Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
658 results about "Tree node" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Extensible markup language (XML) server pages having custom document object model (DOM) tags
InactiveUS6981212B1Improve performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsWebsite content managementComponent Object ModelExtensible markup
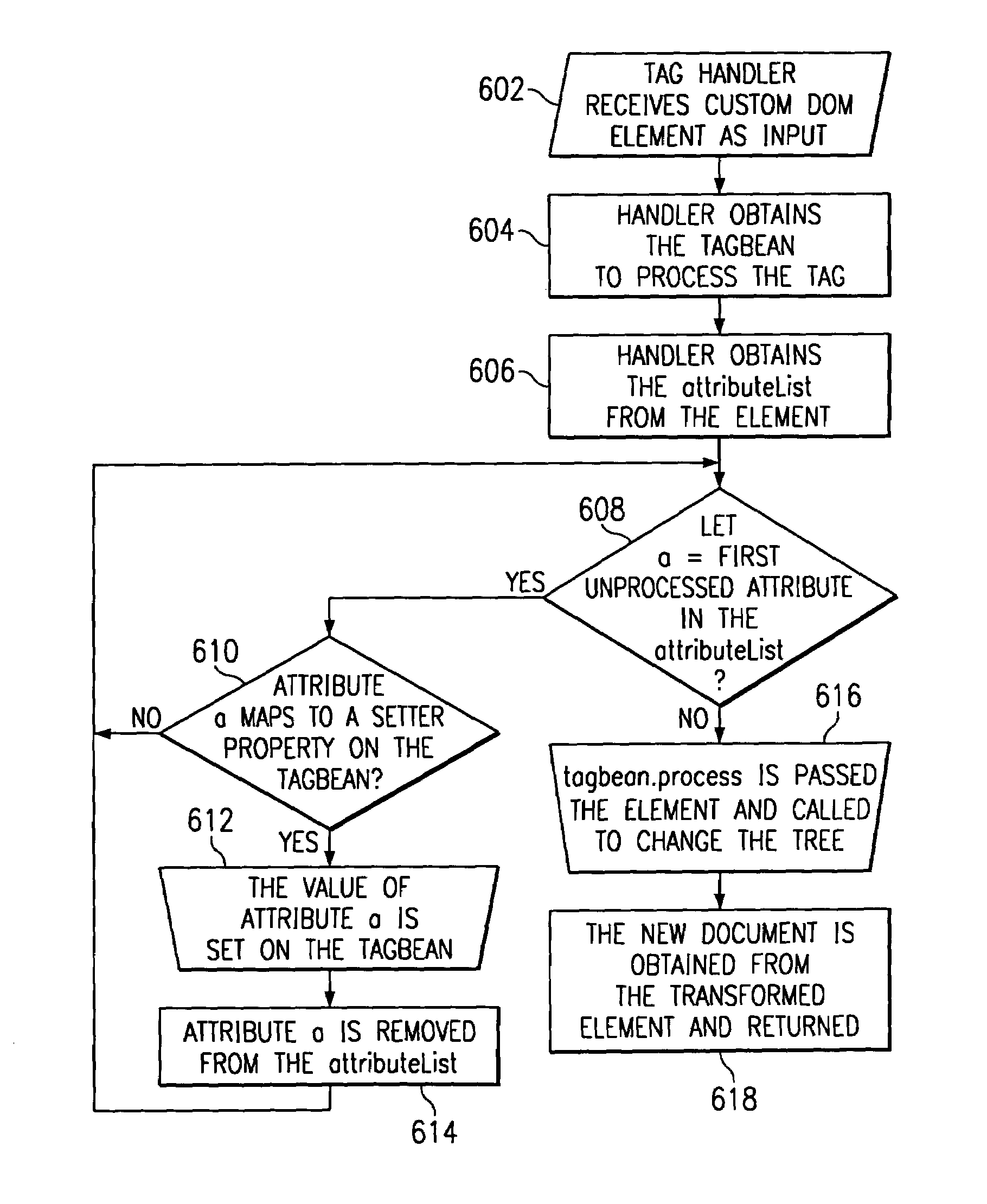
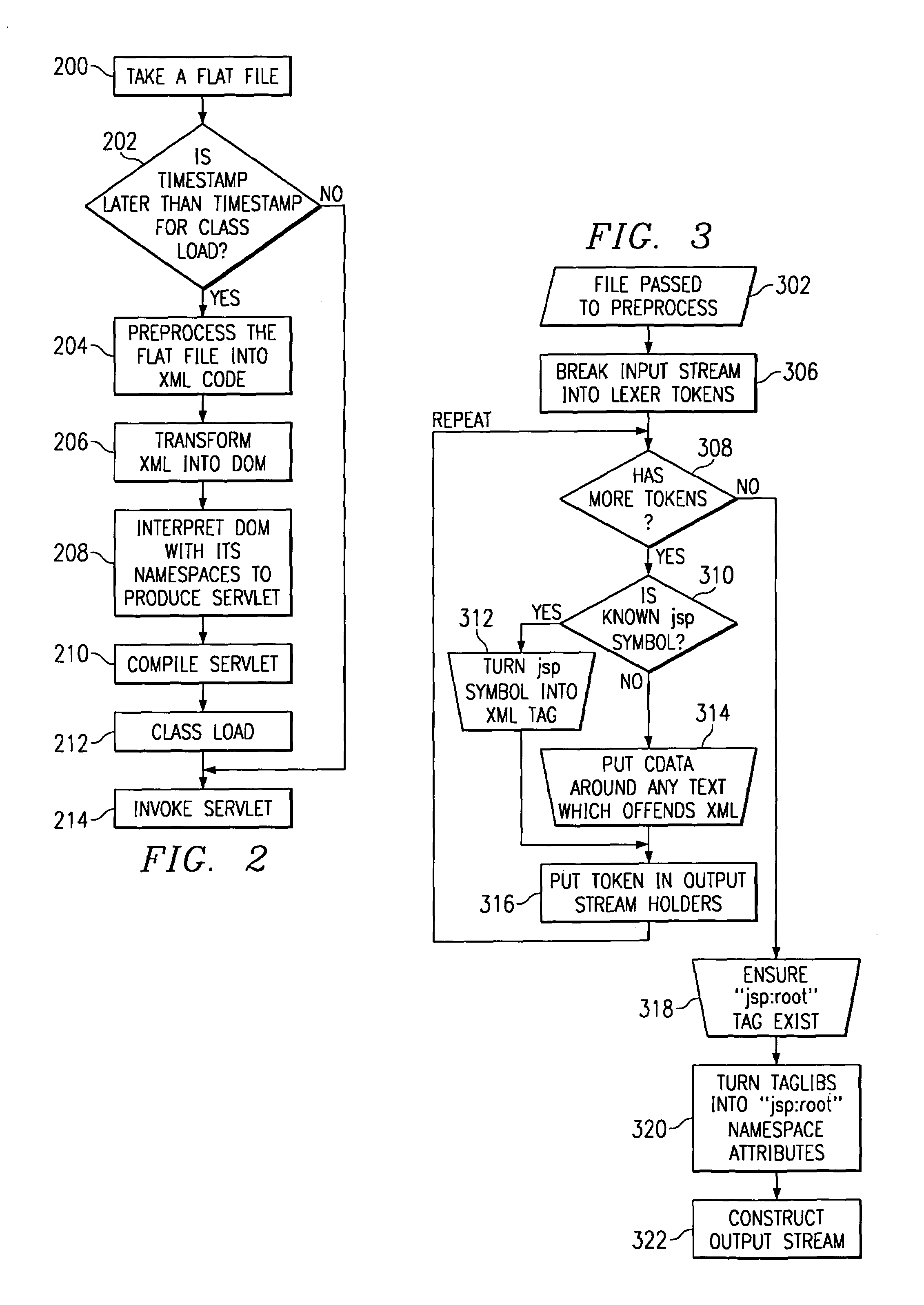
A method for serving a web page uses eXtensible Markup Language (XML) server pages. The first time a page is accessed, a given flat file is parsed into an XML Document Object Model (DOM), and required tag libraries are loaded. The DOM tree is then traversed, preferably in a depth-first, inside-out manner to locate custom tags. Upon locating a custom tag, if the tag is registered as a Java object, the object is loaded. A process method is then called on the object, passing the custom tag's tree node. The Java object then examines the custom tag and replaces it with an object, e.g., script code. Alternatively, if the tag is registered as an XSL stylesheet, the stylesheet is loaded and passed, together with the DOM, to an XSL processor. The processor applies the template to the custom tag and replaces it with given script code. Once all custom tags are reduced to HTML and script code, the DOM is compiled into a Java servlet to service the client request.
Owner:IBM CORP
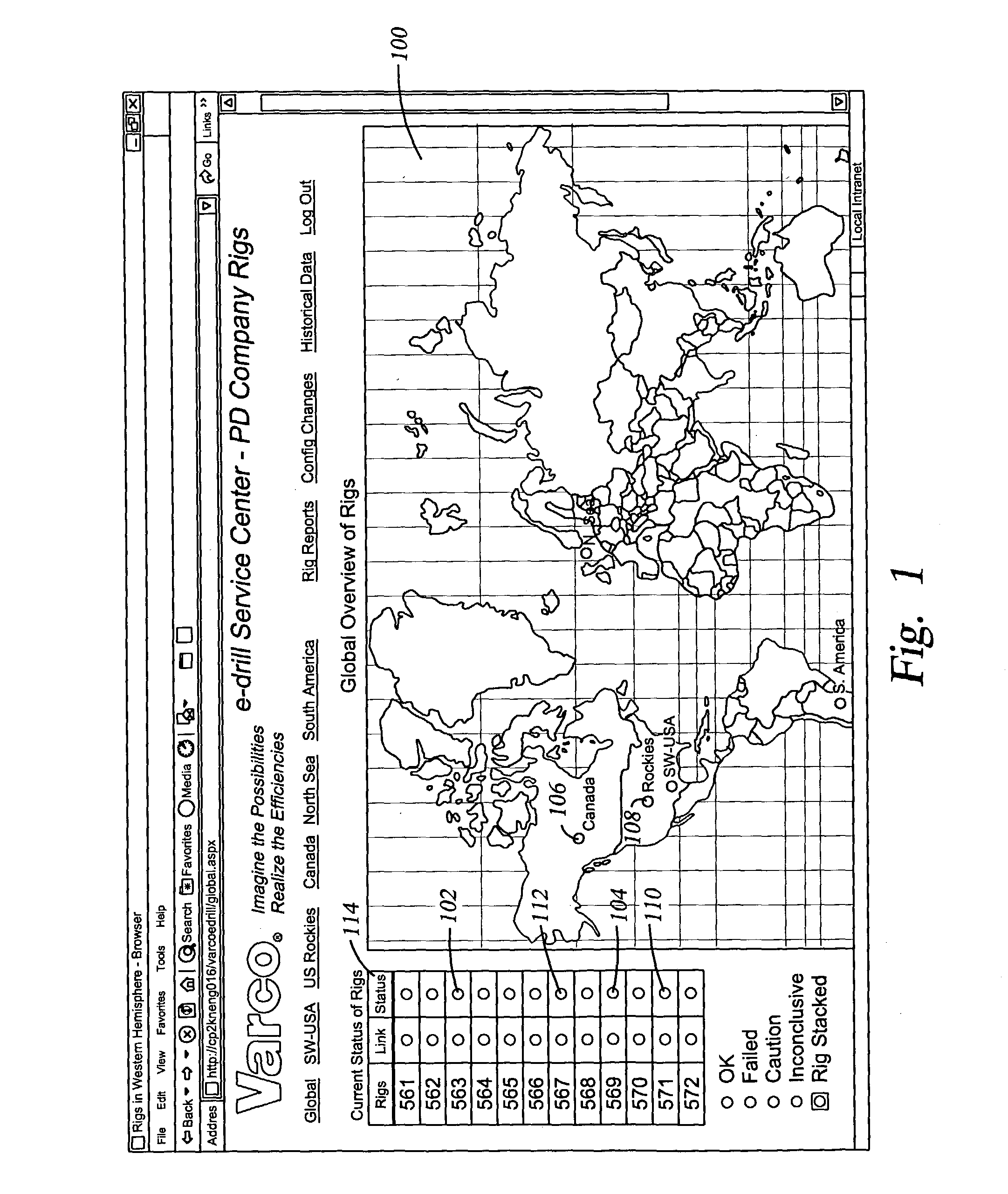
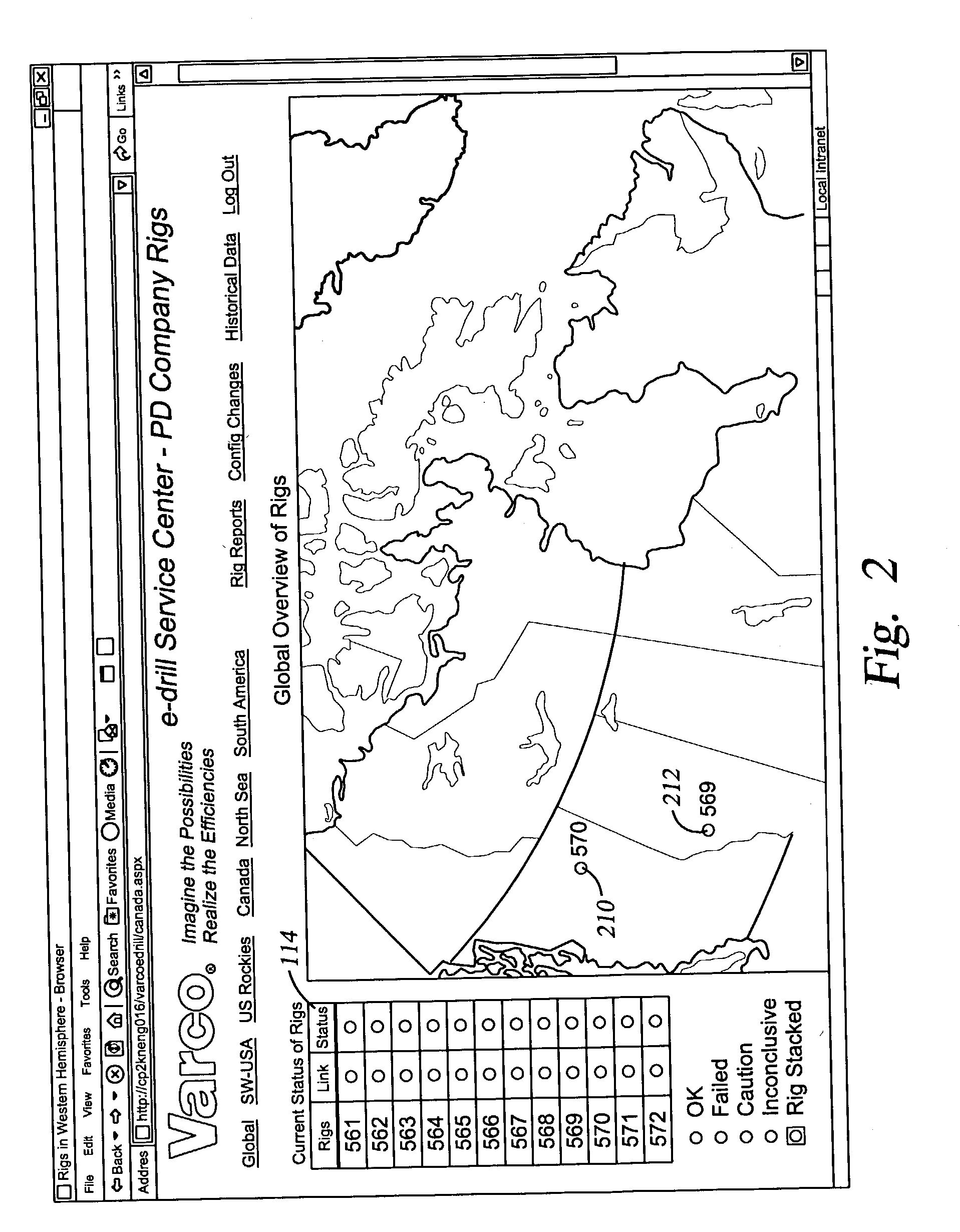
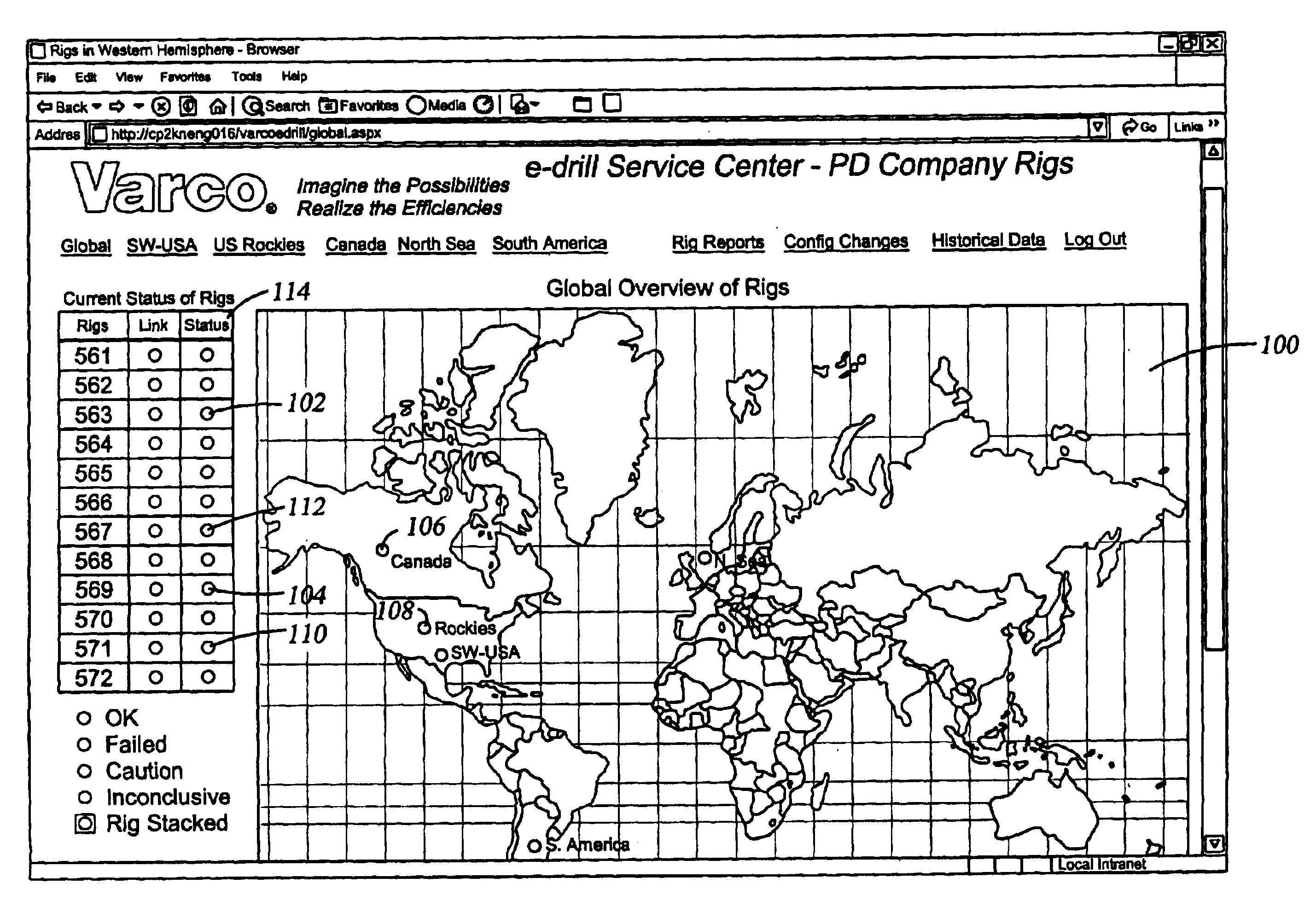
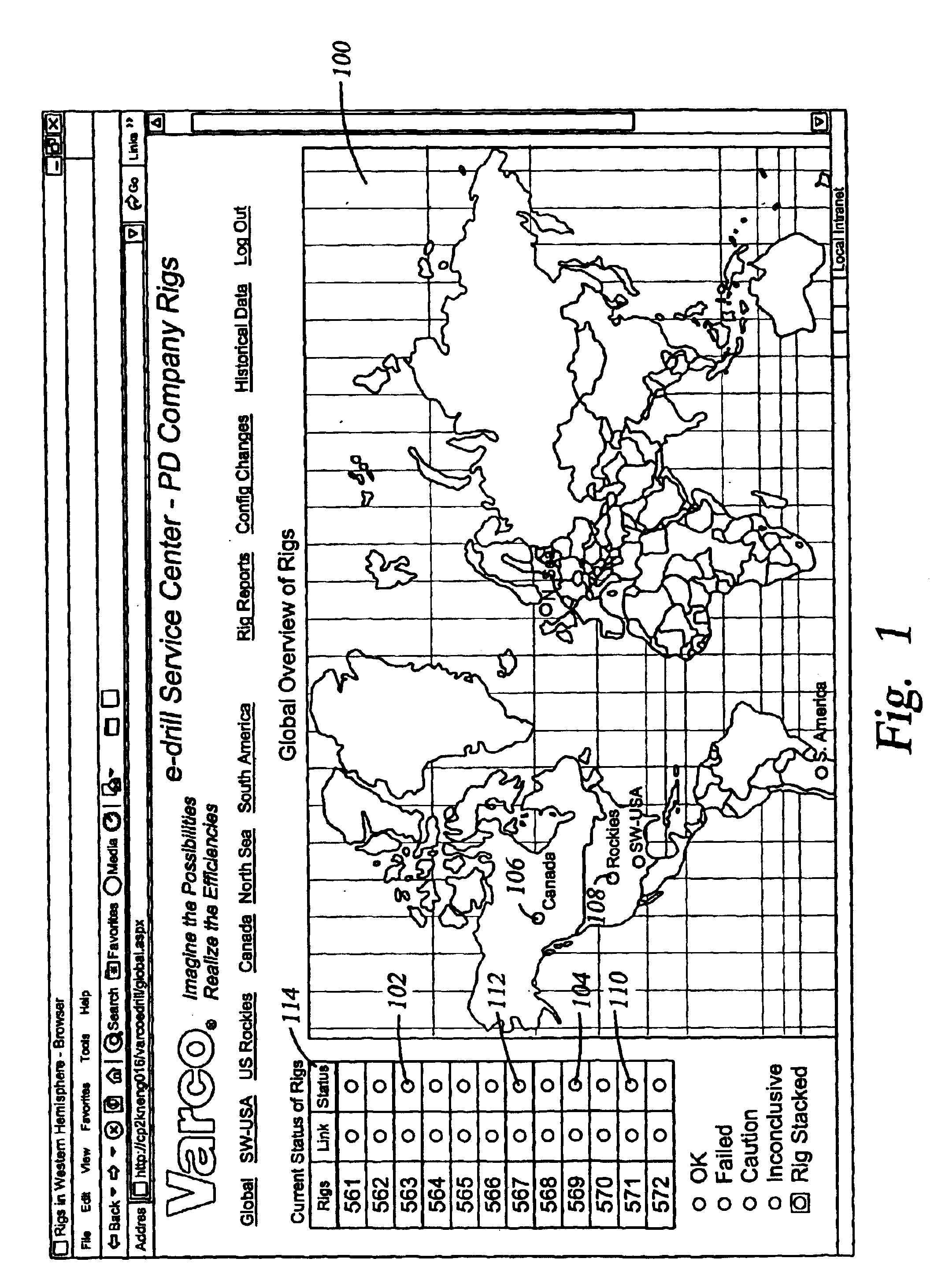
Method and apparatus for dynamic checking and reporting system health
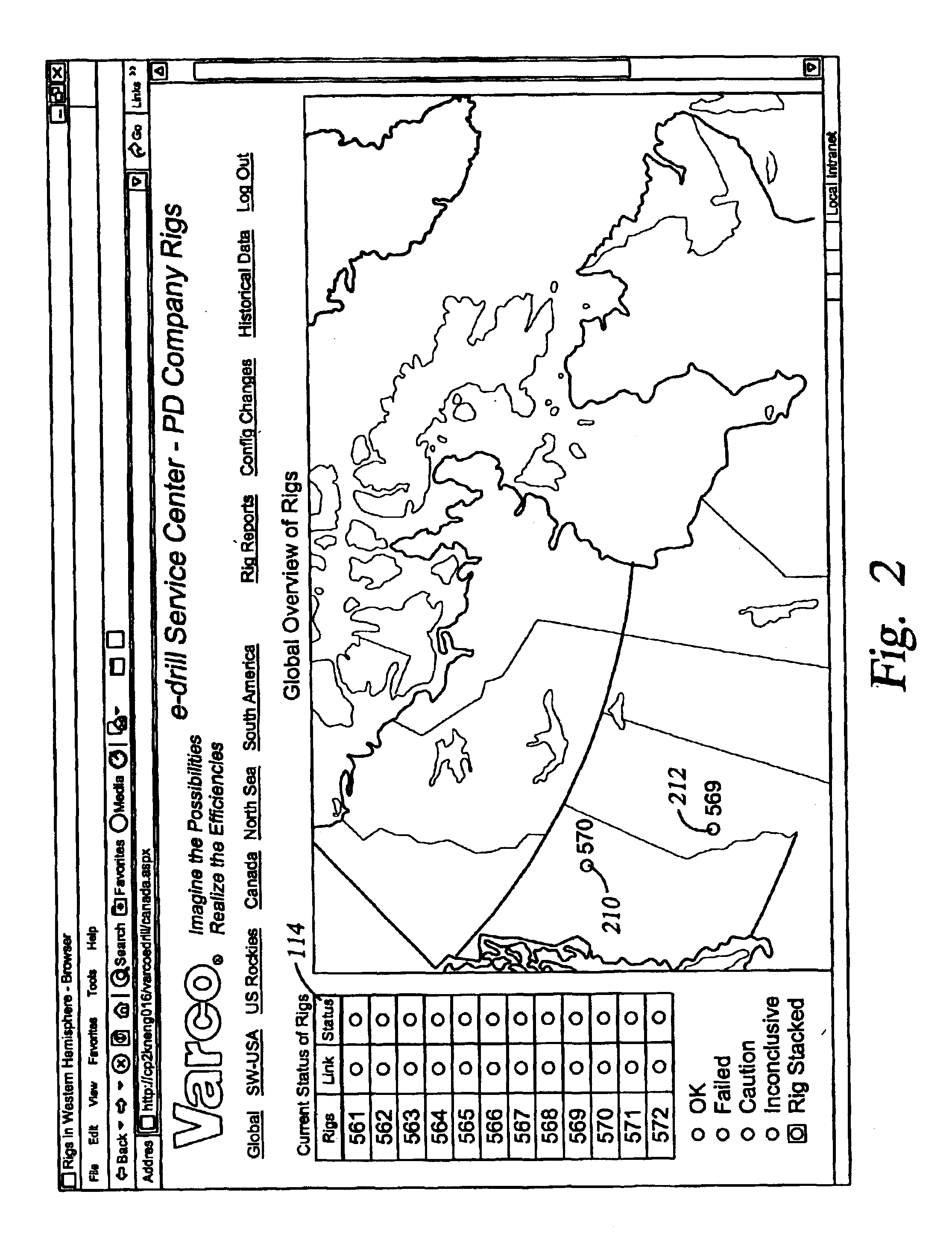
InactiveUS20040088115A1Rapid visual affirmationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingResourcesHealth checkRemote analysis
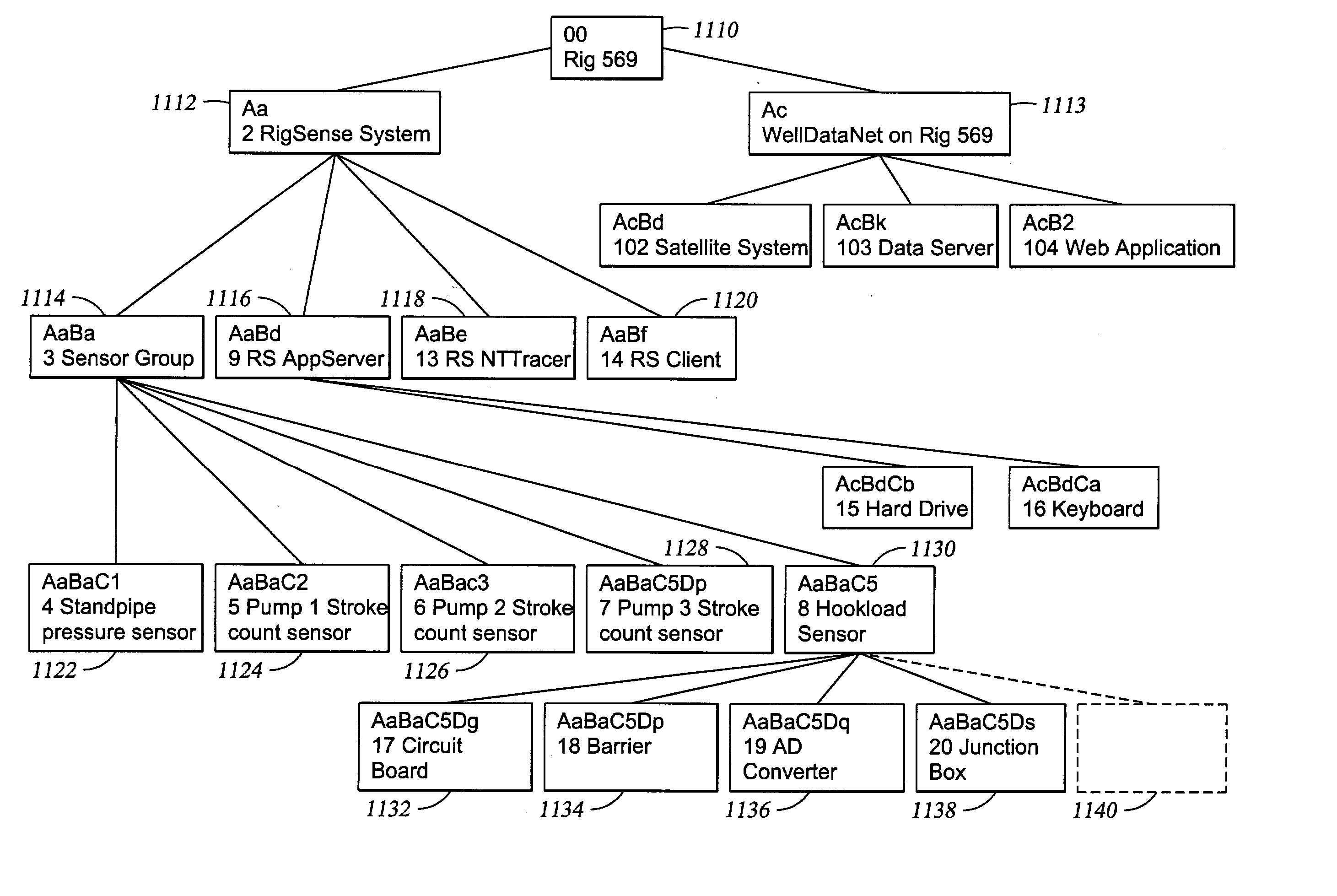
