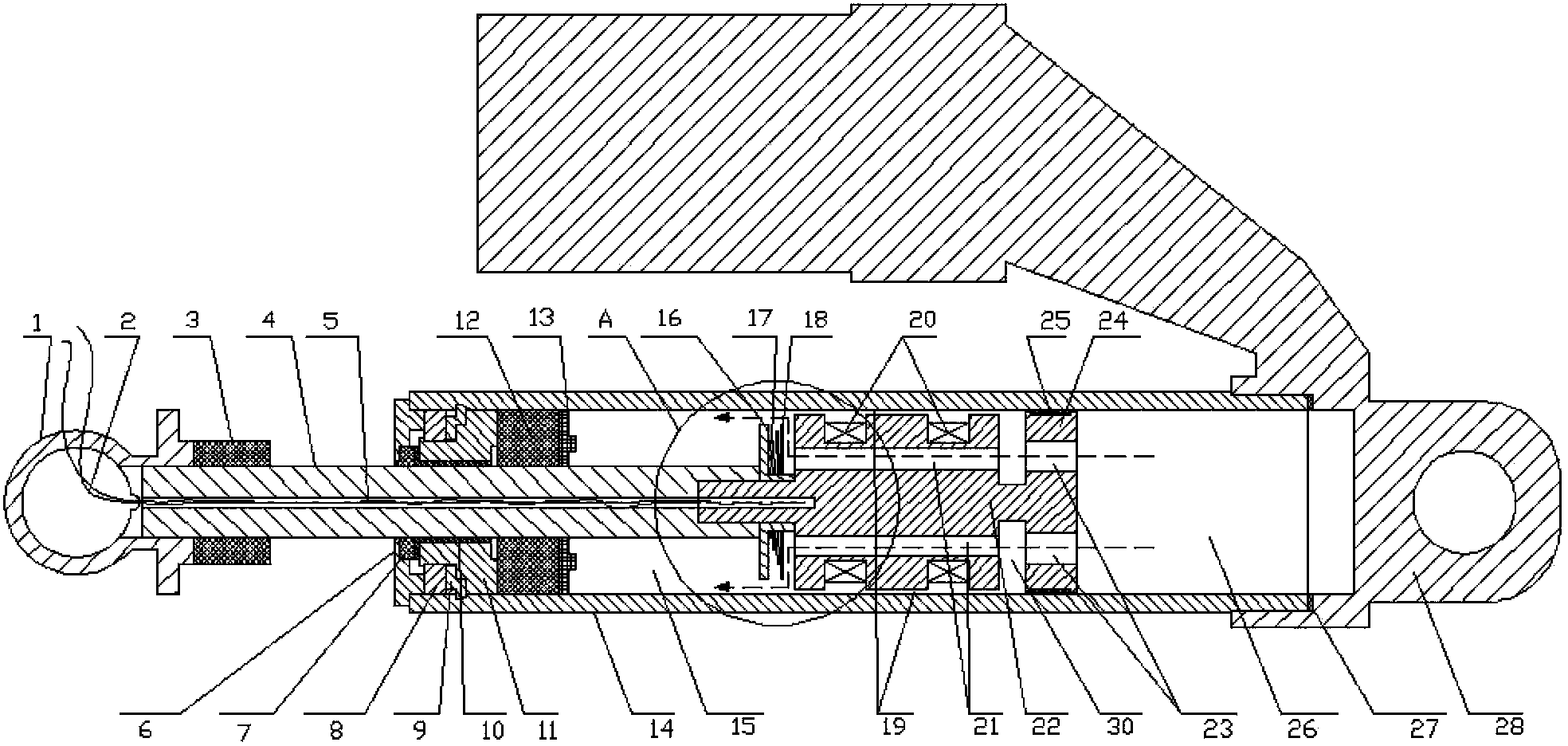
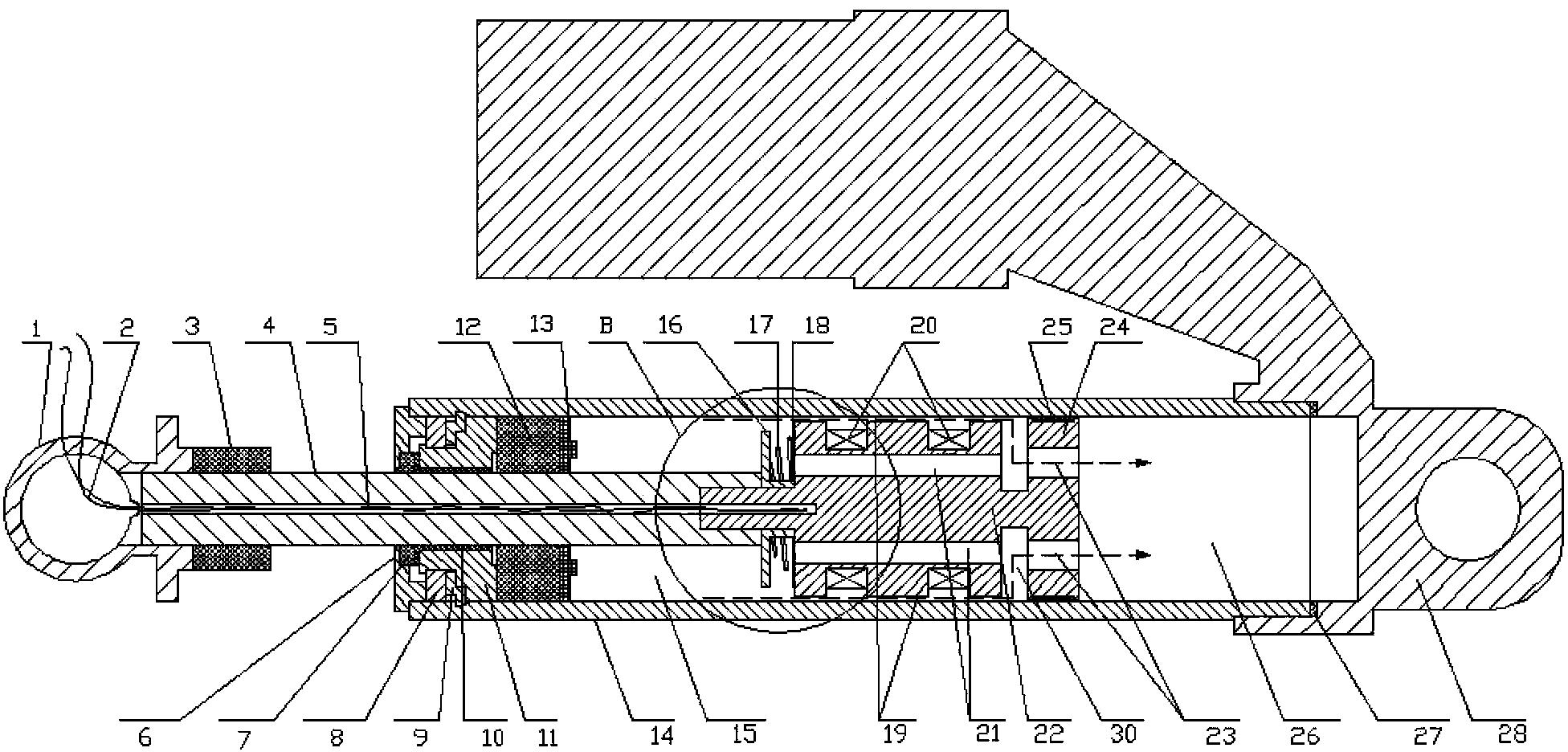
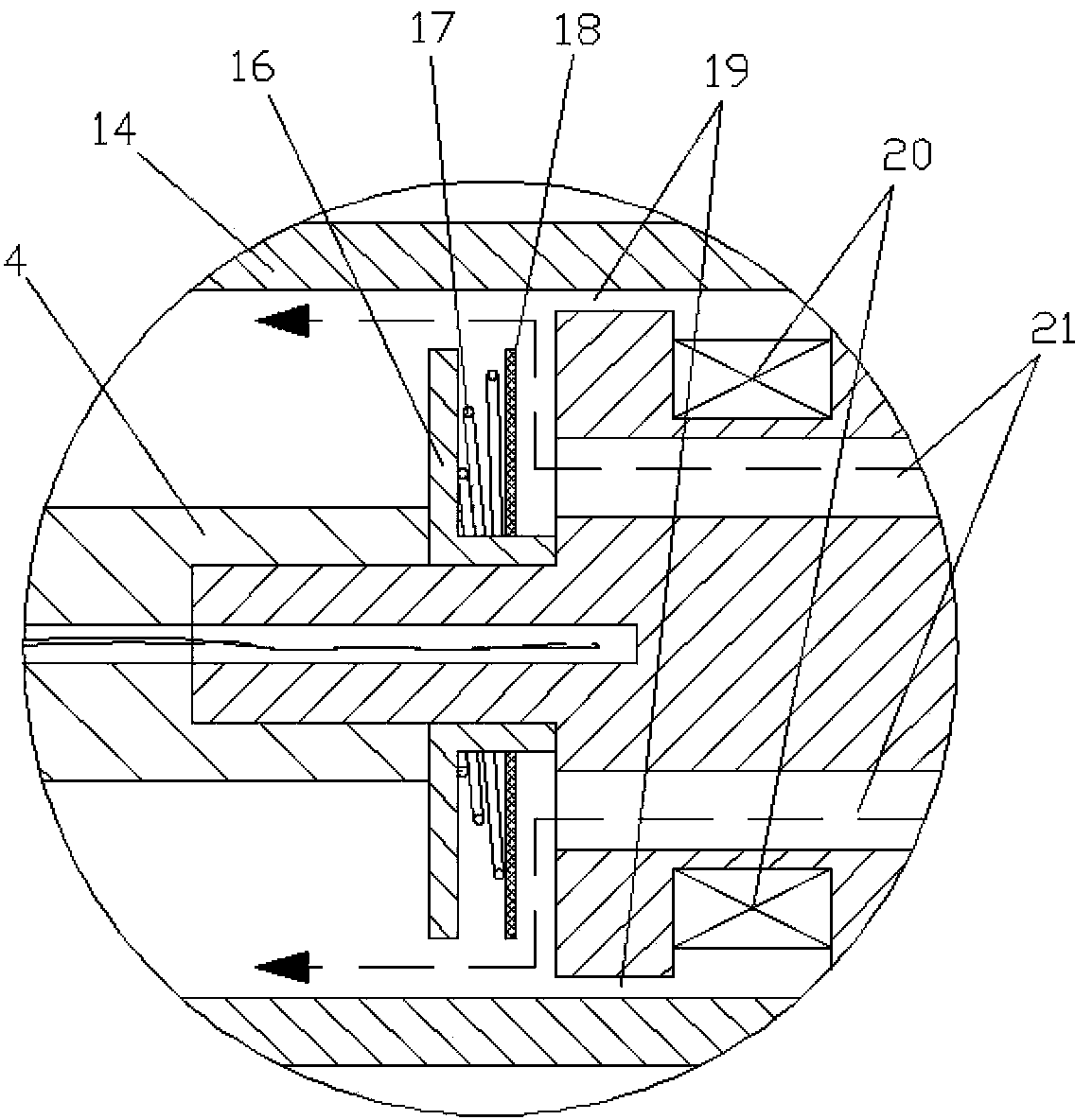
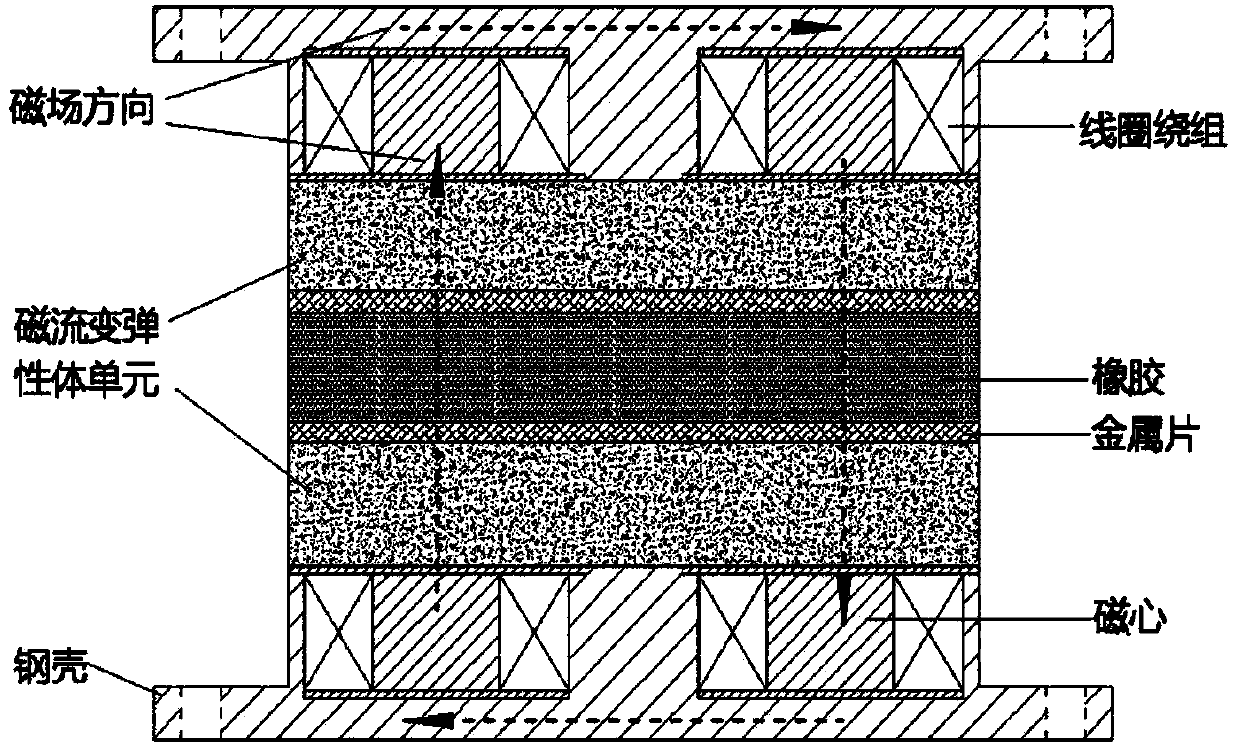
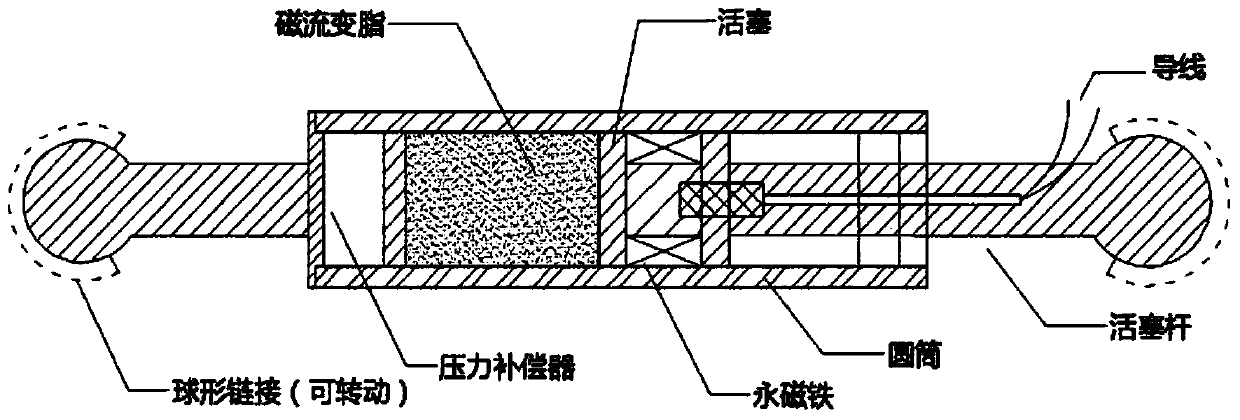
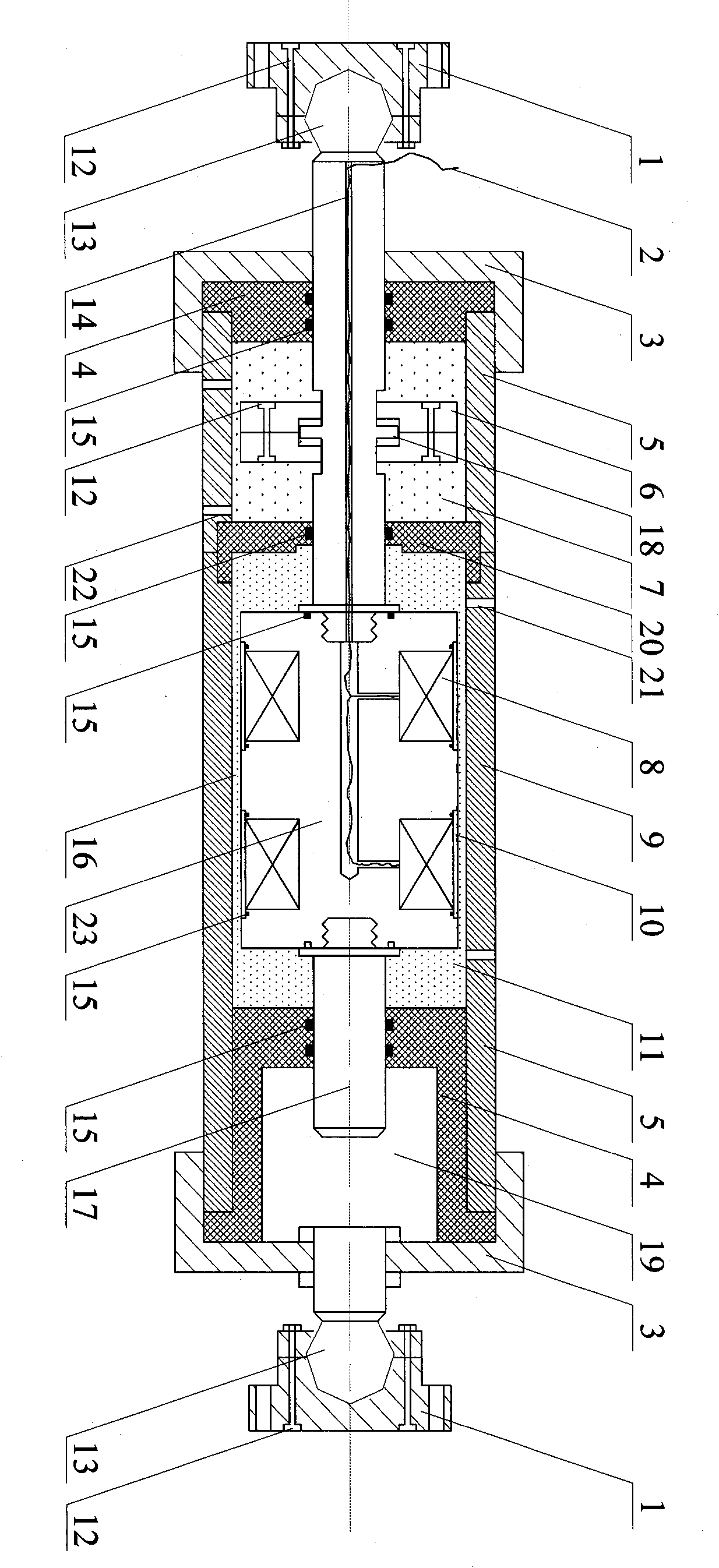
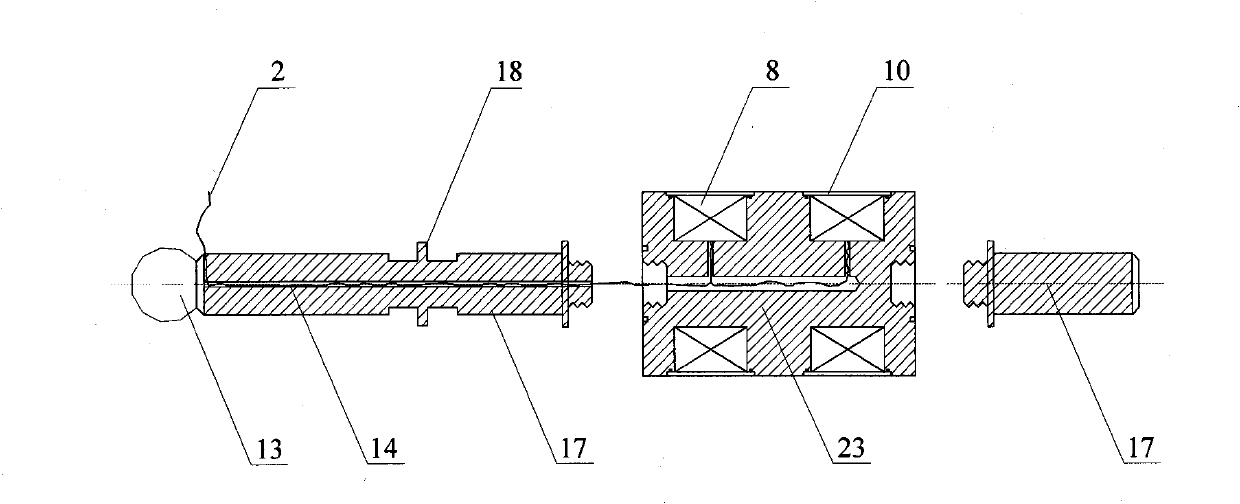
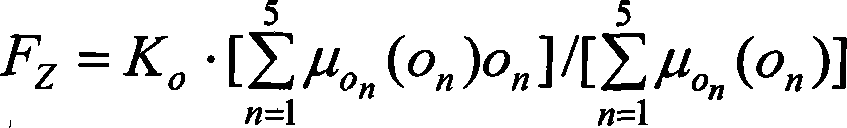Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
875 results about "Magnetorheological damper" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
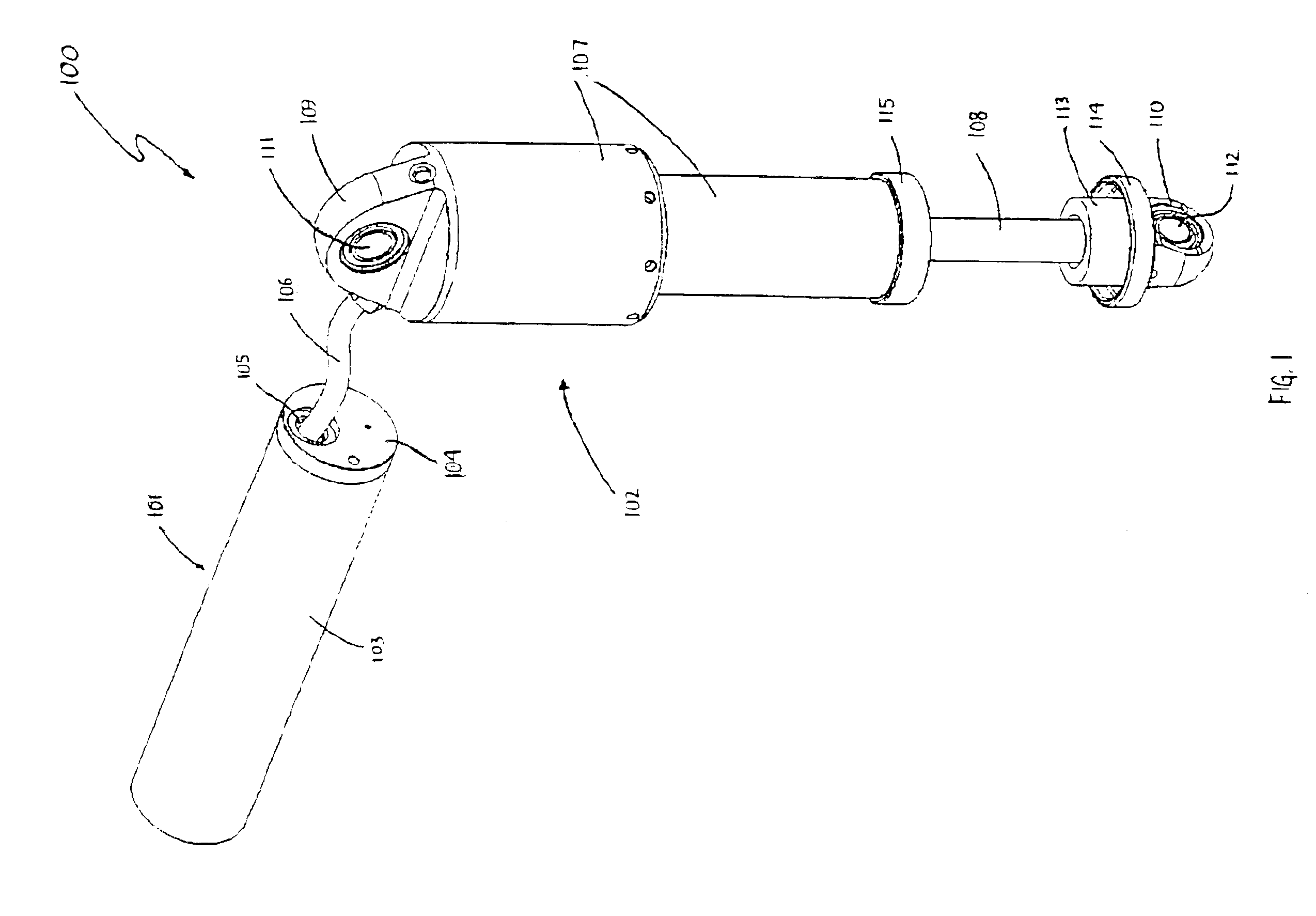
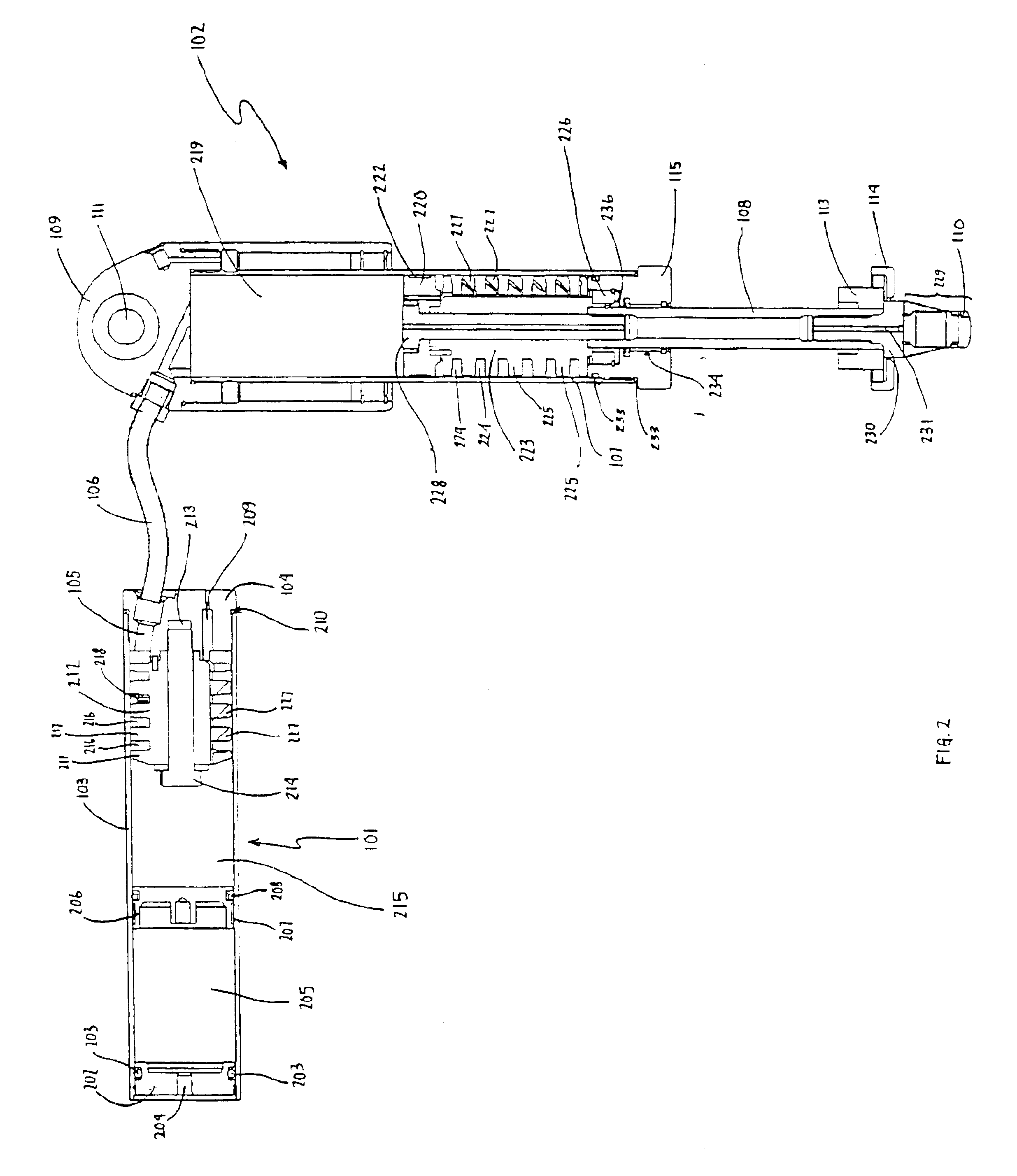
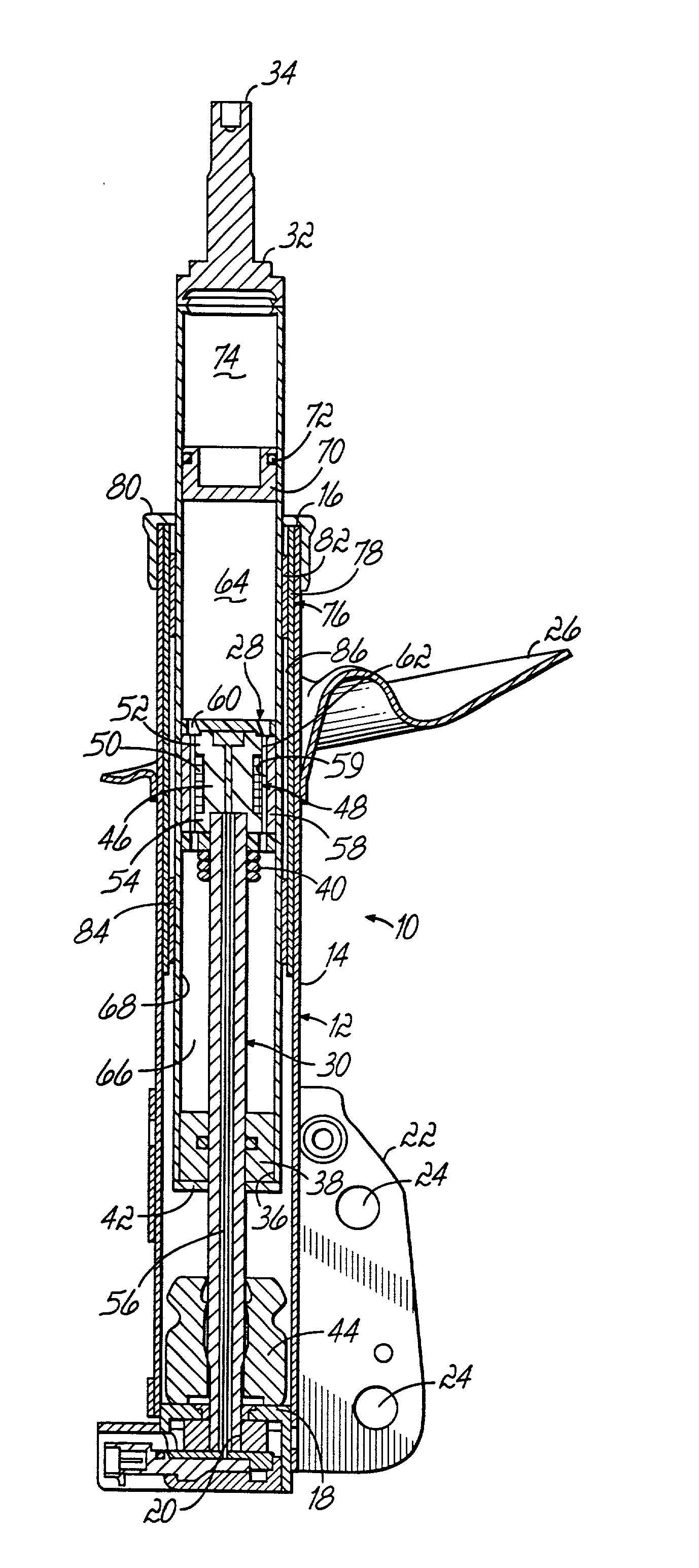
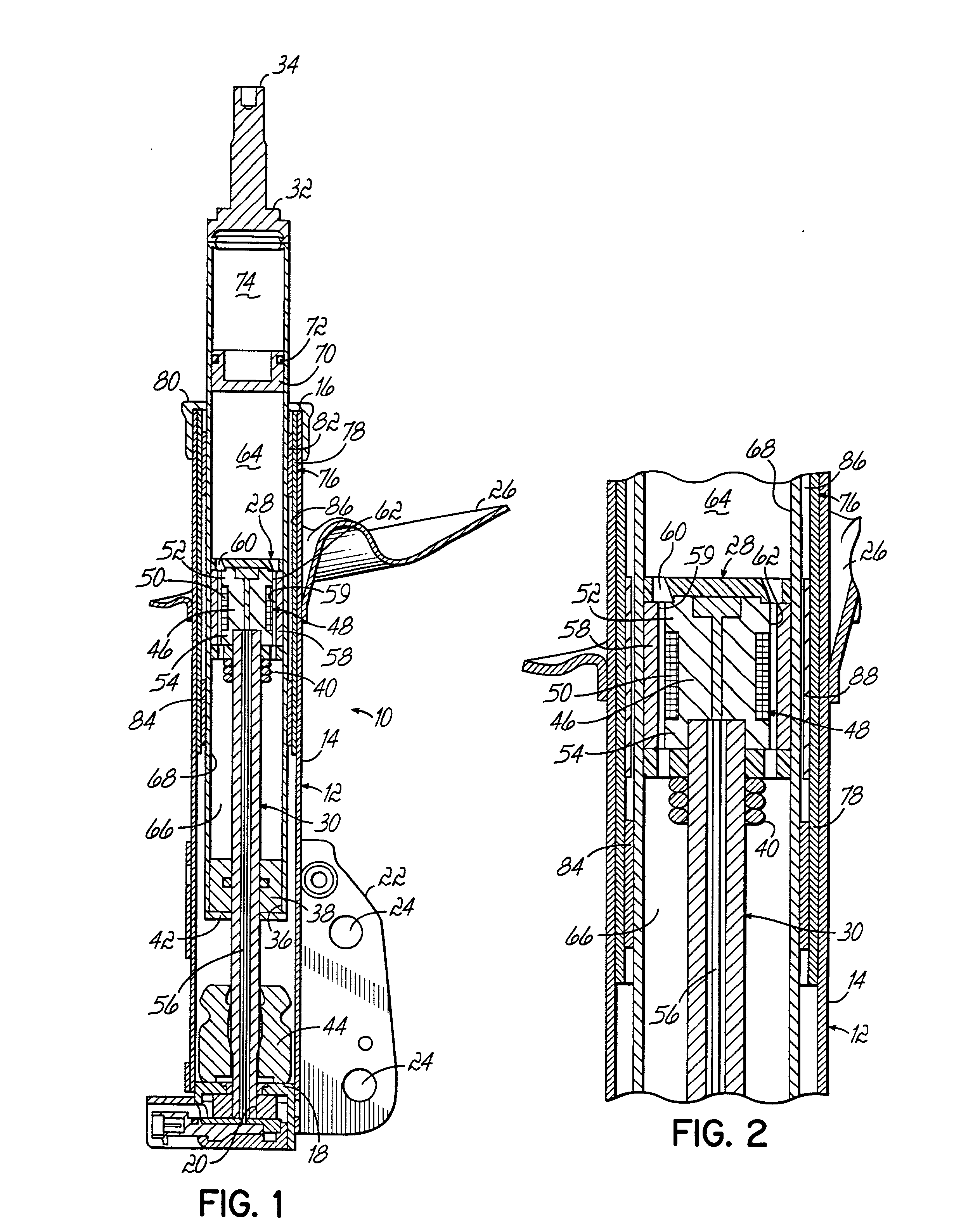
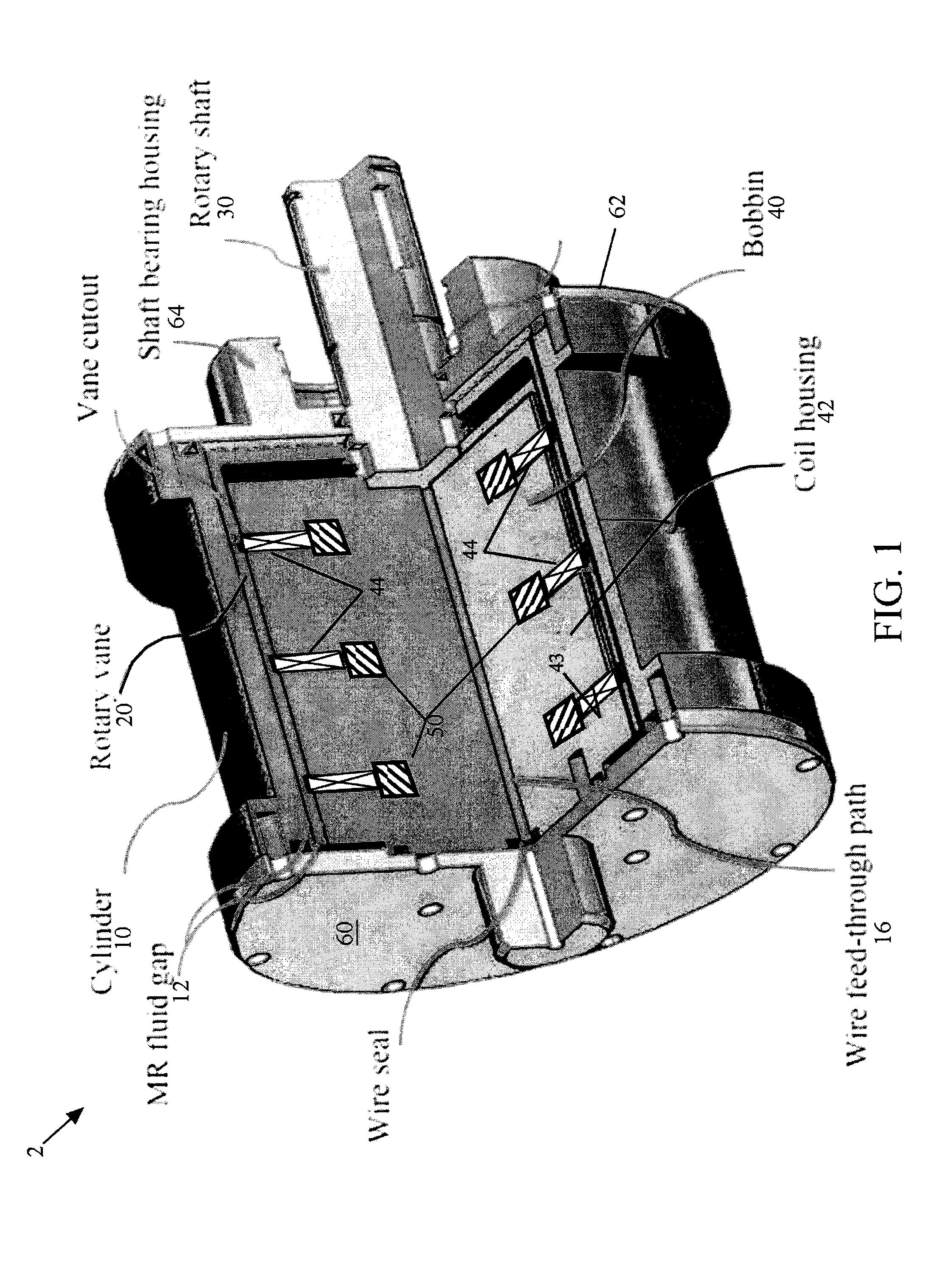
