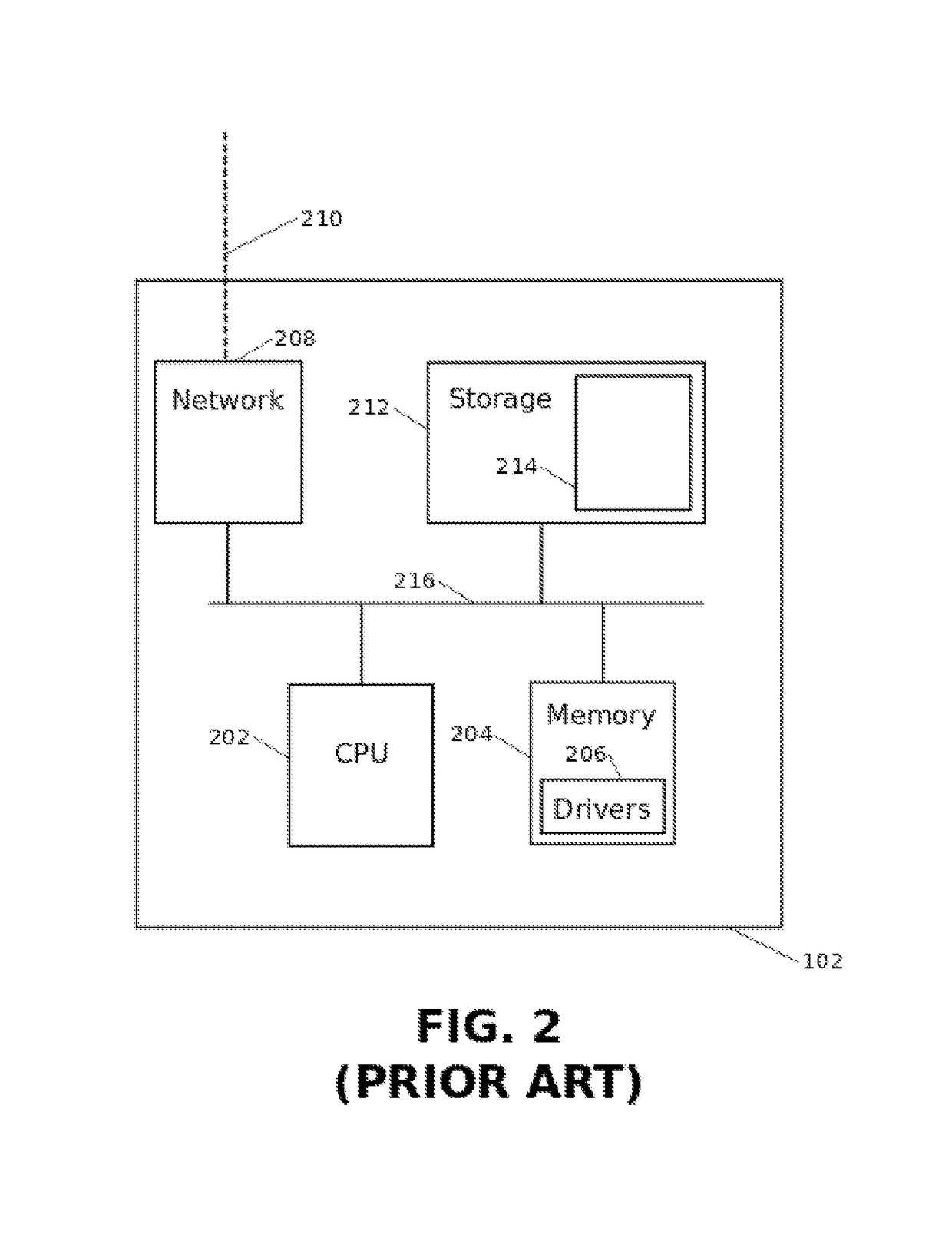
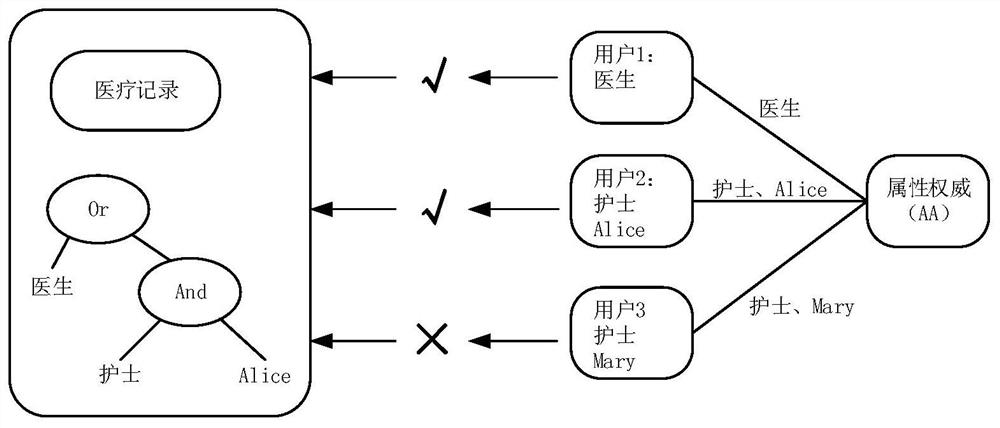
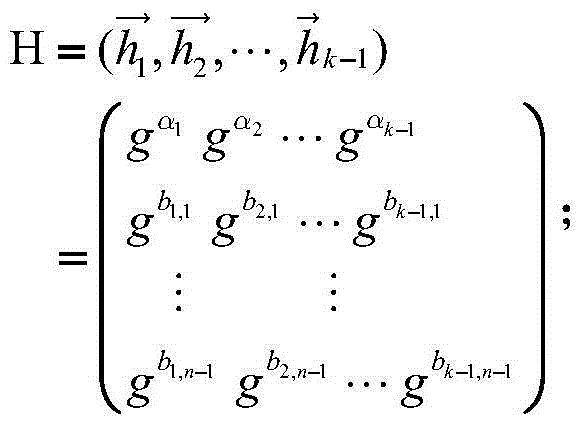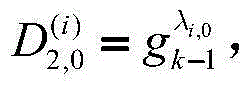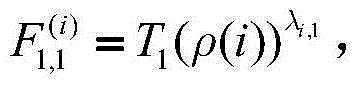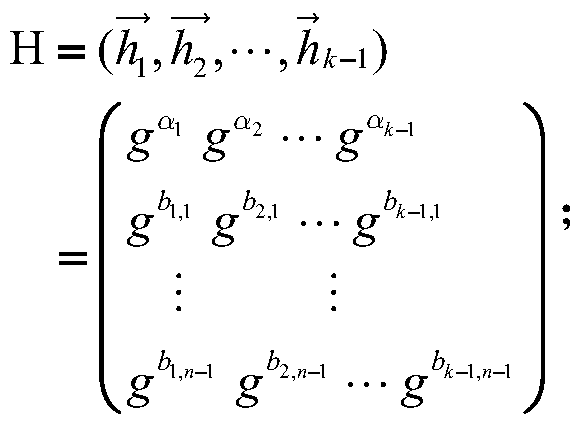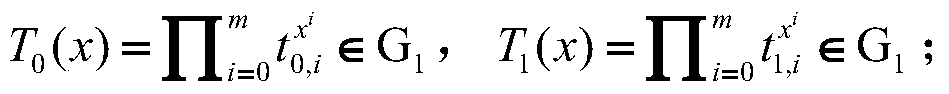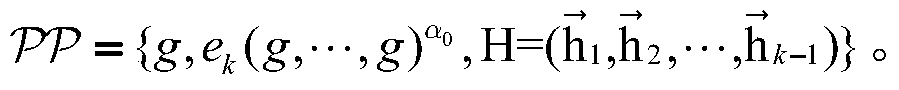Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Key revocation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Key revocation is the manner in which PGP public keys are permanently retired. It is suggested that a key revocation certificate should be generated as soon as the key pair is created. This certificate should be held by a trusted third party, exactly as the key-escrow facility described above.
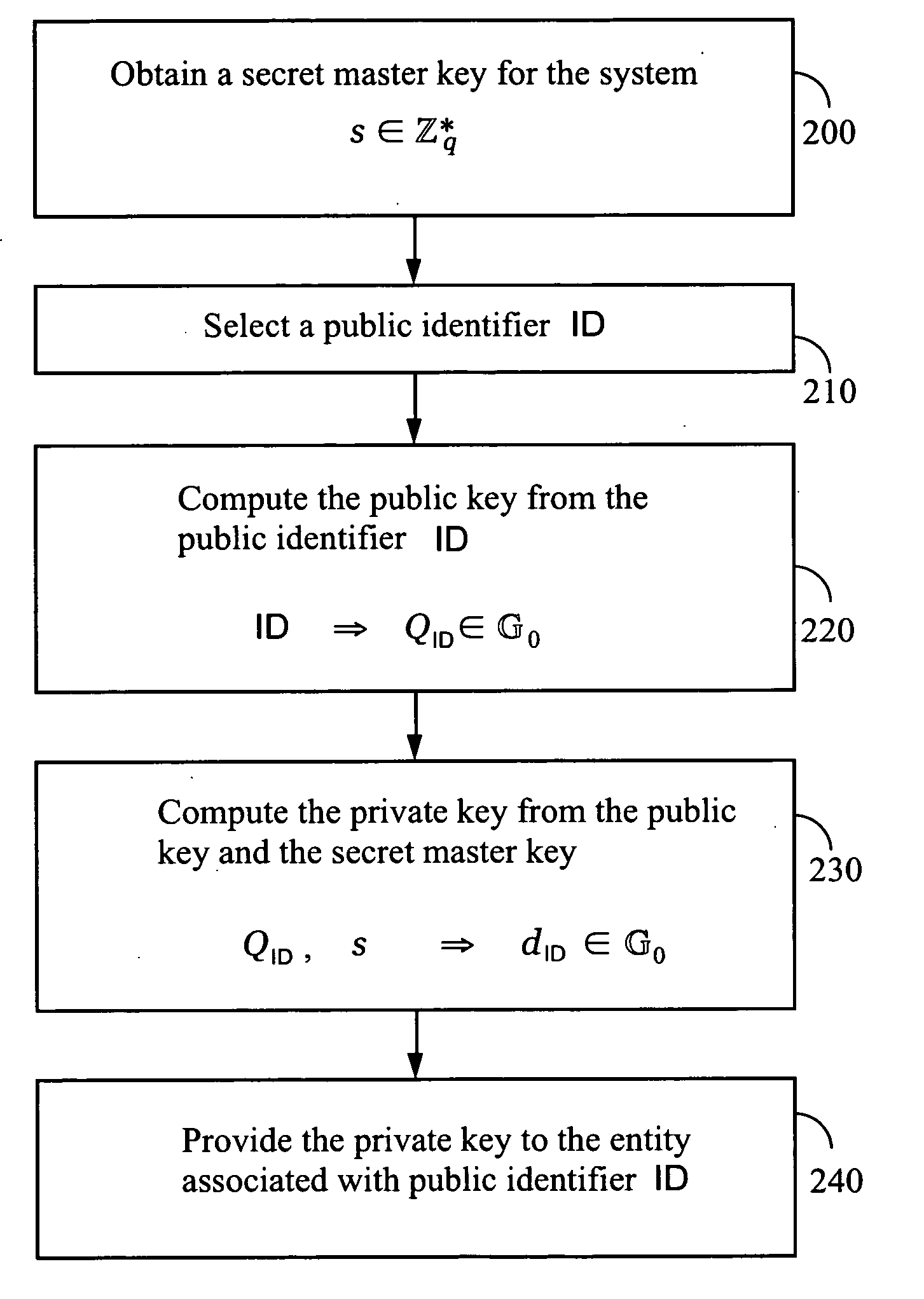
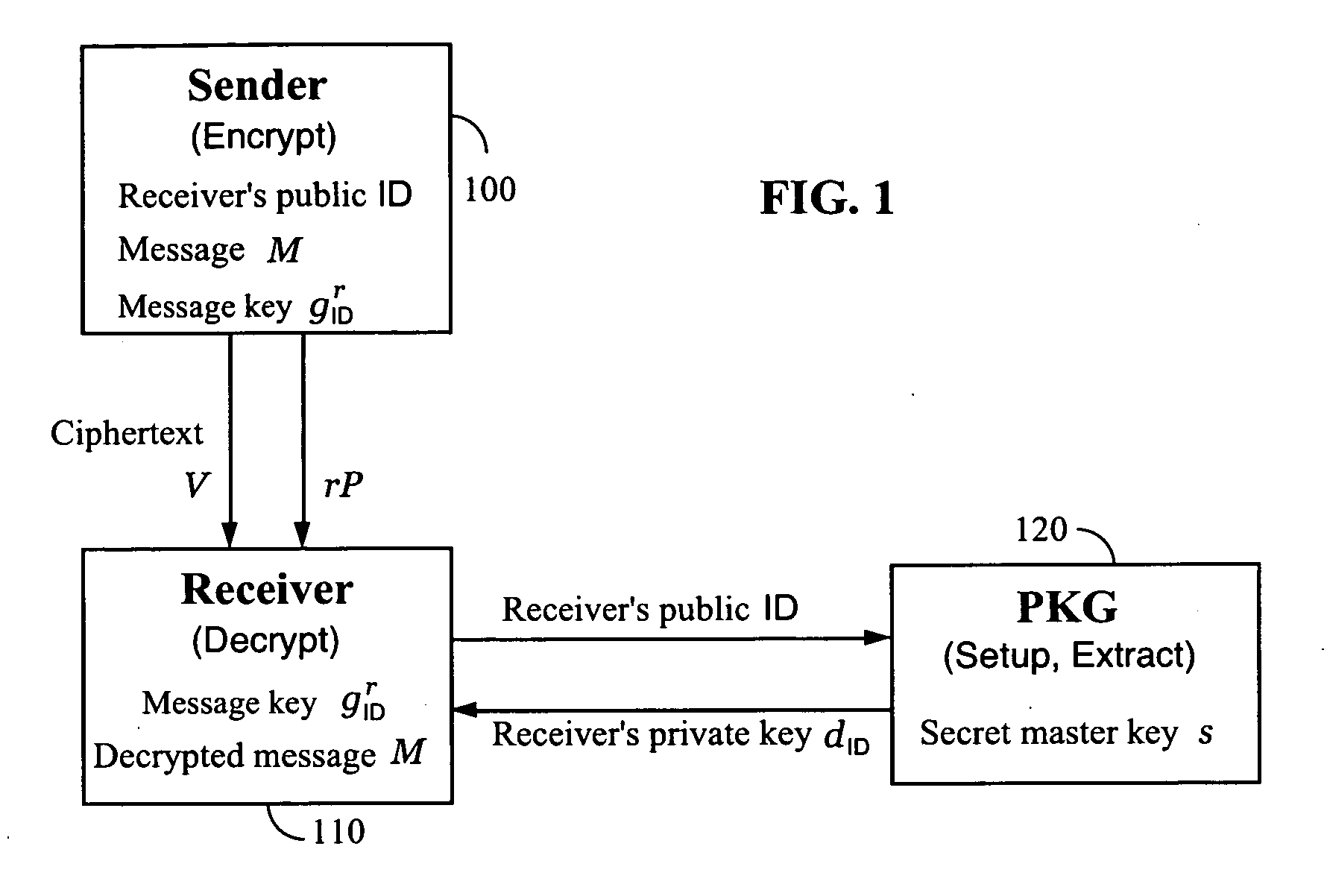
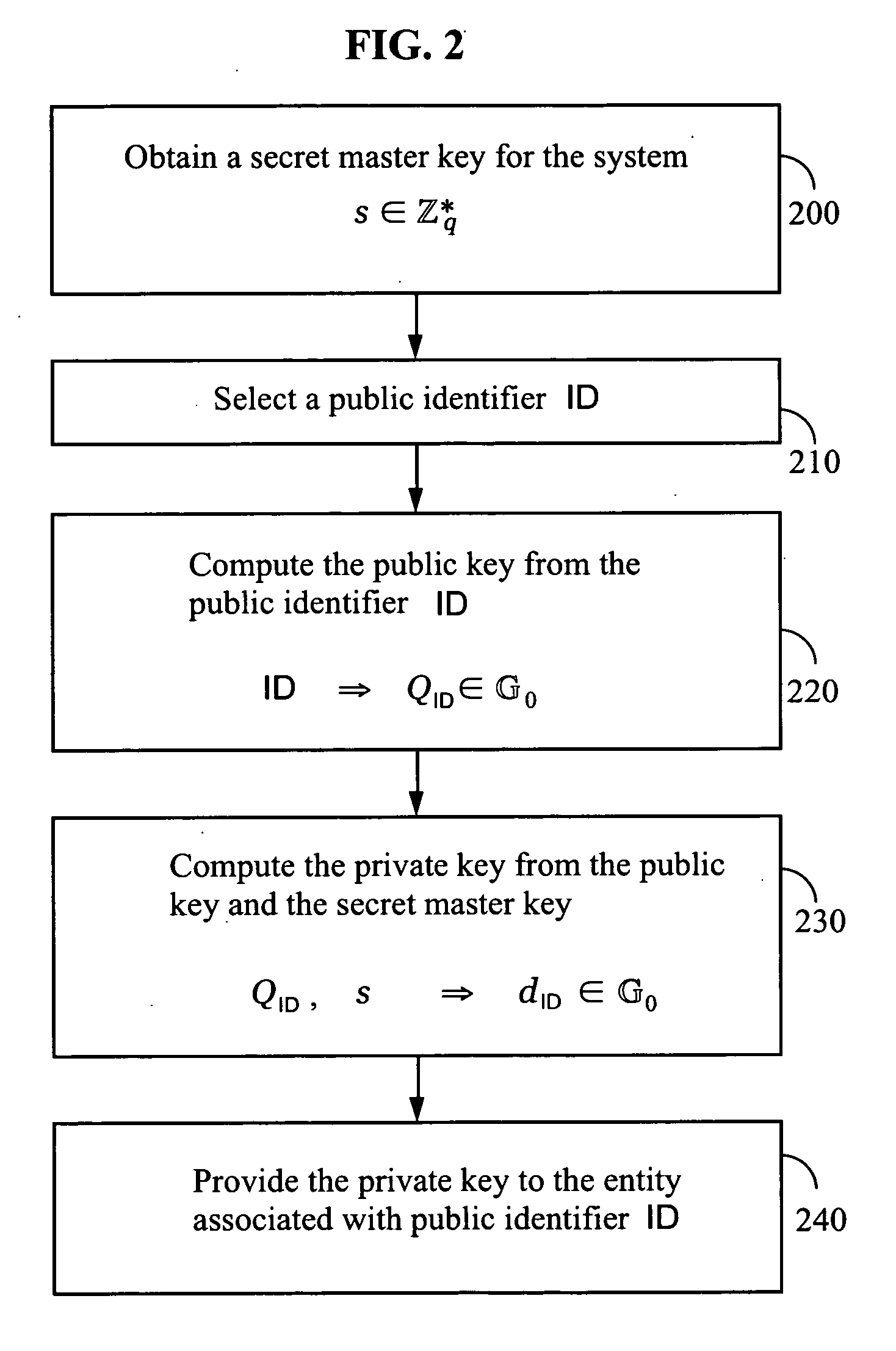
Systems and methods for identity-based encryption and related cryptographic techniques
ActiveUS7113594B2Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationEmail addressCiphertext
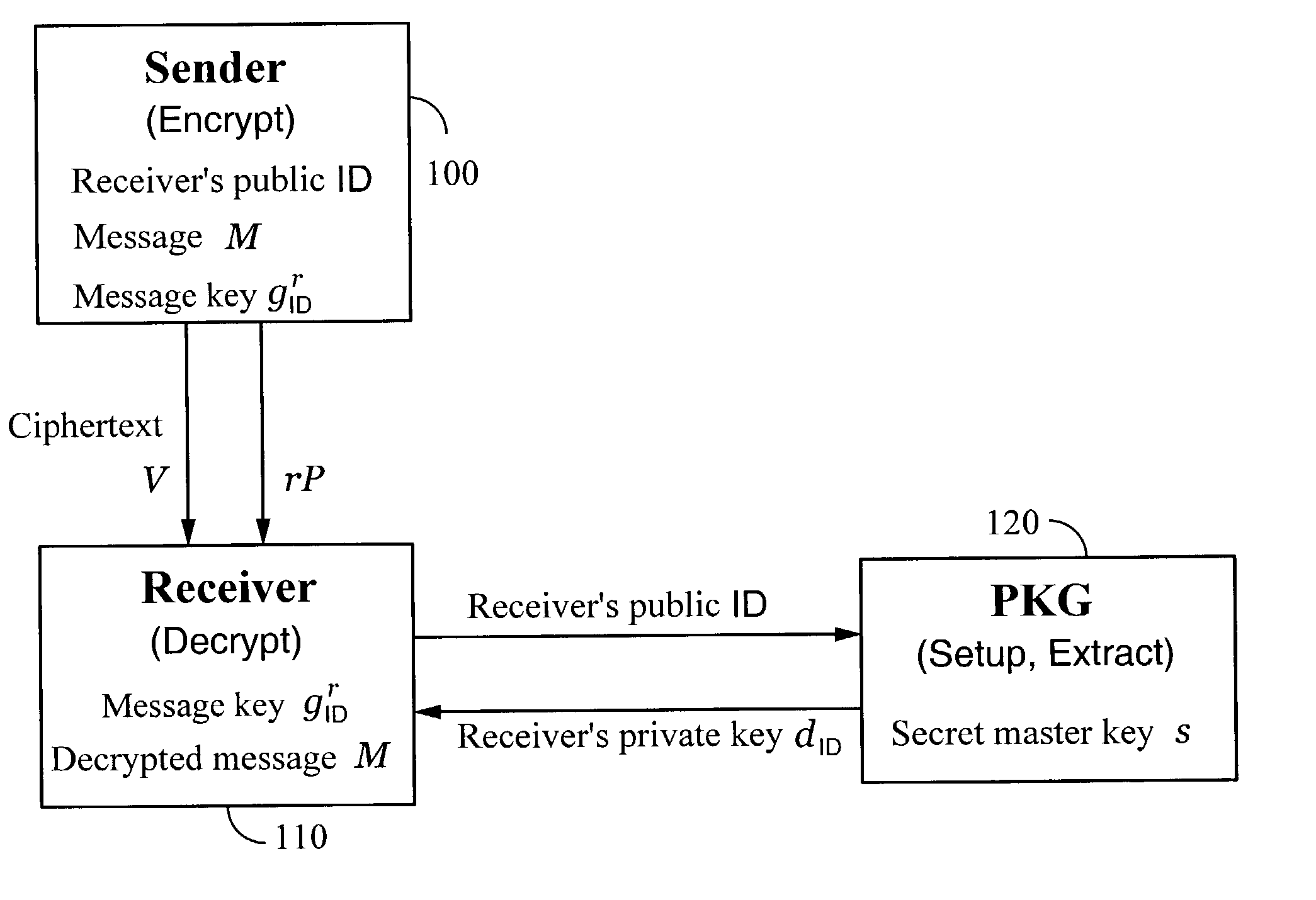
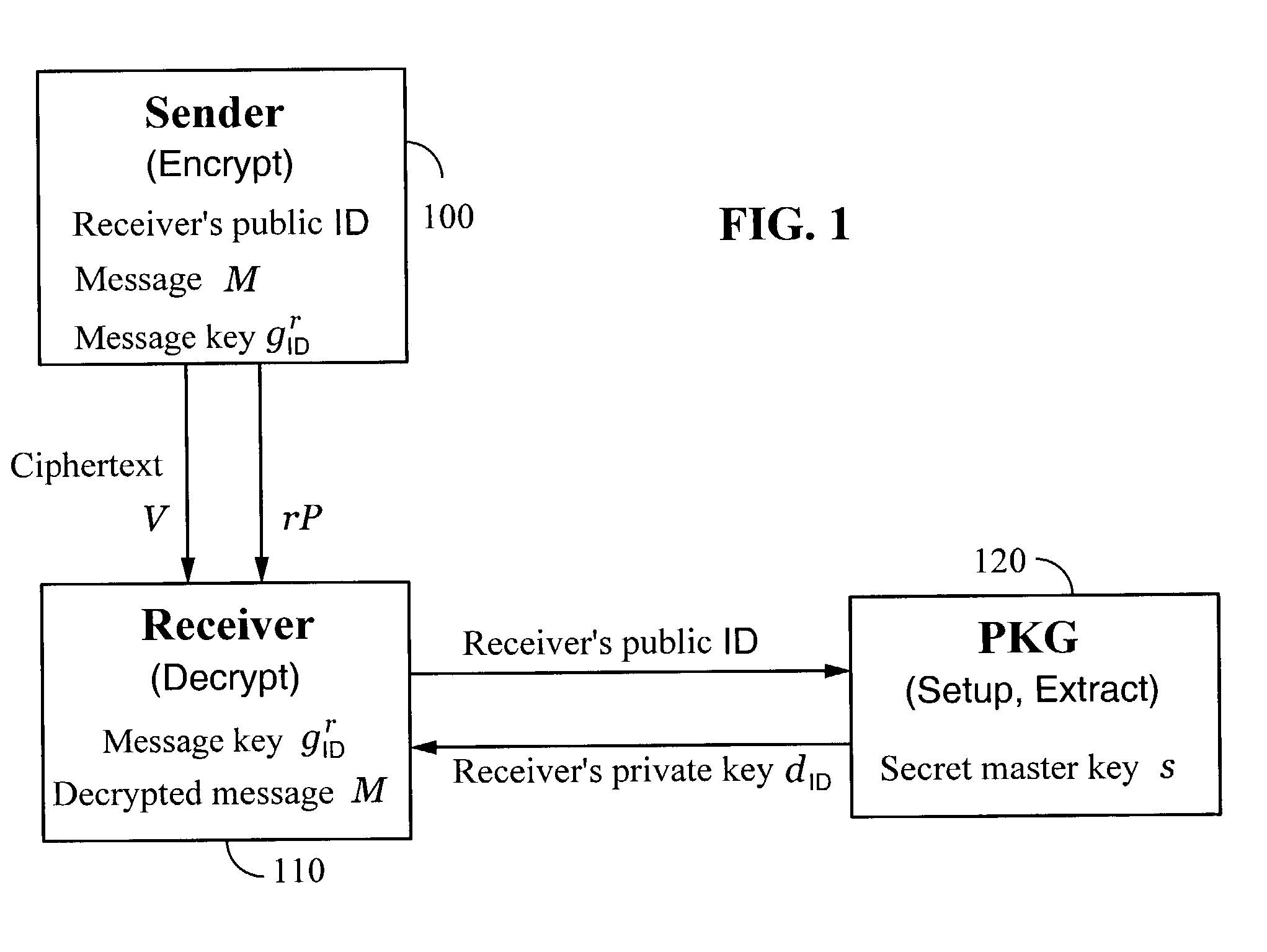
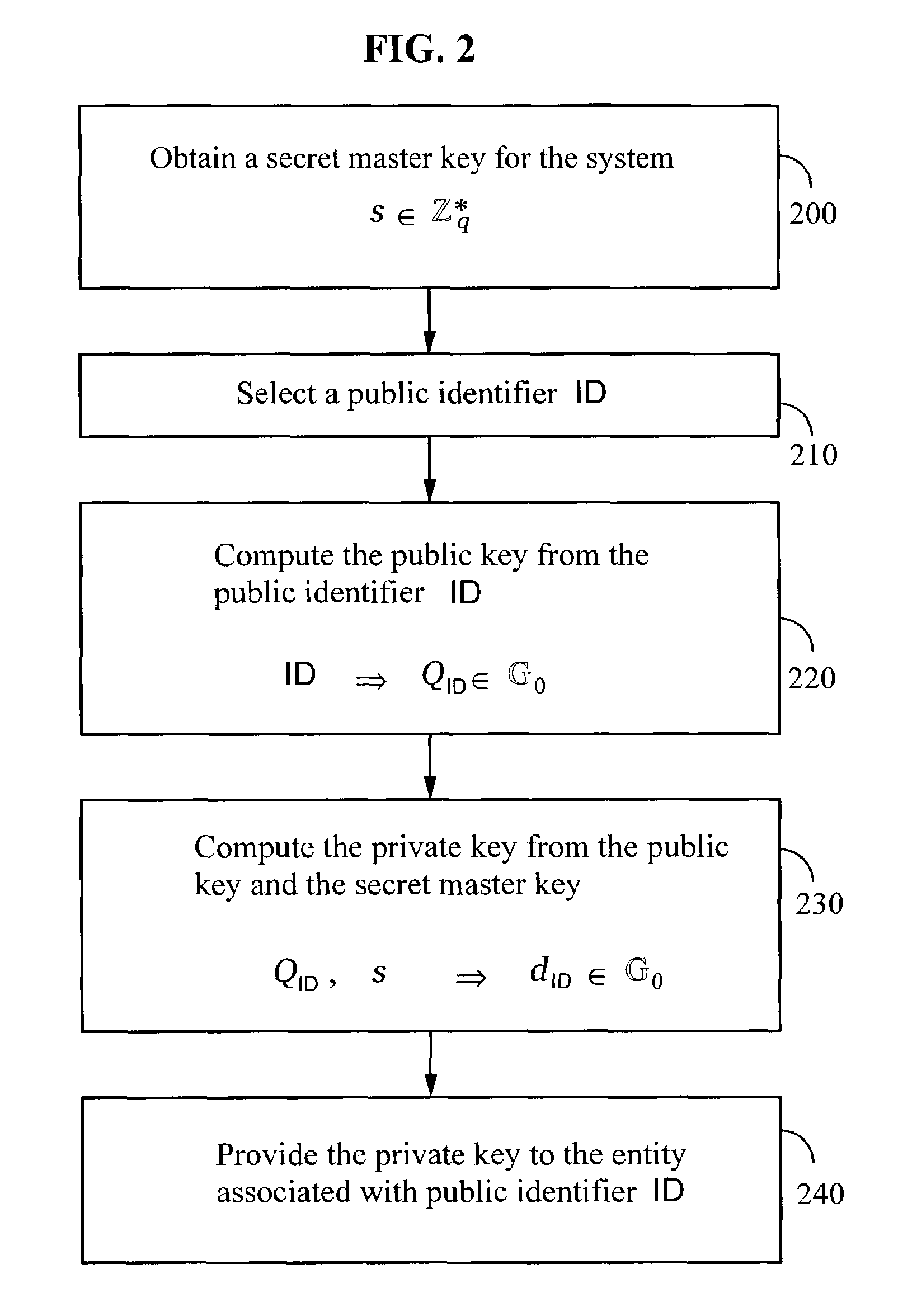
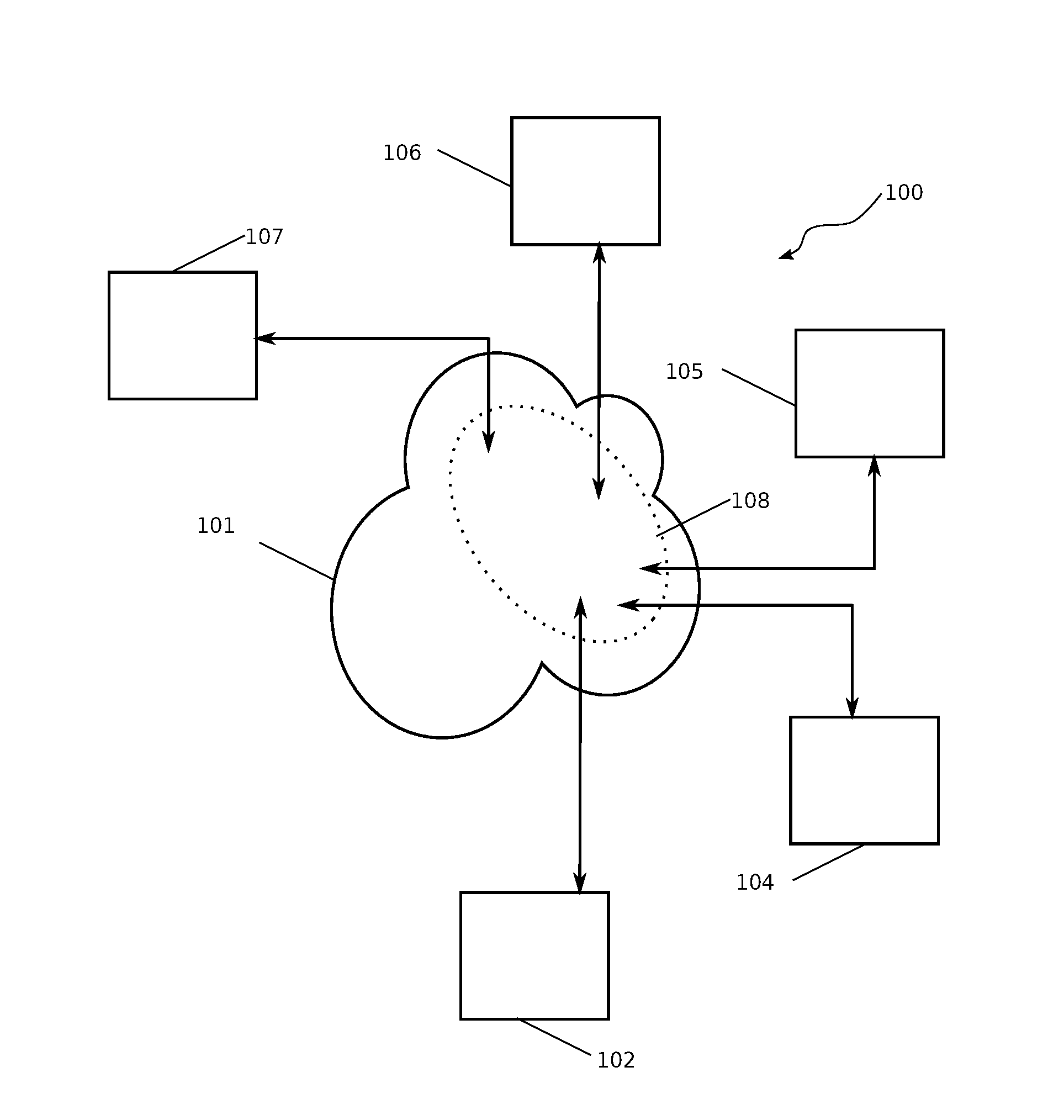
A method and system for encrypting a first piece of information M to be sent by a sender [100] to a receiver [110] allows both sender and receiver to compute a secret message key using identity-based information and a bilinear map. In a one embodiment, the sender [100] computes an identity-based encryption key from an identifier ID associated with the receiver [110]. The identifier ID may include various types of information such as the receiver's e-mail address, a receiver credential, a message identifier, or a date. The sender uses a bilinear map and the encryption key to compute a secret message key gIDr, which is then used to encrypt a message M, producing ciphertext V to be sent from the sender [100] to the receiver [110] together with an element rP. An identity-based decryption key dID is computed by a private key generator [120] based on the ID associated with the receiver and a secret master key s. After obtaining the private decryption key from the key generator [120], the receiver [110] uses it together with the element rP and the bilinear map to compute the secret message key gIDr, which is then used to decrypt V and recover the original message M. According to one embodiment, the bilinear map is based on a Weil pairing or a Tate pairing defined on a subgroup of an elliptic curve. Also described are several applications of the techniques, including key revocation, credential management, and return receipt notification.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
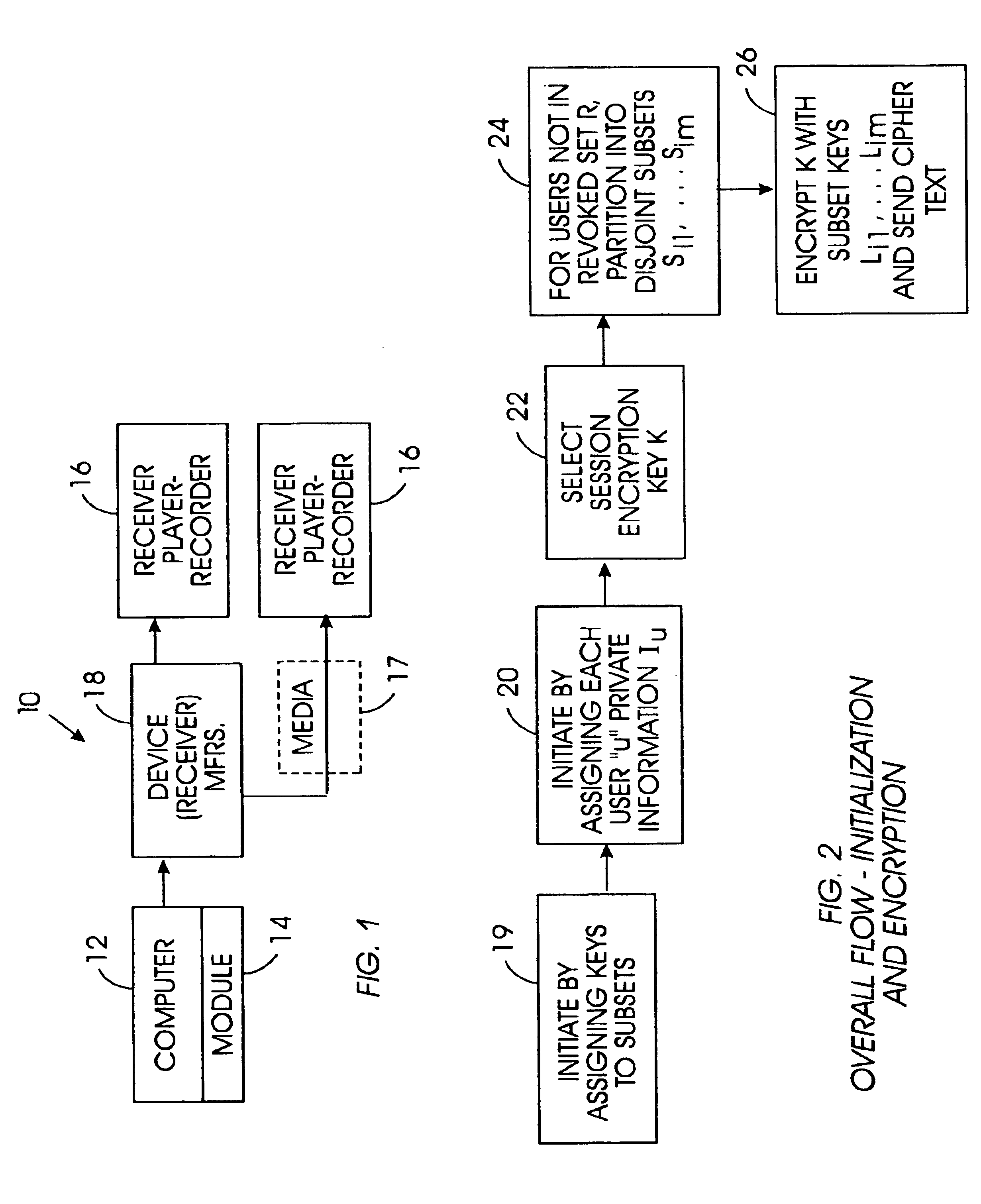
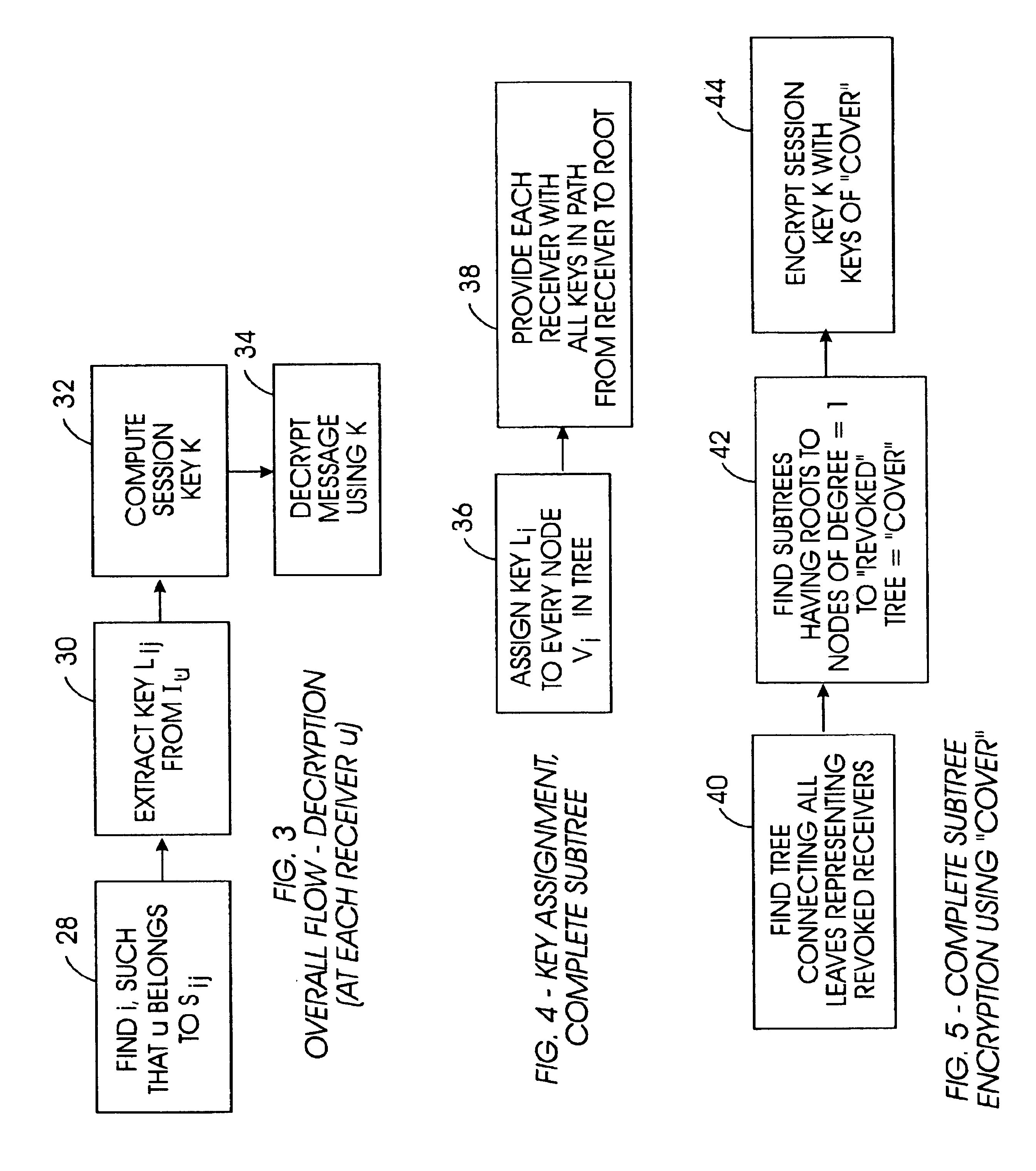
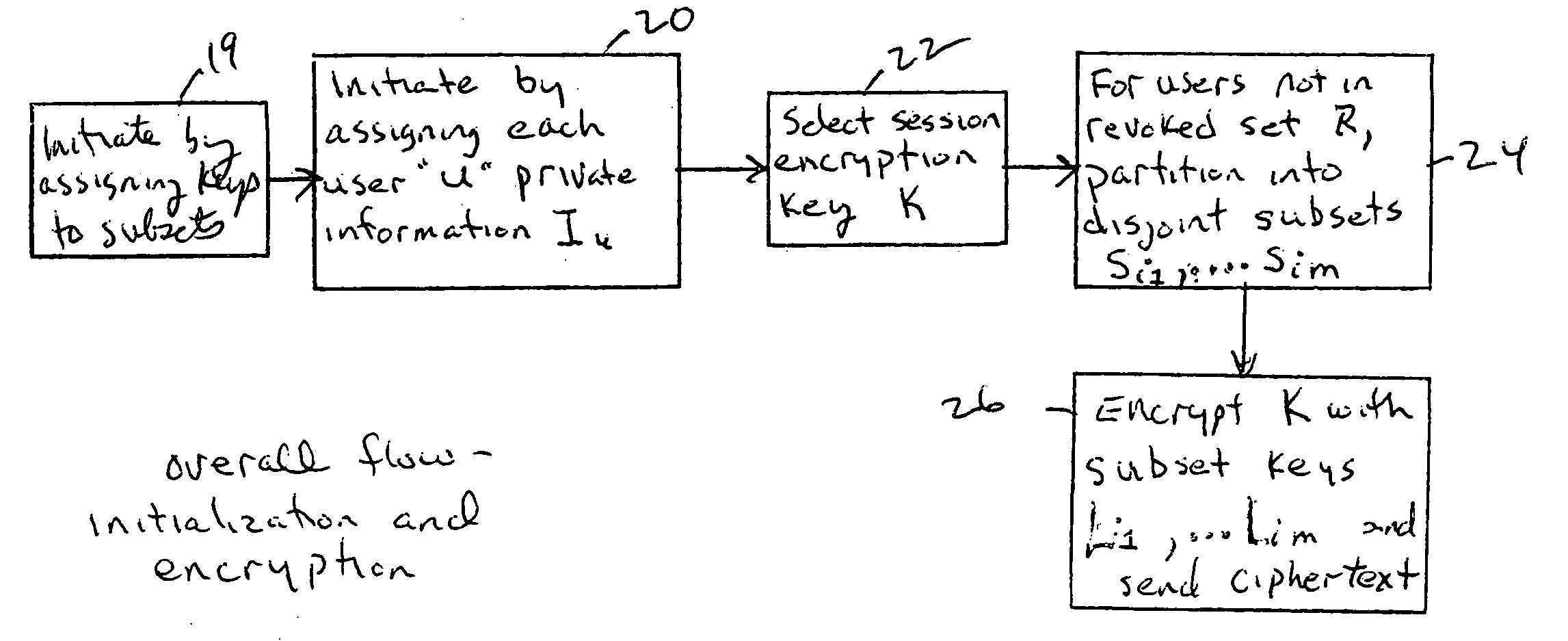
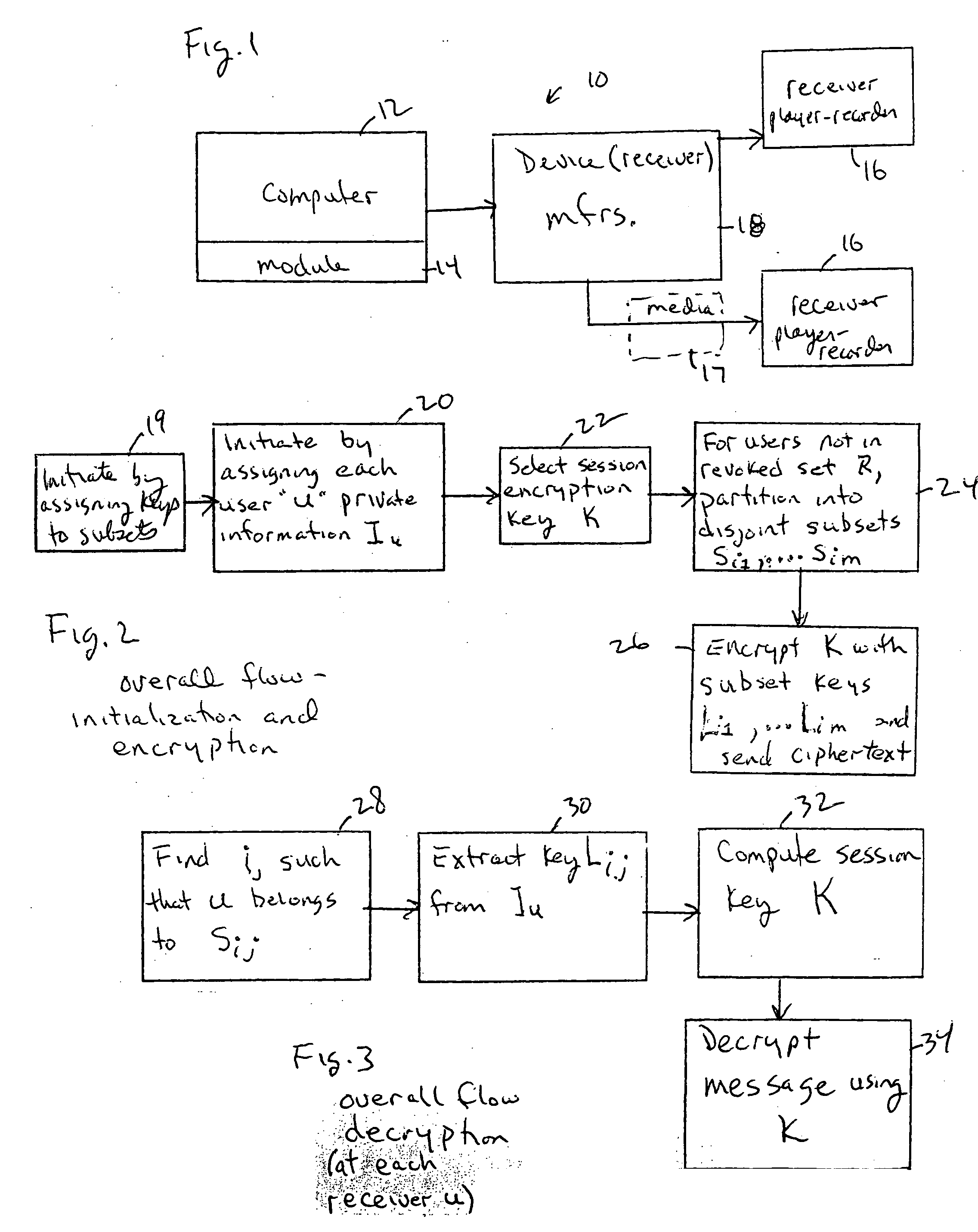
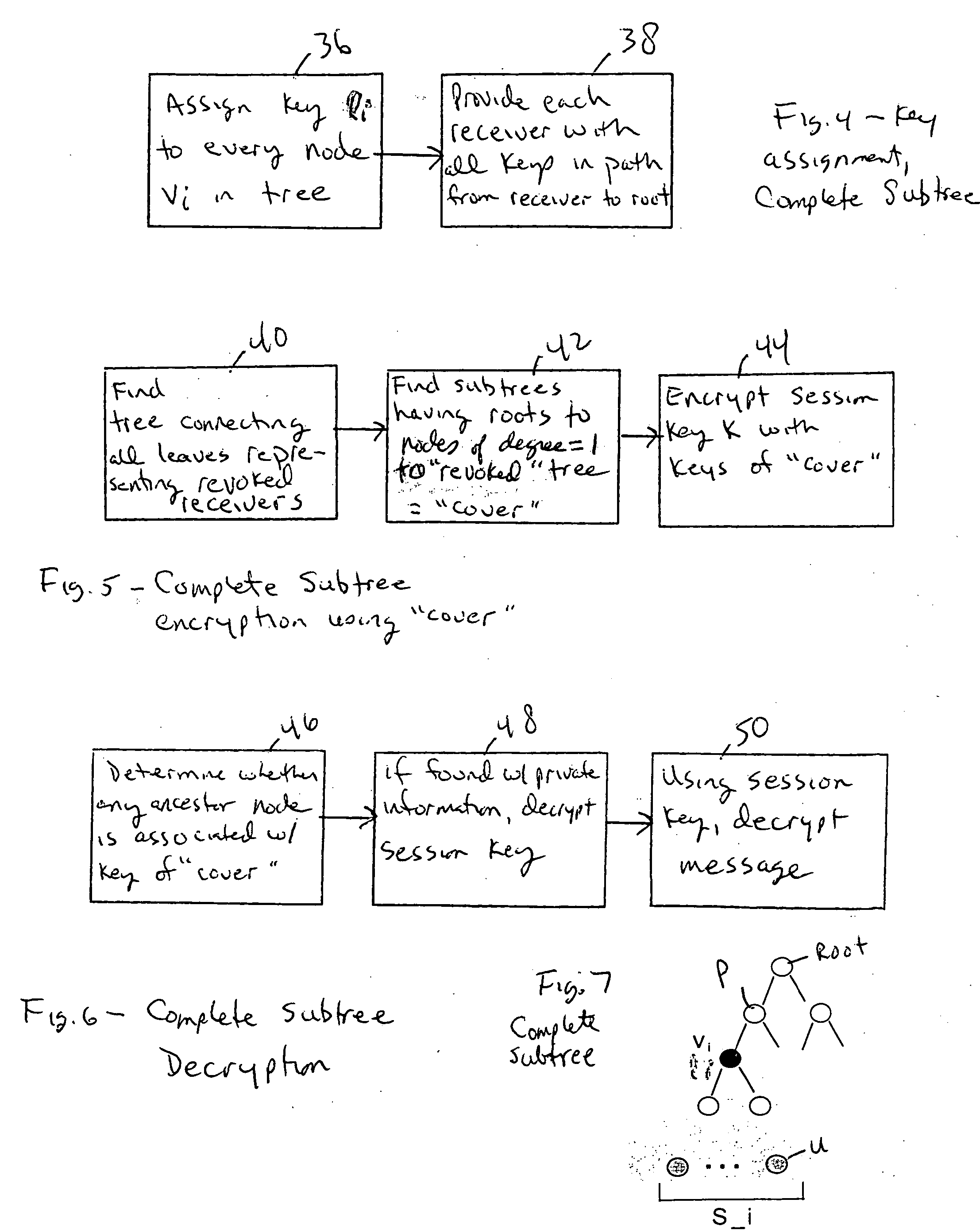
Method for broadcast encryption and key revocation of stateless receivers
InactiveUS7039803B2Special service provision for substationKey distribution for secure communicationBroadcastingSession key
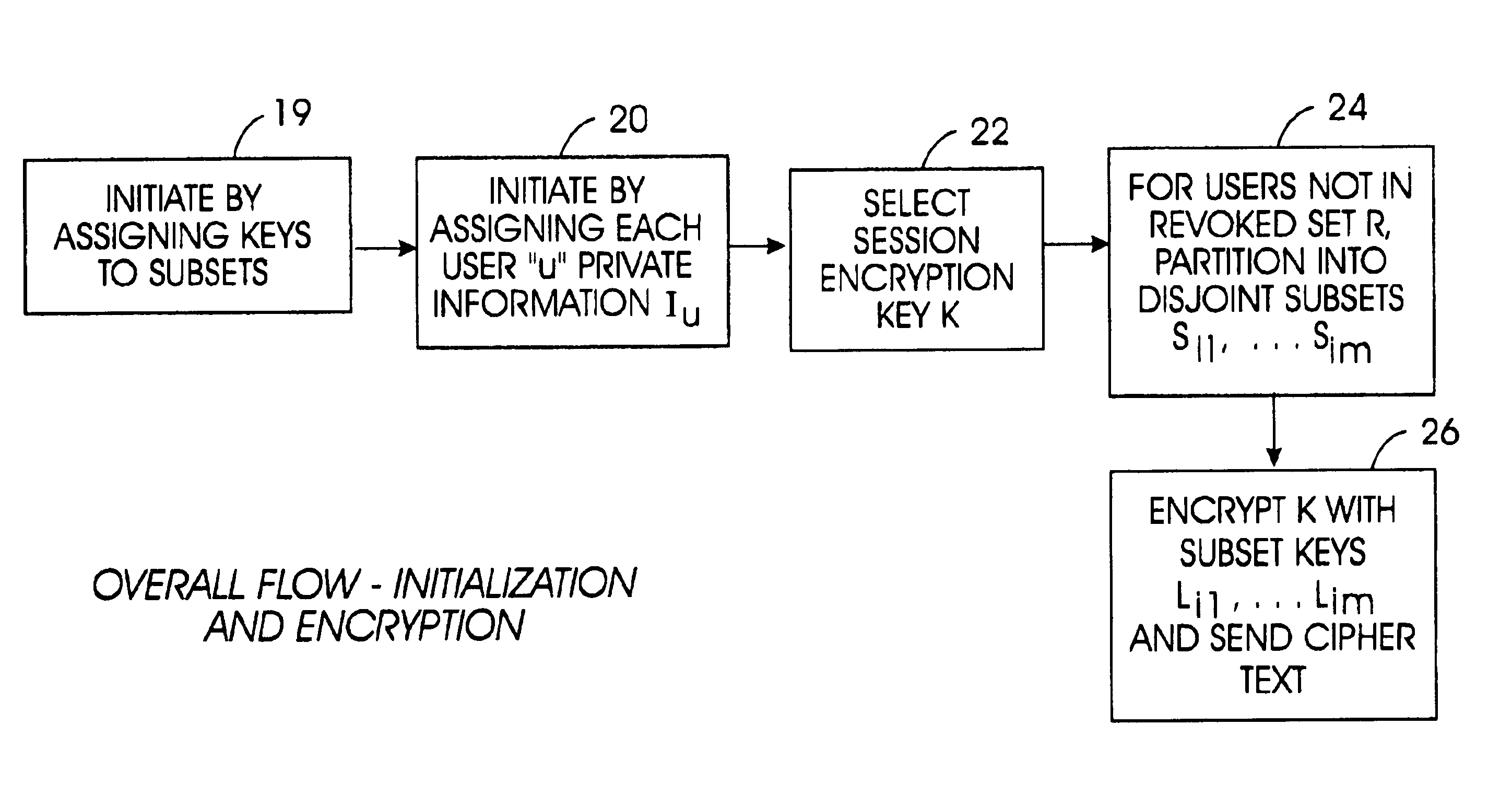
A tree is used to partition stateless receivers in a broadcast content encryption system into subsets. Two different methods of partitioning are disclosed. When a set of revoked receivers is identified, the revoked receivers define a relatively small cover of the non-revoked receivers by disjoint subsets. Subset keys associated with the subsets are then used to encrypt a session key that in turn is used to encrypt the broadcast content. Only non-revoked receivers can decrypt the session key and, hence, the content.
