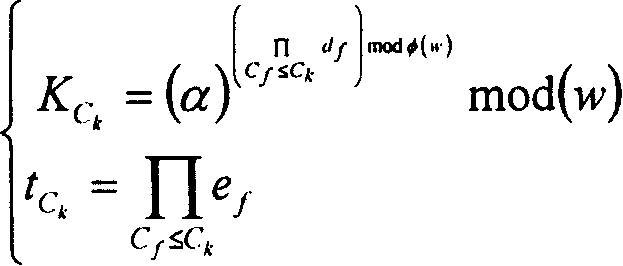Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
65 results about "Key tree" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
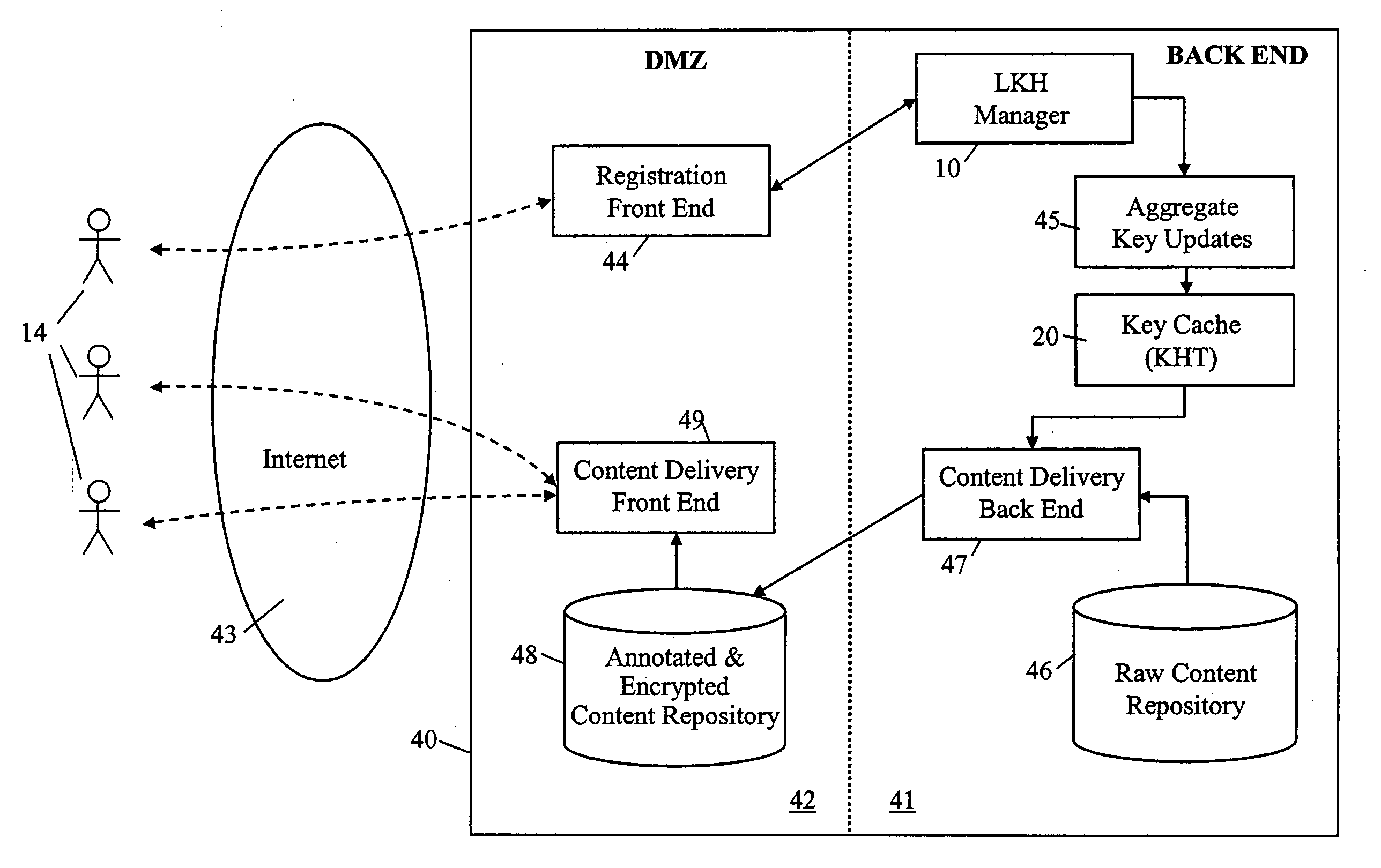
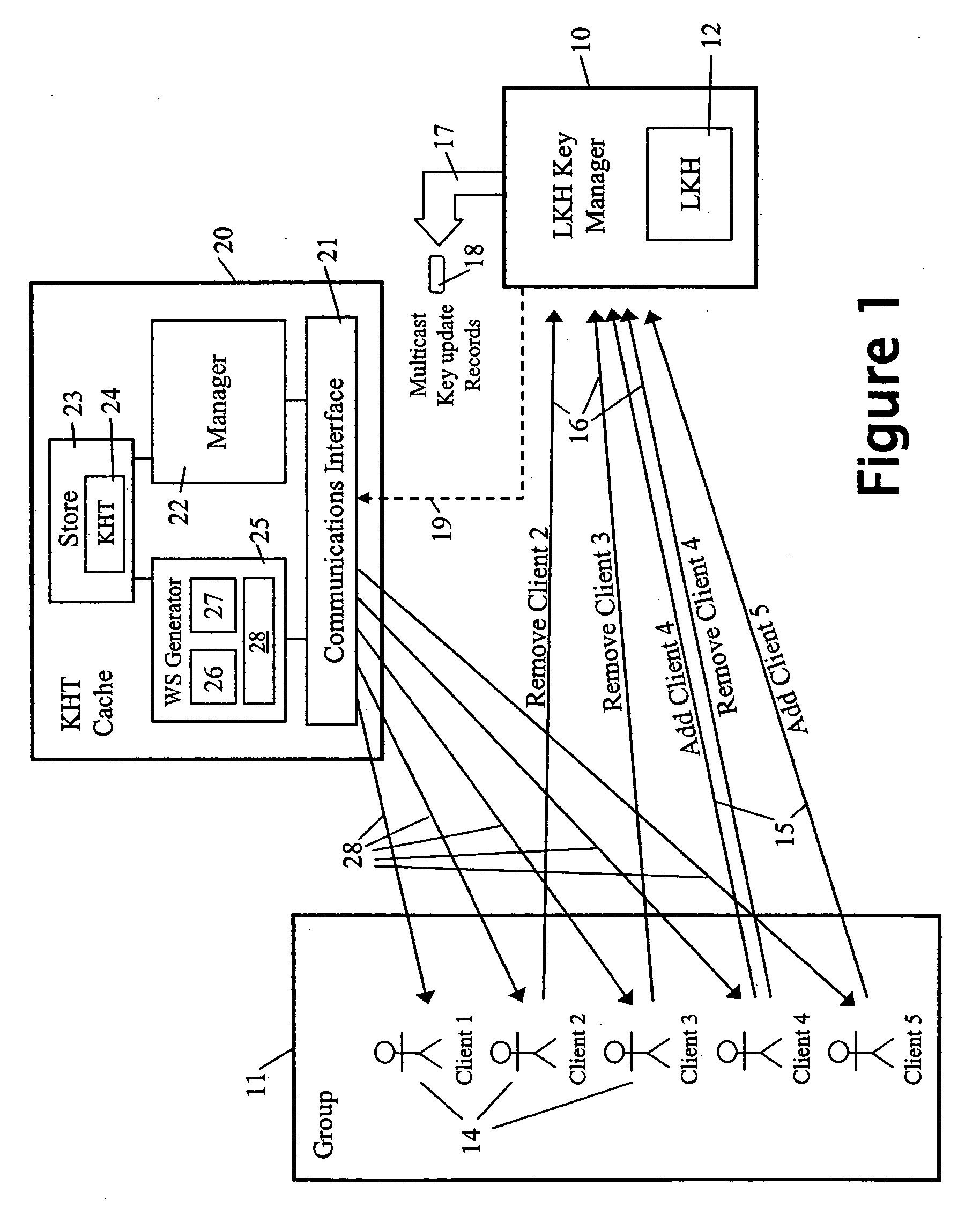
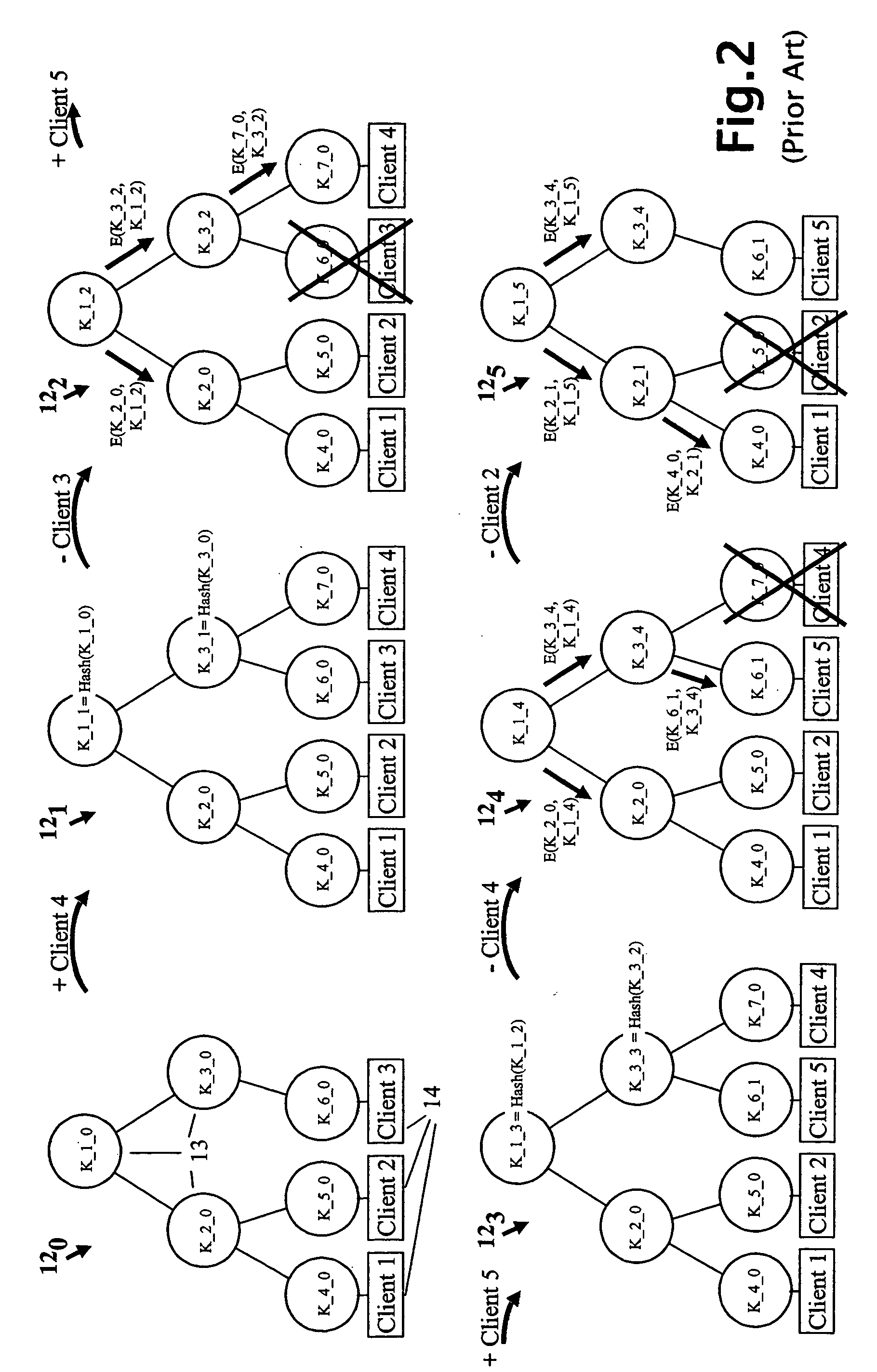
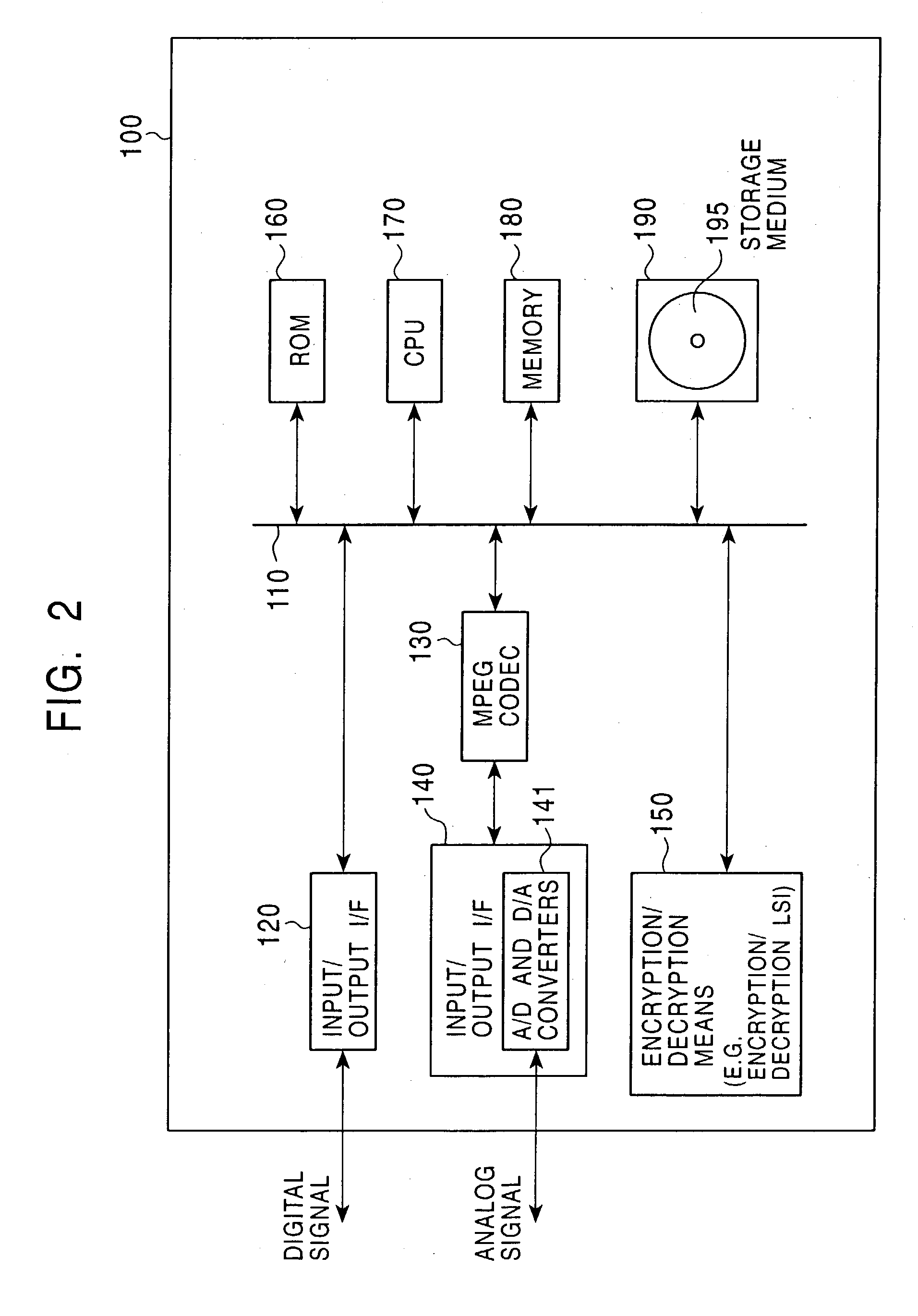
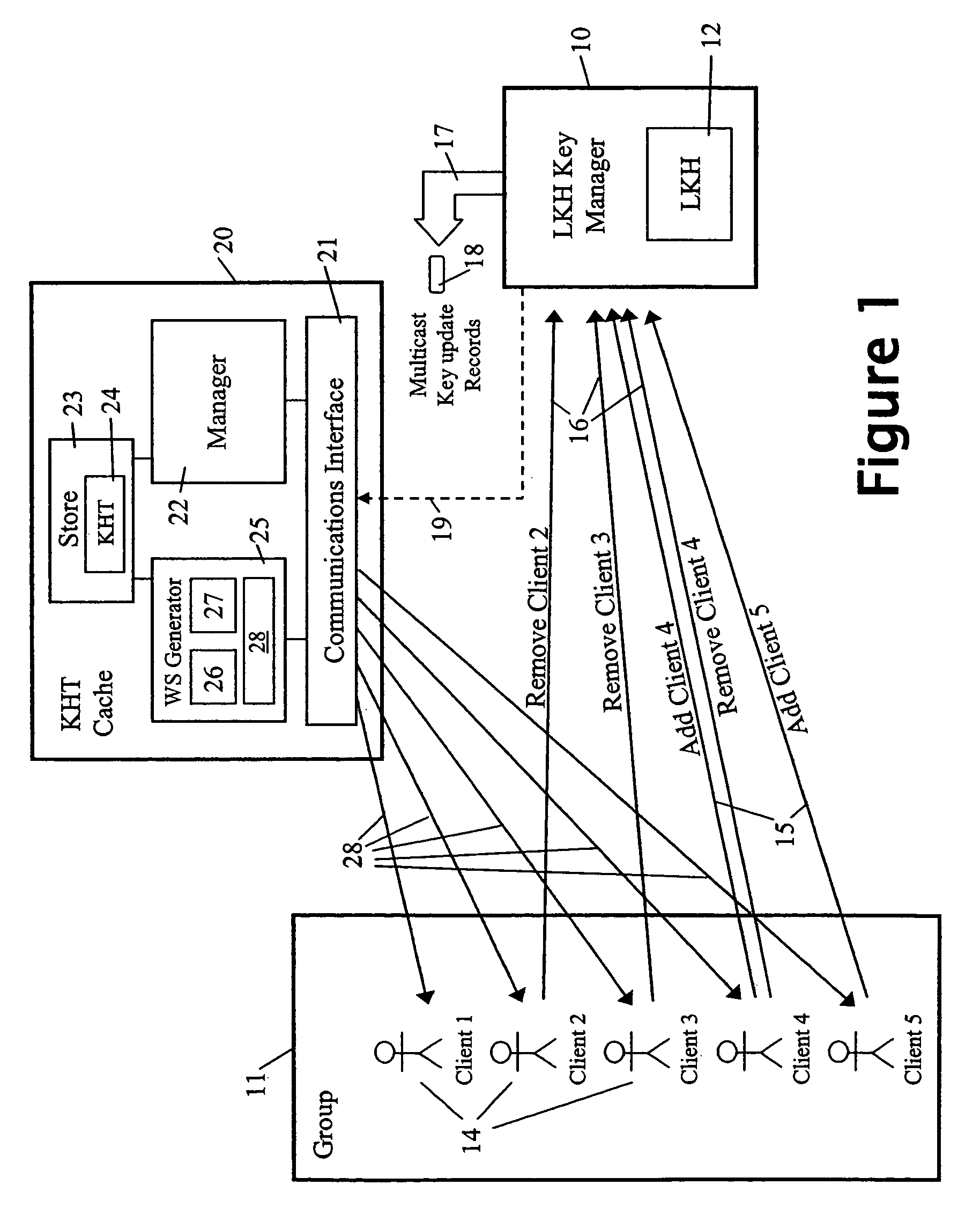
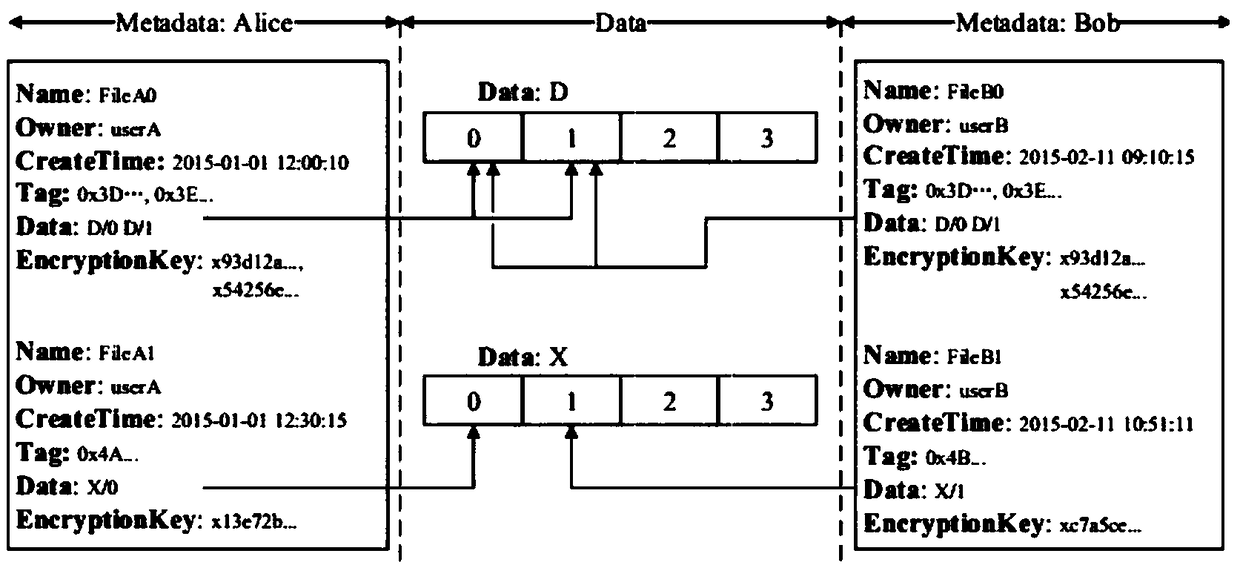
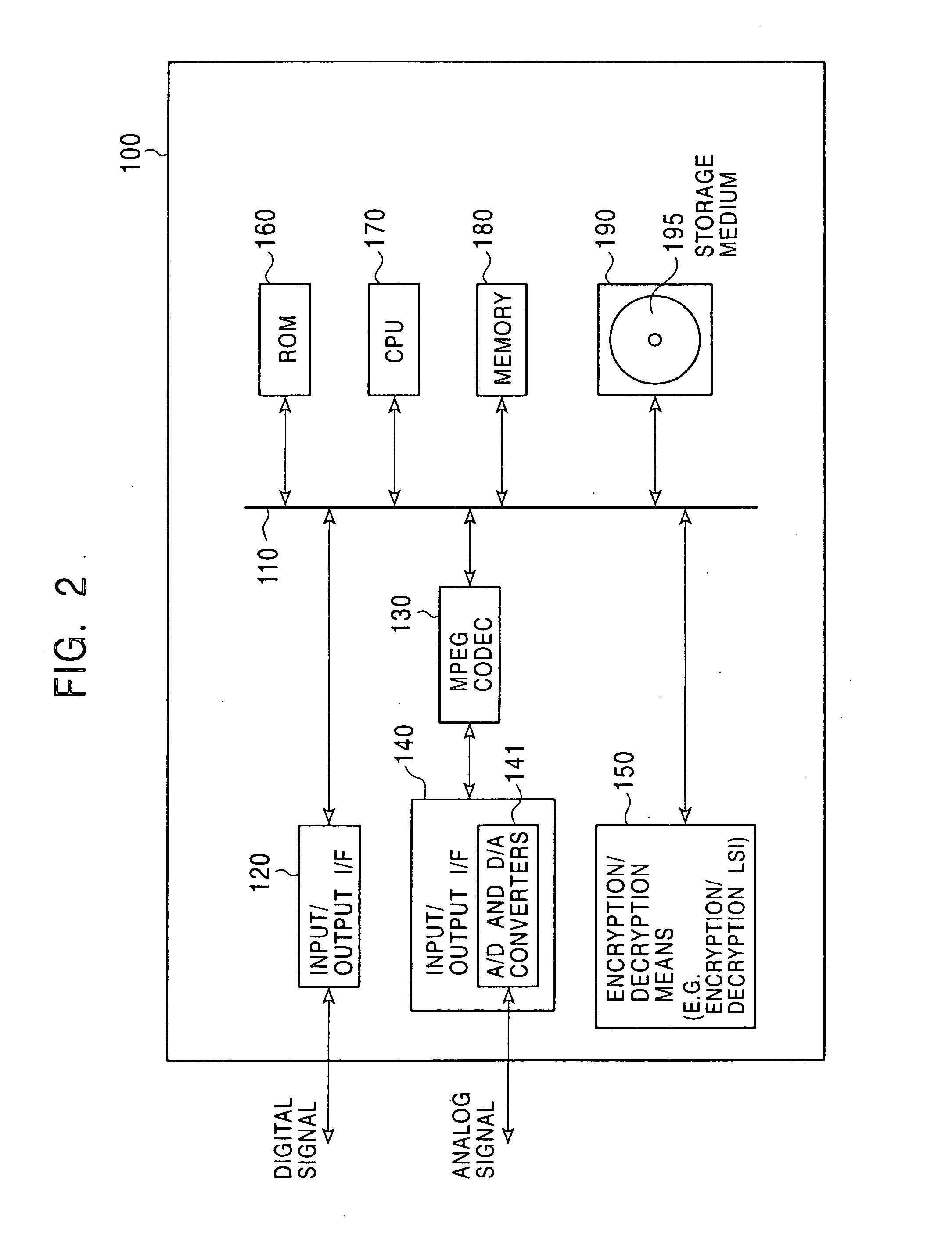
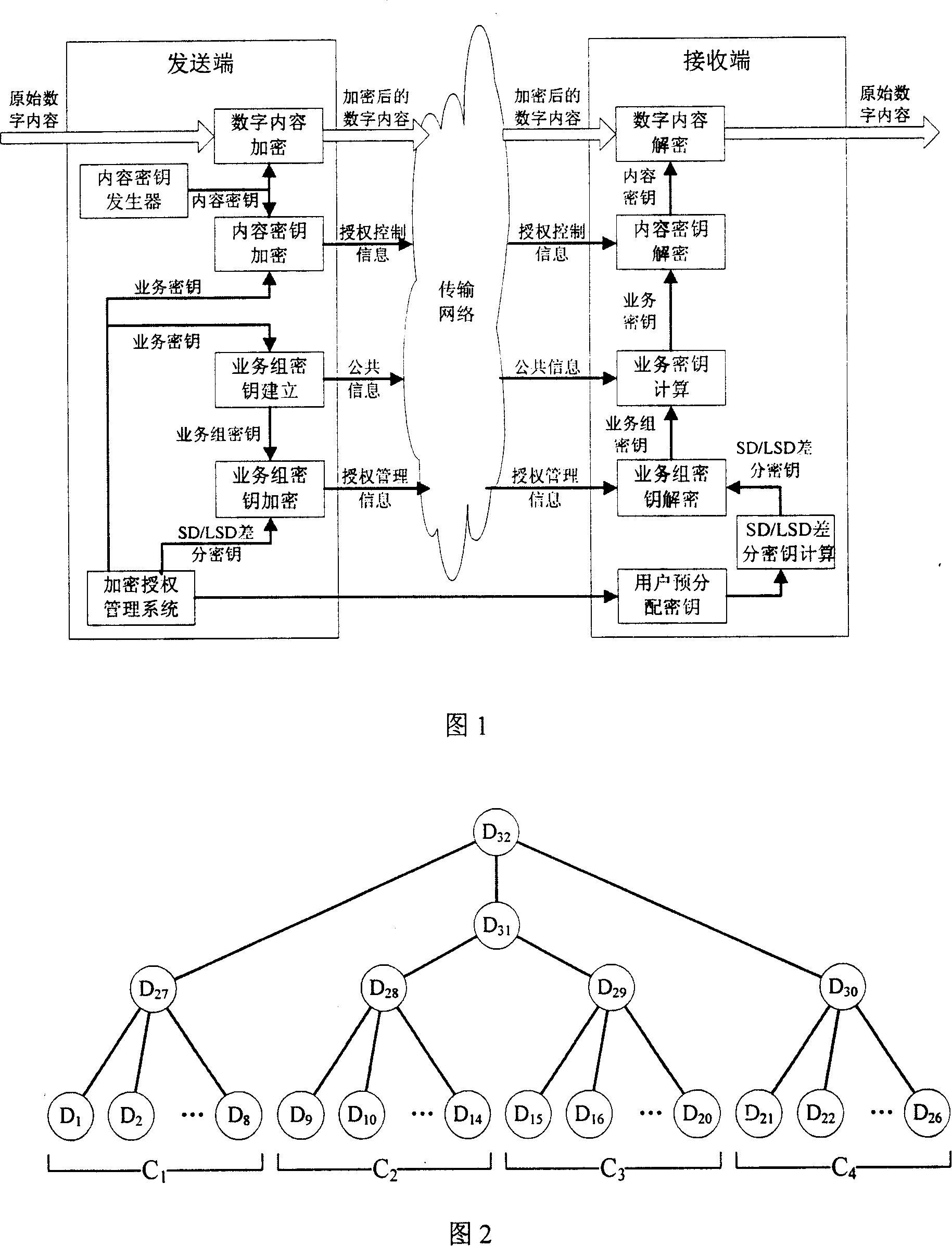
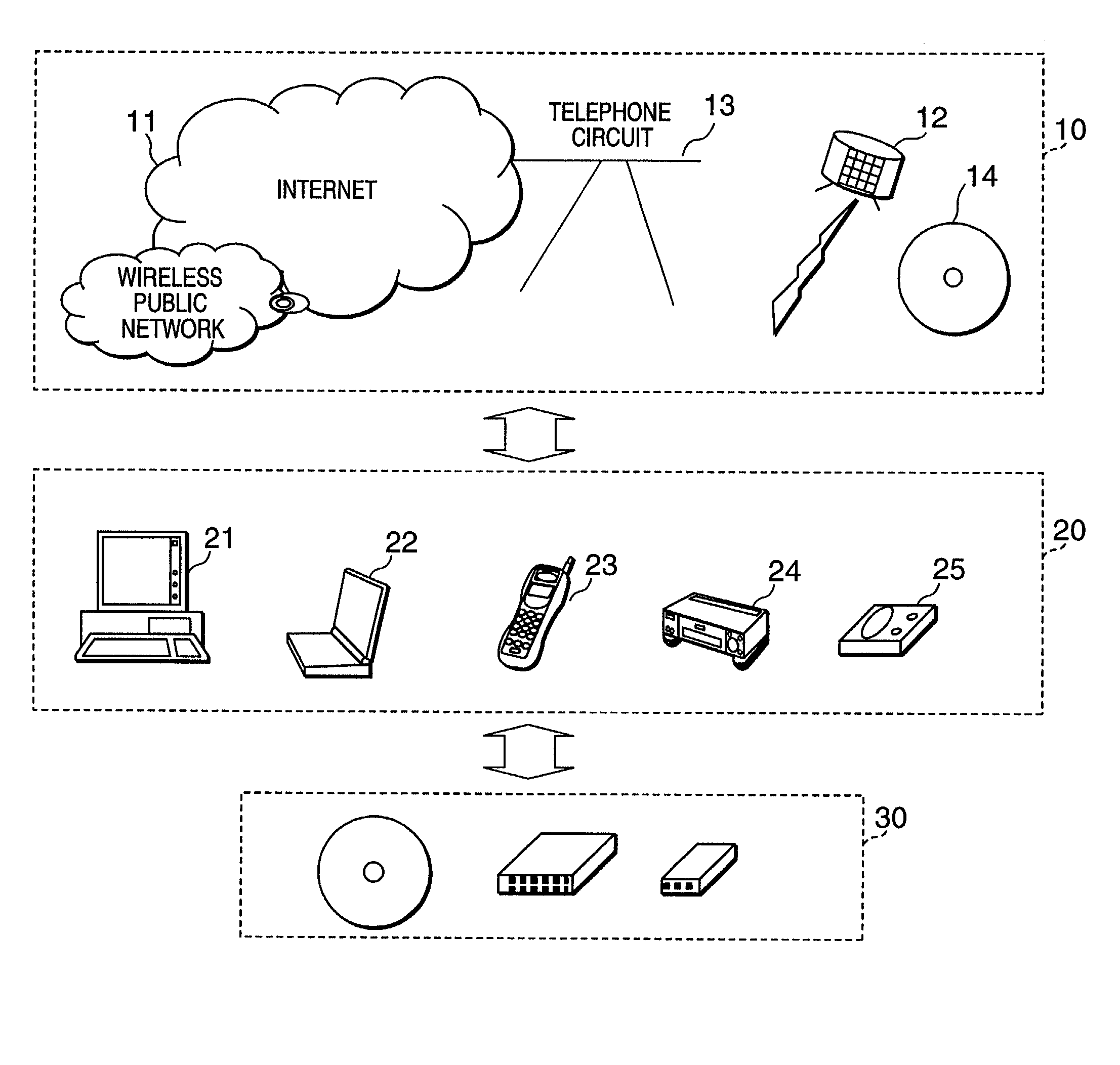
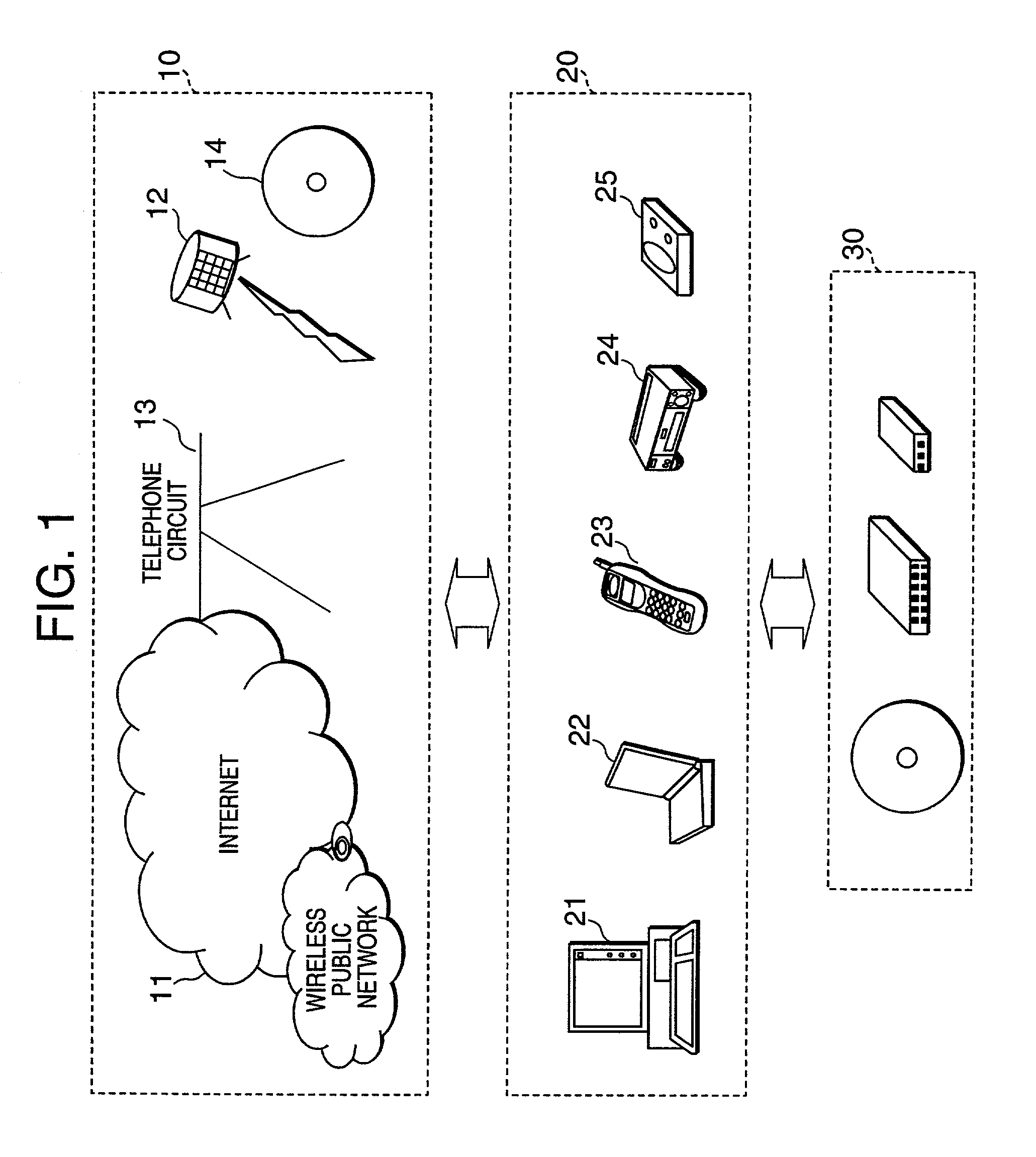
Cryptographic key update management method and apparatus
ActiveUS20050018853A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationMostly TrueRekeying
A method and apparatus is provided for consolidating cryptographic key updates, the consolidated update information enabling, for example, a returning member of a secure group who has been offline, to recover the current group key, at least in most cases. The unconsolidated key updates each comprise an encrypted key, corresponding to a node of a key hierarchy, that has been encrypted using a key which is a descendant of that node. The key updates are used to maintain a key tree with nodes in this tree corresponding to nodes in the key hierarchy. Each node of the key tree is used to store, for each encrypting key used in respect of the encrypted key associated with the node, the most up-to-date version of the encrypted key with any earlier versions being discarded. The key tree, or a subset of the tree, is then provided to group members.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
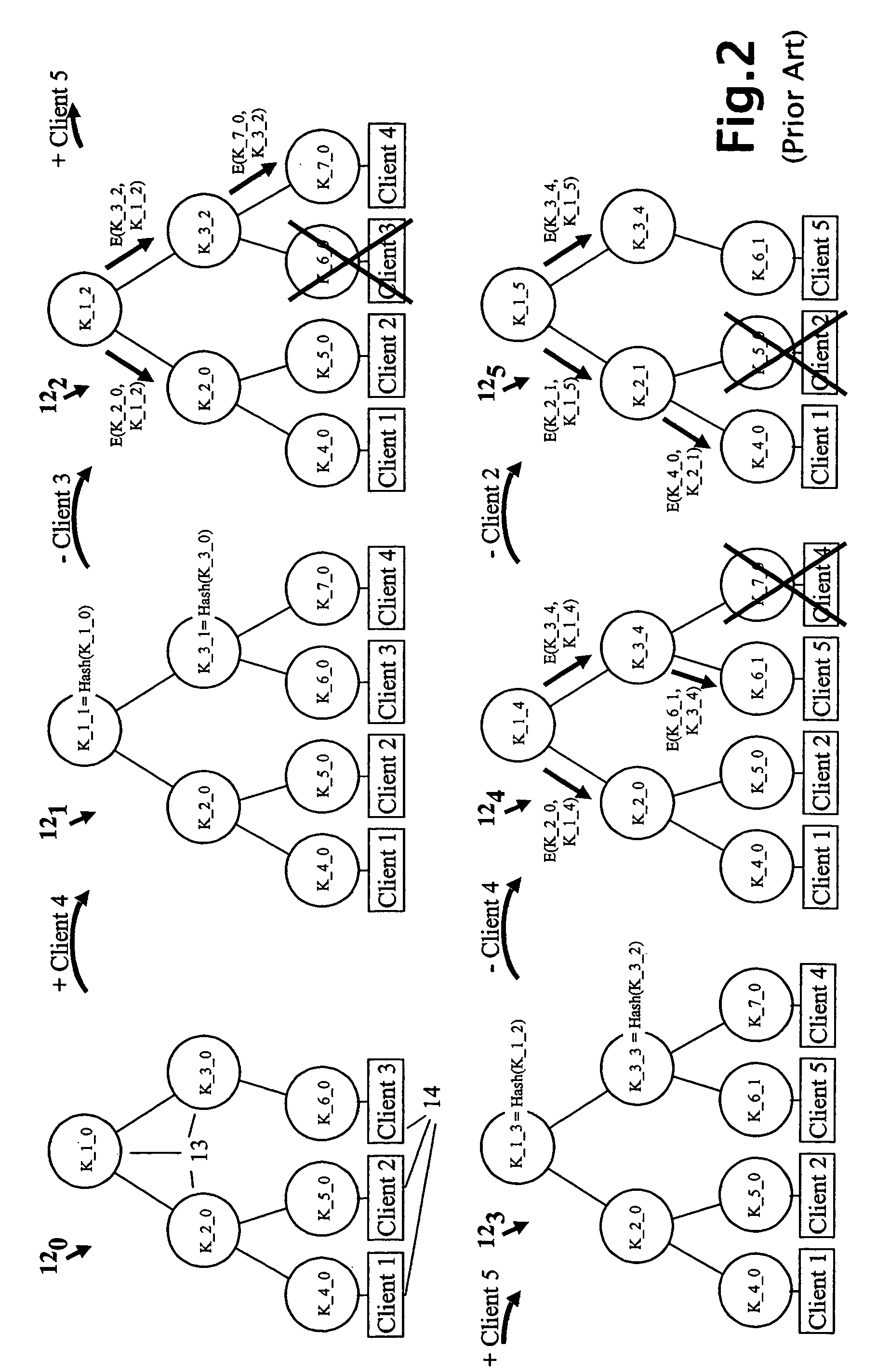
Last hop topology sensitive multicasting key management
ActiveUS20070140245A1Data switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsComputer networkMulticast address
Owner:FOUR BATONS WIRELESS LLC +1
