants with preferred orientation. The operating temperature range for the nano material provided by the invention is approximately minus 197 DEG C-50 DEG C, and the material can keep linear elasticity within the temperature range and has the yield strength of 1.2-1.9 GPa and the linear elasticity strain limit of 4.5%-5.4%.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Multilayered printed circuit board plated-through hole stress-strain model establishing method based on girder construction
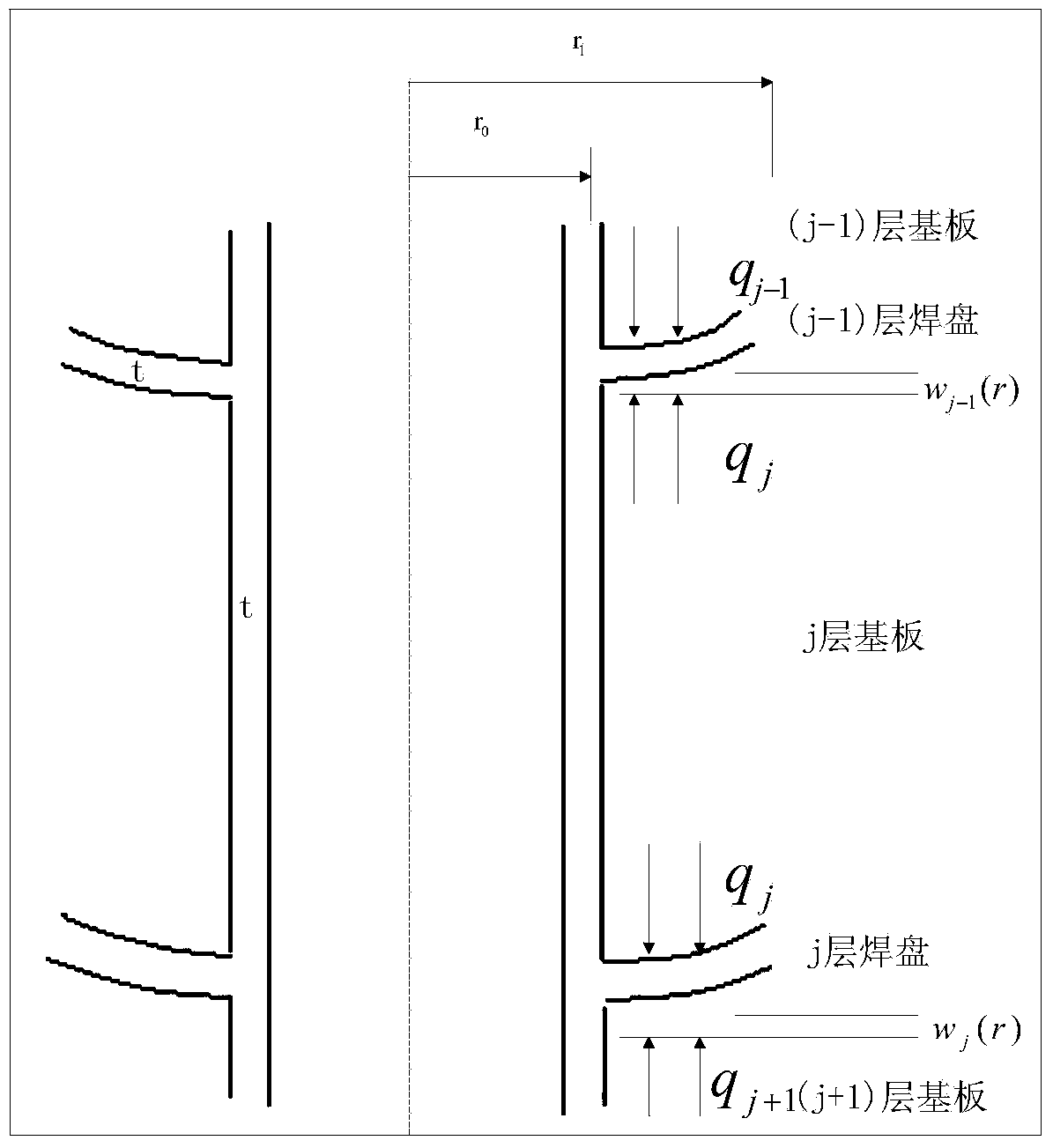
ActiveCN103778293ARapid Assessment of LifespanPossess engineering application valueElectrical connection printed elementsSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringPrinted circuit board
The invention provides a multilayered printed circuit board plated-through hole stress-strain model establishing method based on girder construction. The multilayered printed circuit board type plated-through-hole stress-strain model establishing method based on the girder construction comprises the following steps: 1, simplifying a multilayered printed circuit board plated-through-hole to be the girder construction in axial symmetry, and establishing assumed conditions based on the girder construction; 2, regarding a bonding plate structure as an annular round plate to be uniformly loaded, and setting boundary conditions of inner-diameter simply support and external-diameter free of a bonding plate; 3, writing mechanical ordinary differential equations of the bonding plate based on assumption that the bonding plate is uniformly loaded, and solving a general solution expression of a deflection; 4, determining four coefficients to be determined in the general solution expression by using the boundary conditions, and listing relationship of the load, and the deflection, a bearing force and a thermal strain by combining displacement continuous conditions; 5, determining radial, annular and axial stresses at the position with the maximum stress by combining the boundary conditions and calculating an equivalent stress by using a Mises equivalent stress computational formula; 6, giving a strain analysis expression within a range of elasticity and plasticity of a multilayered printed circuit board plated-through hole according to linear elasticity and linear plasticity stress-strain relationship of a coating material.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
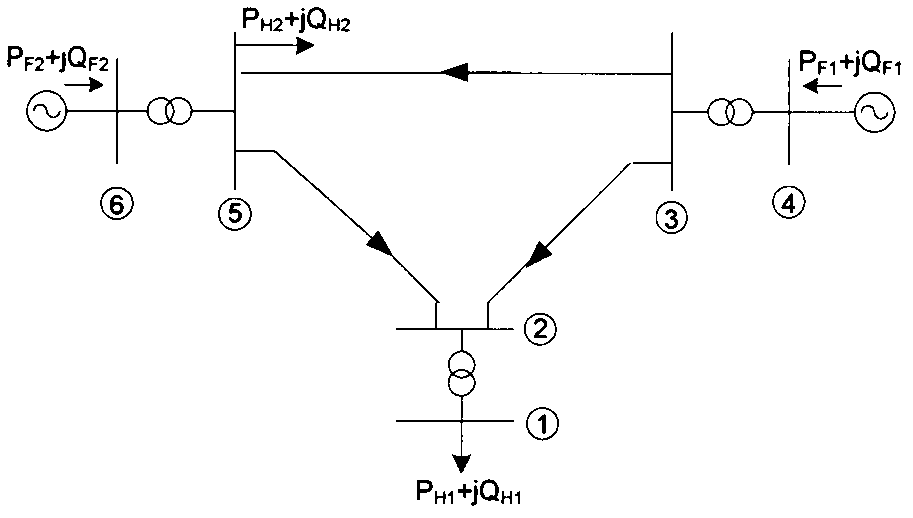
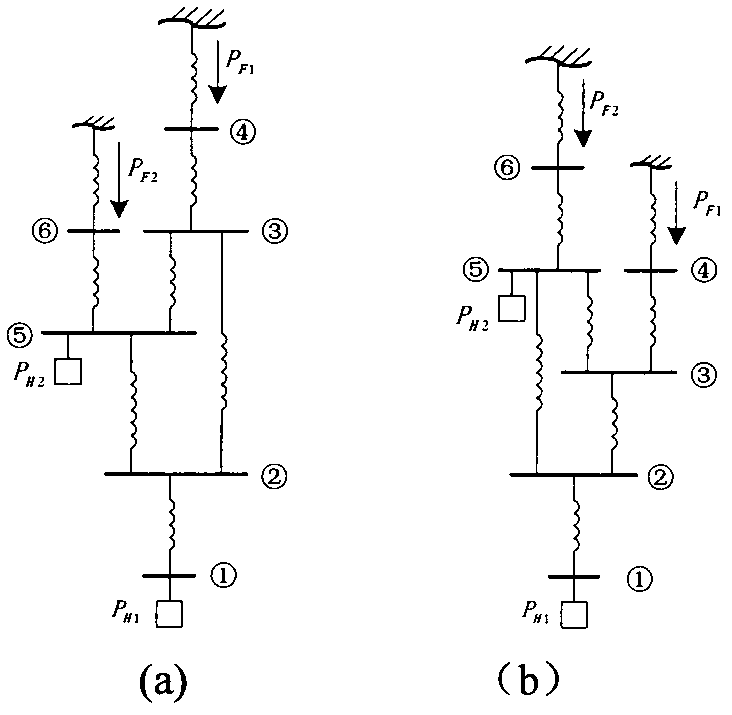
Power grid-elastic mechanics network topology mapping method
ActiveCN102227084BDisplay power angle state changesImprove predictive abilityAc network circuit arrangementsElastic networkWide area