Owner:IBM CORP
Key revocation in a mobile device
ActiveUS20060089126A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsComputer networkMobile device
A system for revoking access to a mobile device comprises a mobile device providing a plurality of applications and an agent providing a plurality of revocation procedures for revoking access by the mobile device to the plurality of applications running on the mobile device. Access to a first application is revoked by the agent using a first revocation procedure, and access to a second application is revoked by the agent using a second revocation procedure.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Key revocation in a mobile device
ActiveUS7860486B2Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsComputer networkMobile device
A system for revoking access to a mobile device comprises a mobile device providing a plurality of applications and an agent providing a plurality of revocation procedures for revoking access by the mobile device to the plurality of applications running on the mobile device. Access to a first application is revoked by the agent using a first revocation procedure, and access to a second application is revoked by the agent using a second revocation procedure.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Revocation of cryptographic keys in the absence of a trusted central authority
ActiveUS20160254910A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationTrusted authorityCryptographic nonce
A method and apparatus is presented for revoking cryptographic keys within a distributed ledger system in which no central trusted authority is available, consisting of sending a key revocation message by a network connected device to other network connected devices over a peer-to-peer network for inclusion in a ledger. In one embodiment the revocation message is signed using a private key of a public / private key pair to be revoked. In another embodiment an authorization for future revocation of the public / private key pair by a plurality of other public / private keys is sent for inclusion in the ledger, and subsequently the key revocation message is signed with one of the private keys of the plurality of public / private key pairs before sending the key revocation message. Once a valid key revocation message is included in the ledger, any future request to include a message signed by the revoked cryptographic key is rejected.
Owner:FINLOW BATES KEIR
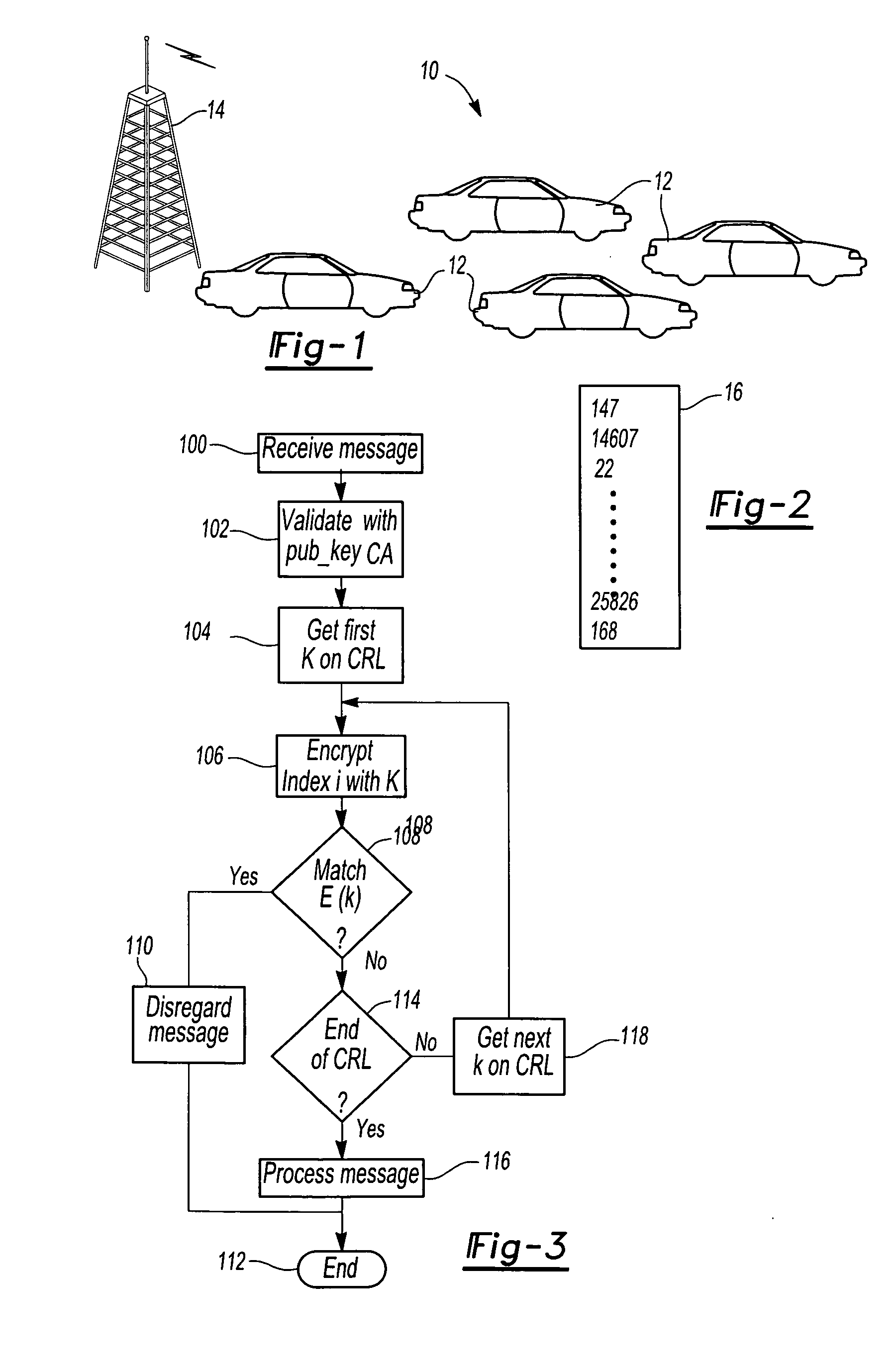
Method for allocating multiple authentication certificates to vehicles in a vehicle-to-vehicle communication network
ActiveUS20090259841A1Ensuring privacyVehicle fittingsEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesEncryptionAuthentication
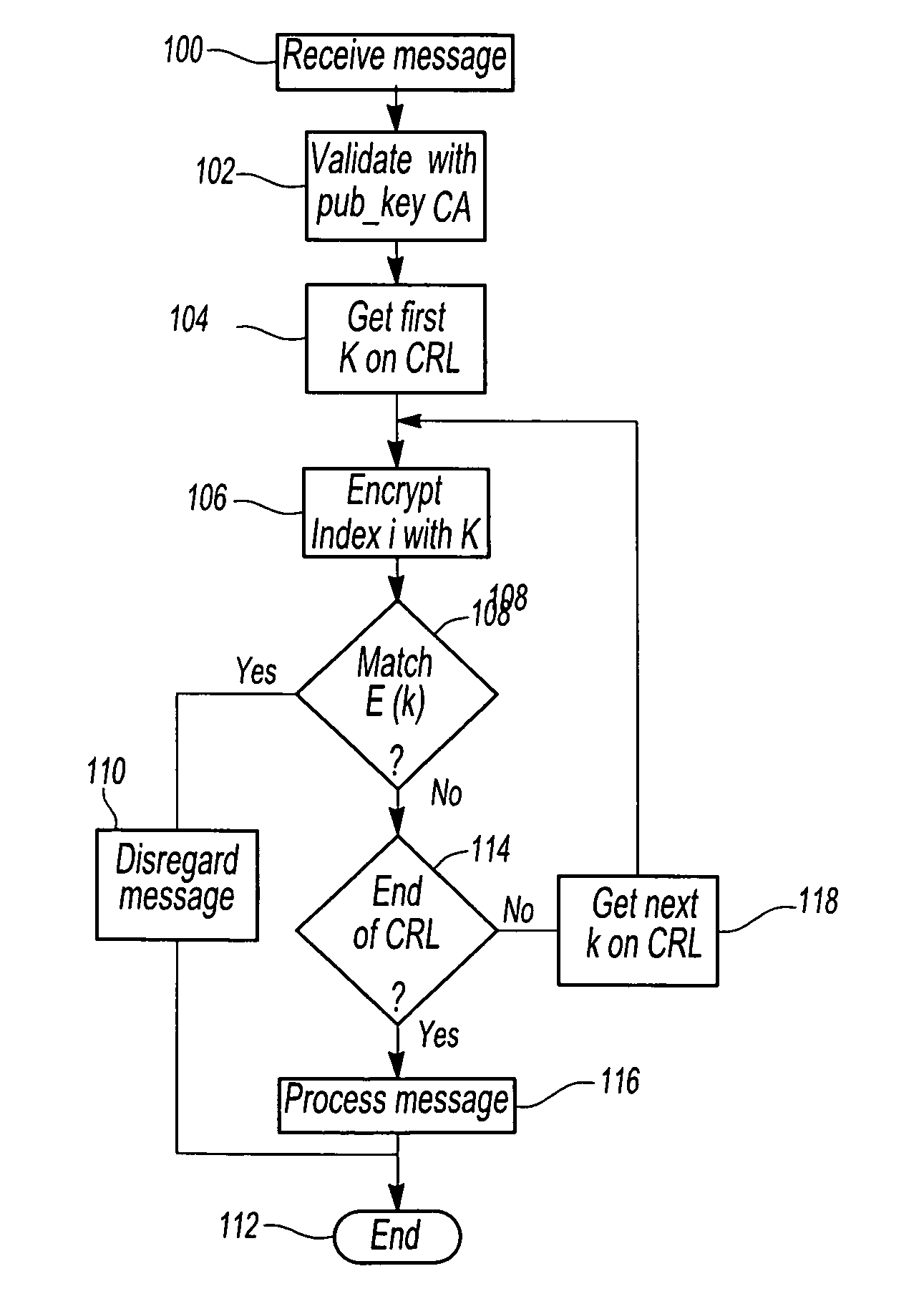
