Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
104 results about "Mass spring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
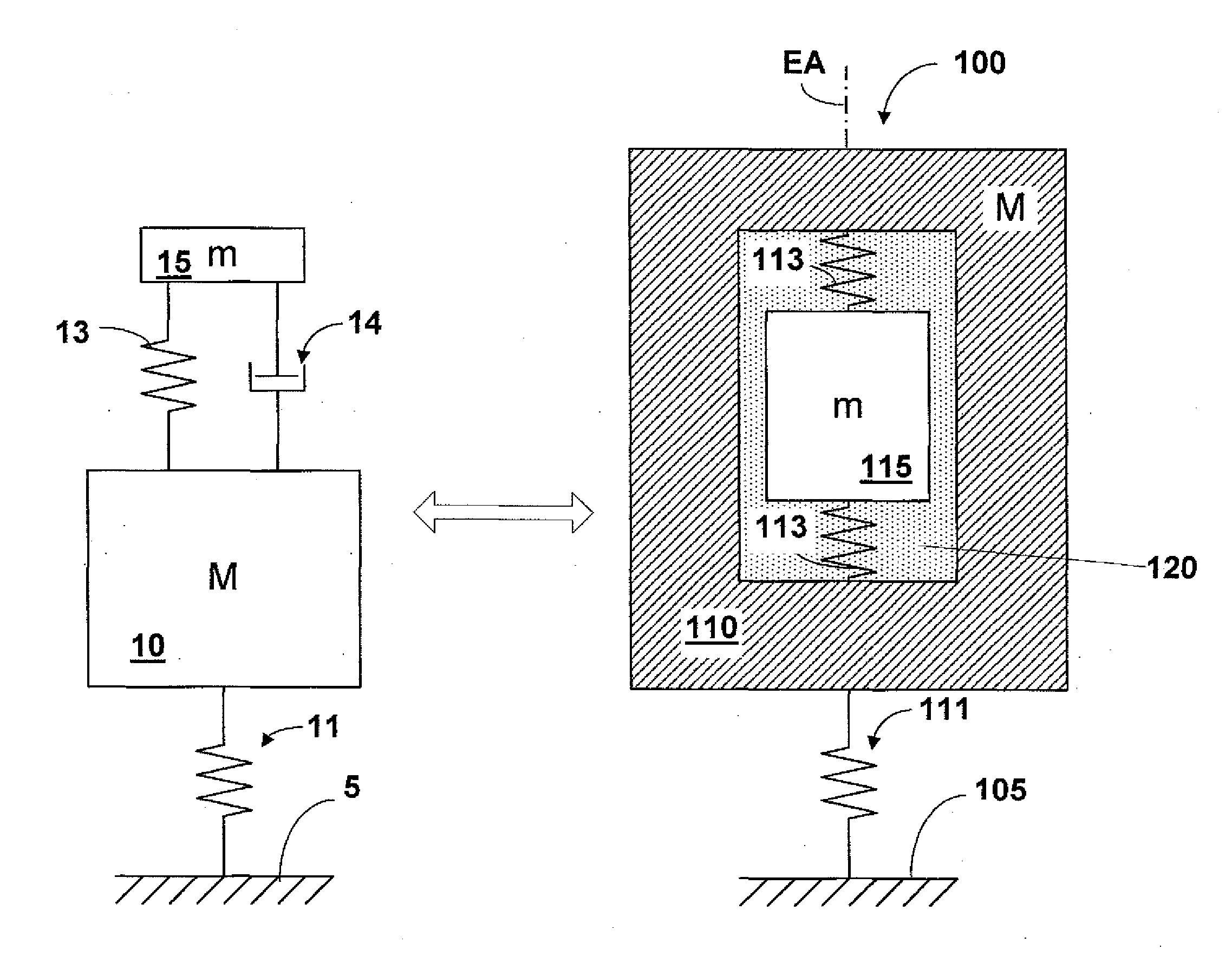
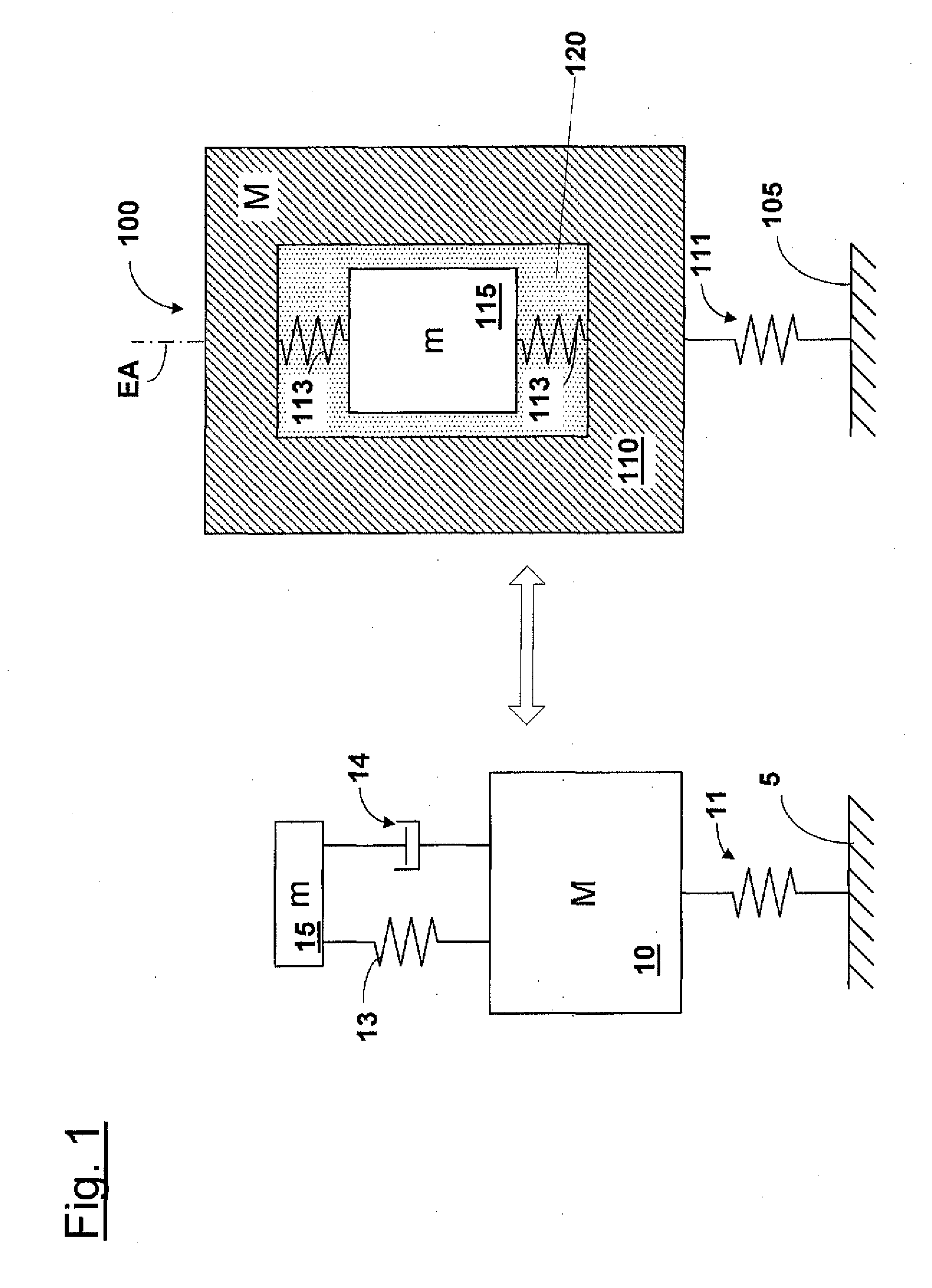
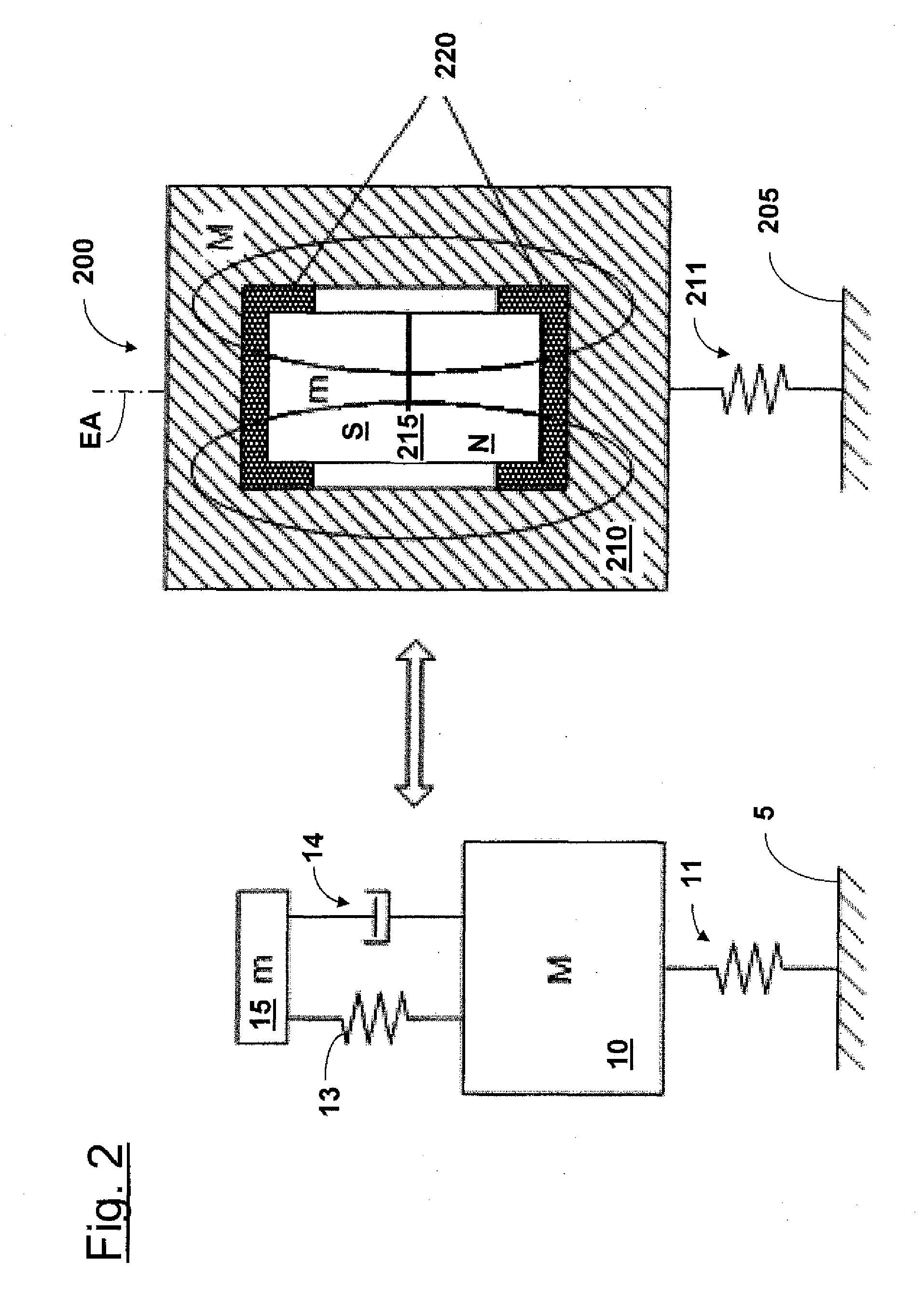
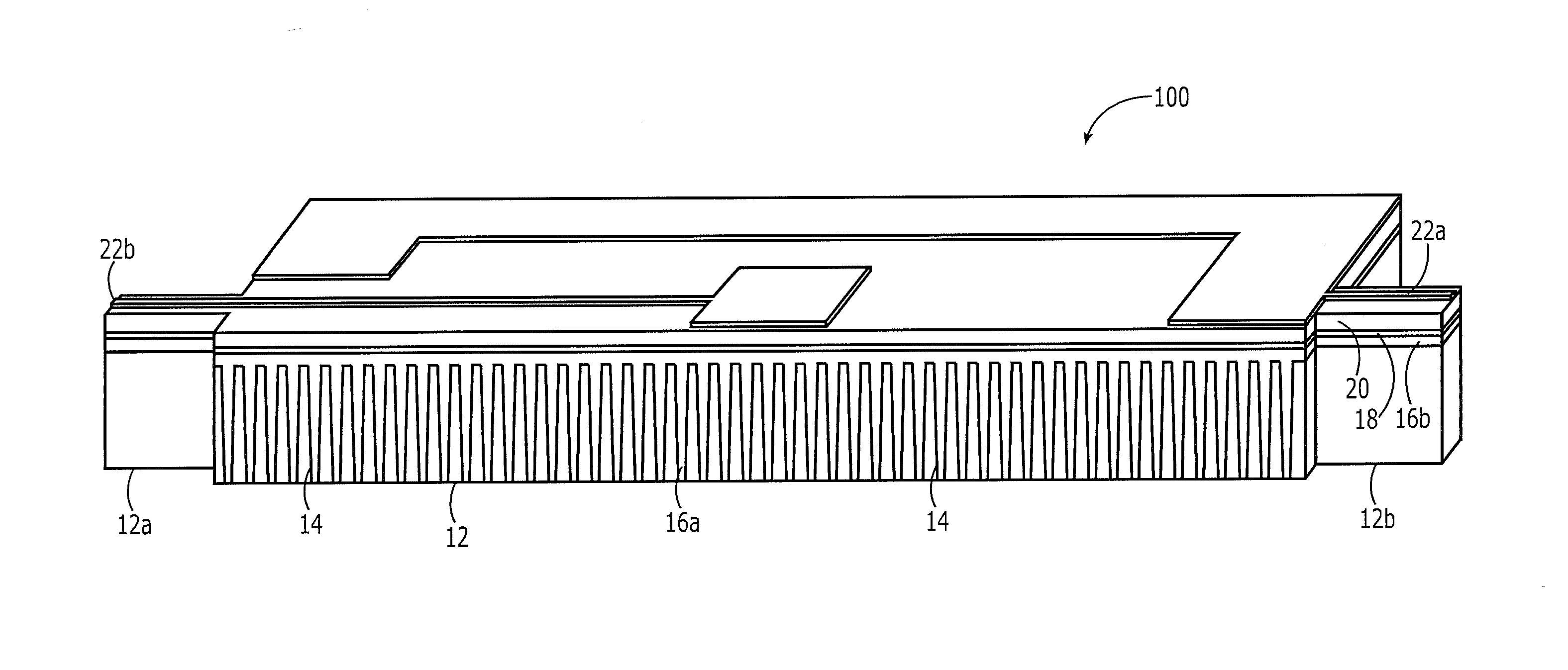
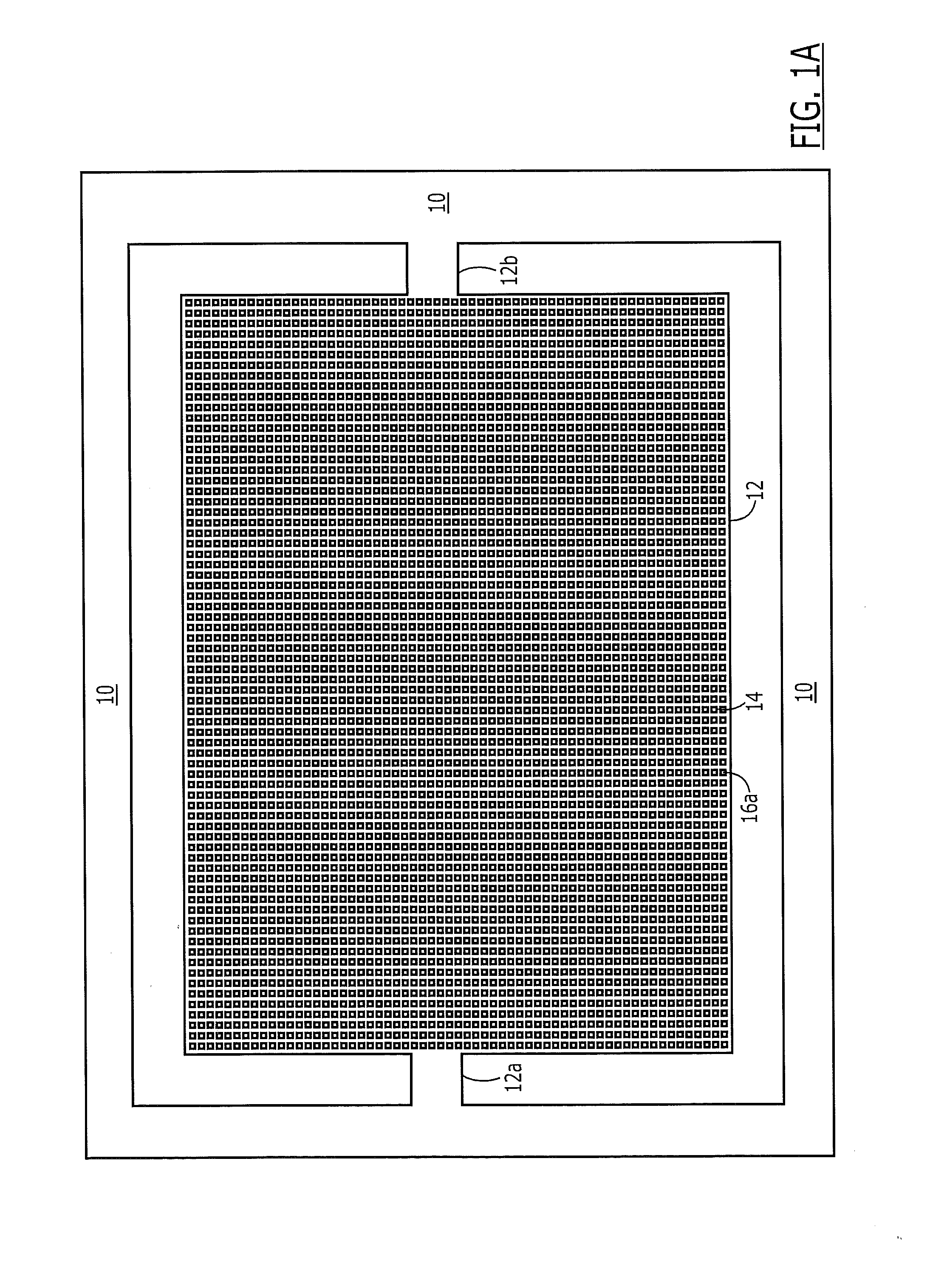
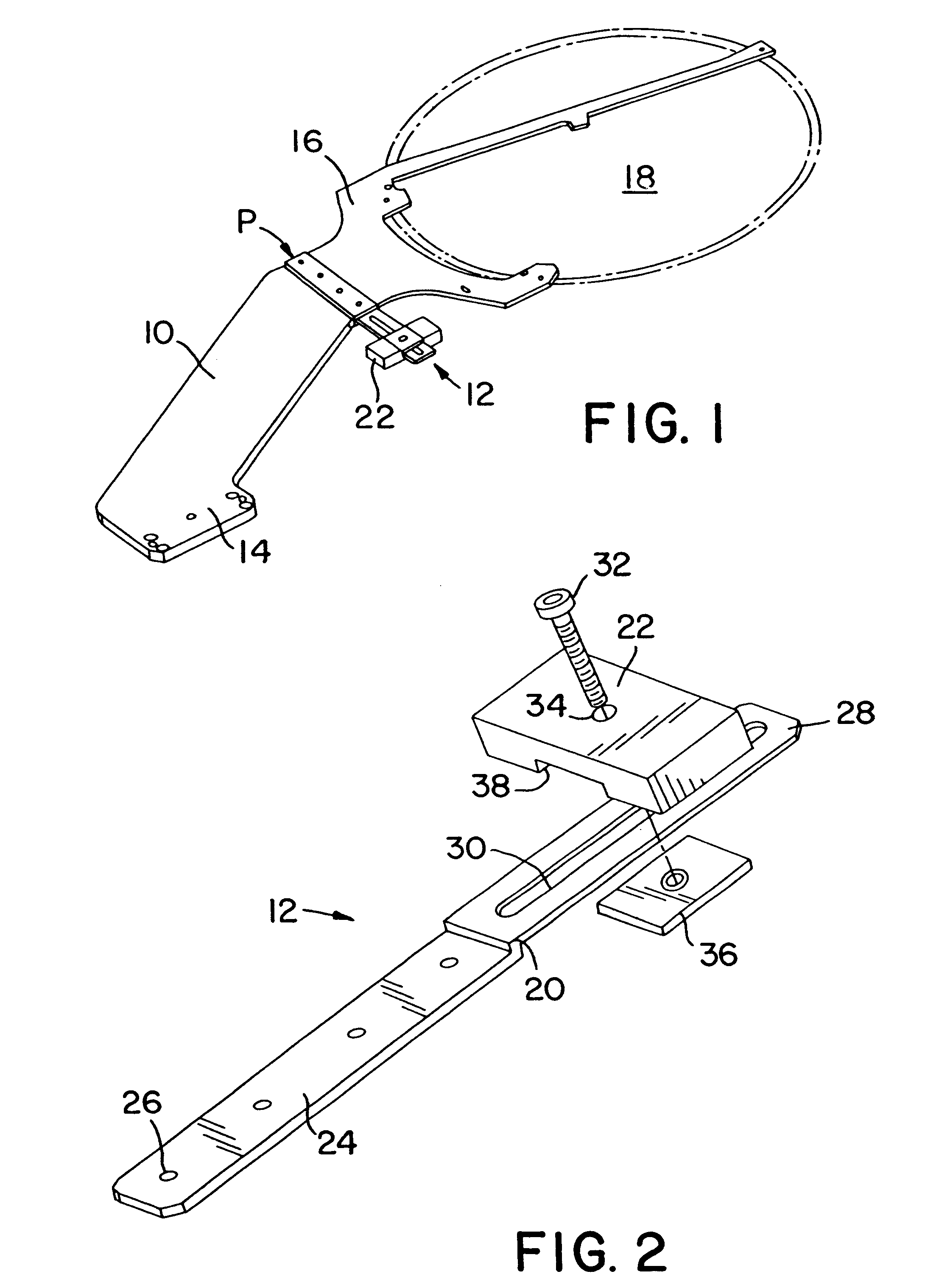
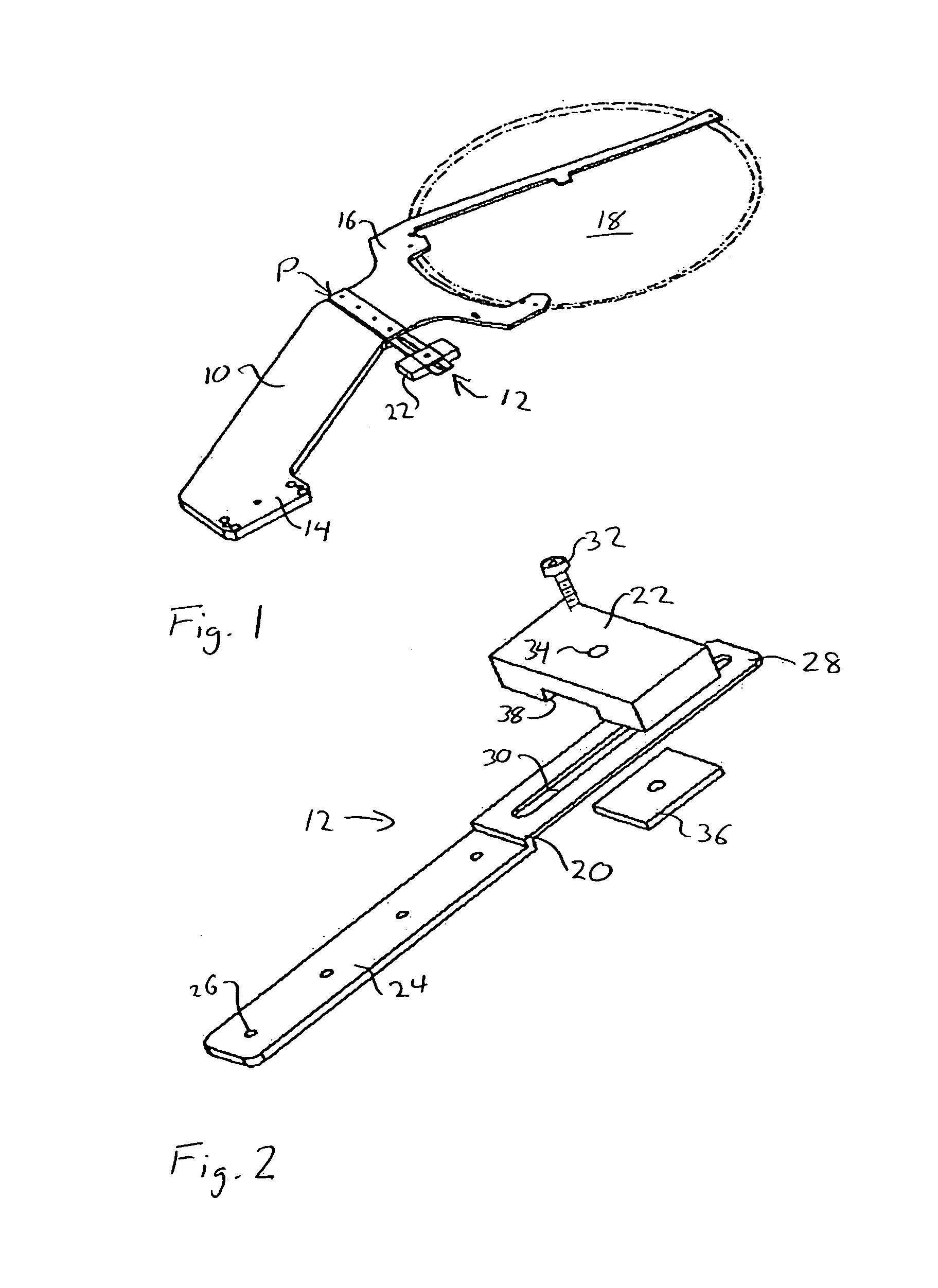
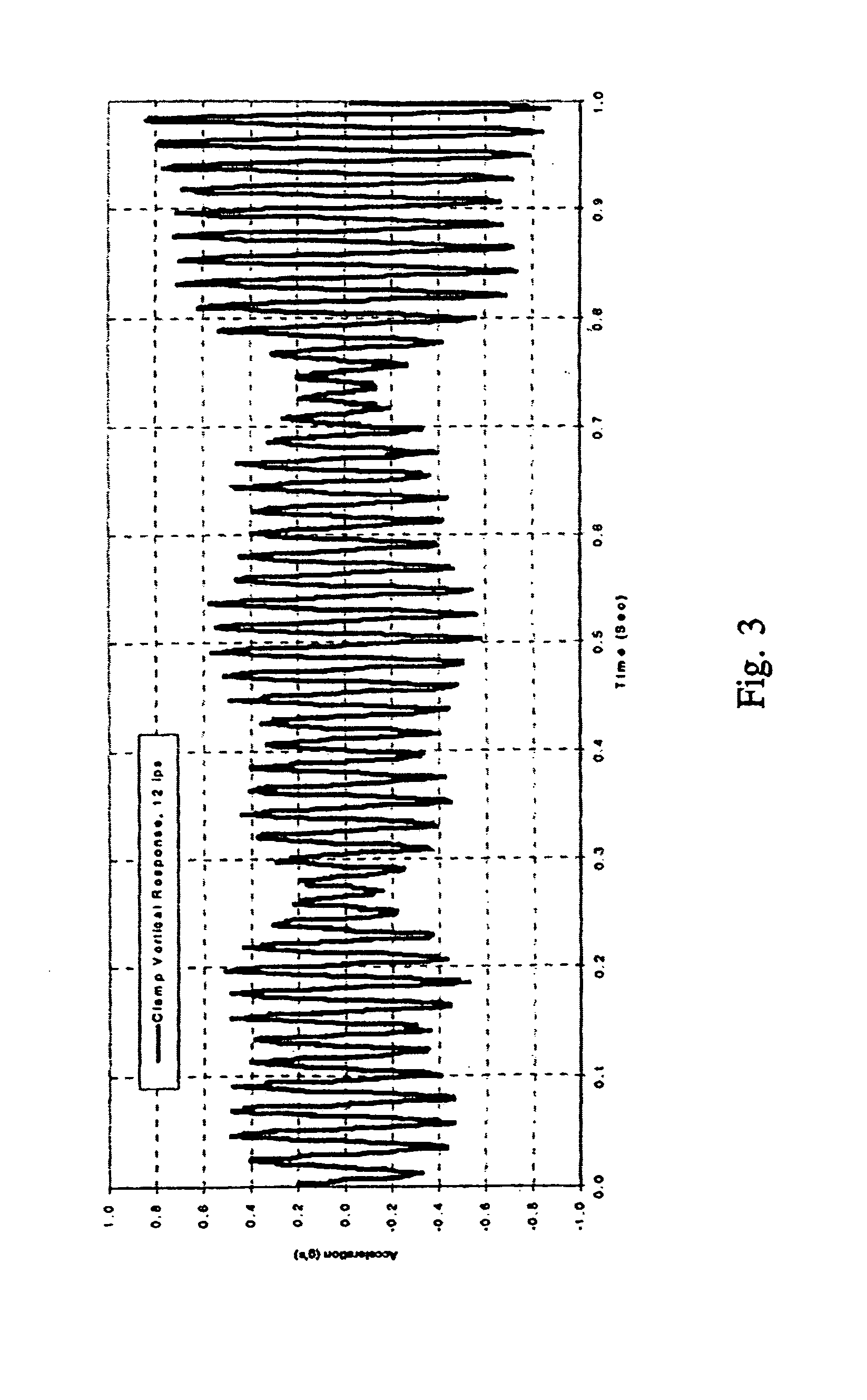
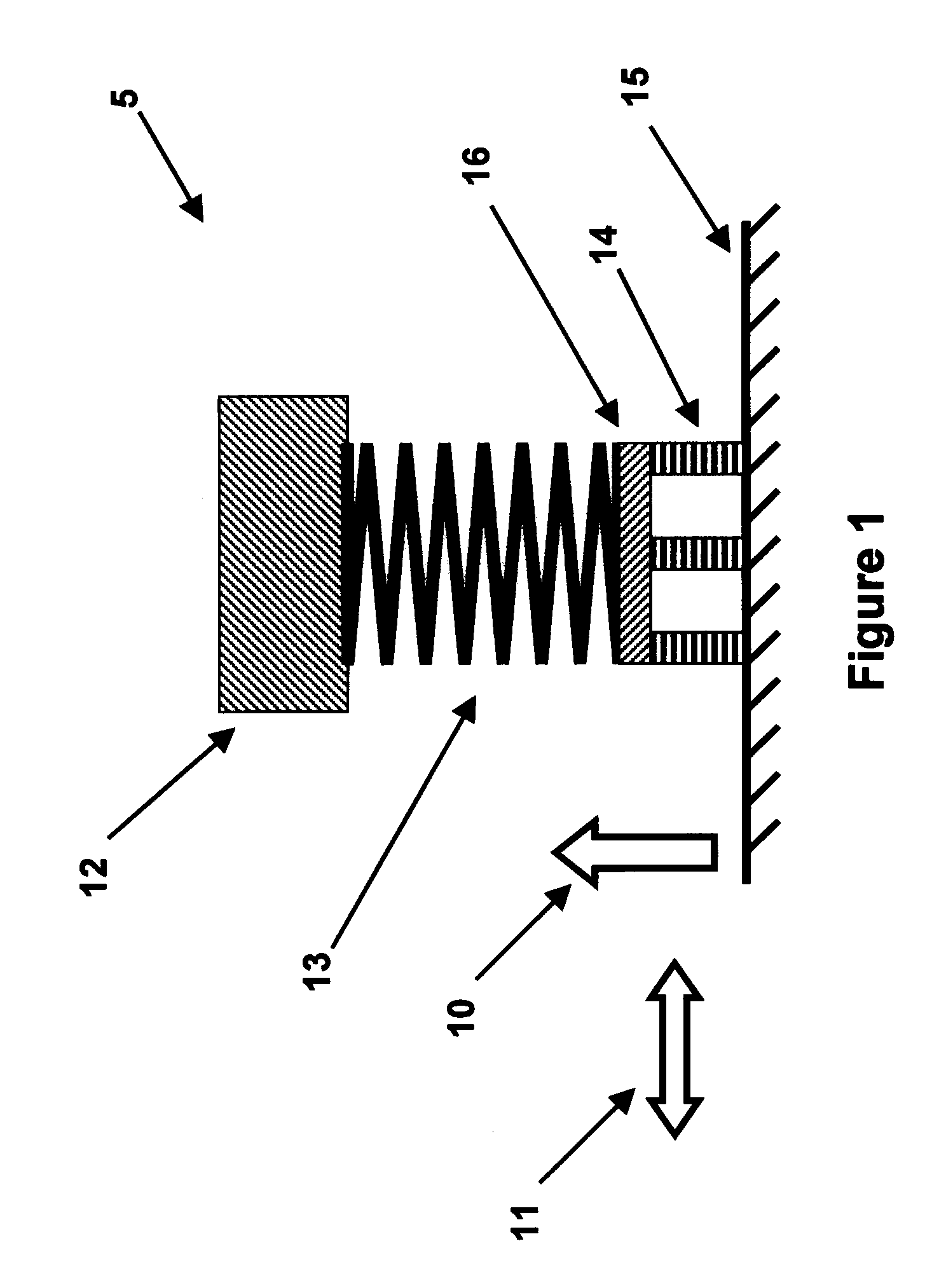
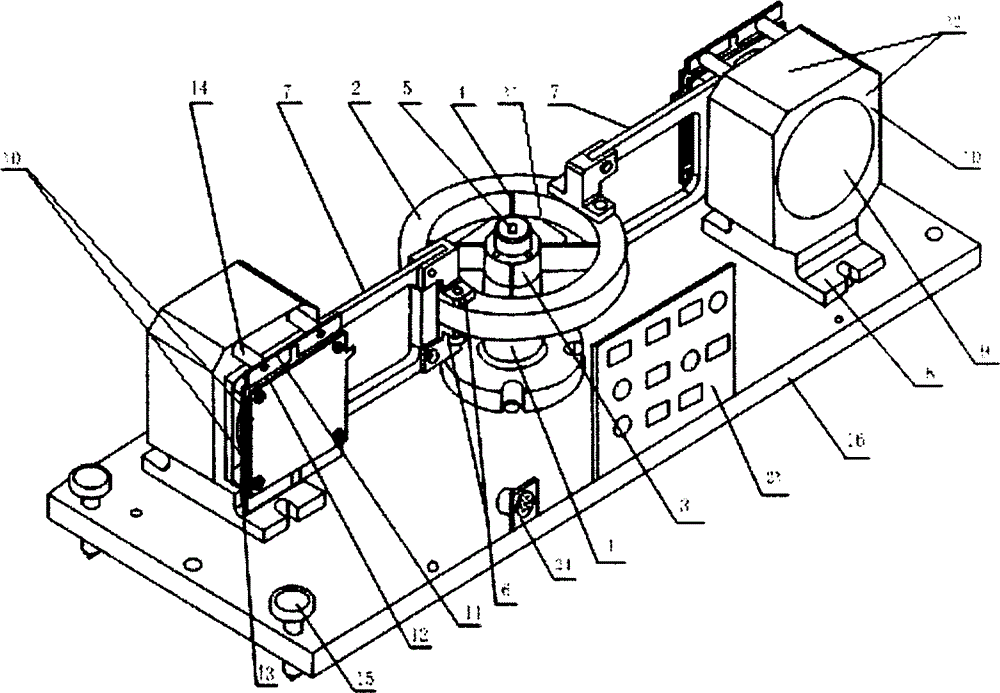
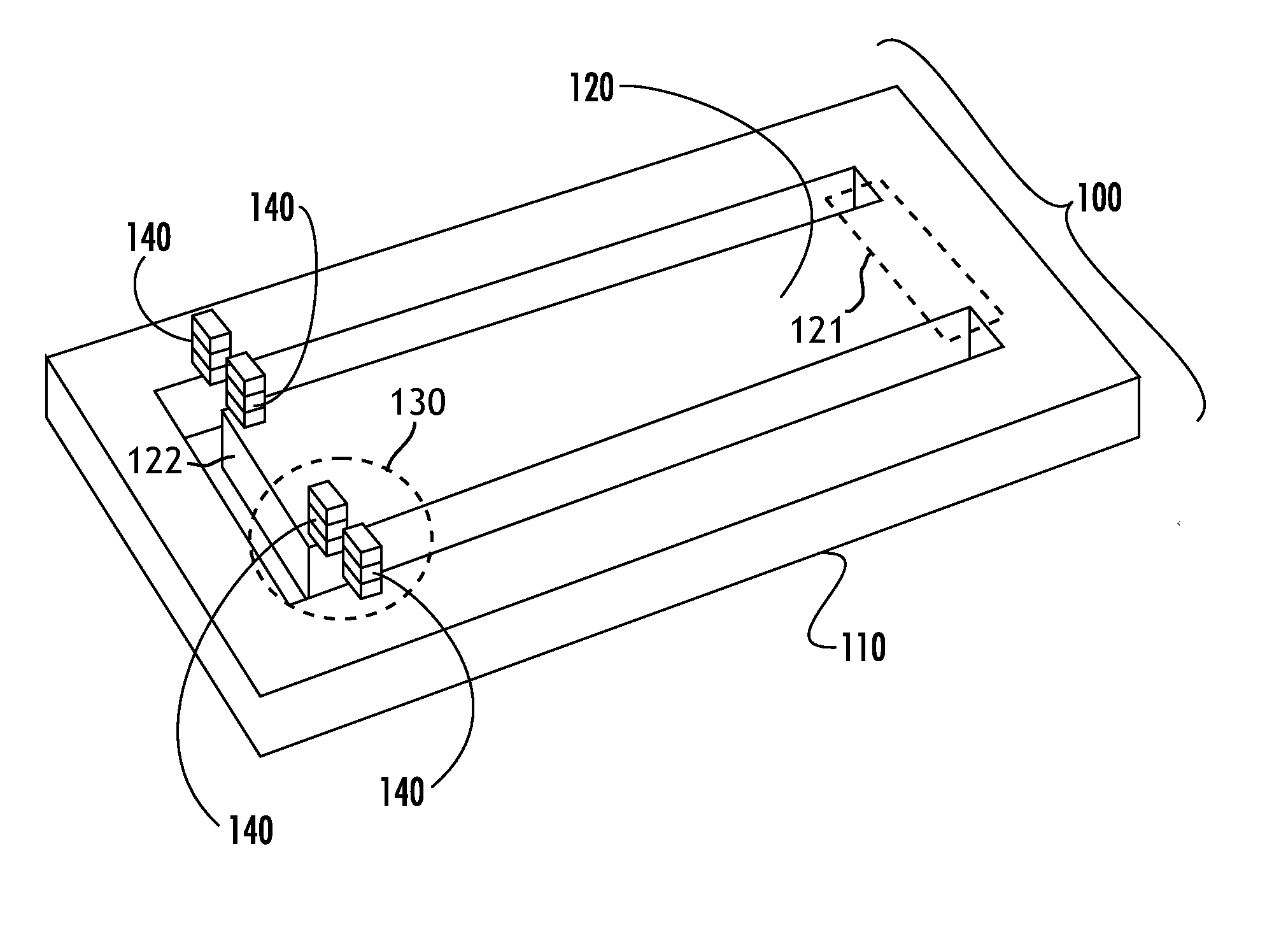
Supporting device, lithographic apparatus, and device manufacturing method employing a supporting device, and a position control system arranged for use in a supporting device
ActiveUS7084956B2Avoid positioningImprove accuracyNon-rotating vibration suppressionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice formEngineering
A supporting device for supporting in a lithographic projection apparatus a supported part relative to a supporting part, is presented. The supporting device includes a first part that engages the supporting part of the lithographic projection apparatus; a second part that engages the supported part of the lithographic projection apparatus; a supporting spring system disposed between the first part and the second part; and a position control system configured to control a position of the supported part. The position control system comprises at least one reference object that is movable relative to the supporting part; a reference support device that supports the reference object relative to the first part, wherein the reference object and the reference support device form a reference mass-spring system; at least one position sensor that detects at least one attribute of the position of the second part relative to at