Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
221 results about "Reference Document" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A document that provides pertinent details for consultation about a subject.
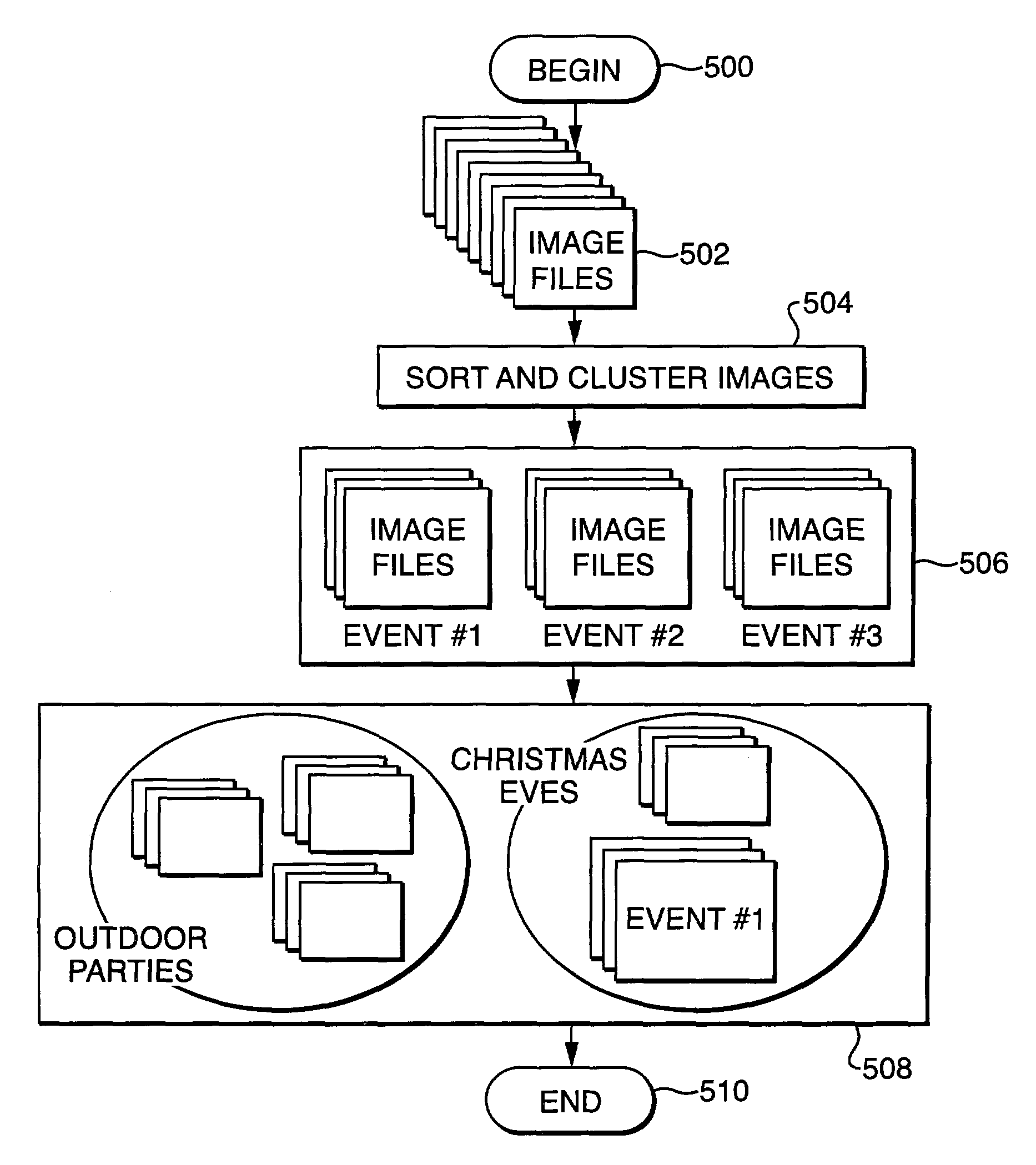
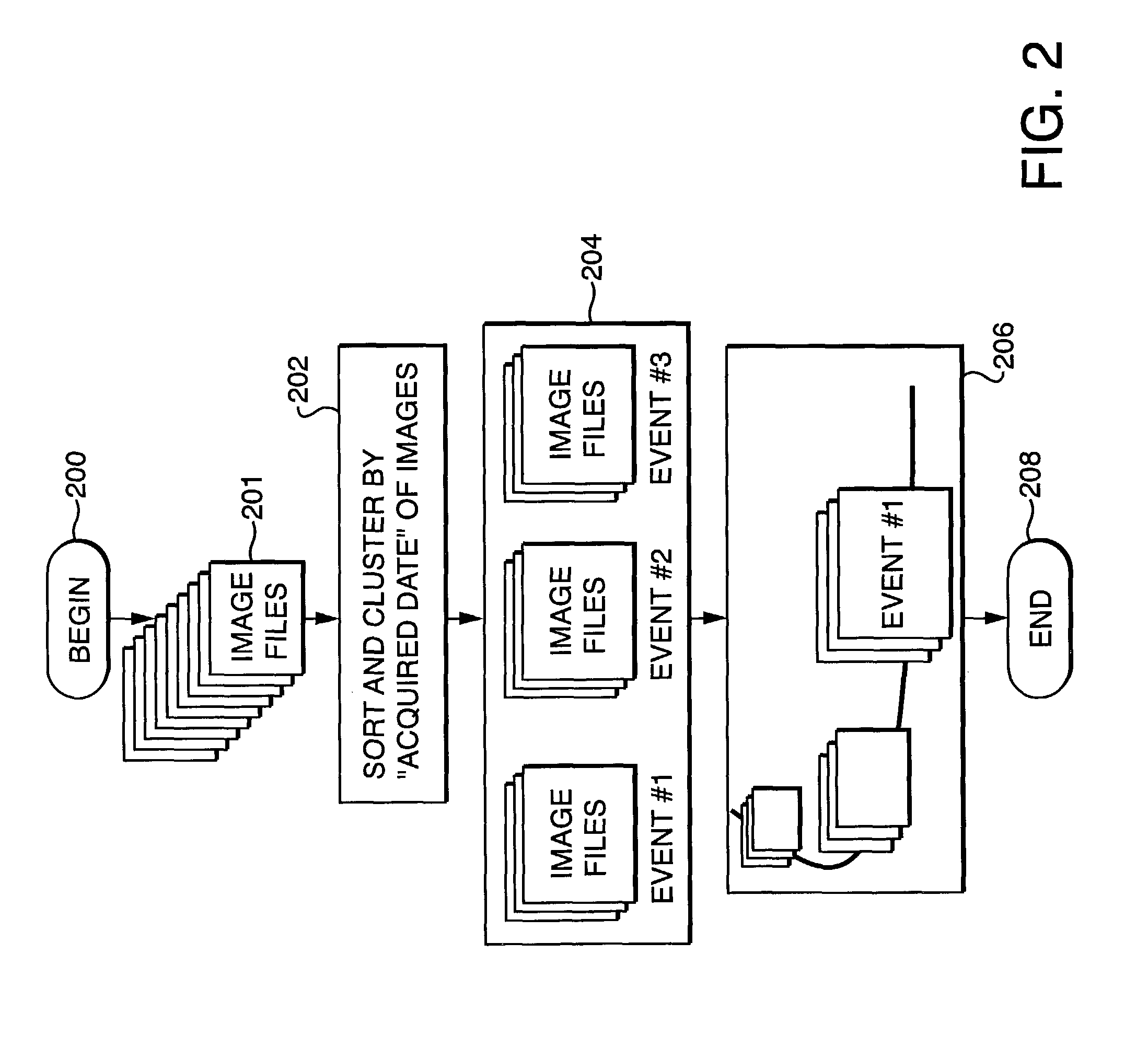
Method and apparatus for archiving and visualizing digital images
ActiveUS7970240B1SuperbEasy to findCharacter and pattern recognitionStill image data indexingGraphicsGraphical user interface
A computer based, digital image management system that visually presents an entire archive in a manner that facilitates easy, non-textual, searching for specific images. The system consists of two main elements; a file management methodology, and a graphical user interface. The file management method utilizes reference files that contain multiple properties (metadata) relating to each image file. Image files are grouped into a multiplicity of collections based on user-defined associations of the properties. The graphical user interface visually represents the groups of image files on 2-dimensional or 3-dimensional graphic metaphors. In addition, the graphical interface uses multiple display variables such as icons, mnemonics, size, movement, color, and luminance to signify relationships between groups, and / or communicate key properties of individual or groups of images.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
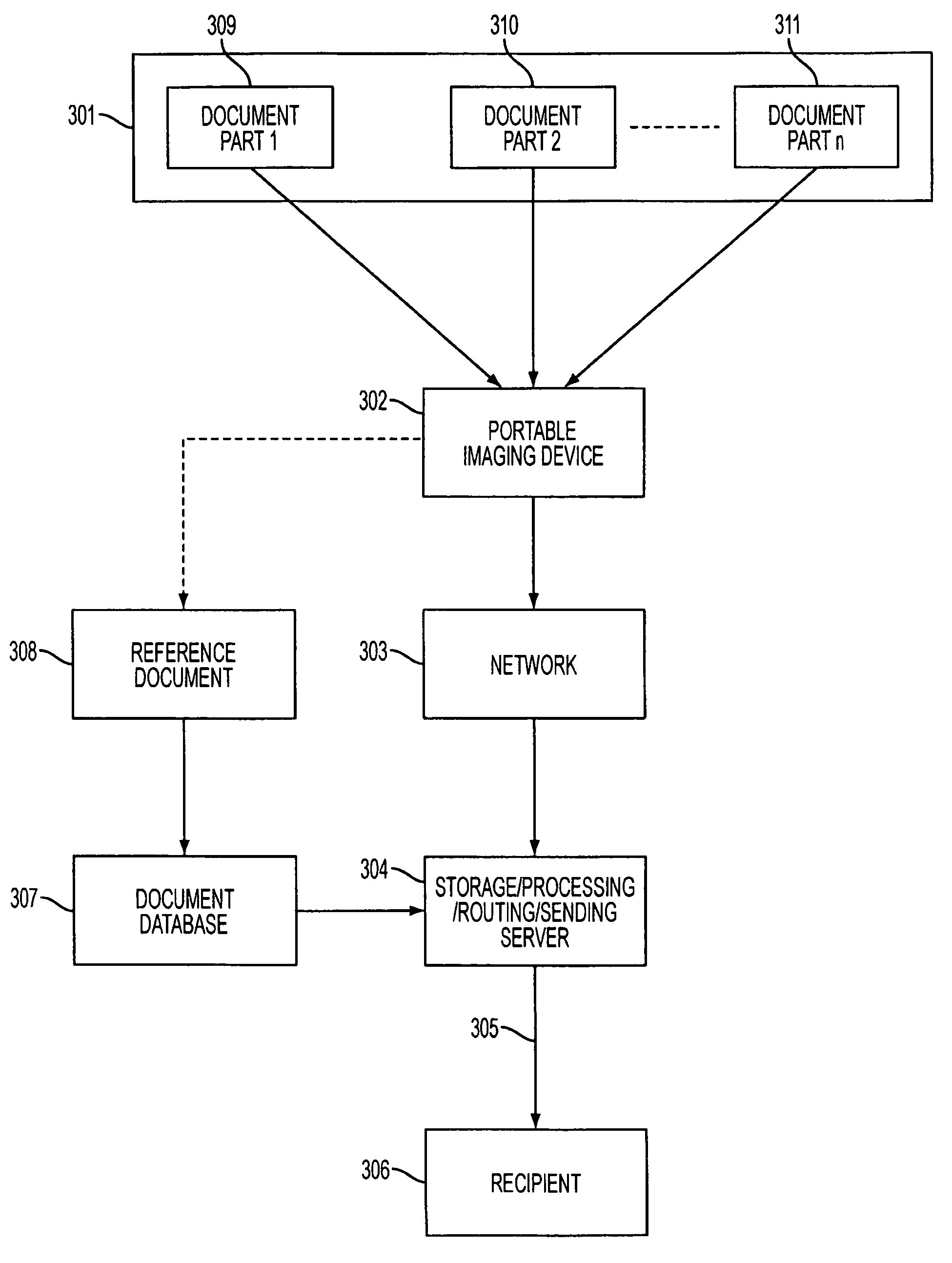
System and method of improving the legibility and applicability of document pictures using form based image enhancement
InactiveUS20060164682A1Easy to convertReliably scannedImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImage enhancementReference Document
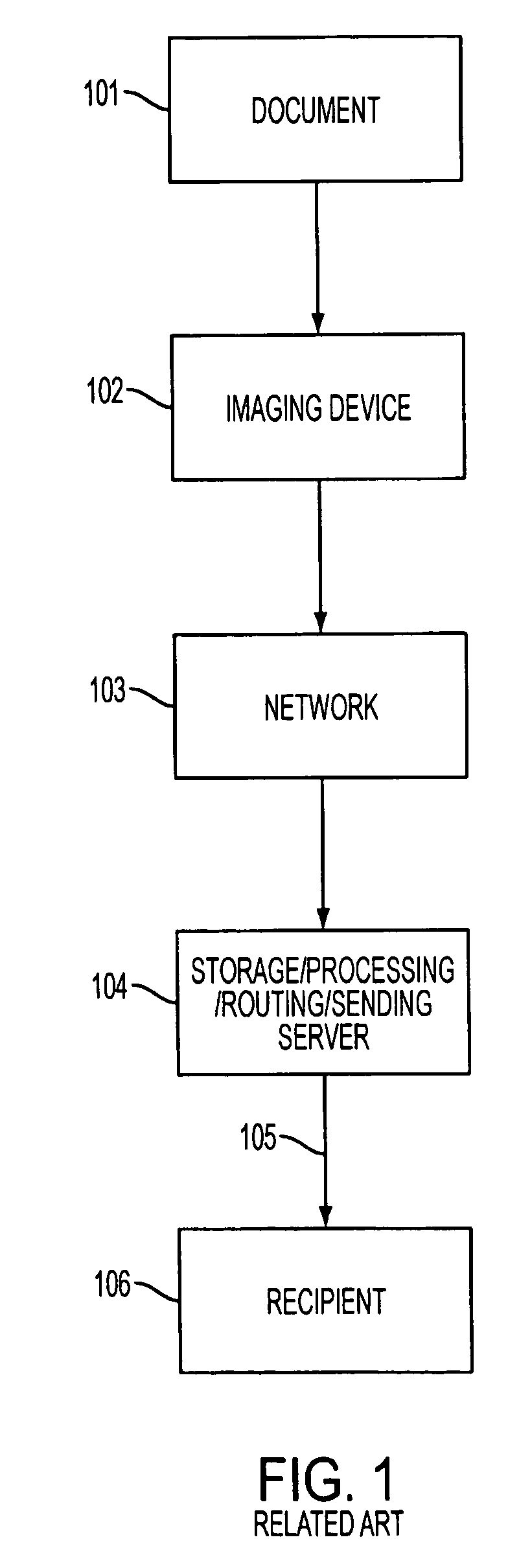
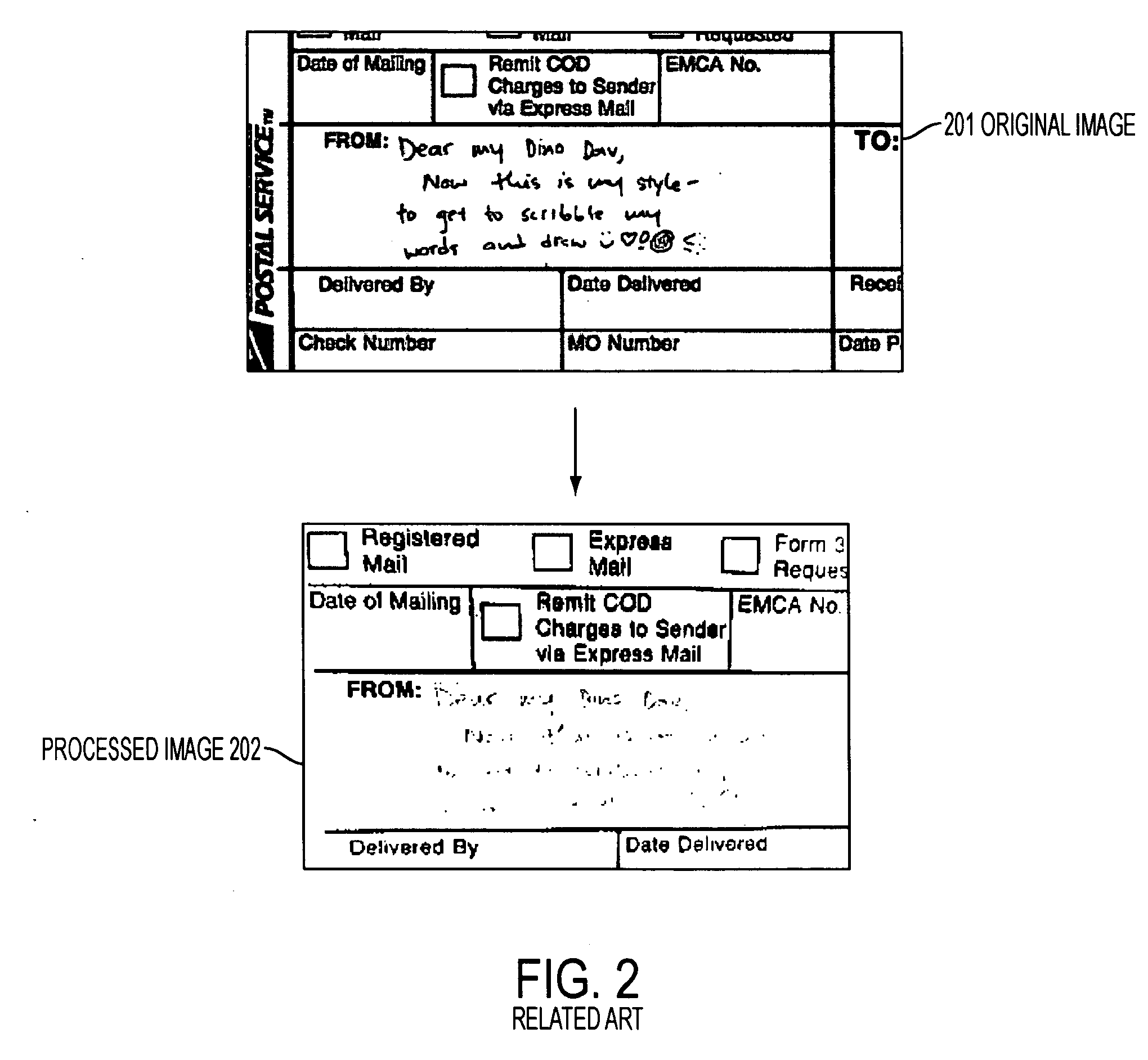
A system and method for imaging a document, and using a reference document to place pieces of the document in their correct relative position and resize such pieces in order to generate a single unified image, including the electronic capturing a document with one or multiple images using an imaging device, the performing of pre-processing of said images to optimize the results of subsequent image recognition, enhancement, and decoding, the comparing of said images against a database of reference documents to determine the most closely fitting reference document, and the applying of knowledge from said closely fitting reference document to adjust geometrically the orientation, shape, and size of said electronically captured images so that said images correspond as closely as possibly to said reference document.
Owner:DSPV
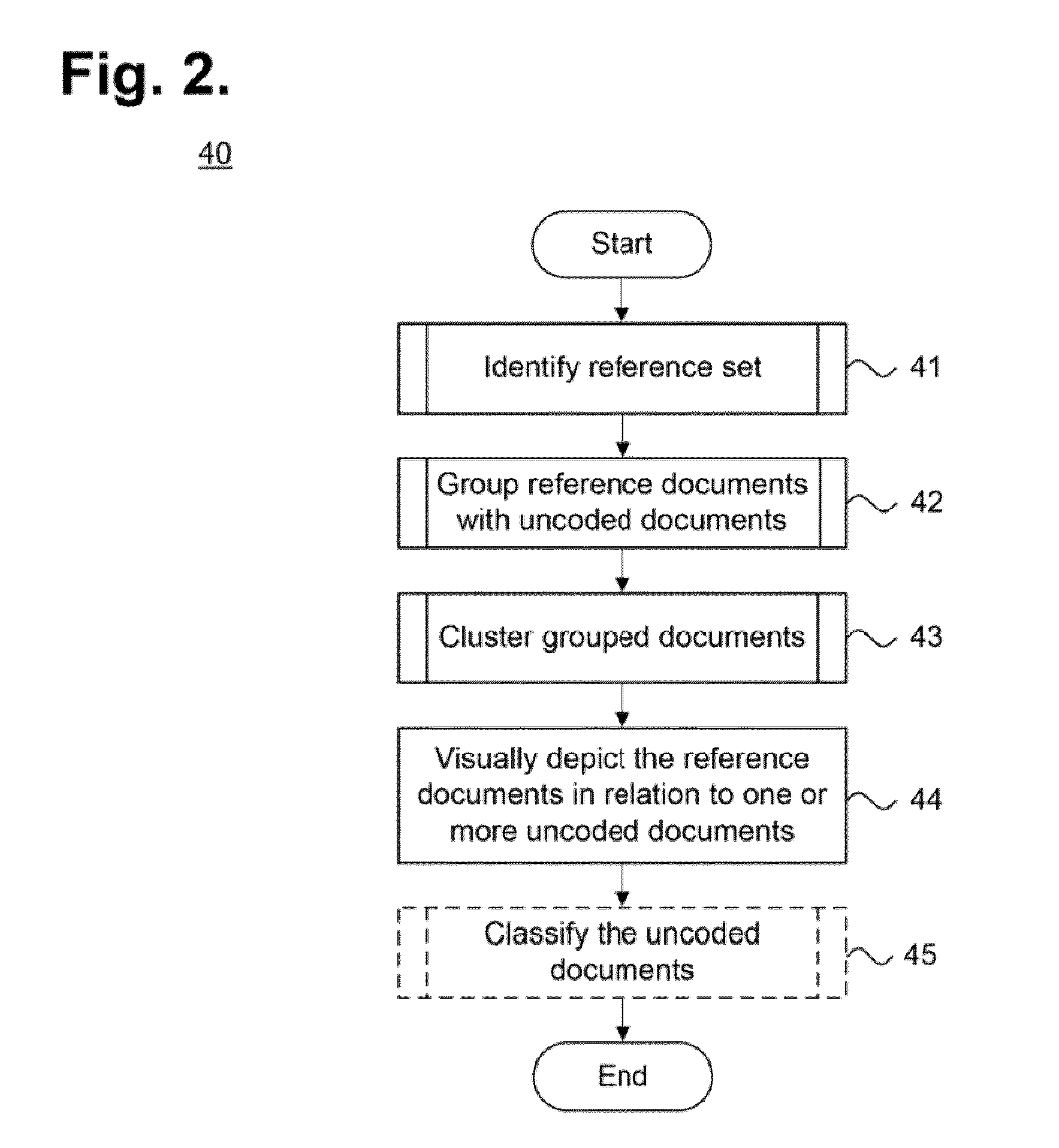
System And Method For Displaying Relationships Between Electronically Stored Information To Provide Classification Suggestions Via Inclusion
ActiveUS20110029526A1Improve review efficiencyMathematical modelsDigital data processing detailsDocumentationLibrary science
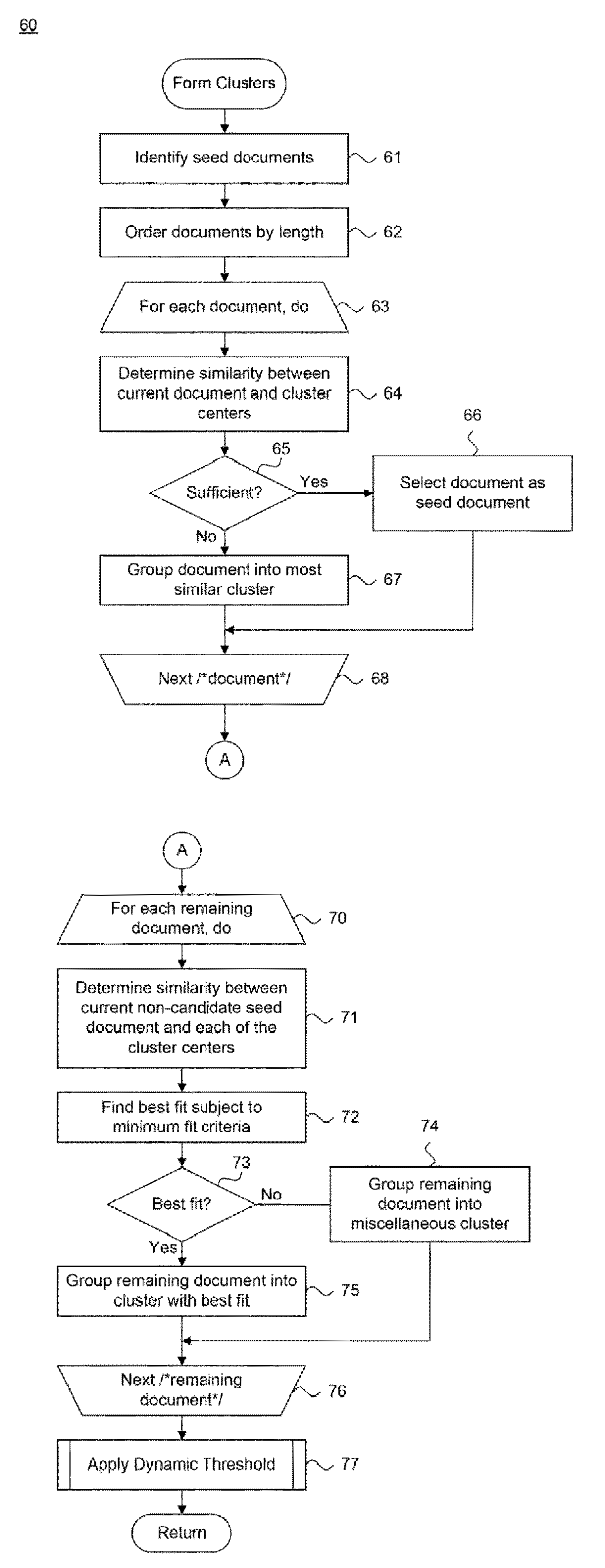
A system and for providing reference documents as a suggestion for classifying uncoded documents is provided. A set of reference electronically stored information items, each associated with a classification code, is designated. One or more of the reference electronically stored information items is combined with a set of uncoded electronically stored information items. Clusters of the uncoded electronically stored information items and the one or more reference electronically stored information items are generated. Relationships between the uncoded electronically stored information items and the one or more reference electronically stored information items in at least one cluster are visually depicted as suggestions for classifying the uncoded electronically stored information items in that cluster.
