Static microrelay based on bistable compliant mechanism
A flexible mechanism and micro-relay technology, applied in the direction of electrostatic relays/electro-adhesion relays, relays, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as complex structures, and achieve the effects of large working strokes, low energy consumption, and low driving voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
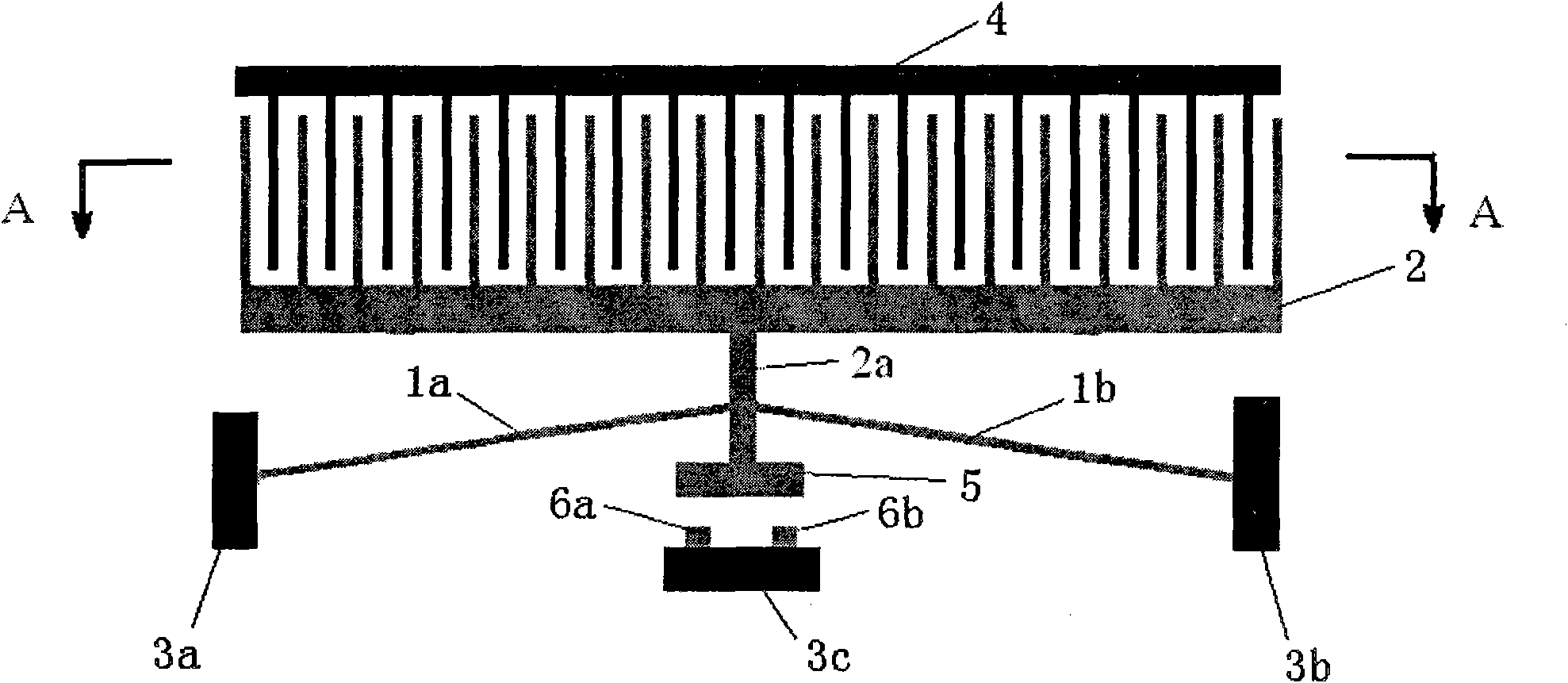
[0034] figure 1 , 2 An electrostatic microrelay based on a bistable flexible mechanism is shown. In the figure, the movable comb 2 and the movable contact 5 are connected into one body by means of a member 2a, and the bistable fully flexible beam adopts two flexible beams, one end of a left flexible beam 1a is fixed on the left insulating anchor point 3a, and the other One end is fixed on the member 2a, and one end of the other right flexible beam 1b is fixed on the right insulating anchor point 3b, and the other end is also fixed on the member 2a. The two stable positions of the bistable fully flexible beam respectively make the micro-relay in two states of closing and opening. The number of movable comb teeth 2 and fixed comb teeth 4 are equal and arranged at intervals, and the generated electrostatic force drives the action of the relay. Directly below the movable contact 5 is a left fixed contact 6a and a right fixed contact 6b fixed on the lower insulation anchor point...
