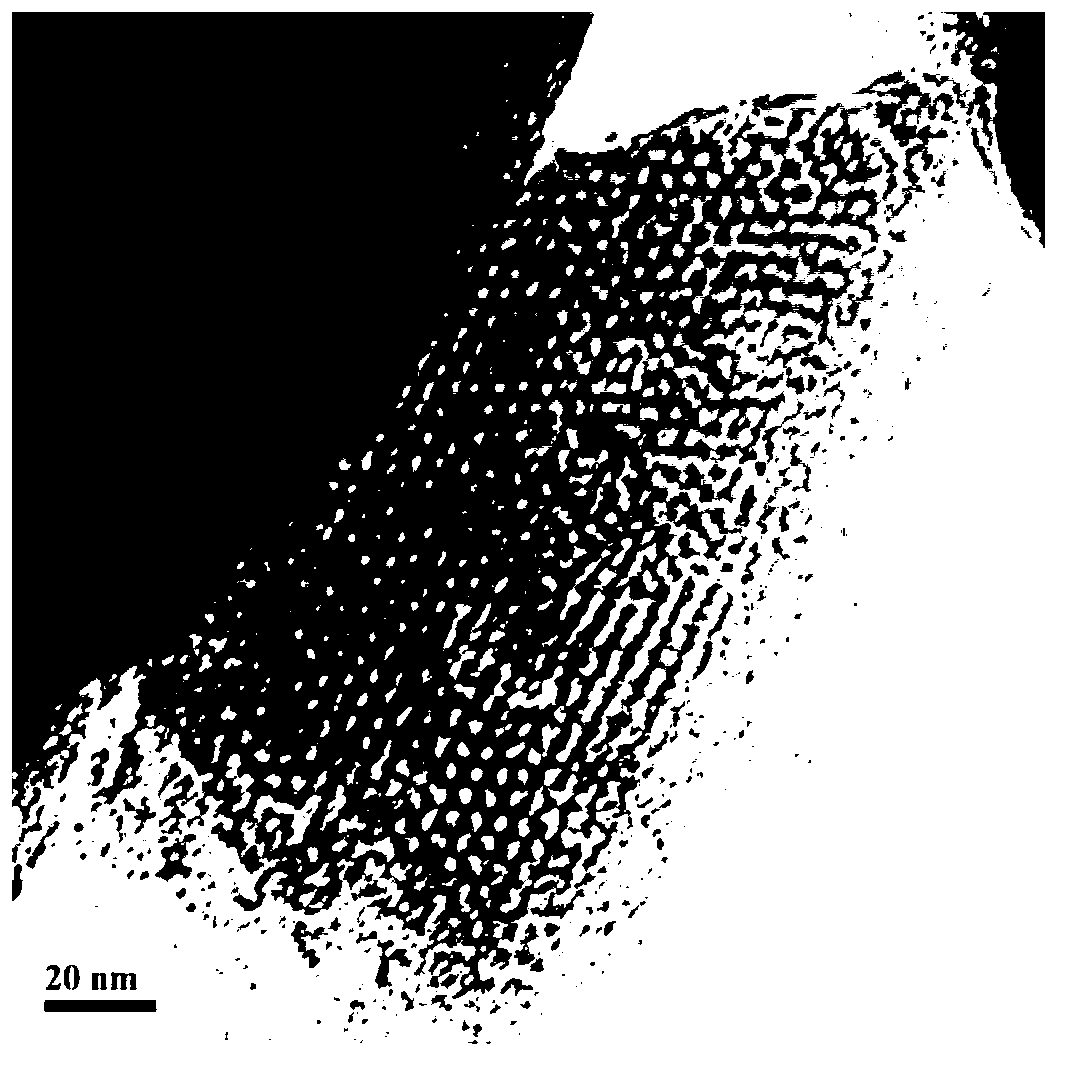
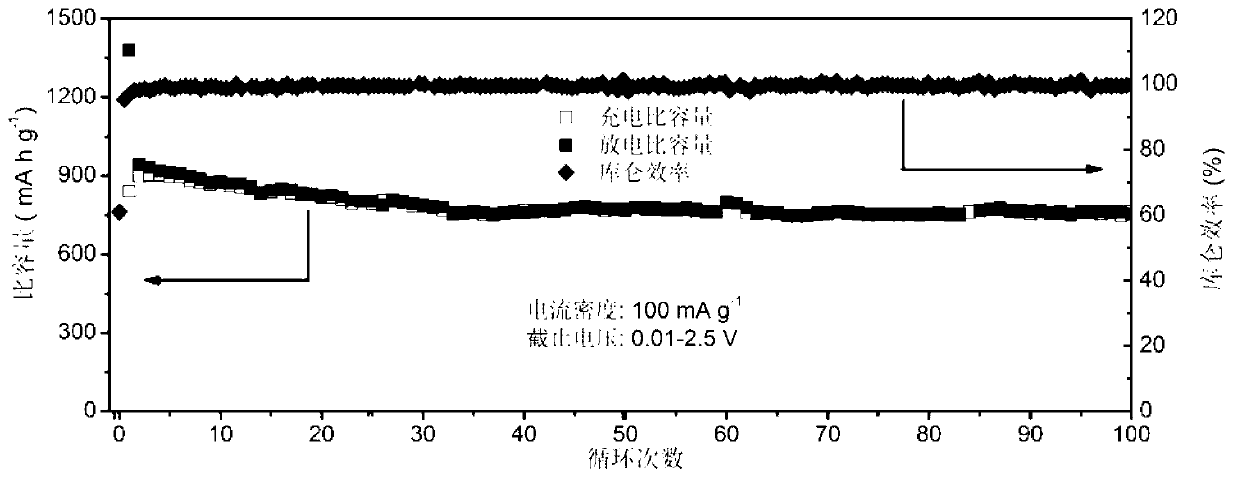
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3193 results about "Hydrothermal treatment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
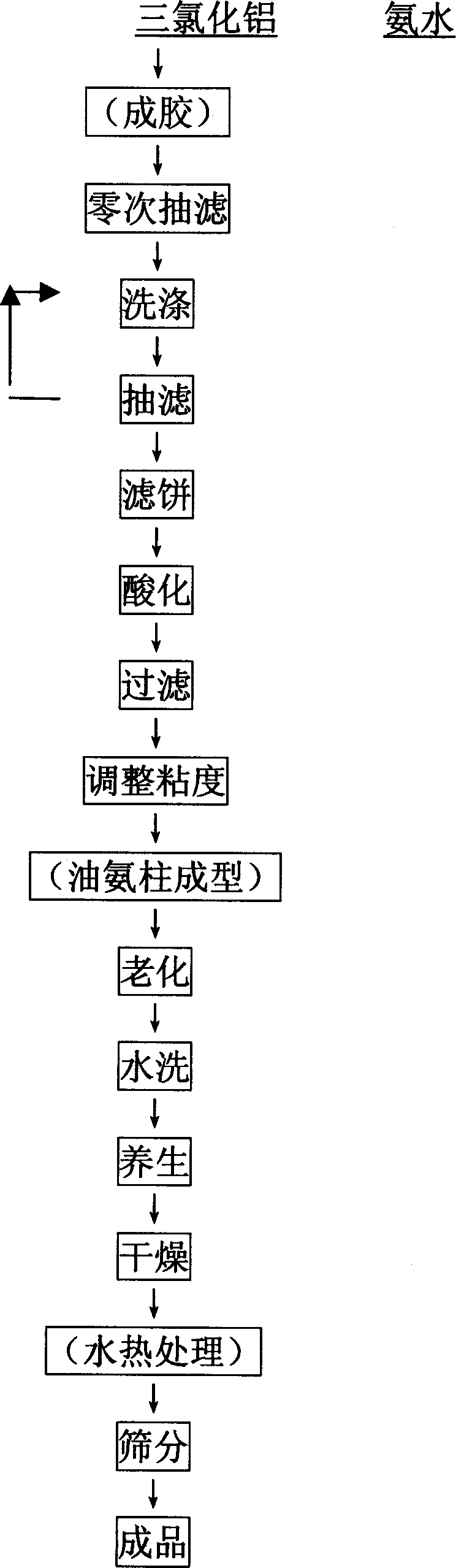
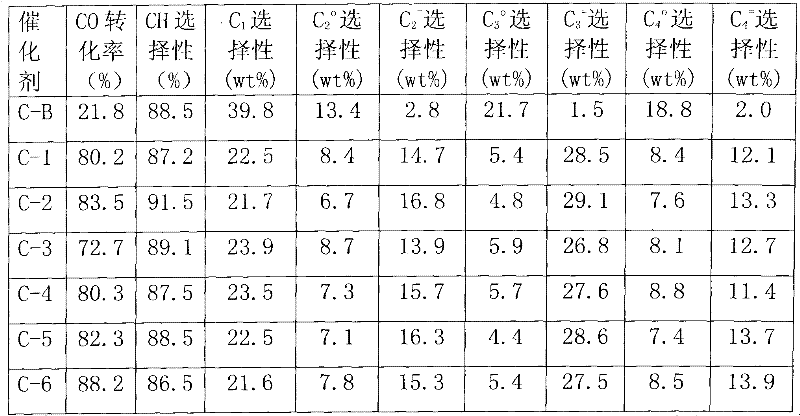
Technology Data. Our Hydrothermal Treatment is a treatment method which generates a reaction of material with high temperature and high pressure steam (Max 230℃/ 3Mph) inside the reactor. After 30 minutes of treatment, a germ free and useful output can be obtained, such as solid fuel, solid fertilizer, liquid fertilizer or livestock food.
