Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
692 results about "Shear modulus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In materials science, shear modulus or modulus of rigidity, denoted by G, or sometimes S or μ, is defined as the ratio of shear stress to the shear strain...
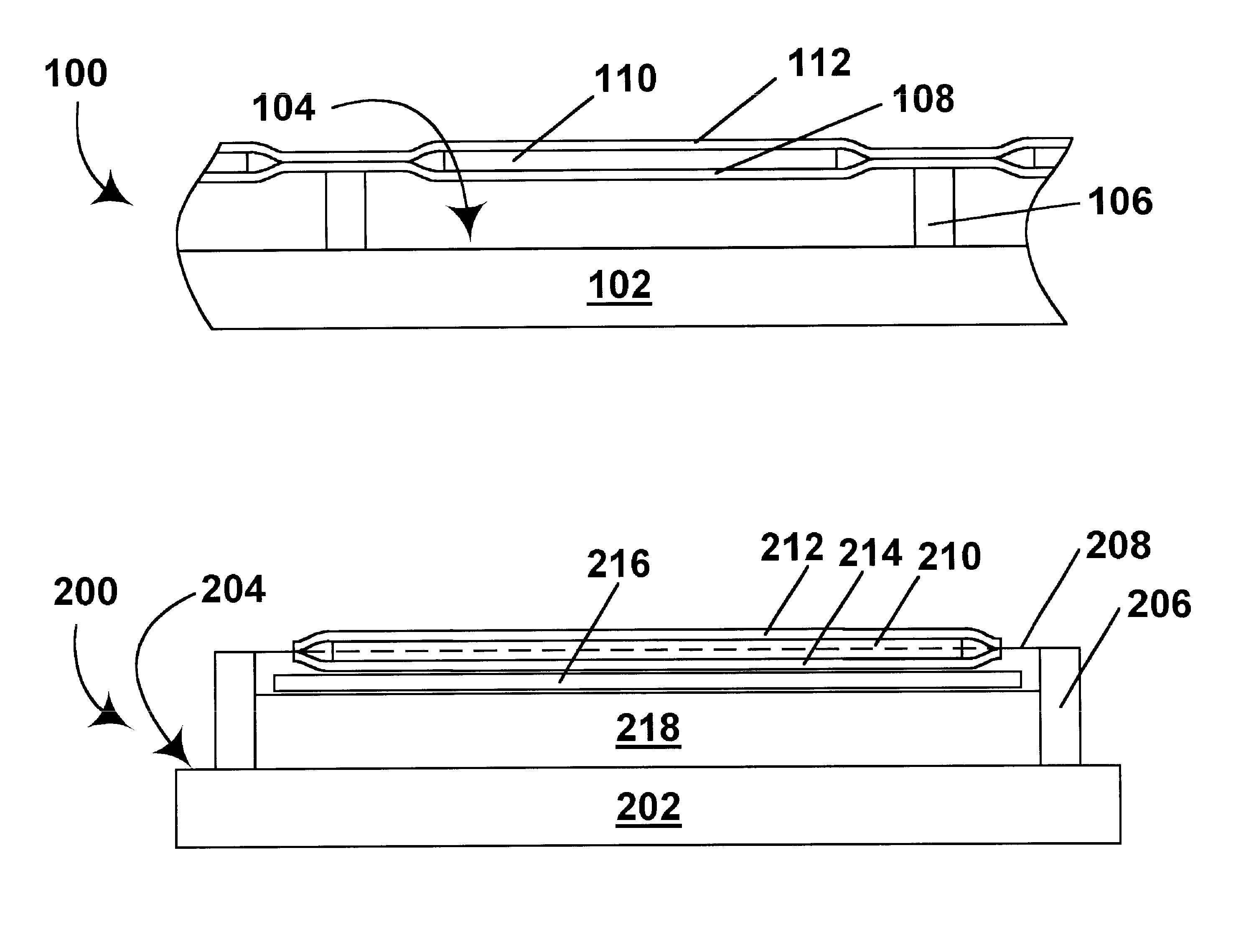
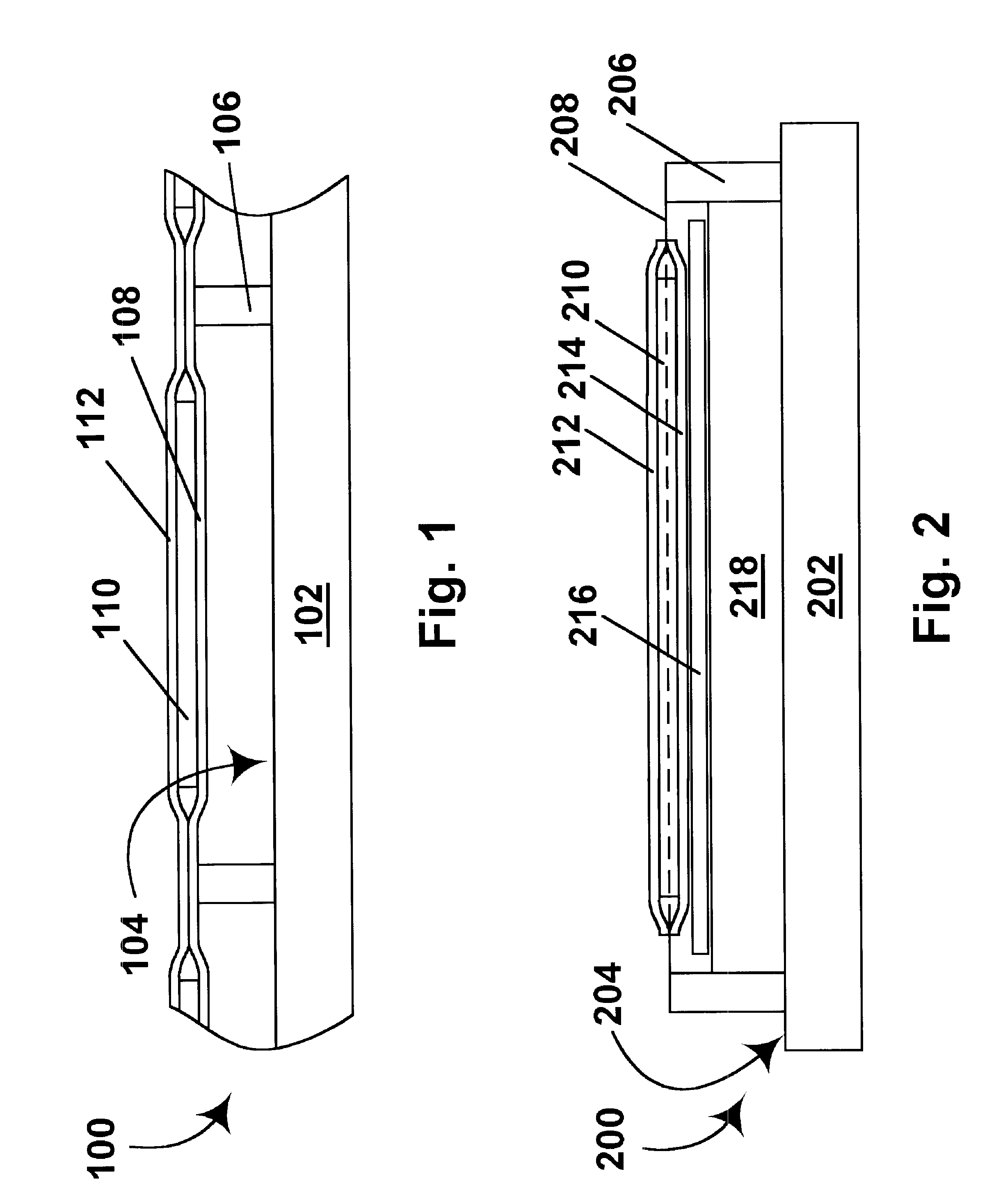
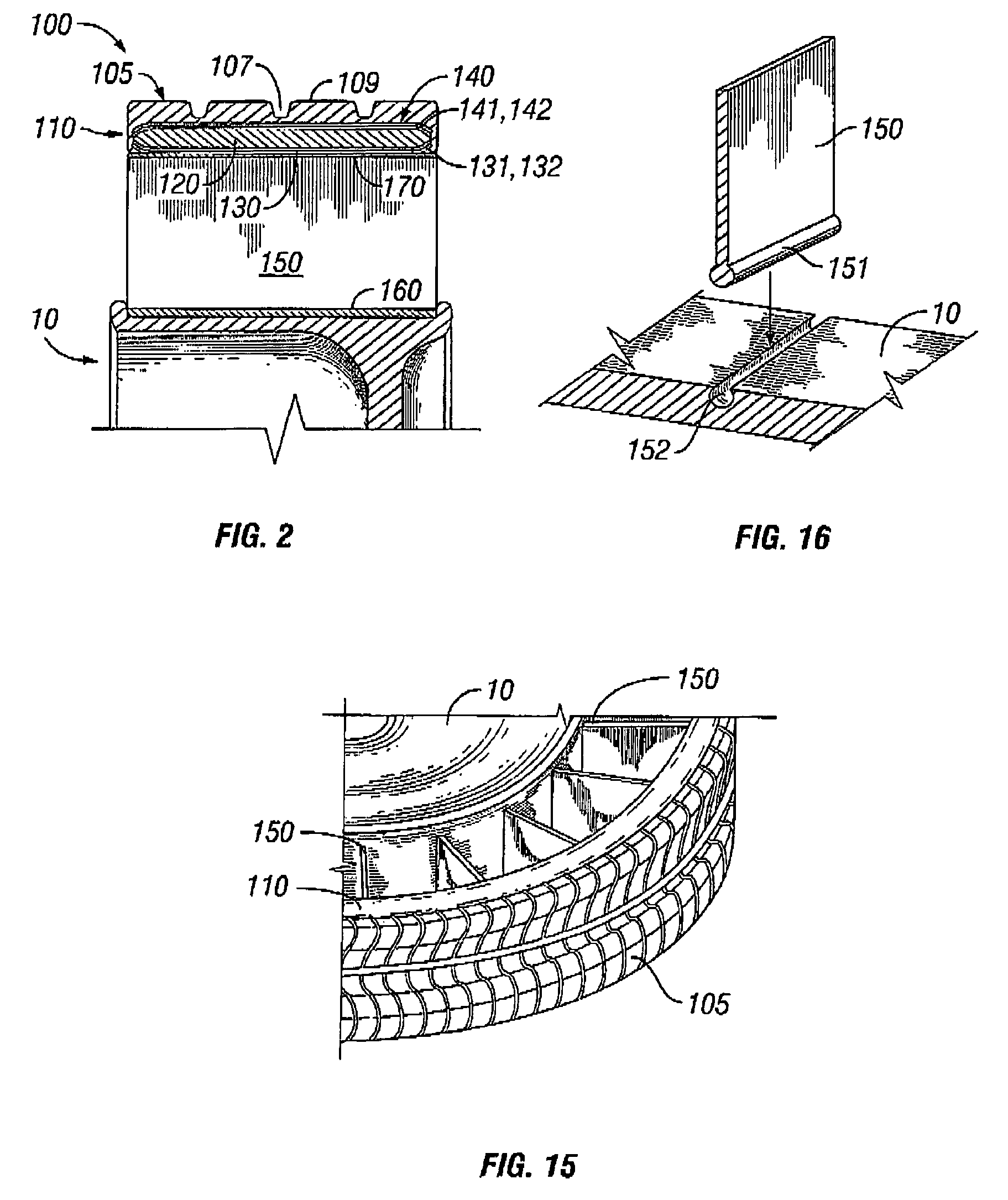
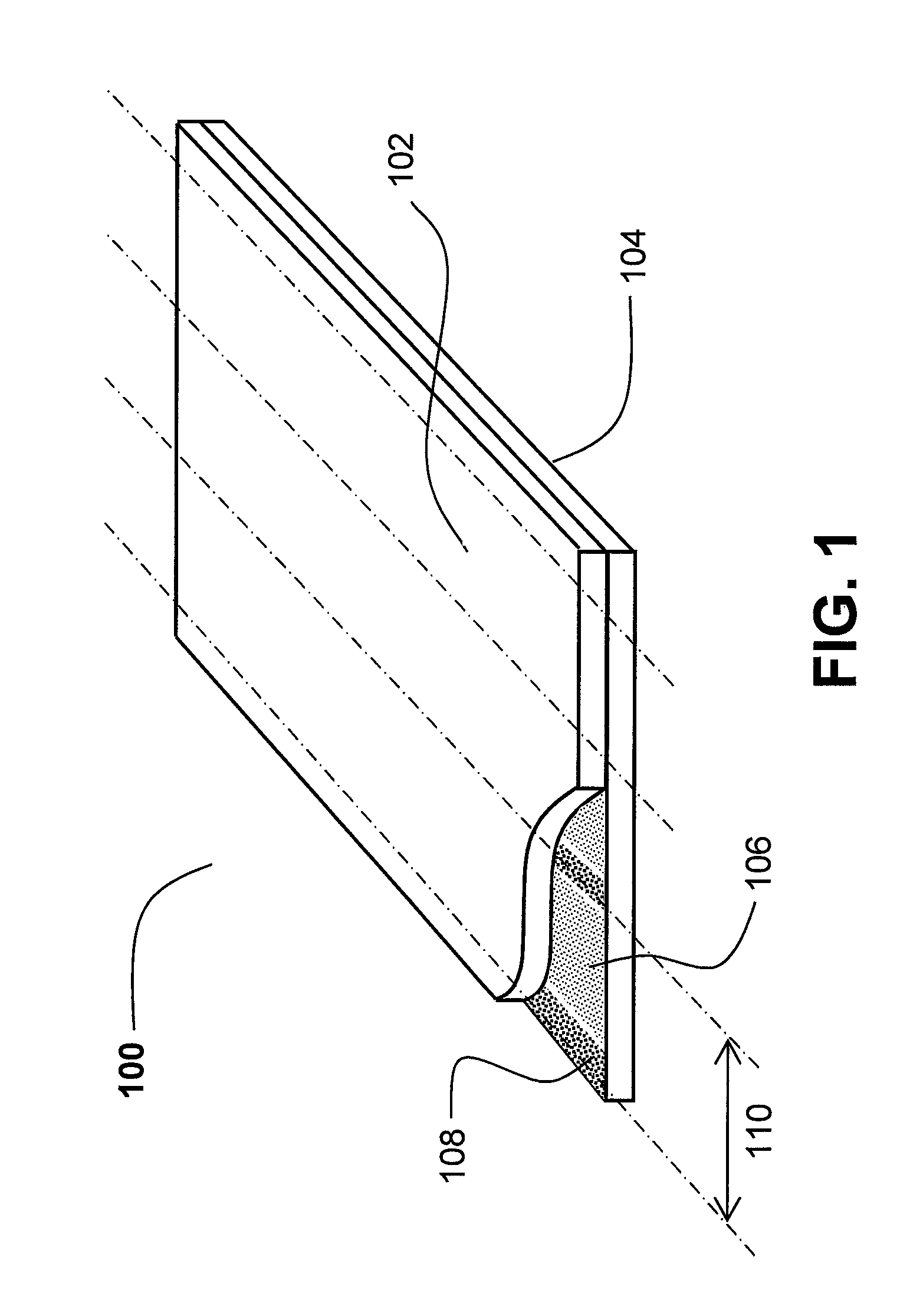
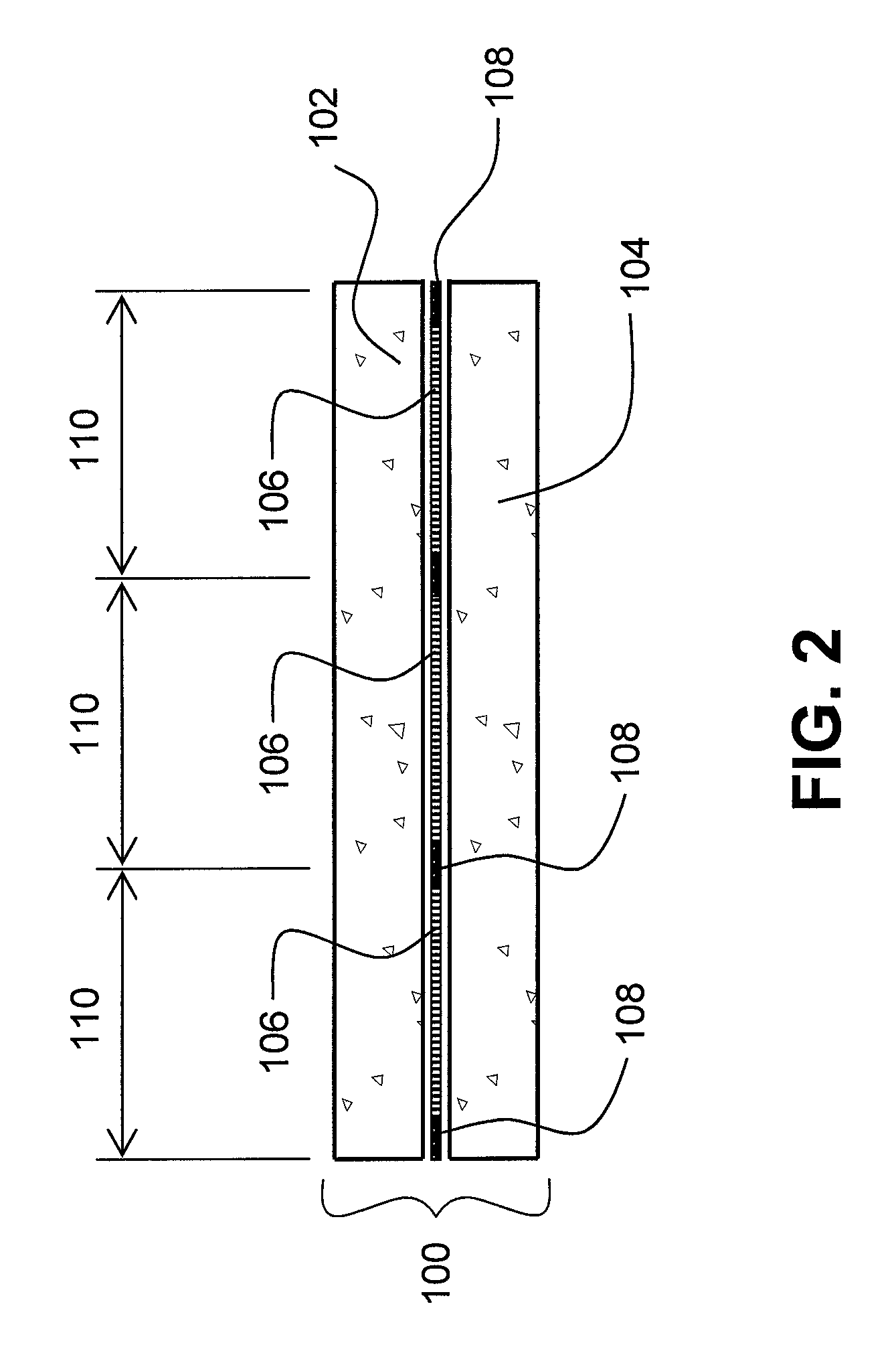
Flexible electro-optic displays
An encapsulated electrophoretic medium comprises a plurality of capsules dispersed in a polymeric binder, each of the capsules comprising a capsule wall, a suspending fluid contained within the capsule wall, and a plurality of electrically charged particles suspended in the suspending fluid and capable of moving therethrough upon application of an electric field to the medium, the polymeric binder having a shear modulus of at least about 10 mPa at 20° C., and preferably over the range of 10-50° C.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
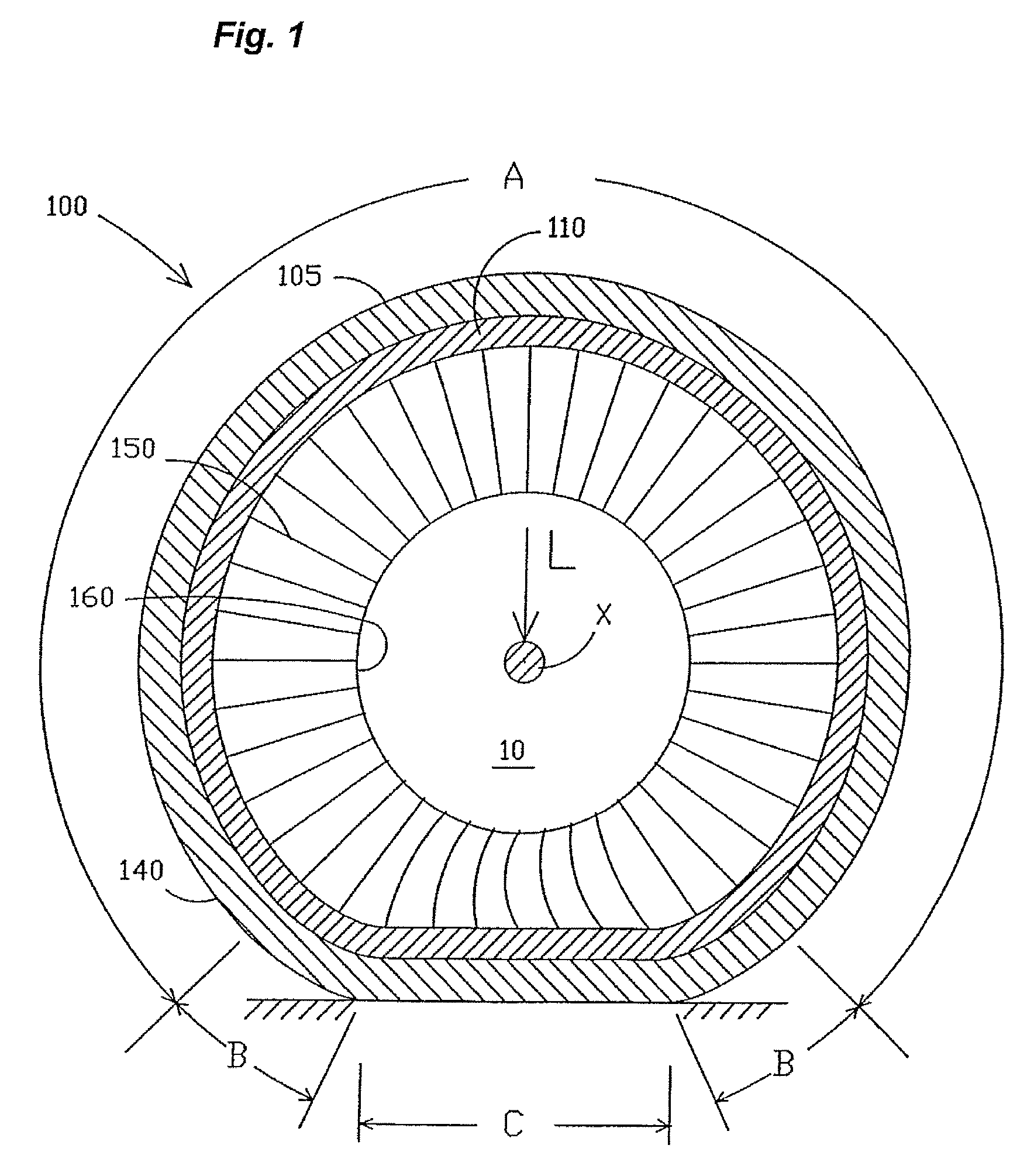
Non-pneumatic tire
InactiveUS7201194B2Supporting massHigh effective radial stiffness in tensionNon-inflatable tyresPneumatic tyre reinforcementsElastomerShear modulus
A structurally supported tire includes a ground contacting tread portion, a reinforced annular band disposed radially inward of the tread portion, and a plurality of web spokes extending transversely across and radially inward from the reinforced annular band and anchored in a wheel or hub. The reinforced annular band comprises an elastomeric shear layer, at least a first membrane adhered to the radially inward extent of the elastomeric shear layer and at least a second membrane adhered to the radially outward extent of the elastomeric shear layer. Each of the membranes has a longitudinal tensile modulus sufficiently greater than the shear modulus of the shear layer so that when under load the ground contacting portion of the tire deforms to a flat contact region through shear strain in the shear layer while maintaining constant the length of the membranes, the web spokes transmitting load forces between the annular band and the hub through tension in the web spokes not connected to the ground contacting portion of the tire.
