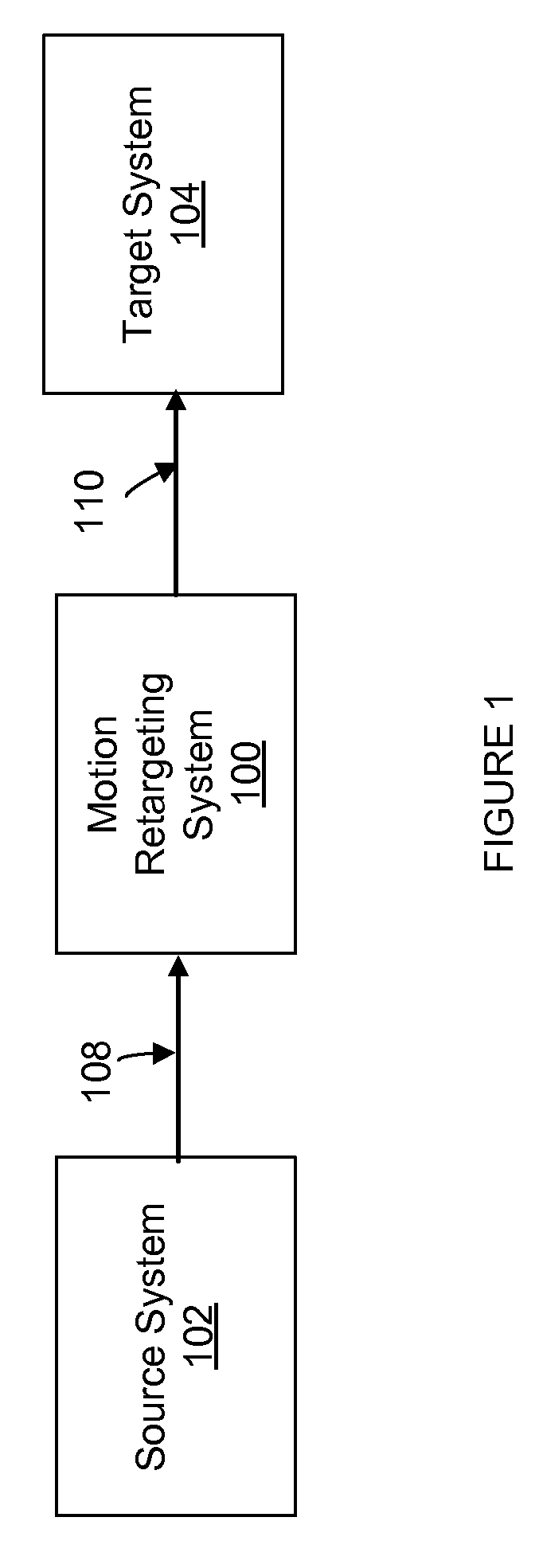
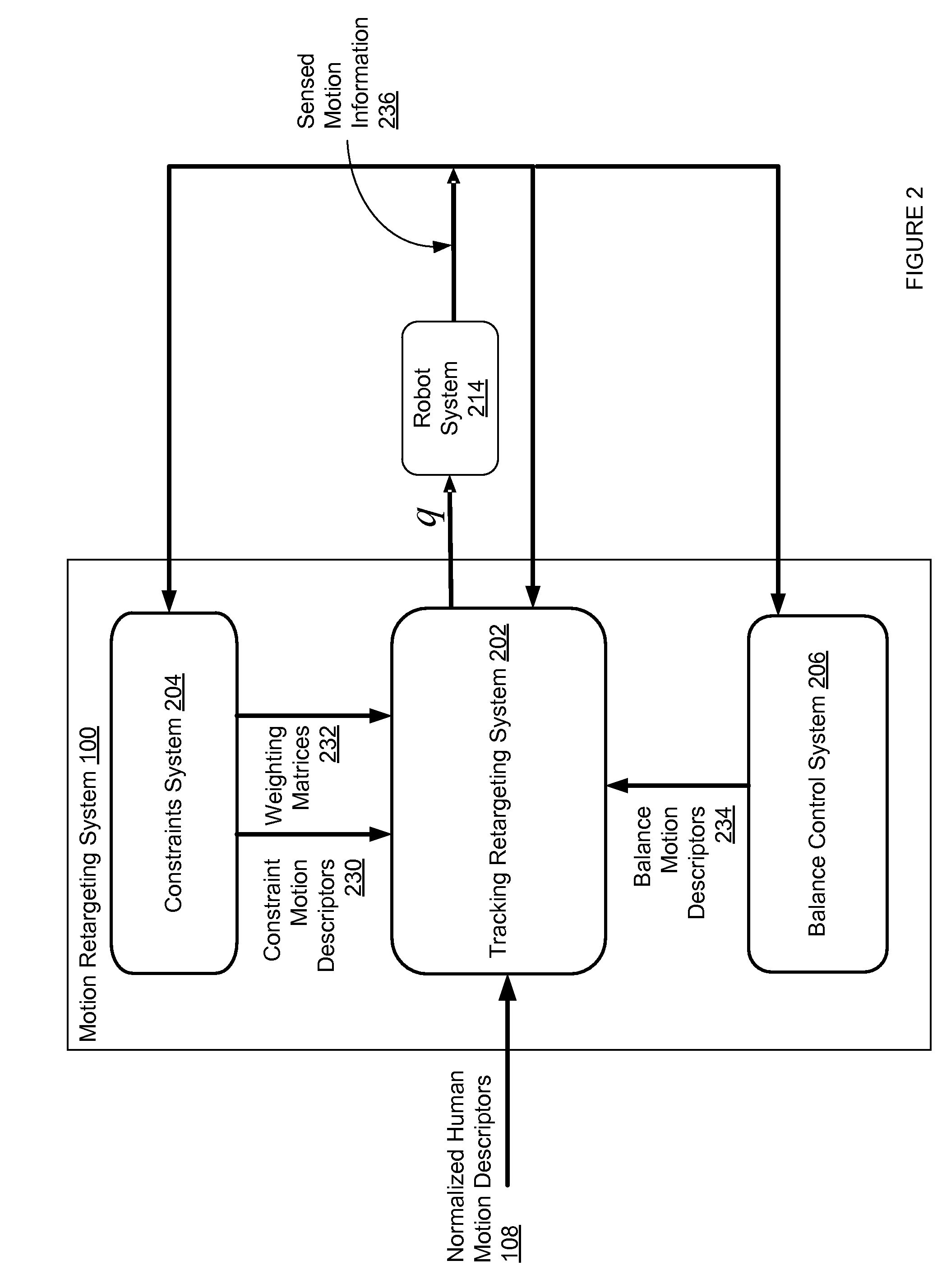
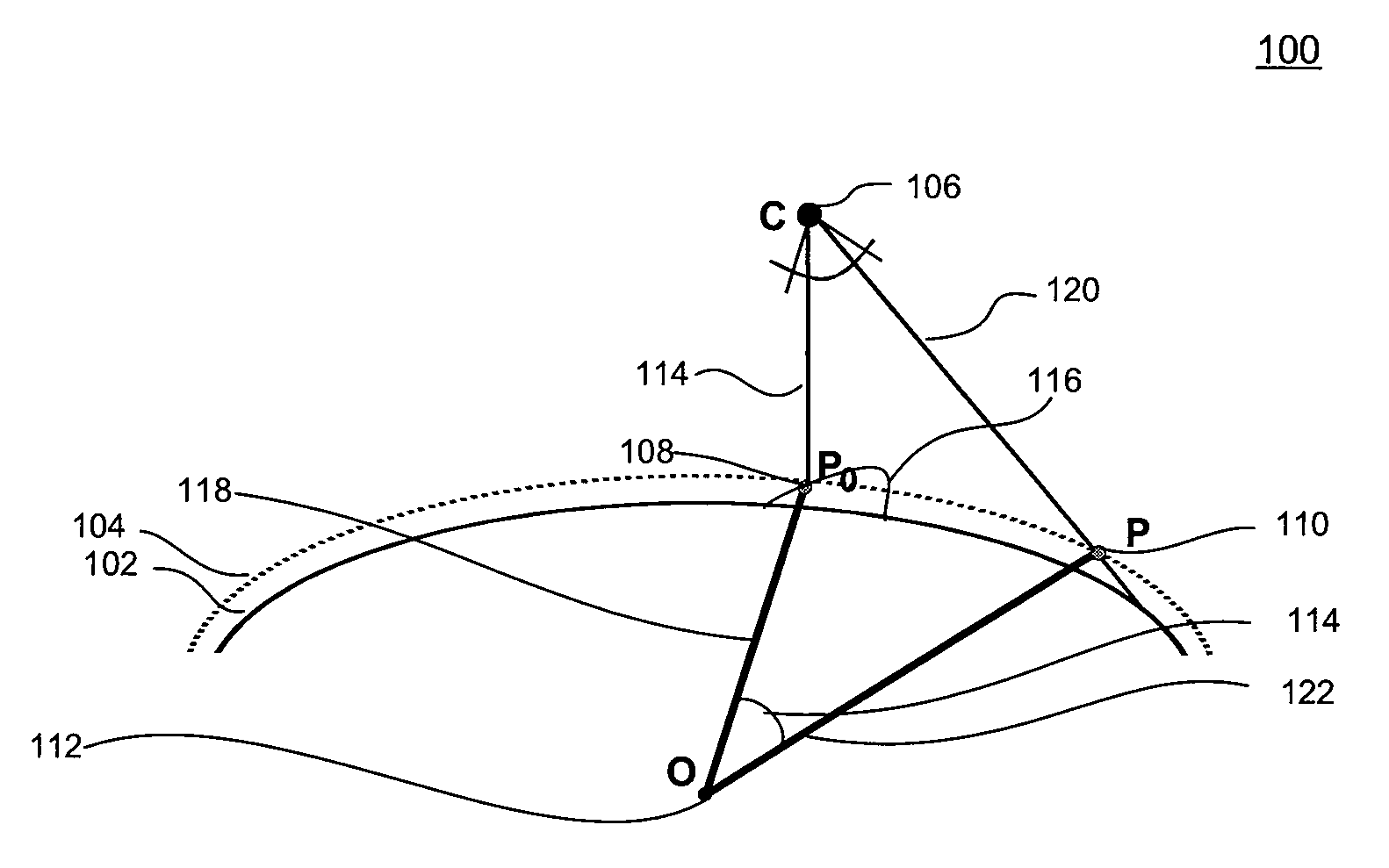
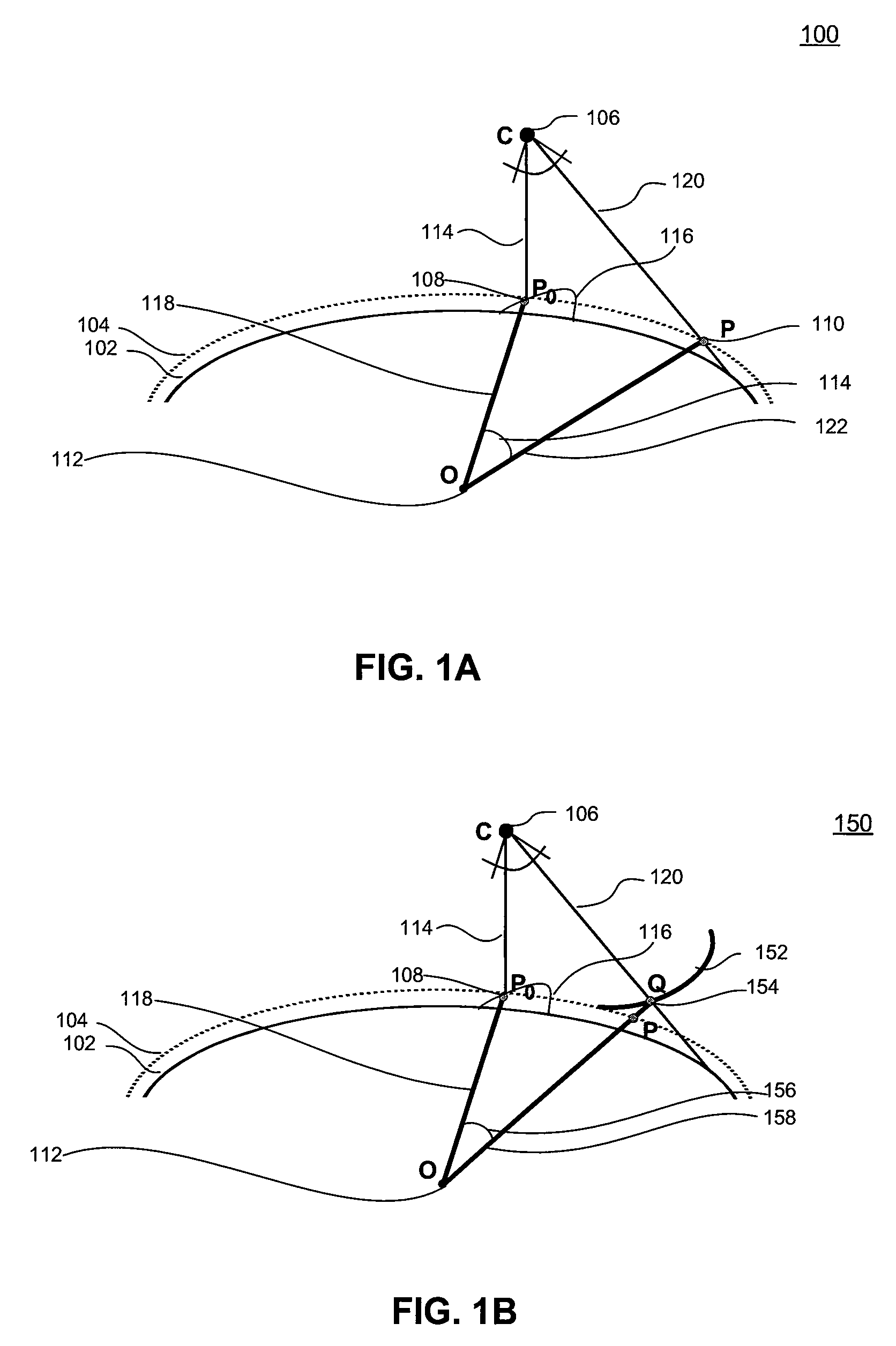
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
243 results about "Virtual surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
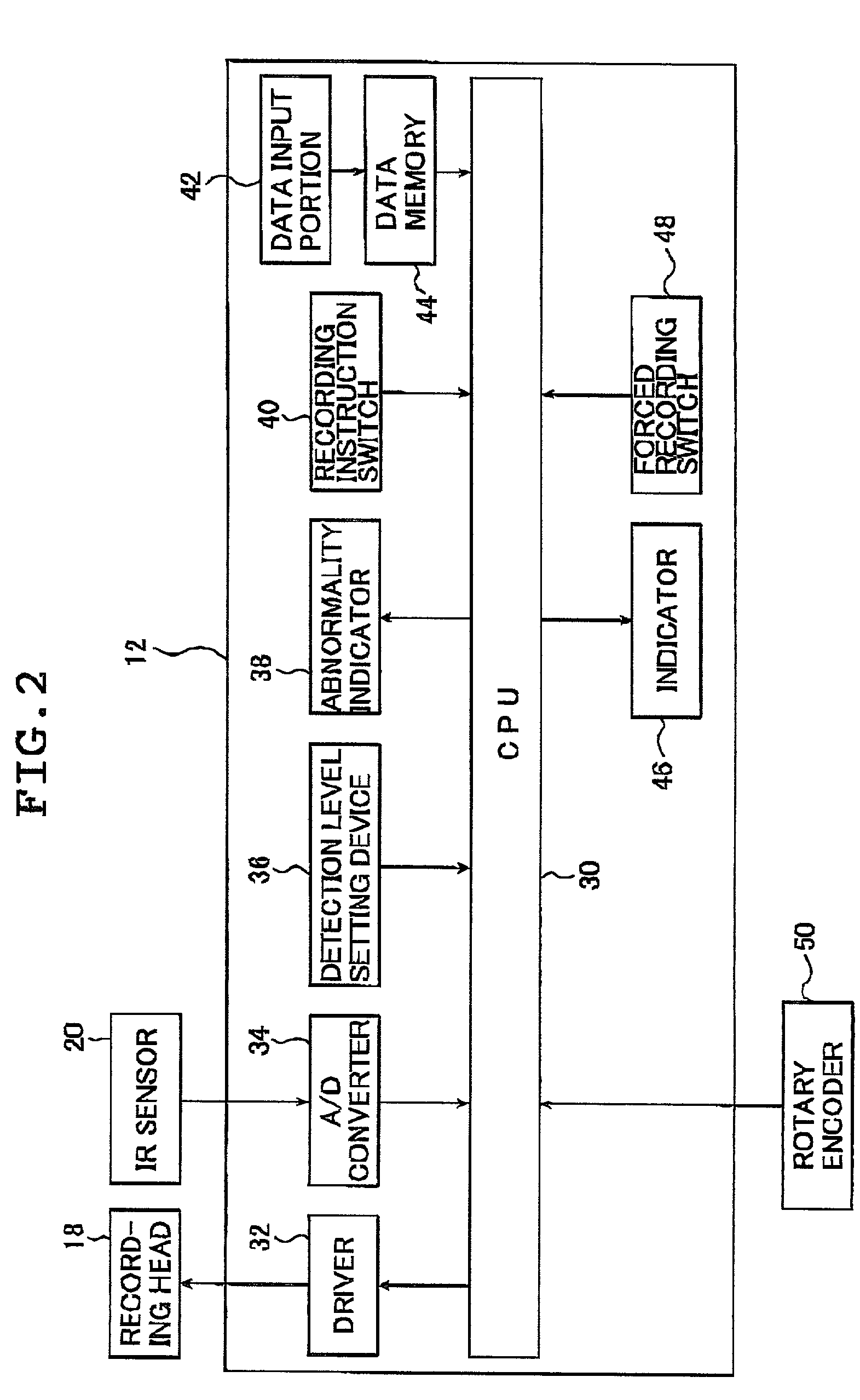
Single or multi-mode cardiac activity data collection, processing and display obtained in a non-invasive manner
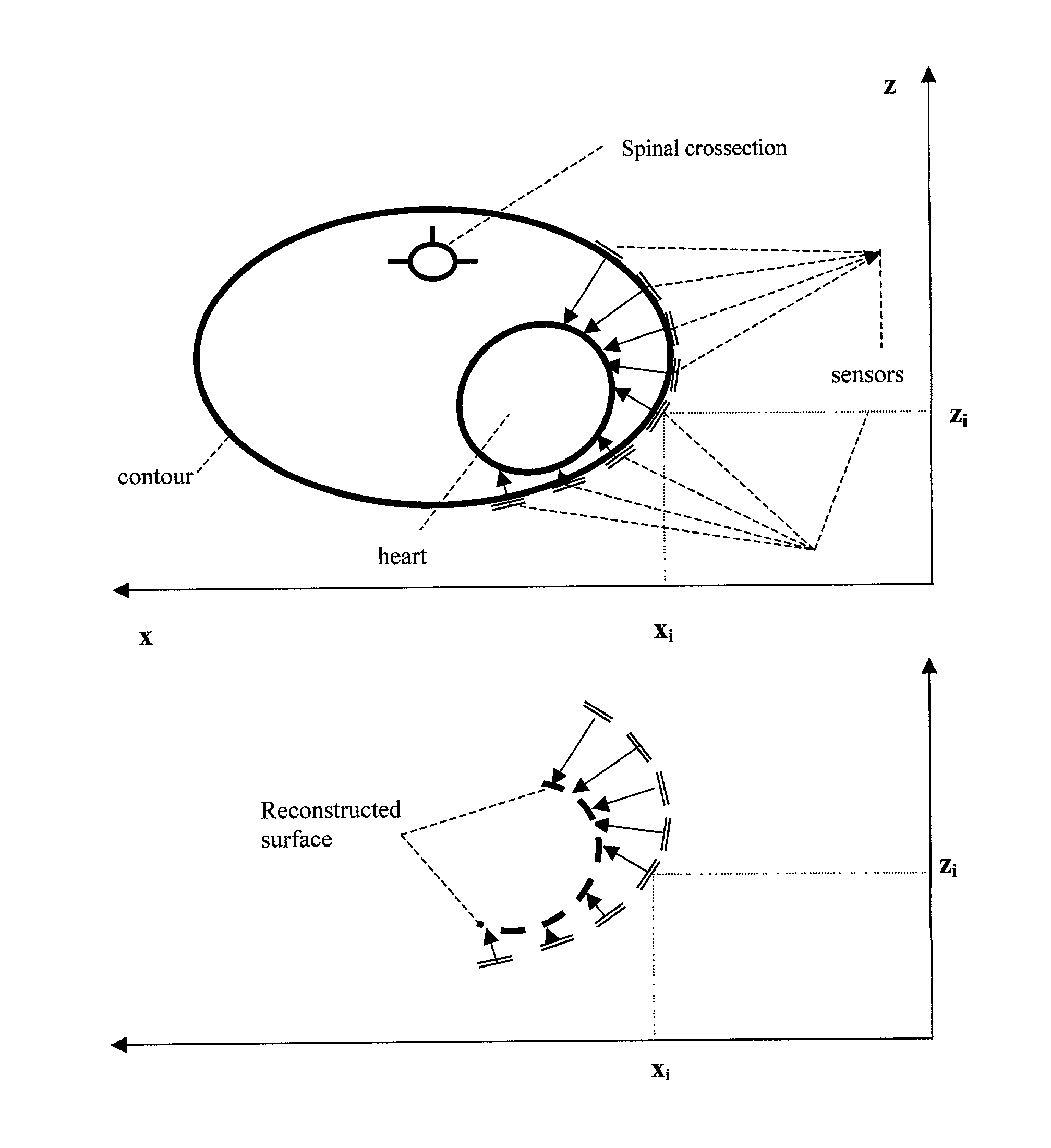
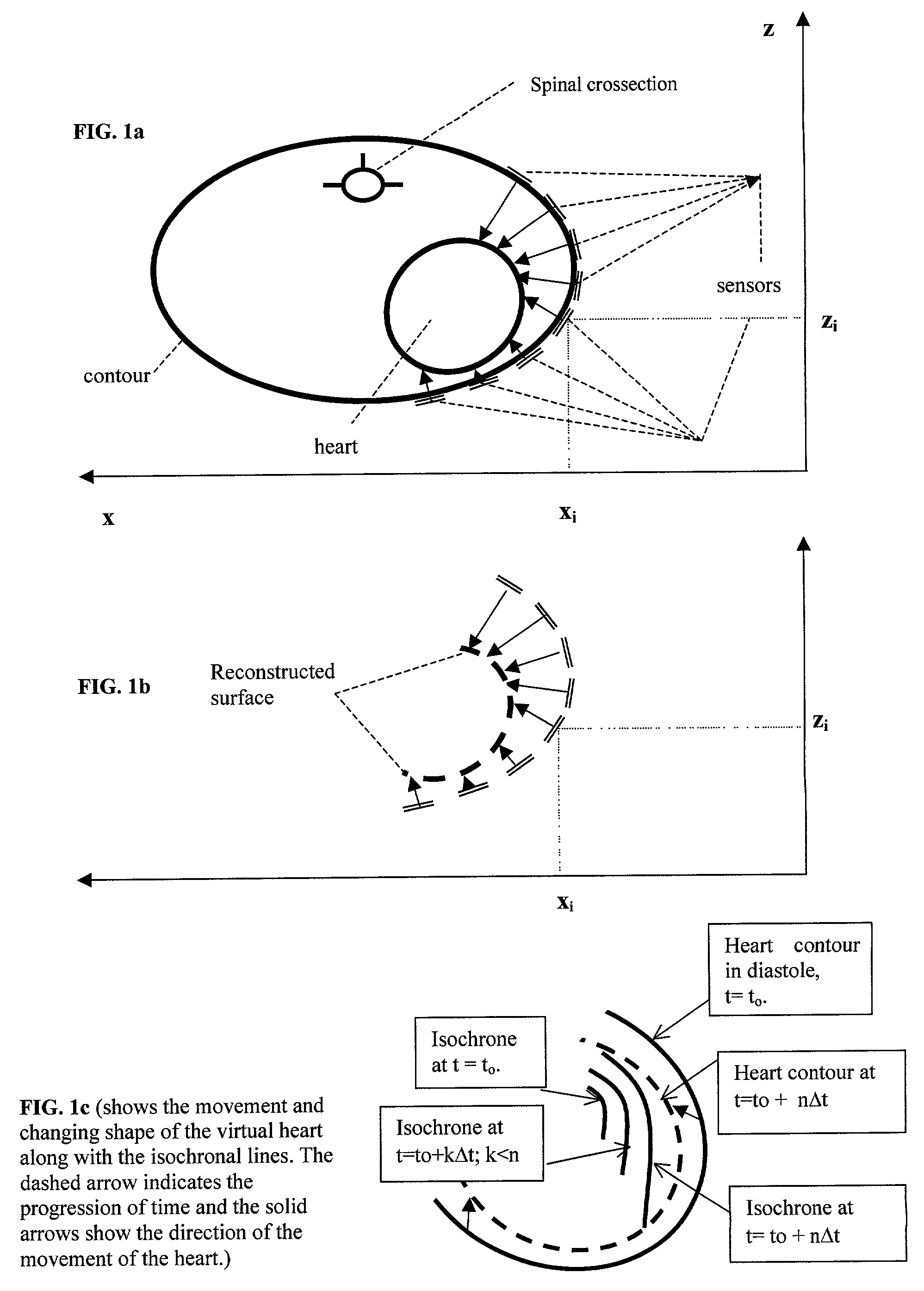
InactiveUS7043292B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioEasy to identifyElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic sensorCardiac surface
The method of presenting concurrent information about the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart using non-invasively obtained electrical and mechanical cardiac activity data from the chest or thorax of a patient comprises the steps of: placing at least three active Laplacian ECG sensors at locations on the chest or thorax of the patient; where each sensor has at least one outer ring element and an inner solid circle element, placing at least one ultrasonic sensor on the thorax where there is no underlying bone structure, only tissue, and utilizing available ultrasound technology to produce two or three-dimensional displays of the moving surface of the heart and making direct measurements of the exact sites of the sensors on the chest surface to determine the position and distance from the center of each sensor to the heart along a line orthogonal to the plane of the sensor and create a virtual heart surface; updating the measurements at a rate to show the movement of the heart's surface; monitoring at each ultrasonic sensor site and each Laplacian ECG sensor site the position and movement of the heart and the passage of depolarization wave-fronts in the vicinity; treating those depolarization wave-fronts as moving dipoles at those sites to create images of their movement on the image of the beating heart's surface; and, displaying the heart's electrical activity on the dynamically changing image of the heart's surface with the goal to display an approximation of the activation sequence on the beating virtual surface of the heart
