Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
512 results about "Group key" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
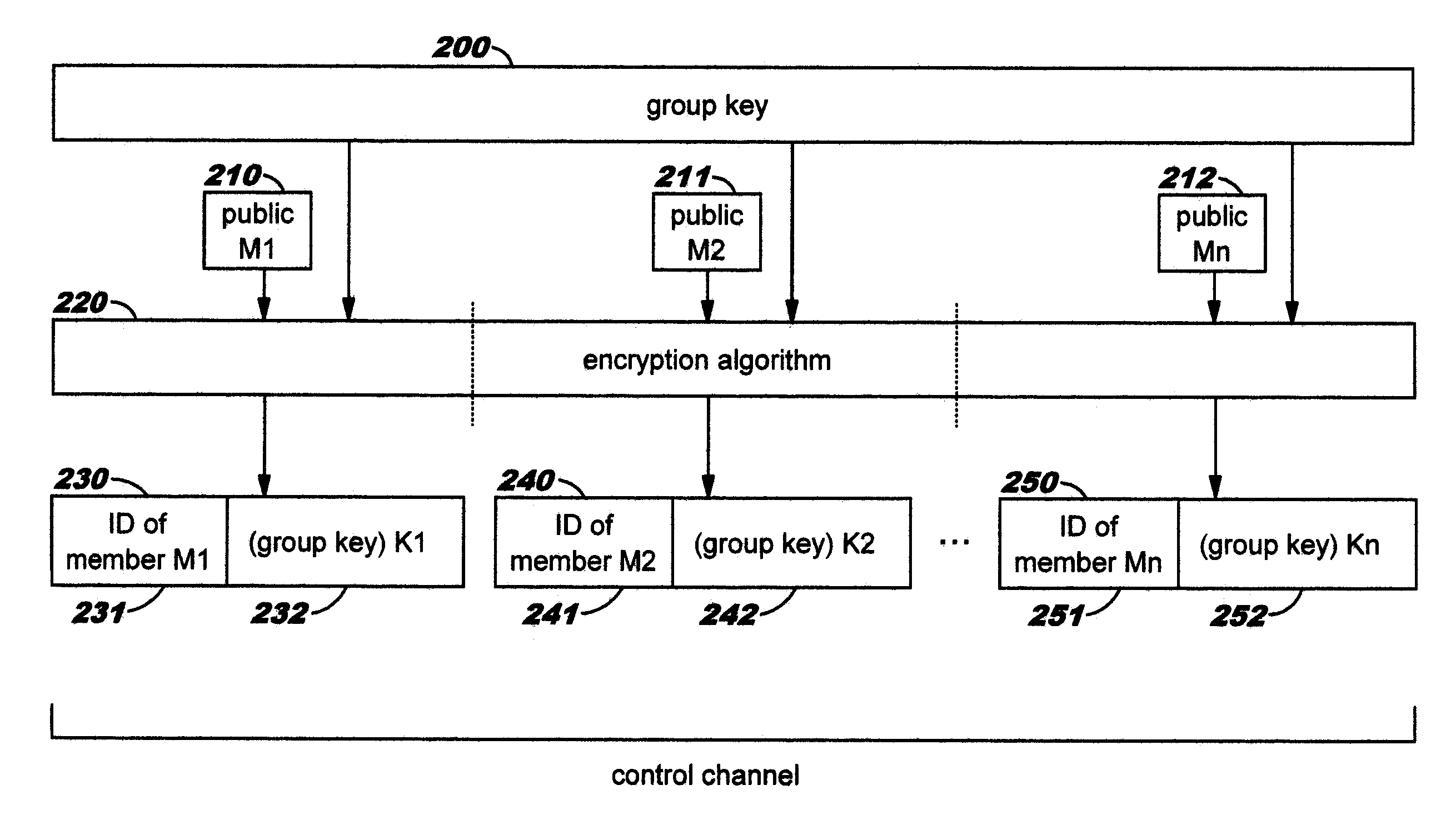
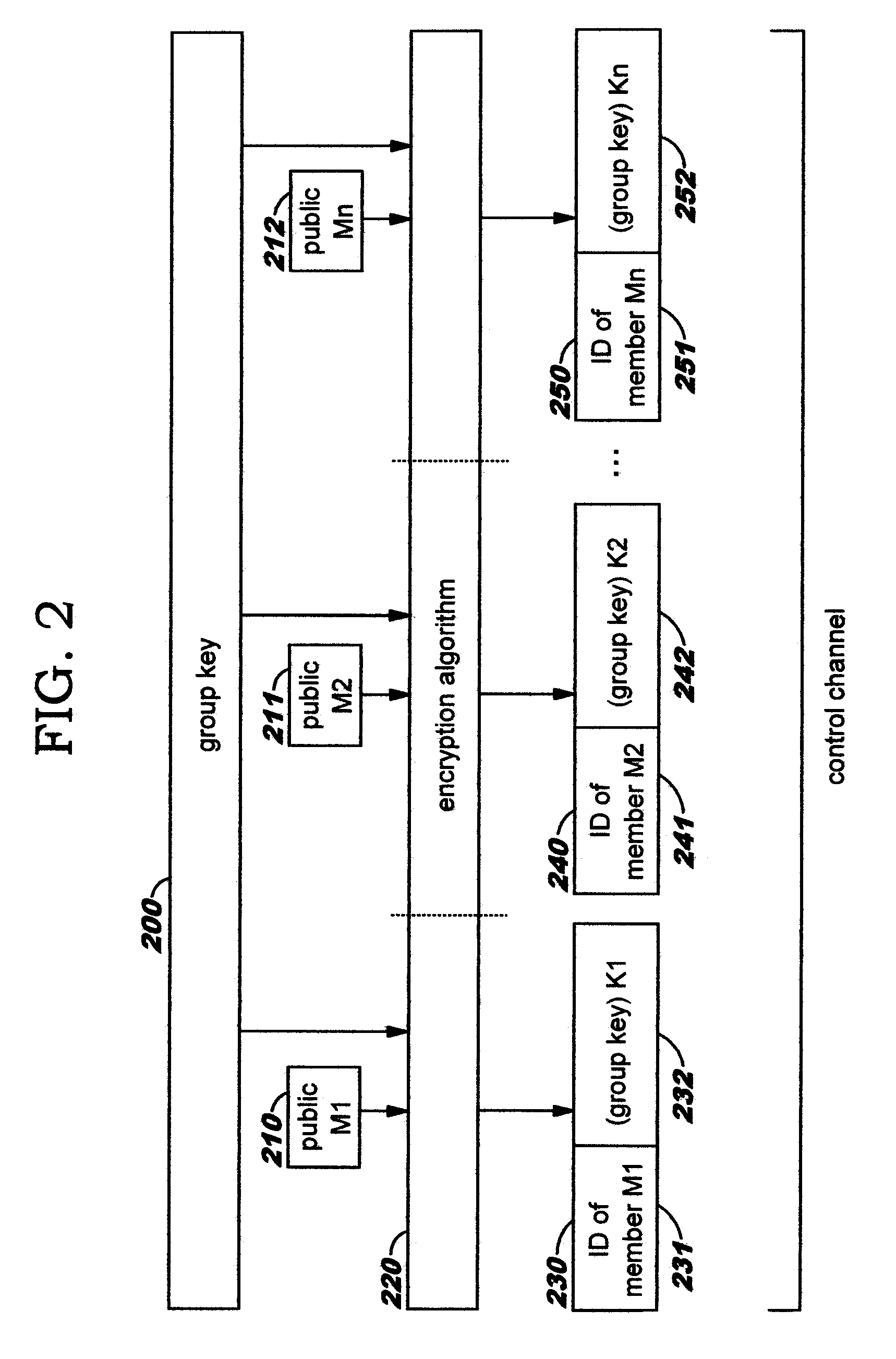
In cryptography, a group key is a cryptographic key that is shared between a group of users. Typically, group keys are distributed by sending them to individual users, either physically, or encrypted individually for each user using either that user's pre-distributed private key.
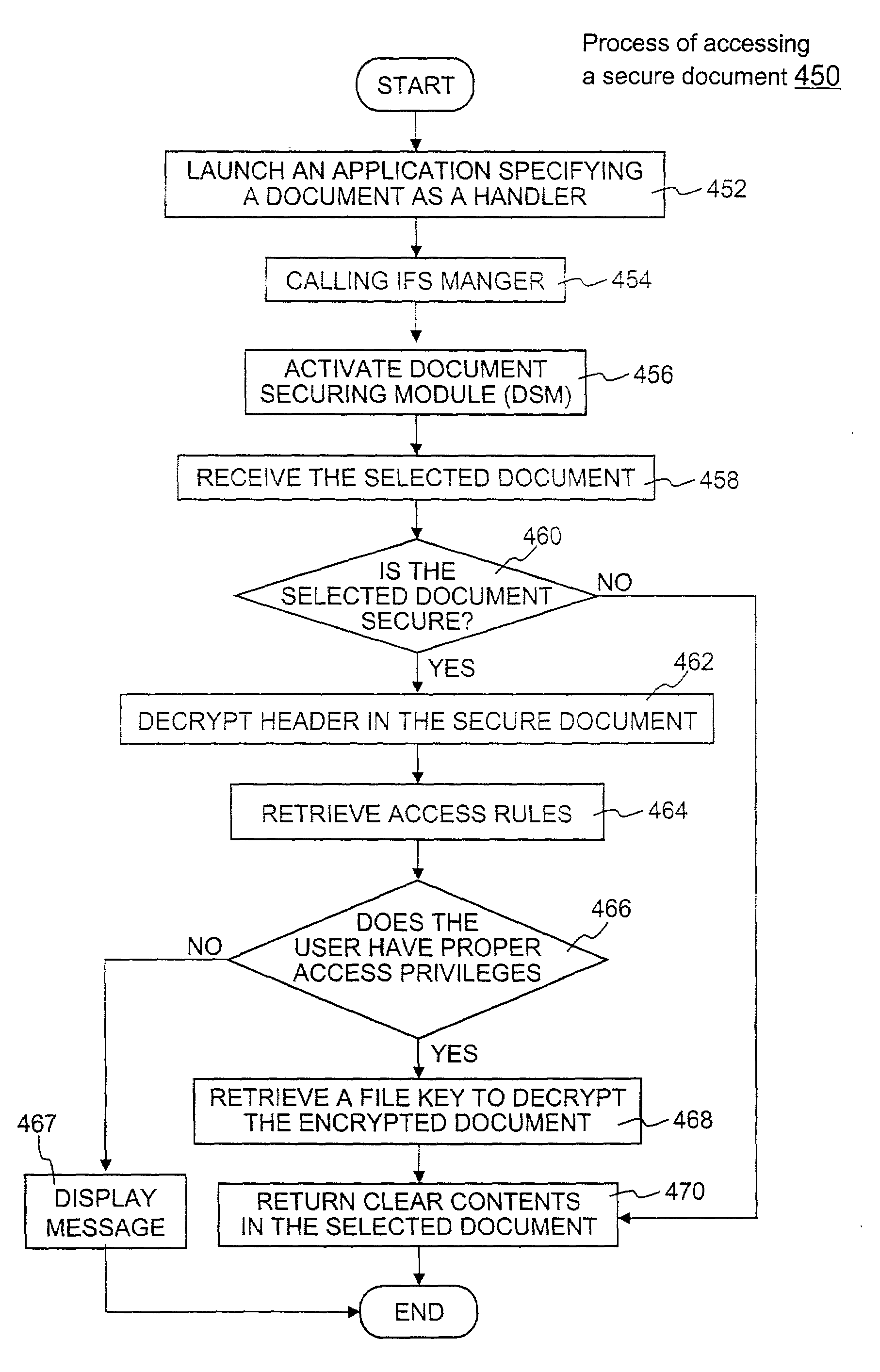
Method and apparatus for securing electronic data
ActiveUS7681034B1Facilitate access control managementGood synchronizationDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionPathPingEngineering
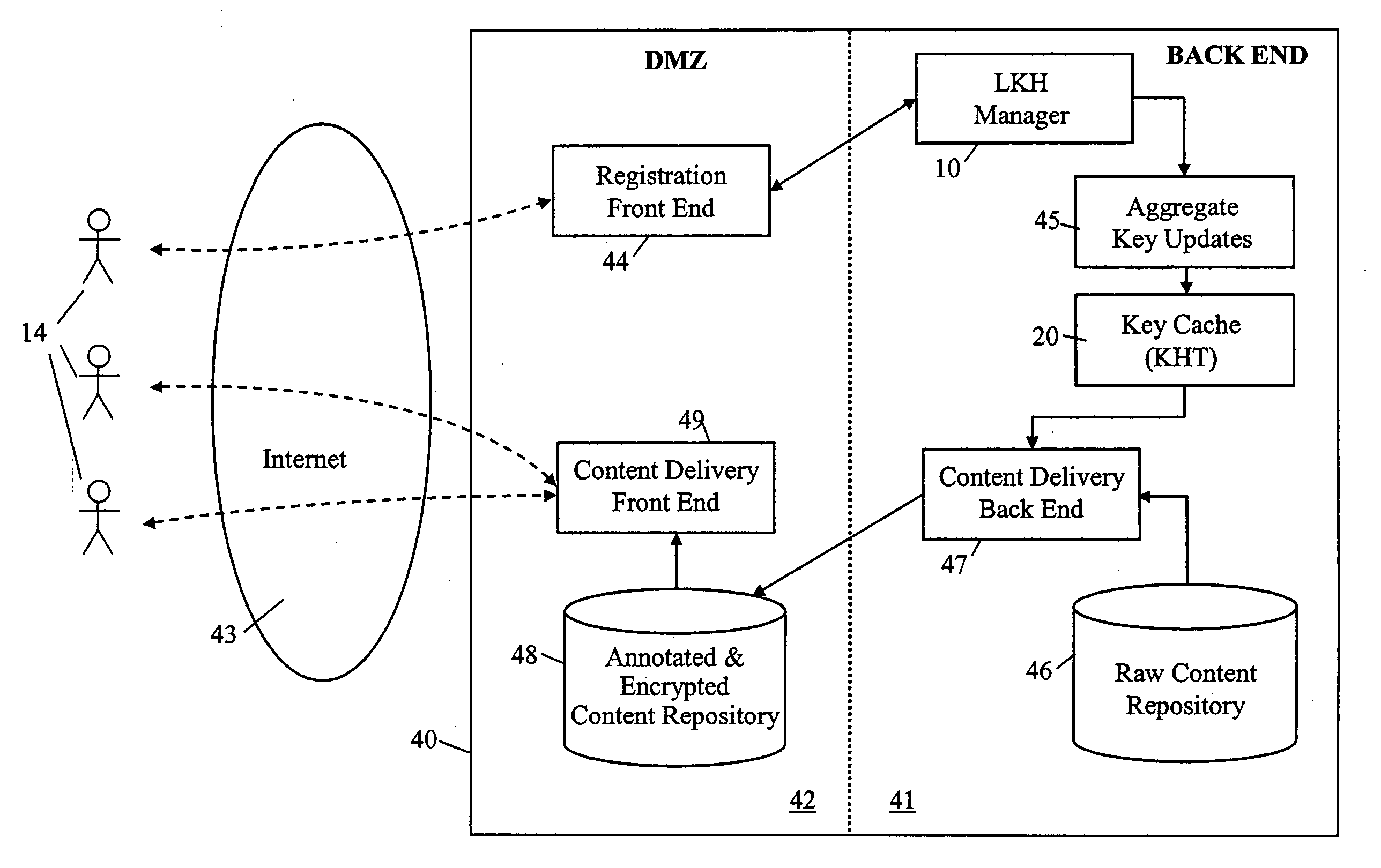
Techniques for securing electronic data and keeping the electronic data secured at all times are disclosed. According to one embodiment, a client module in a client machine is configured to provide access control to secured documents that may be located in a local store, another computer machine or somewhere over a data network. The client module includes a document-securing module configured to operate in a path through which a document being accessed is caused to pass so that the document can be examined or detected for the security nature. If the document is secured, the document-securing module obtains a user or group key to decrypt security information in the secured document for access rules therein. If a user accessing the document is determined to have the access privilege to the secured document, a file key is retrieved from the security information and a cipher module is activated to decrypt the encrypted data portion with the file key. Likewise, if a document is to be secured, the cipher module encrypts clear data from the document to create the encrypted data portion. The document-securing module integrates proper or desired security information with the encrypted data portion to produce the secured document.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
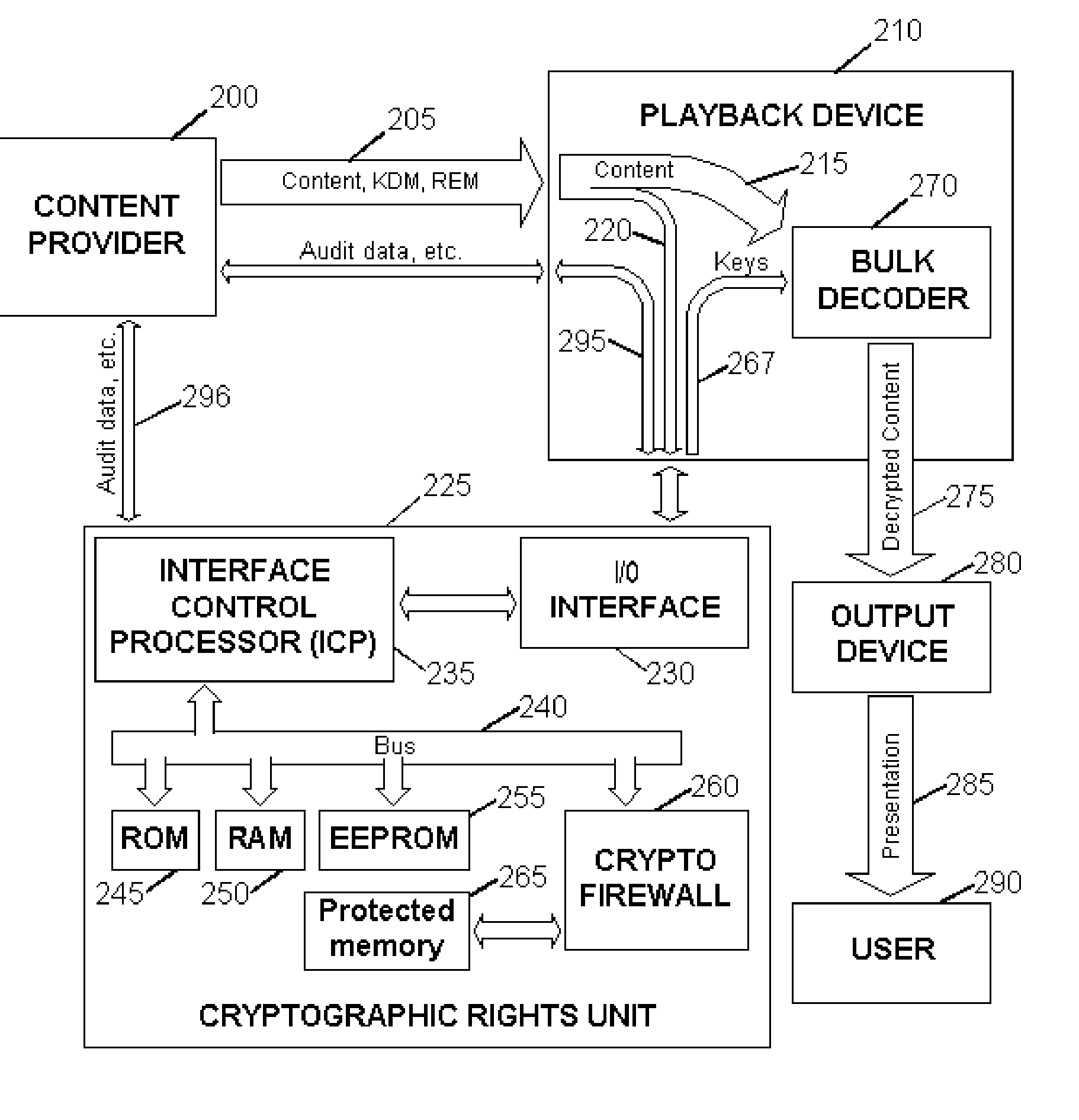
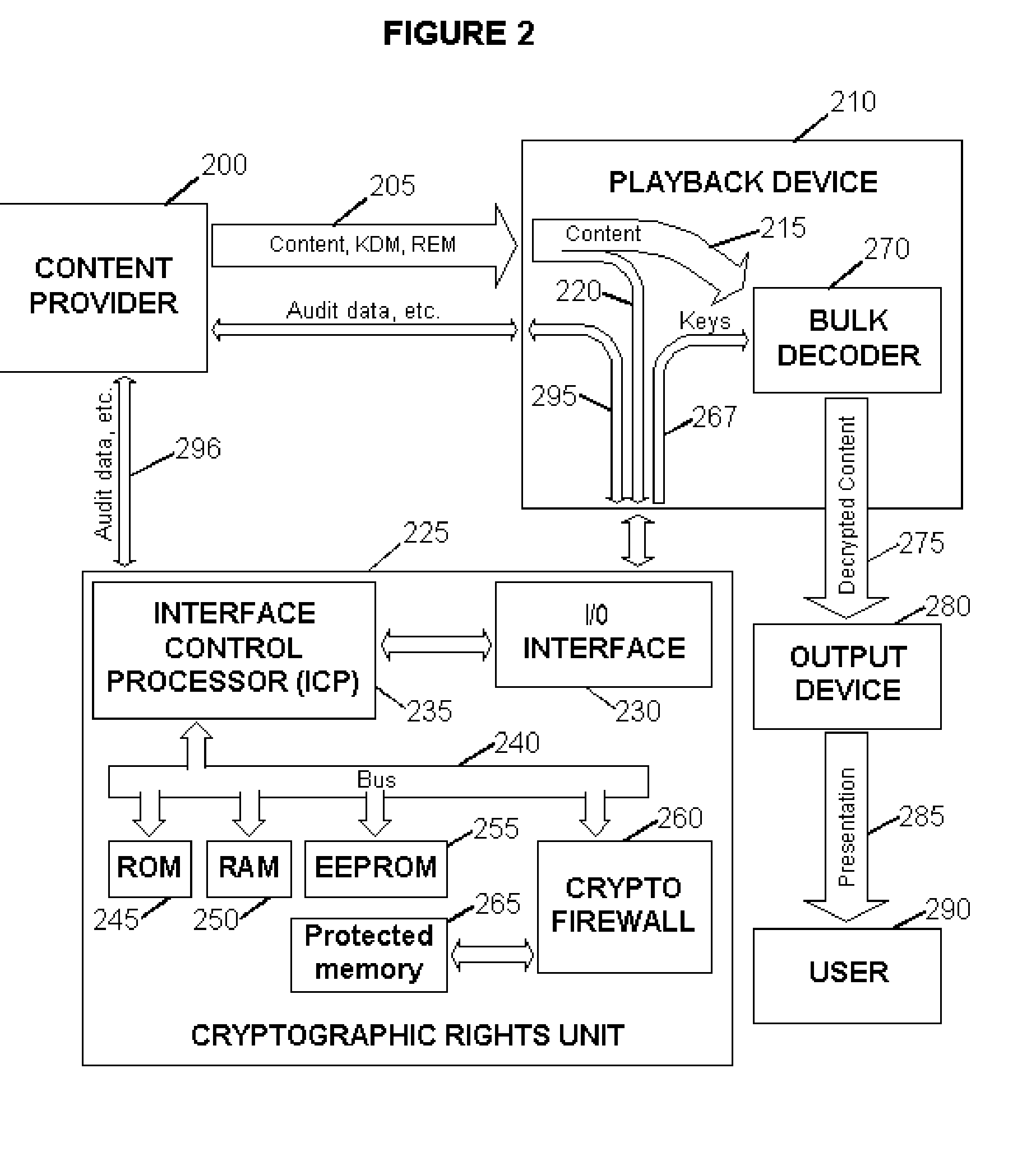
Digital Content Protection Method and Apparatus
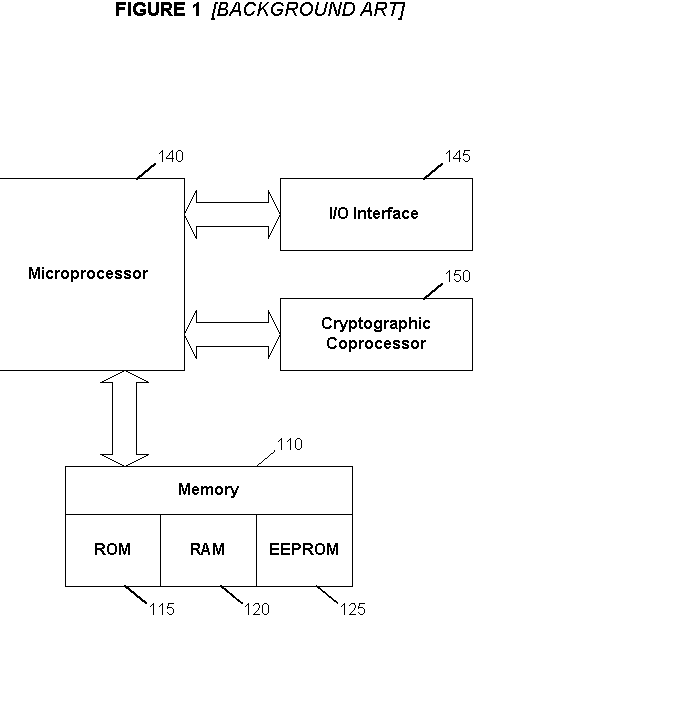
InactiveUS20020099948A1Improve securityMinimizes probabilityKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsDigital signatureDigital content
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> Before use, a population of tamper-resistant cryptographic enforcement devices is partitioned into groups and issued one or more group keys. Each tamper-resistant device contains multiple computational units to control access to digital content. One of the computational units within each tamper-resistant device communicates with another of the computational units acting as an interface control processor, and serves to protect the contents of a nonvolatile memory from unauthorized access or modification by other portions of the tamper-resistant device, while performing cryptographic computations using the memory contents. Content providers enforce viewing privileges by transmitting encrypted rights keys to a large number of recipient devices. These recipient devices process received messages using the protected processing environment and memory space of the secure unit. The processing result depends on whether the recipient device was specified by the content provider as authorized to view some encrypted digital content. Authorized recipient devices can use the processing result in decrypting the content, while unauthorized devices cannot decrypt the content. A related aspect of the invention provides for securing computational units and controlling attacks. For example, updates to the nonvolatile memory, including program updates, are supported and protected via a cryptographic unlocking and validation process in the secure unit, which can include digital signature verification.
Owner:CRYPTOGRAPHY RESEARCH
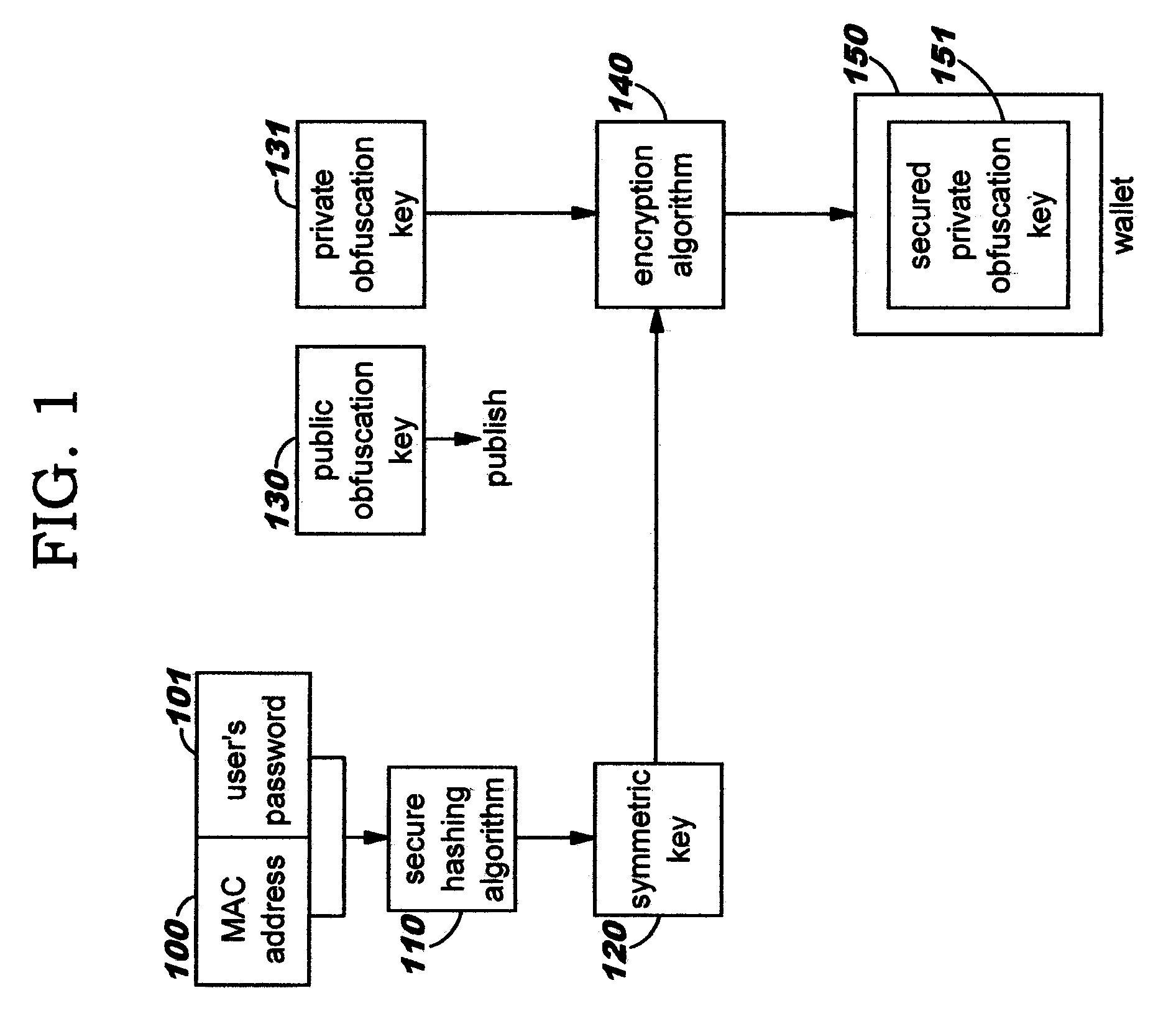
Dynamic, Selective Obfuscation of Information for Multi-Party Transmission
Selectively obfuscating, or obscuring, a portion or portions of information in a multi-party transmission. A user participating in a multi-party exchange signals a communication device (or proxy) that he will provide private information that is to be perceptible only to a subset of the other participants. This user also identifies that subset, preferably by providing a group identifier for a group in which that subset of participants are members. The communication device transmits a member-specific descriptor comprising an encrypted version of a group key, and uses this group key to encrypt the private information that is to be perceptible only to the subset. Device-specific characteristics of participant devices are used, in addition to user-provided data (such as a user's log-on identifier and / or password), as input to create cryptographic key information. Only participants in the subset can decrypt the encrypted private information; other participants preferably receive a filler pattern of some type instead.