Graphene/metal oxide composite cathode material for lithium ion battery and preparation
InactiveCN102646817APromote circulationExcellent rate performanceCell electrodesHigh energyIn situ polymerization
The invention belongs to the fields of material synthesis and energy technology, and especially relates to a graphene / metal oxide composite cathode material for lithium ion batteries and a preparation method thereof. Grapheme is dispersed into various metal oxide precursor salt solutions; a graphene / metal oxide compound is obtained directly by a hydrothermal method, or an graphene / metal oxide compound is obtained by a liquid in-situ polymerization method or a coprecipitation process; and the graphene / metal oxide compound is obtained by heat treatment or hydrothermal treatment. In the invention, the novel three-dimensional composite cathode material of graphene-coated metal oxide or graphene-anchored metal oxide is prepared by carrying metal oxide particles with graphene as a carrier. The obtained composite material can be used as a lithium ion battery cathode, which has a high specific capacity, excellent cycle stability and rate capability, and is expected to be used as a lithium ion battery cathode material with a high energy density and a high power density.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tubular titanium oxide particles, method for preparing the same, and use of the same
InactiveUS20040265587A1Large specific surface areaImprove detection accuracyMaterial nanotechnologyLight-sensitive devicesReduction treatmentSorbent
The process for preparing tubular titanium oxide particles comprises subjecting a water dispersion sol, which is obtained by dispersing (i) titanium oxide particles and / or (ii) titanium oxide type composite oxide particles comprising titanium oxide and an oxide other than titanium oxide in water, said particles having an average particle diameter of 2 to 100 nm, to hydrothermal treatment in the presence of an alkali metal hydroxide. After the hydrothermal treatment, reduction treatment (including nitriding treatment) may be carried out. The tubular titanium oxide particles obtained in this process are useful as catalysts, catalyst carriers, adsorbents, photocatalysts, decorative materials, optical materials and photoelectric conversion materials. Especially when the particles are used for semiconductor films for photovoltaic cells or photocatalysts, prominently excellent effects are exhibited.
Owner:JGC CATALYSTS & CHEM LTD
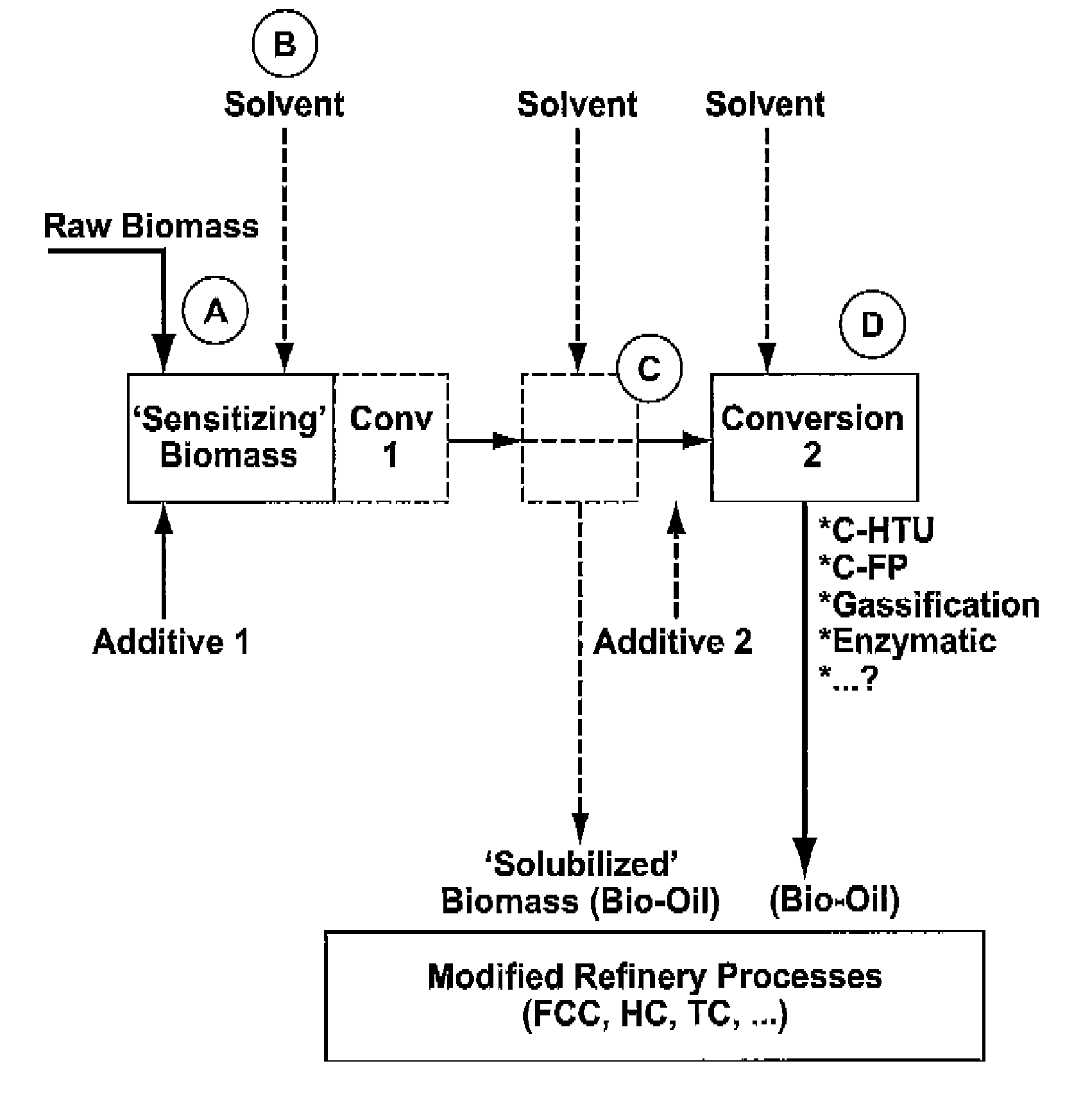
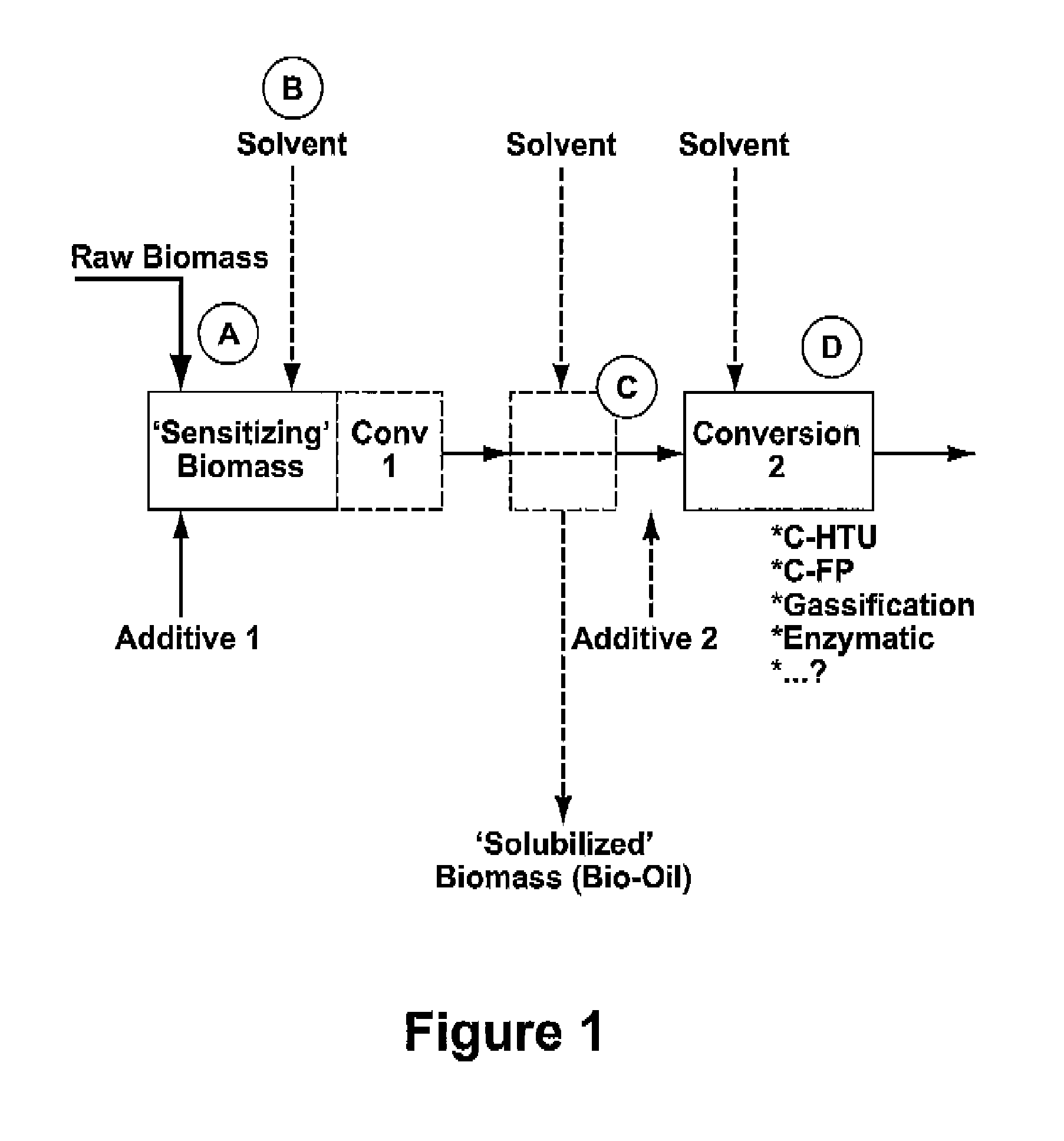
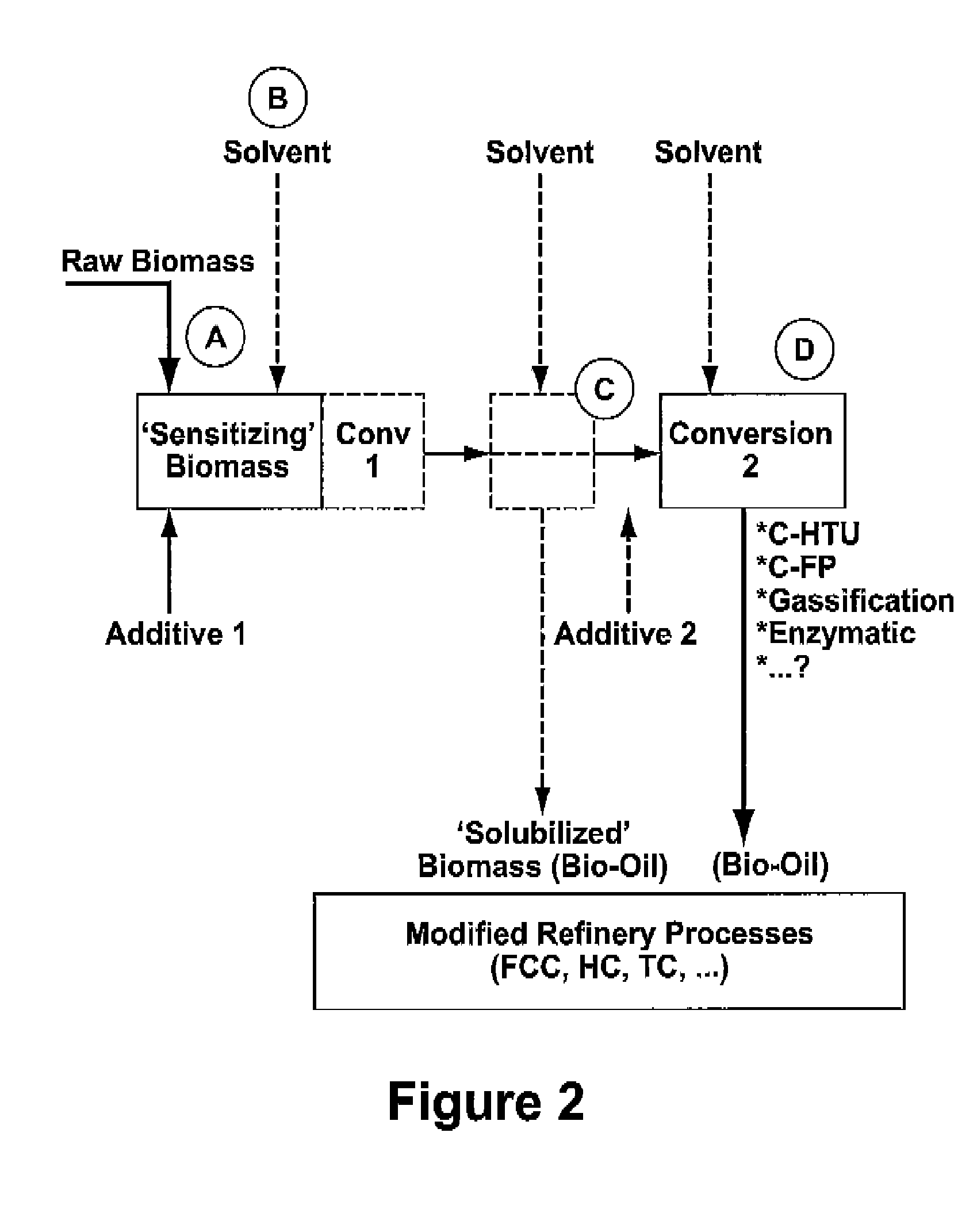
Process for the conversion of biomass to liquid fuels and specialty chemicals
Disclosed is a hydrothermal treatment process for conversion of a carbon-based energy carrier material. The process comprises a step for sensitizing or activating the carbon based energy carrier material to increase its susceptibility to hydrothermal conversion. As a result of the sensitization step, the hydrothermal conversion step itself may be carried out under relatively mild conditions.The process comprises the steps of sensitizing the carbon-based energy carrier material to increase its susceptibility to hydrothermal conversion; and subjecting the sensitized carbon-based energy carrier material to hydrothermal conversion at a temperature of less than 300 degrees centigrade in a hydrothermal treatment reactor.
Owner:MARD INC
NaY-type molecular sieves and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101722023AOrderly formationOrderly and stableMolecular sieve catalystsFaujasite aluminosilicate zeoliteMolecular sieveThermal stability
The invention discloses microcrystal NaY-type molecular sieves and a preparation method thereof. In the microcrystal NaY-type molecular sieves, the molar ratio of SiO2 to Al2O3 is 4.0 to 6.0, and the average particle size is 100 to 700 nanometers. The microcrystal NaY-type molecular sieves are prepared by a method combining low-temperature synthesis directing agent, low-temperature synthesis gel and two-stage variable-temperature dynamic crystallization. The NaY-type molecular sieves have a relative crystallinity of over 80 percent after being roasted in the air at 600 DEG C for 3 hours or after undergoing hydrothermal treatment with vapor at 650 DEG C for 1 hour, as well as high thermostability and hydrothermal stability.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Prepn process of hyperastable Y-type RE molecular sieve
InactiveCN1436728AExcellent anti-vanadium effectMolecular sieve catalystsFaujasite aluminosilicate zeoliteRare earthHigh activity
