Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3355 results about "High dielectric permittivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
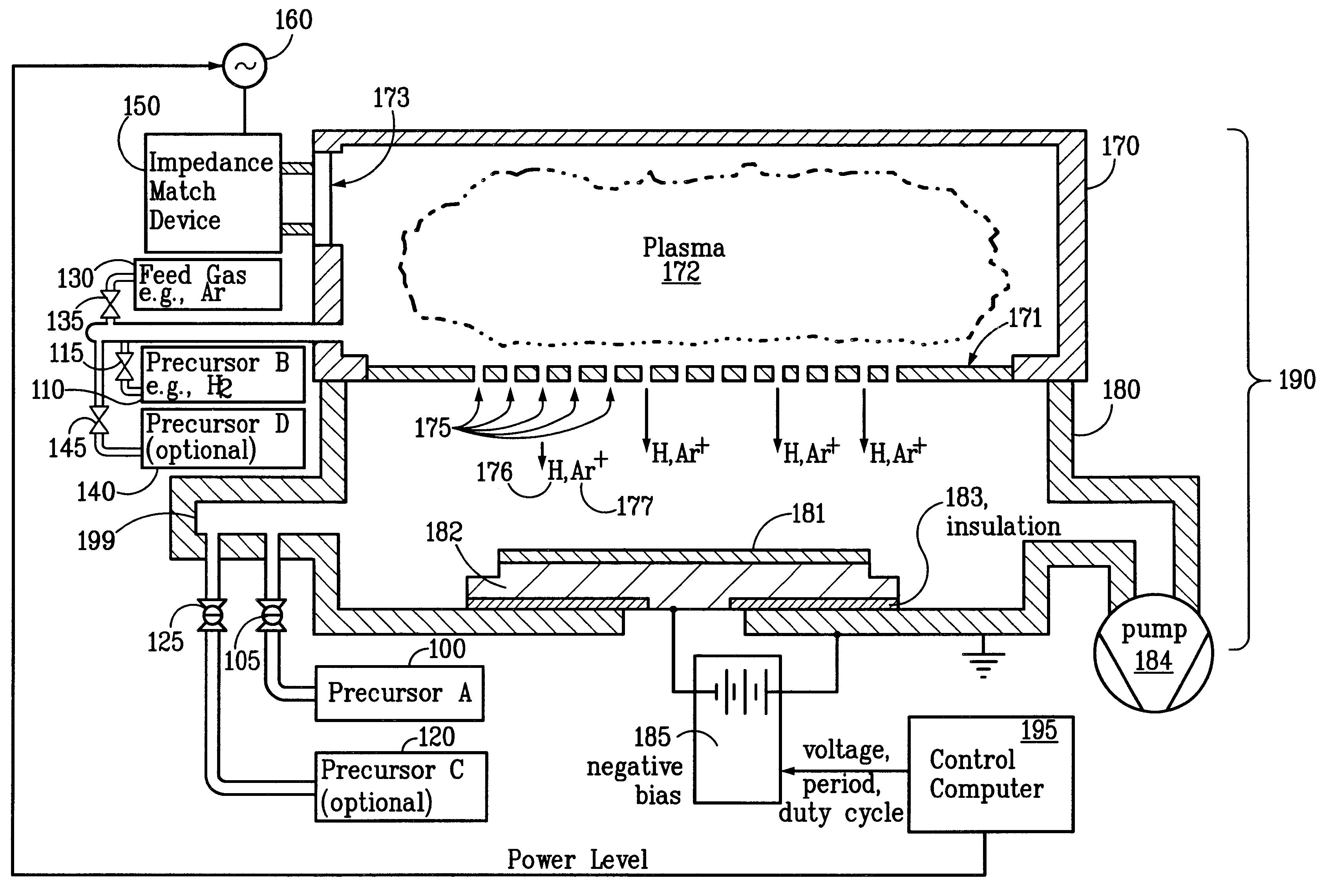
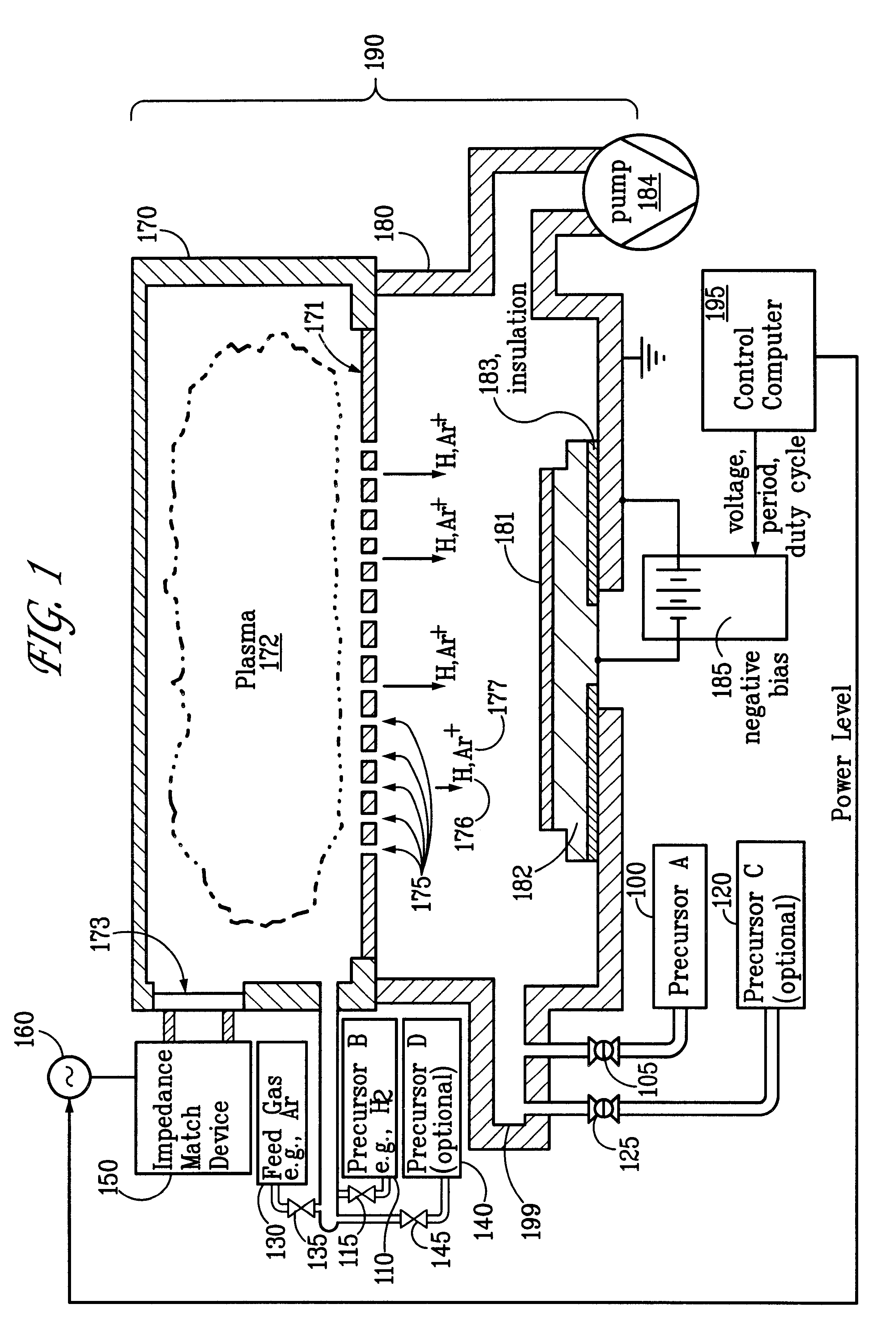
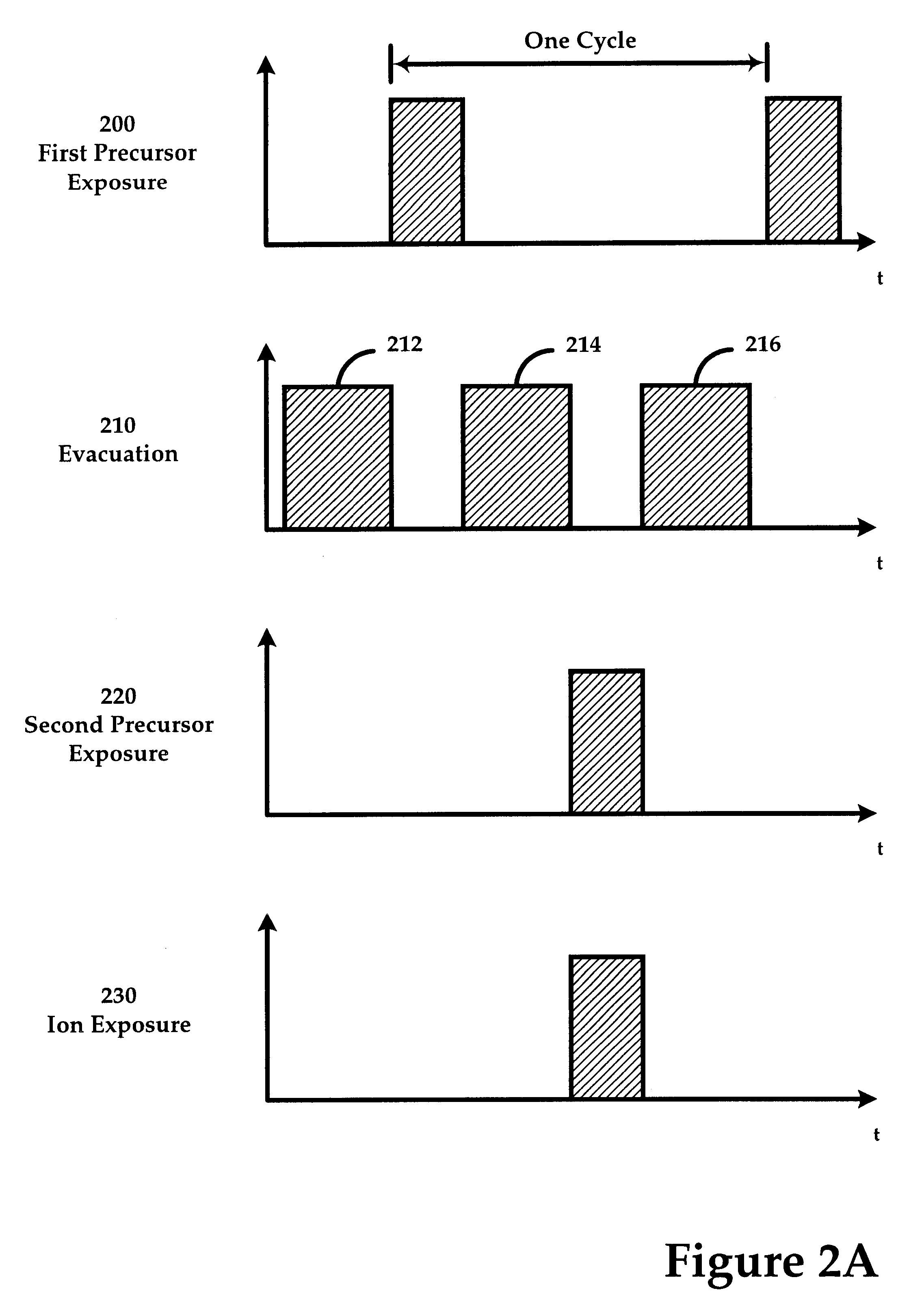
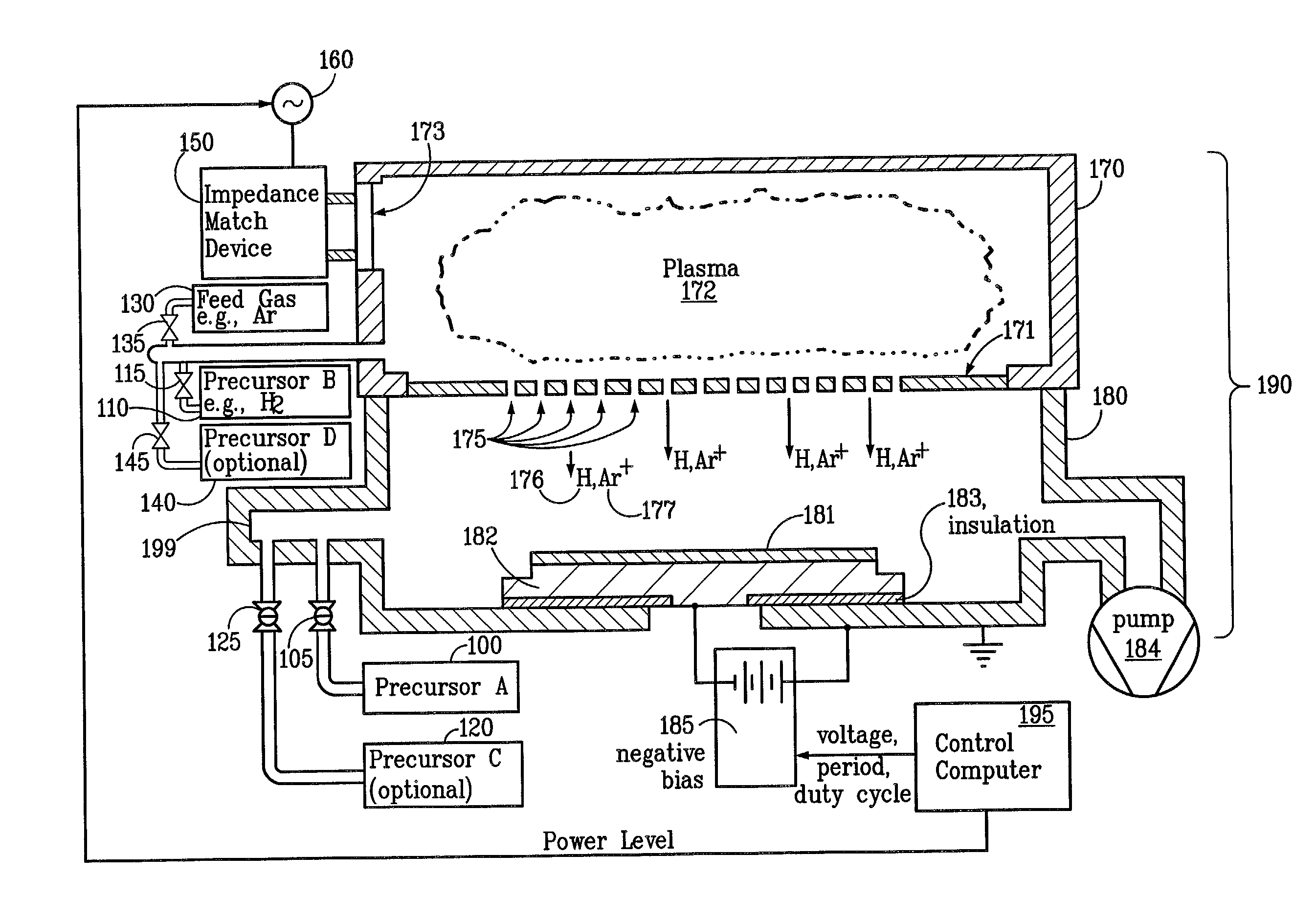
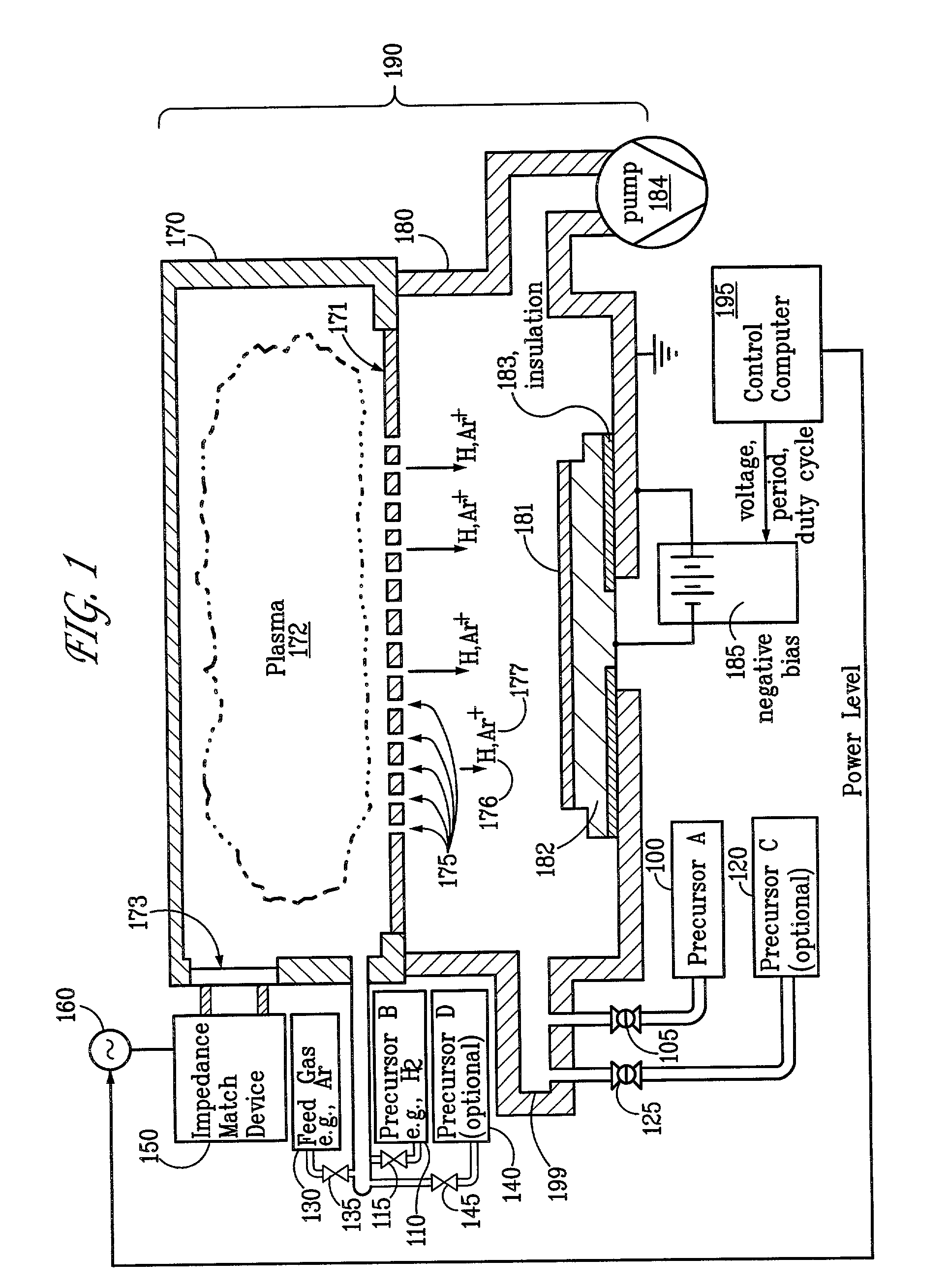
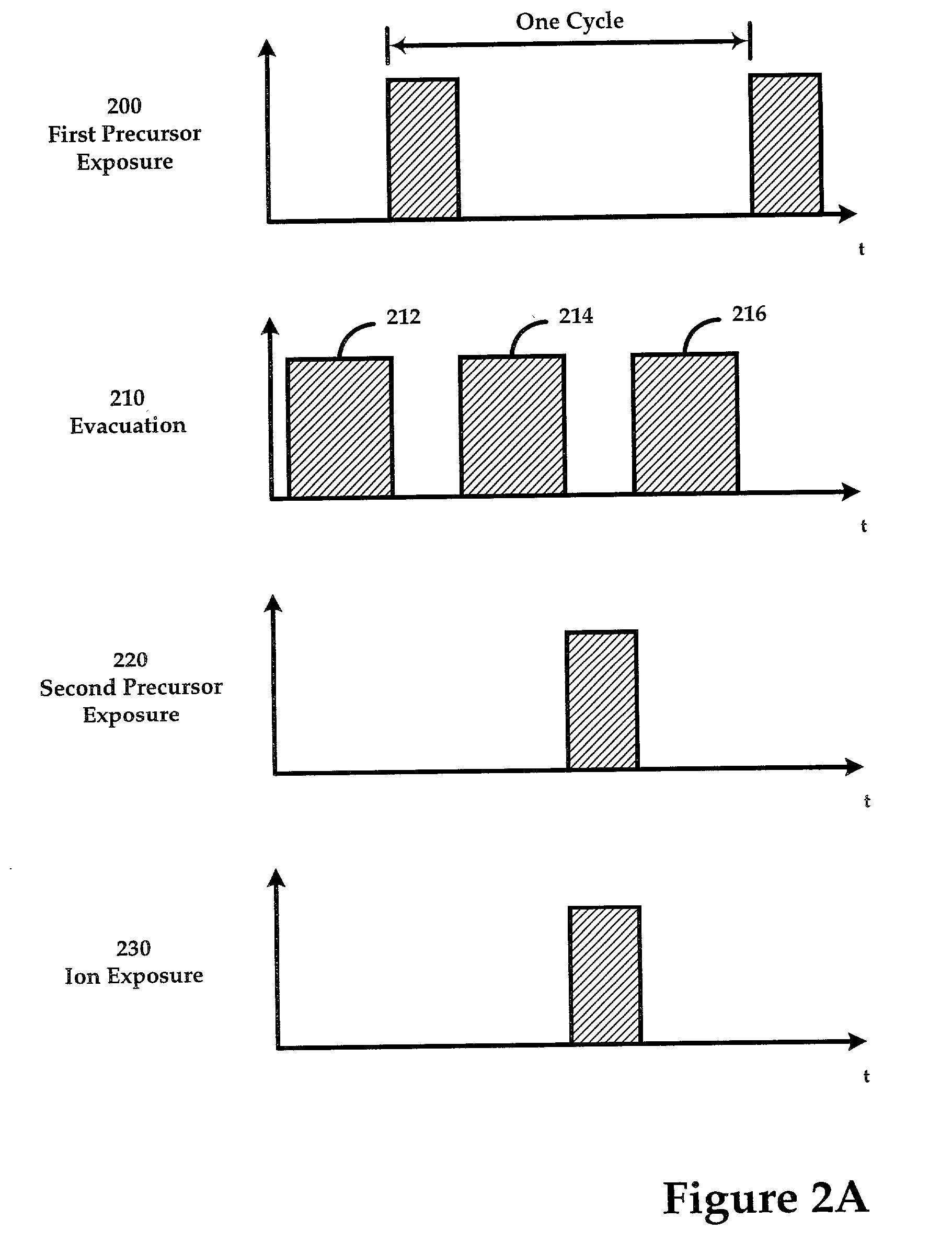
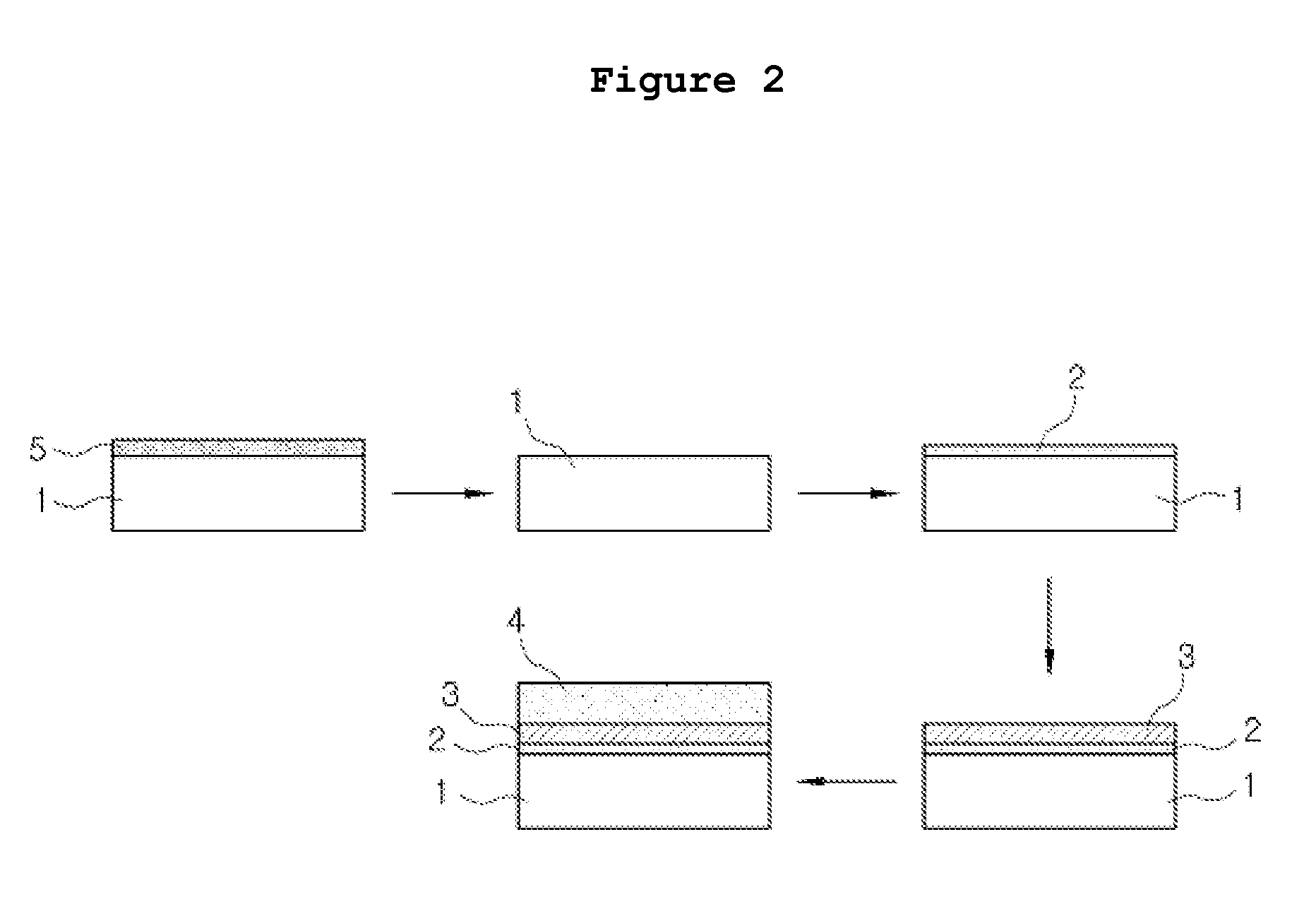
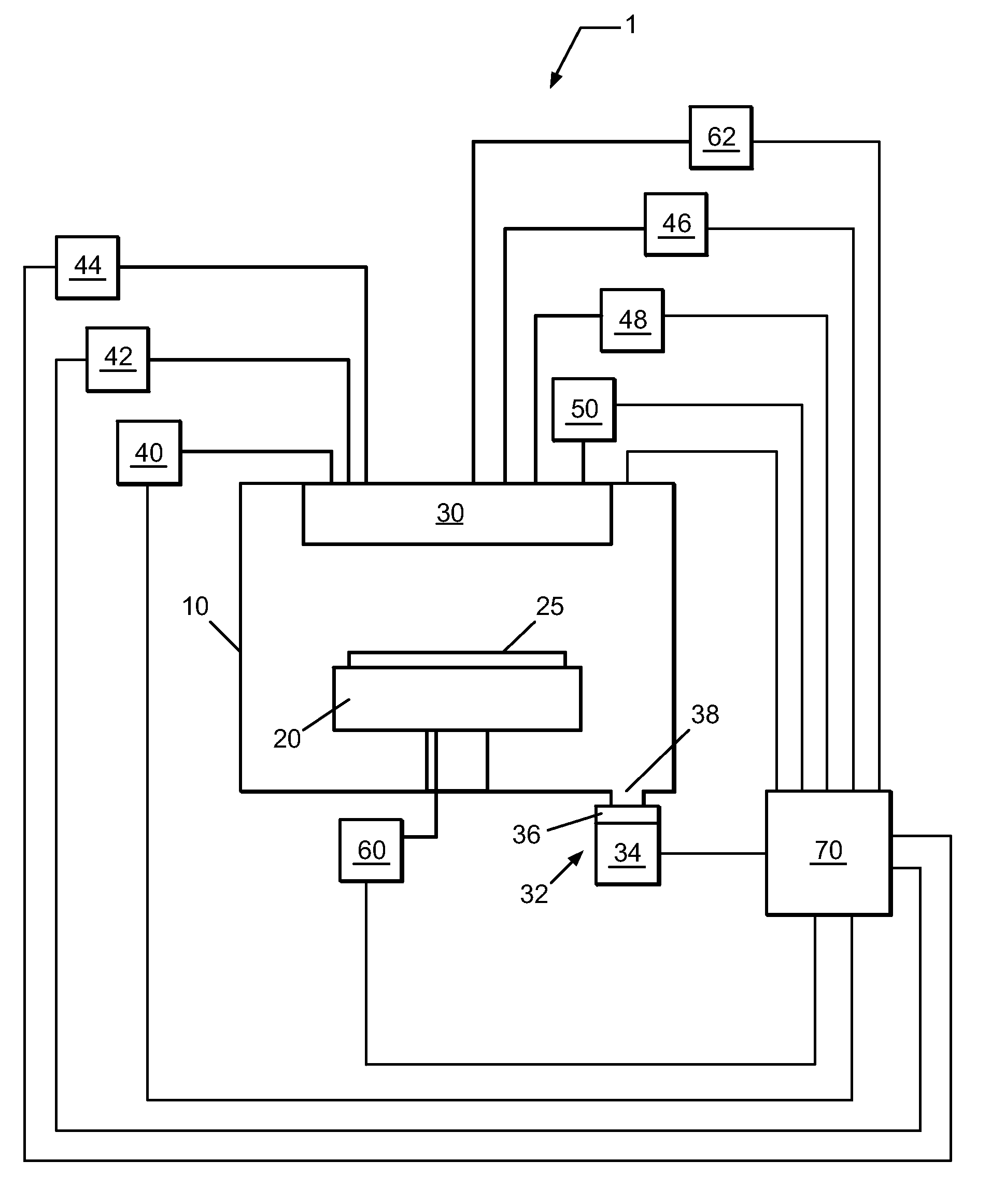
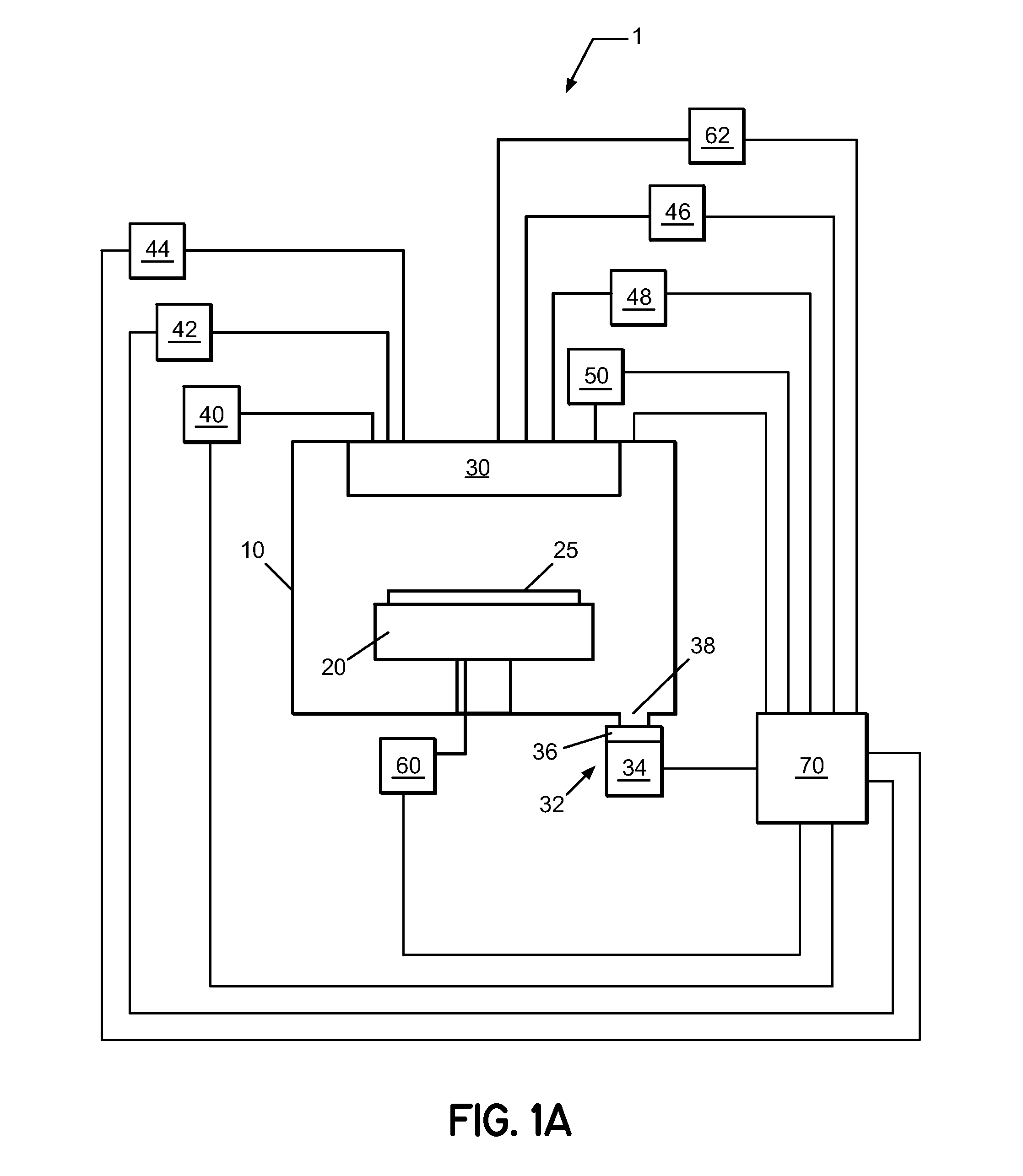
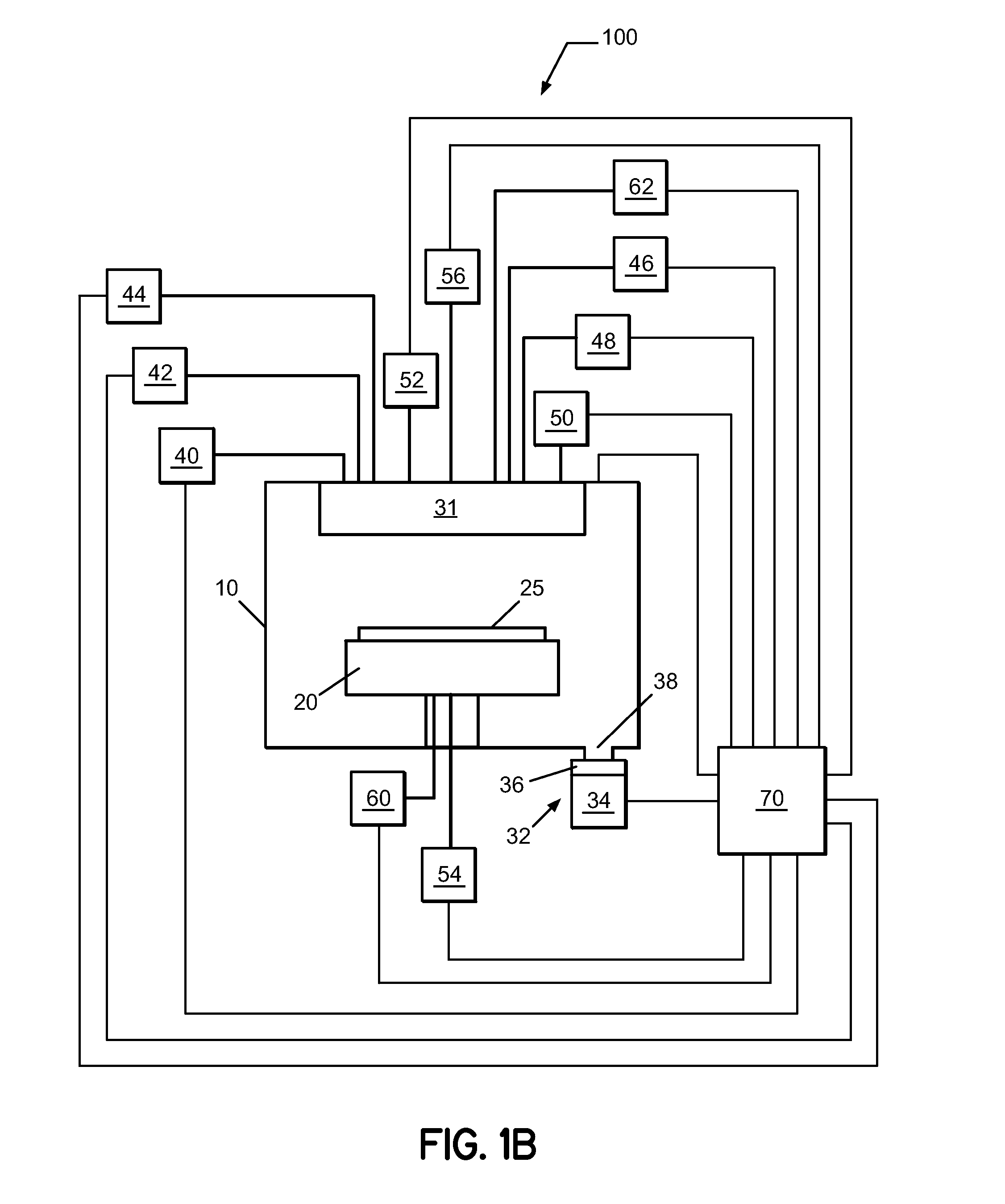
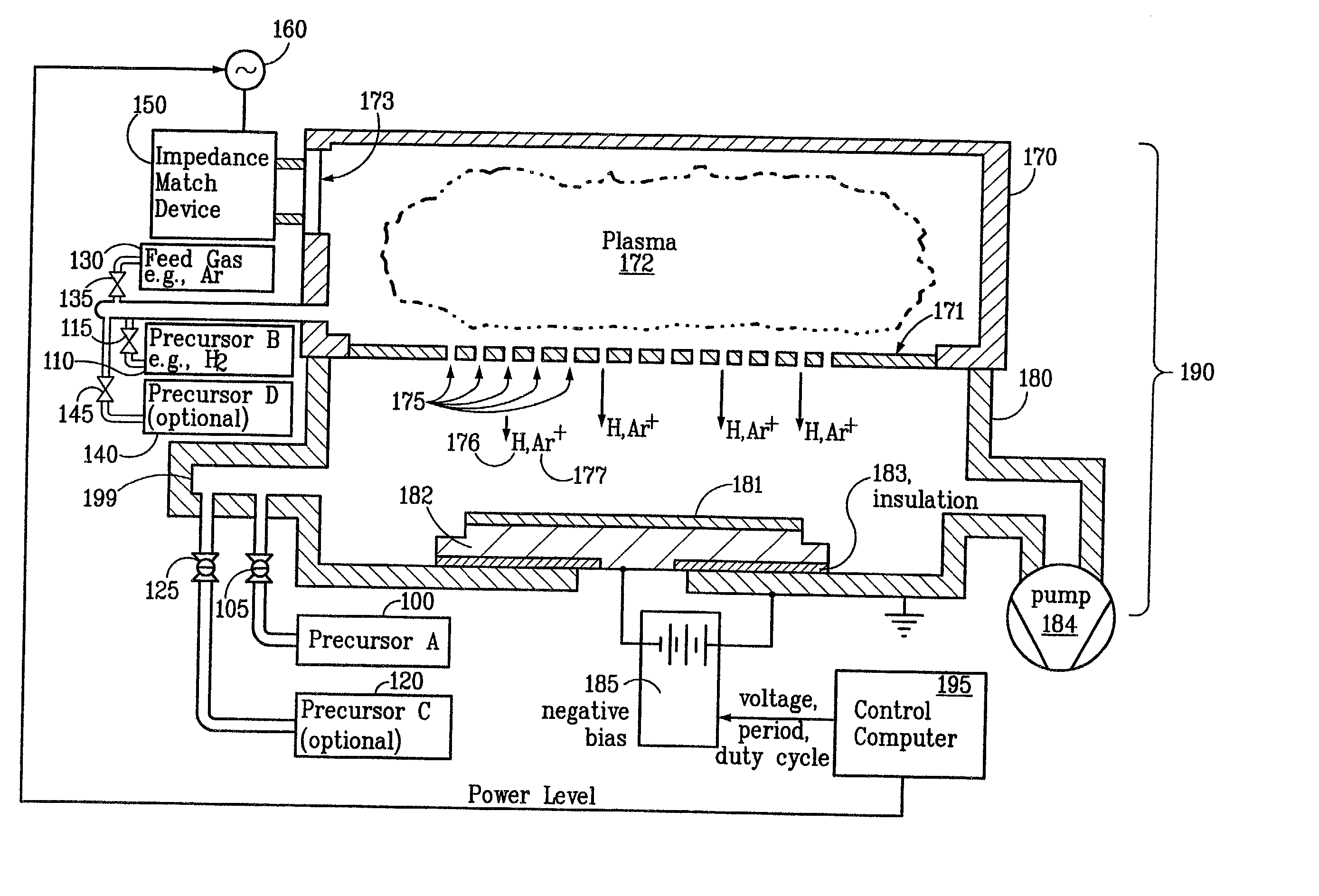
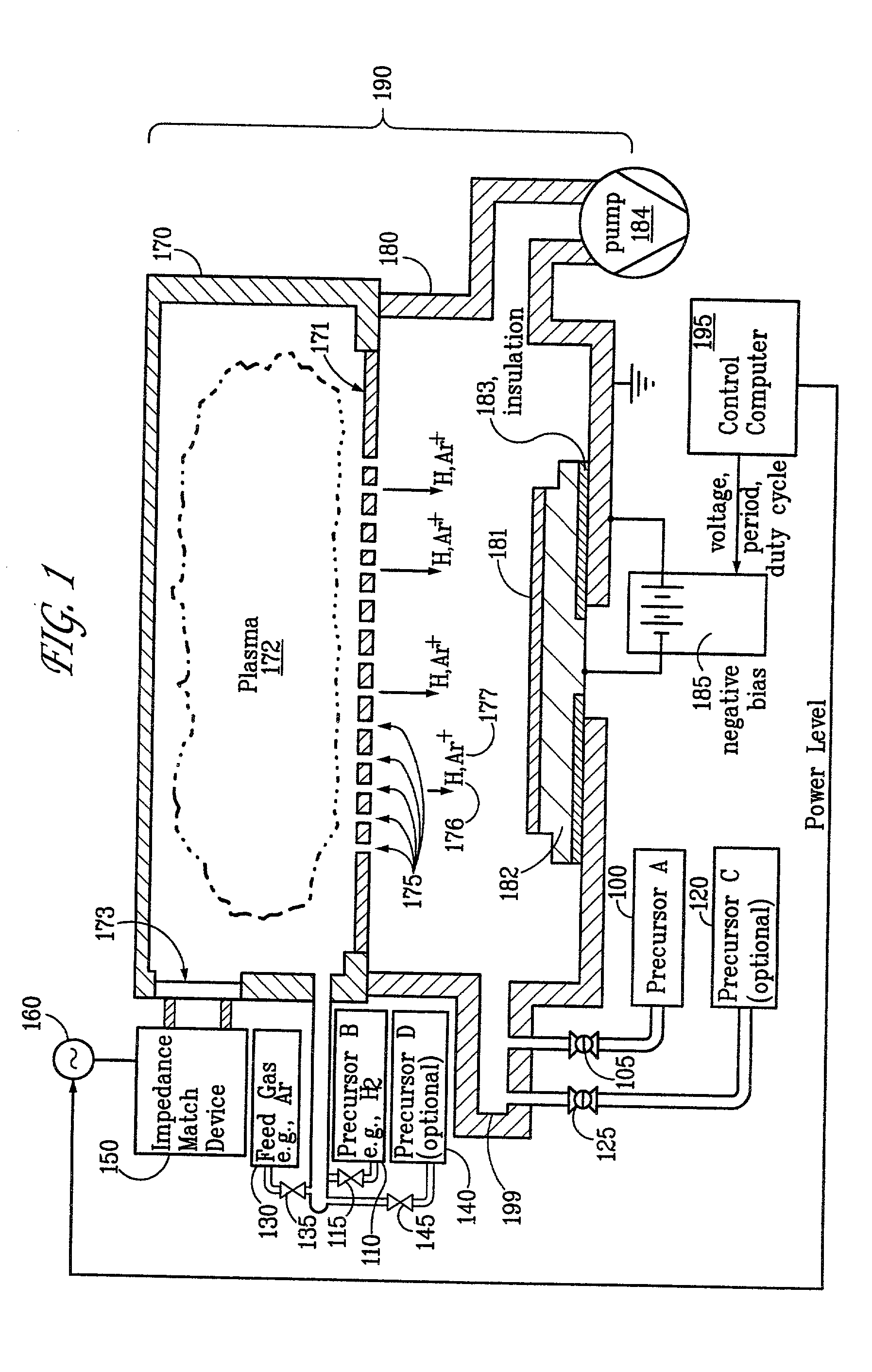
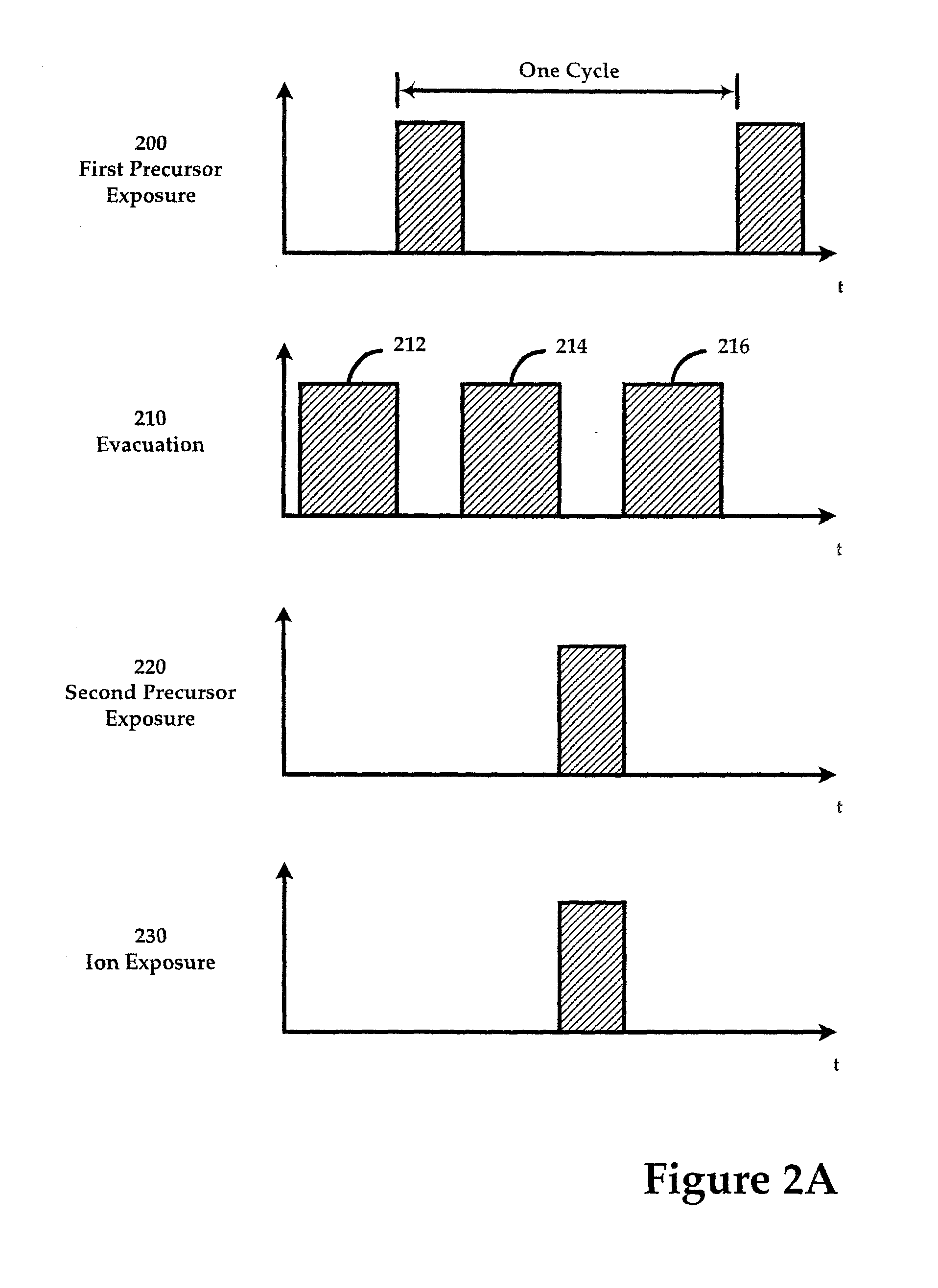
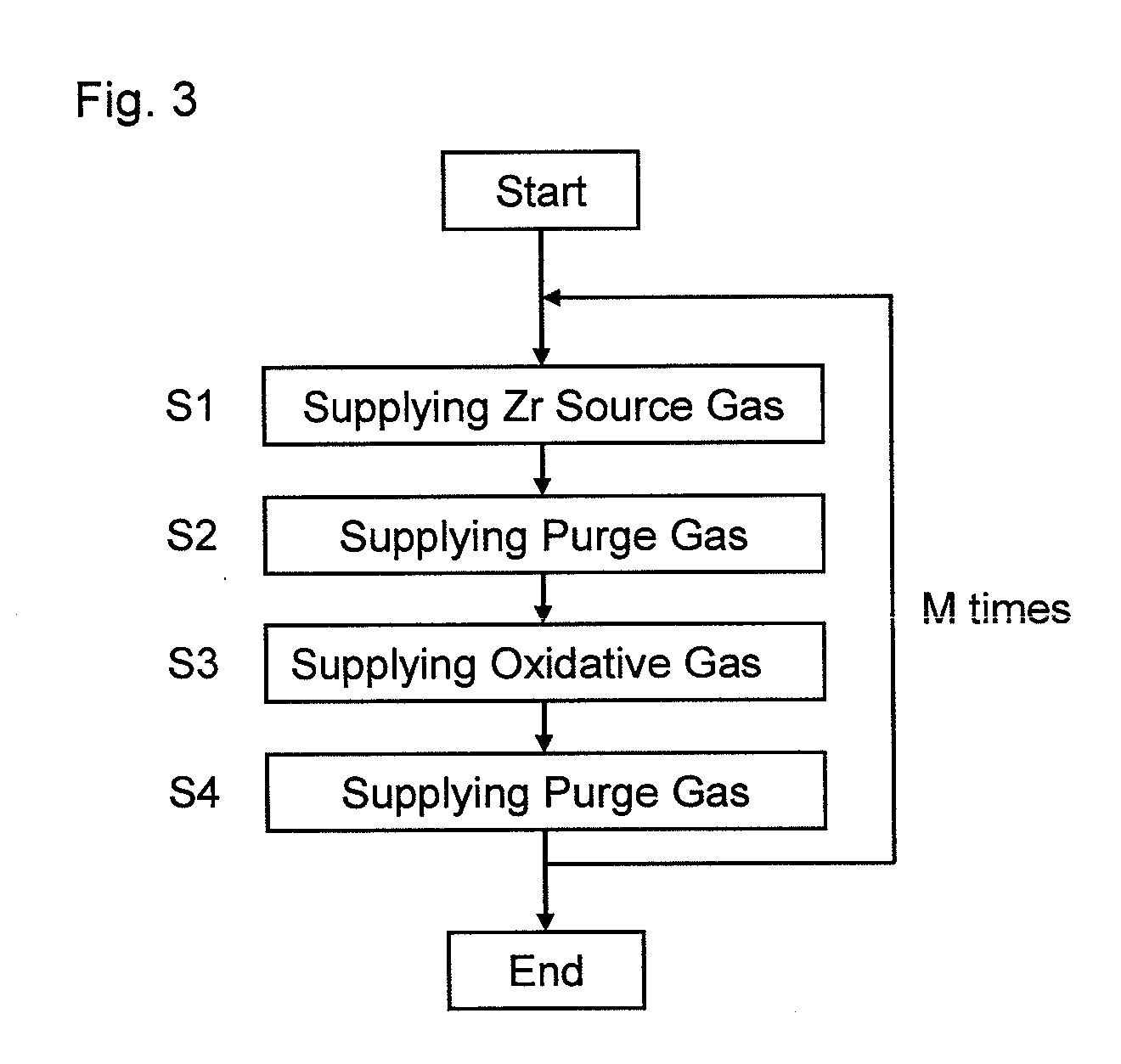
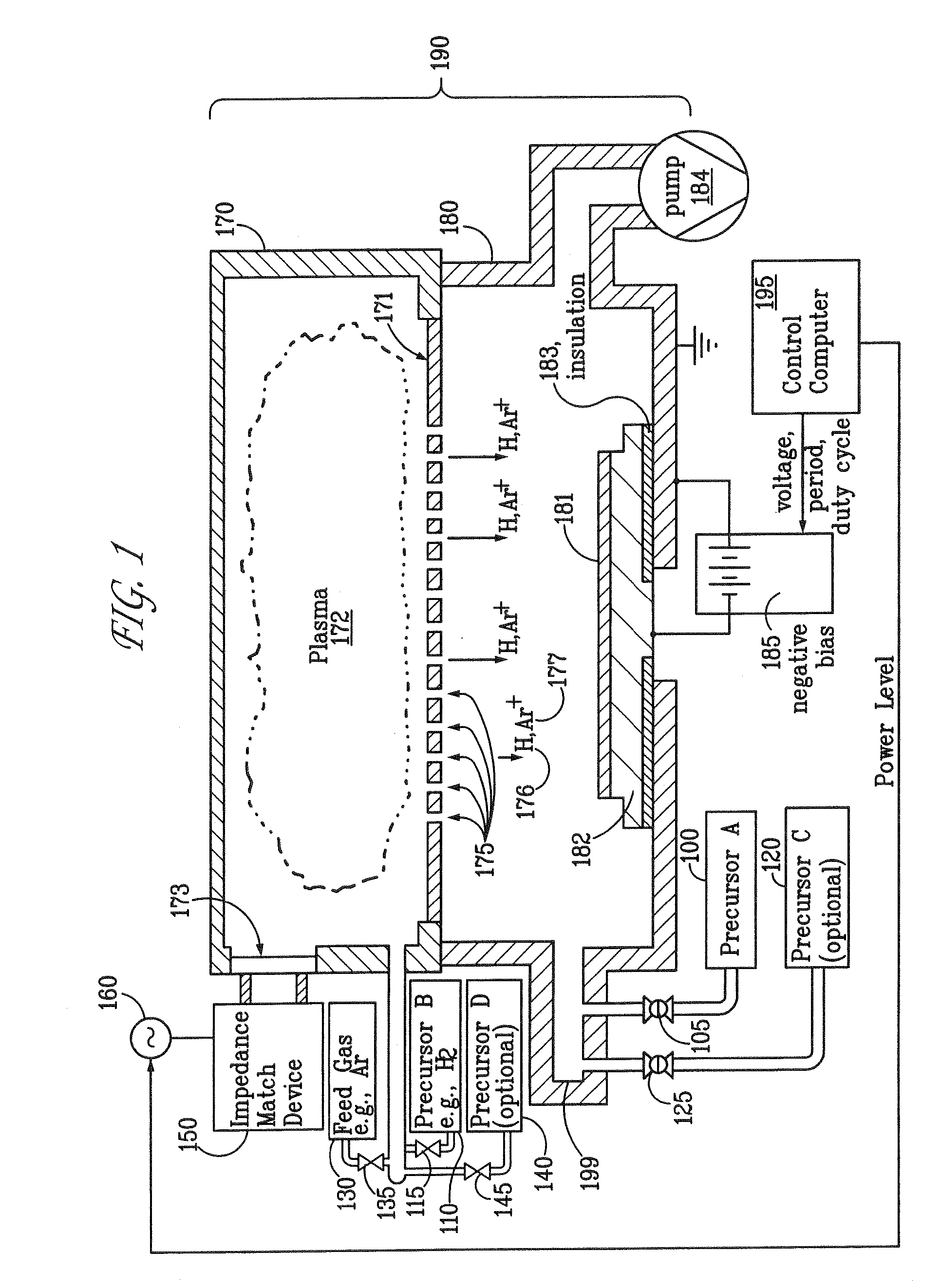
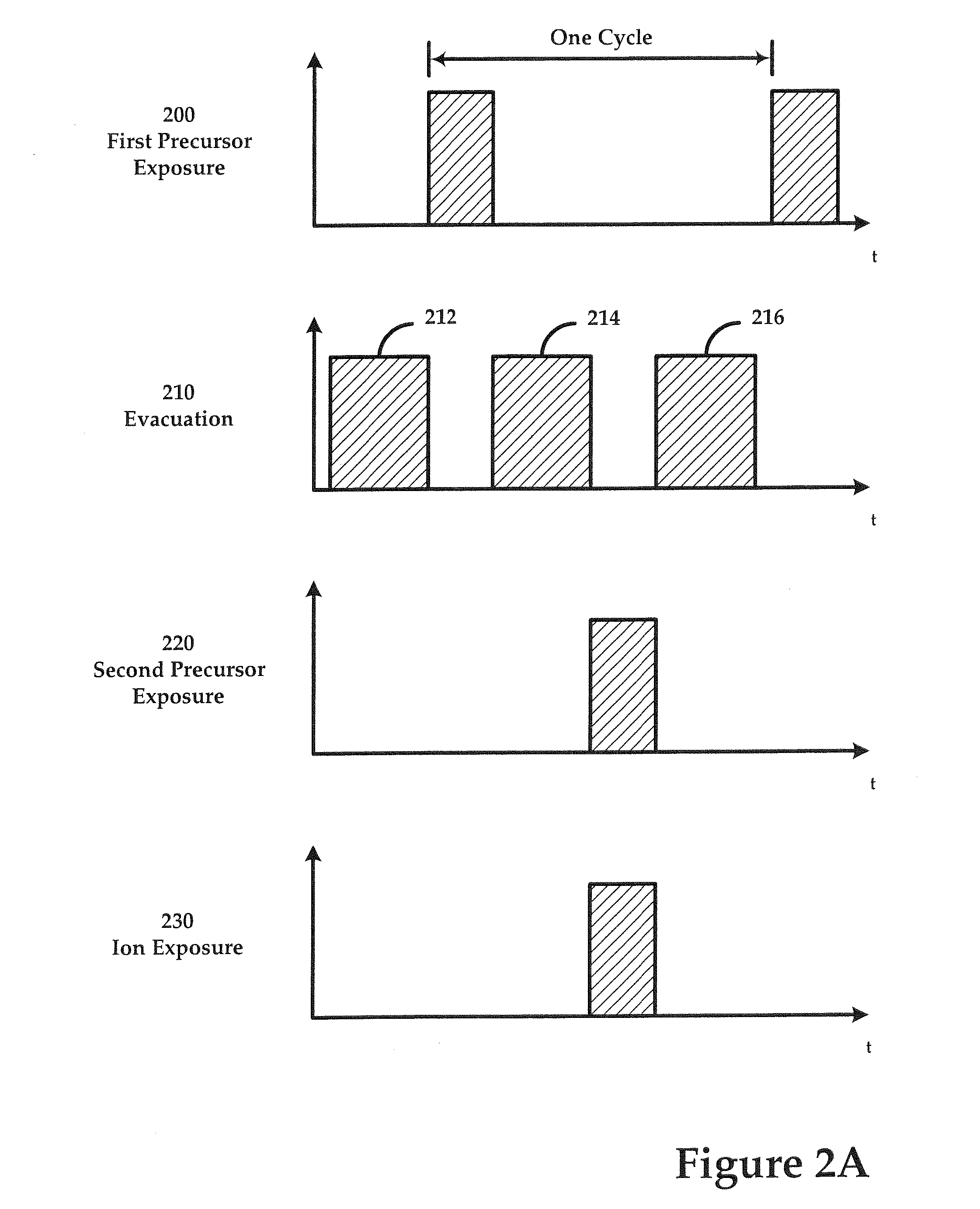
Sequential method for depositing a film by modulated ion-induced atomic layer deposition (MII-ALD)
InactiveUS6428859B1Faster efficient meanSimple methodVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSequential methodHigh density
The present invention relates to an enhanced sequential atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique suitable for deposition of barrier layers, adhesion layers, seed layers, low dielectric constant (low-k) films, high dielectric constant (high-k) films, and other conductive, semi-conductive, and non-conductive films. This is accomplished by 1) providing a non-thermal or non-pyrolytic means of triggering the deposition reaction; 2) providing