least one of the reference objects, the position sensor including a sensor output for outputting a position signal representing at least one of the attributes; and an actuator, communicatively coupled to the position sensor, that is configured to adjust the position of the second part relative to the first part, in response to the position signal.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Simulation Method of Soft Tissue Deformation Based on Meshless Galerkin and Particle Spring Coupling
InactiveCN102262699AImprove continuityImprove stabilitySpecial data processing applicationsComputation complexitySoft tissue deformation
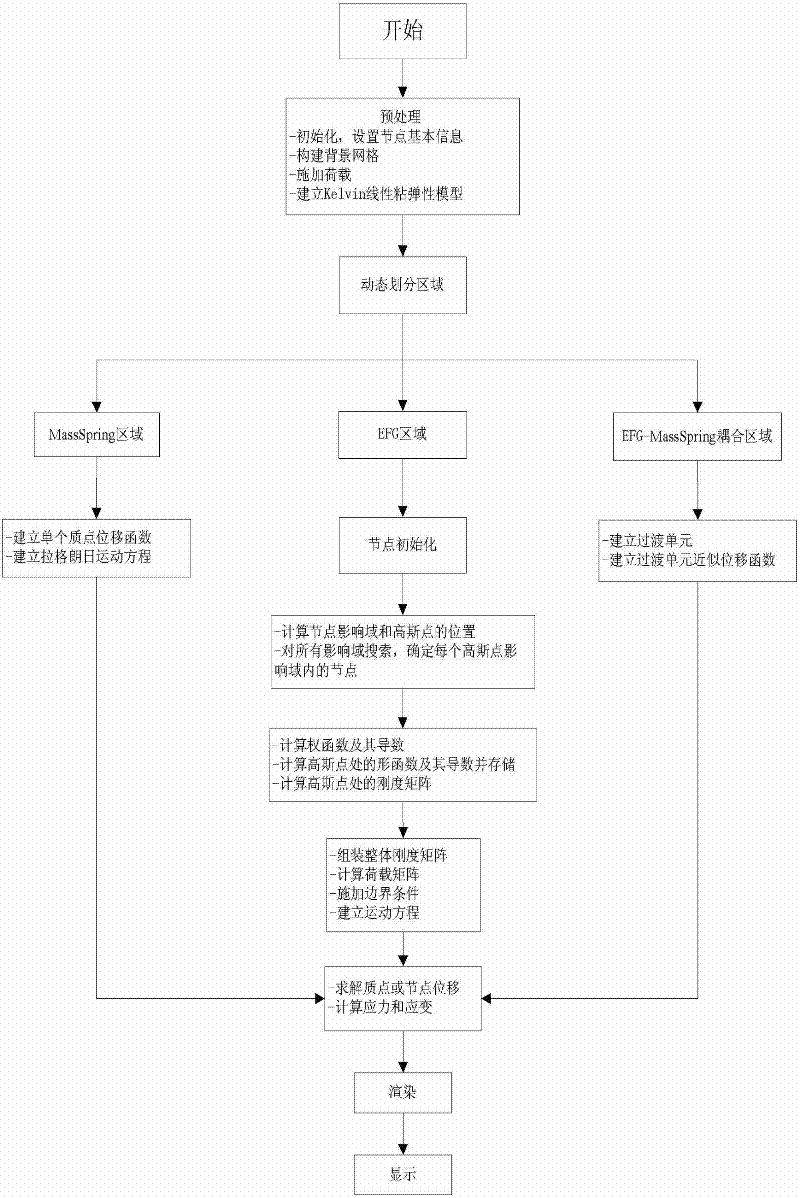
The invention relates to an object deformation real-time simulation graphic processing technique, particularly a soft tissue deformation simulation method based on coupling of mesh-free Galerkin and mass spring, which comprises the following steps: in the pretreatment process, establishing a linear viscoelasticity biomechanical model for soft tissues; in the deformation computation process, dynamically partitioning a mesh-free region and a mass spring region according to the load carried by the soft tissues, establishing a transitional unit of the connection region between the mesh-free region and mass spring region, and constructing a transitional unit approximation displacement function, thereby implementing self-adapting coupling of a mesh-free Galerkin method and a mass spring method;and in the after-treatment process, outputting the state of the mass or node of each time step in the deformation process onto a screen, carrying out illumination rendering, and finally displaying the real-time deformation process of the soft tissue organ under stressed conditions on the screen, thereby implementing visualization effect of dynamic deformation. By