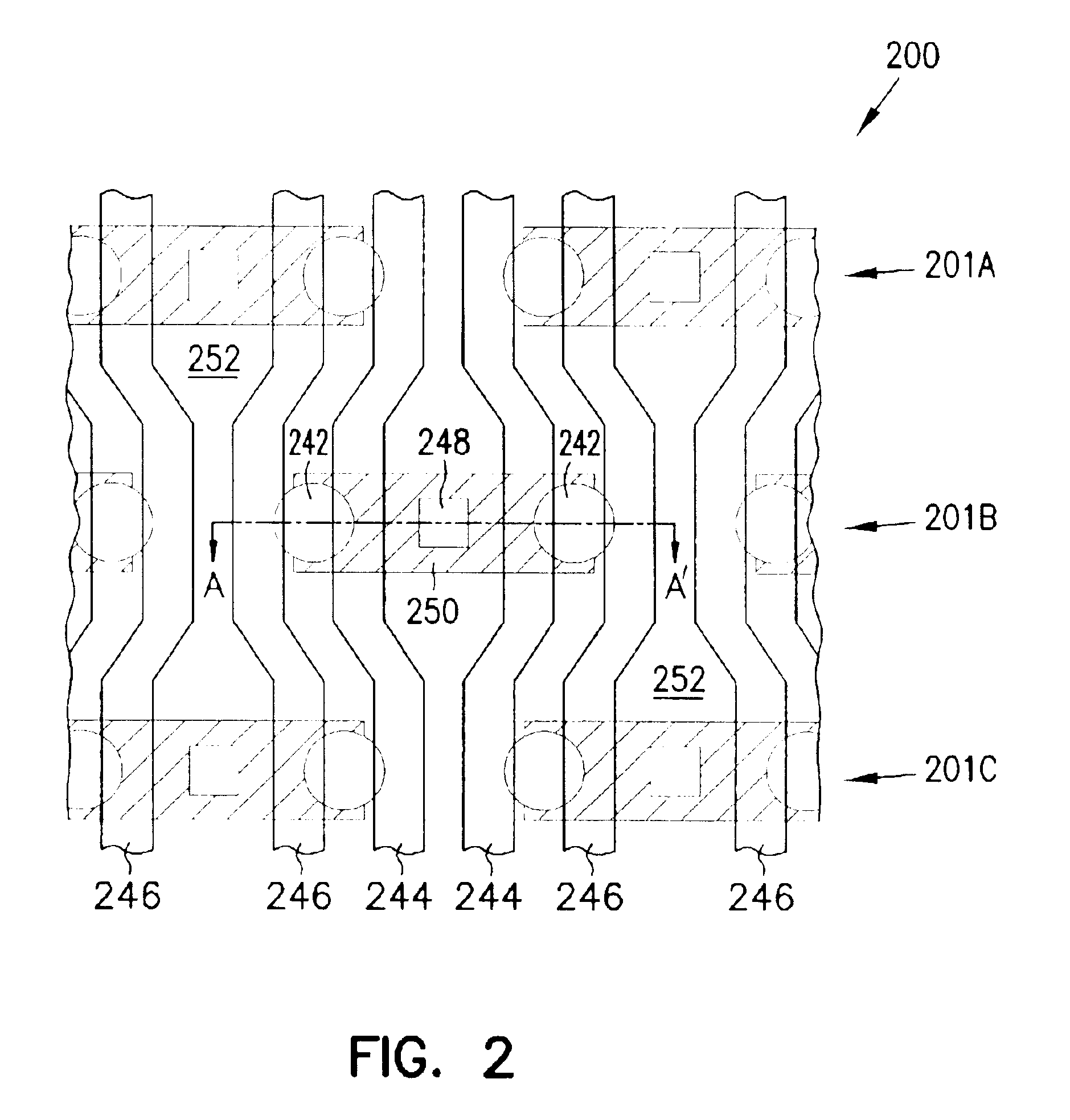
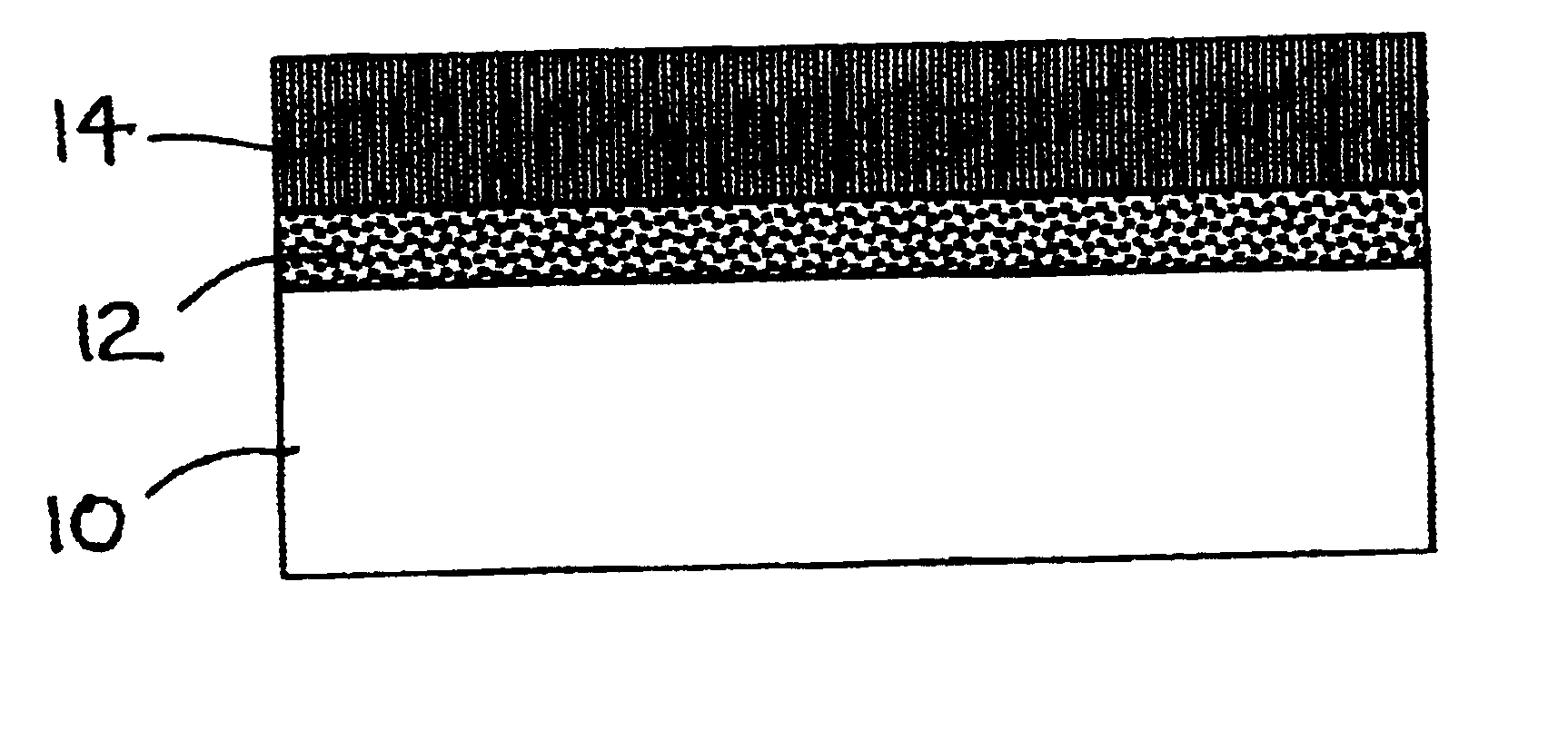
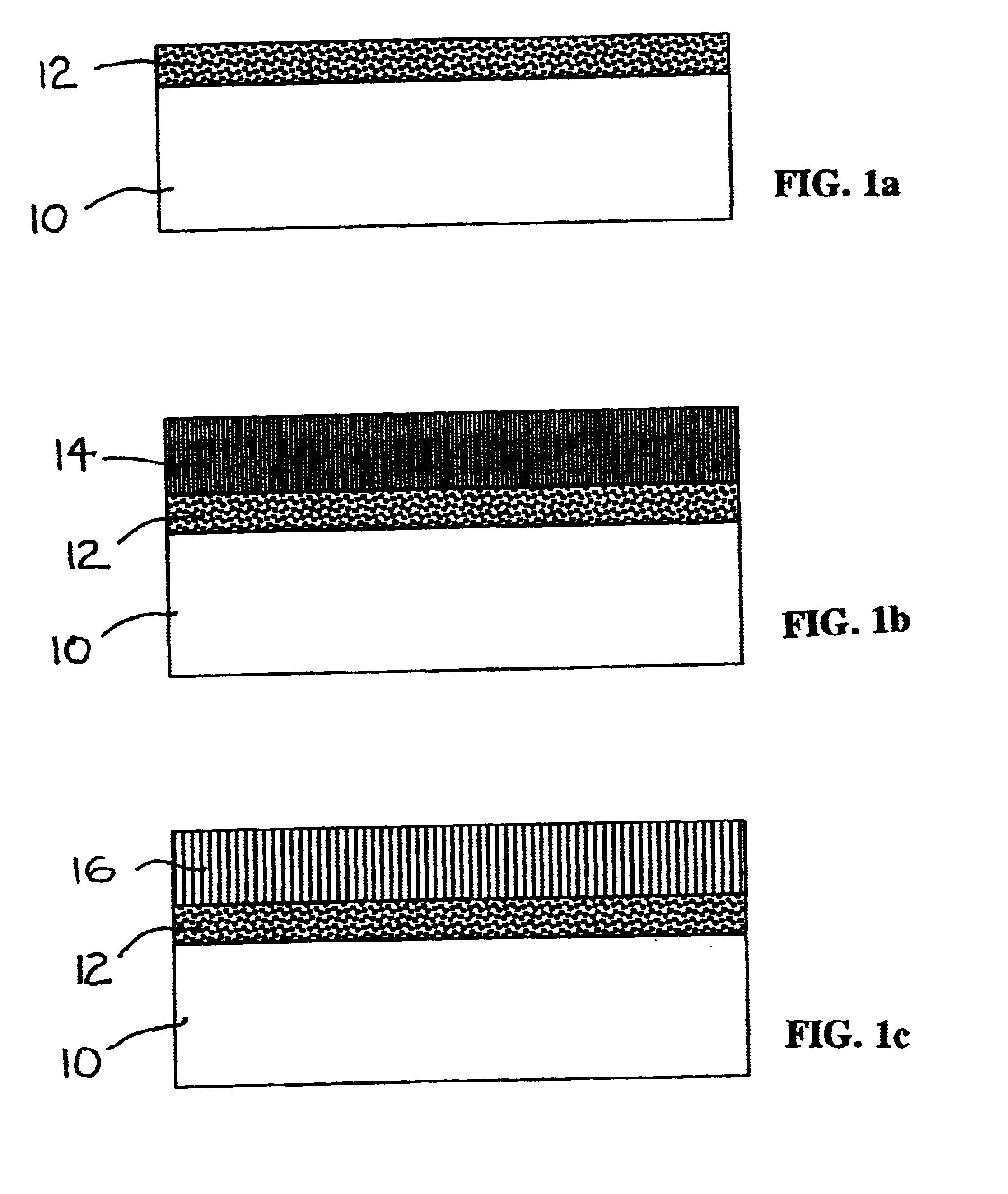
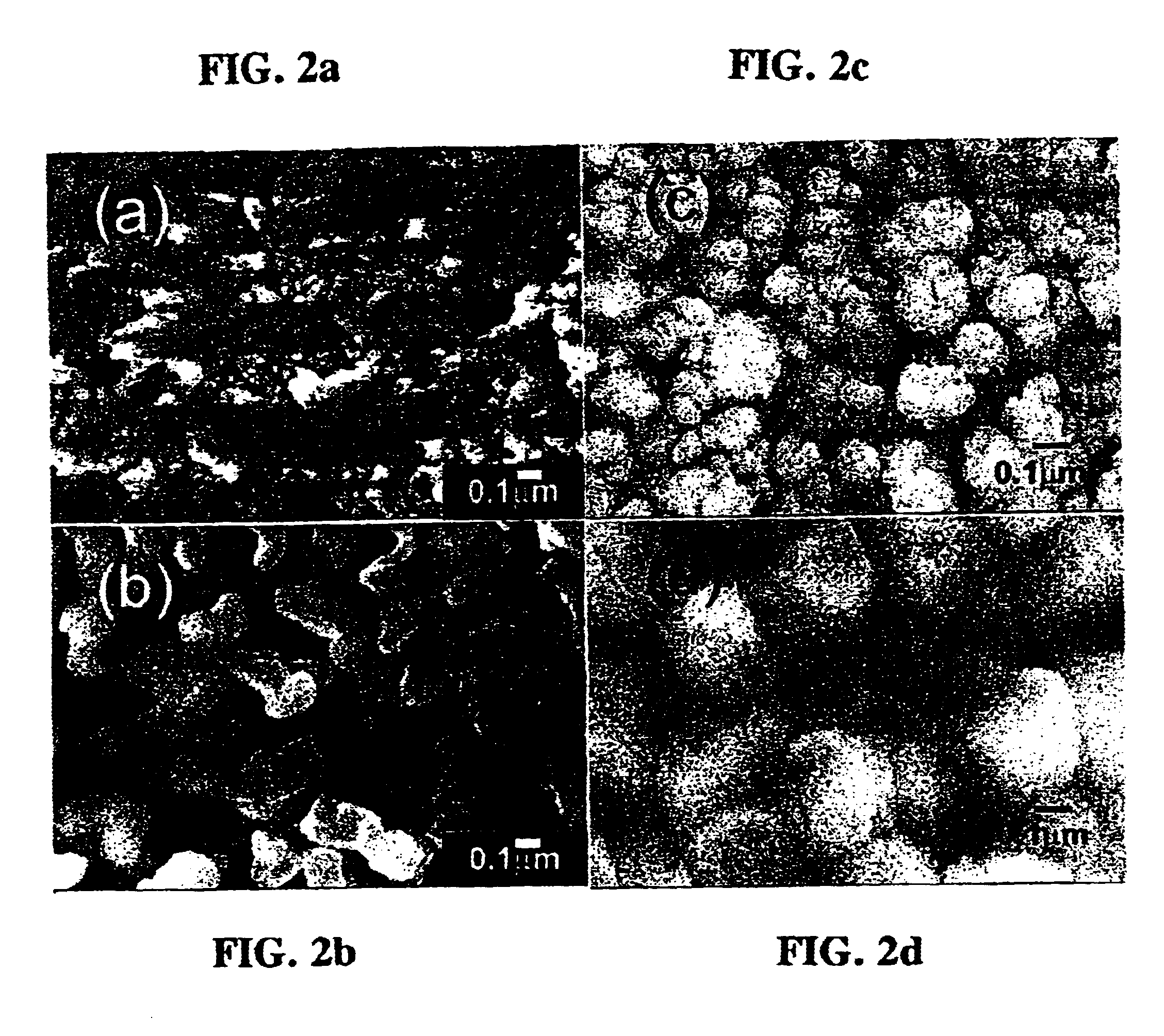
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
371 results about "Barium strontium titanate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
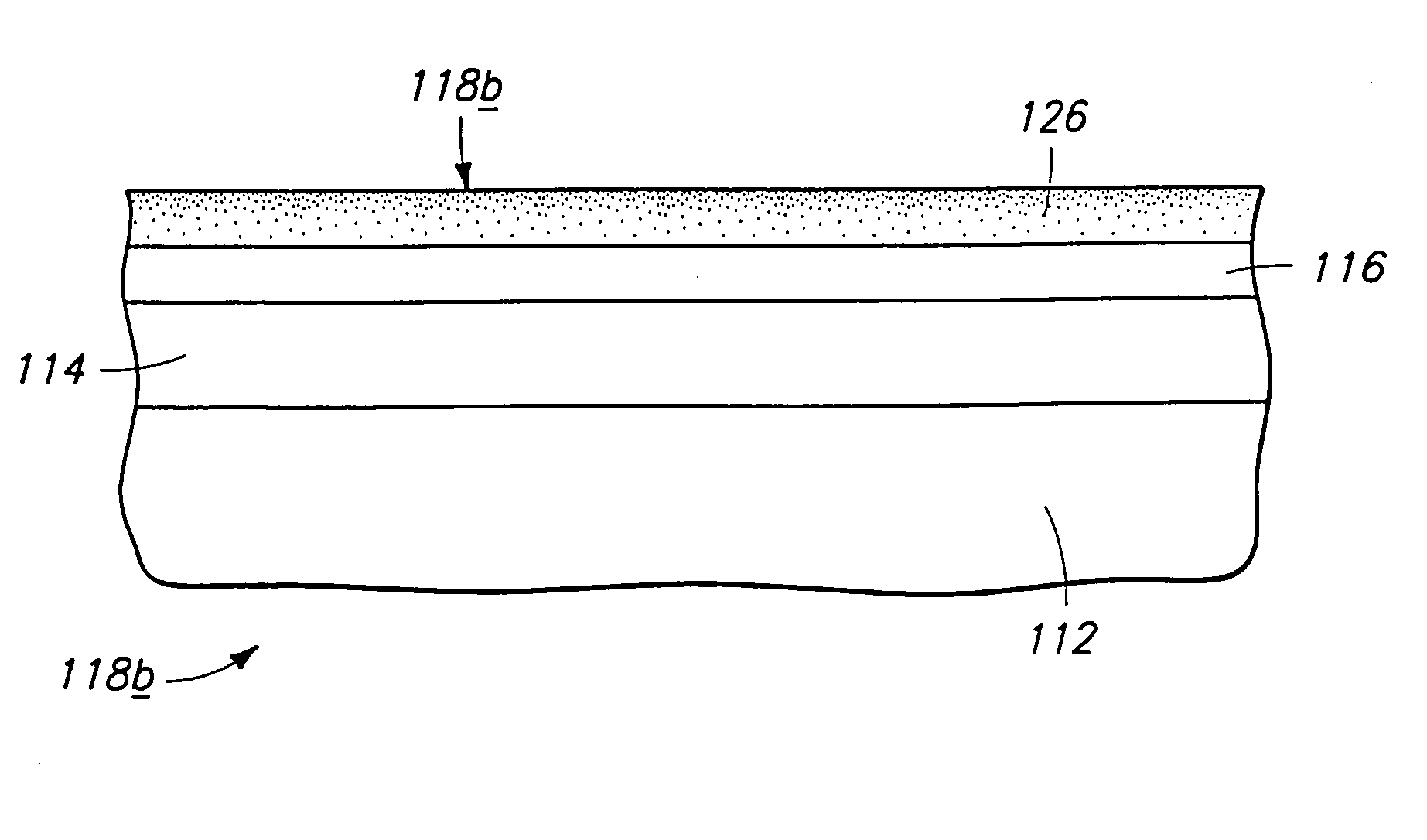
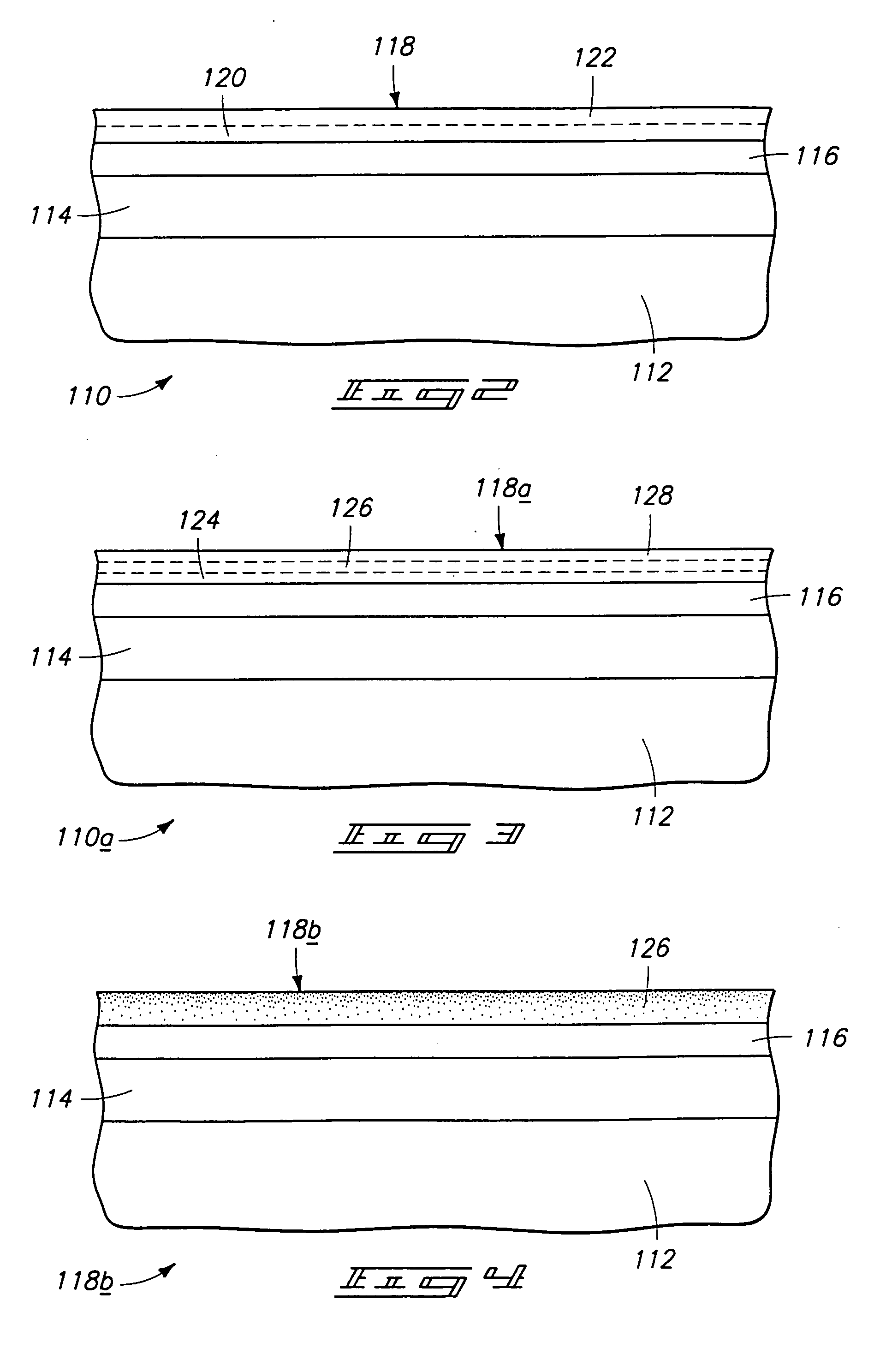
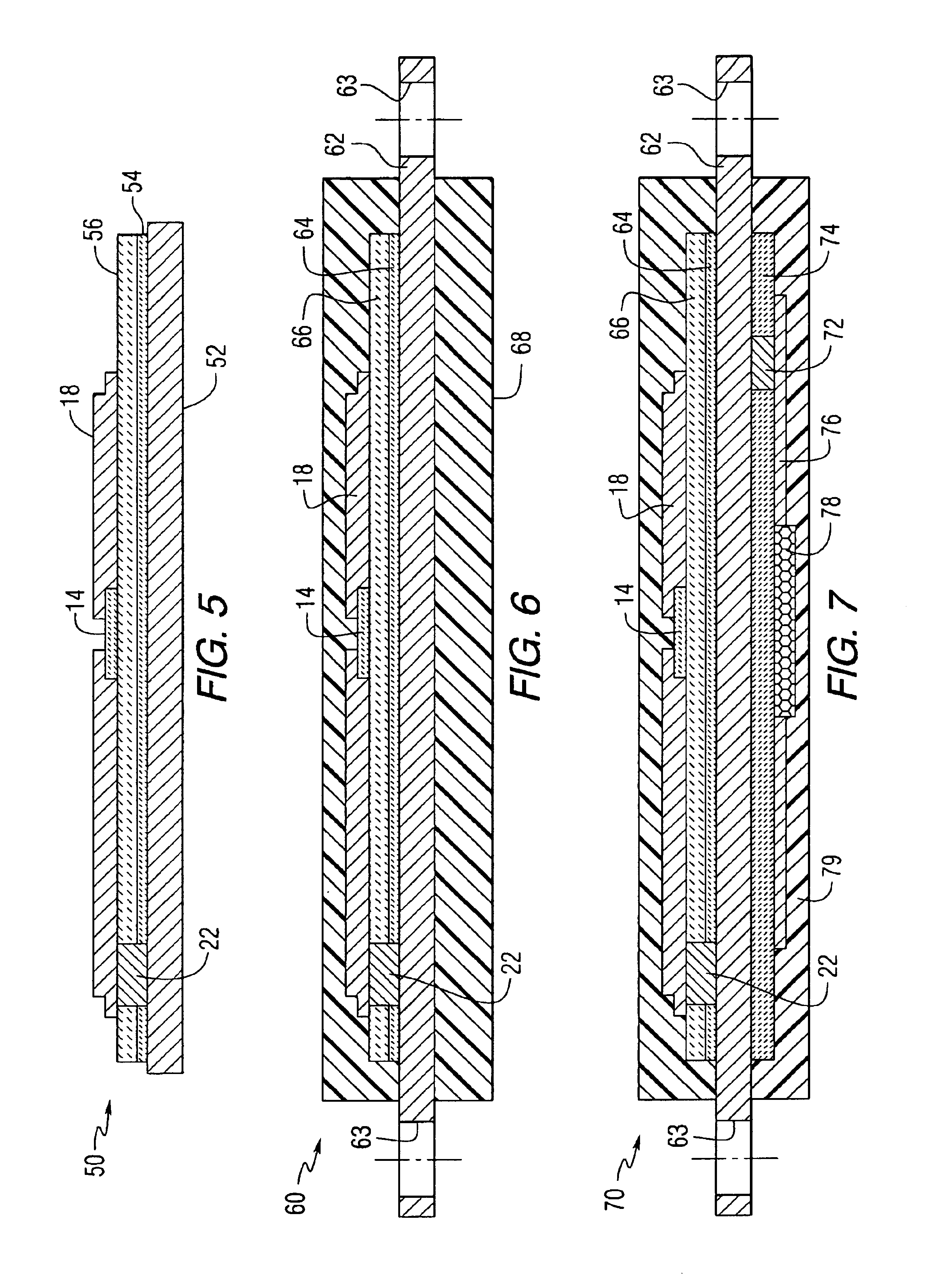
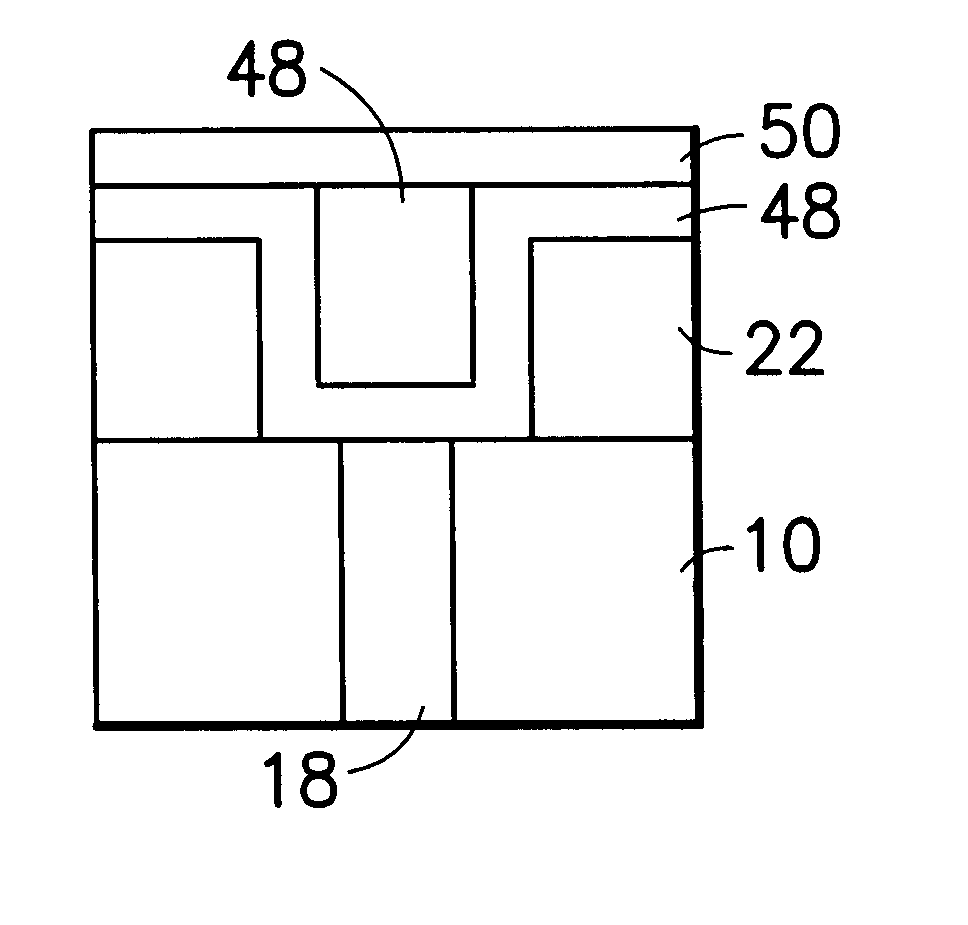
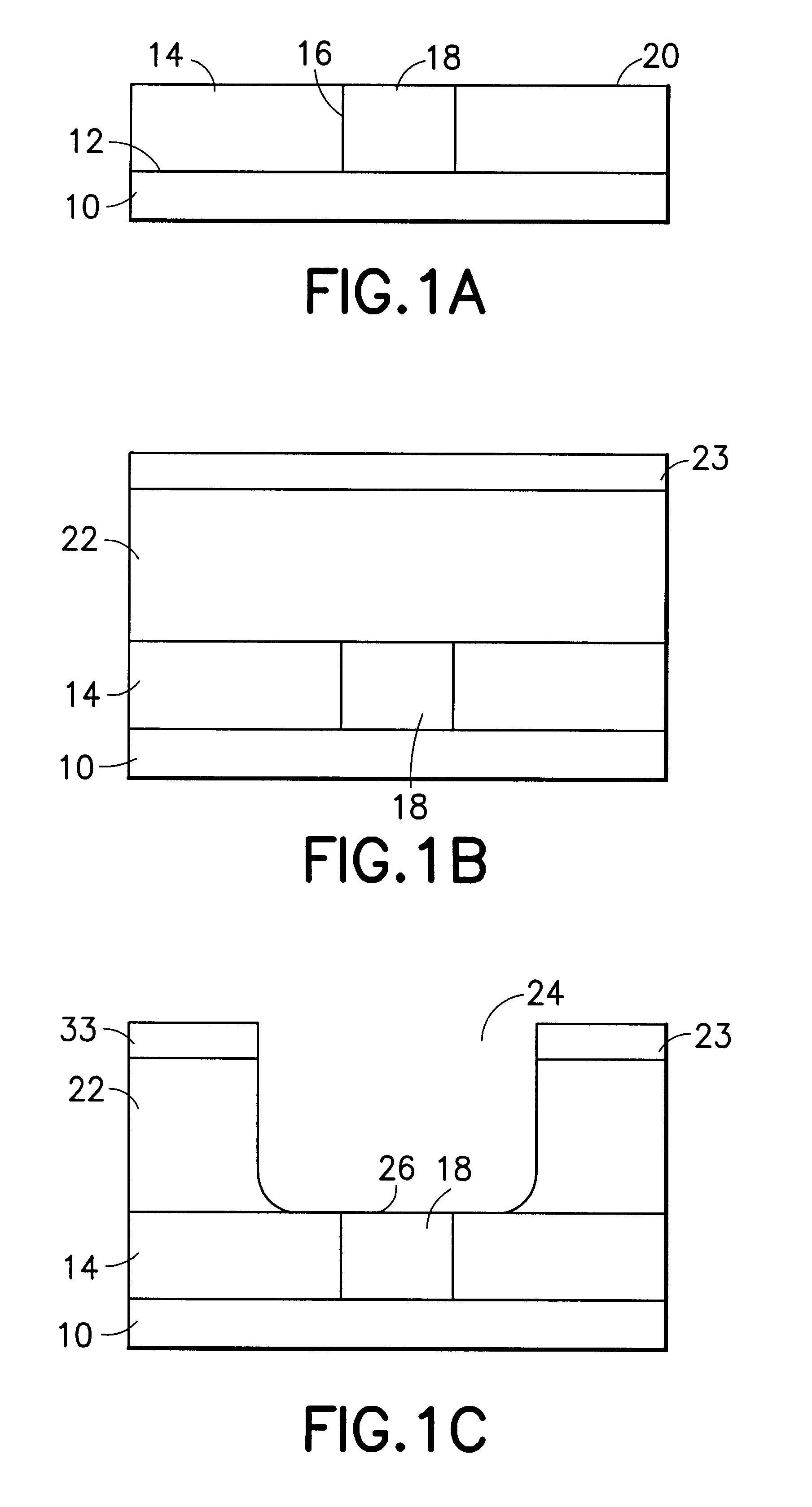
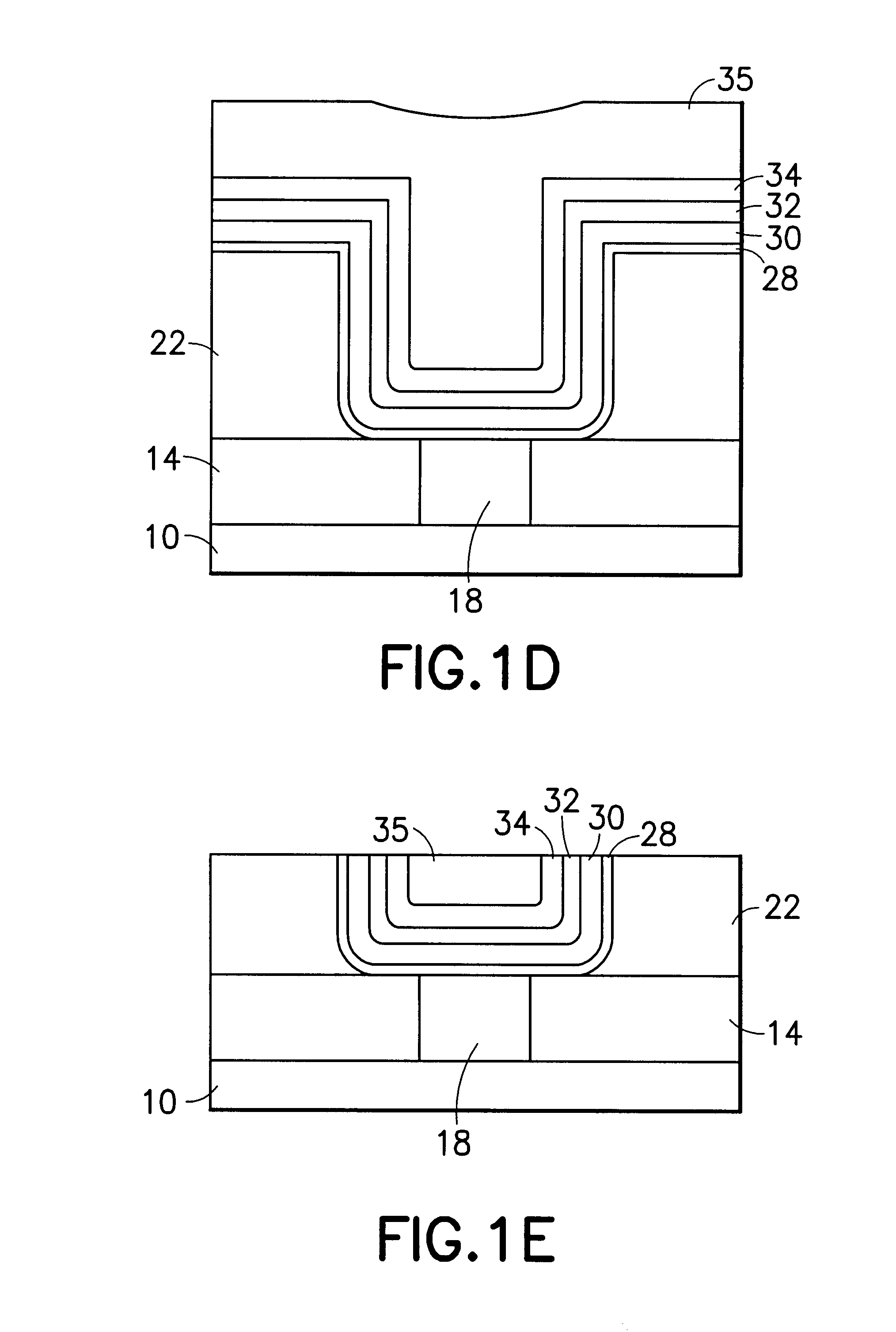
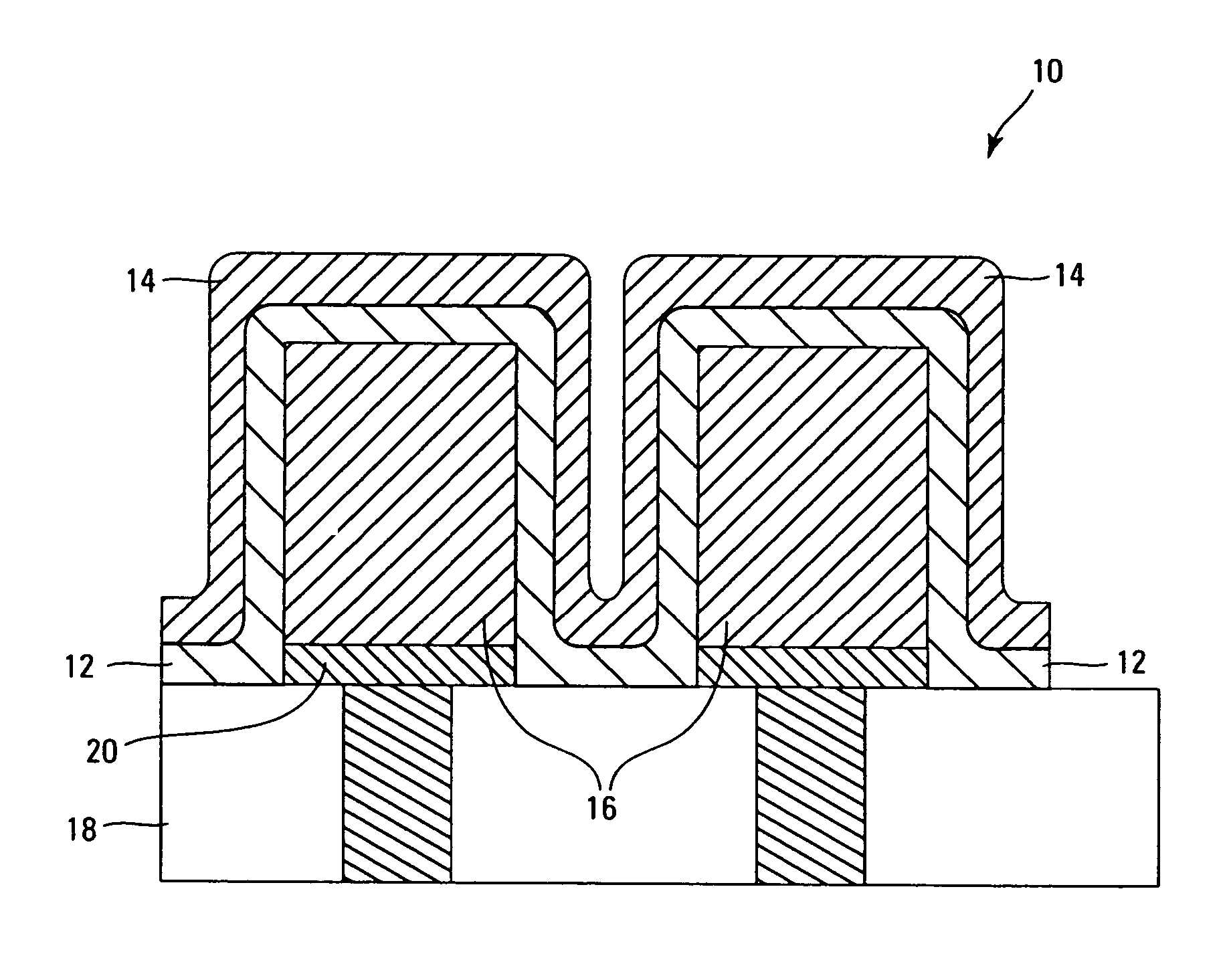
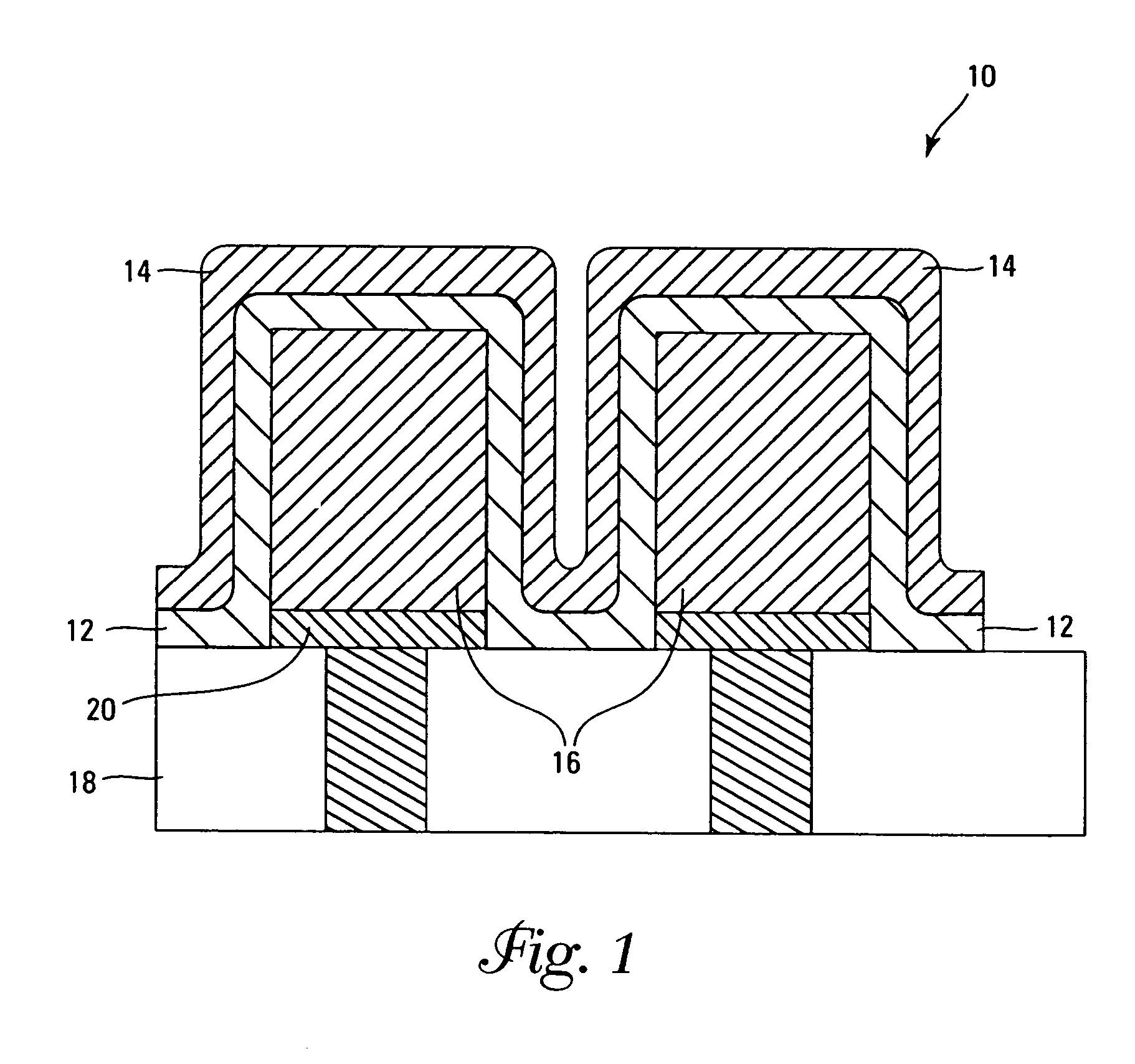
Chemical vapor deposition methods of forming barium strontium titanate comprising dielectric layers, including such layers having a varied concentration of barium and strontium within the layer
The invention includes a chemical vapor deposition method of forming a barium strontium titanate comprising dielectric layer having a varied concentration of barium and strontium, and / or titanium, within the layer. A substrate is positioned within a chemical vapor deposition reactor. Barium and strontium are provided within the reactor by flowing at least one metal organic precursor to the reactor. Titanium is provided within the reactor. One or more oxidizers are flowed to the reactor. In one aspect, conditions are provided within the reactor to be effective to deposit a barium strontium titanate comprising dielectric layer on the substrate from the reactants.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Tunable dielectric compositions including low loss glass
InactiveUS6905989B2Lower sintering temperatureIncrease varietyFixed capacitor dielectricCeramic layered productsBreakdown strengthStrontium titanate