The present invention relates to the preparation of hyperstable Y-type RE molecular sieve for the catalytic cracking of heavy oil and containnig vanadium resisting component. The preparation uses NaY-type molecular sieve as main material and chemical aluminum-eliminating complex containing oxalic acid and / or oxalate and its mixture and through introducing RE ion in the late stage of chemical aluminum elimination reaction to from RE precipitate and hydrothermal treatment to realize hyperstabilizing and introduce RE ion and independent phase Re oxide. The formed precipitate RE precursor includes RE oxalate. Compared with conventional REY, REHY and REUSY, the molecular sieve preparing process is simple and high in RE utilization, and has homogeneously distributed aluminum, more secondary pores high hydrothermal stability, high activity and high vanadium contamination resisting capacity.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Hydrodewaxing catalyst and its preparation method
ActiveCN102451748AImprove the effect of impurity removalInhibit carbon depositionMolecular sieve catalystsRefining to eliminate hetero atomsImpurityChemistry
The invention discloses a hydrodewaxing catalyst and its preparation method. With the weight of the catalyst as the reference, the catalyst contains the following components of: by weight, 5-10% of tungsten oxide, 1-5% of nickel oxide, 40-50% of nanometer ZSM-5 molecular sieve, 10-40% of macroporous alumina and the balance being a binder. The catalyst is prepared by the following steps of: firstly kneading the nanometer ZSM-5 molecular sieve, macroporous alumina and the binder to prepare a carrier, dipping loaded active metal, and finally carrying out hydrothermal treatment. The hydrodewaxing catalyst provided by the invention has a good shape-selective catalysis function and simultaneously has a good hydrofinishing function, and is especially suitable for the hydrofinishing and pour point reduction processes of a waxy hydrocarbon oil material containing high content of impurities such as sulfur, nitrogen and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for preparing mesoporous silica molecular sieve fiber
InactiveCN101387019AIncrease the areaIncrease the apertureInorganic material artificial filamentsMolecular-sieve and base-exchange compoundsFiberNanowire
The present invention discloses a method for preparing a wide aperture mesoporous silica molecular sieve fiber. An industrialized nonionics or cationic surfactant is adopted as a template. An organic or inorganic silicon source is adopted as a precursor. In the state where various auxiliary reagents, such as inorganic salt, alcohol and the like, are added, the fiber is synthesized through the cooperative assembly between a surface active agent and inorganic species and a hydrothermal treatment process. The mesoporous silica molecular sieve fiber is between 3 and 20 nm in aperture, between 0.3 and 2.5 cm^3 / g in pore volume, and between 600 and 1200 cm^2 / g in specific area. The material is easy to obtain, the technical requirements are comparatively simple, and the operation is feasible. The method has a very wide application range in terms of the preparation of composite fortifying fiber and semiconductor porous nanometer tube and nanometer wire in the fields of nanometer microelectrode and aviation material.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Method for preparing fewer-layer graphene on basis of biomass waste
ActiveCN105060289AReduce pollutionAbundant and easy-to-obtain raw materialsCarbon layerArgon atmosphere
The invention discloses a method for preparing fewer-layer graphene on the basis of biomass waste, which comprises the following steps: carrying out hydrothermal treatment on the biomass waste, and carrying out carbonization by heating and calcination, thereby obtaining a carbonization material; immersing the carbonization material in an acid solution to remove impurities, thereby obtaining biomass carbon; and quickly heating the biomass carbon in an argon atmosphere, and carrying out high-temperature graphitization to obtain the biomass fewer-layer graphene. The hydrothermal process is combined with the high-temperature graphitization to directly strip the biomass waste, and the carbonization and high-temperature graphitization are carried out. Thus, the prepared biomass fewer-layer graphene has the advantages of fewer layers (2-10 layers), fewer defects, fewer oxy groups, high electric conductivity and small carbon layer interval. The method is simple to operate, has the advantages of low cost and high graphene yield, and can easily implement industrialized large-scale production. The prepared biomass fewer-layer graphene can be used in the fields of lithium ion batteries, supercapacitors and the like, is beneficial to green production of battery industry, and has important practical value and favorable application prospects.
