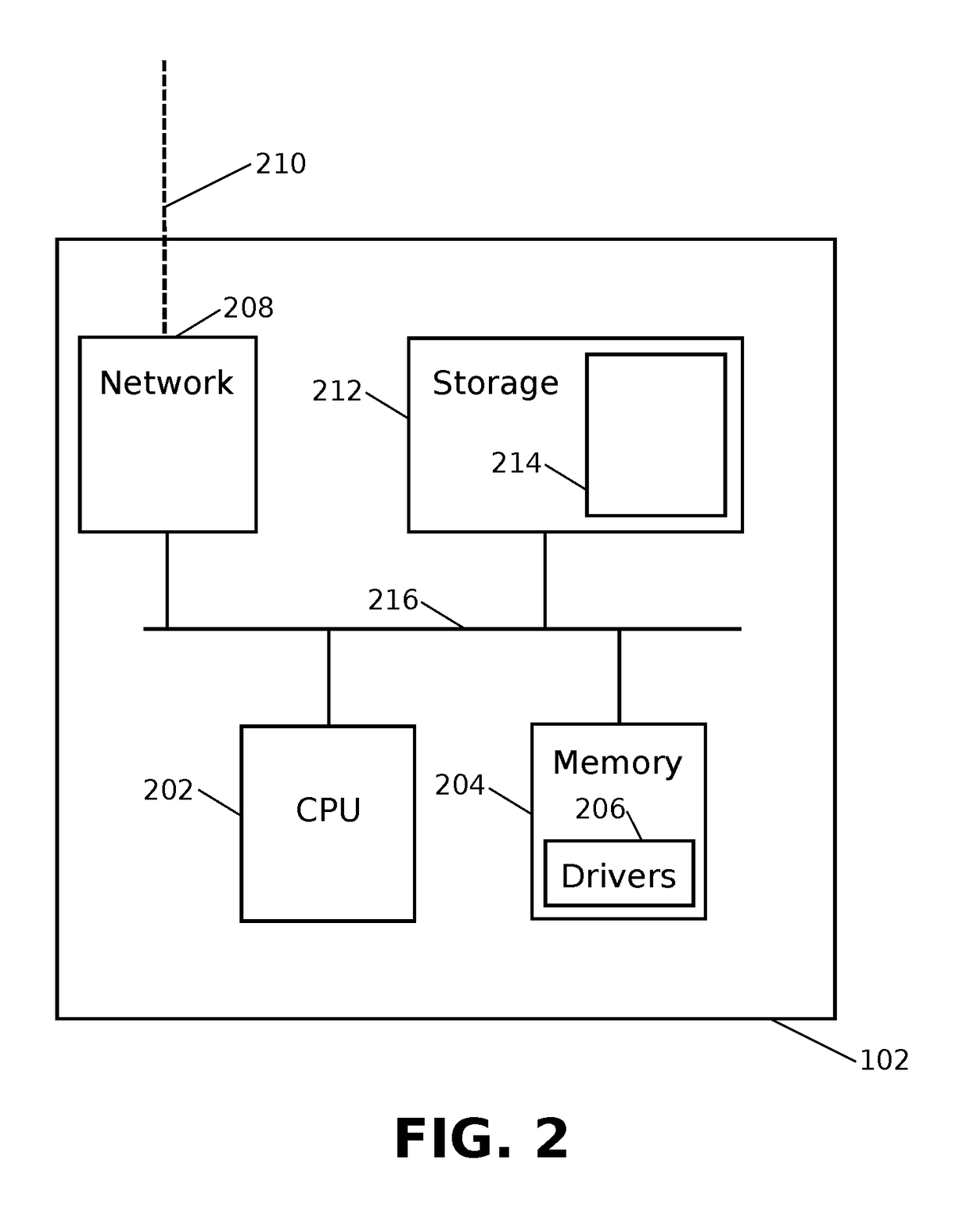
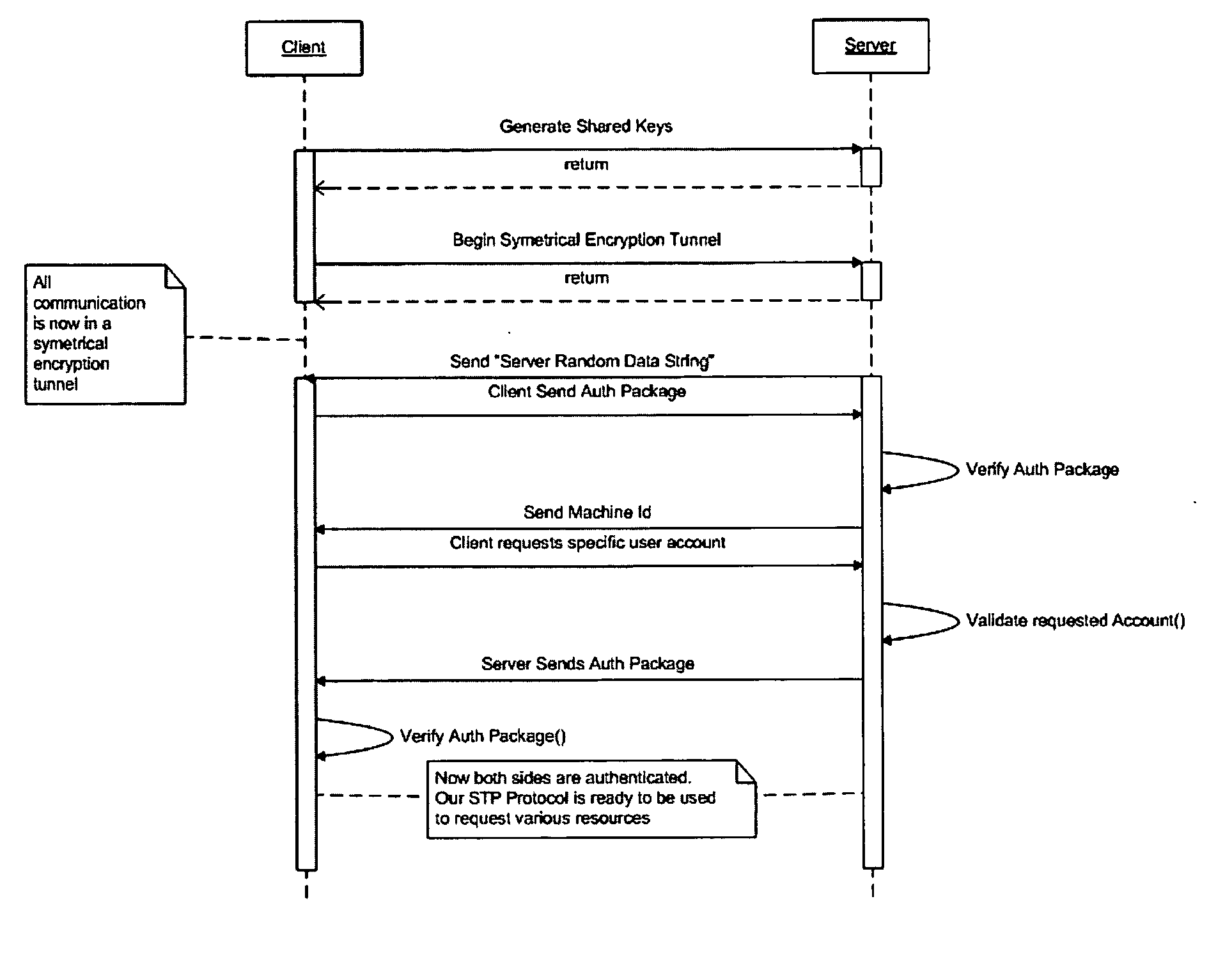
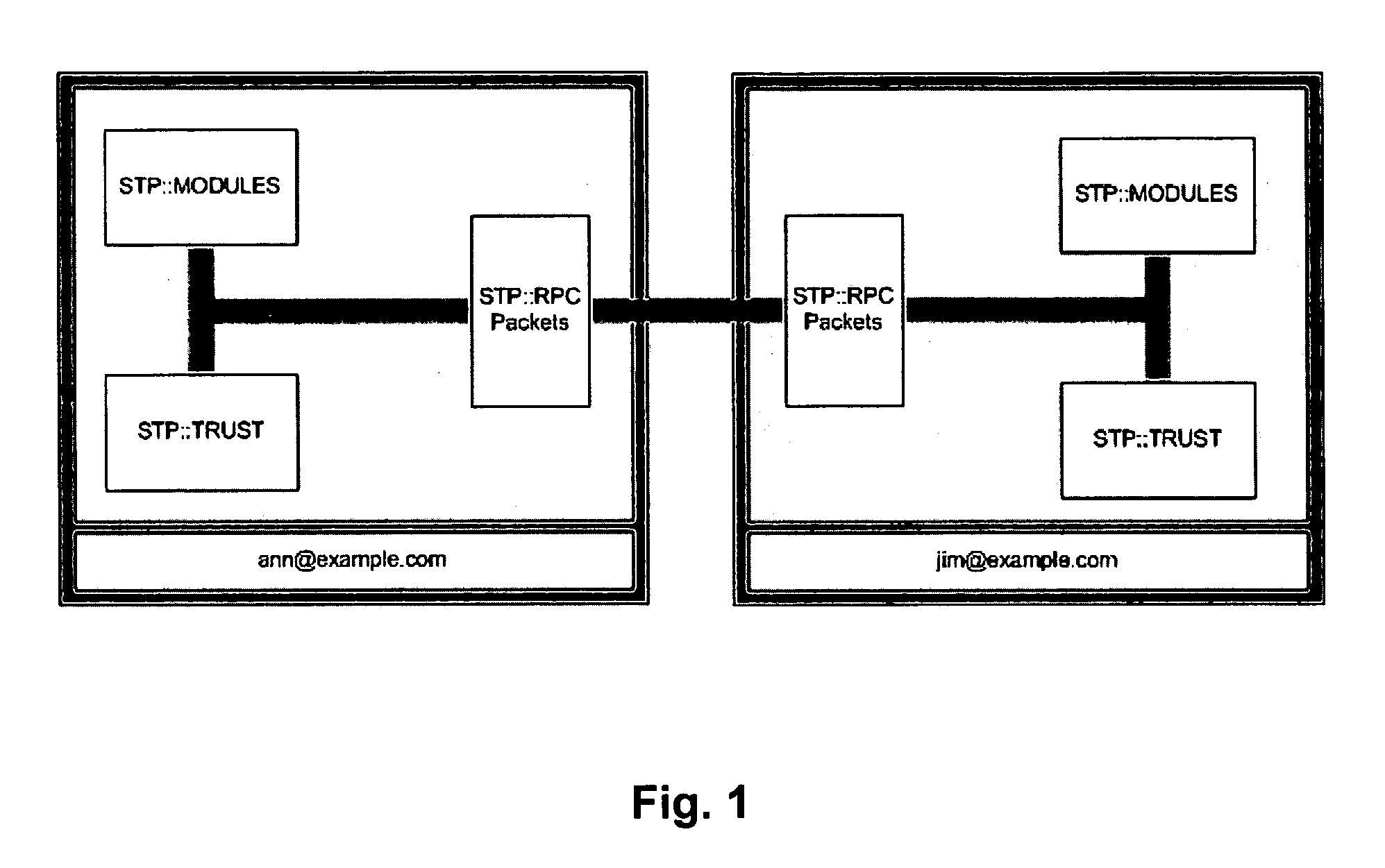
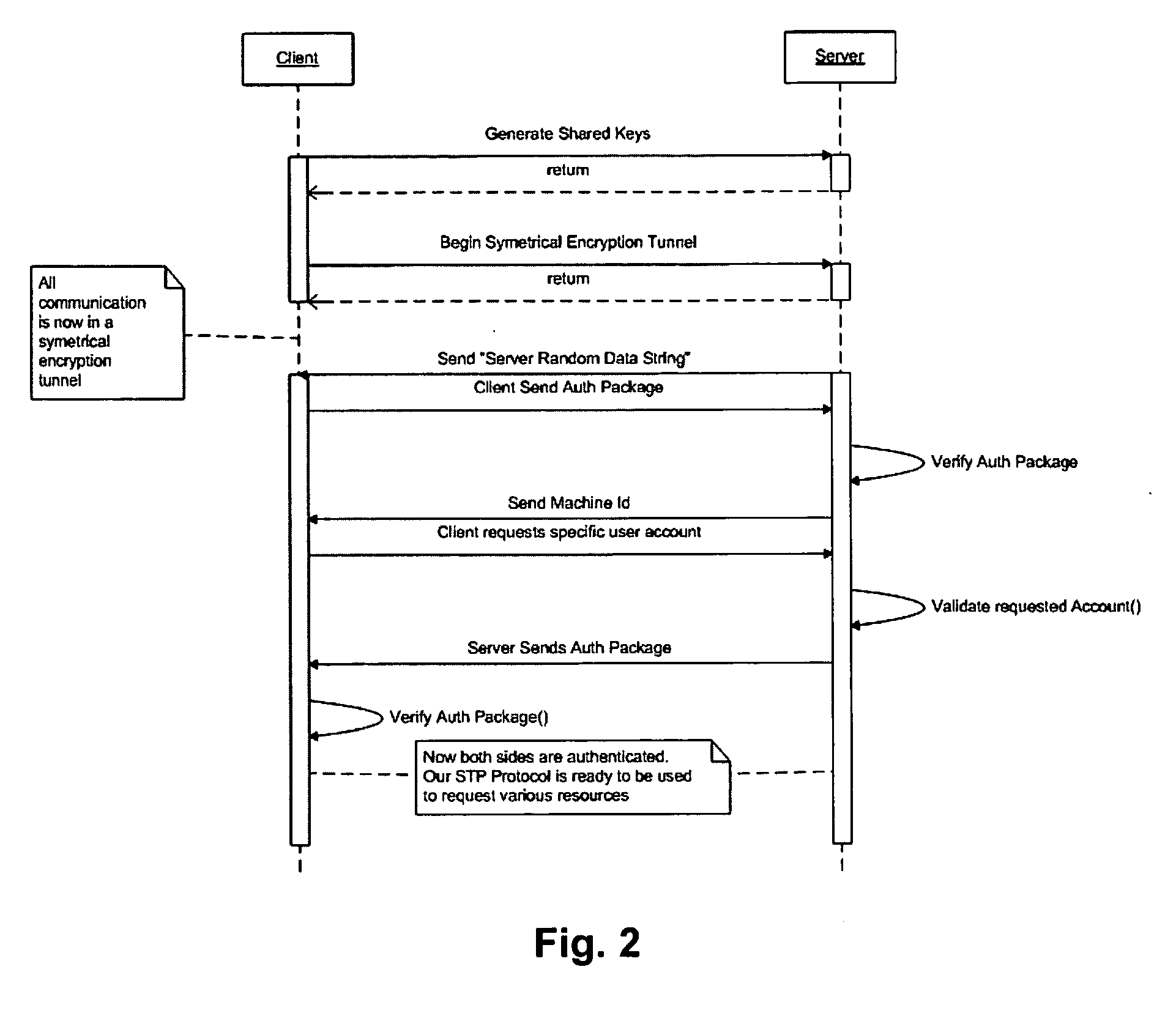
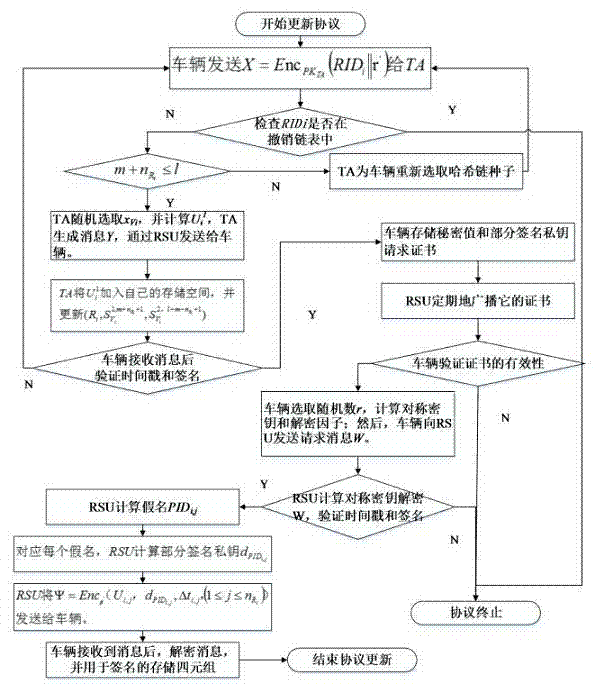
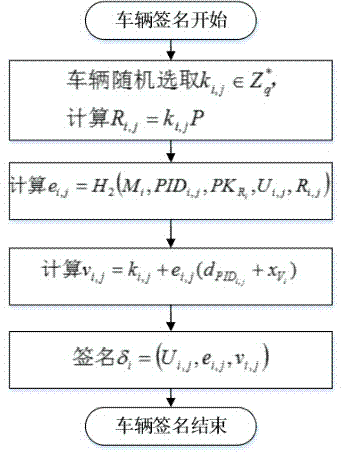
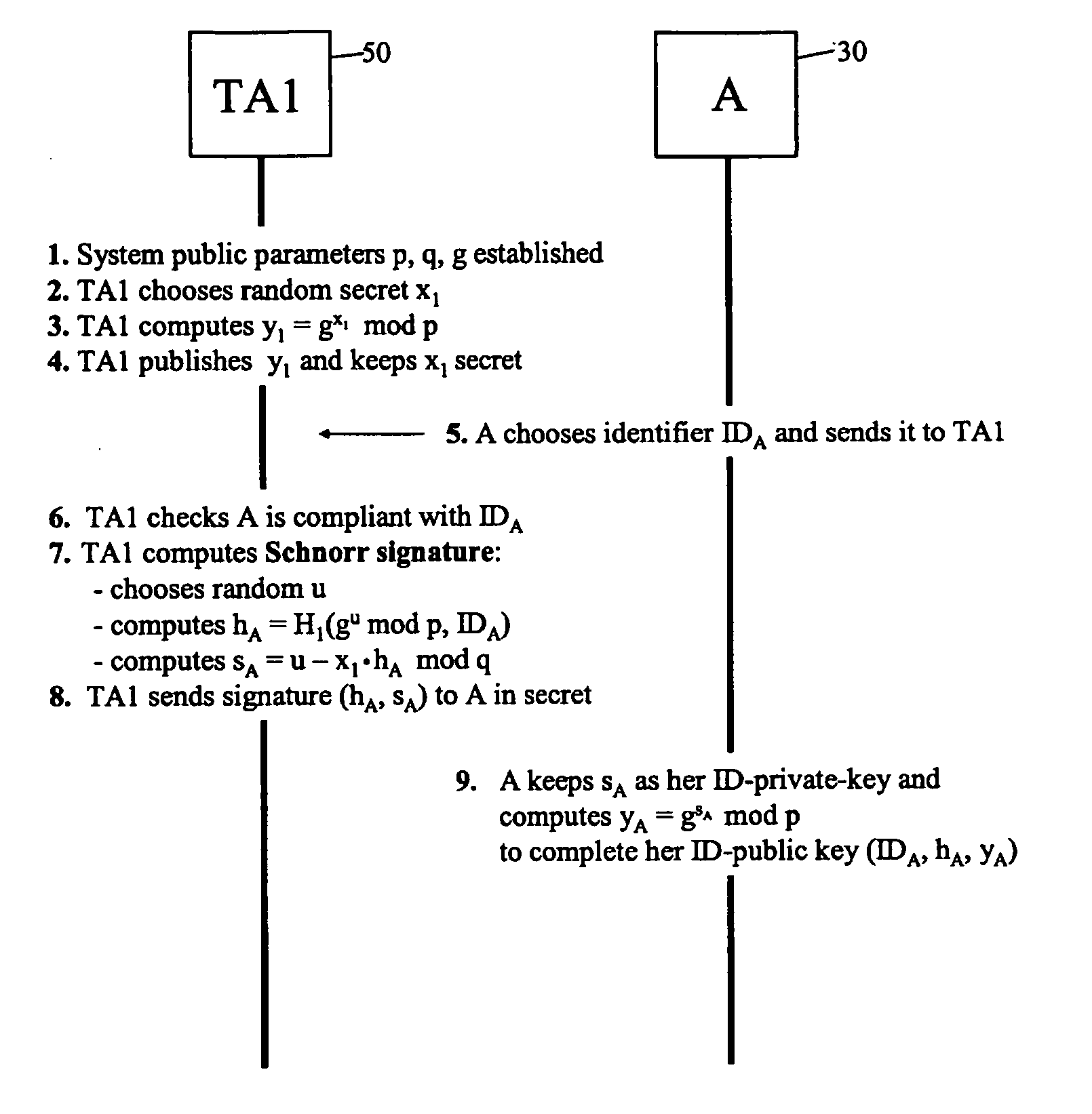
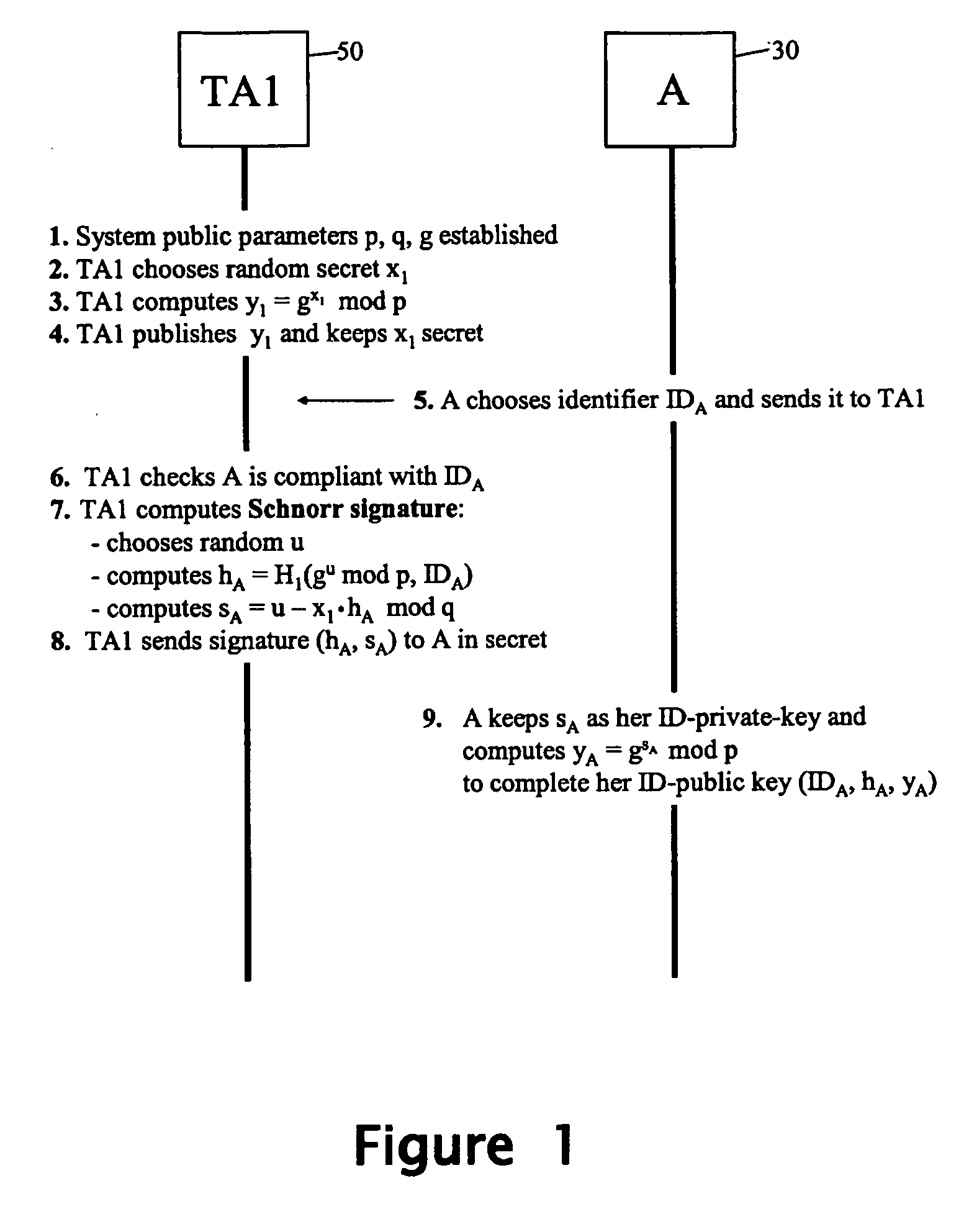
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
194 results about "Trusted authority" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
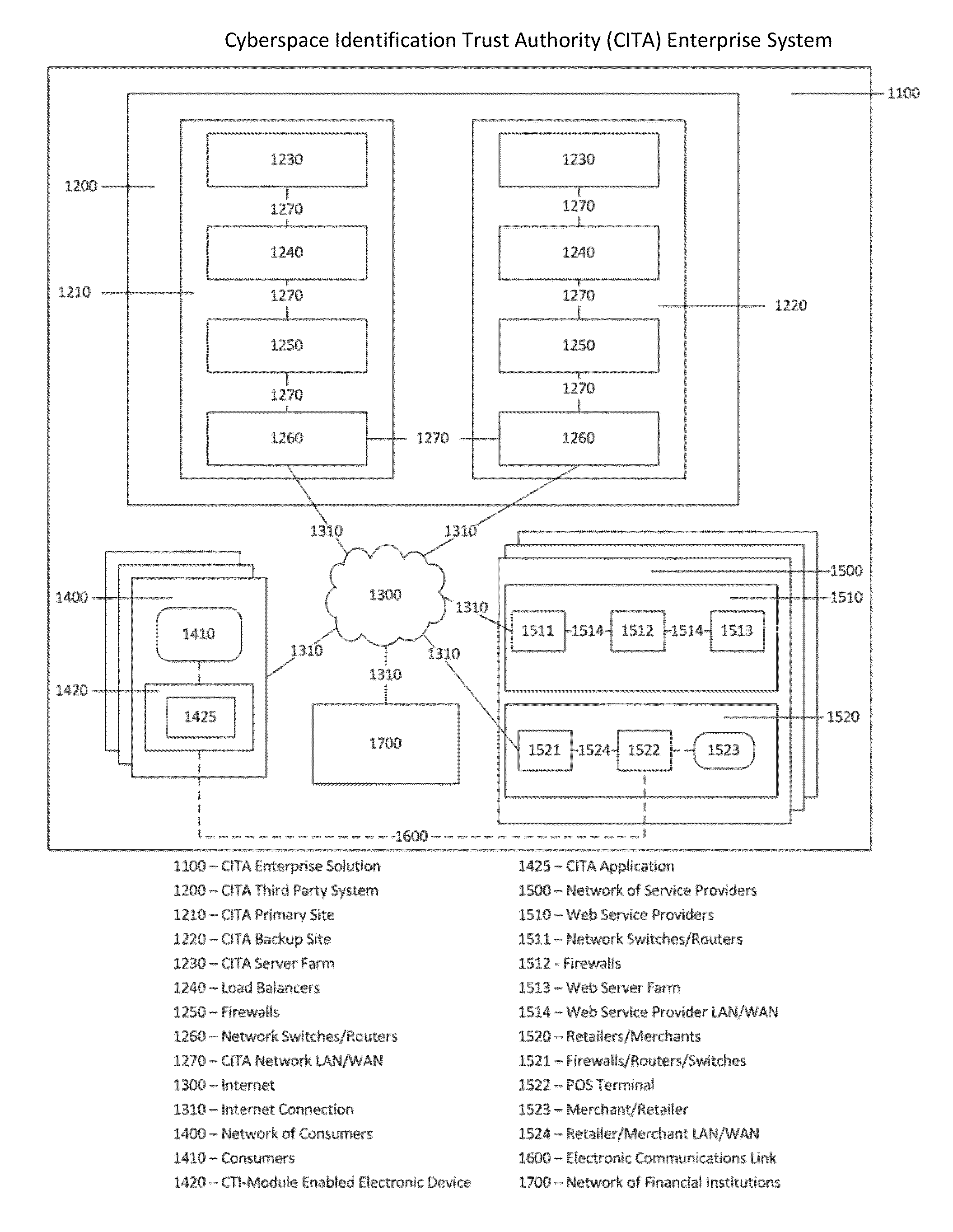
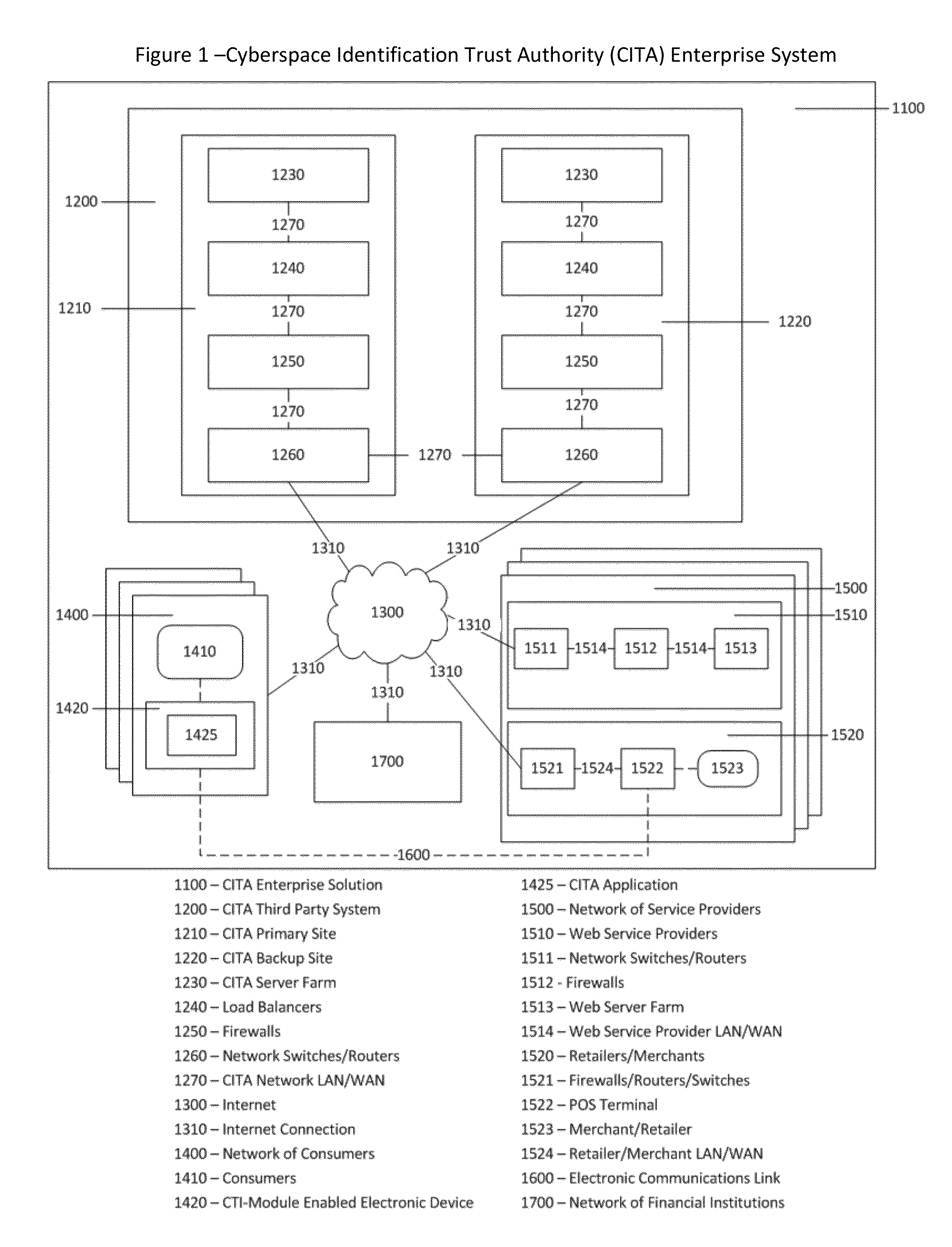
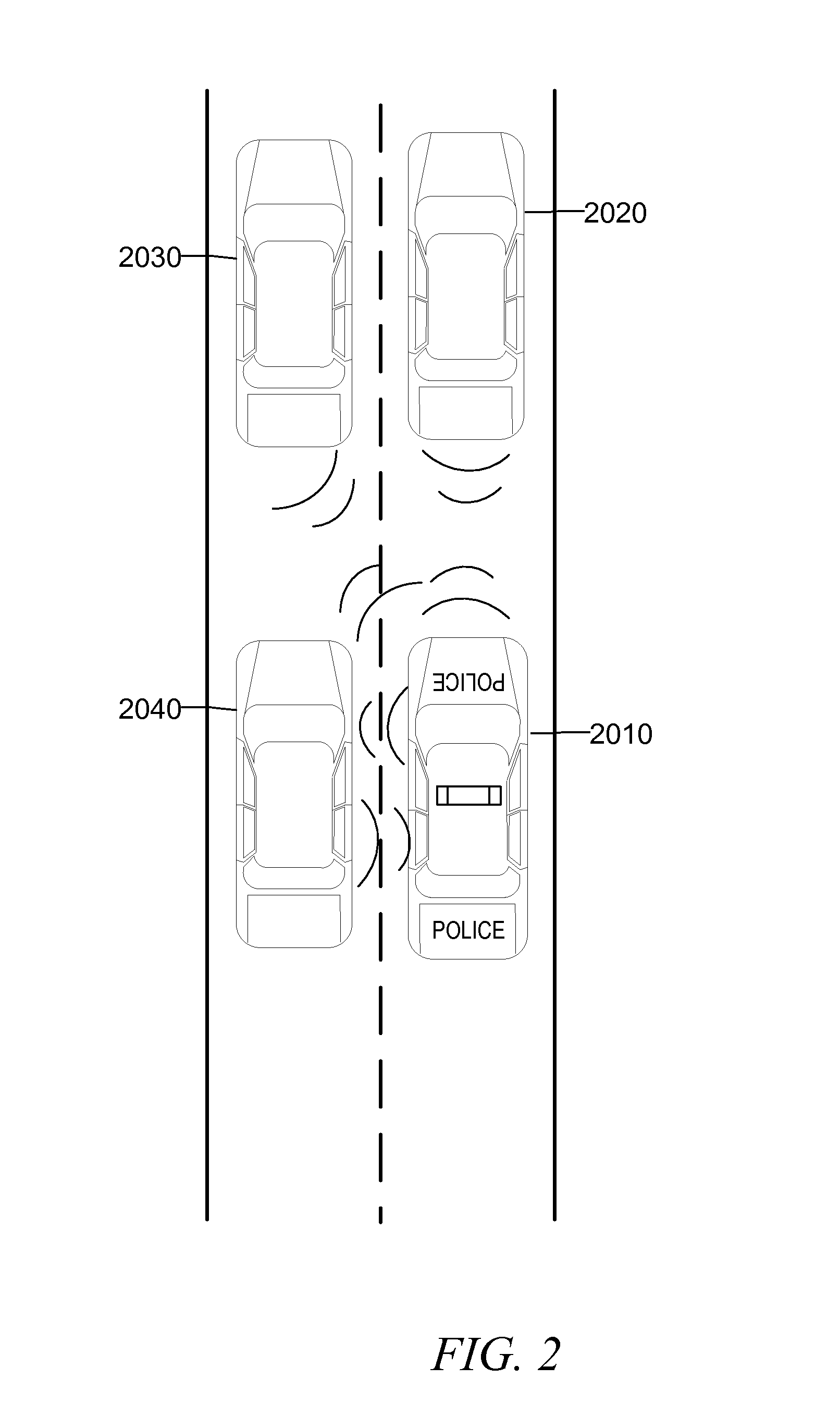
Cyberspace Identification Trust Authority (CITA) System and Method
InactiveUS20130226813A1Eliminate chanceSecure transmissionFinanceProtocol authorisationTrusted authorityPayment
When two parties of a cyberspace transaction register their identity attributes under a CITA system each party is assigned a unique, encrypted and digitally signed identity token. When the consuming party seeks access too, or payment for, cyberspace services, the providing party submits their identity token to the consuming party. The consuming party creates a request token, containing both the consumers' and the providers' identity tokens, and the transaction related information, to the CITA system. The CITA system validates the identity tokens and either creates a payment confirmation token by processing the payment request, or creates an access confirmation token by dynamically defining the minimal consumer identity attributes required to gain access to the provider's service. The confirmation token is encrypted and digitally signed and returned to the consumer, and then forwarded to the provider to complete the transaction without either party openly exchanging personal identity attributes.