utilizing the advantage of high efficiency in the mass spring method and the advantages of high precision and no need of mesh reconstruction in the mesh-free Galerkin method, the invention overcomes the defect that the Galerkin method is not suitable for solving a large-scale problem, thereby effectively lowering the complexity of computation in the soft tissue deformation simulation and enhancing the operation efficiency.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
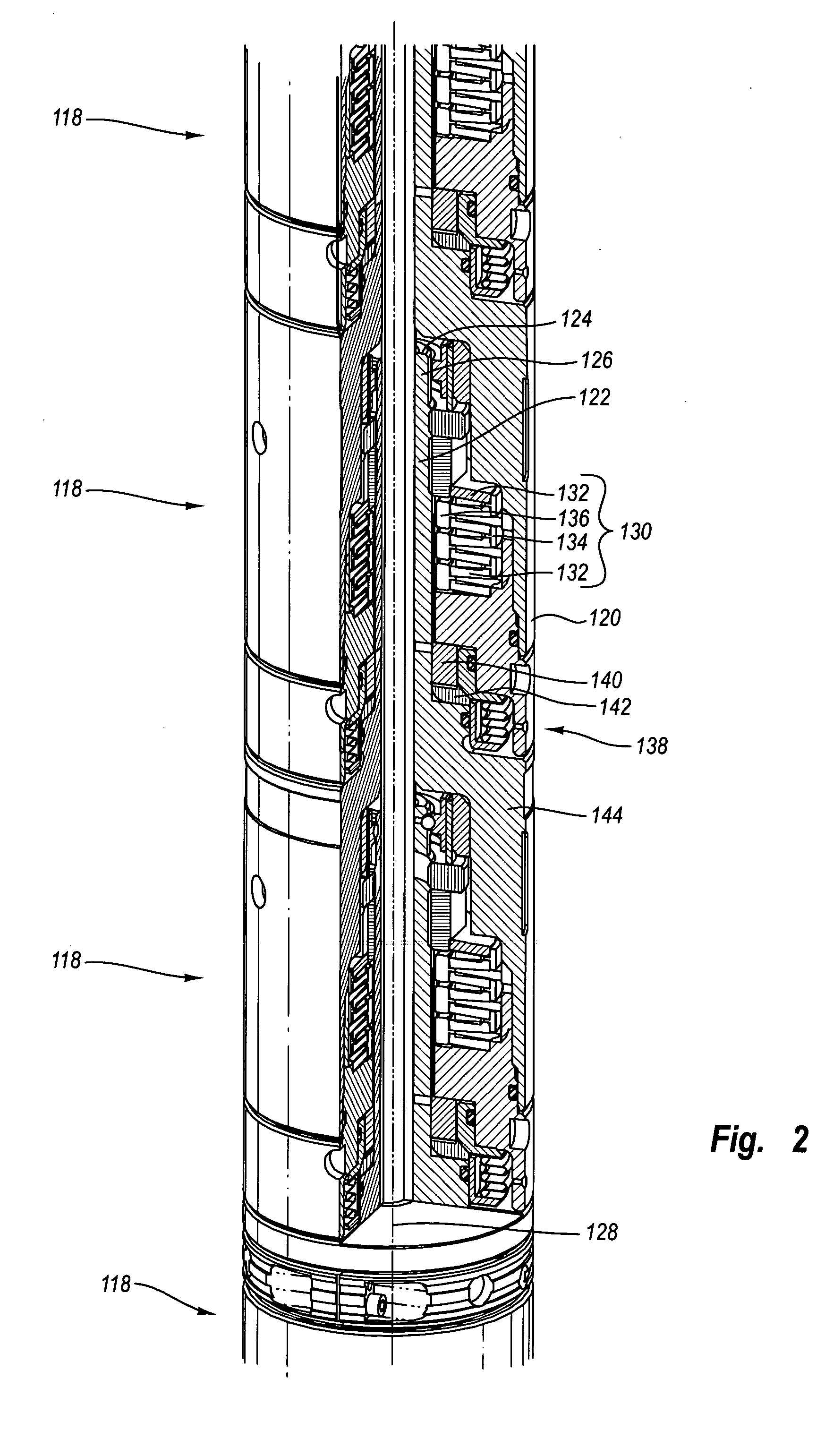
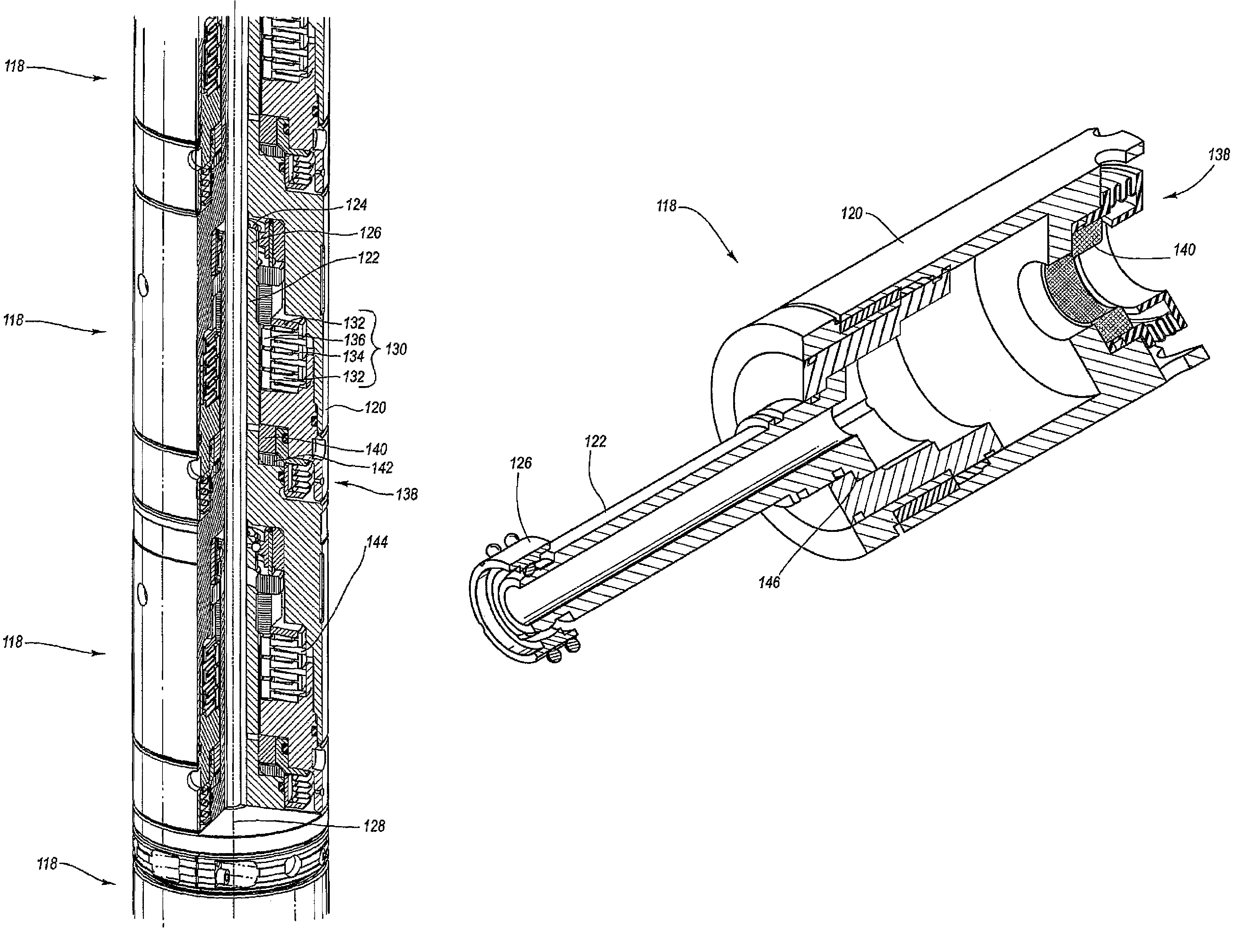
Acoustic isolator between downhole transmitters and receivers
ActiveUS20050167101A1High tensile strengthLower cutoff frequencyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersFluid removalUltrasound attenuationEngineering
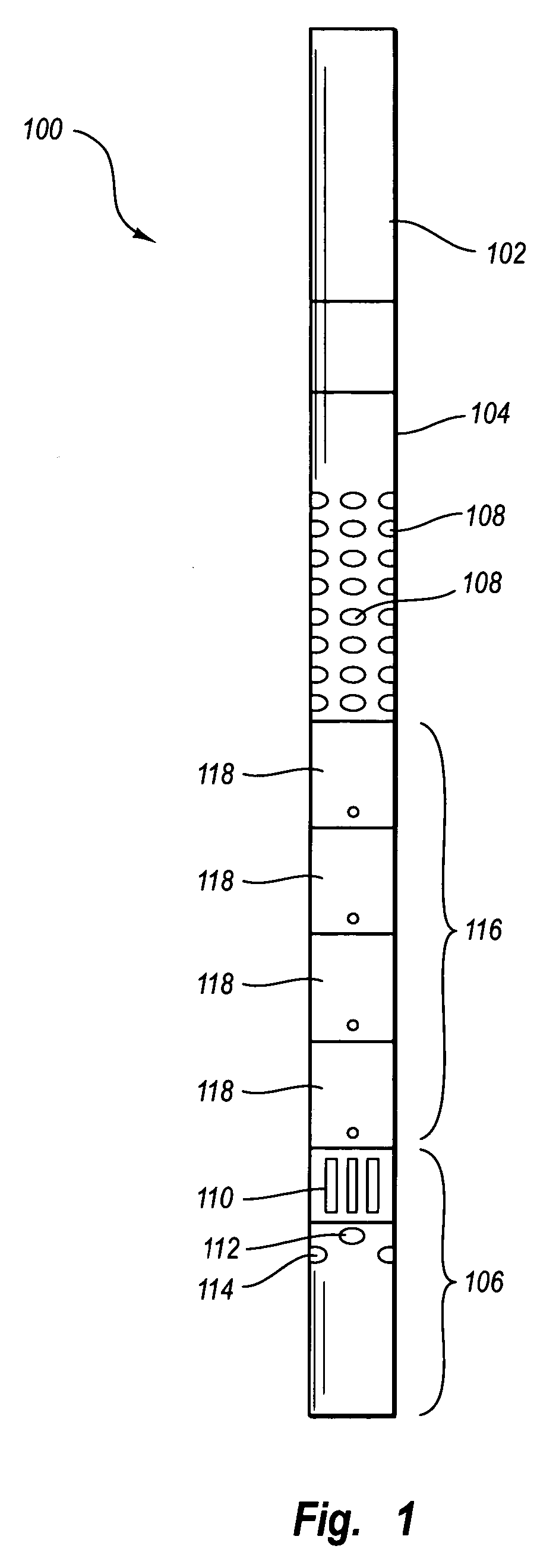
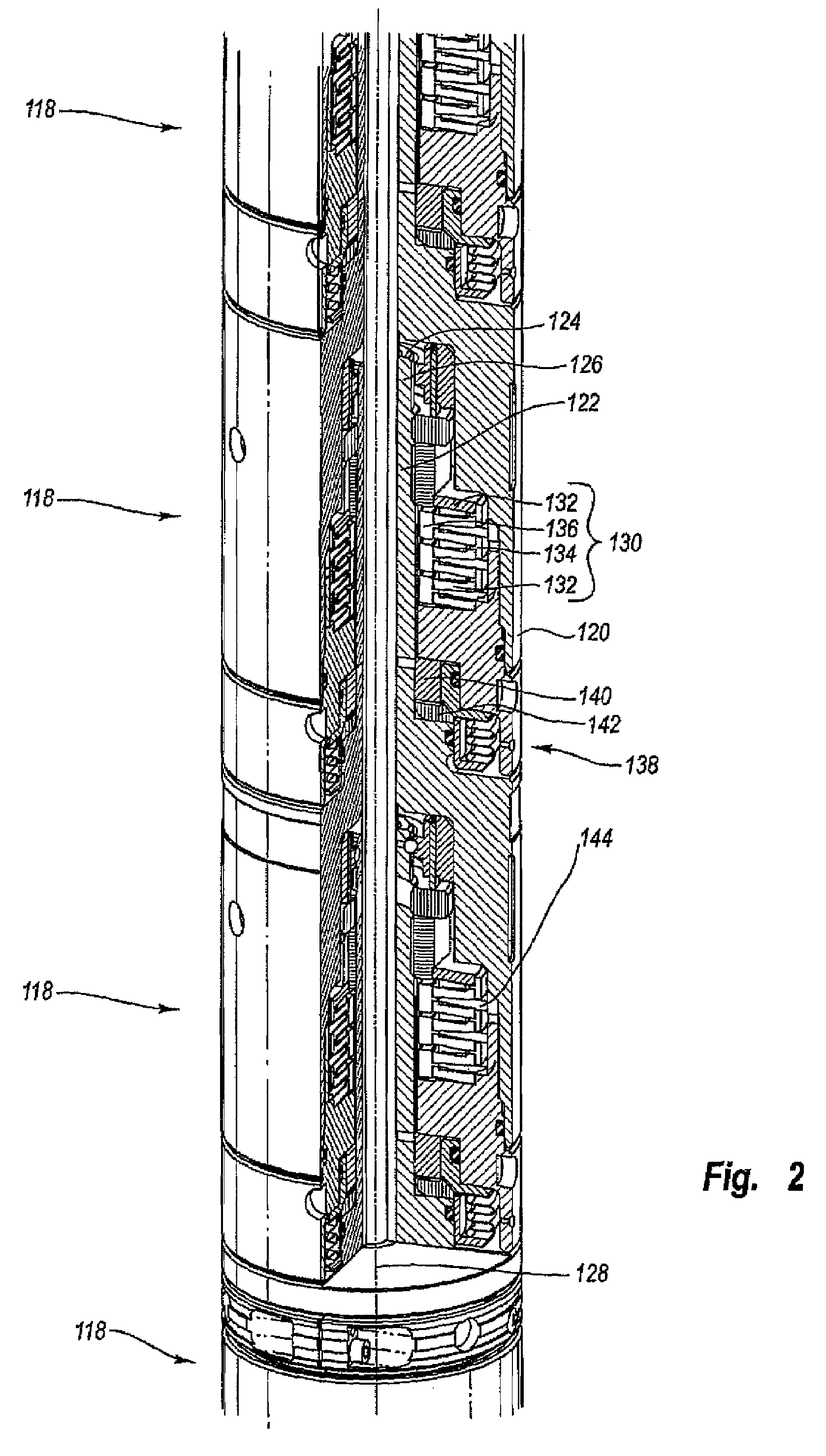
Apparatus and methods for acoustically isolating logging tool receiver and transmitter sections. One or more modular isolators is arranged between the receiver and transmitter sections. The modular isolators comprise a high tensile strength while also providing for a high wave attenuation level. The modular isolators are mechanical mass-spring systems capable of absorbing acoustic waves propagating along the logging tool. The mass is a swinging sleeve, and the spring includes a Belleville spring stack. The use of the strong modular isolators provides acoustic isolation between the transmitters and receivers for the complete sonic frequency band at multiple modes.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Diamond nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center-based acceleration sensor
ActiveCN105352489AHigh measurement accuracySolve the accuracy problemTurn-sensitive devicesMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMicro nanoAccelerometer
