Low temperature thin film transistor fabrication
a thin film transistor and fabrication technology, applied in transistors, thermoelectric devices, solid-state devices, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to withstand temperatures above 150-200 degrees c and meeting all constraints, and achieve the effect of broadening the range of materials and processes availabl
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0041] Substrates such as silicon wafers with a blanket coating of 150 .ANG. titanium followed by 400 .ANG. of platinum can be loaded into a BZT sputter deposition chamber as described in connection with FIG. 7. The chamber is pumped down to a base pressure of 2.1.times.10.sup.-7 torr after which a flow of 10 standard cubic centemeters per minute (sccm) of argon and 2 sccm of oxygen gas are introduced into the chamber through elements 34 and 35. By appropriate valving of the chamber, a total pressure of 2 mtorr is achieved. After purging this gas for 5 minutes, a plasma is ignited in the chamber by applying a radio frequency ac voltage through elements 25 and 26 to the BZT sputter target 23 while maintaining the chamber at ground potential. The ions in the rf plasma thus created is used to reactively sputter the BZT from the target on to the samples 27 loaded in the chamber. A total power of 100 watts which corresponds to a power density of about 0.8 watts / cm.sup.2 is employed to ac...
example 2
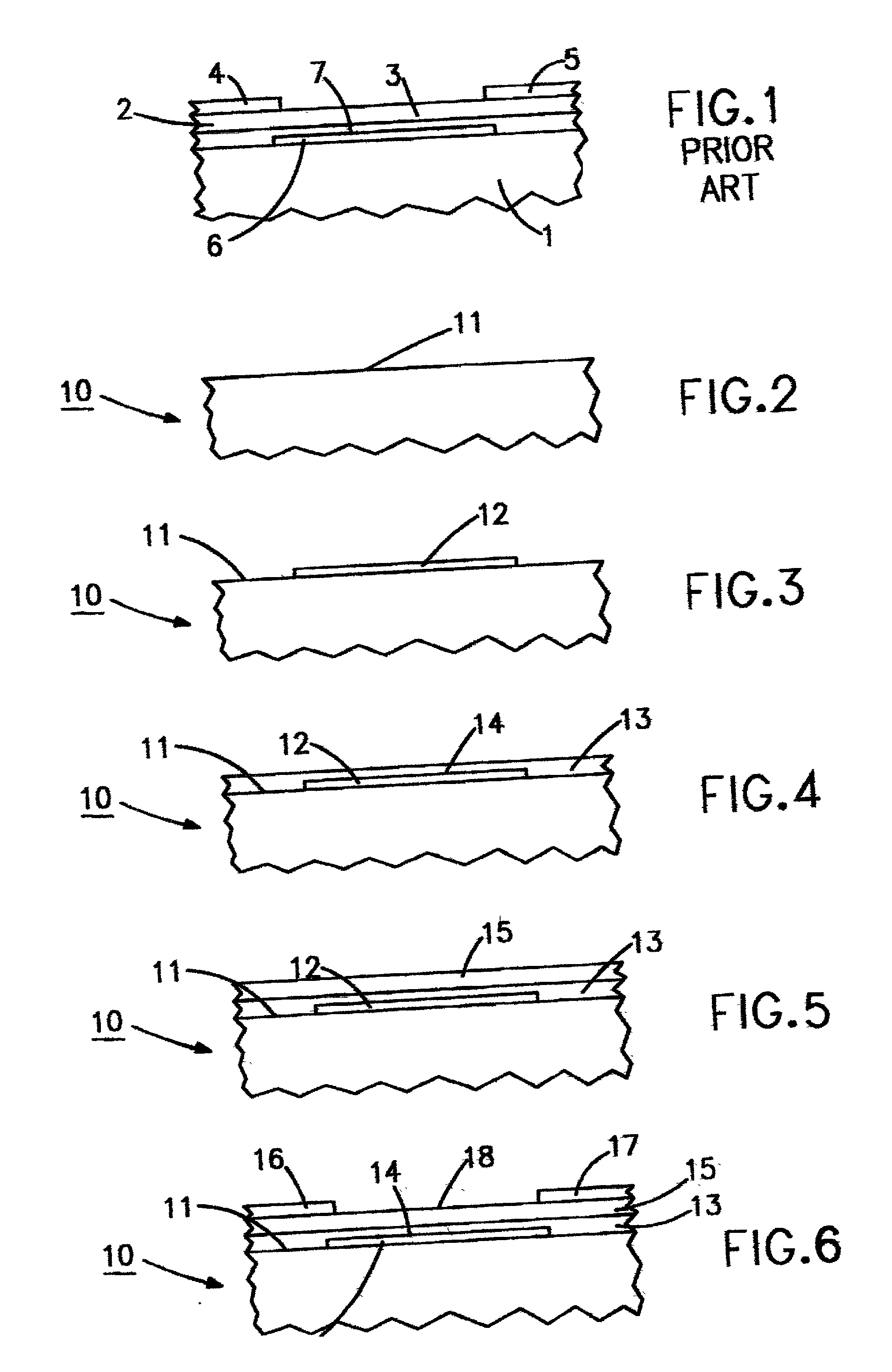
[0044] TFT's having as gate insulator a thin film of barium zirconate titanate (BZT), are fabricated by means of room temperature vicinity type rf sputtering as described in Example 1 together with the TFT fabrication steps described in connection with FIGS. 2-6. In this particular example, oxidized silicon substrates are cleaned in an isopropanol bath using ultrasonic agitation and dried with nitrogen. They are then assembled with a metal mask with openings corresponding to the gate lines and placed and pumped down to high vacuum in an electron beam evaporator. Gate metallization of either 400 .ANG. of aluminum or a bilayer of 150 .ANG. of titanium followed by 300 .ANG. of platinum is deposited on the substrates by electron beam evaporation. Then a gate insulator film 13 of BZT is deposited on top of the gate 12 and the substrate surface 11, as described in example 1.
[0045] An organic semiconductor pentacene layer 15 is deposited on the BZT gate insulator 13 using thermal evaporati...
example 3
[0052] TFT devices are fabricated on transparent polycarbonate substrates that are 0.020" thick which is about 0.5 mm using a sputtered BZT gate insulator that is about 1280 .ANG. in thickness deposited by the sputtering process as described in connection with FIG. 7 and using the steps described in connection with FIGS. 2-6 for depositing the other layers.
[0053] Measurements of TFT characteristics were performed as described in Example 2. Referring to FIG. 16 which shows the drain current versus drain voltage plot for a TFT device on this type of substrate with a channel length of 69 .mu.m and channel width of 1500 .mu.m. The mobility for this device was calculated to be 0.14 cm.sup.2 V.sup.-1 sec.sup.-1 while .mu.=0.20 cm.sup.2 V.sup.-1 sec.sup.-1 in the saturation regime. Mobility values as high as 0.38 cm.sup.2 V.sup.-1 sec.sup.-1 were measured from devices with a W / L ratio of 4. These are the highest reported mobilities from devices fabricated on plastic substrates, and they ar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com