Information processing system and method
InactiveUS7346170B2Secure transmissionReduce data sizeKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationInformation processingTheoretical computer science
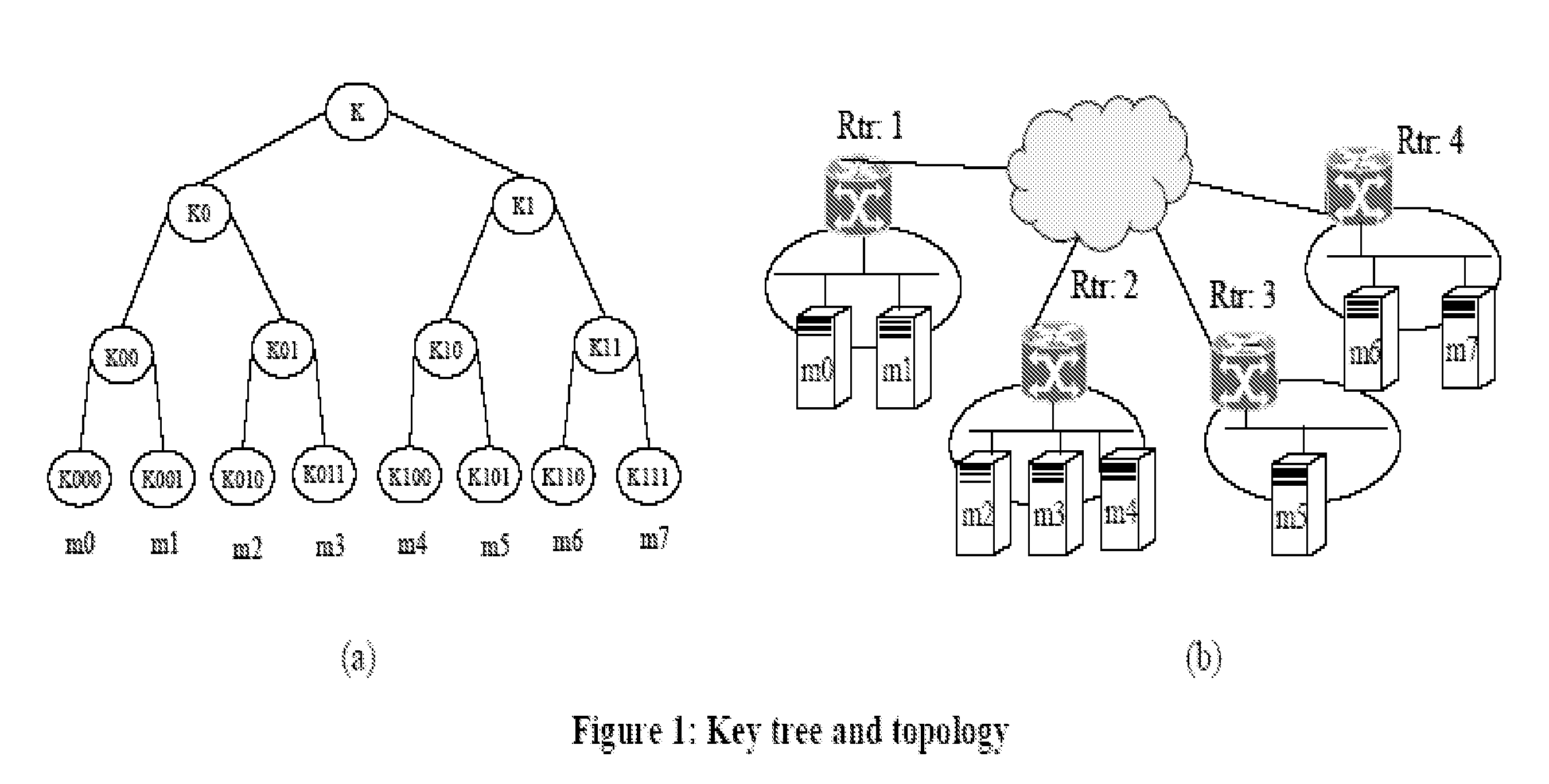
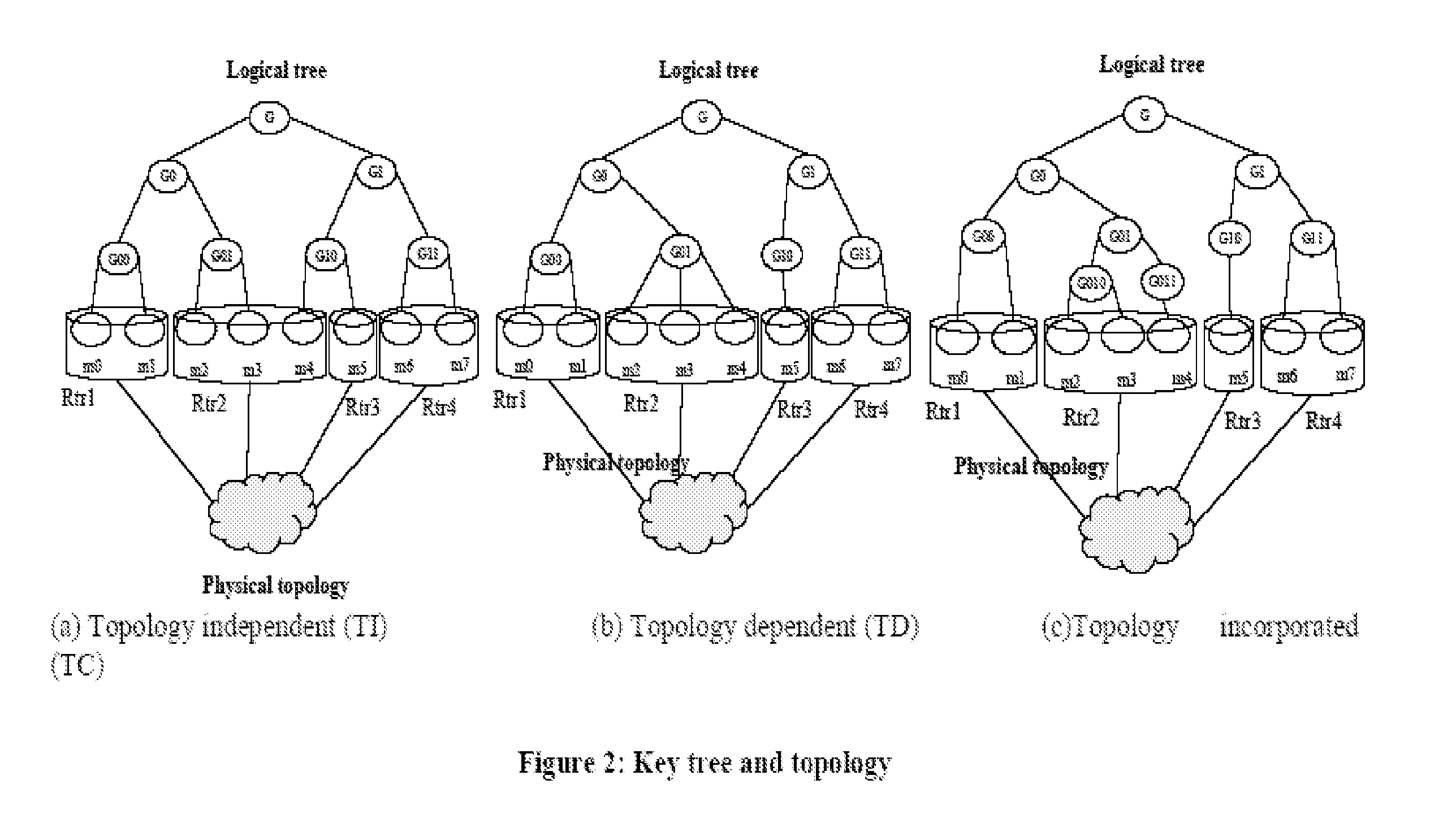
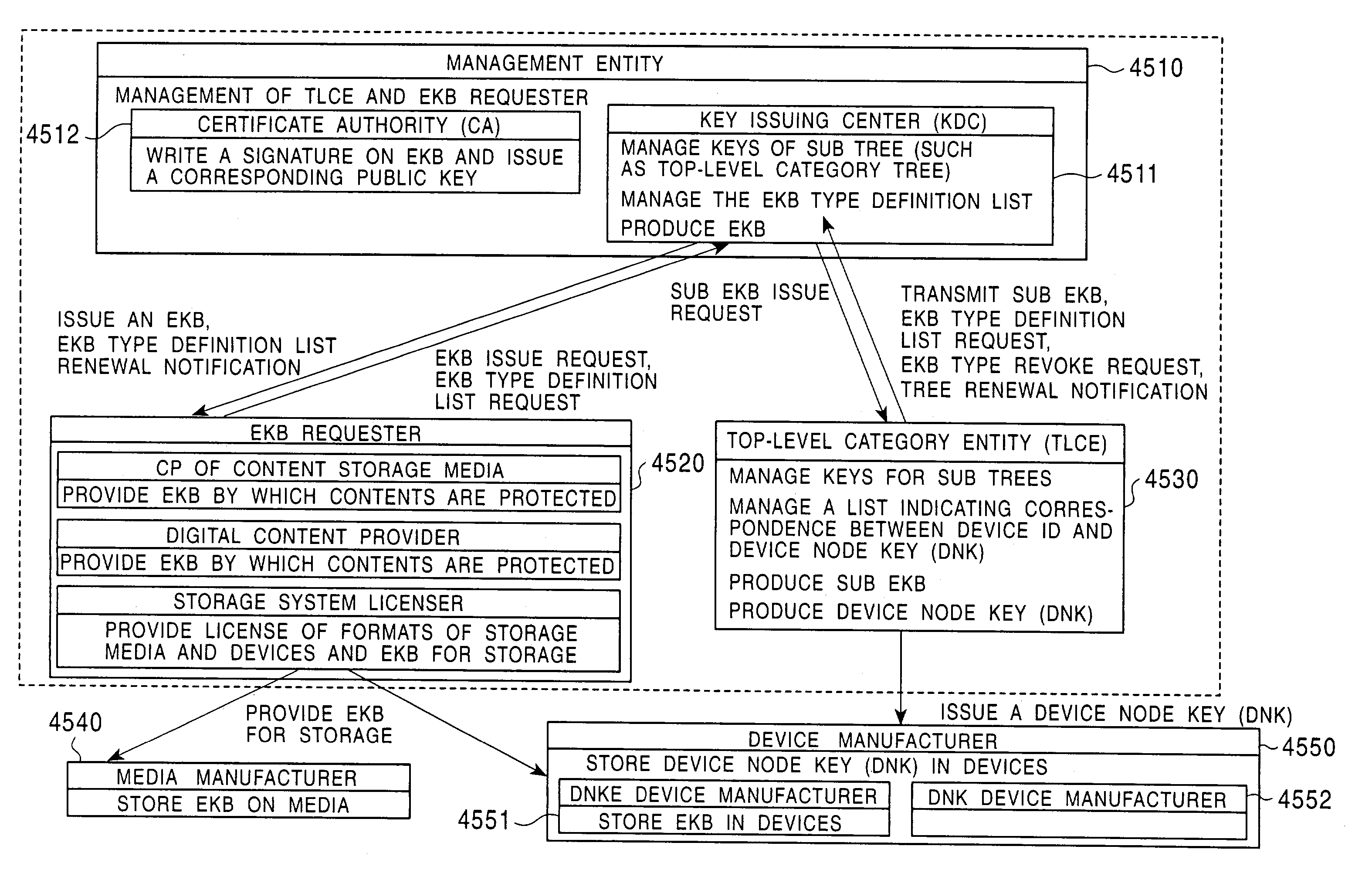
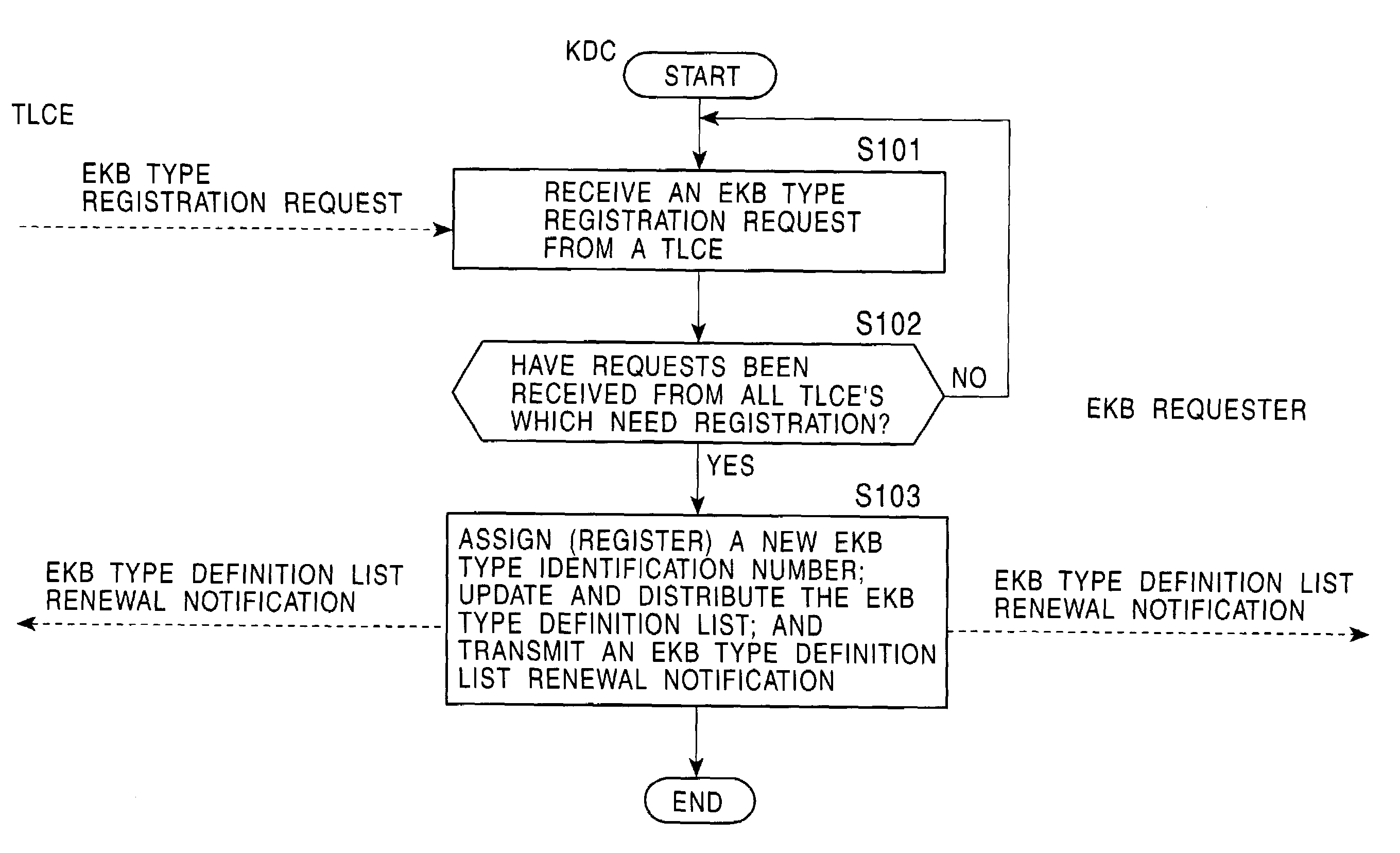
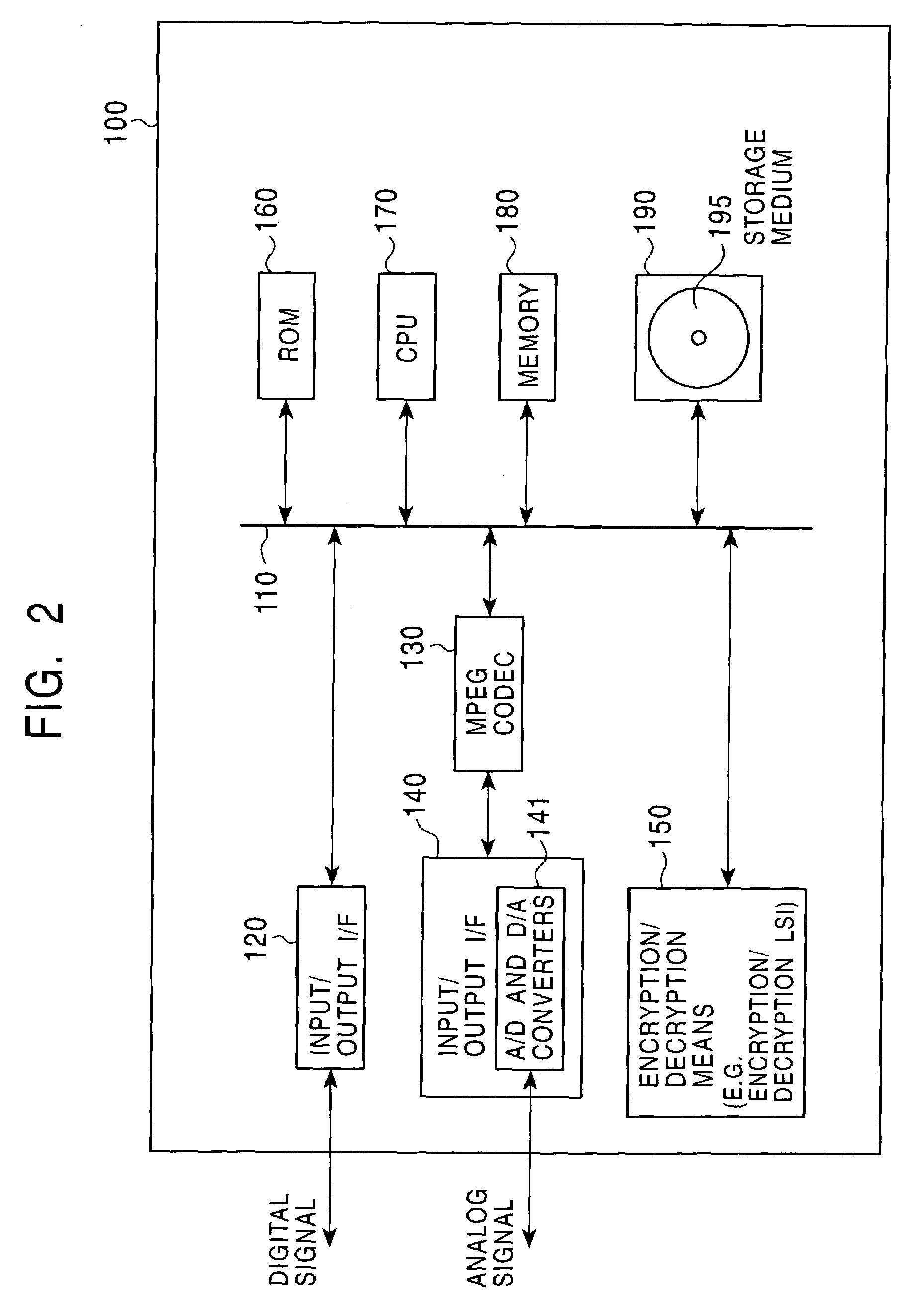
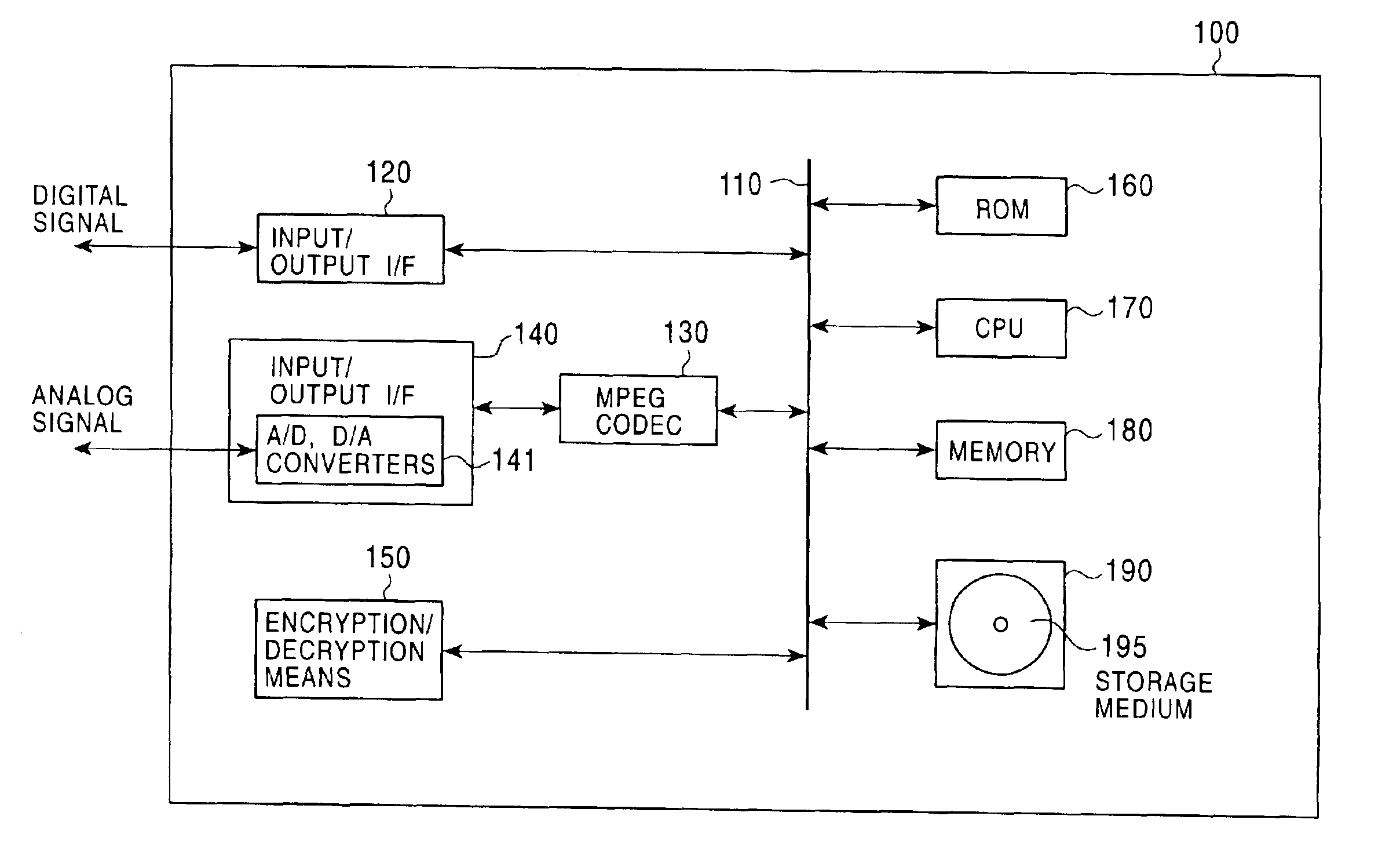
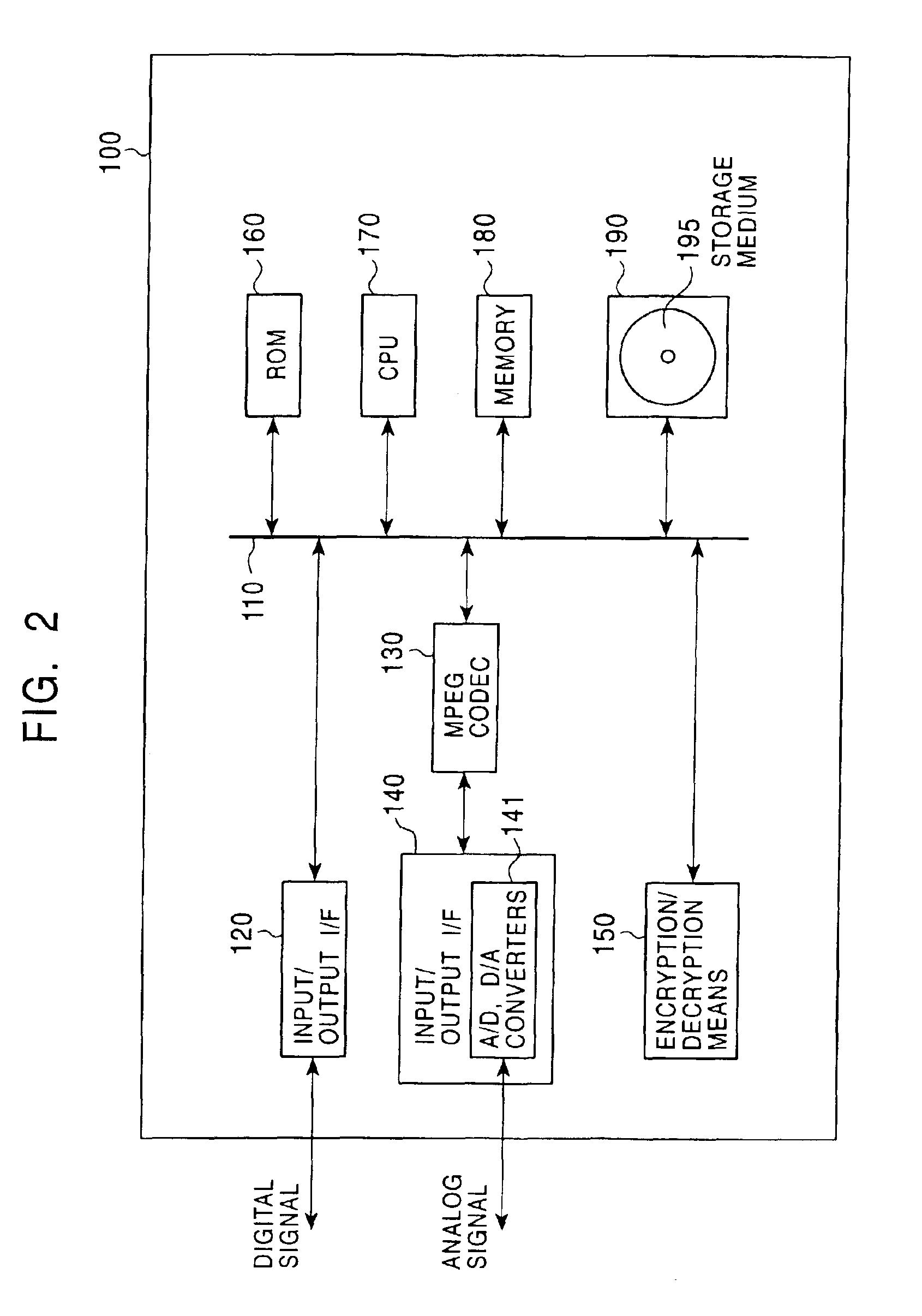
An information processing system and method are disclosed in which information processing is performed using an enabling key block (EKB) in association with a tree structure including category subtrees. A key tree is produced, which include subtrees that are grouped in accordance with categories and are managed by category entities. The EKB includes data produced by selecting a path in the key tree and encrypting a higher-level key in the selected path using a lower-level key in the selected path. The EKB is then provided to a device. A requester, which requests production of the EKB, may produce a root key or may request a key distribution center (KDC) to produce a root key. If the (KDC) produces the EKB, it may also request a category entity to produce a sub-EKB.
Owner:SONY CORP
Information processing system and method
InactiveUS7167564B2Secure transmissionPossible to useKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageInformation processingTheoretical computer science
An information processing system and method are disclosed in which information processing is performed in a highly efficient manner using an enabling key block (EKB) on the basis of a tree structure including category subtrees. A key tree is produced so as to include a plurality of subtrees that are grouped in accordance with categories and managed by category entities. An EKB