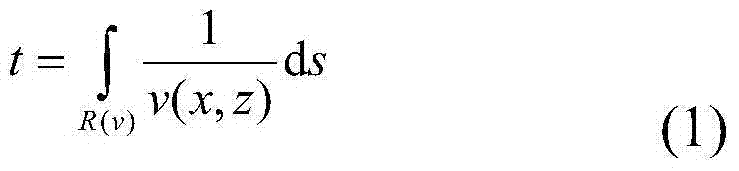Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
113 results about "Algebra over a field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
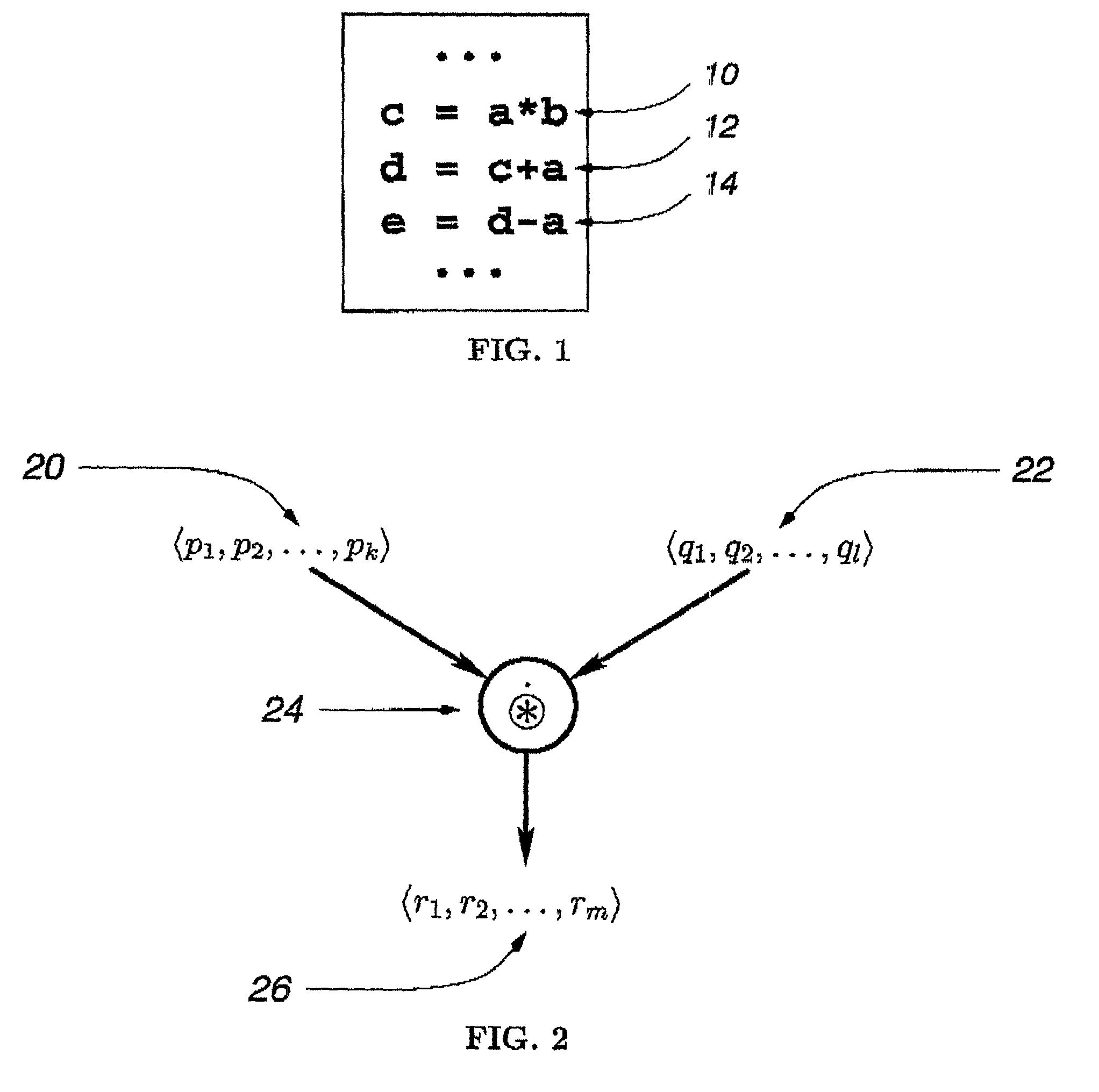
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
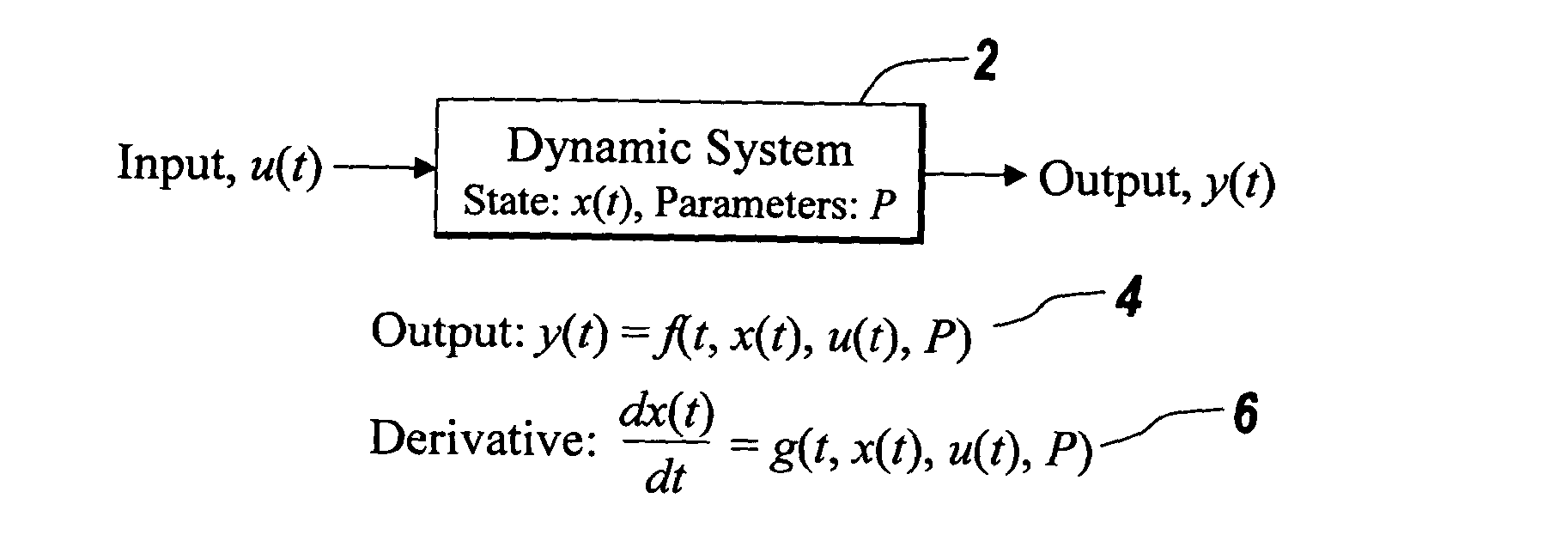
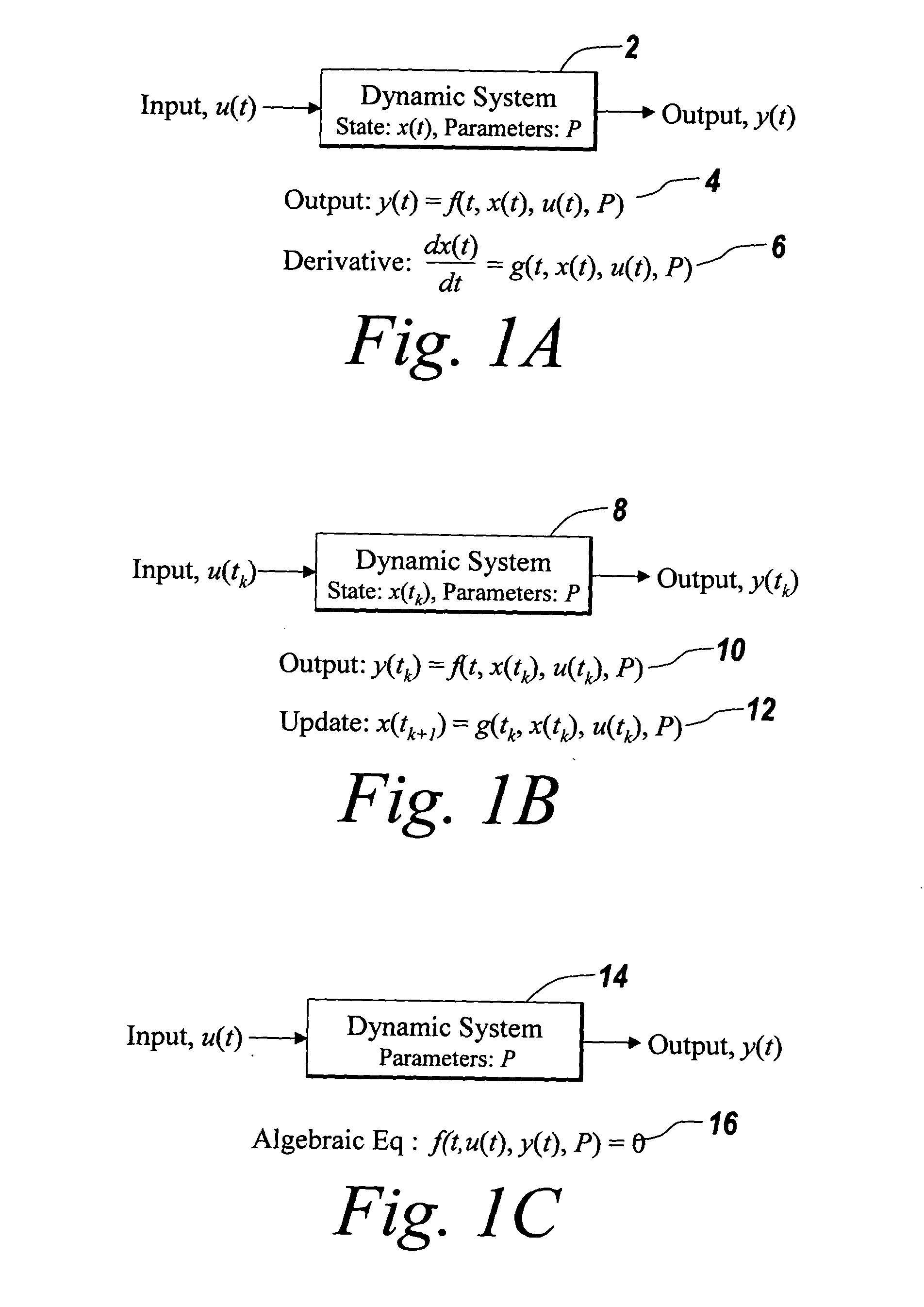
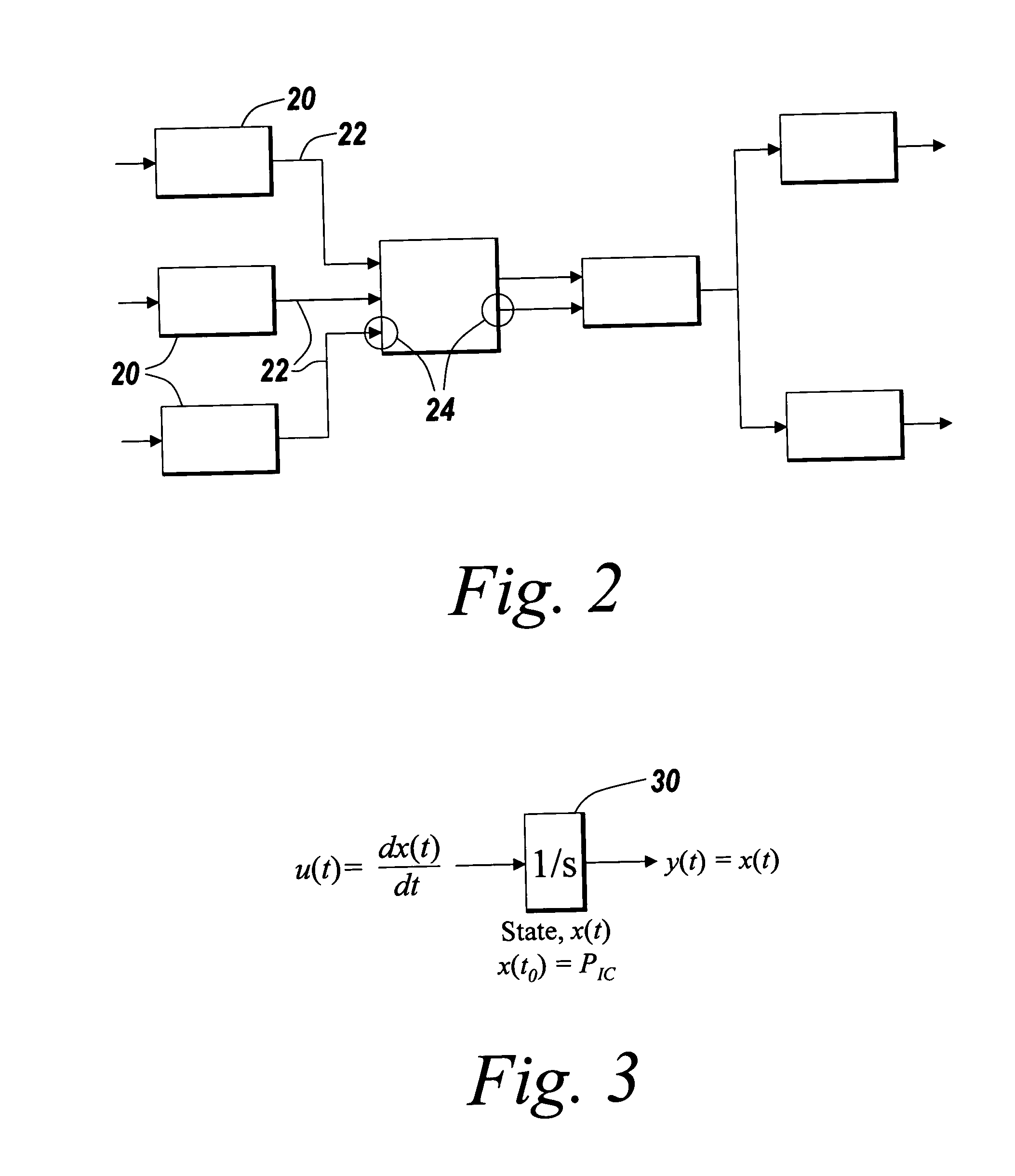
In mathematics, an algebra over a field (often simply called an algebra) is a vector space equipped with a bilinear product. Thus, an algebra is an algebraic structure, which consists of a set, together with operations of multiplication, addition, and scalar multiplication by elements of the underlying field, and satisfies the axioms implied by "vector space" and "bilinear".
