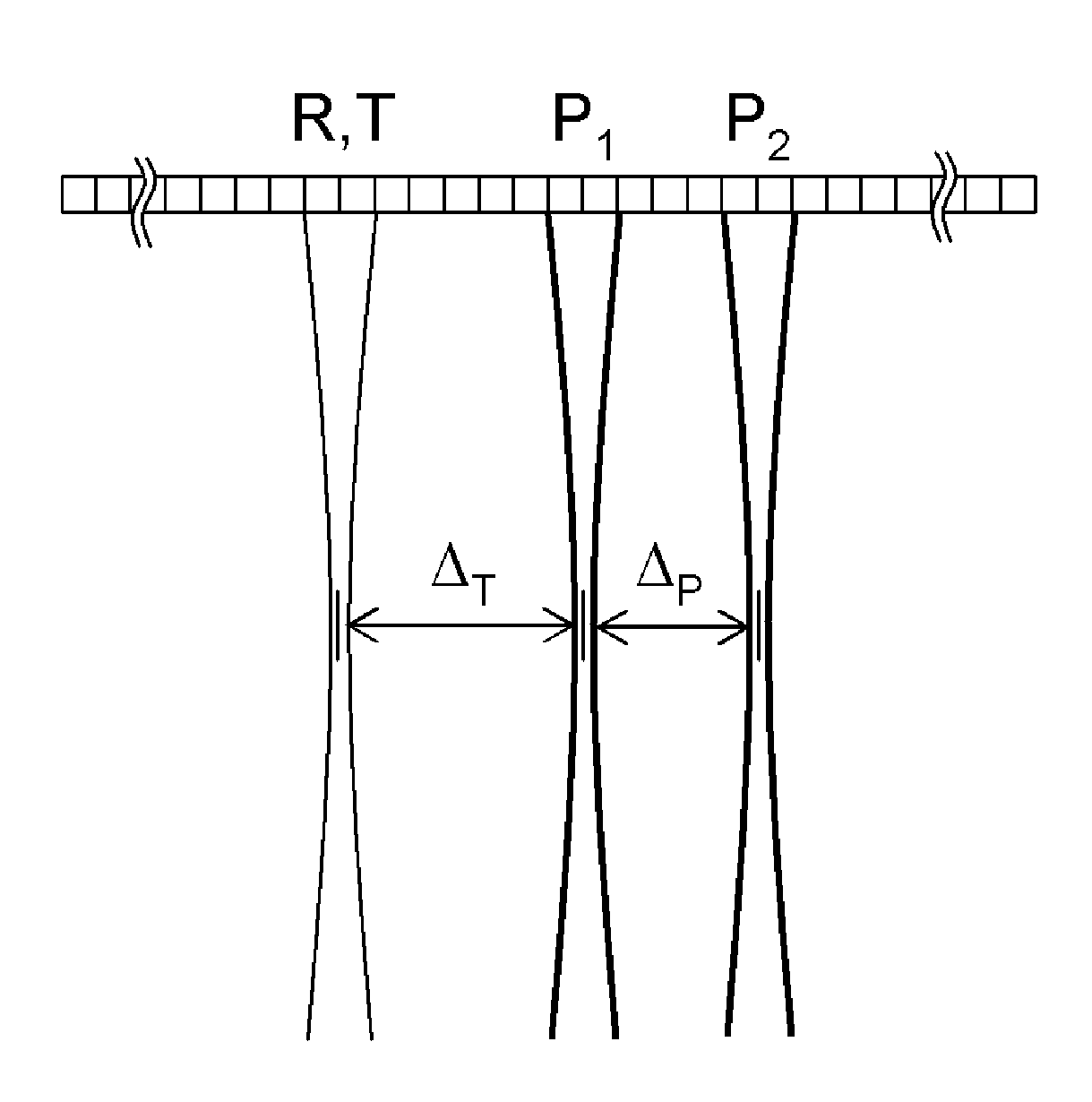
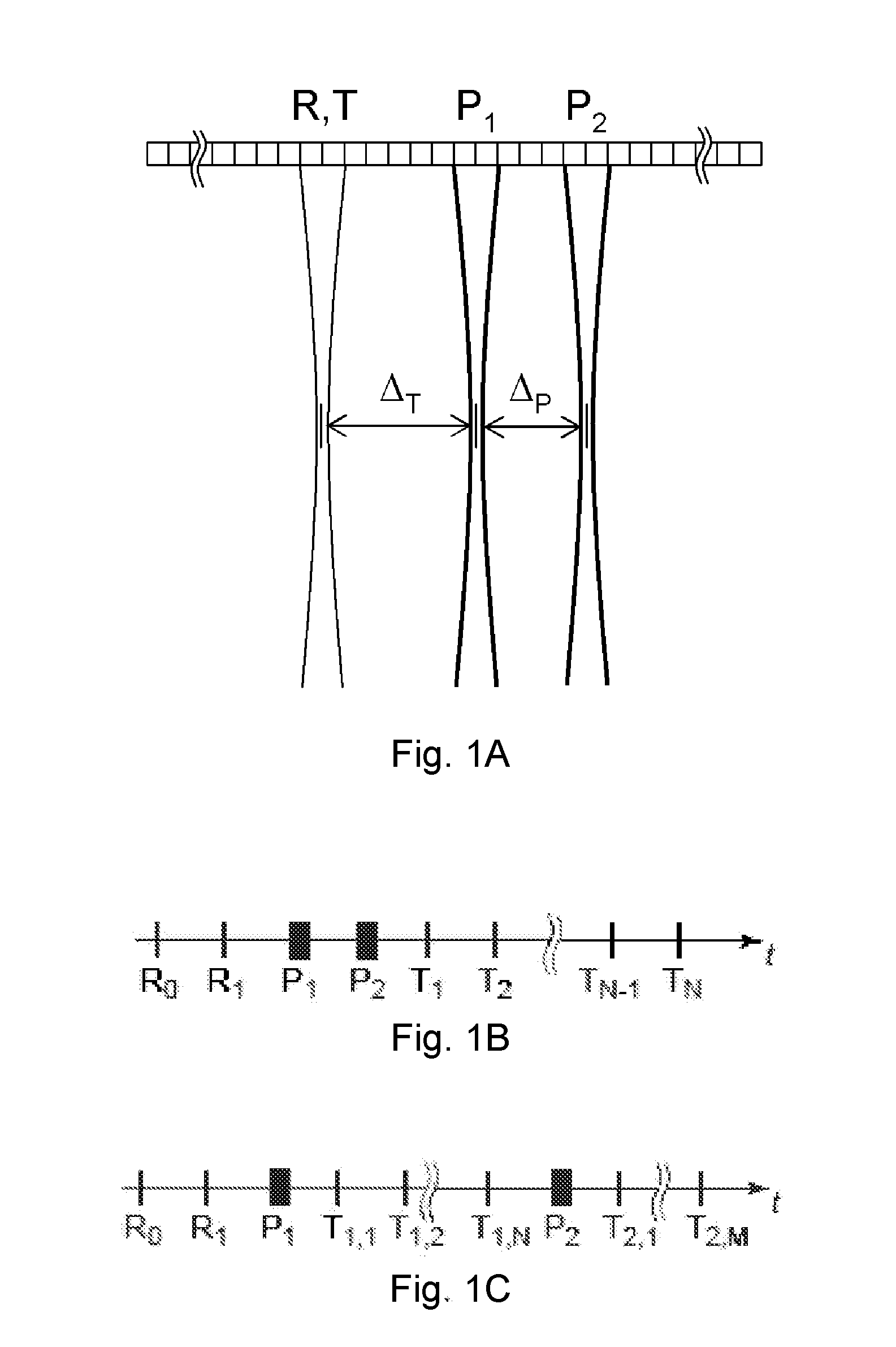
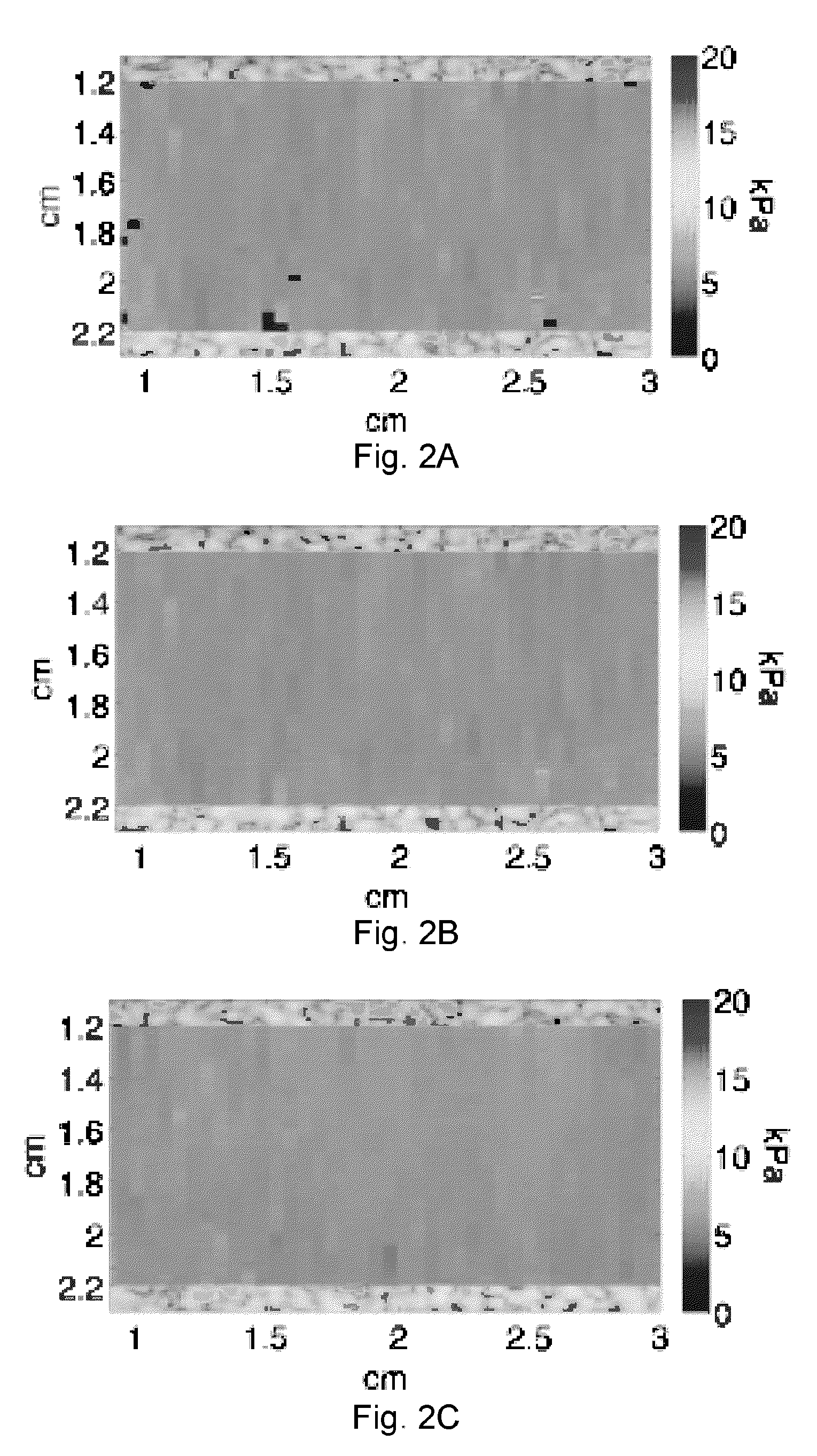
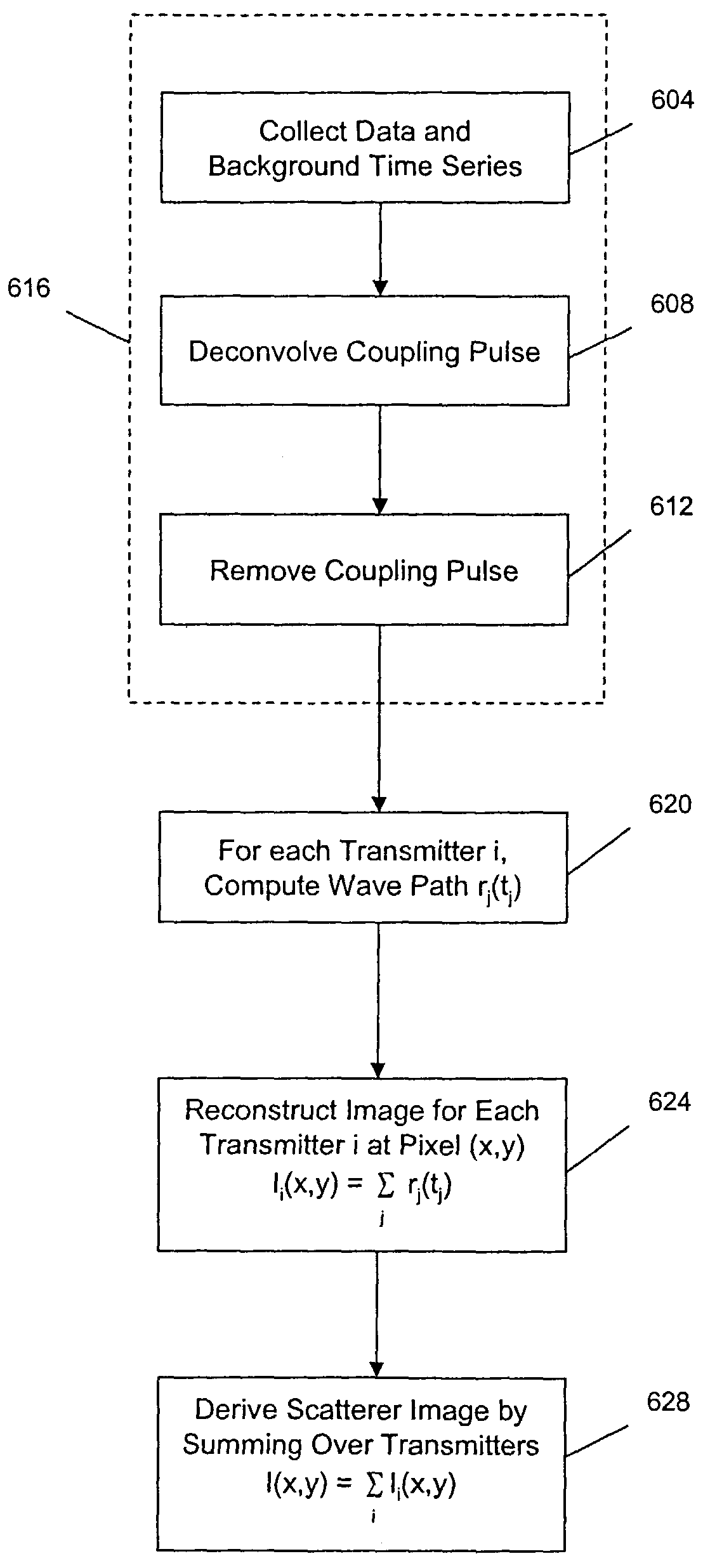
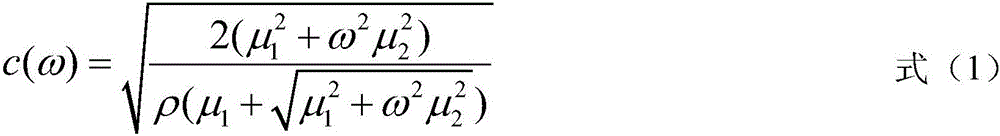Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
199 results about "Acoustic radiation force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
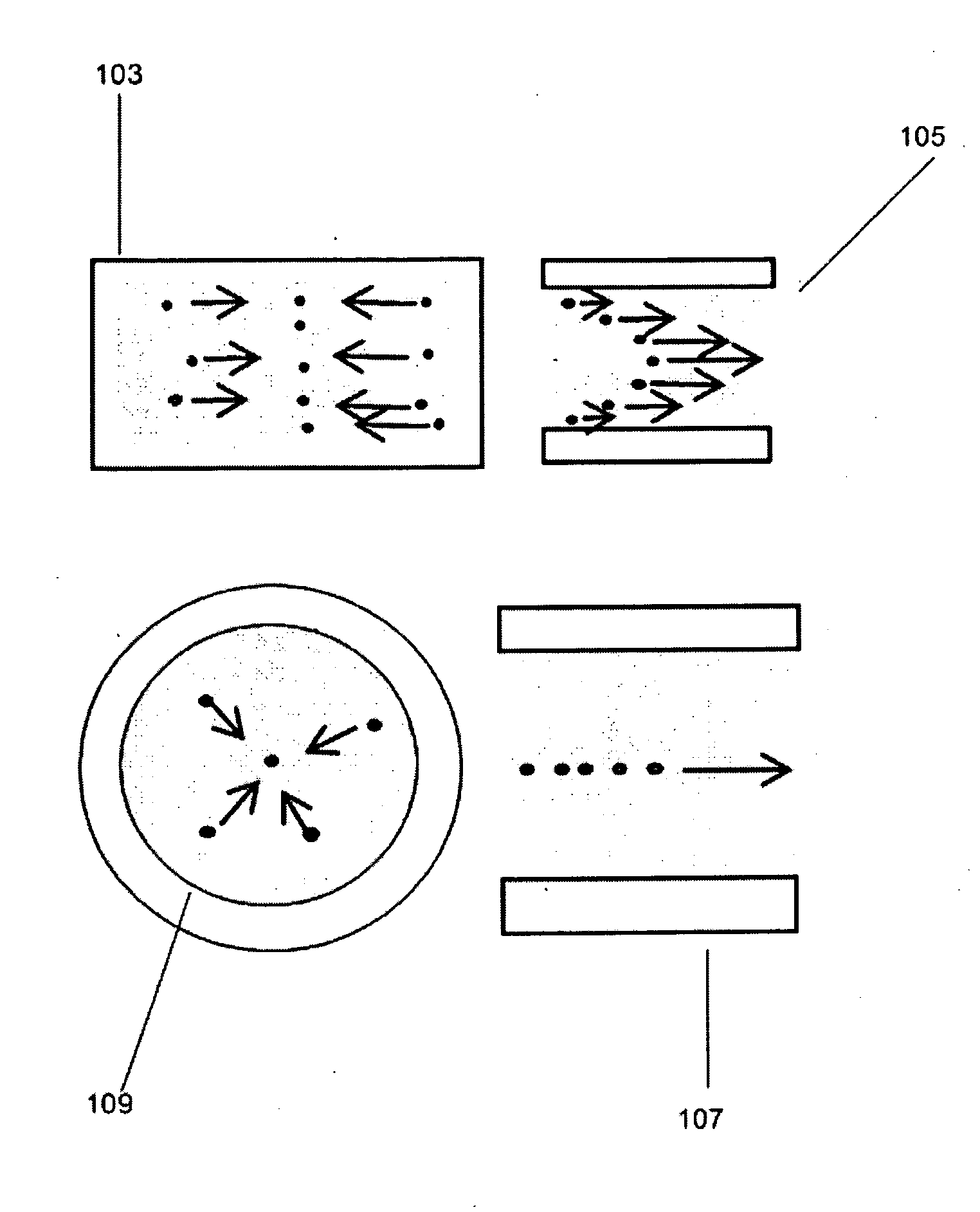
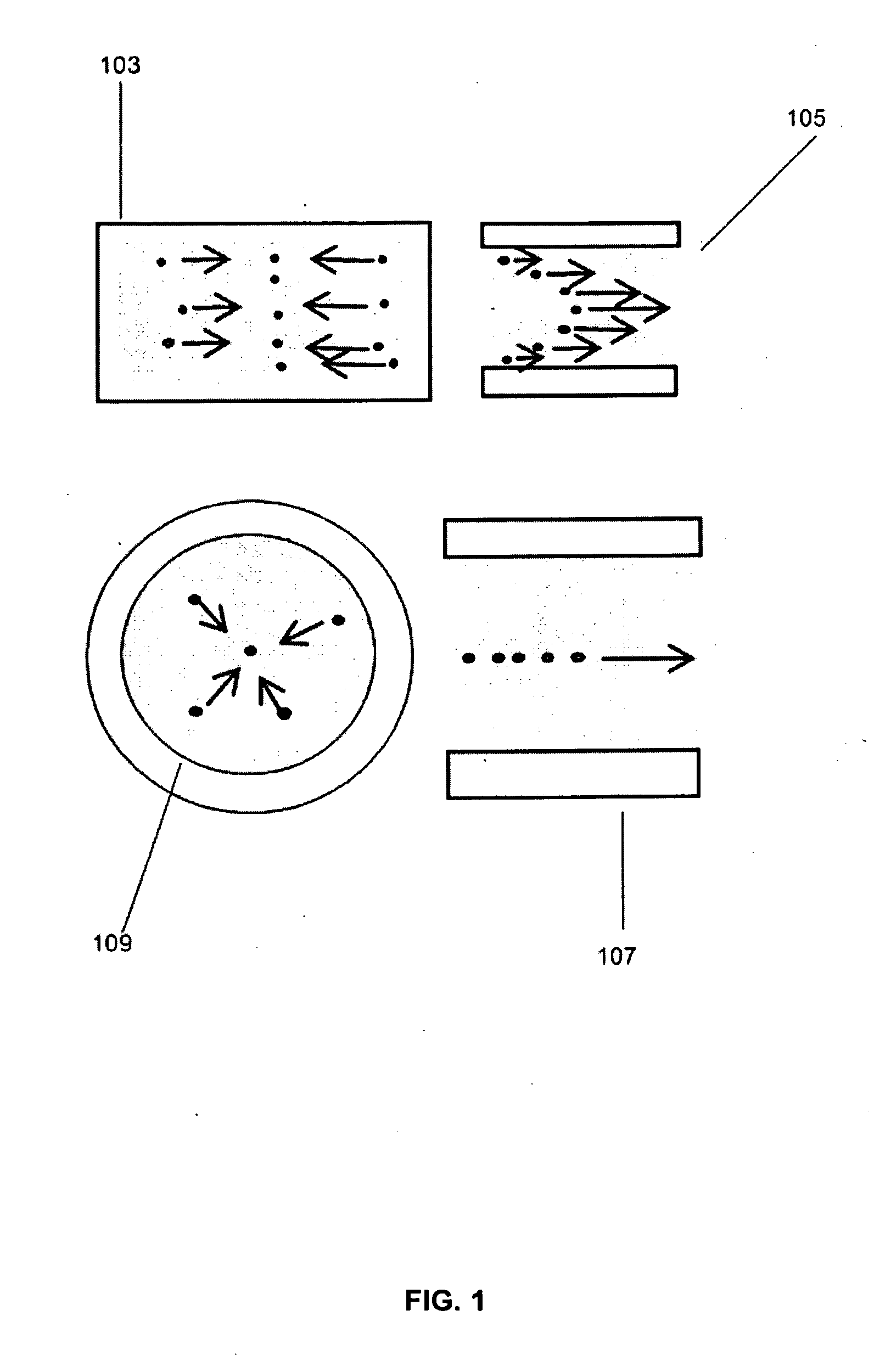
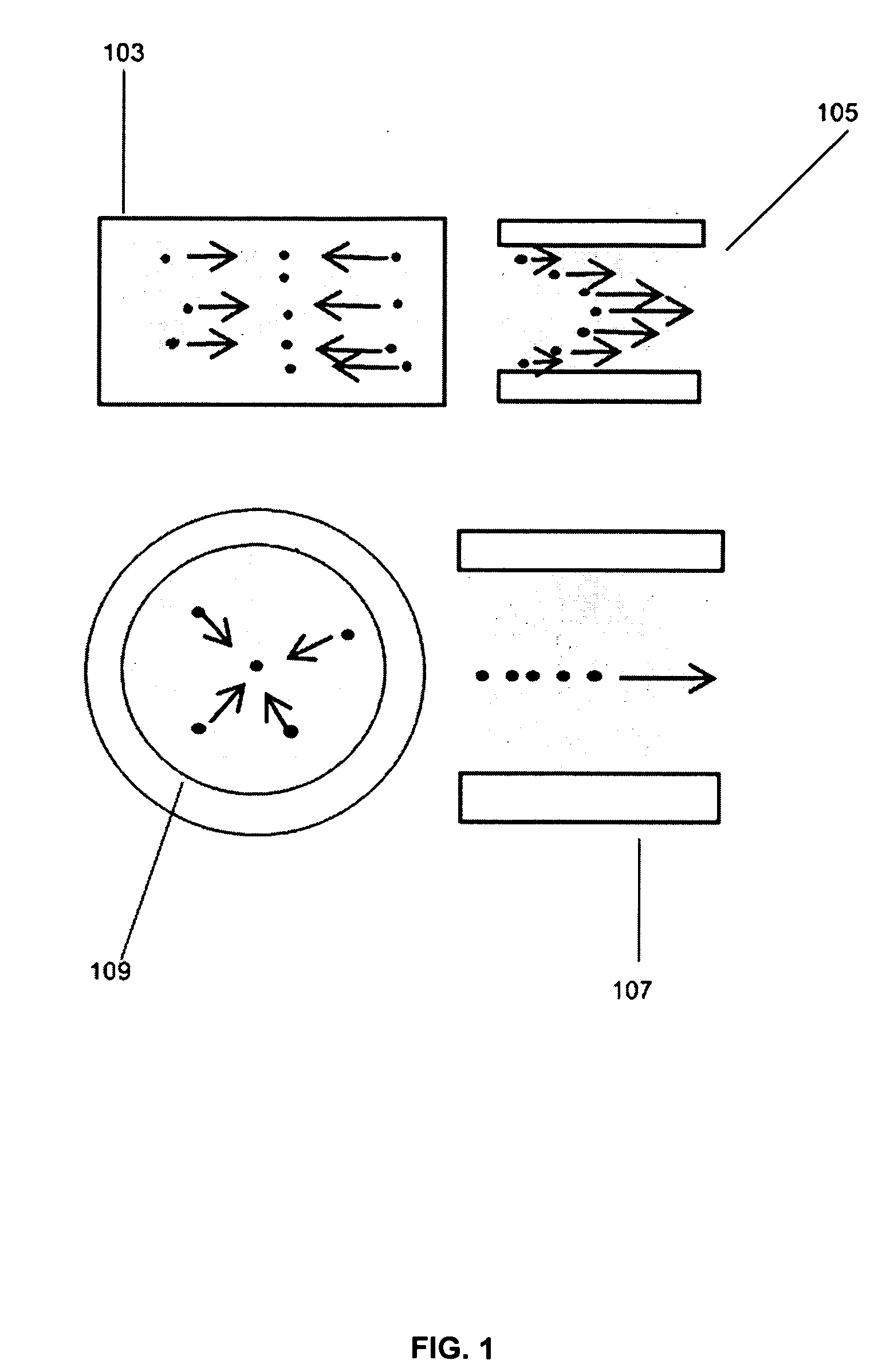
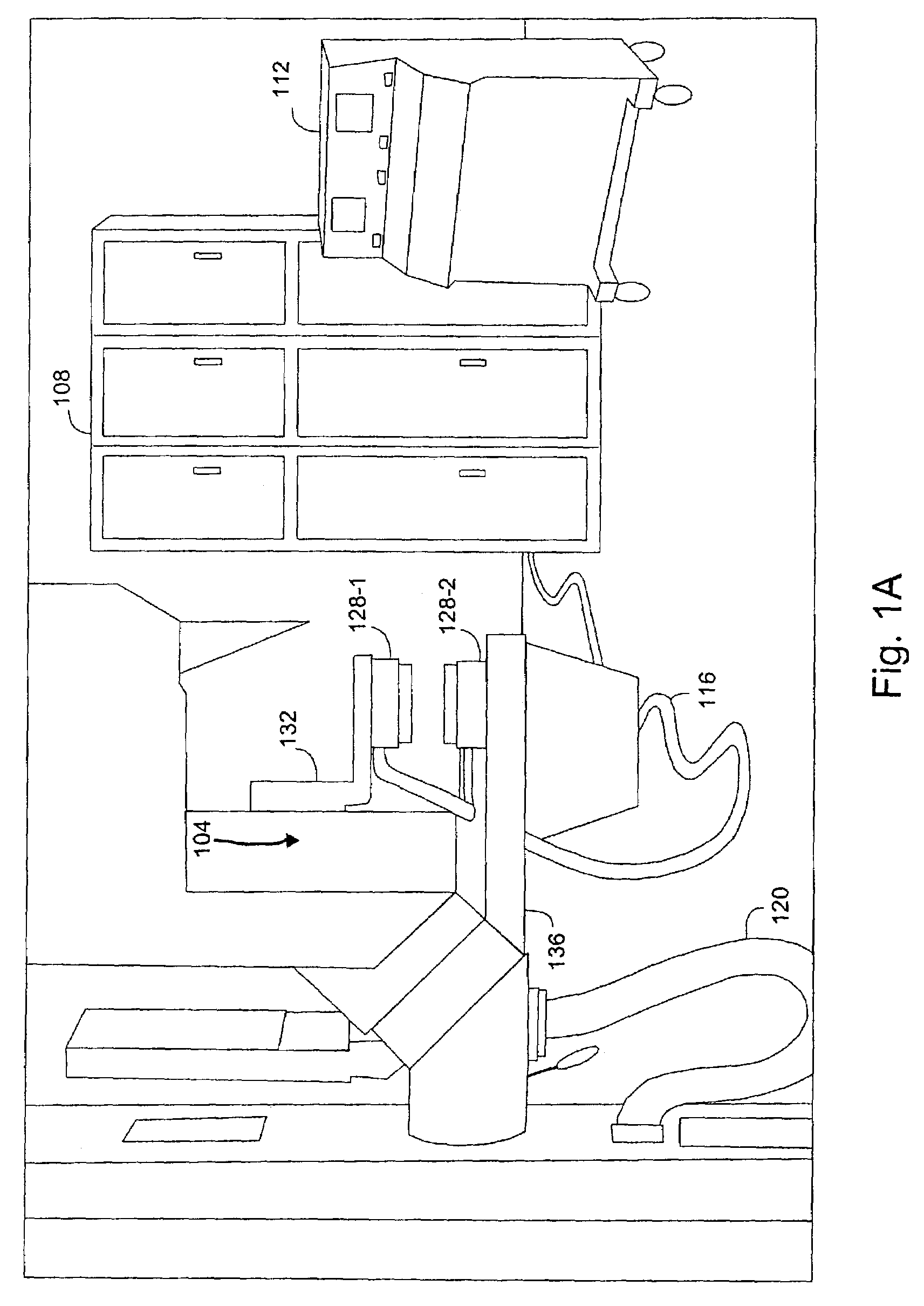
Acoustic radiation force is a physical phenomenon resulting from the interaction of an acoustic wave with an obstacle placed along its path. Generally, the force exerted on the obstacle is evaluated by integrating the acoustic radiation pressure (due to the presence of the sonic wave) over its time-varying surface. The magnitude of the force exerted by an acoustic plane wave at any given location can be calculated as: where F is the force in kg/(s²cm²), α is the absorption coefficient in Np/cm, I is the temporal average intensity of the acoustic wave at the given location in W/cm², and c is the speed of sound in the medium in cm/s.