Owner:IBM CORP
Cryptographic key update management method and apparatus
ActiveUS20050018853A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationMostly TrueRekeying
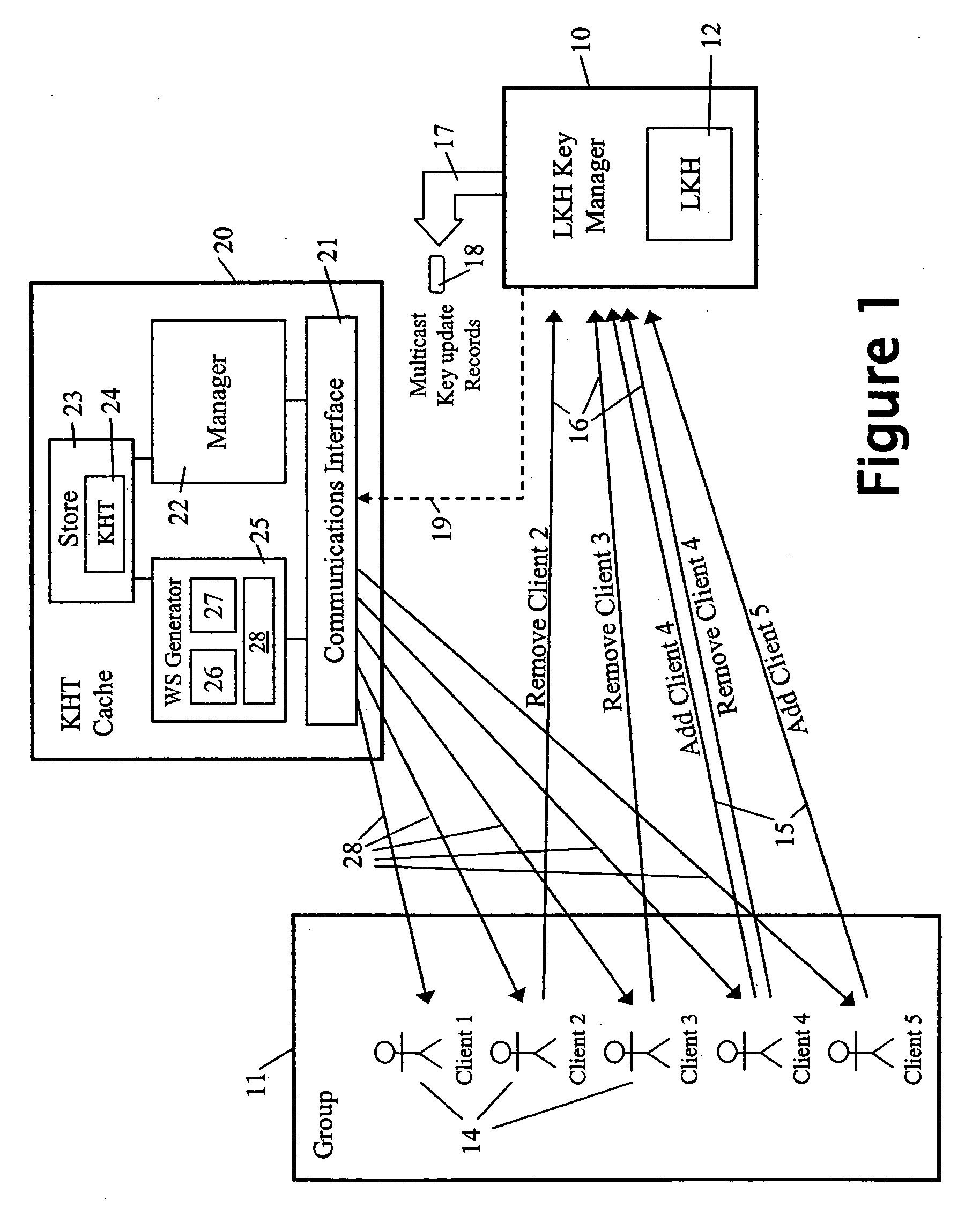
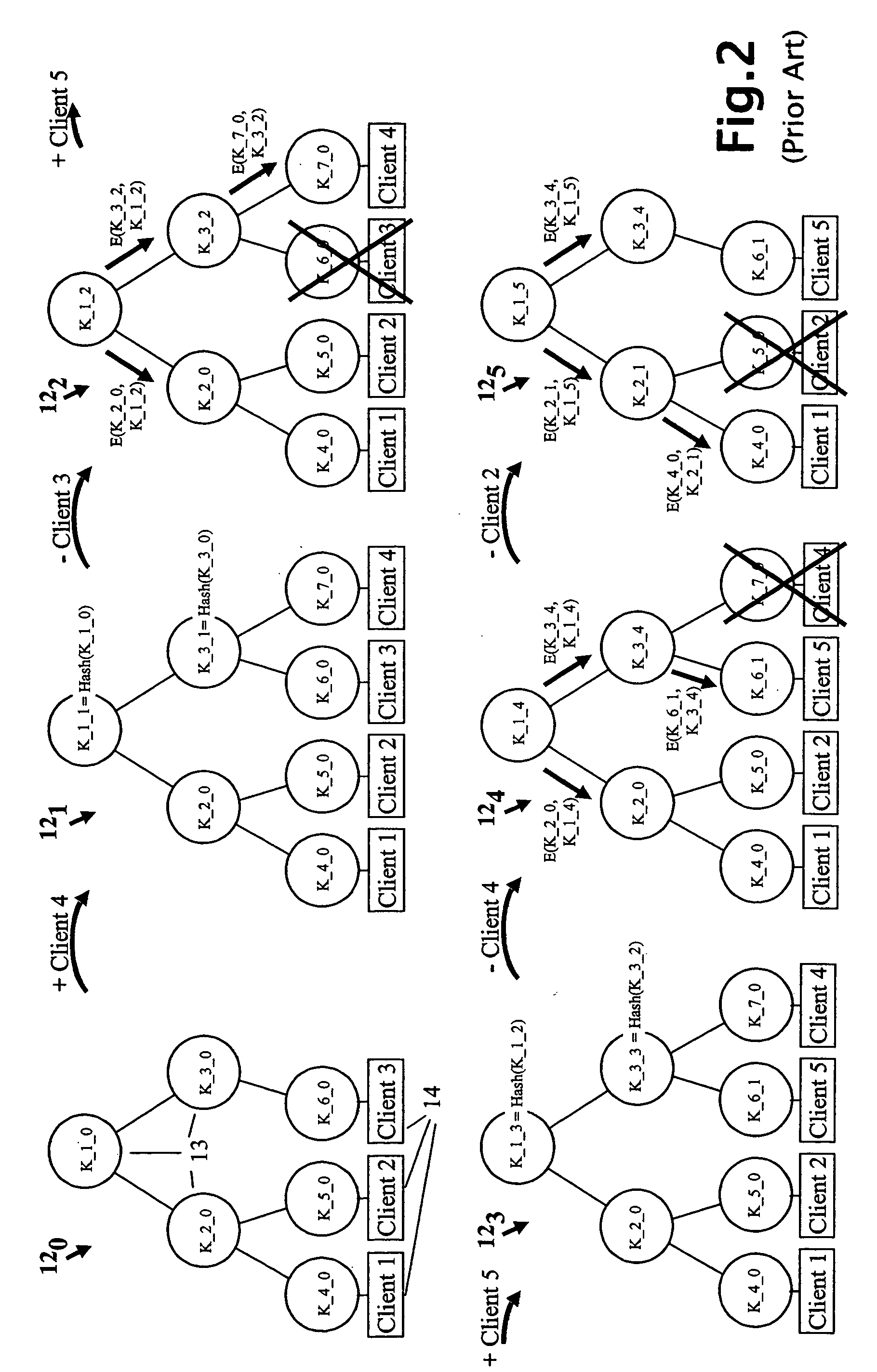
A method and apparatus is provided for consolidating cryptographic key updates, the consolidated update information enabling, for example, a returning member of a secure group who has been offline, to recover the current group key, at least in most cases. The unconsolidated key updates each comprise an encrypted key, corresponding to a node of a key hierarchy, that has been encrypted using a key which is a descendant of that node. The key updates are used to maintain a key tree with nodes in this tree corresponding to nodes in the key hierarchy. Each node of the key tree is used to store, for each encrypting key used in respect of the encrypted key associated with the node, the most up-to-date version of the encrypted key with any earlier versions being discarded. The key tree, or a subset of the tree, is then provided to group members.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
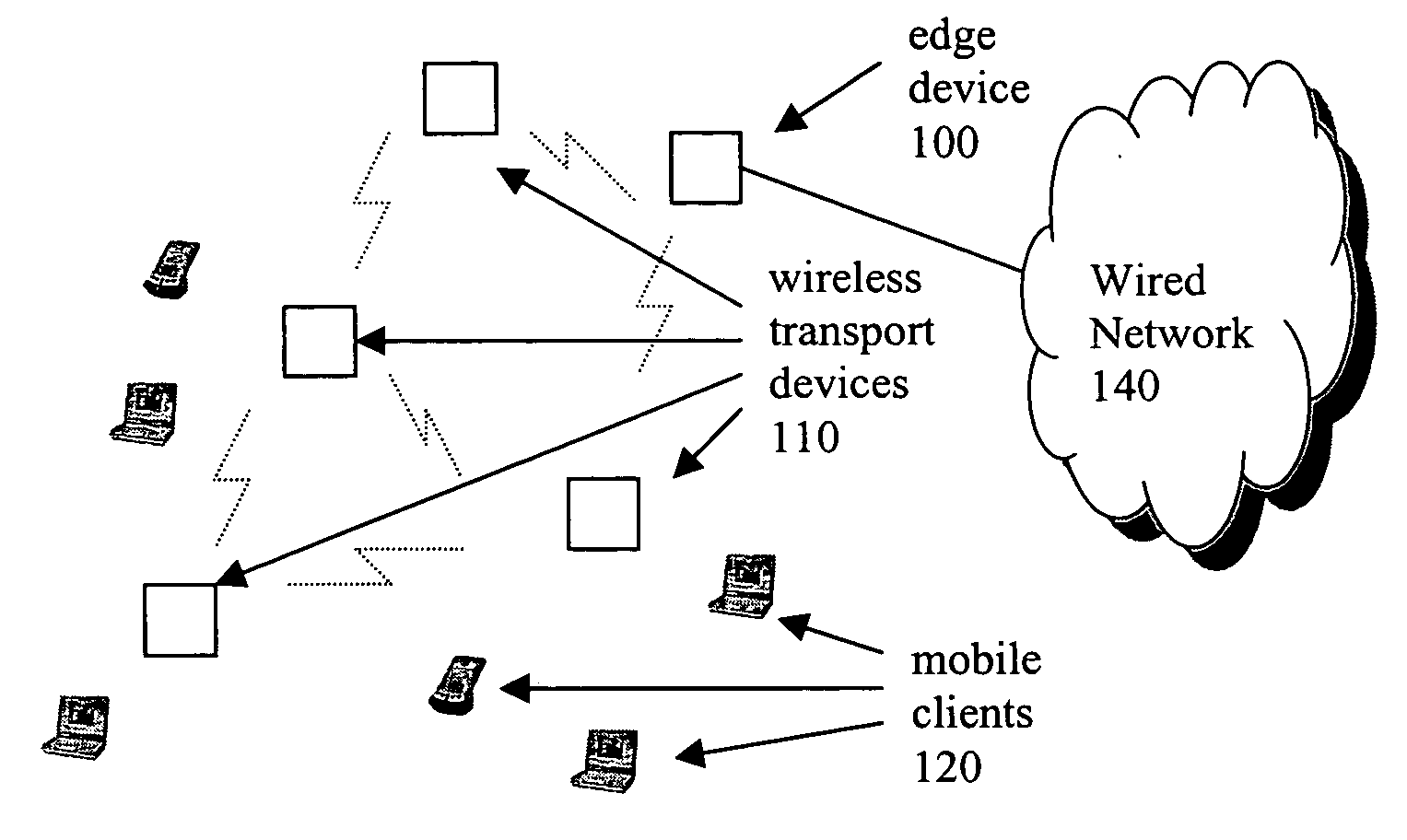
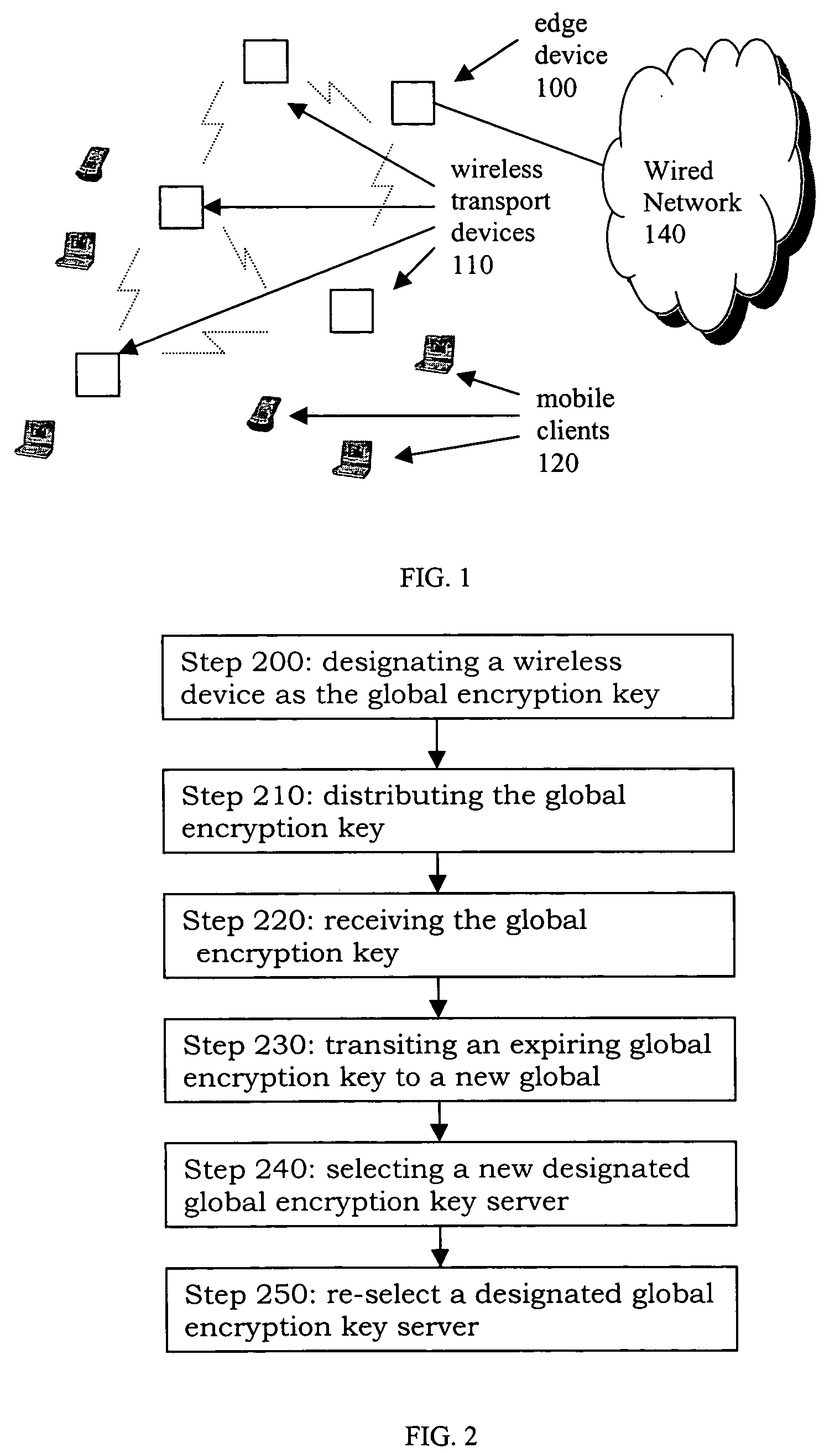
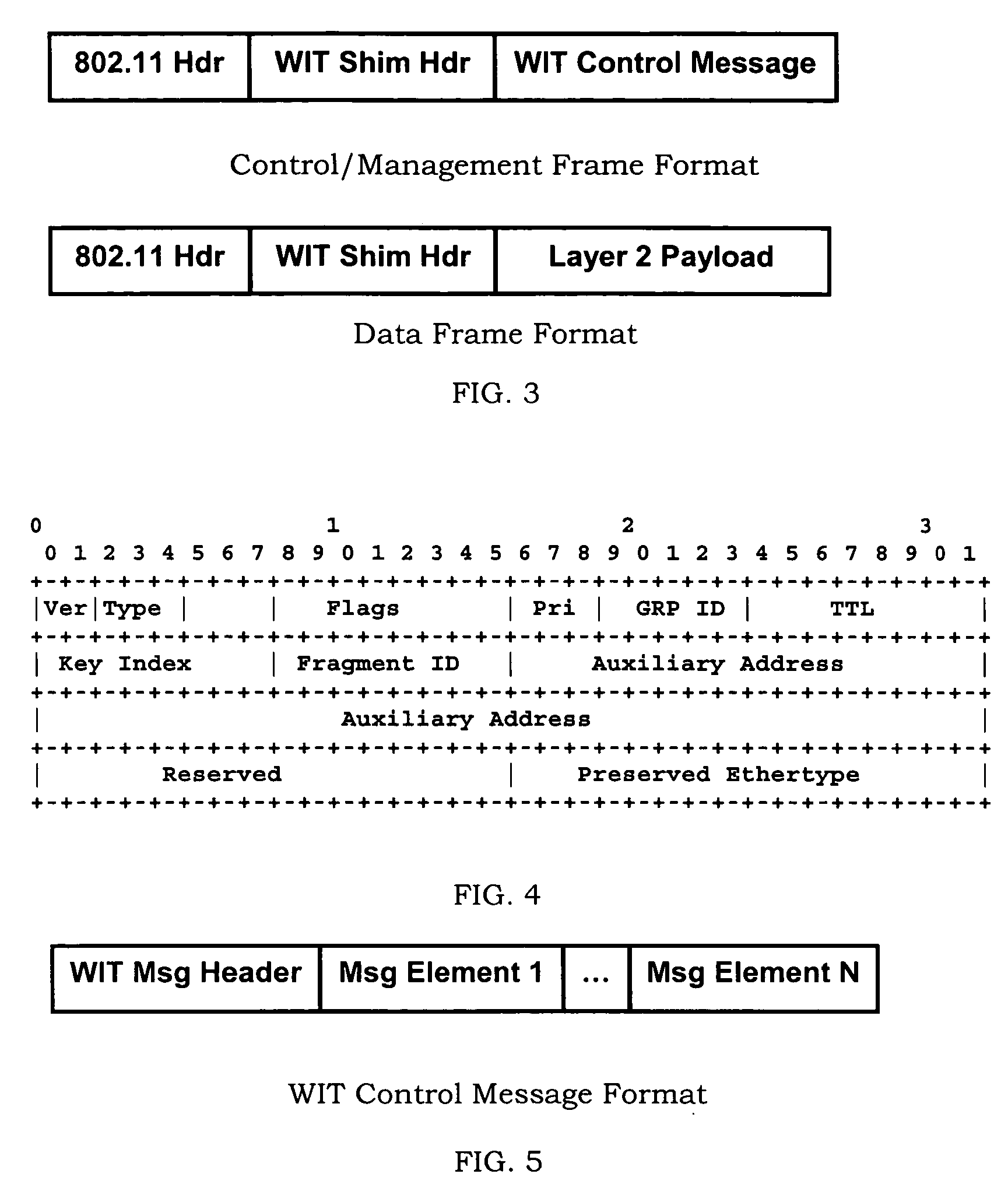
Methods for generating and distribution of group key in a wireless transport network
InactiveUS20050050004A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsWireless transmissionTransport network
The present invention provides a method of distributing a new group key by a designated group key server, comprising: receiving a group key by a wireless device from each of a newly discovered neighbor. The next step is to receive a list of devices that the newly discovered neighbor connects to. Then, the device determines whether or not the received group key is the same with a new group key and a key index from a neighbor Ni and to associate each the group key with the list of device received from the same neighbor. The device compares all the group keys from the each neighbor and merging an associated lists of device into a single list if the group keys are the same. Subsequently, the device selects the group key with the largest associated list of device be a new selected group key.