a means of depositing a purer film of higher density at lower temperatures; and, 3) providing a faster and more efficient means of modulating the deposition sequence and hence the overall process rate resulting in an improved deposition method. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
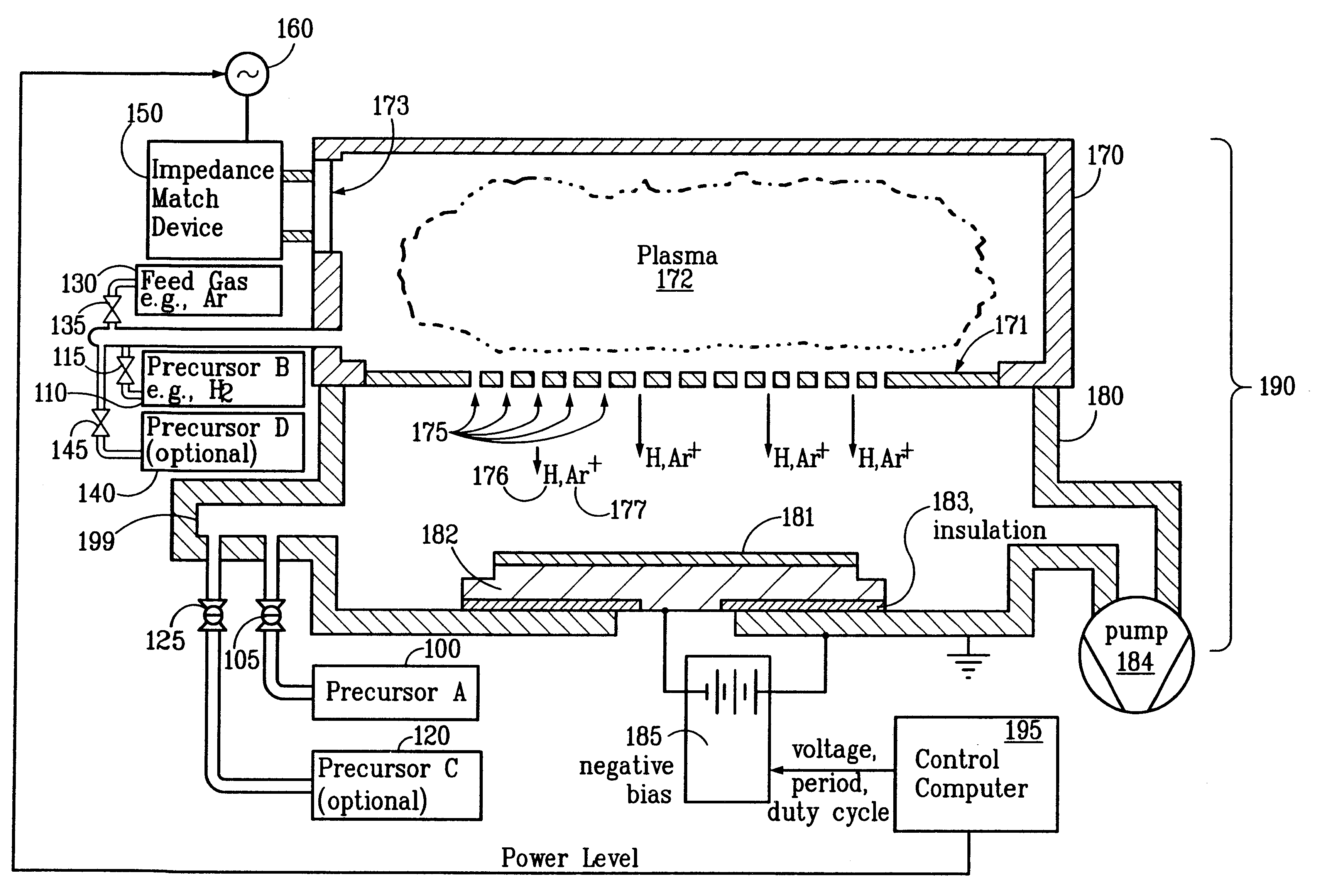
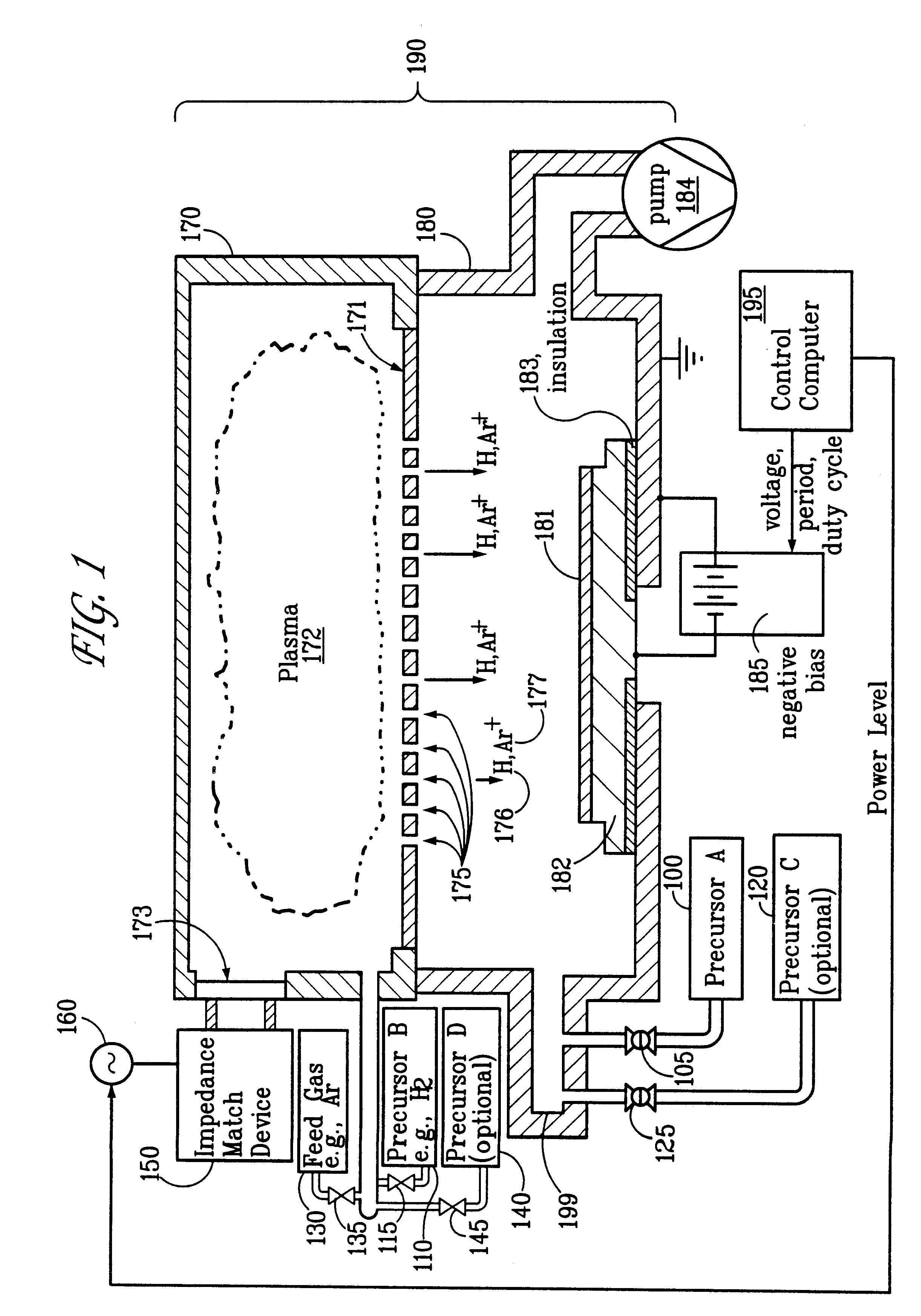
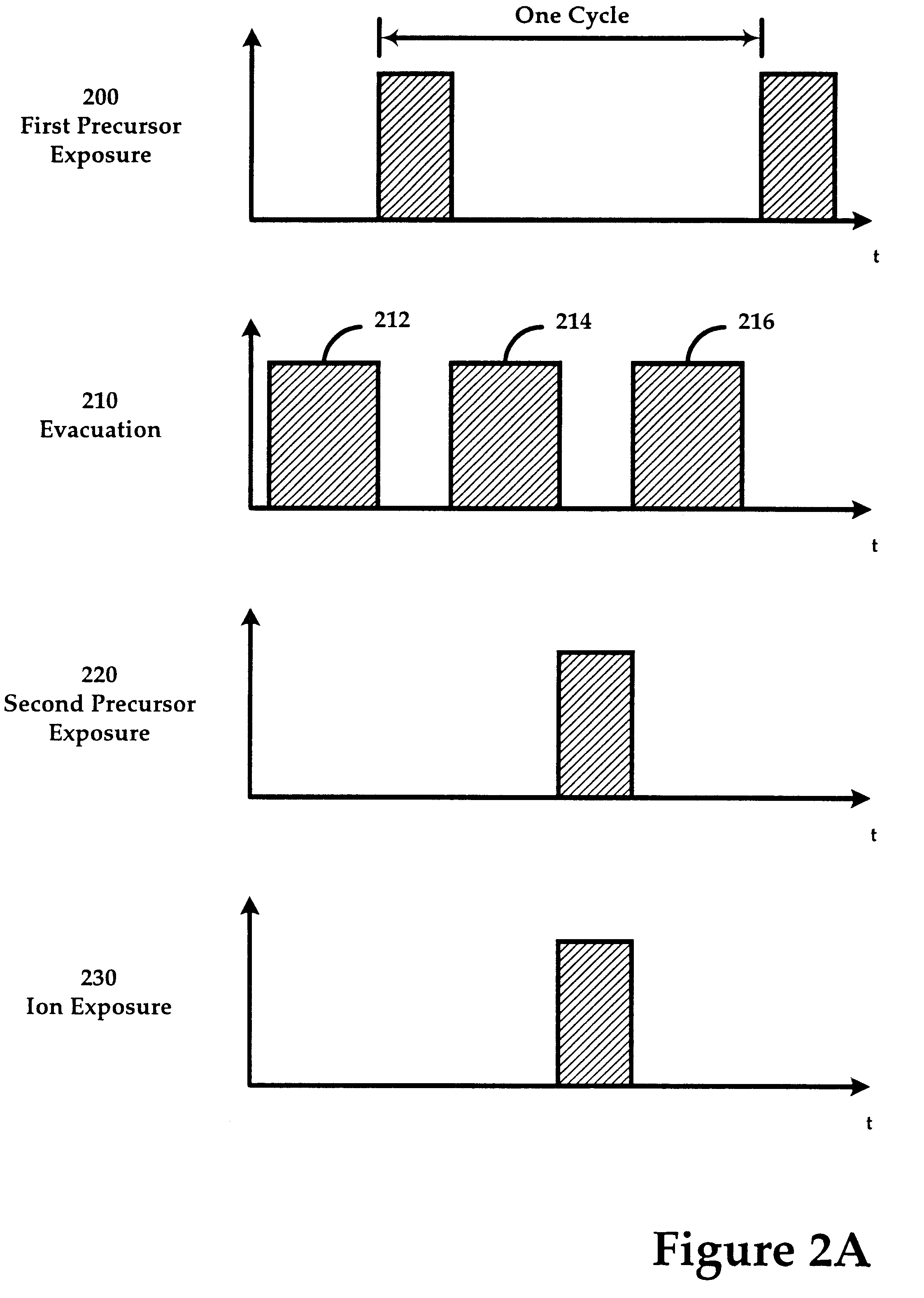
System and method for modulated ion-induced atomic layer deposition (MII-ALD)
InactiveUS20020104481A1Faster efficient meanSimple methodSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHigh densitySubject matter
The present invention relates to an enhanced sequential or non-sequential atomic layer deposition (ALD) apparatus and technique suitable for deposition of barrier layers, adhesion layers, seed layers, low dielectric constant (low-k) films, high dielectric constant (high-k) films, and other conductive, semi-conductive, and non-conductive films. This is accomplished by 1) providing a non-thermal or non-pyrolytic means of triggering the deposition reaction; 2) providing a means of depositing a purer film of higher density at lower temperatures; 3) providing a faster and more efficient means of modulating the deposition sequence and hence the overall process rate resulting in an improved deposition method; and, 4) providing a means of improved radical generation and delivery. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. [37 C.F.R. § 1.72(b)].
