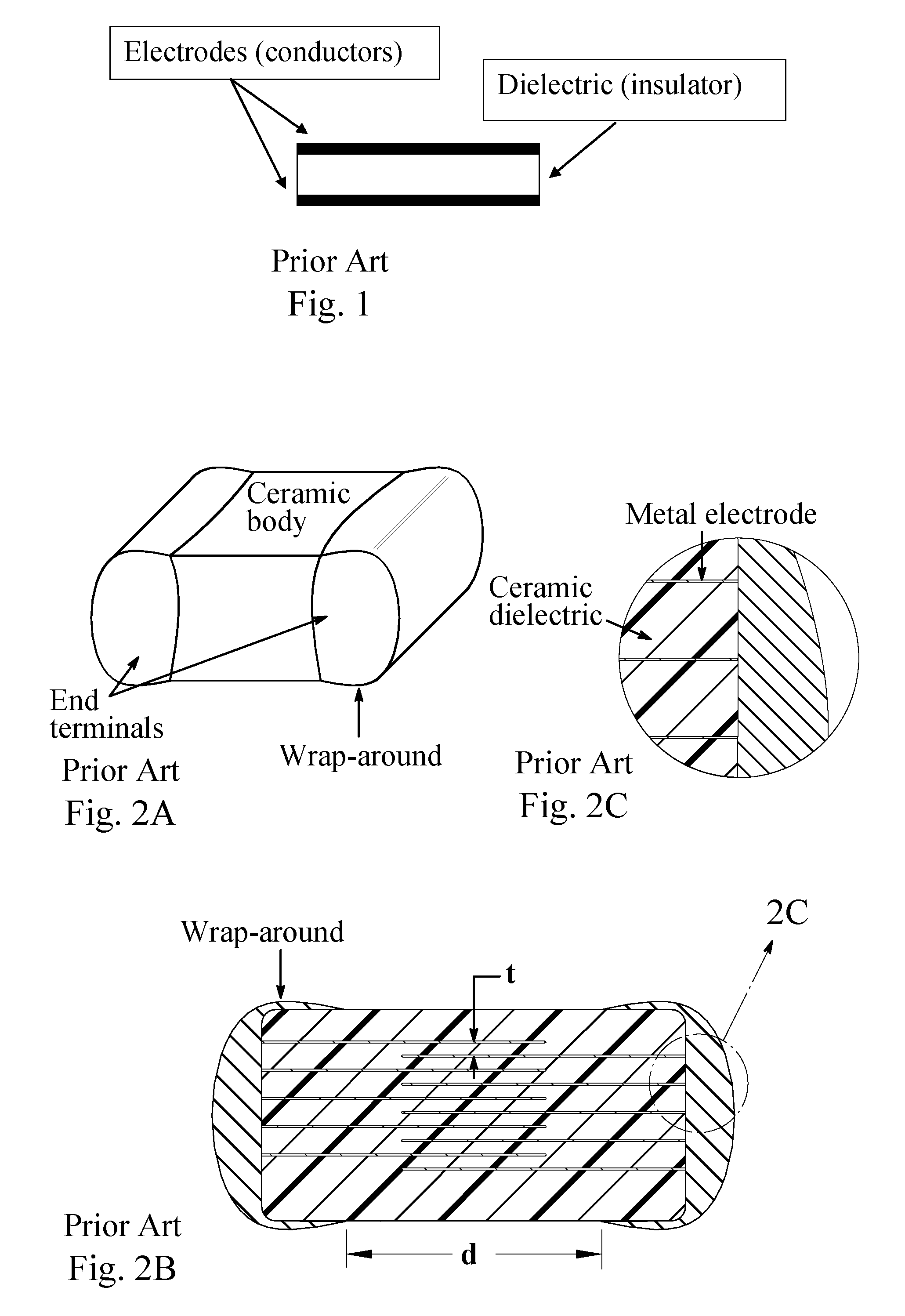
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
8270results about "Stacked capacitors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
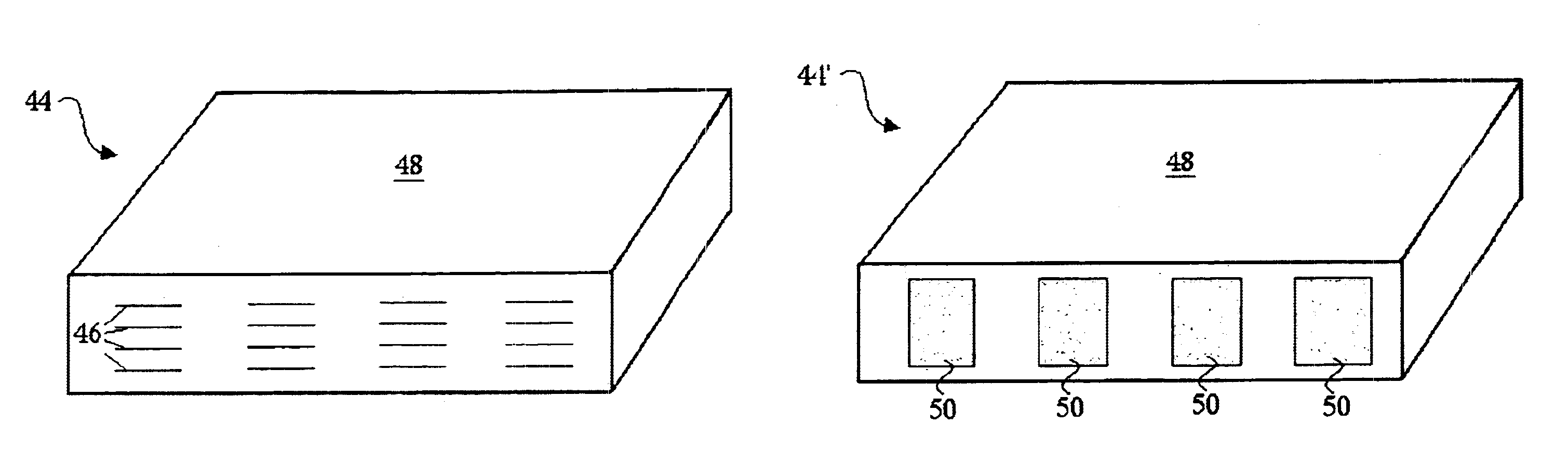
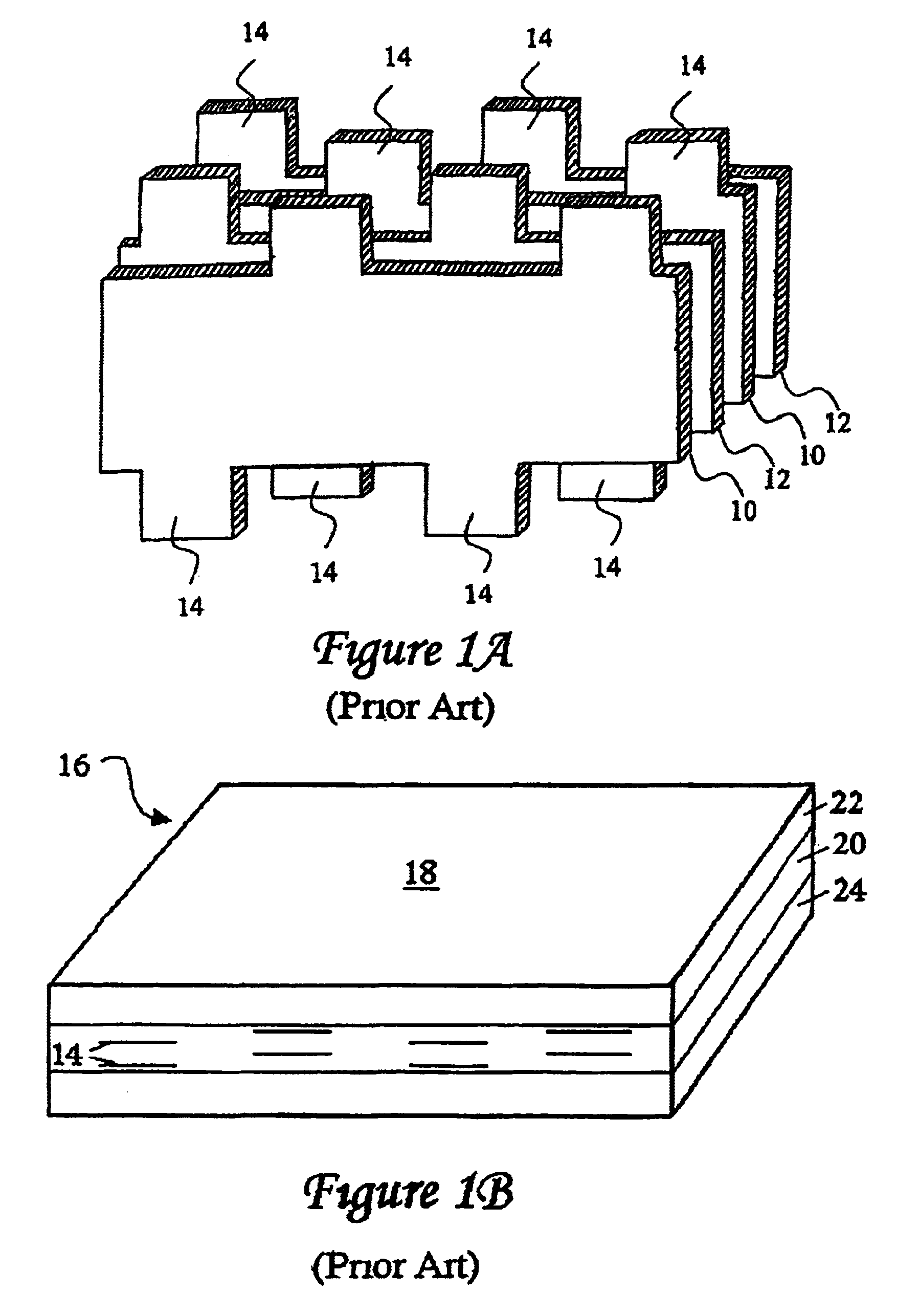
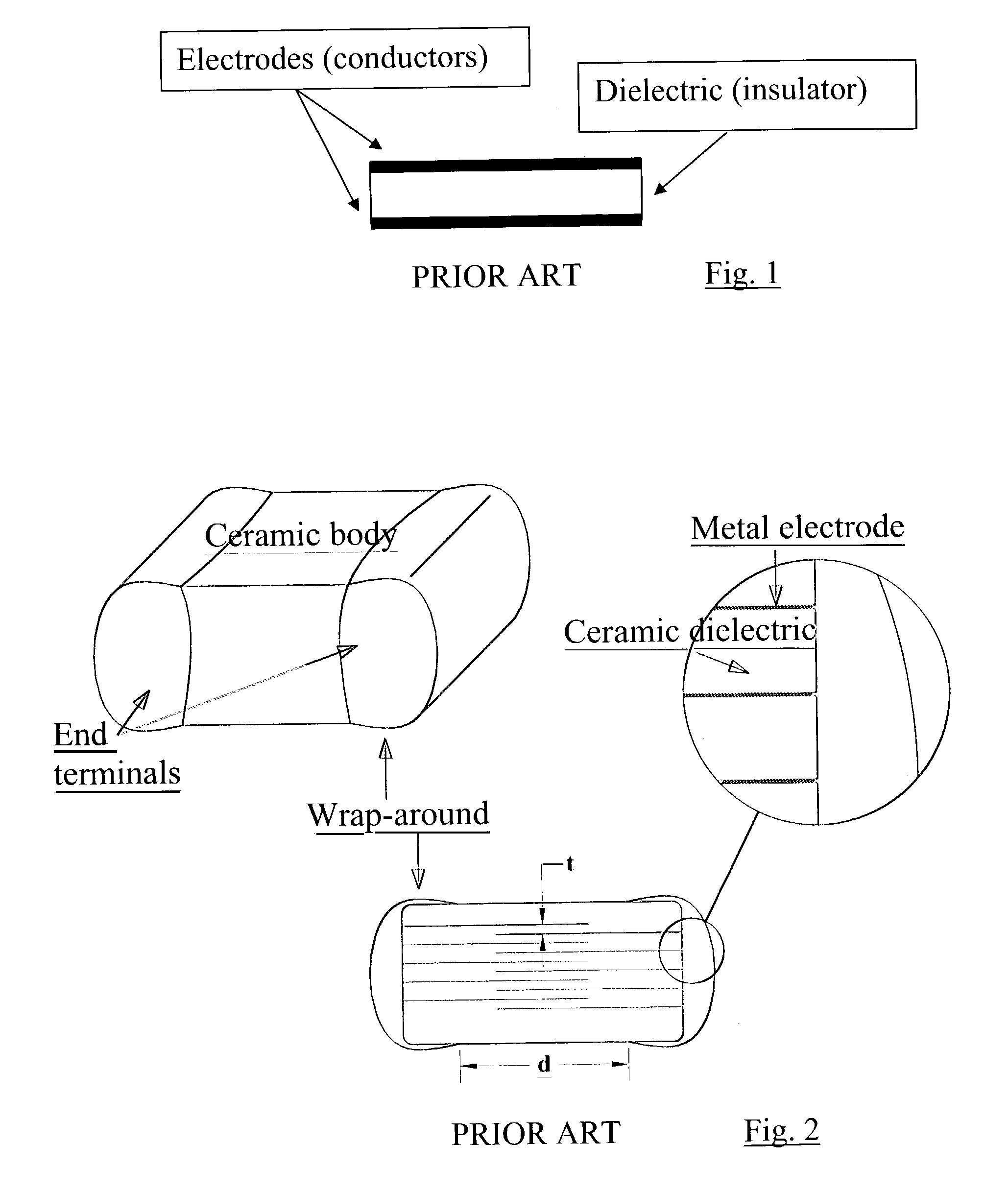
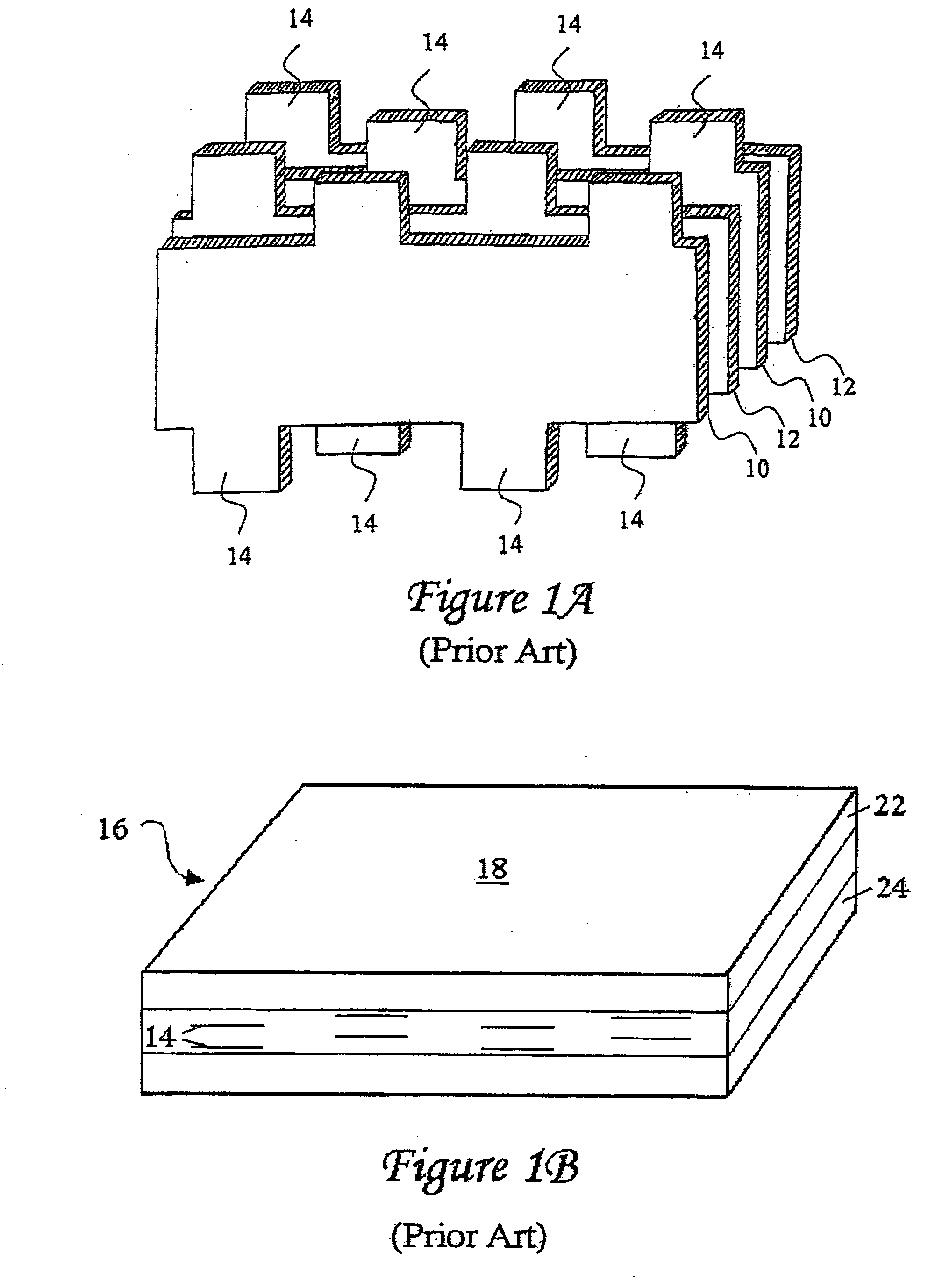
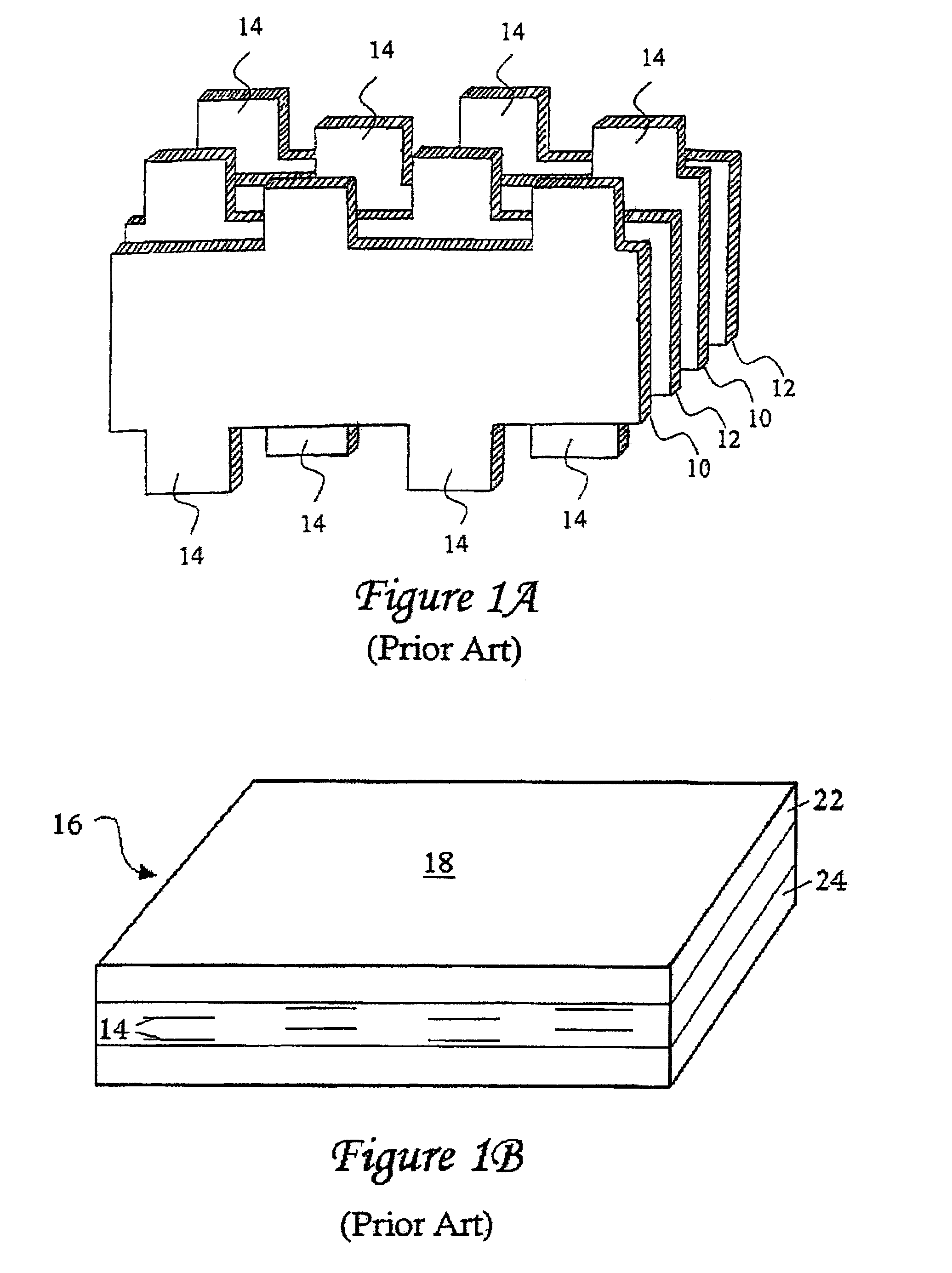
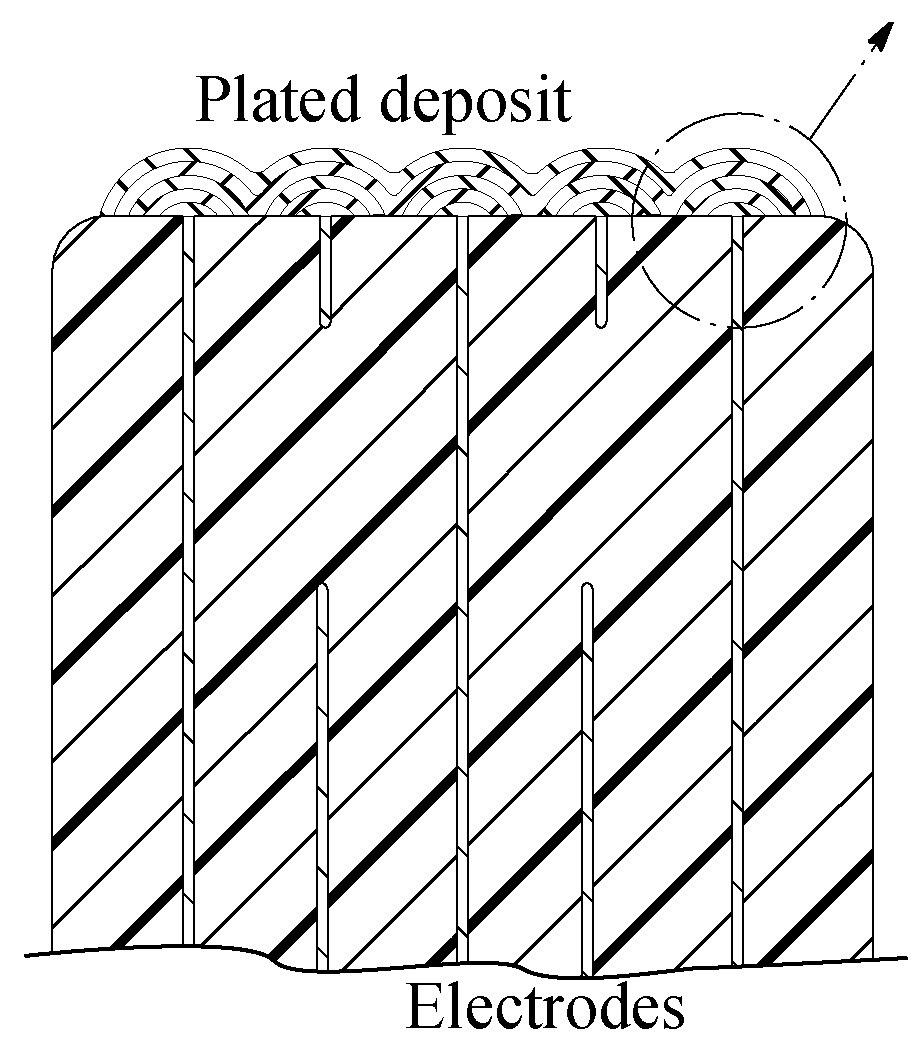
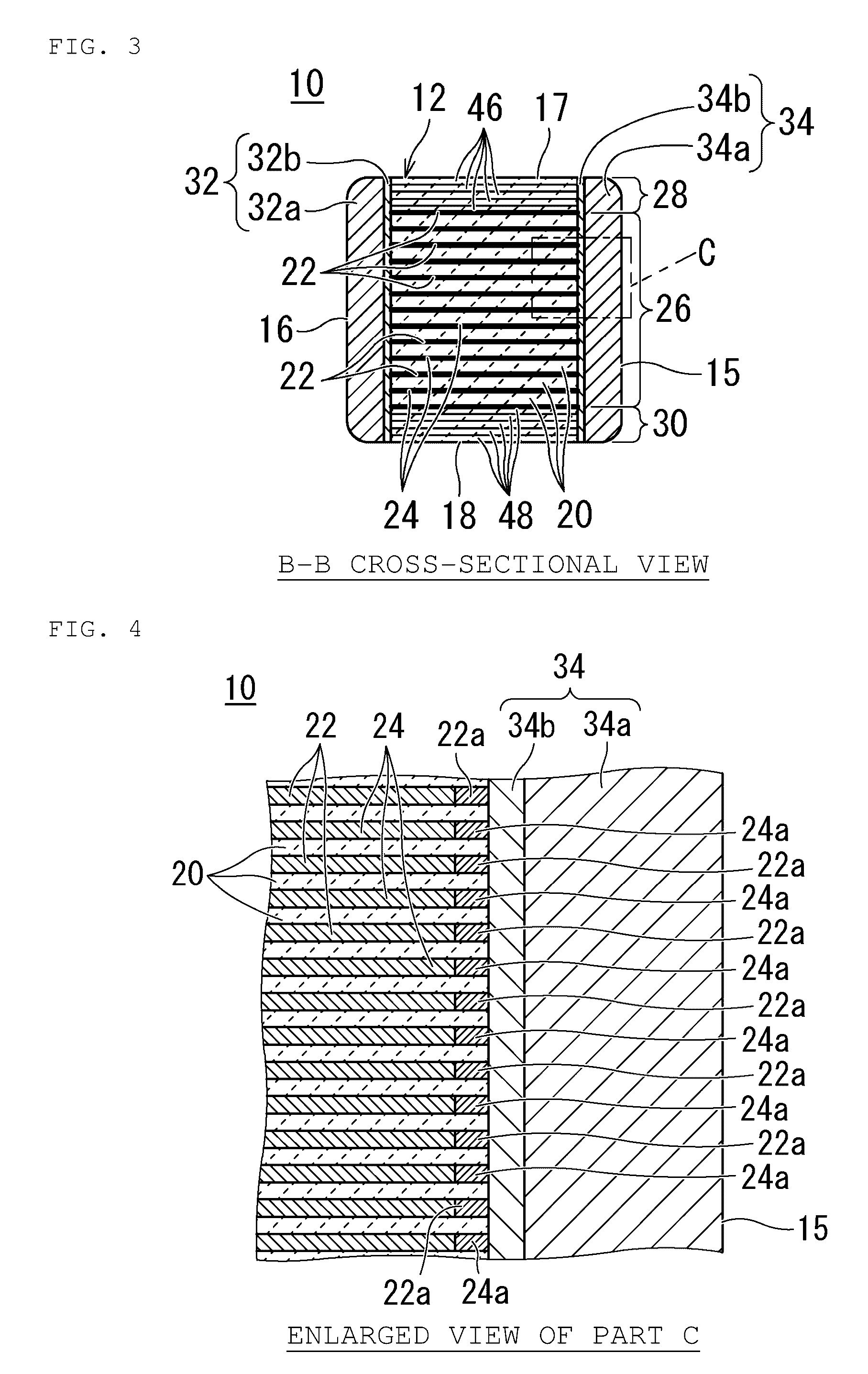
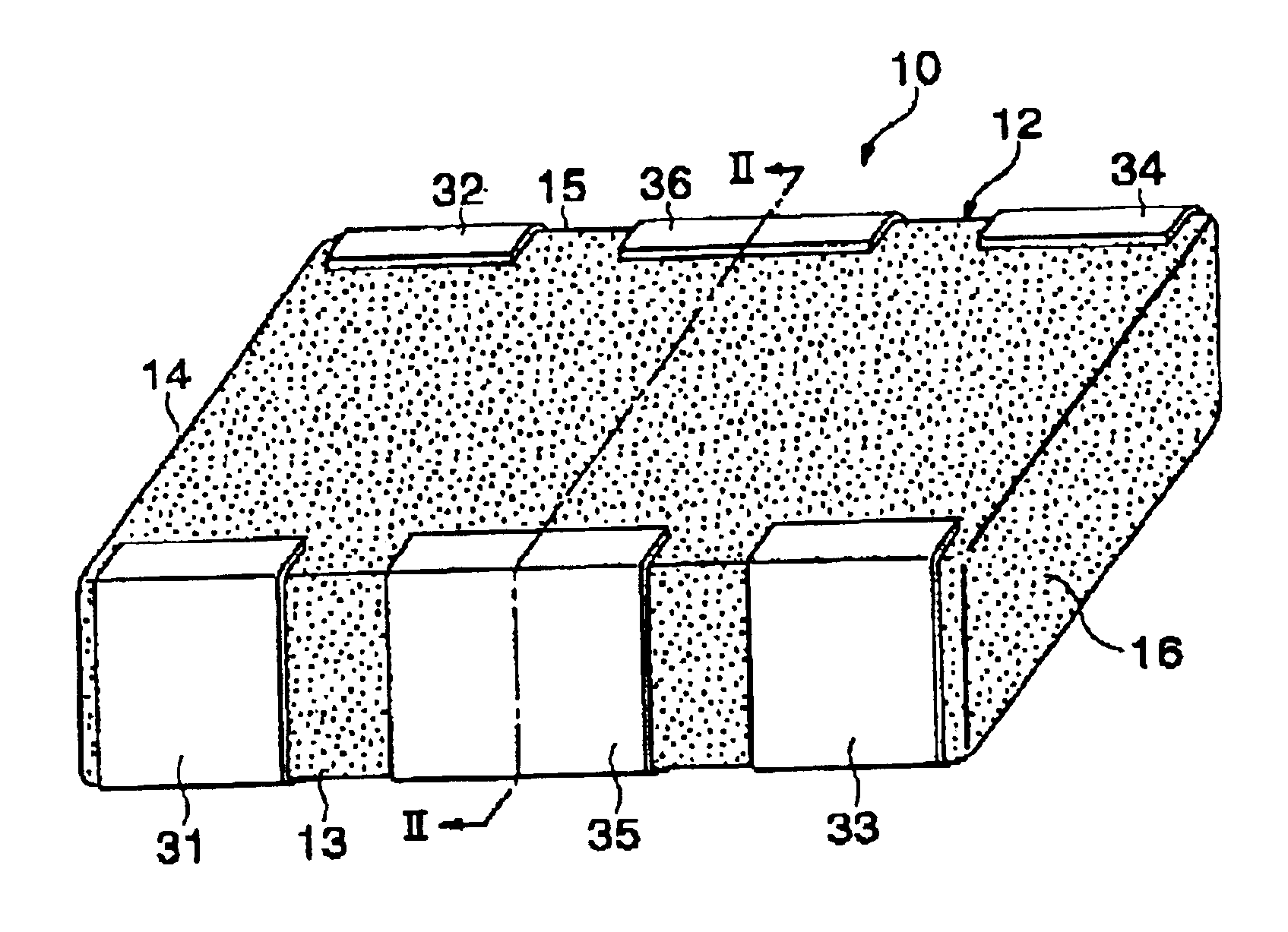
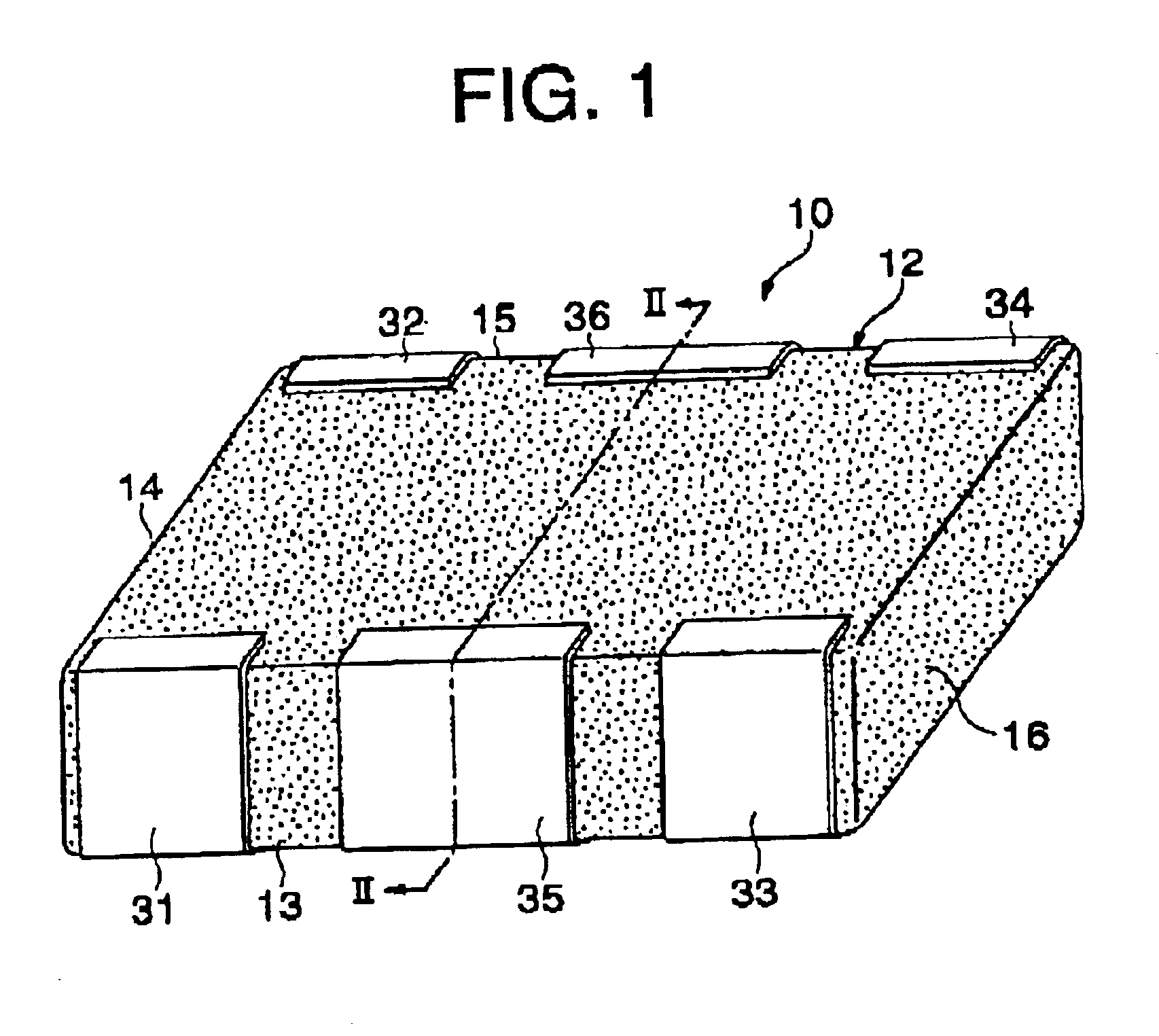
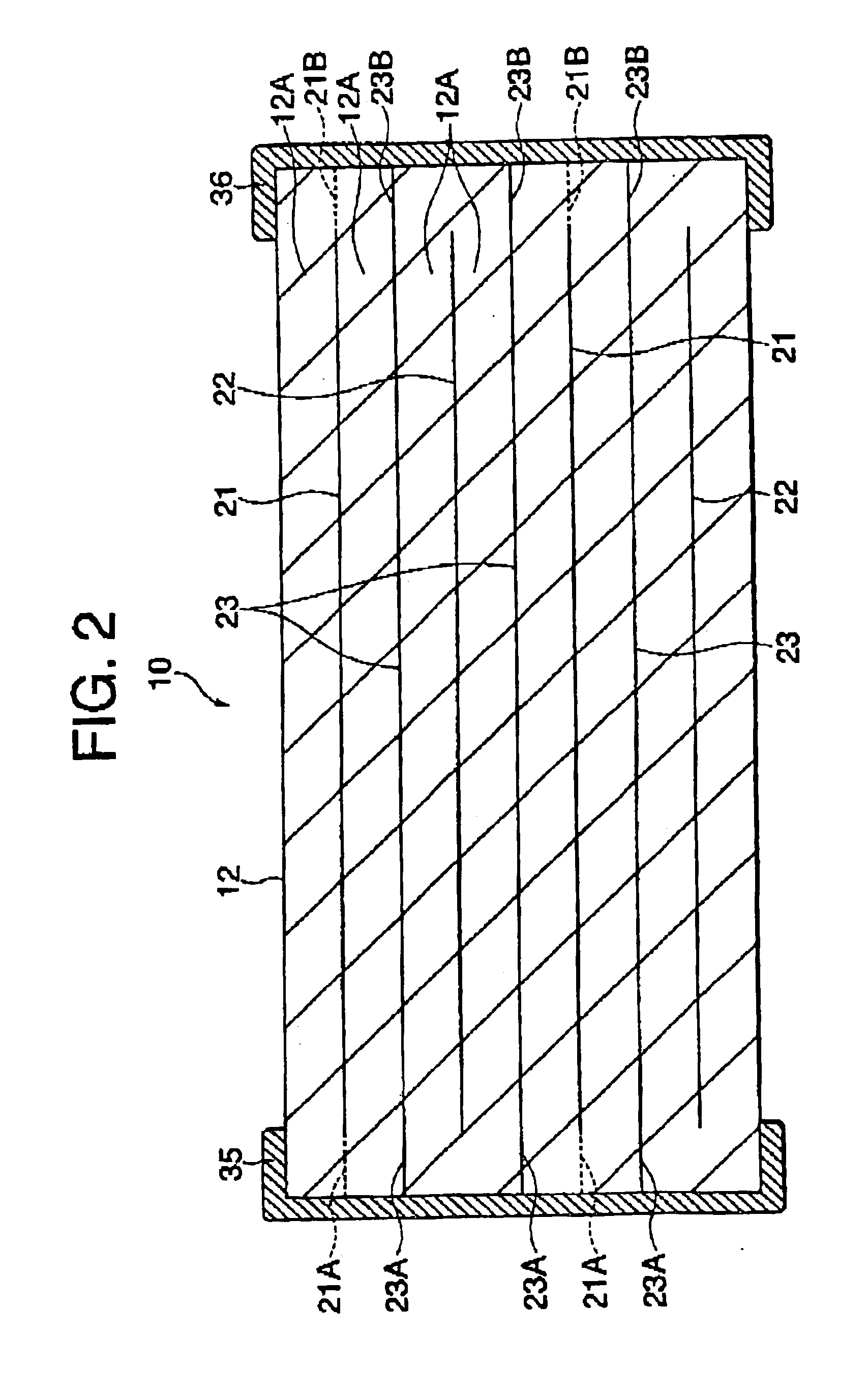
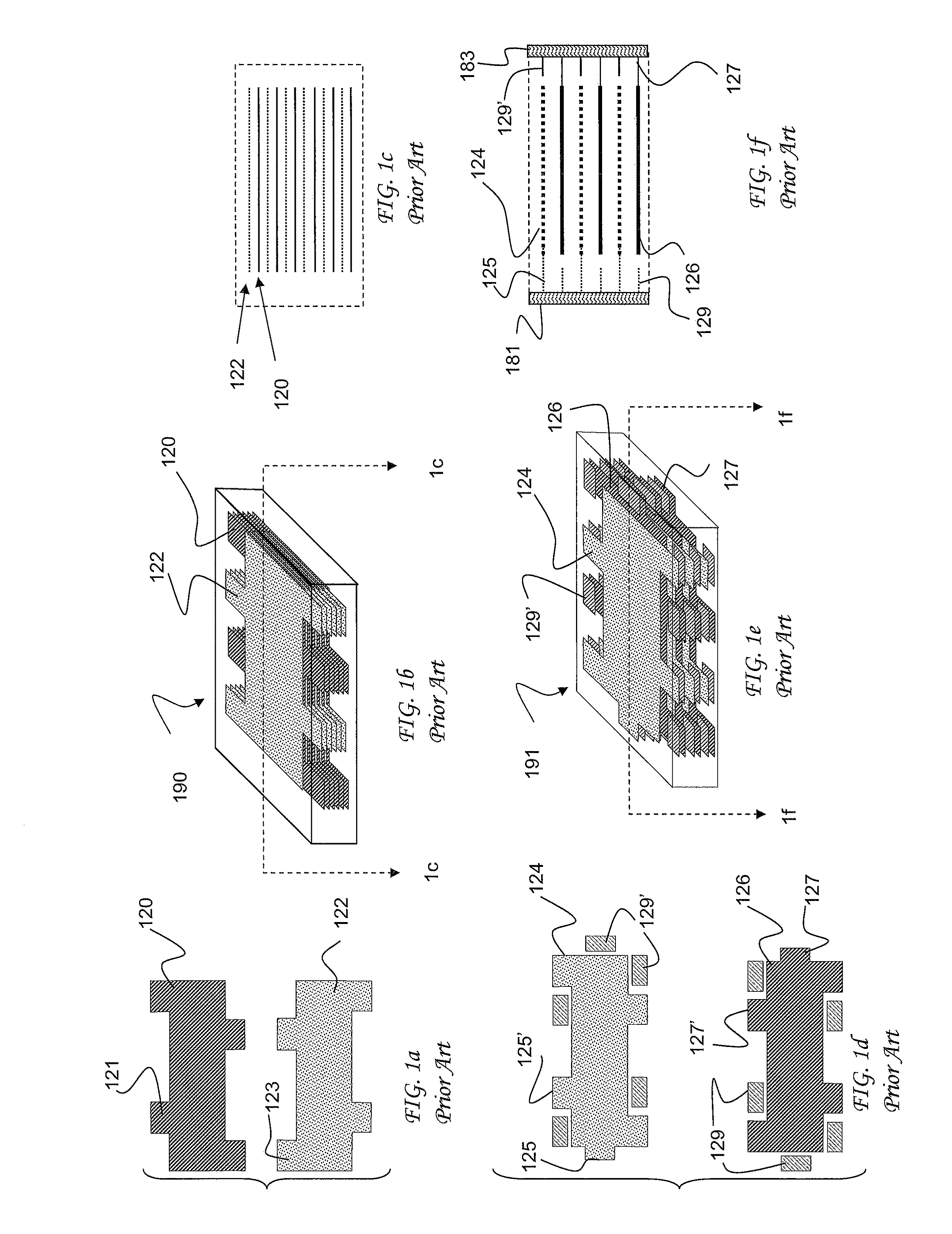
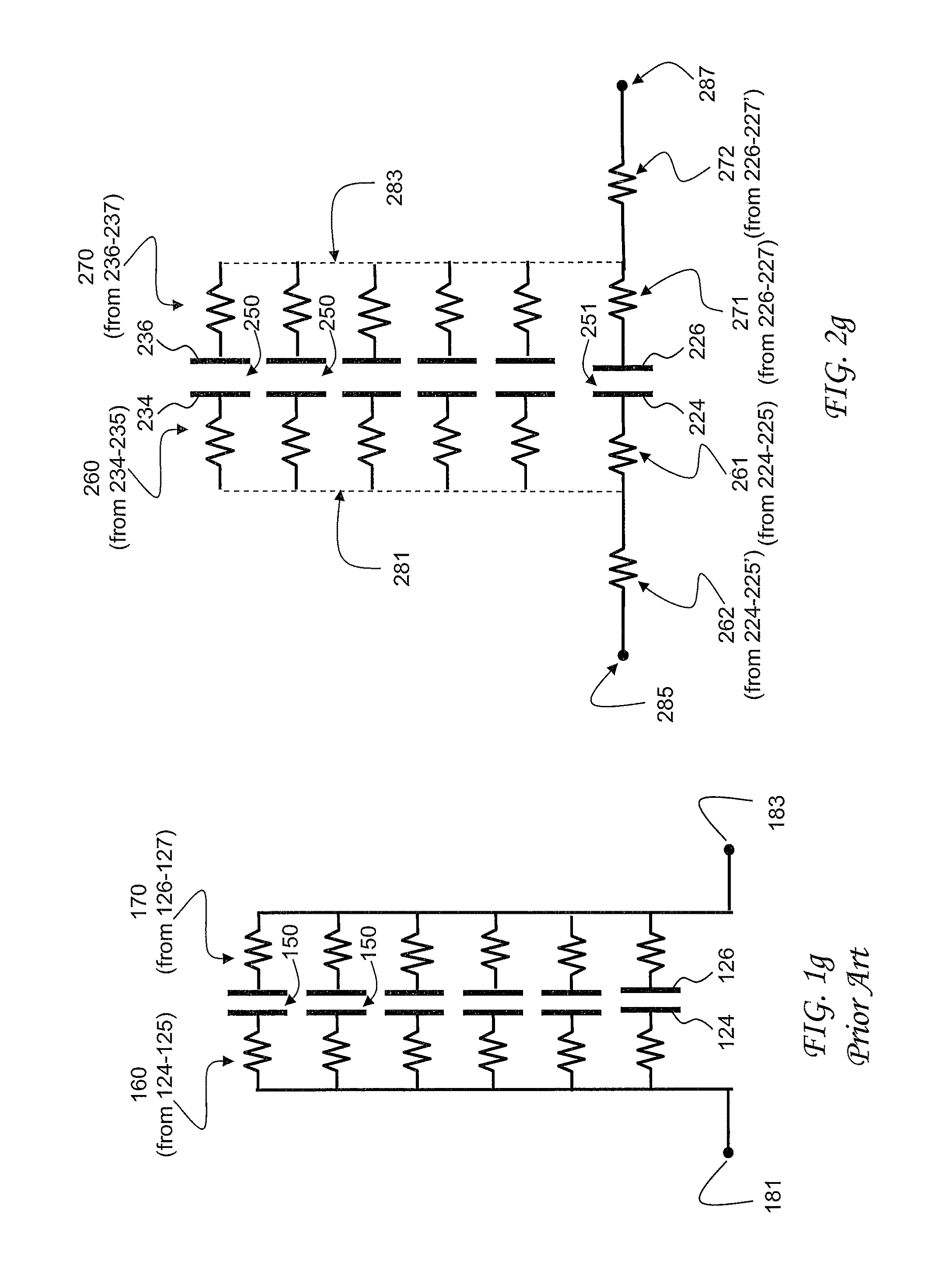
Plated terminations
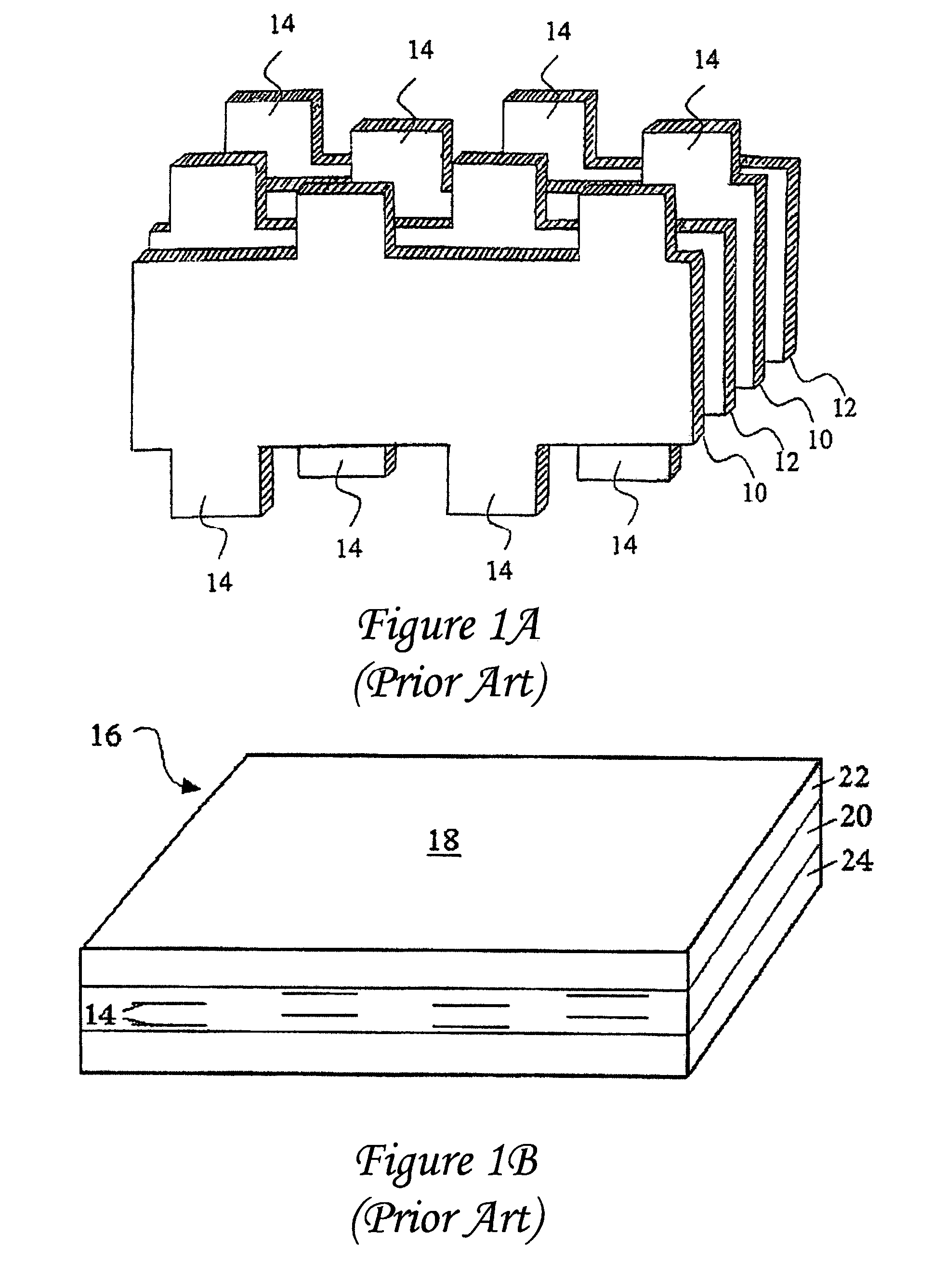
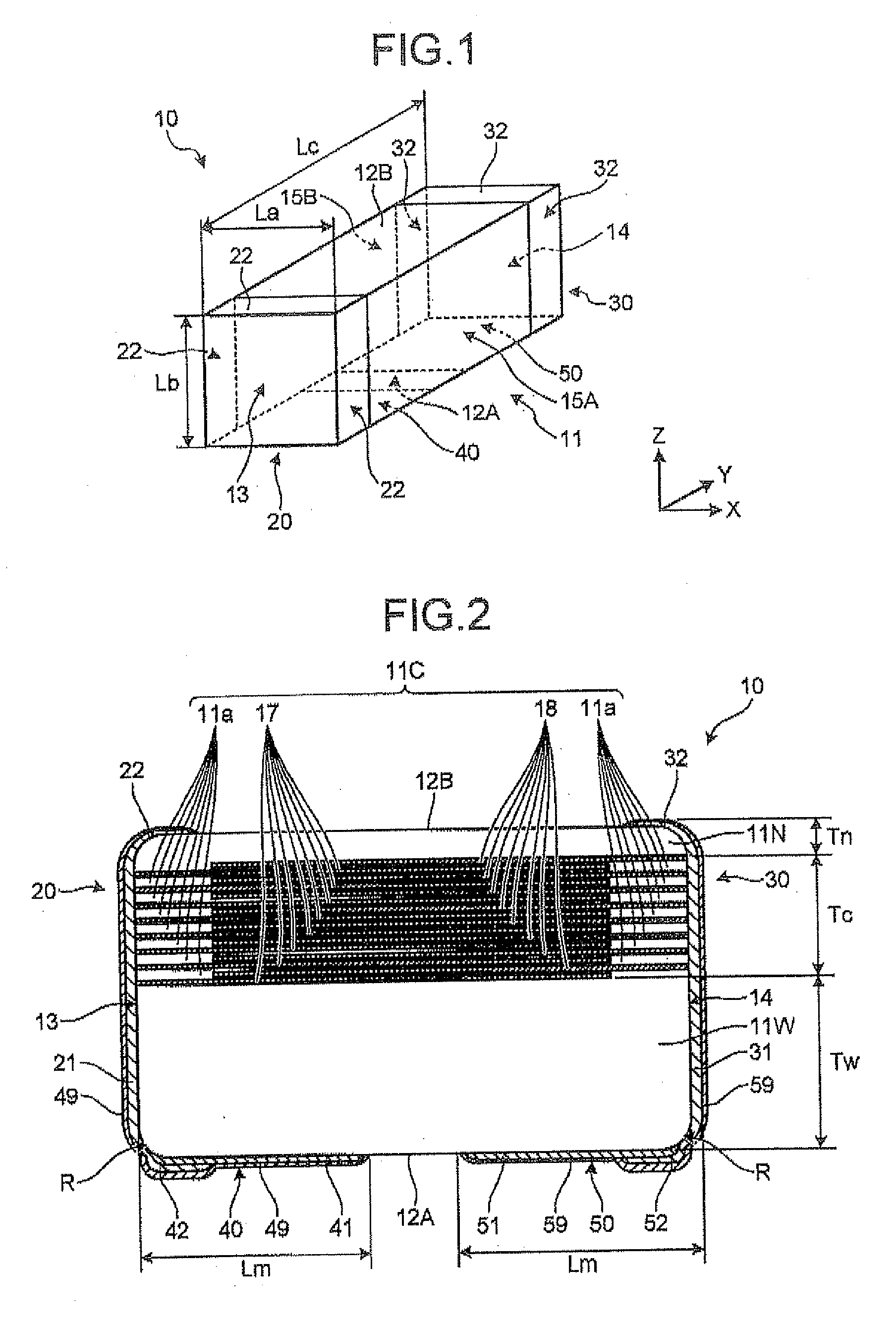
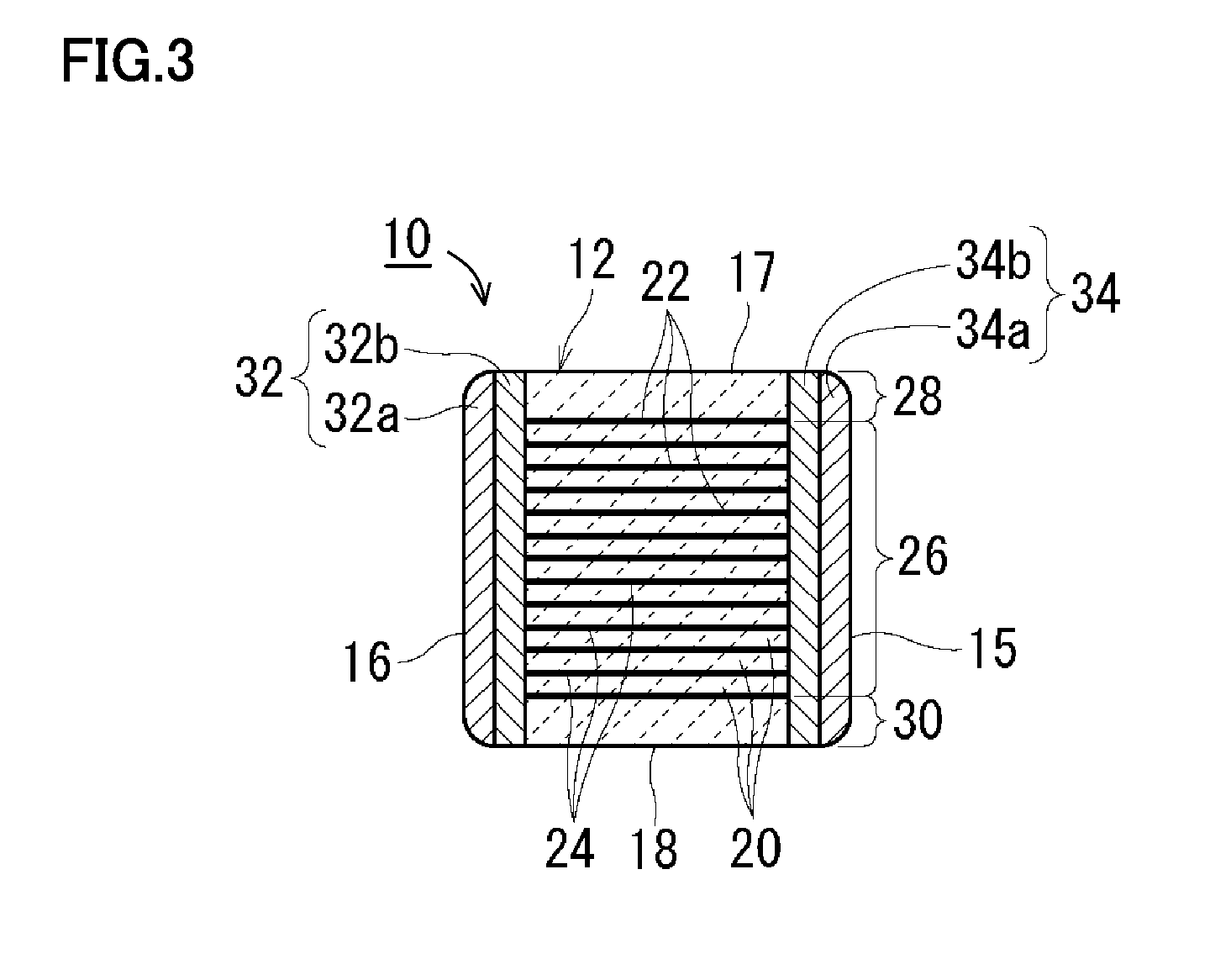
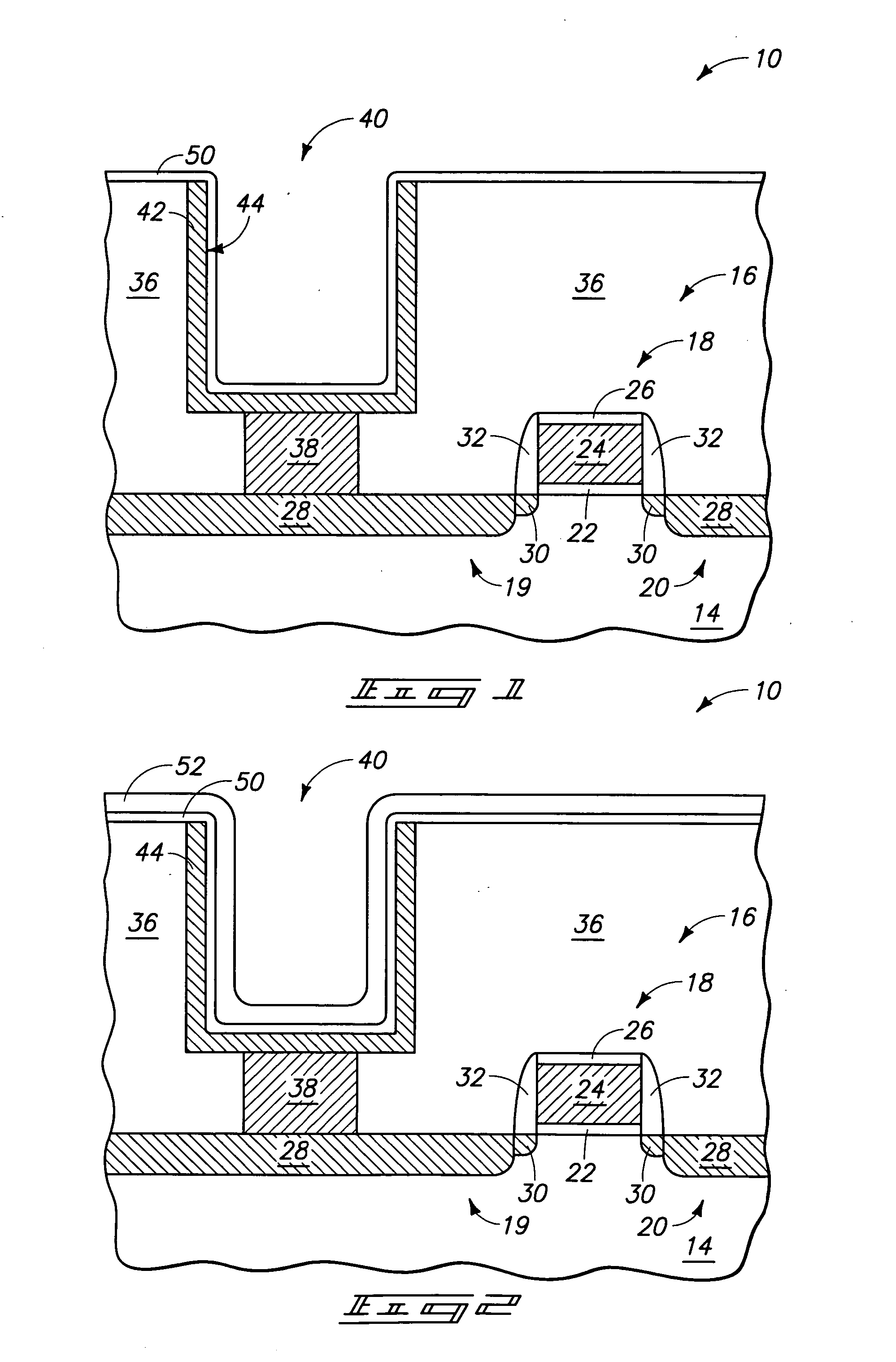
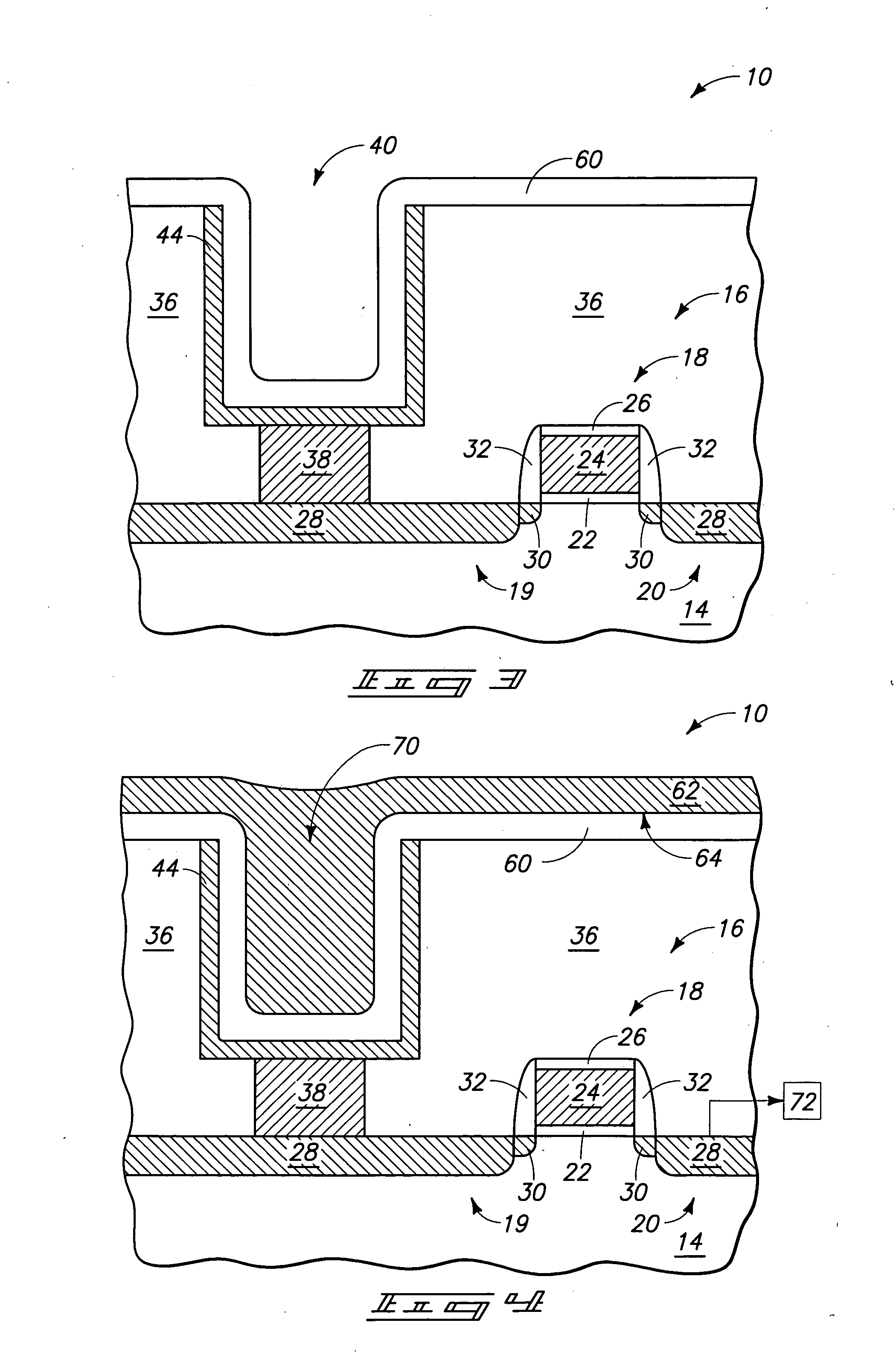
InactiveUS7177137B2Improved termination featureEliminate or greatly simplify thick-film stripesFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricHigh densityEngineering
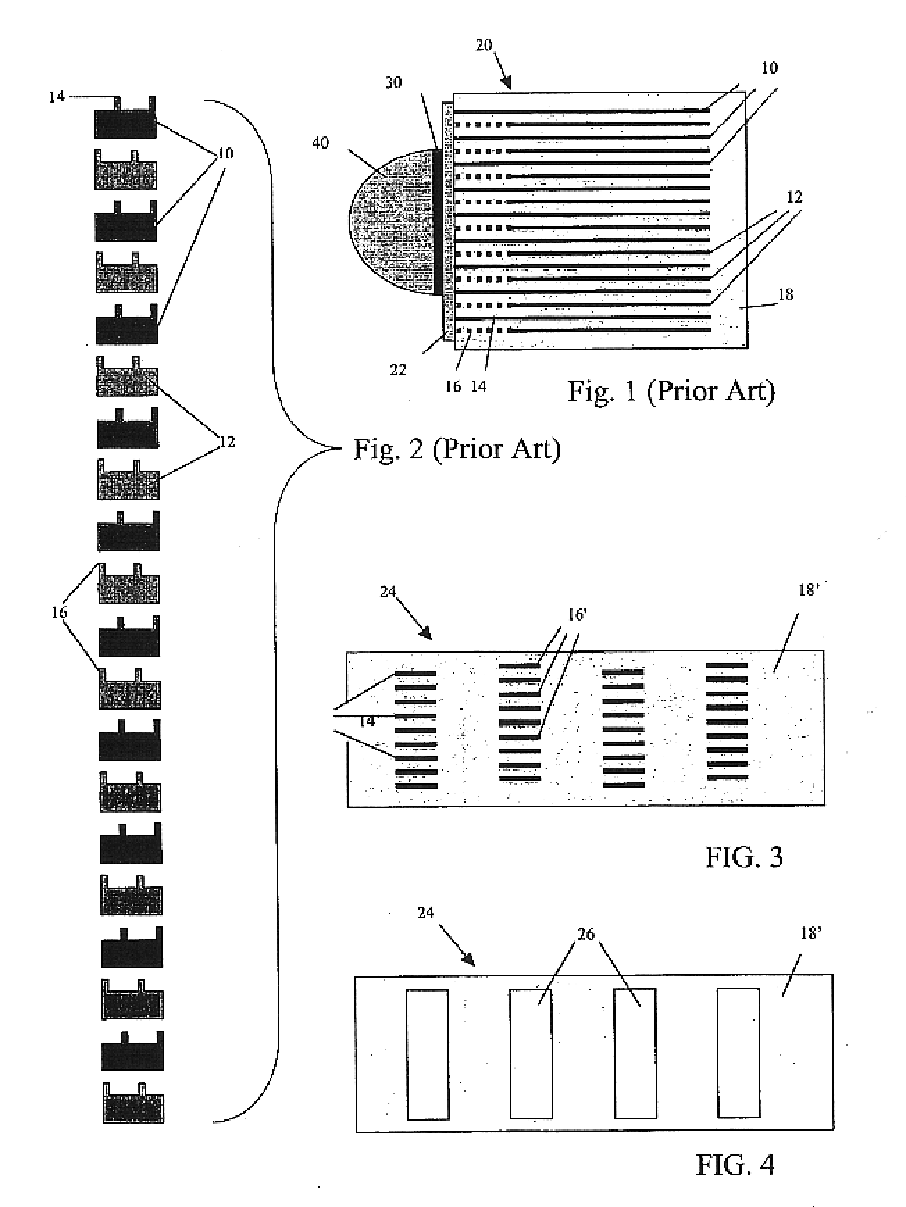
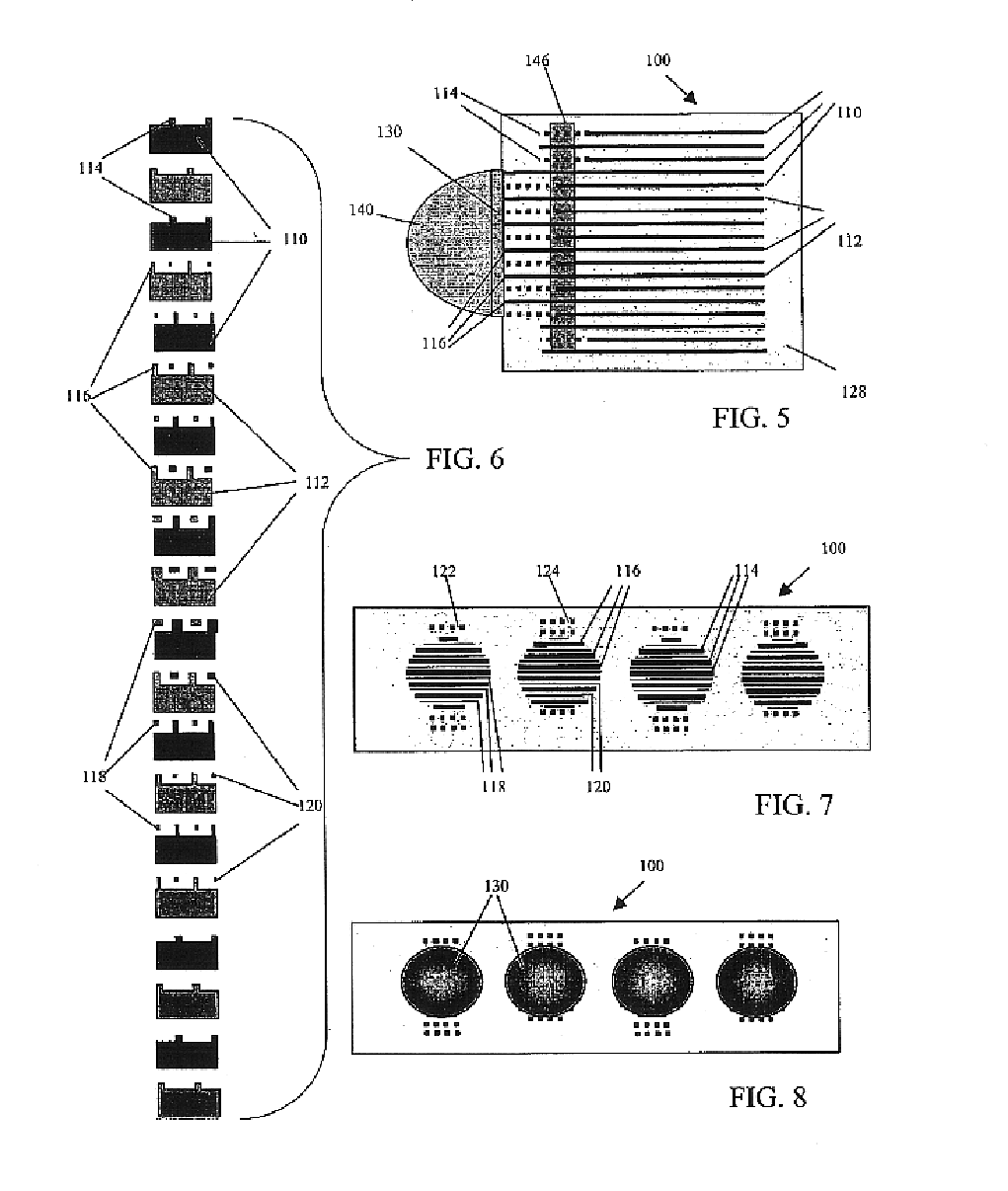