Owner:NUIX NORTH AMERICA
Query-less searching
InactiveUS20060212415A1Web data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsThe InternetDocument recognition
Some embodiments of the invention provide a method for identifying relevant documents. The method receives a set of reference documents. The method analyzes the received set of reference documents. Based on this analysis, the method then identifies one or more documents that are potentially relevant to the discussion in one or more reference documents. In some embodiments, the method identifies the relevant documents by examining candidate documents that are on a computer or are accessible by a computer through a computer network (e.g., a local area network, a wide area network, or a network of networks, such as the Internet). In these embodiments, the method uses its analysis of the reference document set to determine whether the discussion (i.e., content) of the candidate document is relevant to the topics discussed in one or more of the reference documents. If so, the method of some embodiments identifies the candidate document as a potentially relevant document (i.e., as a document that is potentially relevant or related to the reference document set).
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
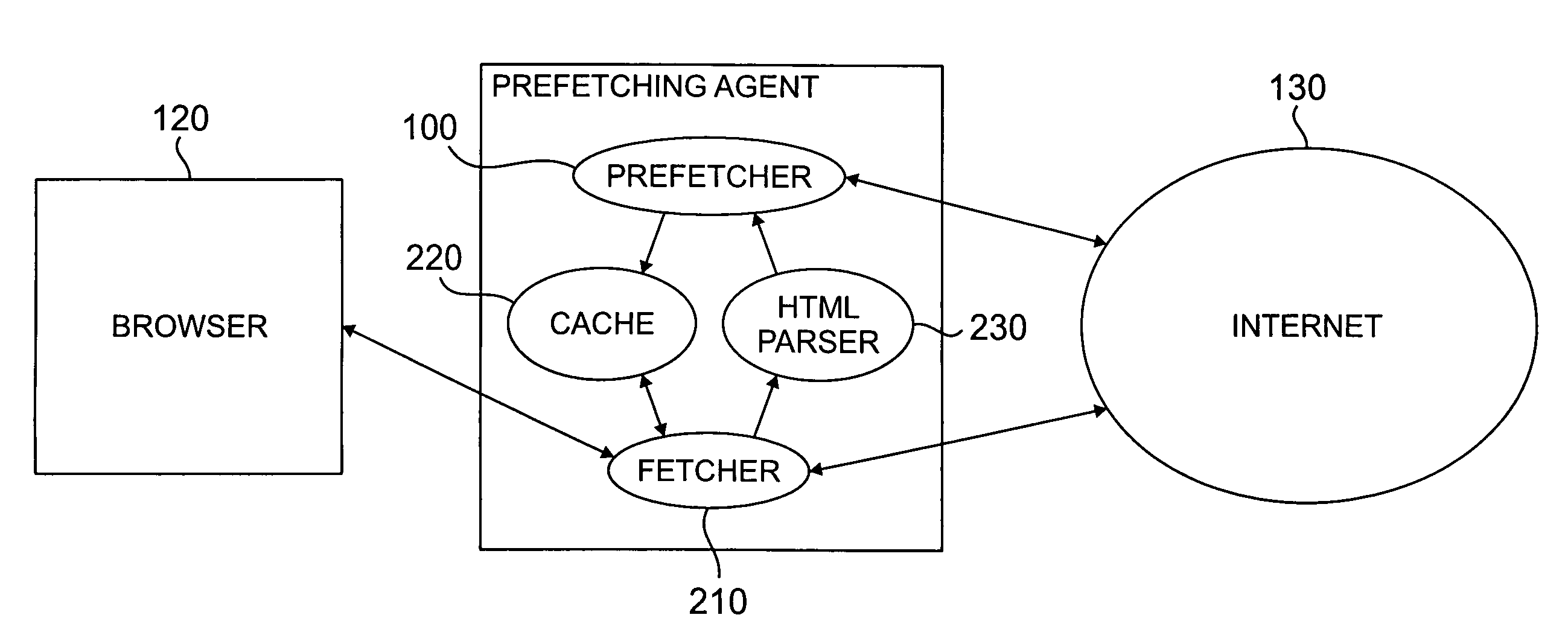
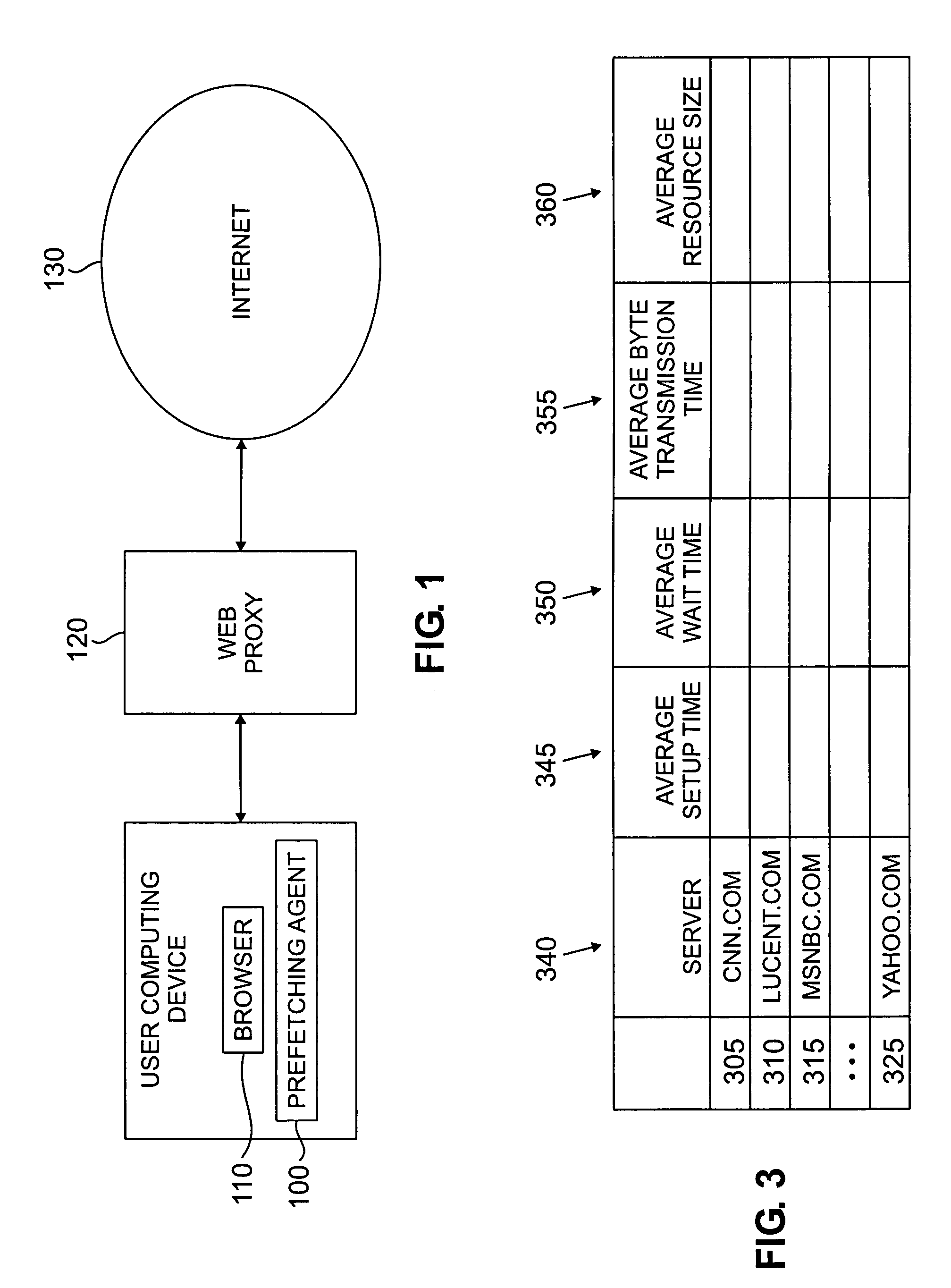
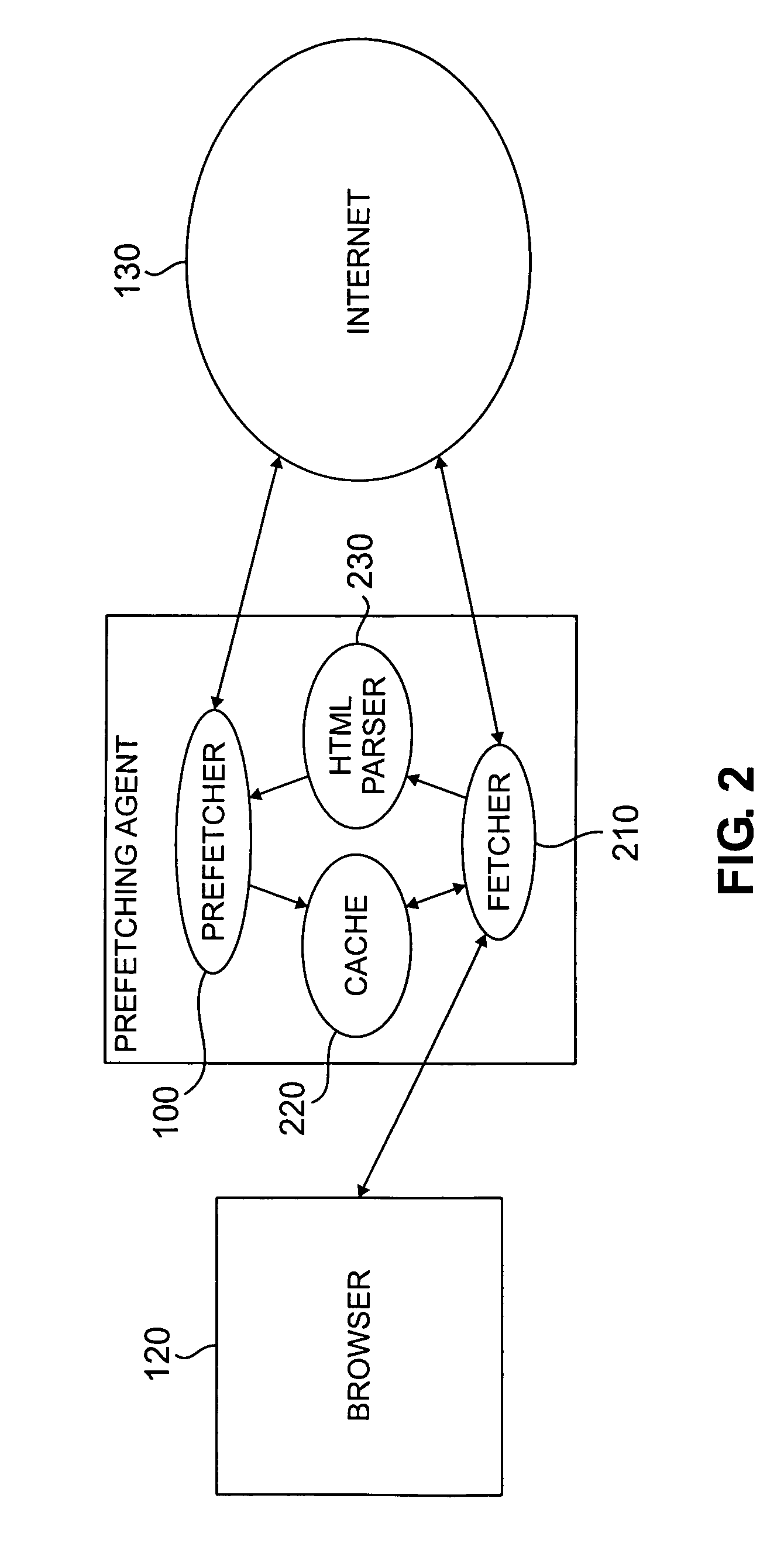
Method and apparatus for prefetching internet resources based on estimated round trip time
InactiveUS6993591B1Shorten access timeMinimizing networkData processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsHyperlinkTTEthernet
A method and apparatus are disclosed for prefetching Internet resources based on the estimated round trip time of the resources. Whenever a user clicks on an embedded hyperlink, the prefetching strategy aims to ensure that the corresponding document has been prefetched or can be fetched very quickly from its origin server. Web access time as perceived by the user is reduced, while also minimizing the network, server and local resource overhead due to prefetching. The estimated round trip time is obtained or approximated for all referenced documents. The “round trip” time or access time of a resource is the time interval between the sending of the first byte of an HTTP request for the resource until the last byte of the server response has arrived at the requesting Web client. Documents with the longest access times are prefetched first and prefetching generally continues until the estimated round trip time falls below a predefined threshold. An HTTP HEAD request may be used to determine the estimated round trip time of a Web resource. The prefetching agent can be configured to prevent prefetching of those documents that are quickly fetchable, dynamically generated or non-HTTP based resources, or those documents whose size exceed a certain limit, to minimize the network, server and local resource overhead due to prefetching. The thresholds applied to the list of documents to be prefetched can be dynamically adjusted by the agent, based on changing network and server conditions.
Owner:SOUND VIEW INNOVATIONS
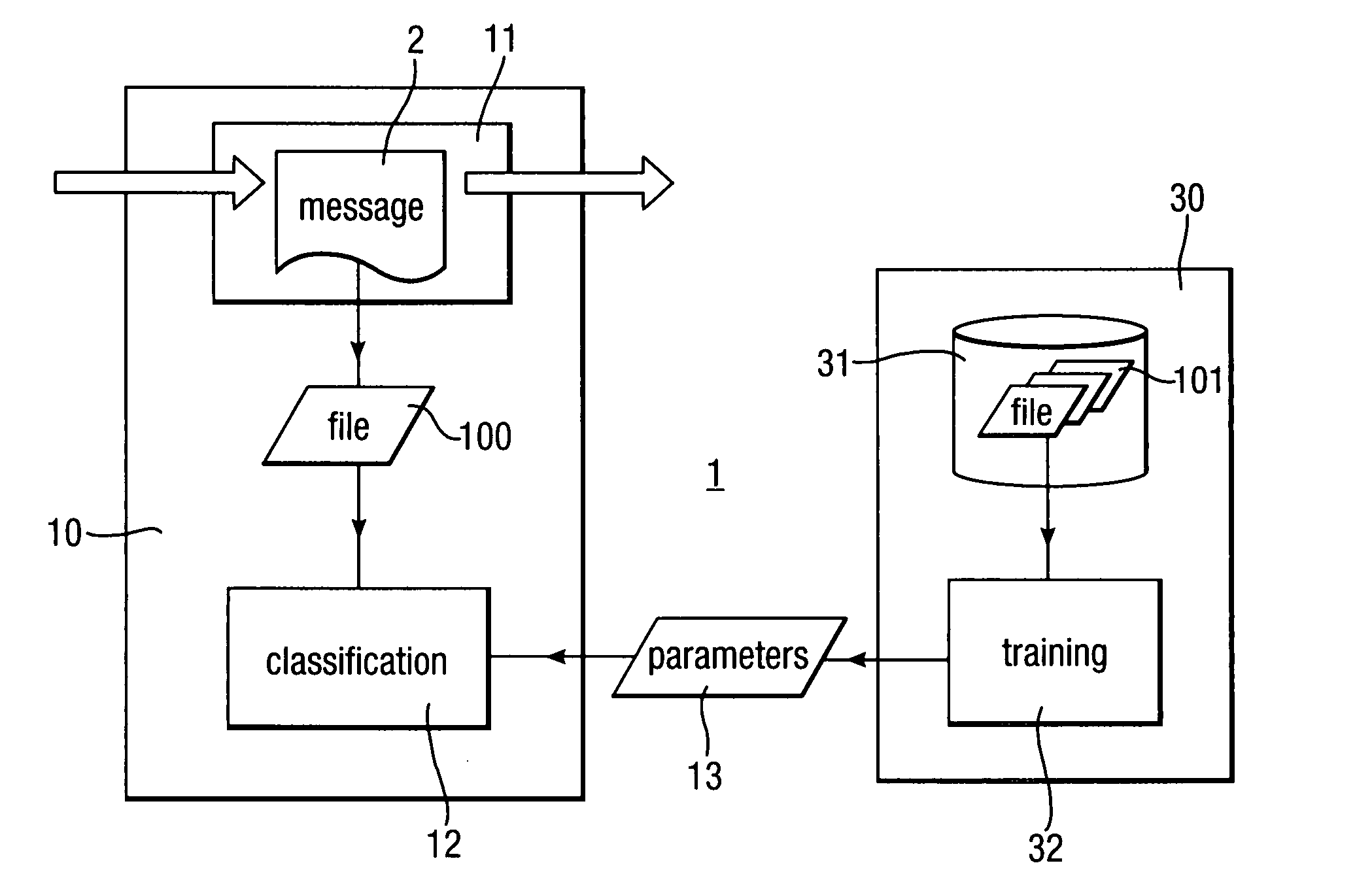
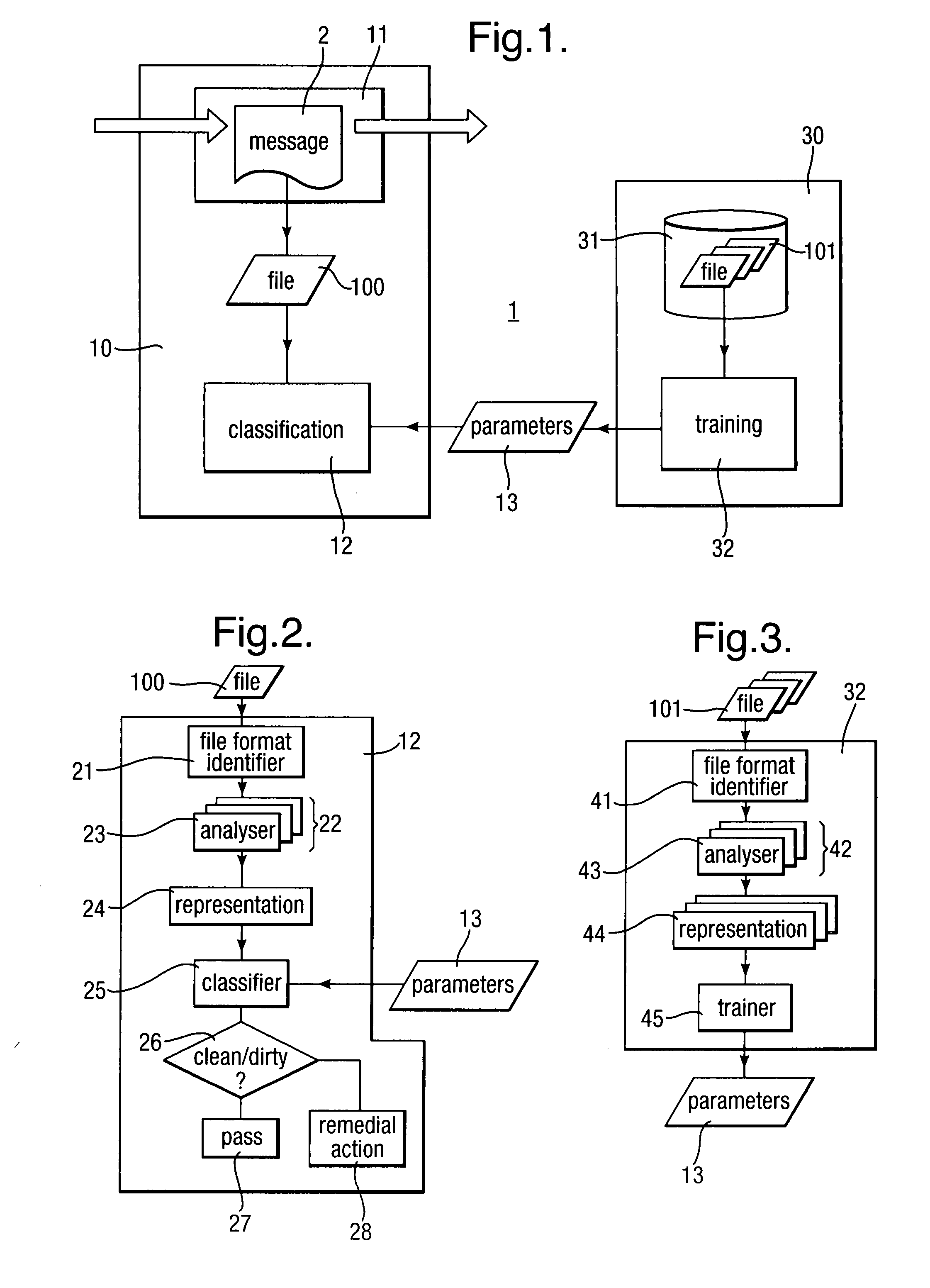
Heuristic detection of malicious code
InactiveUS20090013405A1Avoid the needImprove the detection rateMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionData fieldMalware
Scanning of computer files for malware uses a classifying technique to classify an input file as a clean file or a dirty file. The parameters of the classifying technique are derived to train the classification on a corpus of reference files including clean files known to be free of malware and dirty files known to contain malware. The classification is performed using a representation of the files in a feature space defined by a set of predetermined features for respective file formats, the features being a predetermined value or range of values for one or more data fields of given meanings. The representation of a file is derived by determining the file format, parsing the file on the basis of the structure of data fields in the determined file format to identify the data fields and their meaning, and determining, on the basis of the identified data fields, which of the set of predetermined features are present.