Owner:ANGSTRON SYST
Plasma curing process for porous silica thin film
InactiveUS6558755B2Low dielectric constantHigh elastic modulusSilicaSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon dioxideHeat treated
Low dielectric constant films with improved elastic modulus. The method of making such coatings involves providing a porous network coating produced from a resin containing at least 2 Si-H groups and plasma curing the coating to convert the coating into porous silica. Plasma curing of the network coating yields a coating with improved modulus, but with a higher dielectric constant. The costing is plasma cured for between about 15 and about 120 seconds at a temperature less than or about 350° C. The plasma cured coating can optionally be annealed. Rapid thermal processing (RTP) of the plasma cured coating reduces the dielectric constant of the coating while maintaining an improved elastic modulus as compared to the plasma cured porous network coating. The annealing temperature is typically loss than or about 475° C., and the annealing time is typically no more than or about 180 seconds. The annealed, plasma cured coating has a dielectric constant in the range of from about 1.1 to about 2.4 and an improved elastic modulus.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES +1
Method of depositing nanolaminate film for non-volatile floating gate memory devices by atomic layer deposition
Disclosed herein is a method of depositing a nanolaminate film for next-generation non-volatile floating gate memory devices by atomic layer deposition. The method includes the steps of: introducing a substrate into an atomic layer deposition reactor; forming on the substrate a first high-dielectric-constant layer by alternately supplying an oxygen source and a metal source selected from among an aluminum source, a zirconium source and a hafnium source; forming on the first high-dielectric-constant layer a nickel oxide layer by alternately supplying a nickel source and an oxygen source; and forming on the nickel oxide layer a second high-dielectric-constant layer by alternately supplying an oxygen source and a metal source selected from among an aluminum source, a zirconium source and a hafnium source. The nanolaminate film deposited according to the method shows good memory window characteristics compared to those of memory devices fabricated using nanocrystal floating gates according to the prior physical vapor deposition methods, and thus can be applied to non-volatile floating gate memory devices.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH
Continuous method for depositing a film by modulated ion-induced atomic layer deposition (MII-ALD)
InactiveUS6416822B1Faster efficient meanSimple methodPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention relates to an enhanced non-sequential atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique suitable for deposition of barrier layers, adhesion layers, seed layers, low dielectric constant (low-k) films, high dielectric constant (high-k) films, and other conductive, semi-conductive, and non-conductive films. This is accomplished by 1) providing a non-thermal or non-pyrolytic means of triggering the deposition reaction; 2) providing a means of depositing a purer film of higher density at lower temperatures; and, 3) providing a faster and more efficient means of modulating the deposition sequence and hence the overall process rate resulting in an improved deposition method.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
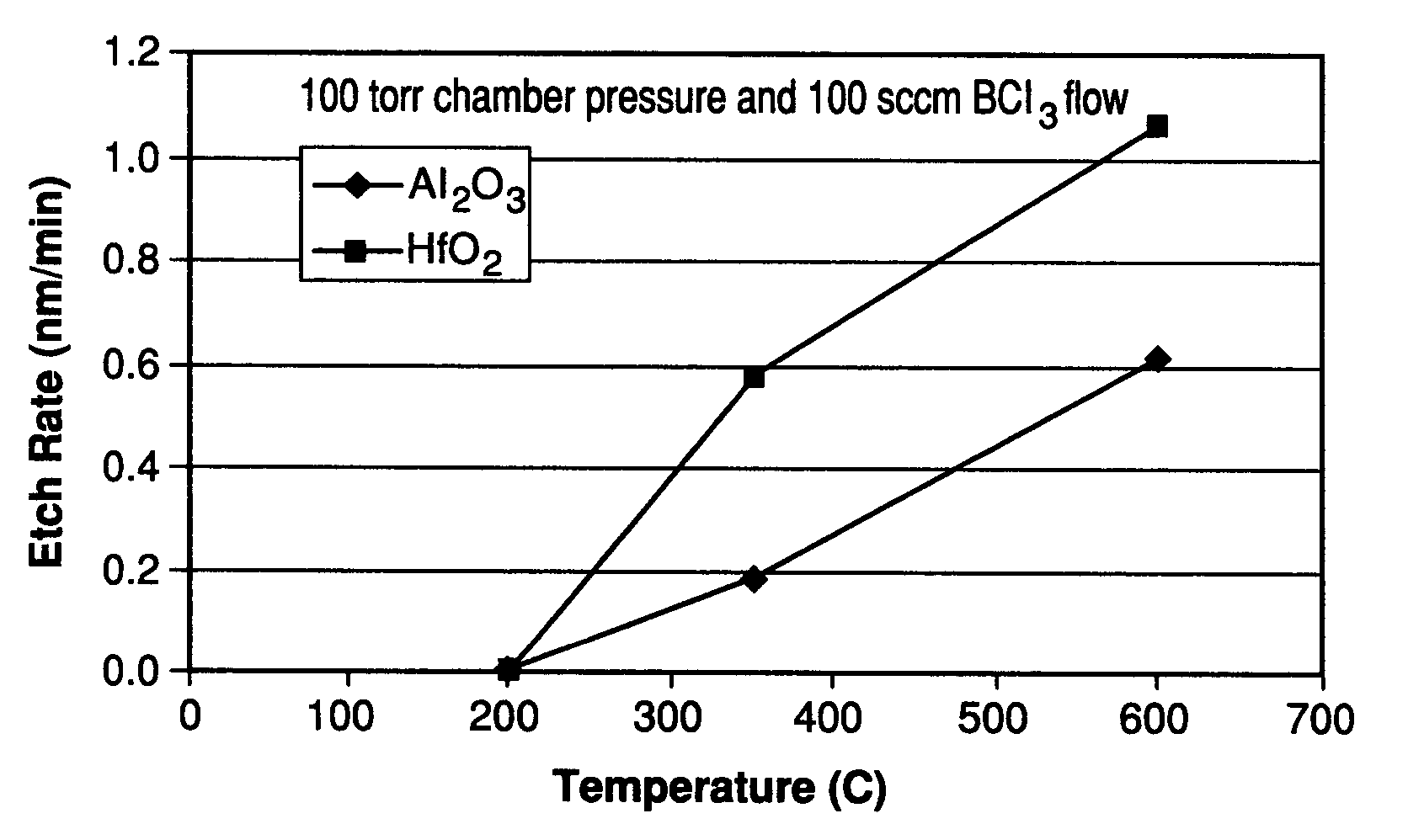
Method for etching high dielectric constant materials and for cleaning deposition chambers for high dielectric constant materials
A process for the removal of a substance from a substrate for etching and / or cleaning applications is disclosed herein. In one embodiment, there is provided a process for removing a substance having a dielectric constant greater than silicon dioxide from a substrate by reacting the substance with a reactive agent that comprises at least one member from the group consisting a halogen-containing compound, a boron-containing compound, a hydrogen-containing compound, nitrogen-containing compound, a chelating compound, a carbon-containing compound, a chlorosilane, a hydrochlorosilane, or an organochlorosilane to form a volatile product and removing the volatile product from the substrate to thereby remove the substance from the substrate.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
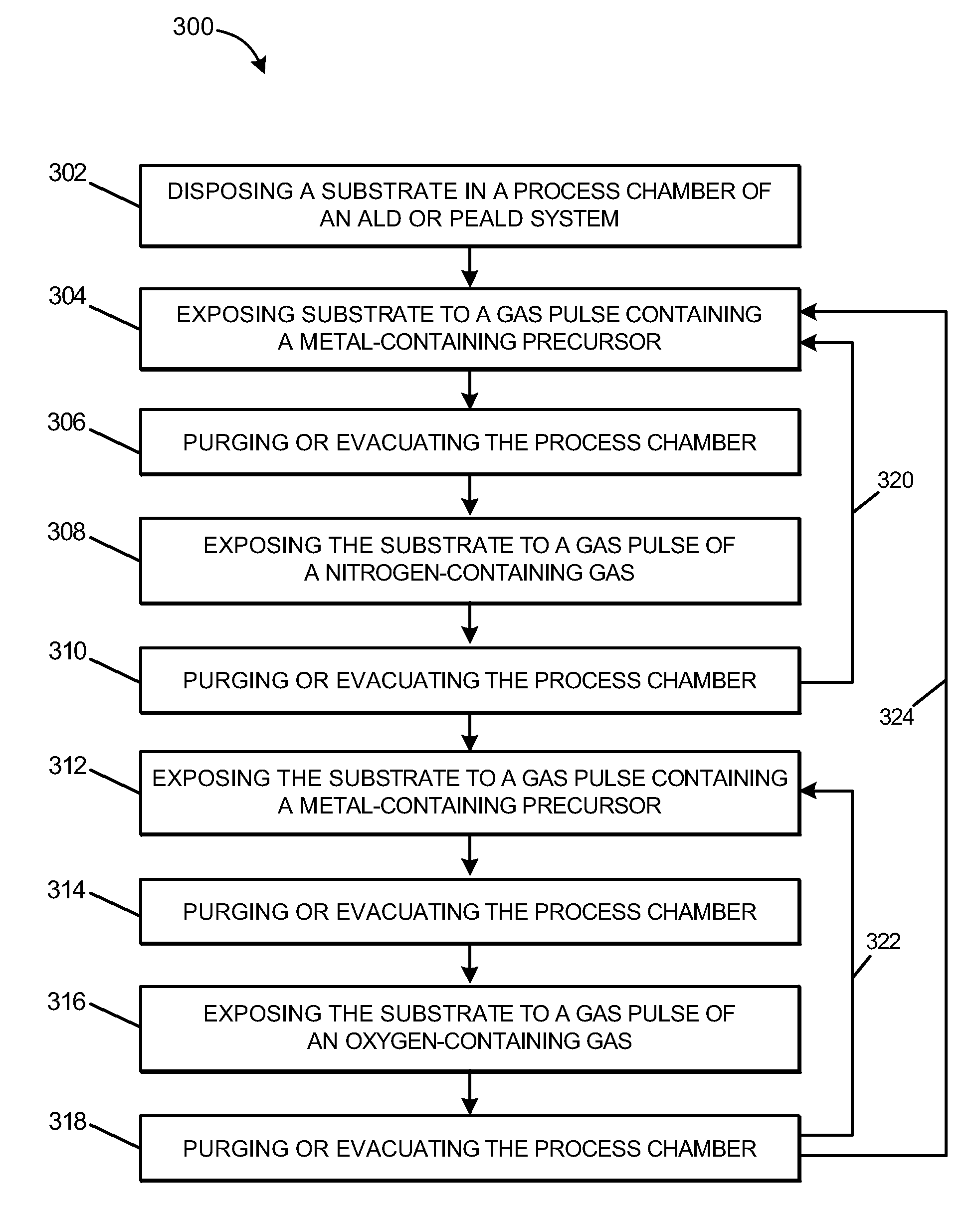
Nitrogen profile engineering in nitrided high dielectric constant films
InactiveUS7767262B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingRare-earth elementNitrogen