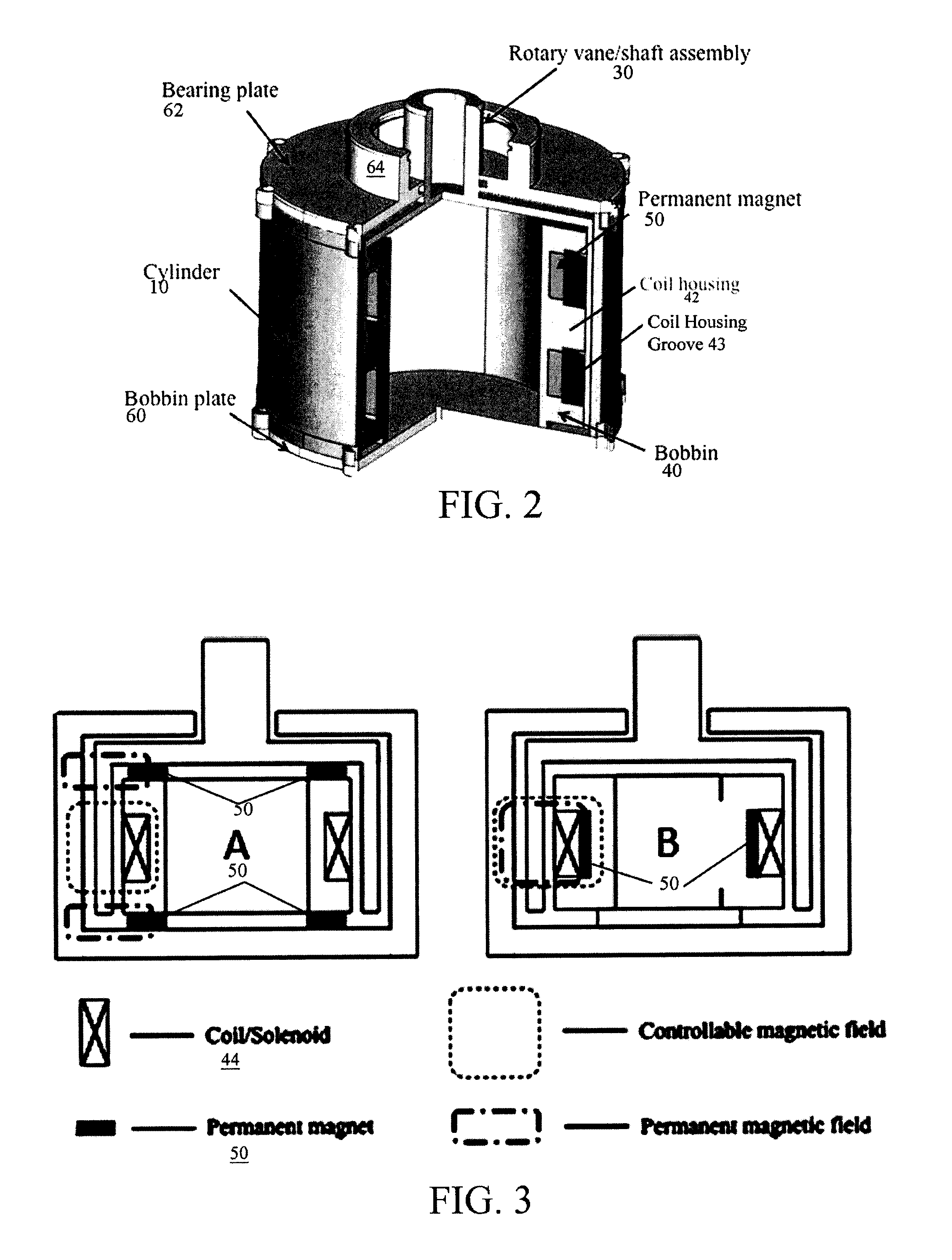
A magnetorheological damper or magnetorheological shock absorber is a damper filled with magnetorheological fluid, which is controlled by a magnetic field, usually using an electromagnet. This allows the damping characteristics of the shock absorber to be continuously controlled by varying the power of the electromagnet. Fluid viscosity increases within the damper as electromagnet intensity increases. This type of shock absorber has several applications, most notably in semi-active vehicle suspensions which may adapt to road conditions, as they are monitored through sensors in the vehicle, and in prosthetic limbs.
