Patents
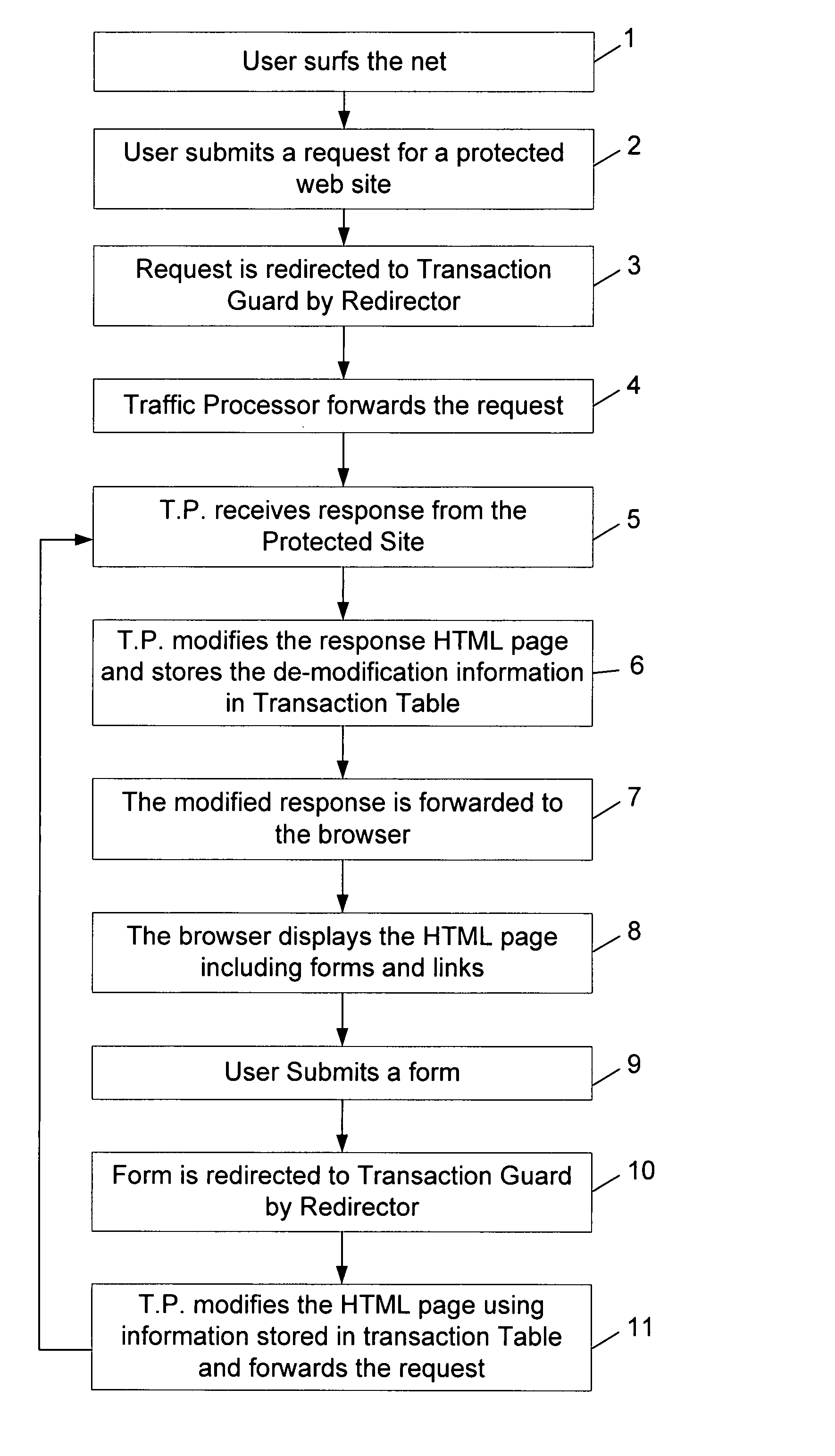
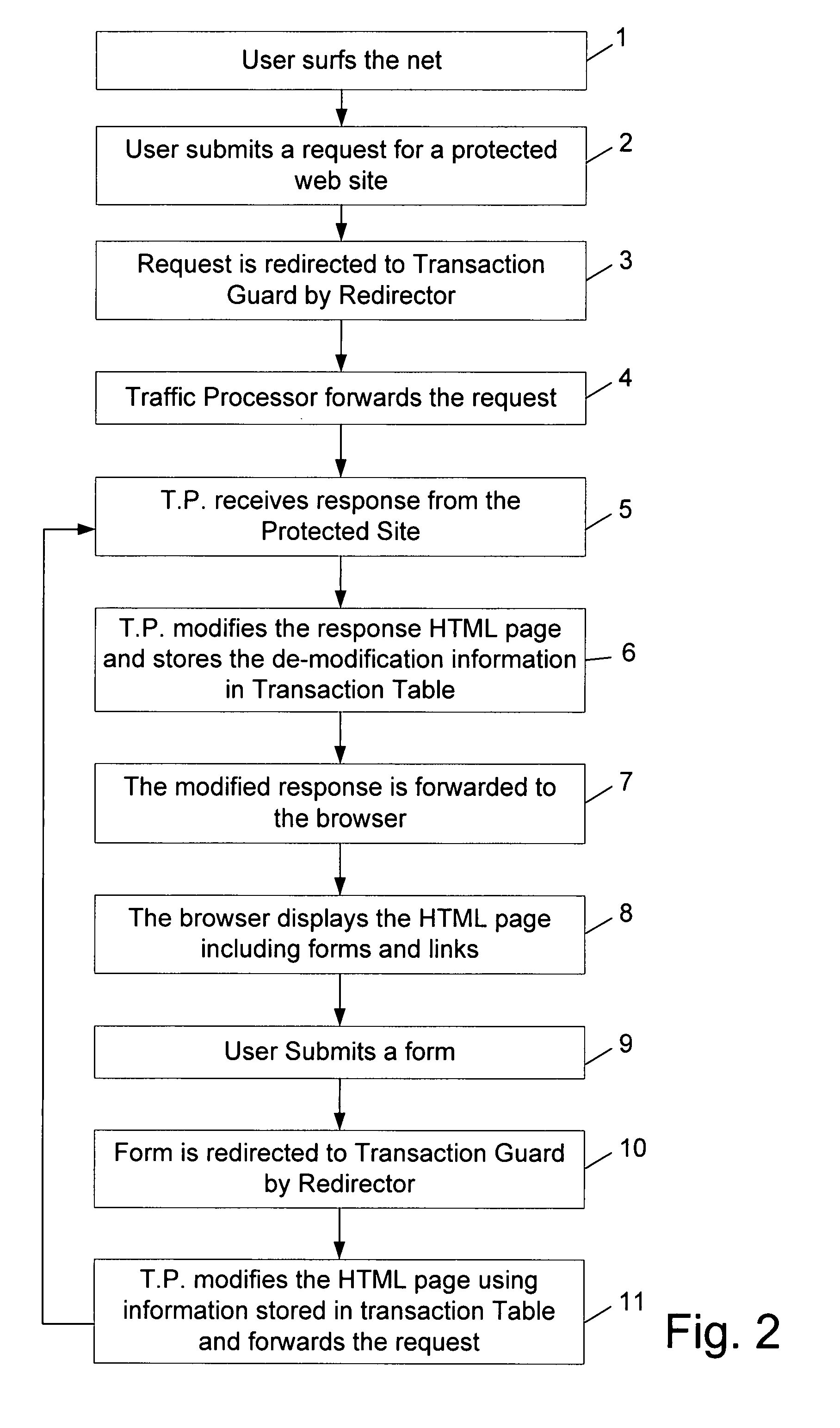
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
409 results about "Obfuscation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Obfuscation is the obscuring of the intended meaning of communication by making the message difficult to understand, usually with confusing and ambiguous language. The obfuscation might be either unintentional or intentional (although intent usually is connoted), and is accomplished with circumlocution (talking around the subject), the use of jargon (technical language of a profession), and the use of an argot (ingroup language) of limited communicative value to outsiders.
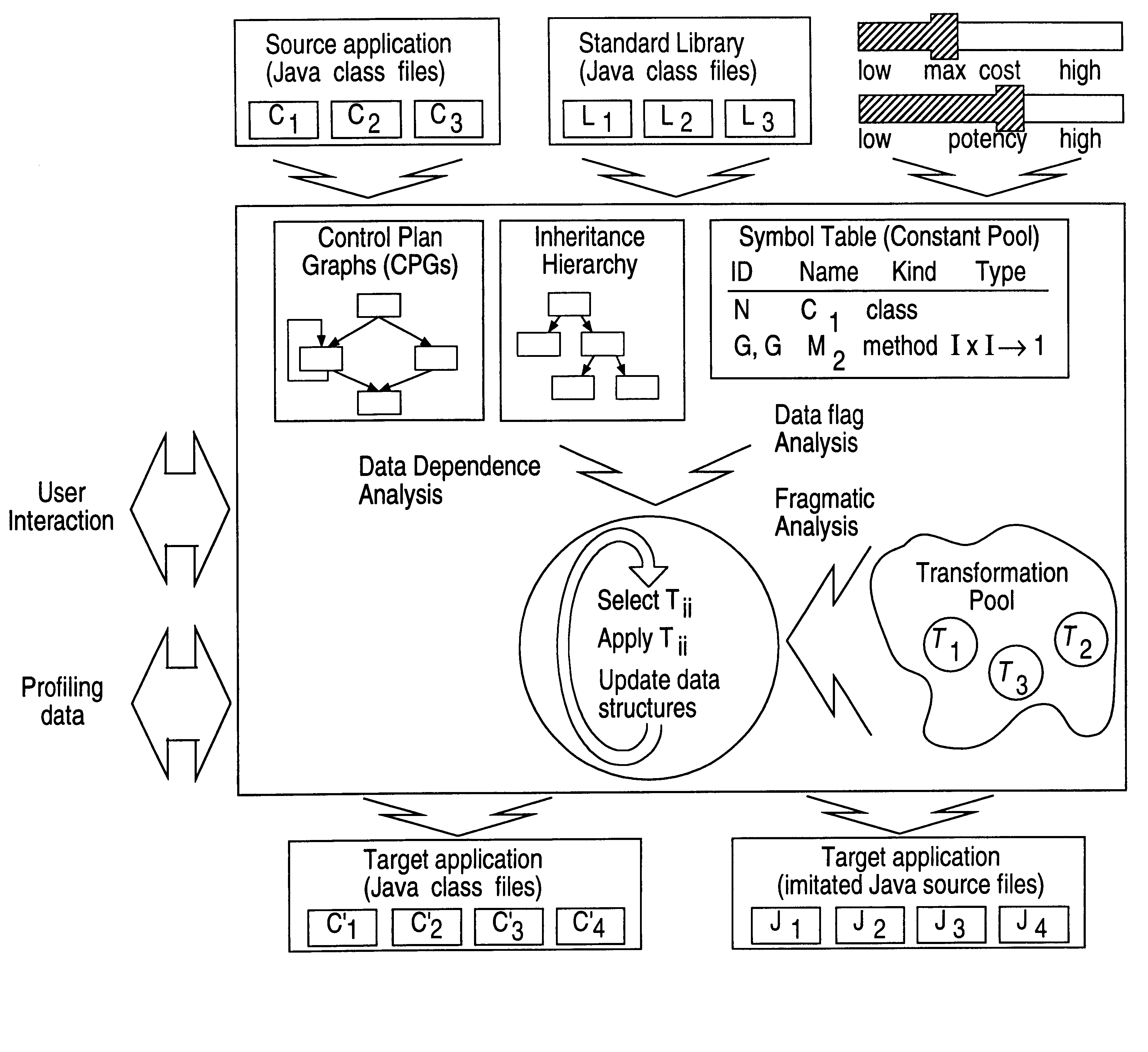
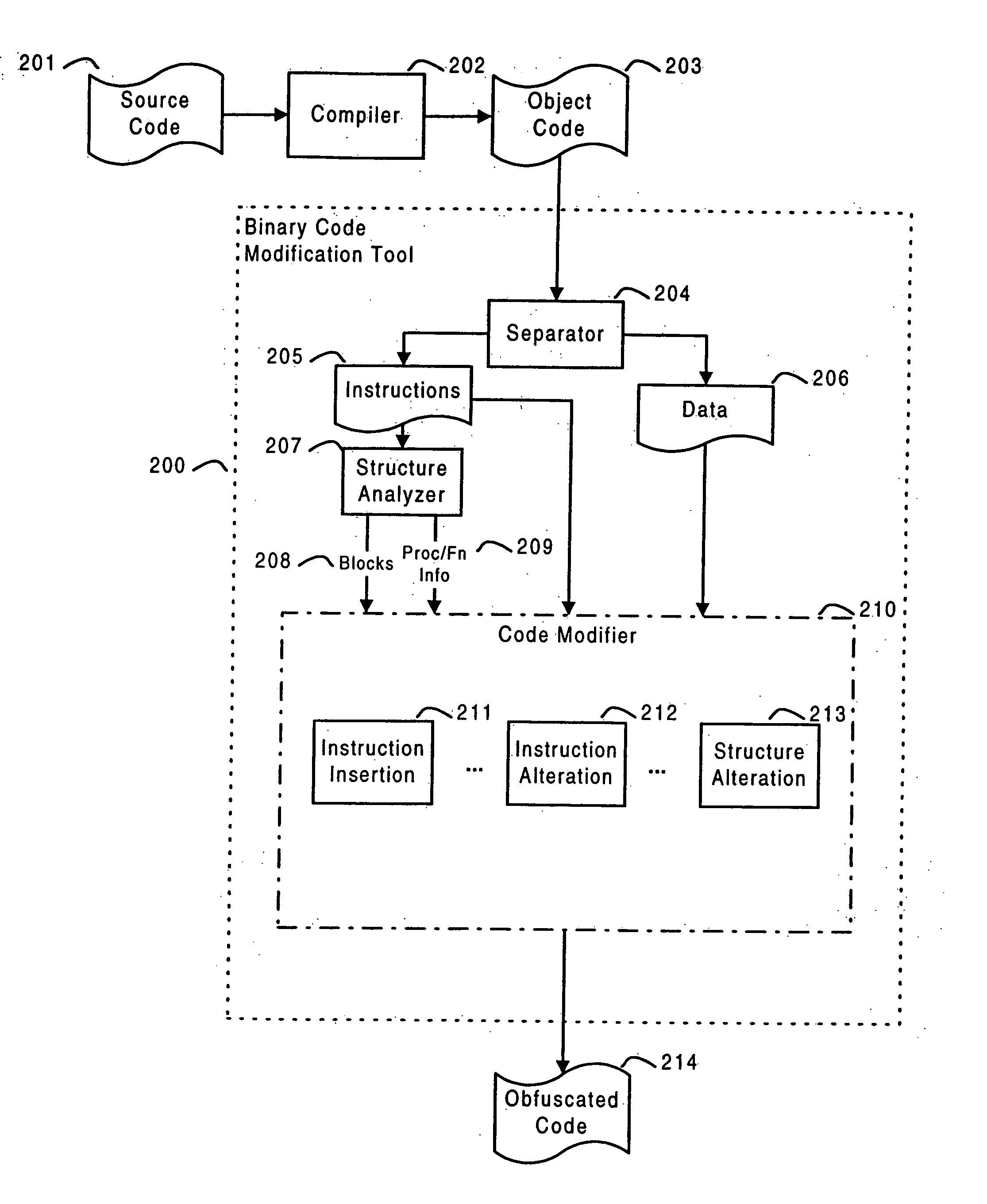
Obfuscation techniques for enhancing software security
InactiveUS6668325B1Guaranteed maximum utilizationDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionObfuscationTheoretical computer science
The present invention provides obfuscation techniques for enhancing software security. In one embodiment, a method for obfuscation techniques for enhancing software security includes selecting a subset of code (e.g., compiled source code of an application) to obfuscate, and obfuscating the selected subset of the code. The obfuscating includes applying an obfuscating transformation to the selected subset of the code. The transformed code can be weakly equivalent to the untransformed code. The applied transformation can be selected based on a desired level of security (e.g., resistance to reverse engineering). The applied transformation can include a control transformation that can be creating using opaque constructs, which can be constructed using aliasing and concurrency techniques. Accordingly, the code can be obfuscated for enhanced software security based on a desired level of obfuscation (e.g., based on a desired potency, resilience, and cost).
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
Software self-defense systems and methods
ActiveUS20050183072A1Error detection/correctionProgram/content distribution protectionTamper resistanceObfuscation
Systems and methods are disclosed for protecting a computer program from unauthorized analysis and modification. Obfuscation transformations can be applied to the computer program's local structure, control graph, and / or data structure to render the program more difficult to understand and / or modify. Tamper-resistance mechanisms can be incorporated into the computer program to detect attempts to tamper with the program's operation. Once an attempt to tamper with the computer program is detected, the computer program reports it to an external agent, ceases normal operation, and / or reverses any modifications made by the attempted tampering. The computer program can also be watermarked to facilitate identification of its owner. The obfuscation, tamper-resistance, and watermarking transformations can be applied to the computer program's source code, object code, or executable image.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
Method and system for providing tamper-resistant software
InactiveUS20060048223A1Performance penaltyImprove tamper resistanceMemory loss protectionDetecting faulty computer hardwareTamper resistanceObfuscation
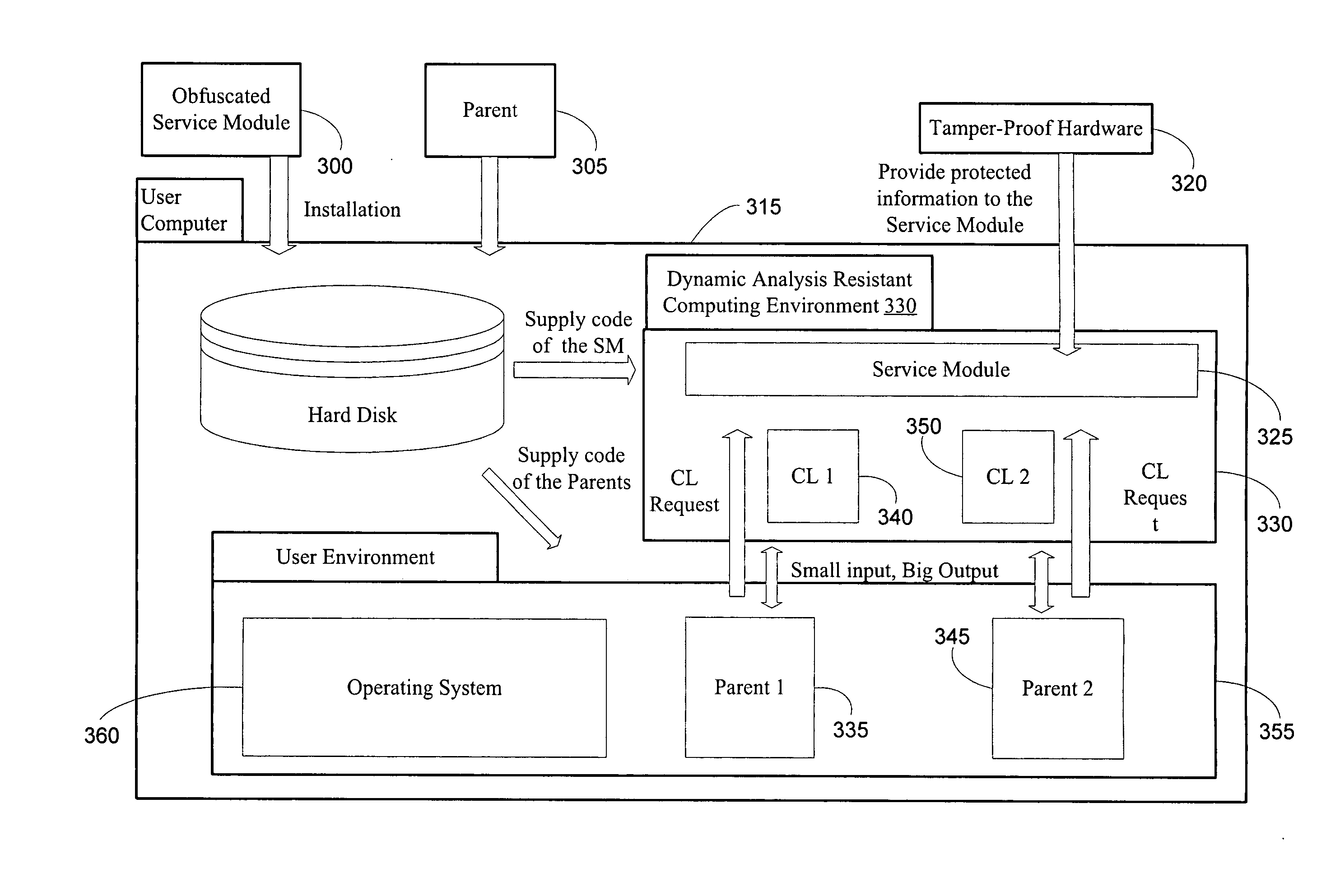
A method and system for protecting only a portion of the software to be protected against tampering is described. Such a portion may be stored in a tamper-resistant physical device, with optional encryption, for downloading when needed for execution. Several layers of tamper resistance are provided without excessively impacting performance of the protected software. For instance, obfuscation is applied to the code for the service module to minimize the large expense associated with obfuscation. The invention includes embodiments that deliver critical logic, policy information and other similar information with the help of mobile agents, which may be hosted by a server in a smart card.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
