Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33results about How to "Large damping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tuneable ferroelectric decoupling capacitor
InactiveUS6888714B2Big lossLarge dampingSolid-state devicesFixed capacitor terminalsSemiconductorDecoupling capacitor
A voltage supply bypass capacitor for use with a semiconductor integrated circuit chip or module comprising a ferroelectric dielectric having electromechanical properties designed to provide maximum losses at selected frequencies.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Acoustical sound proofing material with improved damping at select frequencies and methods for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20090004448A1Improve abilitiesResist transmission of noiseWallsSound proofingShear modulusCellulose
Panels for use in building construction (partitions, walls, ceilings, floors or doors) which exhibit improved acoustical sound proofing in multiple specific frequency ranges comprise laminated structures having as an integral part thereof one or more layers of viscoelastic material of varied shear moduli which also function as a glue and energy dissipating layer; and, in some embodiments, one or more constraining layers, such as gypsum, cement, metal, cellulose, wood, or petroleum-based products such as plastic, vinyl, plastic or rubber. In one embodiment, standard wallboard, typically gypsum, comprises the external surfaces of the laminated structure.
Owner:SERIOUS MATERIALS +1
Acoustical sound proofing material with improved damping at select frequencies and methods for manufacturing same
Panels for use in building construction (partitions, walls, ceilings, floors or doors) which exhibit improved acoustical sound proofing in multiple specific frequency ranges comprise laminated structures having as an integral part thereof one or more layers of viscoelastic material of varied shear moduli which also function as a glue and energy dissipating layer; and, in some embodiments, one or more constraining layers, such as gypsum, cement, metal, cellulose, wood, or petroleum-based products such as plastic, vinyl, plastic or rubber. In one embodiment, standard wallboard, typically gypsum, comprises the external surfaces of the laminated structure.
Owner:SERIOUS MATERIALS +1
Acoustical sound proofing material
Panels for use in building construction (partitions, walls, ceilings, floors or doors) which exhibit improved acoustical sound proofing in multiple specific frequency ranges comprise laminated structures having as an integral part thereof one or more layers of viscoelastic material of varied shear moduli which also function as a glue and energy dissipating layer; and, in some embodiments, one or more constraining layers, such as gypsum, cement, metal, cellulose, wood, or petroleum-based products such as plastic, vinyl, plastic or rubber. In one embodiment, standard wallboard, typically gypsum, comprises the external surfaces of the laminated structure.
Owner:SERIOUS MATERIALS +1
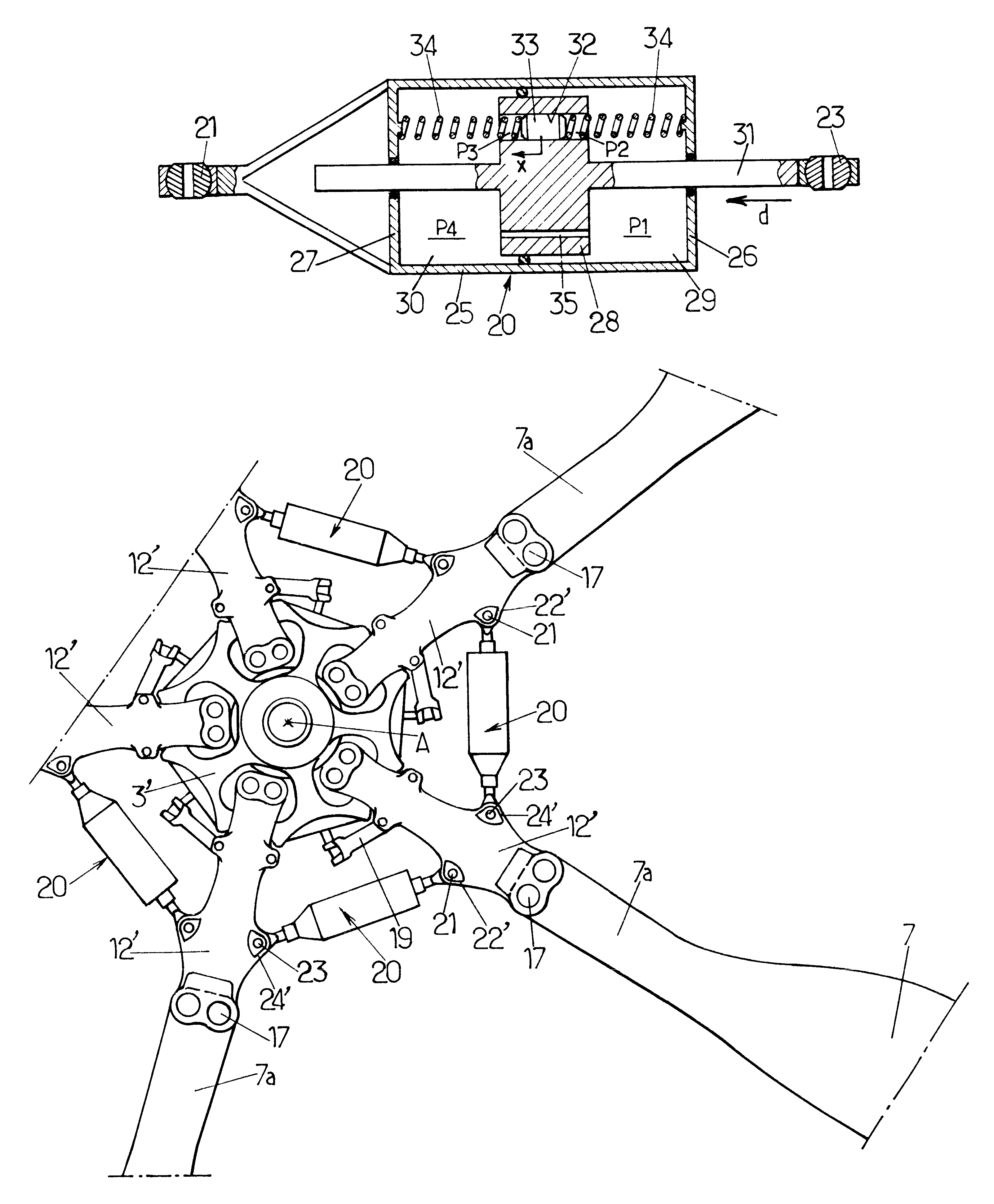
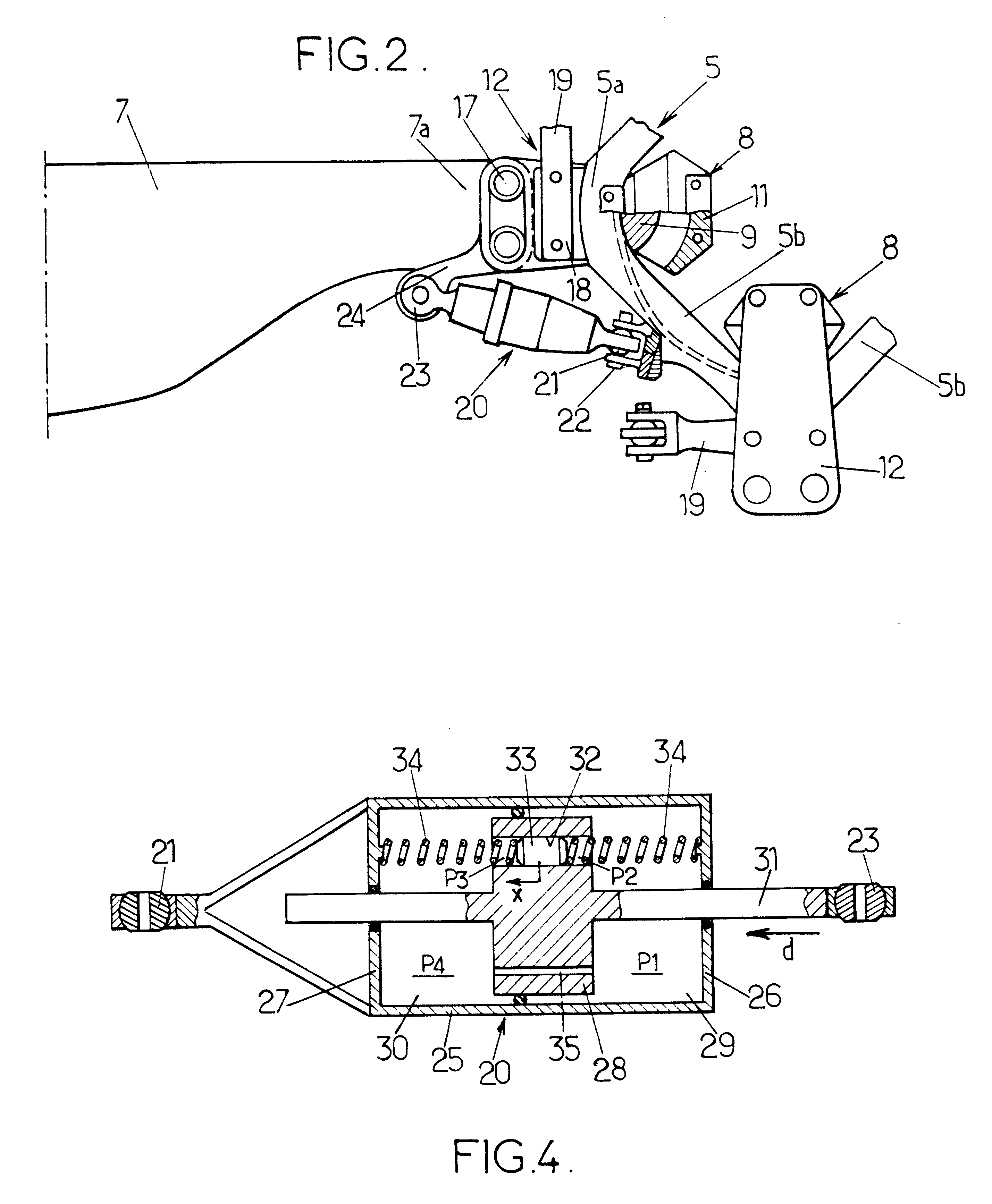
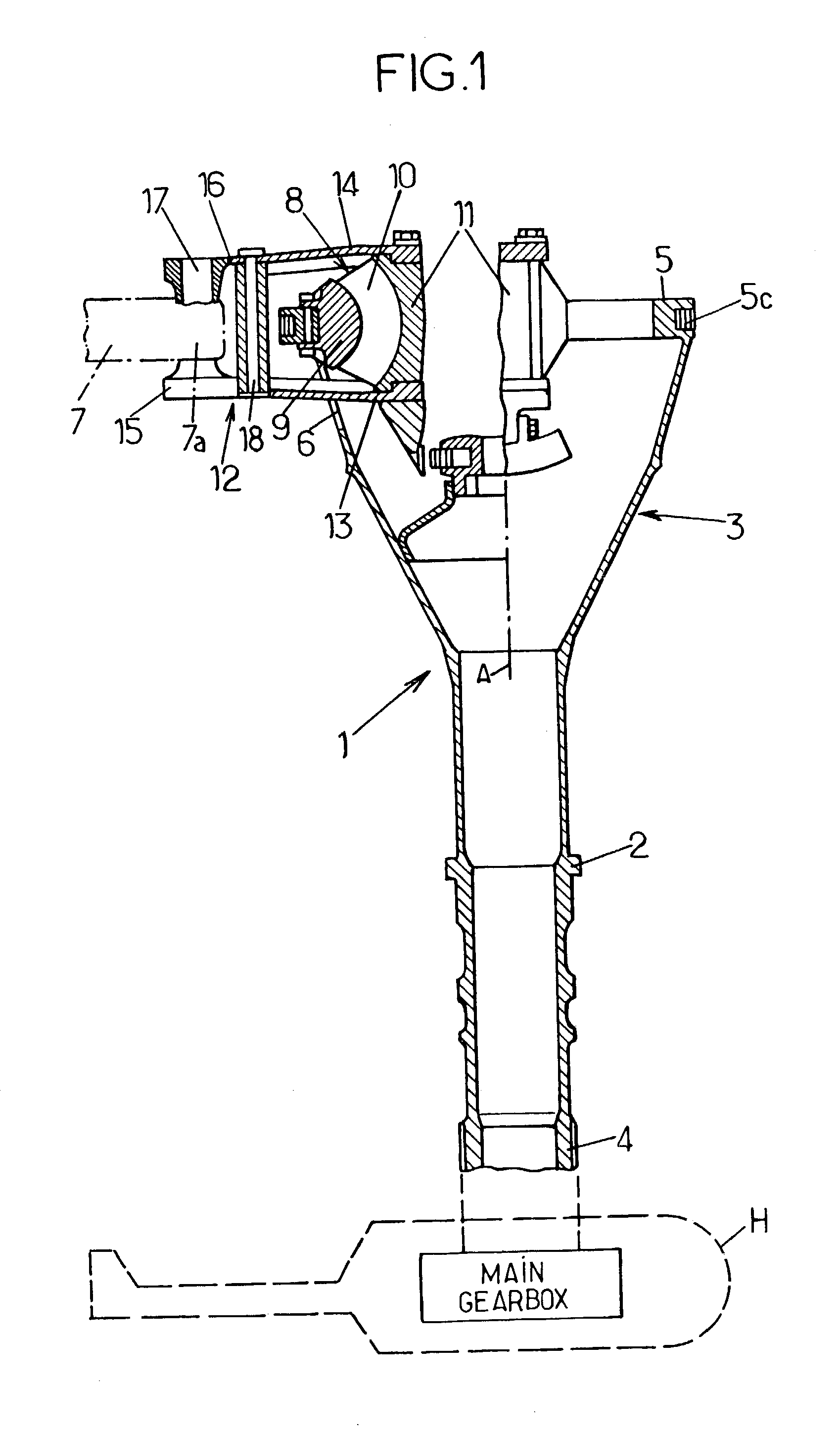
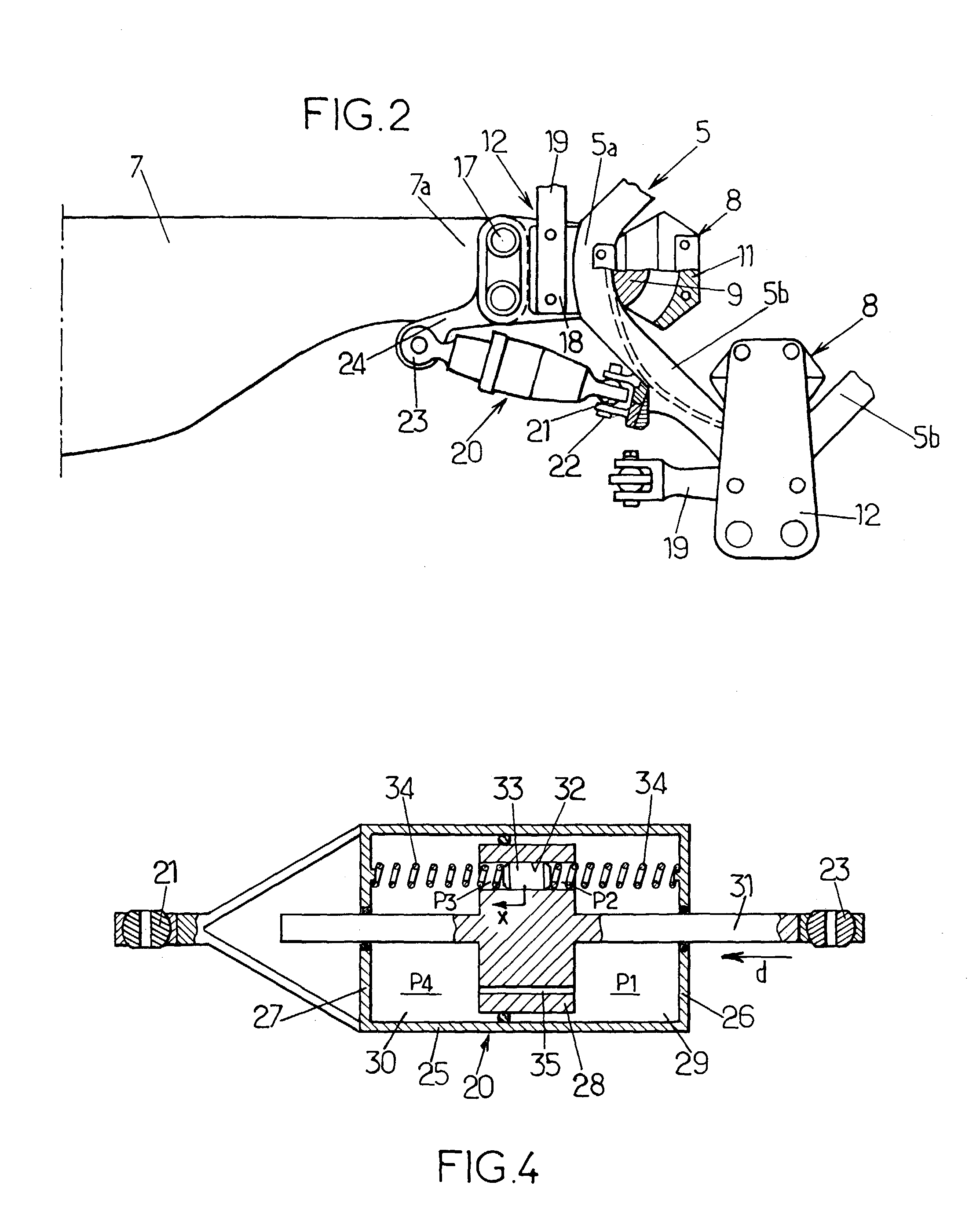
Dual piston drag damper for rotary-wing aircraft rotor