Tunable dielectric materials including an electronically tunable dielectric ceramic and a low loss glass additive are disclosed. The tunable dielectric may comprise a ferroelectric perskovite material such as barium strontium titanate. The glass additive may comprise boron, barium, calcium, lithium, manganese, silicon, zinc and / or aluminum-containing glasses having dielectric losses of less than 0.003 at 2 GHz. The materials may further include other additives such as non-tunable metal oxides and silicates. The low loss glass additive enables the materials to be sintered at relatively low temperatures while providing improved properties such as low microwave losses and high breakdown strengths.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Compositions and structures for chemical mechanical polishing of FeRAM capacitors and method of fabricating FeRAM capacitors using same
InactiveUS6346741B1Easy to manufactureBig advantageOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLead zirconate titanateBarium strontium titanate
An integrated circuit structures formed by chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) process, which comprises a conductive pathway recessed in a dielectric substrate, wherein the conductive pathway comprises conductive transmission lines encapsulated in a transmission-enhancement material, and wherein the conductive pathway is filled sequentially by a first layer of the transmission-enhancement material followed by the conductive transmission line; a second layer of transmission-enhancement material encapsulating the conductive transmission line and contacting the first layer of the transmission-enhancement material, wherein the transmission-enhancement material is selected from the group consisting of high magnetic permeability material and high permittivity material. Such integrated circuit structure may comprise a device structure selected from the group consisting of capacitors, inductors, and resistors. Preferably, the transmission-enhancement material comprises MgMn ferrites, MgMnAl ferrites, barium strontium titanate, lead zirconium titanate, titanium oxide, tantalum oxide, etc.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
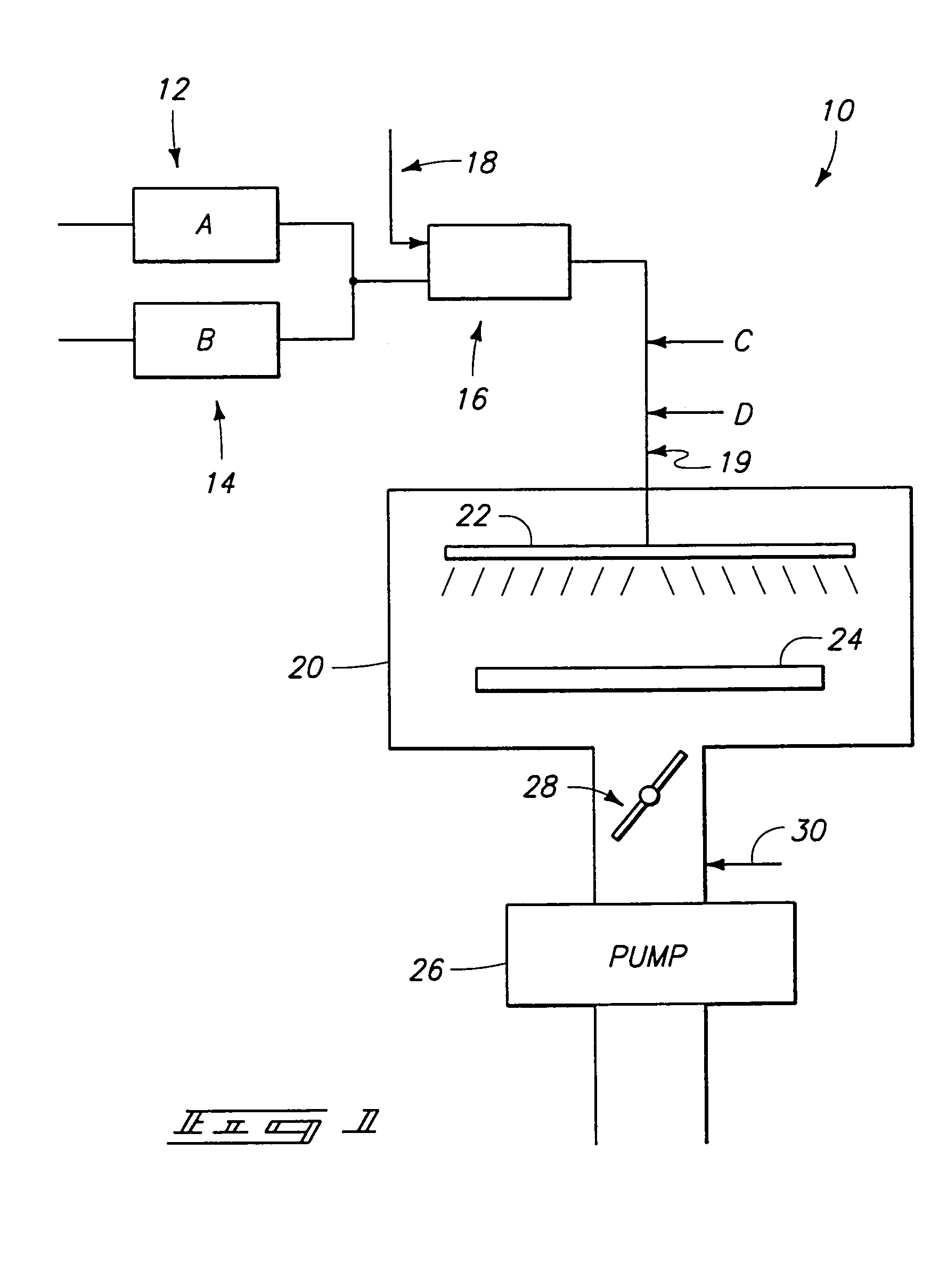
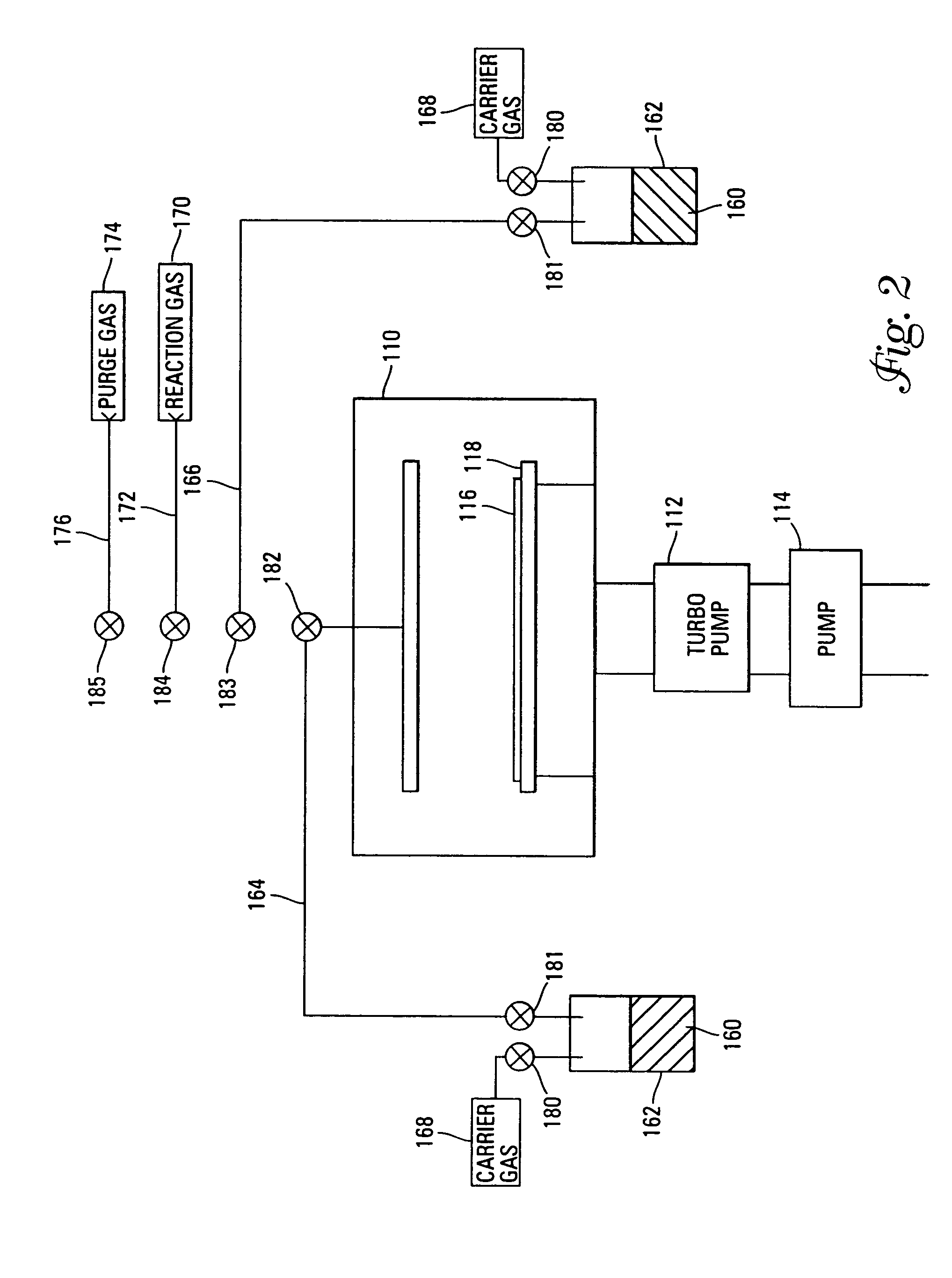
Systems and methods for forming strontium- and/or barium-containing layers
InactiveUS7115166B2Easy to controlMinimizing detrimental gas phase reactionPolycrystalline material growthSolid-state devicesStrontium titanateBarium strontium titanate
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
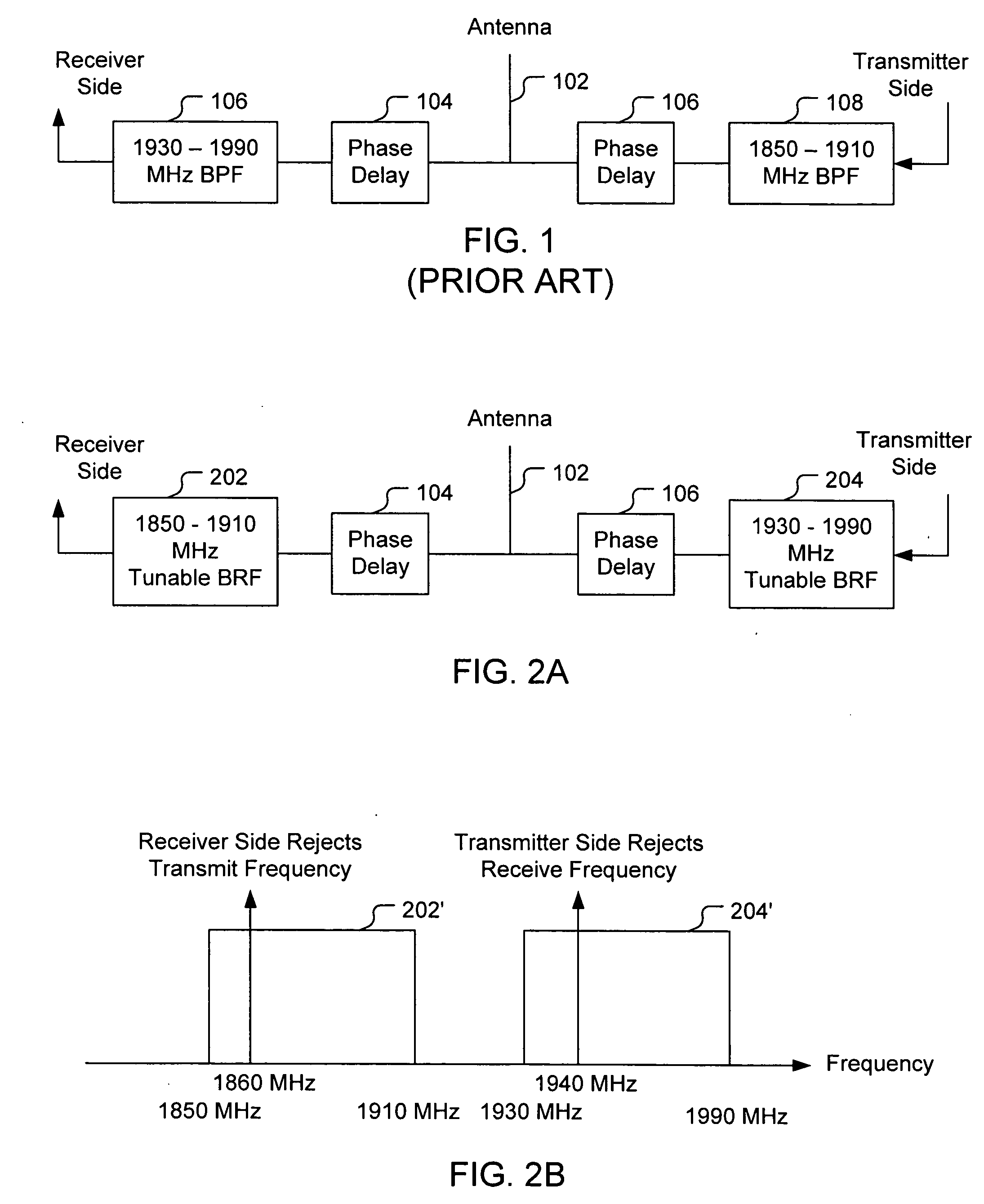
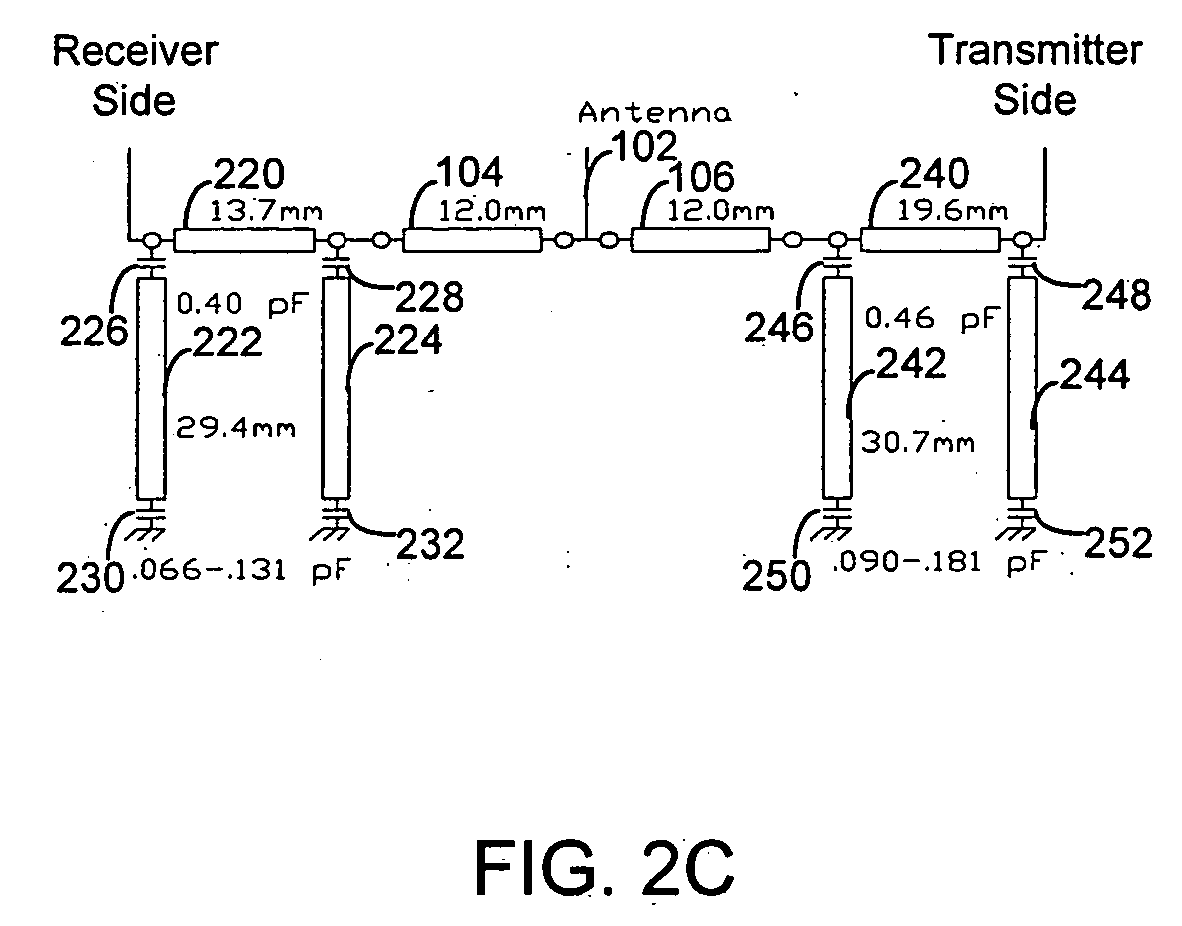
Tunable notch duplexer
InactiveUS20070024393A1Reduce manufacturing costSmall sizeCoupling devicesStrontium titanateCapacitance
A duplexer for bidirectional communication systems includes tunable band reject filters. The tunable band reject filter on the receiver side can be tuned to reject the transmit signal frequency, and the tunable band reject filter on the transmitter side can be tuned to reject the receive signal frequency. Thus, the band reject filters allow for simultaneous tuning of the band reject frequencies on the transmission side and the reception side. The tunable band reject filters can be implemented as resonators including barium strontium titanate (BST) capacitors of which the capacitance can be tuned according to bias voltages applied to the BST capacitors.