Owner:湖南宸宇富基新能源科技有限公司
Preparation method for multi-hole carbon nitride photocatalytic material doped with sulphur
InactiveCN103861632AReduce pollutionGood repeatabilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionSurface-active agentsSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method for a multi-hole carbon nitride photocatalytic material doped with sulphur, belonging to the technical field of synthesis of photocatalytic materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps of preparing a super-molecule polymer through simple hydro-thermal treatment by taking melamine and trithiocyanuric acid as a raw material and taking water as a solvent, and burning in an inert atmosphere so as to obtain a three-dimensional network sulphur-doped multi-hole carbon nitride photocatalytic material. The preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages that simplicity and easiness in preparation are achieved, a method for burning a super-molecule polymer is adopted, any template agent and a surface active agent do not need to be added, a reaction system is simplified, the cost is low, the pollution of a reagent is slight, the reaction repeatability is good, a preparation condition is mild, the time consumption of a synthetic process is short, and the requirement on equipment is high; the multi-hole carbon nitride photocatalytic material doped with sulphur has excellent catalytic activity in a catalyzing hydrogen production reaction, and the hydrogen production rate of the material is 8.3 times and 5.2times that of a product obtained by burning melamine and trithiocyanuric acid under the same condition.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Preparation method of double-hole-structure alumina supporter
ActiveCN102861617ALarge hole volumeNo overheating phenomenonCatalyst carriersMaterials scienceAmmonium bicarbonate
The invention discloses a preparation method of a double-hole-structure alumina supporter. The preparation method comprises the steps of weighing a certain quantity of pseudo-boehmite dry glue powders, evenly mixing the pseudo-boehmite dry glue powder with a certain quantity of peptizing agent and extrusion-auxiliary agent, then adding a certain quantity of ammonium bicarbonate aqueous solution in materials, mixing and nipping obtained materials into a plasticizer, squeezing into stripes and molding, placing molded materials in a sealing container, and roasting to prepare the alumina supporter after hydro-thermal treatment. The temperature of the hydro-thermal treatment is 70-120 DEG C, and the treatment time is 5-10 hours. Roasting is carried out at the temperature of 600-750 DEG C for 2-4 hours. The mass concentration of an ammonium bicarbonate solution is 40%-80%, the adding quantity of the ammonium bicarbonate solution is calculated according to NH<4+> and Al<3+>, and a molar ratio of the NH<4+> to Al<3+> is (0.5-1):1. According to the preparation method, the preparation procedure is simple, the prepared alumina supporter is in double-hole distribution and has good mechanical strength, and the preparation method is suitable to the field of preparation of heavy oil and residual oil hydrodemetallization catalysts and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Hydrocracking catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103100417AHigh selectivityLarge freezing pointMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon oil crackingAlkaneMolecular sieve
The invention discloses a hydrocracking catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The hydrocracking catalyst comprises: a carrier composed of a modified beta molecular sieve, a modified Y type molecular sieve and alumina, and hydrogenation active metal components. Specifically, the modified beta molecular sieve is prepared by: subjecting a crystallized beta molecular sieve slurry directly to ammonium exchange and a template agent removal treatment, then first conducting a hydrothermal treatment, and performing an aluminum salt solution treatment, under the condition of maintaining a high beta molecular sieve crystallinity, removing part of non-framework aluminum uniformly, thus obtaining the beta molecular sieve with the characteristics of high Si / Al ratio, large specific surface area, appropriate acidity and acid distribution, and reasonable structure, etc. The modified beta molecular sieve especially has a suitable cracking effect and a very good isomerization effect on long-chain alkane and the long side chain alkyl of aromatic hydrocarbon and cyclane, and has a synergistic effect with the Y type molecular sieve, so that the hydrocracking catalyst can have very high catalytic activity and middle distillate selectivity. And the condensation point of diesel fraction is substantially reduced, and the product properties of middle distillate are improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
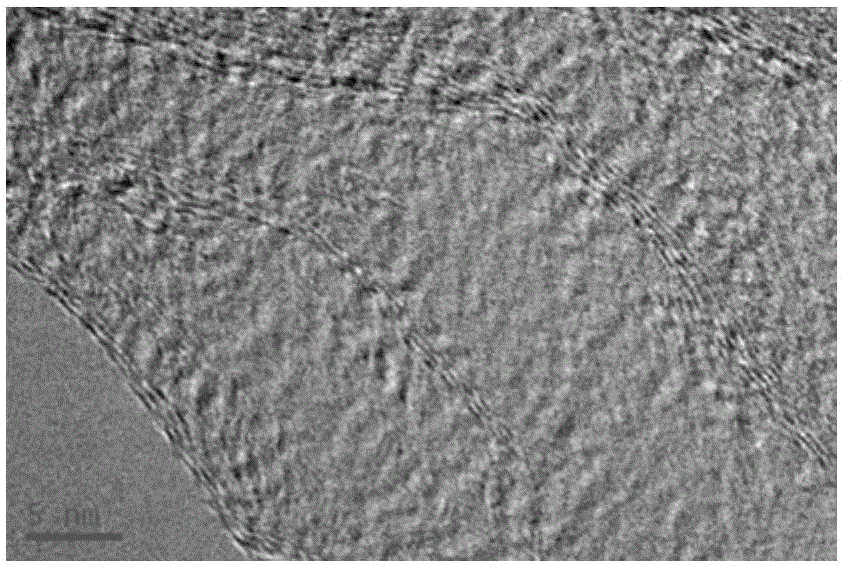
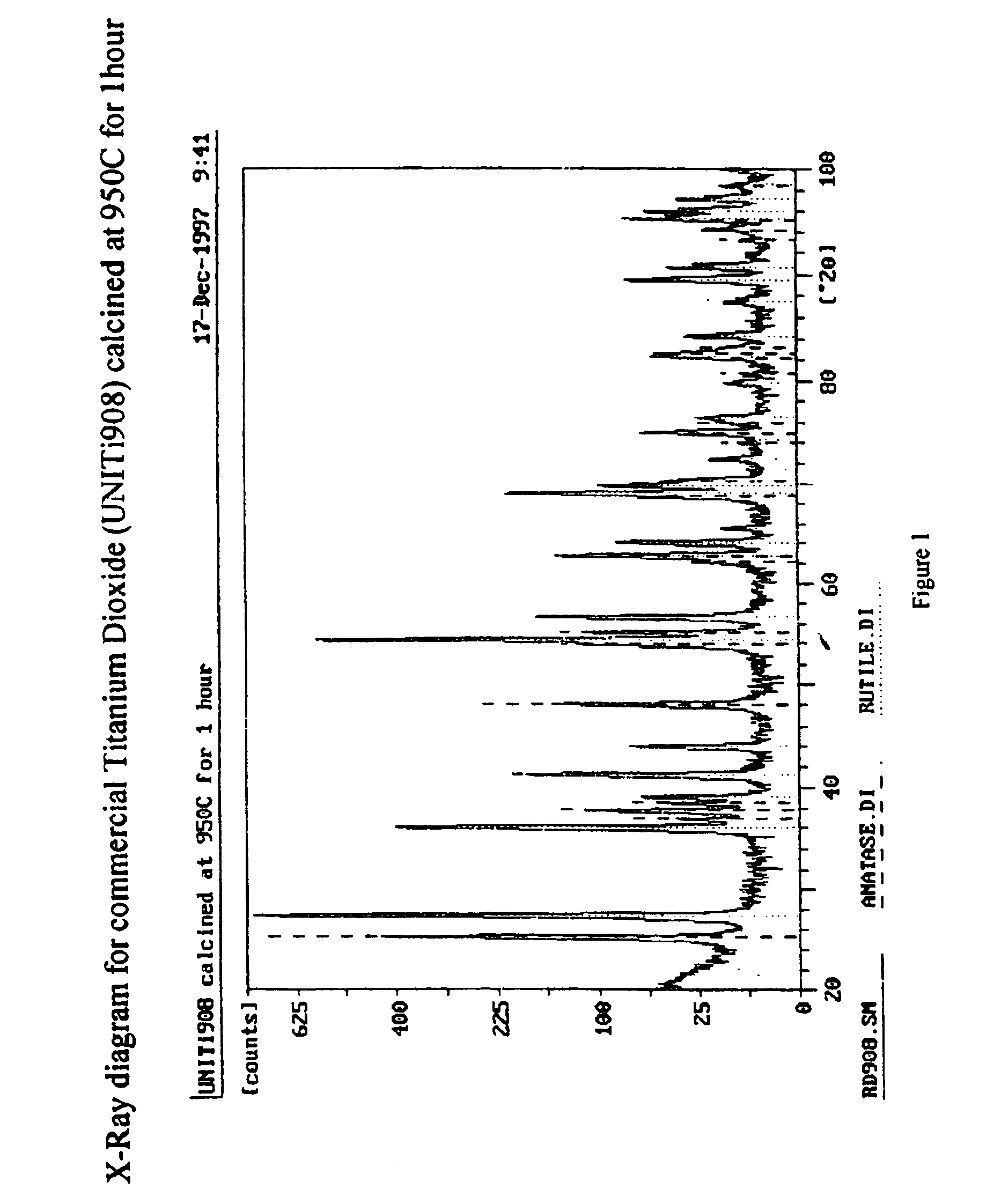
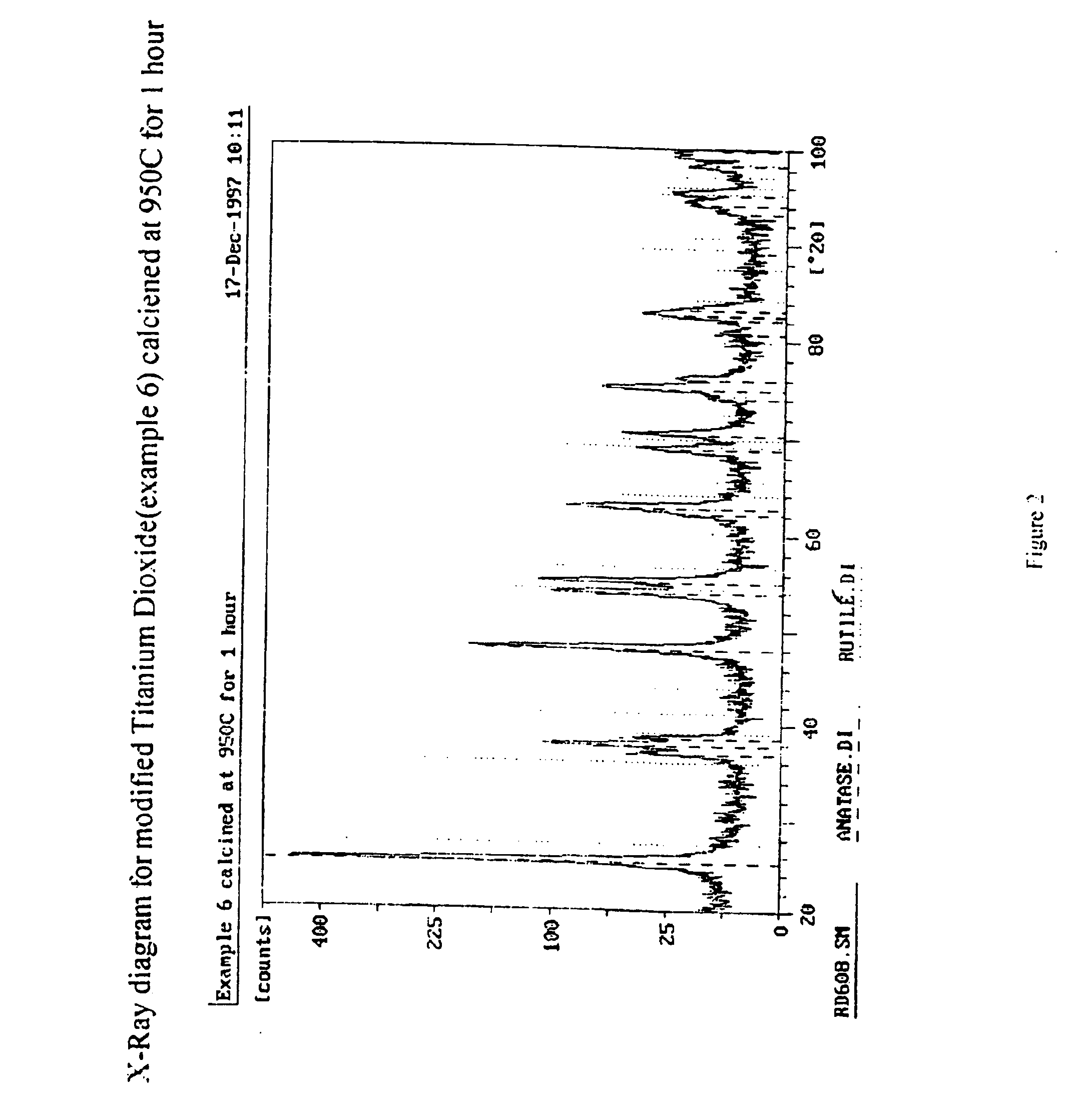
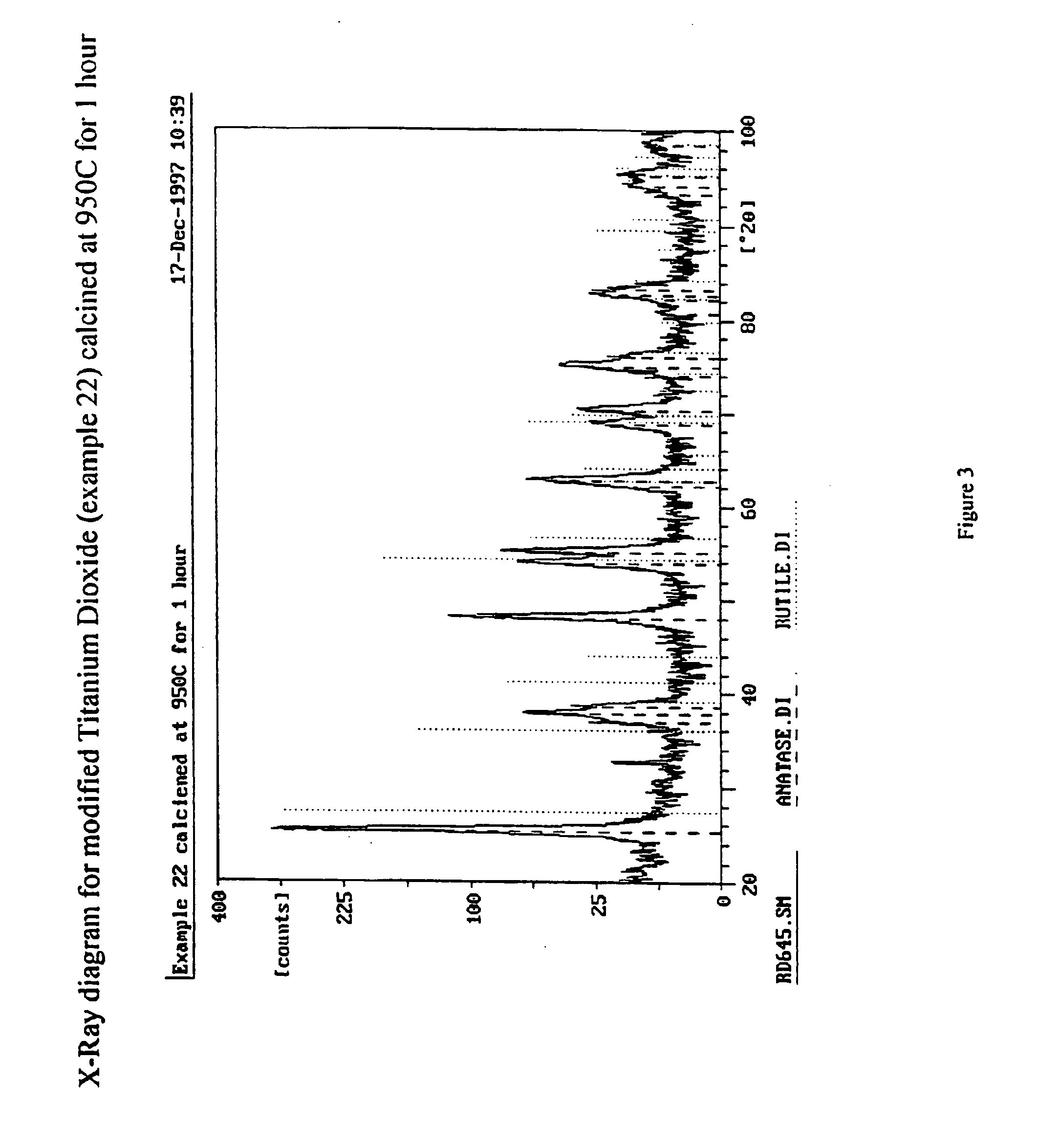
Modified titanium dioxide and a method for its preparation
The invention relates to a composite material comprising silicon and titanium dioxide characterized by an enhanced thermal and hydrothermal stability of the pore structure. The composite is obtainable by precipitating titanium hydroxide from an aqueous solution containing sulfate salts and urea, followed by an hydrothermal treatment in the mother liquor, and by reacting the precipitate with a basic silica sol. The composite has a specific surface area of up to 228 m2 / g for a material calcined at 800° C. for 3 hours, and is suitable for catalyzing a variety of reactions, including Claus reaction and degradation of organic impurities.
Owner:ROTEM AMFERT NEGEV
Preparation method of brain-coral-shaped birnessite type manganese dioxide
InactiveCN102120619AImprove structural stabilityShape unchangedNanotechnologyManganese oxides/hydroxidesStructural stabilityPotassium permanganate
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIV