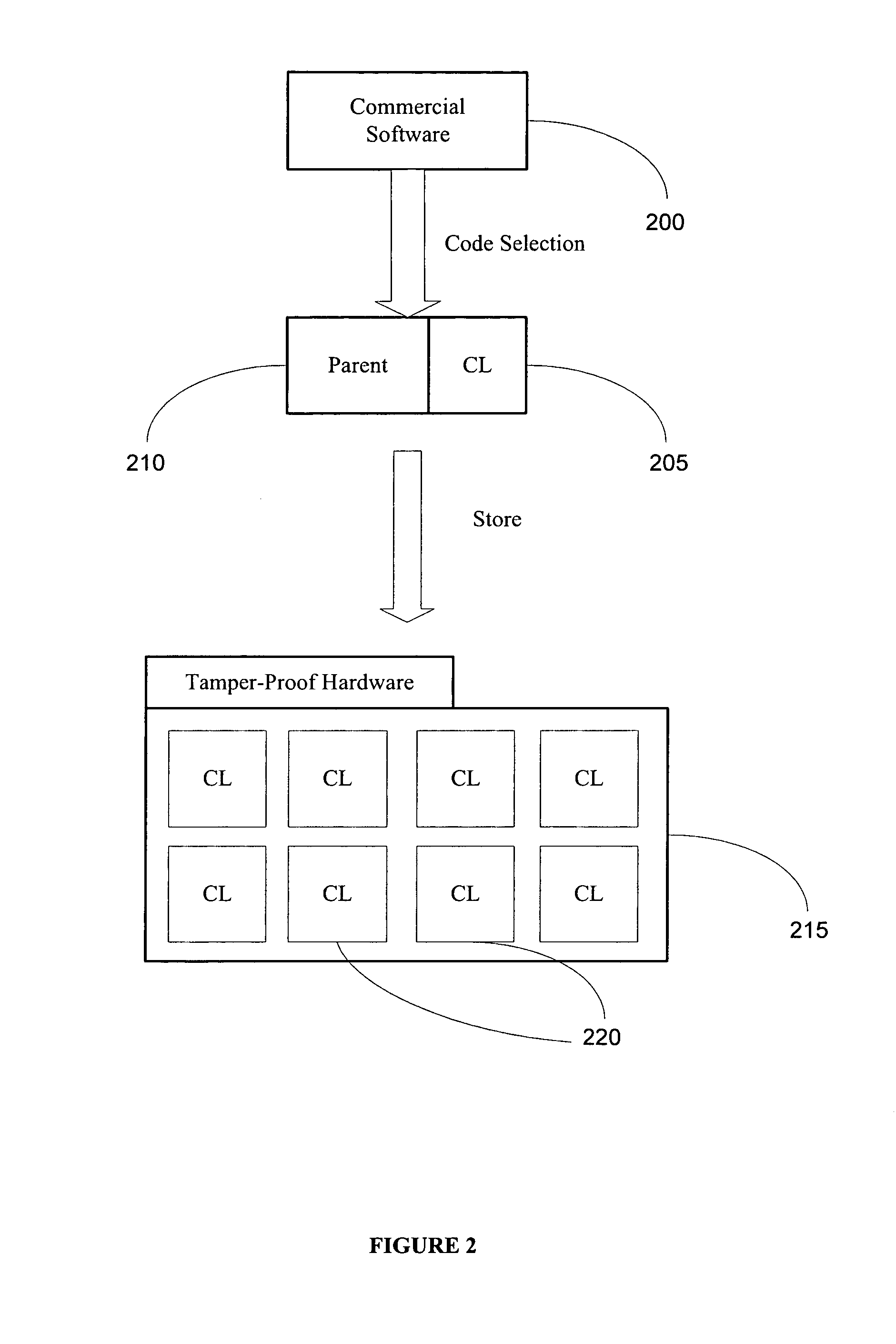
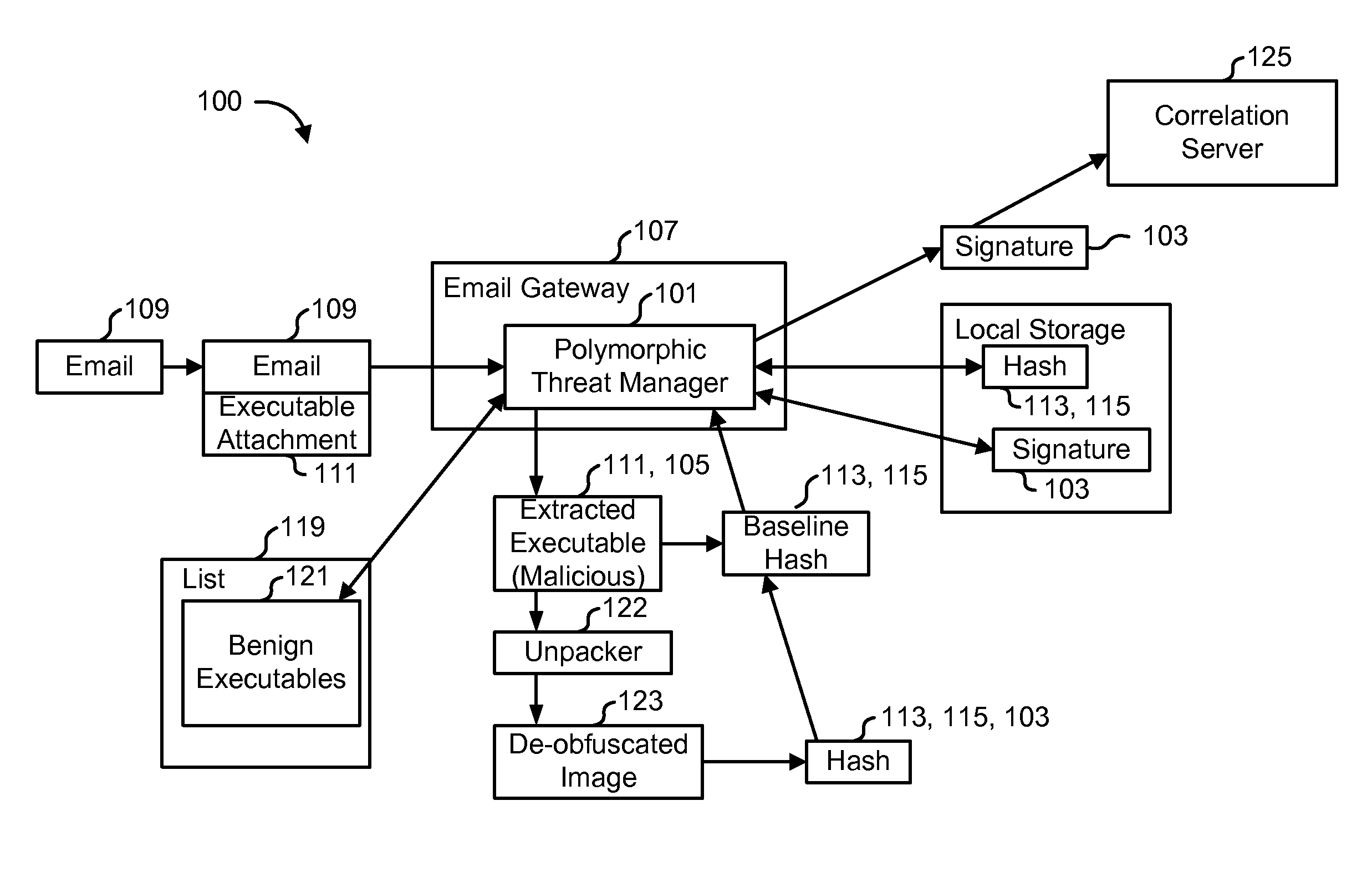
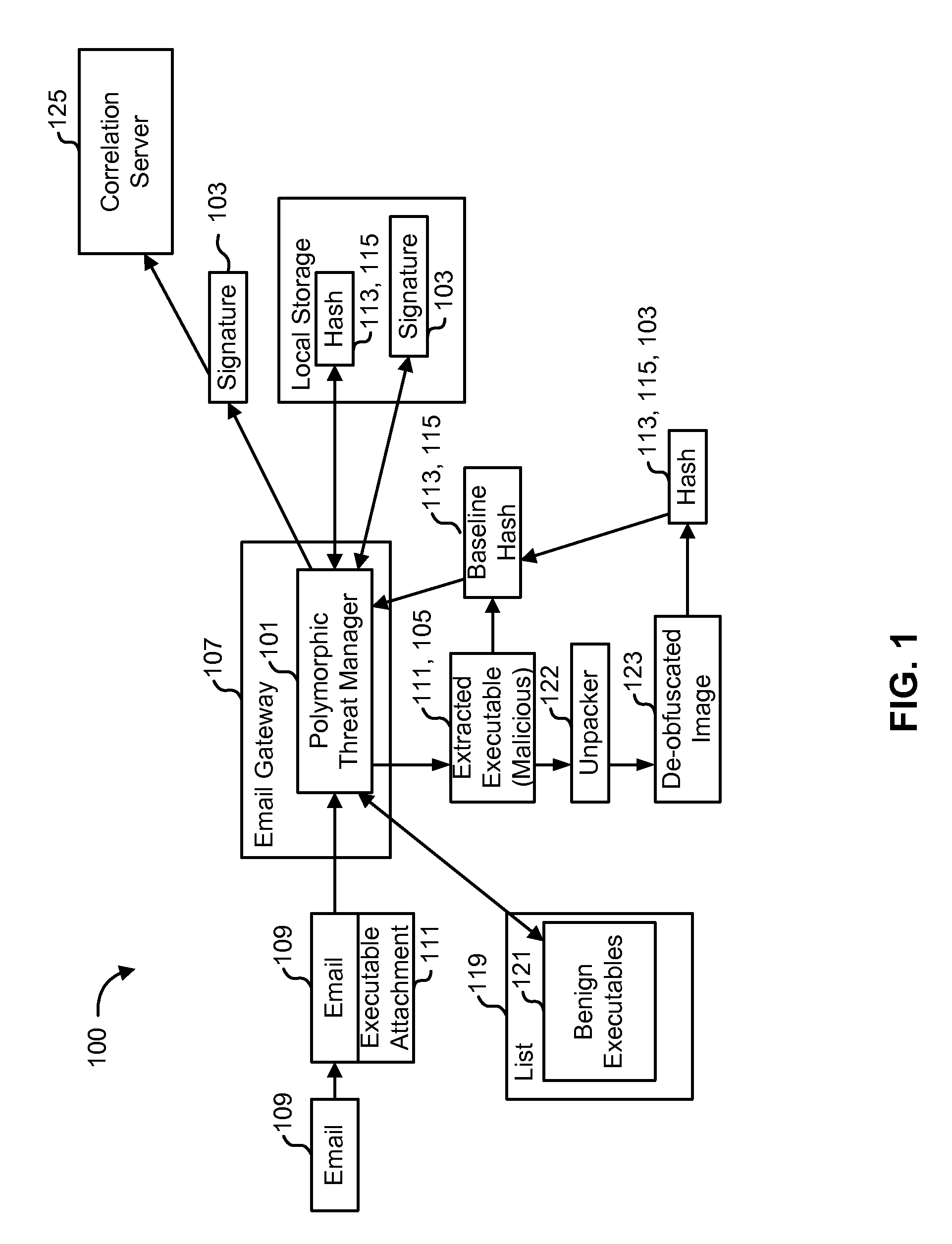
Detecting polymorphic threats
InactiveUS7739740B1Reduce loadMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionObfuscationInternet privacy
A polymorphic threat manager monitors an incoming email stream, and identifies incoming email messages to which executable files are attached. The polymorphic threat manager characterizes incoming executable files according to at least one metric. For example, the polymorphic threat manager can decompose an executable file into fragments, hash some or all of these, and use the hashes as characterization metrics. The polymorphic threat manager subsequently de-obfuscates executable files, and creates corresponding characterization metrics for the de-obfuscated images. The characterizations of executable files before and after de-obfuscation are compared, and if they differ sufficiently, the polymorphic threat manager determines that the file in question is polymorphic. The characterization metrics of such an executable file after de-obfuscation can be used as a signature for that file.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Scrambling HTML to prevent CSRF attacks and transactional crimeware attacks
InactiveUS20080222736A1Preventing unauthorized activityDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsWeb siteTraffic capacity
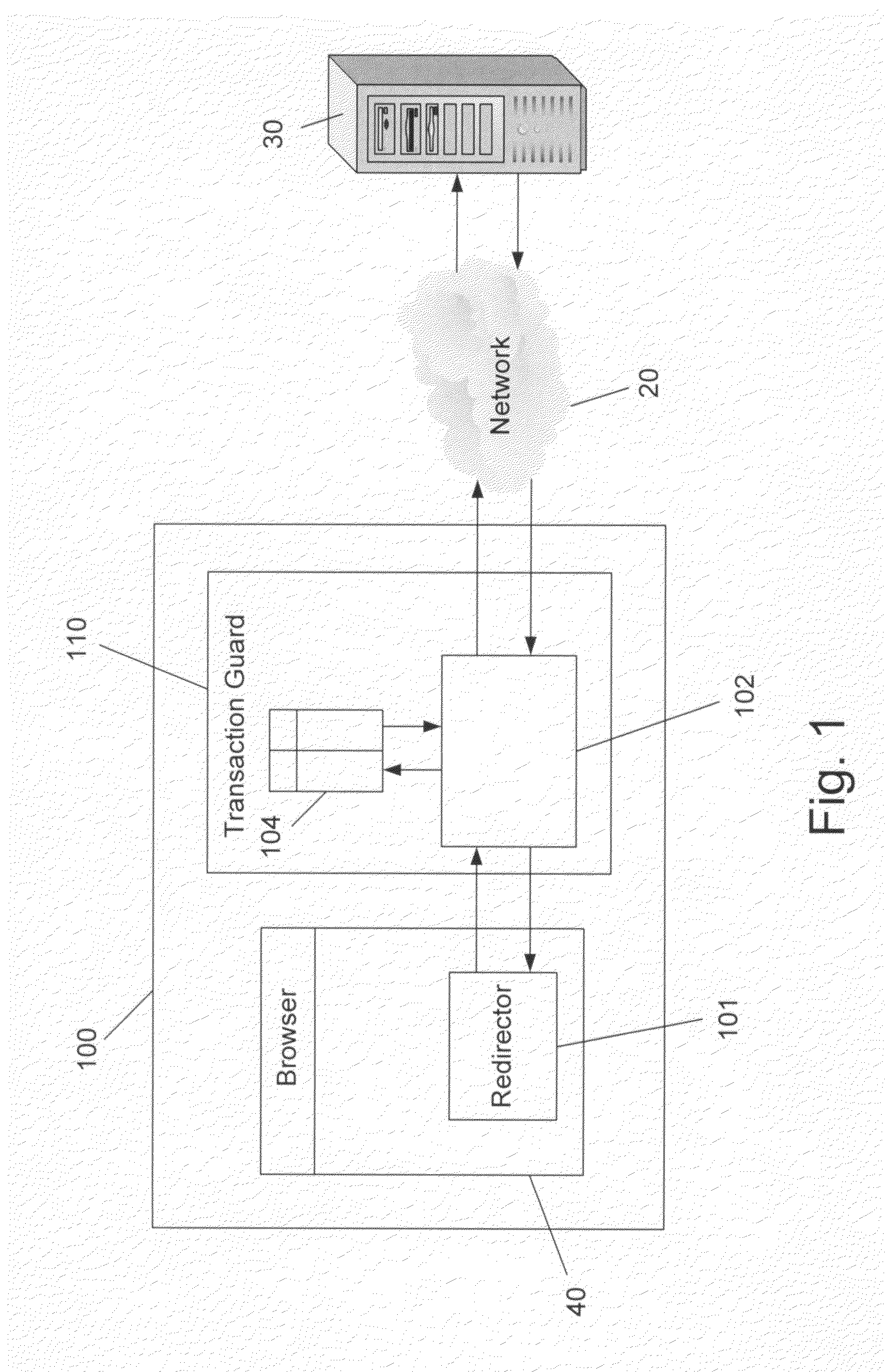
The present invention relates to a method for preventing an unauthorized activity including a transaction in a web site comprising the steps of: (a) receiving a response containing at least one HTML page, from said site, by the traffic processor; (b) modifying said response by obfuscating said at least one HTML page of said response; (c) storing de-obfuscation information in a transaction table; (d) forwarding the modified response from said traffic processor to the client's browser; (e) redirecting a request from said browser to the traffic processor, by the redirector; (f) checking said request for an unauthorized command; (g) de-obfuscating said request using the stored information in said transaction table; and (h) forwarding the modified request to said site.
Owner:TRUSTEER
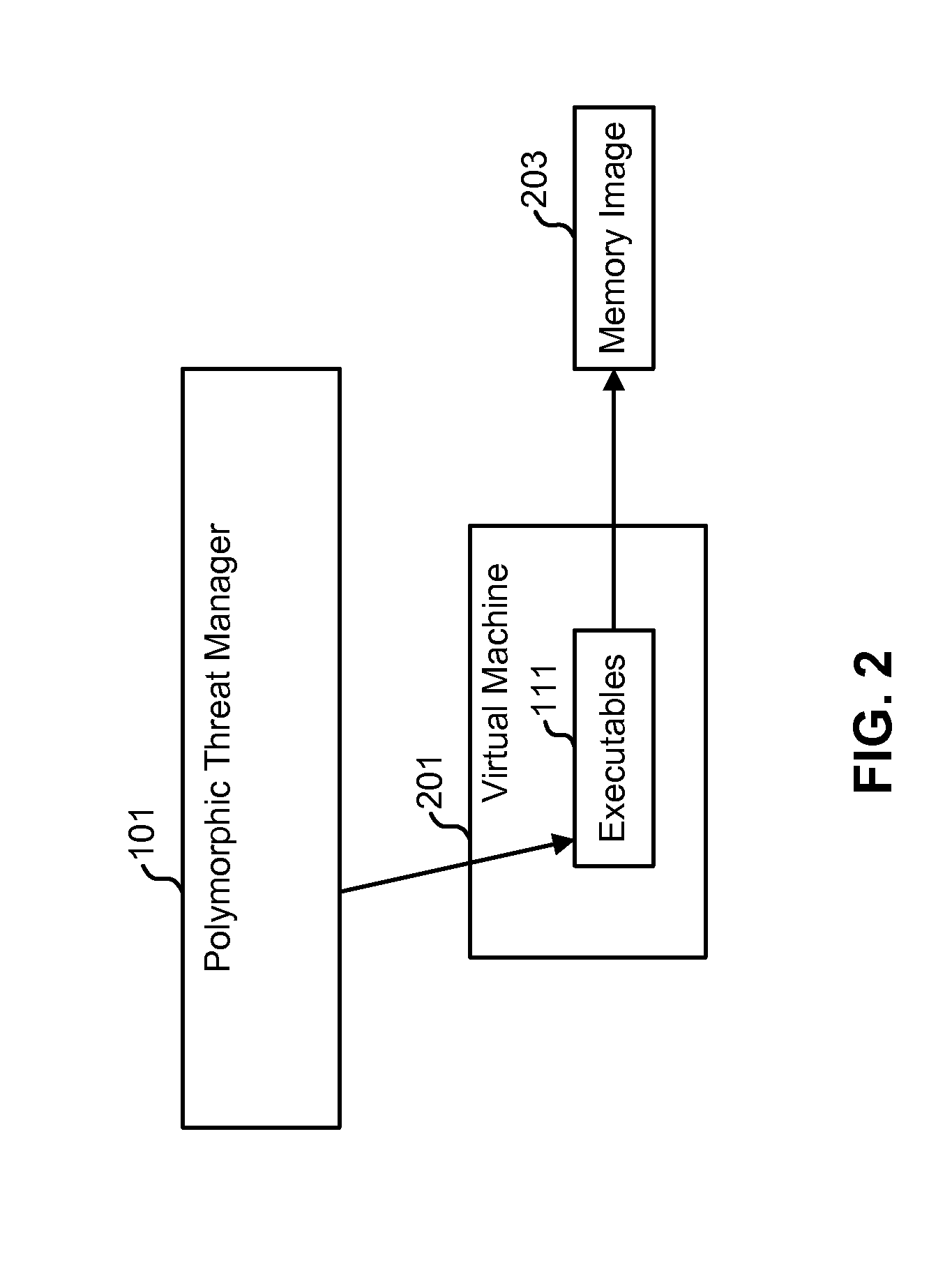
System and method for the programmatic runtime de-obfuscation of obfuscated software utilizing virtual machine introspection and manipulation of virtual machine guest memory permissions
ActiveUS20140189882A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsObfuscationVirtual machine introspection
A system and method operable to programmatically perform runtime de-obfuscation of obfuscated software via virtual machine introspection and manipulation of virtual machine guest memory permissions.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC
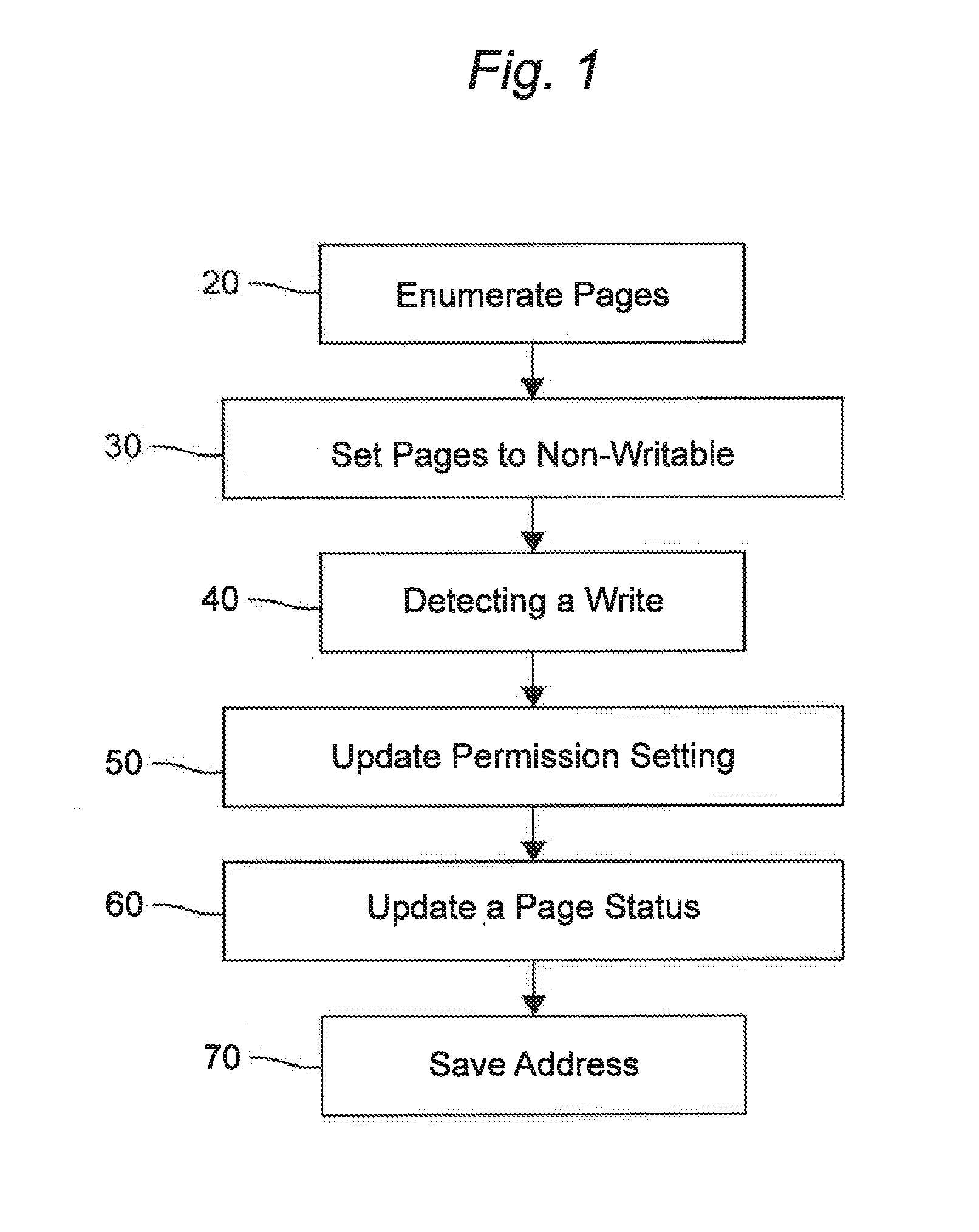
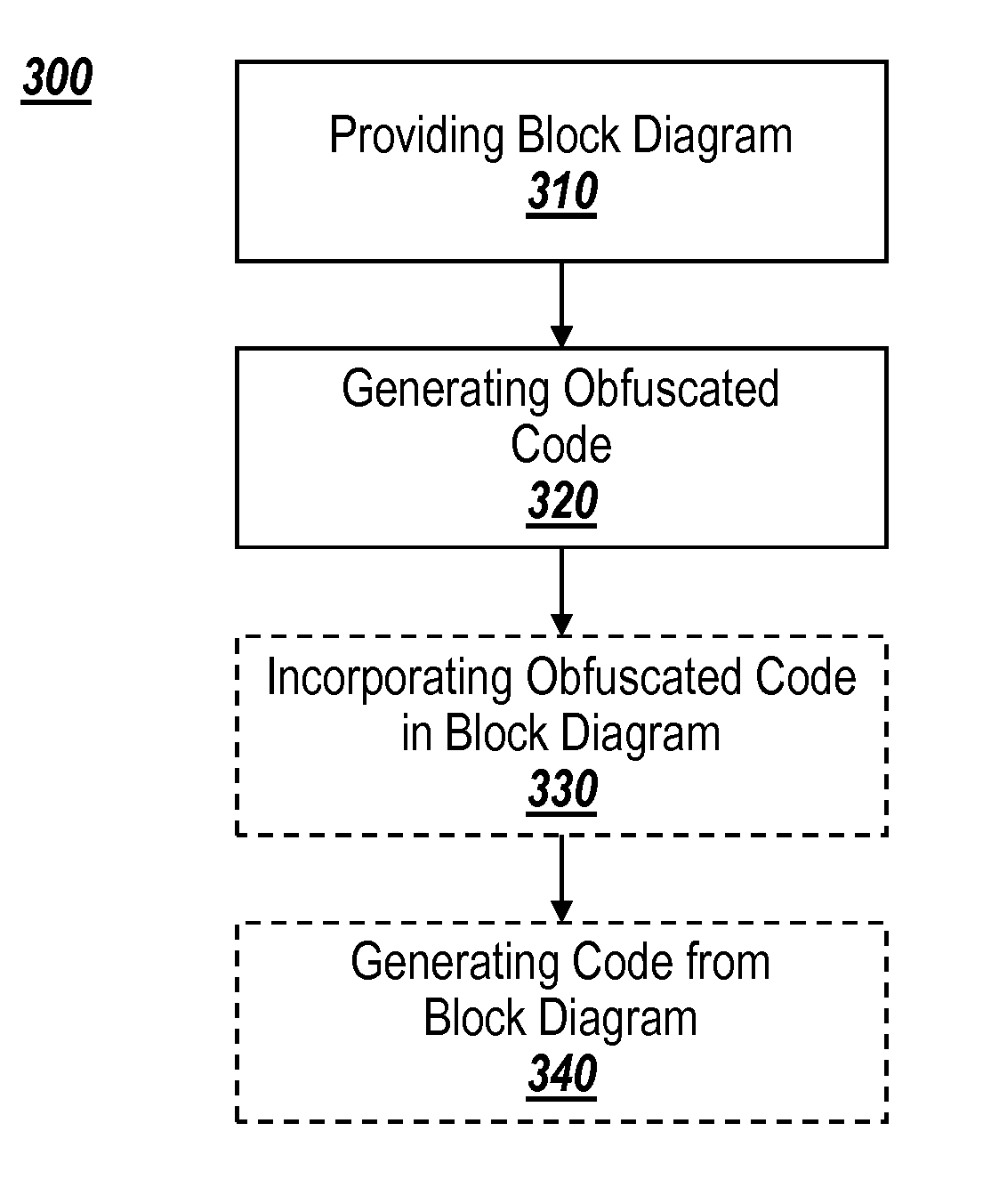
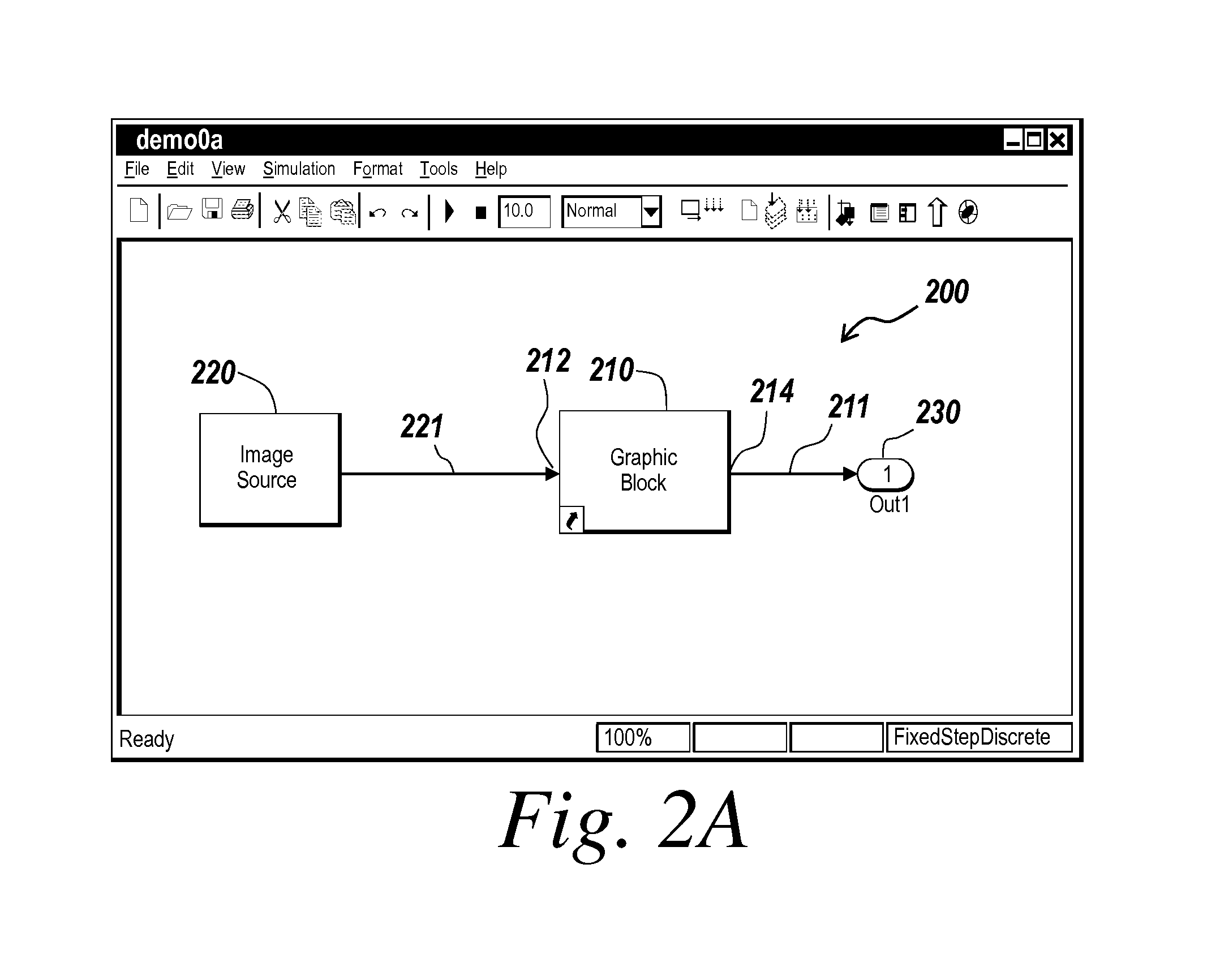
Obfuscation of automatically generated code
ActiveUS8832646B1Visual/graphical programmingProgram/content distribution protectionGraphicsObfuscation
A method is provided for obfuscating code generated from a block diagram model in a graphical programming environment. The obfuscation may be removed through the use of a password. Incorporating the obfuscated code in a block diagram allows for code to be generated from the block diagram incorporating the obfuscated code.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