In a vehicle-to-vehicle communication network utilizing PKI security methods to protect communications and in which the PKI encryption utilizes a Certificate Authority having both a private key and a publicly distributed key, a method for allocating multiple certificates for each vehicle which are assigned to each vehicle in the communication network. The method includes the step of assigning a unique secret key k to each vehicle in the communication network. The Certificate Authority then creates a plurality of public key and private key encryption pairs for each vehicle and each encryption pair is associated with an index i. A plurality of certificates are then created with one certificate for each value of the index. A revocation list comprising the secret keys is maintained by the Certificate Authority so that all encryption pairs assigned to a particular vehicle may be revoked by the secret key k corresponding to that vehicle.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Systems and methods for identity-based encryption and related cryptographic techniques
InactiveUS20070041583A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationID-based encryptionEmail address
A method and system for encrypting a first piece of information M to be sent by a sender [100] to a receiver [110] allows both sender and receiver to compute a secret message key using identity-based information and a bilinear map. In a one embodiment, the sender [100] computes an identity-based encryption key from an identifier ID associated with the receiver [110]. The identifier ID may include various types of information such as the receiver's e-mail address, a receiver credential, a message identifier, or a date. The sender uses a bilinear map and the encryption key to compute a secret message key gIDr, which is then used to encrypt a message M, producing ciphertext V to be sent from the sender [100] to the receiver [110] together with an element rP. An identity-based decryption key dID is computed by a private key generator [120] based on the ID associated with the receiver and a secret master key s. After obtaining the private decryption key from the key generator [120], the receiver [110] uses it together with the element rP and the bilinear map to compute the secret message key gIDr, which is then used to decrypt V and recover the original message M. According to one embodiment, the bilinear map is based on a Weil pairing or a Tate pairing defined on a subgroup of an elliptic curve. Also described are several applications of the techniques, including key revocation, credential management, and return receipt notification.
Owner:UNIV OF CALIFORNIA DAVIS +1
Method for managing wireless multi-hop network key
InactiveUS20100299519A1Improve securityImprove performancePublic key for secure communicationNetwork topologiesNetwork keyLarge networks
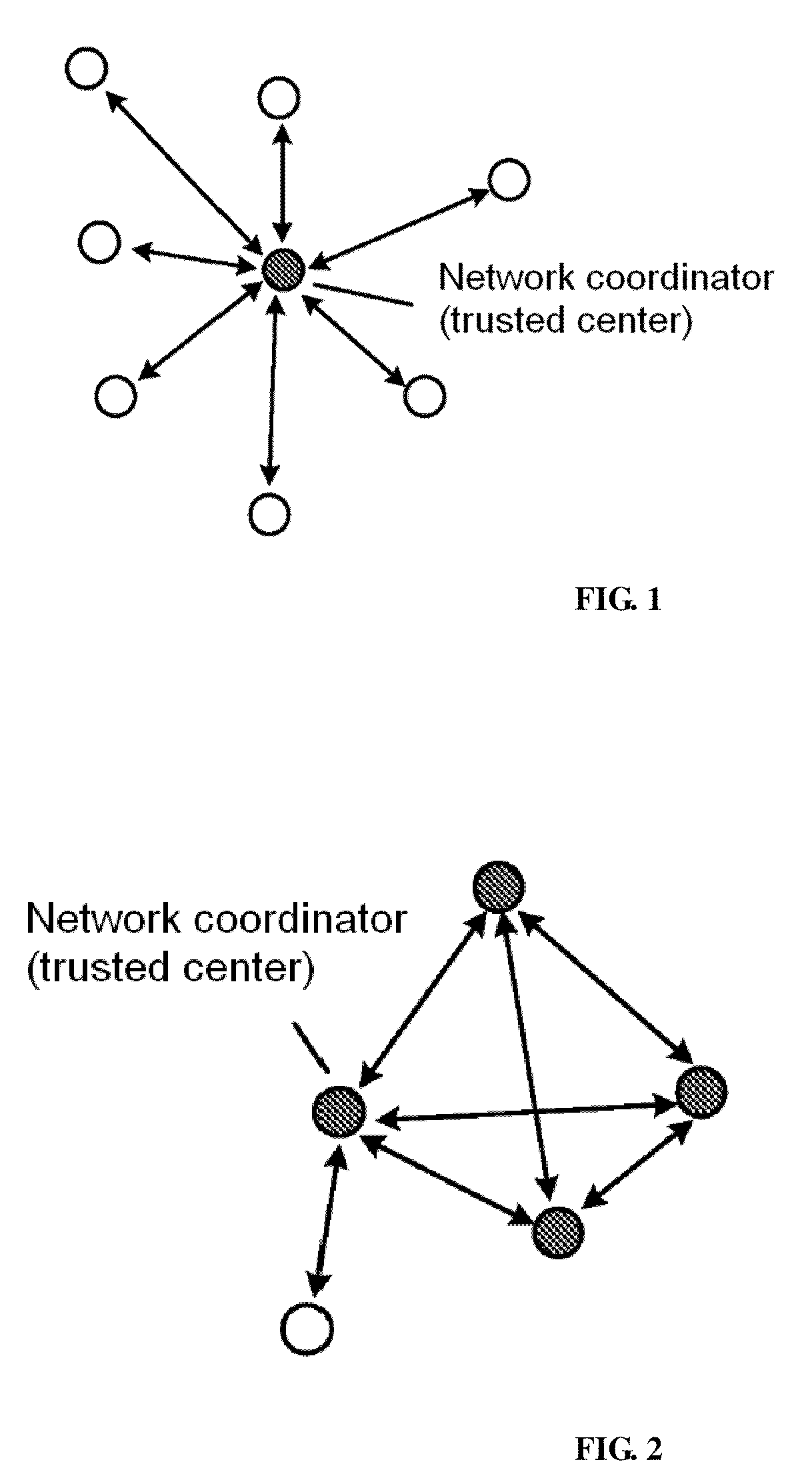
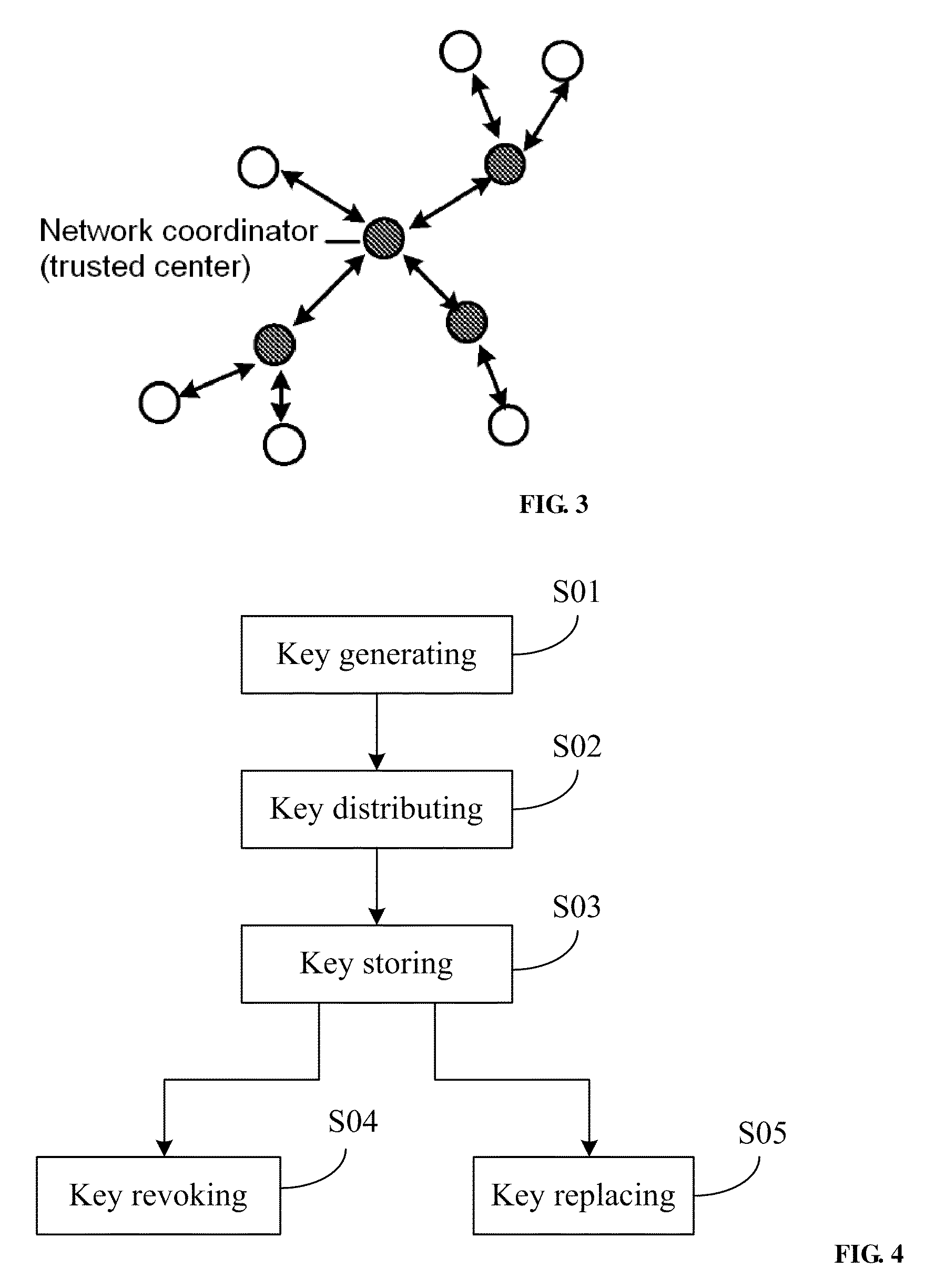
A method for managing wireless multi-hop network key is applicable to a security application protocol when a WAPI frame method (TePA, an access control method based on the ternary peer-to-peer identification) is applied in a concrete network containing a Wireless Local Area Network, a Wireless Metropolitan Area Network AN and a Wireless Personal Area Network. The key management method of the present invention includes the steps of key generation, key distribution, key storage, key modification and key revocation. The present invention solves the technical problems that the prior pre-share-key based key management method is not suitable for larger networks and the PKI-based key management method is not suitable for wireless multi-hop networks; the public-key system and the ternary structure are adopted, thereby the security and the performance of the wireless multi-hop networks are improved.