The invention relates to a diamond nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center-based acceleration sensor. Through high-NV center concentration diamond as a magnetic field sensing element, Rabi-flopping frequency of an NV center ensemble electronic two-level energy system produced by laser pulse is measured by an optical detection magnetic resonance (ODMR) so that under the action of extraneous acceleration, high-precision measurement of a variable magnetic field produced by change of relative displacement of a magnetostatic field and high-NV center concentration diamond is realized and thus acceleration information measurement is realized. Through combination of a traditional acceleration sensor mass-spring structure, a micro-nano light-machine-electricity technology and a diamond NV center quantum manipulation principle and use of the diamond NV center in the ultrahigh precision magnetic field measurement, the acceleration sensor member with a small volume, an ultrahigh precision, high sensitivity and a large measurement scope is obtained. The acceleration sensor has an important value in an accelerometer and a gravimeter.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
MEMS mass-spring-damper systems using an out-of-plane suspension scheme
ActiveUS20110030472A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopeMass spring damper
MEMS mass-spring-damper systems (including MEMS gyroscopes and accelerometers) using an out-of-plane (or vertical) suspension scheme, wherein the suspensions are normal to the proof mass, are disclosed. Such out-of-plane suspension scheme helps such MEMS mass-spring-damper systems achieve inertial grade performance. Methods of fabricating out-of-plane suspensions in MEMS mass-spring-damper systems (including MEMS gyroscopes and accelerometers) are also disclosed.