Owner:SYMANTEC CORP
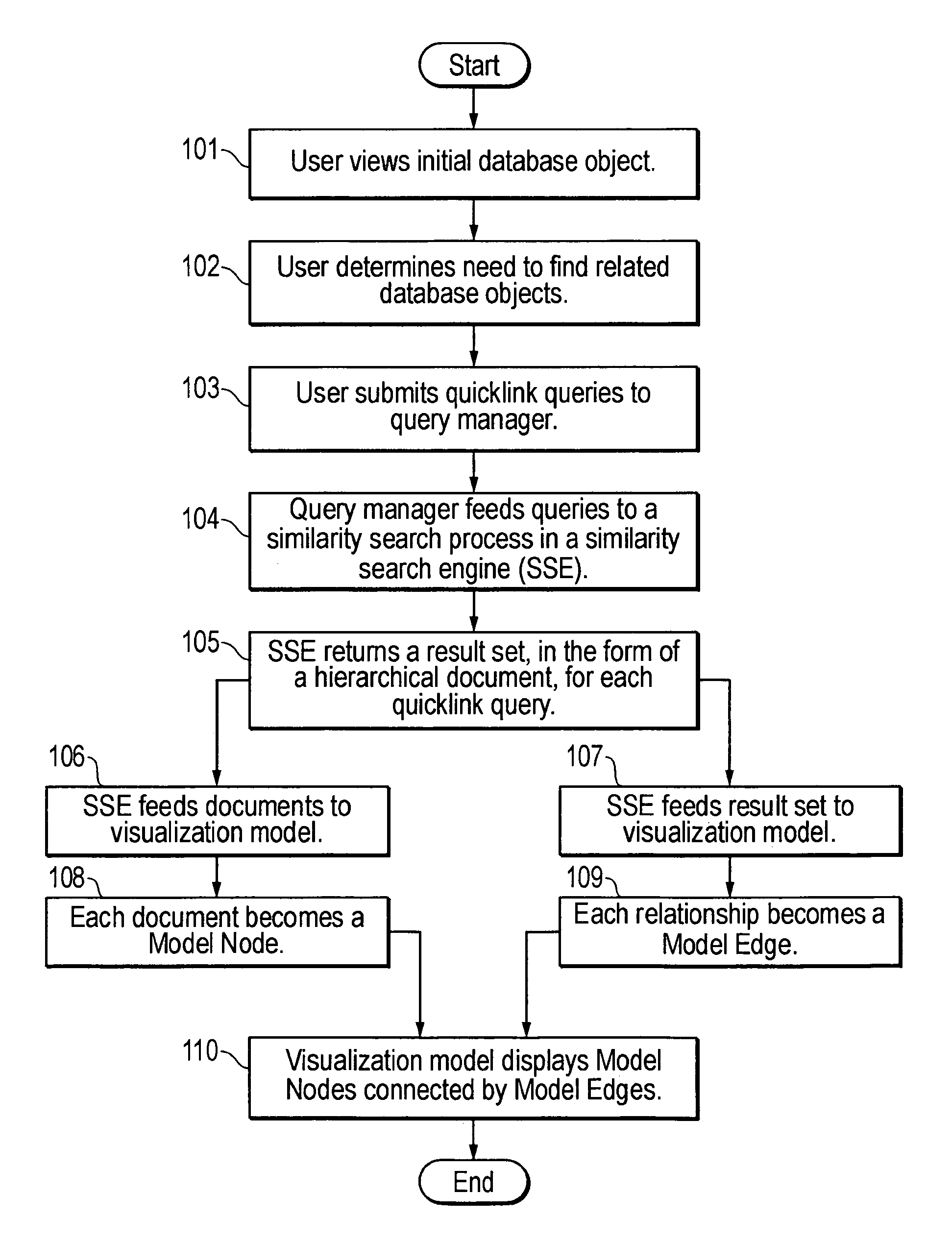
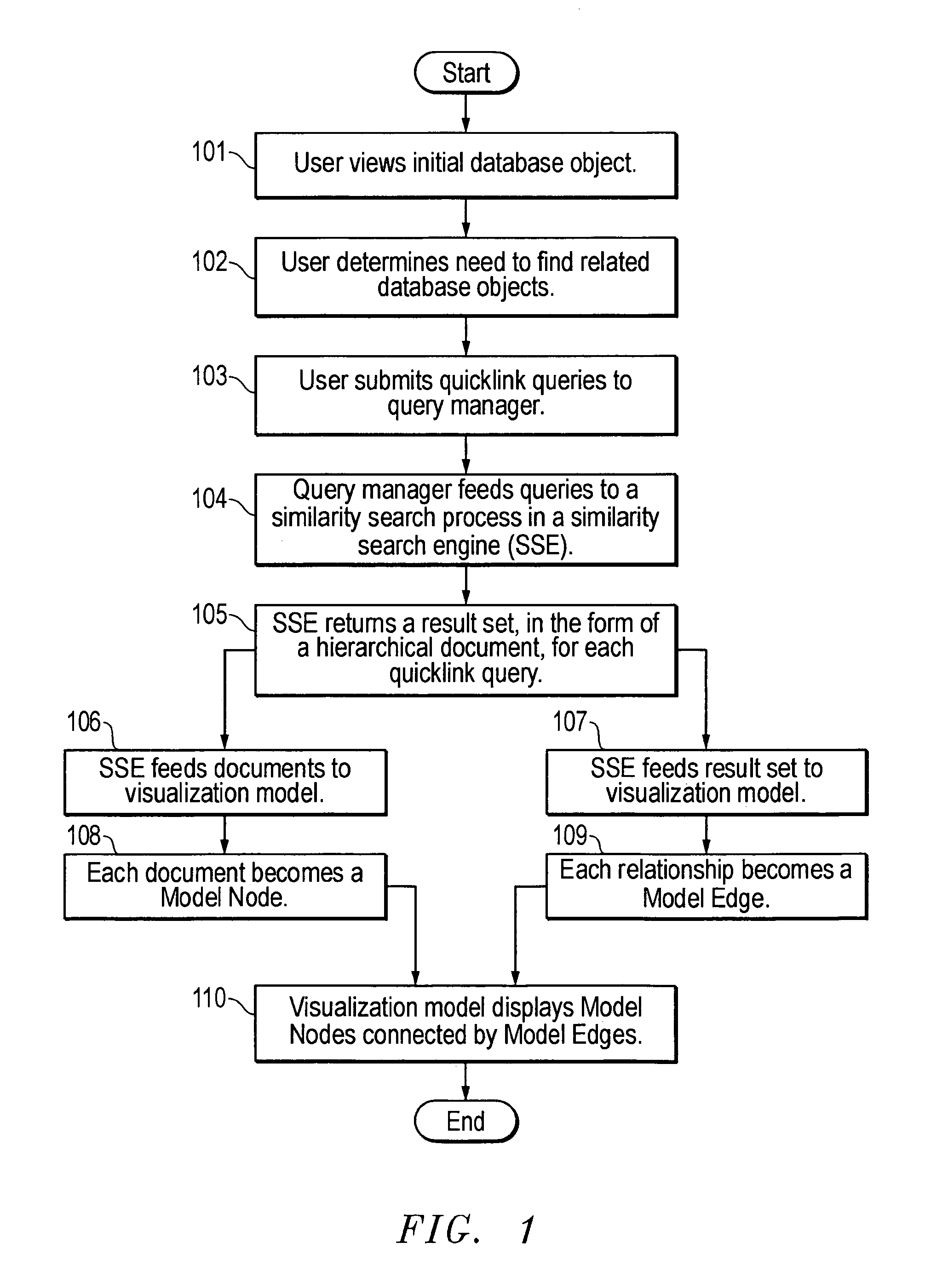
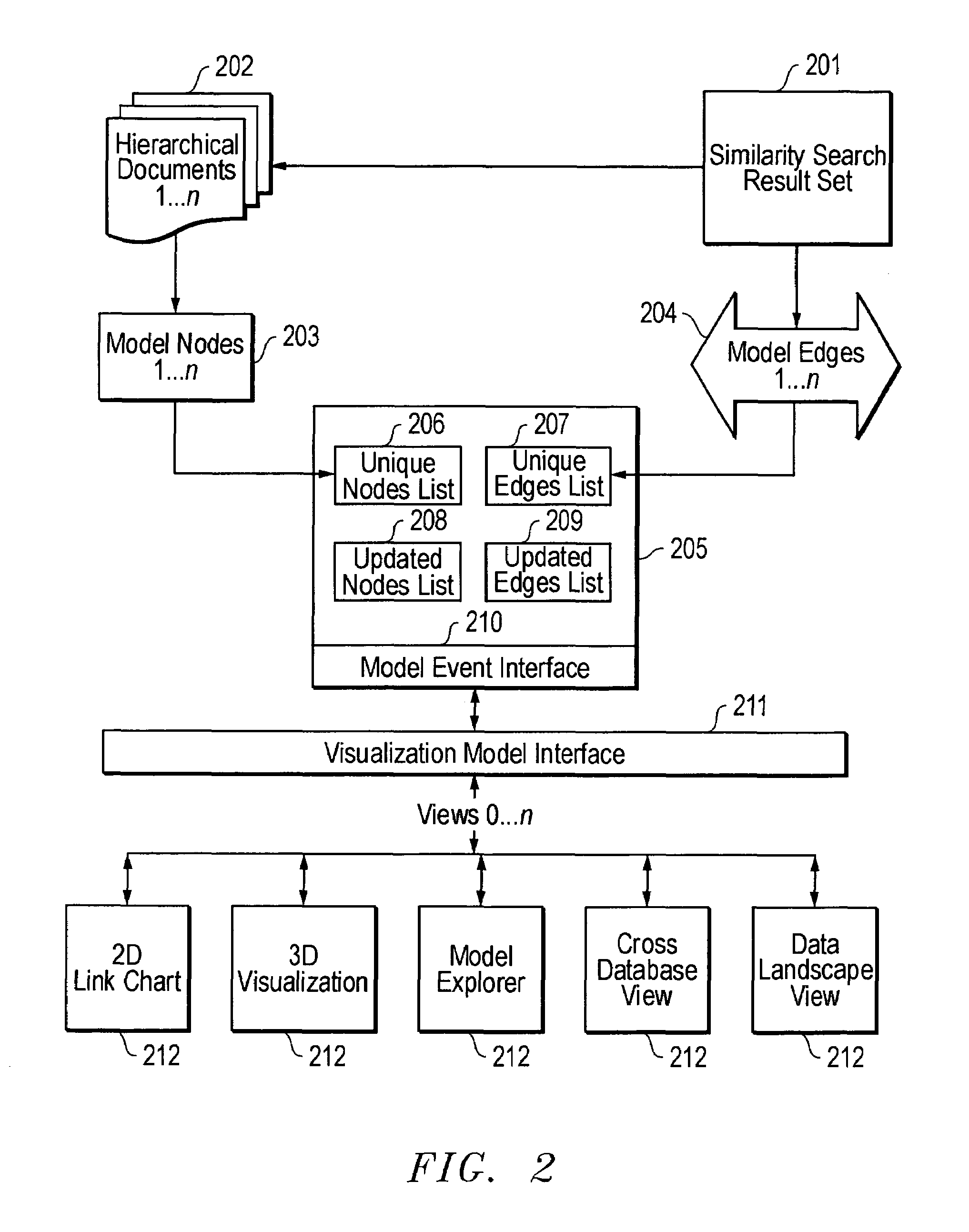
System and method for visually representing a hierarchical database objects and their similarity relationships to other objects in the database
InactiveUS6985898B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalGraphicsReference database
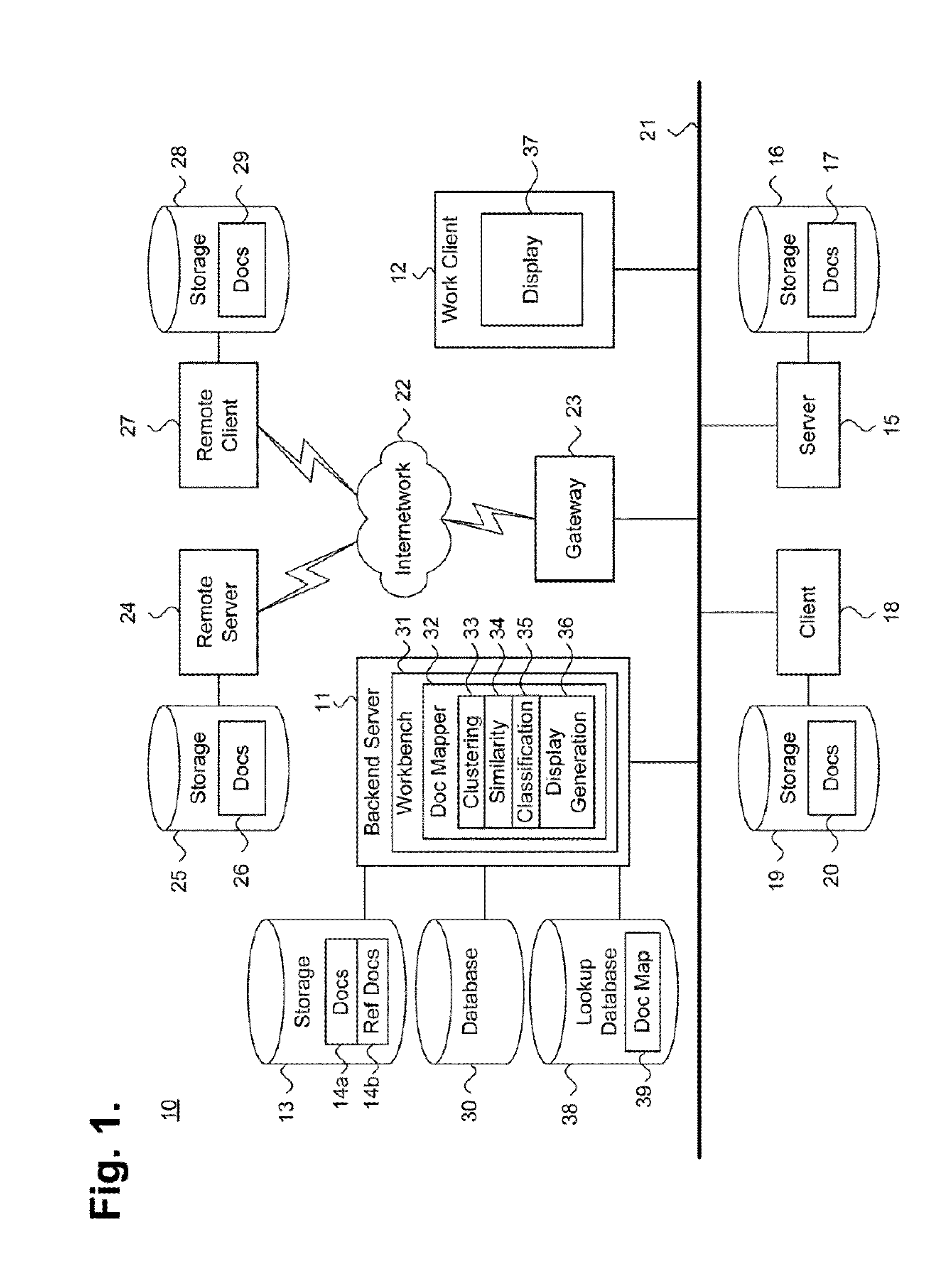
The present invention comprises a computer-implemented visualization model of similarity relationships between documents. It comprises performing a similarity search based on at least one attribute of a reference document to find at least one target document with similar attributes; creating a visual representation of the reference database document and the at least one target document; creating a visual representation of the similarities between the reference document and the at least one target document; and displaying the visual representations of the database documents and their similarities on a graphical user interface. The target documents that are similarity searched may reside in a plurality of databases. The similarity search returns a result set of target documents that are used by the visualization model to create the visual representation of the documents and the similarities between the documents.
Owner:FAIR ISAAC & CO INC
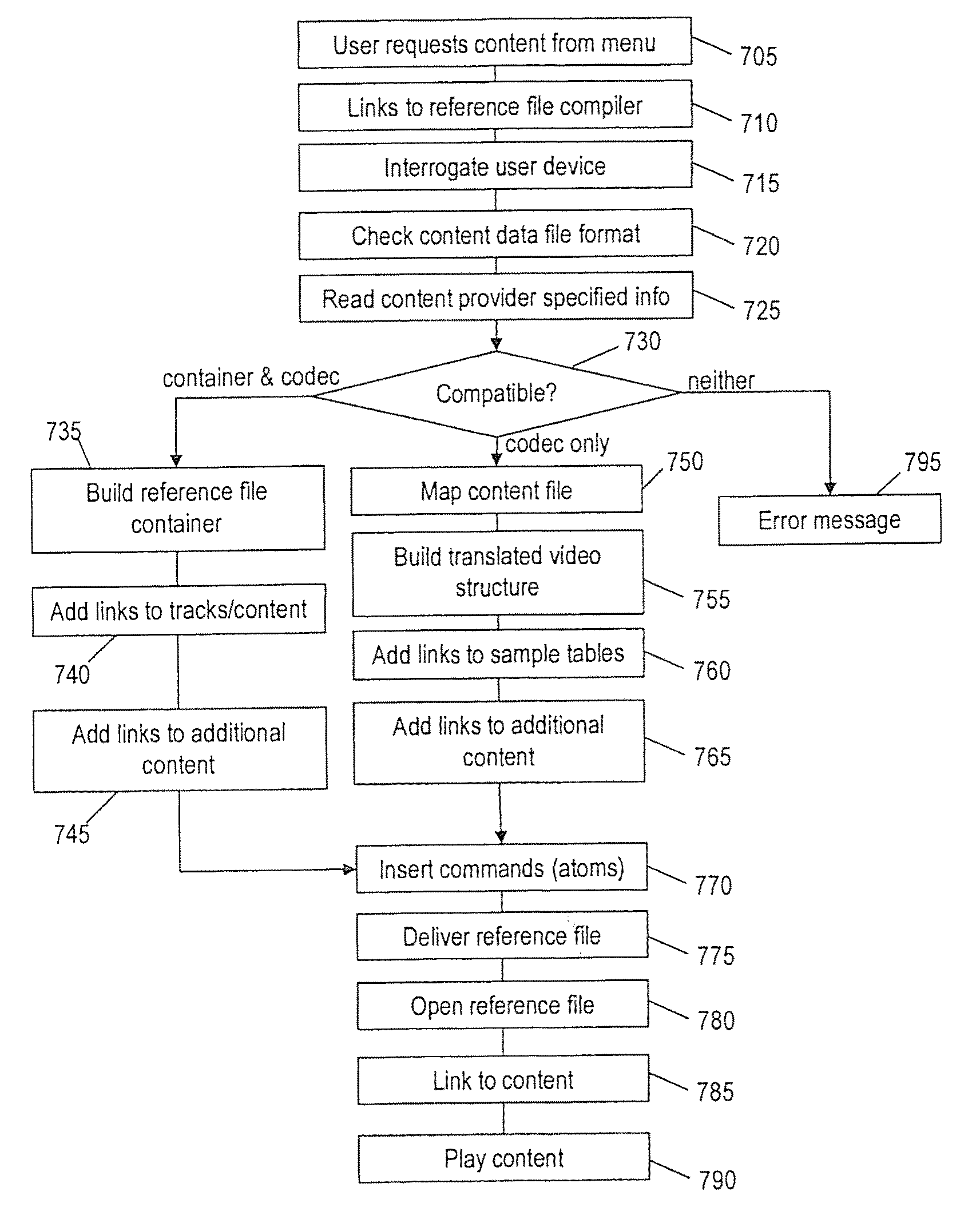
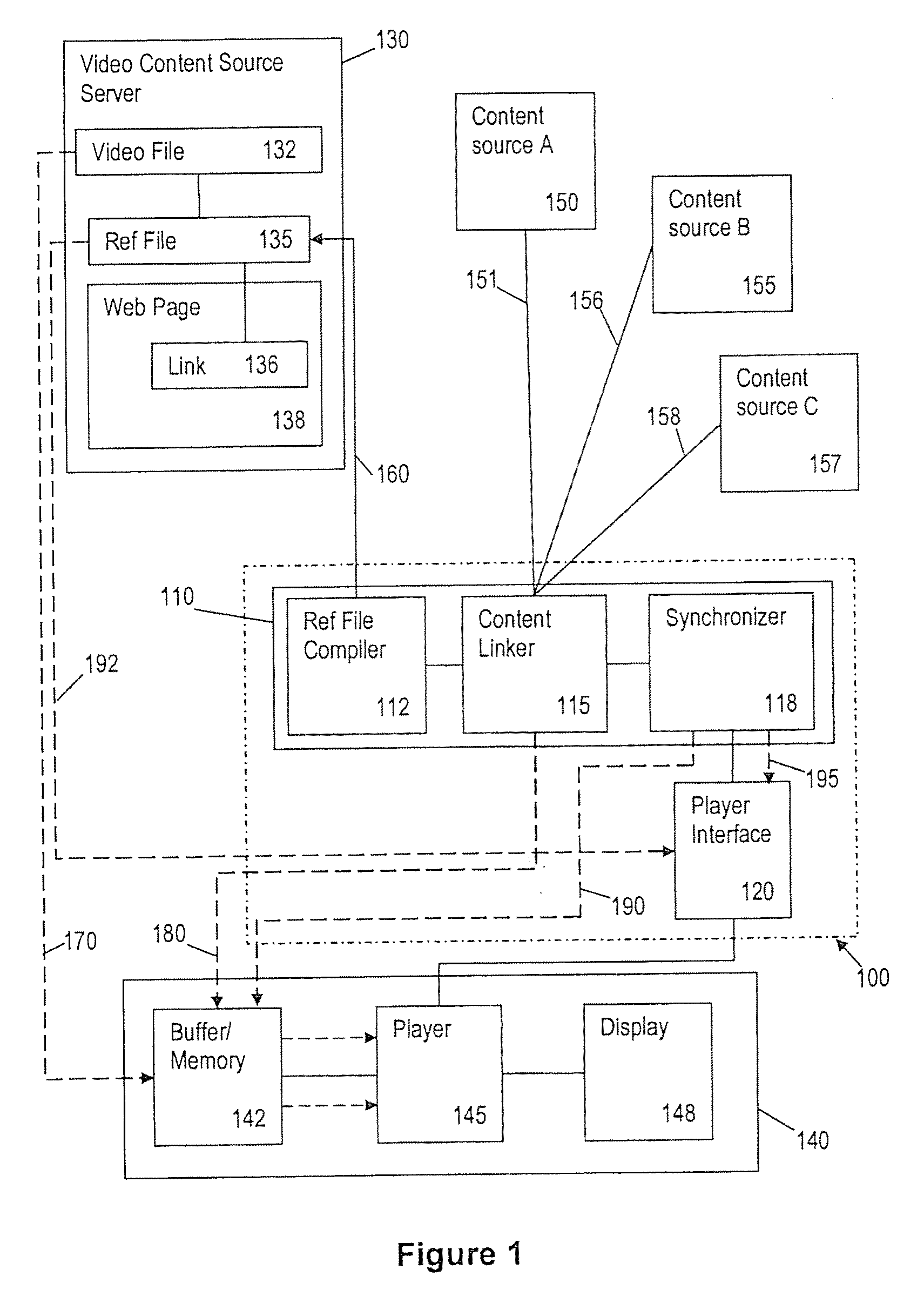
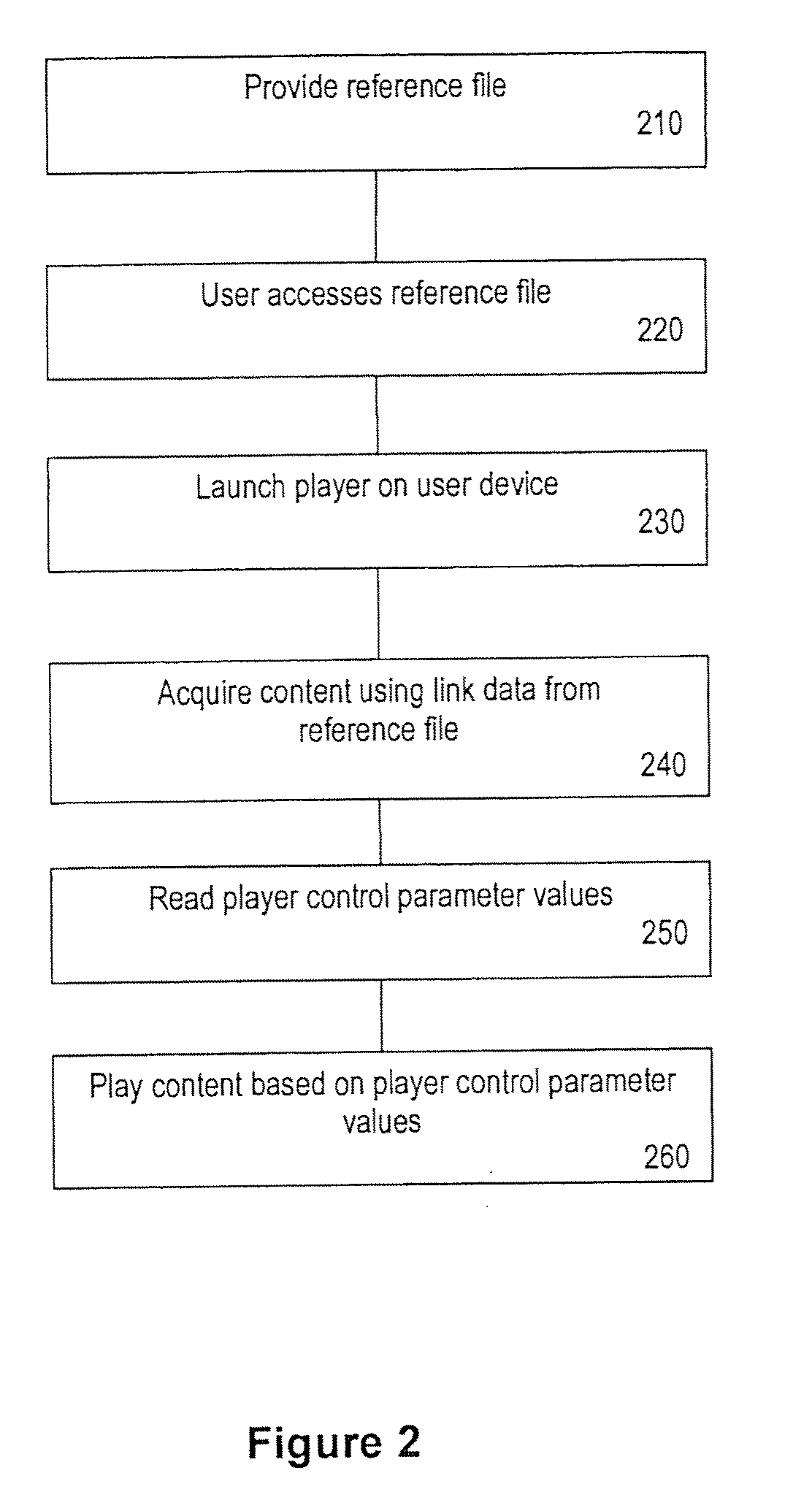
Method and System for Content Delivery
ActiveUS20100257569A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionCarrier indexing/addressing/timing/synchronisingDisplay deviceConnected device
A method and system for providing video content on a data network connected device having a display and a device display controller including a player. The method comprises the steps of a data network connected device, accesses a reference file including a plurality of player control parameter values and linking data for one or more content sources. Play control commands are provided to the player based on the play control parameter values. Content data is acquired by the player from one or more content sources via the data network using the linking data, and the content acquired from each source played on the display in accordance with the player control commands. The reference file may be a pre-existing reference file or a reference file created in response to a request to play the video content data. A reference file compiler is provided for generating the reference file.