is produced so as to include data produced by selecting a path in the key tree and encrypting an upper-level key in the selected path using a lower-level key in the selected path. The resultant EKB is provided to a device. If a change occurs in state of a category tree capable of processing an EKB identified in the EKB type definition list, a notification of the change in state is sent to an entity that uses the EKB thereby making it possible for an EKB requester to perform processing in accordance with a newest EKB.
Owner:SONY CORP
Information Processing Apparatus, Information Recording Medium Manufacturing Apparatus, And Information Recording Medium
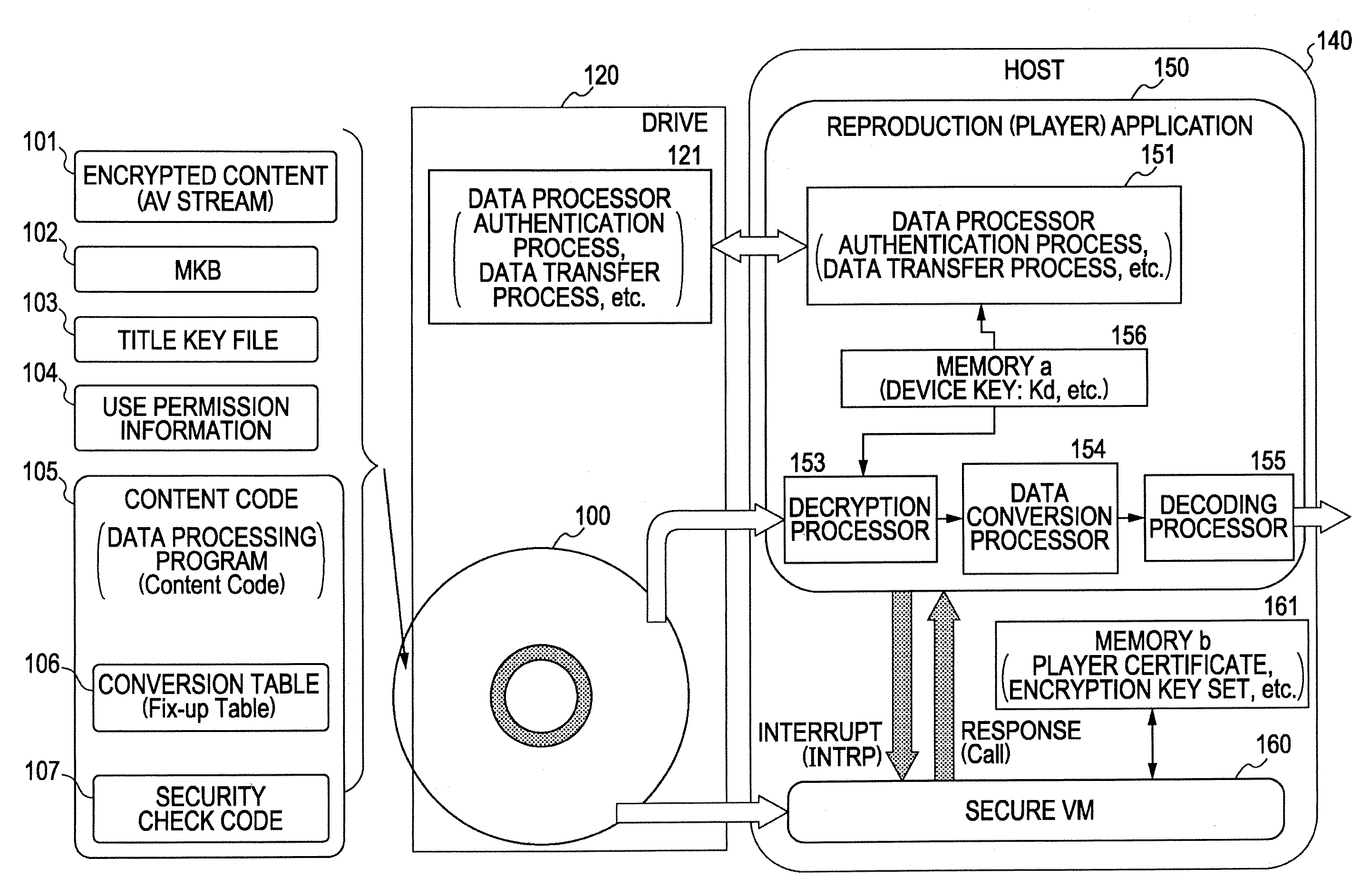
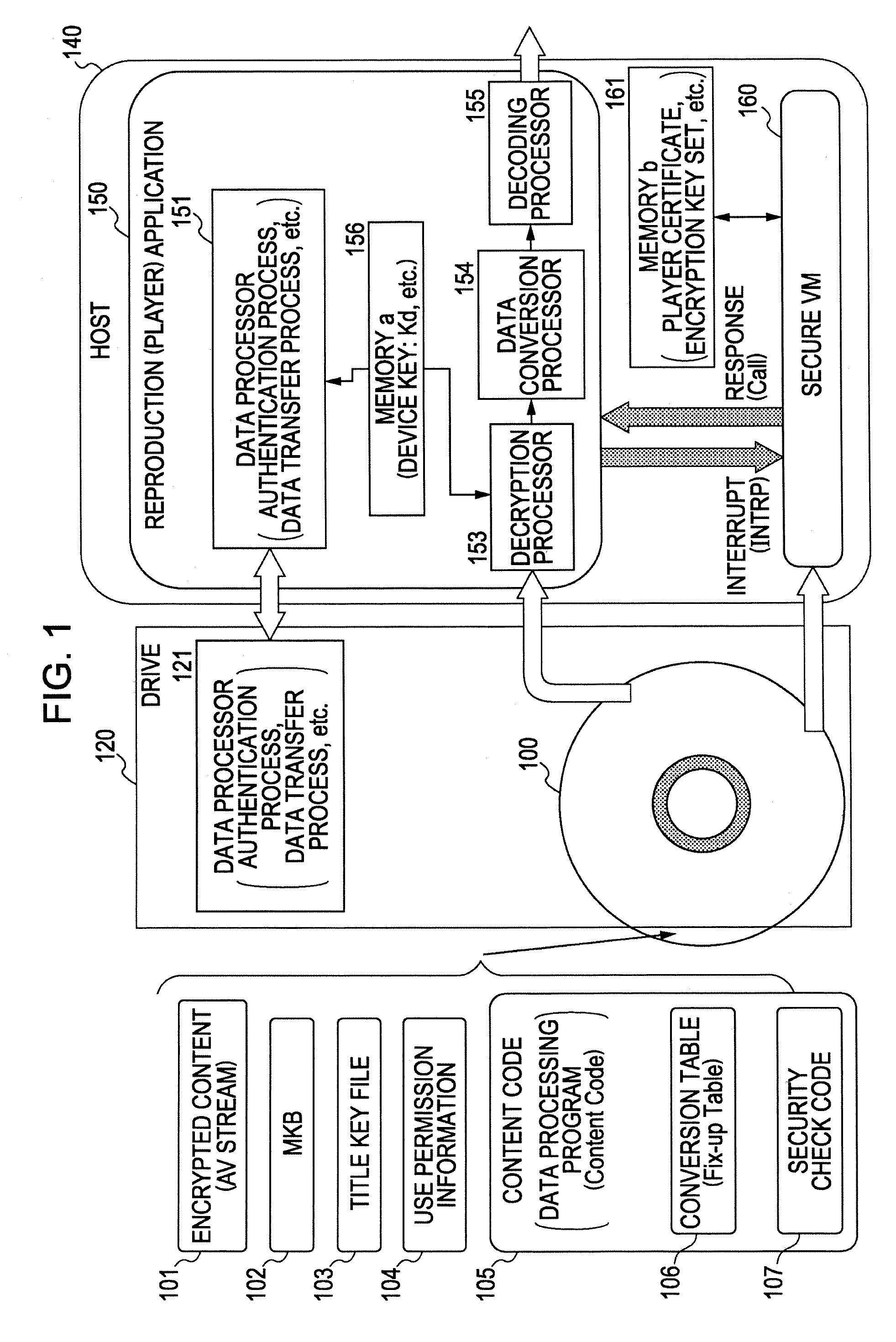
ActiveUS20080210747A1Inhibitory contentReduce processing stepsDigital computer detailsRecord information storageComputer hardwareInformation processing
A configuration is provided for enabling a process in which appropriate content code corresponding to apparatuses and applications of various model types and versions is selected to be performed. In a configuration in which content code recorded on an information recording medium is obtained, and processing, such as a security check in accordance with the content code, conversion of the content data, and embedding of player information into the content, is performed, at least a portion of the content code is set as encrypted data, and as an encryption key therefore, a node key set so as to correspond to a node of a key tree having a hierarchical structure is used. With this configuration, it is possible to specify in advance a player capable of decrypting the encryption part of the content code by using the node key, and only appropriate content code compliant with each player is processed, thereby making it possible to prevent a process of using invalid content code.