Particle Analyzing Systems and Methods Using Acoustic Radiation Pressure
ActiveUS20090029870A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMagnetic measurementsAcoustic radiation forceAcoustics
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Particle Imaging Systems and Methods Using Acoustic Radiation Pressure
ActiveUS20090048805A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansParticle imagingAcoustic radiation force
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Real-time monitoring and control of hifu therapy in multiple dimensions
InactiveUS20130096597A1Reliable indicatorAccurate and fast and low-cost and simple and convenient techniqueUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyAuditory radiationMechanical property
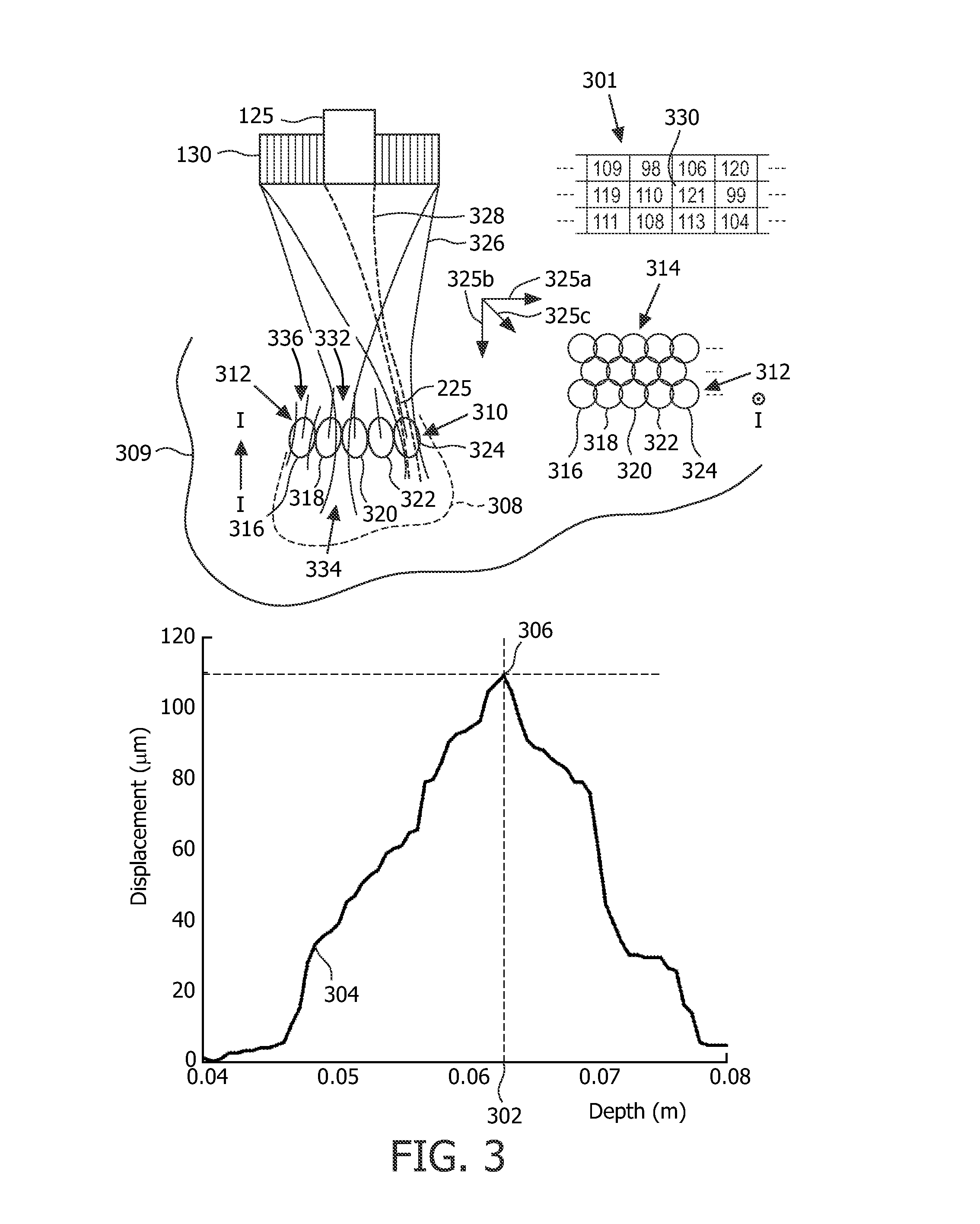
Energy is transferred (336) to cause a mechanical property of biological tissue to change, as in ablation. An effect of the transferring is examined in more than one spatial dimension to, for example, make an ablation halting decision for a treatment region, i.e., line (312) or layer (314), or for a location (316) within the region. Halting decisions can be based on lesion-central and / or lesion-peripheral longitudinal displacement of treated tissue evaluated in real time against a characteristic curve. Steering in the azimuthal and / or elevation direction is afforded by, for example, linear, or 2D, multi-channel ultrasound arrays for therapy and imaging. Protocols includable are region-wide scanning (SI 010) and location-by-location completion for both (HIFU) therapy and tracking (acoustic-radiation-forced-based) displacement of treated tissue. Fine, location- to-location monitoring can be used for relatively inhomogeneous tissue; whereas, quicker, sparser and more generalized monitoring (1 100, 1200) can be employed for relatively homogeneous tissue.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Particle Fusing Systems and Methods Using Acoustic Radiation Pressure
ActiveUS20090042239A1Animal cellsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcoustic radiation forceAcoustics
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Methods And Systems For Spatially Modulated Ultrasound Radiation Force Imaging
ActiveUS20110184287A1Easy to detectAvoid noiseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsShear modulusAcoustic radiation force
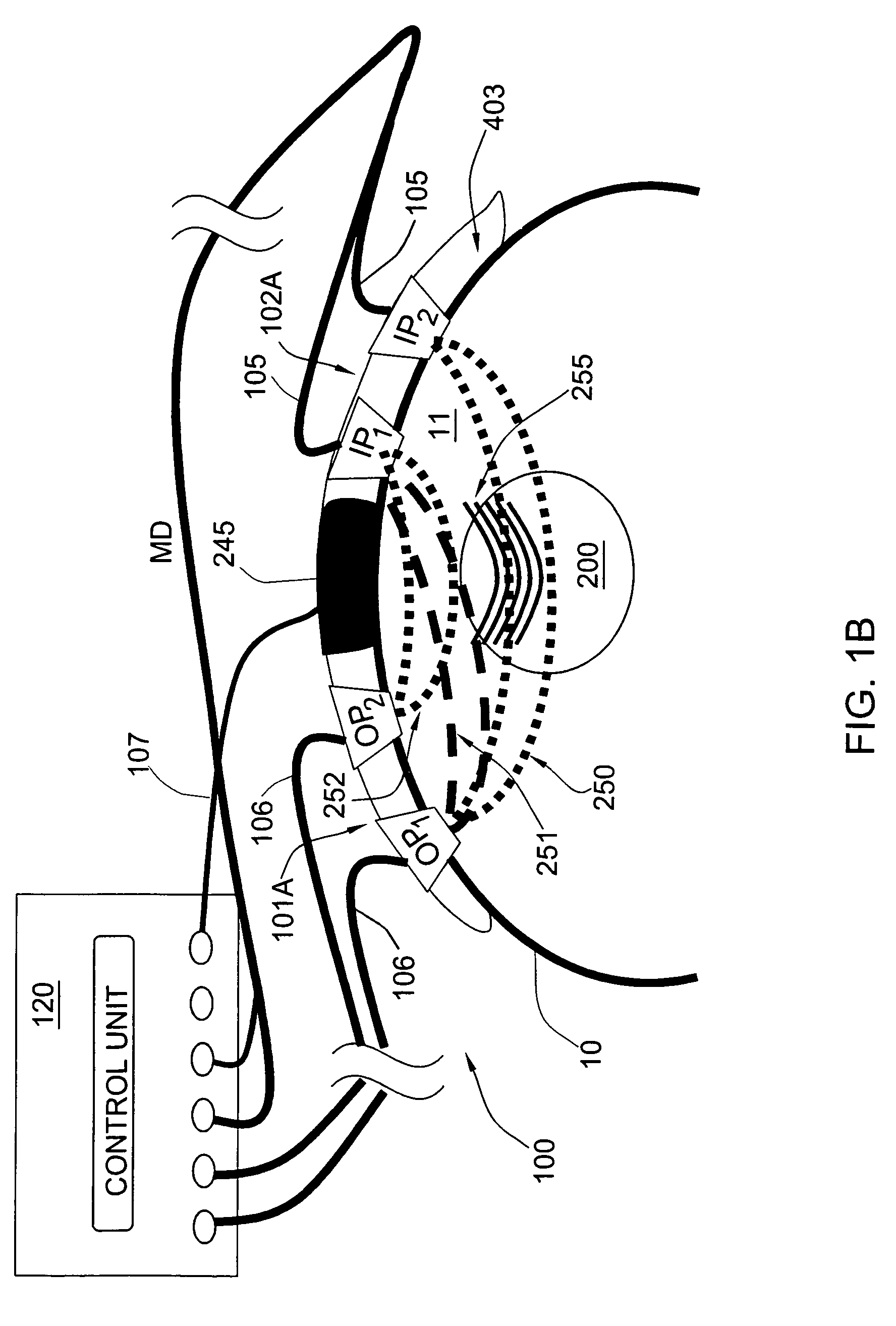
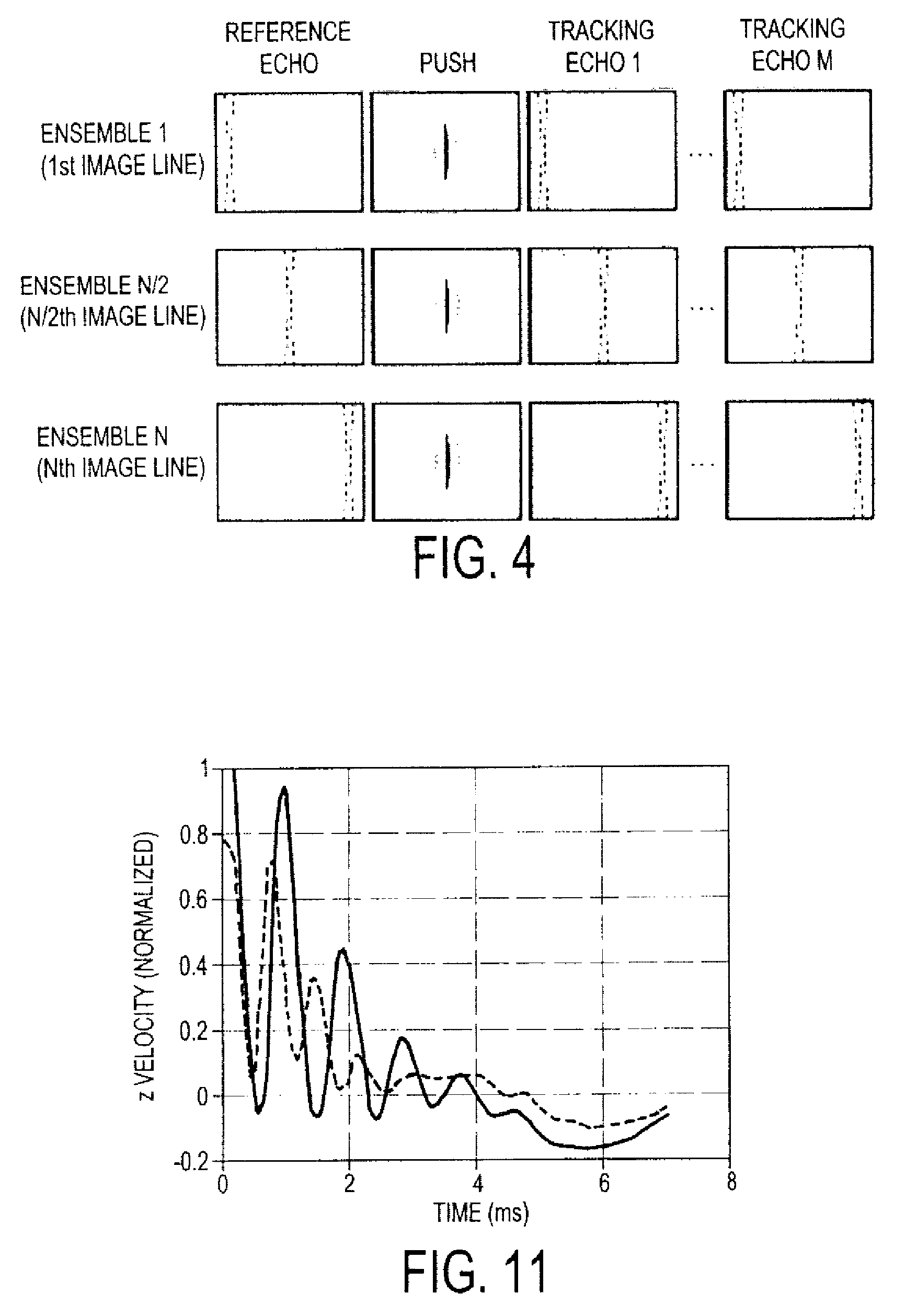
Methods for determining the shear modulus of a tissue of an individual are disclosed. In one embodiment, an acoustic pulse is transmitted and a reference echo signal is received. A first push pulse is transmitted at a second location of the individual. A second push pulse is transmitted at a third location of the individual. A series of tracking pulses are transmitted at the first location and a tracking echo signal is received from each tracking pulse. The effect of the first and second push pulses on the tissue is determined through analysis of the tracking echo signals. The shear modulus of the tissue is calculated based on the effect of the push pulses on the tissue. A system for imaging a region of tissue is presented.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Computerized ultrasound risk evaluation system
InactiveUS7285092B2Improve comfortOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsAuditory radiationSonification
A method and system for examining tissue are provided in which the tissue is maintained in a position so that it may be insonified with a plurality of pulsed spherical or cylindrical acoustic waves. The insonifying acoustic waves are scattered by the tissue so that scattered acoustic radiation including a mix of reflected and transmitted acoustic waves is received. A representation of a portion of the tissue is then derived from the received scattered acoustic radiation.