Owner:KING ABDULLAH UNIV OF SCI & TECH
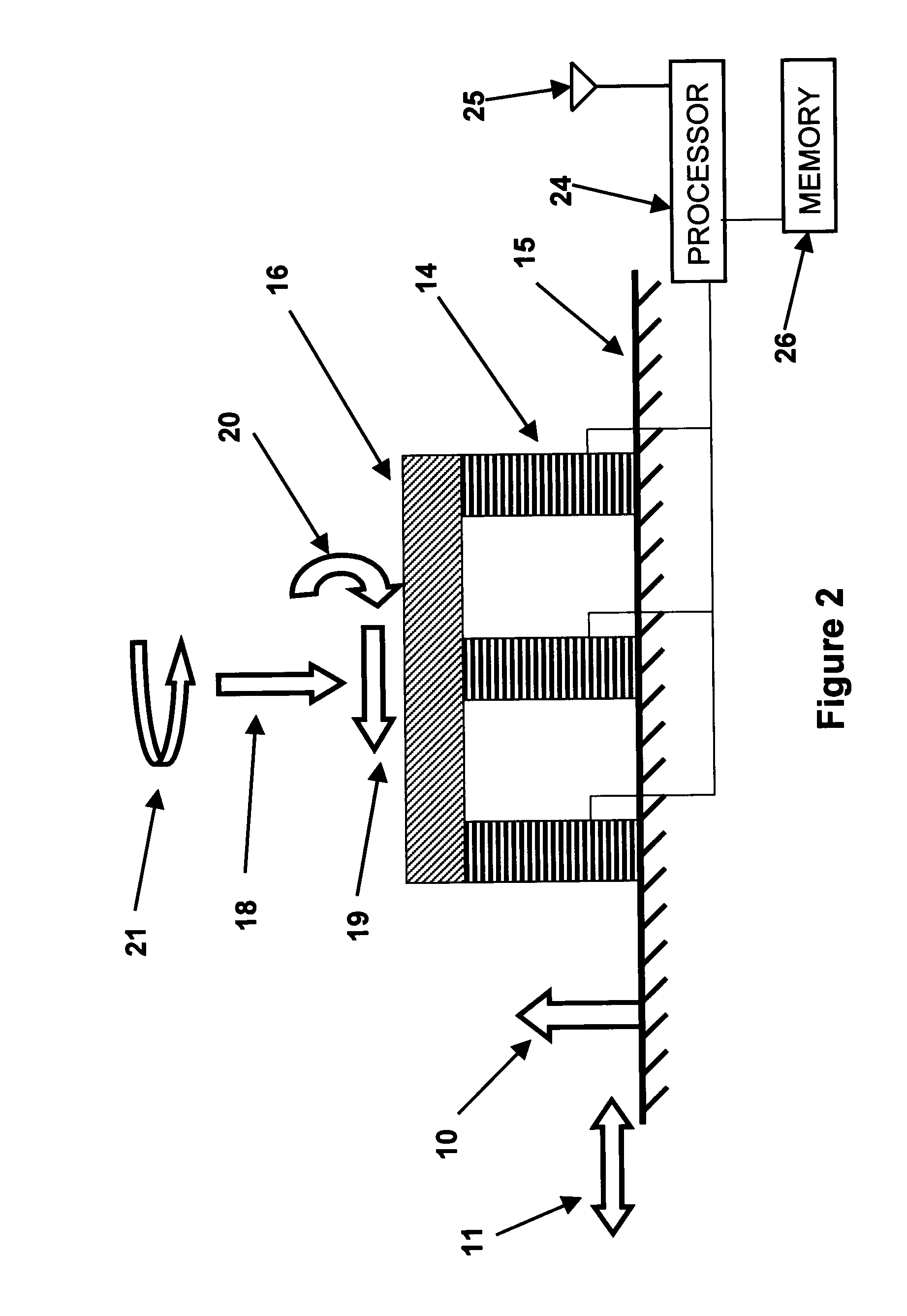
Supporting device, lithographic apparatus, and device manufacturing method employing a supporting device, and a position control system arranged for use in a supporting device
ActiveUS20050018160A1Improve accuracyAvoid positioningNon-rotating vibration suppressionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice formEngineering
A supporting device for supporting in a lithographic projection apparatus a supported part relative to a supporting part, is presented. The supporting device includes a first part that engages the supporting part of the lithographic projection apparatus; a second part that engages the supported part of the lithographic projection apparatus; a supporting spring system disposed between the first part and the second part; and a position control system configured to control a position of the supported part. The position control system comprises at least one reference object that is movable relative to the supporting part; a reference support device that supports the reference object relative to the first part, wherein the reference object and the reference support device form a reference mass-spring system; at least one position sensor that detects at least one attribute of the position of the second part relative to at least one of the reference objects, the position sensor including a sensor output for outputting a position signal representing at least one of the attributes; and an actuator, communicatively coupled to the position sensor, that is configured to adjust the position of the second part relative to the first part, in response to the position signal.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Damping arrangement for dissipating oscillating energy of an element in a system, more particularly in a microlithographic projection exposure apparatus
ActiveUS20140202812A1Optimization of degree of dampingDissipate energyPhotomechanical apparatusShock absorbersElectricityDissipative system
The invention relates to a damping arrangement for dissipating oscillation energy of an element in a system, more particularly in a microlithographic projection exposure apparatus, comprising an absorber mass, which is mounted via a stable mounting with respect to the element, wherein the absorber mass is arranged in a cavity present within the element and is at least partly surrounded by a fluid situated in the cavity, wherein a mass-spring system is formed by the absorber mass, the system damping a translational movement component of an oscillation of the element that exists at the linking point of the absorber mass, and wherein the stable mounting is formed by a rheological fluid that is electrically controllable or controllable via electric or magnetic fields.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
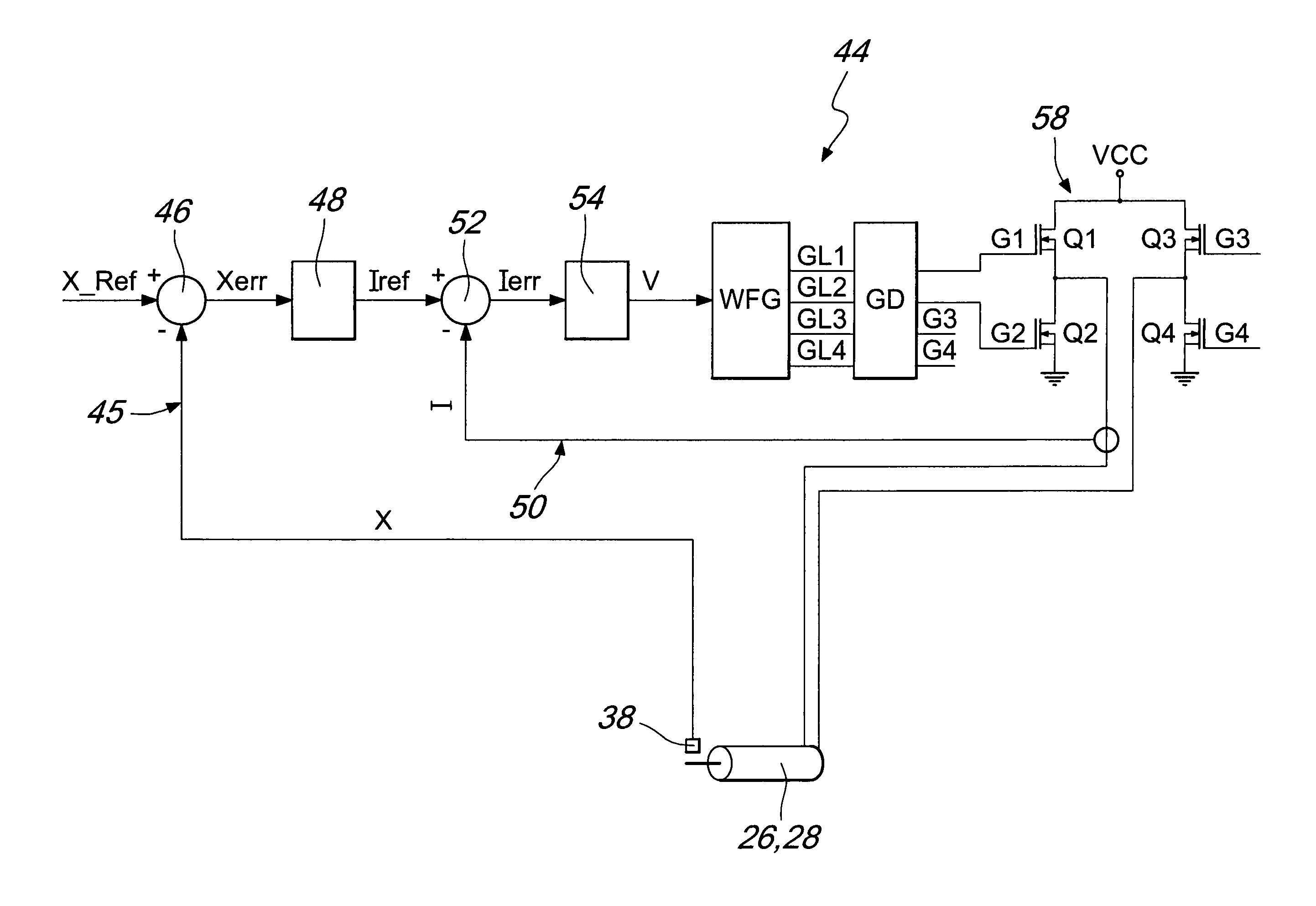
Methods and apparatus for mechanical reserve power sources for gun-fired munitions, mortars, and gravity dropped weapons
ActiveUS8183746B2Improve the level ofSufficient energyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectric fuzesEngineeringGravitation
A power source including: a power generation device; a mass-spring unit having a mass and an elastic element operatively connected to the power generation device; and one or more retention fingers releasably engaged with the mass-spring unit for retaining the mass-spring unit in a position such that potential energy is stored therein and for releasing the potential energy upon occurrence of an event to generate electrical energy in the power generation device, the one or more retention fingers having a first end fixed at a base and a second end releasably engaged with the mass-spring unit. The occurrence of the event can be one or more of an acceleration and spinning of the base. Also disclosed is a power source having one or more retention fingers that are slidable with respect to a base such that the engagement of the first end is released upon a spinning of the base.
Owner:OMNITEK PARTNERS LLC
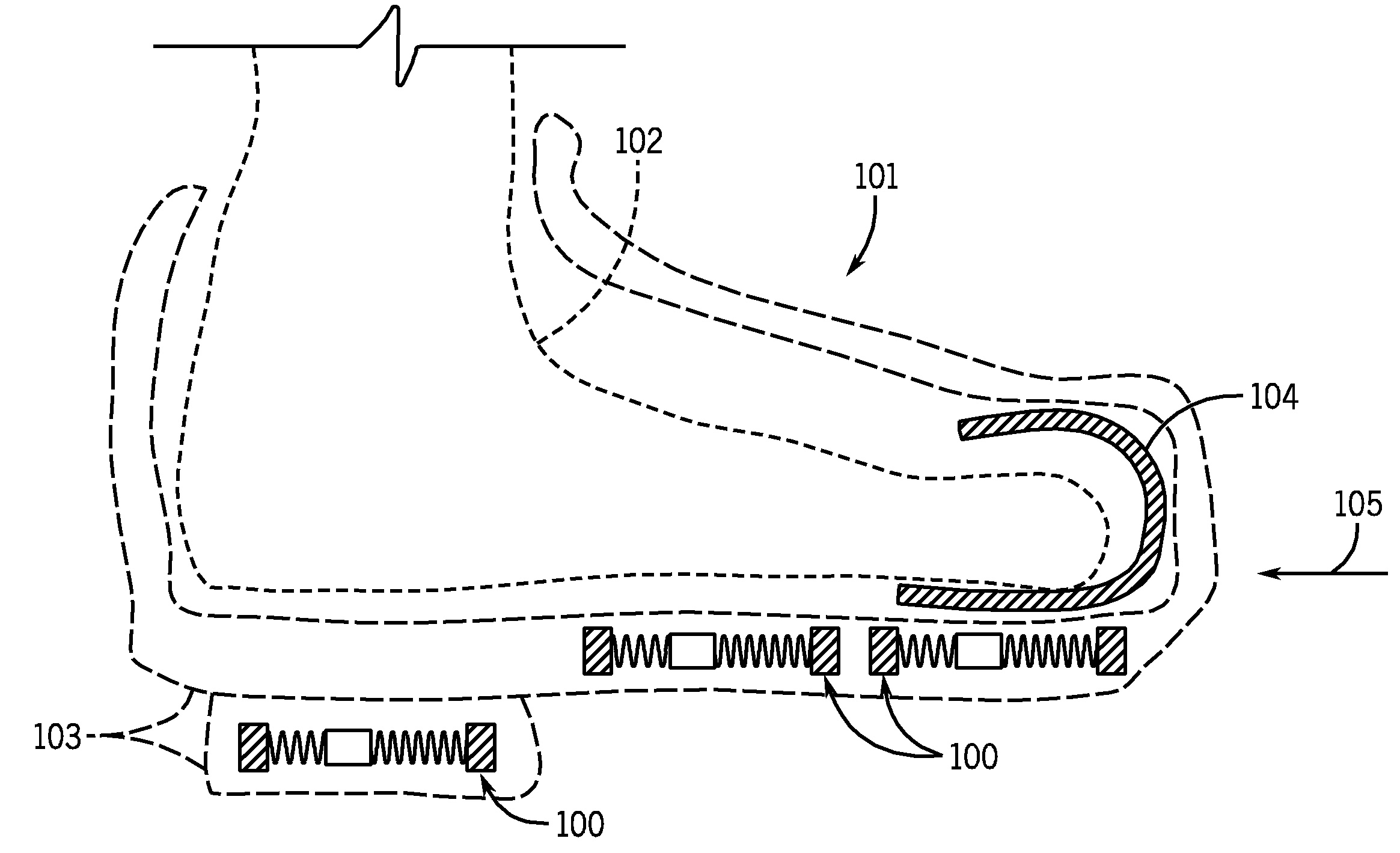
Piezoelectric-based toe-heaters for frostbite protection
InactiveUS8087186B2SolesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityEngineering
A footwear including a body; a base structure; and one or more electrical energy generators disposed in the base structure for generating electrical energy upon application of an impact to the base structure. The footwear is used to produce electrical energy by impacting a base structure of the footwear; and vibrating a mass-spring unit in the base structure to generate an electrical energy.