Owner:CHINA IWNCOMM
Wireless multi-hop network key management method based on ID
InactiveCN101222325AImprove securityImprove performanceKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationStructure of Management InformationNetwork key
The invention discloses an ID-based wireless multi-hop network key management method which is applicable to a safety application protocol when a WAPI frame method (TePA, an access control method based on the ternary peer-to-peer identification) is applied in a concrete network containing a WLAN, a WMAN and a WPAN. The key management method of the invention comprises the steps of key generation, key distribution, key storage, key modification and key revocation. The invention solves the technical problems that the prior pre-share-key based key management method is not suitable for larger networks and the PKI-based key management method is not suitable for wireless multi-hop networks; the public-key system and the ternary structure are adopted, thereby improving the security and the performance of the wireless multi-hop networks.
Owner:CHINA IWNCOMM
Method and device for upgrading secret key
InactiveCN103326853AUpdate at any timeFlexible Security PolicyKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCryptosystemComputer security
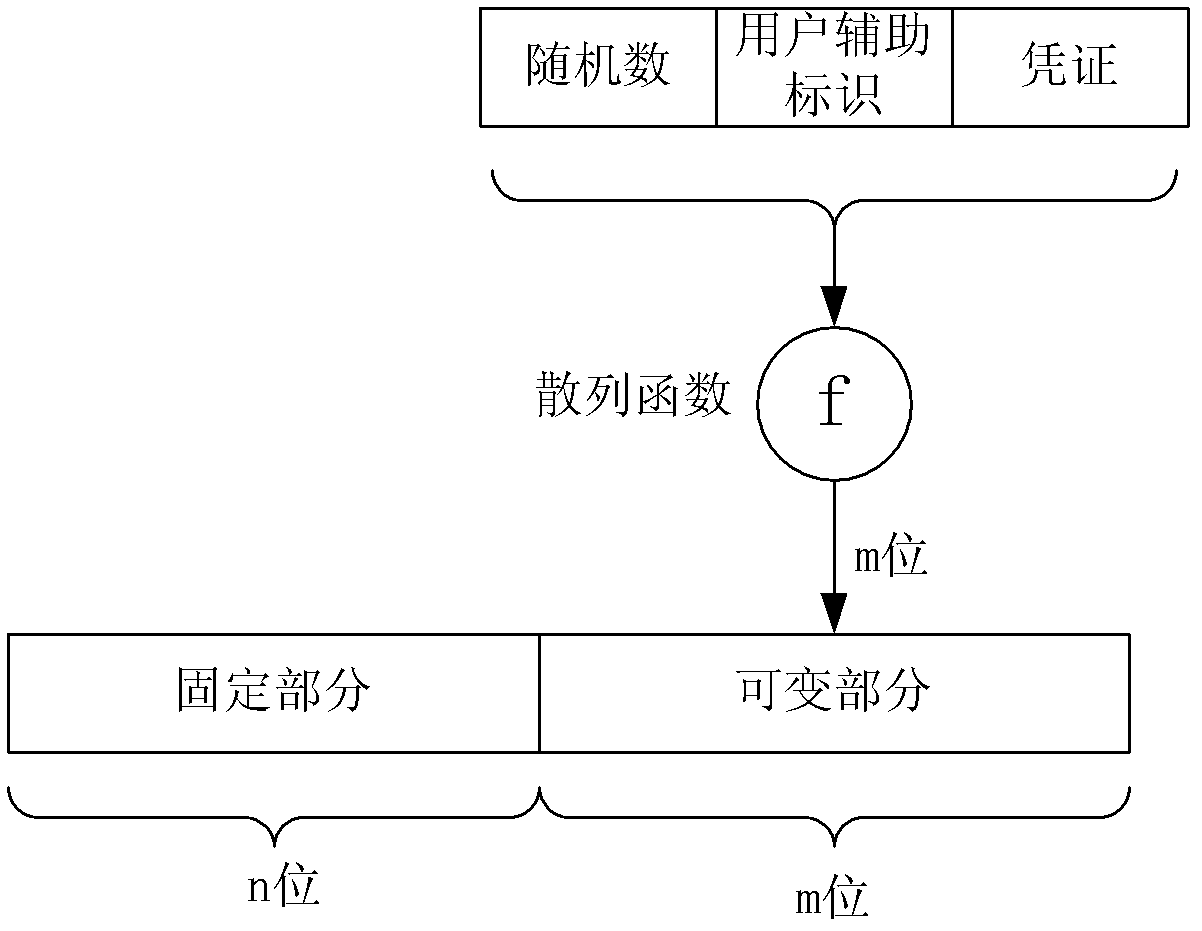
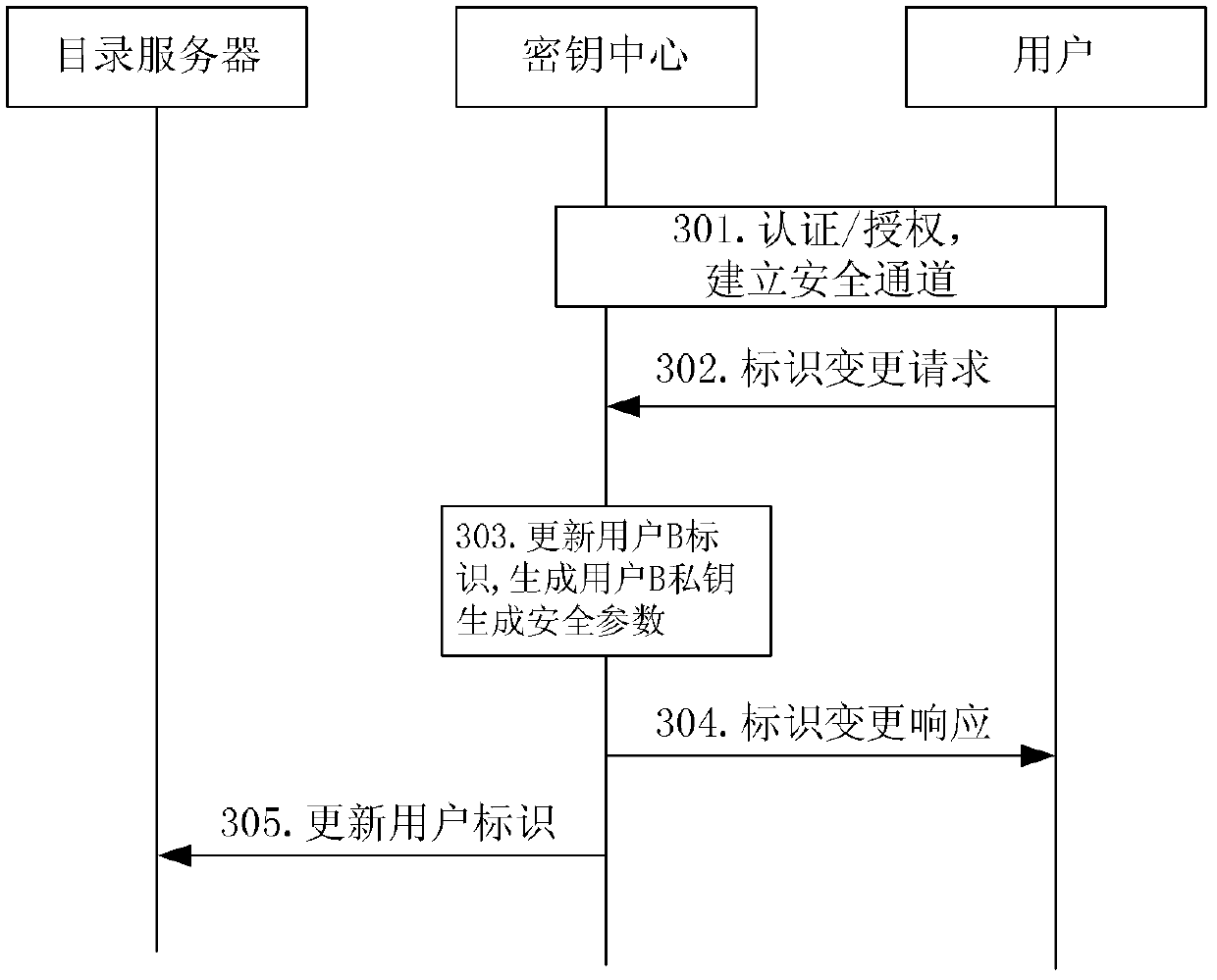
The invention discloses a method and device for upgrading a secret key. The method and device for upgrading the secret key includes the steps that in a cryptosystem (IBC) based on an identification, a secret key center enables a user identification used as a public key is arranged to be a fixed part and a variable part, and the variable part of the user identification is changed to conduct upgrading on the public key. The method and device for upgrading the secret key can effectively solve the problem that the secret key is revoked based on the cryptosystem on the identification, a user can timely conduct secret key revocation, service operators can conveniently conduct safety service, convenience is improved for the user, and the safety of the system is enhanced.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Attribute encryption method based on multi-linear mapping and achieving strategy of secret key revocation in an authority separating way
ActiveCN105162573AGuaranteed validityReduce time consumptionKey distribution for secure communicationAccess structureCiphertext
The invention discloses an attribute encryption method based on multi-linear mapping and achieving a strategy of secret key revocation in an authority separating way, which is provided for single attribute revocation of a user. The user can finish a decryption process only when a cryptograph attribute set satisfies the secret key strategy of the user. Specifically, an authority center makes subordinate authorities. Each subordinate authority commands a main secret key of its own and participates in a public parameter establishing process. An assess strategy is converted into an access structure according to a linear secret sharing algorithm. User private keys under corresponding access structures are generated. According to the attribute set and a known revocation list, information encryption is performed. Whether the user is in the revocation list is further judged. A decryption process is finished. In consideration of known private keys and users, a tracking algorithm is established to judge the relevance of users and private keys. By means of the method provided in the invention, the problem that all attributes of non-users are canceled during a single user attribute revocation process is solved. The relevance of users and private keys is verified. The scheme operation efficiency and the overall safety can be improved. The scheme is enabled to resist quantum attacks.
Owner:深圳天通信息科技有限公司
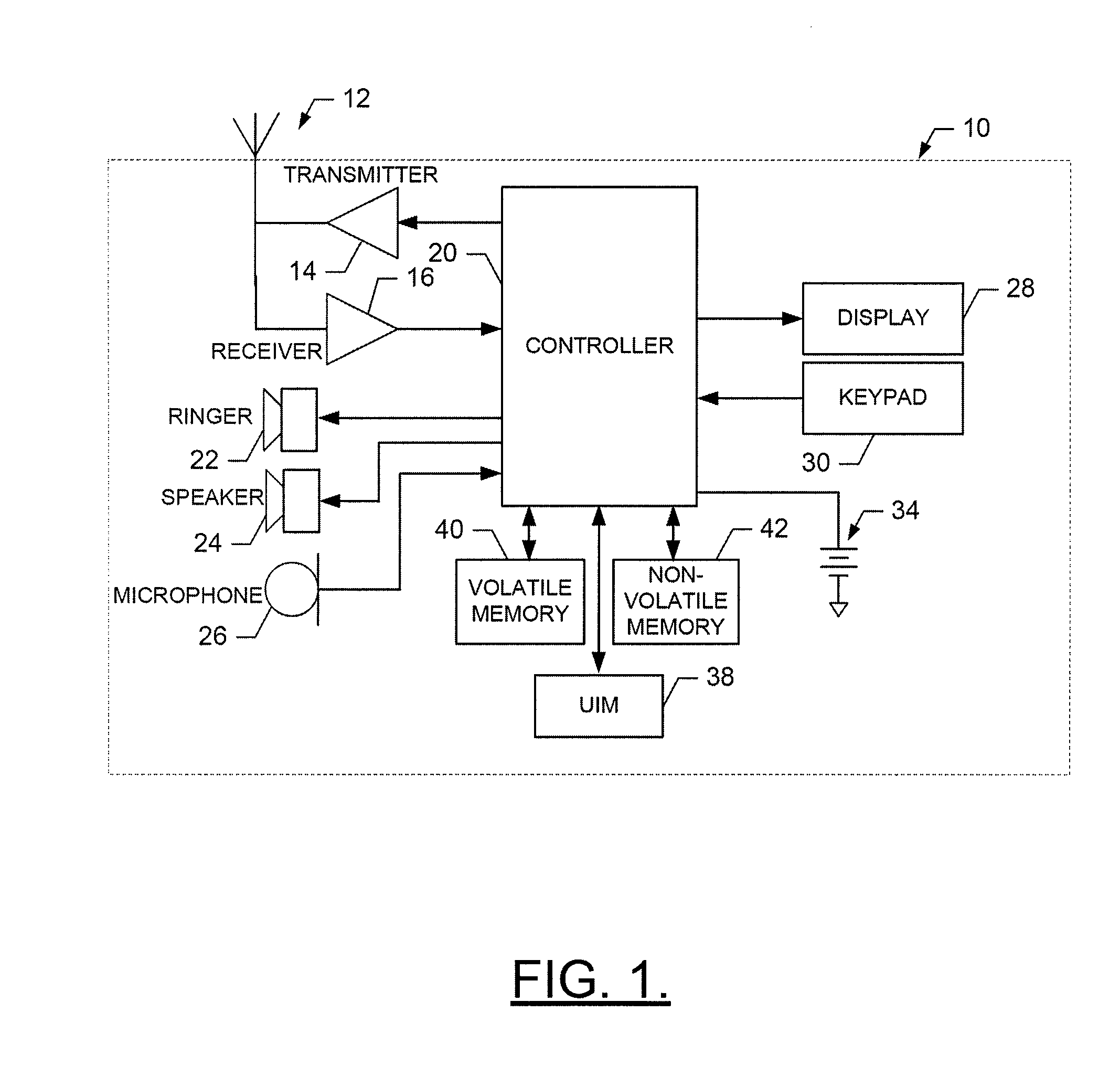
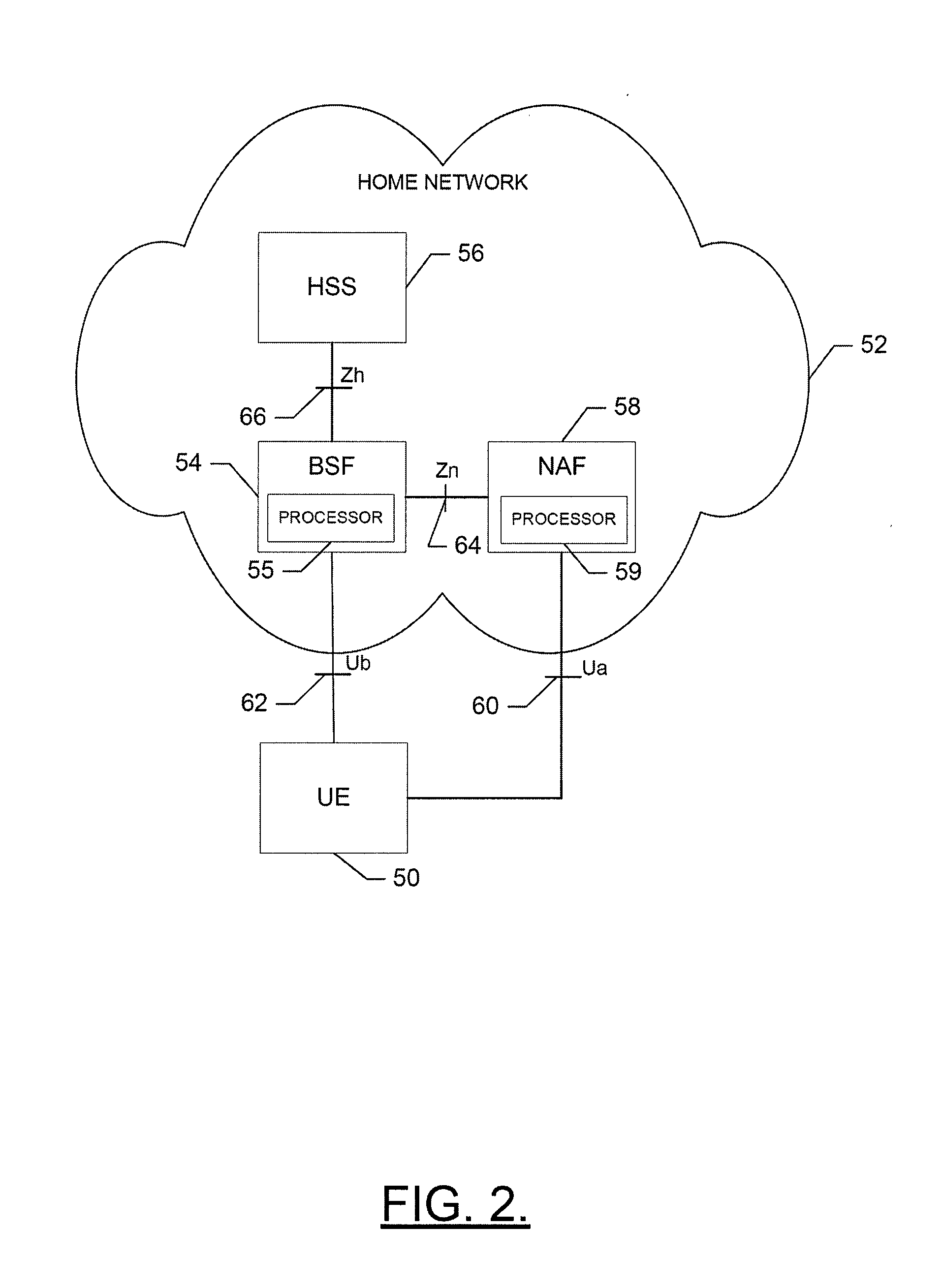
Method, Apparatus and Computer Program Product for Providing Key Management for a Mobile Authentication Architecture
