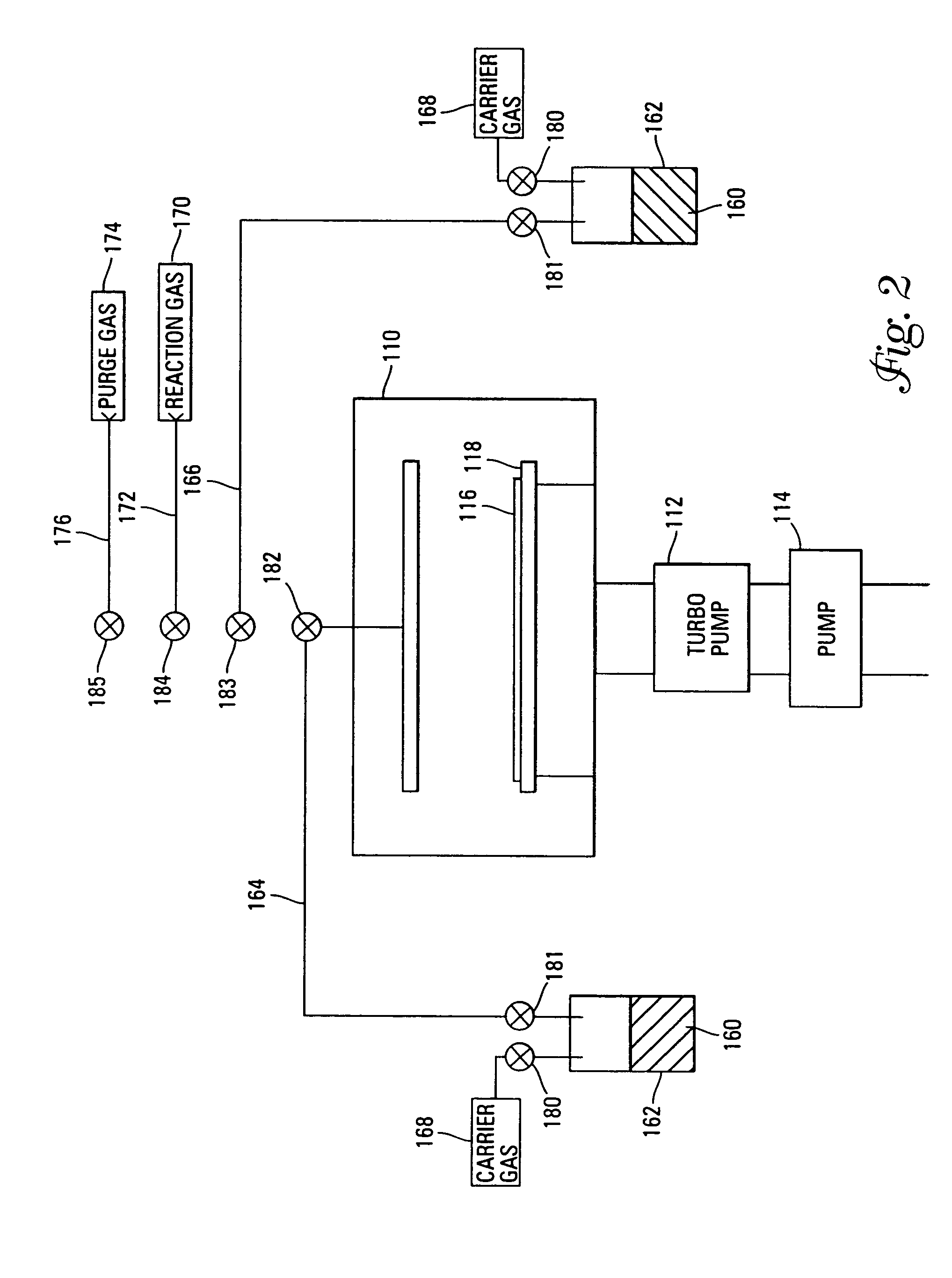
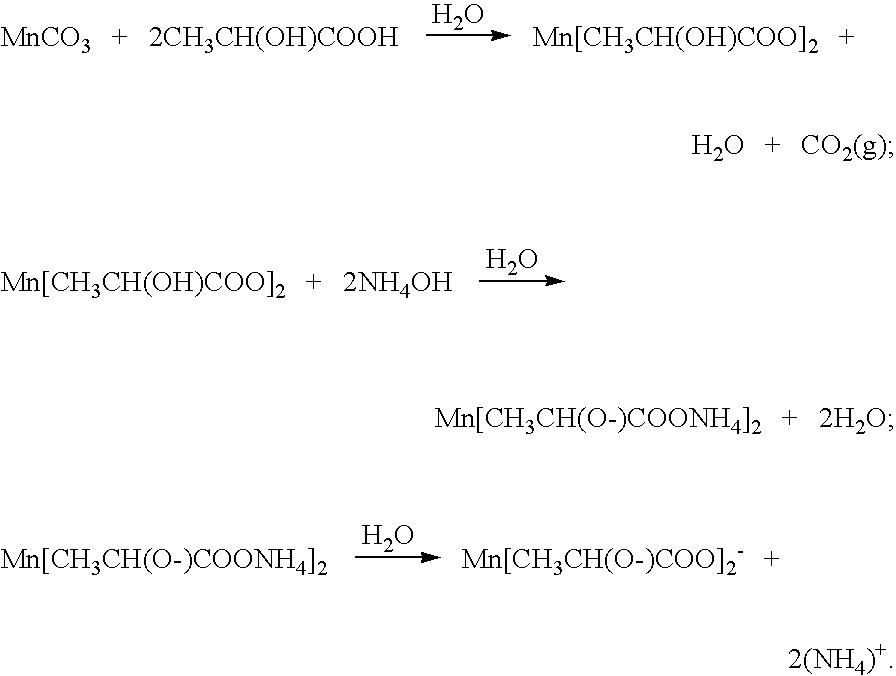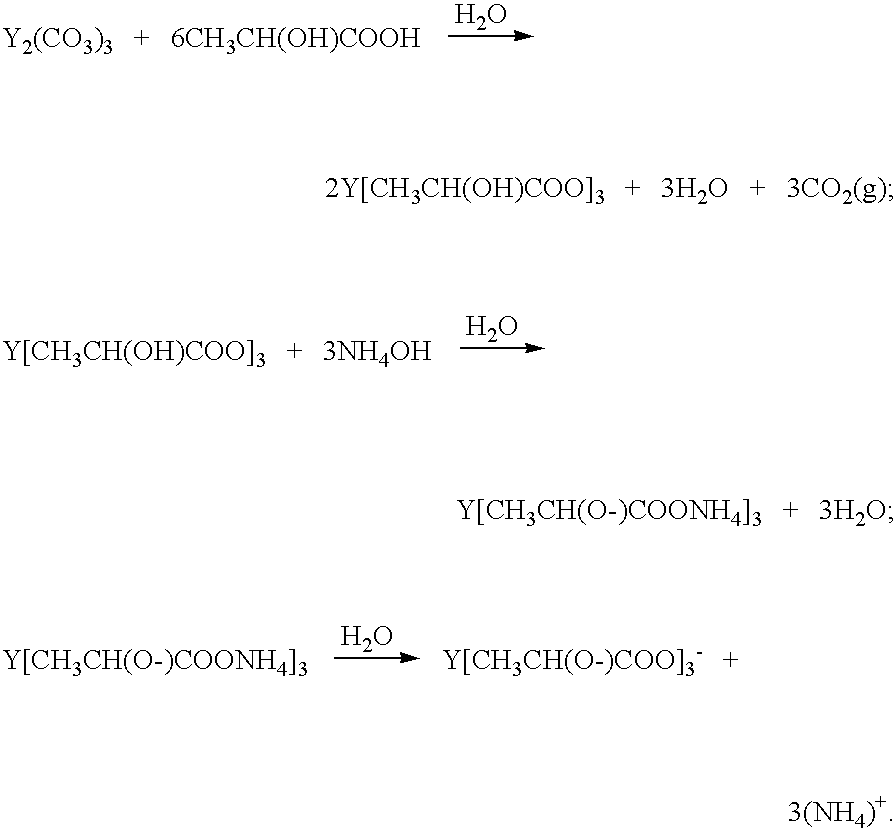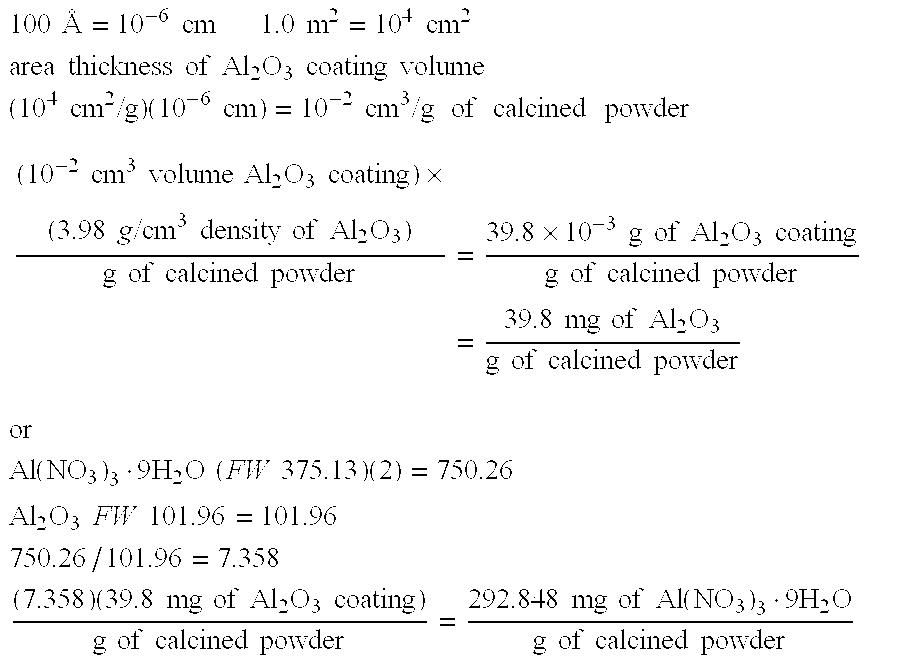Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2491 results about "Barium titanate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Barium titanate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula BaTiO₃. Barium titanate appears white as a powder and is transparent when prepared as large crystals. It is a ferroelectric ceramic material that exhibits the photorefractive effect and piezoelectric properties. It is used in capacitors, electromechanical transducers and nonlinear optics.
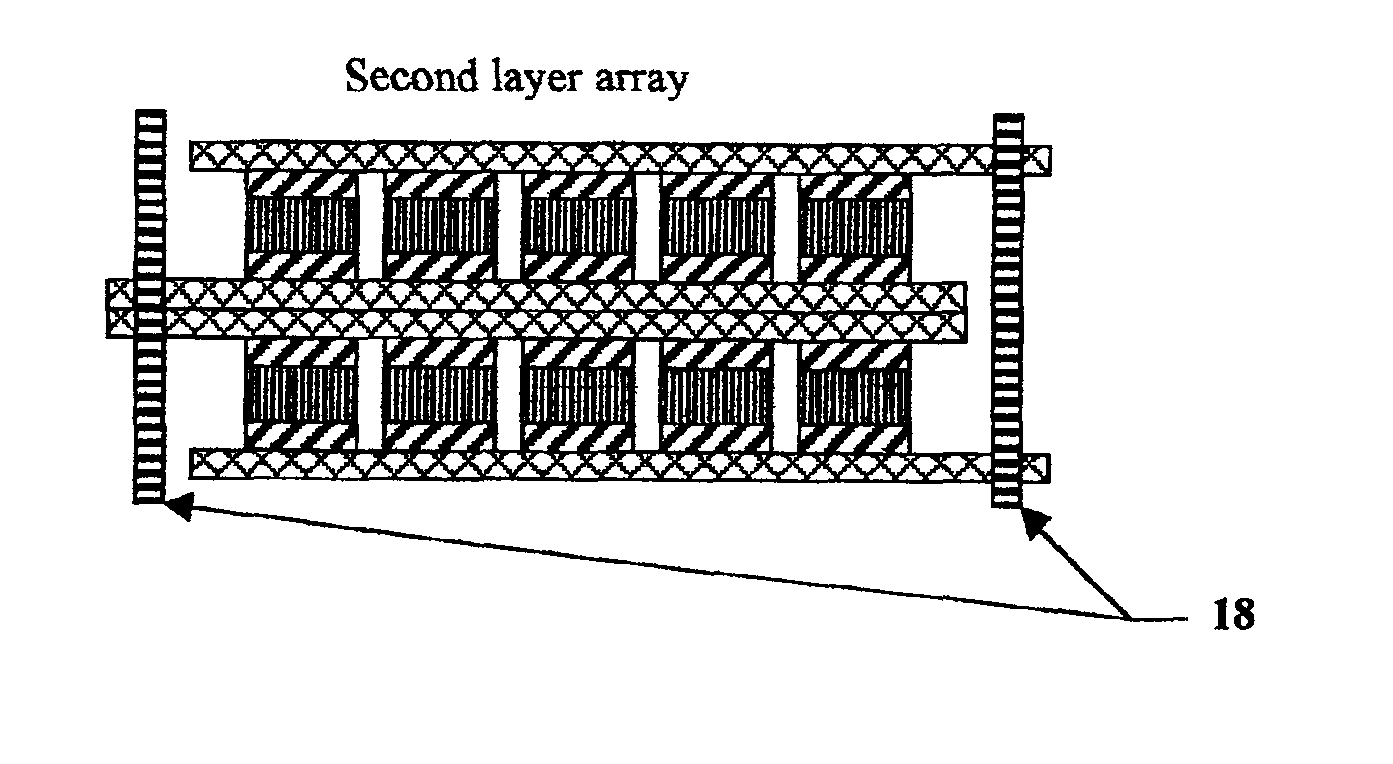
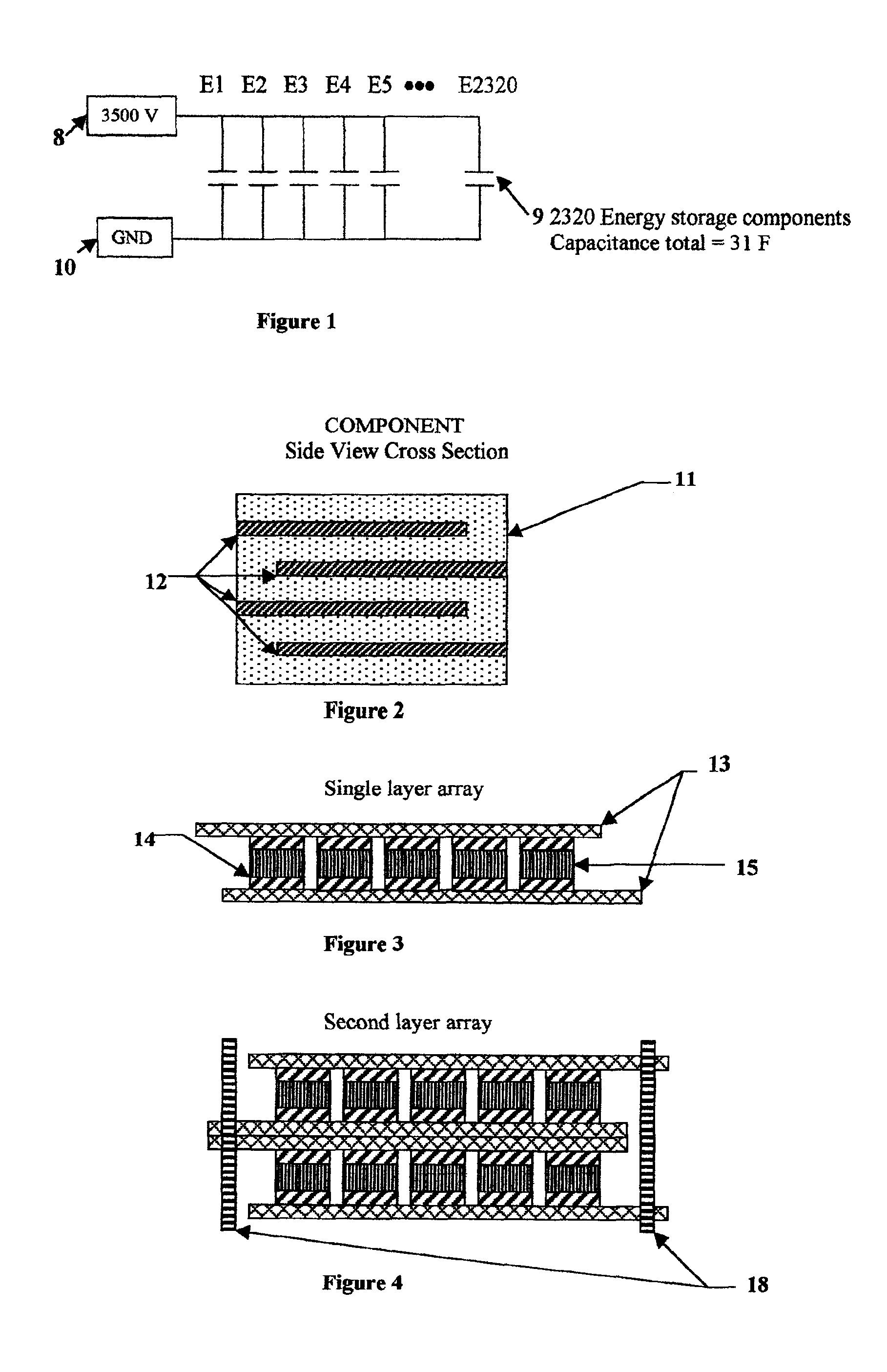
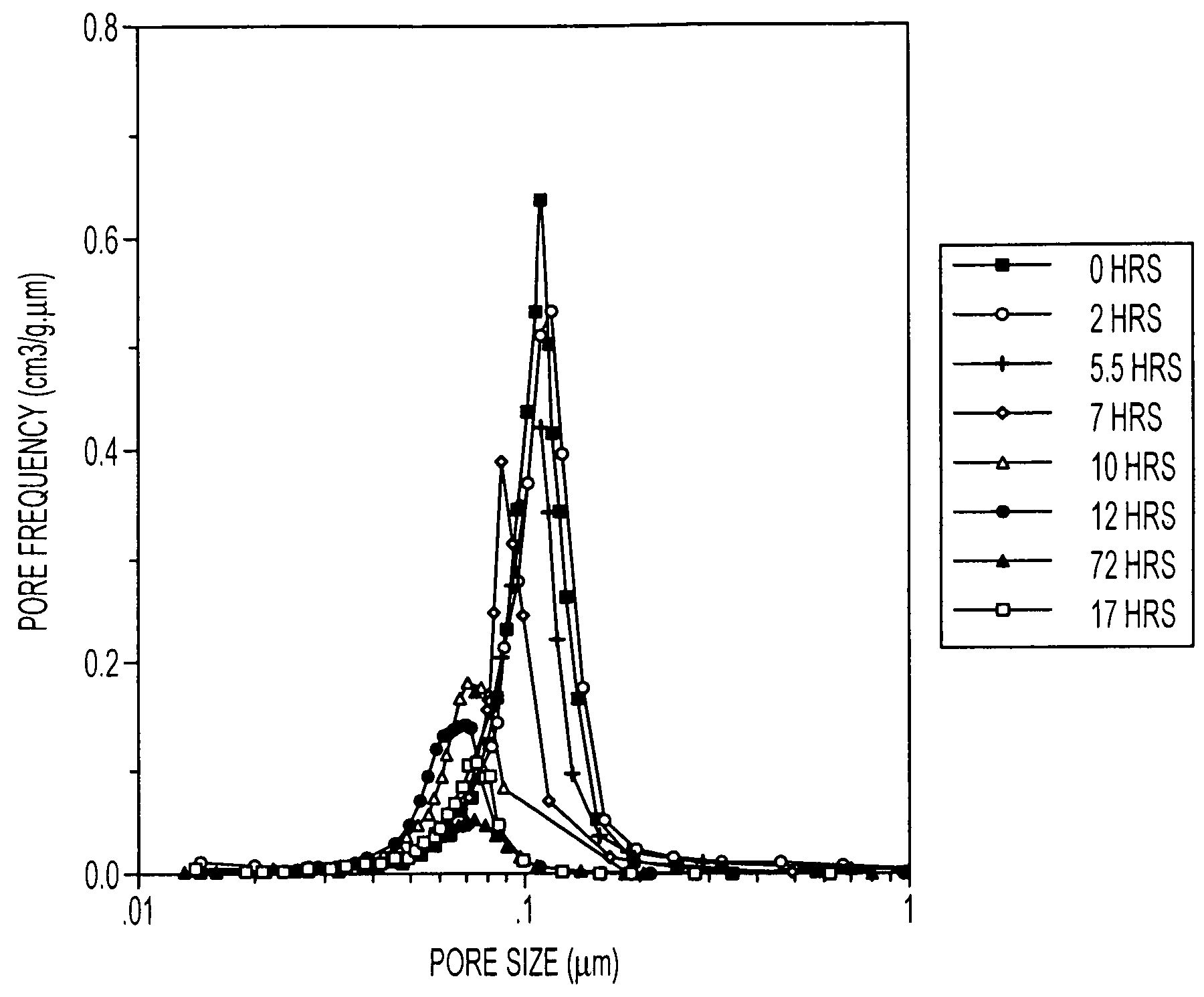