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for remotely analyzing and affirmatively notifying appropriate personnel of problems and events associated with an oil recovery system-comprising hundreds of oil rigs over a vast geographic area. The results of selected Health Checks, which are run on each oilrig, are reported to a central server. The central server populates a data base for the oil recovery system, displays a red / yellow / green color coded electronic notification and status for an entire oil recovery system and affirmatively alerts appropriate personnel of actions required to address events associated with an oilrig in an oil recovery system. The diagnostics run at each oilrig are configurable at the individual rig. The present invention provides a dynamic oilrig status reporting protocol that enables population and display of a tree node structure representing an entire oil recovery system status on a single screen at a top level. Detailed information is available by drilling down in to other screens, enabling rapid visual evaluation of a system Health Check.
Owner:VARCO I P INC
Method and apparatus for dynamic checking and reporting system health
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for remotely analyzing and affirmatively notifying appropriate personnel of problems and events associated with an oil recovery system—comprising hundreds of oil rigs over a vast geographic area. The results of selected Health Checks, which are run on each oilrig, are reported to a central server. The central server populates a data base for the oil recovery system, displays a red / yellow / green color coded electronic notification and status for an entire oil recovery system and affirmatively alerts appropriate personnel of actions required to address events associated with an oilrig in an oil recovery system. The diagnostics run at each oilrig are configurable at the individual rig. The present invention provides a dynamic oilrig status reporting protocol that enables population and display of a tree node structure representing an entire oil recovery system status on a single screen at a top level. Detailed information is available by drilling down in to other screens, enabling rapid visual evaluation of a system Health Check.