Owner:MICHELIN RECH & TECH SA
Methods, Systems and Computer Program Products for Ultrasound Shear Wave Velocity Estimation and Shear Modulus Reconstruction
ActiveUS20080249408A1Wave based measurement systemsOrgan movement/changes detectionShear modulusReconstruction method
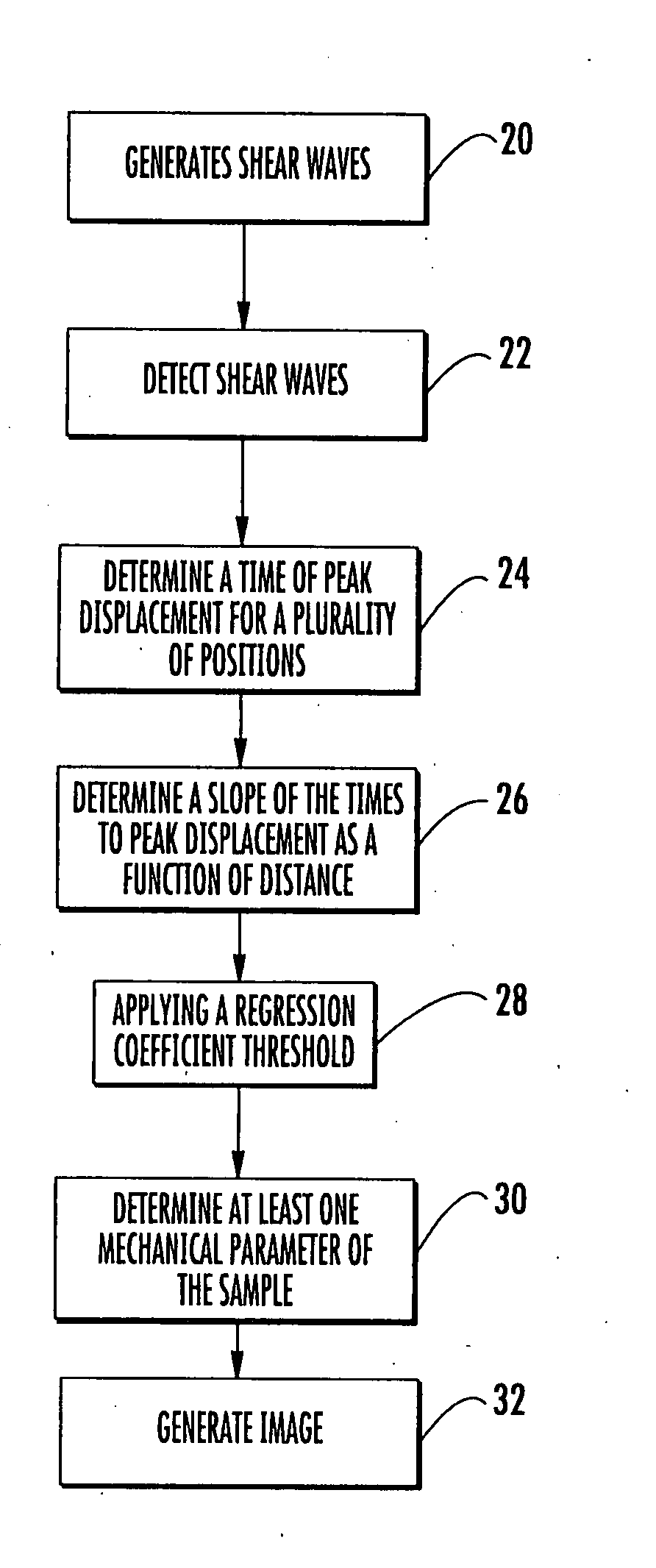
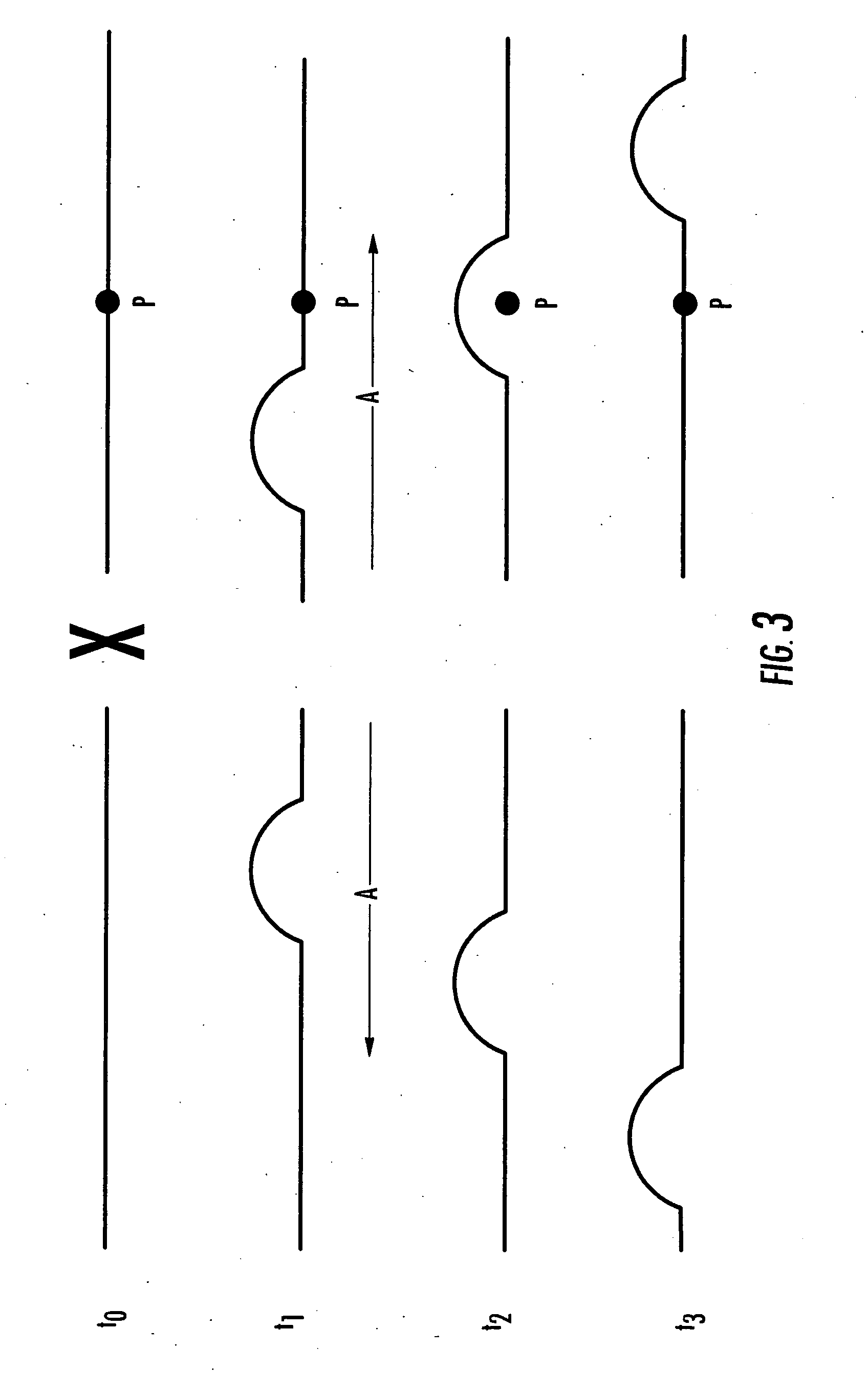
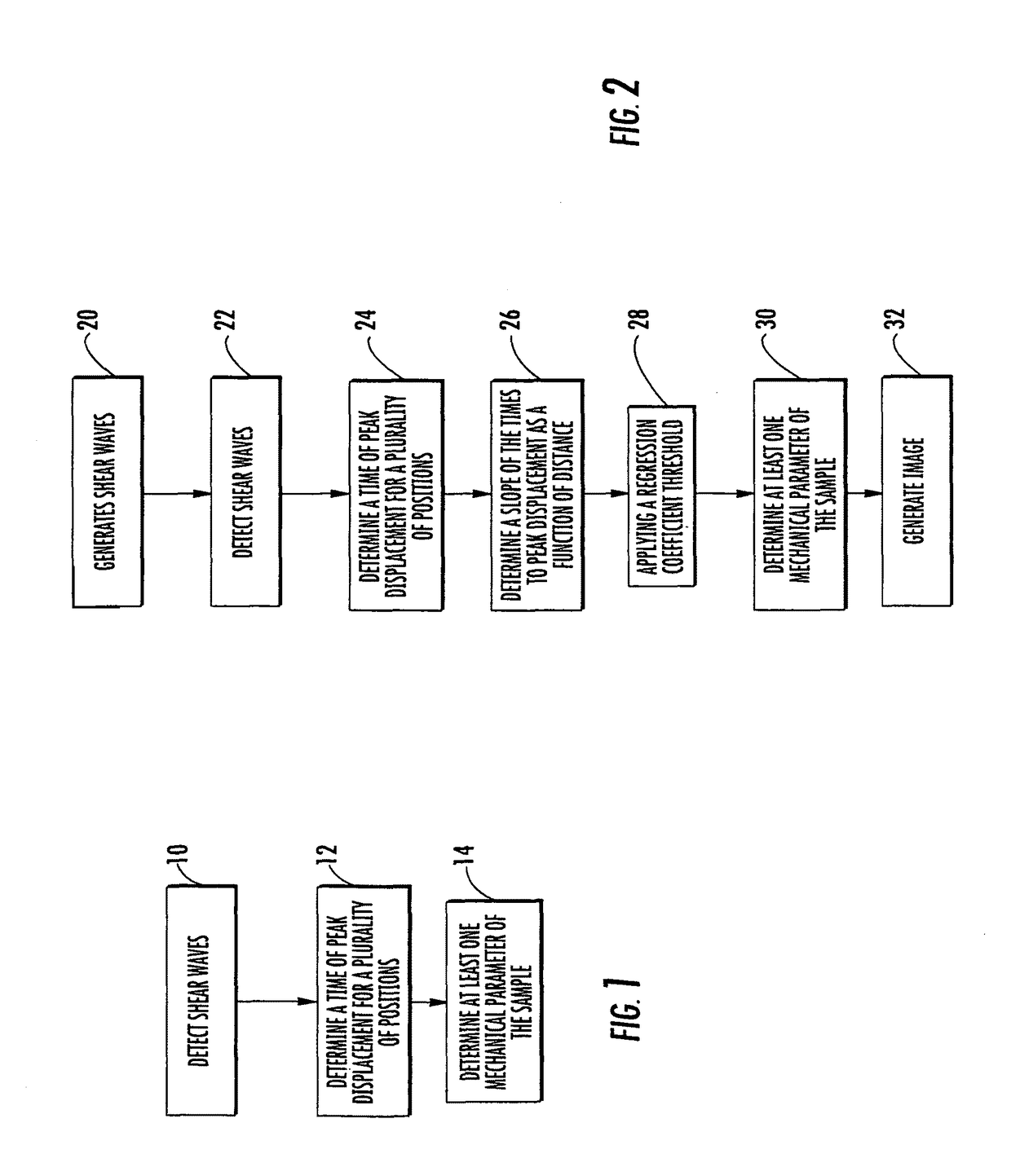
Methods for determining a mechanical parameter of a sample include detecting shear waves that have been generated in the sample by an applied shear wave source. A time of peak displacement of the shear waves for a plurality of sample positions is determined. At least one mechanical parameter of the sample based on the time of peak displacement for the plurality of sample positions is determined.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Tough iron-based bulk metallic glass alloys
A family of iron-based, phosphor-containing bulk metallic glasses having excellent processibility and toughness, methods for forming such alloys, and processes for manufacturing articles therefrom are provided. The inventive iron-based alloy is based on the observation that by very tightly controlling the composition of the metalloid moiety of the Fe-based, P-containing bulk metallic glass alloys it is possible to obtain highly processable alloys with surprisingly low shear modulus and high toughness.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Lightweight thermoplastic composite including reinforcing skins
A lightweight fiber reinforced thermoplastic composite having an improved combination of surface roughness, flexural and shear characteristics. The composite generally comprises a fiber reinforced thermoplastic core containing reinforcing fibers bonded together with a first thermoplastic resin in which the core has a first surface and a second surface and at least one first skin applied to the first surface. The first skin comprises a plurality of fibers bonded together with a second thermoplastic resin, with the fibers in each first skin aligned in a unidirectional orientation within the first skin. The composite satisfies at least one of the conditions: an average surface roughness of the outer surface of the first skin is equal to or less than about 4.0 μm / 10 mm; the flexural modulus and strength are greater than about 10,000 MPa and greater than about 180 MPa, respectively; and the shear modulus and strength are greater than about 3,000 MPa and greater than about 100 MPa, respectively. In another embodiment, a fiber reinforced thermoplastic composite comprises a fiber reinforced thermoplastic core containing reinforcing fibers bonded together with a first thermoplastic resin, the core having a density of about 0.1 gm / cc to about 2.25 gm / cc and a porosity greater than about 0% by volume. The core has a first surface and a second surface and at least one first skin applied to the first surface, each of the first skins comprising fibers bonded together with a second thermoplastic resin. The first skin comprises a thermoplastic melt impregnated continuous fiber prepreg material, or commingled fiber rovings comprising reinforcing fibers and thermoplastic fibers, with the fibers in the first skin aligned in a unidirectional orientation within the first skin.