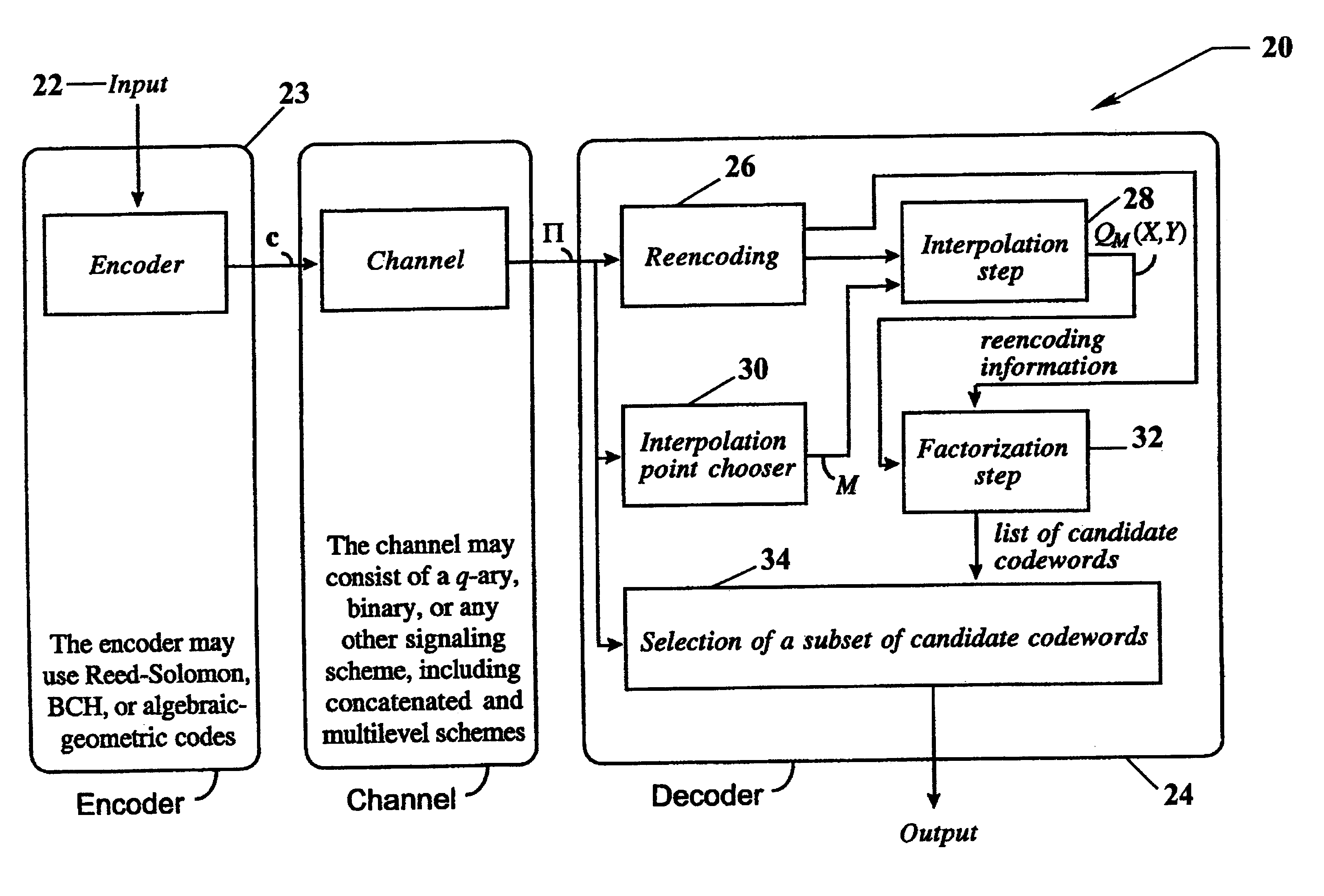
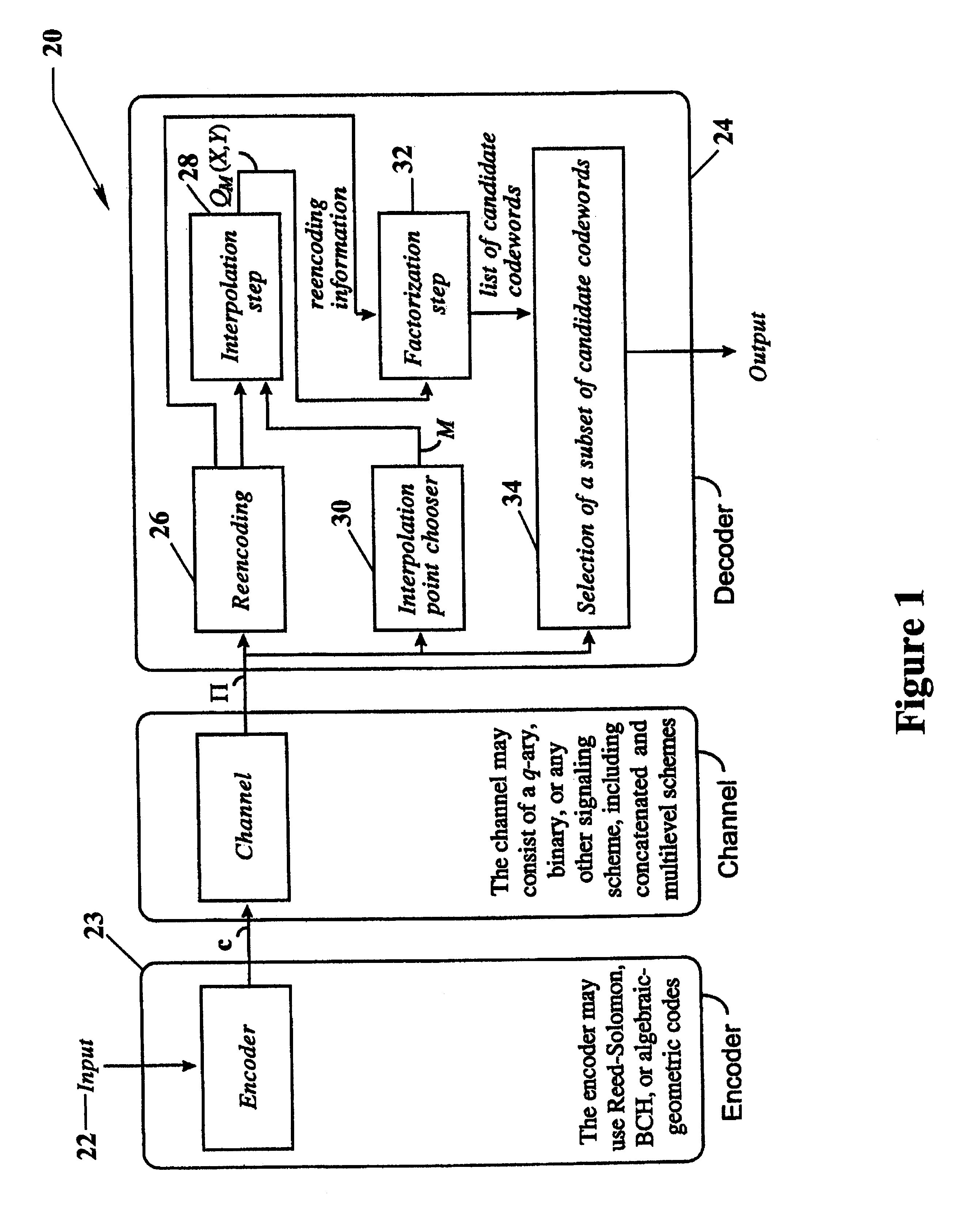
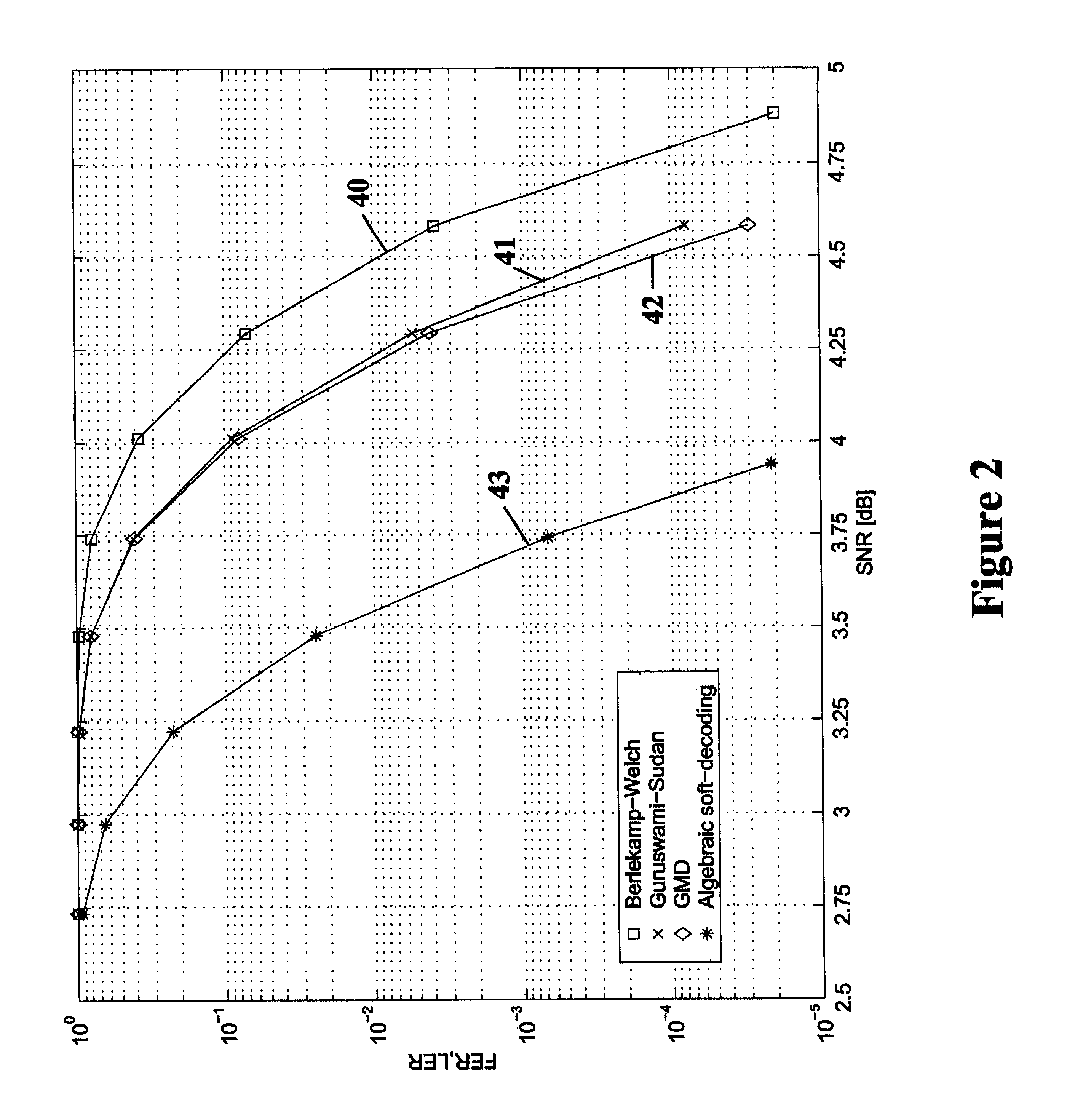
Algebraic soft decoding of reed-solomon codes
InactiveUS6634007B1Maximizes the expected scoreMaximizing the expected scoreOther decoding techniquesAlgebraic geometric codesDecoding methodsRound complexity
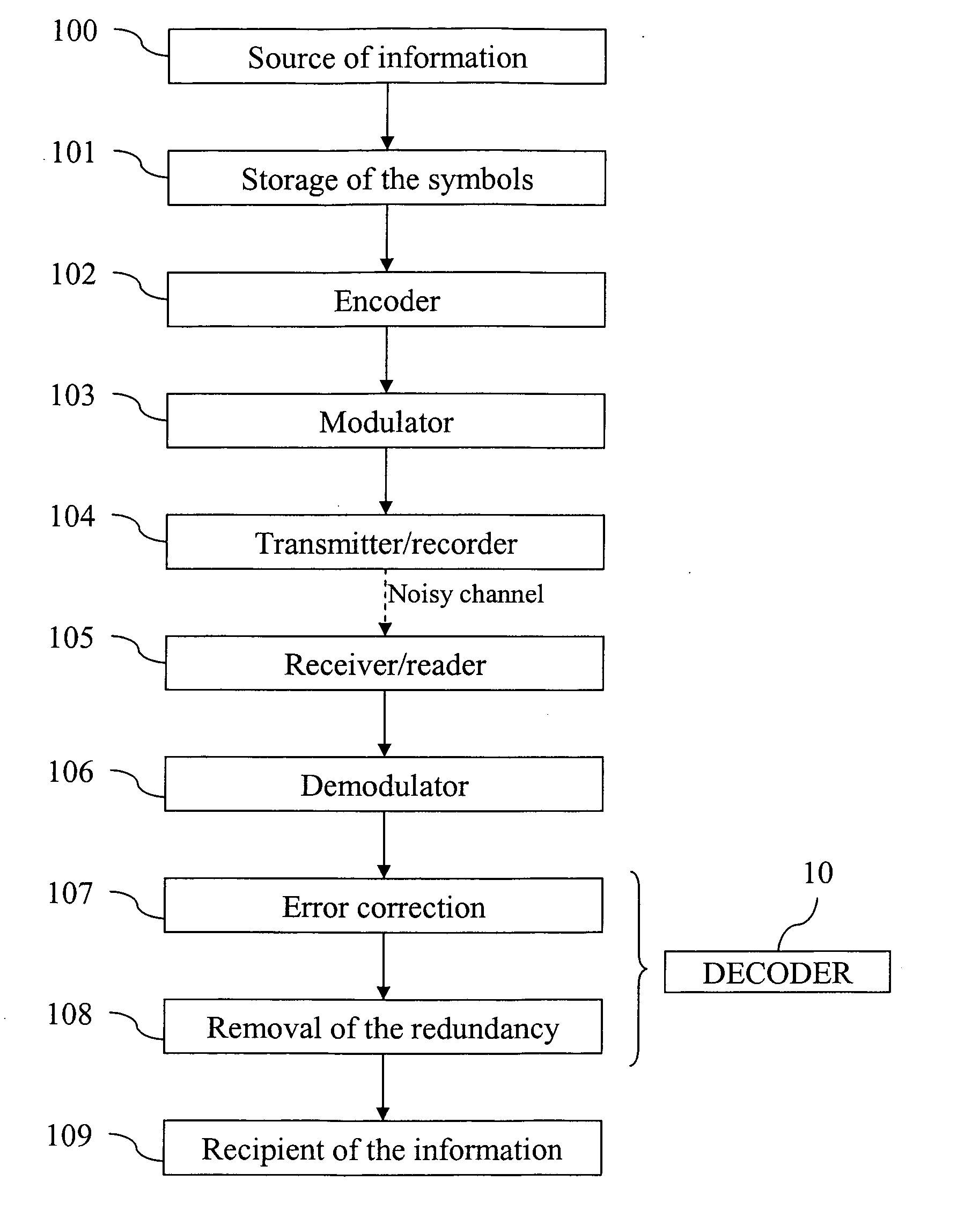
An algorithmic soft-decision decoding method for Reed-Solomon codes proceeds as follows. Given the reliability matrix Pi showing the probability that a code symbol of a particular value was transmitted at each position, computing a multiplicity matrix M which determines the interpolation points and their multiplicities. Given this multiplicity matrix M, soft interpolation is performed to find the non-trivial polynomial Q<HIL><PDAT>M< / SB><PDAT>(X,Y) of the lowest (weighted) degree whose zeros and their multiplicities are as specified by the matrix M. Given this non-trivial polynomial Q<HIL><PDAT>M< / SB><PDAT>(X,Y), all factors of Q<HIL><PDAT>M< / SB><PDAT>(X,Y) of type Y-f(X) are found, where f(X) is a polynomial in X whose degree is less than the dimension k of the Reed-Solomon code. Given these polynomials f(X), a codeword is reconstructed from each of them, and the most likely of these codewords selected as the output of the algorithm. The algorithmic method is algebraic, operates in polynomial time, and significantly outperforms conventional hard-decision decoding, generalized minimum distance decoding, and Guruswami-Sudan decoding of Reed-Solomon codes. By varying the total number of interpolation points recorded in the multiplicity matrix M, the complexity of decoding can be adjusted in real time to any feasible level of performance. The algorithmic method extends to algebraic soft-decision decoding of Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquenghem codes and algebraic-geometry codes.< / PTEXT>
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
Finite element methods and systems
ActiveUS20150120261A1Address limitationsComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationMulticore architectureCpu architecture
The computational efficiency of Finite Element Methods (FEM) on parallel architectures is typically severely limited by sparse iterative solvers. Standard iterative solvers are based on sequential steps of global algebraic operations, which limit their parallel efficiency, and prior art techniques exploit sophisticated programming techniques tailored to specific CPU architectures to improve performance. The inventors present a FEM Multigrid Gaussian Belief Propagation (FMGaBP) technique that eliminates global algebraic operations and sparse data-structures based upon reformulating the variational FEM into a probabilistic inference problem based upon graphical models. Further, the inventors present new formulations for FMGaBP, which further enhance its computation and communication complexities where the parallel features of FMGaBP are leveraged to multicore architectures.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Fully Homomorphic Encryption from Monoid Algebras
ActiveUS20170134158A1Improve securityReduce chancePublic key for secure communicationCommunication with homomorphic encryptionCiphertextSecurity parameter
A blueprint that produces a family of FHE schemes given any homomorphic monoidal encryption scheme. The ciphertext space is a subspace of the monoid algebra over F2 generated by the initial encryption monoid. The method can be generally applied to any monoid encryption schemes. Advantageously, monoid encryption schemes produce efficient FHE schemes with the inventive blueprint. Furthermore, the corresponding FHE scheme can correctly decrypt and efficiently compute circuits with low (polynomial in the security parameter) additive depth, a feature not realized by prior encryption methods.
Owner:CERTSIGN SA
Inverse kinematics solution method for six-degree-of-freedom serial robot
ActiveCN102637158AAvoid problems with rank less than orderIngenious ideaComplex mathematical operationsRobot kinematicsTabu search
The invention discloses an inverse kinematics solution method for a six-degree-of-freedom serial robot. The inverse kinematics solution method comprises the steps of: establishing a connecting rod coordinate system and setting variables theta 1, theta 2, theta 3, theta 4, theta 5 and theta 6; setting an initial configuration; solving theta 4, theta 5 and theta 6 by utilizing a geometric method; and eliminating theta 1, theta 2 and theta 3 by utilizing an algebra elimination method and introducing a tabu search algorithm when solving a non-orthogonal spheroid or the terminal structure of the non-orthogonal spheroid, thereby solving out corresponding numerical solutions. The inverse kinematics solution method is smart in conception and utilizes the geometric method and the algebra elimination method for comprehensive solution, thereby avoiding the problem that the rank of an equation determinant of coefficient is smaller than order caused by arbitrary establishing of equations and correctly obtaining the analytic solutions of six axes efficiently; and for complex-structure trigonometric function relationship, a linear equation in two unknowns can be effectively transformed to a linear equation with one unknown by the elimination method in the use of the geometric method, and therefore a unique corresponding analytic solution is obtained.
