Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
54 results about "Haptic rendering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
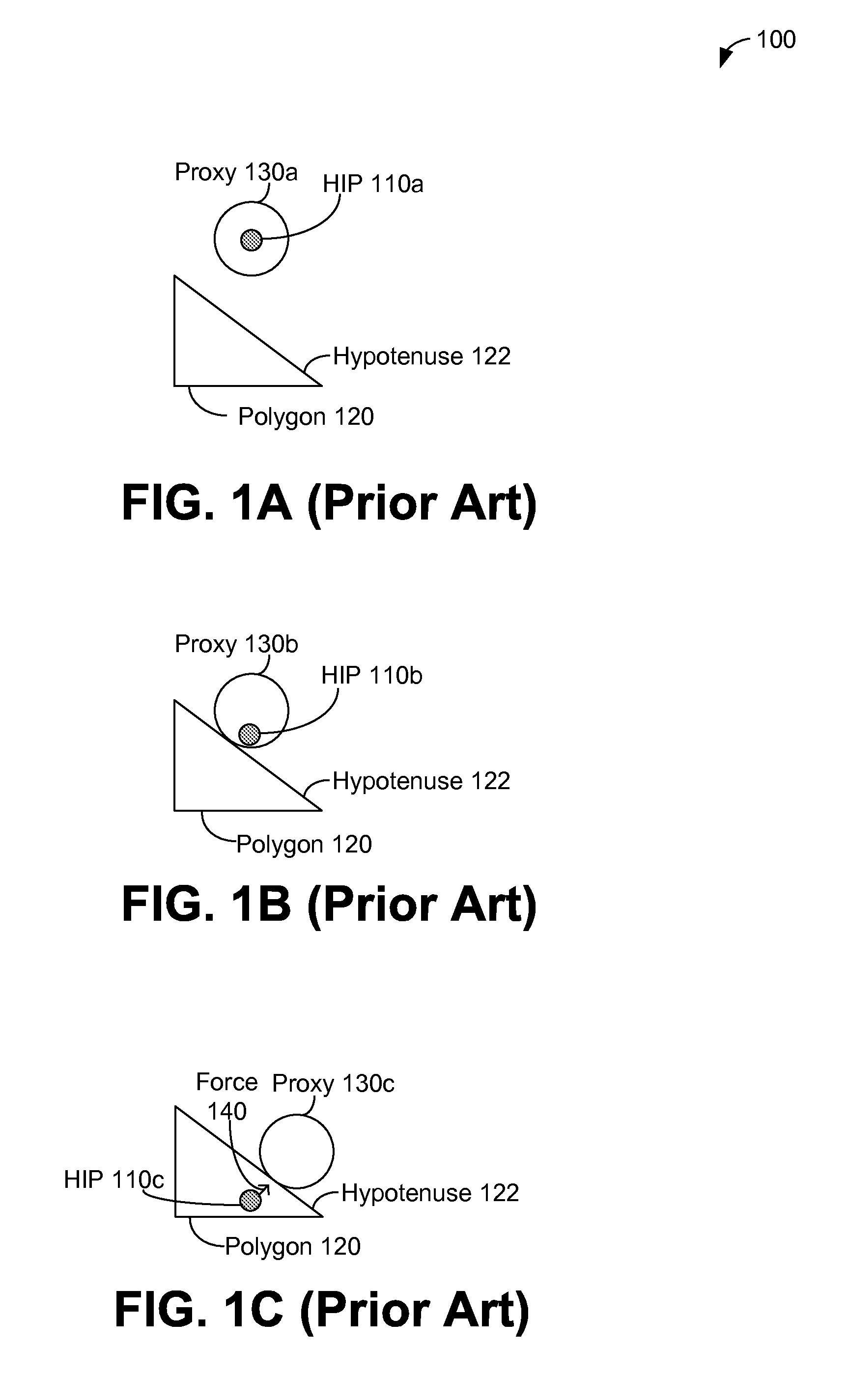
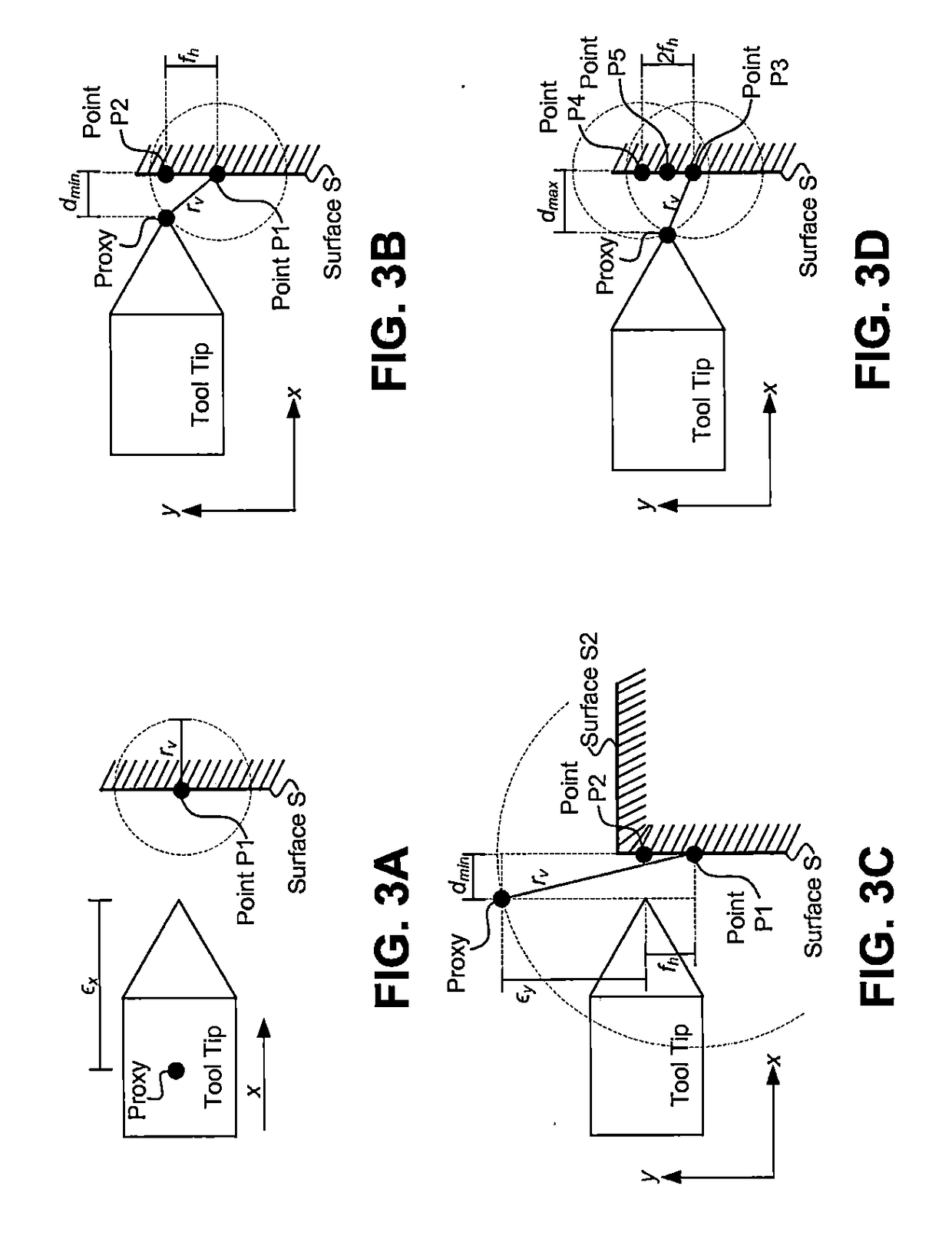
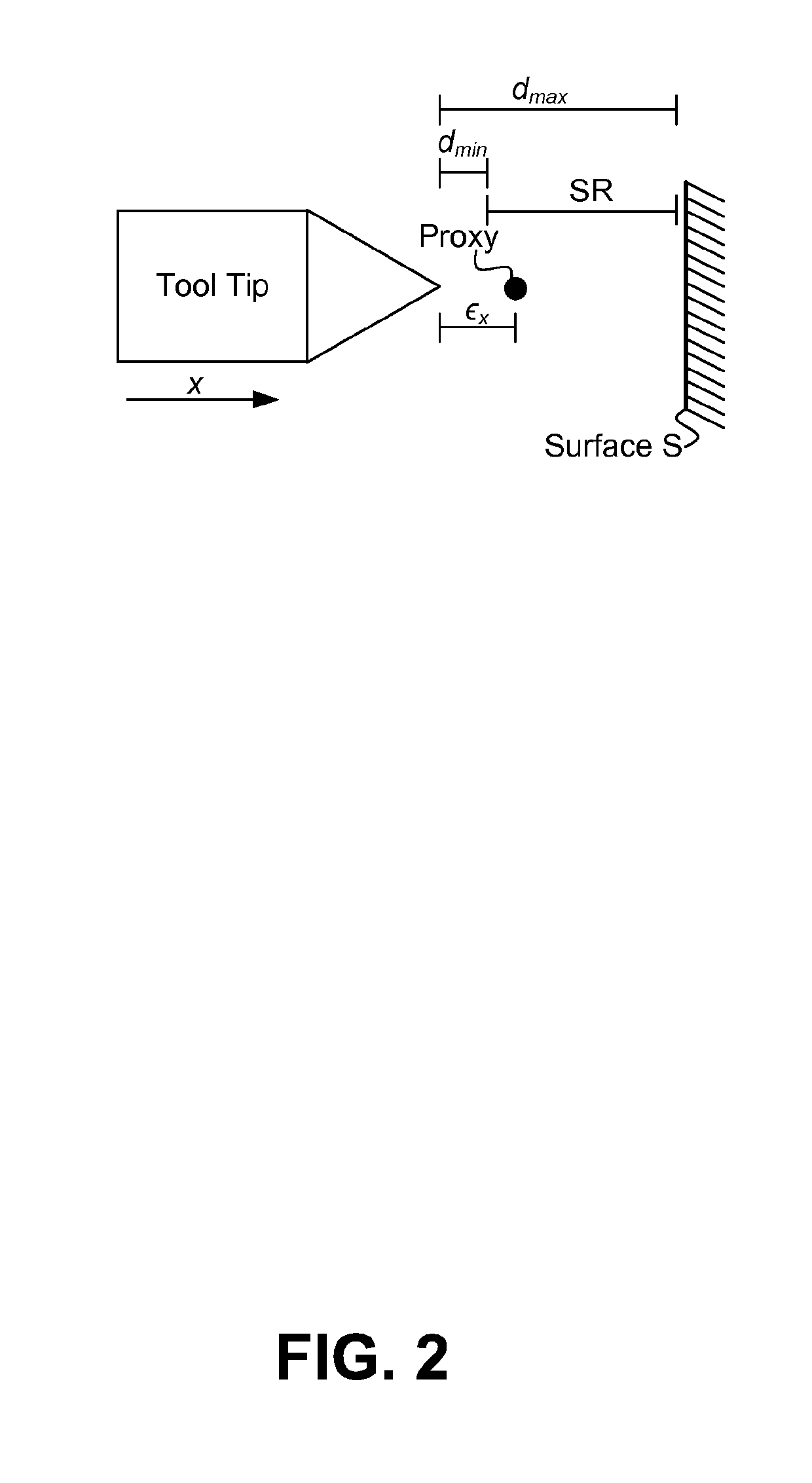
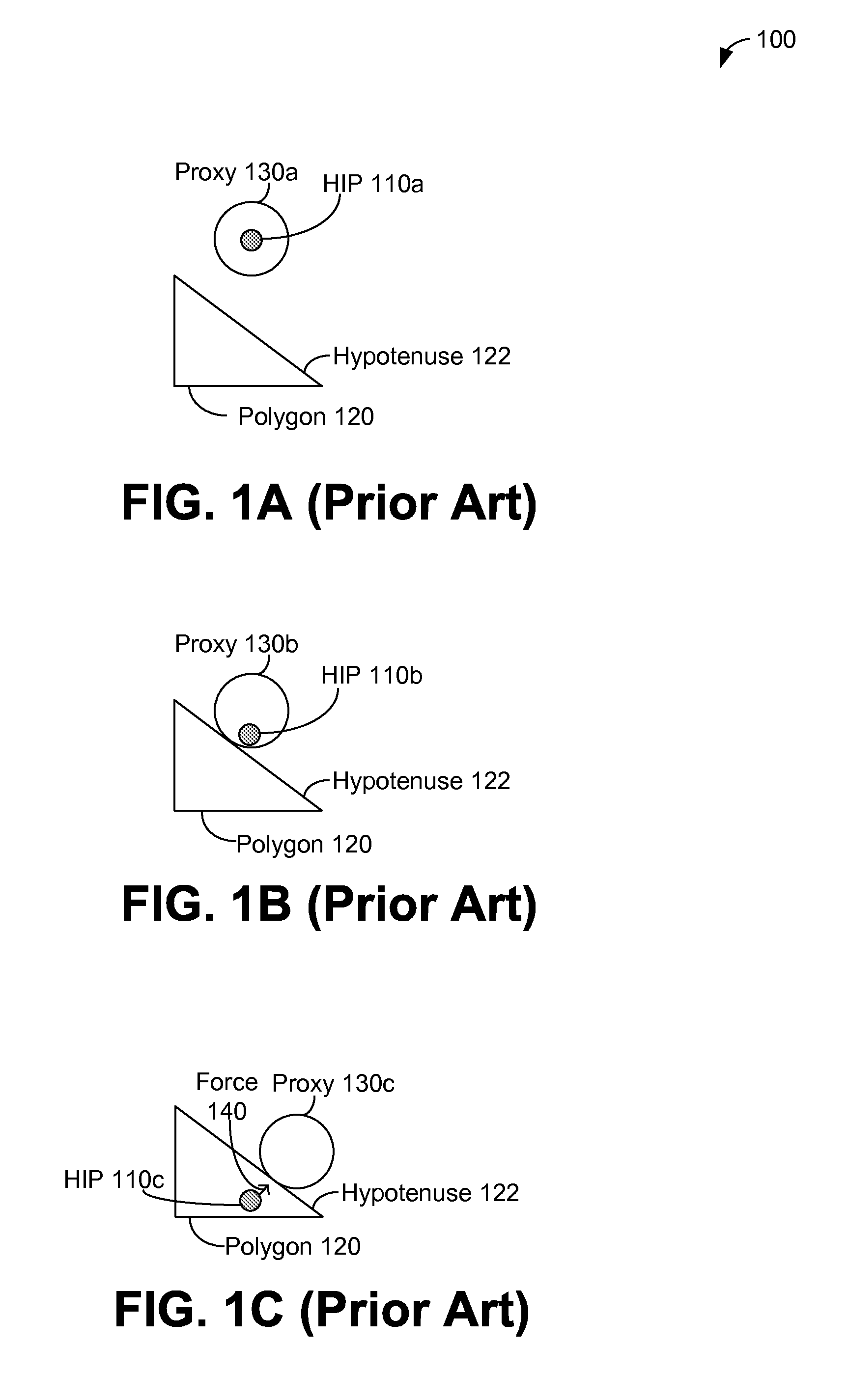
In this regard, haptic rendering can be defined as the process of displaying computer controlled forces on the user to make him or her sense the tactual feel of virtual objects In this tutorial, haptic rendering of 3D polygonal objects is discussed.