Owner:TARJAN PETER P +2
Manipulating virtual environment using non-instrumented physical object
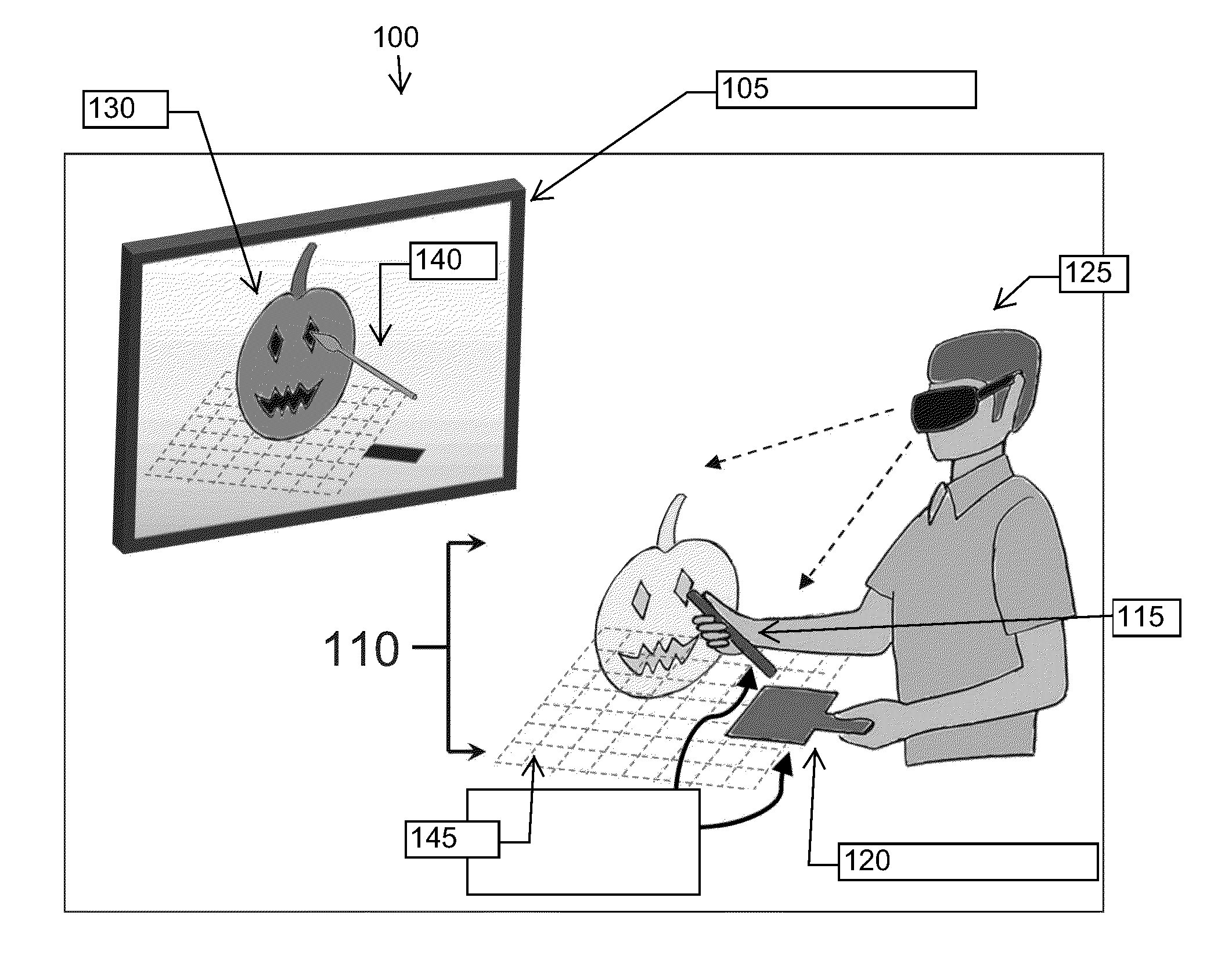
A method of manipulating a three-dimensional image file including a virtual object includes obtaining image information in a processing device of a non-instrumented physical object manipulated by a user, such image information including movement information; and causing virtual movement of the virtual object based on the movement information. A method of shaping a virtual object includes obtaining image information including movement information; and determining a shape of the virtual object based on the movement information. A method of modifying a virtual object includes obtaining image information including movement information; and altering a virtual surface appearance of at least a part of the virtual object based on the movement information. Systems and computer-readable media are also described.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
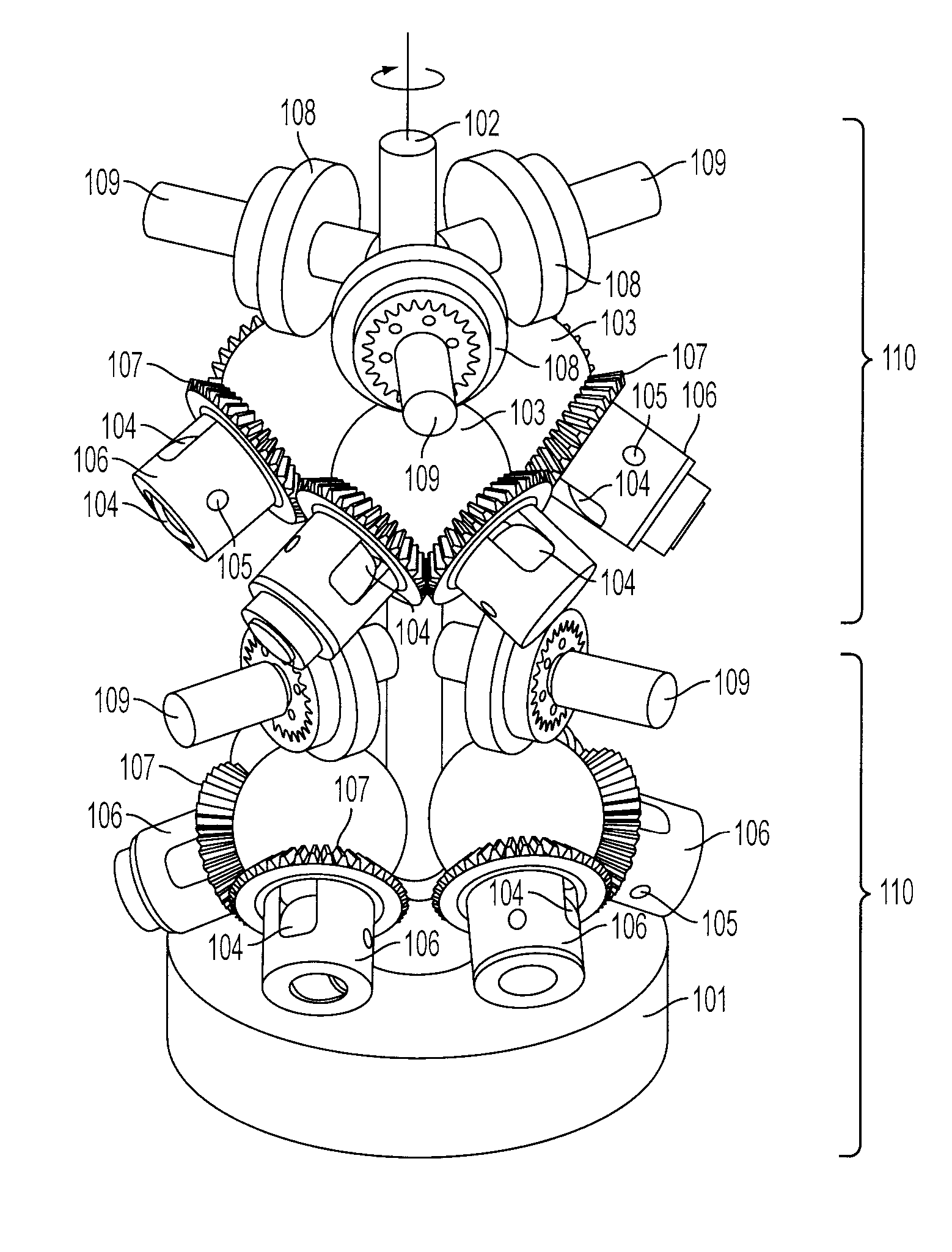
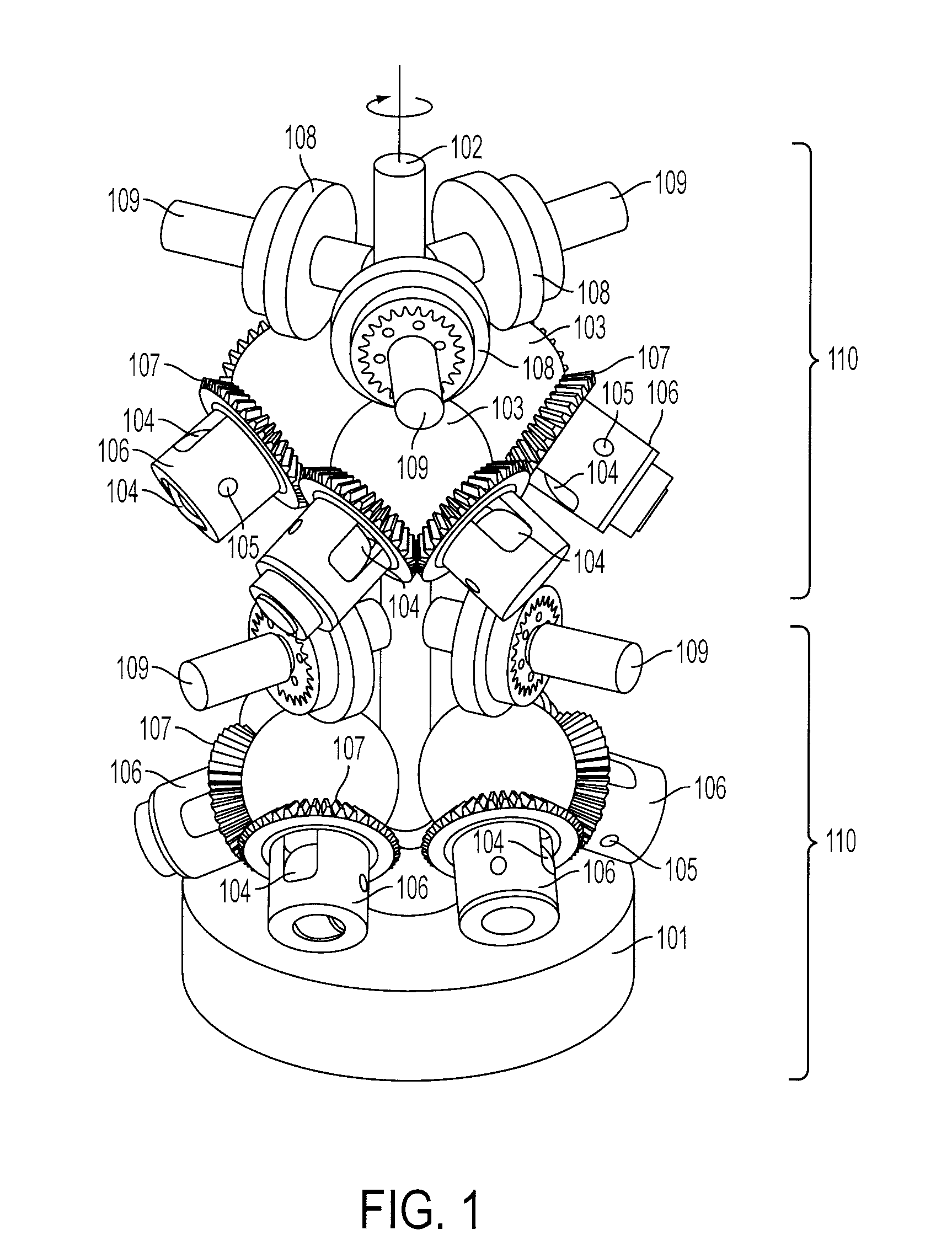
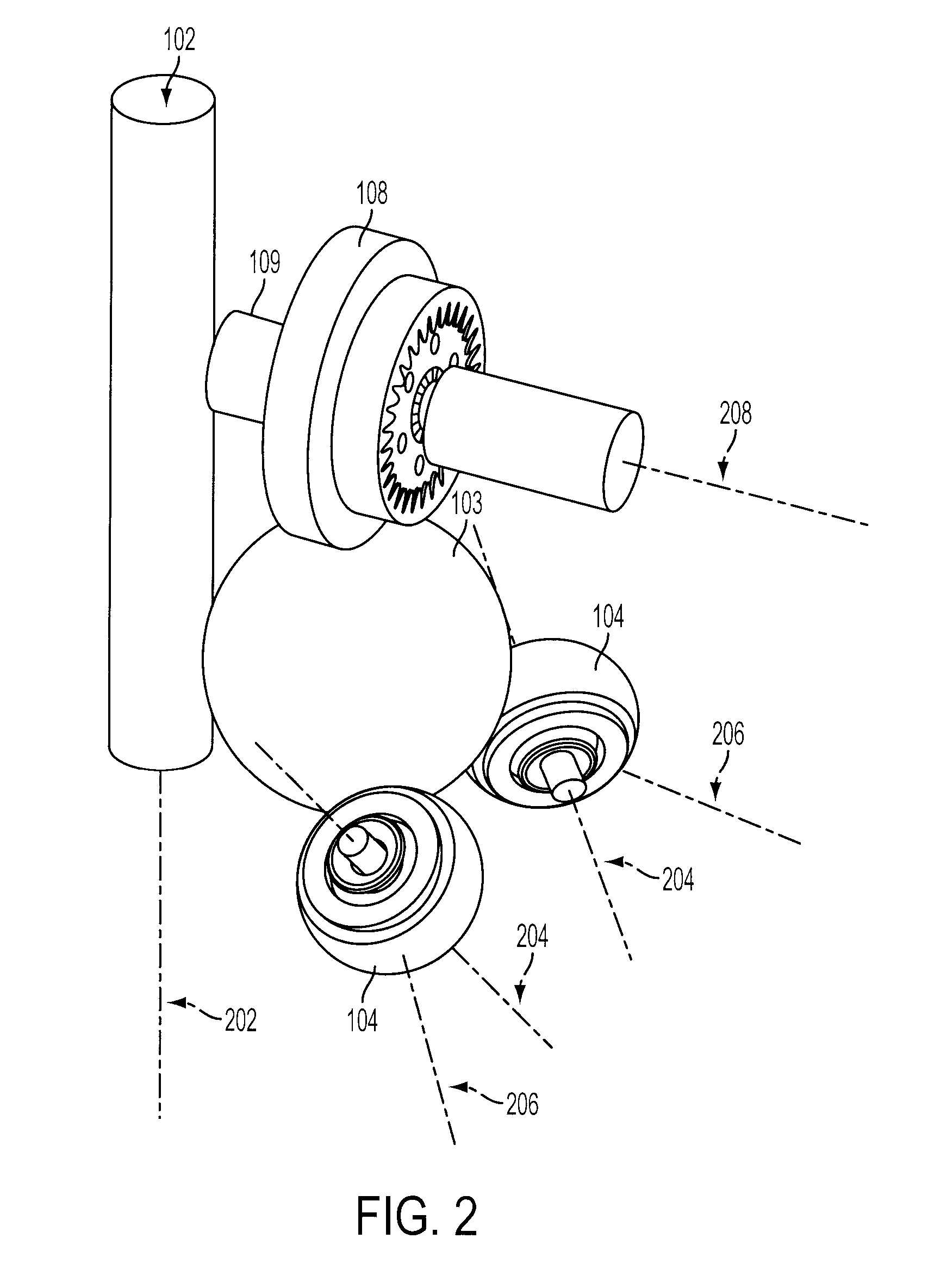
Continuously Variable Transmission with Mutliple Outputs
ActiveUS20080081728A1Efficient power utilizationSaving of weightFriction gearingsManual control with multiple controlling membersEngineeringProsthetic hand
A transmission or actuator offering multiple rotational outputs proportionate in speed to that of a common rotational input, each output according to its own ratio. The ratios are continuously variable between positive and negative values, including zero, and may be varied by electromechanical actuators under computer control. The transmission relates the output speeds one to another under computer control, and thus makes possible the establishment of virtual surfaces and other haptic effects in a multidimensional workspace to which the transmission outputs are kinematically linked. An example of such a workspace is that of a robotic or prosthetic hand.