Owner:ACCTON TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Securing media content using interchangeable encryption key
Owner:SYNAMEDIA LTD
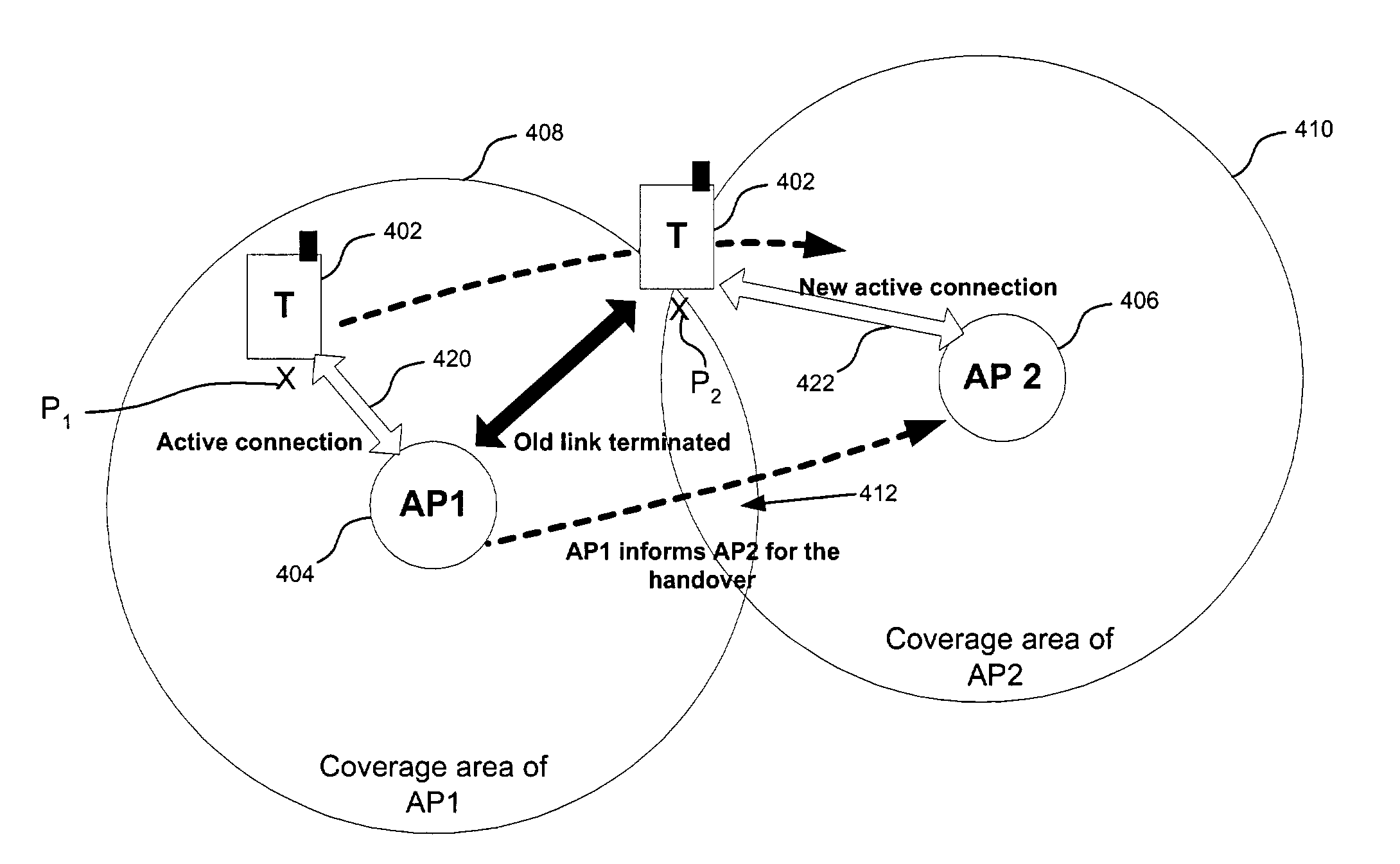
Method and system for access point roaming
InactiveUS7103359B1Improve overall utilizationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsTerminal equipmentGroup key
Efficient access point roaming techniques involve a terminal device handing over a wireless communications session from a first access point to a second access point. The terminal device establishes a link with the second access point; authenticates the link with the second access point using an alternative access point address and a group key associated with the terminal device; and continues the communications session with the second access point using an address of the second access point. Various alternative access point addresses may be used, such as the address of the first access point, or a random address created by the terminal device during initiation of a prior access point connection. The terminal device may transmit a directive to the second access point to employ the alternative access point address.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
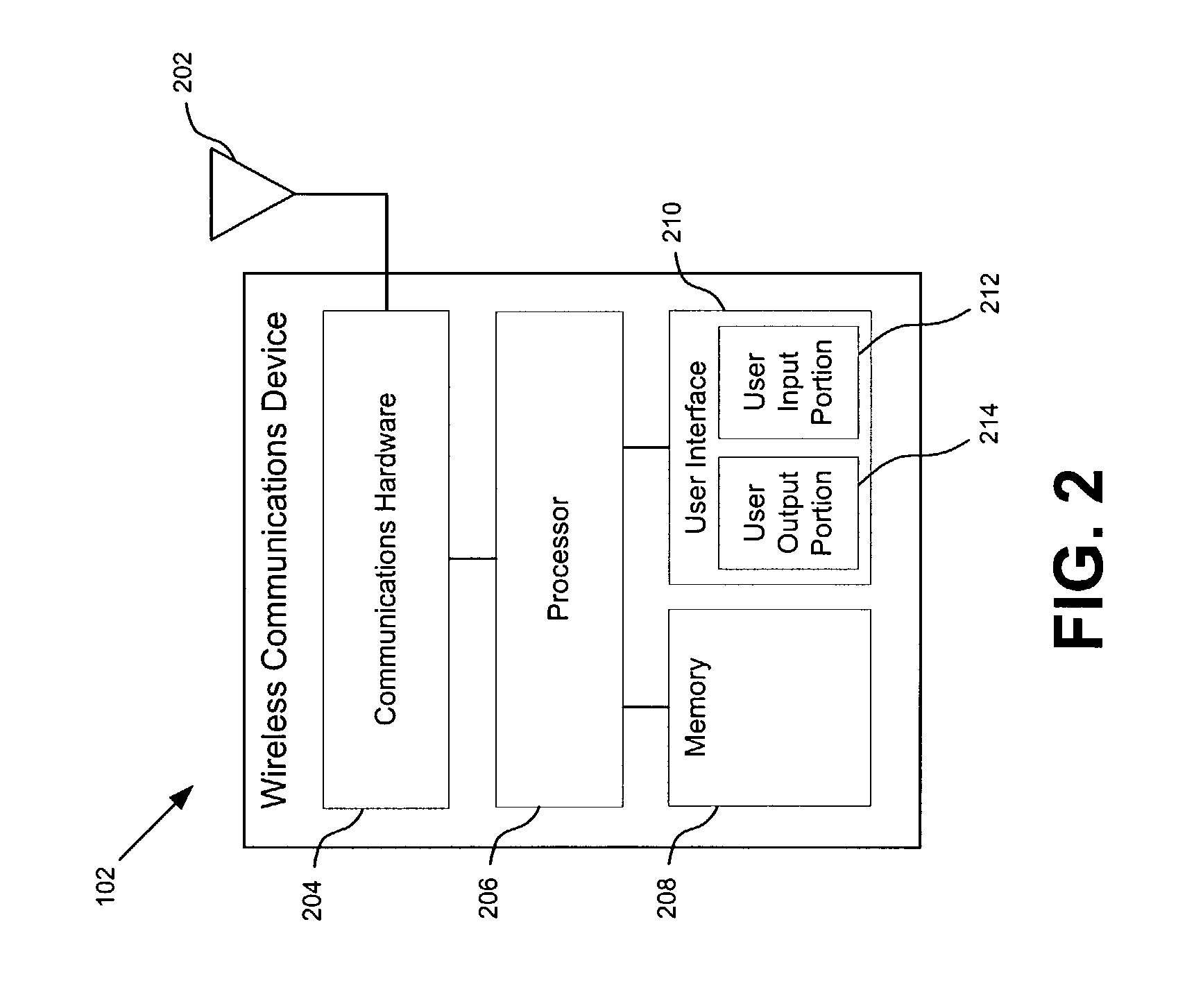
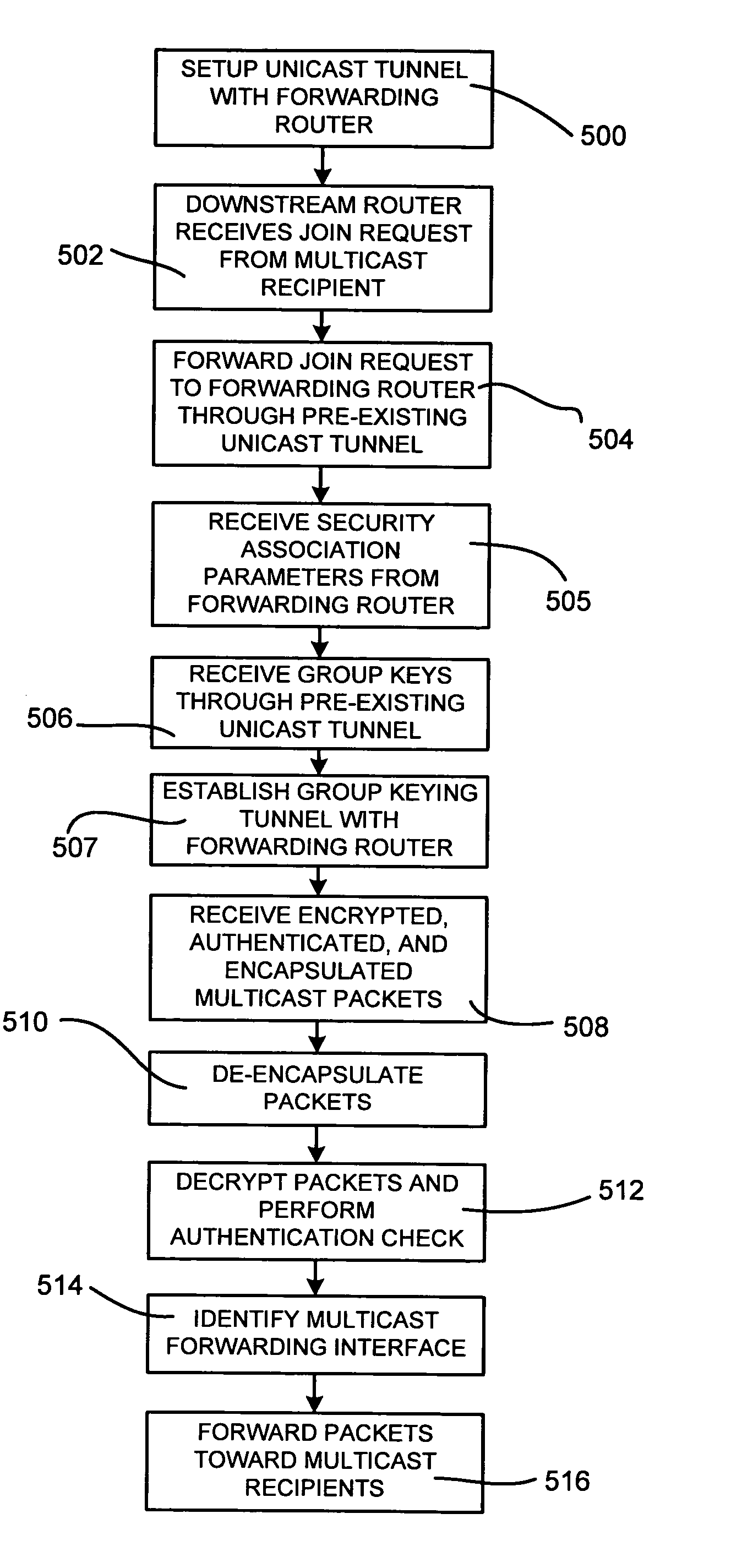
Secure transport of multicast traffic
ActiveUS20050138369A1Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsComputer networkSecure transmission
Secure tunneled multicast transmission and reception through a network is provided. A join request may be received from a second tunnel endpoint, the join request indicating a multicast group to be joined. Group keys may be transmitted to the second tunnel endpoint, where the group keys are based at least on the multicast group. A packet received at the first tunnel endpoint may be cryptographically processed to generate an encapsulated payload. A header may be appended to the encapsulated payload to form an encapsulated packet, wherein the header includes information associated with the second tunnel endpoint. A tunnel may be established between the first tunnel endpoint and the second tunnel endpoint based on the appended header. The encapsulated packet may be transmitted through the tunnel to the second tunnel endpoint. The second tunnel endpoint may receive the encapsulated packet. Cryptographic processing of the encapsulated packet may reveal the packet having a second header. The packet may then be forwarded on an interface toward at least one multicast recipient identified in the second header.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Method and system for network security capable of doing stronger encryption with authorized devices
InactiveUS6965992B1Improve securityKey distribution for secure communicationPresent methodNetwork security policy
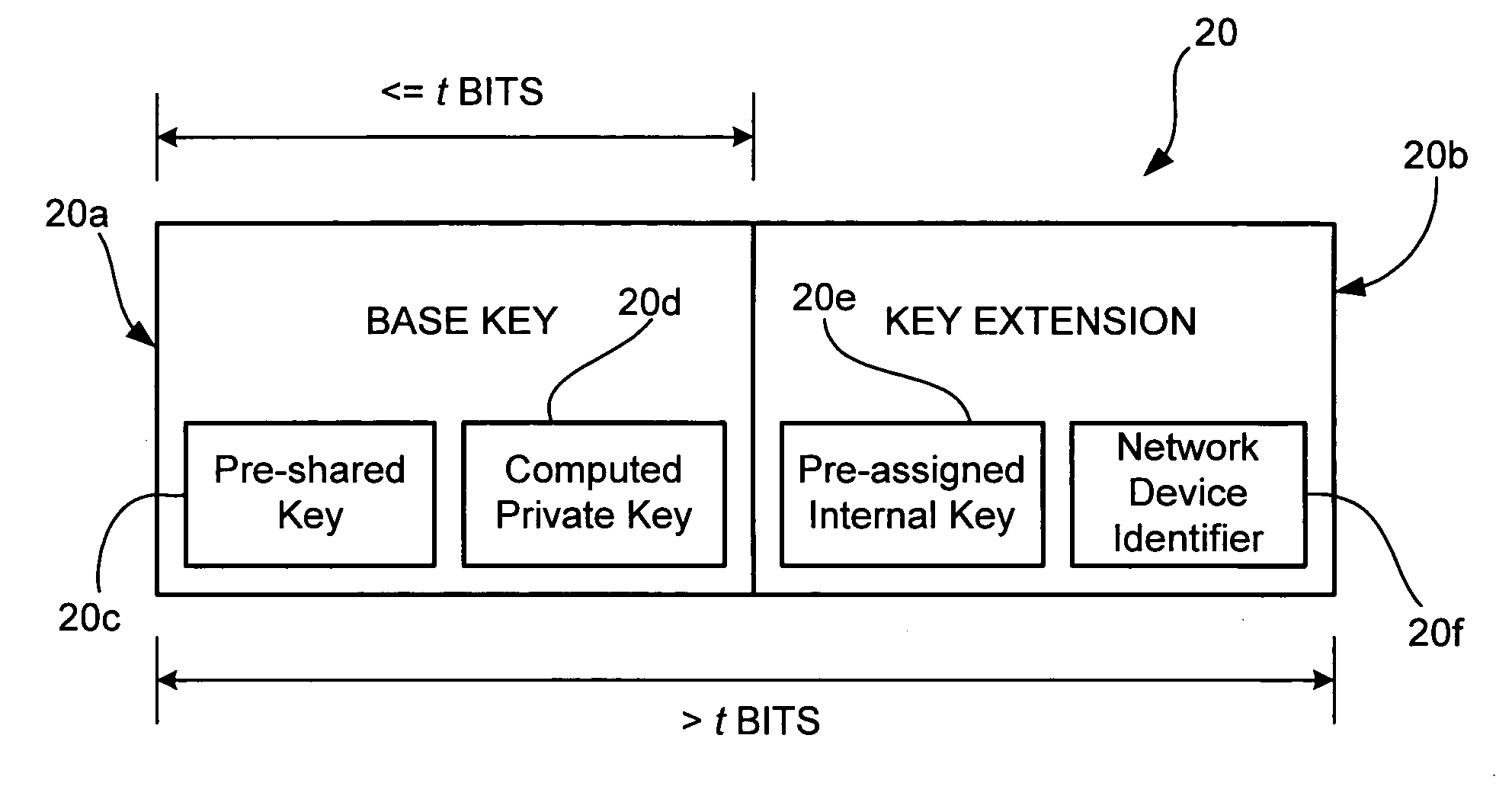
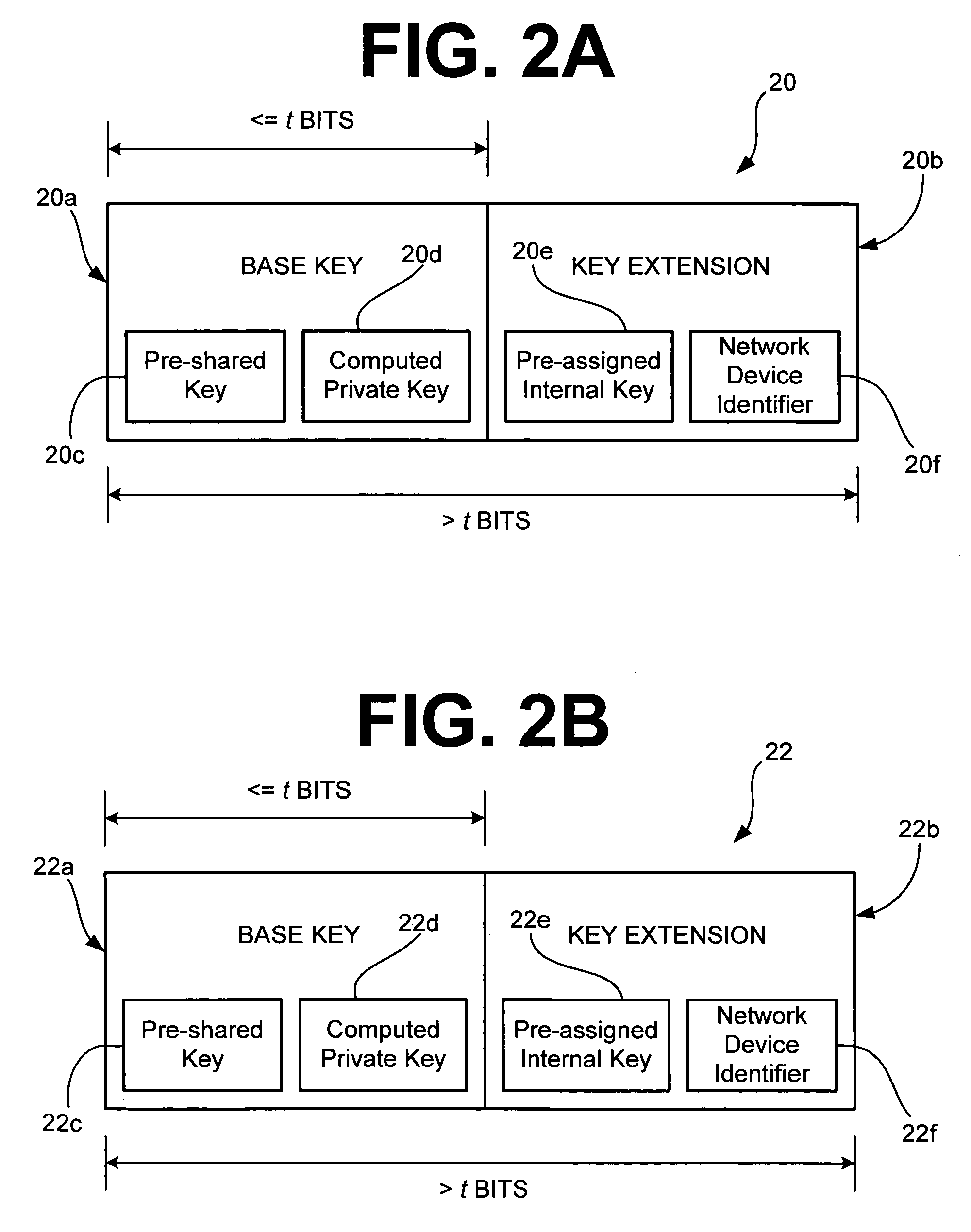
A method and system for network security includes a first network device having a first set of key material with a base key and a key extension, and a second network device also having the first set of key material and a second set of key material with a second base key. The second network device is capable of communicating with the first network device using security determined by the first set of key material. The method and system for network security may further include a third network device having the second set of key material. The third network device is capable of communicating with the second network device using security determined by the second set of key material. For the present method and system, security determined by the first set of key material is stronger than security determined by the second set of key material.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
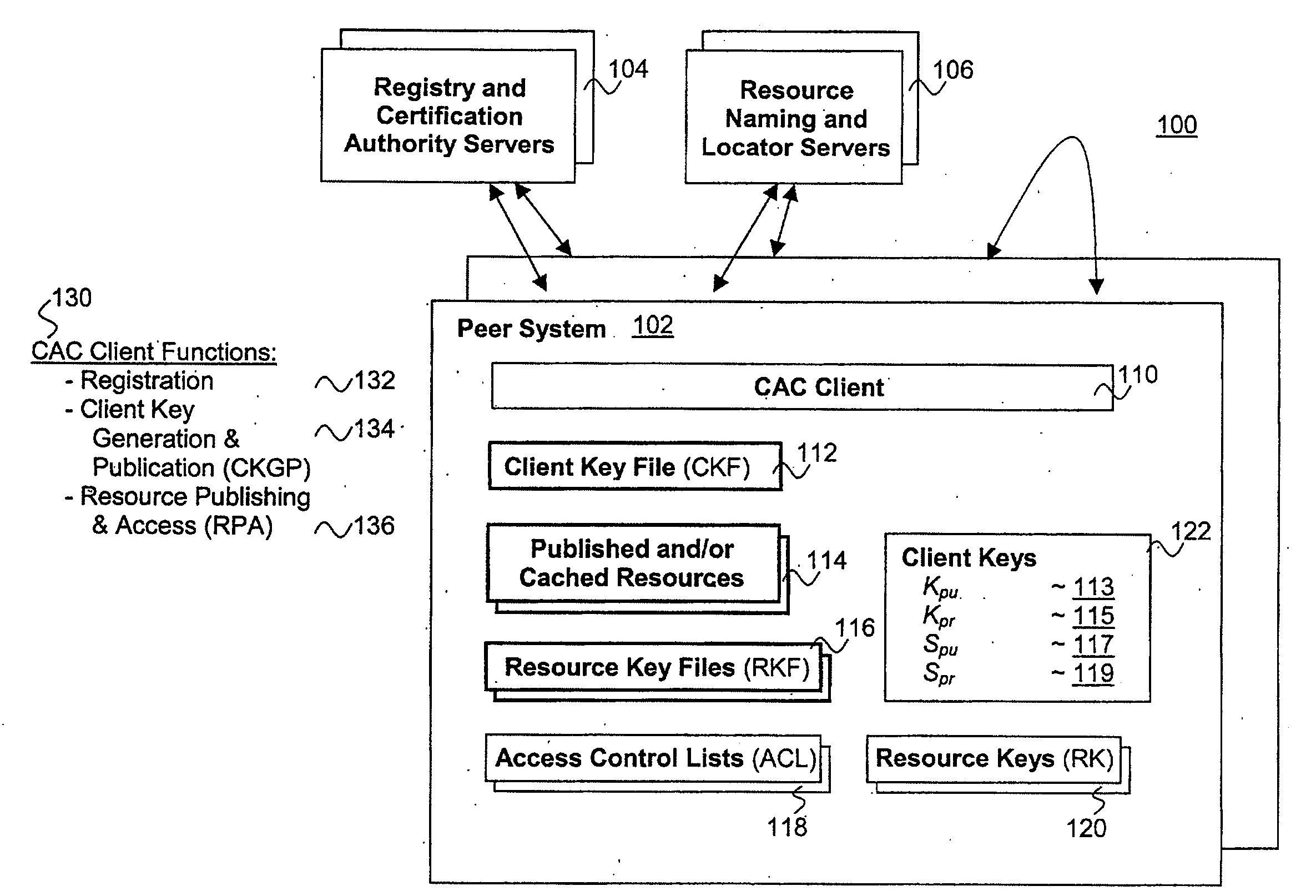
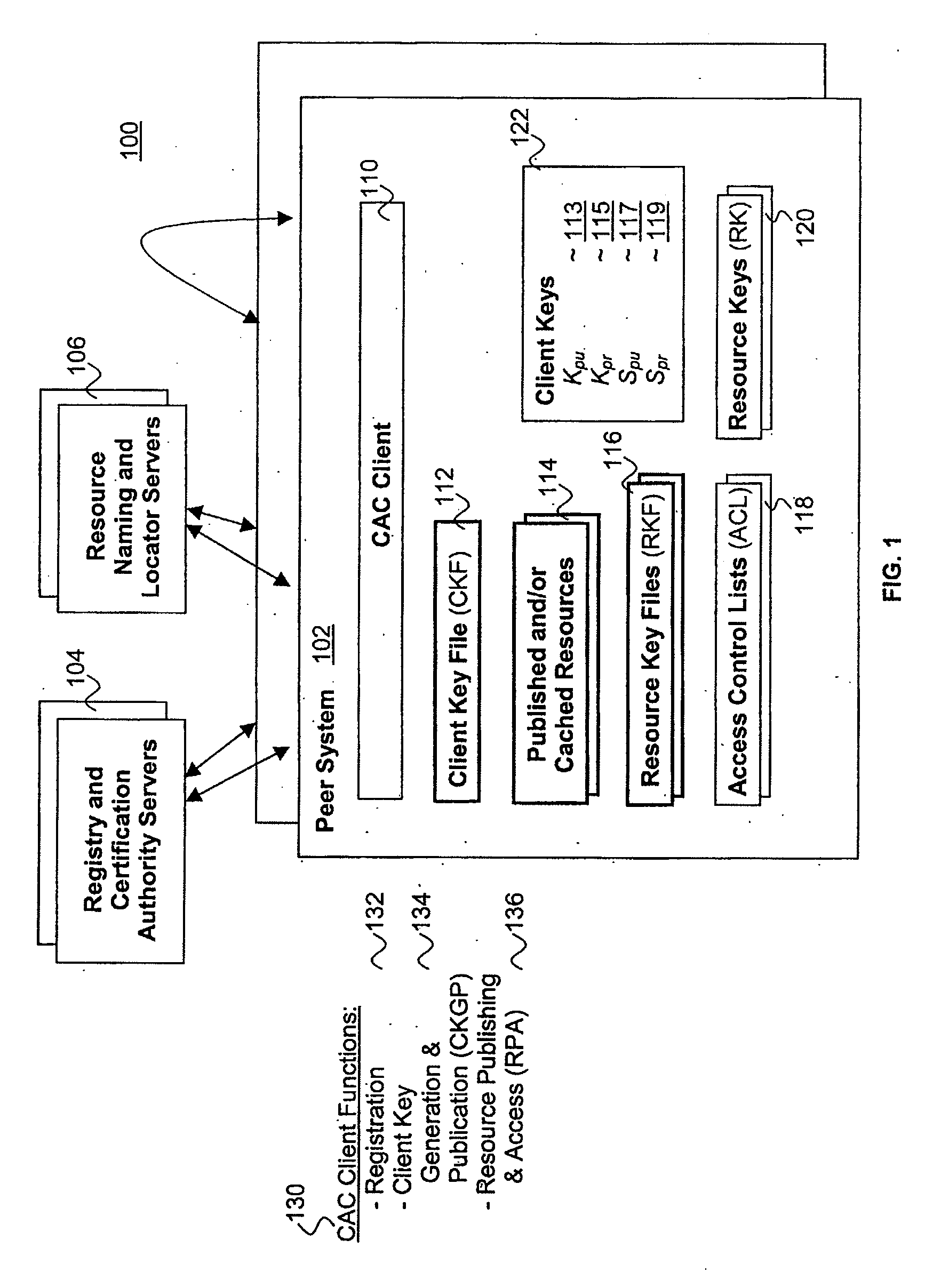
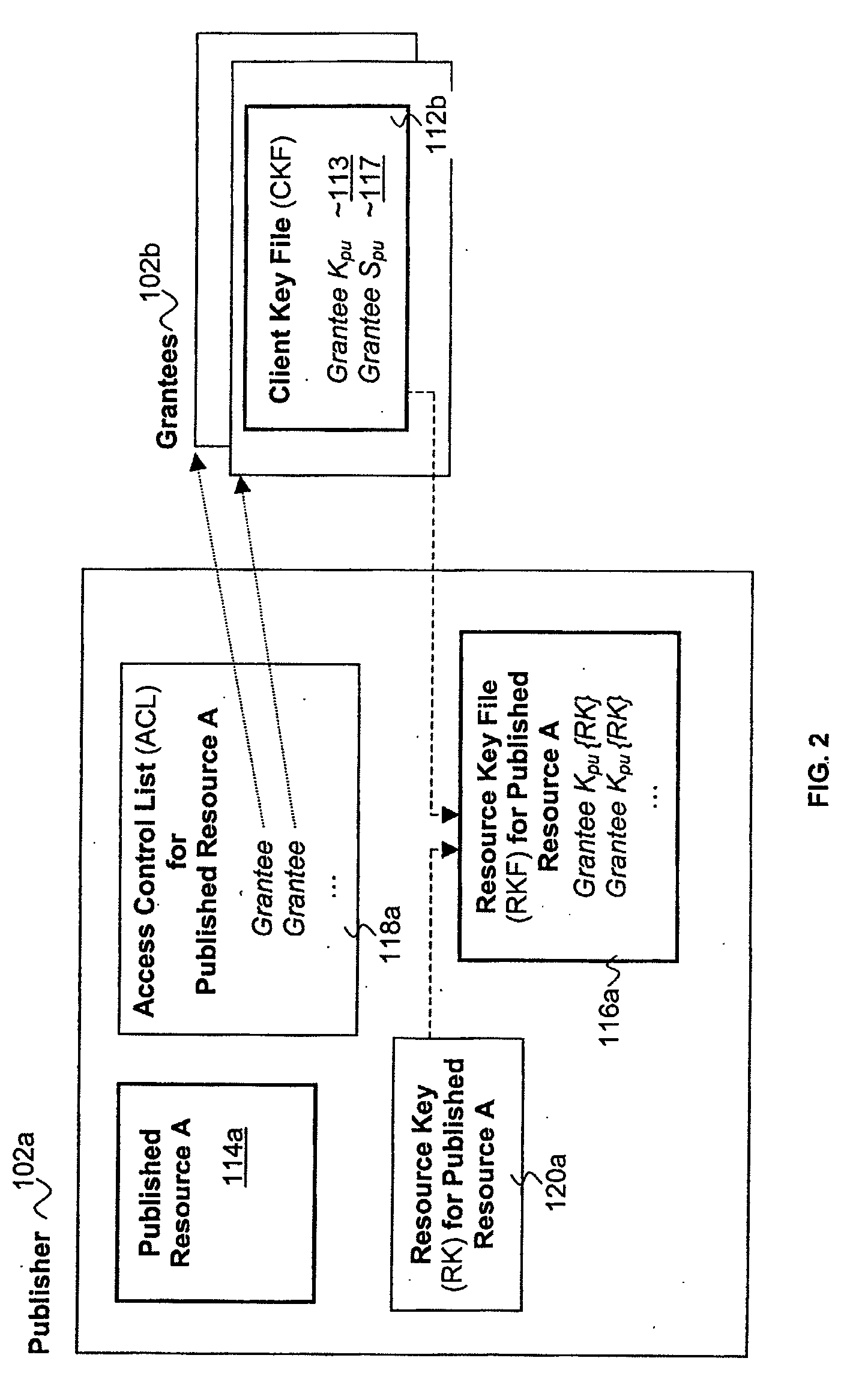
Distributed, scalable cryptographic access control
InactiveUS7509492B2Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationPasswordClient-side
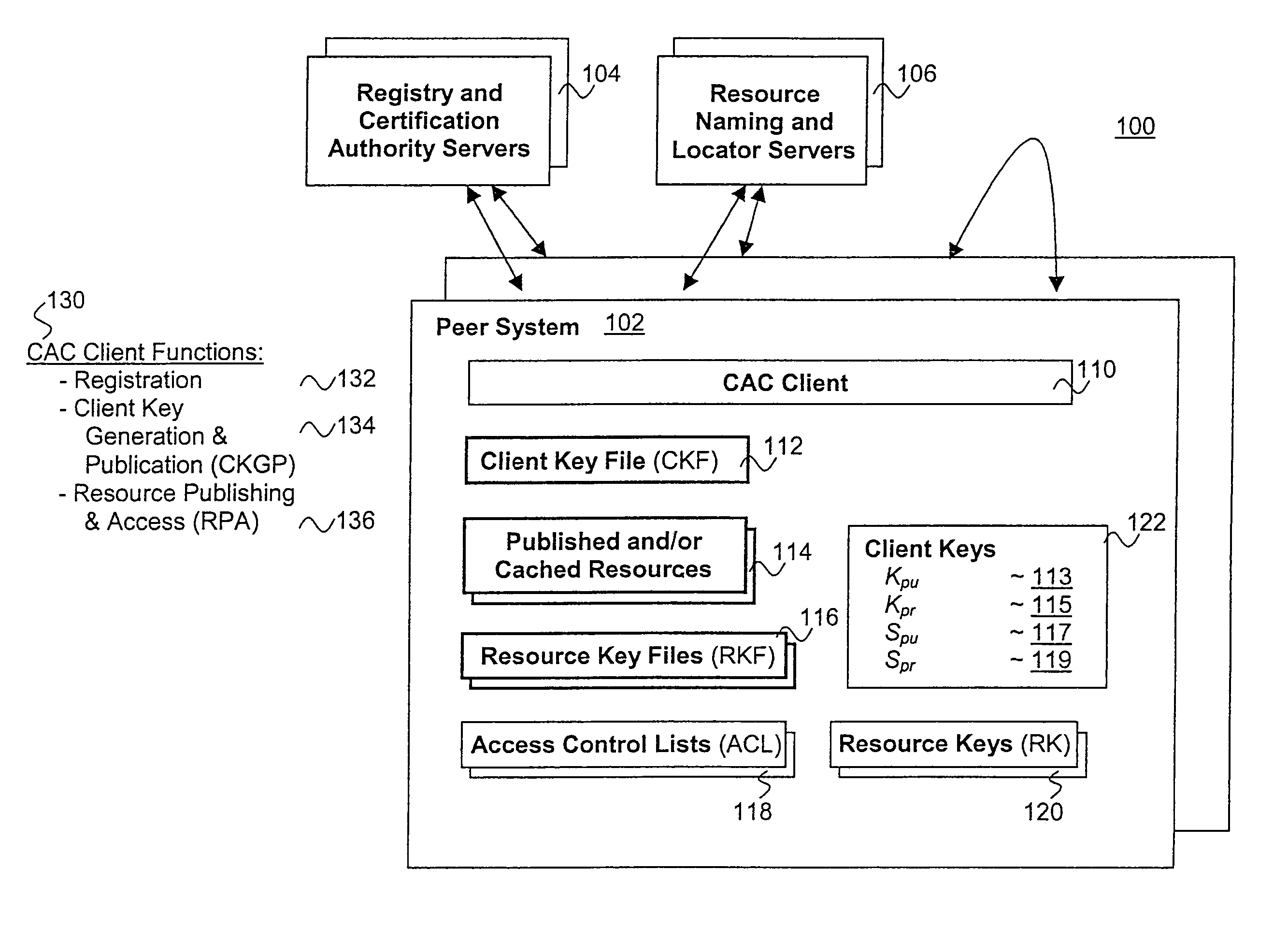
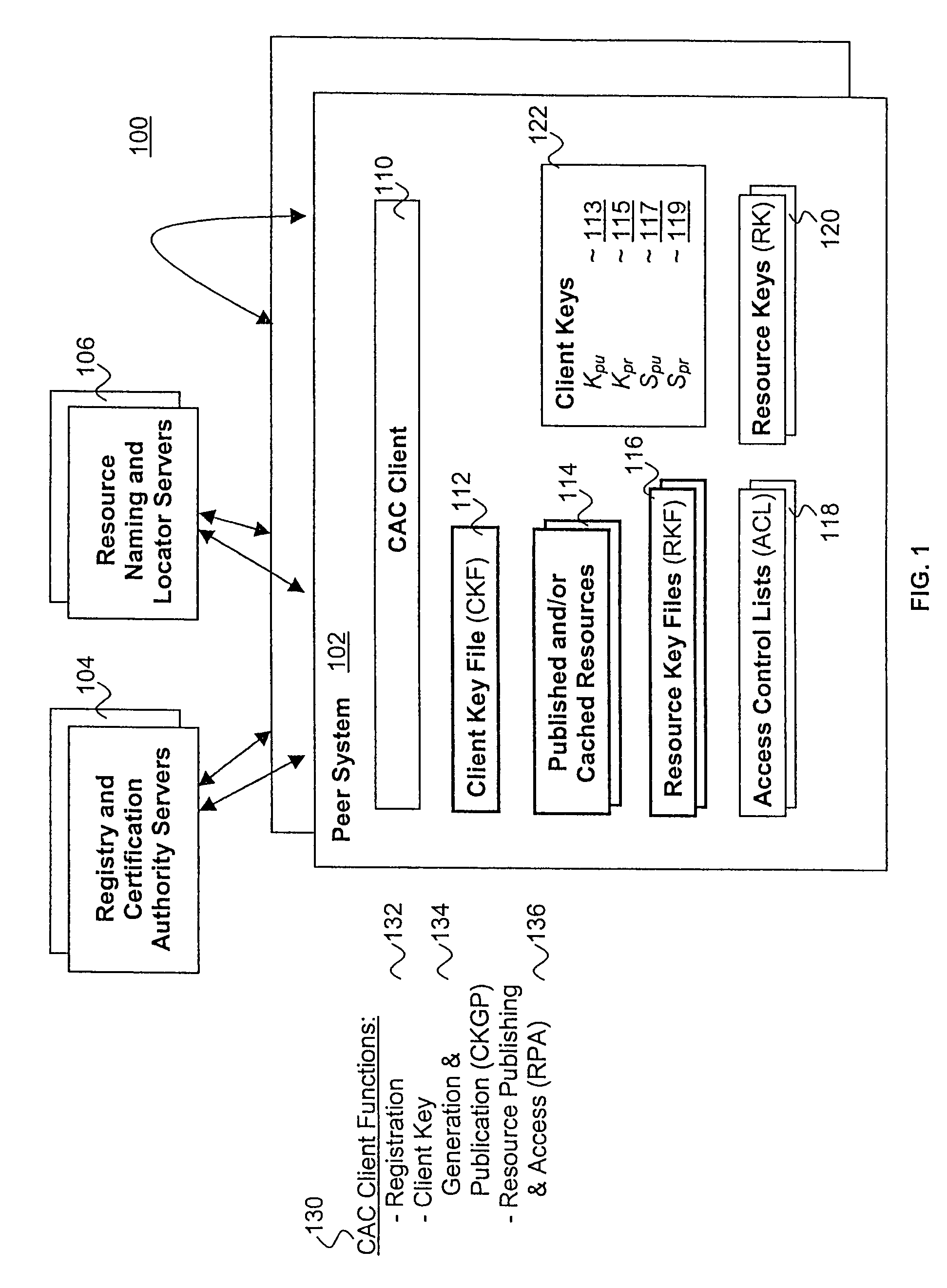
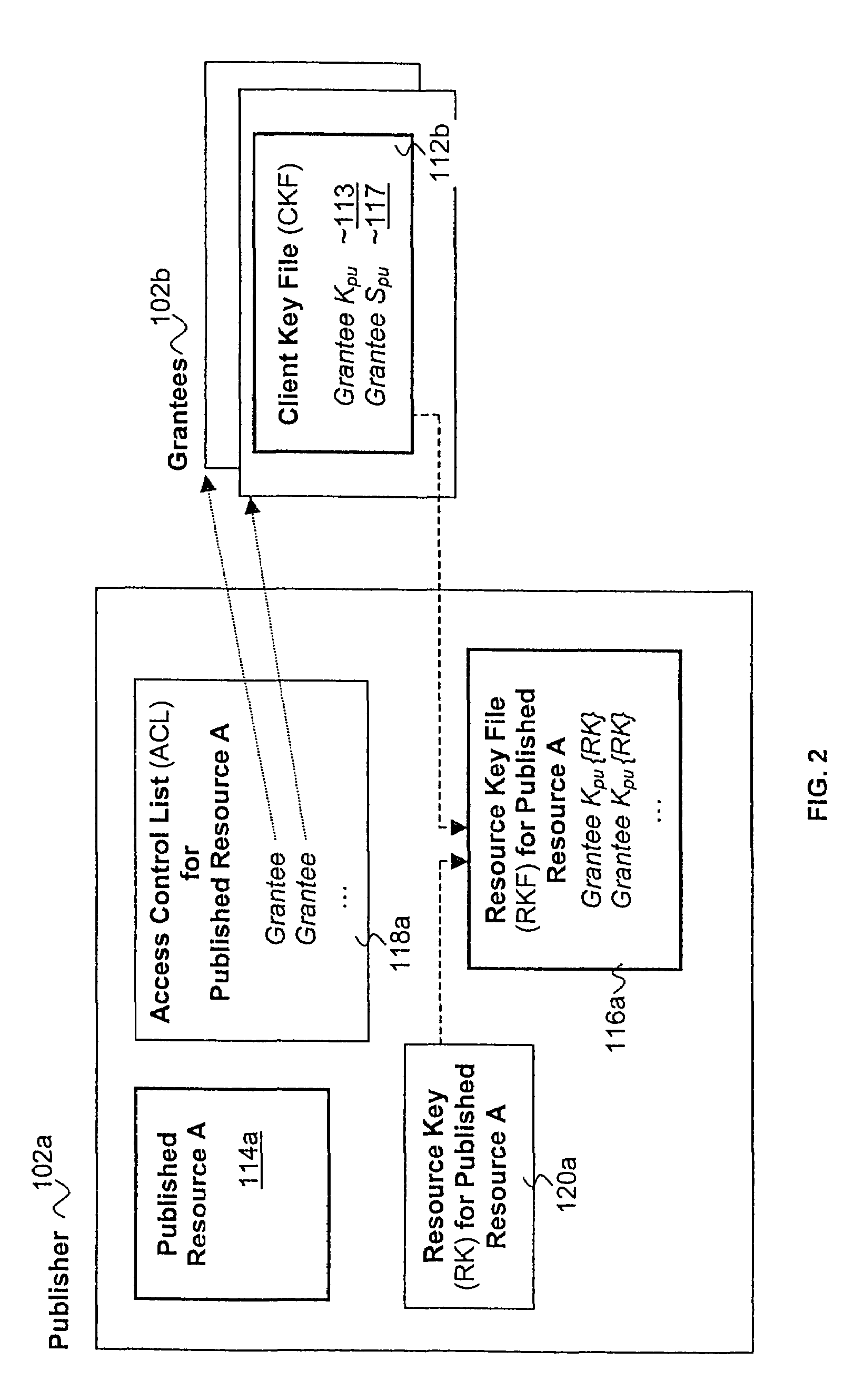
Published resources are made available in an encrypted form, using corresponding resource keys, published through resource key files, with the publications effectively restricted to authorized peer systems only by encrypting the resource keys in a manner only the authorized peer systems are able to recover them. In one embodiment, the resource keys are encrypted using encryption public keys of the authorized peer systems or the groups to which the authorized peer system are members. In one embodiment, the encryption public keys of individual or groups of authorized peer systems are published for resource publishing peer systems through client and group key files respectively. Group encryption private keys are made available to the group members through published group key files. Further, advanced features including but not limited to resource key file inheritance, password protected publication, obfuscated publication, content signing, secured access via gateways, and secured resource search are supported.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