Owner:CYCAD GRP
High dielectric constant composite materials and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS20120245016A1High composite strengthHigh dielectric constantMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsBarium strontium titanateBarium titanate
The present invention relates to composite materials with a high dielectric constant and high dielectric strength and to methods of producing the composite materials. The composite materials have high dielectric constants at a range of high frequencies and possess robust mechanical properties and strengths, such that they may be machined to a variety of configurations. The composite materials also have high dielectric strengths for operation in high power and high energy density systems. In one embodiment, the composite material is composed of a trimodal distribution of ceramic particles, including barium titanate, barium strontium titanate (BST), or combinations thereof and a polymer binder.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Amorphous dielectric capacitors on silicon
InactiveUS6255122B1Improve conformityReduce leakage currentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLead zirconate titanateMaterials science
High-capacity capacitors and gate insulators exhibiting moderately high dielectric constants with surprisingly low leakage using amorphous or low temperature films of perovskite type oxides including a titanate system material such as barium titanate, strontium titanate, barium strontium titanate (BST), lead titanate, lead zirconate titanate, lead lanthanum zirconate titanate, barium lanthanum titanate, a niobate, aluminate or tantalate system material such as lead magnesium niobate, lithium niobate lithium tantalate, potassium niobate and potassium tantalum niobate, a tungsten-bronze system material such as barium strontium niobate, lead barium niobate, barium titanium niobate, and Bi-layered perovskite system material such as strontium bismuth tantalate, bismuth titanate deposited directly on a silicon surface at temperatures about 450° C. or less.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method of patterning lead zirconium titanate and barium strontium titanate
In an embodiment of the present invention, a method is provided of patterning PZT layers or BST layers. For example, a PZT layer or a BST layer is plasma etched through a high-temperature-compatible mask such as a titanium nitride (TiN) mask, using a plasma feed gas comprising as a primary etchant boron trichloride (BCl3) or silicon tetrachloride (SiCi4). Although BCl3 or SiCl4 may be used alone as the etchant plasma source gas, it is typically used in combination with an essentially inert gas. Preferably the essentially inert gas is argon. Other potential essentially inert gases which may be used include xenon, krypton, and helium. In some instances O2 or N2, or Cl2, or a combination thereof may be added to the primary etchant to increase the etch rate of PZT or BST relative to adjacent materials, such as the high-temperature-compatible masking material. A TiN masking material can easily be removed without damaging underlying oxides. The selectivity of PZT or BST relative to TiN is very good, with the ratio of the etch rate of the PZT film to the etch rate of the TiN mask typically being better than 20:1. In addition, the etch rate for PZT using a BCl3-comprising plasma source gas is typically in excess of 2,000 Å per minute. A substrate bias power is applied to direct ions produced from the BCl3 or SiCl4 toward the surface to be etched. The bias power is controlled to avoid sputtering of a conductive layer or layers in contact with the PZT layer, so that the surface of the etched PZT is not contaminated by a conductive material, which can cause the semiconductor device which includes the patterned PZT to short out.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Tunable dielectric compositions including low loss glass
InactiveUS20030073565A1Fixed capacitor dielectricCeramic layered productsStrontium titanateBreakdown strength
Tunable dielectric materials including an electronically tunable dielectric ceramic and a low loss glass additive are disclosed. The tunable dielectric may comprise a ferroelectric perskovite material such as barium strontium titanate. The glass additive may comprise boron, barium, calcium, lithium, manganese, silicon, zinc and / or aluminum-containing glasses having dielectric losses of less than 0.003 at 2 GHz. The materials may further include other additives such as non-tunable metal oxides and silicates. The low loss glass additive enables the materials to be sintered at relatively low temperatures while providing improved properties such as low microwave losses and high breakdown strengths.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Interposer capacitor built on silicon wafer and joined to a ceramic substrate
InactiveUS6791133B2Improve performanceHigh yieldTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLead zirconate titanateBarium strontium titanate
An interposer, located between an integrated circuit having power, ground and signal connections and a ceramic substrate having power, ground and signal connections, that includes an oxide layer formed on a polished surface of a silicon substrate, a thin film dielectric capacitor formed on the oxide layer, a plurality of metallized that electrically connect to either of the electrodes of the thin film dielectric capacitor, and vias than conduct power, ground and signals between a the ceramic substrate and the integrated circuit. The interposer connects the metallized vias to the integrated circuit by solder connections and also connects the vias conducting power, ground and signals from the ceramic substrate to the interposer by solder connections. The dielectric of the thin film dielectric capacitor may be selected from the group of high-K titanates, such as, barium zirconate titanate, barium strontium titanate, pure barium titanate, barium titanate modified with Pb, Nb, W, Ca, Mg, and Zn, lead titanate, lead zirconate titanate, and polycrystalline lanthanum-modified lead zirconate titanate, or other high-K dielectrics, such as, lead niobate and its derivatives, and lead tungstate and its derivatives.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Tetrahydrofuran-adducted group II beta-diketonate complexes as source reagents for chemical vapor deposition
InactiveUS6218518B1Simple methodGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsGroup 2/12 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesHolographic storageBarium strontium titanate
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
Method for producing low-loss tunable ceramic composites with improved breakdown strengths
InactiveUS20030119656A1Improved propertyLow cost productionLayered productsFixed capacitor dielectricBreakdown strengthMicrowave
The production of low-loss, tunable composite ceramic materials with improved breakdown strengths is disclosed. The composite materials comprise ferroelectric perovskites such as barium strontium titanate or other ferroelectric perovskites combined with other phases such as low-loss silicate materials and / or other low-loss oxides. The composite materials are produced in sheet or tape form by methods such as tape casting. The composite tapes exhibit favorable tunability, low loss and tailorable dielectric properties, and can be used in various microwave devices.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Dielectric composite materials including an electronically tunable dielectric phase and a calcium and oxygen-containing compound phase