Owner:VOLTZ ROBERT MATTHEW
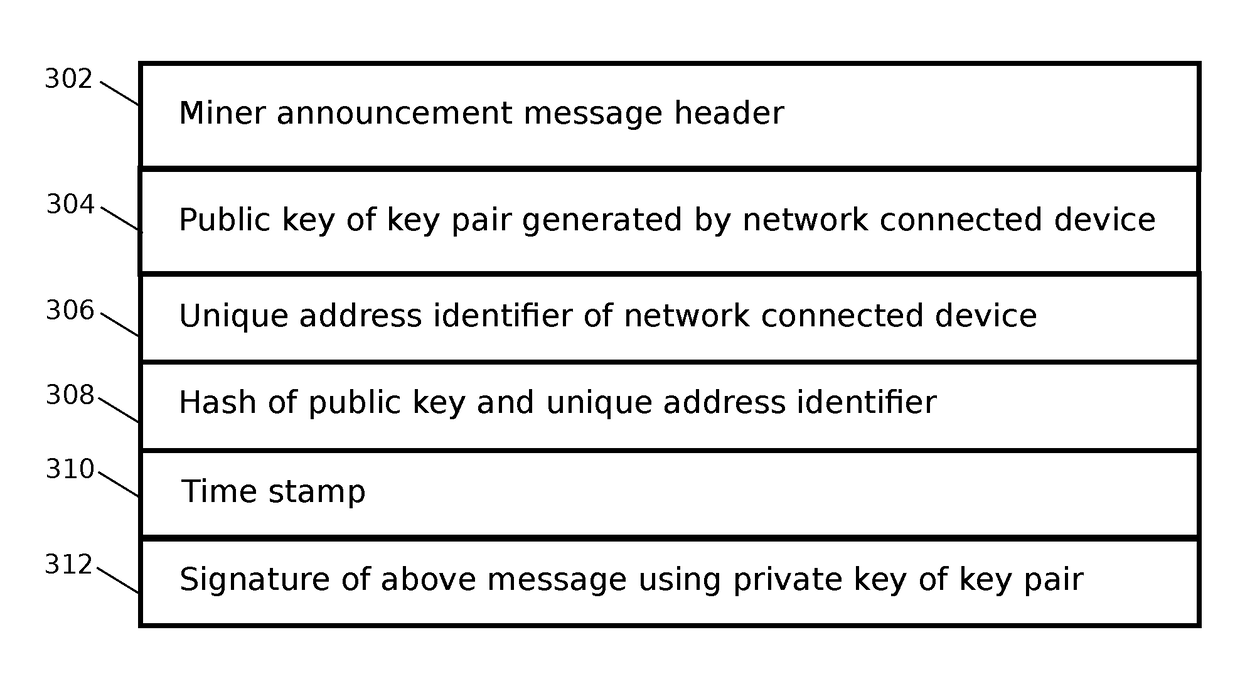
Consensus system and method for adding data to a blockchain
ActiveUS20170075941A1Reduce energy consumptionDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsTrusted authorityWaiting period
A method and apparatus is presented for reaching consensus on adding data to a distributed ledger system in which no central trusted authority is available, comprising sending an announcement message by a network connected device to a plurality of network connected devices over a peer-to-peer network, said message providing an identification of the network connected device using a public key of a public / private key pair, a unique address identifier, and a hash. Subsequently, after a waiting period measured in, for example, time or blocks of data, the network connected device may submit data for inclusion in the distributed ledger. If the announcement message and preceding data in the distributed ledger satisfy a predetermined condition, the plurality of network connected devices may include the data in the distributed ledger. If the network connected device fails to submit the data when the predetermined condition is satisfied, the announcement message may be canceled.
Owner:FINLOW BATES KEIR
Method of providing secure access to computer resources
InactiveUS20070101400A1Easy accessLow level of trustDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer resourcesTrusted authority
A method of providing varying levels of secure access to computer resources. A certificate is used to identify a particular data requester and the certificate is authenticated using asymmetrical encryption techniques, such as public-private key pairs. One or more trust authorities may be consulted to ascribe a trust level to the certificate, which is an indication of the veracity of the identity of the data requester. Individual system users may set differing levels of access to a number of shared system resources for a particular data requester. The authenticated and verified data requester is then provided with the pre-set level of access to the desired shared resource. The level of access to a particular shared system resource therefore depends upon the user the data is being accessed through, the authenticated identity of the data requester, and their ascribed trust level. The shared resource may comprise data and / or an application module that is accessed or executed through a secure symmetric encryption tunnel.
Owner:OVERCOW CORP
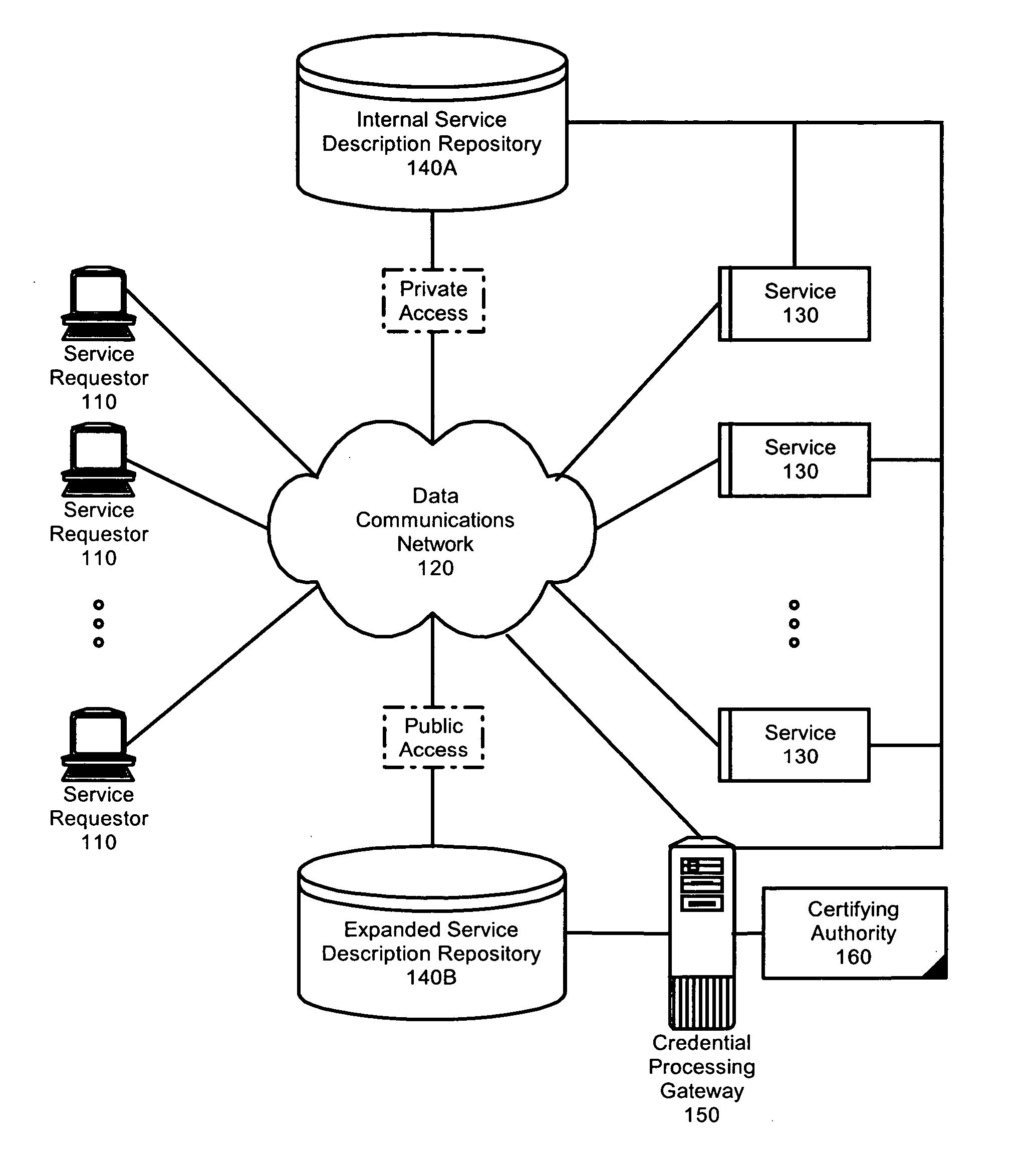
Federated identity brokering
InactiveUS20060021010A1Make up for deficienciesDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTrusted authorityFederated identity
A method, system and apparatus for federated identity brokering. In accordance with the present invention, a credential processing gateway can be disposed between one or more logical services and one or more service requesting clients in a computer communications network. Acting as a proxy and a trusted authority to the logical services, the credential processing gateway can map the credentials of the service requesting clients to the certification requirements of the logical services. In this way, the credential processing gateway can act as a federated identity broker in providing identity certification services for a multitude of different service requesting clients without requiring the logical services to include a pre-configuration for specifically processing the credentials of particular service requesting clients.
Owner:IBM CORP
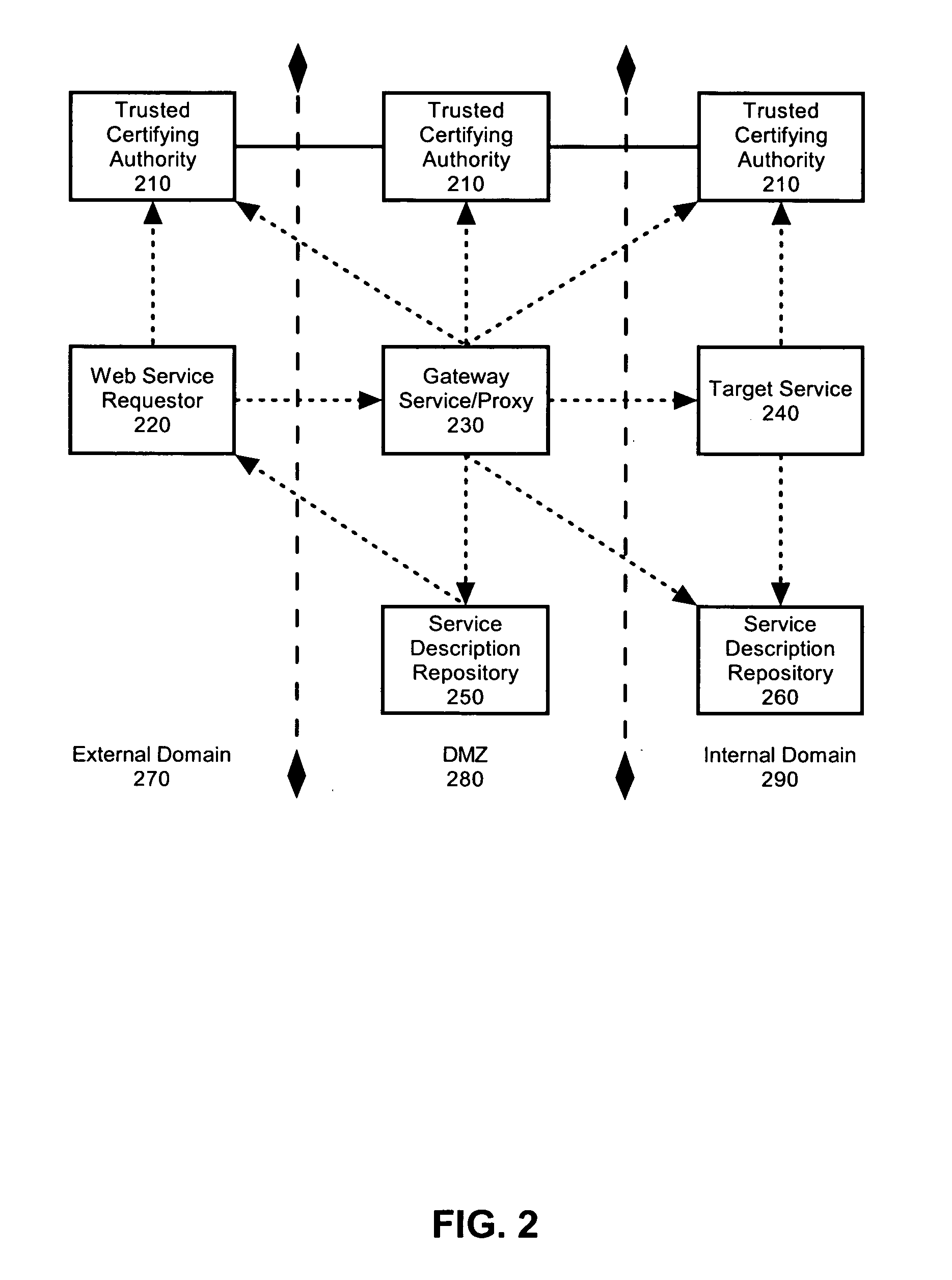
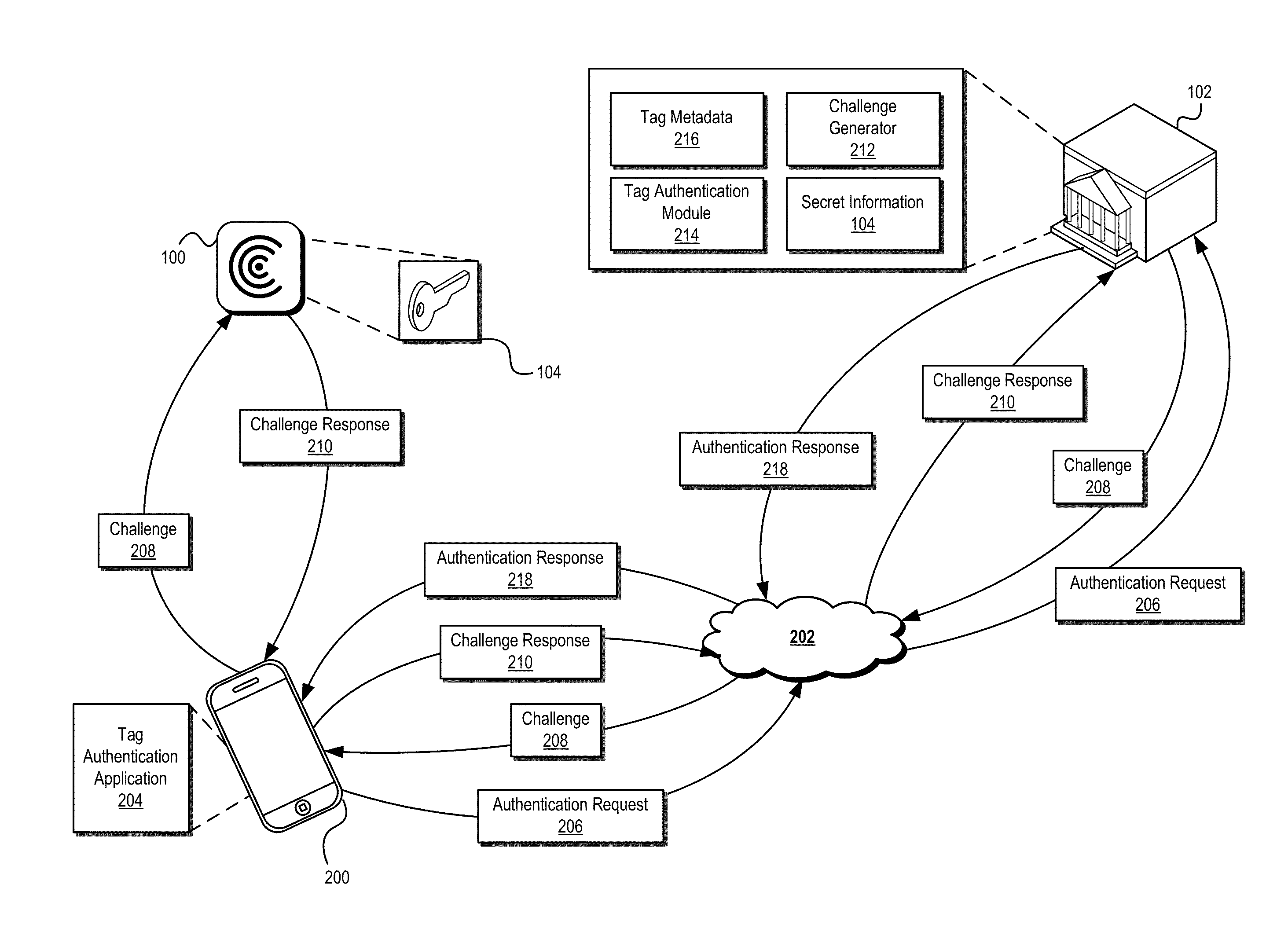
Secure Transaction Systems and Methods
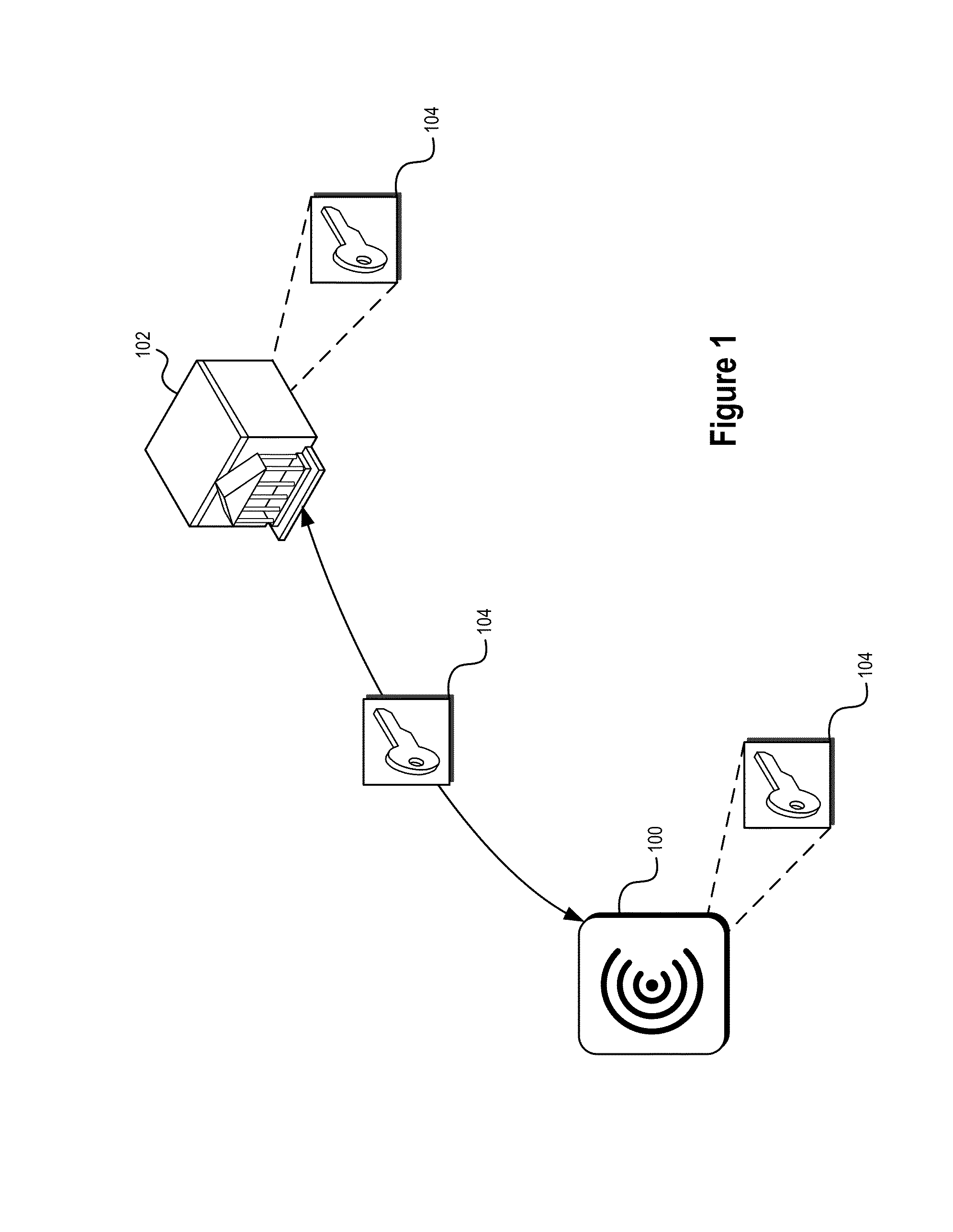
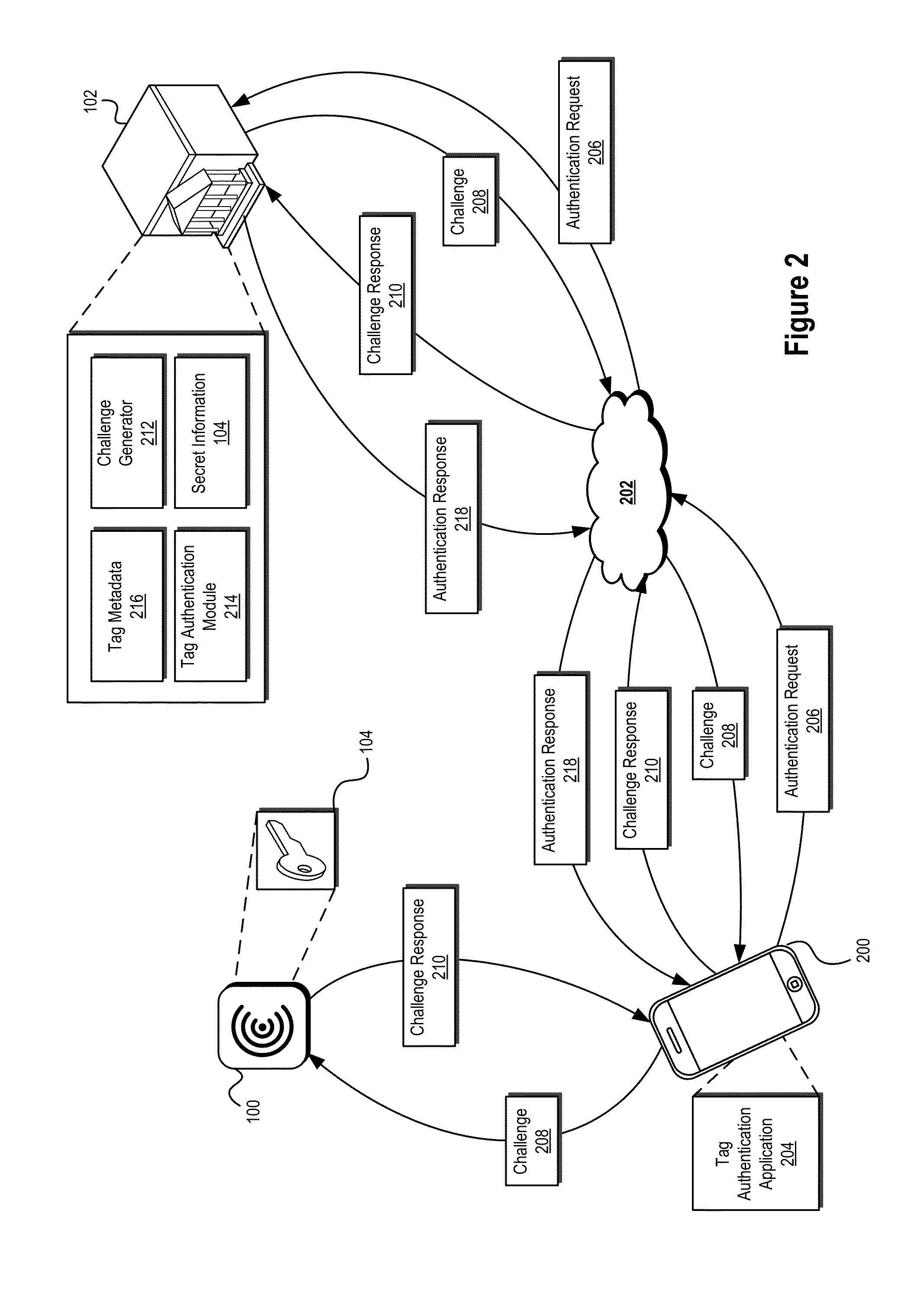
ActiveUS20140282974A1Prevent theftPrevent fraudDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTrusted authorityInformation provision
Systems and methods are described that use tag authentication and presence verification techniques in connection with a variety of transactions. In certain embodiments, an authentication device may verify the authenticity of a secure tag by determining whether the secure tag stores secret information provisioned by a trusted authority. In some embodiments, such an authentication process may be performed without exposing the secret information to the authentication device, thereby maintaining integrity of the secure tag. In other embodiments, insecure tags and / or tags that do not include secret information are used.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