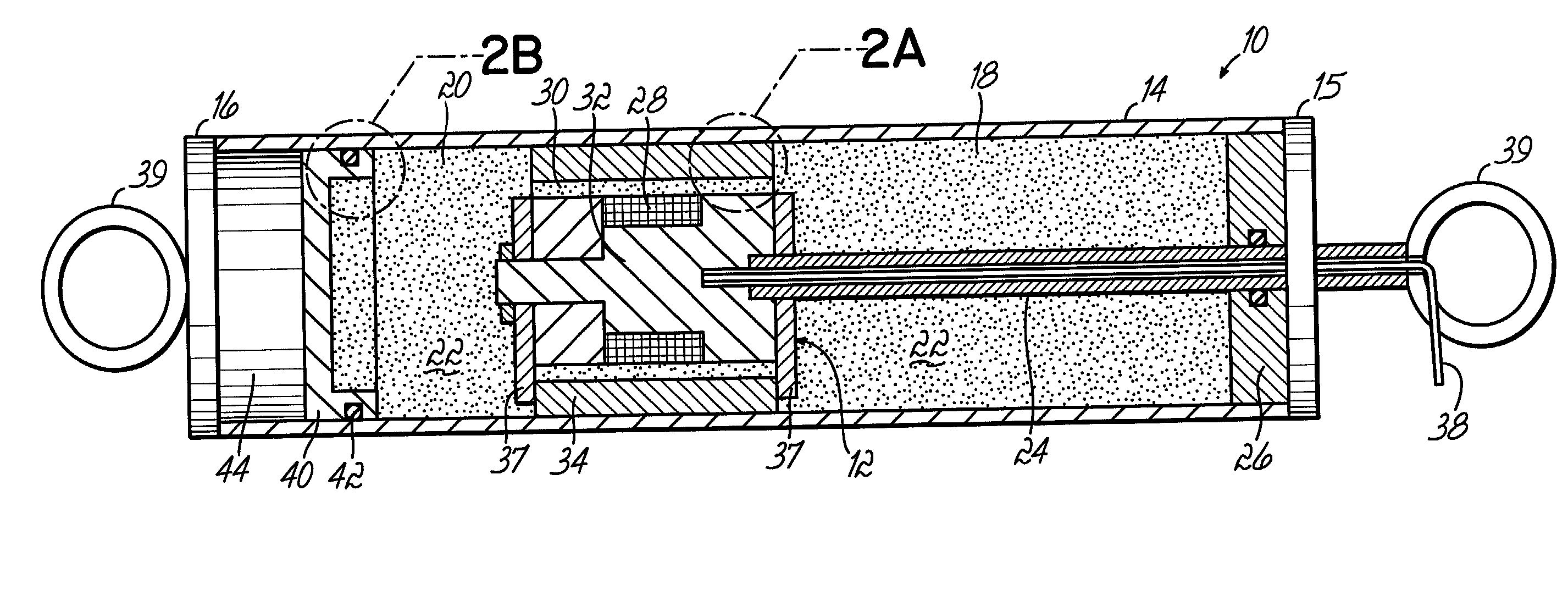
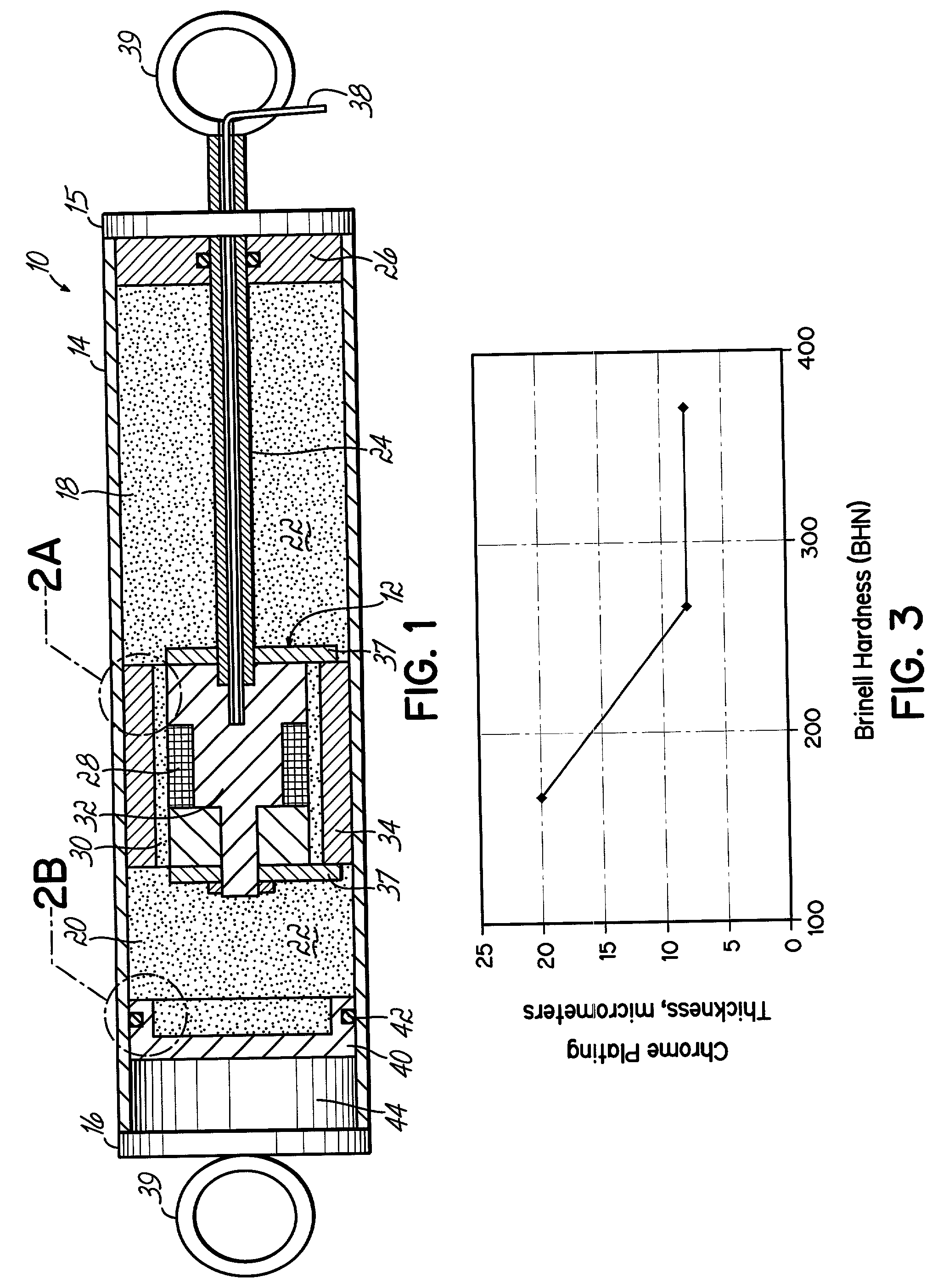
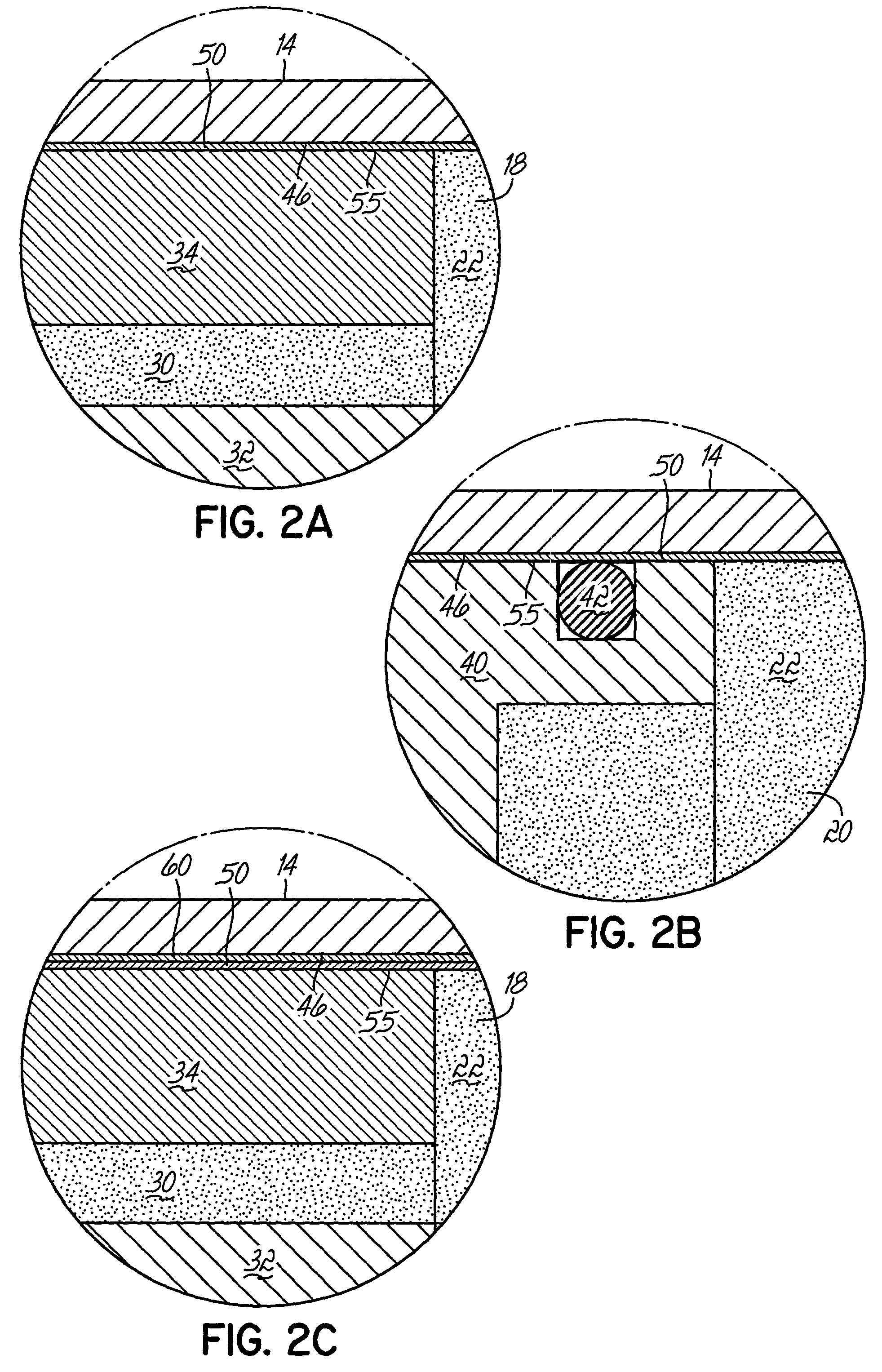
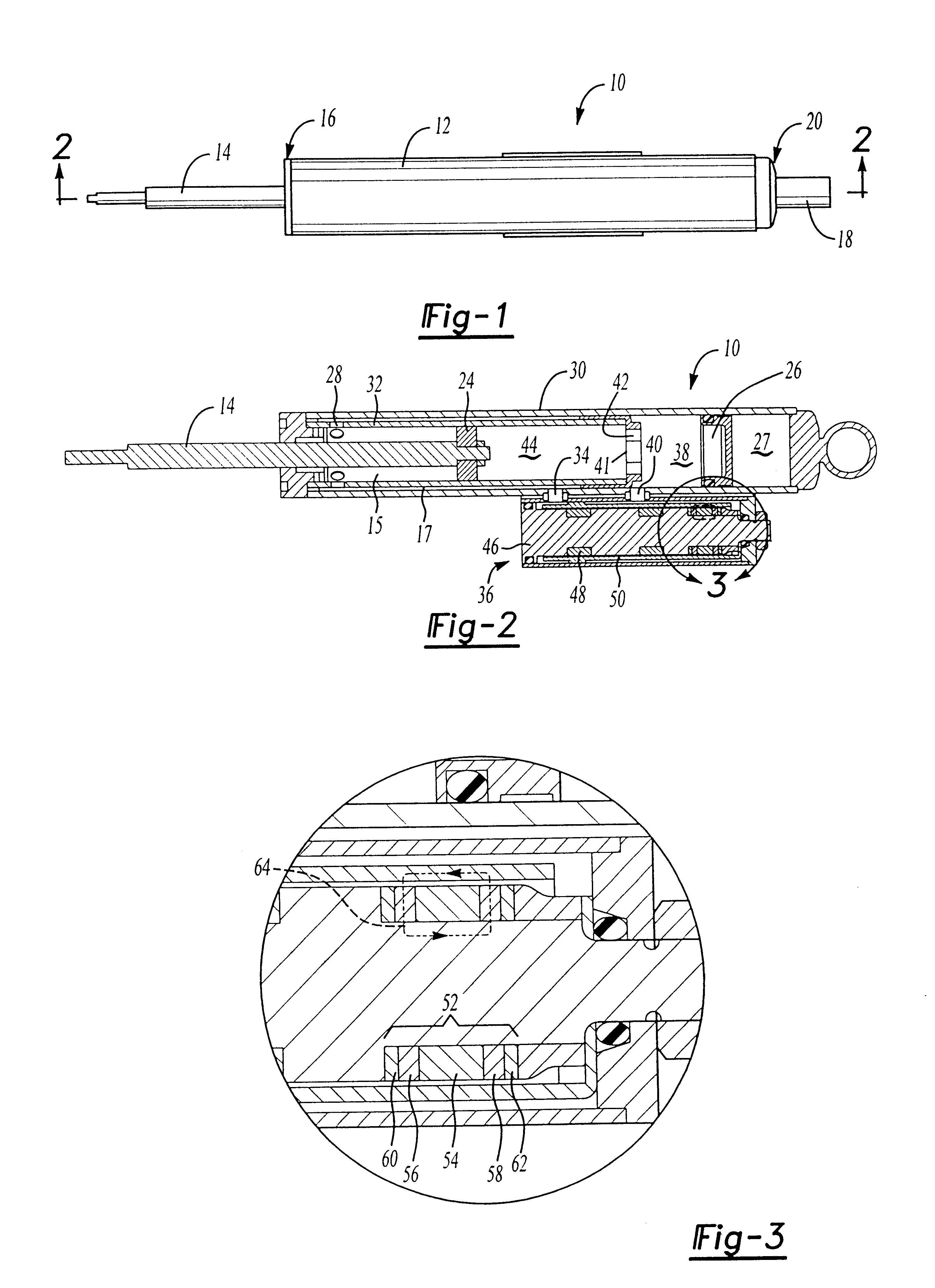
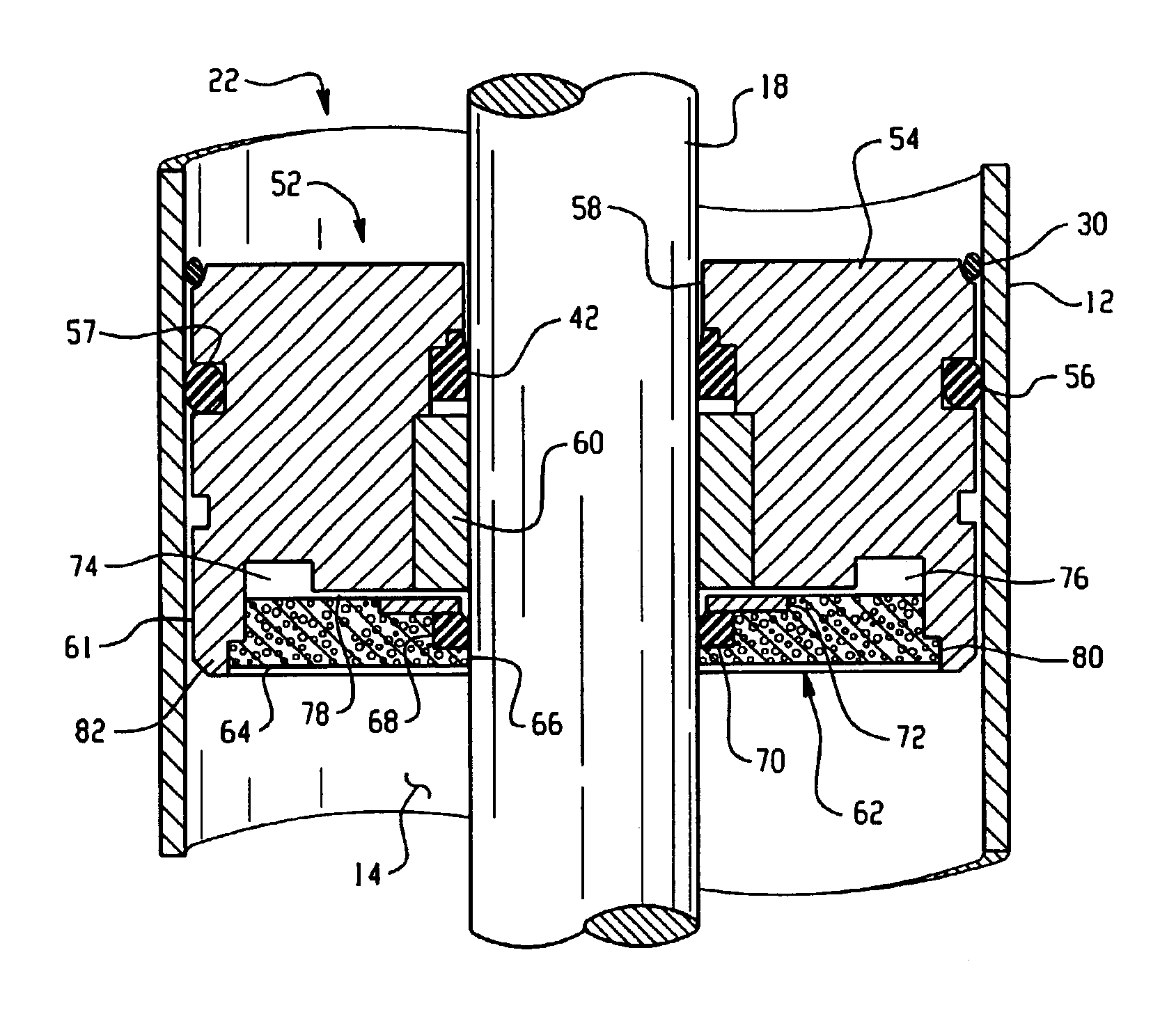
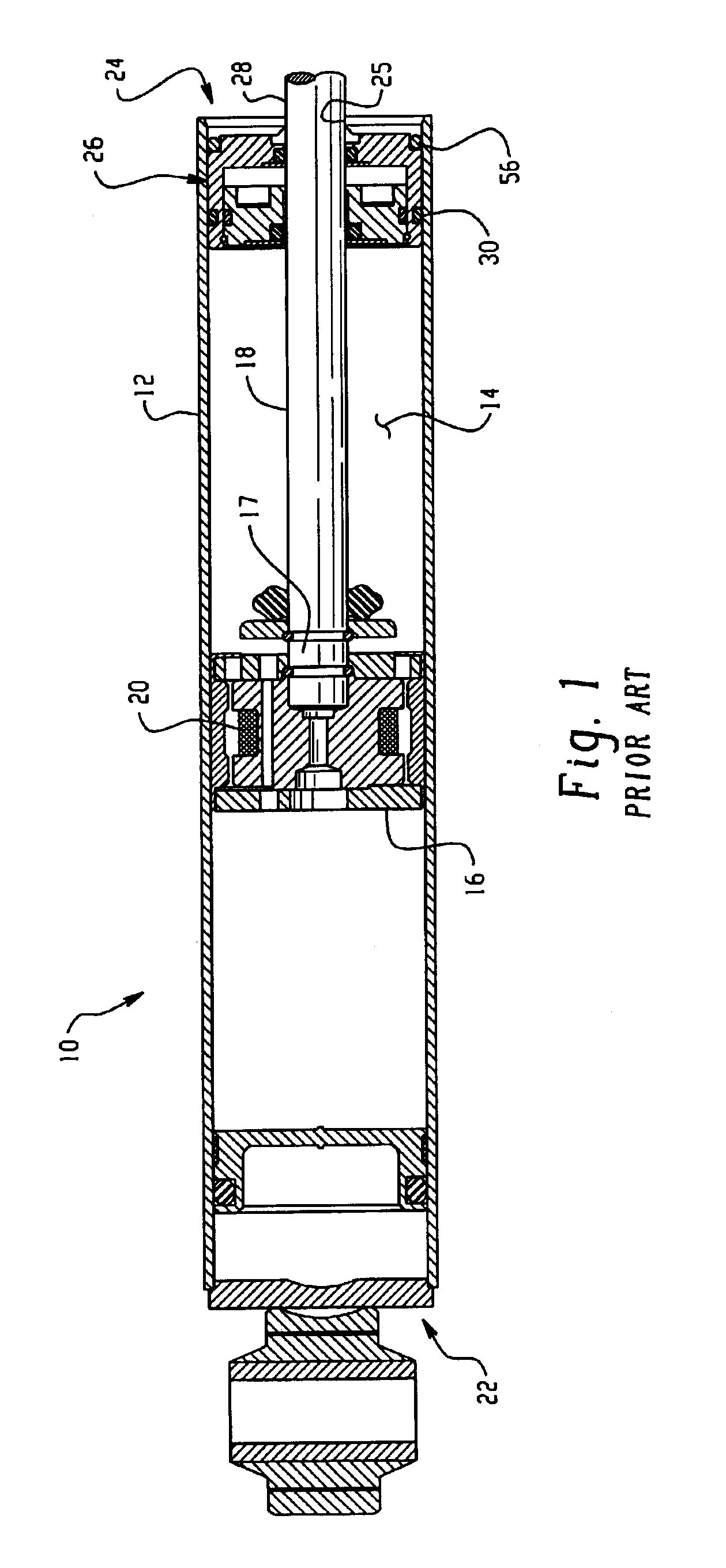
Magnetorheological dampers with improved wear resistance
InactiveUS20020130003A1Improve wear resistanceIncrease effective viscositySpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionEngineeringHardness
A damper body for a magnetorheological (MR) damper and associated methods of forming the damper body. The damper body is formed of a base material, such as a steel, and is coated with an abrasion-resistant layer comprising chromium. The layer of chromium provides a sliding wear surface for sliding contact with a reciprocating piston. To avoid high-stress abrasive wear over the expected service life of the magnetorheological damper, the layer of chromium has a minimum thickness greater than or equal to a minimum thickness of about 8 .mu.m. In other embodiments, be fore applying the abrasion-resistant layer of chromium, the damper body is coated with a layer of a hard coating material having a hardness greater than the hardness of the base material. The effective hardness of the damper body is a composite of the respective hardnesses of the base material comprising the damper body and the layer of hard coating material. The thickness of abrasion-resistant layer of chromium is chosen in direct relation to the effective hardness.
Owner:BWI CO LTD SA +1
Magnetorheological damper system
InactiveUS6953108B2Straightforward to manufactureStraightforward to assembleSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionControl theoryShock absorber
A magnetorheological damper system comprising a reservoir in communication with a damper. The damper comprises a damper cylinder defining a damper chamber, wherein the damper chamber contains a magnetorheological fluid and a movable damper piston. The damper piston comprises at least two coil windings on the outer surface of the damper piston, wherein the damper piston is capable of generating a magnetic field between the damper piston and a wall of the damper cylinder. The reservoir comprises a reservoir cylinder defining a passageway, wherein the reservoir includes a magnetorheological electromagnet capable of generating a magnetic field between the magnetorheological piston and a wall of the passageway. The combination of the an MR reservoir and MR damper leads to a damping system capable of damping a wide range of extreme forces.