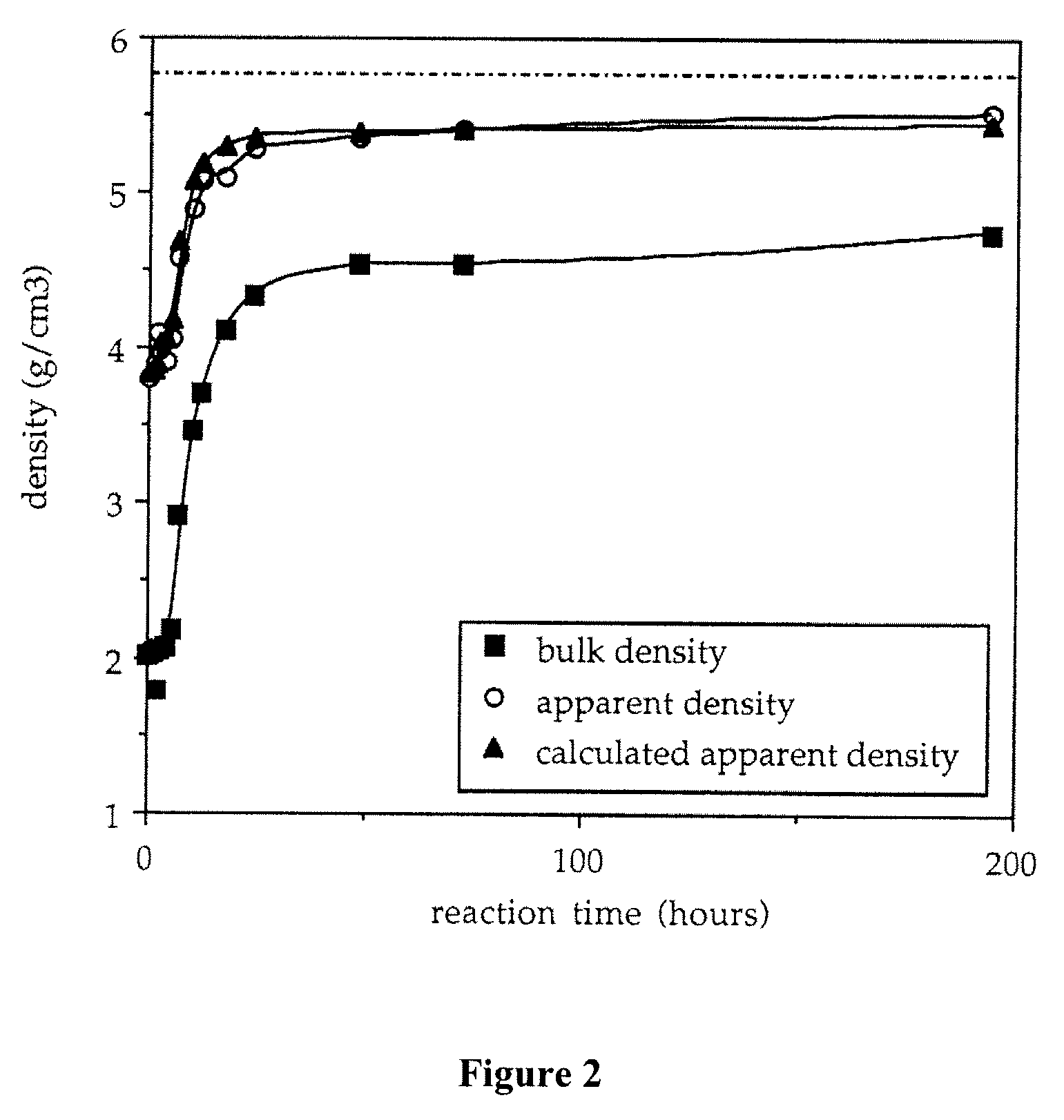
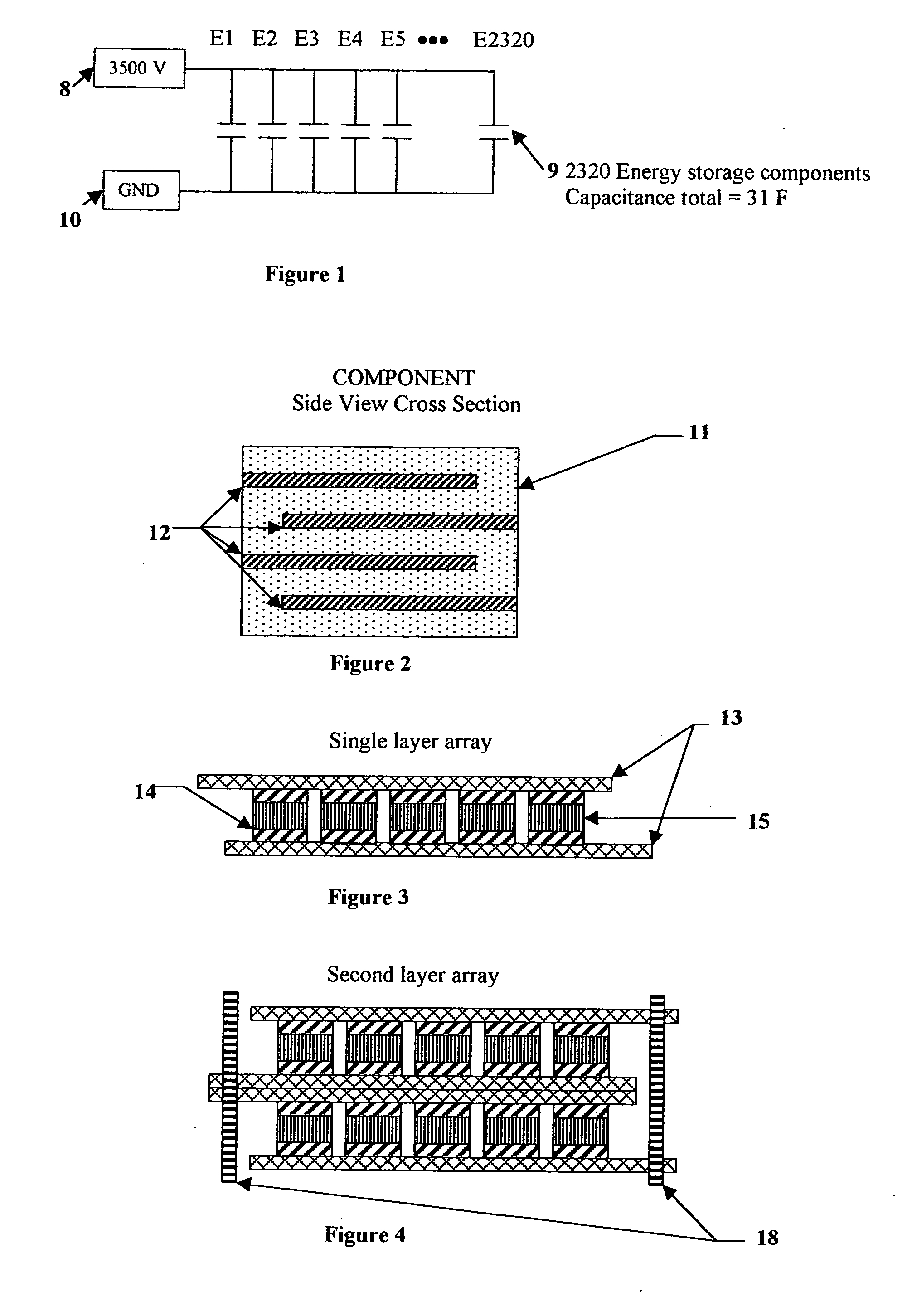
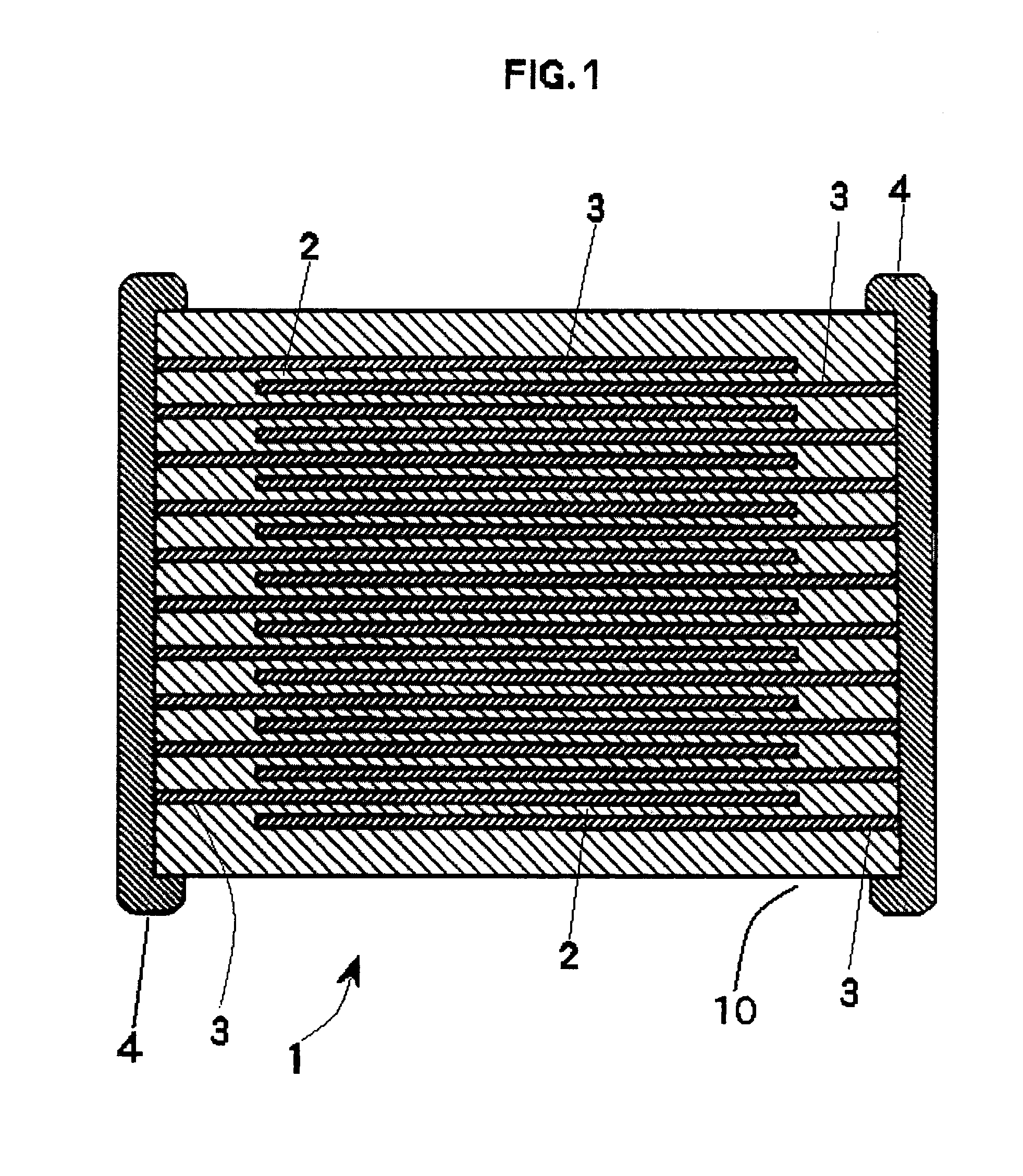
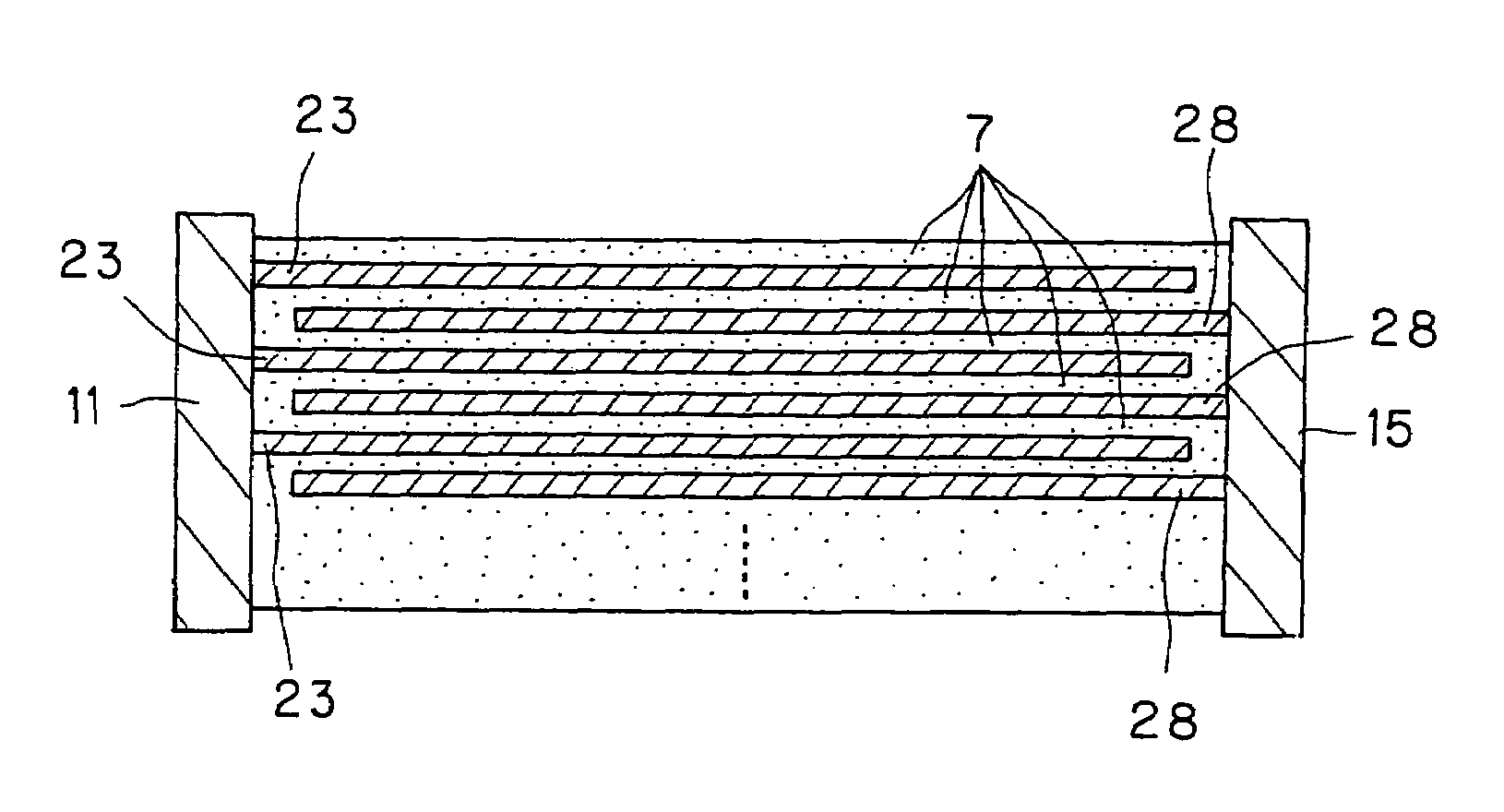
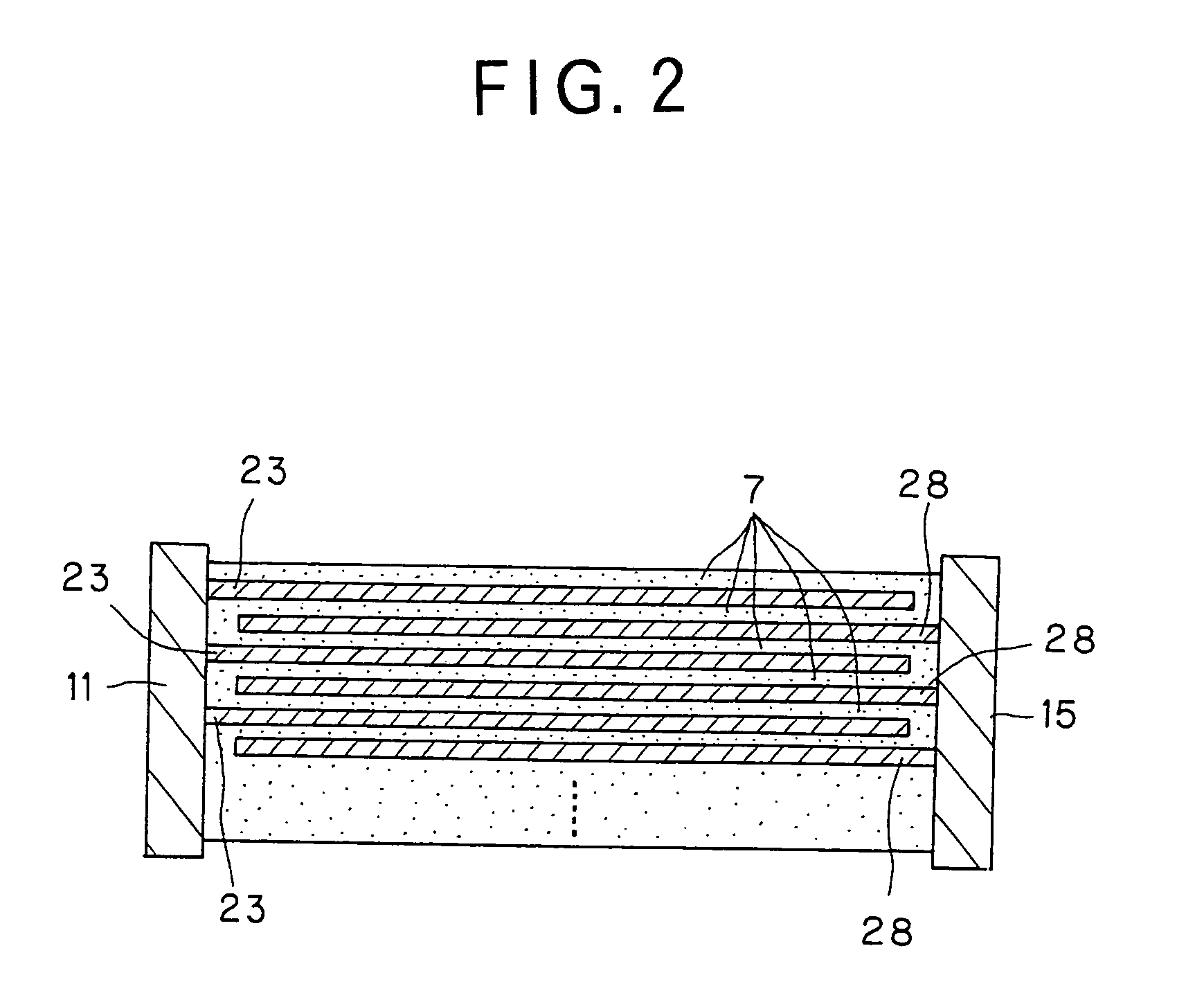
Electrical-energy-storage unit (EESU) utilizing ceramic and integrated-circuit technologies for replacement of electrochemical batteries
InactiveUS7033406B2Reduce sinteringLowering hot-isostatic-pressing temperatureElectrical storage systemFixed capacitor electrodesBarium titanatePermittivity
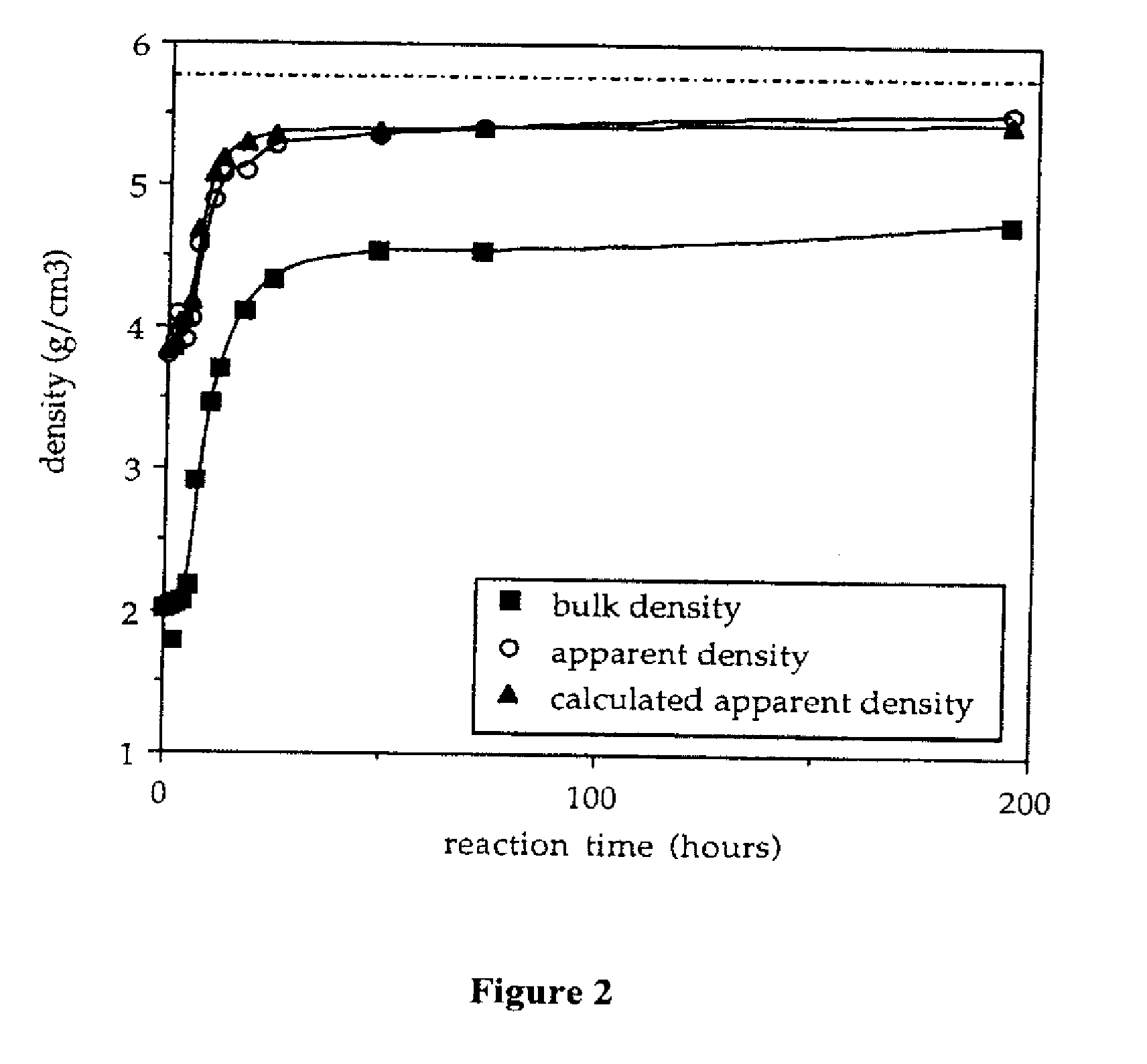
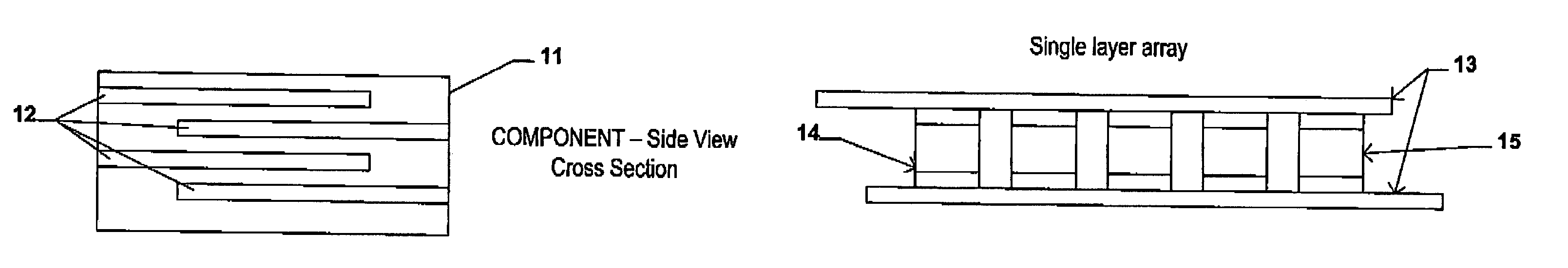
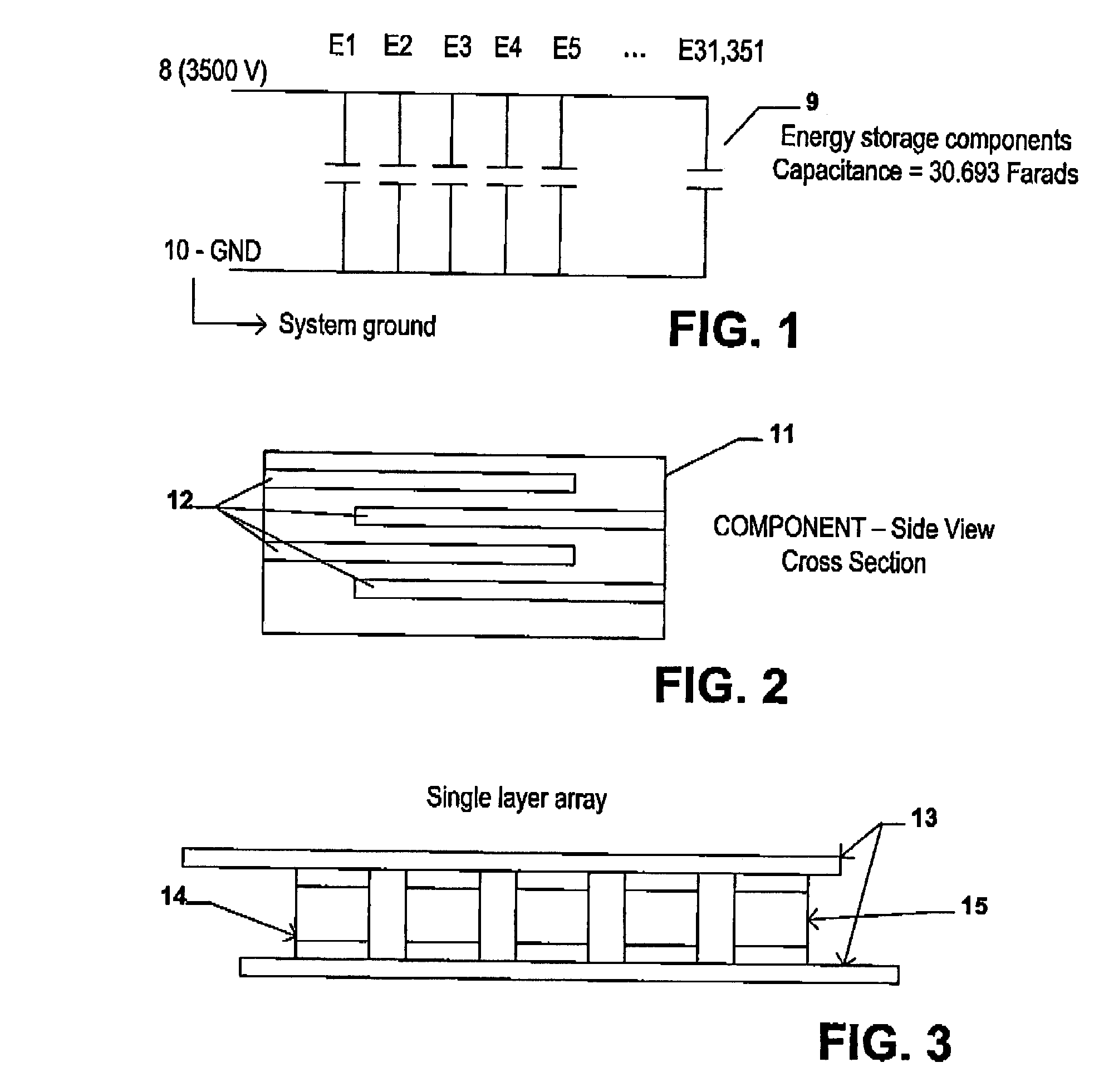
An electrical-energy-storage unit (EESU) has as a basis material a high-permittivity composition-modified barium titanate ceramic powder. This powder is double coated with the first coating being aluminum oxide and the second coating calcium magnesium aluminosilicate glass. The components of the EESU are manufactured with the use of classical ceramic fabrication techniques which include screen printing alternating multilayers of nickel electrodes and high-permittivitiy composition-modified barium titanate powder, sintering to a closed-pore porous body, followed by hot-isostatic pressing to a void-free body. The components are configured into a multilayer array with the use of a solder-bump technique as the enabling technology so as to provide a parallel configuration of components that has the capability to store electrical energy in the range of 52 kW·h. The total weight of an EESU with this range of electrical energy storage is about 336 pounds.