Owner:HDT EXPEDITIONARY SYST
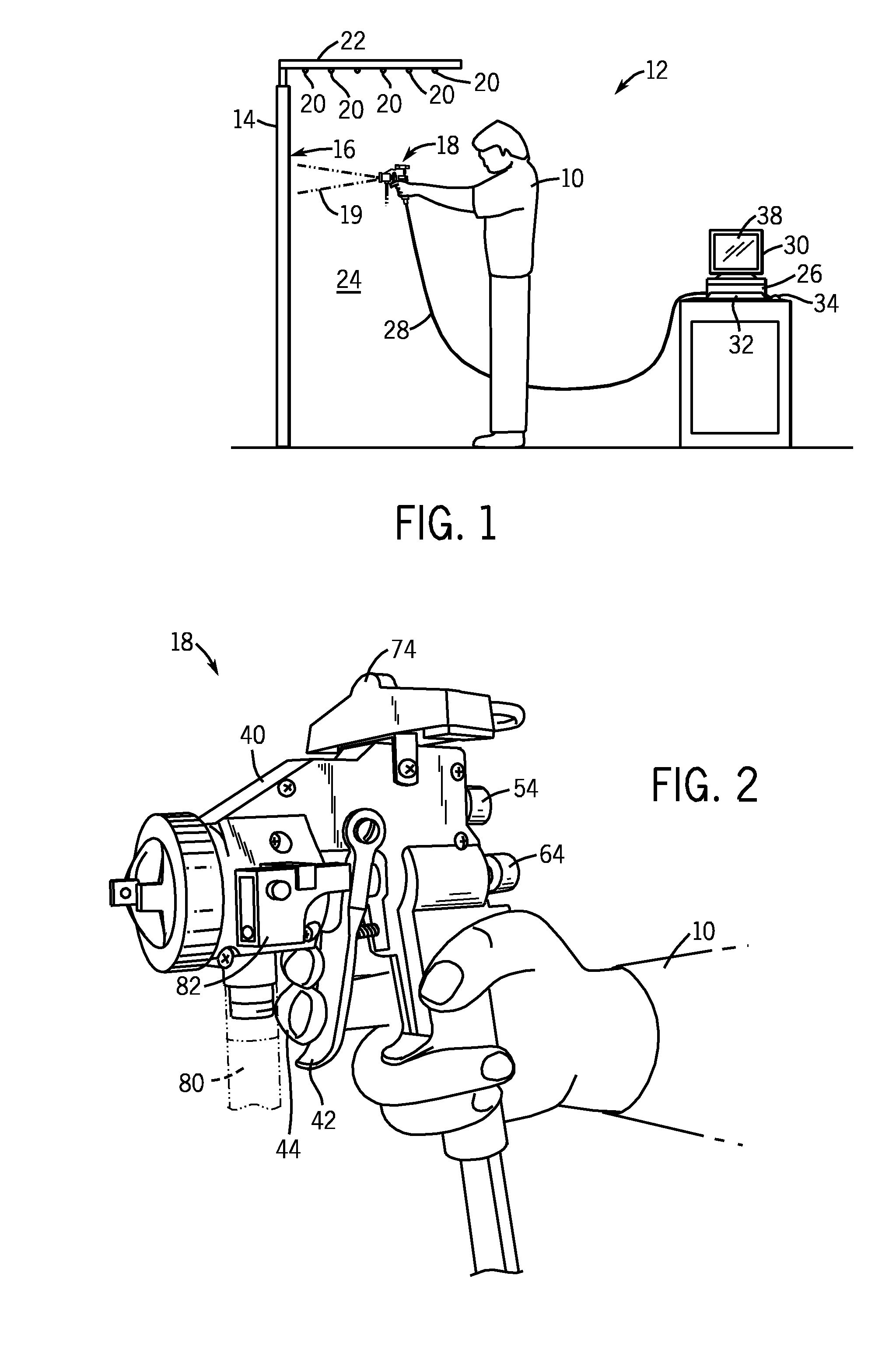
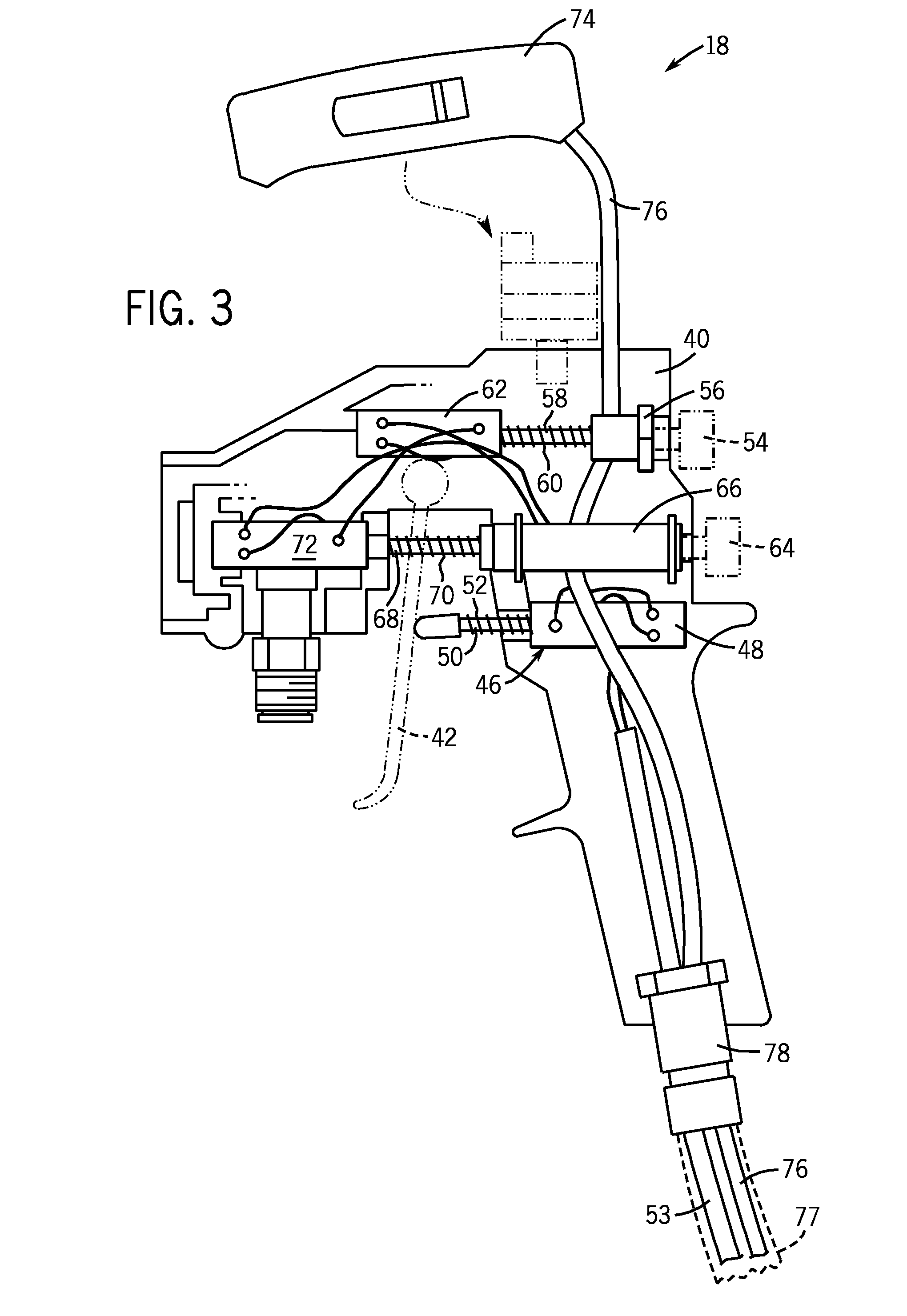
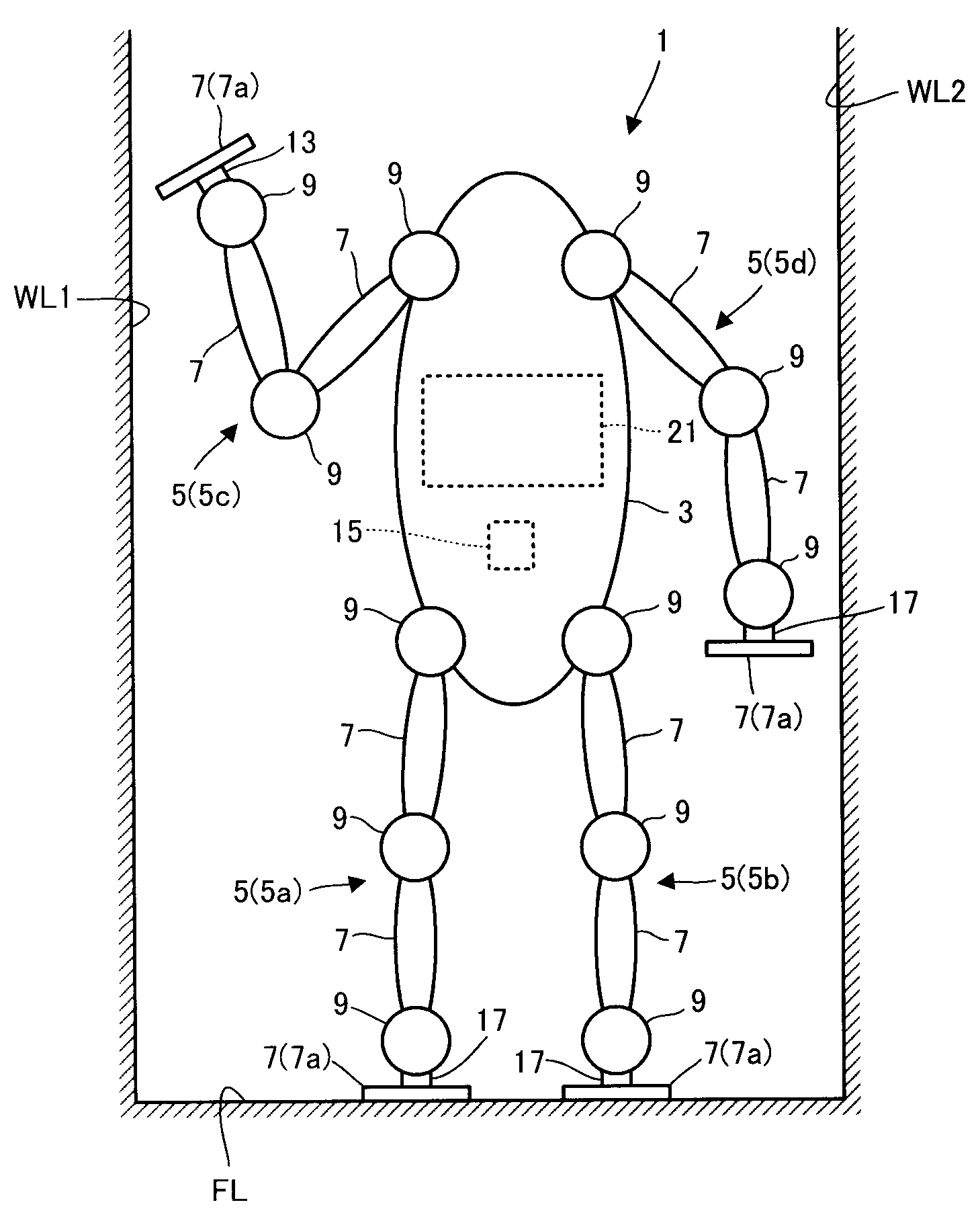
Virtual blasting system for removal of coating and/or rust from a virtual surface
InactiveUS7817162B2High simulationImprove realismCathode-ray tube indicatorsEducational modelsAbrasive blastingElectronic controller
A computer simulation and virtual reality system simulates the use of a blasting nozzle to remove one or more coatings and / or rust from a virtual surface. The user operates an electronic controller in the form of a blasting nozzle that outputs a signal indicating whether the blasting nozzle controller is in an “on” position or in an “off” position. The system also has a motion tracking system that tracks the position and orientation of the blasting nozzle controller with respect to the virtual surface defined on the display screen. Simulation software in a computer generates virtual blast pattern data, and the removal of the virtual coating(s) and / or rust image from the virtual surface is displayed in real time on the display screen.
Owner:UNIV OF NORTHERN IOWA RES FOUND
Virtual coatings application system
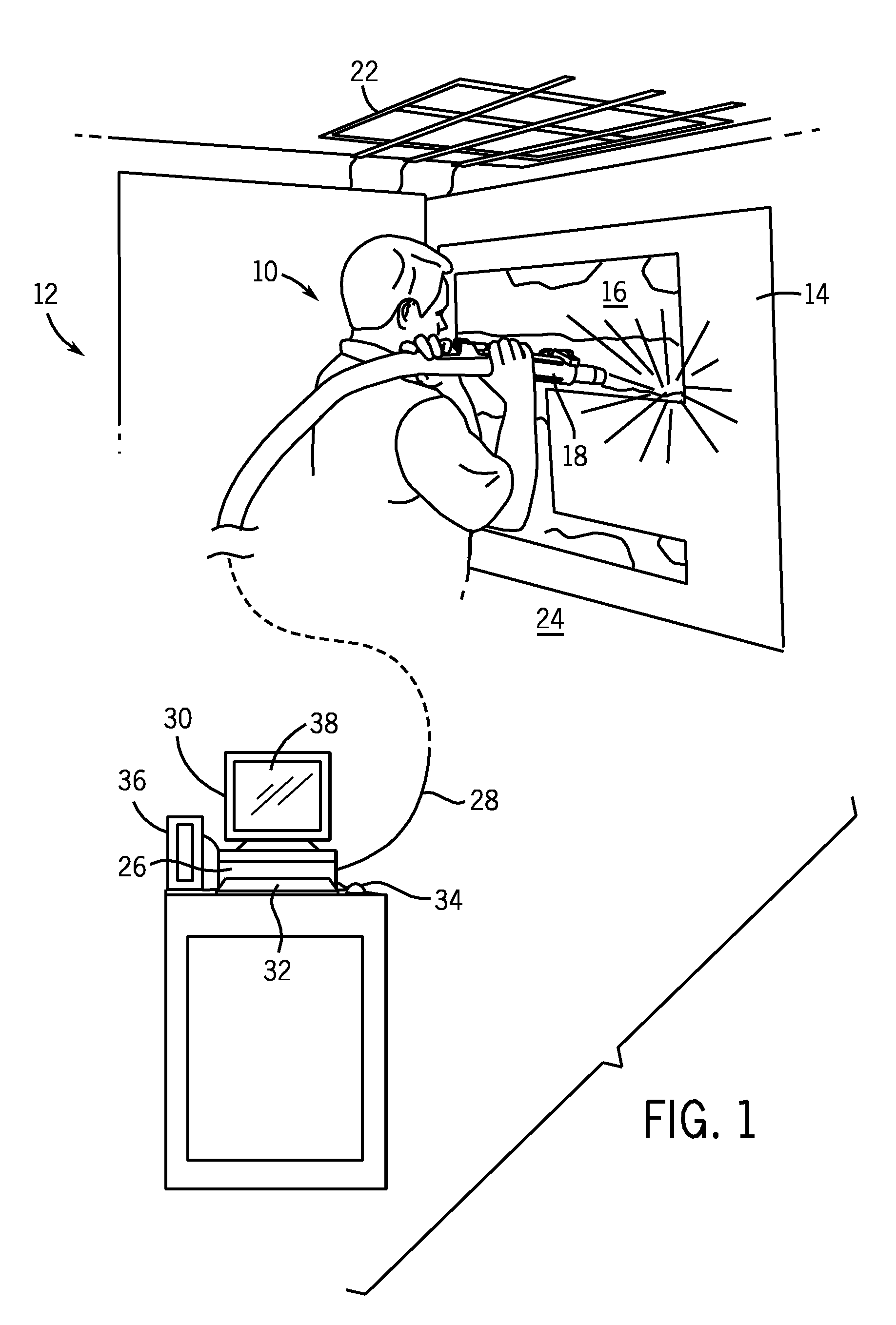
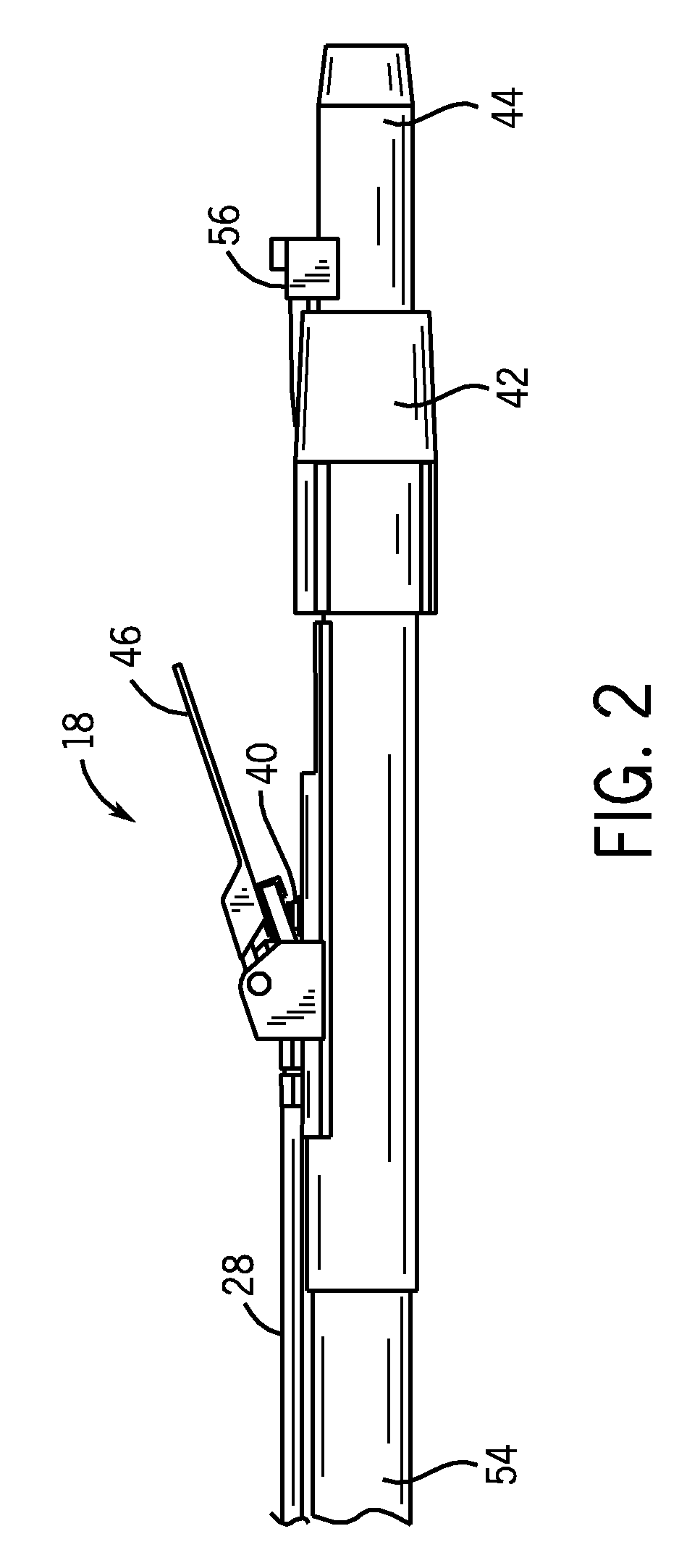
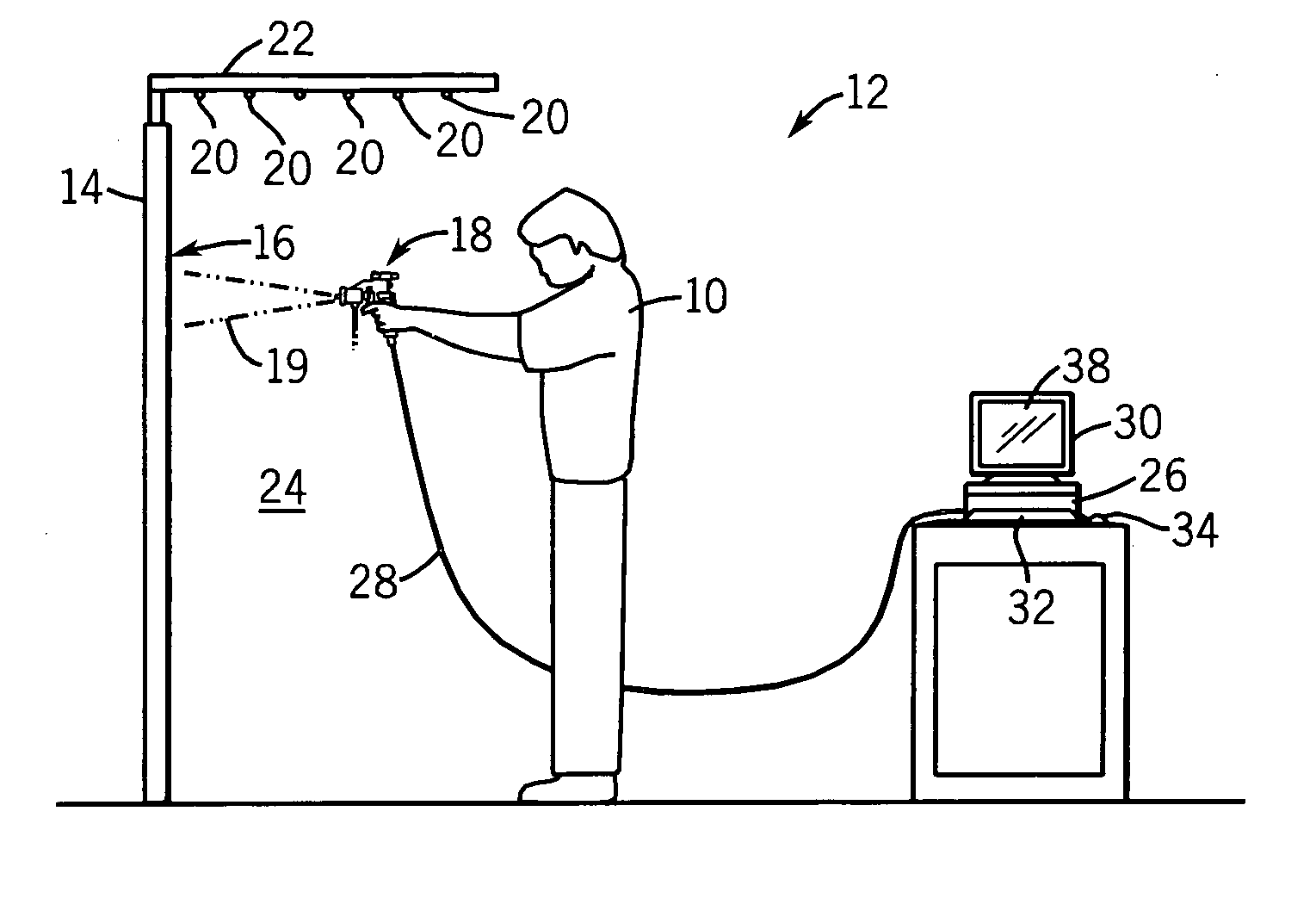
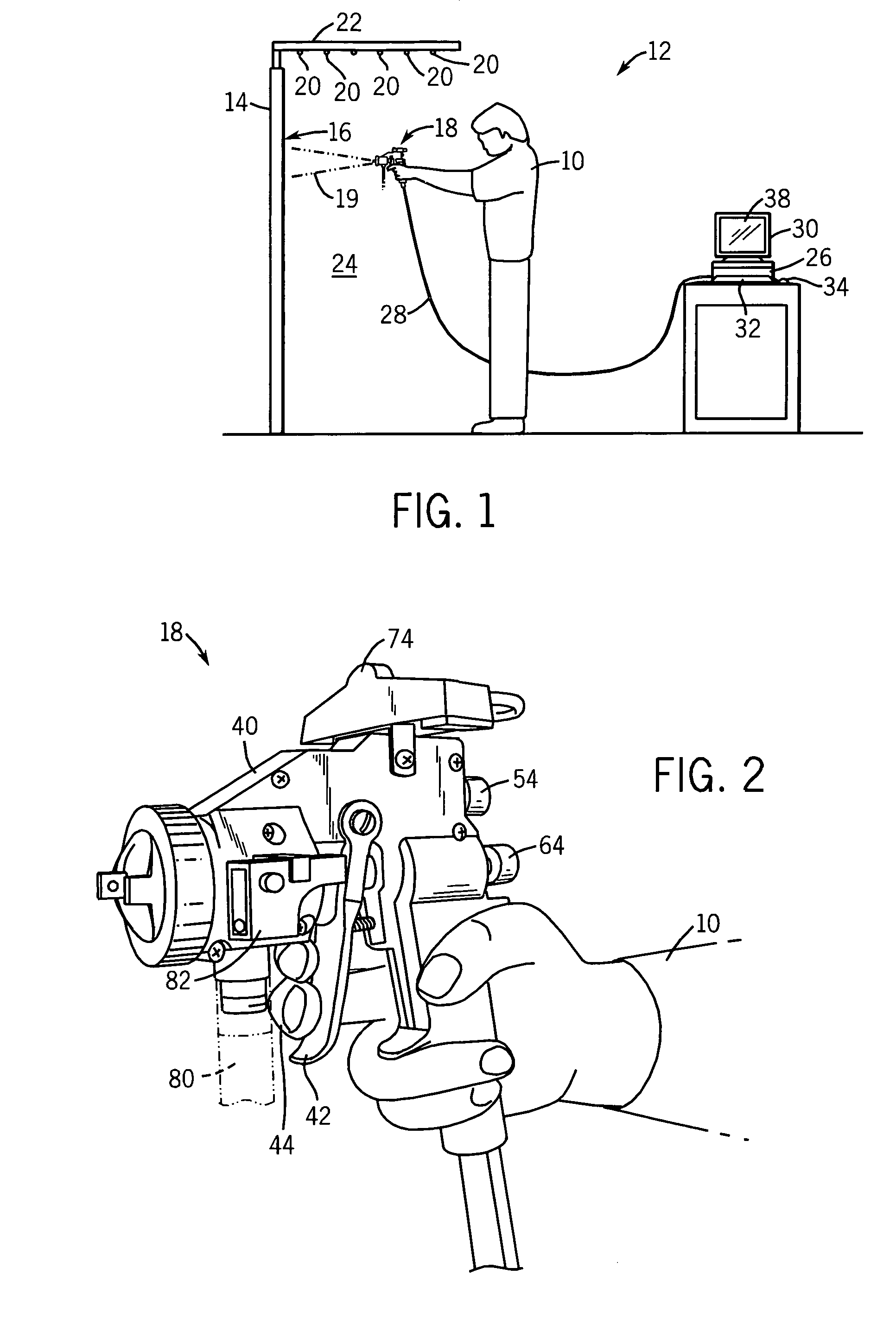
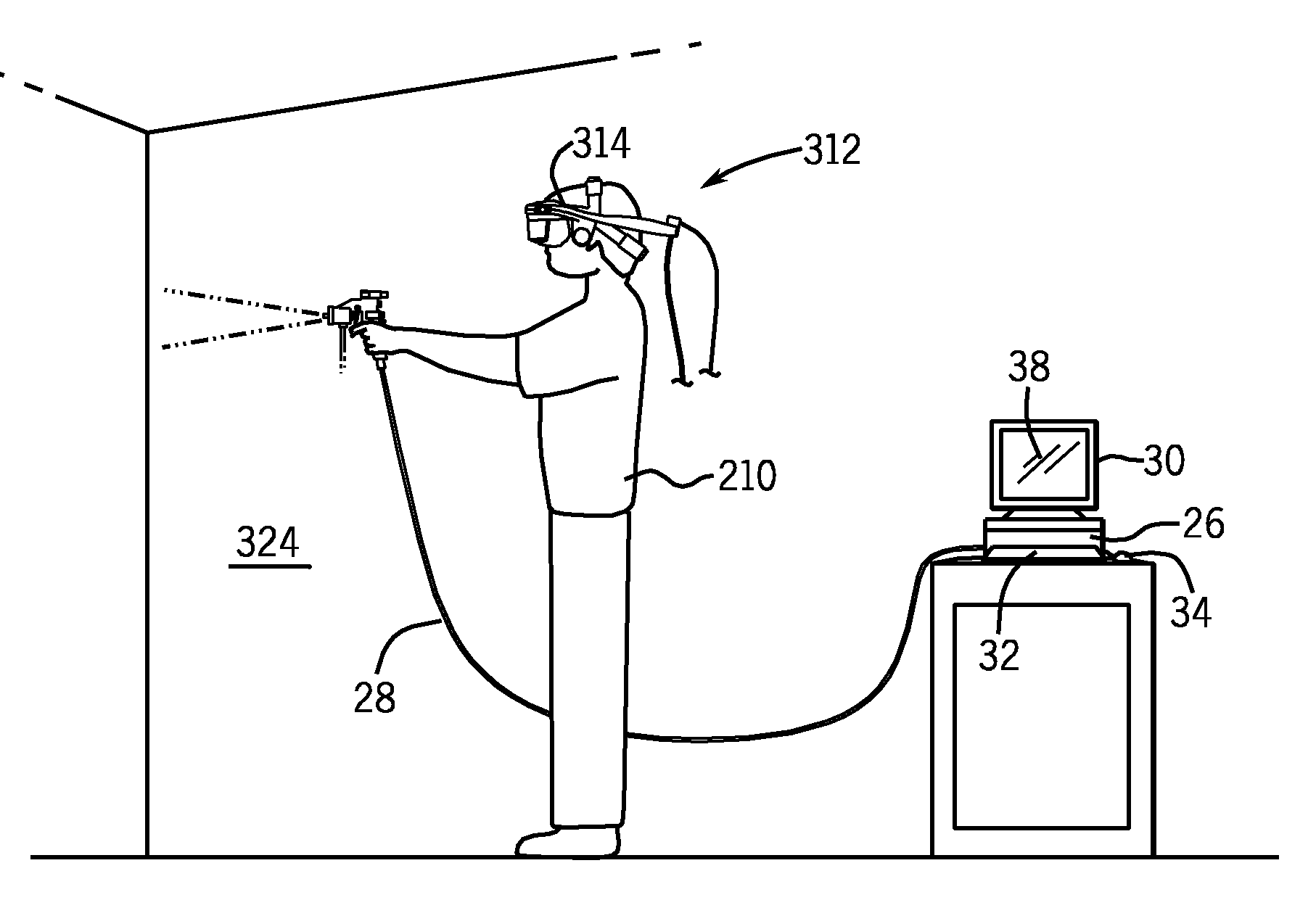
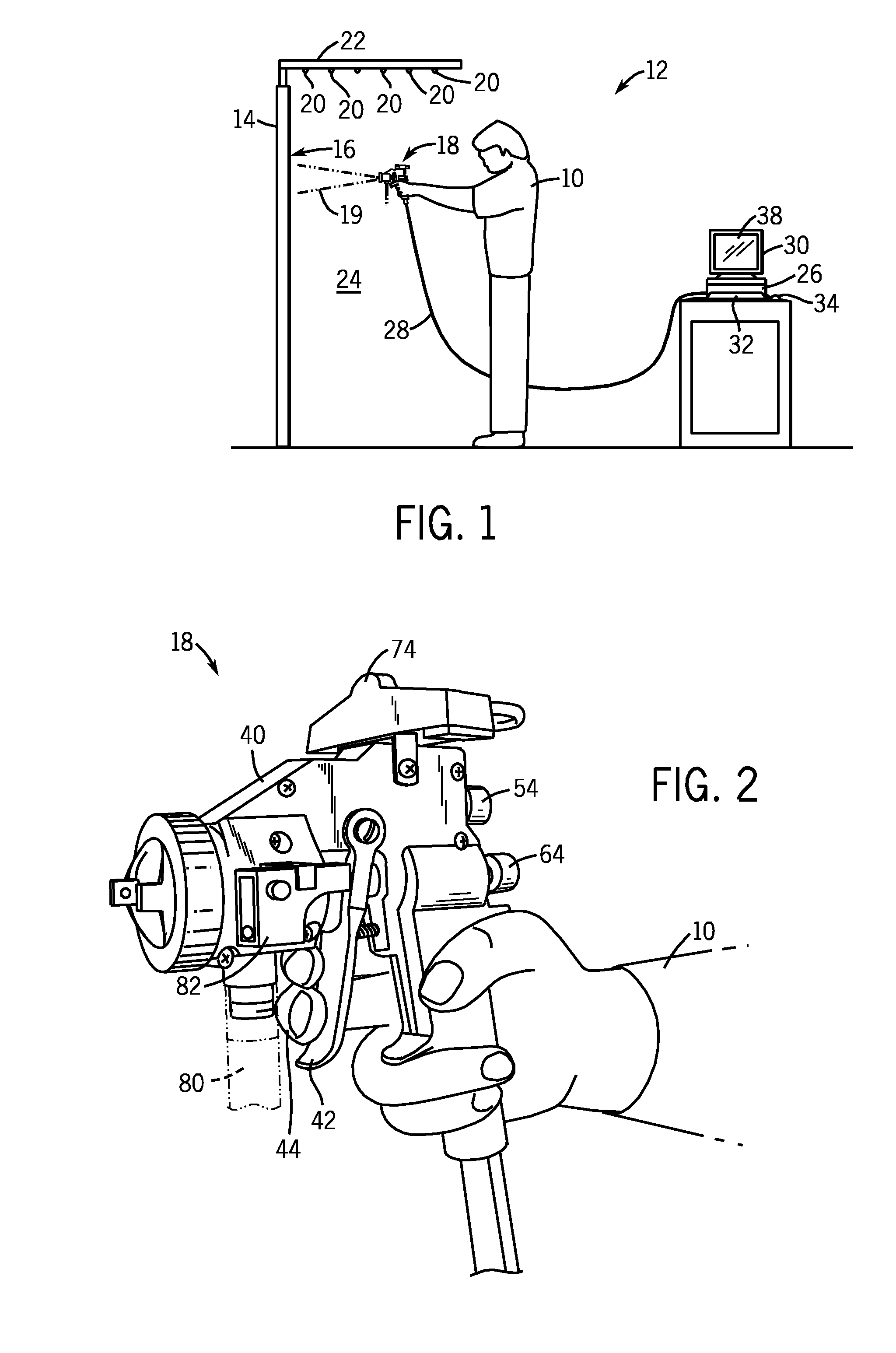
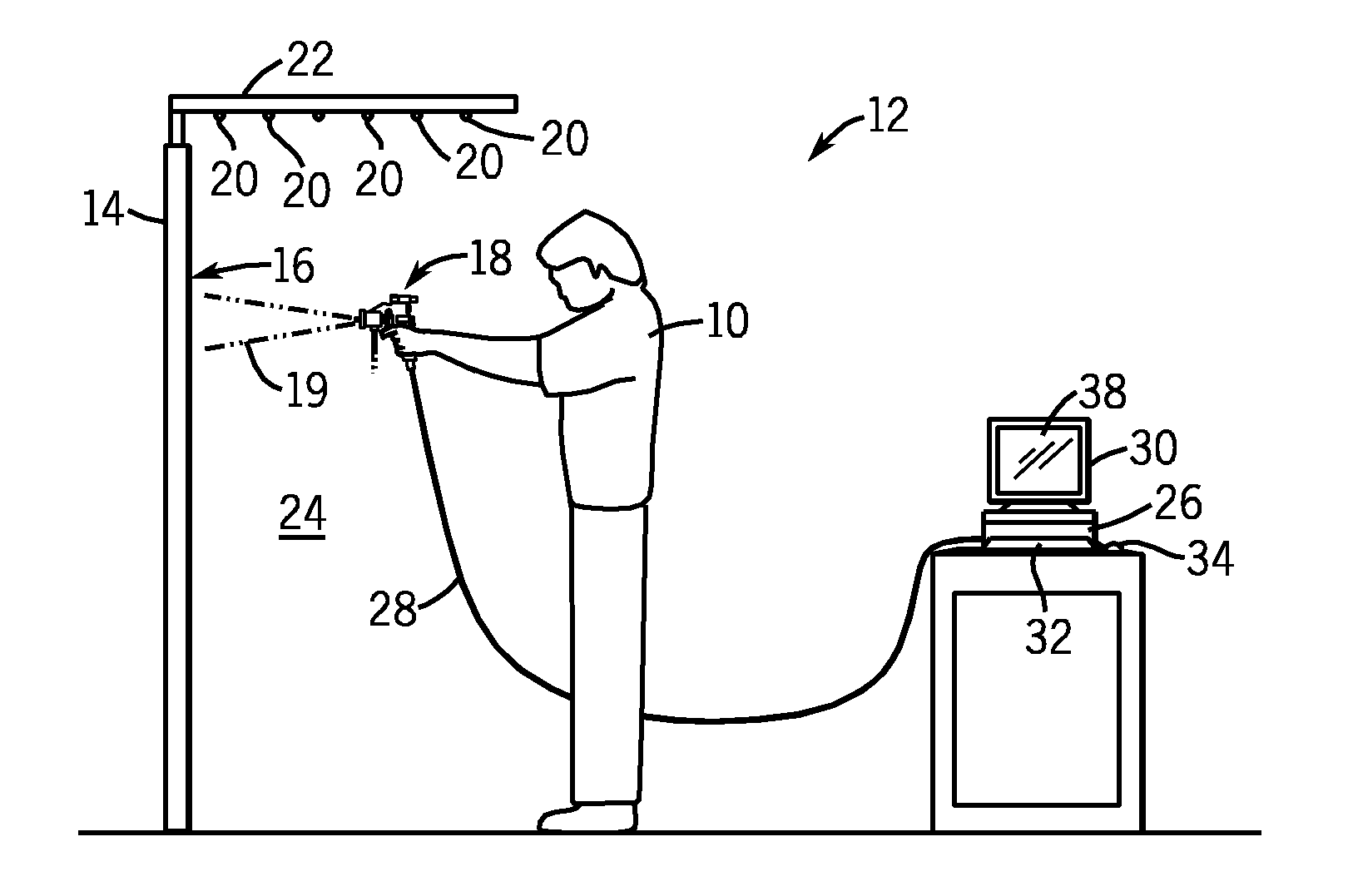
ActiveUS7839416B2Improve realismSimulate the realLiquid surface applicatorsCathode-ray tube indicatorsSimulationMotion tracking system
A virtual coatings application system has several features to enhance the realism of simulated spray painting. The system generally includes a display screen on which is defined a virtual surface (such as a truck door) that is intended to be virtually painted or coated by the user. The user operates an instrumented spray gun controller that outputs one or more signals representing data as to the status of the controls on the spray gun controller. The system also has a motion tracking system that tracks the position and orientation of the spray gun controller with respect to the virtual surface defined on the display screen. Simulation software generates virtual spray pattern data in response to at least the data from the spray gun controller and the position and orientation data received from the tracking system. Virtual spray pattern images are displayed in real time on the display screen in accordance with the accumulation of virtual spray pattern data at each location on the virtual surface.