InactiveUS6960546B2Improve material performanceImprove temperature stabilityLayered productsFixed capacitor dielectricDielectricDopant
Dielectric composite materials including an electronically tunable dielectric phase and a calcium and oxygen-containing compound are disclosed. The tunable phase may comprise a material such as barium strontium titanate. The calcium / oxygen compound may comprise CaO or a transition metal-containing compound such as Ca2Nb2O7 or CaTiO3. The material may also include a rare earth oxide dopant such as CeO2. The materials resist dielectric breakdown and possess improved combinations of electronic properties. The materials may be tailored for specific applications.
Owner:NXP USA INC
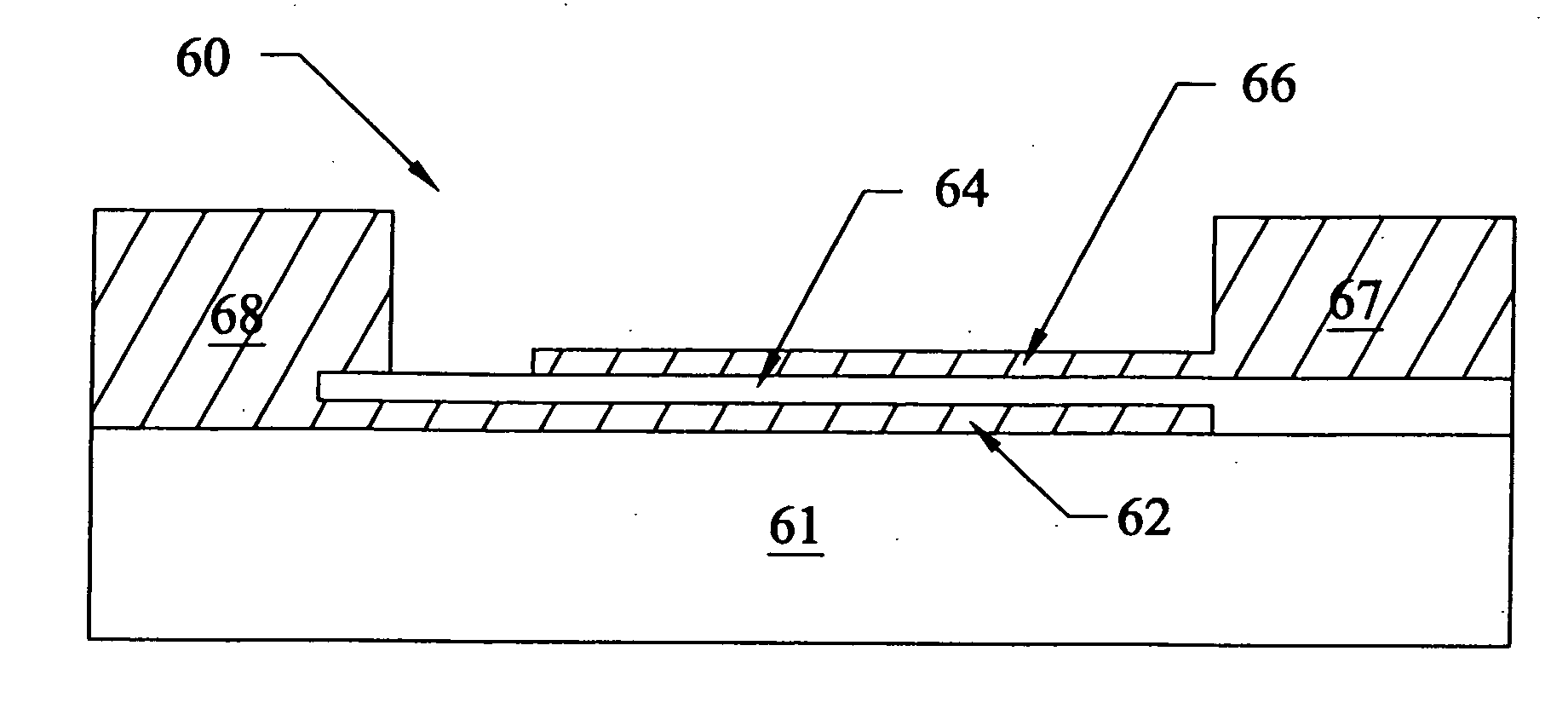
Structures and methods for enhancing capacitors in integrated circuits
InactiveUS6861330B2Inhibit dielectric degradationSimple structureTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricBarium strontium titanate
Systems, devices, structures, and methods are described that inhibit dielectric degradation in the presence of contaminants. An enhanced capacitor in a dynamic random access memory cell is discussed. The enhanced capacitor includes a first electrode, a dielectric coupled to the first electrode, a second electrode coupled to the dielectric, and at least one inhibiting layer that couples to the first electrode, the dielectric, and the second electrode. The inhibiting layer defines a chamber that encloses the capacitor and renders the capacitor impervious to disturbance in its physical or chemical forces in the presence of contaminants. The inhibiting layer includes a nitride compound, an oxynitride compound, and an oxide compound. In one embodiment, the nitride compound includes SixNy. In another embodiment, the oxynitride compound includes SiOxNy. In another embodiment, the oxide compound includes Al2O3 and (SrRu)O3. The variables x and y are indicative of a desired number of atoms. The dielectric includes an oxide compound. In one embodiment, the oxide compound includes barium strontium titanate.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Strain-relieved tunable dielectric thin films
InactiveUS6617062B2Relieves film strainStrain-relieved and defect-reduced tunableVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingBarium strontium titanateDielectric loss
Tunable dielectric thin films are provided which possess low dielectric losses at microwave frequencies relative to conventional dielectric thin films. The thin films include a low dielectric loss substrate, a buffer layer, and a crystalline dielectric film. Barium strontium titanate may be used as the buffer layer and the crystalline dielectric film. The buffer layer provides strain relief during annealing operations.
Owner:NXP USA INC
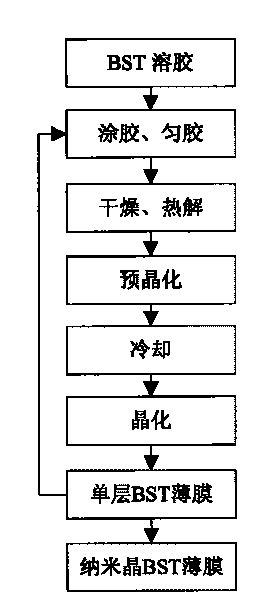
Method for preparing nano-crystalline BST film
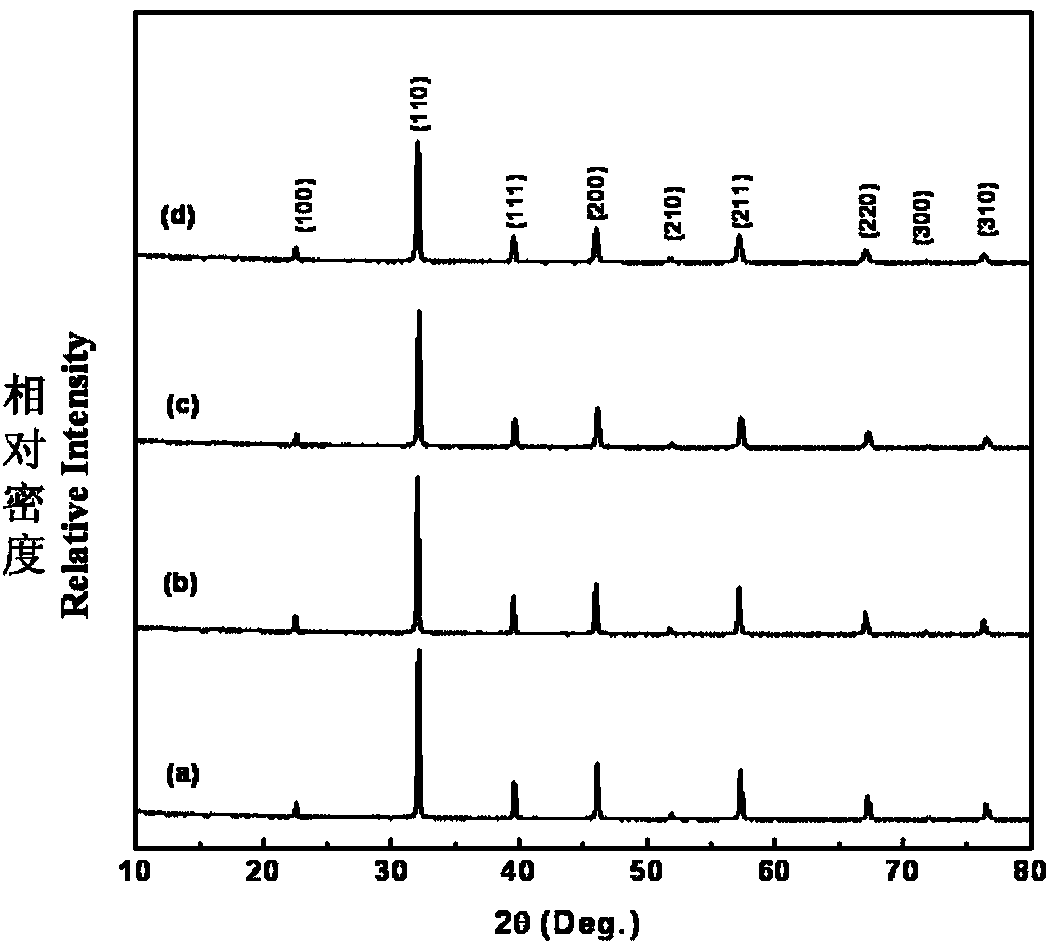
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nano-crystalline barium-strontium titanate film, belongs to the technical field of functional materials, and relates to a method for preparing a nano-crystalline BST film. A pre-crystallization treatment step is added between cooling step and crystallization step of the conventional sol-gel method for preparing the BST film. The nano-crystalline BST film can be grown internally and externally under atmospheric environment, and the obtained film is smooth and compact, and has no crack or shrinkage hole. The method can greatly improve the comprehensive dielectric tuning performance of the nano-crystalline BST film, the capacitance of the obtained nano-crystalline BST film is 58 to 1,840pF, the dielectric tuning rate is over 20.0 percent, the dielectric loss is less than 3.0 percent, the K factor is more than 15.0, and the nano-crystalline BST film has the advantages of high dielectric strength and stable frequency characteristic and temperature characteristic. The nano-crystalline BST film prepared by the method can replace ferrite and semiconductors for preparing a microwave tuning device (such as a phase shifter) so as to remarkably reduce the manufacturing cost of the microwave tuning device; in addition, the nano-crystalline BST film prepared by the method can also be used for magnetic recording, pyroelectric focal plane array and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
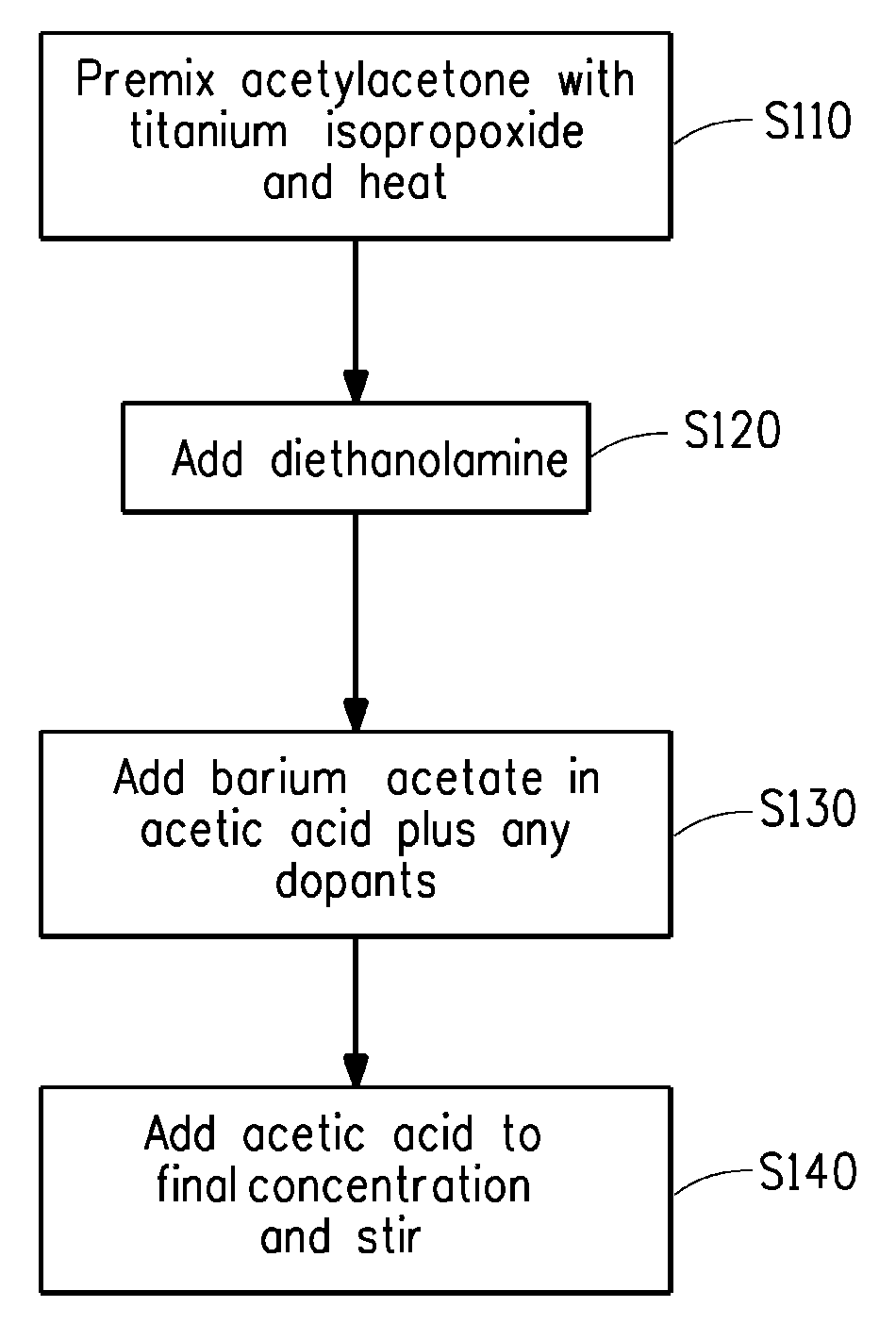
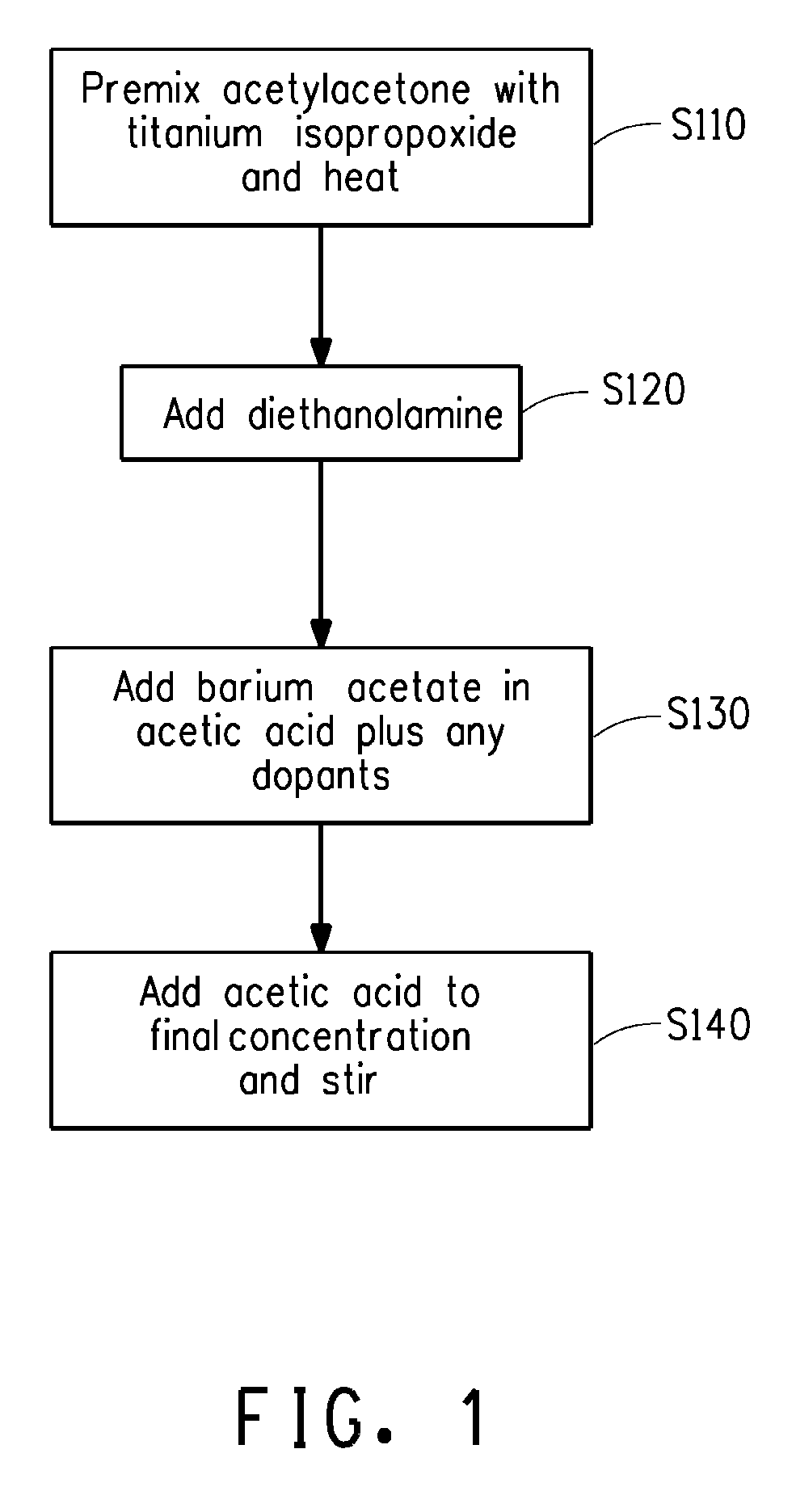
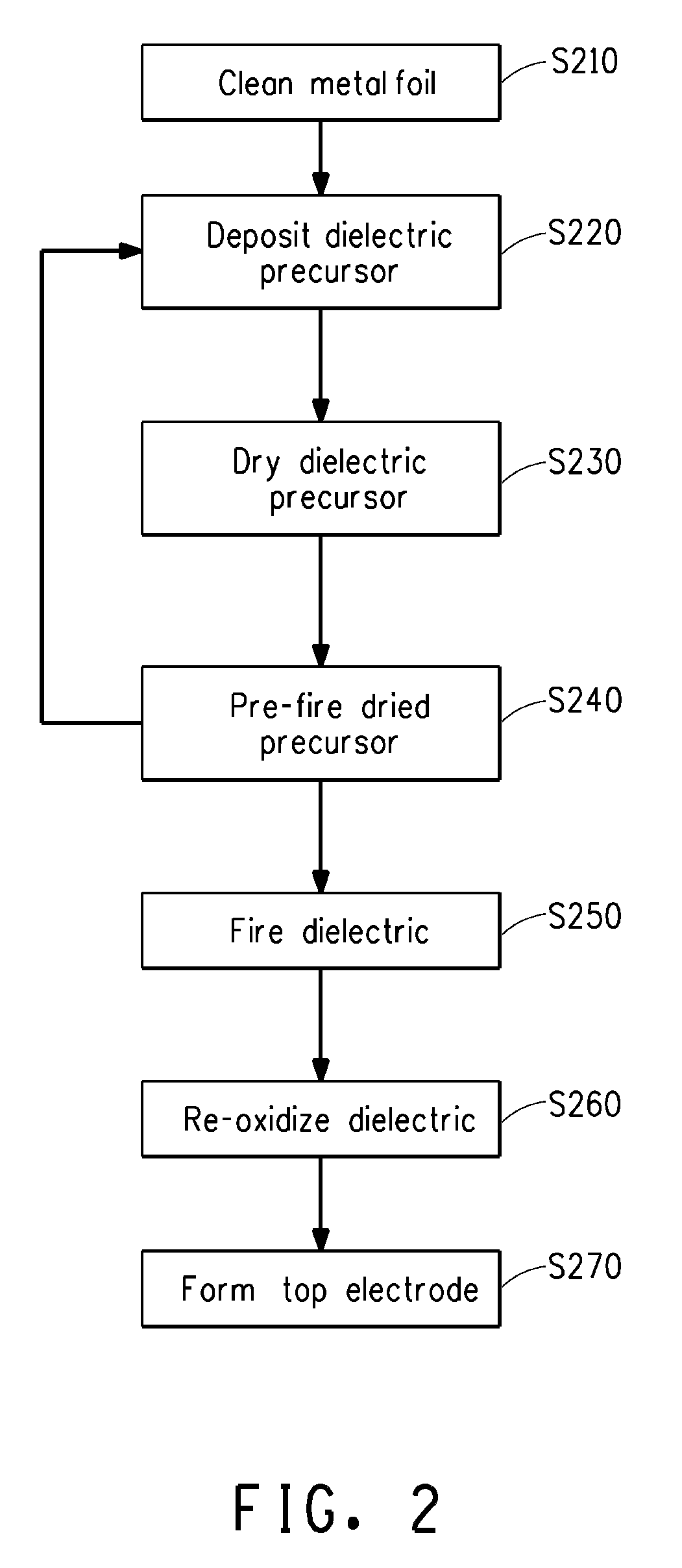
Large area thin film capacitors on metal foils and methods of manufacturing same
InactiveUS20090238954A1Printed circuit assemblingThin/thick film capacitorBarium strontium titanateBarium titanate
Disclosed are a method of making a dielectric on a metal foil, and a method of making a large area capacitor that includes a dielectric on a metal foil. A dielectric precursor layer and the base metal foil are prefired at a prefiring temperature in the range of 350 to 650° C. in a moist atmosphere that also comprises a reducing gas. The prefired dielectric precursor layer and base metal foil are subsequently fired at a firing temperature in the range of 700 to 1200° C. in an atmosphere having an oxygen partial pressure of less than about 10−6 atmospheres to produce a dielectric. The area of the capacitor made according to the disclosed method may be greater than 10 mm2, and subdivided to create a multiple individual capacitor units that may be embedded in printed wiring boards. The dielectric is typically comprised of crystalline barium titanate or crystalline barium strontium titanate.
Owner:CDA PROCESSING LIABILITY
Ferroelectric nanocomposite based dielectric inks for reconfigurable RF and microwave applications
ActiveUS20170009090A1Low loss tangentAntenna arraysPrinted circuit detailsDielectricSemiconductor materials
A novel ferroelectric ink comprising multiphase Barium Strontium Titanate (BST) in a polymer composite is described. The ink can be employed using direct-ink writing techniques to print high dielectric constant, low loss, and electrostatically-tunable dielectrics on substrates. The substrates can be flexible such as plastics or rigid, such as substrates comprising semiconductor materials or ceramics and the like. The dielectric ink is made by suspending pre-sintered nano / submicron-sized particles of BST in a thermoplastic polymer with a solvent. After printing with the ink, a low temperature curing process is performed at temperatures below 200° C., a temperature too low to sinter BST. Fully printed devices, such as a varactor and a phase shifter using direct ink writing methodologies are described.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Strain-relieved tunable dielectric thin films
InactiveUS20030022030A1Relieves film strainStrain-relieved and defect-reduced tunableVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingBarium strontium titanateDielectric loss
Tunable dielectric thin films are provided which possess low dielectric losses at microwave frequencies relative to conventional dielectric thin films. The thin films include a low dielectric loss substrate, a buffer layer, and a crystalline dielectric film. Barium strontium titanate may be used as the buffer layer and the crystalline dielectric film. The buffer layer provides strain relief during annealing operations.