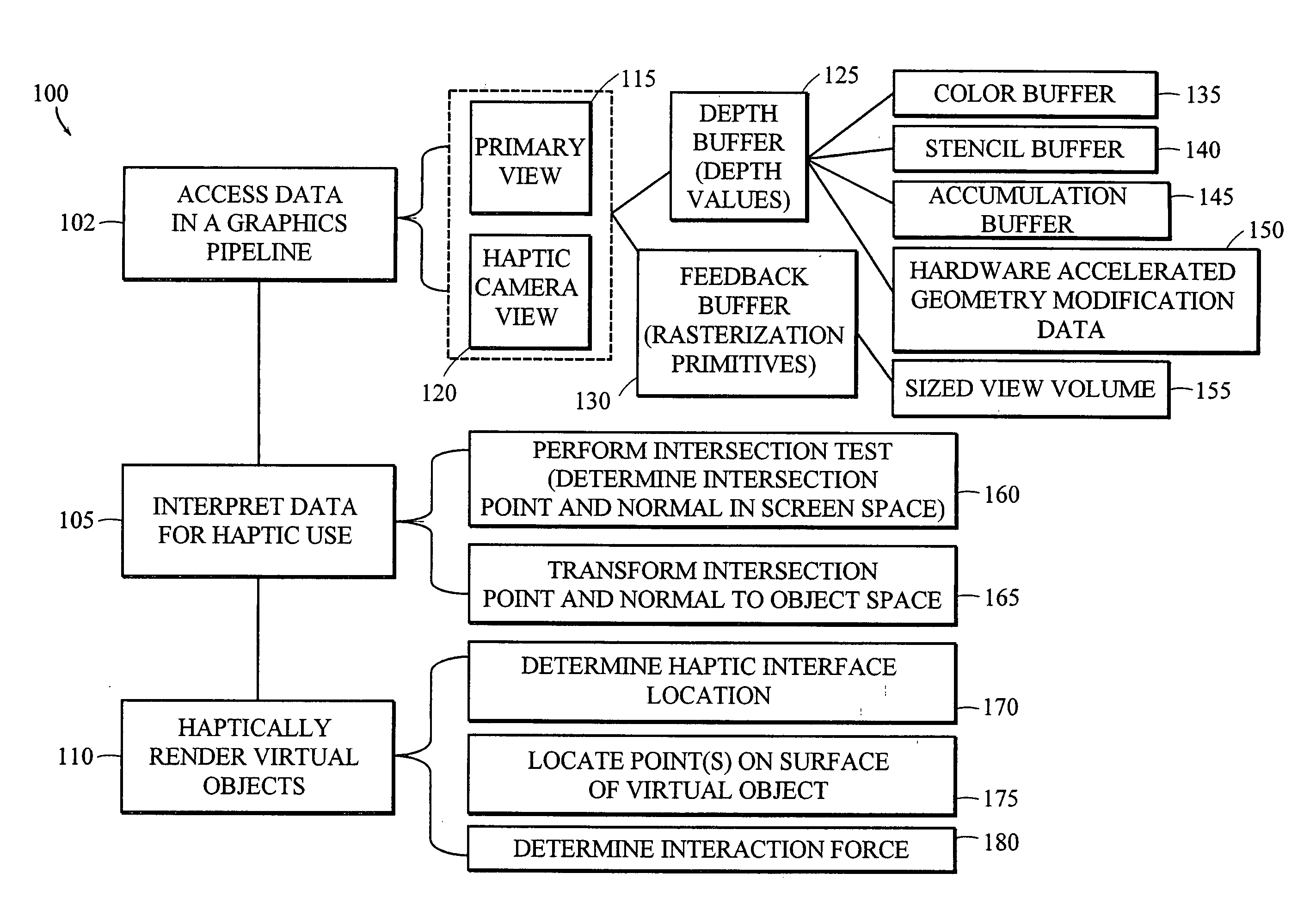
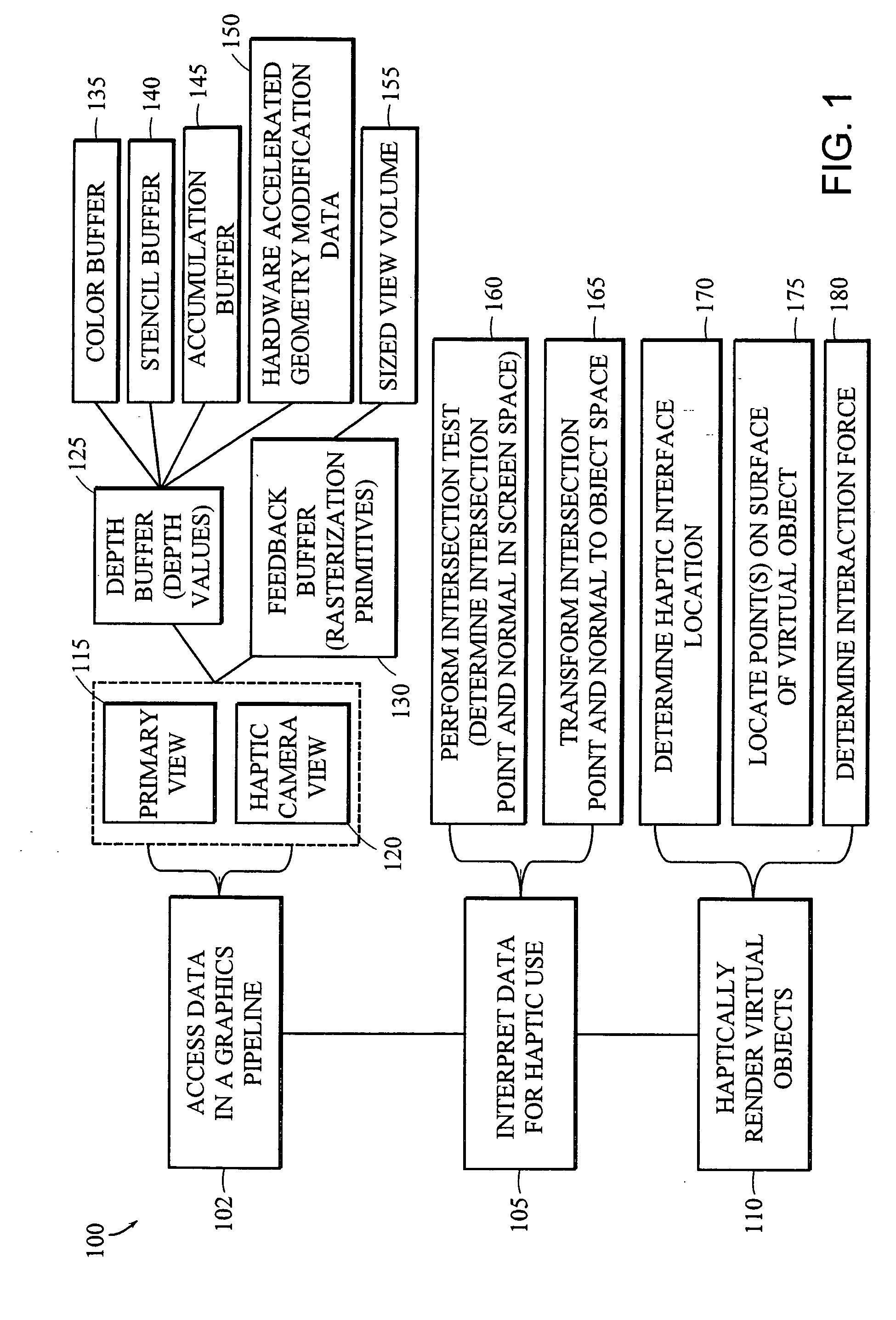
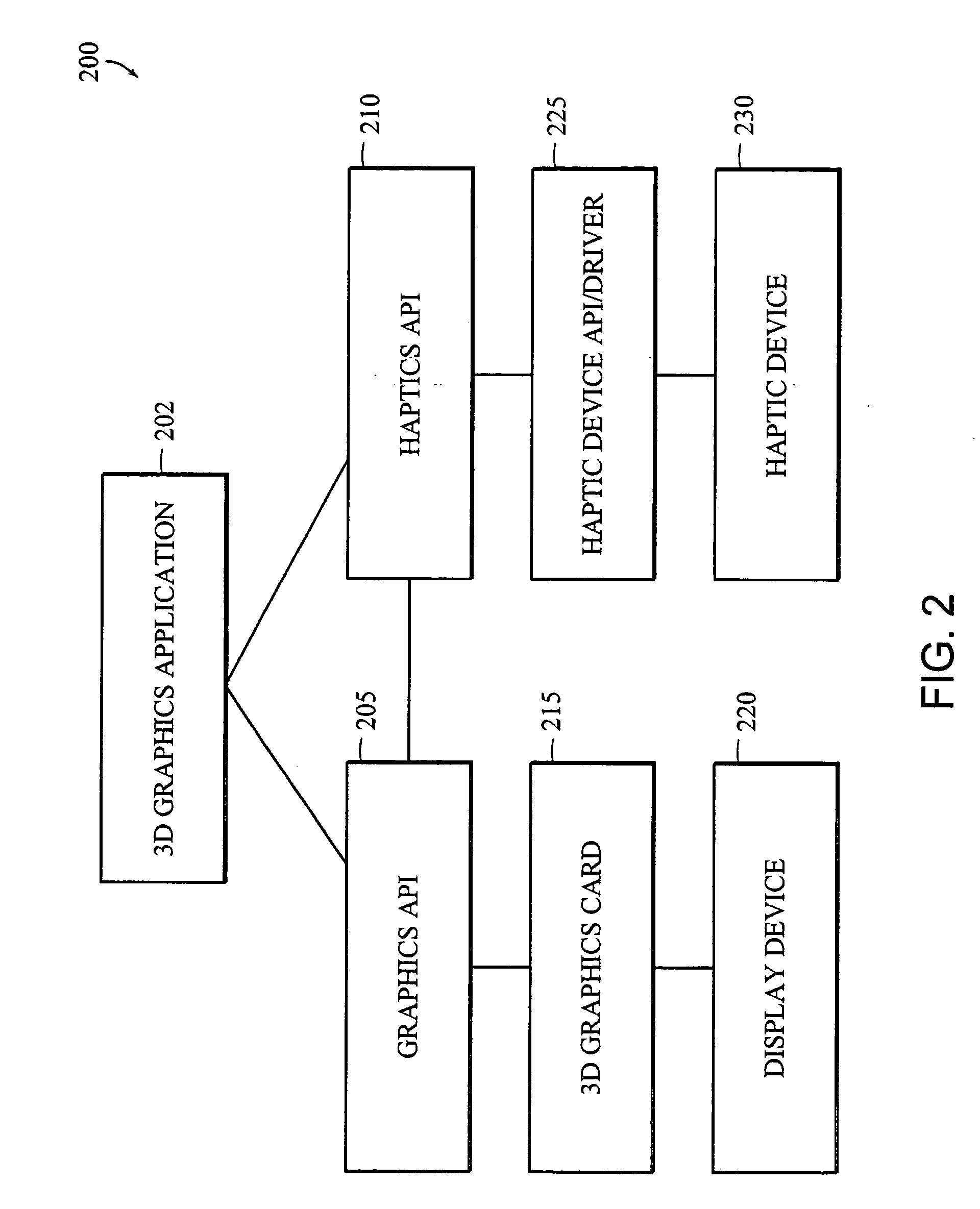
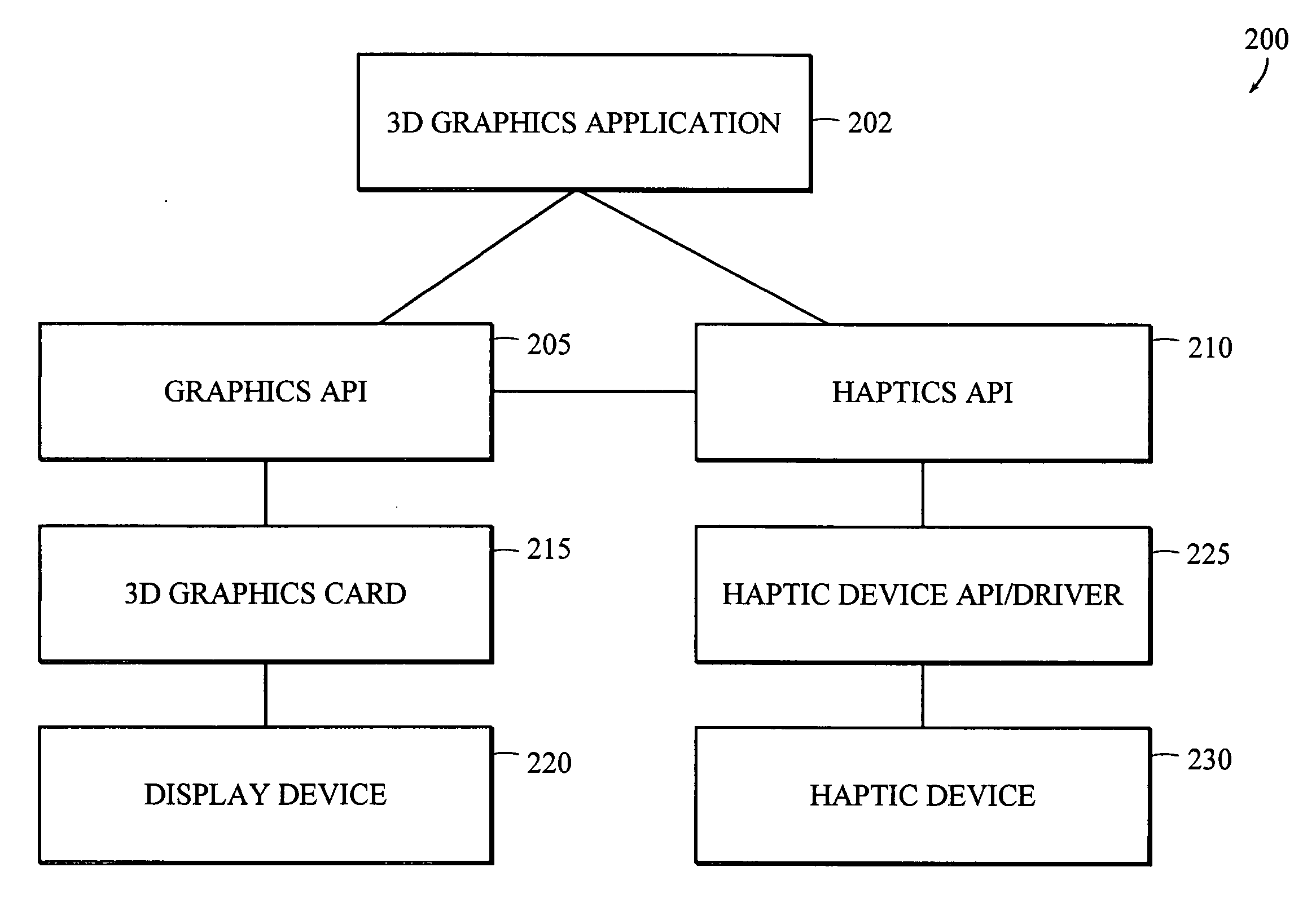
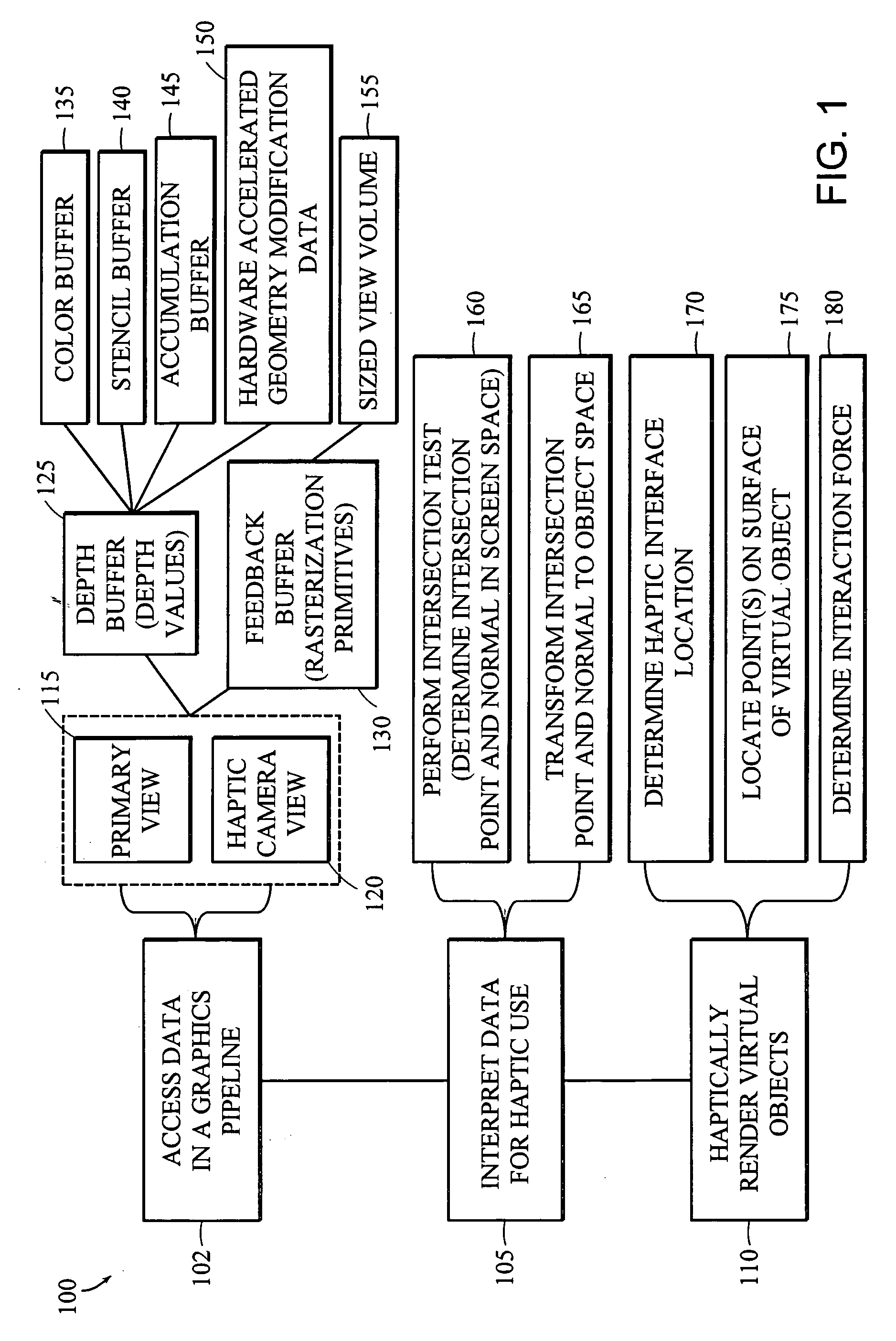
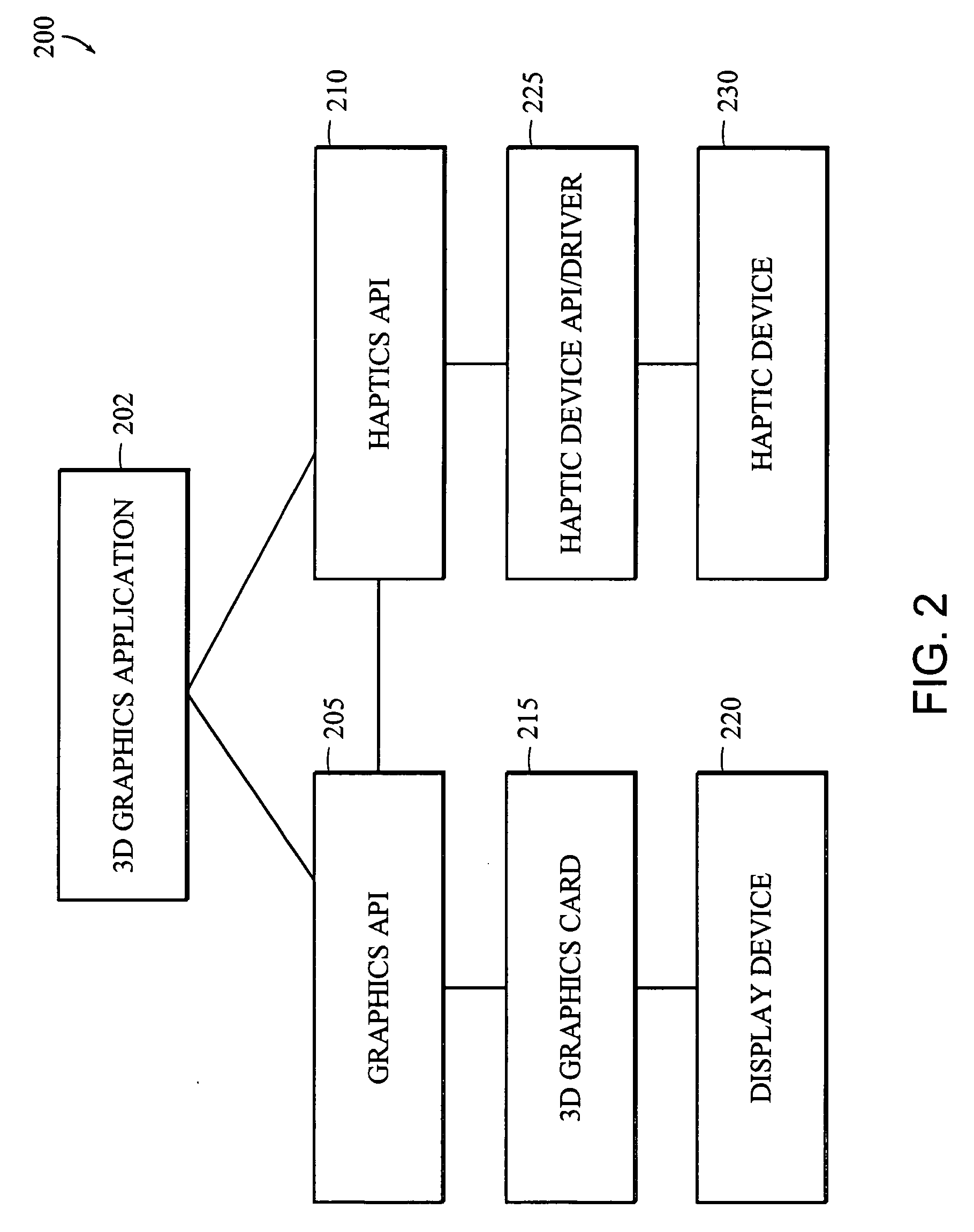
Apparatus and methods for haptic rendering using data in a graphics pipeline
ActiveUS20060109266A1Unleash processing performanceQuick fixGearworksMusical toysGraphicsLine tubing
The invention provides methods for leveraging data in the graphics pipeline of a 3D graphics application for use in a haptic rendering of a virtual environment. The invention provides methods for repurposing graphical information for haptic rendering. Thus, at least part of the work that would have been performed by a haptic rendering process to provide touch feedback to a user is obviated by work performed by the graphical rendering process.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Apparatus and method for haptic rendering
ActiveUS20070142751A1Increasing haptic stabilityMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesPerson identificationHaptic renderingComputer science
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
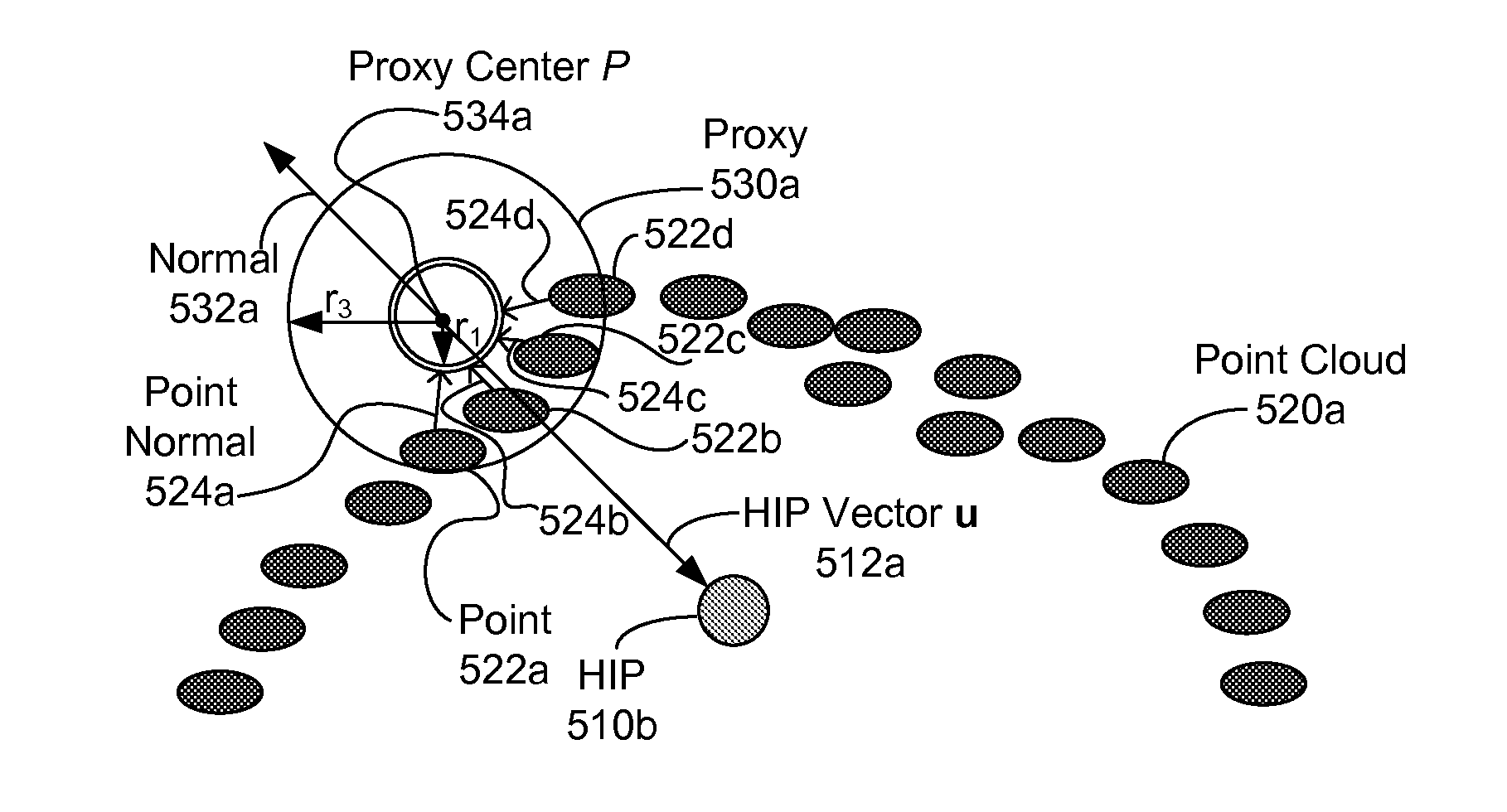
Methods and Systems for Haptic Rendering and Creating Virtual Fixtures from Point Clouds