Owner:DELPHINUS MEDICAL TECH
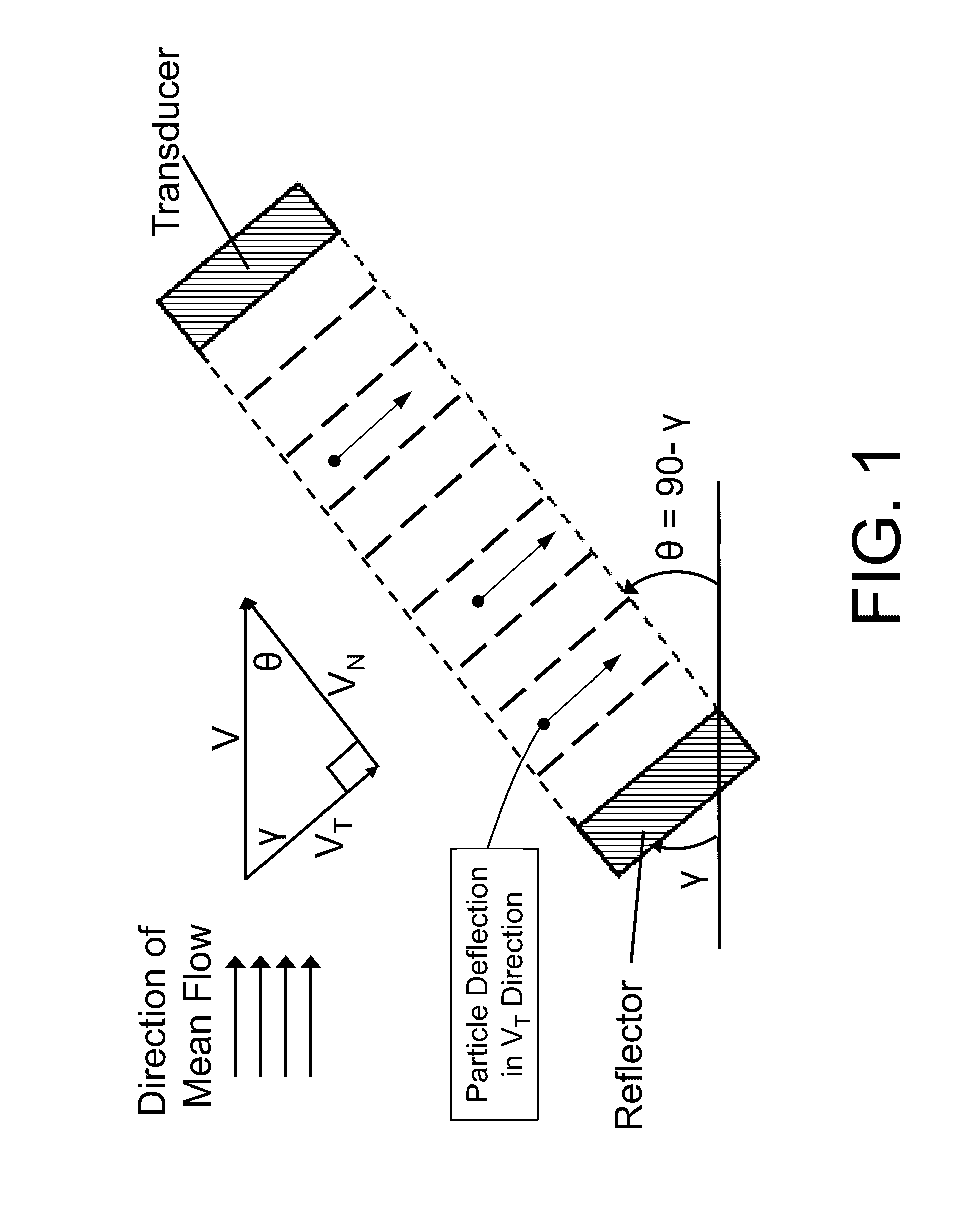
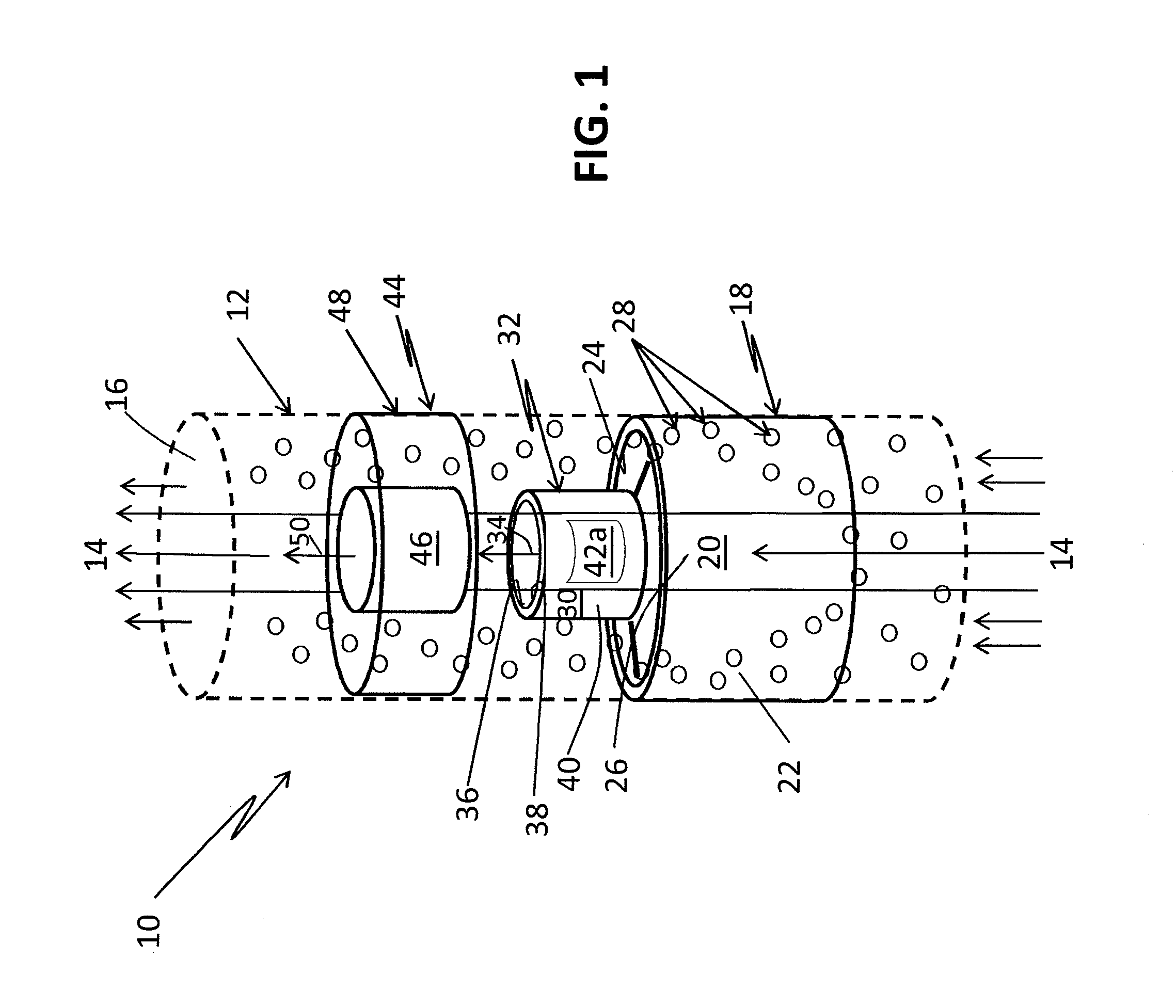
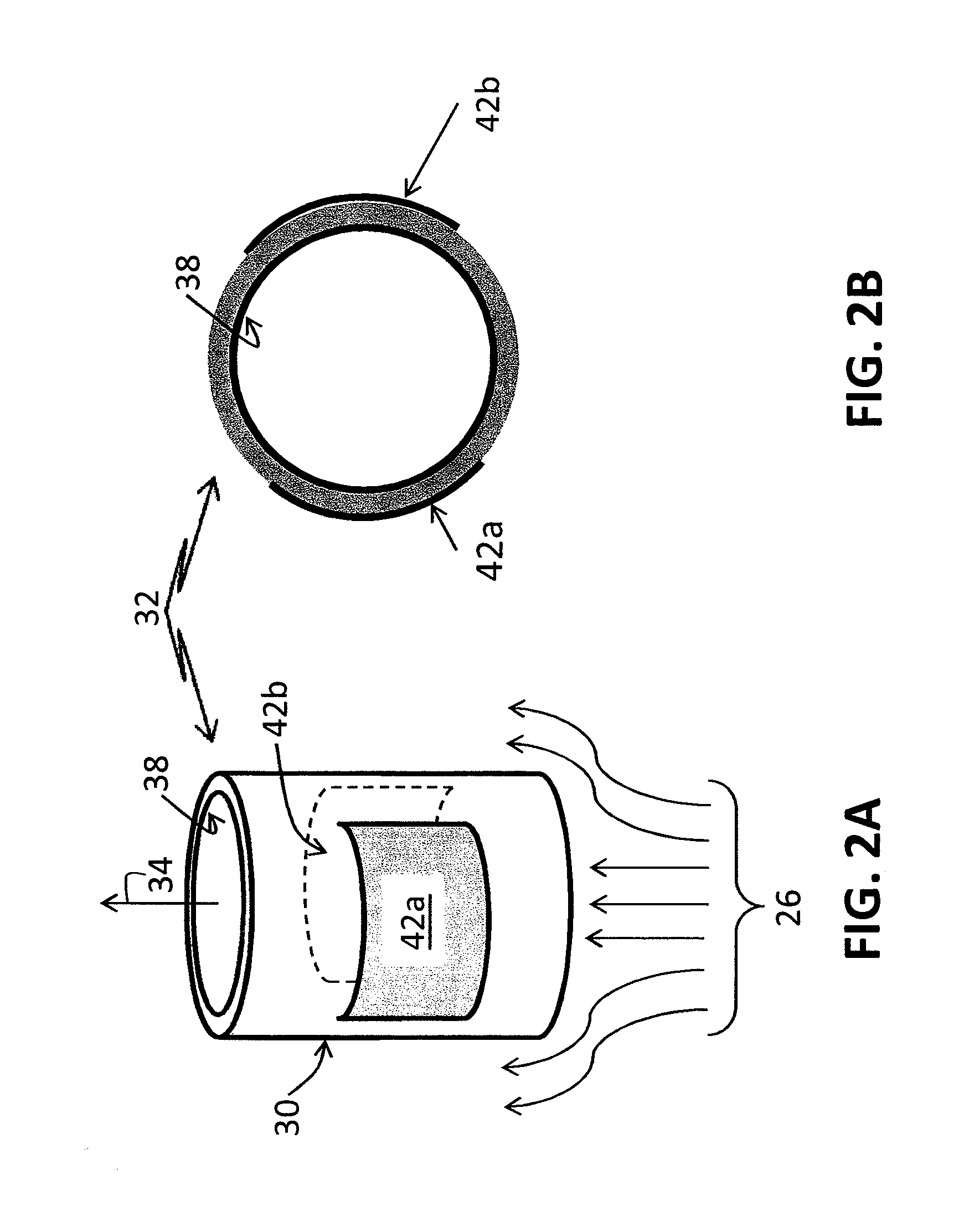
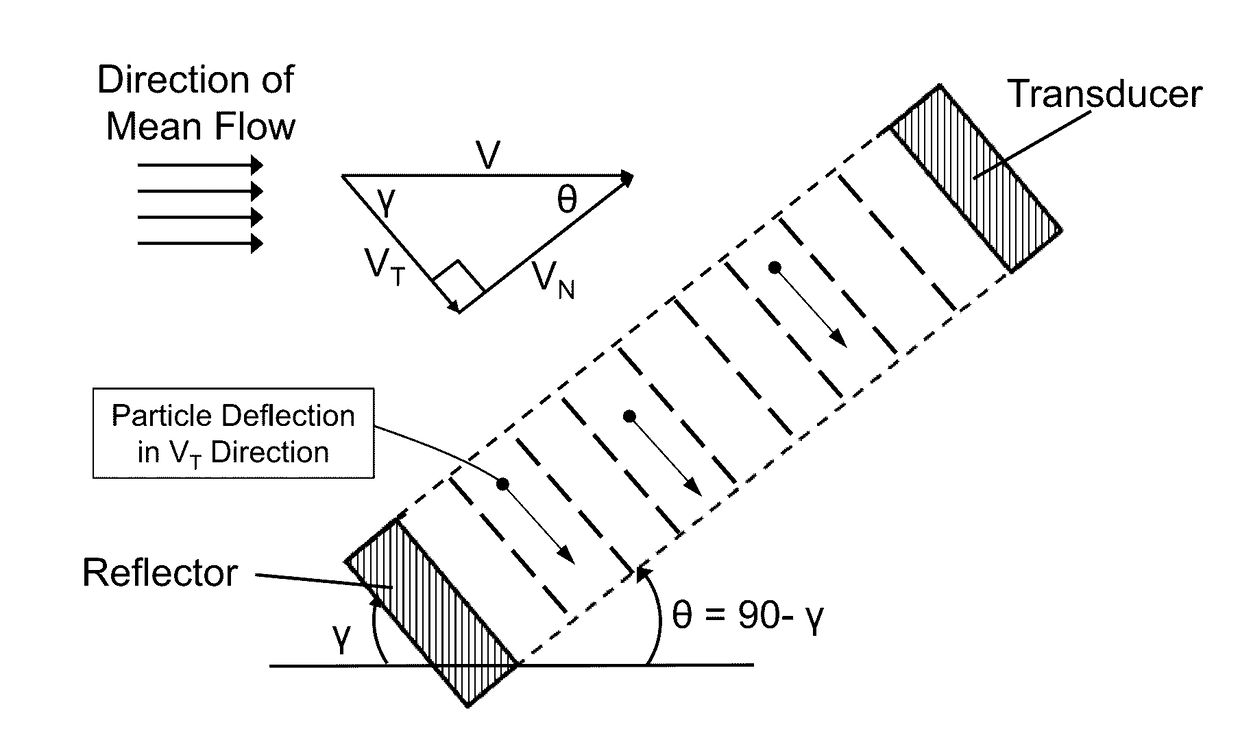
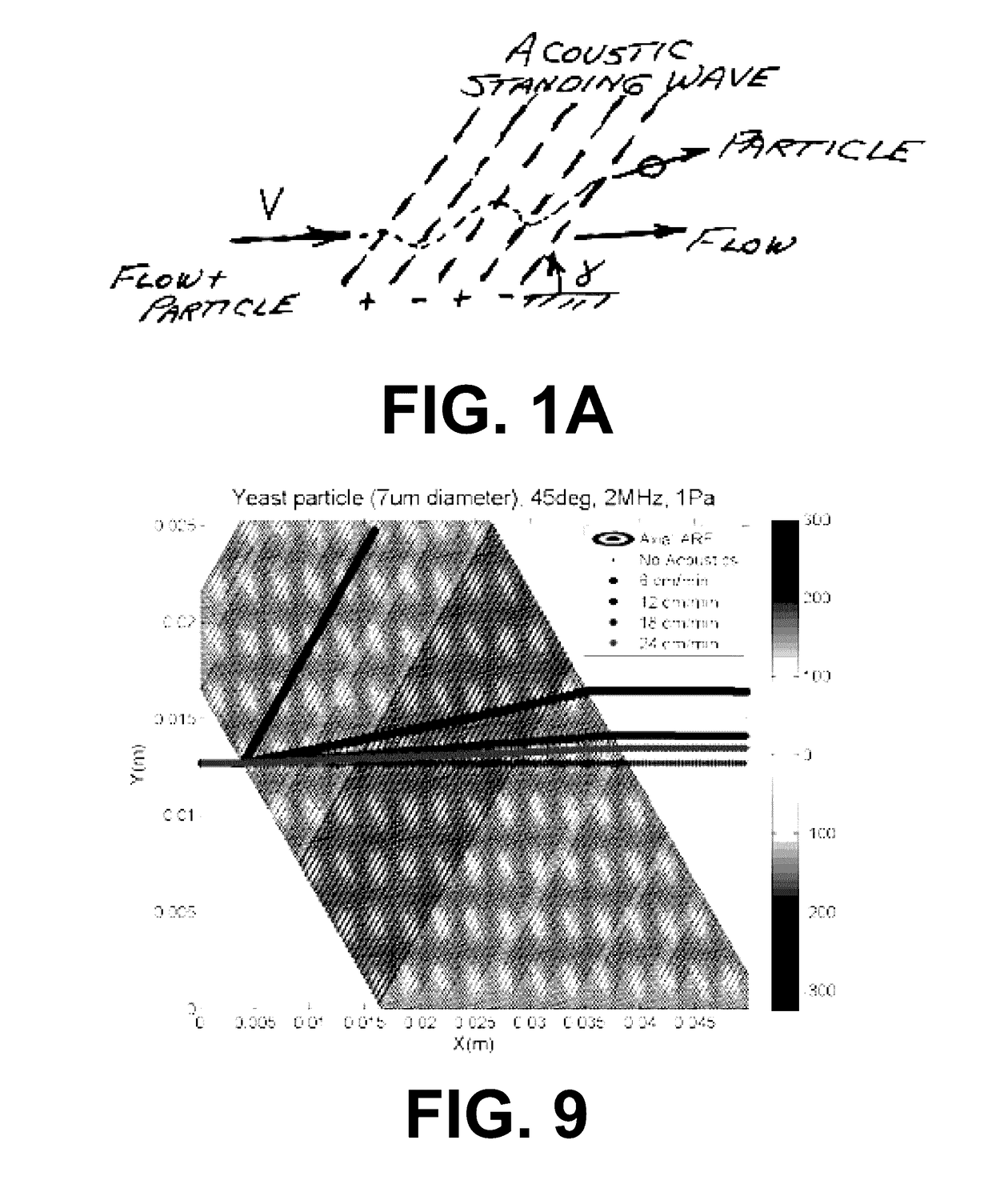
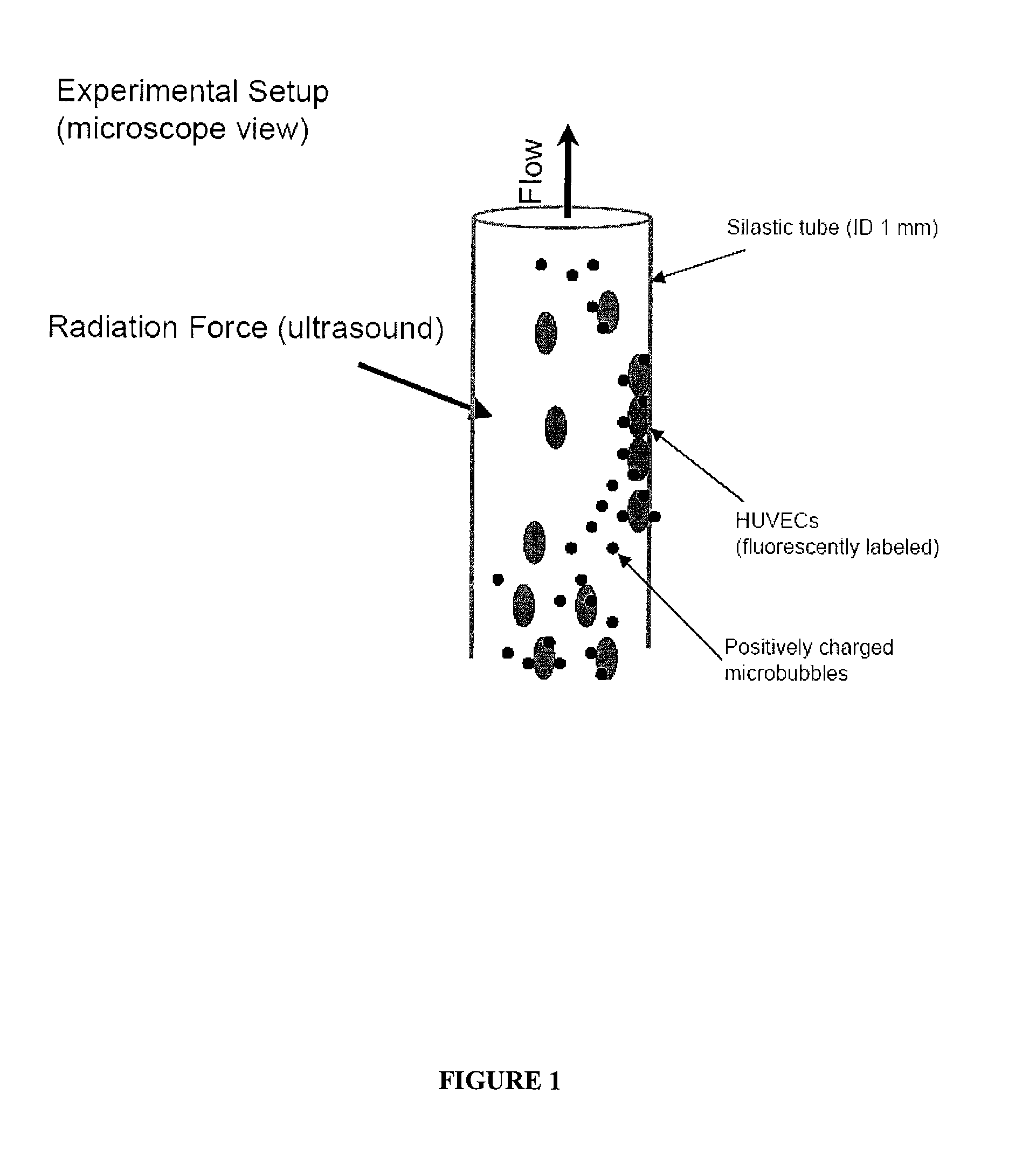
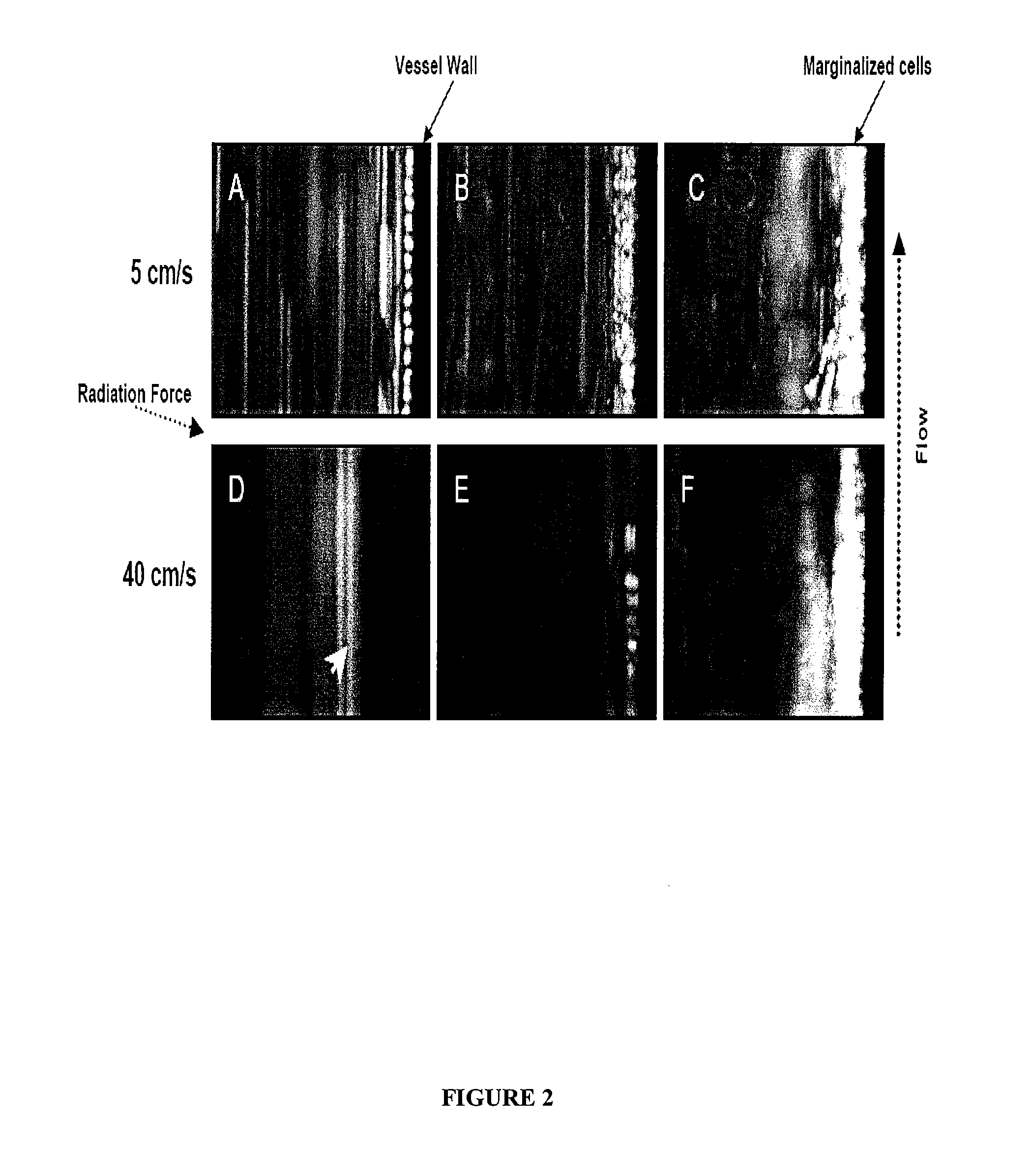
Acoustophoretic device for angled wave particle deflection
ActiveUS20160319270A1Desired deflectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsUltrasonic sensorAcoustic radiation force
Devices for separating materials from a host fluid are disclosed. The devices include a flow chamber, an ultrasonic transducer, and a reflector. The ultrasonic transducer and reflector create an angled acoustic standing wave oriented at an angle relative to the direction of mean flow through the flow chamber. The angled acoustic standing wave results in an acoustic radiation force having an axial force component that deflects the materials, so that the materials and the host fluid can thus be separated. The angled acoustic standing wave can be oriented at an angle of about 20° to about 70° relative to the direction of mean flow through the flow chamber to deflect, collect, differentiate, or fractionate the materials from the fluid flowing through the device at flow rates of about 400 mL / min up to about 700 mL / min.