Owner:SONY CORP
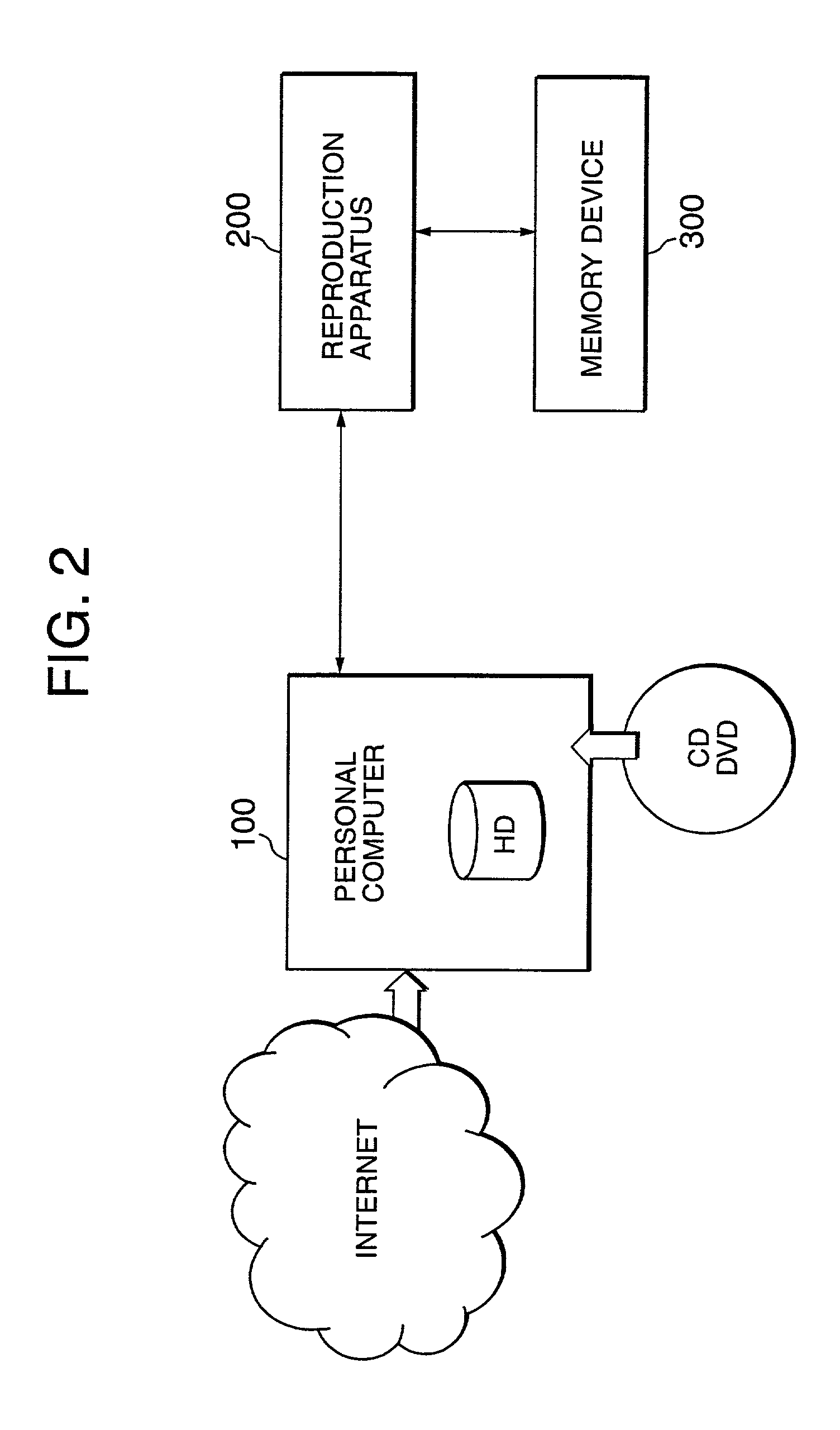
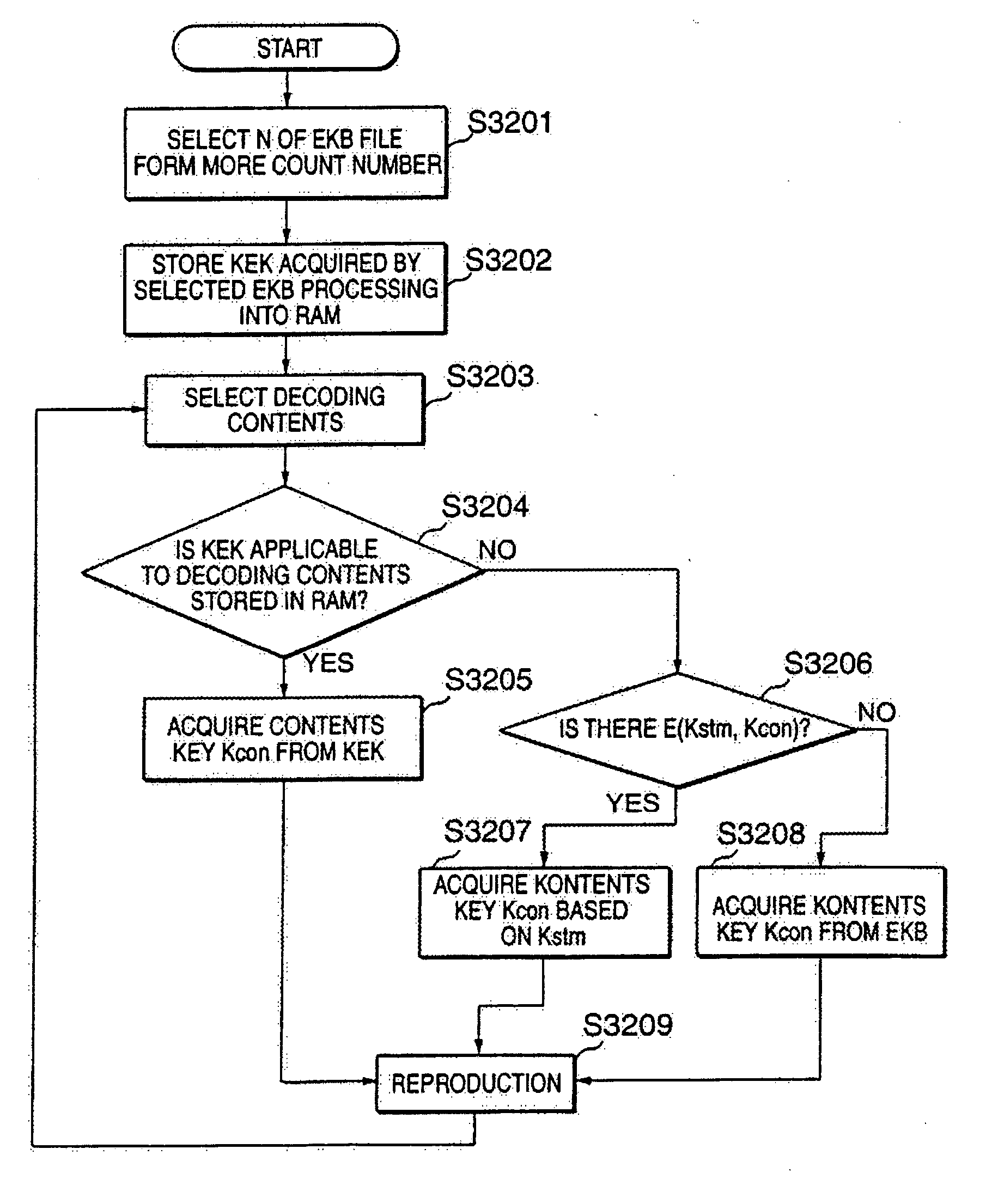
Data processing system, data processing method, and program providing medium
ActiveUS7116785B2Effective method of processingEnsure safe distributionKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationData processing systemData file
The inventive data processing apparatus enables own memory device to store a plurality of key distribution approval data files each containing such a header data comprising a number of “link-count” data units each designating actual number of applicable contents data per decodable contents key based on an enabling key block (EKB) distribution key enciphering key (KEK) enciphered by a corresponding enabling key block (EKB) provided for by a hierarchy key tree structure. When storing a plurality of the enabling key blocks (EKB) in a memory device, such a key enciphering key (KEK) contained in an enabling key block (EKB) having a number of link-count data units is previously decoded and stored in the memory device. By way of applying the stored (KEK) when utilizing contents data, the enabling key block (EKB) processing step is deleted, whereby promoting higher efficiency in the utilization of contents data.
Owner:SONY CORP
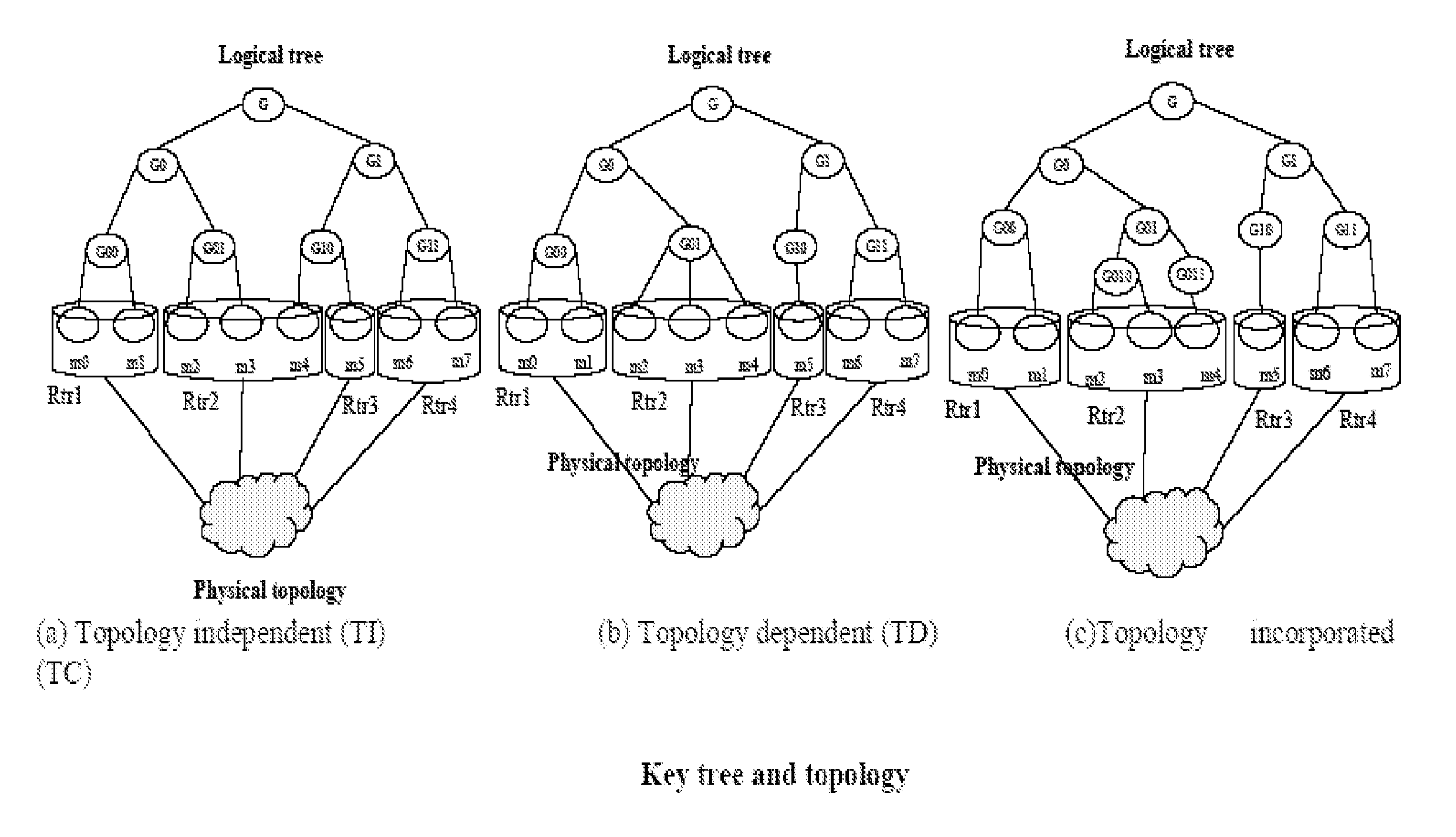
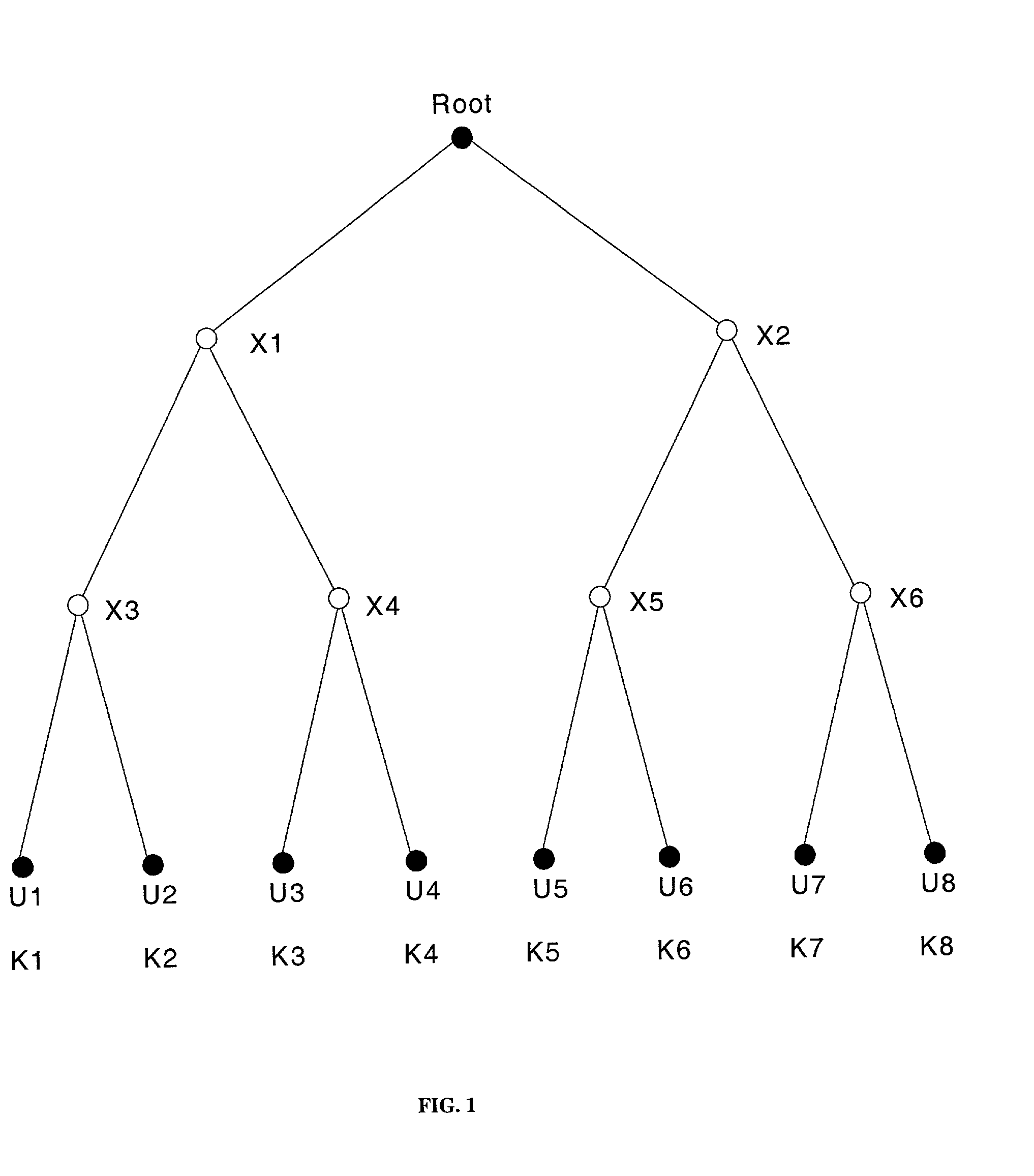
Spatial key trees for key management in wireless environments
InactiveUS6993138B1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageSecure communicationCurrent cell
A system, method, and program code are given for secure communication. Multiple geographic cells are arranged in a hierarchical tree having a root node and internal nodes. The root node and each internal node in the tree have an associated node cryptographic key for secure communication with lower nodes in the tree. Each cell is associated with a leaf node of the tree and a cell cryptographic key for secure communications with devices located within the cell. A key management center is at the root node for determining an anticipated cell path of a mobile device from a current cell to a destination cell. The key management center distributes to the mobile device a set of cryptographic keys from the tree. This set contains a minimum number of cryptographic keys necessary to permit secure communications for the mobile device within each cell along the anticipated cell path, but no other cells.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Information processing system and method
InactiveUS6911974B2Secure transmissionReduce data sizeKey distribution for secure communicationUnauthorized memory use protectionInformation processingTheoretical computer science
An information processing system and method are disclosed in which information processing is performed in a highly efficient manner using an enabling key block (EKB) on the basis of a tree structure including category subtrees. A key tree is formed so as to include a plurality of subtrees serving as category trees categorized in accordance with categories and managed by category entities. An EKB including data produced by selecting a path in a tree and encrypting a higher-level key in the selected path using a lower-level key in the selected path. The resultant EKB is provided to a device. Distribution of EKB's is managed on the basis of an EKB type definition list representing the correspondence between an EKB type identifier and one or more identification data identifying one or more category trees that can process an EKB of an EKB type specified by the EKB type identifier.
Owner:SONY CORP
Information processing system and method using encryption key block
InactiveUS7269257B2Data transmission securitySecure transmissionKey distribution for secure communicationUnauthorized memory use protectionInformation processingComputer hardware
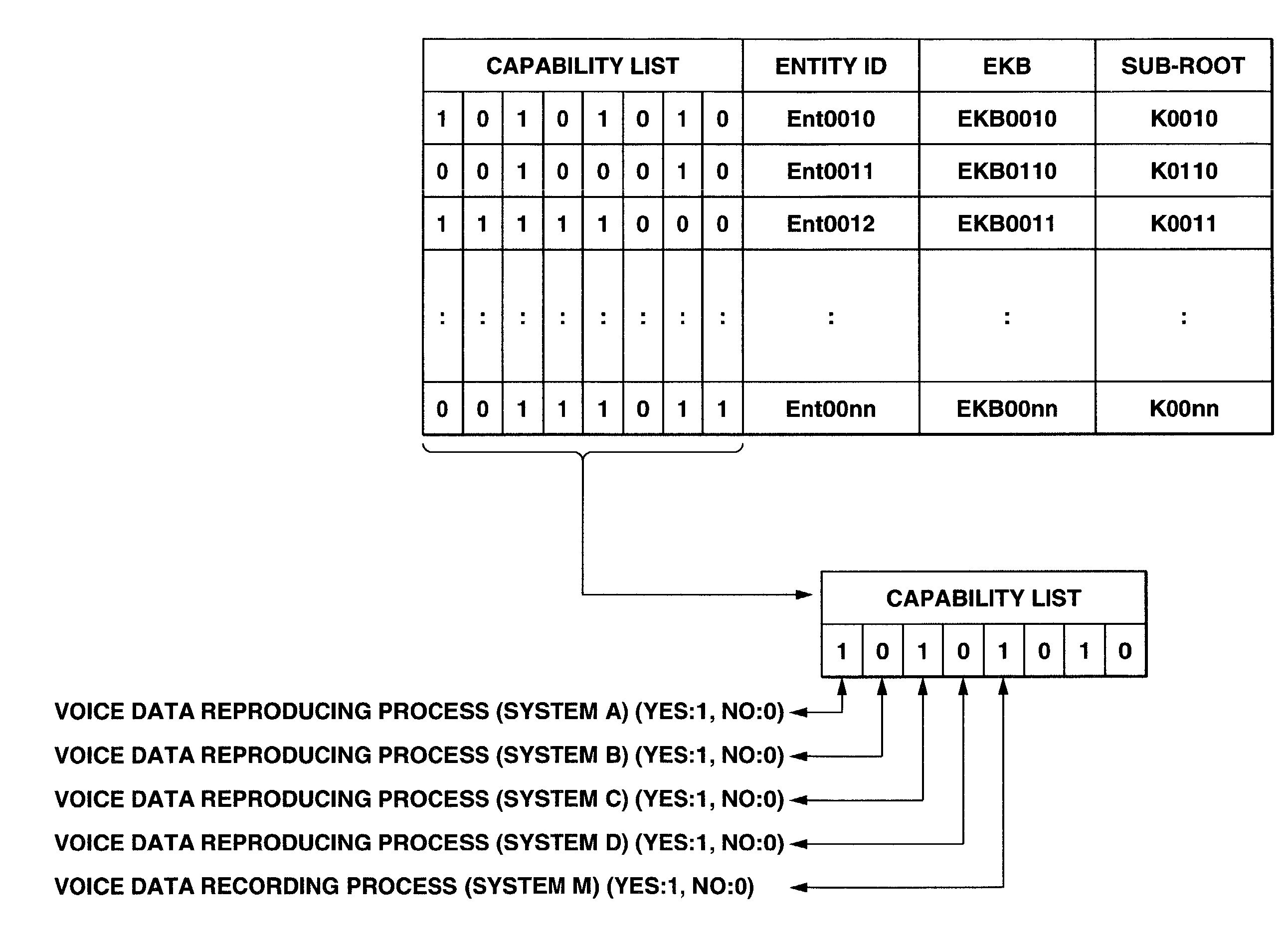
An information processing system and method using an encryption key block sets sub-trees classified based on data processing ability of the devices (capability) in a key tree in which respective keys are corresponded to a root, nodes and leaves of a tree in which a plurality of devices are constituted as the leaves, generates a sub-enabling key block which is effective for an entity in a managing subject of each sub-tree (entity), and generates an enabling key block decodable only by the entities having common capability. Also, an information processing system and method using an encryption key block manages a partial tree of a key tree (sub-tree), generates a sub-enabling key block based only on a key set corresponding to nodes or leaves included in the sub-tree, and generates an enabling key block decodable only by selected entities by using the sub-enabling key block. Thus, it is possible to generate and distribute an enabling key block corresponding to data processing ability of a device and to manage devices by dividing a hierarchical key tree structure.