InactiveUS20090232310A1Improve securityEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesMultiple digital computer combinationsMobile authenticationComputer science
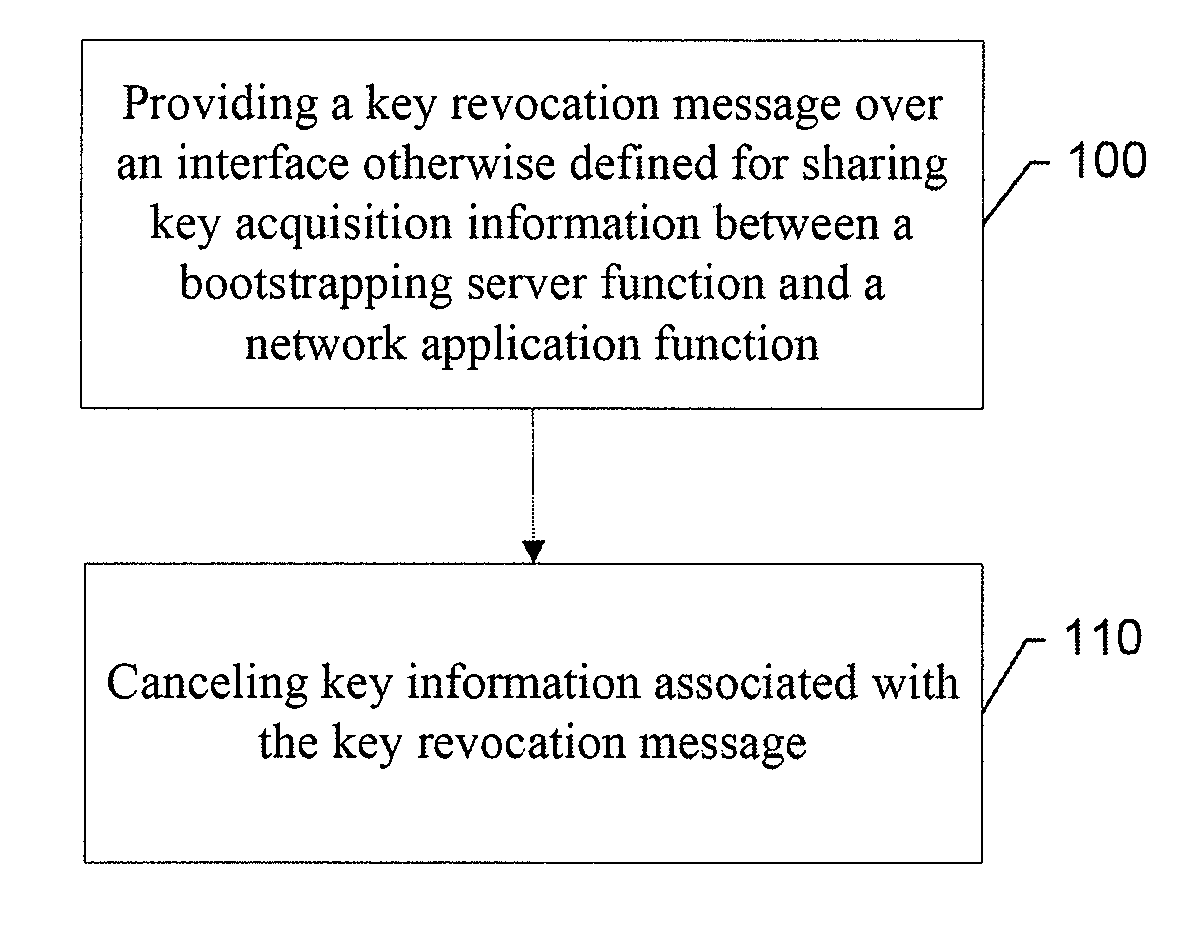
An apparatus for providing key management for a mobile authentication architecture may include a processor. The processor may be configured to provide a request for key revocation over an interface otherwise defined for sharing key acquisition information between a bootstrapping server function and a network application function, and cancel key information associated with the request for key revocation.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
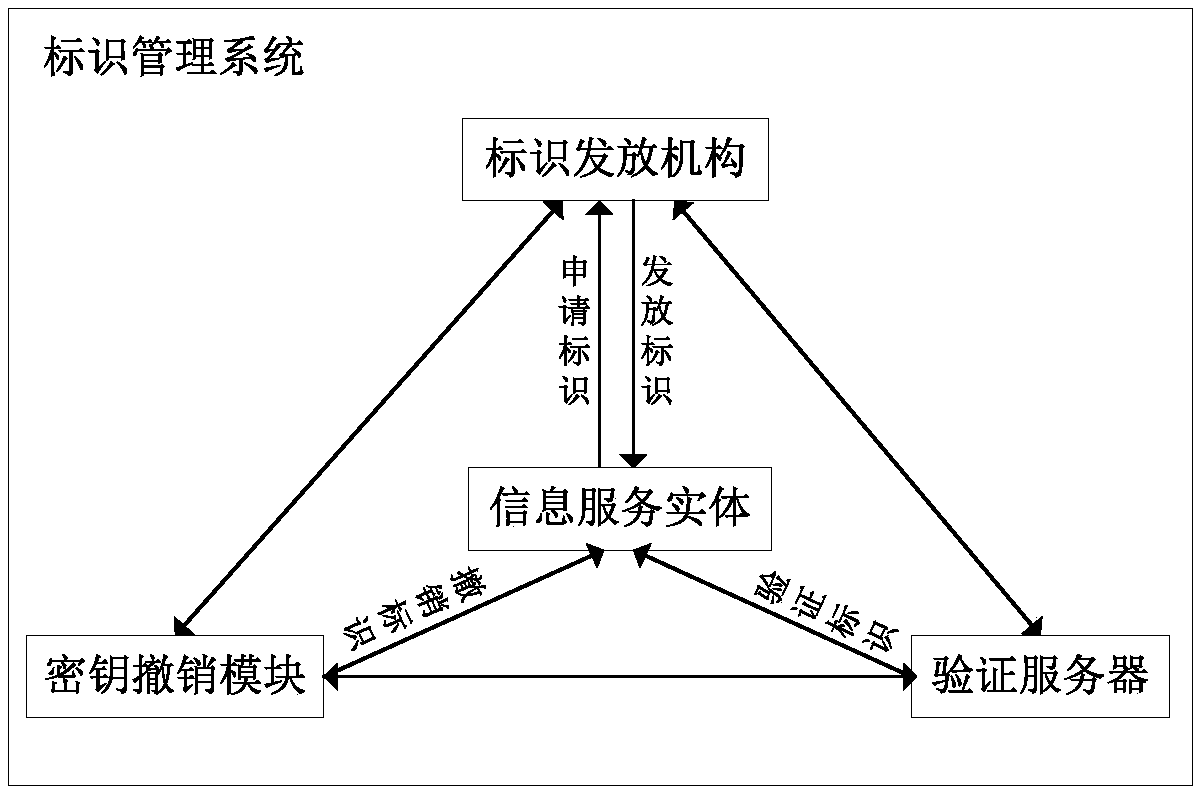
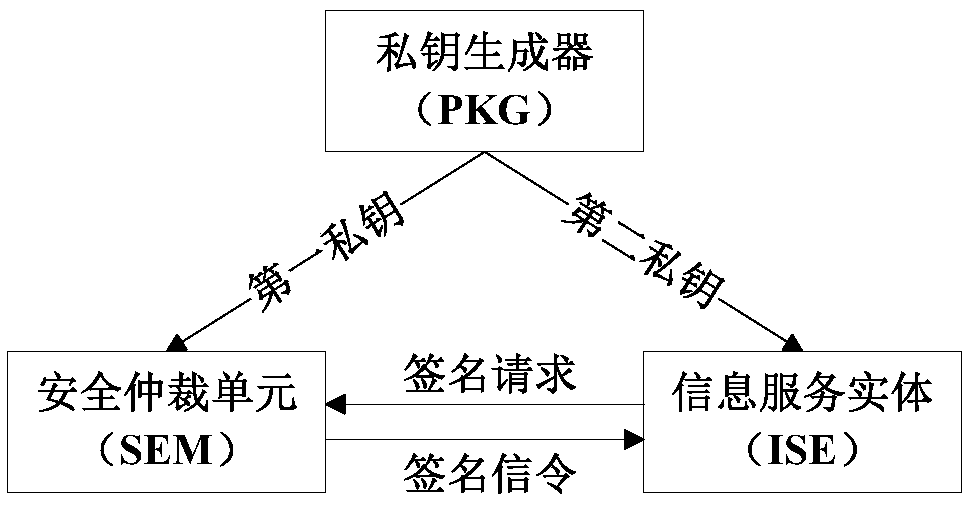
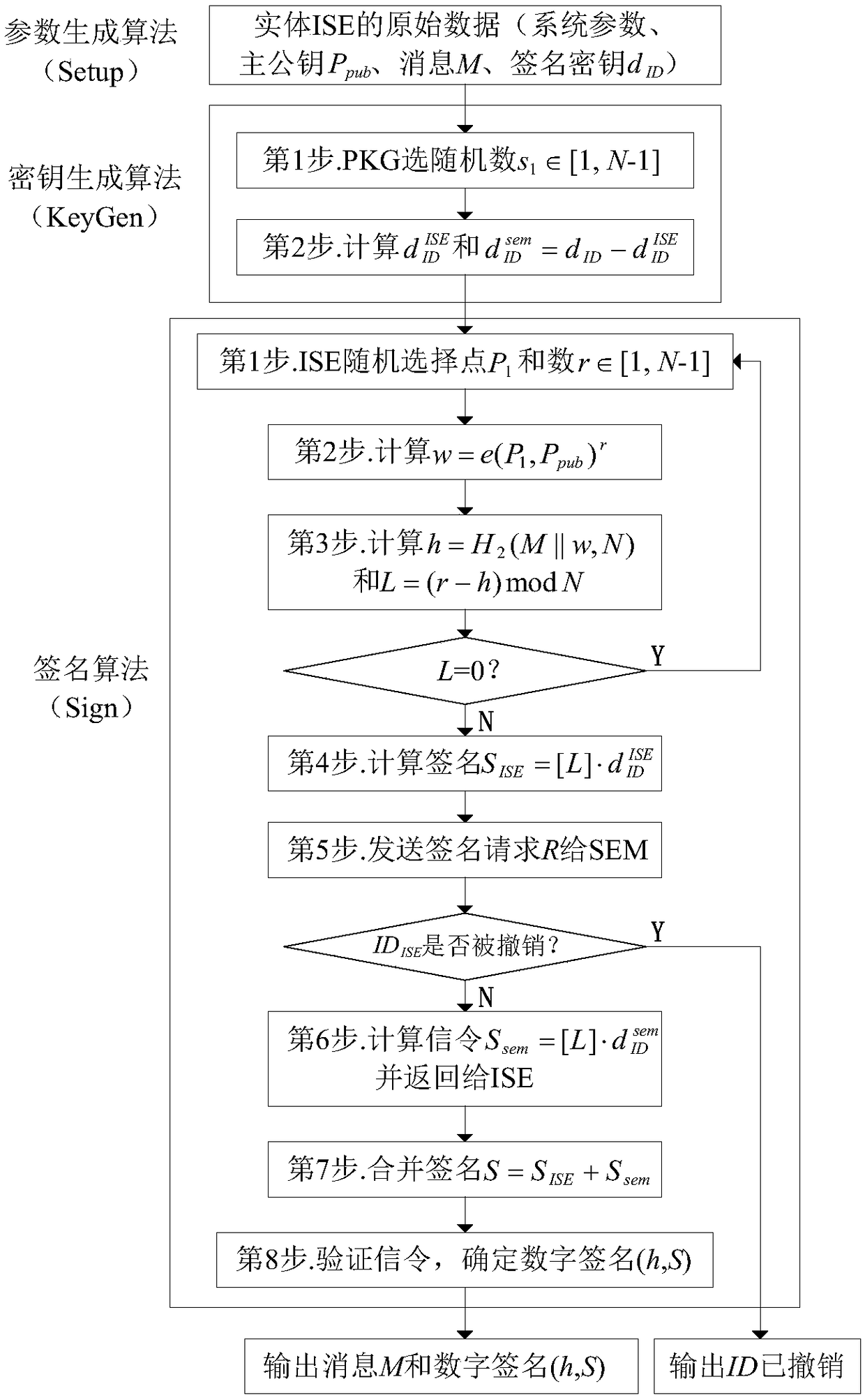
Information service entity identity management system and quick identity revocation method
ActiveCN108737391AImprove manageabilityImprove recognizabilityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationComputational securityDiscrete logarithm
The invention discloses an information service entity identity management system and a quick identity revocation method, which can solve the problem of instant revocation of an entity identity. A keyrevocation module is added in an identity management system, and the key revocation module includes a security arbitration unit, which can quickly revoke the identity of an information service entitywhen services of the information service entity are invalid or illegal. The implementation of the quick revocation method includes the following steps that: system initialization is performed, and keygeneration and segmentation of the information service entity is performed; and the information service entity and the security arbitration unit cooperate with part of private keys to implement the signature of a message, and a verification server verifies the signature of the message to achieve the unified management and authentication of a network space information service entity identity. According to the scheme of the invention, the invalid or illegal identity can be quickly revoked, the computational security is based on the difficulty of solving discrete logarithms on elliptic curves, the characteristic of quick revocation can be realized, high security can also be achieved, and the scheme is suitable for network environments with high security requirements.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
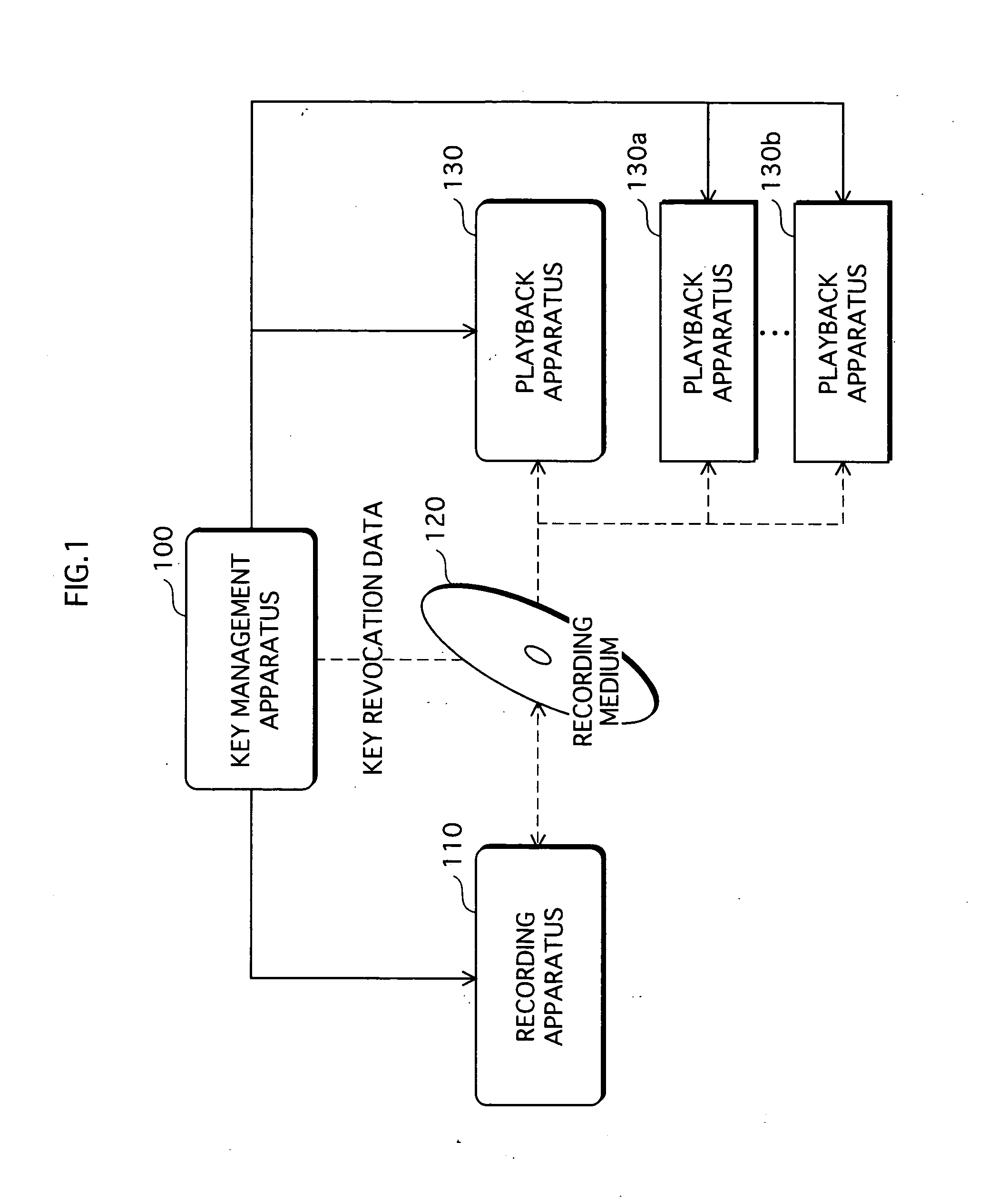
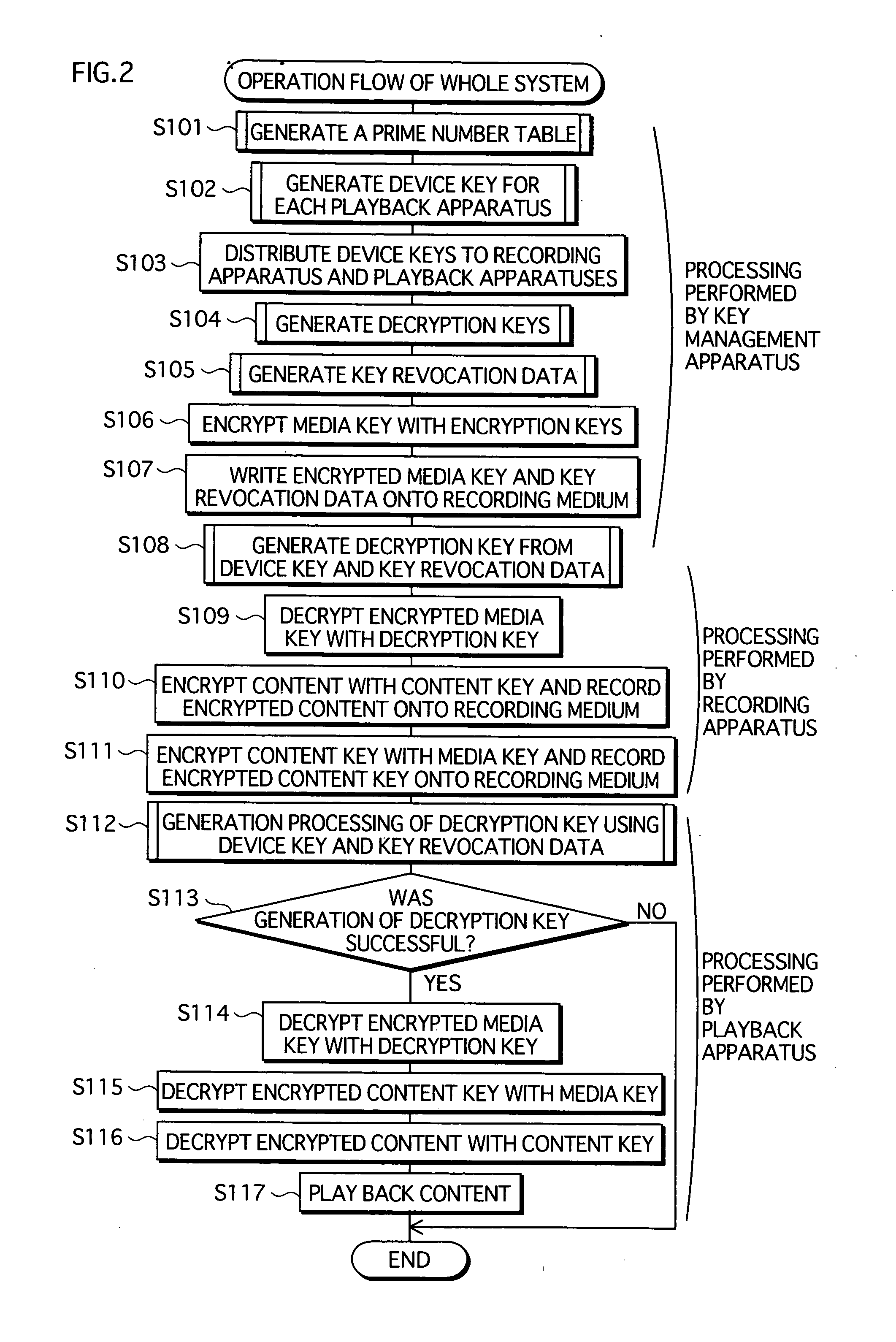
Copyright protection system, modular exponentiation operation apparatus, and modular exponentiation operation method
ActiveUS20070147603A1Easy to operateKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsModularityModular exponentiation
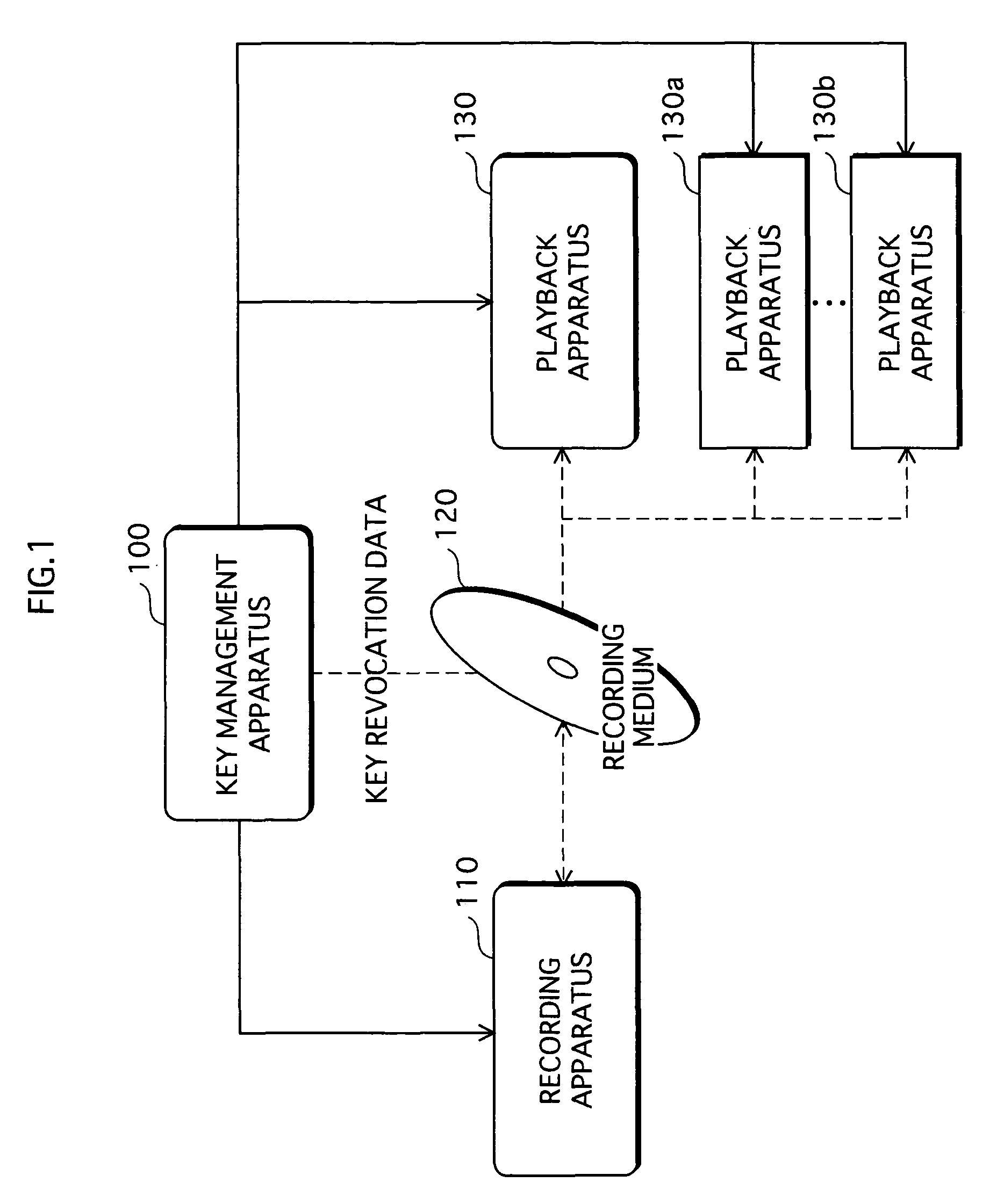
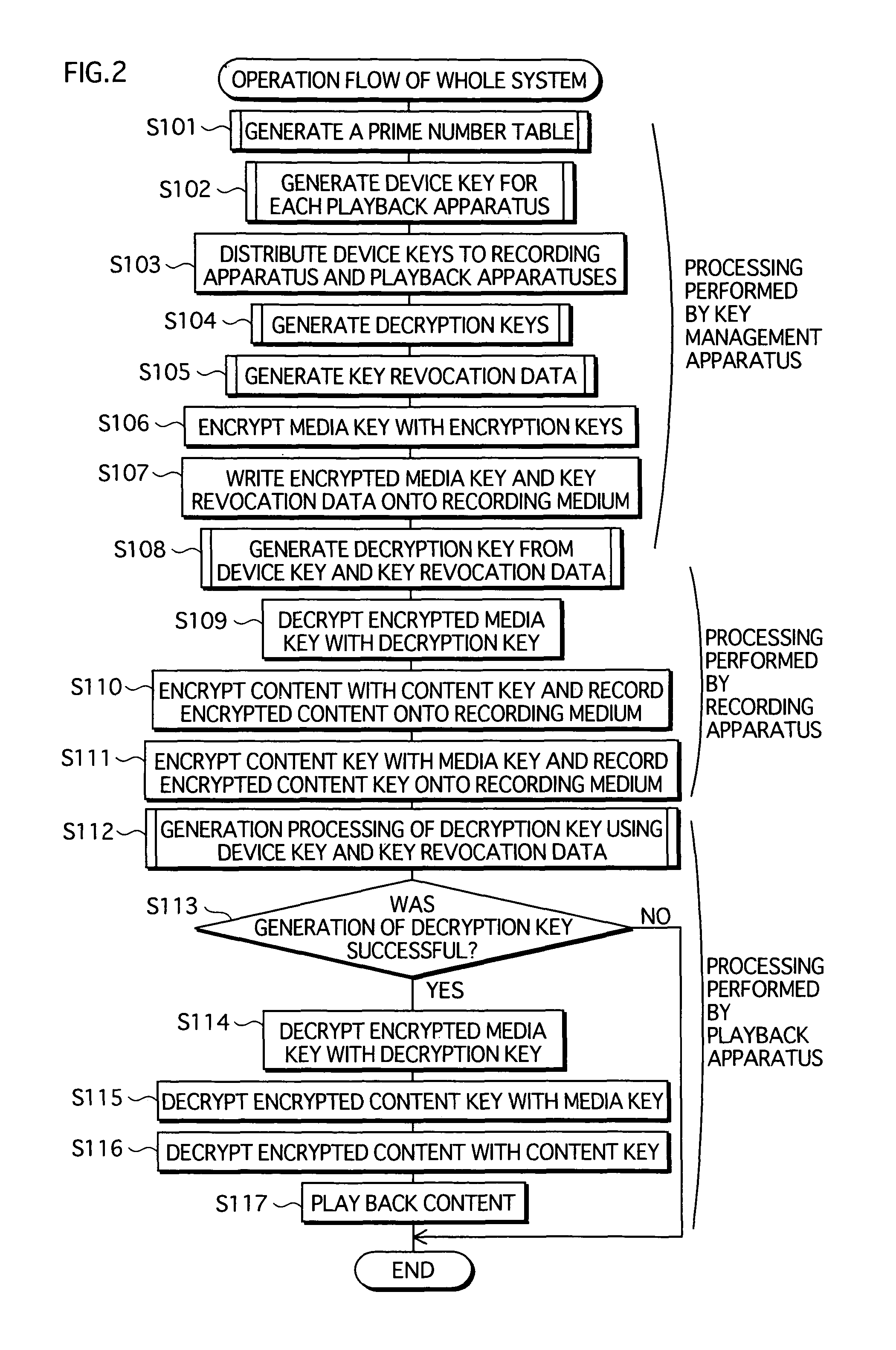
A copyright protection system is provided that keeps manufacturing costs down regardless of the total number of playback apparatuses belonging to the system. In this system, a device key generating unit of a key management apparatus performs a modular exponentiation operation on a random number with an inverse element of a product of predetermined prime numbers, so as to generate and distribute device keys to playback apparatuses in one-to-one correspondence. A key revocation data generating unit generates, as key revocation data, information identifying the prime numbers used by an unrevoked playback apparatus to generate a decryption key from its device key and distributes the key revocation data along with an encrypted content to each playback apparatus. Playback apparatuses each attempt to generate a description key based on the key revocation data, and only those playback apparatuses that have successfully generated a decryption key are able to decrypt the encrypted content.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
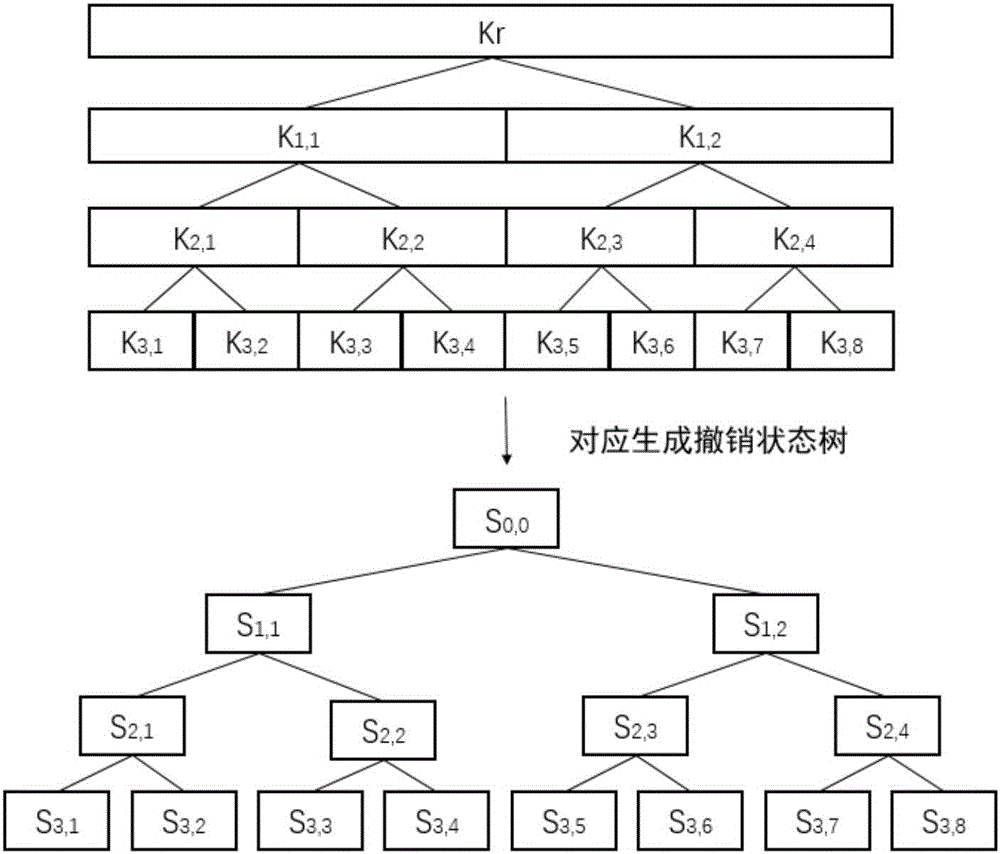
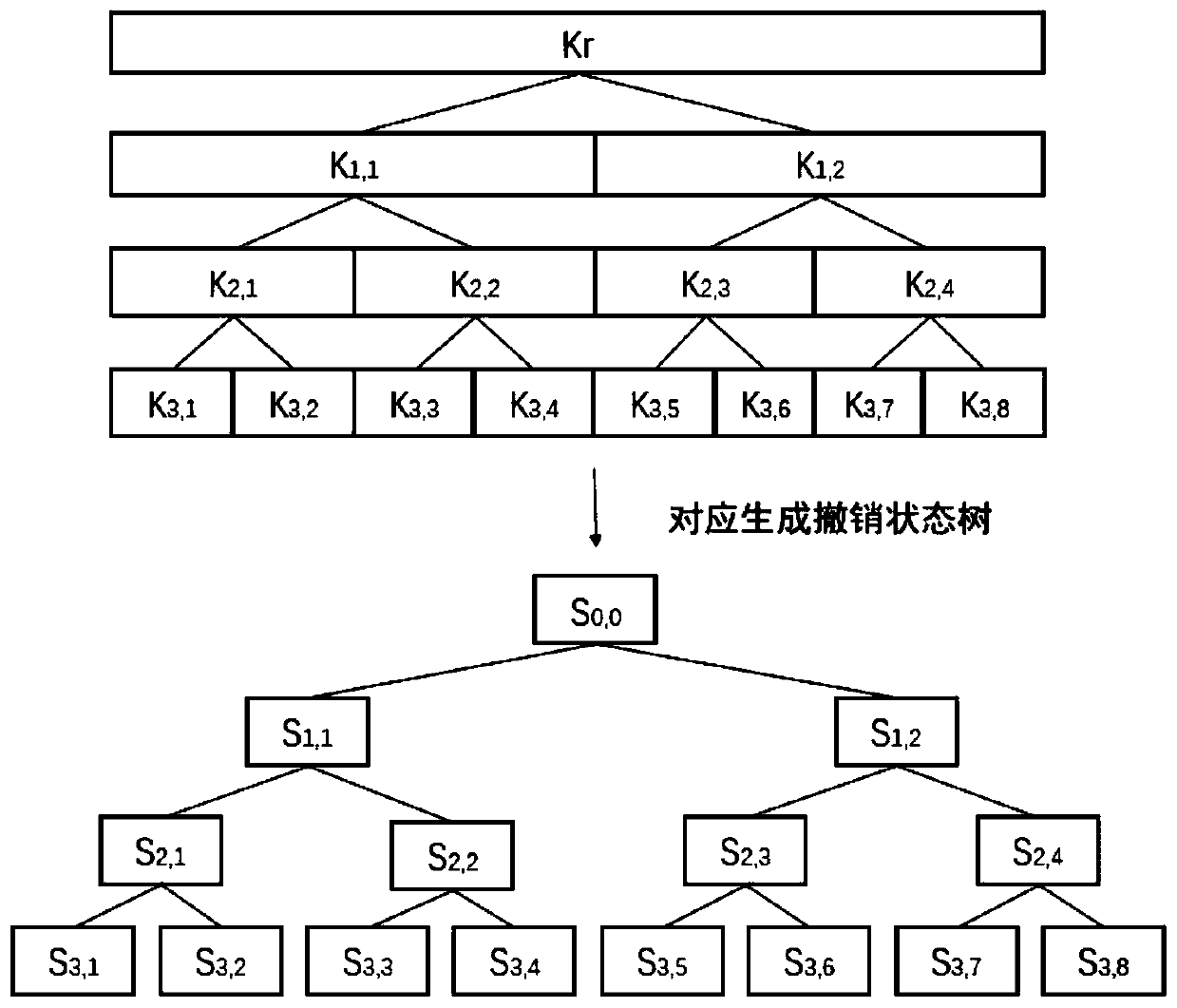
Key revocation method for key management tree in cloud database
ActiveCN106850216ASave on storage overheadSave administrative overheadKey distribution for secure communicationKey storageTree node