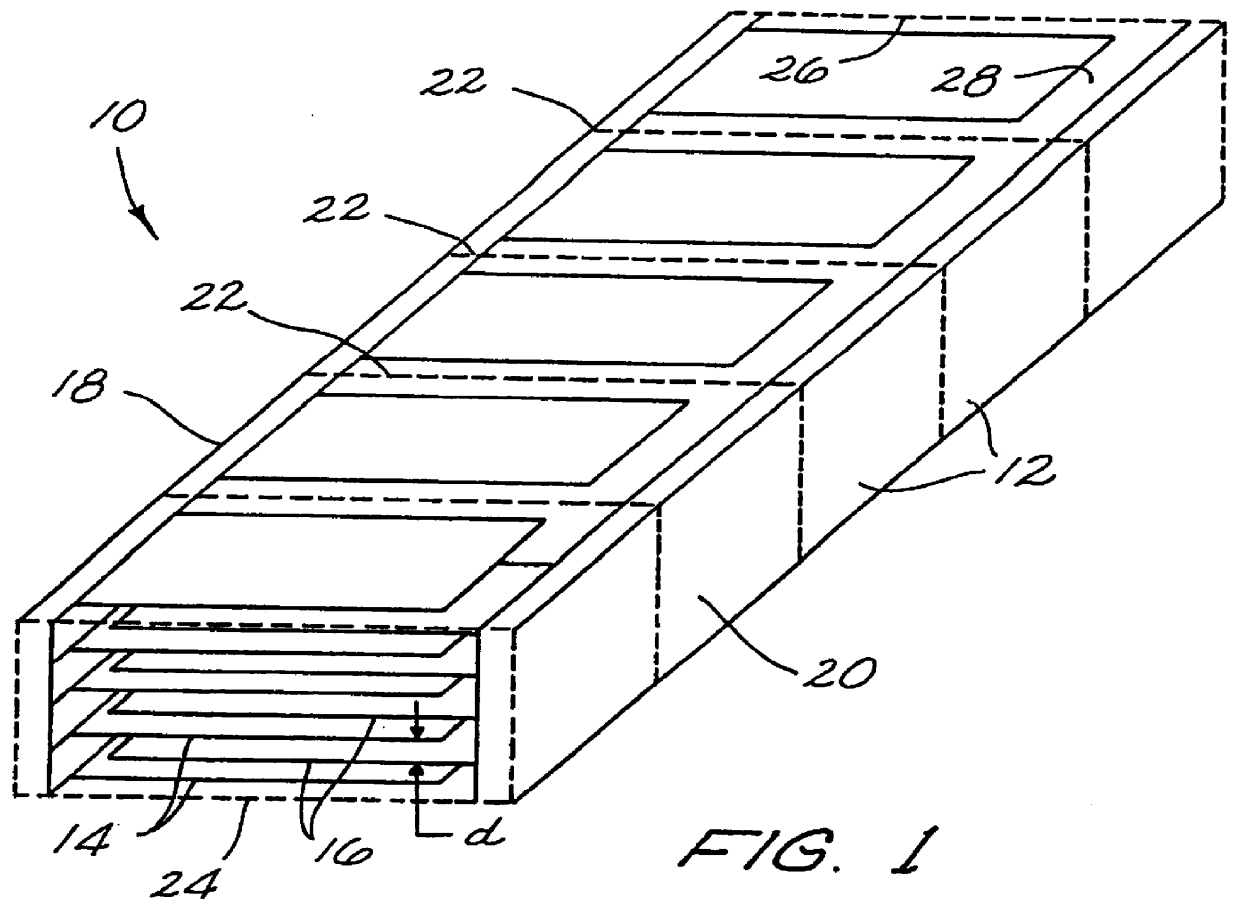
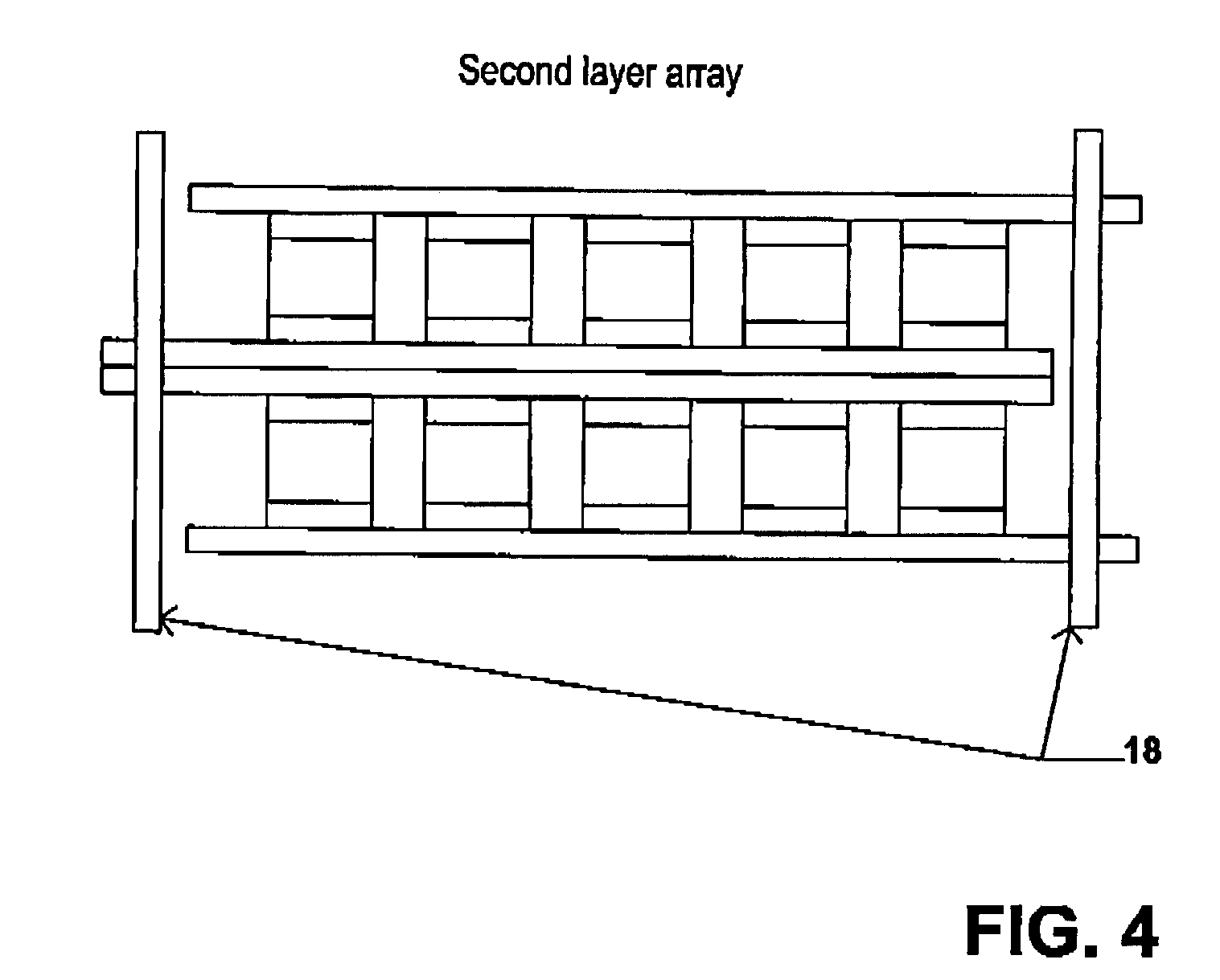
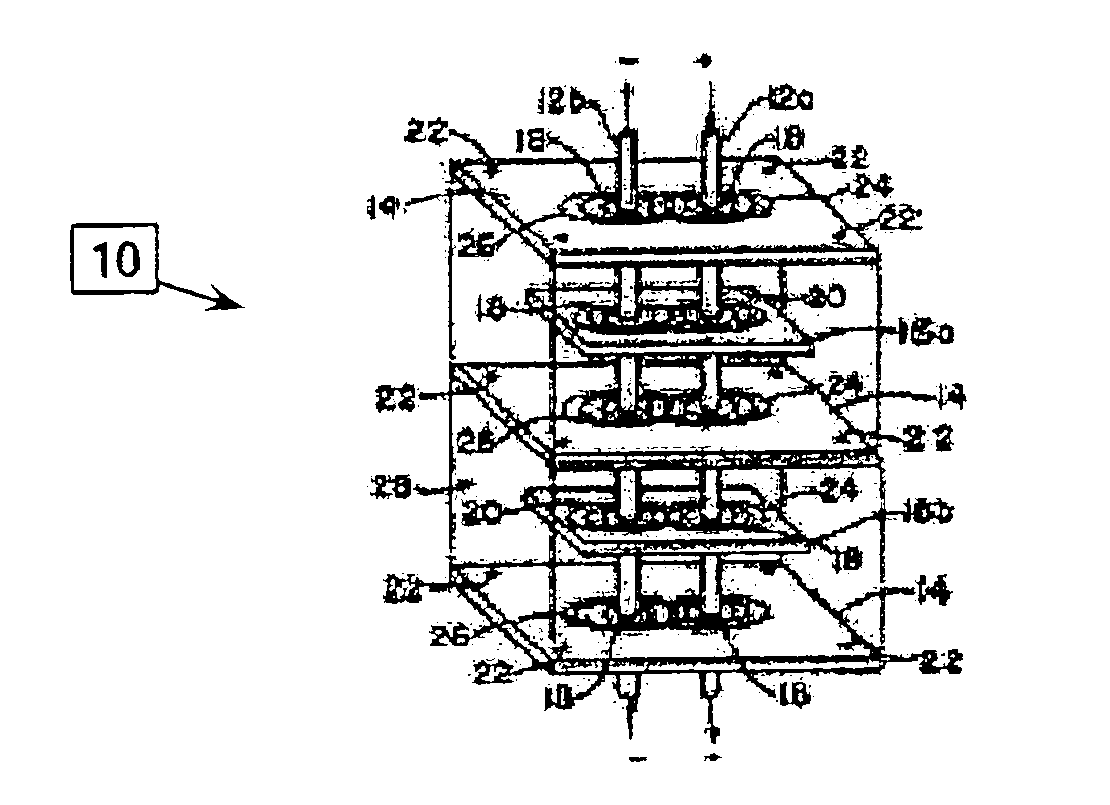
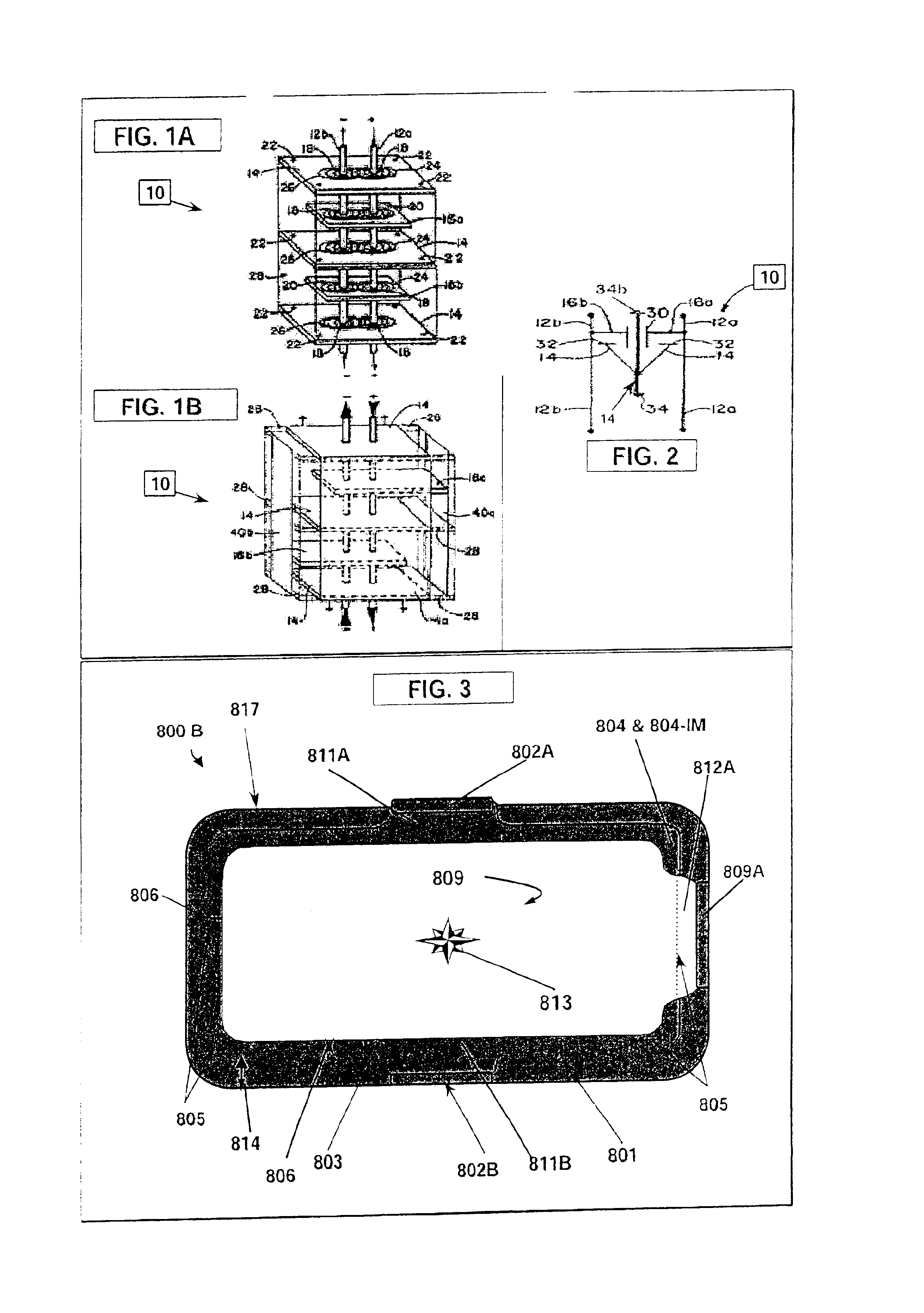
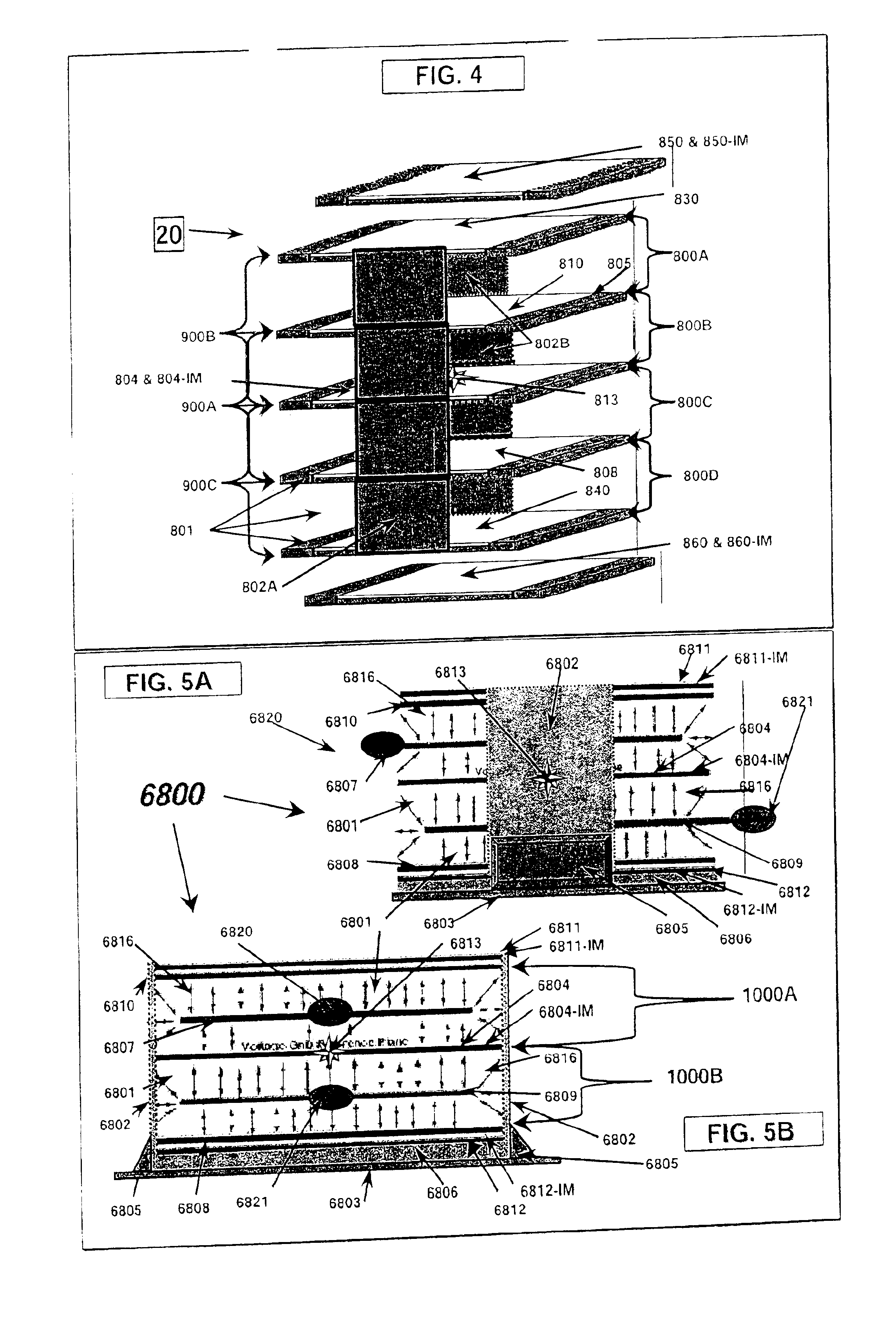
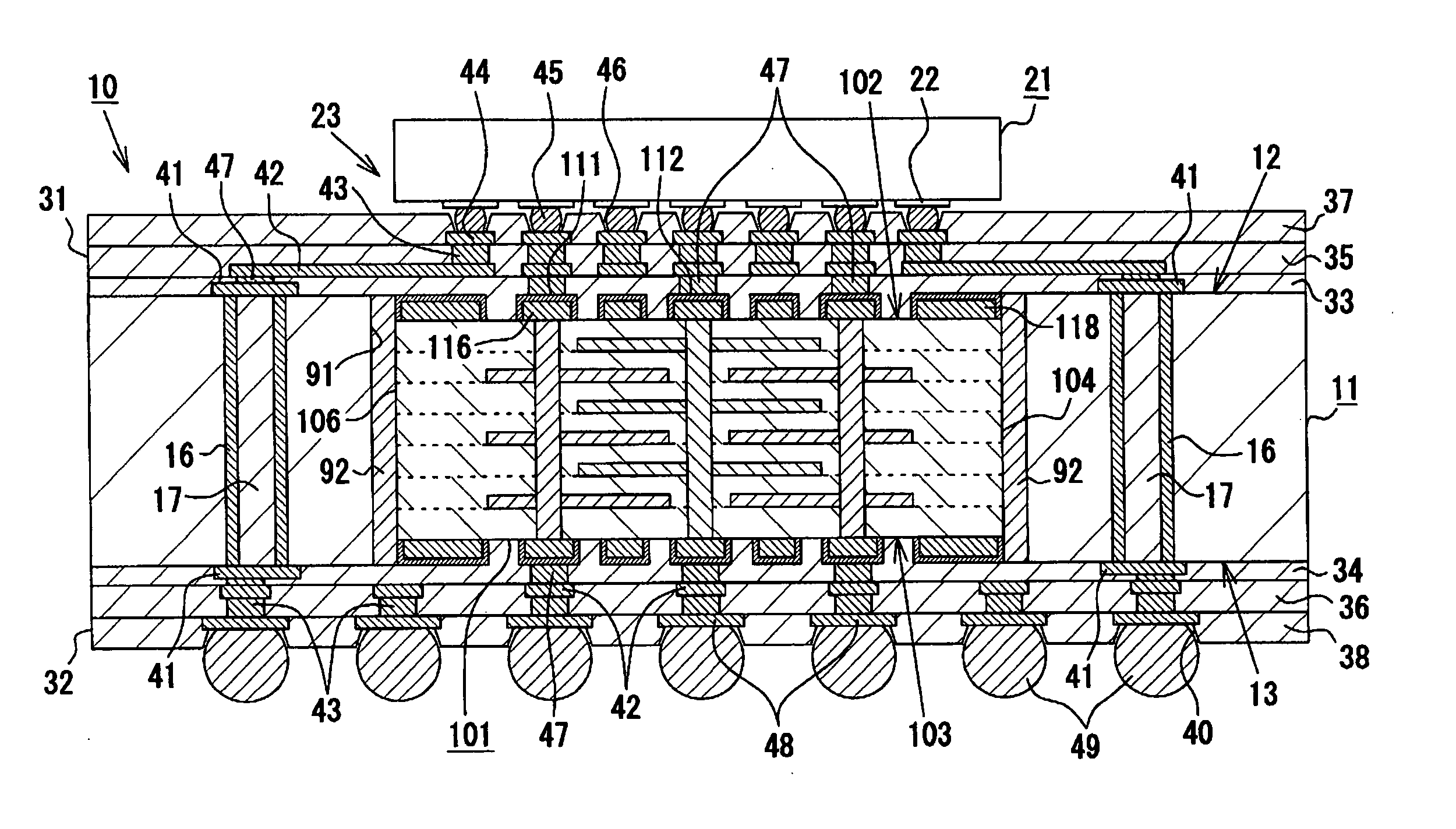
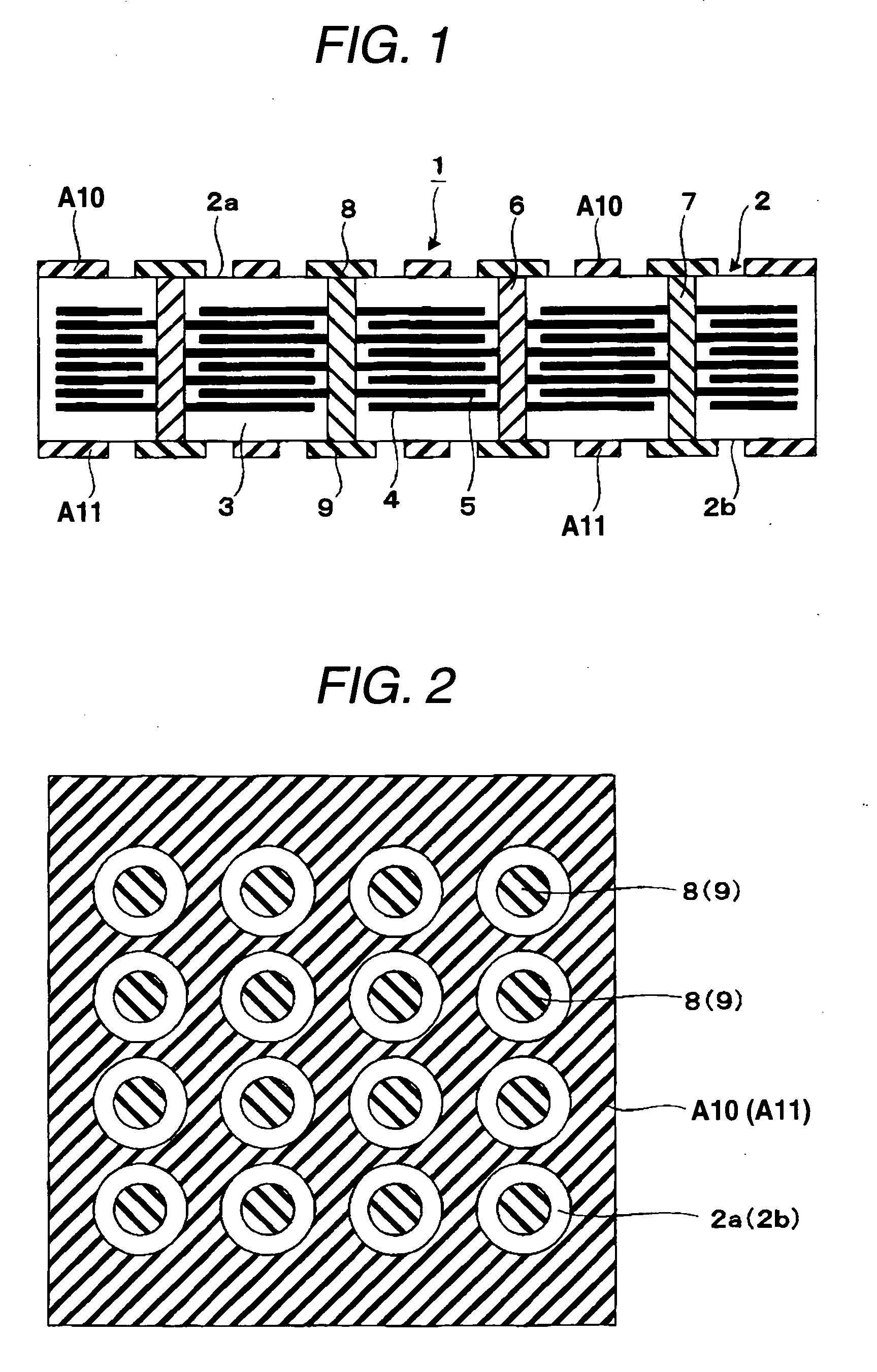
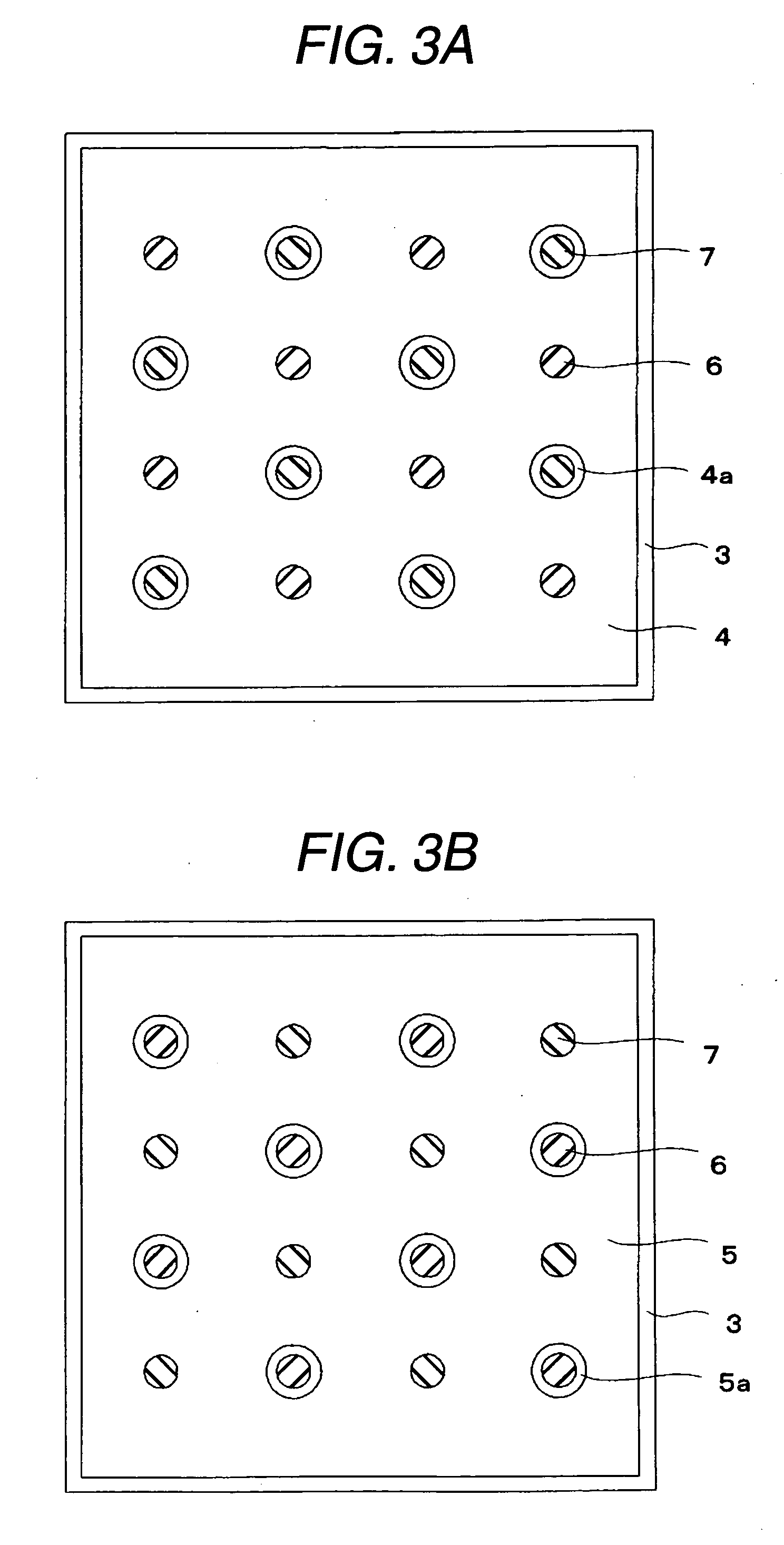
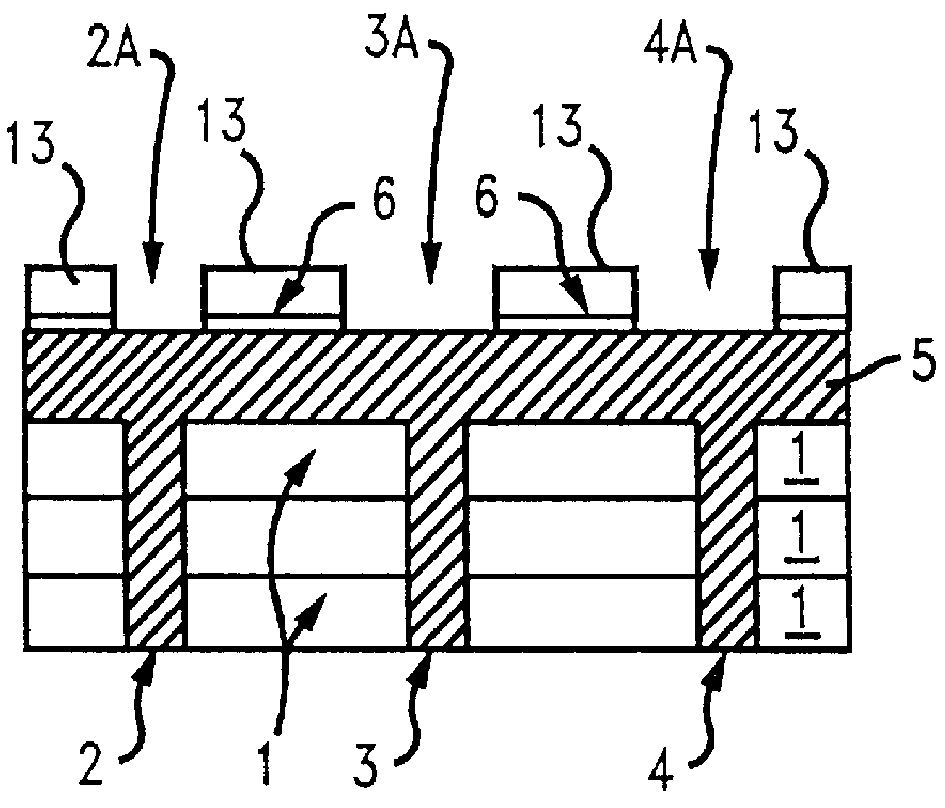
A multilayer electronic component includes a plurality of dielectric layers interleaved with a plurality of internal electrode elements and a plurality of internal anchor tabs. Portions of the internal electrode elements and anchor tabs are exposed along the periphery of the electronic component in one or more aligned columns. Each exposed portion is within a predetermined distance from other exposed portions in a given column such that bridged terminations may be formed by depositing one or more plated termination materials over selected of the respectively aligned columns. Internal anchor tabs may be provided and exposed in prearranged relationships with other exposed conductive portions to help nucleate metallized plating material along the periphery of a device. External anchor tabs or lands may be provided