Owner:CHENGDU CRP ROBOT TECH CO LTD
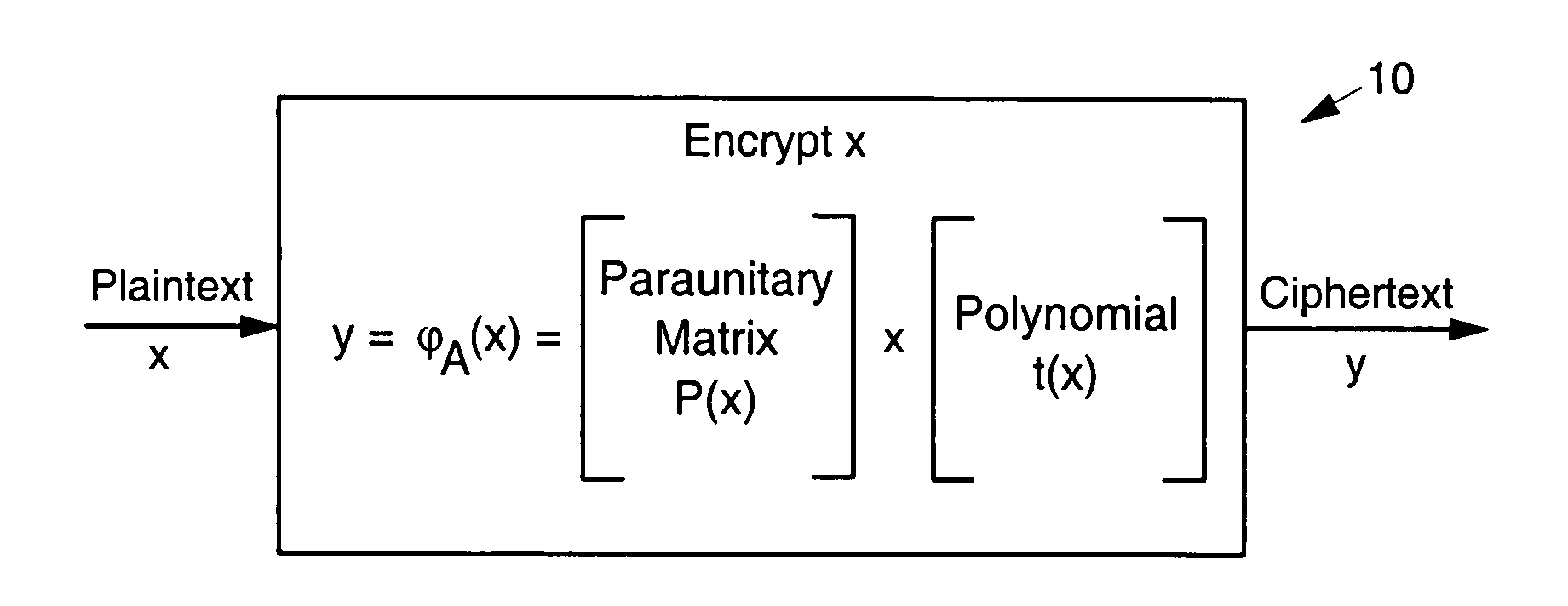
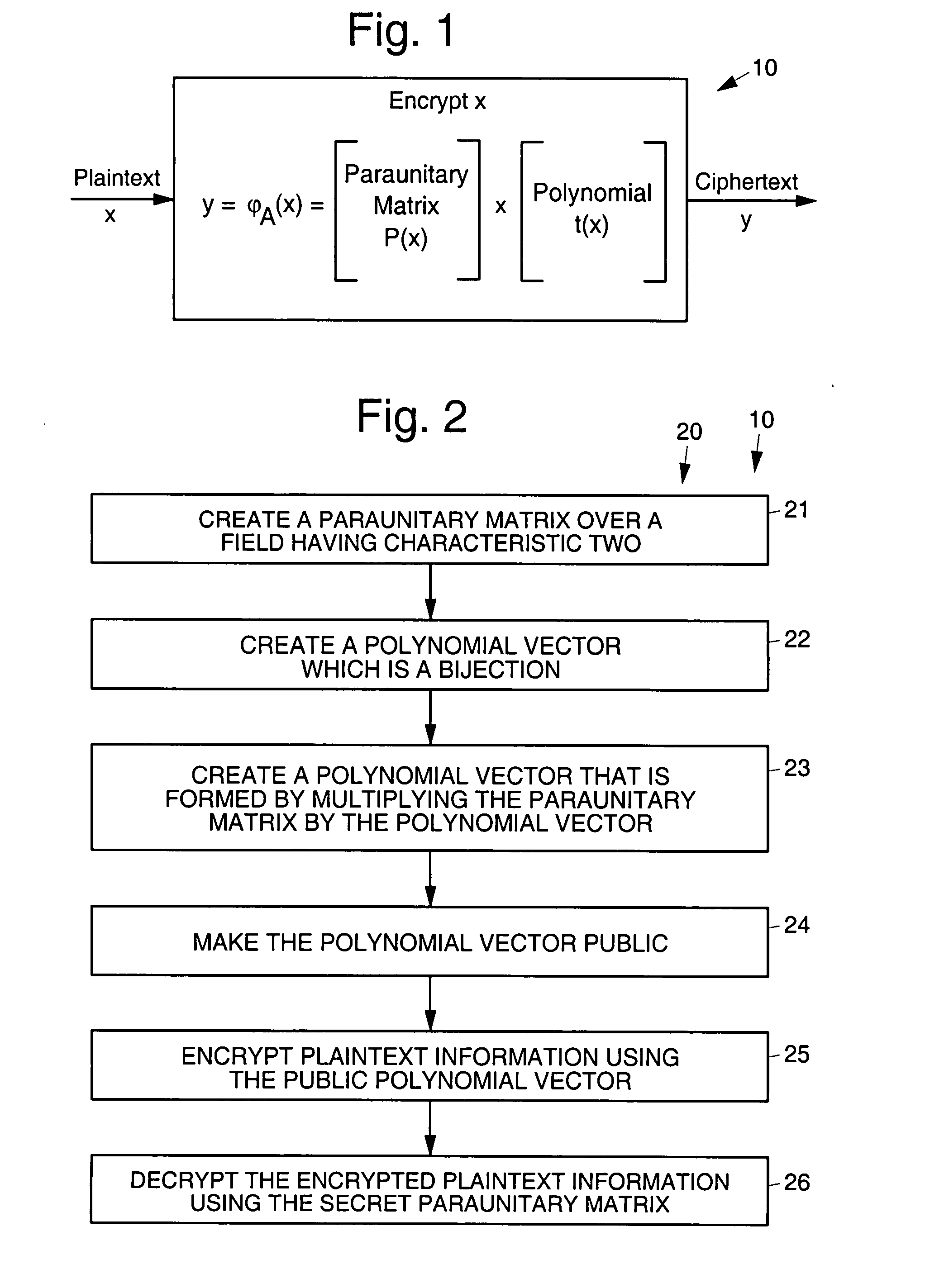
Asymmetric cryptosystem employing paraunitary matrices
InactiveUS20090010428A1Public key for secure communicationSecret communicationNon symmetricCiphertext
Disclosed are multivariate paraunitary asymmetric cryptographic systems and methods that are based on paraunitary matrices. An algebraic approach is employed in designing the multivariate cryptographic systems and methods. The cryptographic systems and methods are based on formulating a general system of multivariate polynomial equations by paraunitary matrices. These matrices are a family of invertible polynomial matrices that can be completely parameterized and efficiently generated by primitive building blocks. Using a general formulation that involves paraunitary matrices, a one-way function is designed that operates over the fields of characteristic two. To include a trapdoor, approximations are made to the paraunitary matrix. The result is a trapdoor one-way function that is efficient to evaluate, but hard to invert unless secret information about the trapdoor is known. An exemplary implementation operates on the finite field GF(256). In this example, the message block includes 16 to 32 symbols from GF(256), i.e., the block size n is an integer between 16 and 32. The ciphertext block takes its elements from the same field and has at least 10 extra symbols.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Automated approach to resolving artificial algebraic loops
ActiveUS7167817B2Accurate calculationAvoid it happening againComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationAlgebraic loopComputational science
A method and apparatus for resolving artificial algebraic loops in model executions include providing an executable process having a plurality of functions. An analysis step identifies whether the process includes at least one potential artificial algebraic loop. If at least one potential artificial algebraic loop exists in the process, an artificial algebraic loop solution manipulates the order or manner by which the functions are executed to eliminate or otherwise resolve the artificial algebraic loop.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
Computer method and apparatus for constraining a non-linear approximator of an empirical process
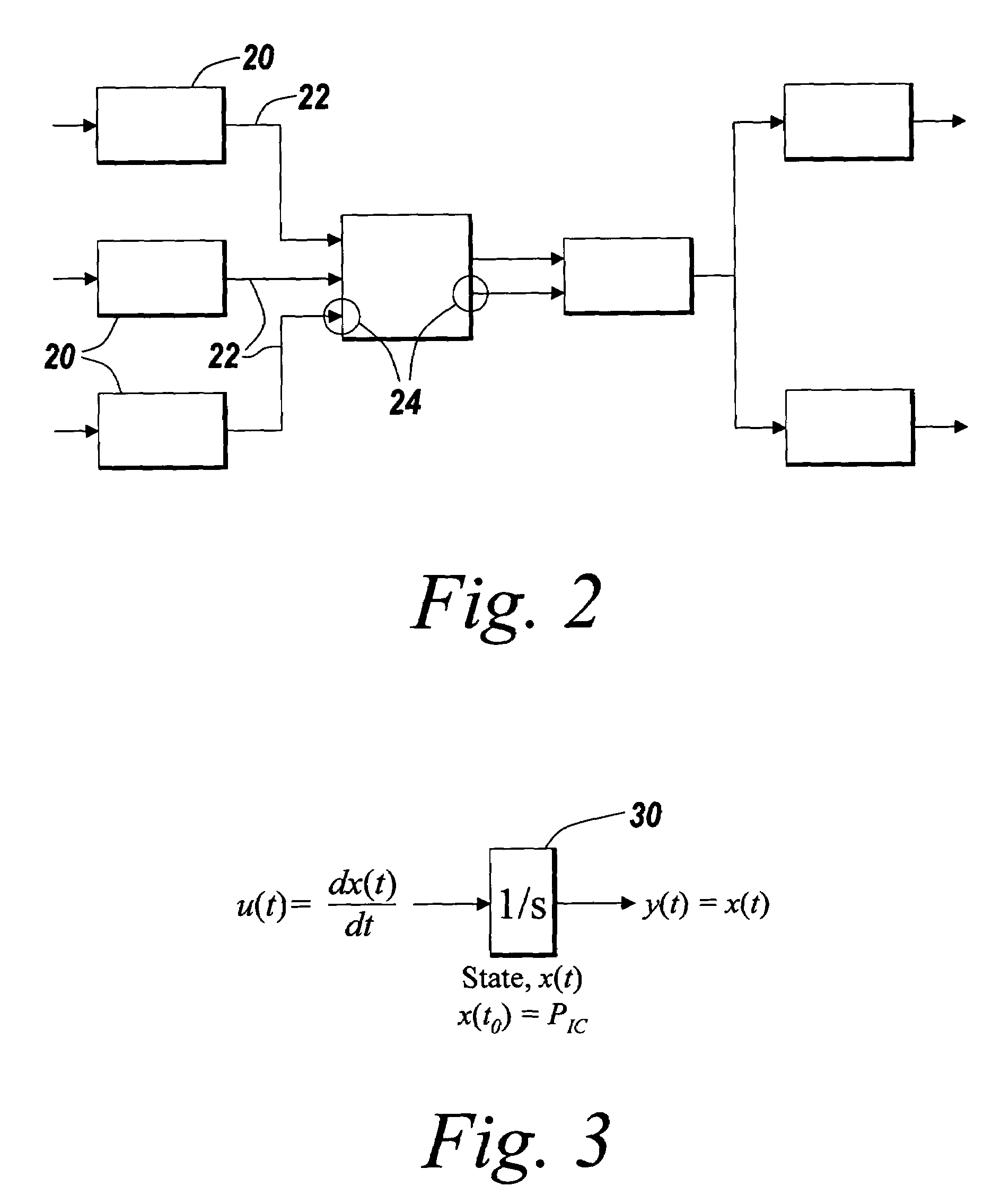
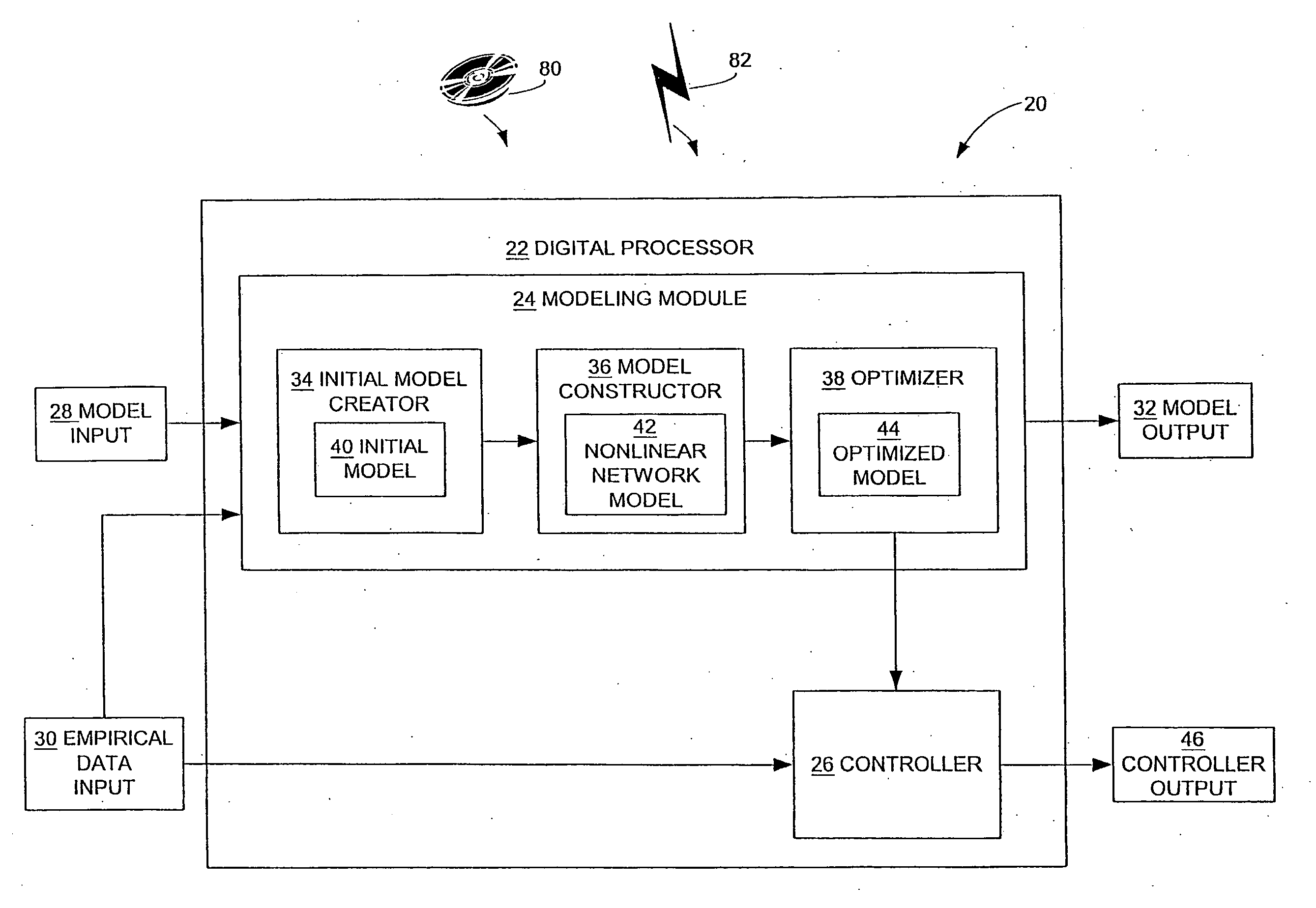
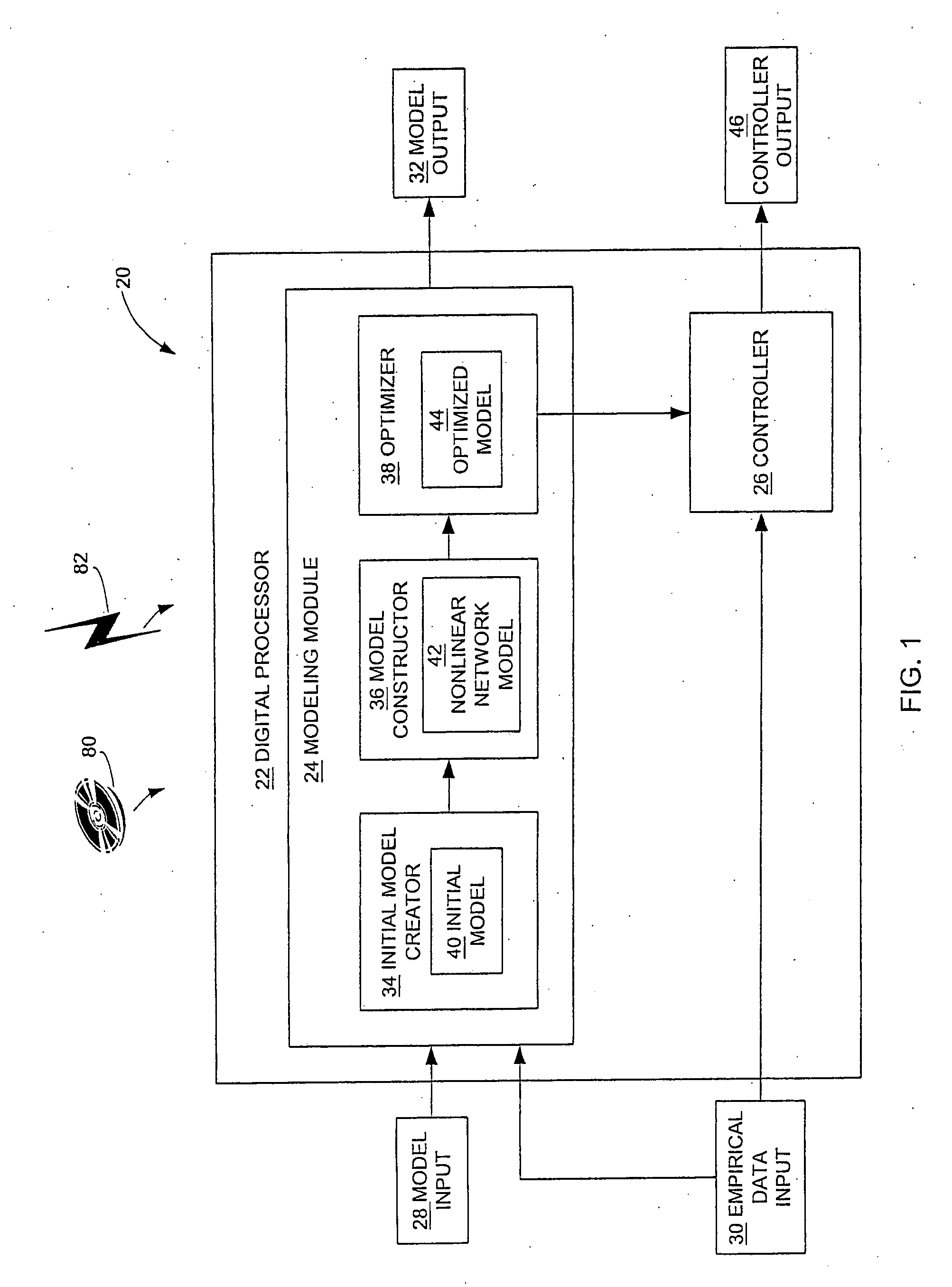
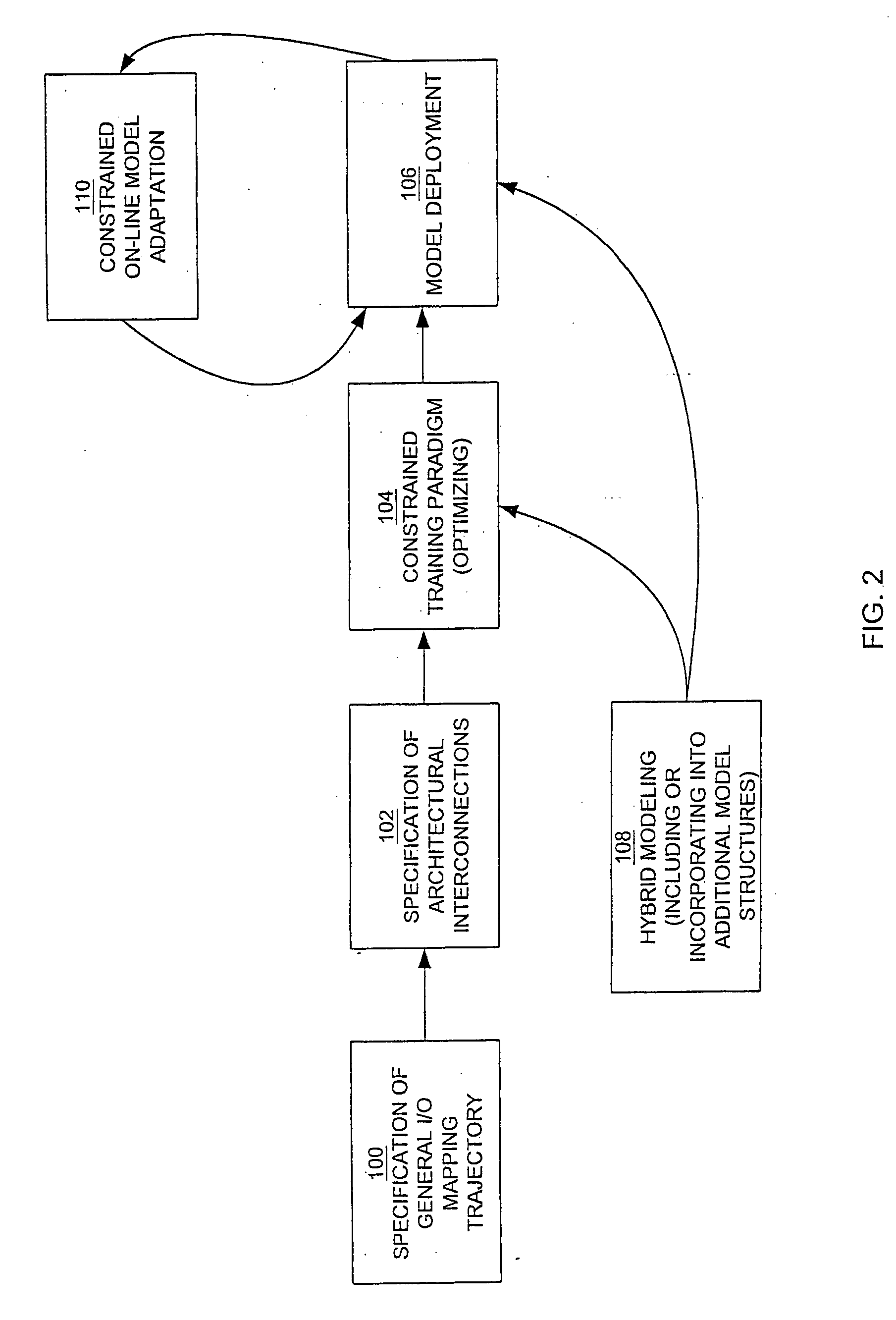
InactiveUS20080071394A1Predict and controlReduce varianceSimulator controlBiological modelsNonlinear approximationLinear relationship
A constrained non-linear approximator for empirical process control is disclosed. The approximator constrains the behavior of the derivative of a subject empirical model without adversely affecting the ability of the model to represent generic non-linear relationships. There are three stages to developing the constrained non-linear approximator. The first stage is the specification of the general shape of the gain trajectory or base non-linear function which is specified graphically, algebraically or generically and is used as the basis for transfer functions used in the second stage. The second stage of the invention is the interconnection of the transfer functions to allow non-linear approximation. The final stage of the invention is the constrained optimization of the model coefficients such that the general shape of the input / output mappings (and their corresponding derivatives) are conserved.