A method of forming a nitrided high-k film by disposing a substrate in a process chamber and forming the nitrided high-k film on the substrate by a) depositing a nitrogen-containing film, and b) depositing an oxygen-containing film, wherein steps a) and b) are performed in any order, any number of times, so as to oxidize at least a portion of the thickness of the nitrogen-containing film. The oxygen-containing film and the nitrogen-containing film contain the same one or more metal elements selected from alkaline earth elements, rare earth elements, and Group IVB elements of the Periodic Table, and optionally aluminum, silicon, or aluminum and silicon. According to one embodiment, the method includes forming a nitrided hafnium based high-k film. The nitrided high-k film can be formed by atomic layer deposition (ALD) or plasma-enhanced ALD (PEALD).
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
In-situ hybrid deposition of high dielectric constant films using atomic layer deposition and chemical vapor deposition
InactiveUS7816278B2Rapid temperature measurementIncrease deposition rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDielectricBatch processing
An in-situ hybrid film deposition method for forming a high-k dielectric film on a plurality of substrates in a batch processing system. The method includes loading the plurality of substrates into a process chamber of the batch processing system, depositing by atomic layer deposition (ALD) a first portion of a high-k dielectric film on the plurality of substrates, after depositing the first portion, and without removing the plurality of substrates from the process chamber, depositing by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) a second portion of the high-k dielectric film on the first portion, and removing the plurality of substrates from the process chamber. The method can further include alternatingly repeating the deposition of the first and second portions until the high-k dielectric film has a desired thickness. The method can still further include pre-treating the substrates and post-treating the high-k dielectric film in-situ prior to the removing.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
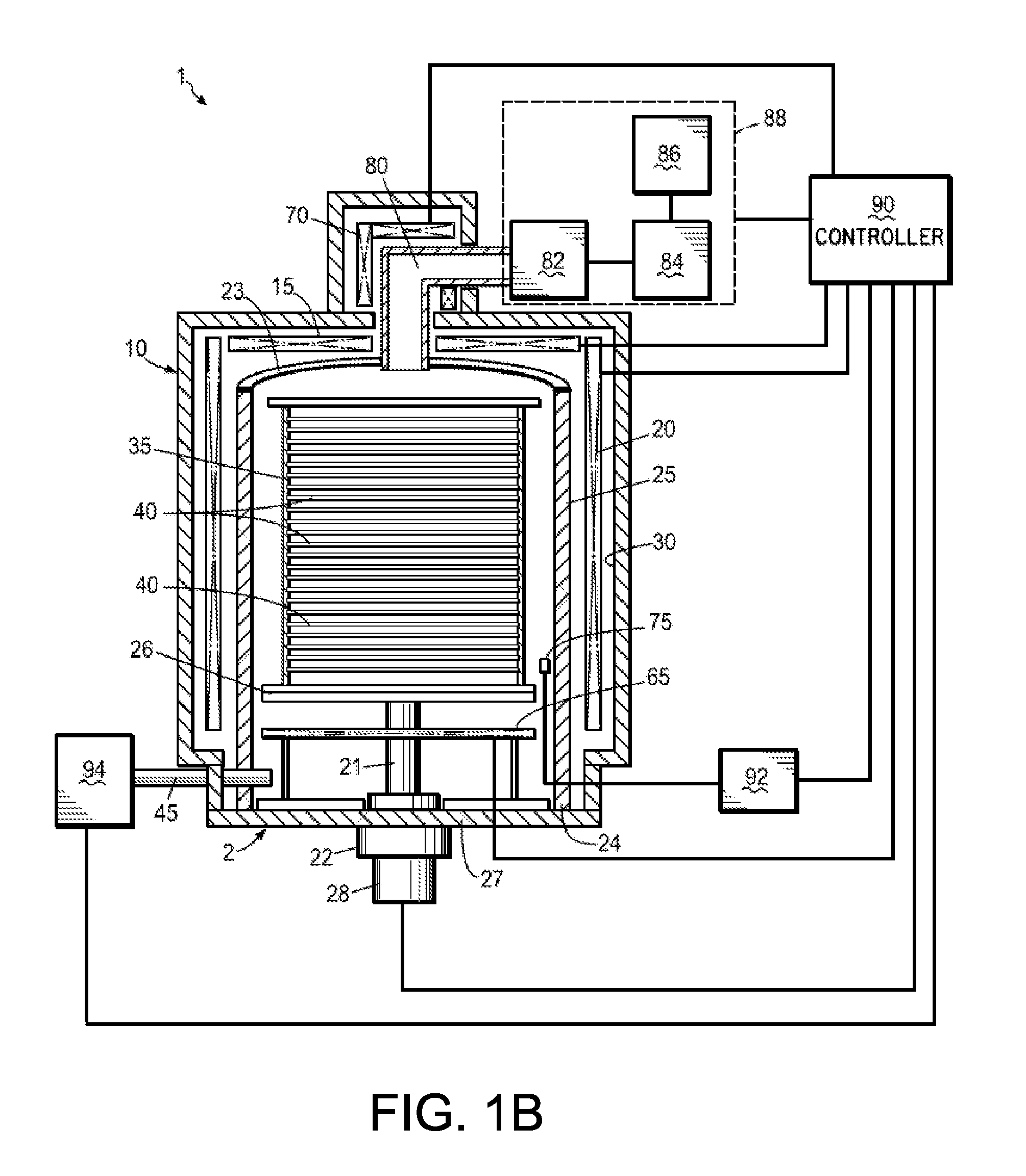
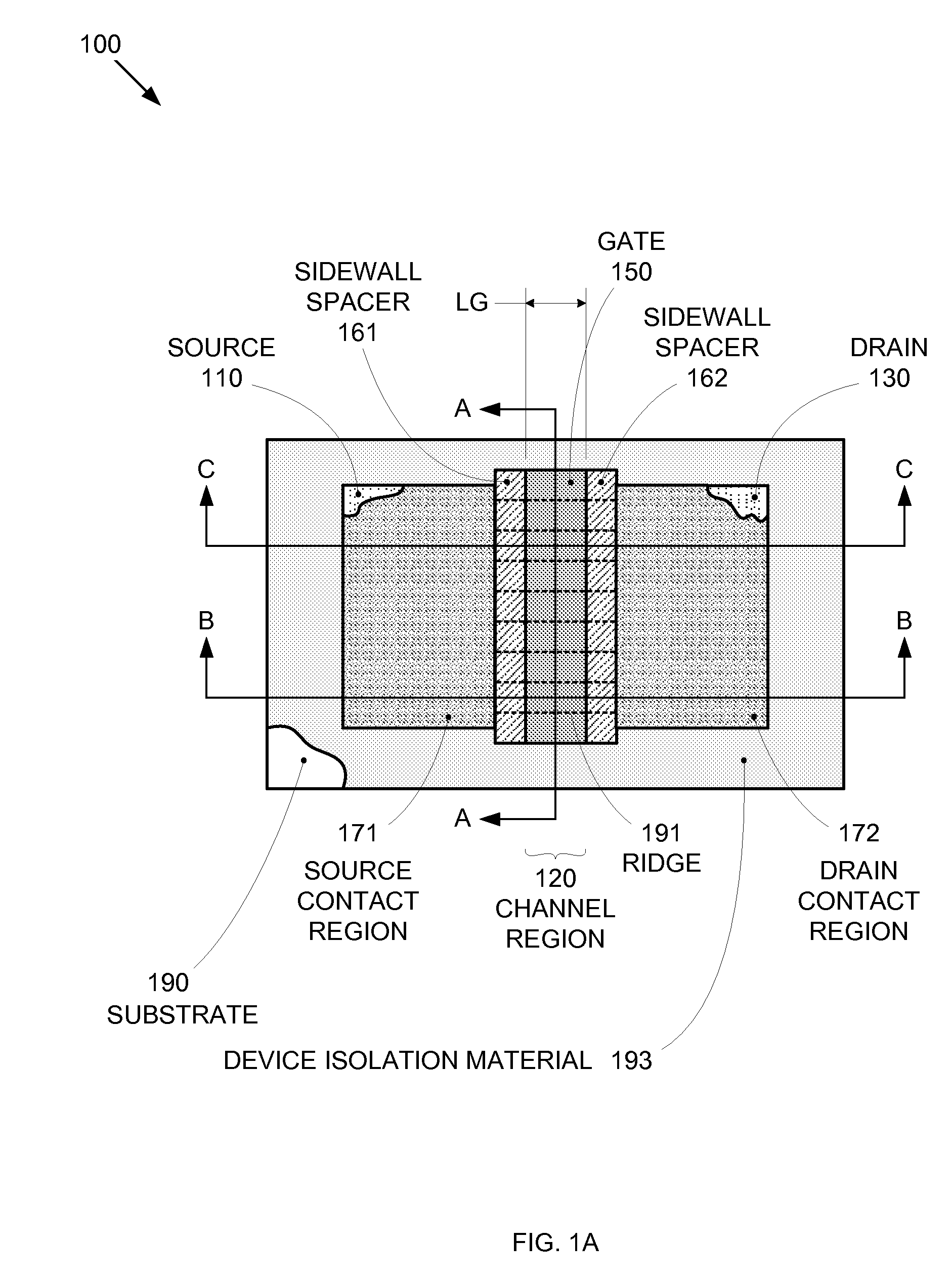
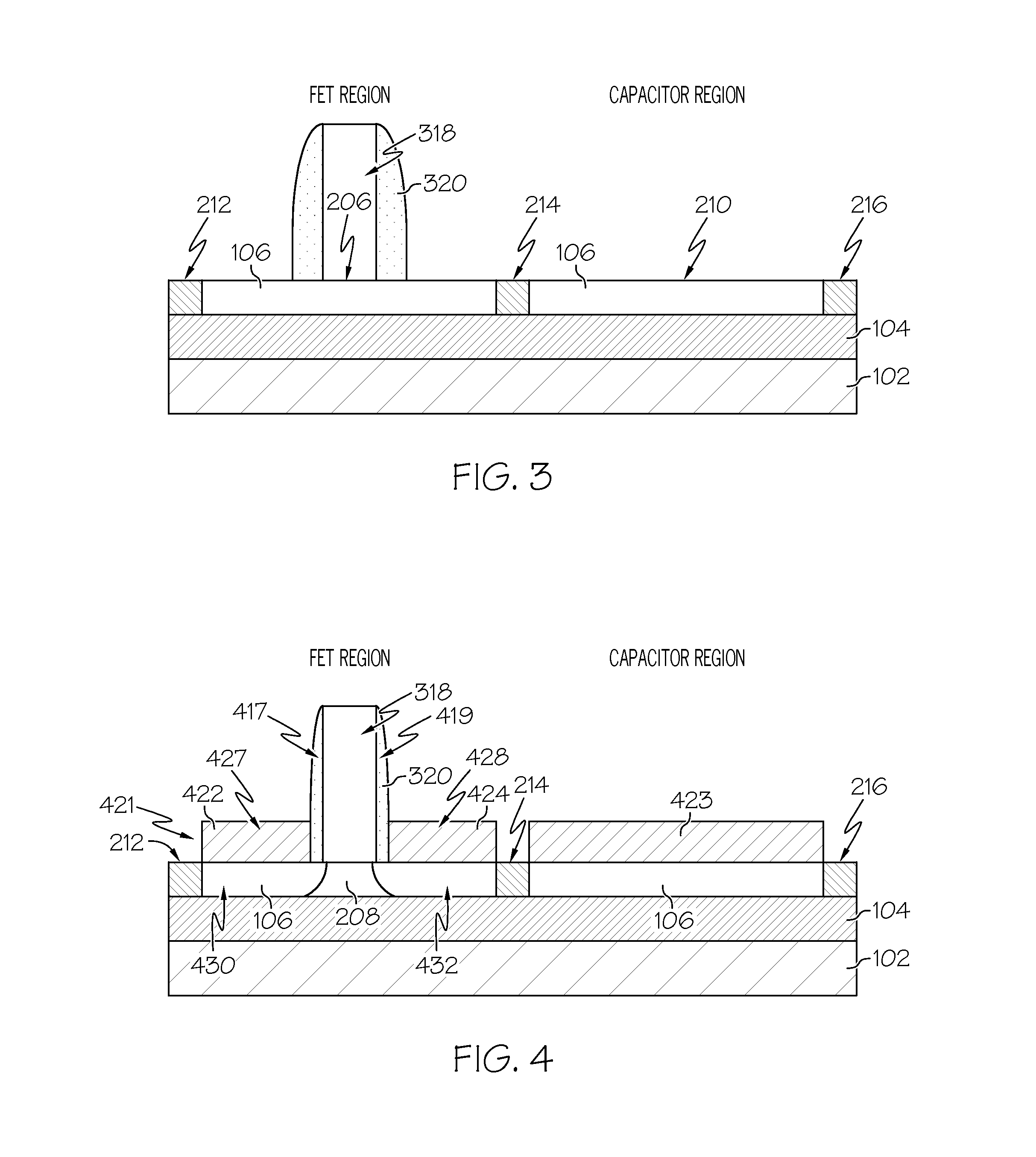
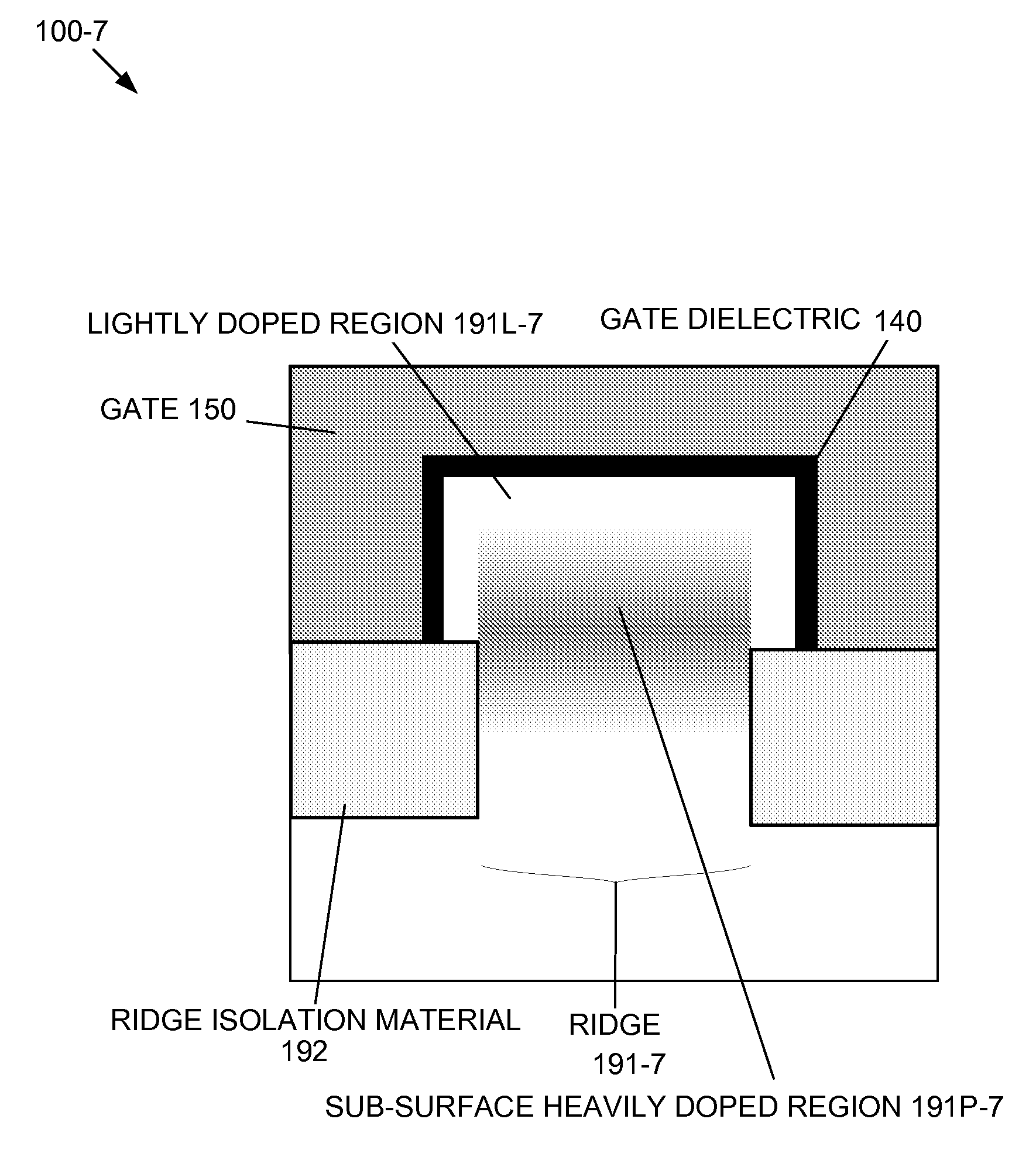
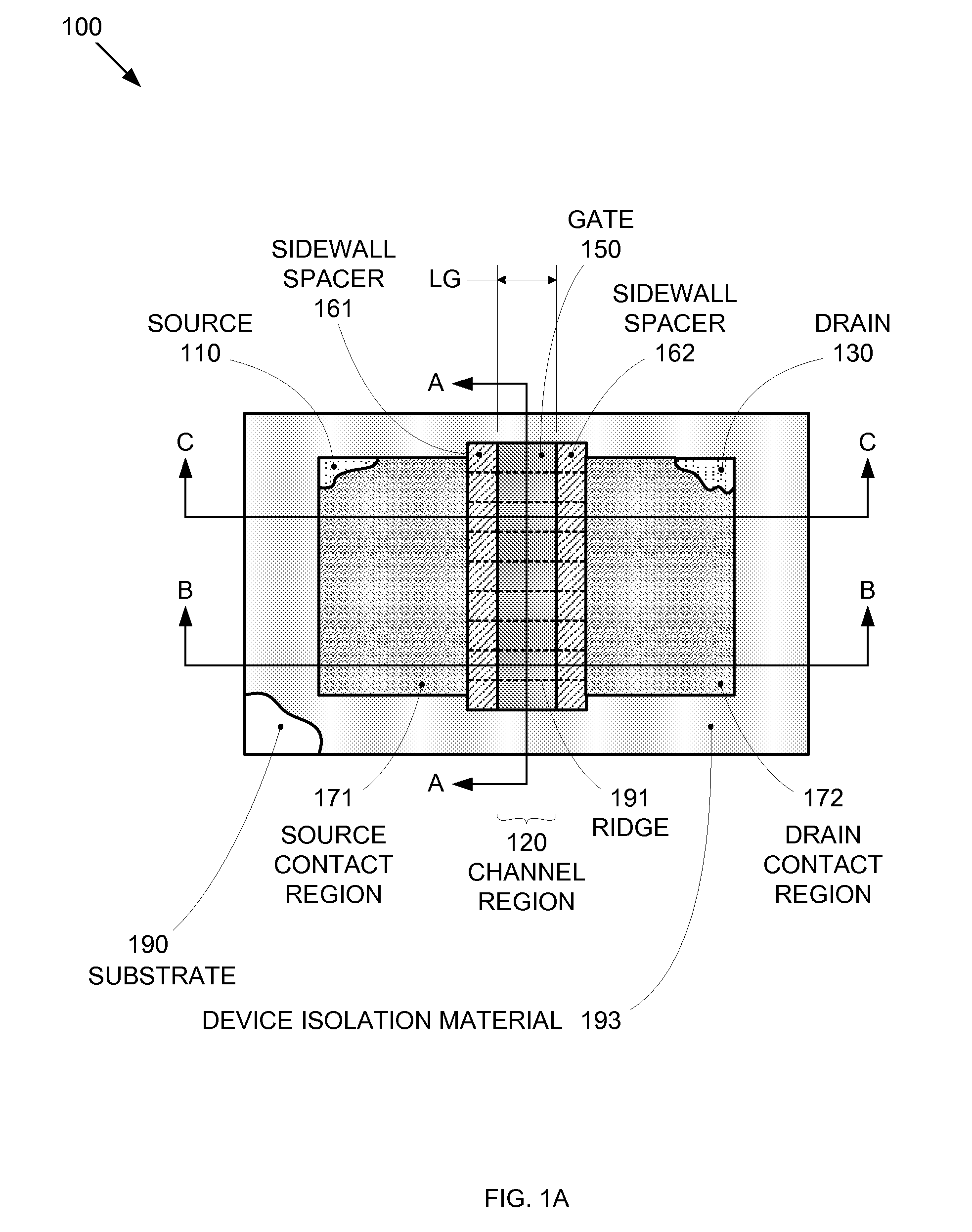
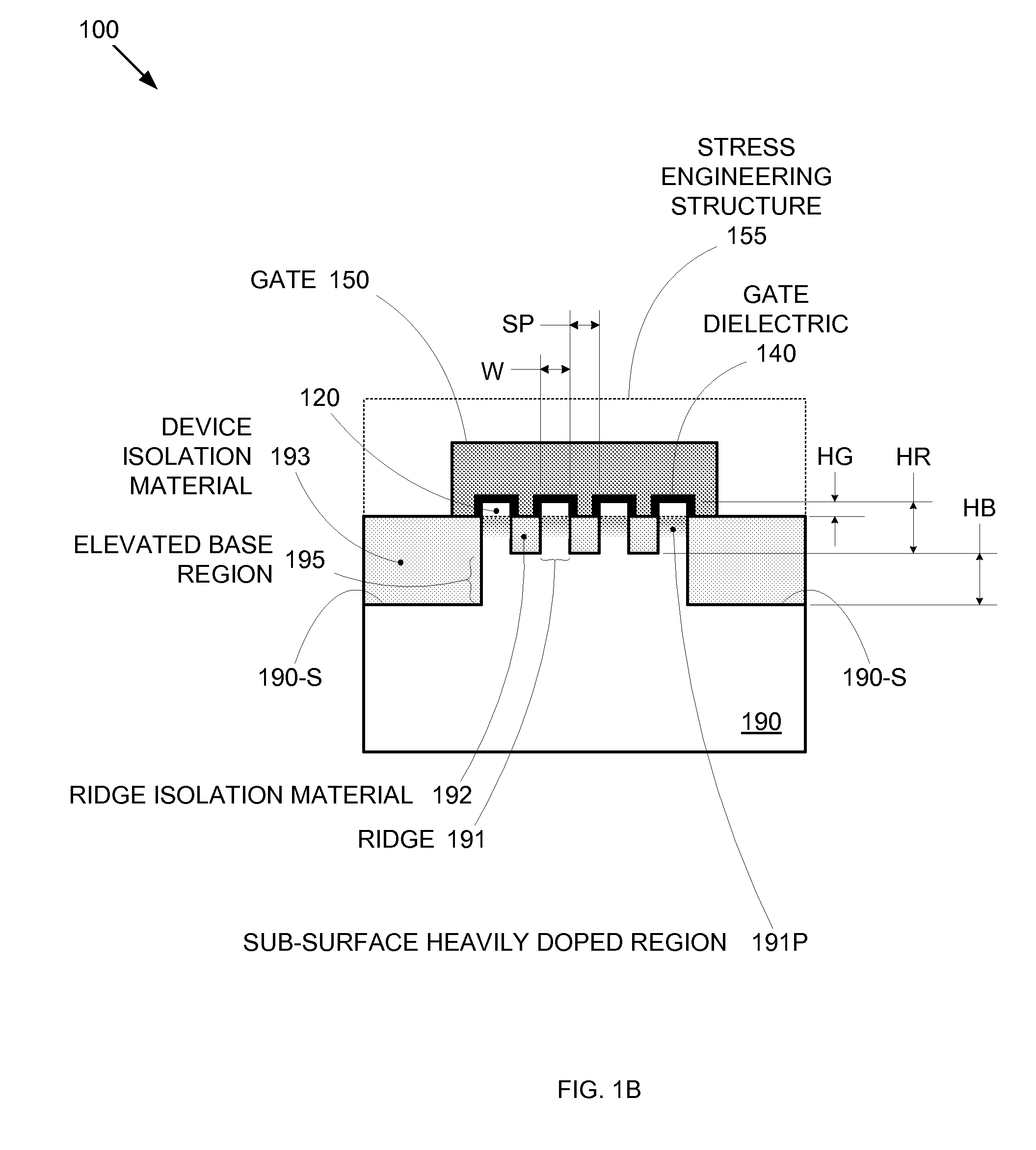
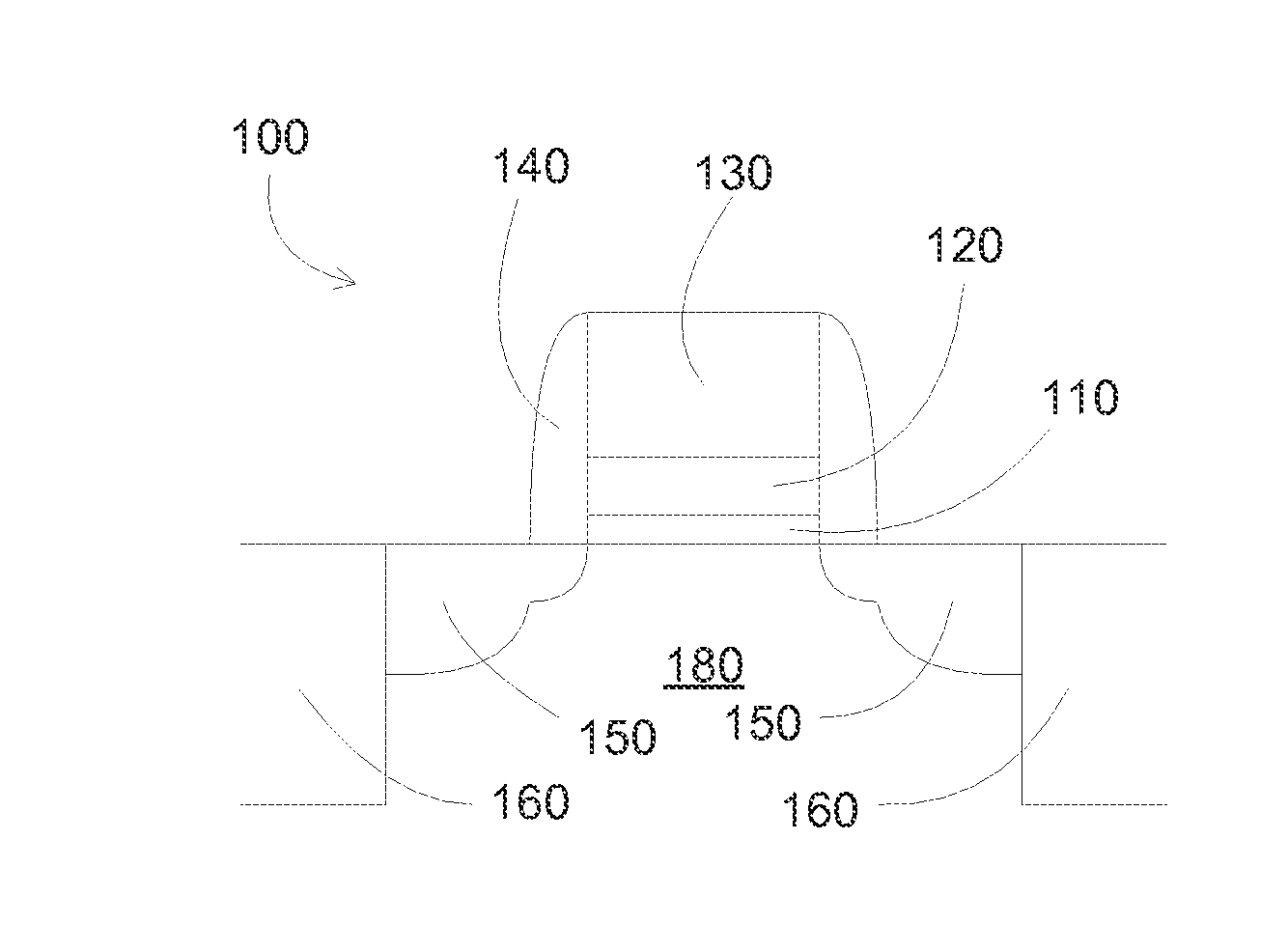
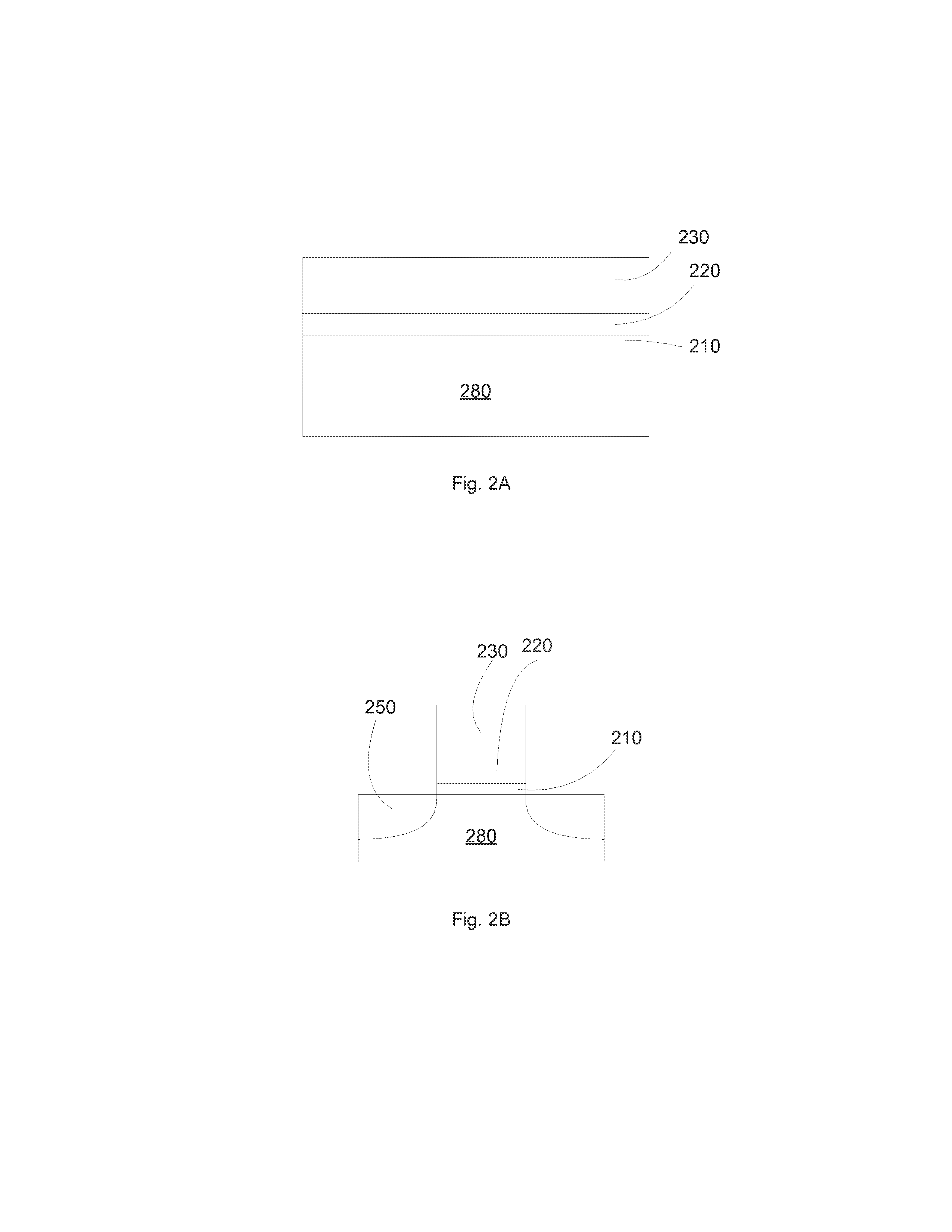
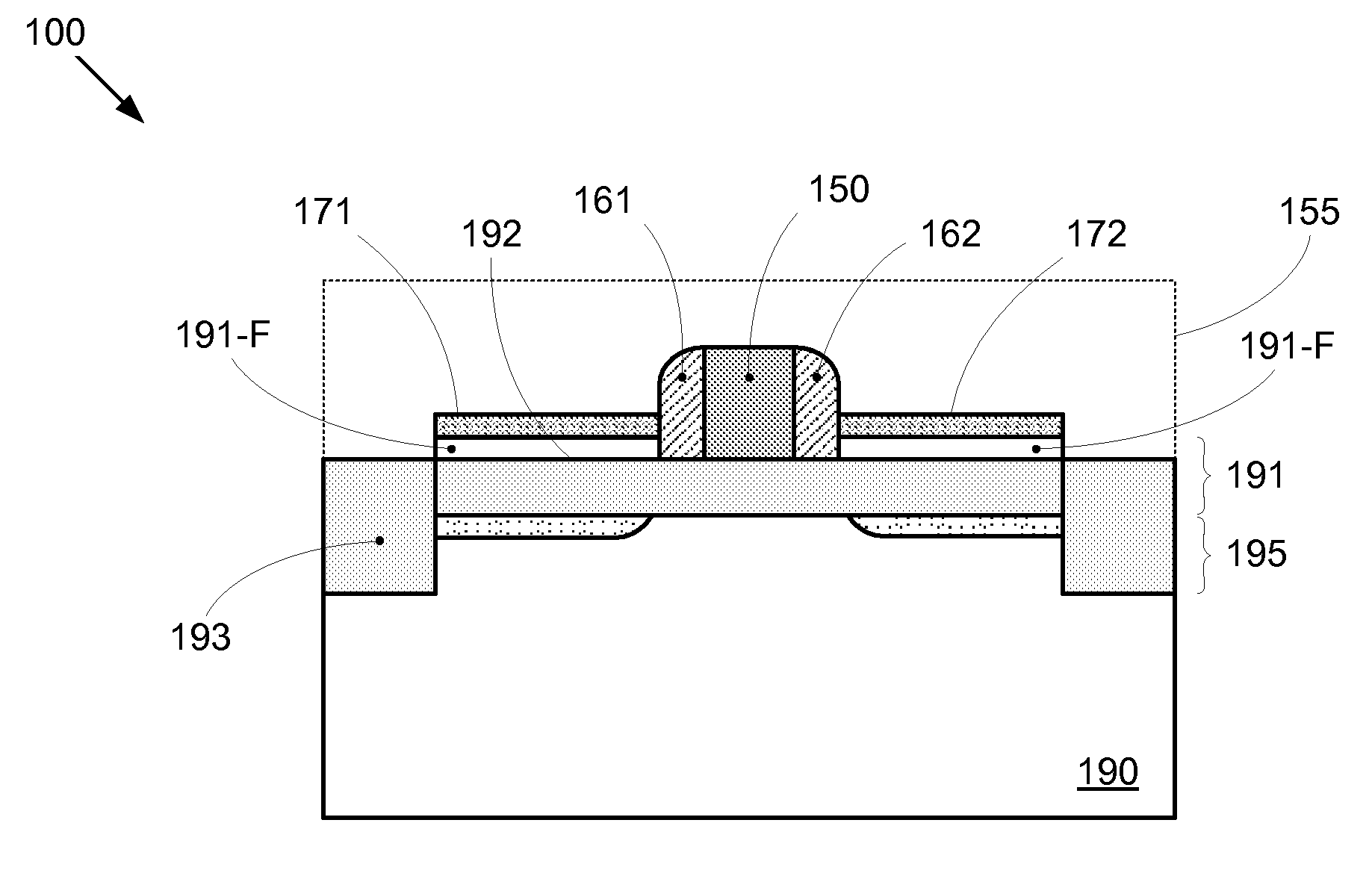
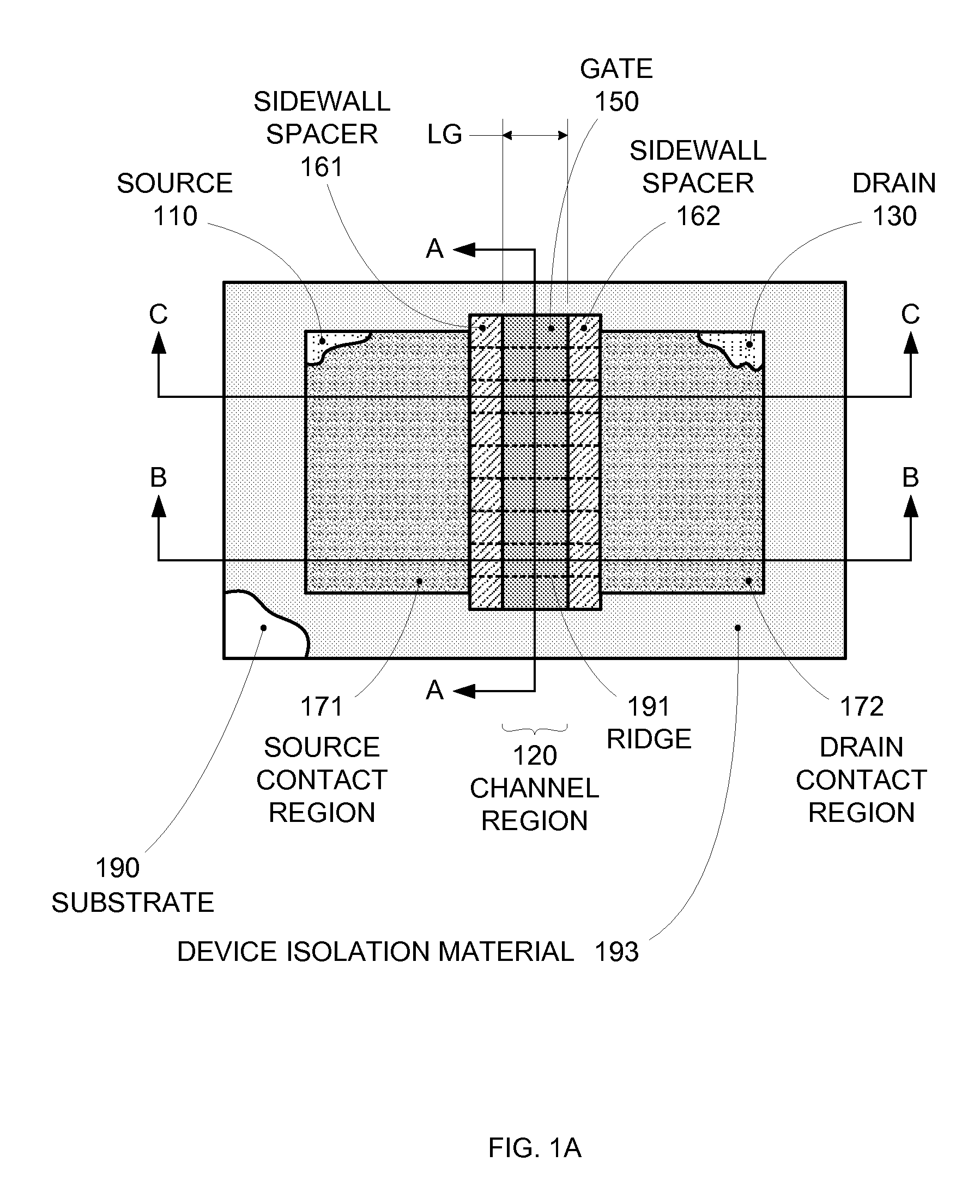
Enhanced Segmented Channel MOS Transistor with Multi Layer Regions
ActiveUS20070120156A1Increase costImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETPerformance enhancement
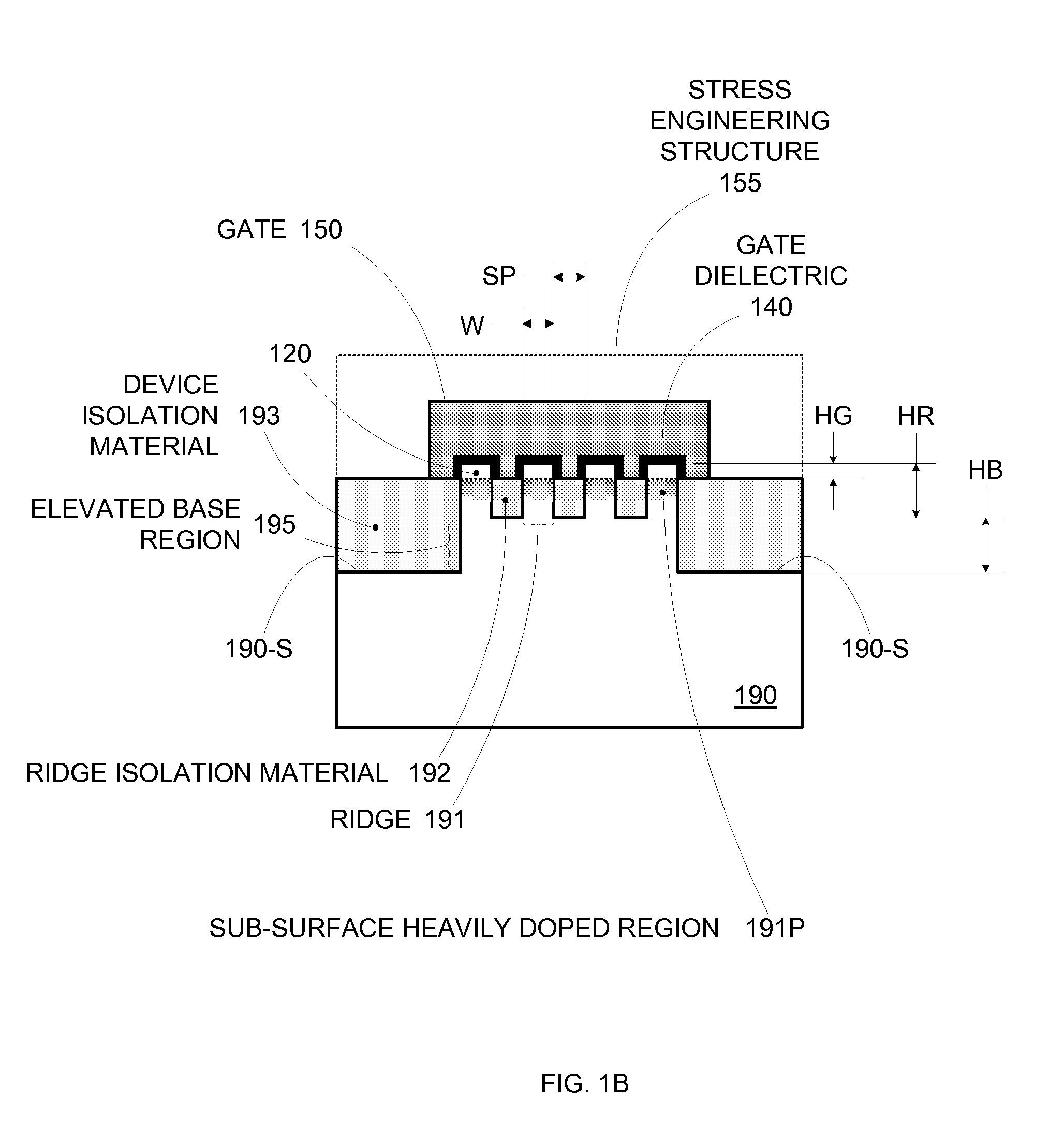
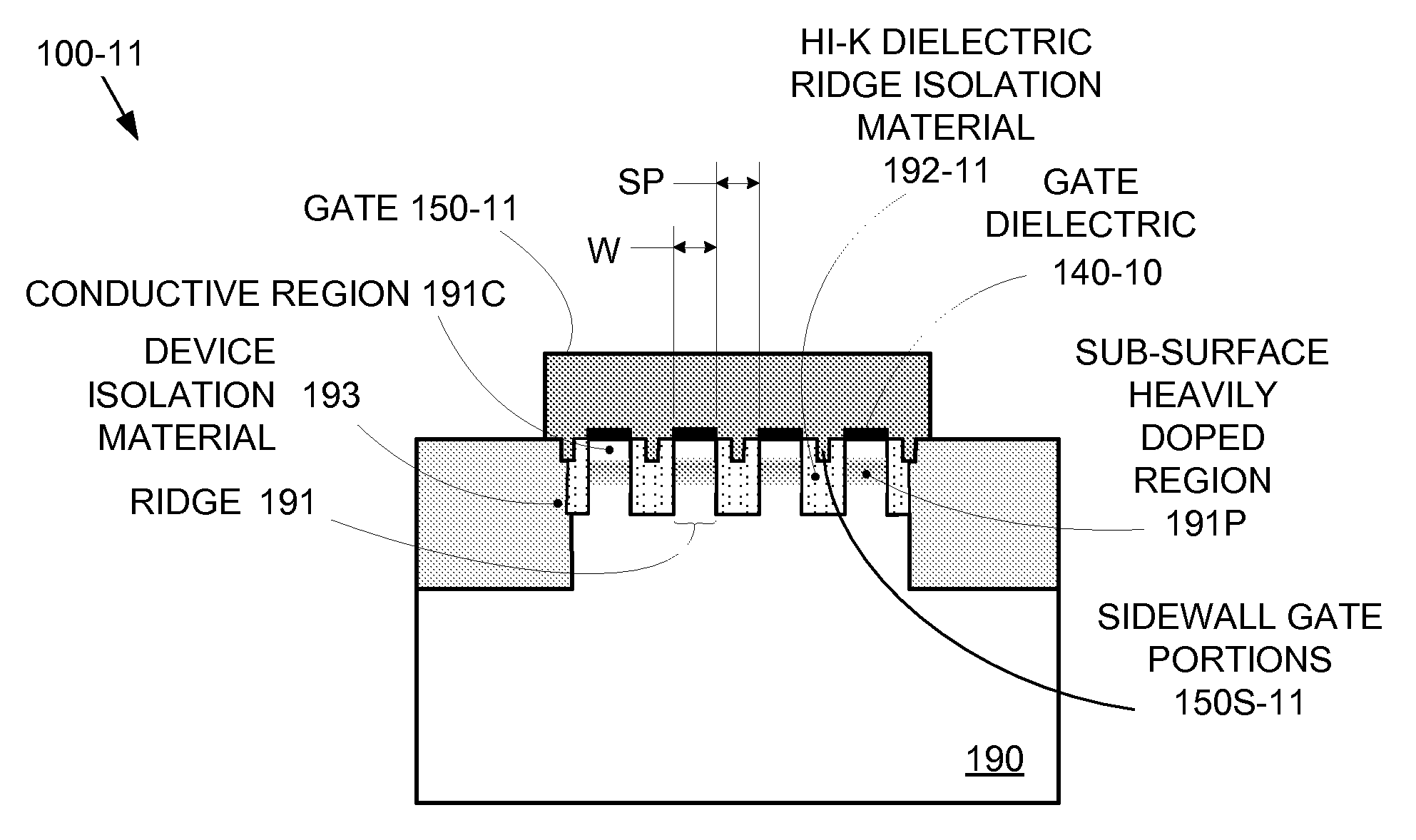
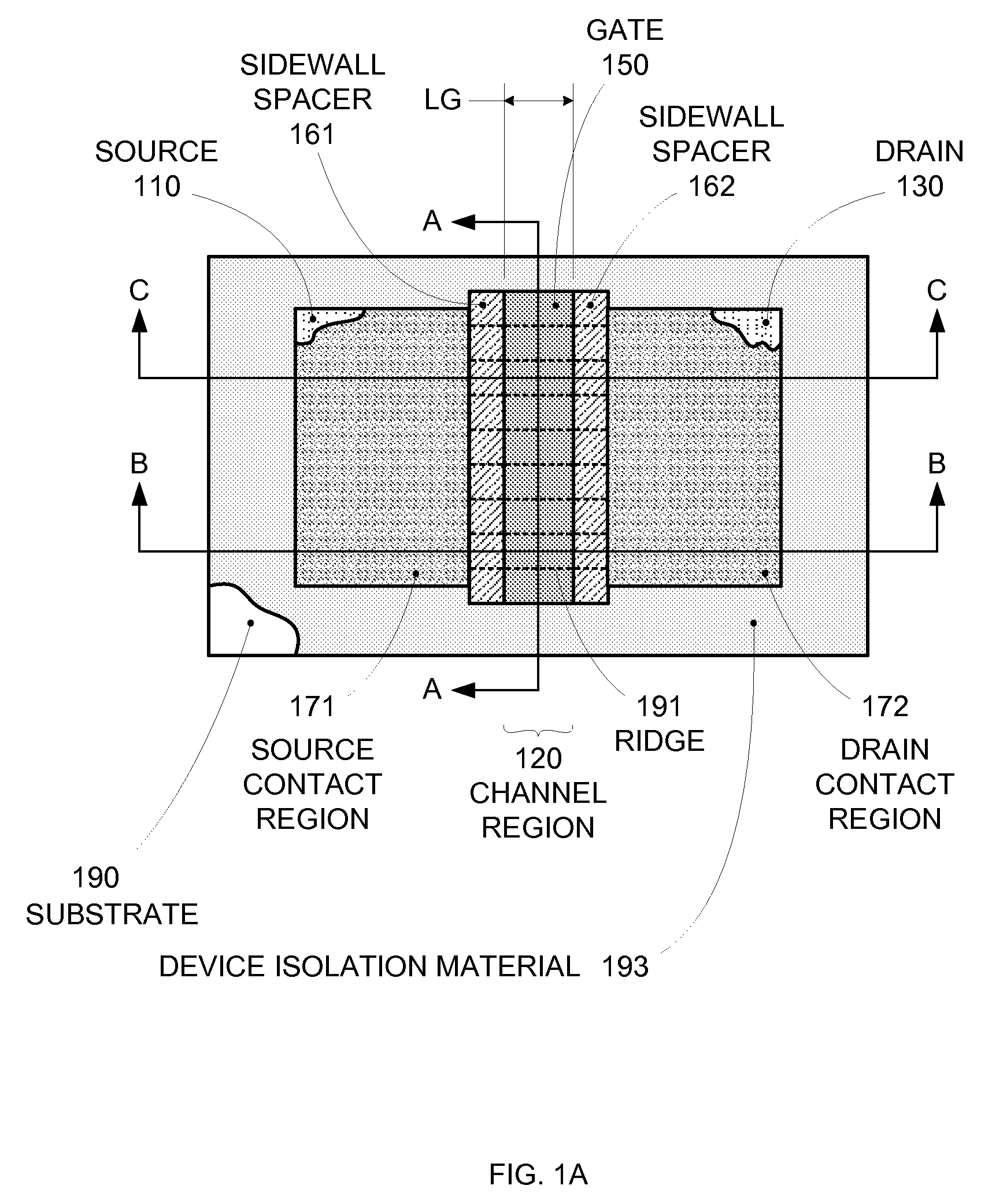
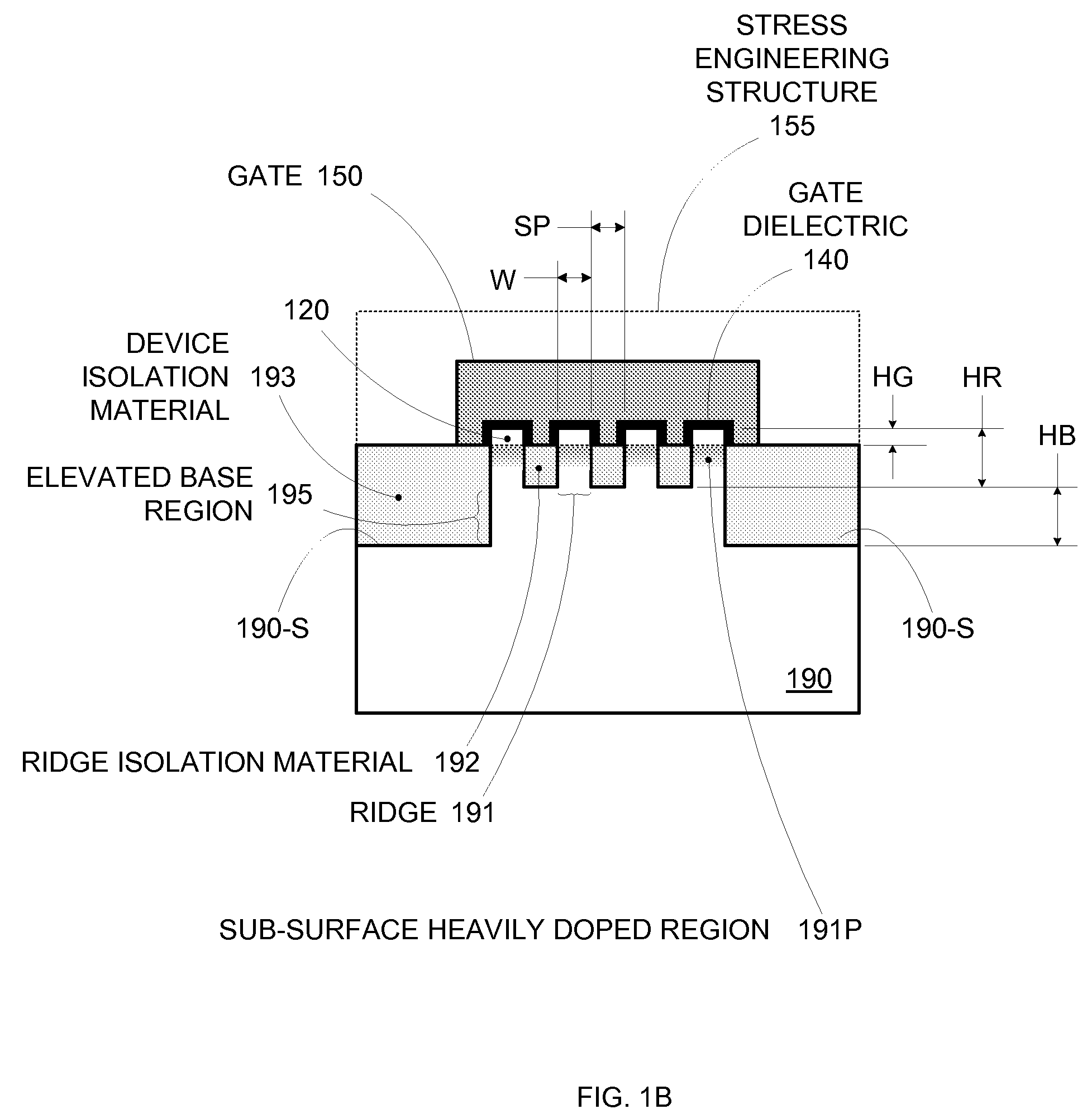
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Nitrogen profile engineering in nitrided high dielectric constant films
InactiveUS20080081113A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingRare-earth elementNitrogen
A method of forming a nitrided high-k film by disposing a substrate in a process chamber and forming the nitrided high-k film on the substrate by a) depositing a nitrogen-containing film, and b) depositing an oxygen-containing film, wherein steps a) and b) are performed in any order, any number of times, so as to oxidize at least a portion of the thickness of the nitrogen-containing film. The oxygen-containing film and the nitrogen-containing film contain the same one or more metal elements selected from alkaline earth elements, rare earth elements, and Group IVB elements of the Periodic Table, and optionally aluminum, silicon, or aluminum and silicon. According to one embodiment, the method includes forming a nitrided hafnium based high-k film. The nitrided high-k film can be formed by atomic layer deposition (ALD) or plasma-enhanced ALD (PEALD).
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Silicon oxide cap over high dielectric constant films
InactiveUS20060211259A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGate dielectricThermal chemical vapor deposition
A method for forming an integrated circuit structure on a semiconductor substrate comprises depositing a high k gate dielectric material over the substrate using an atomic layer deposition process. A silicon oxide capping layer is deposited over the gate dielectric material in a rapid thermal chemical vapor deposition process. A gate electrode is formed over the silicon oxide capping layer.