Owner:AZDEL INC
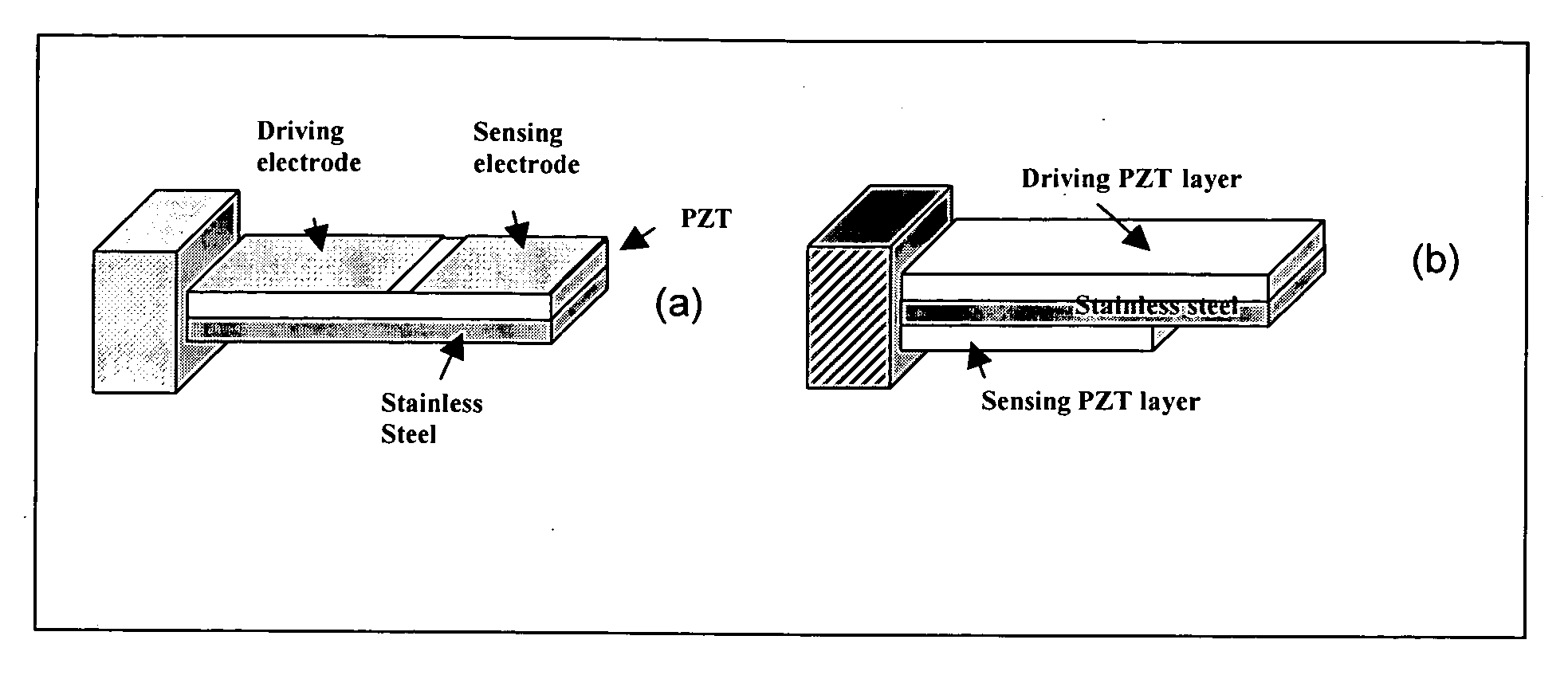
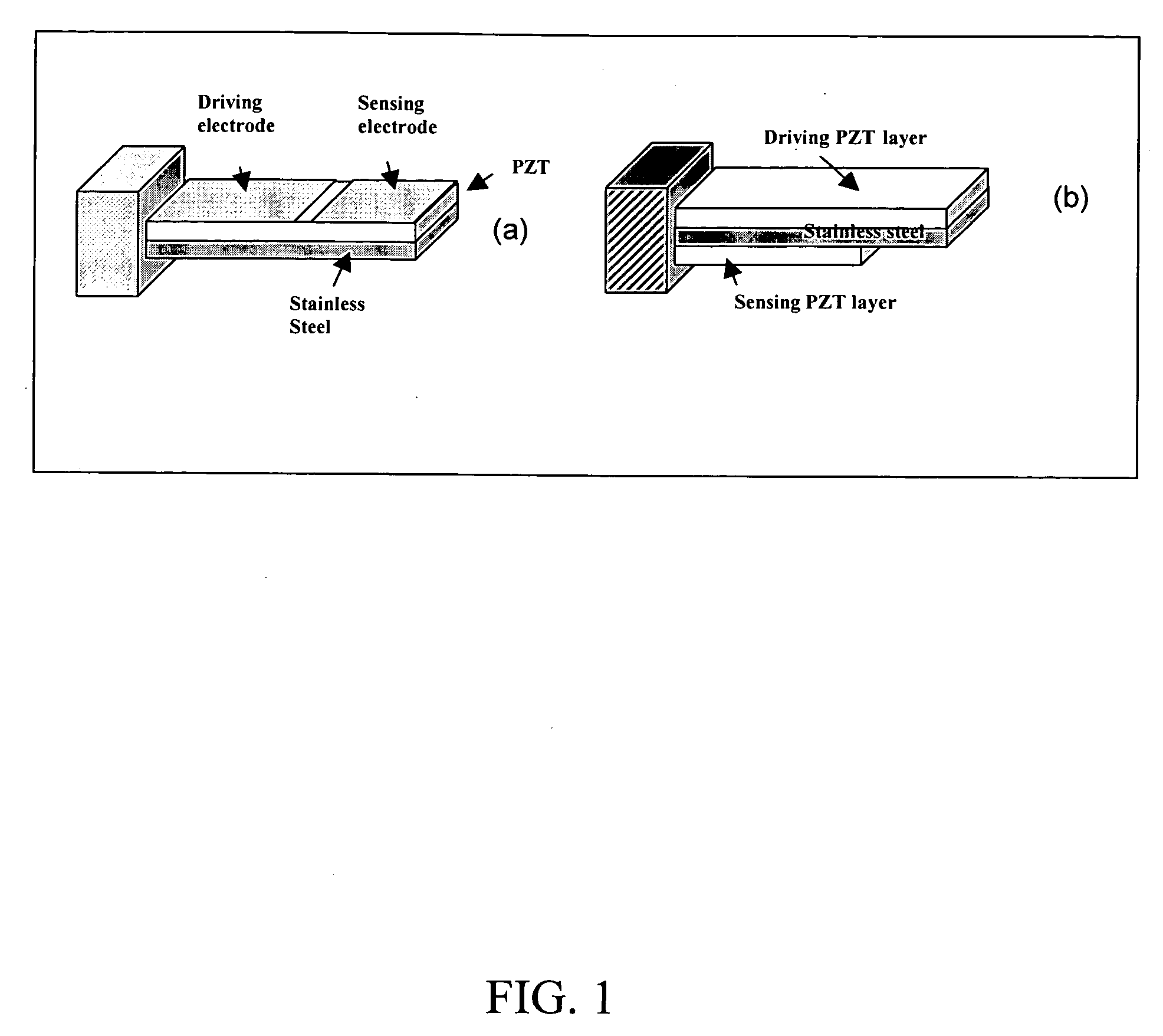
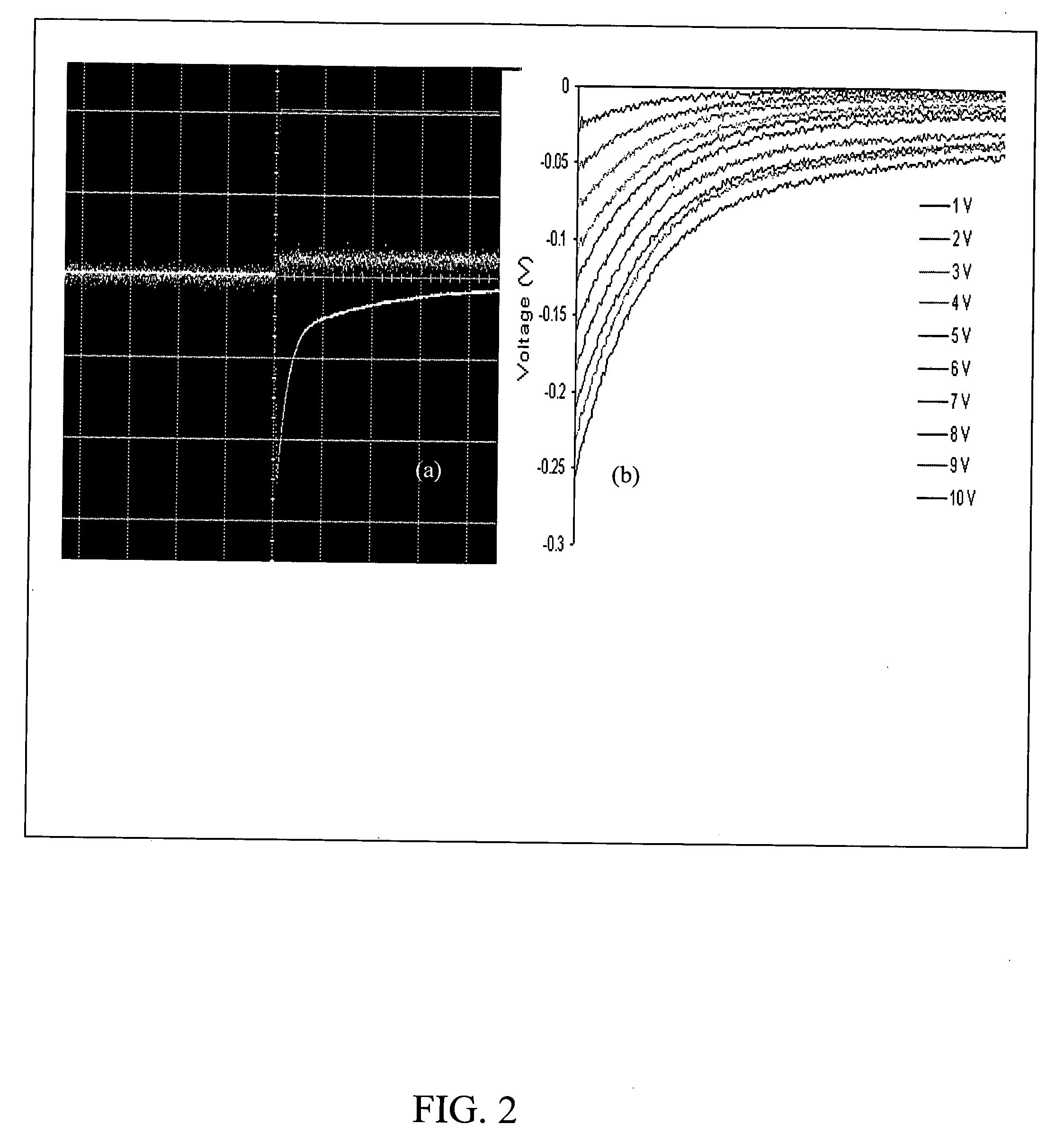
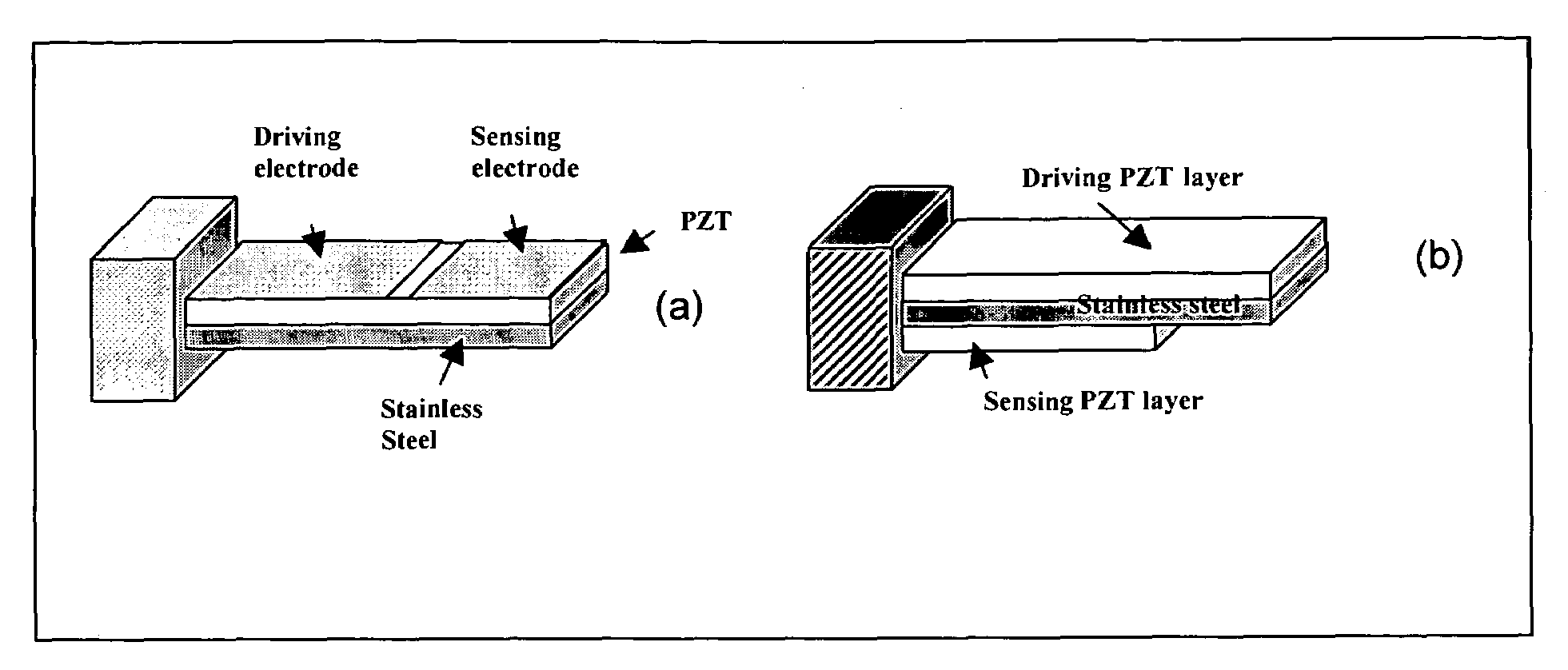
All electric piezoelectric finger sensor (PEFS) for soft material stiffness measurement
A PEFS (Piezoelectric Finger Sensor) acts as an “electronic finger” capable of accurately and non-destructively measuring both the Young's compression modulus and shear modulus of tissues with gentle touches to the surface. The PEFS measures both the Young's compression modulus and shear modulus variations in tissue generating a less than one-millimeter spatial resolution up to a depth of several centimeters. This offers great potential for in-vivo early detection of diseases. A portable hand-held device is also disclosed. The PEF offers superior sensitivity.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Methods, systems and computer program products for ultrasound shear wave velocity estimation and shear modulus reconstruction
ActiveUS8118744B2Wave based measurement systemsOrgan movement/changes detectionShear modulusReconstruction method
Owner:DUKE UNIV
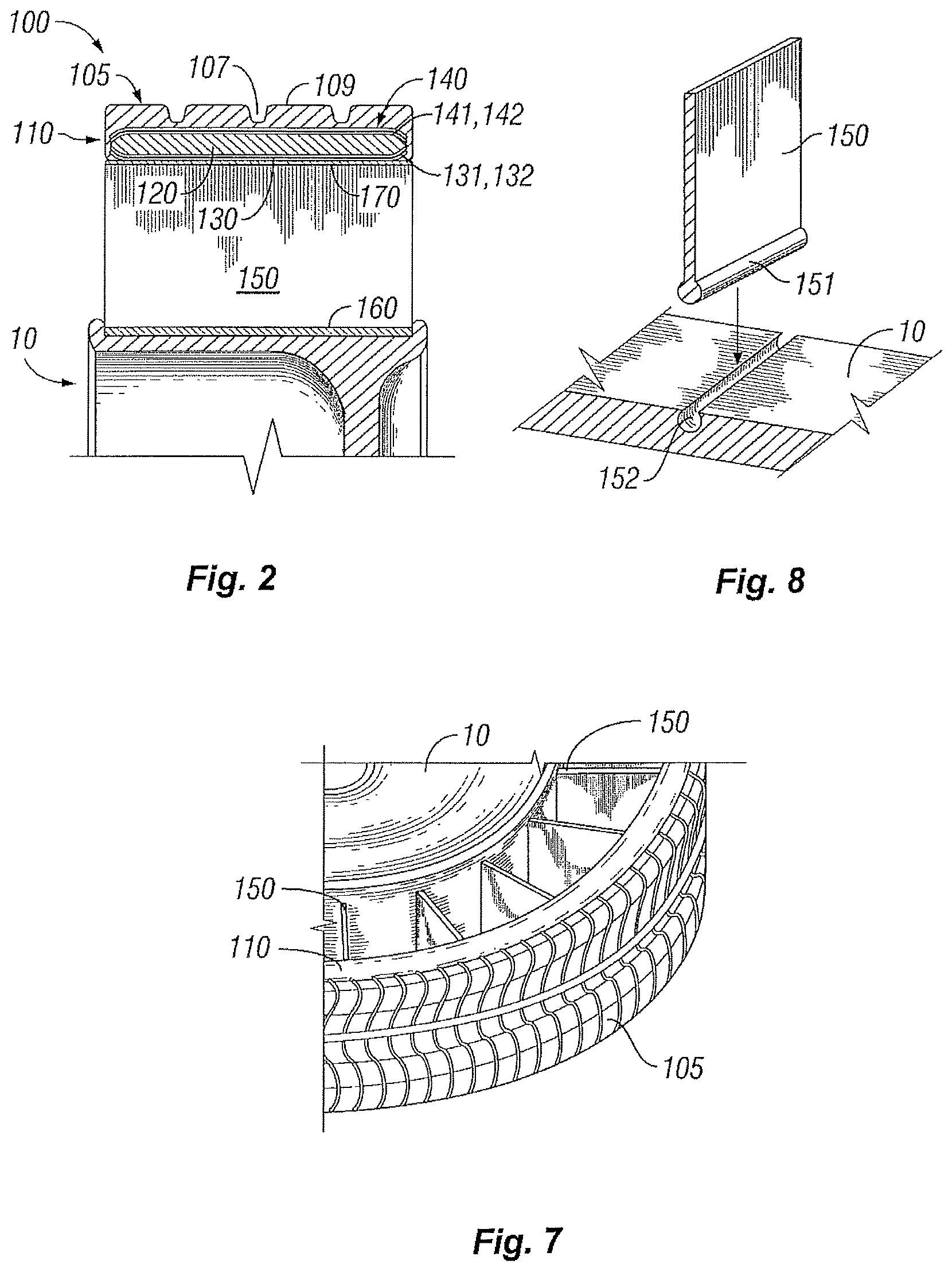
Non-pneumatic tire having web spokes
InactiveUS7650919B2High effective radial stiffness in tensionLow effective radial stiffnessNon-inflatable tyresPneumatic tyre reinforcementsGround contactElastomer
Owner:MICHELIN RECH & TECH SA
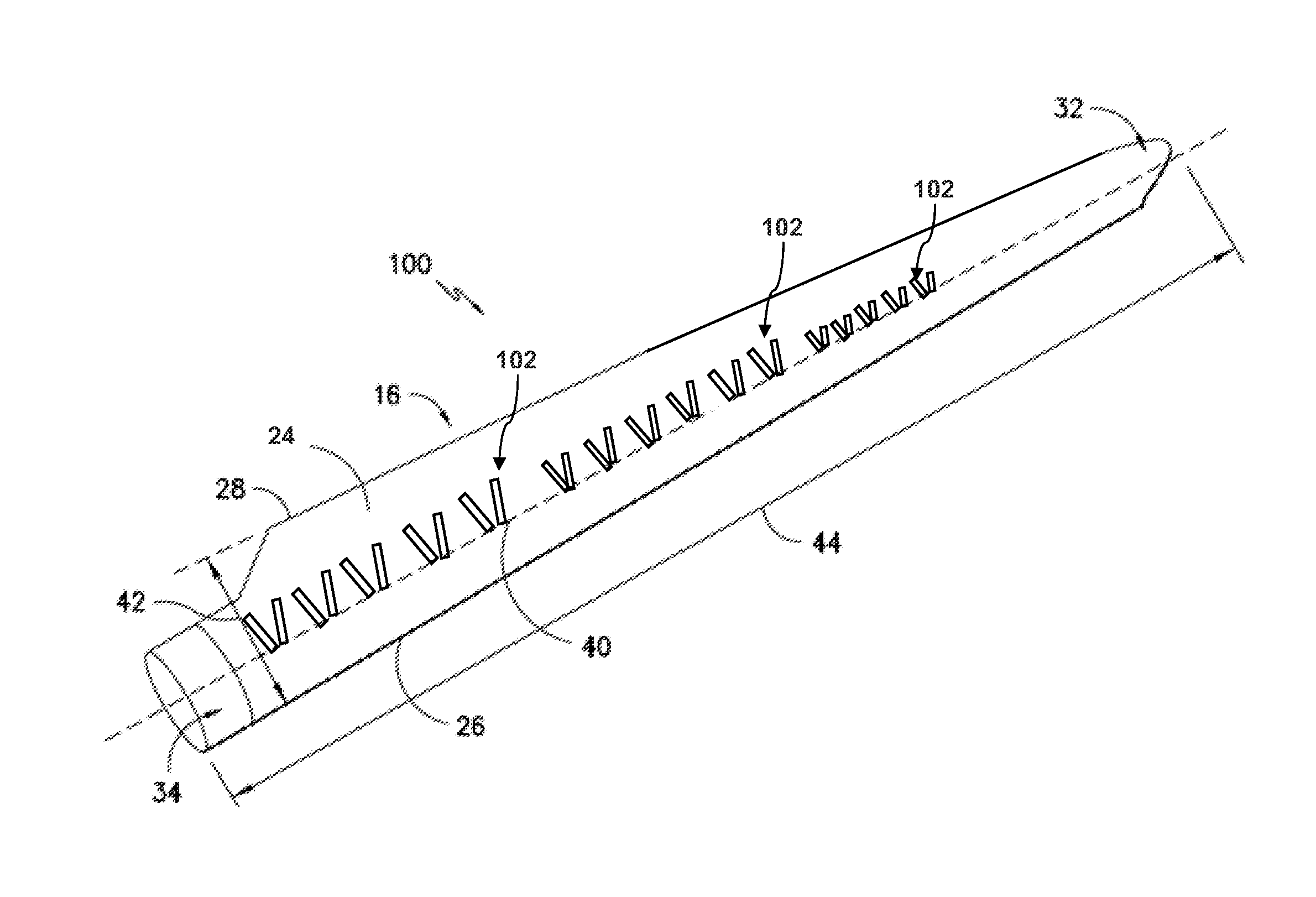
Attachment system and method for wind turbine vortex generators
A rotor blade assembly for a wind turbine includes a rotor blade having a pressure side, a suction side, a leading edge, and a trailing edge. A vortex generator accessory is mounted to either of the suction side or pressure side and includes a base portion and a protrusion member extending upwardly from the base portion. An attachment layer connects the base portion to the suction or pressure side. The attachment layer has a lower shear modulus than the base portion to allow for shear slippage between the base portion and the underlying suction or pressure side.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Surface-mounting coil component and method of producing the same
ActiveUS7209022B2Low costReduced durabilityTransformers/inductances casingsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsShear modulusSurface mounting
A surface-mounting choke coil has a resin coating material with magnetic powder which is filled a space between the upper flange and the lower flange of a drum-type ferrite core, while covering the circumferential of the winding. The resin coating material with magnetic powder has a glass transition temperature Tg of about −20° C. or lower, more preferably about −50° C. or lower in a course of transferring from a glass state to a rubber state during changing of shear modulus with respect to temperature as a physical property when hardening, and the thickness of the upper flange of the drum-type ferrite core is about 0.35 mm or less, and a value of a ratio L2 / L1 of an outer diameter L2 of the upper flange to a diameter L1 of the winding core of the drum-type ferrite core is about 1.9 or more.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
Clinical apparatuses
ActiveUS20060173319A1High measurement accuracySimple calculationDiagnostics using vibrationsOrgan movement/changes detectionShear modulusEngineering
Owner:SUMI CHIKAYOSHI
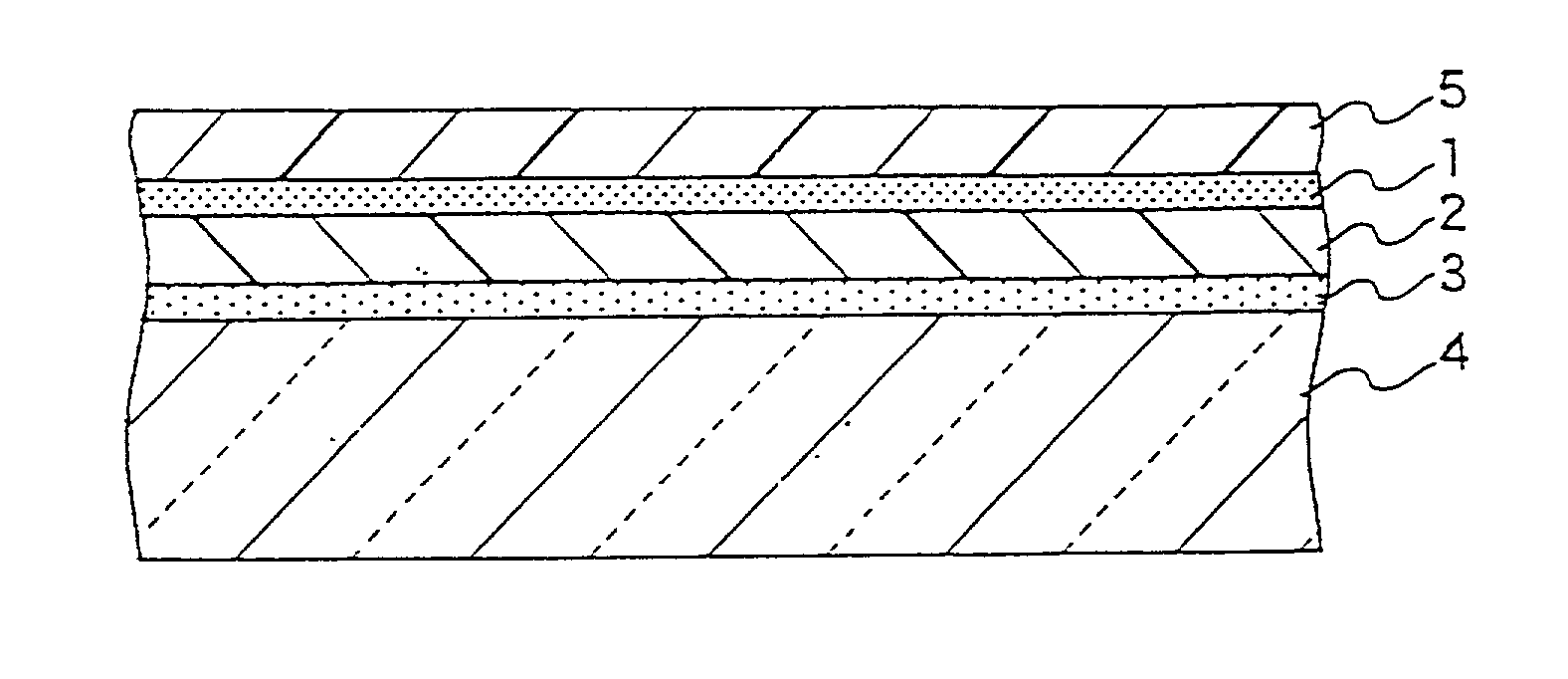
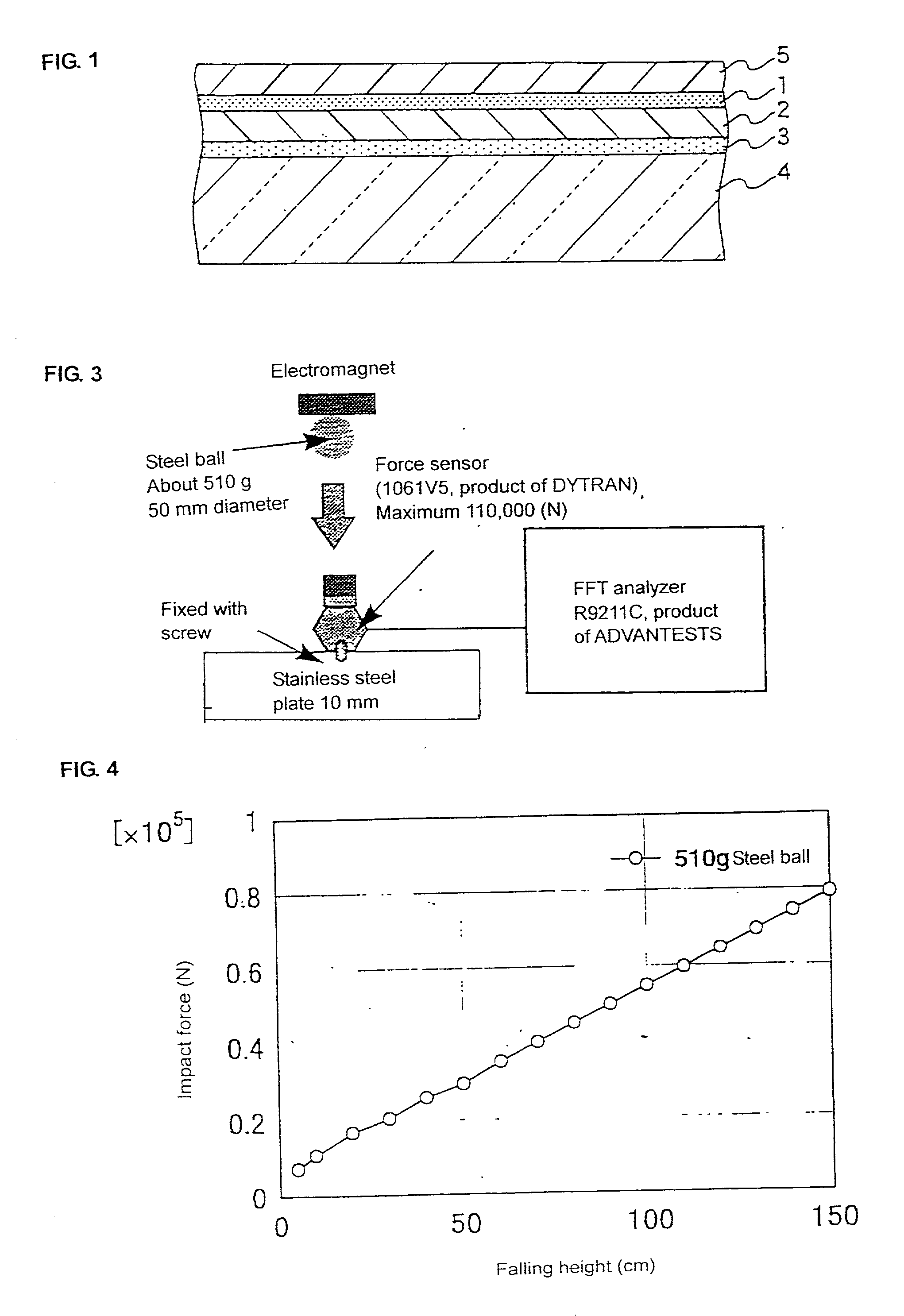
Transparent shock-absorbing laminate and flat panel display using the same