Owner:SONY CORP
Key management method based on wireless Mesh netword
InactiveCN101110670AReduce communication costReduce computational costKey distribution for secure communicationExtensibilityWireless mesh network
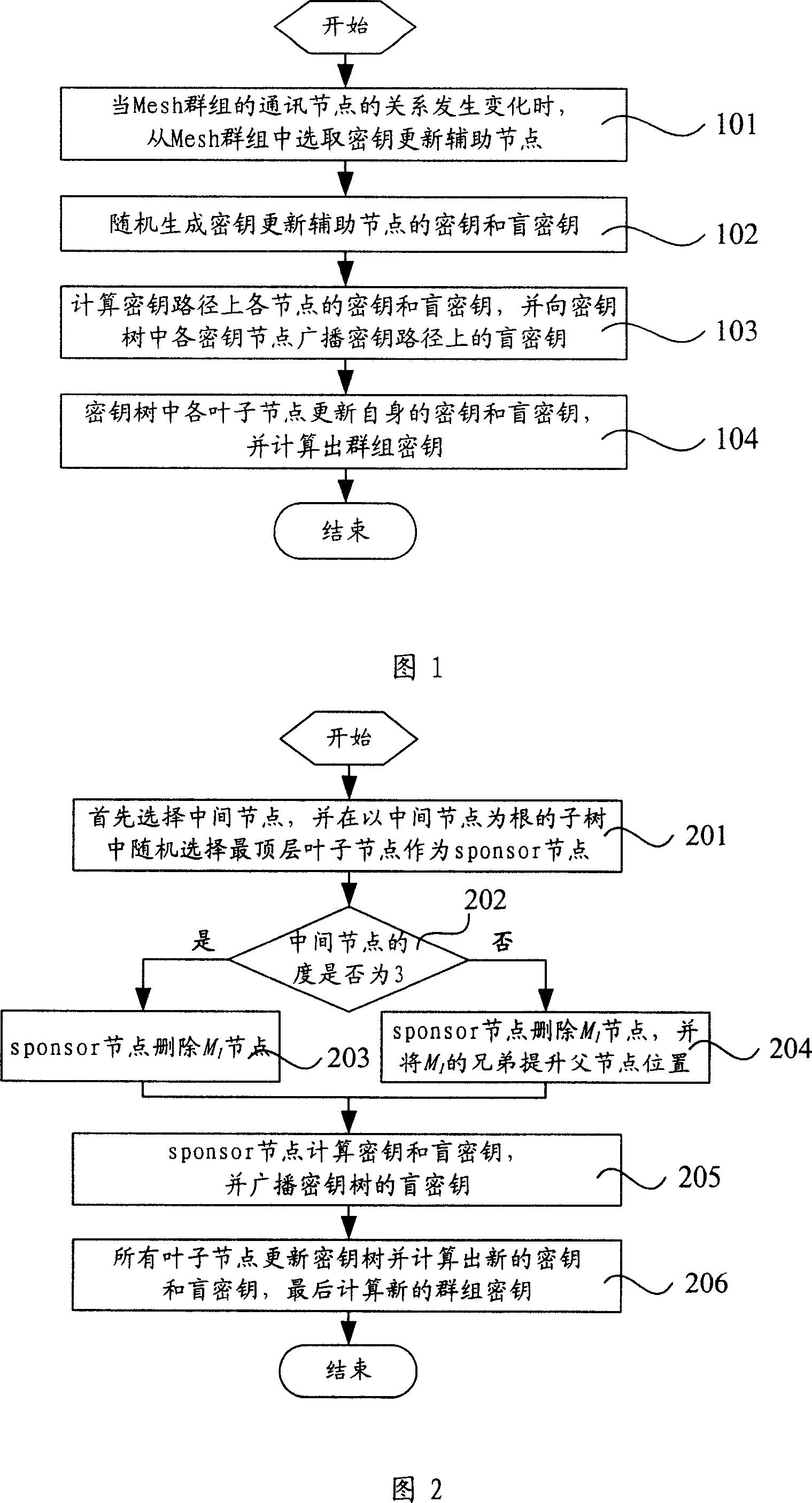
The present invention relates to a key management method based on wireless Mesh network, which is characterized in that the method includes procedures below: As relation amongst communication nodes of a mesh cluster varies, an auxiliary updating node is selected from a key tree in correspondence with the Mesh cluster. Wherein, the key tree is provided with a ternary tree structure. A key and a blind key of the auxiliary updating node are created at random. Keys and blind keys at all key nodes in a key path of the key tree are calculated for the auxiliary updating node. Besides, all key nodes of the key tree broadcast to blind keys of all key nodes on the key path. Each leaf node of the key tree updates its own keys and blind keys and works out cluster keys. The technic proposal of the present invention provides parameters of total information length while nodes are added and leaves, password calculation quantity, total combined cluster information length and so on lower than those of prior arts, thus eliminating conflicts of safety demands of prior arts with expansibility and QoS demands.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
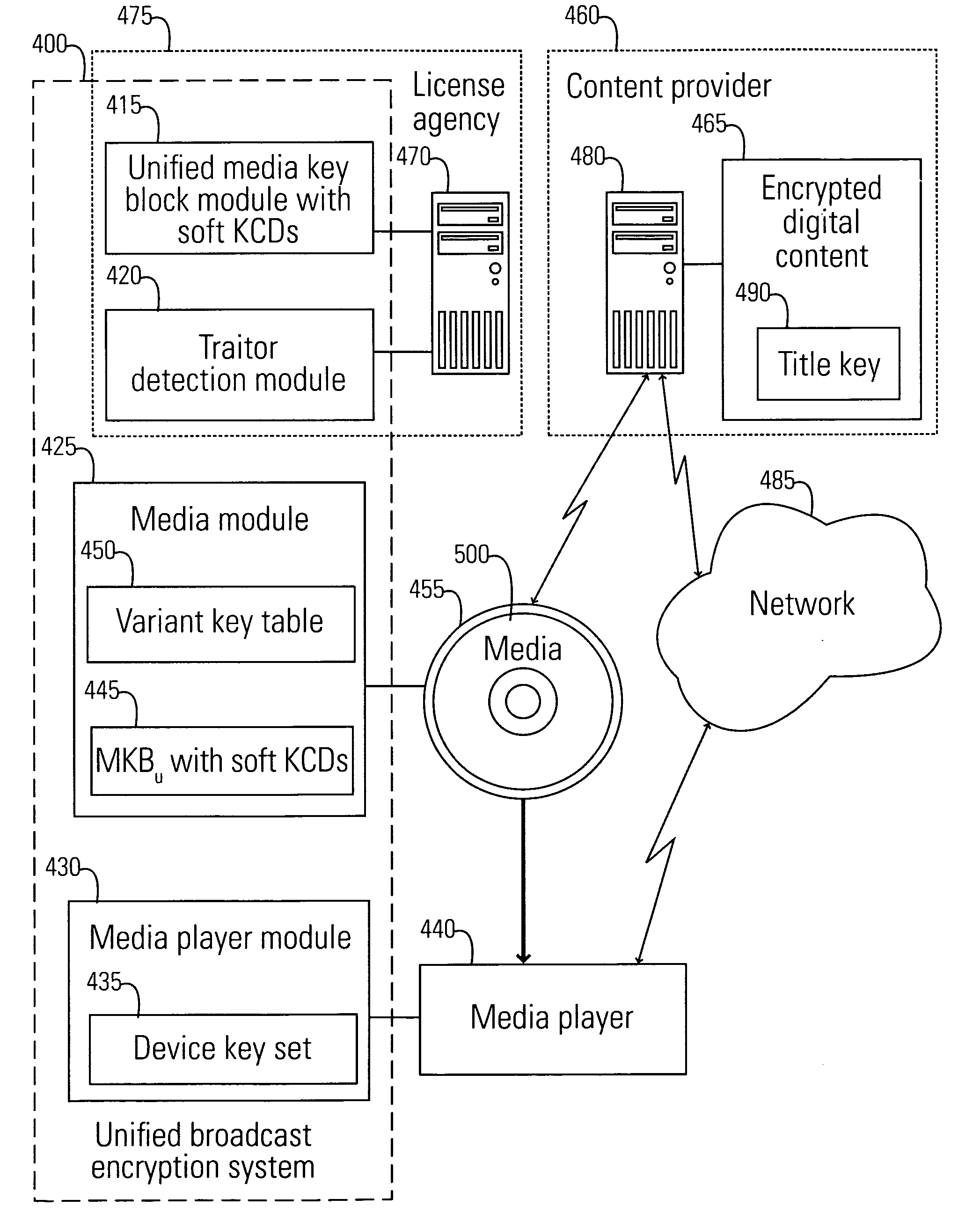
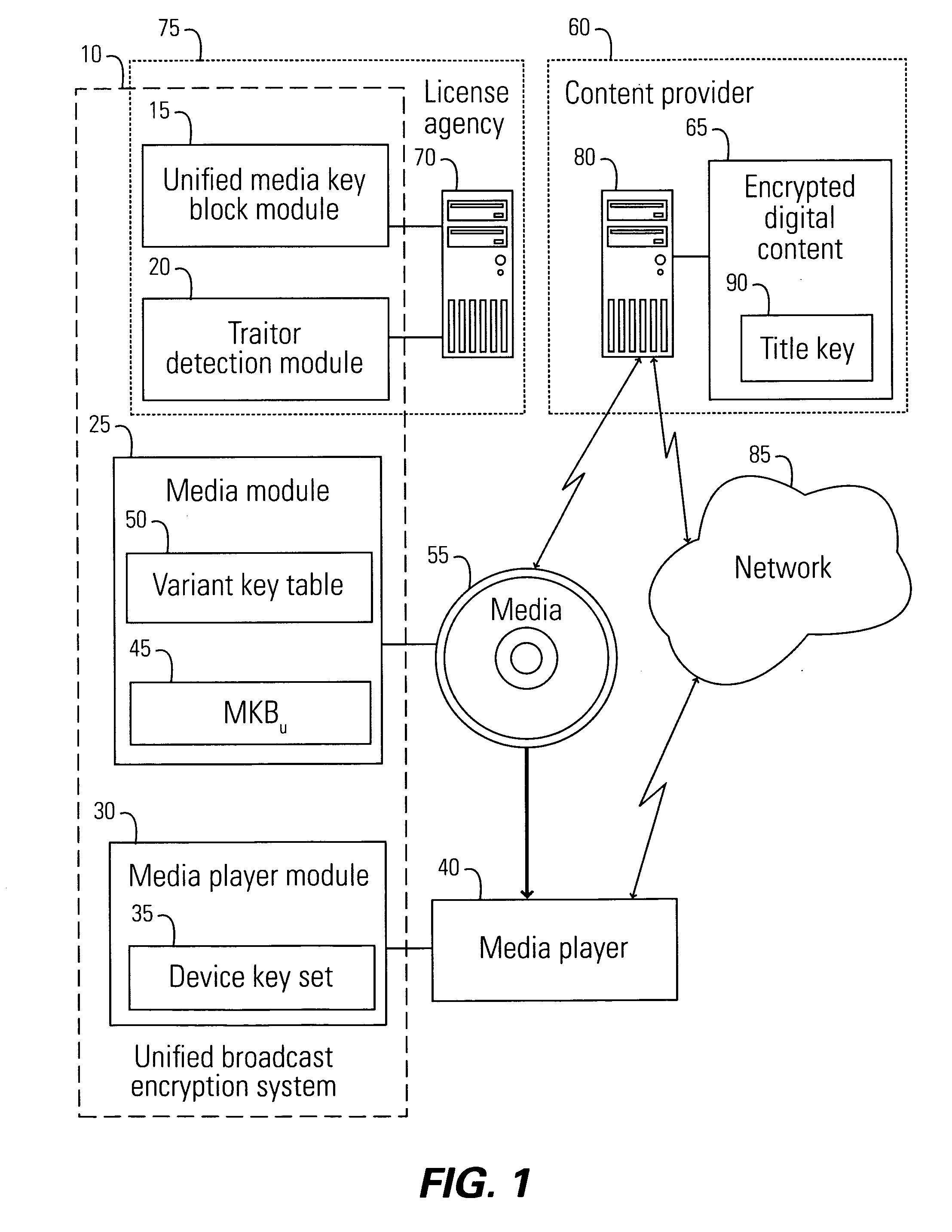
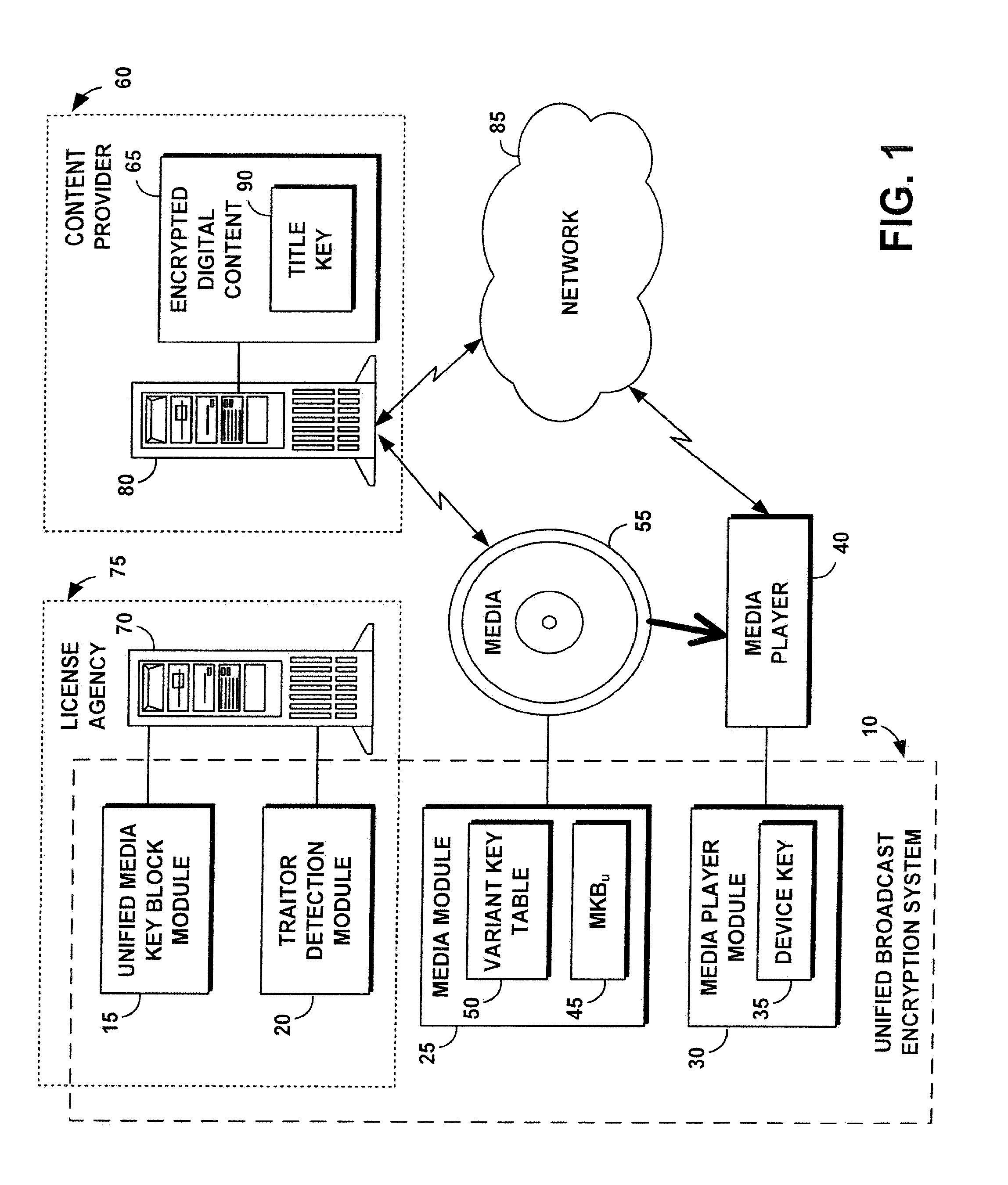
System, method, and service for performing unified broadcast encryption and traitor tracing for digital content
InactiveUS20080279376A1Preventing future piracyImprove abilitiesUser identity/authority verificationRecord information storageComputer hardwareDigital content
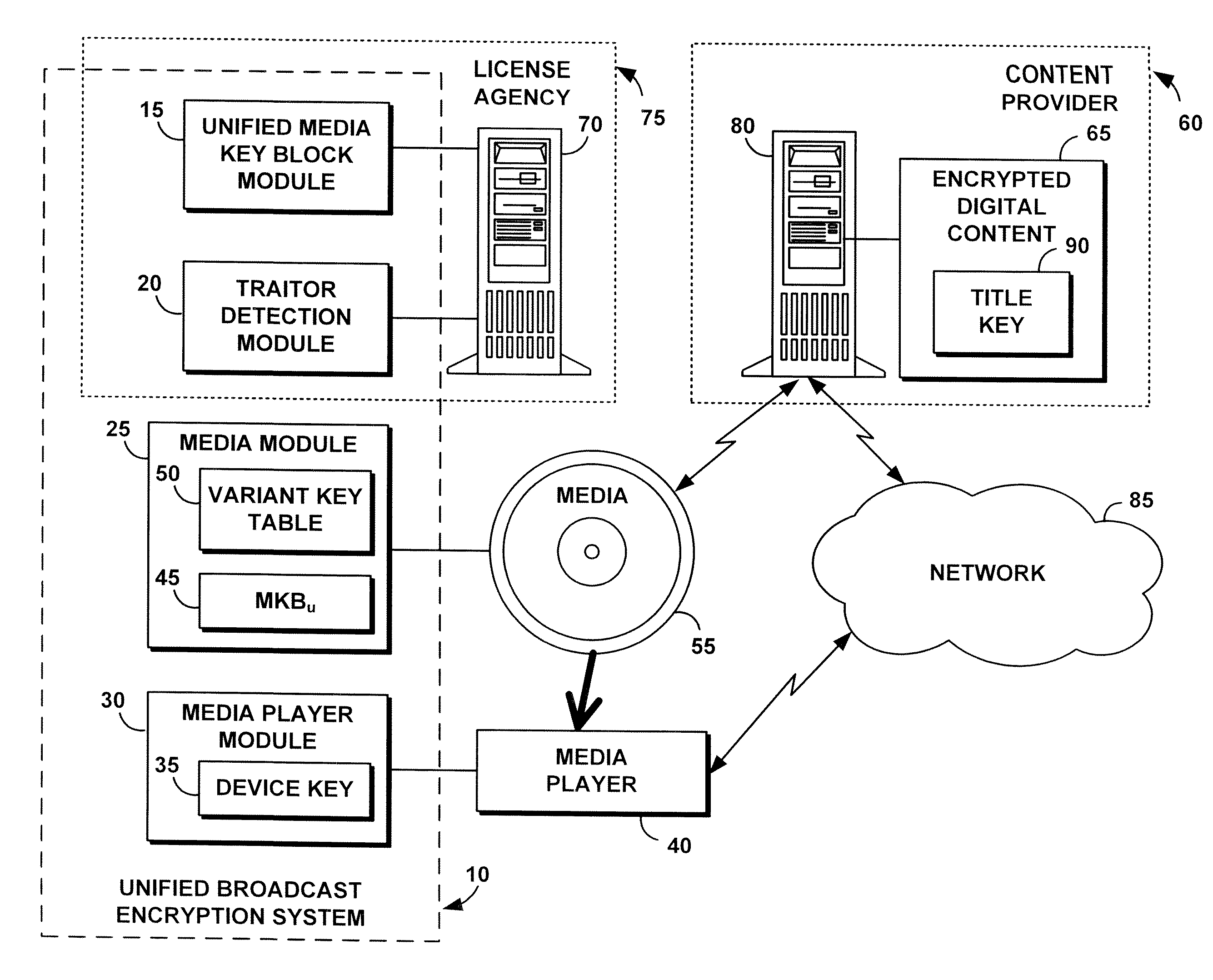
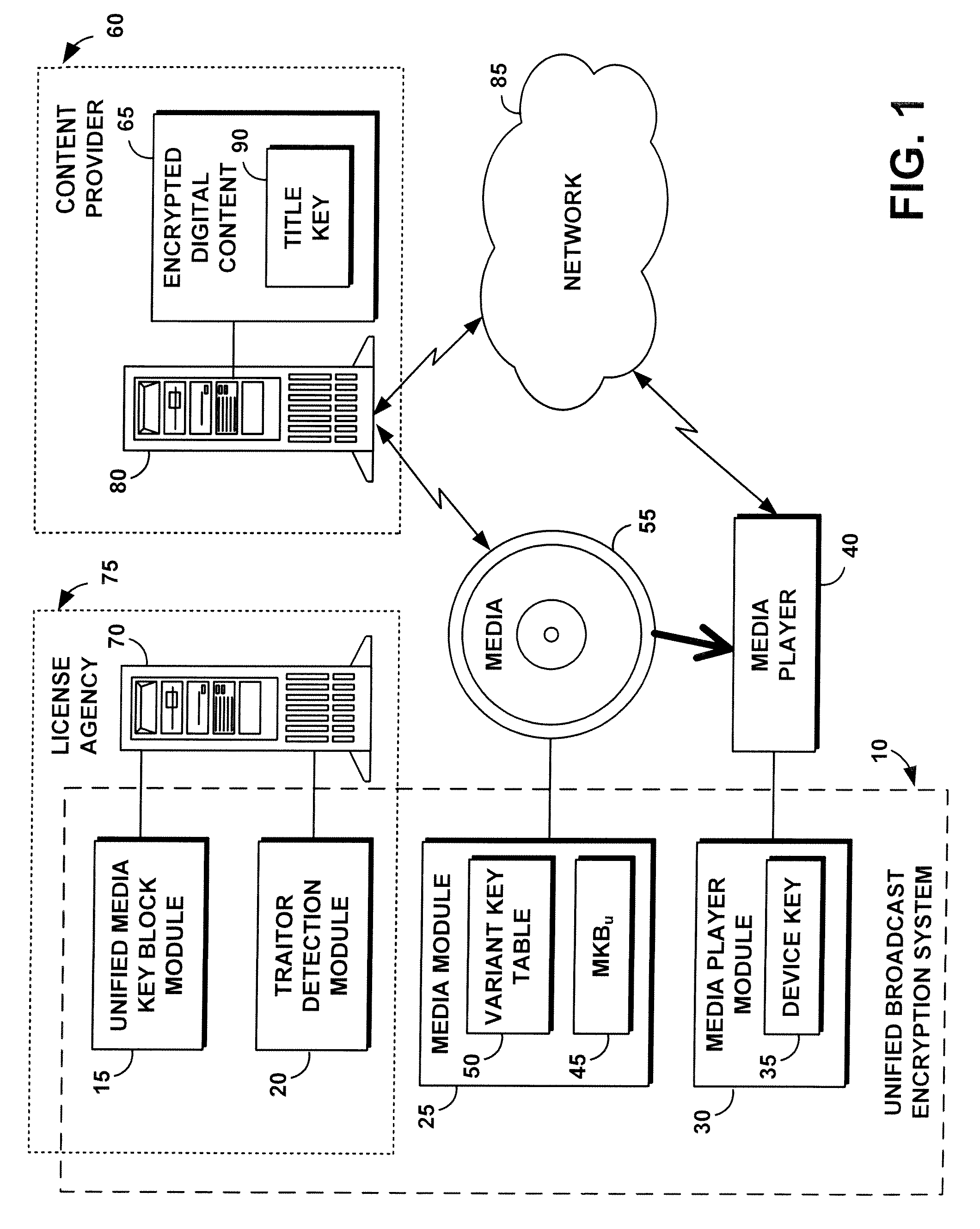
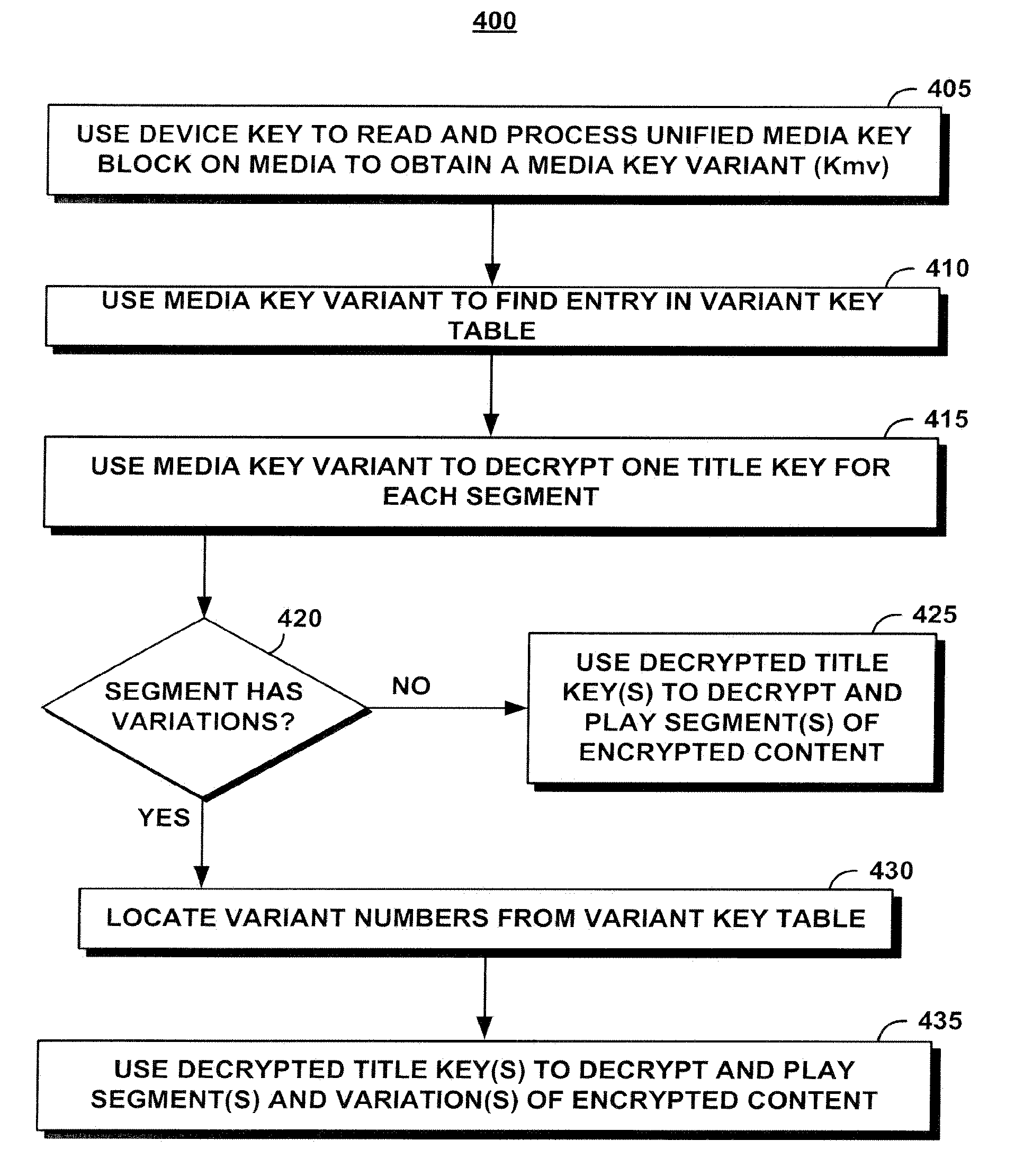
A unified broadcast encryption system divides a media key tree into S subtrees, divides digital content into segments, and converts some of the segments into variations; the number of segments and variations is q. The system subdivides each of the subtrees into q / |S| subdivided subtrees, assigns a key media variant to each of the subdivided subtrees, and generates a unified media key block (MKBu). The system decrypts digital content by obtaining required key media variants from the MKBu, using the key media variant to find an entry in a variant key table, decrypt a title key, and locate a variant number from the variant key table. The system uses the variant number to identify which of the variations may be decrypted by the title key and uses the title key to decrypt segments and variations.