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
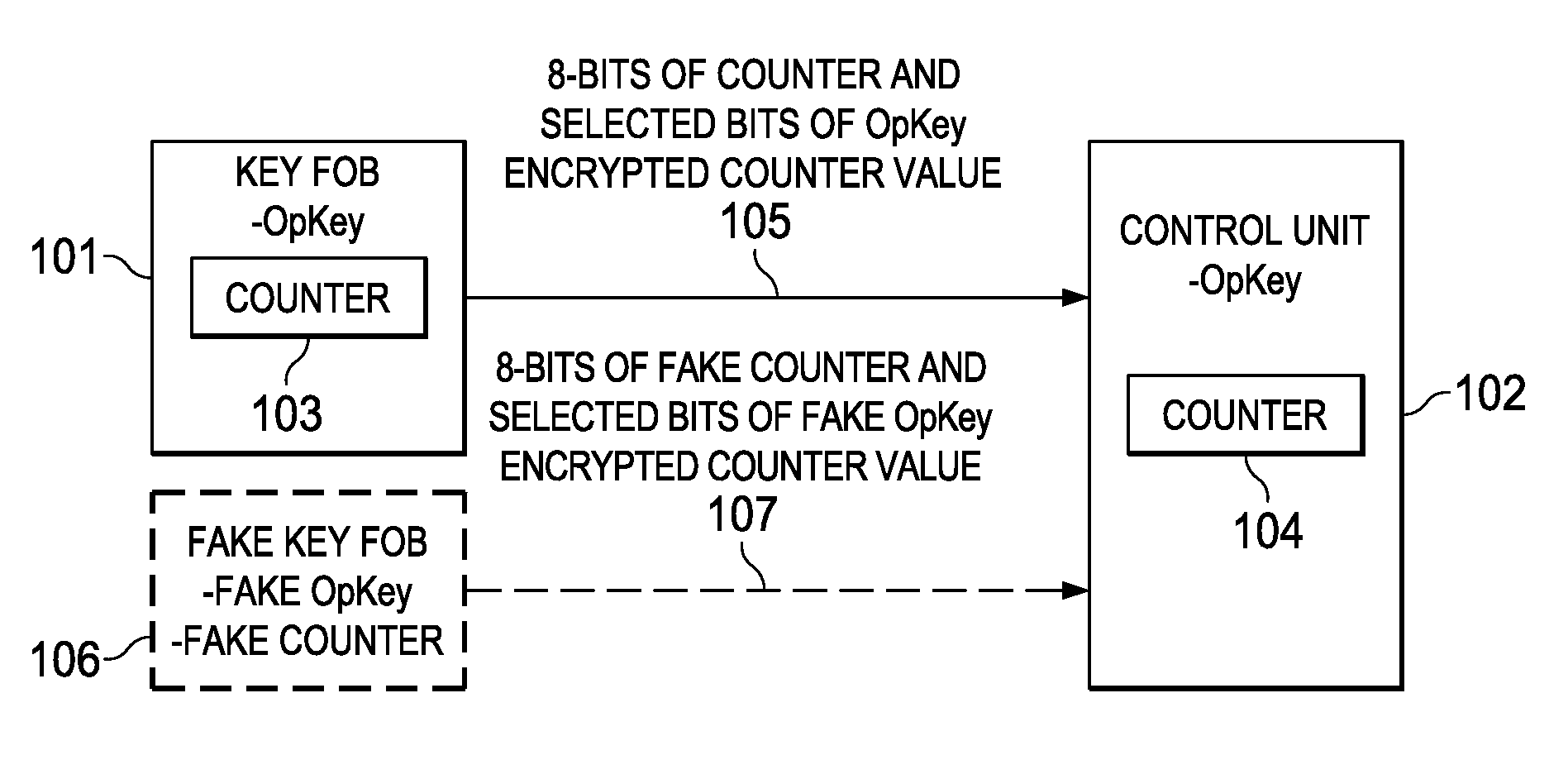
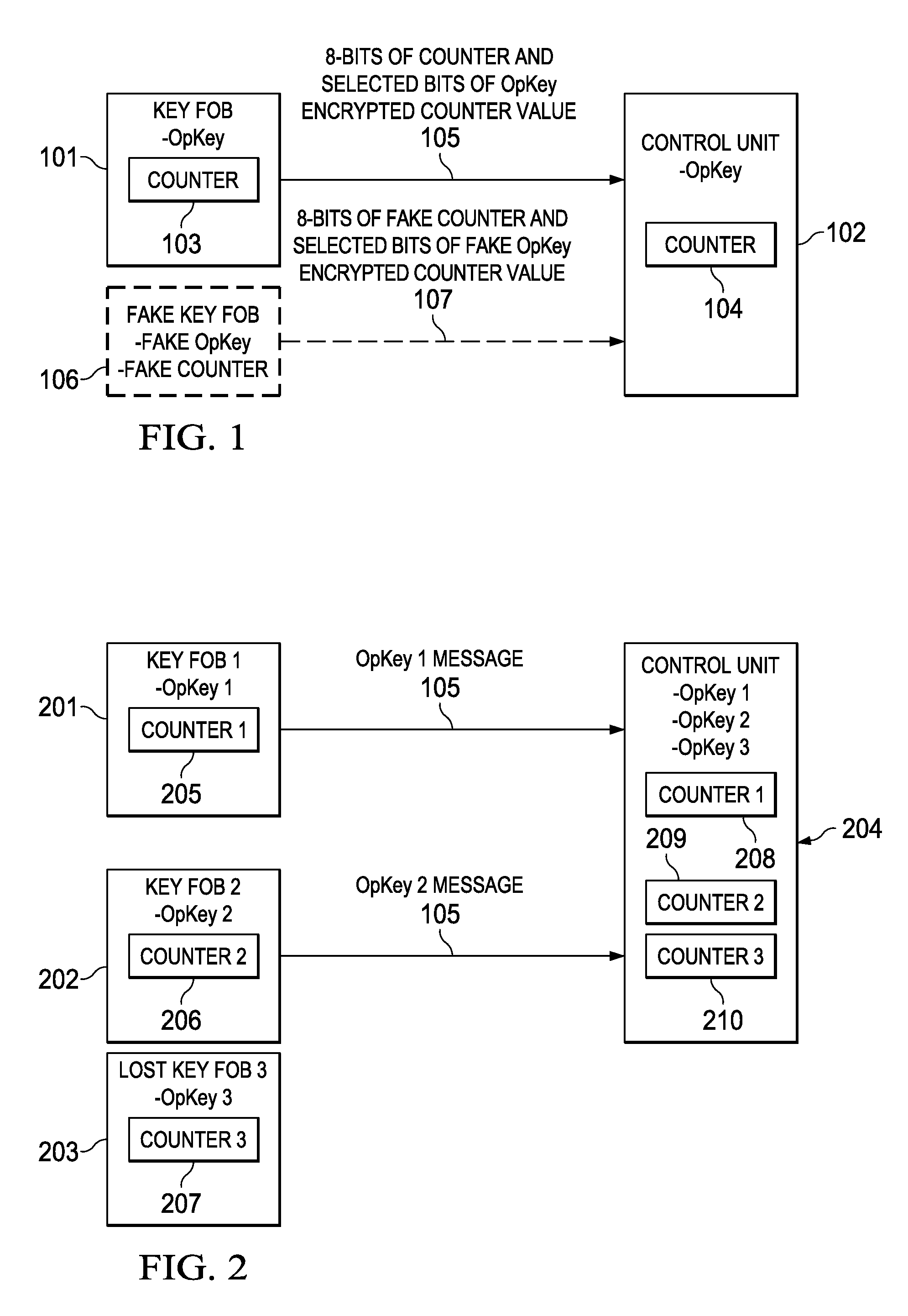
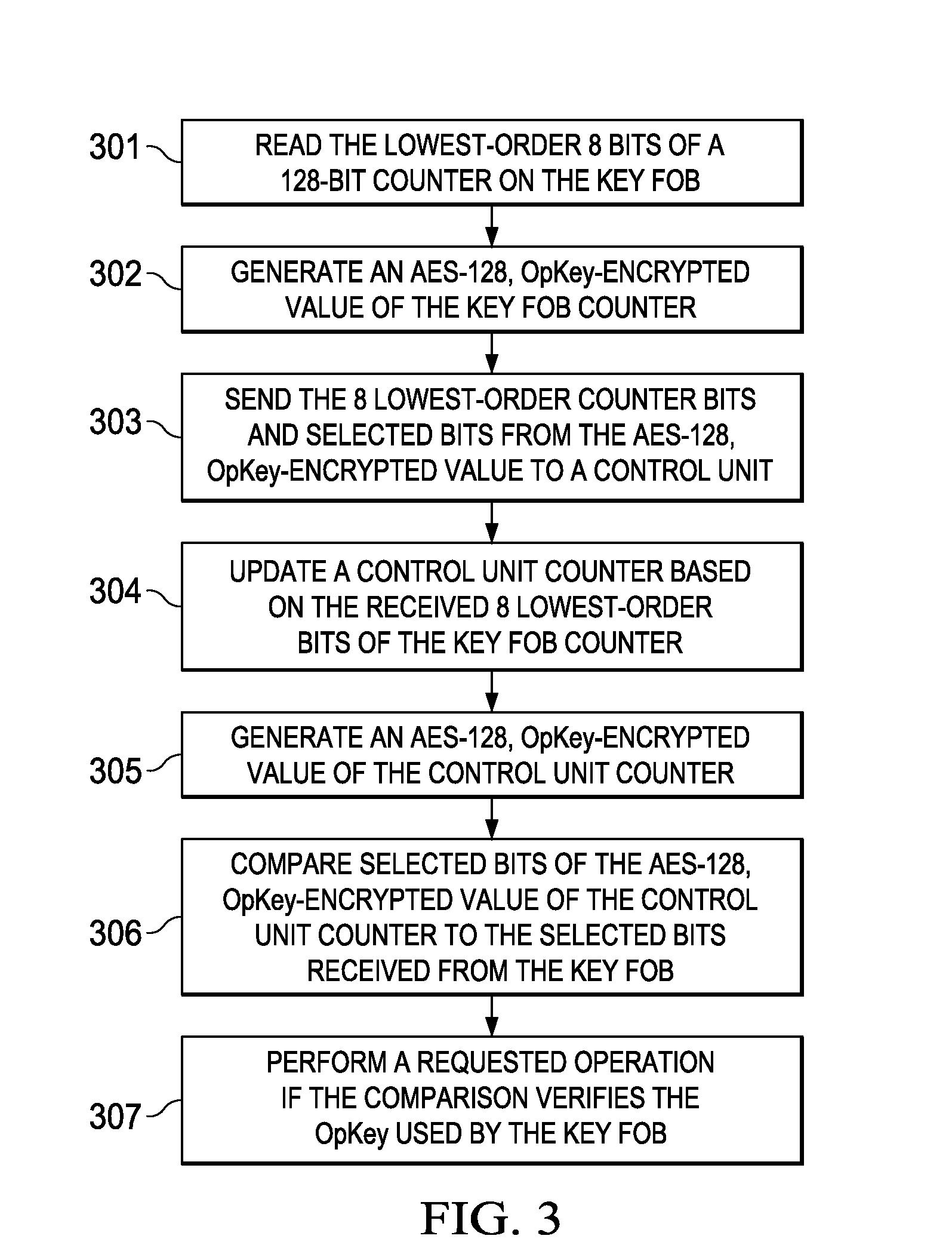
One-way key fob and vehicle pairing verification, retention, and revocation
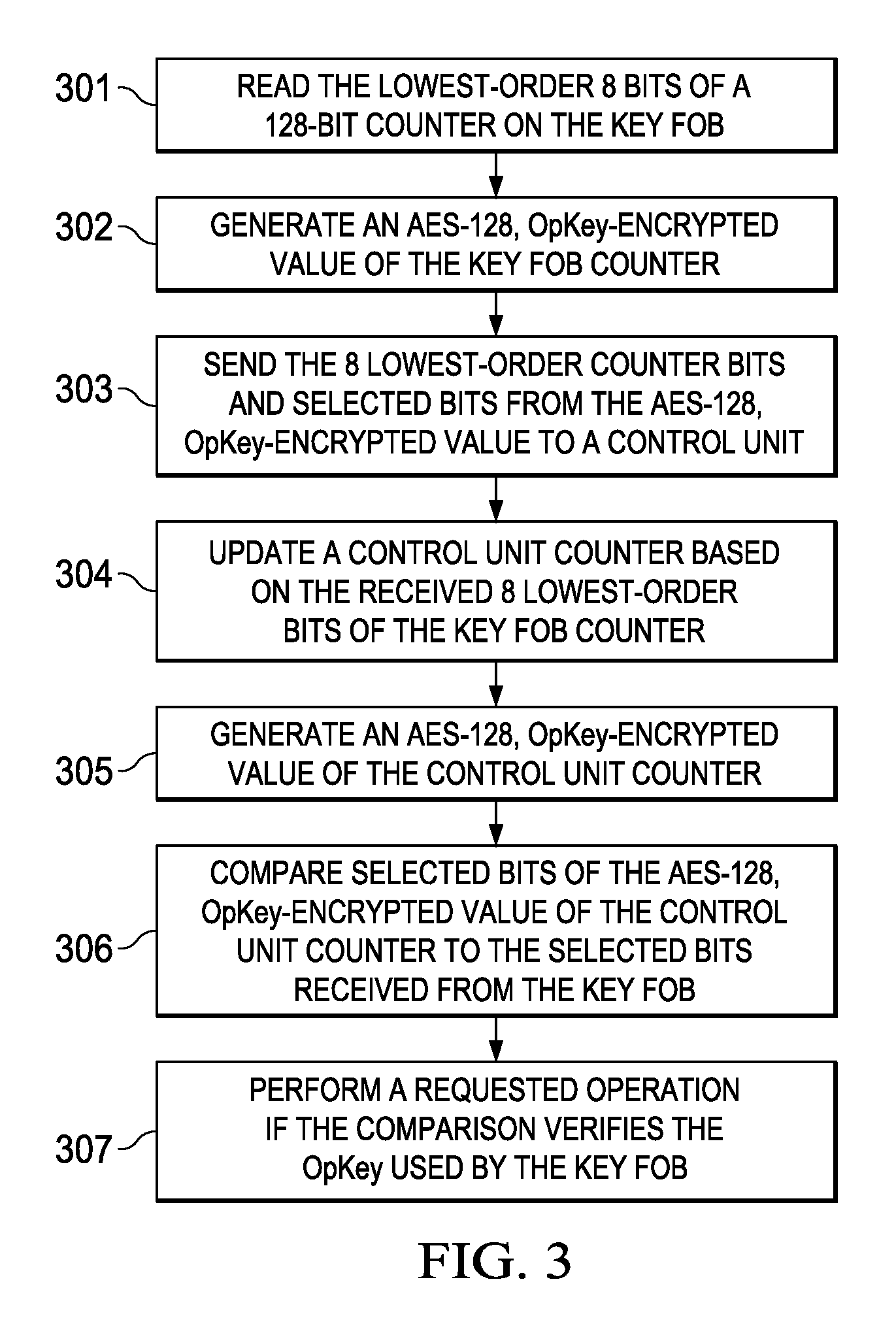
ActiveUS9306743B2Key distribution for secure communicationAnti-theft devicesComputer hardwareControl unit
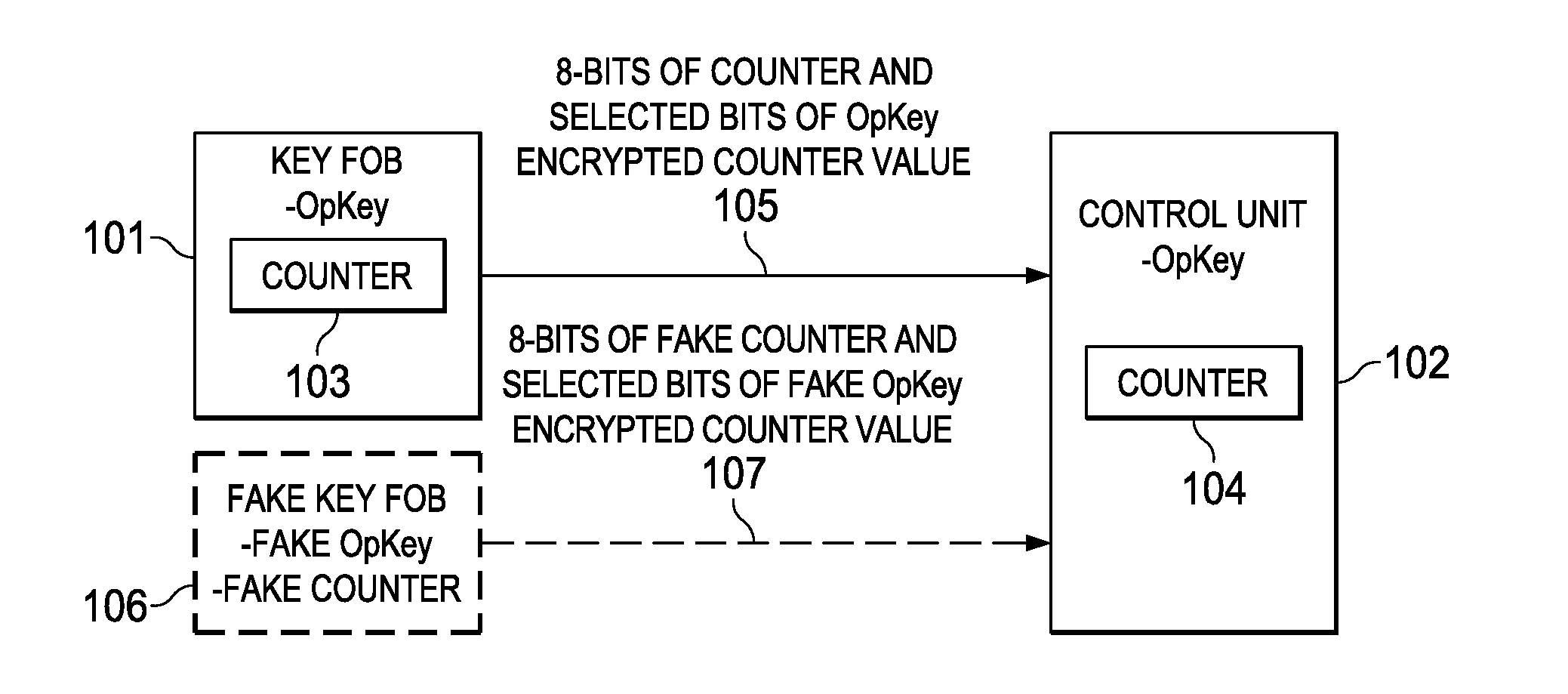
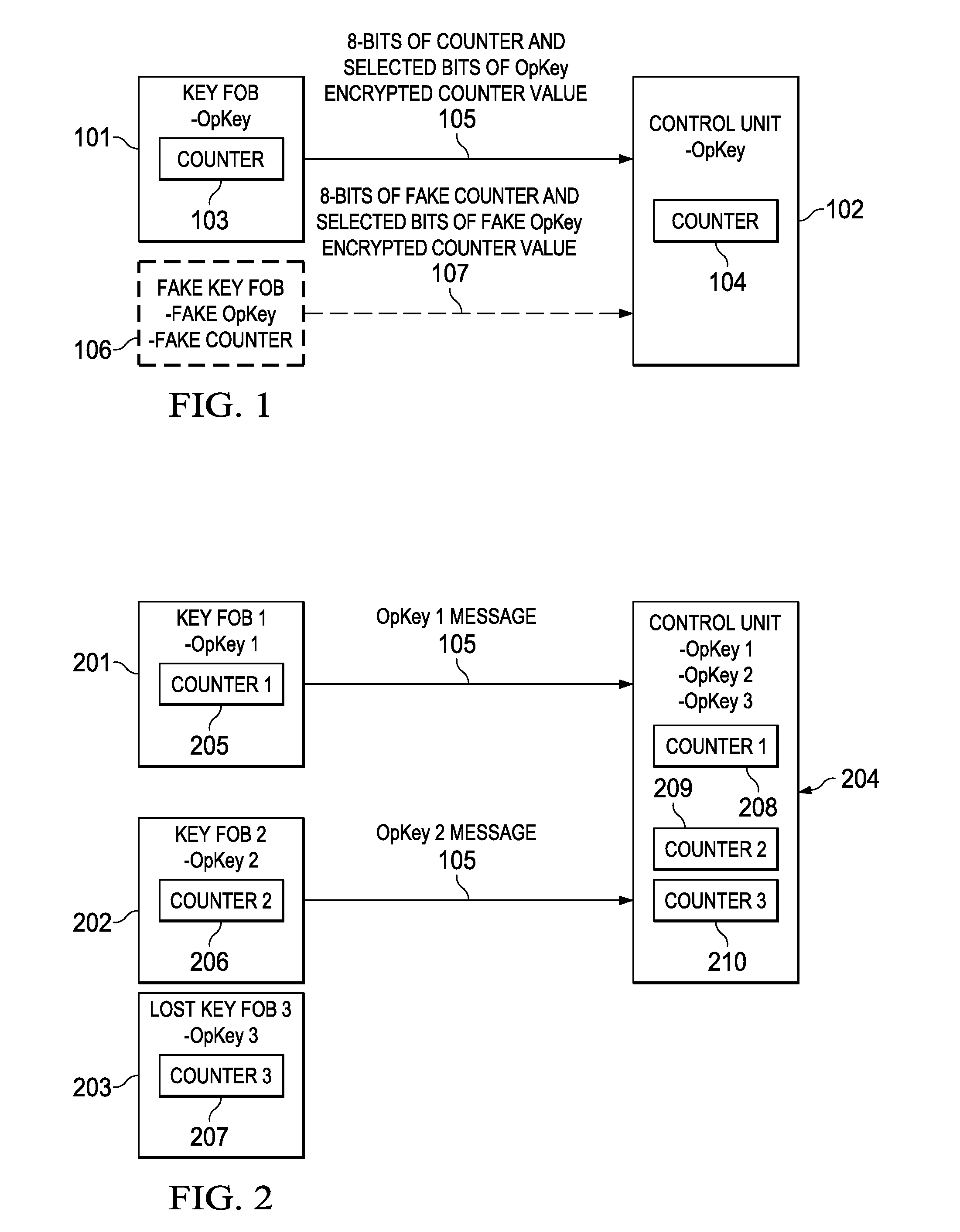
Embodiments of the invention provide methods for key fob to control unit verification, retention, and revocation. After an initial pairing between a key fob and a control unit, the devices share a secret operation key (OpKey). For verification, the key fob sends the 8 lowest-order bits of a 128-bit counter and some bits of an AES-128, OpKey encrypted value of the counter to the control unit. For key revocation and retention, the control unit is prompted to enter an OpKey retention and revocation mode. Subsequently, each of the remaining or new key fobs is prompted by the user to send a verification message to the control unit. When the control unit is prompted to exit the OpKey retention and revocation mode, it retains the OpKeys of only the key fobs that sent a valid verification message immediately before entering and exiting the OpKey retention and revocation mode.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Revocation of cryptographic keys in the absence of a trusted central authority
ActiveUS10135616B2Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationTrusted authorityCryptographic nonce
Owner:FINLOW BATES KEIR
Key updating method and device, multi-attribute authority management system, equipment and medium
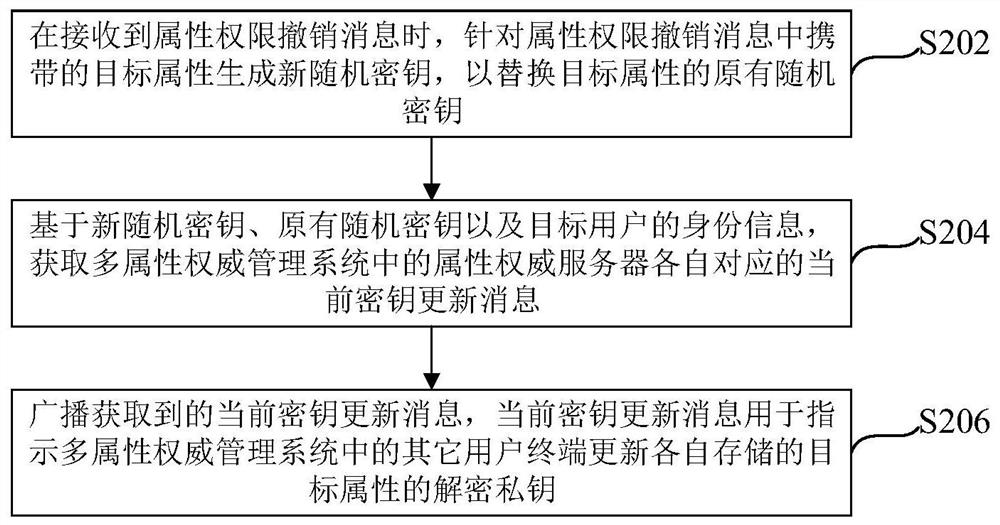
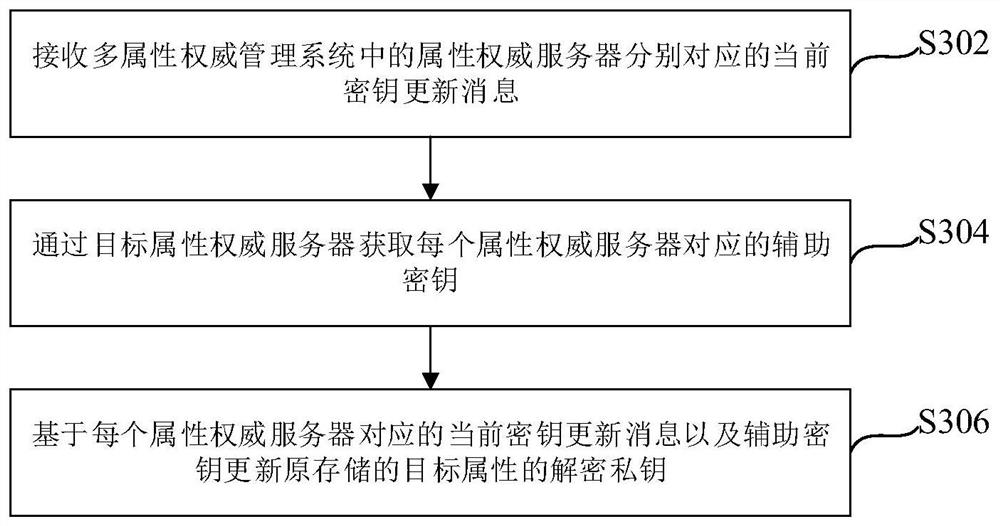
ActiveCN113486384AReduce computational overheadEnsure safetyRandom number generatorsDigital data protectionEngineeringManagement system
The embodiment of the invention relates to a secret key updating method and device, a multi-attribute authority management system, equipment and a medium, wherein the method applied to a target attribute authority server comprises the steps of generating a new random secret key for a target attribute carried in an attribute authority revocation message when the attribute authority revocation message is received, and replacing the original random key of the target attribute; based on the new random key, the original random key and the identity information of the target user, obtaining current key update messages corresponding to attribute authority servers in the multi-attribute authority management system; and broadcasting the obtained current secret key updating message, wherein the current secret key updating message is used for indicating other user terminals in the multi-attribute authority management system to update the decryption private keys of the target attributes stored by the other user terminals respectively. According to the mode, the calculation overhead required by key revocation can be effectively reduced, and the security and reliability of key revocation can be fully guaranteed.
Owner:BEIJING BYTEDANCE NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Method for broadcast encryption and key revocation of stateless receivers
InactiveUS20050195980A1Special service provision for substationKey distribution for secure communicationBroadcastingSession key
A tree is used to partition stateless receivers in a broadcast content encryption system into subsets. Two different methods of partitioning are disclosed. When a set of revoked receivers is identified, the revoked receivers define a relatively small cover of the non-revoked receivers by disjoint subsets. Subset keys associated with the subsets are then used to encrypt a session key that in turn is used to encrypt the broadcast content. Only non-revoked receivers can decrypt the session key and, hence, the content.
Owner:IBM CORP
Digital key authorization issuing and withdrawing method and system
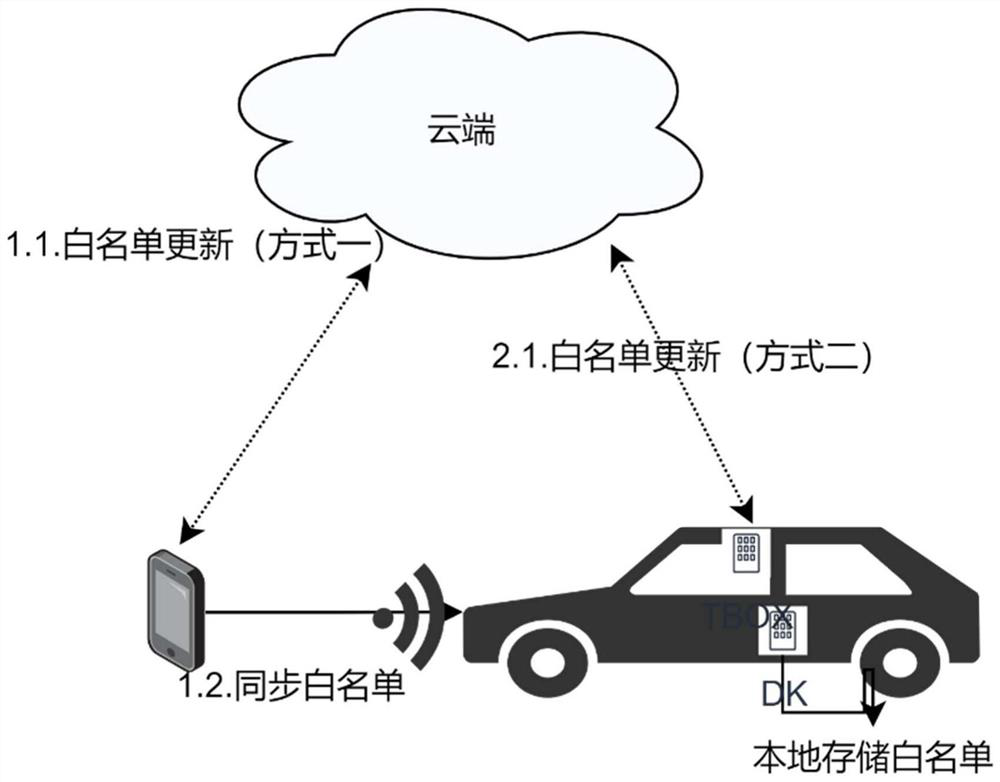
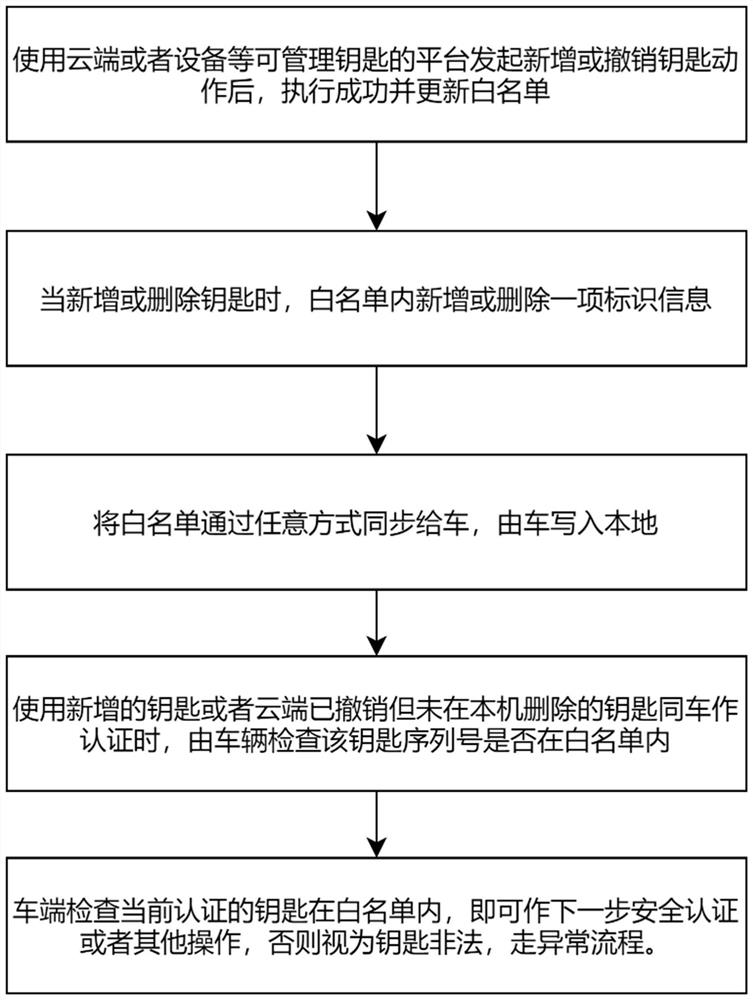