ActiveUS20140168073A1Faster rateInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsPoint cloudSimulation
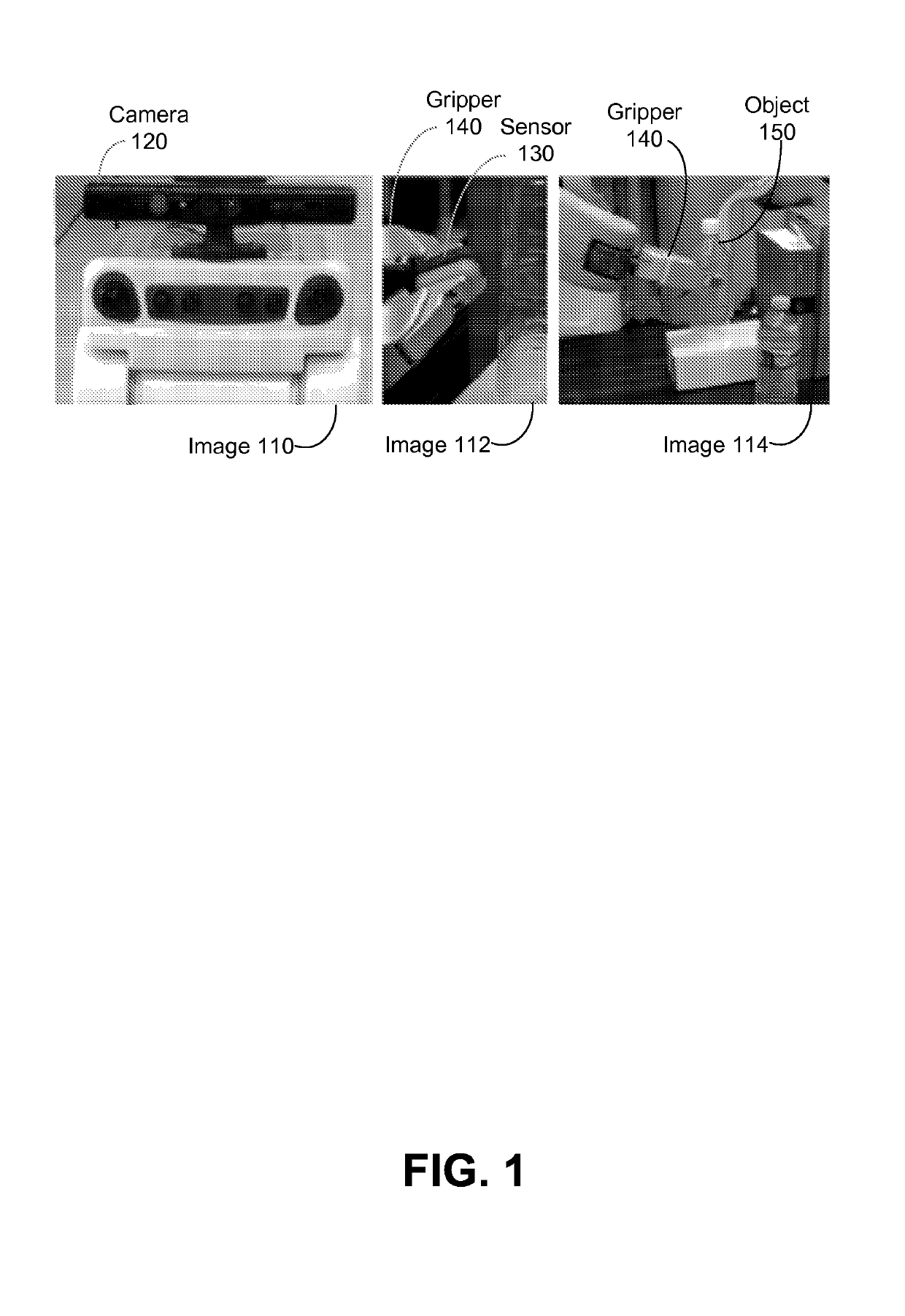
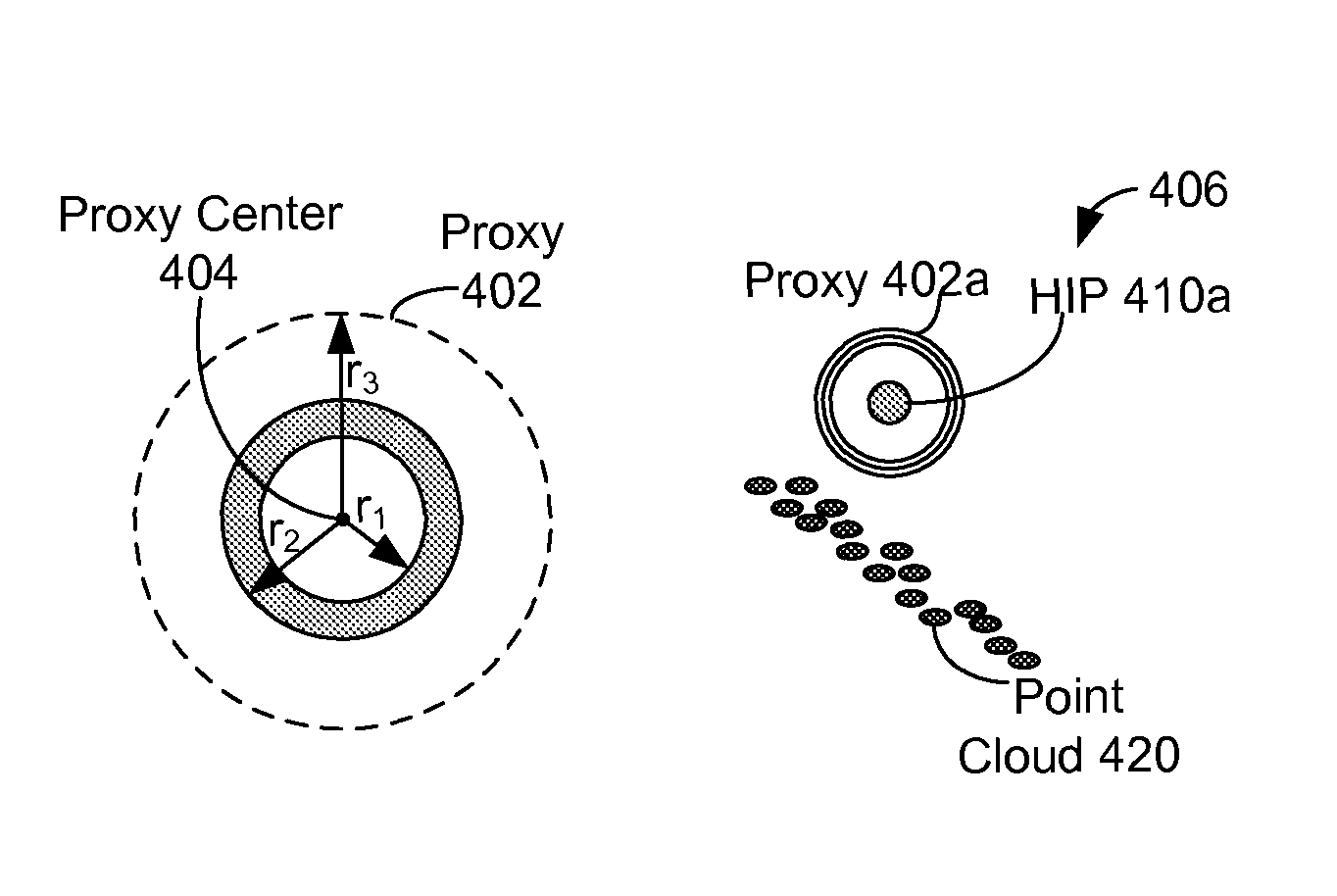
Methods, articles of manufacture, and devices related to generating haptic feedback for point clouds are provided. A computing device receives depth data about an environment. The computing device generates a point cloud from the depth data. The computing device determines a haptic interface point (HIP). The computing device determines a haptic interface point (HIP). The computing device determines a force vector between the HIP and point cloud. The computing device sends an indication of haptic feedback based on the force vector.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Fluid haptic interface with improved haptic rendering using a torque or load sensor
ActiveUS9898032B2Improved haptic renderingReduce, or even suppress, a spatial and time delay in the control of the interfaceControlling membersSpringsMagnetic currentLow speed
A haptic interface, including: a button which can be rotated by a user; an interaction element interacting with a magnetorheological fluid, secured to the button; a mechanism measuring a current position of the button; a brake including a magnetorheological fluid and a generation