Owner:IBM CORP
Cryptographic key update management method and apparatus
InactiveUS8045713B2Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationMostly TrueGroup key
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
Last hop topology sensitive multicasting key management
ActiveUS8306026B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationComputer networkMulticast address
Owner:FOUR BATONS WIRELESS LLC +1
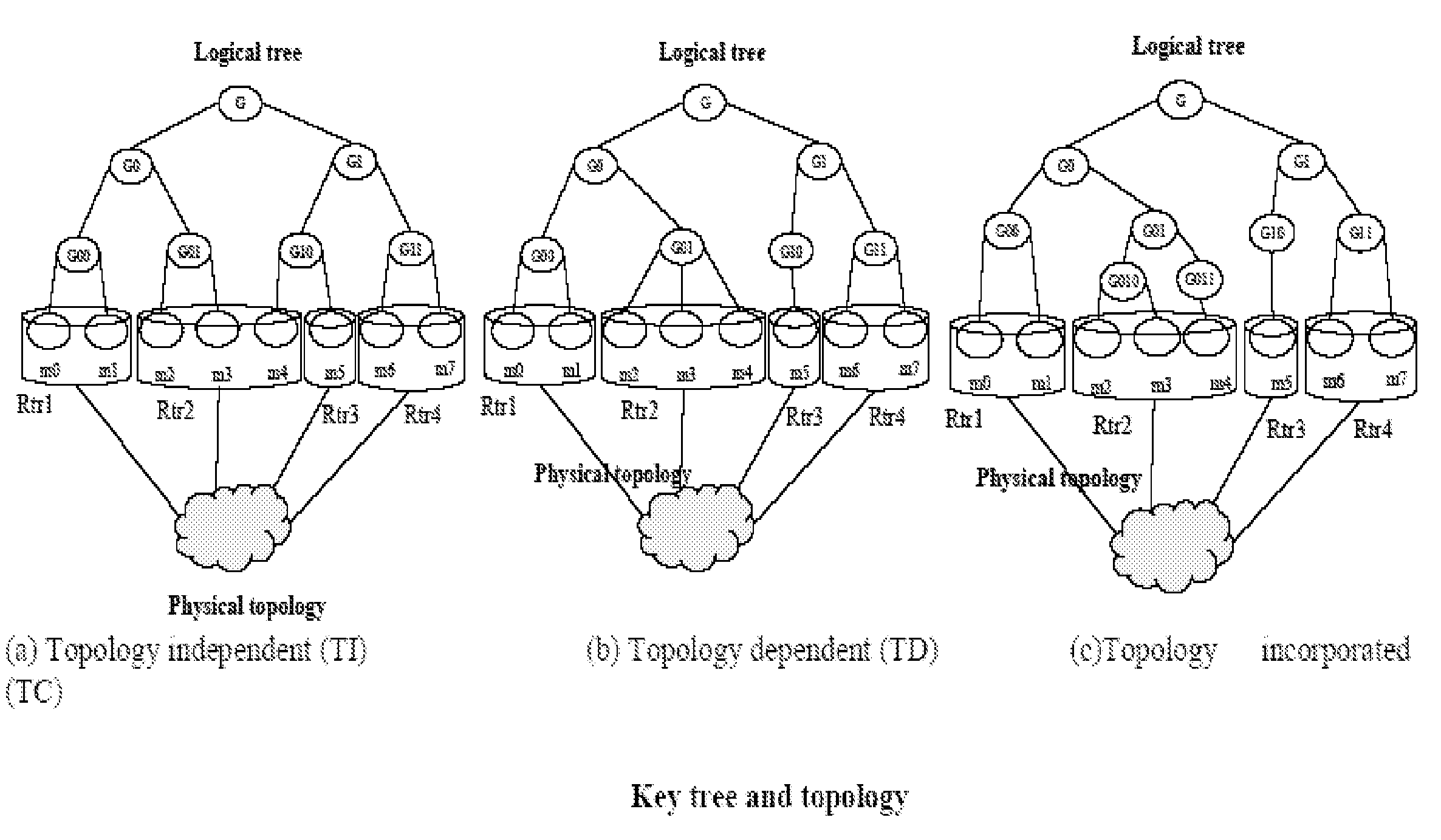
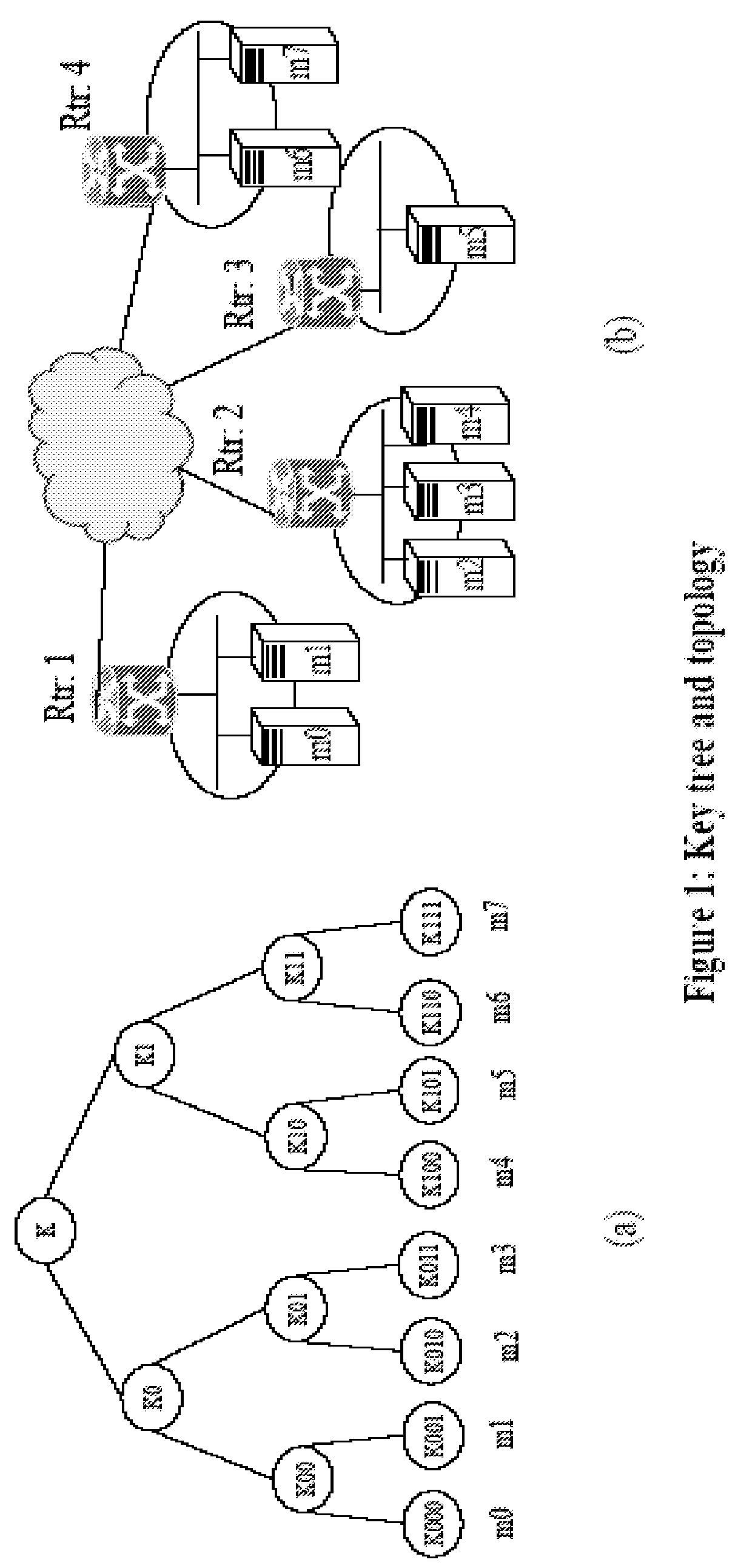
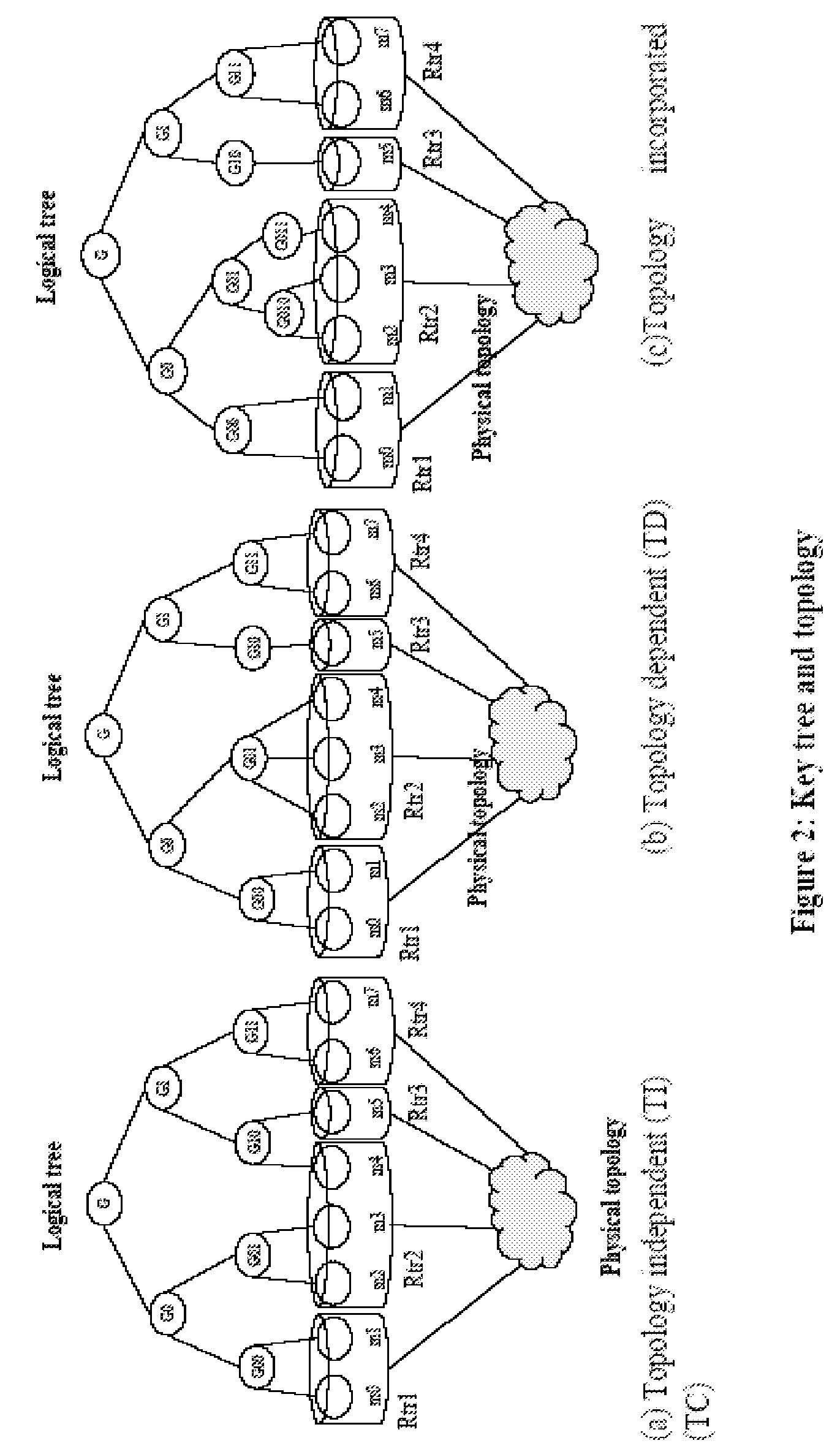
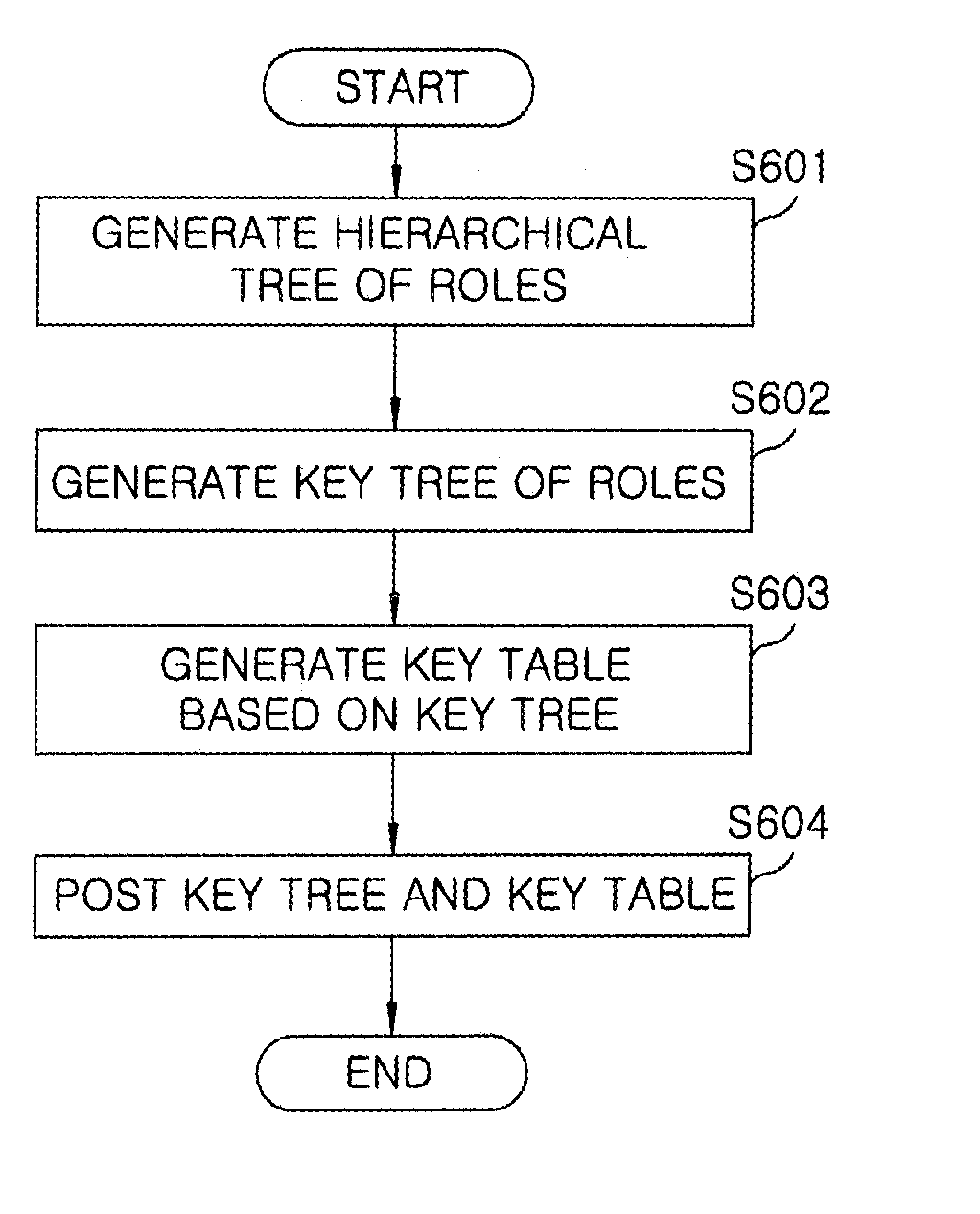
Key tree construction and key distribution method for hierarchical role-based access control
InactiveUS20110150224A1Efficient executionReduce consumptionKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageMedia access controlKey distribution
A key tree construction and key distribution method for hierarchical role-based access control, includes: constructing a key tree including relationships between a hierarchical structure of role groups and data; performing encryption and decryption of data keys and role keys; and generating a key table, in which the data keys required to decrypt encrypted data and the role keys required to decrypt encrypted data keys are stored, with reference to the key tree. Further, the key tree construction and key distribution method for hierarchical role-based access control includes performing management such that a specific role group can obtain a data key by performing decryption based on its own role key by using both the key tree and the key table.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Unified broadcast encryption system
A system and method is disclosed for performing unified broadcast encryption and traitor tracing for digital content. In one embodiment a media key tree is divided into S subtrees, the media key tree including media keys and initial values, which may be random values. The digital content is divided into a plurality of segments and at least some of the segments are converted into a plurality of variations. The random values are transformed into media key variations and a separate media key variant is assigned to each of the subdivided subtrees. A unified media key block including the media key tree is stored on the media.
Owner:IBM CORP
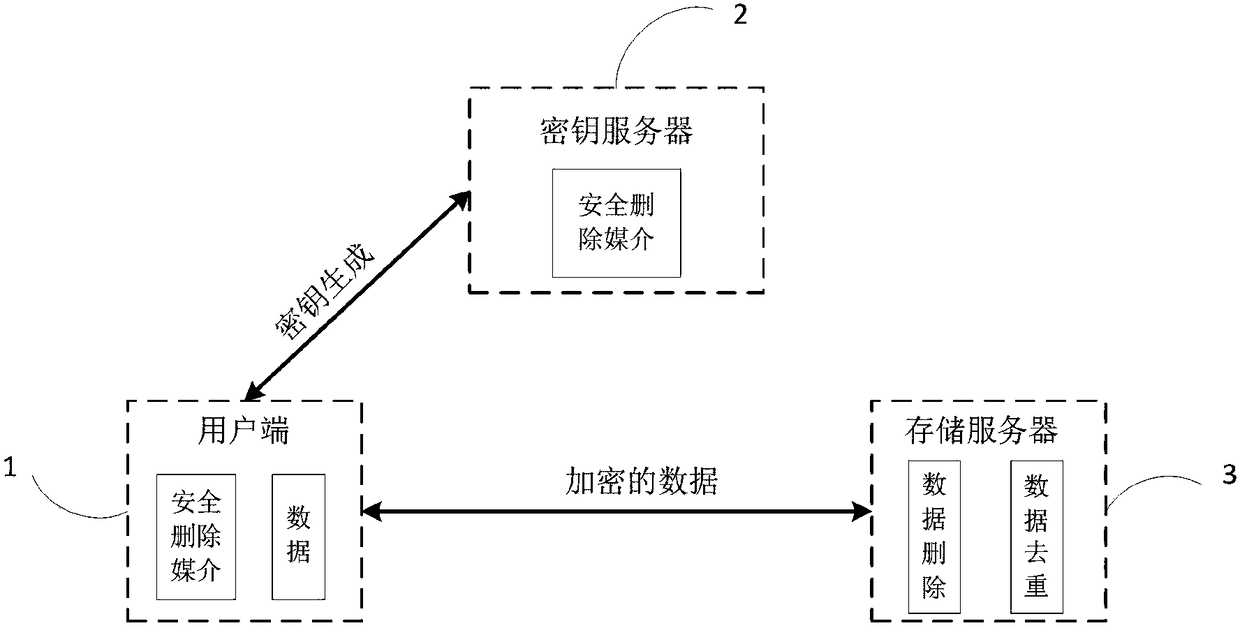
Cloud storage system and method capable of supporting secure data deduplication and deletion
ActiveCN108200172ASupport insertionSupport deleteKey distribution for secure communicationNetwork structureCloud storage system
The invention belongs to the technical field of cloud storage, and discloses a cloud storage system and method capable of supporting secure data deduplication and deletion. The method comprises the following technical algorithms: providing secure data deduplication between different users by adopting a deduplication and encryption scheme and a server-assisted network structure; and building secureand efficient data deletion by using an encapsulation key tree. The invention further can support dynamic data updating, namely supporting interpolation, deletion and alteration operation of data inthe system. Efficient data updating is executed by adopting an increment data updating method, and only updated parts are required to be encrypted and uploaded. Through the combination with an increment updating technology, withdrawing / reworking operation of dynamic data is also considered, so that calculation and communication expenses for cloud storage are greatly reduced. Furthermore, detailedsecurity analysis and performance assessment are performed in the method disclosed by the invention. A result shows that the method disclosed by the invention can fulfill an expected security aim andalso realize efficient data deletion and deduplication operation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Radio frequency recognizing privacy authentication method for dynamic cryptographic key update based on rarefaction tree
InactiveCN101256615AReduce overheadReduce storage overheadDigital data authenticationSensing record carriersRfid authenticationSystem maintenance
The invention relates to a radio frequency identification technology and discloses a method for privacy authentication of radio frequency identification based on dynamic key update of sparse tree, which comprises the following steps that: system initialization step, a read-write machine generates the key of each label stored by the sparse key tree; label identification step, the read-write machine sends an authentication request to the label, the label computes and sends the authentication information to the read-write machine, and the read-write machine identifies the label after receiving the authentication information; key updating step, after the label identification is finished, the read-write machine updates the key tree and sends the synchronous updating authentication information to the label which updates the stored keys; system maintenance step, once the label joins in or level RFID system, the read-write machine maintains the system sparse key tress. The invention is able to efficiently resist various passive and active attacks at present, and in contrast with the RFID authentication method based on the balance tree structure, greatly reduces the storage expense at the label end.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Information processing system and method
InactiveUS20070098177A1Secure transmissionPossible to useKey distribution for secure communicationUnauthorized memory use protectionInformation processingProcessing type
An information processing system and method are disclosed in which information processing is performed in a highly efficient manner using an enabling key block (EKB) on the basis of a tree structure including category subtrees. A key tree is produced so as to include a plurality of subtrees that are grouped in accordance with categories and managed by category entities. An EKB is produced so as to include data produced by selecting a path in the key tree and encrypting an upper-level key in the selected path using a lower-level key in the selected path. The resultant EKB is provided to a device. If a change occurs in state of a category tree capable of processing an EKB identified in the EKB type definition list, a notification of the change in state is sent to an entity that uses the EKB thereby making it possible for an EKB requester to perform processing in accordance with a newest EKB.