to form terminations that extend to top and / or bottom surfaces of the device. Selected of the conductive elements may be formed by a finite volume percentage of ceramic material for enhanced durability, and external lands may be thicker than internal conductive elements and / or may also be embedded in top and / or bottom component surfaces. A variety of potential internal electrode configurations are possible including ones configured for orientation-insensitive component mounting and for high density peripheral termination interdigitated capacitors.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
System and method of plating ball grid array and isolation features for electronic components
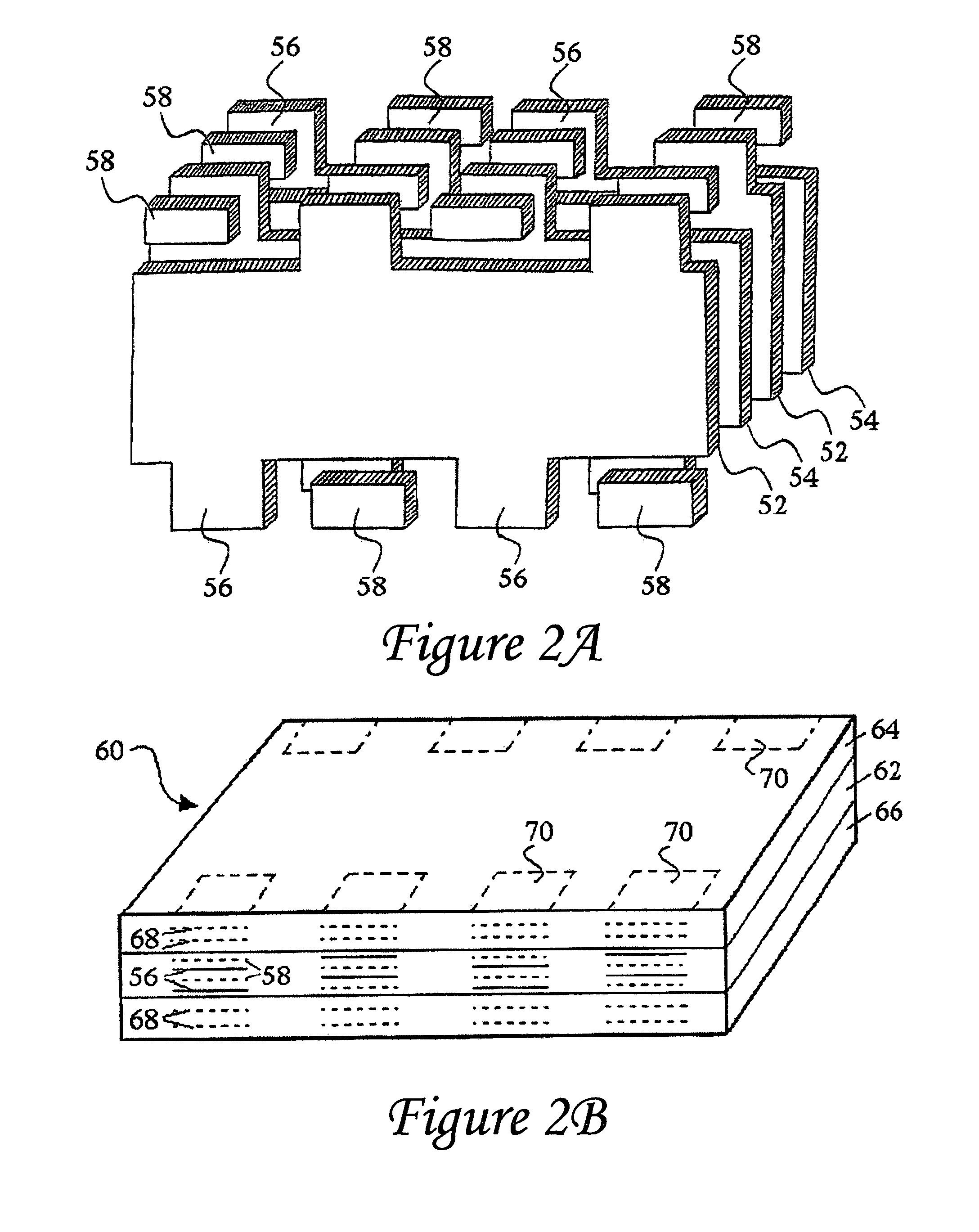
InactiveUS7463474B2Improved termination featureEliminate or greatly simplify thick-film stripesFixed capacitor dielectricStacked capacitorsEngineeringElectronic component
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
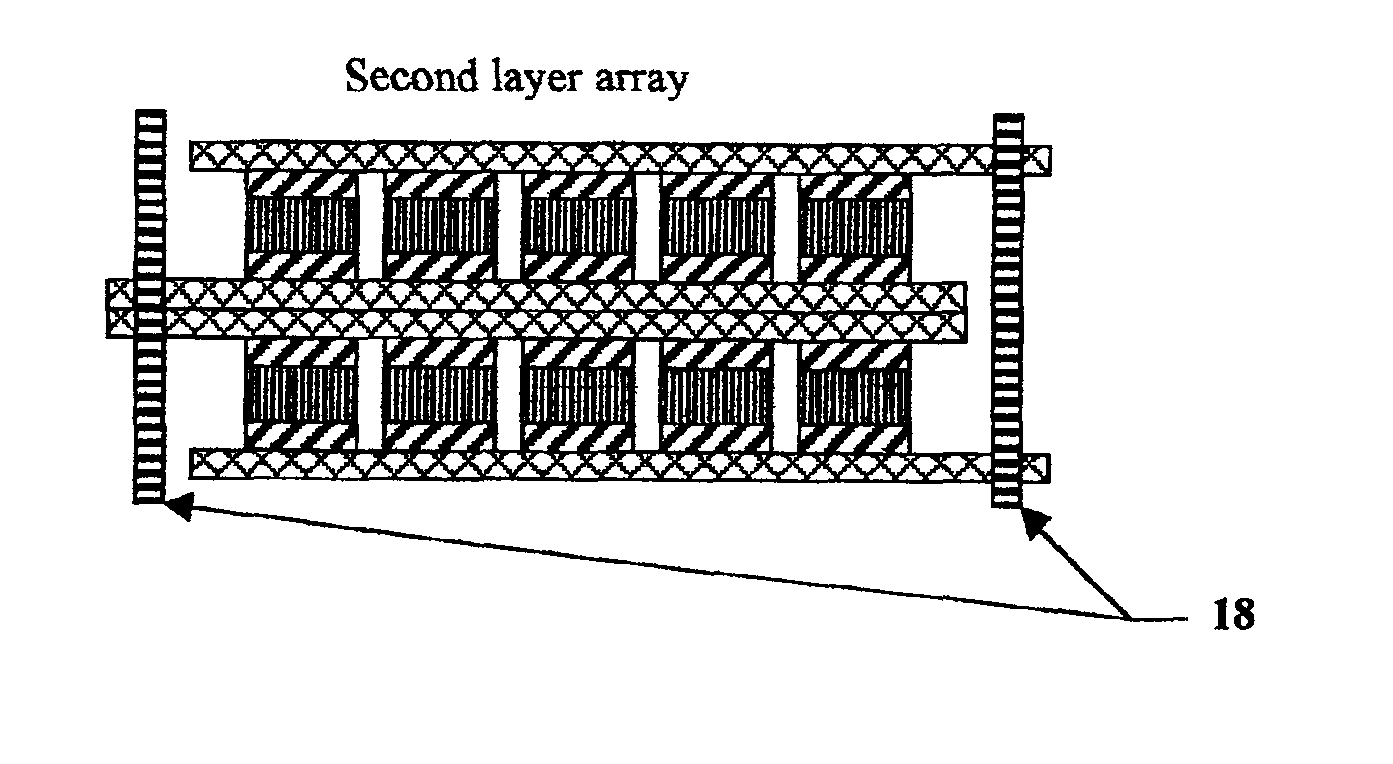
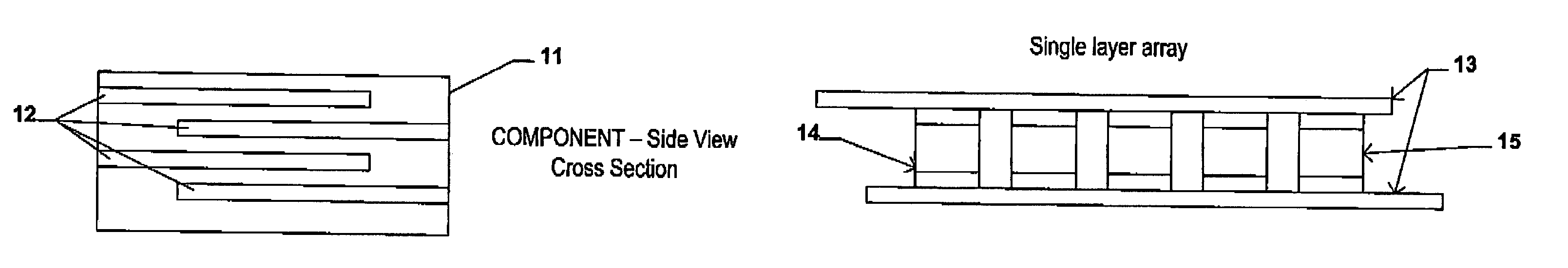
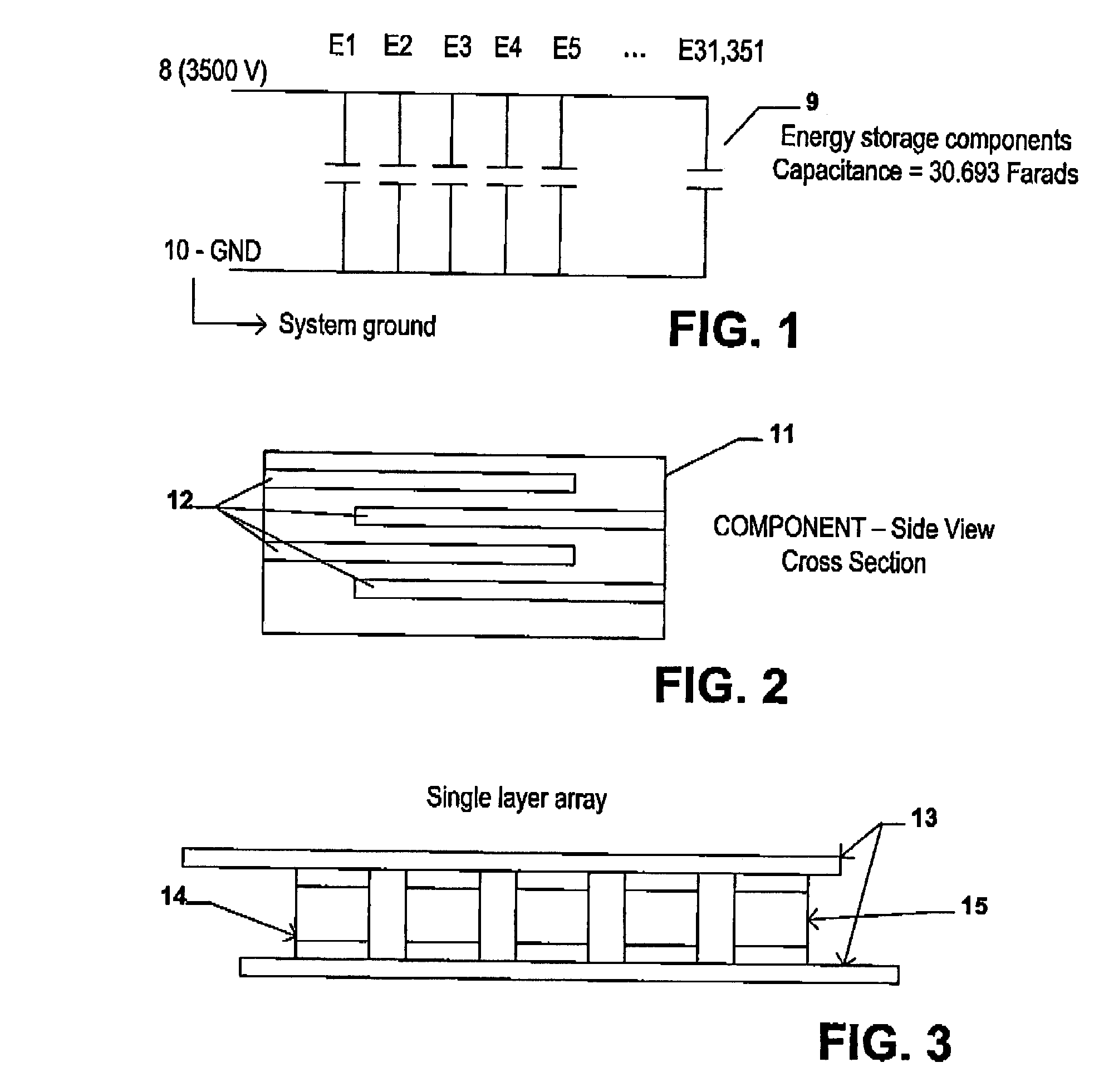
Electrical-energy-storage unit (EESU) utilizing ceramic and integrated-circuit technologies for replacement of electrochemical batteries
InactiveUS7033406B2Reduce sinteringLowering hot-isostatic-pressing temperatureElectrical storage systemFixed capacitor electrodesBarium titanatePermittivity
An electrical-energy-storage unit (EESU) has as a basis material a high-permittivity composition-modified barium titanate ceramic powder. This powder is double coated with the first coating being aluminum oxide and the second coating calcium magnesium aluminosilicate glass. The components of the EESU are manufactured with the use of classical ceramic fabrication techniques which include screen printing alternating multilayers of nickel electrodes and high-permittivitiy composition-modified barium titanate powder, sintering to a closed-pore porous body, followed by hot-isostatic pressing to a void-free body. The components are configured into a multilayer array with the use of a solder-bump technique as the enabling technology so as to provide a parallel configuration of components that has the capability to store electrical energy in the range of 52 kW·h. The total weight of an EESU with this range of electrical energy storage is about 336 pounds.