Owner:VARCO I P INC
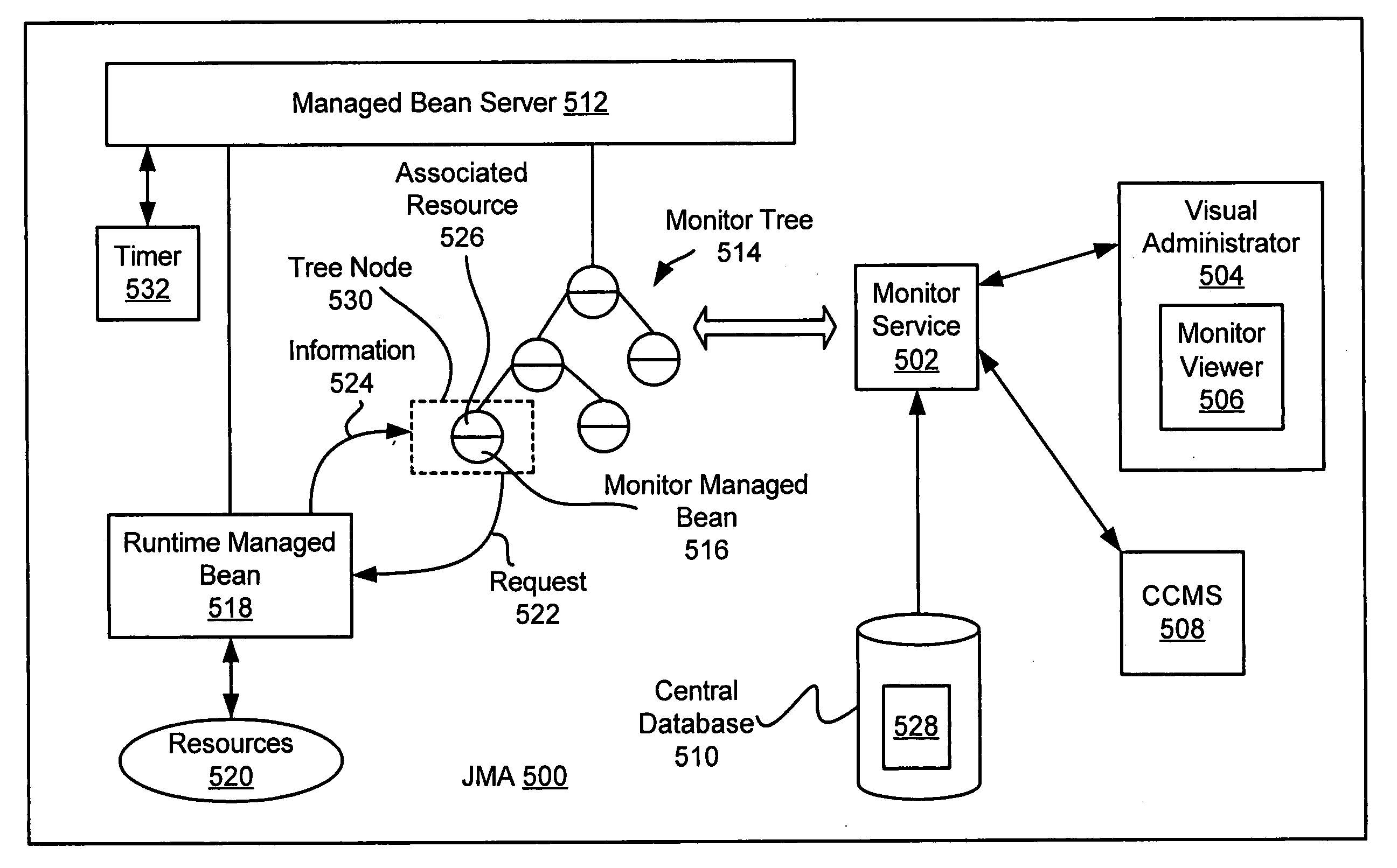
Monitor viewer for an enterprise network monitoring system
InactiveUS20050216585A1Digital computer detailsData switching networksGraphicsGraphical user interface
A method, apparatus, and system are provided for a monitor viewer in an enterprise network monitoring system. In one embodiment, upon selecting a monitor service tree node, a monitor tree (e.g., a graphical representation of one or more monitored / managed resources) is displayed in a graphical user interface. The displayed monitor tree may have one or more selectable monitor tree nodes, wherein each of the monitor tree nodes is a graphical representation of a monitored / managed resource. In an embodiment, a monitor tree node may be selected and configured in the graphical user interface.
Owner:TODOROVA TSVETELINA +2
Visual administrator for specifying service references to support a service
ActiveUS20050216860A1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlGraphicsApplication server
A method, apparatus, and system are provided for a visual administrator for specifying service references to support a service. According to one embodiment, a hierarchical tree structure having one or more tree nodes is displayed in a graphical user interface. Each of the one or more tree nodes may represent a resource of an application server. In an embodiment, at least one of the tree nodes represents a service of the application server. The tree node representing the service may be selected via a cursor control device. In one embodiment, upon selecting the tree node, a list of one or more service references associated with the service is displayed in the graphical user interface. Each listed service reference may include, for example, a server reference name, a service reference type, and / or a relationship value. In one embodiment, the relationship value specifies whether the listed service reference is to be automatically started when the service represented by the selected tree node is started.
Owner:SAP AG
Large-scale data processing system, method, and non-transitory tangible machine-readable medium thereof
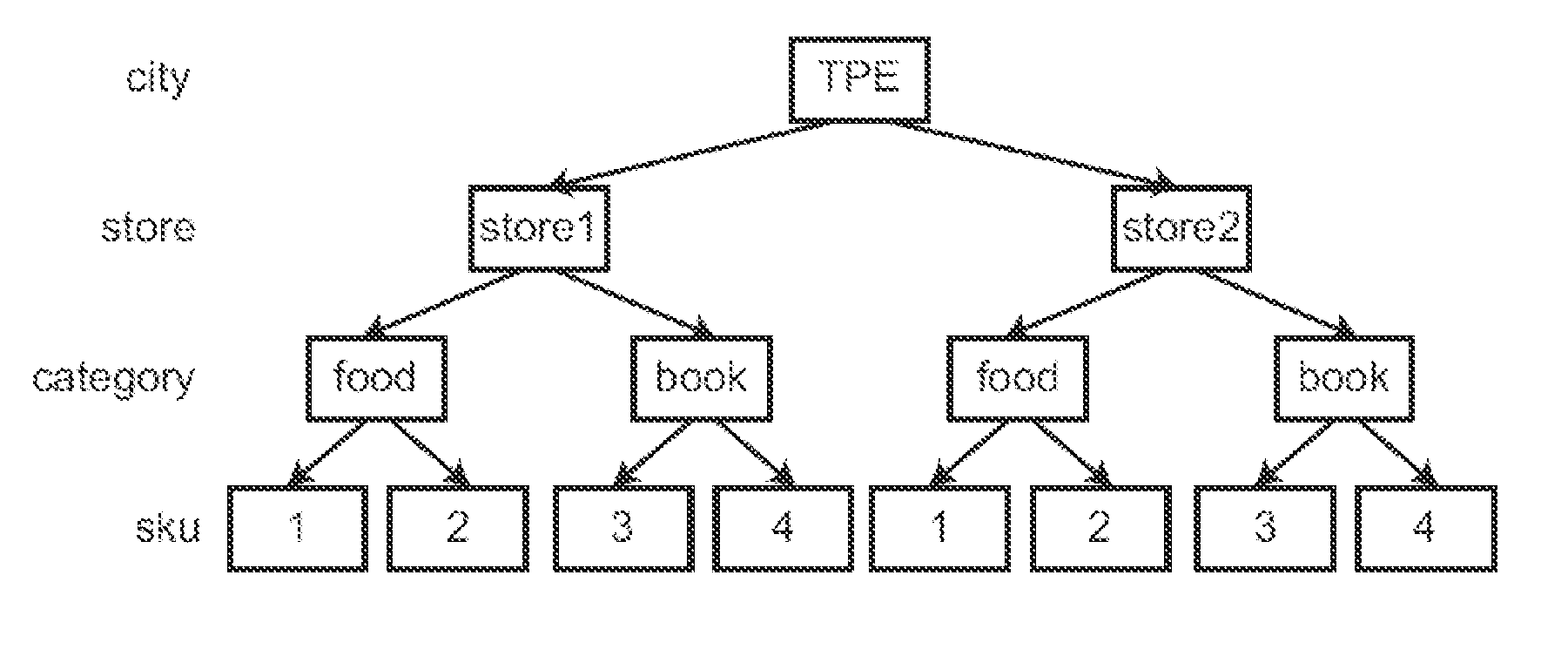
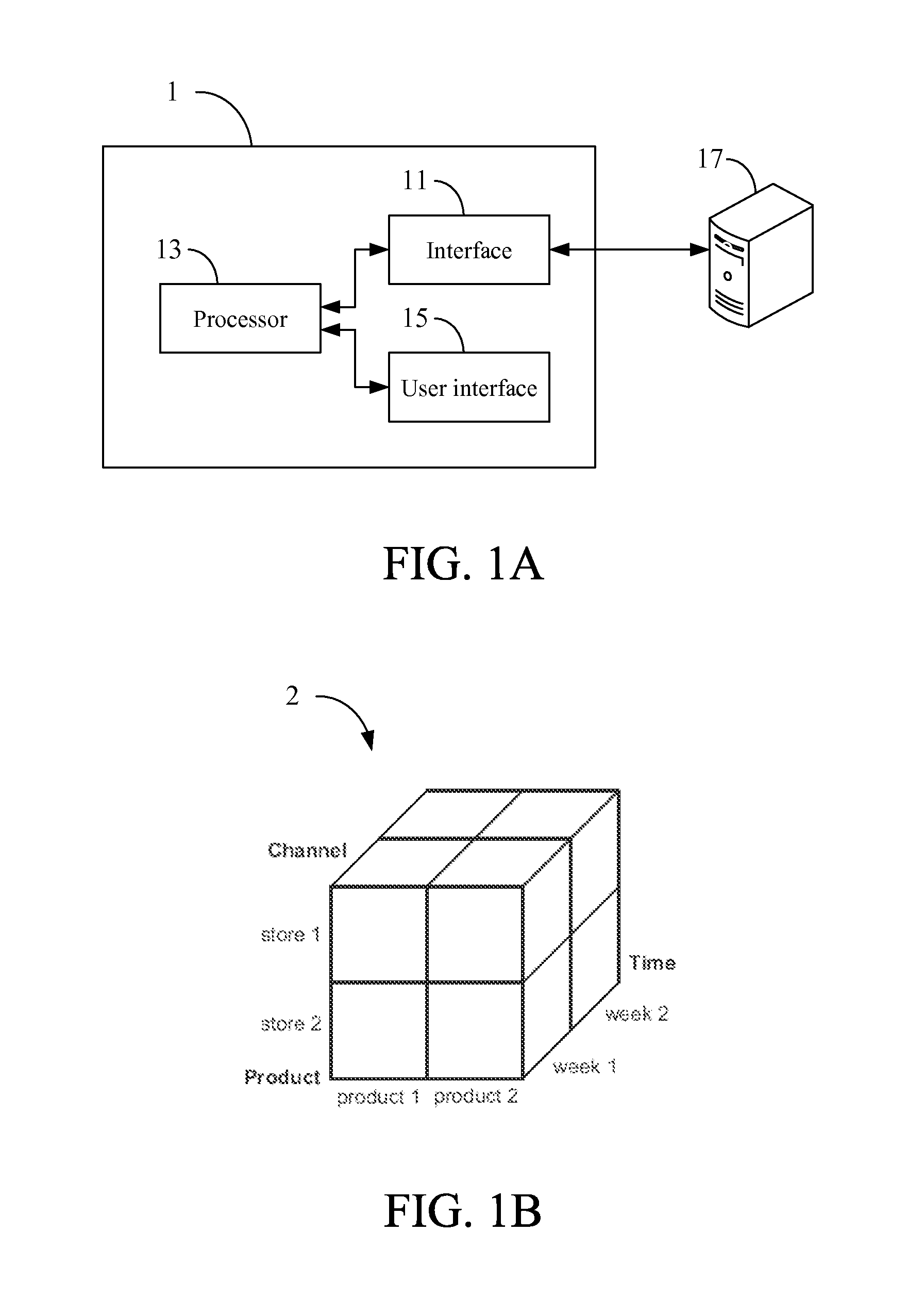
ActiveUS20130238664A1Easy to calculateEasily manipulatedDigital data processing detailsMulti-dimensional databasesLevel orderTree (data structure)
A large-scale data processing system, a large-scale data processing method, and a non-transitory tangible machine-readable medium are provided. The large-scale data processing system comprises an interface and a processor. The interface accesses a multi-dimensional data model, wherein the multi-dimensional data model comprises a plurality of dimensions, the dimensions form a multi-dimensional space of measures, each dimension is a single space comprising a plurality of members with a common set of attributes, and each measure is a data element organized and accessible through the multi-dimensional space of the cross-product of all dimensions. The processor builds at least one Tree Object (TO), wherein the TO is derived by converting the multi-dimensional data model into an N-level tree data structure according to a level order of N attributes, each tree node in the TO meets all conditions of attributes for all ancestor nodes, and N is a positive integer.
Owner:BIGOBJECT
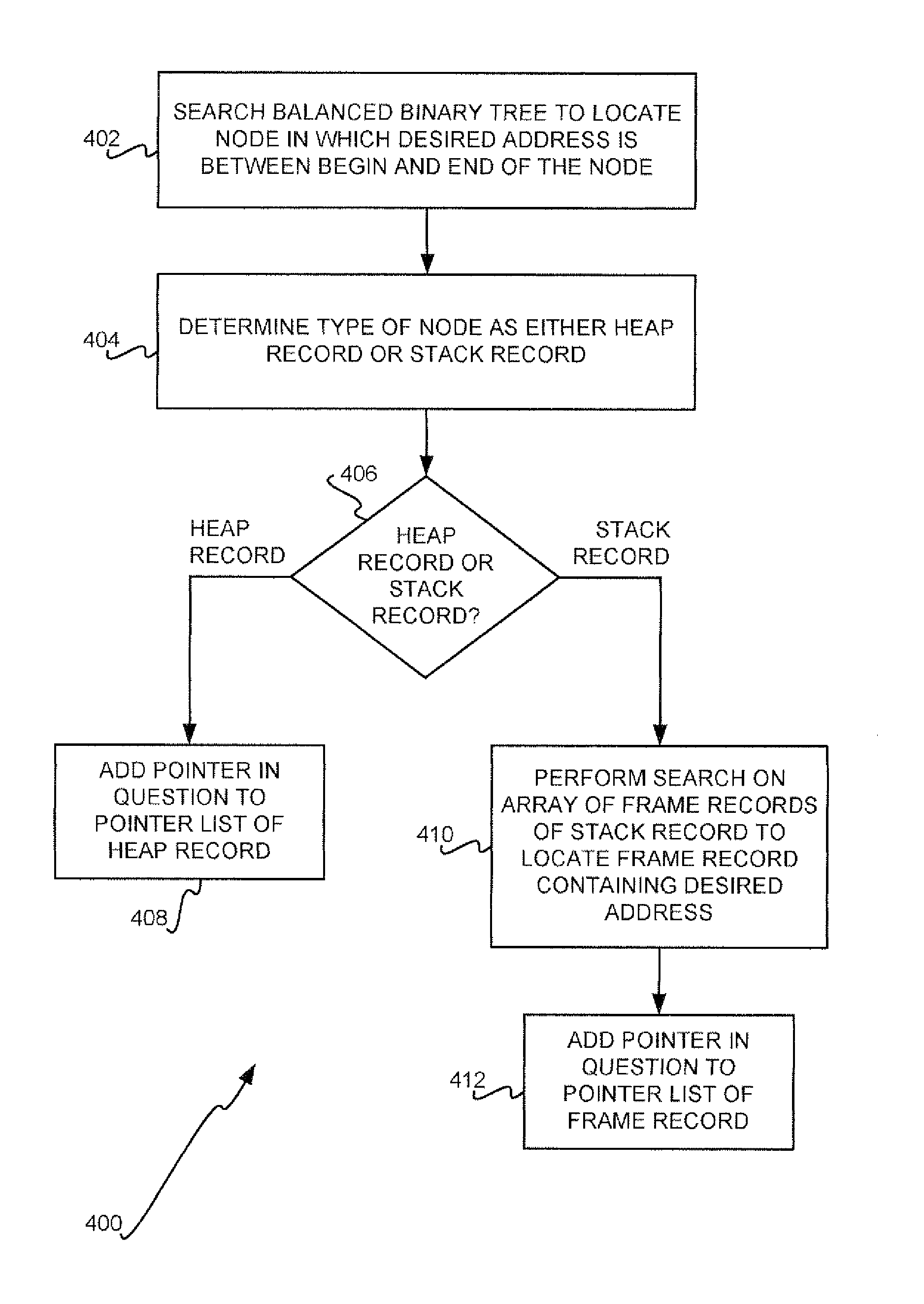
Detecting Dangling Pointers and Memory Leaks Within Software
InactiveUS20080301646A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsParallel computingBinary tree
Dangling pointers and memory leak locations within software are detected. As the software allocates and deallocates memory, lists of pointers referencing the memory, and pointer status, are maintained. As the software writes new addresses within pointers and reads addresses referenced by the pointers, the pointer lists are maintained to determine whether the pointers are dangling and to detect memory leak locations. A balanced binary tree having a number of nodes can be maintained. The nodes represent heap or stack records. Each heap record corresponds to heap memory that has been allocated and has a list of pointers referencing the heap memory. Each stack record corresponds to a stack within which a stack frame is allocated each time a function is entered. The stack record has frame records corresponding to the stack frames. Each frame record has a list of pointers referencing the corresponding stack frame.