Owner:OMNITEK PARTNERS LLC +1
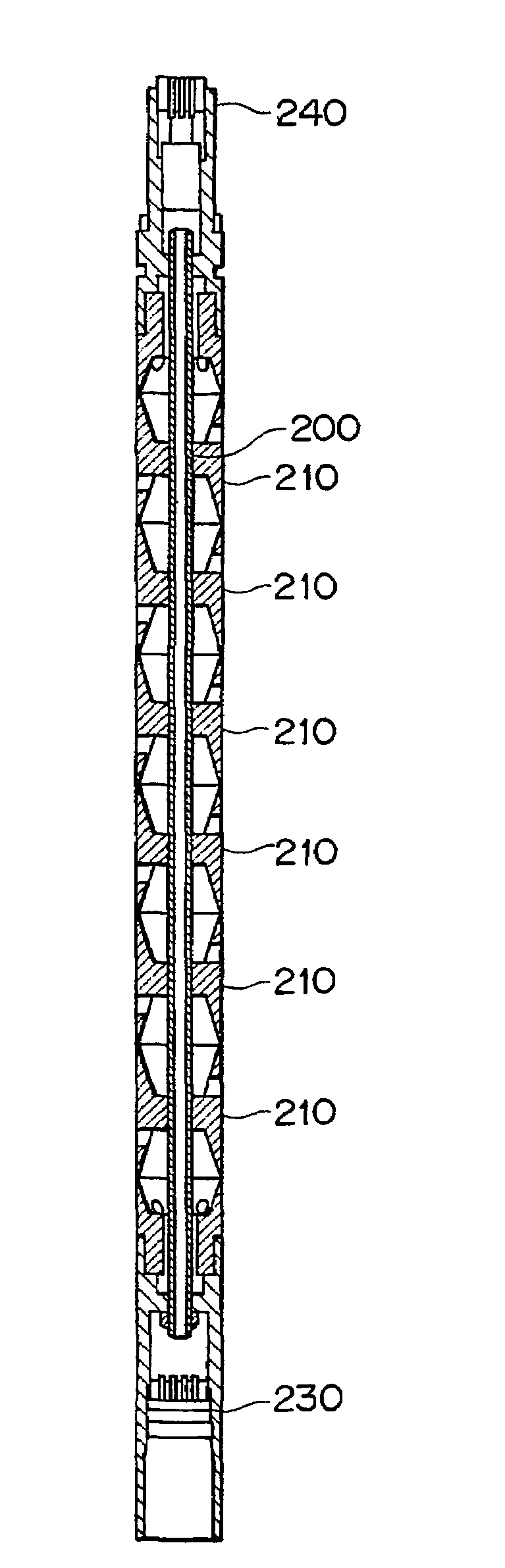
Sonic logging tool including receiver and spacer structure
InactiveUS7336562B1Prevent removalAchieve communicationSeismology for water-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationDispersion curveEngineering
A formation logging tool having a substantially continuous central mandrel with regularly spaced mass blocks disposed thereon, at least some of the mass blocks carrying sensors such as receivers. By adopting this structure, the tool can be made to behave as a mass-spring structure and its flexural and extensional behaviour controlled such that its dispersion curve does not extend into the dispersion curve of the formation to be logged. The structure can be applied to the whole of the logging tool or just to the receiver section and / or any spacer section between the receiver and the transmitter section.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Methods of Forming Micromechanical Resonators Having High Density Trench Arrays Therein that Provide Passive Temperature Compensation
InactiveUS20100319185A1High and low mechanical stressPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksHigh densityNegative temperature
A method of forming a micromechanical resonator includes forming a resonator body anchored to a substrate by at least a first anchor. This resonator body may include a semiconductor or other first material having a negative temperature coefficient of elasticity (TCE). A two-dimensional array of spaced-apart trenches are provided in the resonator body. These trenches may be filled with an electrically insulating or other second material having a positive TCE. The array of trenches may extend uniformly across the resonator body, including regions in the body that have relatively high and low mechanical stress during resonance. This two-dimensional array (or network) of trenches can be modeled as a network of mass-spring systems with springs in parallel and / or in series with respect to a direction of a traveling acoustic wave within the resonator body during resonance.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Acoustic isolator between downhole transmitters and receivers
ActiveUS7216737B2Reduce disruption and disruptionReduce wave propagationPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersSeismic energy generationUltrasound attenuationAcoustic wave
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Local resonance acoustic black hole structure
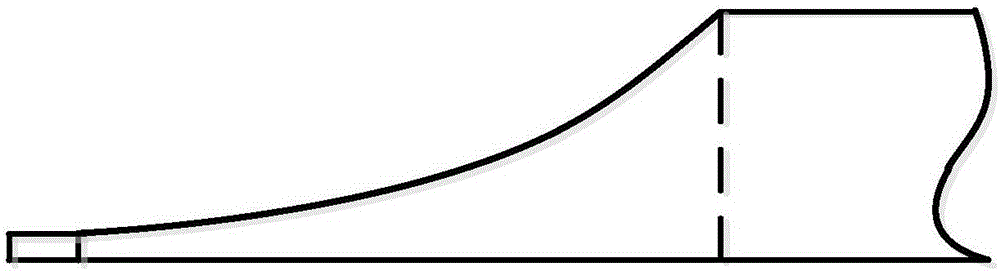
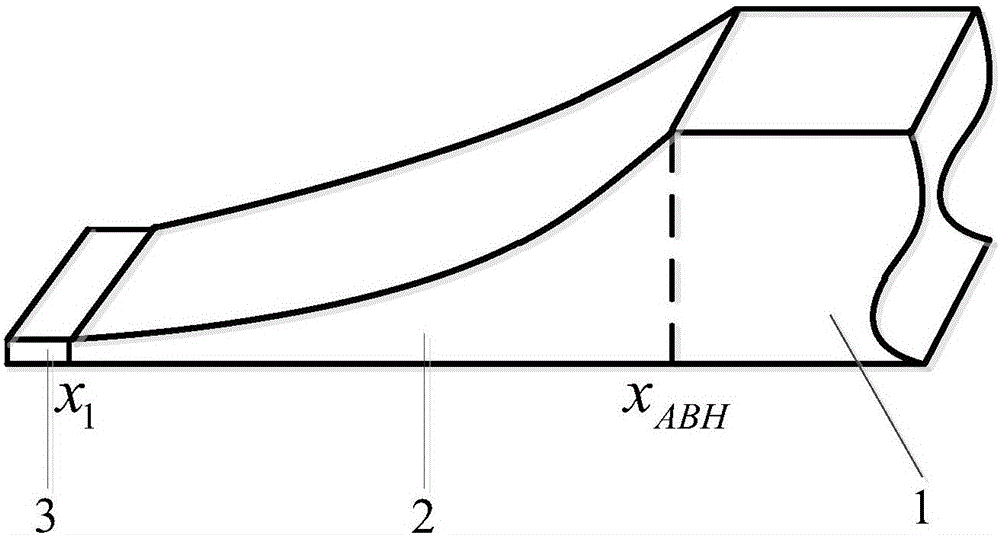
ActiveCN106023979AEasy to adjustReduce weightSound producing devicesVibration controlEffective action
The invention discloses a plate or bridge structure of a local resonance acoustic black hole (ABH). The local resonance acoustic black hole structure comprises an acoustic black hole region (a region which is gradually thinned), a local vibrator (such as a mass spring unit) and an acoustic black hole extension part. According to the local resonance acoustic black hole structure disclosed by the invention, the local vibrator is constituted by units having the properties of a spring vibrator, so that an effective action frequency range of an acoustic black hole effect is reduced, and subsequently, a vibration control effect of the acoustic black hole structure is effectively improved. The local resonance acoustic black hole structure disclosed by the invention has a broad application prospect in vibration absorption and noise reduction of structures.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method and apparatus for damping vibrations in a semiconductor wafer handling arm
InactiveUS6761085B1Reduction in out of plane accelerationReduction in out of plane vibration accelerationPortable framesJointsCantilevered beamControl theory
A vibration damper for a semiconductor wafer handling arm includes a spring and a mass coupled to the spring to form a mass spring system that is tuned to vibrate at a structural resonant frequency of the vibrating wafer handling arm. The spring has temperature insensitive spring characteristics and the mass and spring are constructed of materials that do not outgas or produce contaminants in a semiconductor processing environment. The mass spring system is preferably a cantilever beam spring connected to a high response point on the vibrating arm and oriented to vibrate in a plane perpendicular to the plane of the wafer. The mass is preferably slidably adjustable along the length of the cantilever beam spring to adjust the resonant frequency of the vibration damper. Vibration damping of the wafer handling arm is accomplished by the transfer of kinetic energy from the vibrating wafer handling arm to the mass spring system.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method and apparatus for damping vibrations in a semiconductor wafer handling arm
A method of damping a semiconductor wafer handling arm by attaching a spring and a mass coupled to the spring to form a mass spring system that is tuned to vibrate at a structural resonant frequency of the vibrating wafer handling arm. The spring has temperature insensitive spring characteristics and the mass and spring are constructed of materials that do not outgas or produce contaminants in a semiconductor processing environment. The mass spring system is preferably a cantilever beam spring connected to a high response point on the vibrating arm and oriented to vibrate in a plane perpendicular to the plane of the wafer. The mass is slidably adjustable along the length of the cantilever beam spring to adjust the resonant frequency. Vibration damping of the wafer handling arm is accomplished by the transfer of kinetic energy from the vibrating wafer handling arm to the mass spring system.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Methods and apparatus for integrated energy harvesting power sources and inertial sensors for gun-fired munitions
ActiveUS20100236329A1Improve the level ofSufficient energyAcceleration measurement using interia forcesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityElectric force
A method for generating electrical power from an acceleration of an object is provided. The method including: vibrating a mass-spring unit upon an acceleration of an object; transmitting a force resulting from the acceleration from the mass-spring unit to the one or more piezoelectric elements; converting the vibration of the mass-spring unit to an electrical energy; and calculating at least one of the force and acceleration based on an output of the one or more piezoelectric elements.
Owner:OMNITEK PARTNERS LLC
Automotive noise attenuating trim part
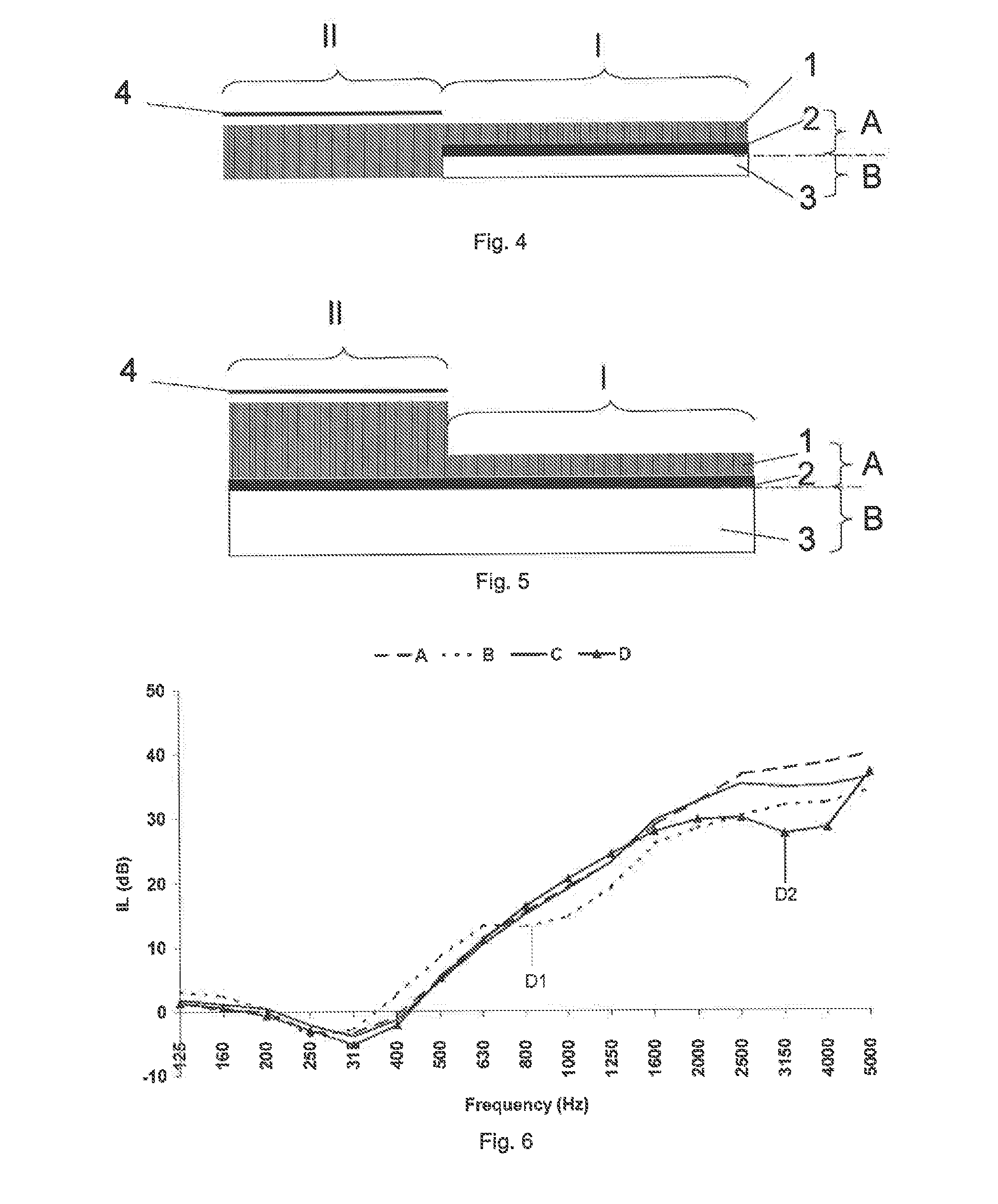
ActiveUS20140014438A1Increase the number ofReduce weightWallsVehicle componentsRadiation frequencyYoung's modulus
A sound attenuating trim part, including at least one insulating area with an acoustic mass-spring characteristics having at least a mass layer and a decoupling layer adjacent to the mass layer, whereby the mass layer consists of a porous fibrous layer and a barrier layer, with the barrier layer being located between the porous fibrous layer and the decoupling layer and all layers are laminated together, and whereby the porous fibrous layer at least in the insulating area has adjusted dynamic Young's modulus (Pa) such that the radiation frequency of is at least 3000 (Hz).