system to generate a magnetic field in the fluid; a controller configured to generate orders for the system to generate a magnetic fluid to modify a value of the magnetic field; and a mechanism to detect torque exerted by a user on the button to know direction of the torque and whether the torque is greater than a given value for a given direction, the controller controlling generation of a magnetic field based on obtained information about the torque at least when the button indicates zero or low speed.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Virtual Fixtures for Improved Performance in Human/Autonomous Manipulation Tasks
InactiveUS20140320392A1Same timeAccurate maneuveringInput/output for user-computer interactionSurgical systems user interfaceInterface pointVirtual fixture
Apparatus and method for defining and utilizing virtual fixtures in haptic rendering sessions interacting with various environments, including underwater environments, are provided. A computing device can receive first depth data about an environment. The computing device can generate a first plurality of points from the first depth data. The computing device can determine a haptic interface point (HIP) and can define a virtual fixture for the environment. The computing device can determine a first force vector between the HIP and the first plurality of points using the computing device, where the first force vector is based on the virtual fixture. The computing device can send a first indication of haptic feedback based on the first force vector.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
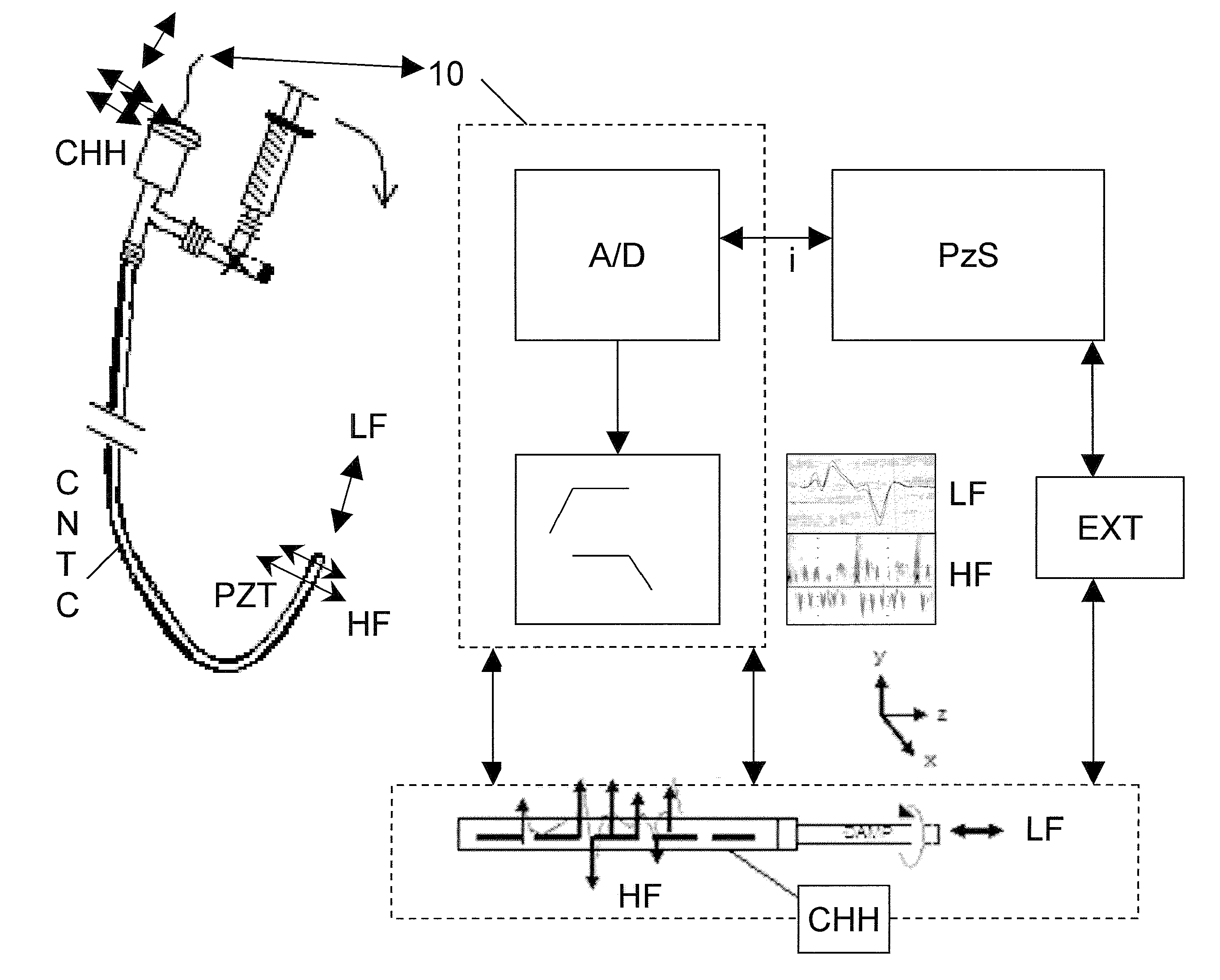
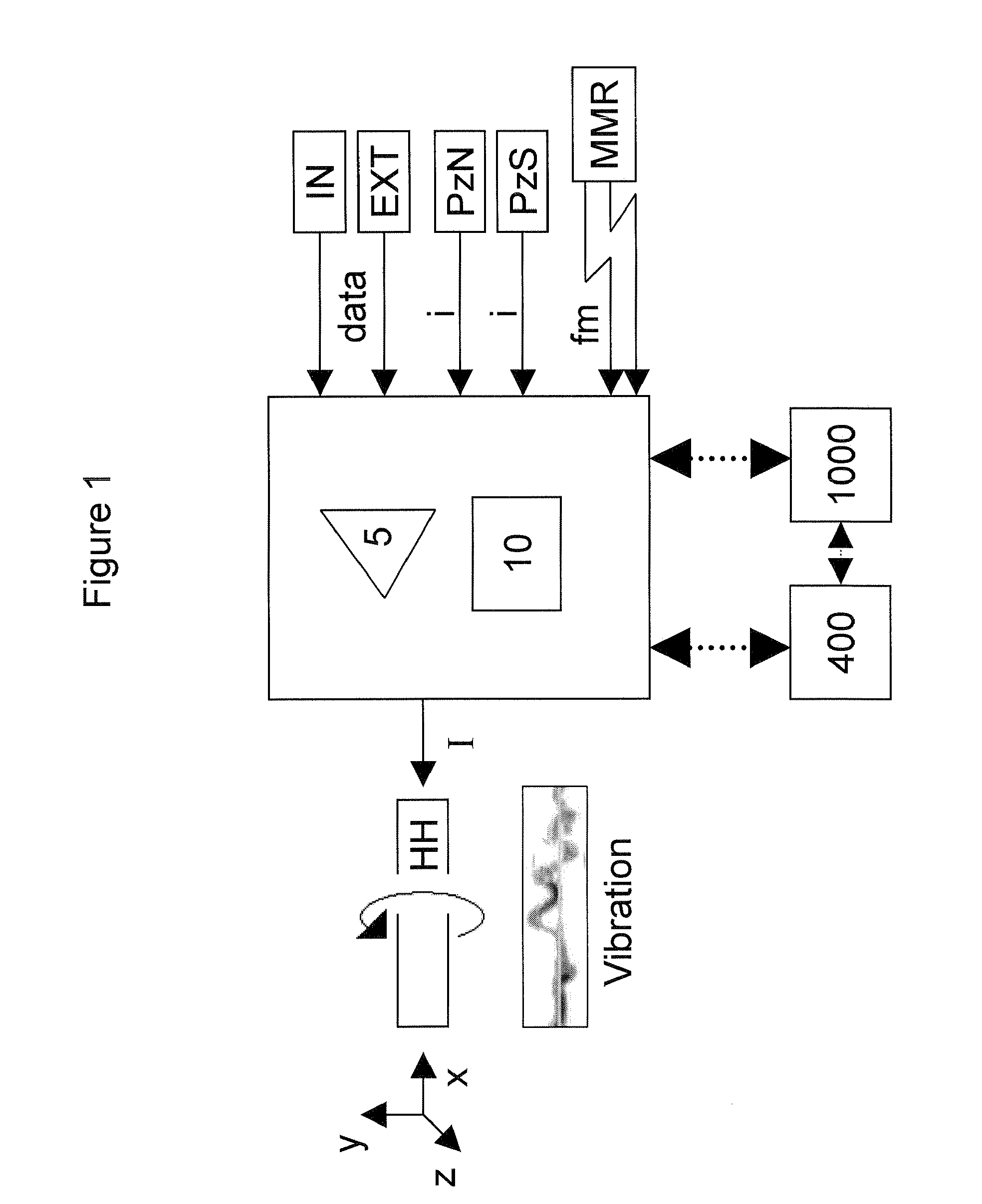
Cardiovascular haptic handle system
Cardiac tissue motion characteristics acquired by novel cardiac sensors are analyzed and processed for the derivation of physiological indices. The indices are output to a hand held local or remote volumetric haptic display and enable an operator to obtain motion related dynamic characteristics of cardiac tissues. The ability to tactually sense the motion of cardiac tissue and the affect on such motion from inserted cardiovascular instrumentation enhances the operator's performance of procedures including the positioning and placement of implanted catheters / sensors, extraction of permanently implanted leads and delivery of cardiovascular therapies. Optimal haptic rendering is achieved by using computational techniques to reconstruct the physically and perceptually relevant aspects of acquired signals and bridge the gap between the inserted catheter and operator's hand / catheter handle.