Owner:LINIUS AUST PTY LTD
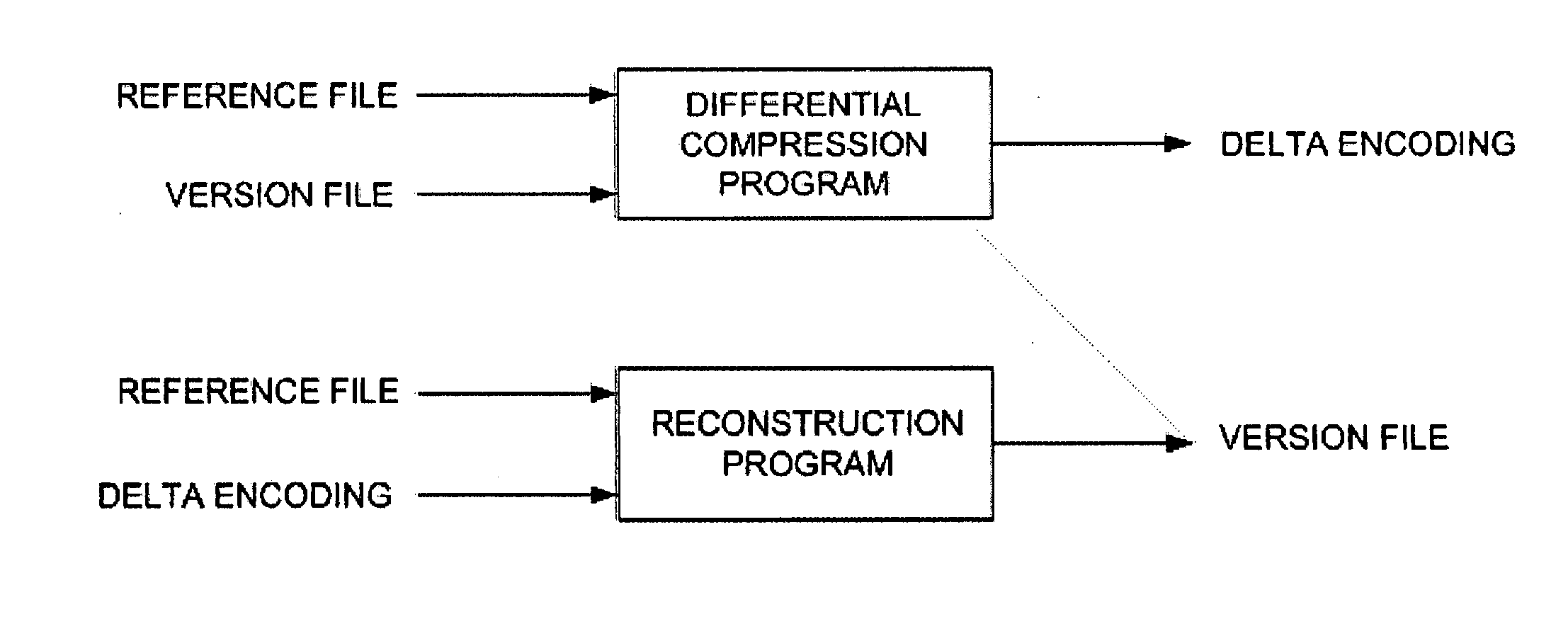
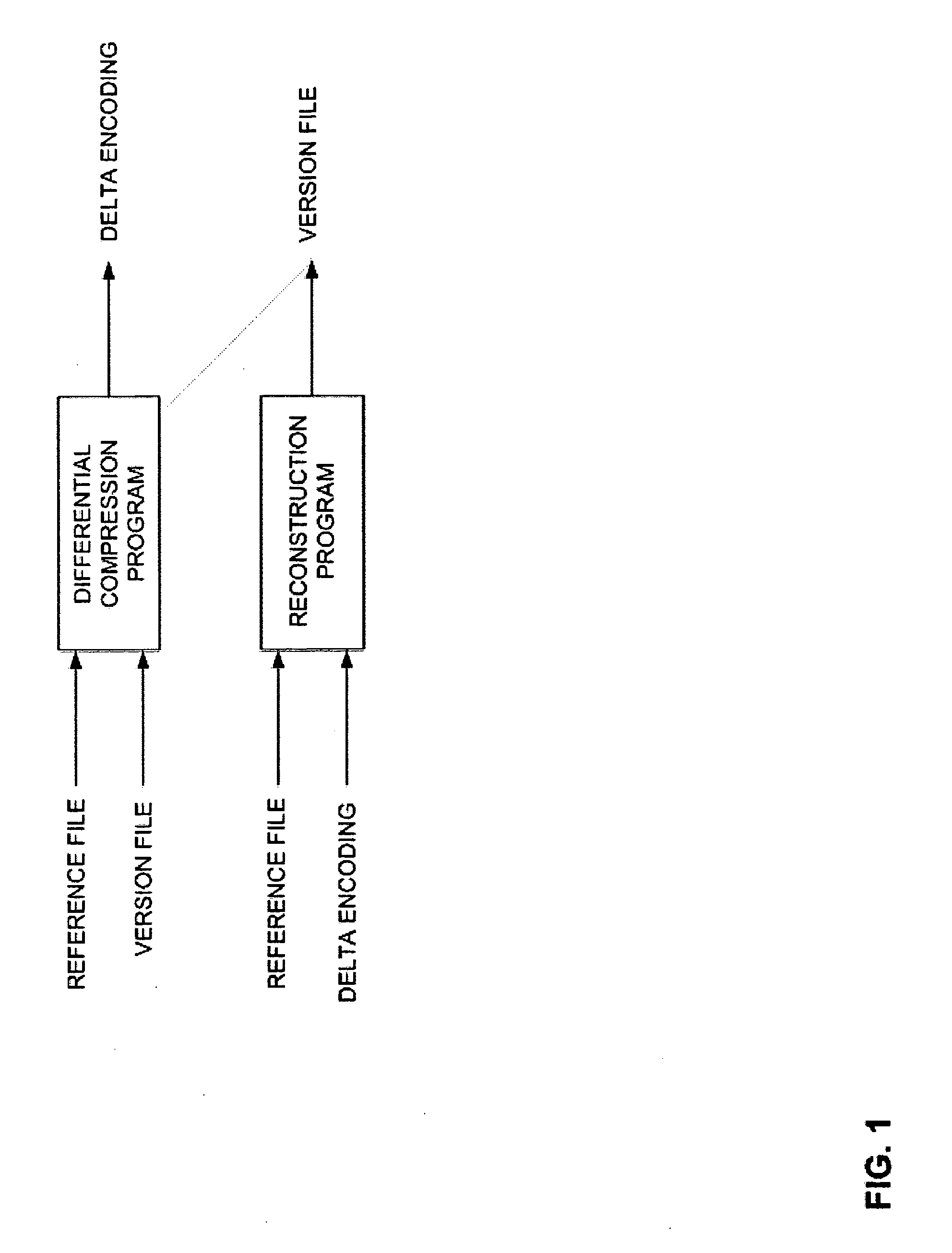
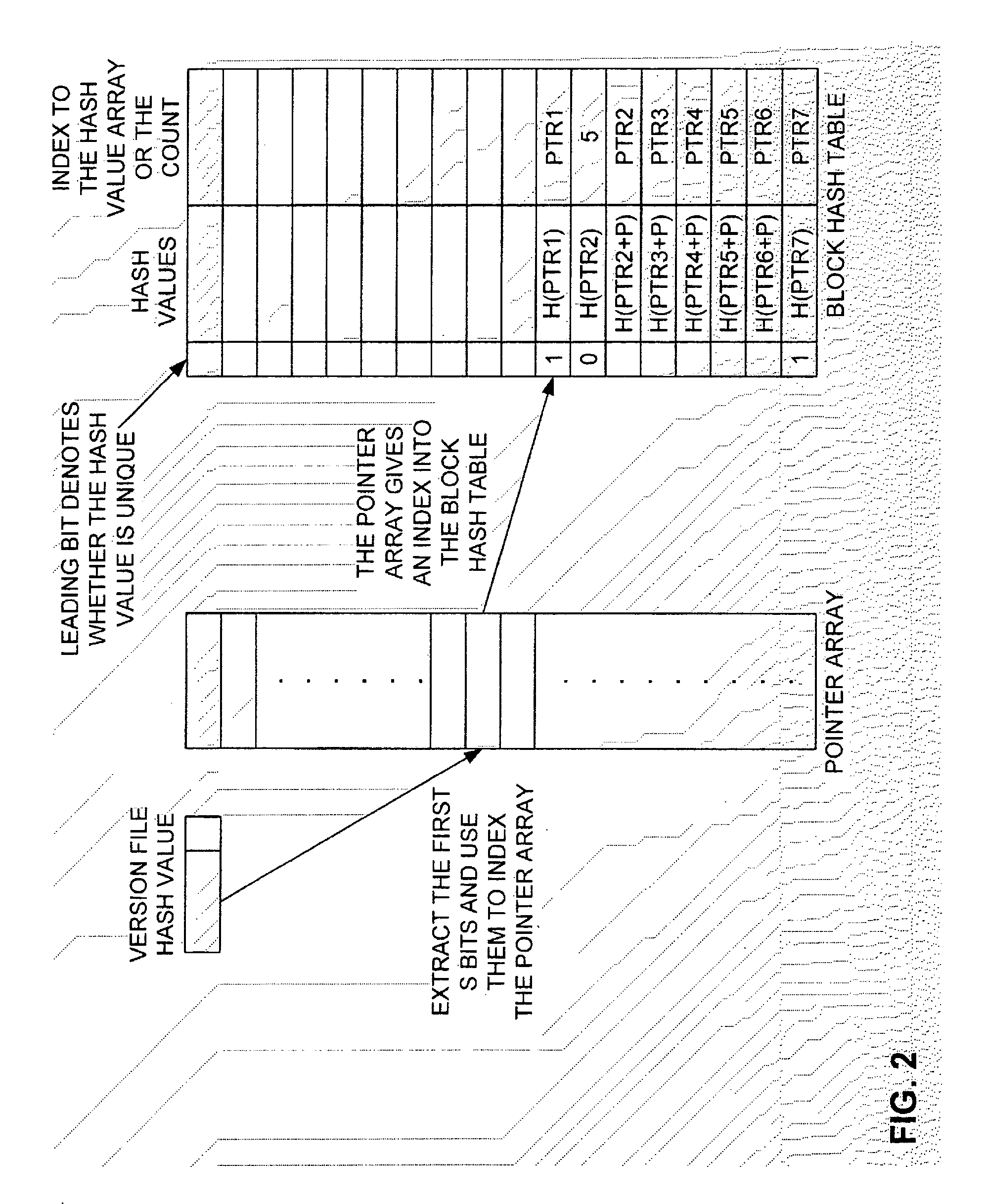
Method and Computer Program Product for Finding the Longest Common Subsequences Between Files with Applications to Differential Compression
InactiveUS20060112264A1Improve I/O performanceLow costCode conversionSecuring communicationLongest common subsequence problemGreedy algorithm
A differential compression method and computer program product combines hash value techniques and suffix array techniques. The invention finds the best matches for every offset of the version file, with respect to a certain granularity and above a certain length threshold. The invention has two variations depending on block size choice. If the block size is kept fixed, the compression performance of the invention is similar to that of the greedy algorithm, without the expensive space and time requirements. If the block size is varied linearly with the reference file size, the invention can run in linear-time and constant-space. It has been shown empirically that the invention performs better than certain known differential compression algorithms in terms of compression and speed.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for cleansing, linking and appending data records of a database
ActiveUS7376680B1Promote resultsLow costDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsReference databaseComputer science
A system and method for reading a data record from an input file only once, processing that data record according to one or more reference files, and then writing out the cleansed and updated data record to a target file such that the data record is read and written to remote storage only once, thereby making a single pass through a given database of data records. Each data record (comprising of multiple data elements) of the input file is reviewed, verified, and corrected against one or more reference databases containing similar information, assigned a unique identifying key, and, optionally, appended with new additional data elements of a matching data record from a new-data database.
Owner:ONEPASS DATA SOLUTIONS
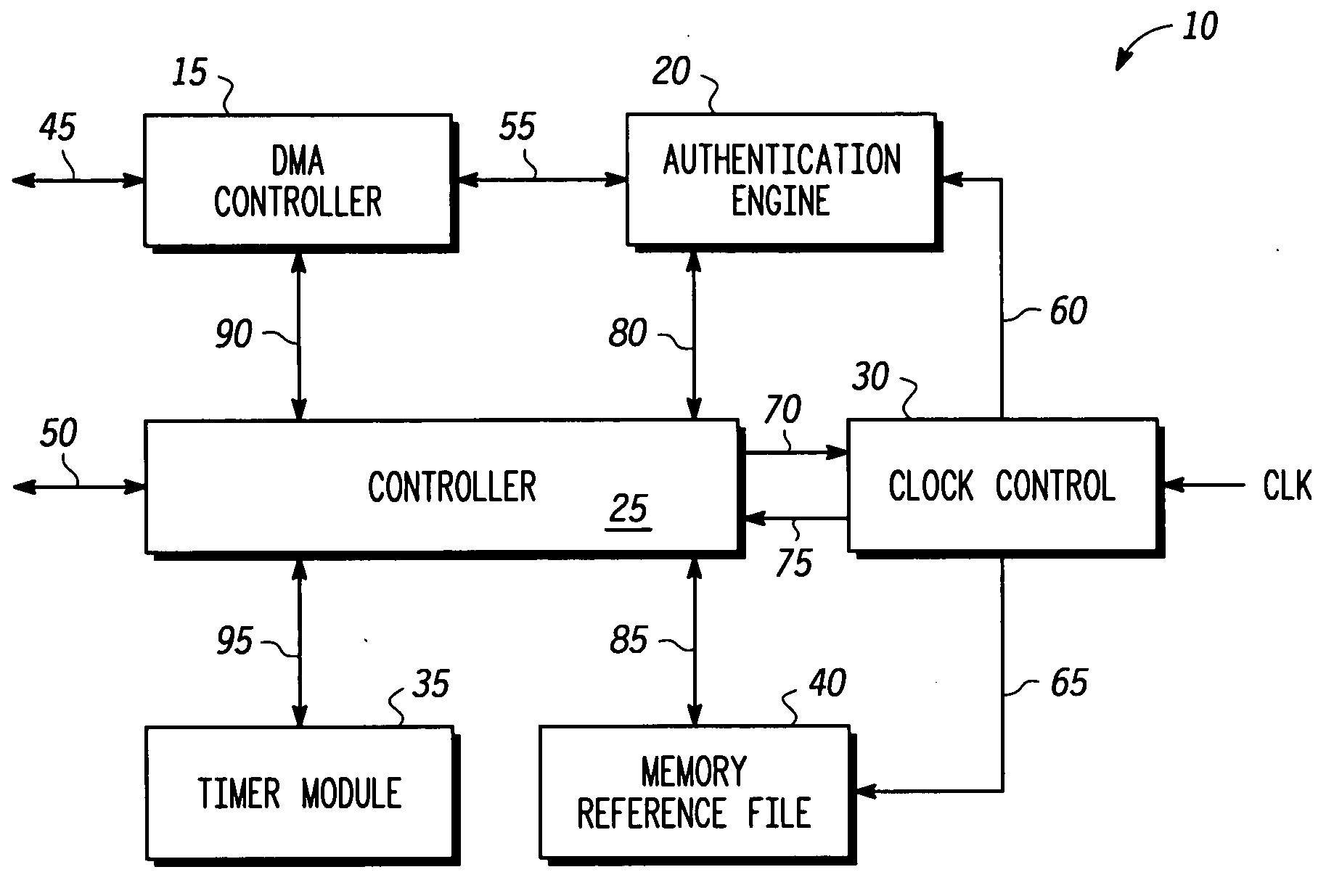
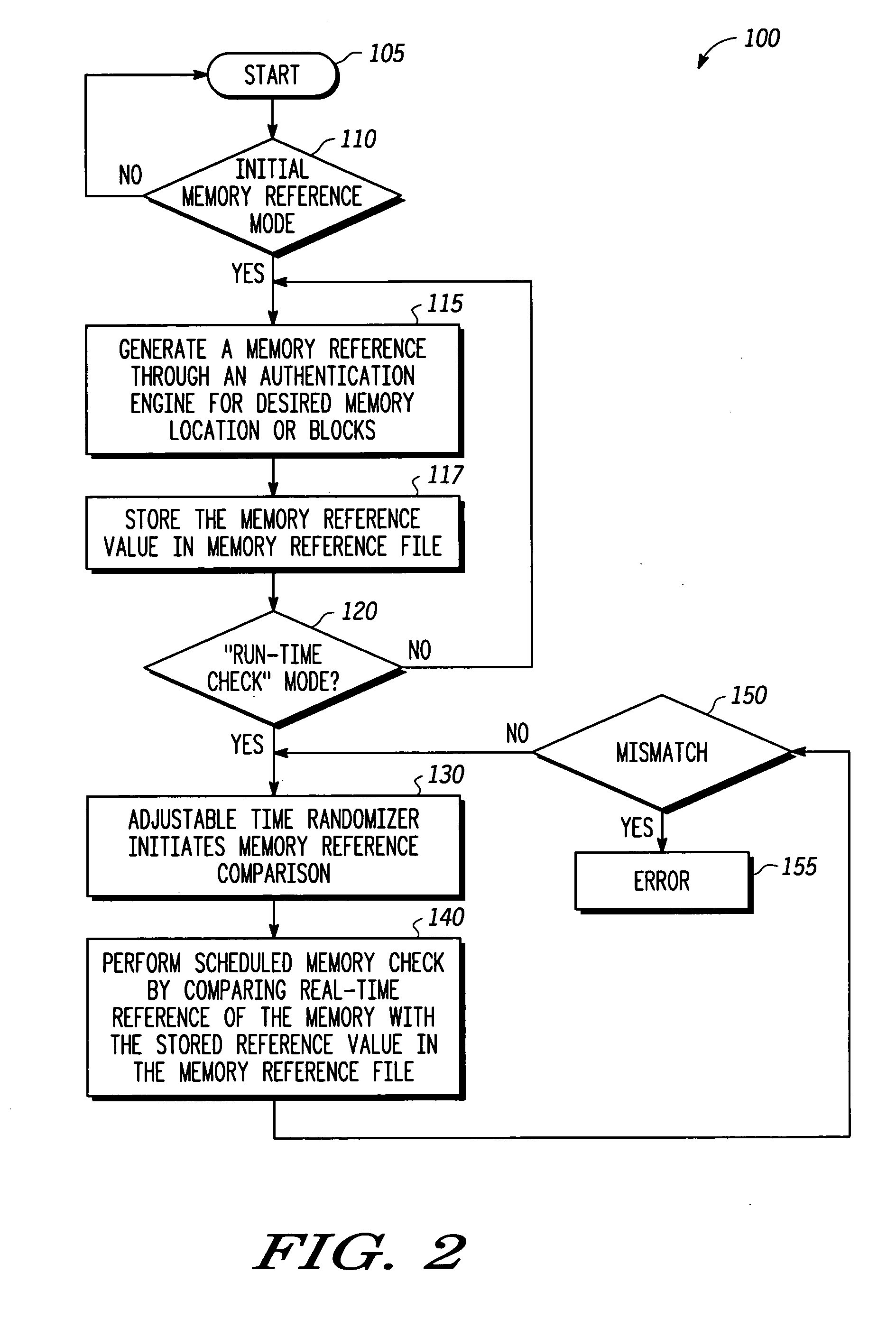
Autonomous memory checker for runtime security assurance and method therefore
ActiveUS20050193217A1Compromise integrityData processing applicationsMemory loss protectionComputer hardwareAuthentication
Methods and apparatus are provided for an electronic device having an autonomous memory checker for runtime security assurance. The autonomous memory checker comprises a controller, a memory reference file coupled to the controller, and an authentication engine coupled to the controller. A check is performed during runtime operation of the electronic device. The autonomous memory checker generates runtime reference values corresponding to trusted information stored in memory. The runtime reference values are compared against memory reference values stored in the memory reference file. The memory reference values are generated from the trusted information stored in memory. An error signal is generated when the runtime reference values are not identical to the memory reference values thereby indicating that the trusted information has been modified.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
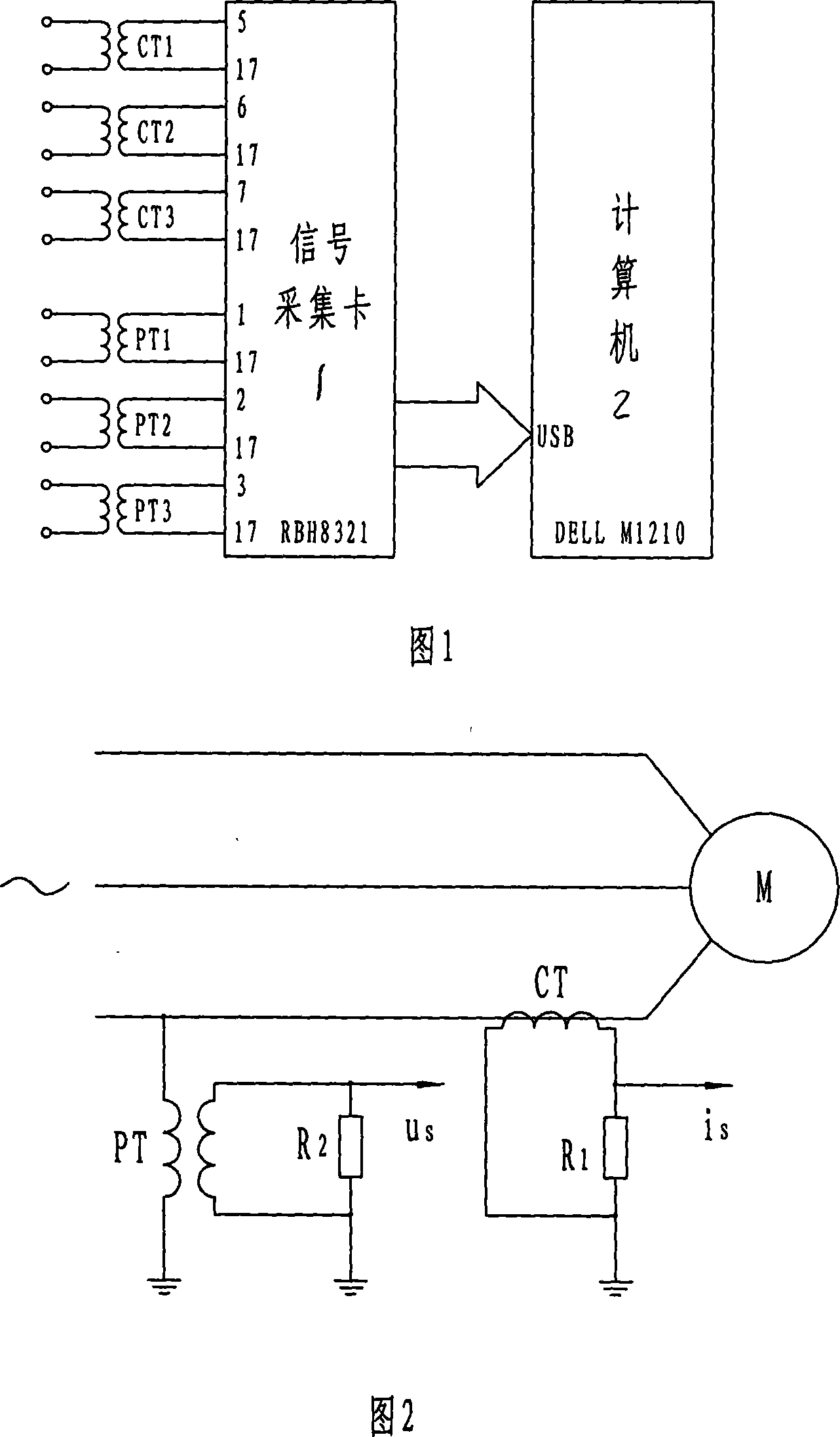
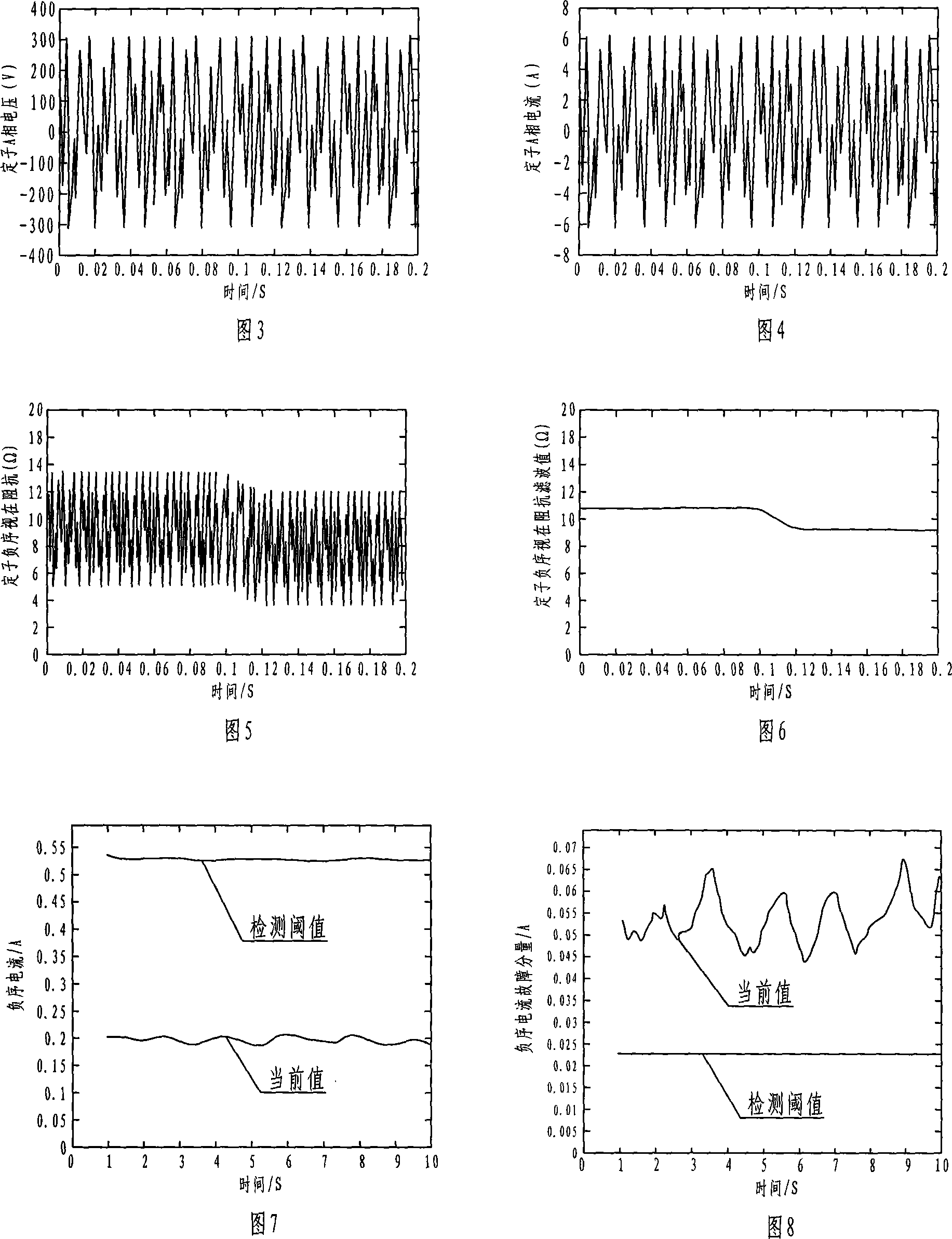
Asynchronous motor stator winding inter-turn short circuit failure on-line detecting method and device
InactiveCN101025434AGuaranteed safe operationAvoid adverse effects of fault detectionDynamo-electric machine testingStator voltageInduction motor
The invention relates to a online testing process for shorted fault of asynchronous motor's stator winding, which is belong to Detecting Technology. It was designed to solve the detecting problem of stator winding. The project is that it figures out the voltage and current of negative sequence and positive sequence of the stator winding by collecting three-phase stator voltage, instantaneous-current signal. Then using of normal motor sample reference document estimated the filter value of the stator negative sequence, figured out the stator negative sequence current fault component. And then base on the threshold of the stator negative sequence current fault component educe failure exponent. Finally according to the index judge whether to exist short circuit failure or not. This invention also gave corresponding detection device. Not only can high sensitivity, high reliability and on-line measurement asynchronous motor stator windings at the beginning of the early short circuit fault, but also can judge short circuit phase. This can effectively ensure the asynchronous motor operating safely.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