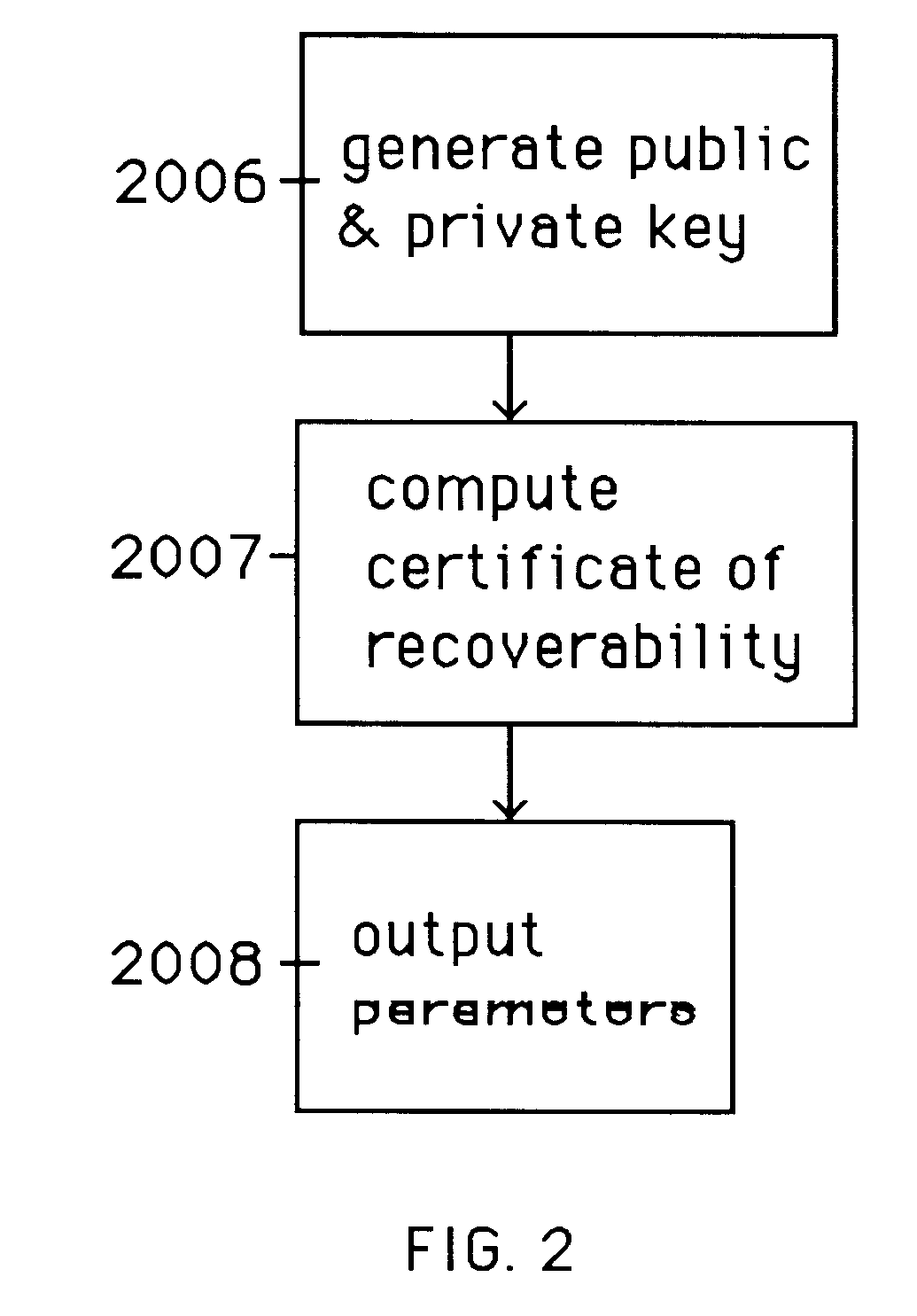
Auto-recoverable and auto-certifiable cryptostem using zero-knowledge proofs for key escrow in general exponential ciphers
InactiveUS6282295B1Fast and easy disseminationEasy to handleKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationTrusted authorityValidation methods
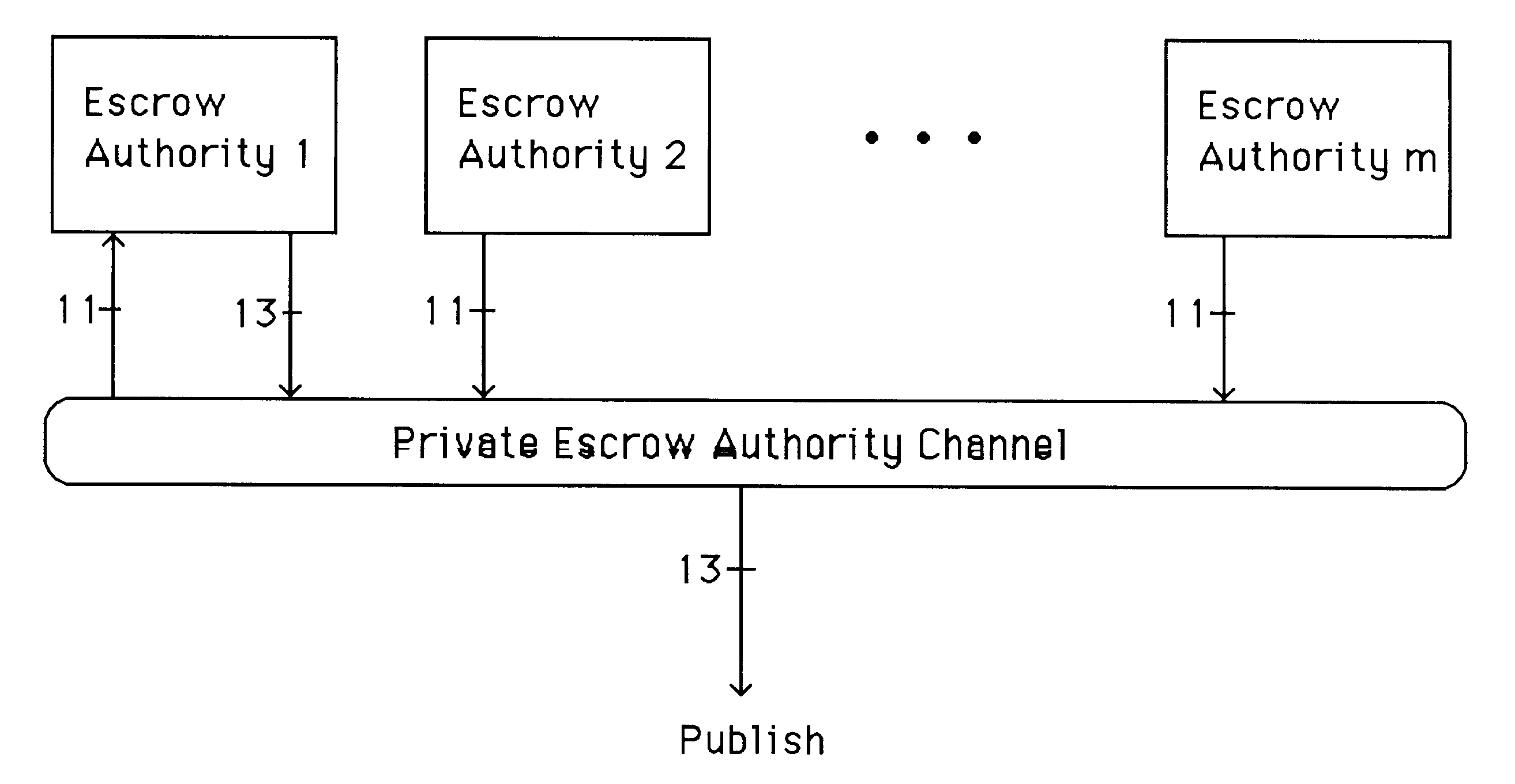
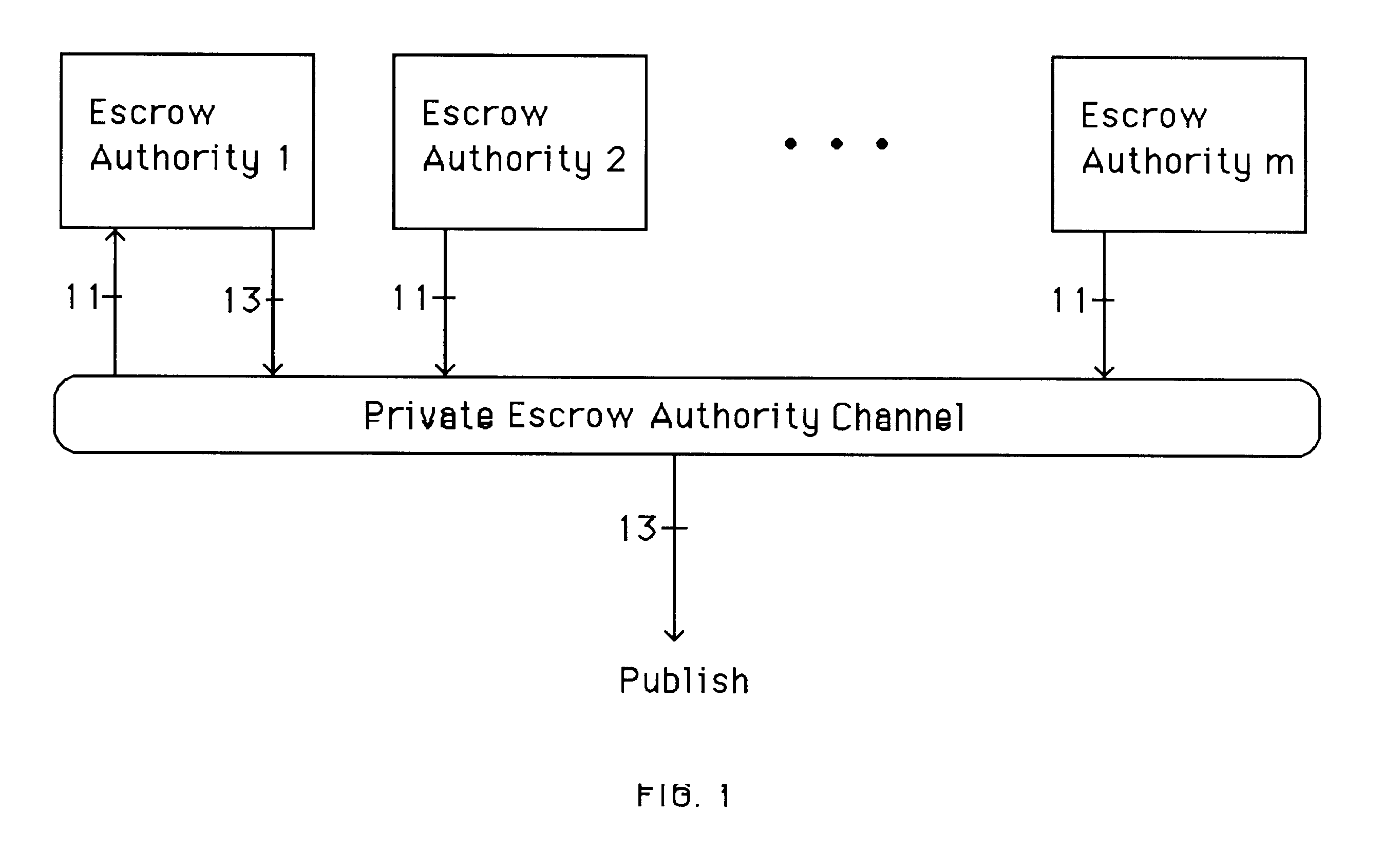
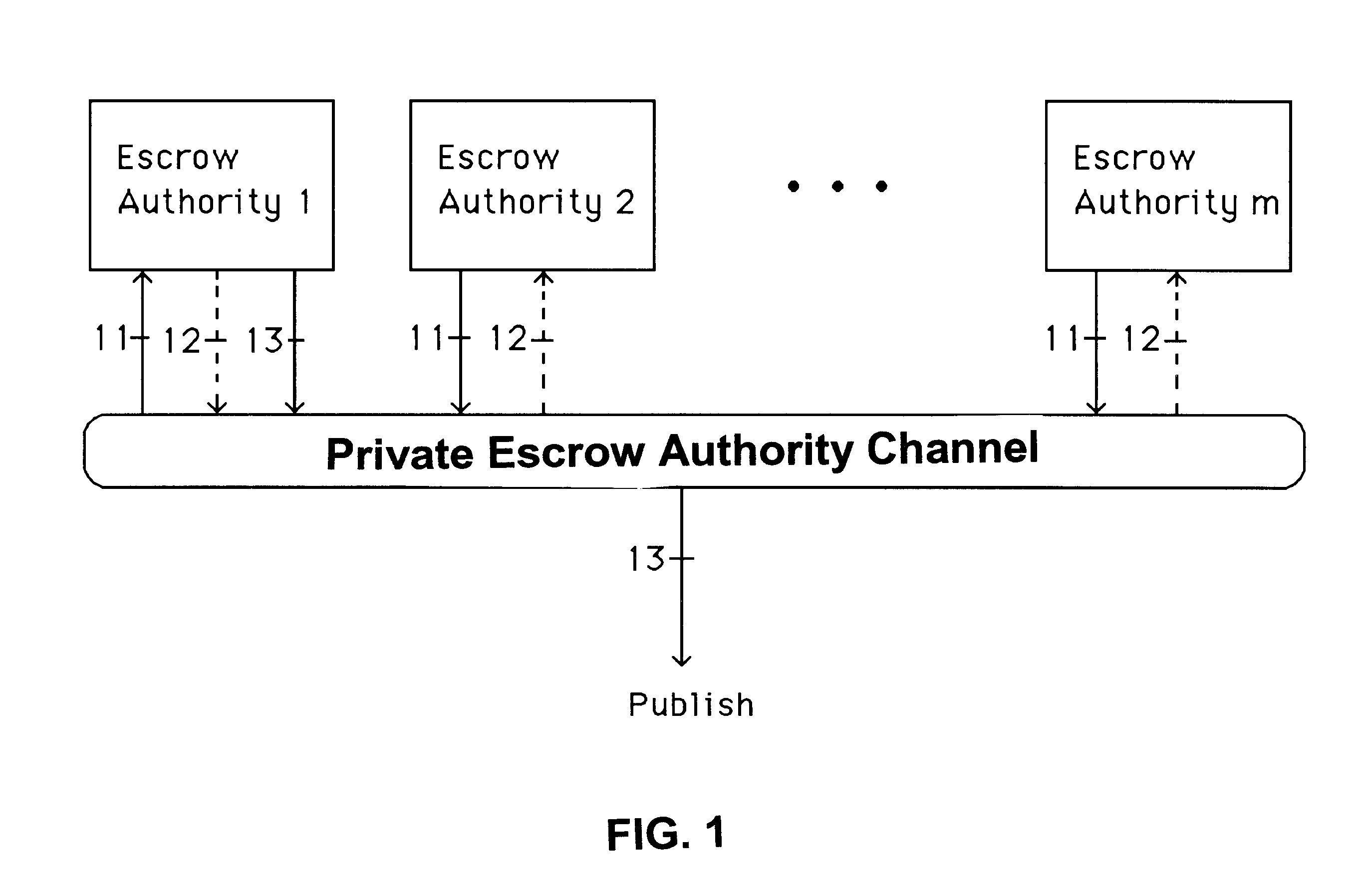
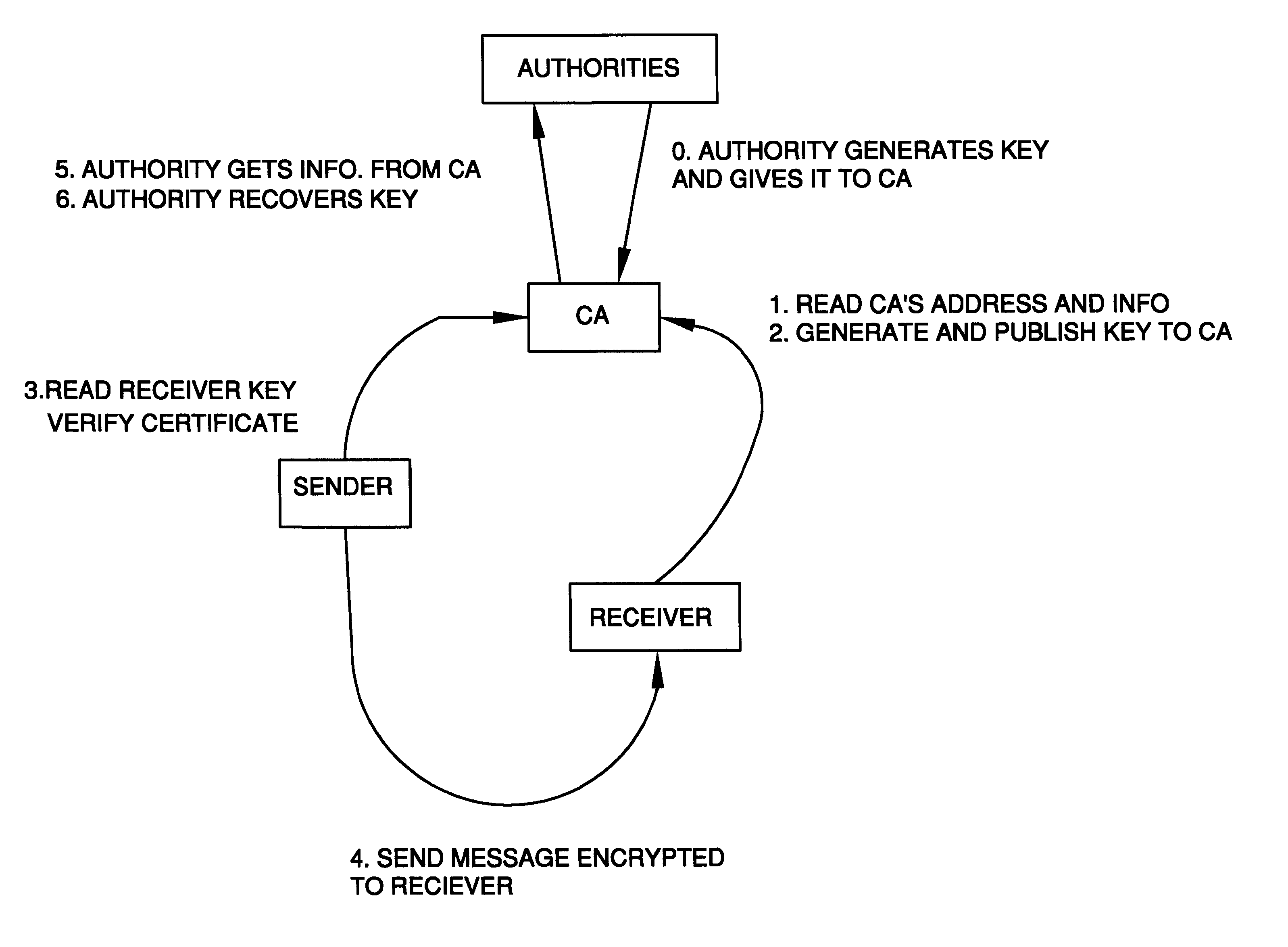
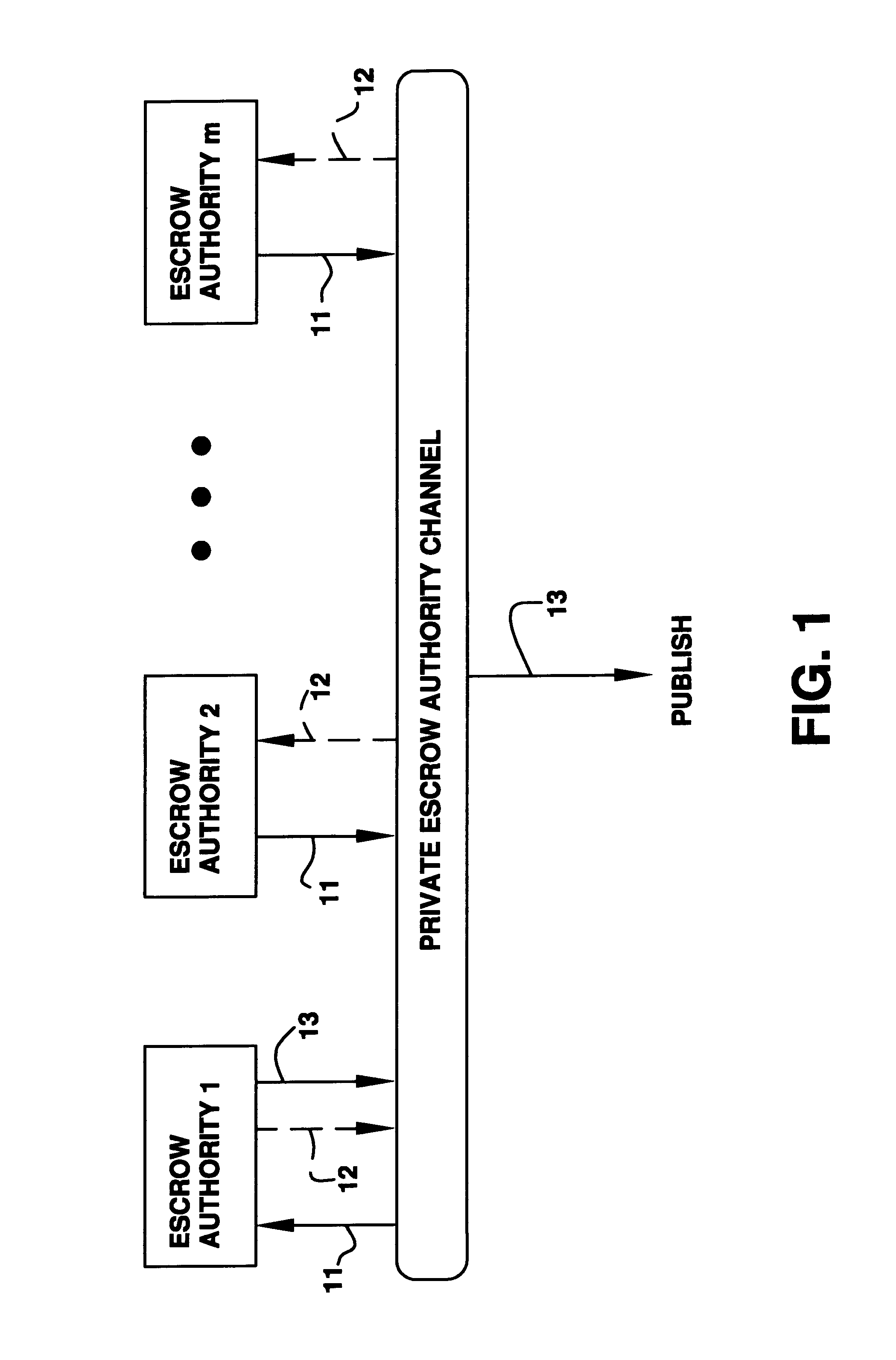
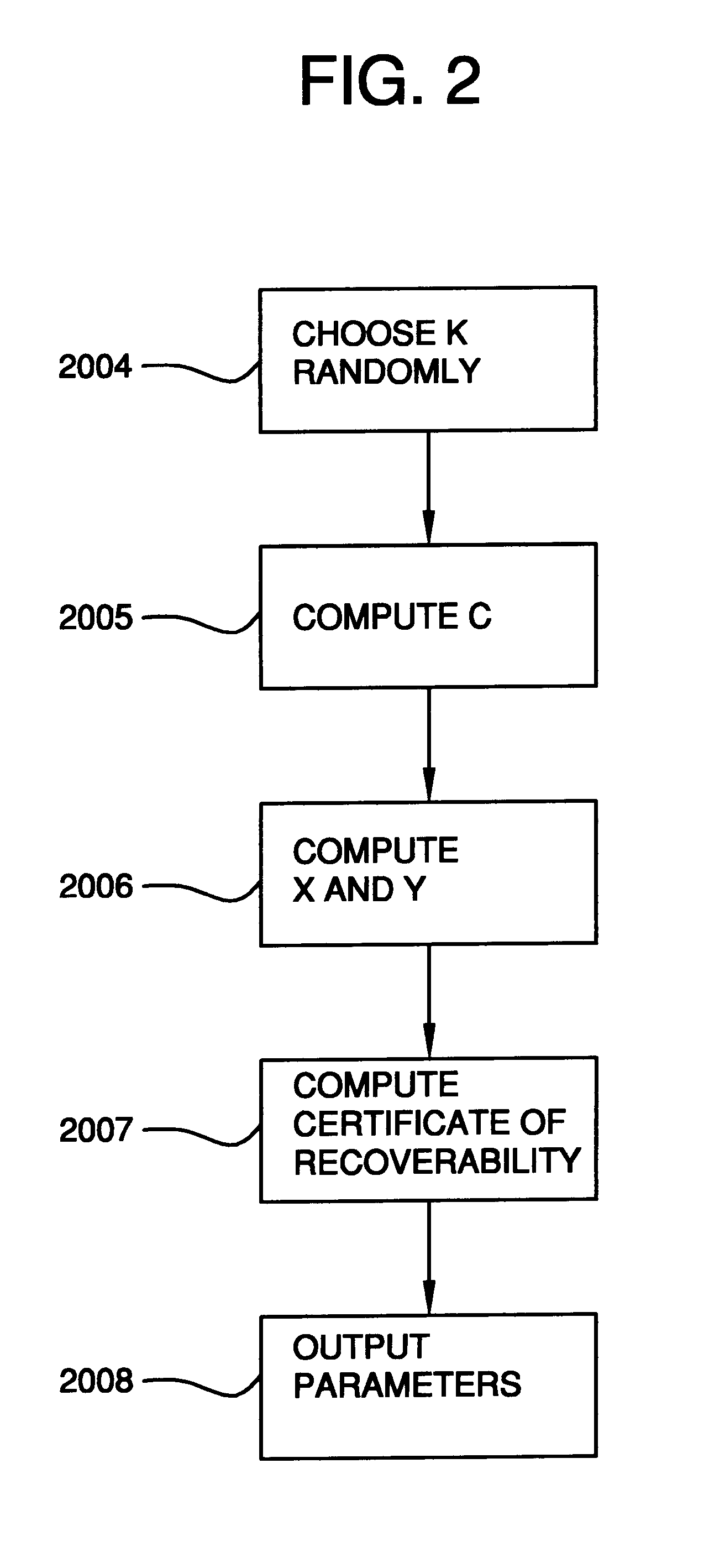
A method is provided for an escrow cryptosystem that is essentially overhead-free, does not require a cryptographic tamper-proof hardware implementation (i.e., can be done in software), is publicly verifiable, and cannot be used subliminally to enable a shadow public key system. A shadow public key system is an unescrowed public key system that is publicly displayed in a covert fashion. The keys generated by the method are auto-recoverable and auto-certifiable (abbrev. ARC). The ARC Cryptosystem is based on a key generation mechanism that outputs a public / private key pair, and a certificate of proof that the key is recoverable by the escrow authorities. Each generated public / private key pair can be verified efficiently to be escrowed properly by anyone. The verification procedure does not use the private key. Hence, the general public has an efficient way of making sure that any given individual's private key is escrowed properly, and the trusted authorities will be able to access the private key if needed. Since the verification can be performed by anyone, there is no need for a special trusted entity, known in the art as a "trusted third party". The proof and verification method involves one party proving to a second party that a third party can gain access to an encrypted value. In addition, the system is designed so that its internals can be made publicly scrutinizable (e.g., it can be distributed in source code form). This differs from many schemes which require that the escrowing device be tamper-proof hardware. The system is efficient and can be implemented as a "drop-in" replacement to an RSA or ElGamal cryptosystem. The system is applicable for lawenforcement, file systems, e-mail systems, certified e-mail systems, and any scenario in which public key cryptography can be employed and where private keys or information encrypted under public keys need to be recoverable. The system security relies solely on the security of cipher systems involved whose security has been extensively studied in the past.
Owner:CRYPTOPEAK SECURITY LLC
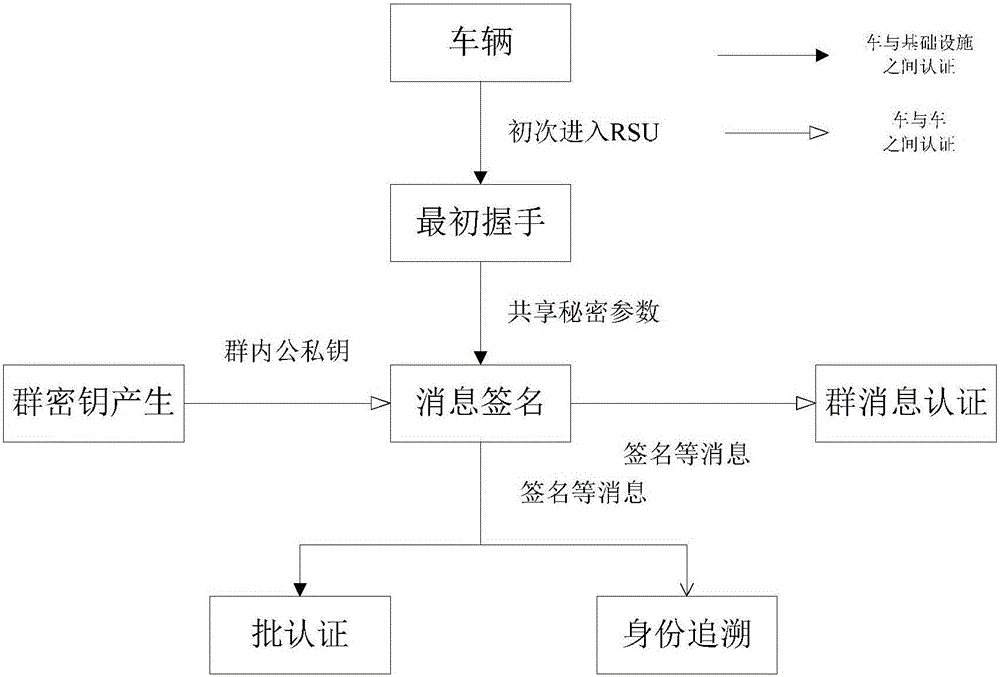
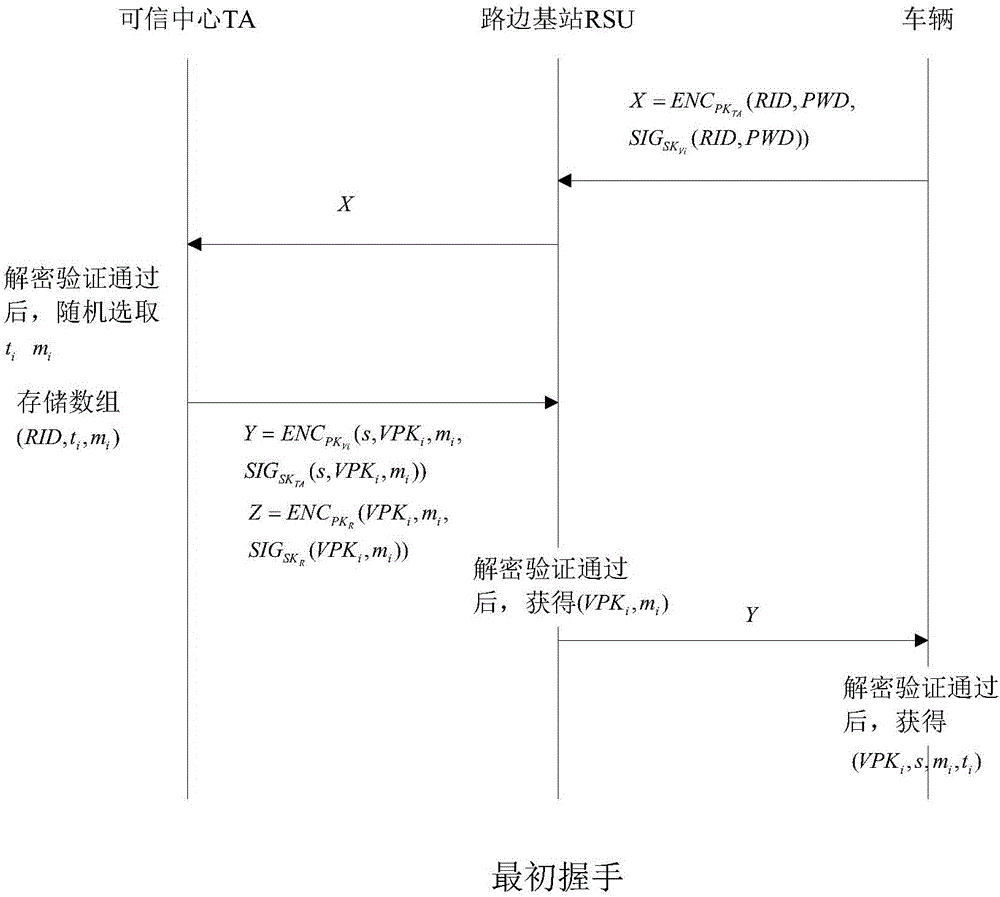
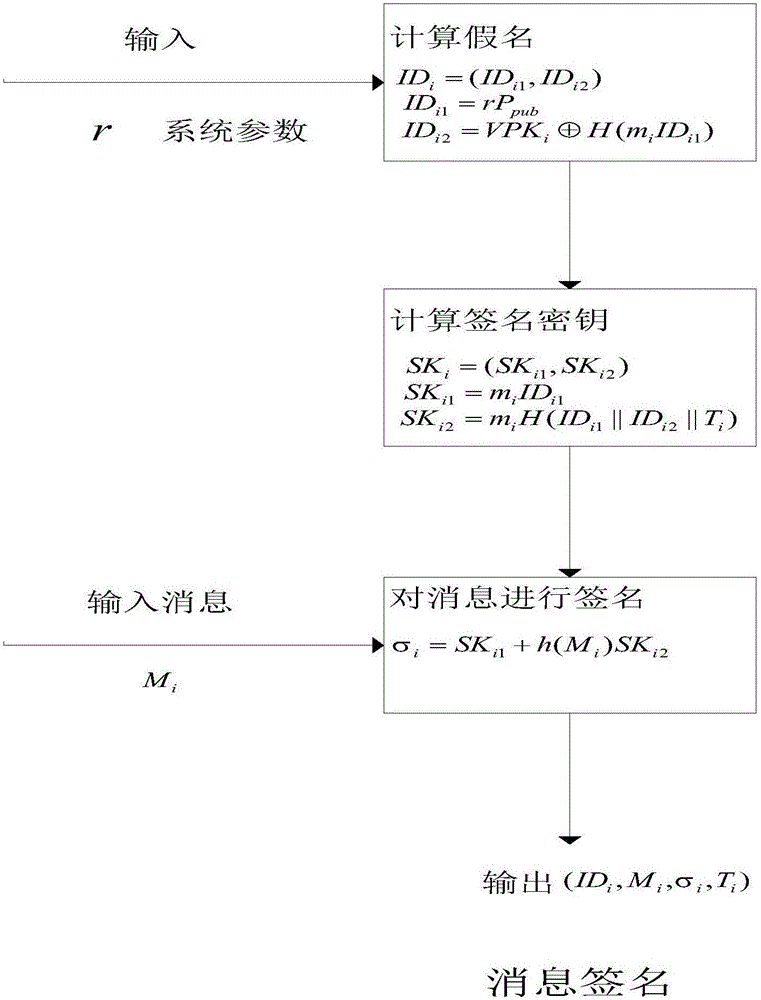
Identity based efficient anonymous batch authentication method in IOV (Internet of Vehicles) environment
ActiveCN105847235AAchieve authenticationImprove securityUser identity/authority verificationTrusted authorityTamper resistance
The invention discloses an identity based efficient anonymous batch authentication method in an IOV (Internet of Vehicles) environment. The identity based efficient anonymous batch authentication method in the IOV environment comprises an initial handshake module, a message signature module, a batch authentication module, an identity tracing module, a group key generation module and a group message signature and authentication module. According to the identity based efficient anonymous batch authentication method in the IOV environment, authentication between vehicles and infrastructures and authentication between vehicles can be realized, no tamper-proofing device is depended, privacy protection is realized by utilizing a pseudonymous name, conditional privacy protection is realized as a TA (Trusted Authority) can trace the real identity of each vehicle if necessary, the efficiency is improved as batch authentication is adopted, and the authentication process is simple and efficient. The message signature process and the group message signature process are same, the operating cost is low, and a replay attack can be borne as a time stamp is added.