Owner:EESTOR
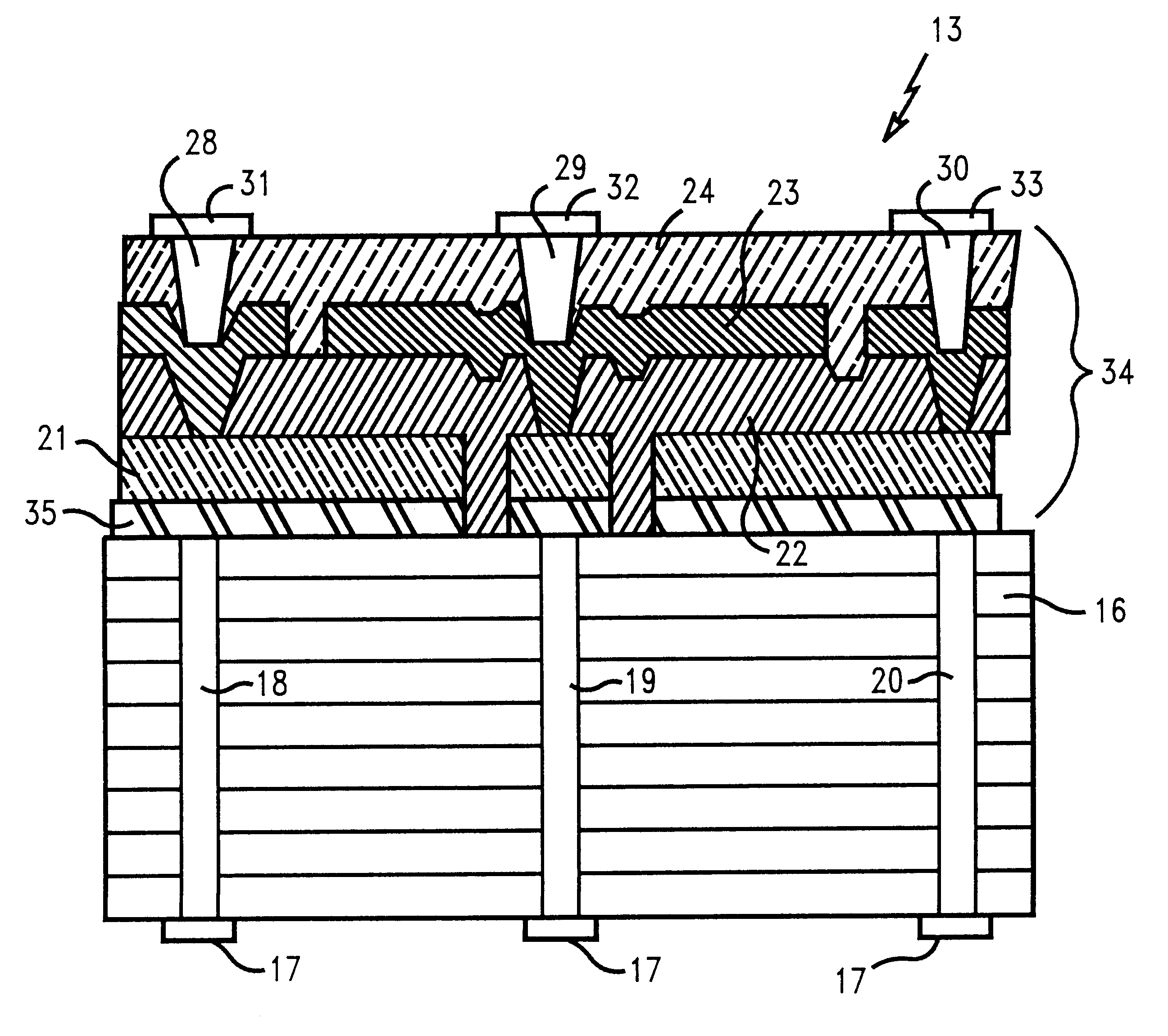
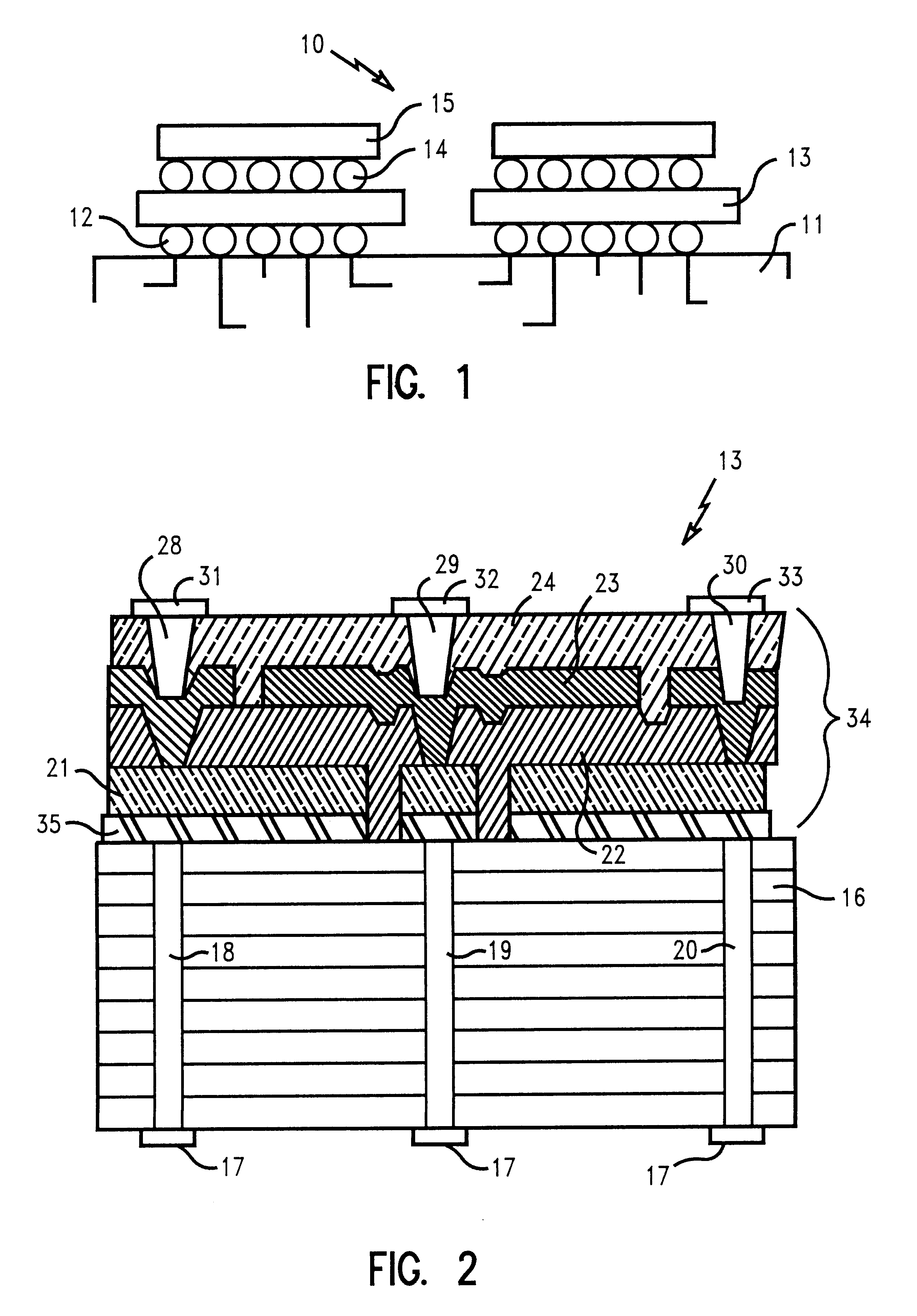
High temperature, conductive thin film diffusion barrier for ceramic/metal systems
A multilayer ceramic substrate having a thin film structure containing capacitor connected thereto is provided as an interposer capacitor, the capacitor employing platinum as the bottom electrode of the capacitor. In a preferred capacitor, a dielectric material such as barium titanate is used as the dielectric material between the capacitor electrodes. The fabrication of the interposer capacitor requires an in-situ or post deposition high temperature anneal and the use of such dielectrics requires heating of the capacitor structure in a non-reducing atmosphere. A layer of a high temperature, thin film diffusion barrier such as TaSiN on the lower platinum electrode between the electrode and underlying multilayer ceramic substrate prevents or minimizes oxidization of the metallization of the multilayer ceramic substrate to which the thin film structure is connected during the fabrication process. A method is also provided for fabricating an interposer capacitor with a multilayer ceramic substrate base and a thin film multilayer structure having at least one capacitor comprising at least one bottom platinum electrode.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method of hydrothermal liquid phase sintering of ceramic materials and products derived therefrom
ActiveUS20090142578A1Improve responseLayered productsPretreated surfacesBarium titanateCeramic materials
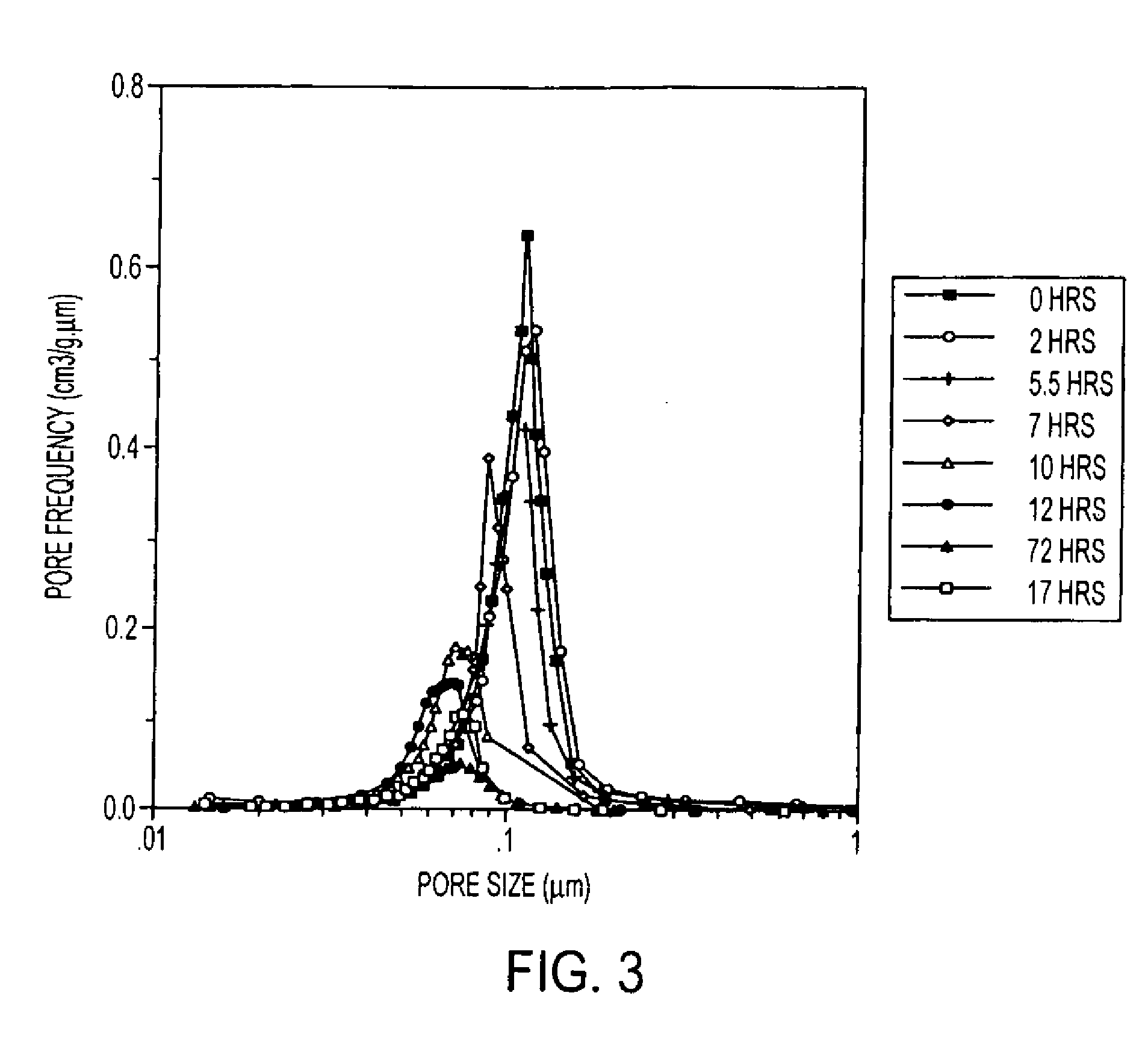
Provided here is a method of producing a monolithic body from a porous matrix, comprising: (i) providing a porous matrix having interstitial spaces and comprising at least a first reactant; (ii) contacting the porous matrix with an infiltrating medium that carries at least a second reactant; (iii) allowing the infiltrating medium to infiltrate at least a portion of the interstitial spaces of the porous matrix under conditions that promote a reaction between the at least first reactant and the at least second reactant to provide at least a first product; and (iv) allowing the at least first product to form and fill at least a portion of the interstitial spaces of the porous matrix, thereby producing a monolithic body, wherein the monolithic body does not comprise barium titanate.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Systems and methods for forming strontium- and/or barium-containing layers
InactiveUS7115166B2Easy to controlMinimizing detrimental gas phase reactionPolycrystalline material growthSolid-state devicesStrontium titanateBarium strontium titanate
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Nitrogen oxide storage material and nitrogen oxide storing catalyst prepared therefrom
InactiveUS6350421B1Determine efficiencyNitrogen compoundsExhaust apparatusAlkaline earth metalCuprate
A nitrogen oxide storage material is disclosed which contains at least one storage component for nitrogen oxides in the form of an oxide, mixed oxide, carbonate or hydroxide of the alkaline earth metals magnesium, calcium, strontium and barium and the alkali metals potassium and caesium on a high surface area support material. The support material can be doped cerium oxide, cerium / zirconium mixed oxide, calcium titanate, strontium titanate, barium titanate, barium stannate, barium zirconate, magnesium oxide, lanthanum oxide, praseodymium oxide, samarium oxide, neodymium oxide, yttrium oxide, zirconium silicate, yttrium barium cuprate, lead titanate, tin titanate, bismuth titanate, lanthanum cobaltate, lanthanum manganate and barium cuprate or mixtures thereof.
Owner:DMC2 DEGUSSA METALS +1
Method of hydrothermal liquid phase sintering of ceramic materials and products derived therefrom
Provided here is a method of producing a monolithic body from a porous matrix, comprising: (i) providing a porous matrix having interstitial spaces and comprising at least a first reactant; (ii) contacting the porous matrix with an infiltrating medium that carries at least a second reactant; (iii) allowing the infiltrating medium to infiltrate at least a portion of the interstitial spaces of the porous matrix under conditions that promote a reaction between the at least first reactant and the at least second reactant to provide at least a first product; and (iv) allowing the at least first product to form and fill at least a portion of the interstitial spaces of the porous matrix, thereby producing a monolithic body, wherein the monolithic body does not comprise barium titanate.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Utilization of poly(ethylene terephthalate) plastic and composition-modified barium titanate powders in a matrix that allows polarization and the use of integrated-circuit technologies for the production of lightweight ultrahigh electrical energy storage units (EESU)
InactiveUS7466536B1Low costLower sintering temperatureCell electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricManufacturing technologyBarium titanate
An electrical-energy-storage unit (EESU) has as a basis material a high-permittivity composition-modified barium titanate ceramic powder. This powder is single coated with aluminum oxide and then immersed in a matrix of poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) plastic for use in screen-printing systems. The ink that is used to process the powders via screen-printing is based on a nitrocellulose resin that provide a binder burnout, sintering, and hot isostatic pressing temperatures that are allowed by the PET plastic. These lower temperatures that are in the range of 40° C. to 150° C. also allows aluminum powder to be used for the electrode material. The components of the EESU are manufactured with the use of conventional ceramic and plastic fabrication techniques which include screen printing alternating multilayers of aluminum electrodes and high-permittivity composition-modified barium titanate powder, sintering to a closed-pore porous body, followed by hot-isostatic pressing to a void-free body. The 31,351 components are configured into a multilayer array with the use of a solder-bump technique as the enabling technology so as to provide a parallel configuration of components that has the capability to store at least 52.22 kW·h of electrical energy. The total weight of an EESU with this amount of electrical energy storage is 281.56 pounds including the box, connectors, and associated hardware.
Owner:EESTOR
Alkali-Free Composite Sealant Materials for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
A sealant composition for use in sealing solid oxide fuel cells is provided which comprises a glass component which comprises a mixture of alkali-free inorganic oxides, and an optional filler component dispersed in the glass component, said filler component being up to 40% by weight of the composition. The glass component can include, on a mole basis, 20 to 50% BaO, 1 to 10% Y2P3, 5 to 20% B2O3, 10 to 30% SiO2, 3 to 35% MgO, 2 to 20% CaO, 1 to 10% ZnO, and 0 to 5% ZrO2, and exemplary filler components include zirconia, alumina, barium titanate, strontium titanate, and combinations thereof.
Owner:CUMMINS ENTERPRISE LLC
Production Of Barium Titanate Compounds
InactiveUS20070202036A1High purityLow costMaterial nanotechnologyAlkaline earth titanatesBarium titanateSpherical shaped
An ultrafine powder of barium titanate including solid solutions and doped compounds that meets up to specific characteristics is produced by method comprising two main steps. The first step is a reaction, typically in a Segmented Flow Tubular Reactor, between reactants to produce cubic-structure barium titanate composed of non-agglomerated ultrafine particles having a shape of given aspect ratio, usually a generally spherical shape, of low density corresponding at most to 90% of the intrinsic density, all particles being smaller than 1 micron and having a narrow particle size distribution and wherein the ratio of Ba:Ti including substitutents and dopants is very close to the ideal stoichiometry. This is followed by subjecting the powder produced in the first step to a second stage solvothermal post treatment typically in an autoclave at temperature less than 400° C. to convert the cubic-structure particles of low density to ultrafine tetragonal particles of increased density corresponding to at least 90% of the intrinsic density while maintaining the same aspect ratio, and maintaining the size of all particles below 1 micron, the narrow particle size distribution span, and the given ideal stoichiometry. The produced particles can have a non-spherical facetted shape such as cube-like.