A transparent shock-absorbing laminate to be formed on a glass substrate for a display panel having a fracture strength such that it is fractured by a falling ball impact (drop height: 1.5 m; ball weight: 510 g) corresponding to 79,000 N, the transparent shock-absorbing laminate comprising a shatterproof layer having a shearing modulus of 2x108 Pa or more, at least two fracture-proof layers having a shearing modulus ranging from 1x104 to 2x108 Pa, each having different modulus, and a transparent pressure-sensitive adhesive layer.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Tough iron-based bulk metallic glass alloys
A family of iron-based, phosphor-containing bulk metallic glasses having excellent processability and toughness, methods for forming such alloys, and processes for manufacturing articles therefrom are provided. The inventive iron-based alloy is based on the observation that by very tightly controlling the composition of the metalloid moiety of the Fe-based, P-containing bulk metallic glass alloys it is possible to obtain highly processable alloys with surprisingly low shear modulus and high toughness. Further, by incorporating small fractions of silicon (Si) and cobalt (Co) into the Fe—Ni—Mo—P—C—B system, alloys of 3 and 4 mm have been synthesized with high saturation magnetization and low switching losses.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
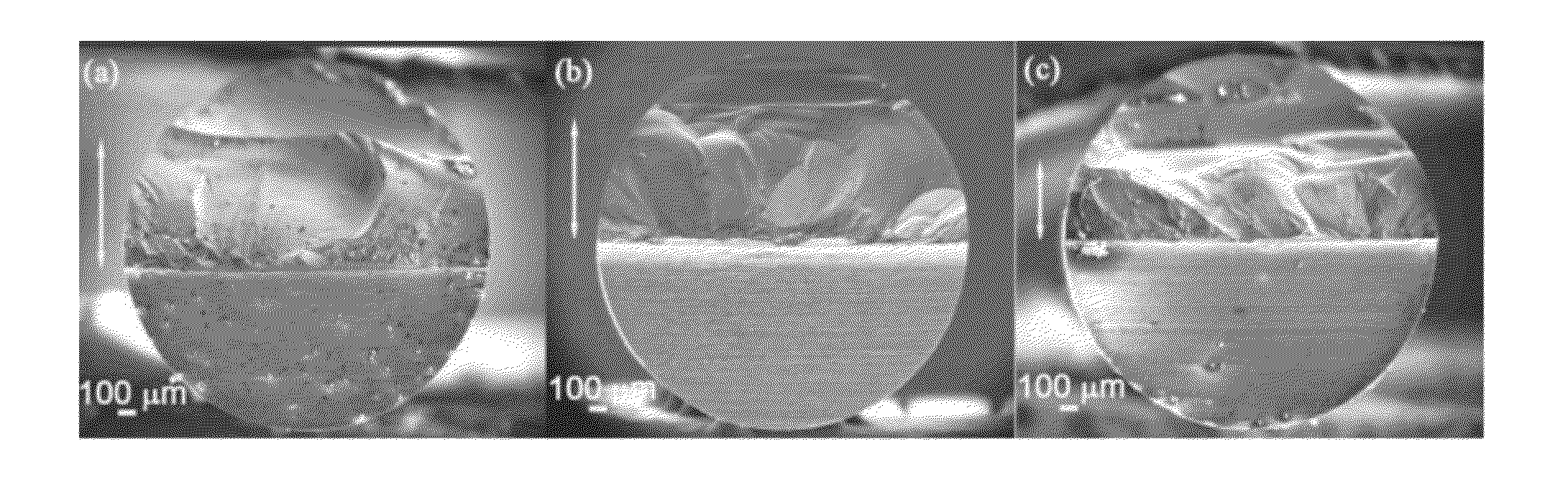
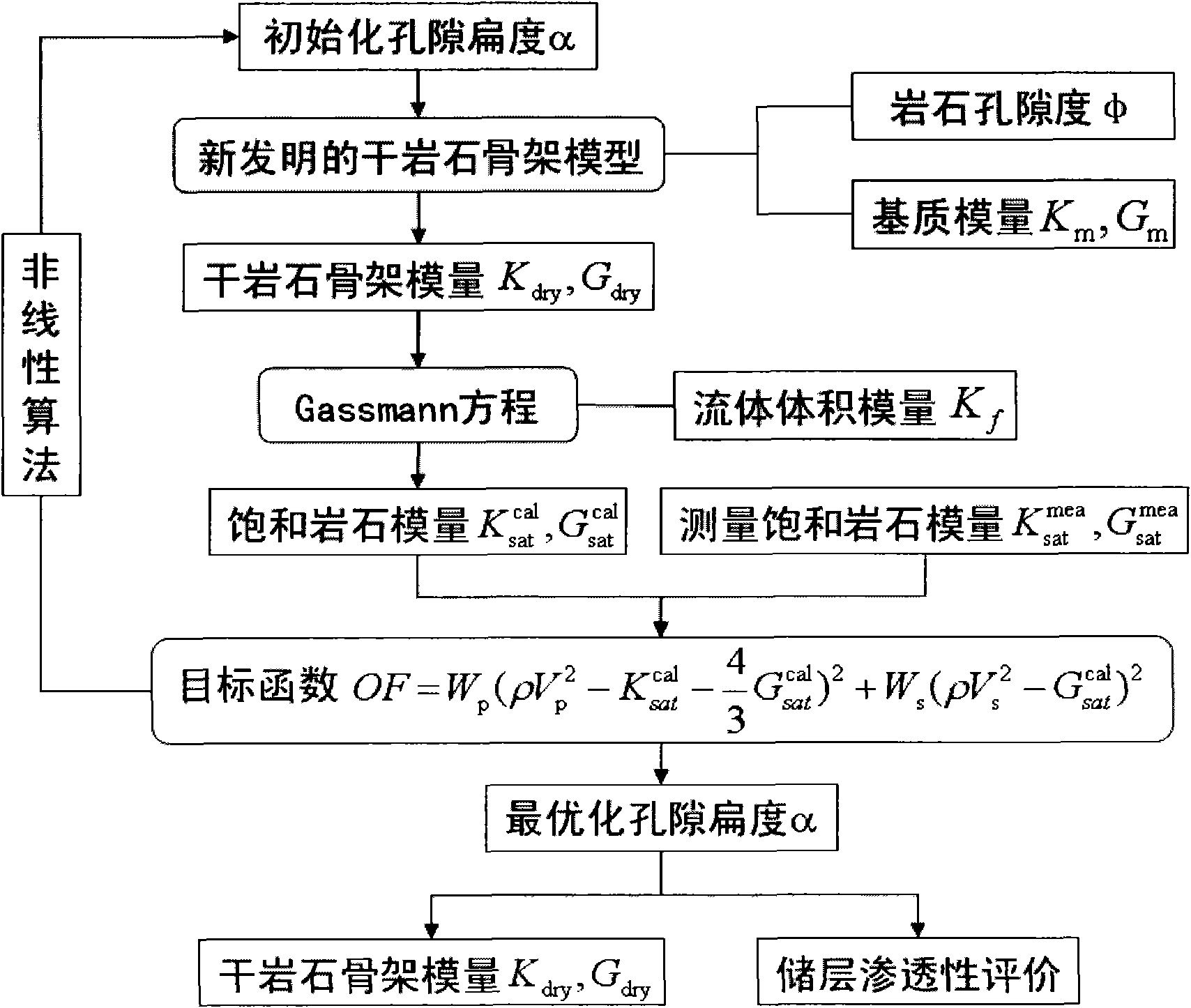
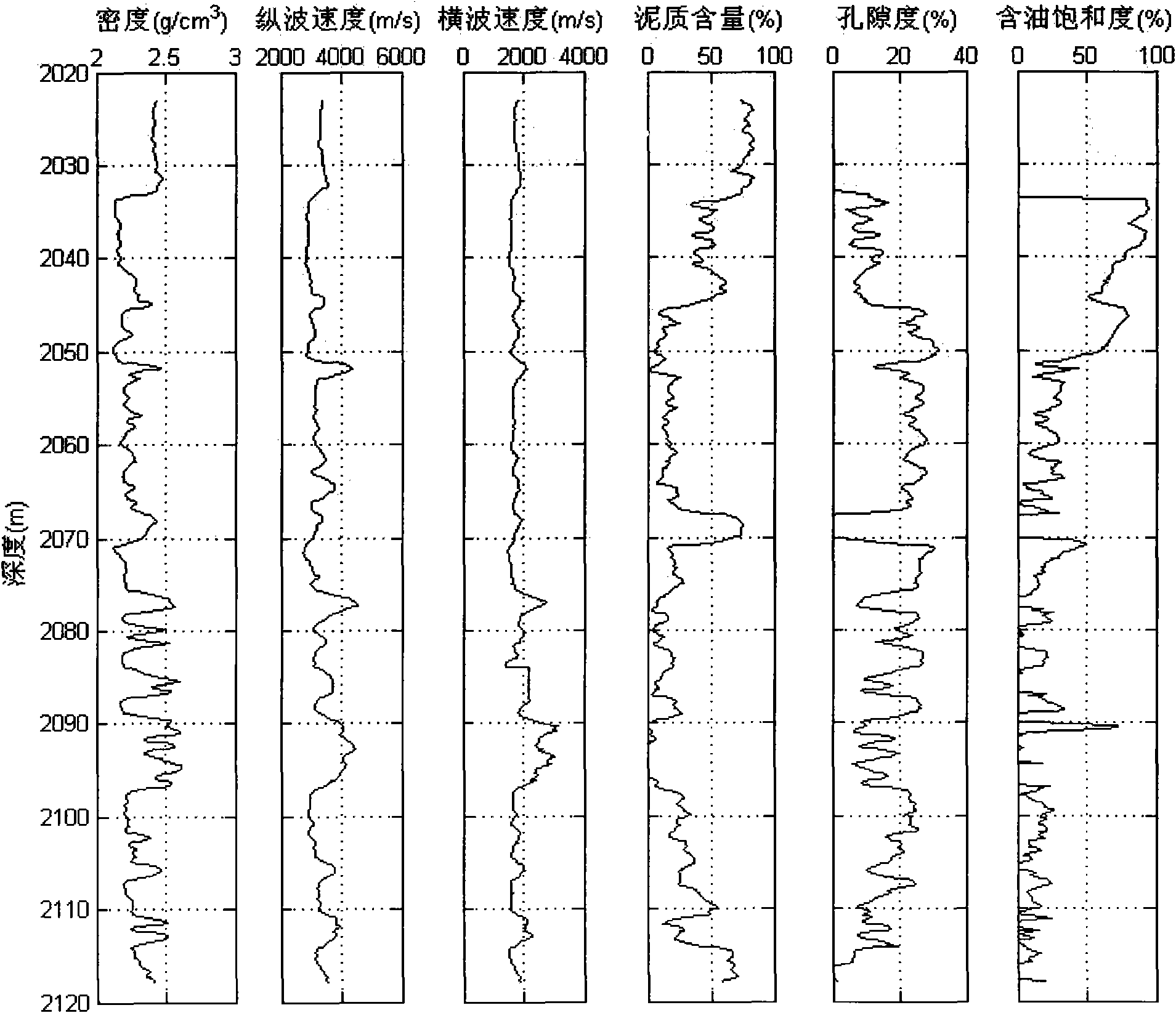
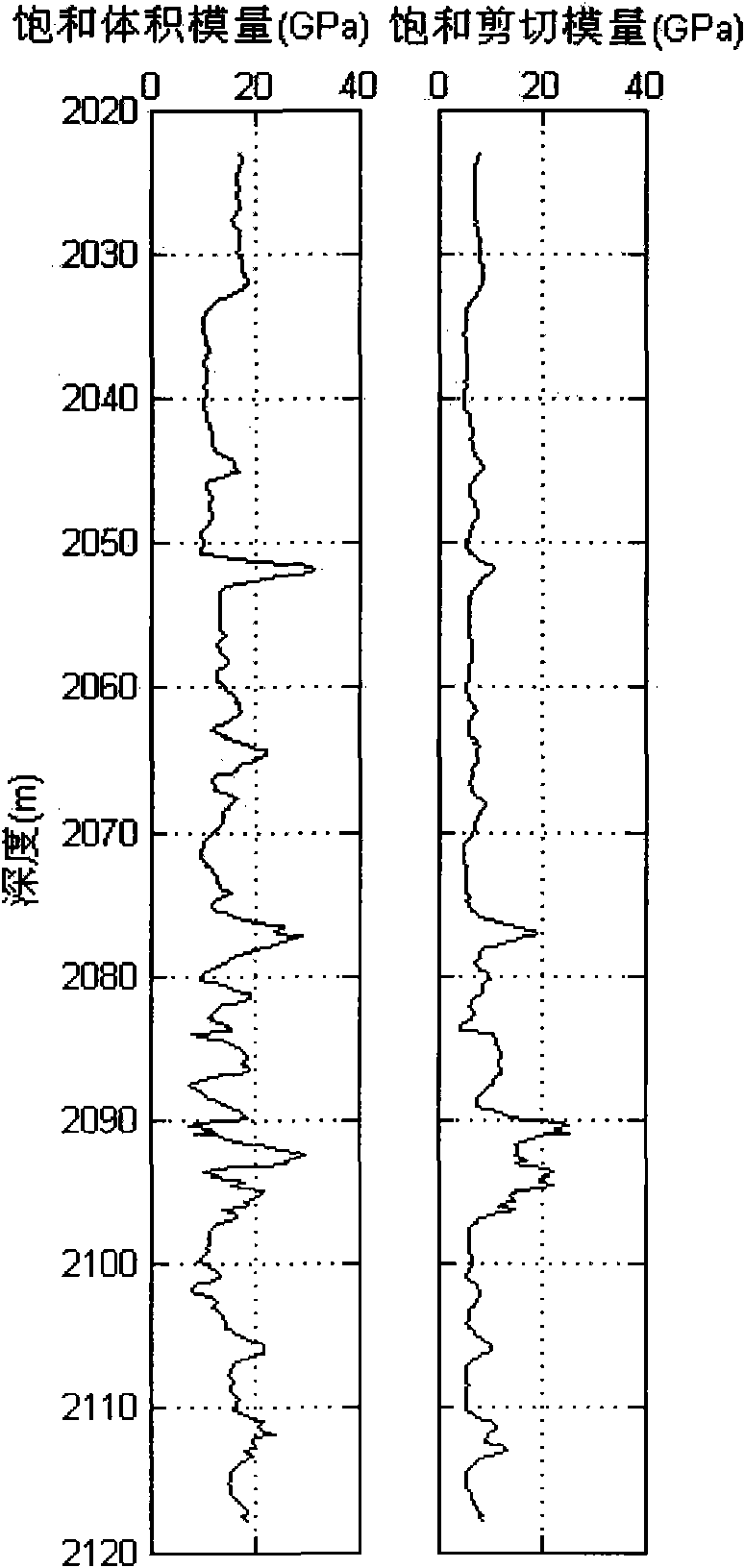
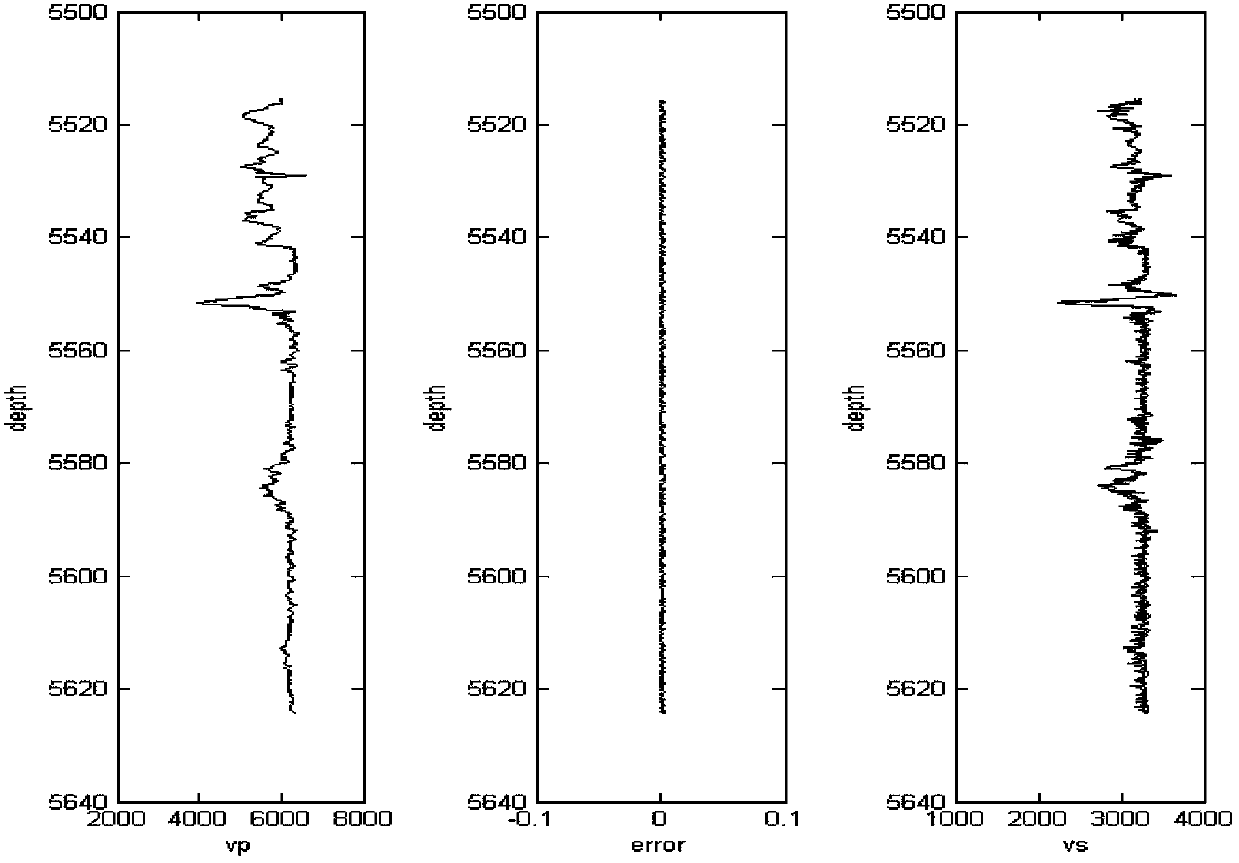
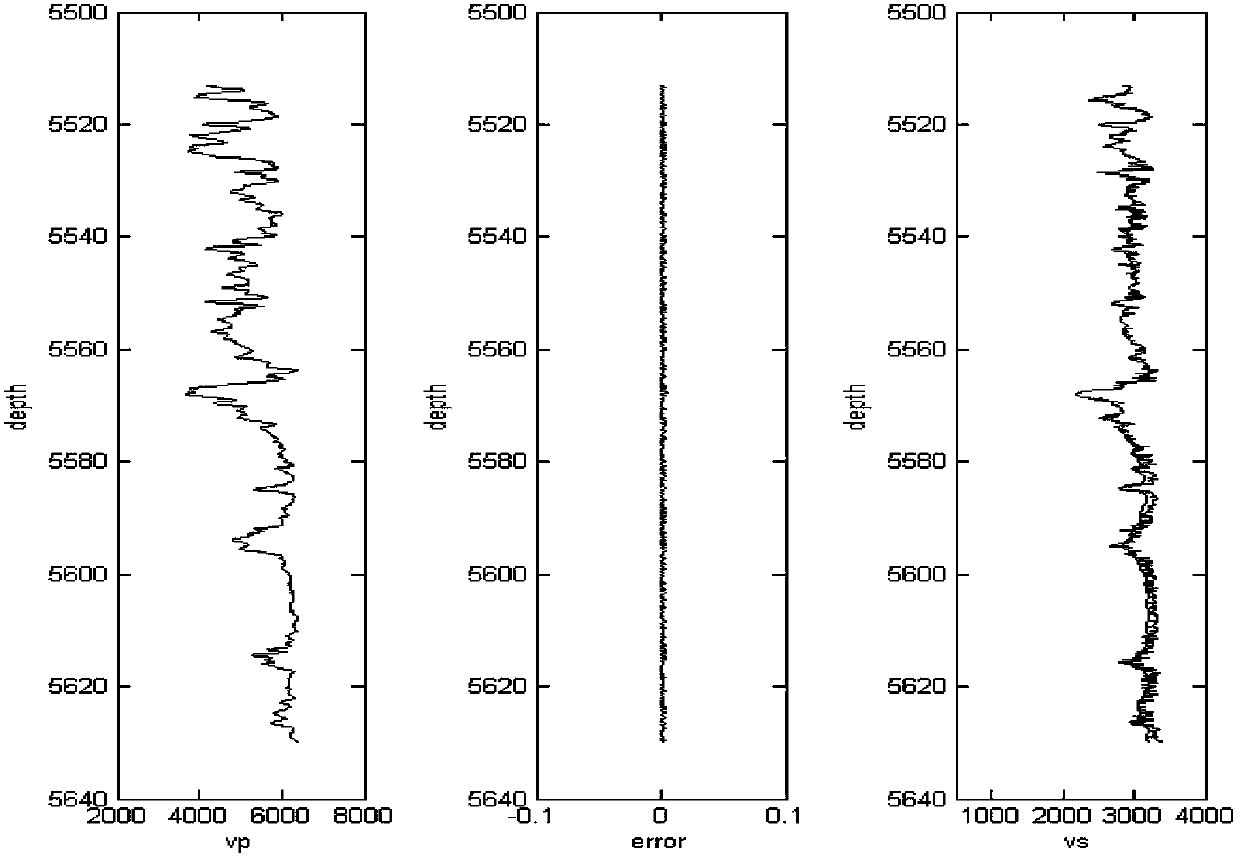
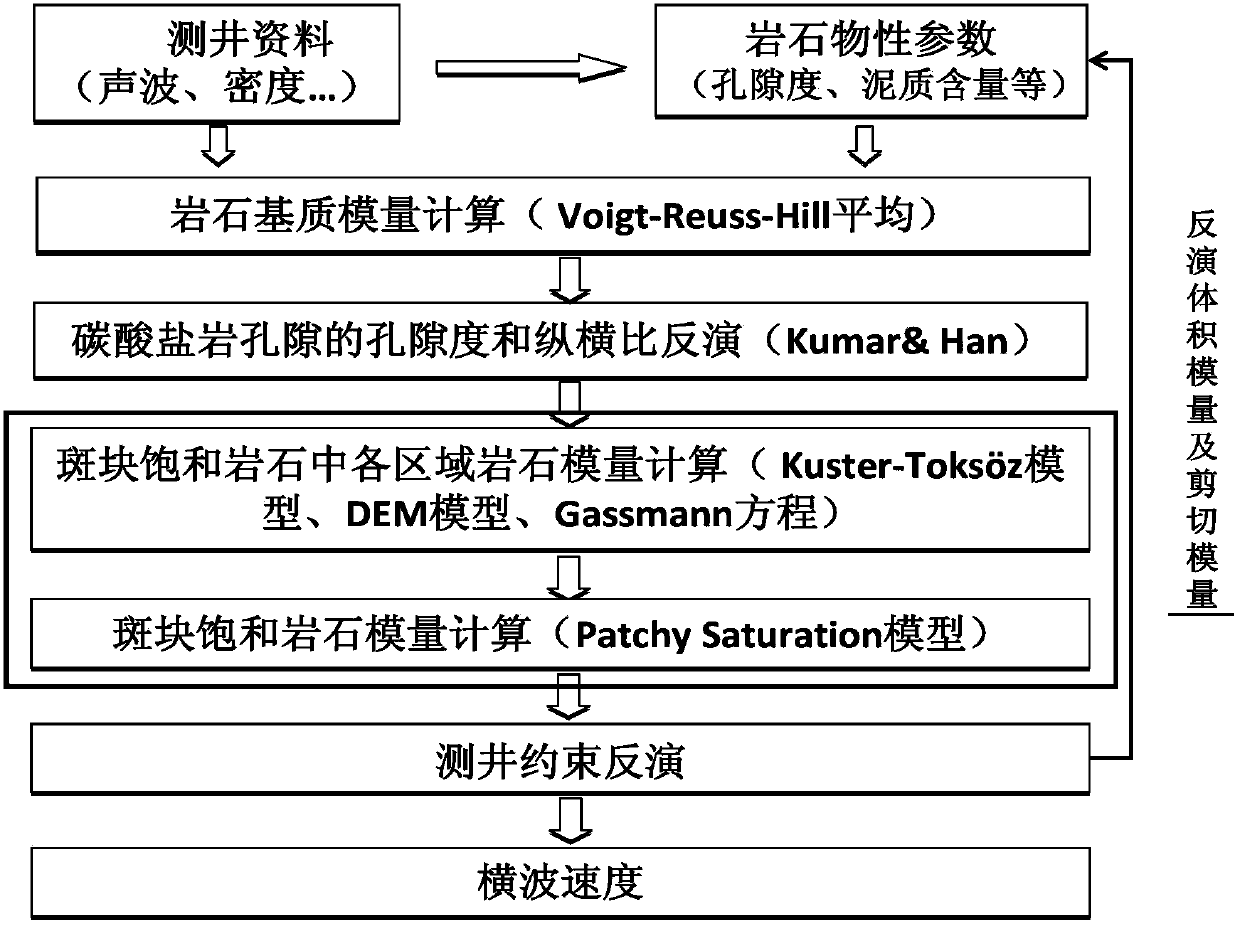
Method for evaluating permeability of reservoir layer according to interval transit time and density inversed pore flat degree
The invention relates to a method for evaluating the permeability of a reservoir layer according to the interval transit time and density inversed pore flat degree, comprising the following steps: collecting the characteristics and physical property parameters of rock; calculating the bulk modulus and shear modulus of saturated rock; calculating the bulk modulus and shear modulus of a rock substrate and the bulk modulus of fluid; setting the initial flat degree of the pores; calculating the change relation of the modulus ratio of a dry rock skeleton along with the porosity; calculating the bulk modulus and shear modulus of the dry rock skeleton; calculating the bulk modulus and shear modulus of fluid saturated rock; comparing the bulk modulus and shear modulus obtained through forward calculation with the bulk modulus and shear modulus actually measured, and calculating the error between the bulk modulus and shear modulus obtained through forward calculation and the bulk modulus and shear modulus actually measured; and modifying the set pore flat degree by adopting a nonlinear global optimizing algorithm, and using the pore flat degree for speed prediction, fluid substitution, inversion of porosity and saturated degree and logging parameter evaluation after accurate moduli of the dry rock skeleton are obtained.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
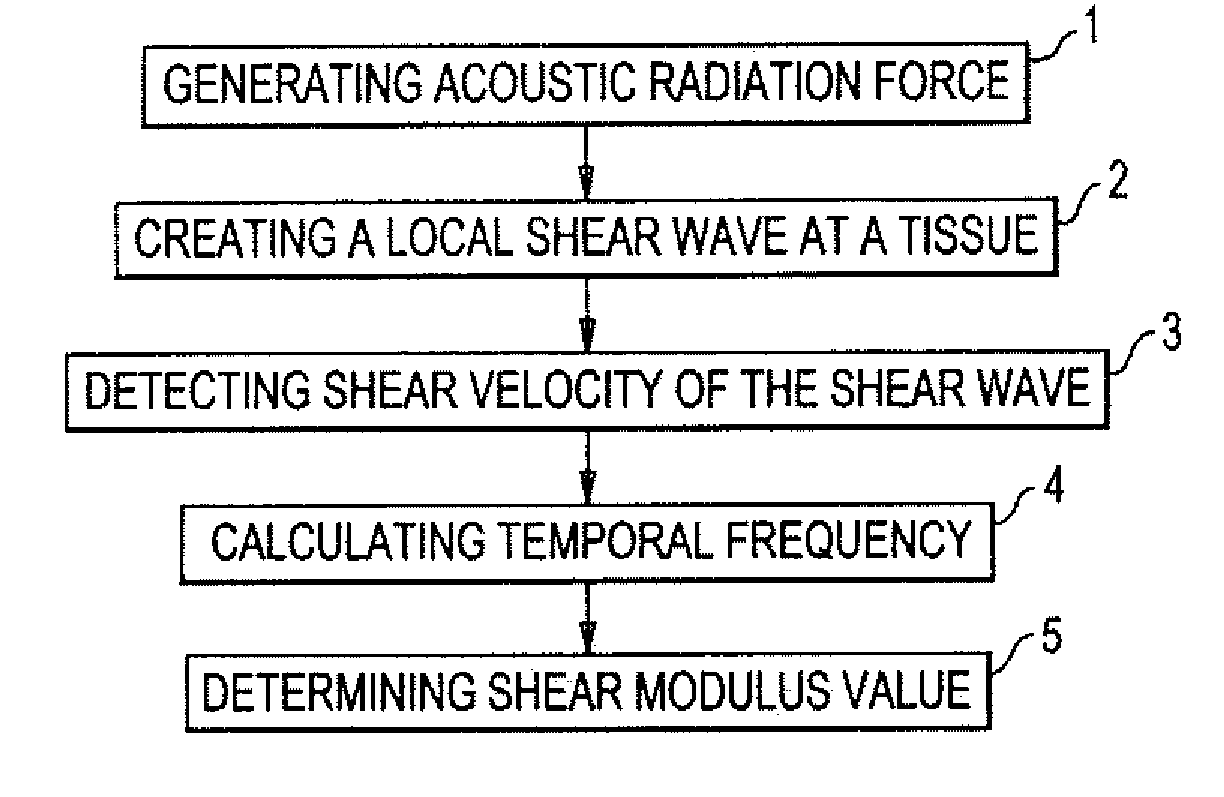
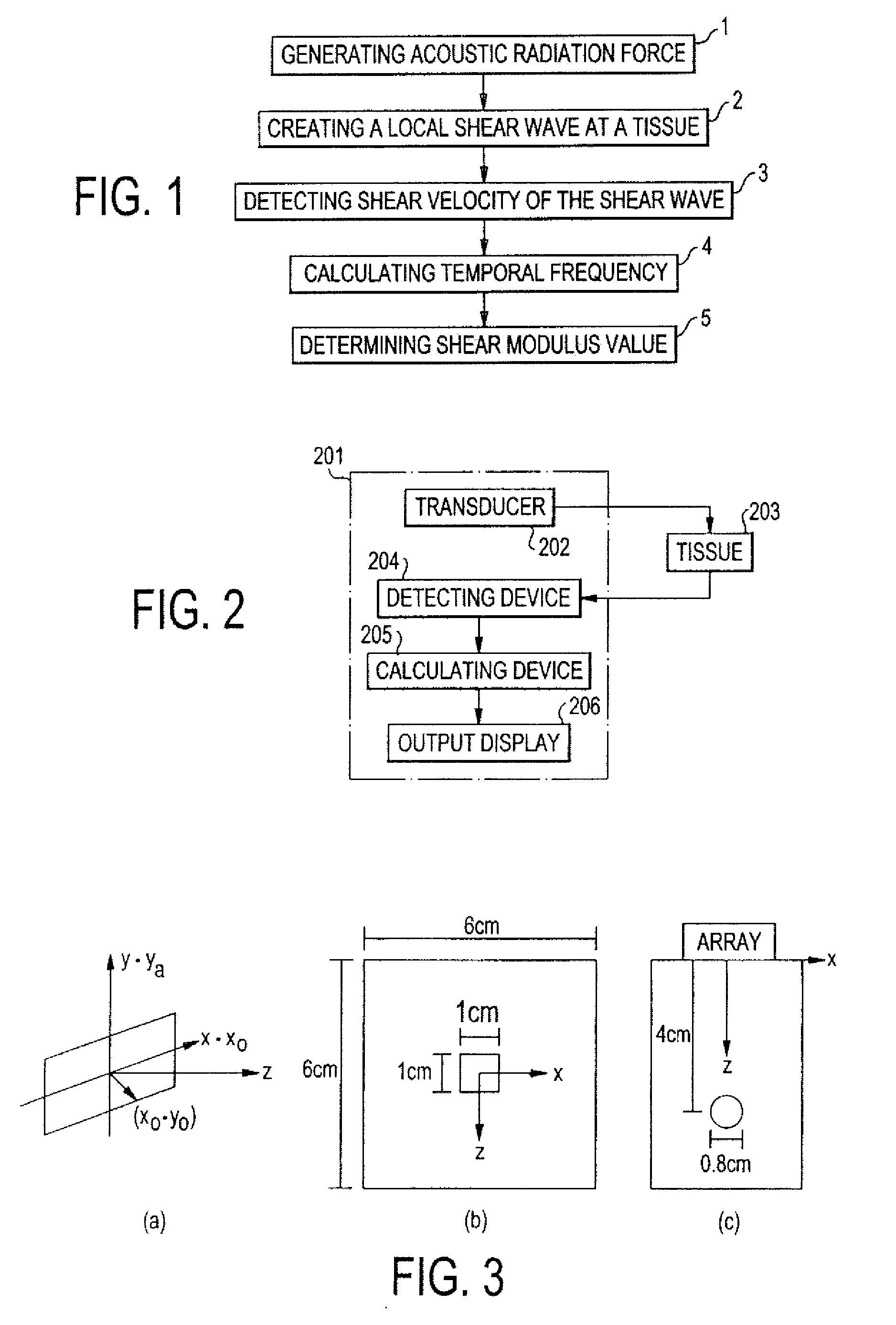
Methods And Systems For Spatially Modulated Ultrasound Radiation Force Imaging
ActiveUS20110184287A1Easy to detectAvoid noiseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsShear modulusAcoustic radiation force