Owner:FLODESIGN SONICS
Ultrasonic imaging method and device
InactiveCN101869485AHigh energyGood cross-correlationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesAcoustic radiation forceSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses ultrasonic imaging method and device. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly carrying out coded modulation on a pulse generating an acoustic radiation force, and exciting a probe to emit an ultrasonic wave to generate a multi-frequency acoustic radiation force to generate tissue vibration; then adopting the coded modulation different from an exciting pulse for the pulse detecting the tissue vibration, ensuring the good correlation between two code words, and eliminating the interference caused by an exciting pulse echo generating the acoustic radiation force for a detection echo by utilizing a CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) technology similar to communication, thereby improving the signal-to-noise ratio and increasing the energy of the acoustic radiation force by more fully utilizing the pulse width and the frequency band width resources of a system.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Magneto-acoustic-electric imaging system and imaging method
ActiveCN102894974AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationHandling system
The invention provides a magneto-acoustic-electric imaging system, mainly comprising an ultrasonic driving excitation source, an ultrasonic probe array, a control system, a magnet system, an electrode pair or a coil, and a signal detection processing system. The ultrasonic probe array is controlled to be at two modes of transmitting or measuring by the control system. An imaging method of the magneto-acoustic-electric imaging system is characterized by adopting acoustic radiation force to generate a focusing region inside a biological tissue and adopting an ultrasonic echo technology to measure the position of the focusing region and a mass point vibration speed. The area of the focusing region is small so that an inner static magnetic field in the focusing region, the mass point vibration speed and a current density of an assumption process are approximate to an average value, so that a linear relation between measured voltage and the current density of the assumption process is established.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
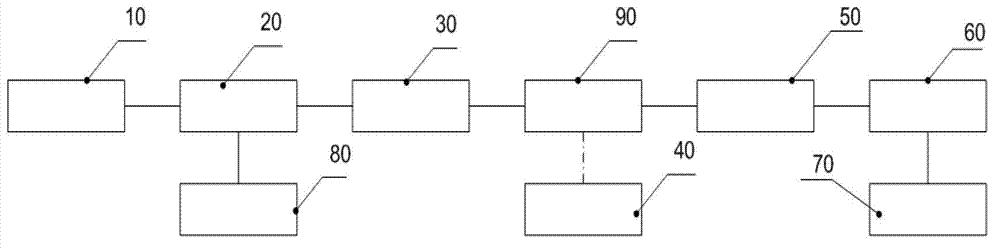
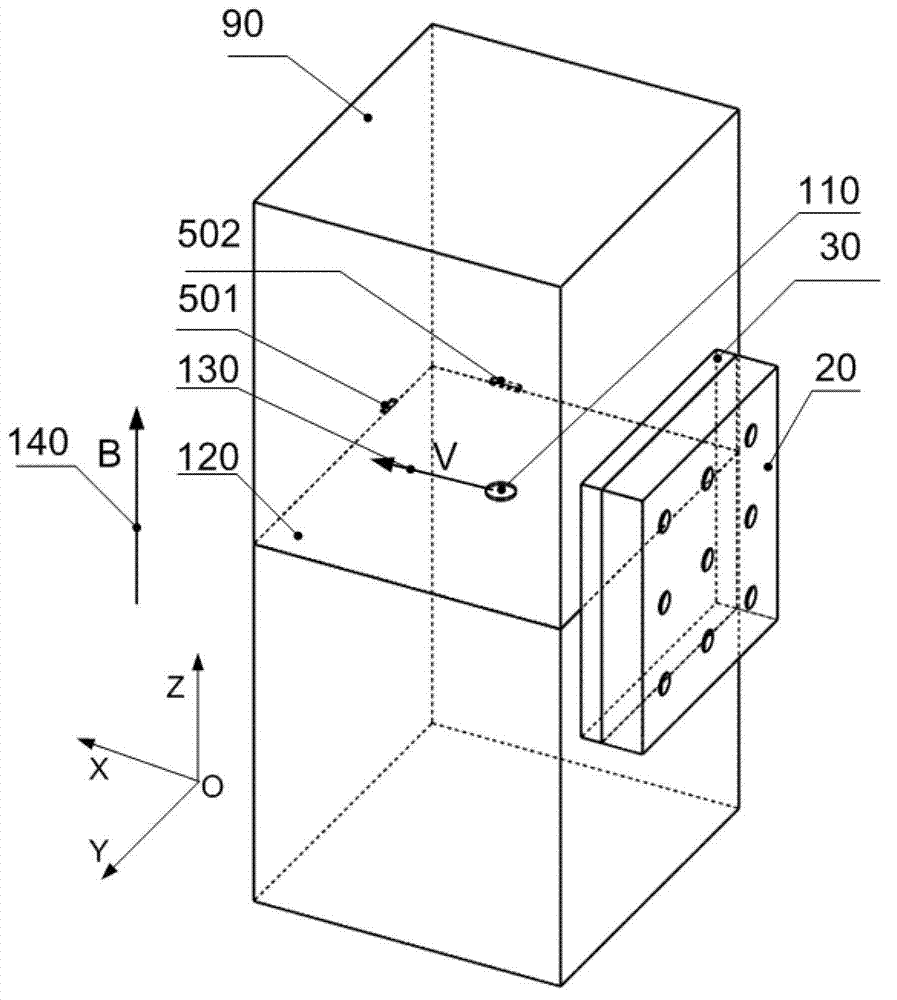
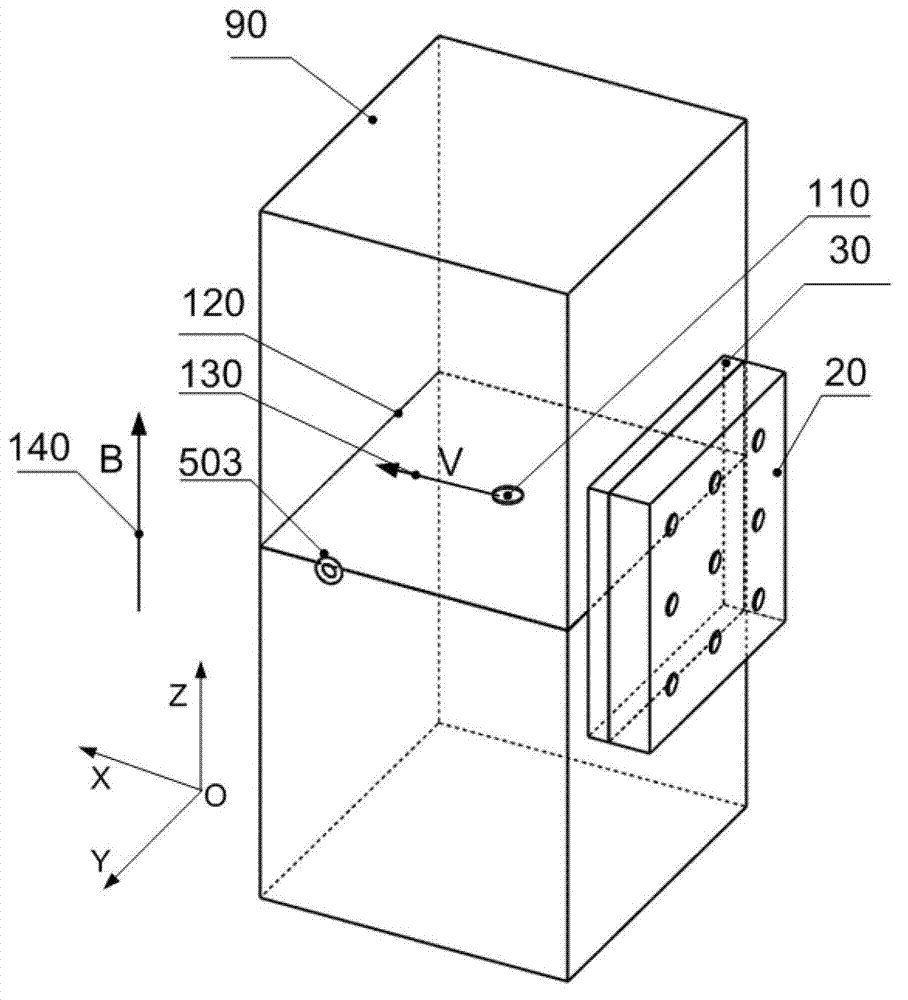
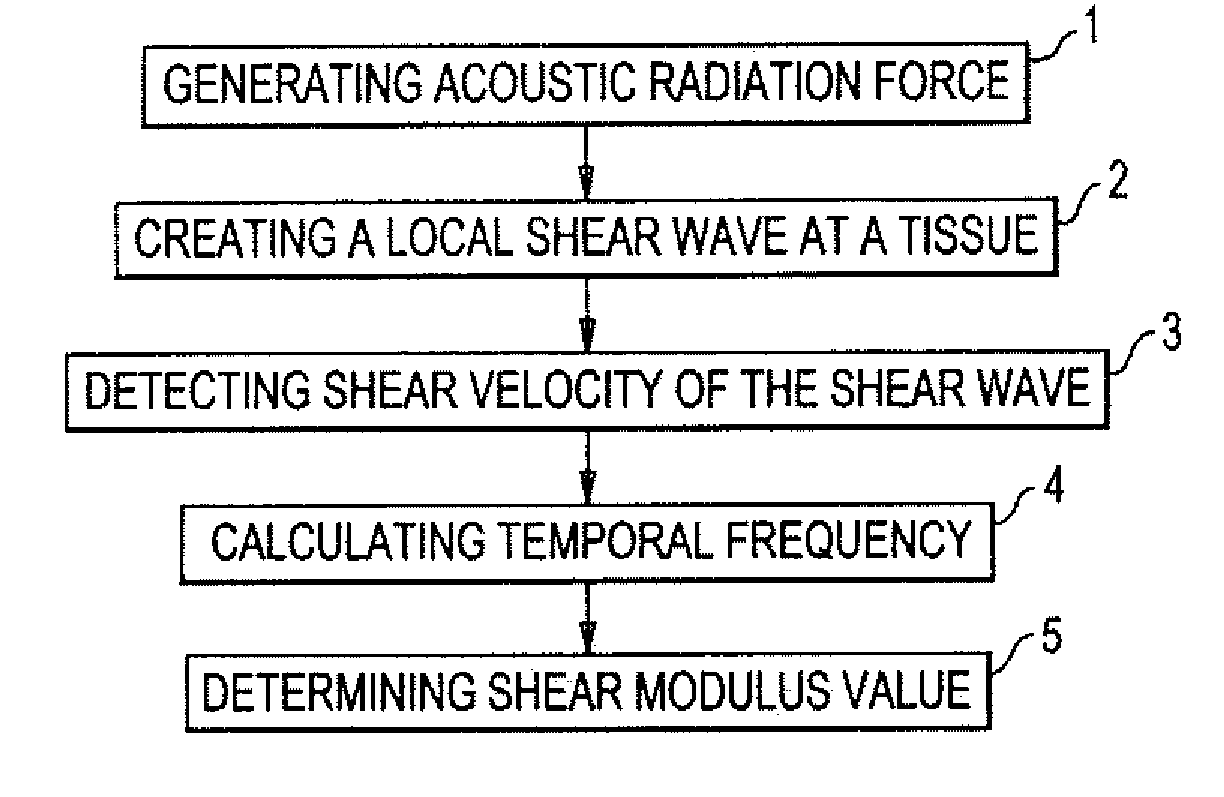
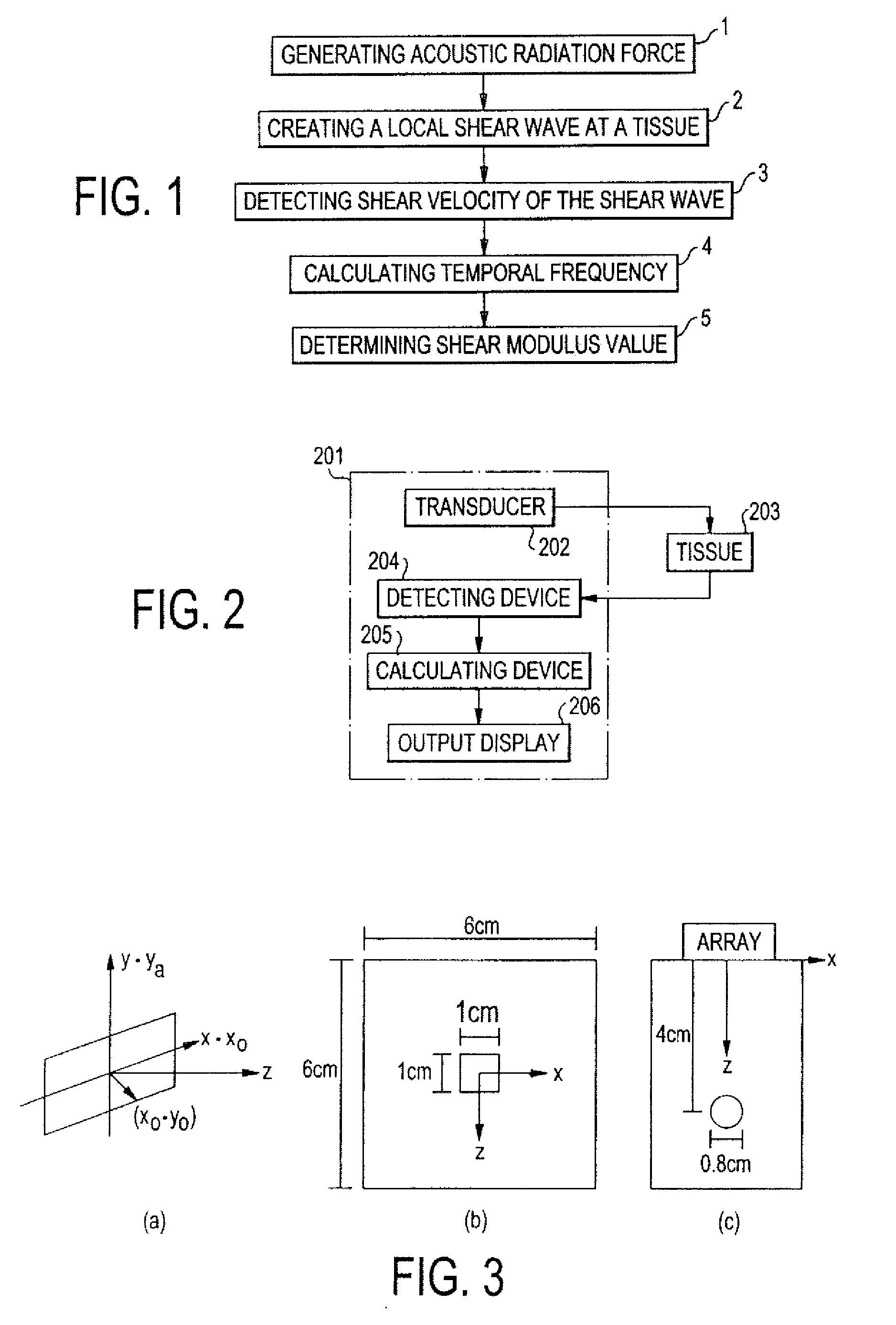
Shear modulus estimation by application of spatially modulated impulse acoustic radiation force approximation
ActiveUS20090056453A1Quantitative measurement of the shear modulus of the tissueVibration measurement in solidsVibration measurement in fluidShear modulusSonification
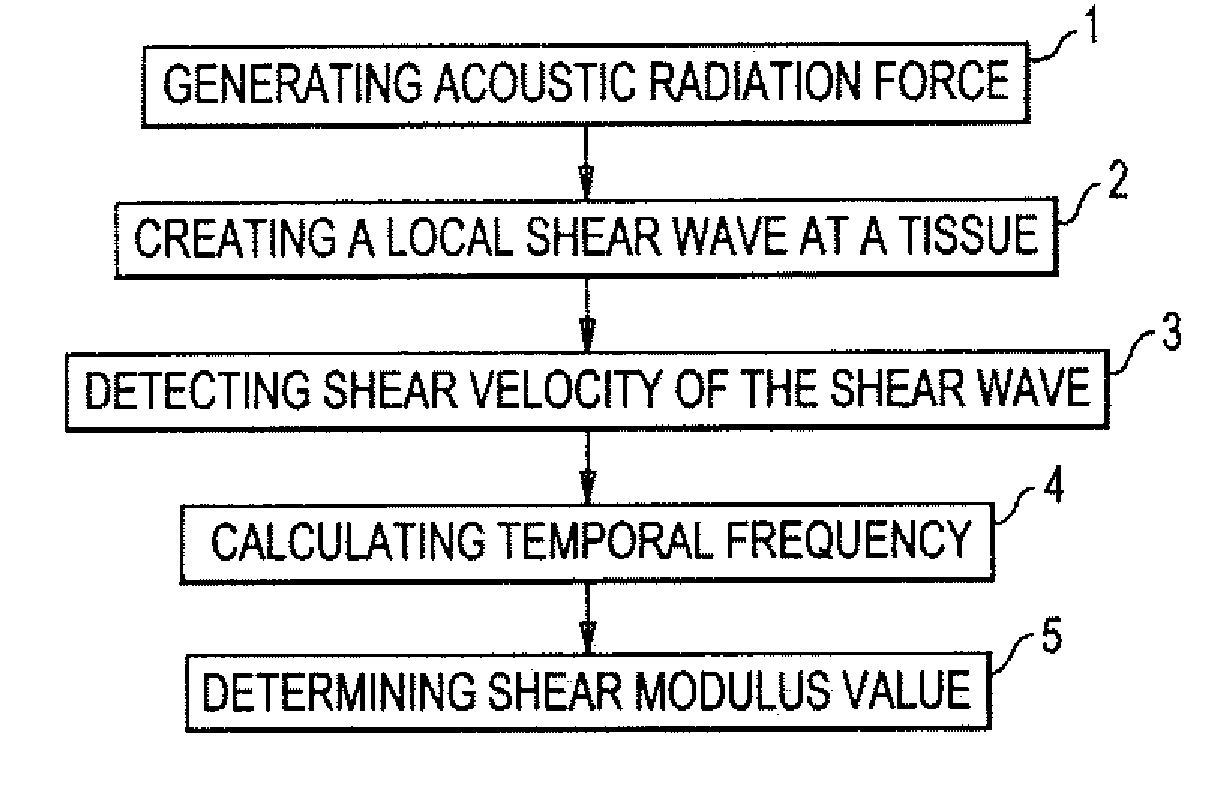
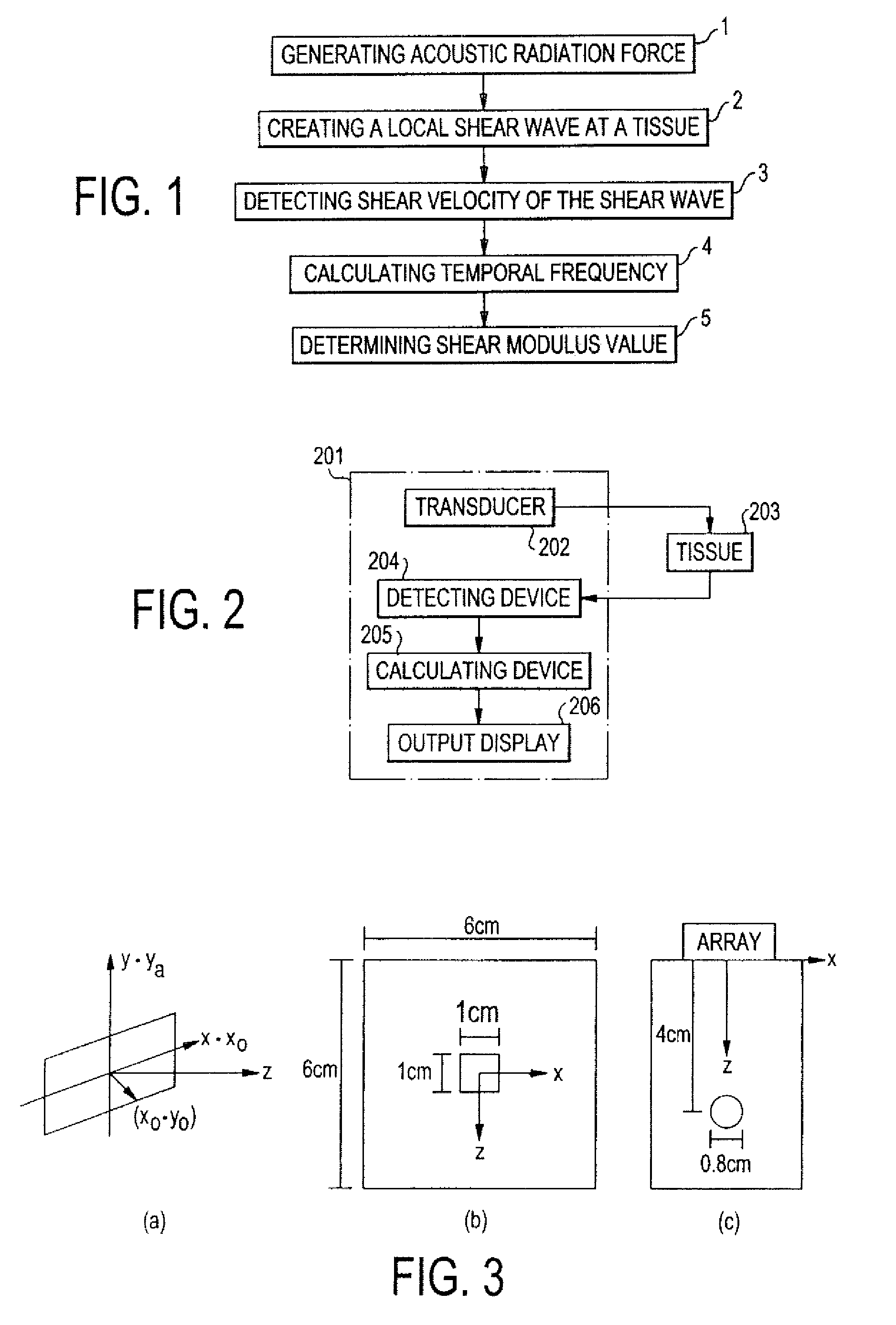
A method for determining a shear modulus of an elastic material with a known density value is provided. In this method, a spatially modulated acoustic radiation force is used to initially generate a disturbance of known spatial frequency or wavelength. The propagation of this initial displacement as a shear wave is measured using ultrasound tracking methods. A temporal frequency is determined based on the shear wave. The shear modulus of the elastic material at the point of excitation may be calculated using the values of the spatial wavelength, material density, and temporal frequency.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Method of making a stratified paper
The present invention provides a method making stratified paper by redistributing the pulp suspension inside the headbox nozzle using acoustic radiation waves. Acoustic radiation forces fractionate fibers based on fiber radius. The acoustic radiation waves separate the fibers by pushing the coarse and longer fibers to the inner area while fines and smaller fibers remain in the outer area. This has a similar effect of multi-layer stratification headbox, and provides paper with a smoother surface.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Acoustic assessment of characteristics of a fluid relevant to acoustic ejection
InactiveUS7354141B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAuditory radiationAcoustic energy
Owner:LABCYTE
Integrated Multimodality Intravascular Imaging System that Combines Optical Coherence Tomography, Ultrasound Imaging, and Acoustic Radiation Force Optical Coherence Elastography
ActiveUS20150351722A1Low costImproved prognosisOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryBiomechanicsMechanical property
A method of using an integrated intraluminal imaging system includes an optical coherence tomography interferometer (OCT), an ultrasound subsystem (US) and a phase resolved acoustic radiation force optical coherence elastography subsystem (PR-RAF-OCE). The steps include performing OCT to generate a returned optical signal, performing US imaging to generate a returned ultrasound signal, performing PR-ARF-OCE to generate a returned PR-ARF-OCE signal by generating a amplitude modulated ultrasound beam or chirped amplitude modulated ultrasound beam to frequency sweep the acoustic radiation force, measuring the ARF induced tissue displacement using phase resolved OCT method, and the frequency dependence of the PR-ARF-OCE signal, processing the returned optical signal, the returned ultrasound signal and the measured frequency dependence of the returned PR-ARF-OCE optical coherence elastographic signal to quantitatively measure the mechanical properties of the identified tissues with both spectral and spatial resolution using enhanced materials response at mechanically resonant frequencies to distinguish tissues with varying stiffness, to identify tissues with different biomechanical properties and to measure structural and mechanical properties simultaneously.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Tissue viscoelasticity measuring method based on shear wave amplitude and phase detection
ActiveCN106175831AGood for expanding the scopeGood for leveling upOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsDiseaseViscoelasticity
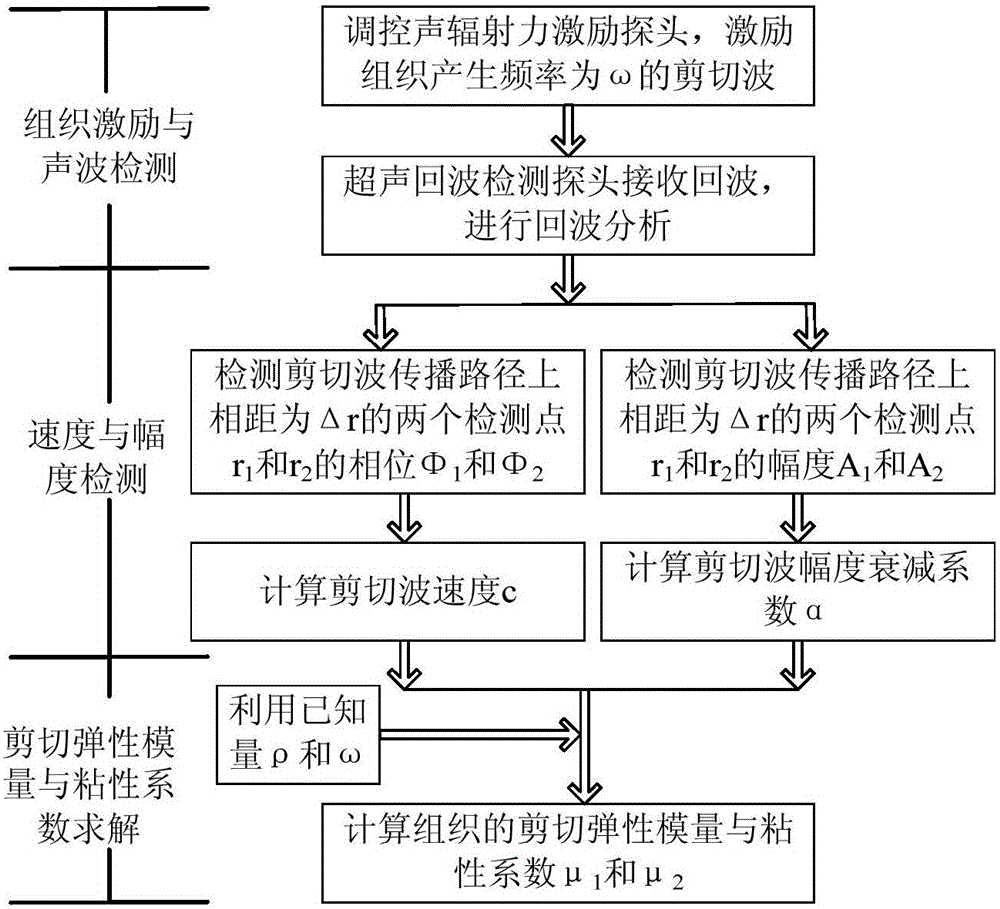
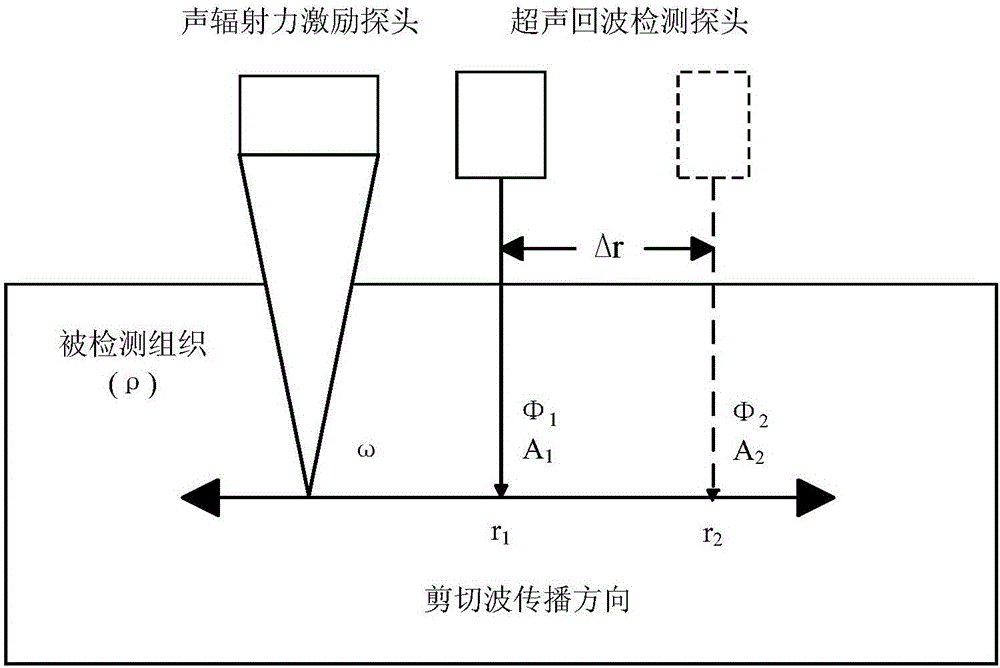
The invention provides a tissue viscoelasticity measuring method based on shear wave amplitude and phase detection. An acoustic radiation force excitation probe and an ultrasonic echo detection probe are used for detection at the same time, the acoustic radiation force excitation probe generates push wave beams, tissue generates shear waves at certain frequency, the ultrasonic echo detection probe generates detection wave beams to detect amplitude attenuation and phase change of the shear waves on a propagation path, the elasticity modulus and viscosity coefficient of the tissue are estimated through an amplitude attenuation coefficient and a speed detection value, in other words, the elasticity modulus and viscosity coefficient of the tissue can be quantitatively detected at the same time, precise and rich mechanical parameter information is provided for diagnosis of multiple diseases, the clinical application range of ultrasonic elastography can be widened, and the level of ultrasonic elastography can be improved. The method can carry out detection through the shear waves at one frequency, the system complexity and design cost are reduced, detection efficiency is improved, phase detection noise caused by high-frequency shear waves is avoided, and the accuracy of mechanical tissue parameter detection is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Acoustic surface wave based microfluidic plasma separating chip and method