Owner:ASM AMERICA INC
Integrated circuit with a thin body field effect transistor and capacitor
An integrated circuit includes a transistor and a capacitor. The transistor includes a first semiconductor layer and a gate stack located on the first semiconductor layer. The gate stack includes a metal layer and a first high-k dielectric layer. A gate spacer is located on sidewalls of the gate stack. The first high-k dielectric layer is located between the first semiconductor layer and the metal layer and between the gate spacer and sidewalls of the metal layer. A first silicide region is located on a first source / drain region. A second silicide region is located on a second source / drain region. The capacitor includes a first terminal that comprises a third silicide region located on a portion of the second semiconductor. A second high-k dielectric layer is located on the silicide region. A second terminal comprises a metal layer that is located on the second high-k dielectric layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Enhanced segmented channel MOS transistor with narrowed base regions
ActiveUS7508031B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably produced. Ridges on the corrugated substrate can be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials, high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Methods of atomic layer deposition of hafnium oxide / erbium oxide bi-layer as advanced gate dielectrics
InactiveUS20130313656A1Improve electrical performanceFew defectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGate dielectricHafnium
Provided is a two-step ALD deposition process for forming a gate dielectric involving an erbium oxide layer deposition followed by a hafnium oxide layer deposition. Hafnium oxide can provide a high dielectric constant, high density, large bandgap and good thermal stability. Erbium oxide can act as a barrier against oxygen diffusion, which can lead to increasing an effective oxide thickness of the gate dielectric and preventing hafnium-silicon reactions that may lead to higher leakage current.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
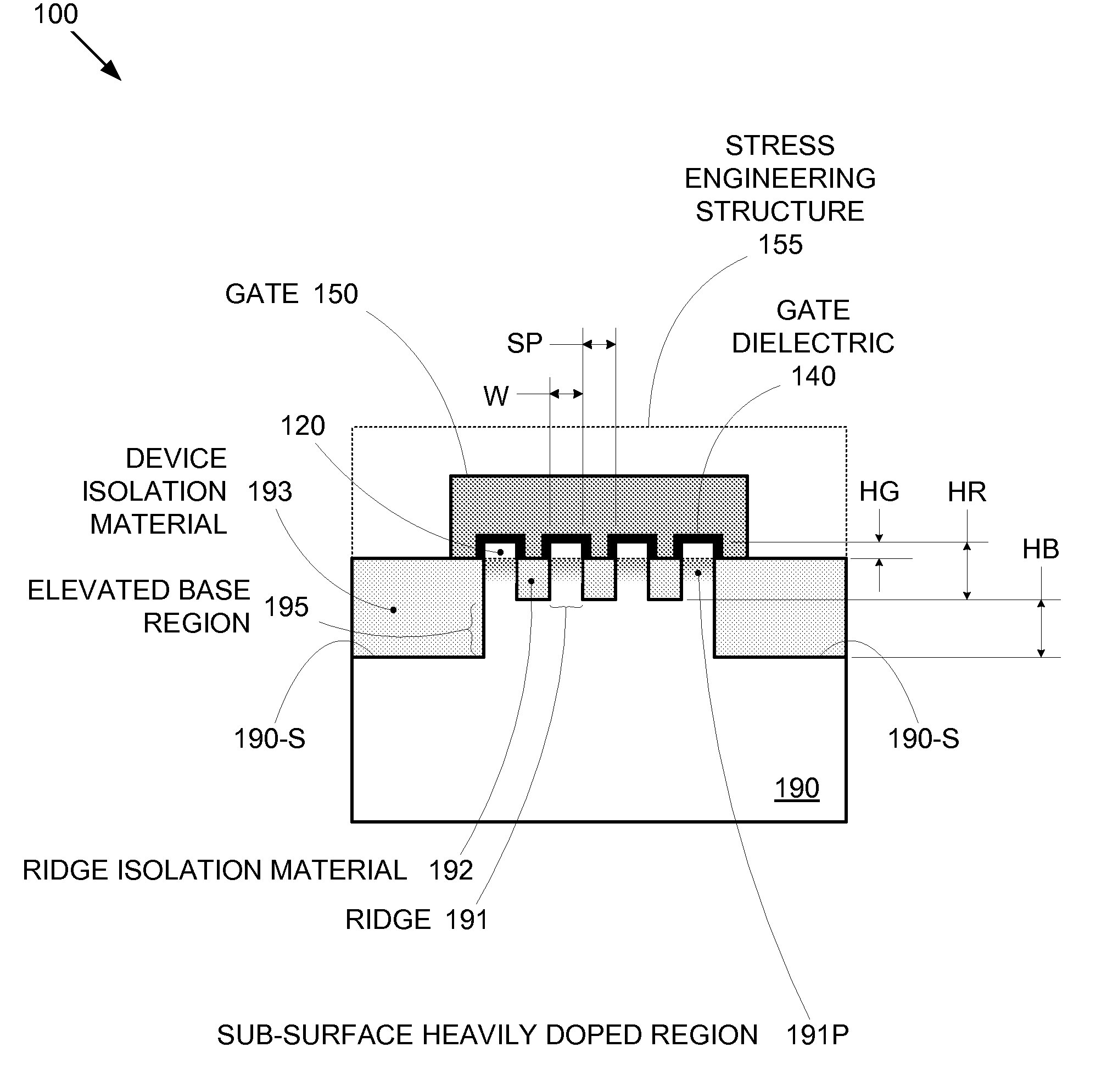
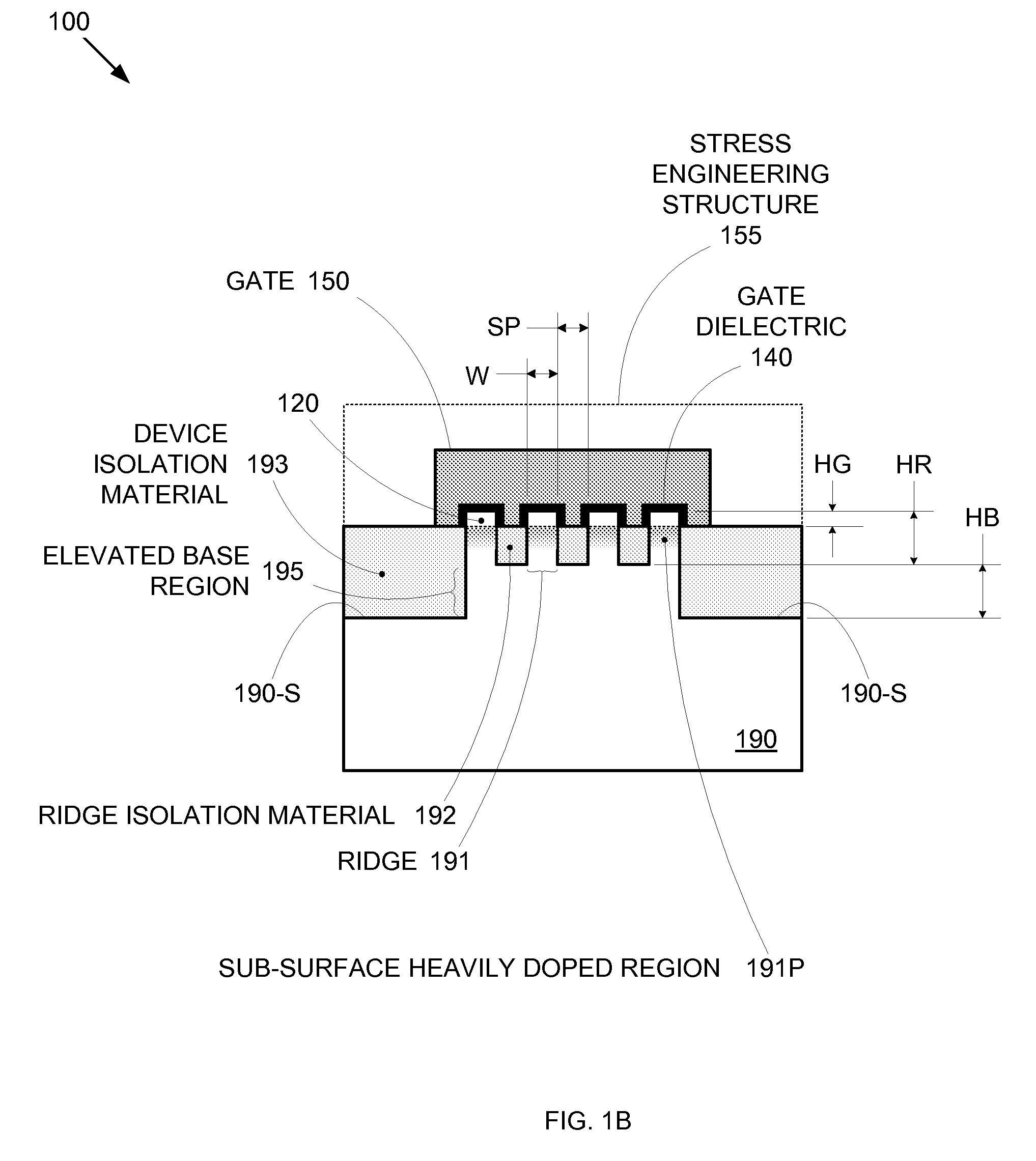
Enhanced Segmented Channel MOS Transistor with High-Permittivity Dielectric Isolation Material
ActiveUS20070122953A1Increase costImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Enhanced segmented channel MOS transistor with high-permittivity dielectric isolation material
ActiveUS7605449B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Continuous method for depositing a film by modulated ion-induced atomic layer deposition (MII-ALD)
InactiveUS20020164423A1Faster efficient meanSimple methodPretreated surfacesSolid state diffusion coatingHigh densityOptoelectronics
The present invention relates to an enhanced sequential atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique suitable for deposition of barrier layers, adhesion layers, seed layers, low dielectric constant (low-k) films, high dielectric constant (high-k) films, and other conductive, semi-conductive, and non-conductive films. This is accomplished by 1) providing a non-thermal or non-pyrolytic means of triggering the deposition reaction; 2) providing a means of depositing a purer film of higher density at lower temperatures; and, 3) providing a faster and more efficient means of modulating the deposition sequence and hence the overall process rate resulting in an improved deposition method.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method of manufacturing capacitive insulating film for capacitor
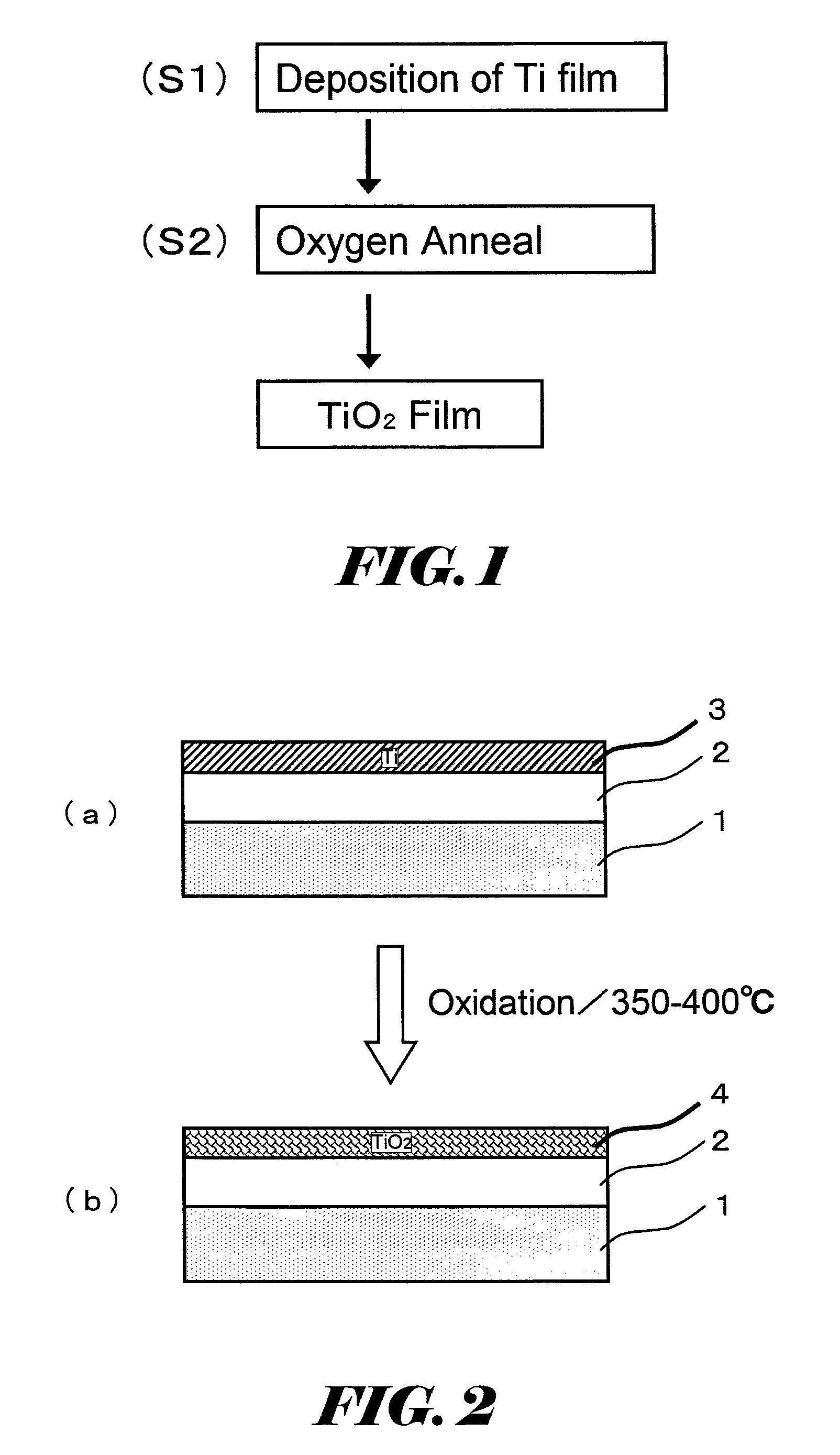
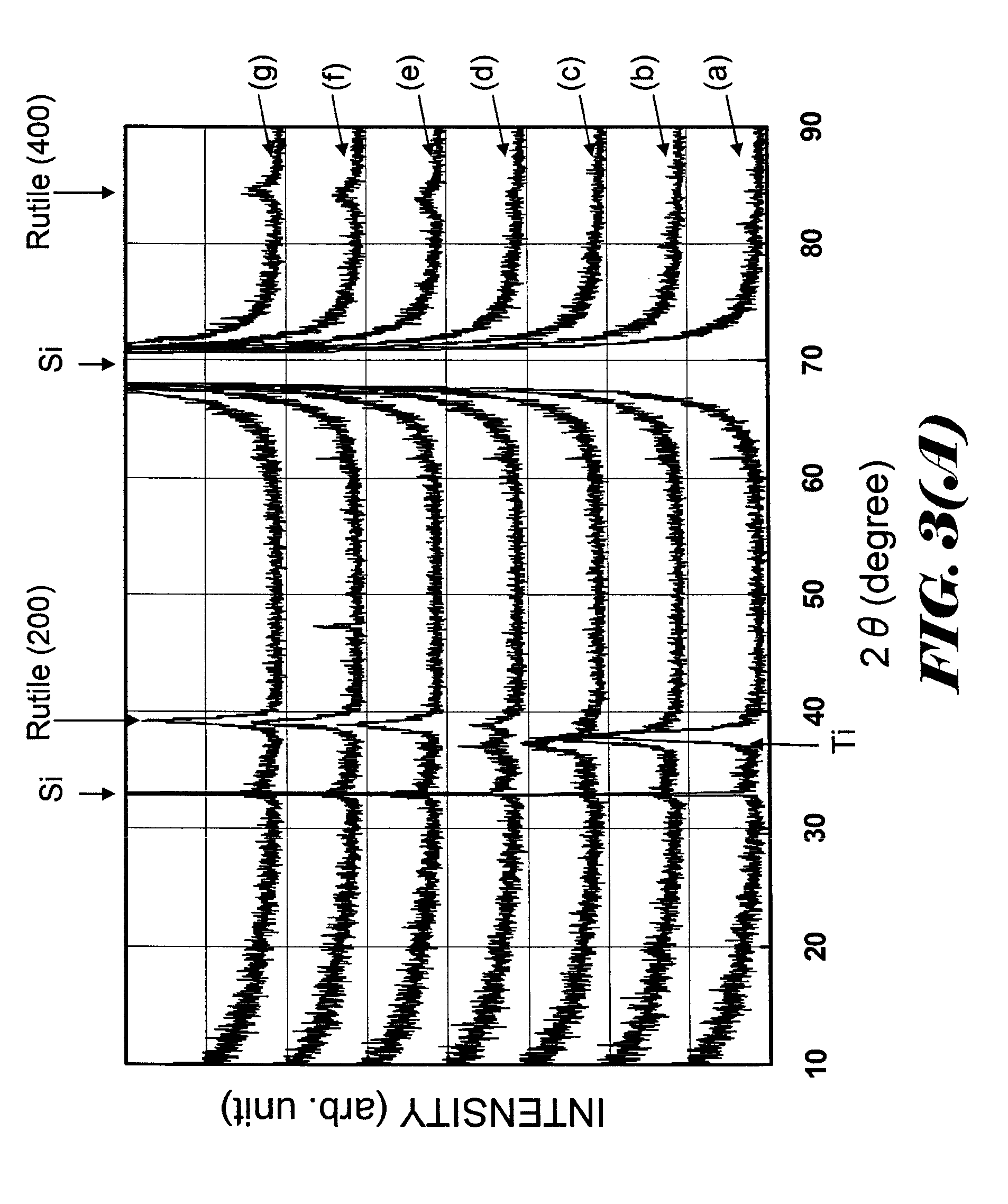
InactiveUS8198168B2Increase capacitanceReduce adverse effectsThin/thick film capacitorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceCrystal structure
According to the invention, a Ti film is formed on a substrate and is annealed at the temperatures of 350° C.-400° C. under oxidative environment, so that a TiO2 film having a rutile crystal structure is formed. Since the TiO2 film having a rutile crystal structure has a high dielectric constant, it is useful for a capacitive insulating film for a capacitor.
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
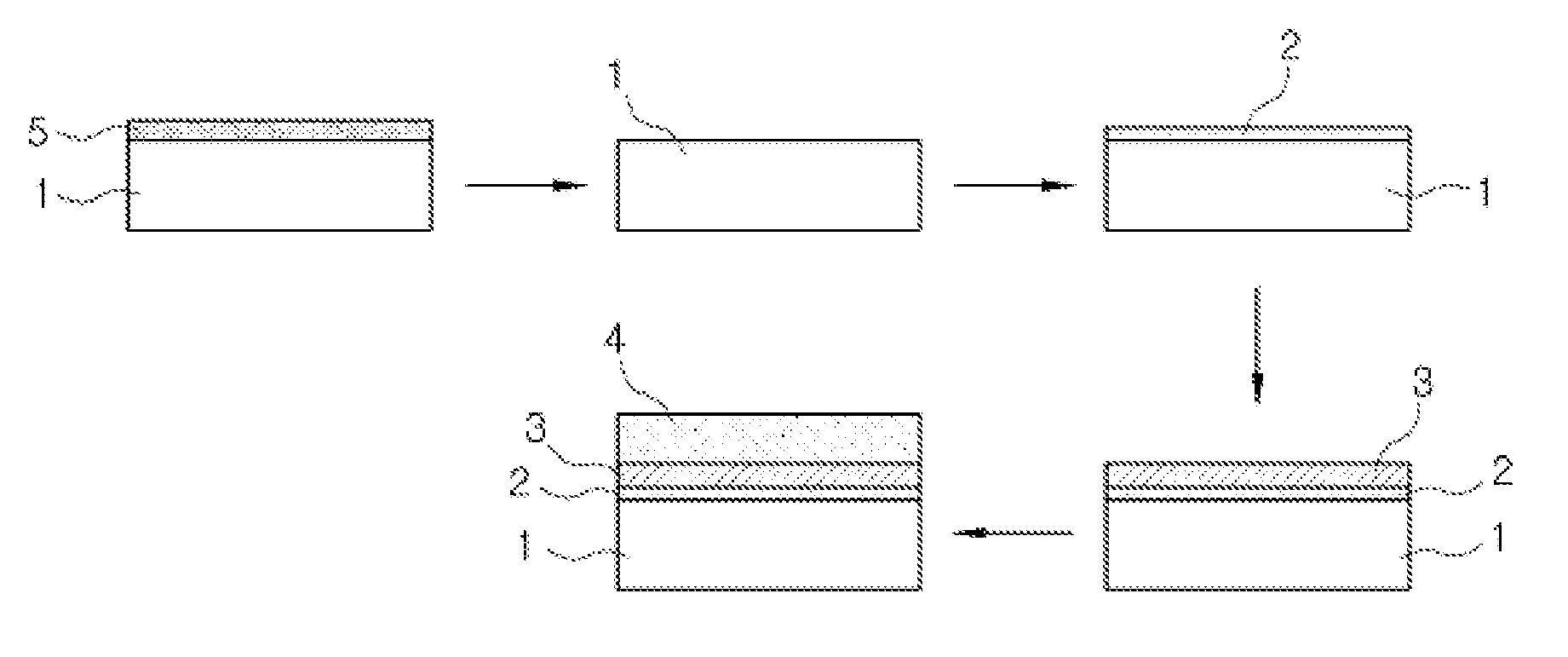