Methods for determining the shear modulus of a tissue of an individual are disclosed. In one embodiment, an acoustic pulse is transmitted and a reference echo signal is received. A first push pulse is transmitted at a second location of the individual. A second push pulse is transmitted at a third location of the individual. A series of tracking pulses are transmitted at the first location and a tracking echo signal is received from each tracking pulse. The effect of the first and second push pulses on the tissue is determined through analysis of the tracking echo signals. The shear modulus of the tissue is calculated based on the effect of the push pulses on the tissue. A system for imaging a region of tissue is presented.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Multifunctional periodic cellular solids and the method of making thereof
ActiveUS20080226870A1Efficient load supportExcellent mechanical impact energy absorptionWeft knittingLaminationPorosityEnergy absorption
A cellular material that can provide a unique combination of properties and characteristics for a variety of applications requiring a cellular solid that possesses one or more of the following characteristics: (1) efficient load support in one or more directions, (2) excellent mechanical impact energy absorption and vibration suppression potential, (3) high convection heat transfer throughout, (4) low pumping requirements for fluid throughput, for example in a second direction orthogonal to one or more load-bearing directions, (5) a substantially linear dependence of the Young's and shear moduli along with the tensile, compressive and shear yield strengths upon relative density (6) a potentially inexpensive textile-based synthetic approach, (7) excellent filtration potential, (8) a high surface area to volume ratio for enhanced activity as a catalyst or catalyst support (9) interconnected, open porosity for device storage, biological tissue in-growth or other functionalities requiring open space, and (10) extendibility to a wide variety of materials.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA +1
Reservoir shear wave velocity prediction method based on rock physics
ActiveCN103424772ASeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingEnvironmental geologyShear modulus
The invention relates to a reservoir shear wave velocity prediction method based on rock physics. The method comprises the steps that (1) supposing that the bulk modulus, the shear modulus and the density of a destination interval mineral are unknown constants, the error between a longitudinal wave velocity and a measured longitudinal wave velocity is acquired according to equation modeling, and the error between the acquired density and the measured density is calculated; (2) according to the minimum error criterion, the bulk modulus, the shear modulus and the density of a mineral component are inverted through a genetic algorithm; (3) and the shear wave velocity is calculated. According to the step (1), supposing that the elastic modulus of each rock component is an unknown constant in a reservoir logging curve section, the objective function of the inversion of the logging curve can be defined that a superscript M represents a simulation longitudinal wave velocity, O represents a logging observation longitudinal wave velocity, and w Rho and w rho represent normalized weighted coefficients; and the objective function is a nonlinear function of the bulk modulus, the shear modulus and the density of each mineral component. The method can be applied to a sand shale reservoir, and carbonate rock and other complex reservoirs.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