Owner:IBM CORP
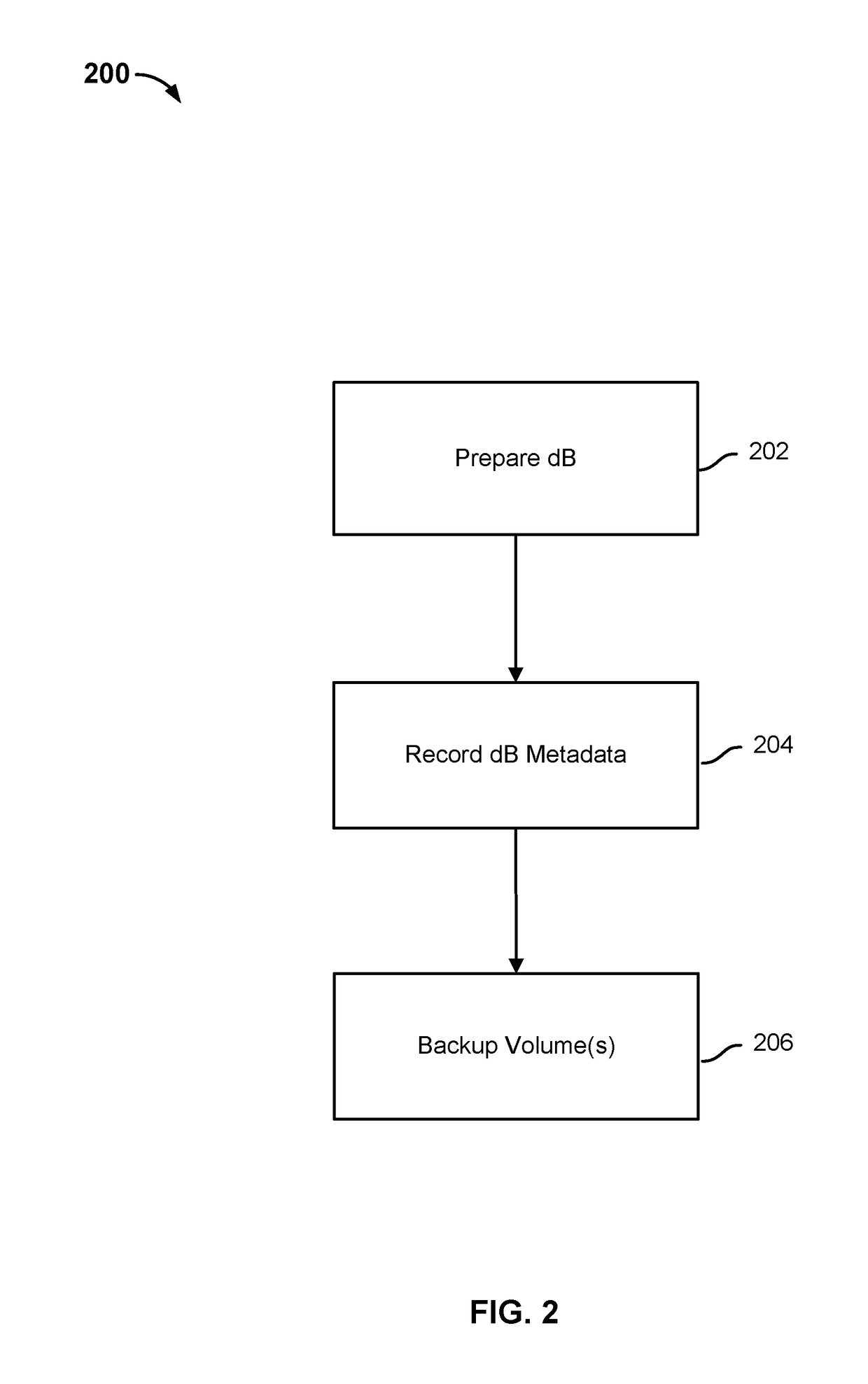
Restoring a database using a fully hydrated backup
ActiveUS20190065322A1Input/output to record carriersDatabase distribution/replicationTree rootTree (data structure)
A backup of a database is determined to be performed. A backup of at least a portion of contents of a storage volume that includes data of the database is performed. The backup includes a step of creating a new metadata tree root node. Creating the new metadata tree root node includes copying from another metadata tree root node of a tree data structure corresponding to a previous backup instance, one or more references to one or more lower tier metadata tree nodes associated with the tree data structure corresponding to the previous backup instance.
Owner:COHESITY
Method for classifying sub-trees in semi-structured documents
InactiveUS20060288275A1Easy to organizeSemi-structured data indexingSemi-structured data queryingDocument structuringClassification methods
A method and system for classifying semi-structured documents by distinguishing sub-tree structural information as a distinct representative characteristic of a fragment of the document structure identified by a sub-tree node therein. The structural information comprises both an inner structure and an outer structure which individually can be exploited as representative data in a probabilistic classifier for classifying the sub-tree itself or the entire document. Additional representative feature data can also be independently used for classification and comprises the data content of the fragment structurally represented by the sub-tree and additionally with node attributes. The classification values independently generated from each of the different sets of features can then be combined in an assembly classifier to generate an automated classification system.
Owner:XEROX CORP
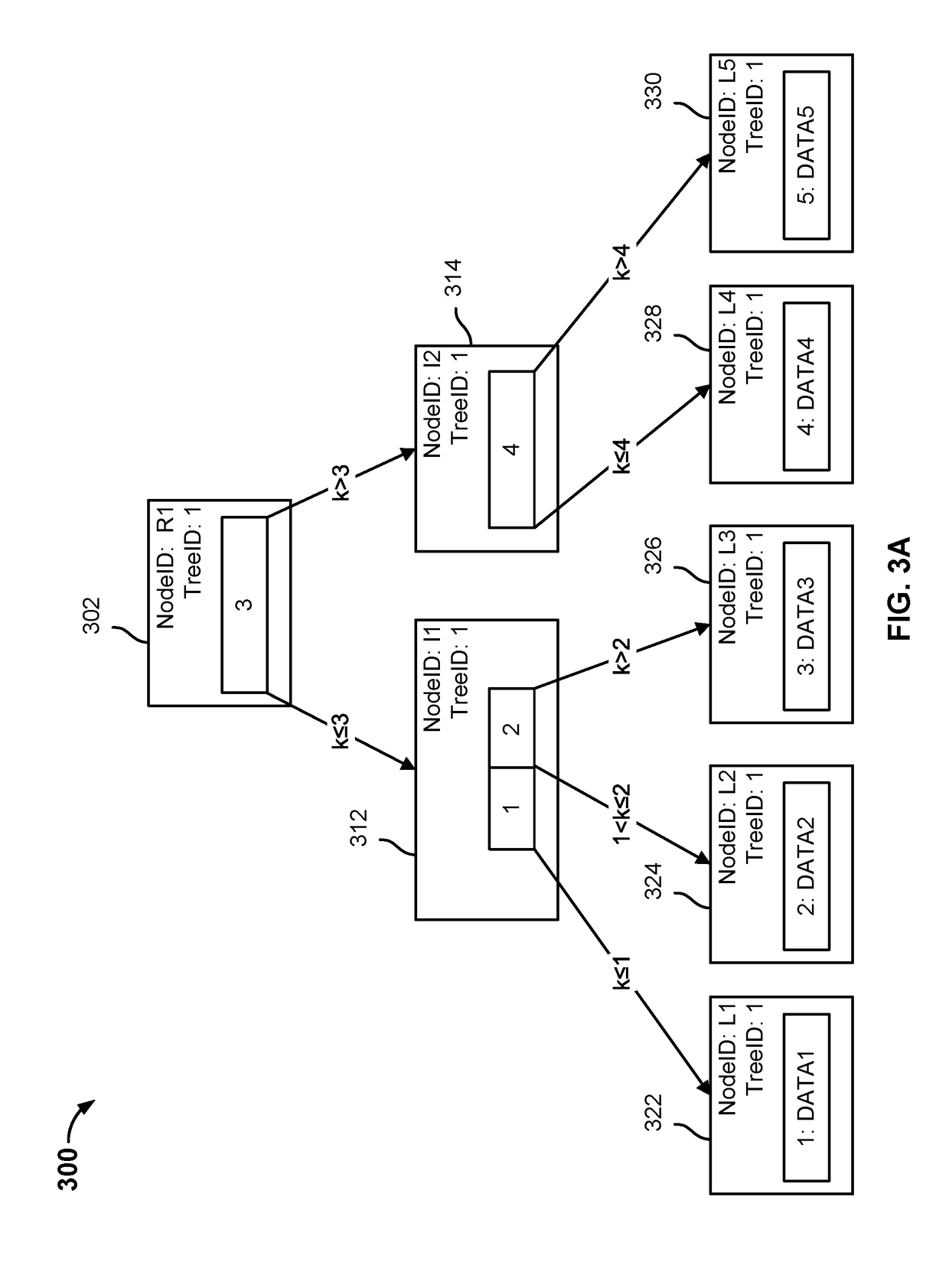
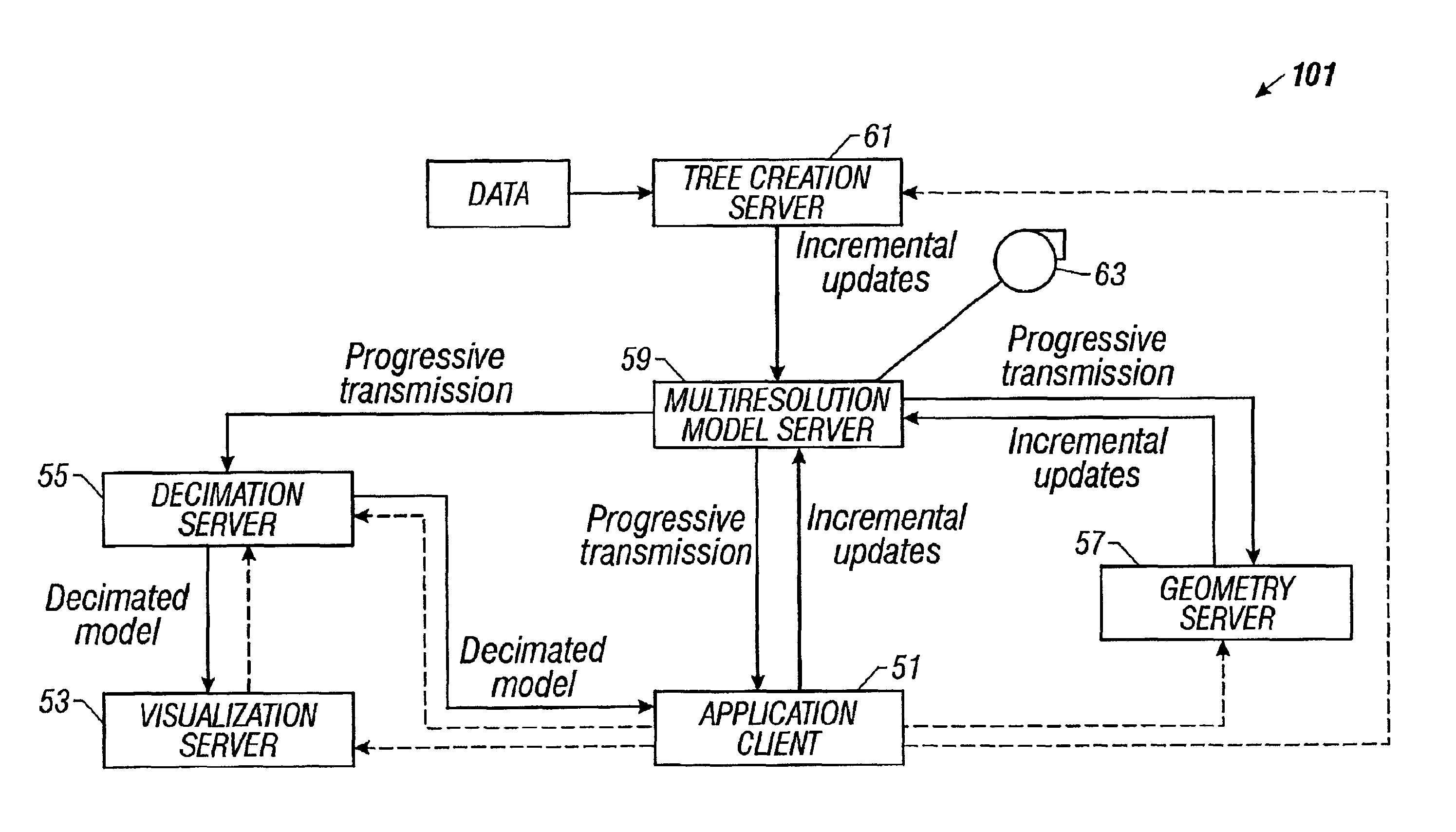
Distributed multiresolution geometry modeling system and method
InactiveUS6910001B2Computation using non-denominational number representationComplex mathematical operationsImage resolutionGeometric modeling
A distributed multiresolution modeling system has a database management system on a first server. The database management system provides access to a hierarchical tree representation of surfaces of geometric models. Client programs executing on computers connected to the first server accesses and updates the model by traversing the hierarchical tree representation until a terminating criterion has been satisfied. During the traversal the client programs request quad-tree nodes from the database management system.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
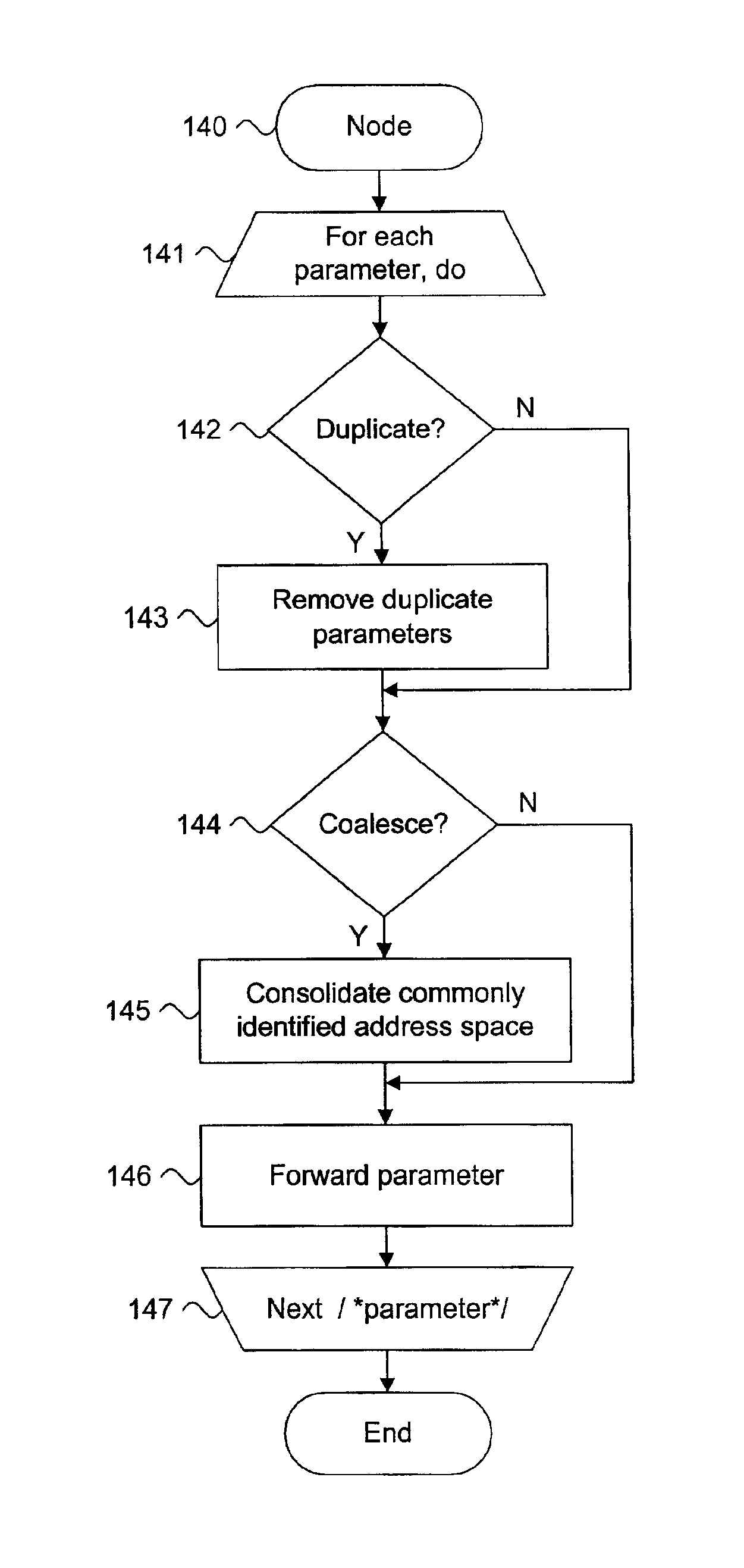
System and method for communicating coalesced rule parameters in a distributed computing environment
InactiveUS6920493B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityDistributed Computing Environment
A system and a method for communicating coalesced rule parameters in a distributed computing environment are described. A plurality of packet validation devices are communicatively interposed between network routing points within the distributed computing environment. The packet validation devices apply parameterized rules to transiting network packet traffic. A plurality of processing tree nodes are configured into a concast tree. In a lowermost layer of the concast tree, each processing tree node collects and coalesces rule parameters from at least one packet validation device. In each successive layer of the concast tree, each processing tree node collects and coalesce the rule parameters from at least one processing tree node in a next lower layer of the concast tree. A control center assembles the coalesced rule parameters from each packet validation device in an uppermost layer of the concast tree. The coalesced rule parameters are forwarded from the control center to each packet validation device along a dissemination path.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
Webpage loading method based on layout zoning
ActiveCN102915375AImprove satisfactionReduce waiting timeTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsComputer graphics (images)Layout manager
The invention provides a webpage loading method based on layout zoning, belonging to the technical field of browsers. The webpage loading method comprises the following steps that: a client sends a request to a server; the client establishes TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) connection together with the server and obtains an HTML (Hyper Text Mark-up Language) file, a CSS (Cascading Style Sheet) file and various resource files; a browser analyzes various kinds of files to respectively generate a DOM (Document Object Model) tree and a style sheet, and generates a render tree; a layout manager carries out layout on the render tree, and starts to generate render layout tree nodes; and when one render layout tree node is generated, a browser interface is drawn by using an increment drawing mode until the whole render layout tree is completely drawn. According to the method, by fully utilizing the characteristic of a small screen of a mobile device, the method of carrying out loading and layout on all webpage contents and then displaying is changed, increment drawing is carried out when one render layout tree node is generated, thus long-time interface blank caused by loading all webpages when a user opens the webpages is avoided, the waiting time is greatly reduced, and the user experience is greatly promoted.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Probabilistic boosting tree framework for learning discriminative models
A probabilistic boosting tree framework for computing two-class and multi-class discriminative models is disclosed. In the learning stage, the probabilistic boosting tree (PBT) automatically constructs a tree in which each node combines a number of weak classifiers (e.g., evidence, knowledge) into a strong classifier or conditional posterior probability. The PBT approaches the target posterior distribution by data augmentation (e.g., tree expansion) through a divide-and-conquer strategy. In the testing stage, the conditional probability is computed at each tree node based on the learned classifier which guides the probability propagation in its sub-trees. The top node of the tree therefore outputs the overall posterior probability by integrating the probabilities gathered from its sub-trees. In the training stage, a tree is recursively constructed in which each tree node is a strong classifier. The input training set is divided into two new sets, left and right ones, according to the learned classifier. Each set is then used to train the left and right sub-trees recursively.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
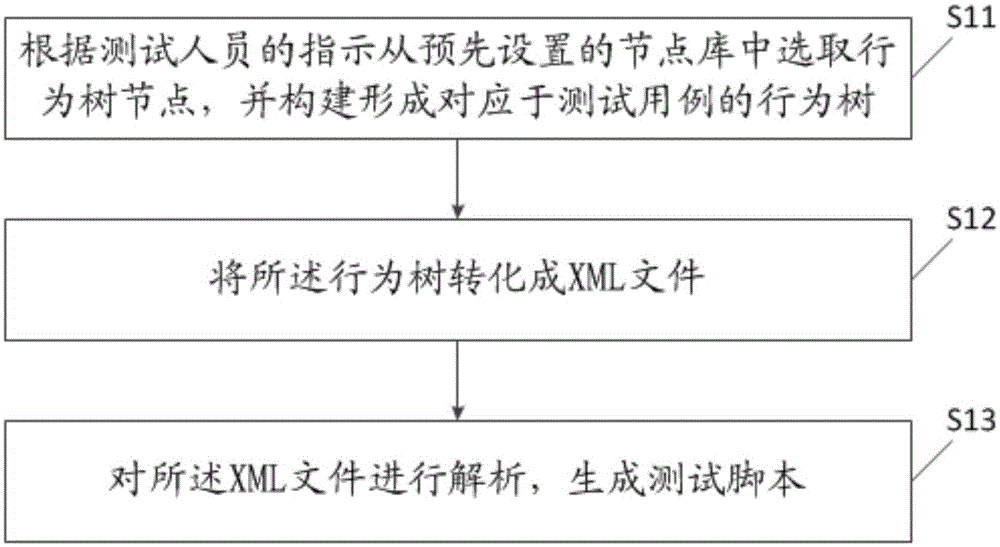
Test script generation method, test script generation device, testing method, testing device and testing system
The invention discloses a test script generation method, a test script generation device, a testing method, a testing device and a testing system. The test script generation method comprises the following steps of: selecting behaviour tree nodes from a preset node library according to instructions of testers, and constructing a behaviour tree corresponding to a test case; transforming the behaviour tree into an XML file; analyzing the XML file, and generating a test script. According to the invention, test processes may be simplified, requirements on technical capacity of the testers may be lowered, and accumulation and reuse of test codes may be facilitated.