Traditional power grid topology can only reflect connections of geography position nodes on two-dimensional plane and can not dynamically show relations between quantities of state. By using the power grid-elastic mechanics network topology mapping method of the invention, the power grid can be mapped to a three-dimensional expansion arrangement and longitudinal bearing elasticity network, which maintains an original topology connection state of the power grid and shows a physical property of power angle. An actual measurement quantity of state of wide-area measurement system (WAMS) is put into the elasticity network model mapped by the method of the invention. Power grid power angle state changes can be visually showed through an elasticity network deformation so as to get rid of dependence on element parameter accuracy. Anticipation ability of the power grid state changes can be raised. The invention possesses practical significance for realizing power grid visualization intelligence analysis and control.
Owner:竺炜
Construction method for layered pouring type concrete beams on soft soil foundation
ActiveCN111560856AImprove stabilityReduce construction costsBridge erection/assemblyBridge materialsConcrete beamsArchitectural engineering
The invention relates to the field of bridge and culvert engineering in the transportation industry, and particularly discloses a construction method for layered pouring type concrete beams on a softsoil foundation. The construction method is based on the elastic mechanics theory, the stress function of the first-layer concrete beam in the second-layer concrete pouring process is derived, and anelastic coefficient of a composite foundation under the stress safety condition of the first-layer concrete beam is determined according to the compressive strength test value of the same batch of concrete cubic test blocks of the first-layer concrete beam. According to the elastic coefficient of the composite foundation, the elastic coefficient of the composite foundation is changed to a reasonable safety range through partial replacement or direct grouting and other construction methods, so that the safer composite foundation is formed to improve the stability of the composite foundation. The method can effectively guide the construction of the layered concrete beam under the soft foundation, is favorable for controlling the early strain of the beam and reducing the later creep and the like so as to reduce the probability of cracking of the concrete. The method not only has higher theoretical value, but also has higher applicability in engineering practice.
Owner:GUANGXI TRANSPORTATION SCI & TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com