Owner:南京秉蔚信息科技有限公司
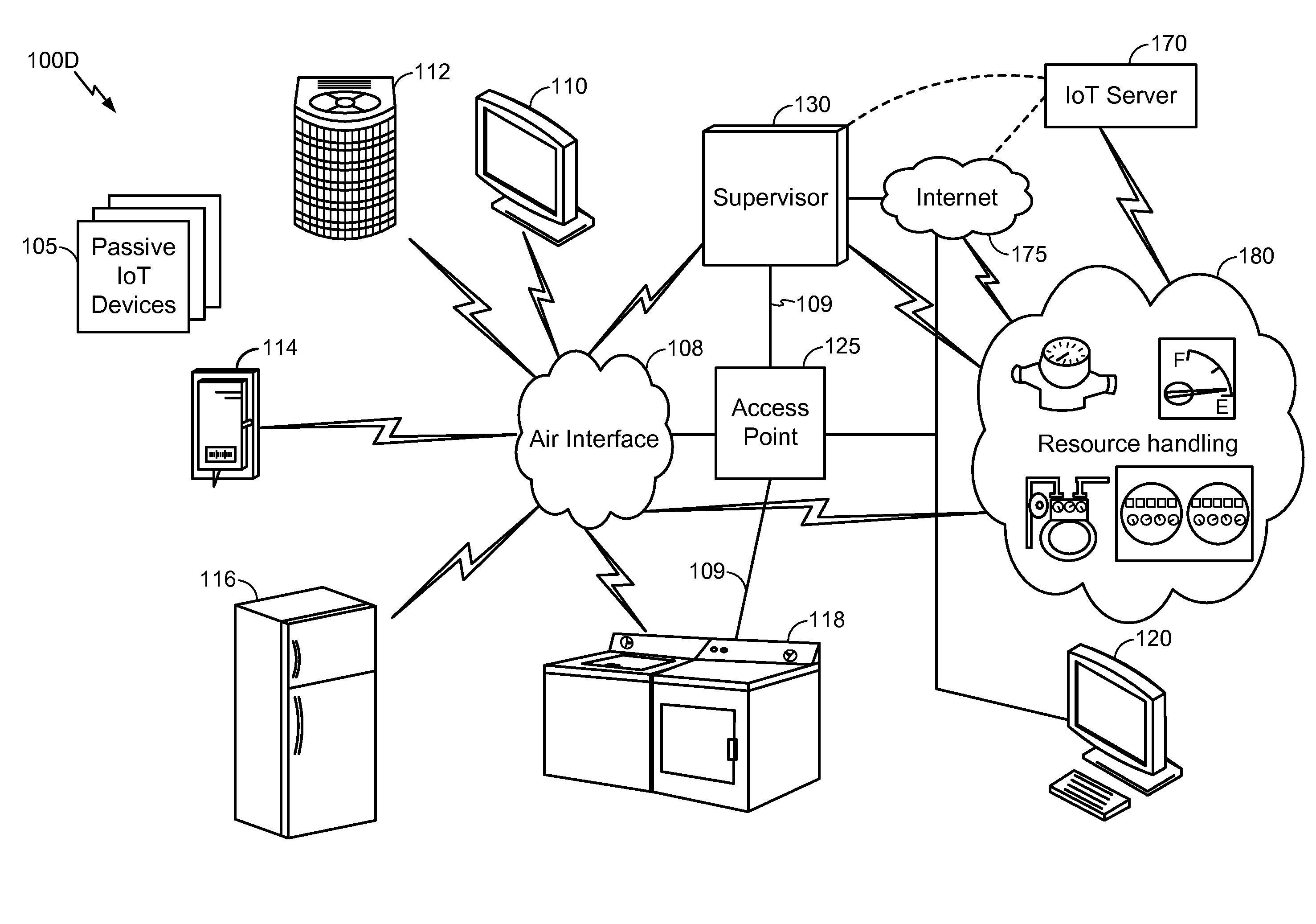
Emergency mode for IoT devices
InactiveUS20140244997A1Minimize damageTransmissionSecurity arrangementTrusted authorityComputer science
Methods and apparatuses for implementing an emergency instruction based on an emergency message from a trusted authority source. The method includes receiving, at an Internet of Things (IoT) device, an emergency secret key from a trusted authority source The method receives, at an IoT device, an emergency message from the trusted authority source; decoding, at an IoT device, the emergency message from the trusted authority source using the emergency secret key to determine a value within the emergency message. The method calculates, at an IoT device, a result based on the determined value. The method implements, at an IoT device, an emergency instruction if the result is above a predetermined threshold.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
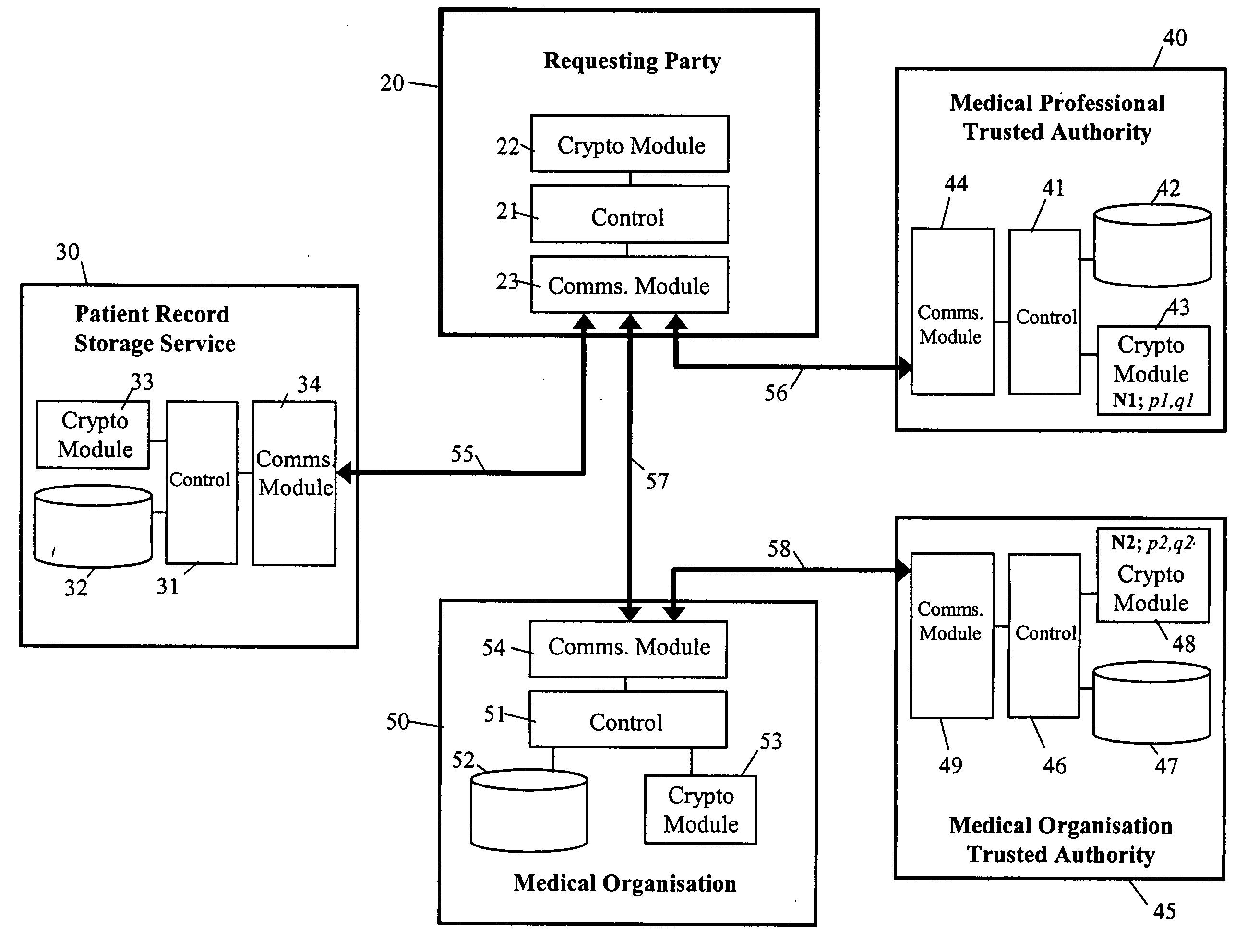
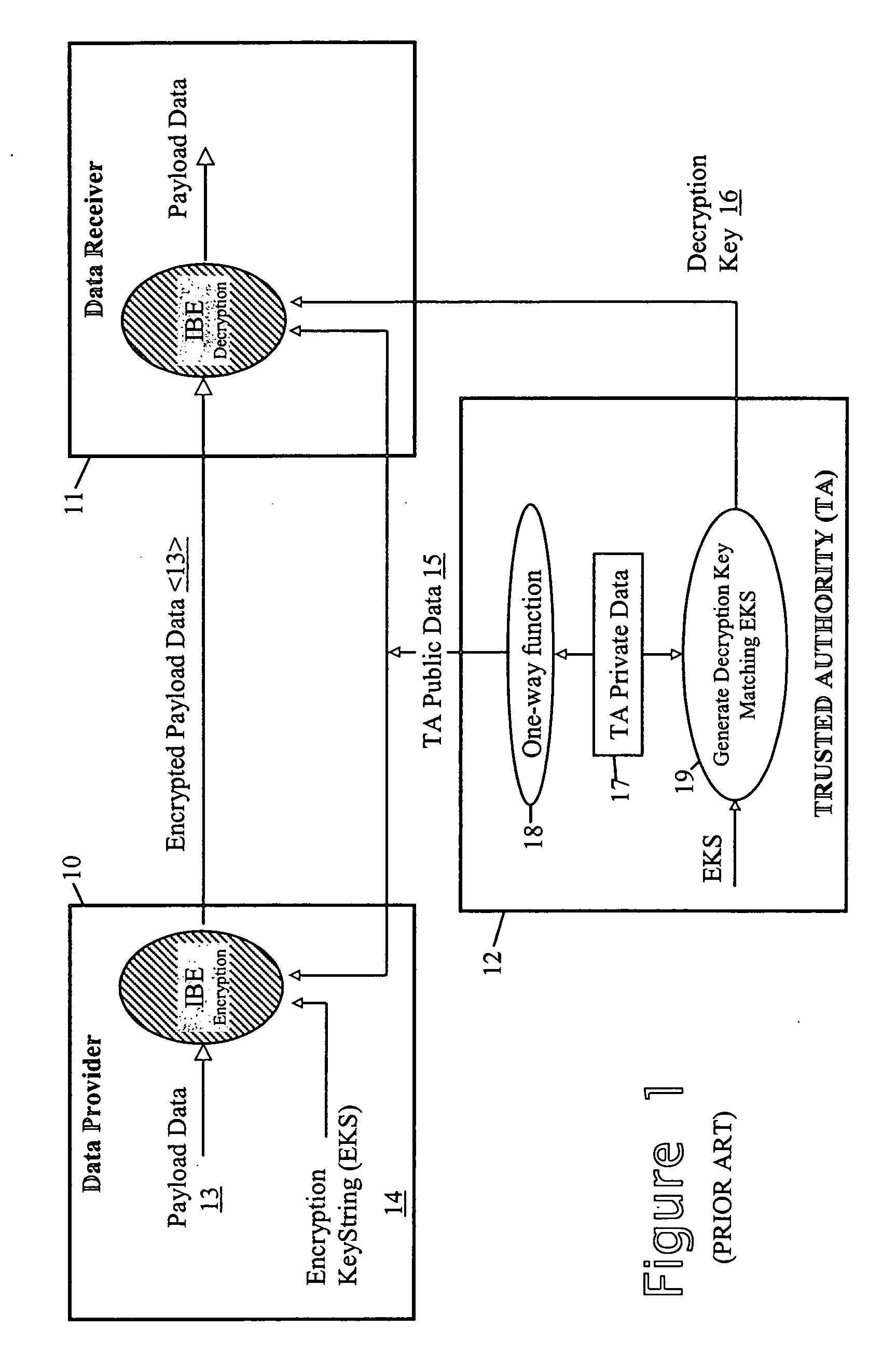
Secure data provision method and apparatus and data recovery method and system
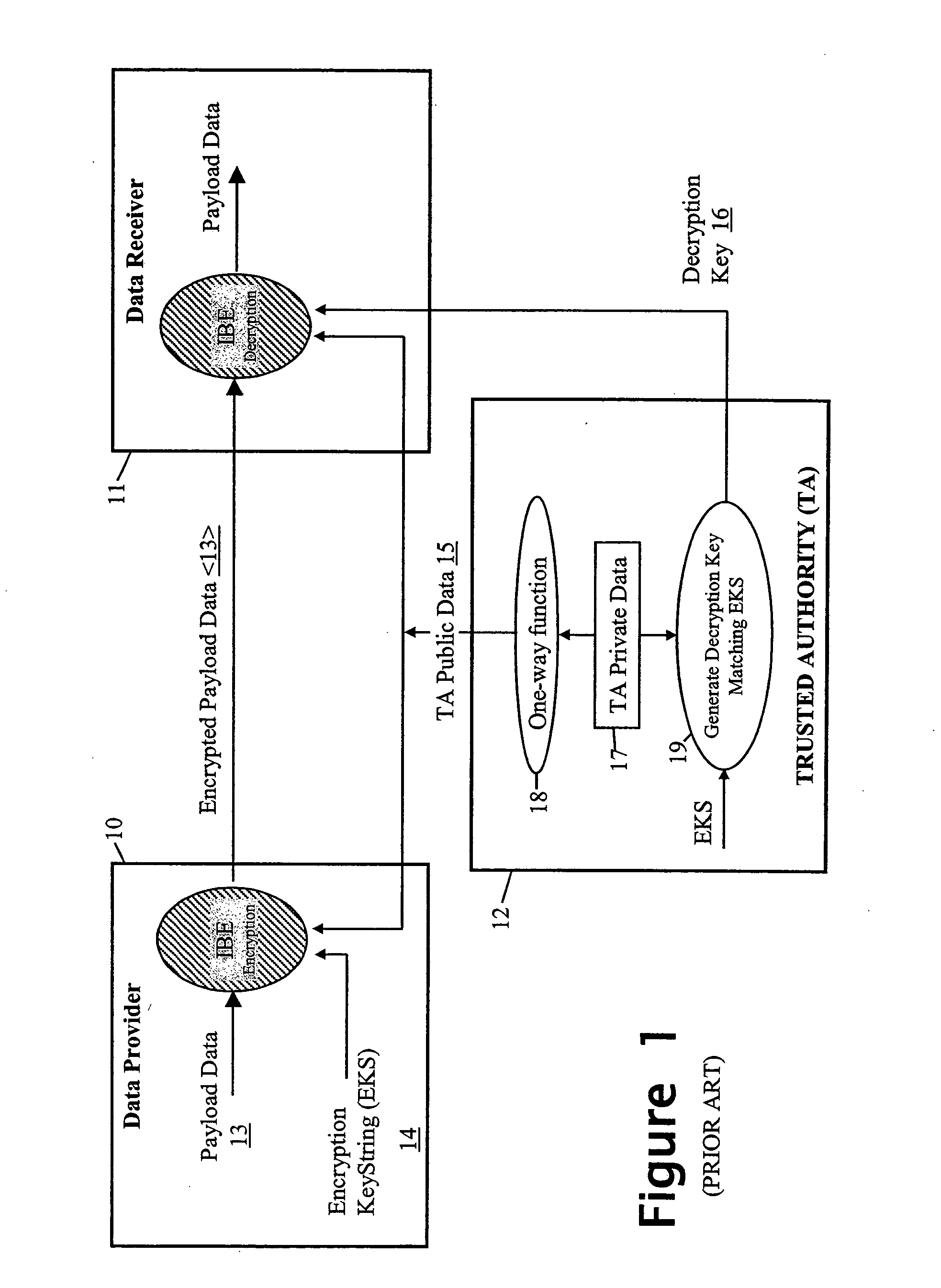
InactiveUS20050010760A1Eliminate needDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionTrusted authorityData set
To control access to target data whilst relieving the data provider of policing obligations, the data provider provides the target data in encrypted form to a requesting party as part of a data set with which first and second trusted authorities are associated in a non-subvertible manner. Recovery of the target data in clear by the party requires the first trusted authority to verify that a specific individual is a professional accredited with it, the second trusted authority to verify that a particular organisation is accredited with it, the particular organisation to verify that the specific individual is engaged by it, and at least one of the particular organisation and the first trusted authority to verify that the party is the specific individual. Various ways of encrypting the target data are provided, the preferred ways being based on Identifier-Based Encryption schemas.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
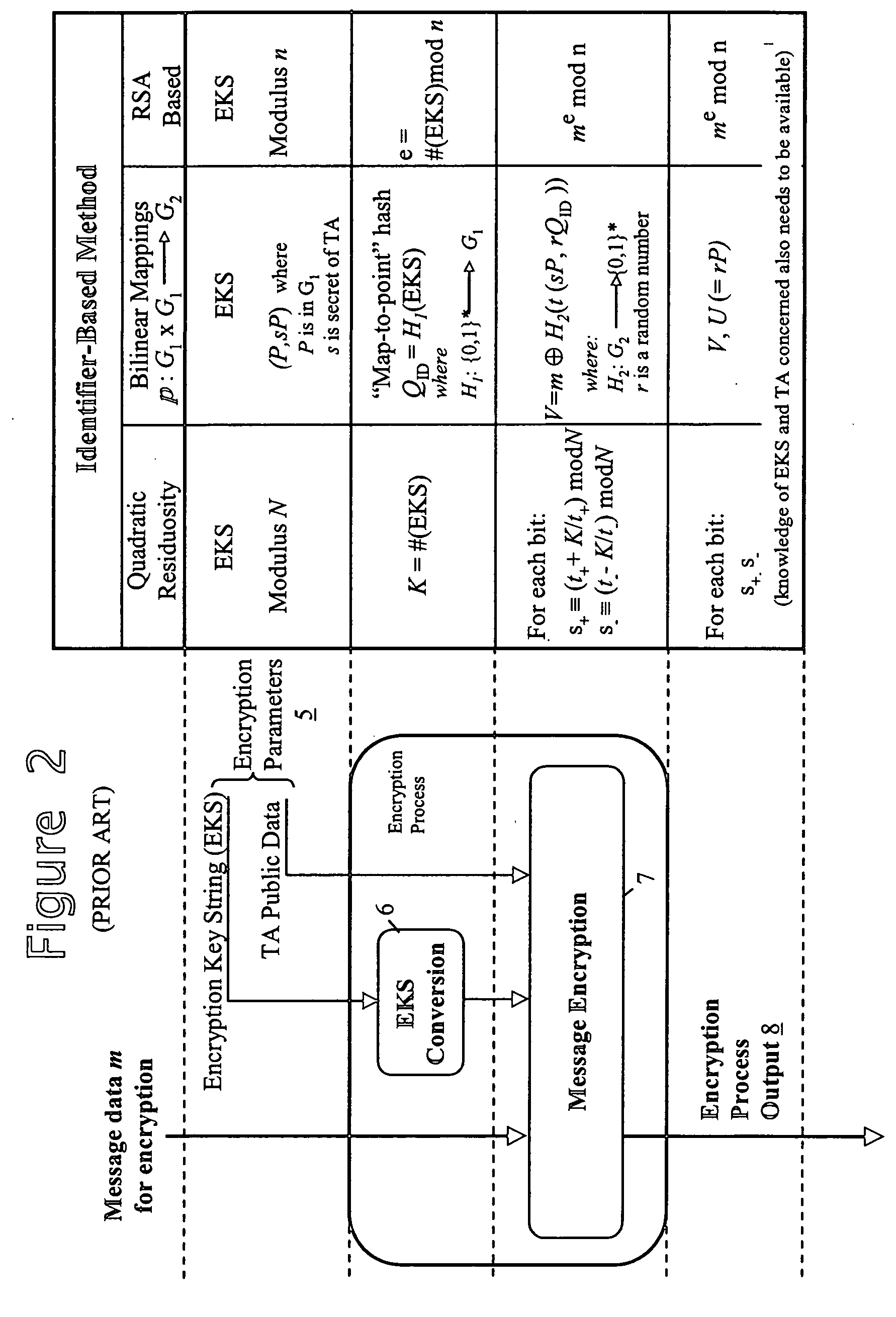
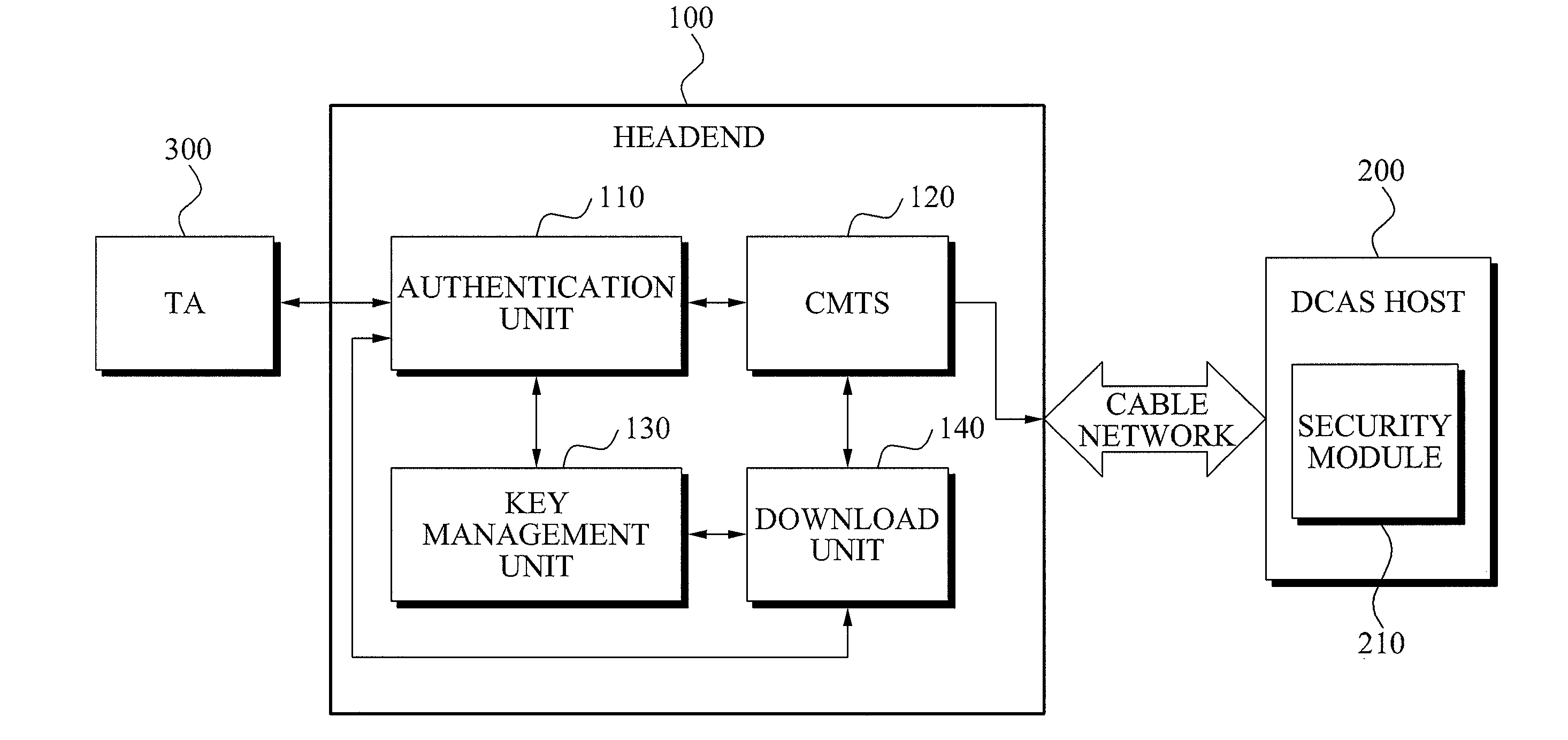
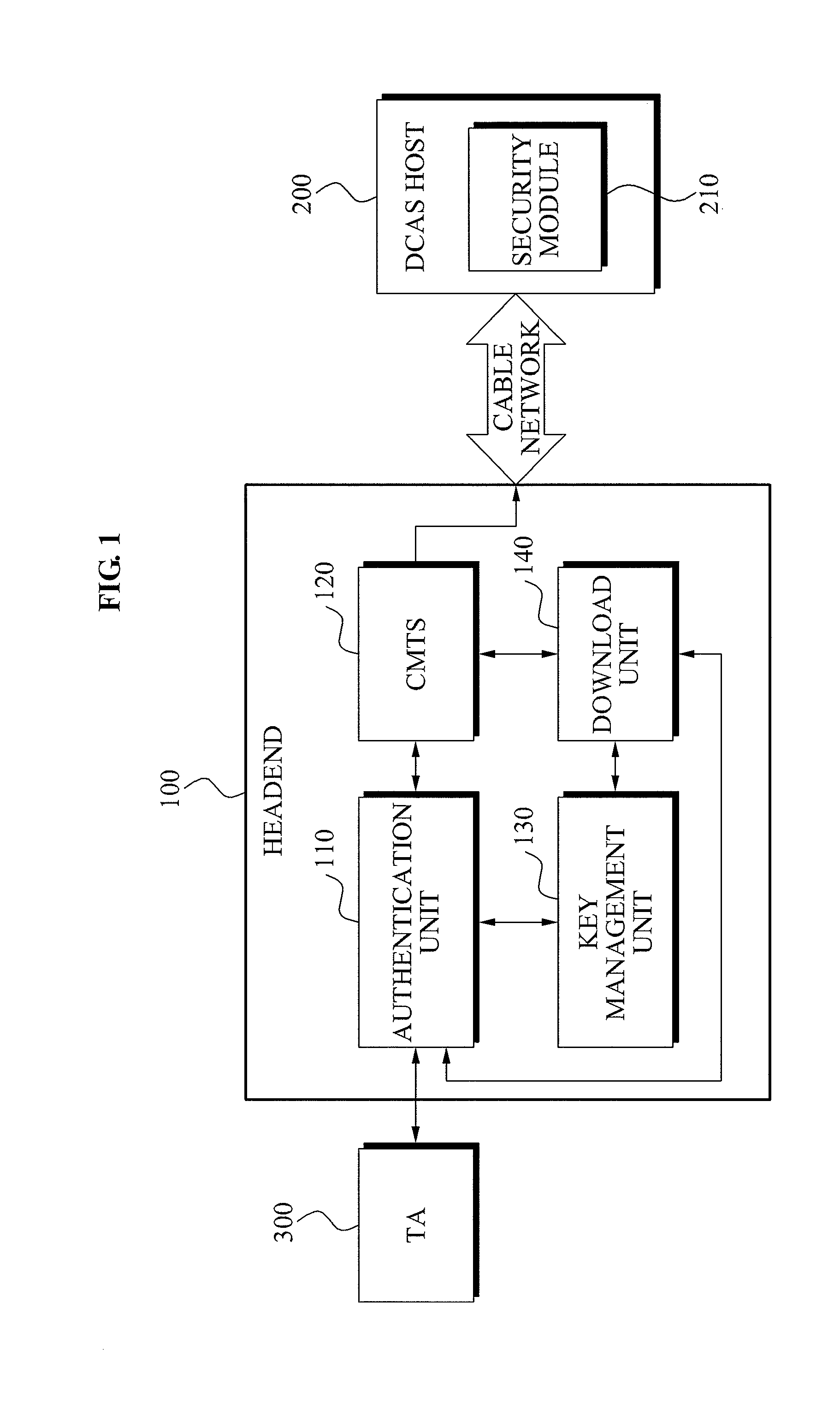
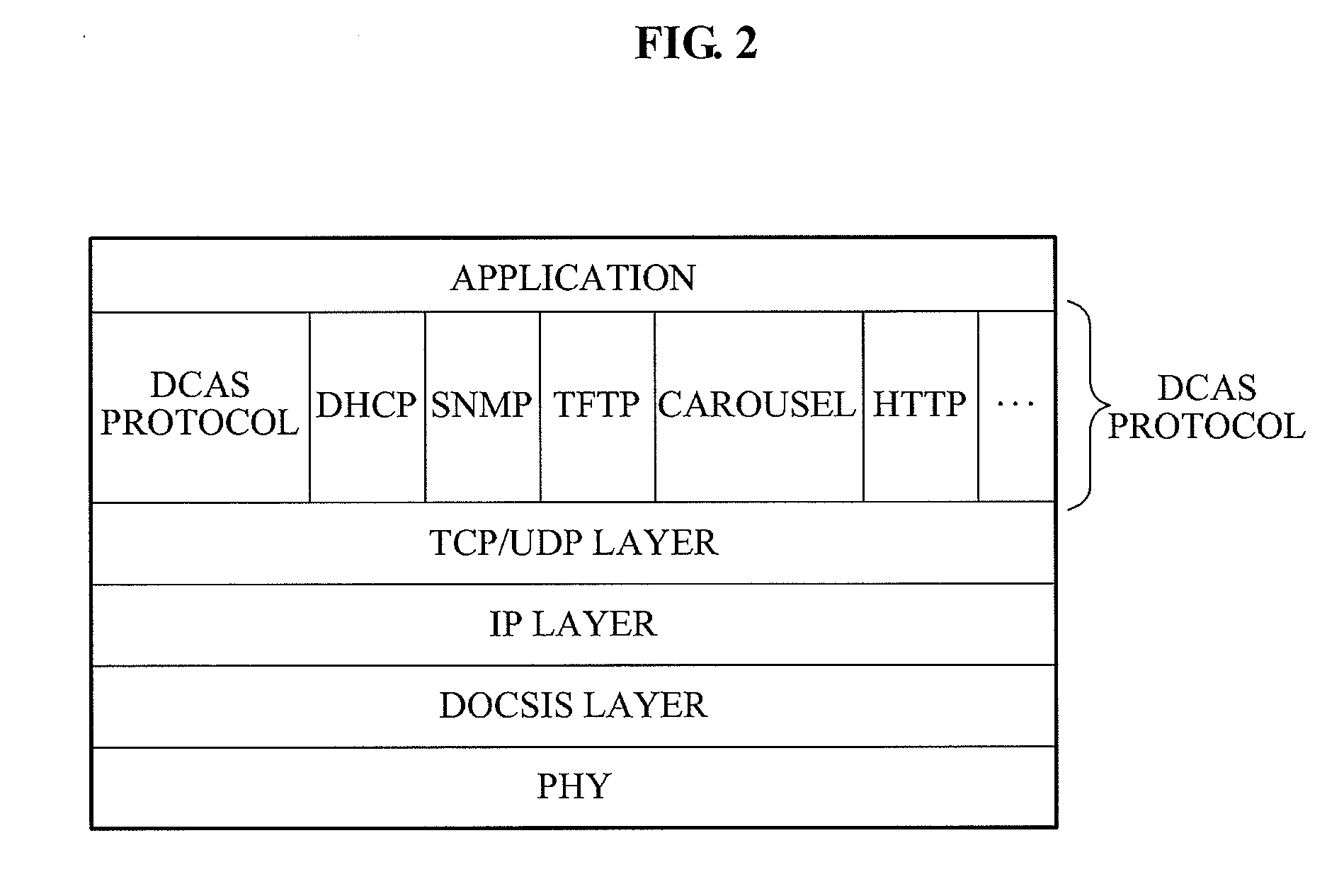
Mutual authentication apparatus and method in downloadable conditional access system
InactiveUS20100161966A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationTrusted authorityDownloadable Conditional Access System
A mutual authentication method in a Downloadable Conditional Access System (DCAS) is provided. The mutual authentication method may receive authentication-related information about authentication between an authentication unit and a security module (SM) from a Trusted Authority (TA), generate an authentication session key using the authentication-related information, transmit the authentication session key by the authentication unit to the SM through a Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS), and control a Conditional Access System (CAS) software to be downloaded to the SM from the authentication unit, when the authentication is completed by the authentication session key.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method, system and device for enabling delegation of authority and access control methods based on delegated authority
ActiveUS20050058294A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationTrusted authorityCryptographic key generation
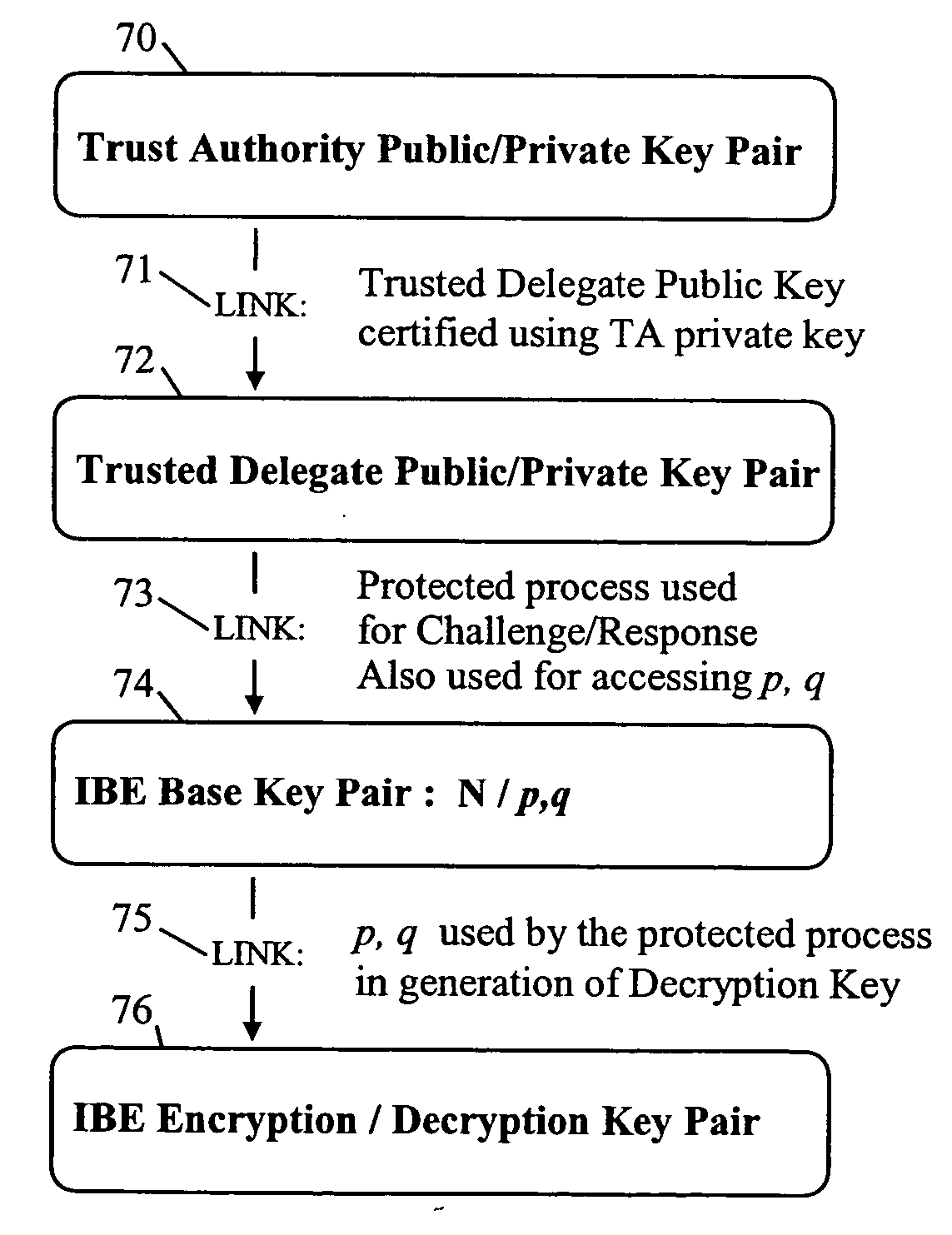
A trusted authority delegates authority to a device. This delegation of authority is effected by providing a yet-to-be completed chain of public / private cryptographic key pairs linked in a subversion-resistant manner. The chain terminates with a penultimate key pair formed by public / private data, and a link towards an end key pair to be formed by an encryption / decryption key pair of an Identifier-Based Encryption, IBE, scheme. The private data is securely stored in the device for access only by an authorized key-generation process that forms the link to the end key pair and is arranged to provide the IBE decryption key generated using the private data and encryption key. This key generation / provision is normally only effected if at least one condition, for example specified in the encryption key, is satisfied. Such a condition may be one tested against data provided by the trusted authority and stored in the device.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method and system for providing an open gateway initiative bundle over the air
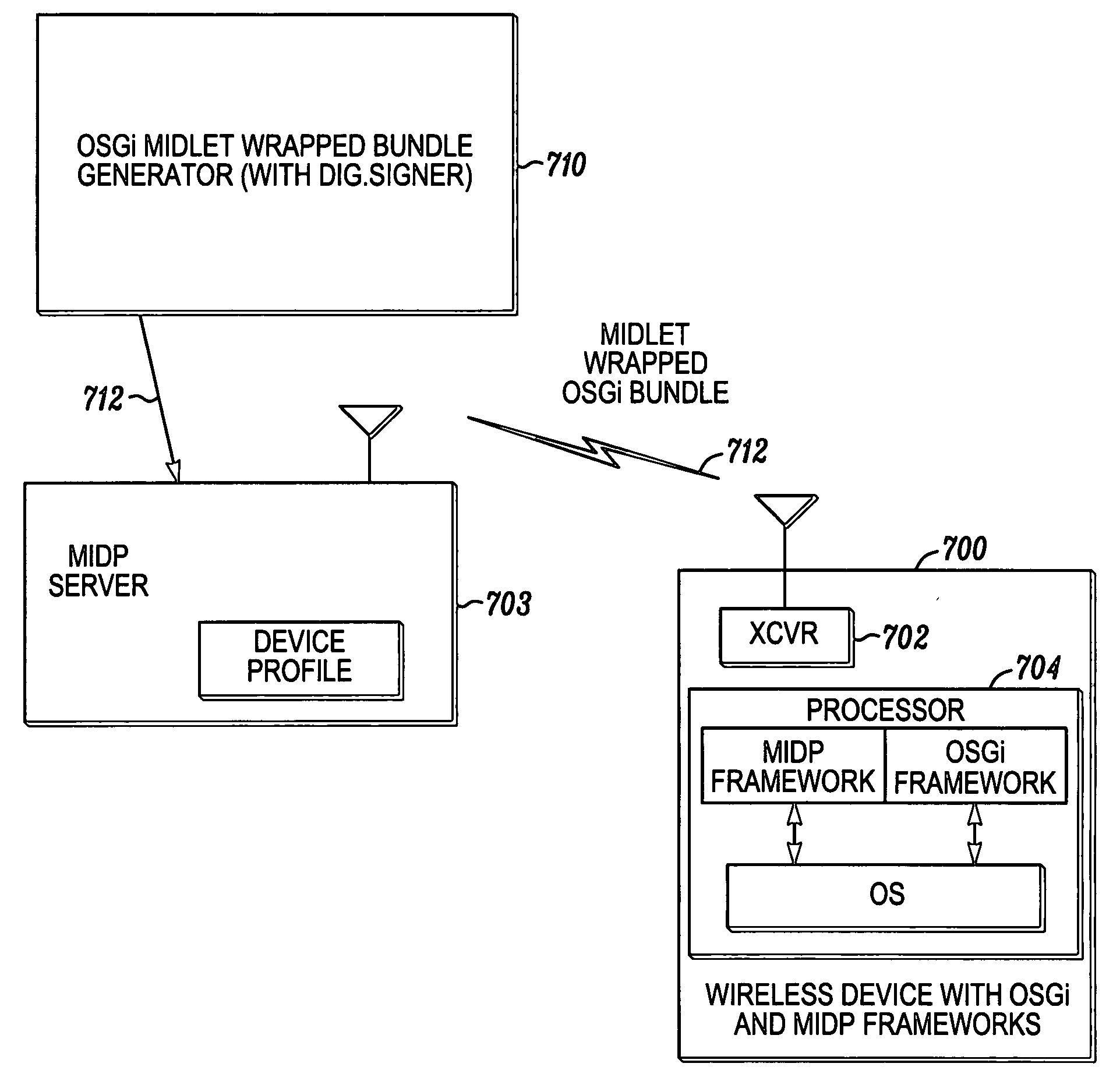
InactiveUS20060140144A1Digital data processing detailsData switching by path configurationTrusted authorityComputer hardware
A method and apparatus provides an open services gateway initiative (OSGi) bundle over the air to a wireless mobile device by obtaining data representing an OSGi bundle in the form of a JAVA archive (JAR) file (802), such as from a trusted authority, or any other suitable source, and generates, for sending to the wireless mobile device, a MIDlet wrapped OSGi bundle (712) that contains data representing a MIDP JAR file (900) containing the OSGi bundle (902) and a corresponding MIDlet (904) operative to invoke an OSGi bundle provisioning application interface (API) (804) on the wireless mobile device to install said bundle. The method may be carried out for example by a network element, or any other suitable element or elements. In one example, a standard MIDP server sends the MIDlet wrapped OSGi bundle to the wireless mobile device since it is in a suitable MIDP format although it contains an OSGi bundle.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
Auto-Recoverable and Auto-certifiable cryptosystems with RSA or factoring based keys
InactiveUS6389136B1Fast and easy disseminationEasy to handleKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationTrusted authorityComposite number
A method is provided for an escrow cryptosystem that is essentially overhead-free, does not require a cryptographic tamper-proof hardware implementation (i.e., can be done in software), is publicly verifiable, and cannot be used subliminally to enable a shadow public key system. The keys generated are based on composite numbers (like RSA keys). A shadow public key system is an unescrowed public key system that is publicly displayed in a covert fashion. The keys generated by the method are auto-recoverable and auto-certifiable (abbrev. ARC). The ARC Cryptosystem is based on a key generation mechanism that outputs a public / private key pair, and a certificate of proof that the key is recoverable by the escrow authorities. Each generated public / private key pair can be verified efficiently to be escrowed properly by anyone. The verification procedure does not use the private key. Hence, the general public has an efficient way of making sure that any given individual's private key is escrowed properly, and the trusted authorities will be able to access the private key if needed. Since the verification can be performed by anyone, there is no need for a special trusted entity, known in the art as a "trusted third party". Furthermore, the system is designed so that its internals can be made publicly scrutinizable (e.g., it can be distributed in source code form). This differs from many schemes which require that the escrowing device be tamper-proof hardware. The system is efficient and can be implemented as a "drop-in" replacement to an RSA or Rabin cryptosystem. The system is applicable for law-enforcement, file systems, e-mail systems, certified e-mail systems, and any scenario in which public key cryptography can be employed and where private keys or information encrypted under public keys need to be recoverable. Another aspect of the system is the possibility to organize it in a hierarchical tree structure, where each element in the tree is an escrow authority (or authorities) capable to recover keys and / or information encrypted under these keys within the subtree rooted at the authority (or authorities) and only within this subtree.