Peer-to-peer privacy panel for audience measurement
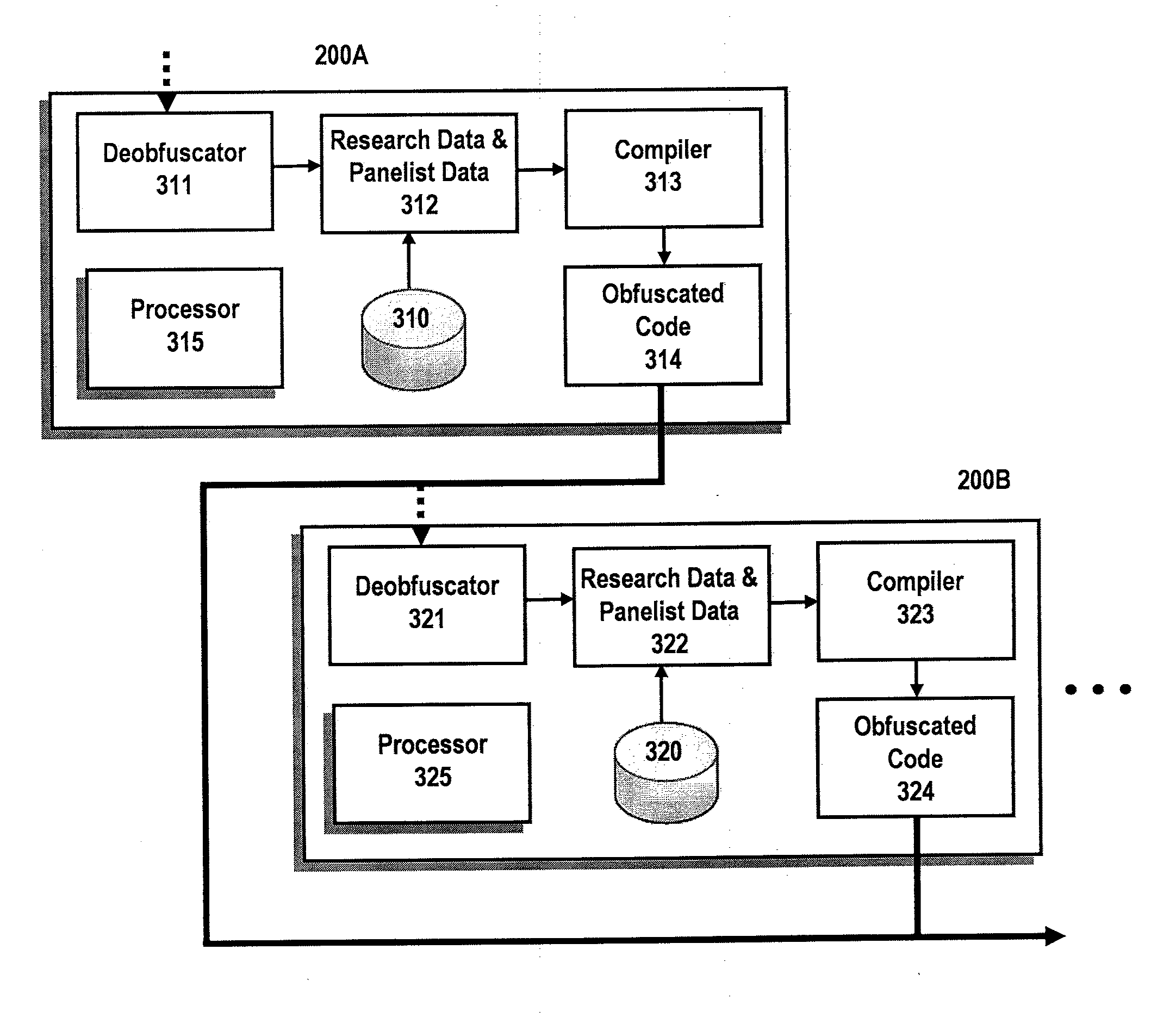
InactiveUS20110153391A1Privacy protectionReliable resultsMarket predictionsMultiple digital computer combinationsObfuscationInternet privacy
Systems and methods for operating an anonymous peer-to-peer (“P2P”) privacy panel for audience measurement is disclosed. A plurality of portable devices are configured to record and process research data pursuant to a research operation. Each of the panelists associated with each portable devices provide panelist data to a central site, where the panelist data includes demographic information, previous media exposure data, and other data. In accordance with panelist data, a customized P2P network is created where media exposure data is obfuscated and communicate among portable devices in the network. By utilizing a P2P network together with obfuscation techniques, panelist privacy is greatly increased.
Owner:THE NIELSEN CO (US) LLC +1
System and Method for Permissioned Distributed Block Chain
The invention is a method for providing a permissioned distributed ledger to a requesting client, and comprises the steps of: receiving a client request for a specified distributed ledger; retrieving the specified distributed ledger from one of a document server or a computer-readable storage medium; associating client access permission criteria with the distributed ledger; performing at least one of a filtering, an obfuscation, and an encryption to produce a modified distributed ledger in conformance with the client permission criteria; and sending the modified distributed ledger to the client.
Owner:KUNSTEL MICHAEL
Method and system for tamperproofing software
InactiveUS20060031686A1User identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionCoding blockObfuscation
Method of protecting host application code comprising a plurality of code blocks. The method includes steps of preprocessing the host application code; obfuscating the host application code; installing guards in the host application code to protect client blocks; randomly rearranging the code blocks of the host application code; linking the rearranged host application code with other resources to produce a binary executable image; and patching the binary executable image with data values to be used by the guard. The method can be used to install a plurality of guards to form a distributed network of guards that cooperatively protect the host application code and the other guards in the network. The installation of the guards can be performed automatically using a guard formation graph; and guard formation graph customization parameters. The obfuscation step can include control flow graph merging, cloning, and data-aliasing.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
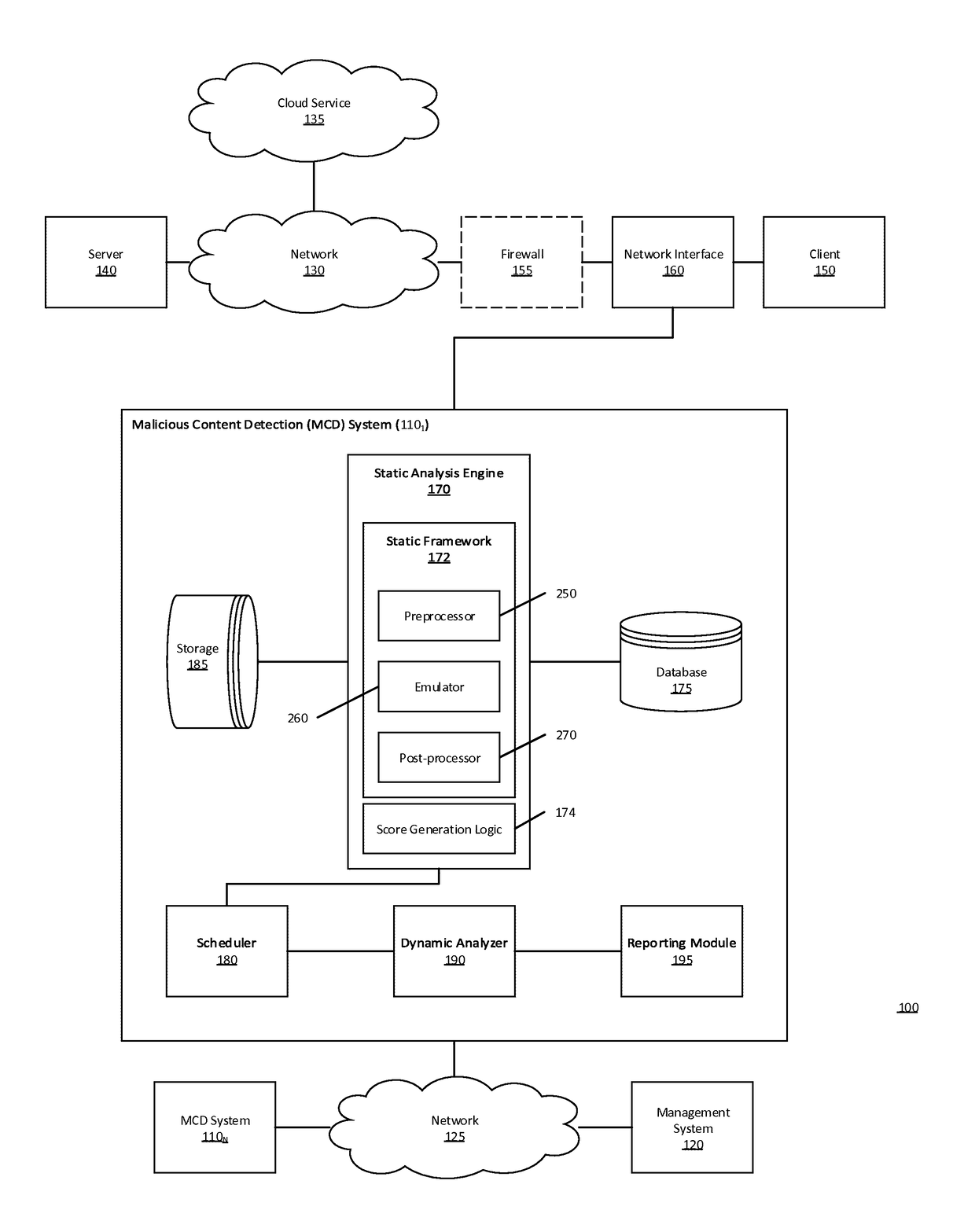
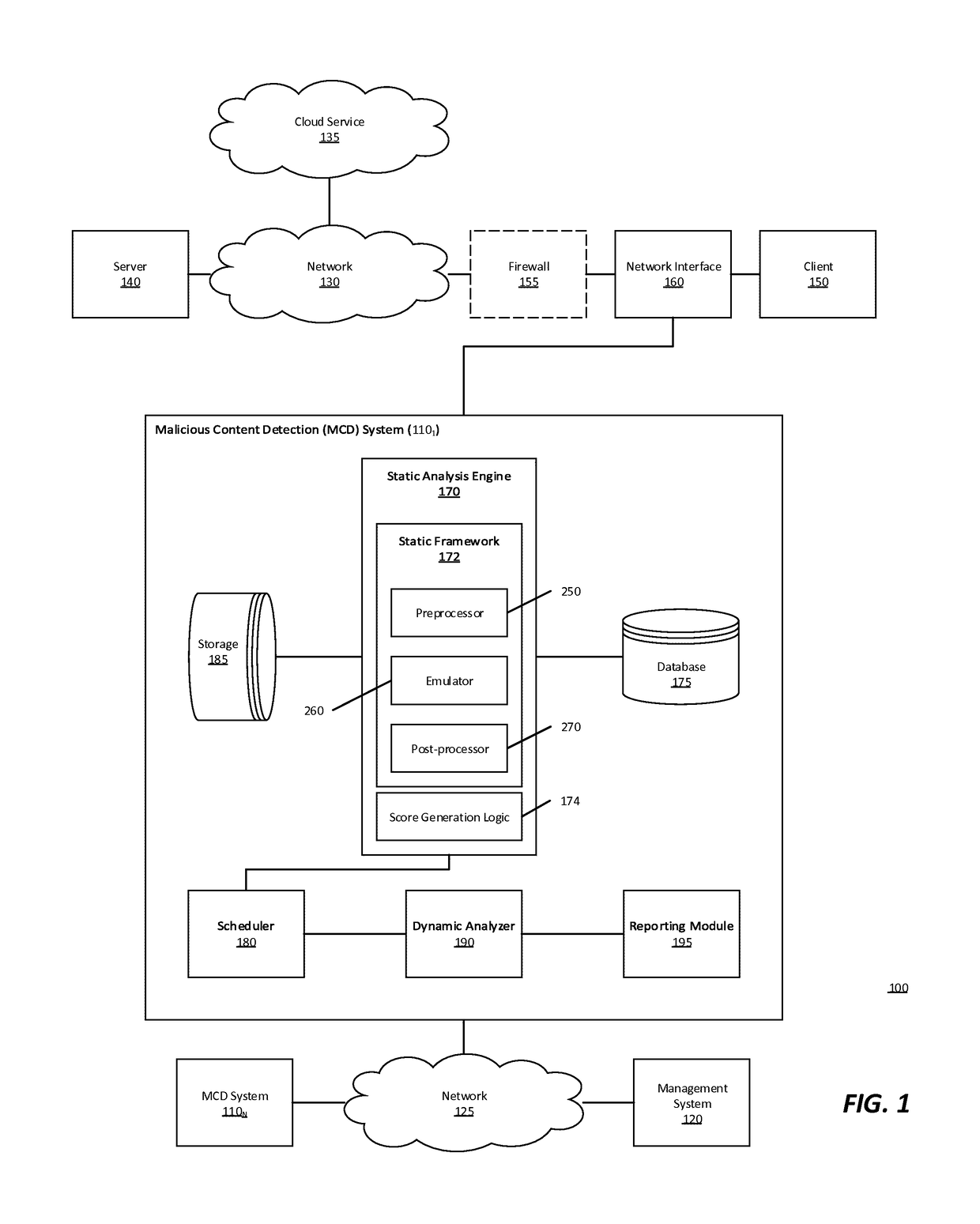
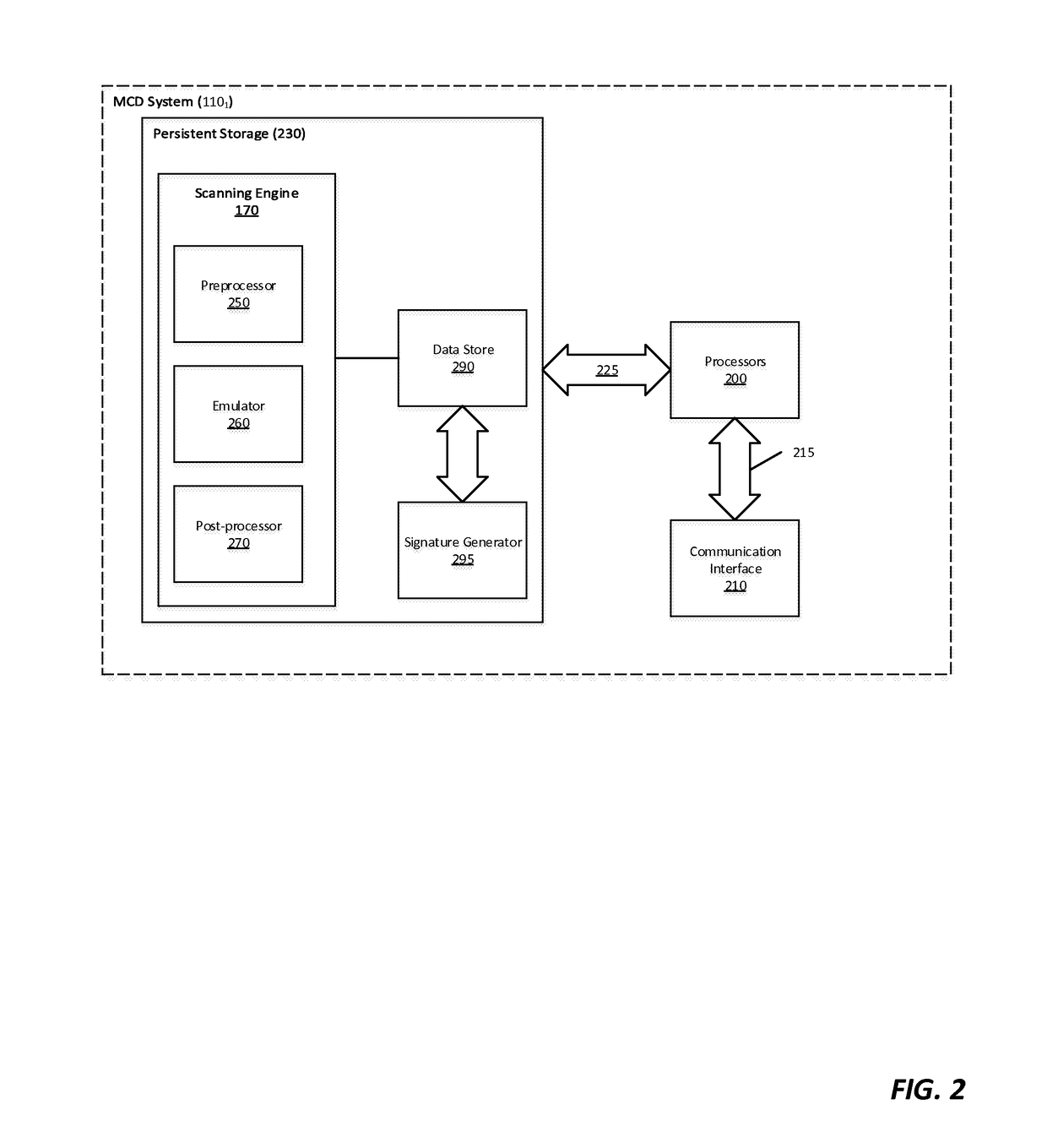
Multistage system and method for analyzing obfuscated content for malware
A malware detection system configured to detect suspiciousness in obfuscated content. A multi-stage static detection logic is utilized to detect obfuscation, make the obfuscated content accessible, identify suspiciousness in the accessible content and filter non-suspicious non-obfuscated content from further analysis. The system is configured to identify obfuscated content, de-obfuscate obfuscated content, identify suspicious characteristics in the de-obfuscated content, execute a virtual machine to process the suspicious network content and detect malicious network content while removing from further analysis non-suspicious network content.