A drag damper for use on a rotary wing aircraft rotor comprises a body defining two variable volume chambers linked by a piston. The chambers are filled with fluid and are connected by a restriction port (35) and by a channel (32) of larger cross-section than the restriction port. A secondary piston slidable and pressure-tight piston is fitted in the channel and loaded by an elastic bias (34). The equivalent mass of this secondary piston (33) and of the fluid which it displaces, and the stiffness of the elastic bias (34) are such that the secondary piston is resonant in the channel (32) at the rotation frequency of the rotor, to filter the dynamic component at this frequency of stresses applied to the damper (20). Furthermore at the natural drag frequency of the corresponding blade, the elastic bias substantially blocks the secondary piston (33) in its channel (32), and the flow of fluid between the chambers (29, 30) of the damper (20) takes place mainly via the restriction port (35) calibrated to provide substantial damping at this frequency.
Owner:EUROCOPTER
Flanged shim for disc brake squeal attenuation
ActiveUS20090223753A1Large dampingArea maximizationFluid actuated brakesNoise/vibration controlUltrasound attenuationEngineering
A brake pad assembly provided for a disc brake apparatus. The brake pad assembly comprises a backing plate having a flat inner face and a flat outer face oriented opposite to the inner face, a friction member fixed to the inner face of the backing plate, and an anti-squeal shim attached to the outer face of the backing plate. The anti-squeal shim includes a flat support plate attached to the outer face of the backing plate and a straight flat flange plate. The support plate of the anti-squeal shim has a peripheral edge including opposite outer and inner edges and opposite side edges. The flange plate is in the form of a flexible cantilever formed integrally with the support plate of the anti-squeal shim and extends away from one of the outer, inner and opposite side edges of the support plate of the anti-squeal shim.
Owner:WOLVERINE ADVANCED MATERIALS
Acoustical sound proofing material with improved damping at select frequencies and methods for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20090000866A1Improve abilityResist transmission of noiseLayered product treatmentWallsGypsumCellulose
Panels for use in building construction (partitions, walls, ceilings, floors or doors) which exhibit improved acoustical sound proofing in multiple specific frequency ranges comprise laminated structures having as an integral part thereof one or more layers of viscoelastic material of varied shear moduli which also function as a glue and energy dissipating layer; and, in some embodiments, one or more constraining layers, such as gypsum, cement, metal, cellulose, wood, or petroleum-based products such as plastic, vinyl, plastic or rubber. In one embodiment, standard wallboard, typically gypsum, comprises the external surfaces of the laminated structure.
Owner:SERIOUS MATERIALS +1
Dual piston drag damper for rotary-wing aircraft rotor
A drag damper for use on a rotary wing aircraft rotor comprises a body defining two variable volume chambers linked by a piston. The chambers are filled with fluid and are connected by a restriction port (35) and by a channel (32) of larger cross-section than the restriction port. A secondary piston slidable and pressure-tight piston is fitted in the channel and loaded by an elastic bias (34). The equivalent mass of this secondary piston (33) and of the fluid which it displaces, and the stiffness of the elastic bias (34) are such that the secondary piston is resonant in the channel (32) at the rotation frequency of the rotor, to filter the dynamic component at this frequency of stresses applied to the damper (20). Furthermore at the natural drag frequency of the corresponding blade, the elastic bias substantially blocks the secondary piston (33) in its channel (32), and the flow of fluid between the chambers (29, 30) of the damper (20) takes place mainly via the restriction port (35) calibrated to provide substantial damping at this frequency.