Owner:EESTOR
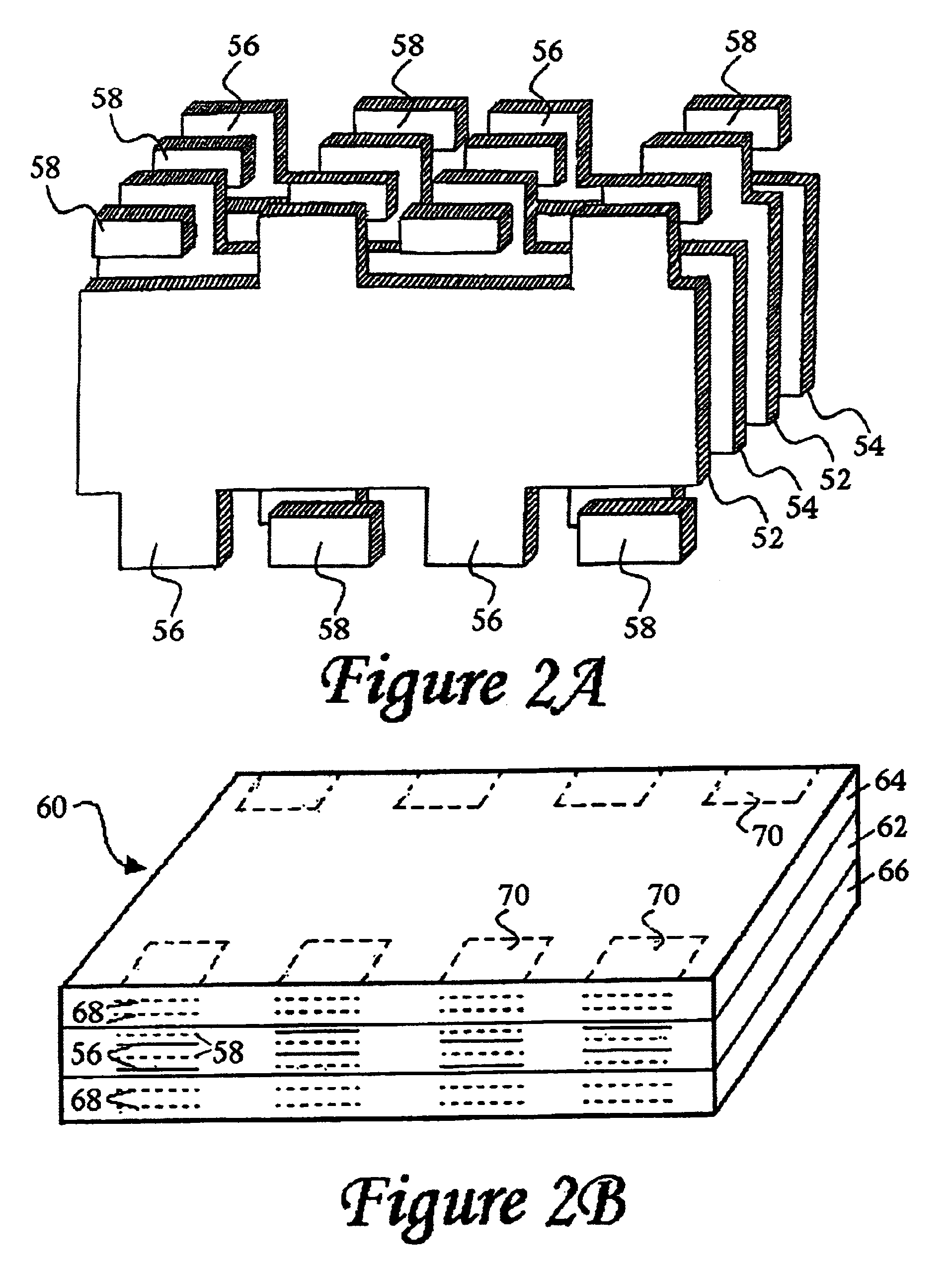
Plated terminations
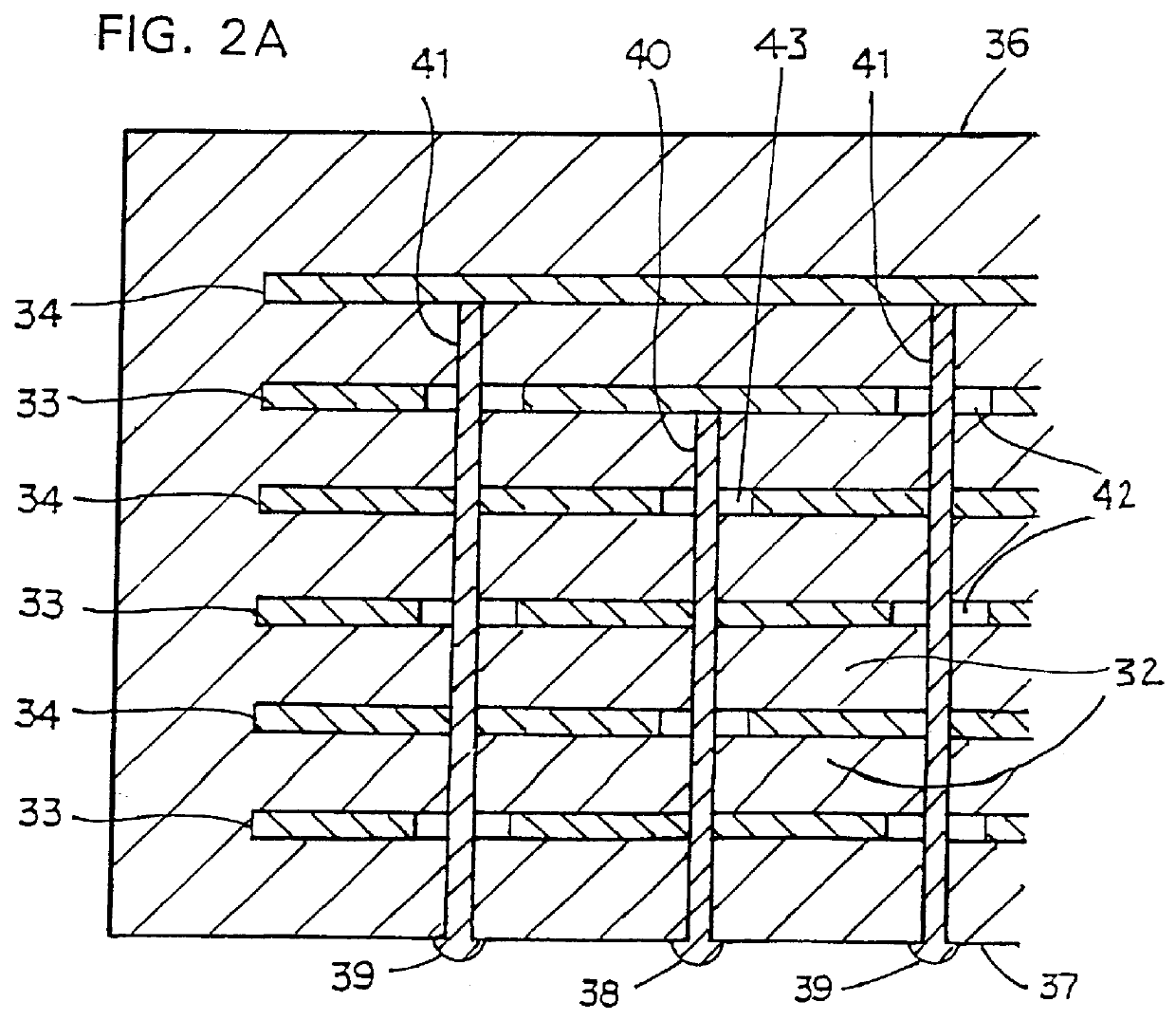
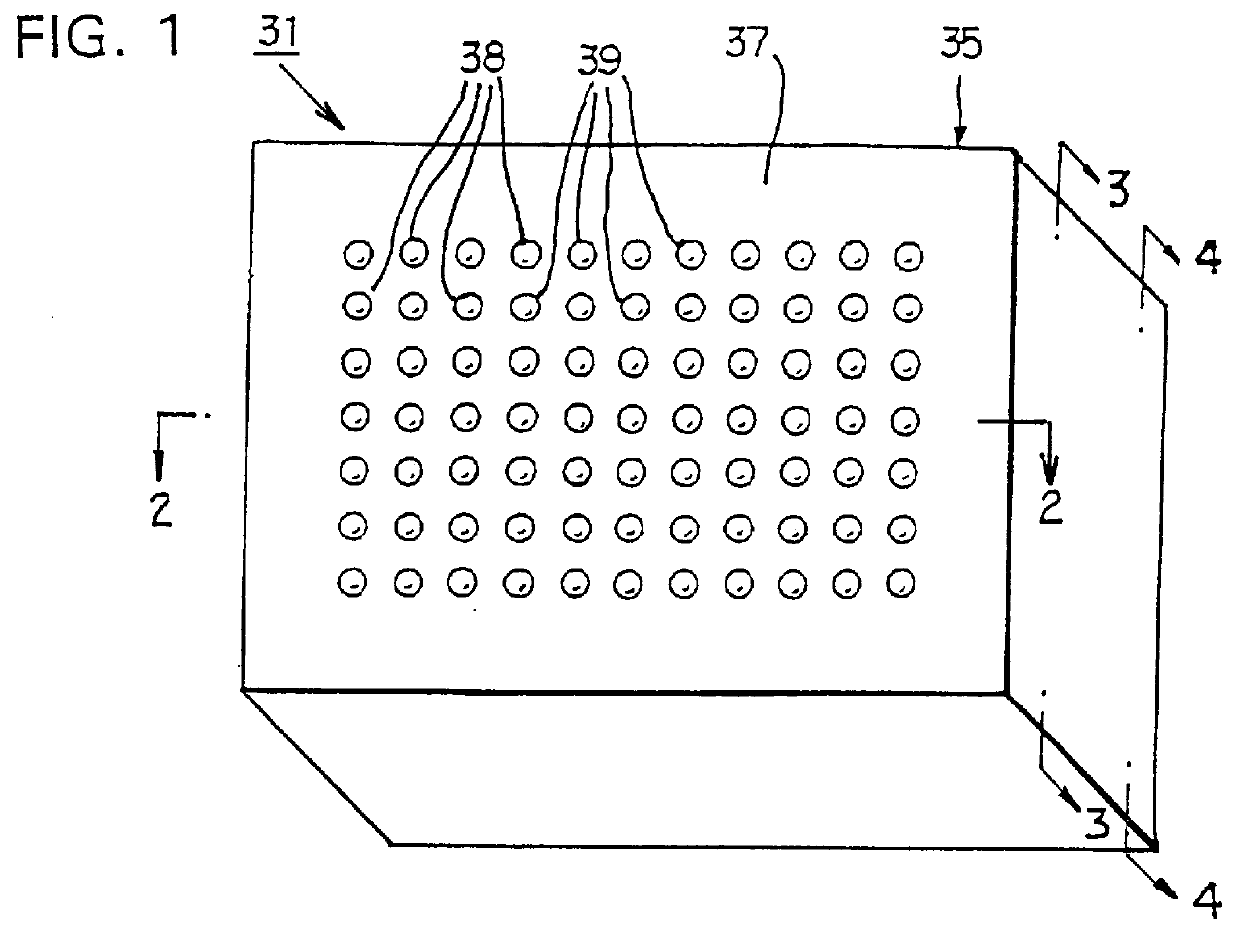
InactiveUS6960366B2Improved termination featureEliminate and greatly simplifyResistor terminals/electrodesFinal product manufactureTermination problemEngineering
Improved termination features for multilayer electronic components are disclosed. Monolithic components are provided with plated terminations whereby the need for typical thick-film termination stripes is eliminated or greatly simplified. Such termination technology eliminates many typical termination problems and enables a higher number of terminations with finer pitch, which may be especially beneficial on smaller electronic components. The subject plated terminations are guided and anchored by exposed internal electrode tabs and additional anchor tab portions which may optionally extend to the cover layers of a multilayer component. Such anchor tabs may be positioned internally or externally relative to a chip structure to nucleate additional metallized plating material. External anchor tabs positioned on one or both of top and bottom surfaces of a monolithic structure can facilitate the formation of selective wrap-around plated terminations. The disclosed technology may be utilized with a plurality of monolithic multilayer components, including interdigitated capacitors, multilayer capacitor arrays, and integrated passive components. A variety of different plating techniques and termination materials may be employed in the formation of the subject self-determining plated terminations.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
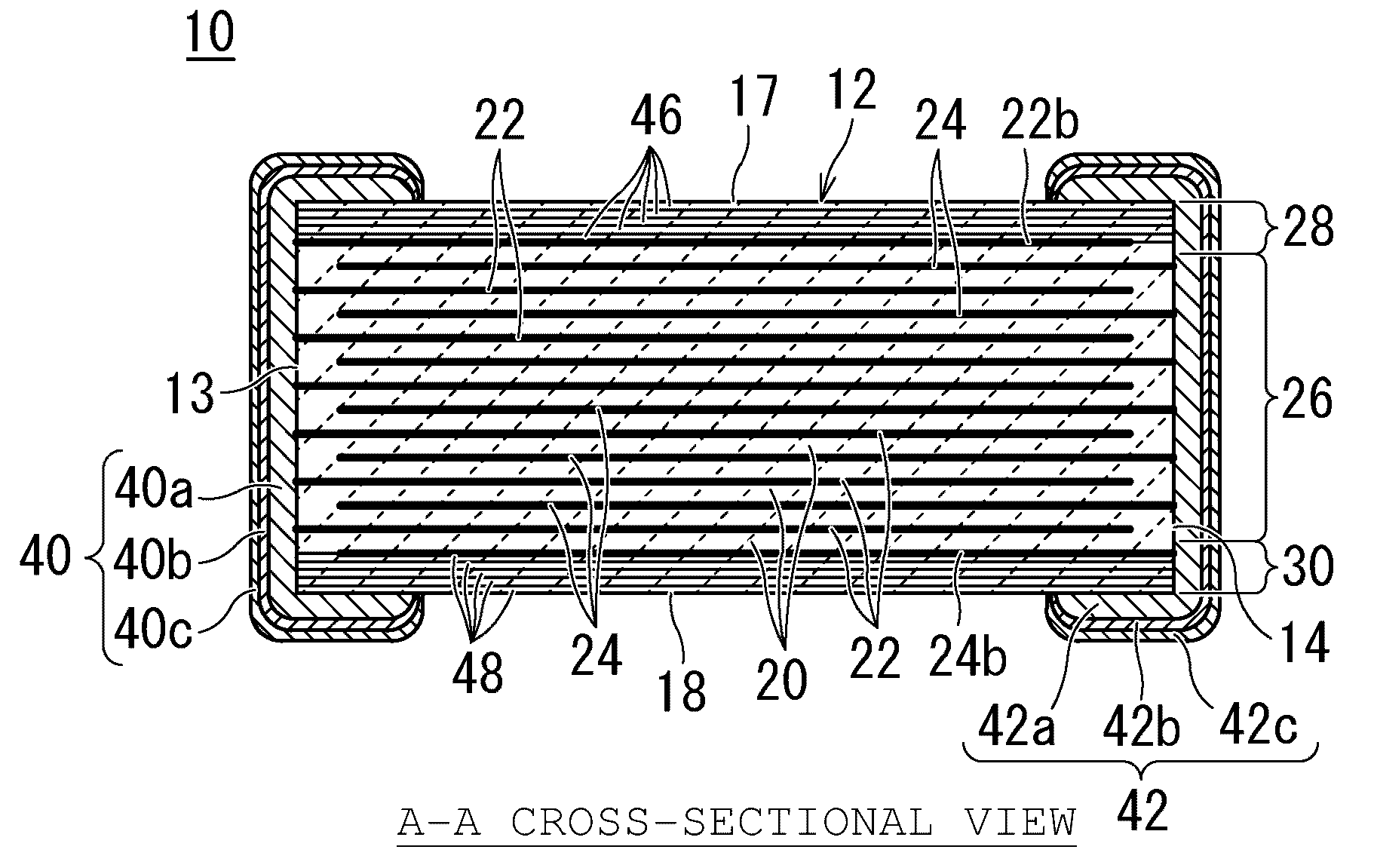
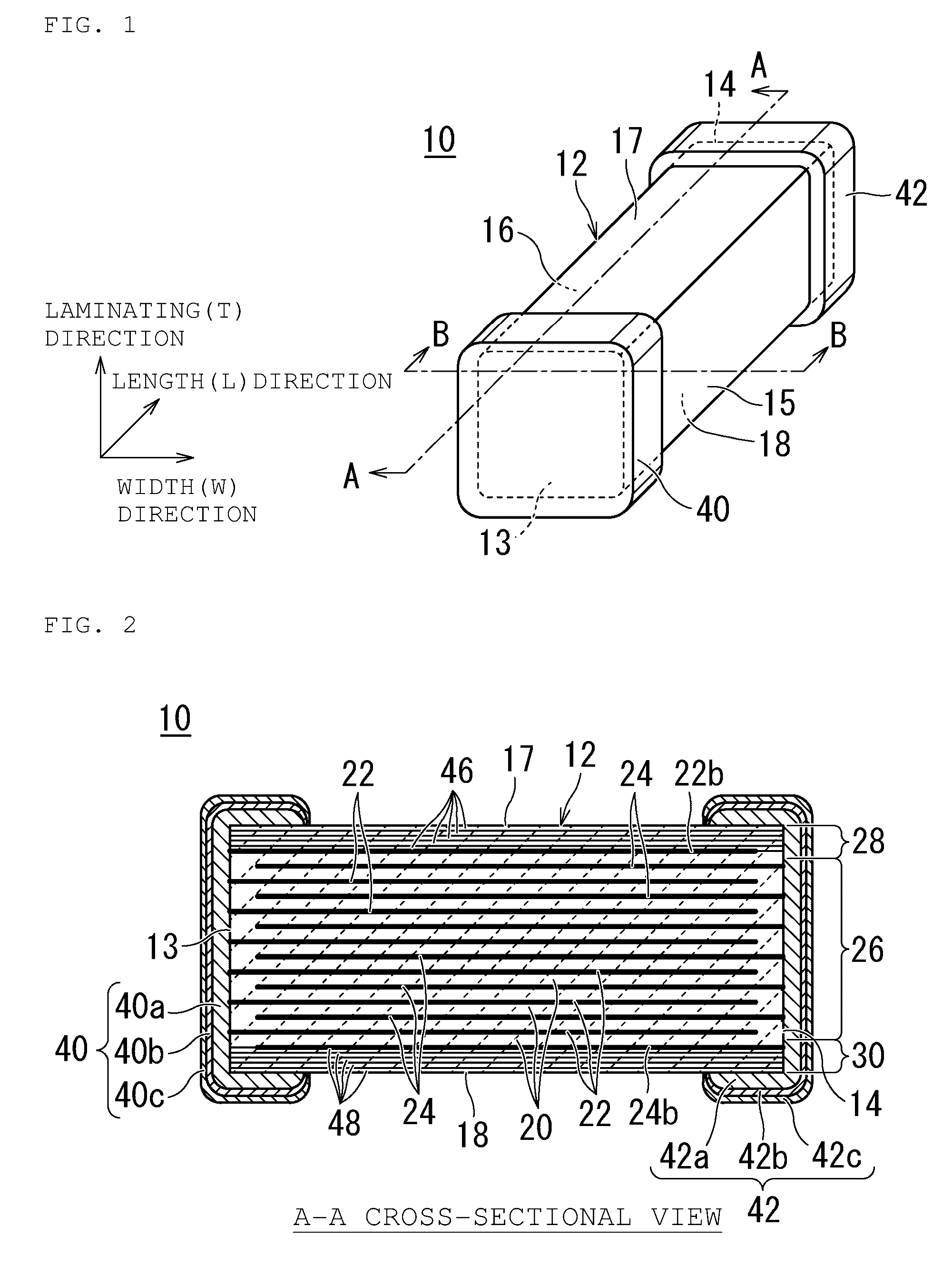
Multilayer capacitor and method for manufacturing the same
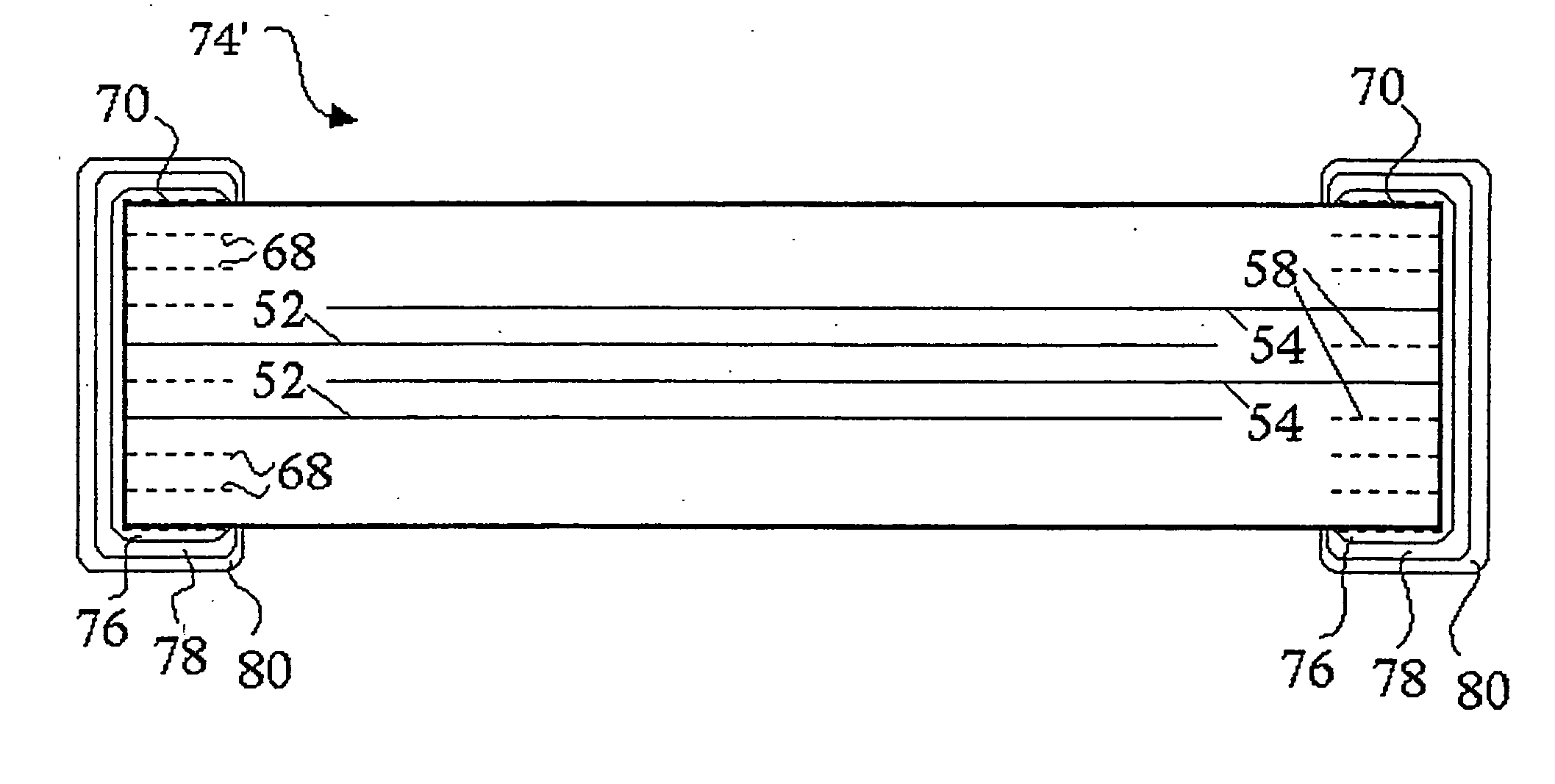
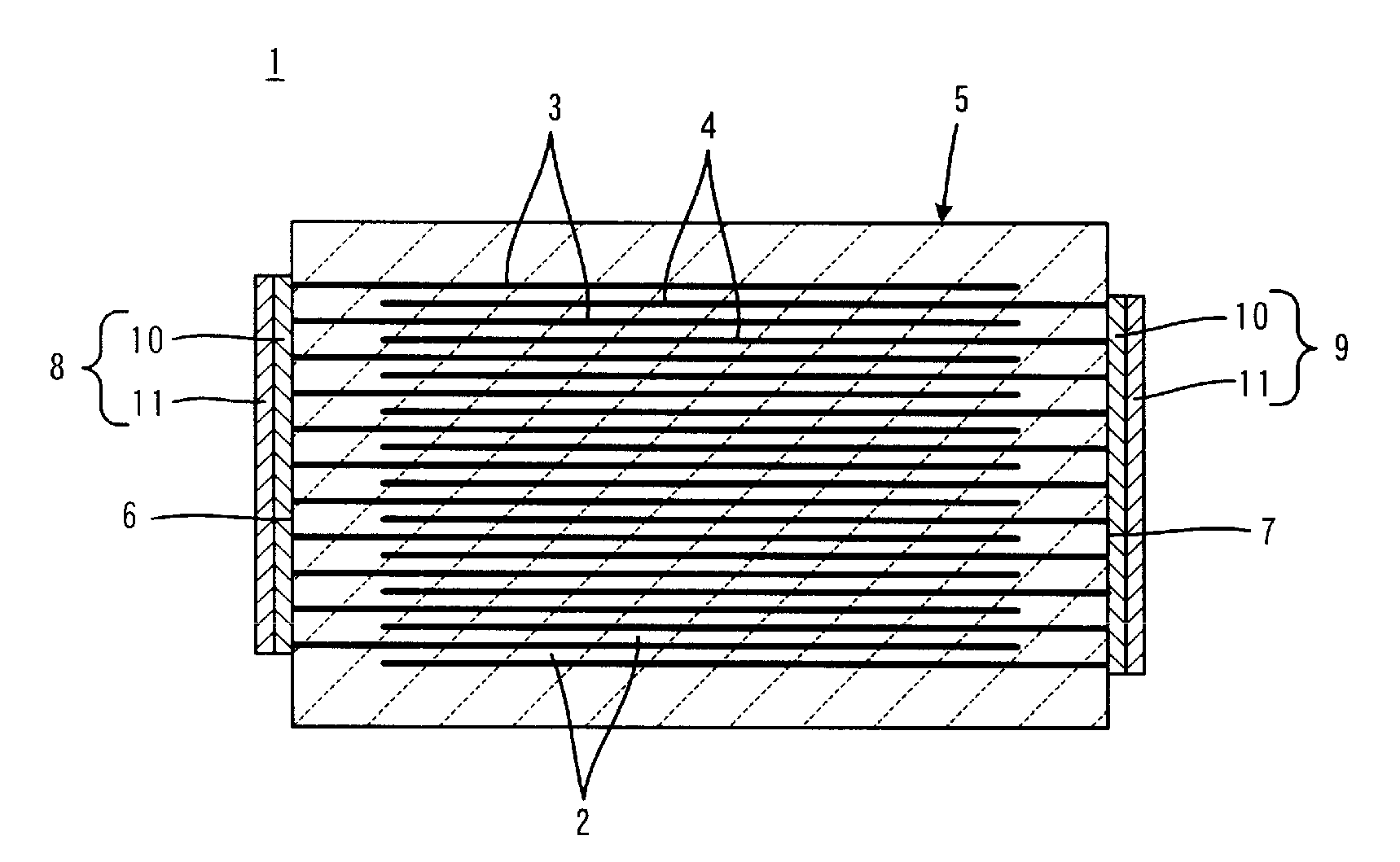
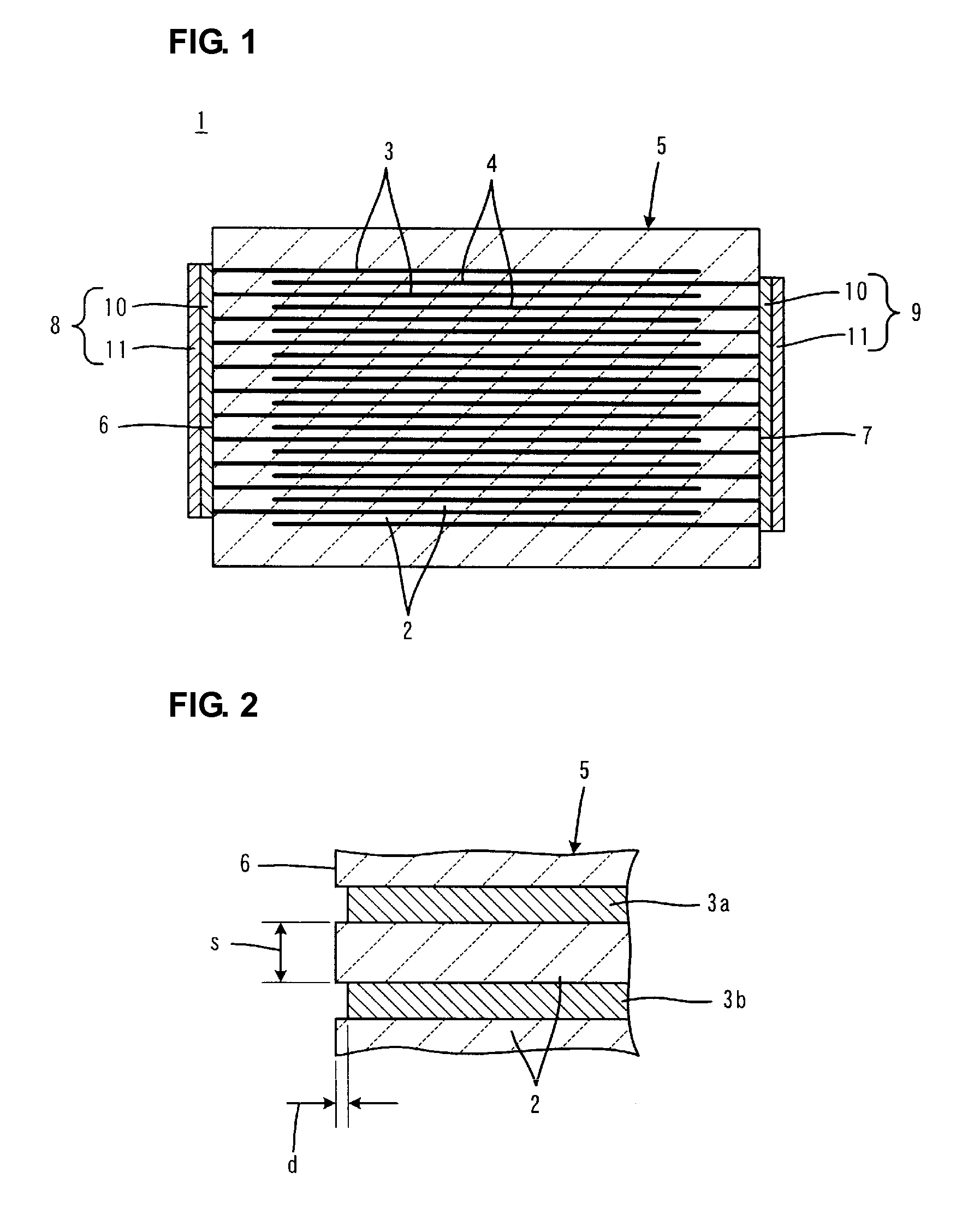
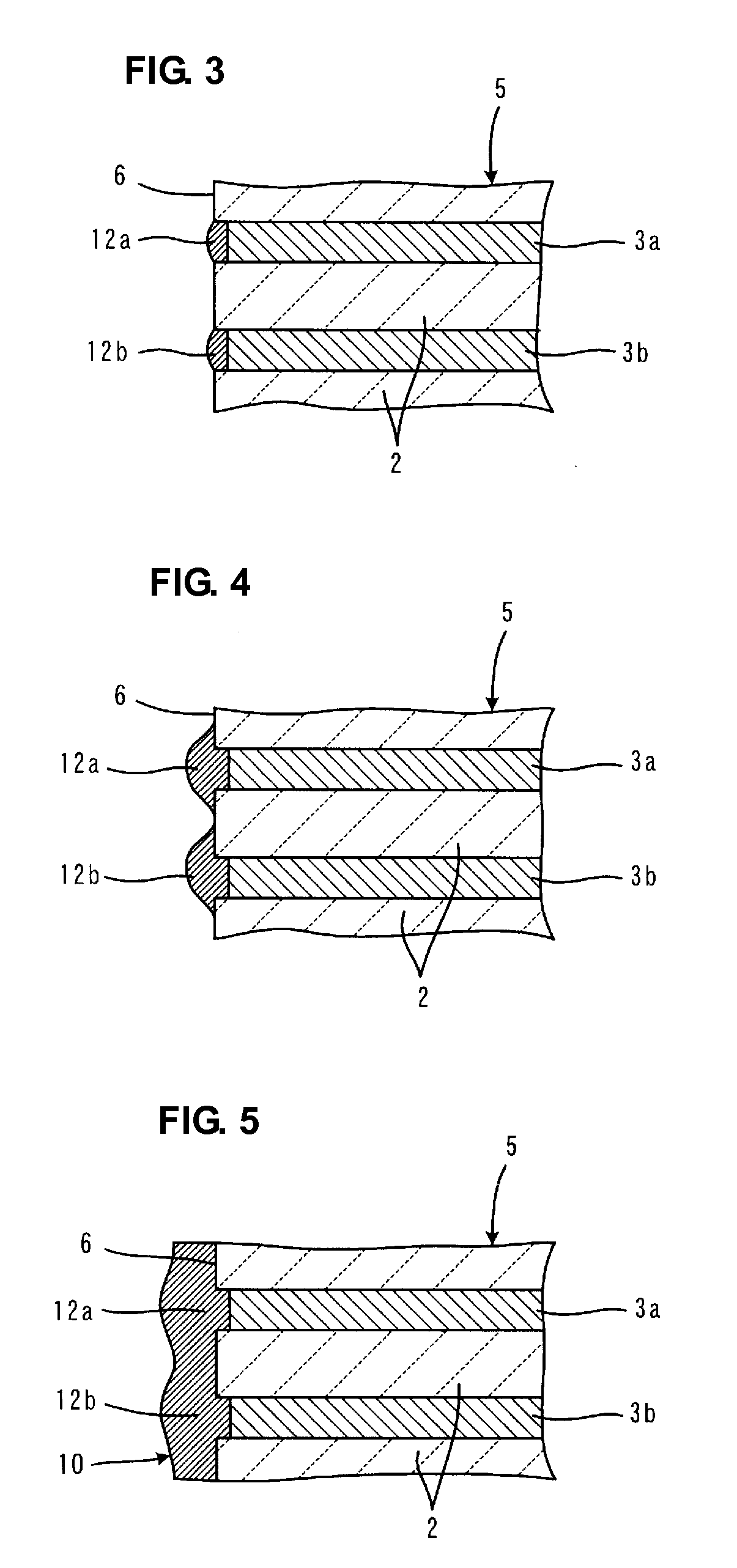
In a multilayer capacitor, a first dielectric layered product including a first body principal face is formed to be thicker than a second dielectric layered product including a second body principal face in a stacking direction thereof. A first external electrode and a second external electrode extend only to the first body principal face from a first body end face and a second body end face. Alternatively, the first external electrode and the second external electrode extend at least to the first body principal face from the first body end face and the second body end face and extend also to at least one of the second body principal face, a first body lateral face, and a second body lateral face.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Multilayer capacitor
First and second external terminal electrodes are formed on the same principal surface of a capacitor main body. The connection between first internal electrodes in the capacitor main body, the first external terminal electrode and the mutual connection between the plurality of first internal electrodes is achieved by a first connection portion. The connection between second internal electrodes, the second external terminal electrode and the mutual connection between the plurality of second internal electrodes is achieved by a second connection portion. The first and second connection portions are arranged alternately. Currents flow through the connection portions in opposite directions with the result that components of magnetic flux generated by such currents are cancelled and the ESL is reduced.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Plated terminations and method of forming using electrolytic plating
InactiveUS20070014075A1Improved termination featureEliminate and greatly simplifyElectrolytic capacitorsResistor terminals/electrodesCombined useEngineering
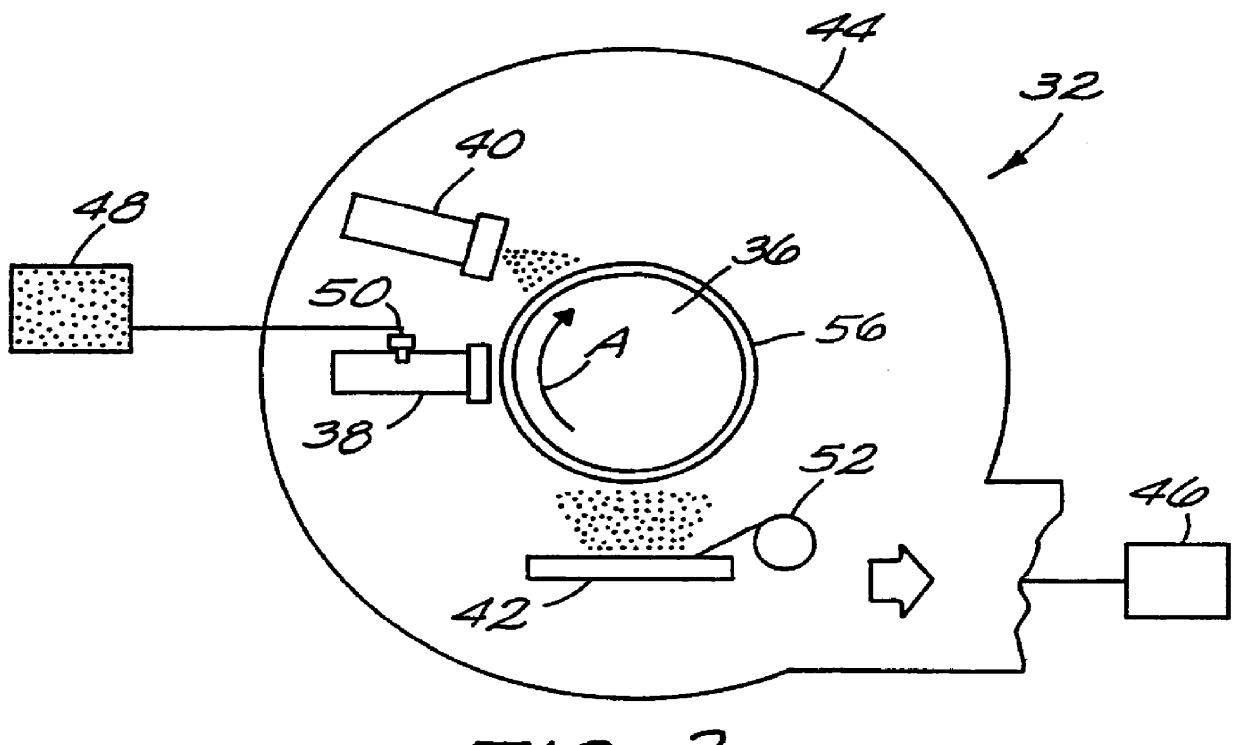
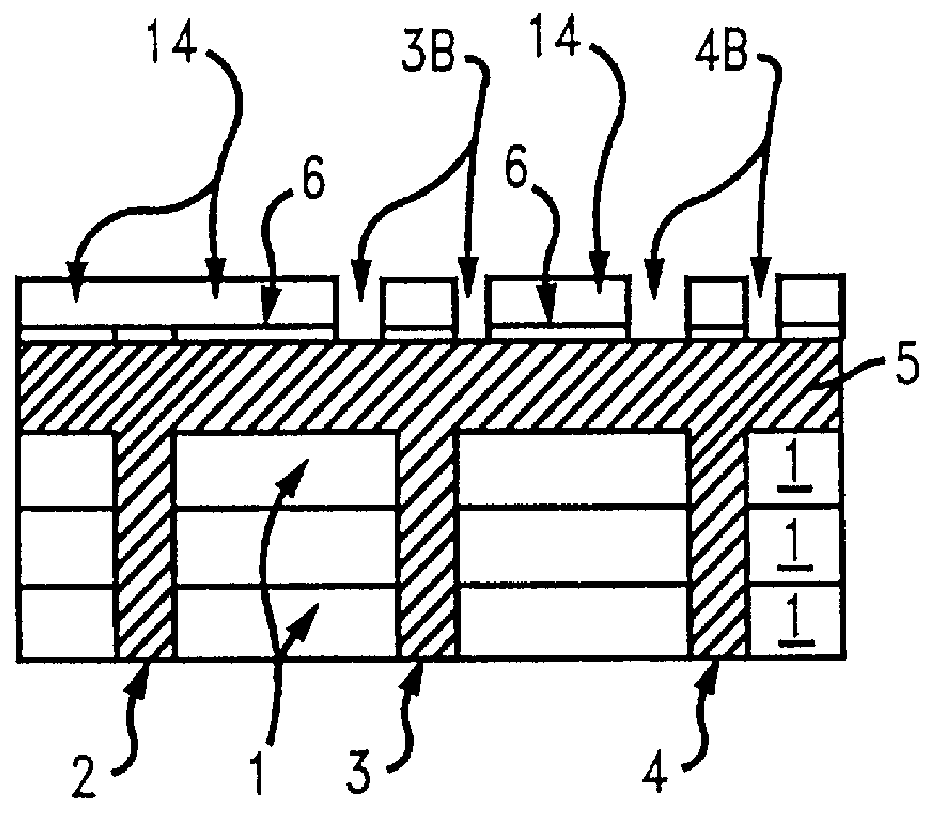
A multilayer electronic component includes a plurality of dielectric layers interleaved with a plurality of internal electrodes. Internal and / or external anchor tabs may also be selectively interleaved with the dielectric layers. Portions of the internal electrodes and anchor tabs are exposed along the periphery of the electronic component in respective groups. Each exposed portion is within a predetermined distance from other exposed portions in a given group such that termination structures may be formed by deposition and controlled bridging of a thin-film plated material among selected of the exposed internal conductive elements. Electrolytic plating may be employed in conjunction with optional cleaning and annealing steps to form directly plated portions of copper, nickel or other conductive material. Once an initial thin-film metal is directly plated to a component periphery, additional portions of different materials may be plated thereon.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
Multilayer ceramic capacitor with terminal formed by electroless plating
InactiveUS7345868B2High strengthFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricElectrolysisCeramic capacitor