Owner:NXP USA INC
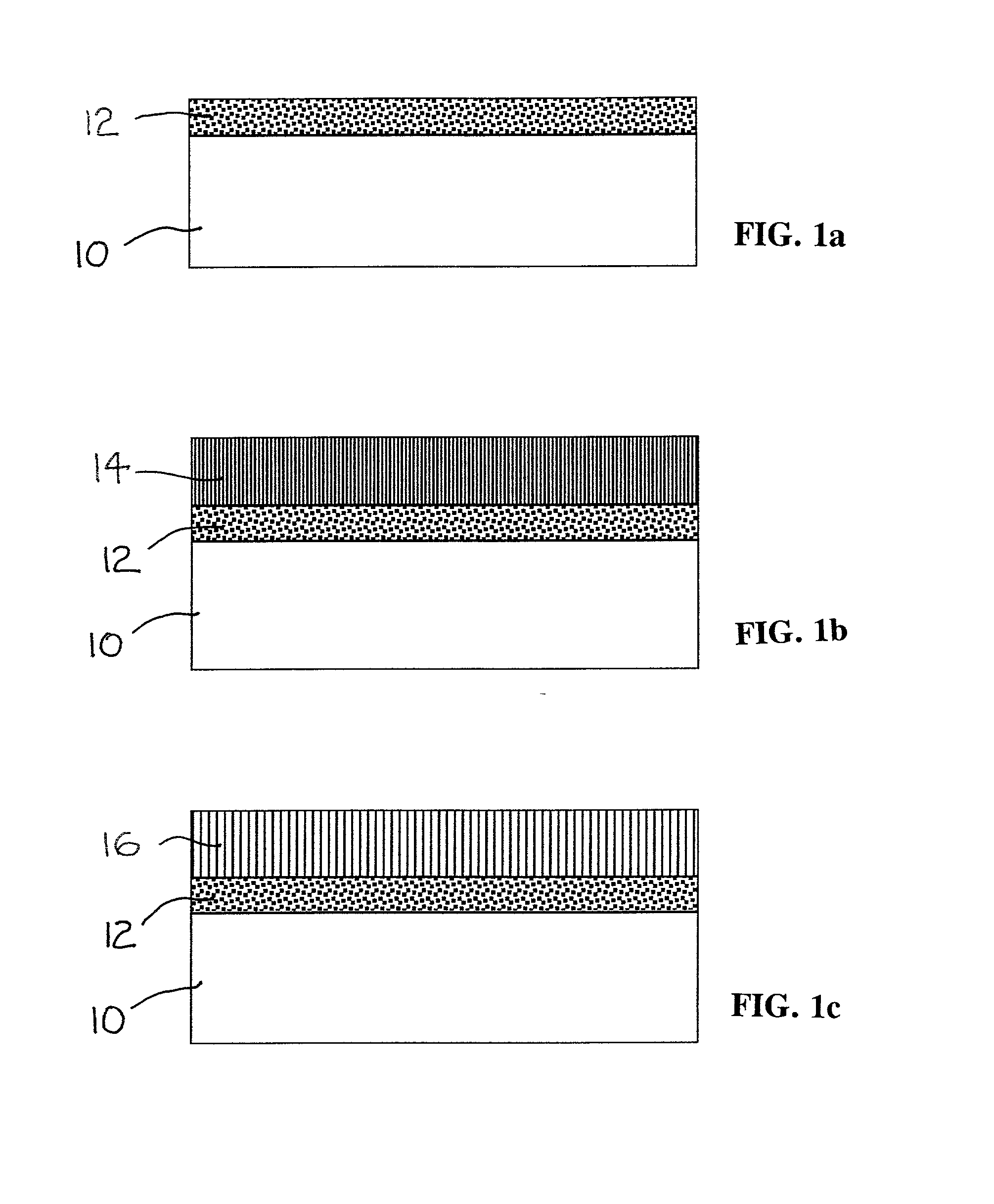
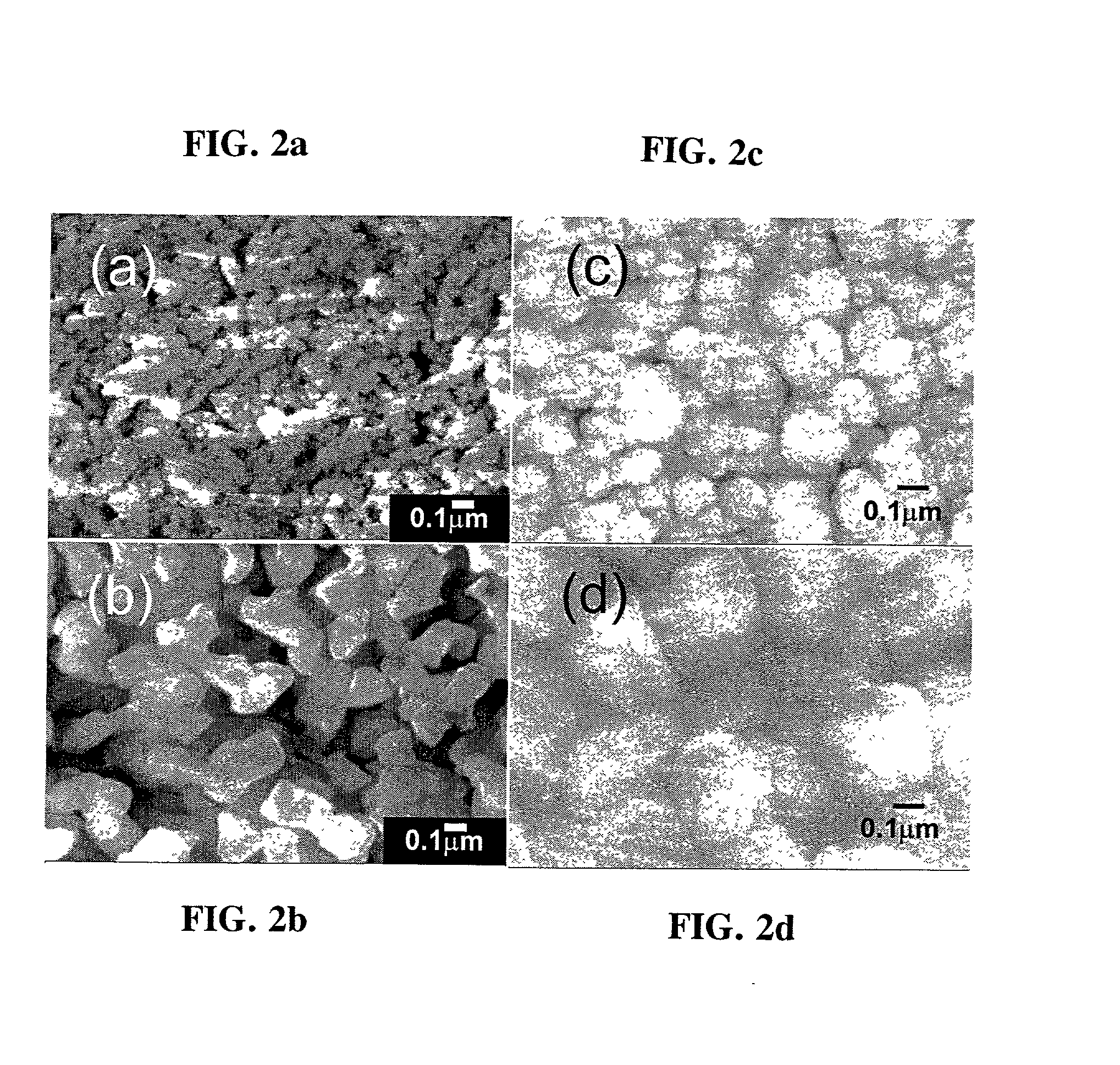
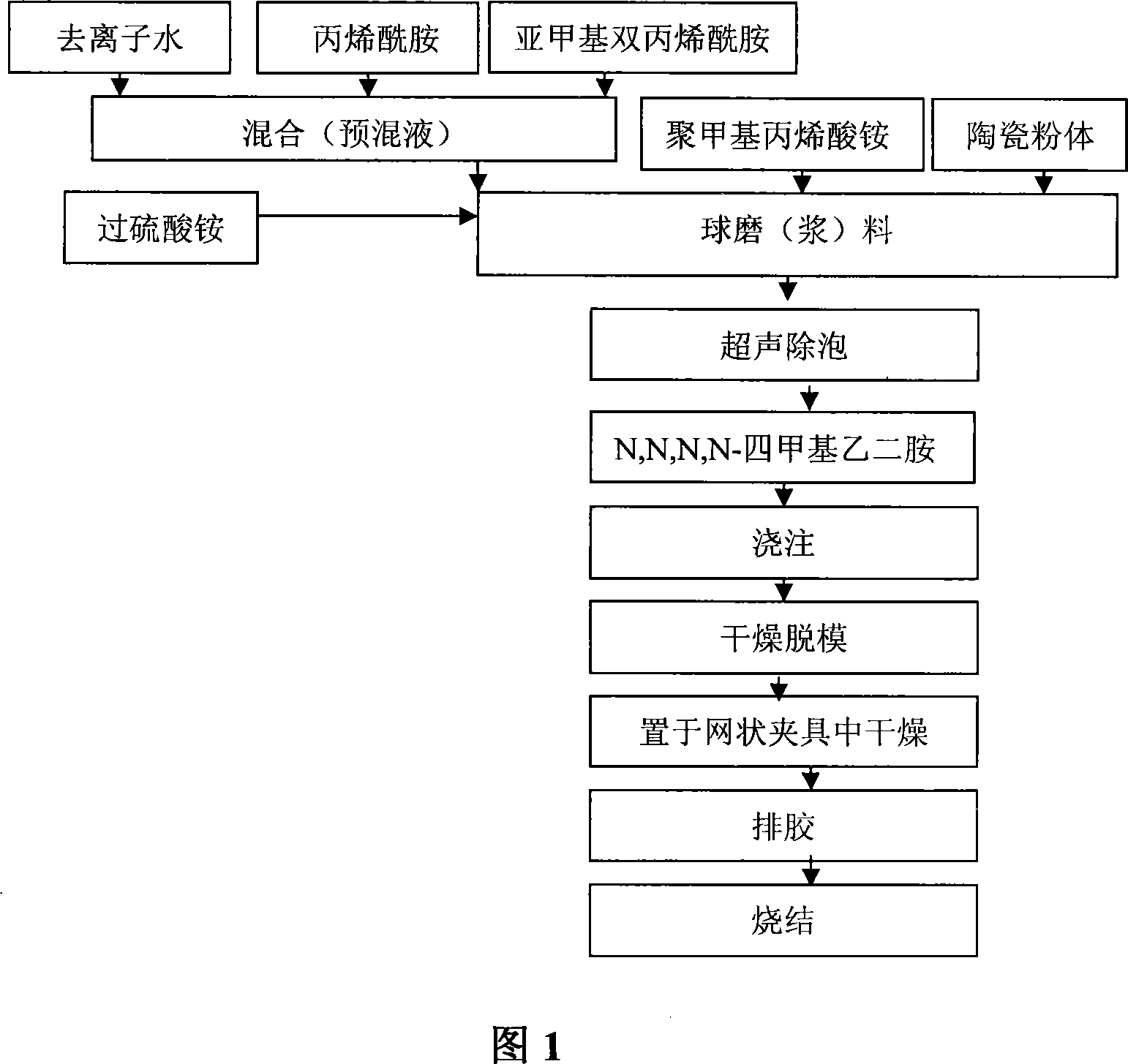
Method of preparing functional ceramic material
ActiveCN101125757AImprove uniformityGuaranteed uniformityLead zirconate titanateBarium strontium titanate
The invention discloses a preparation method of functional ceramics material and comprises the steps: (1) suspending liquid containing organic monomer, cross linker, evocating agent, dispersant and ceramics powder lot is prepared; (2) catalyst is added, slurry is injected into a ring mental die to be solidified in situ and wet rough-body of large size ceramics is obtained; (3) after being demoulded, the rough-body is put into a net clamp, the clamp is put into a climatic chamber to be dried and then put into an oven to be dried after a plurality of days; (4) the dried rough-body is batched out under certain temperature rising system and sintered into ceramics under high temperature. The invention prepares large size high performance lead zinc niobate-lead zirconate titanate piezoceramics, barium strontium titanate pyroelectric ceramics, lead manganese niobate-lead manganese stibate-lead zirconate titanate pyroelectric ceramics.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
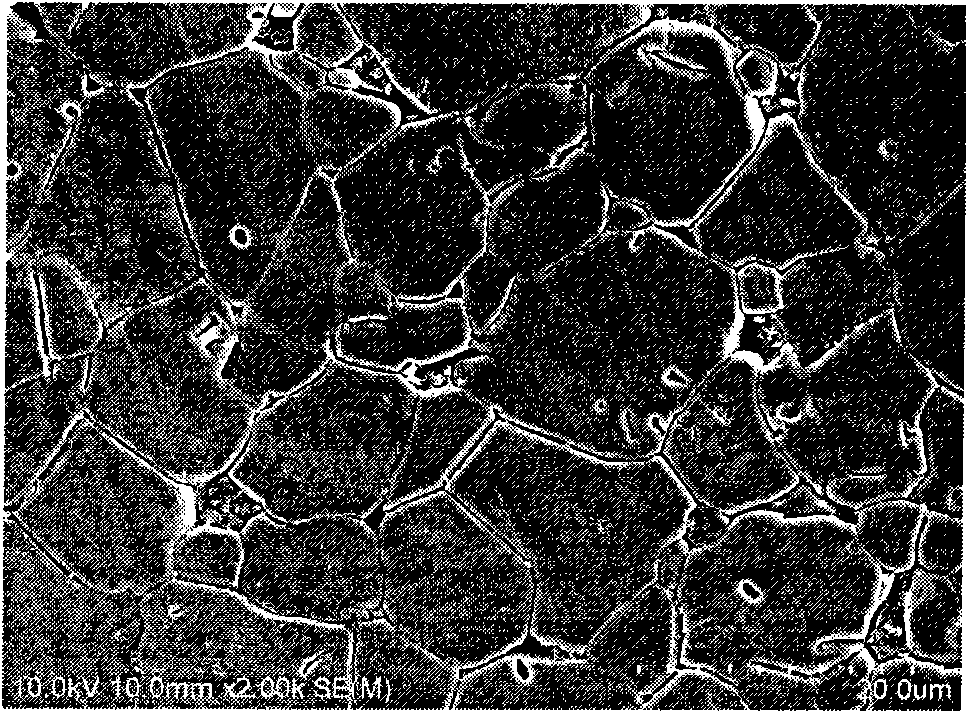
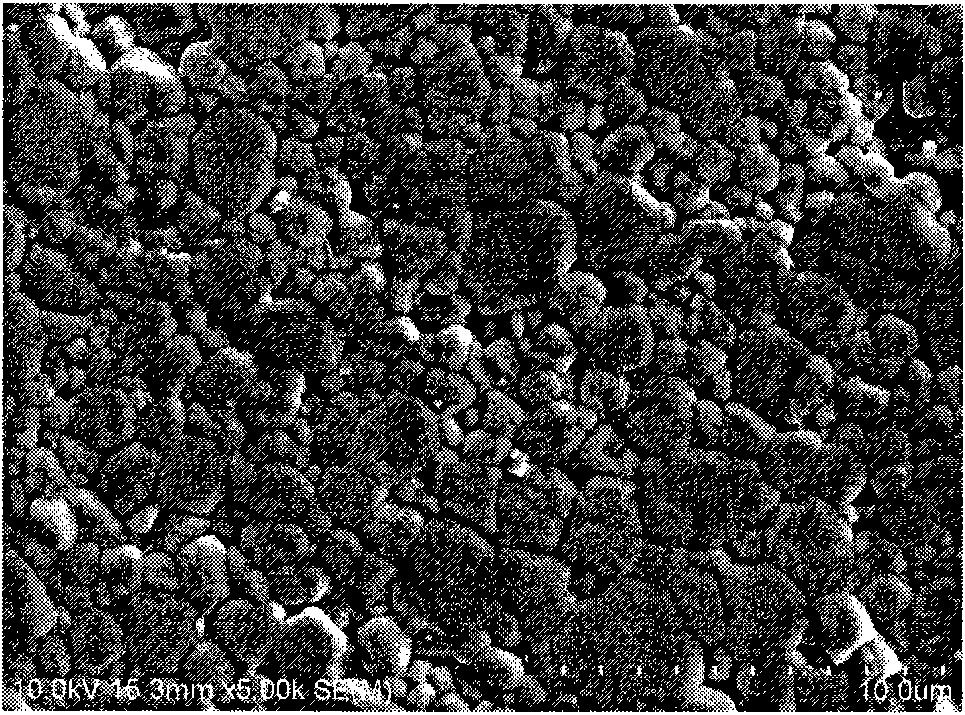
Barium strontium titanate ceramic capacitor material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101659546ALower sintering temperatureShort holding timeFixed capacitor dielectricBarium strontium titanateDielectric loss
The invention relates to a barium strontium titanate ceramic capacitor material and a preparation method thereof. The material is characterized by comprising the following components: 80 to 98 volumepercent of BaxSr1-xTiO3 and 2 to 20 volume percent of BaO-SiO2-B2O3 glass, wherein the range of x is between 0.2 and 0.5; and the molar contents of the compositions in BaO-SiO2-B2O3 glass are: 48 to 49 percent of BaO, 20 to 21 percent of SiO2, 26 to 27 percent of B2O3, 1 to 2 percent of SrO, 1 to 2 percent of ZrO2, 0.5 to 1 percent of Al2O3, 0.1 to 0.4 percent of MgO and 0.1 to 0.3 percent of Bi2O3. The barium strontium titanate ceramic capacitor material and the preparation method thereof provided by the invention can reduce the sintering temperature of barium strontium titanate by 250 to 400DEG C and the holding time to 1 hour, refine crystal grains to 1 to 3 micrometre, maintain dielectric loss at 1*10<-3> and increase pulse breakdown field strength to 40kV / mm, thereby meeting the requirements of a ceramic capacitor.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
Bismuth ferrite base film layer stacked structure capacitor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102222672AGood lattice matchingImprove insulation performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBarium strontium titanateLanthanide
The invention discloses a bismuth ferrite base film layer stacked structure capacitor and a preparation method thereof, wherein the capacitor comprises a bottom electrode, a substrate, a buffer layer, a ferroelectric film layer and a metal point electrode in sequence from the bottom to top; the buffer layer is a manganese-doped barium strontium titanate film, the chemical formula is Ba0.6Sr0.4Ti(1-x)MnxO3, x is the mole equivalent of element manganese, and x is equal to 0.005-0.05; and the ferroelectric film layer is a bismuth ferrite base film, the chemical formula is Bi(1-y)LnyFeO3, wherein Ln is one of lanthanide, y is the mole equivalent of lanthanide, and y is equal to 0.01-0.2. The preparation method is simple, and the obtained capacitor is a storage cell of a ferro-electric field effect transistor; and the capacitor overcomes the defects that the bismuth ferrite base film capacitor on ordinary silicon substrate has the defects of poor interface performance and high working voltage, and has good energy storage performance.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Capacitive strain sensor and preparation method therefor
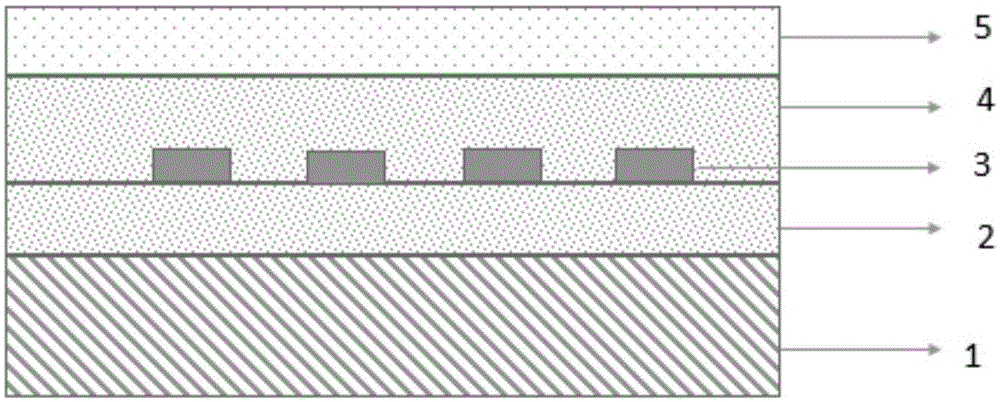
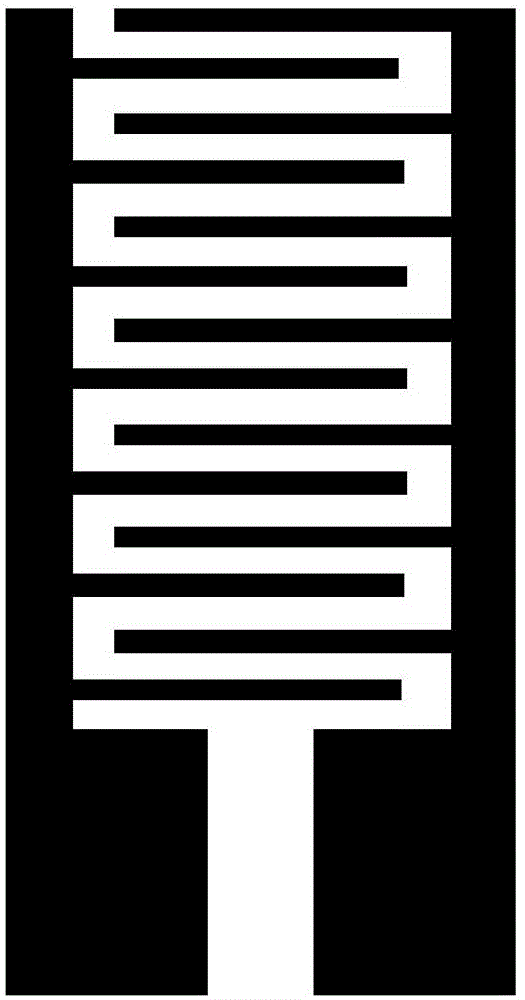
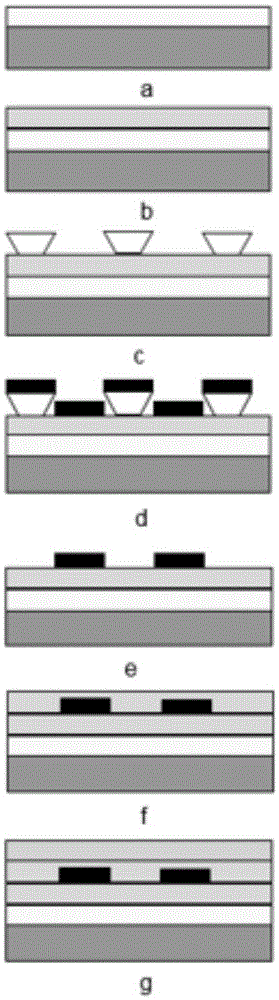
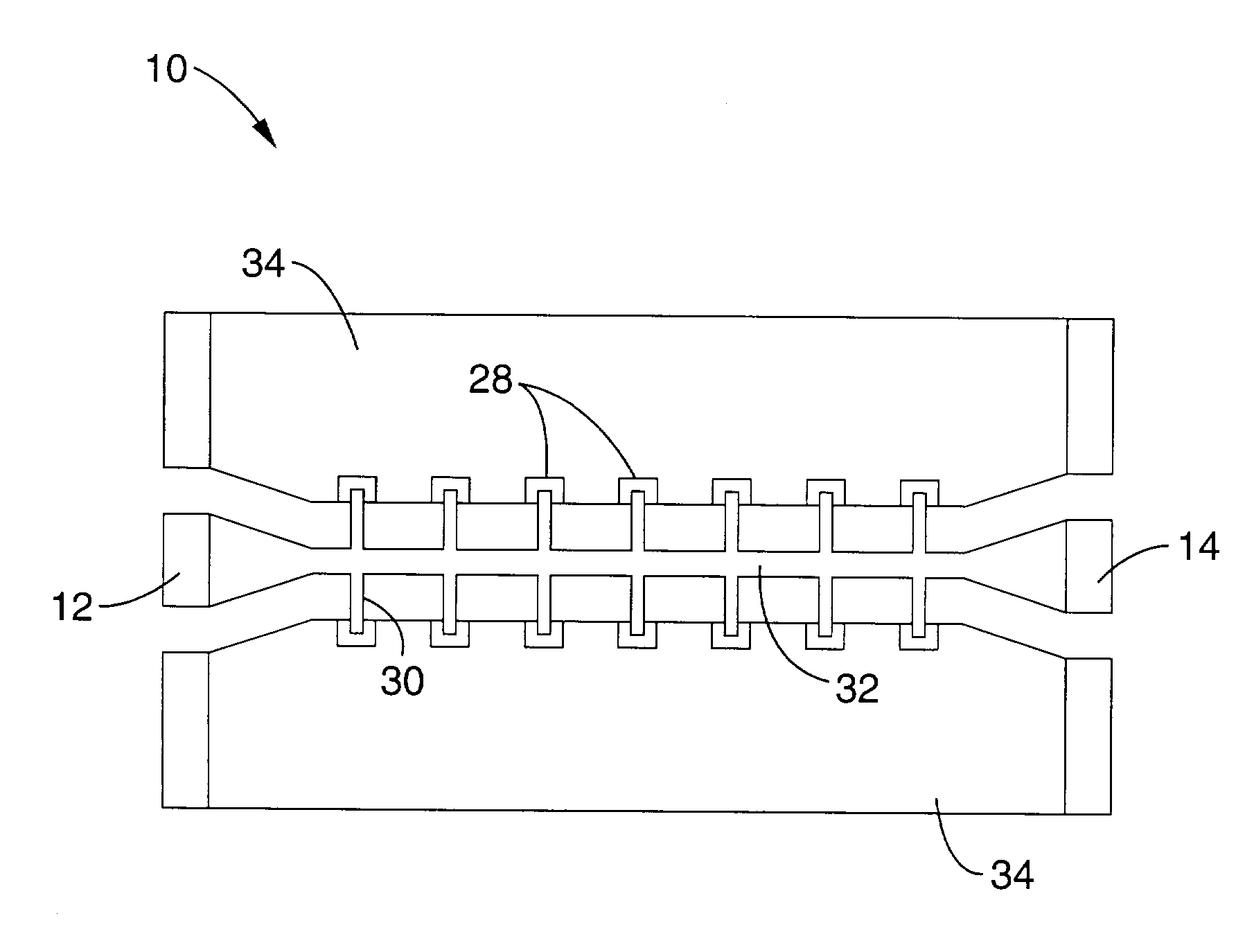
ActiveCN105021120AIncreased strain sensitivityLarge GF factorElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementStrontium titanateCapacitance
The invention provides a capacitive strain sensor and a preparation method therefor, and belongs to the technical field of sensor design and production. The sensor is sequentially provided with a substrate, a first barium strontium titanate dielectric film layer, a PdCr electrode layer, a second barium strontium titanate dielectric film layer and an Al2O3 protection layer from the bottom to the top, wherein the PdCr electrode layer is in an interdigital electrode structure. The sensor employs an interdigital capacitive plane structure, takes barium strontium titanate (Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3) as a dielectric material, takes PdCr as an electrode material, and achieves a purpose of stable operation under bigger strain (2500 mu*epsilon) and higher temperature (500 DEG C) employs a preparation technology combining magnetron sputtering coating with the photoetching technology.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Preparation method of nano flaky ferroelectric material for photocatalysis
InactiveCN103523824ASmall particle sizeHigh crystallinityMaterial nanotechnologyTitanium compoundsBarium strontium titanateBarium salt
The invention relates to a preparation method of a nano flaky ferroelectric material for photocatalysis. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing barium salt, strontium salt and titanium salt to obtain premix according to a barium strontium titanate (BaxSr1-xTiO3) molecular formula, mixing barium salt and strontium salt according to proportions and dissolving in water, adding NaOH, dissolving titanium salt in absolute ethyl alcohol, uniformly mixing the raw materials, carrying out thermal reaction for 24 hours in a high-pressure kettle at 160-200 DEG C, cooling to room temperature in air, filtering, washing and drying the mixture to obtain nano flaky barium strontium titanate powder. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method has the advantages that the process is simple and few aggregation phenomena of prepared nano particles exist; in comparison with barium strontium titanate nano powder prepared by a conventional hydrothermal method, the preparation method, which adopts butyl titanate as a titanium source, has the characteristics of high purity of a prepared sample, good crystallinity of powder and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Electronic and optical devices and methods of forming these devices
InactiveUS20060228064A1Reduce lossesAlign dielectric changeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBarium strontium titanatePhotonics
Electronic and optical (or photonic) devices with variable or switchable properties and methods used to form these devices, are disclosed. More specifically, the present invention involves forming layers of conductive material and dielectric material or materials with varying conductivity and indexes of refraction to form various electronic and optical devices. One such layer of adjustable material is formed by depositing epitaxial or reduced grain boundary barium strontium titanate on the C-plane of sapphire.