Owner:CRYPTOPEAK SECURITY LLC
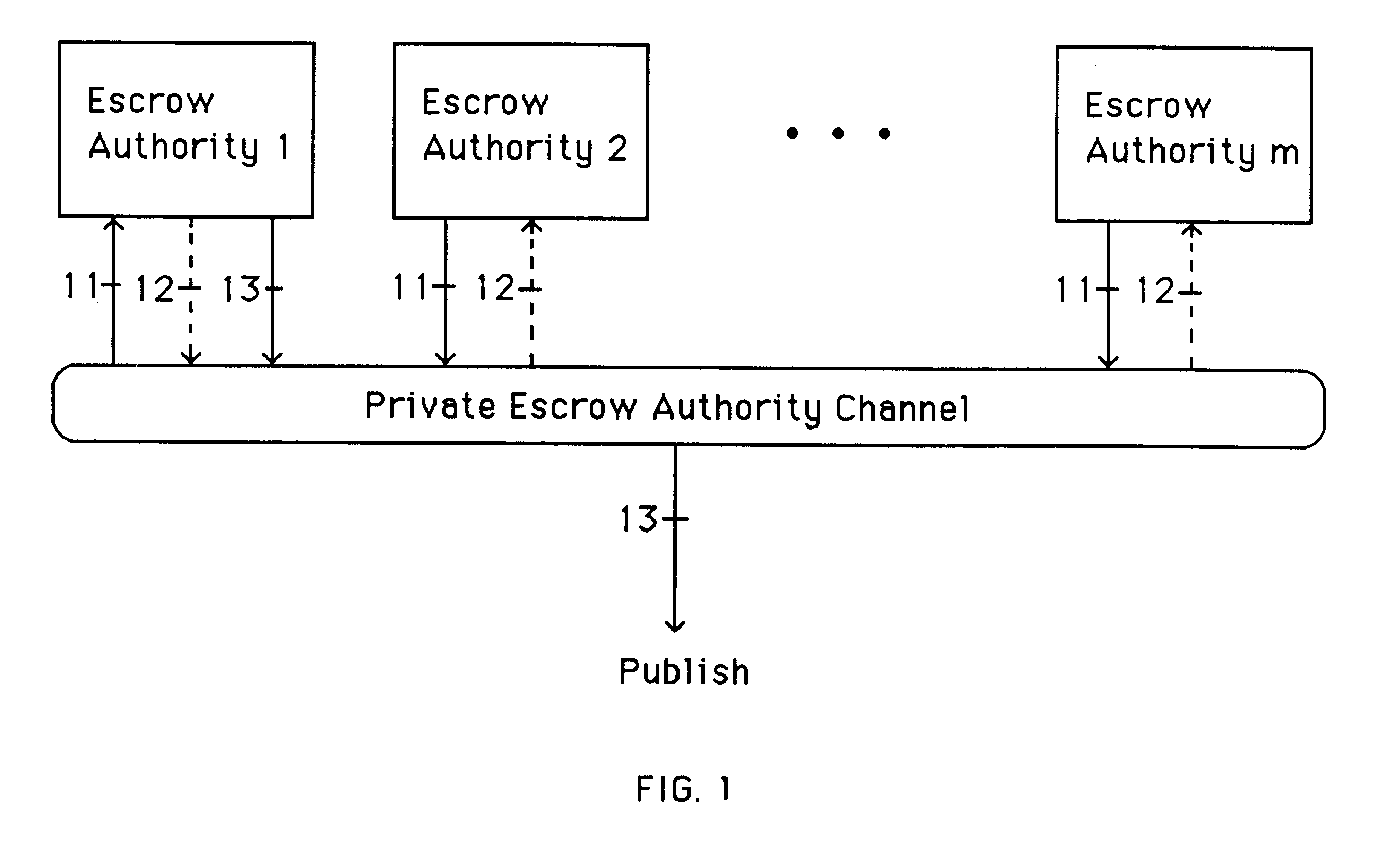
Auto-escrowable and auto-certifiable cryptosystems
InactiveUS6202150B1Fast and easy disseminationEasy to handleKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationTrusted authorityTamper proof hardware
A method is provided for an escrow cryptosystem that is overhead-free, does not require a cryptographic tamper-proof hardware implementation (i.e., can be done in software), is publicly verifiable, and cannot be used subliminally to enable a shadow public key system. A shadow public key system is an unescrowed public key system that is publicly displayed in a covert fashion. The key generated by the method are auto-recoverable and auto-certifiable (abbrev. ARC). The ARC Cryptosystem is based on a key generation mechanism that outputs a public / private key pair, and a certificate of proof that the key was generated according to the algorithm. Each generated public / private key pair can be verified efficiently to be escrowed properly by anyone. The verification procedure does not use the private key. Hence, the general public has an efficient way of making sure that any given individual's private key is escrowed properly, and the trusted authorities will be able to access the private key if needed. Since the verification can be performed by anyone, there is no need for a special trusted entity, known in the art as a "trusted third party". The cryptosystem is overhead free since there is no additional protocol interaction between the user who generates his or her own key, and the certification authority or the escrow authorities, in comparison to what is required to submit the public key itself in regular certified public key systems. Furthermore, the system is designed so that its internals can be made publicly scrutinizable (e.g., it can be distributed in source code form). This differs from many schemes which require that the escrowing device be tamper-proof hardware.
Owner:CRYPTOPEAK SECURITY LLC
Security method and apparatus using biometric data
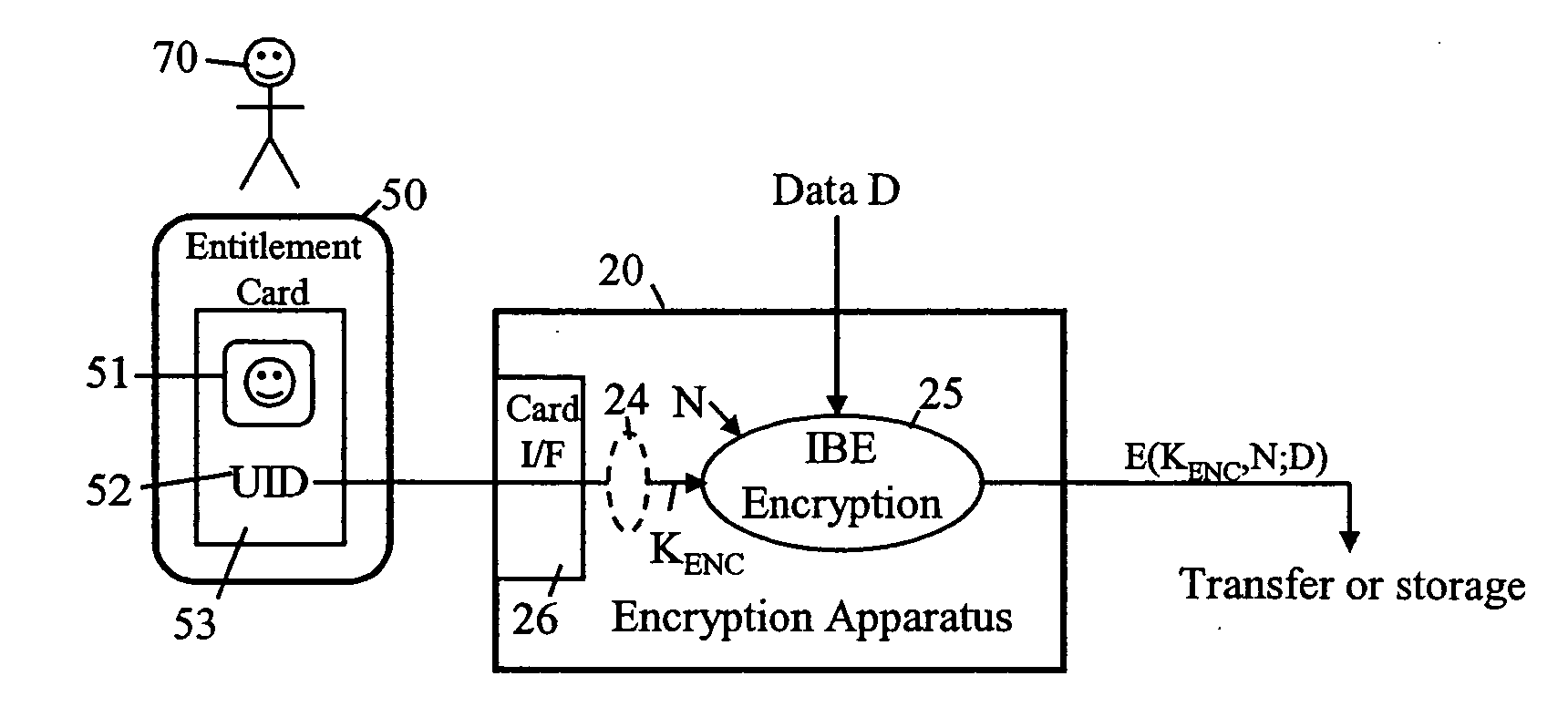
InactiveUS20050005136A1Public key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationTrusted authorityBiometric data
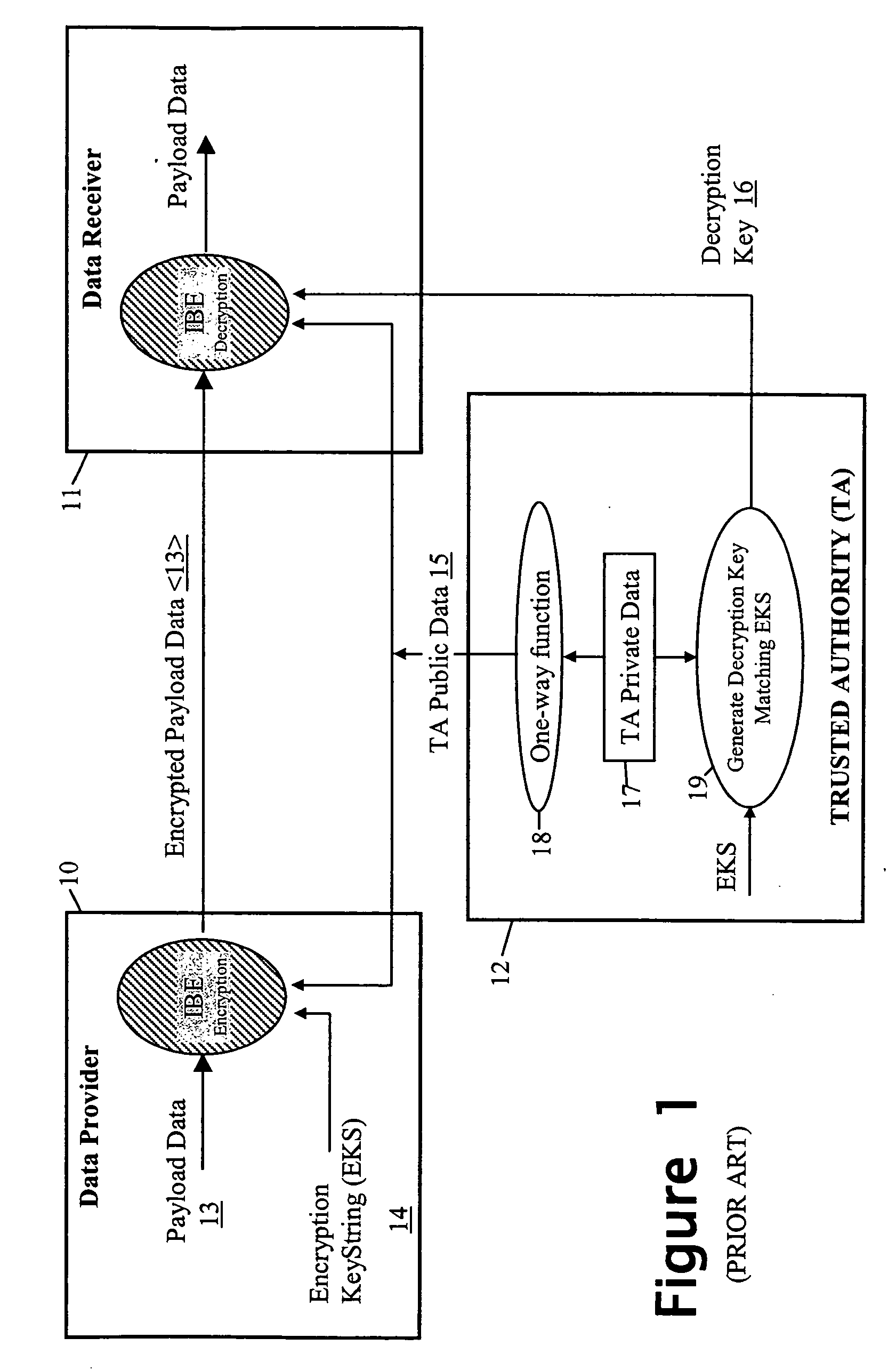
A security method and apparatus is provided in which a trusted authority is arranged to read in identity data from a memory device presented by an individual. This identity data comprises both biometric data of a specific individual and additional identity data concerning the same individual. The trusted authority uses the biometric data as a biometric reference for comparison with biometric characteristics of the individual presenting the memory card in order to determine whether the latter is the individual represented by the biometric data. The trusted authority uses the additional identity data or matching data, together with private data of the trusted authority, to generate a decryption key. This decryption key is apt to decrypt data encrypted using both an encryption key string comprising the additional identity data of the specific individual and public data of the trusted authority.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Revocable key external package decryption method based on content attributes
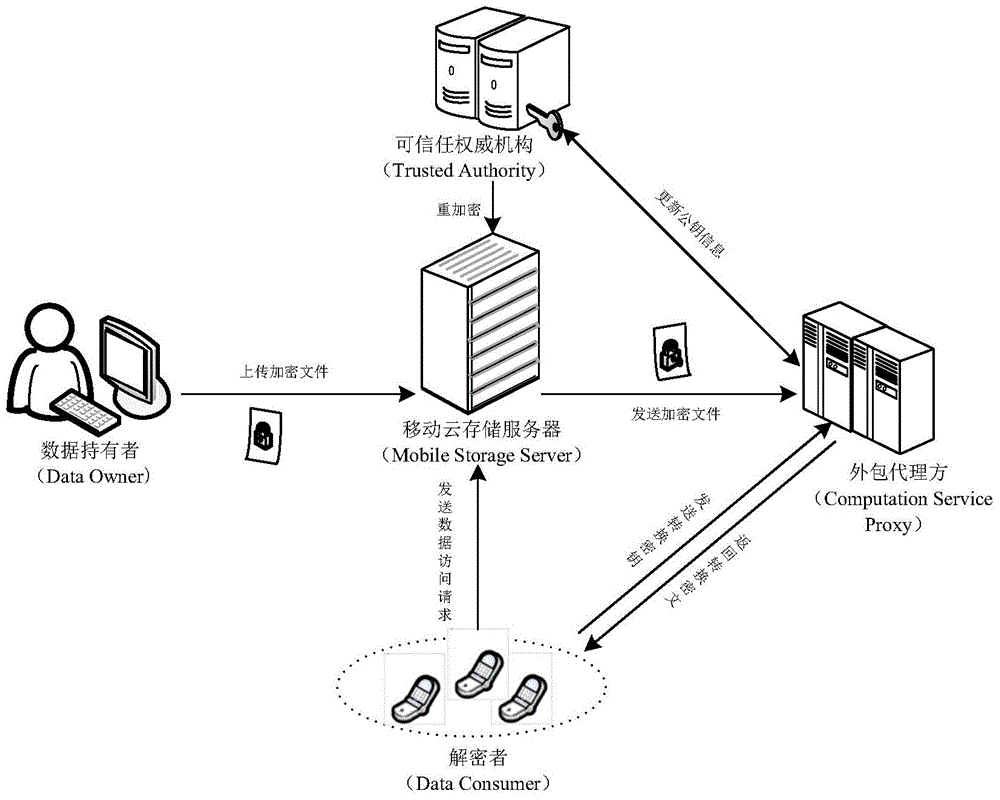
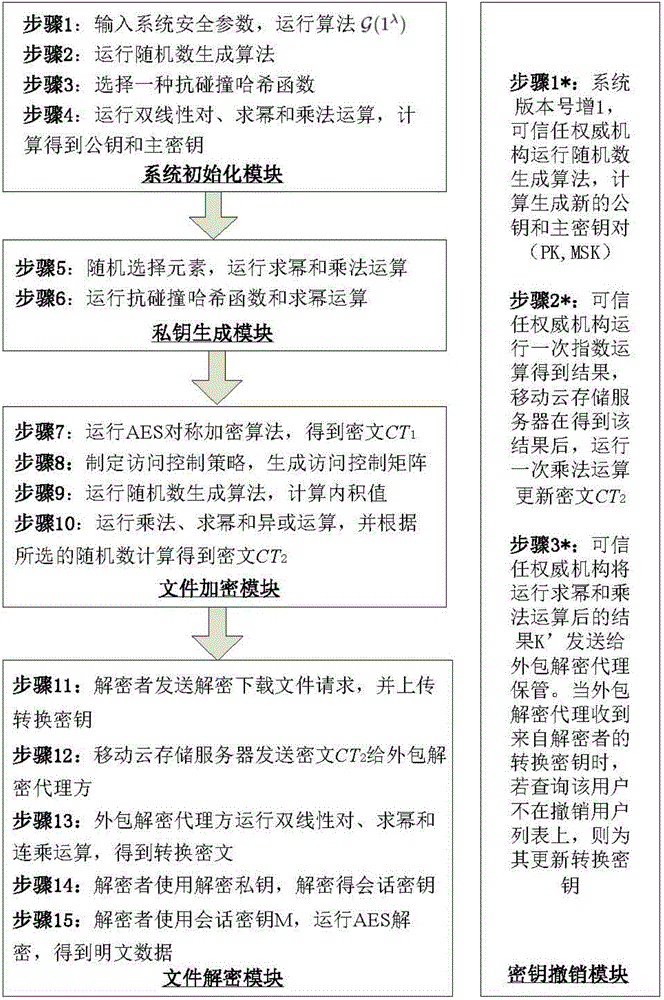
ActiveCN104486315APrevent unauthorized accessProtection securityUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareTrusted authority
The invention relates to a revocable key external package decryption method based on content attributes. For a trusted authority, 1, initialization is carried out, and system parameters are output; 2, a random number generation algorithm operates; 3, a collision-resistant Hash function is selected, and the Hash value is calculated; 4, a public key and a main key are calculated; 5, the random number is selected, and exponentiation calculation and multiplication are carried out; 6, the collision-resistant Hash function operates, the exponentiation operation is carried out, and a decryption key is obtained. For a data holder, 7, AES data encryption is carried out; 8, an access control matrix is generated; 9, a random number is selected, and an inner product is calculated; 10, multiplication, exponentiation and exclusive-or operation is operated, and ciphertexts are obtained. For a decryption operator, 11, a decryption request and a transformation key are sent. For a mobile storage serve provider, 12, CT2 is sent to an external package decryption agency. For the external package decryption agency, 13, the transformation key is utilized, and the transformation ciphertext is calculated. For the decryption operator, 14, a conversation key is obtained through calculation; 15, AES data decryption is carried out.