Owner:MILLENWORKS
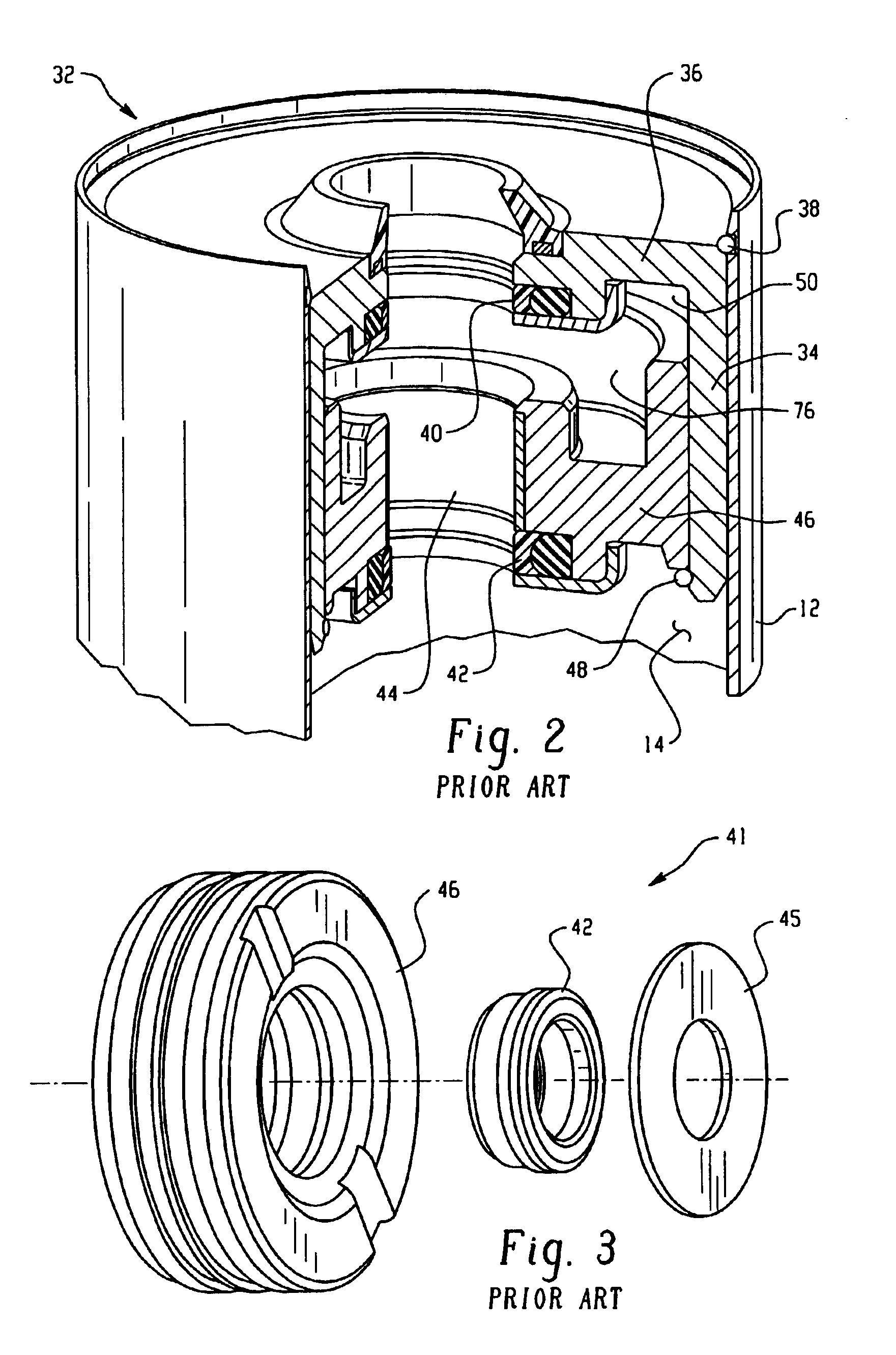
Magneto-rheological damper with ferromagnetic housing insert
InactiveUS20020130000A1Improve performanceDecreased damping capacitySpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagneto rheologicalControl theory
A magneto-rheological ("MR") damper having a damper body tube containing an MR fluid. A piston assembly is disposed in the damper body tube and forms an annular flow gap between the piston assembly and the damper body tube. The piston assembly has a piston core containing ferrous material and an electromagnetic coil mounted on the piston core for generating a magnetic field. The damper further includes a ferromagnetic member positioned outside of the damper body tube substantially adjacent the piston assembly for providing at least a part of a magnetic flux return path for the magnetic field.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC +1
Magnetorheological damper system
InactiveUS20070119669A1Reduce forceAvoid cavitationMachine framesNon-rotating vibration suppressionEngineeringControl theory
A magnetorheological damper system comprising a reservoir in communication with a damper. The damper comprises a damper cylinder defining a damper chamber, wherein the damper chamber contains a magnetorheological fluid and a movable damper piston. The damper piston comprises at least two coil windings on the outer surface of the damper piston, wherein the damper piston is capable of generating a magnetic field between the damper piston and a wall of the damper cylinder. The reservoir comprises a reservoir cylinder defining a passageway, wherein the reservoir includes a magnetorheological electromagnet capable of generating a magnetic field between the magnetorheological piston and a wall of the passageway. The combination of the an MR reservoir and MR damper leads to a damping system capable of damping a wide range of extreme forces.