Owner:MANDIANT +1
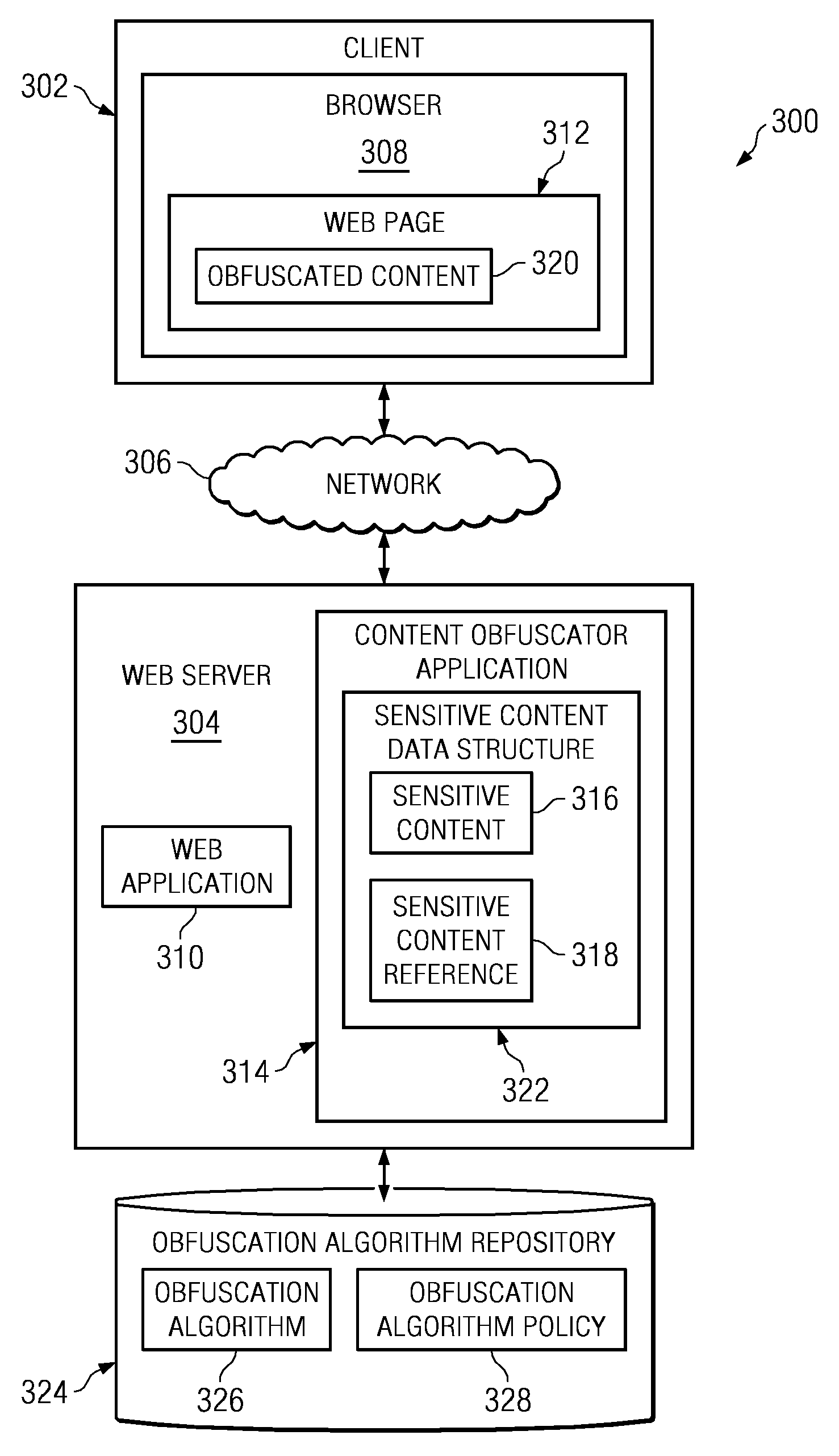
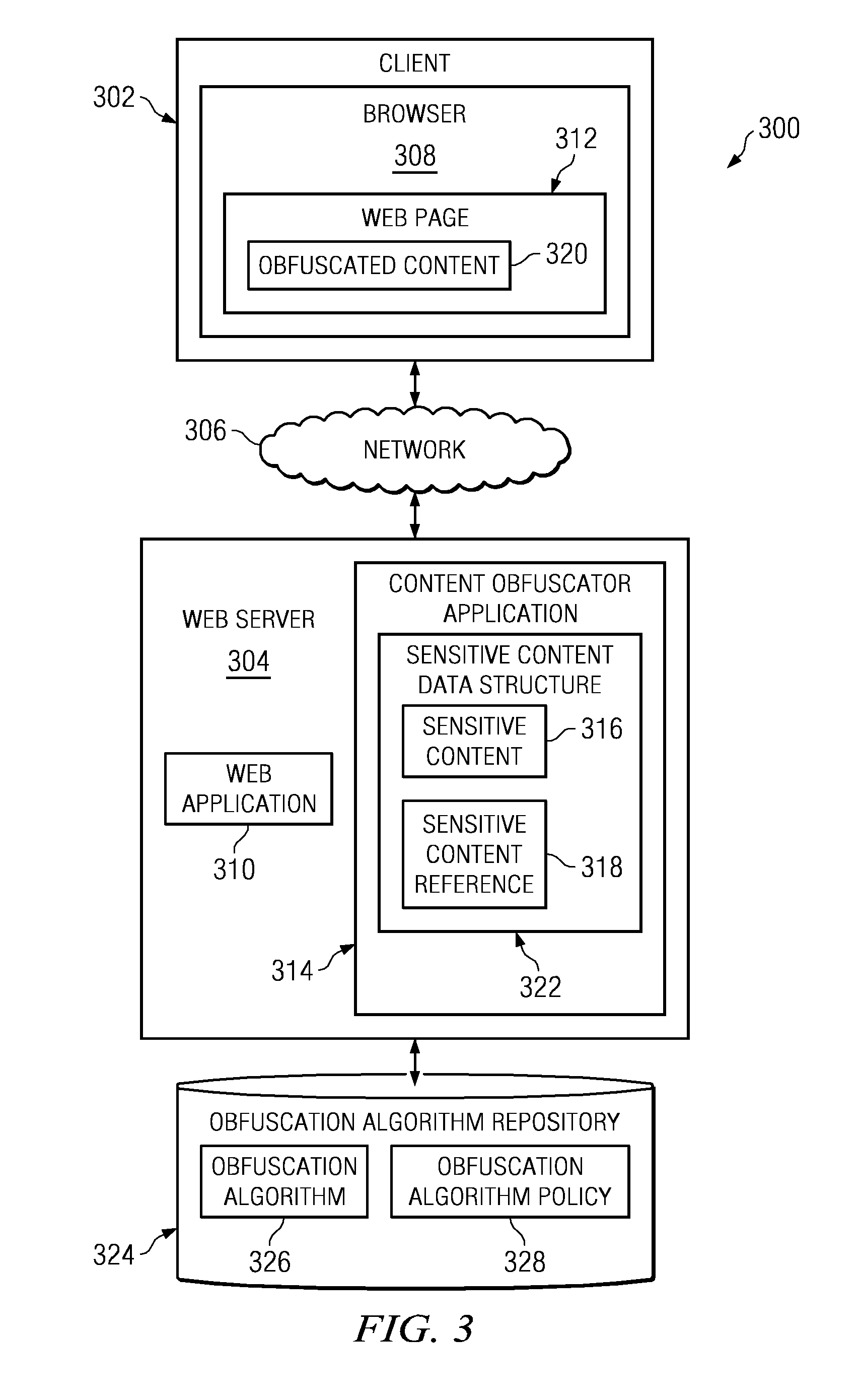
Method and apparatus to protect sensitive content for human-only consumption
InactiveUS20090144829A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsObfuscationWorld Wide Web
A computer implemented method, apparatus, and computer usable program product for protecting sensitive content. In response to receiving a selection of content, the process determines whether the content is of a sensitive content type based on a policy. The process then designates the content as the sensitive content in response to the content being of a sensitive content type. Thereafter, the process generates a sensitive content reference for publication and stores the sensitive content in a data structure, wherein the data structure associates the sensitive content with the sensitive content reference. Subsequently, in response to receiving a request from a requester for the sensitive content reference, the process obfuscates the sensitive content using a selected obfuscation algorithm to form obfuscated content, and returns the obfuscated content to the requester.
Owner:IBM CORP
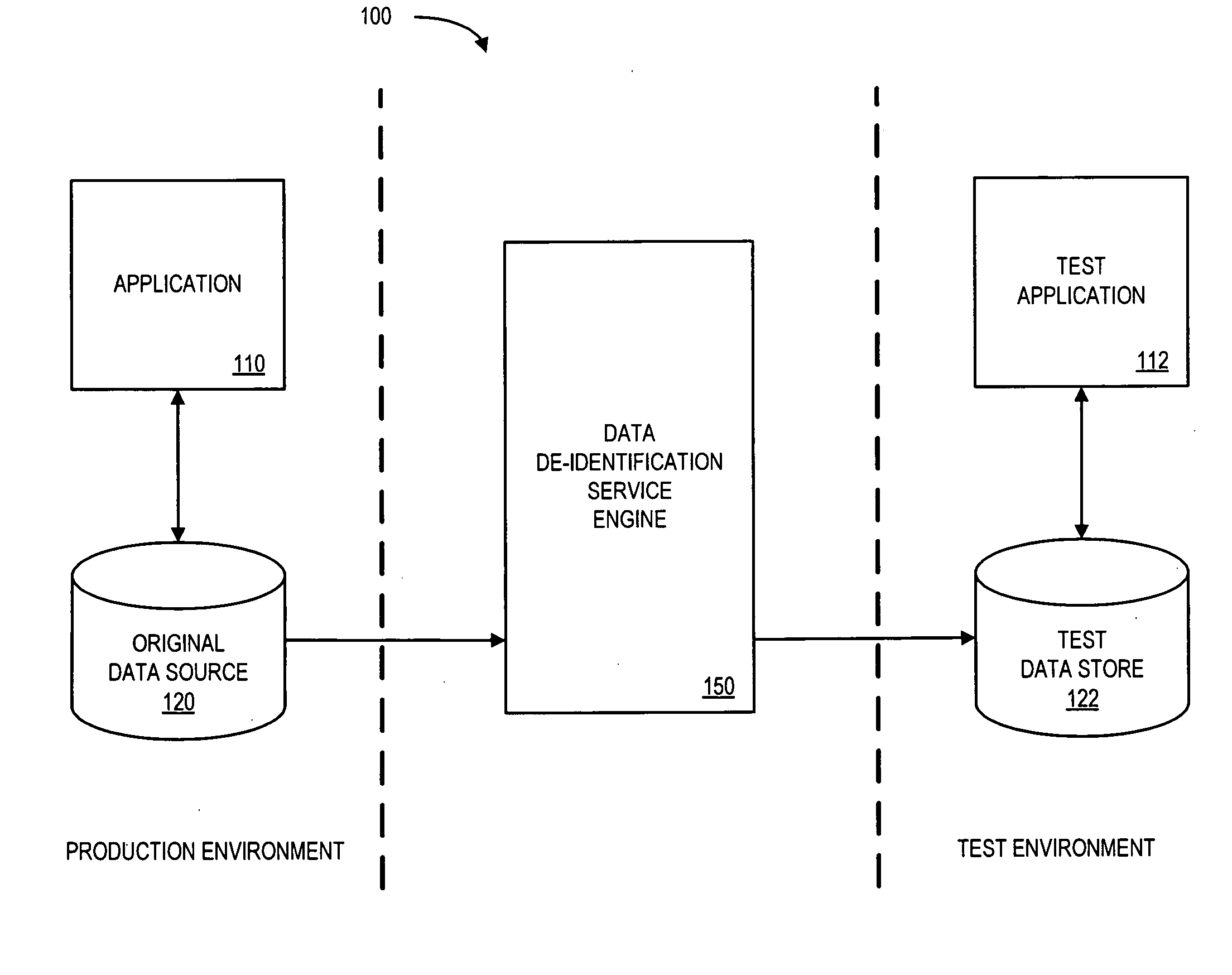
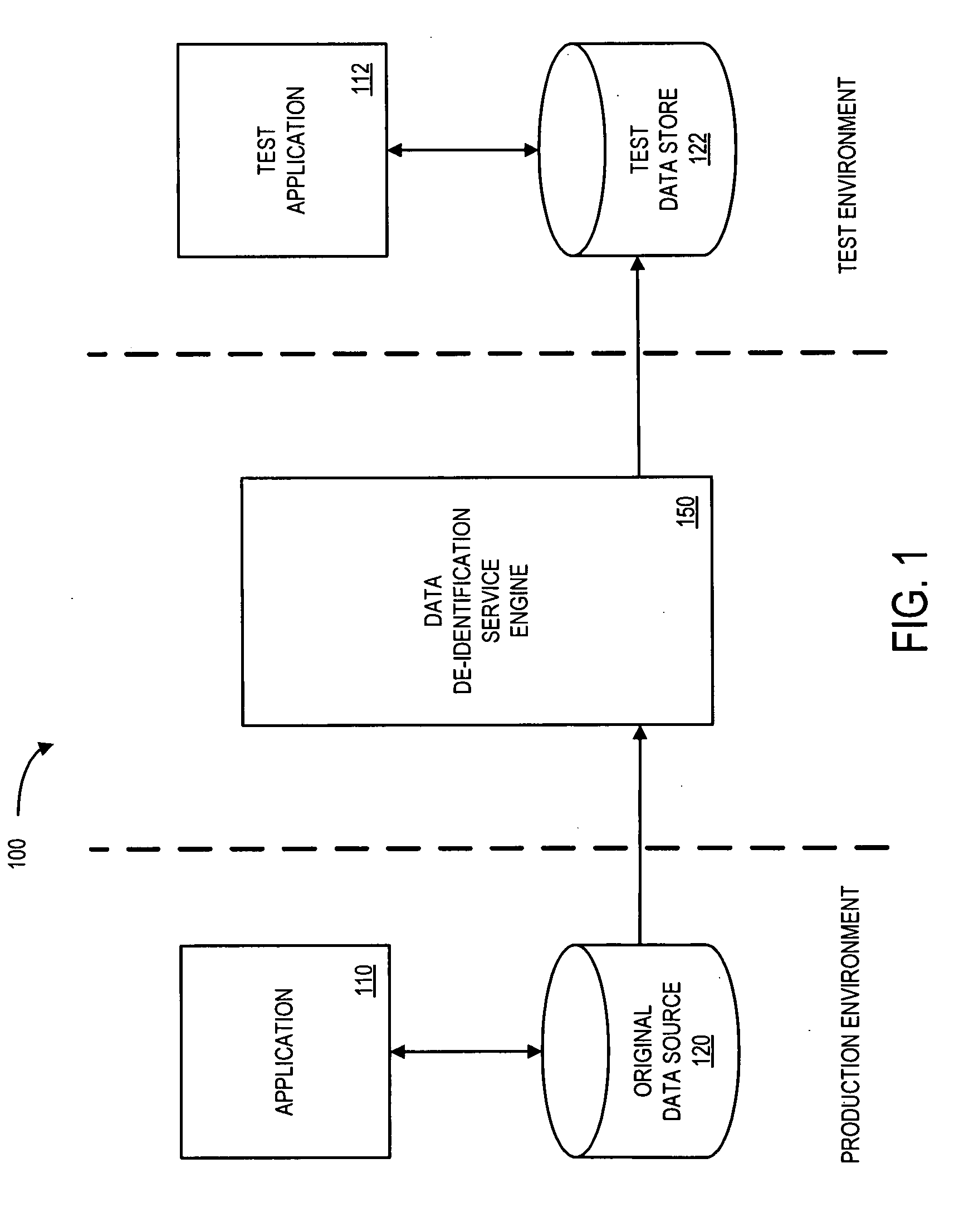
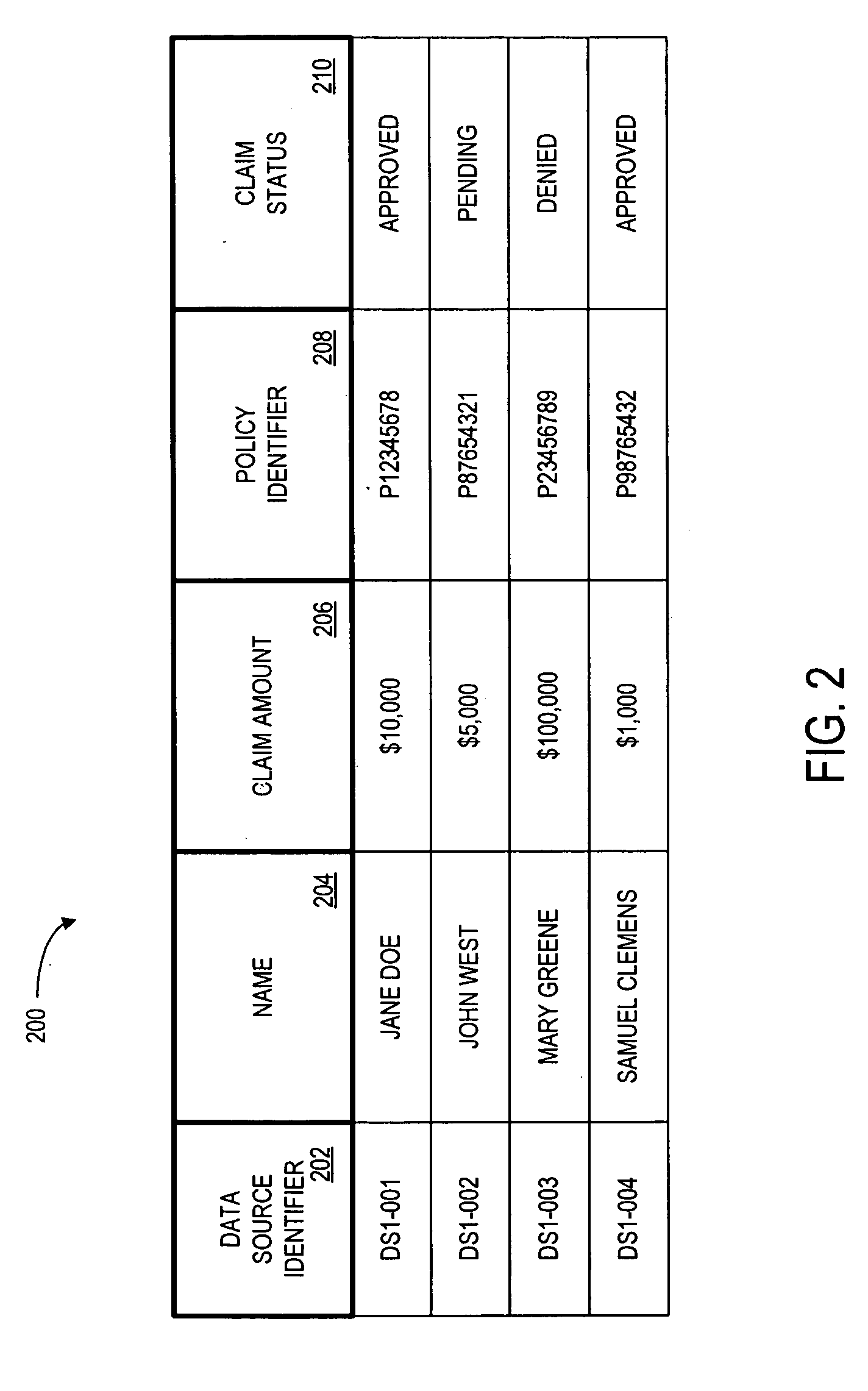
Systems and methods for de-identification of personal data
According to some embodiments, original data is retrieved from an original data source. The original data may be automatically searched for potential personal information, such as a person's name, address, or Social Security number. An obfuscation method may be selected from a plurality of potential obfuscation methods. The potential personal information in the original data may then be automatically replaced with fictional data in accordance with the selected obfuscation method.
Owner:HARTFORD FIRE INSURANCE
System and method for the programmatic runtime de-obfuscation of obfuscated software utilizing virtual machine introspection and manipulation of virtual machine guest memory permissions
ActiveUS9459901B2Platform integrity maintainanceProgram/content distribution protectionObfuscationVirtual machine introspection
A system and method operable to programmatically perform runtime de-obfuscation of obfuscated software via virtual machine introspection and manipulation of virtual machine guest memory permissions.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC
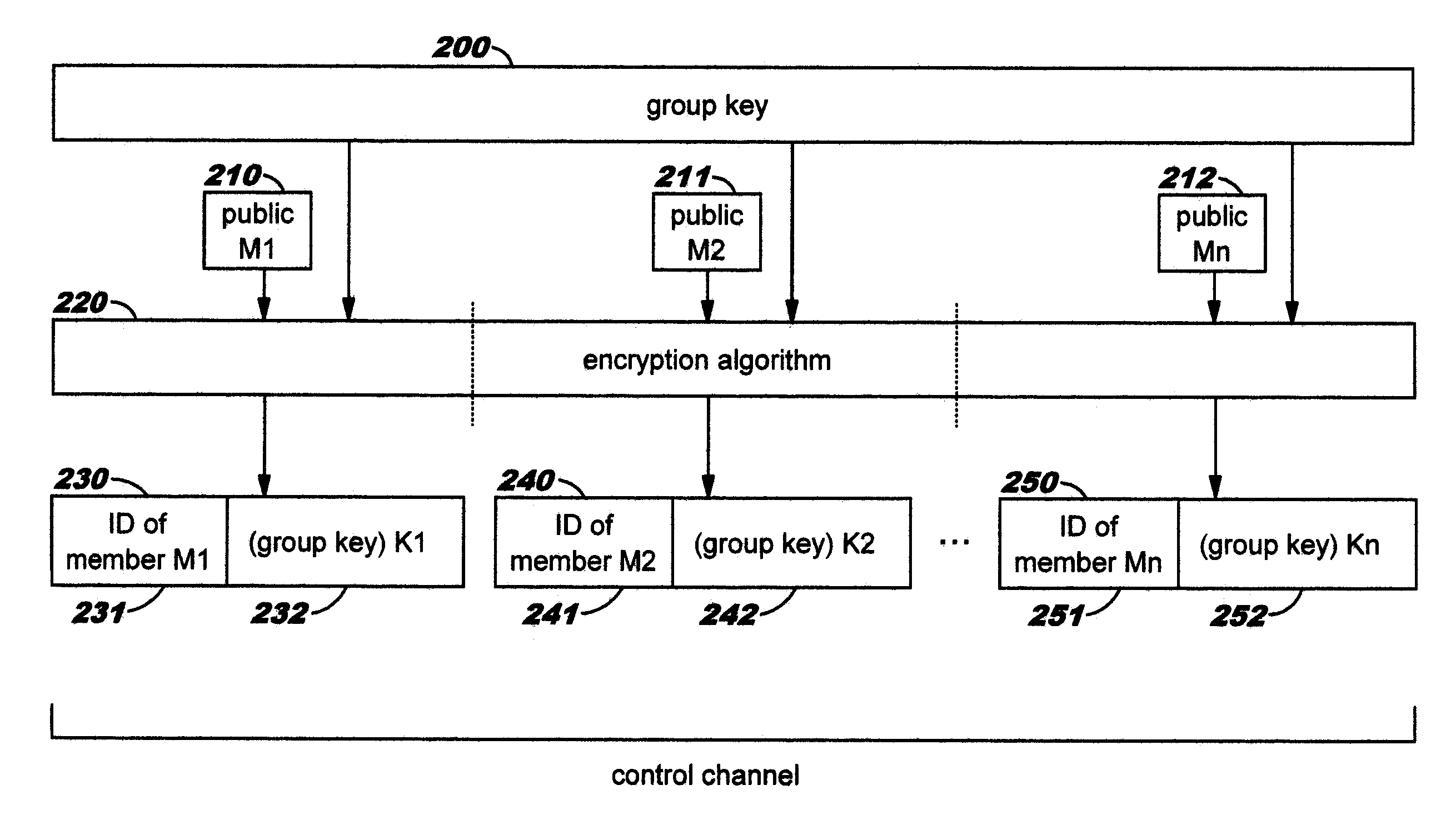
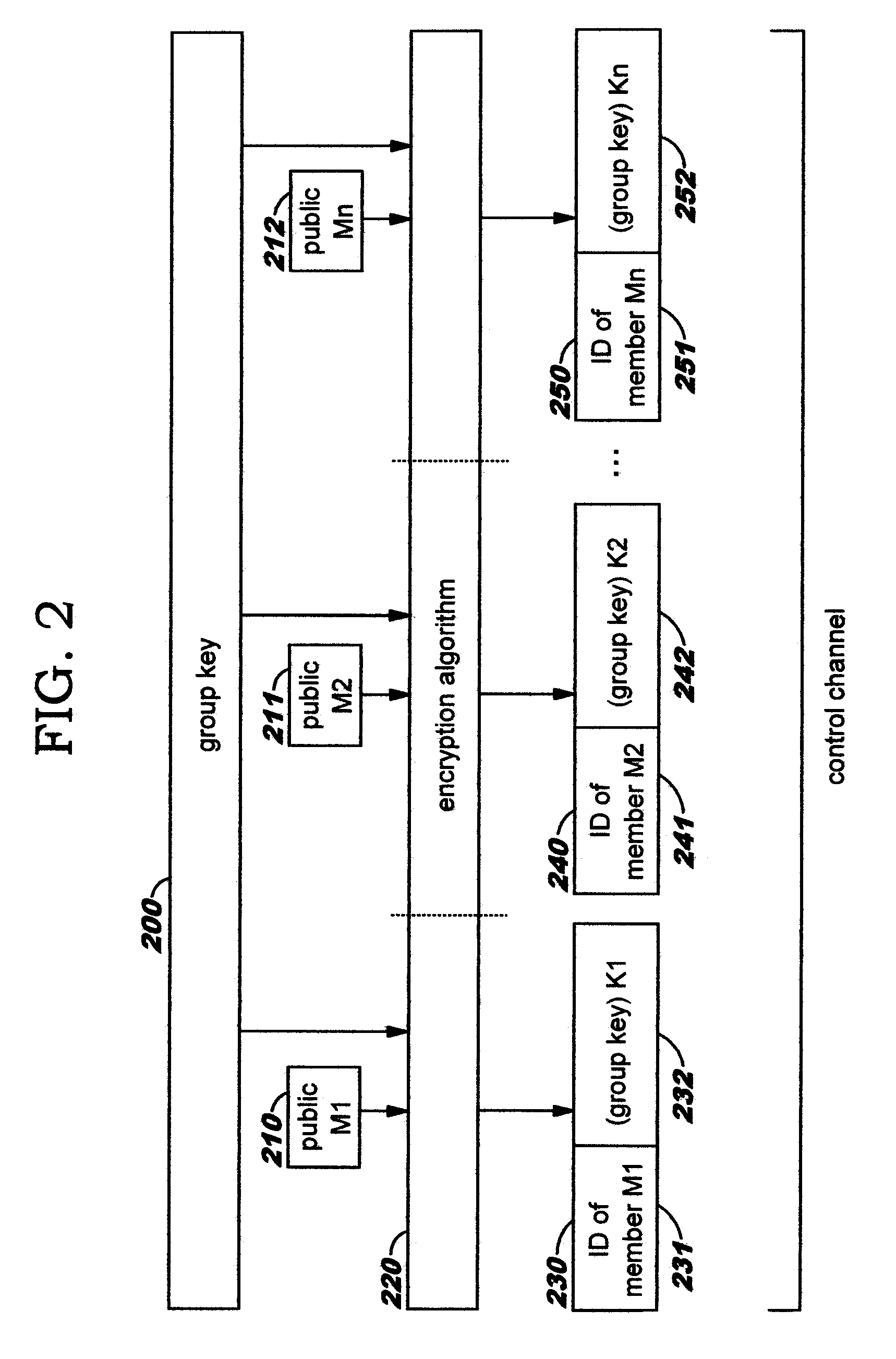
Dynamic, Selective Obfuscation of Information for Multi-Party Transmission
Selectively obfuscating, or obscuring, a portion or portions of information in a multi-party transmission. A user participating in a multi-party exchange signals a communication device (or proxy) that he will provide private information that is to be perceptible only to a subset of the other participants. This user also identifies that subset, preferably by providing a group identifier for a group in which that subset of participants are members. The communication device transmits a member-specific descriptor comprising an encrypted version of a group key, and uses this group key to encrypt the private information that is to be perceptible only to the subset. Device-specific characteristics of participant devices are used, in addition to user-provided data (such as a user's log-on identifier and / or password), as input to create cryptographic key information. Only participants in the subset can decrypt the encrypted private information; other participants preferably receive a filler pattern of some type instead.