Straight chain paraffin dehydrogenation catalyst carrier production process
InactiveCN1579616AAdapt to the needs of dehydrogenation catalytic reactionImprove stabilityCatalyst carriersAluminium oxides/hydroxidesAlkaneDehydrogenation
The invention relates to linear alkanes dehydrogenation catalyst carrier technics used in petrochemical industry. Its aperture distribution can be adjusted through producing macroporous alumina globule. Then add surface active agent in globule dropping process. Finally conduct hydrothermal treatment in supporter producing process. On base of self-research, globule dropping technics is designed by self to make product cost reduce remarkably. Using self produced macroporous alumina dropping globule, side pressure intensity of alumina globule can reach more than 20N per grain. Using self-researched macroporous gamma-Al2O3 with binocular construction, reaction performance of linear alkanes dehydrogenation catalyst can reach conversion>12-13 percent and selectivity>90 percent. Compared with international like products, its stability is better.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Method for preparing low-carbon olefin catalyst by high-activity-stability carrier-type iron-based synthetic gas
ActiveCN102441384AHigh activityHigh selectivityHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesCatalyst activation/preparationWater vaporActive component
The invention discloses a method for preparing a low-carbon olefin catalyst by high-activity-stability carrier-type iron-based synthetic gas. Silica gel is taken as a carrier, and a metal promoter and an active component Fe are loaded by adopting an immersion method, wherein the used silica gel carrier is firstly subjected to hydrothermal treatment, and the condition for the hydrothermal treatment is that 50%-100% water vapor is used for carrying out the hydrothermal treatment for 0.5-20h at the temperature of 150-600 DEG C. After the silica gel carrier used in the method disclosed by the invention is subjected to the hydrothermal treatment, the strong interaction between the carrier and the active component is overcome, and thus, the activity and the selectivity of the catalyst are improved. The catalyst prepared by the method disclosed by the invention is applicable to the reacting processes of preparing the low-carbon olefins, such as ethylene, propylene, butylene and the like, from the synthetic gas.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
High molecule polymer template synthetic composite hole zeolite molecular sieve and its preparing method
InactiveCN1749162AHigh catalytic activityCrystalline aluminosilicate zeolitesCalcinationHeat treated
The present invention relates to inorganic chemistry, physical chemistry and catalytic chemistry technology. The present invention prepares composite pore zeolite molecular sieve with common silicon source, aluminum source and hybrid metal atom source, and through hydrothermal treatment and calcinations process. In the hydrothermal treatment, material powder is prepared with composite template of mixture comprising quaternary ammonium salt polymer and organic amine or organic quaternary ammonium salt, or template of quaternary ammonium salt polymer. The hydrothermal treatment is in 100-180 deg c and has setting time of 1-7 days. The prepared molecular sieve m is then calcined at 300-800 deg c for 0.5-24 hr to obtain opened channels. The prepared molecular sieve has composite pore structure and high catalytic activity, and may have various metal atoms introduced. The prepared molecular sieve may be used widely as adsorbent, catalyst and catalyst carrier.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Preparation method of mesoporous-microporous composite molecular sieve
ActiveCN103100399ALarge hole volumeLarge specific surface areaMolecular sieve catalystsFaujasite aluminosilicate zeoliteMolecular sieveFiltration
The invention discloses a preparation method of a mesoporous-microporous composite molecular sieve. The preparation method comprises the following steps of adding a microporous molecular sieve subjected to hydrothermal treatment into a mixed system of a silicon source, an acid solution and a surfactant, then carrying out crystallization, filtration and washing, and then carrying out drying and calcination to obtain the mesoporous-microporous composite molecular sieve. The preparation method fully utilizes non-framework aluminum falling from the microporous molecular sieve, avoids an aluminum source used by the conventional molecular sieve preparation technology, is conducive to improvement of a silica-alumina ratio of the mesoporous-microporous composite molecular sieve, realizes a high degree of crystallization, and improves hydrothermal stability and thermostability of the mesoporous-microporous composite molecular sieve. The mesoporous-microporous composite molecular sieve is suitable for the field of macromolecule catalysis, is conducive to improvement of a reaction conversion ratio and reaction selectivity, and is especially suitable for being used in a cracking catalyst for maximum-degree production of middle distillate from heavy oil as a raw material.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Preparation method and application of nitrogen-doped starch-based activated carbon microsphere material
ActiveCN105948045AMicrostructure is easy to controlGood dispersionHybrid capacitor electrodesDispersityMicrosphere