ActiveCN104726331AReduce volumeReduce difficultyStress based microorganism growth stimulationHigh energySeparation technology
The invention discloses an acoustic surface wave based microfluidic plasma separating chip and method. The chip comprises a piezoelectric substrate, a set of interdigital transducer arranged on the piezoelectric substrate and a flow microchannel system which is arranged on the piezoelectric substrate in a bonding manner, located on one side of the interdigital transducer and has a necking structure. According to the chip, by use of width change of a microchannel, blood cells gradually shift to one side of a runner under the action of an acoustic radiation force, thus realizing the separation of plasma and blood cells. The chip takes such good advantages of the acoustic surface wave based microfluidic particle separation technology as high energy density and easy integration and manufacturing; in addition, only one set of interdigital transducer is arranged on the piezoelectric substrate and the distribution of an acoustic surface standing wave field is defined by a special geometrical shape of the PDMS flow microchannel; therefore, the defect that the existing acoustic surface wave based microfluidic particle separation technology requires two sets of interdigital transducer at the same time is overcome, the size of the separation chip is reduced further, and the requirement on alignment precision of the interdigital transducer and the microchannel system is reduced greatly.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for intravascular ultrasound multi-slice shear wave elastography
InactiveCN104055541AAchieve early diagnosisStrengthening Early Diagnosis CapabilitiesOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryPulse beamMulti slice
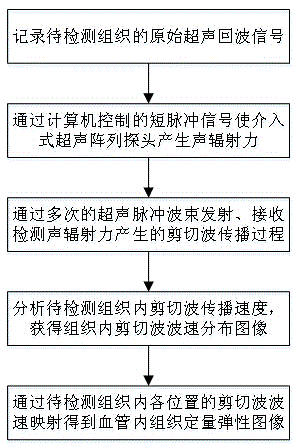
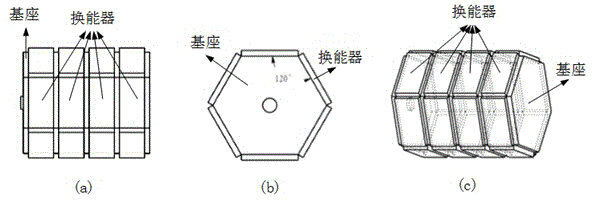
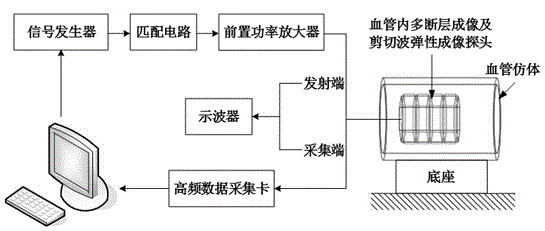
The invention discloses a method for intravascular ultrasound multi-slice shear wave elastography. The method comprises the following steps of recording an original ultrasound echo signal of a tissue to be detected; enabling an interventional ultrasound array probe to generate acoustic radiation force by virtue of a short-pulse signal controlled by a computer; emitting ultrasonic pulse beams for many times to accept and detect a propagation process of shear waves generated by the acoustic radiation force; analyzing the propagation speed of the shear waves in the tissue to be detected to obtain a wave speed distribution image of the shear waves in the tissue; performing wave speed mapping on the shear waves at each position in the tissue to be detected to obtain a quantitative elastic image of the intravascular tissue. The method has the advantages of real time performance, quantification, high speed, high resolution and the like; a multi-array element intravascular transducer array is used for performing vascular wall tissue elastic information quantitative analysis to excite and track the shear waves; the further popularization and application of intravascular elastography are favorably promoted, and the early diagnosis capability of people in cardiovascular diseases is enhanced.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Integrated acoustic phase separator and multiphase fluid composition monitoring apparatus and method
InactiveUS20120055262A1Avoid large pressure differencesMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesConstructionsCapacitanceAcoustic radiation force
An apparatus and method for down hole gas separation from the multiphase fluid flowing in a wellbore or a pipe, for determining the quantities of the individual components of the liquid and the flow rate of the liquid, and for remixing the component parts of the fluid after which the gas volume may be measured, without affecting the flow stream, are described. Acoustic radiation force is employed to separate gas from the liquid, thereby permitting measurements to be separately made for these two components; the liquid (oil / water) composition is determined from ultrasonic resonances; and the gas volume is determined from capacitance measurements. Since the fluid flows around and through the component parts of the apparatus, there is little pressure difference, and no protection is required from high pressure differentials.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
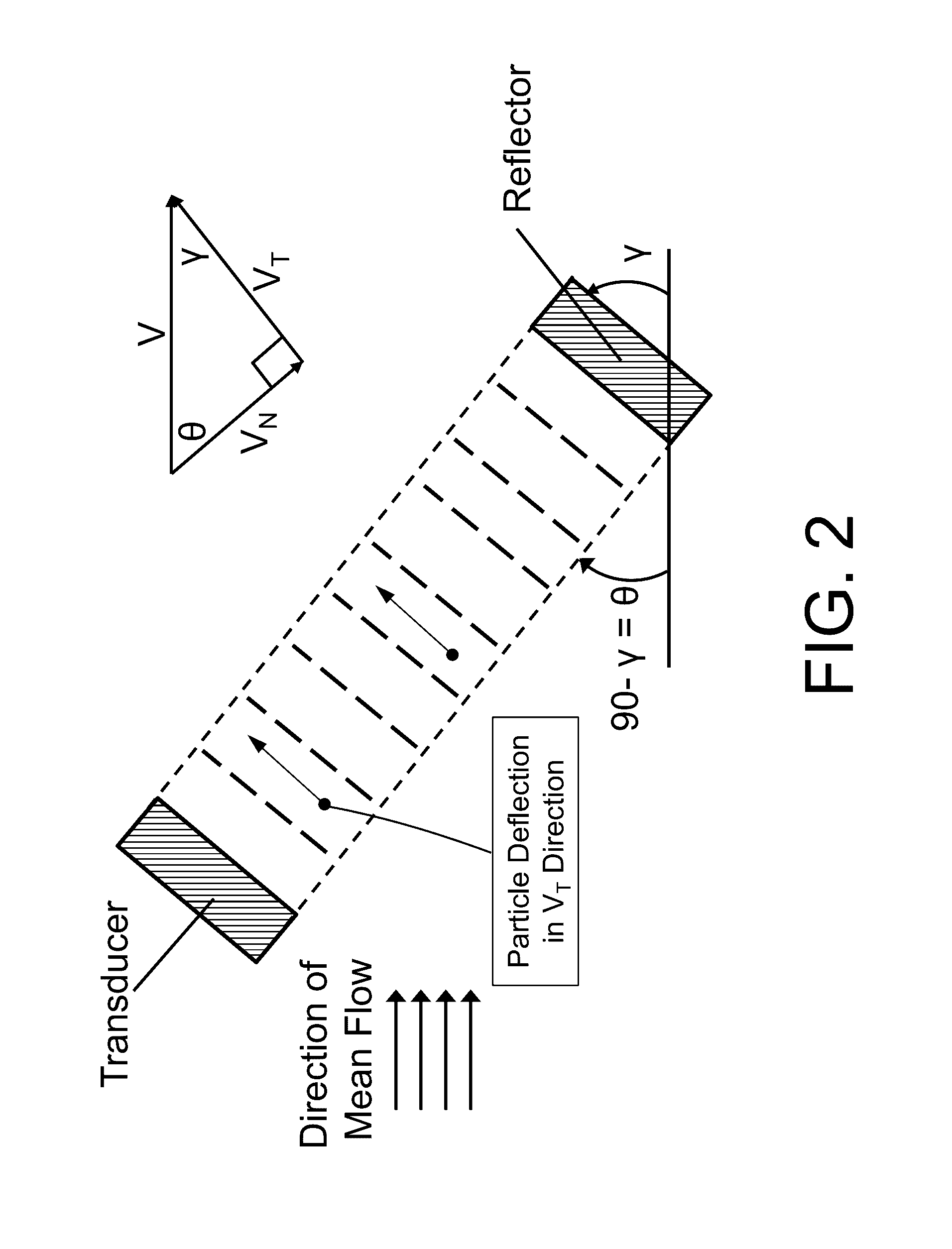
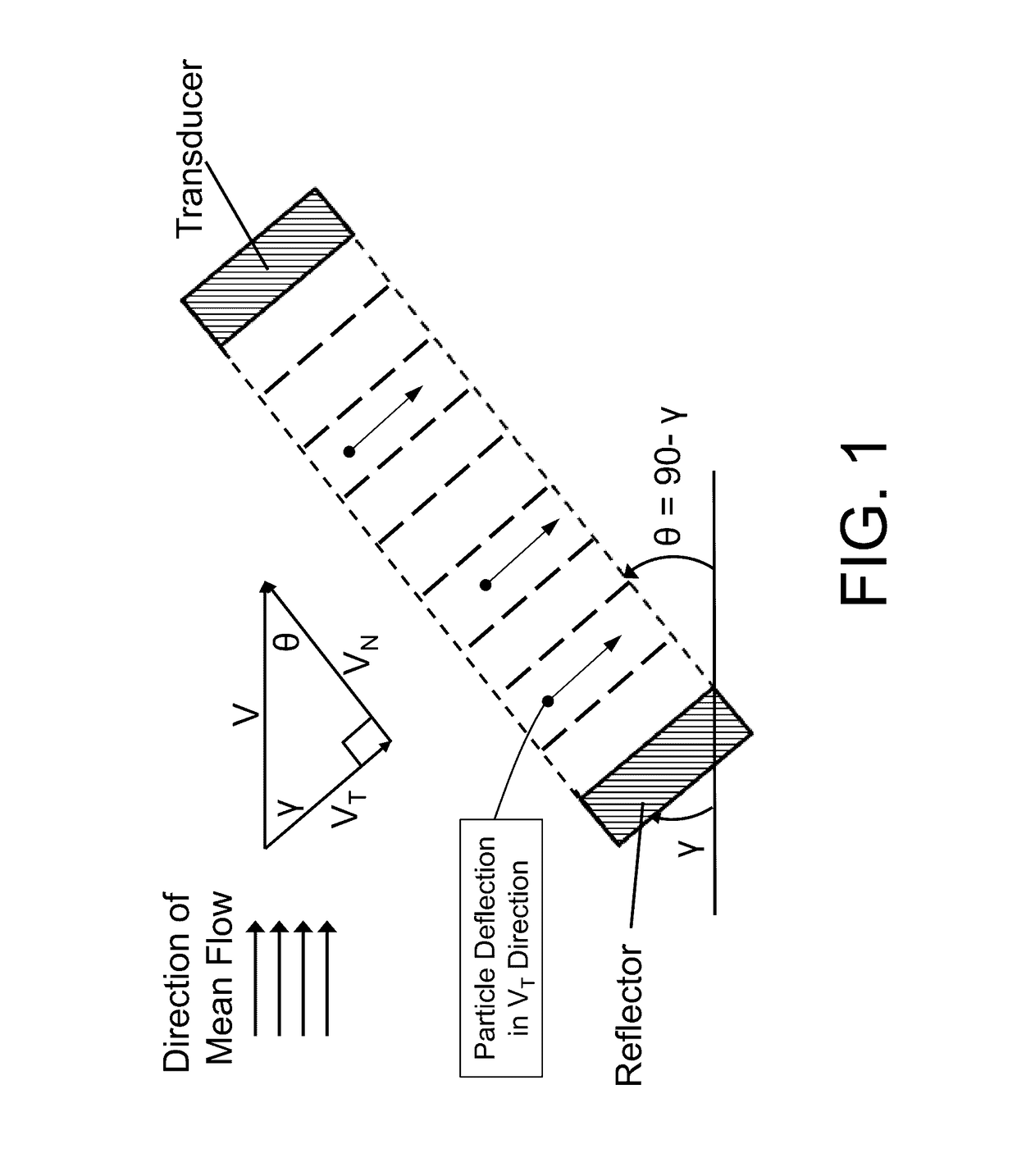
Acoustophoretic device for angled wave particle deflection
ActiveUS9670477B2Desired deflectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic sensorAcoustic radiation force
Devices for separating materials from a host fluid are disclosed. The devices include a flow chamber, an ultrasonic transducer, and a reflector. The ultrasonic transducer and reflector create an angled acoustic standing wave oriented at an angle relative to the direction of mean flow through the flow chamber. The angled acoustic standing wave results in an acoustic radiation force having an axial force component that deflects the materials, so that the materials and the host fluid can thus be separated. The angled acoustic standing wave can be oriented at an angle of about 20° to about 70° relative to the direction of mean flow through the flow chamber to deflect, collect, differentiate, or fractionate the materials from the fluid flowing through the device at flow rates of about 400 mL / min up to about 700 mL / min.
Owner:FLODESIGN SONICS
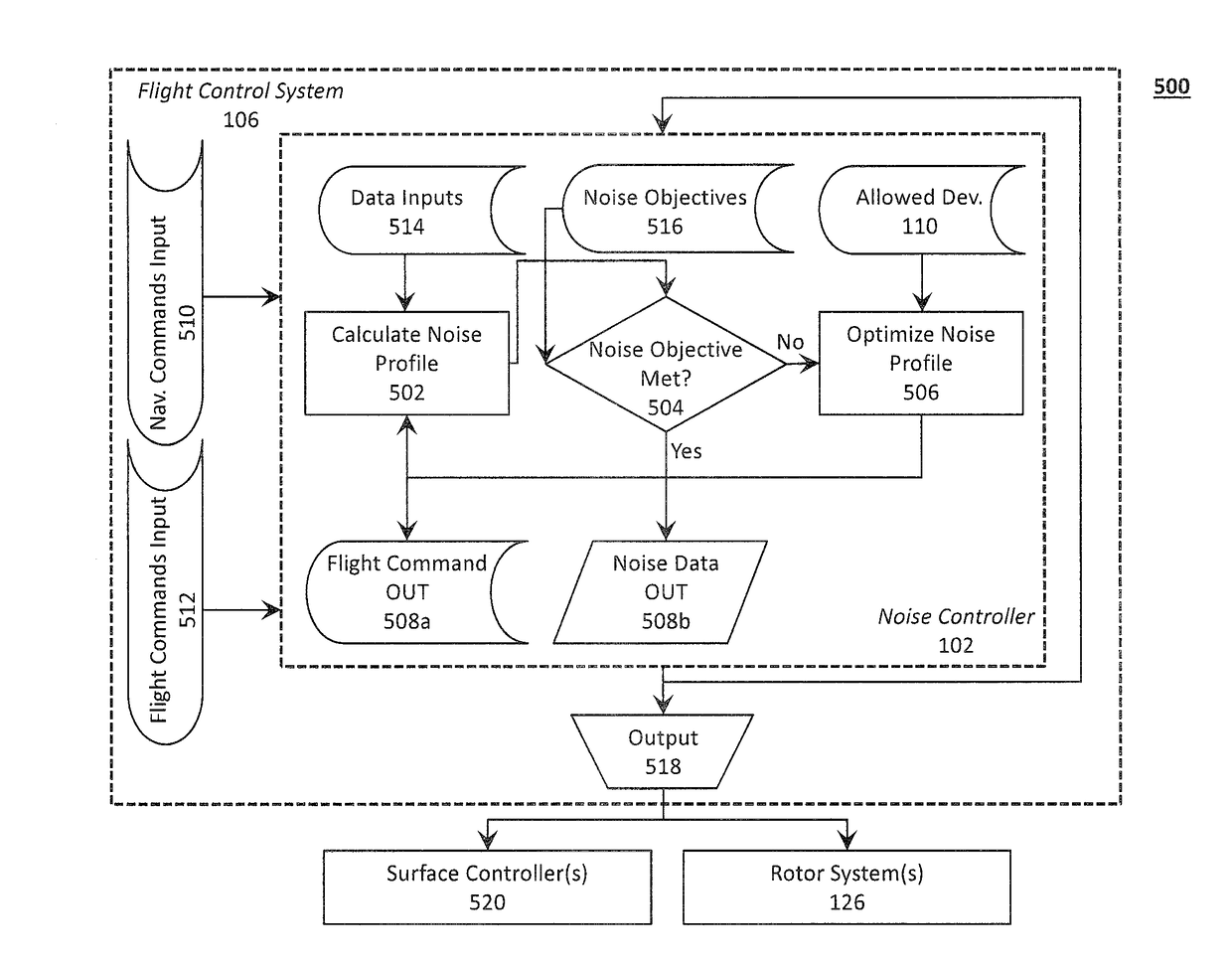
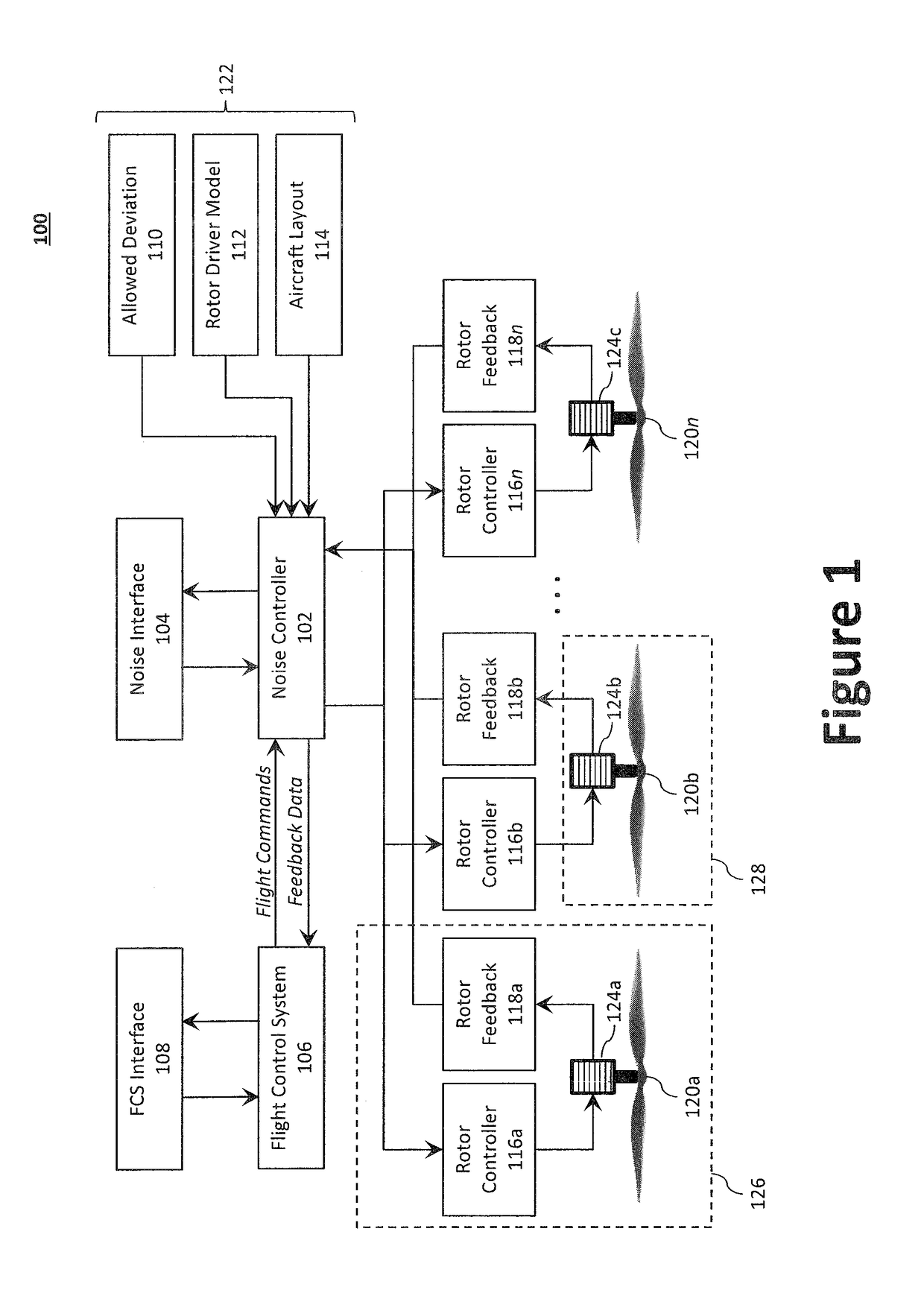
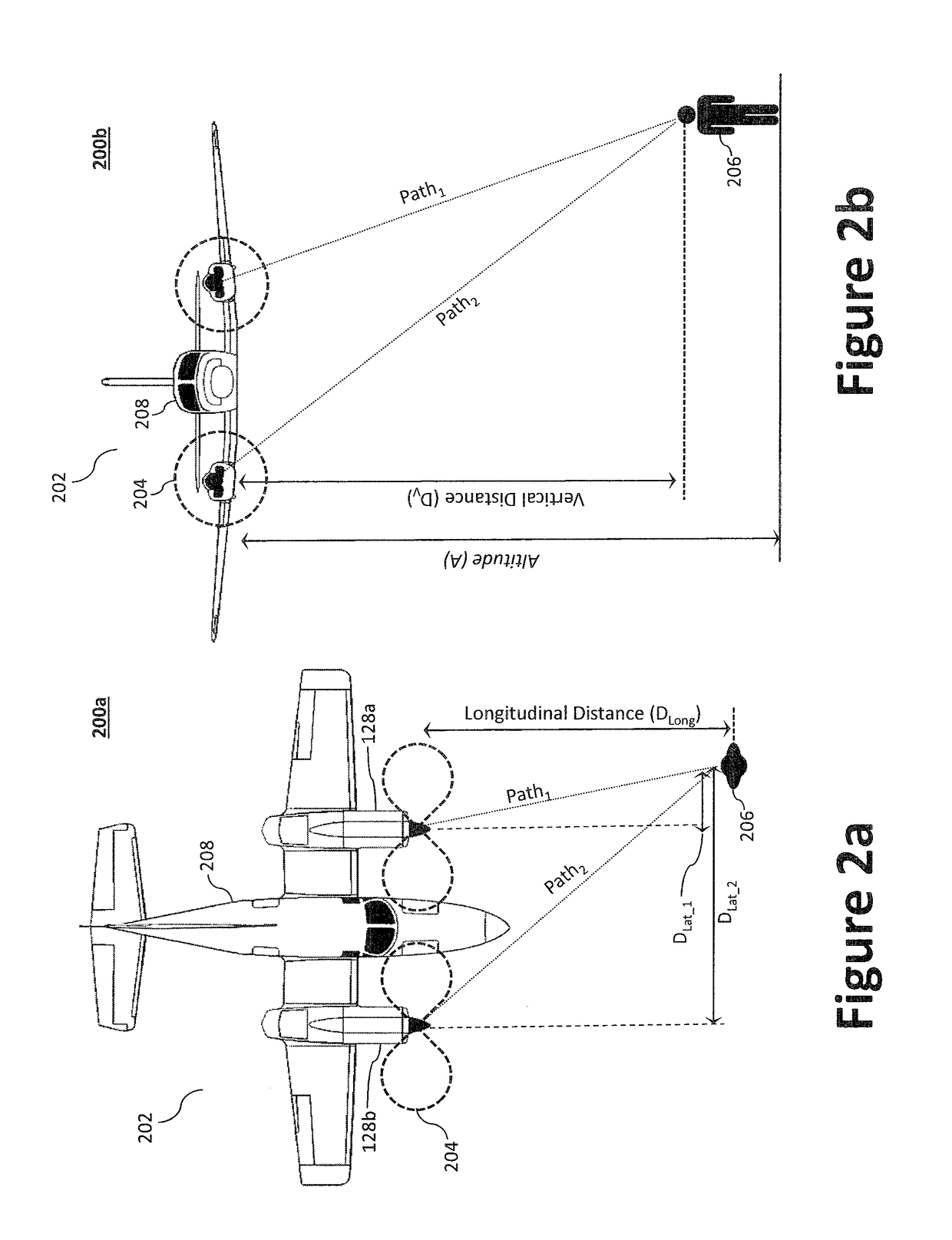
Systems and Methods for Acoustic Radiation Control
ActiveUS20180319491A1Diminishing detectabilityPropellersUnmanned aerial vehiclesAuditory radiationNoise control
Disclosed is a system for controlling acoustic radiation from an aircraft. The system comprising a plurality of rotor systems (one or more) and a noise controller configured to regulate acoustic radiation from the plurality of rotor systems. The noise controller can be configured to regulate a commanded flight setting from the flight control system and to output a regulated flight setting to the plurality of rotor systems. Based on the regulated flight setting, the plurality of rotor systems are configured to generate, individually and in aggregate, acoustic radiation having a target acoustic behavior. The target acoustic behavior may be achieved using beamforming techniques to, for example, change the directionality of acoustic radiation from the plurality of rotor systems, or otherwise tune the acoustic radiation to reduce detectability and / or annoyance.