Owner:ASPENTECH CORP
Automated approach to resolving artificial algebraic loops
ActiveUS20050060129A1Accurate calculationAvoid it happening againComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationComputational scienceAlgebraic loop
A method and apparatus for resolving artificial algebraic loops in model executions include providing an executable process having a plurality of functions. An analysis step identifies whether the process includes at least one potential artificial algebraic loop. If at least one potential artificial algebraic loop exists in the process, an artificial algebraic loop solution manipulates the order or manner by which the functions are executed to eliminate or otherwise resolve the artificial algebraic loop.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
Intelligent bus scheduling calculation method
InactiveCN102737356ARealize rational utilizationData processing applicationsGenetic modelsMathematical modelGenetic algorithm
The invention discloses an intelligent bus scheduling calculation method, which comprises the following steps of: constructing a math model of a genetic algorithm; and then designing specific solution steps of the genetic algorithm by the math model, wherein the termination condition of the algorithm is that a genetic algebra Gen is equal to the set maximum genetic algebra. By the intelligent bus scheduling calculation method, the comprehensive benefit between a bus company and passengers can be comprehensively considered; and the shortcomings about solution for multi-target non-linear problems in the conventional bus scheduling algorithm are overcome.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Adaptively determined parameter values in iterative reconstruction method and system
InactiveUS20130336562A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionAlgorithmReconstruction algorithm
The CT imaging system optimizes its image generation by adaptively changing parameters in an iterative reconstruction algorithm based upon certain information such as statistical information. The coefficients for the parameters include at least a first coefficient for a predetermined data fidelity process and a second coefficient for a predetermined regularization process in an iterative reconstruction algorithm. The iterative reconstruction algorithm includes the ordered subsets simultaneous algebraic reconstruction technique (OSSART) and the simultaneous algebraic reconstruction technique (SART). The first coefficient and the second coefficient are independently determined using some predetermined statistical information such as noise and or error in matching the real data.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
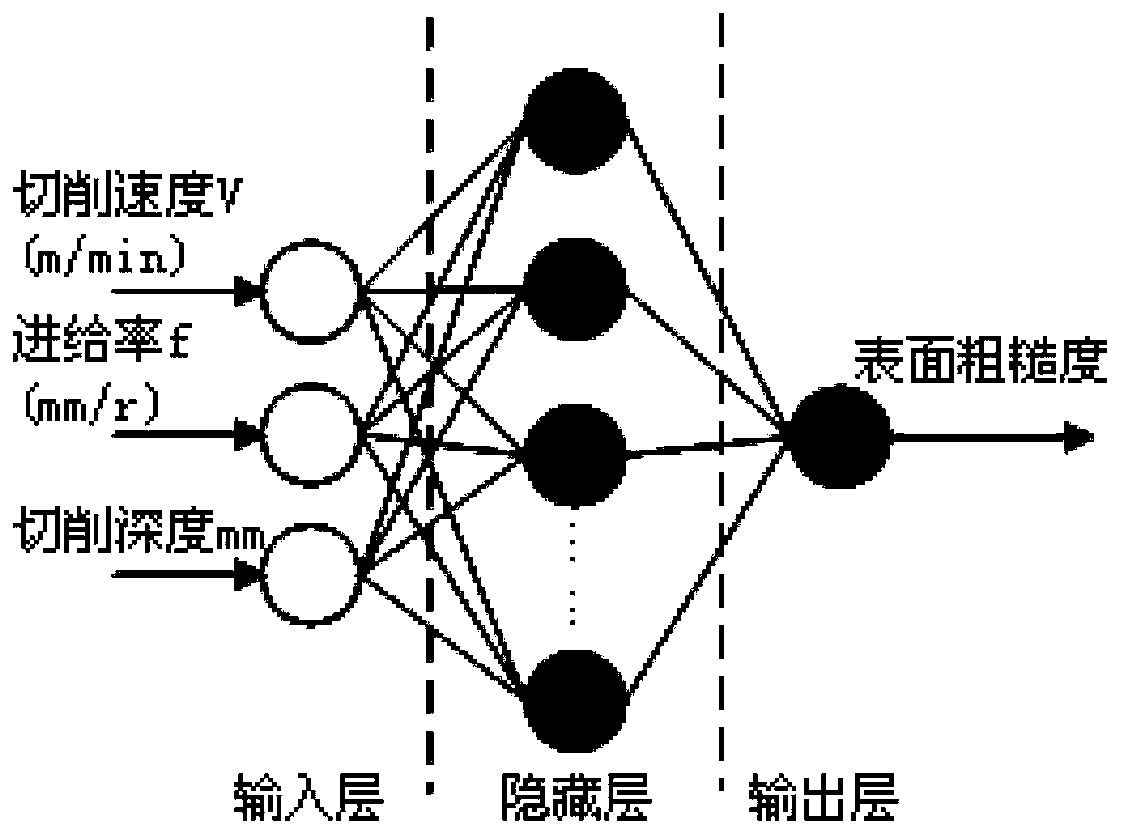
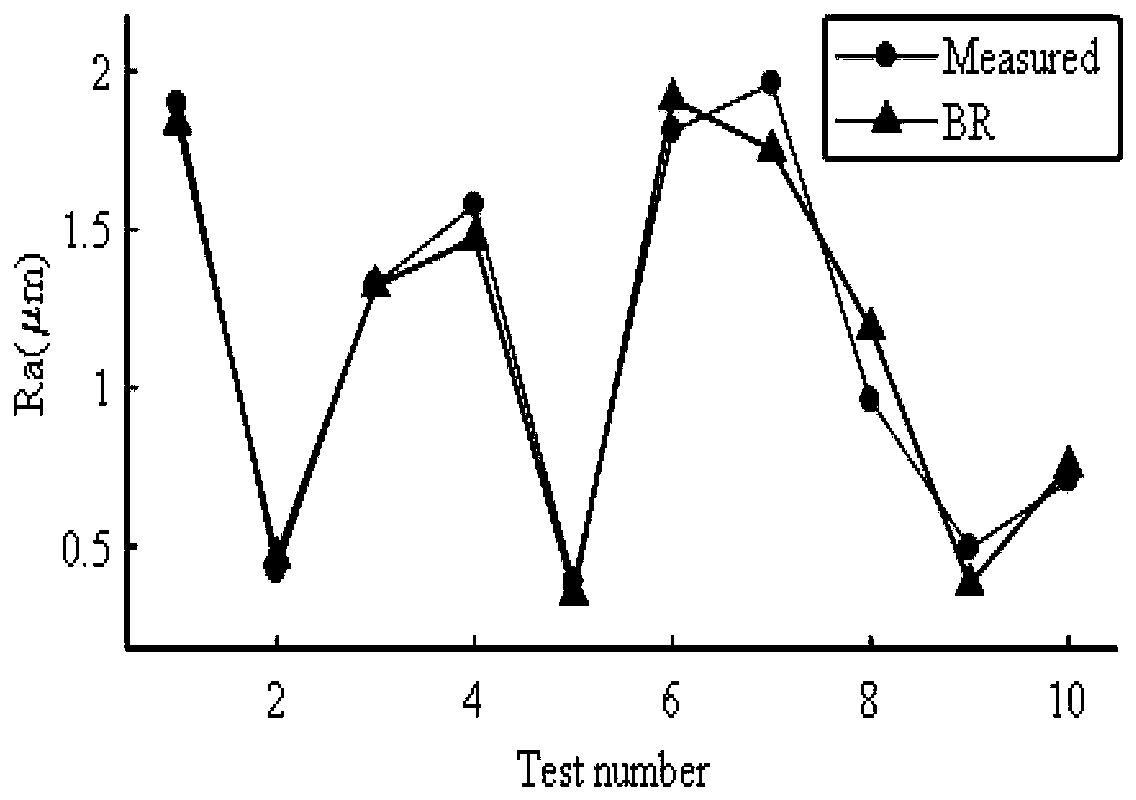
Surface roughness prediction method based on GA-GBRT and method for optimizing process parameters
ActiveCN109828532AImprove test accuracyImprove generalization abilityProgramme controlComputer controlOptimality modelData set
The invention discloses a surface roughness prediction method based on GA-GBRT and a method for optimizing process parameters. The method comprises the steps of: collecting data to construct a data set, and dividing the data set to training set data and test set data, and employing the training set data to perform training of key parameters of a GBRT model; b, performing parameter coding and population initialization: randomly generating a chromosomal sequence for increasing the number of iterations, the maximum depth of the individual regression estimator and the learning rate; c, employing the k-folded cross-validation method to train the GBRT model, and employing the genetic algorithm to calculate the fit goodness fitting value of each individual; d, when the number of cycles does not reach the maximum number of iterations, allowing the population to be selected, crossed and mutated to produce a new generation of populations, and continuously performing training of the GBRT model; and e, repeatedly performing the steps c and d until the number of cycles reaches the maximum evolution algebra or exceeds the maximum number of iterations to obtain the optimal model parameters. The surface roughness prediction method based on GA-GBRT and the method for optimizing process parameters are high in test precision and superior in prediction performance and improves the surface processing precision of the workpiece.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Server load balancing method based on genetic algorithm
ActiveCN105704255AOptimize allocationMeasure fitnessTransmissionResource utilizationA moderate amount
The invention discloses a server load balancing method based on a genetic algorithm, and relates to the technical field of load balancing. The server load balancing method comprises the following steps that 1) candidate solutions of space are coded by adopting a decimal system, and a moderate amount of initial string structure data are randomly generated to act as initial populations; 2) iteration is performed on the initial populations by adopting the genetic algorithm, and the algorithm ends when the difference between adaptability of the optimal character string and the minimum adaptability value is less than e or iteration reaches the preset number; 3) assessment detection of resource utilization rate and an execution time adaptability value is performed through a Mean-Variance model; and 4) the character strings of high adaptability are selected according to a roulette method, and crossover and mutation operation is performed on the selected character strings so that new character strings are generated to enter the next round of iteration and the process returns to the step 2. The Mean-Variance model is applied to assessment of adaptability so that the mode of a conventional target function is improved, the adaptability of the character strings can be more effectively measured by the obtained resource use balancing situation and execution time, and thus the load balancing performance can be enhanced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Improved particle swarm algorithm for automatic optimization of control law parameters of unmanned aircraft