PendingCN113706743ASupport undo operationAvoid infinite growthSubstation equipmentIndividual entry/exit registersSecurity authenticationWhitelist
The invention provides a digital key authorization issuing and withdrawing method and system, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, a key management platform carries out the operation of adding or deleting a key, a white list is locally updated after the operation succeeds, and the data in the white list is a set of key serial numbers; S2, other equipment synchronizes the updated white list to the vehicle end; S3, the vehicle end checks the validity of the white list and stores the white list, whether the serial number corresponding to the key is in the white list or not is checked through security authentication, and if the serial number does not exist in the white list, it is judged that the key is illegal. According to the method and system, a data list capable of identifying corresponding key information is maintained, and the list of the data corresponding to the key information effectively supports key revocation operation; issuing and withdrawing operations of the digital key are effectively supported; and on the premise that the number of available keys is always limited, the reliability of the operation of recording the key state is kept by the vehicle end.
Owner:SHANGHAI TRUSTKERNEL INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Novel message signature method for sparse movable Ad Hoc network
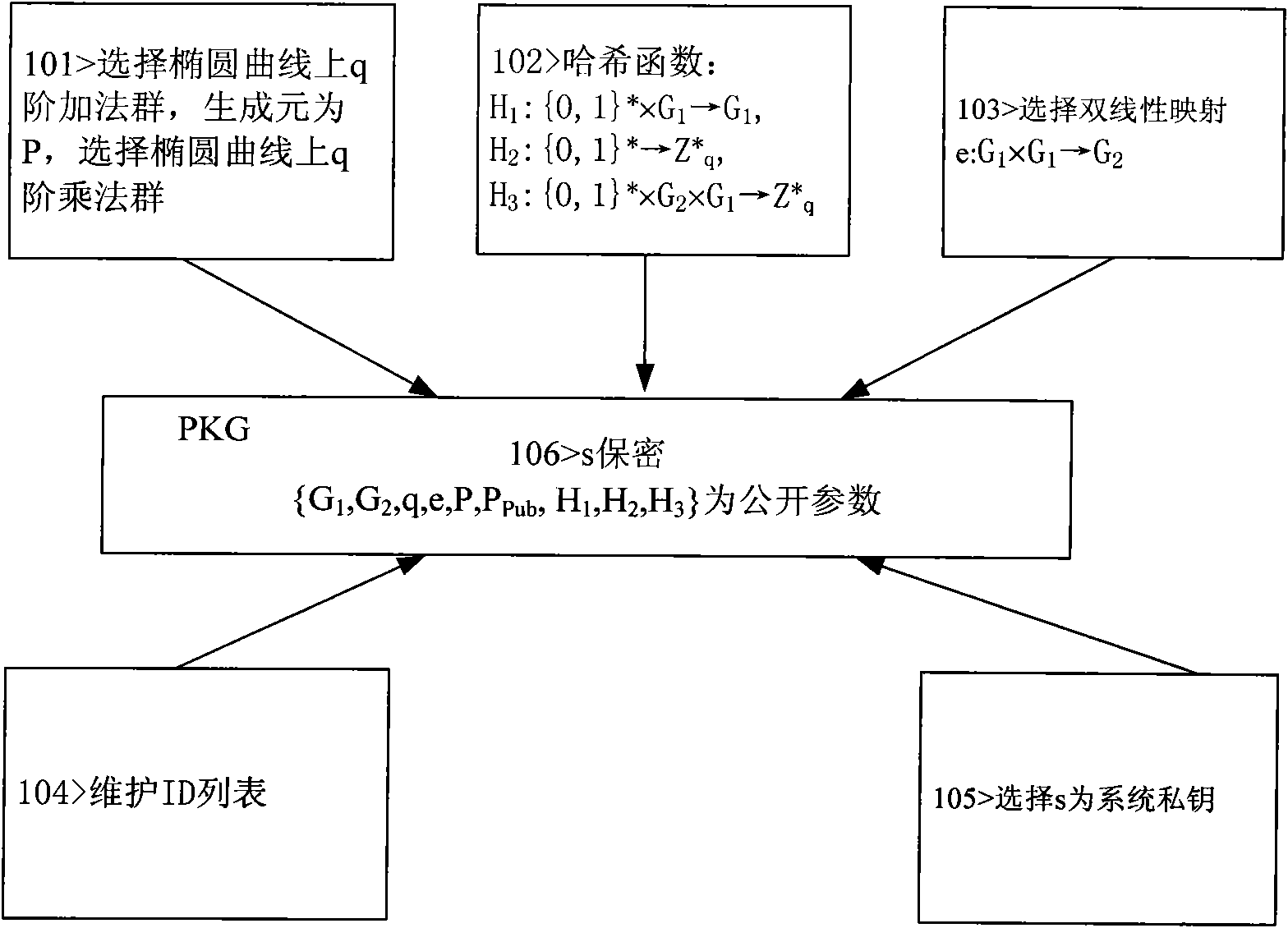
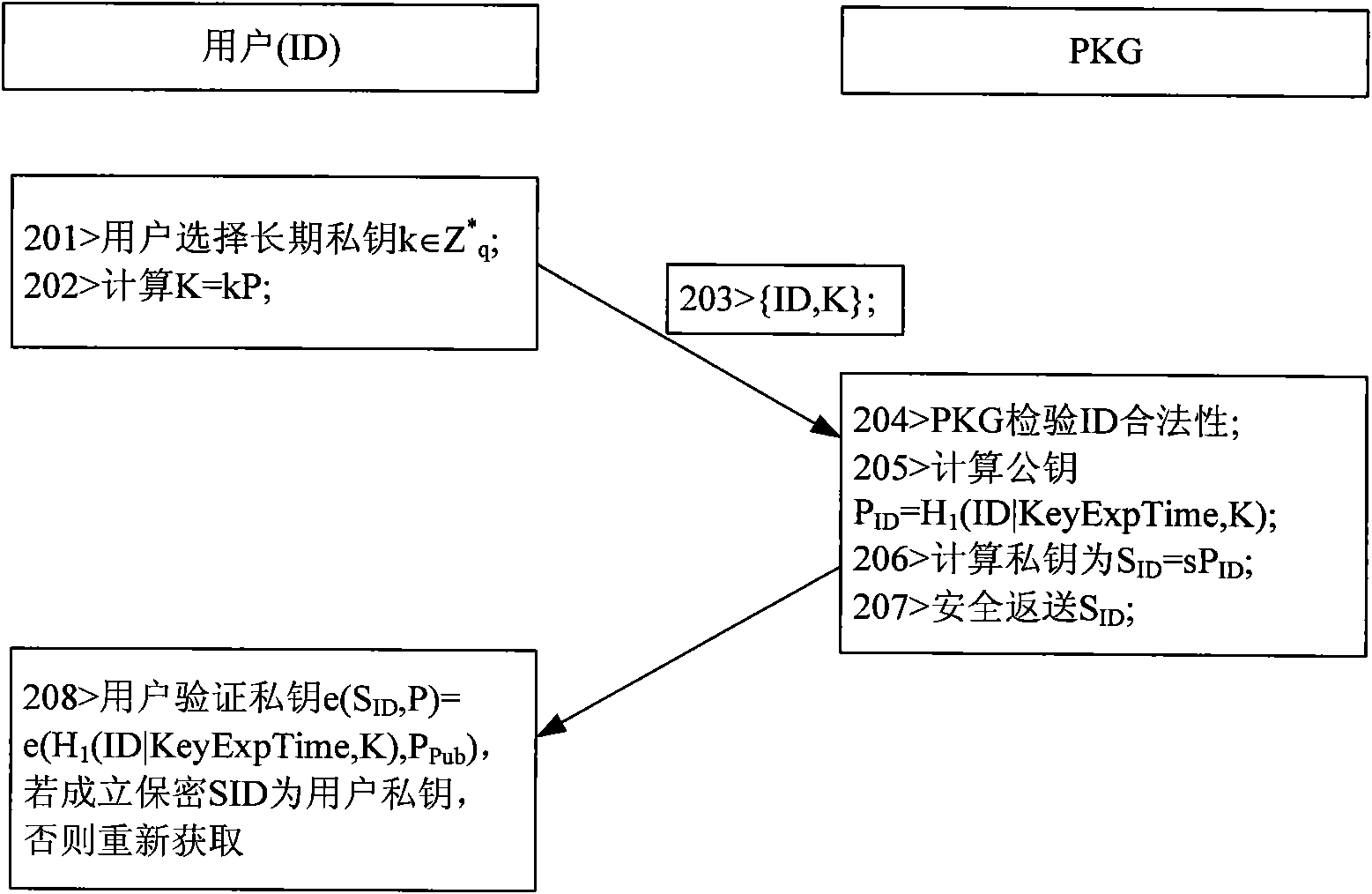
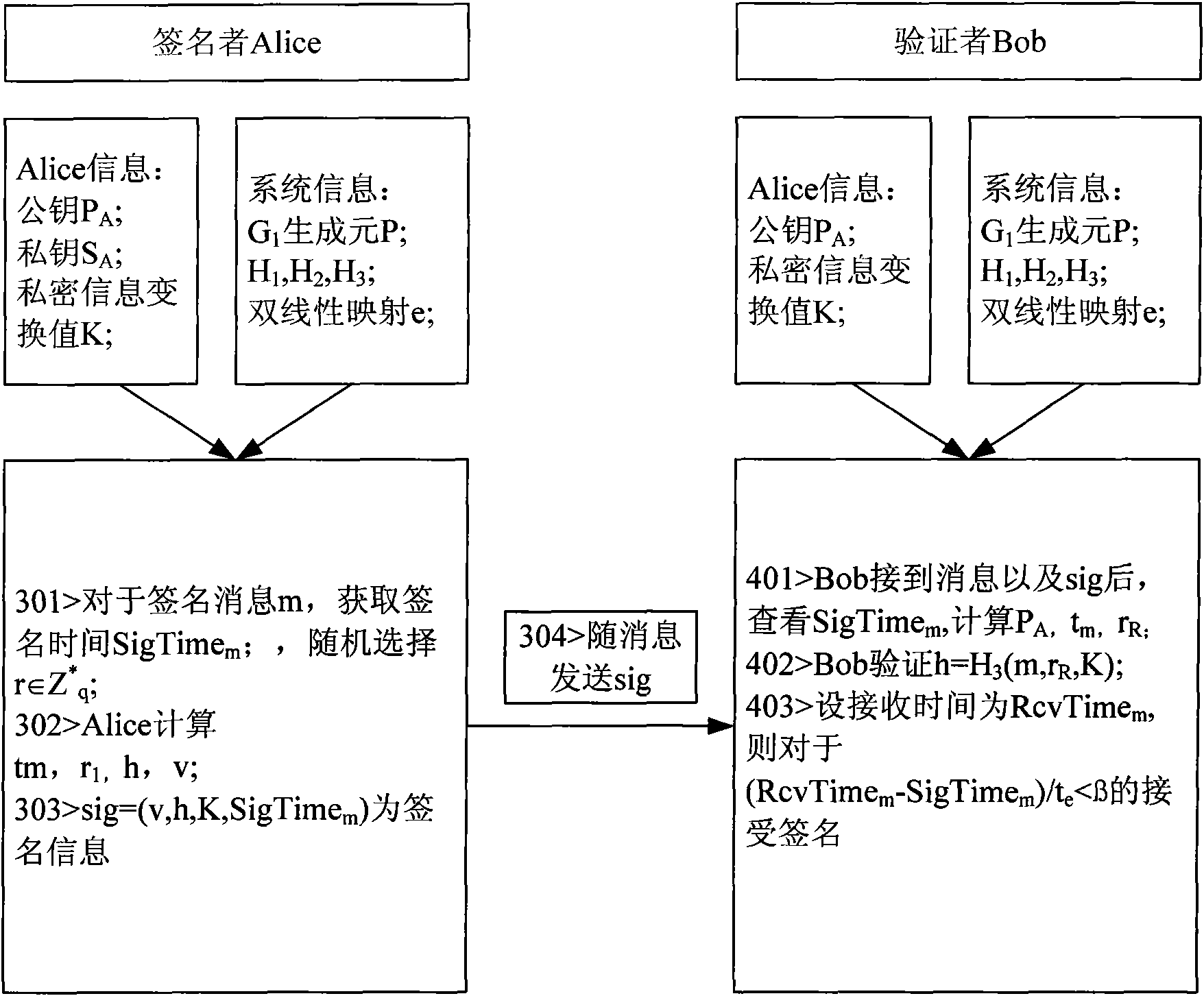
The invention discloses a novel message signature method for a sparse movable Ad Hoc network, which can be used for the message signature authentication of the sparse Ad Hoc network, and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication networks. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a system, generating a private key, executing a signature algorithm and executing a verification algorithm. In the method, the need of a signing and authenticating third party is obviated by adopting an identity-based cryptosystem; key revocation is performed by using key survival time; a node private value is added in the process of generating the private key to solve the problem of key escrow; the harm to the network due to key revealing is limited by using a message signature survival time threshold value; and the signature by elliptic curve bilinear pair reduces key length, calculated amount, signature length, storage space and the bandwidth of a communication link.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
General identifier representation method for identifier password updating and revoking
The invention provides a general identifier representation method for identifier password updating and revocation. The method comprises the following identification forms: identifier password identifier = body identifier + aging identifier + version number, time efficiency identifier = time slice level + time slice serial number, wherein the identifier password identifier is composed of the body identifier, the time efficiency identifier and the version number; the time efficiency identifier consists of the time slice level and the time slice serial number, and the time efficiency is used forperiodically updating the identifier; the version number is used for revoking the identifier in the validity period, and the version number is accumulated from 0 to top; the time efficiency identifieradopts a form of an effective time slice grade and an effective time slice serial number, along with the improvement of the time slice level, the time length represented by the time slice is increased exponentially, and the time slices of all levels adopt the same starting time. According to the relation between secret key updating and secret key revocation in the identification password system,the characteristics of the layered identifier password system are combined, and secret key revocation comprises two parts of revocation when a secret key expires and active application revocation before the secret key expires.