Owner:HANGZHOU INNOVATION RES INST OF BEIJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Internet of Vehicles distributed authentication method based on controllable privacy
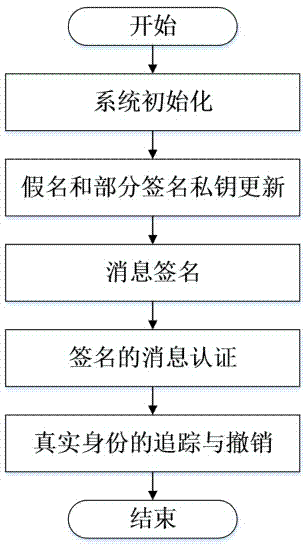
InactiveCN104853351AReduce the burden onSolve the problem of non-repudiationSecurity arrangementTrusted authorityStructure of Management Information
The invention discloses an Internet of Vehicles distributed authentication method based on controllable privacy, relates to the field of vehicle network communication safety, and specifically relates to an Internet of Vehicles distributed authentication method based on controllable privacy. The method specifically includes five following steps: system initialization; private key update of fake names and a part of signatures; message signature; message authentication of signatures; and real identity tracking and revocation. According to the method, the double hash chain is employed to establish the fake names, the communication cost for invalidating a vehicle identity is irrelevant to the numbers of the fake names and a part of the signature private keys of the vehicle, a vehicle user can update multiple parts of signature private keys by the adoption of one authorization, and the burden of trusted authority (TA) and road-side units (RSU) is reduced; when a message with a controversial signature occurs, the TA can distinguish whether the signature is forged by the RSU according to re-signature of the message uploaded by the vehicle, and the problem of non-repudiation in the distributed environment is solved. According to the method, the security is high, the cost is low, and the method is applicable to node high-speed movement, topology structure volatility, and large-scale VANET network.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
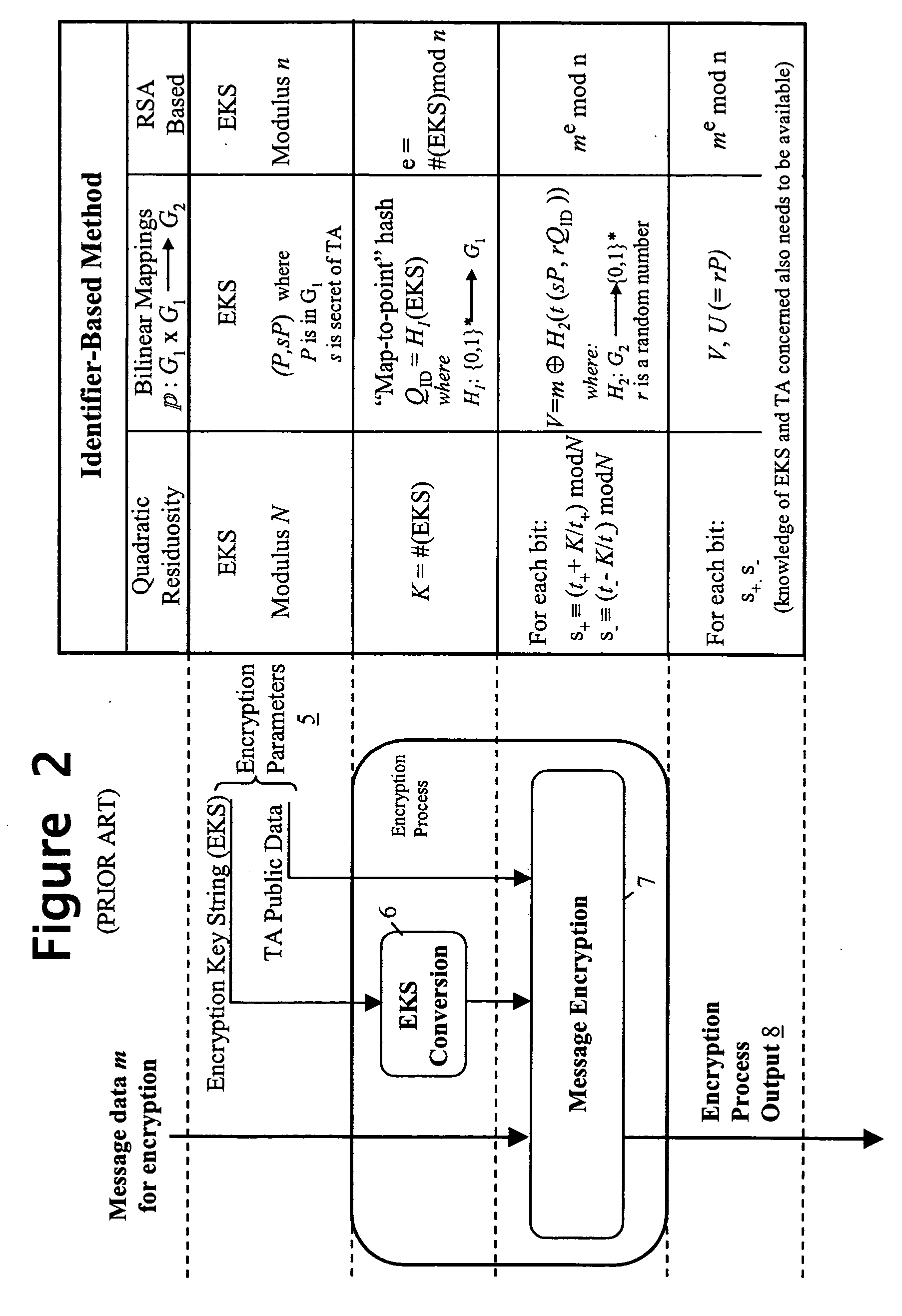
Method and apparatus for generating an identifier-based public/private key pair
An identifier-based public / private key pair is generated for a first party with the involvement of a trusted authority that has an associated secret. An identifier of the first party is signed by the trusted party to produce a multi-component signature. This signature is converted into the first-party identifier-based key pair; the private key of this key pair comprises a component of the signature provided confidentially to the first party, and the public key being formed using at least another component of the signature and the first-party identifier. The signature used by the trusted authority is, for example, a Schnorr signature or a DSA signature.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method and system for encryption of messages in land mobile radio systems
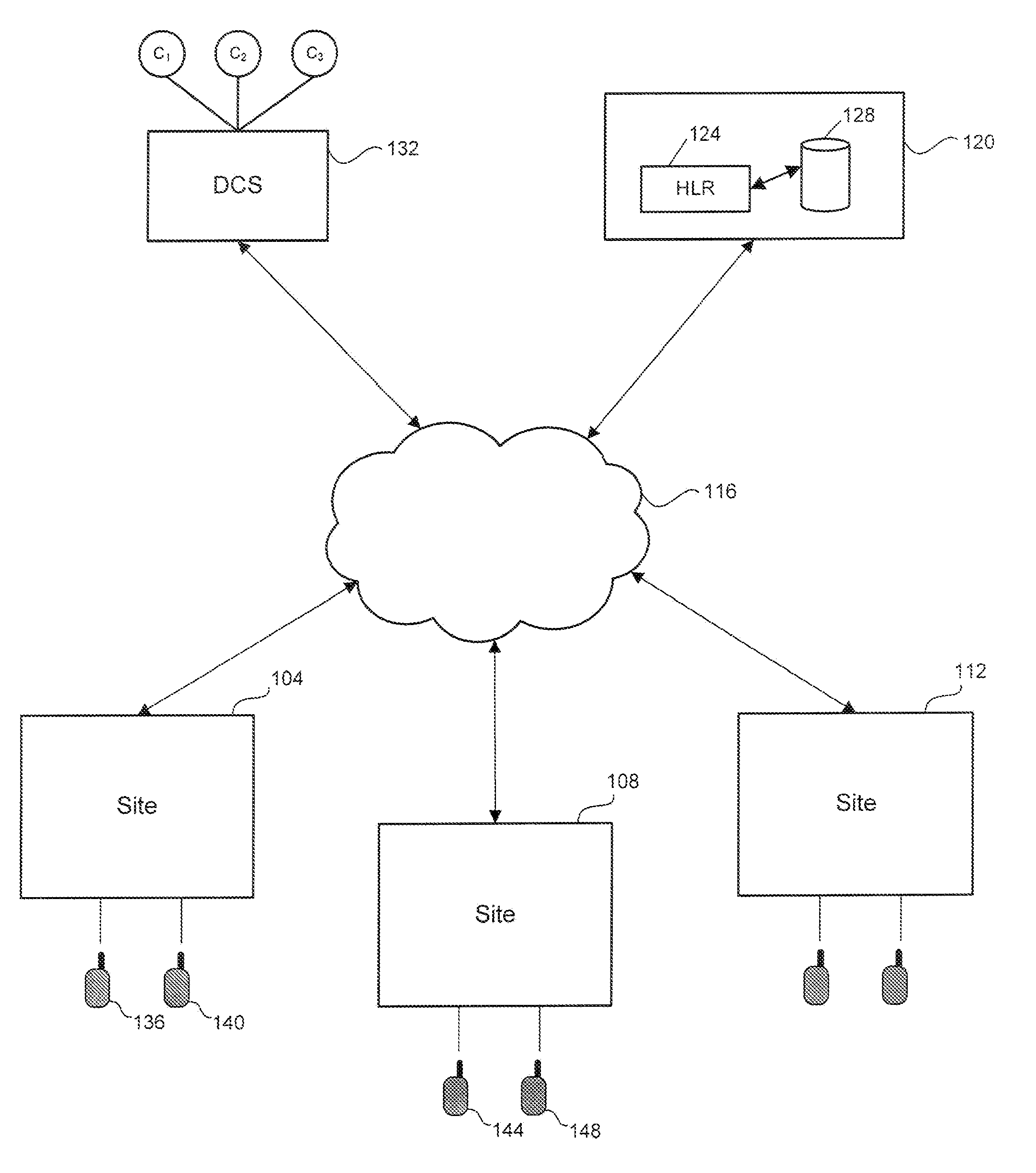
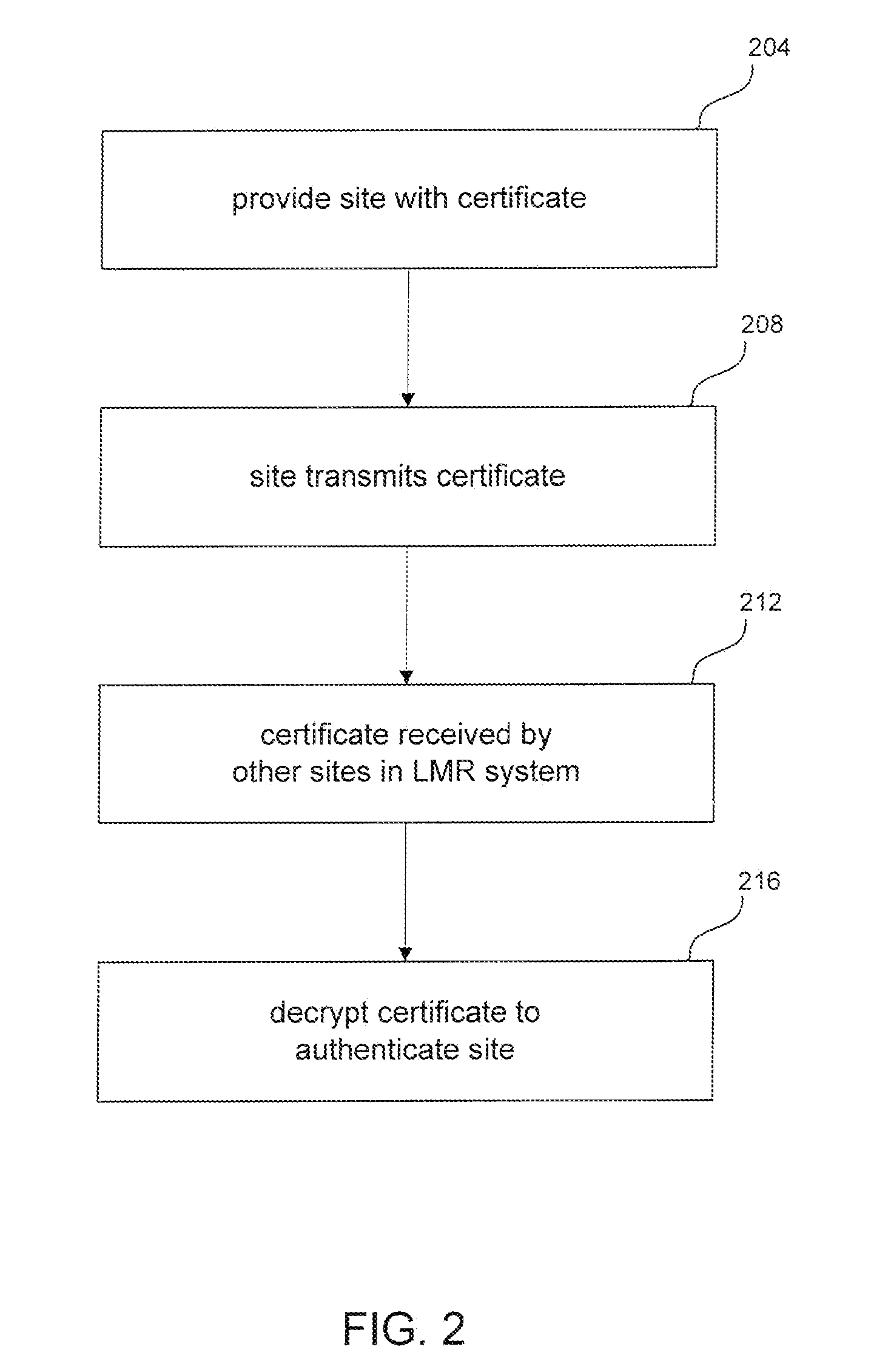
ActiveUS20090024845A1Improve securityQuick changeDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTrusted authorityRelevant information
A method and system for authentication of a plurality of sites in a land mobile radio (LMR) system and for encryption of messages exchanged by the sites. The plurality of sites are connected by a data network (e.g., IP network). The method includes transmitting by a first site its certificate. The certificate is created by a trusted authority by applying a selected function to the public key, the ID and other relevant information of the first site with the trusted authority's private key to generate a reduced representation and then encrypting the reduced representation with the trusted authority's private key. The method further includes receiving, by the other sites in the LMR system, the certificate transmitted by the first site. The method further includes decrypting, by the other sites, the certificate transmitted by the first site and authenticating the first site, wherein the certificate is decrypted using the trusted authority's public key. The method further includes generating a session key, encrypting the session key with the public key of the first site, and transmitting the encrypted session key to the first site. The method further includes decrypting, by the first site, the encrypted session key with the first site's private key, and transmitting, by the first site, a message encrypted with the shared session key. The method further includes multicasting the encrypted message over the data network. The method further includes receiving, by the other sites in the LMR system, the encrypted message transmitted by the first site, and decrypting the message with the session key.
Owner:E F JOHNSON CO
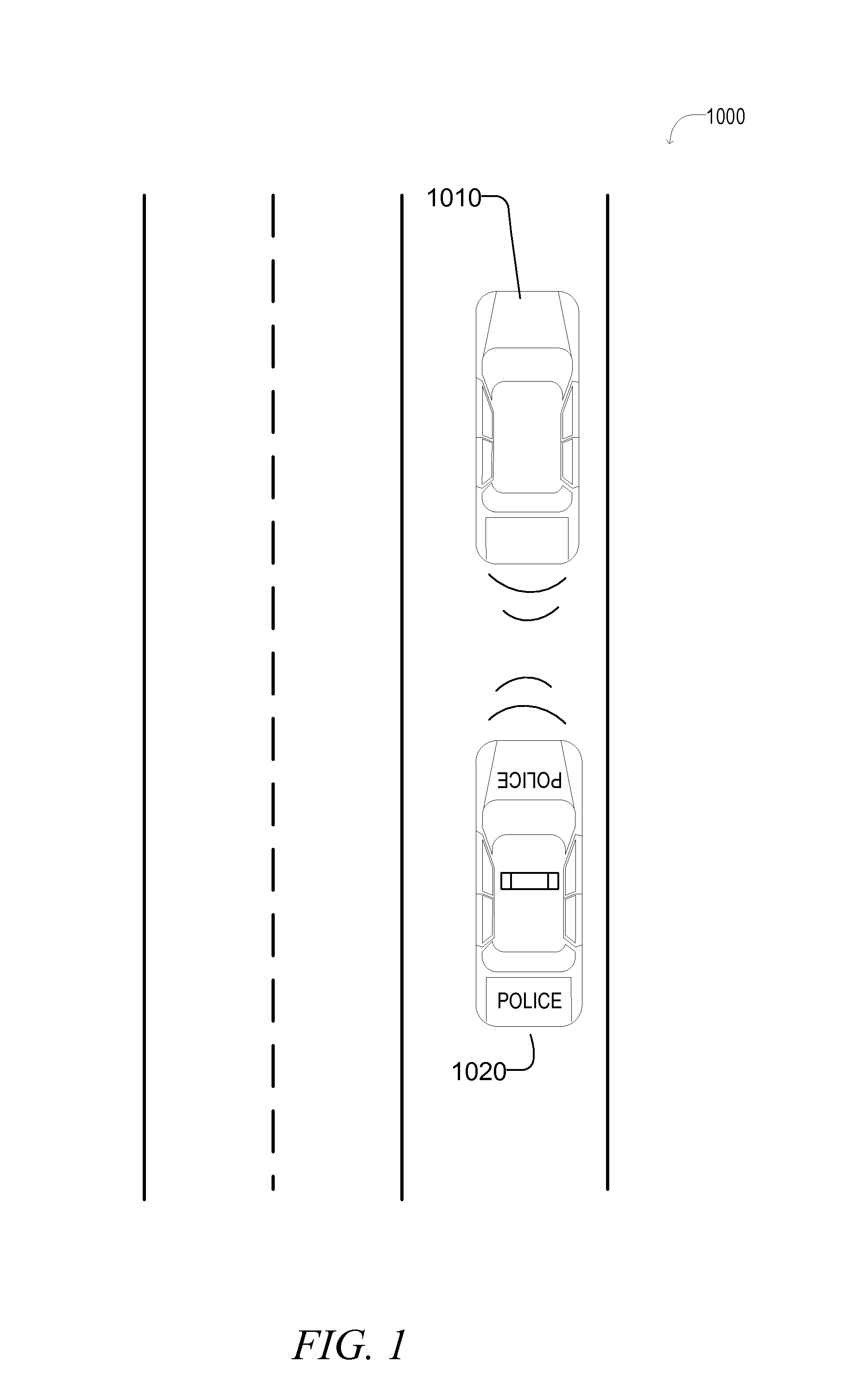
Authorized access to vehicle data
ActiveUS20150057838A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsTrusted authorityMachine-readable medium
Disclosed in some examples are methods, systems, and machine readable mediums which provide for controlled access of vehicle information by trusted authority systems. These systems may allow for police and other authority figures to utilize the onboard systems of the vehicle or obtain other information about the vehicle and occupants while safely in their own vehicles prior to an initial encounter with the vehicle and occupants.
Owner:INTEL CORP
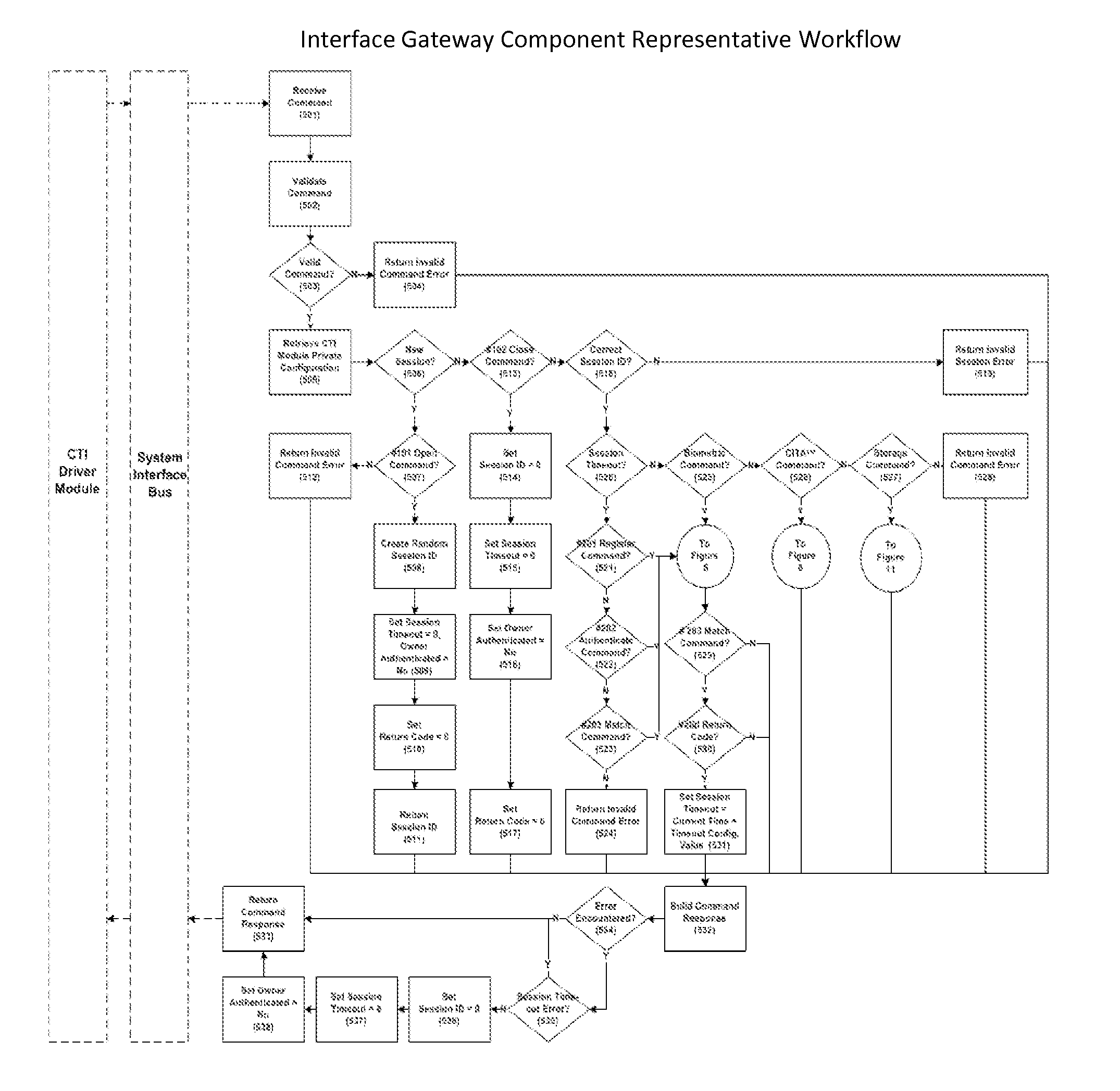
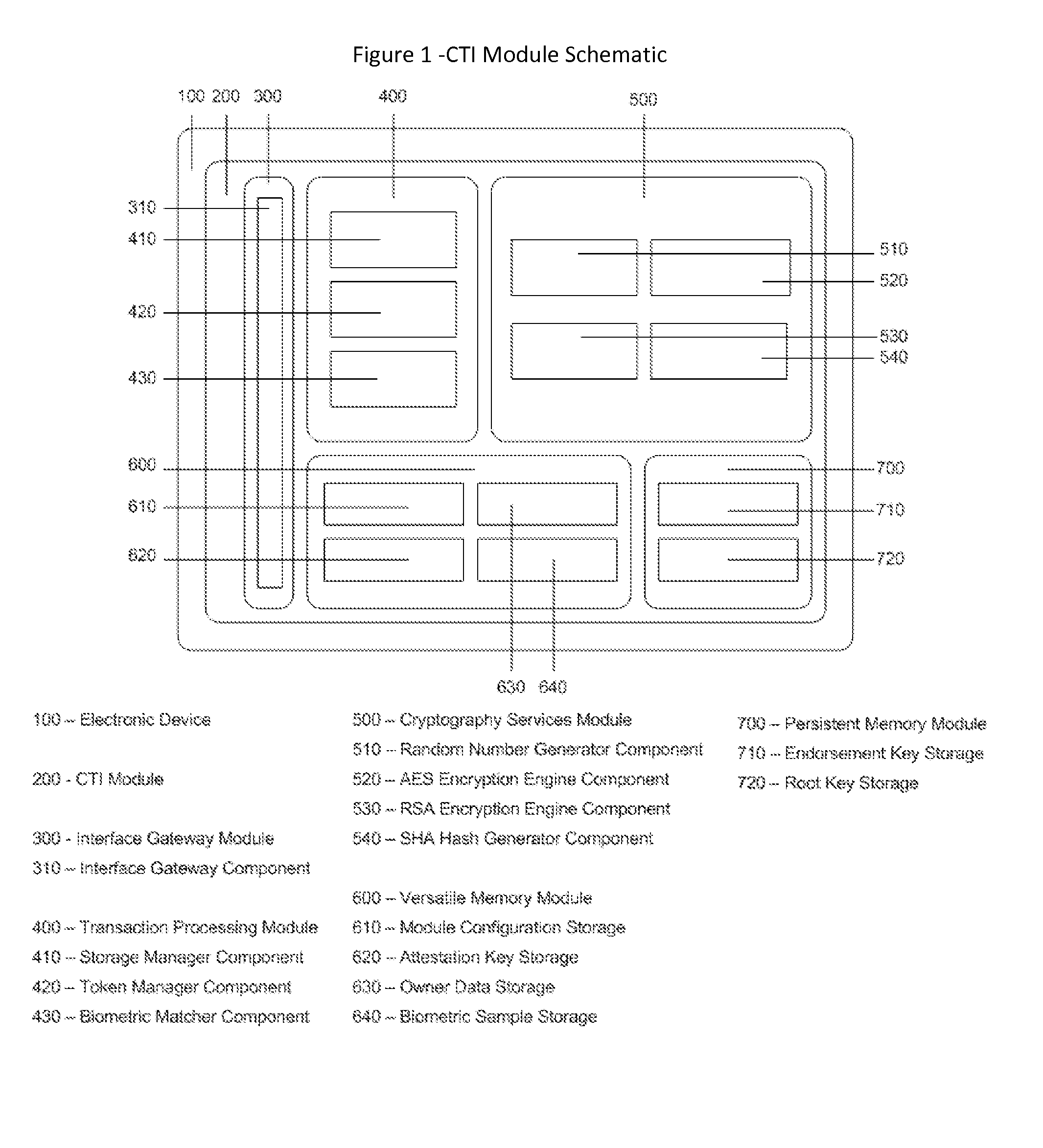
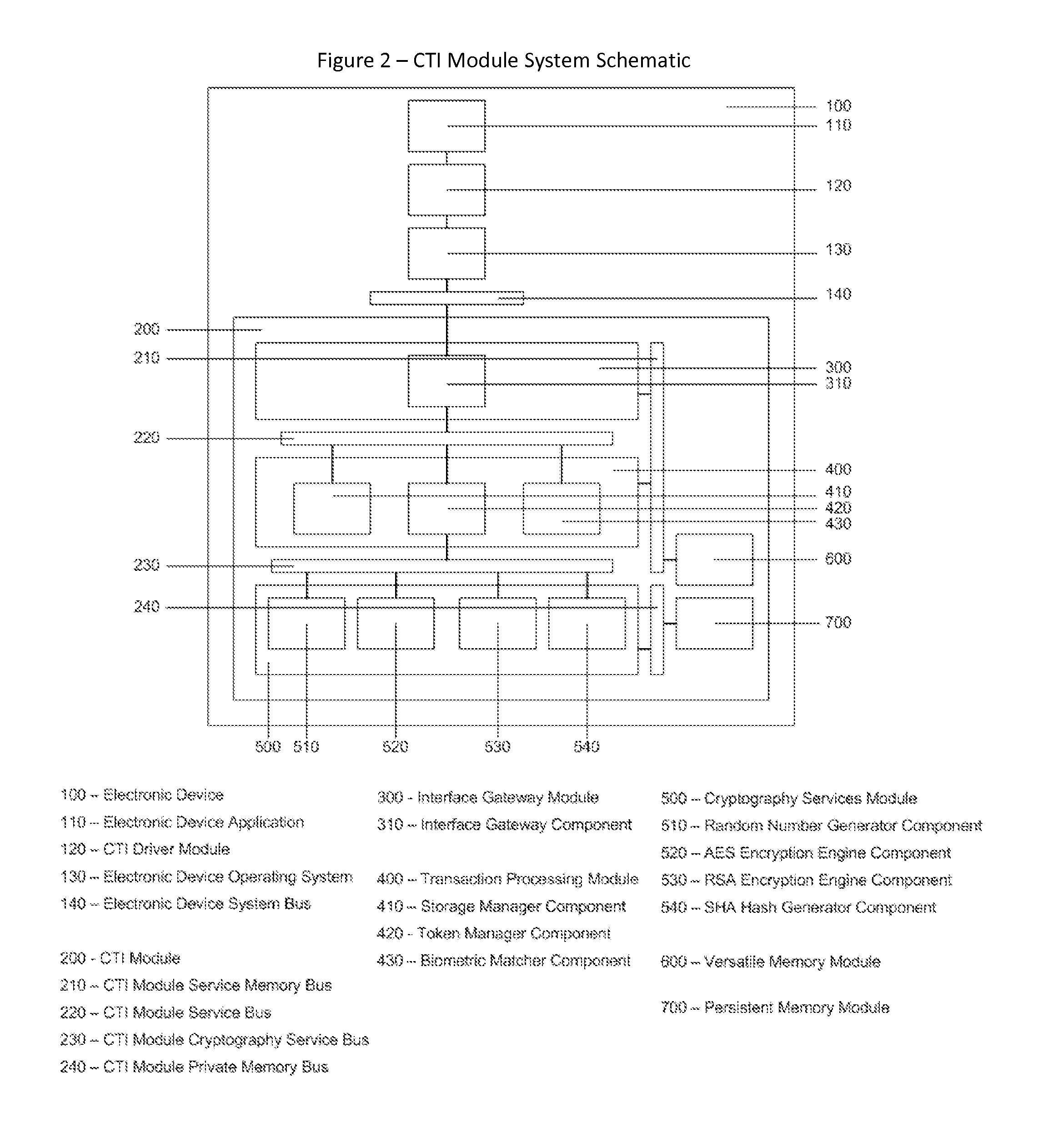
Cyberspace Trusted Identity (CTI) Module
InactiveUS20130219481A1Eliminate needIncrease storage capacityDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsTrusted authorityDigital identity
The Cyberspace Trusted Identity (CTI) module provides secure storage of a cyberspace user's personal identity information and a security infrastructure to guarantee the integrity and privacy of a cyberspace transaction. When the owner of an electronic device registers their biometric samples on the CTI module the module becomes locked and the information stored on the module can only be accessed when the device owner provides a live biometric sample, which matches the registered biometric sample. When the CTI Module is registered under a trusted third party system; a Cyberspace Identification Trust Authority (CITA) system, the module provides a secure mechanism for storing a cyberspace user's digital identity tokens and for conducting safe and reliable cyberspace transactions between two cyberspace users. The CTI Module eliminates the need to carry man-made identity tokens, or the need to remember and / or openly exchange personal identity information, when conducting a cyberspace transaction.