Owner:AURORA FLIGHT SCI CORP
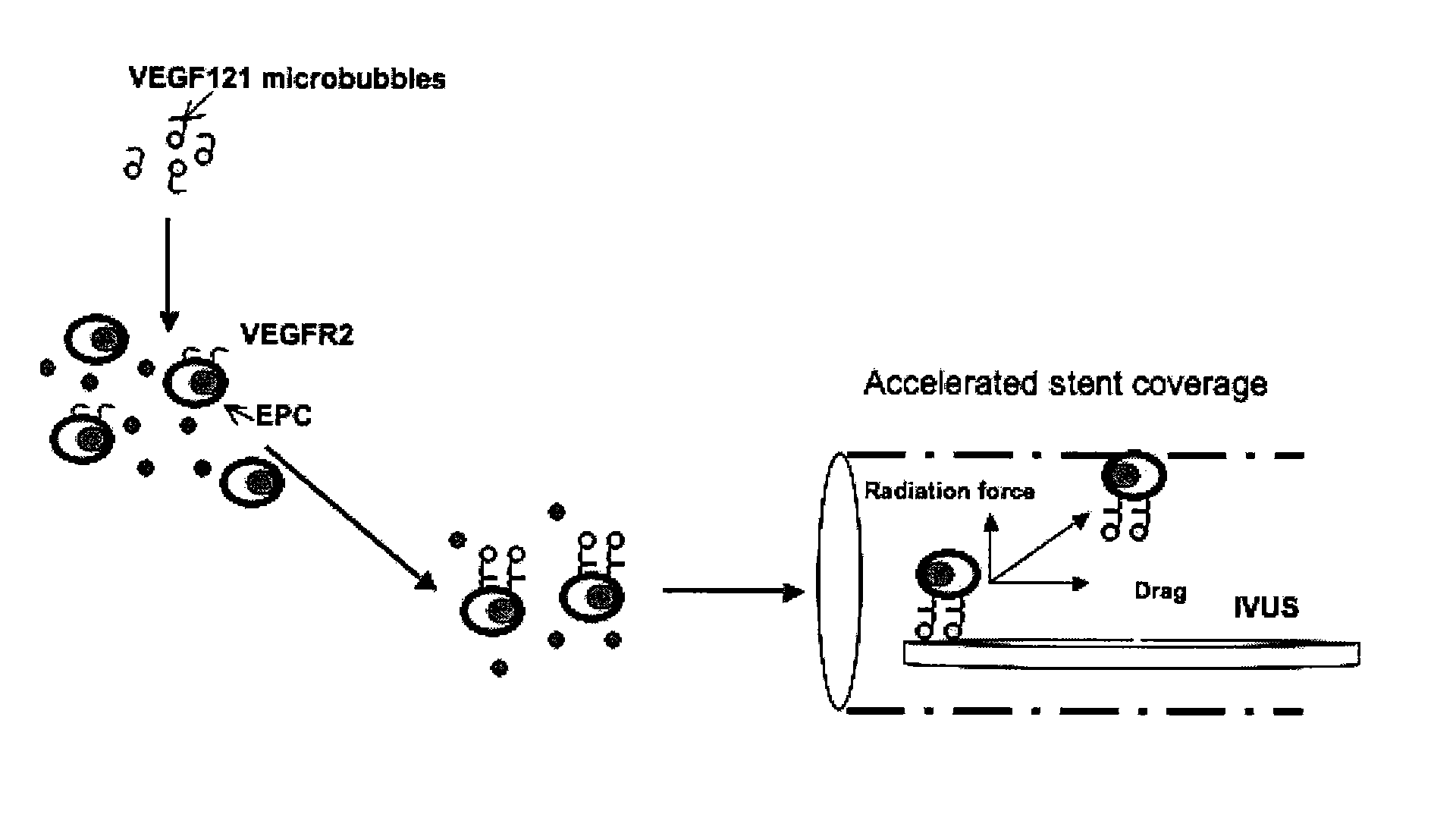
Directed Cell-Based Therapy Using Microbubble Tagged Cells
ActiveUS20110208113A1Promote tissue growthImprove satisfactionBiocideUltrasound therapyAuditory radiationProgenitor
The disclosed technology describes compositions and methods useful for providing cell based therapy. For example, one embodiment of cell based therapy involves the regeneration of injured tissue and / or promoting wound healing. Certain embodiments provide improved therapeutic compositions using microbubbles by delivering biological progenitor cells to the injured tissues. The administration of the microbubbles is directed by acoustic radiation forces that interact with embodiments of microbubbles comprising an acoustically active gas. As such, a high efficiency of progenitor cell delivery to injured tissue is realized. One advantage of this technique over targeted delivery of pharmaceutical compounds, is that the delivered progenitors cells may be derived from the patient (i.e., personalized therapy), thereby avoiding side effects, allergic reactions, and overall problems associated with refractive drug responses.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
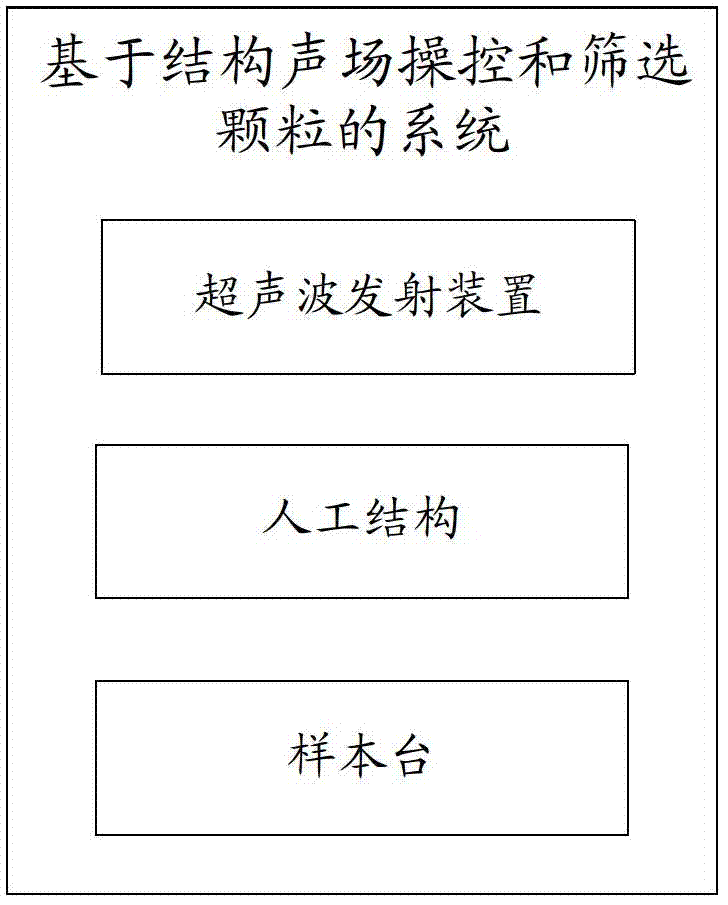
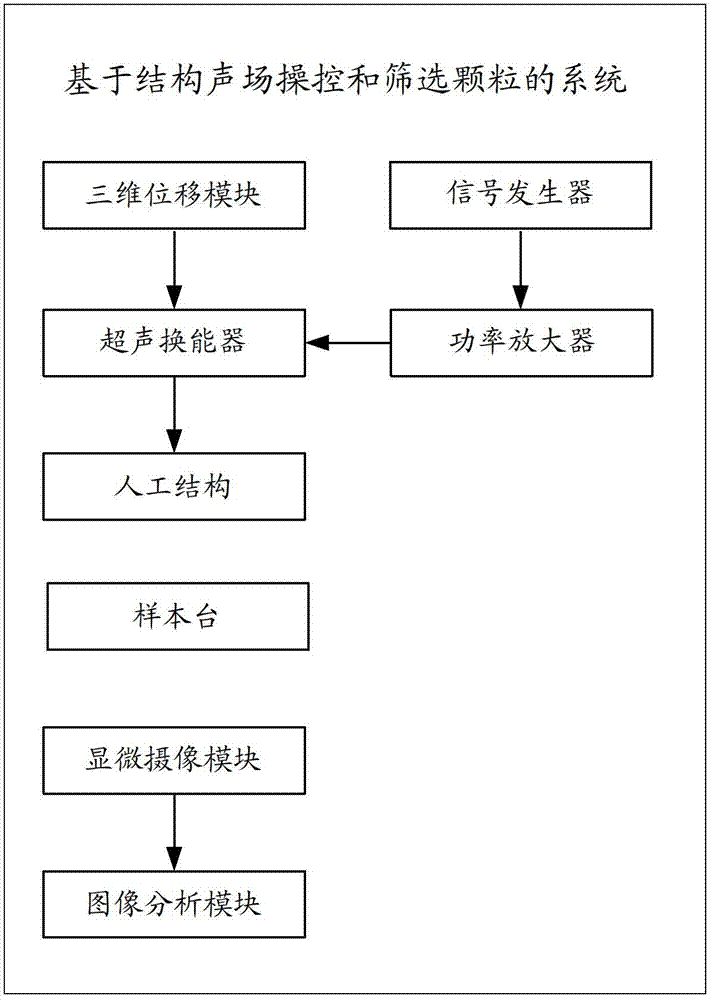
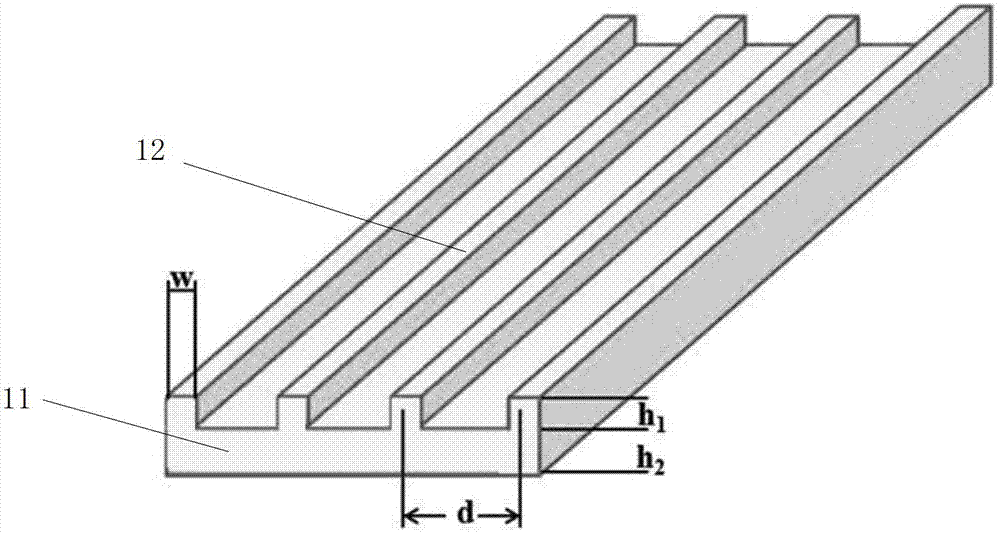
System and method for controlling and selecting granules on basis of structural sound field
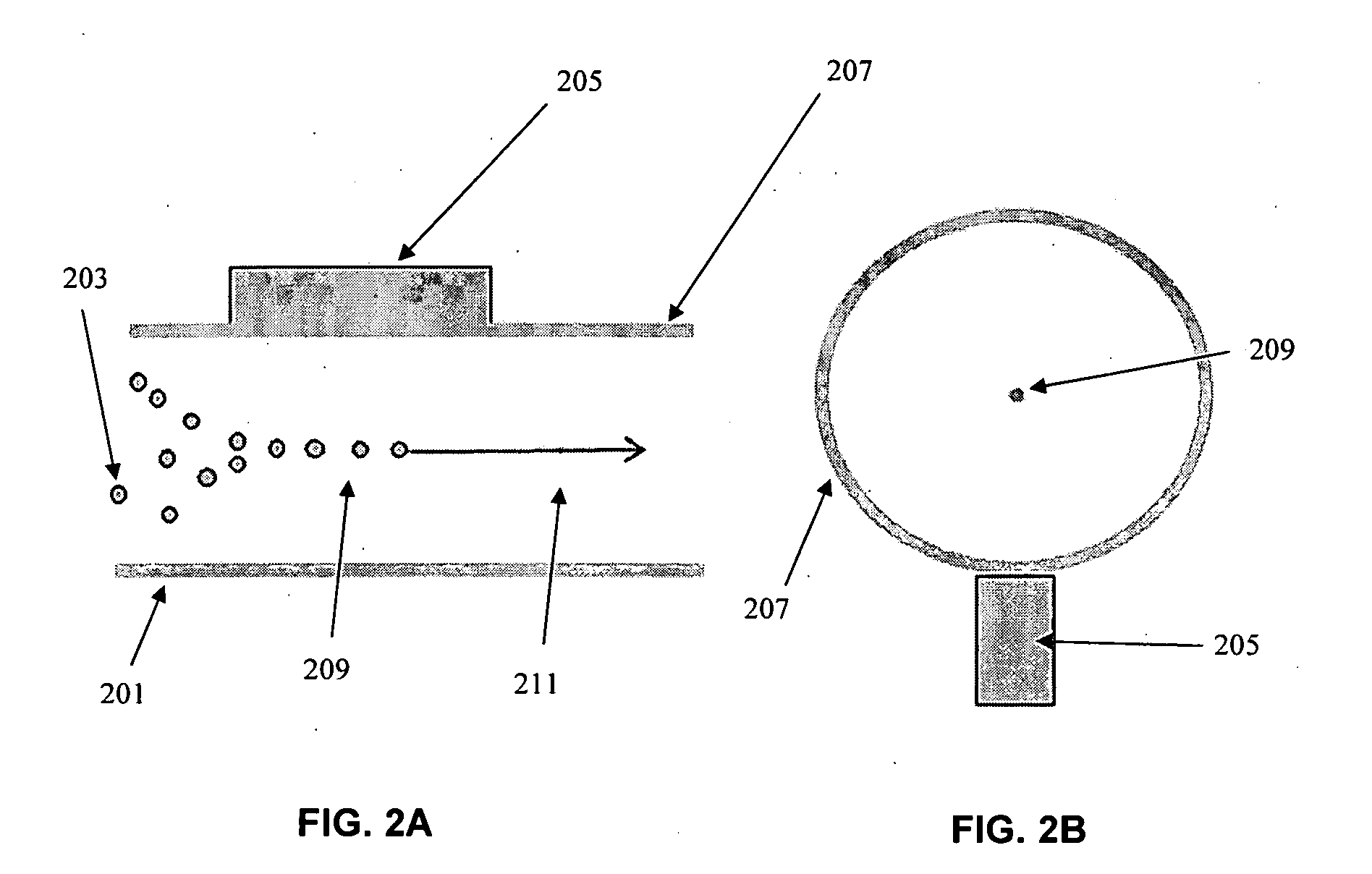
ActiveCN103203328AQuick filterFilter batchParticle size analysisIndividual particle analysisAcoustic radiation forceSpecific granule
The invention discloses a system for controlling and selecting granules on basis of the structural sound field. The system comprises a sample table, an ultrasonic emitter and a manual structure. The sample table is used for storing to-be-selected granules, the ultrasonic emitter is used for emitting ultrasonic waves, and the manual structure is a circular structure and is used for modulating the sound field to generate stronger sound emissive power and to select the to-be-selected granules. The invention further discloses a method for controlling and selecting granules on basis of the structural sound field. The system comprises the sample table, the ultrasonic emitter and the manual structure, the ultrasonic emitter is used for emitting ultrasonic waves, the manual structure is a circular structure and is used for selecting the to-be-selected granules, a plurality of granules can be placed on the sample table, the manual structure can be used for modulating the sound field to generate stronger sound emissive power and can capture specific granules on the lower surface of the manual structure, so that the granules can be rapidly and massively selected and efficiency is improved.
Owner:深圳中科乐普医疗技术有限公司
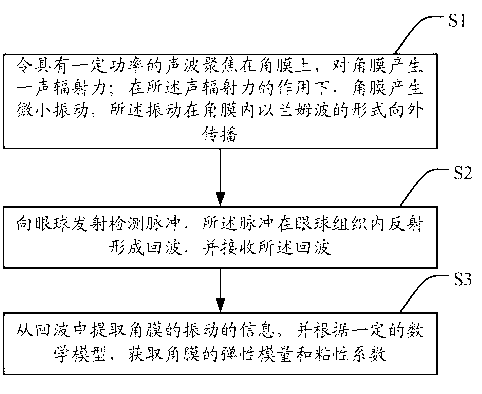
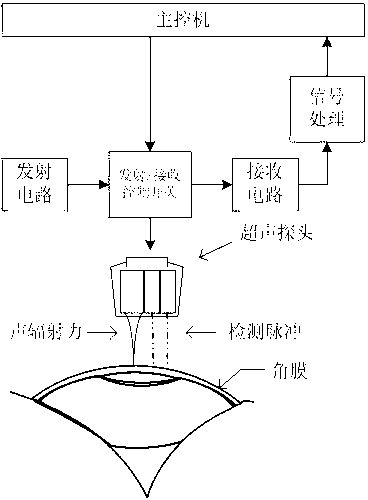
Method and system for ultrasonic detection of cornea viscoelasticity
InactiveCN103006274AComprehensive description of mechanical propertiesSimple structureEye diagnosticsEye inspectionMathematical modelViscoelasticity
The invention discloses a method and system for ultrasonic detection of cornea viscoelasticity. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, focusing sound waves with certain power onto a cornea to generate a sound radiant force on the cornea; under the action of the sound radiant force, the cornea generating slight vibration, and the vibration propagating outwards in the cornea in a Lamb wave way; then, transmitting a detection pulse to an eyeball, the pulse reflecting in the tissues of the eyeball to form echo, and receiving the echo; and finally, extracting the vibration information of the cornea from the echo, and according to a certain mathematical model, obtaining an elastic module and a viscosity coefficient of the cornea. The elastic module and the viscosity coefficient can be simultaneously and quantitatively measured, and mechanical properties of the cornea are fully described. Meanwhile, the system has the advantages that the structure is simple, easy implementation is realized, the cost is low, and the like. The system can be used as independent equipment, and also can be used as an additional function module to be loaded onto the existing color ultrasonic system for use, so the market population prospect is better.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