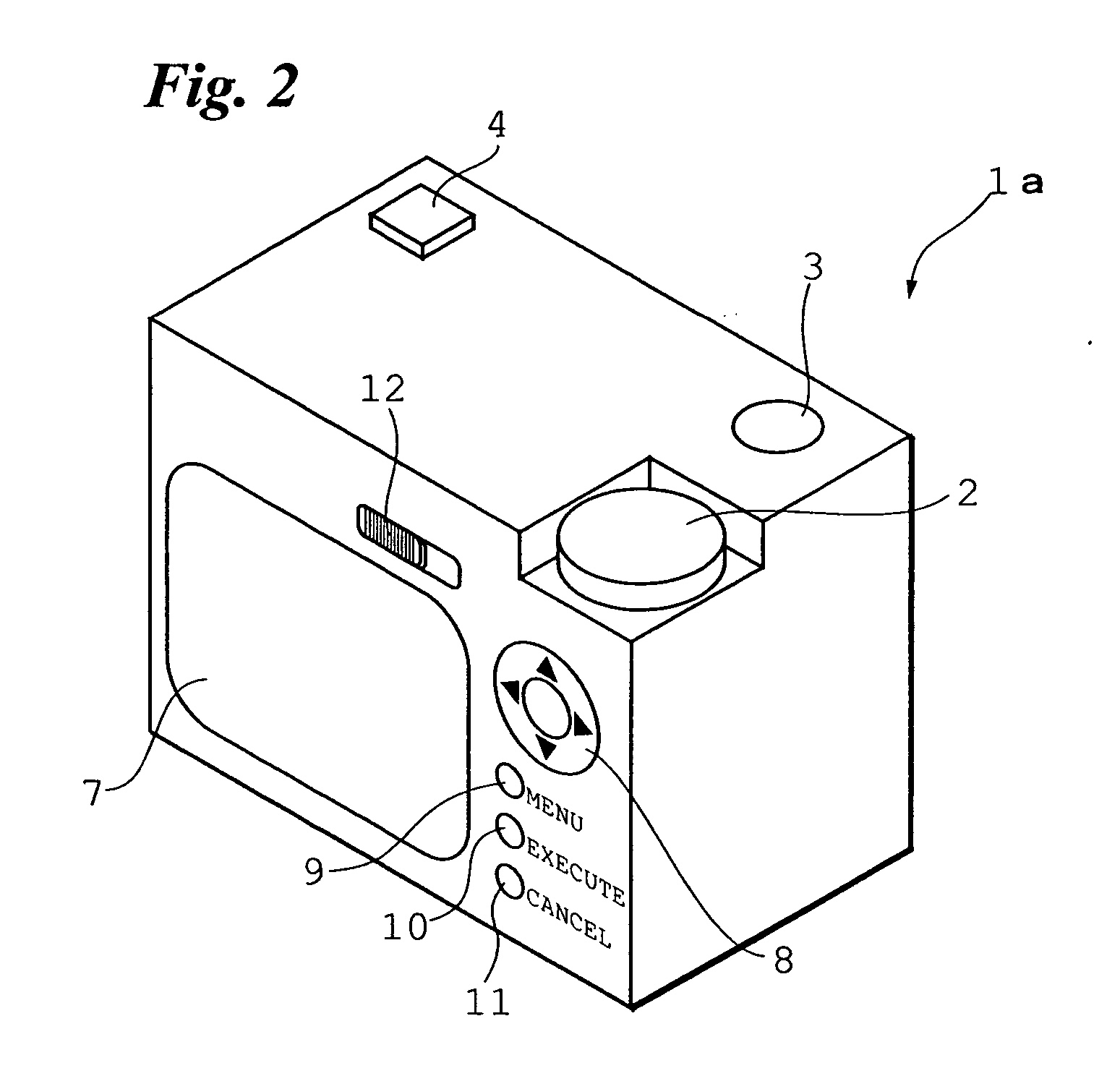
Image file sharing method, and digital camera and center server used in image file sharing system
InactiveUS20050213147A1Good choiceEfficient downloadStill image data retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer graphics (images)Information access
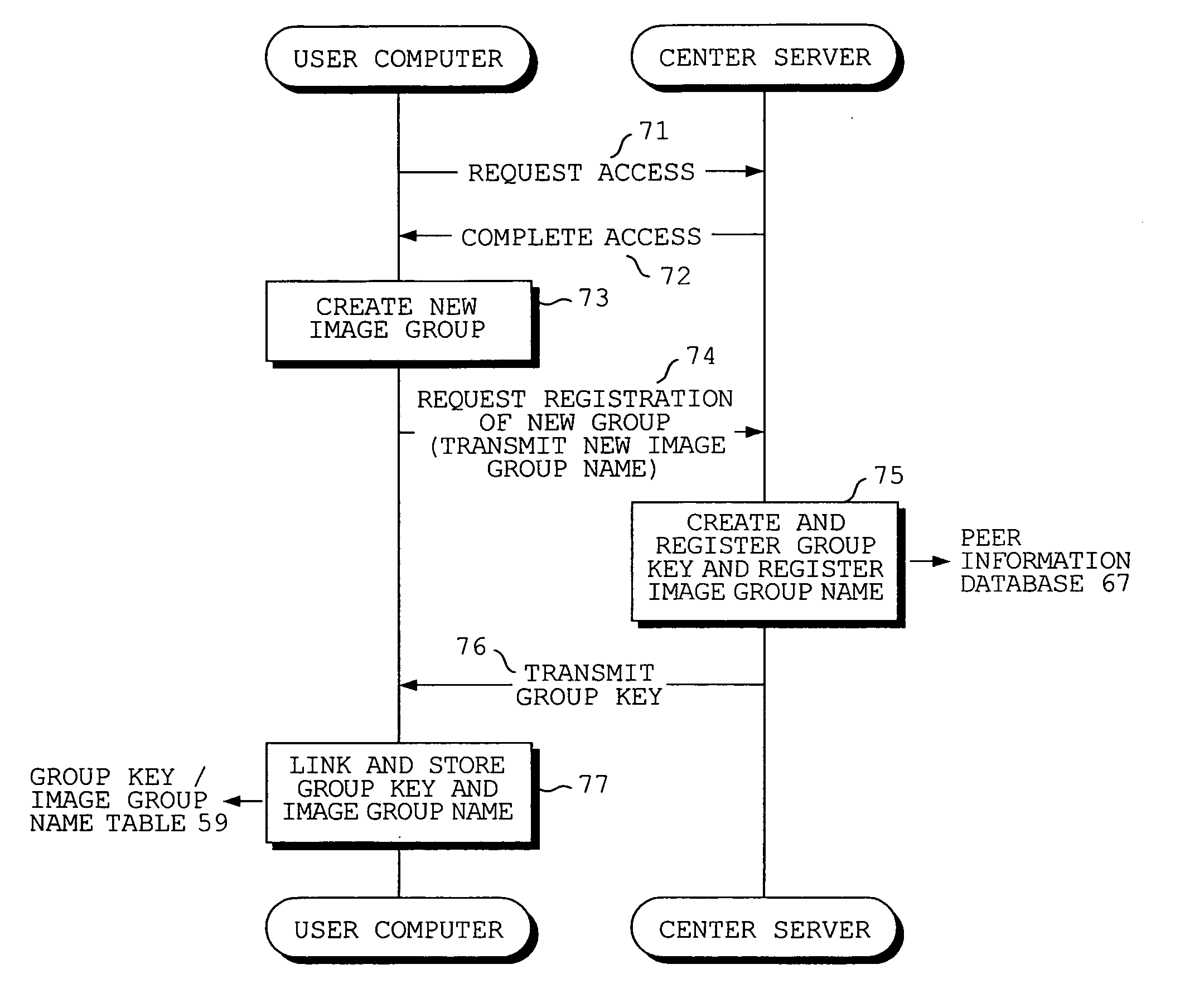
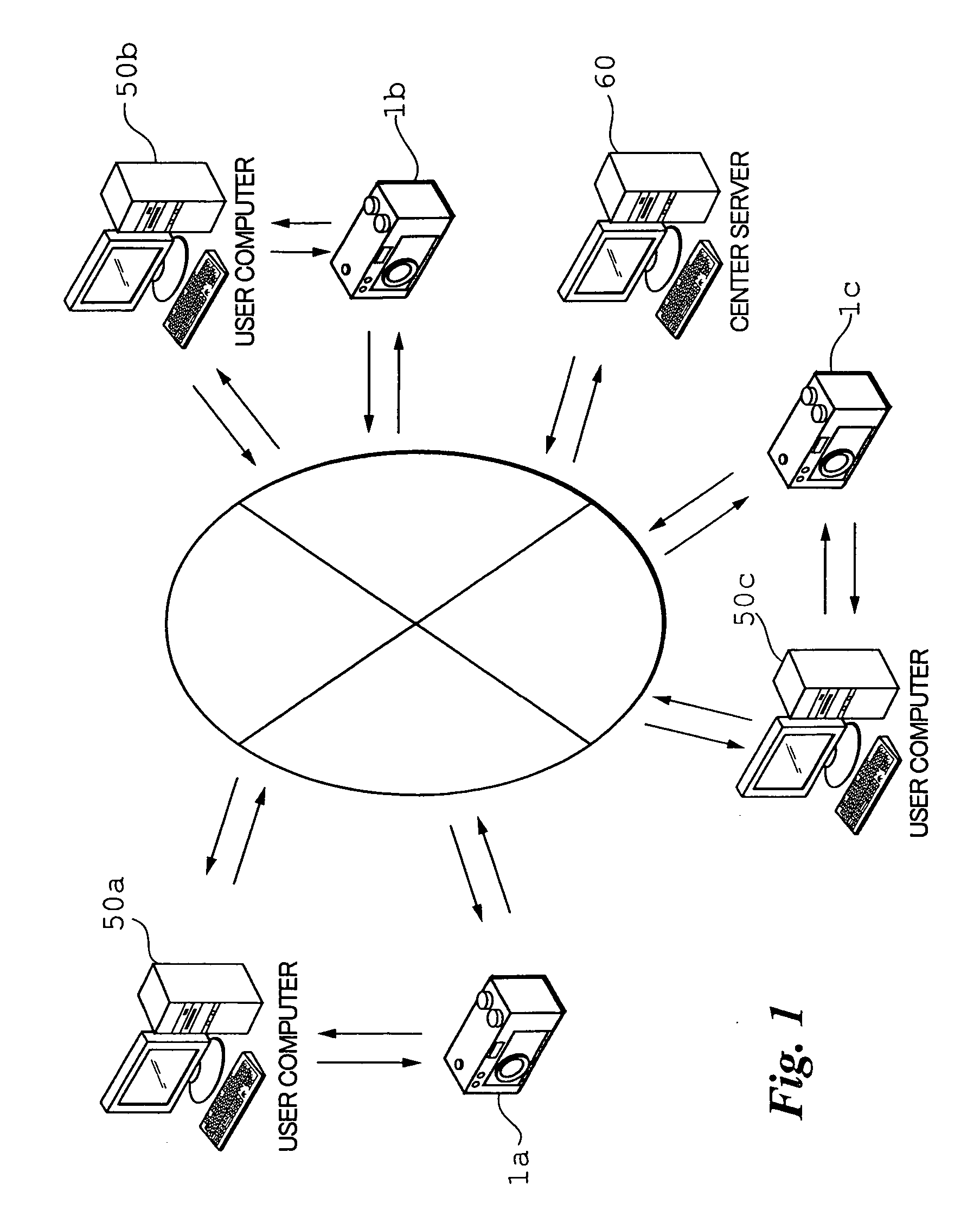
Group keys and image group names of image groups to which the owner of a digital camera belongs are transmitted from a server to the digital camera. The image group names are displayed in list form and an image group name is selected from the list. The group key of the selected image group is transmitted from the digital camera to the server. The server sends the digital camera access information for accessing the user computer of another user who belongs to the image group identified by the received group key. The digital camera accesses the user computer based upon the access information and receives the image file desired.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Distributed scalable cryptographic access control
InactiveUS20090141891A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsPasswordClient-side
Published resources are made available in an encrypted form, using corresponding resource keys, published through resource key files, with the publications effectively restricted to authorized peer systems only by encrypting the resource keys in a manner only the authorized peer systems are able to recover them. In one embodiment, the resource keys are encrypted using encryption public keys of the authorized peer systems or the groups to which the authorized peer system are members. In one embodiment, the encryption public keys of individual or groups of authorized peer systems are published for resource publishing peer systems through client and group key files respectively. Group encryption private keys are made available to the group members through published group key files. Further, advanced features including but not limited to resource key file inheritance, password protected publication, obfuscated publication, content signing, secured access via gateways, and secured resource search are supported.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Control device with easy lock feature
InactiveUS6947101B2Improve distributionEasily identifiableTelevision system detailsTransmission systemsSoft keyRemote control
Methods for identifying control keys with particular devices are disclosed along with methods of assigning control keys to particular devices. In particular, a remote control comprises a set of hard keys comprising channel group keys and volume group keys and a set of soft keys activated via a touch screen display. The display identifies the device the volume group keys are set to control and the device the channel group keys are set to control. Selecting the device currently controlled by the channel group keys by, for example, depressing the device indicator on the display screen, initiates a set up mode that displays numerous devices that may be controlled by the channel group keys. Selecting one of the numerous devices assigns the channel group keys to that device.
Owner:UNIVERSAL ELECTRONICS INC
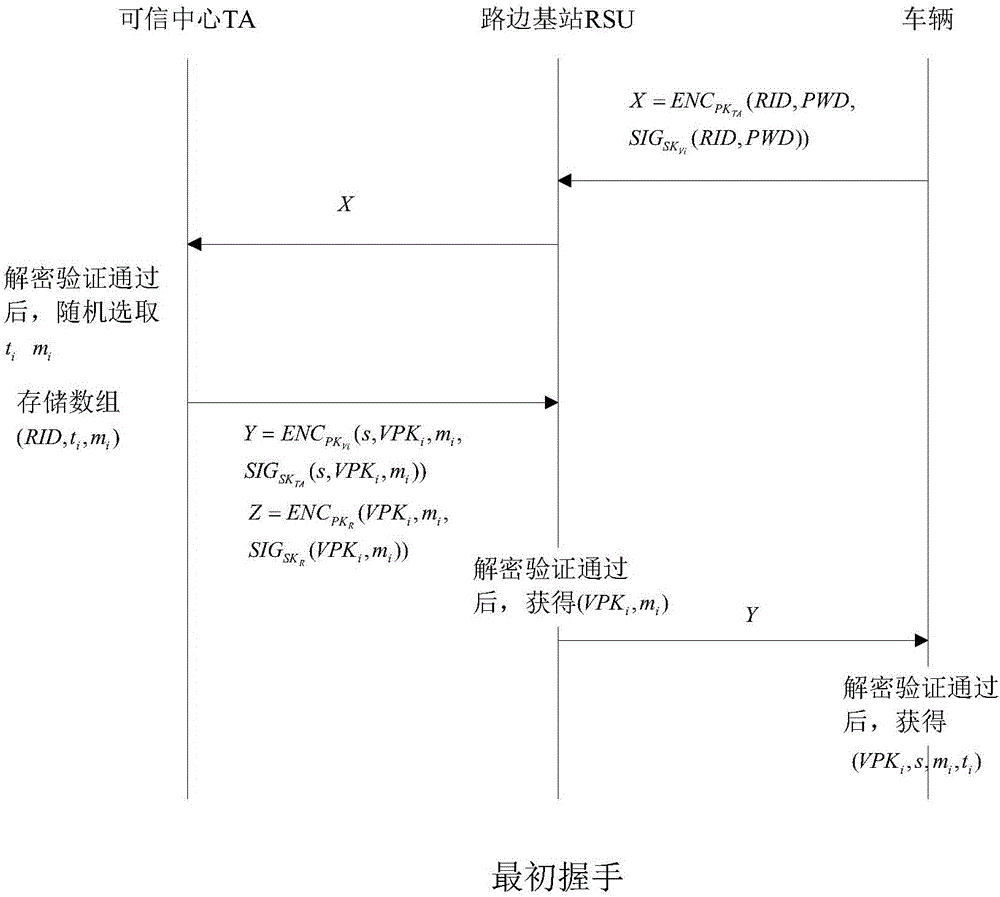
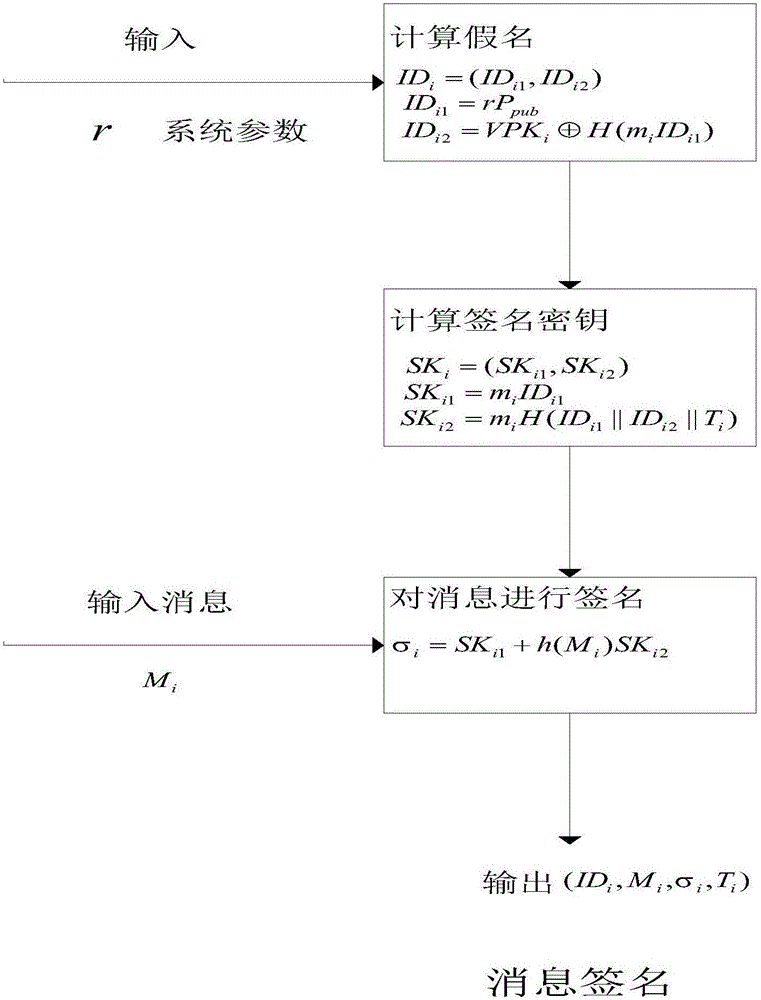
Identity based efficient anonymous batch authentication method in IOV (Internet of Vehicles) environment
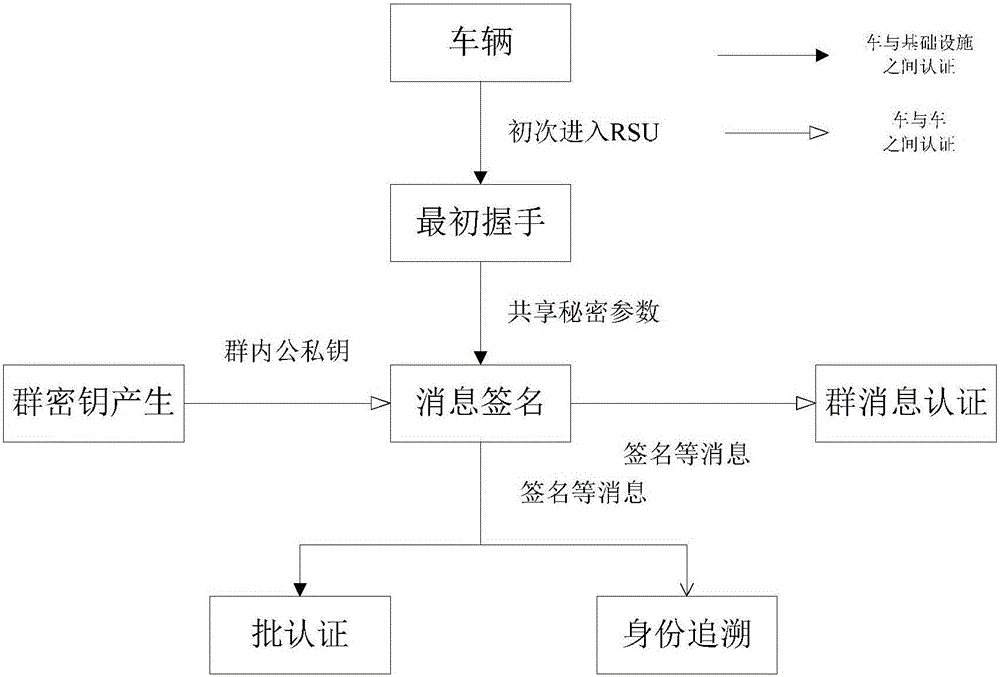
ActiveCN105847235AAchieve authenticationImprove securityUser identity/authority verificationTrusted authorityTamper resistance
The invention discloses an identity based efficient anonymous batch authentication method in an IOV (Internet of Vehicles) environment. The identity based efficient anonymous batch authentication method in the IOV environment comprises an initial handshake module, a message signature module, a batch authentication module, an identity tracing module, a group key generation module and a group message signature and authentication module. According to the identity based efficient anonymous batch authentication method in the IOV environment, authentication between vehicles and infrastructures and authentication between vehicles can be realized, no tamper-proofing device is depended, privacy protection is realized by utilizing a pseudonymous name, conditional privacy protection is realized as a TA (Trusted Authority) can trace the real identity of each vehicle if necessary, the efficiency is improved as batch authentication is adopted, and the authentication process is simple and efficient. The message signature process and the group message signature process are same, the operating cost is low, and a replay attack can be borne as a time stamp is added.