Owner:SONY CORP
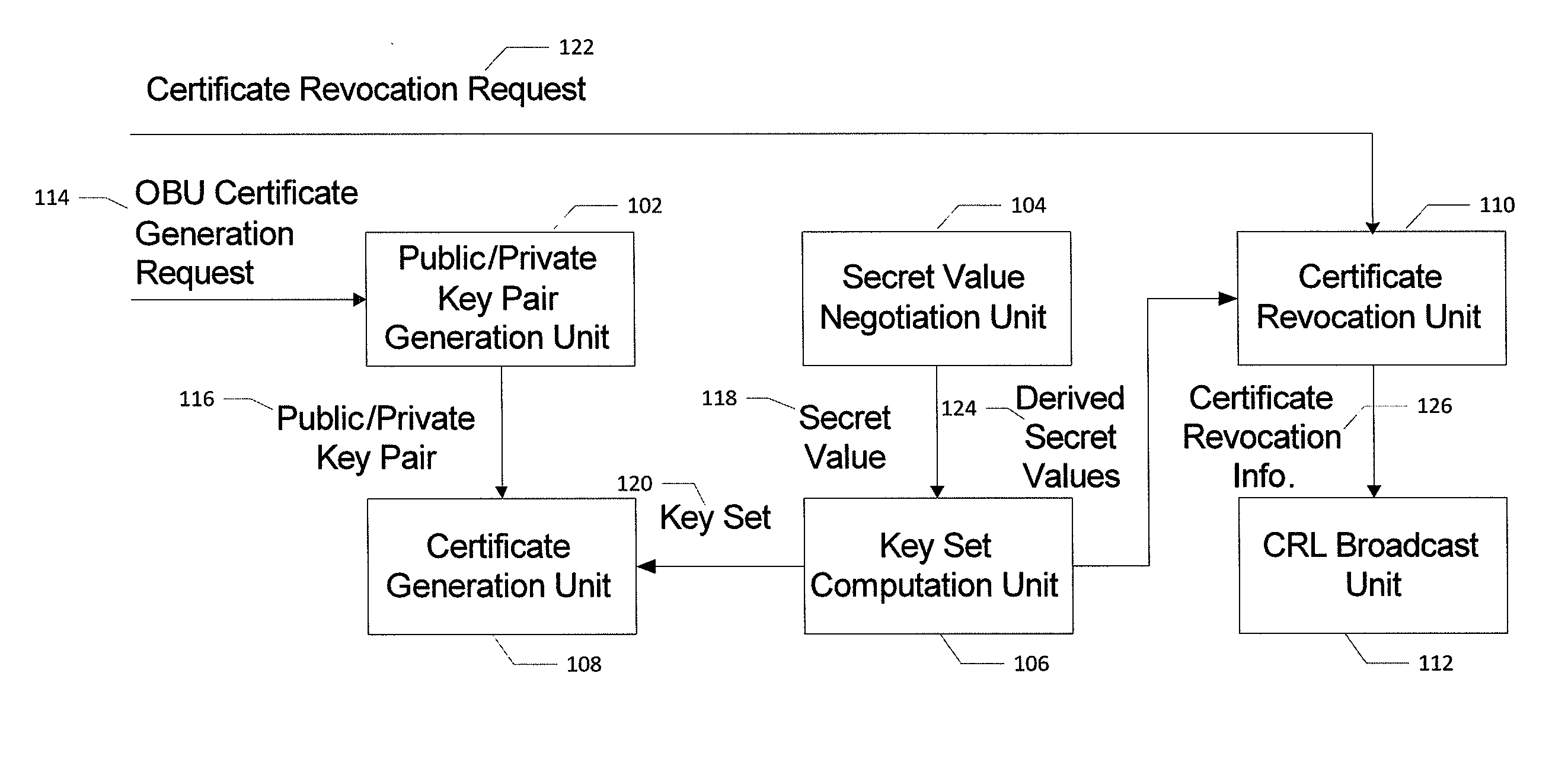
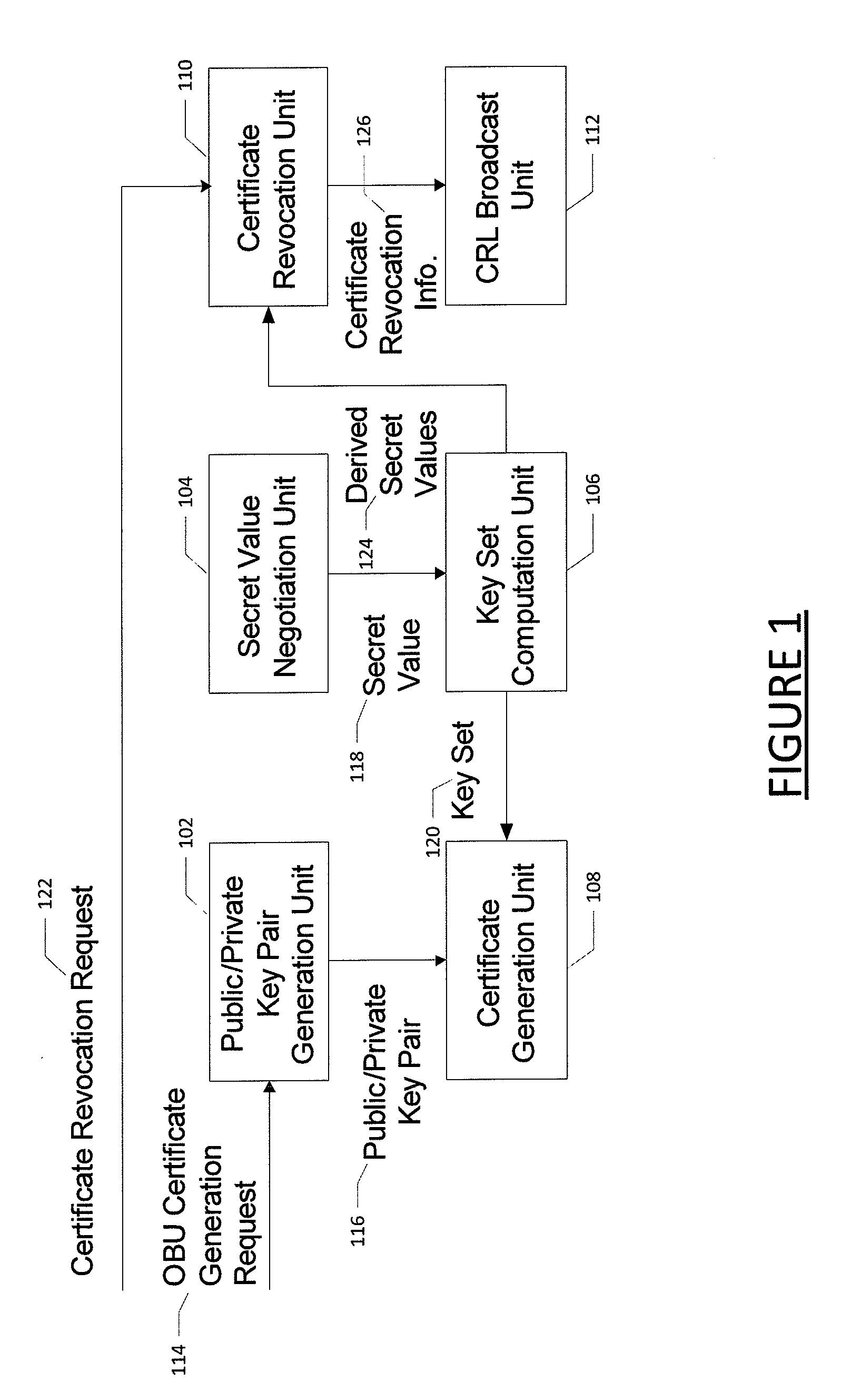
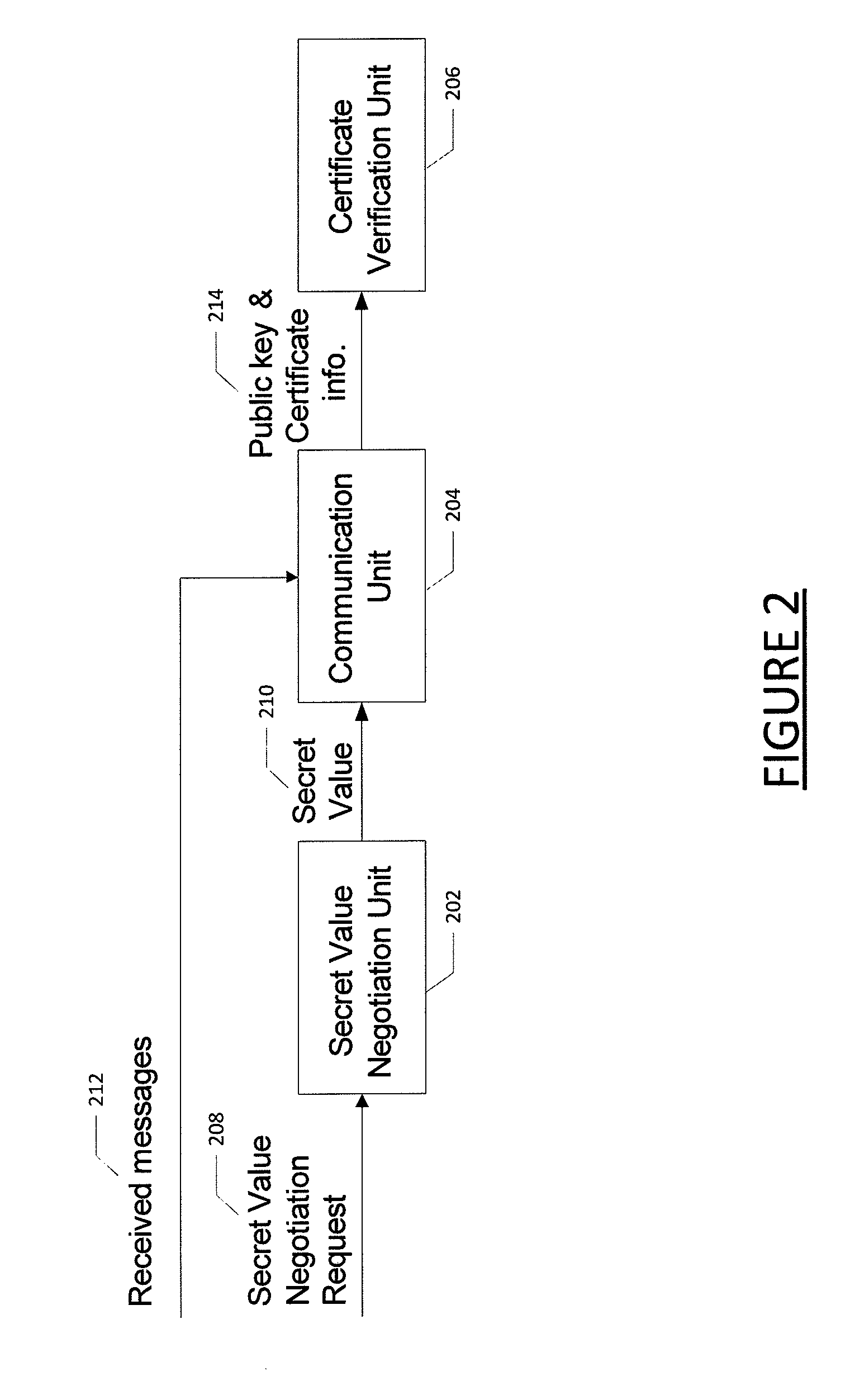
Method for certificate generation and revocation with privacy preservation
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to methods and systems for generating and revoking, as well as validating, certificates used to protect communications within networks while maintaining privacy protection. In the context of a method, certificate generation and revocation with privacy preservation comprises determining a secret value to be used by a certificate authority and an entity; constructing a key tree based on the secret value, wherein the leaves of the key tree represent derived keys for the certificates for the entity; and generating certificates for the entity based in part on the key tree leaves. The method further comprises determining that one or more of the certificates should be revoked; determining a minimum key node set that covers the certificates to be revoked; adding the minimum key node set to a certificate revocation list; and providing the certificate revocation list to one or more entities. Corresponding apparatuses and computer program products are also provided.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
A L4 encryption method of double group of encrypted authorization management system
InactiveCN101150395AReduce overheadReduce communication burdenSpecial service provision for substationKey distribution for secure communicationSubset differenceBroadcasting
This invention discloses a four-layer encryption method for double grouping an encrypted authorization management system including the following steps: setting up a user ciphered key tree according to a subset difference / hierarchical subset difference unit when settin up the encrypted authorization management system to distribute pre-distributed key of users, the ciphered authorization and management system applies a four-layer of ciphered structure of double grouping to service and users to encrypt digit content in real time when distributing digit content to set up broadcasting authorization information and authorization management information to all users to be analyzed and de-ciphered by the receiving end to compute content key to decipher the digit content.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
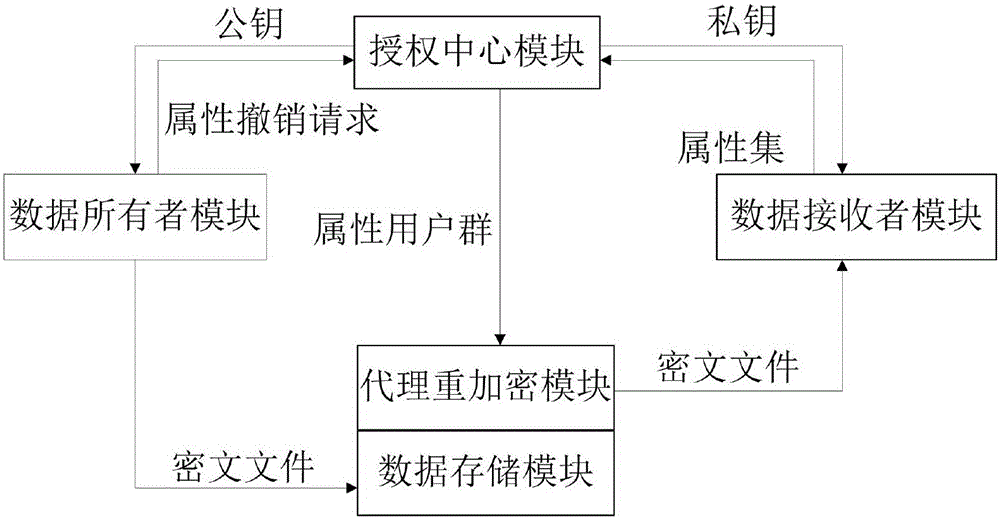
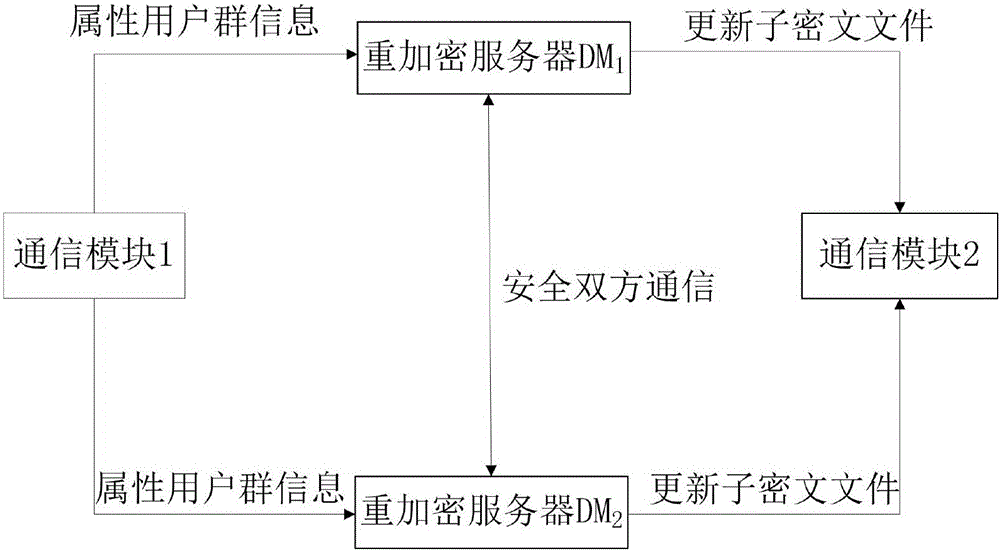
Encryption system and method for resisting re-encryption key leakage and capable of cancelling attributes
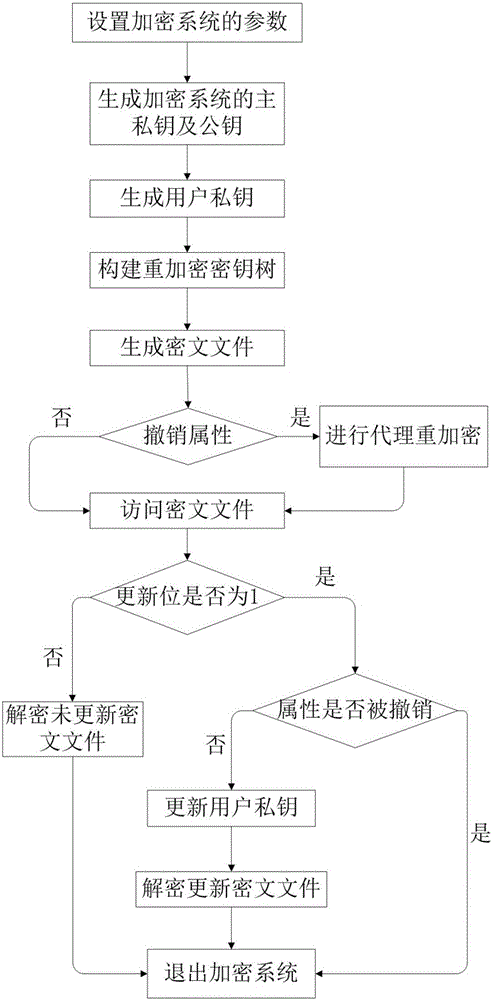
ActiveCN106059768ALeak resistanceOvercoming property revocation flawsKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationCiphertextDisk encryption
The present invention provides an encryption system and method for resisting re-encryption key leakage and capable of cancelling attributes. The method comprises: 1, setting the parameters of an encryption system; 2, generating the main private key and the public key of the encryption system; 3, generating a user private key; 4, building a re-encryption key tree; 5, generating a cryptograph file; 6, cancelling attributes; 7, performing re-encryption agency; 8, accessing the cryptograph file; 9, determining whether the update position of the cryptograph file is 1 or not; 10, decrypting an un-updating cryptograph file; 11, updating the private key; 12, decrypting the update cryptograph file; and 13, quitting the encryption system. Through adoption of a dual-agency re-encryption server model, the encryption system and method for resisting re-encryption key leakage and capable of cancelling attributes can resist the leakage of the re-encryption key. When the attributes are cancelled, an attribute user group is employed to construct the re-encryption key tree so as to effectively, timely and accurately cancel the indirect attributes. When the encryption is performed, the secret is dispersed to resist the conspiracy attack.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Information processing system and method
InactiveUS20050228809A1Secure transmissionReduce data sizeKey distribution for secure communicationUnauthorized memory use protectionInformation processingTheoretical computer science
An information processing system and method are disclosed in which information processing is performed in a highly efficient manner using an enabling key block (EKB) on the basis of a tree structure including category subtrees. A key tree is formed so as to include a plurality of subtrees serving as category trees categorized in accordance with categories and managed by category entities. An EKB includes data produced by selecting a path in a tree and encrypting a higher-level key in the selected path using a lower-level key in the selected path. The resultant EKB is provided to a device. Distribution of EKB's is managed on the basis of an EKB type definition list representing the correspondence between an EKB type identifier and one or more identification data identifying one or more category trees that can process an EKB of an EKB type specified by the EKB type identifier.