Embodiment 2
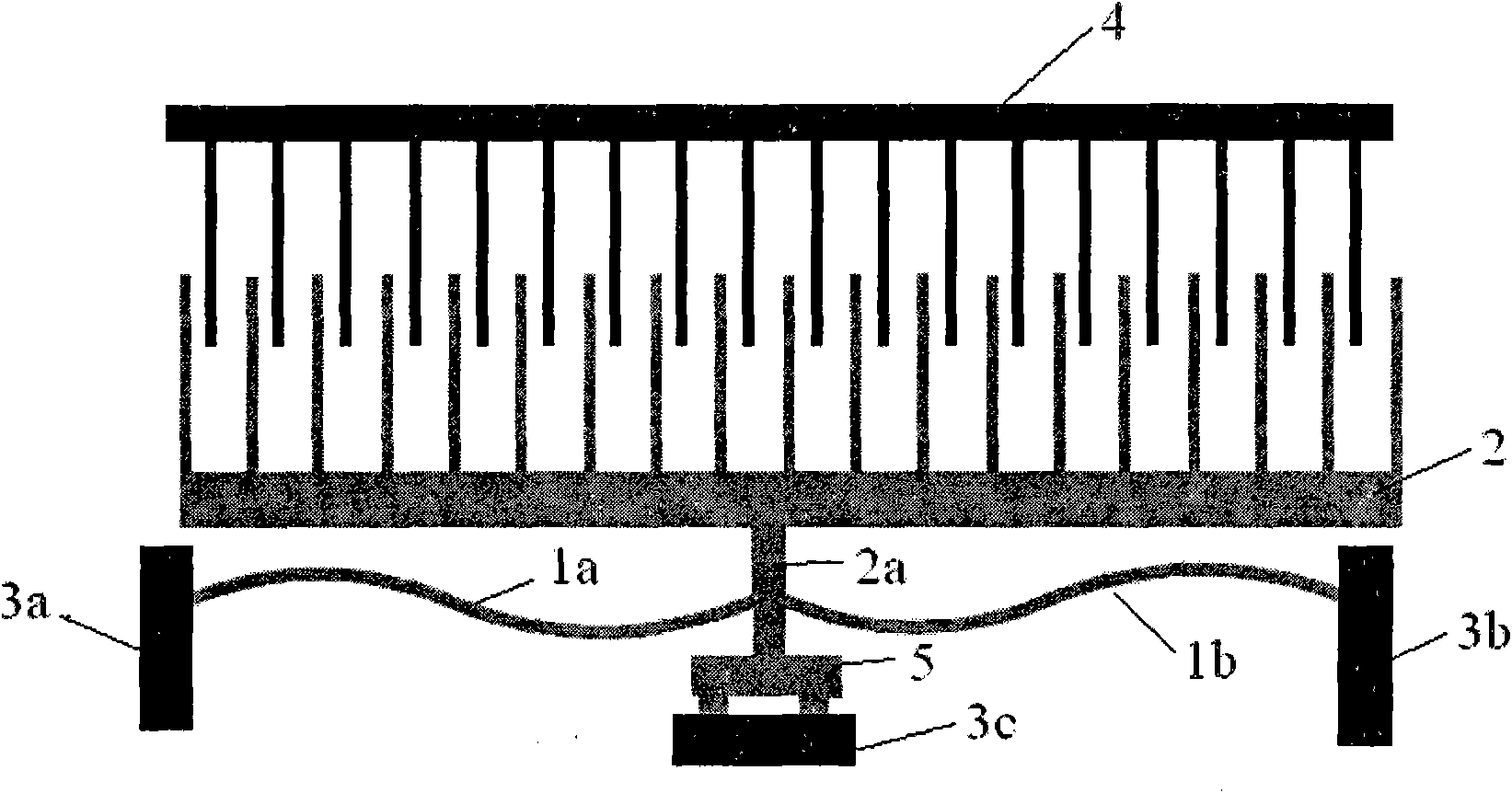
[0047] Figure 13 A schematic structural diagram of an electrostatic micro-relay with two bistable flexible mechanisms is shown. On the basis of the first embodiment, two bistable micro-relays are realized with multi-point control by adopting MEMS integration technology. When the driving voltage is applied, the upper movable comb 2 drives the upper movable contact 5 to move laterally, and conducts the upper fixed contact to realize the conduction of the upper relay. At the same time, the lower movable comb 2 drives the lower movable contact 5 to generate lateral movement, and closes the lower fixed contact to realize the conduction of the lower relay. The fixed comb teeth 4 of the upper and lower relays apply the voltage in the same direction, and the action control of the upper and lower relays can be realized only by changing the input voltage direction of the upper movable comb teeth 2 and the lower movable comb teeth 2 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com