Owner:JONGEN NATHALIE +1
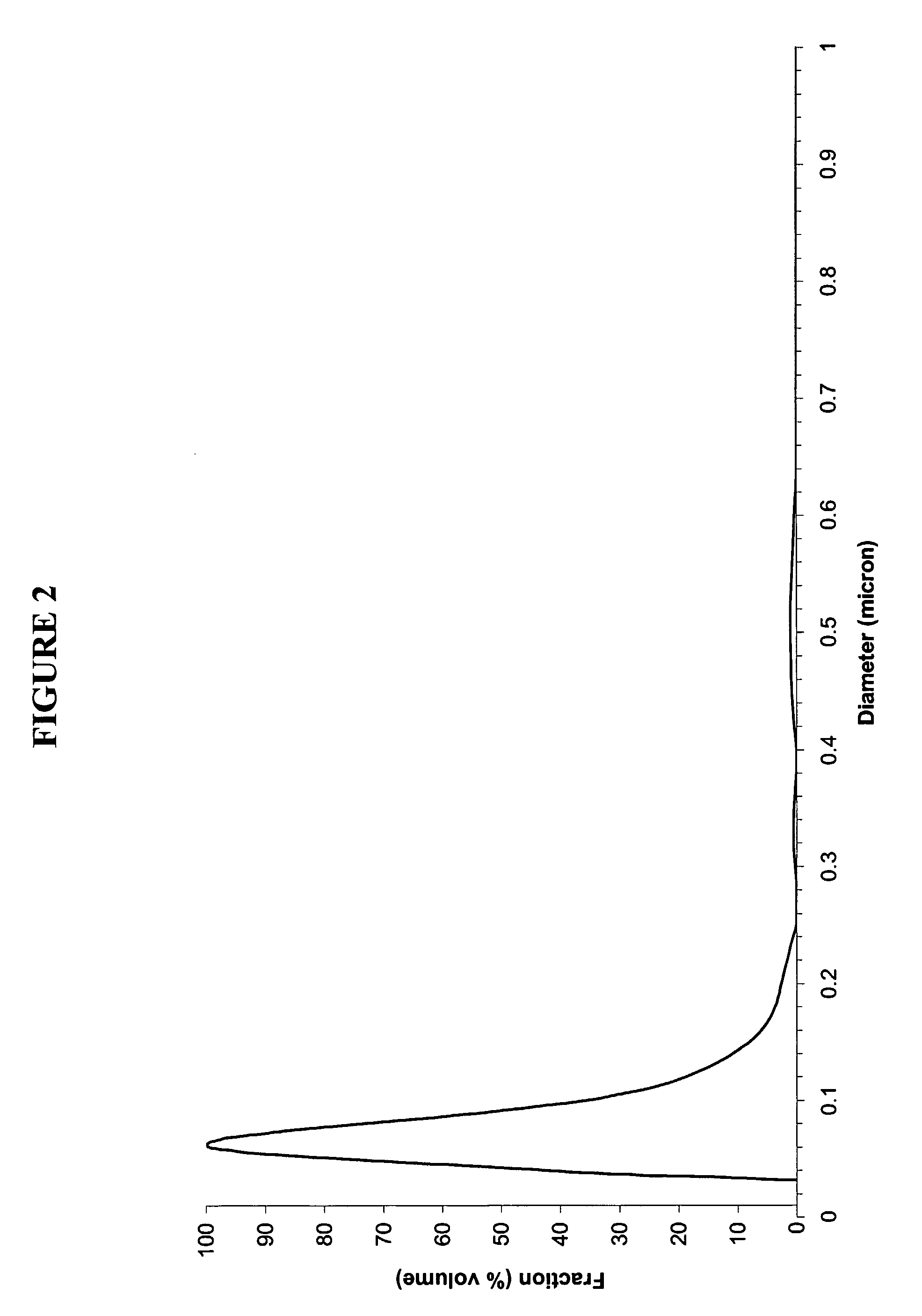
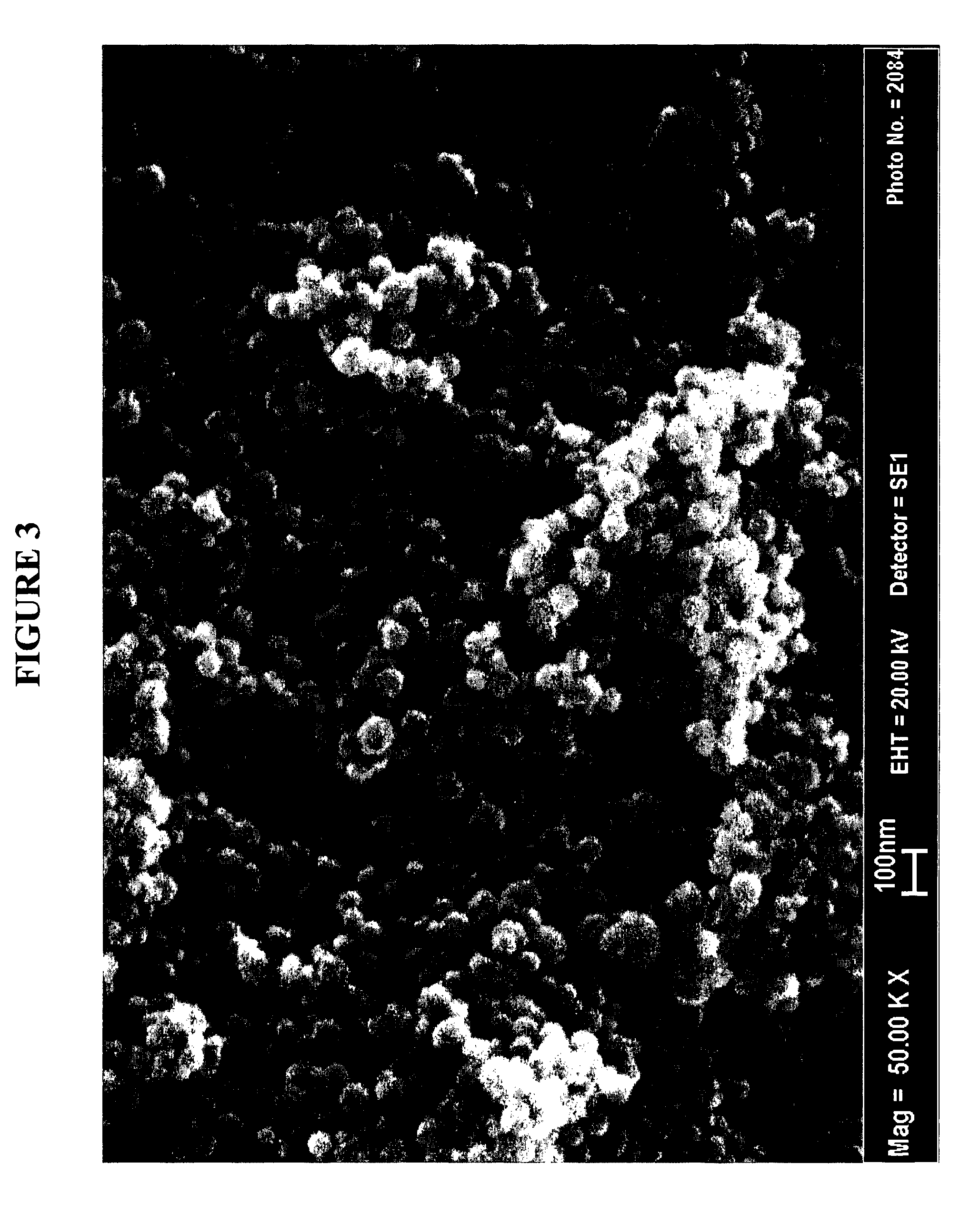
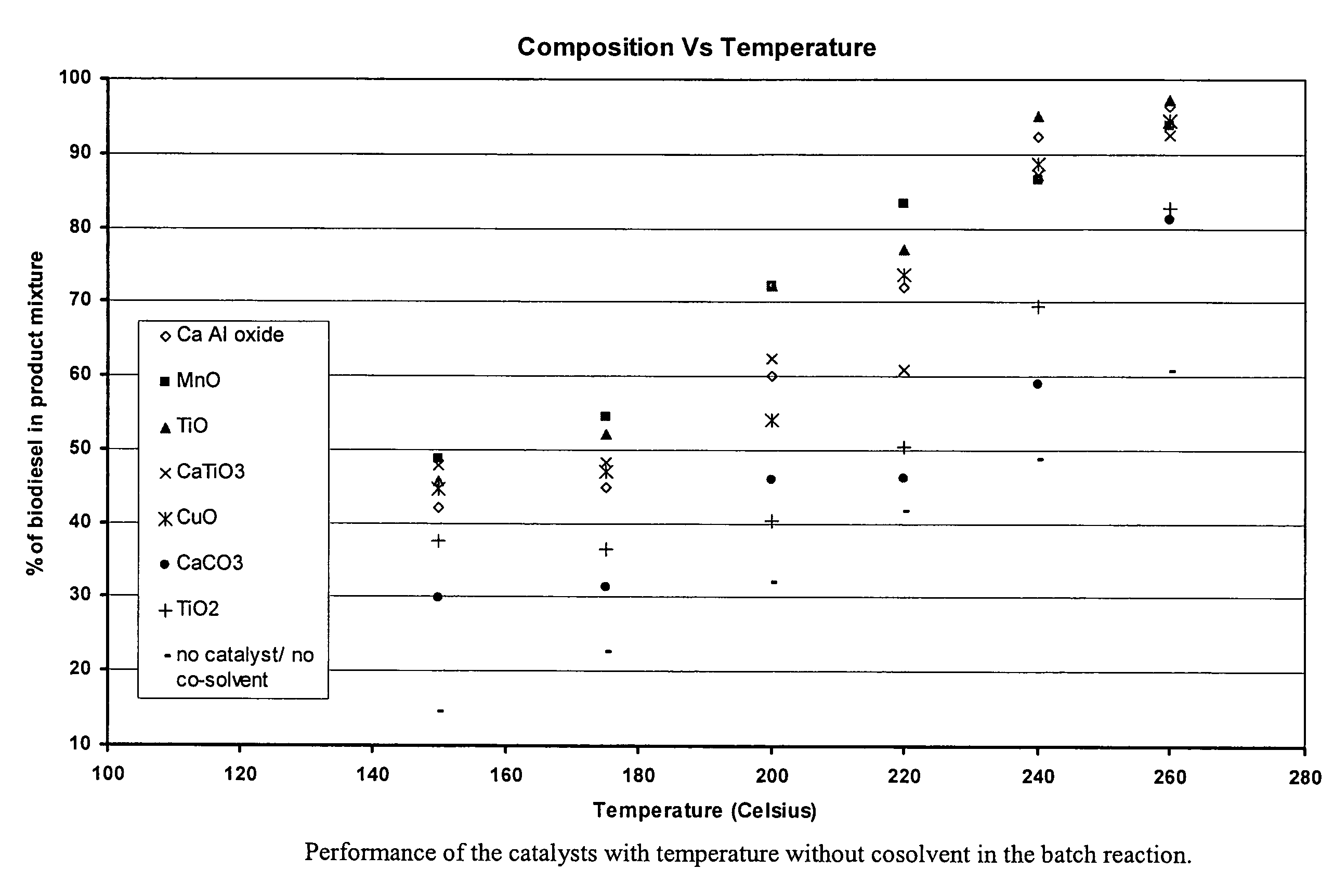
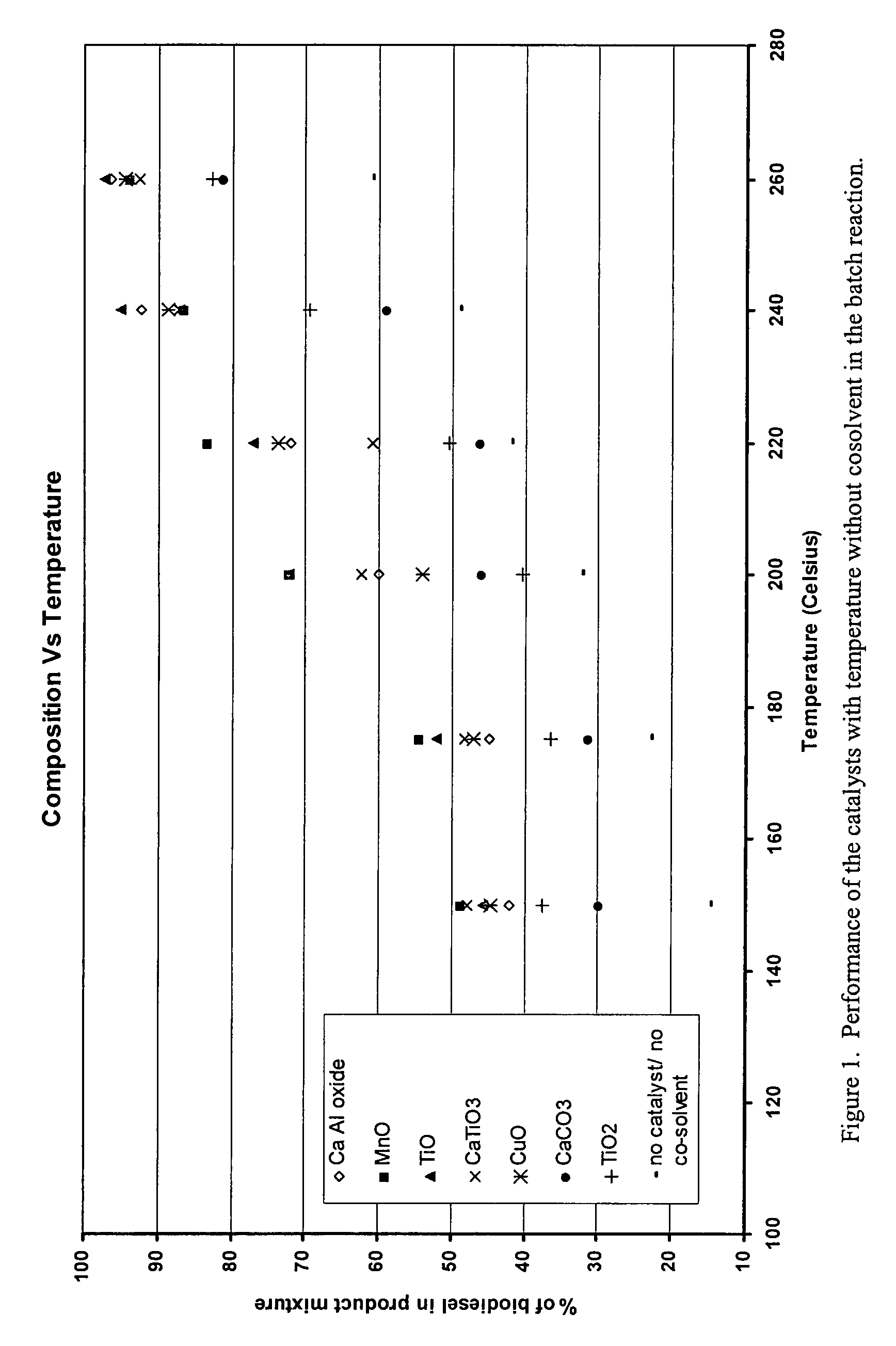
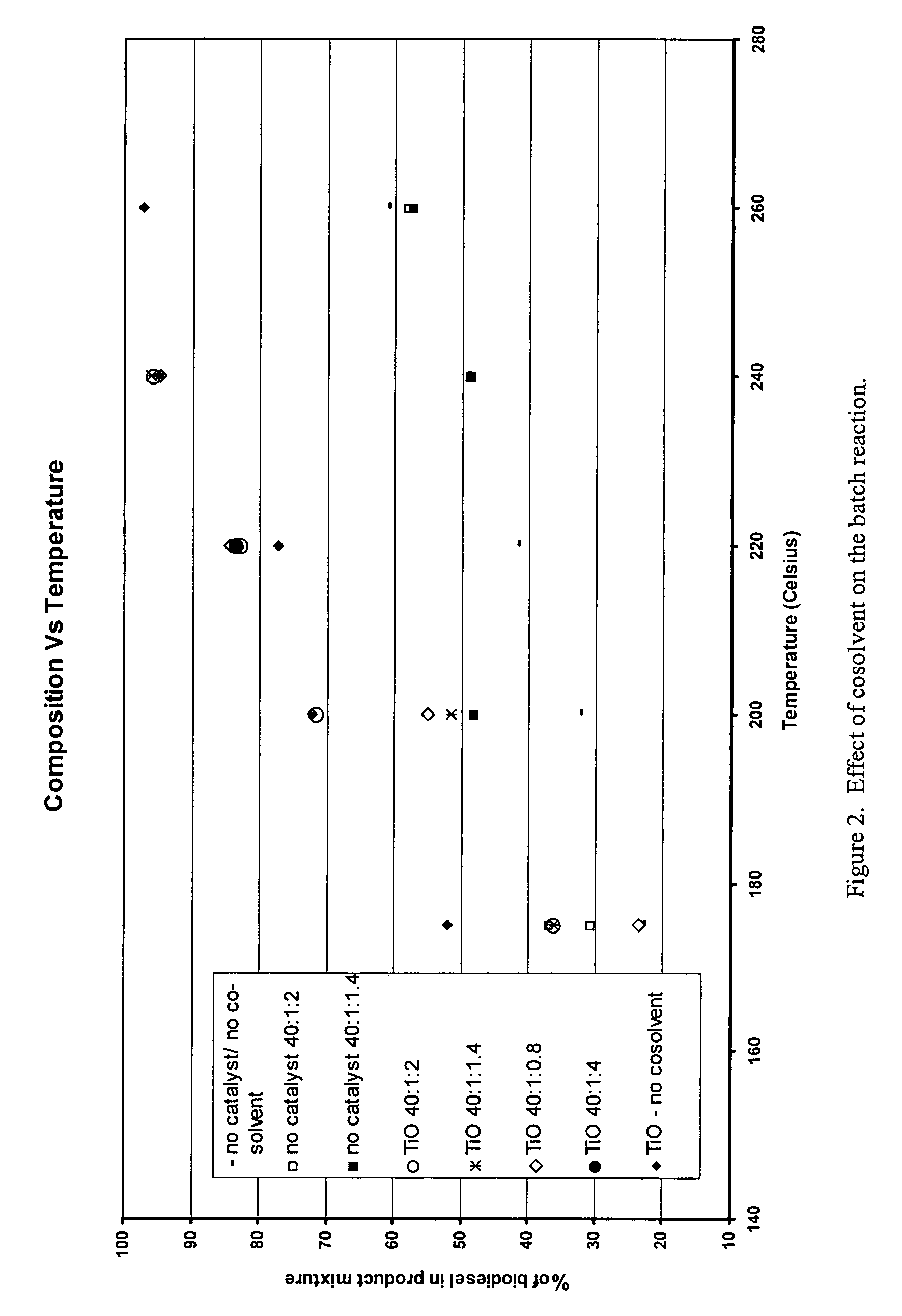
Green biodiesel
InactiveUS7563915B2Reduce wasteSignificant energyFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationCalcium silicateBiodiesel
Methods for improved manufacture of green biodiesel focus on the selection and use of one or more solid metallic oxide base catalyst(s) selected from the group consisting of calcium oxide (CaO), calcium aluminum oxide (CaO—Al2O3), calcium titanate (CaTiO3), barium titanate (BaTiO3), magnesium aluminum oxide (MgO—Al2O3), zinc oxide (ZnO), copper (II) oxide (CuO), nickel oxide (NiO), manganese oxide (MnO), titanium oxide (TiO), vanadium oxide (VO), cobalt oxide (CoO), iron oxide (FeO), chromite (FeCr2O4), hydrotalcite (Mg6Al2(CO3)(OH)16.4(H2O), magnetite (Fe3O4), magnesium silicate and calcium silicate.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
High dielectric constant composite materials and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS20120245016A1High composite strengthHigh dielectric constantMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsBarium strontium titanateBarium titanate
The present invention relates to composite materials with a high dielectric constant and high dielectric strength and to methods of producing the composite materials. The composite materials have high dielectric constants at a range of high frequencies and possess robust mechanical properties and strengths, such that they may be machined to a variety of configurations. The composite materials also have high dielectric strengths for operation in high power and high energy density systems. In one embodiment, the composite material is composed of a trimodal distribution of ceramic particles, including barium titanate, barium strontium titanate (BST), or combinations thereof and a polymer binder.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
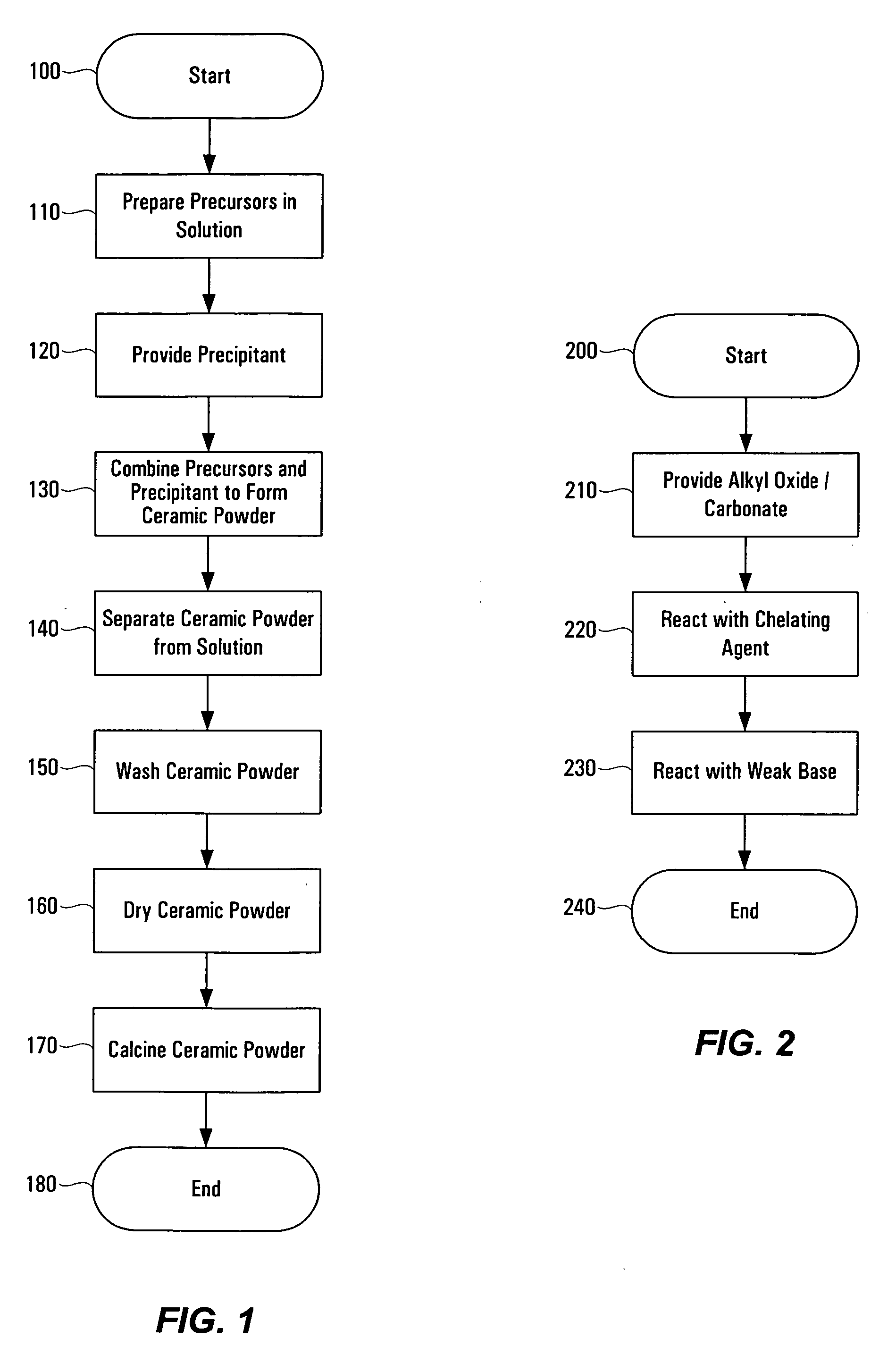
Method of preparing ceramic powders using chelate precursors
InactiveUS20070148065A1Oxide/hydroxide preparationStacked capacitorsBarium titanateAmmonium hydroxide
Wet-chemical methods involving the use of water-soluble hydrolytically stable metal-ion chelate precursors and the use of a nonmetal-ion-containing strong base can be used in a coprecipitation procedure for the preparation of ceramic powders. Examples of the precipitants used include tetraalkylammonium hydroxides. A composition-modified barium titanate is one of the ceramic powders that can be produced. Certain metal-ion chelates can be prepared from 2-hydroxypropanoic acid and ammonium hydroxide.