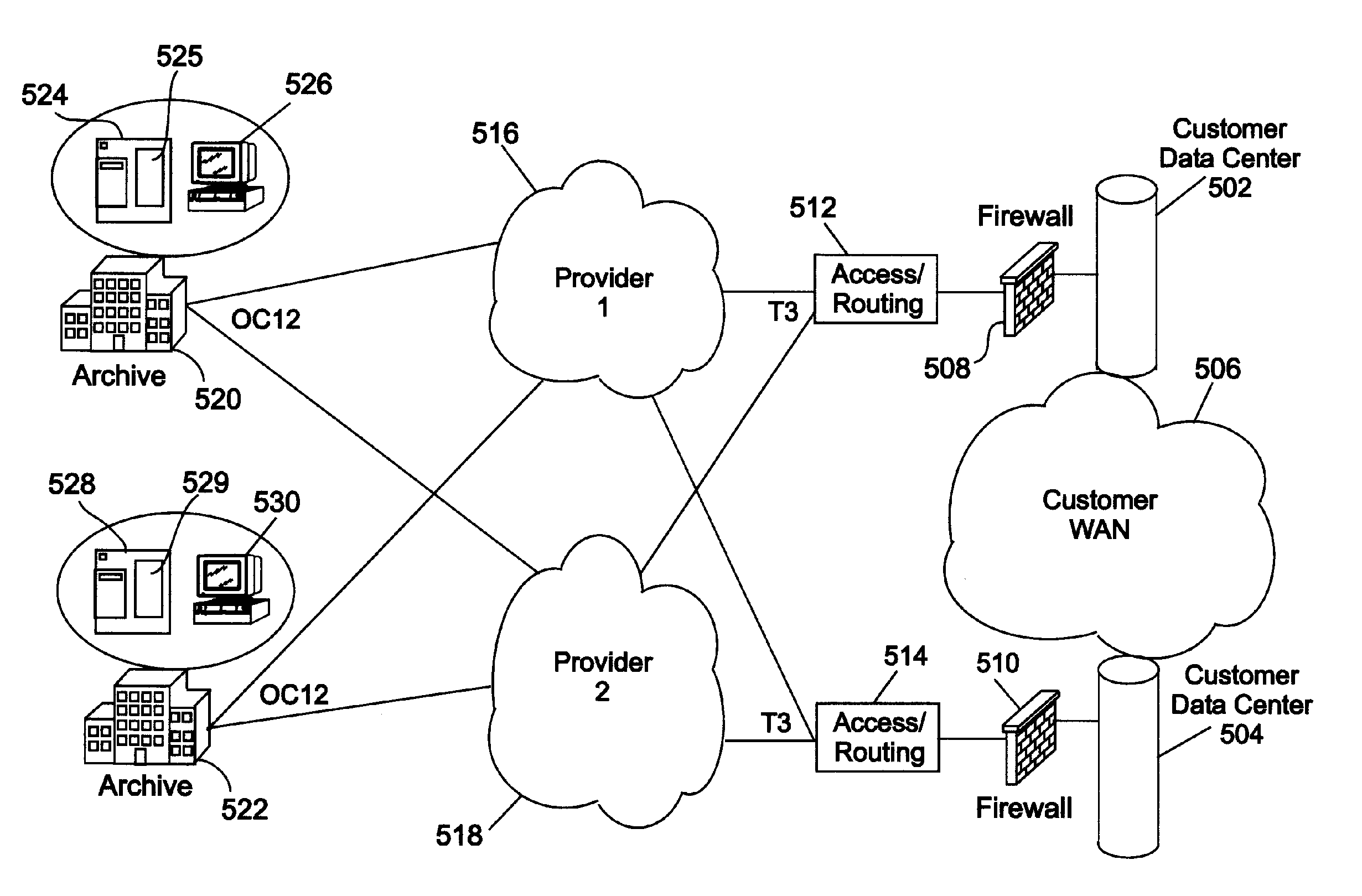
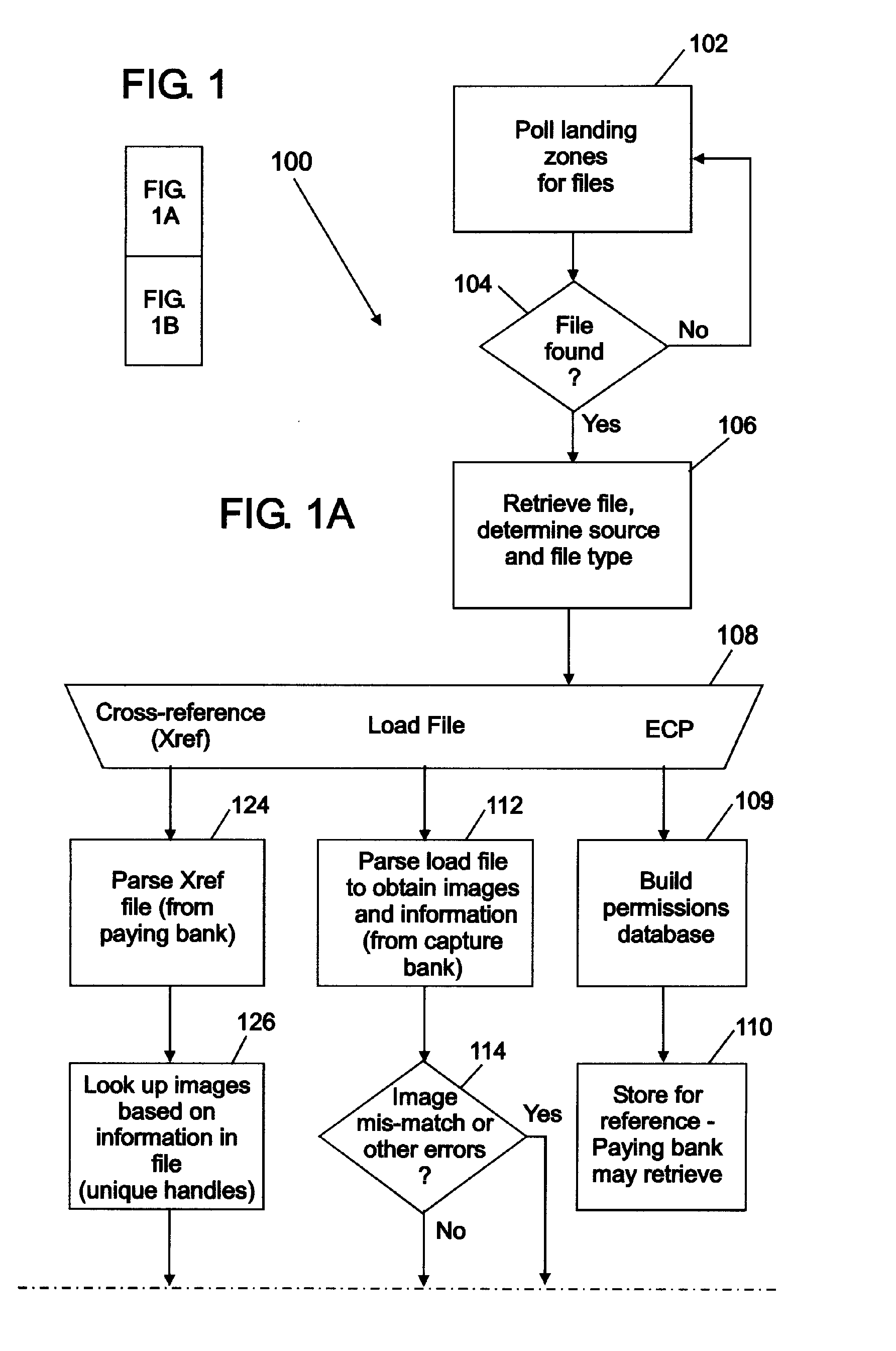
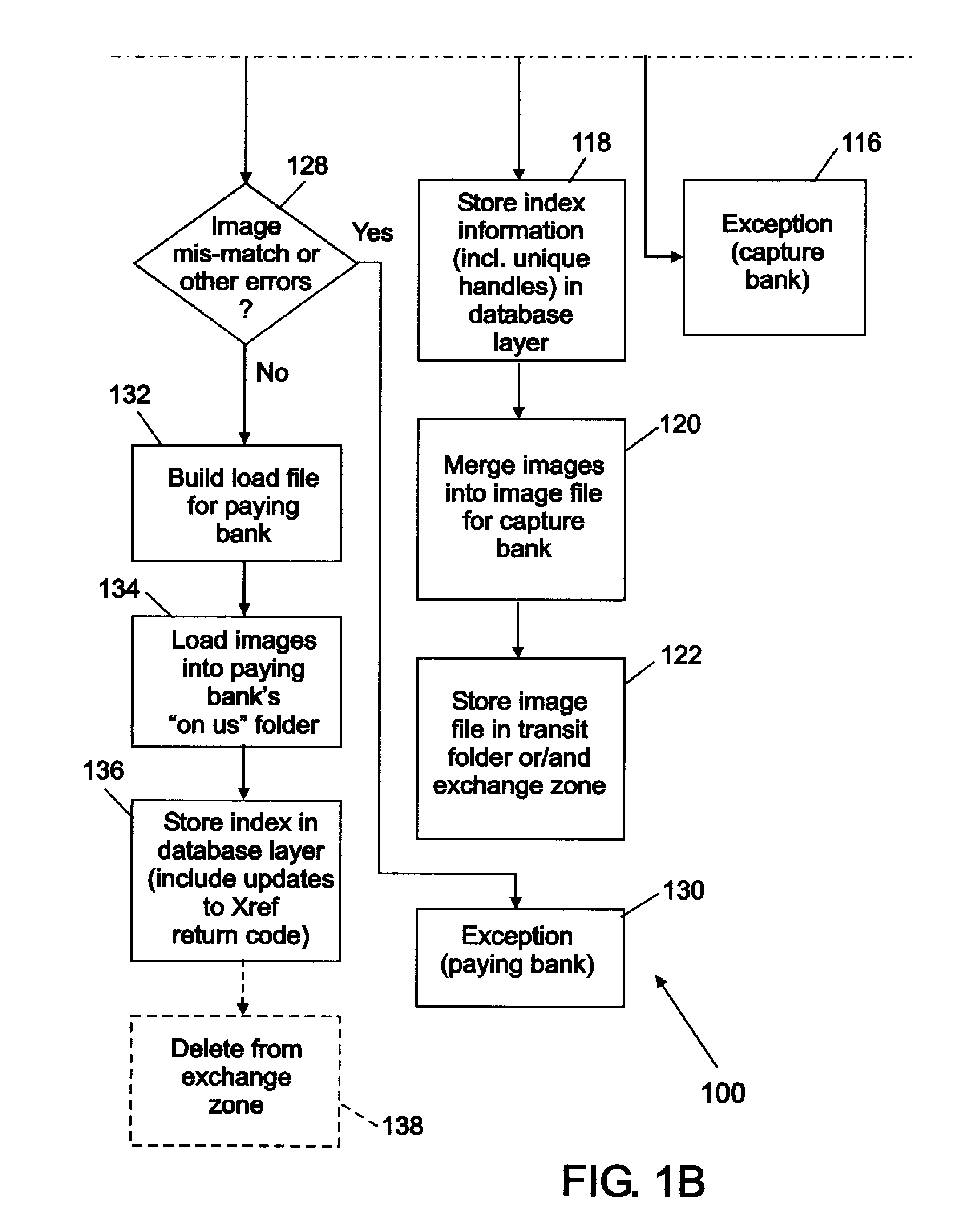
Centralized check image storage system
ActiveUS20050216409A1Reduce on-site image archive storage needSpeed reconciliationFinancePayment architectureInformation supportLanding zone
Centralized check image storage system. The present invention provides for sharing check images stored in a substantially centralized storage system between and / or among banks in support of the check collection process. In some embodiments, check images are received from the capture bank via a landing zone at the centralized storage facility. These images and information supporting the check collection process can be in the form of load file. A cross-reference file including information supporting the check clearing process such as unique handles identifying the check images is received from a paying bank, possibly also via a landing zone. Check images can be identified based on these unique handles, so that the check images can be made accessible to both the capture bank and the paying bank from the substantially centralized storage system.
Owner:VIEWPOINTE ARCHIVE SERVICES
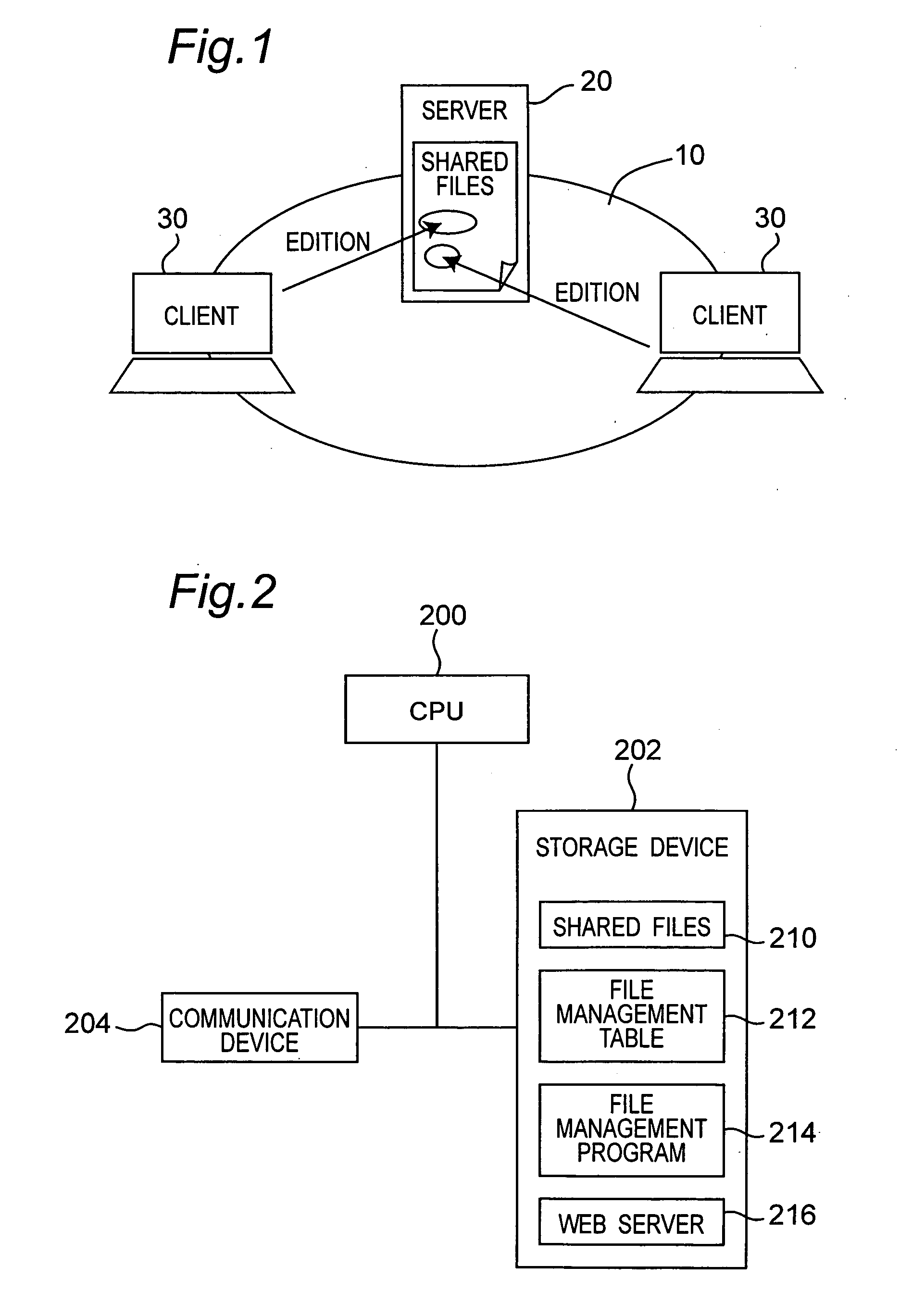
System and server for managing shared files
ActiveUS20050289512A1Data processing applicationsMultiprogramming arrangementsGraphicsGraphical user interface
In a system where files are shared by a plurality of client apparatuses through a network, when an access to a file in the shared files by a first client apparatus is received, it is decided whether the file is under editing by a second client apparatus or not, with reference to file management data. When the accessed file is not edited by a second client apparatus, the second client apparatus editing the file including a portion which the first client apparatus intends to edit, a first graphic user interface is presented for notifying whether the second apparatus permits or rejects editing of the portion by the first client apparatus. When a notification to permit editing of the portion is received, the first client apparatus is allowed to open the file in a status wherein editing of the portion is permitted.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA BUSINESS TECH INC
Repository for jobseekers' references on the internet
InactiveUS6904407B2Elimination of repeated contactEliminate lossOffice automationResourcesWeb siteElectronic mail
An electronic repository for jobseekers' references on the Internet. The jobseeker registers himself and his reference sources on an Internet site. The references are notified via e-mail, they subsequently log in and enter their personal or professional reference or letter of reference for the jobseeker. The jobseeker gives perspective Recruiters / Employers information on accessing his references. The list of references is available at no charge, but the detail of the reference document can be purchased by the Recruiter / Employer. All required security is implemented. The advantages of this process include: (1) elimination of repeated contact of jobseekers' references for positions that change frequently; (2) virtually instant checking of references, eliminating loss of potential employee through extended process; and (3) significant reduction in cost and time of checking reference by recruiter / Employer.
Owner:RITZEL WILLIAM D
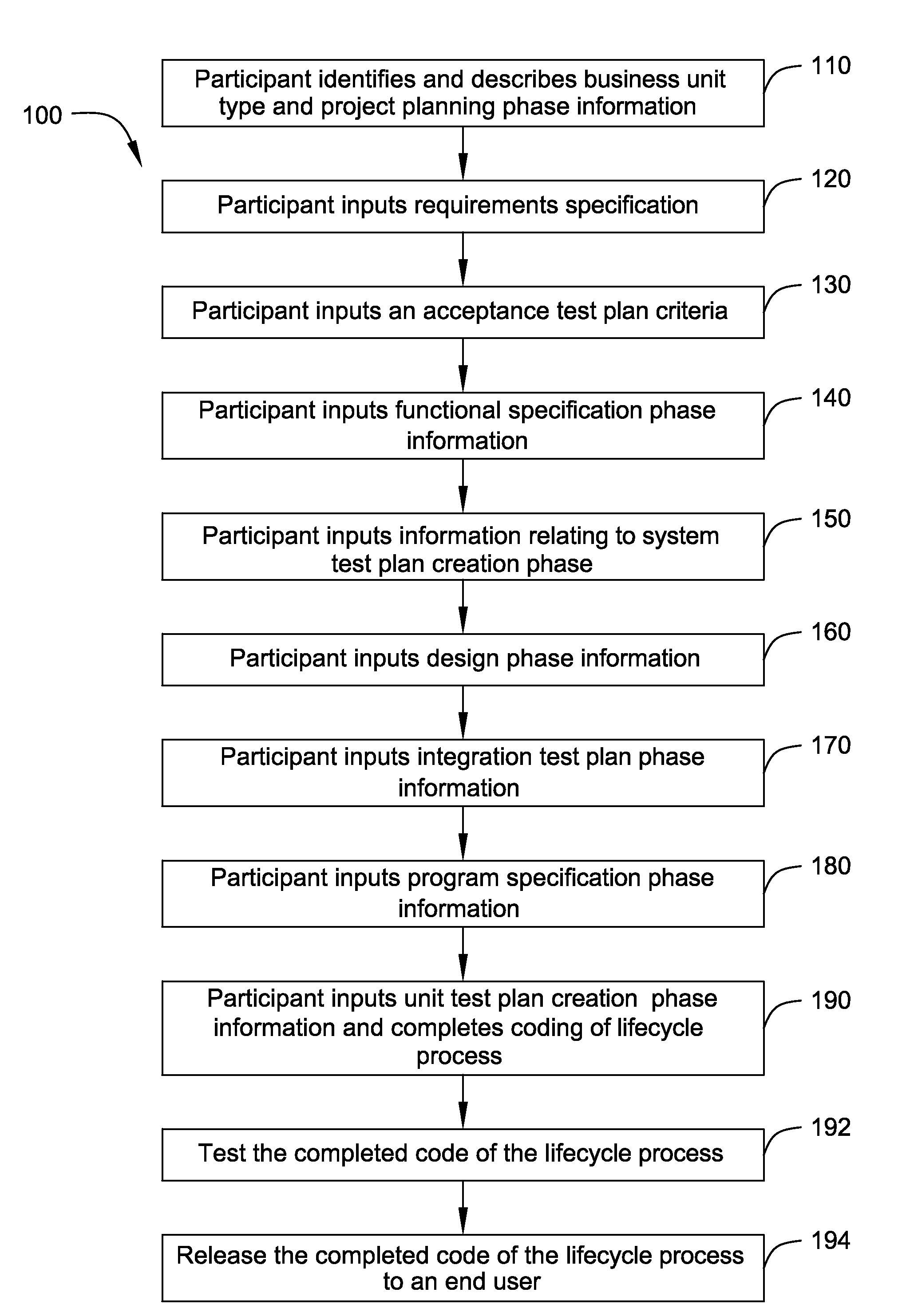
System and method for software lifecycle management
InactiveUS20080034347A1Software maintainance/managementSpecific program execution arrangementsManagement toolSoftware development
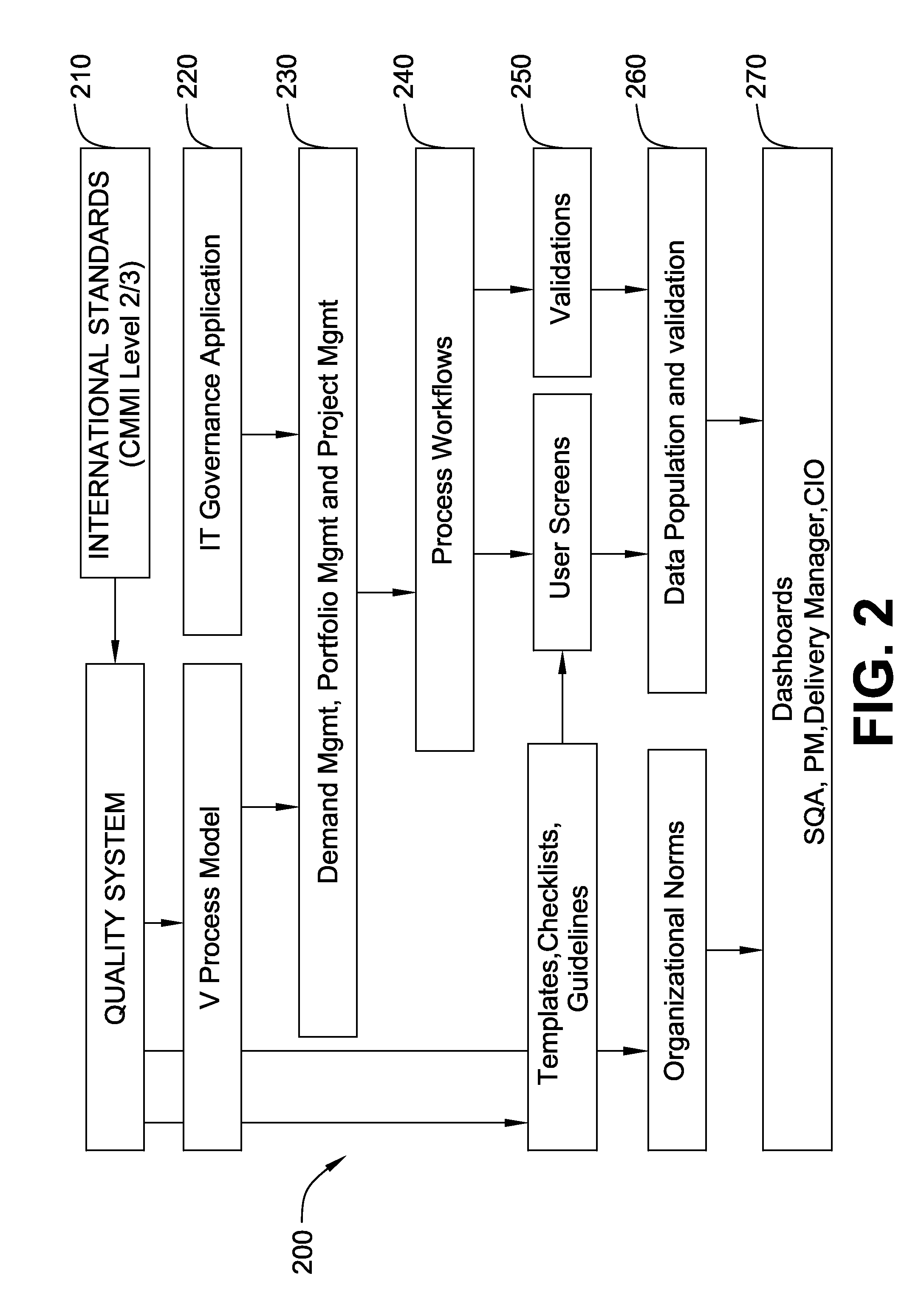
A computerized tool and techniques for enabling a software lifecycle management tool for an end user is provided. In one example embodiment, this is accomplished by using a V-process software development lifecycle model built with a workflow engine on an IT governance application. The technique provides an end-to-end life cycle with automatic review processes that complies with an external quality standard, such as level 2 CMMI. Further, the technique provides an on-line reference document including best practices at each phase in the V-process lifecycle.