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a nitrogen-doped starch-based activated carbon microsphere material. The nitrogen-doped starch-based activated carbon microsphere material is prepared by taking starch as the carbon source and taking a nitrogen-containing compound as the nitrogen source through the steps of gelatinization, hydrothermal treatment, carbonization, activation and the like. The diameters of prepared carbon microspheres range from 0.5 micrometer to 10 micrometers, the particle size is controllable, the dispersity is good, the specific surface area ranges from 1,000 m<2> / g to 3,000 m<2> / g, and the nitrogen content ranges from 0.2% to 15%. The prepared material relates to the application fields of electrochemical energy storage, adsorption separation, catalyst carriers, drug carriers and the like and is particularly applicable to electrochemical energy storage. Green biomass is adopted as the carbon source, sources are wide, the price is low, and the preparation technology is simple, easy to control, environmentally friendly and suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Bismuth vanadate powder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101318700AHigh activityImprove visible light absorptionVanadium compoundsBismuth compoundsBismuth vanadateIon exchange
The invention discloses bismuth vanadate powder and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, bismuth-bearing compounds and vanadium-bearing compounds are respectively dissolved in a nitric acid, mixed and then added with a hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide solution, the mol ratio of bismuth to vanadium to the nitric acid to hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide is 1 to 1 to 2.5 to 0.025, and the mixture is stirred for 1 to 2 hours by magnetic force so as to form a bismuth vanadate precursor; the bismuth vanadate precursor is placed in a reaction kettle, undergoes hydrothermal treatment for 70 to 75 hours at a temperature of between 80 and 200 DEG C, cooled, centrifugally separated, and then added with a saturated sodium chloride solution of anhydrous ethanol and deionized water; ion-exchange is performed after the bismuth vanadate precursor is completely immersed, and then centrifugal separation is performed; and finally the bismuth vanadate precursor is washed for 3 to 5 times by mixture of the deionized water and ethanol, then the bismuth vanadate powder with microspheric and / or micro-flaky particles is prepared. The method has simple operation and mild conditions; and bismuth vanadate powder particles prepared are uniform, have large specific surface area, have the characteristics of good visible light response and high photocatalytic activity, and are suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Zeolite catalyst with improved NOX reduction in SCR
InactiveUS20070134146A1Improved selective catalytic reductionImprove performanceNitrous oxide captureAluminium compoundsIon exchangeLow sodium
The present invention is directed to a novel metal-promoted zeolite catalyst, a method of producing the catalyst and a method of using the catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with improved hydrothermal durability. The novel metal-promoted zeolite is formed from a low sodium zeolite and is hydrothermally treated after metal ion-exchange.
Owner:BASF CORP
Process for slurry phase hydroconversion of heavy hydrocarbon feeds and/or coal using a supported catalyst
InactiveUS20080149531A1Catalyst activation/preparationHydrocarbon oil crackingSlurry reactorSpherical shaped
The invention concerns a process for converting heavy feeds carried out in a slurry reactor in the presence of hydrogen and in the presence of a catalyst comprising at least one catalytic metal or a compound of a catalytic metal from group VIB and / or VIII supported on alumina, the pore structure of which is composed of a plurality of juxtaposed agglomerates each formed by a plurality of acicular platelets, the platelets of each agglomerate being generally radially oriented with respect to the others and with respect to the centre of the agglomerate, said catalyst having an irregular and non-spherical shape and being mainly in the form of fragments, obtained using a process including the following steps:a) granulation starting from an active alumina powder having a low crystallinity and / or amorphous structure, to obtain agglomerates in the form of beads;b) maturing in a moist atmosphere between 60° C. and 100° C. then drying said beads;c) sieving to recover a fraction of said beads;d) crushing said fraction;e) calcining at least a portion of said crushed fraction at a temperature in the range 250° C. to 900° C.;f) impregnating with acid and hydrothermal treatment at a temperature in the range 80° C. to 250° C.;g) drying then calcining at a temperature in the range 500° C. to 1100° C.h) depositing at least one catalytic metal or compound of a catalytic metal from group VIB and / or group VIII by impregnation.The process of the invention employs a catalyst with a specific pore texture, shape and granulometry, resulting in improved performances.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Preparation method for photocatalytic material with strong adsorption and high visible light degradation of performance
The invention discloses a gahnitem, zinc oxide and nickel zinc nano-composite photocatalytic material which has a high specific surface area and a mesoporous structure and is prepared by roasting at high temperature by taking ternary hydrotalcite as a precursor. The material is used for the adsorption and the degradation of organic pollutants. The photocatalytic material is prepared by taking zinc nitrate, nickel nitrate, aluminum nitrate, sodium carbonate, sodium hydroxide and the like as raw materials; preparing the raw materials into salt solutions and alkali solutions respectively; mixing the solutions by using a constant-flow pump at the temperature of 80 DEGC with magnetic stirring, transferring the mixed solution into a hydrothermal reaction kettle; performing hydrothermal treatment at 130 to 180 DEG C; performing suction filtration, washing and drying to the precursor; roasting the precursor in Muffle furnace for 2 to 6 hours at the temperature of 400 to 600 DEG C to obtain the product, wherein the specific surface area is greater than 150 m<2>.g<-1>. The photocatalyst disclosed by the invention has regular shape, large specific surface area, and super-high capacity for adsorbing and degrading organics, and can be reused; the raw materials for preparing the composite photocatalyst are abundant, the cost is low, and the process is simple.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method of hierarchical porous titanium silicon molecular sieve