Owner:南京秉蔚信息科技有限公司
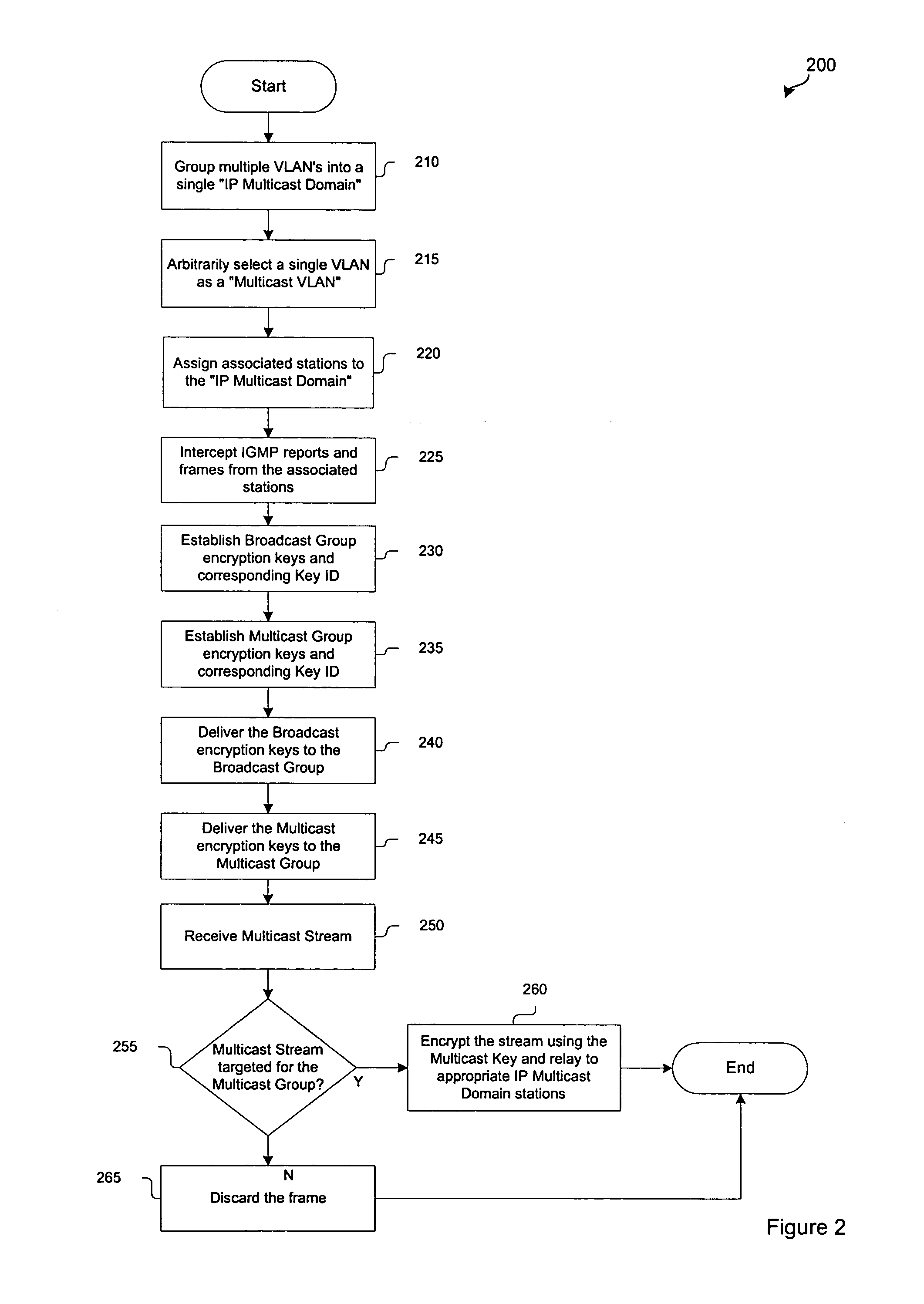
System and method for grouping multiple VLANs into a single 802.11 IP multicast domain
ActiveUS20050025160A1Special service provision for substationBroadcast with distributionVirtual LANIP multicast
A system and method for identifying and grouping multiple virtual local area networks into a single multicast domain is provided. The system and method may be configured to designate a virtual local area network within as a multicast virtual local area network to streamline the delivery of multicast messages via a network. A station may be configured with multiple group keys so that it can receive messages from multiple broadcast or multicast domains.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
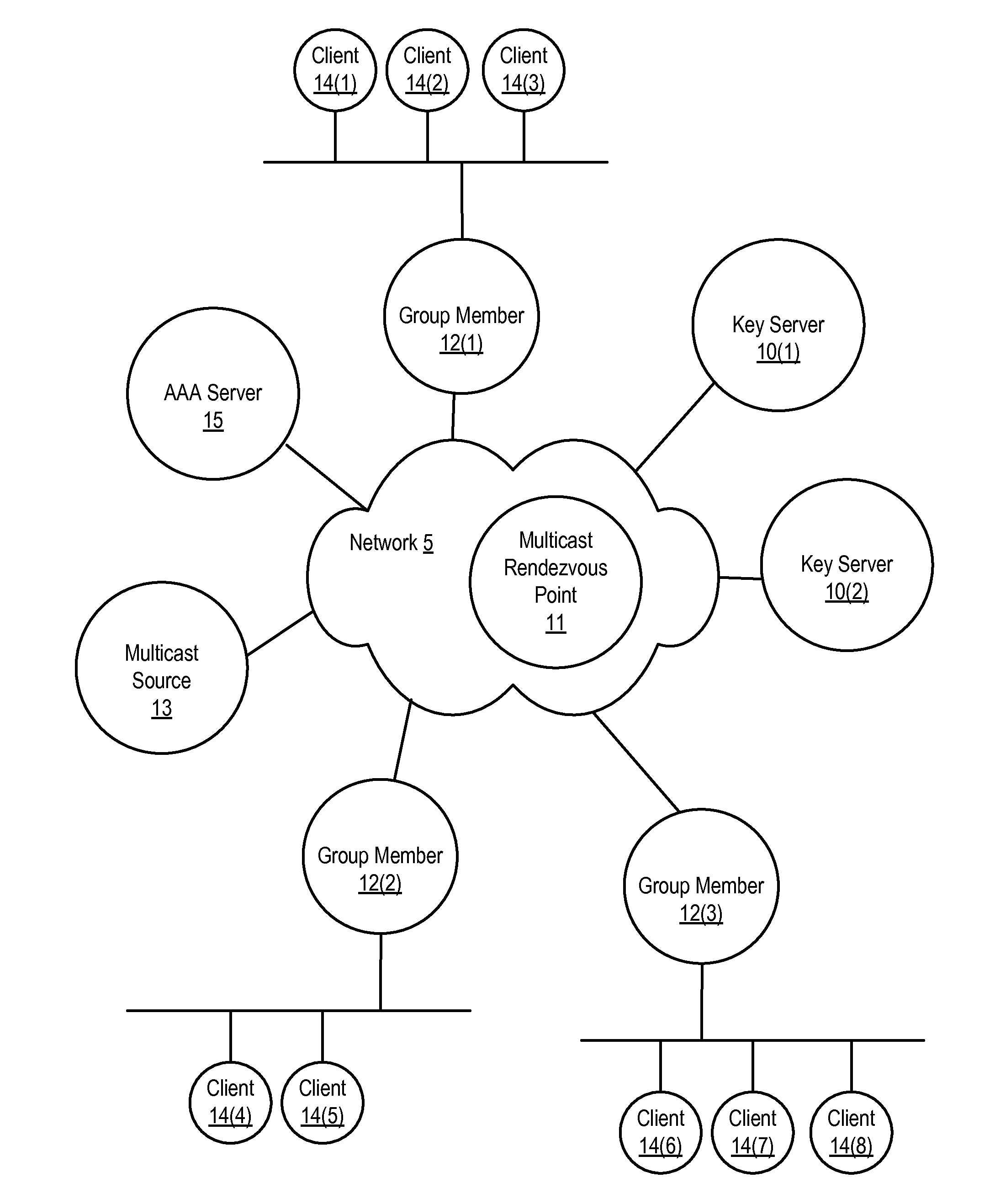
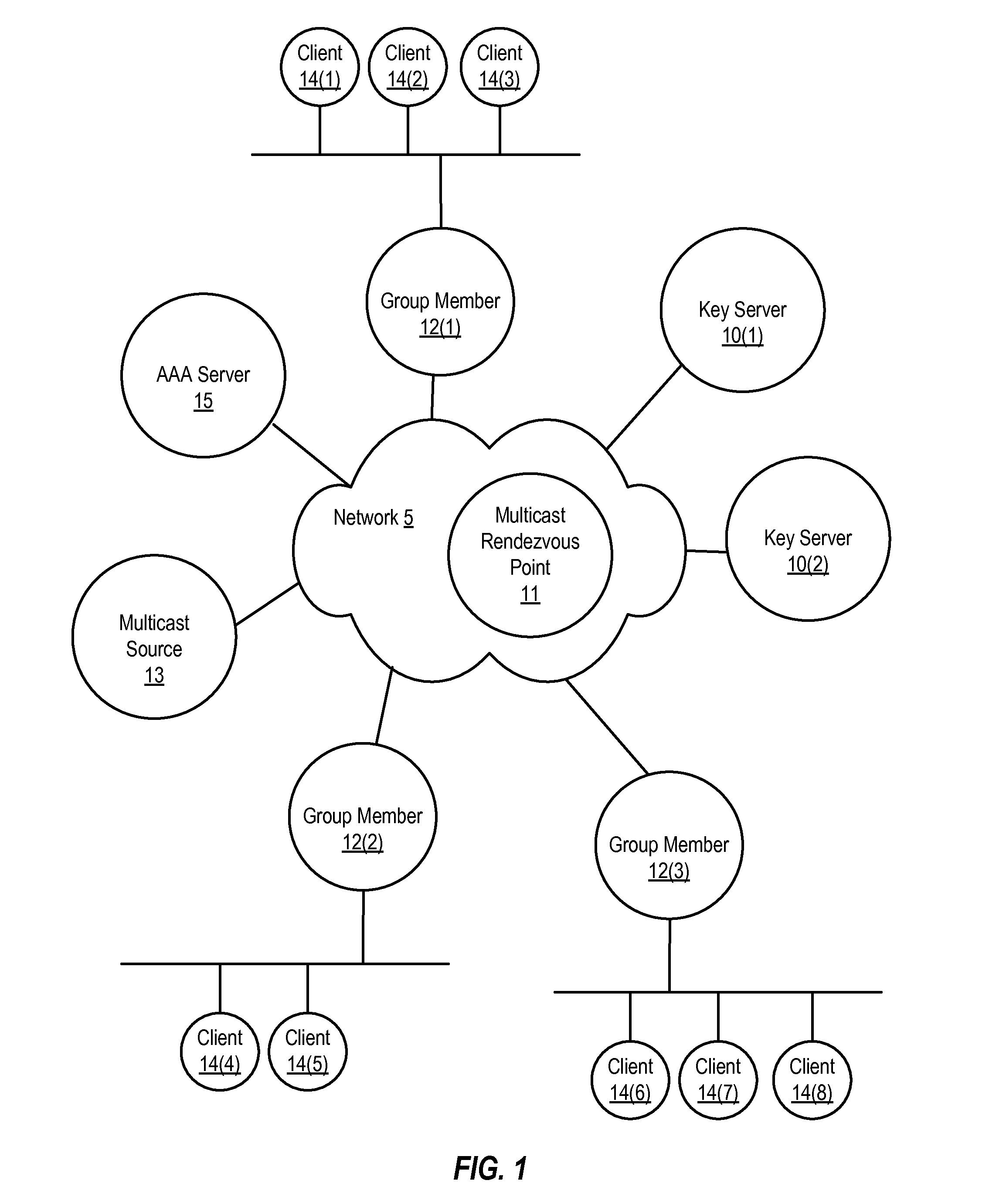
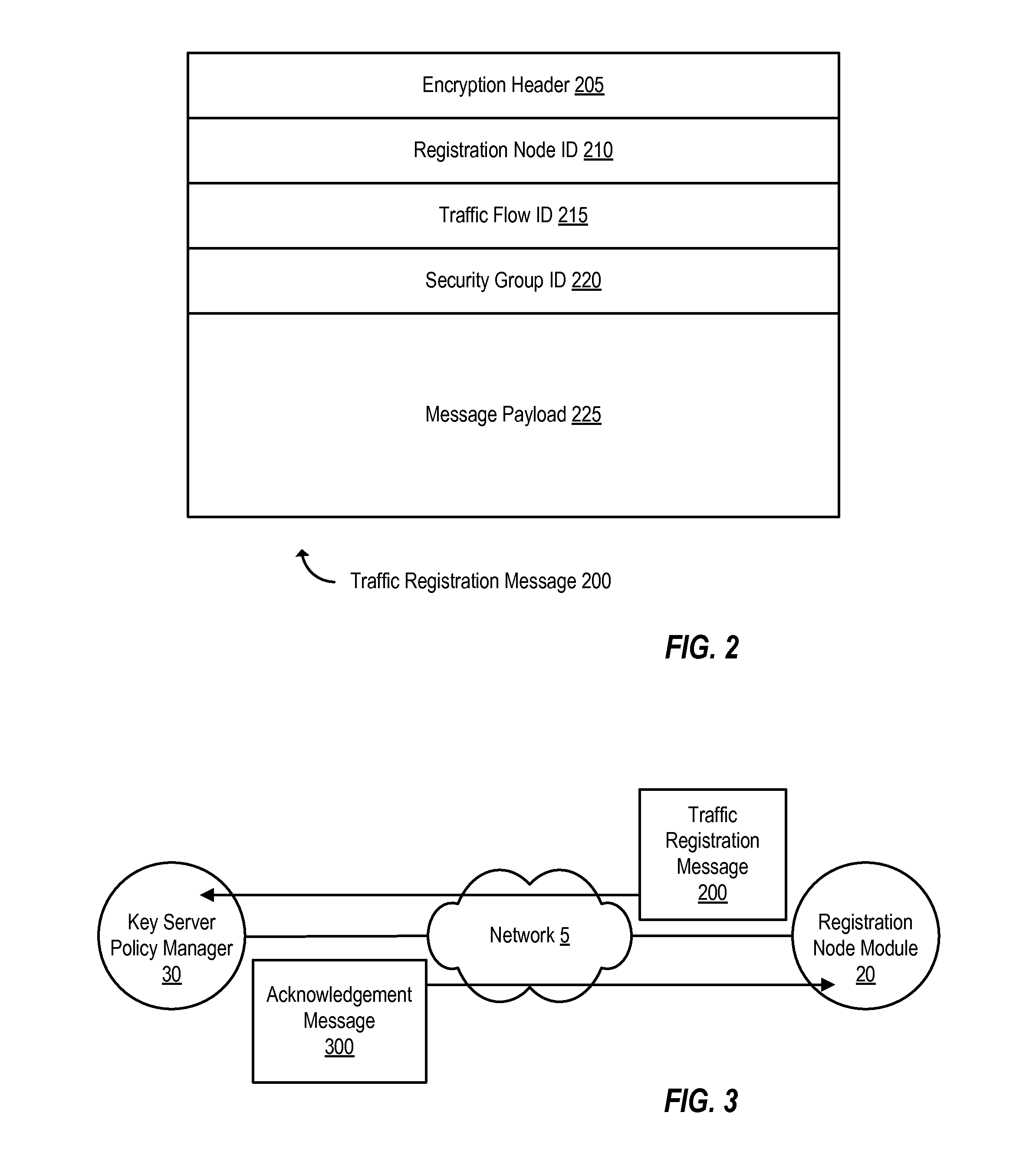
Dynamic group creation and traffic flow registration under a group in a group key infrastructure
ActiveUS20130219035A1Digital computer detailsElectric digital data processingTraffic capacityGroup Policy
Upon detection of a new traffic flow, a registration node can dynamically register the new traffic flow with a key server policy manager by sending a registration request on behalf of the new traffic flow. A registration request indicates the new traffic flow should be protected by a security group. A registration request may also include a request to dynamically generate a new security group to protect the traffic flow. The registration request is received by a key server policy manager, which performs authentication and authorization checks of the requesting registration node, and determines whether to accept or reject the registration request. If accepted, the key server policy manager registers the new traffic flow by including a description of the traffic flow in a group policy of an existing security group or a newly created security group, depending on the registration request.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Quantum-key distribution method between a plurality of users or groups
InactiveUS20050249352A1Improve securitySecure distributionKey distribution for secure communicationPump componentsComputer scienceQuantum state
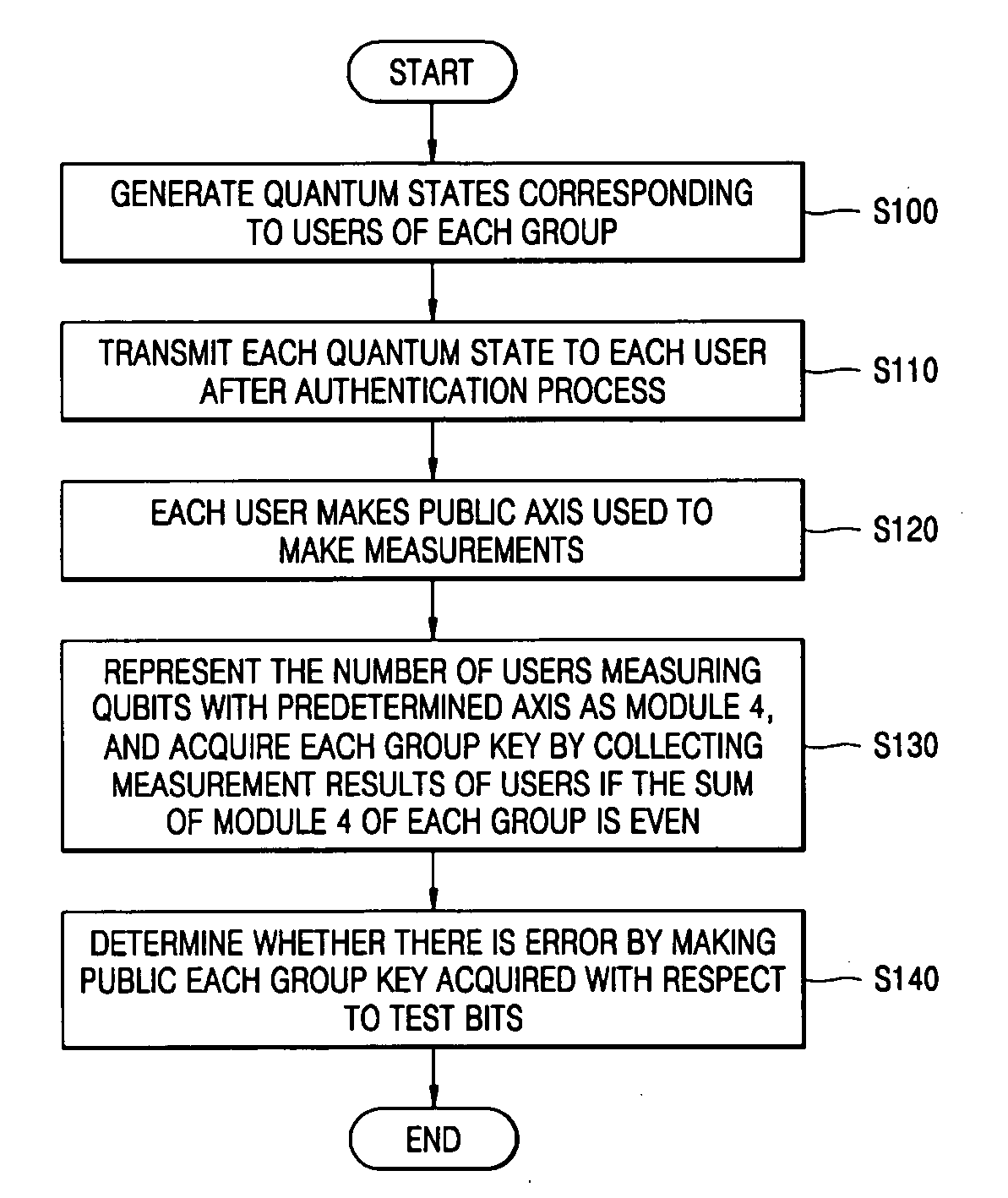
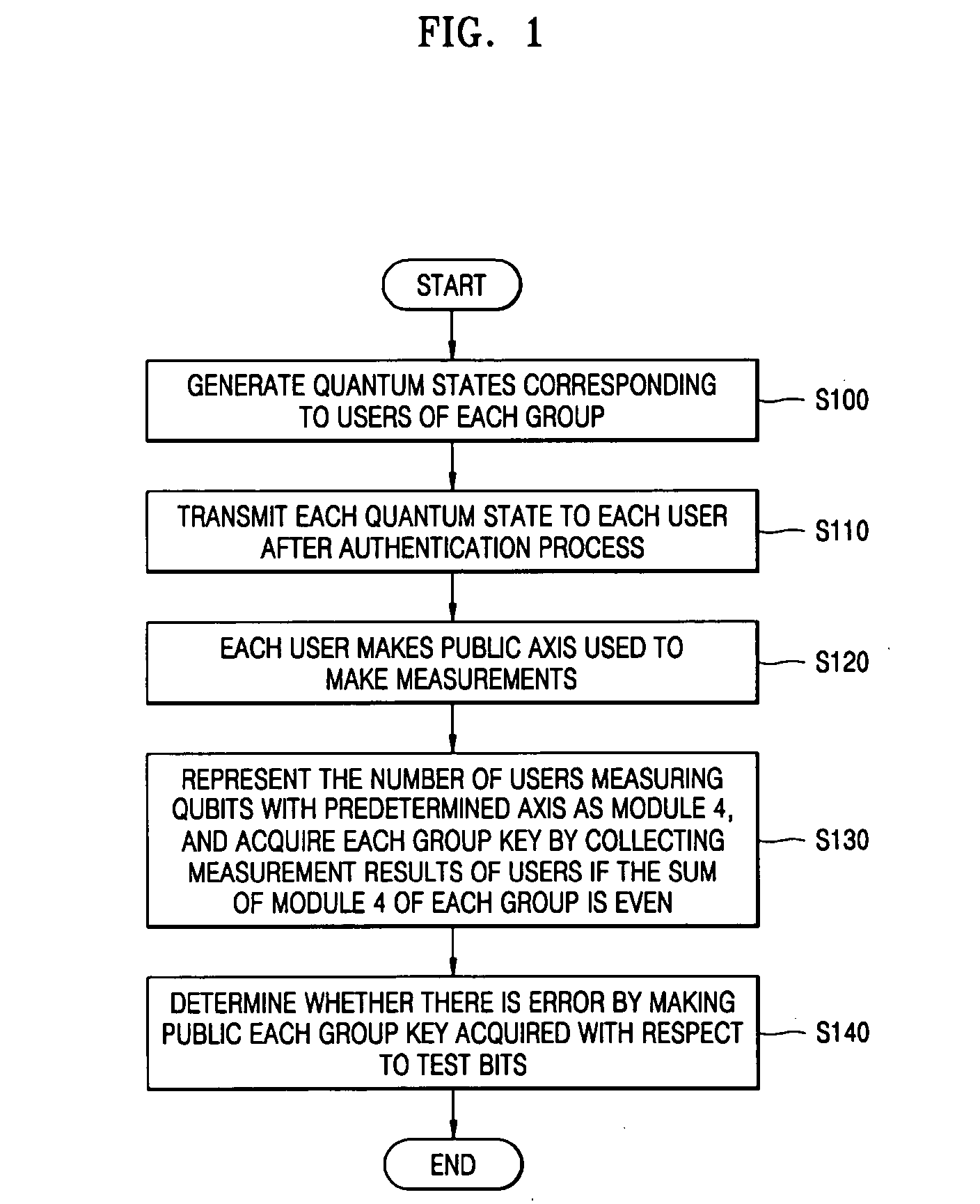
There is provided a quantum-key distribution method between a plurality of users or groups. A center prepares a predetermined number of entangled states consisting of qubits equal to the number of the users, and generates quantum states consisting of the qubits belonging to each of the entangled states and corresponding to each of the users. The center transmits each of the quantum states to each of the users after an authentication process. Each of the users receiving the quantum state makes public an axis used to measure each of the qubits constituting the quantum states. The number of users in each group measuring the qubits with a predetermined axis is represented by module 4. If the sum of the module 4 of each group is even, each group collects the qubit measurement results of the users and acquires each group key. Therefore, it is possible to provide a high-security quantum-key distribution method between an unspecified number of users or groups.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Key distribution system
InactiveUS20100296655A1Improve securityMore bandwidthKey distribution for secure communicationTelevision systemsKey distributionComputer science
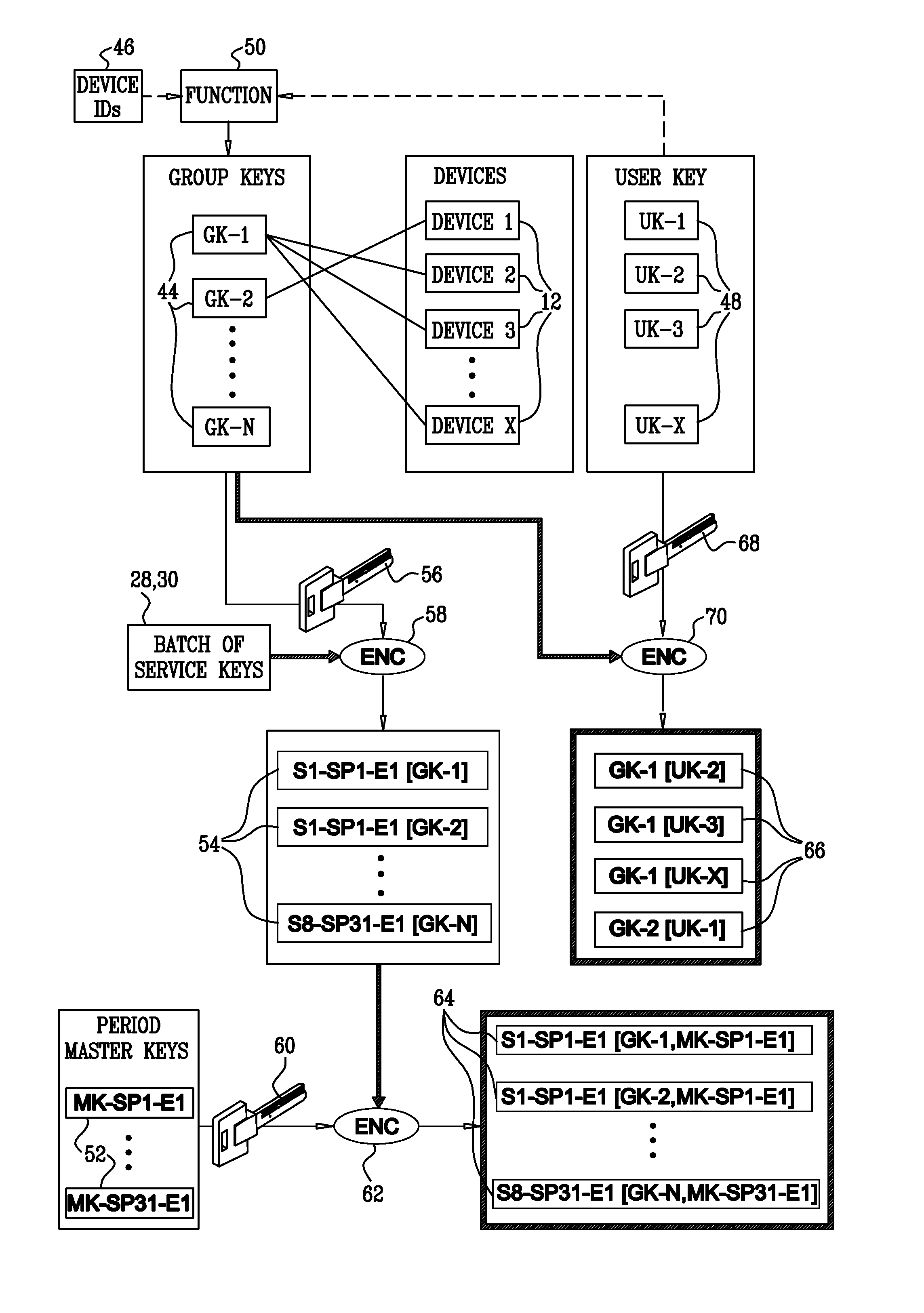
A key distribution system for controlling access to content by rendering devices, comprising an epoch module to provide epochs, each epoch including service key periods, a service key module to provide a batch of service keys, a group module to provide group keys for each epoch such that each rendering device is assigned a group key grouping together the devices having the same group key, thereby defining groups, in different epochs the devices are grouped differently, an encryption module to encrypt, for each epoch, each service key in the batch of service keys, individually with each group key yielding a plurality of group-key-encrypted service keys from each service key, and a delivery module to distribute to the devices, for each one of the epochs, the group-key-encrypted service keys for the batch of service keys and the group keys of the one epoch. Related apparatus and methods are also described.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
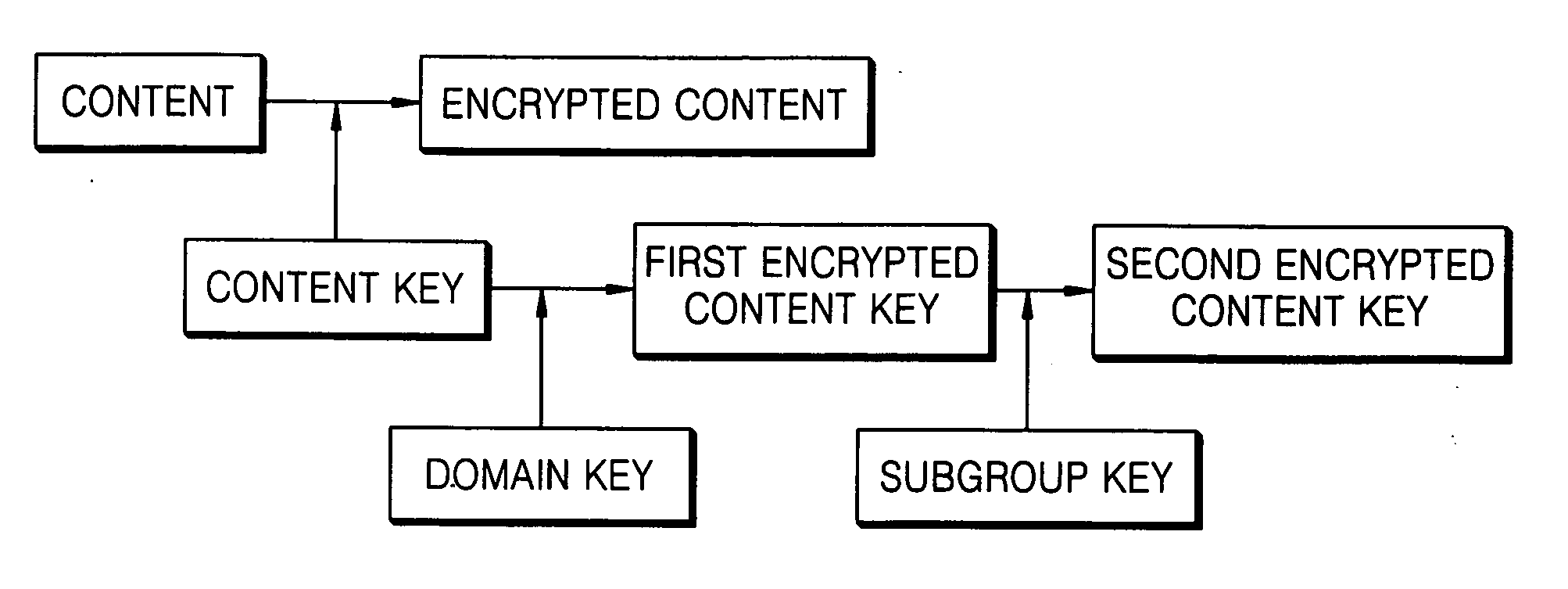
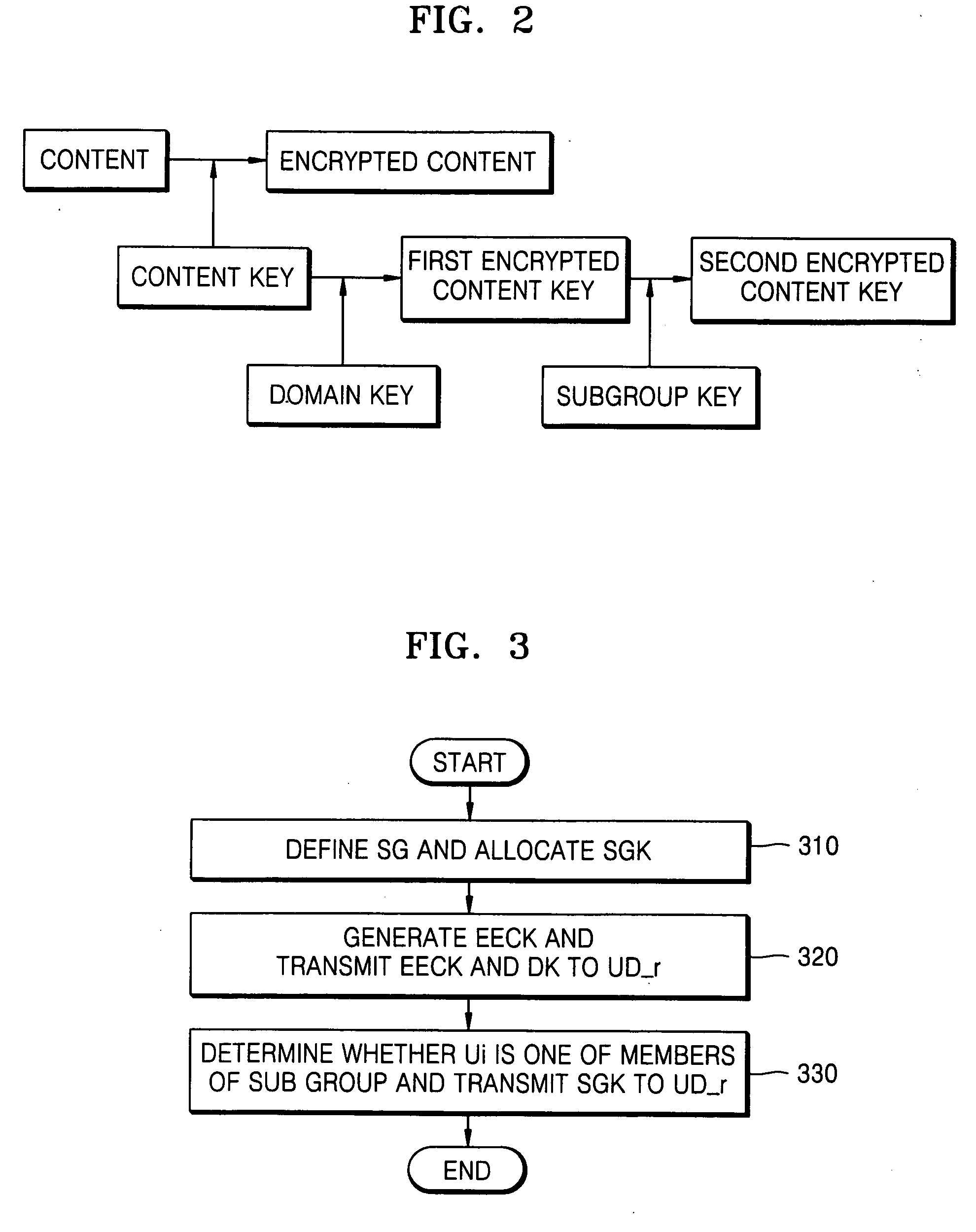
Method of controlling content access and method of obtaining content key using the same
InactiveUS20060179478A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationUser deviceA domain
Provided is a method of controlling content access in a home network. The method includes: (a) defining a predetermined sub group and allocating a sub group key for the sub group; and (b) checking whether a user belongs to the sub group and transmitting the sub group key to a user device requested by the user, wherein the user device obtains an encrypted content key using a domain key and the sub group key. Since a content key is twice encrypted using a domain key and a sub group key and transmitted to a user device, it is possible to provide authorized content access to a user.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Identity-based safety signature method
The invention relates to an identity-based safety signature method which comprises the steps of: allocating a secret key offline, signing online and setting a secret key service life for realizing updating of a communication group secret key, wherein a unique identification of a sensor node, i.e. a public key of the node, is used as identity information. Based on a public parameter of a system and a main secret key of the system and according to identity information of each node, a private key of the node is figured out. After a wireless sensor network is configured, a system parameter and a private key are stored in each node, when identity authentication is required between two or among more nodes, a sender can use the private key of the sender to sign a pre-appointed authentication quantity. With identity information of the sender as a public key, a receiver verifies the received information according to a signature verification algorithm in the signature scheme so as to determine the identity of the sender. The storage space in the safety signature method is a constant, therefore, the safety signature method is more suitable for being used in a wireless sensor.