Owner:EUROCOPTER
Damping and denoising water-soluble damping coating for passenger vehicle and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103980789AImprove the shock and noise reduction effectImprove mechanical propertiesCoatingsEmulsionWater soluble
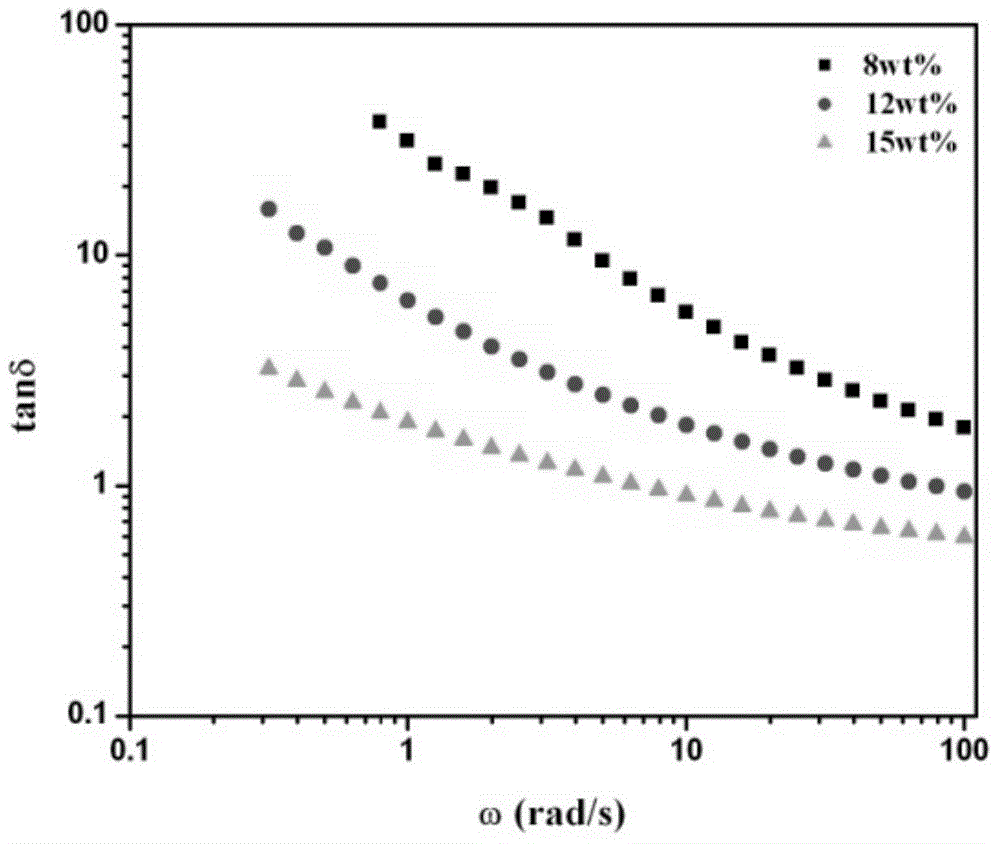
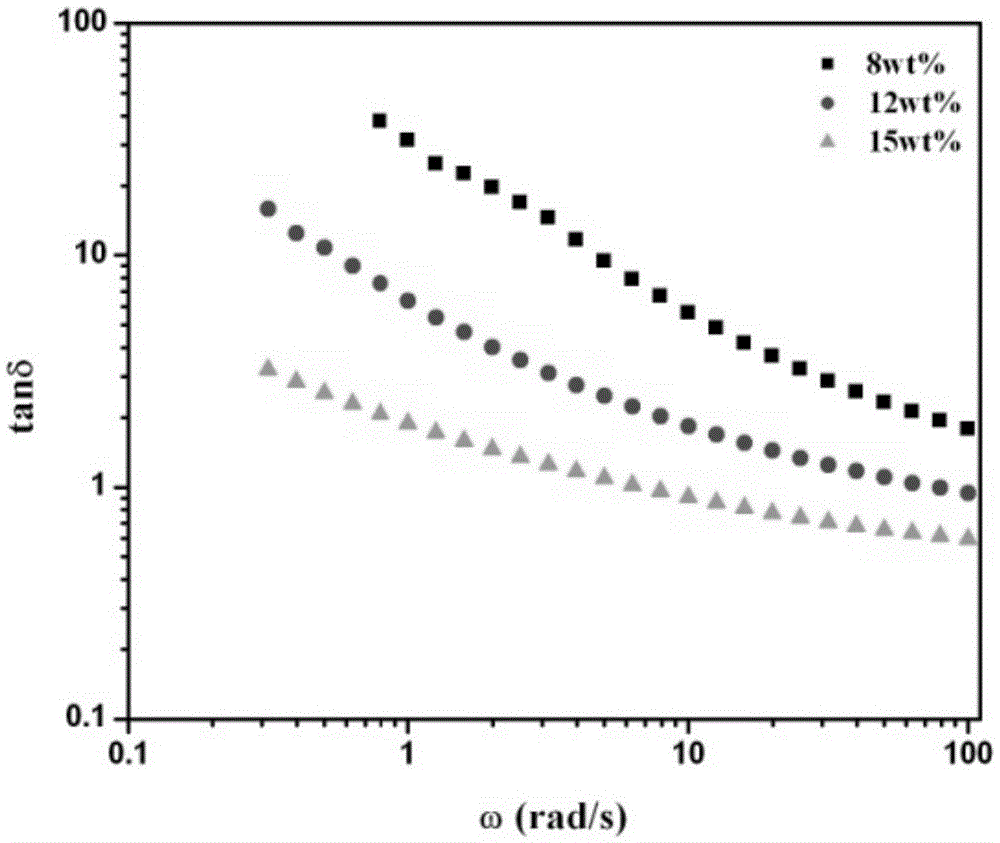
The invention discloses a damping and denoising water-soluble damping coating for passenger vehicles, and a preparation method thereof. The coating comprises 10-15wt% of 'core-shell' type silicone-acrylic-phase-change material emulsion, 5-15wt% of acrylate copolymer emulsion, 5-15wt% of benzene-acrylic copolymer emulsion, 30-55wt% of inorganic filler, 2-5wt% of assistant and 15-25wt% of deionized water, wherein the 'core-shell' type silicone-acrylic-phase-change material emulsion is a significant component for remarkably enhancing the damping property of the coating, and is prepared by synthesizing an organic phase-change micro-capsule wrapped with silicon dioxide, and further wrapping the silicon dioxide with a polysiloxane-acrylate copolymer, thereby obtaining the silicone-acrylic-phase-change material emulsion with a double-layer wrapped 'core-shell' structure.
Owner:HANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED MATERIAL BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
Vibration reduction in a combustion chamber
InactiveUS20020162336A1Large dampingIncrease frequencyBurnersTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsCombustion chamberCombustor
A combustion chamber according to the invention has a number b0 of annularly arranged burners, of which a number k of modulatable burners have means for modulating a fuel mass flow, k being k<b0, and the modulatable burners being arranged in such a way that between every pair of adjacent modulatable burners are arranged in each case a1, a2, . . . ak nonmodulatable burners, and that the values a1+1, a2+1, . . . , ak+1 are not integral divisors of b0. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, a highest value of <paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>LCM(b0, a1+1), LCM(b0, a2+1), . . . LCM(b0, ak+1) < / in-line-formula>is maximum, LCM designating the lowest common multiple. It thereby becomes possible to damp a maximum number of azimuthal vibration modes of the combustion chamber by means of a minimum number of modulatable burners. Each pair of modulatable burners gives rise to at least one undesirable vibration or instability which, however, is damped by the other modulatable burner or burners arranged according to the invention.
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
Multistage composite type energy absorption and dissipation damping device, application and method
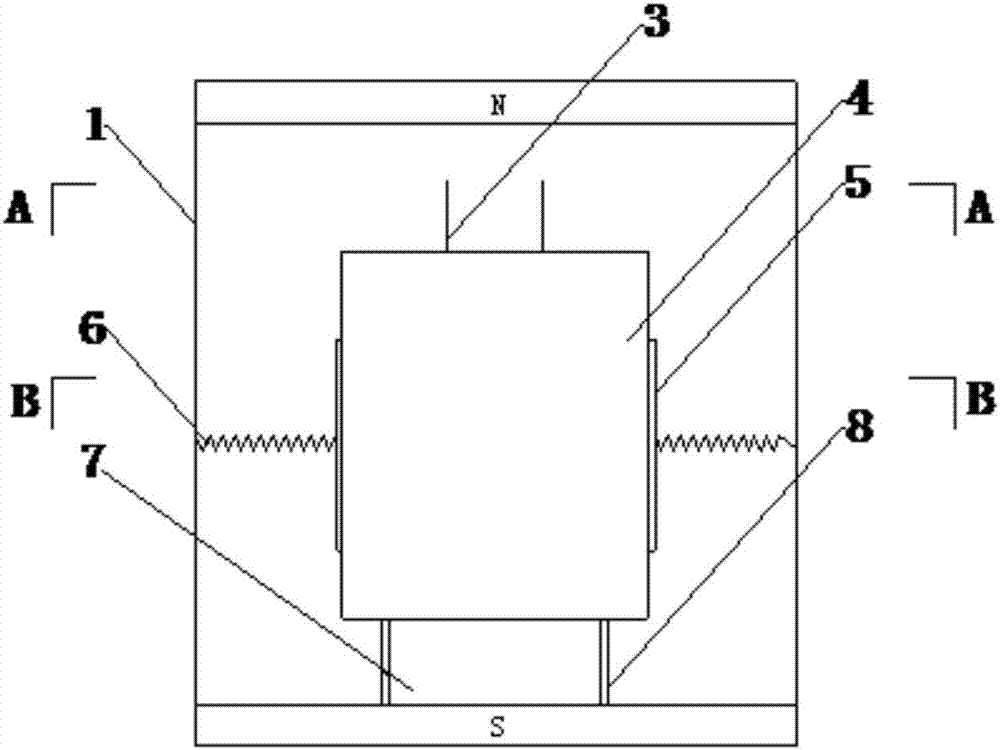
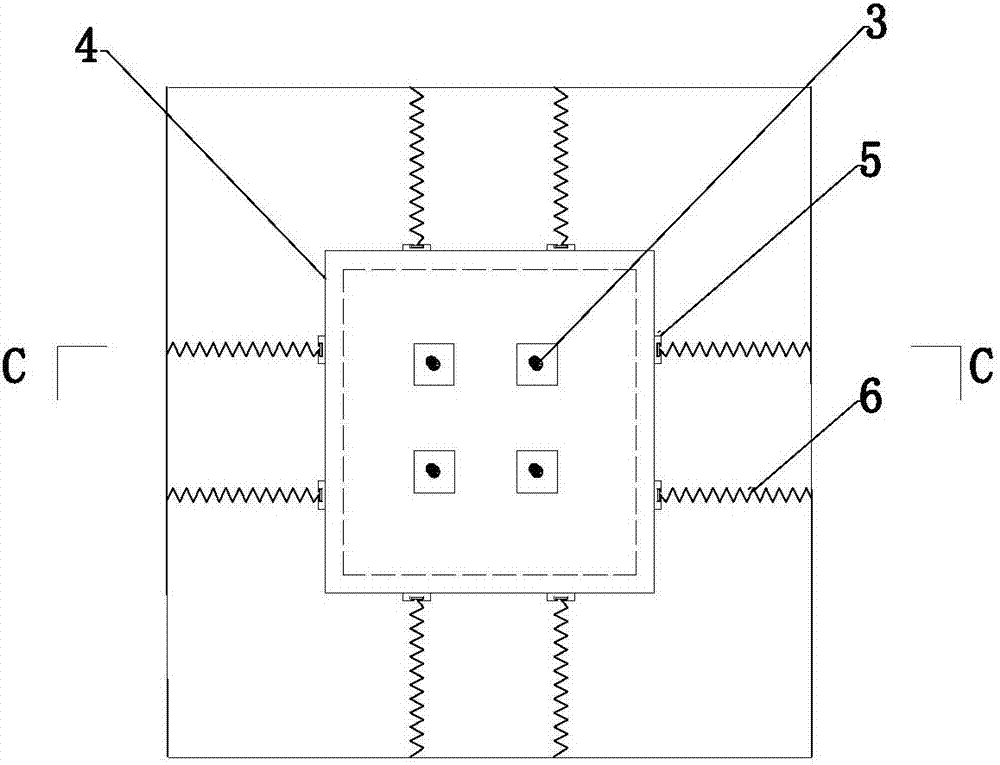
ActiveCN106907042AEffective Vibration ControlReduce loadDevices for damping mechanical oscillationsTowersEnergy absorptionMechanical energy
The invention discloses a multistage composite type energy absorption and dissipation damping device, an application and a method. According to the multistage composite type energy absorption and dissipation damping device, the defect that in the prior art, in complex load action, energy dissipation in multiple directions cannot be conducted is overcome, and multistage and polydirectional damping can be effectively realized. According to the scheme, the device comprises an outer box, a mass block and a liquid container, wherein permanent magnets are arranged on the top and at the bottom of the outer box correspondingly, and magnet poles of the two permanent magnets are opposite; the mass block is arranged inside the outer box, and the side face of the mass block is connected with the inner wall of the outer box through a first elastic damping assembly to realize the energy dissipation and damping effects of the mass block in the horizontal direction; the liquid container is arranged below the mass block, liquid with a set volume is contained in the liquid container, the liquid container is internally provided with a second elastic damping assembly, the bottom end of the second elastic damping assembly is connected with the inner bottom of the liquid container, and the top end of the second elastic damping assembly is fixed to the mass block; and meanwhile in the moving process of the mass block, magnetic induction lines generated by the two permanent magnets are cut to conduct dissipating in the mode that mechanical energy is transformed into electric energy.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Multirod bow stabilizer