All electric piezoelectric finger sensor (PEFS) for soft material stiffness measurement
A PEFS (Piezoelectric Finger Sensor) acts as an “electronic finger” capable of accurately and non-destructively measuring both the Young's compression modulus and shear modulus of tissues with gentle touches to the surface. The PEFS measures both the Young's compression modulus and shear modulus variations in tissue generating a less than one-millimeter spatial resolution up to a depth of several centimeters. This offers great potential for in-vivo early detection of diseases. A portable hand-held device is also disclosed. The PEF offers superior sensitivity.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
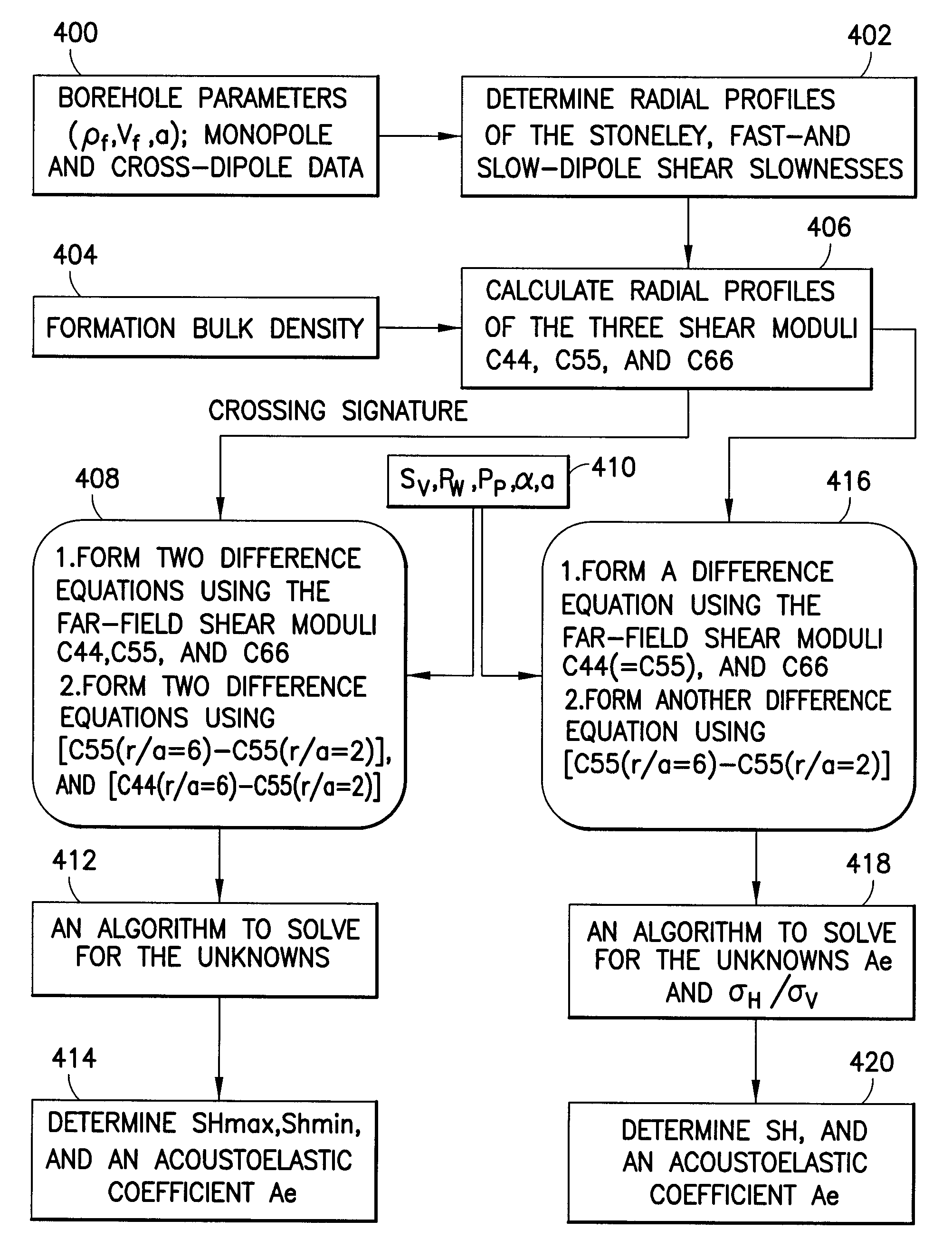
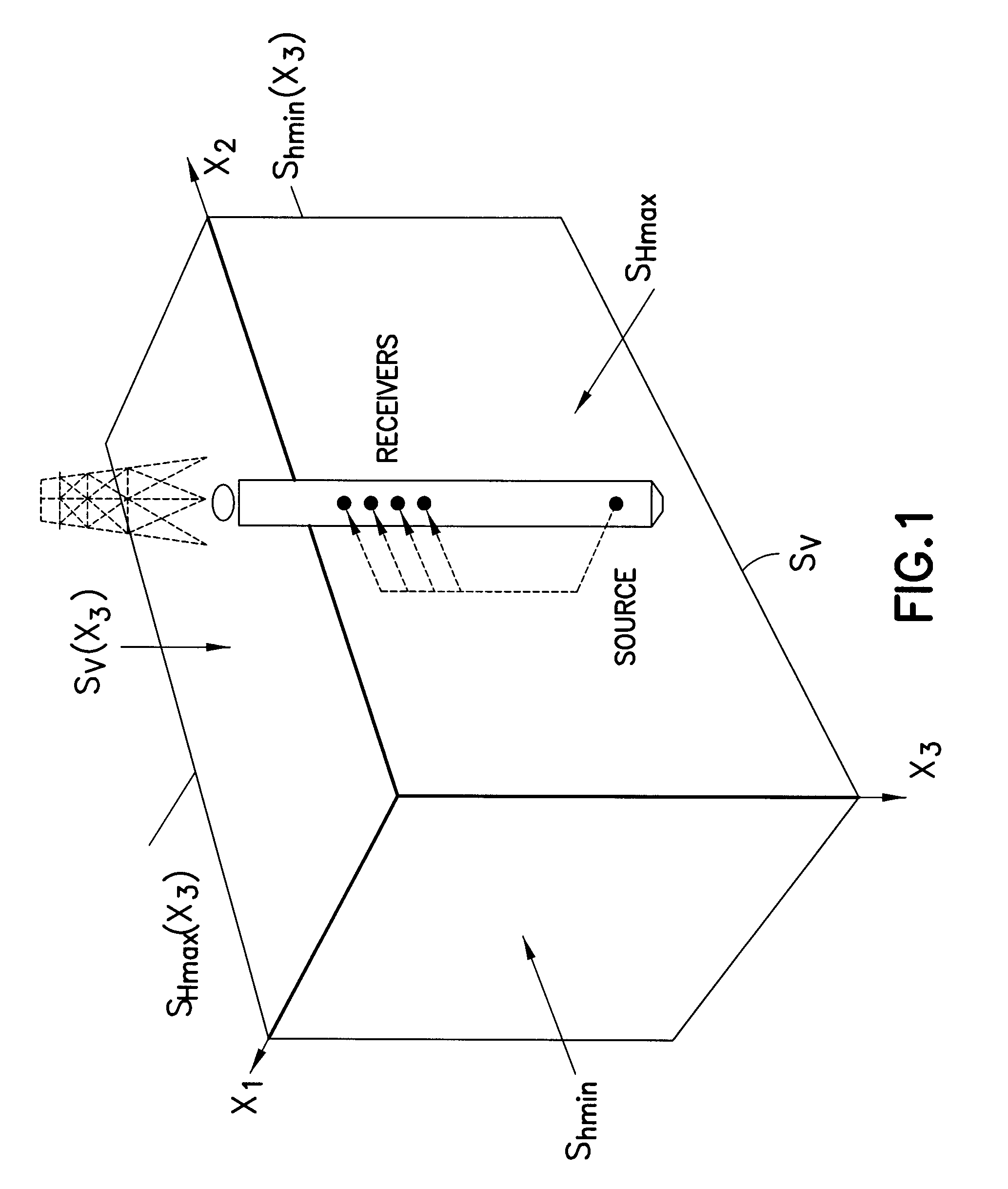
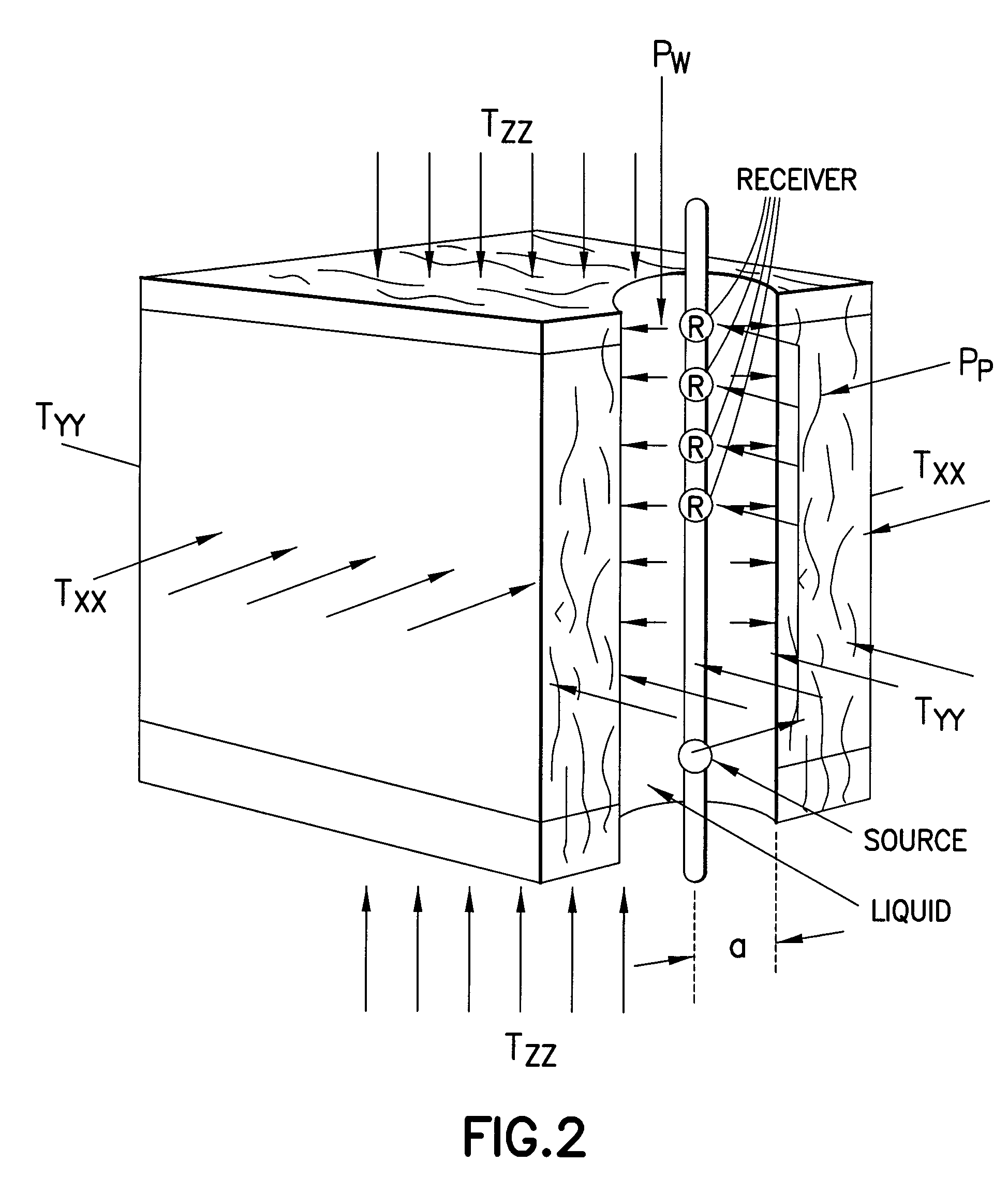
Estimating formation stresses using radial profiles of three shear moduli
ActiveUS20100020642A1Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingStress concentrationShear modulus
Maximum and minimum horizontal stresses, and horizontal to overburden stress ratio, are estimated using radial profiles of shear moduli. Inversion enables estimation of maximum and minimum horizontal stresses using radial profiles of three shear moduli associated with an orthogonal set of axes defined by the three principal stress directions. Differences in the far-field shear moduli are inverted together with two difference equations obtained from the radial profiles of the dipole shear moduli C44 and C55, and borehole stresses in the near-wellbore region. The horizontal to overburden stress ratio is estimated using differences in the compressional, dipole shear, and Stoneley shear slownesses at two depths in the same lithology interval where the formation exhibits azimuthal isotropy in cross-dipole dispersions, implying that horizontal stresses are nearly the same at all azimuths. The overburden to horizontal stress ratio in a formation with axial heterogeneity may also be estimated using the far-field Stoneley shear modulus C66 and dipole shear modulus C55 together with the radial variation of the dipole shear modulus C55 caused by near-wellbore stress concentrations.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
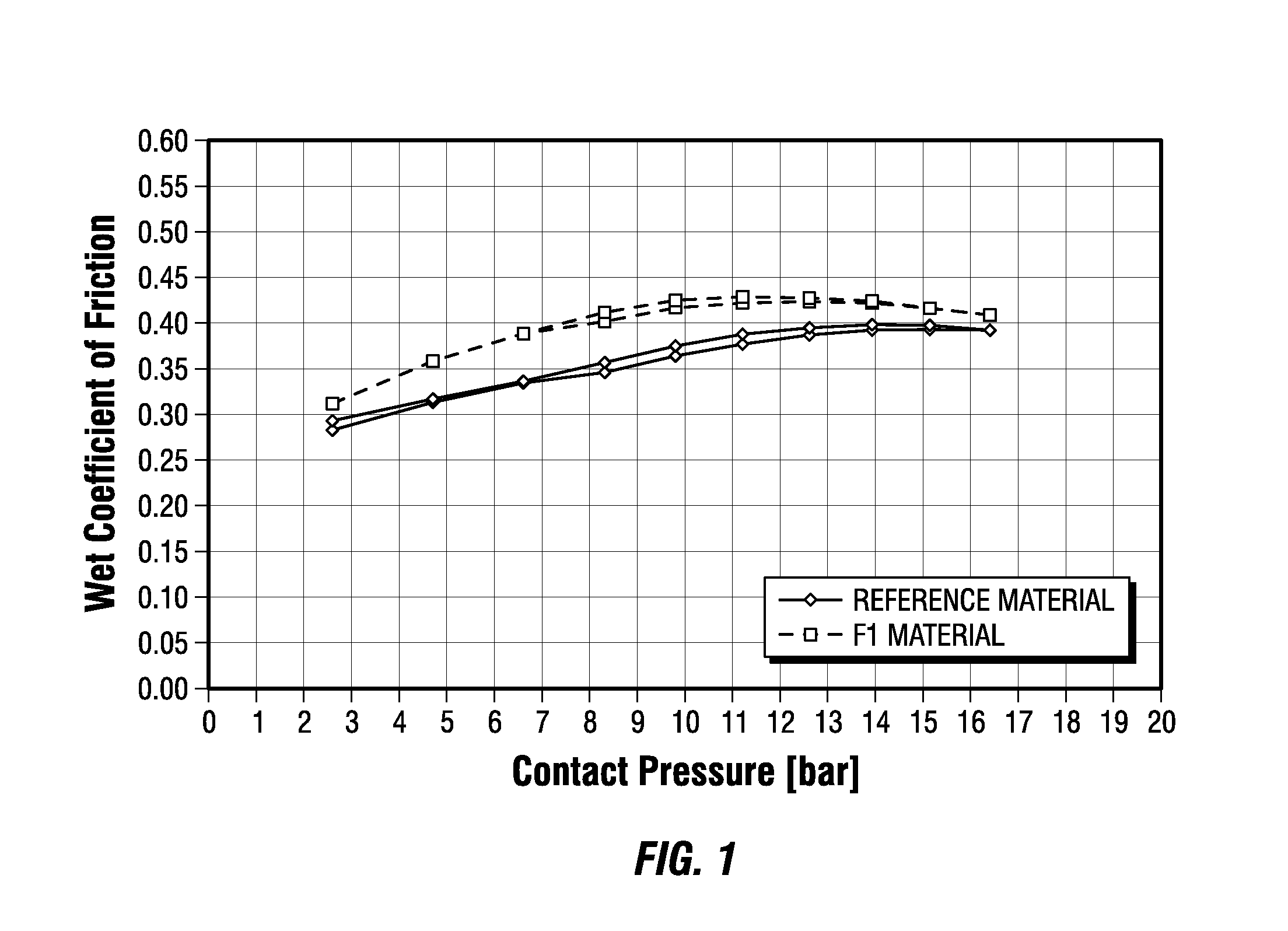
Tire with tread having improved wet traction
Owner:PIFFARD OLIVIER +3
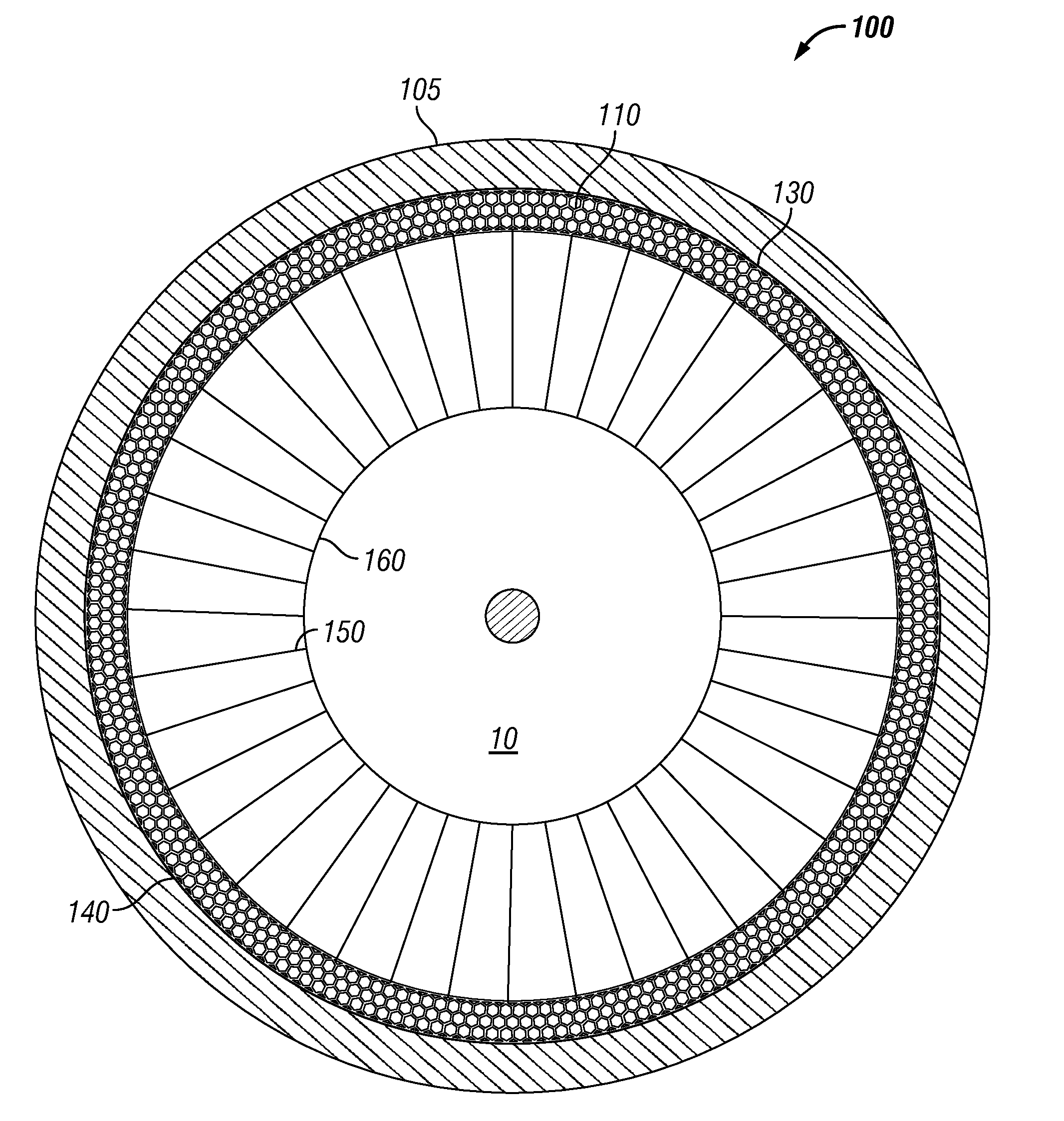
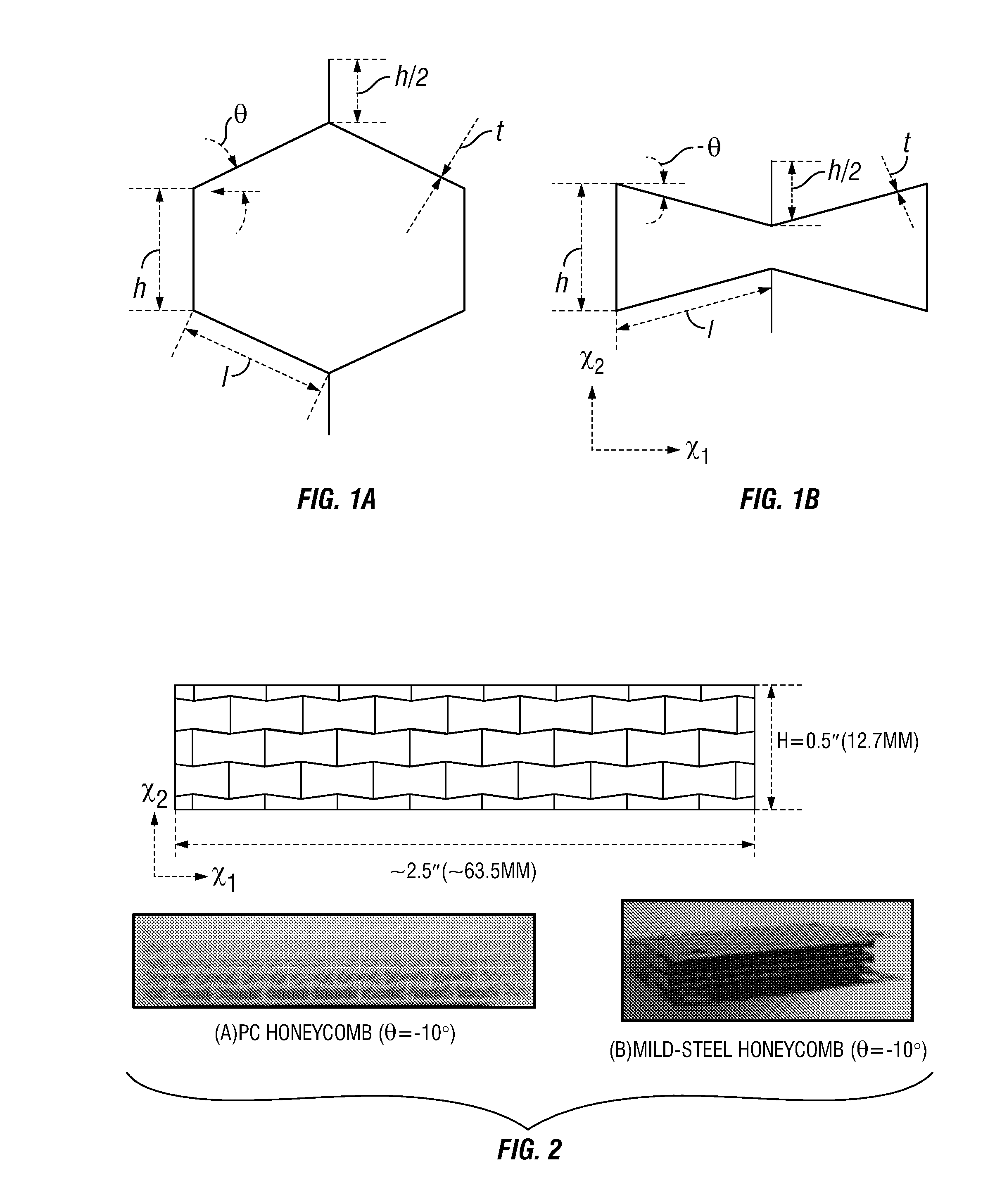
Honeycomb structures for high shear flexure
The present invention provides an improved shear band for use in non-pneumatic tires, pneumatic tires, and other technologies. The improved shear band is uniquely constructed of honeycomb shaped units that can replace the elastomeric continuum materials such as natural or synthetic rubber or polyurethane that are typically used. In particular, honeycomb structures made of high modulus materials such as metals or polycarbonates are used that provide the desired shear strains and shear modulus when subjected to stress. When used in tire construction, improvements in rolling resistance can be obtained because of less mass being deformed and reduced hysteresis provided by these materials. The resulting mass of the shear band is greatly reduced if using low density materials. Higher density materials can be used (such as metals) without increasing mass while utilizing their characteristic low energy loss.