Owner:EESTOR
Modified zirconium oxide ceramic material and application thereof
InactiveCN104446457ARich Appearance StyleHigh dielectric constantBarium titanateUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a modified zirconium oxide ceramic material. The modified zirconium oxide ceramic material comprises the following components in percentage by molar concentration: 0-6mol% of yttrium oxide, 0-15mol% of cerium oxide, 0.02-1mol% of titanium oxide, 0-20mol% of aluminum oxide, 0-5mol% of barium titanate and the balance of zirconium oxide. The invention also discloses zirconium oxide ceramic and a dielectric cover plate prepared from the modified zirconium oxide ceramic material. The dielectric cover plate prepared from the modified zirconium oxide ceramic material has the advantages of high hardness, good toughness, high strength and high dielectric constant.
Owner:CHAOZHOU THREE CIRCLE GRP
Low temperature thin film transistor fabrication
The invention broadens the range of materials and processes that are available for Thin Film Transistor (TFT) devices by providing in the device structure an organic semiconductor layer that is in contact with an inorganic mixed oxide gate insulator involving room temperature processing at up to 150 degrees C. A TFT of the invention has a pentacene semiconductor layer in contact with a barium zirconate titanate gate oxide layer formed on a polycarbonate transparent substrate employing at least one of the techniques of sputtering, evaporation and laser ablation.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Hydrothermal synthesis of perovskite nanotubes
ActiveUS20050036939A1Reduce the amount requiredThe instrumentation is simpleDigital storageGermanium dioxideStrontium titanateBarium titanate
A low-temperature hydrothermal reaction is provided to generate crystalline perovskite nanotubes such as barium titanate (BaTiO3) and strontium titanate (SrTiO3) that have an outer diameter from about 1 nm to about 500 nm and a length from about 10 nm to about 10 micron. The low-temperature hydrothermal reaction includes the use of a metal oxide nanotube structural template, i.e., precursor. These titanate nanotubes have been characterized by means of X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy, coupled with energy dispersive X-ray analysis and selected area electron diffraction (SAED).
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Amorphous dielectric capacitors on silicon
InactiveUS6255122B1Improve conformityReduce leakage currentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLead zirconate titanateMaterials science
High-capacity capacitors and gate insulators exhibiting moderately high dielectric constants with surprisingly low leakage using amorphous or low temperature films of perovskite type oxides including a titanate system material such as barium titanate, strontium titanate, barium strontium titanate (BST), lead titanate, lead zirconate titanate, lead lanthanum zirconate titanate, barium lanthanum titanate, a niobate, aluminate or tantalate system material such as lead magnesium niobate, lithium niobate lithium tantalate, potassium niobate and potassium tantalum niobate, a tungsten-bronze system material such as barium strontium niobate, lead barium niobate, barium titanium niobate, and Bi-layered perovskite system material such as strontium bismuth tantalate, bismuth titanate deposited directly on a silicon surface at temperatures about 450° C. or less.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
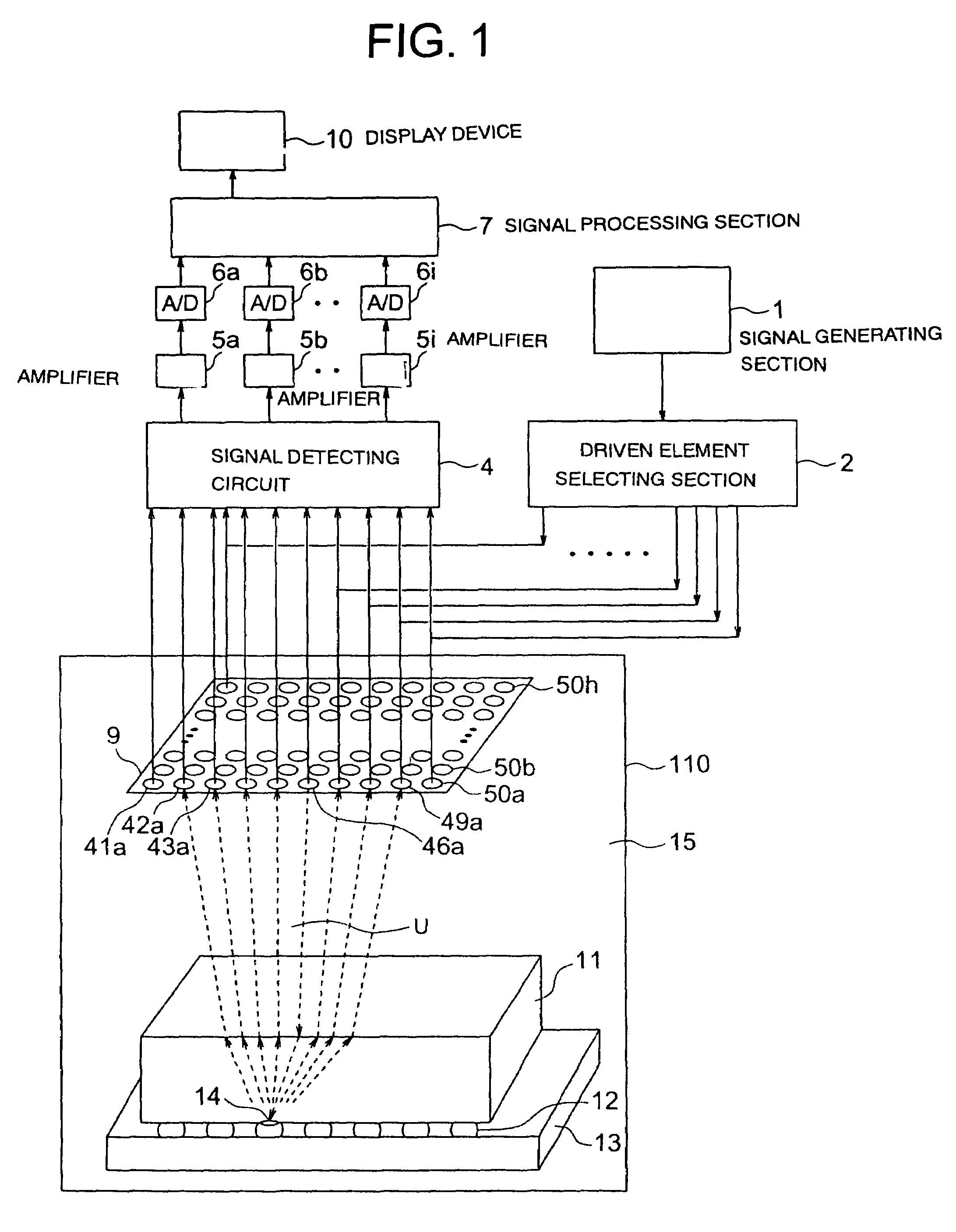
Ultrasonograph, ultrasonic transducer, examining instrument, and ultrasonographing device
ActiveUS7421900B2Transmission propertyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesLead zirconate titanateElectricity
An ultrasonograph, an ultrasonic transducer, an inspection device, and an ultrasonic imaging device enabling easy and quick inspection and high-resolution or high-speed processing are provided. Barium titanate (BaTiO3) or lead zirconate titanate (PZT) is used for a piezoelectric material constituting the ultrasonic transducer, and the thickness thereof is 0.1 μm to 100 μm. Included therein are a drive section capable of driving an arbitrary one of piezoelectric layers, a detecting section detecting electrical signals generated by the plural piezoelectric layers based on echoes from an inspection object, the echoes being originated from an ultrasonic wave generated by the driven piezoelectric layer, and a processing section performing processing for visualizing a state of the inspection object based on the detected electrical signals.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
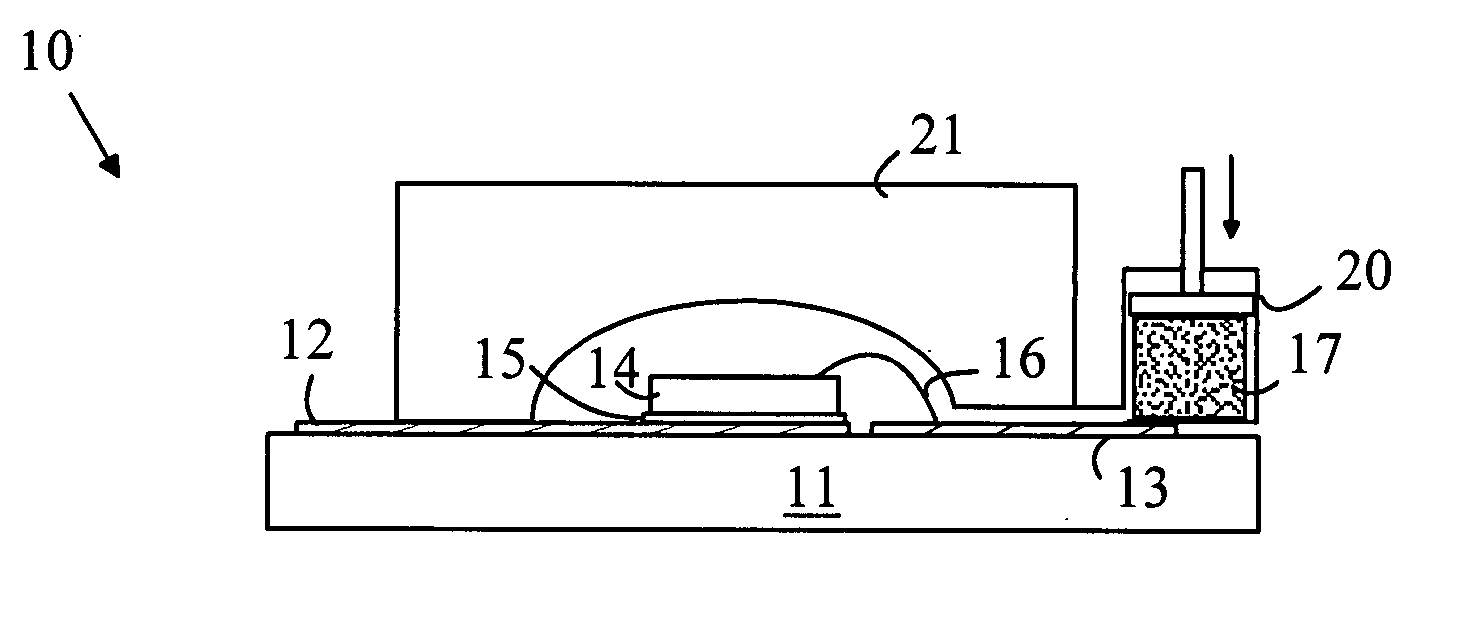
Mold compound with fluorescent material and a light-emitting device made therefrom
InactiveUS20050264194A1Improve adhesionDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesEpoxyBarium titanate
A phosphor composition and light emitting device utilizing that composition is disclosed. The composition includes a suspension of phosphor particles that are uniformly distributed in a transparent medium that includes an epoxy, and a diffusive agent that includes diffusive particles of a transparent material. In one embodiment, the diffusive particles have a median particle size between 1 μm-5 μm. The diffusive agent can be made from both inorganic and organic material such as Barium Titanate, titanium Oxide, aluminum oxide, silicone oxide, calcium carbonate, melanin resin, CTU guanamine resin or benzoguanamine resin. Embodiments that further include adhesion promoters, hydrophobic agents, thixotropic agents and UV inhibitors are also disclosed. In one embodiment, the composition is in the form of a pellet suitable for transfer molding.