Owner:LEVEN INDS
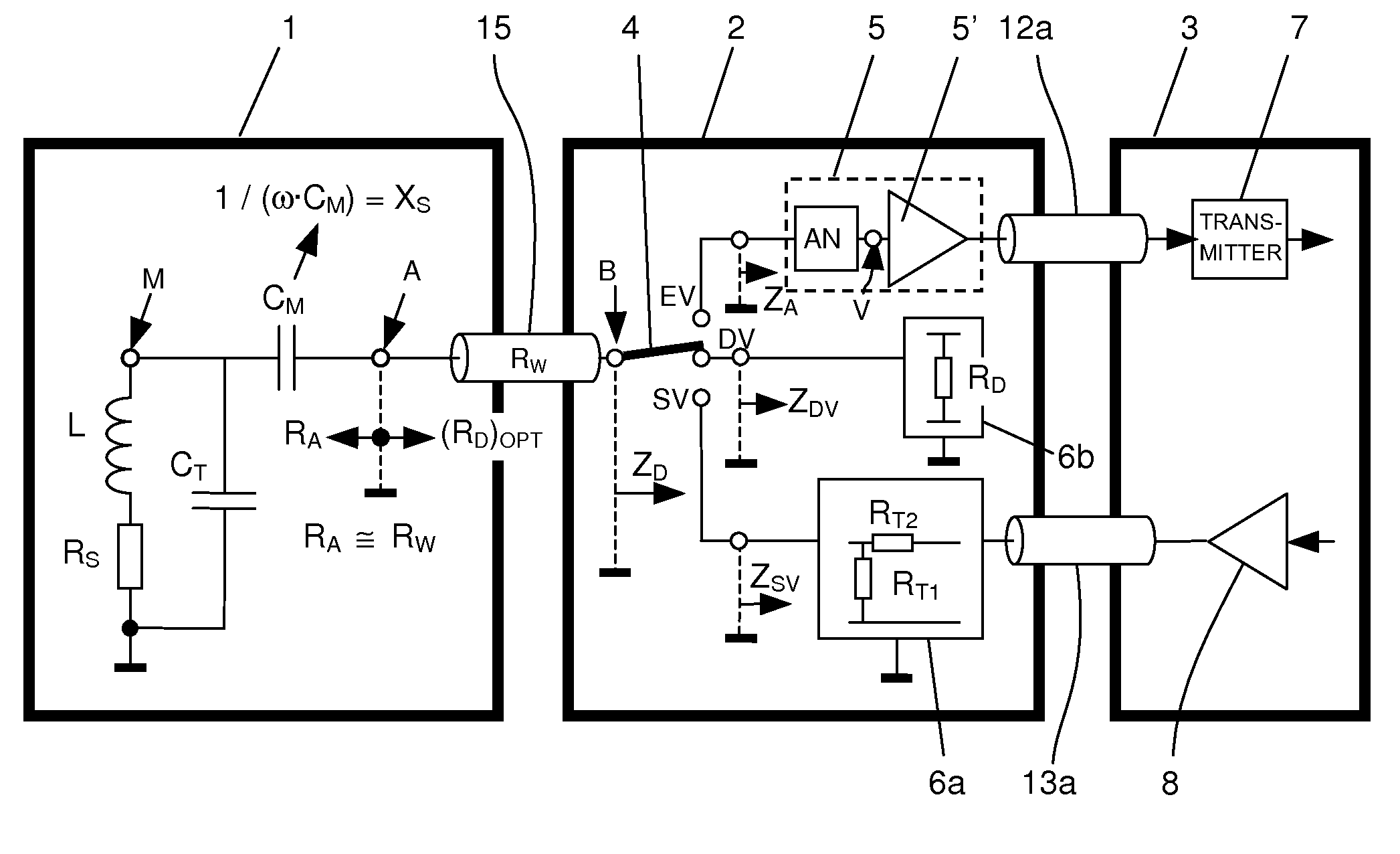
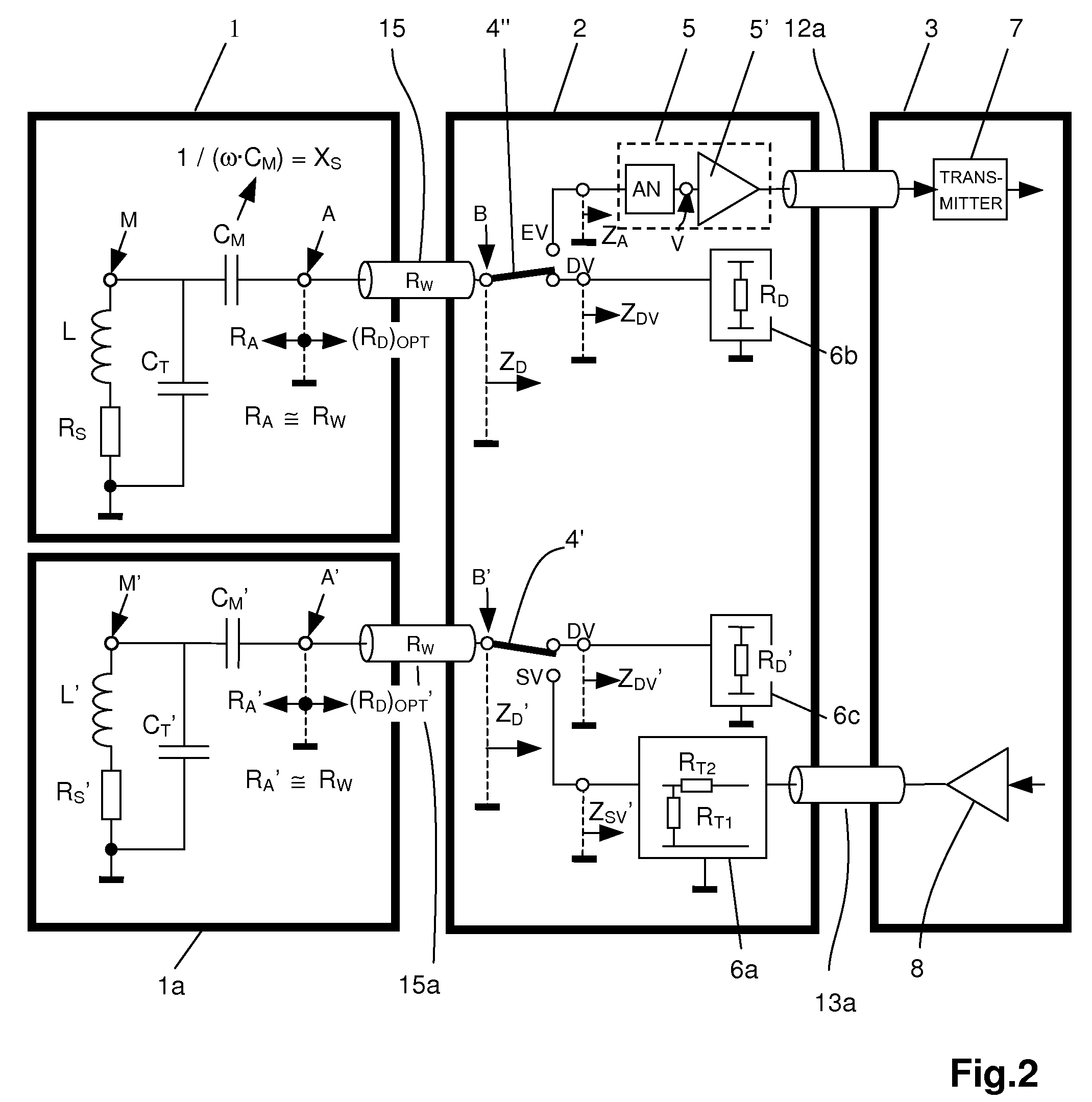
Passively damped magnetic resonance (MR) detection configuration
InactiveUS7723988B2Preventing any disturbance of the sensitive surroundingsLarge dampingMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionAudio power amplifierResonance
A magnetic resonance (MR) detection configuration comprising at least one RF resonant circuit with an inductance, a preamplifier module and an RF receiver, wherein a reactive transformation circuit is connected between a high-impedance point of the inductance and a low-impedance connecting point of the RF resonant circuit, which acts as an impedance transformer and wherein the low-impedance connecting point is connected to the preamplifier module via an RF line having a characteristic impedance, is characterized in that at least one passive damping impedance is provided in the preamplifier module downstream of the RF line, wherein the passive damping impedance can be connected to the resonant circuit by a switching means during a damping and / or transmitting process, and wherein the respective amount of the complex reflection factor of passive damping impedance relative to the characteristic impedance of the RF line exceeds a value of 0.5. This presents an MR detection configuration with an extensive damping concept, wherein all three processes (transmitting, damping and receiving processes) are optimized.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
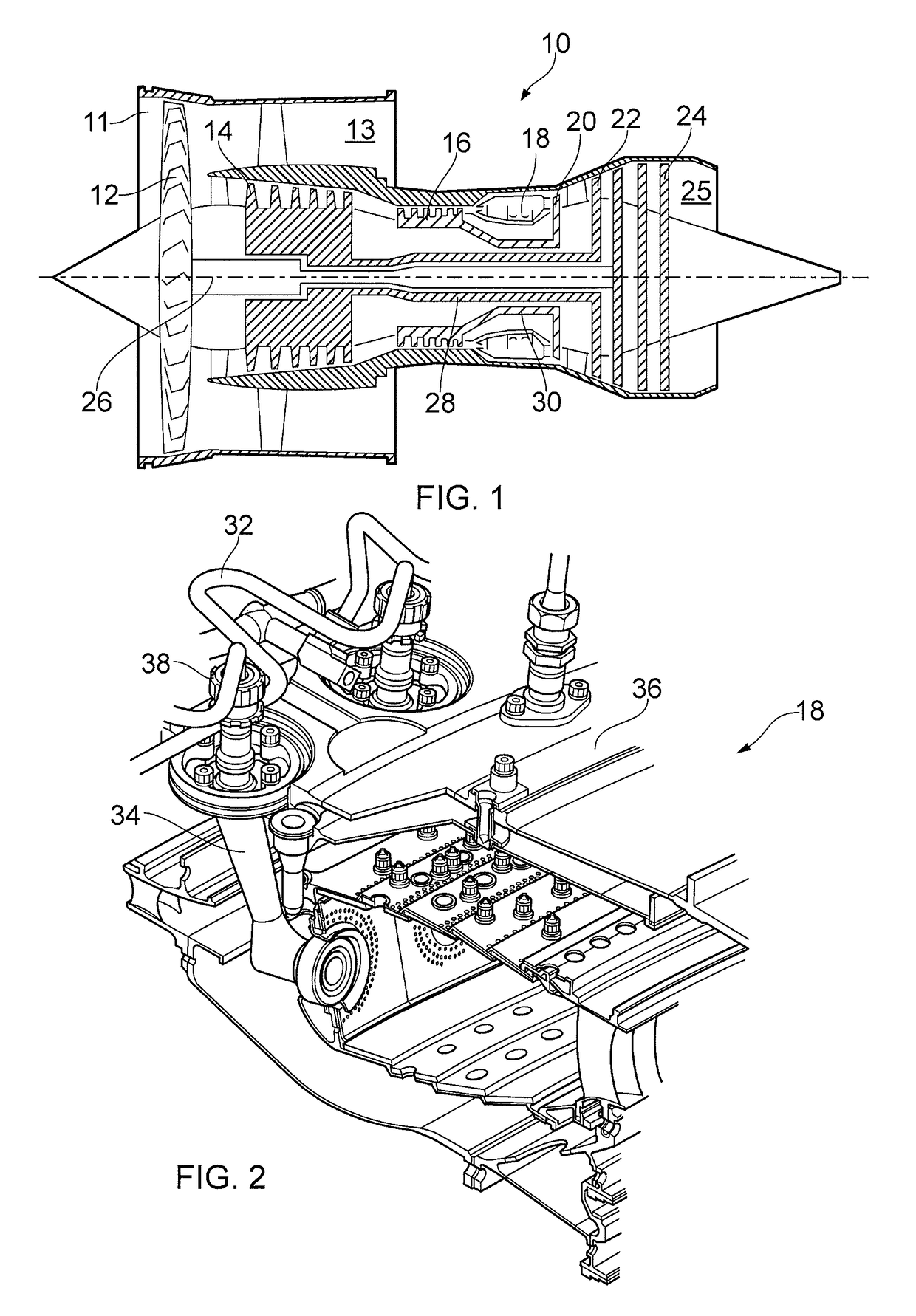
Fluid conduit
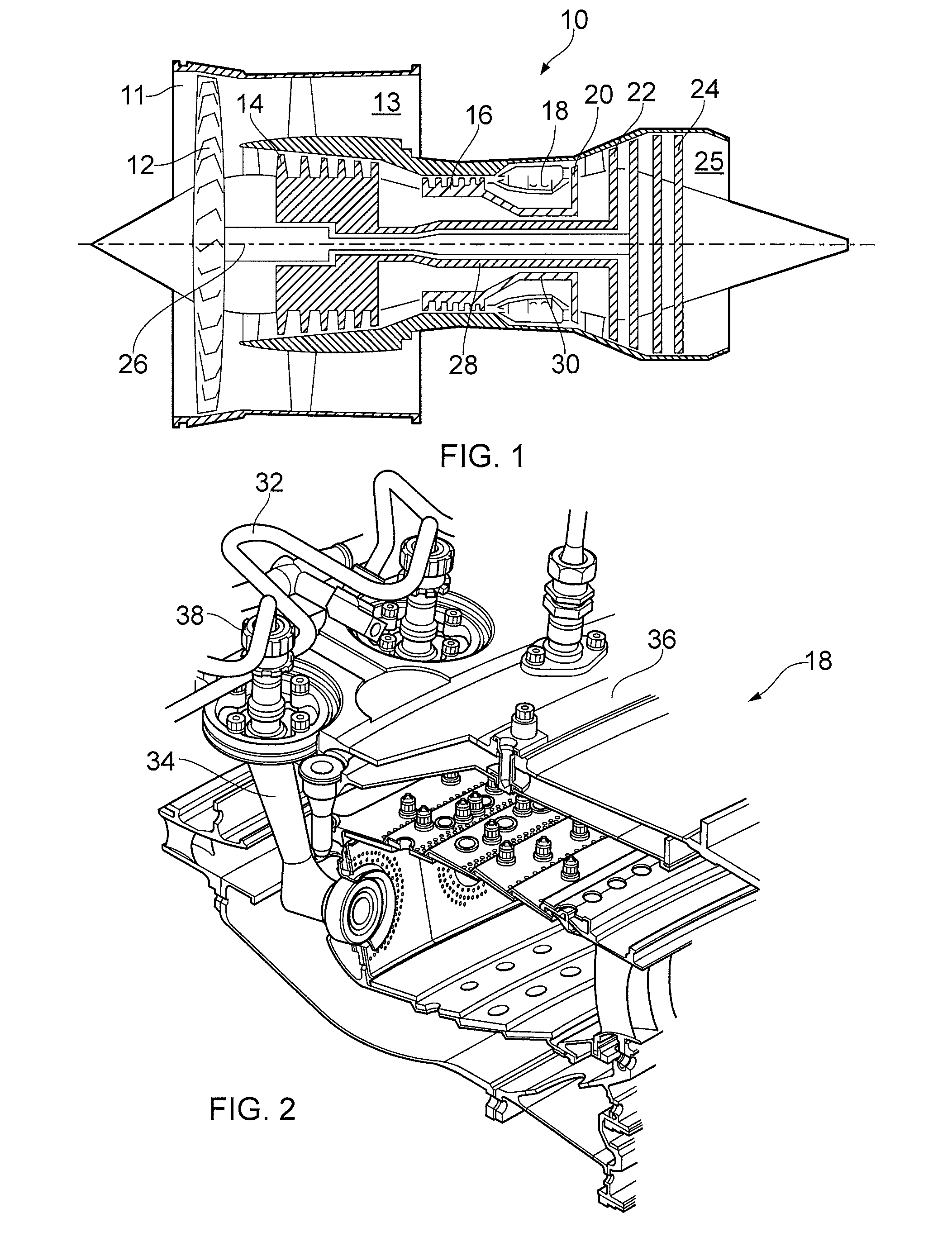
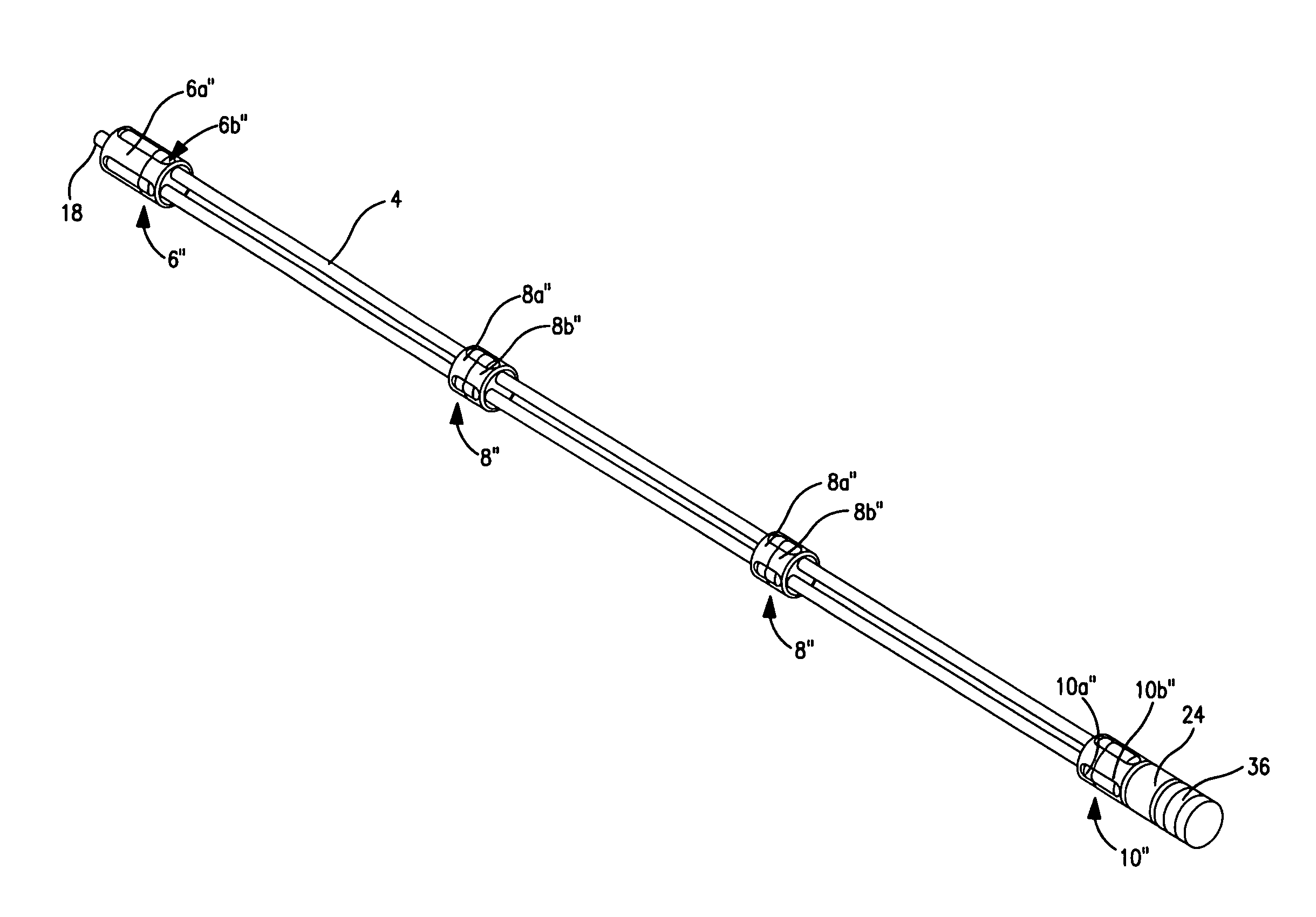
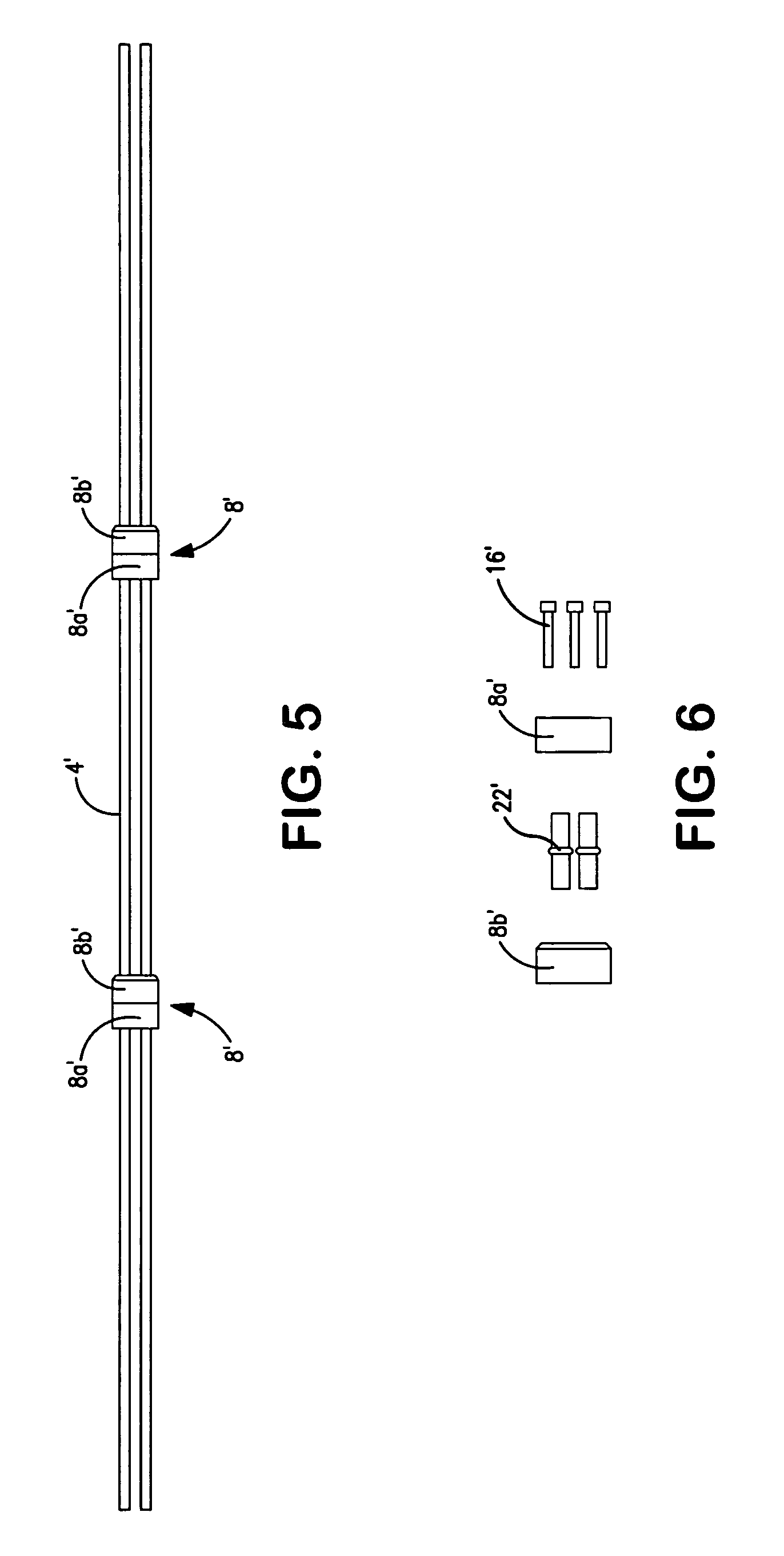
ActiveUS20160108818A1Minimize resonanceLarge dampingGeometric CADContinuous combustion chamberCatheterEngineering
A fluid conduit for a gas turbine engine. The conduit includes a superelastic material such as TNTZ or Ti2448. The conduit is installed such that at least part of the conduit is subject to a stress which lies in one of a superelastic and a plastic region of the material in use.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Multirod bow stabilizer