Owner:AUTONEUM MANAGEMENT AG
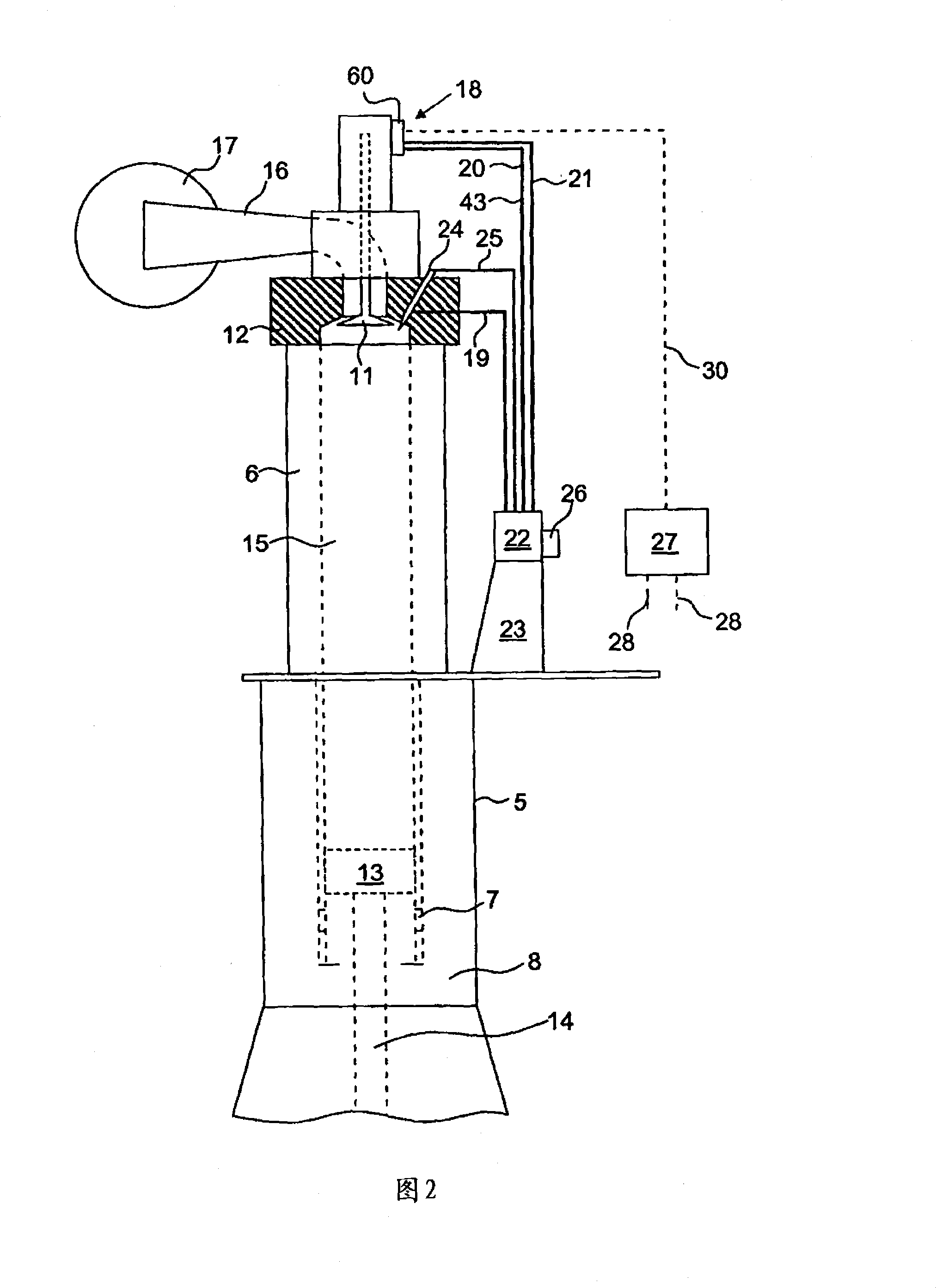
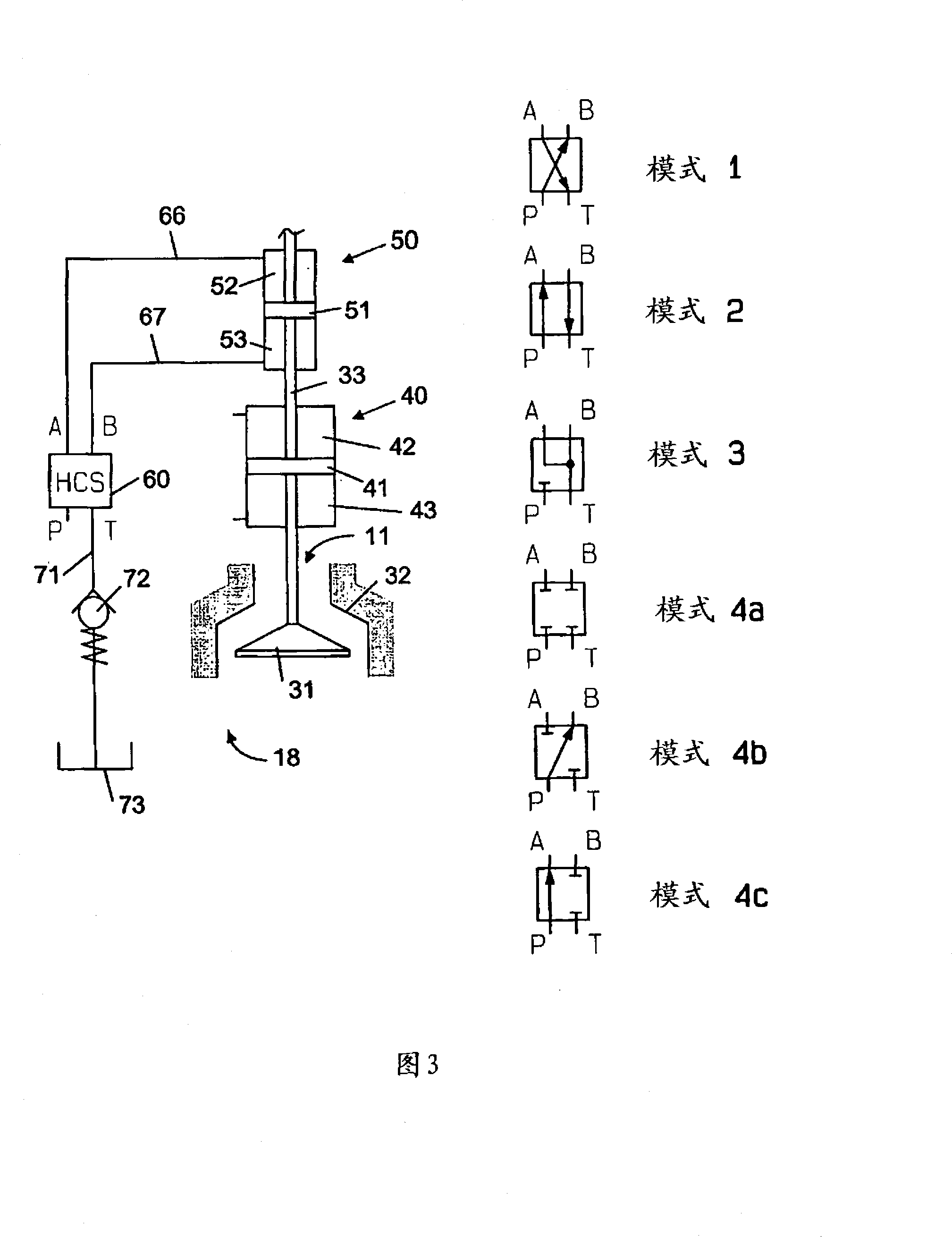
Exhaust valve assembly for a large two-stroke diesel engine
InactiveCN101160457ALess hydraulic energyEasy to useCasingsCombustion enginesExhaust valveFuel efficiency
The present invention relates to an exhaust valve assembly (18) for a large two-stroke diesel engine (1). The assembly (18) includes an exhaust valve (11) that is movable in opposite directions between a closed position and a open position. A double acting spring assembly (40) is operably connected to the exhaust valve (11) and forms a mass-spring system together with the exhaust valve (11) and the mass of any other parts moving in unison with the exhaust valve (11). The double acting spring assembly (40) stores energy during translation of the exhaust valve (11) back and forth between the closed and open position for subsequent propulsion of the exhaust valve (11) in an opposite direction. Hydraulic means (50) hold the exhaust valve (11) on command from a controller (27) in the closed or in the open position.
Owner:MAN B & W DIESEL AS
Rotation acceleration meter for earthquake
InactiveCN103149583ACompact structureReasonable designAcceleration measurementSeismic signal receiversCapacitor voltageEngineering
The invention relates to a rotation acceleration meter for earthquake. The meter comprises a shell and a bottom plate. A spoke type mass spring device, two groups of symmetrically and reversely installed swinging type differential capacitive transducers, two groups of moveable coil dampers and a circuit board are arranged in the shell. The spoke type mass spring device is located between the two groups of swinging type differential capacitive transducers which respectively comprise an outer moveable polar plate, an inner moveable polar plate and a fixed polar plate. The circuit board comprises two capacitor voltage converting circuits, two conditioning circuits, a synthetic circuit and two damp adjusting circuits. The rotation acceleration meter for earthquake provided by the invention is compact in structure, reasonable in design, high in monitoring precision, good in reliability and wide in application range.
Owner:INST OF ENG MECHANICS CHINA EARTHQUAKE ADMINISTRATION +2
Compaction device for compacting moulded bodies from granular substances and method for using said device
InactiveUS7025583B2Easy to useHigh repeatabilityConfectioneryCeramic shaping apparatusSystem qualityResonance
Apparatus and method for carrying out compaction operations on molded bodies that consist of granular materials and are placed on pallets, the compaction being achieved by impact of a vibrating table on the underside of the pallet. The vibrating table, together with a spring system forms a mass-spring system, which acts as a vibrator capable of oscillation that is excited by an excitation device to produce forced vibrations. The spring system, together with the system mass, is designed to develop at least one individual frequency within the range of the compaction frequency, whereby it is also possible to adjust the individual frequency gradually or continuously. This, together with the fact that the excitation frequency can be adjusted, allows the vibrator to be operated partially or completely in resonance mode over the whole frequency range of the compaction.
Owner:GEDIB ING & INNOVATIONSBERATUNG
Control unit for yarn-braking devices in weft feeders for looms, and tuning method therefor
InactiveUS7584014B2Improve automationShort execution timeLoomsFilament handlingYarnReference current
Owner:L G L ELECTRONICS
Hybrid modeling method of virtual flexible cable
ActiveCN105160098ASolve the characteristicsSolve the requestSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringPhysical property
The invention provides a hybrid modeling method of a virtual flexible cable, and belongs to the technical field of flexible object modeling. The cable is divided into N sections, sub-cables which require high static attitude fidelity are modeled by an energy optimization method, the sub-cables which require high dynamic real-time attitude fidelity are modeled by a mass spring method, a constraint that two sub-cable segments connected on a connection point pass the same fixed point, and a constraint that the two connected sub-cable segments on the connection point have the consistent tangent direction are set, and finally, a hybrid model of the flexible cable is determined. The cable constraints including an endpoint constraint and a hoop constraintare processed according to practical situations. By means of the hybrid modeling method, the instantaneity requirement of virtual environment on a cable moving posture can be met, the physical properties of the cable can be considered as much as possible in a cable model, the authenticity of the flexible cable model is improved and a support for subsequent virtual cable layout, assembling, final assembly troubleshooting and maintenance simulation is provided.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
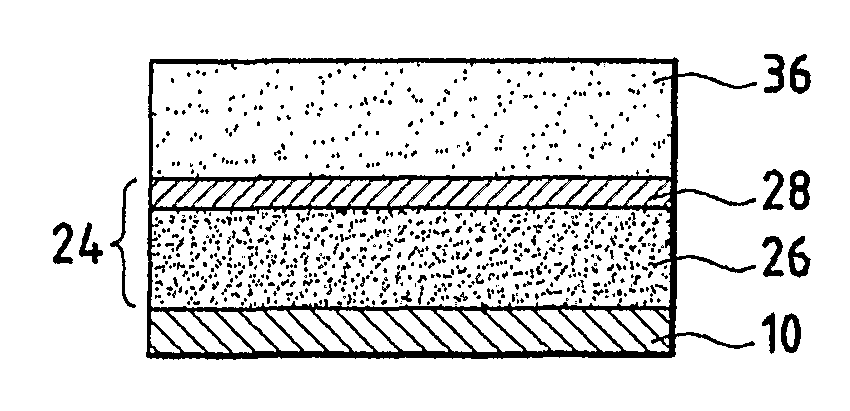
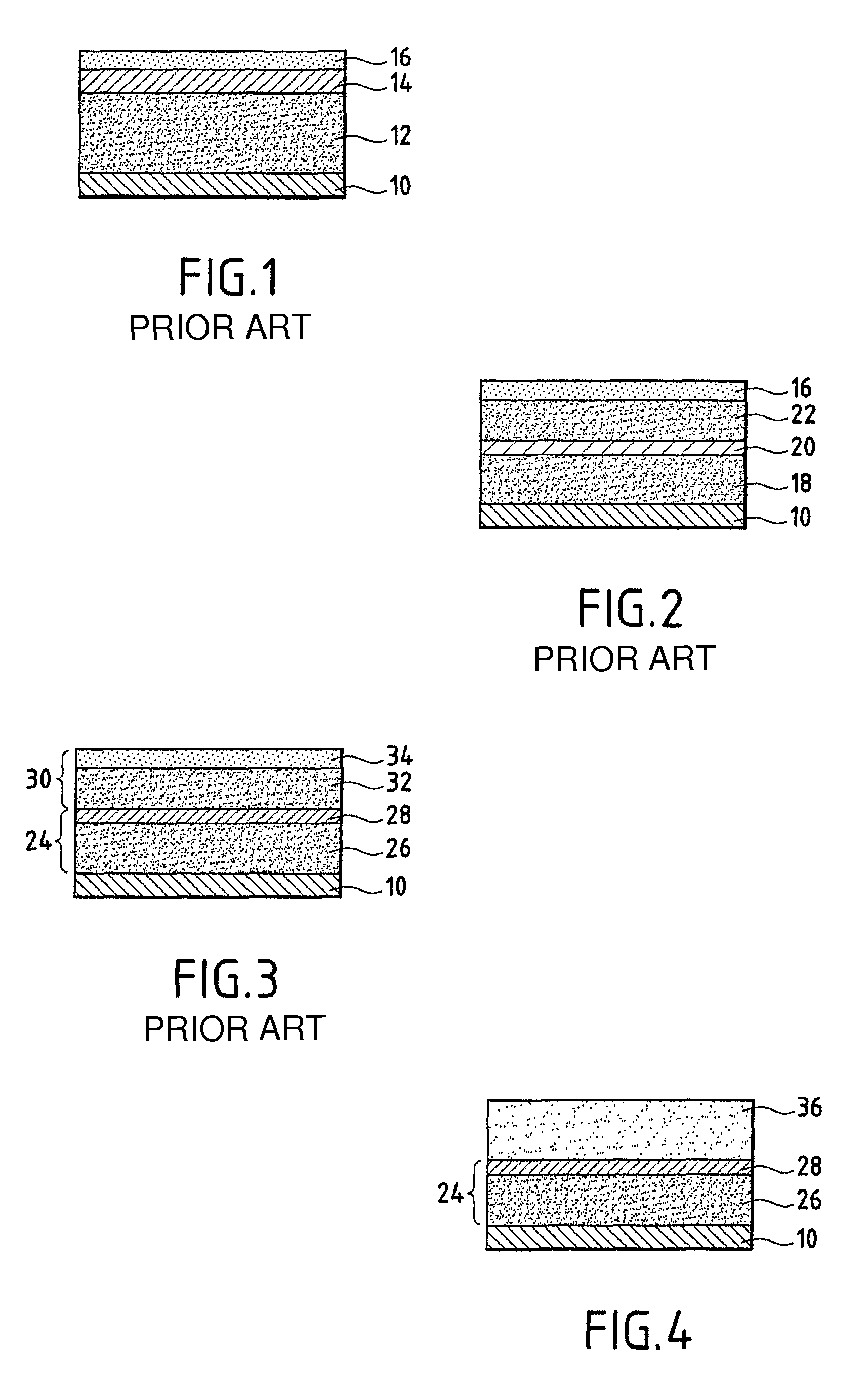
Soundproofing assembly, use for soundproofing enclosed spaces, and method for making same
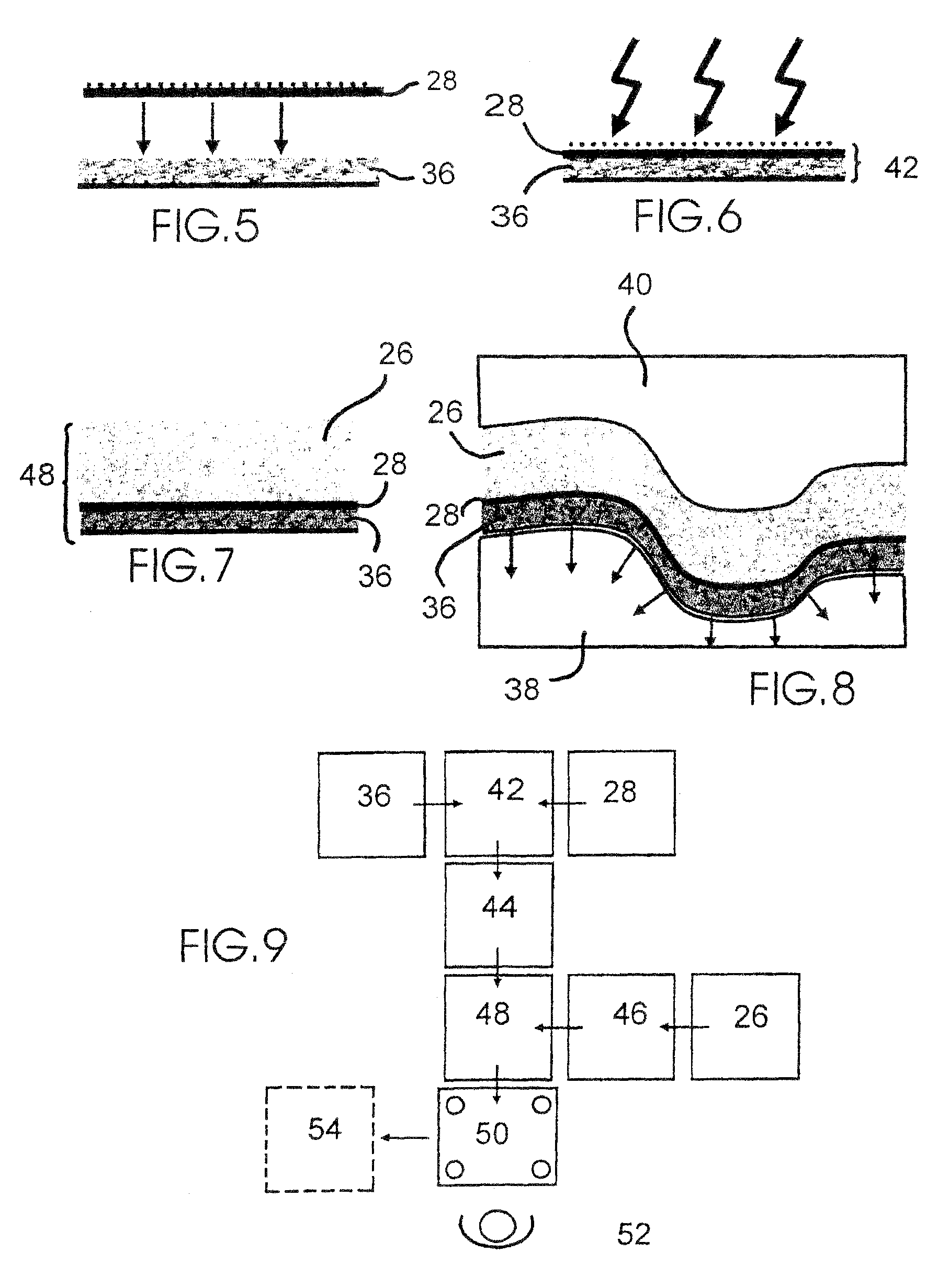
ActiveUS7789197B2Improve sound insulationIncreased tortuosityLamination ancillary operationsWallsEngineeringAcoustic wave
A soundproofing assembly includes stacked layers in the form of a first set of layers (36) having good resistance to the passage of air, and a second set of layers (24) with mass-spring function including a layer (28) having a heavy viscoelastic mass and a spring type layer (26); the first set of layers includes a layer (36) of a foam with open cells of high porosity, high tortuosity and good resistance to the passage of air, the layer (36) having, owing to its high tortuosity, excellent sonic absorption properties at medium and high frequencies. The invention is useful for soundproofing motor car passenger compartments.
Owner:FAURECIA AUTOMOTIVE IND
Coupled Mass-Spring Systems and Imaging Methods for Scanning Probe Microscopy
InactiveUS20100257644A1Improve abilitiesImprove performanceNanotechnologyScanning probe microscopyPhase shiftedResonance
A novel way for constructing and operating scanning probe microscopes to dynamically measure material properties of samples, mainly their surface hardness, by separating the functions of actuation, indentation and sensing into separate dynamic components. The amplitude and phase shift of higher modes occurring at periodic indentations with the sample are characteristic values for different sample materials. A separate sensor cantilever, connected to the indentation probe tip, has the advantage of a high mechanical amplification of a desired higher mode while suppressing the actuation signal itself. The operational range of the sensor can be extended just by switching the actuation signal to another submultiple of the sensor cantilever's resonance frequency and / or by using more than one sensor cantilever for each indentation tip.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Automotive trim part for sound insulation and absorption