Owner:YUELIANG CHUANQI TECH CO LTD
Digital Copyright Management Using Secure Device
InactiveUS20070276760A1Copyright protectionUnnecessary operationTelevision system detailsKey distribution for secure communicationDigital rights managementLicense
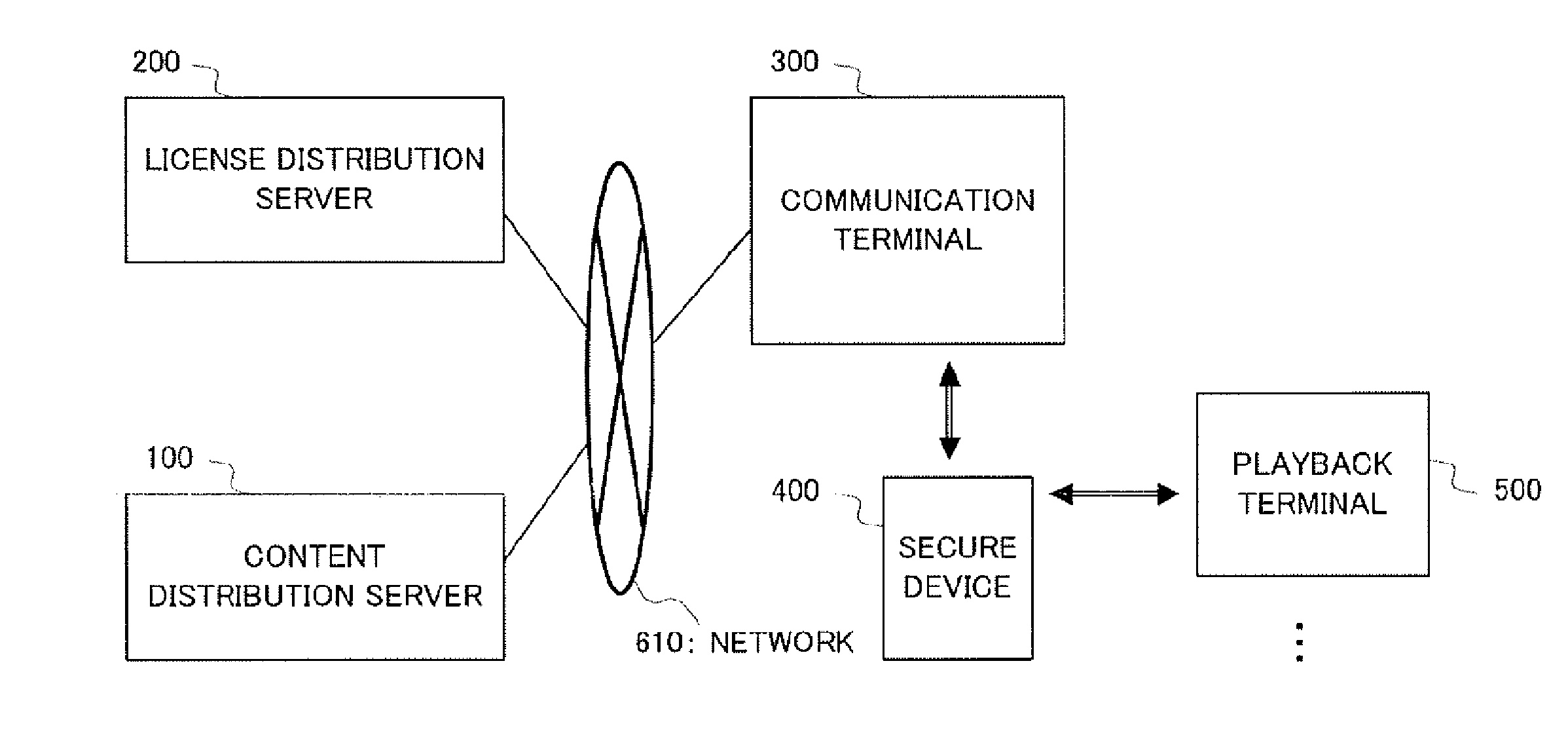
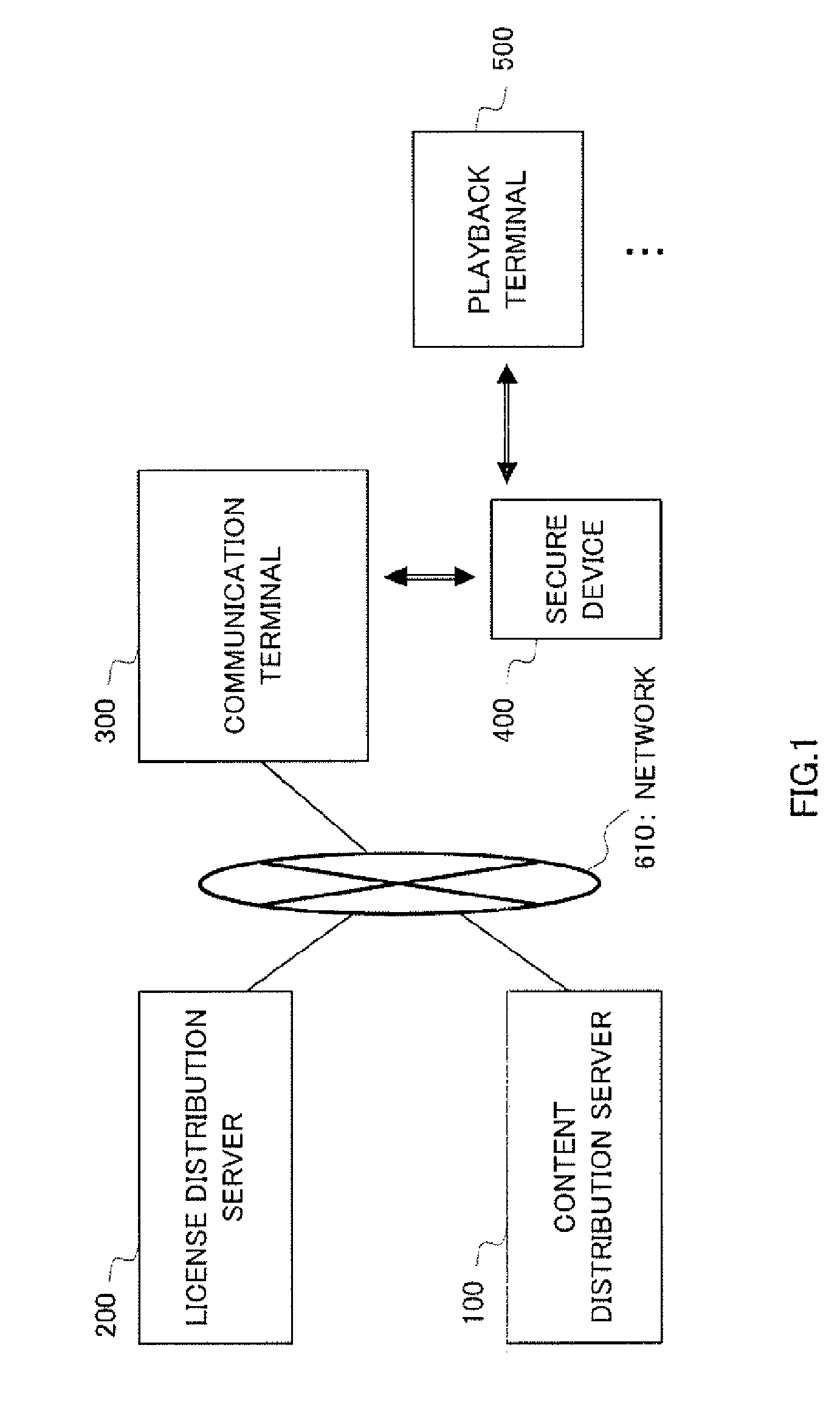
There is provided a content use management method capable of preventing unauthorized distribution of a content and improving user-friendliness. In this method, the same group key is stored in a secure device (400) and a playback terminal (500). Moreover, a license issuing application is received from a license distribution server (200) and stored in the secure device (400). After this, a license encrypted by the group key is sent to the playback terminal (500) and the license encrypted by the group key is stored in the playback terminal (500). Upon playback of the encrypted content, the playback terminal (500) decrypts the license by using the group key and acquires the content decryption key, thereby decrypting the encrypted content. Even when the encrypted license flows into the network, it cannot be decrypted by a playback terminal not having the same group key and the copyright is protected. Moreover, the playback terminal (500) which already holds the group key and the license encrypted by the group key does not need the secure device when reproducing the encrypted content.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
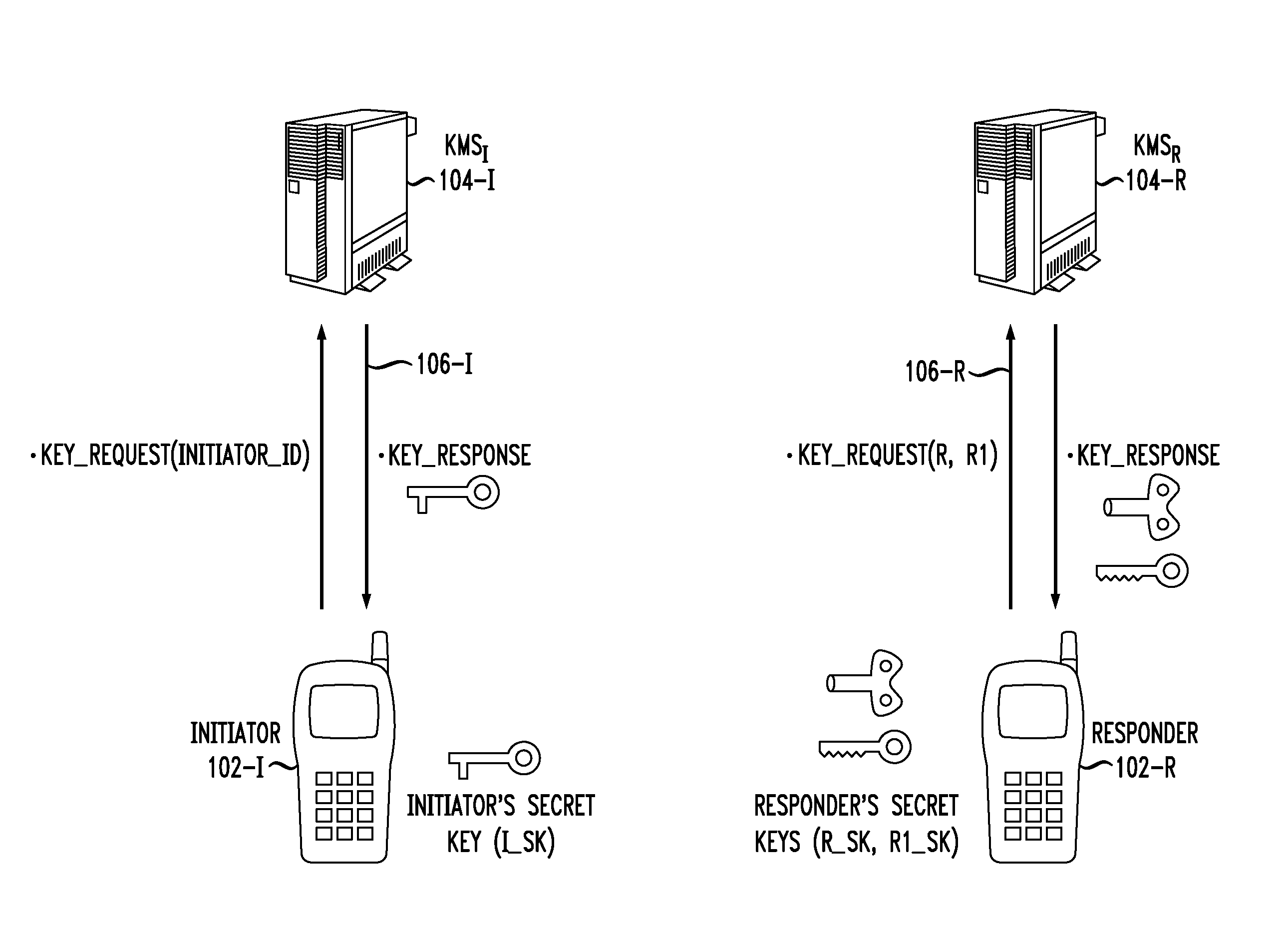
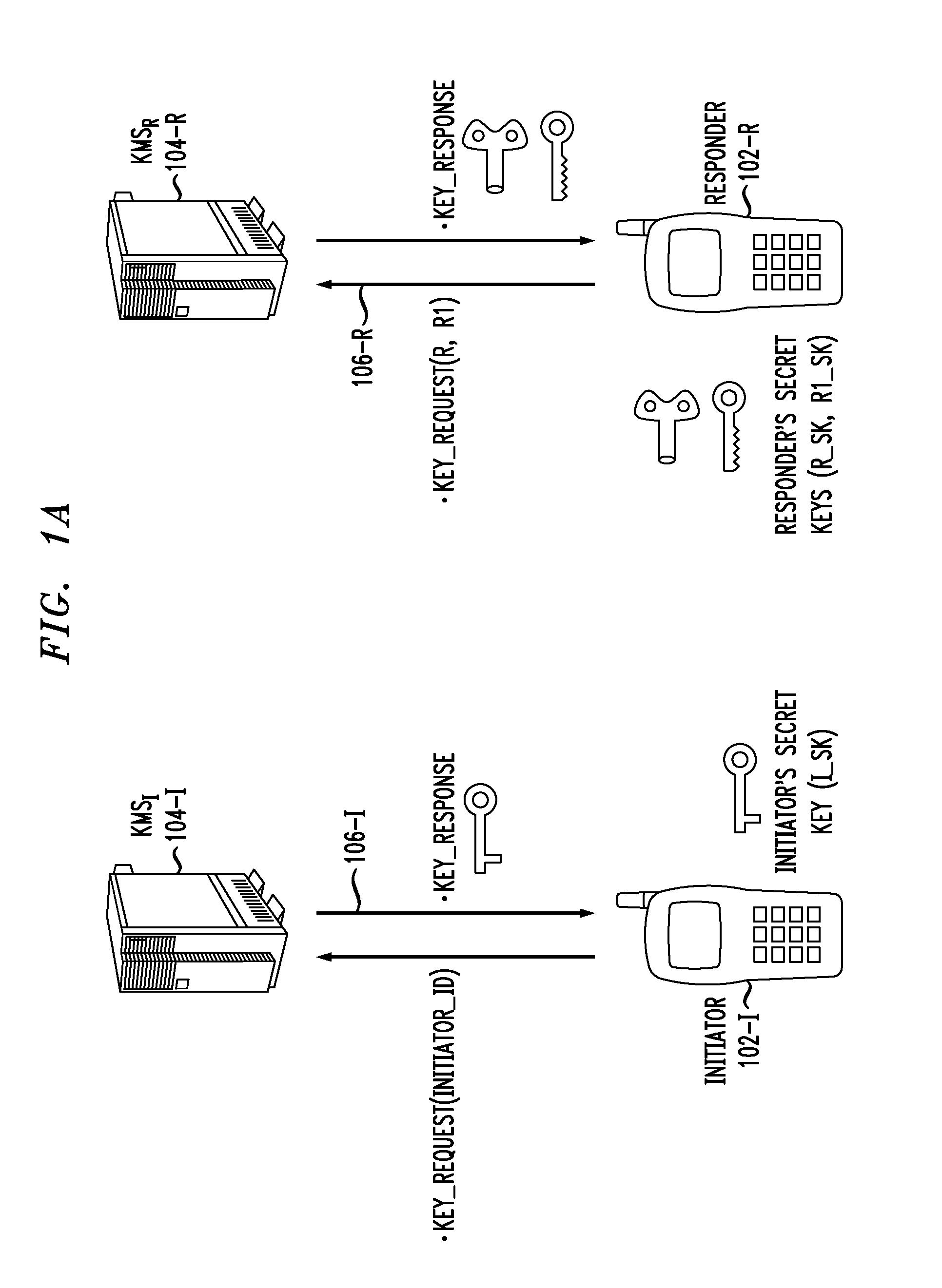
Key negotiation and management for third party access to a secure communication session
ActiveUS20070198836A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationThird partySecure communication
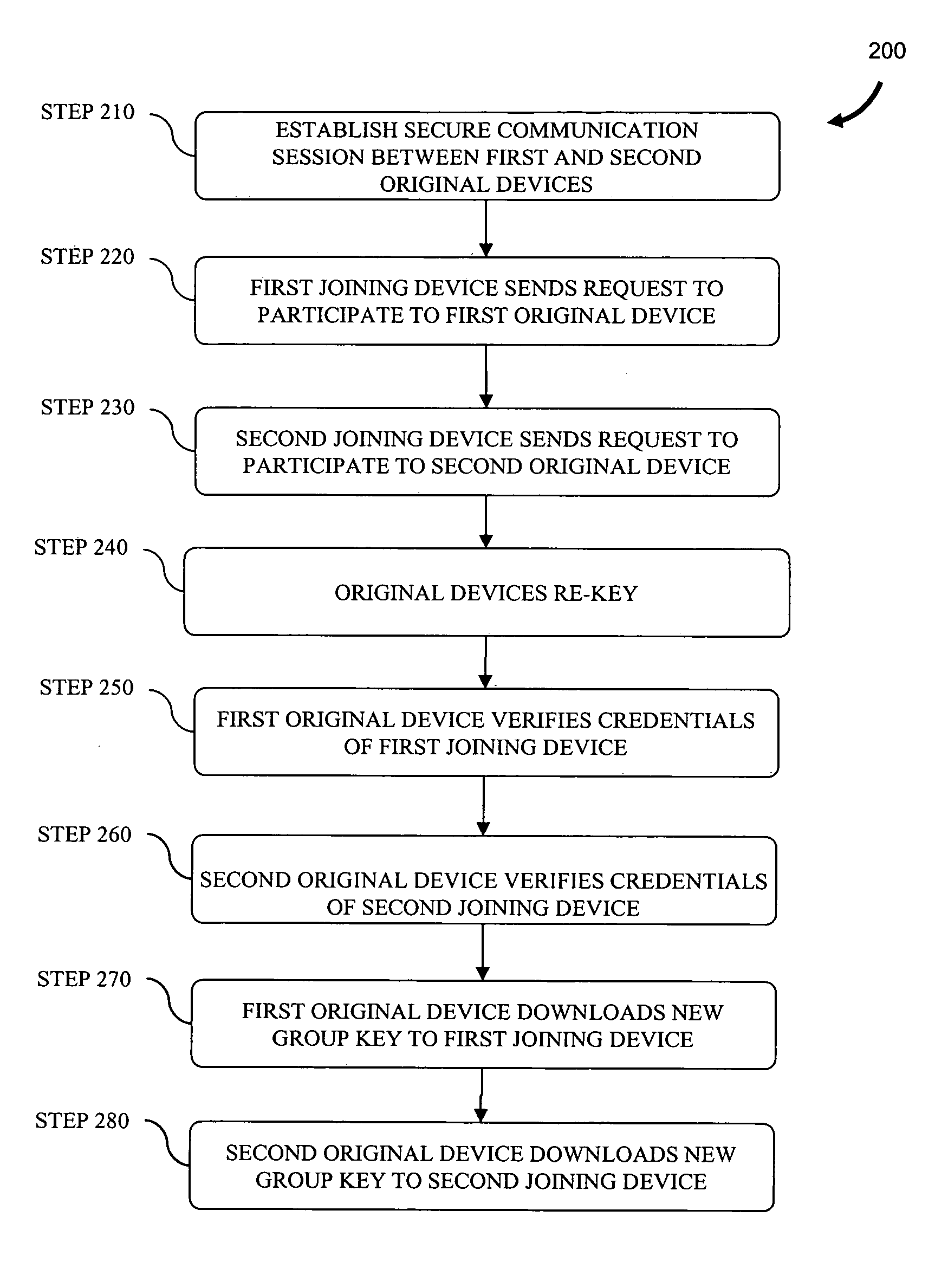
Described are a method and system for establishing a secure communication session with third-party access at a later time. A first communication subsession is established between two original devices using a first key generated by a two-party key and security association protocol. At least one of the original devices is established as a group key server. A request from a joining device to join the secure communication session is received and a second communication subsession is established between the original devices using a second key generated by the two-party key and security association protocol. The second key is provided to the joining device to enable participation in the second communication subsession.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
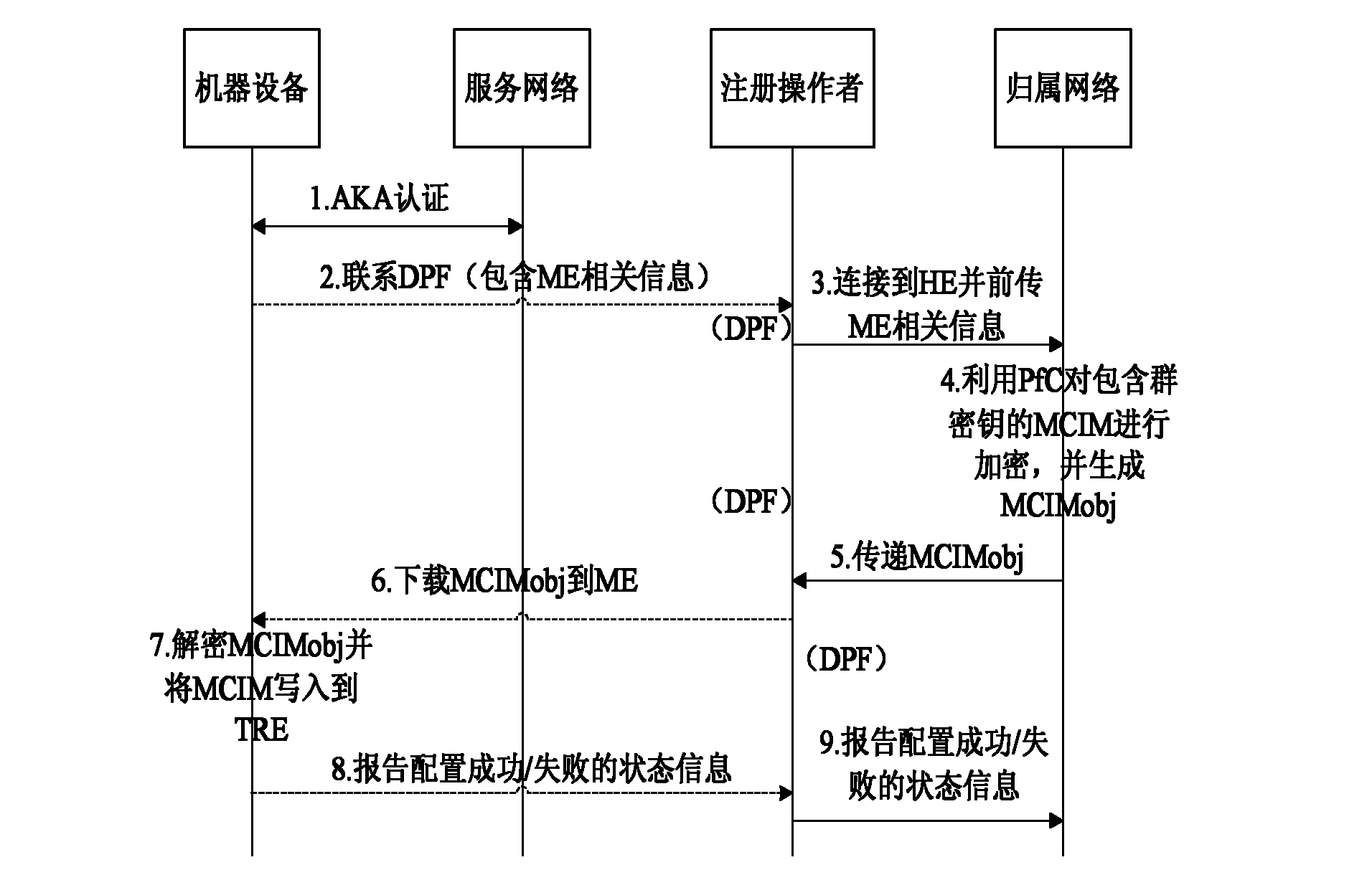
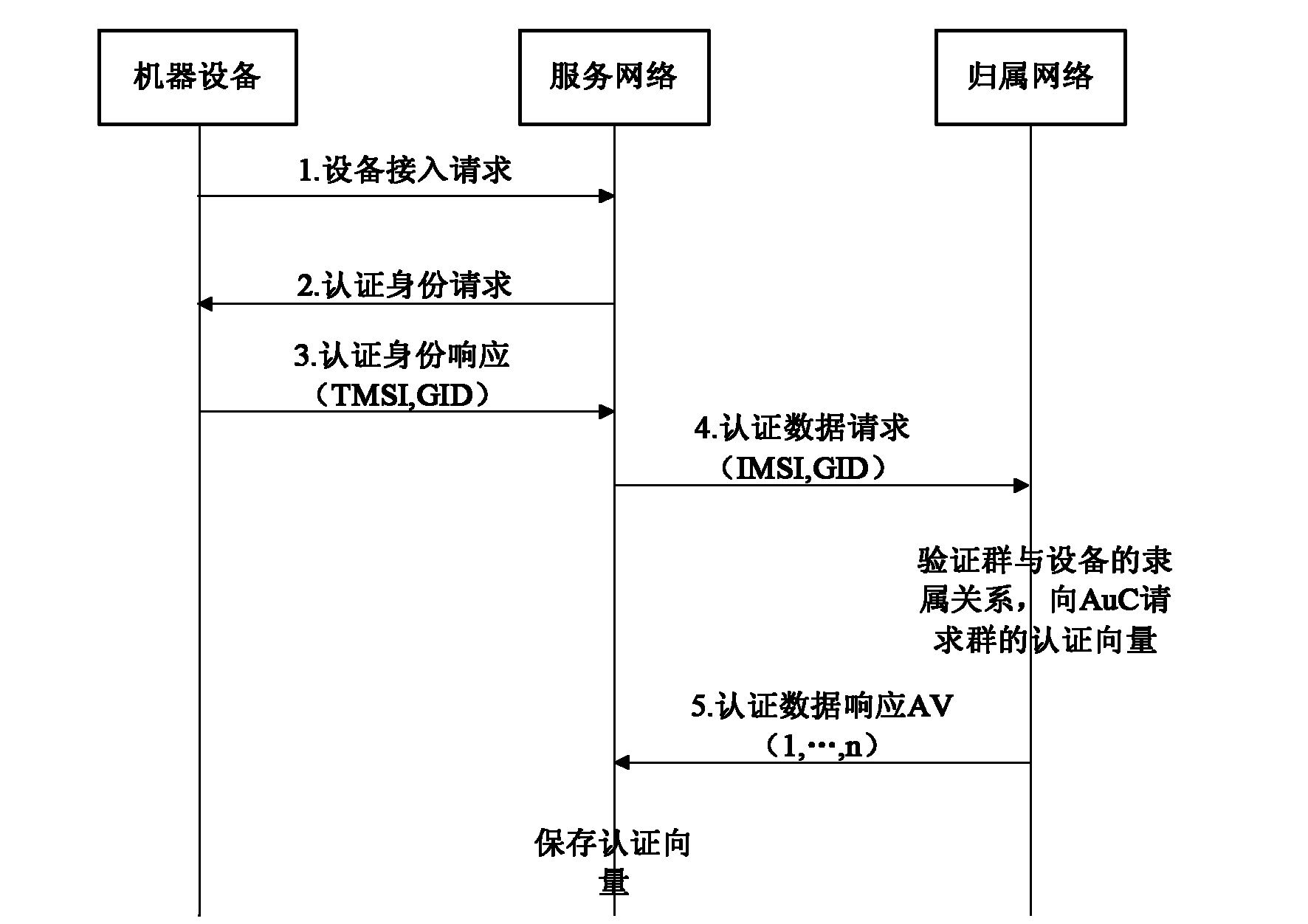
Authentication method based on shared group key in machine type communication (MTC)
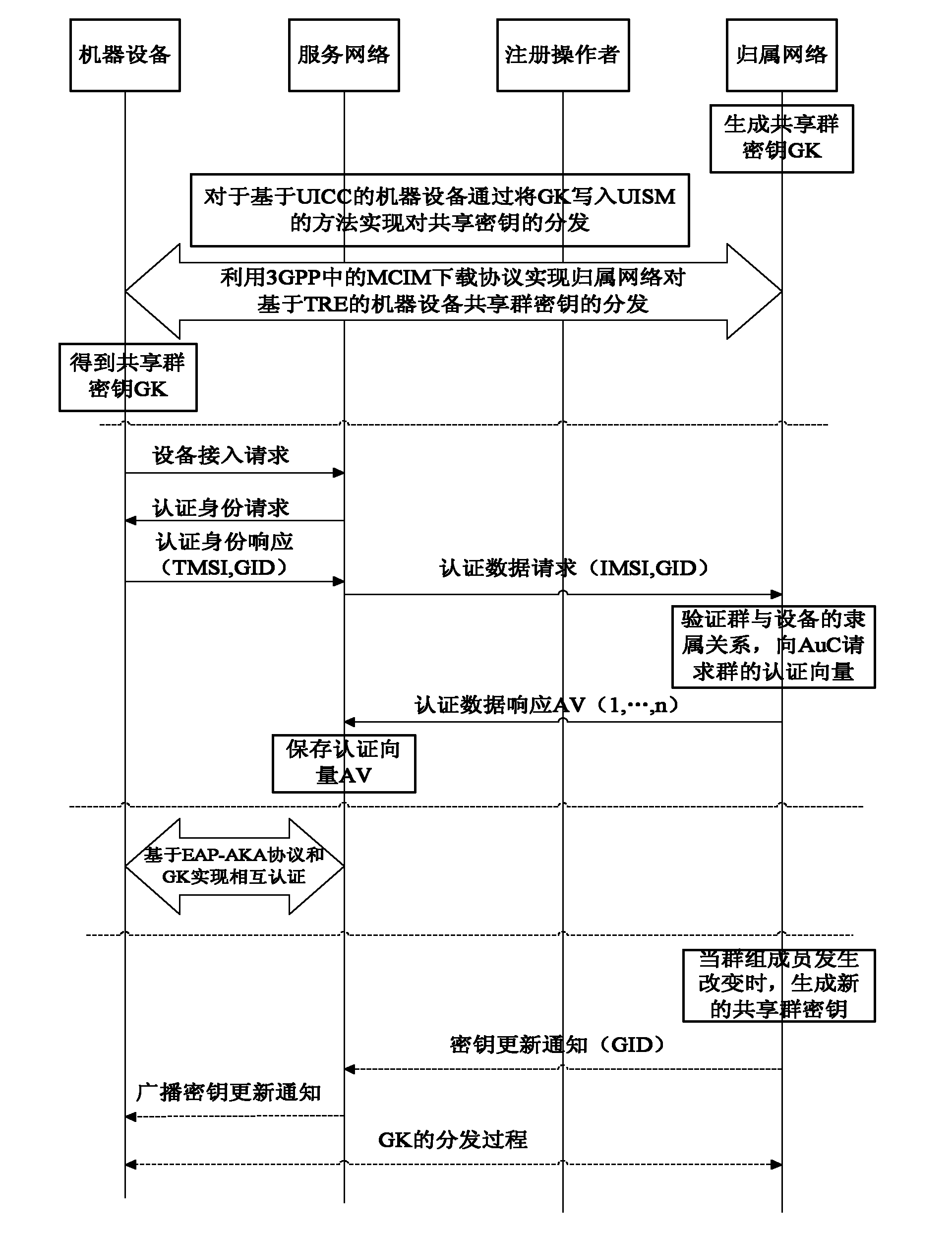
ActiveCN102137397AOptimizing Signaling DataReduce congestionSecurity arrangementBroadcastingService networks
The invention discloses an authentication method based on a shared group key in machine type communication (MTC), mainly solving the defect of lack of an authentication mechanism based on an MTC group in the existing standard. The authentication process comprises the following steps that: (1) a home network (HN) generates a shared group key (GK), and writes the generated GK into a universal subscriber identity module (USIM) or distributes the generated GK as part of a machine to machine (M2M) communication identity module (MCIM) to all machinery equipment (ME) in the group; (2) the HN sends authentication data generated based on the GK to a service network (SN); (3) the SN performs mutual authentication on the ME in the group by using the obtained authentication data; and (4) when the relation among the group members is changed, the HN broadcasts a key updating notification message to all the ME belonging to the group, and realizes update of the shared GK between the HN and the ME according to the step (1). The authentication method optimizes the signal data generated by authentication between the SN and the HN, reduces congestion of a link between the SN and the HN, and is safe, fast and suitable for fast access authentication of an ME group in MTC.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
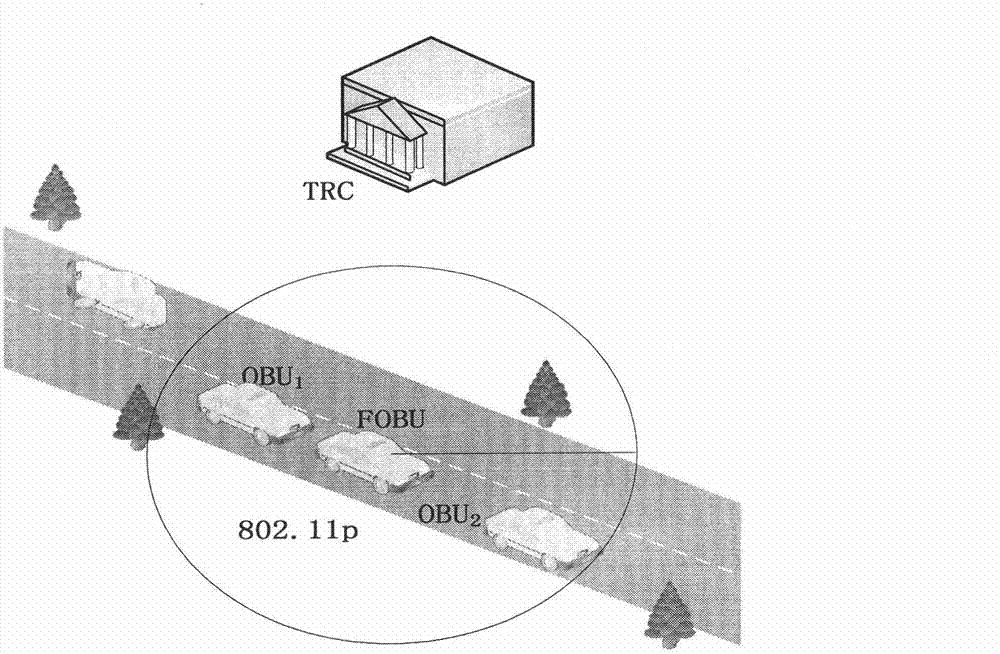
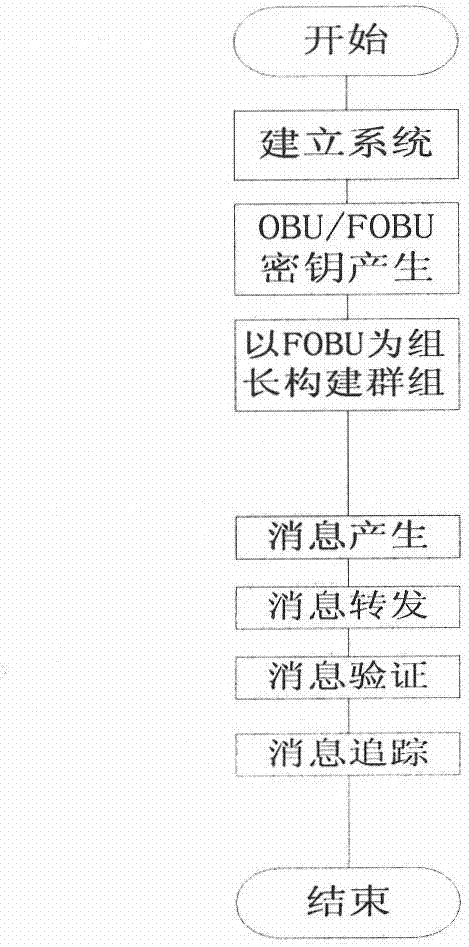
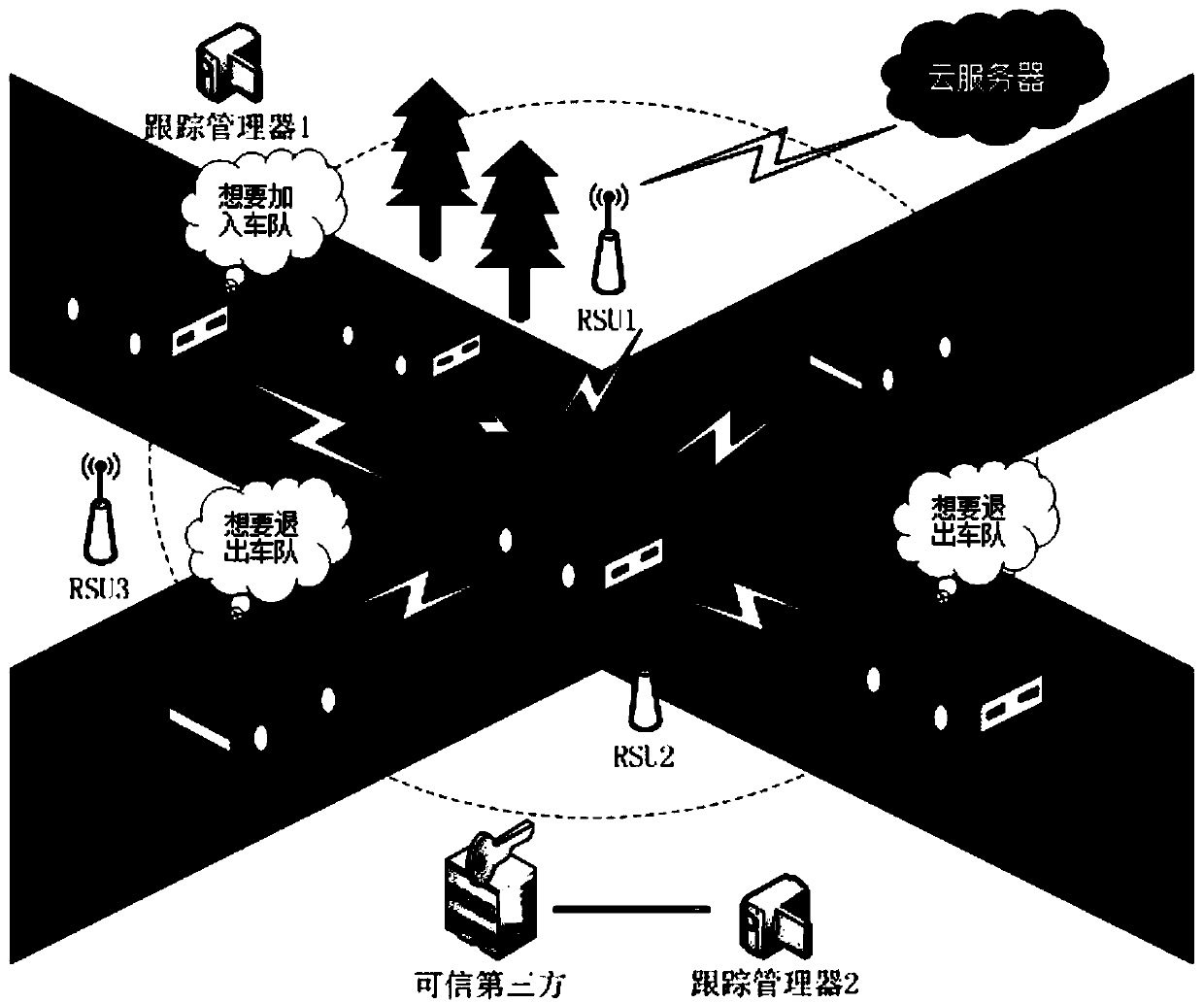
Floating vehicle-based traceability vehicle self-networking communication privacy protection method
InactiveCN102740286AIncrease coverageReduce overheadNetwork topologiesSecurity arrangementPrivacy protectionEngineering