Owner:IBM CORP
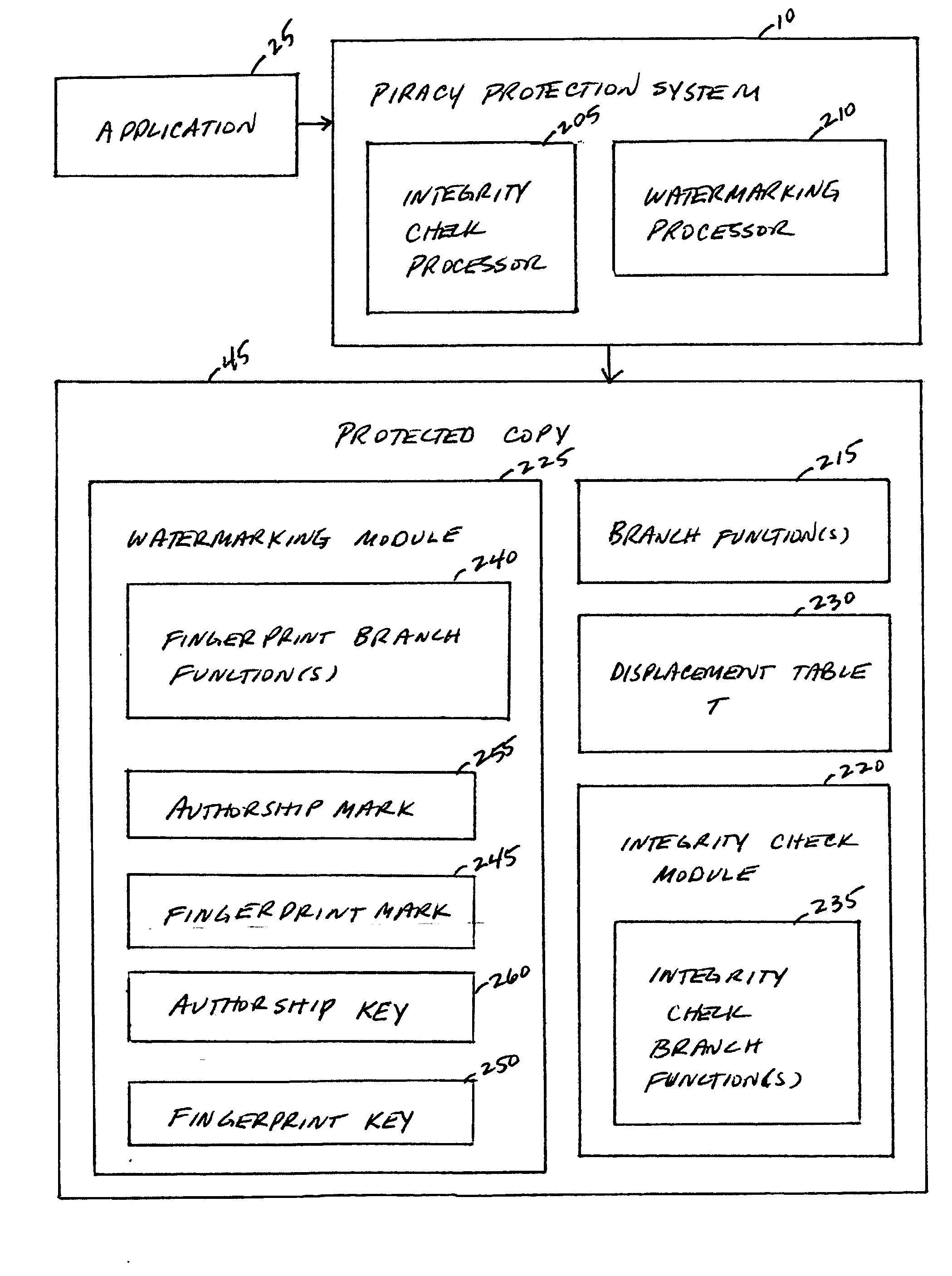
System, method, and service for detecting improper manipulation of an application
InactiveUS20060195906A1Eliminate loopholesMore robustnessDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationObfuscationApplication procedure
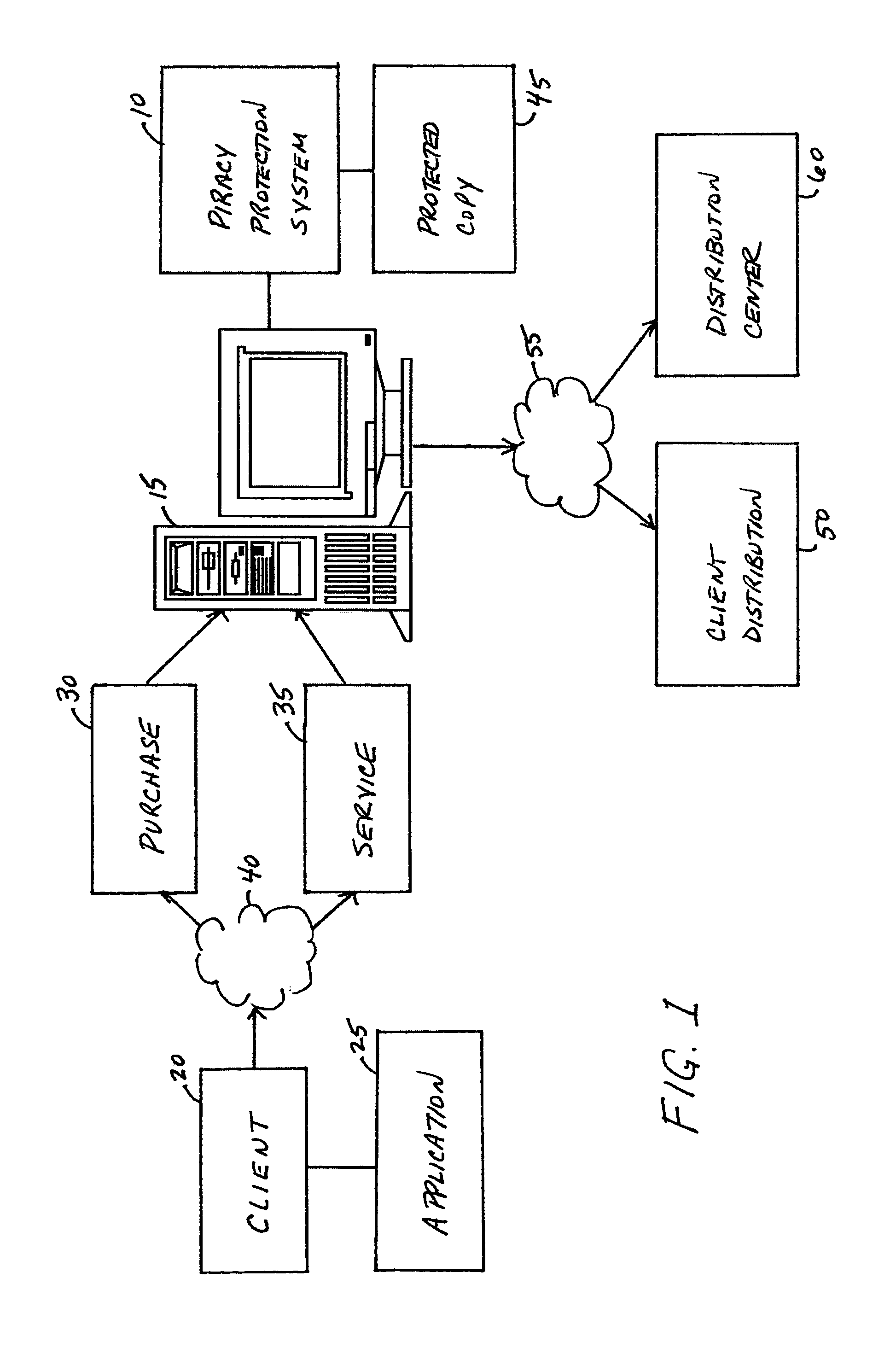
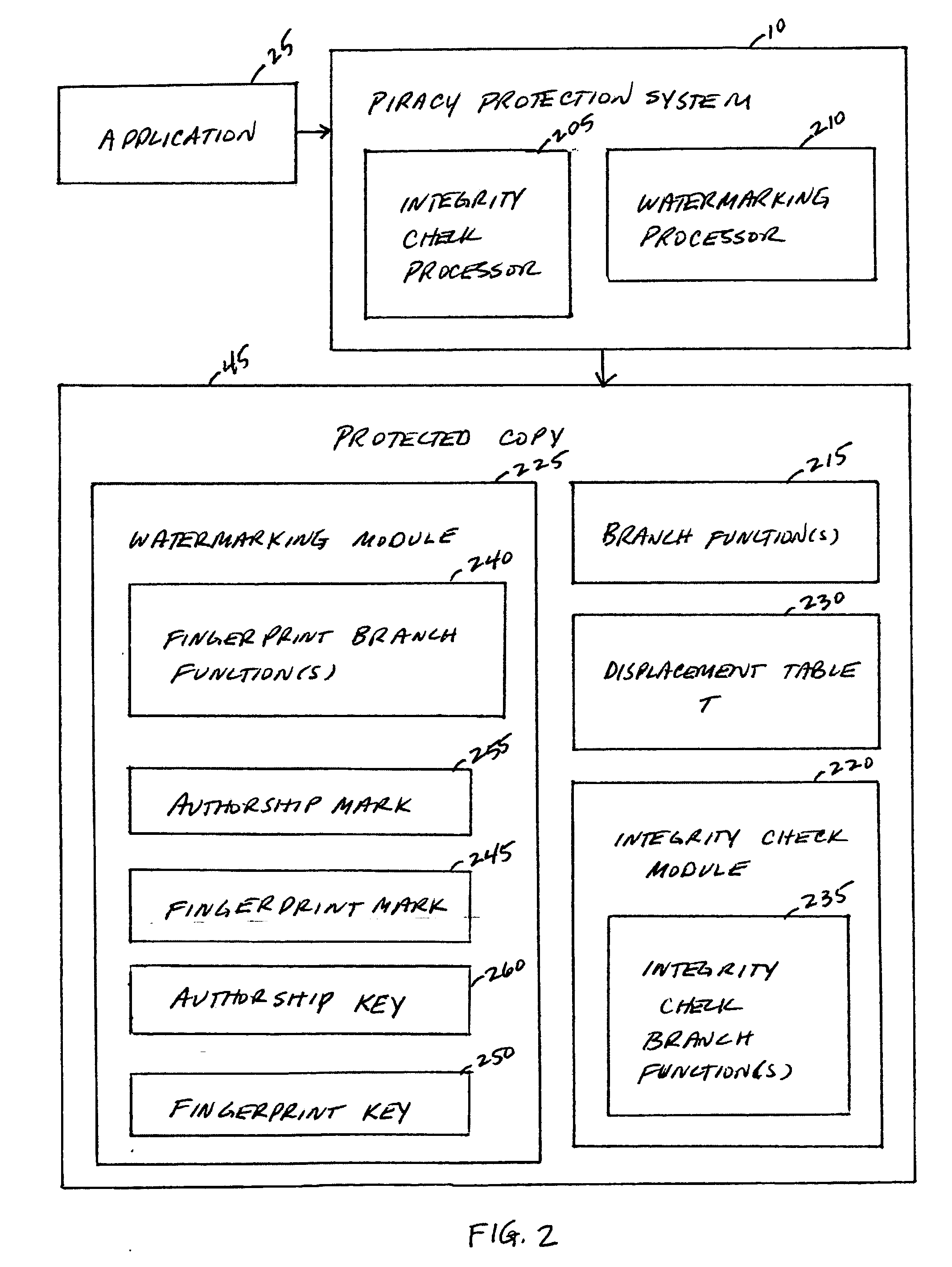
A piracy protection system incorporates tamper detection capabilities into a protected copy of an application by disassembling a statically linked binary of the application, modifying some of the instructions in the application, and then rewriting all of the modified and unmodified instructions to a new executable file, a protected copy. The piracy protection system comprises an offline tamper detection technique in which the software itself detects the tampering and causes the program to fail, therefore protecting itself from malicious attacks. The system further comprises a dynamic software-watermarking process that incorporates code obfuscation to prevent reverse engineering.
Owner:IBM CORP
Network infrastructure obfuscation
ActiveUS20140115706A1Maximize chanceMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionObfuscationIp address
A shadow network, which can be a virtual reproduction of a real, physical, base computer network, is described. Shadow networks duplicate the topology, services, host, and network traffic of the base network using shadow hosts, which are low interaction, minimal-resource-using host emulators. The shadow networks are connected to the base network through virtual switches, etc. in order to form a large obfuscated network. When a hacker probes into a host emulator, a more resource-intensive virtual machine can be swapped in to take its place. When a connection is attempted from a host emulator to a physical computer, the a host emulator can step in to take the place of the physical computer, and software defined networking (SDN) can prevent collisions between the duplicated IP addresses. Replicating the shadow networks within the network introduces problems for hackers and allows a system administrator easier ways to identify intrusions.
Owner:ACALVIO TECH
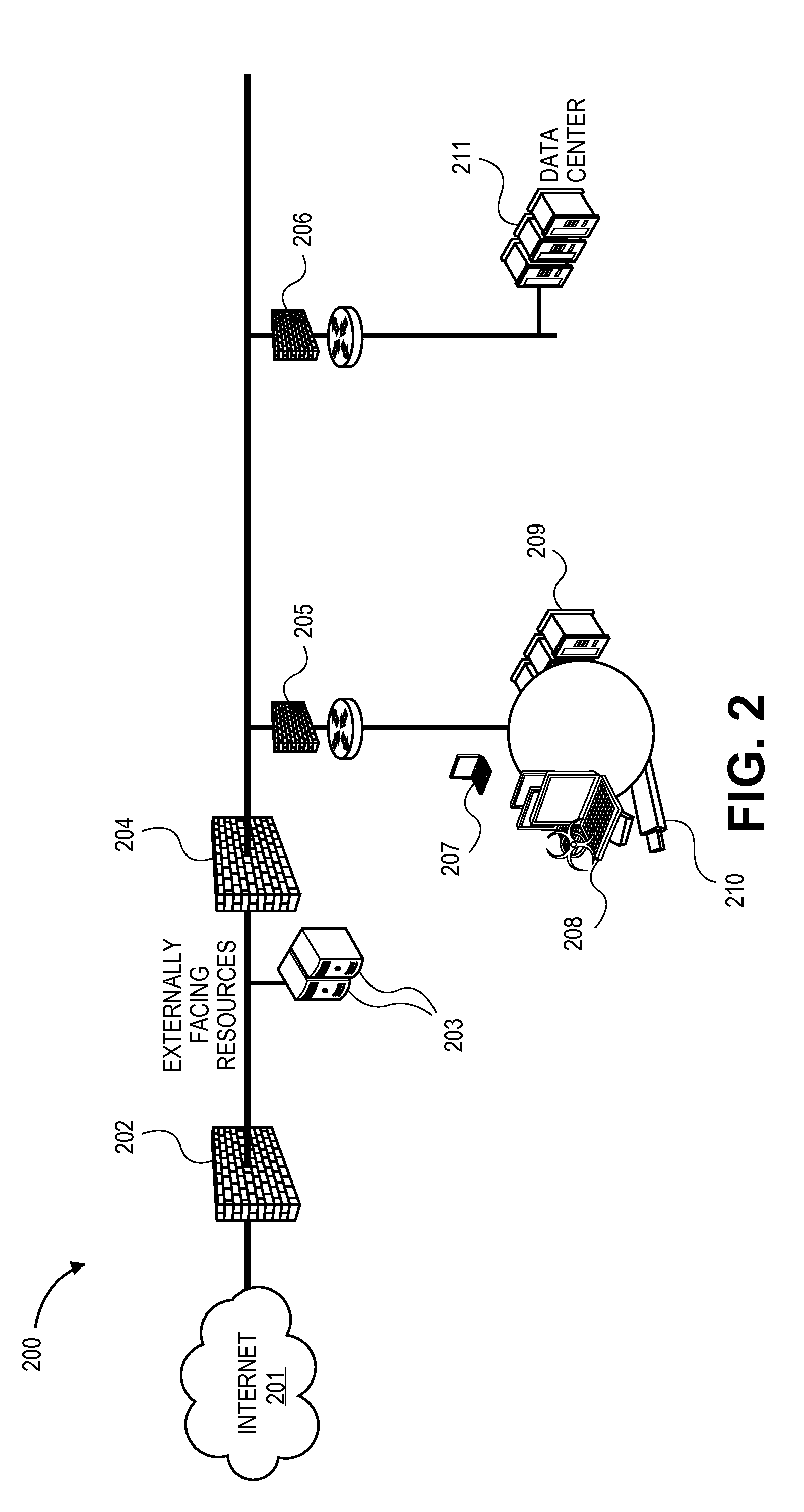
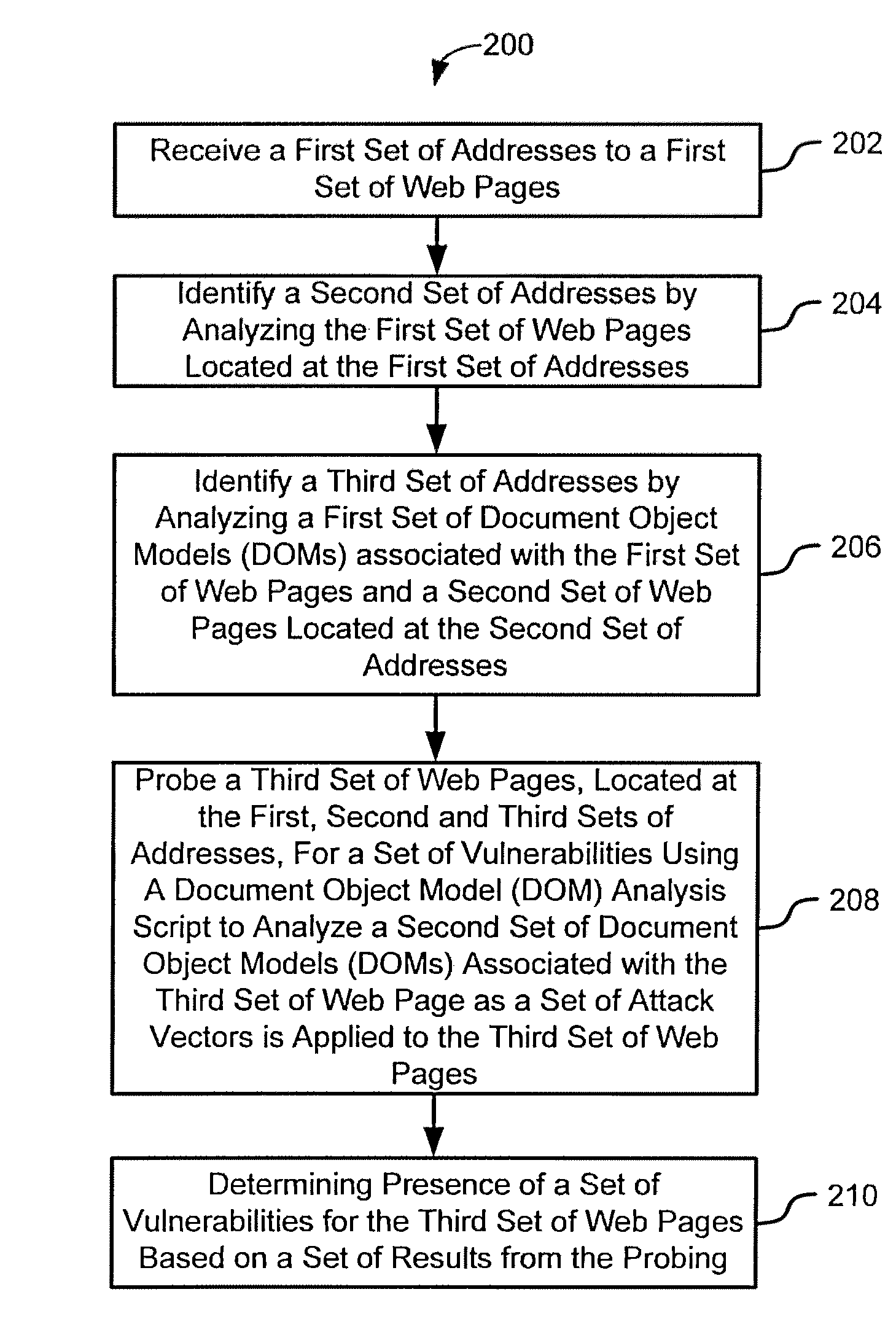
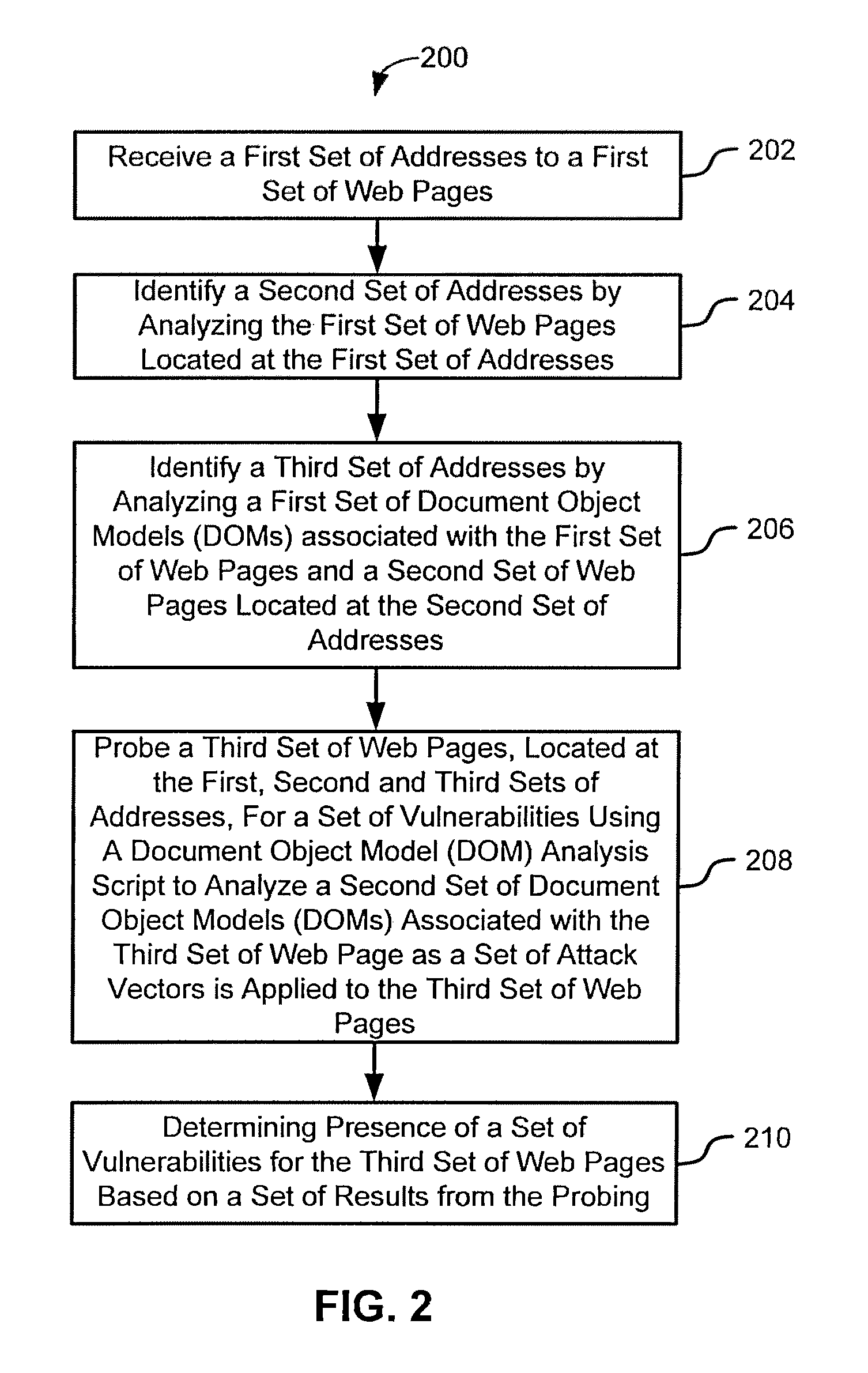
Systems and methods for client-side vulnerability scanning and detection
InactiveUS8752183B1Avoid hard activationImprove accuracyMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionObfuscationWeb browser
Various embodiments presented herein relate to scanning for and detecting web page vulnerabilities, including cross-site scripting (XSS). Some embodiments are configured to scan for and detect vulnerabilities of a target web page using a client-based approach, which may employ a remotely-controlled web browser application capable of generating a document object model (DOM) for the target web page as it is accessed. Some embodiments may scan for and detect web page vulnerabilities by monitoring the DOM associated with a targeted web page as one or more attack vectors are applied to the target web page. Certain embodiments are capable of detecting web page vulnerabilities independent of the complexity or presence of an event model, or obfuscation of the malicious code (e.g., XSS code). Target web pages that are scanned may include those associated with an application coded in a web browser-supported language, such a Rich Internet Application (RIA).