Owner:MILLENWORKS
A self-supplied magnetic current damper
InactiveCN101550982AMeet the needs of workNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagnetic currentRare earth
The invention presents a self-supplied magnetic current damper, which includes a magnetic current damper, a vibration energy collector, and an energy storage management module. The energy collector is a multi-vane disc shaped electro-magnetism type mechanical energy collector installed on the piston bottom of the magnetic current damper, which is composed of multiple impellers and disc shaped magnetoelectric transducers, wherein, the disc shaped magnetoelectric transducers are mounted on the piston, the multiple impellers are mounted on the rotor of the disc shaped magnetoelectric transducers, and the energy produeced by the disc shaped magnetoelectric transducers is lead out by the coil on the stator. The output lines of the disc shaped magnetoelectric transducers are connected to the energy storage management module, and the output of the energy storage management module is connected to the magnetizing coil of the magnetic current damper. During work, the magnetic current liquid impacts the vanes, the impeller converts the fluid washing into the rotation of the disc shaped stator inlaid on the rare-earth permanent magnet, the magnetic flux of the coil on the disc shaped stator is changed, in order to achieve effective collection of mechanical energy, and greatly reduce the transducer volume.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Power-off damping in MR damper
InactiveUS6419057B1High than minimum level of dampingMore operating rangeSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionElectricityEngineering
A magneto-rheological (MR) damper provides a higher than minimum level of damping when a power source to the MR damper is not supplying a control current. The present invention damper includes magnets positioned to direct a magnetic flux across a MR fluid path. The fluid path is created when a rod and piston assembly stroke the fluid though a control valve assembly attached to a damper chamber causing a resistance to MR fluid flow. An electric coil cancels an effect of the permanent magnets when the control current is available to allow a control circuit more operating range. The permanent magnets allow for damping when no control current is available.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC +1
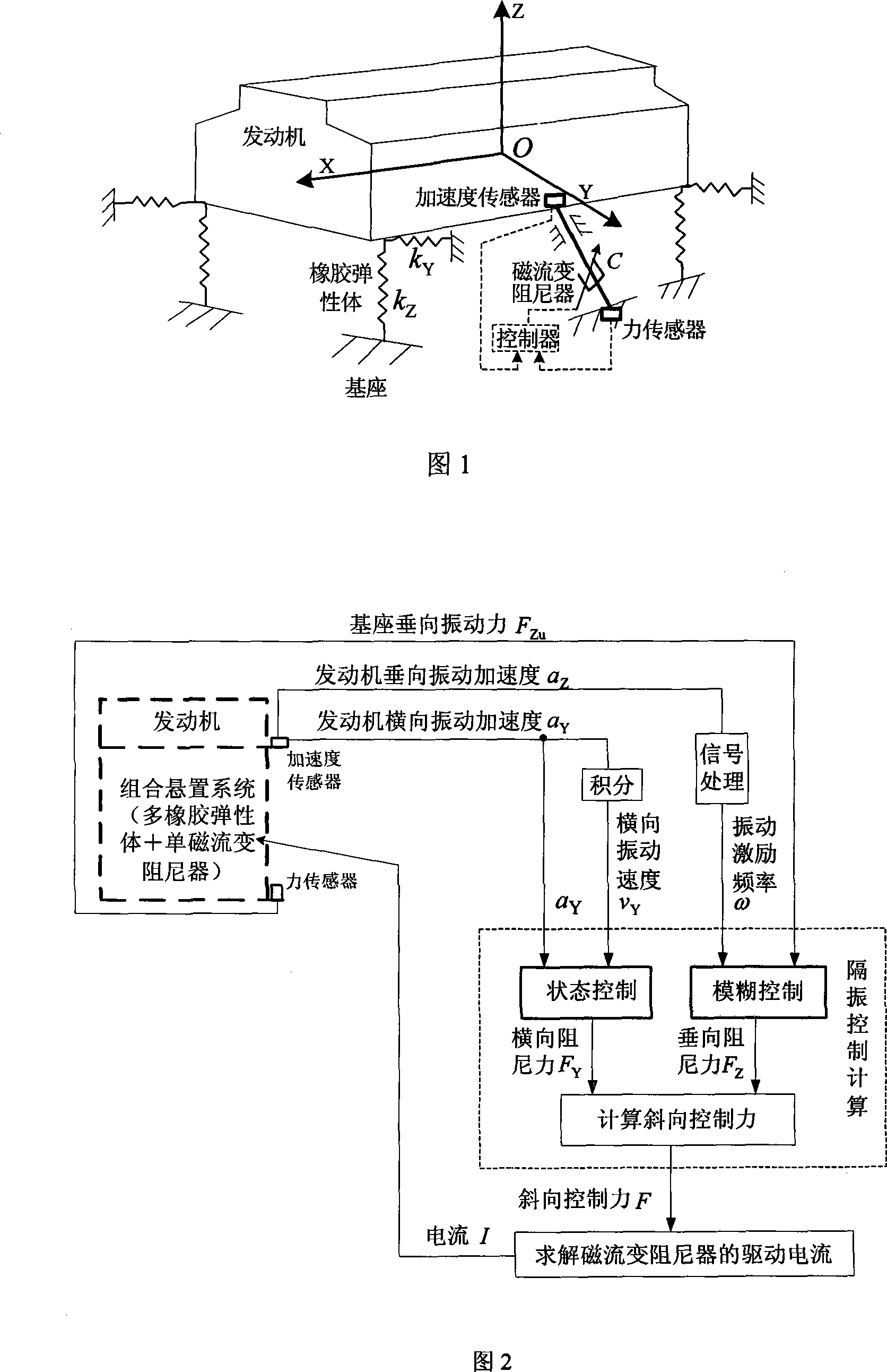
Engine vibration isolation system based on combined suspension and its control method
InactiveCN101220845AEffective vibration isolationChange the strength of the magnetic fieldNon-rotating vibration suppressionPower plants being motor-drivenVertical vibrationElastomer
The invention provides an engine vibration isolation system which is based on a combination suspension and a control method, relating to the automatic control technical field. The invention forms the combination suspension by a plurality of passive rubber elastomers and a single controllable magneto-rheological damper which is obliquely arranged between the middle part of the engine and a base; an acceleration sensor and a force sensor respectively extract the vertical and transverse vibration acceleration of the engine body and the vertical vibration force of the base, so as to calculate the vibration excitation frequency and the transverse vibration speed of the engine; an engine vertical vibration isolation fuzzy control rule and a transverse damping state control rule are established in a controller, and an oblique control force of the magneto-rheological damper is calculated; the driving current of the magneto-rheological damper is determined by an oblique control force, the damping force of the combination suspension is adjusted in real-time, the transmission of the vibration energy of the engine is restricted. The invention can lead to effective vibration isolation of the engine in wide-frequency range, reduces the self vibration of the engine, and improves the durability and the riding comfort of a carrier.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
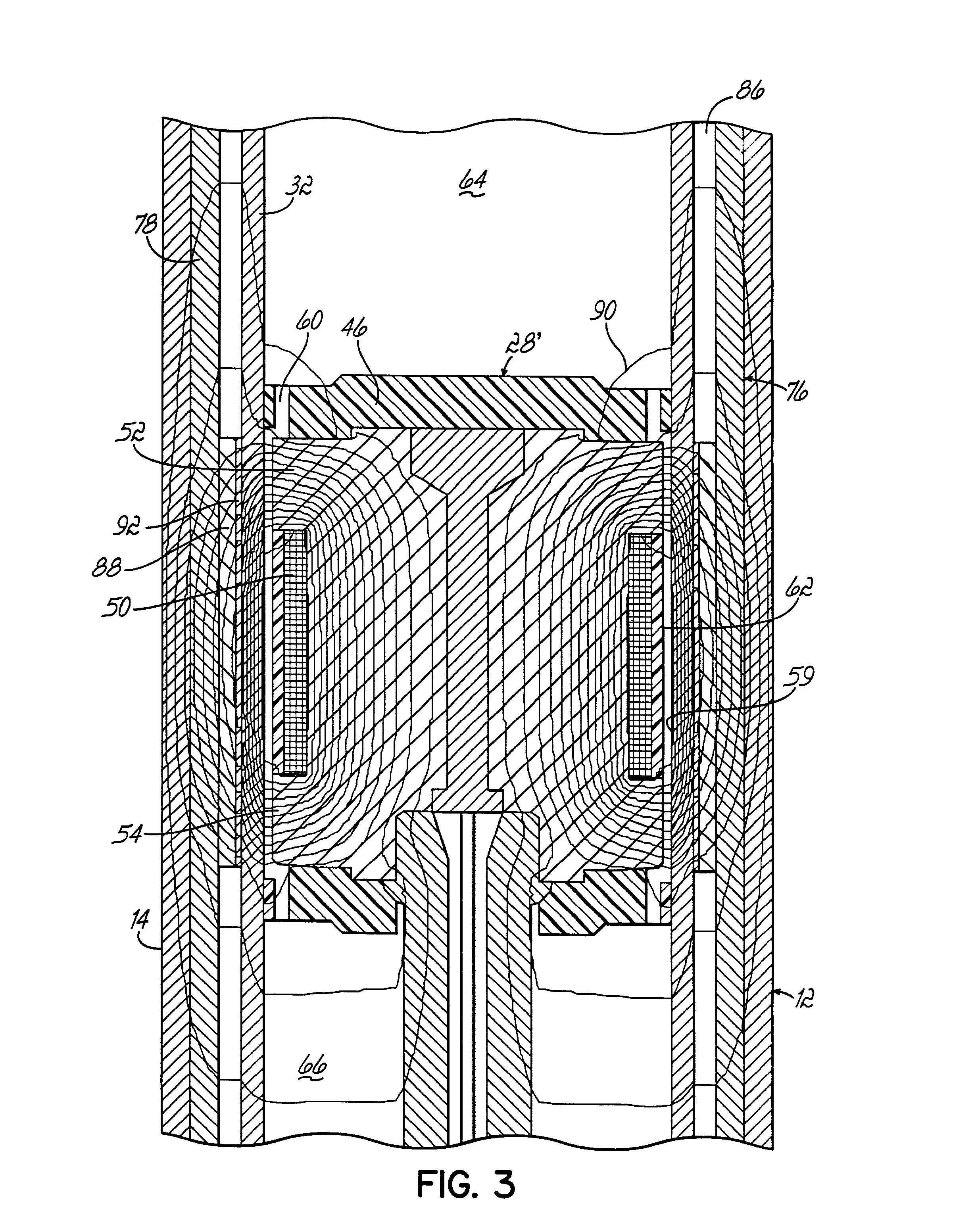
Closing system for a magneto-rheological damper
A closing system for use with a magneto-rheological (MR) damper. The closing system provides lubrication for a piston rod without a need for periodic replenishment. According to an embodiment of the present invention, a lubrication chamber of the closing system utilizes a carrier fluid portion of MR fluid present in a fluid reservoir of the damper as lubricant for a piston rod guide and the piston rod. A seal retainer comprised of a porous material acts as a selective barrier to the micro-particles in the MR fluid in the fluid reservoir, allowing the MR carrier fluid portion to pass through the porous seal retainer to the lubrication chamber while restraining the micro-particles in the fluid reservoir. The seal retainer thus acts as a filter to segregate the abrasive particles of the MR fluid and allows the MR carrier fluid portion of the MR fluid to continuously replenish the lubrication chamber and lubrication passage to lubricate the piston rod guide and piston rod.
Owner:BWI CO LTD SA +1
Magnetorheological fluid damper
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and method for damping vibration in a drill string using a magnetorheological damper
ActiveUS20100224410A1Change viscosityReduce induced remanent magnetic fieldSurveyDrilling rodsAlternatorEngineering
A system for damping vibration in a drill string can include a magnetorheological fluid valve assembly having a supply of a magnetorheological fluid, a first member, and a second member capable of moving in relation to first member in response to vibration of the drill bit. The first and second members define a first and a second chamber for holding the fluid. Fluid can flow between the first and second chambers in response to the movement of the second member in relation to the first member. The valve assembly can also include a coil for inducing a magnetic field that alters the resistance of the magnetorheological fluid to flow between the first and second chambers, thereby increasing the damping provided by the valve. A remanent magnetic field is induced in one or more components of the magnetorheological fluid valve during operation that can be used to provide the magnetic field for operating the valve so as to eliminate the need to energize the coils during operation except temporarily when changing the amount of damping required, thereby eliminating the need for a turbine alternator power the magnetorheological fluid valve. A demagnetization cycle can be used to reduce the remanent magnetic field when necessary.
Owner:APS TECH
Automotive energy-regenerative active suspension system with rigidity and damping variable
ActiveCN104015582AImprove handling stabilityEasy rideAuxillary drivesResilient suspensionsControl systemElectric machinery
The invention discloses an automotive energy-regenerative active suspension system with rigidity and damping variable. The suspension system comprises a suspension variable-rigidity mechanism, a suspension energy-regenerative mechanism and an active suspension control system. The suspension variable-rigidity mechanism comprises a low-rigidity spring, a magneto-rheological damper and a high-rigidity spring. The suspension energy-regenerative mechanism is formed by bi-directionally connecting a linear motor, an energy-regenerative circuit and a storage battery in sequence. The active suspension control system includes a controller. The data input end of the controller is connected with a vibration measuring and processing circuit. The magneto-rheological damper and the control input end of the linear motor are respectively connected with the control output end of the controller. The suspension system can automatically adjust the damping and rigidity at the same time, so that the good steering stability and ride comfort of a finished automobile are achieved; the control system is high in response speed; energy consumption is substantially lowered, and therefore the economy requirement of the finished automobile is met; moreover, the structure and a control algorithm are simple, working is stable and reliable, service life is long, and the suspension system can be conveniently applied to an existing automotive suspension so that real-time control can be achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Failsafe magnetorheological (MR) energy absorber
ActiveUS20140152066A1Boost and reduces baseline magnetic fieldReduce energy impactSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionLinear motionMagnetic current
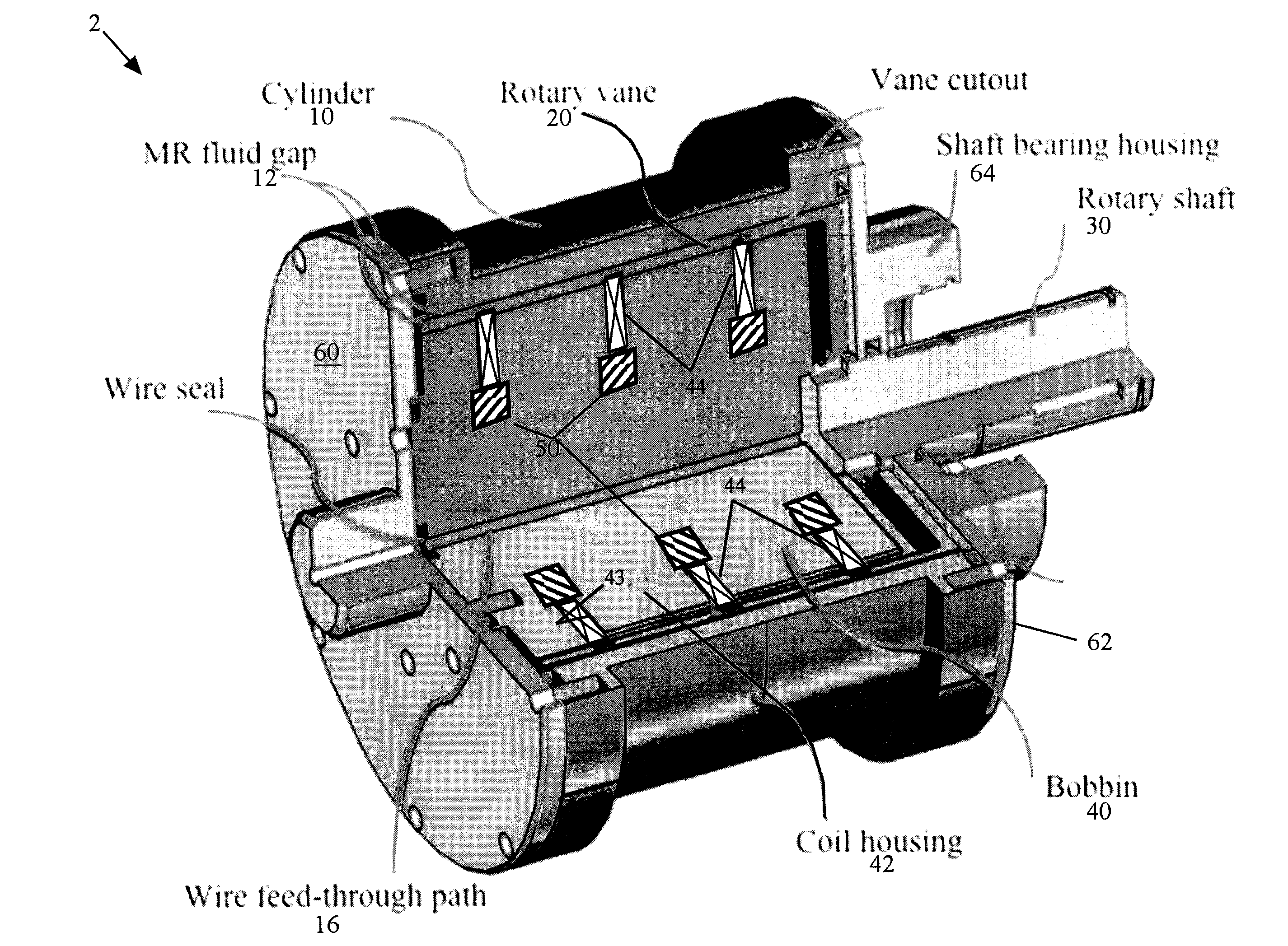
A compact and failsafe magnetorheological energy absorber design including both a light weight piston (LWP) embodiment in which linear motion is subjected to a linear damping force, and a light weight rotary vane (LWRV)embodiment in which linear motion is converted into rotary motion and is subjected to a rotary damping force. Both embodiments allow increased damper stroke within a compact mechanical profile. A new lightweight Magnetorheological energy attenuation system (LMEAS) for a vehicle seat is also disclosed using the new LMRW MREA.
Owner:INNOVITAL LLC +1
Variable-stiffness variable-damping shock absorber based on magnetorheological damper