Owner:SONY CORP
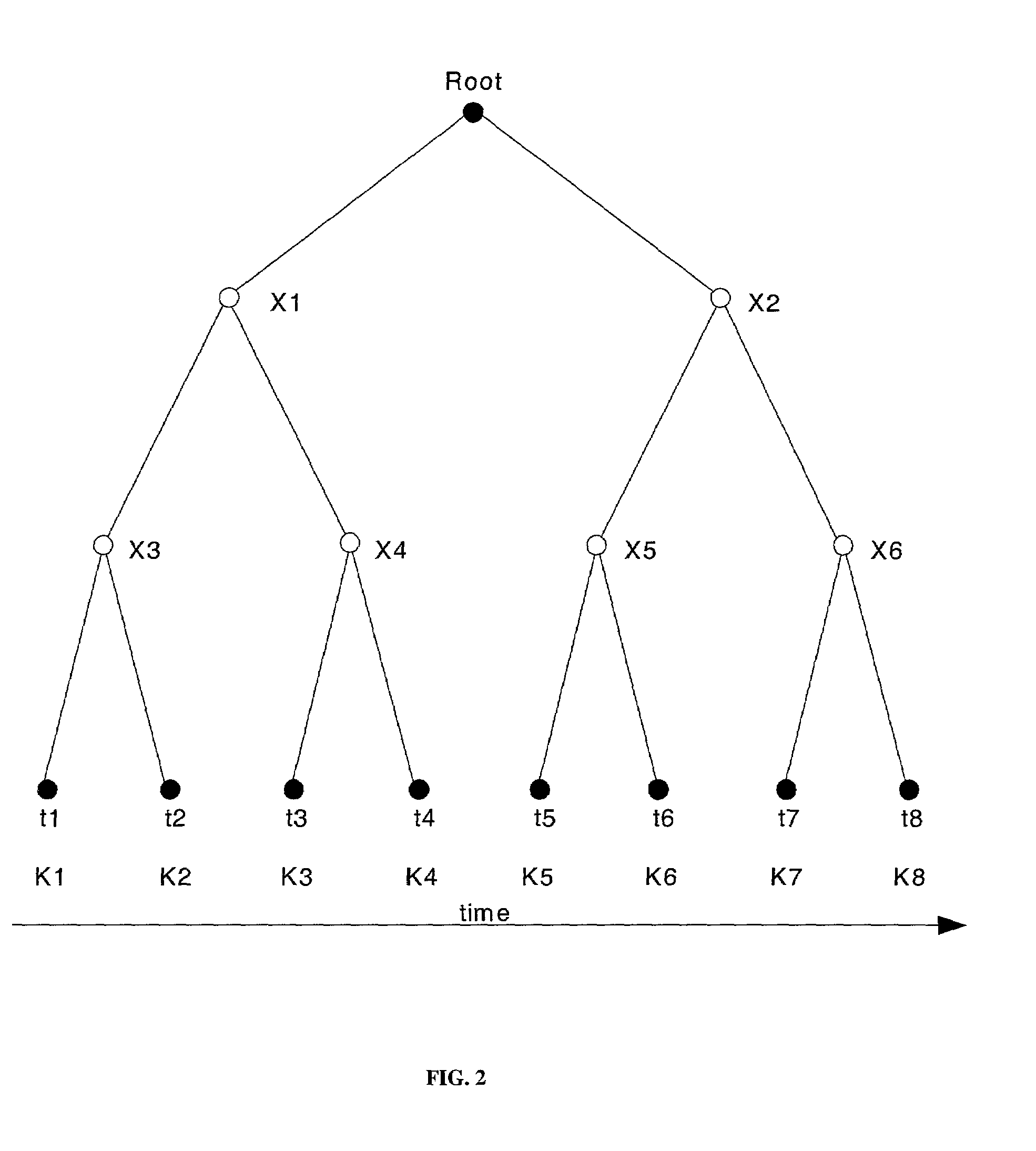
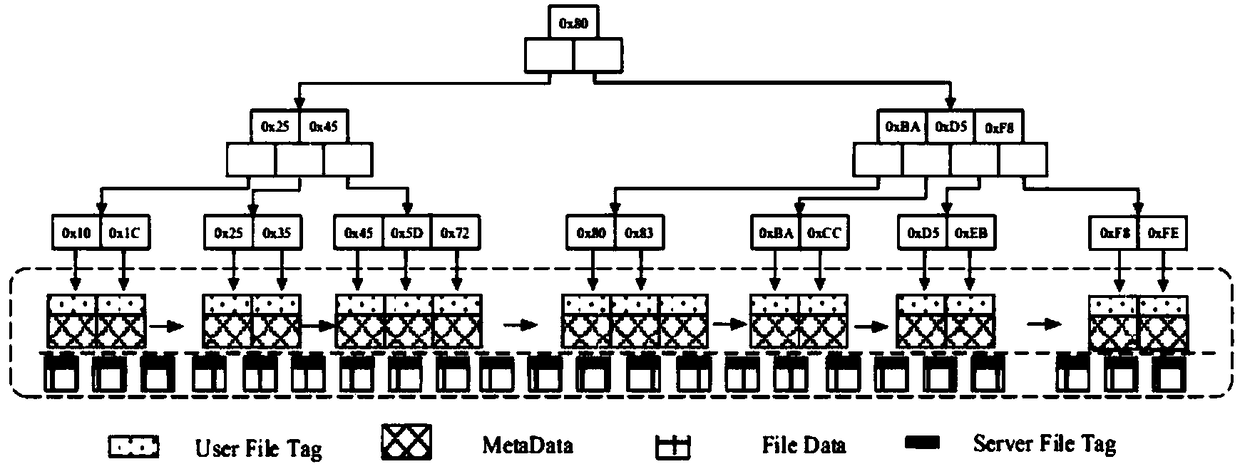
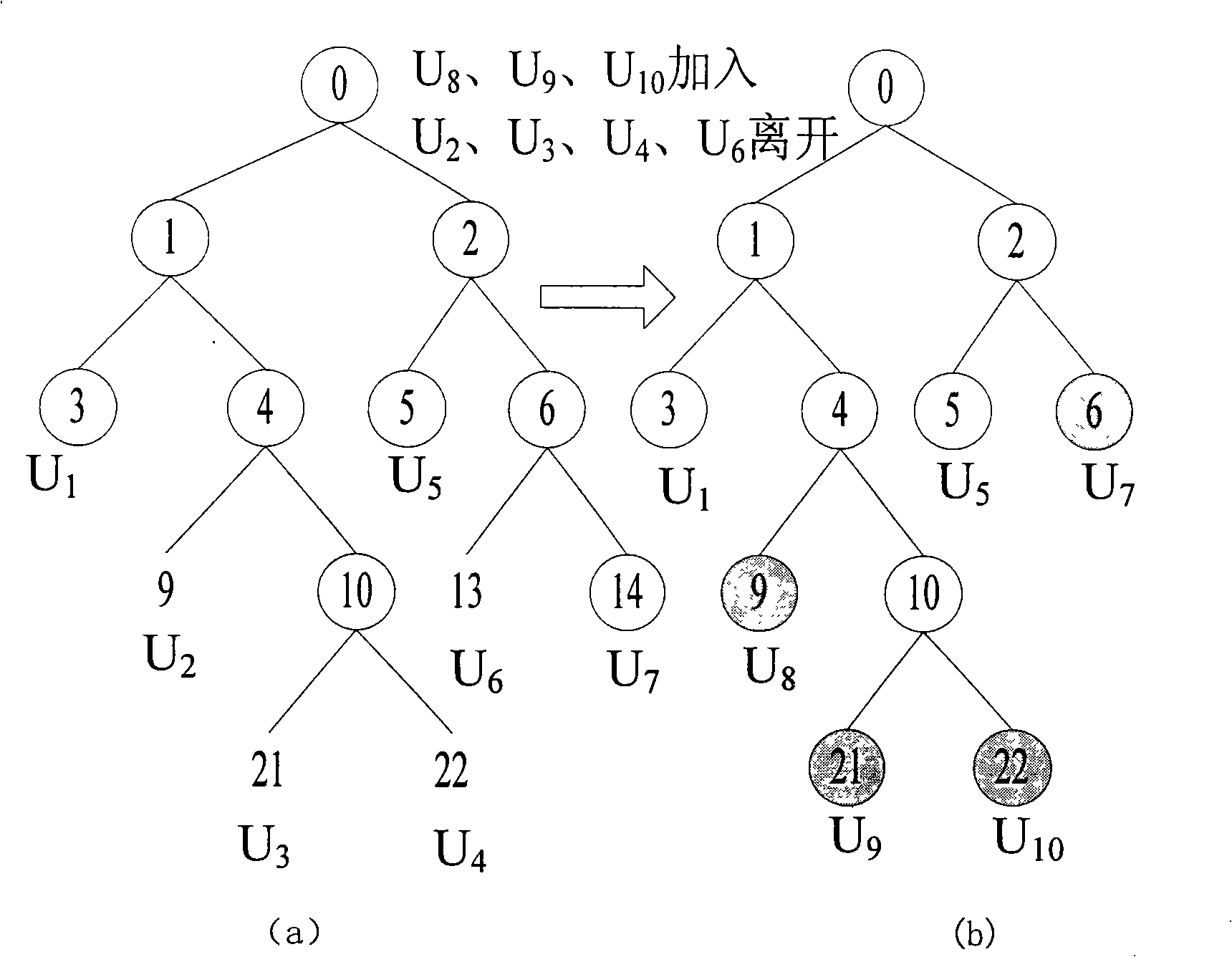
Method for updating distributed cipher key based on AVL tree
ActiveCN101257382AReduce consumptionLow number of stored keysSpecial service provision for substationKey distribution for secure communicationTheoretical computer scienceOne-way function
The invention relates to a distributed group key updating method based on the AVL tree, belonging to the computer network security field. The method comprises: subkey tree forming step, subkey tree combining step, AVL rotating step; if newly formed key tree is loss of balance, rotating the new key tree in the AVL mode until recovering the balance; selecting the leaf nodes at the far left of the subtree whose all of the leaf nodes are newly jointed nodes of the new key tree as the triggering node; initiating the key updating process of the whole key tree. The invention effectively solves key tree unbalance problem in the key management plan completely based on the one-way function tree due to the perfect balance ability of AVL tree and reduces the storage spending of the users.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
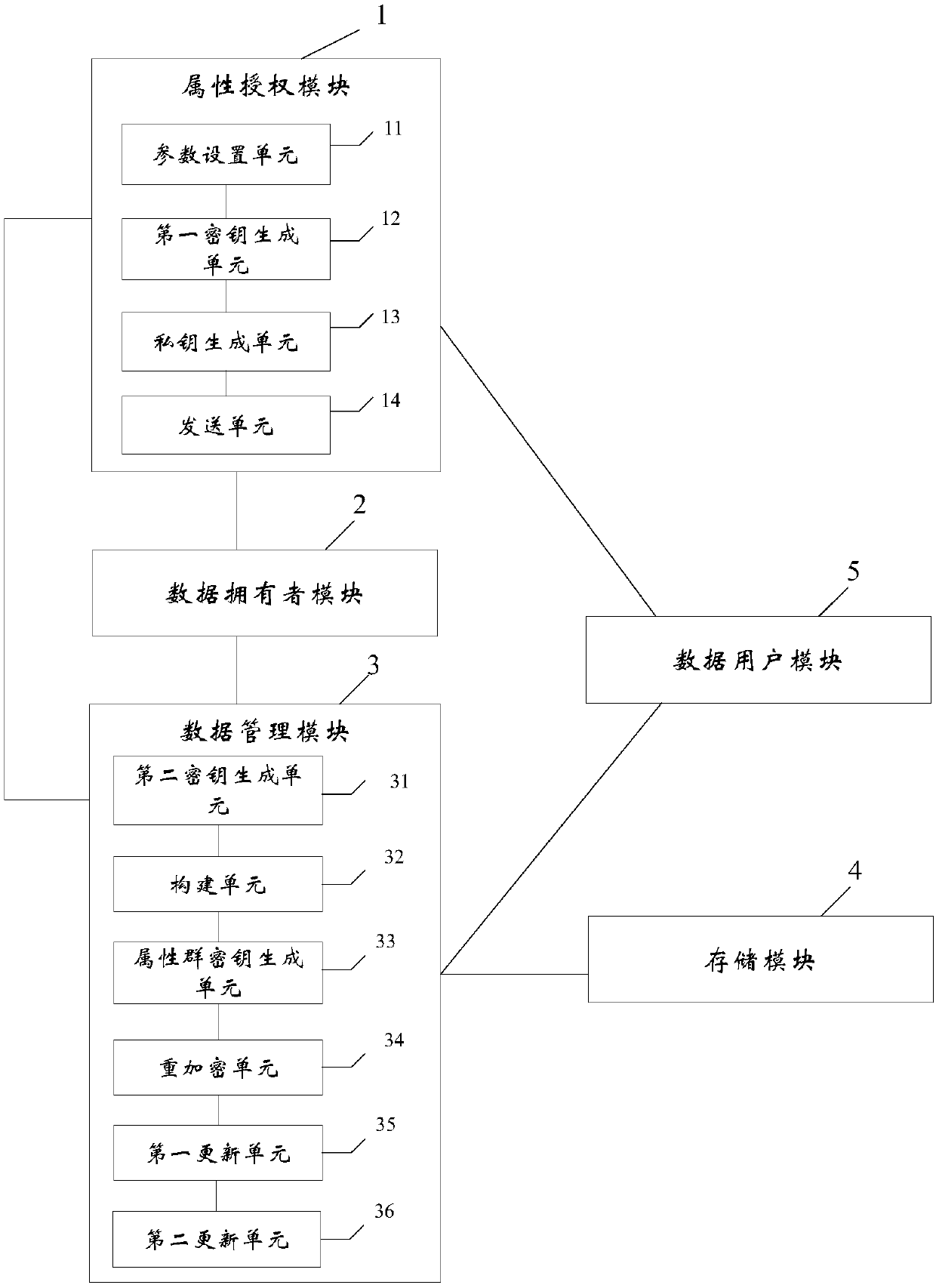
Revocable attribute-based encryption system and method for cloud storage
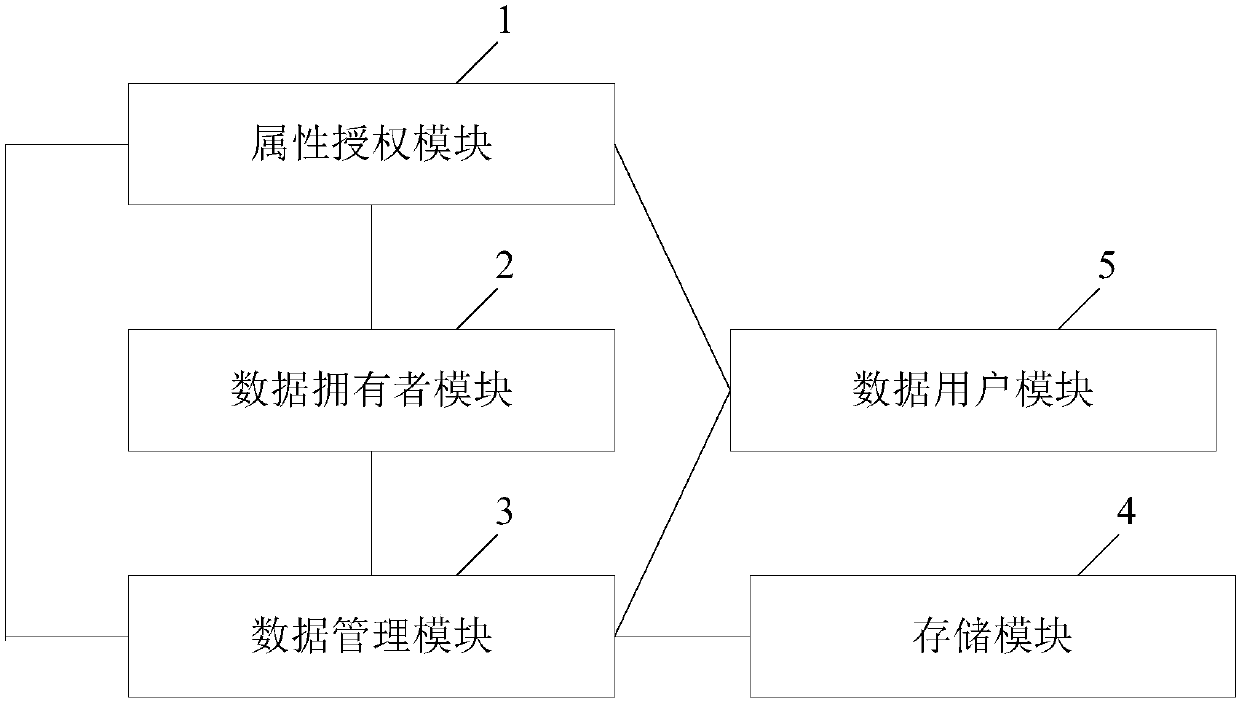
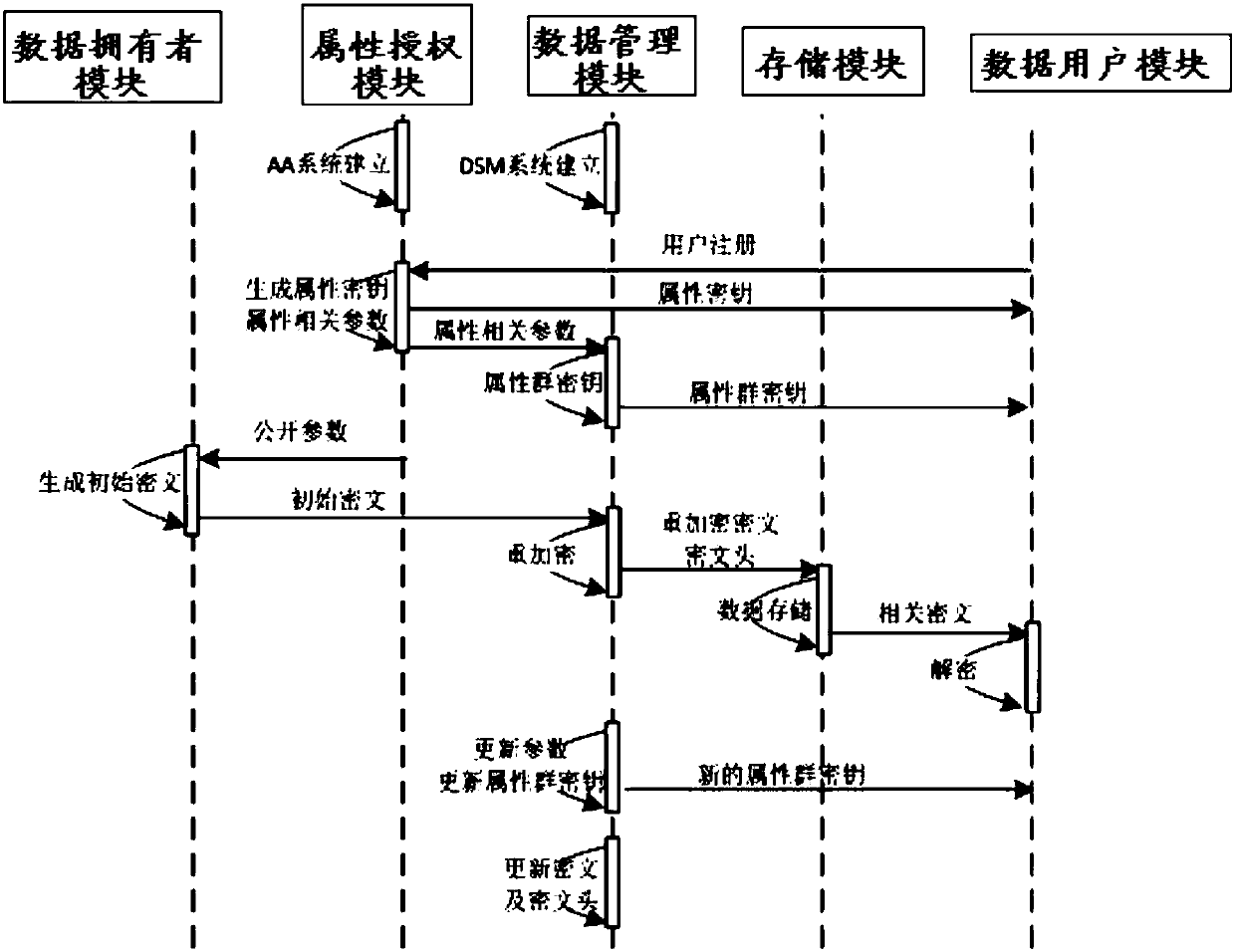
ActiveCN108200181ALighten the computational burdenConstant lengthKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usagePlaintextData access
The invention discloses a revocable attribute-based encryption system and method for cloud storage. An attribute authorization module generates a public key and a main private key of an encryption system, and an attribute private key and an attribute group initial key of a data user; a data owner module constructs a data access structure, and obtain initial ciphertext by encrypting the plaintext;a data management module generates a attribute group key through the constructed key encryption key tree, performs re-encryption processing on the initial ciphertext to generate a ciphertext file anda ciphertext header of the ciphertext file, and stores the ciphertext file via a storage module; the data management module can also update the attribute group key after the data user module attributeis revoked, and process to obtain an updated ciphertext file. The data user module accesses the ciphertext file and decrypts the ciphertext file to obtain a plaintext corresponding to the ciphertextfile. Therefore, the attribute-level user revocation capability is implemented, the collusion attack between a revoking user and a non-revoking user can be resisted, and fixed-length ciphertext lengthand higher efficiency are achieved.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
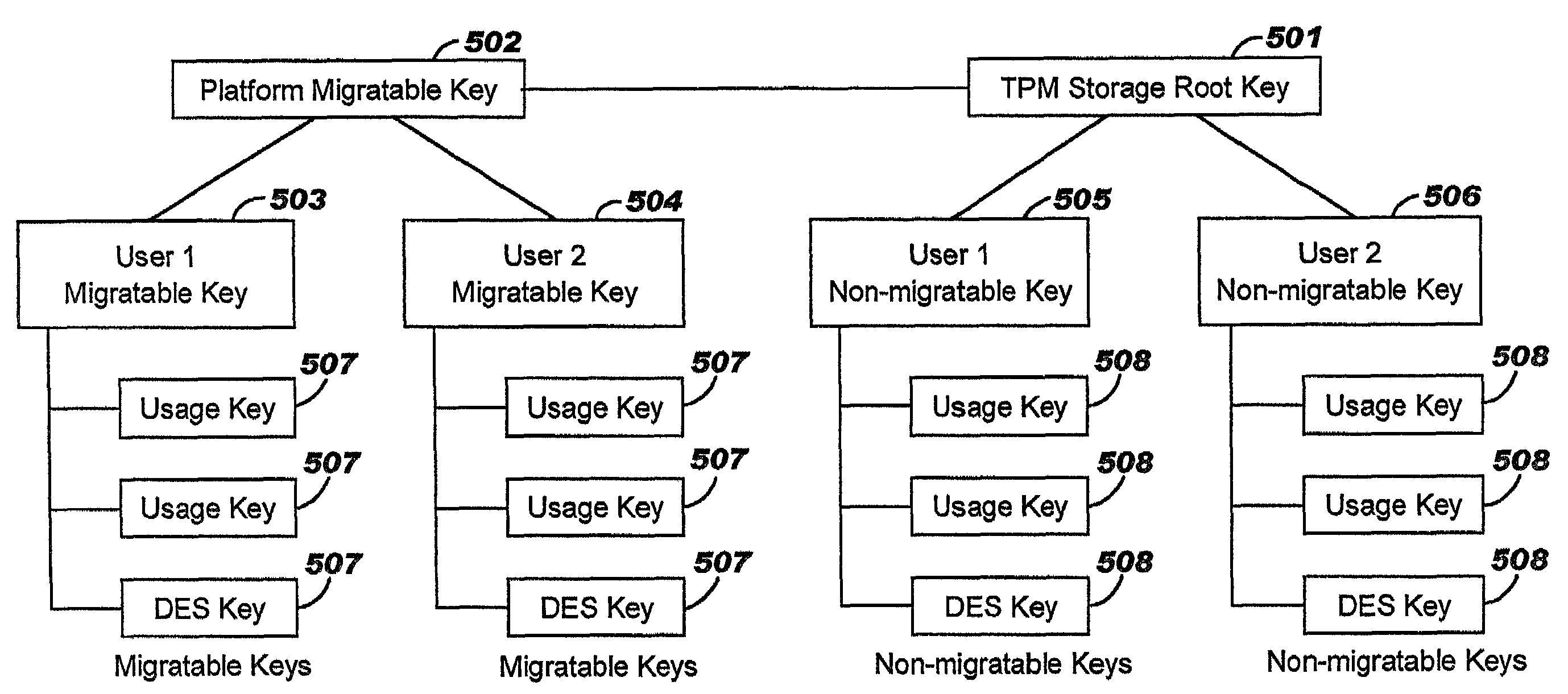
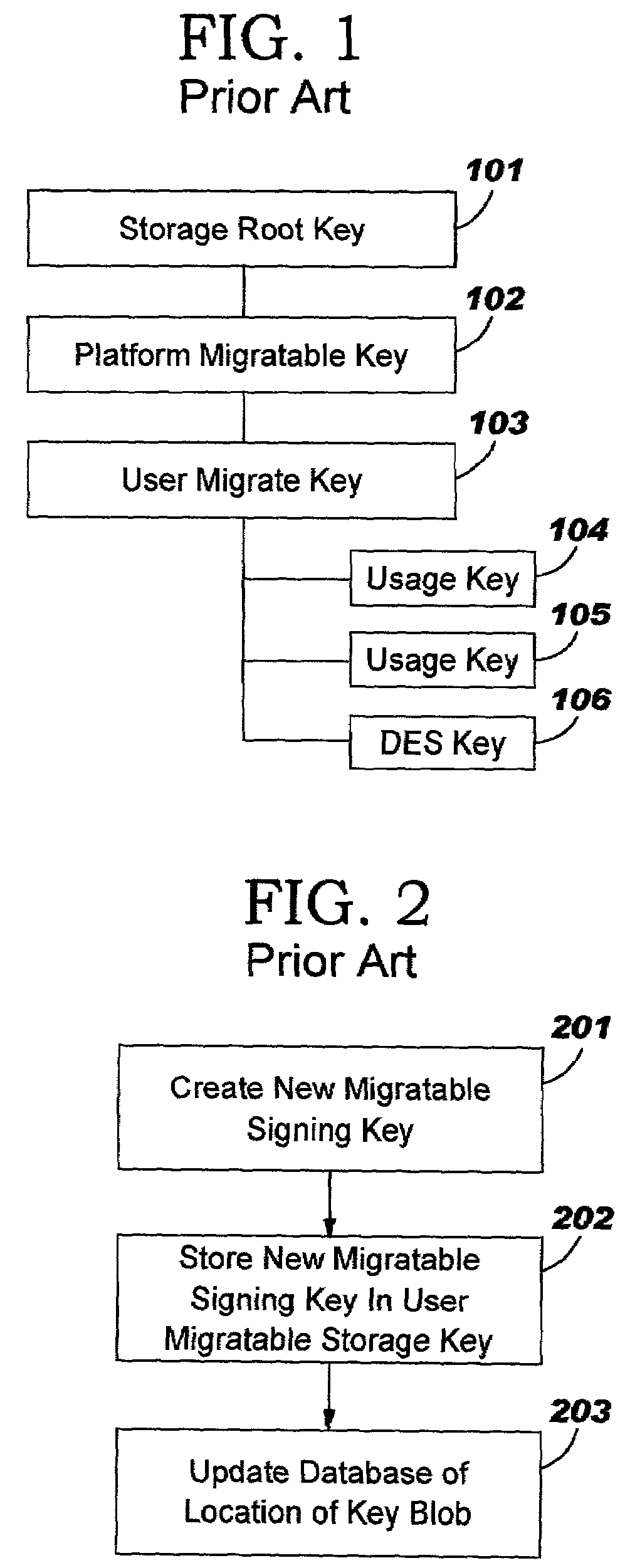
Trusted computing platform with dual key trees to support multiple public/private key systems
ActiveUS7281010B2Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsTrusted ComputingTheoretical computer science
The present invention addresses the foregoing need by creating two identically structured storage trees with a single storage root key. As envisioned in the current art (e.g., the TCPA specification), all migratable keys will be stored in a migratable storage tree. These migratable keys will be storage keys except at the extreme end of any branch, where the key (known as a leaf key) will be a user key. However, an additional storage tree will also be created which shadows the migratable storage key. This second storage tree will be comprised entirely of non-migratable storage keys of the quicker loading type except for the leaf keys (which will be identical to the leaf keys in the migratable storage tree (MST). The second storage tree (SST) will have a storage key for every migratable storage key in the MST. The use authorization for the keys in the SST will be identical to the use authorization for the MST.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
Data processing system, data processing method, data processing apparatus, and program providing medium
ActiveUS7131010B2Good effectKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationData processing systemComputer science
The data processing system is realizable by executing a step of ciphering contents keys used for decoding ciphered contents data by applying mutually different ciphering keys before storing ciphered contents keys in memory as header data of the corresponding contents data. One of the ciphered contents keys comprises ciphered data ciphered by a ciphering key provided for by enabling key block comprising such data composition which is solely decodable by specific device by way of disposing related keys in such corresponding nodes on the path ranging from roots to leaves of a key tree structure for distributing keys. The other ciphered contents key comprises such data ciphered by a specific key proper to a corresponding storage device to enable the device for reproducing contents data to properly and selectively utilize data of ciphered key, whereby enabling the data processing system to properly reproduce decoded contents data.
Owner:SONY CORP
Data processing system, data processing method, and program providing medium
InactiveUS20070121950A1Key distribution for secure communicationUnauthorized memory use protectionData processing systemData file
The inventive data processing apparatus enables own memory device to store a plurality of key distribution approval data files each containing such a header data comprising a number of “link-count” data units each designating actual number of applicable contents data per decodable contents key based on an enabling key block (EKB) distribution key enciphering key (KEK) enciphered by a corresponding enabling key block (EKB) provided for by a hierarchy key tree structure. When storing a plurality of the enabling key blocks (EKB) in a memory device, such a key enciphering key (KEK) contained in an enabling key block (EKB) having a number of link-count data units is previously decoded and stored in the memory device. By way of applying the stored (KEK) when utilizing contents data, the enabling key block (EKB) processing step is deleted, whereby promoting higher efficiency in the utilization of contents data.
Owner:SONY CORP
Specific text infor mation processing method based on key tree and system therefor
ActiveCN1979482AImprove search speedImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsInformation processingData mining
The invention provides a key tree-based specific text information processing method and system, comprising the steps of: storing specific text information; generating a key tree including the specific text information; searching whether the given character string is included in the specific text information the key tree includes according to the key tree and then outputting the searching result. And the invention is used to raise specific text information processing rate, reduce misreporting and raise processing rate of the whole service.
Owner:INDUSTRIAL AND COMMERCIAL BANK OF CHINA
System, method, and service for performing unified broadcast encryption and traitor tracing for digital content
ActiveUS20090323936A1Improve abilitiesUser identity/authority verificationRecord information storageComputer hardwareDigital content
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Key tree construction and key distribution method for hierarchical role-based access control
InactiveUS8447037B2Efficient executionReduce consumptionKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageRole-based access controlKey distribution
A key tree construction and key distribution method for hierarchical role-based access control, includes: constructing a key tree including relationships between a hierarchical structure of role groups and data; performing encryption and decryption of data keys and role keys; and generating a key table, in which the data keys required to decrypt encrypted data and the role keys required to decrypt encrypted data keys are stored, with reference to the key tree. Further, the key tree construction and key distribution method for hierarchical role-based access control includes performing management such that a specific role group can obtain a data key by performing decryption based on its own role key by using both the key tree and the key table.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com