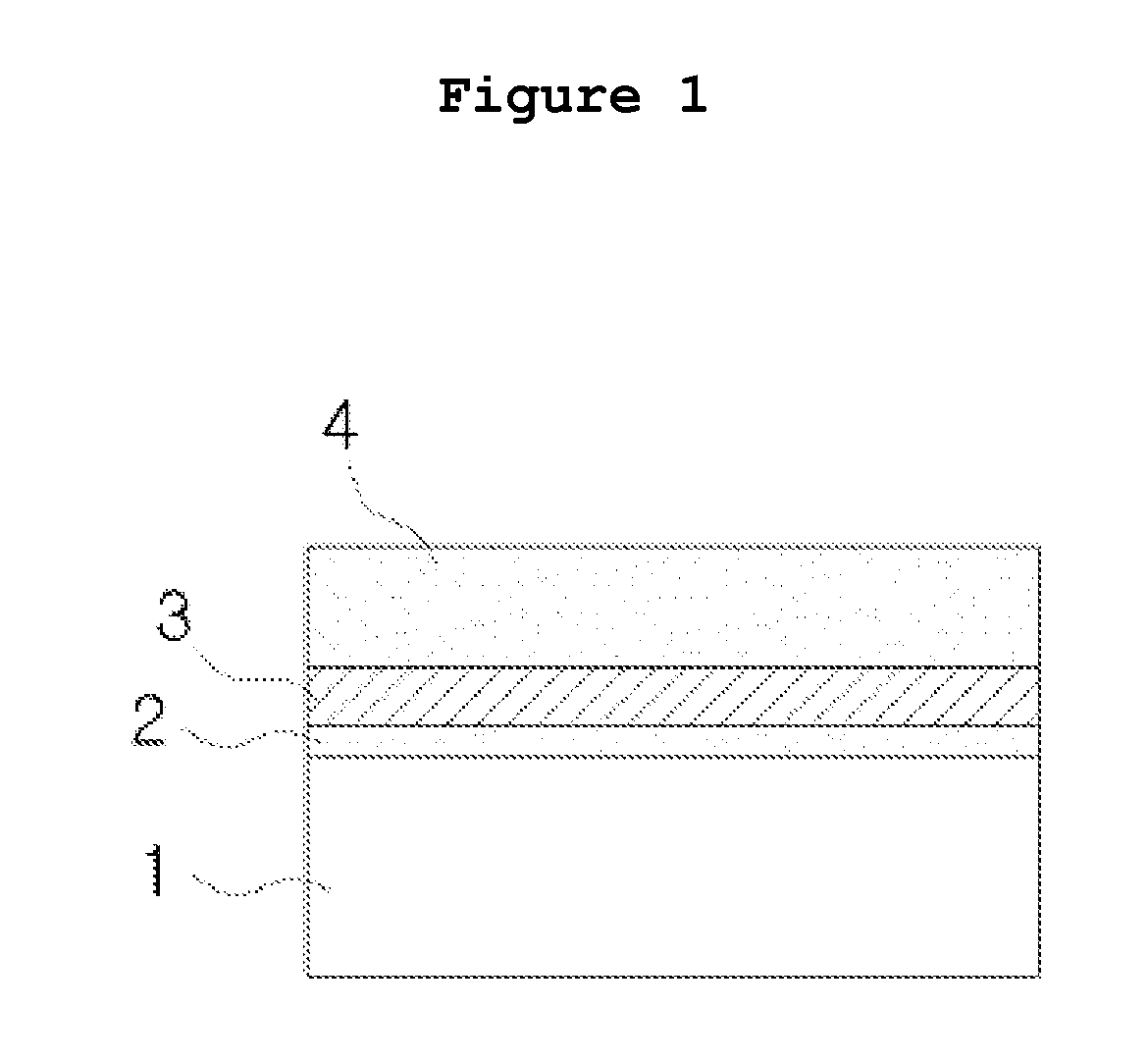
Insulating film, method of manufacturing the same, and semiconductor device
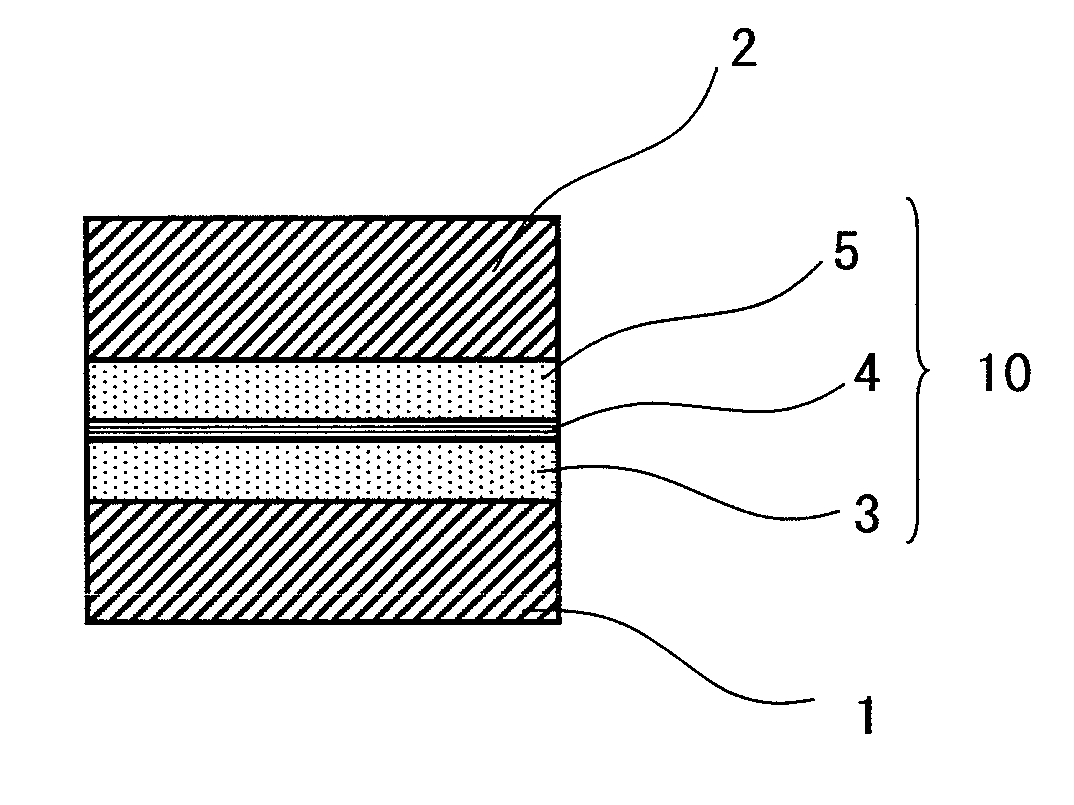
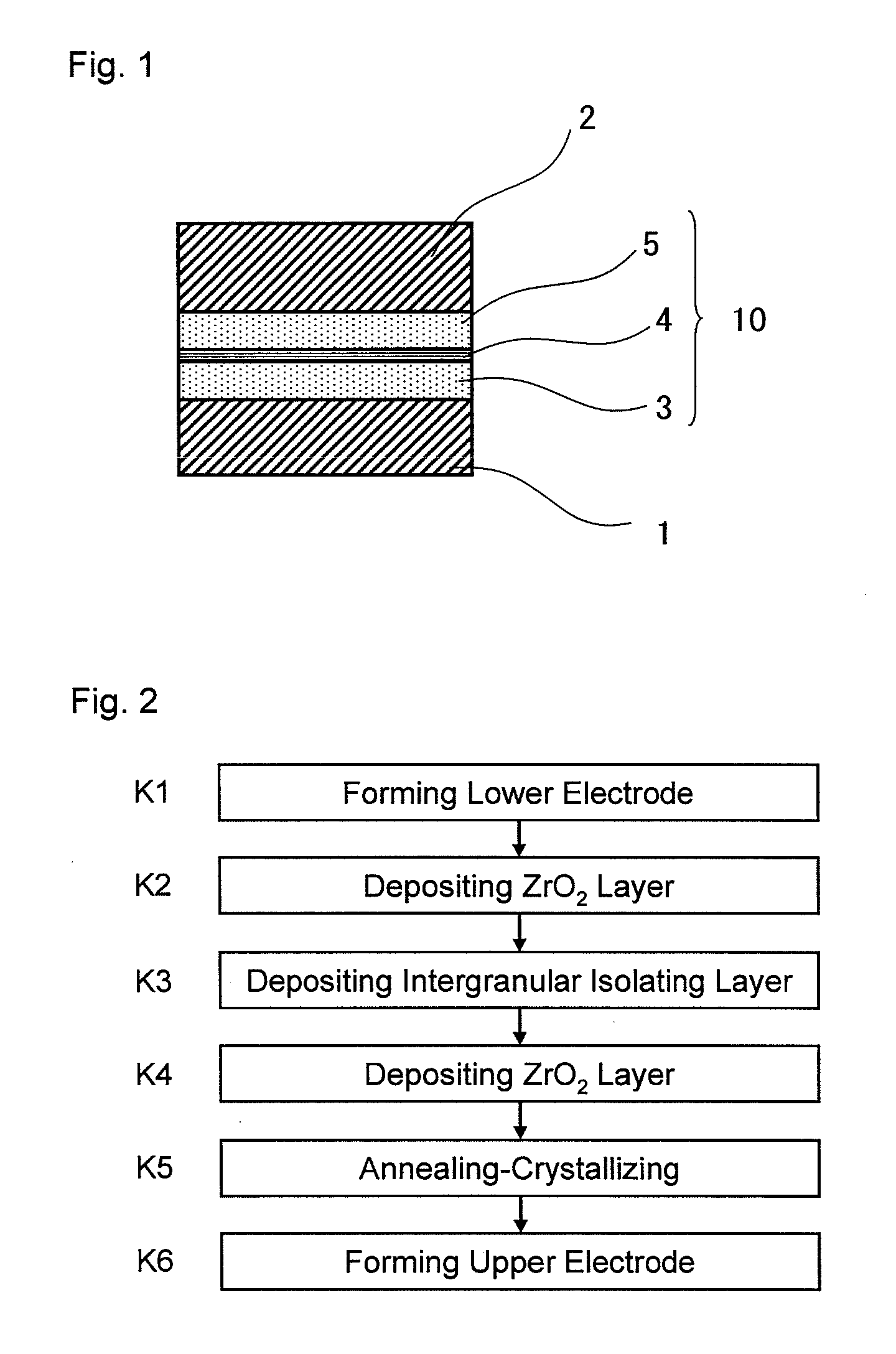
InactiveUS20110048769A1High dielectric constantSmall currentThin/thick film capacitorCeramicsCapacitanceSemiconductor
An exemplary aspect of the invention provides an insulating film which has a high dielectric constant and has small leakage current even when it is sandwiched between electrodes. The insulating film comprises two zirconium oxide layers in crystallized state; and an intergranular isolating layer composed of an amorphous material having a dielectric constant higher than that of zirconium oxide in crystallized state; wherein the intergranular isolating layer is sandwiched between the two zirconium oxide layers. The insulating film is properly used as a capacitive insulating film in a semiconductor device comprising a memory cell including a capacitor element having the capacitive insulating film between an upper electrode and a lower electrode, or as an intergate insulating film in a semiconductor device comprising a nonvolatile memory device having the intergate insulating film between a control gate electrode and a floating gate electrode.
Owner:ELPIDA MEMORY INC
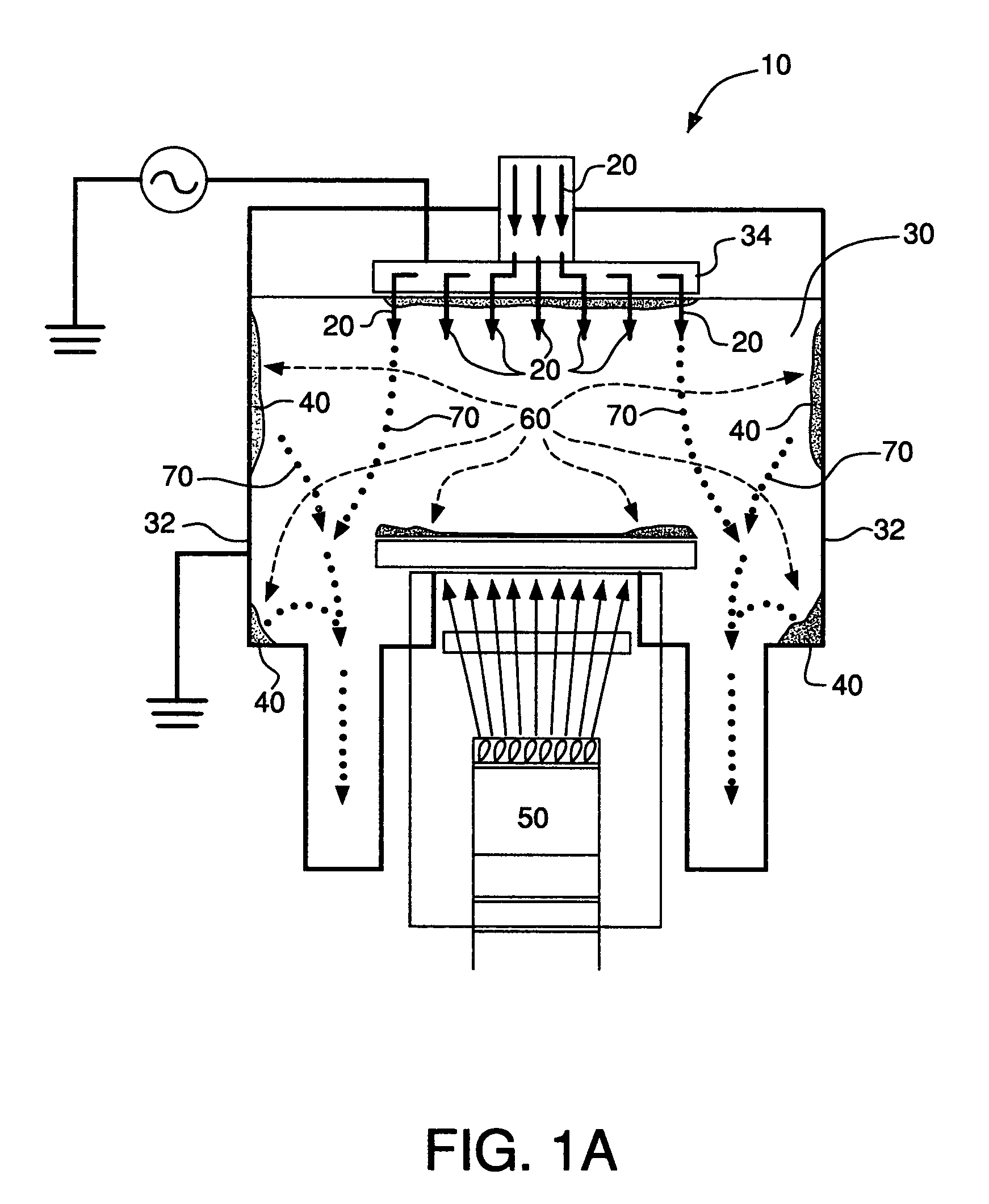
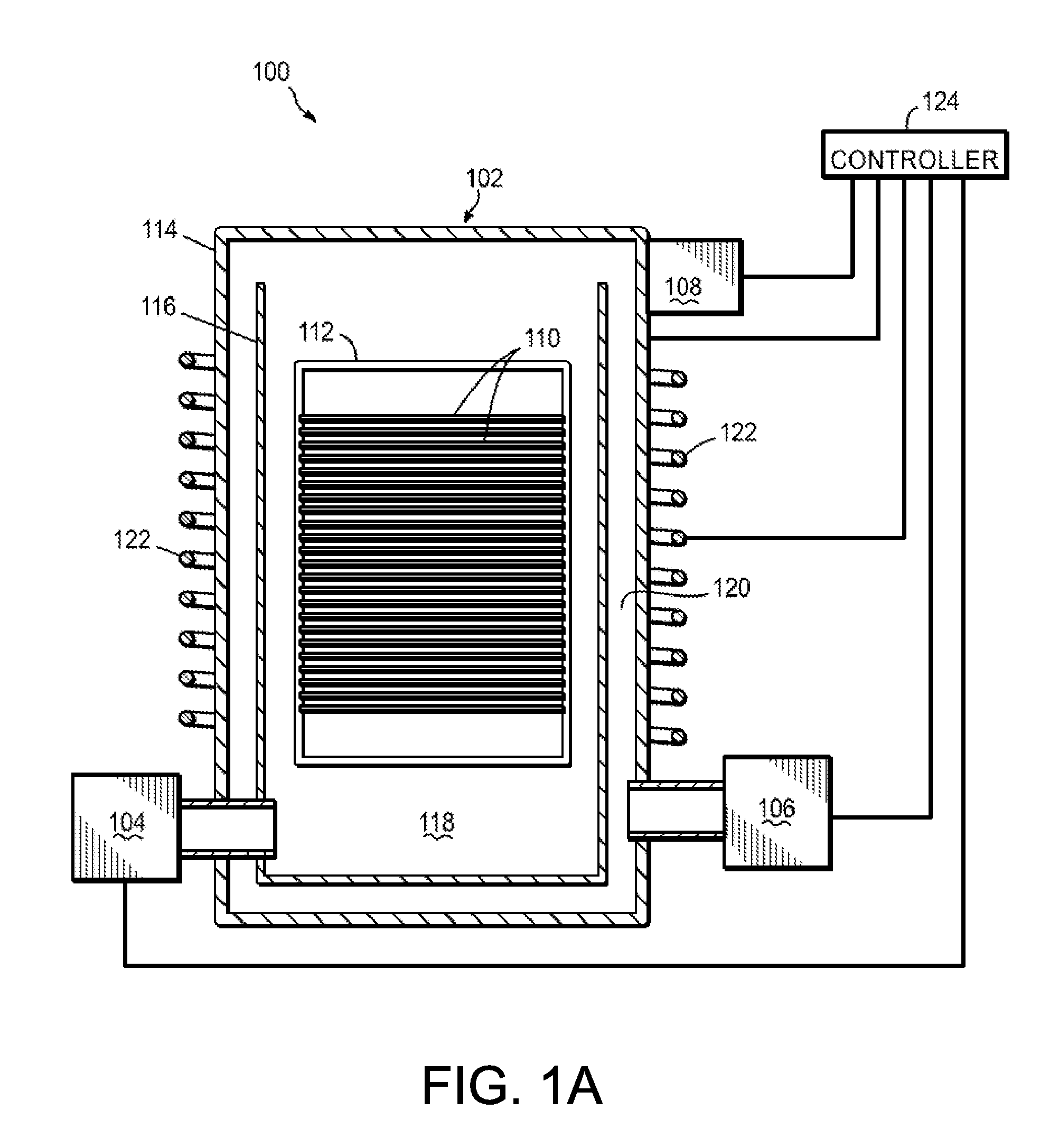
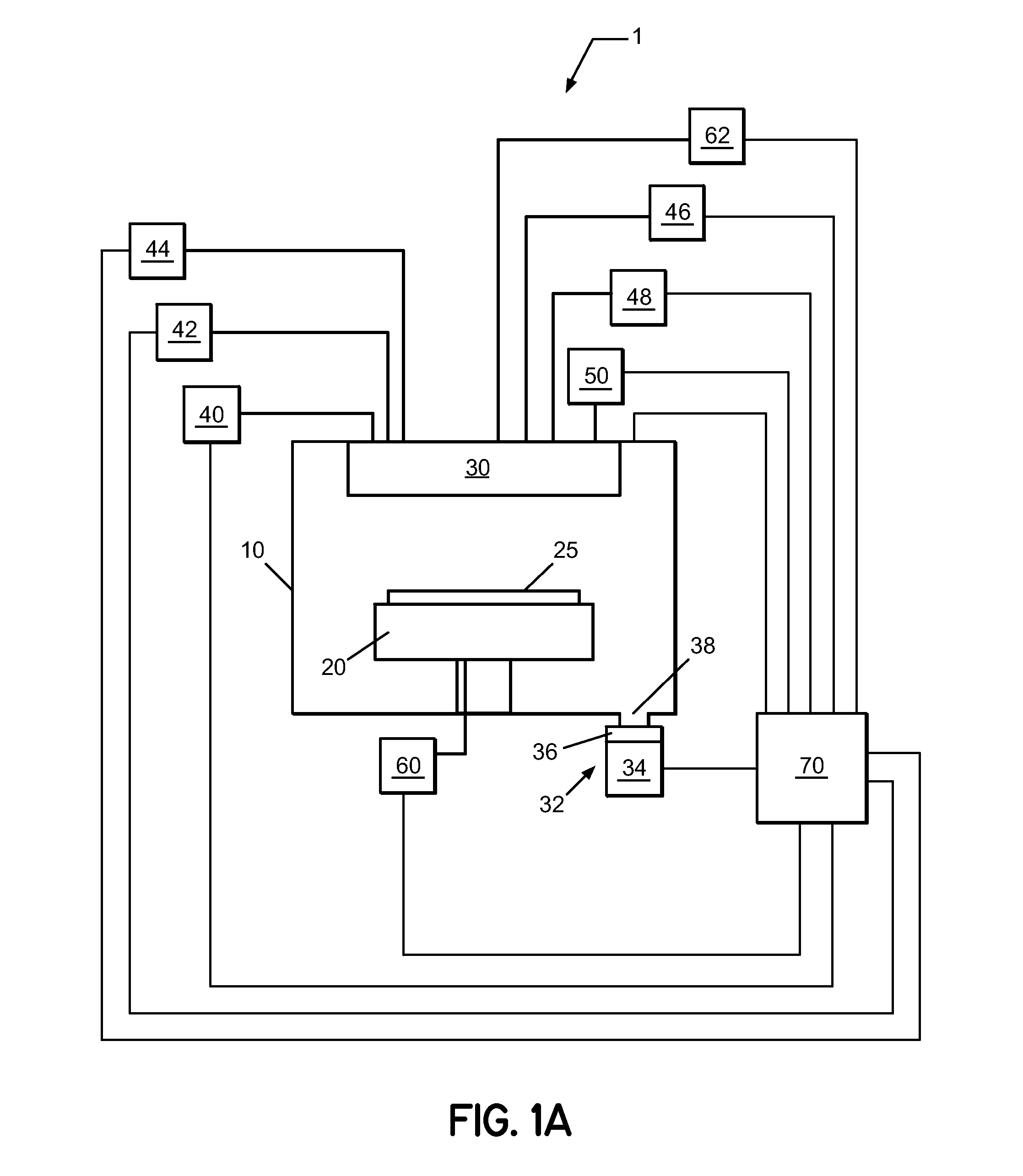
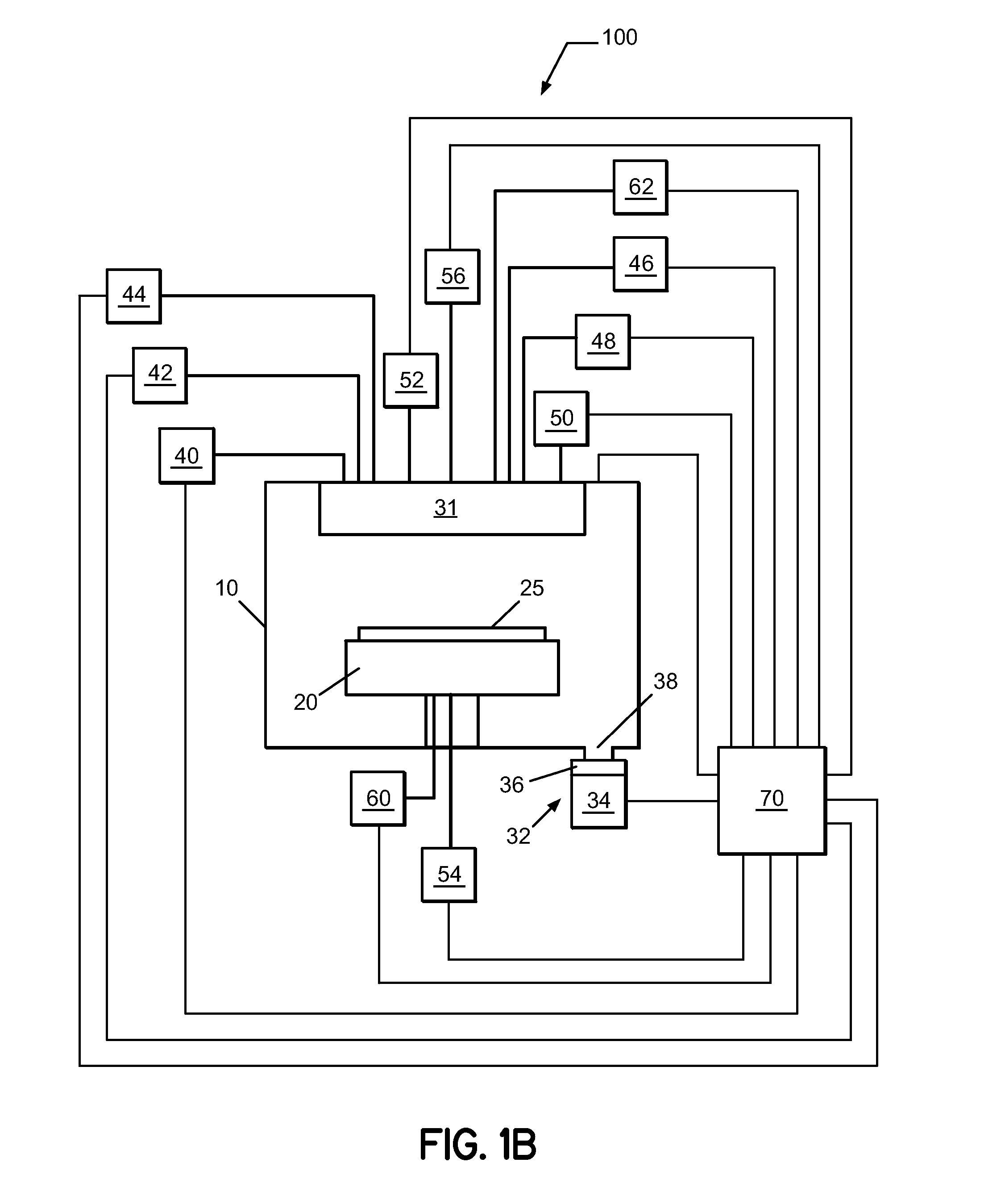
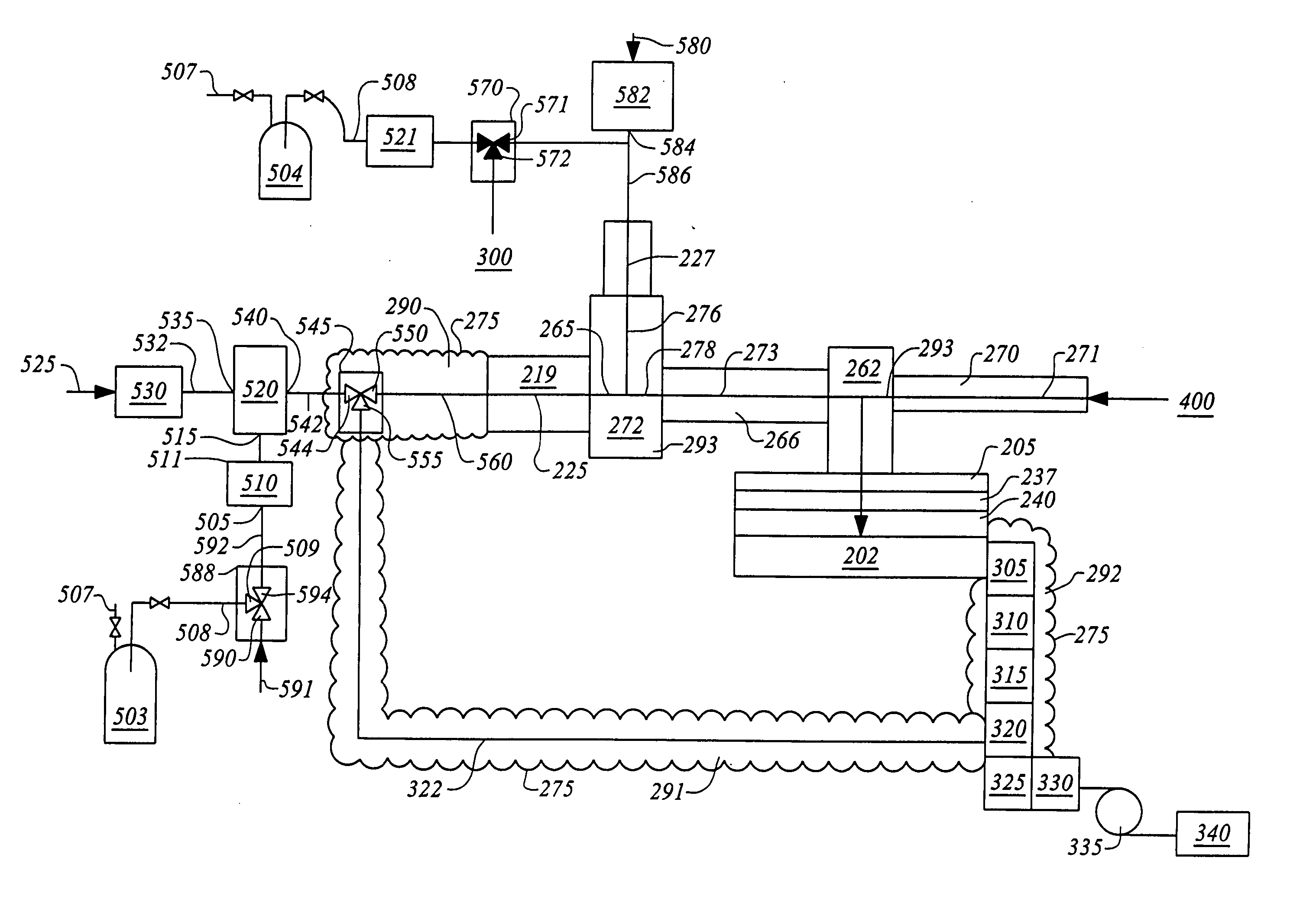
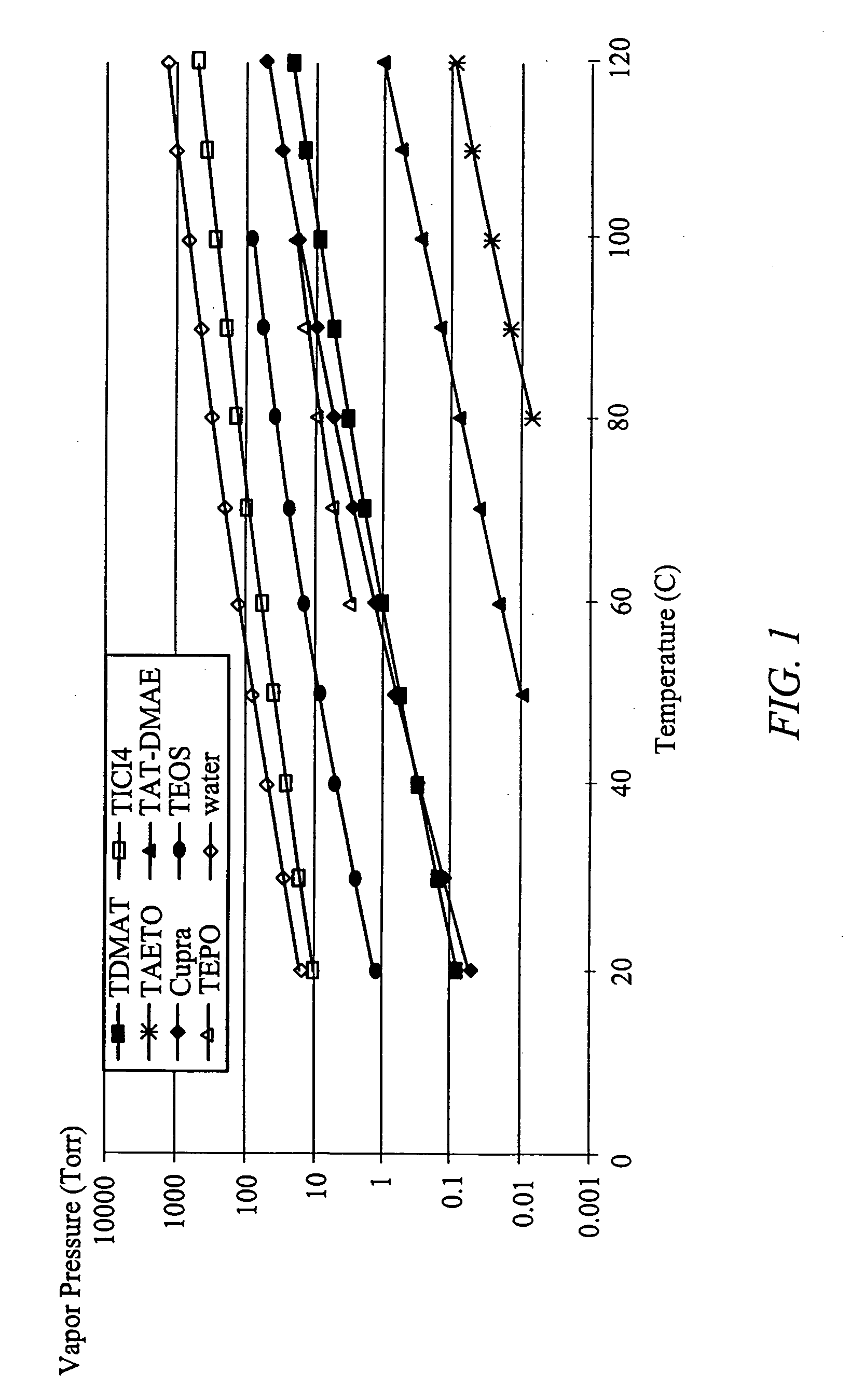
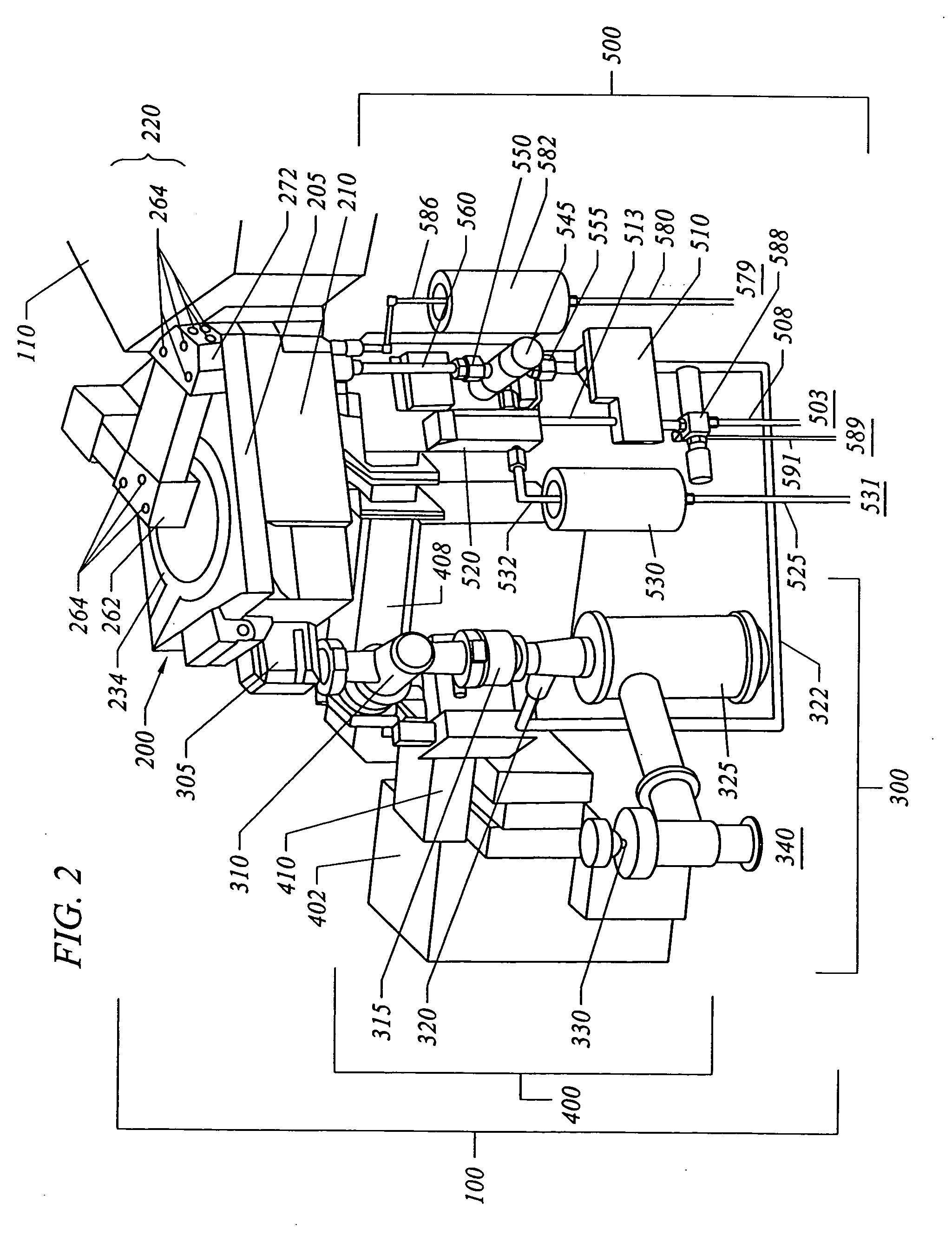
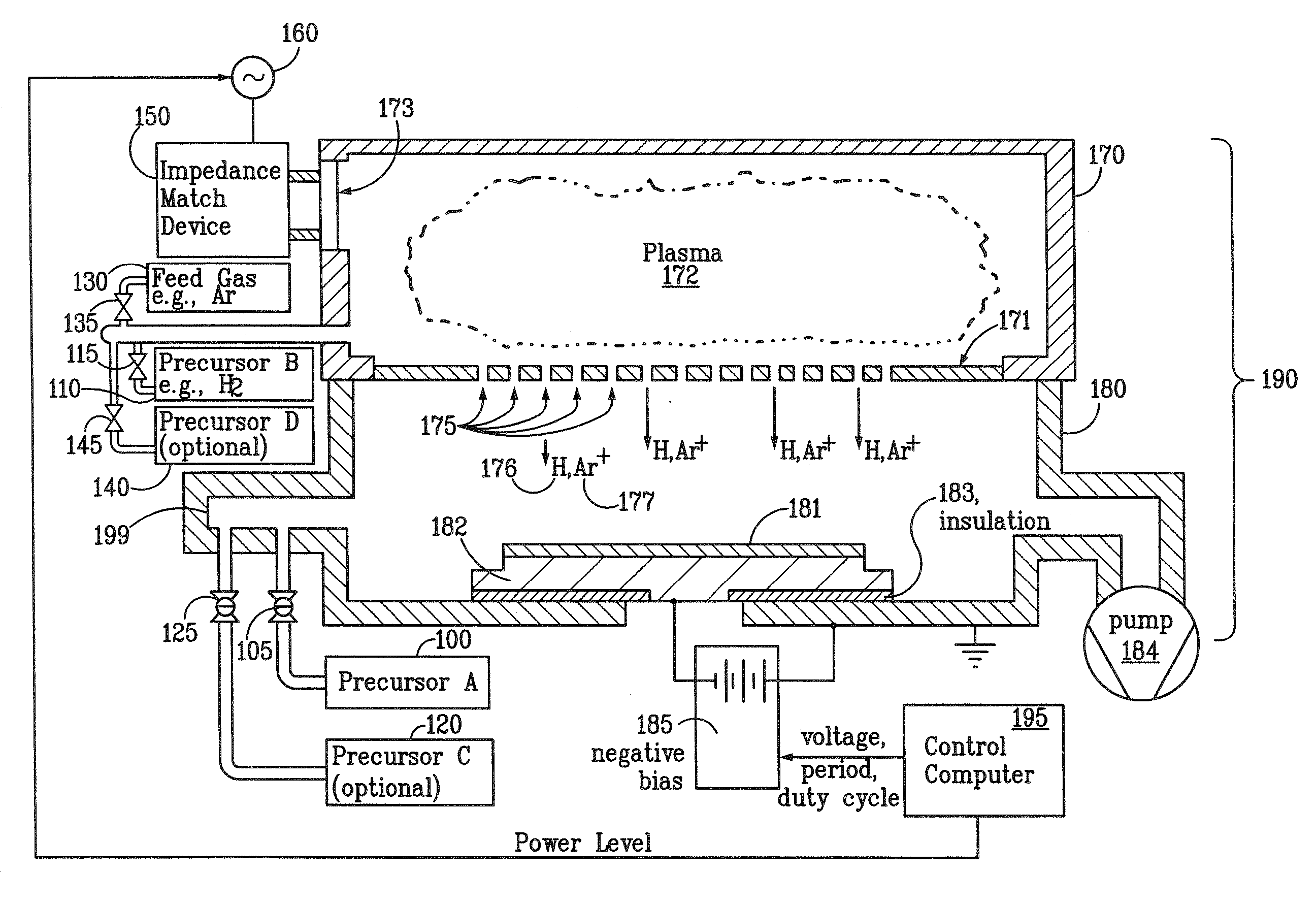
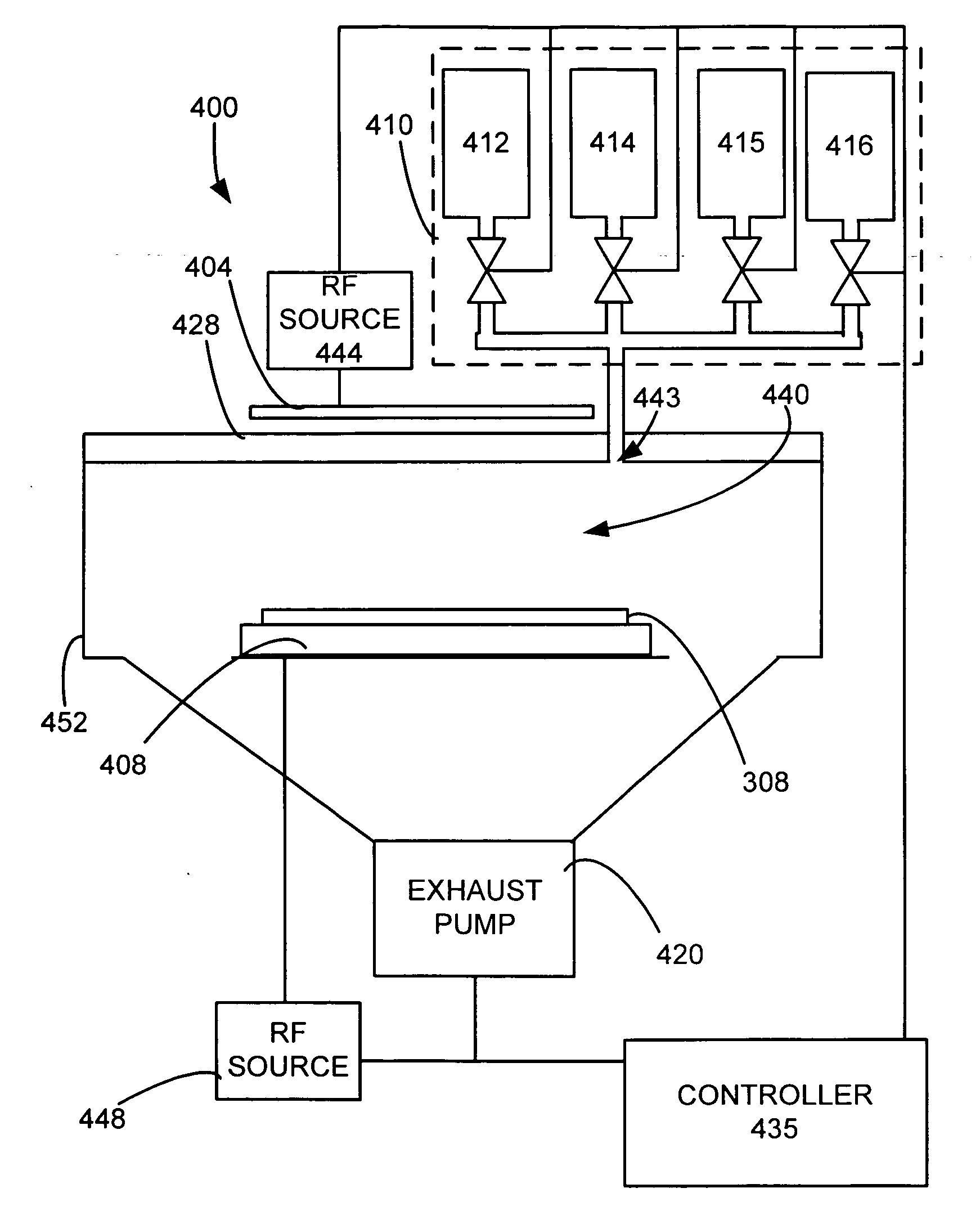
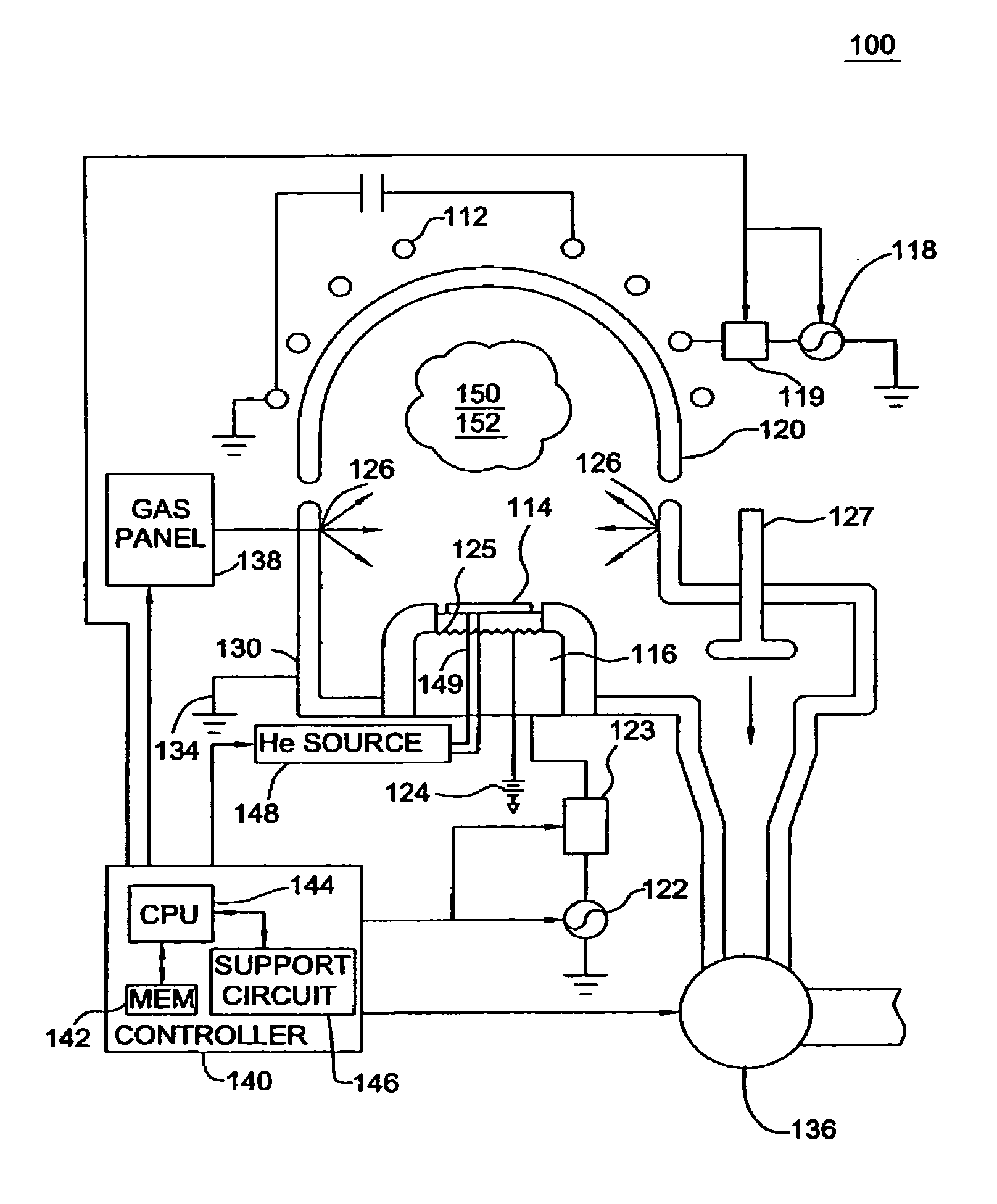
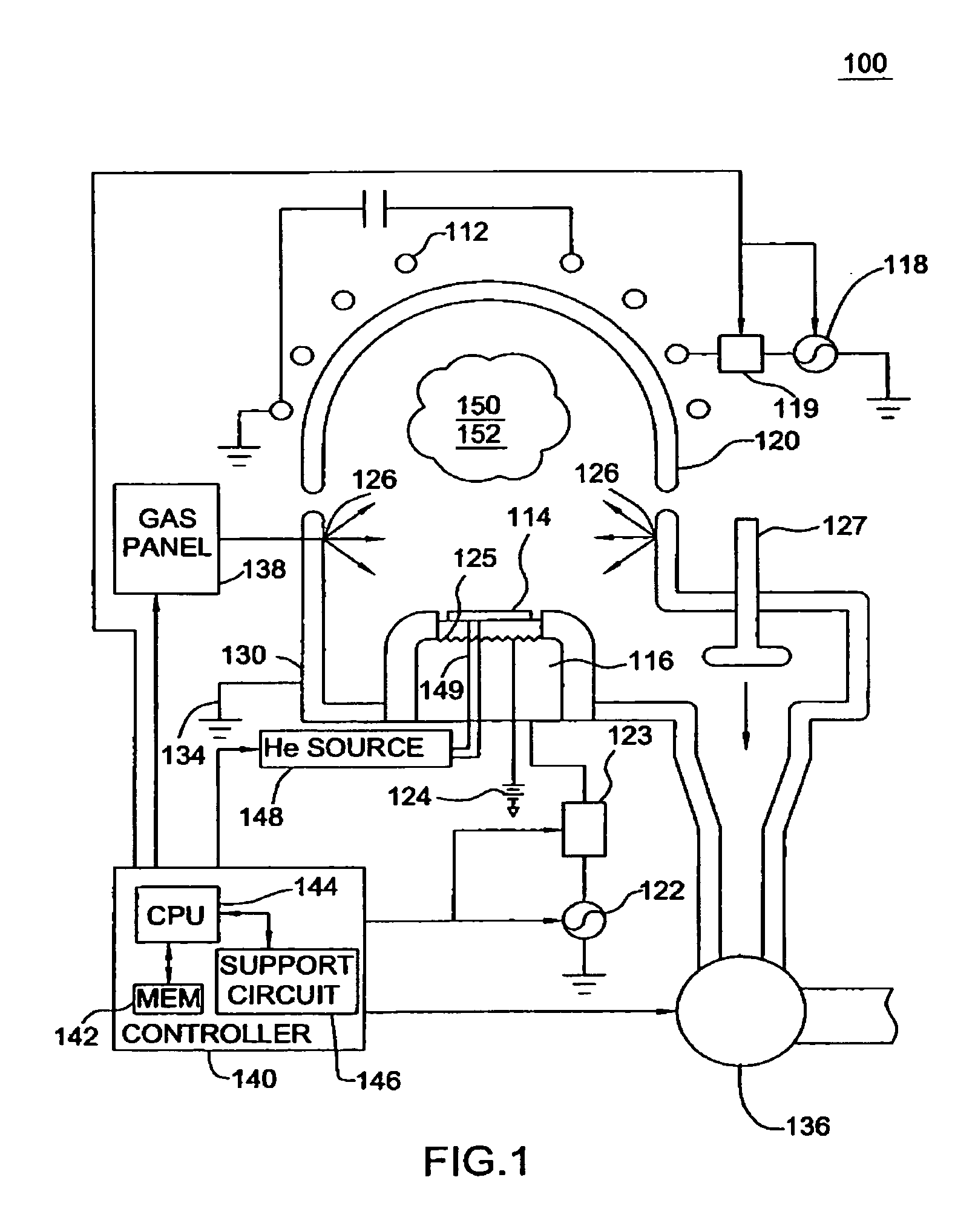
Apparatus for the deposition of high dielectric constant films
InactiveUS20060196421A1Precise temperature controlEasy temperature controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDielectricElectricity
An integrated deposition system is described that is capable of vaporizing low vapor pressure liquid precursors and conveying the vapor to a processing region to fabricate advanced integrated circuits. The integrated deposition system includes a heated exhaust system, a remote plasma generator, a processing chamber, a liquid delivery system, and a computer control module that together create a commercially viable and production worthy system for depositing high capacity dielectric materials from low vapor pressure precursors.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
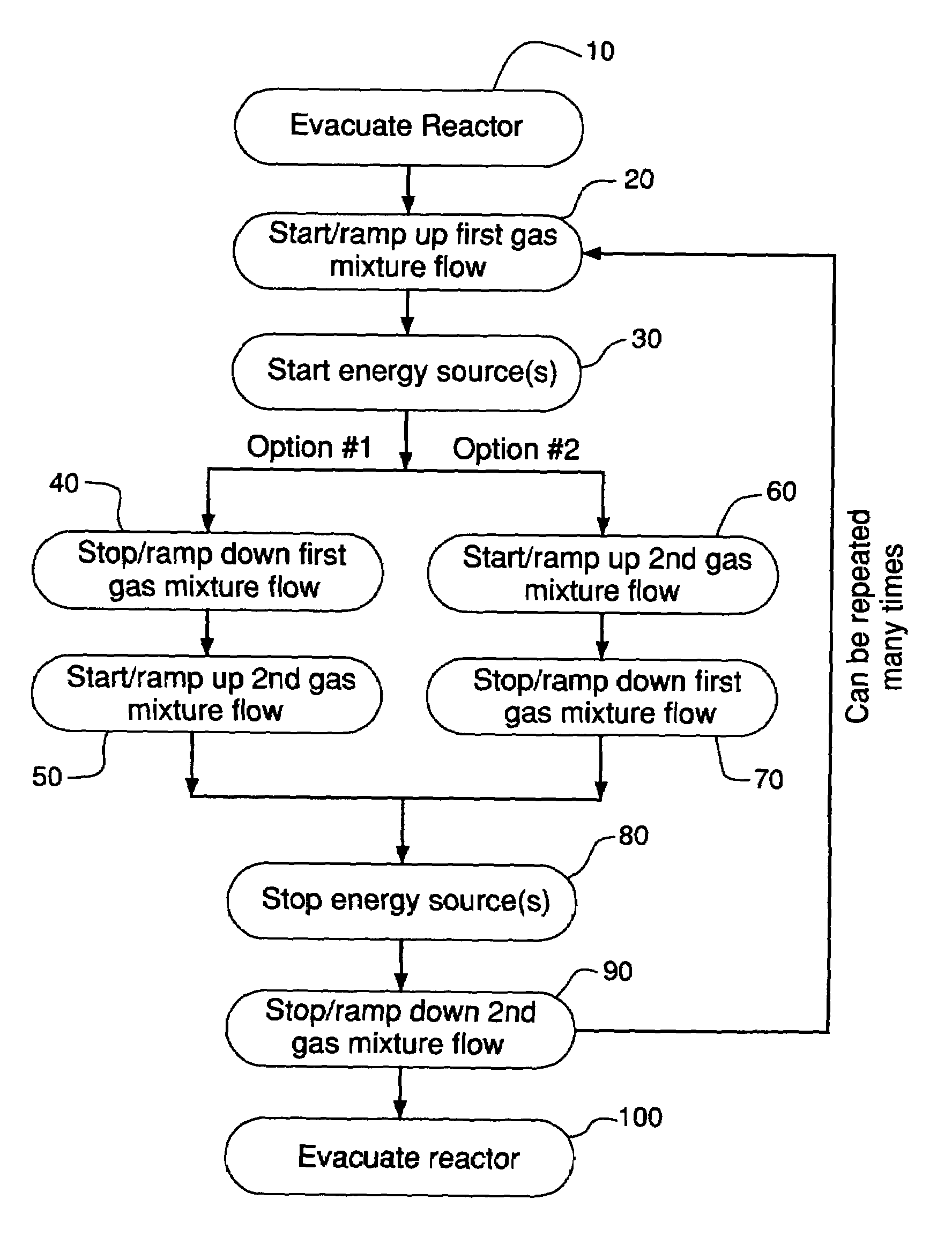
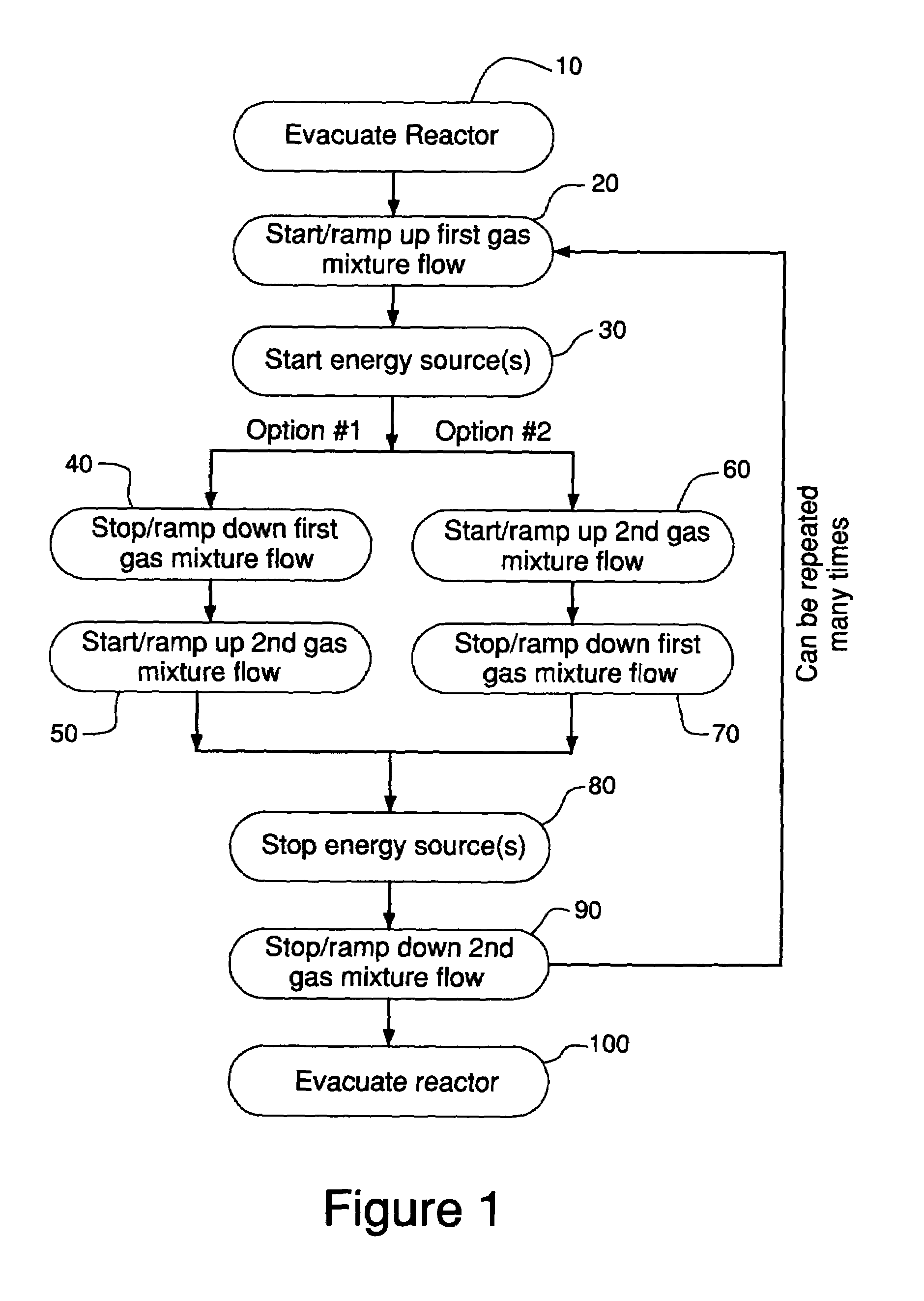
Method for cleaning deposition chambers for high dielectric constant materials
A method for dry etching and chamber cleaning high dielectric constant materials is disclosed herein. In one aspect of the present invention, there is provided a process for cleaning a substance comprising a dielectric constant greater than the dielectric constant of silicon dioxide from at least a portion of a surface of a reactor comprising: introducing a first gas mixture comprising a boron-containing reactive agent into the reactor wherein the first gas mixture reacts with the substance contained therein to provide a volatile product and a boron-containing by-product; introducing a second gas mixture comprising a fluorine-containing reactive agent into the reactor wherein the second gas mixture reacts with the boron-containing by-product contained therein to form the volatile product; and removing the volatile product from the reactor.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
System for Depositing a Film by Modulated Ion-Induced Atomic Layer Deposition (MII-ALD)
InactiveUS20110017139A1Faster efficient meanSimple methodElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention relates to an enhanced sequential atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique suitable for deposition of barrier layers, adhesion layers, seed layers, low dielectric constant (low-k) films, high dielectric constant (high-k) films, and other conductive, semi-conductive, and non-conductive films. This is accomplished by 1) providing a non-thermal or non-pyrolytic means of triggering the deposition reaction; 2) providing a means of depositing a purer film of higher density at lower temperatures; and, 3) providing a faster and more efficient means of modulating the deposition sequence and hence the overall process rate resulting in an improved deposition method.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