Owner:AVAGO TECH ECBU IP (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
All-solid polymer electrolyte, and preparation method and application of all-solid polymer electrolyte
InactiveCN104538670AImprove conductivityHigh mechanical strengthSolid electrolytesFinal product manufacturePolyethylene oxideBarium titanate
The invention discloses an all-solid polymer electrolyte, and a preparation method and an application of the all-solid polymer electrolyte, and belongs to the field of lithium ion batteries. The all-solid polymer electrolyte comprises polyethylene oxide, lithium salt, inorganic nano particles and ion liquid, wherein a mass ratio of the lithium salt to polyethylene oxide is 0.1-0.5; the mass sum of the inorganic nano particles and the ion liquid is 10-30% of the mass of the all-solid polymer electrolyte; the lithium salt comprises one or several of bistrifluoromethane sulfonimide lithium salt, lithium tetrafluoroborate, lithium perchlorate, lithium hexafluorophosphate, lithium hexafluoroarsenate, lithium trifluoromethanesulfonate and lithium bis borate; and the inorganic nano particles comprise one or several of nano aluminum oxide, nano silicon oxide, nano zirconium oxide and nano barium titanate. The all-solid polymer electrolyte has better mechanical strength and higher ion conductivity. The method is simple in technology and low in cost; and raw materials are easy to obtain.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH RES INST SHENZHEN
Piezoelectric ceramic fibers having metallic cores
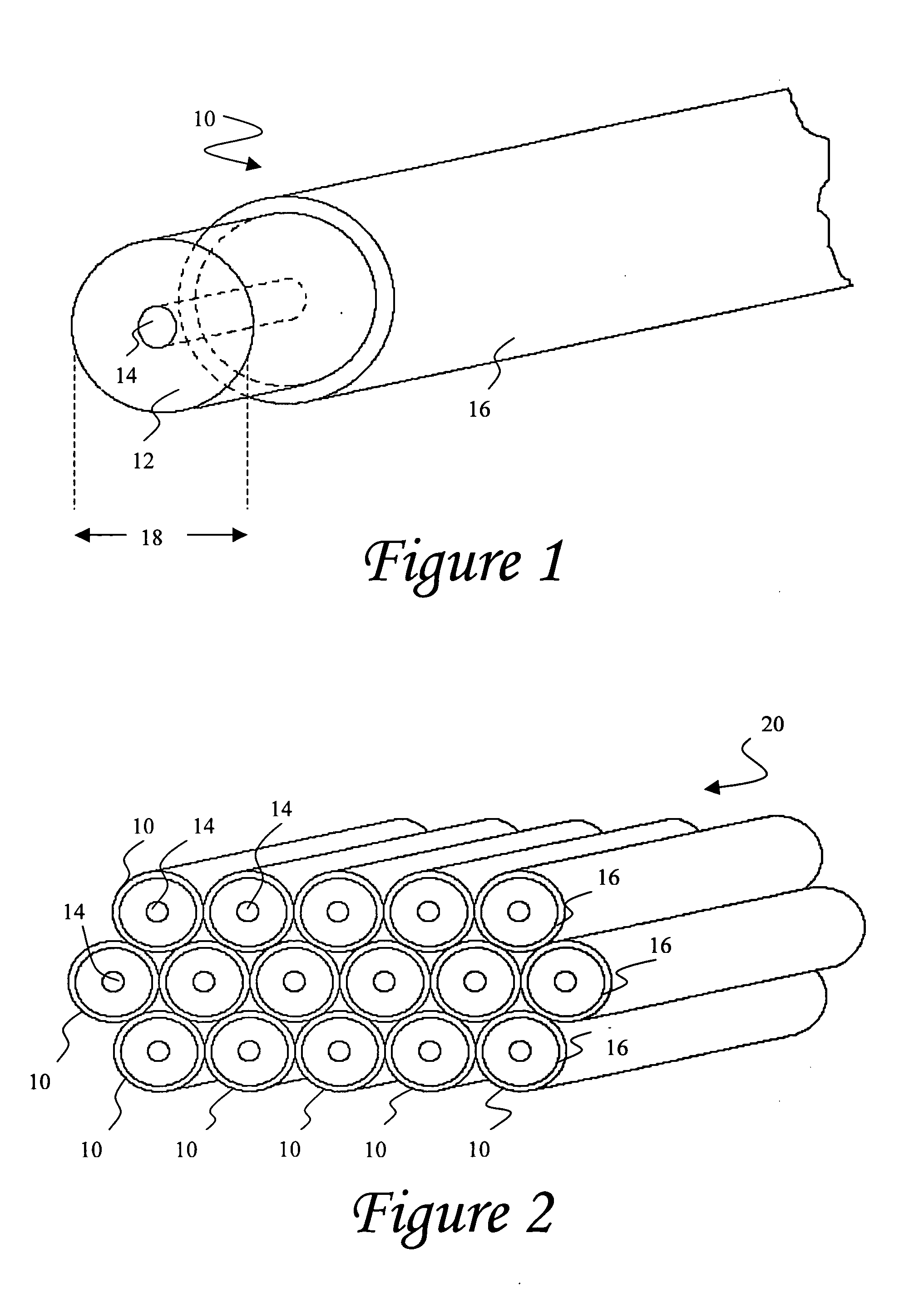
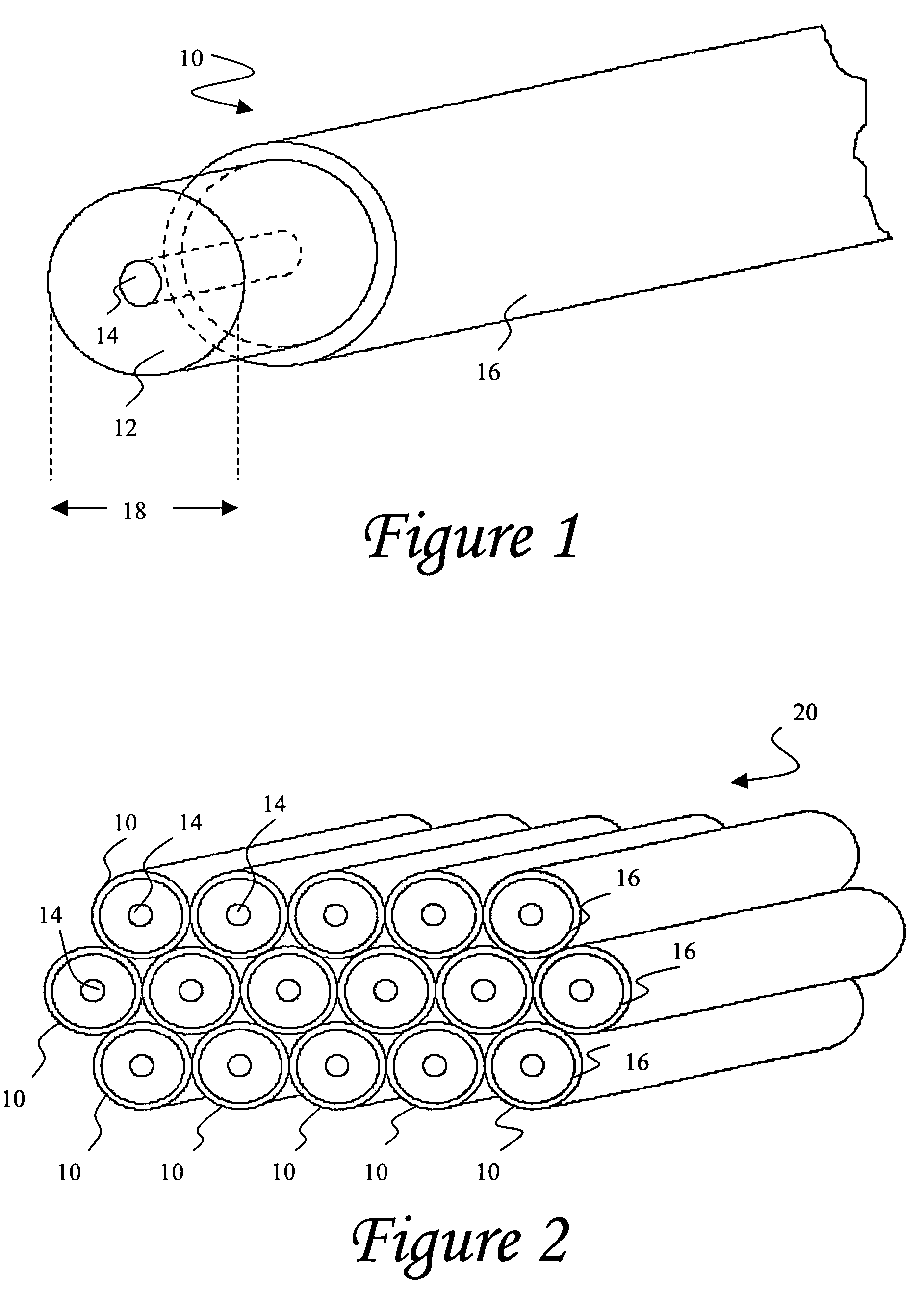
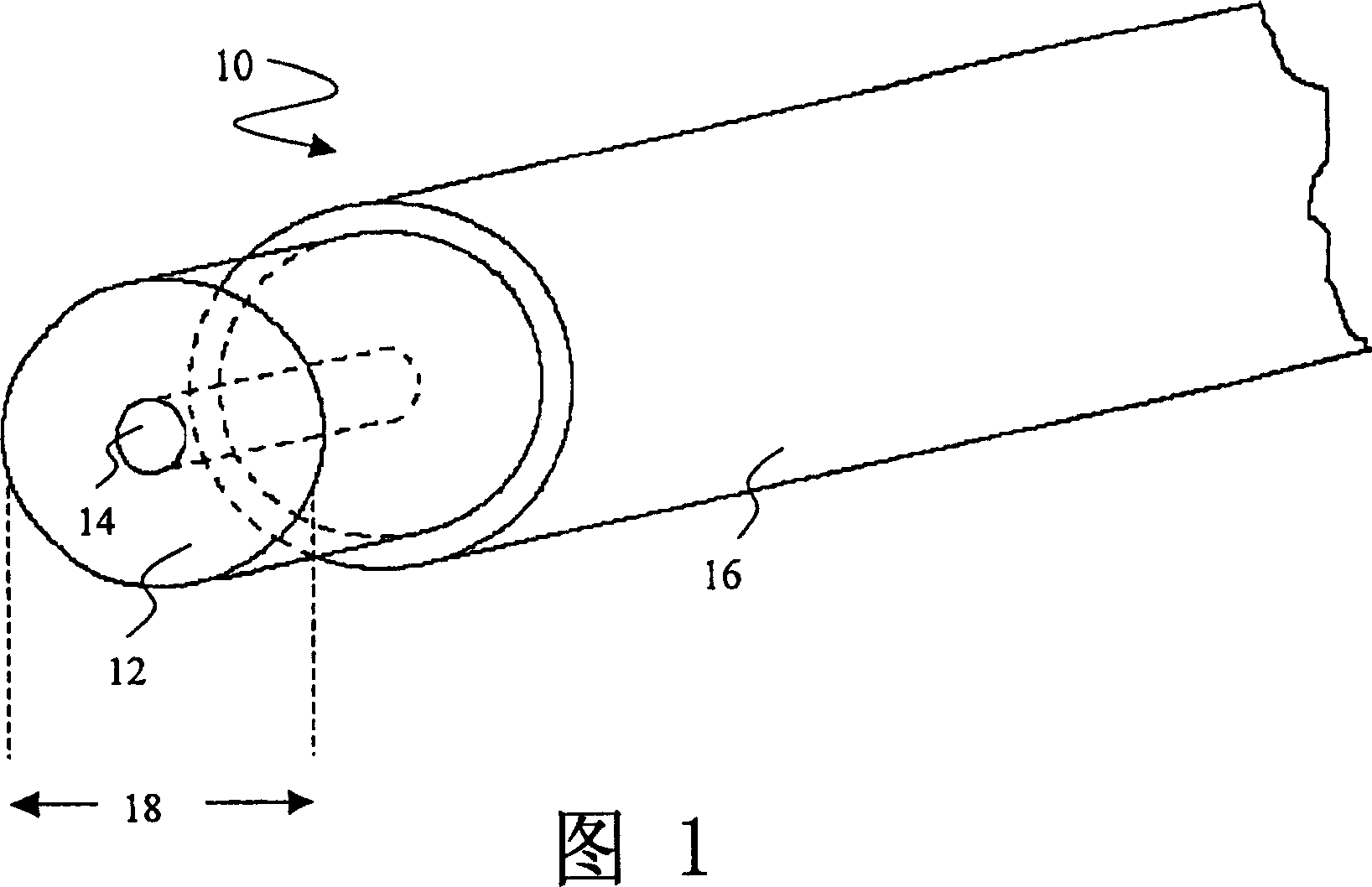
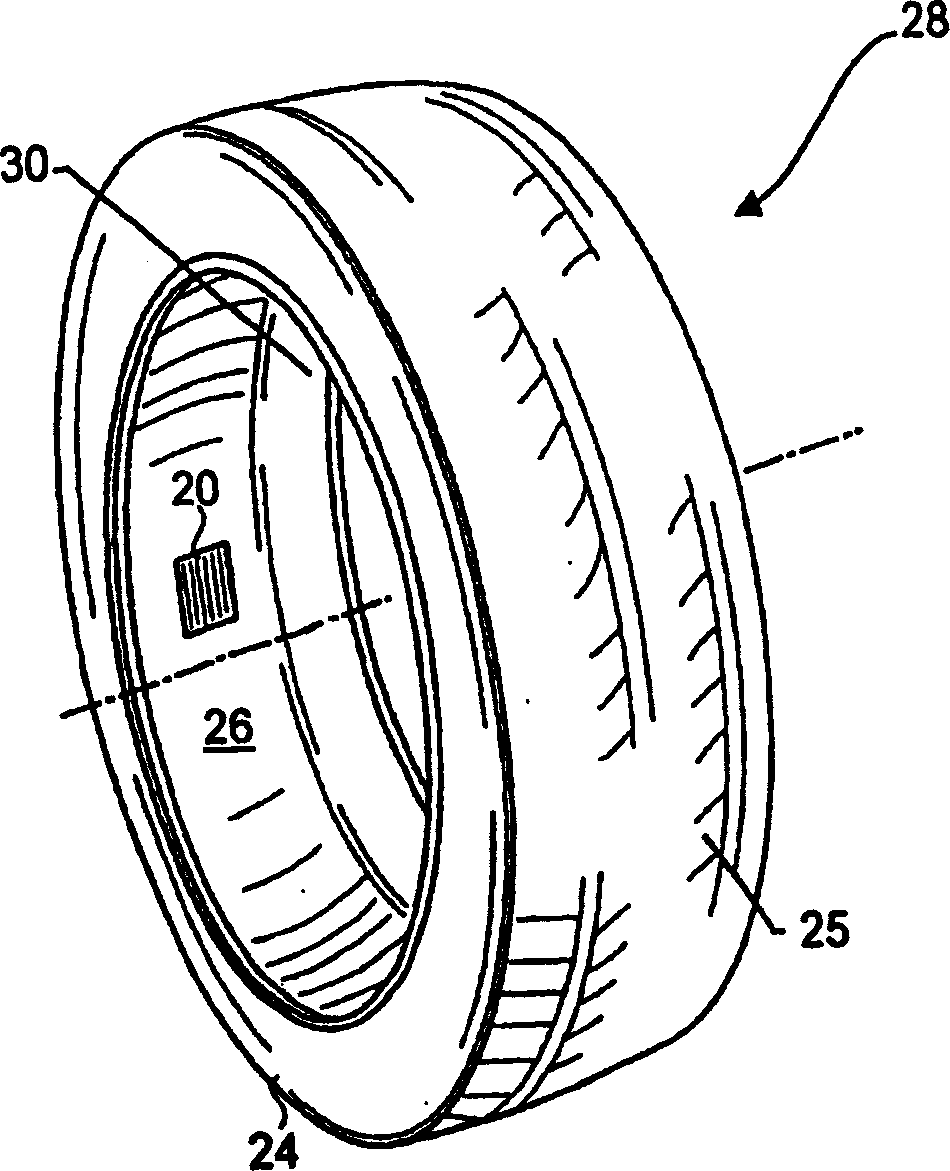
ActiveUS20050274176A1Simple structureReduce the voltage rangePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTyre measurementsMicrocontrollerFiber
An enhanced piezoelectric wire structure includes an elongated portion of piezoelectric material, a metallic core, and an outer conductive sheath. The metallic core is substantially surrounded by the elongated portion of piezoelectric material and configured to function as a first electrode for the piezoelectric structure. The conductive outer sheath preferably covers selected areas of the elongated portion of piezoelectric material and functions as a second electrode for the structure. The piezoelectric material may correspond to barium titanate ceramic fibers, such that a lead-free structure is effected, however other piezoelectric materials may also be utilized. The disclosed structure can be poled with a reduced poling voltage and lower temperature level, and also requires a reduced voltage potential level required for mechanical actuation. A collection of such piezoelectric structures can be provided together in a modular patch assembly that may be formed in a variety of customized configurations for integration with various environments, and can function as a mechanical actuator device, a condition-responsive device (e.g., a sensor) and / or as a power generation device. When utilized as a power generation device, the subject piezoelectric assembly can power tire electronics components such as a revolution counter, a sensor, a rechargeable battery, a flashing light assembly, a microcontroller, a global positioning system (GPS), and a radio frequency (RF) device.
Owner:MICHELIN RECH & TECH SA
Electrical-energy-storage unit (EESU) utilizing ceramic and integrated-circuit technologies for replacement of electrochemical batteries
InactiveUS20060210779A1Fast chargingSolution to short lifeStacked capacitorsPrimary cellsBarium titanateElectrical battery
An electrical-energy-storage unit (EESU) has as a basis material a high-permittivity composition-modified barium titanate ceramic powder. This powder is double coated with the first coating being aluminum oxide and the second coating calcium magnesium aluminosilicate glass. The components of the EESU are manufactured with the use of classical ceramic fabrication techniques which include screen printing alternating multilayers of nickel electrodes and high-permittivitiy composition-modified barium titanate powder, sintering to a closed-pore porous body, followed by hot-isostatic pressing to a void-free body. The components are configured into a multilayer array with the use of a solder-bump technique as the enabling technology so as to provide a parallel configuration of components that has the capability to store electrical energy in the range of 52 kW·h. The total weight of an EESU with this range of electrical energy storage is about 336 pounds.