The invention discloses a floating vehicle-based traceability vehicle self-networking communication privacy protection protocol, which is characterized in that a floating vehicle is used as a mobile RSU (Remote Subscriber Unit), a floating vehicle auxiliary grouping technology is adopted, the floating vehicle F adopts V2V communication, vehicles running in the same direction in an effective communication radius are united to spontaneously form a group, F is used as a group leader and is in charge of authorizing the validity of the vehicles and maintaining a group key and a specified group parameter; and F and all members respectively have a one-to-one secret channel negotiated by anonymous certificates issued by an authentication center (TA), the members sends messages to be broadcasted to the F by using the channels, the F is subjected to the message anonymilization and encrypted by using a group key-based symmetric encryption algorithm and then forwarded to other members or other groups, and when the messages are disputed, under the authorization of the TA, the real identity of the vehicle generating the messages can be accurately located.
Owner:杨涛
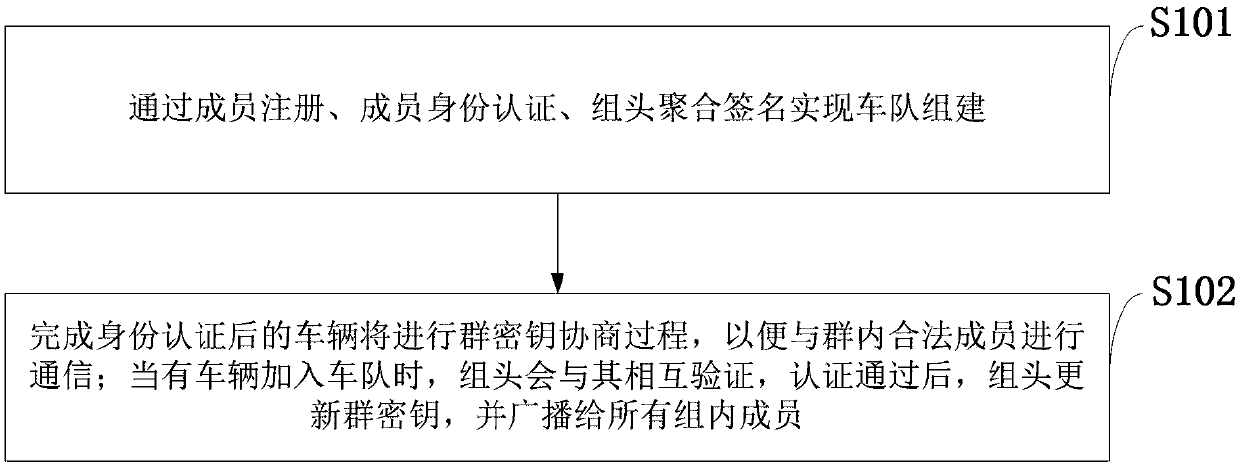
Motorcade establishment and management method and system based on block chain and PKI authentication mechanism
ActiveCN109687976ASolve authentication problemsTroubleshoot account management issuesKey distribution for secure communicationParticular environment based servicesSecure communicationThe Internet
The invention belongs to the technical field of safety communication between motorcades in Internet of Vehicles, and discloses a motorcade establishment and management method and system based on a block chain and a PKI authentication mechanism. The method is mainly divided into two parts of motorcade establishment and group key agreement and update; the motorcade establishment part comprises the following main processes of member registration, member identity authentication and group head aggregate signature; and the group key agreement and update part comprises the following main processes ofgroup key agreement and group key update for dynamic joining and exiting of a vehicle. According to the method and the system, the block chain is combined with the PKI authentication mechanism, a problem of identity authentication of the vehicle, a server and an RSU in the Internet of Vehicles is solved; the motorcade establishment is completed based on an elliptic curve, a bilinear pairing technology and an aggregate signature; and the group key agreement and update can be realized based on a DDH difficulty problem, the forward and backward safety is achieved, and the safety of member communication in the motorcade is ensured.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
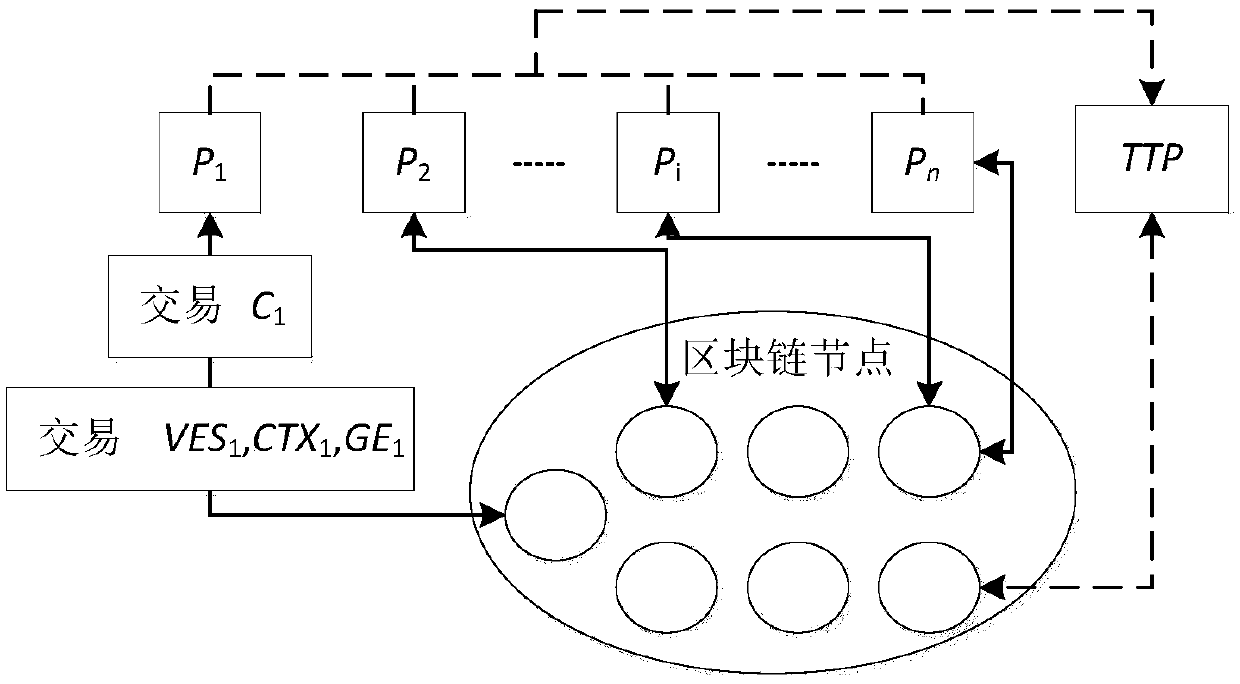
Multiparty fair PDF contract signing method based on block chain
ActiveCN108833115AKey distribution for secure communicationData processing applicationsDigital signatureCiphertext
The invention relates to a multiparty fair PDF contract signing method based on a block chain. Participants comprise a plurality of contract signers P<1>,... and P<n>, a trusted third party (TTP) andblock chain nodes. The method comprises the steps that the P<1> generates a verifiable encryption signature VES<1> of a contract, calculates a hash context CTX<1> of contract content, generates elements GE<1> of a group key negotiation agreement GKA, packages the VES<1>, the CTX<1> and the GE<1> into block chain transaction and sends the block chain transaction to any block chain node; a P verifies VES<i-1> of a P<i-1>, wherein the i is greater than 1 and is smaller than or equal to the n, after the verification is successful, the P generates a new VES, CTX and GE, and sends theVES, CTX and GE to any block chain node through transaction; after the P<n> finishes operation, a P<j> calculates a group encryption key GK, wherein the j is greater than or equal to 1 and is smaller than or equal to the n, the P<j> encrypts a digital signature of a PDF document to form a ciphertext C<j>, packages the C<j> into the transaction and sends the transaction to the block chainnode; the P<j> queries block chain data, decrypts the block chain data through utilization of the GK and then combines the block chain data into a complete PDF contract; and if the P<j> does not obtain the block chain data after the P<j> is overtime, the P<j> communicates with the TTP to process an exception. According to the method, the dependence on the TTP is relatively weak, and the efficiency is relatively high.