Owner:UNIV OF NORTHERN IOWA RES FOUND
Enhancing video using a virtual surface
InactiveUS6864886B1Avoid operation failureTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVideo imageVirtual surface
A system is disclosed for enhancing video by use of a virtual surface. One or more positions are identified in a first image. These one or more positions are transformed to one or more locations in relation to the virtual surface. In subsequent video images (e.g. fields, frames, or other units), the one or more locations in relation to said virtual surface are transformed to one or more positions in the subsequent video images. The subsequent video images are enhanced based on the one or more transformed positions.
Owner:SPORTSMEDIA TECH CORP
Virtual coatings application system
InactiveUS20070209586A1Accurate dataAvoid interferenceProgramme controlLiquid surface applicatorsSimulationMotion tracking system
A virtual coatings application system has several features to enhance the realism of simulated spray painting. The system generally includes a display screen on which is defined a virtual surface (such as a truck door) that is intended to be virtually painted or coated by the user. Alternatively, the system includes a head-mounted display unit that displays a virtual spray painting environment in which the virtual surface is defined. The user operates an instrumented spray gun controller that outputs one or more signals representing data as to the status of the controls on the spray gun controller. The system also has a motion tracking system that tracks the position and orientation of the spray gun controller with respect to the virtual surface. Simulation software generates virtual spray pattern data in response to at least the data from the spray gun controller and the position and orientation data received from the tracking system. Virtual spray pattern images are displayed in real time on the virtual surface in accordance with the accumulation of virtual spray pattern data at each location on the virtual surface.
Owner:UNIV OF NORTHERN IOWA RES FOUND
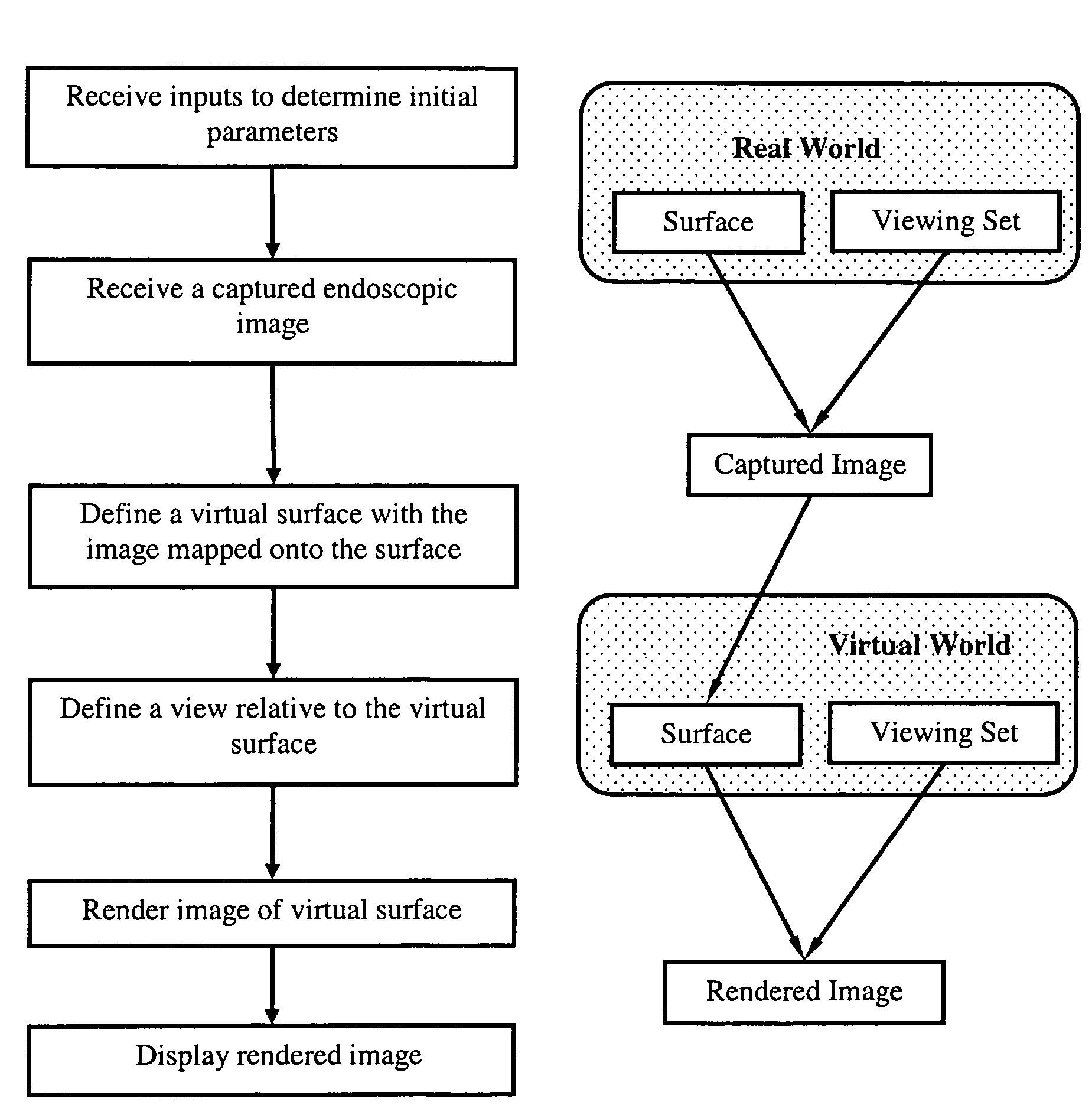
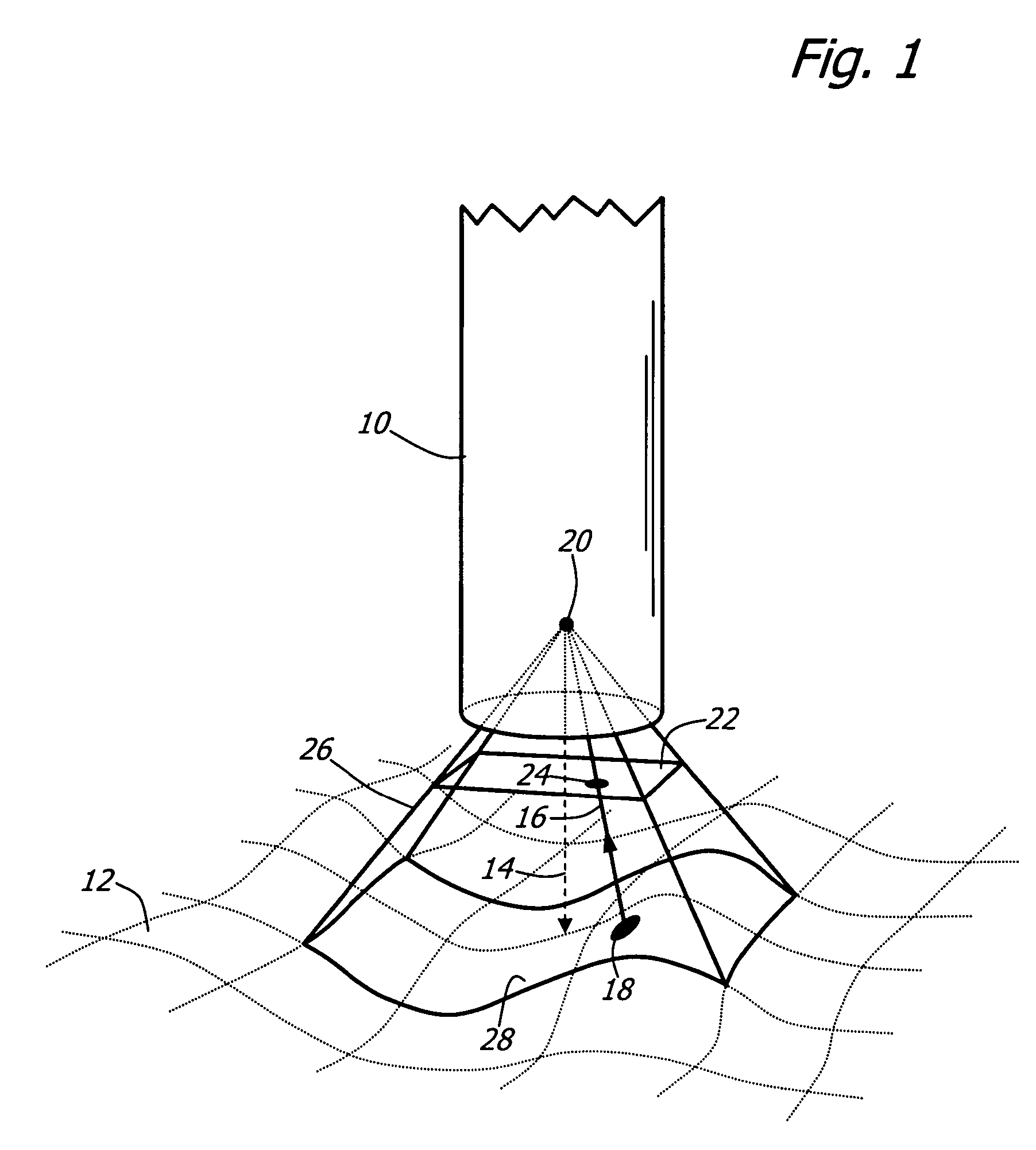
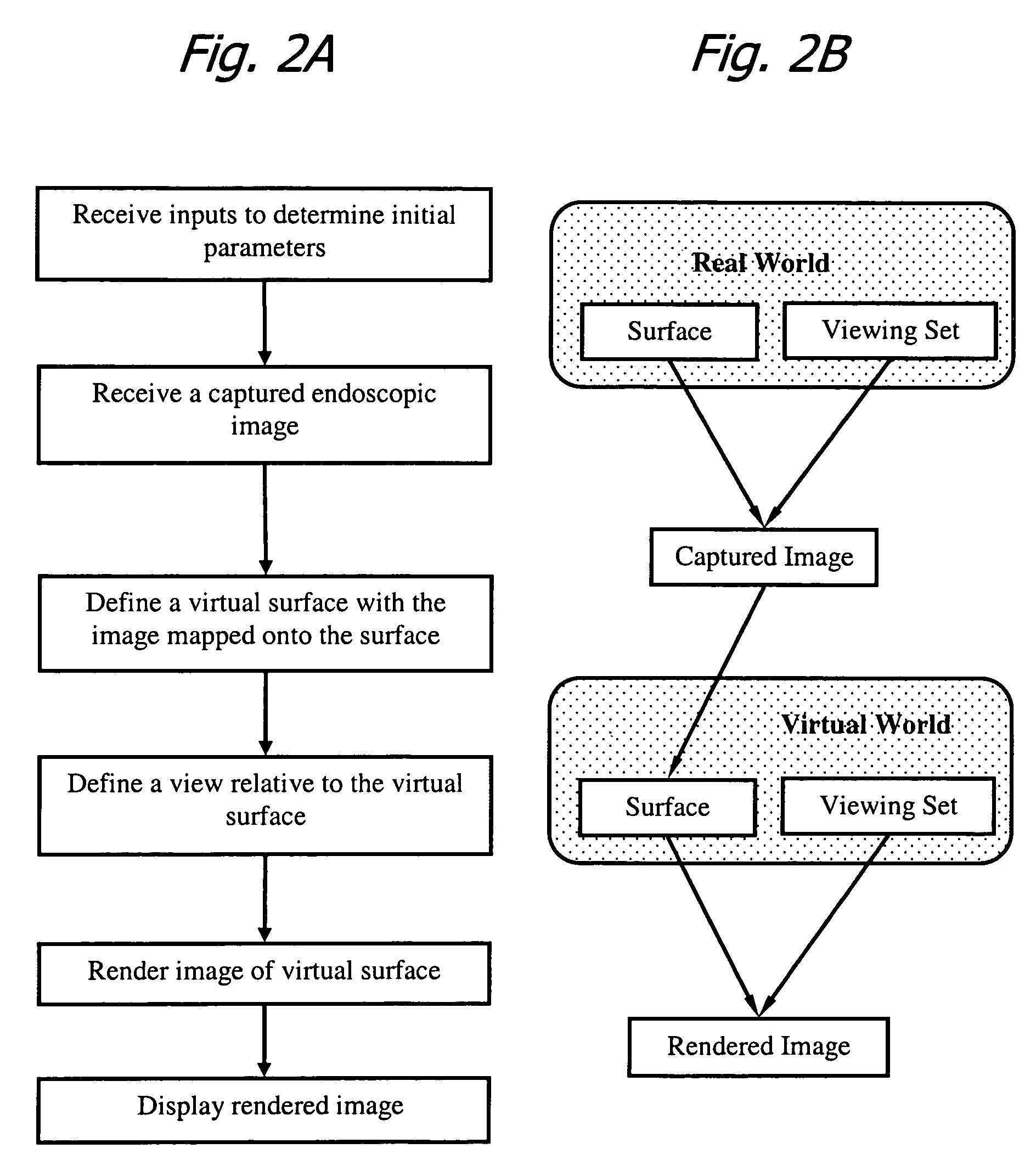
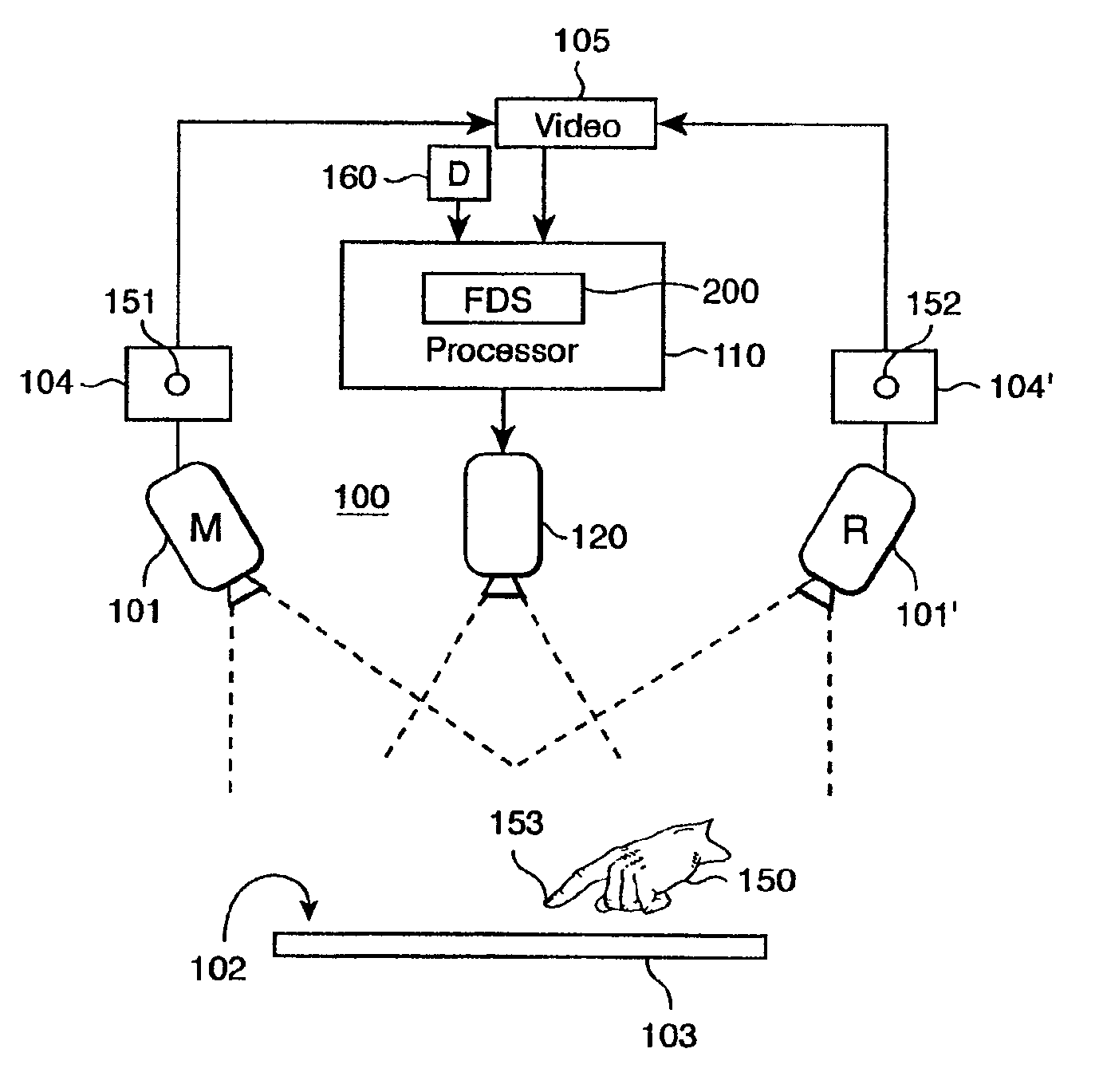