Owner:MICHELIN NORTH AMERICA
Sound Proofing material with improved damping and structural integrity
ActiveUS8424251B2Improve abilitiesImproves Structural IntegrityAdhesive processesCeilingsCelluloseShear modulus
Panels for use in building construction (partitions, walls, ceilings, floors or doors) which exhibit improved acoustical sound proofing in multiple specific frequency ranges and also present improved structural integrity, are provided. The improved performance is achieved through the use of one or more layers of glue such that at least one layer of glue includes a viscoelastic material in a first pattern and a structural adhesive in a second, non-overlapping pattern. The viscoelastic material may have a varied shear moduli and functions as a glue and energy dissipating layer. In some embodiments, one or more constraining layers separating one layer of glue may be included. The constraining layer may be formed of a material such as gypsum, cement, metal, cellulose, wood, or petroleum-based products such as vinyl, plastic, or rubber. In some embodiments, standard wallboard, typically gypsum, comprises the external surfaces of the laminated panel.
Owner:PABCO BUILDING PROD
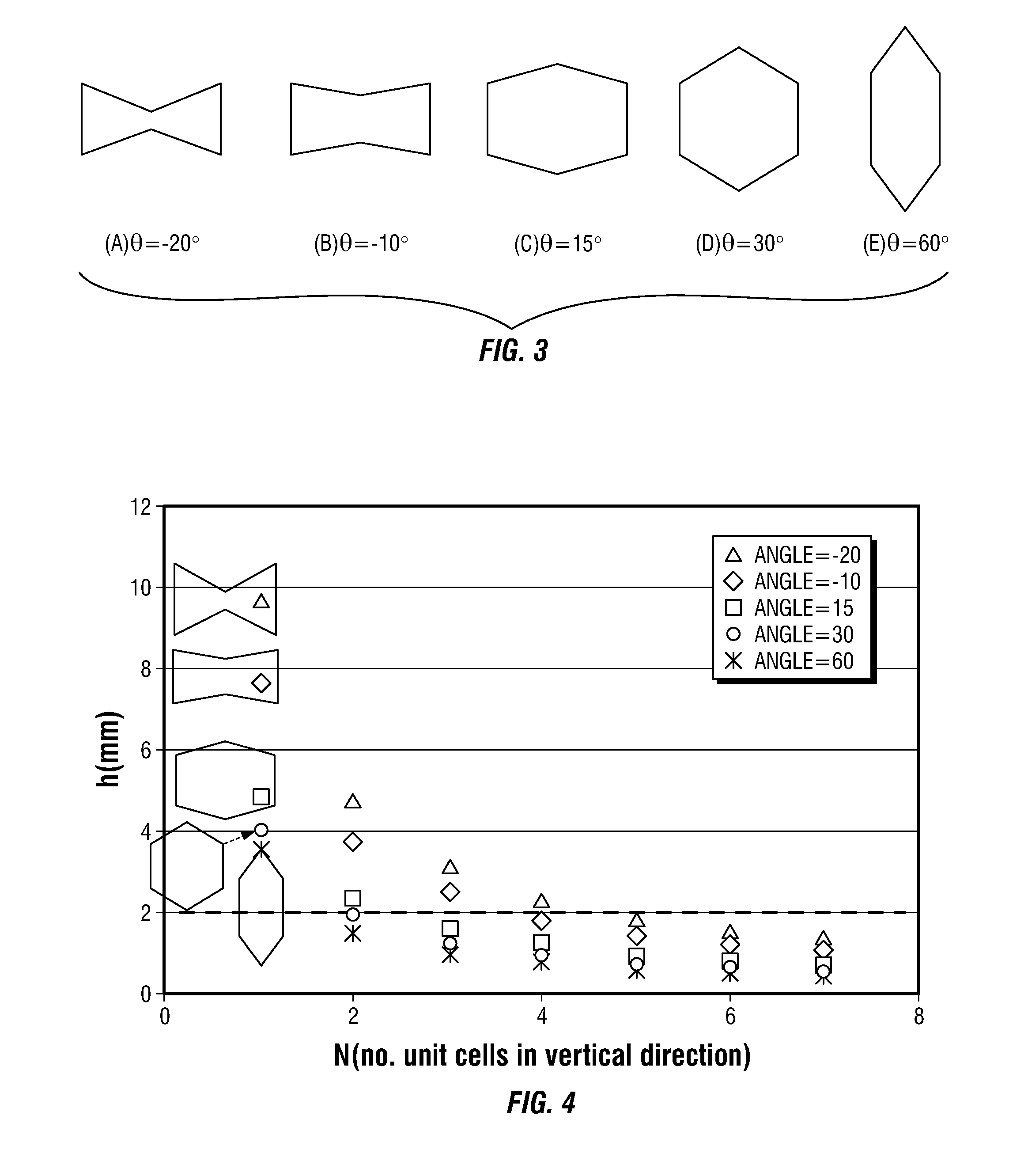
Shear modulus estimation by application of spatially modulated impulse acoustic radiation force approximation
ActiveUS20090056453A1Quantitative measurement of the shear modulus of the tissueVibration measurement in solidsVibration measurement in fluidShear modulusSonification
A method for determining a shear modulus of an elastic material with a known density value is provided. In this method, a spatially modulated acoustic radiation force is used to initially generate a disturbance of known spatial frequency or wavelength. The propagation of this initial displacement as a shear wave is measured using ultrasound tracking methods. A temporal frequency is determined based on the shear wave. The shear modulus of the elastic material at the point of excitation may be calculated using the values of the spatial wavelength, material density, and temporal frequency.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
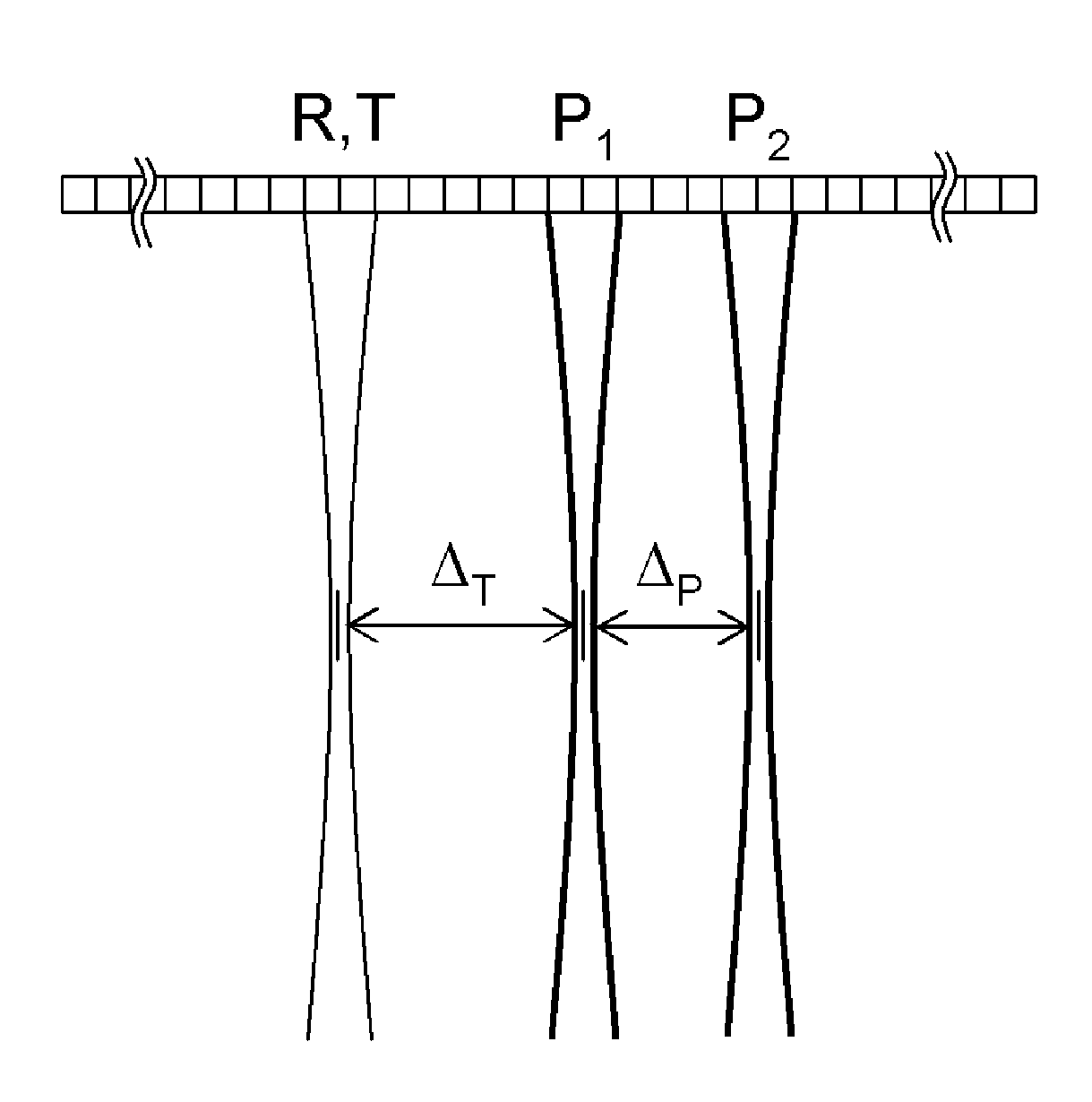
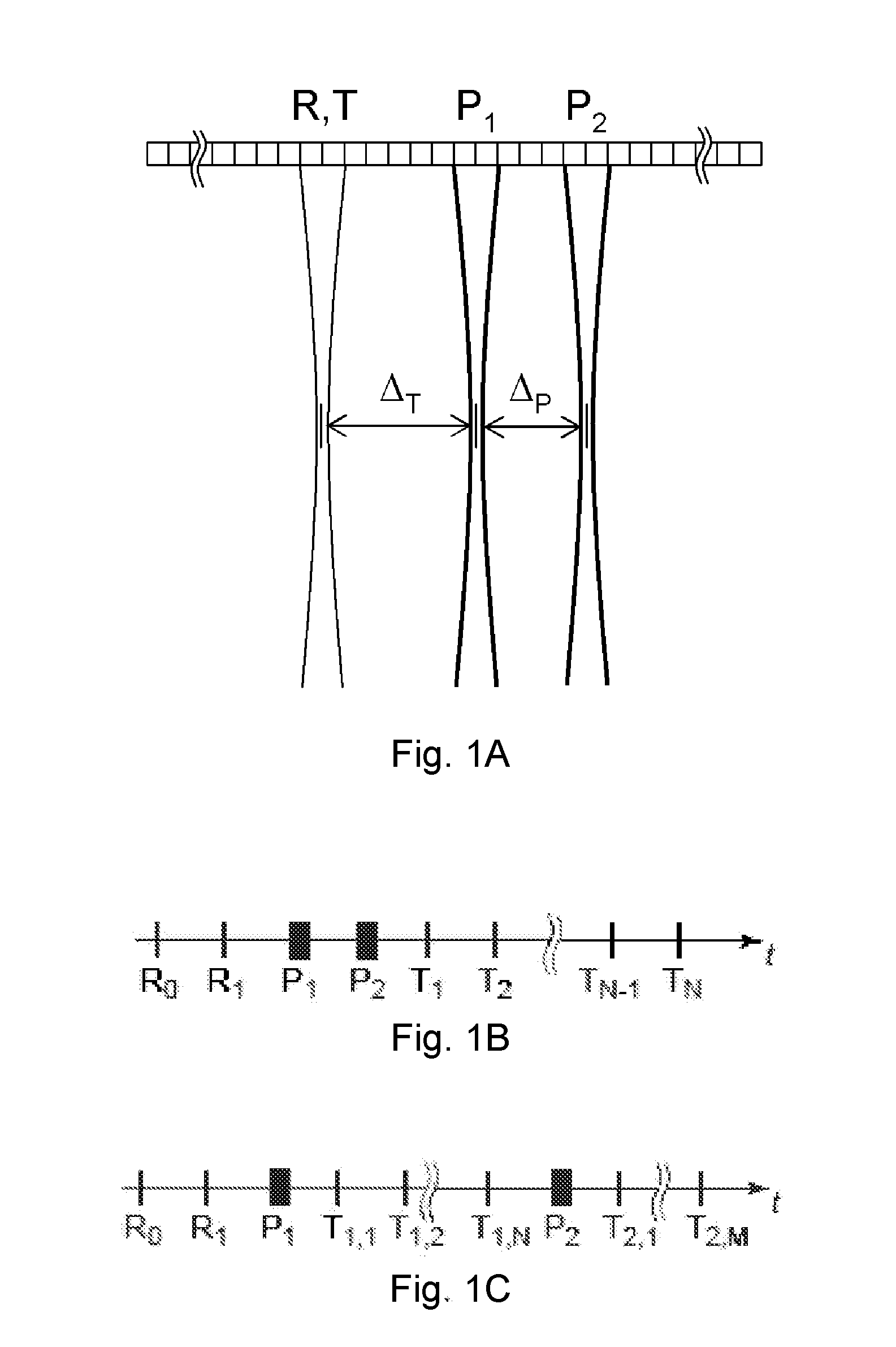
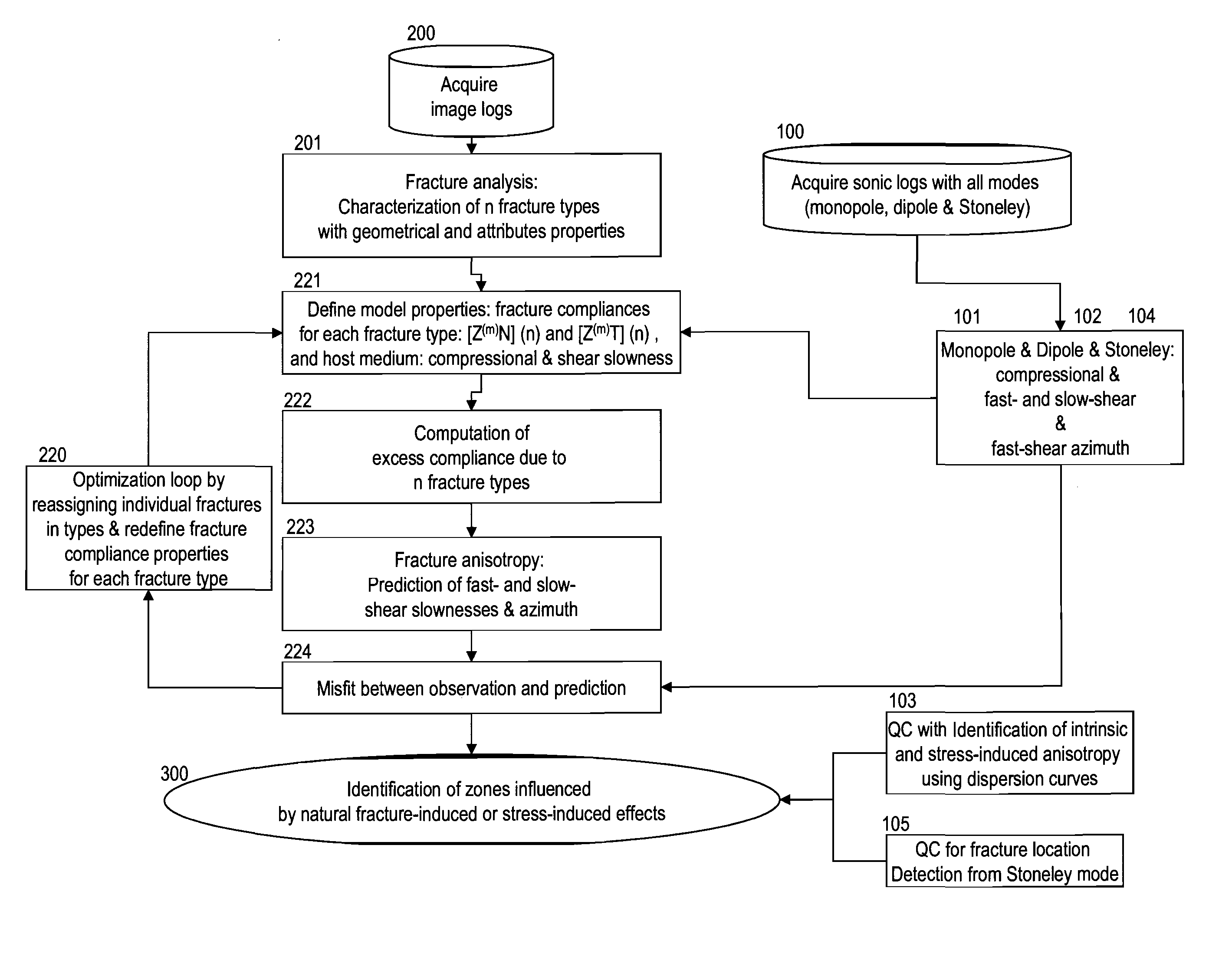
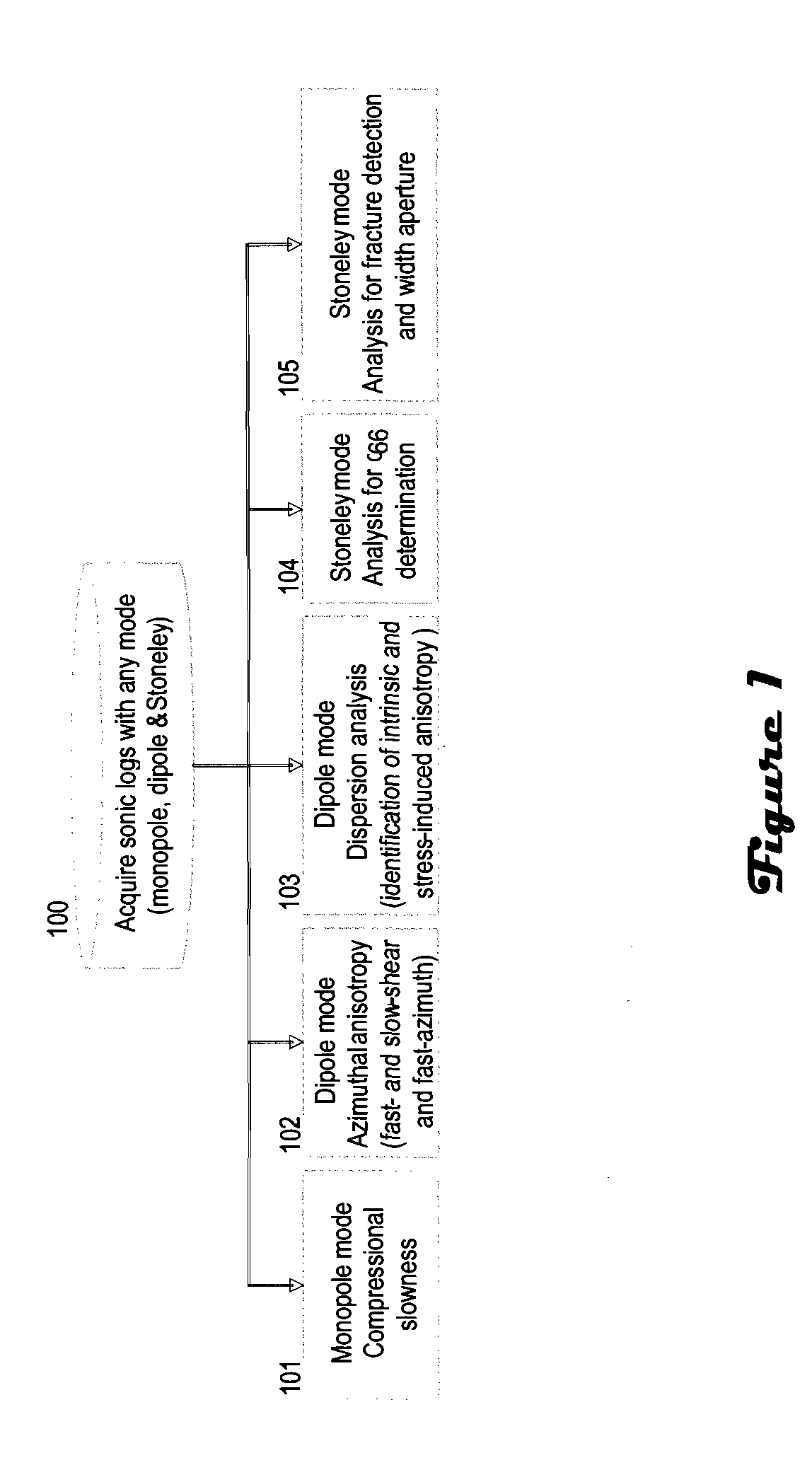
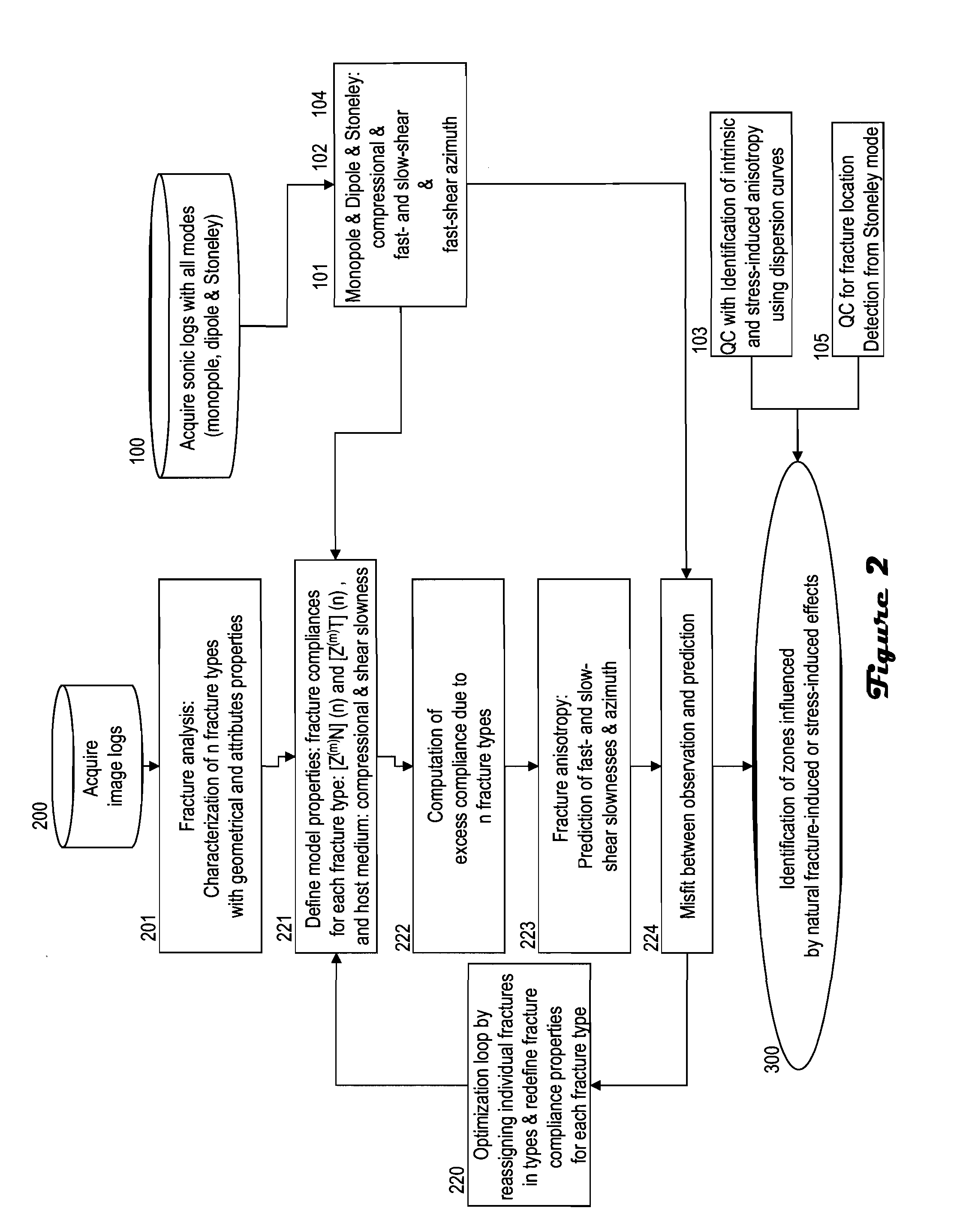
Discriminating natural fracture- and stress-induced sonic anisotropy using a combination of image and sonic logs
Fracture- and stress-induced sonic anisotropy is distinguished using a combination of image and sonic logs. Borehole image and sonic logs are acquired via known techniques. Analysis of sonic data from monopole P- and S-waves, monopole Stoneley and cross-dipole shear sonic data in an anisotropic formation are used to estimate at least one compressional and two shear moduli, and the dipole fast shear direction. Fracture analysis of image logs enables determination of fracture types and geometrical properties. Geological and geomechanical analysis from image logs provide a priori discrimination of natural fractures and stress-induced fractures. A forward quantitative model of natural fracture- and stress-induced sonic anisotropy based on the knowledge of fracture properties interpreted from image logs allows the computation of the fast-shear azimuth and the difference in slowness between the fast- and slow-shear. The misfit between predicted and observed sonic measurements (i.e. fast-shear azimuth and slownesses) is then optimized in order to discriminate depth zones with an elastic medium as being influenced by the presence of open natural fractures, closed natural fractures and fractures induced by non-equal principal stress effects.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method of determining, displaying and using the relative changes of elastic modulus and density of underground rock
InactiveUS6091669AReduce riskIncrease the number ofSeismic signal processingShear modulusClassical mechanics
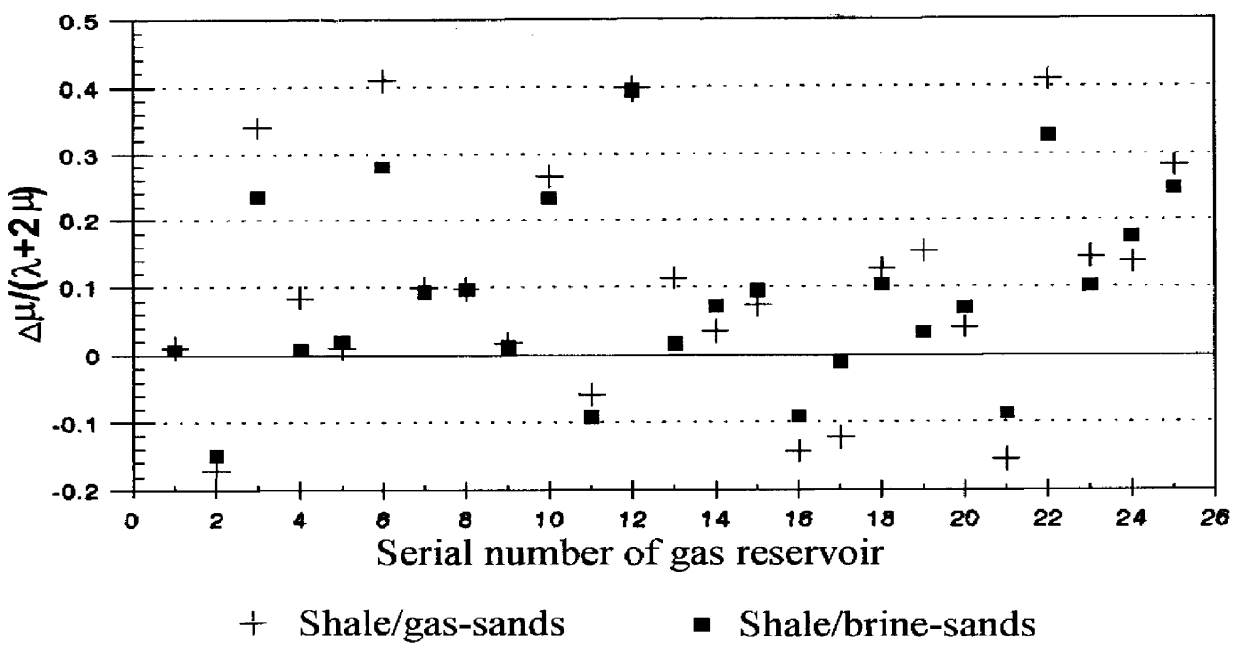
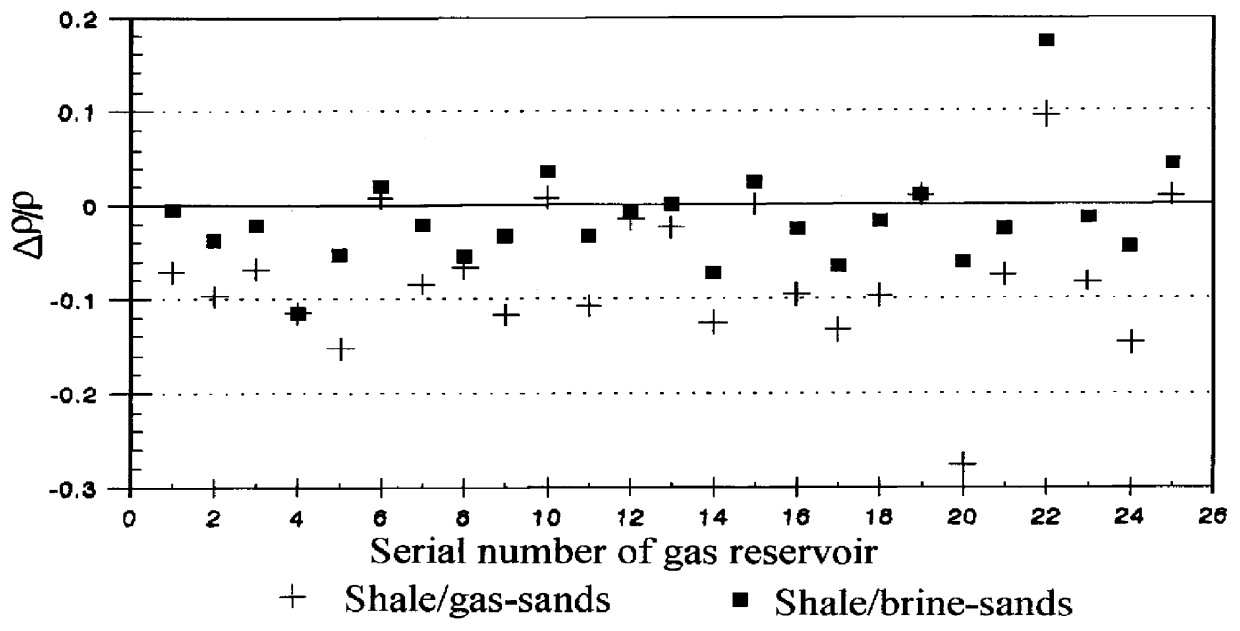
PCT No. PCT / CN96 / 00104 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 29, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 29, 1998 PCT Filed Nov. 20, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 19370 PCT Pub. Date May 29, 1997The general object of the present invention is to provide a method for determining and displaying the relative changes of elastic moduli and that of density of geologic formations and for utilizing these relative changes and plottings for gas / oil exploration, especially for direct gas and light oil detection. The said relative changes of elastic moduli are the relative change of Lame constant DELTA lambda / ( lambda +2 mu ), the relative change of shear modulus DELTA mu / ( lambda +2 mu ) and / or DELTA mu / [ kappa +(4 / 3) mu ], the relative change of bulk modulus DELTA kappa / [ kappa +(4 / 3) mu ]; and the relative change of density is DELTA rho / rho .
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP
Acoustical sound proofing material with improved damping at select frequencies and methods for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20090004448A1Improve abilitiesResist transmission of noiseWallsSound proofingShear modulusCellulose