Owner:V SUBRAMANYAM +1
Document creation, linking, and maintenance system
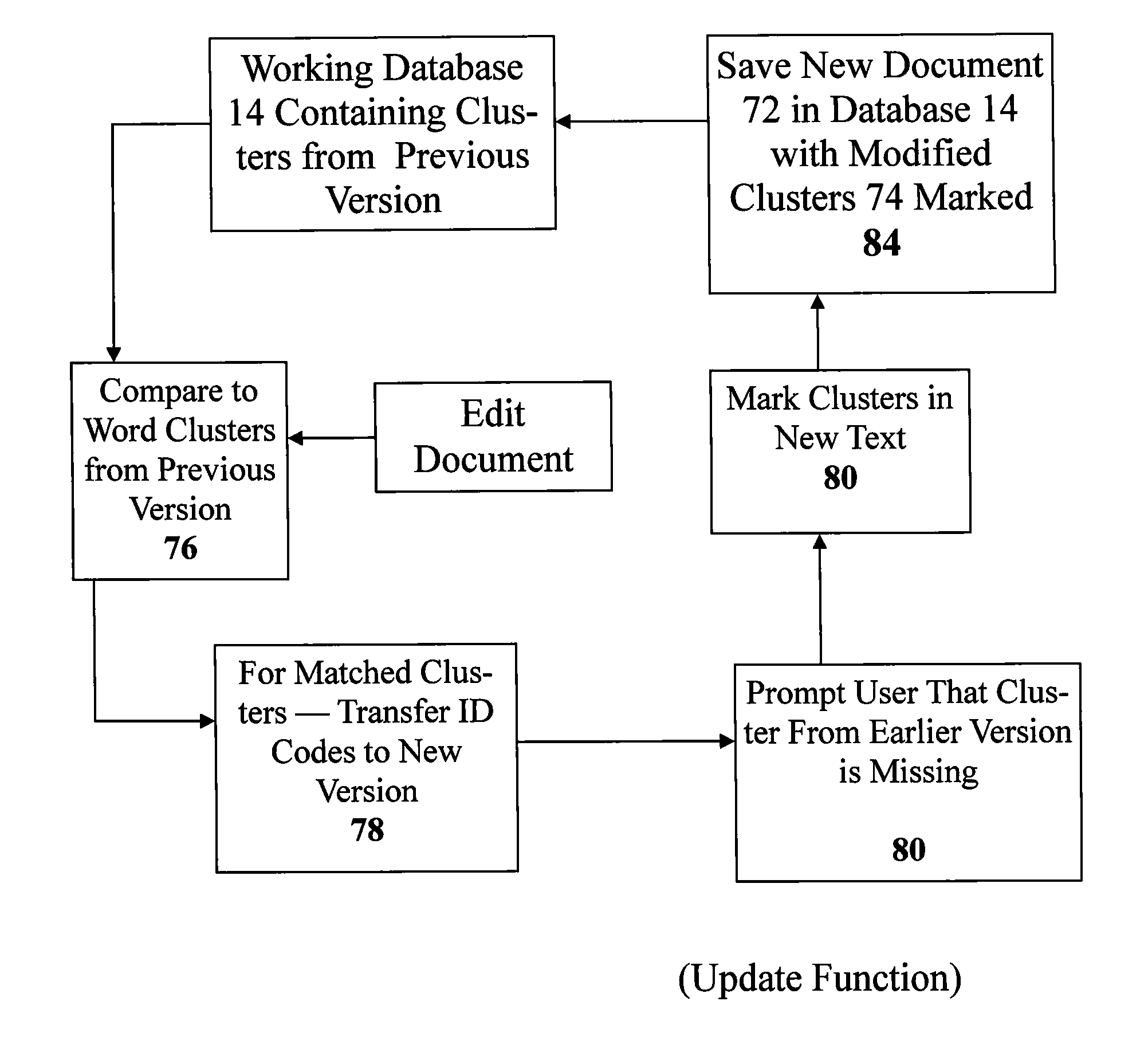
InactiveUS20090043824A1Easy to moveMaintain alignmentDigital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsAs DirectedSystems design
A document creation and citation system designed to maintain a database of reference documents. The content of a selected document may be automatically scanned and indexed by the system. The selected documents may also be manually indexed by a user prior to the upload. The indexed documents may be uploaded and stored within a database for later use. The system allows a user to generate new documents by selecting content within the reference documents stored within the database and inserting the selected content into a new document. The system allows the user to customize and augment the content of the new document. The system also generates citations to the selected content retrieved from the reference documents. The citations may be inserted into the new document in the appropriate location and format, as directed by the user. The new document may be uploaded into the database and included with the other reference documents. The system also maintains the database of reference documents so that when changes are made to a reference document, the author of a document referencing the changed document will be alerted to make appropriate changes to his document. The system also allows visual comparison of documents so that the user may see differences in the text of the documents.
Owner:CLAGHORN RONALD
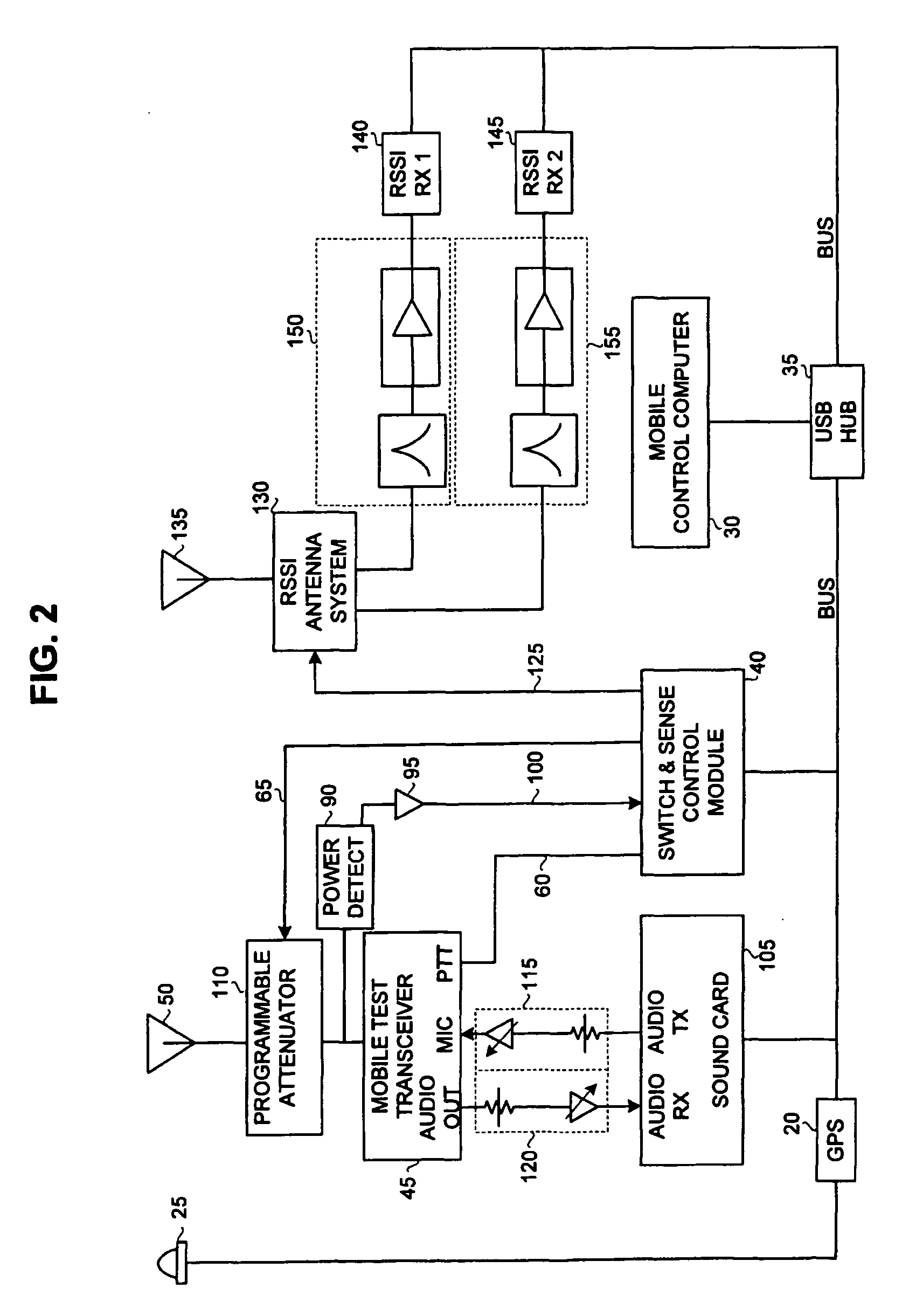
Method and System for Evaluating Radio Coverage
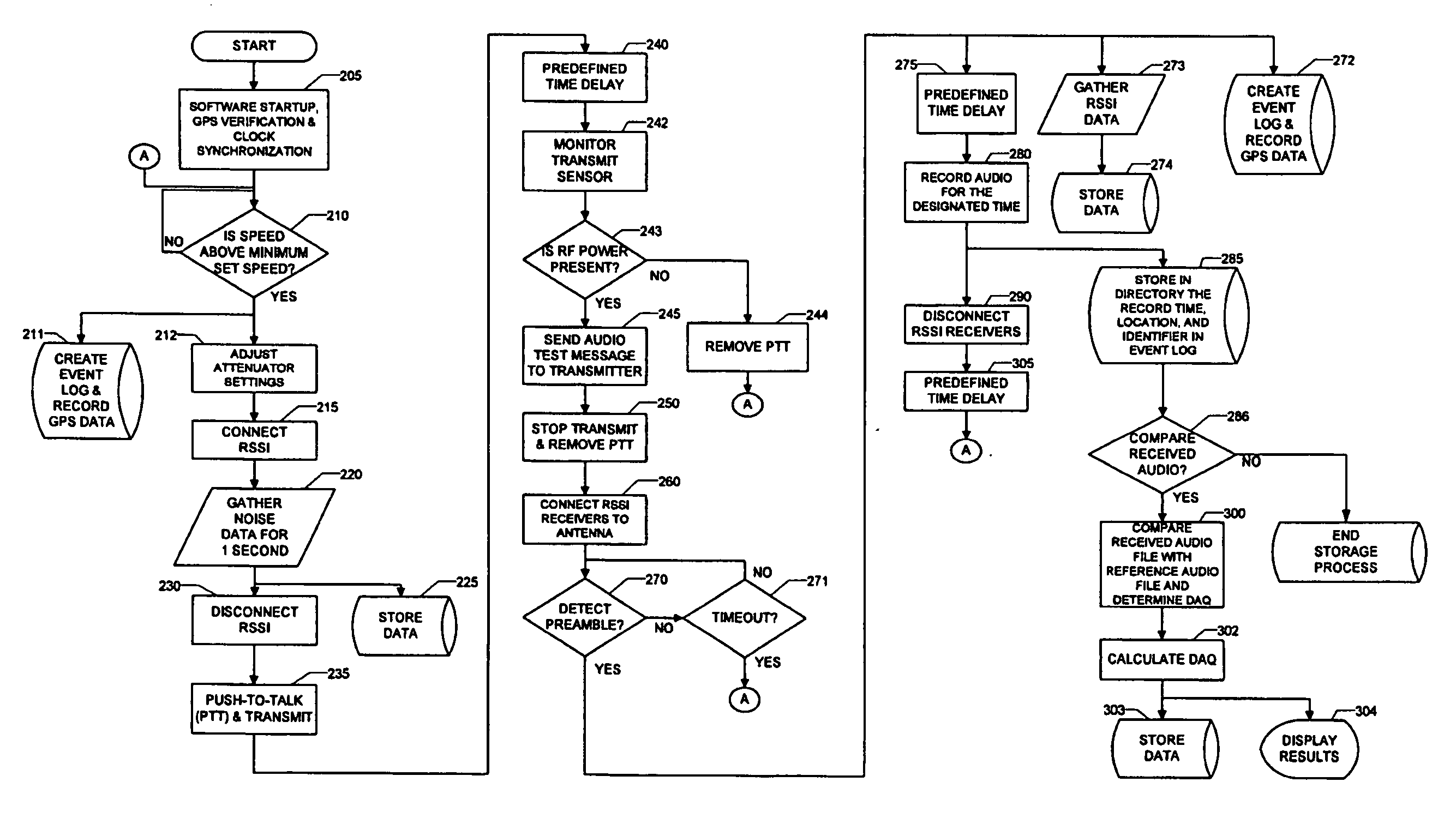
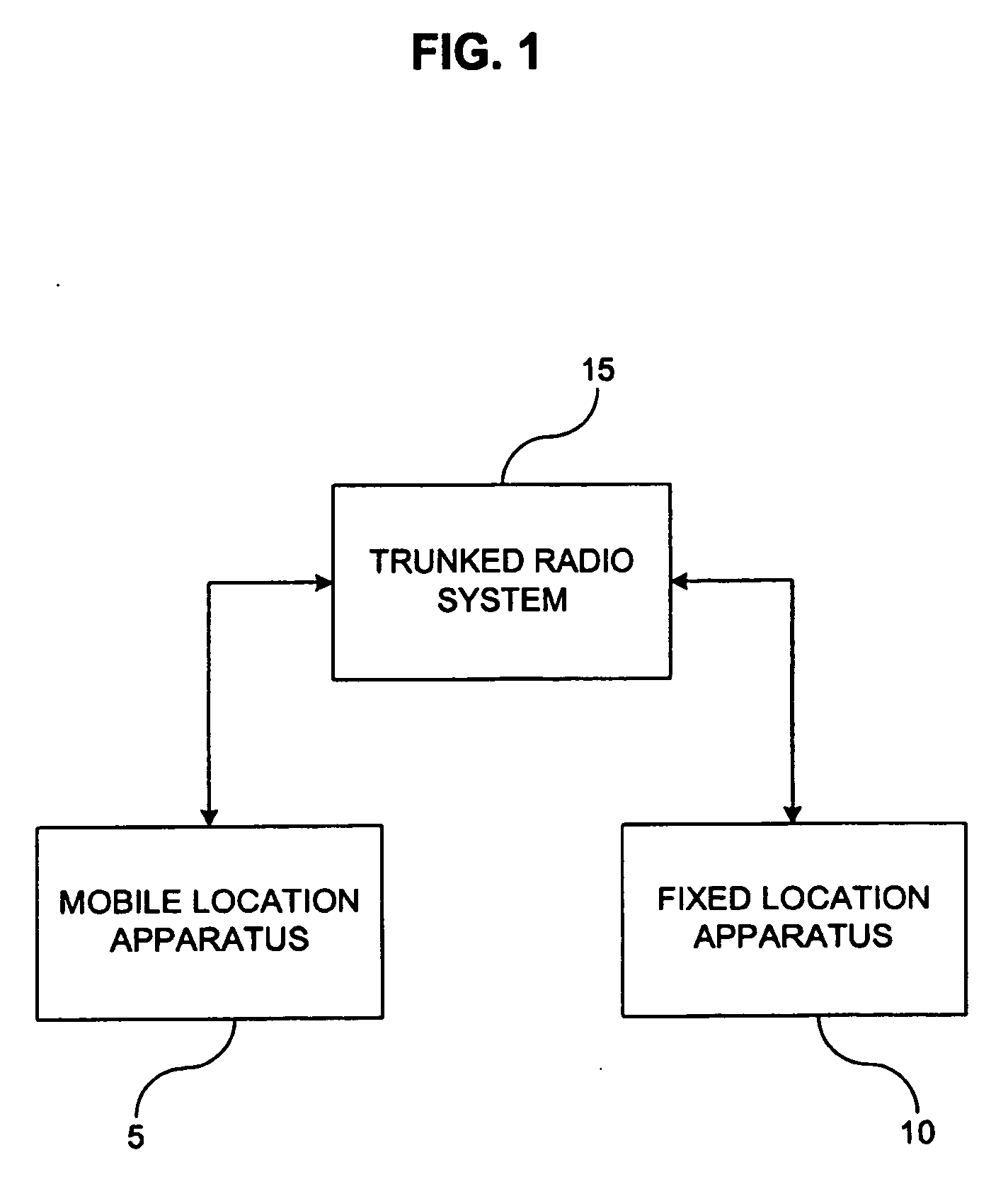
InactiveUS20070010241A1Speech analysisRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio coverageEngineering
A system and method for testing radio coverage of a land mobile radio system. The system configuration generally employs a fixed unit, a mobile unit and the two-way radio system (not part of the invention) subject to testing. The test system and method are compatible with any land-mobile radio system (conventional, trunked, using proprietary or standards-based protocols, FDMA or TDMA) operating in any frequency band. One of three methods may be selected to perform testing at any one time: continuous testing, grid testing or receive-only testing. In the continuous and grid modes, both the talk-out and talk-in paths are measured. Test results are recorded in a computer file after being converted to a digital format, and are compared to an original “reference file” via the Perceptual Evaluation of Speech Quality (PESQ) algorithm as defined by ITU-T standard P.862. The PESQ output is then converted to a Delivered Audio Quality (DAQ) score by application of an empirical set of weighting factors to certain of the PESQ parameters.
Owner:CTA COMM
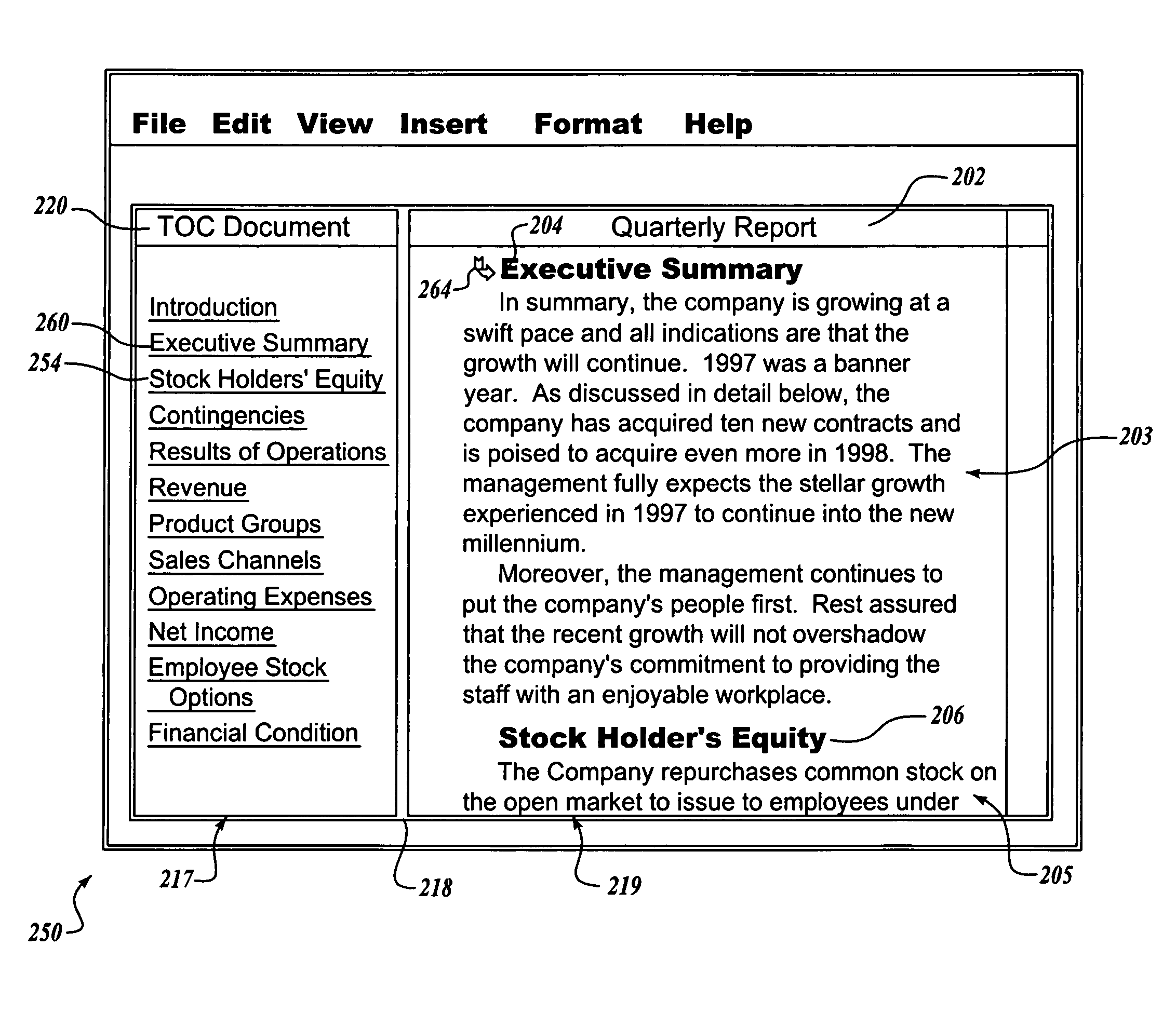
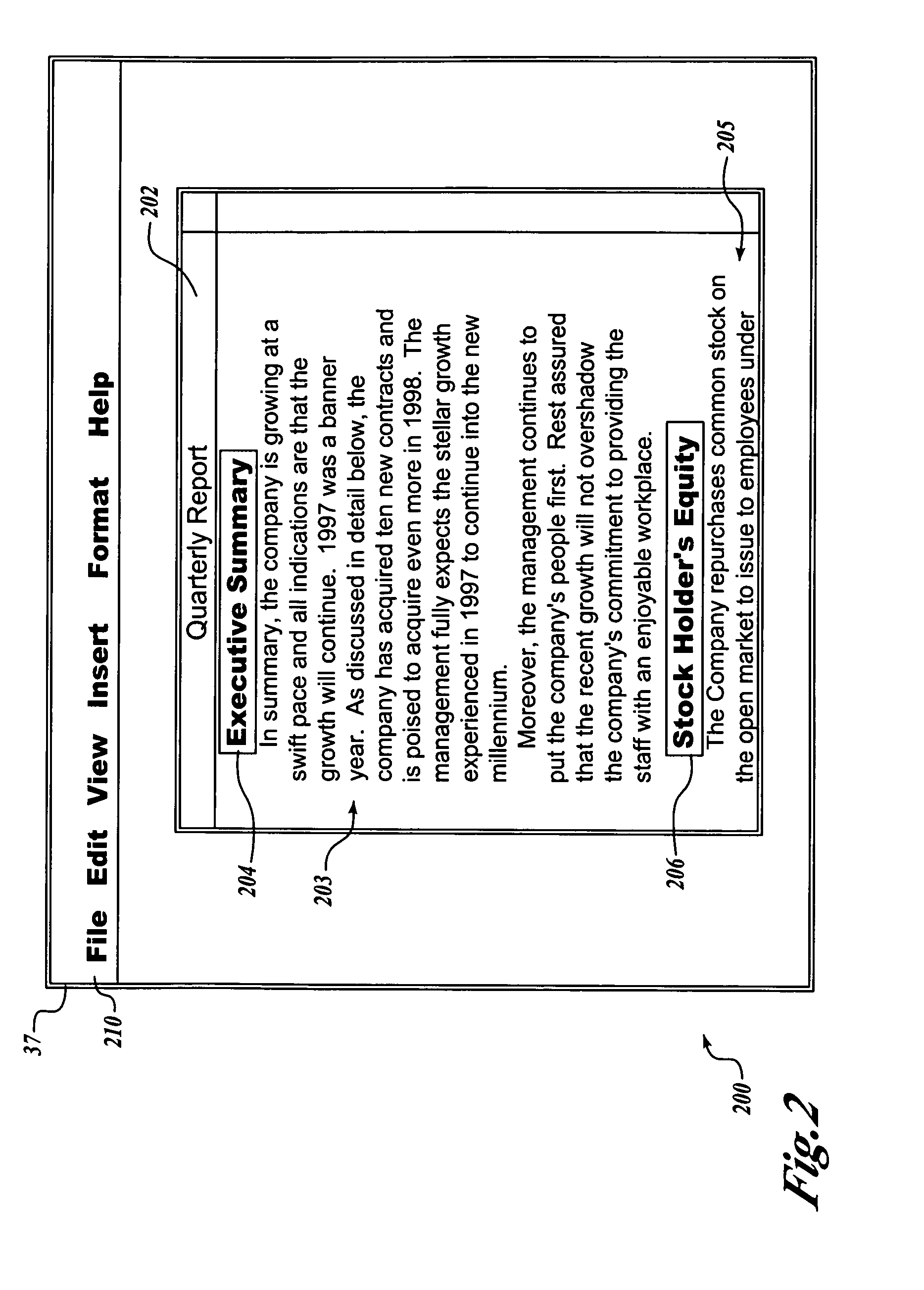
System and method for updating a table-of-contents in a frameset
InactiveUS20050010865A1Scroll fastOvercome disadvantagesDigital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsHyperlinkPaper document
A self-updating frameset having a target document in one frame and a Table-of-Contents (TOC) document in another frame hyperlinked to the target document. A reference document (RD) field is inserted into the TOC document to identify the target document as the target of the TOC. A TOC field in the TOC document scans the target document to identify selected headings as entries in the TOC document. When the selected headings are identified, the TOC field creates hyperlink entries in the TOC document, each hyperlink entry having a corresponding anchor at a selected heading in the target document. The hyperlink entries in the TOC document can be automatically updated each time the fields in the TOC document are recalculated.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Process of localizing objects in markup language documents
A method and system that facilitates localization of objects in markup language documents so that a single set of markup language documents (the set including one or more documents) provide support for displaying portions of the documents in a language selected from among a plurality of different languages. Localized objects are included within in markup language documents through the use of placeholder variables in the documents. The placeholder variables are linked to localized objects through a reference file having entries populated with localized objects that are extracted from a dynamic link library based on a language selected by a user. Before loading each markup language document into a browser, the placeholder variables are replaced with their associated localized objects during a pre-rendering operation. When the markup language documents are rendered by the browser, display pages are produced containing localized objects in the language selected by the user. The present invention also provides for localizing composite graphic objects, which include a global portion, such as a trademark logo, and a localized portion, such as a phrase, through the use of cascading style sheets, thereby enabling the phrase to be rendered in a specified language.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Search system and method with text function tagging
ActiveUS20080059451A1Increase delayQuick identificationDatabase queryingWeb data indexingHyperlinkPaper document
A search system with a user interface module that generates a search engine results page including a listing of reference documents, each with a hyperlink to at least one secondary document relevant to the reference document. The search system also includes a text function tagger that parses text excerpts of the documents, and applies text function tags thereto. A secondary processing module is provided which identifies those secondary documents that have a text function tag that matches a text function tag of a reference document, so that selection of the hyperlink generates a display of secondary documents that are determined to at least have a text function tag that matches a text function tag of the reference document for which corresponding hyperlink was selected. A method and computer readable medium are also provided.