Owner:VOLTZ ROBERT MATTHEW
Scoring Persons and Files for Trust in Digital Communication
ActiveUS20100169265A1Multiple digital computer combinationsFuzzy logic based systemsTrusted authorityInternet privacy
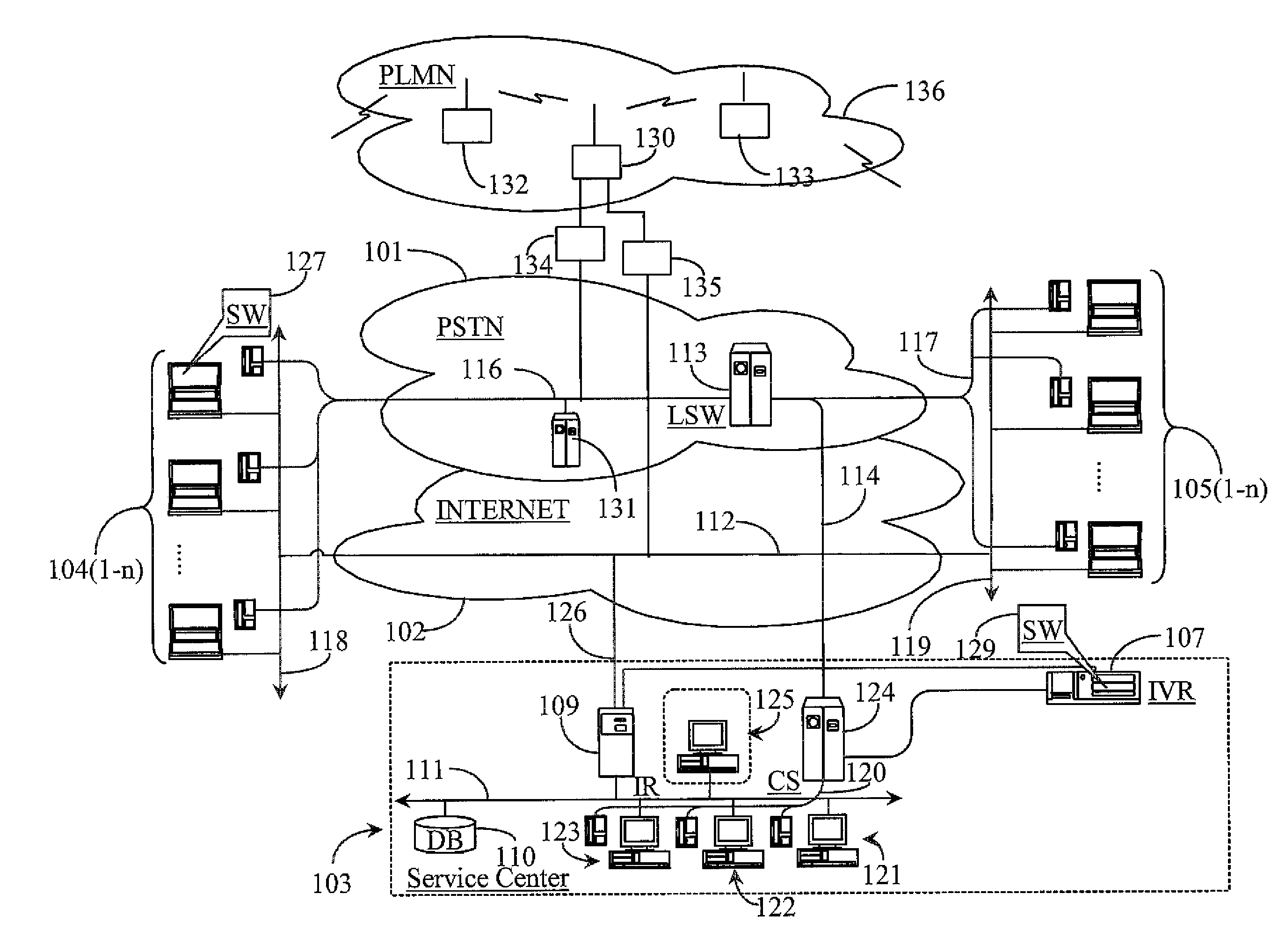
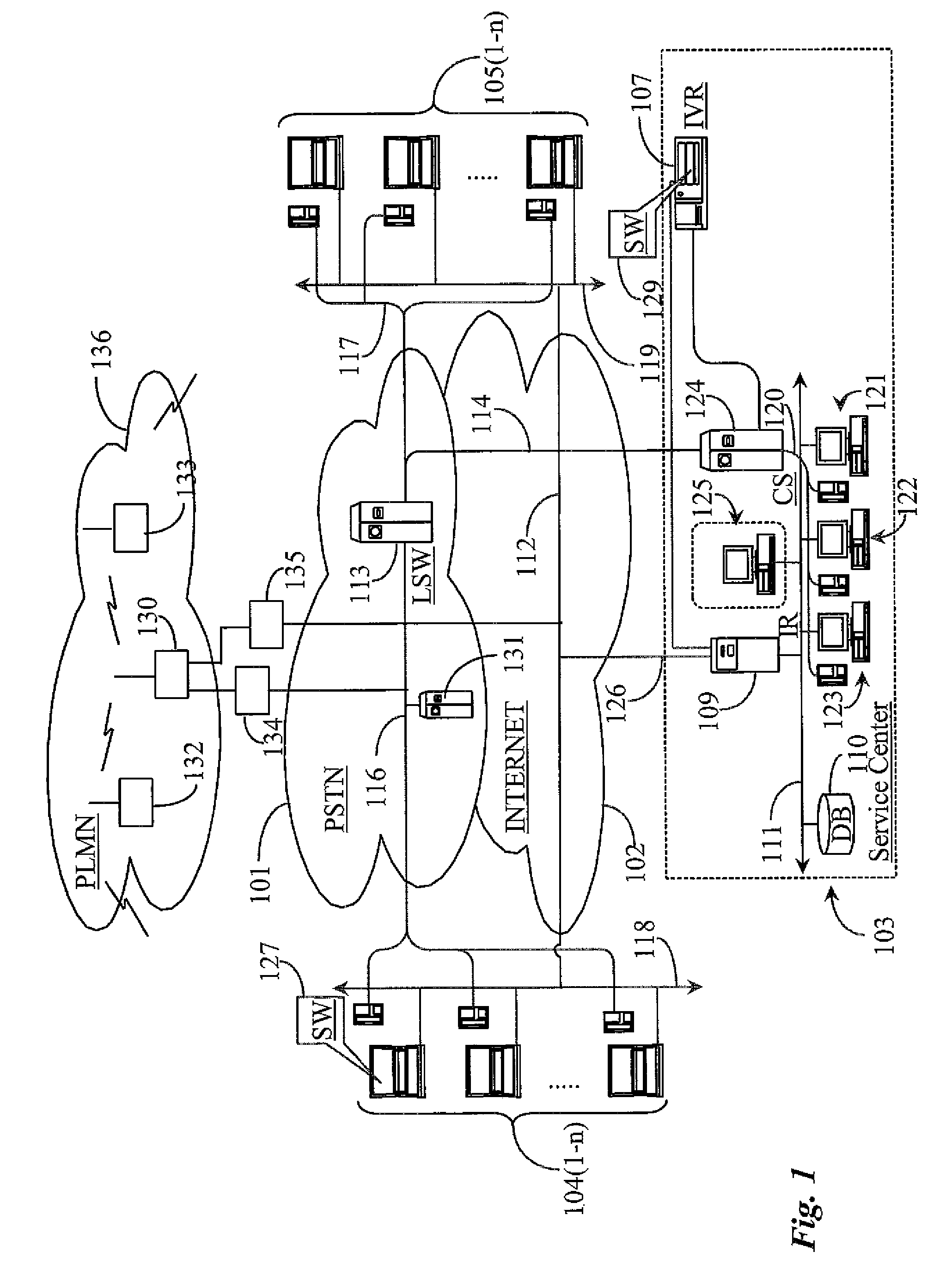
Owner:GENESYS TELECOMMUNICATIONS LABORATORIES INC
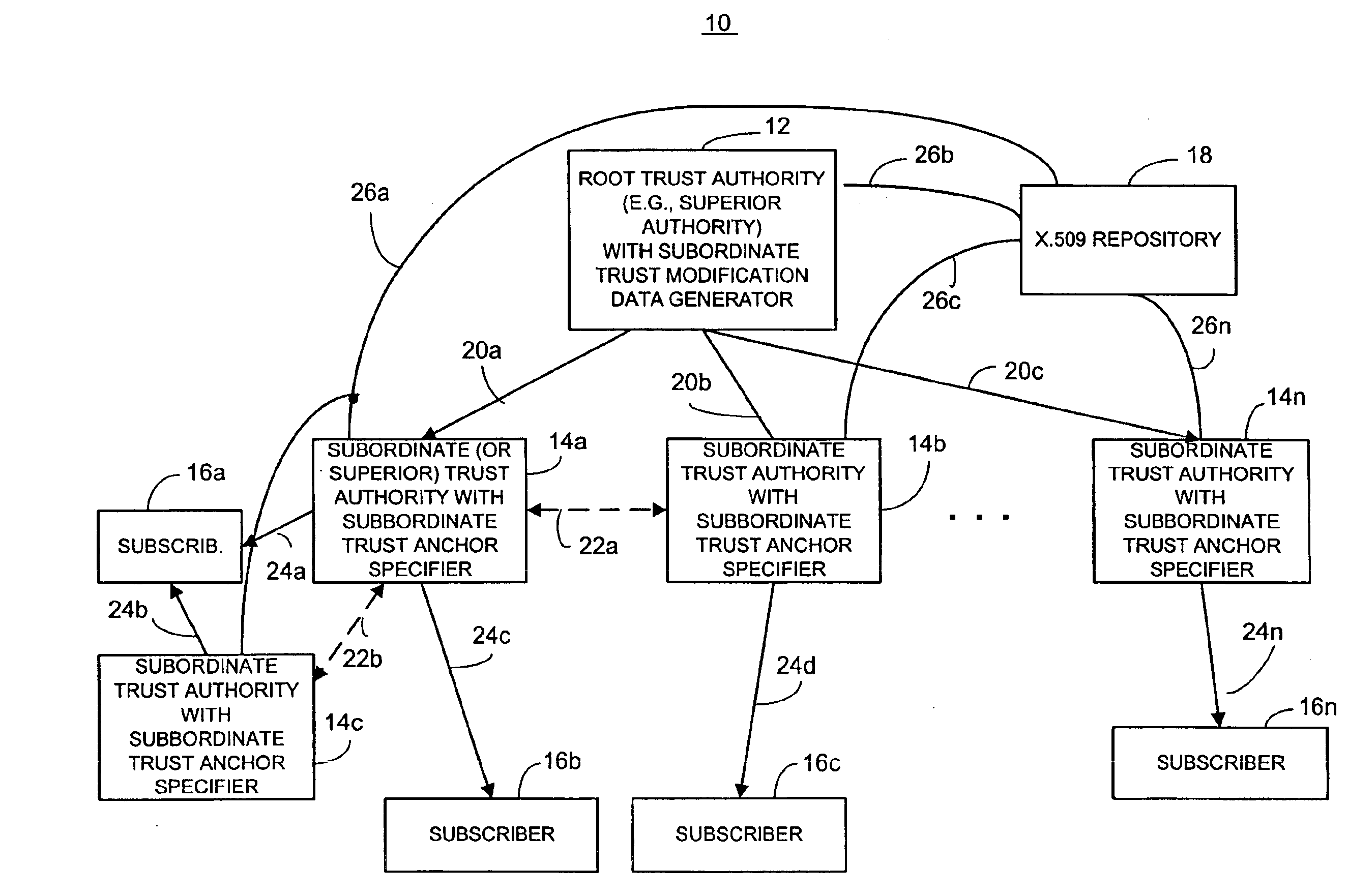
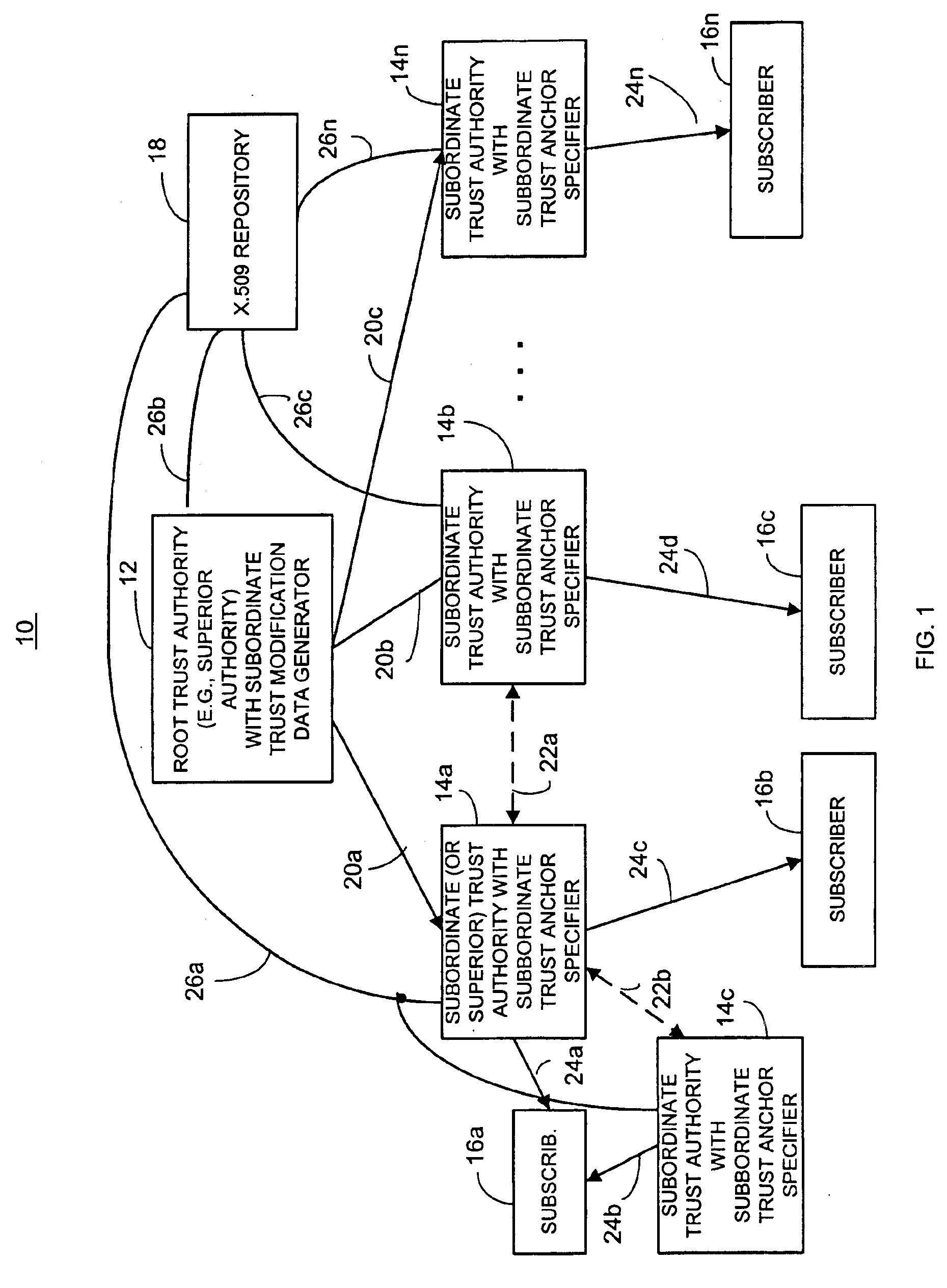
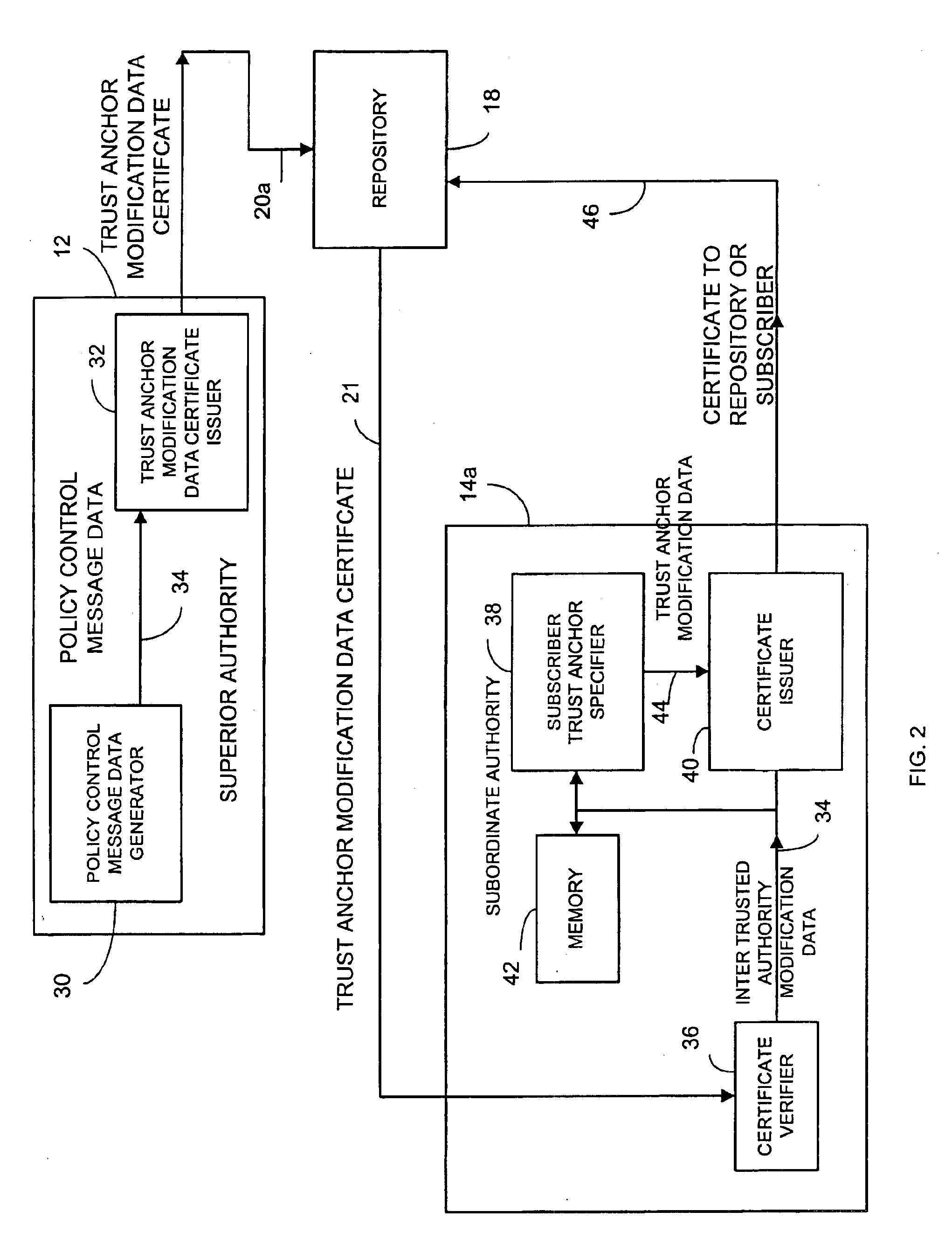
Dynamic trust anchor system and method
InactiveUS6865674B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTrusted authorityInternet privacy
An information security network provides a plurality of trusted authorities configurable in a rooted hierarchical structure. At least one of the trusted authorities is a superior authority and at least one of the trusted authorities are subordinate authorities. The trust authorities are capable of issuing digitally signed data structures, referred to as certificates. The superior authority is operative to generate policy control message data, such as separate message data or a certificate containing policy information, to dynamically vary policy control data to facilitate trust authority policy delegation among subordinate authorities. The policy control data includes, among other things, inter-trusted authority trust modification data to dynamically vary validation starting authorities among subordinate authorities.
Owner:ENTRUST
Revocation of cryptographic keys in the absence of a trusted central authority
ActiveUS20160254910A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationTrusted authorityCryptographic nonce
A method and apparatus is presented for revoking cryptographic keys within a distributed ledger system in which no central trusted authority is available, consisting of sending a key revocation message by a network connected device to other network connected devices over a peer-to-peer network for inclusion in a ledger. In one embodiment the revocation message is signed using a private key of a public / private key pair to be revoked. In another embodiment an authorization for future revocation of the public / private key pair by a plurality of other public / private keys is sent for inclusion in the ledger, and subsequently the key revocation message is signed with one of the private keys of the plurality of public / private key pairs before sending the key revocation message. Once a valid key revocation message is included in the ledger, any future request to include a message signed by the revoked cryptographic key is rejected.
Owner:FINLOW BATES KEIR
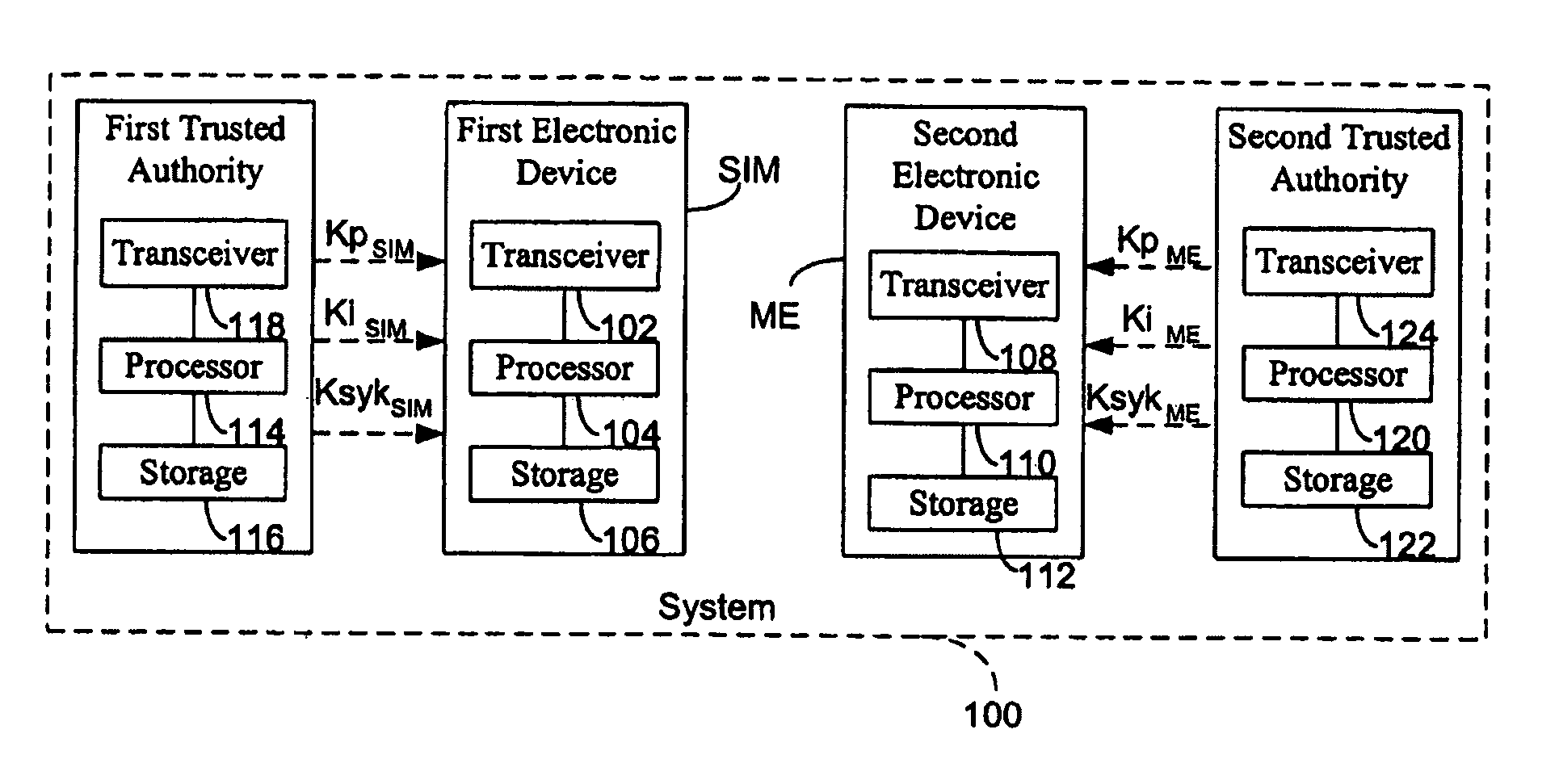
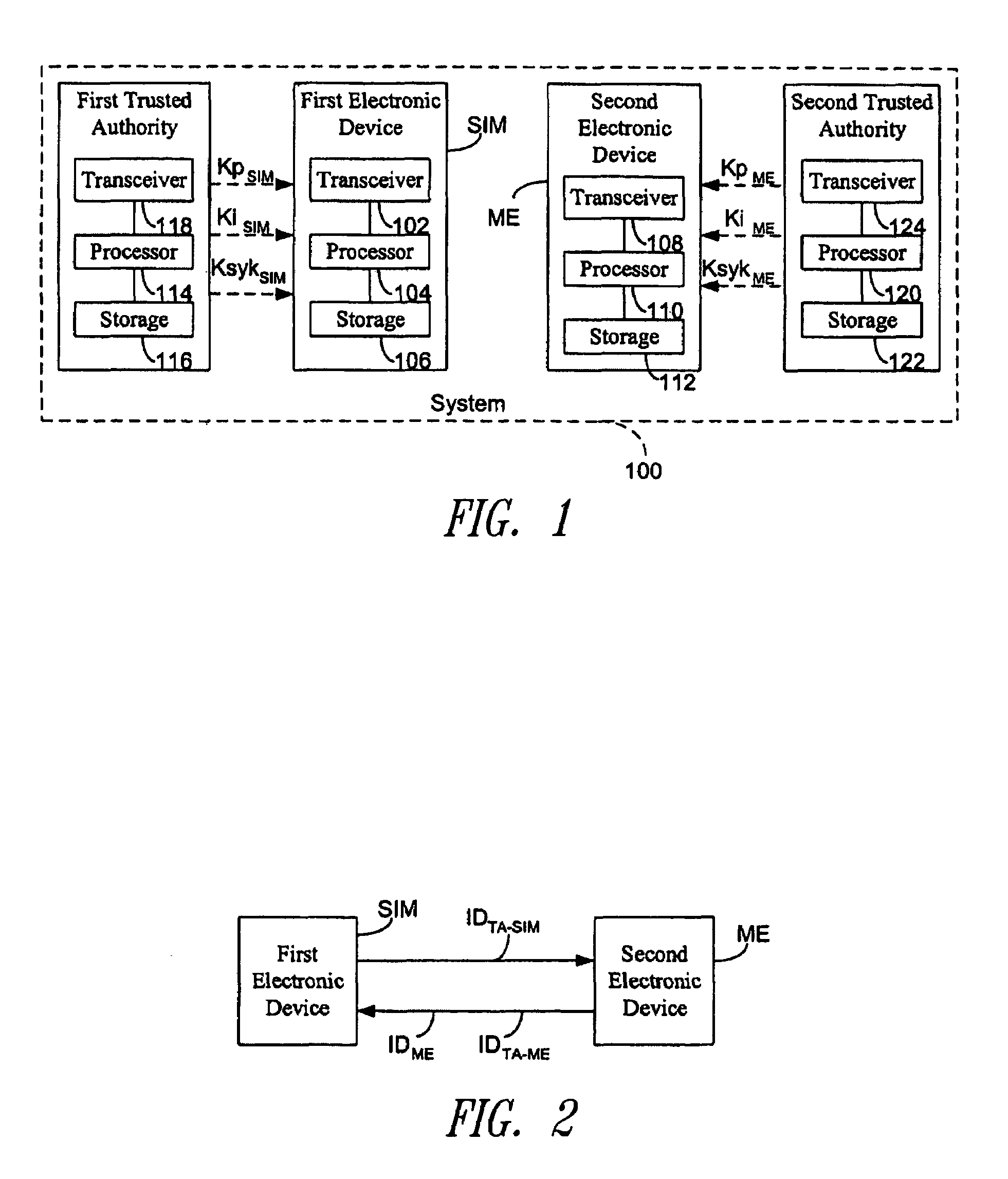
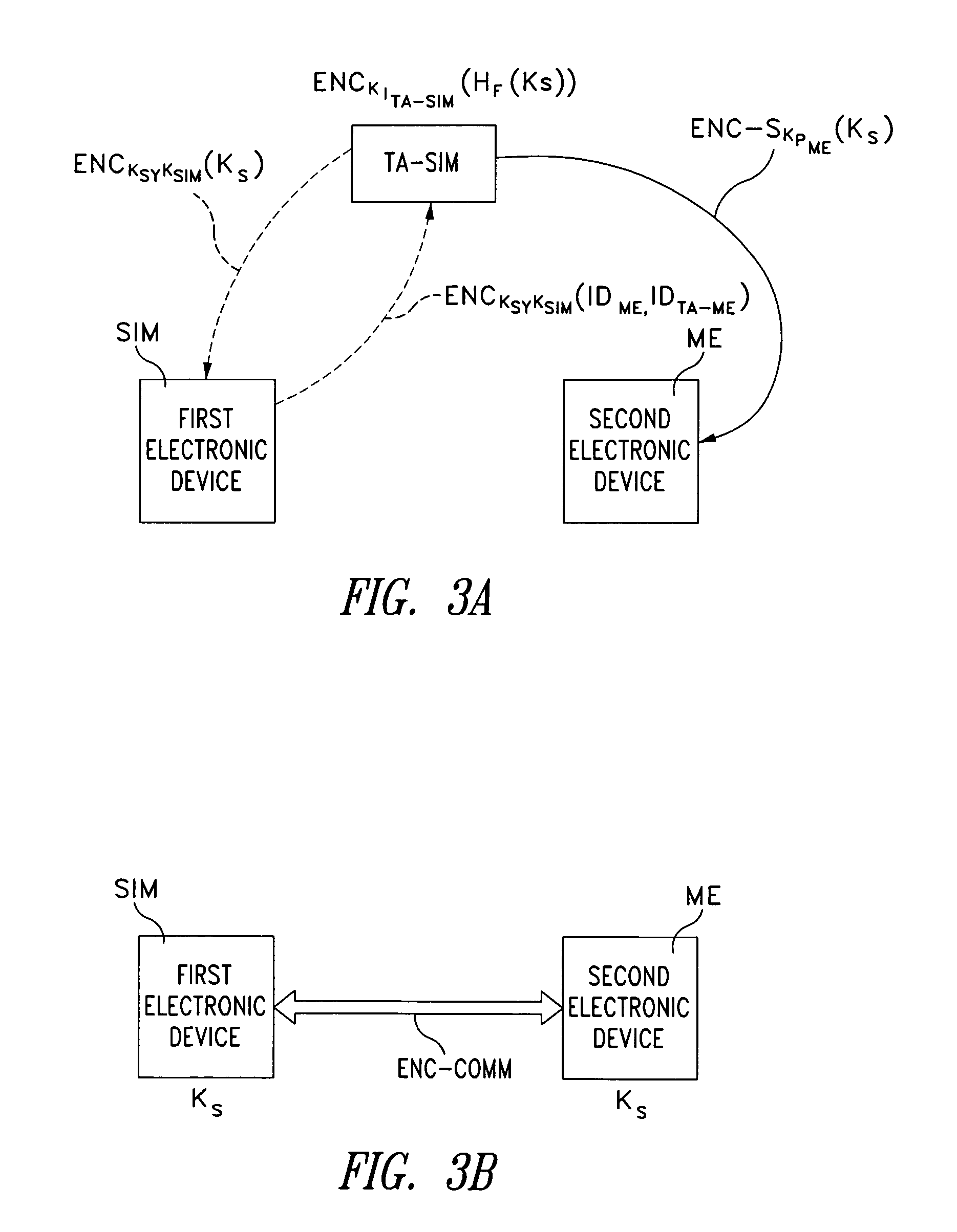
Method for establishing a communication between two devices
ActiveUS7716483B2Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationTrusted authorityElectronic equipment
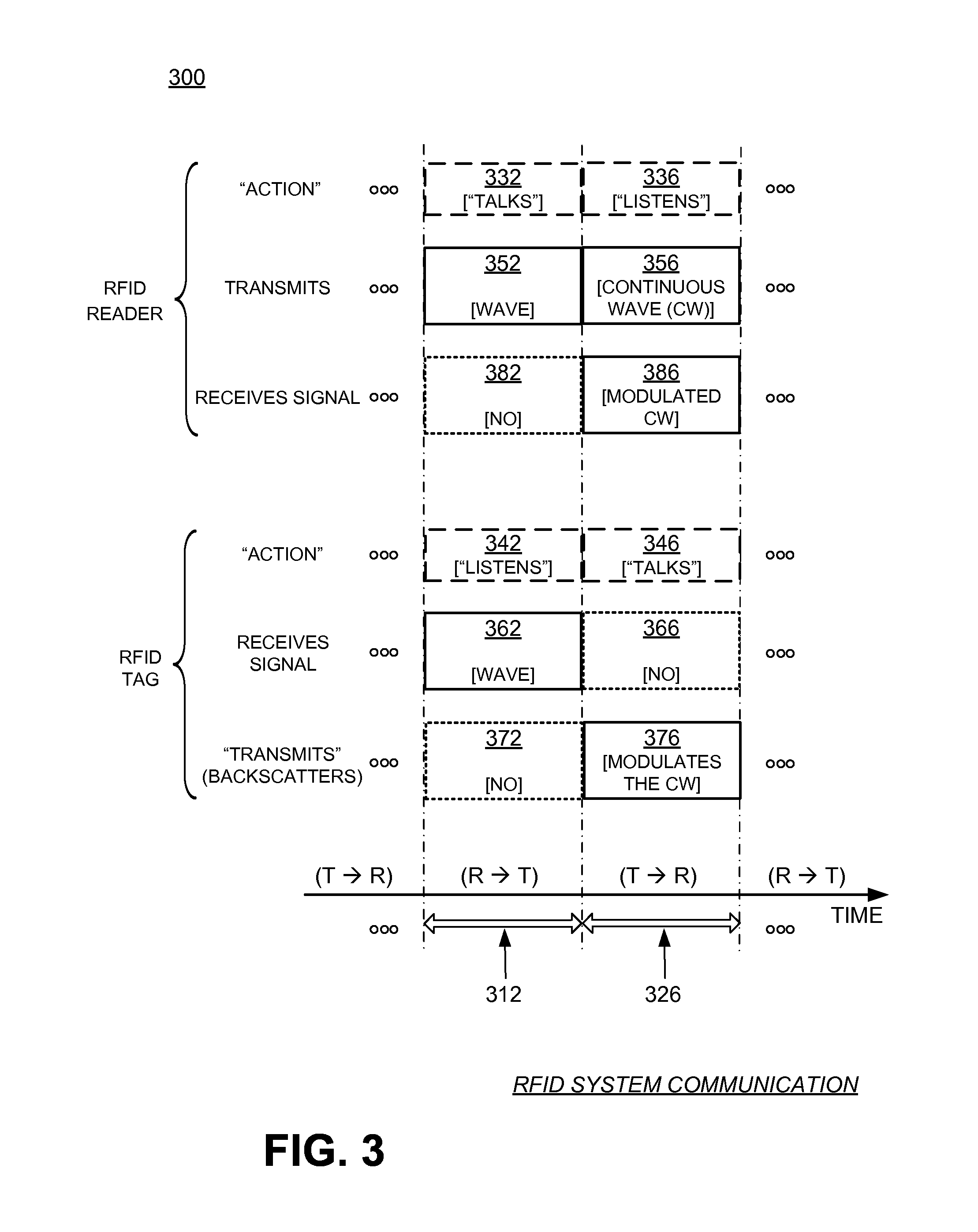
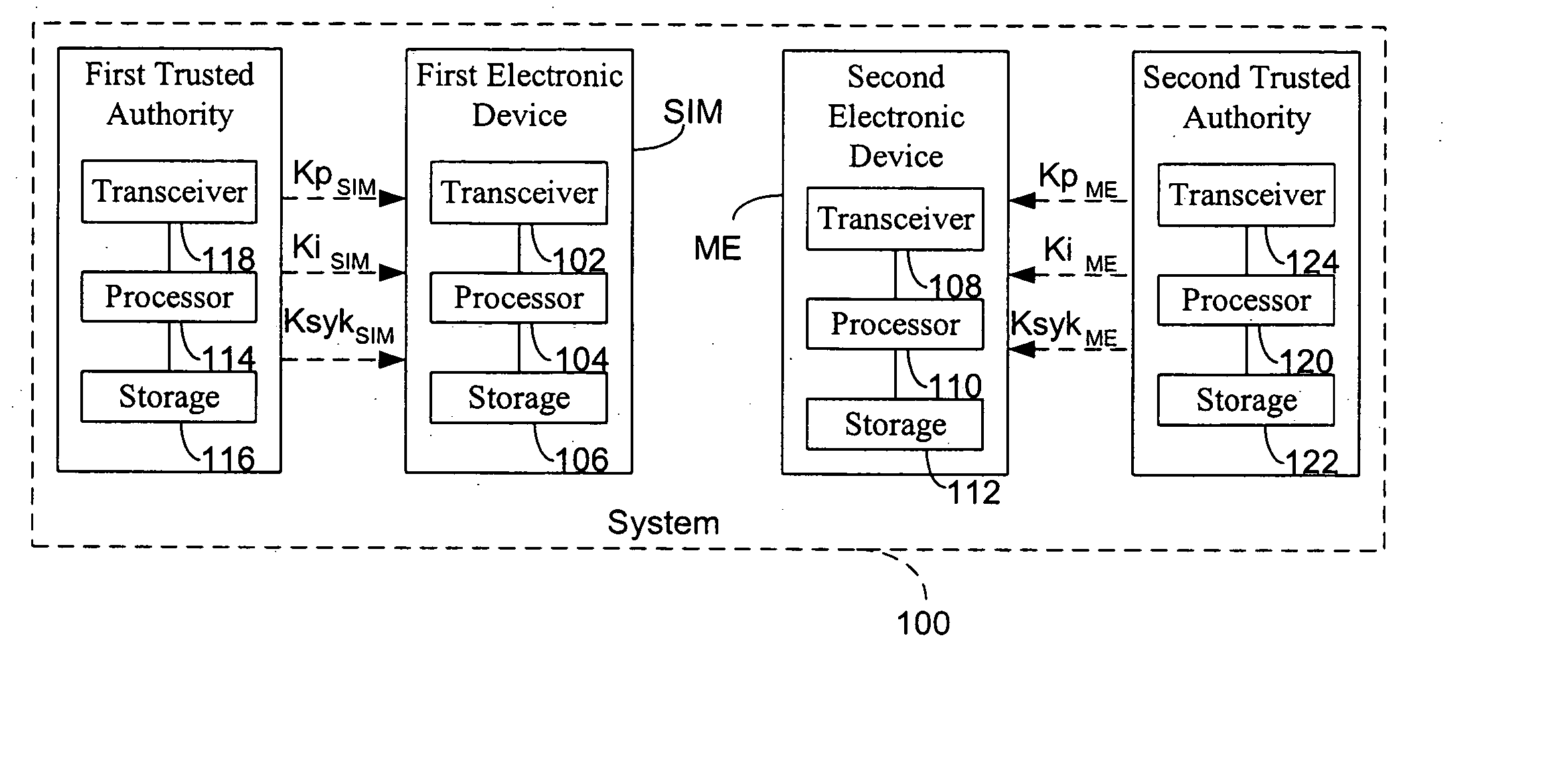
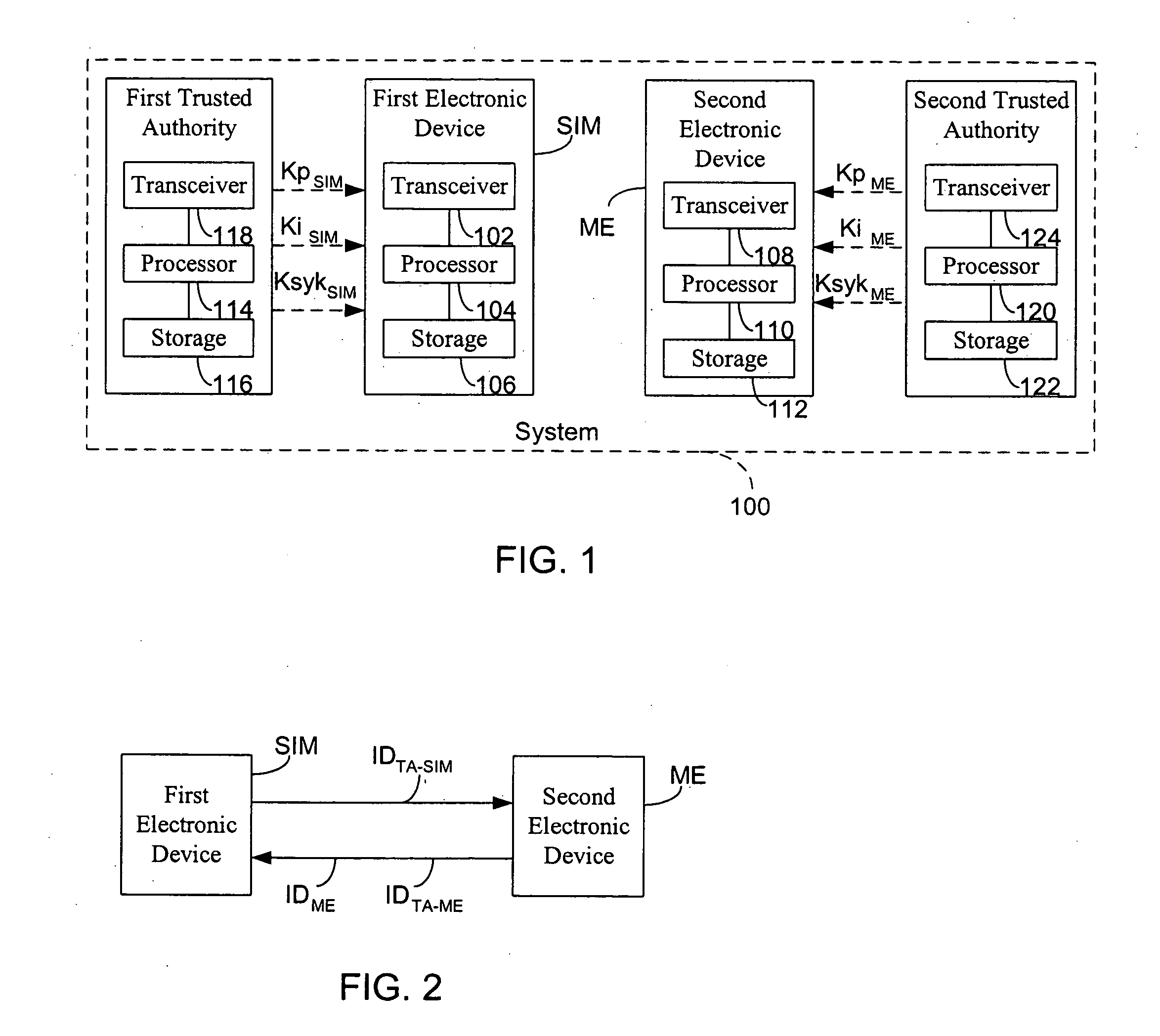
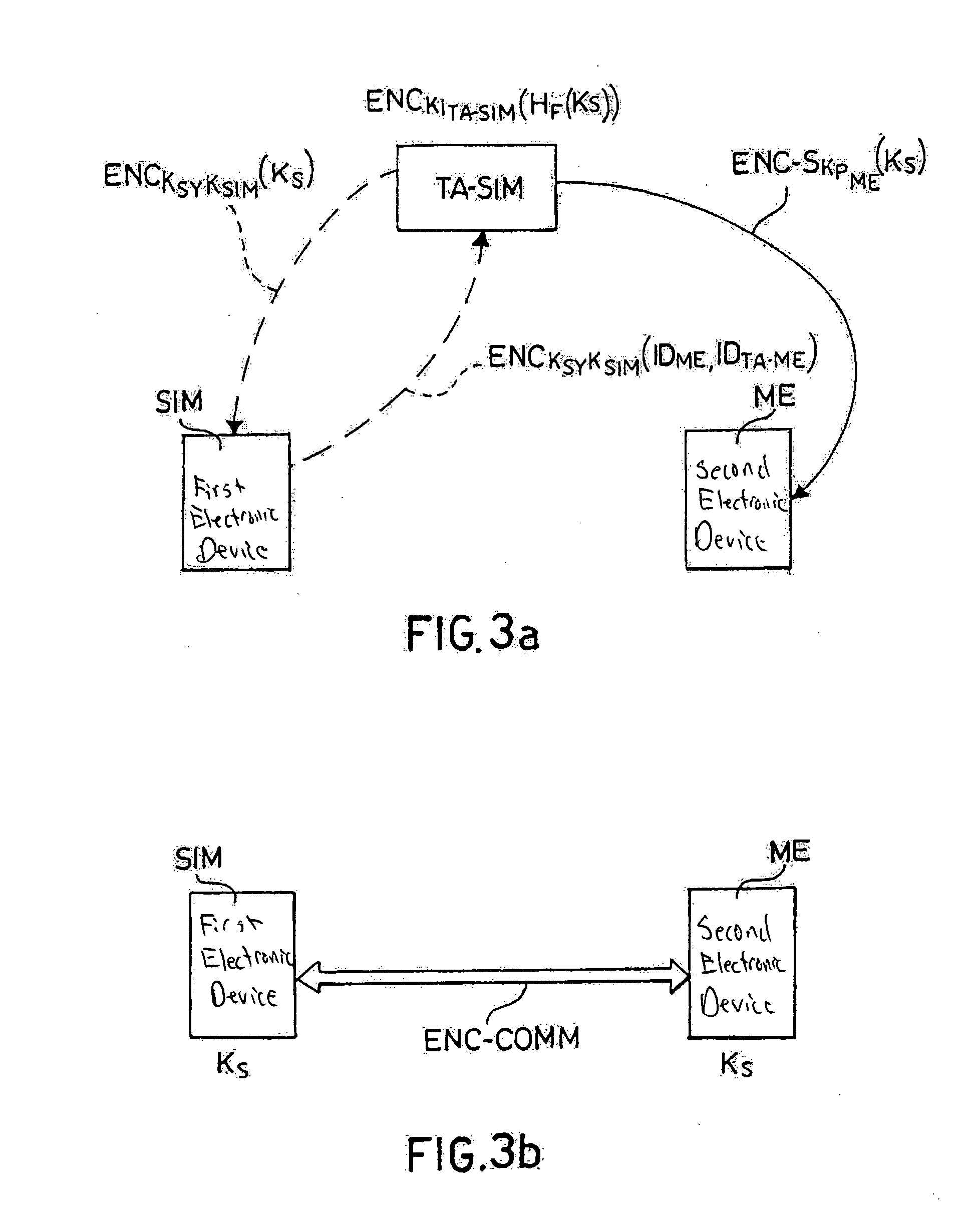
A method establishes a communication between a first electronic device associated with a first trusted authority and a second electronic device. The method includes: making a first key available to the first device for the communication between the first authority and the first device. A second trusted authority, associated with the second device and distinct and autonomous with respect to the first authority, generates a second key in order to communicate with the second device. Furthermore, the method includes: making the second key available to the second device; and providing the first and second devices with a communication key, to be used communication between the first and second devices, through at least one of the first and second authorities.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
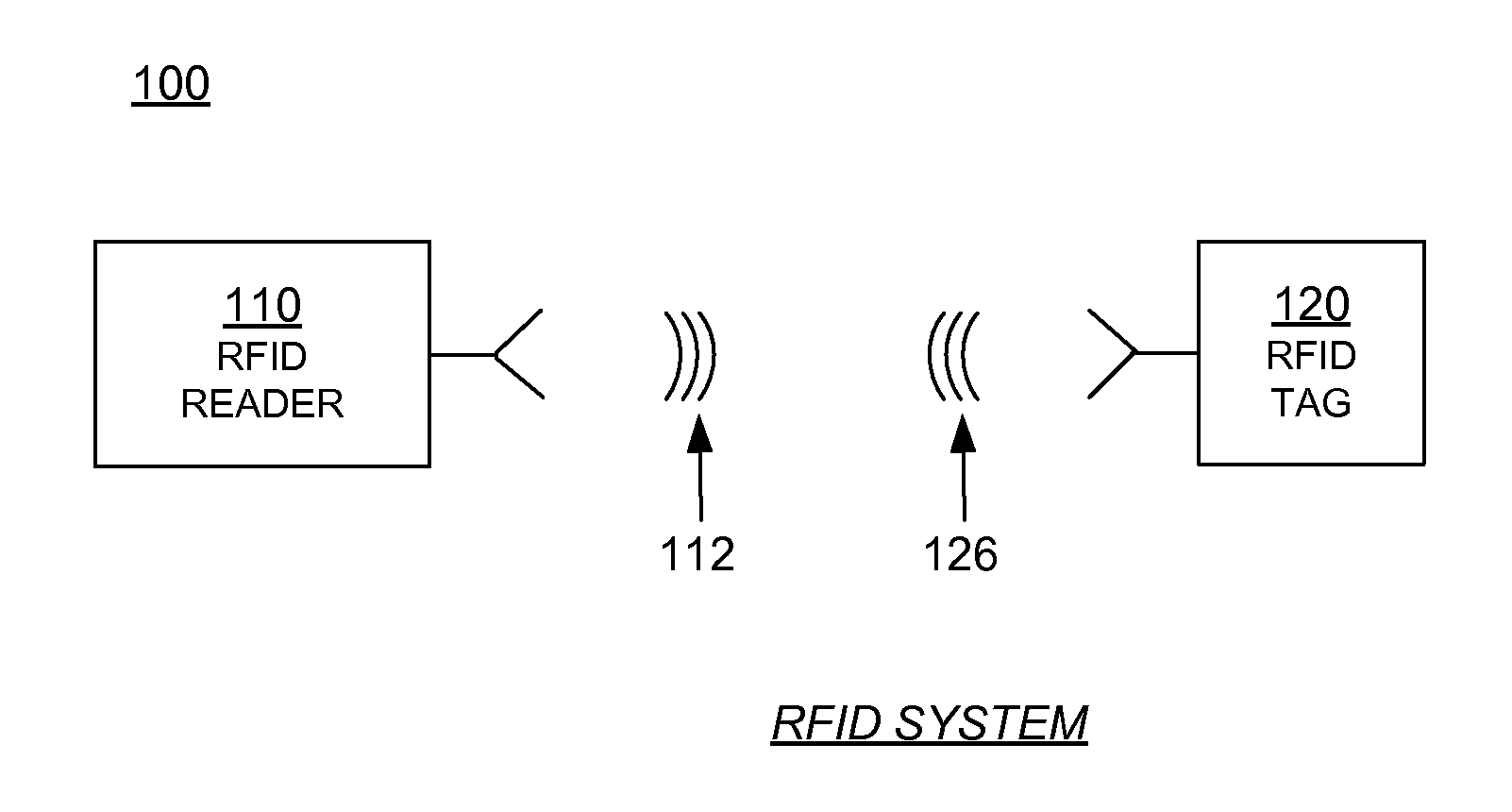
RFID tag and reader authentication by trusted authority
ActiveUS8866594B1Well formedMultiplex system selection arrangementsSensing record carriersComputer hardwareTrusted authority
A Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) reader containing a reader key authenticates an RFID tag containing a tag key by receiving a reader challenge from a verification authority; determining a reader response based at least on the reader challenge and the reader key; sending a first message including at least the reader response but not the reader key to the verification authority; receiving a tag identifier from the tag; challenging the tag with a tag challenge; receiving a tag response based at least on the tag challenge and the tag key but not including the tag key; sending a second message including at least the tag identifier and the tag response to the verification authority; and receiving an electronically-signed reply from the verification authority. The reader validates the verification authority reply by checking the signature. The verification authority may notify a designated party if a response is incorrect.
Owner:IMPINJ
Method for establishing a communication between two devices
ActiveUS20050125670A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationTrusted authorityElectronic equipment