Owner:NETEASE (HANGZHOU) NETWORK CO LTD
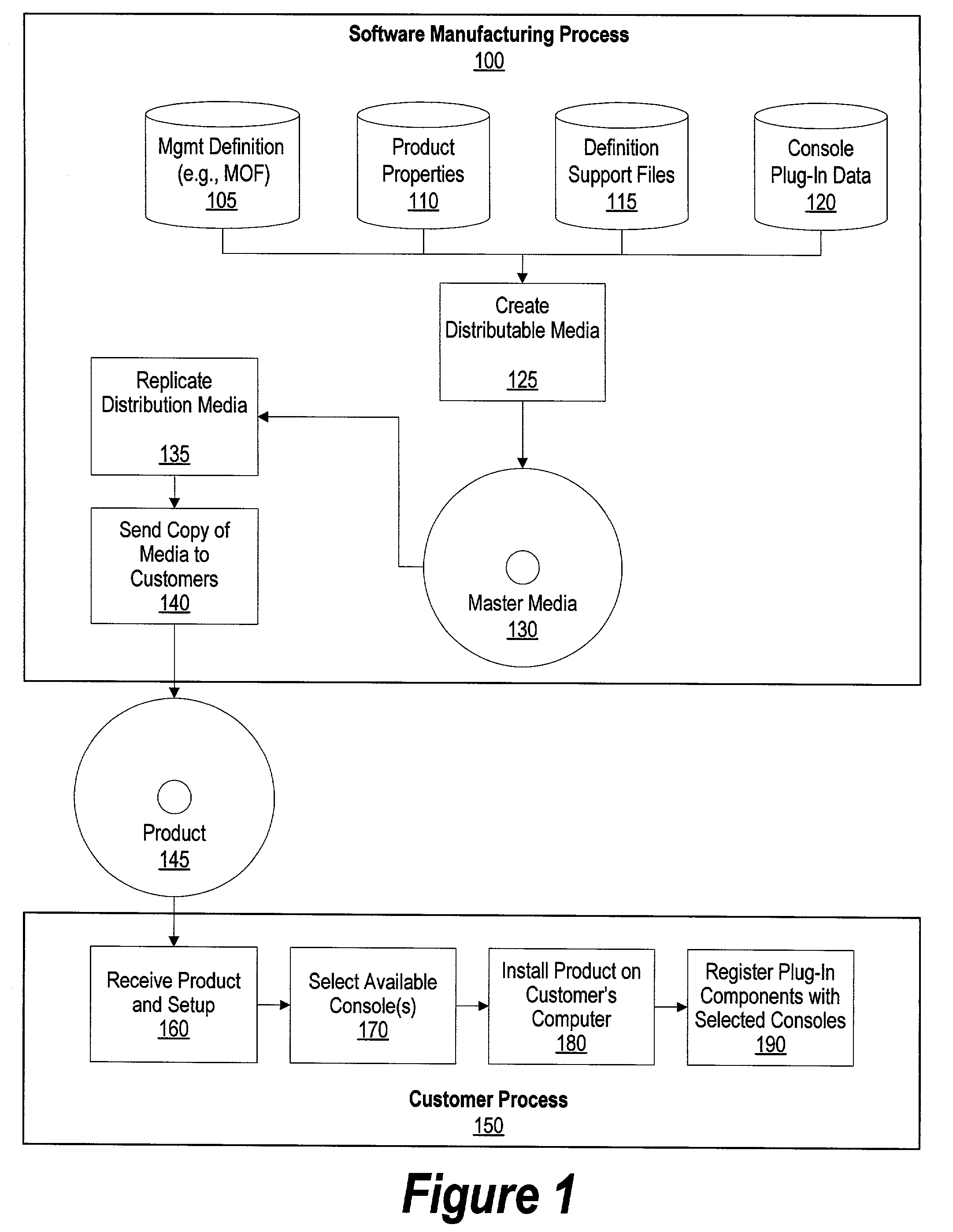
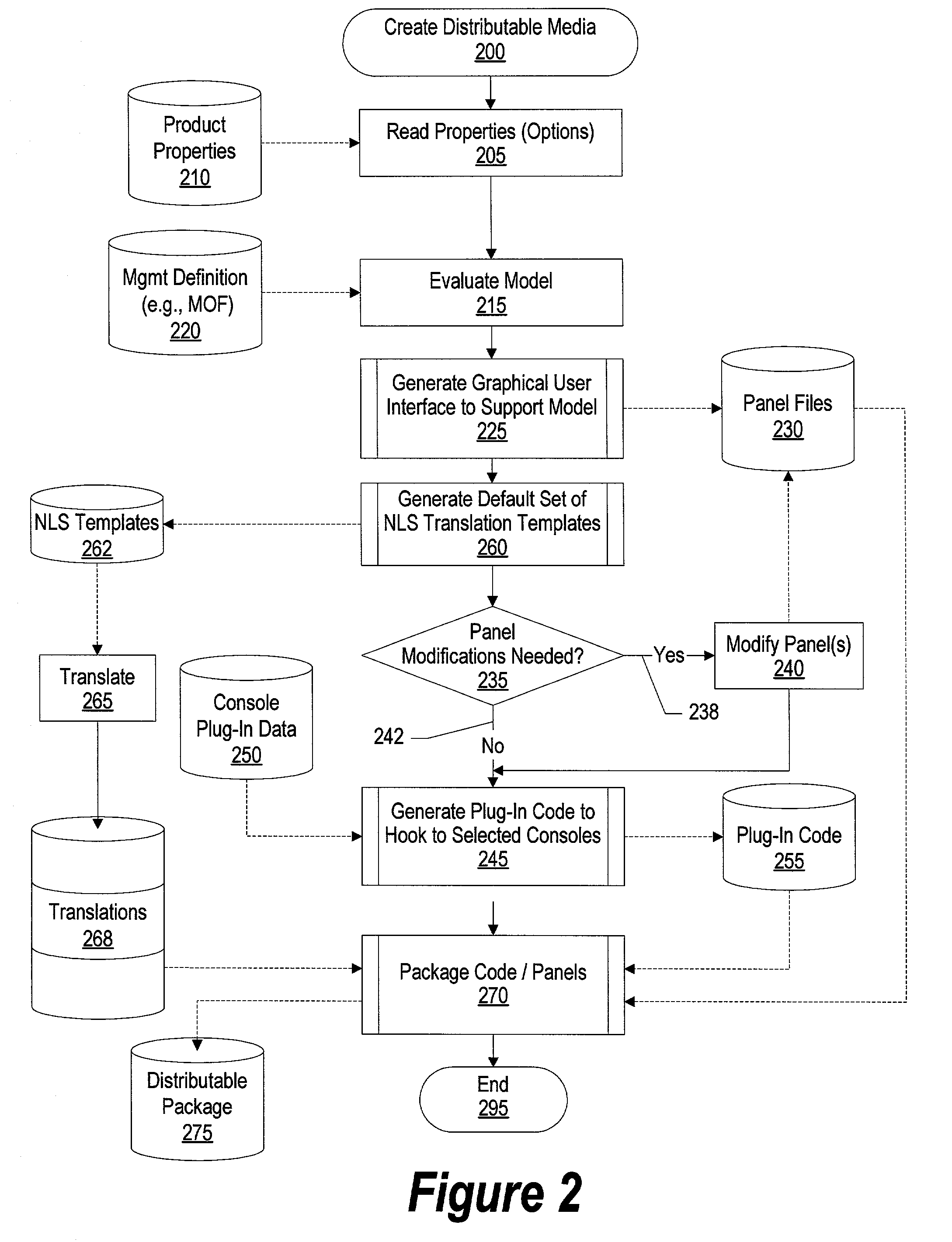
System and method for converting management models to specific console interfaces
InactiveUS7065744B2Address be challengeInterprogram communicationDigital computer detailsComputer scienceManagement model
A system and method for converting management models to specific console interfaces is provided. A plug-in builder process is used to read a management definition object. The plug-in builder process derives display information and method information from the management definition object. Console interface information is used to take the management definition object and transform it into a format suitable for the selected consoles. The management definition object information includes information used to display tree nodes in a management console. The plug-in builder process retrieves methods from the management definition object that corresponds to the displayed nodes. In this manner, when a user selects a tree node from a management console, the method included in the management definition object that was written to support the displayed node is executed. National language files can be used by the plug-in builder process in order to support various national languages used by users.
Owner:IBM CORP
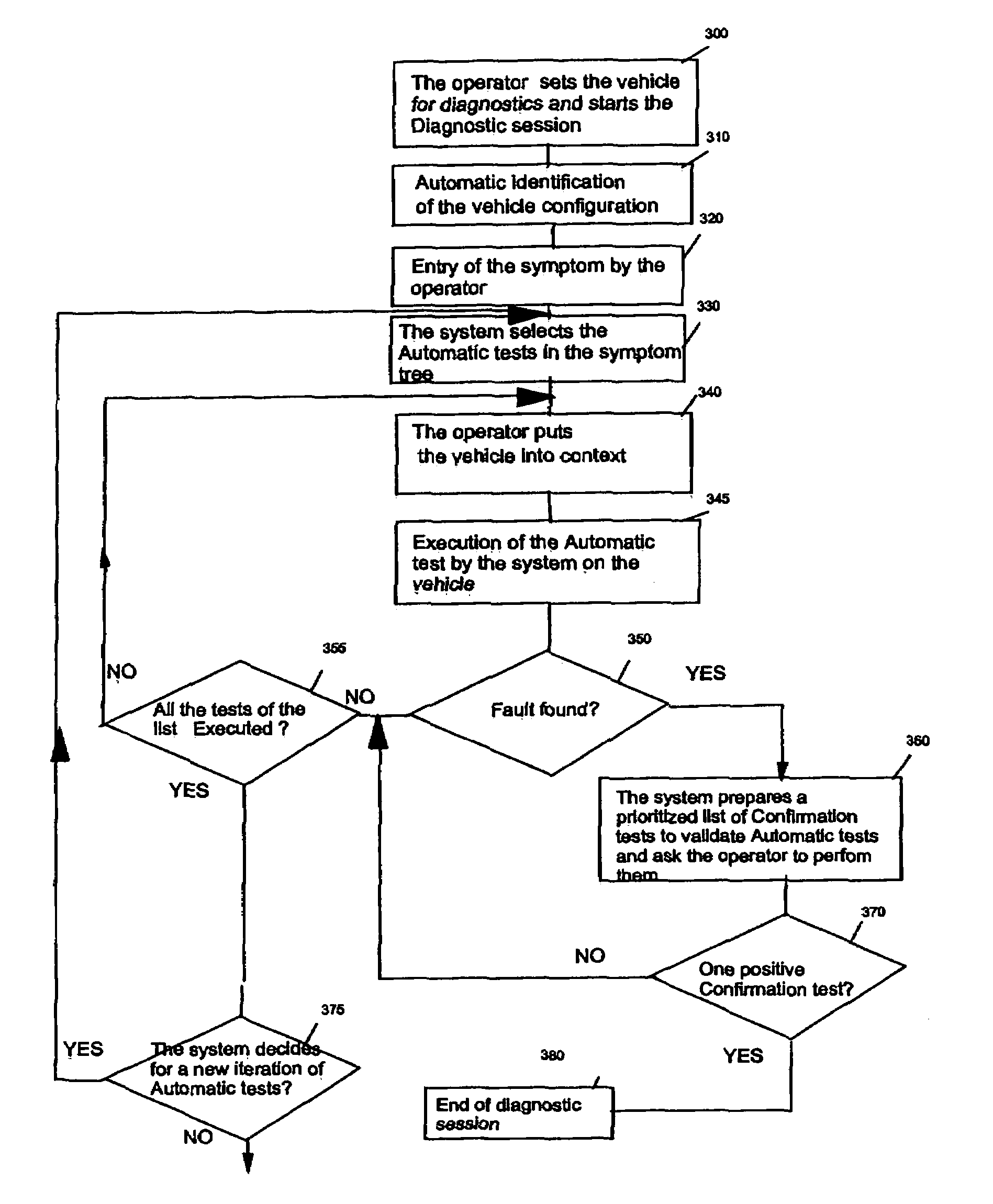
Diagnostic method and system
InactiveUS7409317B2Easy to understandData integrationVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesSystem under testComputer science
A method and system comprising a diagnostic symptom tree system for diagnosing a failing system element causing a symptom in a system-under-test. A diagnostic symptom tree comprises symptom roots and dependent lower function nodes and sub-function nodes. Element nodes depend from the function or sub-function nodes, and a plurality of penultimate failure mode leaves depend from the element nodes. The function and sub-function nodes and the failure mode leaves comprise test information. Responsive to positive test results, the diagnostic symptom tree is configured to identify a function or sub-function or element node associated to a lowest symptom tree node or failure mode leaf for which a test is positive, or advise that no failing function or sub-function or element is found. In one aspect of the invention, nodes may include parameter values allowing successive selections of the nodes of the symptom tree for test iterations according to the parameter values.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS MACHINE CORPORATION
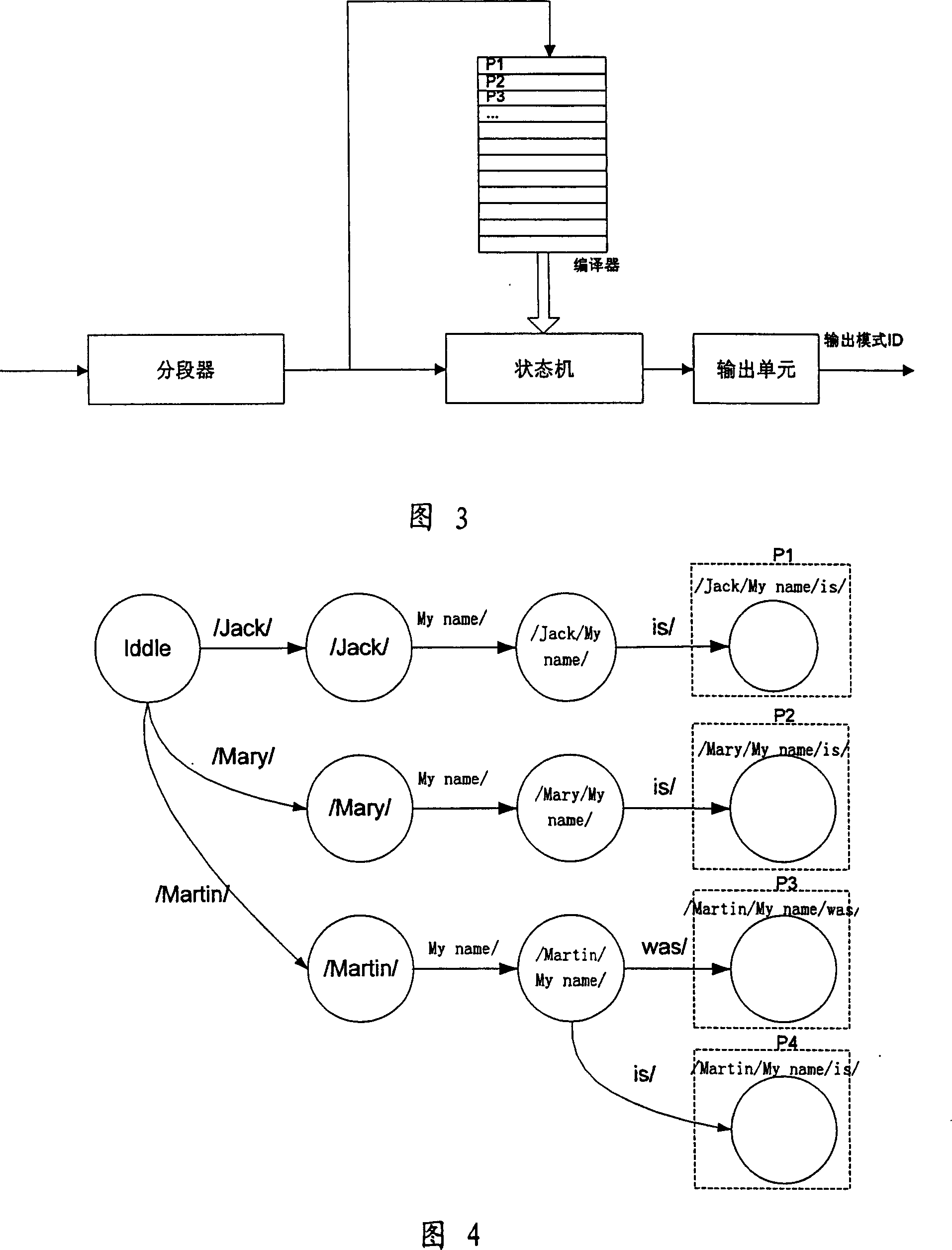
Partitioned pattern matching method and device thereof
InactiveCN101154228AFast pattern matchingFast convergenceSpecial data processing applicationsUser inputResource consumption
The present invention relates to a character string pattern matching, in particular to a subsection pattern matching method and the device. The invention solves the disadvantages of large resource consumption and high hardware requirement in the prior pattern matching; the method of the invention: character strings of keywords can be divided up to at least one character string segment of keywords according to a preconcerted rule; the character string segments of keywords are generated into a keyword tree; according to the preconcerted rule, pending character strings input by users are divided into at least one pending character string segment as the input of a state machine; according to AC matching algorithm, the state machine has matching operation on pending character string segments in the keyword tree nodes; the judging condition of each node branch is the character string segment of keywords; if the pending character string segments succeed in matching, a matching pattern ID is returned. The invention has the advantages of improving the efficiency of character string pattern matching and reducing the requirement on hardware source.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG
Diagnostic method and system
InactiveUS20060150018A1Low effortEasy to understandVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesSystem under testComputer science