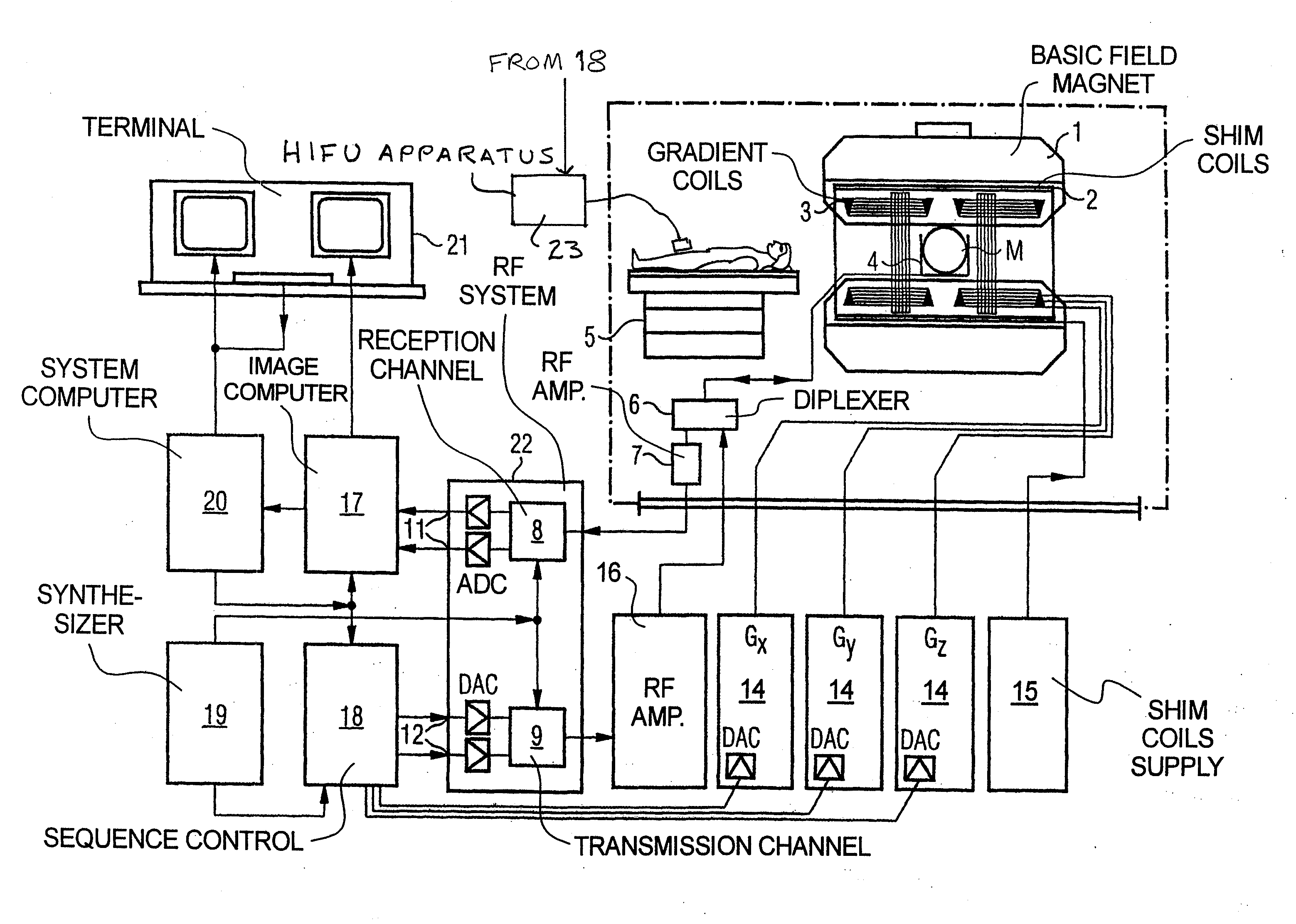
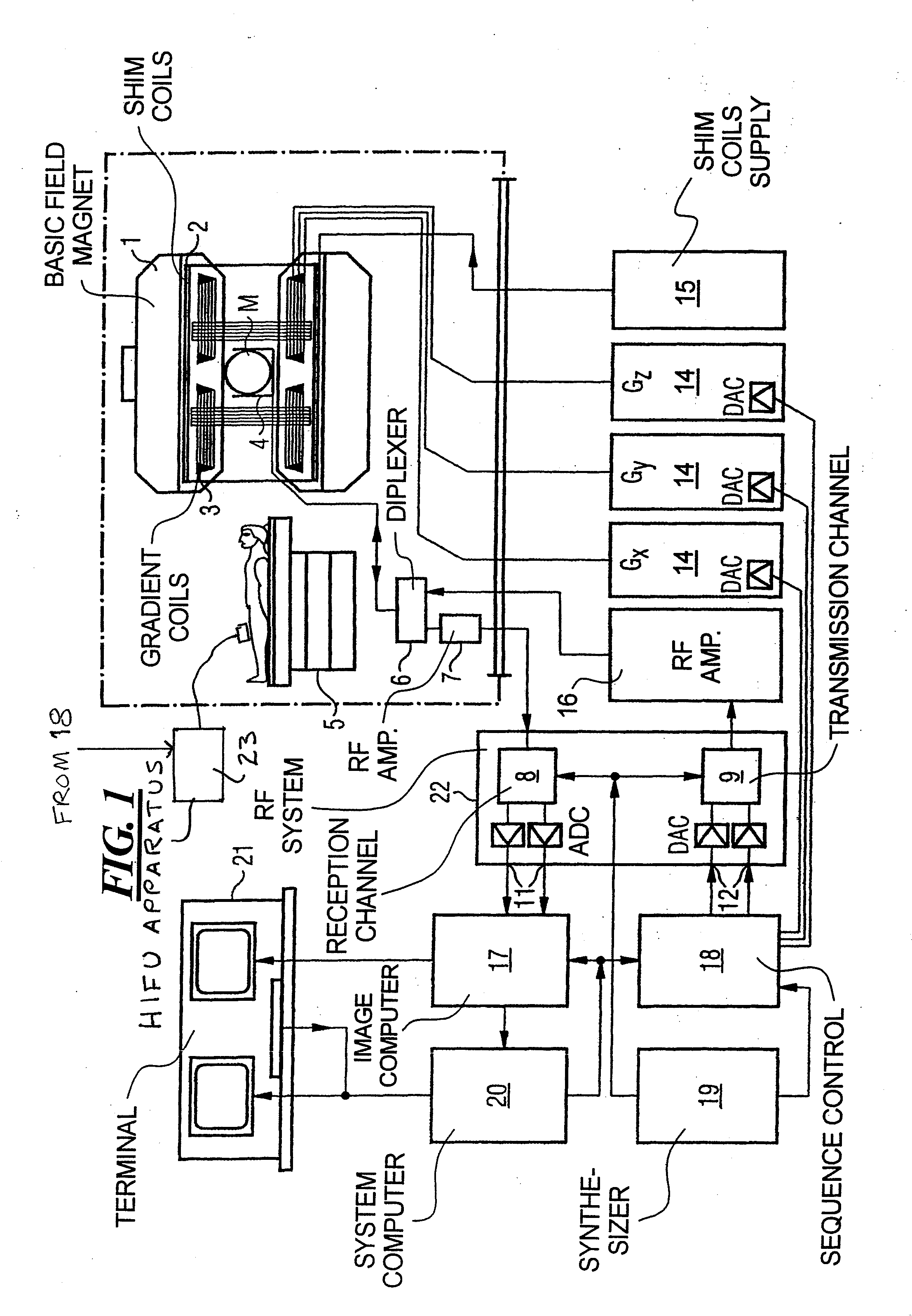
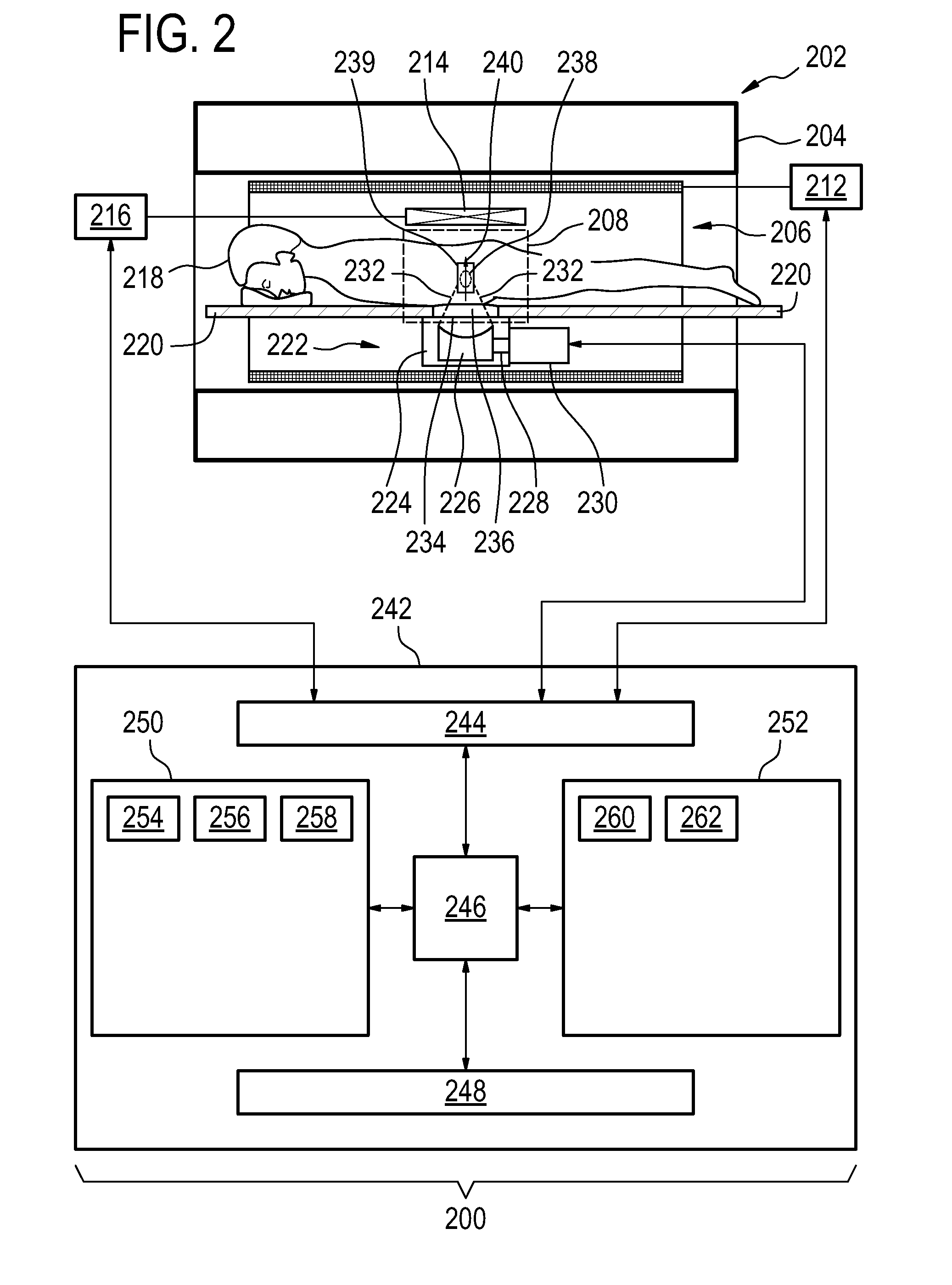
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance guided high intensity focused ultrasound focusing under simultaneous temperature monitoring
ActiveUS20110248714A1Precise positioningHigh resolutionElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRSonificationTissue heating
In a method and an apparatus for magnetic resonance guided high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), precise localization of the focal point of the HIFU is determined by imaging an examination subject in parallel with GRE sequences that respectively include a positive monopolar gradient pulse and a negative monopolar gradient pulse, that respectively encode the acoustic radiation force (ARF)-induced phase shift that is induced by the simultaneous activation of HIFU during the sequences. A GRE phase image is reconstructed from each acquisition sequence, and a difference image is formed between the two GRE phase images, from which the HIFU focal point is determined. An average image is formed of the two GRE phase images from which PRFS temperature map is determined simultaneously to ARFI map. The use of parallel imaging and the use of partial Fourier reconstruction for reconstructing the GRE phase images allows the data to be acquired sufficiently rapidly so as to minimize the adverse effect of tissue heating that occurs with conventional longer-duration, and repetitious, techniques.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
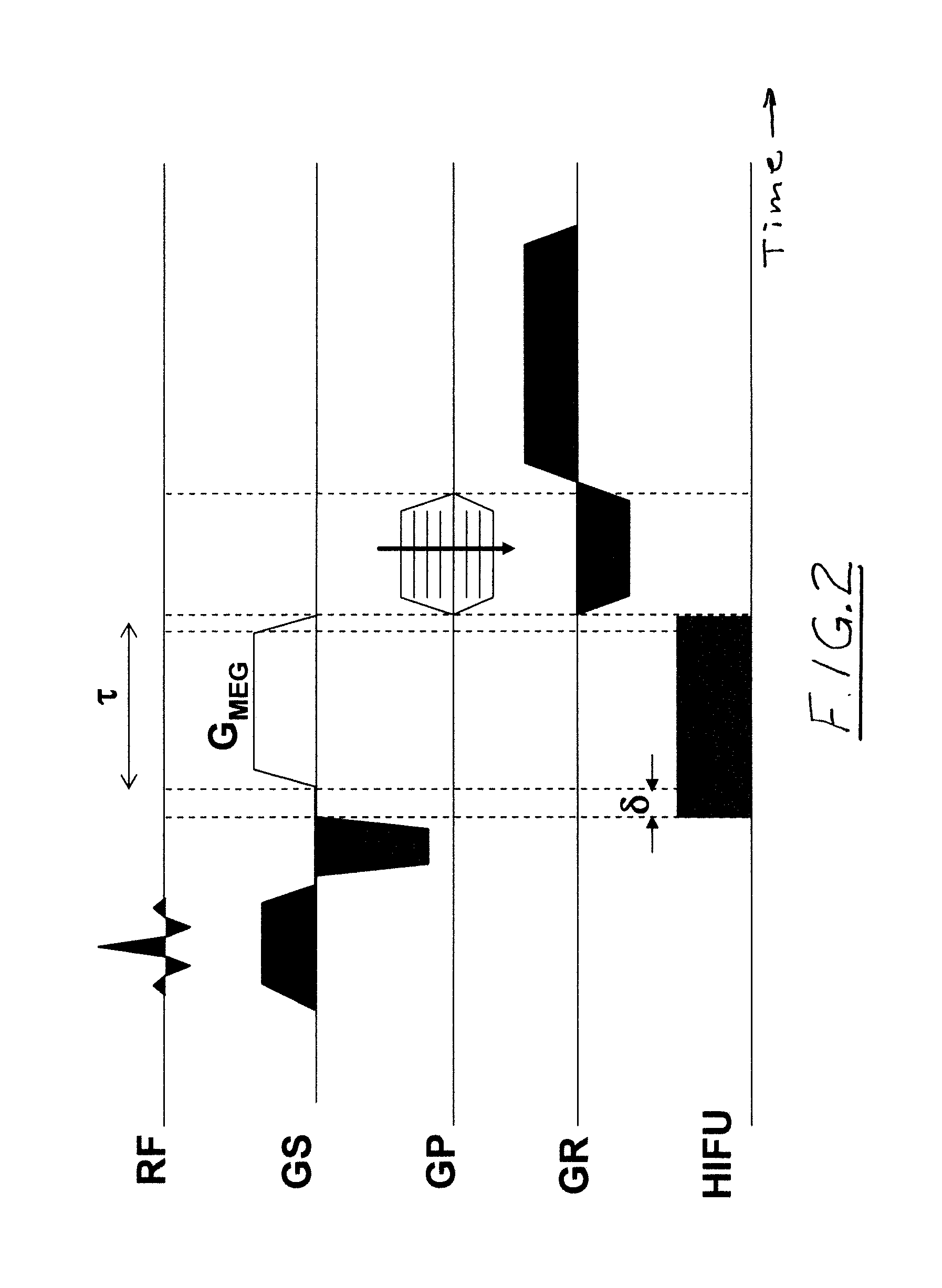
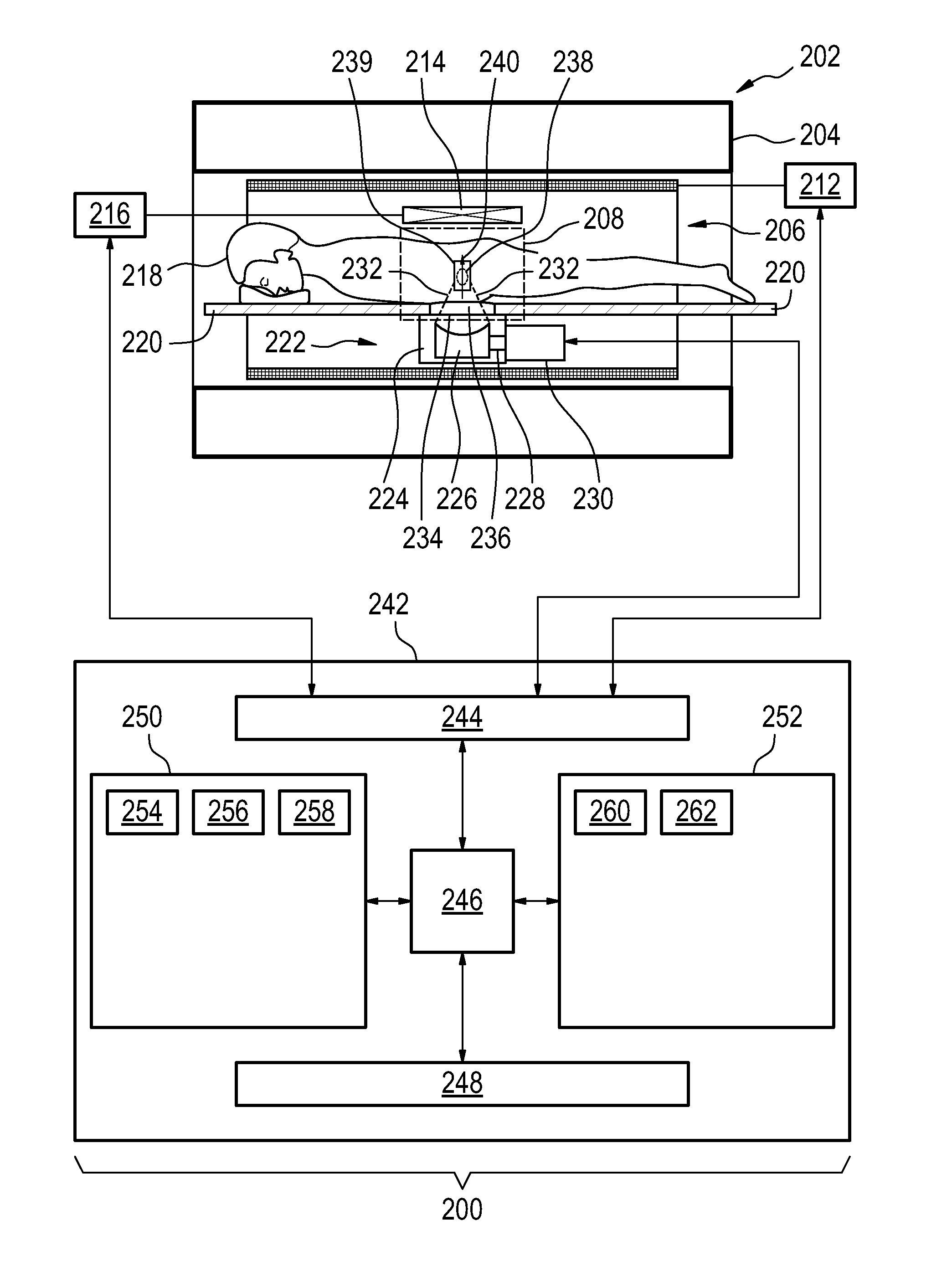
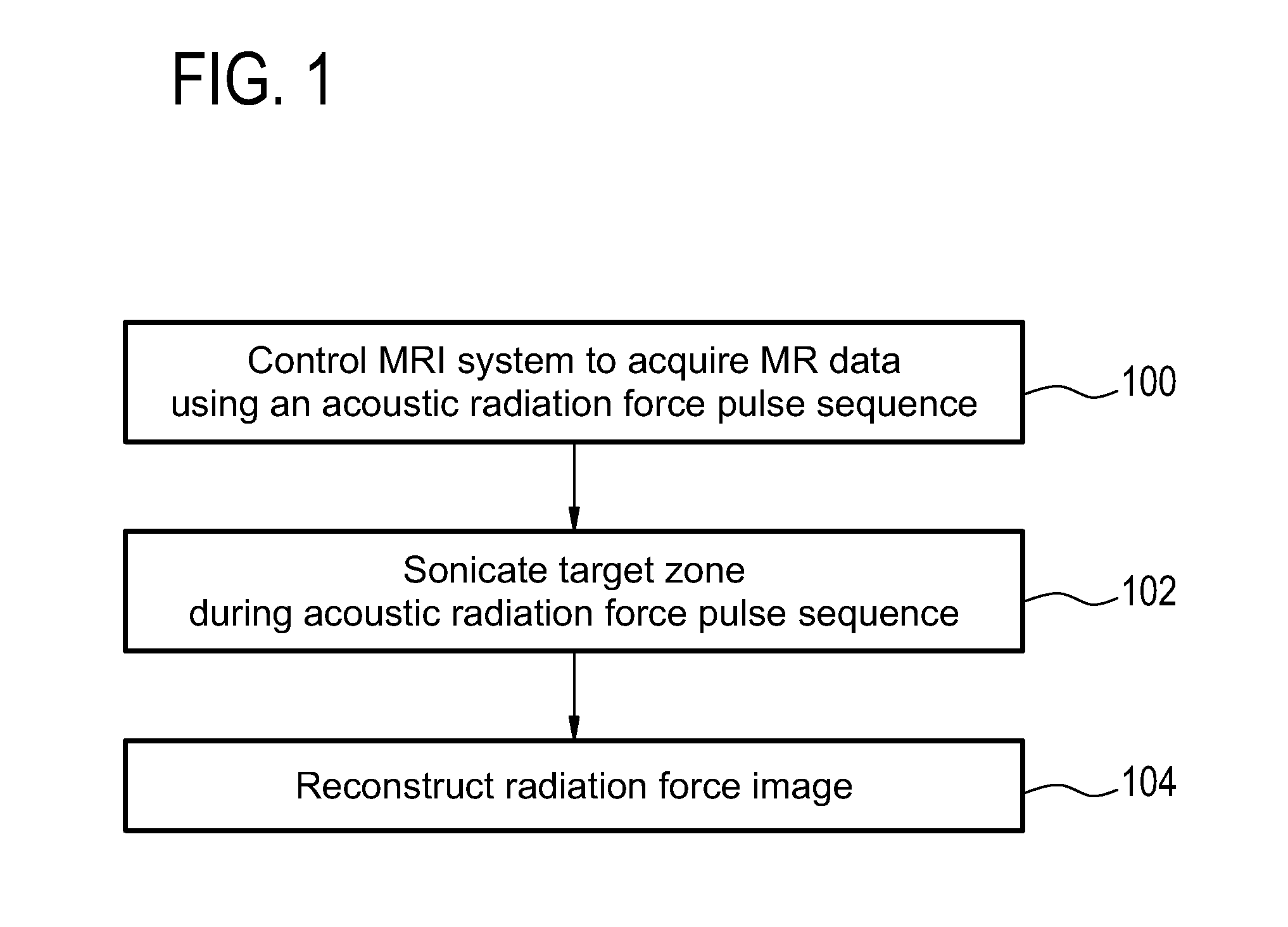
Acoustic radiation force magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20150190659A1Accurate valueSpeeding acquisitionUltrasound therapySurgical instrument detailsSonificationPulse sequence
The invention provides for medical instrument (200, 400) comprising a magnetic resonance imaging system (202) and a high intensity focused ultrasound system (222). A processor (246) controls the medical instrument. Instructions cause the processor to control (100) the magnetic resonance imaging system to acquire the magnetic resonance data using a pulse sequence (254). The pulse sequence comprises an acoustic radiation force imaging pulse sequence (500, 600). The acoustic radiation force imaging pulse sequence comprises an excitation pulse (512) and a multi-dimensional gradient pulse (514) applied during the radio frequency excitation pulse for selectively exciting a region of interest (239) encompassing a target zone and at least a portion of the beam axis. The instructions cause the processor to control (102) the high intensity focused ultrasound system to sonicate the target zone during the acoustic radiation force imaging pulse sequence and reconstruct (104) a radiation force image (258) using the magnetic resonance data.
Owner:PROFOUND MEDICAL
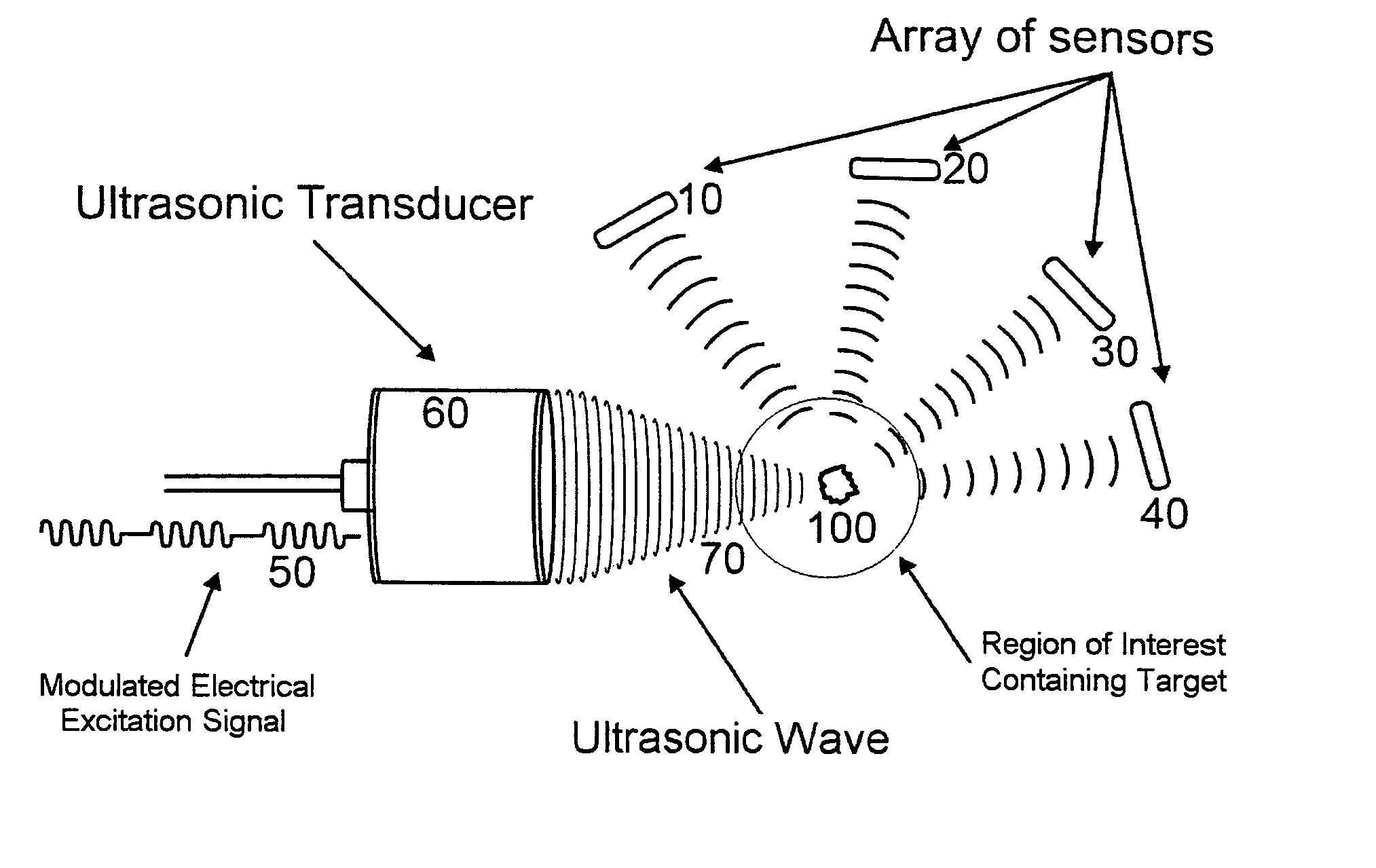
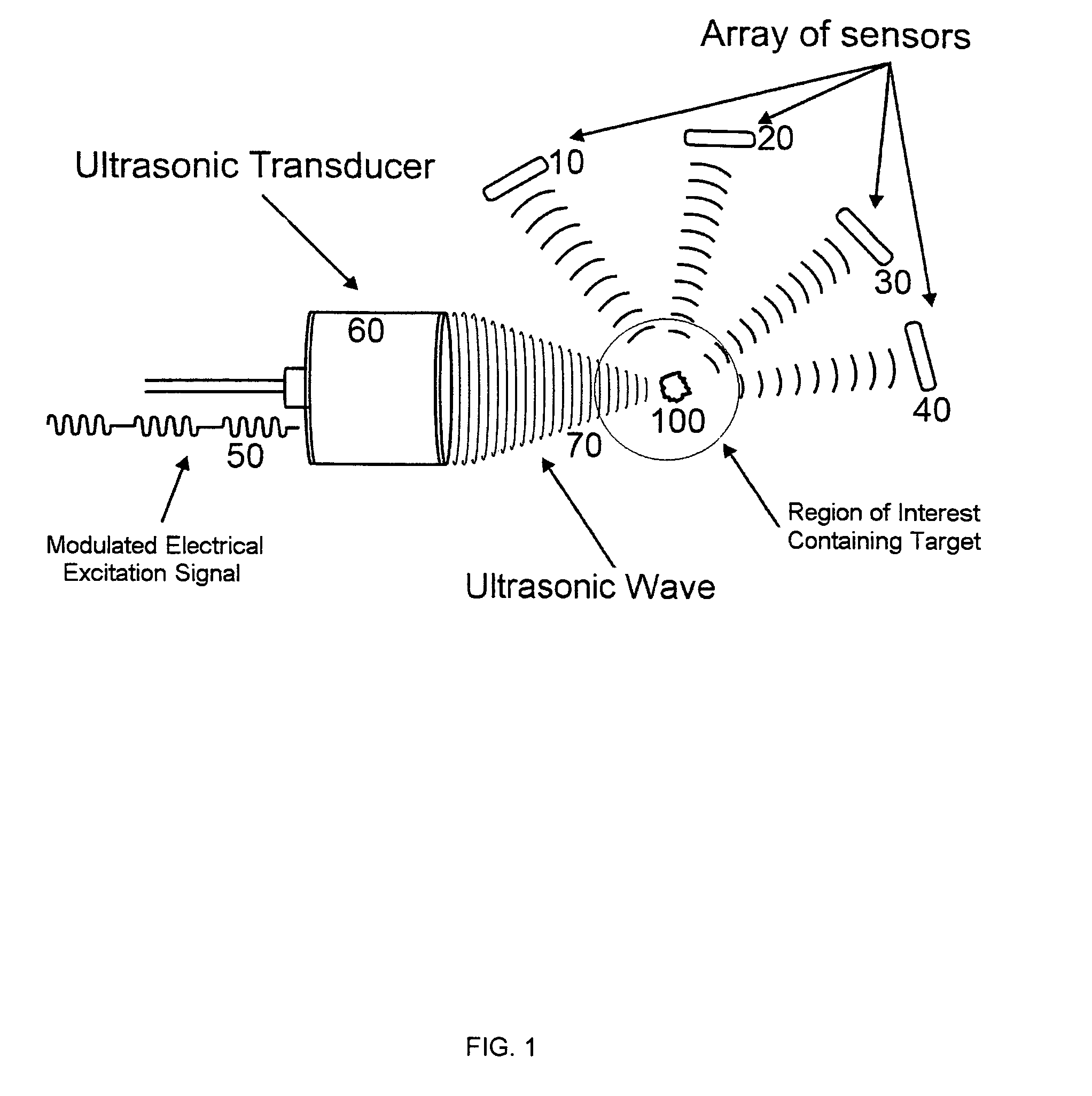
Method of locating the position of a microcalcification in a human breast
InactiveUS8622909B1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasonographySonification
This invention relates to diagnostic and screening medical ultrasound in general and to ultrasound-stimulated detection and location, Image-based Dynamic Ultrasound Spectrography, Acoustic Radiation Force Imaging, and similar modalities in particular. In this invention, an ultrasound signal is emitted into tissue and the resulting radiation force induces localized lower frequency oscillations, which are then received by various acoustic sensors and analyzed to determine certain features or characteristics of the interrogated region. The sensors can be arranged in the form of a ring, in any random arrangements, or positioned in specifically chosen locations. An ultrasonic imaging and excitation transducer generates certain stimulating signals which are received by the breast tissues and which, if they contact a microcalcification, other target, or any region with sharply different mechanical and visco-elastic properties, will result in reflected, demodulated, or re-radiated signals. These signals will propagate away from the targets and detected by the various receiving sensors.