Owner:TEXTDIGGER
Apparatus and method for retrieval of documents
InactiveUS20050091204A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsPaper documentDocument preparation
A system for support and management of search for documents is presented. The system includes a knowledge-database, query interface and communication to a database of documents to be searched. Information generated during a search session is collected by the system and is added to the knowledge-database. The information is ranked automatically according to the usage of that information by the user. During successive search session or during a search made by another user, the system uses the knowledge-database to support the users with keywords, queries and reference documents.
Owner:UBER TECH INC
Method and system for document presentation and analysis
InactiveUS20120204104A1Rapid positioningQuickly assess relevance of a documentSpecial data processing applicationsText database clustering/classificationDocument analysisDocument preparation
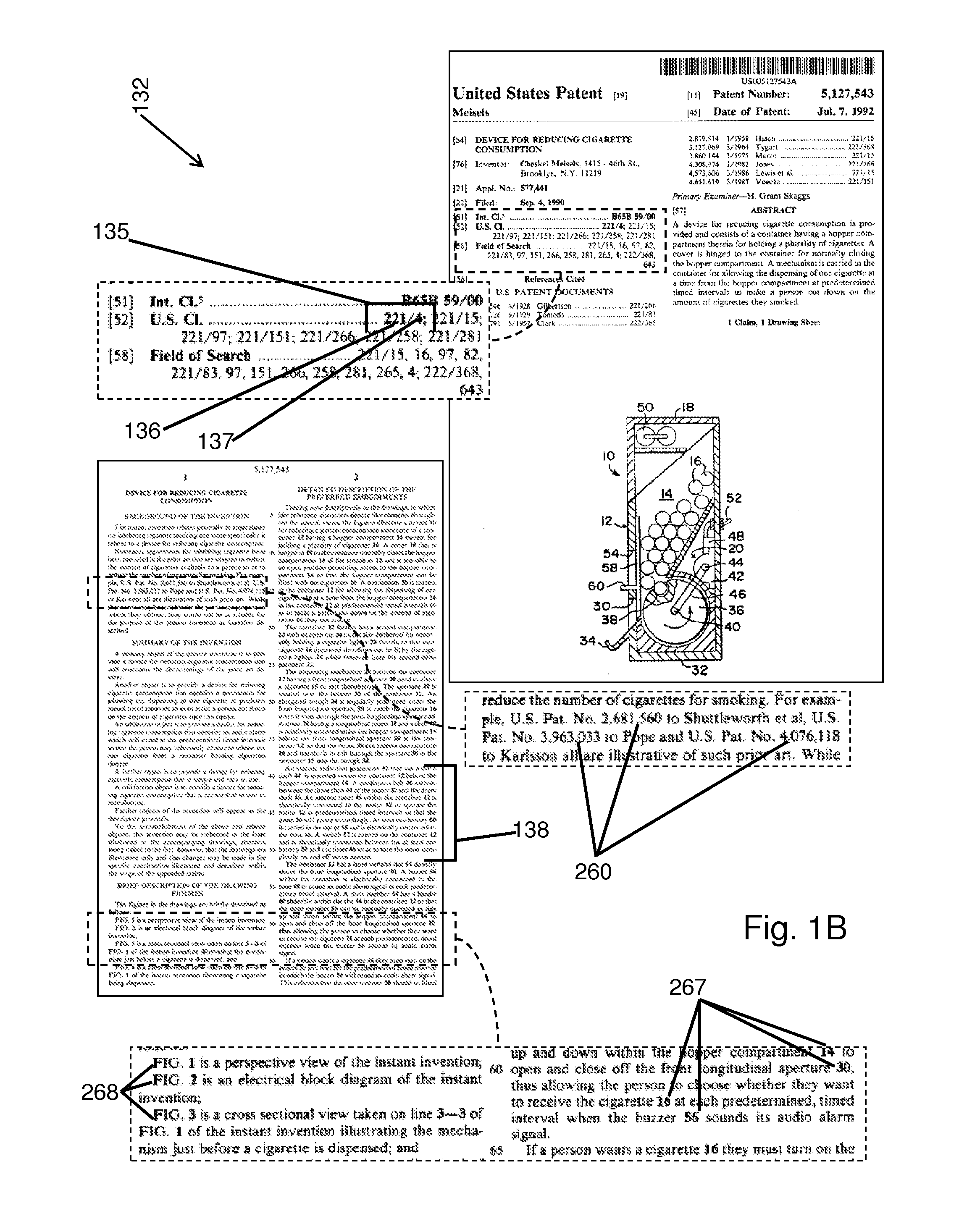
A document analysis system receives multiple concepts along with multiple reference documents and generates sensory indicators that assist a researcher in assessing the relevance of each of the documents to the concepts. In one exemplary aspect, the document analysis system displays a table of keywords separated into blocks, each block of keywords corresponding to one of the concepts. Each block is colored according to the prevalence of any keyword within a given keyword group. The color of a block thus indicates the relative presence of a concept in the document. The document analysis system also determines a unique color for each block of keywords for highlighting in the text of the document. In this manner a researcher can quickly identify passages that contain multiple concepts. Additionally, the researcher is provided the ability to quickly locate reference characters, figure numbers and patent numbers in the document.
Owner:WALSH PATRICK SANDER
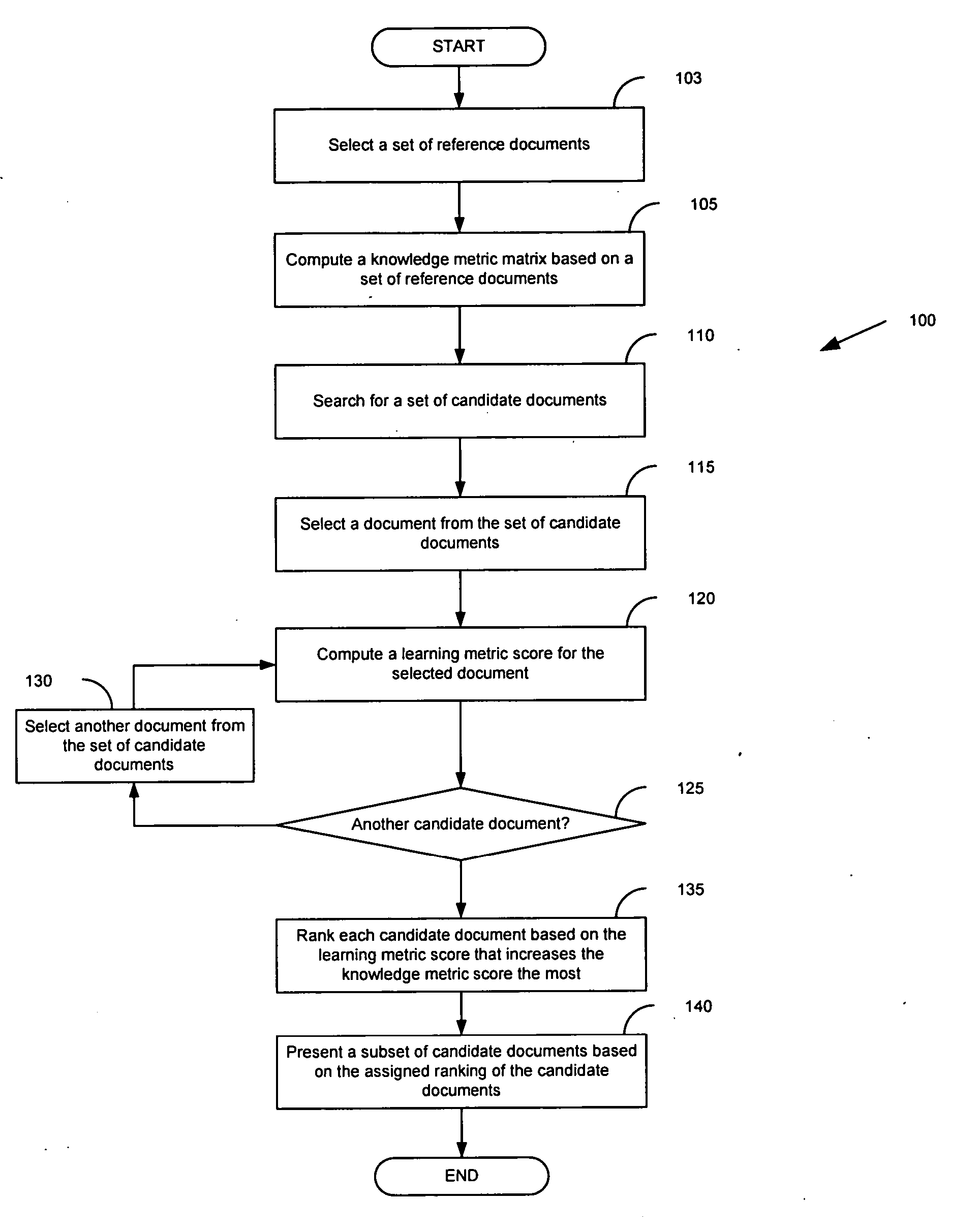
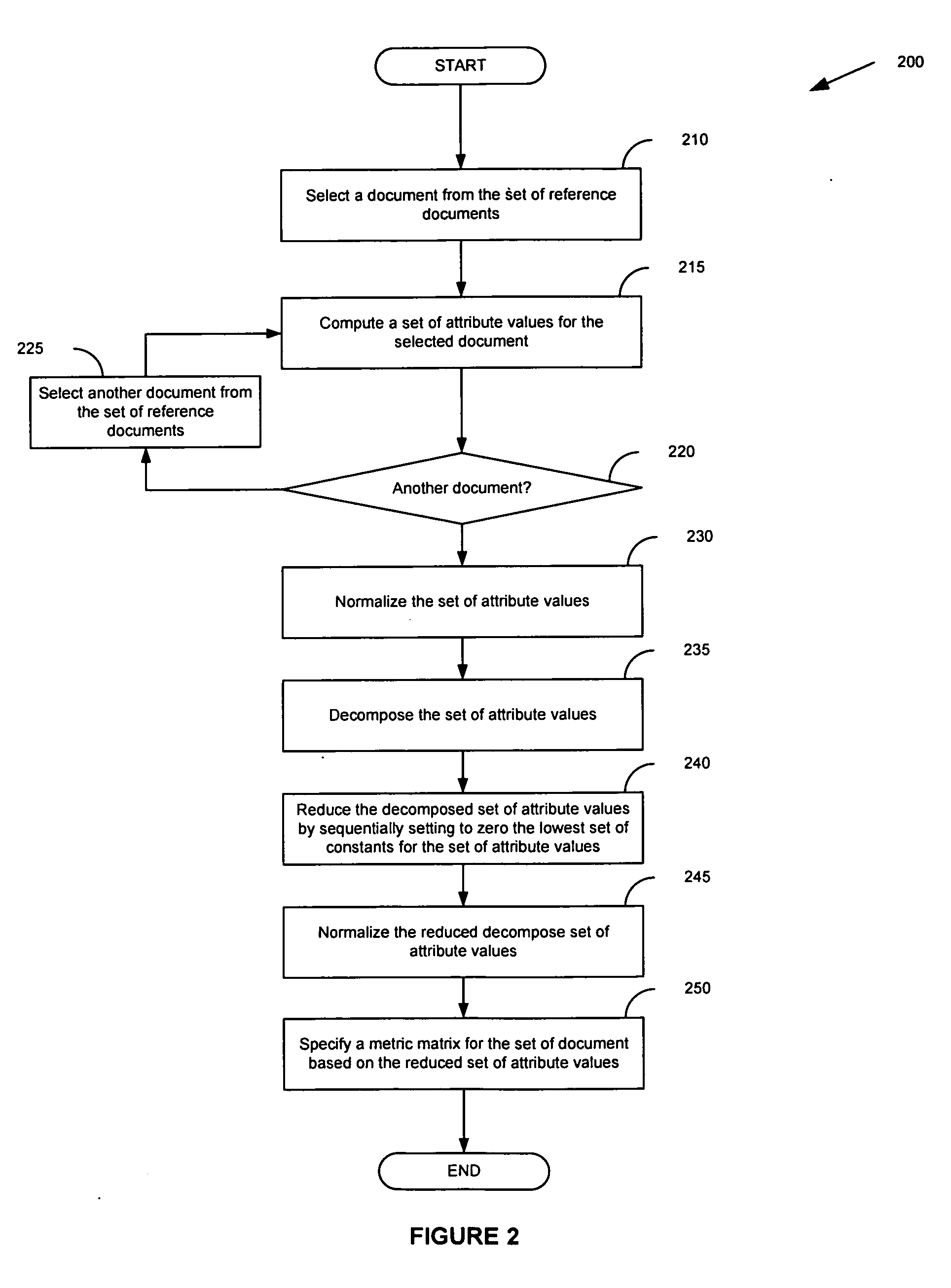
Information search using knowledge agents
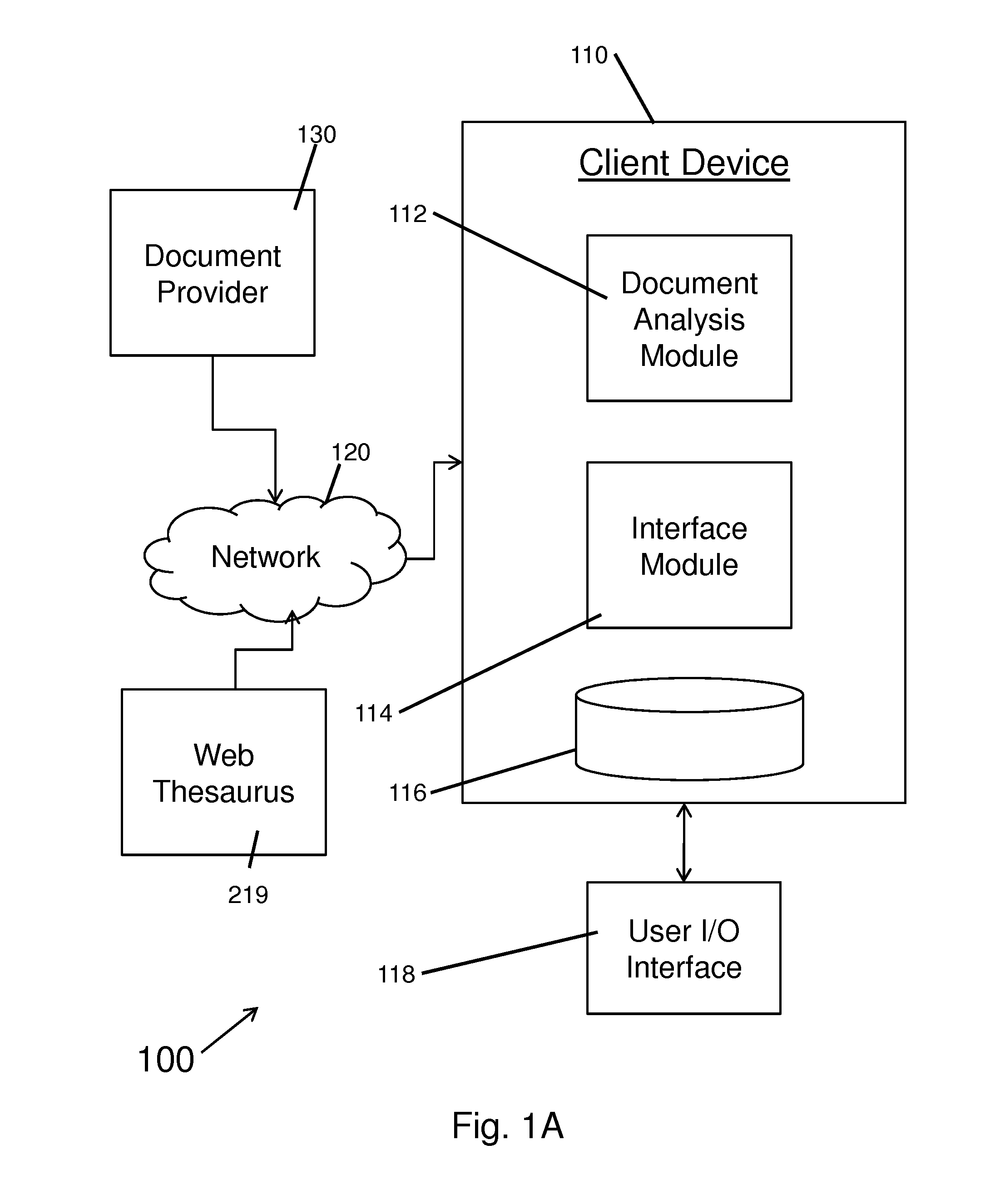
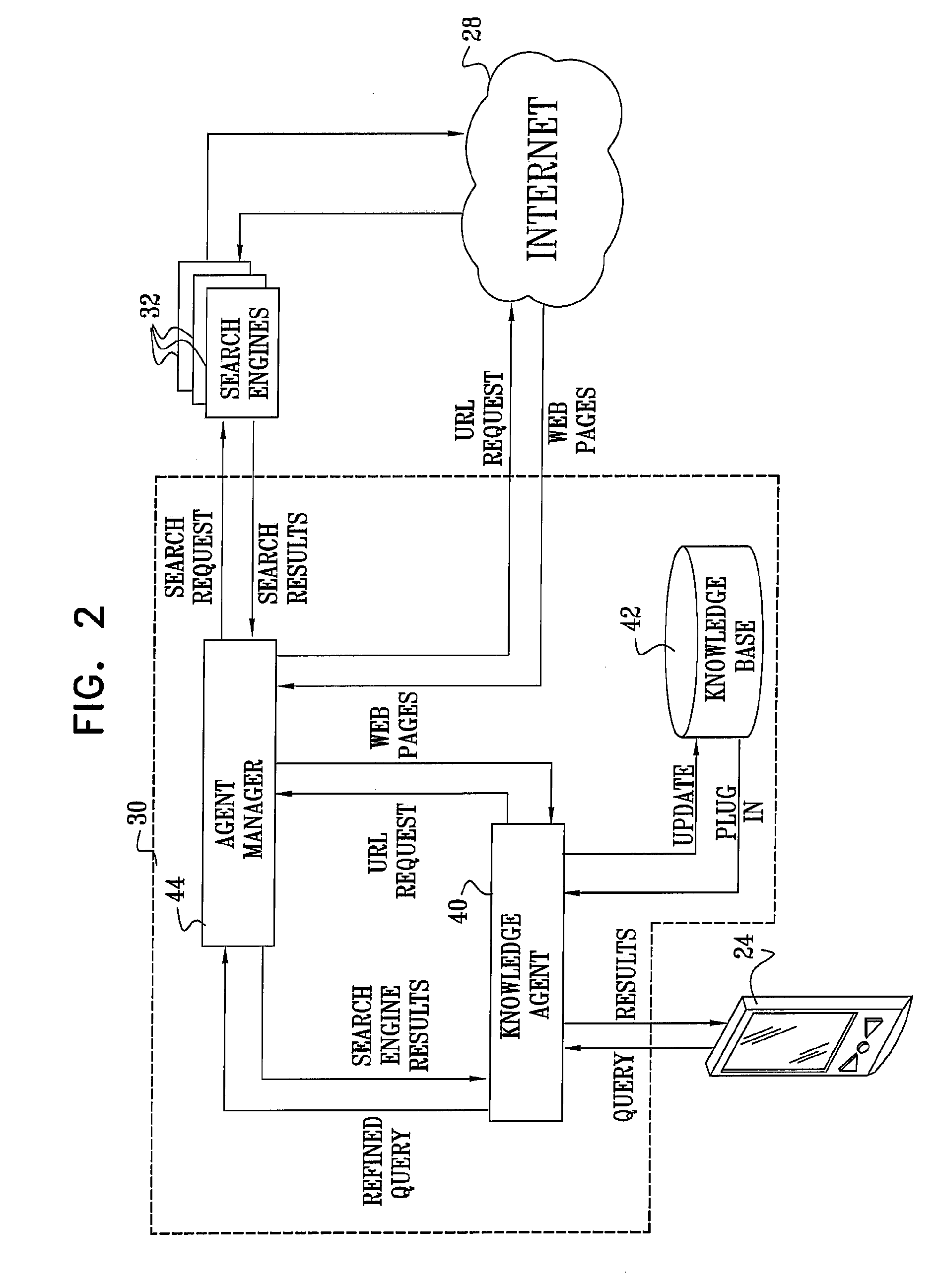
InactiveUS20080147644A1High precisionLow utilizationData processing applicationsWeb data indexingPaper documentInformation searching
A method for searching a corpus of documents, such as the World Wide Web, includes defining a knowledge domain and identifying a set of reference documents in the corpus pertinent to the domain. Upon inputting a query, the corpus is searched using the set of reference documents to find one or more of the documents in the corpus that contain information in the domain relevant to the query. The set of reference documents is updated with the found documents that are most relevant to the domain. The updated set is used in searching the corpus for information in the domain relevant to subsequent queries.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
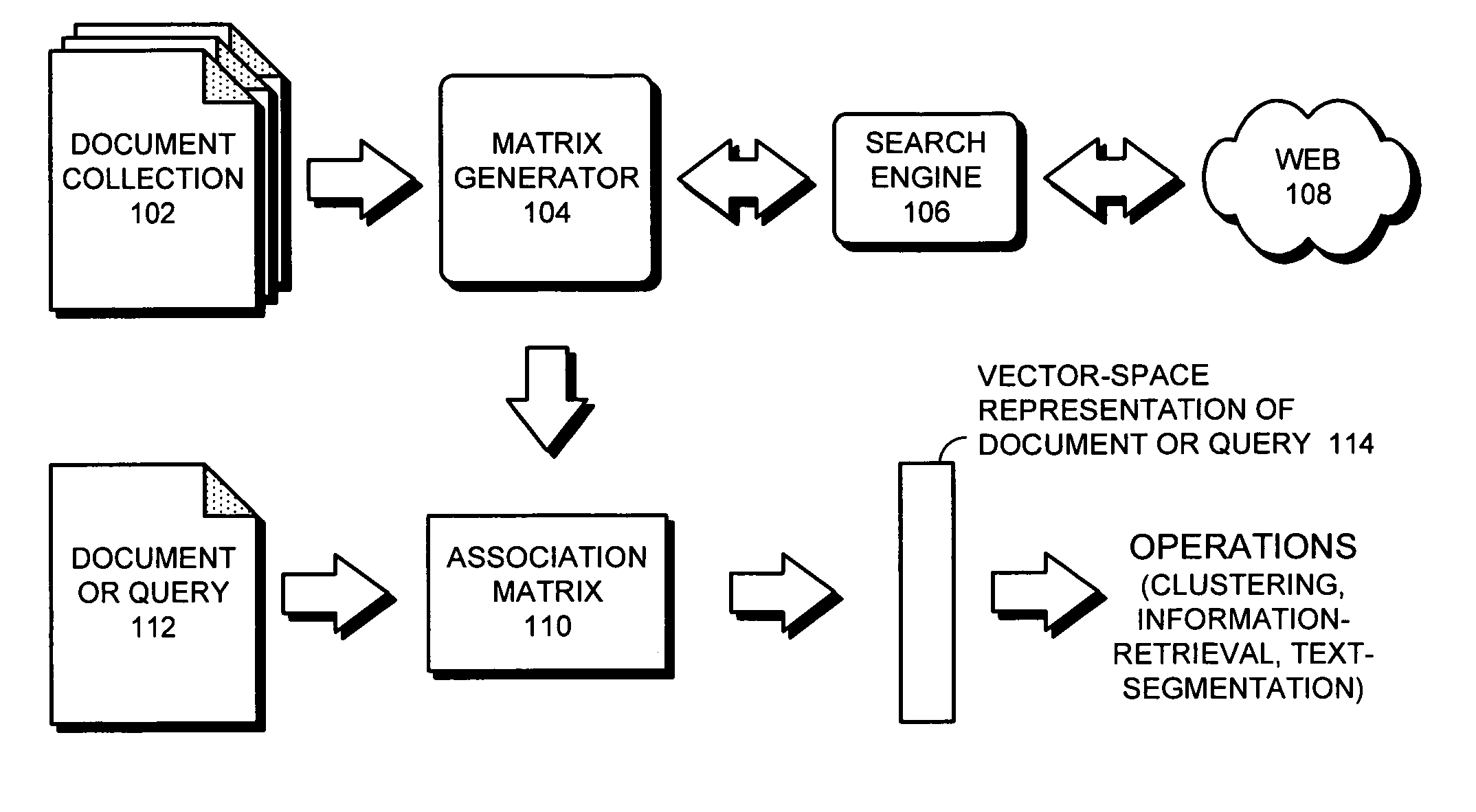
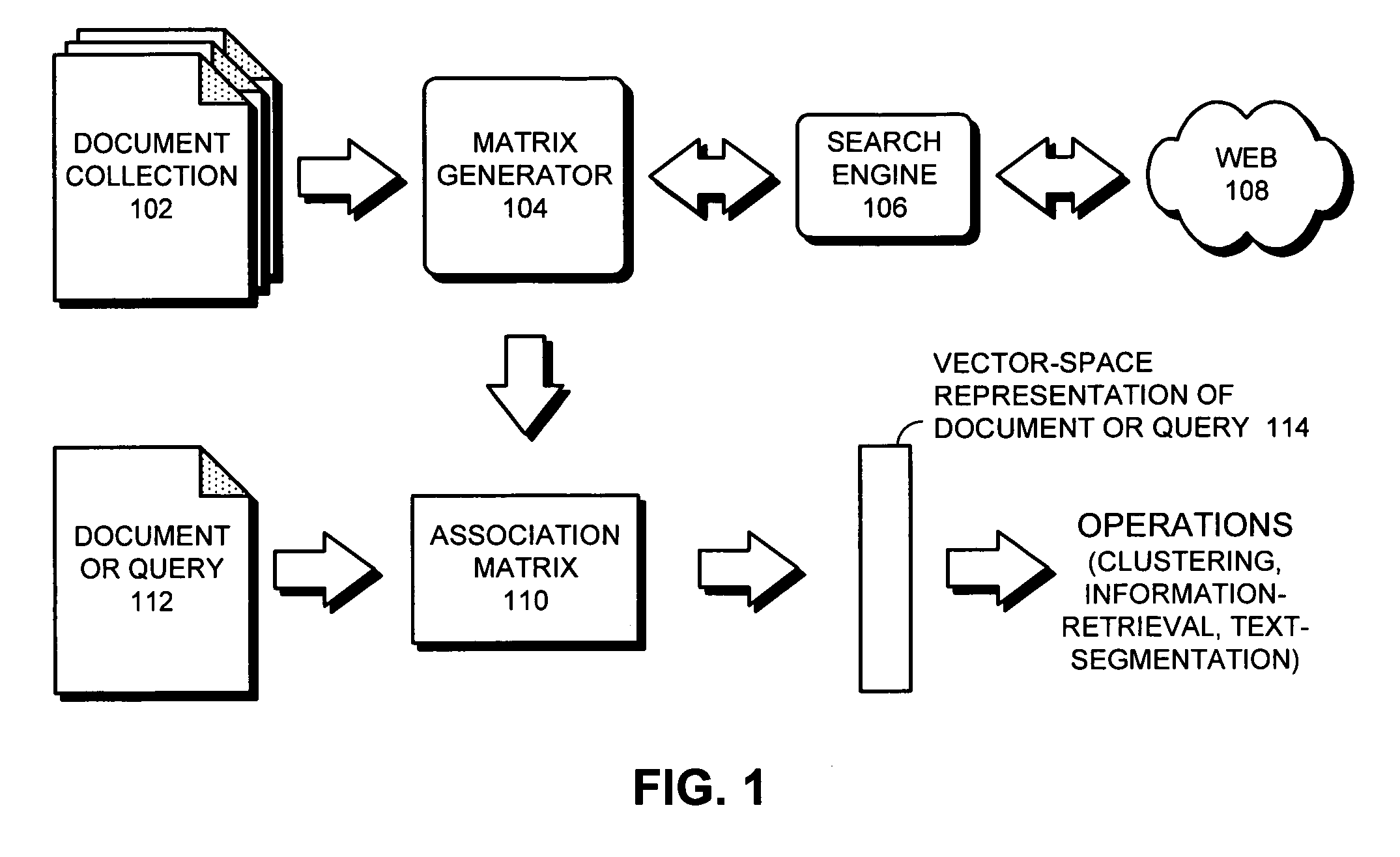
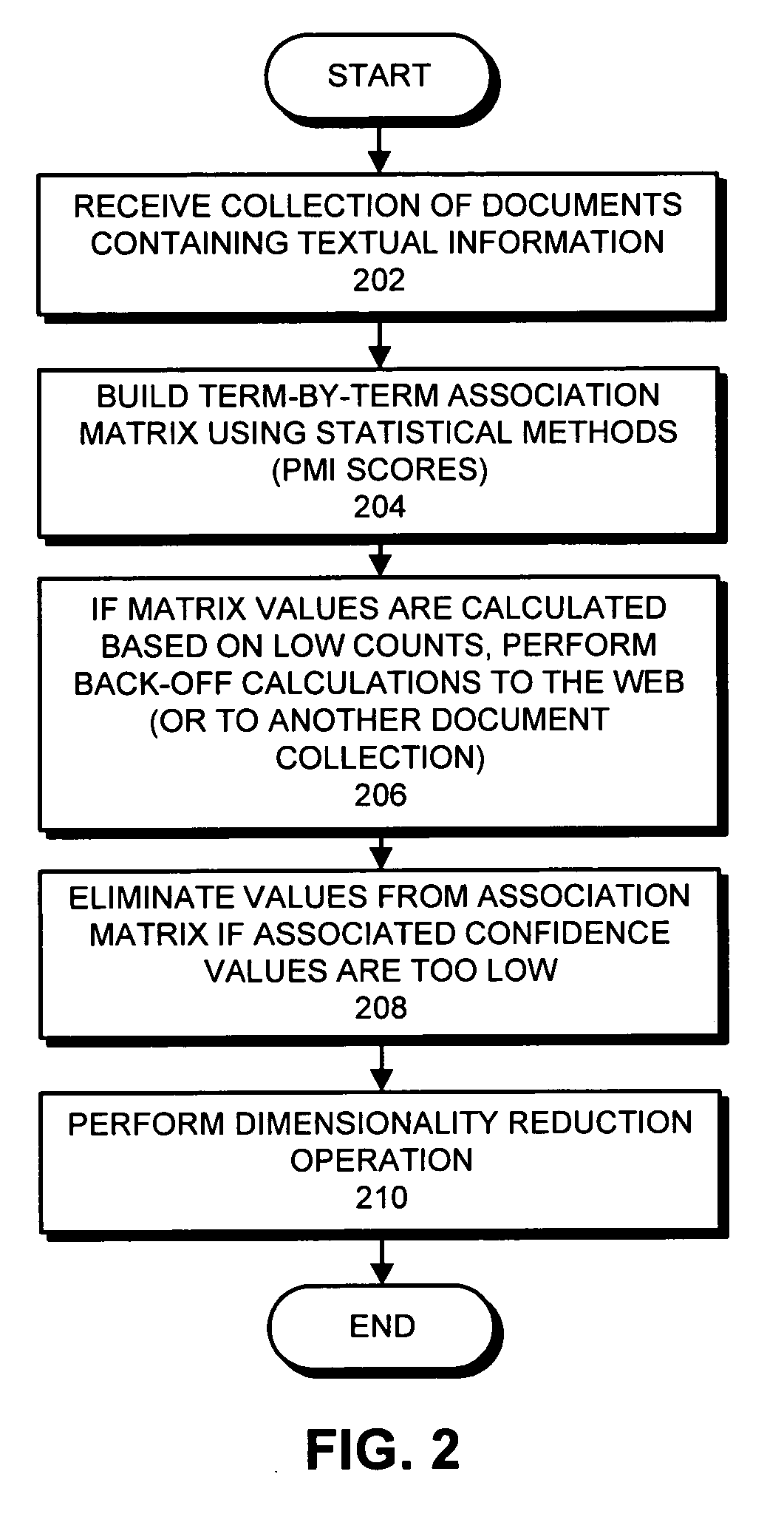
Generalized latent semantic analysis
InactiveUS20070067281A1Facilitate documentFacilitate word-level processing operationDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsAlgorithmPaper document
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that builds an association tensor (such as a matrix) to facilitate document and word-level processing operations. During operation, the system uses terms from a collection of documents to build an association tensor, which contains values representing pair-wise similarities between terms in the collection of documents. During this process, if a given value in the association tensor is calculated based on an insufficient number of samples, the system determines a corresponding value from a reference document collection, and then substitutes the corresponding value for the given value in the association tensor. After the association tensor is obtained, a dimensionality reduction method is applied to compute a low-dimensional vector space representation for the vocabulary terms. Document vectors are computed as linear combinations of term vectors.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Systems and methods for comparing documents containing graphic elements
A system and methods for comparing graphic elements in a changed document to those in a reference document is described. Attributes of selected graphic elements are first adjusted before comparing so that comparing does not identify certain document changes.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