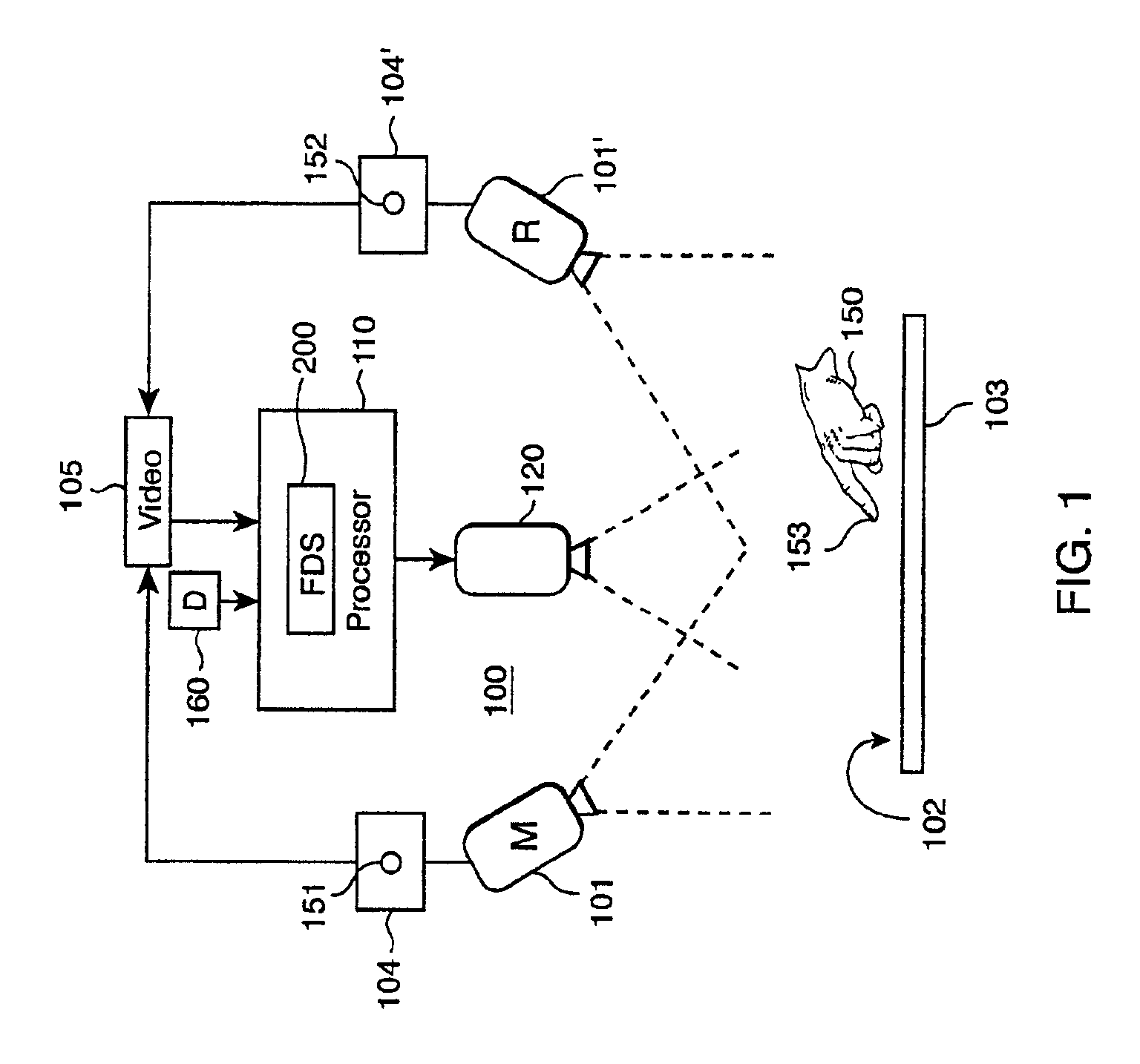
Method and apparatus for displaying endoscopic images
Owner:KARL STORZ IMAGING INC
Computer vision depth segmentation using virtual surface
InactiveUS6911995B2Easy to identifyComplex structureImage enhancementTelevision system detailsParallaxReference image
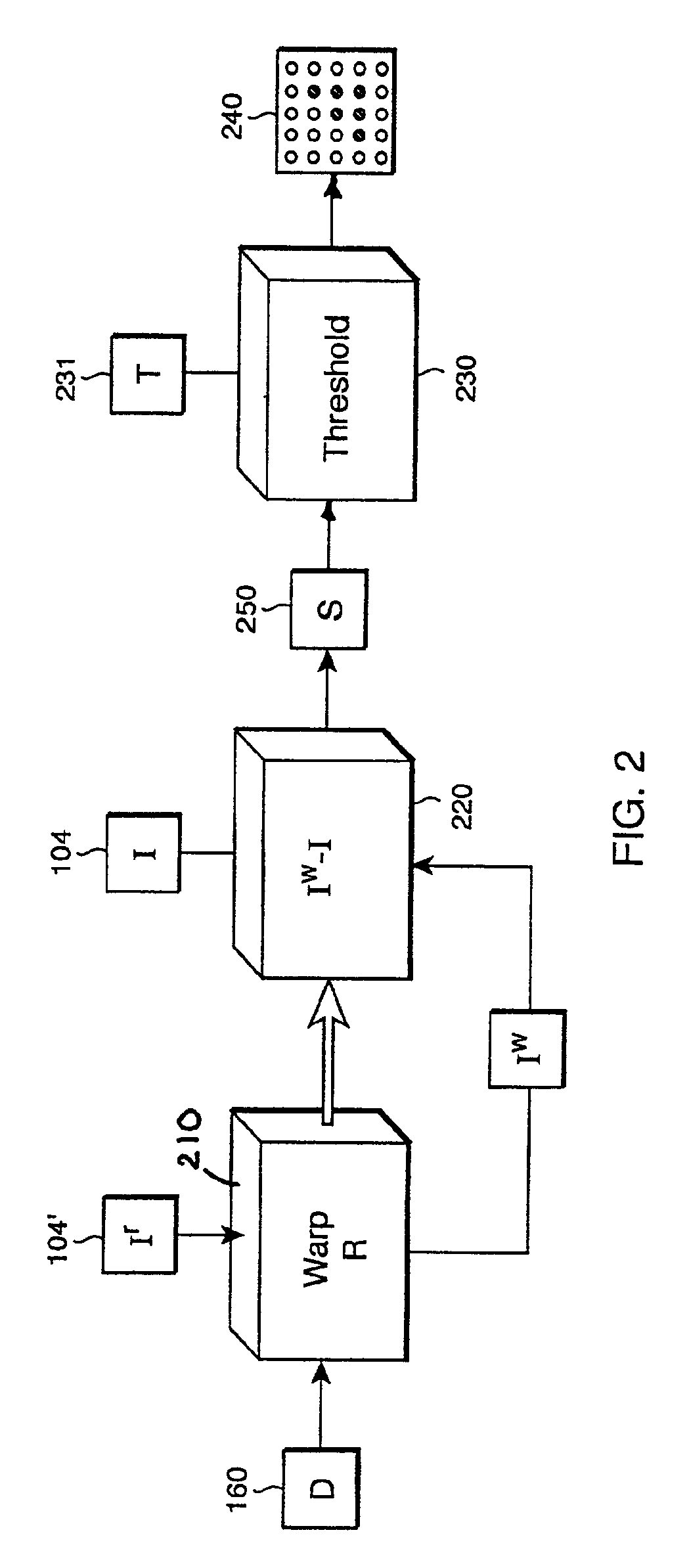
The location of an object in a physical scene is identified with a stereo camera. A virtual surface is identified in the physical scene, and an approximate disparity set is constructed for the virtual surface. A main and a reference image of the scene are acquired by the stereo camera. The reference image is warped according to the disparity set, and subtracted from the main image to determine a set of depth residual values. Pixels having a substantially non-zero residual are identified with a surface of the object not coincident with the virtual surface.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method for texturizing virtual three-dimensional objects
ActiveUS8705843B2Extensive automationImprove competitivenessCharacter and pattern recognition3D-image renderingFeature vectorFeature set
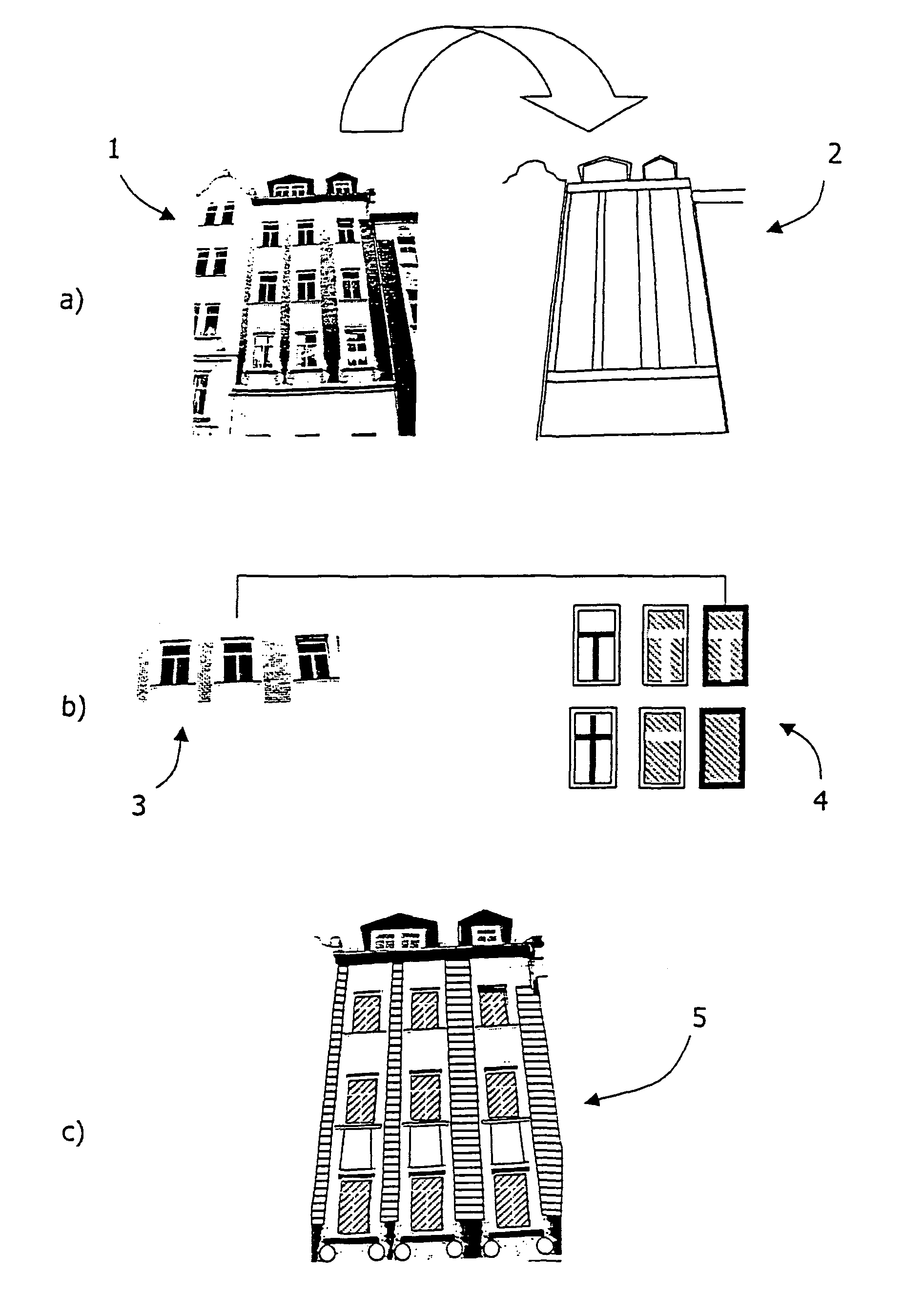
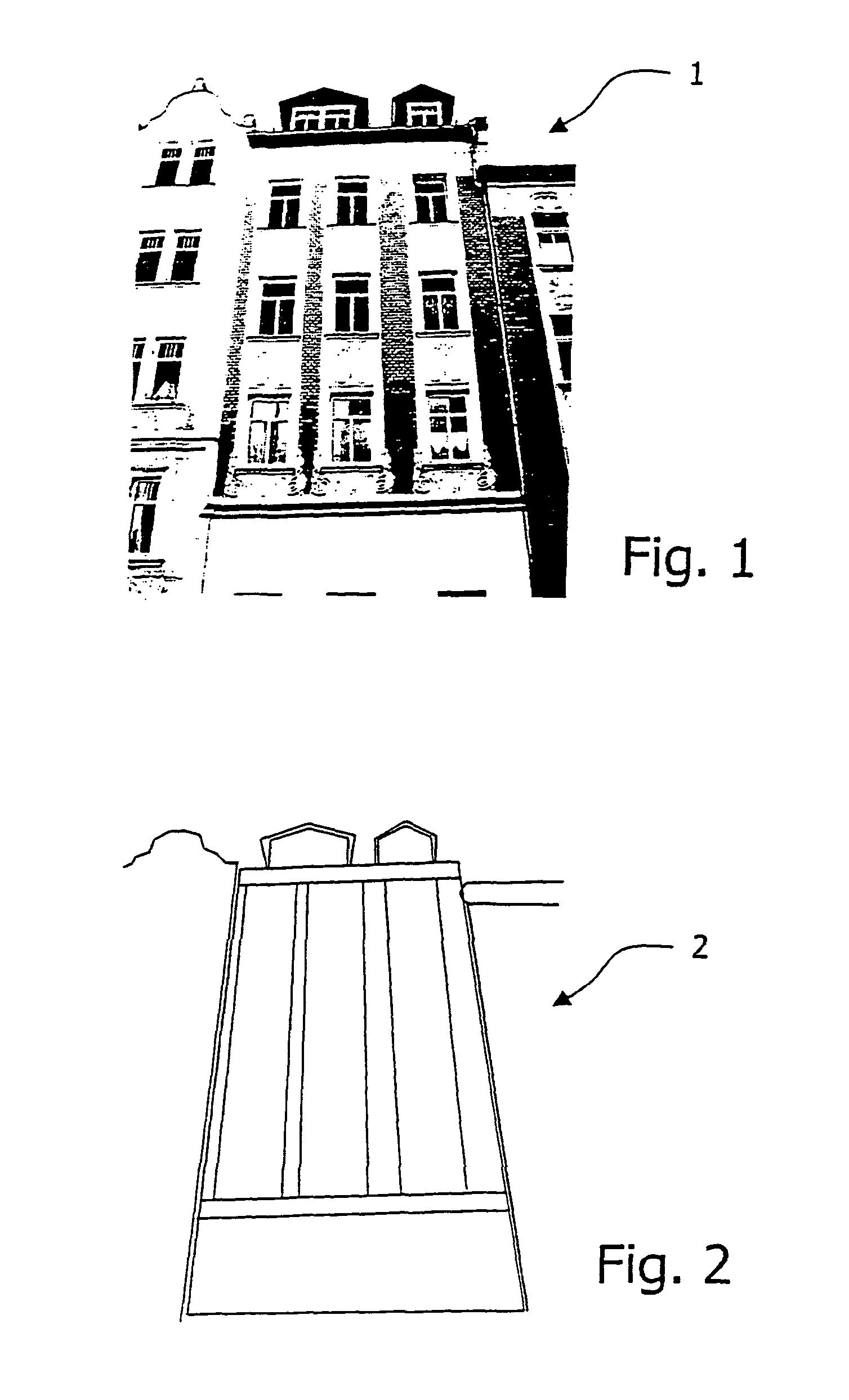
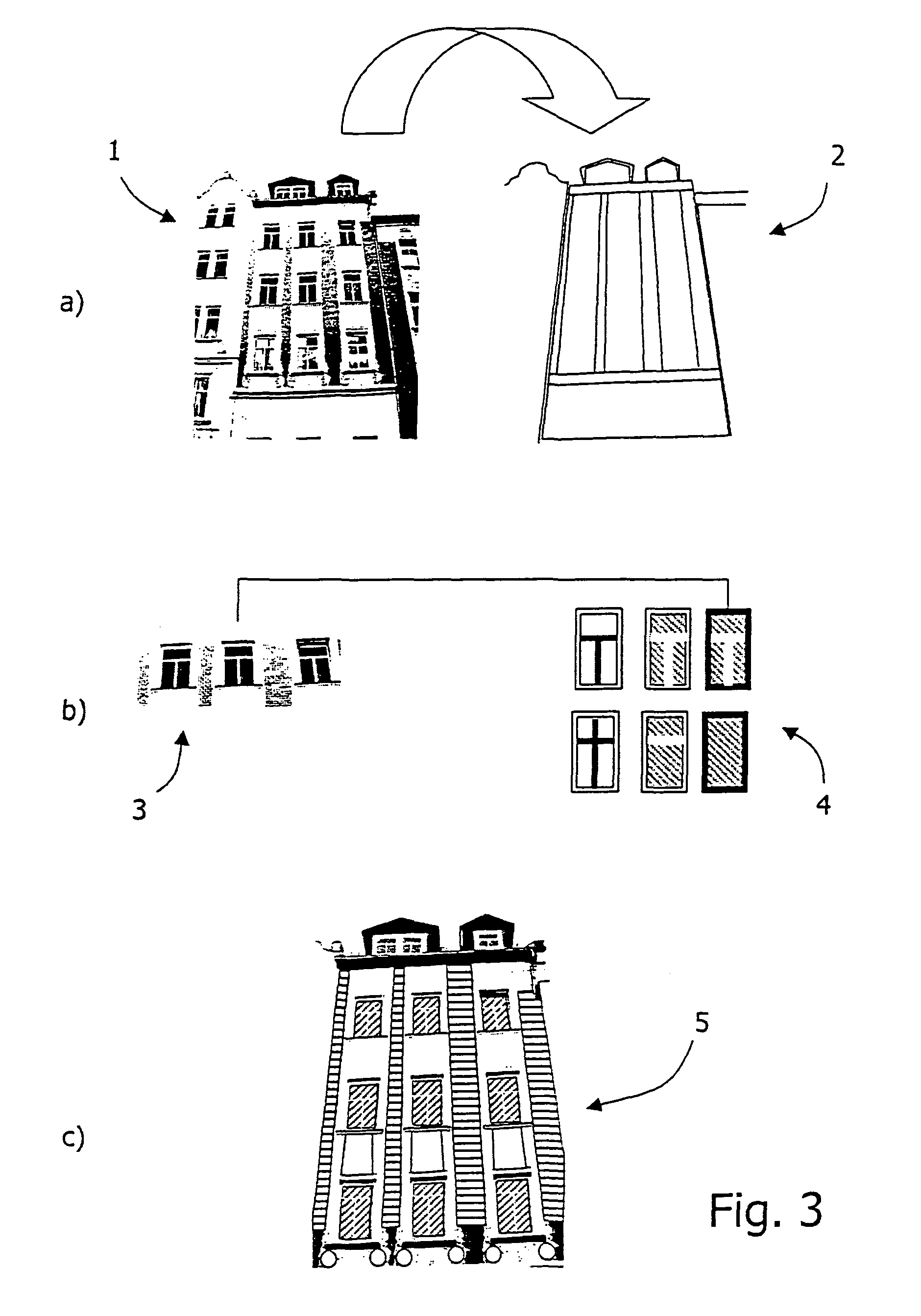
The invention relates to a method for texturizing virtual three-dimensional objects, particularly virtual three-dimensional building objects and city models with a photographic image (1) of a real object, particularly of a picture of a façade. The method is characterized by the following steps: Projecting the photographic image (1) onto a virtual surface (2) of the virtual three-dimensional object to produce a raw texture; localizing a raw texture element (3) in the raw texture by using a classification method; computer-compatible description of the localized raw texture element by a formal feature set for the raw texture element, particularly a feature vector; comparing the formal feature set of the raw texture element with each feature set of predefined library elements (4), and determining degrees of similarity between the raw texture element and each library element; replacing the localized raw texture element with at least one library element when a predefined degree of similarity is present, and reshaping the raw texture into a generalized texture (5) of the virtual object by replacing all raw texture elements with library elements.