Panels for use in building construction (partitions, walls, ceilings, floors or doors) which exhibit improved acoustical sound proofing in multiple specific frequency ranges comprise laminated structures having as an integral part thereof one or more layers of viscoelastic material of varied shear moduli which also function as a glue and energy dissipating layer; and, in some embodiments, one or more constraining layers, such as gypsum, cement, metal, cellulose, wood, or petroleum-based products such as plastic, vinyl, plastic or rubber. In one embodiment, standard wallboard, typically gypsum, comprises the external surfaces of the laminated structure.
Owner:SERIOUS MATERIALS +1
Acoustical sound proofing material with improved damping at select frequencies and methods for manufacturing same
Panels for use in building construction (partitions, walls, ceilings, floors or doors) which exhibit improved acoustical sound proofing in multiple specific frequency ranges comprise laminated structures having as an integral part thereof one or more layers of viscoelastic material of varied shear moduli which also function as a glue and energy dissipating layer; and, in some embodiments, one or more constraining layers, such as gypsum, cement, metal, cellulose, wood, or petroleum-based products such as plastic, vinyl, plastic or rubber. In one embodiment, standard wallboard, typically gypsum, comprises the external surfaces of the laminated structure.
Owner:SERIOUS MATERIALS +1
Heat-Peelable Pressure-Sensitive Adhesive Sheet and Method for Processing Adherend Using the Heat-Peelable Pressure-Sensitive Adhesive Sheet
InactiveUS20080019078A1Avoid deformationEasy to peelLayered productsFixed capacitor dielectricShear modulusFoaming agent
Disclosed is a heat-peelable pressure-sensitive adhesive sheet that can prevent the deformation of a pressure-sensitive adhesive layer due to pressurization in a pressing process and can be easily peeled off from the processed article. The heat-peelable pressure-sensitive adhesive sheet includes a substrate, and a heat-expandable pressure-sensitive adhesive layer arranged on or above at least one side of the substrate and containing a foaming agent, in which the heat-expandable pressure-sensitive adhesive layer has a shear modulus (23° C.) in an unfoamed state of 7×106 Pa or more. The heat-expandable pressure-sensitive adhesive layer preferably has a shear modulus (95° C.) in an unfoamed state of less than 7×106 Pa. The foaming agent in the heat-expandable pressure-sensitive adhesive layer preferably has a foam initiating temperature higher than 80° C.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Insulation block and method of using thermal insulation mortar to prepare insulation block
InactiveCN101781918AImprove mechanical propertiesIncreased durabilityConstruction materialShear modulusThermal insulation
The invention relates to an insulation block and a method of using thermal insulation mortar to prepare the insulation block. The insulation block comprises a hollow block, wherein an insulation block is filled in the hollow part of the hollow block. The preparation method of the insulation block comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing thermal insulation mortar with good flowing property; secondly, filling the thermal insulation mortar in the hollow part of the hollow block; and finally, connecting the hardened thermal insulation mortar with the hollow block to obtain the insulation block. The thermal insulation mortar is one kind of cement mortar, wherein the aggregate is selected from light particles with low coefficient of thermal conductivity. By using the method of the invention, the insulation block with 5-40MPa of compression strength, 0.20-0.70MPa of bending tensile strength, 0.20-0.70MPa of shear strength, 1*10<3>-3*10<3>MPa of elastic modulus, 500-1000MPa of shear modulus, 0-0.04% of coefficient of linear expansion and 0.20-0.40W / (m2.K) of heat transfer coefficient can be prepared and the insulation block can be used in various thermal insulation works of buildings.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
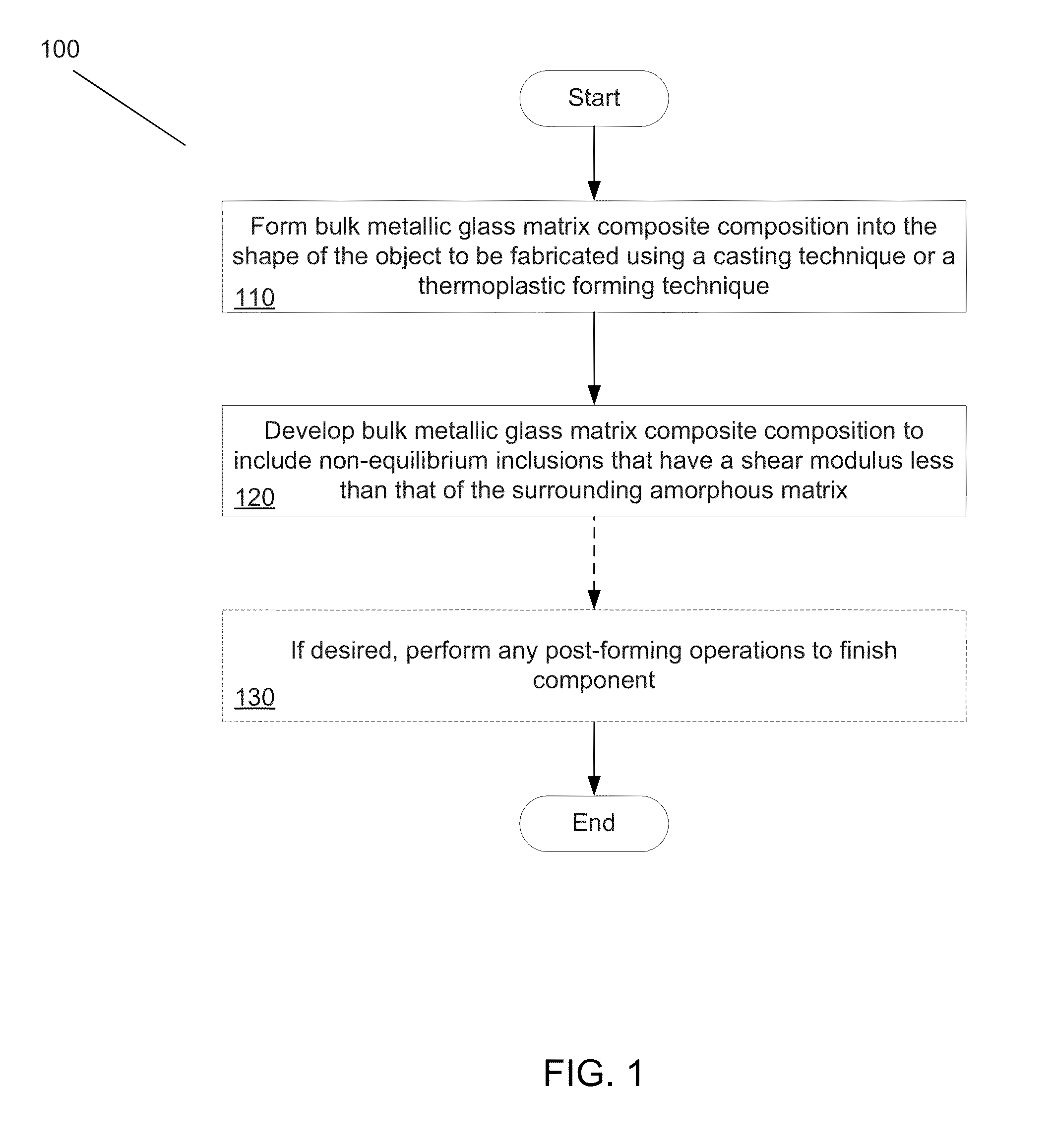
Systems and methods for fabricating objects from bulk metallic glass matrix composites using primary crystallization
Systems and methods in accordance with embodiments of the invention implement bulk metallic glass matrix composites in the fabrication of objects. In one embodiment, a method of fabricating an object including a bulk metallic glass matrix composite includes: forming a bulk metallic glass matrix composite composition into the shape of the object to be fabricated; and developing the bulk metallic glass matrix composite composition to include non-equilibrium inclusions that are softer than the surrounding matrix as measured by one of: the shear modulus, the elastic limit, and the hardness; where the bulk metallic glass matrix composite composition is such that the extent of the presence of the inclusions can be made to vary.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com