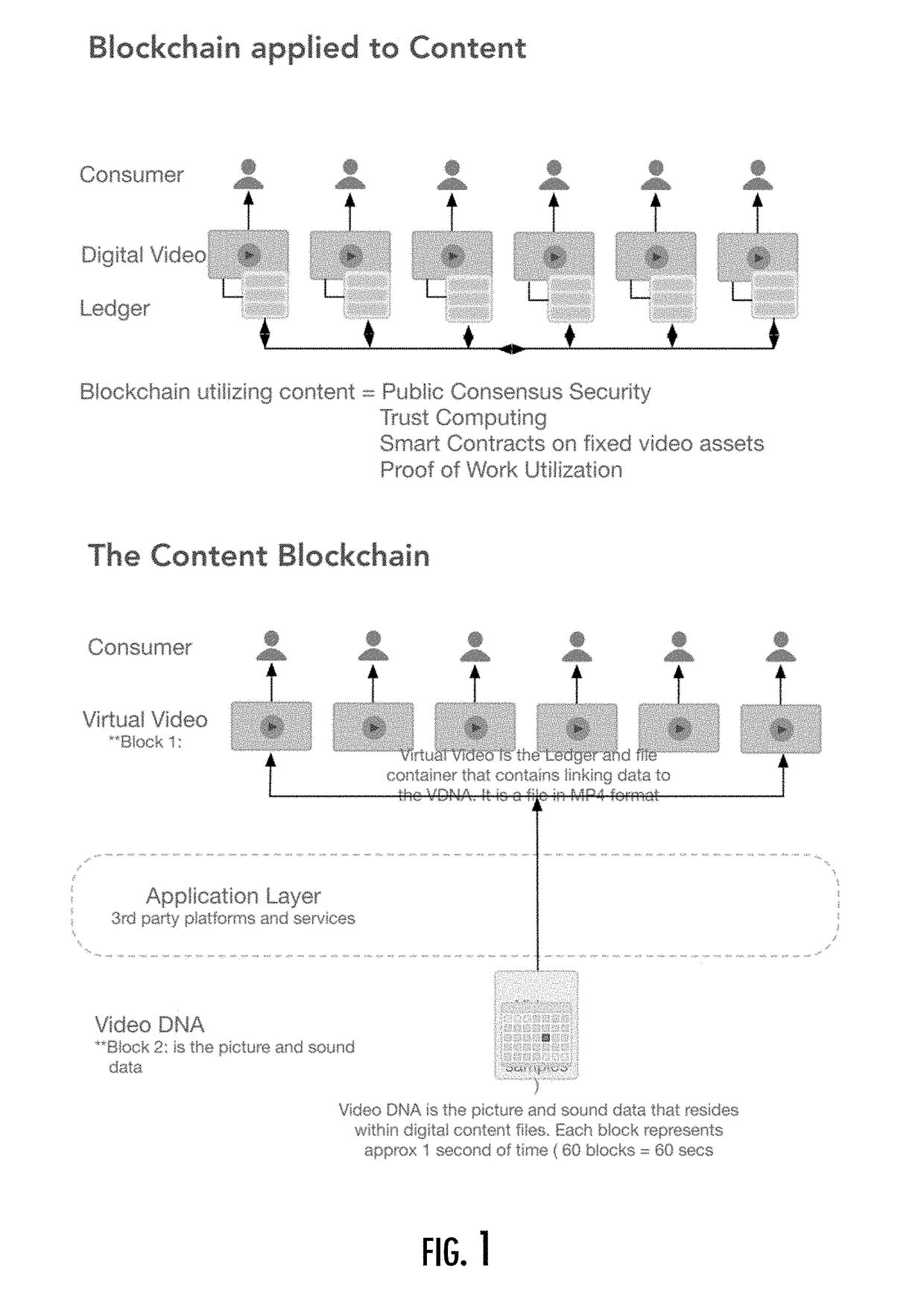
Systems and mehtods of content transaction consensus
ActiveUS20180352268A1Easy to controlIncrease flexibilityProgram/content distribution protectionSelective content distributionData fileConnected device
A method of content transaction consensus includes receiving a request to initiate a transaction for play of video or audio content, the request being received from a data network connected device having a native player. The transaction is validated by consensus in a peer-to-peer network that maintains a distributed ledger, and a record of the transaction is stored in the distributed ledger only when the transaction is validated. The record including a reference file for the video or audio content with a plurality of player control parameter values and linking data for one or more designated content sources outside the peer-to-peer network. And the method includes providing access to the reference file by the data network connected device to enable the data network connected device to play the video or audio content using the reference file and a content data file.
Owner:LINIUS AUST PTY LTD
Image matching apparatus, image matching method, and image data output processing apparatus
ActiveUS20090067727A1Improve accuracySmall sizeCharacter recognitionPictoral communicationImage matchingImaging data
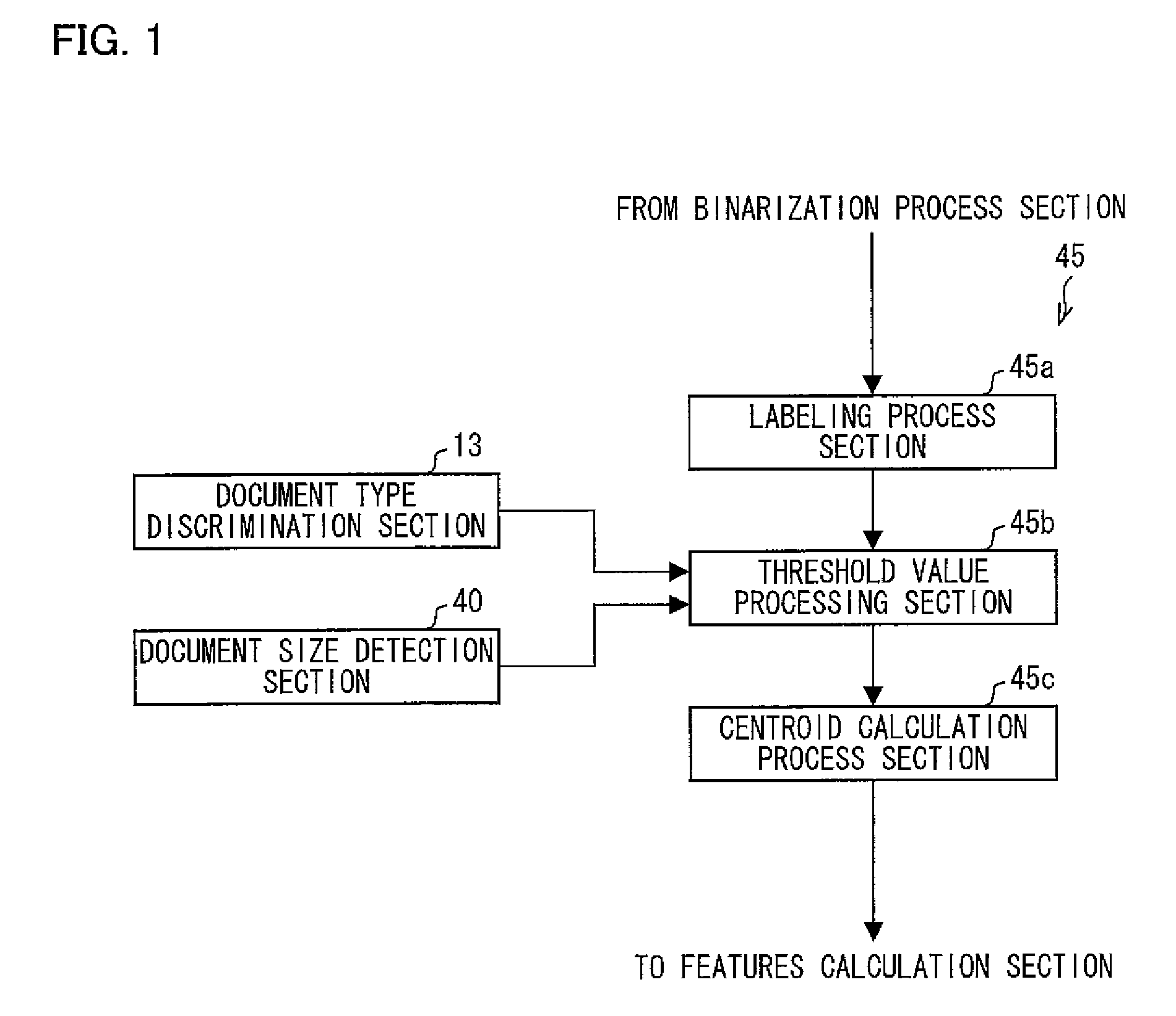
In an image matching apparatus of the present invention, only a connected region in which the number of pixels included therein exceeds a threshold value, among connected regions that are specified by a labeling process section, is sent to a centroid calculation process section from a threshold value processing section, and a centroid (feature point) of the connected region is calculated. When it is determined that a target document to be matched is an N-up document, the threshold value processing section uses, instead of a default threshold value, a variant threshold value that varies depending on the number of images laid out on the N-up document and a document size that are found and detected by an N-up document determination section and a document size detection section. This makes it possible to determine a similarity to a reference document with high accuracy even in a case of an N-up document, i.e., a case where each target image to be matched is reduced in size from an original image.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method and system for processing xml-type telecommunications documents
InactiveUS20100299590A1Remove restrictionsSoftware engineeringProgram controlTelecommunications networkData set
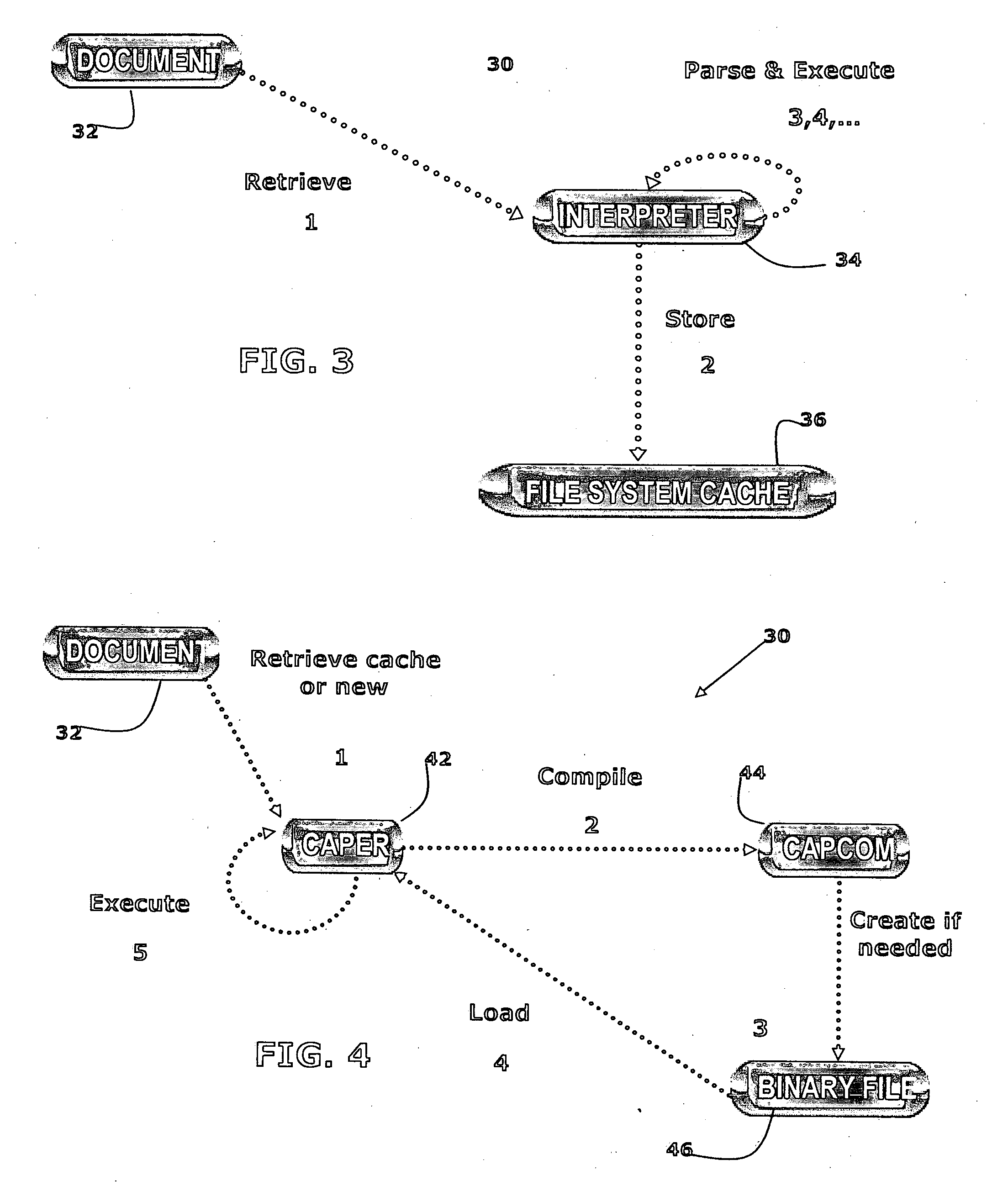
Techniques for use in telecommunications products and services for processing XML-type (e.g., CCXML or VXML) documents in association with the operation of a telecommunications network include parsing a XML-type document a single time for all instruction execution relating to the XML-type document for generating an XML-type reference document. Compiling the XML reference document occurs next for generating a XML-type binary reference file comprising a plurality of binary data sets derived from the XML-type reference document. Then, the method and system convert the XML-type binary reference file to an object tree for use of the contents of the XML-type binary reference file at essentially execution speeds. The method and system provide for storing data in a cache memory, the data relating to the XML-type binary reference file at a point essentially approximating the execution point of the data in the processing of the XML-type document. Furthermore, the method and system execute instructions for the processing of the XML-type document using the data and the XML-type binary reference file.
Owner:INTERACT SOFTWARE SYST
Information search using knowledge agents
InactiveUS7318057B2High precisionLow utilizationData processing applicationsWeb data indexingInformation searchingDocument preparation
A method for searching a corpus of documents, such as the World Wide Web, includes defining a knowledge domain and identifying a set of reference documents in the corpus pertinent to the domain. Upon inputting a query, the corpus is searched using the set of reference documents to find one or more of the documents in the corpus that contain information in the domain relevant to the query. The set of reference documents is updated with the found documents that are most relevant to the domain. The updated set is used in searching the corpus for information in the domain relevant to subsequent queries.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com