Owner:STUART SCHECTER LLC
Apparatus and methods for texture mapping
ActiveUS7095418B2Improved allocationImprove textureDrawing from basic elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsMapping techniques
Owner:3D SYST INC
Apparatus and methods for texture mapping
ActiveUS20050093874A1Improved allocationImprove textureDrawing from basic elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsPattern recognitionGraphics
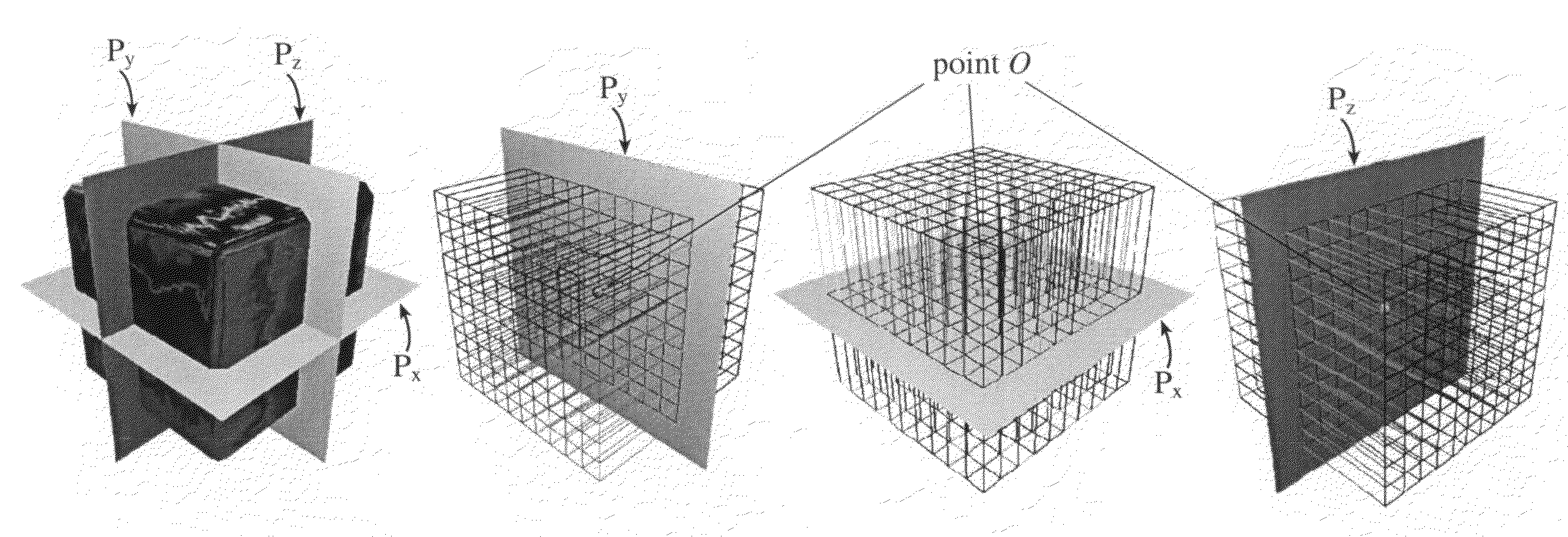
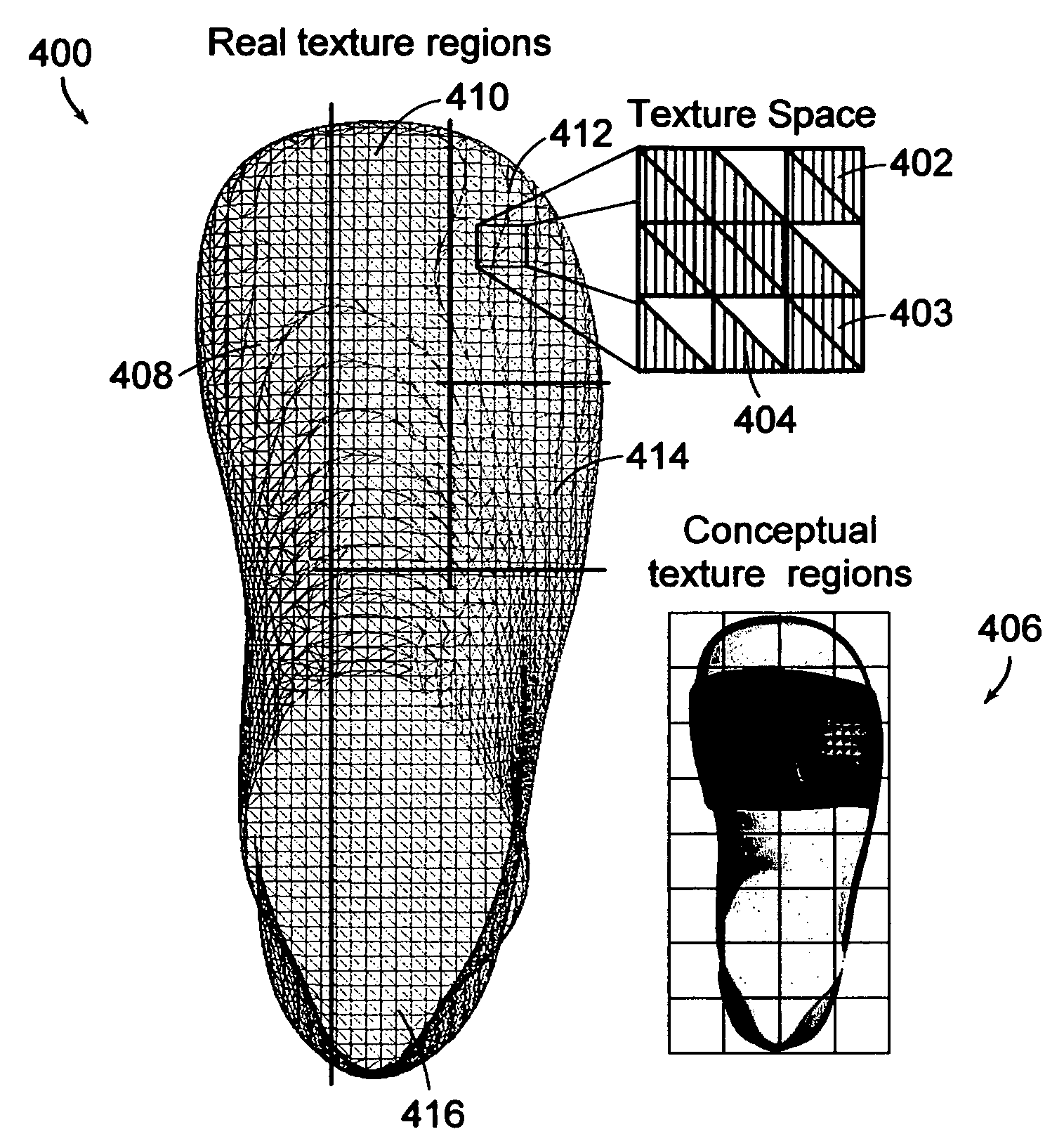
The invention provides texture mapping techniques that facilitate interactive painting of a three-dimensional virtual surface by a user in object space, without requiring global parameterization. The texture mapping techniques feature rendering texture for a given virtual object using a plurality of composite textures, each formed by blending collapsible texture layers. Texture coordinates in texture space are derived using information determined at the time of surface mesh generation. The invention features dynamic texture allocation and deallocation, allowing a user to interactively modify the shape of a painted, three-dimensional model. Finally, the invention features an architecture for combined graphical rendering and haptic rendering of a virtual object, allowing a user to experience force feedback during the painting of the object in object space.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Long elements method for simulation of deformable objects
InactiveUS7363198B2Real timeImprove accuracyAnalogue computers for chemical processesComputation using non-denominational number representationGraphicsBoundary element method
Long Elements Method (LEM) for real time physically based dynamic simulation of deformable objects. The LEM is based on a new meshing strategy using long elements whose forms can be straight or arbitrary. The LEM implements a static solution for elastic global deformations of objects filled with fluid based on the Pascal's principle and volume conservation. The volumes are discretised in long elements, defining meshes one order of magnitude smaller than meshes based on tetrahedral or cubic elements. The LEM further combines static and dynamic approaches to simulate the same deformable medium, allowing modeling a three-dimensional internal state at any point inside the deforming medium from a reduced number of explicitly updated elements. Complex elastic and plastic deformations can be simulated in real time with less computational effort. The LEM is particularly useful in real time virtual interactions, soft tissue modeling, and graphic and haptic rendering.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Haptic interface with improved haptic rendering
ActiveUS20170227980A1Improved haptic renderingReduce, or even suppress, a spatial and time delay in the control of the interfaceControlling membersSpringsTouch PerceptionHaptic sensing
A haptic interface, including: a button which can be rotated by a user; an interaction element interacting with a magnetorheological fluid, secured to the button; a mechanism measuring a current position of the button; a brake including a magnetorheological fluid and a generation system to generate a magnetic field in the fluid; a controller configured to generate orders for the system to generate a magnetic fluid to modify a value of the magnetic field; and a mechanism to detect torque exerted by a user on the button to know direction of the torque and whether the torque is greater than a given value for a given direction, the controller controlling generation of a magnetic field based on obtained information about the torque at least when the button indicates zero or low speed.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Apparatus and methods for texture mapping
InactiveUS20070018993A1Improved allocationImprove textureCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsHaptic rendering
The invention provides texture mapping techniques that facilitate interactive painting of a three-dimensional virtual surface by a user in object space, without requiring global parameterization. The texture mapping techniques feature rendering texture for a given virtual object using a plurality of composite textures, each formed by blending collapsible texture layers. Texture coordinates in texture space are derived using information determined at the time of surface mesh generation. The invention features dynamic texture allocation and deallocation, allowing a user to interactively modify the shape of a painted, three-dimensional model. Finally, the invention features an architecture for combined graphical rendering and haptic rendering of a virtual object, allowing a user to experience force feedback during the painting of the object in object space.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Integration of Auxiliary Sensors with Point Cloud-Based Haptic Rendering and Virtual Fixtures
ActiveUS20180232052A1Input/output for user-computer interactionImage analysisPoint cloudVirtual fixture
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Haptic rendering method based on texture image
ActiveCN103869984ASimple calculationImprove discriminationInput/output for user-computer interactionImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Microscopic scale
The invention discloses a haptic rendering method based on a texture image. The haptic rendering method comprises the following steps that (10) texture features are extracted, wherein the texture features comprises the texture surface microscopic height and the dynamic friction coefficient for rendering texture roughness; (20) on the basis of the texture features extracted in the step (10), haptic modeling is performed, and the resultant force of texture force is measured and calculated; (30) the resultant force of texture force measured and calculated in the step (20) is output and fed back to an operator through a hand controller. According to the haptic rendering method based on the texture image, the dynamic friction coefficient of virtual texture can be obtained with no need for specific measurement equipment, and the roughness of the virtual texture can be passed to humans without a special texture expression device.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Apparatus and methods for haptic rendering using a haptic camera view
InactiveUS20060284834A1Improve efficiencyInteractionCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage renderingGraphicsHaptic rendering
The invention provides systems and methods for using a “haptic camera” within a virtual environment and for using graphical data from the haptic camera to produce touch feedback. The haptic camera obtains graphical data pertaining to virtual objects within the vicinity and along the trajectory of a user-controlled haptic interface device. The graphical data from the camera is interpreted haptically, thereby allowing touch feedback corresponding to the virtual environment to be provided to the user.
Owner:3D SYST INC
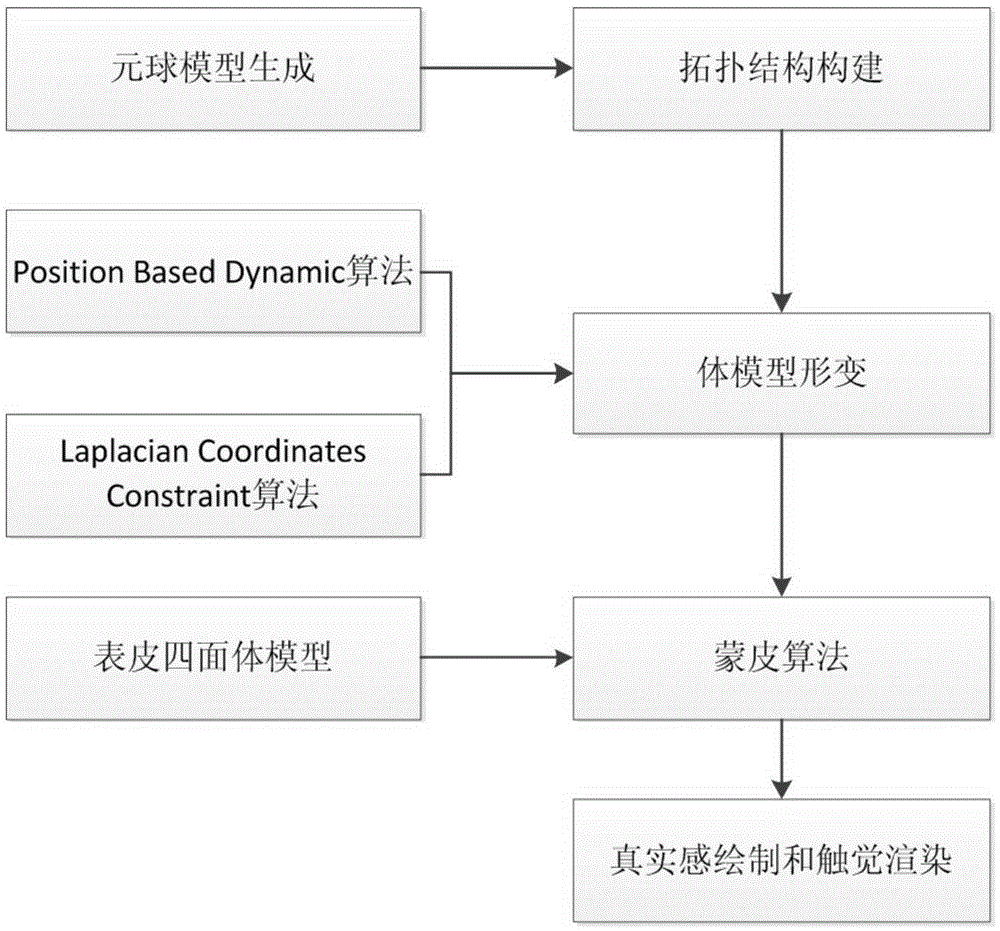
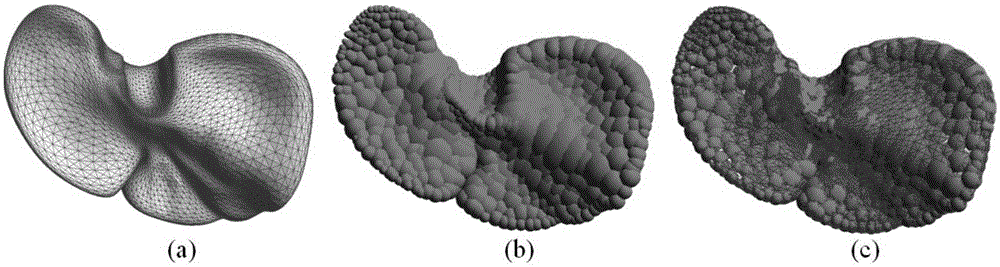
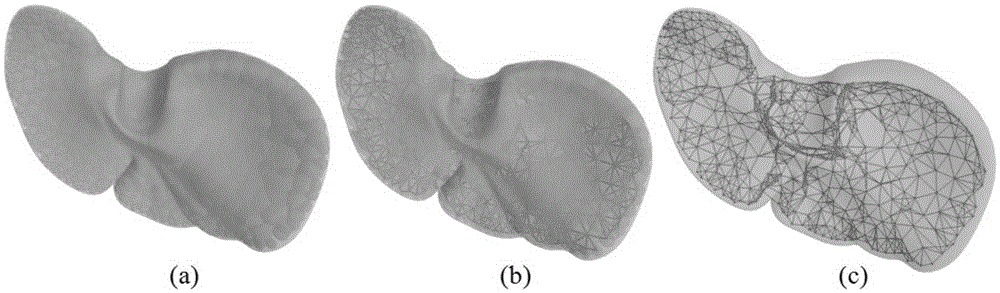
Metaball model based soft tissue deformation method
InactiveCN105302972AOvercome limitationsPhysical authenticity no lessSpecial data processing applications3D-image renderingField functionLaplacian coordinates
The invention provides a metaball model based soft tissue deformation method. The method comprises the four steps of: a stage of constructing a topological structure of a metaball model, wherein a Voronoi diagram is generated according to an original grid model by using a Bradshow Gareth ball tree generation algorithm, the metaball model is generated, and the topological structure of the metaball model is constructed with a threshold setting method; a stage of calculating deformation of the metaball model, wherein a deformation process of a soft tissue model is simulated in combination with Laplacian coordinate restriction by using a Position Based Dynamic (PBD) algorithm; a stage of realizing a skin process of the soft tissue model, wherein distance field functions are established for metaballs in a body model respectively, and a mapping relationship between the body model and a skin grid model is established, so that the skin process is realized; and a stage of realistic rendering and real-time haptic rendering, wherein the realistic rendering is performed according to the physical deformation of soft tissues, and the real-time haptic rendering is performed based on a Geomagic Touch force feedback device. The method can truly simulate the deformation process of the soft tissues in operation and has the characteristics of strong physical realism and good timeliness.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