Owner:HOYT TECH
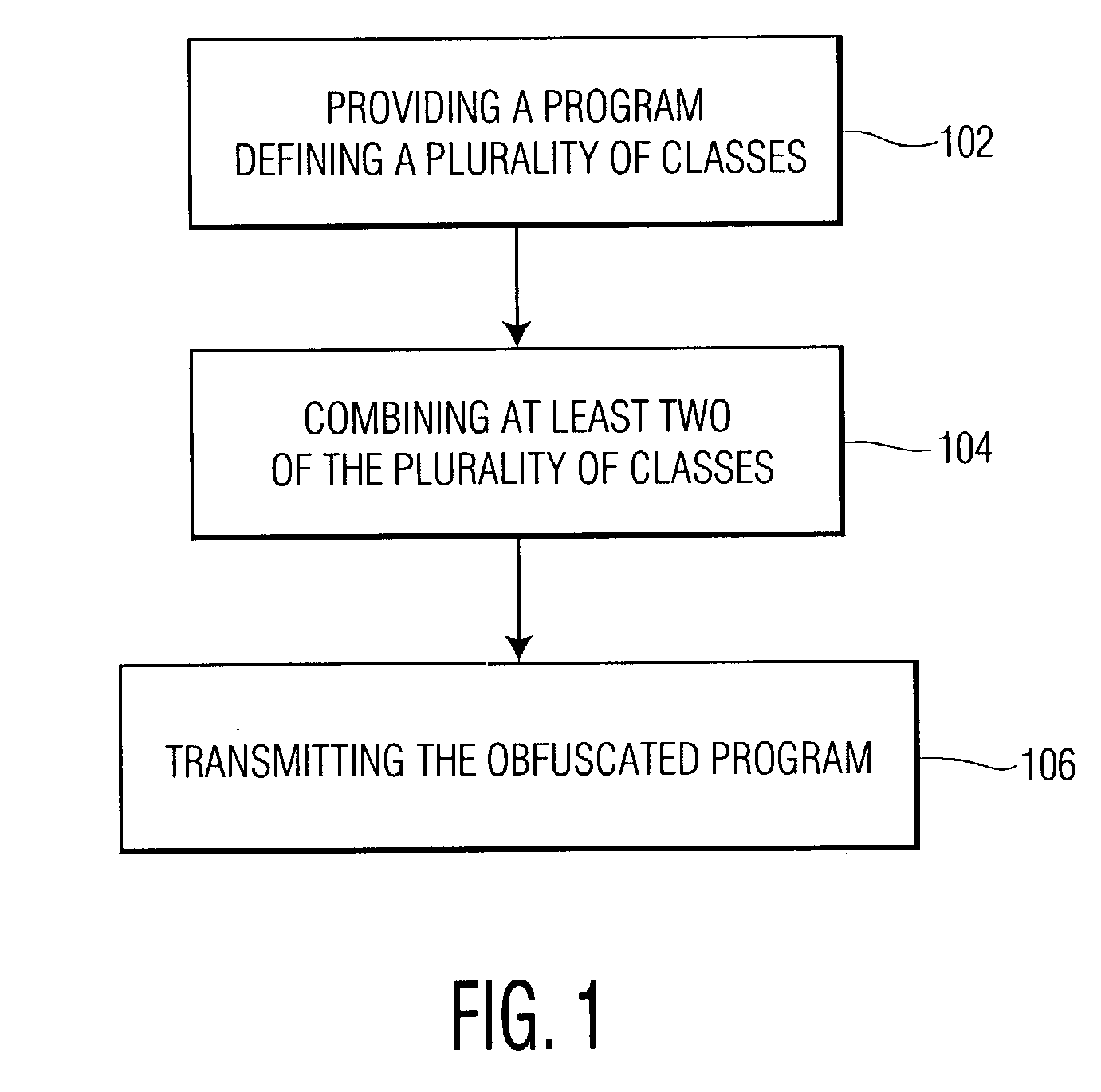
Class coalescence for obfuscation of object-oriented software
InactiveUS7150003B2User identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionObfuscationCombinatorial class
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
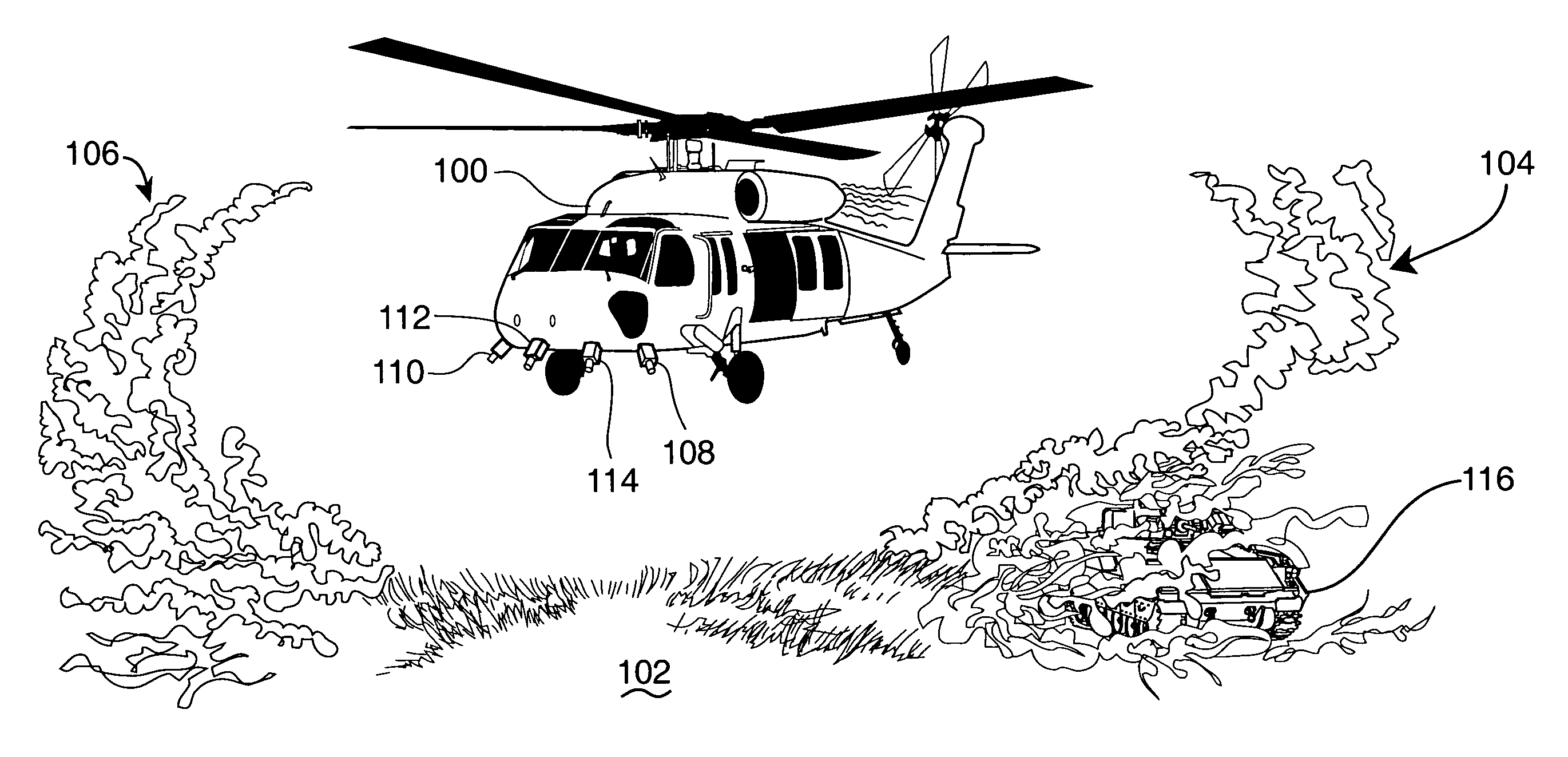
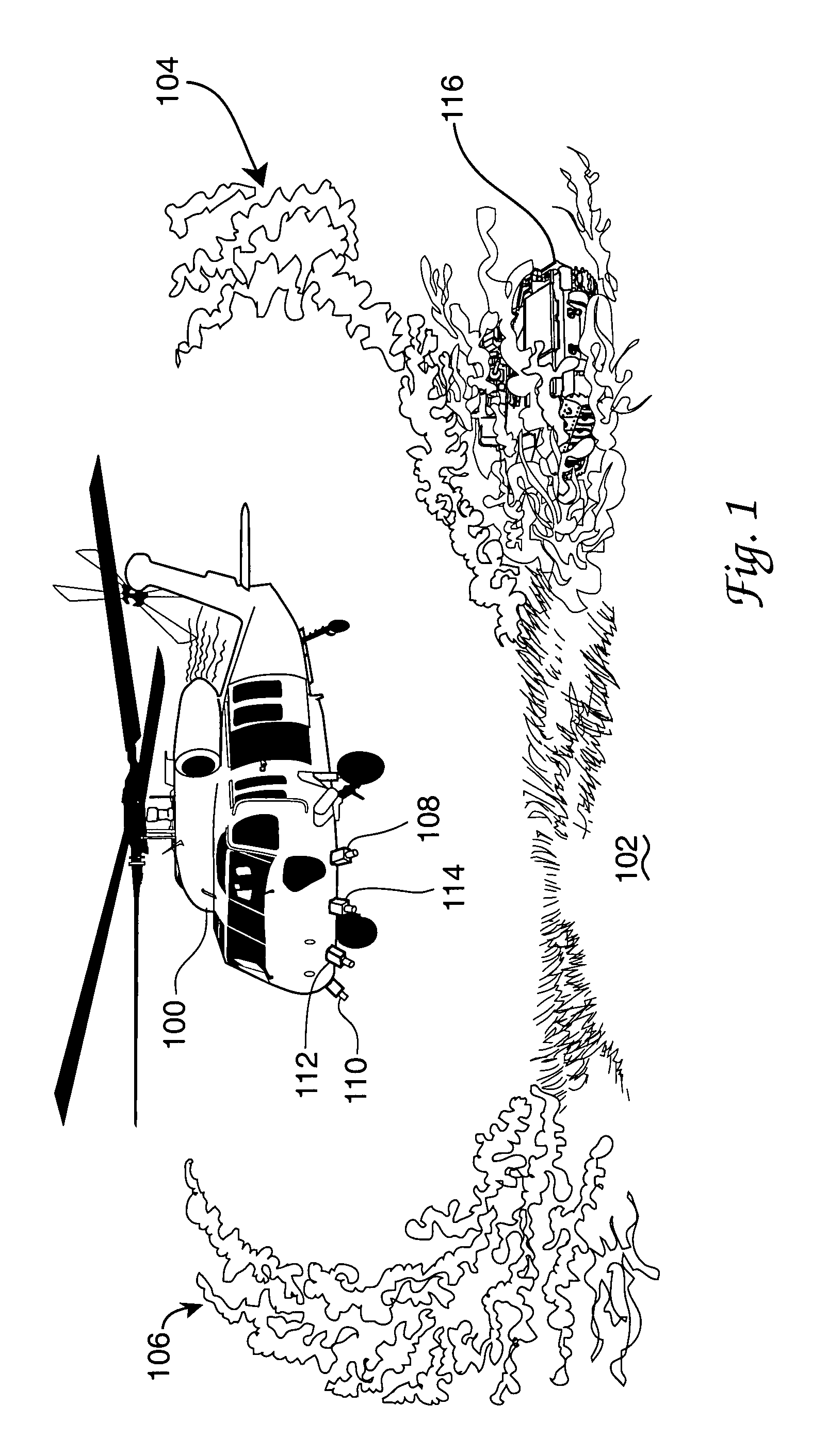
Helicopter brown-out landing
InactiveUS7642929B1Broaden their knowledgeAnalogue computers for trafficCathode-ray tube indicatorsObfuscationImaging processing
An electromagnetic emissions free optical signal based helicopter landing assistance arrangement wherein helicopter rotor wash dust cloud-caused obfuscation of the intended landing site and other landing threats are overcome. Real time optical sourced data is collected early and used during helicopter approach to the intended landing site. Upgrading of this data for use during dust cloud presence is accomplished with image processing techniques applied in response to such inputs as helicopter flight data. Military use of the invention especially in current theatre conflict environments is contemplated. Dust cloud related landing hazards are disclosed as a significant difficulty in such environments and generate need for the invention.
Owner:AIR FORCE US SEC THE THE
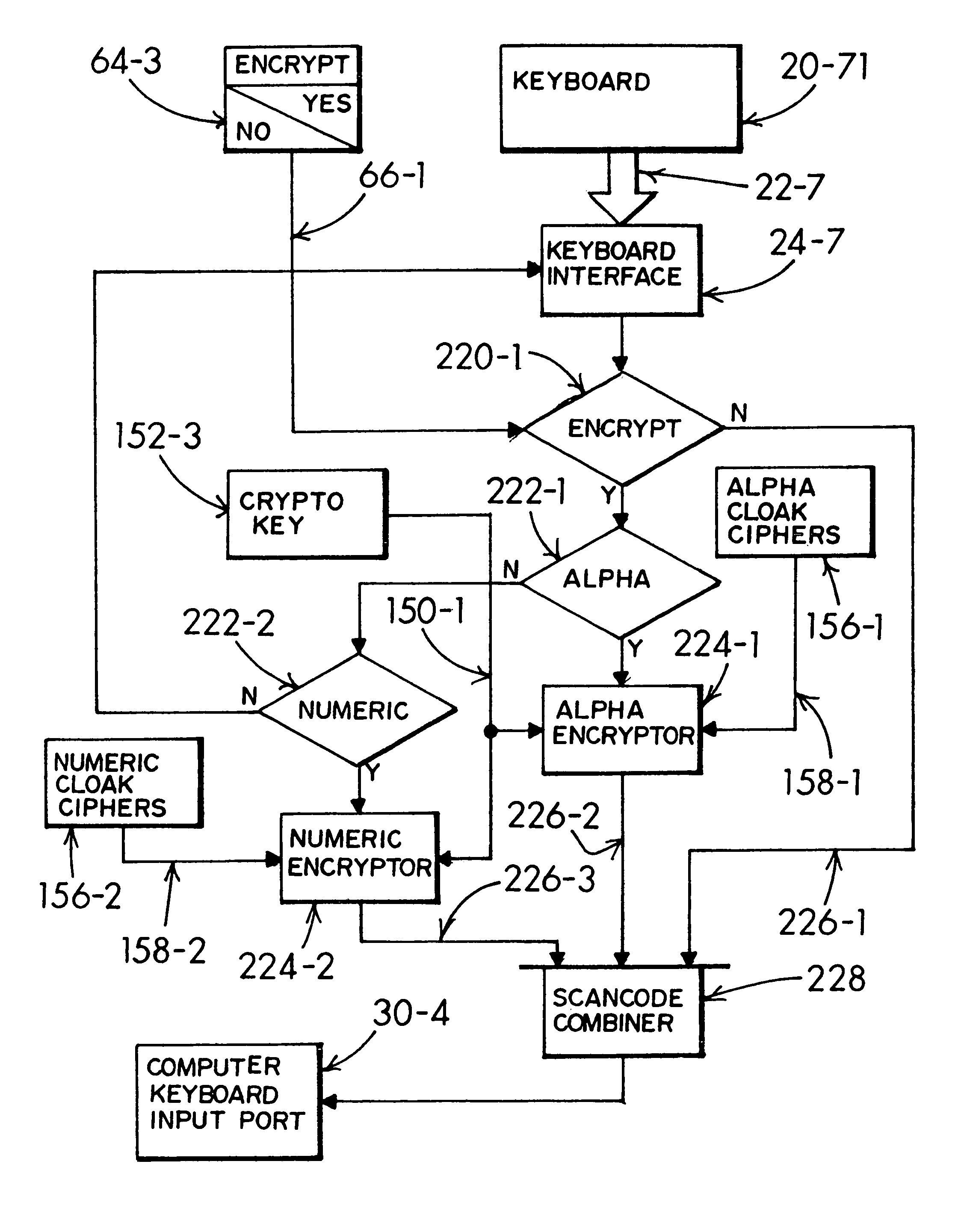
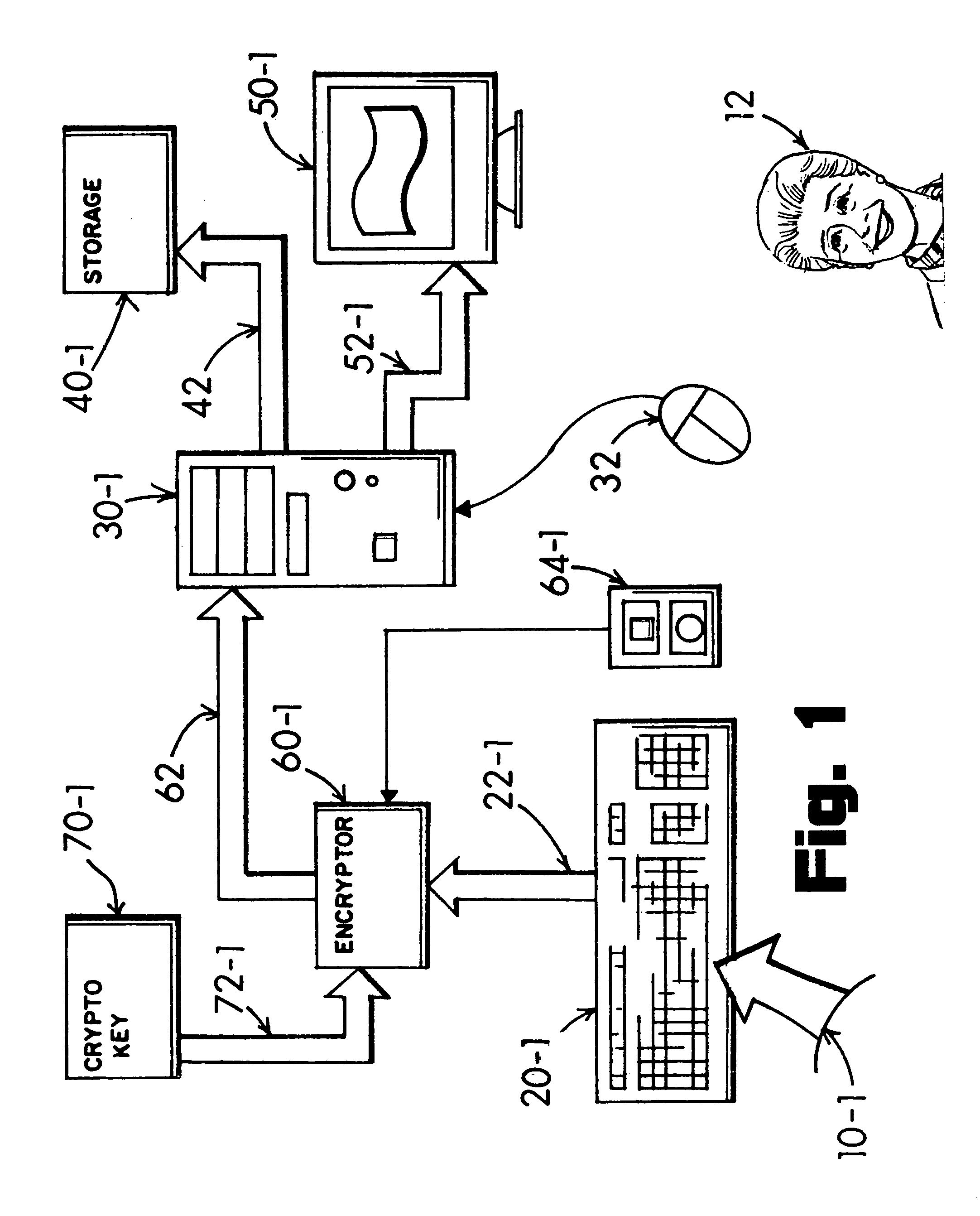
Selected text obfuscation and encryption in a local, network and cloud computing environment
InactiveUS8347398B1Easy typingImprove abilitiesDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionObfuscationData store
A keyboarded a mix of private and public text composing a source-text document is submitted through an encryption adapter intersituated in a data signal link between the keyboard and a computer system. A user selects and obfuscates the private text character portions with surrogate cloak characters in concurrent alternation with direct entry of the public text characters. A resultant protected document's data signal is safeguarded for editing and data storage without revelation of the private text content. The protected document is sufficiently secure for submission into a cloud computing environment and is immune to key-entry tracking malware. Clandestine hacking of residual data remaining in the computer firmware is negated in interpretative value by enabling the user's selective obfuscation of the source-text document's private text character content with surrogate cloak characters prior to entry into the computer system's keyboard input port.
Owner:SAVVYSTUFF PROPERTY TRUST
Acorn: providing network-level security in P2P overlay architectures
InactiveUS20070149279A1Broadcast specific applicationsDigital computer detailsObfuscationComputer science
To address the problem of providing network-based security to mitigate and detect cheating in peer-to-peer (P2P) gaming architecture, an architecture suite called architectures with coordinator obfuscation for resilient P2P gaming networks (ACORN) is presented that uses a combination of low overhead, per-packet access authentication, moving-coordinator and cheat detection mechanisms to effectively mitigate security threats.
Owner:RPX CORP
Software self-defense systems and methods
ActiveUS20050204348A1Error detection/correctionProgram/content distribution protectionTamper resistanceObfuscation
Systems and methods are disclosed for protecting a computer program from unauthorized analysis and modification. Obfuscation transformations can be applied to the computer program's local structure, control graph, and / or data structure to render the program more difficult to understand and / or modify. Tamper-resistance mechanisms can be incorporated into the computer program to detect attempts to tamper with the program's operation. Once an attempt to tamper with the computer program is detected, the computer program reports it to an external agent, ceases normal operation, and / or reverses any modifications made by the attempted tampering. The computer program can also be watermarked to facilitate identification of its owner. The obfuscation, tamper-resistance, and watermarking transformations can be applied to the computer program's source code, object code, or executable image.