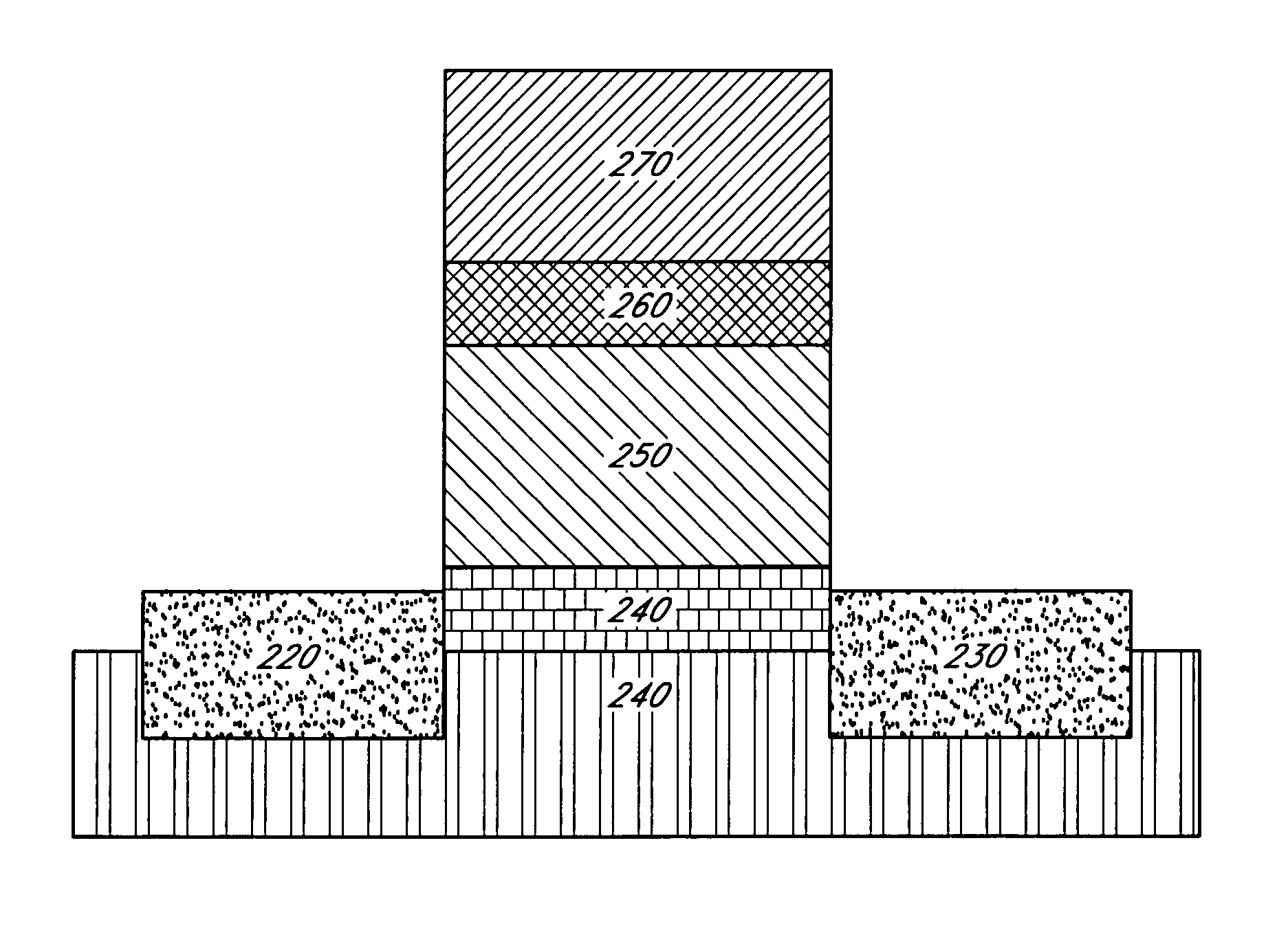
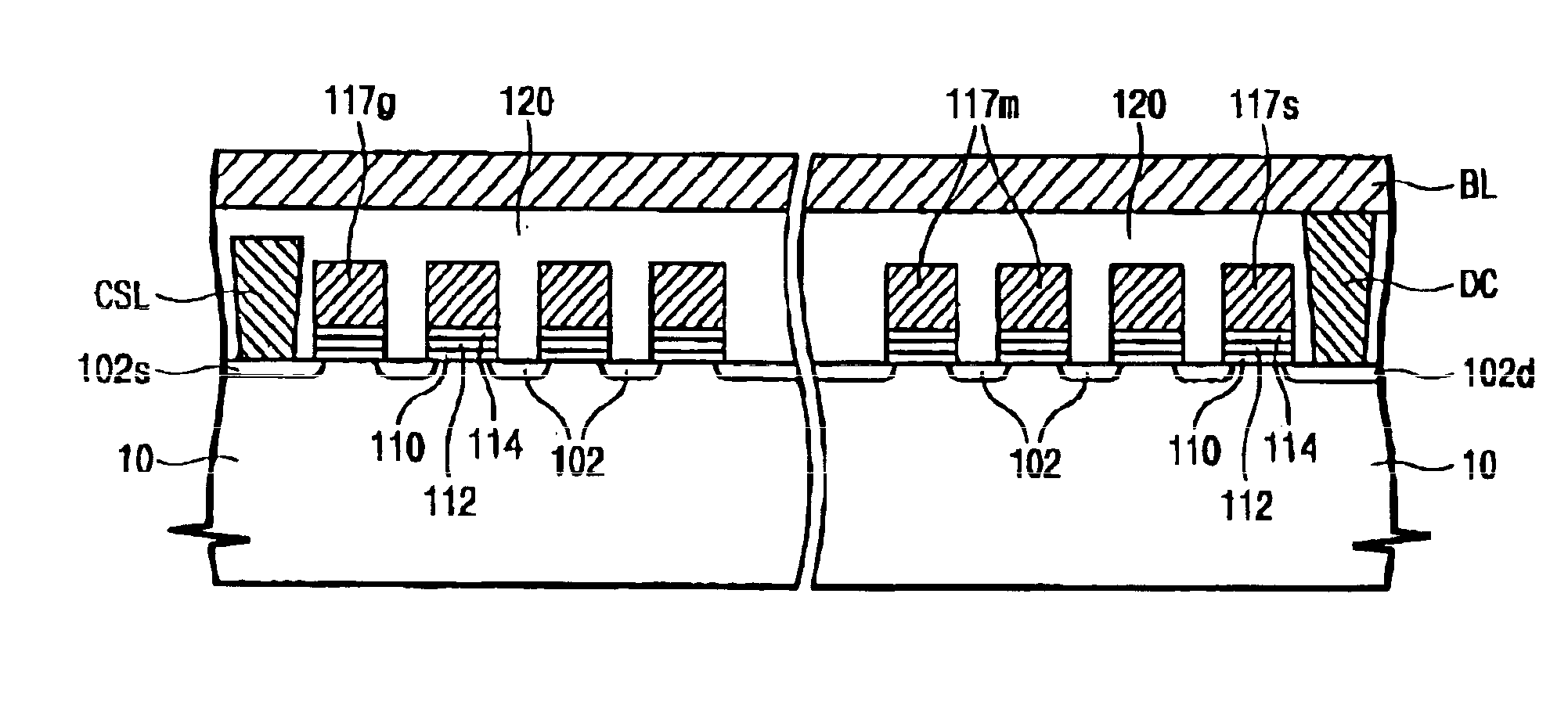
Floating trap non-volatile semiconductor memory devices including high dielectric constant blocking insulating layers
Floating trap non-volatile memory devices and methods are provided. The memory devices include a semiconductor substrate and an adjacent gate electrode. Between the substrate and the gate electrode may be a tunneling insulating layer having a first dielectric constant, a blocking insulating layer having a second dielectric constant that is greater than the first dielectric constant, and a charge storage layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
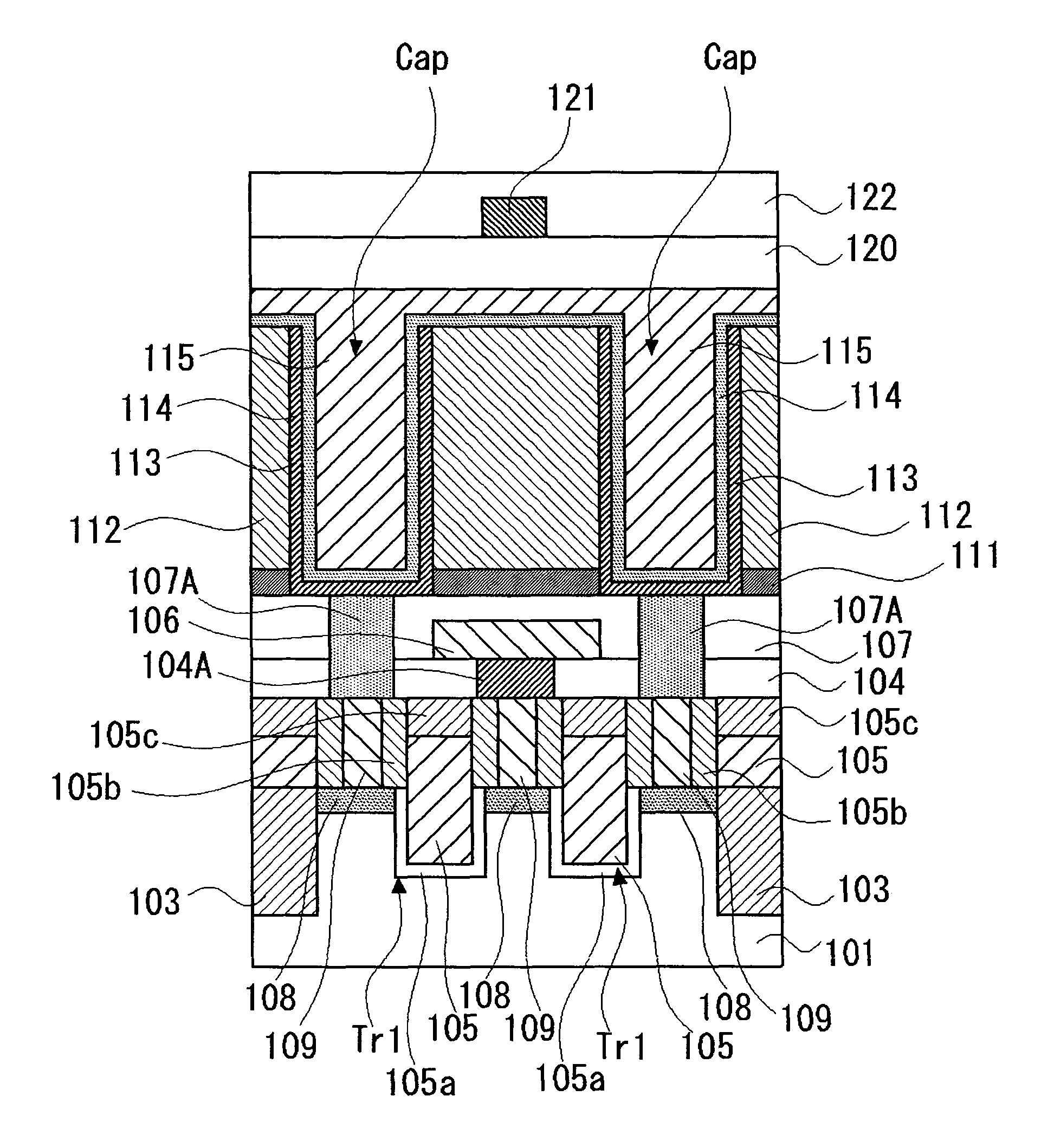
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20120043617A1Work lessTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialPermittivity
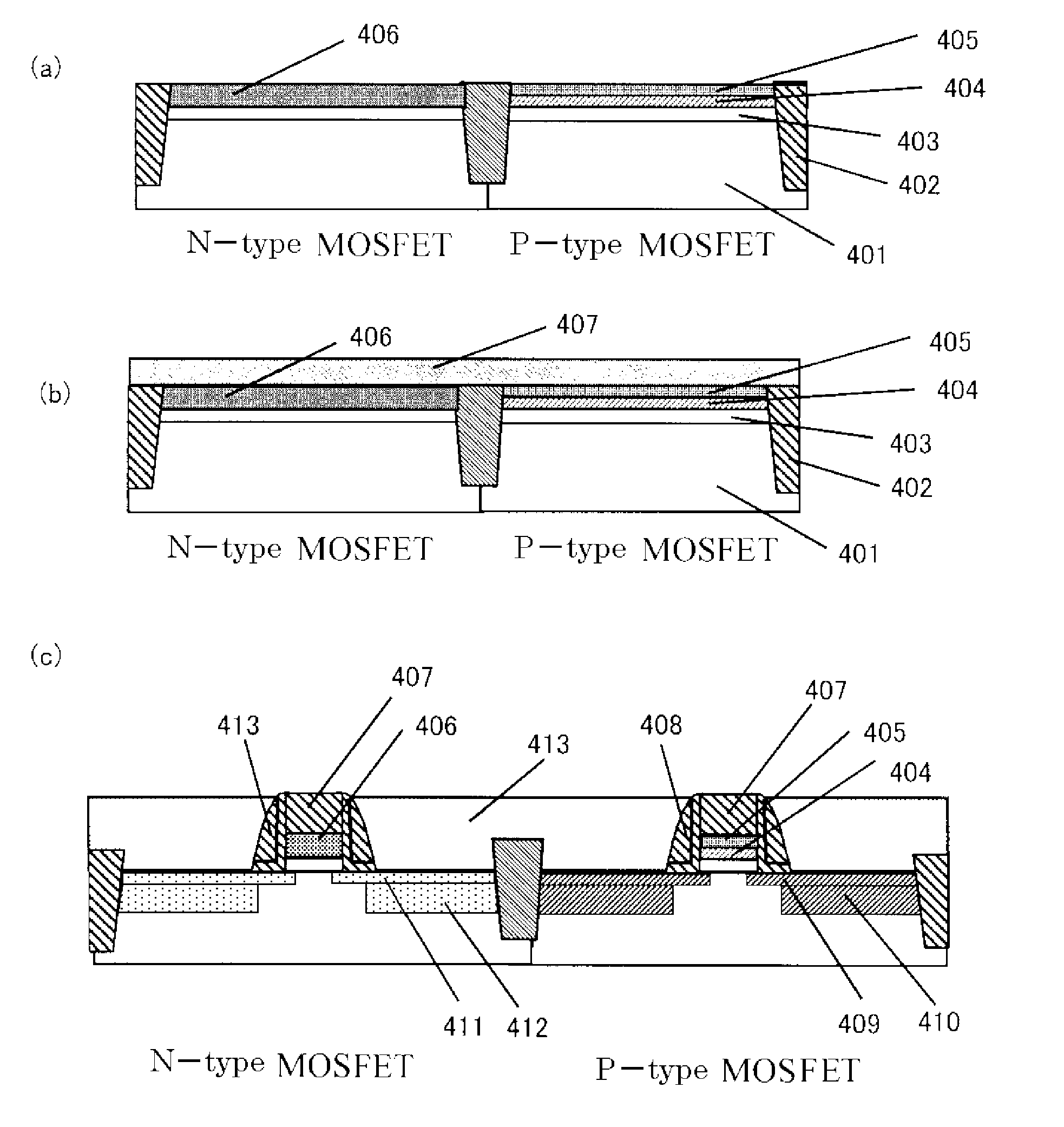
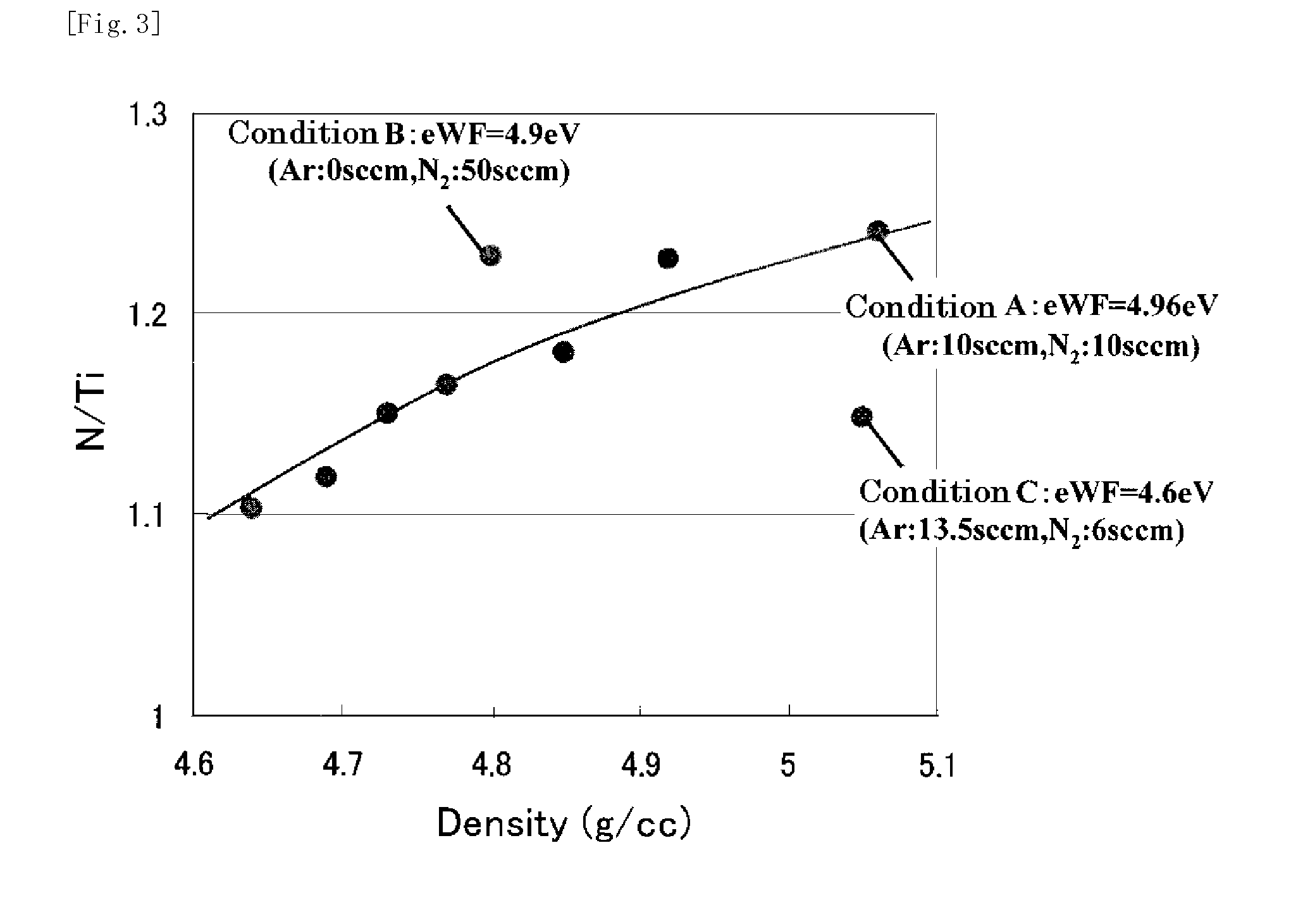
This invention provides a semiconductor device having a field effect transistor comprising agate electrode comprising a metal nitride layer and a polycrystalline silicon layer, and the gate electrode is excellent in thermal stability and realizes a desired work function.In the semiconductor device, a gate insulating film 6 on a silicon substrate 5 has a high-permittivity insulating film formed of a metal oxide, a metal silicate, a metal oxide introduced with nitrogen, or a metal silicate introduced with nitrogen,the gate electrode has a first metal nitride layer 7 provided on the gate insulating film 6 and containing Ti and N, a second metal nitride layer 8 containing Ti and N, and a polycrystalline silicon layer 9, in the first metal nitride layer 7, a molar ratio between Ti and N (N / Ti) is not less than 1.1, and a crystalline orientation X1 is 1.1<X1<1.8, andin the second metal nitride layer 8, the molar ratio between Ti and N (N / Ti) is not less than 1.1, and a crystalline orientation X2 is 1.8≦X2.
Owner:CANON ANELVA CORP
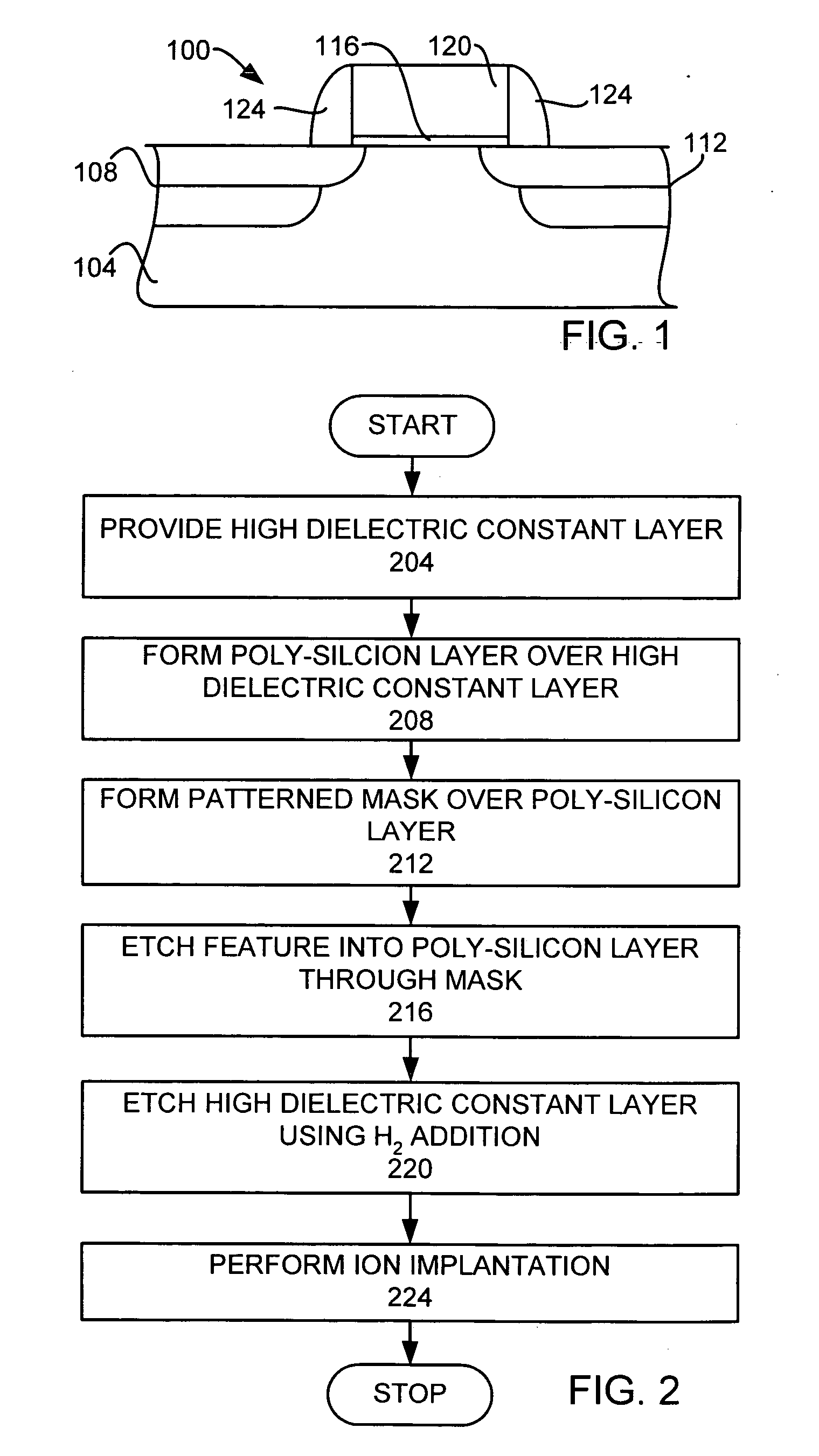
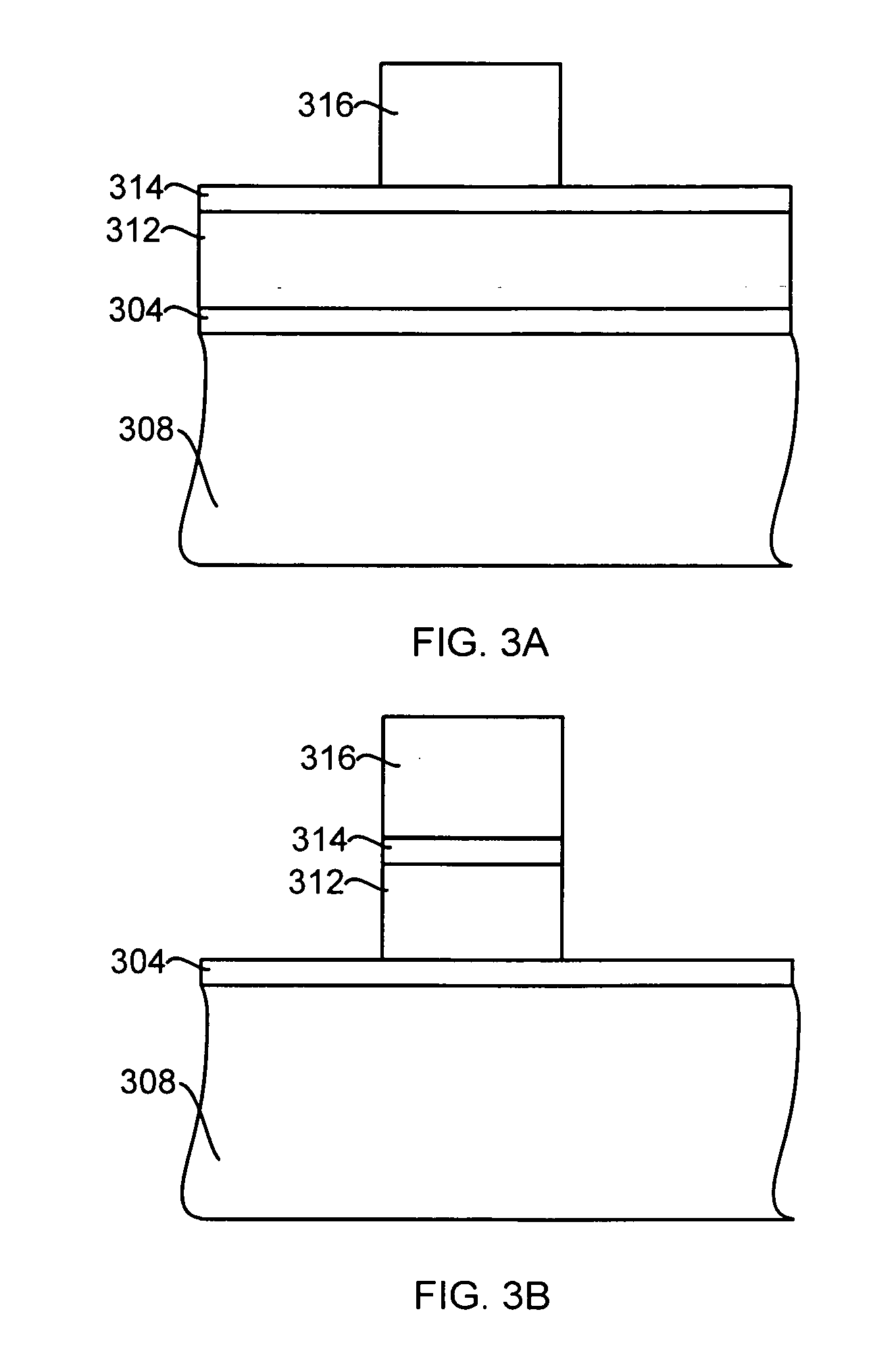
Method of making semiconductor device
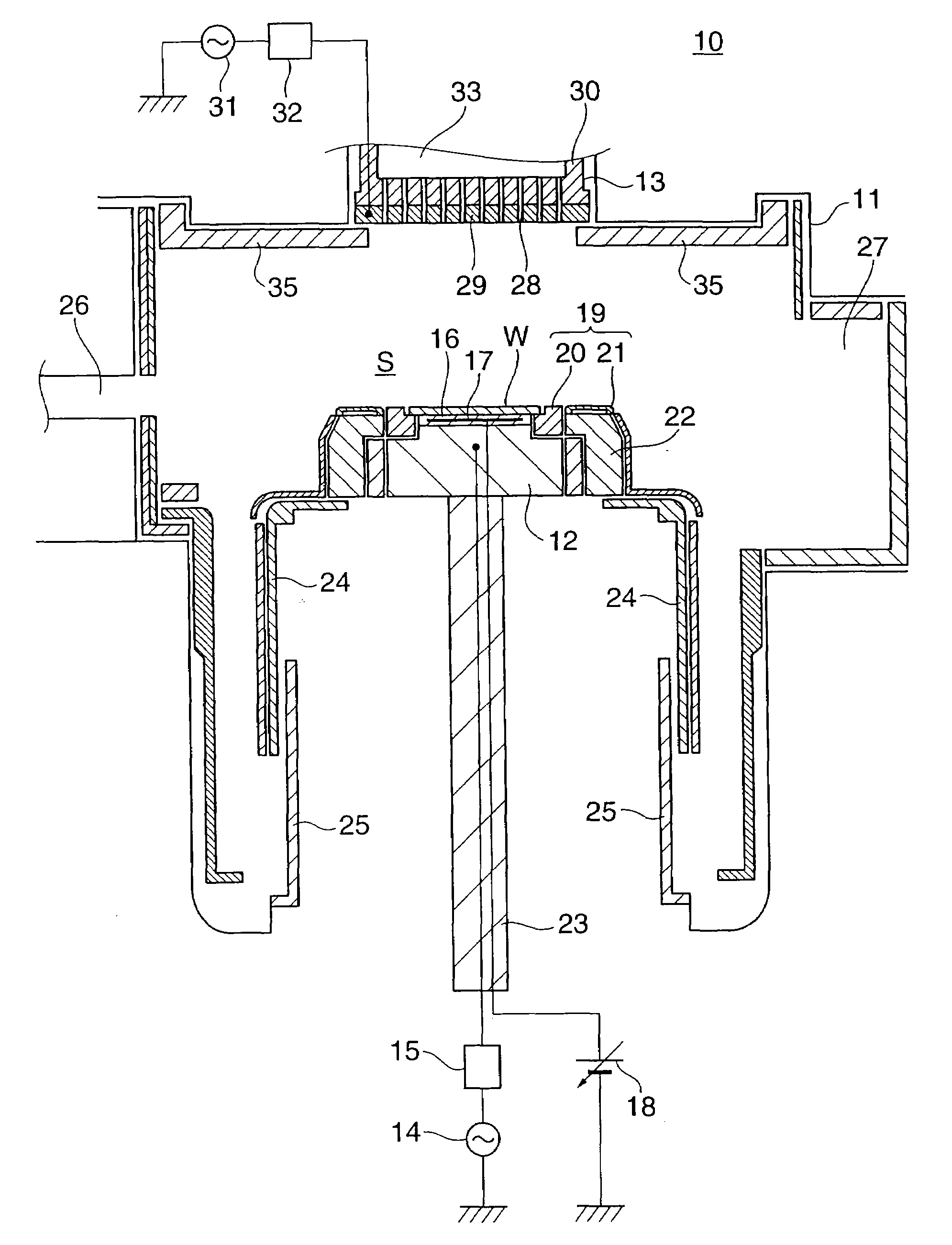
InactiveUS20080261404A1Improve controllabilityGood etchingElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNoble gasControllability
A plasma processing method, which enables the etching controllability for a high-dielectric-constant insulating film to be improved. A substrate having a high-dielectric-constant gate insulating film and a hard mask formed thereon is subjected to etching processing using a plasma of a processing gas containing a noble gas and a reducing gas.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Compositions and structures for chemical mechanical polishing of FeRAM capacitors and method of fabricating FeRAM capacitors using same
InactiveUS6346741B1Easy to manufactureBig advantageOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLead zirconate titanateBarium strontium titanate
An integrated circuit structures formed by chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) process, which comprises a conductive pathway recessed in a dielectric substrate, wherein the conductive pathway comprises conductive transmission lines encapsulated in a transmission-enhancement material, and wherein the conductive pathway is filled sequentially by a first layer of the transmission-enhancement material followed by the conductive transmission line; a second layer of transmission-enhancement material encapsulating the conductive transmission line and contacting the first layer of the transmission-enhancement material, wherein the transmission-enhancement material is selected from the group consisting of high magnetic permeability material and high permittivity material. Such integrated circuit structure may comprise a device structure selected from the group consisting of capacitors, inductors, and resistors. Preferably, the transmission-enhancement material comprises MgMn ferrites, MgMnAl ferrites, barium strontium titanate, lead zirconium titanate, titanium oxide, tantalum oxide, etc.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