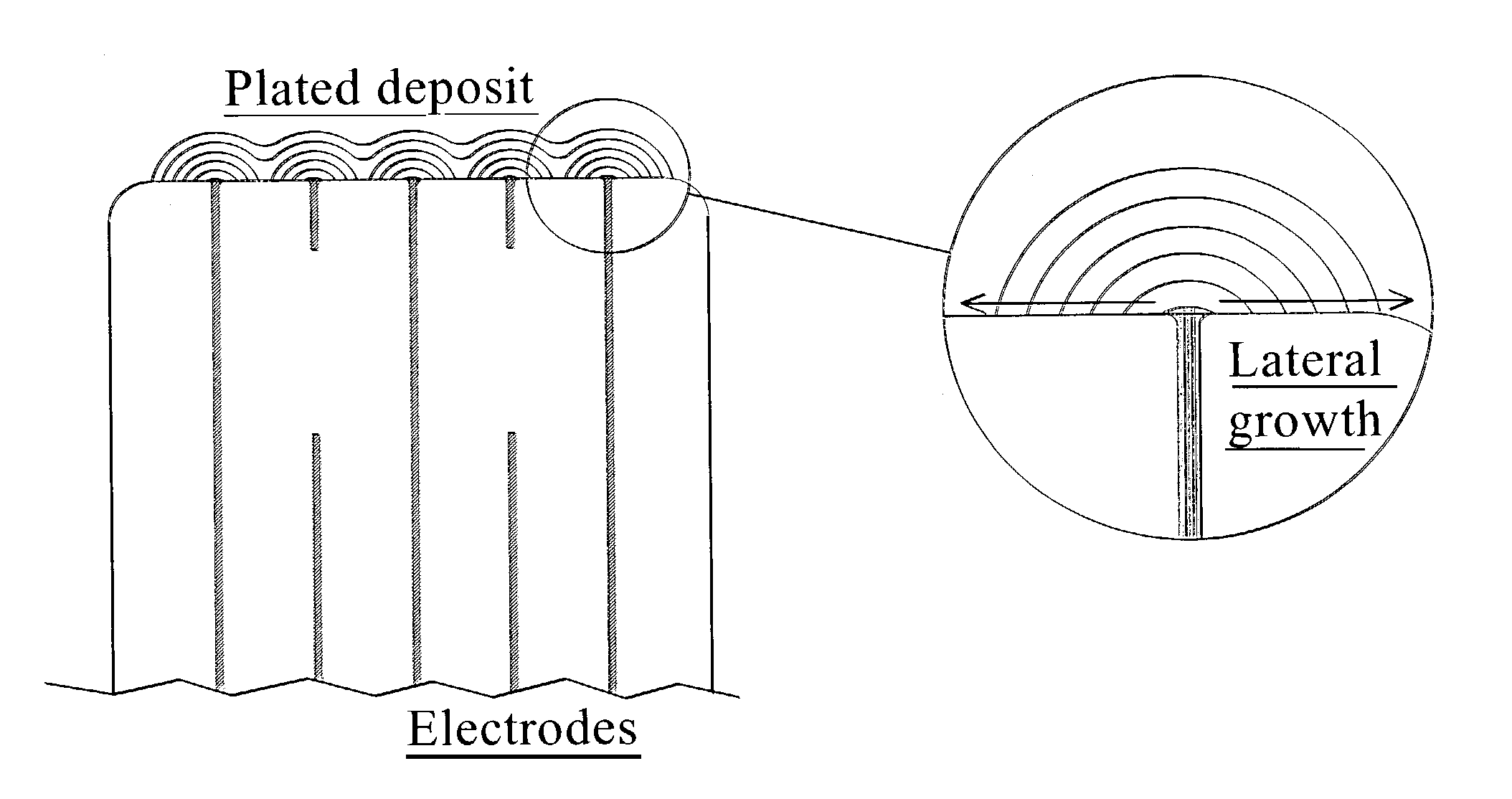
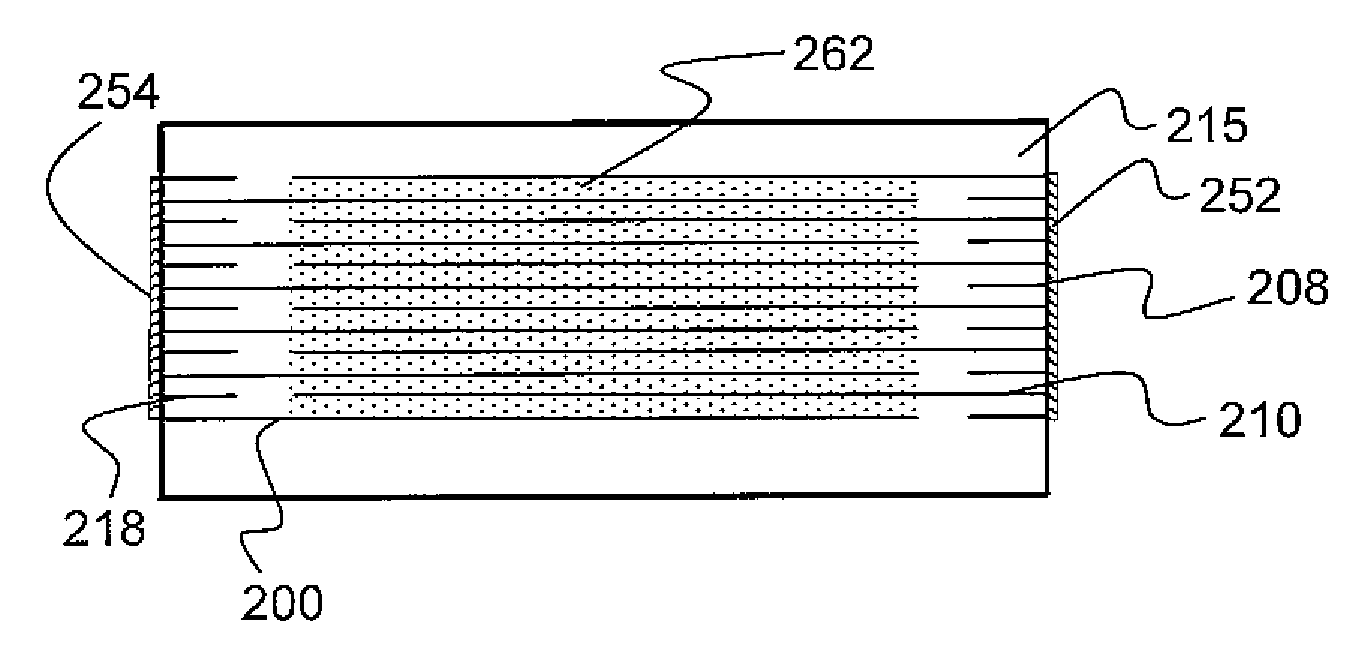
A terminal to, most commonly, a ceramic capacitor, most commonly a multilayer ceramic capacitor (MLCC), is formed by electroless plating, also known as electroless deposition or simply as electrodeposition. In the MLCC having a multiple parallel interior plates brought to, and exposed at, at least one, first, surface, an electrically-conductive first-metal layer, preferably Cu, is electrolessly deposited upon this first surface directly in contact with, mechanically connected to, and electrically connected to, the edges of these interior plates. Lateral growth of the electrolessly-deposited first-metal is sufficient to span from exposed plate to exposed plate, electrically connecting the plates. One or more top layers, preferably one of Ni and one of Sn and Pb, are deposited, preferably by plating and more preferably by electrolytic plating, on top of the electrolessly-deposited Cu.
Owner:PRESIDIO COMPONENTS
Plated terminations
InactiveUS20050046536A1Improved termination featureEliminate and greatly simplifyWave amplification devicesResistor terminals/electrodesTermination problemEngineering
Improved termination features for multilayer electronic components are disclosed. Monolithic components are provided with plated terminations whereby the need for typical thick-film termination stripes is eliminated or greatly simplified. Such termination technology eliminates many typical termination problems and enables a higher number of terminations with finer pitch, which may be especially beneficial on smaller electronic components. The subject plated terminations are guided and anchored by exposed internal electrode tabs and additional anchor tab portions which may optionally extend to the cover layers of a multilayer component. Such anchor tabs may be positioned internally or externally relative to a chip structure to nucleate additional metallized plating material. External anchor tabs positioned on top and bottom sides of a monolithic structure can facilitate the formation of wrap-around plated terminations. The disclosed technology may be utilized with a plurality of monolithic multilayer components, including interdigitated capacitors, multilayer capacitor arrays, and integrated passive components. A variety of different plating techniques and termination materials may be employed in the formation of the subject self-determining plated terminations.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
Plated terminations
InactiveUS7154374B2Improved termination featureEliminate or greatly simplify thick-film stripesResistor terminals/electrodesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTermination problemEngineering
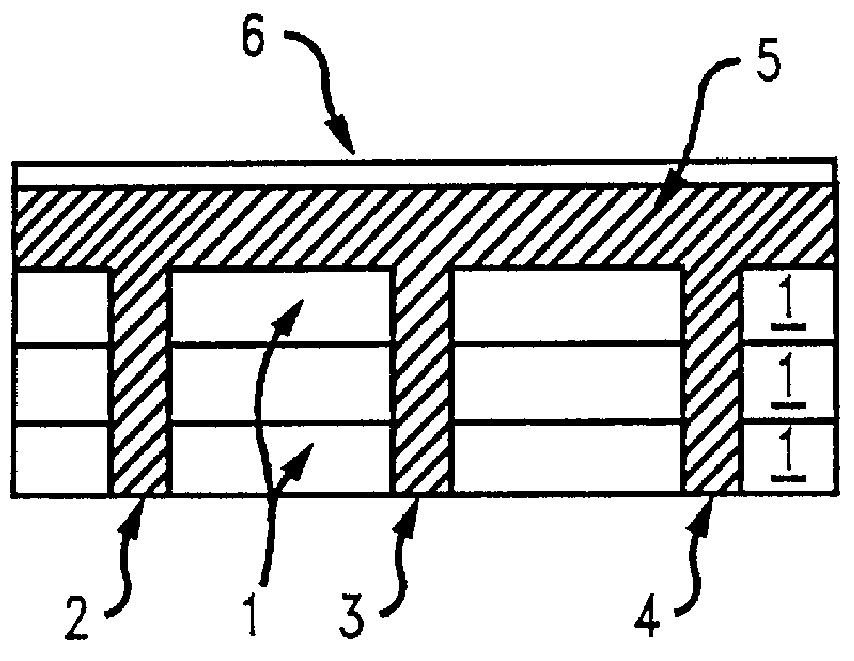
Improved termination features for multilayer electronic components are disclosed. Monolithic components are provided with plated terminations whereby the need for typical thick-film termination stripes is eliminated or greatly simplified. Such termination technology eliminates many typical termination problems and enables a higher number of terminations with finer pitch, which may be especially beneficial on smaller electronic components. The subject plated terminations are guided and anchored by exposed internal electrode tabs and additional anchor tab portions which may optionally extend to the cover layers of a multilayer component. Such anchor tabs may be positioned internally or externally relative to a chip structure to nucleate additional metallized plating material. External anchor tabs positioned on top and bottom sides of a monolithic structure can facilitate the formation of wrap-around plated terminations. The disclosed technology may be utilized with a plurality of monolithic multilayer components, including interdigitated capacitors, multilayer capacitor arrays, and integrated passive components. A variety of different plating techniques and termination materials may be employed in the formation of the subject self-determining plated terminations.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
Laminated electronic component and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080123248A1Improve the effective volume ratioImprove moisture resistanceCellsStacked capacitorsEngineeringElectronic component
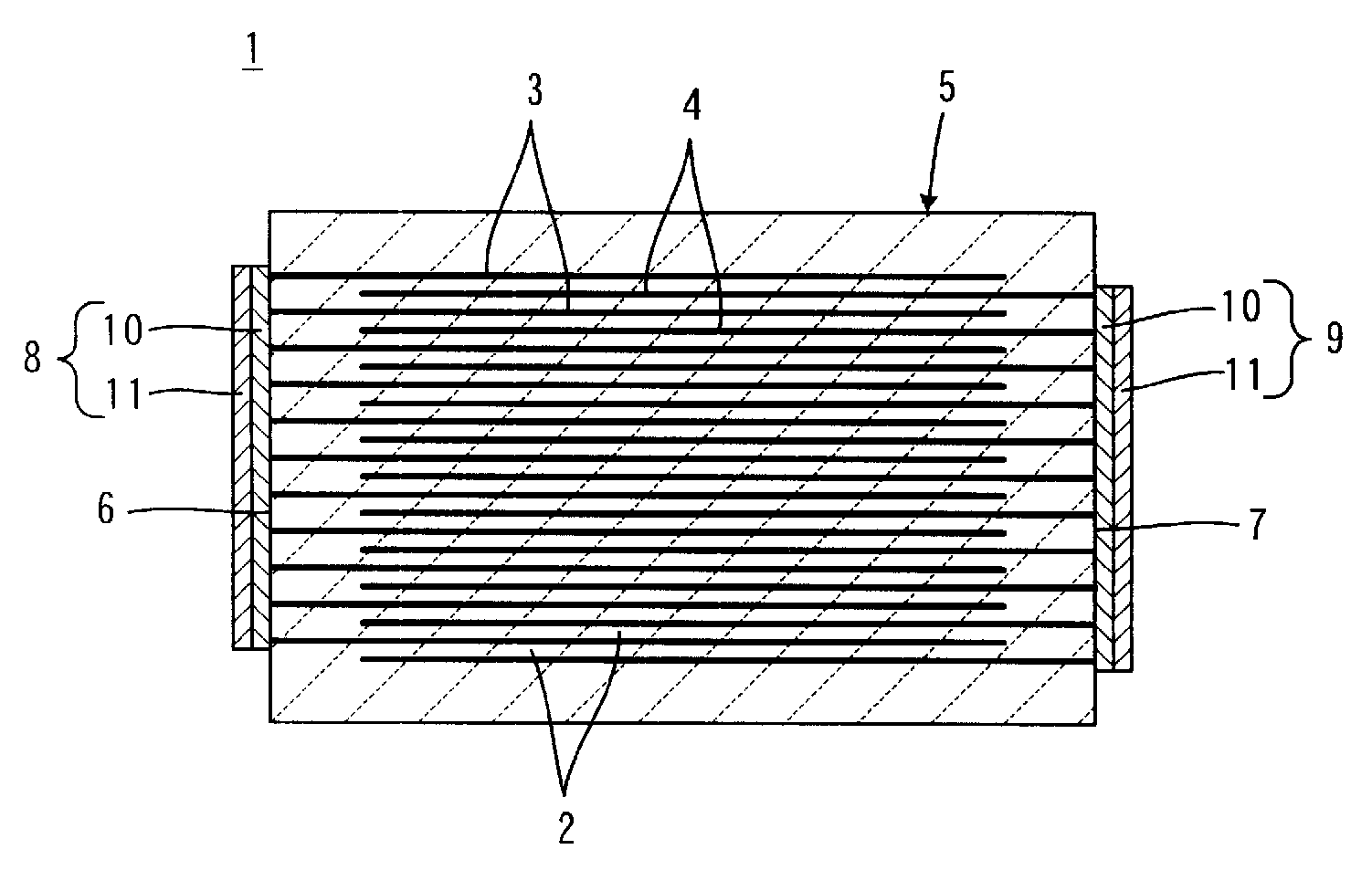
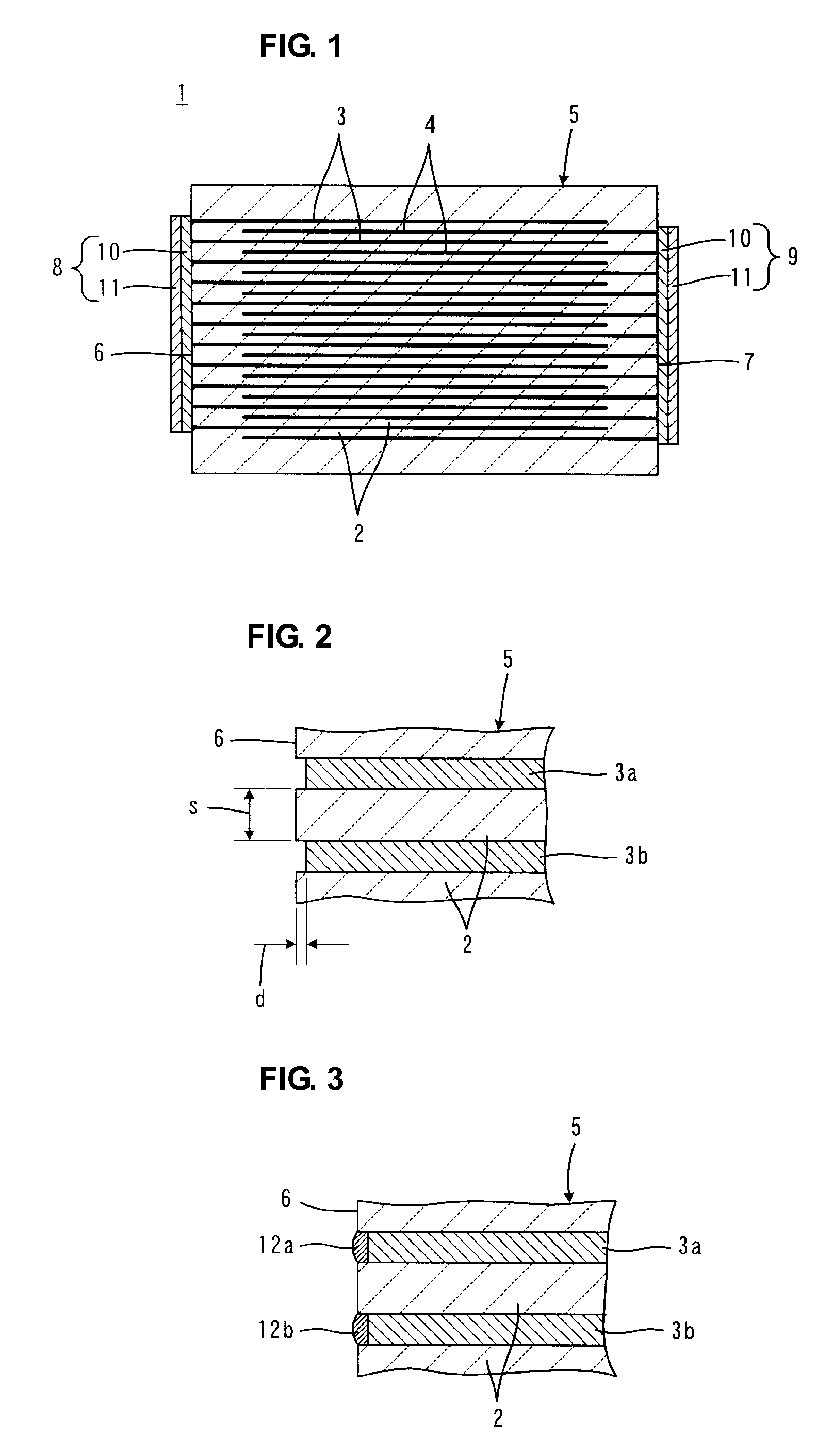
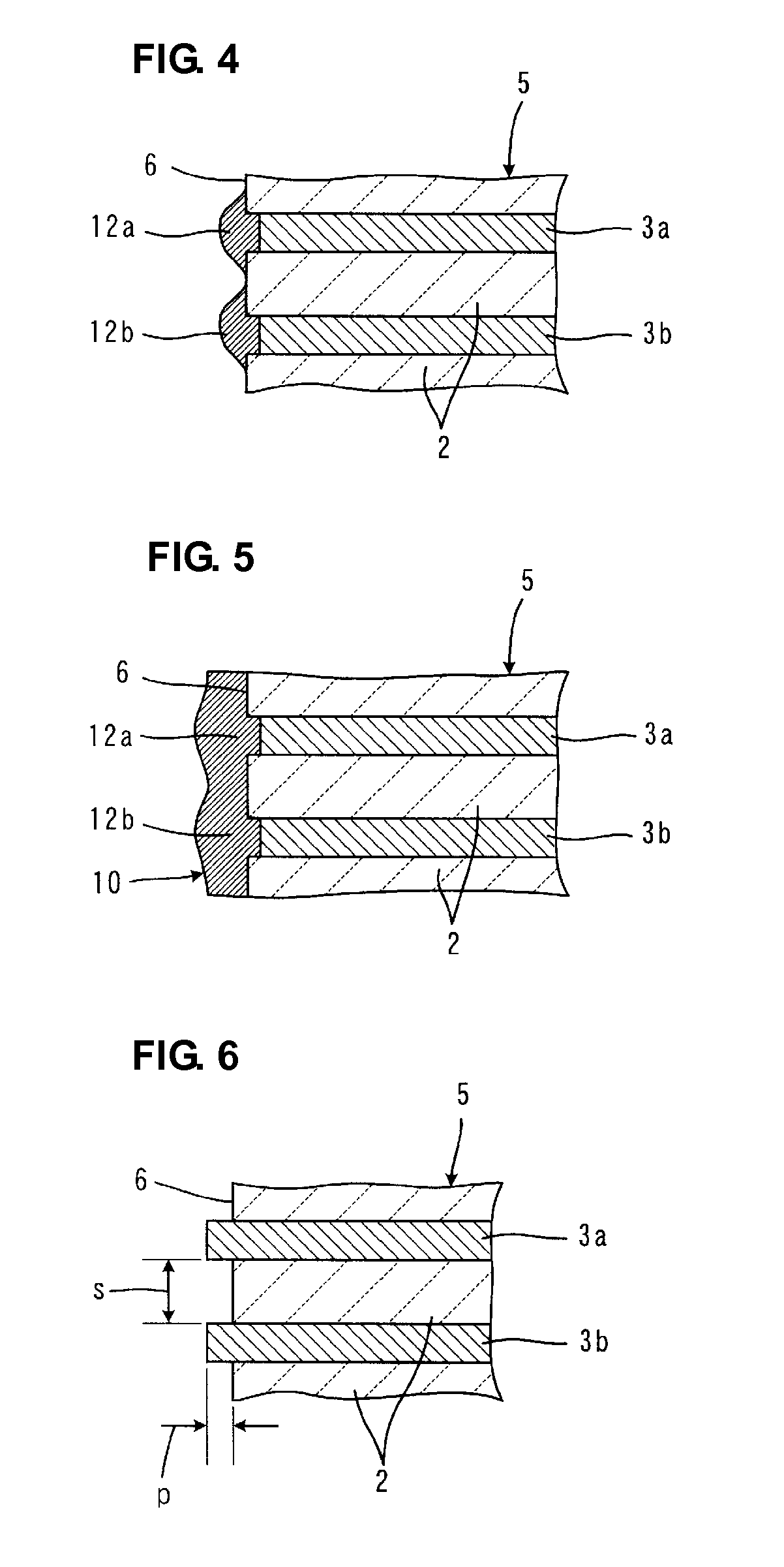
A laminate is prepared in which adjacent internal electrodes are electrically insulated from each other at an end surface at which the internal electrodes are exposed, a space between the adjacent internal electrodes, which is measured in the thickness direction of insulating layers, is about 10 μm or less, and a withdrawn distance of the adjacent internal electrodes from the end surface is about 1 μm or less. In an electroplating step, electroplating deposits deposited on the ends of the adjacent internal electrodes are grown so as to be connected to each other.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