ActiveCN104315073AGood vibration dampingIncrease the itinerarySpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionVariable stiffnessEngineering
The invention discloses a variable-stiffness variable-damping shock absorber based on a magnetorheological damper. The shock absorber is characterized in that an outer cylinder body is glidingly mounted on the outer side of the magnetorheological damper; a spring mounted in the outer cylinder body is connected with the piston rod of the magnetorheological damper; when the magnetorheological damper and the spring vibrate by external pressure, the outer cylinder body slides on the outer side of the magnetorheological damper to change the travel of the whole shock absorber, and meanwhile, the electrification coil of the magnetorheological damper is electrified and the shape of a magnetorheological fluid is changed to change the damping of the shock absorber. According to the shock absorber, the magnetorheological damper is combined with the spring, so that the stiffness and damping of the shock absorber can be changed; the shock absorber is large in travel and can meet the requirements of an environment in need of the shock absorber with large travel.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Positive and negative stiffness parallel three-translation vibration and impact isolation platform
InactiveCN101871505AImprove the dynamic environmentGuaranteed operating vibration parametersNon-rotating vibration suppressionAviationVibration control
The invention discloses a positive and negative stiffness parallel three-translation vibration and impact isolation platform, and belongs to the field of the multi-axis vibration control technology and multi-axis vibration control devices, which comprises an upper platform (1), a lower platform (9), eight elastic branched-chain structures and a silica gel magnetorheological damper (11), wherein the eight elastic branched-chain structures are fixed between the upper platform (1) and the lower platform (9) two by two in an orthogonally symmetrical four-point supporting mode; the axes of the two elastic branched-chain structures of each point are vertical mutually; and the silica gel magnetorheological damper (11) is arranged in the geometric center between the upper platform (1) and the lower platform (9). The positive and negative stiffness parallel three-translation vibration and impact isolation platform can be widely used for instruments and equipment in fields of aviation, space flight, weapons, vehicles, ships, construction, nuclear industry, mechanical industry, optical industry, semiconductor industry, photosensitive chemistry and the like, and has the advantages of large carrying capacity, high stability, small volume, low natural frequency, controlled damping, low cost of manufacturing and maintenance and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI HIGHER MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL
Magneto-rheological damper of automobile engine suspension system
InactiveCN102829127ASuppression of high frequency dynamic hardeningImprove the vibration isolation effectNon-rotating vibration suppressionPower flowExcitation current
The invention discloses a magneto-rheological damper of an automobile engine suspension system, comprising a main rubber spring, a throttling disk, a magnetic core assembly and a decoupling film, wherein the damper is used for regulating the magnetic induction intensity at a magneto-rheological liquid channel in the magnetic core assembly through controlling the excitation current of an electromagnetic coil and then regulating the viscosity of magneto-rheological liquid at the magneto-rheological liquid channel to achieve the optimal damping effect. When the magneto-rheological damper is used, the turbulence level of the magneto-rheological liquid in a liquid feeding chamber can be increased through the throttling disk, the high-frequency dynamic hardening of the damper can be effectively inhibited, and the effectively damping frequency range can be widened. The damper has a more ideal dynamic characteristic and meets the use requirement for damping the automobile engine suspension system with high rotating speed; in addition, the damping capacity, the work stability and the convenience in assembly of the damper are improved through improving a floating decoupling film type decoupler, a sealing structure of the magnetic core assembly, a liquid injection hole structure and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
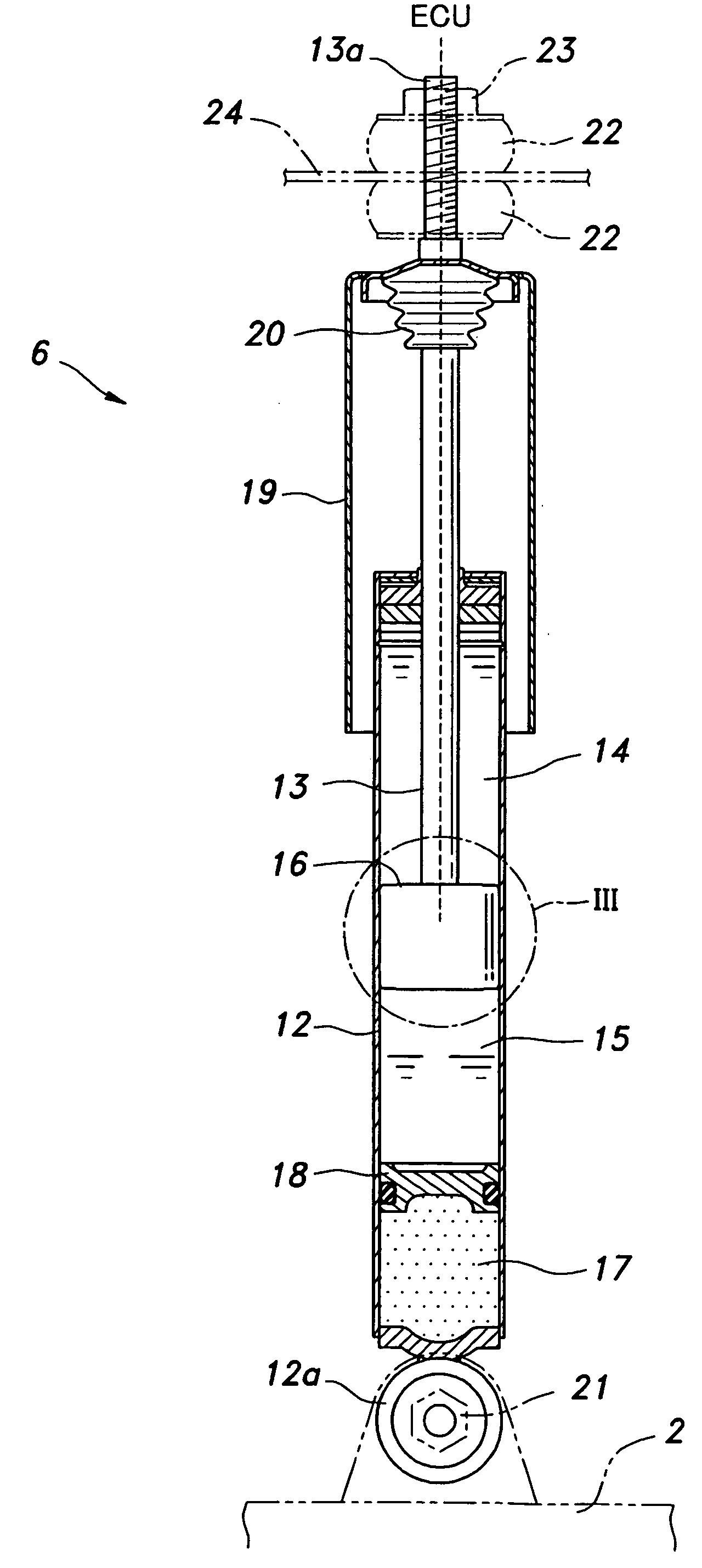
Magneto-rheological damper
InactiveUS20090107779A1Increased durabilityHigh magnetic flux densitySpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionWear resistantVolumetric Mass Density
In a magneto-rheological variable damper (6), the piston (16) comprises an inner yoke (32), an outer yoke (31) concentrically surrounding the inner yoke and held in position by pair of end plates (33, 34) made of non-magnetic material and disposed on either axial end surfaces of the piston. The piston may be circumferentially surrounded by a piston cover (30) that may be made of non-magnetic material and serves a slide member that engages the inner circumferential surface of a cylinder (12). Alternatively, the end plates may serve as the slide member. In either case, the durability of the damper can be improved by using a wear resistant material for the slide member. In particular, the outer yoke may be made of material such as Permendur which has a high saturation magnetic flux density but a poor mechanical property. Thereby, the range of the damping force can be expanded. The slide member may be made of non-magnetic material having a favorable wear resistance such as austenite stainless steel and aluminum alloy. It is also possible to apply a plating or other surface processing to the sliding surface of the slide member to improve the wear resistance thereof.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
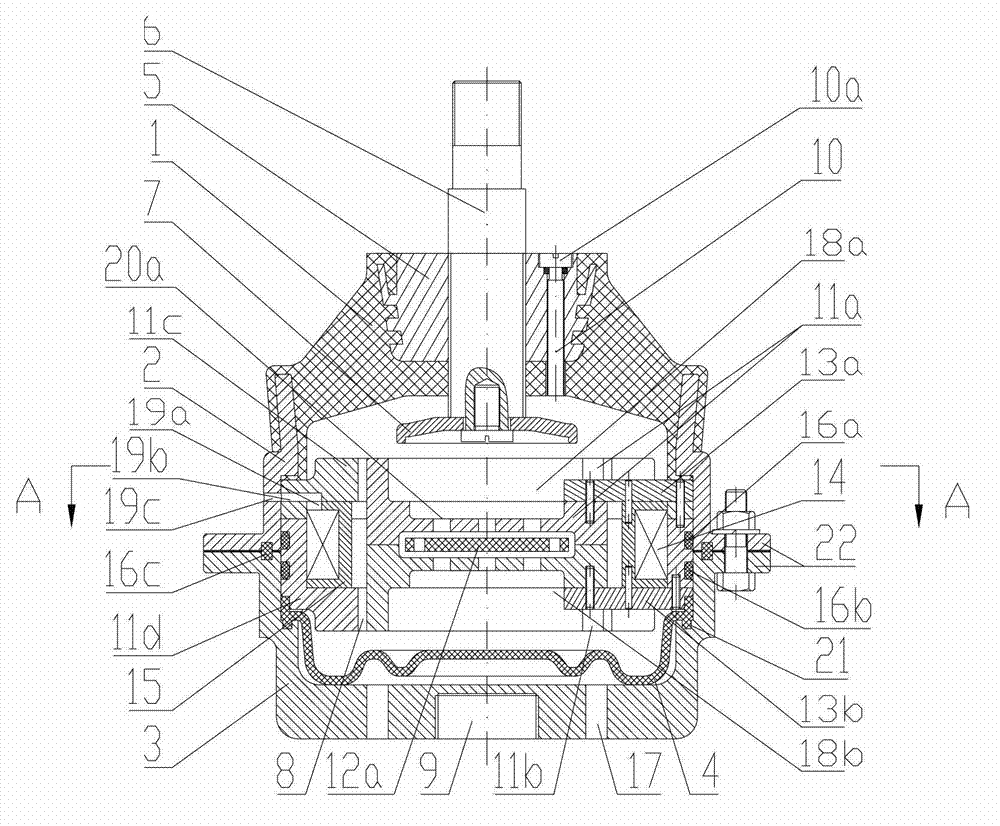
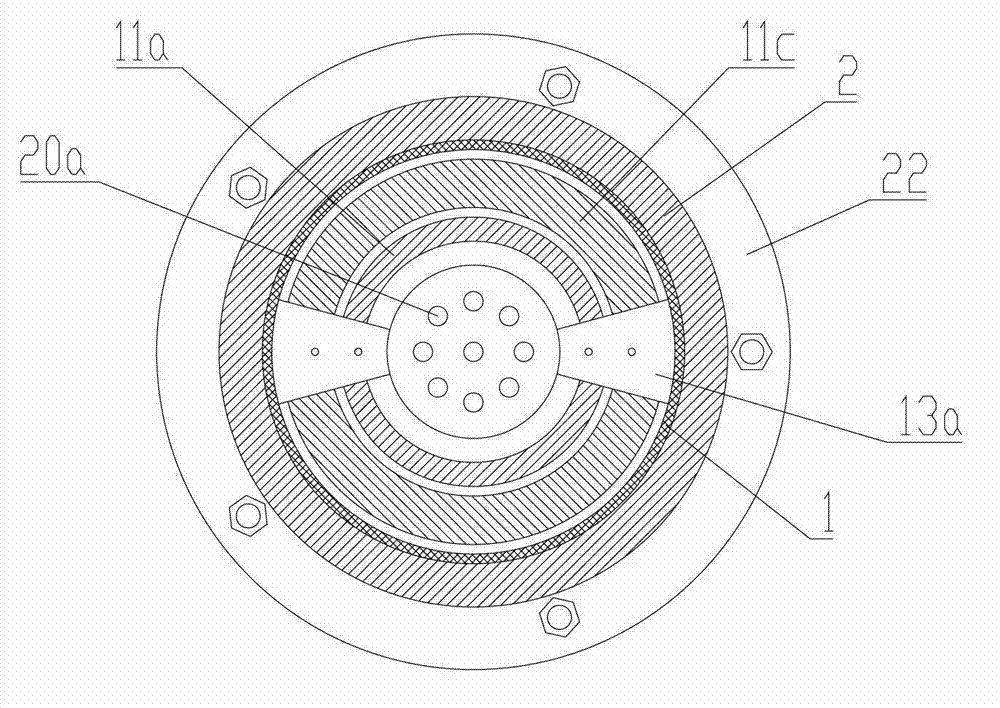
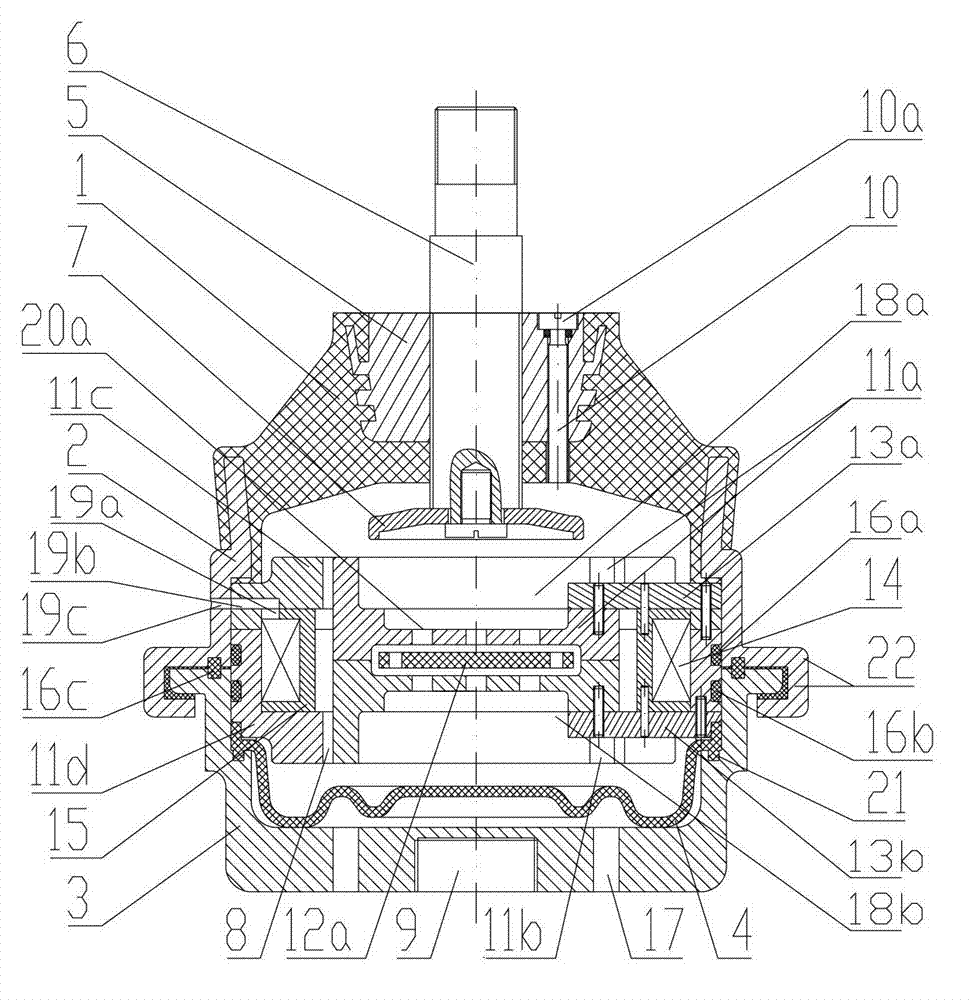
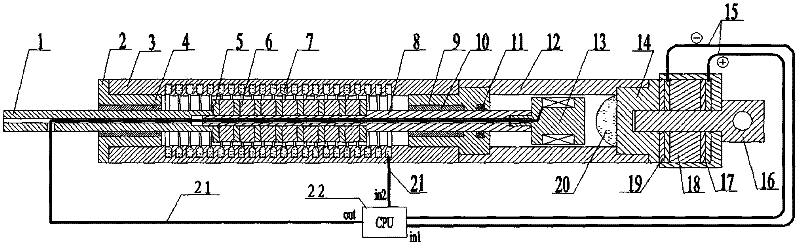
Magneto-rheological shock absorber without external power supply
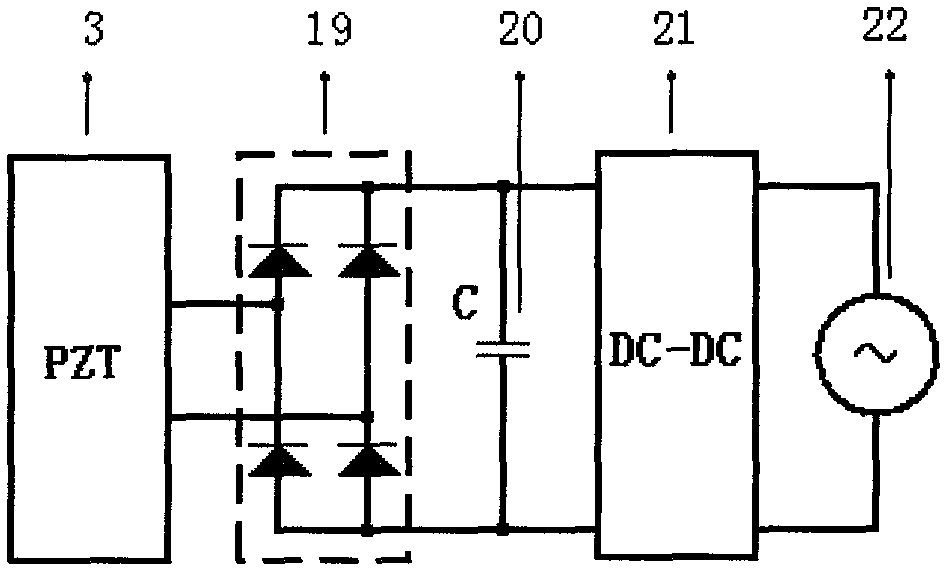
The invention provides a magneto-rheological vibration damper without an externally-connected power supply, comprising an earring, a supporting disc, a piezoelectric pile structure, a lower gland, a bottom end cover, an air bag, a cylinder body, a piston with winded coils, a piston rod, an upper end cover, a spring, an upper gland, a locking member, and an electric energy conditioning module. Wherein, one end of the spring is connected with a piezoelectric generating device, the other end is connected with the piston rod, when the piston rod moves up and down along the cylinder body under outside vibration, external force is applied to the piezoelectric generating device via pressing of a spring mechanism. Under the effect of pressure, the piezoelectric generating device generates electric energy, and the electric energy conditioning module converts high voltage AC electric energy generated by the piezoelectric generating device to low voltage DC electric energy, and applies the low voltage DC electric energy to the piston coils to generate an excitation magnetic field, make magneto-rheological fluid solidified, and improve damping force, thereby reducing vibration of the piston rod. compared with a conventional magneto-rheological damper structure, the magneto-rheological vibration damper without an externally-connected power supply can capture outside vibration energy to supply power to itself, forming a self-energy-providing magneto-rheological vibration damper system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
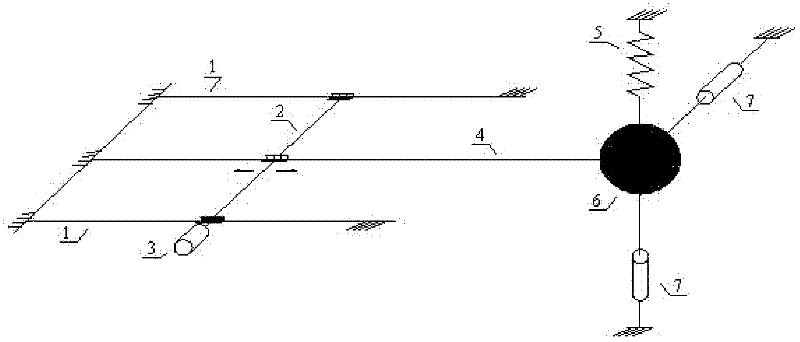
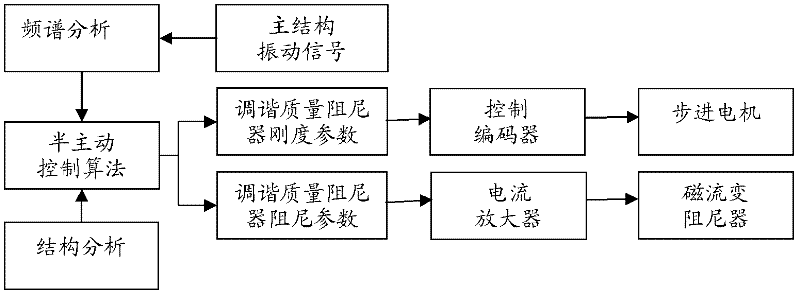
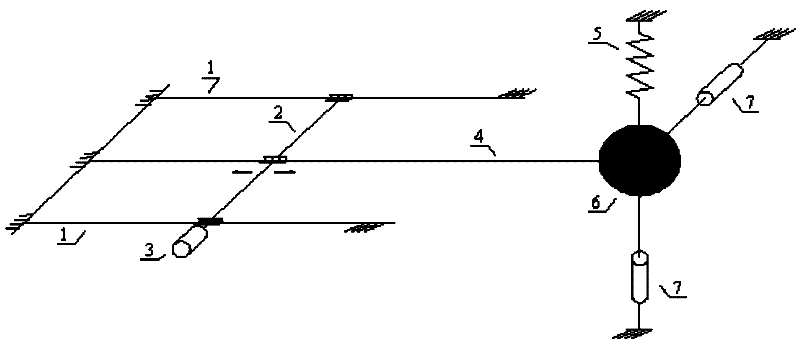
Variable-rigidity and variable-damping tuned mass damper
ActiveCN102345333AWorking principle is clearGood vibration reduction effectArtificial islandsBridge structural detailsSemi activePower flow
The invention discloses a variable-rigidity and variable-damping tuned mass damper, which is mainly applied to vibration control over multi-frequency structures such as high-rise buildings or long-span bridges, ocean platforms and the like. The tuned mass damper comprises a mass block, wherein a vertical spring is connected to the upside of the mass block in a vertical direction, and magnetorheological dampers are respectively arranged on the mass block in a horizontal direction and a vertical direction; and a cantilever spring is arranged horizontally and longitudinally, one end of the cantilever spring is connected with the mass block, the other end of the cantilever is connected with a traveling mechanism. Two ends of the traveling mechanism are placed on a rigid guide rail, and the traveling is driven by a stepping motor to move longitudinally. The length of the cantilever spring is regulated by the movement of the stepping motor, so that the tuning frequency of the tuned mass damper is further regulated; and by regulating currents of the magnetorheological dampers to change the damping ratio of the tuned mass damper, the rigidity and the damping are regulatable continuously, so that the vibration control in the vertical direction and the horizontal direction. The variable-rigidity and variable-damping tuned mass damper disclosed by the invention has a clear working principle and has the advantages of easiness for realizing semi-active control property, good damping effect, fast response, high precision and the like in engineering application.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Magneto-rheological damper with asymmetrical controllable damping characteristic