InactiveCN101551642AFaster convergence timeImprove performanceVehicle position/course/altitude controlAdaptive controlPerformance indexParticle swarm algorithm
The invention relates to an improved particle swarm algorithm for automatic optimization of control law parameters of an unmanned aircraft. The particle swarm algorithm is based on an iterative optimized algorithm; control parameters are initialized to be a group of random solutions; and optimal values are found by iteration; the improved particle swarm algorithm is characterized by comprising the following steps of: in the particle swarm algorithm, introducing a crossover operator, selecting a plurality of particles in which the optimal position value of single particle is positioned in the middle to carry out random two-two crossover; generating offspring particles with the same number; replacing parent particles with offspring particles; selecting crossover time according to convergent algebra of the standard particle swarm algorithm, namely, 17 to 20 generations for pitching and yawing channel and 7 to 10 generations for rolling channel; and selecting algebra of disturbing start as follows: starting from twelfth generation for the pitching and yawing channel and starting from fourth generation for the rolling channel. The improved particle swarm algorithm expands the range of understanding the space, has total searching capacity; the obtained parameters can meet given performance indexes; and the algorithm can save design time and has application value of engineering.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
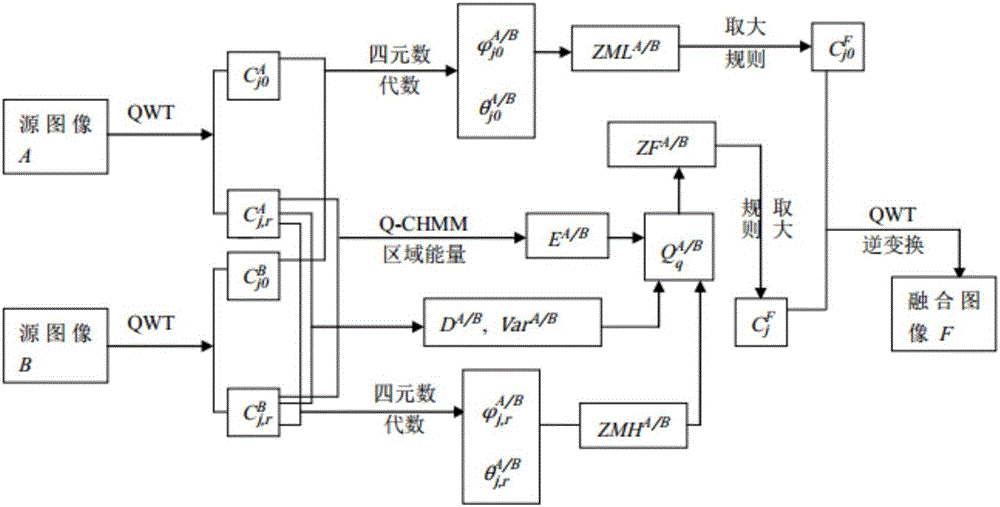
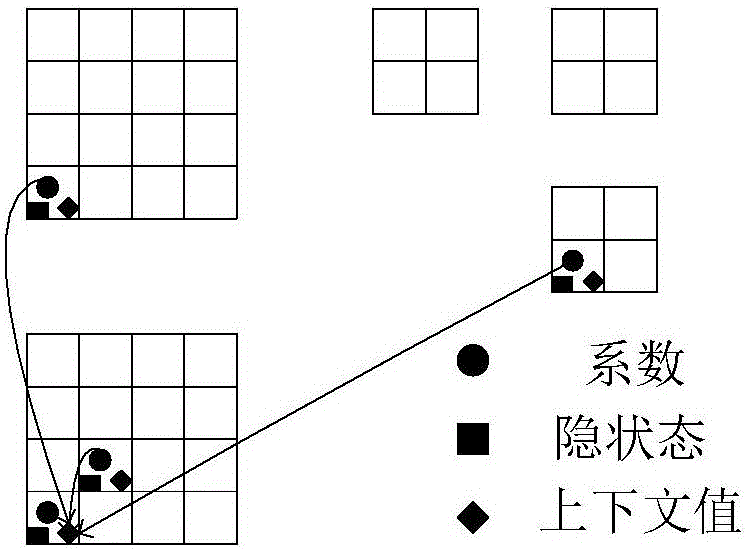
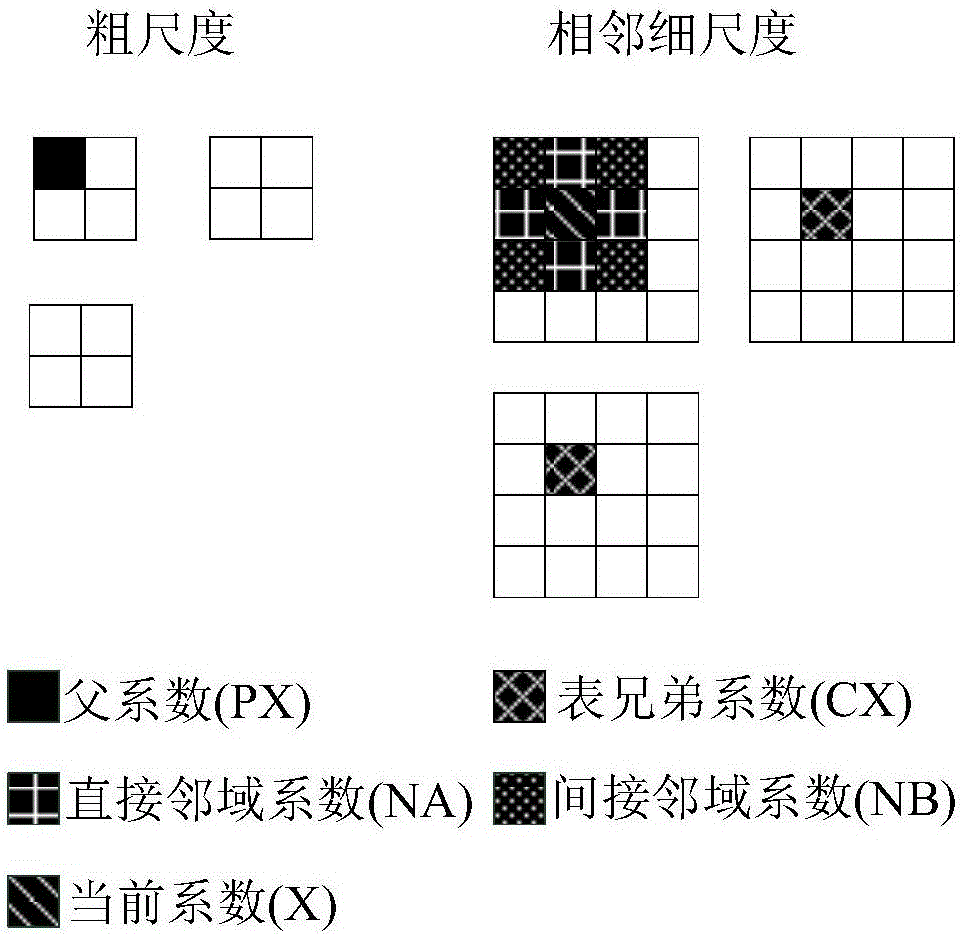
Multi-focus image fusion method based on quaternion wavelet transform
InactiveCN106803242AOvercoming the lack of phase informationInformativeImage enhancementImage analysisThree-phaseSource image
The invention discloses a multi-focus image fusion method based on quaternion wavelet transform in order to more accurately integrate the information in a source image into a fusion image. The method comprises steps of: 1) subjecting two multi-focus images to be fused to quaternion wavelet transform in order to obtain a low-frequency sub-band (LL) and three high-frequency sub-bands (LH, HL, HH) of each layer, wherein each sub-band corresponds to four quaternion coefficient sub-bands, the four quaternion coefficient sub-bands can be transformed to an amplitude sub-band and three phase sub-bands by quaternion algebraic operation; 2) subjecting the low-frequency sub-band to fusion by a fusion rule based on improved phase gradient characteristic value maximization, and subjecting the high-frequency sub-bands to fusion by a fusion method based on quaternion matrix comprehensive multi-features; and 4) subjecting the fused high and low frequency sub-band coefficients to quaternion wavelet transform to obtain a fused image. The method can fully extract the features of the source image and accurately represent the source image so as to avoid introducing error information into the fused image and to improve a visual effect, and greatly improves the quality of the fused image compared with a traditional fusion method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
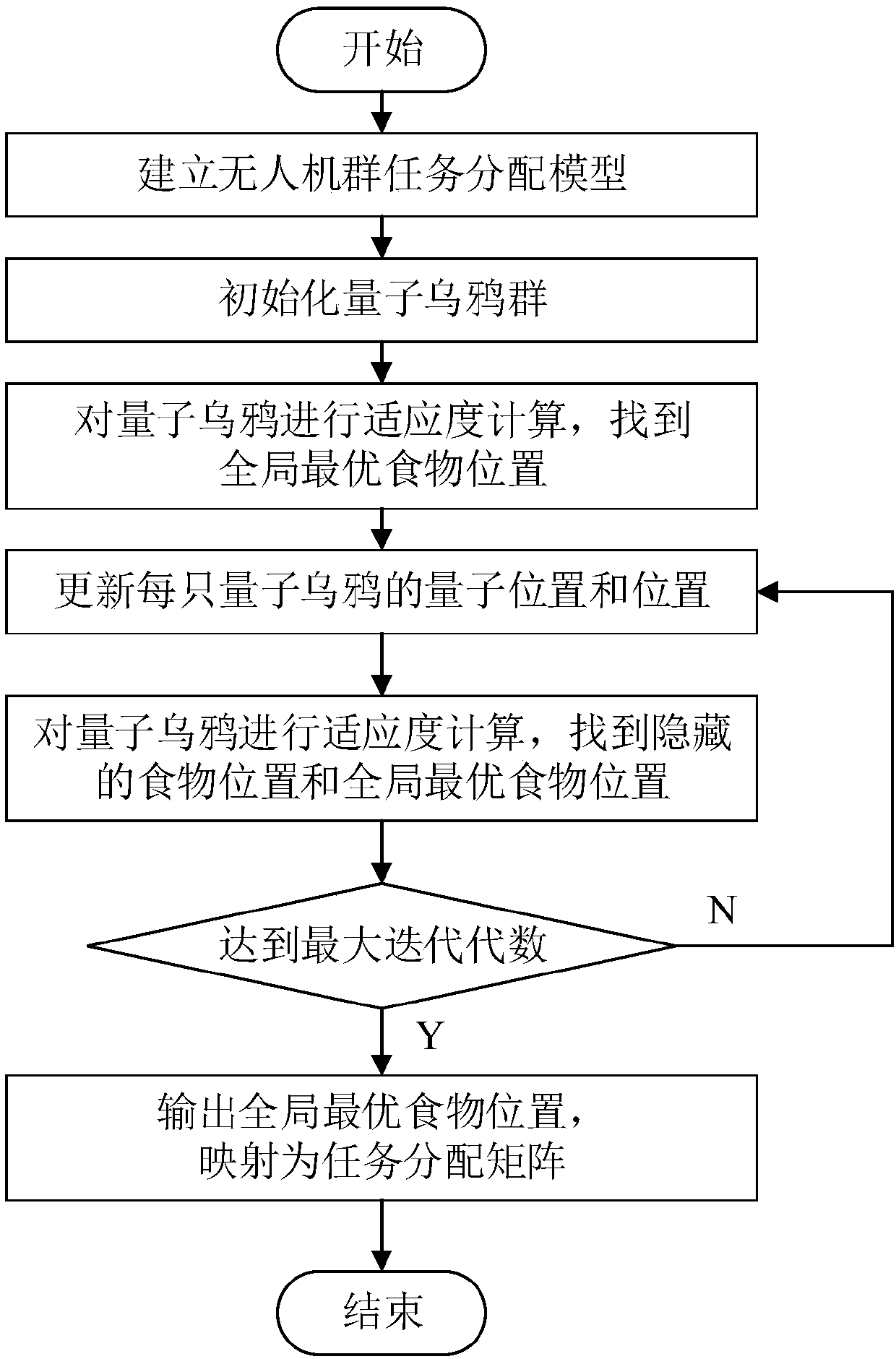
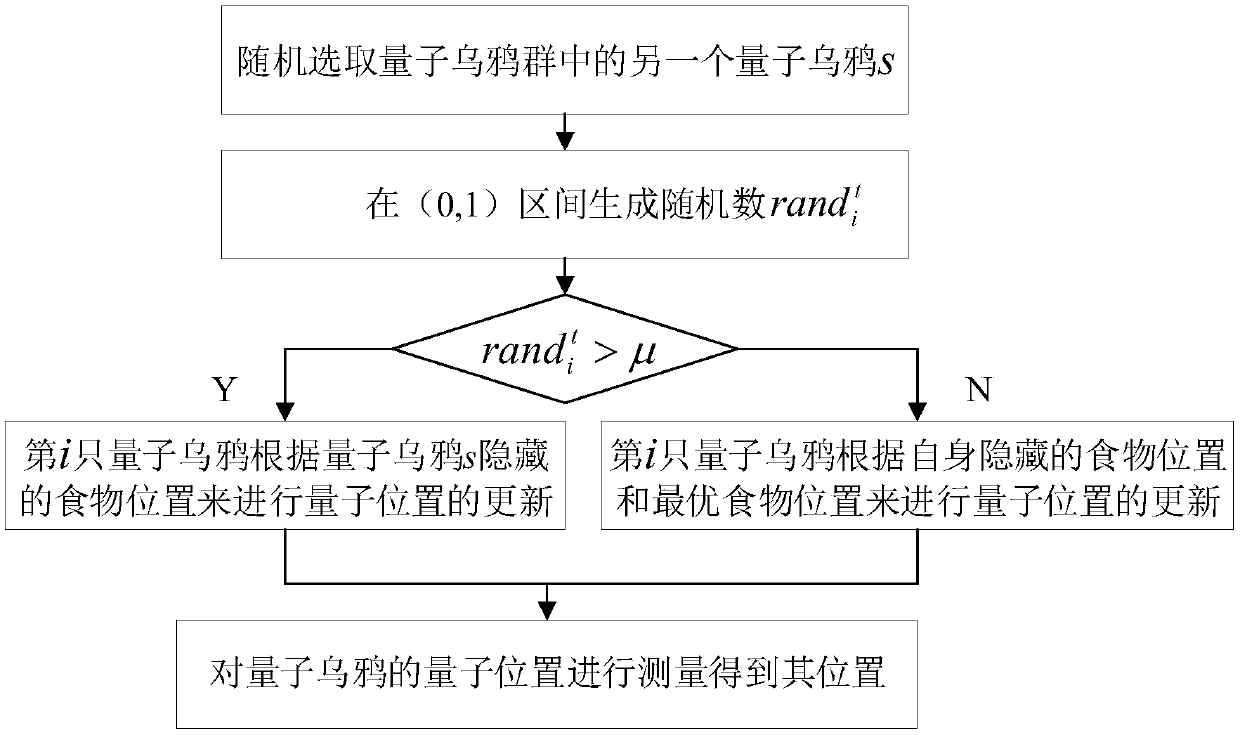
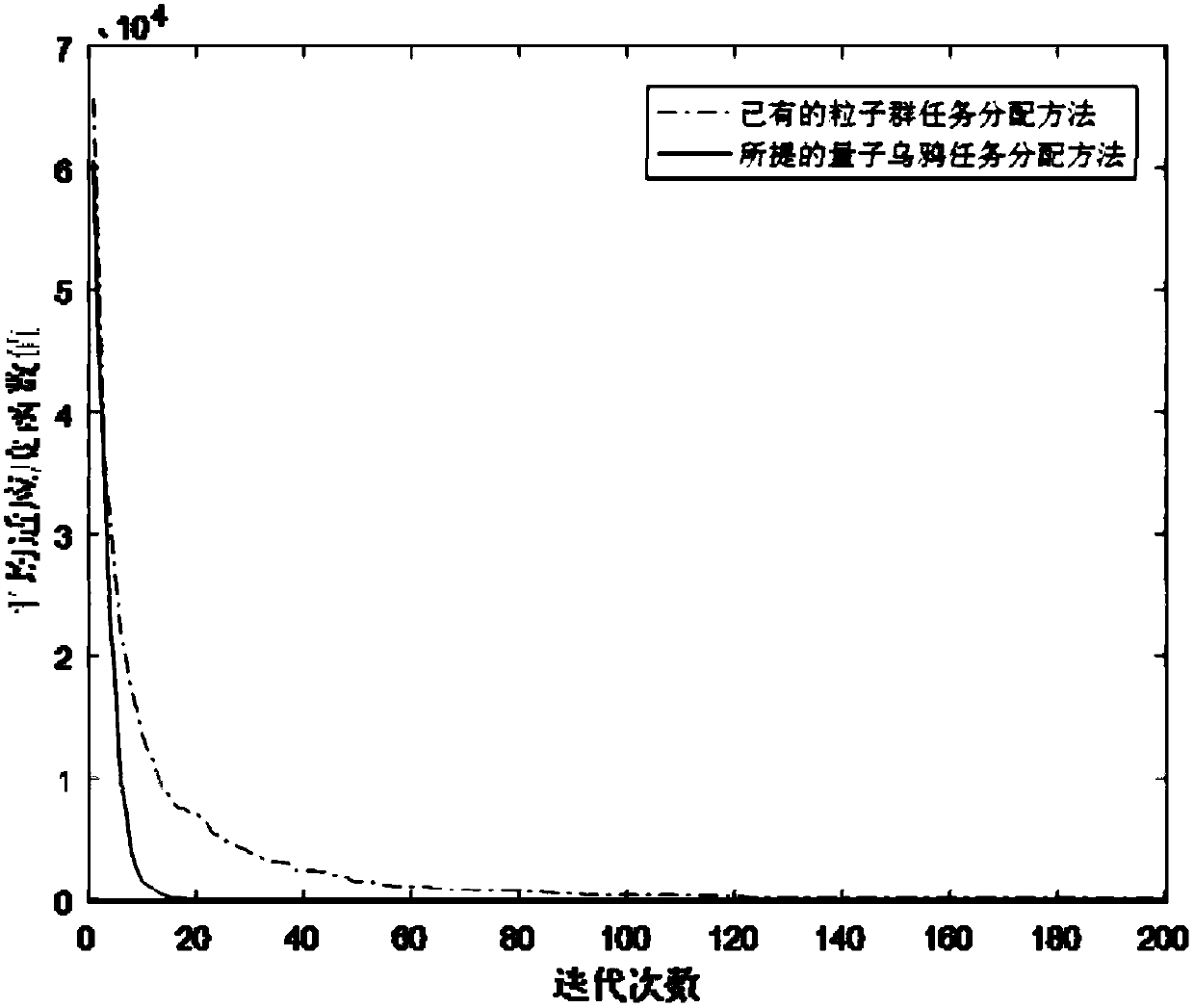
UAV group task allocation method based on quantum crow group search mechanism
ActiveCN108549402ASolve problemsFast convergencePosition/course control in three dimensionsModel NumberComputer science
The invention relates to a UAV group task allocation method based on a quantum crow group search mechanism. The UAV group task allocation method comprises the steps of: establishing a UAV group task allocation model from a plurality of start points to a plurality of tasks, wherein the UAV group task allocation model comprises UAV model numbers, start and end points, and an allocation model; initializing a quantum crow group; calculating the fitness of each quantum crow according to a fitness function, and storing a position of the quantum crow corresponding to the minimum value of the fitnessfunction as a globally optimal food position; updating a quantum position and the position of each quantum crow; and calculating the fitness of each quantum crow according to a fitness function, determining a hidden food position of each quantum crow, finding the optimal food position so far, outputting the globally optimal food position if the maximum iteration algebra is reached, and mapping themaximum iteration algebra into a task allocation matrix. The UAV group task allocation method solves the discrete multi-constrained objective function solving problem, designs a discrete quantum crowalgorithm as an evolution strategy, and has the advantages of fast convergence speed and high convergence precision.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
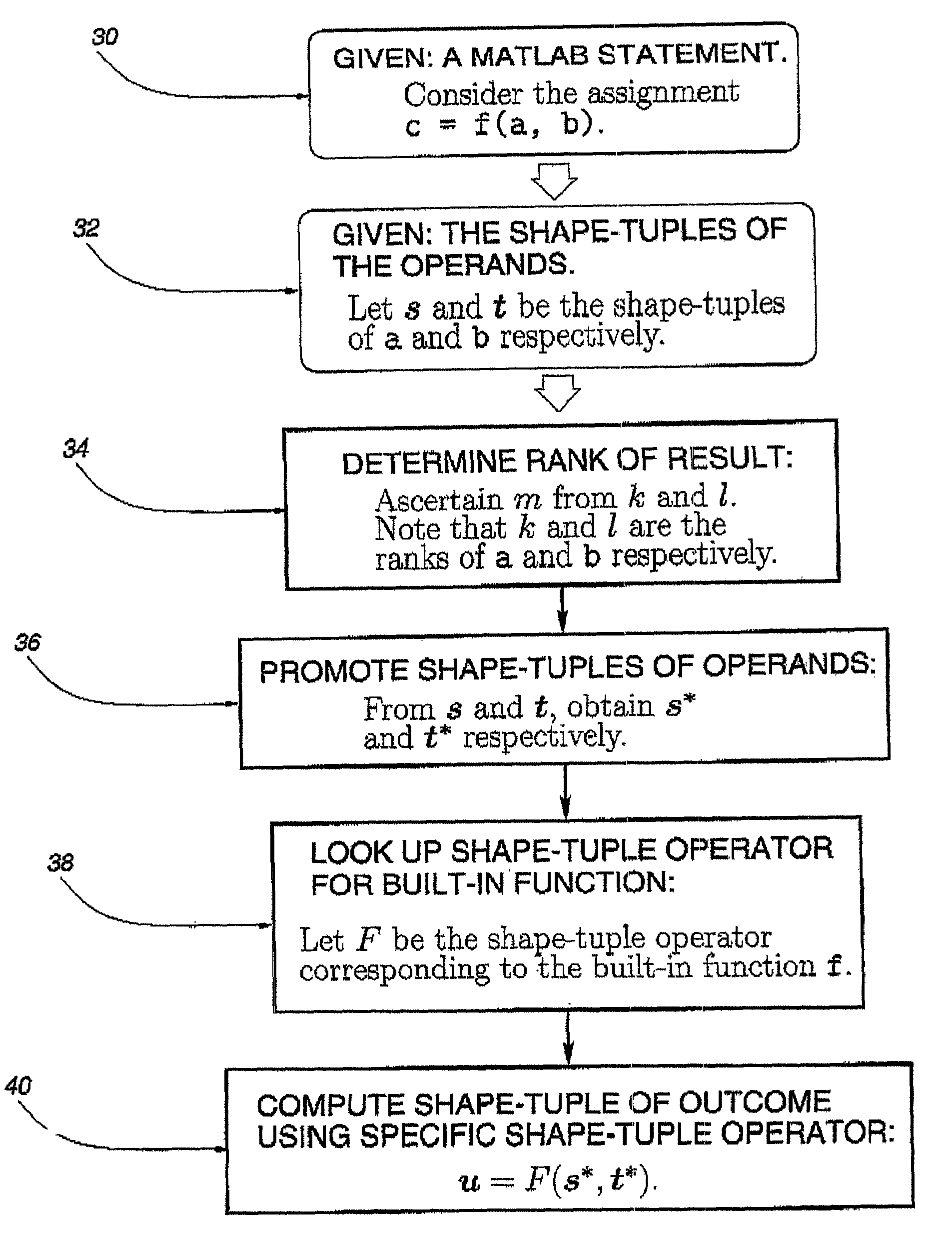
Method for array shape inferencing for a class of functions in MATLAB
InactiveUS7086040B2Optimize allocationOptimal codeSoftware engineeringProgram controlArray data structureTheoretical computer science
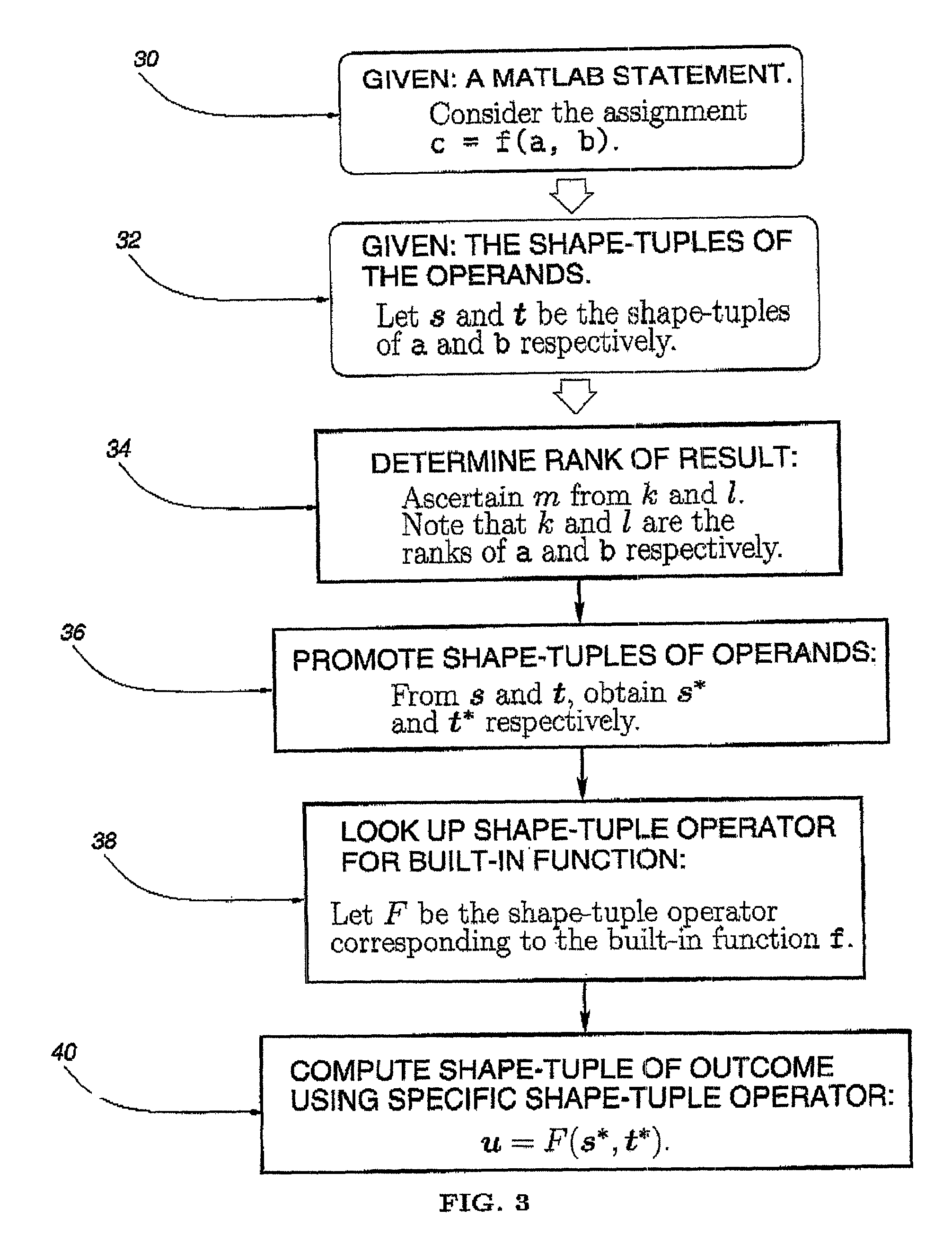