Owner:信睿吉科技(北京)有限公司
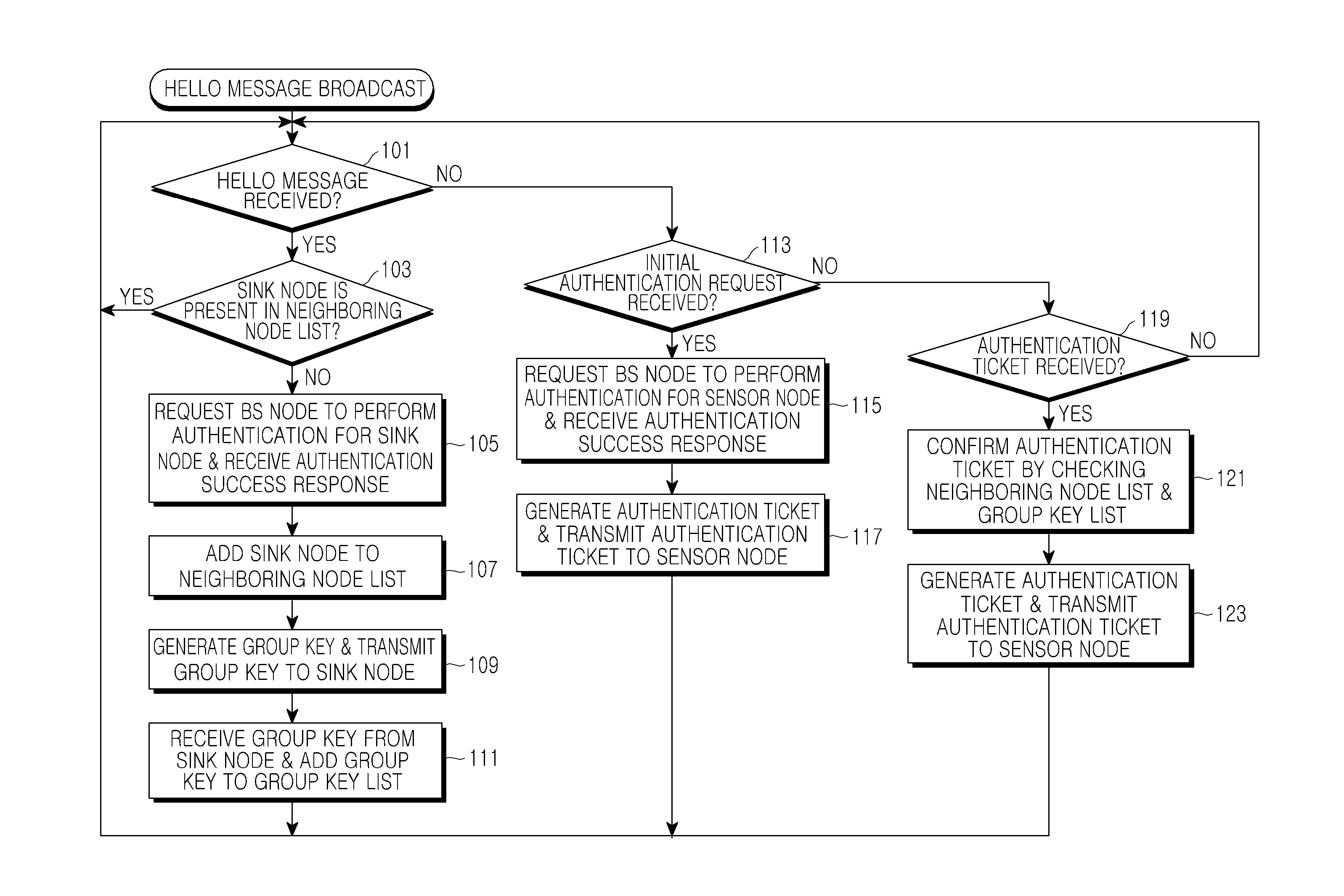
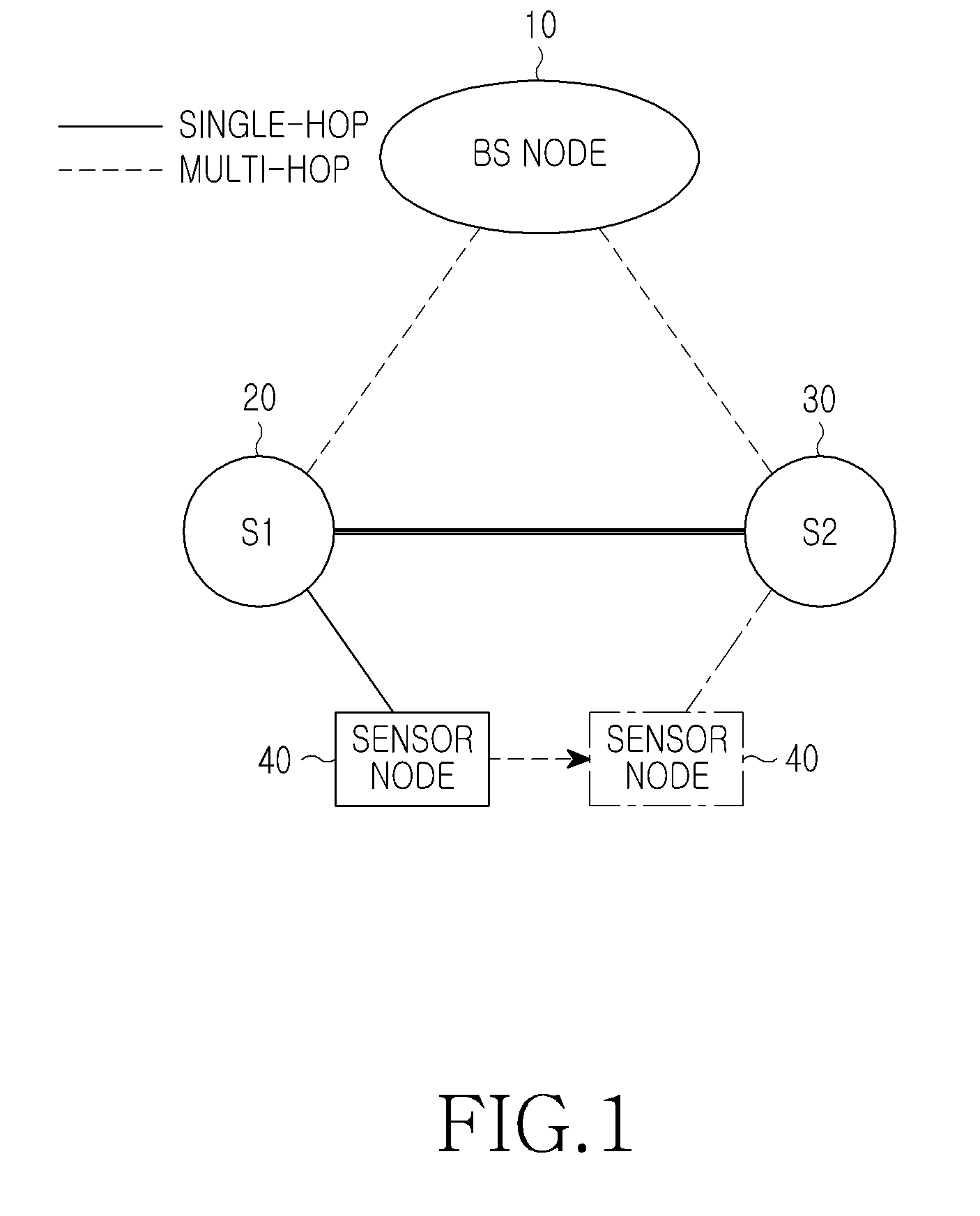
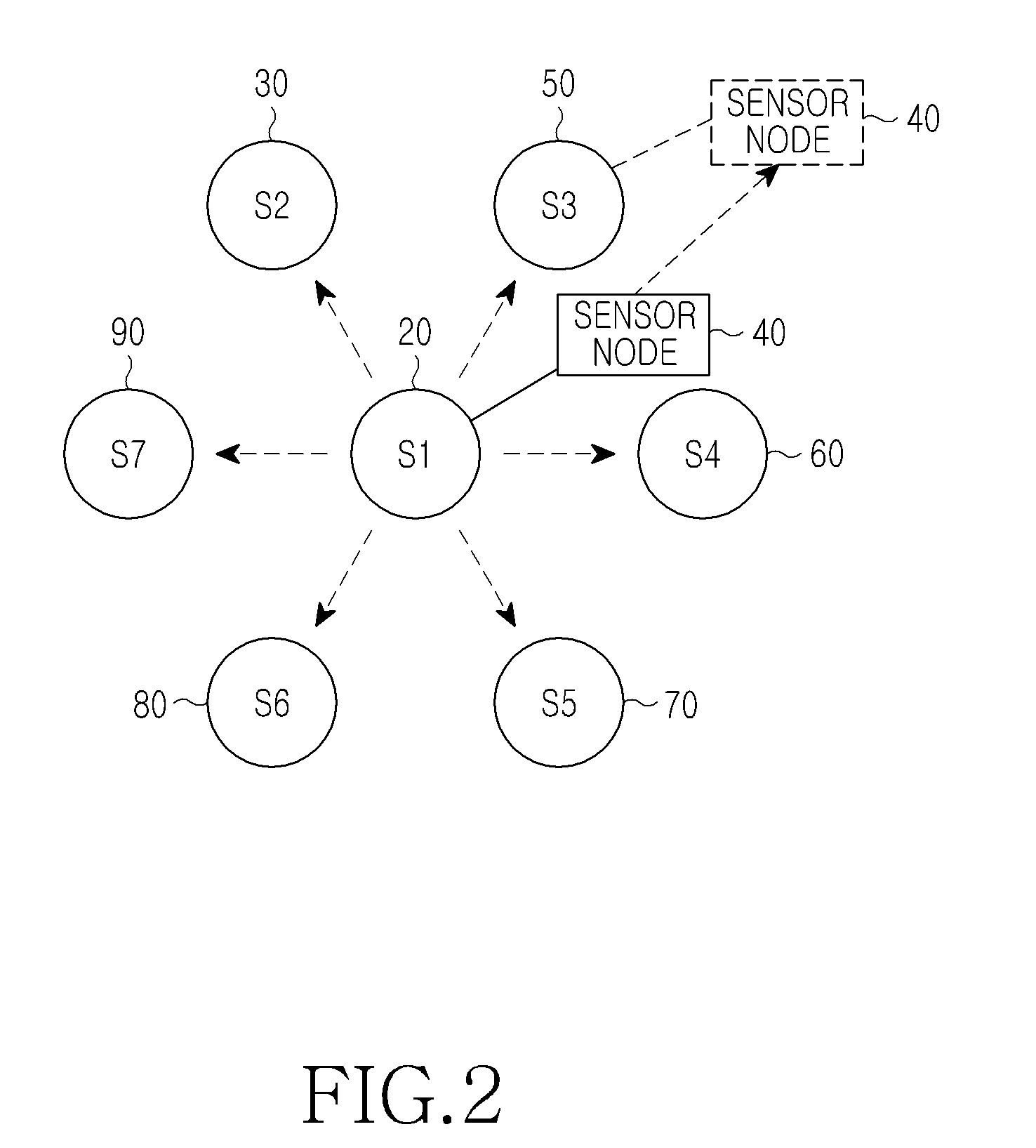
Method and apparatus for authenticating a sensor node in a sensor network
ActiveUS20100332831A1Efficiently reauthenticateFast authenticationDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationSensor nodeGroup key
A method and apparatus for authenticating a sensor node in a sensor network. The method for authenticating a sensor node by a first sink node in a sensor network includes receiving an authentication request using an authentication ticket from the sensor node, identifying a second sink node which has issued the authentication ticket, decoding the authentication ticket using a group key, which is previously stored in correspondence to the second sink node to confirm the validity of the authentication ticket, when the second sink node is included in a neighboring node list, normally processing authentication for the sensor node, generating an authentication ticket using a group key of the first sink node, and transmitting the generated authentication ticket to the sensor node.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Secure Key Management in Conferencing System
InactiveUS20110051912A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCommunications systemConference management
Principles of the invention provide one or more secure key management protocols for use in a communication environment such as a conferencing system. For example, a method for managing a conference between two or more parties in a communication system comprises the following steps. An identity based authenticated key exchange operation is performed between a conference management element of the communication system and each of the two or more parties seeking to participate in the conference, wherein messages exchanged between the conference management element and the two or more parties are encrypted based on respective identities of recipients of the messages, and further wherein the conference management element receives from each party during the key authentication operation a random key component that is computed based on a random number selected by the party. The conference management element sends to each party a set comprising the random key components computed by the parties. The conference management element receives from each party a random group key component, wherein the random group key component is computed by each party via a computation based on the random number used by the party during the key authentication operation and the random key components computed by a subset of others of the two or more parties seeking to participate in the conference. The conference management element sends to each party a set comprising the random group key components computed by the parties such that each party can compute the same group key for use in communicating with each other party through the conference management element.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Device authentication method using broadcast encryption (BE)
InactiveUS20080010242A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationAuthentication serverBroadcasting
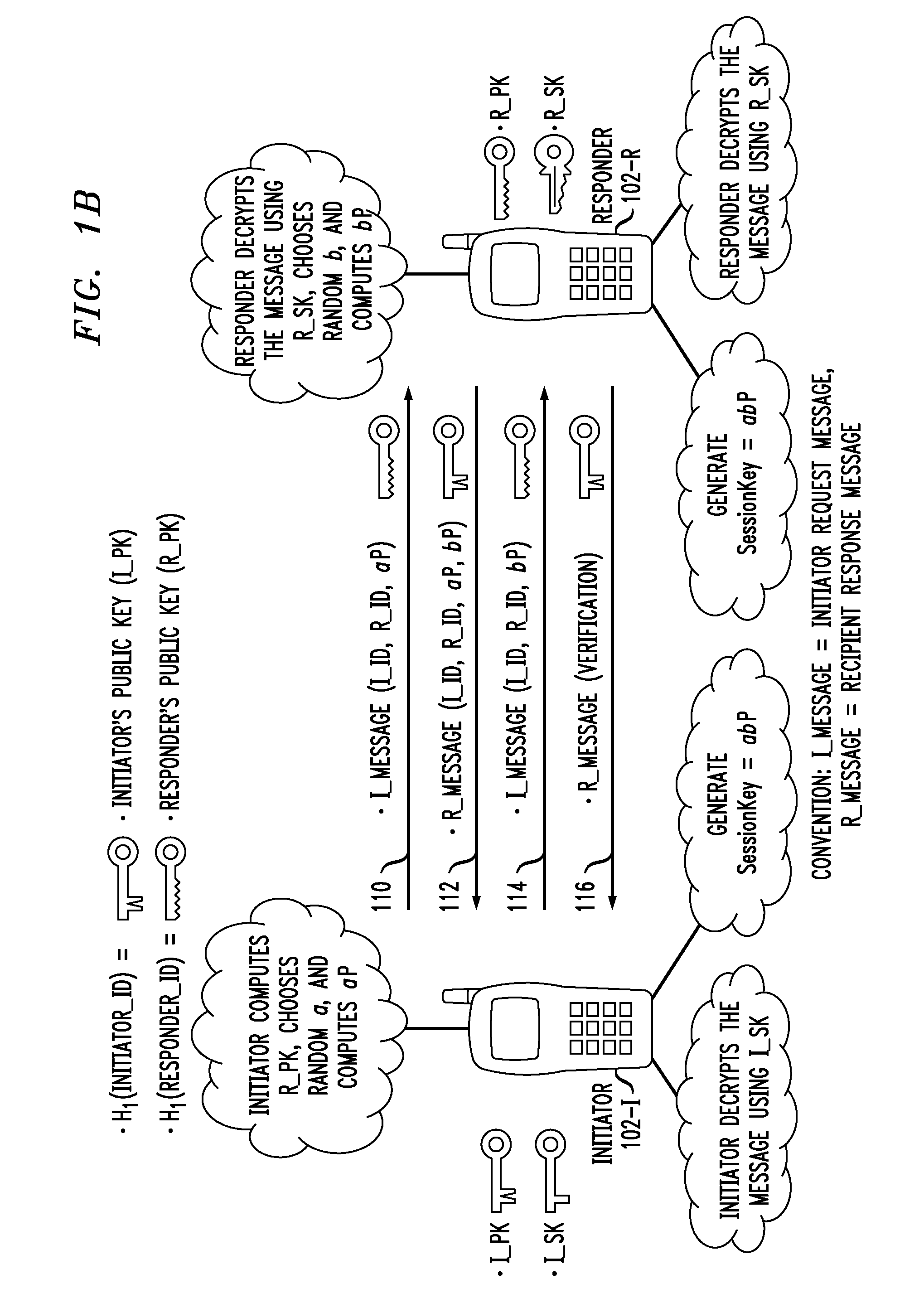
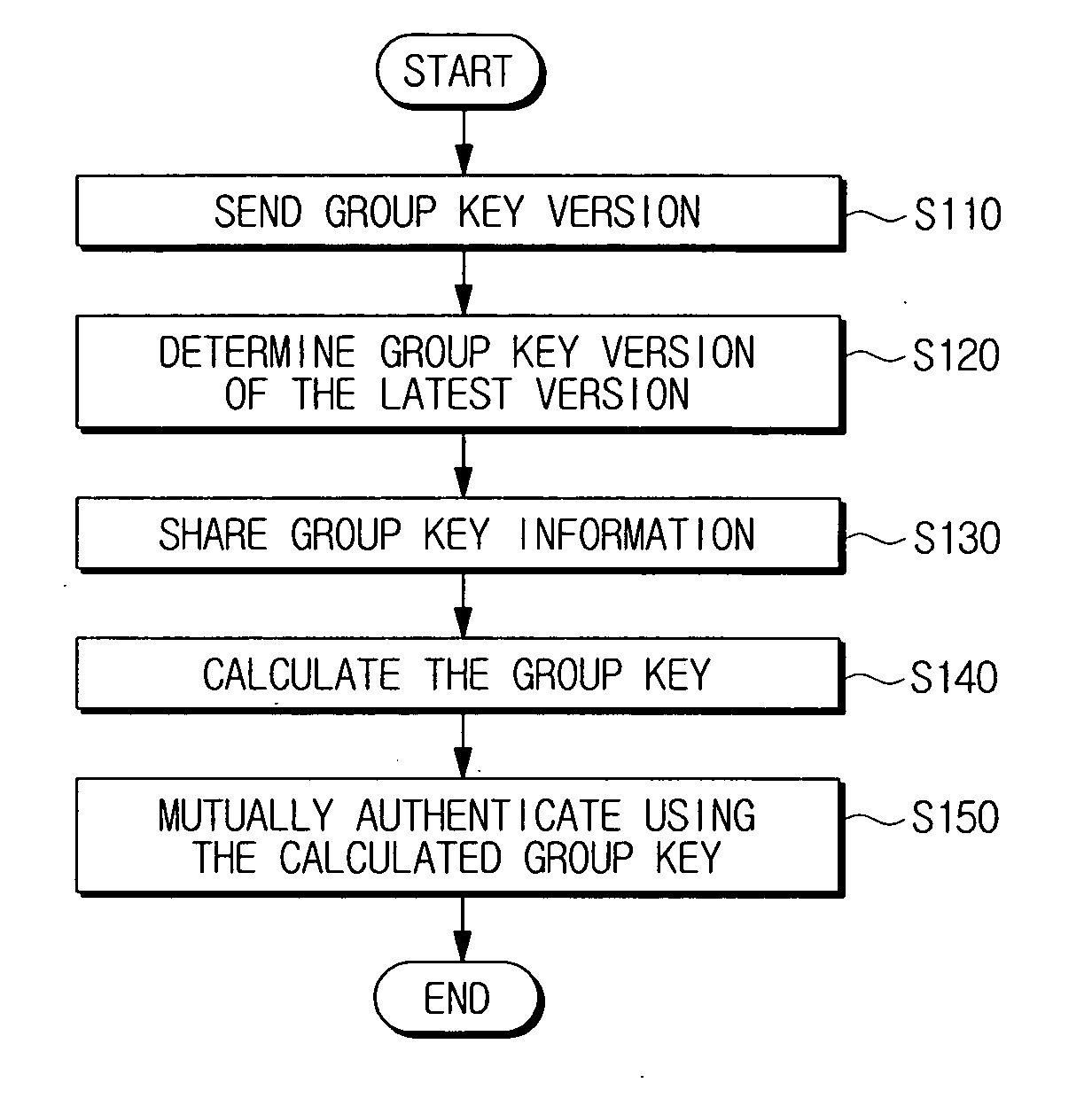
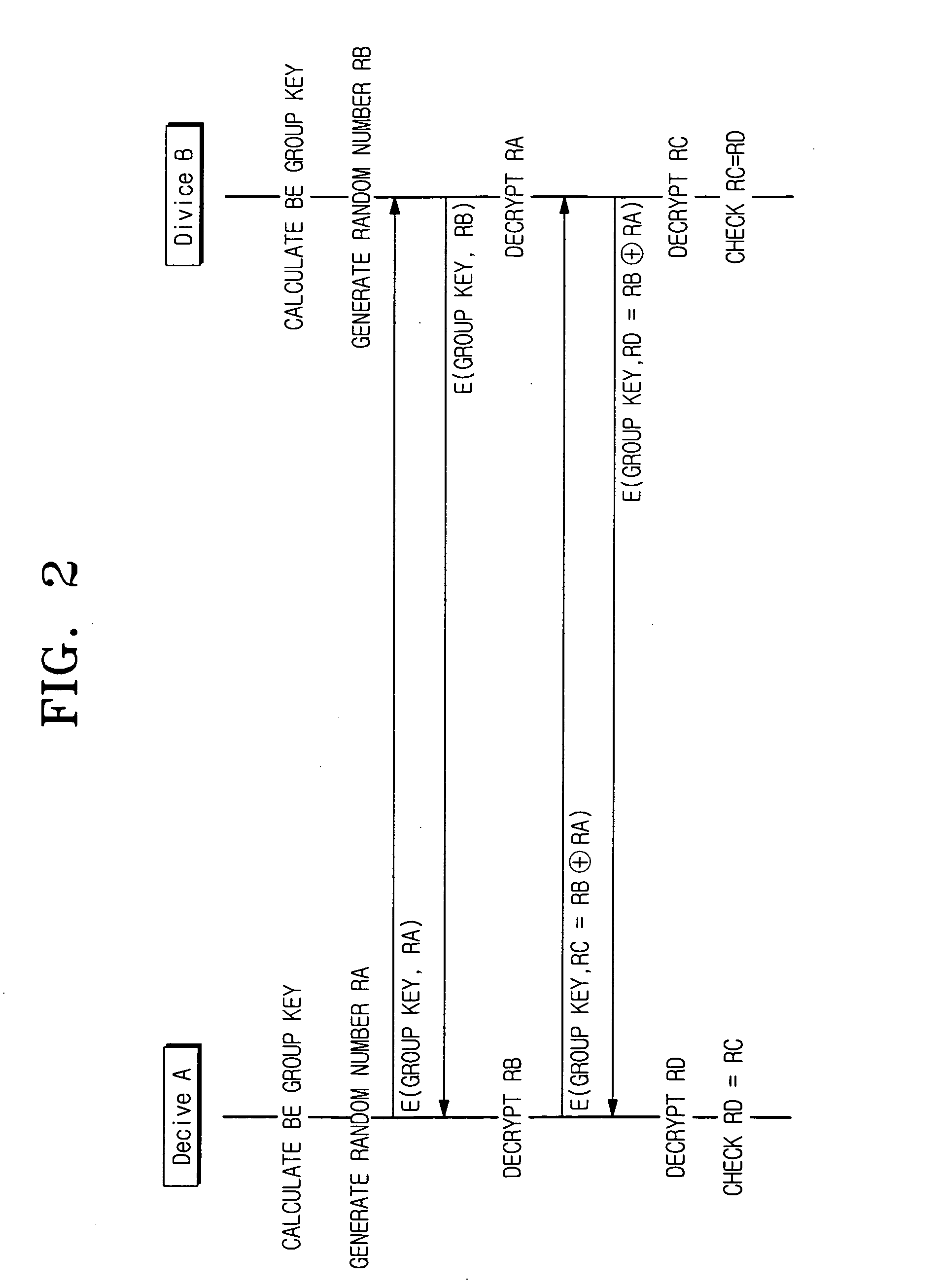
A device authentication method using broadcast encryption is provided, in which, a hash value corresponding to a group key version is generated, the generated hash value is encrypted with a group key, group key information comprising the encrypted hash value is generated, and the generated group key information including a signature of an authentication server for the group key information is transmitted. Accordingly, mutual authentication is accomplished by using the group key version including in the group key information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method, equipment and system for updating group cipher key
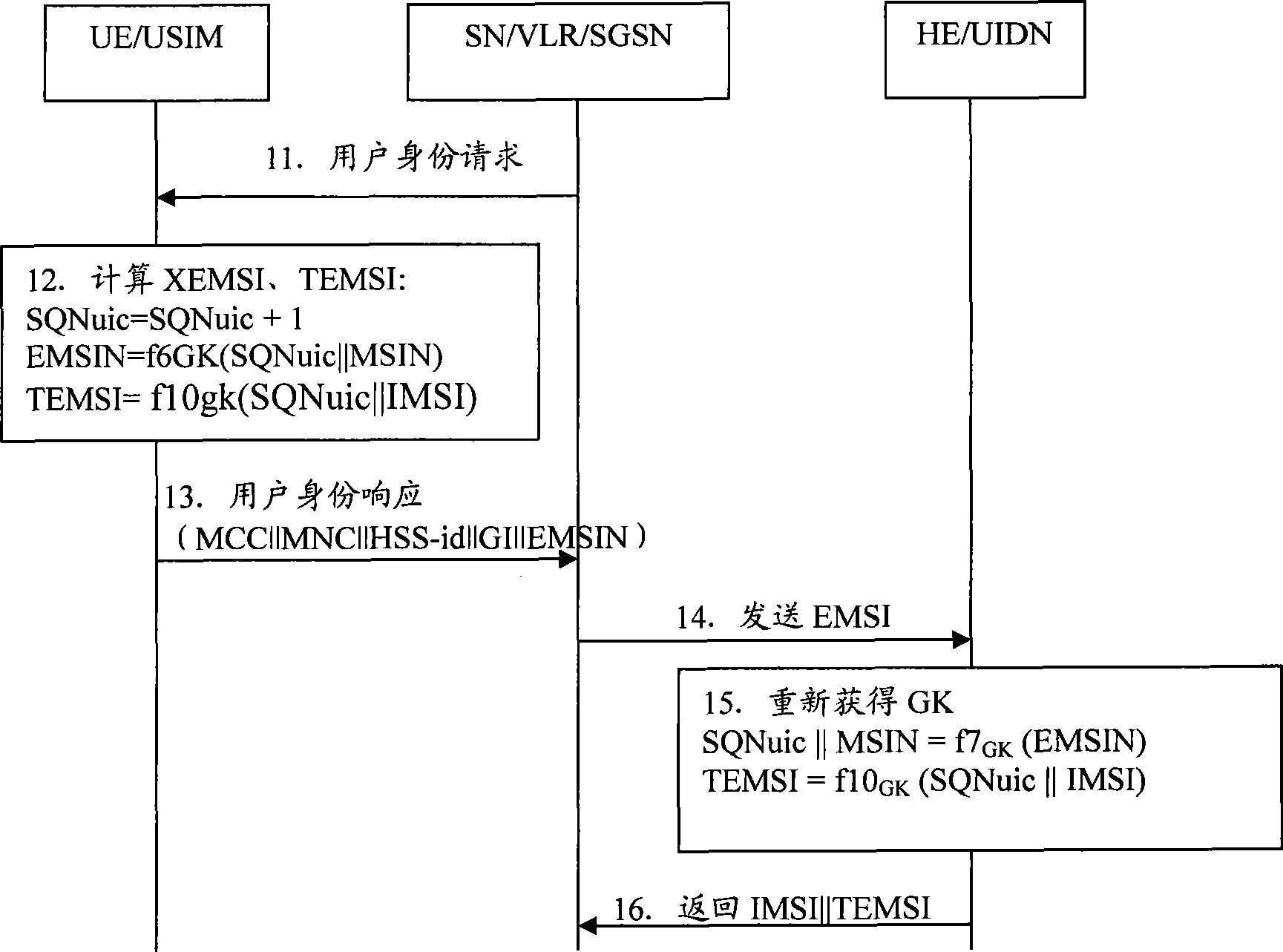
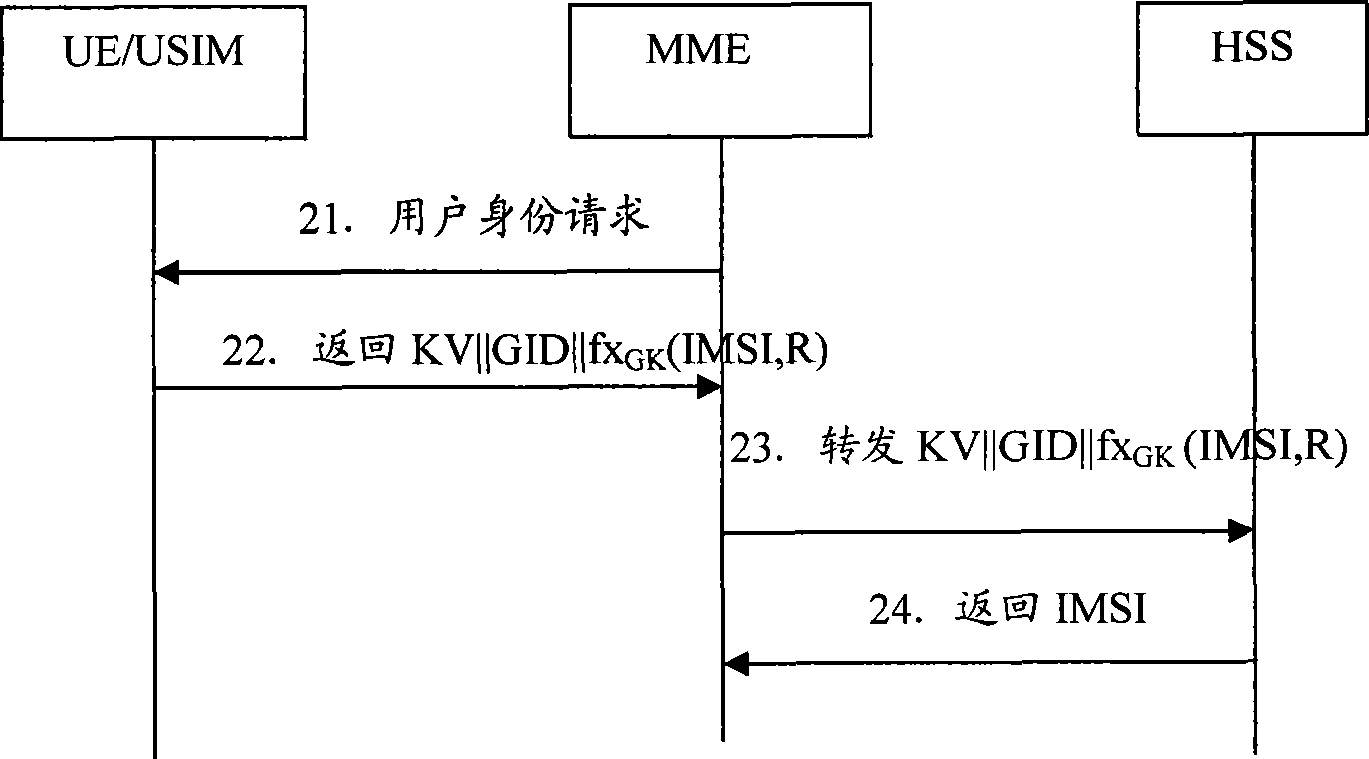
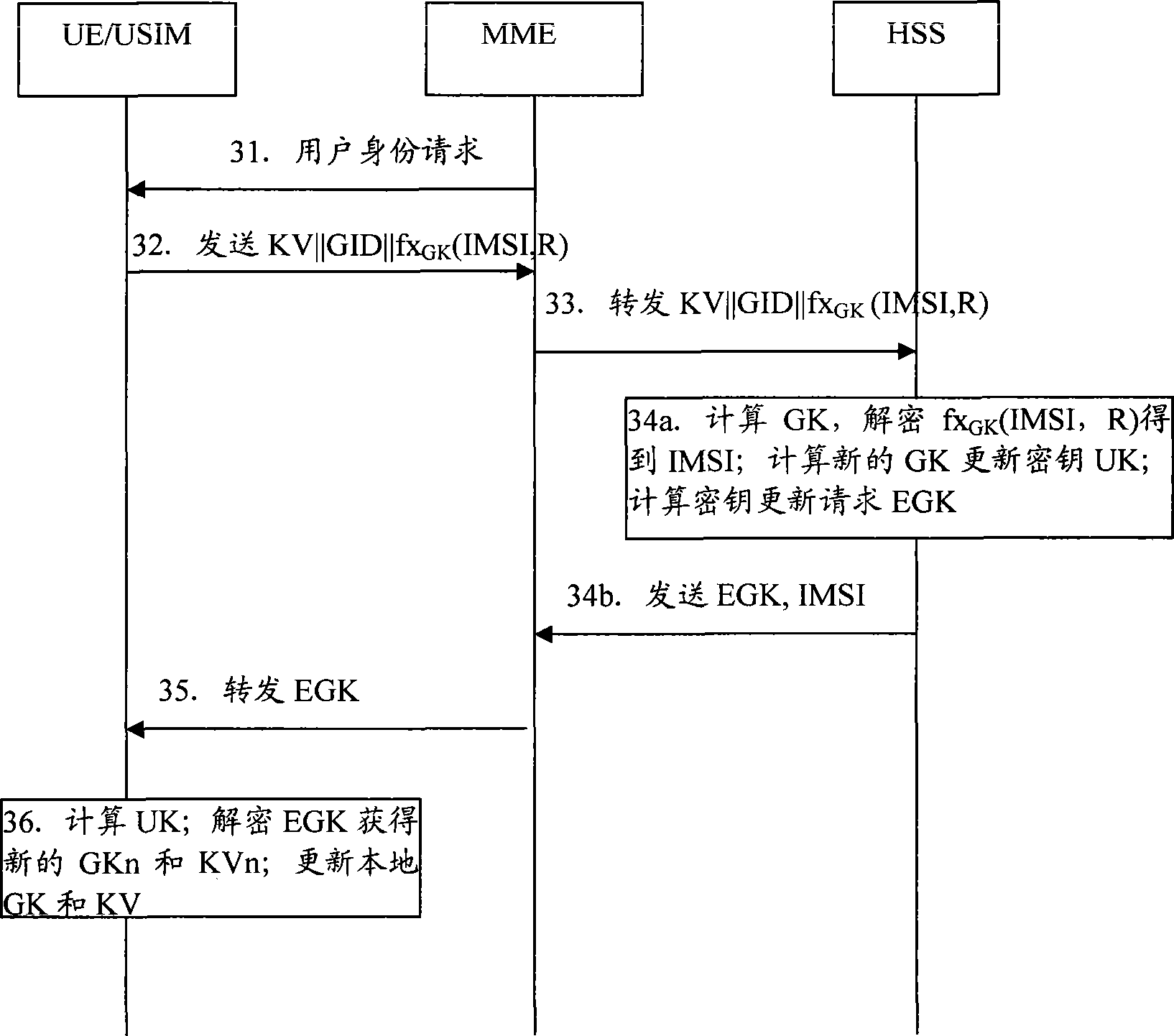
ActiveCN101511082AReduce the Threat of ExposureReduce guessworkSecurity arrangementCommunications systemUser equipment
The invention discloses a method for updating group key which includes steps as follows: an attribute network entity obtains GK according with a version number KV of a group sign GID and a group key GK, and a local boot key SK(GID) for deciphering an internal mobile user identifying code IMSI encrypted by GK provided by an user equipment; the attribute network entity generates new group key GKn according with GID, KVn, SK(GID) when KV differs from the local version number KVn; the attribute network entity generates updating key UK according with IMSI, user's authentication key K, uses UK for encrypting GID, KVn and GKn, and providing to an user equipment; the user equipment generates UK according with IMSI, K, deciphers out GID, KVn and GKn, updates the group key GK and the version number KV. The invention also discloses the attribute network entity and a communication system. The method can improve IMSI security and solve threaten of exposing IMSI.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com