A method and system comprising a diagnostic symptom tree system for diagnosing a failing system element causing a symptom in a system-under-test. A diagnostic symptom tree comprises symptom roots and dependent lower function nodes and sub-function nodes. Element nodes depend from the function or sub-function nodes, and a plurality of penultimate failure mode leaves depend from the element nodes. The function and sub-function nodes and the failure mode leaves comprise test information. Responsive to positive test results, the diagnostic symptom tree is configured to identify a function or sub-function or element node associated to a lowest symptom tree node or failure mode leaf for which a test is positive, or advise that no failing function or sub-function or element is found. In one aspect of the invention, nodes may include parameter values allowing successive selections of the nodes of the symptom tree for test iterations according to the parameter values.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and methods that utilize machine learning algorithms to facilitate assembly of aids vaccine cocktails
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
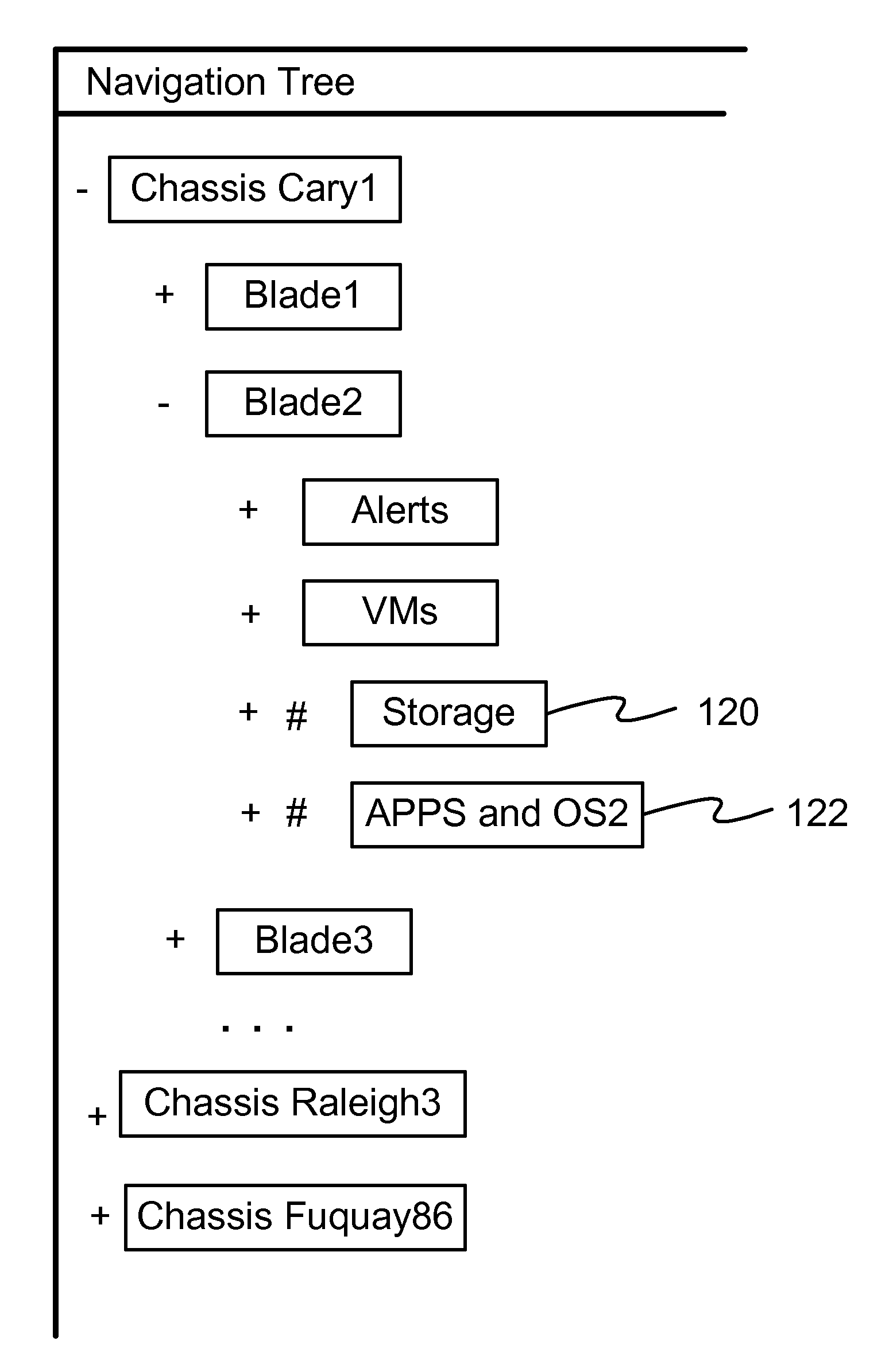
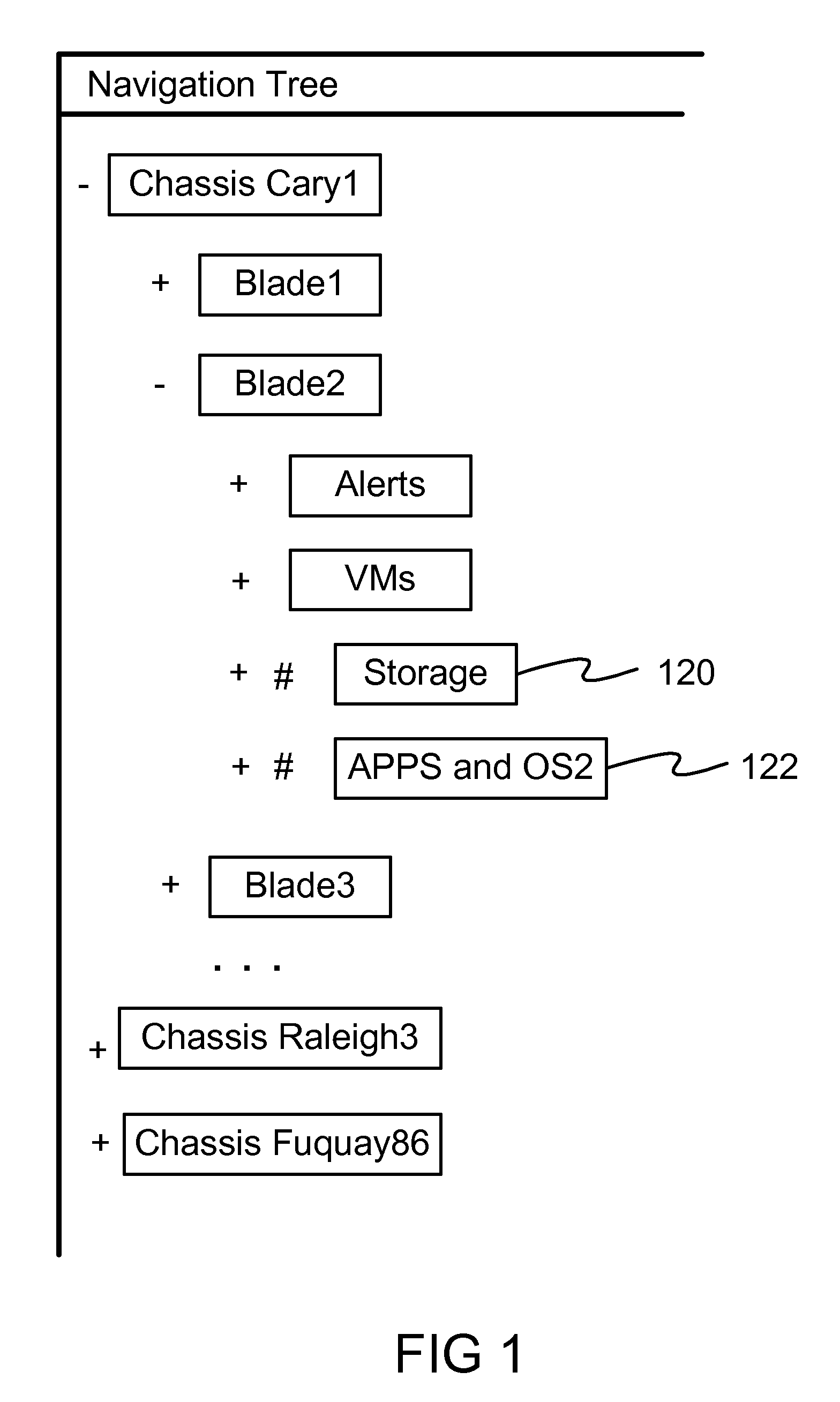
Reorienting navigation trees based on semantic grouping of repeating tree nodes
InactiveUS7669147B1More disorderlyLot of screen spaceDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsRedundant codeTheoretical computer science
Non-hierarchical relationship UIs (“topology UIs”) are difficult to scale to hundreds or more items. An embodiment of this invention provides indicators and quick access controls for the nodes in navigation tree that appear more than once in a hierarchy—where a pure hierarchical navigational tree falls short. The navigational tree is structured by grouping all matching nodes together. The display area displays the most frequent and the concatenated labels of the semantically grouped redundant nodes. A set of contextual proximity and similarity information and an exception list are stored in a semantic database which is configurable by system administrators. These navigation area controls and indicators will preemptively handle non-hierarchies directly within the navigation tree.
Owner:IBM CORP
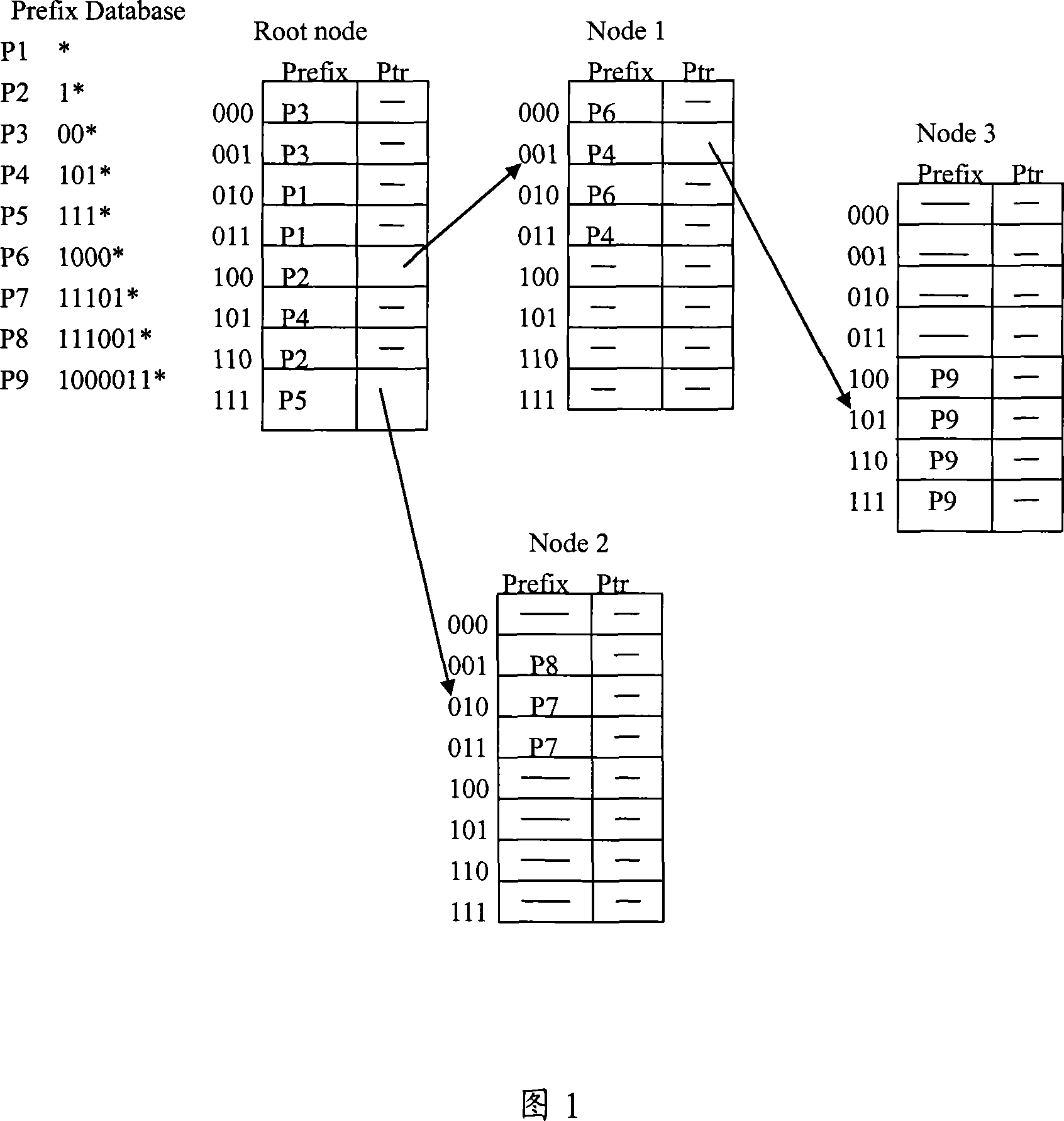
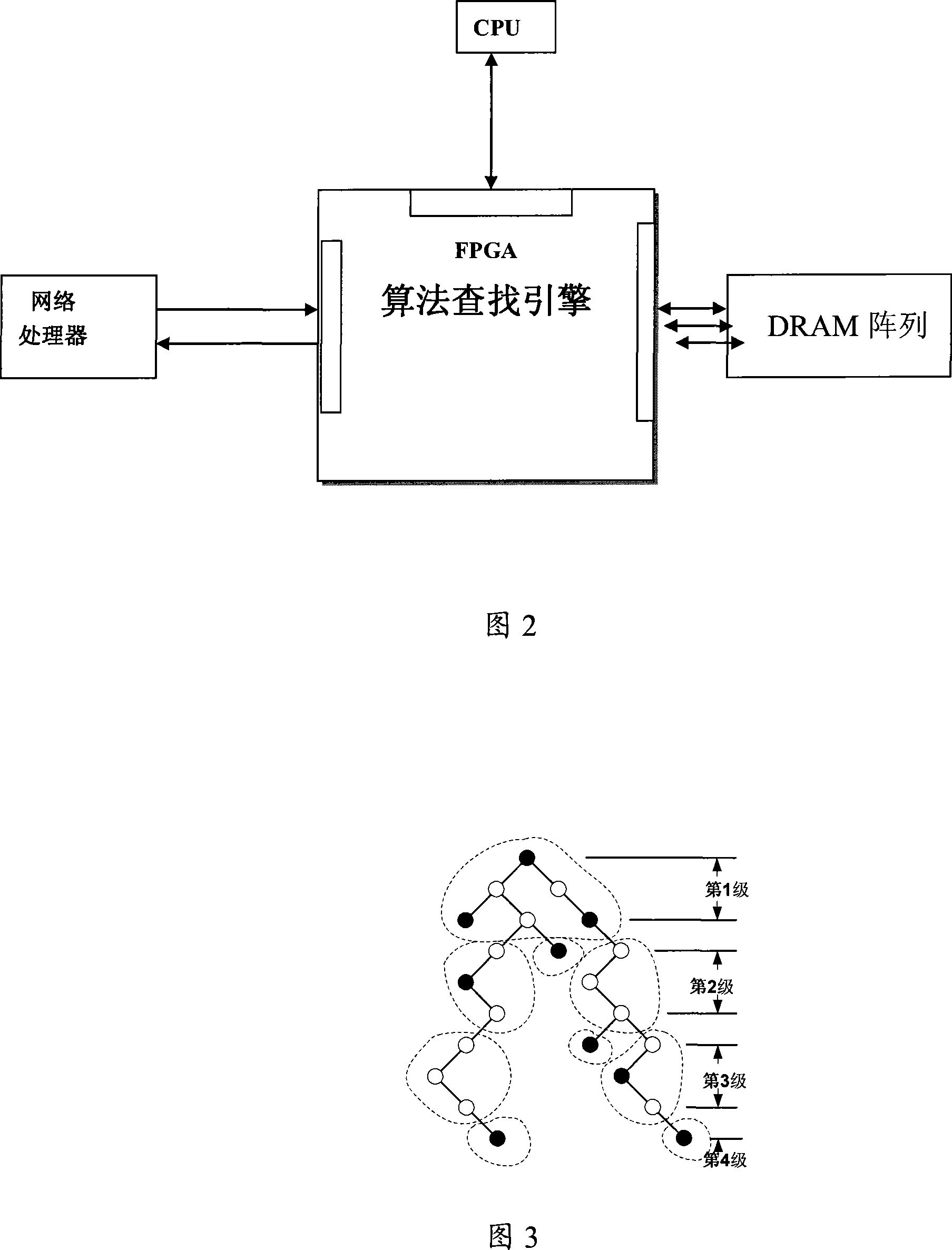
Reinforcement multidigit Trie tree searching method and apparatus
InactiveCN101141389ALarge capacityLow costData switching networksSpecial data processing applicationsTraffic capacityWire speed
The present invention relates to a searching technology for the routing forwarding table, in particular to a searching technology and a device which can enhance a multidigit Trie tree. Through optimizing and improving the searching method to the multidigit Trie, and the data structure of a tree node, particularly the relation between an expansion bitmap and an inferior tree node, and though adopting an FPGA and a DDRII SDRAM, the searching of the high-capacity routing forwarding table is realized, as well as the wire-speed searching under the 20 Gbps flow, even the 40 Gbps flow, and the present invention has obvious advantages in the aspects of table capacity and the cost etc. compared with the commercial three-state content addressable memorizer.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Quick file comparison method, system and client side
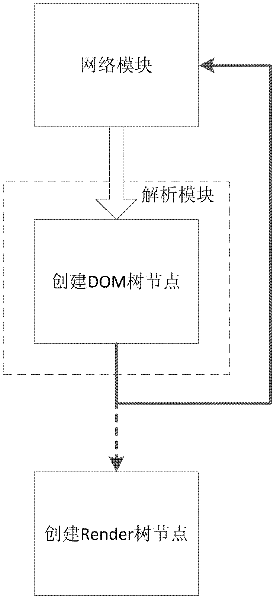
ActiveCN102693302AImprove comparison efficiencyImprove performanceSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemFile comparison
The invention relates to a quick file comparison method, a quick file comparison system and a quick file comparison client side. The quick file comparison method comprises the steps of: e scanning and analyzing a local file directory by the client side; according to the variation of the local file system, updating a first identification tree maintained by the client side; corresponding a node in the first identification tree to each local directory of the client side, wherein node information comprises a node identification and relevant directory information; comparing a second identification tree maintained by server side equipment with the first identification tree node by node by the client side; recording a difference node and a variation file corresponding to the difference node; and according to the difference node and the variation file, providing data to the server side equipment section by the client side so as to update the second identification tree maintained by server side equipment and a stored file. According to the quick file comparison method, a mode of comparing node information for reflecting the local file system of the client side is adopted, and due to the mode, the quickness is realized, the mode is more suitable for bigger and a more complex file system, and the file comparison efficiency and performance can be effectively improved.