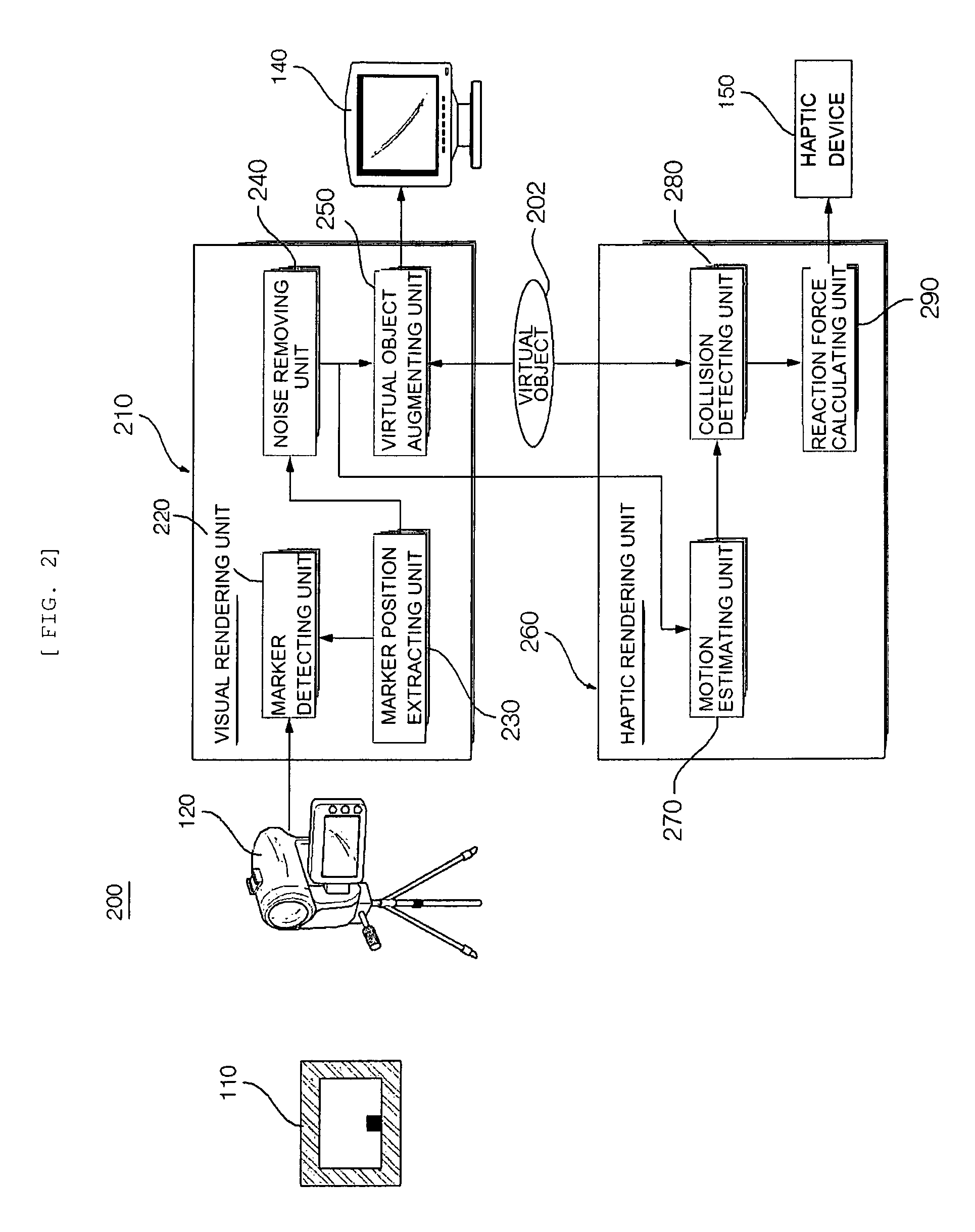
Method and system for haptic interaction in augmented reality
InactiveUS8243099B2Effectively removing noiseMinimizing any discontinuityInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementHaptic interactionHaptic rendering
The present invention relates to a method and system for haptic interaction in augmented reality that can effectively remove noise from real images captured by an image capturing device and minimize discontinuity of force generated in the haptic interaction for the stable and smooth haptic interaction in the augmented reality. The augmented reality system comprising: a marker detecting unit that detects a markers in images; a marker position extracting unit that extracts the positions of the detected markers; a noise removing unit that removes noise from positional information of the markers; a visual rendering unit that augments virtual objects; a motion estimating unit that estimates the motion of the markers over a time; a collision detecting unit that detects collision between the virtual objects and an end point of the haptic device; and a haptic rendering unit that calculates reaction force to be provided through the haptic device.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
Integration of auxiliary sensors with point cloud-based haptic rendering and virtual fixtures
ActiveUS10394327B2Input/output for user-computer interactionImage analysisPoint cloudVirtual fixture
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Apparatus and method for implementing haptic-based networked virtual environment which supports high-resolution tiled display
ActiveUS20130050062A1Improve efficiencyLimited resourceCathode-ray tube indicatorsTactile signalling systemsGraphicsDisplay device
An apparatus and method of implementing haptic-based networked virtual environments supporting high-resolution tiled displays. A haptic rendering process of detecting collision between a user of a haptic-device over a virtual environment and each of at least one virtual object and providing a physical force corresponding to a detection result to the haptic-device is performed, and a graphic rendering process of converting each virtual object represented as 3-D data into an object stream represented as 2-D data such that each virtual object is displayed as a 2-D image, and assigning a priority and a frame rate to each converted object stream according to a preset assignment criterion is performed. A plurality of displays provide a display image, including object streams of the virtual objects and background pixels, so that a virtual environment allowing the user of the haptic-device to visually and tactilely immerse thereto is effectively realized by utilizing limited resources.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
Methods and systems for haptic rendering and creating virtual fixtures from point clouds
ActiveUS9471142B2Input/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingPoint cloudComputer graphics (images)
Methods, articles of manufacture, and devices related to generating haptic feedback for point clouds are provided. A computing device receives depth data about an In-Contact environment. The computing device generates a point cloud from the depth data. The computing device determines a haptic interface point (HIP). The computing device determines a haptic interface point (HIP). The computing device determines a force vector between the HIP and point cloud. The computing device sends an indication of haptic feedback based on the force vector.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Minitype haptic rendering method based on active and passive devices
ActiveCN107229334AImprove realismImprove immersionInput/output for user-computer interactionTactile signalling systemsPower flowEngineering
The invention discloses a minitype haptic rendering method based on active and passive devices. The method comprises the steps of firstly conducting calibration on a magnetorheological damper and a continuous current dynamo, and obtaining a relationship of an input current and output torque; converting an expected force / torque value to a current of the magnetorheological damper to input, the corresponding torque is output through the magnetorheological damper, and exerting the torque to the body of an operation person through a force tactile transmission device; secondly, measuring actually exerted force / torque through a sensor installed at a force / torque point of action, comparing an actually output force / torque value with the expected force / torque value, and calculating a force / torque error; finally, converting the force / torque error to an input signal of the continuous current dynamo, and driving the continuous current dynamo to generate torque corresponding to the error. According to the minitype haptic rendering method based on the active and passive devices, minitype devices can output large-range and high-precision force / torque, thus haptic rendering equipment is more light and exquisite, and the fidelity of haptic interaction is improved; the method can be widely applied to the fields of virtual reality, teleoperation robot control, medical service and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Texture haptic reproduction method based on image gray scale recovery shape technology
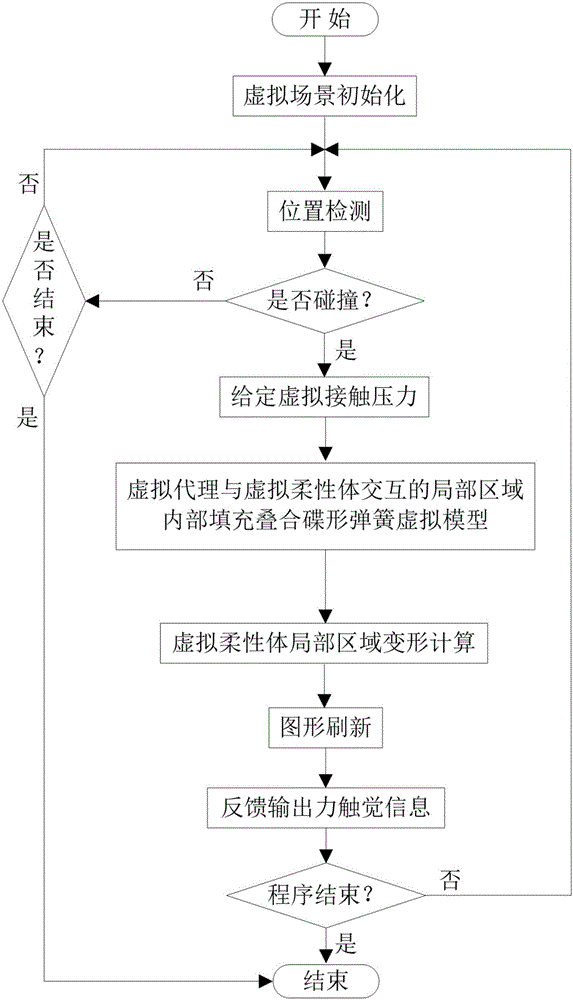
InactiveCN107346552ASmall color differenceImprove realismImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageColor correction
The invention discloses a texture haptic reproduction method based on image gray scale recovery shape technology. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of 1, restoring a three-dimensional contour from a single image frame, performing color correction on acquisition equipment and acquiring color images in different angles by means of the acquisition equipment, fusing the color images, restoring a photographed image by means of a color restoring method based on polynomial regression, processing the images in different angles for obtaining gray scale images, and fusing the gray scale images; establishing a light reflection model; establishing an equation according to the gray scale and the light reflection model, and calculating the height of each point on the surface, and establishing a virtual surface triangular mesh model; and 2, performing haptic rendering on the virtual surface by means of a texture haptic model. The texture haptic reproduction method reduces a color image aberration and improves real feeling in haptic reproduction.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Cardiovascular haptic handle system
Cardiac tissue motion characteristics acquired by novel cardiac sensors are analyzed and processed for the derivation of physiological indices. The indices are output to a hand held local or remote volumetric haptic display and enable an operator to obtain motion related dynamic characteristics of cardiac tissues. The ability to tactually sense the motion of cardiac tissue and the affect on such motion from inserted cardiovascular instrumentation enhances the operator's performance of procedures including the positioning and placement of implanted catheters / sensors, extraction of permanently implanted leads and delivery of cardiovascular therapies. Optimal haptic rendering is achieved by using computational techniques to reconstruct the physically and perceptually relevant aspects of acquired signals and bridge the gap between the inserted catheter and operator's hand / catheter handle.