ActiveCN106145149AHigh crystallinityAdjustable hole structureCrystalline aluminosilicate zeolitesMolecular sieveTitanium
The invention discloses a method for preparing a multi-level porous titanium-silicon molecular sieve, which comprises the following steps: (1) After mixing the silicon source, the structure-directing agent, the titanium source and water uniformly in a certain proportion, directly adding a silylating agent or first After pre-crystallization, a silylating agent is added to obtain a reaction mixture containing a silylating agent; (2) the reaction mixture containing a silylating agent is crystallized under certain conditions in a pressure-resistant airtight container, and then recovered to obtain a crystallized product; (3) the recovered crystallized product is roasted and then treated with alkali to obtain an alkaline mixture; (4) the alkaline mixture is hydrothermally treated in a pressure-resistant airtight container, and the product is recovered. The hierarchically porous titanium-silicon molecular sieve obtained by the technical scheme has the advantages of high crystallinity, high macromolecular reactivity and selectivity, and adjustable pore structure.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
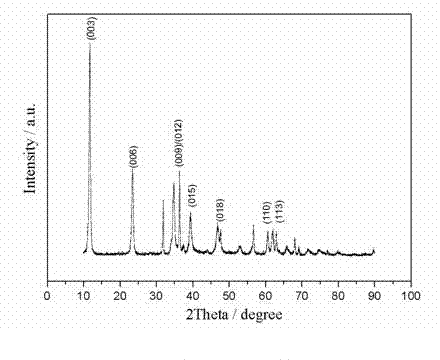
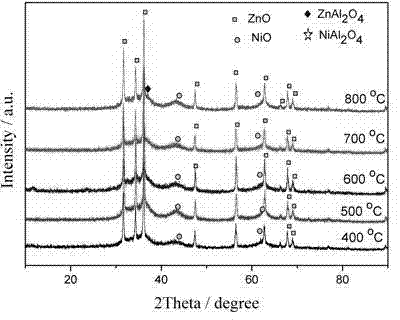
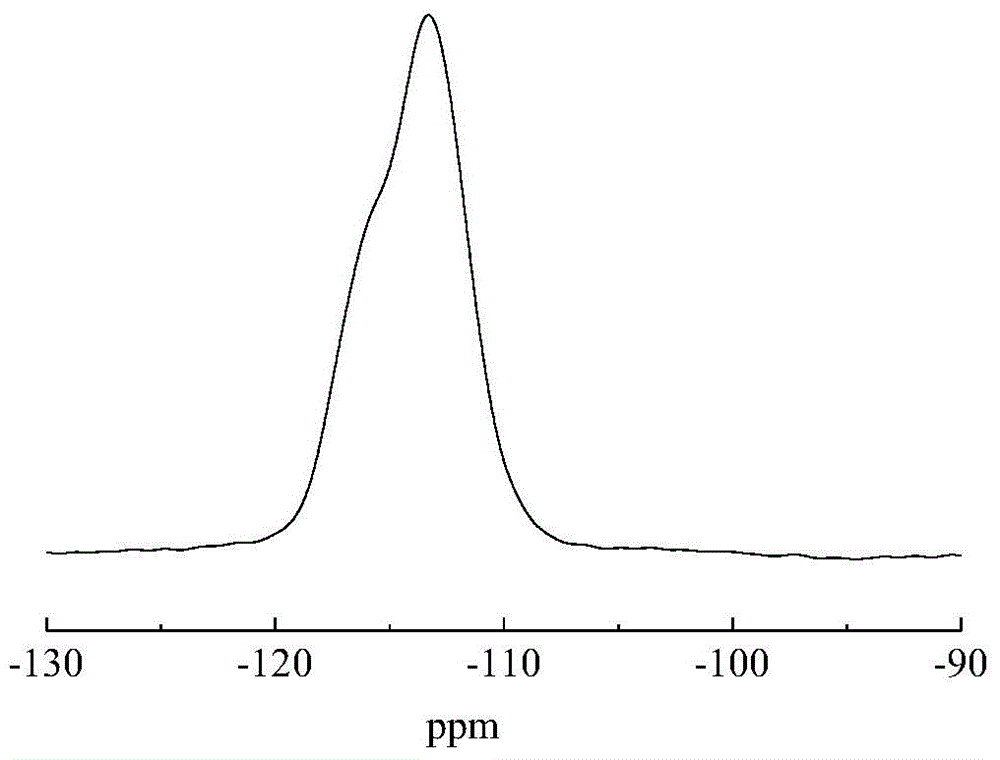
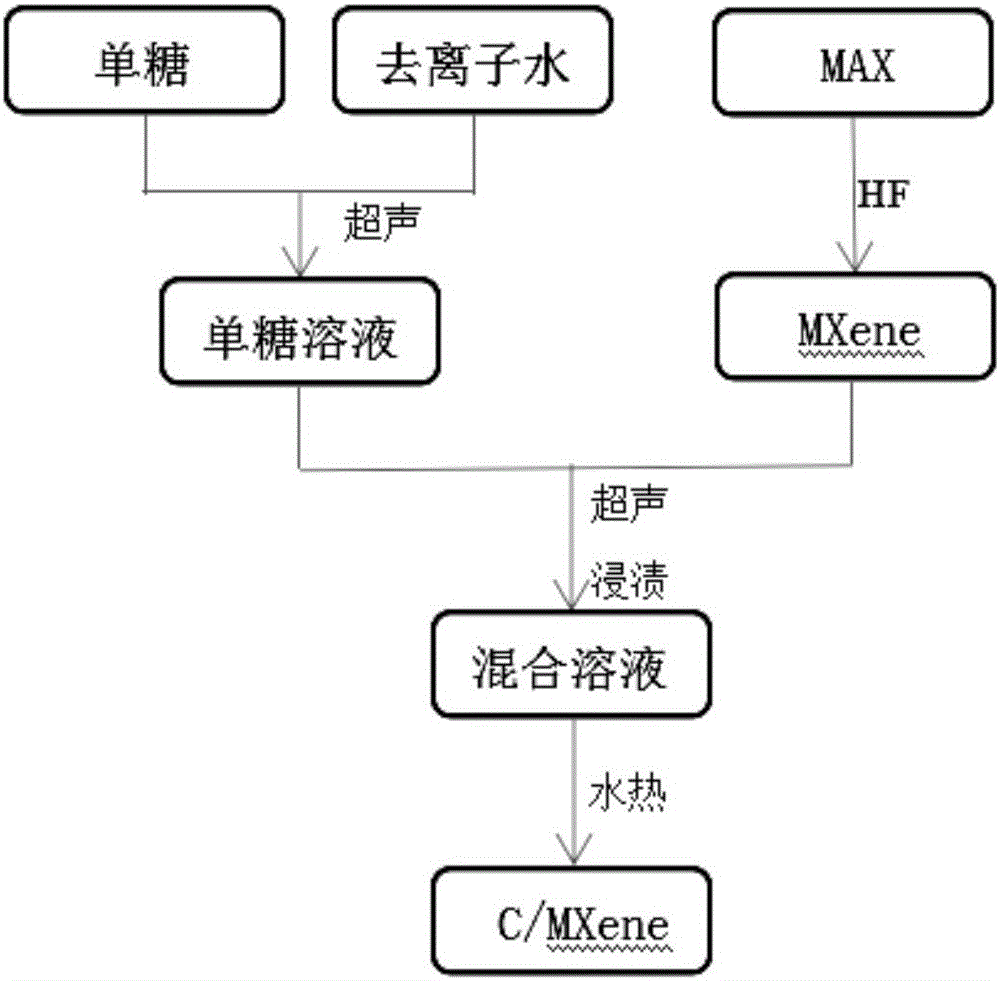
Method for preparing carbon nanoparticle/two-dimensional layered titanium carbide composite material
InactiveCN106185937AImprove mechanical propertiesSimple methodMaterial nanotechnologyHydrofluoric acidSupercapacitor
The invention relates to a method for preparing a carbon nanoparticle / two-dimensional layered titanium carbide composite material. The method includes the steps that a two-dimensional layered titanium carbide nano material MXene (Ti3C2 / Ti2C) is prepared through hydrofluoric acid corrosion; the material MXene (Ti3C2 / Ti2C) and monosaccharide are processed through ultrasonic treatment, vacuum impregnation, hydrothermal treatment and other steps, so carbon nanoparticles are generated between layers and on the surface of the MXene (Ti3C2 / Ti2C) material, and the carbon nanoparticle / two-dimensional layered titanium carbide composite material is obtained. Raw materials which are not toxic and easy to obtain are adopted, the preparation process is simple, the technology is controllable, cost is low, repeatability is good, the layered structure of the prepared two-dimensional layered MXene (Ti3C2 / Ti2C) is uniform and complete, the carbon nanoparticles are evenly distributed between the layers and on the surface of the MXene (Ti3C2 / Ti2C) material, and the prepared composite material has the advantages of being large in specific surface area, good in conductivity, good in hydrophilic property and the like and can be used in the fields such as functional ceramic, wave-absorbing materials, supercapacitors and ion batteries.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method for preparing extrafine anatase titanium dioxide nano rods
InactiveCN101559979ADopingTransparent highNanostructure manufactureTitanium dioxideHydrolysisUltrasonic dispersion
The invention relates to a method for preparing extrafine anatase titanium dioxide nano rods, which comprises that: (1) titanium containing inorganic substances are hydrolyzed, the temperature is raised to be between 20 and 100 DEG C, inorganic base solution is added for heat preservation and hydrolysis and neutralizes pH to between 7 and 8, and precipitation of hydrous titanium dioxide is obtained; (2) the precipitation is repeatedly washed, added with oxyful, stirred and subjected to ultrasonic dispersion, the temperature is raised to be between 0 and 50 DEG C and the heat is preserved for 1 to 24 hours; and (3) water solution of pertitanic acid is diluted by deionized water, then filled into a hydrothermal reaction kettle, subjected to hydrothermal treatment at a temperature between 100 and 250 DEG C for 2 to 48 hours, and cooled to room temperature. The preparation method is simple; the obtained sol does not contain organic stabilizer; and the titanium dioxide in the sol is anatase, has a rod-shaped structure and high length-diameter ratio, and can form extrafine rod-shaped nanocrystal titanium dioxide.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of carbon quantum dots
InactiveCN108083259ASimple preparation processEasy access to raw materialsNanotechnologyNano-carbonEnvironmental resistanceAgricultural residue
The invention provides a preparation method of carbon quantum dots and belongs to the technical field of preparation of nano luminescent materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps: weighing forestry and agricultural residues, kitchen garbage and mixture of one or more of vegetables, fruits, grains, flowers and Chinese herbal medicines in a ratio of parts by weight of 1:(1-100):(0.5-100) as raw materials; pulverizing the weighed raw materials, sieving the pulverized raw materials, performing uniform mixing, and adding organic acid or strong base or weak base to the treatedmixed liquid; and performing ultrasonic treatment, hydrothermal treatment and centrifugal treatment to obtain a solution, putting the obtained solution after centrifugal treatment into a dialysis bag,and putting the dialysis bag in a beaker filled with distilled water to be subjected to dialysis treatment so as to obtain the carbon quantum dots. The yield of the carbon quantum dots provided by the invention is 50-90%, and the sizes of the prepared carbon quantum dots are 1-2nm; and compared with the existing preparation method of the carbon quantum dots, the preparation method provided by theinvention has the advantages that the preparation process is simple, the raw materials are easy to obtain, and the preparation method is environmentally friendly and harmless.