Owner:湖南安方信息技术有限公司
Copyright protection system, modular exponentiation operation apparatus, and modular exponentiation operation method
ActiveUS7925893B2Easy to operateKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsEngineeringModular exponentiation
A copyright protection system is provided that keeps manufacturing costs down regardless of the total number of playback apparatuses belonging to the system. In this system, a device key generating unit of a key management apparatus performs a modular exponentiation operation on a random number with an inverse element of a product of predetermined prime numbers, so as to generate and distribute device keys to playback apparatuses in one-to-one correspondence. A key revocation data generating unit generates, as key revocation data, information identifying the prime numbers used by an unrevoked playback apparatus to generate a decryption key from its device key and distributes the key revocation data along with an encrypted content to each playback apparatus. Playback apparatuses each attempt to generate a description key based on the key revocation data, and only those playback apparatuses that have successfully generated a decryption key are able to decrypt the encrypted content.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
One-Way Key Fob and Vehicle Pairing Verification, Retention, and Revocation
ActiveUS20140161252A1Key distribution for secure communicationAnti-theft devicesComputer hardwareControl unit
Embodiments of the invention provide methods for key fob to control unit verification, retention, and revocation. After an initial pairing between a key fob and a control unit, the devices share a secret operation key (OpKey). For verification, the key fob sends the 8 lowest-order bits of a 128-bit counter and some bits of an AES-128, OpKey encrypted value of the counter to the control unit. For key revocation and retention, the control unit is prompted to enter an OpKey retention and revocation mode. Subsequently, each of the remaining or new key fobs is prompted by the user to send a verification message to the control unit. When the control unit is prompted to exit the OpKey retention and revocation mode, it retains the OpKeys of only the key fobs that sent a valid verification message immediately before entering and exiting the OpKey retention and revocation mode.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
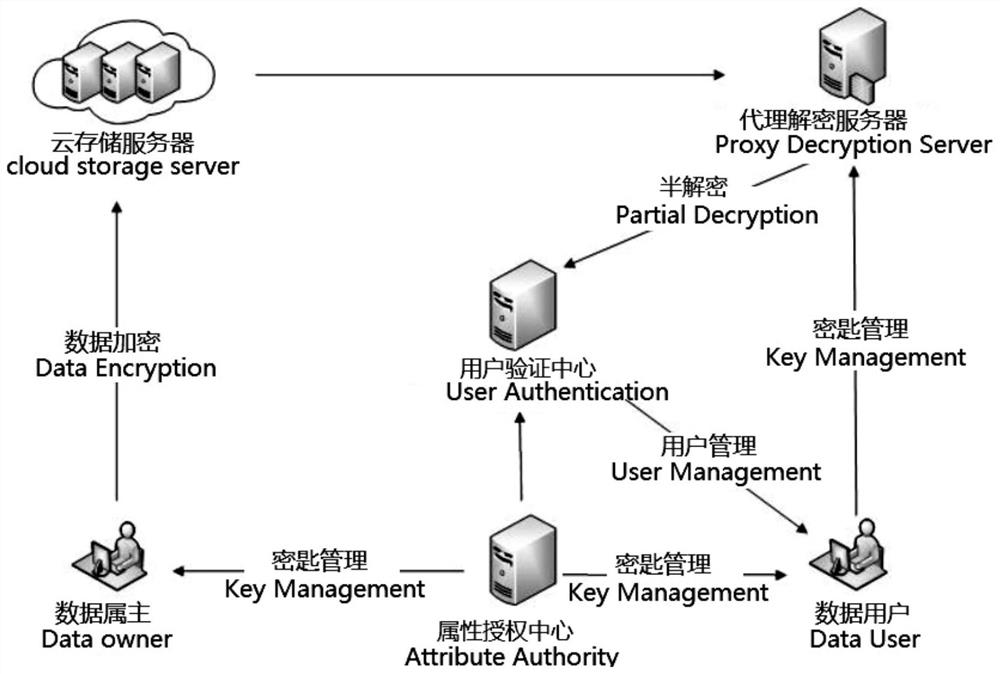
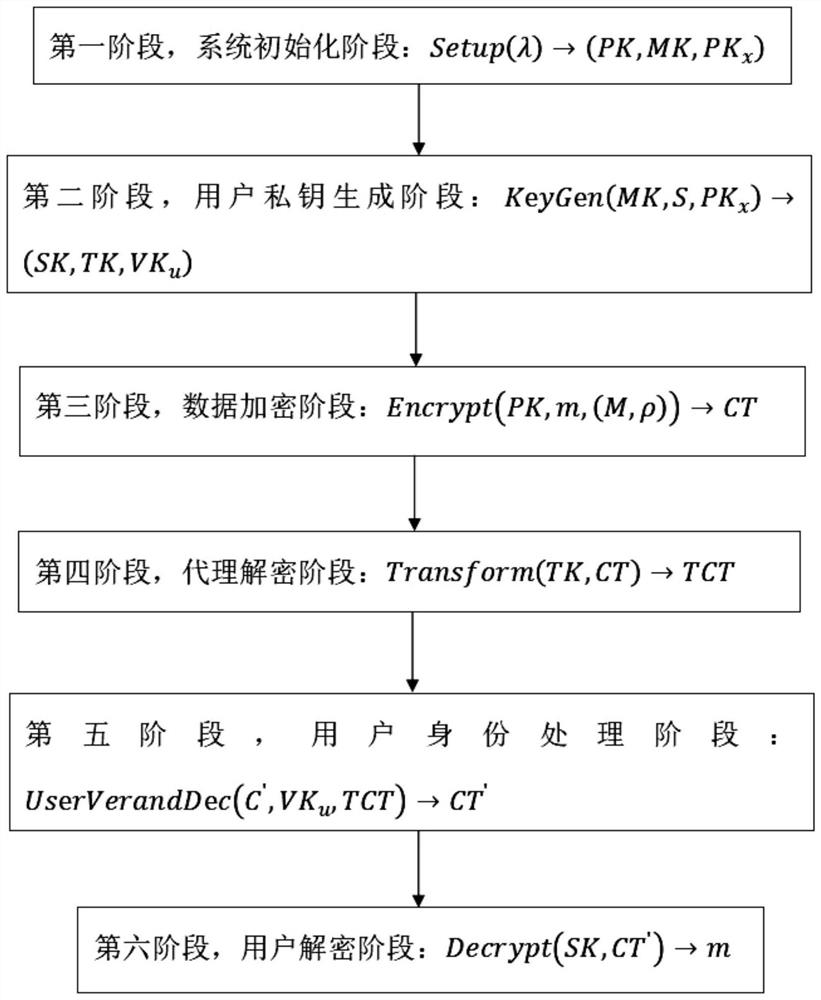
Power data privacy protection system, implementation method thereof and encryption attribute revocation method
PendingCN114244501APrivacy protectionAvoid malicious accessKey distribution for secure communicationUser verificationServer agent
The invention relates to a power data privacy protection system, an implementation method thereof and an encryption attribute revocation method. The power data privacy protection system comprises six entities: an attribute authorization center, a power data owner, a power data user, a cloud storage server, a proxy decryption server and a user verification center, and the six entities communicate with one another through the Internet; an attribute encryption technology is introduced, a private key revocation scheme is given, the fine-grained decryption permission of a user is realized through an attribute-based encryption mode, whether the user has the decryption permission or not is judged through user attributes, and the privacy of the electricity user is protected. The method is used for protecting user privacy data and preventing malicious access.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH +2
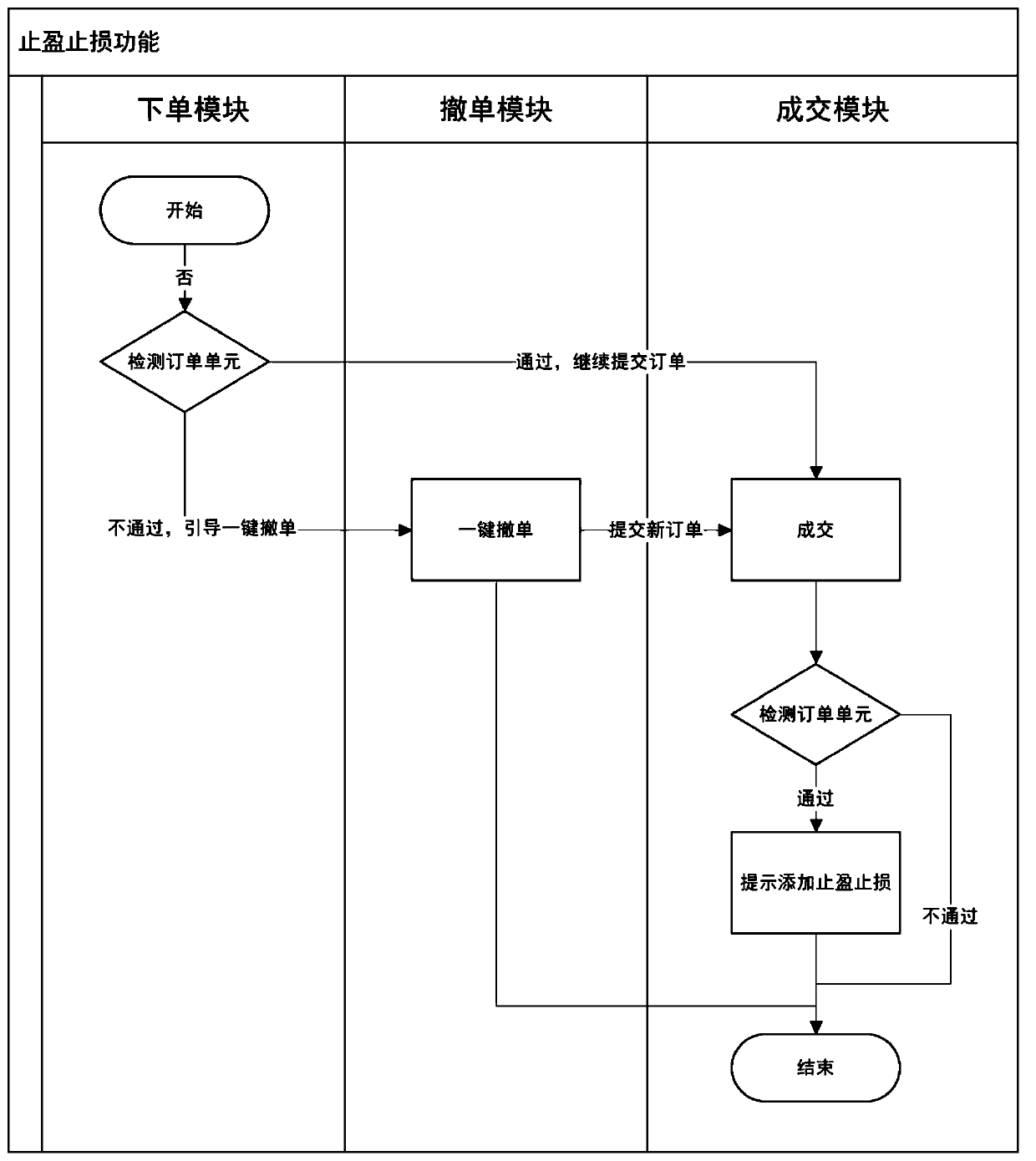
Interference and loss stopping delegation and position holding strong binding method and system
ActiveCN111476665AReduce investment lossAvoid misuseFinanceManufacturing computing systemsInformatizationStrong binding
The invention provides an interference and loss stopping delegation and position holding strong binding method and system. The method comprises the steps of: carrying out first order detection for theorder elements of a delegation order, continuing to submit the delegation order if the delegation order passes detection, otherwise, carrying out the operation guidance of one-key order withdrawal; triggering a one-key revocation function key by sending out a prompt message, immediately revoking position binding of the delegation order after one-key revocation is triggered, and meanwhile, sendingout a new delegation order and setting position binding; and determining the transaction of the delegation order, performing second order detection on the delegation order, if the position binding ofthe delegation order does not belong to the strong binding relationship, prompting to add interference and loss stopping settings, and otherwise, stopping the transaction if the delegation order doesnot pass detection. Synchronous one-key operation is realized for operations such as client delegation and unbinding by adopting an informatization means, so that misoperation of a client is avoidedto a great extent.
Owner:上海樊迪信息技术有限公司
Method for managing wireless multi-hop network key
InactiveUS8688974B2Improving security and performanceImprove performanceDigital data processing detailsPublic key for secure communicationNetwork keyKey generation
A method for managing wireless multi-hop network key is applicable to a security application protocol when a WAPI frame method (TePA, an access control method based on the ternary peer-to-peer identification) is applied in a concrete network containing a Wireless Local Area Network, a Wireless Metropolitan Area Network AN and a Wireless Personal Area Network. The key management method of the present invention includes the steps of key generation, key distribution, key storage, key modification and key revocation. The present invention solves the technical problems that the prior pre-share-key based key management method is not suitable for larger networks and the PKI-based key management method is not suitable for wireless multi-hop networks; the public-key system and the ternary structure are adopted, thereby the security and the performance of the wireless multi-hop networks are improved.
Owner:CHINA IWNCOMM
Attribute Encryption Method Based on Reversible Partial Authoritative Key Strategy Based on Multilinear Mapping
ActiveCN105162573BGuaranteed validityReduce time consumptionKey distribution for secure communicationAccess structureCiphertext
The invention discloses an attribute encryption method based on multi-linear mapping and achieving a strategy of secret key revocation in an authority separating way, which is provided for single attribute revocation of a user. The user can finish a decryption process only when a cryptograph attribute set satisfies the secret key strategy of the user. Specifically, an authority center makes subordinate authorities. Each subordinate authority commands a main secret key of its own and participates in a public parameter establishing process. An assess strategy is converted into an access structure according to a linear secret sharing algorithm. User private keys under corresponding access structures are generated. According to the attribute set and a known revocation list, information encryption is performed. Whether the user is in the revocation list is further judged. A decryption process is finished. In consideration of known private keys and users, a tracking algorithm is established to judge the relevance of users and private keys. By means of the method provided in the invention, the problem that all attributes of non-users are canceled during a single user attribute revocation process is solved. The relevance of users and private keys is verified. The scheme operation efficiency and the overall safety can be improved. The scheme is enabled to resist quantum attacks.
Owner:深圳天通信息科技有限公司
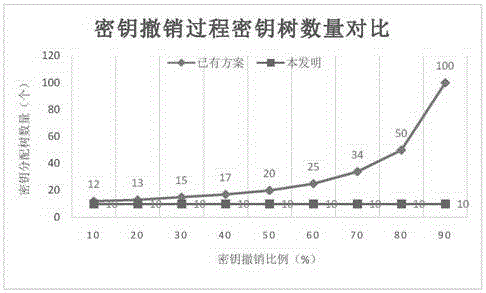
A key revocation method for key management tree in cloud database
The invention discloses a key revocation method for a key management tree in a cloud database. The method comprises the steps of correspondingly generating a key revocation management tree for an existing key management tree structure of the cloud database while the tree structure is generated; recording the revocation state of each key management tree node of the cloud database; and when a user carries out revocation operation, updating corresponding key revocation management tree state, and thus completing the revocation process. The problems of increased storage expense and management difficulty and a lot of computation expense in a re-encryption process due to the fact that the key storage expense is increased along with an increase of the revocation times when key revocation is carried out on the key management tree in an existing cloud database are solved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
MLDP-oriented multi-party access control method and system based on SGX
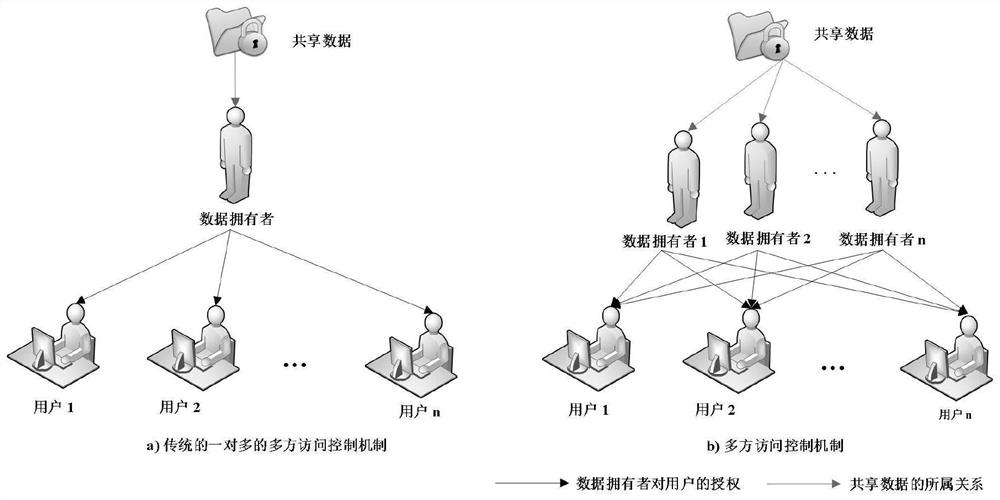
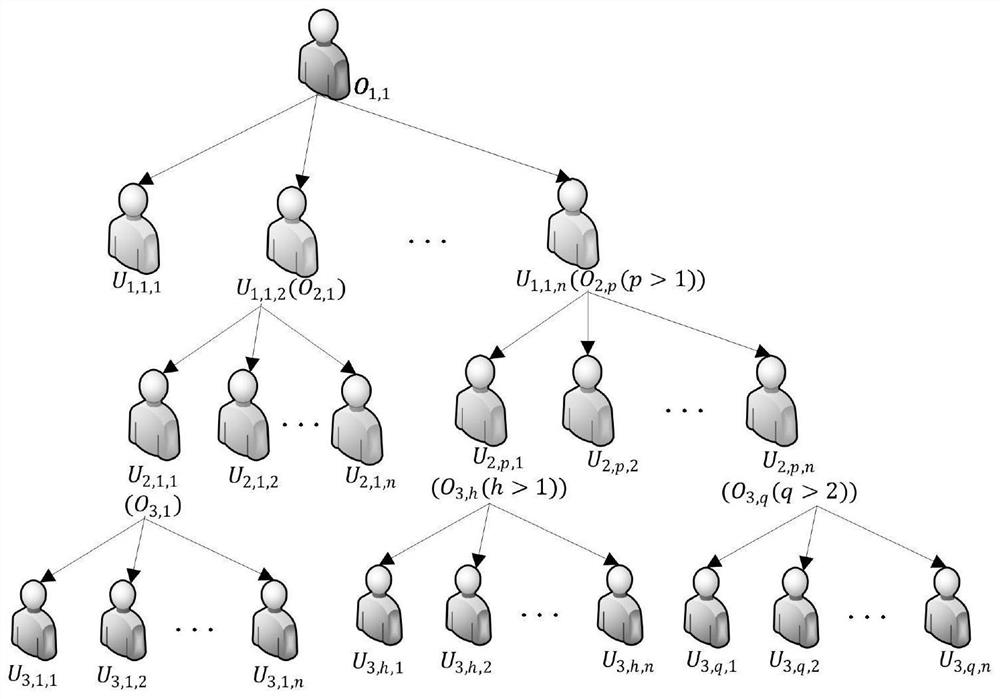
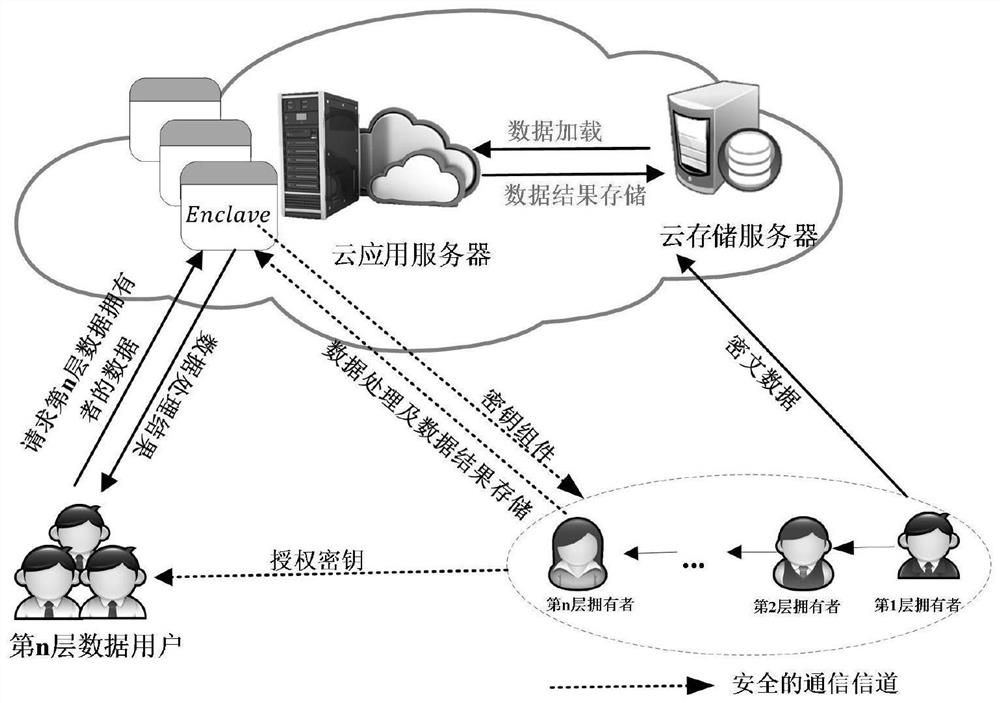
ActiveCN111695145AUndo problem solvingIncreased risk of leakageDigital data protectionProgram/content distribution protectionProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network AccessKey generation
The invention belongs to the technical field of cloud computing, and discloses an MLDP-oriented multi-party access control method and system based on SGX. A lightweight key management algorithm basedon the SGX supports multi-party access control of a data result in an MLDP scene, solves the key revocation problem of the SGX, and is responsible for encryption key generation of a data owner and authorization generation, data encryption and decryption of a user. Based on the secret key management scheme, an efficient, safe and flexible multi-party access control framework is designed, the framework is called an EMPAC framework for short, and the framework supports safe data processing and multi-party access control of data results; the invention also provides a data protection method based on the game theory, and the reward and punishment of the behaviors of the non-root data owners are performed through setting the convenience police, and all non-root data owners are driven to be executed honest according to the protocol of the EMPAC framework. According to the method, the problem that a non-root data owner privately leaks data to seek benefits is finally solved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com