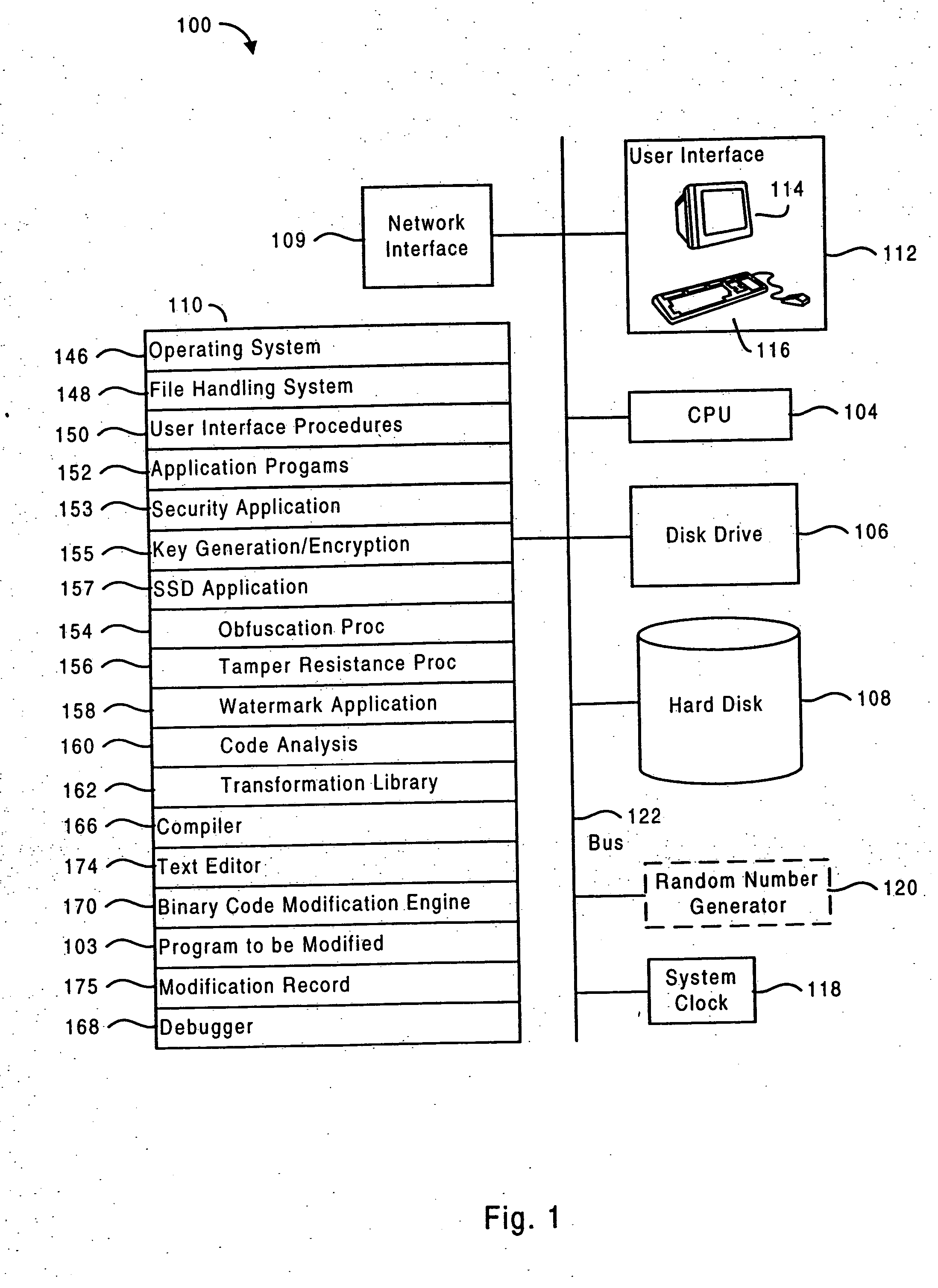
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
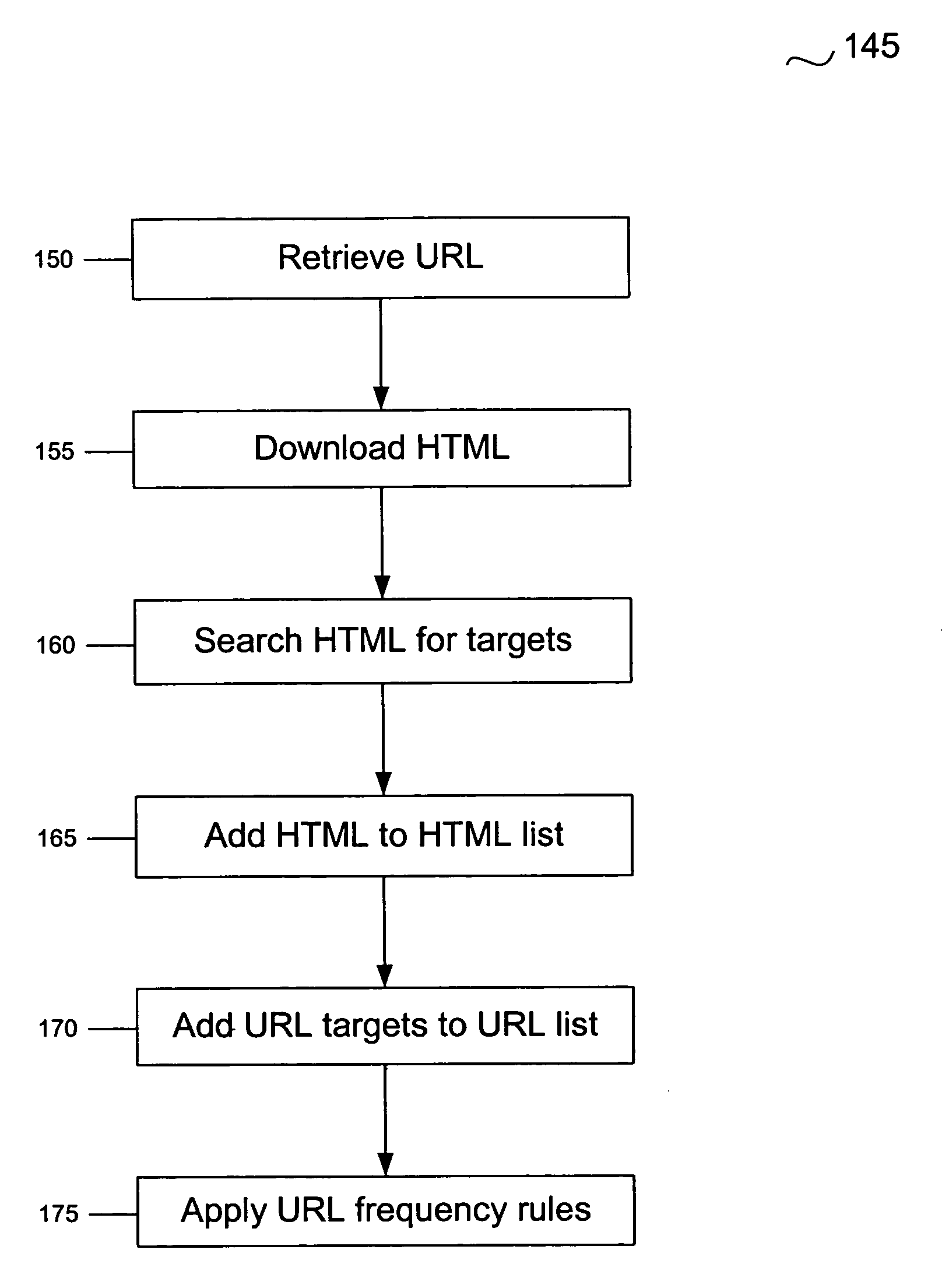
System and method for locating malware
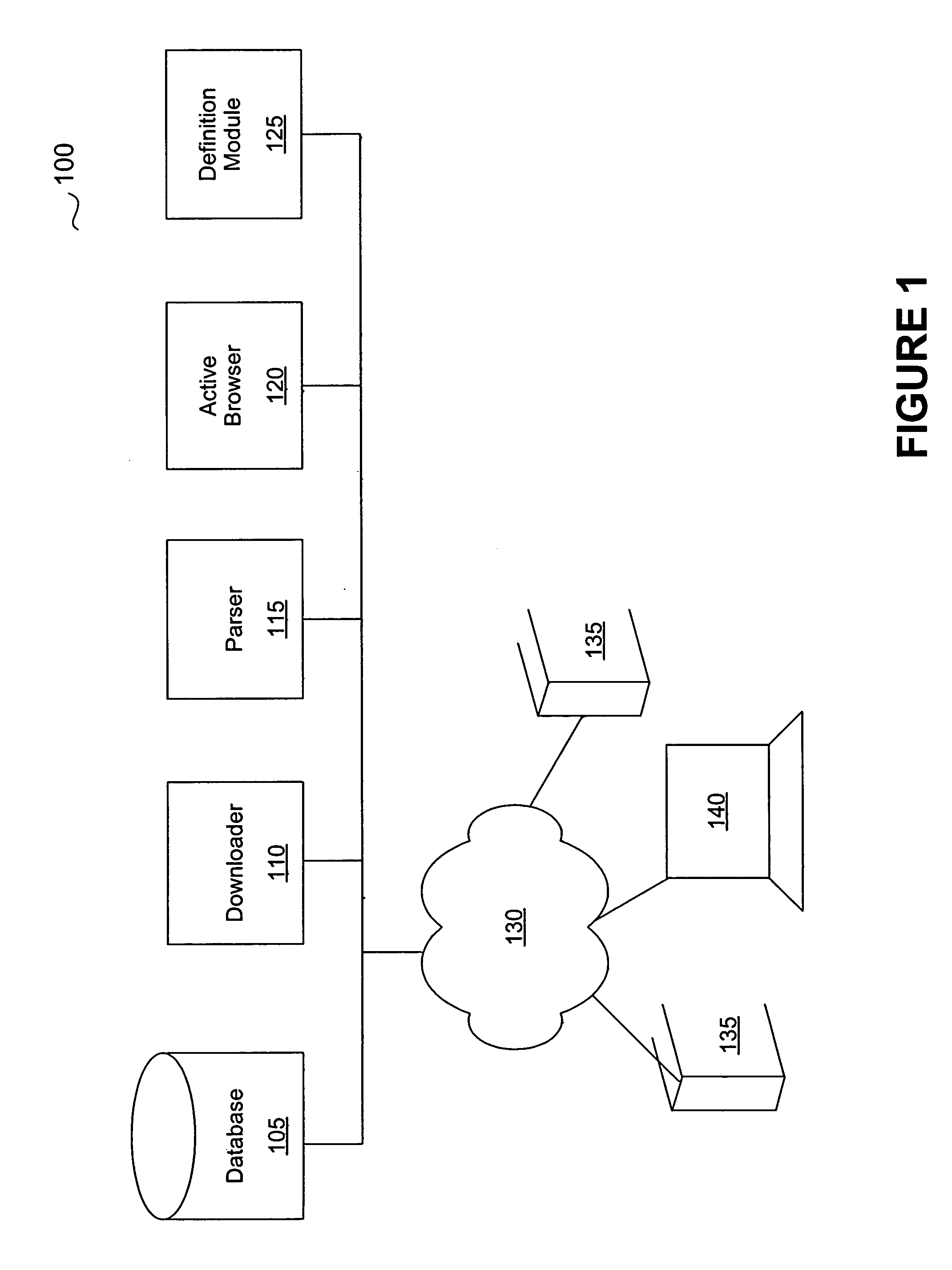
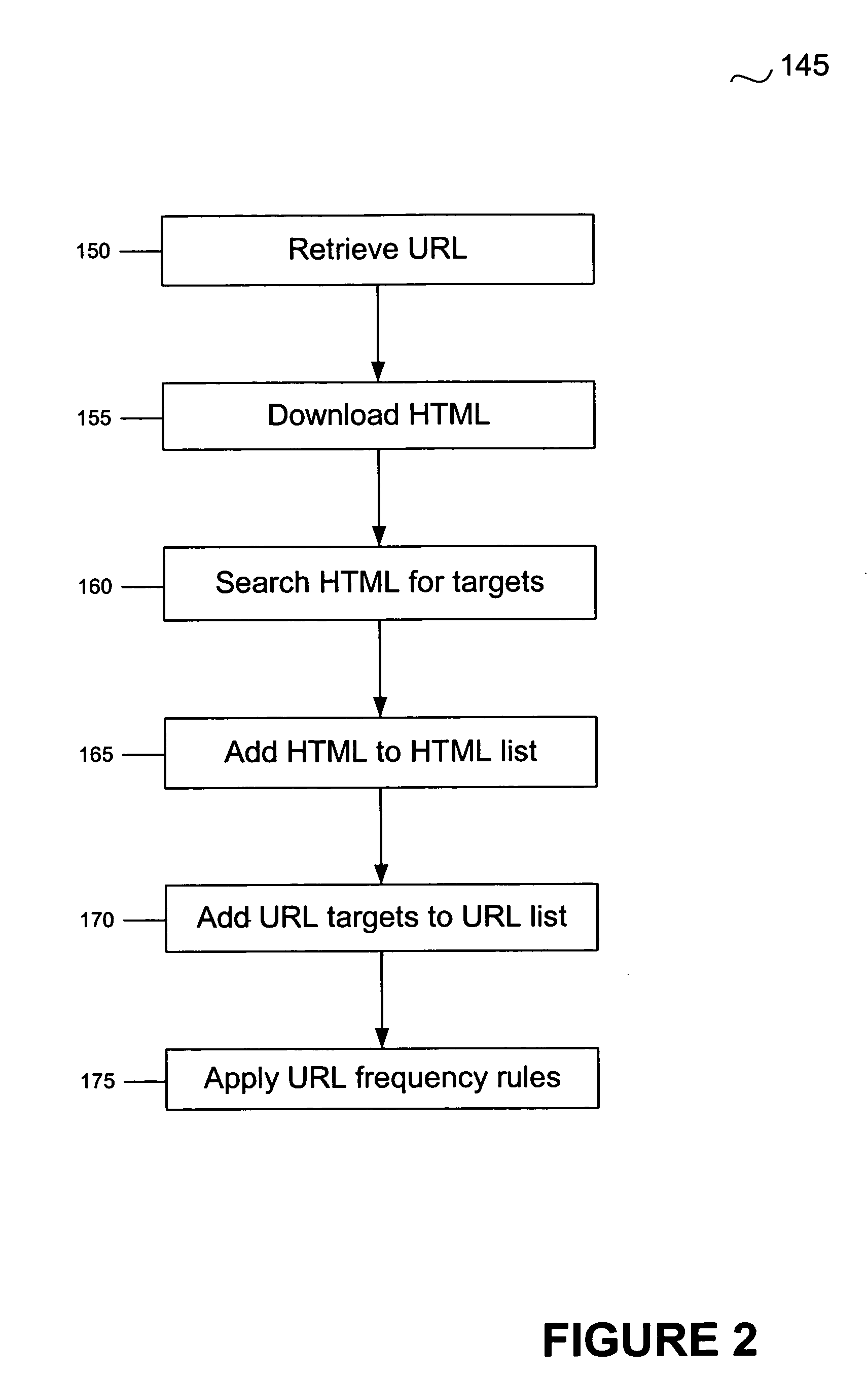
A system and method for managing malware is described. One embodiment is designed to receive an initial URL associated with a Web site; download content from that Web site; identify any obfuscation techniques used to hide malware or pointers to malware; interpret those obfuscation techniques; identify a new URL as a result of interpreting the obfuscation techniques; and add the new URL to a URL database.
Owner:OPEN TEXT CORPORATION
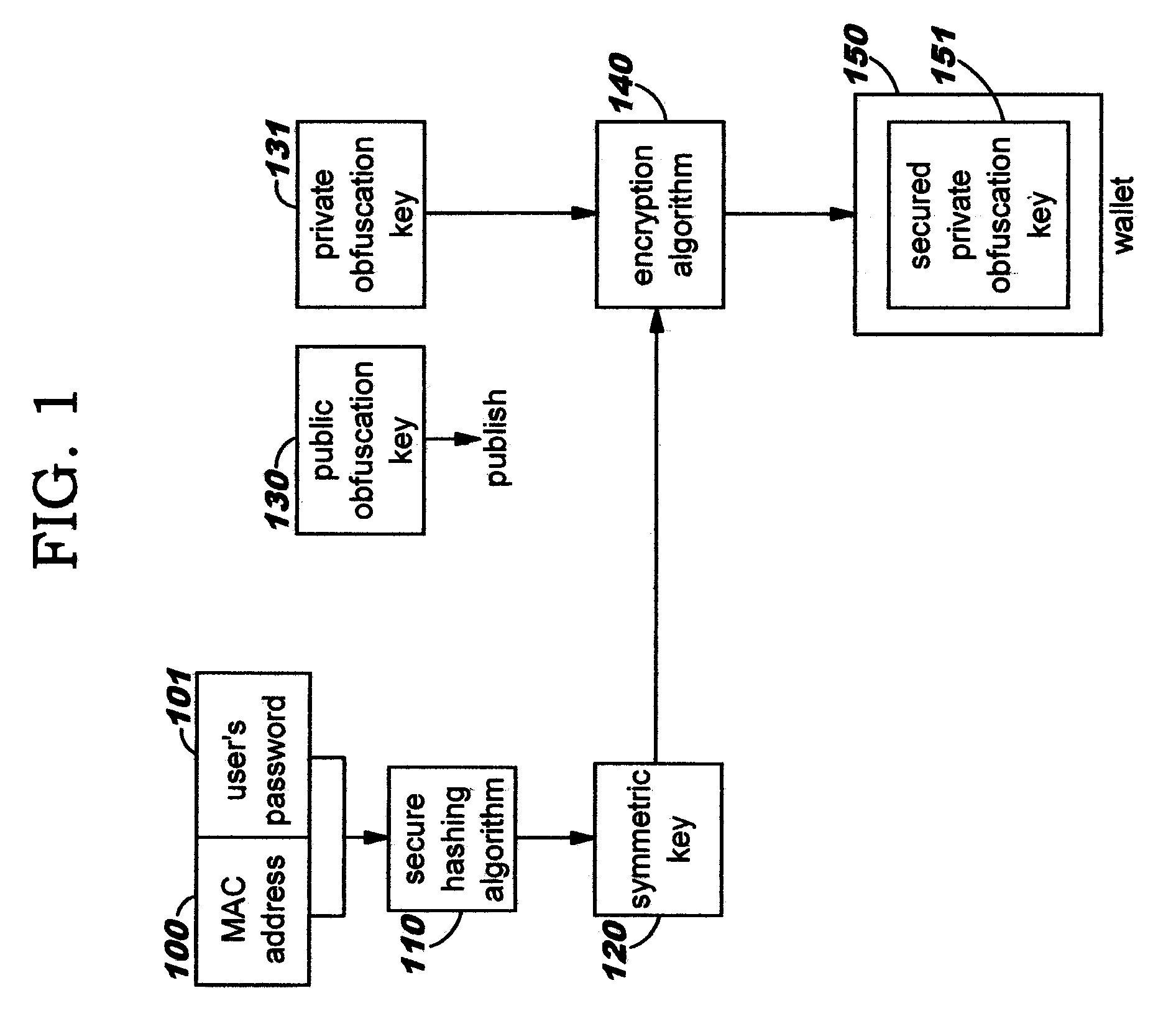
Data privacy management system and method
InactiveUS20050251865A1Minimize impactKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationObfuscationInternet privacy
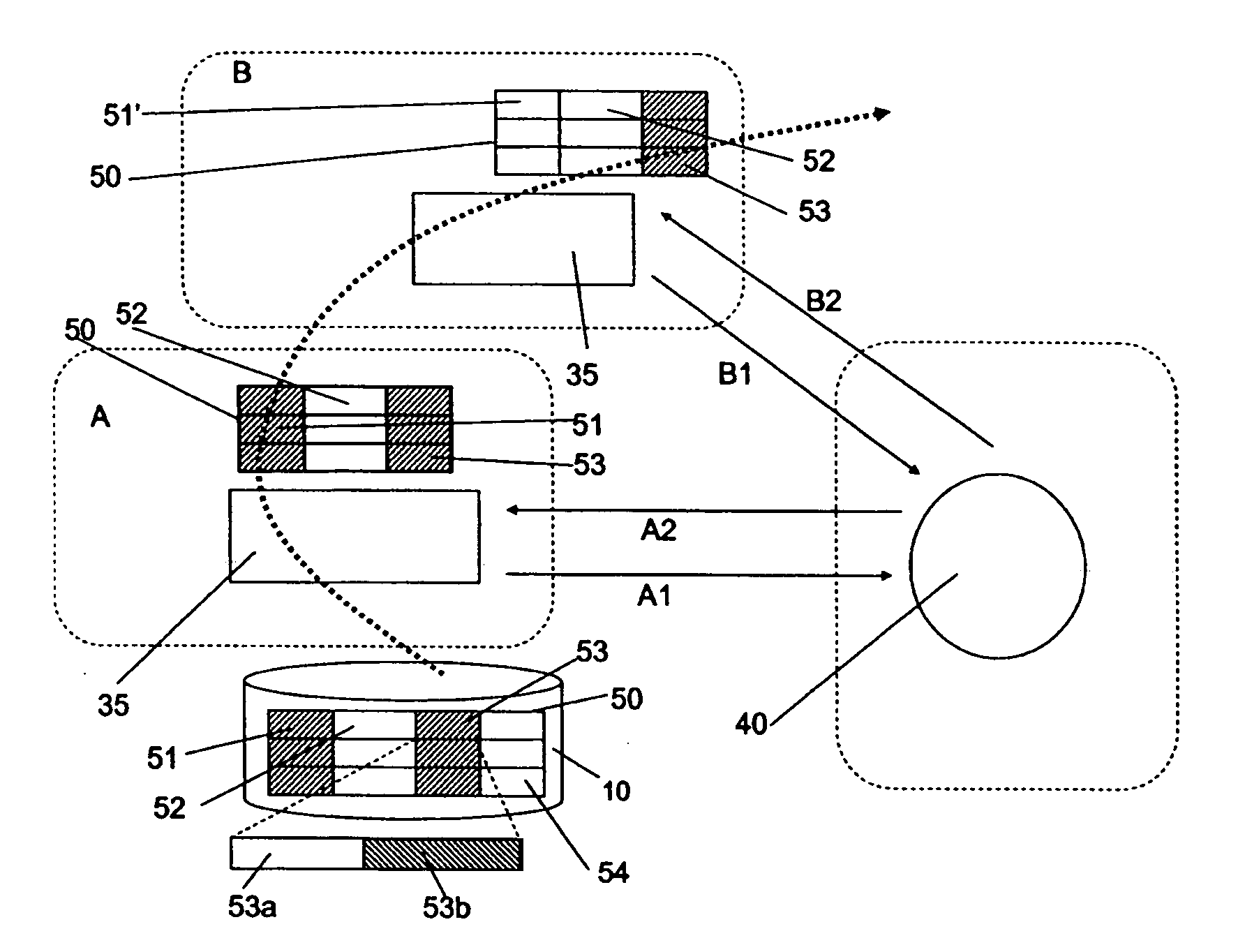
A data privacy management system includes a data repository, a private data mediating system and a privacy manager. The data repository stores private data items in an obfuscated form. Each private data item has associated privacy policy data a defining conditions to be met to ensure the privacy of the data item. A private data mediating system communicates with the privacy manager to obtain de-obfuscated private data items that are extracted from the data repository 10. De-obfuscation of the data 51, 53 is subject to satisfaction of the privacy manager that the respective conditions ensuring privacy of the data item are met.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
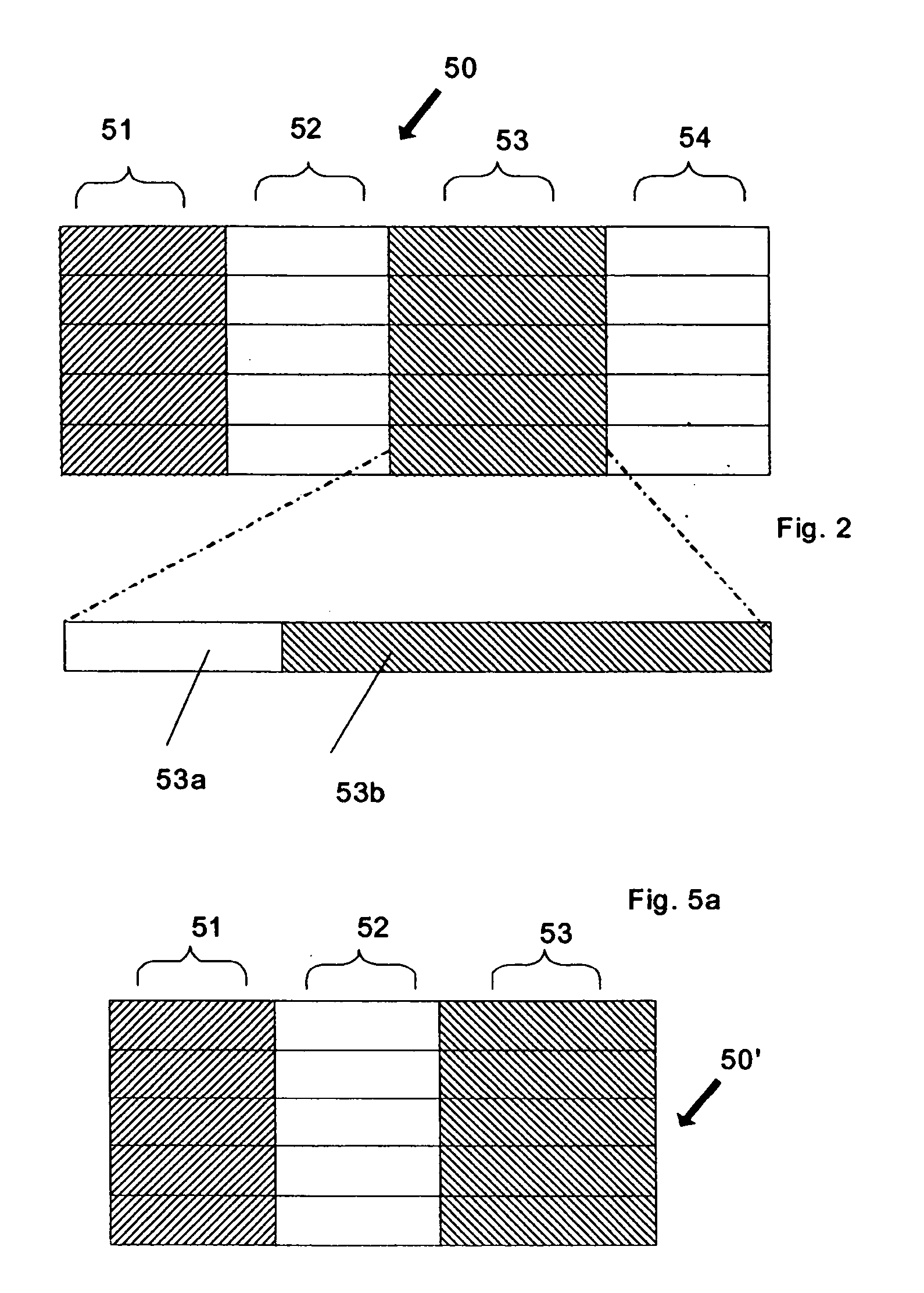
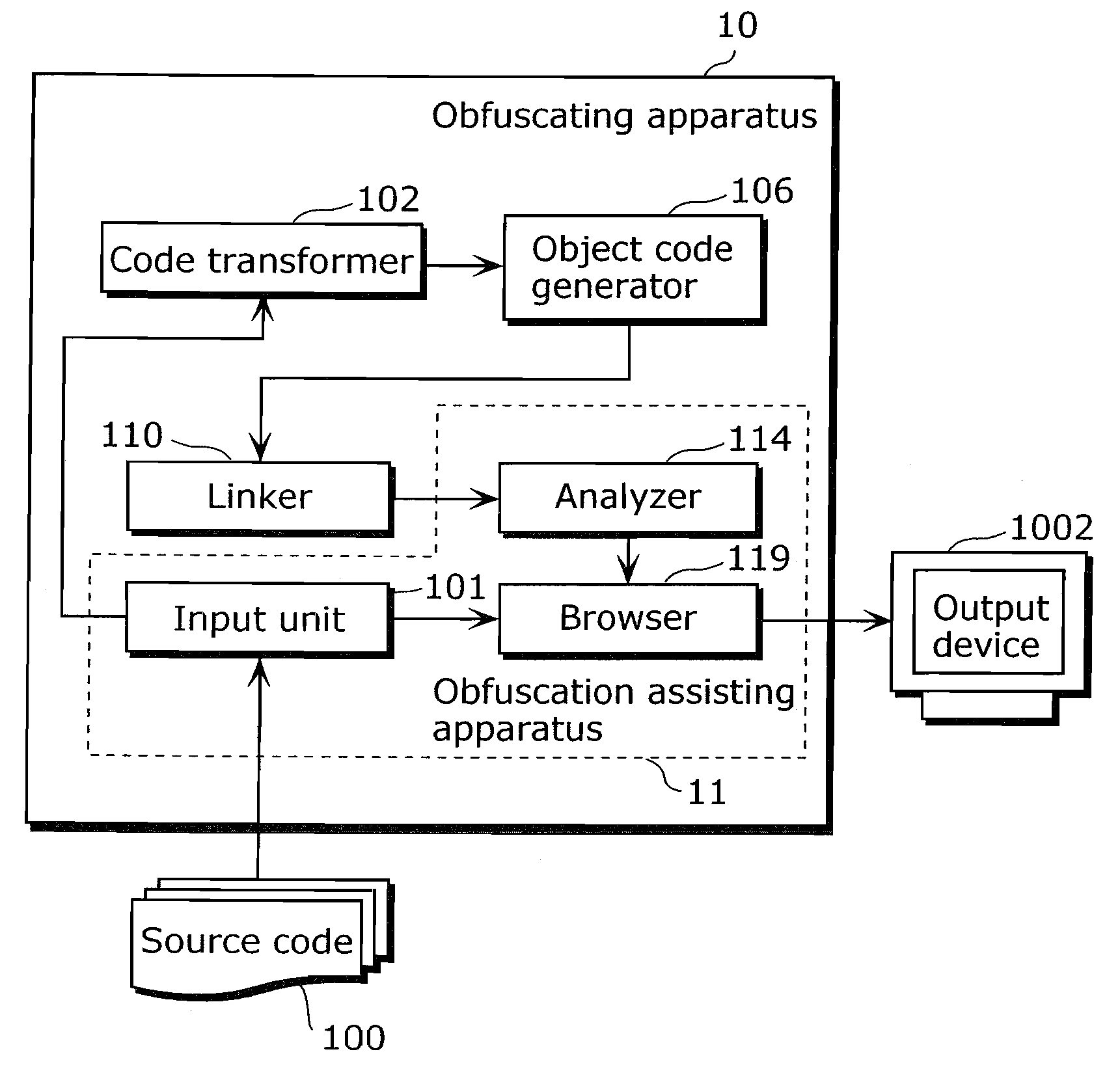
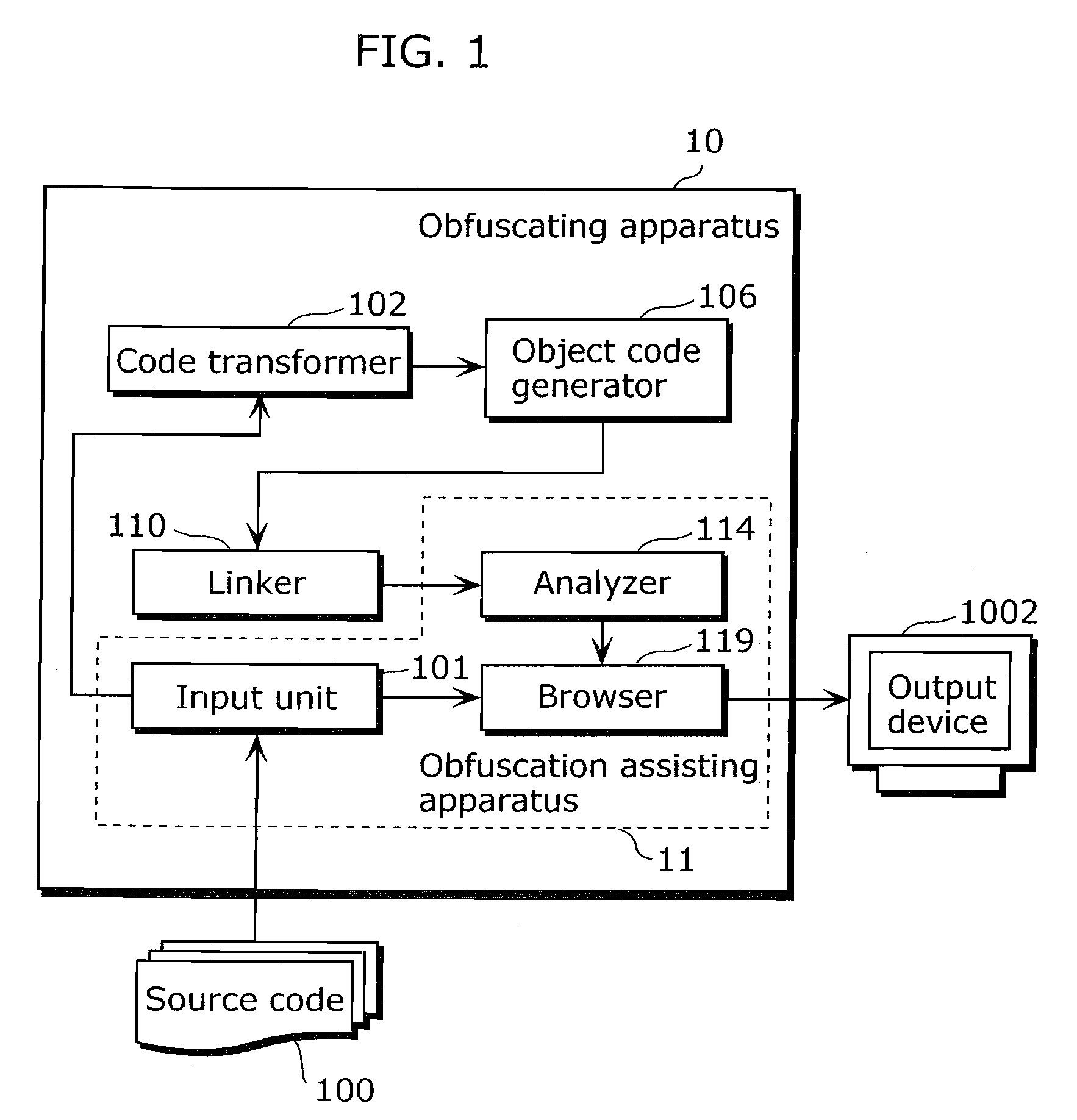
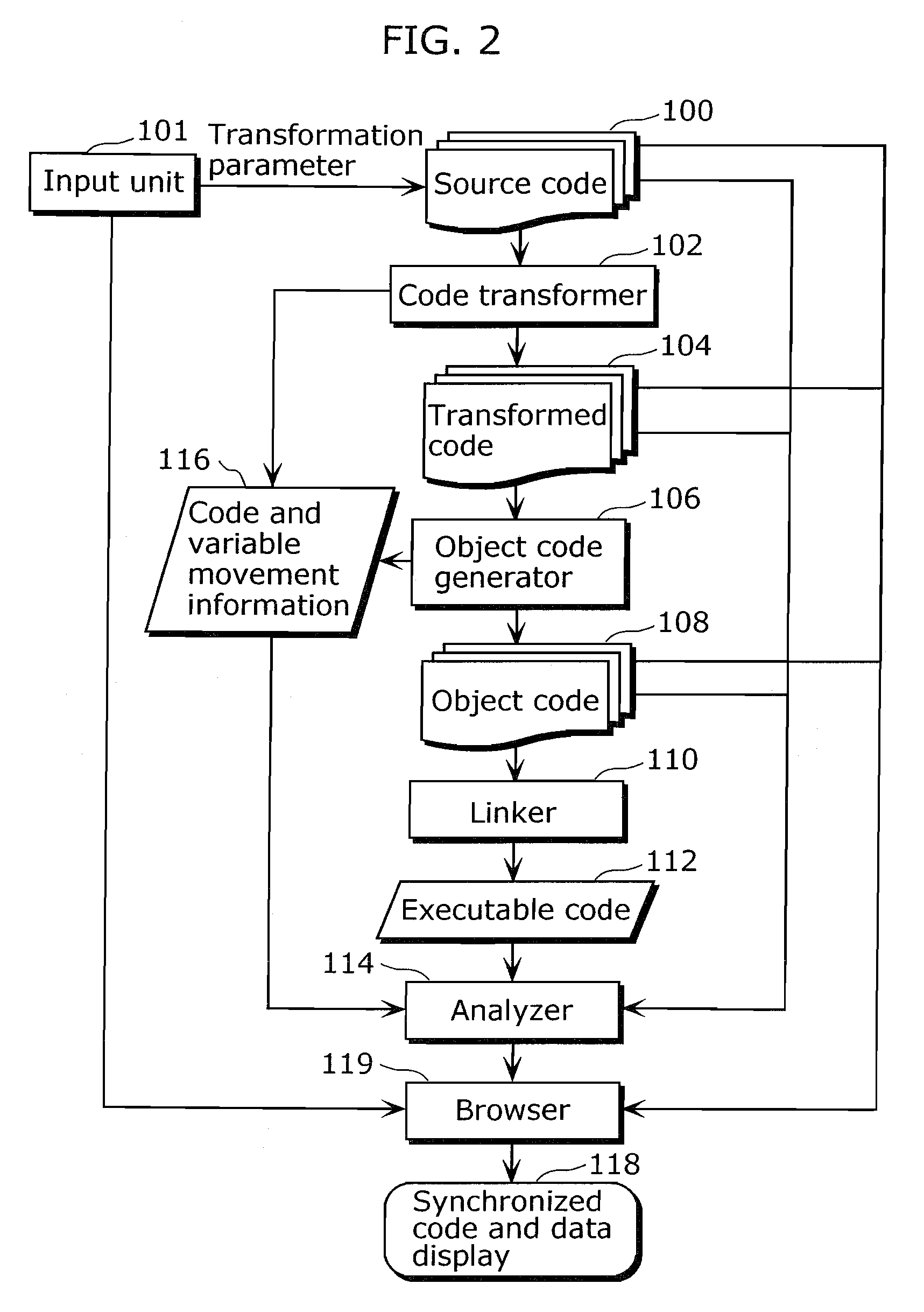
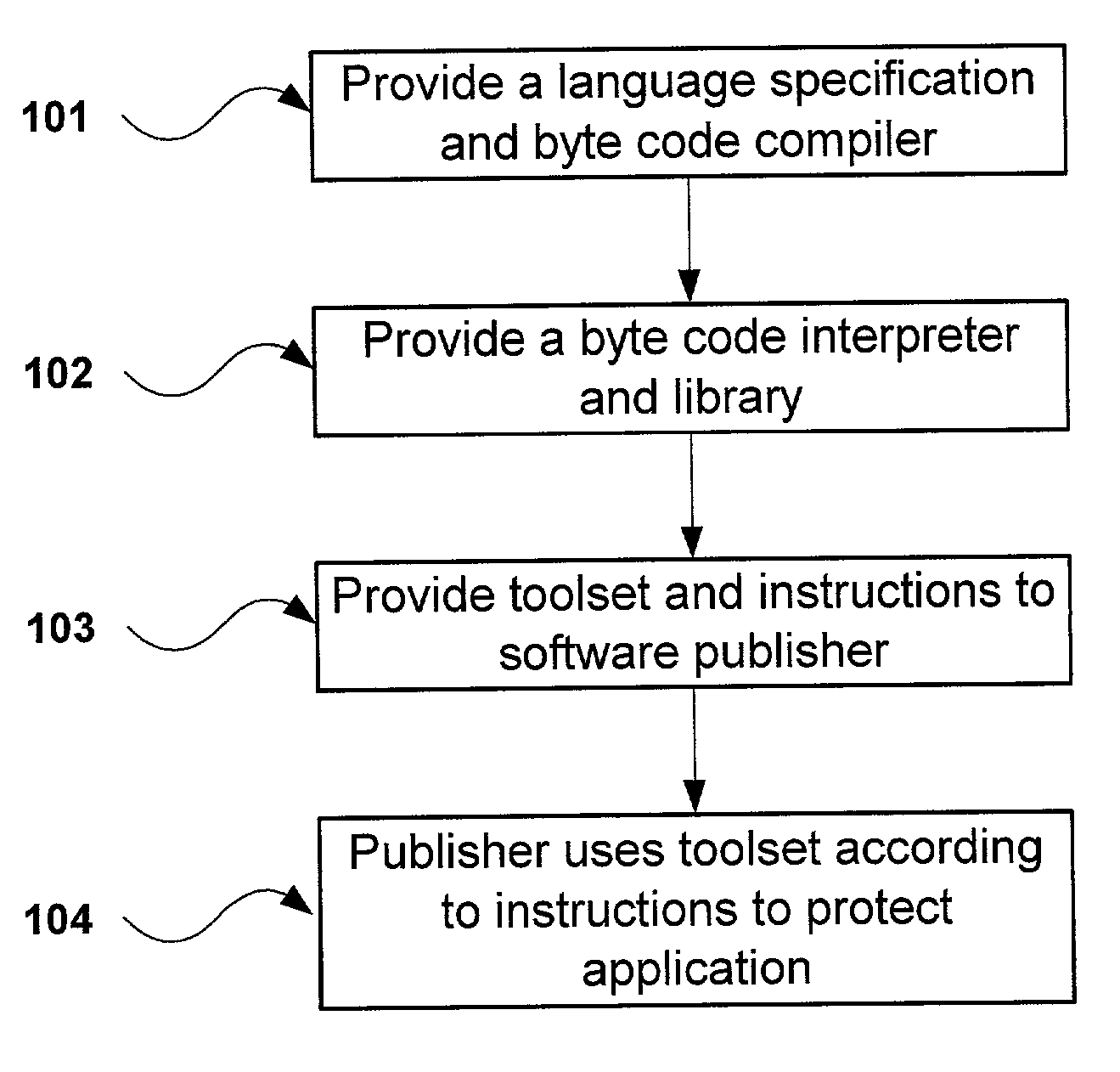
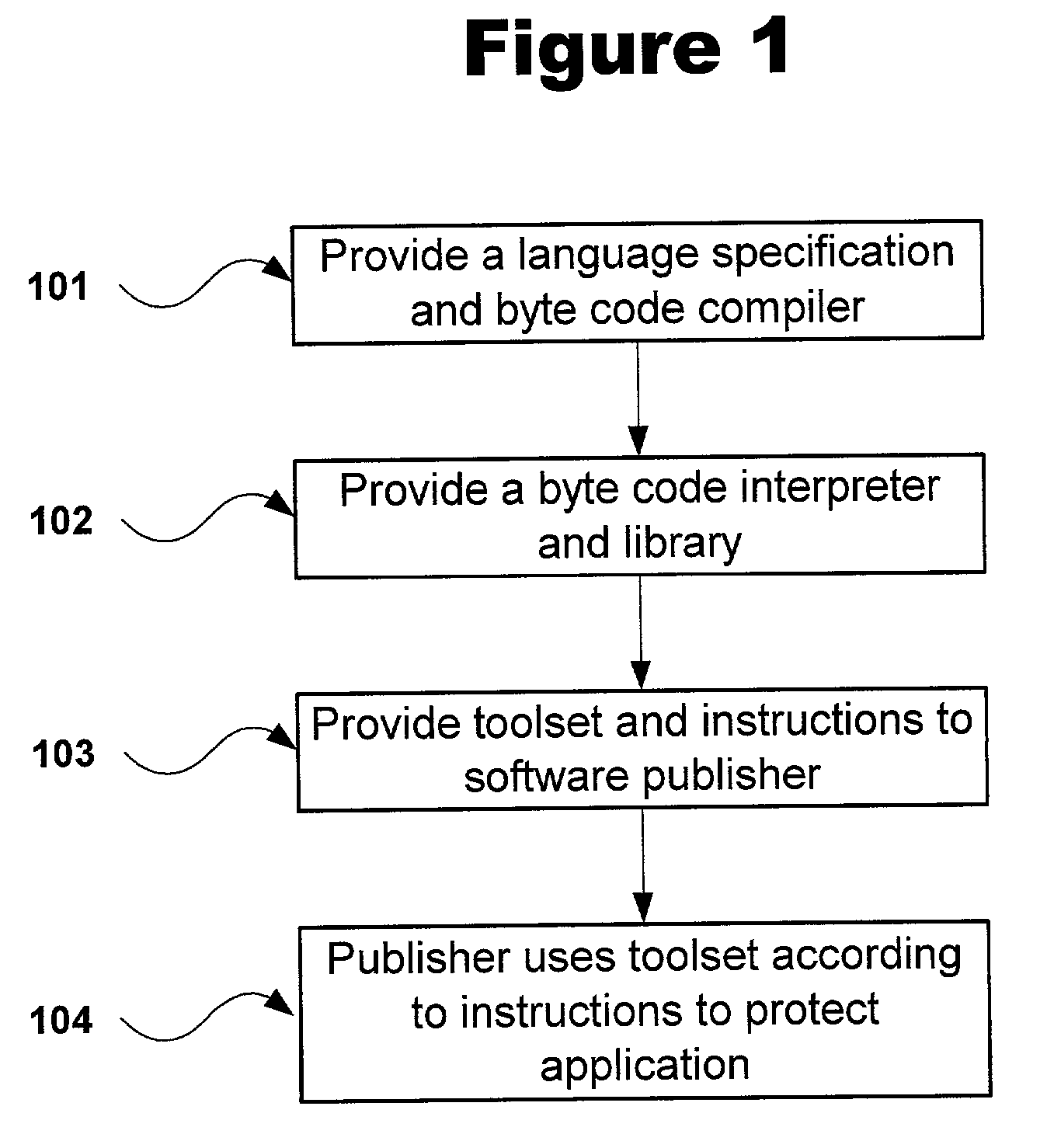
Obfuscation assisting aparatus
ActiveUS20100180346A1Quality improvementEasy to carryDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsObfuscationOutput device
To provide, in order that proper obfuscation of a source code (100) can be easily performed, an obfuscation assisting apparatus (11) which can sufficiently assist the obfuscation. The obfuscation assisting apparatus (11) includes: an analyzer (114) which identifies corresponding respective blocks in the source code (100) and in a transformed code (104) generated through the obfuscation of the source code (100); and a browser (119) which obtains obfuscation information relating to obfuscation of the respective blocks of the source code (100) and the transformed code (104), and causes an output device (1002) to display the respective parts of the source code (100) and the transformed code (104), and the obfuscation information in association with each other.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Apparatuses, systems and methods for determining installed software applications on a computing device