A method for inferring the shape and dimension of arrays for high-level, array-based languages such as MATLAB is presented. The method uses the algebraic properties that underlie MATLAB's shape semantics and infers the shape that the program expression assumes. In one embodiment, a shape-tuple of the result of a program expression is inferred by creating a shape-tuple expression comprising the shape-tuples of the operands and the shape-tuple operator.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
White-box cryptograph non-linear encoding protection method based on table lookup
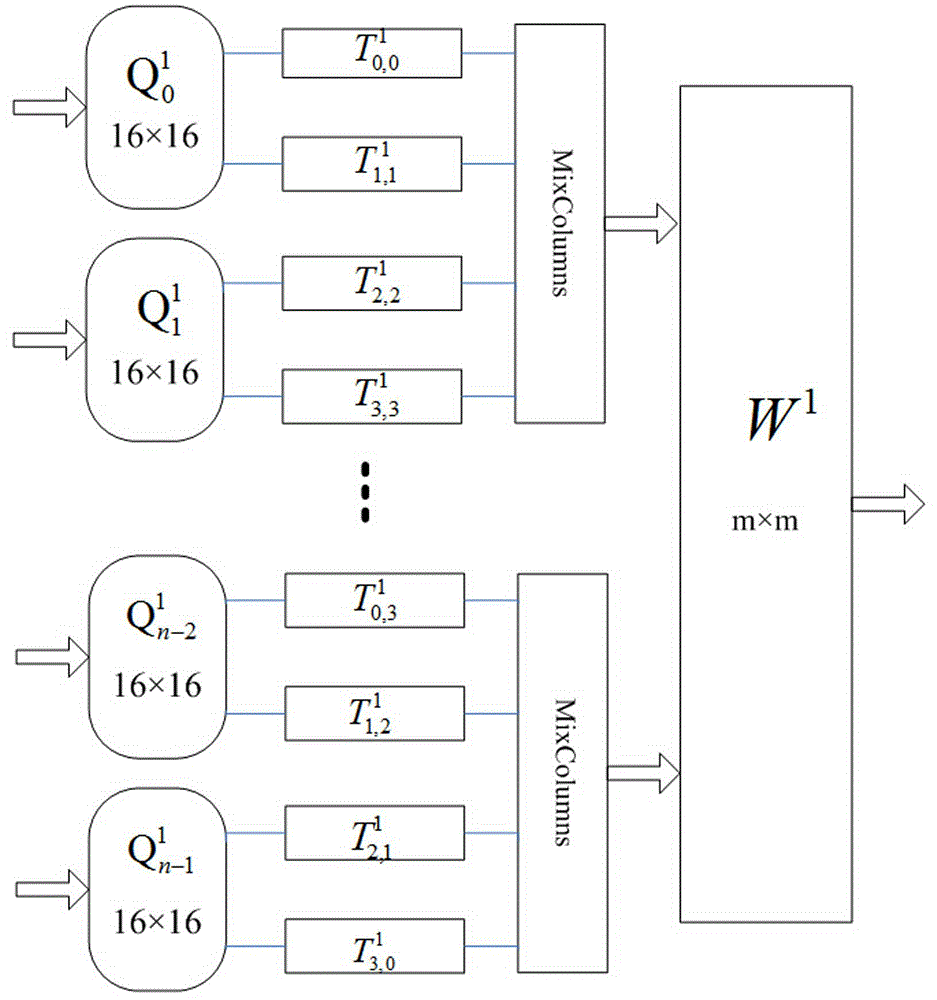
InactiveCN105591734AAlgebra times will not increaseReduce operationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesObfuscation16-bit
The invention discloses a white-box cryptograph non-linear encoding protection method based on table lookup. The white-box cryptograph non-linear encoding protection method comprises the steps of: dividing m variables of a cryptographic algorithm into n groups, wherein each group comprises 16 bits, and subjecting the groups to Q0<1>, Q1<1>, ... , Qn-1<1> nonlinear transformation in sequence; regarding output results as input of an internal obfuscation part of the cryptographic algorithm of an SP structure, taking an AES algorithm for an example, and carrying out T transformation and MixColumns transformation; subjecting obtained results to one-time m bit input and m bit output nonlinear W<1>transformation; and acquiring final results of this turn of iteration, and sending the final results to the subsequent turn of iteration step. According to the white-box cryptograph non-linear encoding protection method, internal and external codes are subjected to non-linear bijective conversion simultaneously, and required operation is small since the algebraic degree of a single S box is no more than 8 and cannot be increased by MixColumn components and external radiation obfuscation codes; in addition, a master cryptography key is not directly restored when facing external algebra interpolation attacks, but an equivalent decrypting Boolean system is constructed, thus the security of the white-box cryptograph non-linear encoding protection method is higher.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Decoding and error correction for algebraic geometric codes
InactiveUS20050204268A1Easy to implementCorrection errorAlgebraic geometric codesCode conversionComputer scienceAlgebra over a field
A method of decoding a one-point algebraic geometric code defined on an algebraic curve of the kind C(a,b), represented by an equation of degree b in X and of degree a in Y, comprises, for any received word, a step of locating transmission errors affecting said received word. The correction of errors in said word, which belongs to an algebraic geometric code, is then reduced to the correction of errors in a certain number, at most equal to a, of words belonging to a Reed-Solomon code. Devices and apparatuses adapted to implement this method are also described.
Owner:CANON KK
Nonlinear transformation method for symmetric key encryption and implementation method thereof
InactiveCN102006161ASimple structureReduce complexityEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesS-boxTheoretical computer science
The invention provides a nonlinear transformation method and a nonlinear transformation device for symmetric key encryption. Nonlinear transformation can be used directly as an S box; the S box uses function complex affine transformation in a finite field; and on the basis of keeping the original structure and code cryptographic characteristics of the S box of advanced encryption standard (AES), by increasing the times of nonlinear operation, the algebraic immunity of the S box is improved without reducing the complexity of the implementation mode of complex field hardware of the S box. The invention also provides a method for implementing the hardware of the S box. In the method, the complex field representation of elements is introduced, the inversion of an original field is converted into the inversion of a complex field, a plurality of linear and affine transformations are combined, and sub-field operations involved in the inversion of the complex field, such as multiplication, square operation, constant multiplication and inversion are all converted into inter-bit exclusive or operation and and operation. The whole S box hardware implementation process only requires a simple logic gate circuit, table lookup is avoided, hardware implement expense is reduced and the path delay is reduced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Structured constitution method of high enclose long low code rate multi-scale LDPC code
InactiveCN101252360AError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTheoretical computer scienceEuclidean vector
The invention relates to a construction method of structured non-binary LDPC code with large girth and low bit-rate based on finite field. The method includes the following steps: 1, parameters m and s are selected; 2, a subset B of GF(2) is constructed; 3, a base matrix W is constructed on the GF(2) by taking use of the subset B; 4, each element of the base matrix W is replaced with the address vector of the element and the nary numbers of the none-zero elements of the address vector are selected according to the nary numbers of the LDPC code to be constructed; in this way the LDPC code can be constructed. The construction method of check matrices provided by the invention is capable of constructing non-binary LDPC codes with any minimum length. Simulation results show that algebraic non-binary LDPC codes constructed through the construction method are obviously improved as compared with Mackay non-binary stochastic LDPC codes with the same parameters.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