A method establishes a communication between a first electronic device associated with a first trusted authority and a second electronic device. The method includes: making a first key available to the first device for the communication between the first authority and the first device. A second trusted authority, associated with the second device and distinct and autonomous with respect to the first authority, generates a second key in order to communicate with the second device. Furthermore, the method includes: making the second key available to the second device; and providing the first and second devices with a communication key, to be used communication between the first and second devices, through at least one of the first and second authorities.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
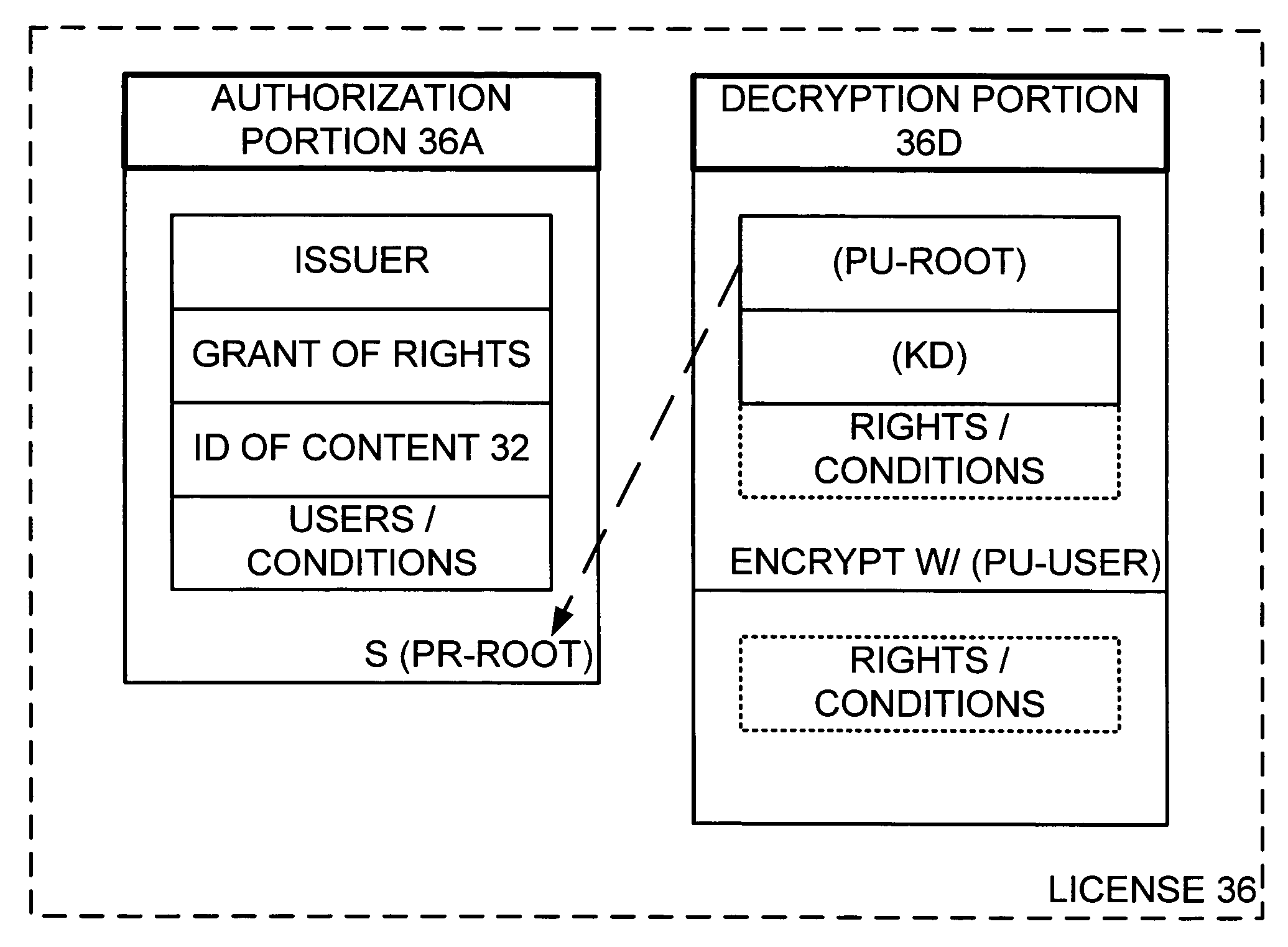
Flexible licensing architecture in content rights management systems
InactiveUS20060173788A1Satisfies needTelevision system detailsComputing modelsTrusted authorityDigital signature
A license is issued to a user as decryption and authorization portions. The decryption portion is accessible only by such user and has a decryption key (KD) for decrypting corresponding encrypted digital content and validating information including an identification of a root trust authority. The authorization portion sets forth rights granted in connection with the digital content and conditions that must be satisfied to exercise the rights granted, and has a digital signature that is validated according to the identified root trust authority in the decryption portion. The user issued accesses the decryption portion and employs the validation information therein to validate the digital signature of the authorization portion. If the conditions in the authorization portion so allow, the rights in the authorization portion are exercised by decrypting the encrypted content with the decryption key (KD) from the decryption portion and rendering the decrypted content.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
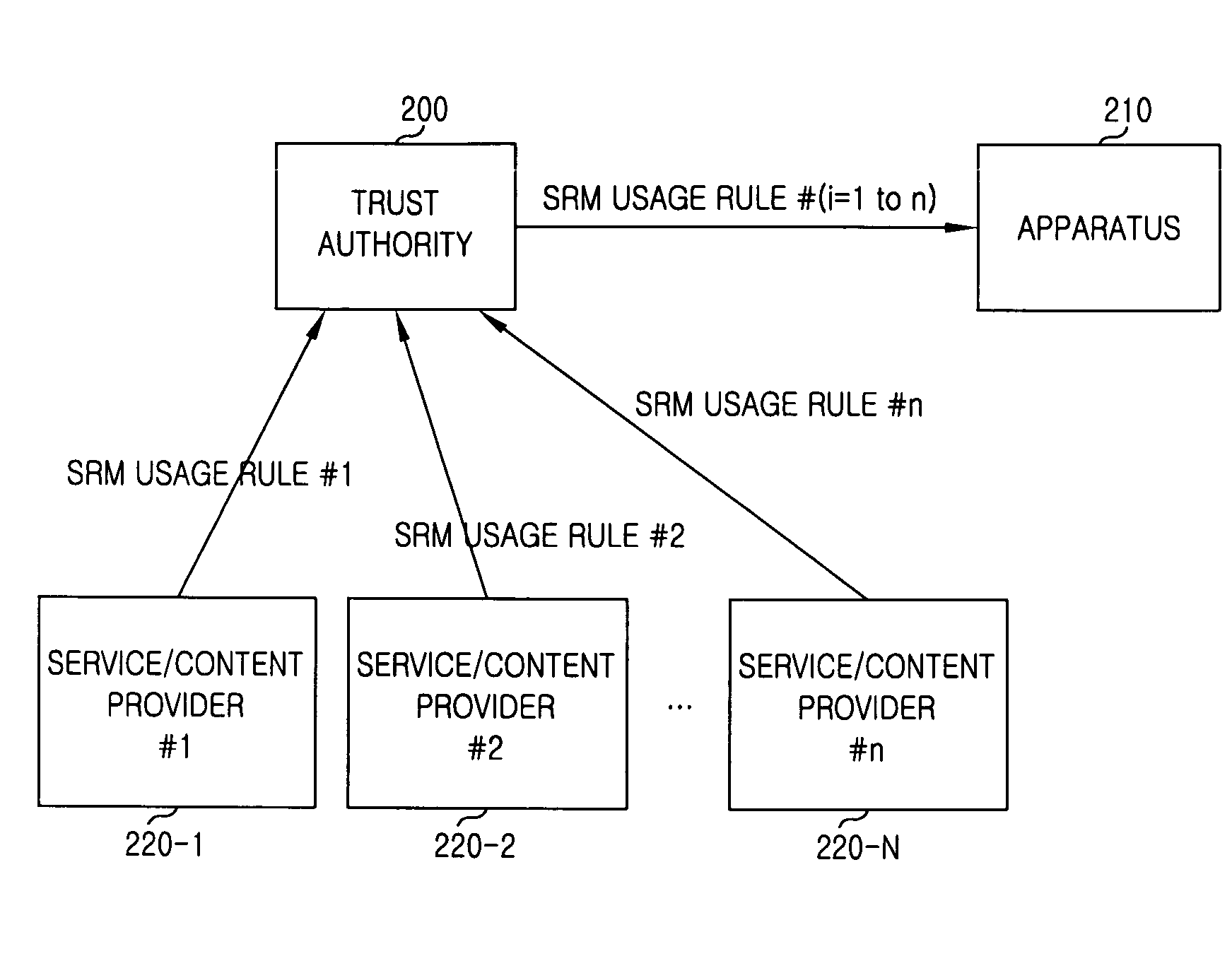
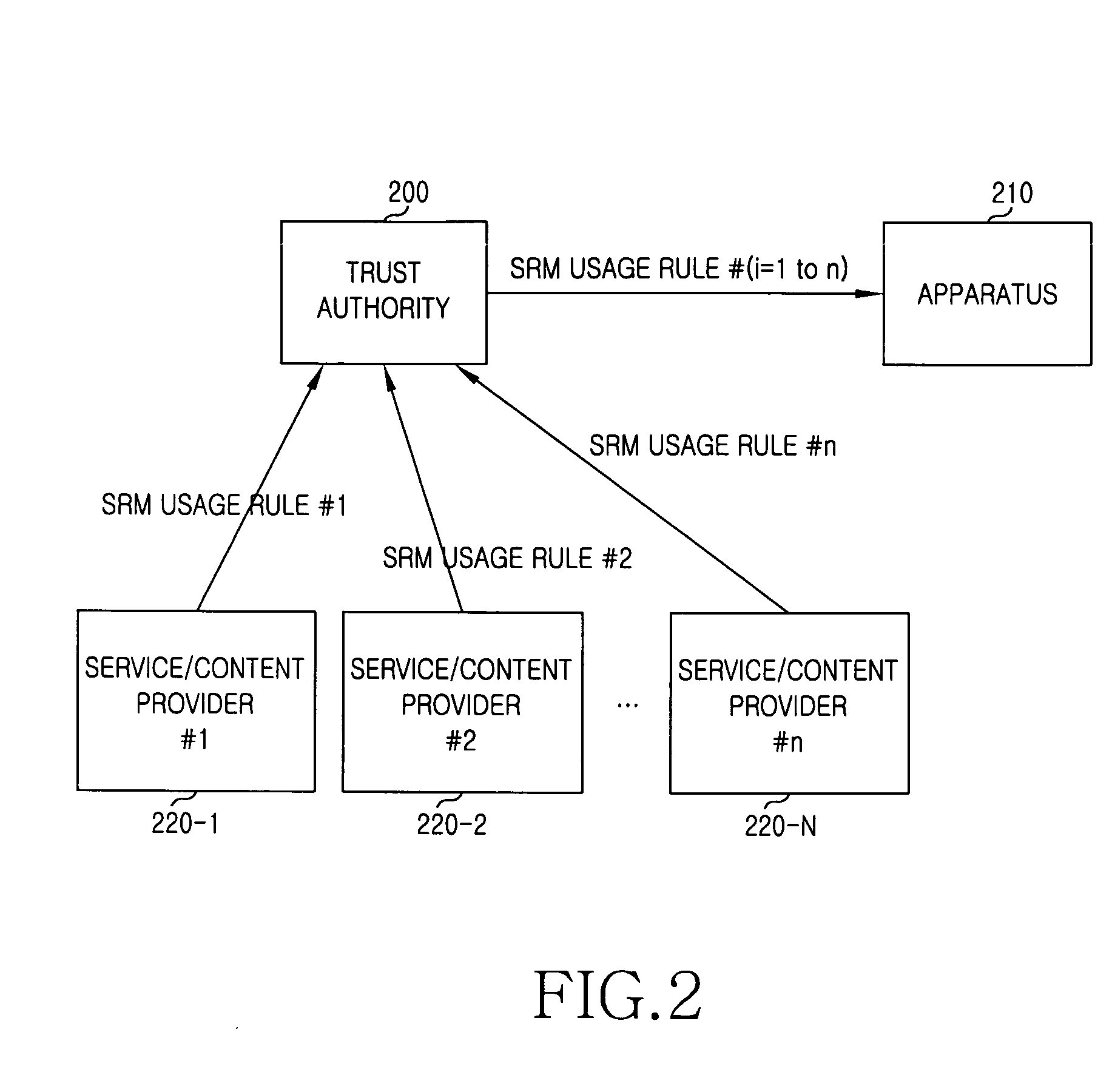
Apparatus and Method for Using Secure Removable Media (SRM) in Digital Rights Management
InactiveUS20100049971A1User identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsTrusted authorityRemovable media
An apparatus and a method for using a Secure Removable Media (SRM) in Digital Rights Management (DRM) are provided. The method for using the SRM in Digital Rights Management (DRM) includes determining, at a plurality of content service providers, an SRM usage rule and providing the determination to a trust authority using an eXtensible Markup Language (XML); receiving messages comprising the SRM usage rule from the content service providers and sending the messages to an apparatus together with an electronic signature; and receiving the messages comprising the SRM usage rule and changing an operation of the apparatus according to requirements of at least one content service provider. Thus, various content business models can be realized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
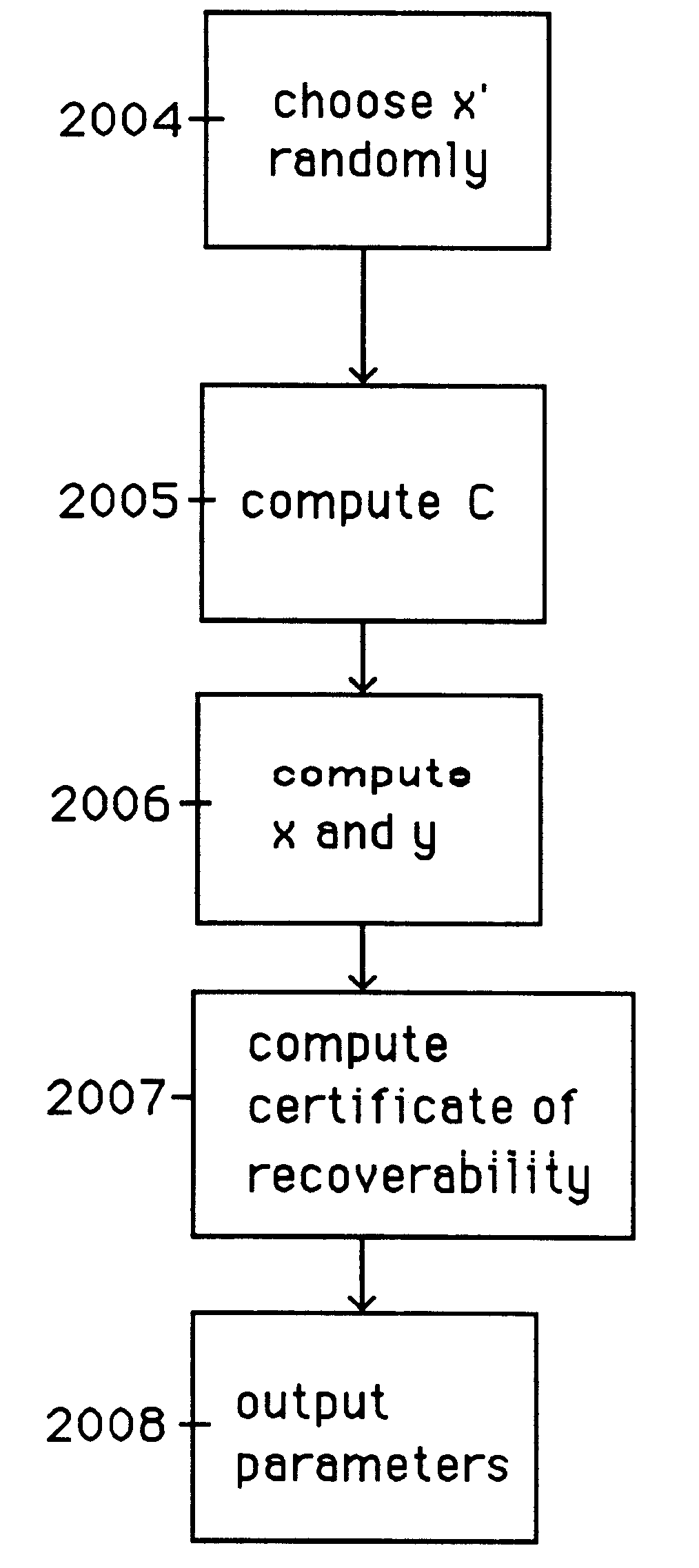
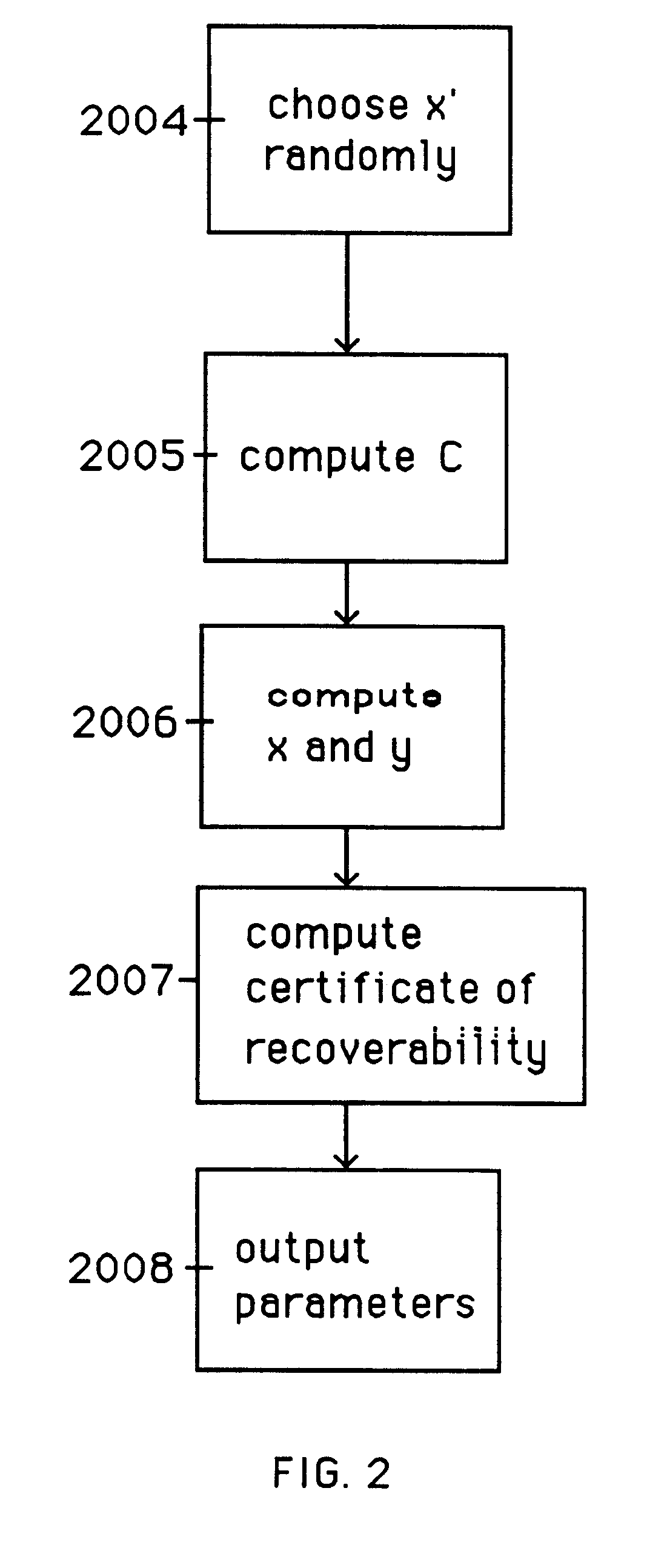
Auto-escrowable and auto-certifiable cryptosystems with fast key generation
InactiveUS6243466B1Fast and easy disseminationEasy to handleKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationTrusted authorityCryptosystem
A method is provided for an escrow cryptosystem that is overhead-free, does not require a cryptographic tamper-proof hardware implementation (i.e., can be done in software), is publicly verifiable, and cannot be used subliminally to enable a shadow public key system. A shadow public key system is an unescrowed public key system that is publicly displayed in a covert fashion. The keys generated by the method are auto-recoverable and auto-certifiable (abbrev. ARC). The ARC Cryptosystem is based on a key generation mechanism that outputs a public / private key pair, and a certificate of proof that the key was generated according to the algorithm. Each generated public / private key pair can be verified efficiently to be escrowed properly by anyone. The verification procedure does not use the private key. Hence, the general public has an efficient way of making sure that any given individual's private key is escrowed properly, and the trusted authorities will be able to access the private key if needed. Since the verification can be performed by anyone, there is no need for a special trusted entity, known in the art as a "trusted third party". Furthermore, the system is designed so that its internals can be made publicly scrutinizable (e.g., it can be distributed in source code form). This differs from many schemes which require that the escrowing device be tamper-proof hardware. The system has a novel feature that the system parameters can be generated very efficiently and at the same time provide a very high level of security. Another novel feature is a method for making the certificates of recoverability publishable. The system is applicable for law-enforcement, file systems, e-mail systems, certified e-mail systems, and any scenario in which public key cryptography can be employed and where private keys or information encrypted under public keys need to be recoverable.
Owner:CRYPTOPEAK SECURITY LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com