Owner:EESTOR
Dielectric compositions and methods to form the same
InactiveUS6673274B2Improve insulation performanceReduce dissipationLiquid organic insulatorsFixed capacitor dielectricLow dissipationDopant
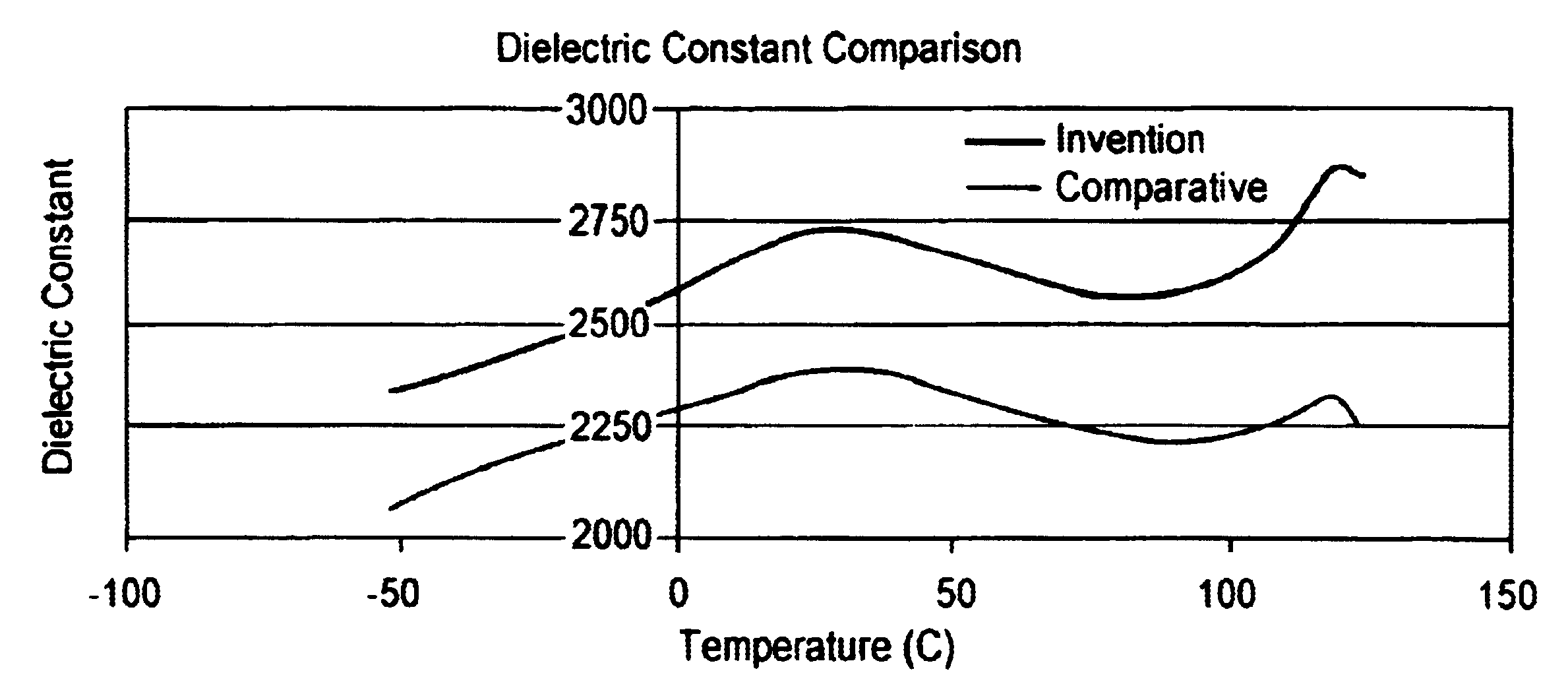
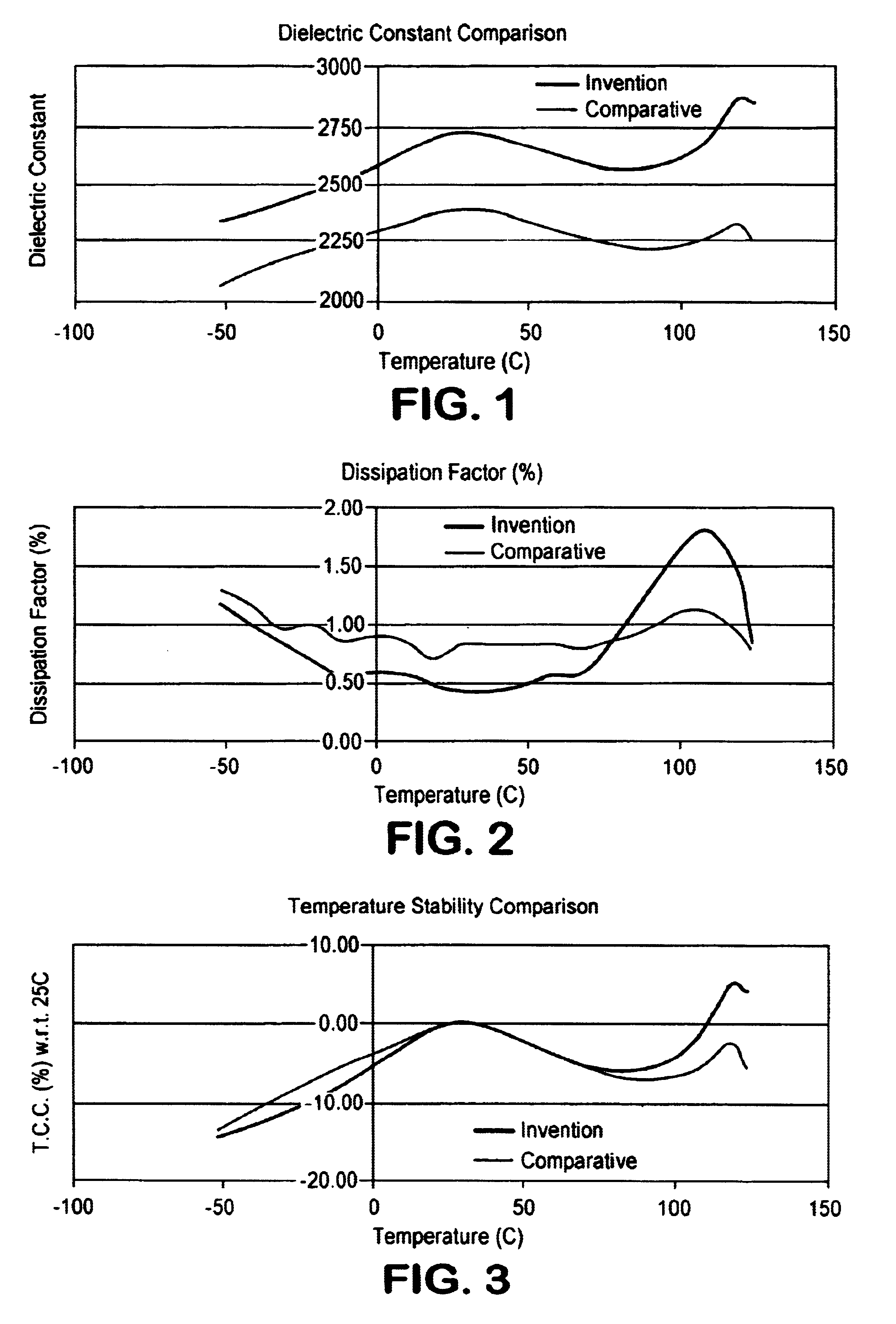
The invention provides dielectric compositions and methods of forming the same. The dielectric compositions may be used to form dielectric layers in electronic devices such as multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) and, in particular, MLCCs which include base metal electrodes. The dielectric compositions include a barium titanate-based material and several dopants. The type and concentration of each dopant is selected to provide the dielectric composition with desirable electrical properties including a stable capacitance over a temperature range, a low dissipation factor, and a high capacitance. Preferably, MLCCs including dielectric layers formed with the composition satisfy X7R and / or X5R requirements.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Piezoelectric ceramic fibers having metallic cores
ActiveUS7047800B2Reduce the voltage rangeWeakening rangePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTyre measurementsFiberMicrocontroller
An enhanced piezoelectric wire structure includes an elongated portion of piezoelectric material, a metallic core, and an outer conductive sheath. The metallic core is substantially surrounded by the elongated portion of piezoelectric material and configured to function as a first electrode for the piezoelectric structure. The conductive outer sheath preferably covers selected areas of the elongated portion of piezoelectric material and functions as a second electrode for the structure. The piezoelectric material may correspond to barium titanate ceramic fibers, such that a lead-free structure is effected, however other piezoelectric materials may also be utilized. The disclosed structure can be poled with a reduced poling voltage and lower temperature level, and also requires a reduced voltage potential level required for mechanical actuation. A collection of such piezoelectric structures can be provided together in a modular patch assembly that may be formed in a variety of customized configurations for integration with various environments, and can function as a mechanical actuator device, a condition-responsive device (e.g., a sensor) and / or as a power generation device. When utilized as a power generation device, the subject piezoelectric assembly can power tire electronics components such as a revolution counter, a sensor, a rechargeable battery, a flashing light assembly, a microcontroller, a global positioning system (GPS), and a radio frequency (RF) device.
Owner:MICHELIN RECH & TECH SA
Piezoelectric ceramic fibers having metallic cores
ActiveCN1707934AEasy to combinePromote reductionPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTyre measurementsFiberBarium titanate
The improved piezoelectric wire structure includes an elongated portion of the piezoelectric portion, a metallic core, and an outer conductive layer. The metal core is substantially surrounded by the elongated portion of piezoelectric material and is provided as a first electrode of the piezoelectric structure. The outer conductive layer preferably covers selected areas of the elongated portion of piezoelectric material and serves as the second electrode of the structure. The piezoelectric material may be barium titanate ceramic fibers, allowing for an effective lead-free construction, however, other materials may also be used. The disclosed structures can be restored with reduced reduction voltages and lower temperatures, and also require reduced voltage levels required for mechanical actuation. Such collections of piezoelectric structures can also be provided together in modular patch assemblies that can be formed in a variety of specialized structures for combination with a variety of environments and can be used as mechanical actuators, conditions respond to devices (e.g. sensors) and / or act as power generating devices.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO (CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN)
Method for producing aluminum titanate sintered object
InactiveUS20030015829A1Reduction factorImprove corrosion resistanceCeramic shaping apparatusTitanium compoundsBarium titanateThermal expansion
The present invention provides a process for preparing an aluminum-titanate-based sintered body comprising the step of firing, at 1250 to 1700° C., a formed product prepared from a raw material mixture containing 100 parts by weight of a mixture of TiO2 and Al2O3 in a weight ratio of TiO2:Al2O3=40:60 to 60:40, and 1 to 15 parts by weight of an alkali feldspar represented by the formula:(NaxK1-x)AlSi3O8 wherein 0<=x<=1. According to the process of the present invention, it is possible to obtain an aluminum-titanate-based sintered body in which inherent properties of an aluminum titanate, i.e., a low coefficient of thermal expansion and high corrosion resistance are maintained, the mechanical strength thereof is improved, and which can be stably used even under high temperature conditions.
Owner:OHCERA CO LTD
COG dielectric composition for use with copper electrodes
ActiveUS7161795B1Small dielectric lossImprove reliabilityFixed capacitor dielectricStacked capacitorsLow dissipationBarium titanate
Multilayer ceramic chip capacitors which satisfy COG requirements and which are compatible with reducing atmosphere sintering conditions so that non-noble metals such as copper and copper alloys thereof may be used for internal and external electrodes are made in accordance with the invention. The capacitors exhibit desirable dielectric properties (high capacitance, low dissipation factor, high insulation resistance), excellent performance on highly accelerated life testing, and very good resistance to dielectric breakdown. The dielectric layers comprise a composite oxide formed by calcining rare earth titanates, barium titanate, together with other metal oxides such as MgO, CaO, ZnO, MnO2, ZrO2, SiO2, Ga2O3, Nd2O3, Nb2O5, and Y2O3.
Owner:FERRO CORP
Multilayer ceramic capacitor
InactiveUS7061748B2Improve reliabilityImprove featuresFixed capacitor dielectricFixed capacitor terminalsRare-earth elementBarium titanate
A multilayer ceramic capacitor containing dielectric layers, in which each of the dielectric layers has a main component containing barium titanate, a first auxiliary component containing at least one kind selected from MgO, CaG, BaO, and SrO, a second auxiliary component containing a silicon oxide as a main component, a third auxiliary component containing at least one kind selected from the group consisting of V2O5, MoO3, and WO3, a fourth auxiliary component containing an oxide of at least one kind of first rare-earth element (R1) selected from Sc, Er, Tm, Yb, and Lu, a fifth auxiliary component containing CaZrO3 or a mixture (CaO+ZrO2) of CaO and ZrO2, and a liquid phase addition of organic metal salts of Zr and Ca.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Hydrothermal synthesis of perovskite nanotubes
ActiveUS7147834B2The instrumentation is simpleReduce the amount requiredNanoinformaticsDigital storageStrontium titanateBarium titanate
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Lead And Cadmium Free, Low Temperature Fired X7R Dielectric Ceramic Composition And Method Of Making
ActiveUS20100220427A1Stable dielectric constantSmall dielectric lossFixed capacitor dielectricStacked capacitorsCeriumCadmium Cation
Multilayer ceramic chip capacitors (MLCC's) which satisfy X7R TCC requirements and which are compatible with silver-palladium internal electrodes. The MLCC's exhibit desirable dielectric properties—high capacitance, low dissipation factor, high insulation resistance, stable TCC—and excellent performance on highly accelerated life testing, and good resistance to dielectric breakdown. The dielectric layers comprise a lead-free and cadmium-free barium titanate base material doped with other metal oxides such oxides of zinc, boron, bismuth, barium, titanium, praseodymium, cerium, tungsten, neodymium, tungsten, tin, niobium, copper, and / or manganese in various combinations. The dielectric ceramic materials herein can be fired at less than 1150° C. with an inner electrode having 70 wt % or more Ag and 30 wt % or less Pd to form an MLCC.
Owner:FERRO CORP
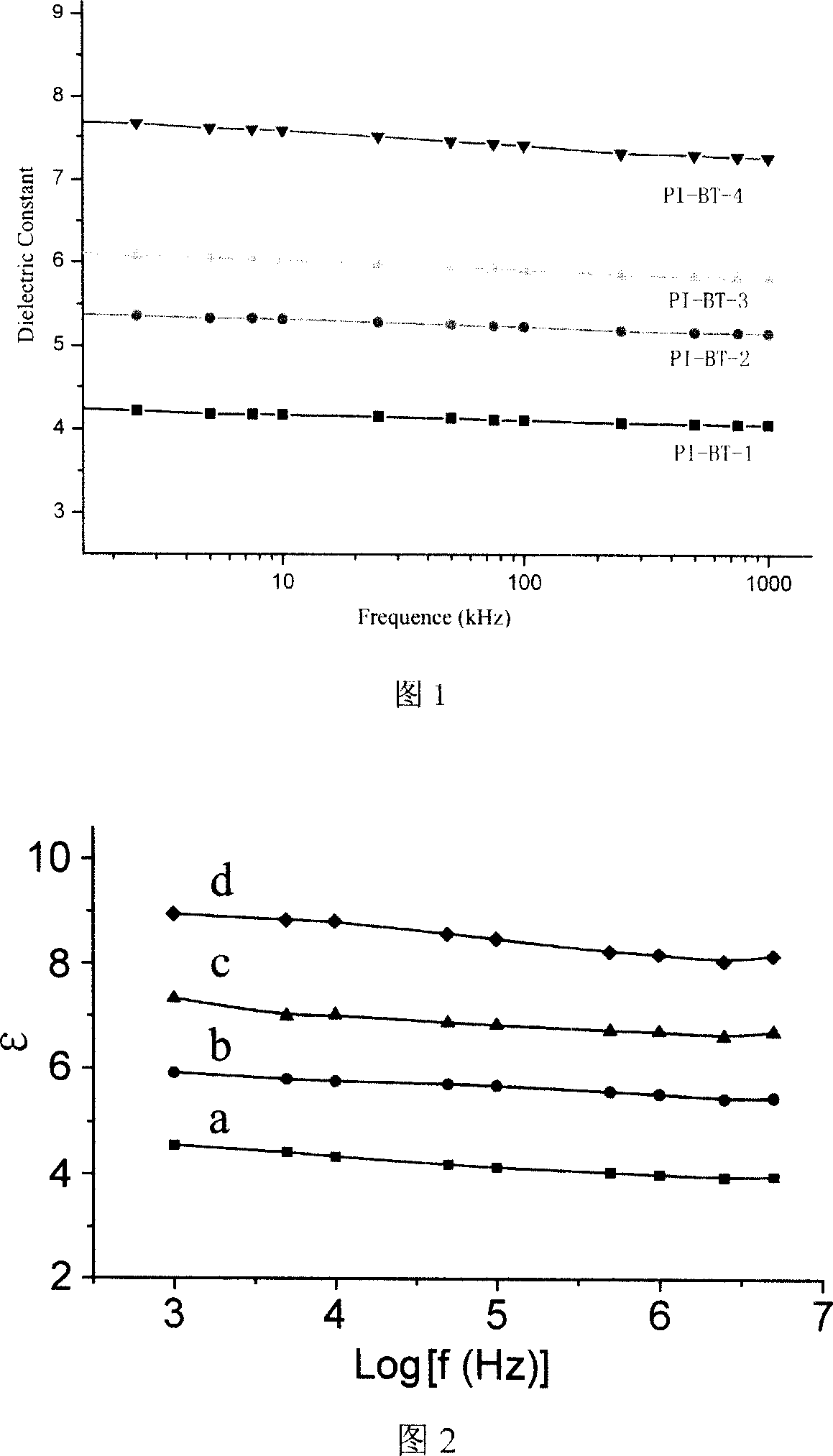
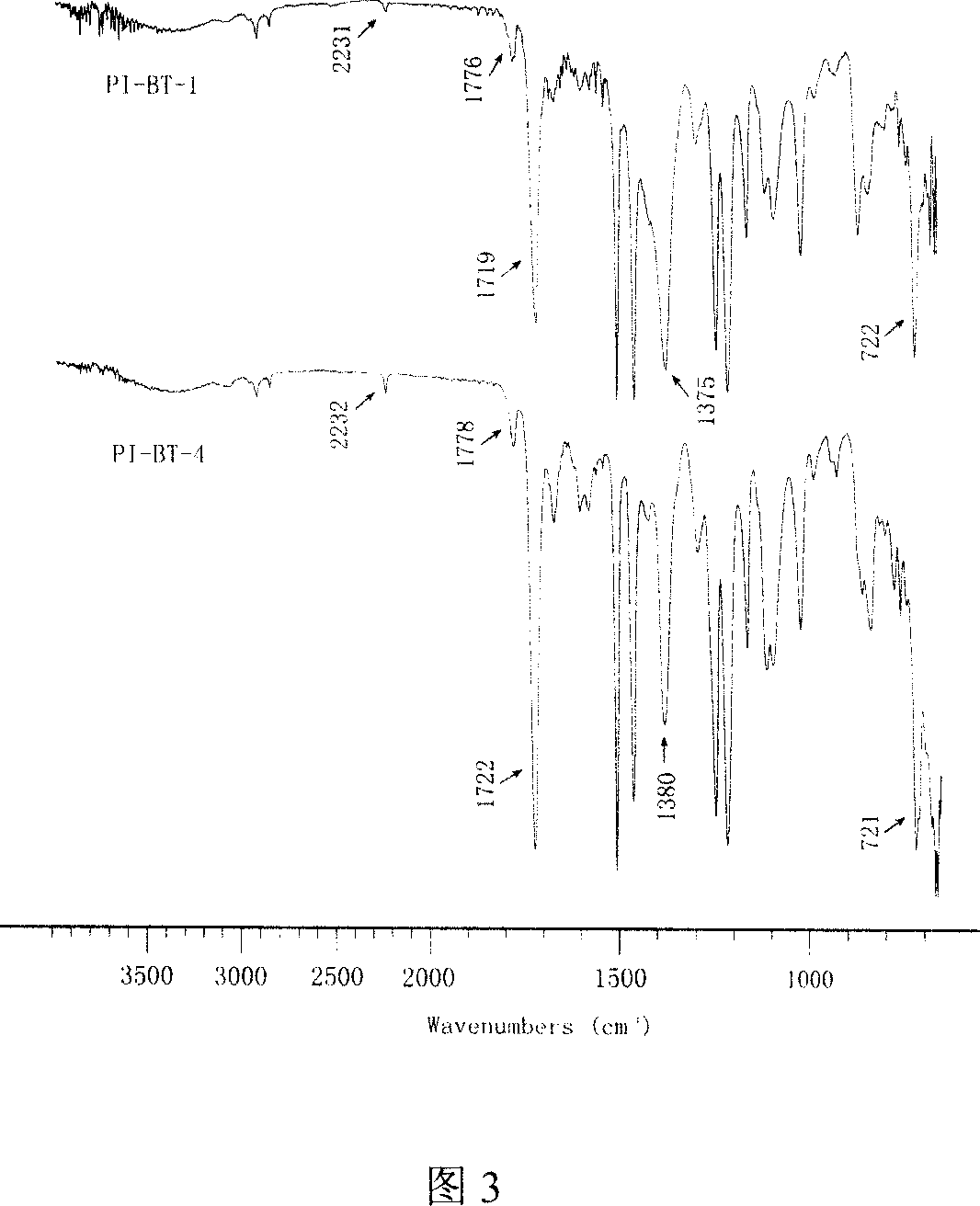
Process for synthesizing composite film of polyacylimide/nano barium phthalate with high deelectric constant
The process of synthesizing composite polyimide / nanometer barium titanate film with high dielectric constant includes the following steps: adding maleic anhydride and diamine in the same molar amount into N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone or N, N-dimethyl acetamide as solvent to compound solution with solid content of 10-20 %, adding nanometer modifying barium titanate particle in the amount less than 40 % of the composite film weight into the solution and ultrasonically dispersing, stirring continuously at room temperature for 18-24 hr to obtain polyamic acid, pouring the polyamic acid on glass plate mold, and vacuum heating to eliminate solvent and iminate to obtain the composite polyimide / nanometer barium titanate film. Thus prepared film has excellent heat stability, high oxidative degradation resistance, high dielectric constant and low dielectric loss, and may be used for wound film capacitor, printed circuit board, semiconductor device, etc.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com