A method of geostationary satellite orbit uncertainty evolution based on differential algebra
ActiveCN109255096AReduce computing timeHigh precisionComplex mathematical operationsNatural satelliteDynamic models
The invention discloses an orbital uncertainty analysis method based on differential algebra technology. Based on Taylor expansion of multivariate functions and polynomial operation framework, and based on the dynamic model of geosynchronous satellite orbit element description, solar pressure to the kinetic model, the third gravitational perturbation and the three perturbation terms of the Earth'soblateness are added in the dynamic model , the right term of the dynamic model is expanded along the nominal orbit by Taylor expansion, the expansion polynomial with initial deviation as variable isobtained, Under the frame of differential algebra, the orbital state expressed by the polynomial with the initial deviation as variable at any time is obtained, and the concrete value of the initialdeviation is brought into the polynomial result to obtain the state of the final spacecraft. The invention analyzes the optimal expansion order, the balance calculation time and the calculation precision according to different perturbation forces. The method can be used to analyze the orbit evolution of geostationary satellites with initial state deviation and parameter uncertainty, and can also be used in other spacecraft orbit evolution and attitude evolution missions.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
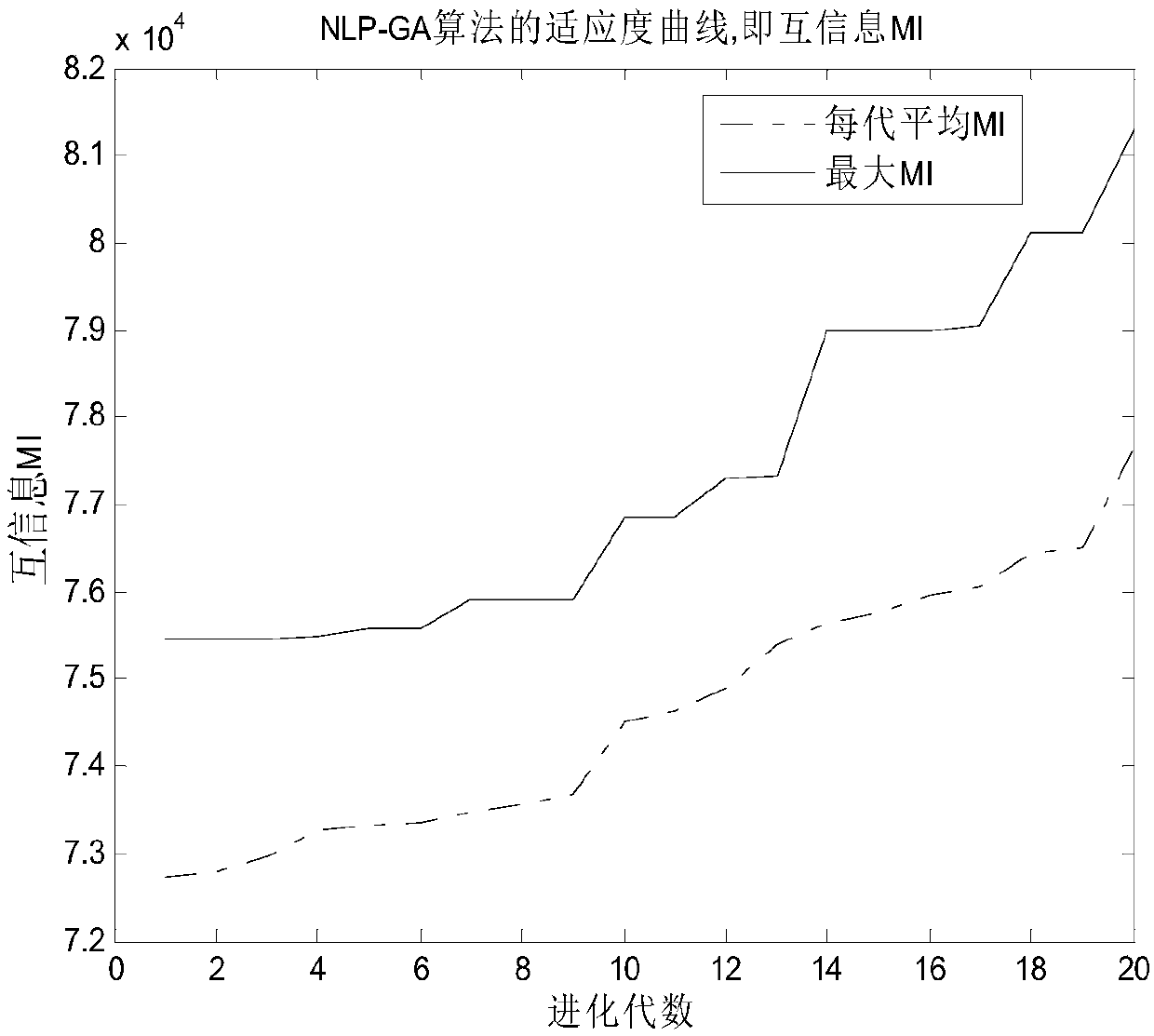
Method for optimizing maximum MI waveforms of cognition radar based on IGA-NP algorithm
ActiveCN107462875AFast convergenceImprove mutual informationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAlgebra over a fieldEnergy constraint
The invention discloses a method for optimizing maximum MI waveforms of the cognition radar based on an IGA-NP algorithm. The method comprises steps of determining the cognition radar, wherein target signals exist in a detection range of the cognition radar, carrying out calculation to obtain target signal spectrum variance, clutter spectrum variance and a noise power spectrum and setting a to-be-optimized waveform power spectrum; determining an energy constraint condition of the to-be-optimized waveforms and carrying out problem modeling; setting iteration times and carrying out integar algebras of non-linearity programming optimization; setting the number of chromosomes, the crossover probability and the mutation probability; calculating an initial population Code; carrying out initialization: making h represent the hth iteration, wherein h belongs to {1, 2,..., G}, and G represents the set biggest evolution algebra and calculating the iterated k-opt searching population shown in the description and the optimal chromosome after the hth iteration; and finishing the iteration until the h=G, and using the corresponding optimal chromosome when the iteration is stopped as the global optimal chromosome, wherein the global optimal chromosome is the to-be-optimized waveform power spectrum.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
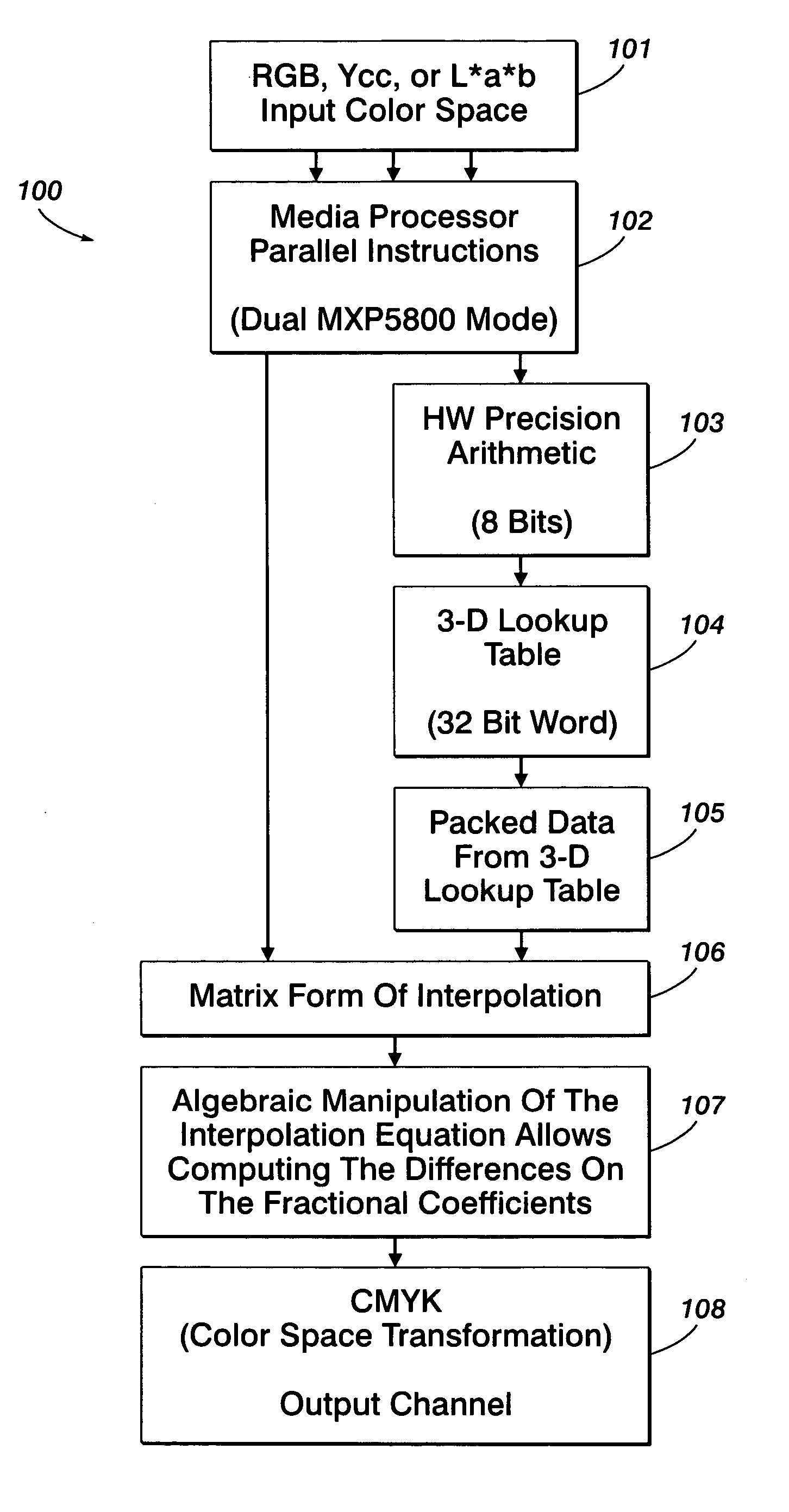
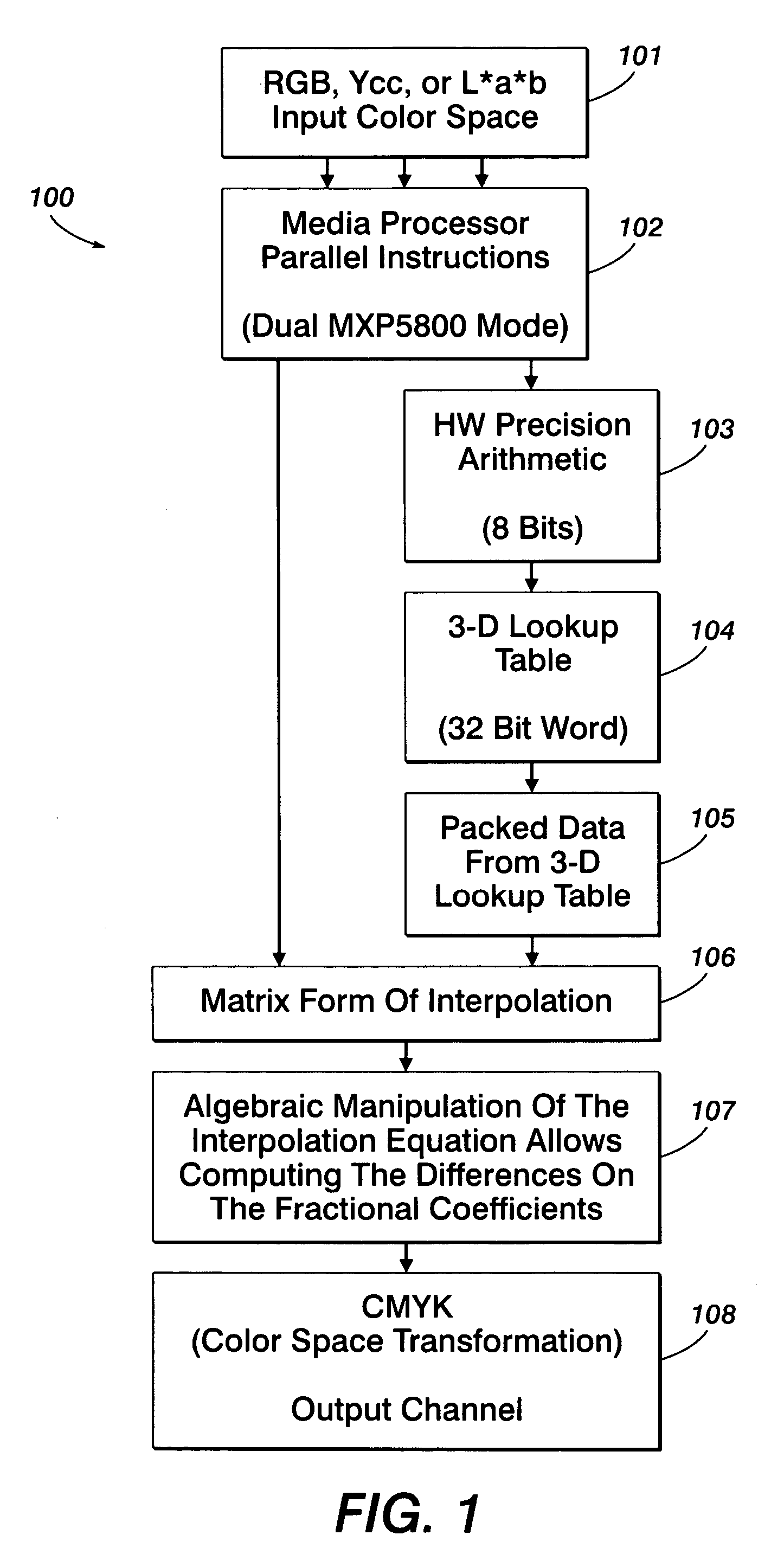
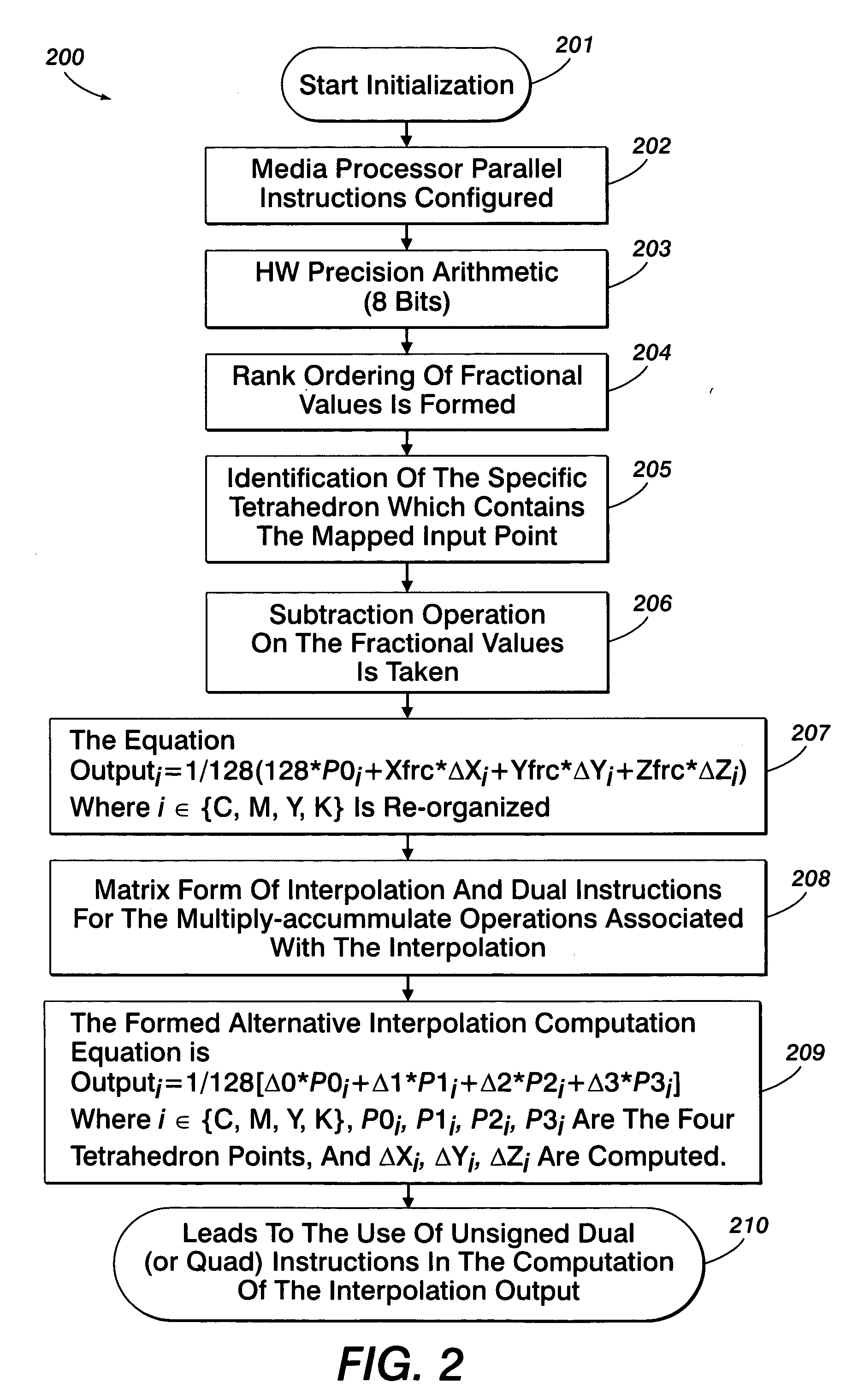
Method for tetrahedral interpolation computations using data-level parallelism
InactiveUS20070247648A1Effective calculationQuick implementationDigitally marking record carriersColor signal processing circuitsParallel computingPerformance rate
A system and method for tetrahedral interpolation computations using data-level parallelism that takes advantage of data-level parallelism in media processors. If the tetrahedron points in a 3D lookup table are packed together in a memory, the interpolation computation can be implemented without extra instructions to unpack them. An algebraic manipulation of the interpolation equation allows computing the difference on the fraction coefficients instead of the tetrahedron node values. Not only will this technique preserve the full precision without over or underflow, but the packed data from the 3D lookup can be used directly, thereby allowing a faster implementation of the color space transformation overall and implementing as part of a direct-copy image path on a media processor. Such a system and method allows the implementation of the direct copy pipeline to function at the required performance rate as requested by a customer specification while obtaining the required product design speed.
Owner:XEROX CORP
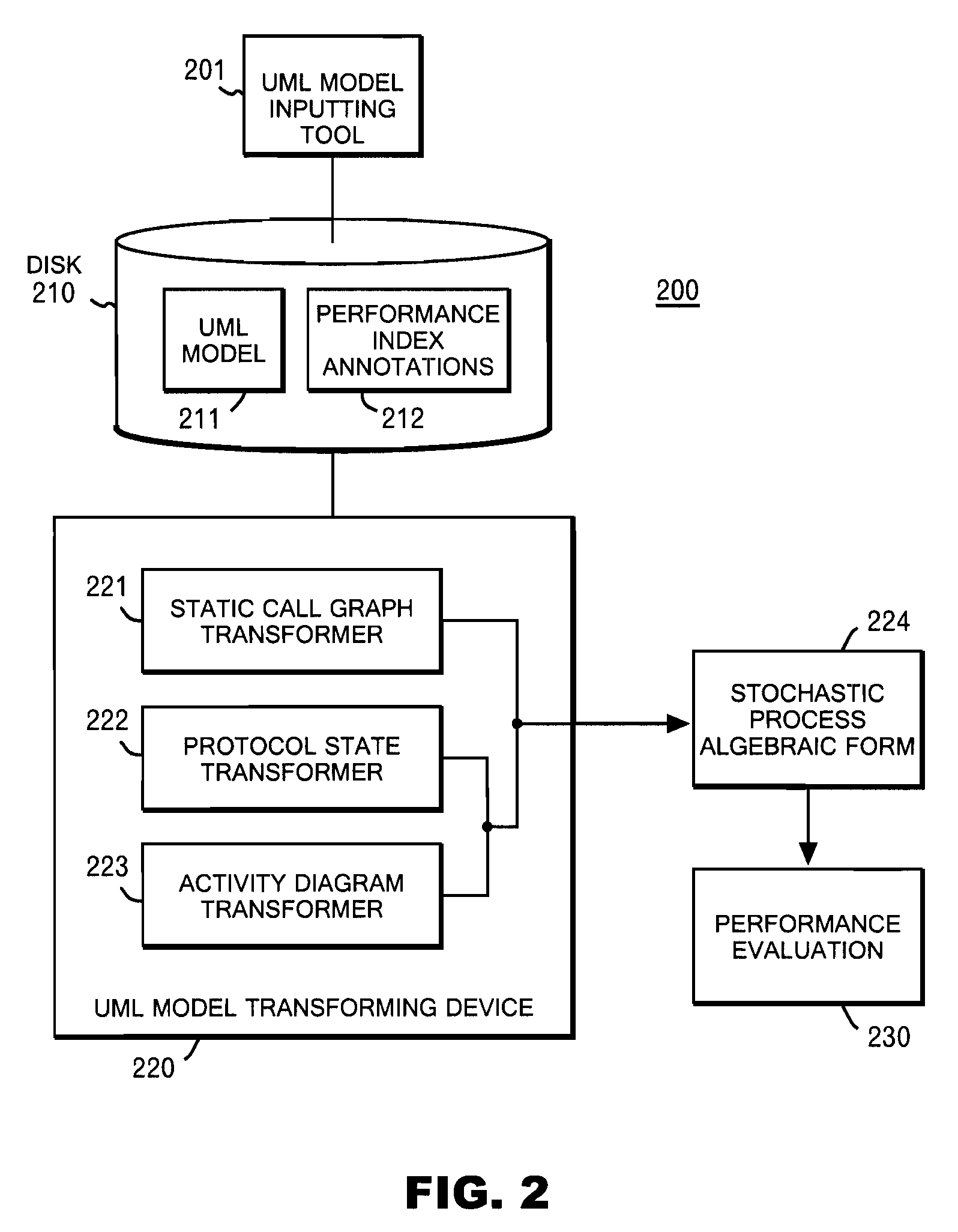
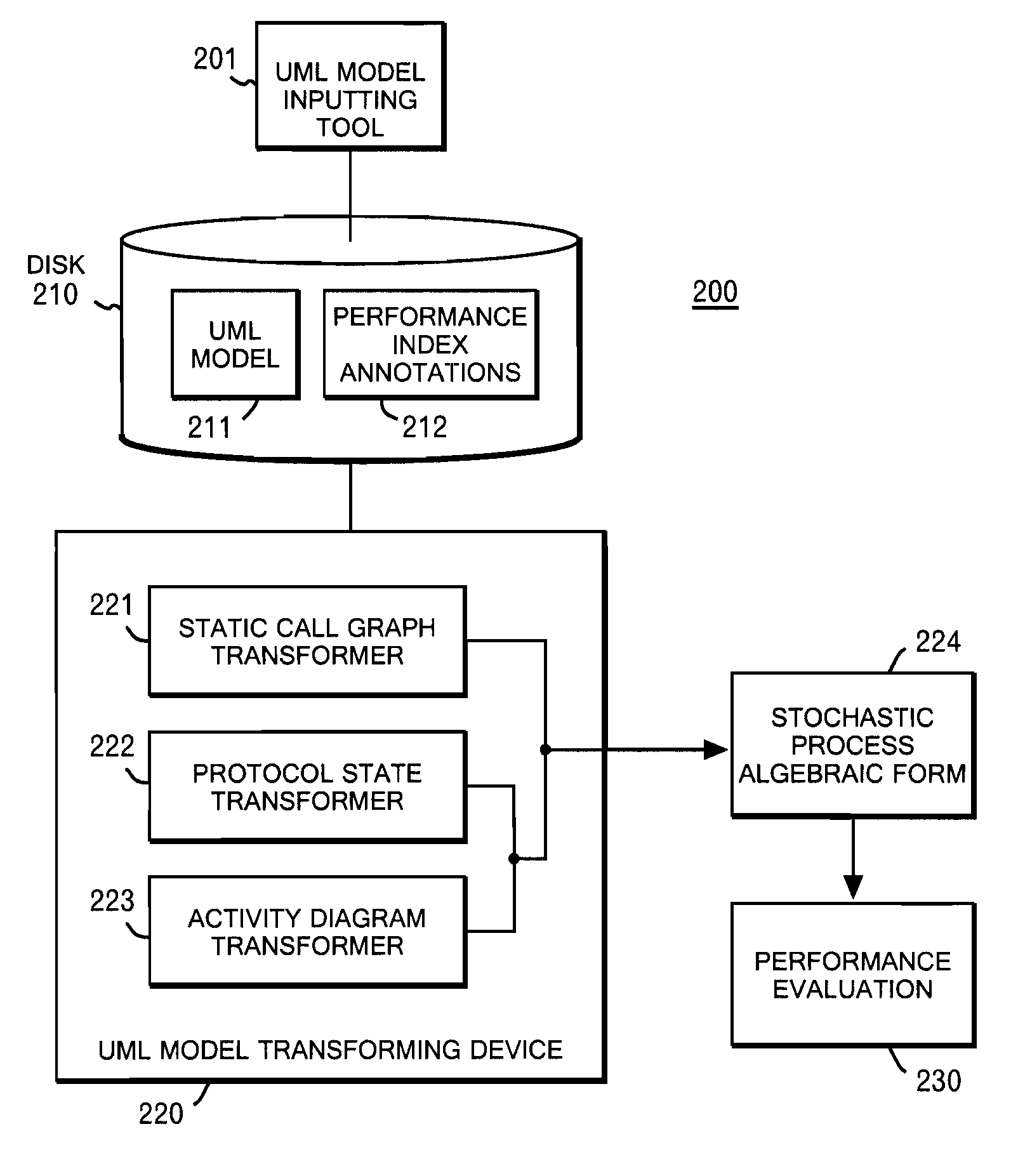
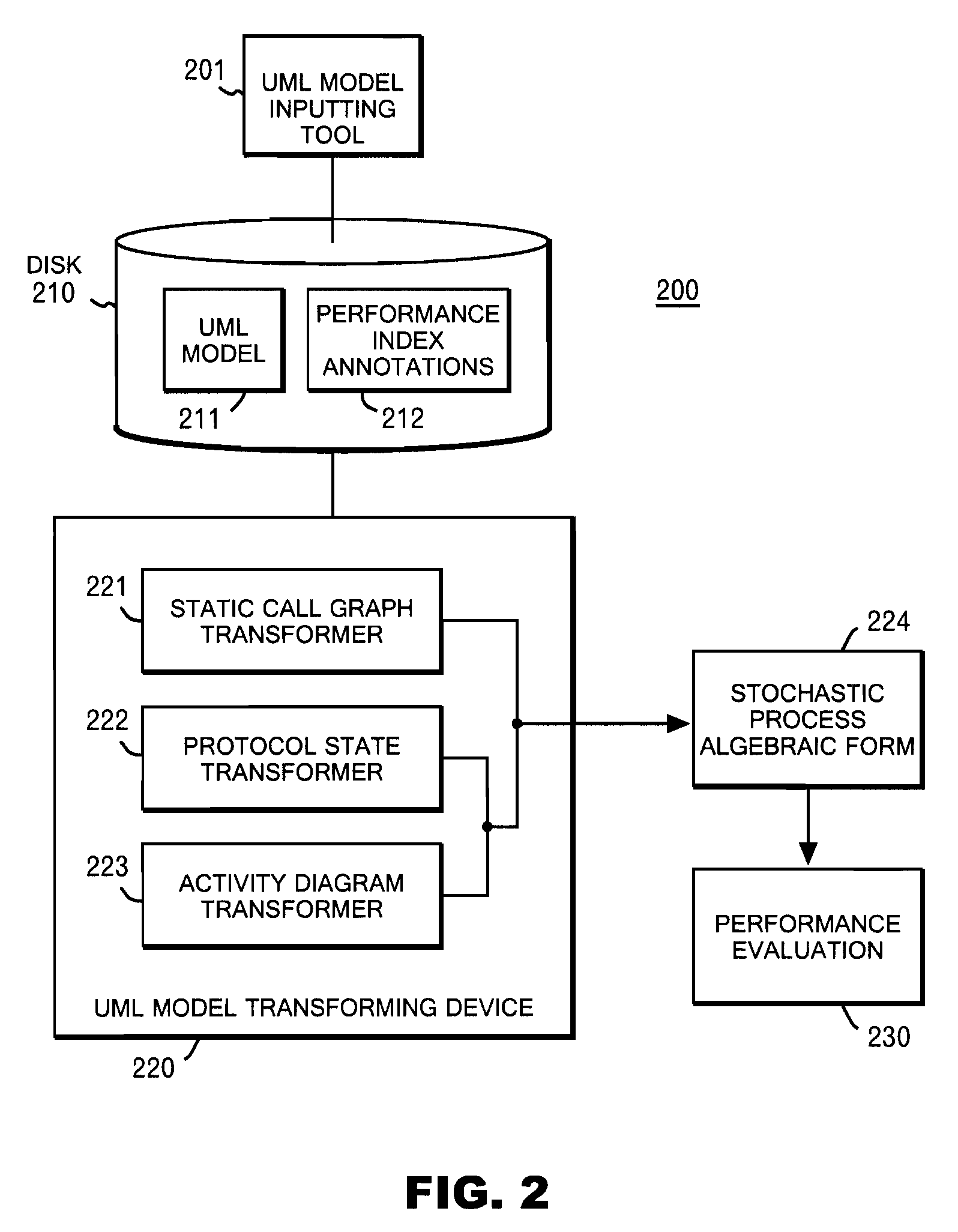
System and method for deriving stochastic performance evaluation model from annotated uml design model
InactiveUS20070150875A1Easy to exportRequirement analysisSpecific program execution arrangementsActivity diagramState diagram
The computer program enables a computer to function as: means for transforming a static call graph into a syntax tree having a binary tree structure; means for transforming a protocol state diagram into a stochastic process algebraic form; means for transforming an activity diagram into a stochastic process algebraic form; means for obtaining a stochastic process algebraic form of each of classes by merging the stochastic process algebraic form of the protocol state diagram, and the stochastic process algebraic form of the activity diagram; and means for obtaining a stochastic algebraic form of a whole system from the syntax tree, and from the stochastic process algebraic forms of the classes.