Owner:LEVEN INDS
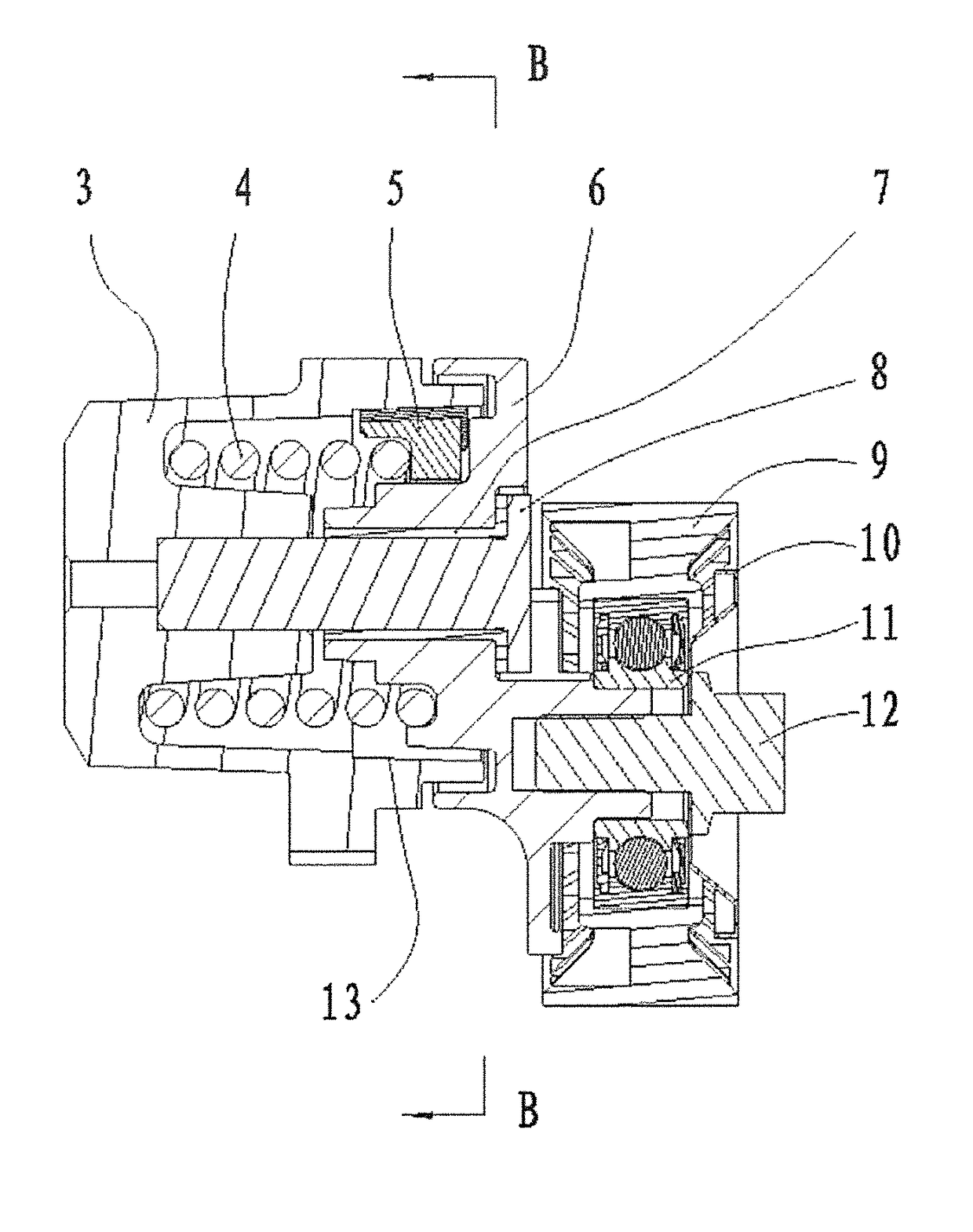
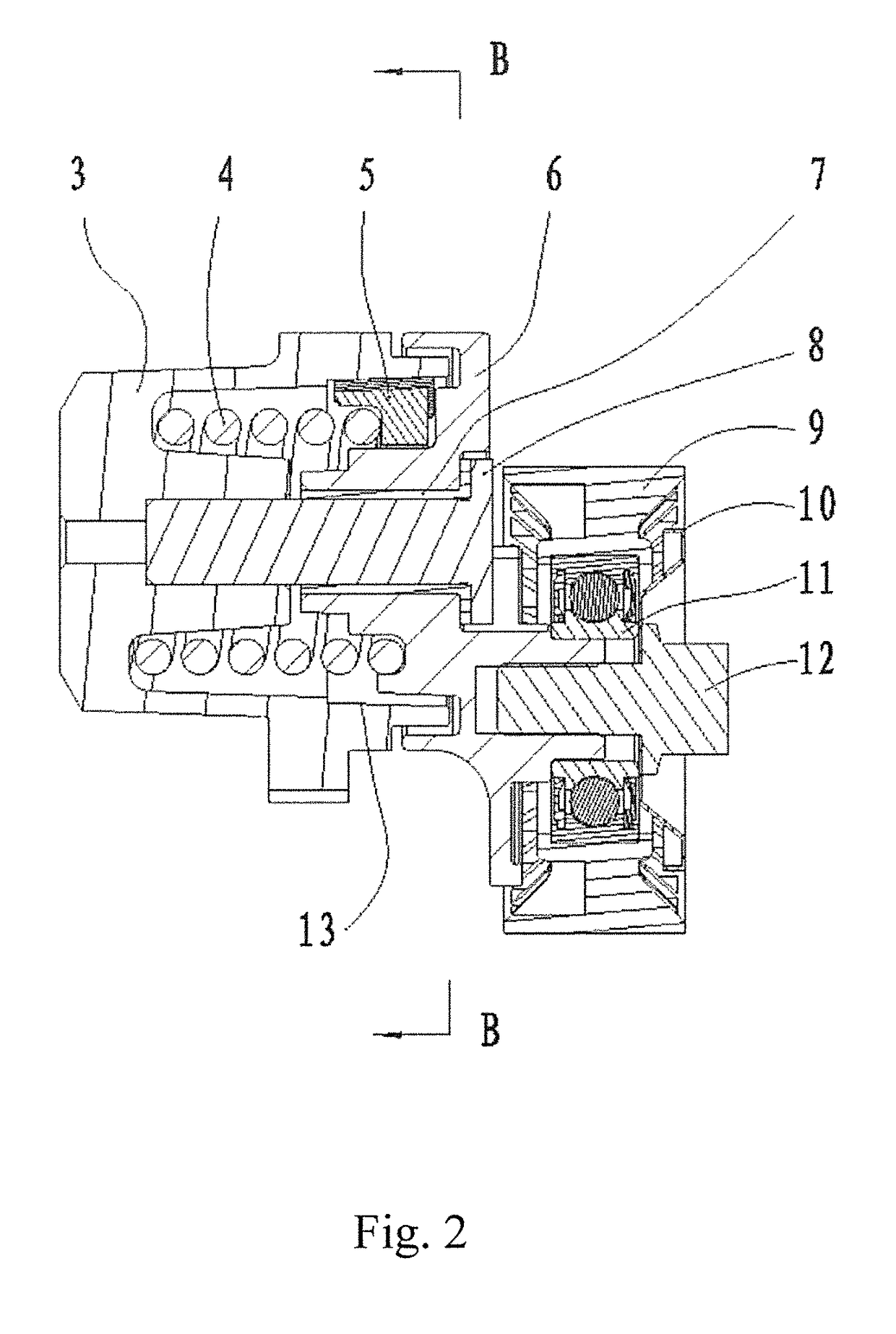
Tensioner for Engine with Large and Stable Damping and Minimum Deflection o f Shaft
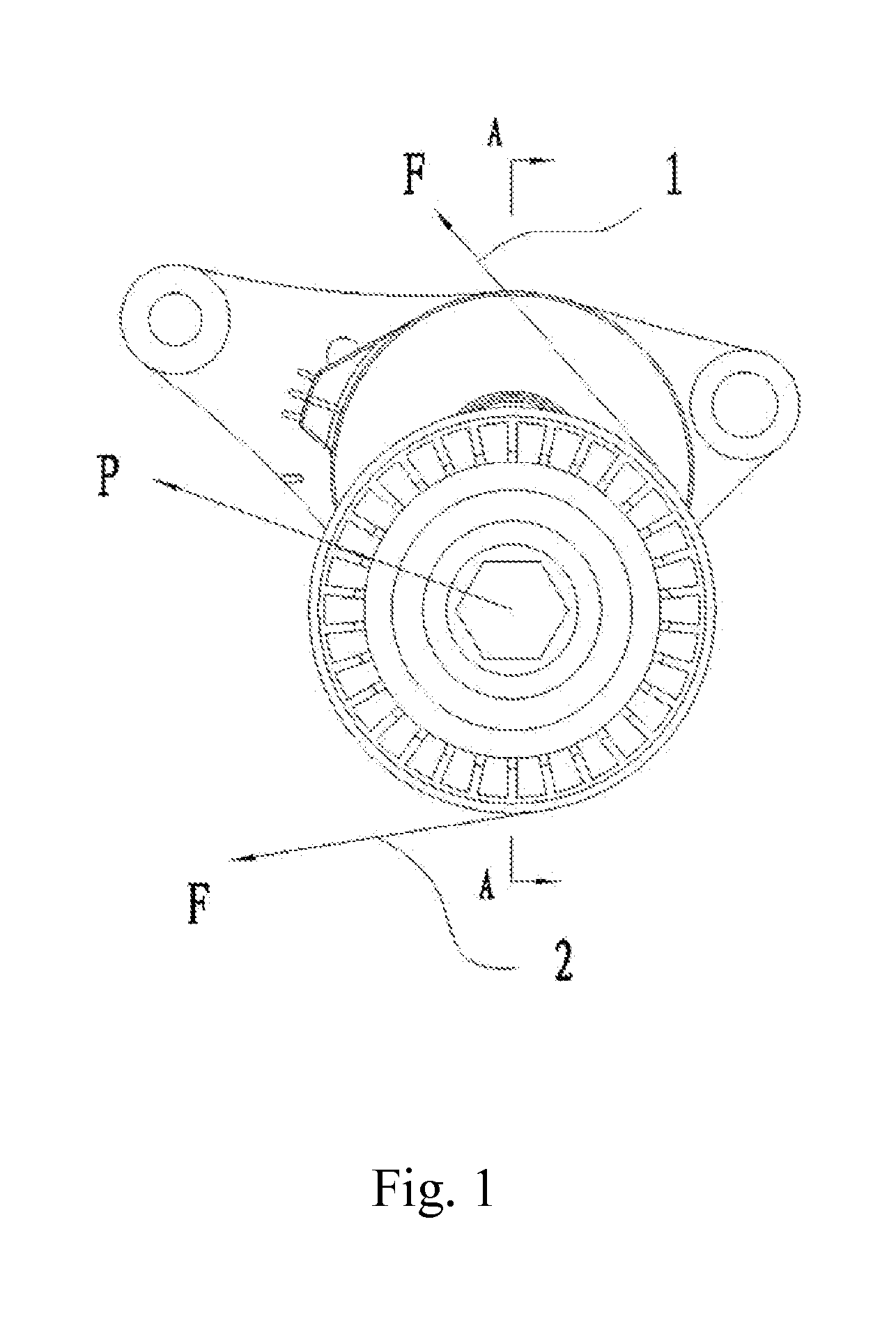
ActiveUS20150276024A1Large and stable damping effectDamping will not be dramatically decreasedGearingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A tensioner includes a base, a tension arrangement rotatable at the base, a damping member being rotated in a loading direction by the tension arrangement, and an elastic member biasing against the damping member. The position of the damping member depends by the layout geometry of the specific application and is directly in opposition to the hub load. The reaction force of the cylindrical surface of the base on the damping member is very near to the plan of the external forces represented by the hub load to minimize the deflection of the shaft. The tension arrangement is rotated to push the damping member for generating a first positive tension between the damping member and the base, and to expand the elastic member radially for generating a second positive tension between the elastic member and the damping member, so as to enhance a damping force of the tensioner.
Owner:NINGBO FENGMAO FAR EAST RUBBER
Honeycomb core composite structural material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104057658AHigh strengthHigh dampingSynthetic resin layered productsRubber layered productsComposite constructionFilling materials
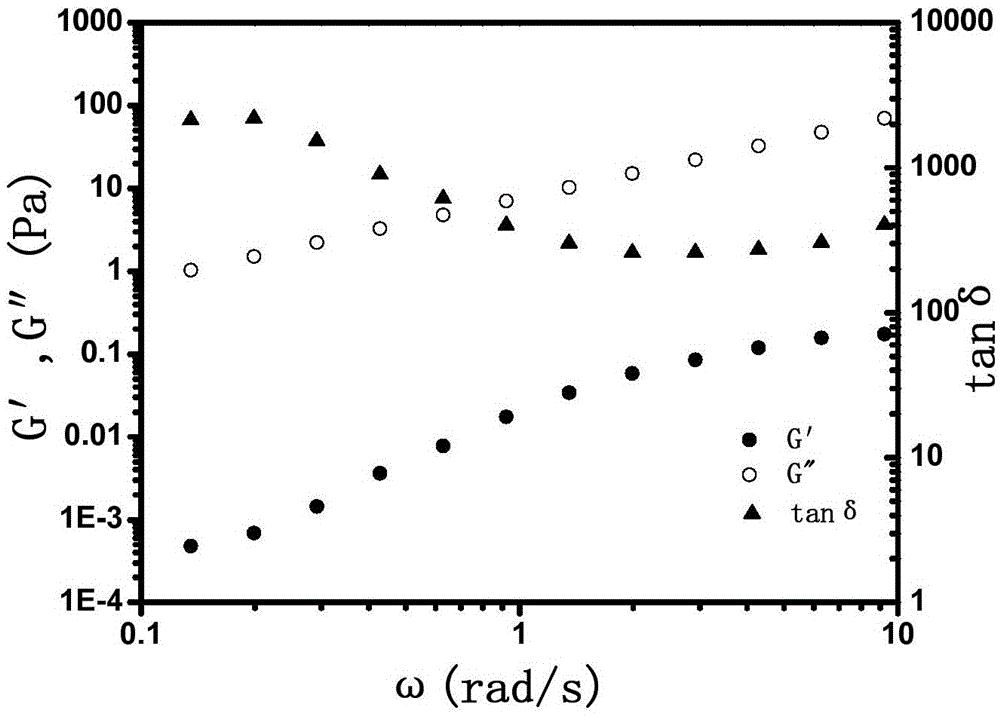
The invention discloses a honeycomb core composite structural material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material comprises a honeycomb base material, a filling material and sealing layers, wherein the filling material is embedded into the honeycomb base material; the sealing layers are positioned on the upper and lower surfaces of the honeycomb base material; the filling material is a damping material, and specifically is macromolecule fluid with viscoelasticity. Compared with a conventional damping material, the structural