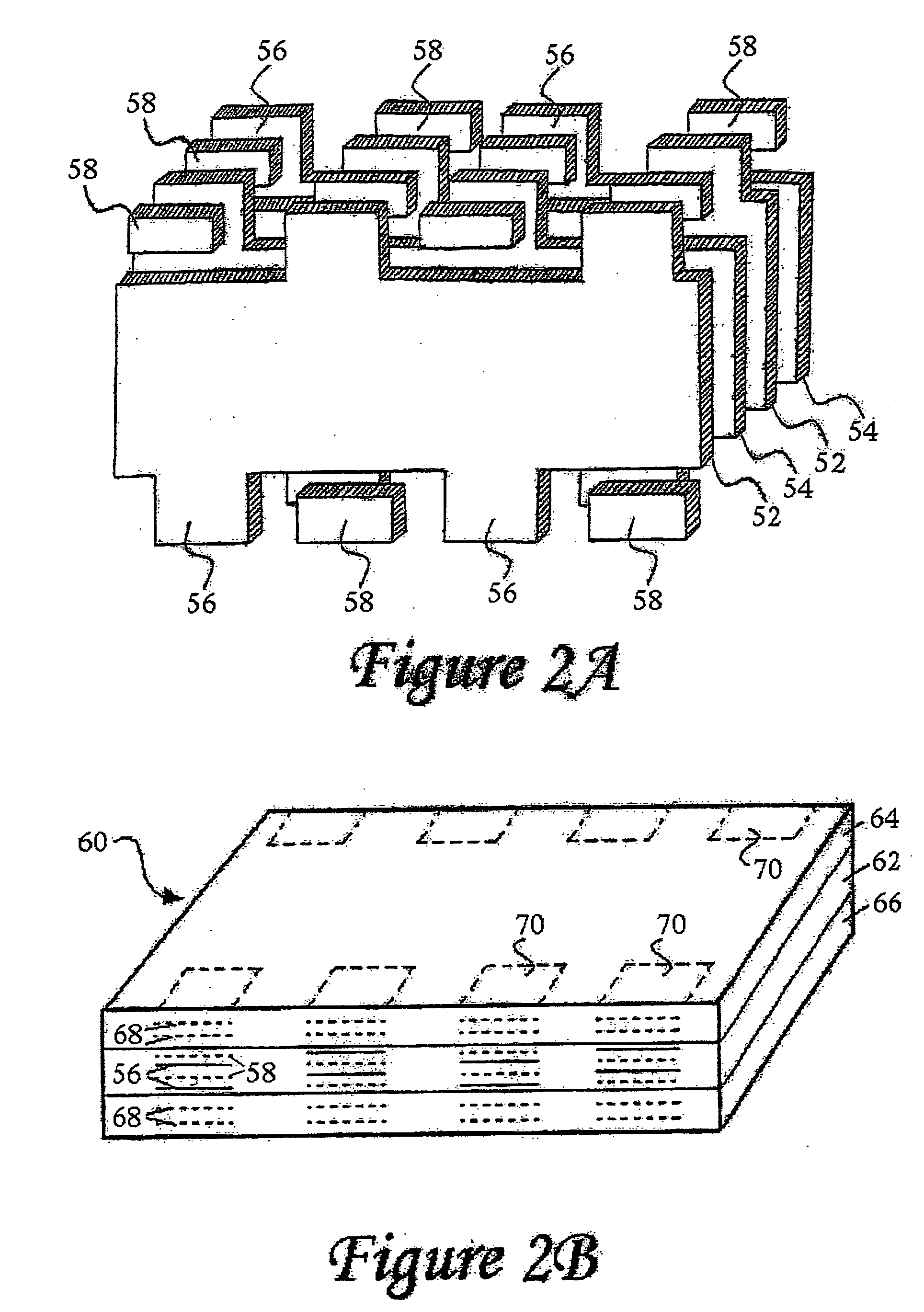
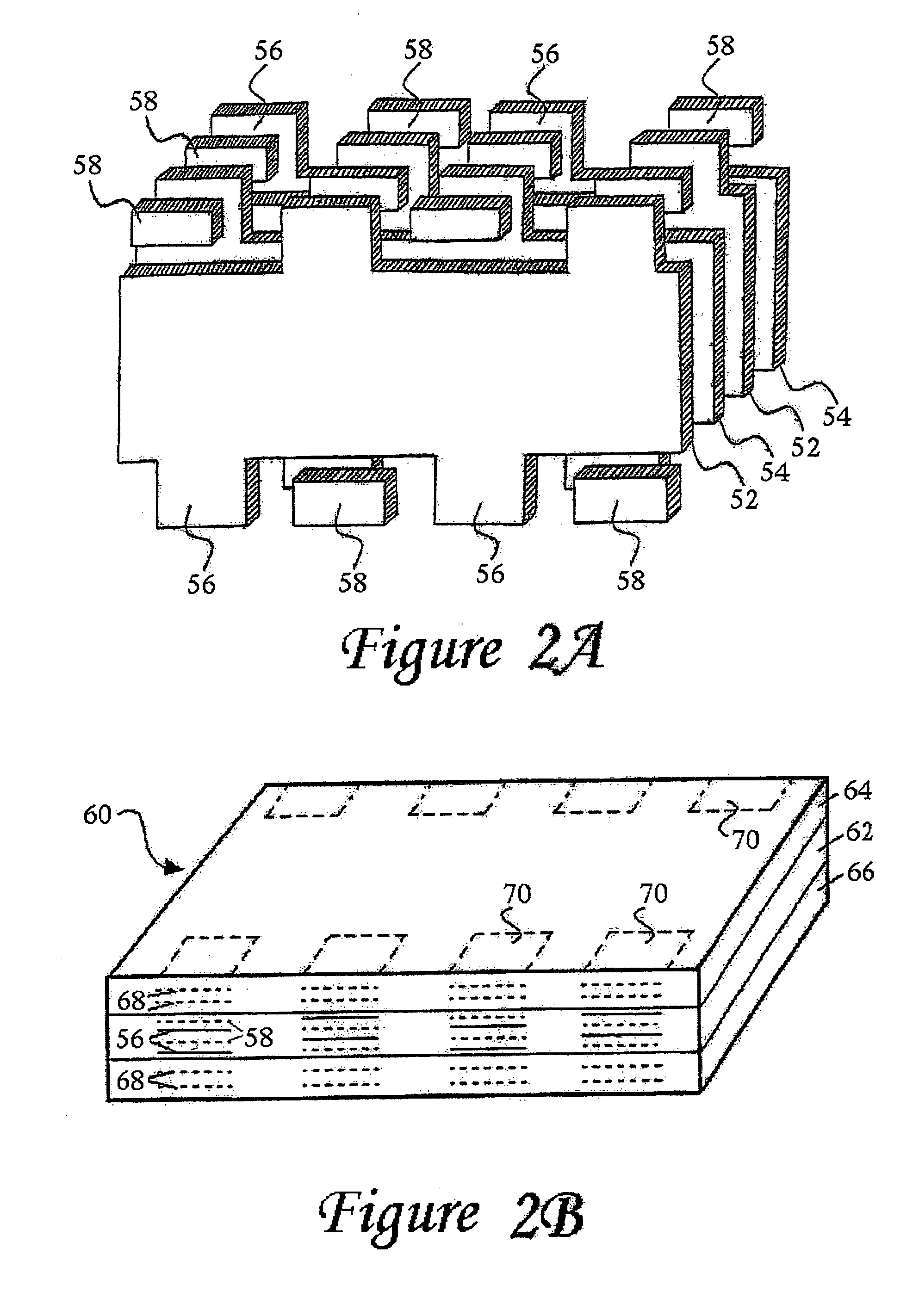
Component formation via plating technology
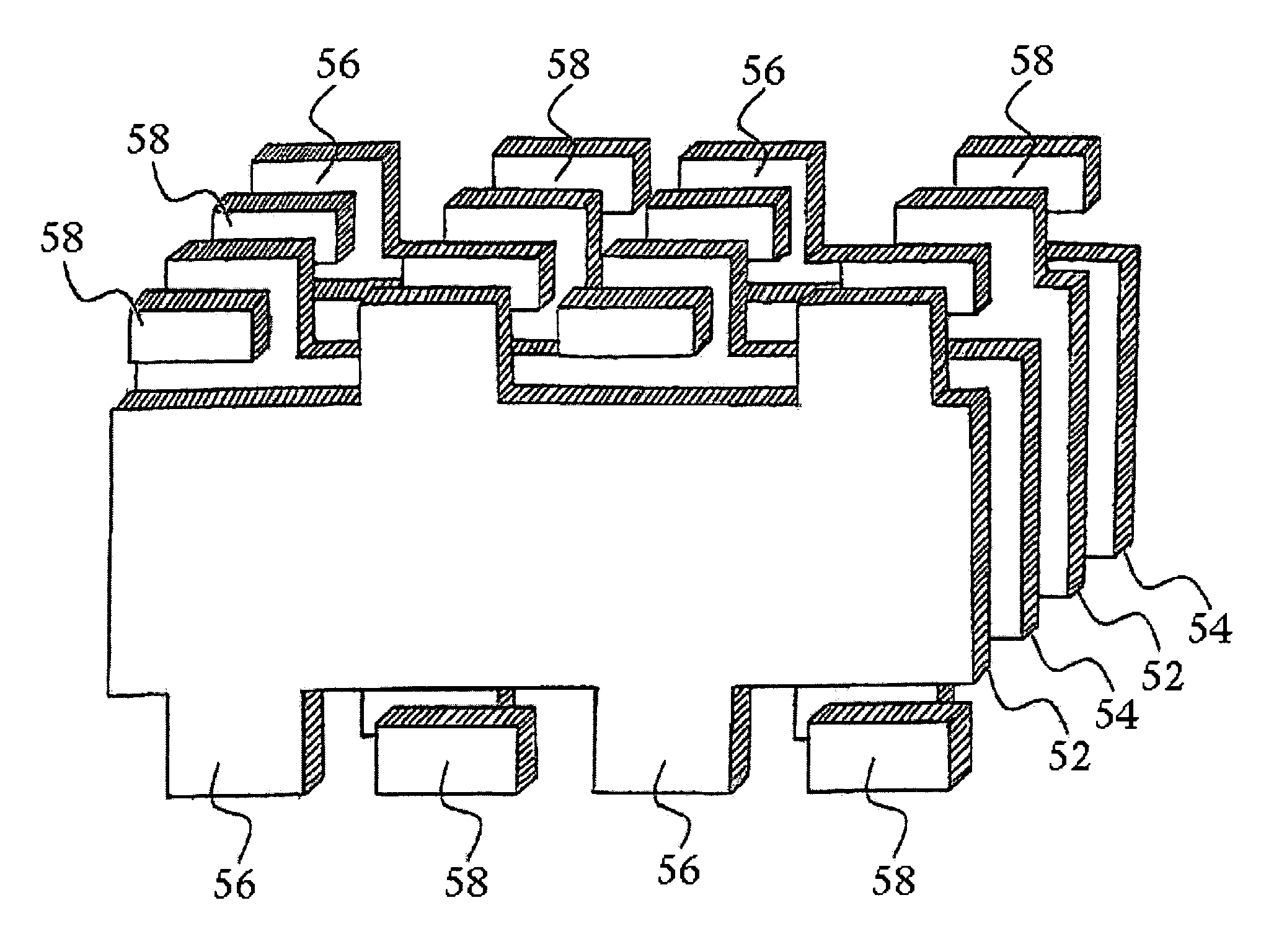
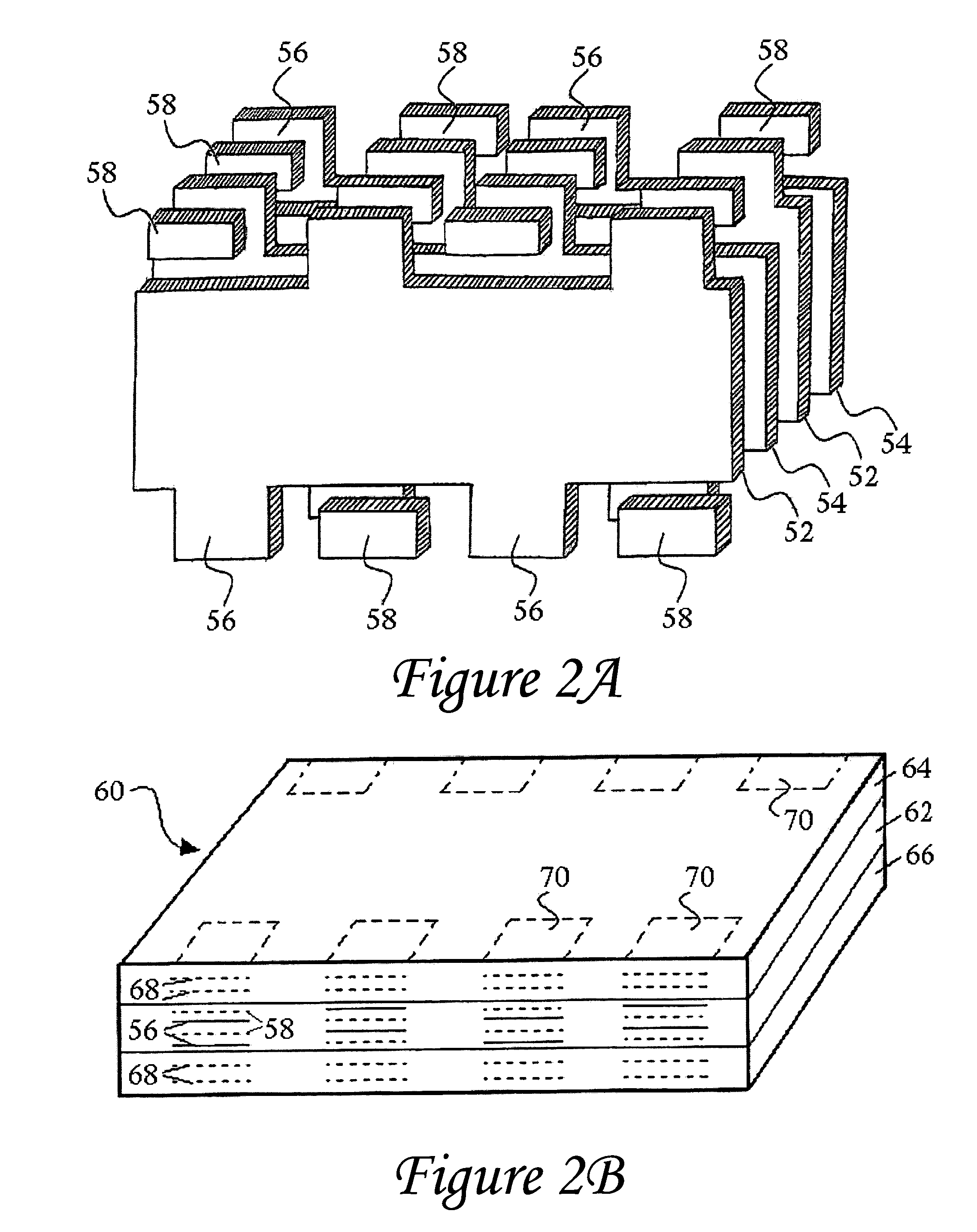
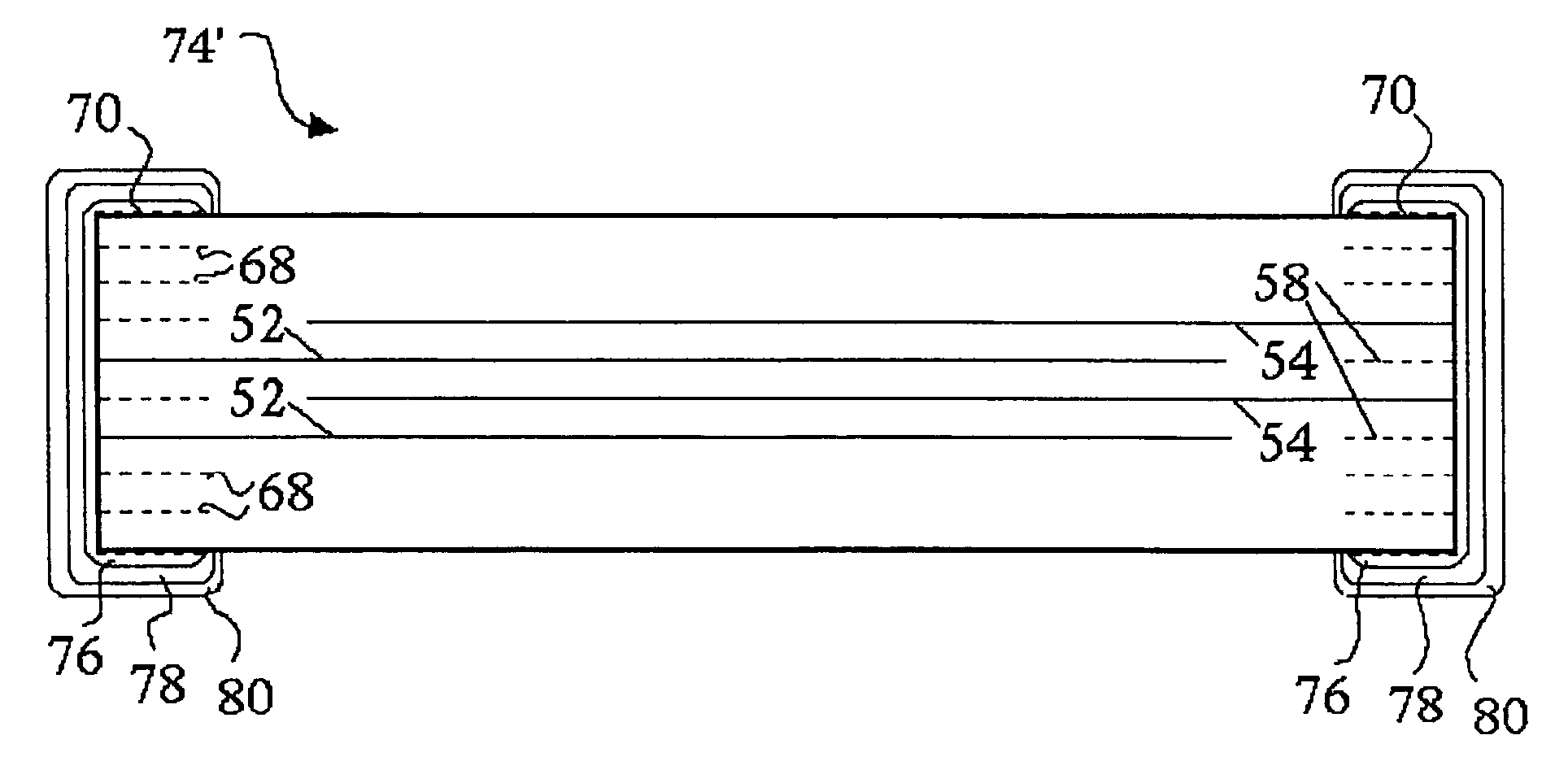
InactiveUS6982863B2Improved termination featureEliminate or greatly simplify thick-film stripesStacked capacitorsWound capacitorsTermination problemSolder ball
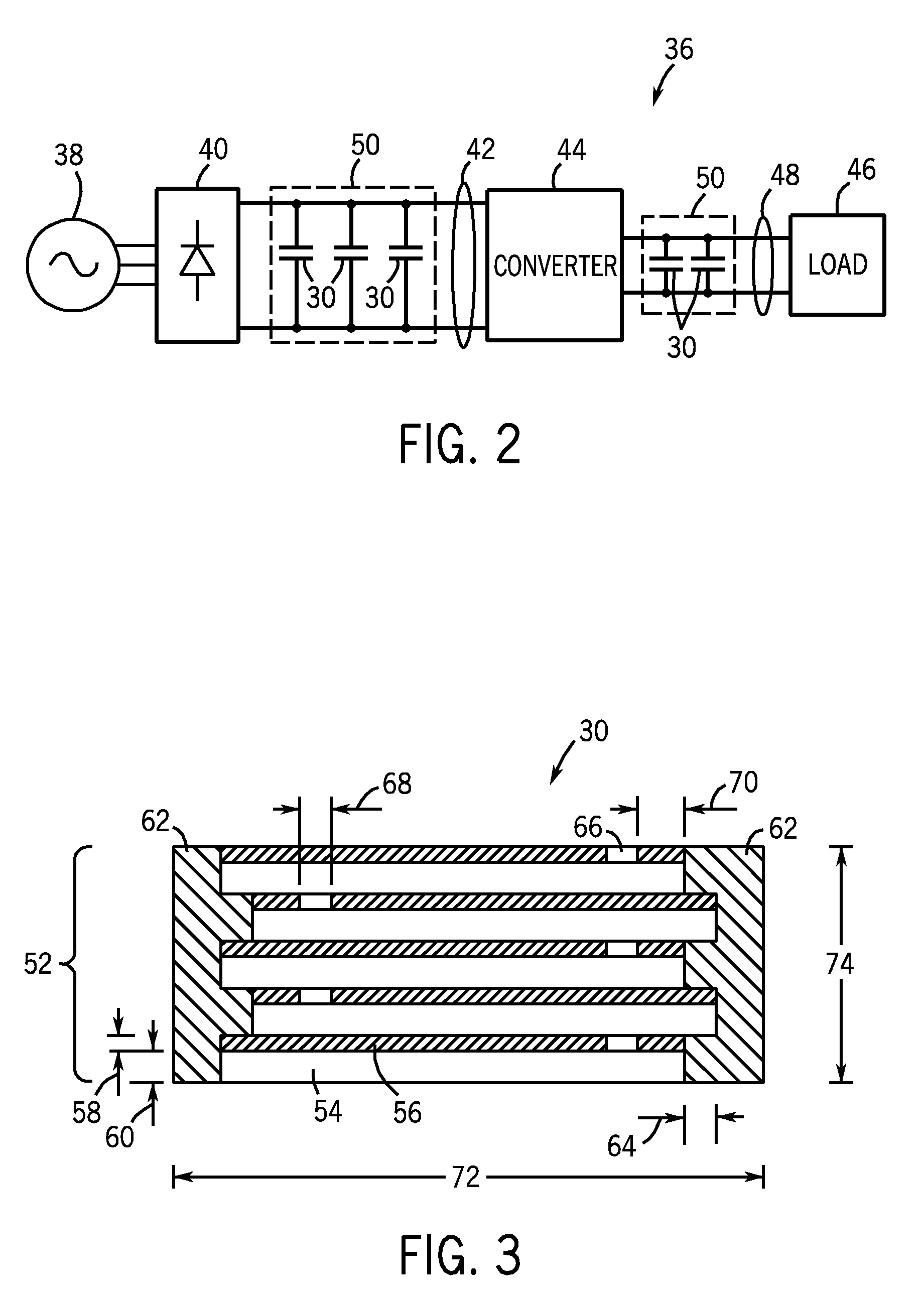
Improved terminations, interconnection techniques, and inductive element features for multilayer electronic components are formed in accordance with disclosed plating techniques. Monolithic components are provided with plated terminations whereby the need for typical thick-film termination stripes is eliminated or greatly simplified. Such plated termination technology eliminates many typical termination problems and enables a higher number of terminations with finer pitch, which may be especially beneficial on smaller electronic components. The subject plated terminations are guided and anchored by exposed varying width internal electrode tabs and additional anchor tab portions. Such anchor tabs may be positioned internally or externally relative to a chip structure to nucleate additional metallized plating material. The combination of electrode tabs and anchor tabs may be exposed in respective arrangements to form generally discoidal portions of plated material. Such plated material may ultimately form generally round portions of ball limiting metallurgy (BLM) to which solder balls may be reflowed. The disclosed technology may be utilized with a plurality of monolithic multilayer components, including interdigitated capacitors, multilayer capacitor arrays, and integrated passive components. A variety of different plating techniques and materials may be employed in the formation of the subject self-determining plated terminations and inductive components.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
High energy density capacitor
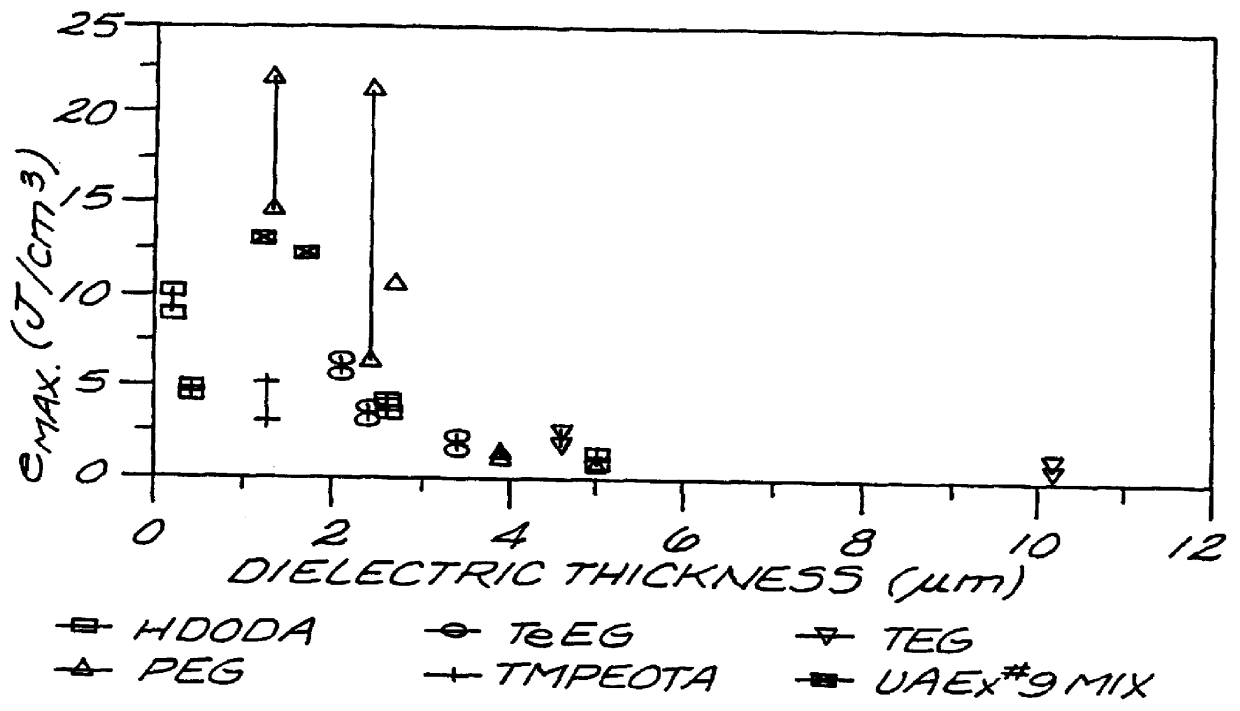
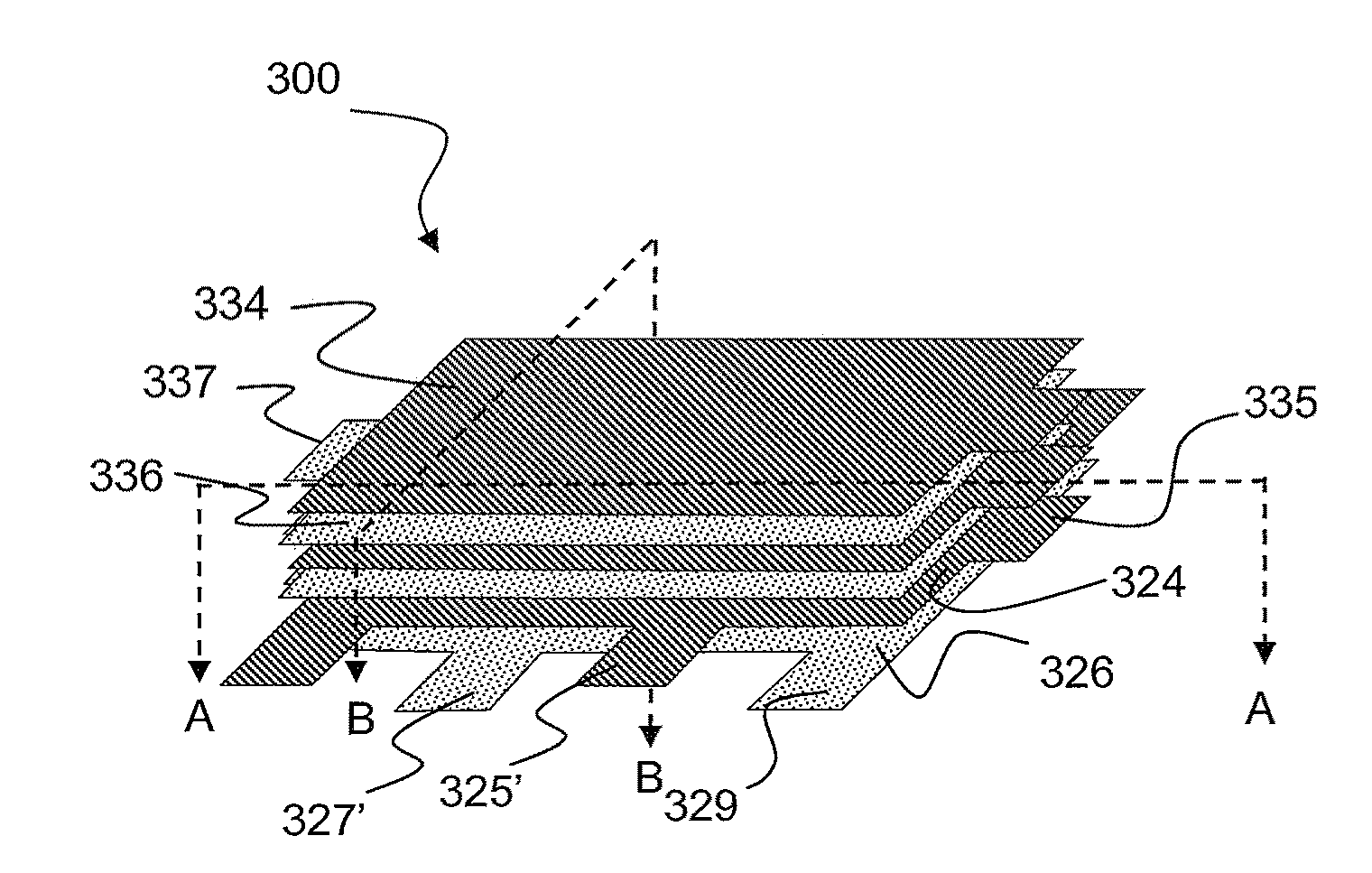
A high energy density, high power density capacitor having an energy density of at least about 0.5 J / cm3 is provided. The capacitor comprises a plurality of interleaved metal electrode layers separated by a polymer layer. The interleaved metal electrode layers terminate at opposite ends in a solder termination strip. The high energy density aspect of the capacitors of the invention is achieved by at least one of the following features: (a) the dielectric thickness between the interleaved metal electrode layers is a maximum of about 5 mu m; (b) the polymer is designed with a high dielectric constant kappa of at least about 3.5; (c) the metal electrode layers within the polymer layer are recessed along edges orthogonal to the solder termination strips to prevent arcing between the metal electrode layers at the edges; and (d) the resistivity of the metal electrode layers is within the range of about 10 to 500 ohms per square, or a corresponding thickness of about 200 to 30 ANGSTROM .
Owner:SIGMA LAB OF ARIZONA
Laminated electronic component and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080123249A1Improve the effective volume ratioImprove reliabilityFixed capacitor dielectricStacked capacitorsElectronic componentElectron
A laminated body is prepared, in which at an end surface at which internal electrodes are exposed, the internal electrodes disposed adjacently are electrically isolated from each other, and a distance between the internal electrodes disposed adjacently is about 20 μm or less when measured along the thickness direction of an insulator layer, and a withdrawn-depth of the internal electrodes is about 1 μm or less when measured from the end surface. In a step of electroless plating, plating deposits formed at the end portions of the plurality of internal electrodes are increased in size so as to be connected to each other.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Multilayer ceramic capacitor with terminal formed by electroless plating
InactiveUS20080158774A1High strengthFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricCeramic capacitorElectroless deposition
A terminal to, most commonly, a ceramic capacitor, most commonly a multilayer ceramic capacitor (MLCC), is formed by electroless plating, also known as electroless deposition or simply as electrodeposition. In the MLCC having a multiple parallel interior plates brought to, and exposed at, at least one, first, surface, an electrically-conductive first-metal layer, preferably Cu, is electrolessly deposited upon this first surface directly in contact with, mechanically connected to, and electrically connected to, the edges of these interior plates. Lateral growth of the electrolessly-deposited first-metal is sufficient to span from exposed plate to exposed plate, electrically connecting the plates. One or more top layers, preferably one of Ni and one of Sn and Pb, are deposited, preferably by plating and more preferably by electrolytic plating, on top of the electrolessly-deposited Cu.