Owner:QUANTASON
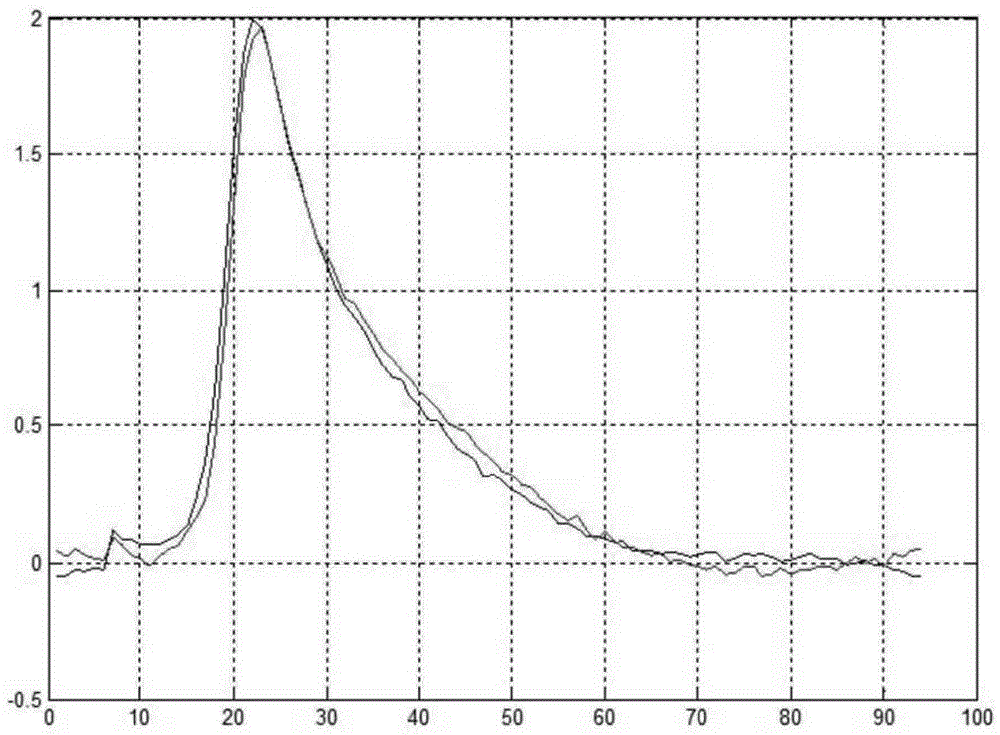
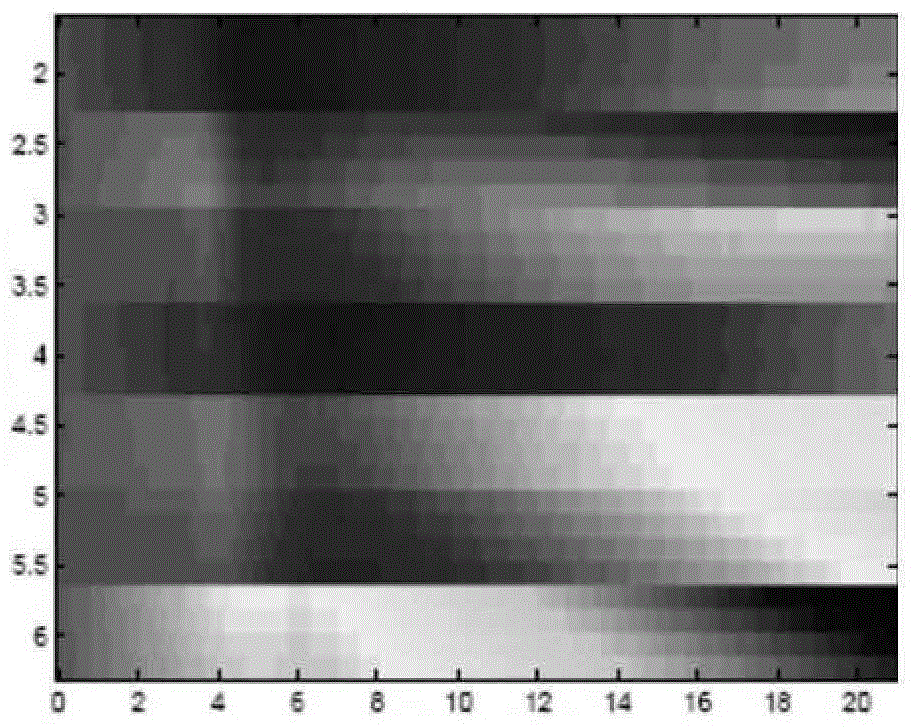
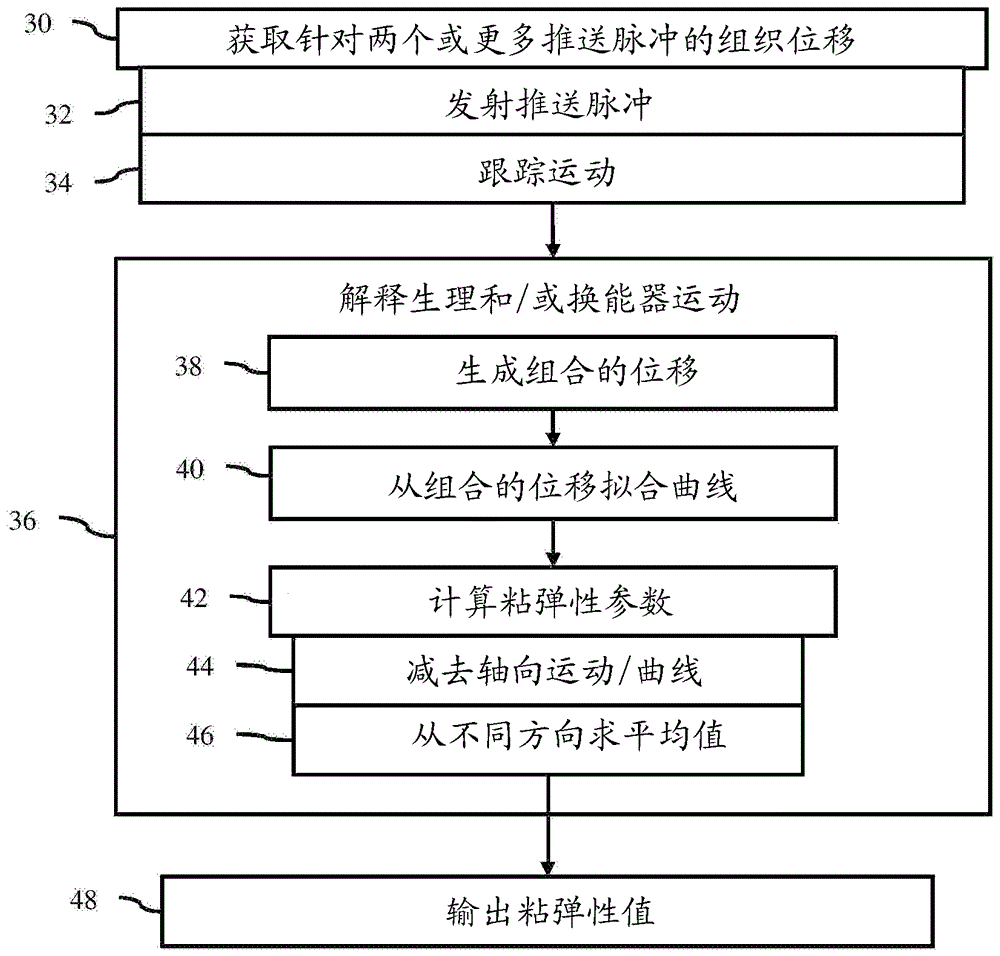
Adaptive motion estimation in acoustic radiation force imaging
For acoustic radiation force ultrasound imaging, multiple displacement profiles (30) for a given location are acquired. Physiological and / or transducer axial and / or lateral motion are accounted for using the displacements from the different acoustic radiation force impulses. For axial motion, a difference (38) between the displacements of the different profiles provides information about motion during displacement at the location caused by just the undesired motion. A more accurate estimate of the undesired motion for removing from the displacement profile is provided. For lateral motion, the displacement profiles are obtained using waves traveling from different directions relative to the given location. An average (46) of velocities (42) estimated from the different profiles removes undesired lateral motion.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Medical ultrasound device with force detection
ActiveUS20120165669A1Minimal space requirementMitigate, alleviate or eliminate oneUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonographyAuditory radiation
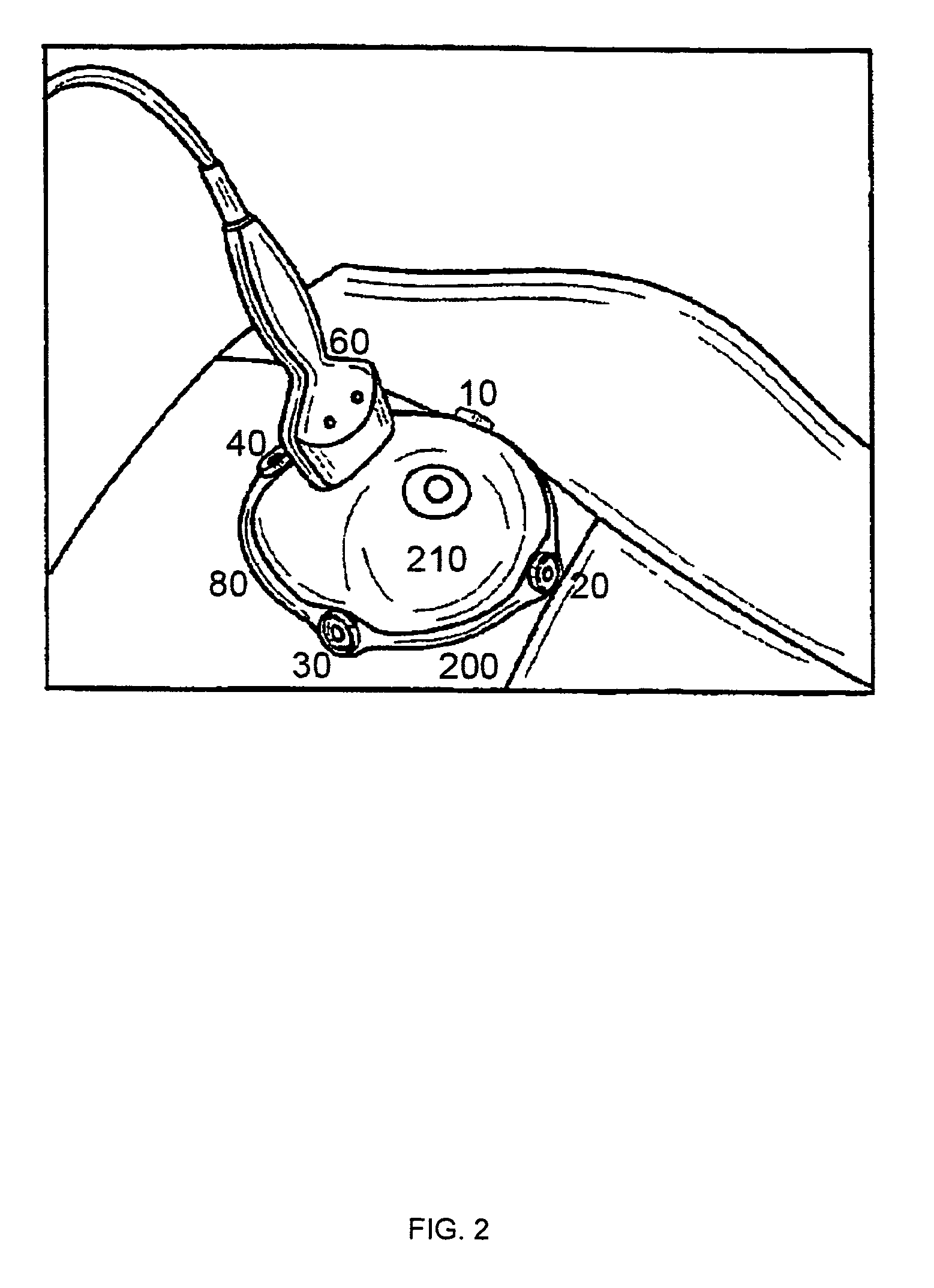
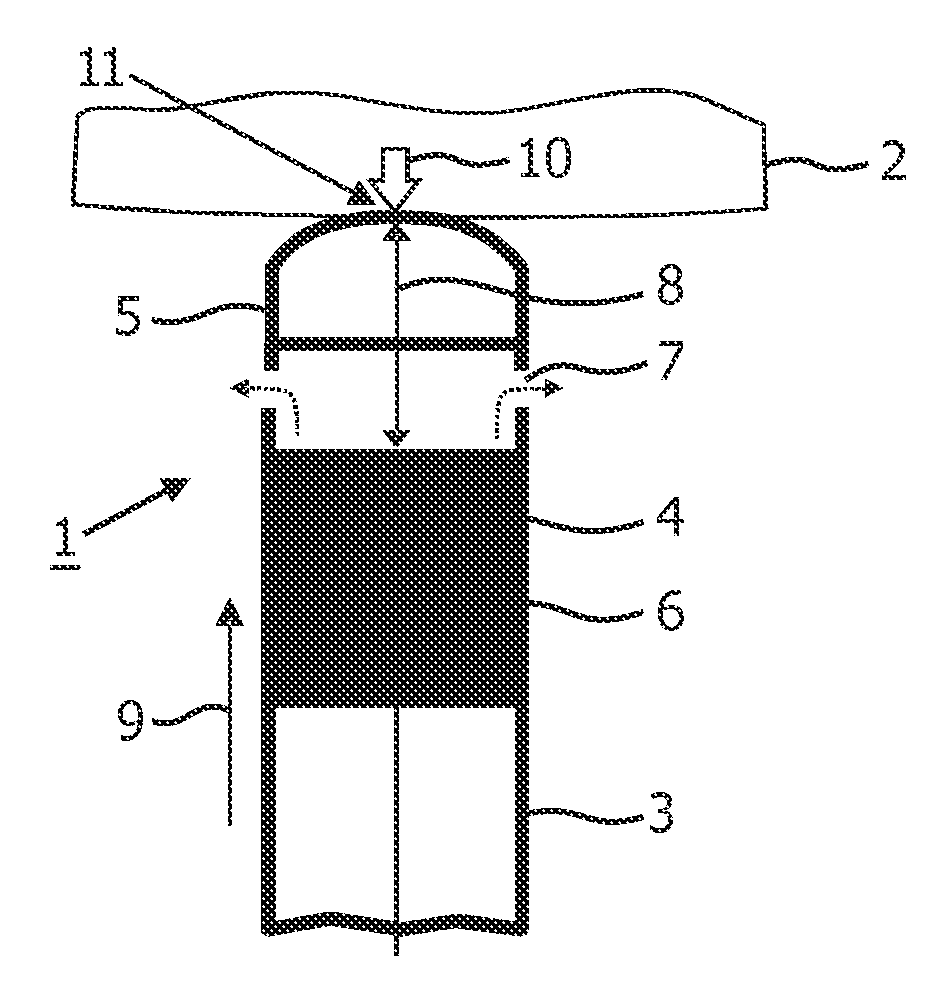
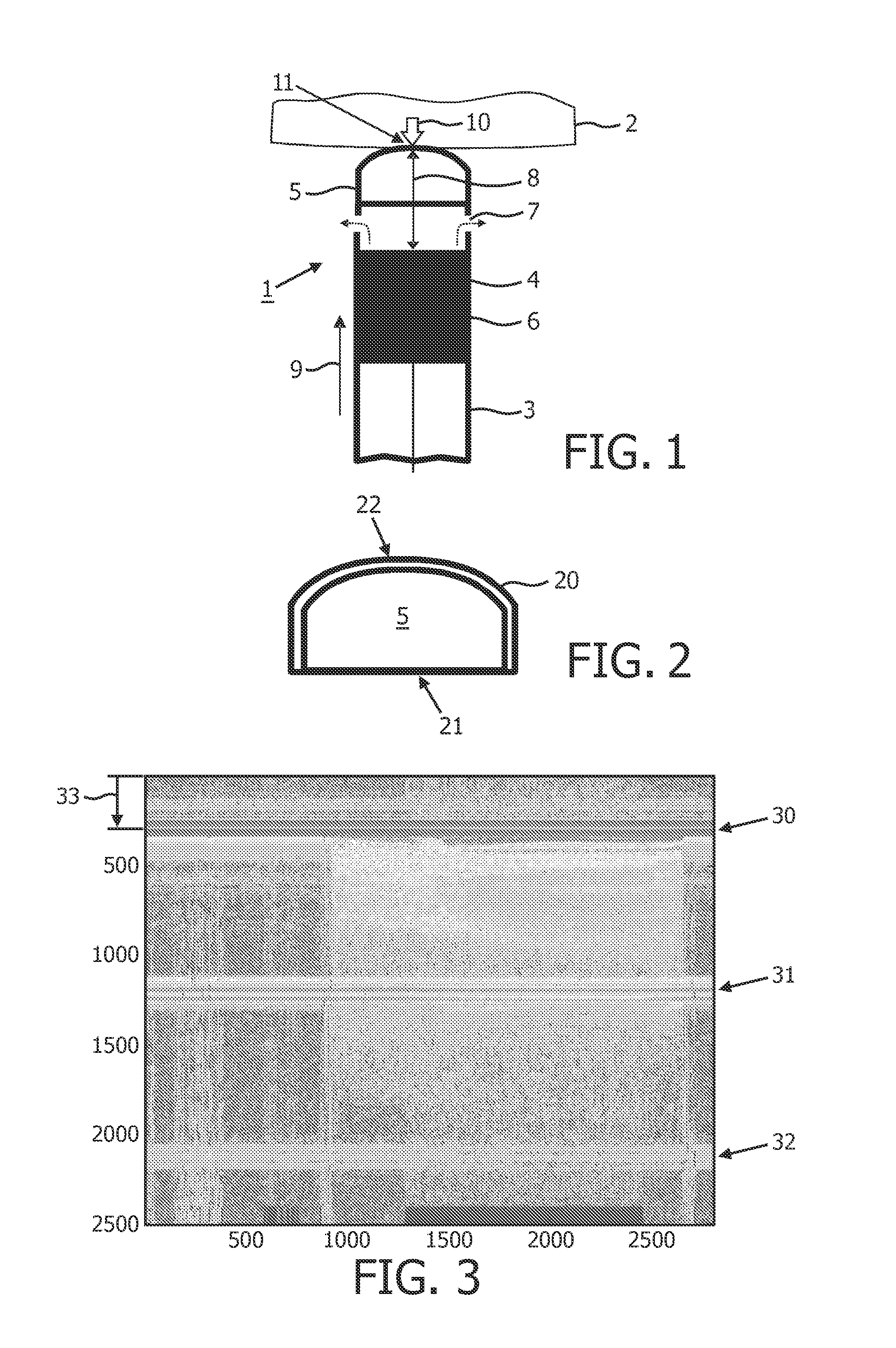
A medical ultrasound device is disclosed. The device comprises an elongated body having a proximal end and a distal end region (1). One or more ultrasound transducers (4) for generating acoustic radiation are positioned in the distal end region, inside the elongated body. A transmission element (5) which is substantially transparent to acoustic radiation is positioned in the radiation path of the acoustic radiation, and a controller unit is operatively connected to the ultrasound transducer. The transmission element and the one or more ultrasound transducers are mounted so that an acoustic path length (8) between the transmission element (5) and the ultrasound transducer (4) varies with contact force (10) imposed to the distal end region. The controller unit detects the acoustic path length between the ultrasound transducer and the transmission element and determines the contact force from the detected acoustic path length. In an embodiment, the medical device is an ultrasound RF ablation catheter.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Piezoelectric underwater sound transducer acoustic radiation mode measurement method and system
InactiveCN103743469AAddressed issue where reconstruction accuracy was often much lower than acoustic pressure reconstruction accuracyPrevent leakageSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementAuditory radiationSound pressure
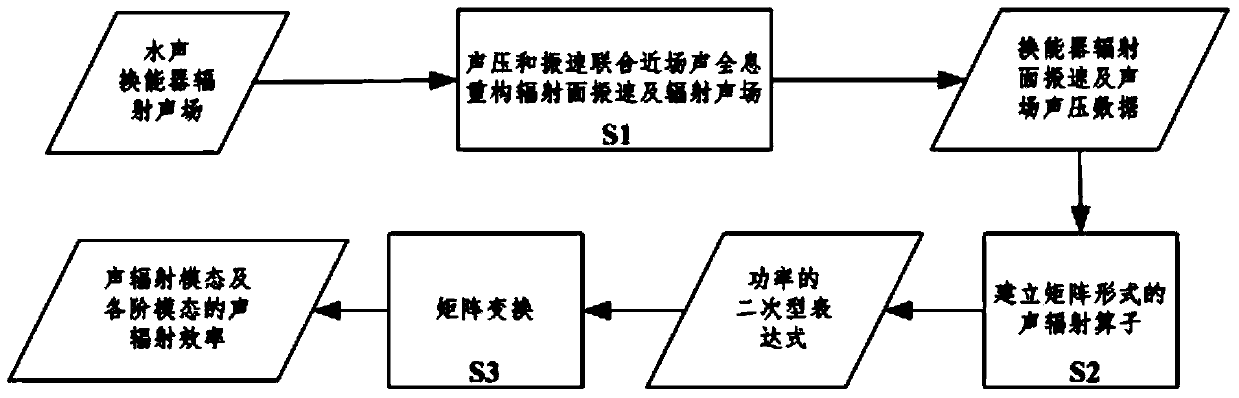
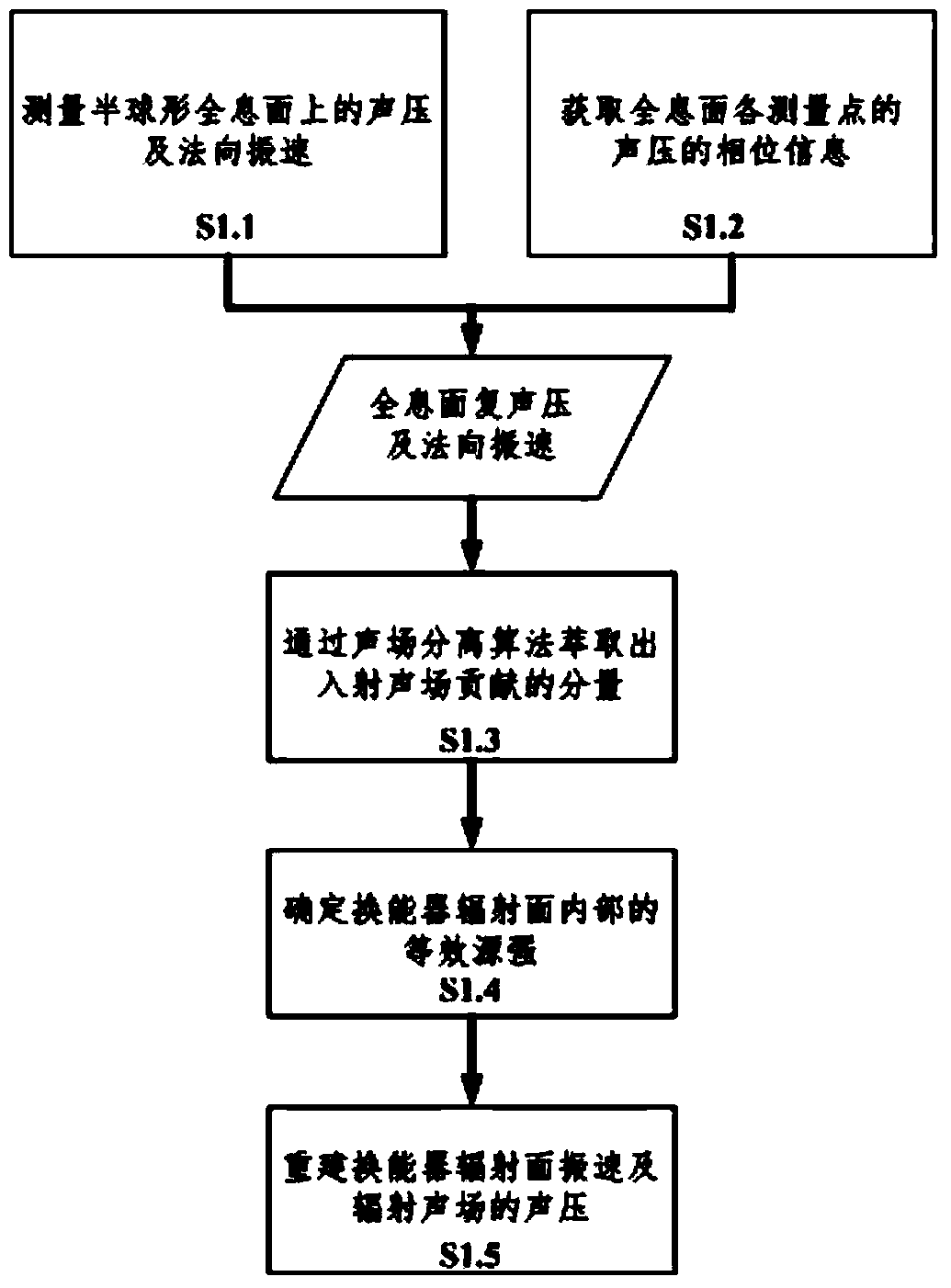
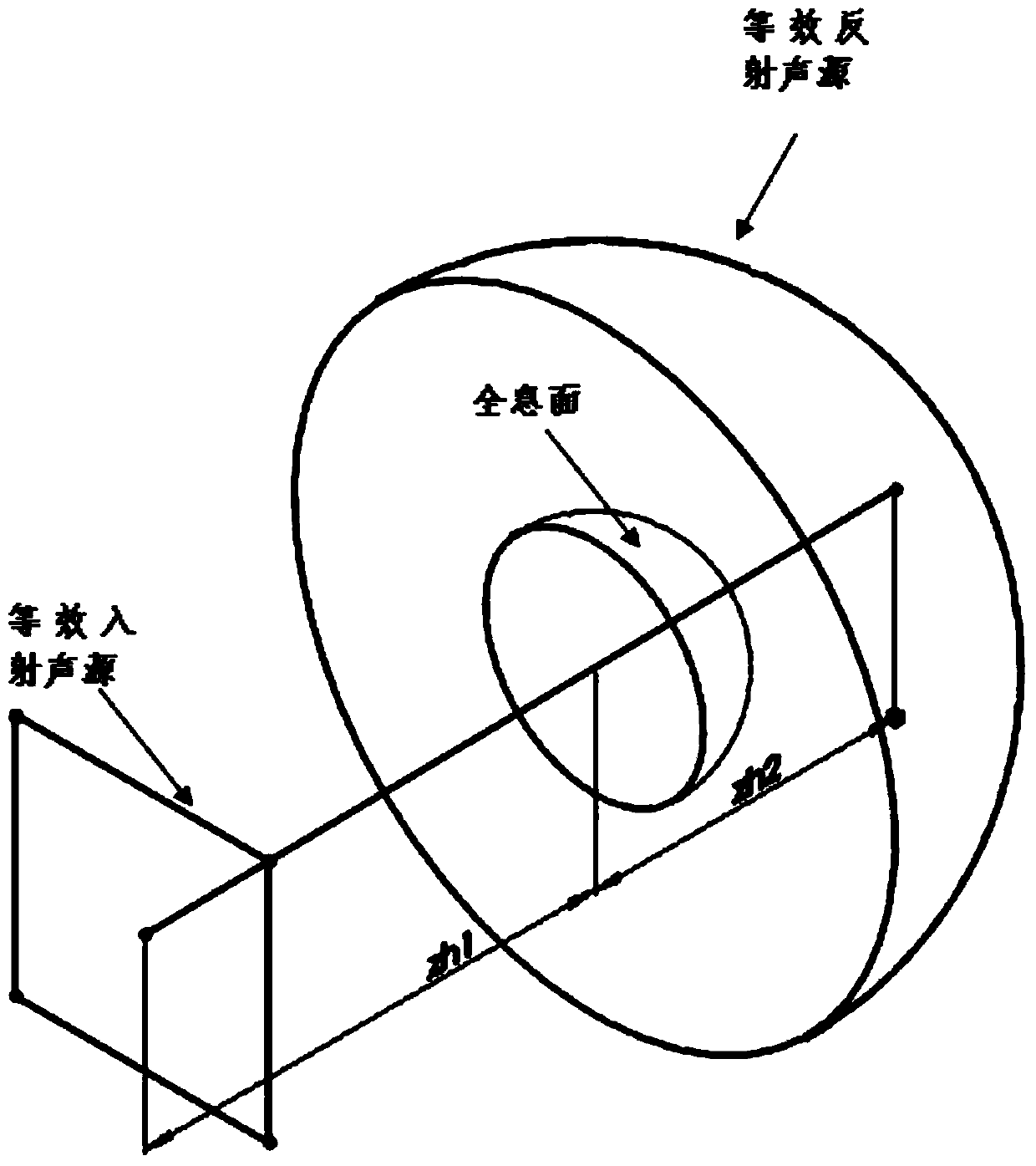
The invention provides a piezoelectric underwater sound transducer acoustic radiation mode measurement method and system based on combination near-field acoustical holography. In the method, the combination near-field acoustical holography is utilized to reestablish sound field, sound pressure and radiation surface vibration velocity; on the basis of an acoustic radiation operator matrix obtained based on measurement data and with the sound field radiation theory being combined, the acoustic radiation power of a piezoelectric underwater sound transducer is expressed to be a positive definite quadric form; and positive definite and conjugate performance of the matrix are utilized to obtained an acoustic radiation mode of the structure. The system comprises a glass water tank, an industrial control computer with PXI bus, a transducer excitation module based on the PXI bus, a sound pressure and vibration velocity acquisition module and a three-dimensional motion platform. The method and system in the invention break the limitation that acoustic radiation mode in the current complex underwater structure can only be solved numerically, provide a new idea for research on the piezoelectric underwater sound transducer, and also provide basis for structure optimization of the piezoelectric underwater sound transducer.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Noninvasive measurements in a human body
InactiveUS8423116B2Easy to measureEasy to operateBlood flow measurement devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringHuman bodyAuditory radiation
A measurement system and method are presented for use for non-invasive measurements in a human body. Acoustic radiation is applied to a certain illuminated region in the body, with at least two different conditions of the applied radiation achievable by varying at least one characteristic of the acoustic radiation. Light scattered from the body part is detected, and measured data indicative of detected photons tagged and untagged by the acoustic radiation is generated. The measured data is analyzed to extract therefrom a data portion corresponding to the tagged photons and being therefore associated with a light response of said certain region, thereby enabling determination of tissue properties of said certain region based on a relation between the measured data portions corresponding to the at least two different operating conditions.
Owner:OR NIM MEDICAL
Shear modulus estimation by application of spatially modulated impulse acoustic radiation force approximation
ActiveUS8225666B2Quantitative measurement of the shear modulus of the tissueVibration measurement in solidsVibration measurement in fluidShear modulusSonification
A method for determining a shear modulus of an elastic material with a known density value is provided. In this method, a spatially modulated acoustic radiation force is used to initially generate a disturbance of known spatial frequency or wavelength. The propagation of this initial displacement as a shear wave is measured using ultrasound tracking methods. A temporal frequency is determined based on the shear wave. The shear modulus of the elastic material at the point of excitation may be calculated using the values of the spatial wavelength, material density, and temporal frequency.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com