Apparatuses, systems and methods are disclosed which provide for determining identification of software installed on a device using one or more of information about the file system structure, and operation wherein the step of determining the identification of software is performed real-time. The apparatuses, systems and methods can be used to identify applications regardless of any security or obfuscation processes employed by the device.
Owner:MEDL MOBILE
Obfuscating the display of information and removing the obfuscation using a filter
InactiveUS20110206285A1Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsObfuscationDisplay device
This is directed to obfuscating a display to secure the display of information provided to a user. An electronic device can modulate the display of information using different approaches, including for example by adding artifacts or changing the color, frequency or polarity of displayed information, thus obfuscating the display. To view the displayed information, a user can place a filter between the user and the display (e.g., as part of glasses) such that the filter can remove or undo the obfuscation. In some embodiments, the device can display different confidential information for several users simultaneously, where different obfuscation approaches are used for each user. This can allow several users to interact with the device simultaneously while ensuring that each user's information remains confidential.
Owner:APPLE INC
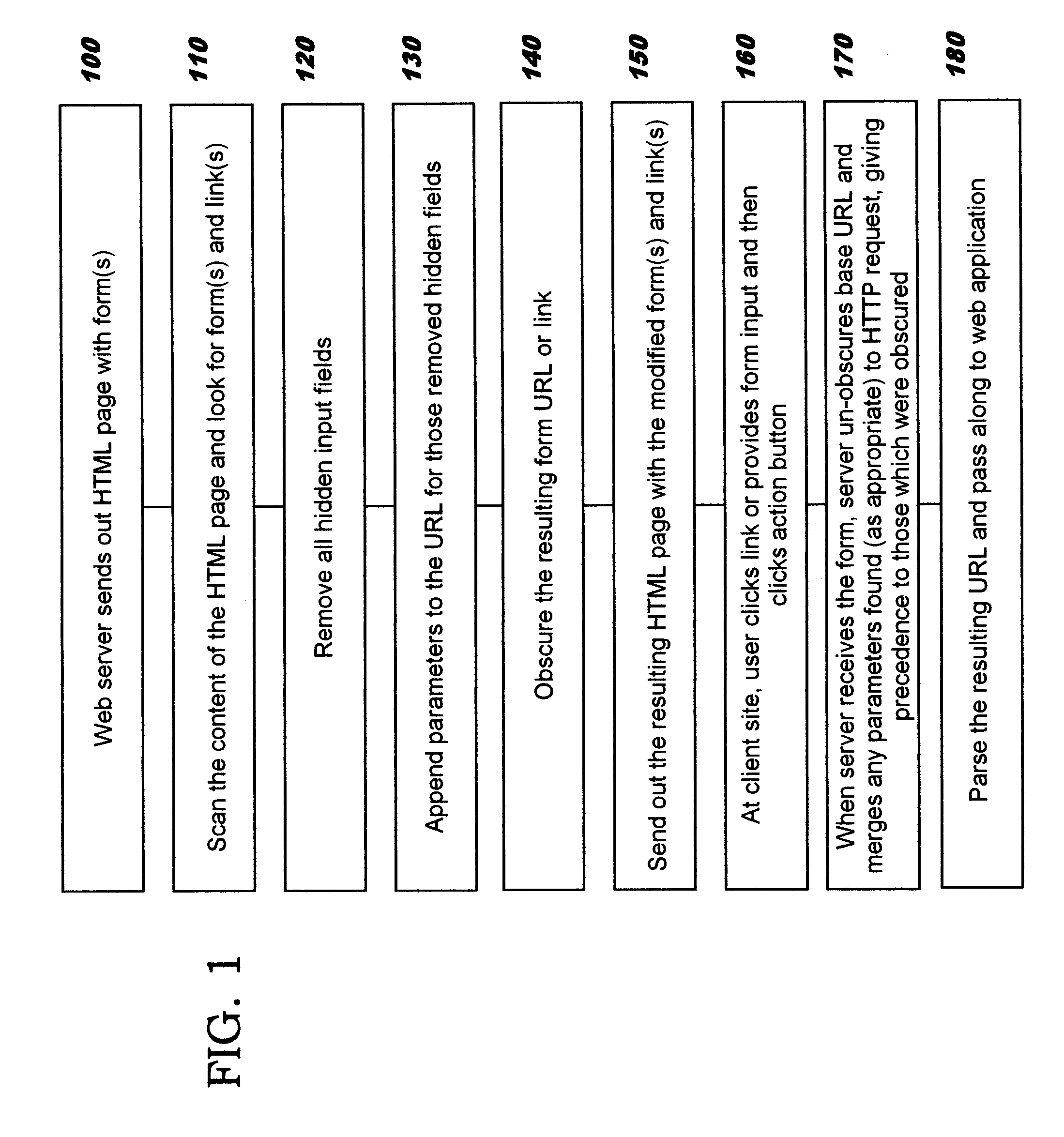
Obscuring form data through obfuscation
InactiveUS20110107077A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsObfuscationUniform resource locator
Obscuring form data to be passed in forms that are sent in messages over a communications network. The form data to be obscured is removed from a form and inserted as a portion of a Uniform Resource Location (“URL”) string. The obscured form data may comprise hidden fields and / or links. An obfuscation is then applied to the portion of the URL string, thereby obscuring the information for sending on an outbound message. The original information is recovered from an inbound message which contains the obscured information by reversing the processing used for the obscuring. In one aspect, the obfuscation comprises encryption. In another aspect, the obfuscation comprises creating a tiny URL that replaces the portion of the URL string.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com