Owner:STUART SCHECTER LLC
A three-dimensional haptic rendering device and method based on plane interaction
ActiveCN109144261AChange tangential forceChange normal forceInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingTangential forceSignal generator
The invention relates to a three-dimensional haptic rendering device and a method based on plane interaction, belonging to the field of human-computer interaction. The device includes a positioning unit, a processing unit, a signal generator and an interaction unit, which can obtain the gray value and calculate the change rate of the corresponding gray value according to the position information of the finger on the image in real time, and further provide the tangential force by vibration, and provide the normal force by electrostatic force or air pressure film, and present the contour information by the three-dimensional haptic reproduction method based on the plane interaction. The advantages are: the portability of the device is good, at the same time, a tangential force and a normal force can be simultaneously applied to the finger, the feedback force is expanded from one dimension to two dimensions breaks through the restriction that electrostatic force only has feedback functionin the process of motion, the device and method realize the two-way width adjustment that the tangential force can be increased or decreased, and have more real three-dimensional haptic reproduction effect, which can be widely used in the field of human-computer interaction.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Apparatus and method for implementing haptic-based networked virtual environment which supports high-resolution tiled display
InactiveUS9041621B2Efficient implementationInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsLimited resourcesGraphics
An apparatus and method of implementing haptic-based networked virtual environments supporting high-resolution tiled displays. A haptic rendering process of detecting collision between a user of a haptic-device over a virtual environment and each of at least one virtual object and providing a physical force corresponding to a detection result to the haptic-device is performed, and a graphic rendering process of converting each virtual object represented as 3-D data into an object stream represented as 2-D data such that each virtual object is displayed as a 2-D image, and assigning a priority and a frame rate to each converted object stream according to a preset assignment criterion is performed. A plurality of displays provide a display image, including object streams of the virtual objects and background pixels, so that a virtual environment allowing the user of the haptic-device to visually and tactilely immerse thereto is effectively realized by utilizing limited resources.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
Compensated haptic rendering for flexible electronic devices
InactiveCN107807733AInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsContact forceFlexible electronics
A device comprises a housing, a sensor, a controller and an actuator. The sensor is configured to detect a contact force exerted on the housing. The controller is communicatively coupled to the sensorand is configured to determine a change in a haptic effect caused by the contact force. The controller is additionally configured to generate an output instruction to deliver the haptic effect in a compensated form that is operable to correct the change. The actuator is configured to receive the output instruction and deliver the compensated haptic effect at the housing.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Dynamic video tactile feature extraction and rendering method
ActiveCN111291677AReal-time tactile experienceFriendlyImage enhancementImage analysisSaliency mapSpace time domain
The invention relates to a dynamic video tactile feature extraction and rendering method, and belongs to the field of virtual reality and human-computer interaction. The method comprises the steps ofdecompressing a received video, preprocessing the video, segmenting shots based on inter-frame color histogram features, extracting saliency maps fused with time-space domain tactile saliency featuresfrom all the segmented frames in each shot, and performing pixel-level tactile rendering according to the saliency maps of the video frames. According to the method, the video content is divided intothe salient region and the non-salient region by extracting the video frame salient features fused with the space-time characteristics. And pixel-level tactile stimulation is applied to the video frame by adopting a one-to-one mapping relationship between the visual channels and the tactile channels. And real-time tactile feedback is generated through the terminal, so that the realistic experience of watching the video by the user is enriched. The method can be widely applied to video education, multimedia entertainment and human-computer interaction.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Access control method by haptic feedback
ActiveUS20150248162A1Improve securityDifficult to discoverInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data authenticationSignal onHuman–computer interaction
An access control method is performed on an equipment item linked to elements for rendering at least one haptic signal on a haptic rendering surface, wherein the haptic signal is a touch-discernible texture. The method includes, after an access request has been obtained: ordering rendering of a haptic signal; obtaining information on detection of a gesture of response to the signal; of validating the gesture of response when the gesture detected corresponds to a gesture previously associated with the haptic signal rendered; and authorizing access following the validation of the gesture.
Owner:ORANGE SA (FR)
Ultrasonic aerial tactile rendering method based on three-dimensional grid model
ActiveCN111340961ASure easyRefine the tactile sensation3D modellingPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
The invention relates to an ultrasonic aerial tactile rendering method based on a three-dimensional grid model, and belongs to the field of human-computer interaction and virtual reality. Positioningof a hand ultrasonic focus point and description of local features of a three-dimensional graph are completed in a grid model mode. Grid vertexes of the three-dimensional model obtain three-dimensional coordinates through specific software; and according to the finger joint coordinates and the distance information between the palm plane and the vertex of the three-dimensional graph grid, positioning of a hand ultrasonic focus point, is completed and ultrasonic focusing is performed on positions such as edges and vertexes of the three-dimensional graph by adopting different intensities and frequencies to complete rendering of local features of the three-dimensional graph. The method has the advantages that the hand part is divided into the finger part and the palm part, ultrasonic focusingis conducted on the finger part and the palm part respectively, ultrasonic focusing is conducted on edges, vertexes and other positions of the three-dimensional graph through different intensities andfrequencies, rendering of local features of the three-dimensional graph is completed, the recognition rate of a user for the three-dimensional graph is increased, and the trueness of the three-dimensional graph is further improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Master-slave guide wire control method
ActiveCN111797506AGuaranteed calculation accuracyLess freedomMedical automated diagnosisComputer-aided planning/modellingTouch SensesCollision detection
The invention relates to a master-slave guide wire control method. The method is master-slave guide wire control based on virtual reality haptic rendering. Force touch representation is carried out atthe main hand end through force touch rendering; an operator controls a slave hand end guide wire to move through force touch information, and the force touch rendering model is a guide wire-vascularwall efficient contact detection algorithm based on any Lagrange Euler (ALE), which adopts one-dimensional arc length coordinates to determine the position of a contact detection point in any Lagrange Euler (ALE) guide wire unit. According to the method, the one-dimensional arc length coordinates are used for replacing three-dimensional Cartesian coordinates in the prior art to determine the position of the contact detection point in the ALE guide wire unit, the contact detection process between the guide wire and the blood vessel wall is simplified, and the collision detection efficiency isimproved on the premise that the precision is not changed.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF ENG SCI
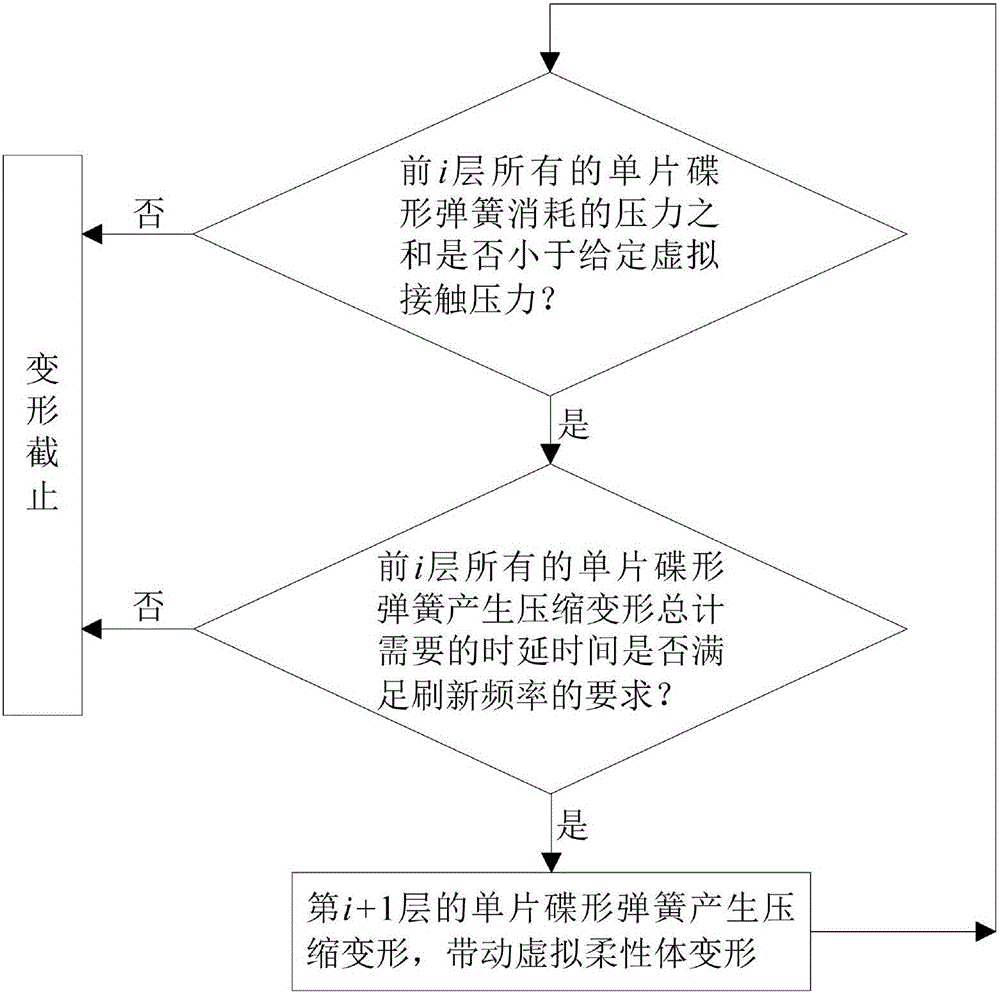
Building method of superimposed disc spring virtual model for flexible haptic rendering
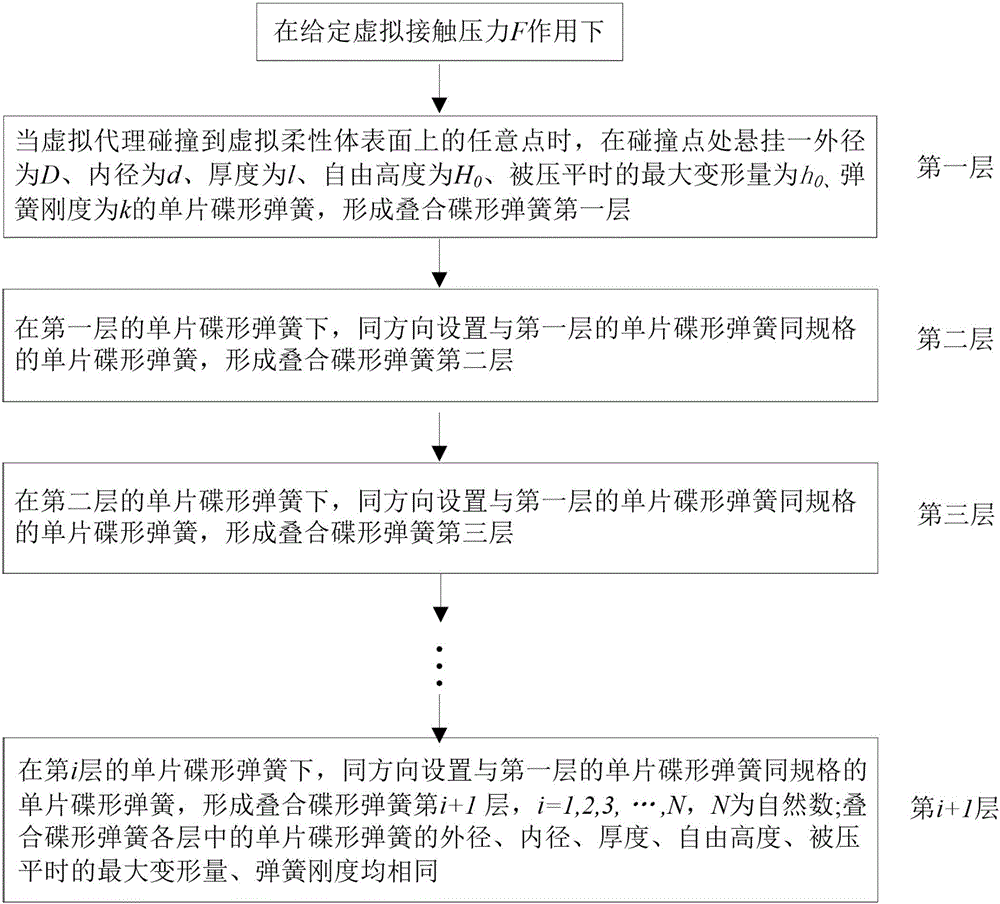
InactiveCN106295085ACalculation speedGuaranteed realismDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsContact pressureSimulation
The invention discloses a building method of superimposed disc spring virtual model for flexible haptic rendering. The building method is characterized in that when the circumstance that a virtual agent collides with any point on the surface of a virtual flexible body is detected, under action of given virtual contact pressure, the inside of a local area in which the virtual agent interacts with the virtual flexible body is filled with the superimposed disc spring virtual model; in the process of interaction, a signal reflecting haptic information of real-time deformation simulation of the flexible body under pressure action and calculated by adopting the superimposed disc spring virtual model is output and fed back ; addition of sums of deformation of disc springs on each layer in the superimposed disc spring virtual model is externally equivalent to deformation of the surface of the flexible body, and sum of pressure consumed when the superimposed disc springs on each layer are compressed. By the building method, the deformation process of the flexible body can be vividly simulated in real time, haptic information which is fed back is real and stable, and a feasible path is sought for practically using virtual operation simulating.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com