Owner:史书亭
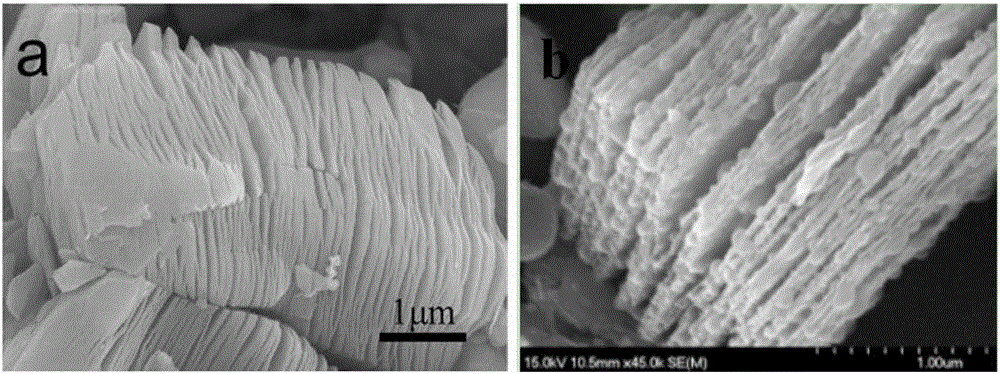
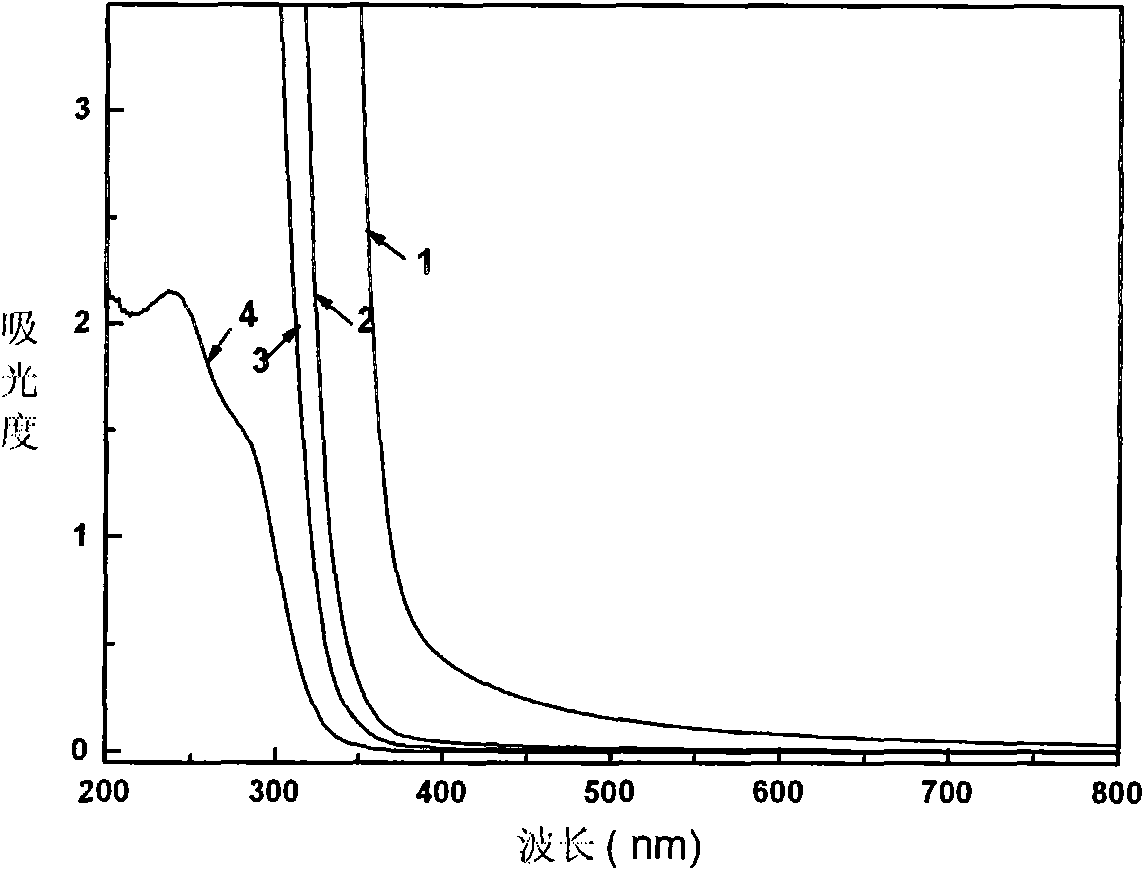
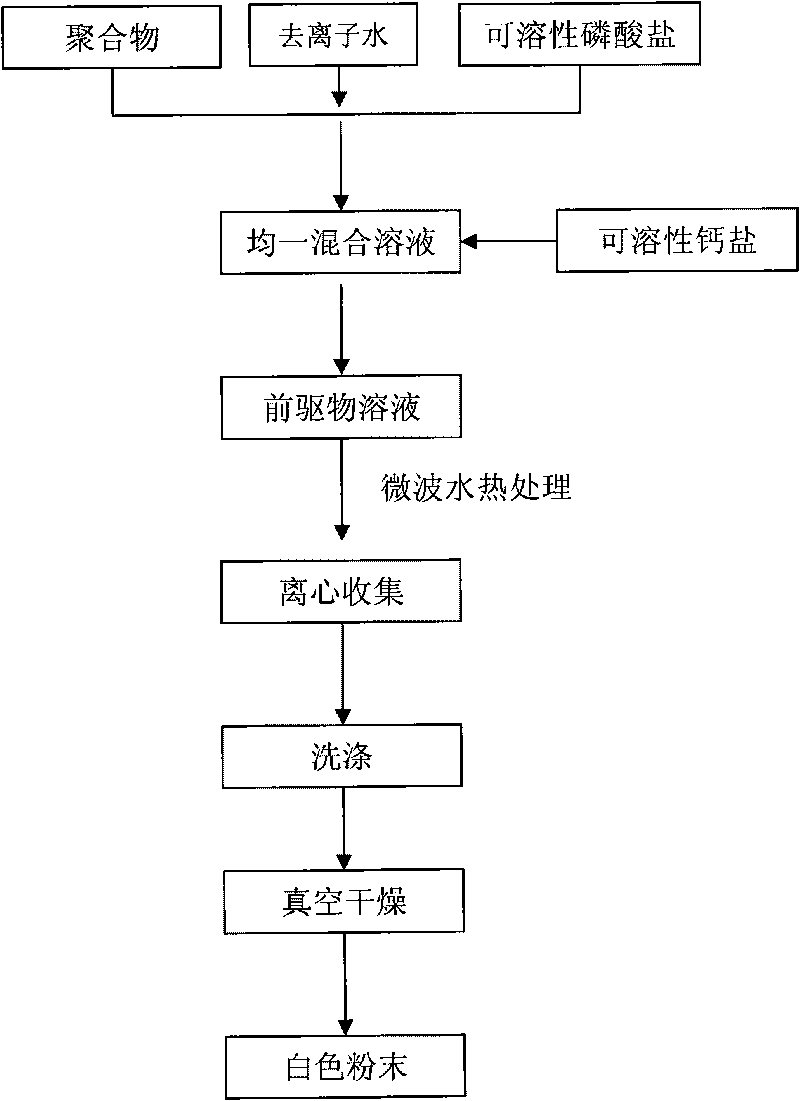
Calcium phosphate nano-structure hollow microsphere and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101759169AShort manufacturing timeReduce energy consumptionIndividual molecule manipulationPhosphorus compoundsCalcium biphosphateNano structuring
The invention belongs to the field of nano biomaterials and relates to a calcium phosphate nano-structure hollow microsphere and a preparation method thereof. The calcium phosphate nano-structure hollow microsphere is prepared by the following steps: dissolving biocompatible polymer, soluble calcium salt and soluble phosphate in water to form a uniform precursor solution, and carrying out the microwave heating hydrothermal treatment on the solution. The prepared calcium phosphate nano-structure hollow microsphere comprises various chemical components of calcium phosphate and hydroxyapatite (Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2); a shell of the hollow microsphere is a porous structure formed by the assembly of nano calcium phosphate pieces with the thickness of 10-50nm; and the diameter of the hollow microsphere is 1-10 micro meters. The invention has the advantages of fast preparation, simple process and low cost, and the prepared nano-structure hollow microsphere has the advantages of favorable biocompatibility and the like, thereby having good application prospects in the field of biomedicine.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Preparation method of biomass pomelo peel derived activated carbon serving as electrode material of super capacitor
InactiveCN105152169ANo pollution in the processRich hierarchical pore structureHybrid capacitor electrodesPotassium hydroxideCarbonization
The invention discloses a preparation method of biomass pomelo peel derived activated carbon serving as an electrode material of a super capacitor. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a pomelo peel is subjected to hydrothermal treatment for mild carbonization firstly, a pomelo peel adopting a porous structure is obtained, a hydrothermal product of the pomelo peel and potassium hydroxide are mixed for soaking, so that potassium hydroxide sufficiently diffuses into the pomelo peel, a mixture is calcined at a high temperature finally, carbon balls are activated by potassium hydroxide, and a honeycomb activated carbon material adopting leveled hole structures is prepared. Honeycomb activated carbon prepared with the method has rich leveled hole structures and larger specific surface area, the electrode capacity is as high as 300 F / g when the activated carbon serves as the electrode material of the super capacitor, and the method has the characteristics of simplicity in process operation, high repeatability and low cost.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Synthesis method of nano-molybdenum carbide
InactiveCN103936008ALarge specific surface areaSmall particle sizeTungsten/molybdenum carbideSynthesis methodsFiltration
The invention relates to a synthesis method of nano-molybdenum carbide. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: dissolving a molybdenum precursor in hydrogen peroxide, dissolving carbohydrates in water, mixing the molybdenum precursor with the carbohydrates, stirring, loading a mixed solution into a hydrothermal kettle, and performing hydrothermal treatment to obtain a black product; cooling the black product, then washing and performing suction filtration on the product, drying, baking in a passivation gas atmosphere, replacing with passivation gas when the temperature is reduced to room temperature, and performing passivation treatment to obtain the nano-molybdenum carbide. The synthesis method provided by the invention has the advantages of simplicity, easiness in control, economical efficiency, reasonableness and large specific surface area with mesoporous structure.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of mesoporous SiOx/C composite negative material of lithium-ion battery
ActiveCN103280560ASmall particlesUniform particle sizeCell electrodesMesoporous silicaSurface-active agents
The invention discloses a preparation method of a mesoporous SiOx / C composite negative material of a lithium-ion battery, and belongs to the fields of new materials and electrochemistry. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: taking polyvinylpyrrolidone as an auxiliary template agent, taking an organic surface active agent as a template agent and organic silicon as a silicon source, obtaining mesoporous silica precursor by hydrothermal treatment, adding a carbon source, and preparing SiOx / C composite negative material with a mesoporous structure by carbothermic reduction reaction occurring in the process of high-temperature thermal treatment. The preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the specific capacity of the material is high, the structure is novel, and simultaneously the cycling stability is good; the yield is high; and the prepared SiOx / C composite material is fine in particle, uniform in particle size and component distribution, high in specific capacity and good in cycling stability, is an ideal composite negative material of the lithium-ion battery, and can be widely applied in the fields such as various portable electronic equipment, electric vehicles and aerospace.
Owner:DONGGUAN KAIJIN NEW ENERGY TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com