Owner:GTA GEOINFORMATIK
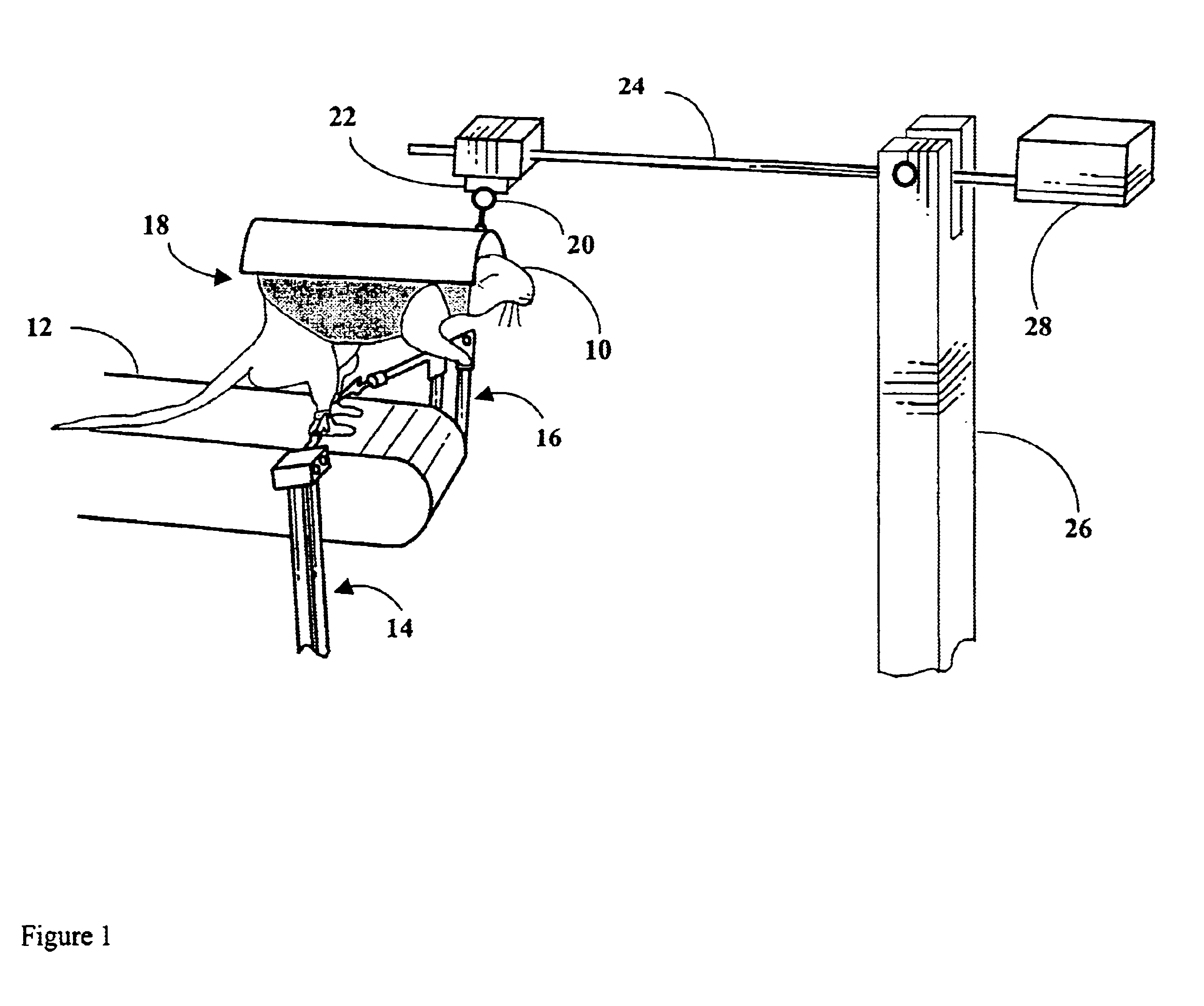
Robotic device for locomotor training
InactiveUS6880487B2Easy to testAssessing the efficacy of potential therapeutic interventionsChiropractic devicesWalking aidsRobotic systemsRobotic arm
A robotic system and method for locomotion assessment and training of a mammal, exemplified by a rodent. A neurologically impaired animal is suspended over a moving surface in a harness, and the animal's hindlimbs are connected to robotic arms that apply force to the hindlimbs or measure limb movement characteristics. The moving surface can be a physical or virtual surface. A single robotic mechanism comprising two robotic arms can simultaneously apply force, measure limb movement, and provide a virtual surface. Manual or automatic adjustment of load support allows the mammal to step at varying body weight loads.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Liquid droplet ejecting apparatus
The liquid droplet ejecting apparatus includes an ejecting head having a plurality of nozzles for ejecting liquid droplets and a plurality of liquid droplet ejecting devices arranged in correspondence with the plurality of nozzles, respectively, and driven with modulation in response to signals, a detection unit for detecting a condition of a virtual surface opposed to the ejecting head or an angle detection unit for detecting an angle made by a direction, in which liquid droplets are ejected from at least a part of the plurality of nozzles of the ejecting head, and a preset reference direction, and a unit for prohibiting liquid droplet ejection from at least a part of the plurality of nozzles of the ejecting head depending on a result of detection by the detection unit or an angle detected by the angle detection unit.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP
Dynamic virtual articulator
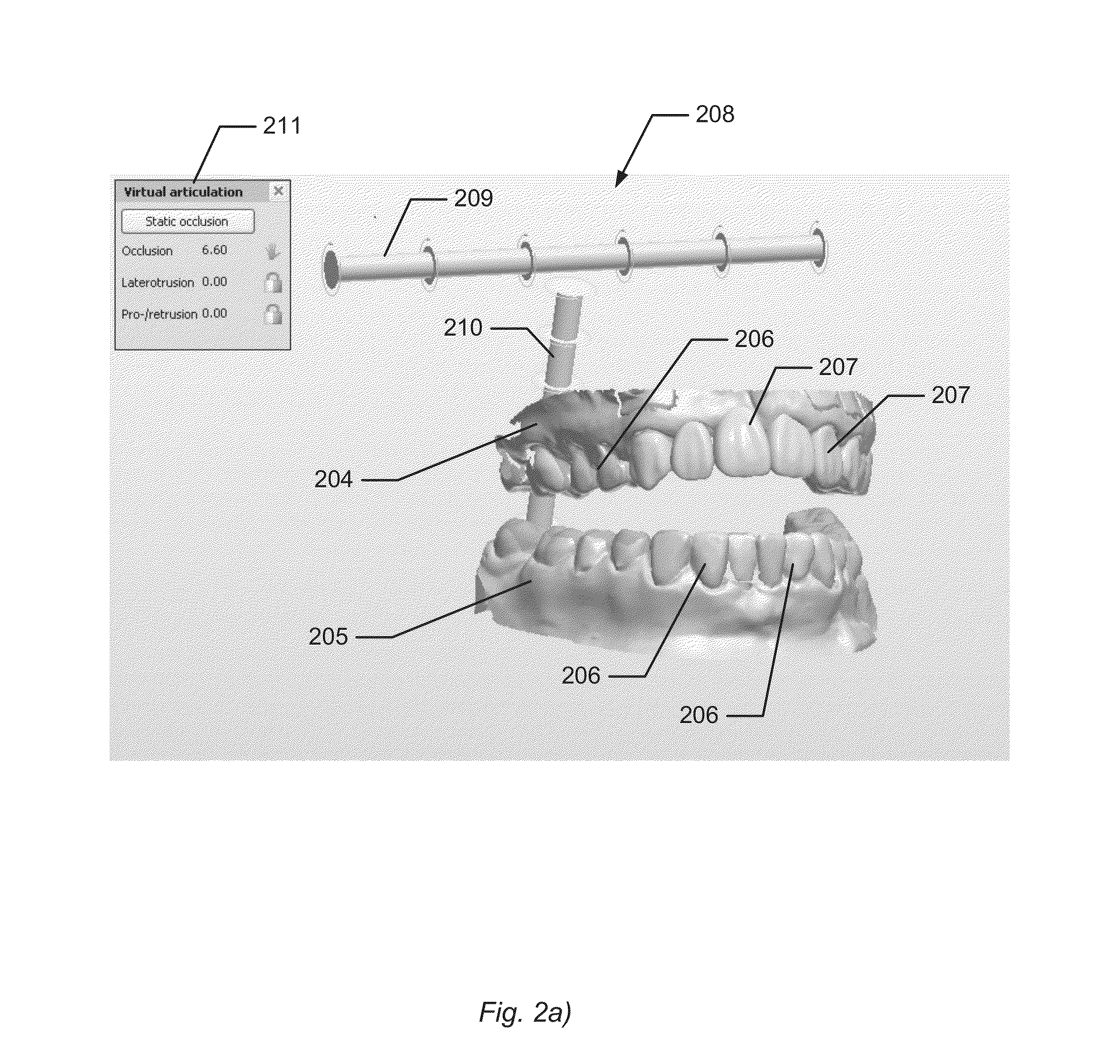
InactiveUS20130066598A1Providing distanceFunction is testedImpression capsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesComputer Aided DesignDental Articulators
Disclosed is a computer-implemented method of using a dynamic virtual articulator for simulating occlusion of teeth, when performing computer-aided designing of one or more dental restorations for a patient, where the method comprises the steps of:providing the virtual articulator comprising a virtual three-dimensional model of the upper jaw and a virtual three-dimensional model of the lower jaw resembling the upper jaw and lower jaw, respectively, of the patient's mouth;providing movement of the virtual upper jaw and the virtual lower jaw relative to each other for simulating dynamic occlusion, whereby collisions between teeth in the virtual upper and virtual lower jaw occur;wherein the method further comprises:providing that the teeth in the virtual upper jaw and virtual lower jaw are blocked from penetrating each other's virtual surfaces in the collisions.
Owner:3SHAPE AS
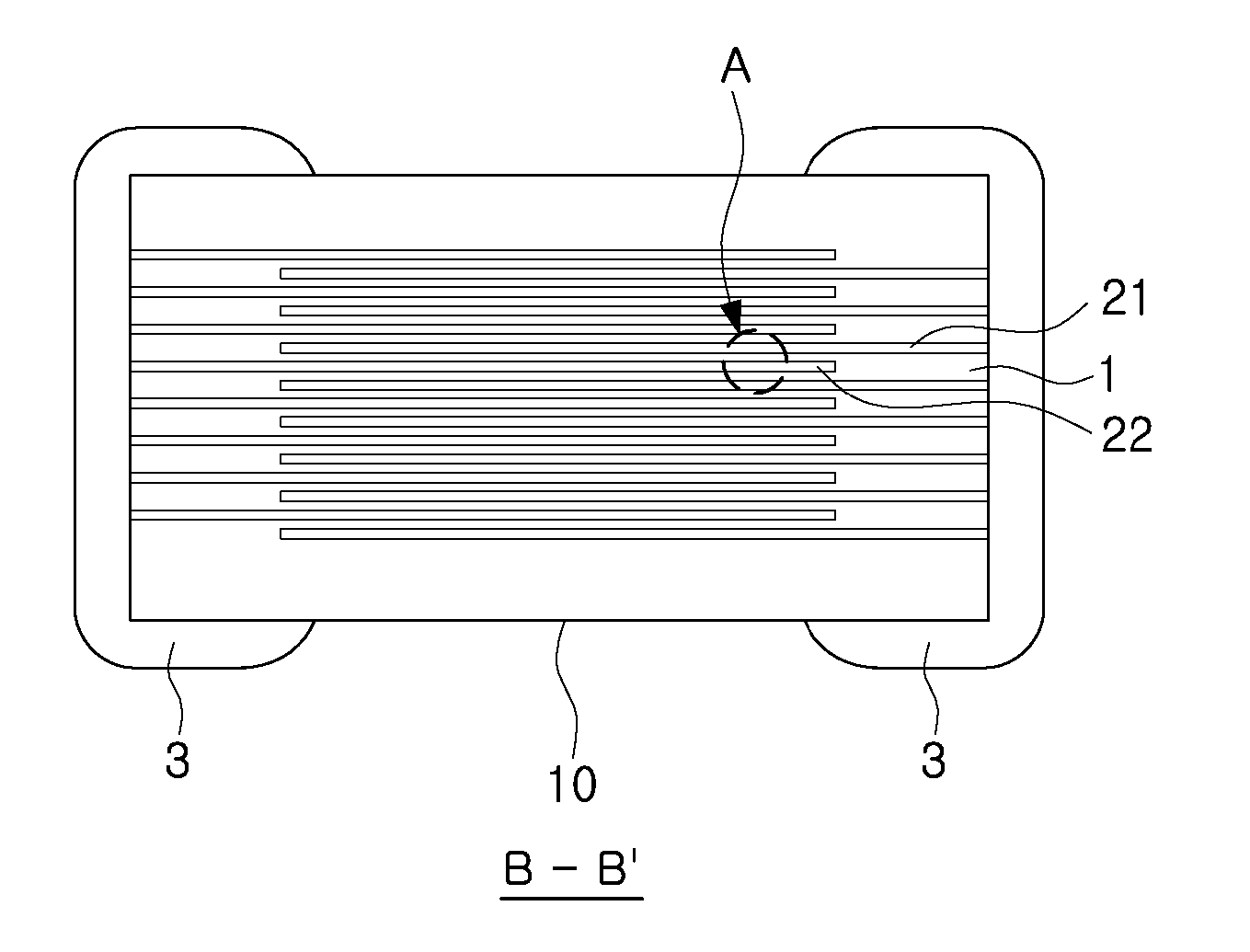
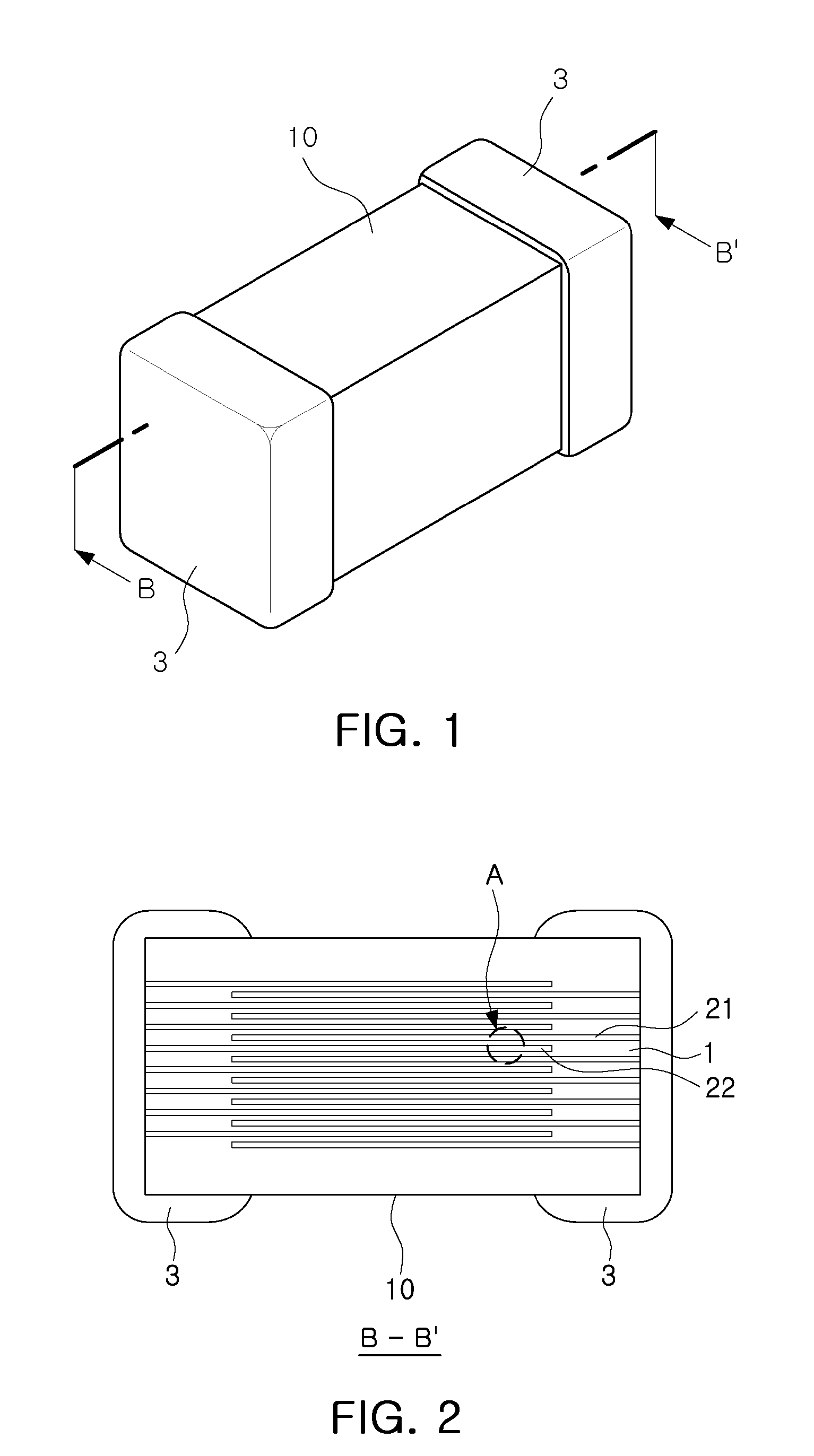
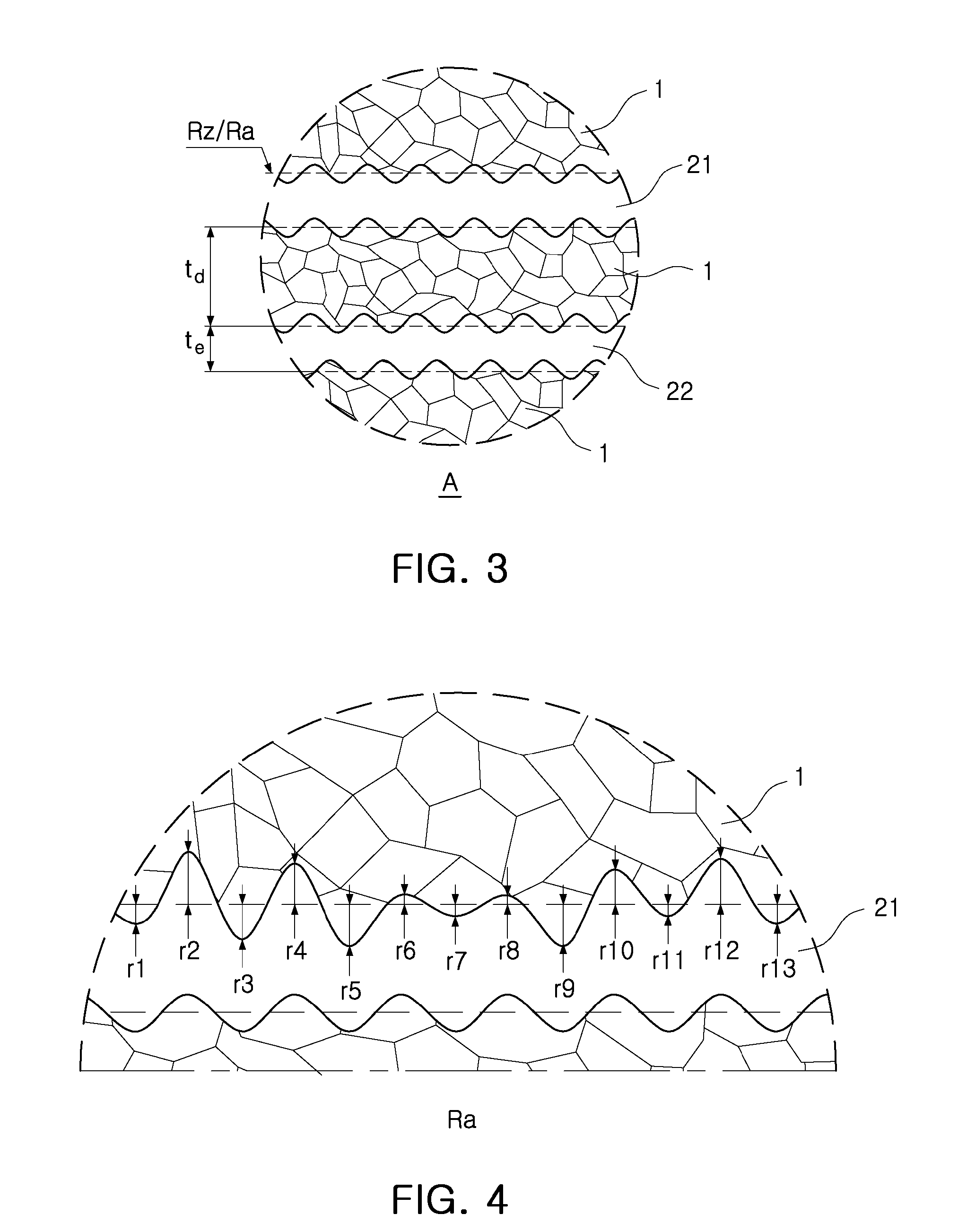
Multilayer ceramic electronic component and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS20130063862A1Improve adhesion strengthLamination ancillary operationsFixed capacitor electrodesSurface roughnessElectronic component
There is provided a multilayer ceramic electronic component, including: a ceramic main body including a dielectric layer; and inner electrodes disposed to face each other within the ceramic main body, with the dielectric layer interposed therebetween, wherein, when an average thickness of the dielectric layer is td and an average thickness of the inner electrodes is te, 0.1 μm≦te≦0.5 μm and (td+te) / te≦2.5 are satisfied, and when an average surface roughness on a virtual surface roughness center line of the inner electrode is Ra and an average roughness of ten points of the inner electrode is Rz, 5 nm≦Ra≦30 nm, 150 nm≦Rz≦td / 2, and 8≦Rz / Ra≦20 are satisfied. The multilayer ceramic electronic component has excellent reliability by improving adhesion strength between the dielectric layer and the inner electrodes and withstand voltage characteristics.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
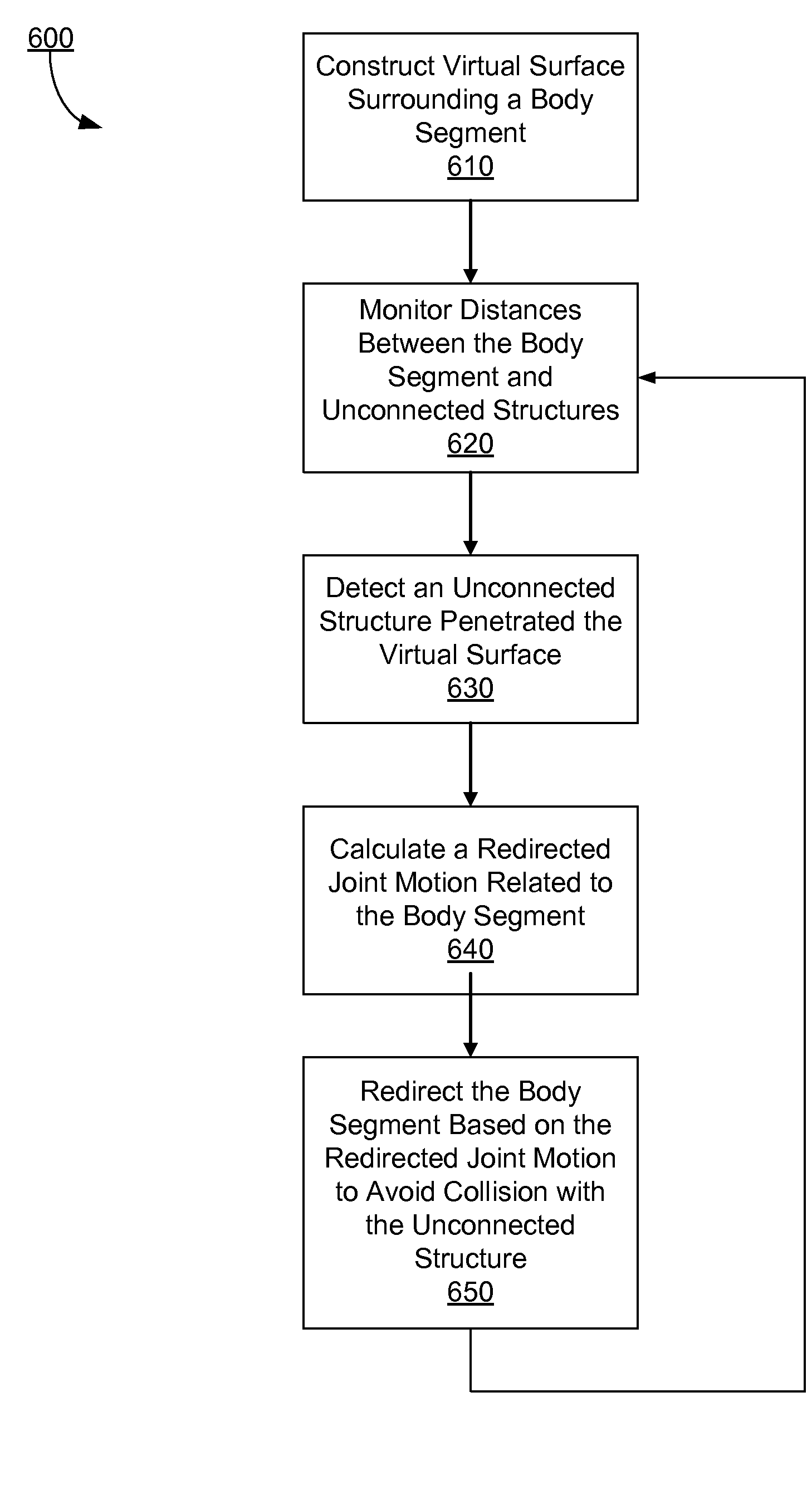
Real-time self collision and obstacle avoidance
ActiveUS20090074252A1Avoid collisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorRead-only memoriesEngineeringObstacle avoidance
A system, method, and computer program product for avoiding collision of a body segment with unconnected structures in an articulated system are described. A virtual surface is constructed surrounding an actual surface of the body segment. Distances between the body segment and unconnected structures are monitored. Responding to an unconnected structure penetrating the virtual surface, a redirected joint motion that prevents the unconnected structure from penetrating deeper into the virtual surface is determined. The body segment is redirected based on the redirected joint motion to avoid colliding with the unconnected structure.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Panning Using Virtual Surfaces
ActiveUS20090256840A1Translation stabilizationReduce exercise3D-image renderingVirtual cameraThree dimensional model
The present invention relates to panning a virtual camera in a three dimensional environment. In an embodiment of the present invention, a computer-implemented method pans a virtual camera in a three dimensional environment. In the method embodiment, a first point is determined on a three dimensional model in the three dimensional environment. According to the first point, the three dimensional model, and a position of a virtual camera in the three dimensional environment, a virtual surface is determined. A second point is determined on the virtual surface. Finally, a location of the three dimensional model is changed according to the first point and the second point.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Electronic device with digital reverberator and method
ActiveUS20130202125A1Easy to useImprove realismGain controlSound producing devicesAbsorption filterDigital surface
Electronic devices having digital reverberators are disclosed, together with a method of reproducing sound for a user with the digital reverberator. The digital reverberator uses digital surface absorption filters positioned in the reverberator to simulate absorption of energy as digital audio data samples are reflected from virtual surfaces. The position of the digital surface absorption filters enables known frequency-dependent surface absorption characteristics of real materials to be directly implemented using the filter coefficients of each digital surface absorption filter. This enables virtual acoustic spaces to be designed quickly without the need for the digital reverberator to be manually tuned for each space.