Owner:NGIMAT CO
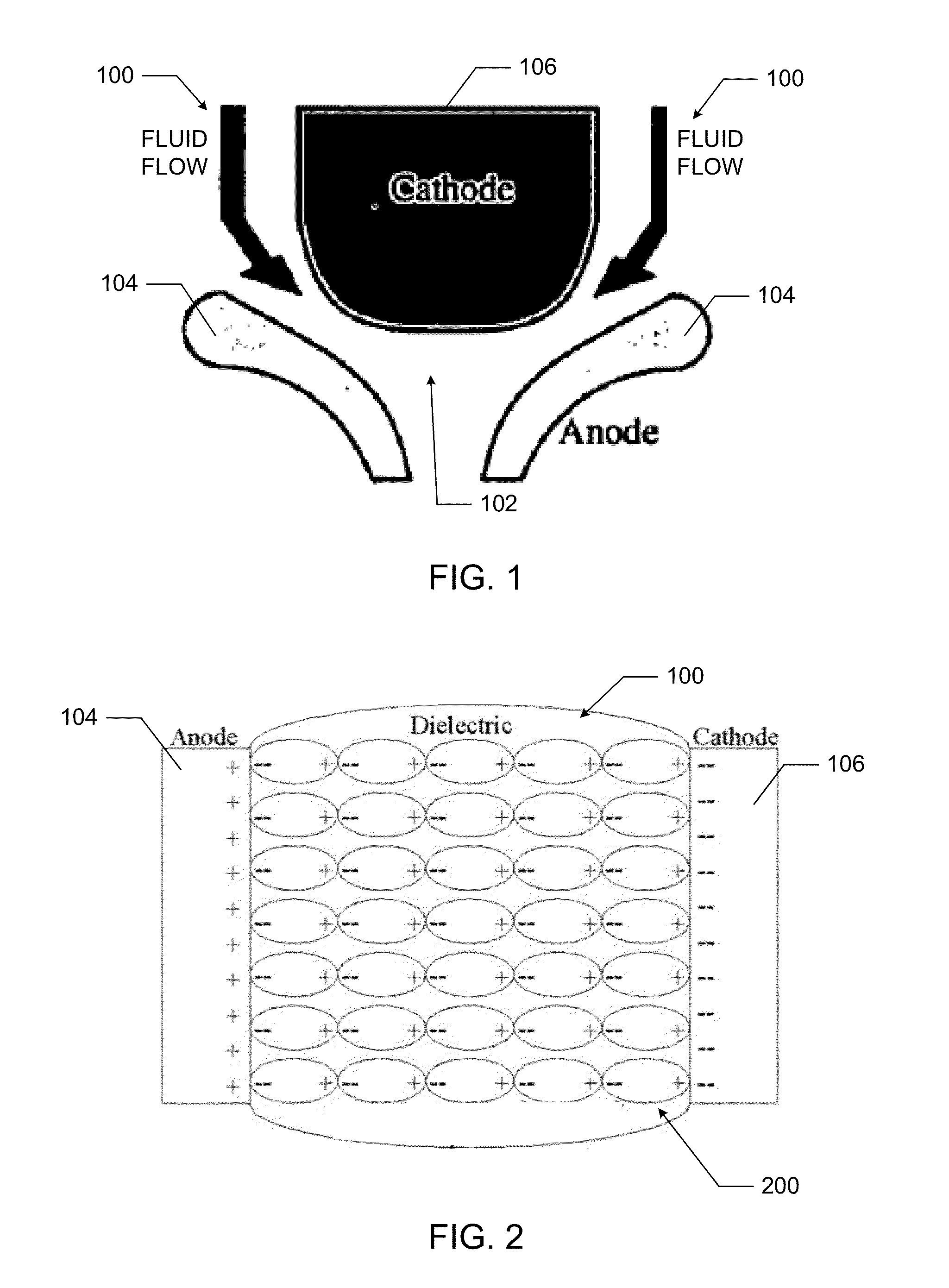
Dielectric loaded fluids for high voltage switching
InactiveUS20130062314A1Increased formationReduce voltageMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid organic insulatorsElectricityBarium strontium titanate
This disclosure relates to methods and systems to reduce high voltage breakdown jitters in liquid dielectric switches. In particular, dielectric liquids have been produced that contain a suspension of nanoparticles and a surfactant to reduce the breakdown jitter. In one embodiment, the suspended nanoparticles are Barium Strontium Titanate (BST) nanoparticles.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Preparation method of barium strontium titanate ceramic
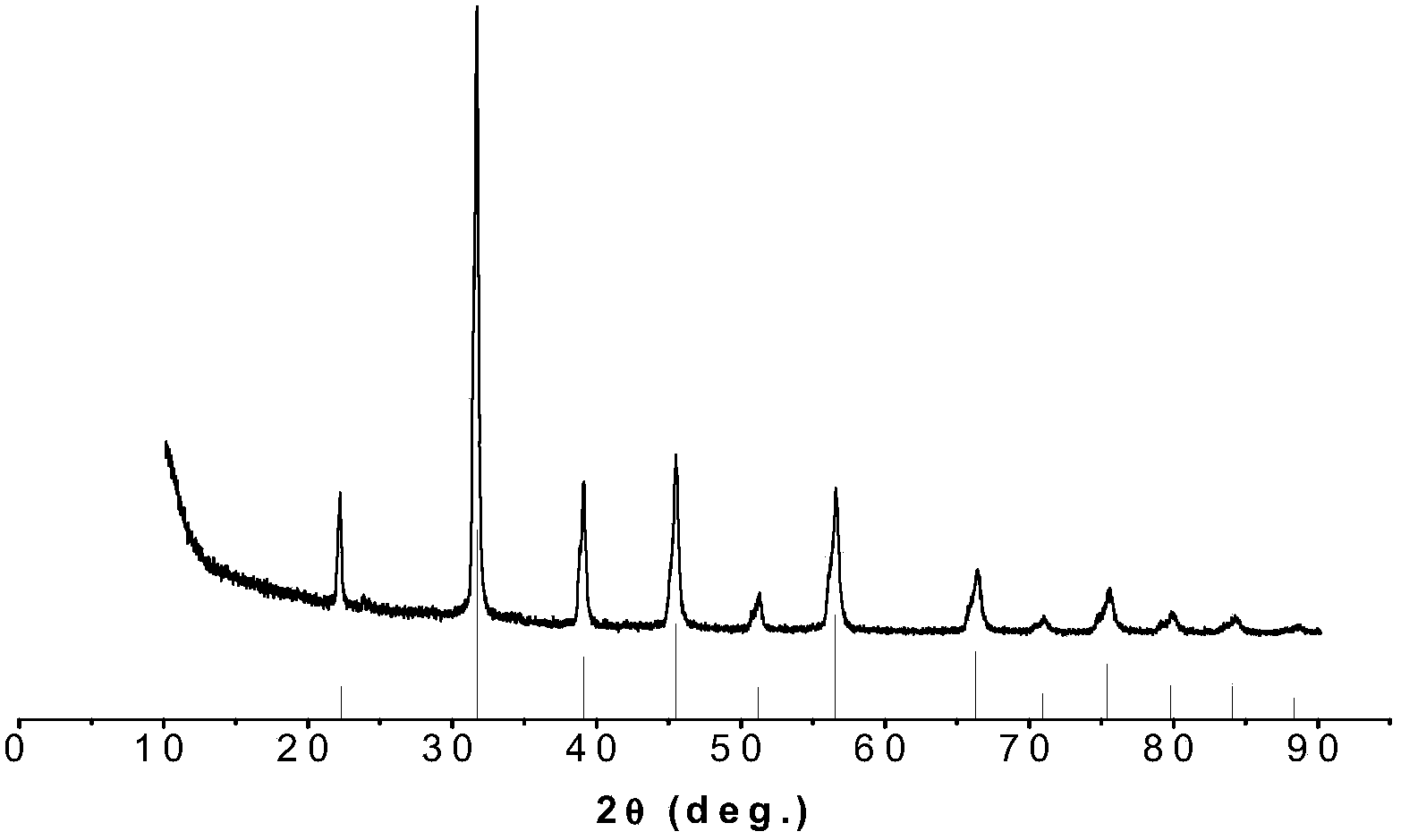
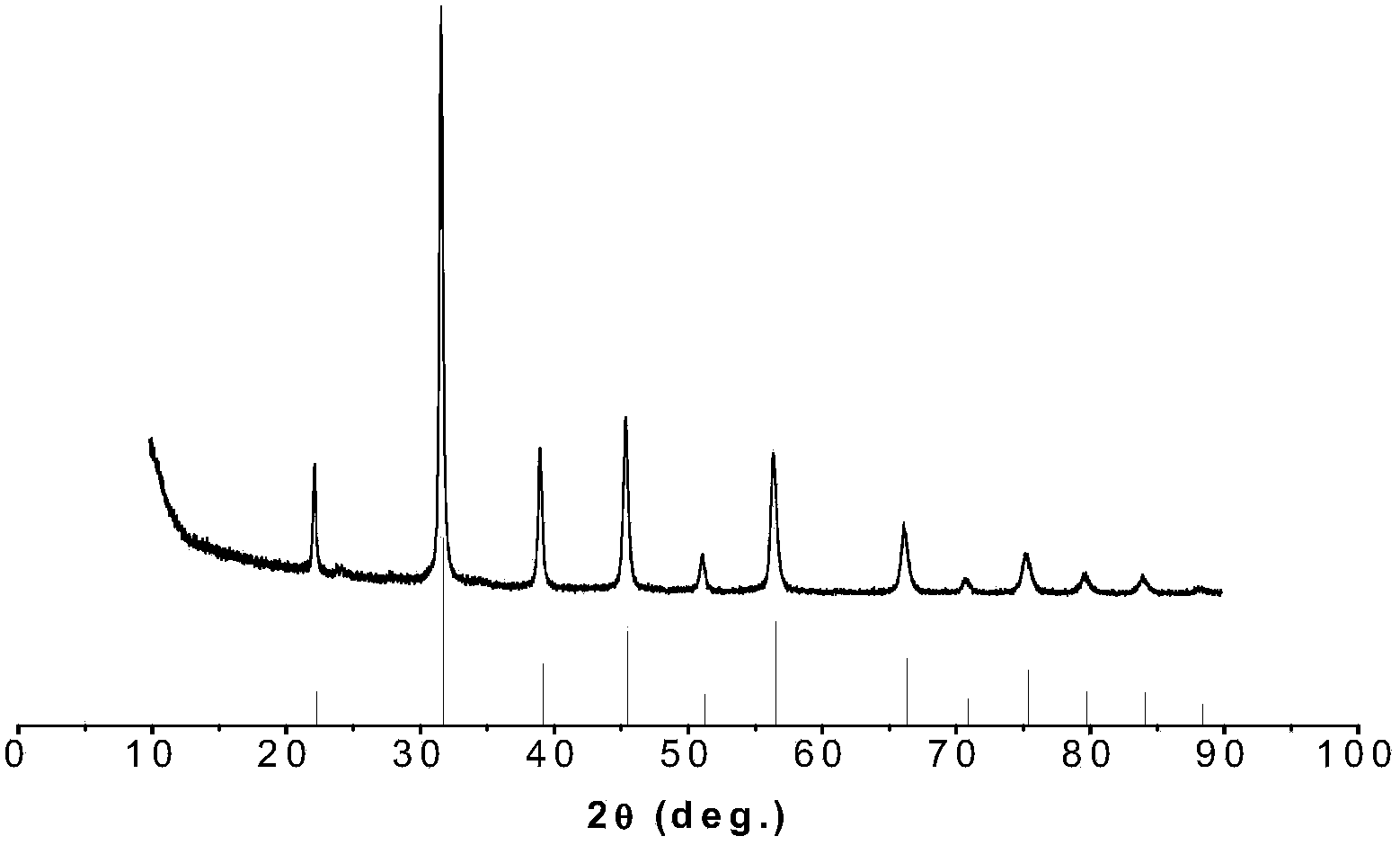
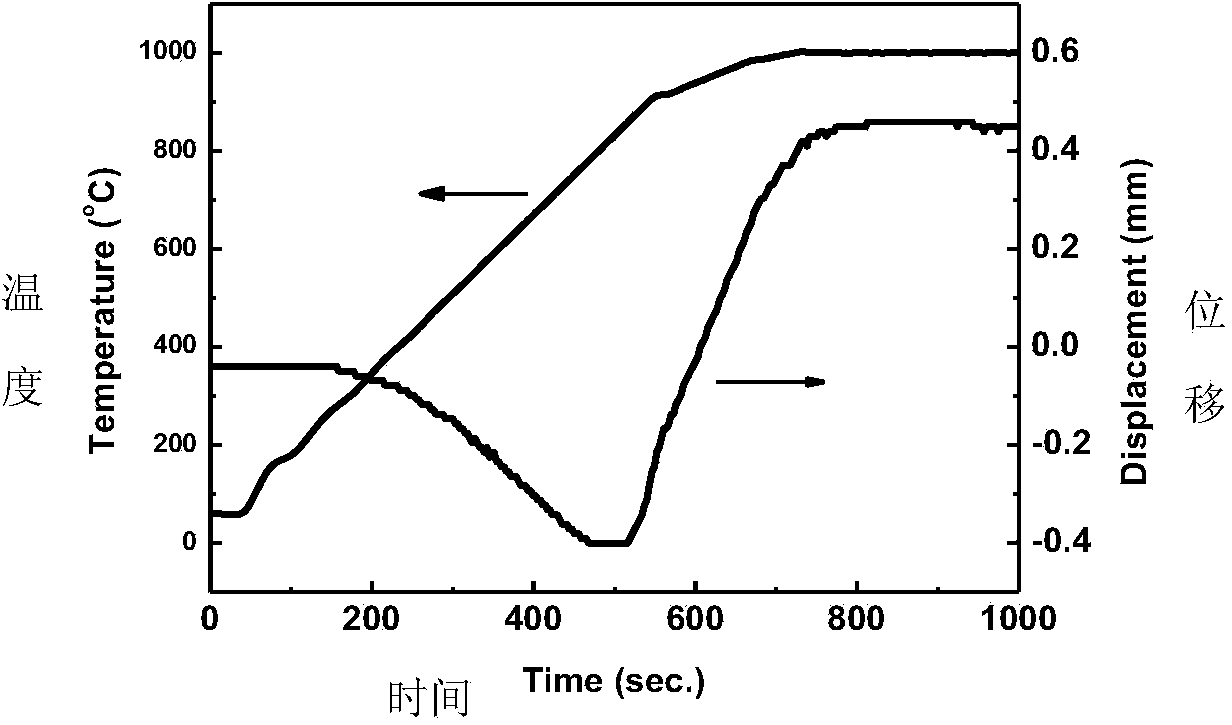
InactiveCN103739283AImprove dielectric breakdown strengthHigh energy storage densityAir atmosphereCeramic sintering
The invention discloses a preparation method of a barium strontium titanate ceramic. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing raw materials of BaCO3, SrCO3, and TiO2 according to a chemical formula Ba<1-x>Sr<x>TiO3, grinding, then drying, sieving; (2) calcinating the powder obtained in the step (1) at a temperature of 1100 to 1250 for 1 to 5 hours, then sieving; (3) loading the powder obtain in the step (2) into a mould, sintering the mould at a temperature of 900 to 1050 DEG C under vacuum environment by using a spark plasma sintering system so as to obtain a ceramic sintered body; (4) performing a thermal treatment on the sintered body at a temperature of 800 to 1100 DEG C in the air for 1 to 5 hours so as to obtain the barium strontium titanate ceramic. The Ba<1-x>Sr<x>TiO3 ceramic has an energy density, which can reach 1.13 J / cm3 or more, and the energy density of the Ba<1-x>Sr<x>TiO3 ceramic is at least two times higher than that of ceramics which are prepared by the conventional sintering method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
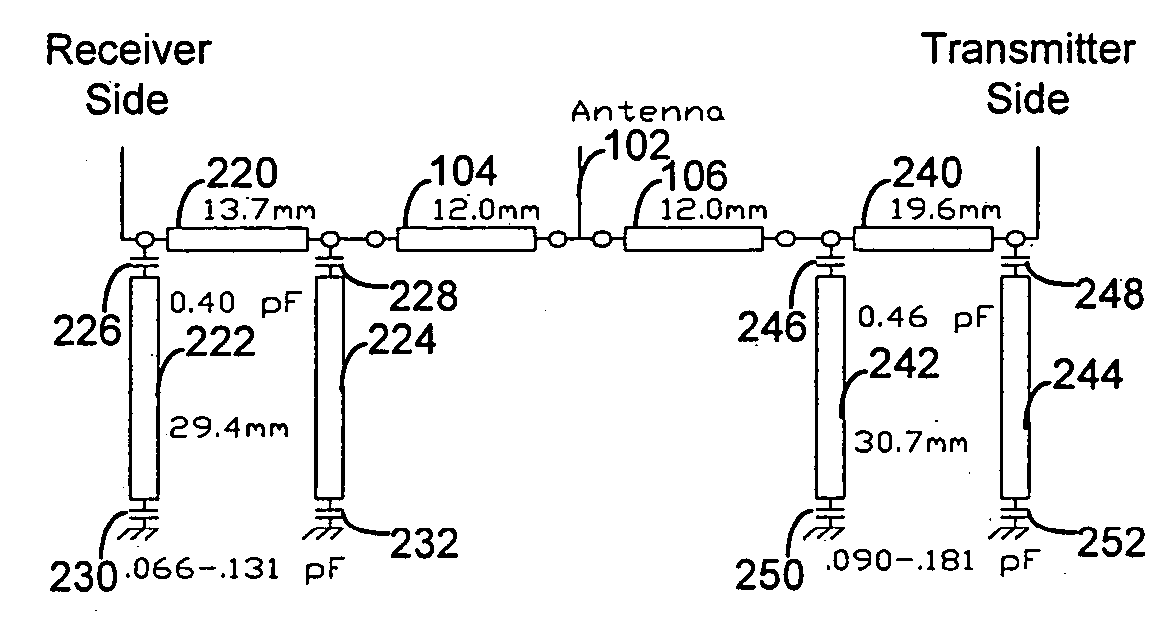
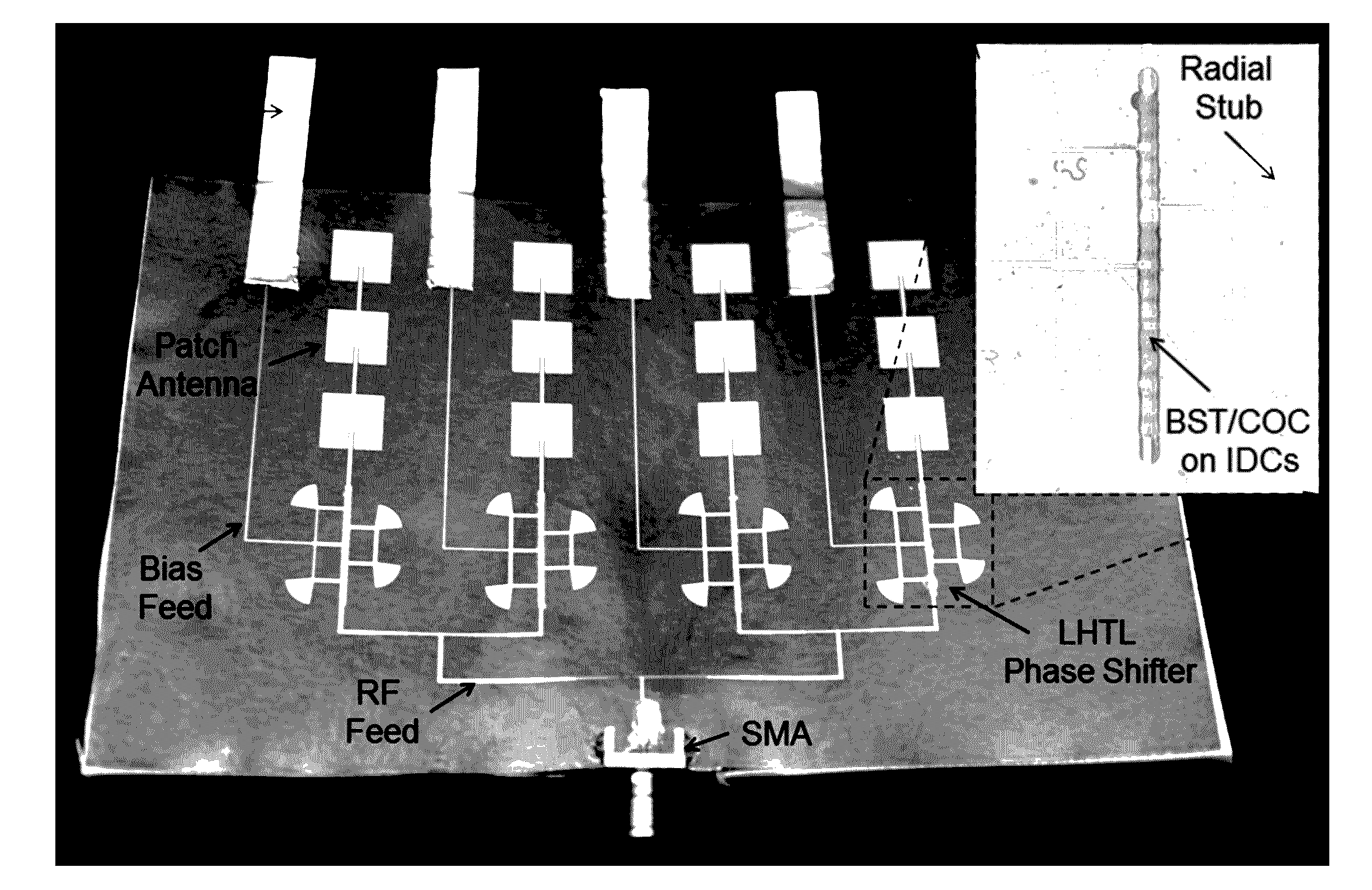
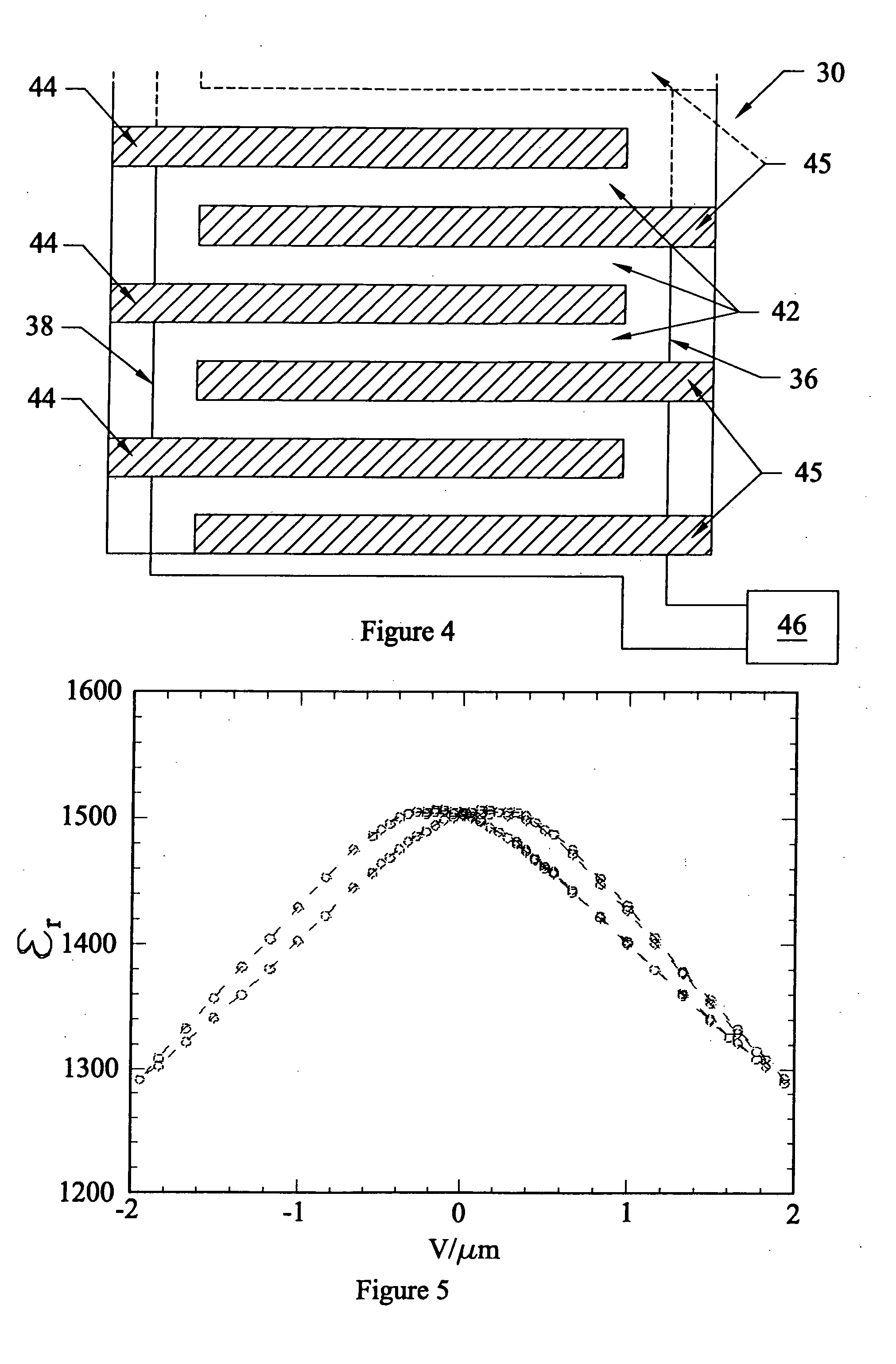
Phase shifters using transmission lines periodically loaded with Barium Strontium Titanate (BST) capacitors
InactiveUS20040017270A1Increase volumeLow costDelay linesWaveguidesSputteringBarium strontium titanate
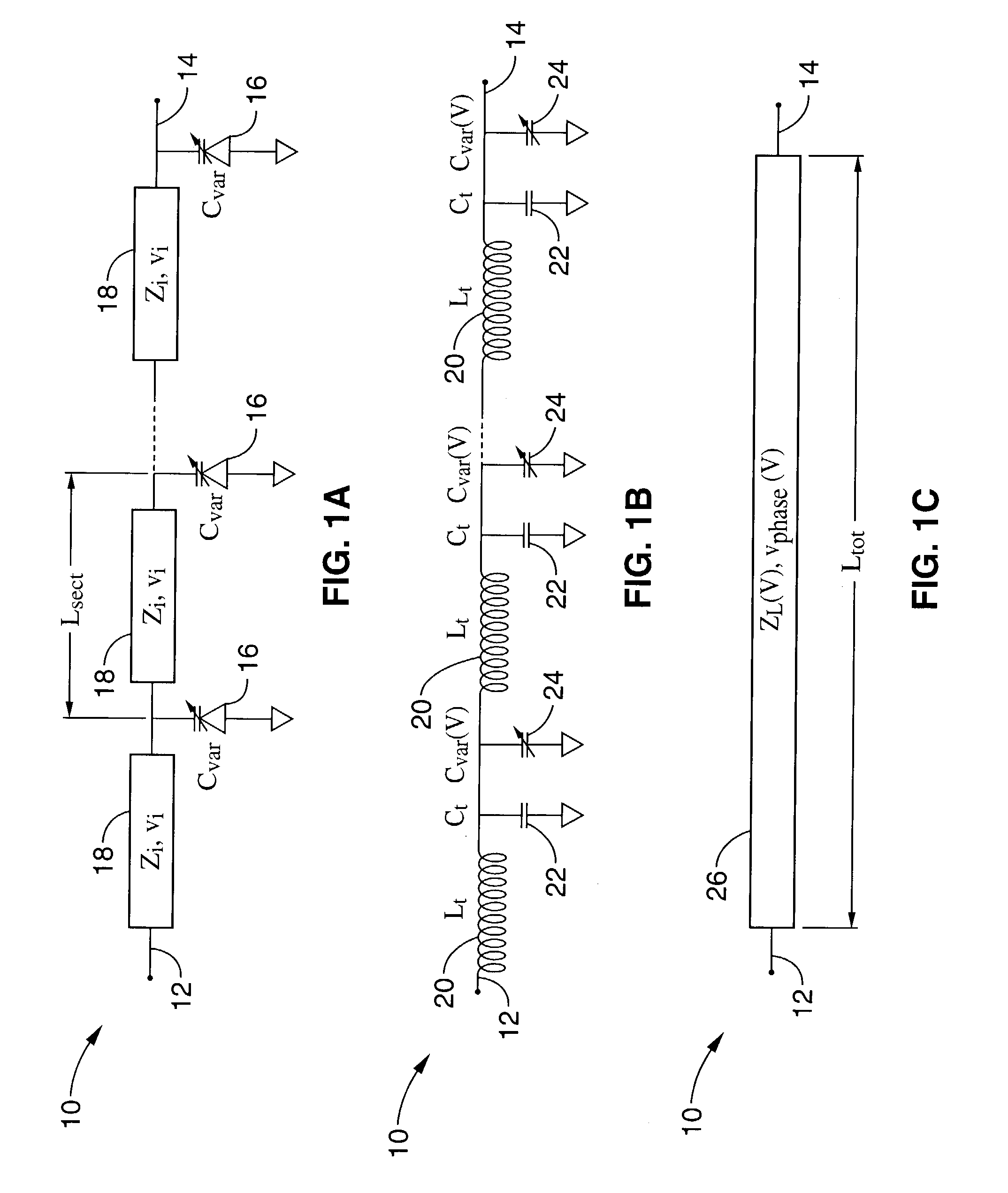
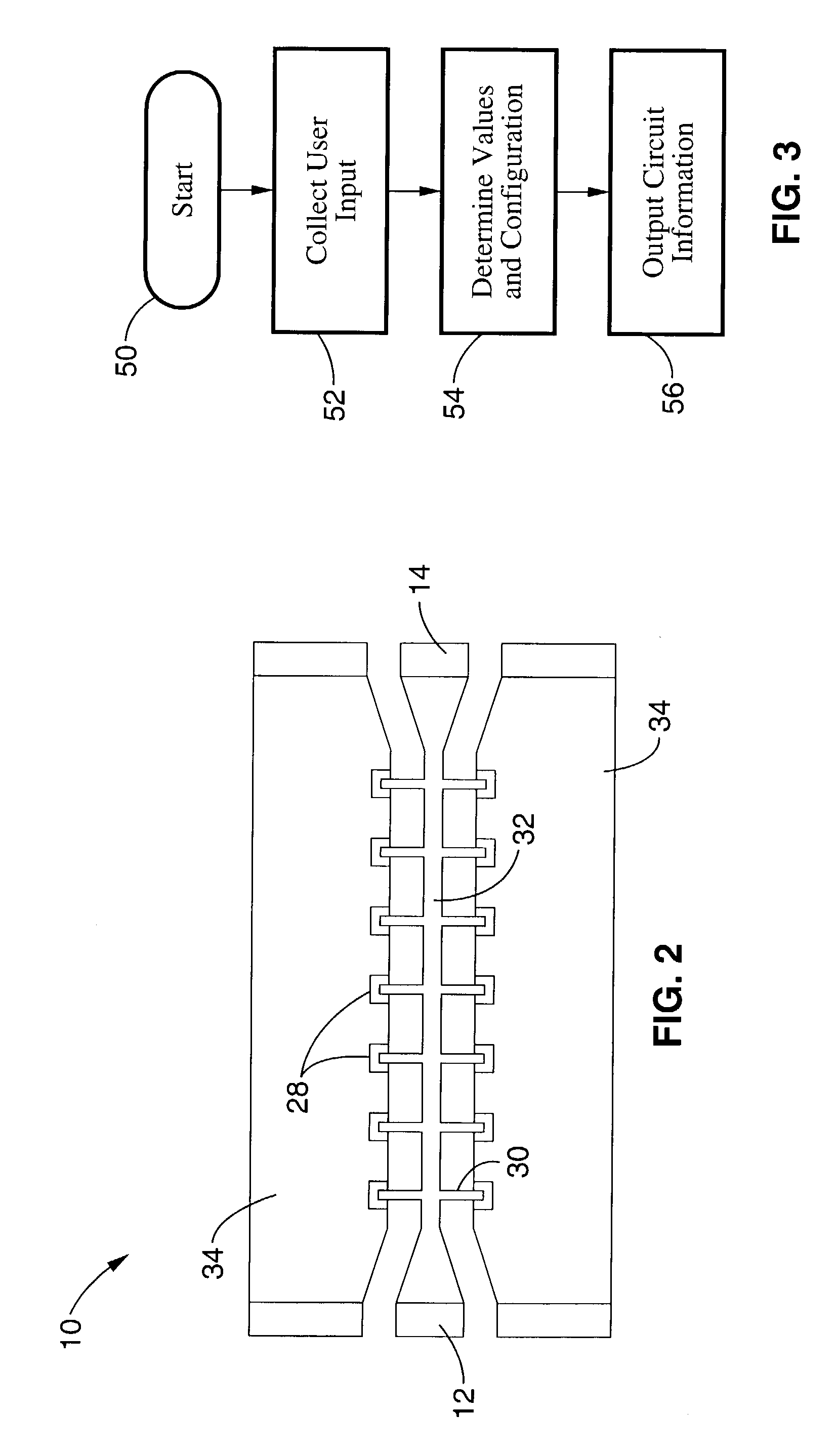
A phase shifter, such as for use in phased antenna arrays, comprising thin film BST capacitors periodically loading a transmission line. The BST thin films can be deposited using RF sputtering on a variety of substrates, and the capacitors can be of a parallel plate configuration or of an interdigitated configuration. An aspect of the invention additionally provides for the use of periodically distributed lumped-element inductors comprising the transmission line. A further aspect provides for programmatic determination of circuit design and configuration parameters based on the input of desired characteristics and materials for the phase shifter.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Process for producing thin-film capacitor