A sound insulating trim part with at least one area with predominantly sound absorbing characteristics (absorbing area), at least one other area with acoustic mass-spring characteristics (insulating area), characterised in that the mass layer of the insulating area consists of the same porous fibrous layer as the absorbing area, in the insulating area adjusted to a dynamic Young's modulus (Pa) of at least (96-AW-t) with AW area weight (g / m2), and t thickness (mm) of the porous fibrous layer, and at least an impervious thin barrier layer between the porous fibrous layer and the decoupling layer.
Owner:AUTONEUM MANAGEMENT AG
Design and structure of self-locking type rail base dynamic vibration absorber
The invention discloses the design and a structure for a self-lock type rail bottom dynamic vibration absorber. An elastic element (3) is paved under a steel rail (1); the middle part of the elastic element is buried with one or more resonant mass blocks (4, 5) in an adhesion mode or an non-adhesion mode; the mass and the distribution positions of the resonant mass blocks are optimized according to the maximum vibration-absorbing amplitude; the elastic element and the resonant mass blocks form a multi-mode dynamic resonant mass-spring unit; and a self-lock type magazine clip (2) passes through the elastic element along the vertical direction of the steel rail and then is clamped at side edges of both ends of a rail root of the steel rail to firmly lock the elastic element on the bottom of the steel rail; when the steel rail vibrates, the dynamic resonant mass-spring unit produces the resonance, thereby realizing the suppression to the vibration of the steel rail and the transfer and absorption to vibration energy, attenuating the amplitude of the steel rail, and reducing the noise radiation of the steel rail caused by the vibration; at the same time, the design can also inhibit the generation and increase of the waviness corresponding to resonant frequency bands of the wave of the steel rail, thereby controlling the excitation of the waviness of the steel rail to a wheel rail and the produced vibration and noise, reducing the action force of the wheel rail, and increasing the riding comfortableness .
Owner:洛阳双瑞橡塑科技有限公司
Time Domain Sensor Systems, Devices, and Methods Using Enhanced Nonlinear Least-Squares Curve Fitting
A time domain sensor system operable via a set of executable instructions storable in relation to a memory device for transforming output data by performing a nonlinear least-squares curve fitting, involving: a time domain sensor device having a mass-spring oscillator including a frame portion and a cantilever portion having a proximal end and a distal end, the cantilever portion coupled with the frame portion; and a plurality of proximity switches having a movable portion and a fixed portion in relation to the frame portion, each proximity switch of the plurality of proximity switches having at least one proximity tip, and each proximity switch configured to trigger in response to an acceleration experienced by the cantilever portion; and a processor operatively coupled with the time domain sensor device and configured to operate via the set of executable instructions for transforming the output data by performing a nonlinear least-squares curve fitting.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
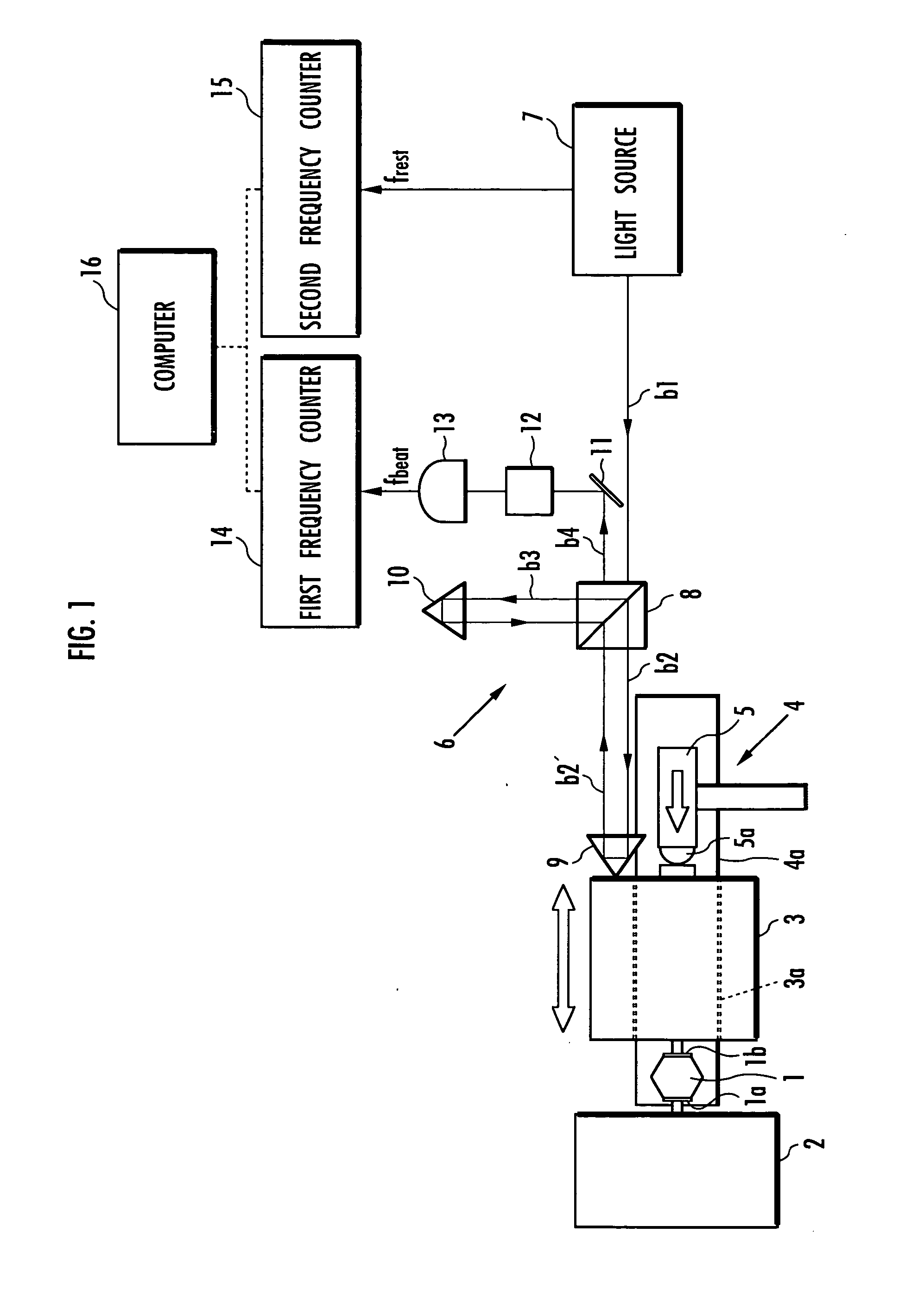
Material testing method
InactiveUS20050097964A1Guaranteed accuracyAccurate assessmentAcceleration measurement using interia forcesForce measurementMaterials testingEngineering
The present invention aims to achieve accurate measurement and evaluation of mechanical properties of an object to be measured 1 without use of a force sensor. A weight 3 is attached to the object to be measured 1 to form a mass-spring system in which the object to be measured 1 serves as a spring element. Then vibration is applied to the mass-spring system to measure the inertial force acting on the weight 3 and the displacement of the weight 3 so that the mechanical properties of the object to be measured 1 will be evaluated based on the inertial force and displacement. A light wave interferometer 6 measures the displacement velocity of the weight 3 to calculate the inertial force from the acceleration determined by differentiating measured values of the displacement velocity of the weight 3 and calculate the displacement of the weight 3 by integrating the measured values of the displacement velocity of the weight 3.
Owner:GUNMA UNIVERSITY
A method for calculating a sound absorption coefficient of a porous material
ActiveCN109388886ASimplify complex calculationsContribute to theoretical researchGeometric CADSustainable transportationMATLABEquivalent model
The invention discloses a method for calculating a sound absorption coefficient of a porous material, comprising the following five steps: Step 1: the sound absorption model of the single hole is equivalent, including obtaining the stiffness k of the single hole sound absorption equivalent model based on the analogy equivalent theory of the acoustic force line, and obtaining the damping loss factor eta through the sound absorption simulation calculation of the single hole; Step 2: creating a random distribution function, generating a 3D Voronoi diagram in Matlab software, and getting the coordinates of the point; Step 3: performing modeling with the Java language combined with Matlab and finite element analysis software; Step 4: establishing a spatial random array mass-spring-damping system equivalent model of the porous material; Step 5: performing simulation analysis to obtain the energy loss curve, that is, the sound absorption coefficient curve. The invention can establish an acoustic equivalent model of the porous material which is simple and applicable, and simplifies the complicated calculation of the sound absorption performance of the porous material; the method reduces the design and experiment cost, and accelerate the development speed of the product.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Piezoelectric-based toe-heaters for frostbite protection
InactiveUS20090229142A1SolesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityEngineering
A footwear including a body; a base structure; and one or more electrical energy generators disposed in the base structure for generating electrical energy upon application of an impact to the base structure. The footwear is used to produce electrical energy by impacting a base structure of the footwear; and vibrating a mass-spring unit in the base structure to generate an electrical energy.
Owner:OMNITEK PARTNERS LLC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com