material successfully achieves combination of high strength and high damping property, meanwhile has the advantages of simplicity and stability of preparation process, long service life and the like, and meets the requirements of the field with special demands, such as the communication and transportation industry and the spaceflight industry.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Material testing of optical test pieces
ActiveUS20210279858A1Simple technologyEasy to detectImage enhancementImage analysisNerve networkEngineering
The invention relates to techniques for material testing of optical test pieces, for example of lenses. Angle-variable illumination, using a suitable illumination module, and / or angle-variable detection are carried out in order to create a digital contrast. The digital contrast can be, for example, a digital phase contrast. A defect detection algorithm for automated material testing based on a result image with digital contrast can be used. For example, an artificial neural network can be used.
Owner:CARL ZEISS JENA GMBH
Vibrating machine with a bearing device and method of operating a vibrating machine
ActiveUS20200300332A1Increased displacement is preventedReduce displacementSievingScreeningMachine partsAir spring
A vibrating machine including a first machine part that vibrates in operation, a second machine part connected to an installation area of the vibrating machine, and a vibratory drive. A resilient bearing is arranged between the machine parts and has at least one air spring per support point and at least one compressed air reservoir fluidically connected to the air spring. A throttle is switched intermediate the air spring and the compressed air reservoir. The first machine part bearing has a resonant or natural frequency lower than an operating frequency of the vibrating machine. The bearing system has a frequency-dependent lower stiffness level with high damping at low frequencies, an upper stiffness level with low damping at higher frequencies, and a transition zone at an intermediate transitional frequency. The throttle is dimensioned such that the transitional frequency is close to, preferably slightly above, the resonant or natural frequency.