Owner:ZHENGJIANG PUBLIC INFORMATION
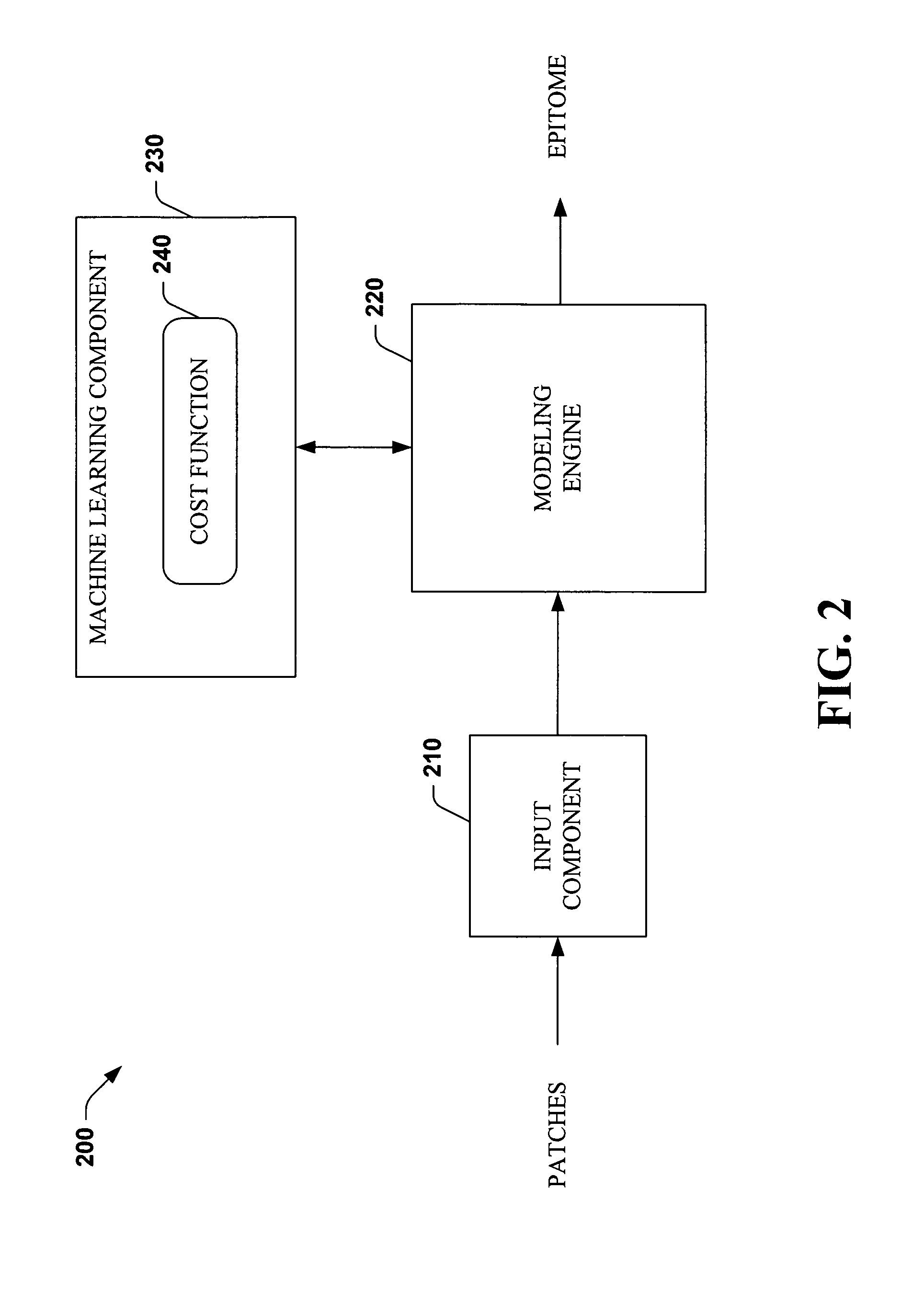
Systems and methods that utilize machine learning algorithms to facilitate assembly of aids vaccine cocktails
The subject invention provides systems and methods that facilitate AIDS vaccine cocktail assembly via machine learning algorithms such as a cost function, a greedy algorithm, an expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm, etc. Such assembly can be utilized to generate vaccine cocktails for species of pathogens that evolve quickly under immune pressure of the host. For example, the systems and methods of the subject invention can be utilized to facilitate design of T cell vaccines for pathogens such HIV. In addition, the systems and methods of the subject invention can be utilized in connection with other applications, such as, for example, sequence alignment, motif discovery, classification, and recombination hot spot detection. The novel techniques described herein can provide for improvements over traditional approaches to designing vaccines by constructing vaccine cocktails with higher epitope coverage, for example, in comparison with cocktails of consensi, tree nodes and random strains from data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
WebKit browser webpage content loading method and device
InactiveCN102346770AHigh speedShorten the timeWebsite content managementSpecial data processing applicationsDocumentationDocument Object Model
Owner:MSTAR SOFTWARE R&D (SHENZHEN) LTD +1
Dynamic tree structured directory retrieval method in BS (browser/server) structure software
The invention discloses a dynamic tree structured directory retrieval method in BS (browser / server) structure software. The method comprises the following steps: 1) taking out the information of a tree node; 2) carrying out data caching; 3) judging whether the node contains retrieval items; 4) carrying out structure transformation on expected data; and 5) carrying out data interaction. In the step 4), the expected data is used for synchronously generating a data format required by a tree directory structure according to JSON (java-script serialized object notation) specification; and in the step 5), the background processing contents of a WEB page timely return the expected JSON-format data to a foreground WEB page by a preset Ajax (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) callback function, and the JSON-format data is analyzed by using a JavaScript built-in method so as to generate a tree structured expression of the expected data.
Owner:LINKAGE SYST INTEGRATION
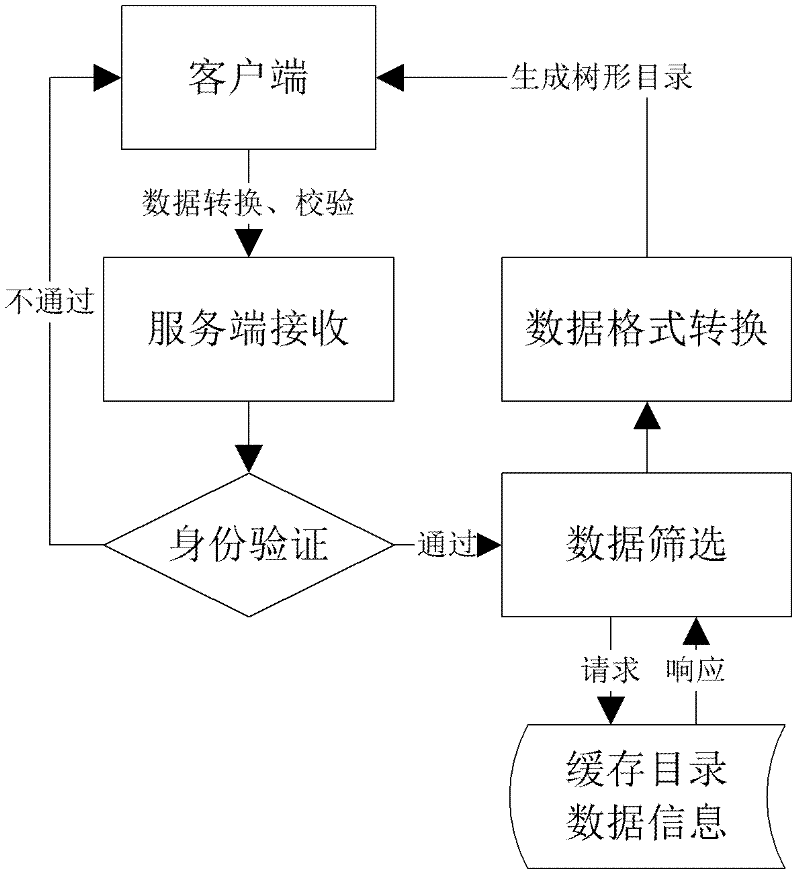
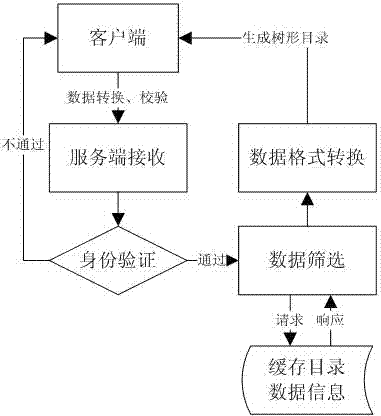
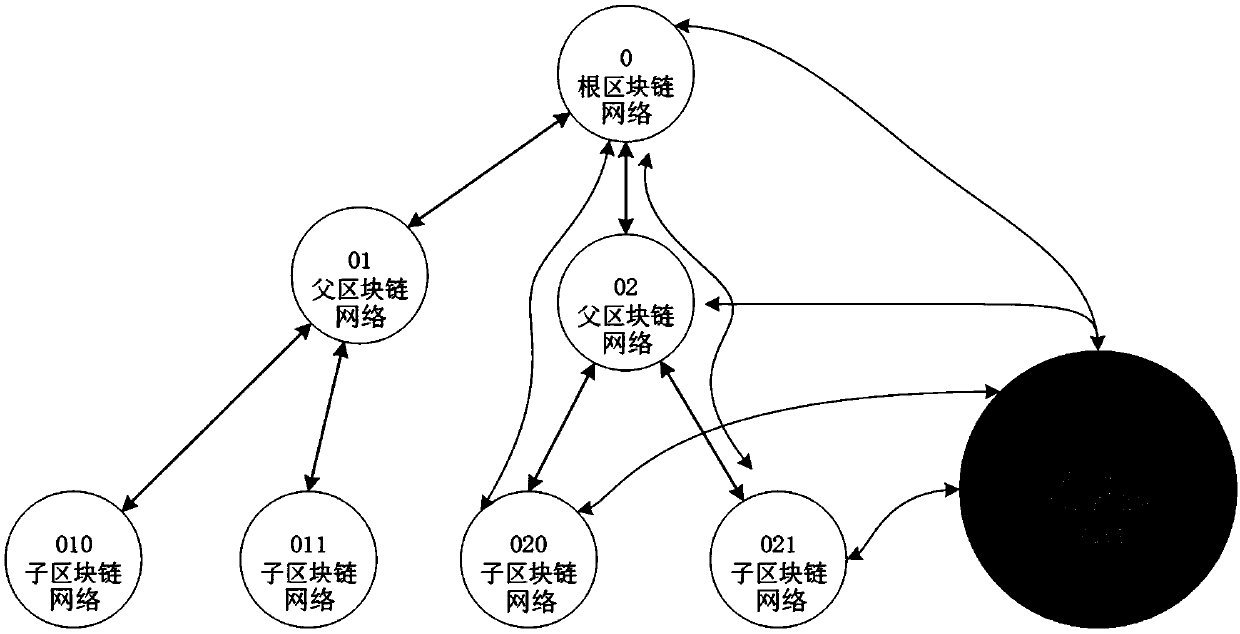
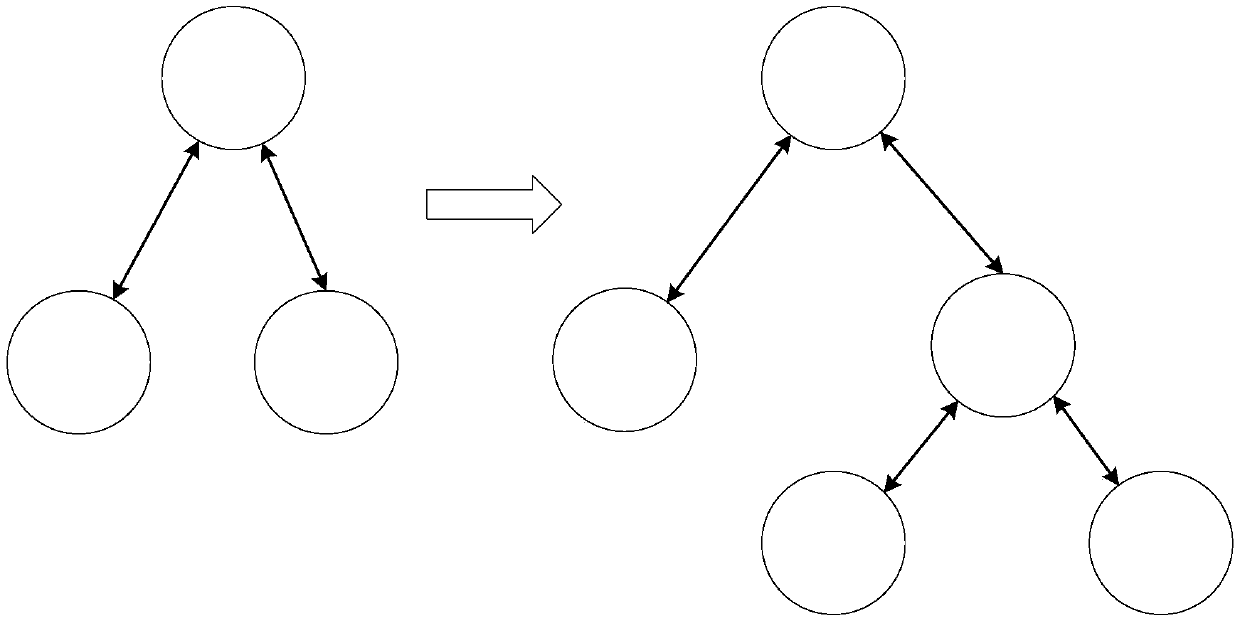
Data summarization method and device based on tree block chain network, equipment and medium
InactiveCN109635165ABreakthrough performanceBreak through the storage bottleneckOther databases indexingData switching networksStructure of Management InformationPooling data
The embodiment of the invention discloses a data summarization method and device based on a tree block chain network, equipment and a medium. The method comprises: when it is detected that a pre-deployed summary contract is triggered, the node attribute of a tree node corresponding to a target block chain network where the tree node is located in a tree hierarchical structure is acquired; processing the data in the target block chain according to a data summarization strategy matched with the node attribute to form target summarized data; and if it is determined that the node attribute is a non-root node, sending the target summarized data to a parent block chain network of the target block chain network through a cross-chain protocol. According to the technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, based on cross-chain interaction between parent and child block chain networks and a tree layering technology, the performance and storage bottleneck of a traditional single-chain structure are broken through, the problem of information islands incompatible with each other between different block chain networks is solved, and extensible application scenarios such as multi-service chains and polymorphic chains can be supported.