Owner:DE SENA ENZO +2
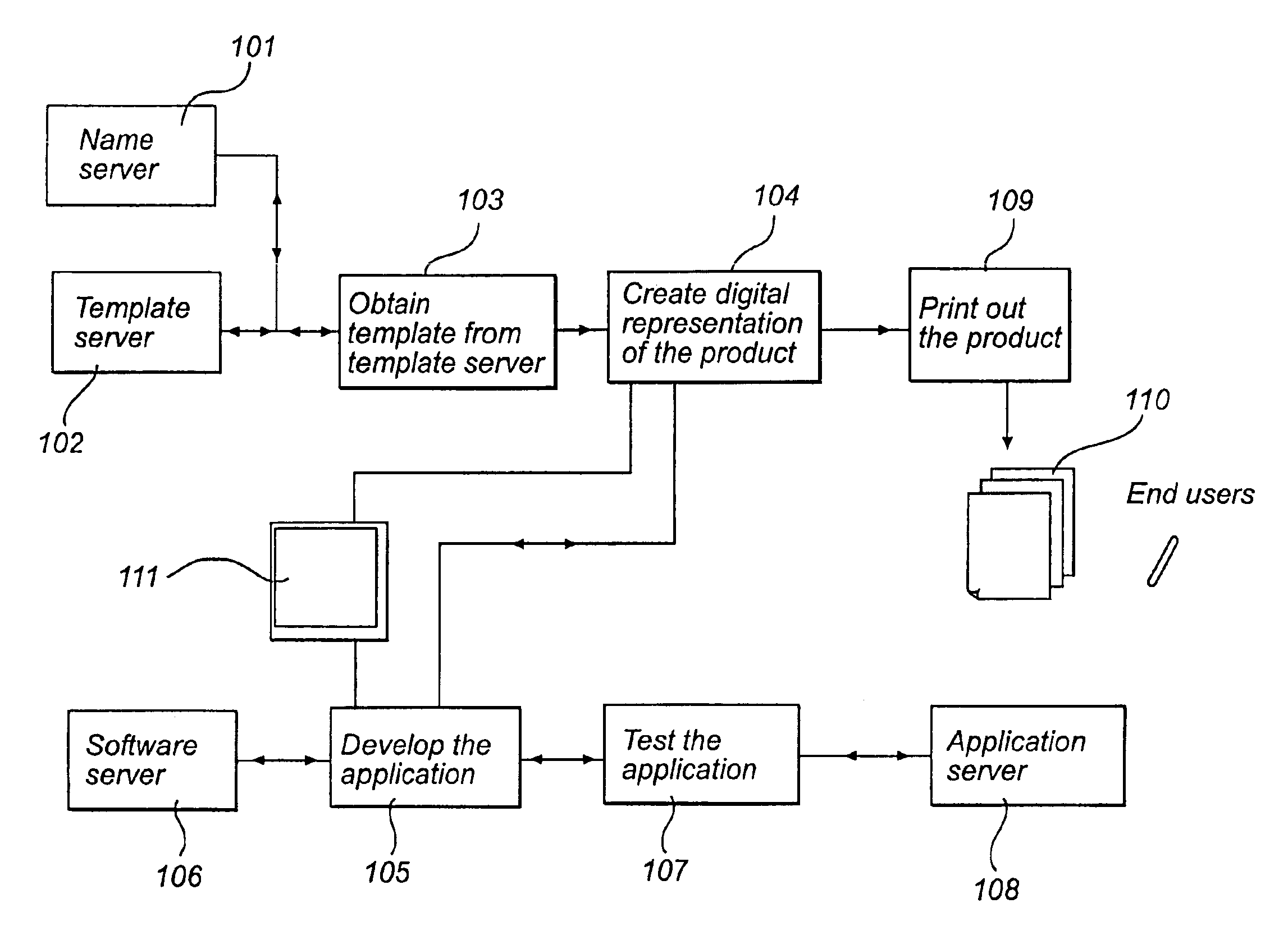
Method for making a product
InactiveUS6958747B2Made simpleEasy to testTransmission systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Biological activation
A method and a computer program are described for developing a product (110), and services associated with the product, which product has at least one activation area (308) which is provided with a position code (403) that codes at least one position on an imaginary surface (601), which position causes a device (710) that detects the position code (403) to initiate an operation that utilizes information recorded by the device (710). A digital representation of at least part of the product comprising image points is produced, each image point in the digital representation of the activation area (308) corresponding to a position the imaginary surface (601). A digital template that can be used for making the digital representation on the product is also described
Owner:ANOTO AB
Systems and methods for capturing and recreating the feel of surfaces
ActiveUS20120026180A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsSpecial data processing applicationsComputer graphics (images)Texture model
Systems and methods for capturing and recreating the feel of a surface are disclosed. A method for capturing a feel of a surface comprises contacting the surface with a handheld tool, recording data measured by the tool, and generating a texture model of the surface based on the recorded data. A method for recreating a feel of a surface comprises contacting a virtual surface with a handheld tool, determining an estimated contact force based on the data measured by the tool, generating a vibration waveform from a texture model based on the data measured by the tool; and actuating at least one actuator of the tool according to the vibration waveform. A system for capturing and recreating a feel of a surface comprises a handheld tool, a storage device, and a processor.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method for reproducing texture force touch based on shape-from-shading technology
InactiveCN101615072AImprove realismStrong real-timeInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingComputer graphics (images)Robot control
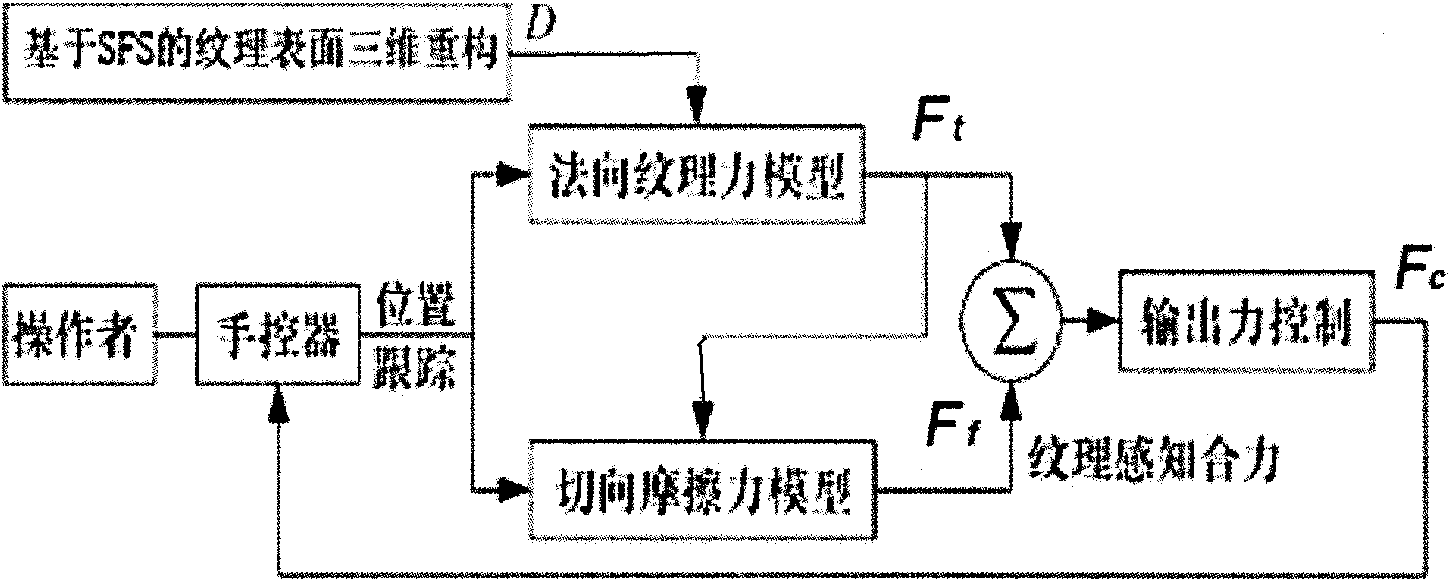
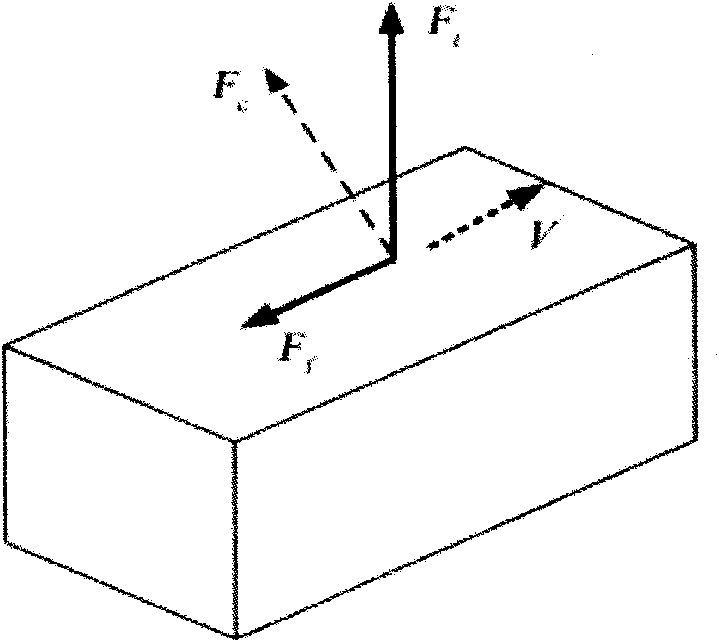
The invention aims at the problem how to reproduce the force touch of image textures and provides a method for reproducing the texture force touch based on a shape-from-shading technology from grey scales of an image. The method is characterized by processing the grey scales of a texture image; extracting the micro three-dimensional contour information of the true textures from the grey scale information of the image to be drawn into a virtual surface; rendering the textures of the virtual surface by a force touch model; and outputting calculated force from a general manual controller to an operator. The invention has the advantages that the miniature contour of an object surface is needless to be measured by a special instrument, a special texture force touch expression device is needless to design, and the like and can be used in the fields for simulating virtual environments, controlling remotely-operated robots, browsing remote museums and online shops, simulating surgeries, and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU HONGBO MACHINERY MFG +1
Virtual coatings application system
InactiveUS7839417B2Improve realismEnhance three-dimensional natureProgramme controlLiquid surface applicatorsSimulationMotion tracking system
A virtual coatings application system has several features to enhance the realism of simulated spray painting. The system generally includes a display screen on which is defined a virtual surface (such as a truck door) that is intended to be virtually painted or coated by the user. Alternatively, the system includes a head-mounted display unit that displays a virtual spray painting environment in which the virtual surface is defined. The user operates an instrumented spray gun controller that outputs one or more signals representing data as to the status of the controls on the spray gun controller. The system also has a motion tracking system that tracks the position and orientation of the spray gun controller with respect to the virtual surface. Simulation software generates virtual spray pattern data in response to at least the data from the spray gun controller and the position and orientation data received from the tracking system. Virtual spray pattern images are displayed in real time on the virtual surface in accordance with the accumulation of virtual spray pattern data at each location on the virtual surface.
Owner:UNIV OF NORTHERN IOWA RES FOUND
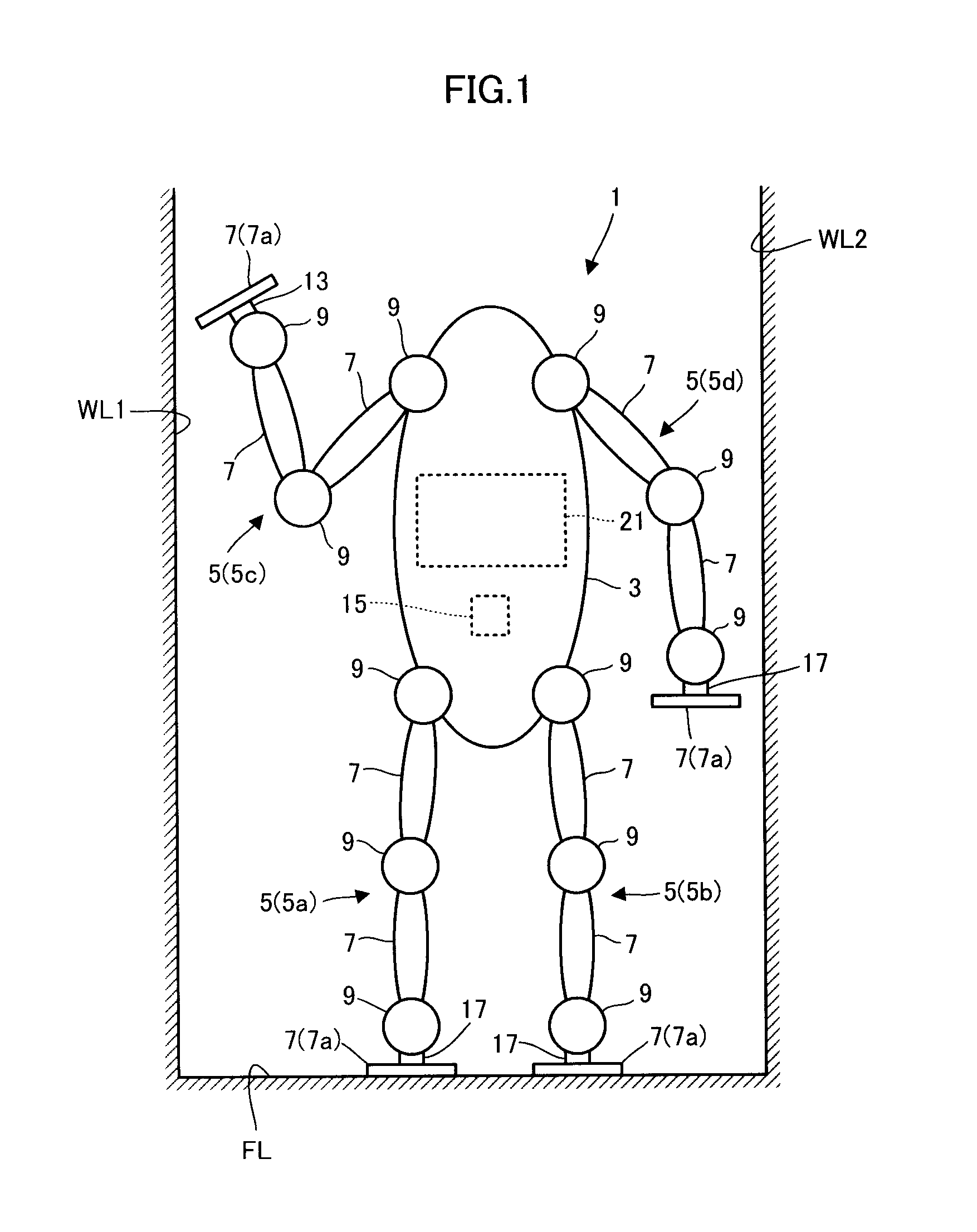
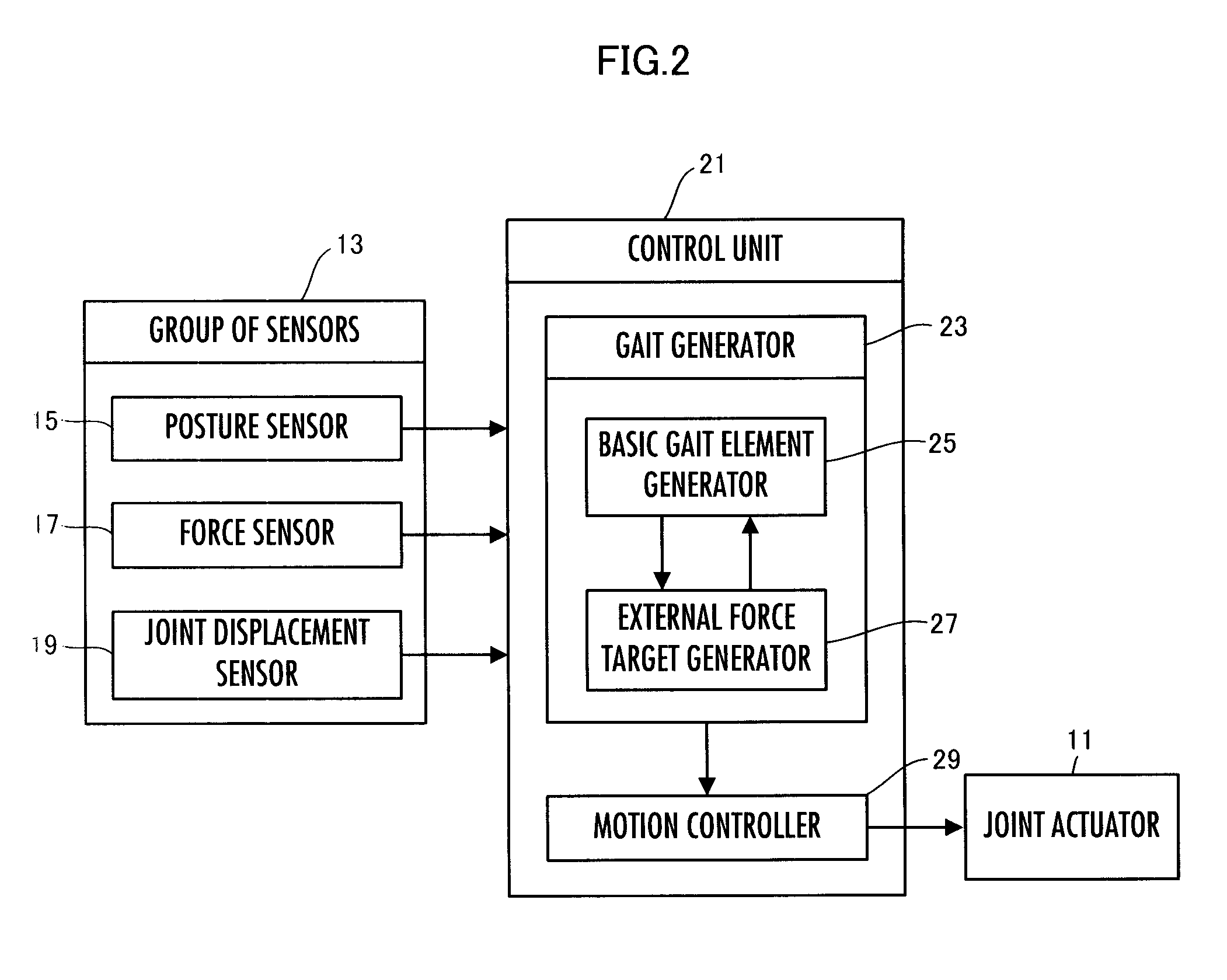
Gait generating device of legged mobile robot
ActiveUS8396593B2Efficiently and properly determiningComputer controlSimulator controlSimulationMobile robot
A gait generating device of a legged mobile robot uses virtual surfaces to approximate a plurality of surfaces to be contacted in an operating environment of a robot, and determines the provisional values of the required virtual surface translational forces to be applied from the virtual surfaces to the robot in order to implement a translational motion of a desired motion of the entire robot. Further, to implement a rotational motion of the desired motion of the entire robot, the gait generating device determines moment compensation amounts to be combined with the provisional values of the required virtual surface translational forces and then determines the desired external forces to be applied from the surfaces to be contacted to the robot and the desired external force action points on the basis of the combinations of the provisional values of the required virtual surface translational forces and the moment compensation amounts.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
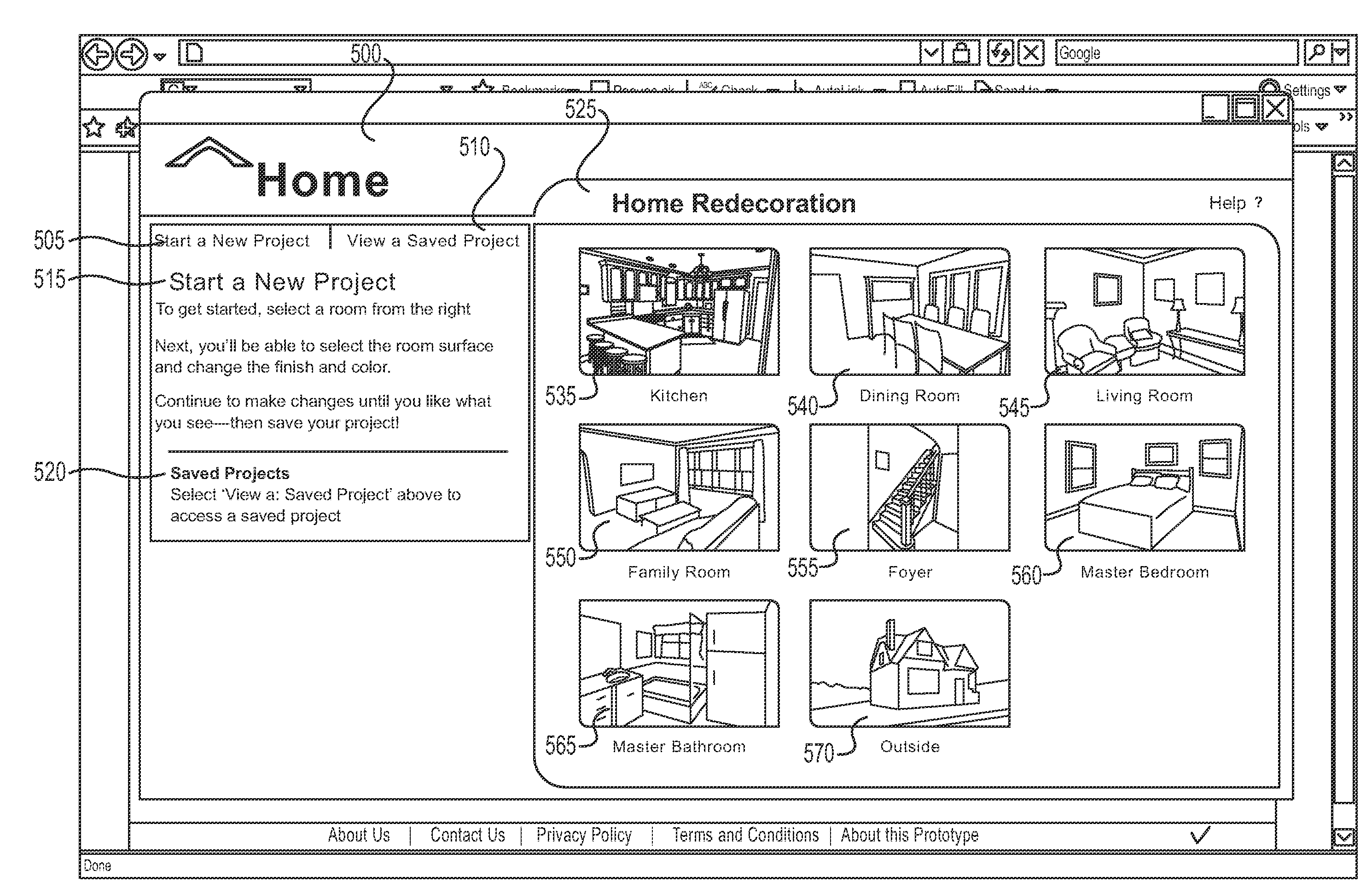
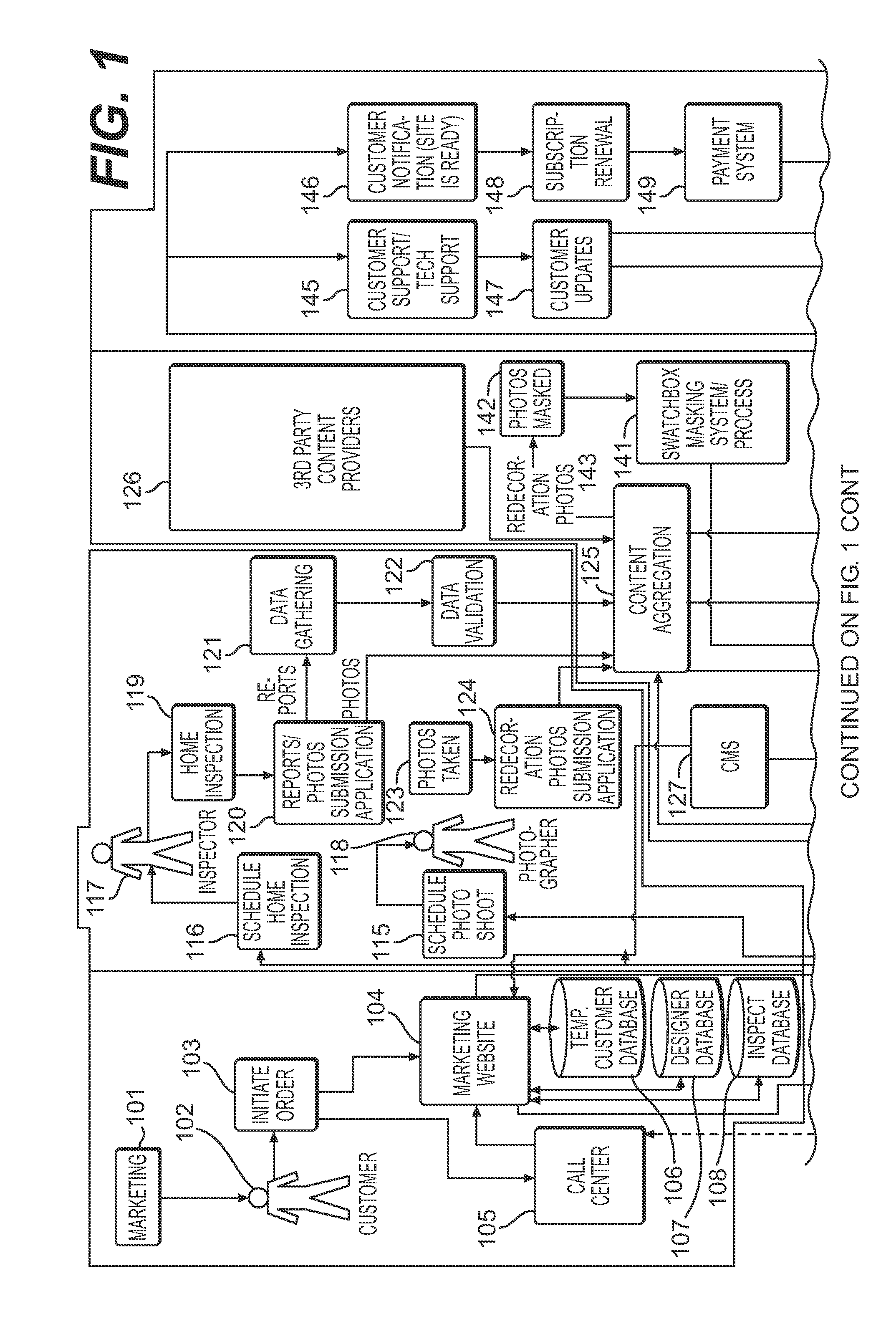
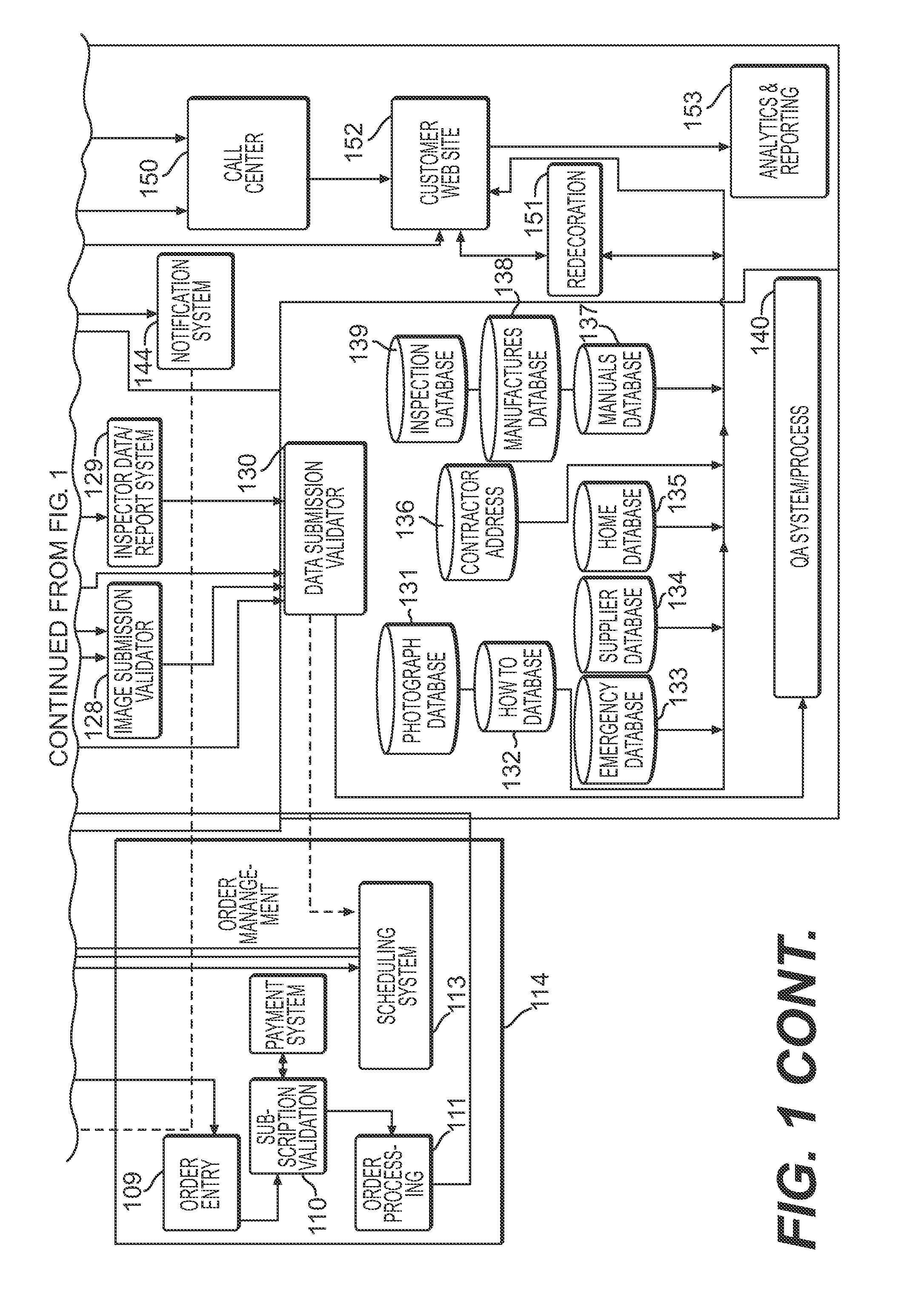
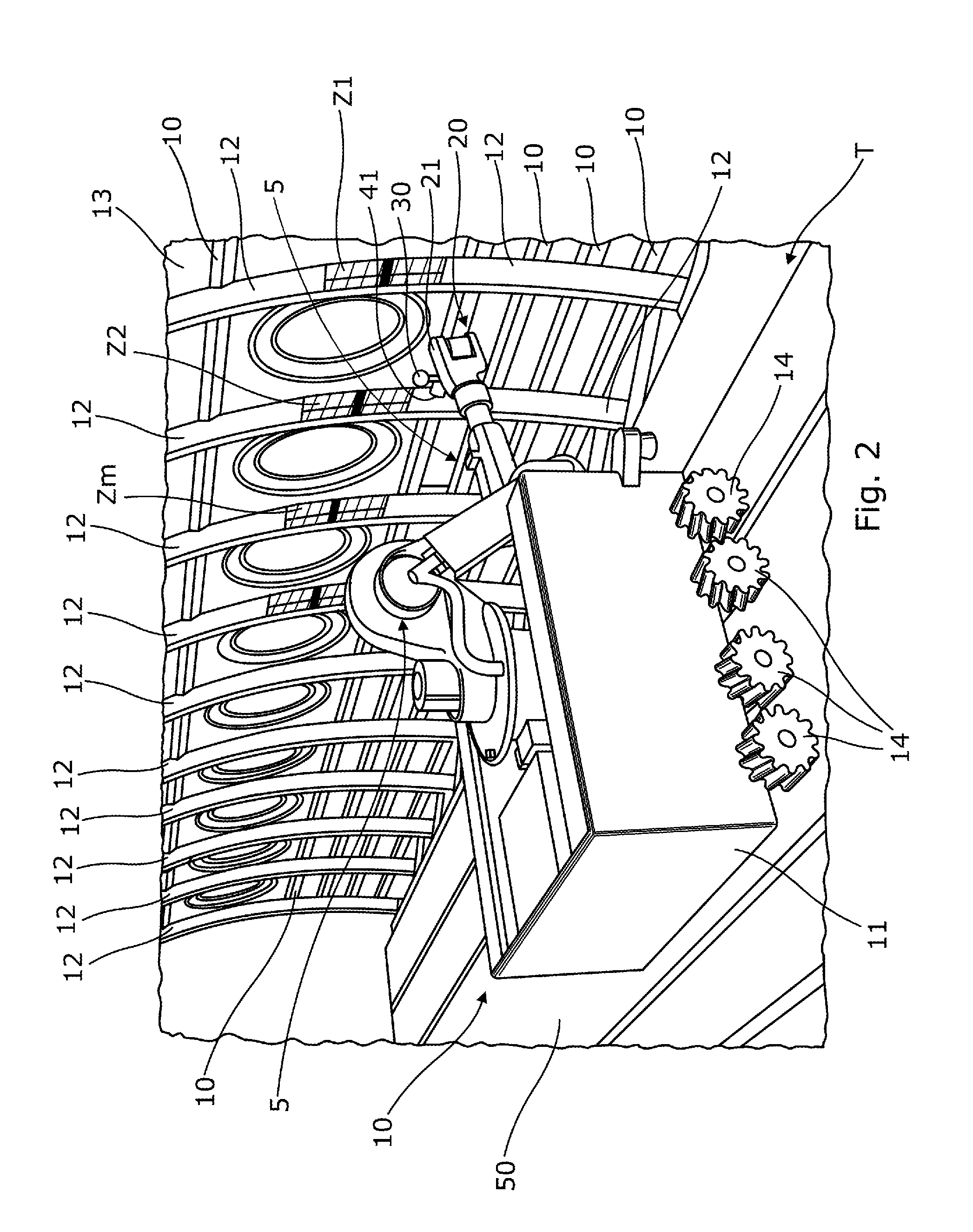
Home management, maintenance, repair, remodeling and redecoration system and method