Owner:SPALECK GMBH & CO KGAA
Tensioner for engine with large and stable damping and minimum deflection o f shaft
ActiveUS9829081B2Large and stable damping effectDamping will not be dramatically decreasedGearingThumb oppositionEngineering
A tensioner includes a base, a tension arrangement rotatable at the base, a damping member being rotated in a loading direction by the tension arrangement, and an elastic member biasing against the damping member. The position of the damping member depends by the layout geometry of the specific application and is directly in opposition to the hub load. The reaction force of the cylindrical surface of the base on the damping member is very near to the plan of the external forces represented by the hub load to minimize the deflection of the shaft. The tension arrangement is rotated to push the damping member for generating a first positive tension between the damping member and the base, and to expand the elastic member radially for generating a second positive tension between the elastic member and the damping member, so as to enhance a damping force of the tensioner.
Owner:NINGBO FENGMAO FAR EAST RUBBER
Decoupling film rigidity-variable semi-active suspension
ActiveCN105822717AReduce labor intensityIncrease productivitySpringsJet propulsion mountingSemi activeEngineering
The invention discloses a decoupling film rigidity-variable semi-active suspension. The decoupling film rigidity-variable semi-active suspension comprises a shell module, a runner module, a leather bowl, a decoupling film, a sealing piece and a driving mechanism; the shell module includes an inner core, a rubber main spring, an outer skeleton and a base; a liquid inlet hole is formed in the shell module; the inner core, the rubber main spring, the outer skeleton and the base surround an accommodating space; the runner module is positioned in the accommodating space, and is provided with a liquid passing hole and an inertia channel; an upper liquid cavity is formed between one side surface of the runner module and the rubber main spring, and is communicated with the external through the liquid inlet hole; and in order to conveniently mount and machine, the runner module can be divided into two parts: an upper runner plate and a lower runner plate. The leather bowl is positioned on one side, far from the upper liquid cavity, of the runner module; a lower liquid cavity is formed between the leather bowl and the runner module, and is communicated with the upper liquid cavity through the inertia channel; the decoupling film is positioned on one side, far from the upper liquid cavity, of the runner module; and the accommodating space is formed between the decoupling film and the runner module, and is communicated with the upper liquid cavity through the liquid passing hole. The decoupling film rigidity-variable semi-active suspension is simple in structure and convenient for use.
Owner:ASIMCO NVH TECH CO LTD ANHUI
Upright post module of fabricated building
InactiveCN112854597AImprove stabilityEasy to adjustStrutsProtective buildings/sheltersArchitectural engineeringRebar
The invention discloses an upright post module of a fabricated building. The upright post module comprises a connecting piece, a post body and baffles, wherein damping steel bars are fixedly mounted in the post body; the connecting piece is fixedly mounted at the top of the periphery of the post body; a connecting bolt is fixedly mounted between the connecting piece and the post body; connecting holes are formed in the surfaces of the two sides of the connecting piece; damping posts are fixedly mounted on the surfaces of the two sides of the post body; damping rings are arranged on the peripheries of the damping posts; and the baffles are fixedly mounted on the two sides of the damping posts. According to the upright post module, the damping and buffering effects can be provided for the baffles through the damping posts and the damping rings, the stability of the baffles is improved, when the post body is impacted, part of impact force generated by impact can be buffered through the baffles, so that the post body can be prevented from being damaged by impact, and the upright post module is very practical.
Owner:HENAN YUZHUO INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Superelastic fluid conduit for a gas turbine engine
ActiveUS9970357B2Easy to useReduce needContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion fuel flow conduitsEngineeringGuide tube
A fluid conduit for a gas turbine engine. The conduit includes a superelastic material such as TNTZ or Ti2448. The conduit is installed such that at least part of the conduit is subject to a stress which lies in one of a superelastic and a plastic region of the material in use.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Tensioner for Engine with Large and Stable Damping and Minimum Deflection o f Shaft
ActiveUS20160290448A1Large and stable damping effectDeflection of shaft is minimizedGearingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A tensioner includes a base, a tension arrangement rotatable at the base, a damping member being rotated in a loading direction by the tension arrangement, and an elastic member biasing against the damping member. The position of the damping member depends by the layout geometry of the specific application and is directly in opposition to the hub load. The reaction force of the cylindrical surface of the base on the damping member is very near to the plan of the external forces represented by the hub load to minimize the deflection of the shaft. The tension arrangement is rotated to push the damping member for generating a first positive tension between the damping member and the base, and to expand the elastic member radially for generating a second positive tension between the elastic member and the damping member, so as to enhance a damping force of the tensioner.
Owner:NINGBO FENGMAO FAR EAST RUBBER
Tensioner for engine with large and stable damping and minimum deflection of shaft
ActiveUS9982760B2Large and stable damping effectDamping will not be dramatically decreasedGearingEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:NINGBO FENGMAO FAR EAST RUBBER
A kind of shock-absorbing and noise-reducing water-based damping coating for passenger cars and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103980789BImprove the shock and noise reduction effectImprove mechanical propertiesCoatingsEmulsionWater soluble
Owner:HANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED MATERIAL BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
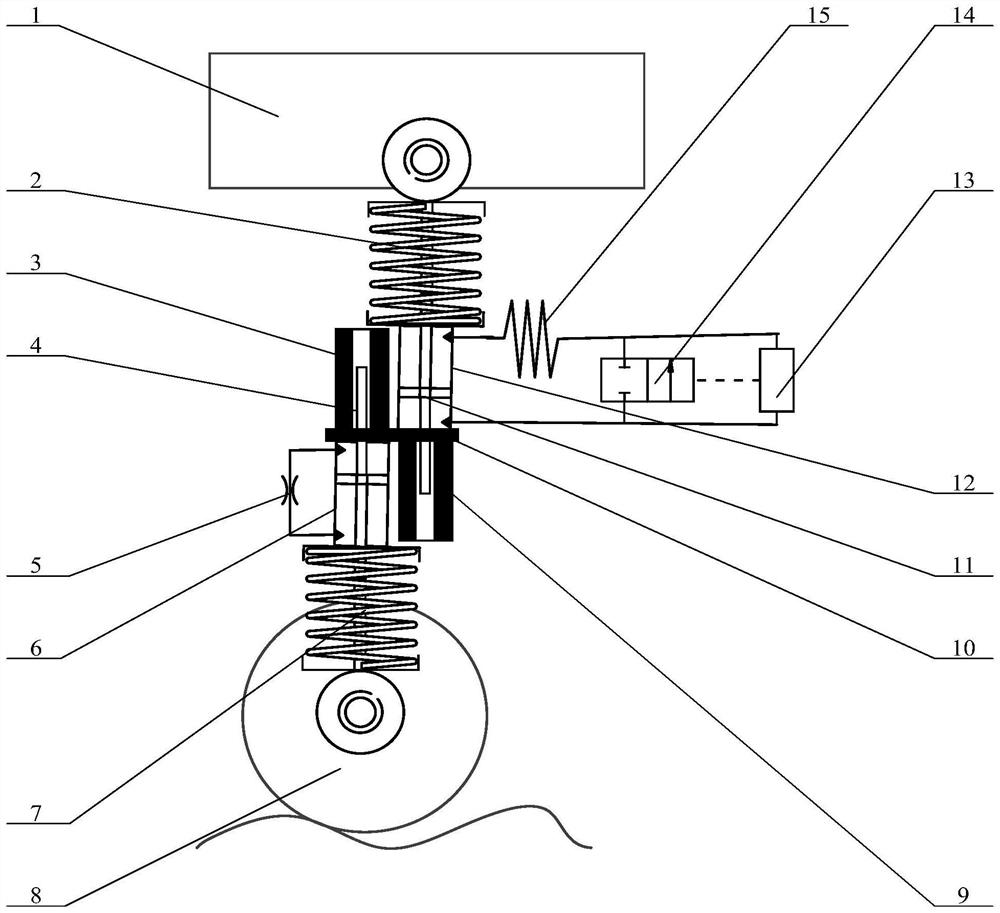
Autonomous intelligent self-energy-supply active suspension adopting double-head oil cylinder and working method of autonomous intelligent self-energy-supply active suspension
PendingCN114435053AImprove driving safetyImprove ride comfortResilient suspensionsVehicle springsDriving safetySmart control
The invention discloses an autonomous intelligent self-energy-supply active suspension adopting a double-head oil cylinder and a working method, and belongs to the field of automobiles, the autonomous intelligent self-energy-supply active suspension comprises a traditional vibration reduction structure and an anti-resonance vibration reduction structure, the anti-resonance vibration reduction structure is provided with the double-head oil cylinder, and the double-head oil cylinder is composed of a second oil cylinder arranged up and down and a second piston with piston rods at the upper end and the lower end; the upper portion of an upper oil cavity of the second oil cylinder is sequentially connected with an inerter spiral pipe, an intelligent control switch and the lower portion of a lower oil cavity of the second oil cylinder through a hydraulic pipeline, and the two ends of the intelligent control switch are connected with a normally-closed electromagnetic valve which is closed in a delayed mode in parallel. The intelligent control switch automatically changes the equal-inertial-capacity value and the equal-damping value of the anti-resonance vibration reduction structure along with changes of the vibration frequency of the automobile, when the vibration frequency of the automobile is low, large equal-inertial-capacity and equal-damping are provided to improve the driving safety, and when the vibration frequency of the automobile is high, small equal-inertial-capacity and equal-damping are provided to improve the riding comfort.
Owner:尨腾汽车科技(南京)有限公司
Scanning probe microscope with a reduced Q-factor
ActiveUS9897626B2Large dampingIncrease in in propertiesScanning probe microscopyScanning electron microscopeRelative motion
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK TNO
Vibrating machine with a bearing device and method of operating a vibrating machine
ActiveUS11268591B2Increased displacement is preventedReduce displacementSievingScreeningMachine partsAir spring
A vibrating machine including a first machine part that vibrates in operation, a second machine part connected to an installation area of the vibrating machine, and a vibratory drive. A resilient bearing is arranged between the machine parts and has at least one air spring per support point and at least one compressed air reservoir fluidically connected to the air spring. A throttle is switched intermediate the air spring and the compressed air reservoir. The first machine part bearing has a resonant or natural frequency lower than an operating frequency of the vibrating machine. The bearing system has a frequency-dependent lower stiffness level with high damping at low frequencies, an upper stiffness level with low damping at higher frequencies, and a transition zone at an intermediate transitional frequency. The throttle is dimensioned such that the transitional frequency is close to, preferably slightly above, the resonant or natural frequency.
Owner:SPALECK GMBH & CO KGAA
A kind of honeycomb sandwich composite structure material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104057658BHigh strengthIncrease dampingSynthetic resin layered productsRubber layered productsComposite constructionFilling materials
The invention discloses a honeycomb core composite structural material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material comprises a honeycomb base material, a filling material and sealing layers, wherein the filling material is embedded into the honeycomb base material; the sealing layers are positioned on the upper and lower surfaces of the honeycomb base material; the filling material is a damping material, and specifically is macromolecule fluid with viscoelasticity. Compared with a conventional damping material, the structural material successfully achieves combination of high strength and high damping property, meanwhile has the advantages of simplicity and stability of preparation process, long service life and the like, and meets the requirements of the field with special demands, such as the communication and transportation industry and the spaceflight industry.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com