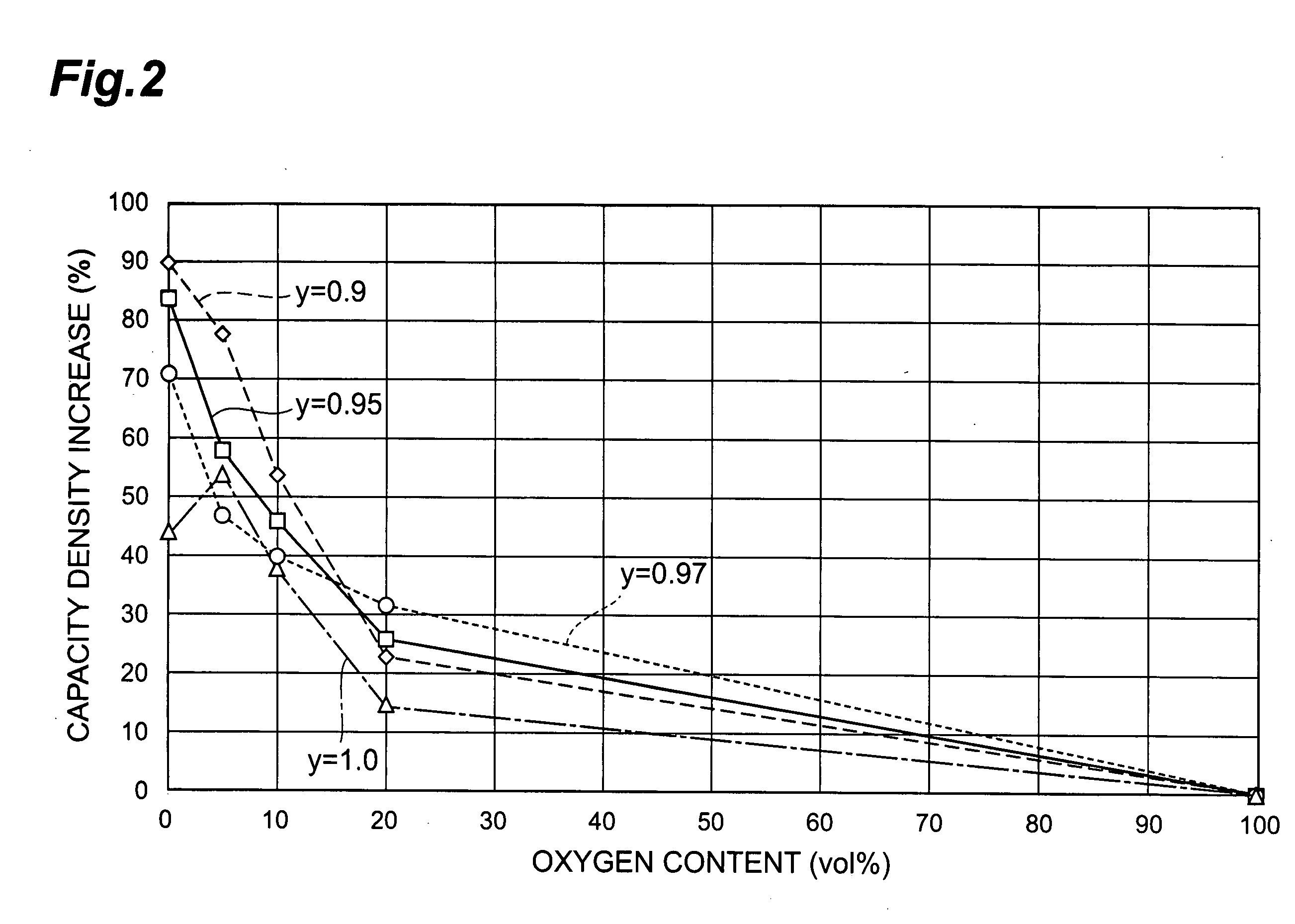
ActiveUS20090176345A1High capacity densityReduced leak current densityThin/thick film capacitorSolid-state devicesBarium strontium titanateLeakage current density
It is an object of the invention to provide a process for production of a thin-film capacitor that can simultaneously achieve improved capacity density and reduced leakage current density for barium strontium titanate thin-films. There is provided a process for production of thin-film capacitors that includes a metal oxide thin-film forming step in which an organic dielectric starting material is fired to form a barium strontium titanate thin-film, wherein the firing atmosphere used is an oxygen-containing inert gas atmosphere, and the barium strontium titanate thin-film formed by the process has a larger capacity density than the capacity density of the barium strontium titanate thin-film fired in an oxygen atmosphere.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
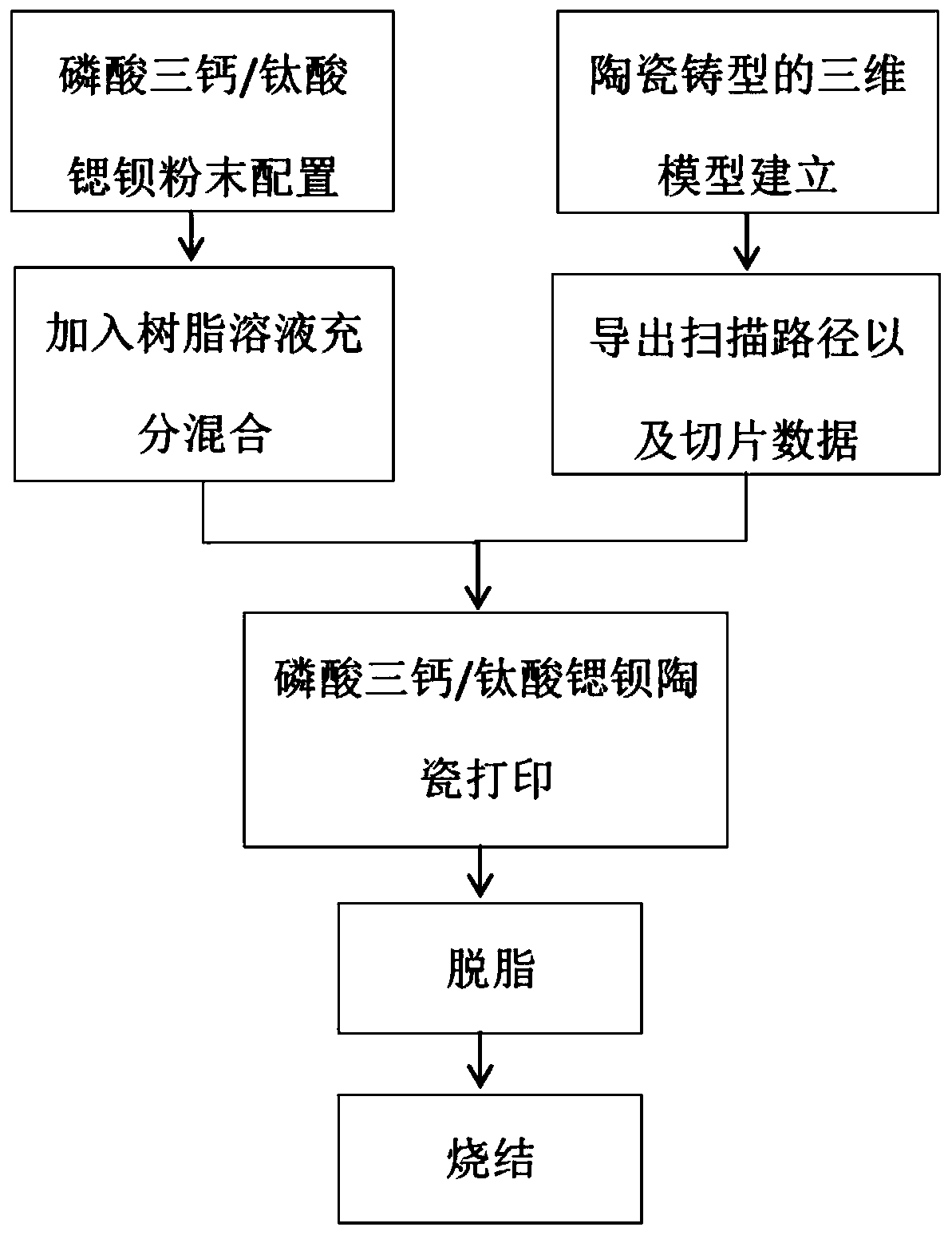
Method for preparing tricalcium phosphate/barium strontium titanate composite biological ceramic with minimum curved surface structures on basis of 3D (three-dimensional) printing technologies
ActiveCN109734434AImprove high temperature stabilityImprove antioxidant capacityAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusBarium strontium titanatePhosphate
The invention discloses a method for preparing tricalcium phosphate / barium strontium titanate composite ceramic with minimum curved surface structures by means of 3D (three-dimensional) printing, andbelongs to the field of 3D printing technologies and biological ceramic. Compositions for the tricalcium phosphate / barium strontium titanate composite ceramic mainly include 35-70 vol% of tricalcium phosphate / barium strontium titanate composite ceramic powder and 30-65 vol% of photosensitive resin premixed liquid. The method has the advantages that DLP (digital light processing) (digital light curing) 3D printing technologies are high in forming speed and printing model precision and low in cost; Rhino software designs are used, minimum curved surface models are optimized, models are importedinto Q3DP software, scanning data are sliced and exported, slurry is prepared according to certain proportions, ball-milling is carried out, the slurry is led into resin grooves of BESK printers, printing is started, printed bodies are further placed into medium-sized furnaces to be degreased and sintered, accordingly, the tricalcium phosphate / barium strontium titanate composite ceramic with the stable structure, excellent mechanical properties, piezoelectric properties and biocompatibility can be ultimately obtained, and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com