ActiveCN103352956ASmall size impactReduce use costSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionSemi activePower flow
The invention discloses a magneto-rheological damper with an asymmetrical controllable damping characteristic. The magneto-rheological damper comprises a magneto-rheological damper body, wherein a piston head of the magneto-rheological damper body is provided with a magnet exciting coil and separates an inner cavity of a cylinder barrel into a first accommodating cavity close to the lower end of the cylinder barrel and a second accommodating cavity close to the upper end of the cylinder barrel; convection holes which are communicated with the first accommodating cavity and the second accommodating cavity are formed inside the piston head; and valve components which are used for performing one-way throttling on a magneto-rheological fluid from the second accommodating cavity to the first accommodating cavity are arranged in the convection holes. The magneto-rheological damper with the asymmetrical controllable damping characteristic can enable recovery and controllable damping force to be larger than compression controllable damping force, can produce larger recovery damping force under smaller current, can prolong the recovery time, and is applicable to a vibration control system such as a motorcycle rear suspension or other vehicle suspension system, which requires asymmetrical controllable damping, and semi-active vibration control is realized by changing current of the magnet exciting coil of the magneto-rheological damper; and the magneto-rheological damper is simple in structure, can realize asymmetrical controllable damping force, and is low in use cost and beneficial to popularization and utilization.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
High-performance piston core for a magnetorheological damper
ActiveUS6948312B1High magnetic flux densityPrevent magnetic saturationSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionHigh fluxMagnetic reluctance
A high-performance piston core including a first piston cylinder and a second piston cylinder, with a piston center longitudinally disposed between and magnetically coupling the first piston cylinder and the second piston cylinder. The piston center is made of high-performance magnetic material, such as Cobalt steel (CoFe), Silicon steel (SiFe), Vanadium / Cobalt steel (Permendur), alloys thereof, or the like. The high-performance magnetic materials exhibit high magnetic permeability and reduce the magnetic reluctance of flux bottlenecks. In addition, high-performance magnetic materials typically saturate at a higher flux density than the conventional magnetic materials. The first piston cylinder and the second piston cylinder can be made of conventional magnetic material, such as low-carbon steel. The first piston cylinder can include a ring disposed about an end, where the end is longitudinally attached and magnetically coupled to the piston center.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC +1
Electromagnetism and magnetorheological fluid mixed shock absorber
InactiveCN102588497AAchieve vibration reductionReduce energy consumptionNon-rotating vibration suppressionSemi activeNitrogen
The invention discloses an electromagnetism and magnetorheological fluid mixed shock absorber which can realize active control, is low in energy consumption and can recover energy. The electromagnetism and magnetorheological fluid mixed shock absorber comprises an upper shell and a lower shell which are connected together; an intermediate connecting plate is arranged at the connecting part of the two shells; a piston rod penetrates into the two shells and is connected with a piston body after penetrating through the intermediate connecting plate; the upper shell and the piston body are internally provided with an electromagnetic device respectively; the two electromagnetic devices are both connected with a control unit, and the control unit is connected with a signal end of a sensor; the lower shell at the lower part of the piston body is internally provided with a moving piston; a magnetorheological fluid cavity is respectively arranged between the piston shell of the piston body and the intermediate connecting plate and between the piston shell of the piston body and the moving piston, and the two magnetorheological fluid cavities are communicated by a communicating structure of the piston body; and a nitrogen cavity is arranged between the moving piston and the lower shell. The electromagnetism and magnetorheological fluid mixed shock absorber combines the advantages and disadvantages of the magnetorheological fluid semi-active control and the magnetism active control of the shock absorber, and has the advantages of being good in shock absorbing effect, low in energy consumption and recoverable in energy.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
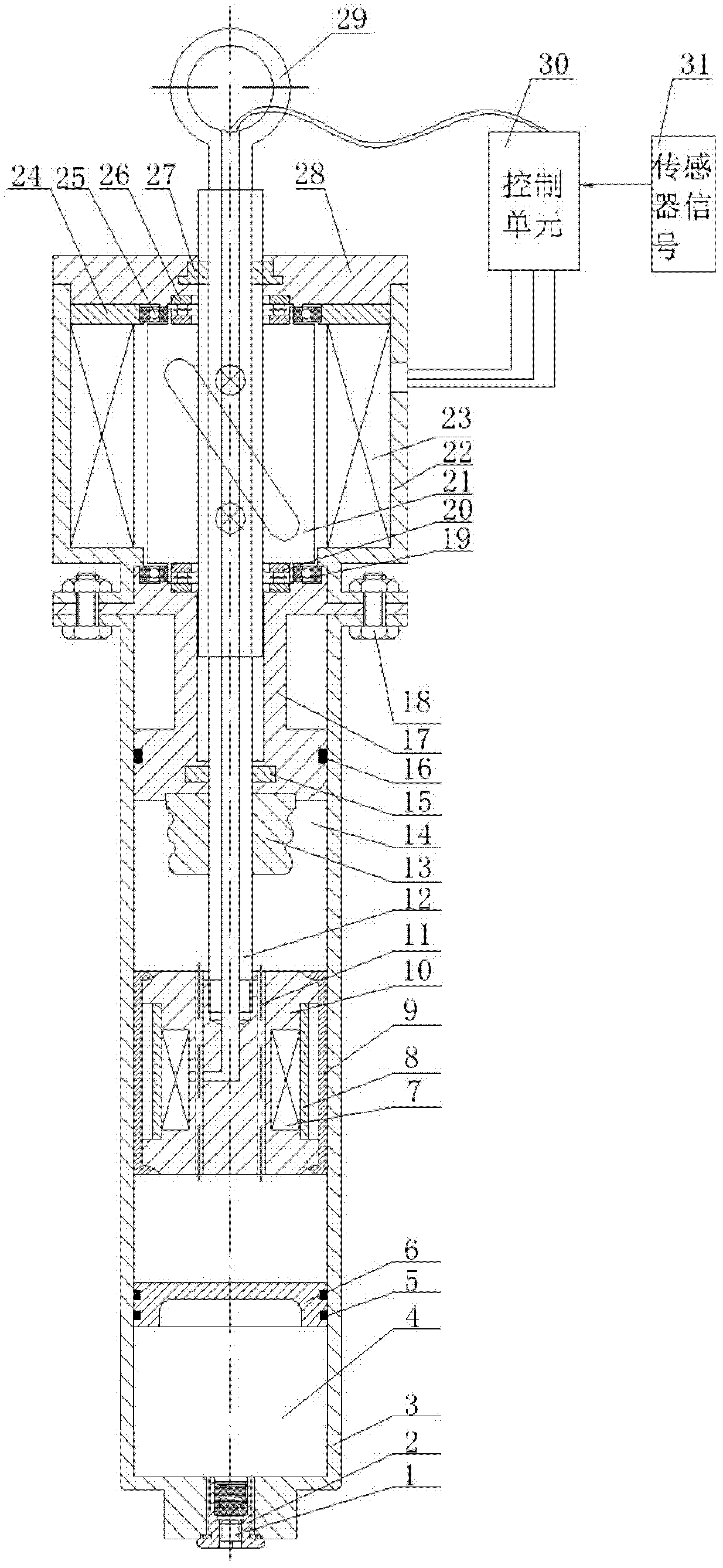
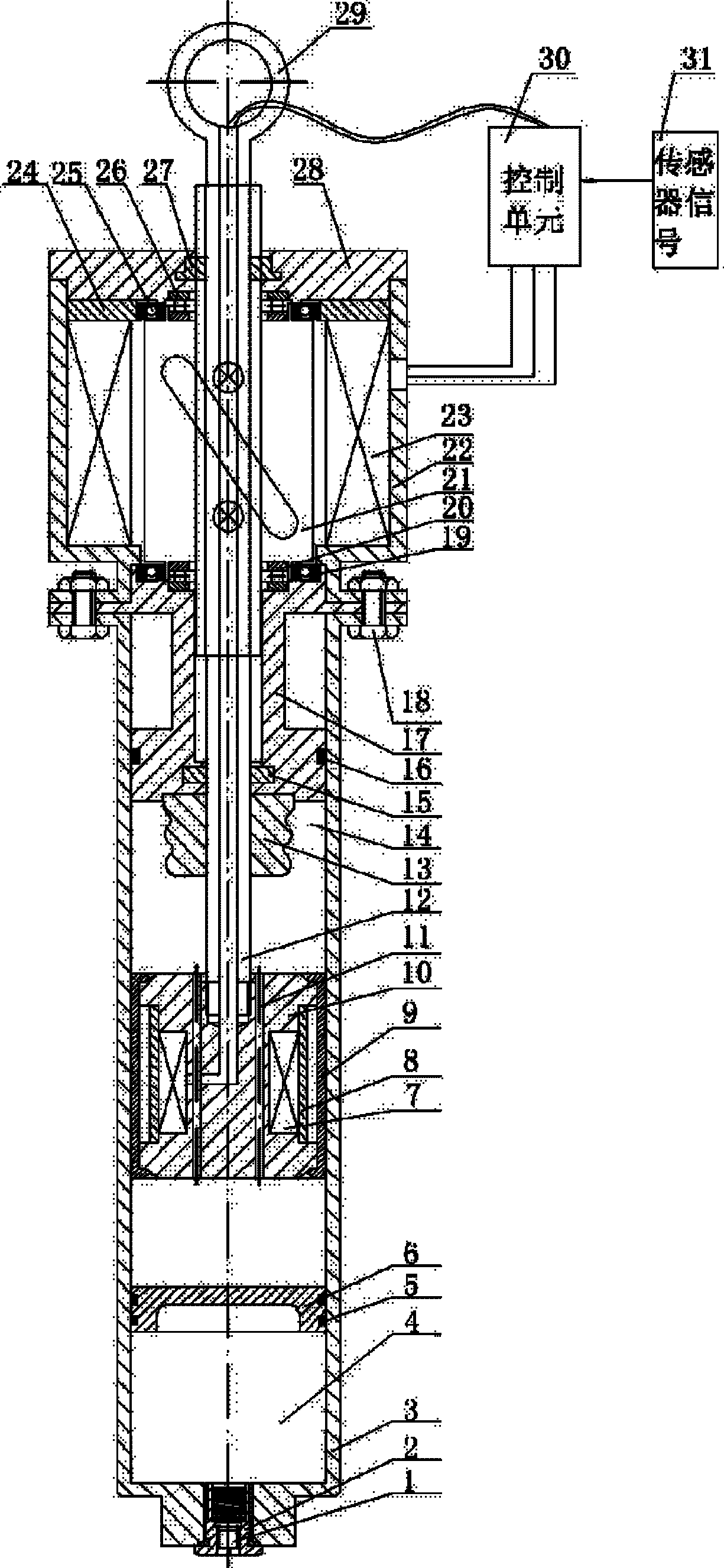
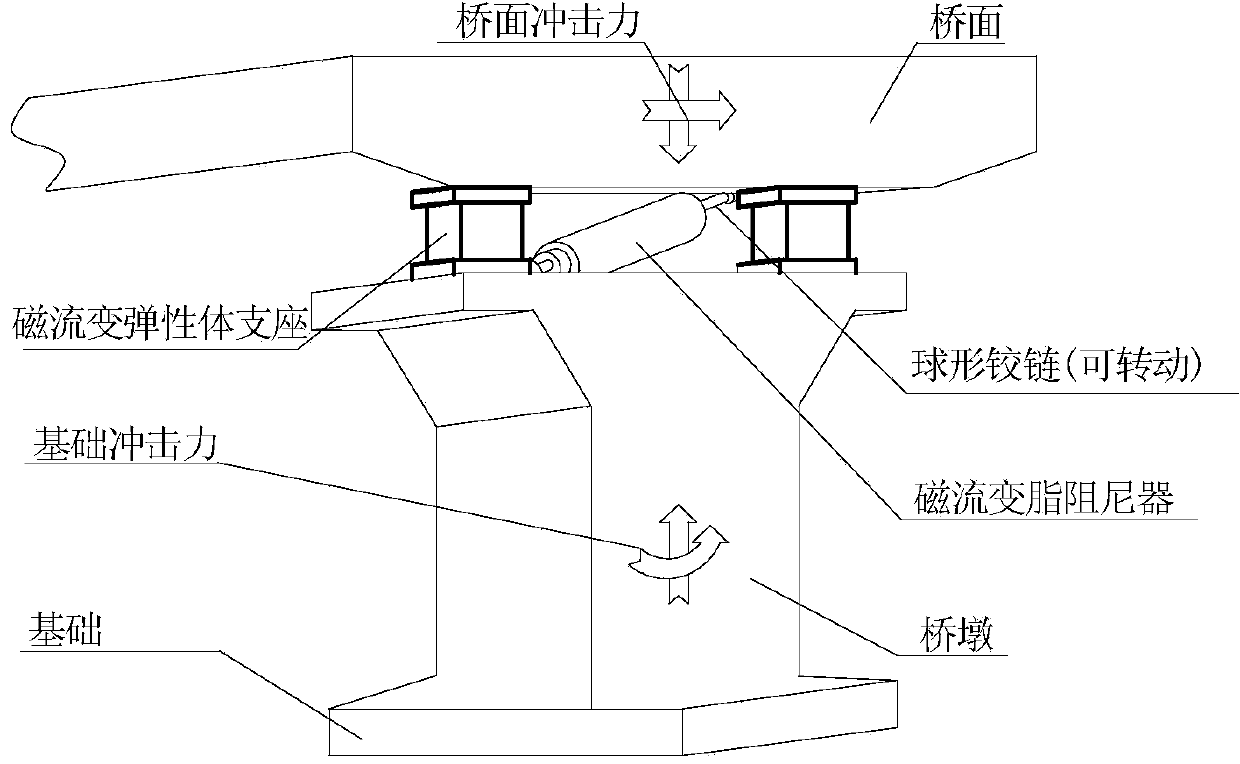
Design method and device of anti-impact vibration isolation type magnetorheological pier bearing-damper system
ActiveCN104179118AInhibition shiftEnhanced vertical strengthBridge structural detailsElastomerDamping ratio
The invention relates to a design method and a device of an anti-impact vibration isolation type magnetorheological pier bearing-damper system. According to the method, magnetorheological elastomers which are large in vertical stiffness, high in structural strength and adjustable in elasticity modulus are used as bearing bodies, and impact resistance and vibration isolation of a pier-beam structure under the action of large load are realized by adjustment of pier stiffness; a magnetorheological damper capable of providing large damping without medium settlement is used as a damping device, three-dimensional rotation capacity of the damper is improved by using a ball-and-socket joint mode at two ends thereof, and pier-beam displacement is restrained by damping adjustment for further vibration reduction and energy dissipation; magnetorheological elastomer bearings, the magnetorheological damper and a controller jointly form an anti-impact vibration-isolation pier bearing device, the controller intelligently adjusts stiffness and damping of the bearing-damper system by detecting the impact vibration of a bridge, structural strength of the pier-beam structure is improved while damping ratio thereof is increased, and when the bridge is under large-load impact vibration, impact transmission is slowed down or isolated and pier-bean displacement is restrained so as to guarantee structural safety of the bridge.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Three-cylinder type large-capacity magneto-rheological damper
InactiveCN101793302AMeet the needs of earthquake resistance and wind resistanceIncreased sensitivityNon-rotating vibration suppressionSolid based dampersVibration controlControl theory
The invention discloses a three-cylinder type large-capacity magneto-rheological damper for vibration control of a large civil engineering structure, which comprises a magneto-rheological damping cylinder (9), a puddle damping cylinder (5), an auxiliary cylinder (19), a magneto-rheological main piston (23), a puddle piston (6), a piston rod (17), a sealing baffle (20), a damping channel (16), a cylinder cover (3) and a spherical hinge joint (13), wherein magneto-rheological liquid (11) is filled in the magneto-rheological damping cylinder, and an annular excitation coil (8) capable of generating a magnetic field is arranged in the magneto-rheological damping cylinder; and the puddle damping cylinder is arranged adjacent to the magneto-rheological damping cylinder, and elastic puddle (7) is filled in the inner cavity of the puddle damping cylinder, thus the damper can generate large damping under the condition of large displacement, and the safety of the damper can be improved. By arranging a displacement splitting mechanism (18), the magneto-rheological damper has high rigidity and large damping in a low-frequency region and has low rigidity and small damping in a high-frequency region. Compared with the traditional magneto-rheological damper with the same size, the maximum capacity of the damper of the invention is improved by more than one time, and the vibration control of the large civil engineering structure is more effective.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Soft touch joint based on joint cross structure