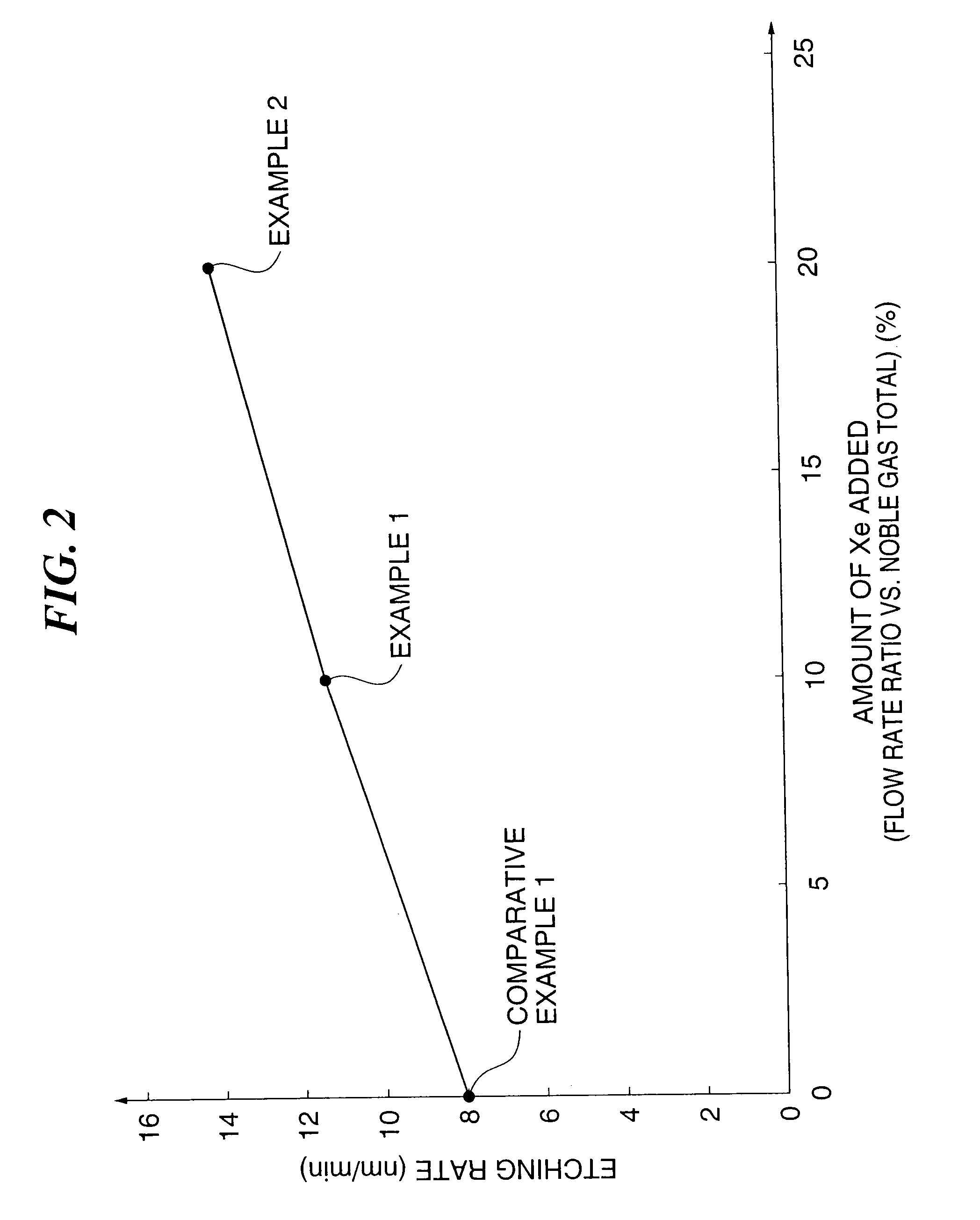
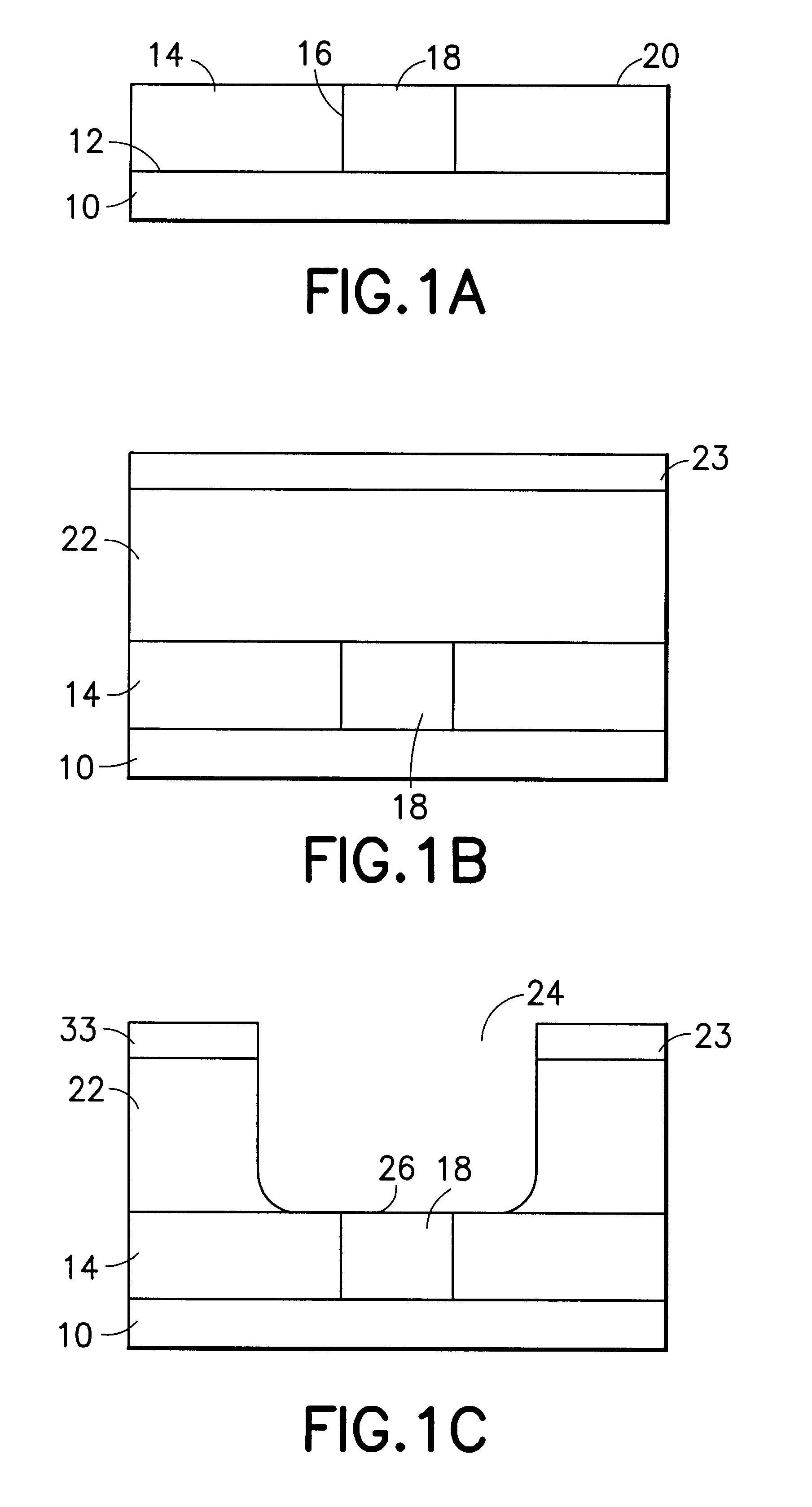
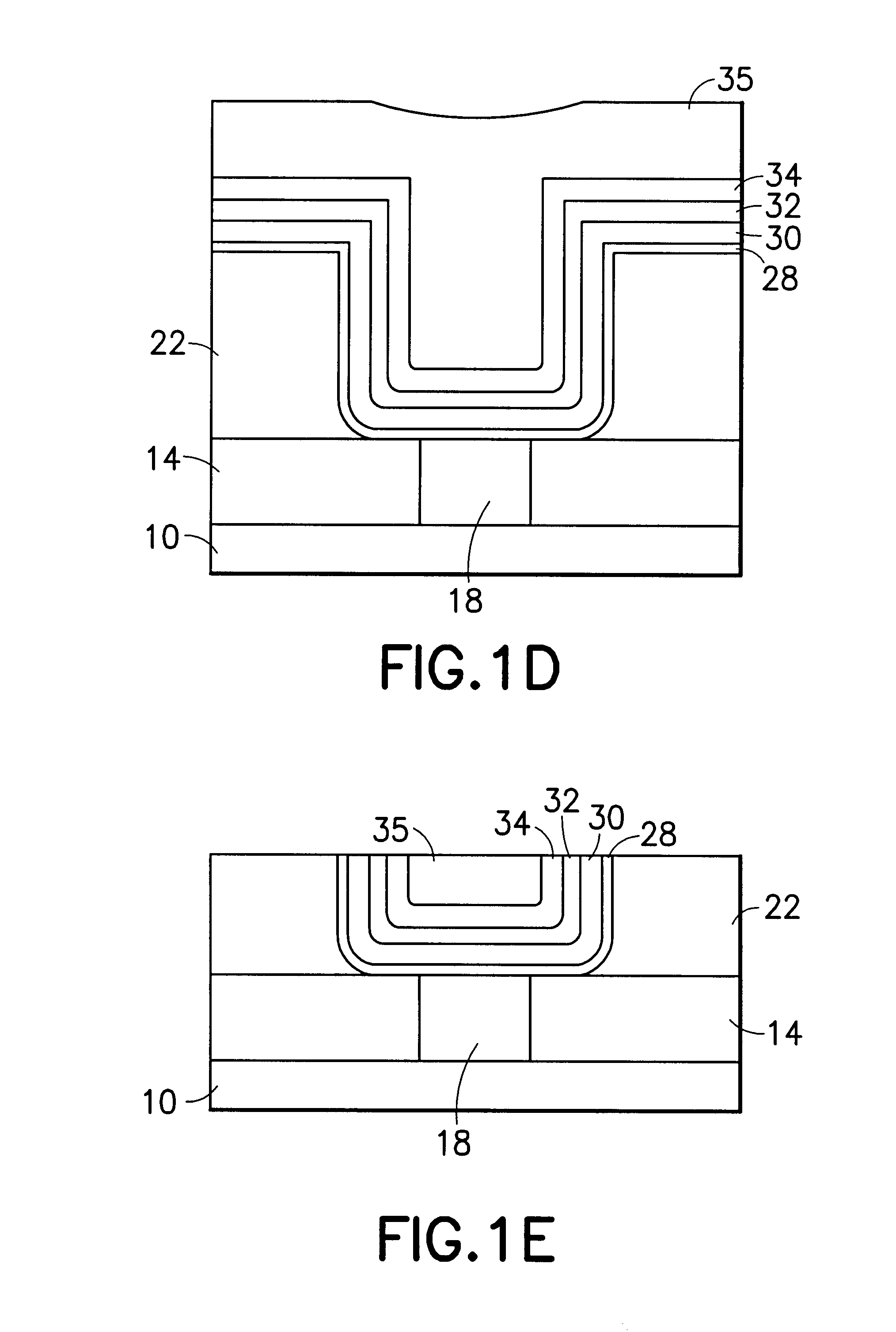
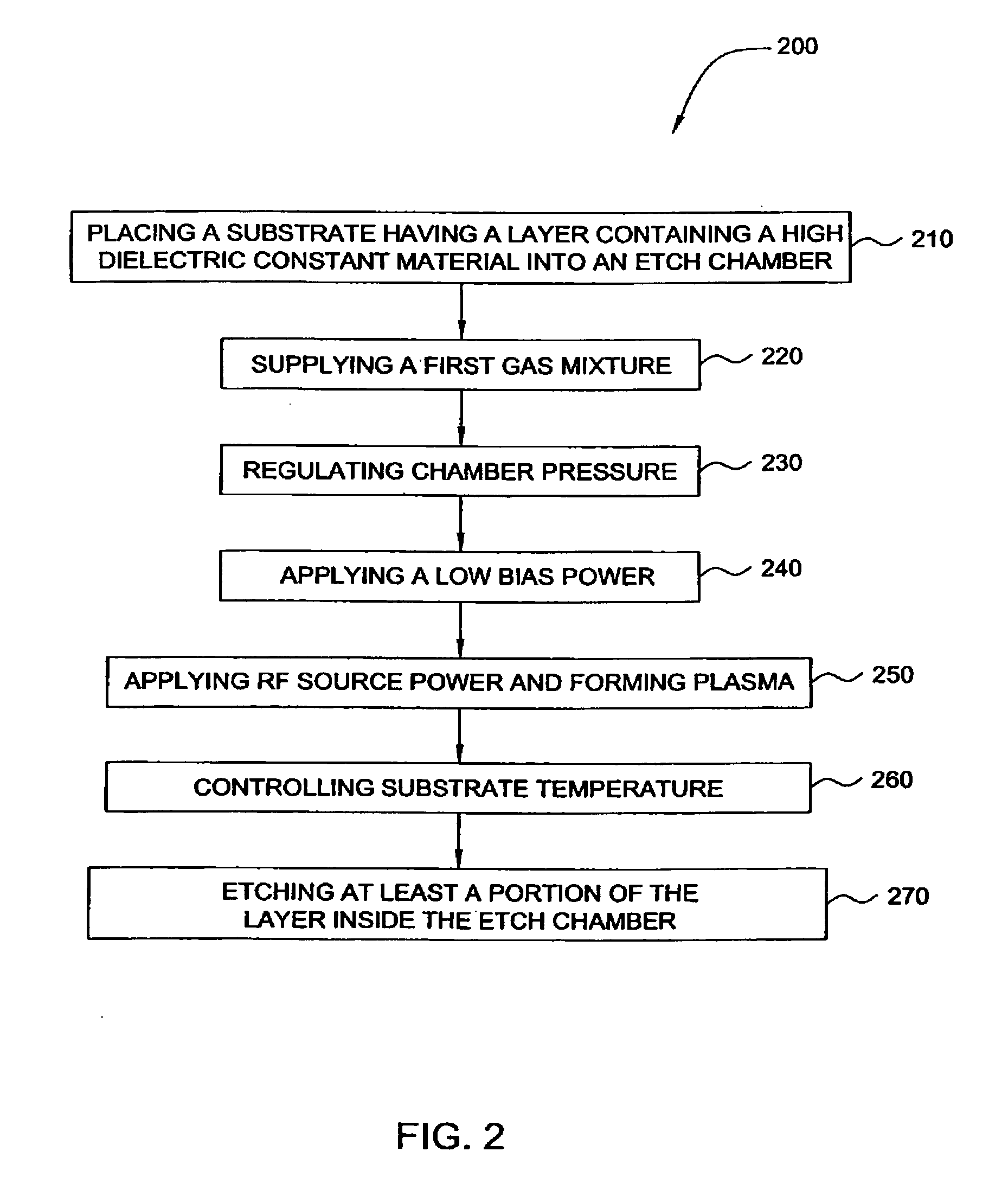
Selective etch of films with high dielectric constant with H2 addition
InactiveUS20070056925A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAtomic physicsHigh dielectric permittivity
A method for selectively etching a high k layer with respect to a silicon based material is provided. The high k layer is placed into an etch chamber. An etchant gas is provided into the etch chamber, wherein the etchant gas comprises H2. A plasma is generated from the etchant gas to selectively etch the high k layer with respect to a silicon based material.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
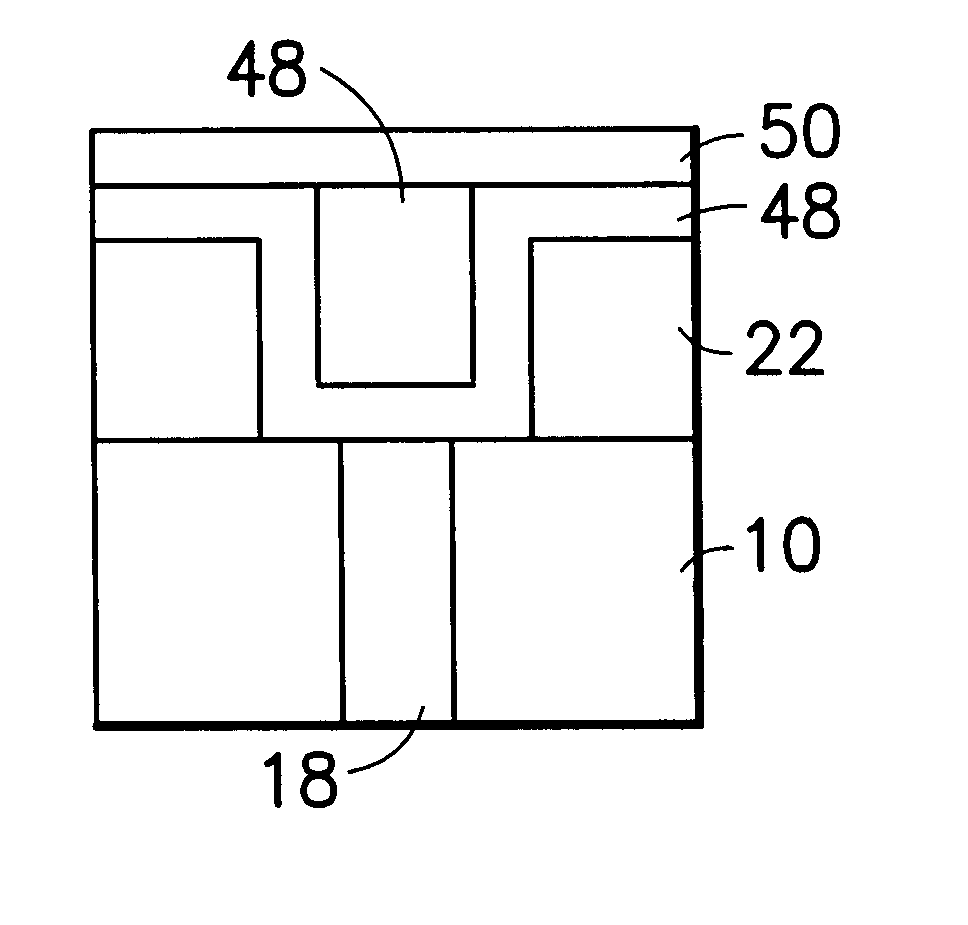
Etching high-kappa dielectric materials with good high-kappa foot control and silicon recess control
InactiveUS20060252265A1High selectivityDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricHalogen
An apparatus and a method for etching high dielectric constant (high-κ) materials using halogen containing gas and reducing gas chemistries are provided. One embodiment of the method is accomplished by etching a layer using two etch gas chemistries in separate steps. The first etch gas chemistry contain no oxygen containing gas in order to break through etching of the high dielectric constant materials, to dean any residues left from previous polysilicon etch process resulting in less high-κ foot, and also to control silicon recess problem associated with an underlying silicon oxide layer. The second over-etch gas chemistry provides a high etch selectivity for high dielectric constant materials over silicon oxide materials to be combined with low source power to further reduce silicon substrate oxidation problem.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Electrical-energy-storage unit (EESU) utilizing ceramic and integrated-circuit technologies for replacement of electrochemical batteries
InactiveUS7033406B2Reduce sinteringLowering hot-isostatic-pressing temperatureElectrical storage systemFixed capacitor electrodesBarium titanatePermittivity
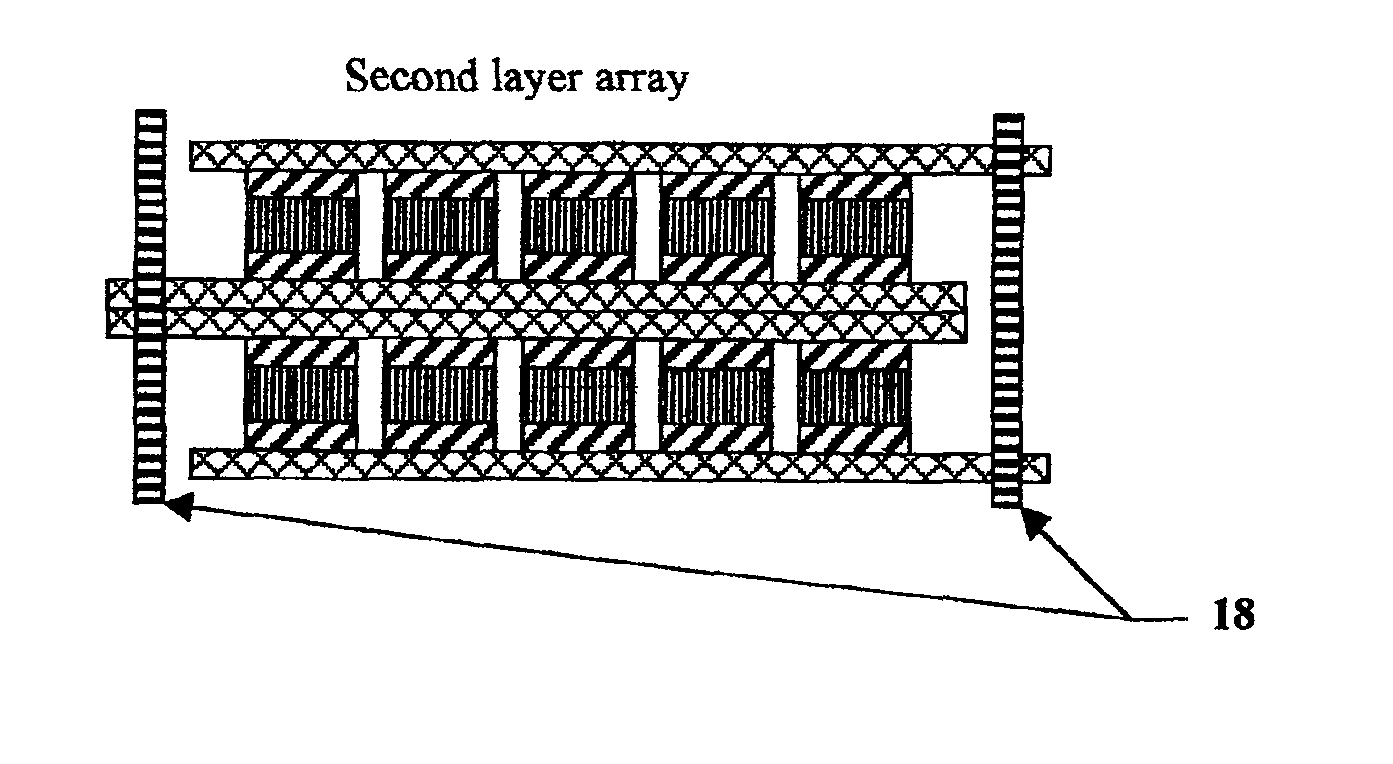
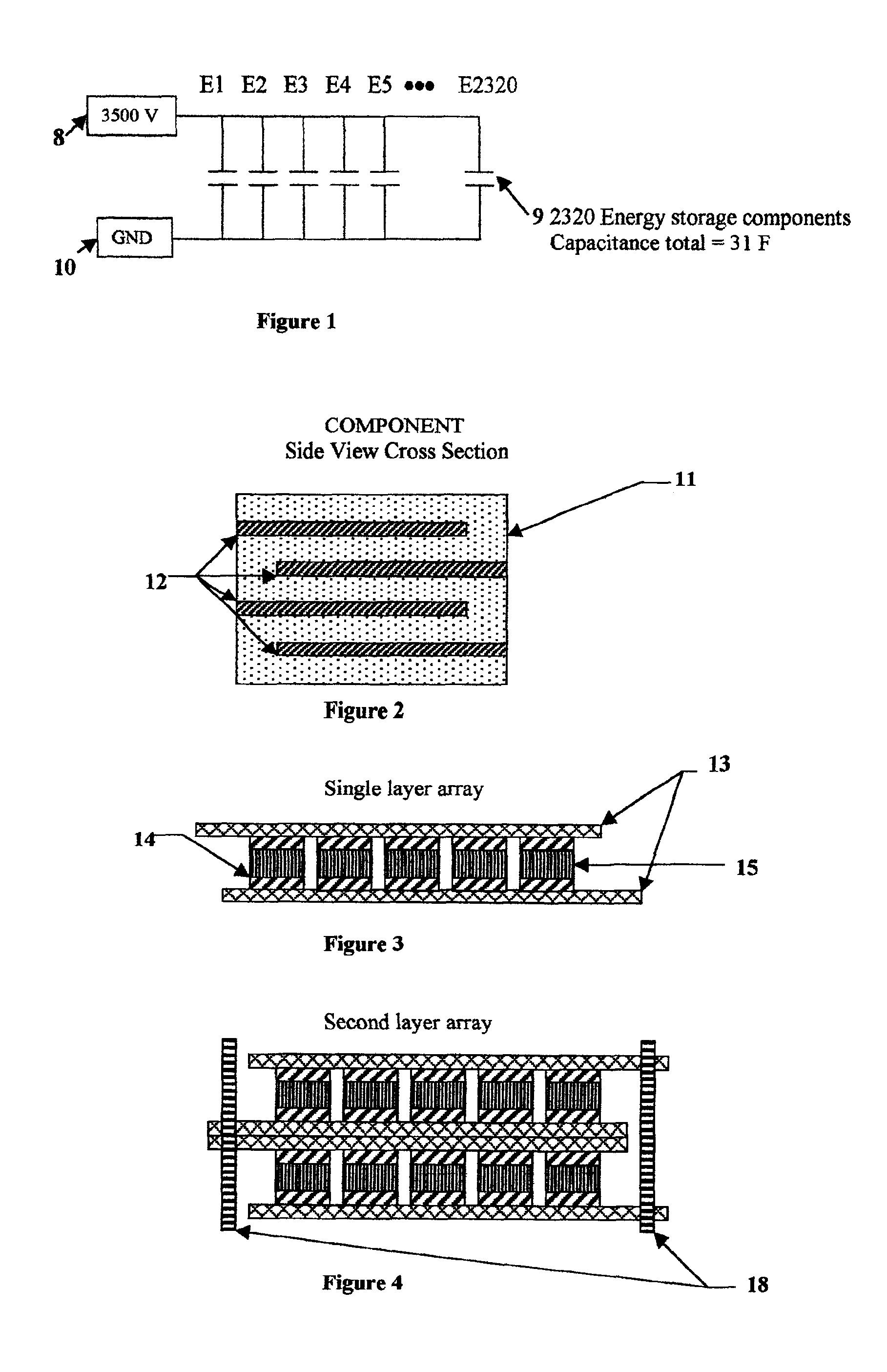
An electrical-energy-storage unit (EESU) has as a basis material a high-permittivity composition-modified barium titanate ceramic powder. This powder is double coated with the first coating being aluminum oxide and the second coating calcium magnesium aluminosilicate glass. The components of the EESU are manufactured with the use of classical ceramic fabrication techniques which include screen printing alternating multilayers of nickel electrodes and high-permittivitiy composition-modified barium titanate powder, sintering to a closed-pore porous body, followed by hot-isostatic pressing to a void-free body. The components are configured into a multilayer array with the use of a solder-bump technique as the enabling technology so as to provide a parallel configuration of components that has the capability to store electrical energy in the range of 52 kW·h. The total weight of an EESU with this range of electrical energy storage is about 336 pounds.
Owner:EESTOR
Circular-polarization dipole helical antenna
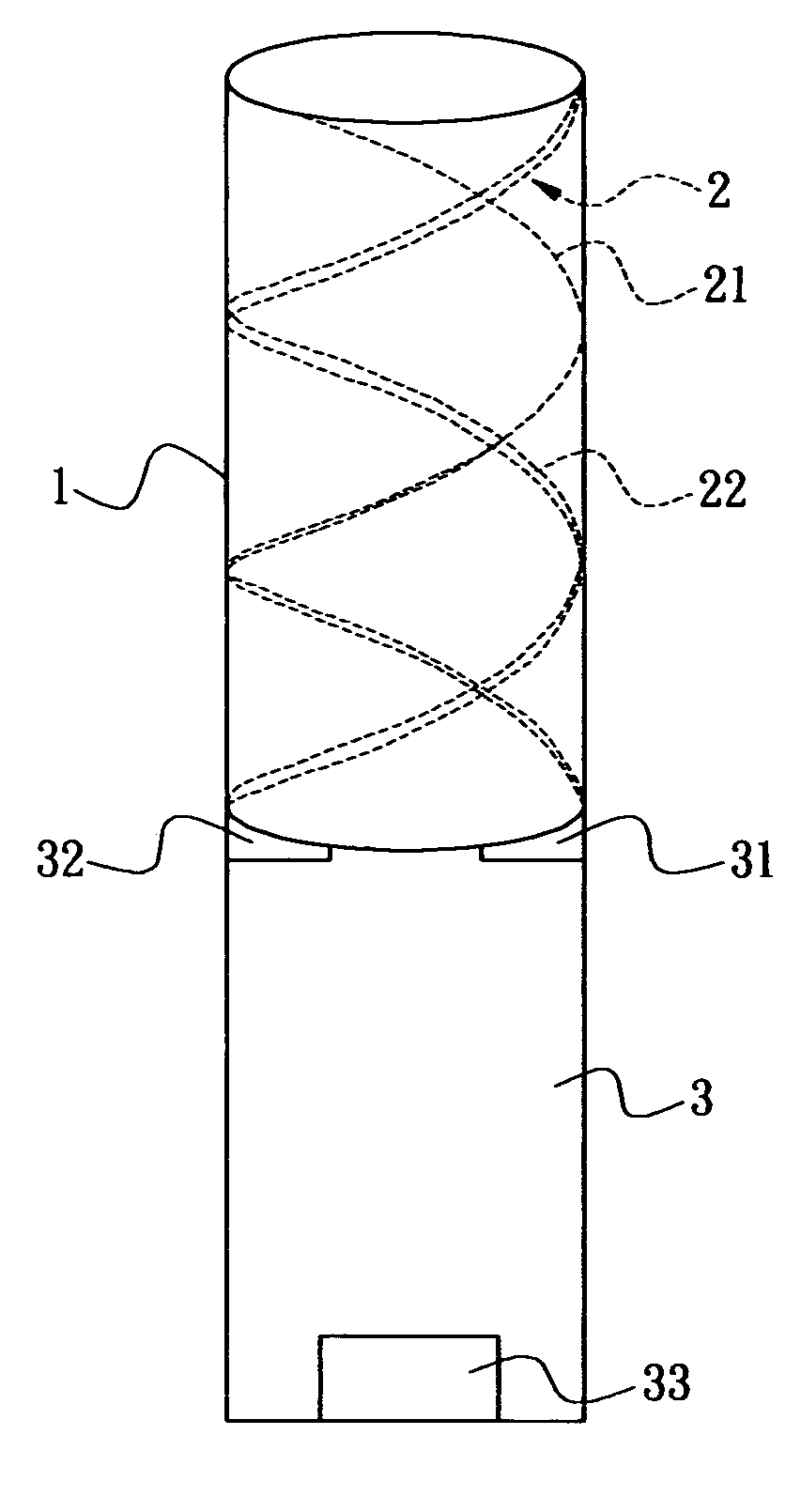
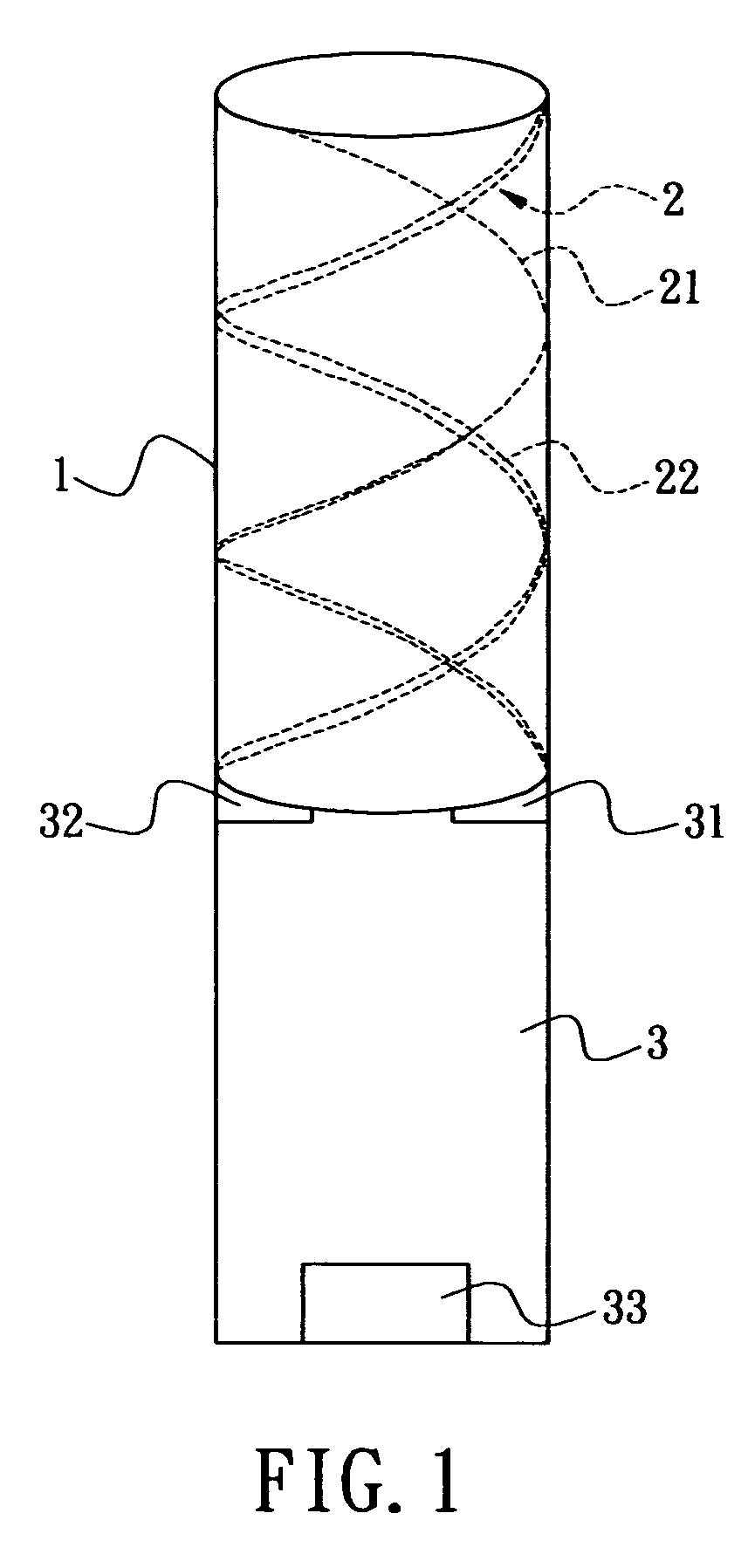
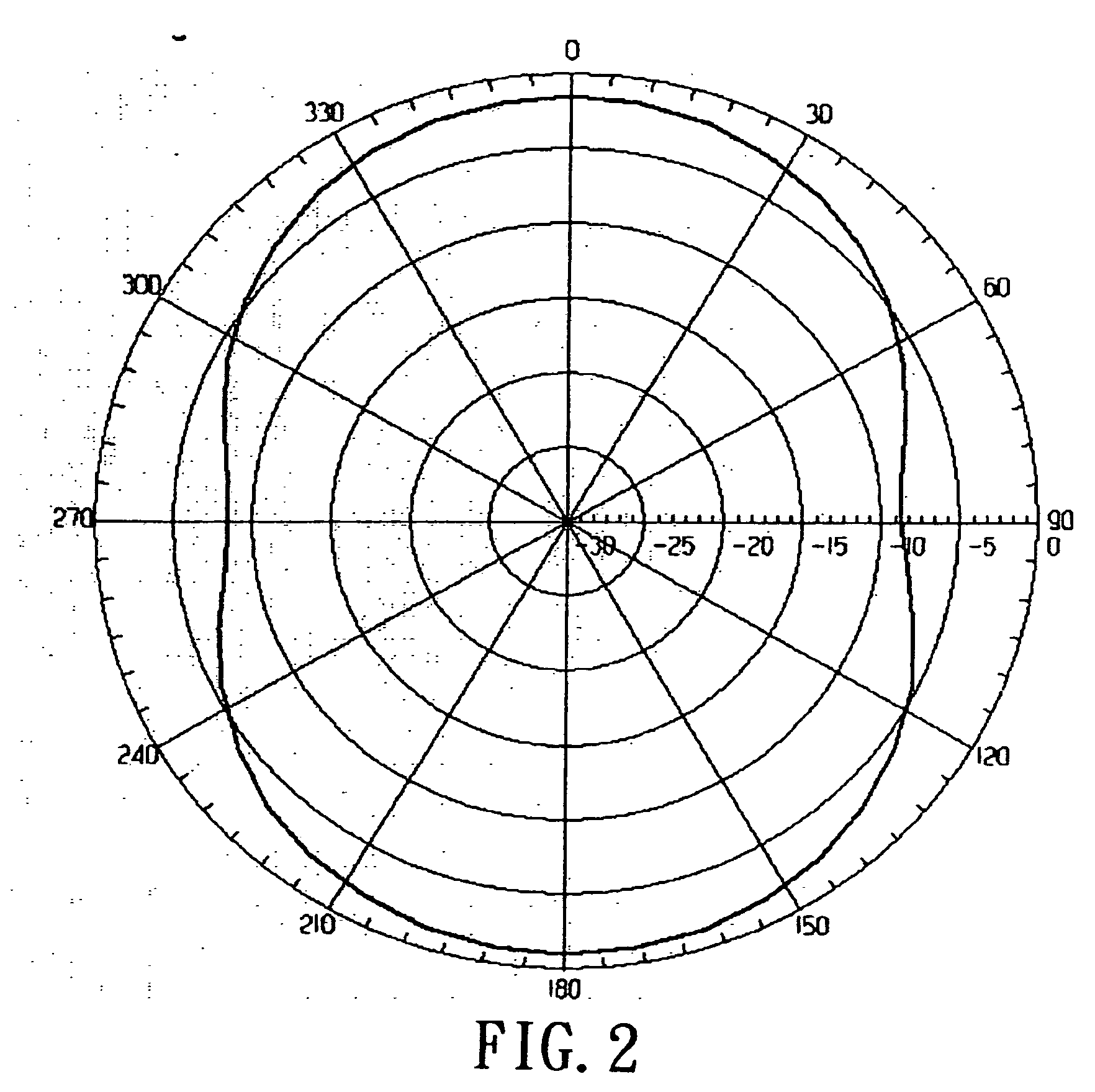
InactiveUS20060232493A1Quick fine-tuningReduce lossRadiating elements structural formsHelical antennasElectrical conductorPhase difference
A circular-polarization dipole helical antenna is used for electronic device and satellite terminal and includes a base, and an antenna conductor arranged on surface of the base. The antenna conductor includes a plurality of metal conductors with high Q value and anti-oxidation property and continuously and helically coated on surface of the base. The base is made of low loss and high dielectric constant material. An unbalance-to-balance circuit module connects two signal-feeding ends to the base with phase difference of 180 degree. The problems of narrow bandwidth, low efficiency, complicated structure and precise manufacture can be solved.
Owner:CIREX TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com