Quick file comparison method, system and client side
A local file system and client technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of performance degradation, data search performance degradation, and reduce equipment processing efficiency, etc., to achieve the effect of improving efficiency and performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
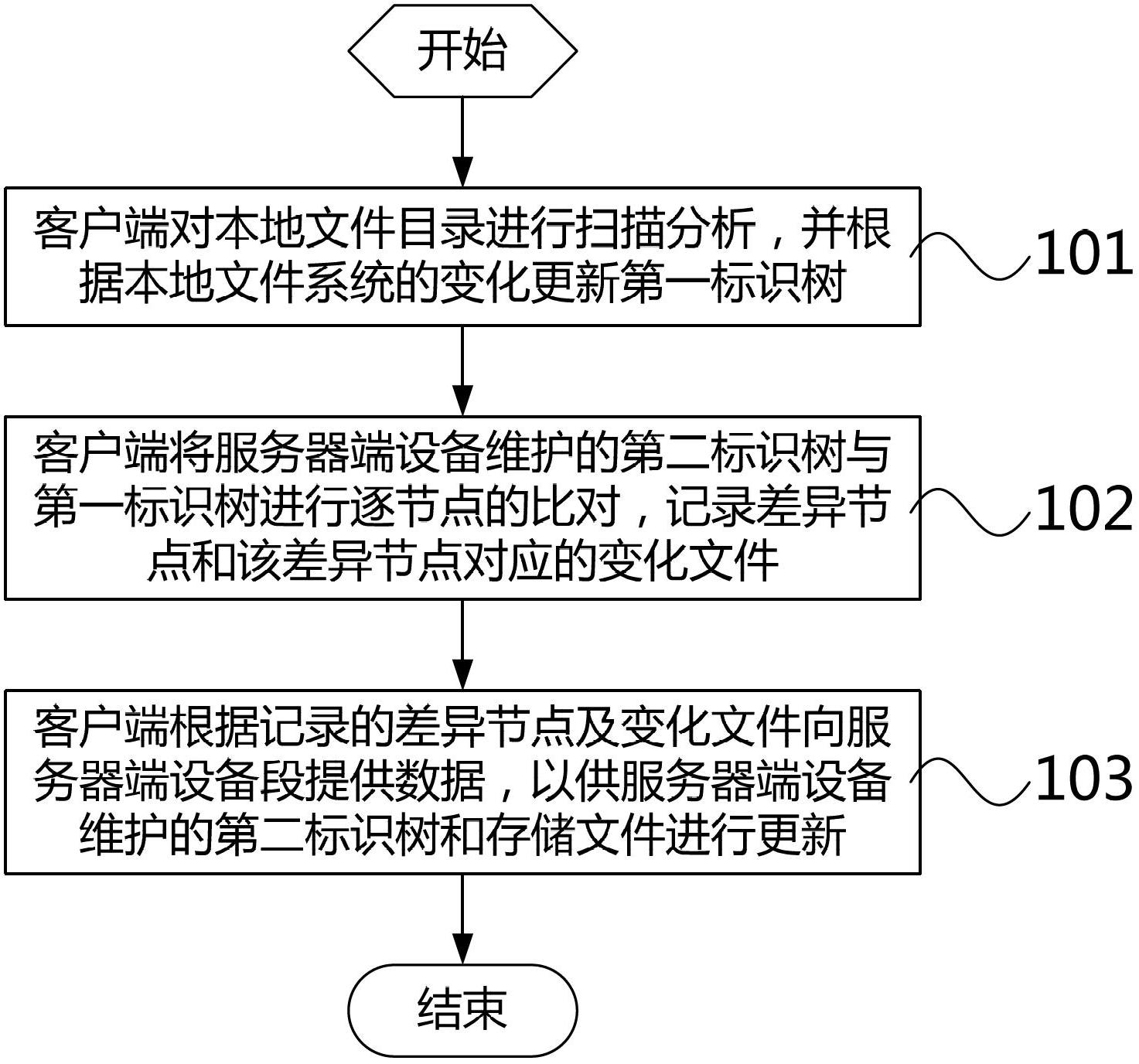
[0067] The technical solutions of the present invention will be described in further detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[0068] First, the data structures involved in each embodiment of the present invention are briefly described.
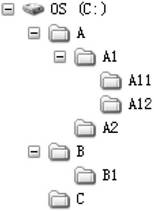
[0069] Such as figure 1 As shown in , it is a schematic diagram of the general file system in the client hard disk. Such a filesystem has at least one root directory ( figure 1 The middle is the drive letter C:), which can include directories (the directories under the directory can also be called subdirectories) and files under the root directory, and can further include Directories and files, the corresponding different files or directories have absolute path information, including the real path from the root directory to the current file or directory, for example, the absolute path of directory A11 is C:\A\A1\A11.
[0070] The root directory is not necessarily limited to the location represented by the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com