The invention relates to the field of space robot researching and engineering, in particular to a soft touch joint based on a joint cross structure. The soft touch joint based on the joint cross structure comprises a driving transmission mechanism, a damping assembly and a sensing component. The driving transmission mechanism comprises motor driving units, controllers, inner shells, outer shells, sliding blocks, sliding rails and the like. The damping assembly comprises linear type magnetorheological dampers, clutches, rotary type magnetorheological dampers, spring mechanisms, torsion spring mechanisms and the like. The sensing component comprises encoders, linear displacement sensors and the like. The mechanical arm joint mainly utilizes the clutches and the magnetorheological dampers in the damping assembly to control the total flexibility of the soft touch joint, mutual conversion between a pitching and yawing two-freedom-degree rigidity driving function and space six-dimensional momentum unloading can be achieved according to operation tasks, and therefore soft touch of space operations is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
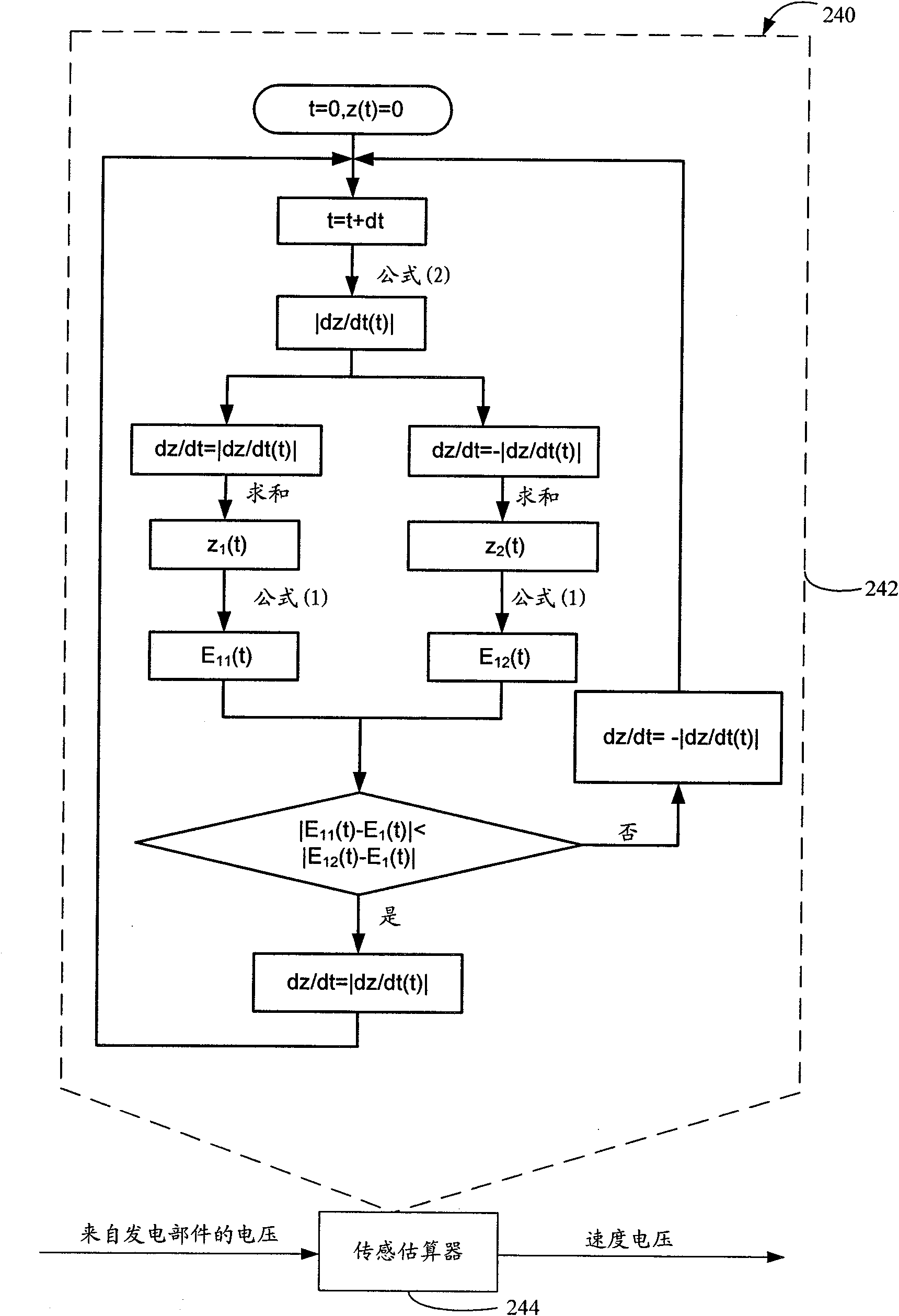
Magnetic current changeing dumper of integrated related speed sensing function and method of adaptive damping
InactiveCN1598350AWith damping functionRealize adaptive vibration reduction functionSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagnetic currentRelative motion
A self-adapting vibration reduction method and a magnetic rheology damper which has integration relative velocity conversion function. The damper is made up of cylinder body, magnetic rheology liquid, exciting coil on the piston head, induction coil in the piston rod, accumulator, and dirt shroud, and so on; the exciting coil and the induction coil are constituted a active magnetoelectricity type relative velocity transducer, it integrates the magnetic rheology damper structure to a unit. Its vibration reduction method is that exciting coil is loaded a medium-low frequency voltage sign as the transducer's exciting coil detection signal, common frequency alternating magnetic field which is produced by the method is formed to a closure work magnetic loop in the damper structure; axial direction relative motion between the piston of magnetic rheology damper and cylinder body make magnetic linkage of the induction coil occur to correspond change and induced obtain conversion output signal which reflects the axial direction relative motion; according to the conversion signal, controller self-adapting adjusts the drive current which is overlap on the exciting coil by current drive to control the magnetic field strength of the exciting coil to realize the self-adapting vibration reduction of the magnetic rheology.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
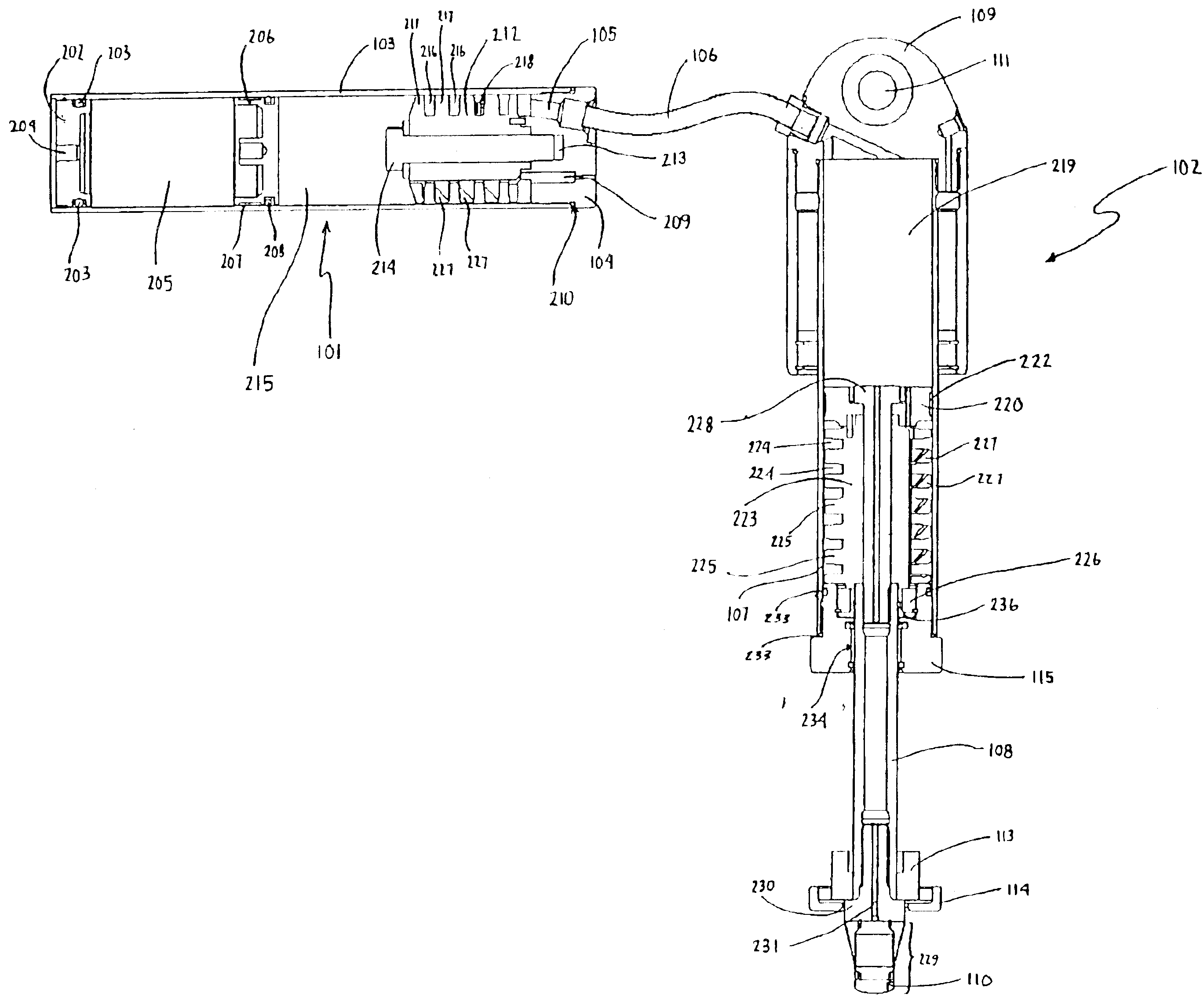
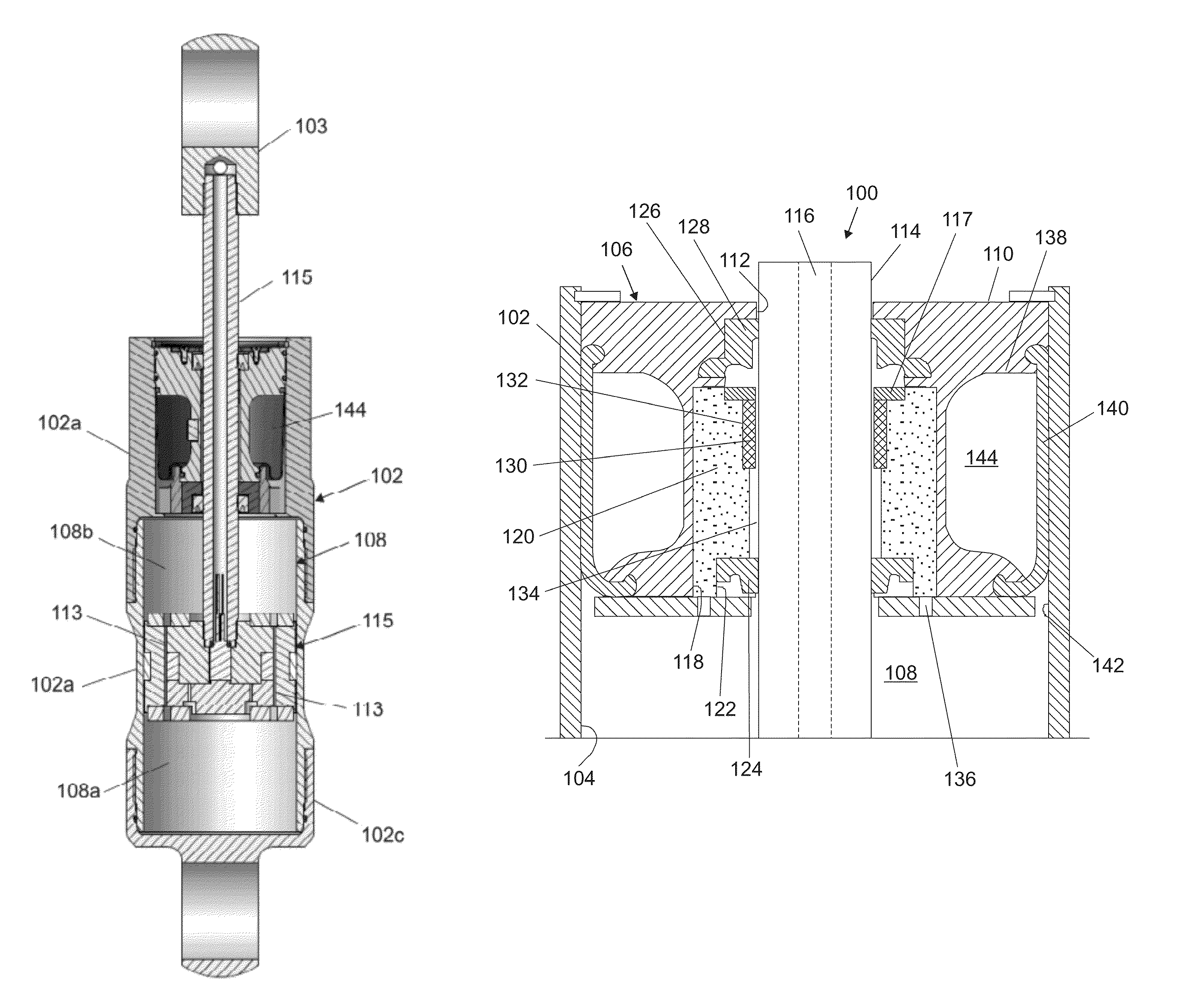
Magneto-rheological dampers for semi-active suspension systems
A magneto-rheological fluid damper includes a damper body having a reservoir for a magneto-rheological fluid, a piston rod, a piston rod guide disposed within the damper body, where the piston rod guide has a passage therein for receiving the piston rod. The magneto-rheological fluid damper further includes at least a first piston rod seal and at least a second piston rod seal arranged to seal between the piston rod guide and the piston rod. The magneto-rheological fluid damper further includes a fluid chamber defined between the piston rod guide and the piston rod, the fluid chamber being in communication with the reservoir. The magneto-rheological fluid damper further includes a piston rod guide filter arranged in a communication path between the fluid chamber and the reservoir to filter particulates out of the magneto-rheological fluid entering the fluid chamber. The magneto-rheological fluid damper further includes an accumulator arranged between the piston rod guide and the damper body.
Owner:LORD CORP
Device for calibrating relationship between current of electric machine of numerically controlled machine and cutting load
InactiveCN101434045ACompact structureHigh precisionMeasurement/indication equipmentsNumerical controlPower flow
The invention discloses a device for calibrating a numerical control machine tool motor current-cutting load relation, which comprises a magnetorheological rotation damper, a controller of the magnetorheological rotation damper, a data acquisition card, a calibration processor, a Hall transducer, a coupling, a simulated cutting tool, a slide block, a rack and a support, wherein the magnetorheological rotation damper is connected with a main shaft of the machine tool through a gear, the rack, the simulated cutting tool or the coupling; and primary motion or feed motion of the machine tool is transformed into rotation of a shaft of the magnetorheological rotation damper. The magnitude of simulated cutting load can be obtained according to different control parameters so as to detect current data and feed the current data to the calibration processor for recording and processing, thereby realizing the calibration of the relation between the machine motor current and the cutting load. The device can be widely applied to calibration on the numerical control machine tool under the condition of a production workshop, and has the advantages of extremely quick response velocity, high precision, strong environmental adaptability, small noise and no pollution.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Magneto-rheological damper suitable for high-speed impact/low-speed vibration control system
ActiveCN103527702AReduced Viscous Damping ForceIncrease shear areaNon-rotating vibration suppressionVibration controlLow speed
The invention discloses a magneto-rheological damper suitable for a high-speed impact / low-speed vibration control system. The magneto-rheological damper comprises a cylinder body I, a cylinder body II and a piston, wherein the cylinder body I comprises an inner cavity, and the piston can slide along the inner wall of the cylinder body I. The cylinder body I is arranged in the cylinder body II, and an outer cavity is formed between the cylinder body I and the cylinder body II. Magneto-rheological fluid is filled into the inner cavity and the outer cavity, and the inner cavity and the outer cavity are communicated with each other through flowing holes formed in the two ends of the cylinder body I. At least one groove where an electromagnetic coil is wound is formed in the outer wall of the cylinder body I and / or the inner wall of the cylinder body II. On the premise that the external dimension, field current and energy consumption of an existing magneto-rheological damper are not increased, the speed ratio of the movement of the piston to a magneto-rheological fluid flowing channel (the outer cavity) can be effectively lowered, and the requirements for a controllable damping ratio and a controllable speed range of the magneto-rheological damper of the high-speed impact and low-speed vibration control system can be met.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
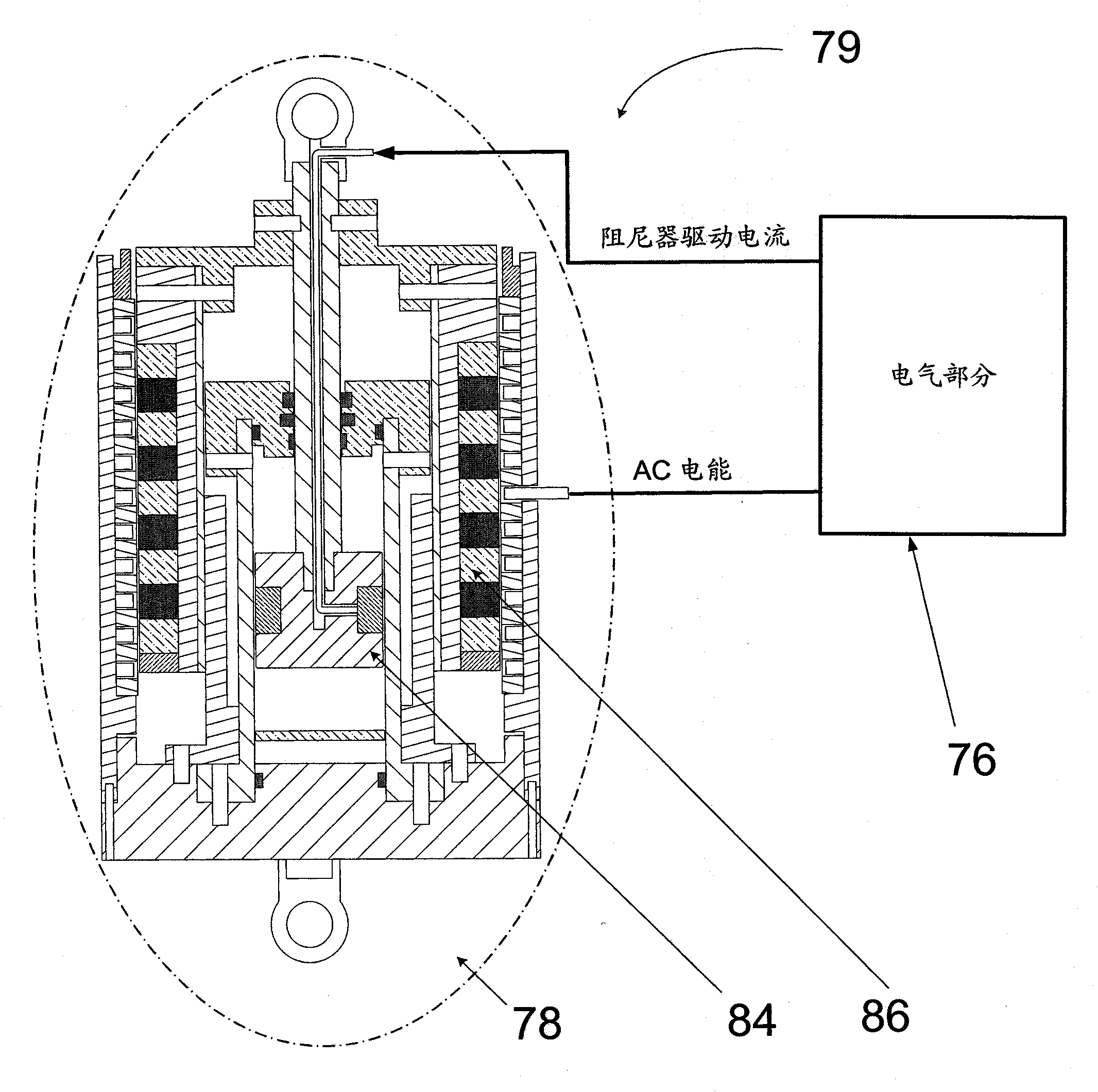
Self-powered and self-sensing magnetorheological (MR) fluid damper
ActiveCN102374255ASmall sizeReduce weightSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionDriving currentSelf sensing
The invention discloses a self-powered and self-sensing magnetorheological (MR) fluid damping device, which comprises an MR damper component, a generating component, a control unit and a sensing component, wherein the MR damper component is provided with a damper piston assembly and a damper cylinder; the damper piston assembly can shift relative to the damper cylinder under external excitation; the generating component is used for generating a voltage signal according to the shift of the damper piston assembly; the control unit is used for estimating the shifting speed according to the generated voltage signal, and outputting damping drive current based on the estimated speed; the sensing component is provided with at least one coil for generating MR fluid field strength; and the sensing component is used for receiving the damping drive current to change the field strength, and thereby, the MR damper component is controlled to provide an adjustable damping force.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
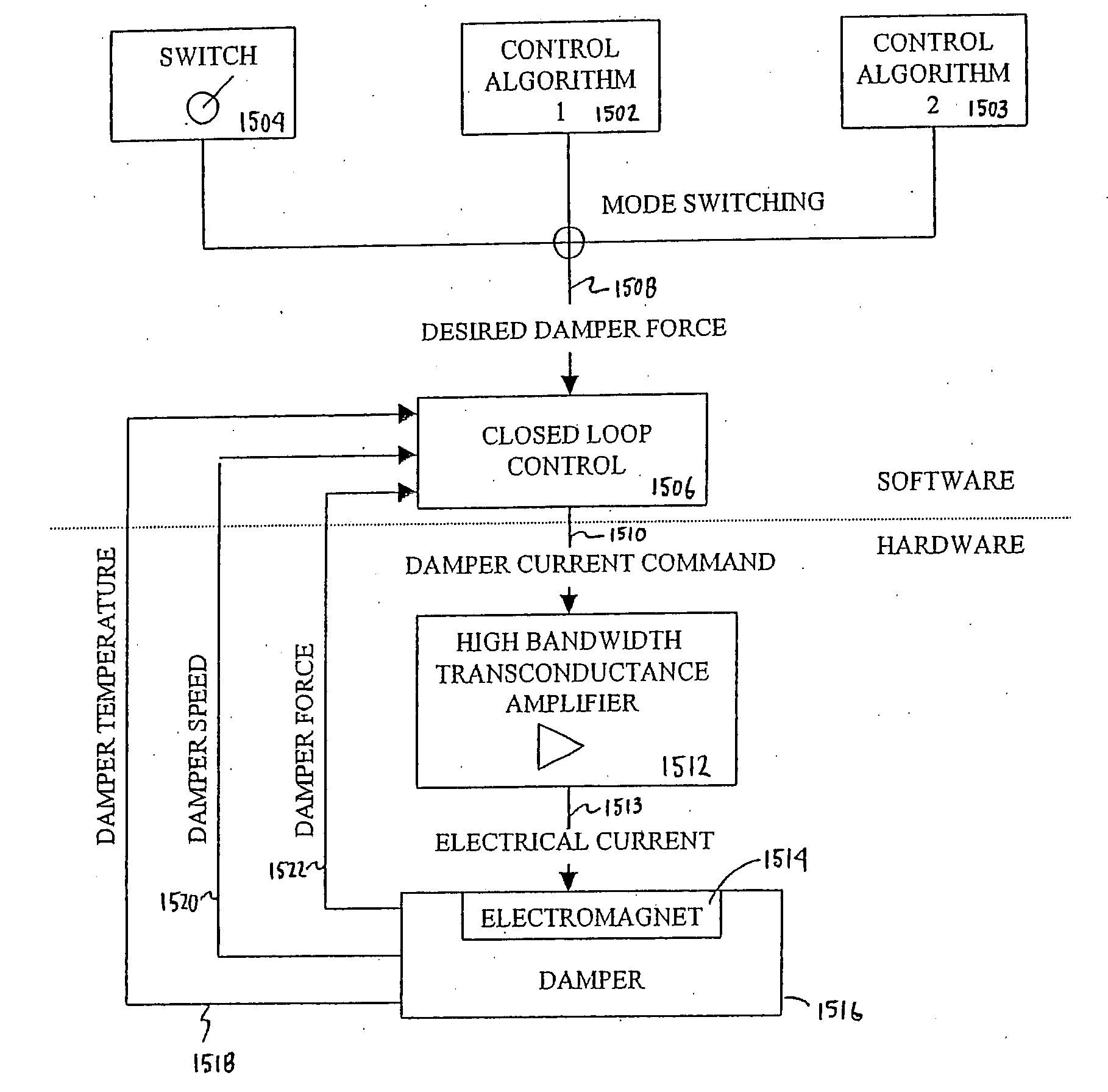
Self-powered self-inductive magnetorheological damper
InactiveCN102287474ARealize intelligent closed-loop controlLow application costNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagnetic polesClosed loop
A self-powered self-induction magneto-rheological damper, including a connecting rod, an upper end cover, a stator, a first guide sleeve, a magnetic pole, a permanent magnet, an electromagnetic coil, a piston rod, a connecting end cover, a second guide sleeve, a seal, and a cylinder Body, piston with coil, bottom end cover, charge signal line, bottom earring, piezoelectric electrode, piezoelectric sheet, rubber sheet, air bag, wire and electric energy signal control module. The invention can adjust the size of the output damping force in real time according to the size of the external vibration force, thereby realizing the intelligent closed-loop control of the external vibration. The structural vibration control system based on the self-powered self-induction magneto-rheological damper will become very simple and greatly reduce the application cost because it does not require additional power input equipment and external vibration force test equipment, and is especially suitable for Applications where space is limited and power supply is inconvenient, such as: large buildings and bridges, etc.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com