Embodiments of the invention provide a home management system and method with a 360-degree virtual surface rendering application. Embodiments of the invention generate a listing of home improvement projects from the inspection report to be viewed through a user interface. Homeowners may manage, prioritize, rank, and educate themselves on each listed home improvement project. Embodiments of the invention may contain a 360-degree virtual surface rendering application allowing a homeowner to select different surface types for a room, and then view them on a re-rendered image of the room before purchasing the new surfaces.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO
Apparatus and methods for texture mapping
ActiveUS7095418B2Improved allocationImprove textureDrawing from basic elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsMapping techniques
Owner:3D SYST INC
Device and Method for Designing a Garment
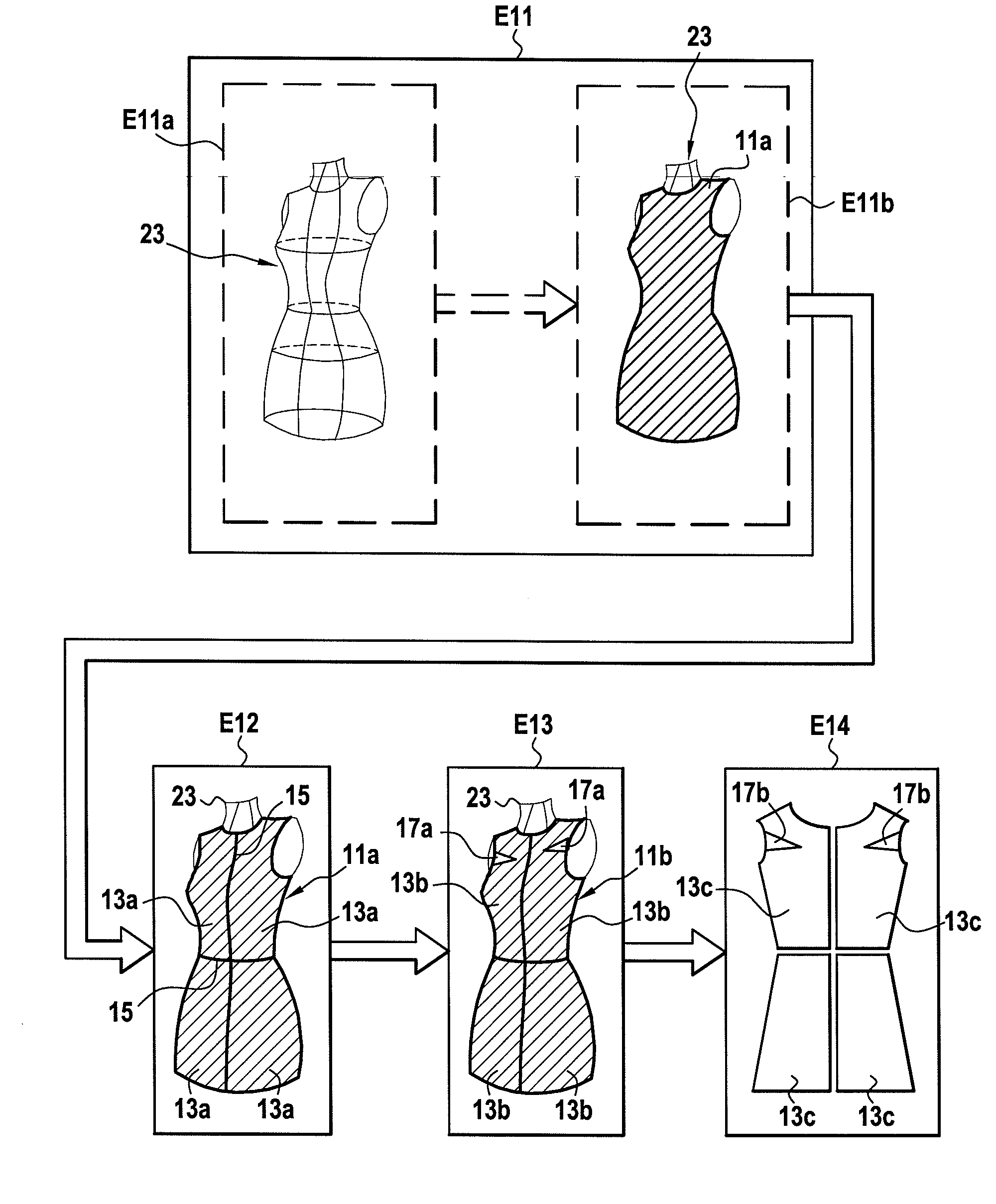
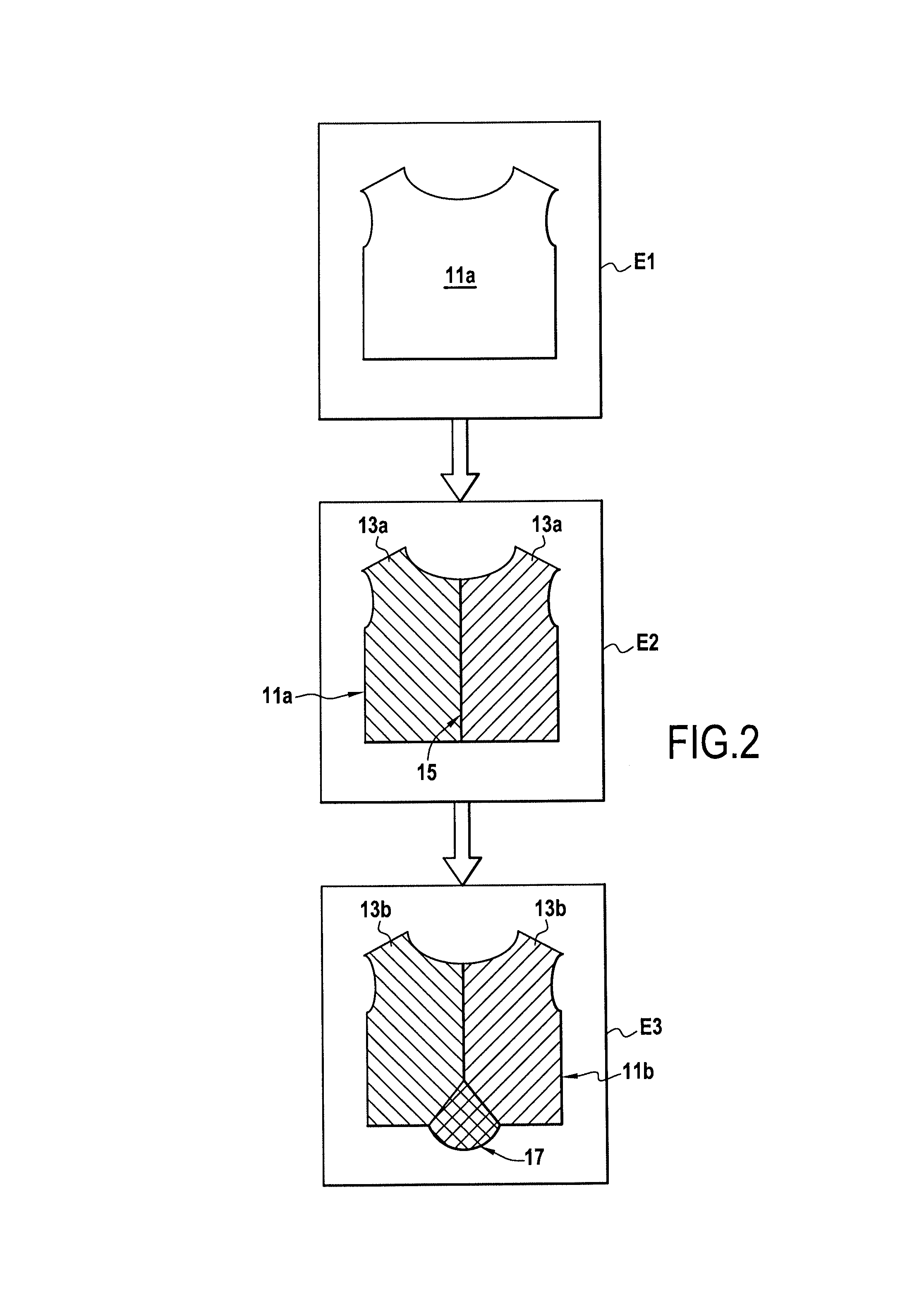
ActiveUS20090099683A1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer Aided DesignComputer graphics (images)
The invention relates to a system and a method for the computer-aided design of a garment occupying a virtual surface represented by data stored in a memory of a computer including the following steps:generating base patterns (11a) on said virtual surface (13a),adding at least one style effect (17, 17a) on at least one base pattern (11a) transforming said at least one base pattern into at least one stylised base pattern (13b), andforming a stylised virtual surface (11b).
Owner:LECTRA SA (FR)
Plate-like particle for cathode active material of a lithium secondary battery, and a lithium secondary battery
InactiveUS20100159333A1Increase battery capacityDeintercalation of lithium ions is facilitatedPositive electrodesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesPorosityLithium
By exposing the crystal plane (a plane other than the (003) plane: e.g., the (101) plane and (104) plane) through which lithium ions are favorably intercalated and deintercalated, more to an electrolyte, characteristics such as cell capacity is improved. The present invention relates a plate-like particle for a lithium secondary battery cathode active material. The particle has a layered rock salt structure. The (003) plane is oriented in a direction intersecting a particle plate surface. The porosity is 10% or less. The ratio of an observed surface area (β) determined from a measured value of a BET specific surface area to a virtual surface area (α) of the particle which is defined by the planar shape and thickness of the particle on the assumption that the plate surface is smooth, β / α is 3 or more and 10 or less
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Process and device for direct fabrication of a part on a structure
A process for direct fabrication of a part at a predetermined structural position. The process comprises: a) scanning, via a three-dimensional scanner, the structure in the region of the predetermined position; b) comparing a virtual surface mesh of the predetermined position with a real surface mesh of the predetermined position, the real surface mesh calculated based on data obtained from the scanning; c) determining the gaps between the two meshes; d) calculating the data for modeling an inserted part, the dimensions of which fill up the determined gaps, to obtain an inserted part model; e) merging of a virtual model of a part, linked with the predetermined position, with the inserted part model, to obtain a model adjusted to the geometry of the structure in the region of the predetermined position; f) fabricating, by material deposition, an adjusted part at the predetermined position based on the adjusted model.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Device and method for designing a garment
ActiveUS8249738B2Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer Aided DesignData storing
Owner:LECTRA SA (FR)
Method, system and product for information management
InactiveUS7002559B2Facilitate communicationInput/output for user-computer interactionTransmission systemsReal-time computingInformation management
A method, a system and a product for managing information uses of an absolute position-coding pattern formed of marks positioned on one or more products. The coordinates of the marks define an imaginary surface, which includes all marks which the absolute position-coding pattern has the capacity to code. The imaginary surface is divided into at least two regions, the coordinates of which can be separated from each other. The information is generated by passing a sensor device over the marks on the product and reading the absolute coordinates of the position of the sensor device. Reading of coordinates from the first region results in a information management function of the sensor device, such as a send function, and reading of coordinates from the second region forms message information.
Owner:ANOTO AB
Method for photographing panoramic picture
InactiveUS20090058991A1Easy to operateAccurate detectionTelevision system detailsImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Unit of time
A panoramic picture photographing method permits more accurate photographing of an image, particularly a panoramic image of a subject, without additional equipment, or separate devices and hardware. The method includes projecting an image, which is successively inputted in every predetermined unit of time, to an imaginary surface having a same focal distance in photographing each image constituting a panoramic picture to obtain a projected image; confirming movement of a corresponding photographing apparatus so that the projected image is compared with a previous image in real time by using a motion estimation technique, to which exposure correction has been applied; determining a photographing time point of each image by confirming the confirmed movement of the corresponding photographing apparatus according to a photographing direction has reached a predetermined critical value; and photographing each image at the photographing time point of each image according to a passive input or automatically.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com