Owner:北京磁云数字科技有限公司
Data query method, data query system and computer readable and writable recording medium
InactiveUS20110093486A1Reduce in quantityIncreasing data query rateDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsExtensible markupData query
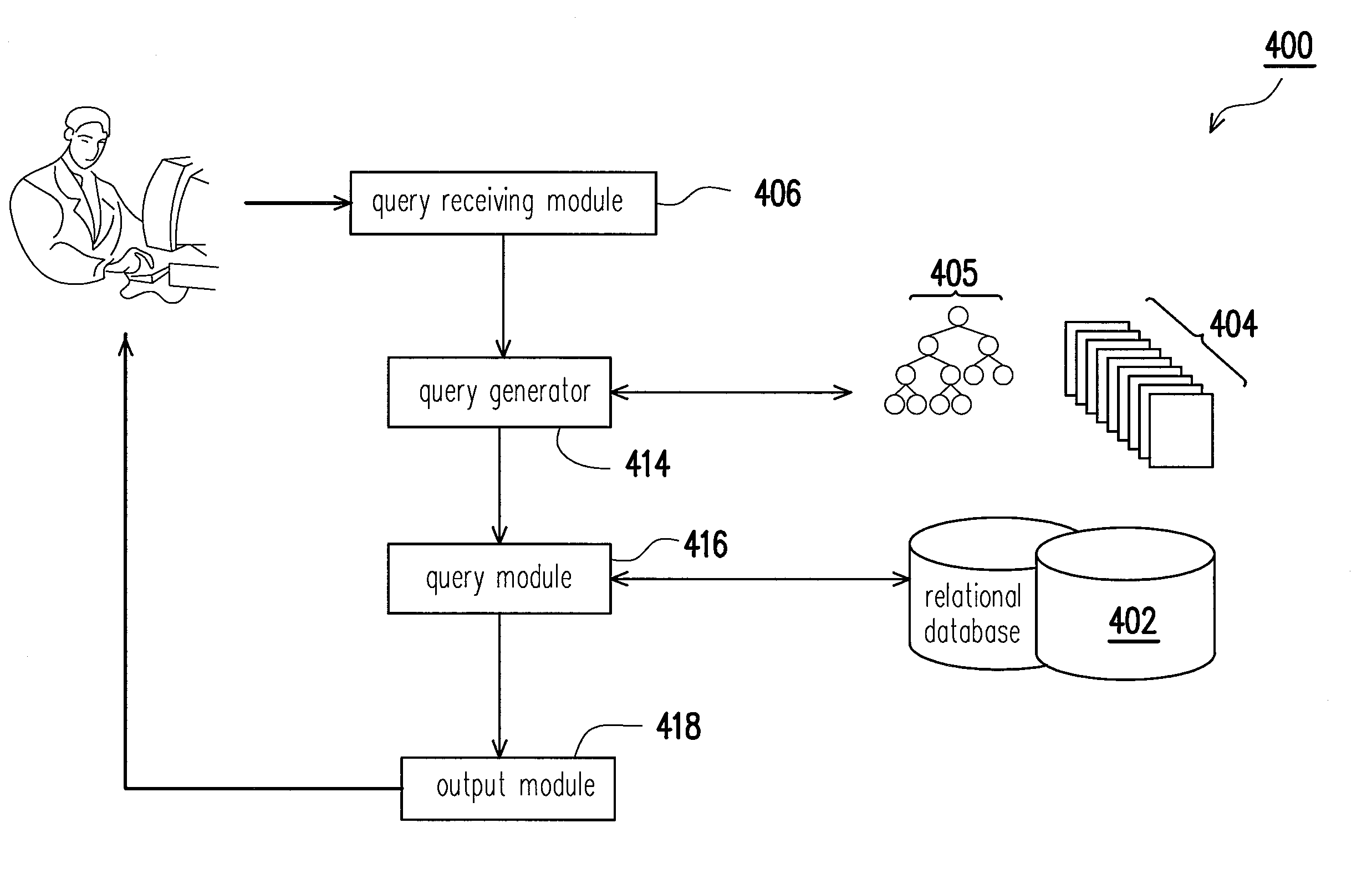
A relational database query system for a relational database is provided, wherein the relational database comprises several relational tables including at least one constant table storing several unique data. The relational database query system comprises a query receiving module for receiving an extensible-markup-language query (XML query); at least a constant mapping tree respectively corresponds to one of the at least constant tables, wherein the at least constant mapping tree comprises several tree nodes respectively with node numbers respectively corresponding to the unique data in the at least constant table; a query generator for converting the XML query to be a structured query language (SQL) query according to the at least constant mapping tree; a query module for querying the relational database with the SQL query.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR INFORMATION INDUSTRY
Method and system for presenting relationships
InactiveUS20060059428A1Large viewDigital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsData miningTree node
One aspect of the invention is a method for presenting relationships. An example of the method includes specifying a set of objects. This example also includes designating a root node of the set of objects. This example also includes selecting a first level object type for a first level. This example further includes, for at least one object having the first level object type, providing and associating therewith a corresponding first level container tree node connected to the root node. Additionally, this example includes adding a child container tree node at a level below the first level, wherein the child container tree node is added only if an object associated with the child container tree node is not in a path between the child container tree node and the root node.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and System for Object Detection Using Probabilistic Boosting Cascade Tree
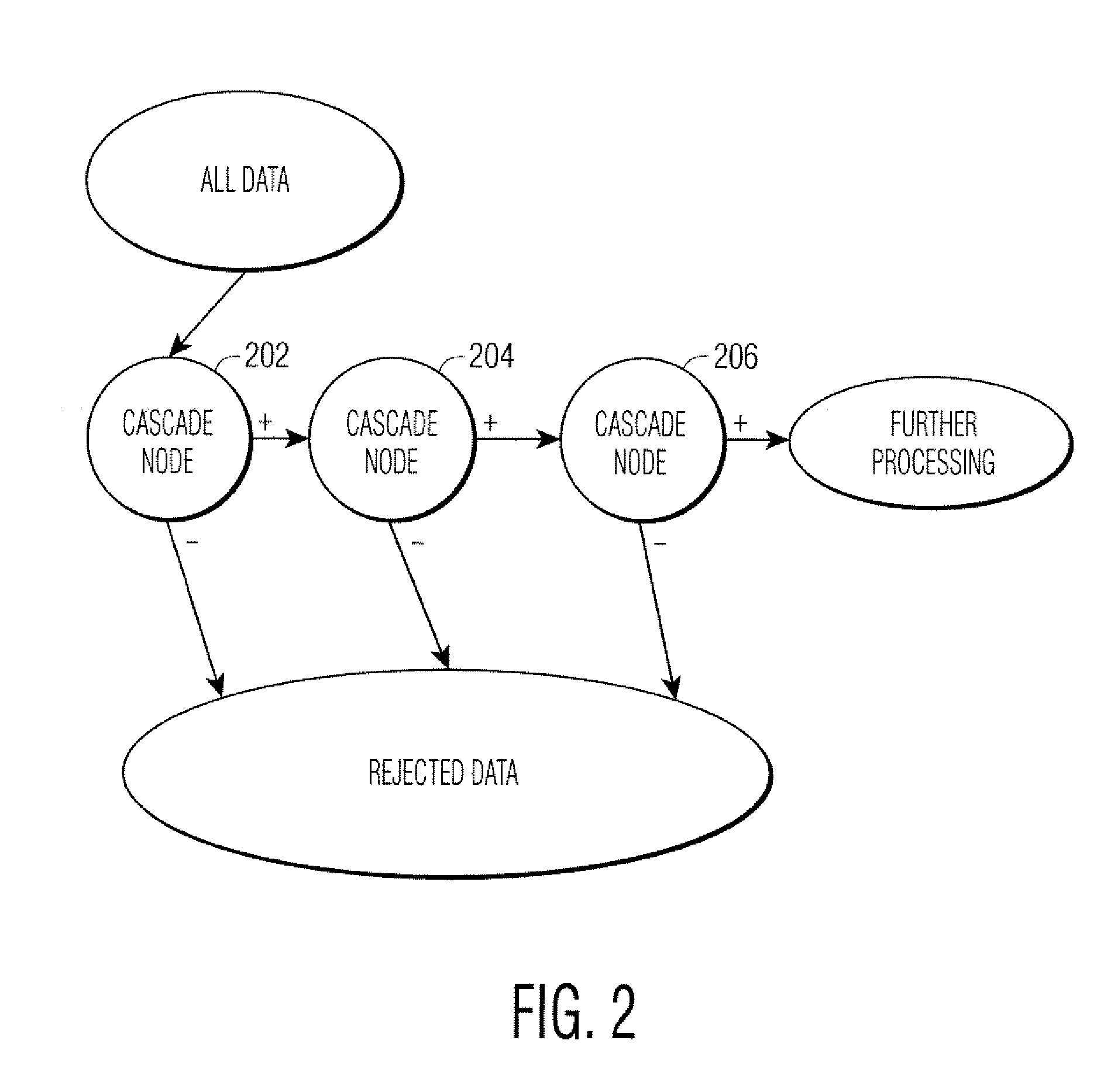
InactiveUS20080071711A1Powerful in learningDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionLearning basedUser input
A method and system for object detection using a probabilistic boosting cascade tree (PBCT) is disclosed. A PBCT is a machine learning based classifier having a structure that is driven by training data and determined during the training process without user input. In a PBCT training method, for each node in the PBCT, a classifier is trained for the node based on training data received at the node. The performance of the classifier trained for the node is then evaluated based on the training data. Based on the performance of the classifier, the node is set to either a cascade node or a tree node. If the performance indicates that the data is relatively easy to classify, the node can be set as a cascade node. If the performance indicates that the data is relatively difficult to classify, the node can be set as a tree node. The trained PBCT can then be used to detect objects or classify data. For example, a trained PBCT can be used to detect lymph nodes in CT volume data.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Multidimensional database query method and apparatus
ActiveCN105550241AConvenient lengthReduce maintenance difficultyMulti-dimensional databasesSpecial data processing applicationsDatabase queryTheoretical computer science
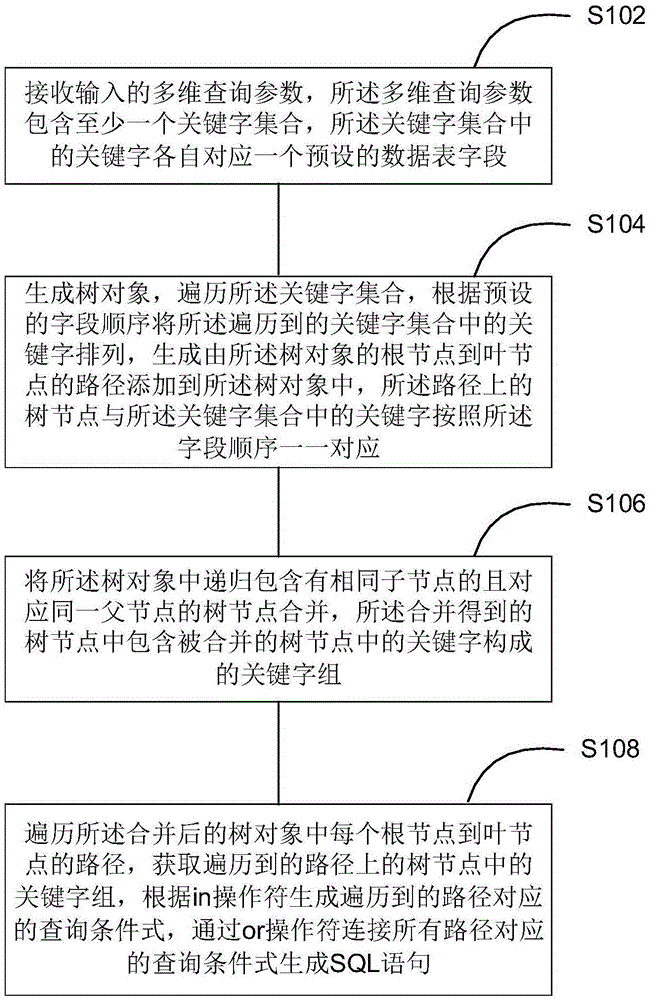
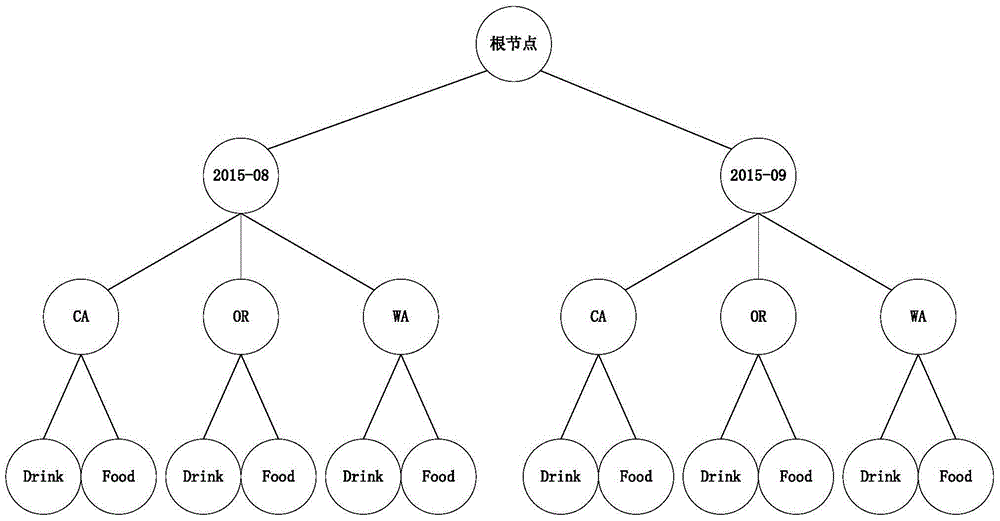
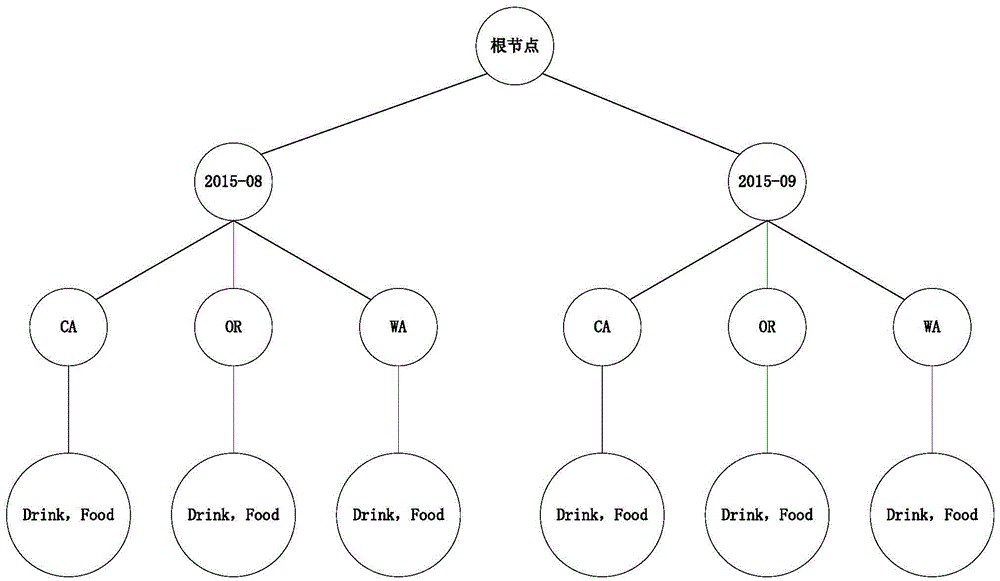
The embodiment of the invention discloses a multidimensional database query method which comprises the steps of: receiving input multidimensional query parameters; generating a tree object, traversing a keyword set, arranging keywords in the traversed keyword set according to a preset field sequence, generating paths from root nodes of the tree object to leaf nodes of the tree object, and adding the path into the tree object; merging tree nodes in the tree object, which recursively comprise the same child nodes and correspond to the same parent node; and traversing the paths from each root node to the leaf nodes in the merged tree object, acquiring keyword sets in the tree nodes on the traversed paths, generating query condition expressions corresponding to the traversed paths according to an in operator, and by an or operator, connecting the query condition expressions corresponding to all the paths to generate an SQL (Structured Query Language) statement. The multidimensional database query method disclosed by the invention can generate the short SQL statement, and is beneficial to maintenance.
Owner:珠海多玩信息技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com