Owner:LINKEDIN
White-box password nonlinear coding protection method based on combination of table look-up and disturbance scrambling
InactiveCN105656622AAlgebra times will not increaseReduce operationKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesPasswordInterpolation attack
The invention discloses a white-box password nonlinear coding protection method based on combination of table look-up and disturbance scrambling. The white-box password nonlinear coding protection method comprises the following steps of: averagely dividing 32-bit sensitive variables in a password algorithm operation process into four sets, namely x<0,0>, x<0,1>, x<0,2> and x<0,3>, and sequentially performing nonlinear scrambling shown in the specification; adding disturbance information (beta*, Y, phi*), and calculating beta*=F(x<0,0>, x<0,1>, x<0,2> and x<0,3>) as an initial disturbance item; sequentially transforming results in two steps through T<3>, T<2>, T<1>, T<0> and phi*; taking an output result as column promiscuous transformation; and then, sequentially performing nonlinear displacement through Q<3>, Q<2>, Q<1>, Y and Q<0> to obtain an input variable for the next round of iteration, such that a final output result of a white box is obtained. According to the invention, nonlinear bijection transformation of internal and external coding is adopted simultaneously; because the algebraic time of a single S box is not beyond 8 and the algebraic time cannot be increased by a column promiscuous part and external radiation scrambling coding, required operation is relatively low; furthermore, when an external algebra interpolation attack occurs, a main key cannot be recovered directly; an equivalent decoding Boolean system is constructed; and thus, the safety of the white-box password nonlinear coding protection method disclosed by the invention is relatively high.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Hybrid network minimum travel time ray tracing tomography method
InactiveCN103698810AReduce the numberSolve the problems of poor parameterization flexibility and low accuracy of speed interface descriptionSeismic signal processingAcoustic waveTomography
The invention discloses a hybrid network minimum travel time ray tracing tomography method which comprises the steps that a two-dimensional complicated external geometric boundary and an imaging area of an internal complicated space structure are split into regular rectangular sub-areas and irregular sub-areas according to geometric structures of the geometric boundary and the imaging area; the regular rectangular sub-areas are subjected to rectangular mesh subdivision; the irregular sub-areas are subjected to triangular mesh subdivision; the sound wave first arrival travel time is computed by a hybrid network wave travel plane extension method; a ray path from any receiving point to an excitation point is traced; ray path information forms a matrix equation; the matrix equation is solved by an extrapolation sequence acceleration algebra reconstruction technique; velocity distribution of a model is obtained; and finally regular mesh imaging data is formed. The method effectively solves the problem existing in single mesh subdivision, the problems of great memory capacity, long computation time, great difficulty and low efficiency during forward modelling, and the problems of poor equation condition and solving difficulty during chromatography inversion.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
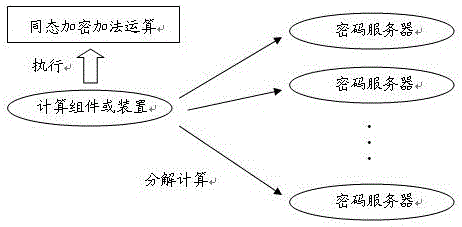
Operation method and system for ciphertext numbers
ActiveCN106254073APrevent leakageCooperative Cheating AvoidPublic key for secure communicationCommunication with homomorphic encryptionPlaintextComputer hardware
The present invention relates to an operation method and system for ciphertext numbers. The operation method for ciphertext numbers includes the following steps that: when carrying out algebraic operation involving ciphertext numbers, a calculation component or apparatus exports n groups of numbers from numbers to be operated, and then, submits the n groups of numbers to n password servers for carrying corresponding algebraic operation, wherein each group of numbers includes ciphertext numbers; after receiving each group of numbers, the n password servers decrypt the ciphertext numbers in each group of numbers, carries out operation required by the calculation component or apparatus by using plaintext numbers obtained after the decryption, and returns the ciphertext number of calculation results to the calculation component or apparatus; and after receiving the ciphertext number results returned by the n password servers, the calculation component or apparatus obtains final operation results through homomorphic encryption additive operation. With the method and system of the invention adopted, the multiplication, division and exponentiation operation of a ciphertext can be carried out through only using the additive homomorphic encryption algorithm with the origin plaintext numbers of the ciphertext numbers involved in operation not leaked.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
System and method for deriving stochastic performance evaluation model from annotated UML design model
InactiveUS7788636B2Easy to exportRequirement analysisSpecific program execution arrangementsActivity diagramState diagram
Owner:LINKEDIN
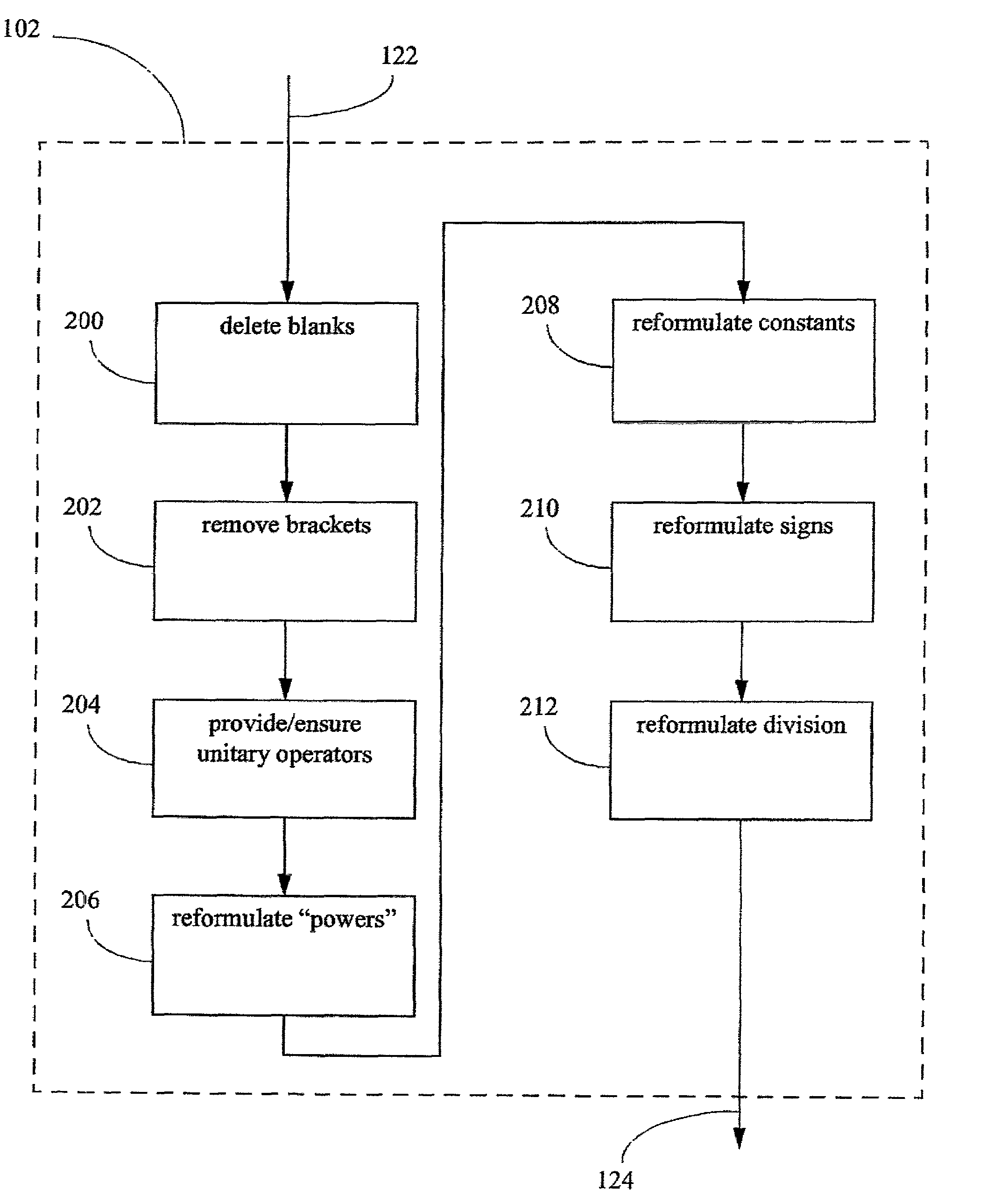
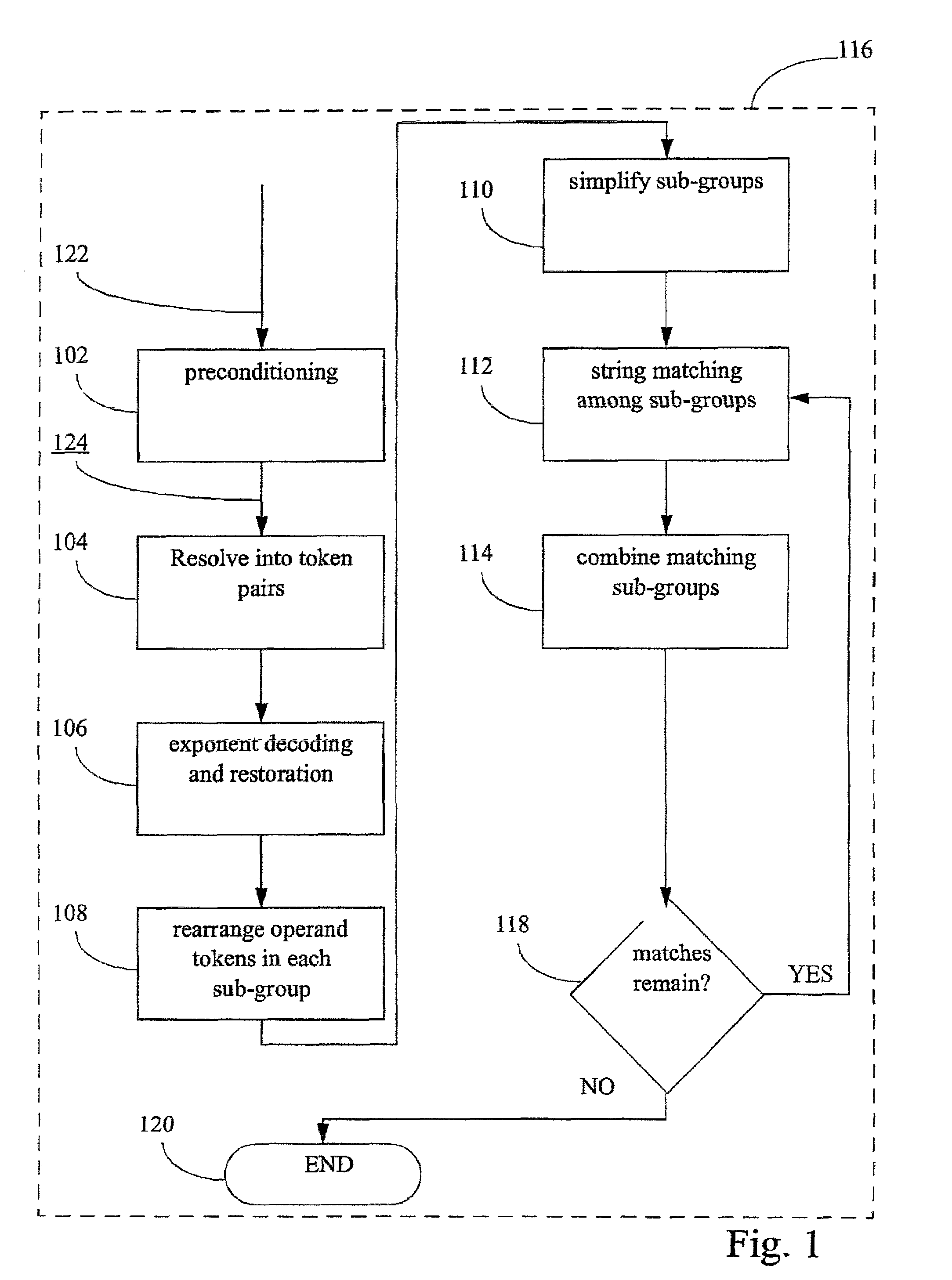
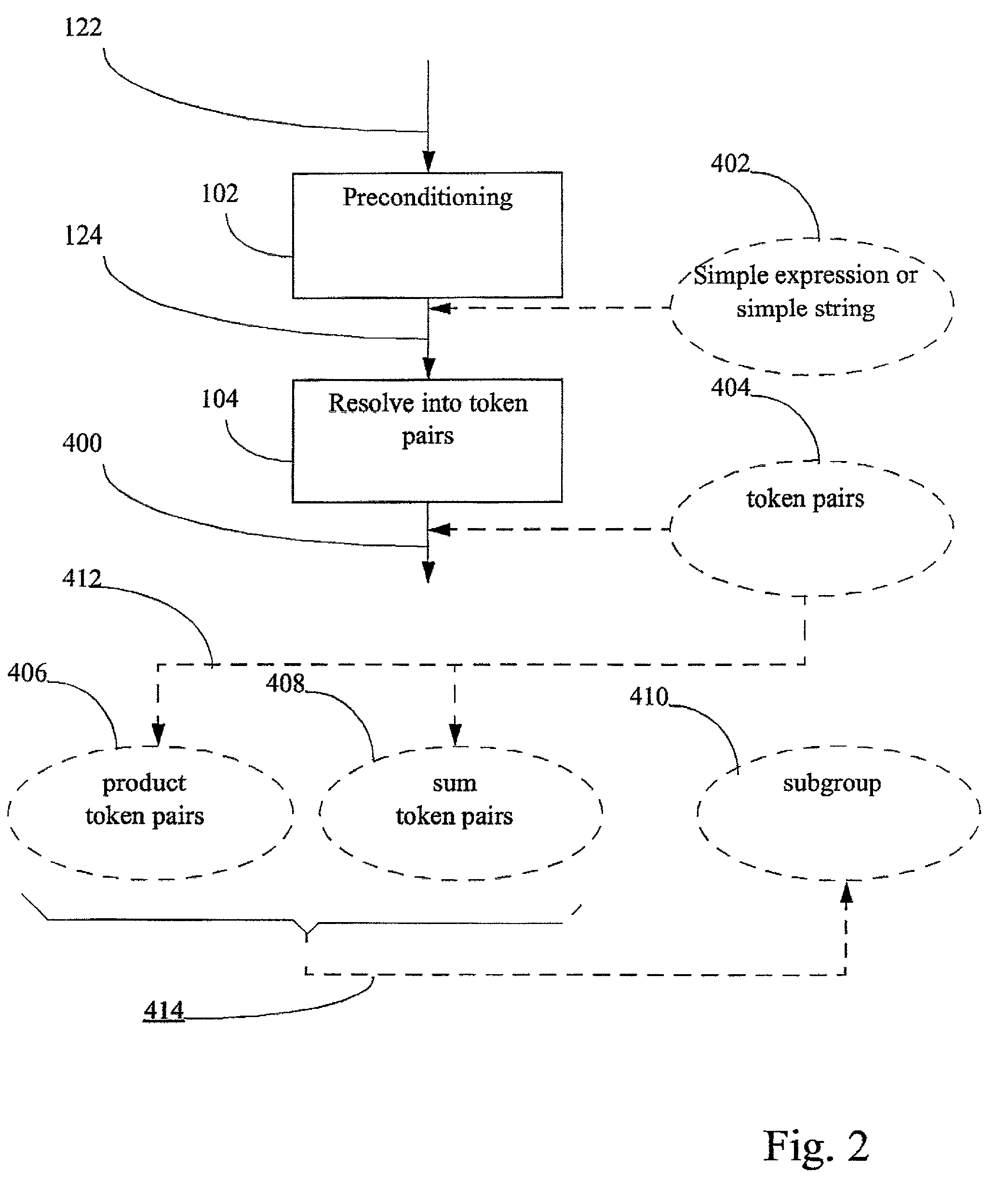
Compiler optimisation of source code by determination and utilization of the equivalence of algebraic expressions in the source code
InactiveUS7337437B2More disadvantageSoftware engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsObject codeTheoretical computer science
A method, apparatus, and computer program product for determining, in a computer environment, the equivalence, if any, of two algebraic expressions. The expressions are recast into a form of one or more token pairs arranged sequentially in a string, such that each token pair includes an operator followed by an operand. The strings are reduced in accordance with a set of predetermined simplifying rules. The reduced strings are compared by matching, to detect equivalence of the two algebraic expressions. The source code is compiled into object code, wherein the source code includes the two algebraic expressions, and wherein the compiling includes the recasting, the reducing, and the comparing. The method, apparal us, and computer program product may be used in compiler optimisation of source code and like computing tasks.
Owner:IBM CORP
Data processing system utilizing topological methods to manipulate and categorize n-dimensional datasets
Methods are constructed for defining equivalence relations on embedded manifolds. A continuous path in the space of equivalence relations that spans from “homologous” to “diffeomorphic” and another similar path with endpoints “homologous” and “isometric” are given. Underlying the methodology is a convolution algebra of homology sampling functions. The methodology has applications for describing geometrical arrangements in material science, molecular biology, data science and physics. The methods are implemented in program code stored in a computer readable media and executable on a computer system to provide data analysis functions for a user.
Owner:KLING DANIEL H
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com