Owner:PRESIDIO COMPONENTS
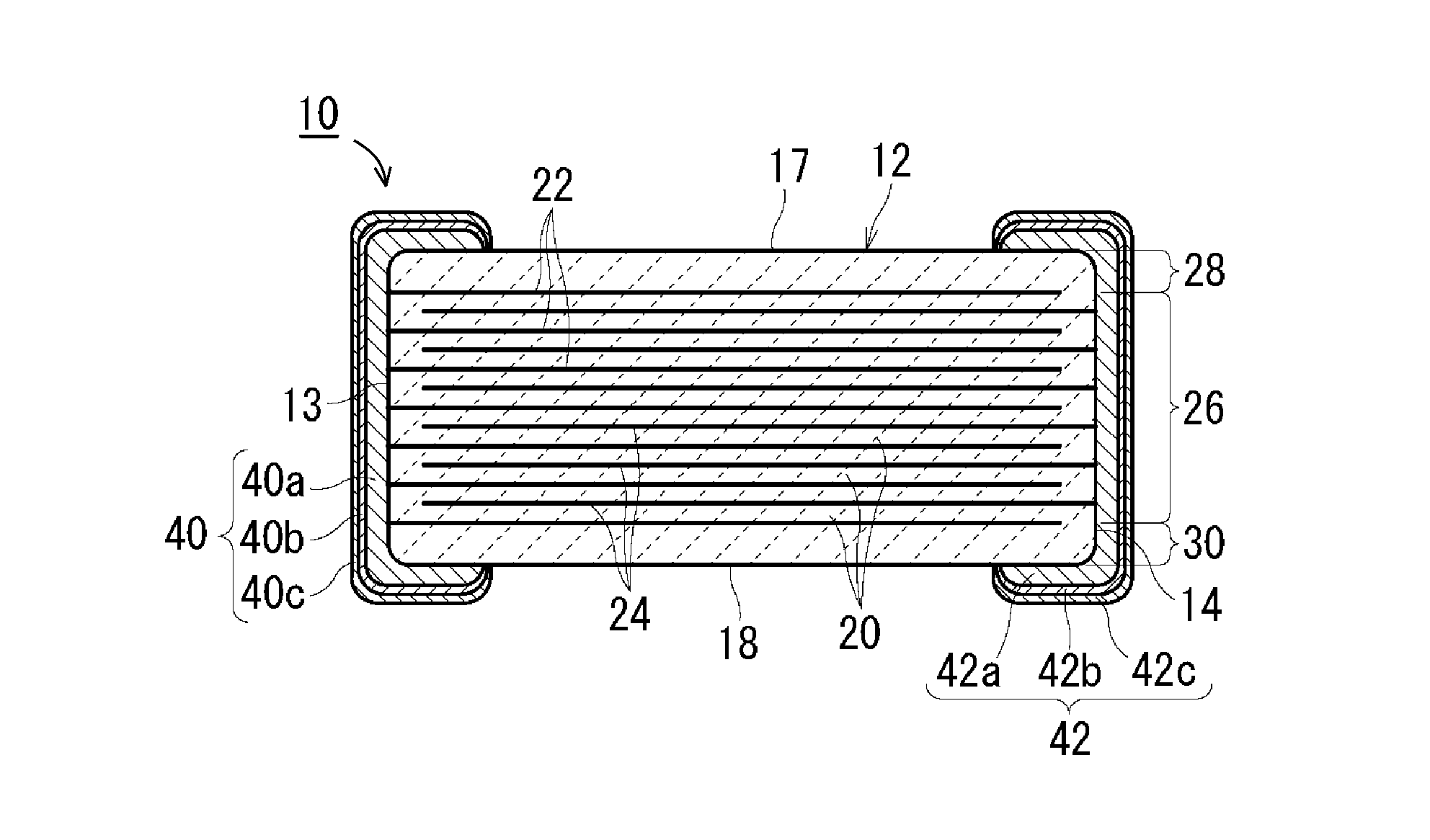
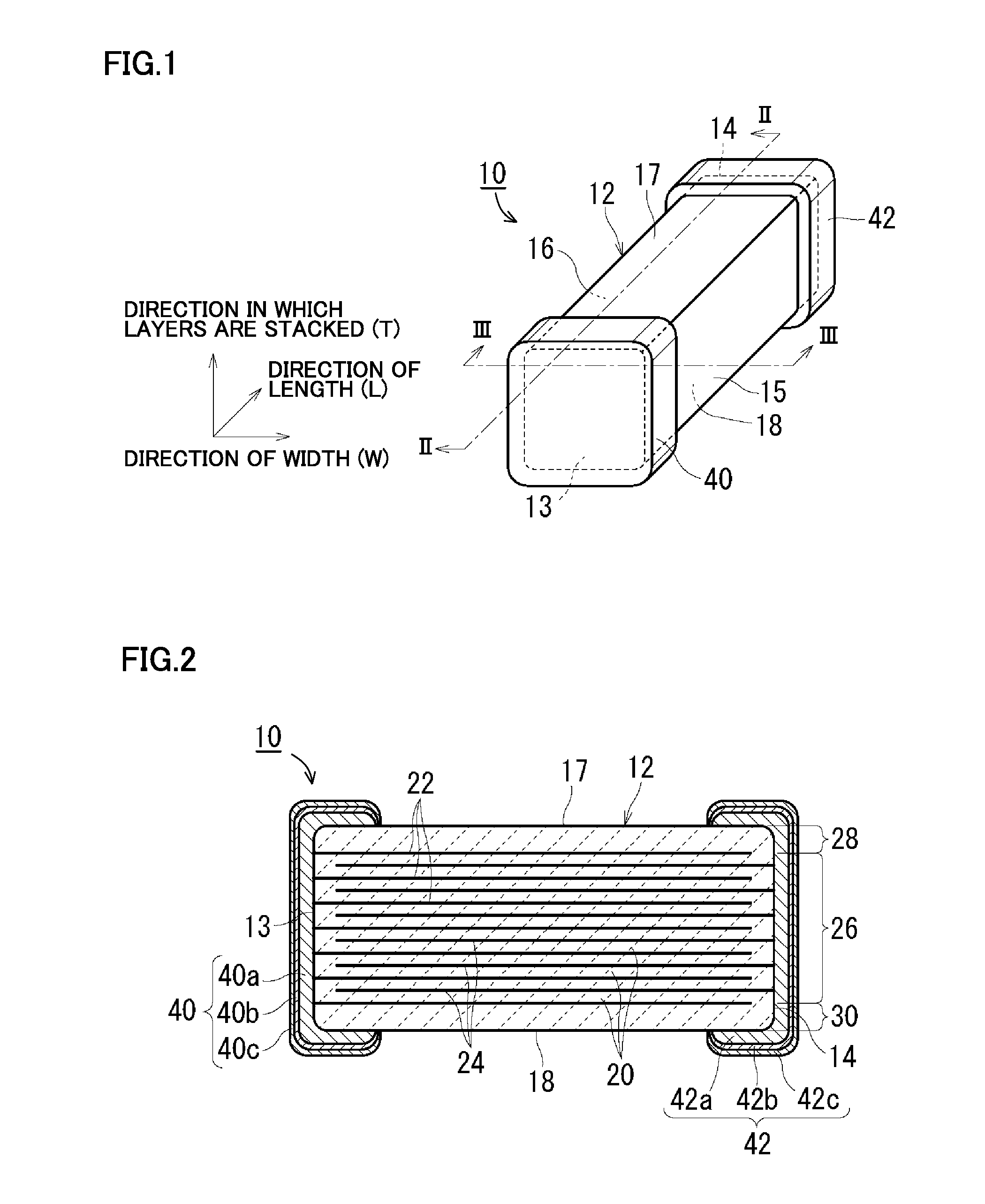
Multilayer ceramic capacitor
ActiveUS20170018363A1Solve the lack of reliabilityImprove side strengthFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricCeramic capacitorMaterials science
A multilayer ceramic capacitor includes a laminated body and first and second external electrodes respectively on both end surfaces of the laminated body. When regions where first internal electrodes or second internal electrodes are not present are regarded as side margin portions in a cross section of the laminated body as viewed from the laminating direction, the side margin portions include multiple side margin layers, and the content of Si in the side margin layer closest to the internal electrode is lower than that in the side margin layer other than the side margin layer closest to the internal electrode.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Multilayer feedthrough capacitor
InactiveUS6768630B2Reduce common mode noiseESL is further reducedAnti-noise capacitorsFixed capacitor electrodesElectrical conductorEngineering
A multilayer feedthrough capacitor having a first internal conductor arranged in a dielectric body, an intermediate internal conductor arranged in the dielectric body and stacked with the first internal conductor via a ceramic layer, a second internal conductor arranged in the dielectric body and stacked with the intermediate internal conductor via a ceramic layer, a first terminal electrode formed at an outside surface of the dielectric body and connected to the first internal conductor, a second terminal electrode formed at the outside surface of the dielectric body and connected to the second internal conductor, and an intermediate terminal electrode formed at the outside surface of the dielectric body and connected to the intermediate internal conductor. The intermediate terminal electrode is connected to the ground, while the first terminal electrode and the second terminal electrode are connected to paths for transmitting signals. The first internal conductor and the second internal conductor have currents flowing through them in opposite directions.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
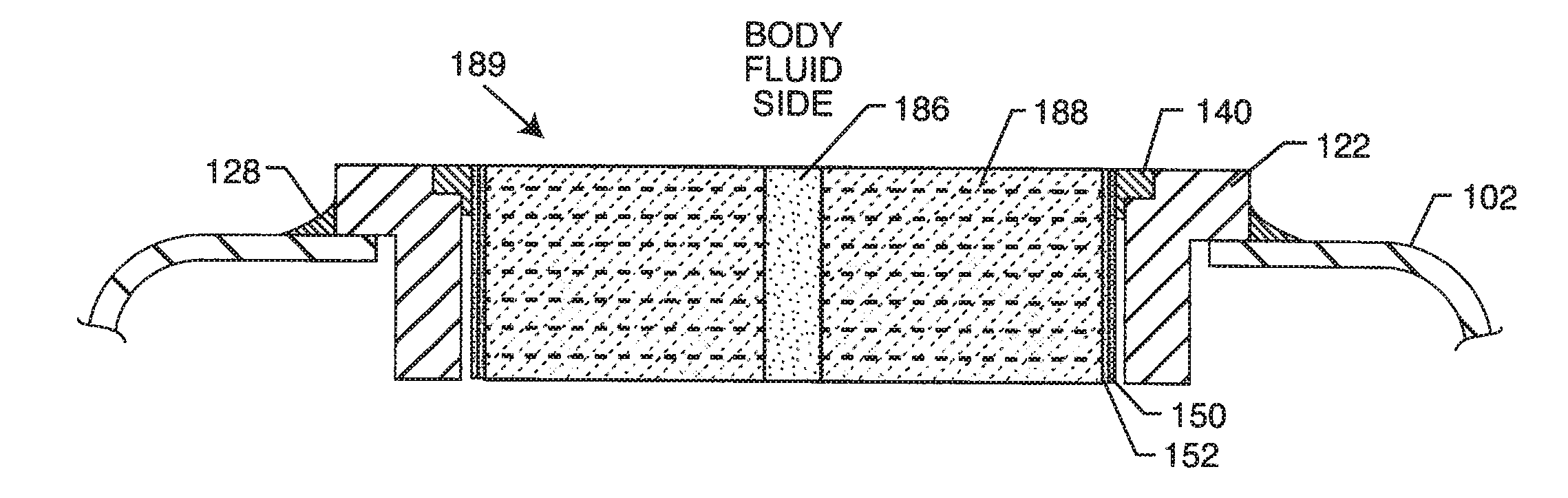
Elevated Hermetic Feedthrough Insulator Adapted for Side Attachment of Electrical Conductors on the Body Fluid Side of an Active Implantable Medical Device
ActiveUS20130184796A1Minimizes damaging tensile stressTensile stress is particularly damagingAnti-noise capacitorsLine/current collector detailsElectricityElectrical conductor
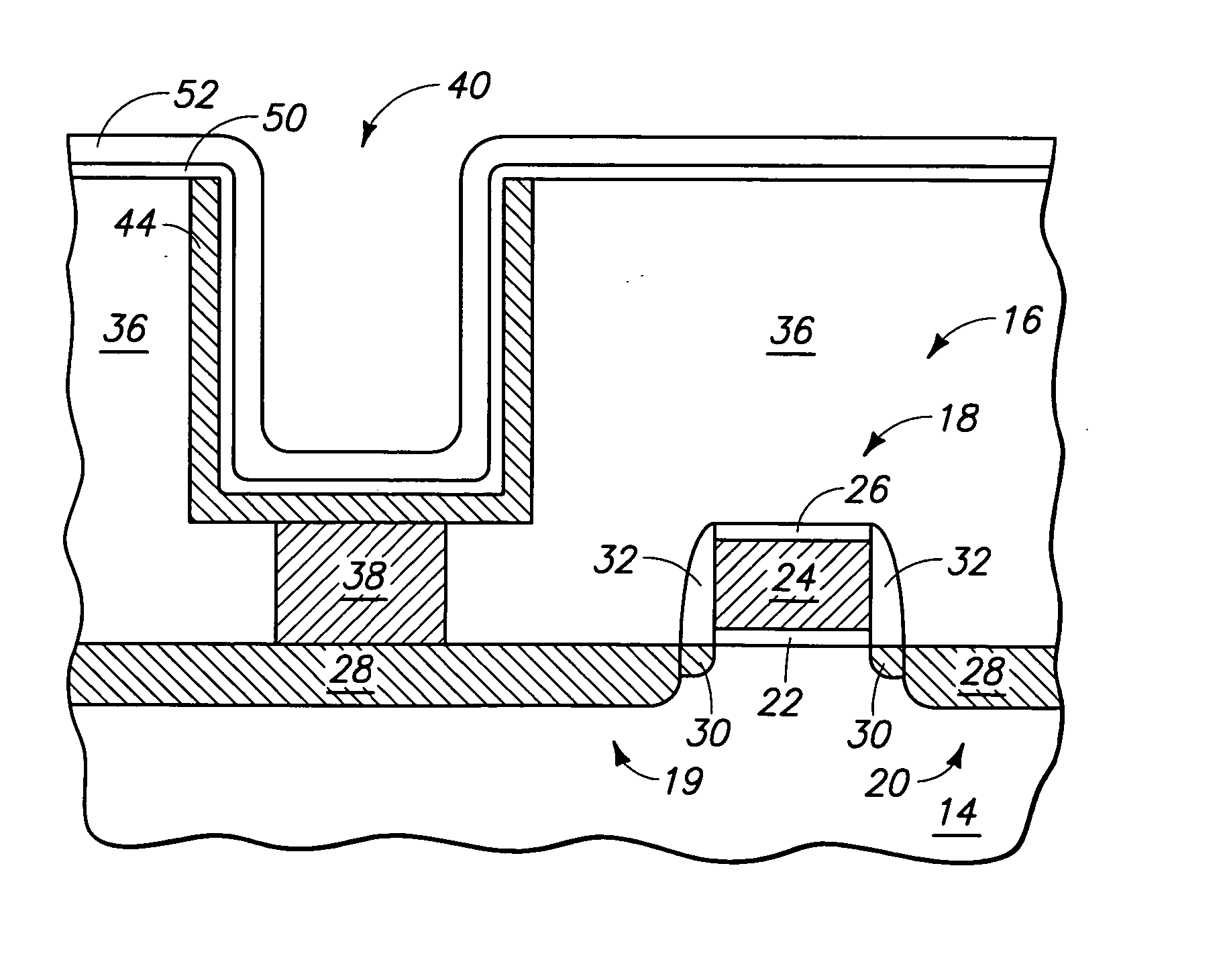
An elevated feedthrough is attachable to a top or a side of an active implantable medical device. The feedthrough includes a conductive ferrule and a dielectric substrate. The dielectric substrate is defined as comprising a body fluid side and a device side disposed within the conductive ferrule. The dielectric substrate includes a body fluid side elevated portion generally raised above the conductive ferrule. At least one via hole is disposed through the dielectric substrate from the body fluid side to the device side. A conductive fill is disposed within the at least one via hole forming a hermetic seal and electrically conductive between the body fluid side and the device side. A leadwire connection feature is on the body fluid side electrically coupled to the conductive fill and disposed adjacent to the elevated portion of the dielectric substrate.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
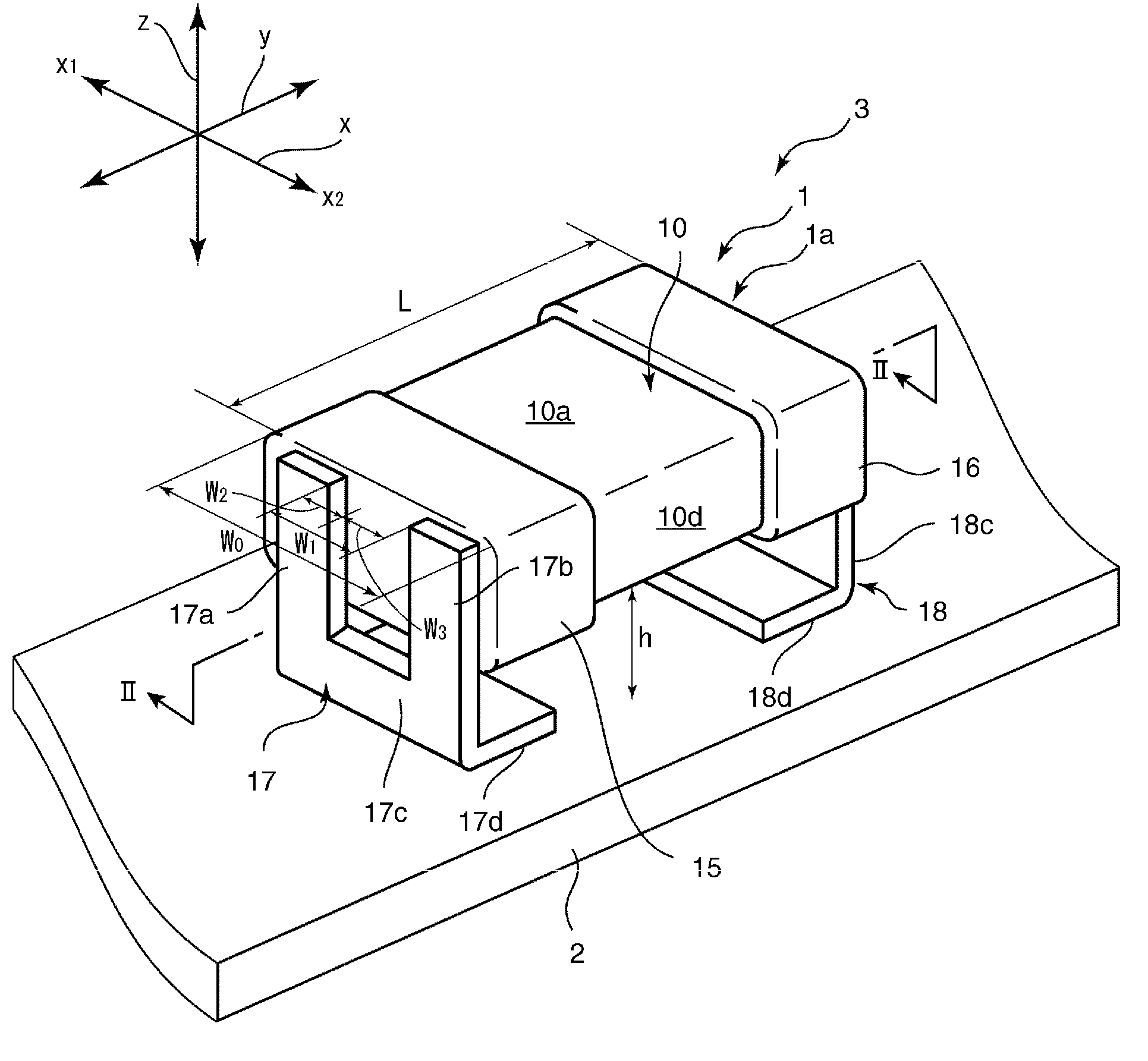
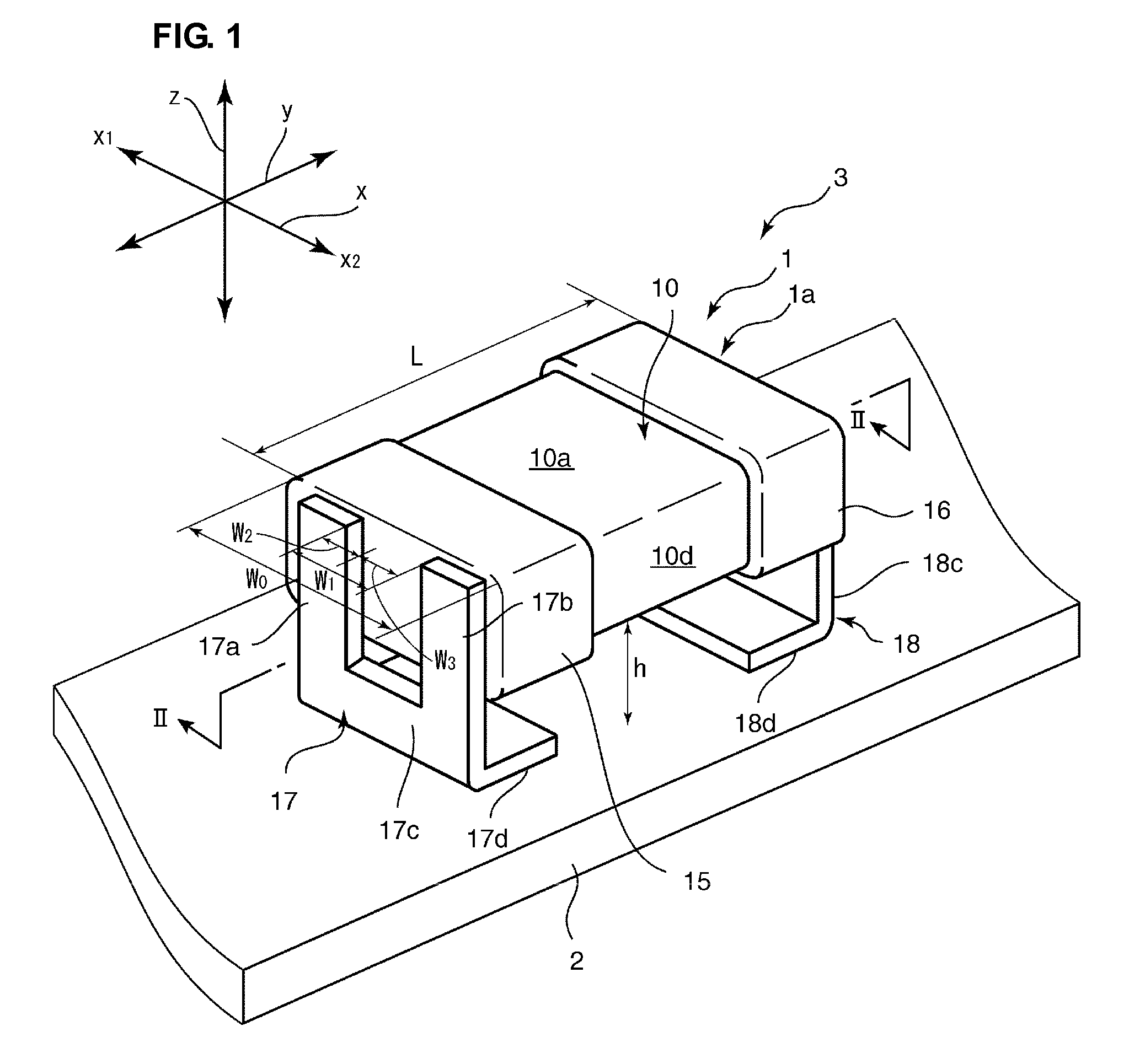
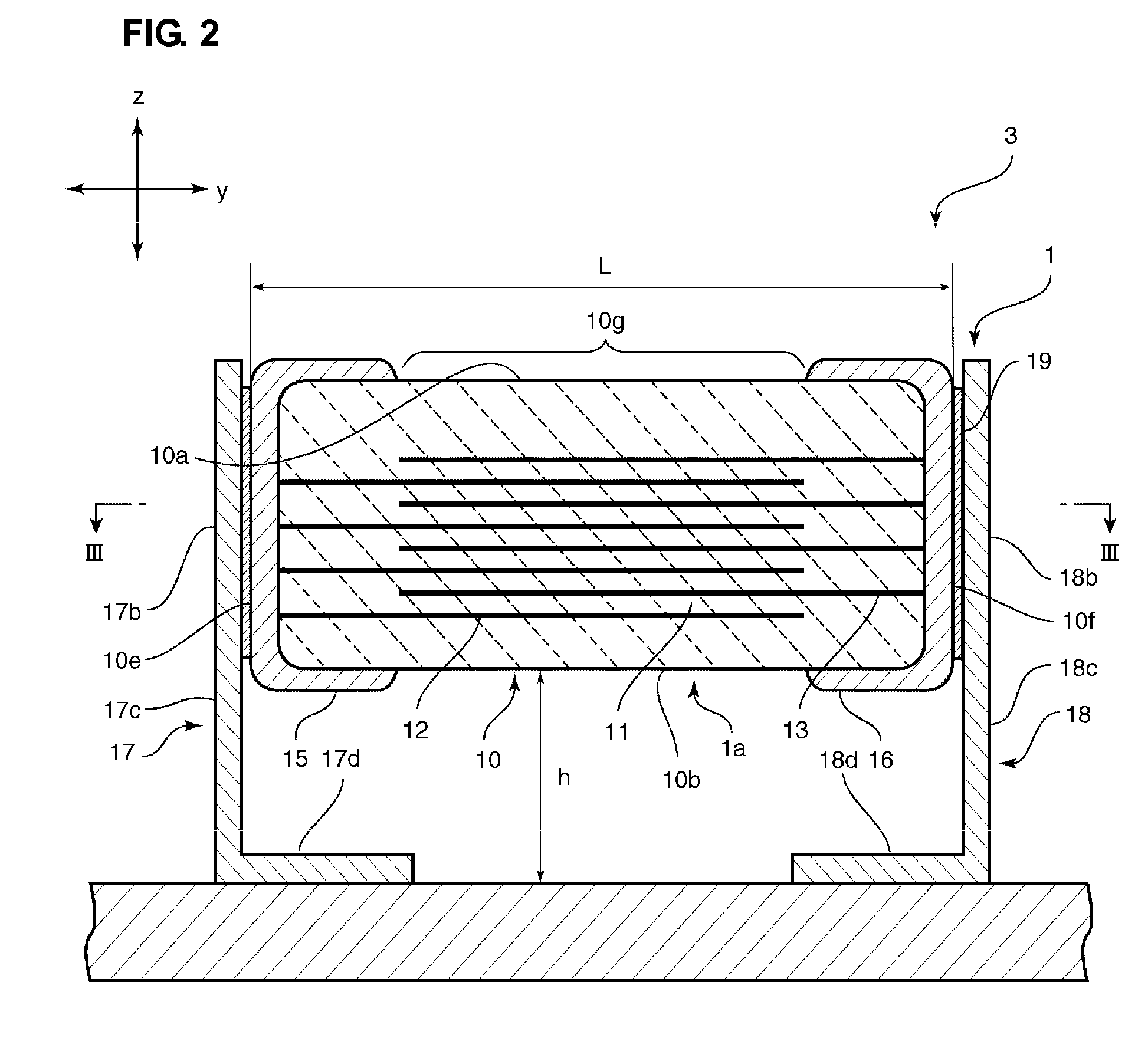
Ceramic capacitor and electronic component including the same
ActiveUS20100123995A1Avoid noiseFinal product manufactureFixed capacitor dielectricCeramic capacitorElectronic component
In a ceramic capacitor, first and second electrode terminals each include a bonded-to-substrate portion, a first bonded-to-electrode portion bonded to a first edge of one of first and second external electrodes, a second bonded-to-electrode portion bonded to a second edge of the one of first and second external electrodes and disposed at a distance from the first bonded-to-electrode portion in the first directions, and a connecting portion connecting the first and second bonded-to-electrode portions and the bonded-to-substrate portion. W1 / W0 is about 0.3 or more, and h / L is about 0.1 or more.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
High-temperature capacitors and methods of making the same
High-temperature, multiple-layer polymer (MLP) capacitors with a stacked electrode arrangement are disclosed. The capacitor electrodes are separated by a polymer dielectric that is stable at high temperatures. In some embodiments, the polymer dielectric also has a high permittivity and is filled with high-permittivity nanoparticles, which enables the capacitor to achieve a very high capacitance density.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ultra broadband capacitor
ActiveUS20100039749A1Efficient and less-expensiveReduce in quantityFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricUltra-widebandBroadband
Disclosed are apparatus and methodology for inexpensive realization of one or more secondary capacitors within a monolithic body that already includes a first, larger capacitor to provide ultra wideband structures. Alternating layers of electrodes are provided with arm portions that embrace portions of adjacent electrode layers so as to create additional coupling effects within the capacitor structure thereby producing multiple additional equivalent capacitor structures within the device.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
Method for manufacturing dielectric capacitor, dielectric memory device
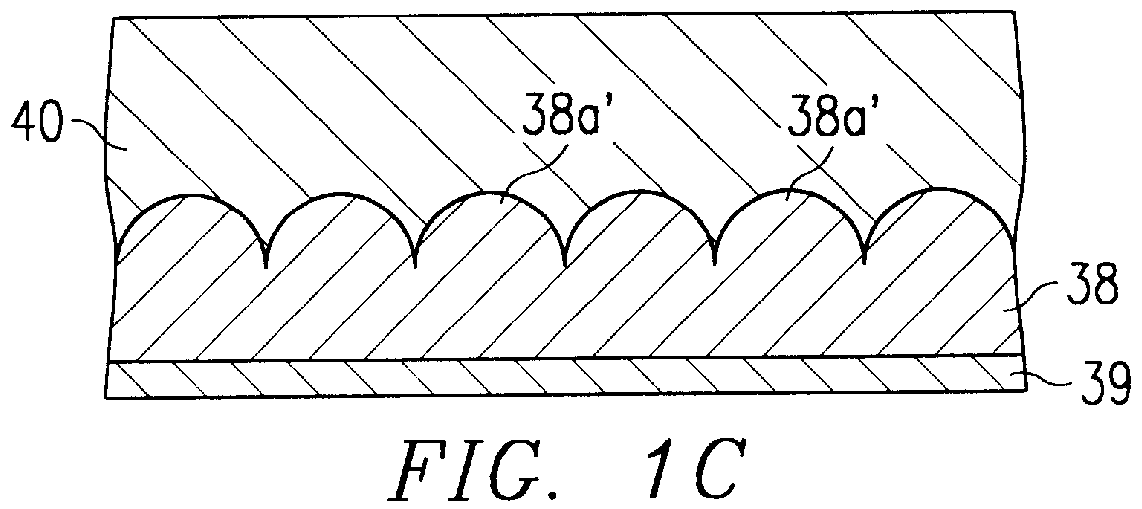
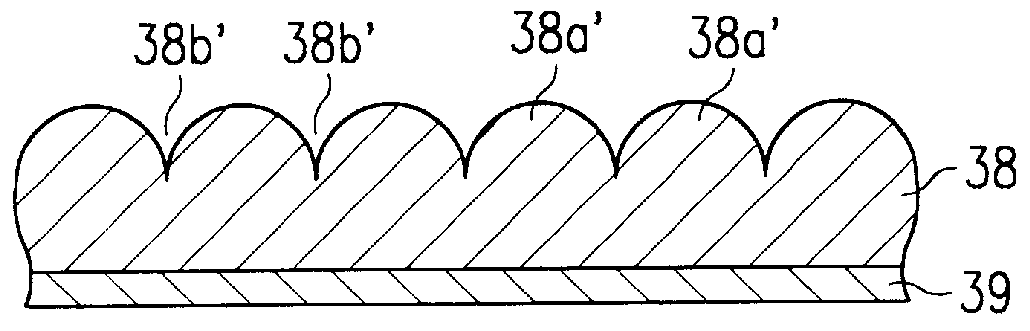
InactiveUS6033953AReduce leakage currentImprove flatnessTransistorThin/thick film capacitorElectrolysisCapacitor
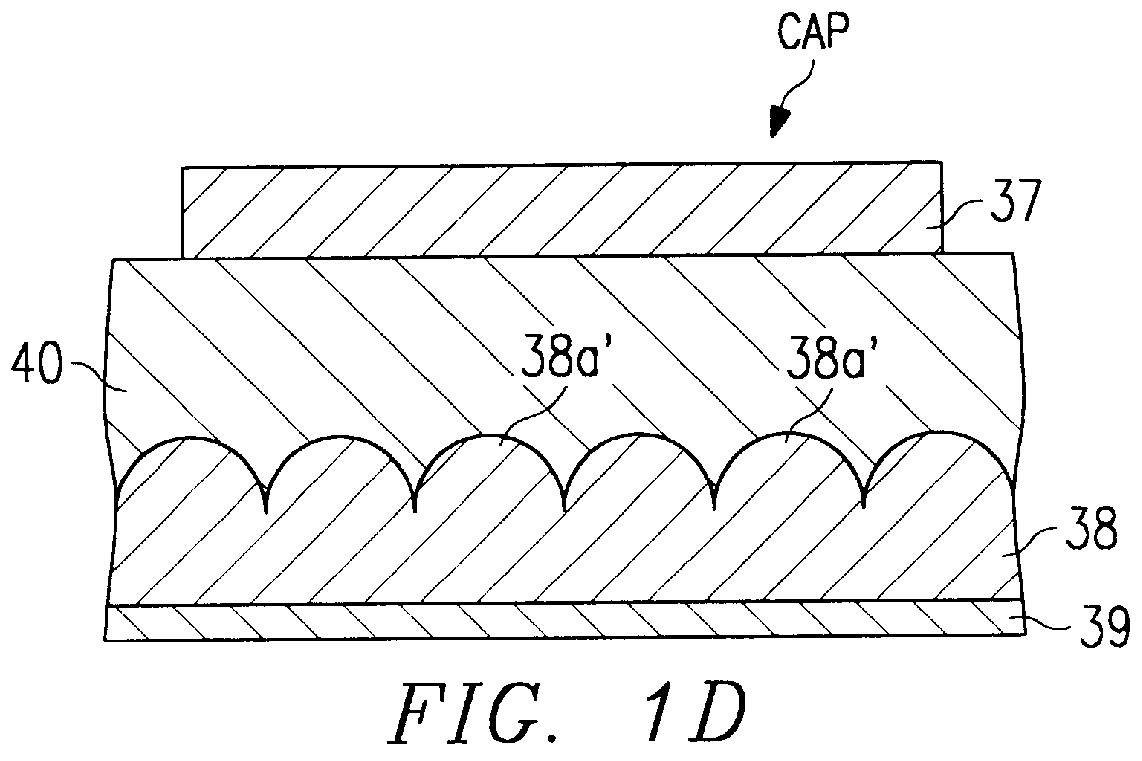
A dielectric capacitor is provided which has a reduced leakage current. The surface of a first electrode (38) of the capacitor is electropolished and a dielectric film (40) and a second electrode (37) are successively laminated on it. The convex parts pointed end (38a) existing on the surface of the first electrode is very finely polished uniformly by dissolving according to electropolishing, a spherical curved surface in which the radius of curvature has been enlarged is formed, and the surface of the first electrode is flattened. Therefore, concentration of electrolysis can be prevented during the operation at the interface of the first electrode and the dielectric film, and the leakage current can be reduced considerably.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
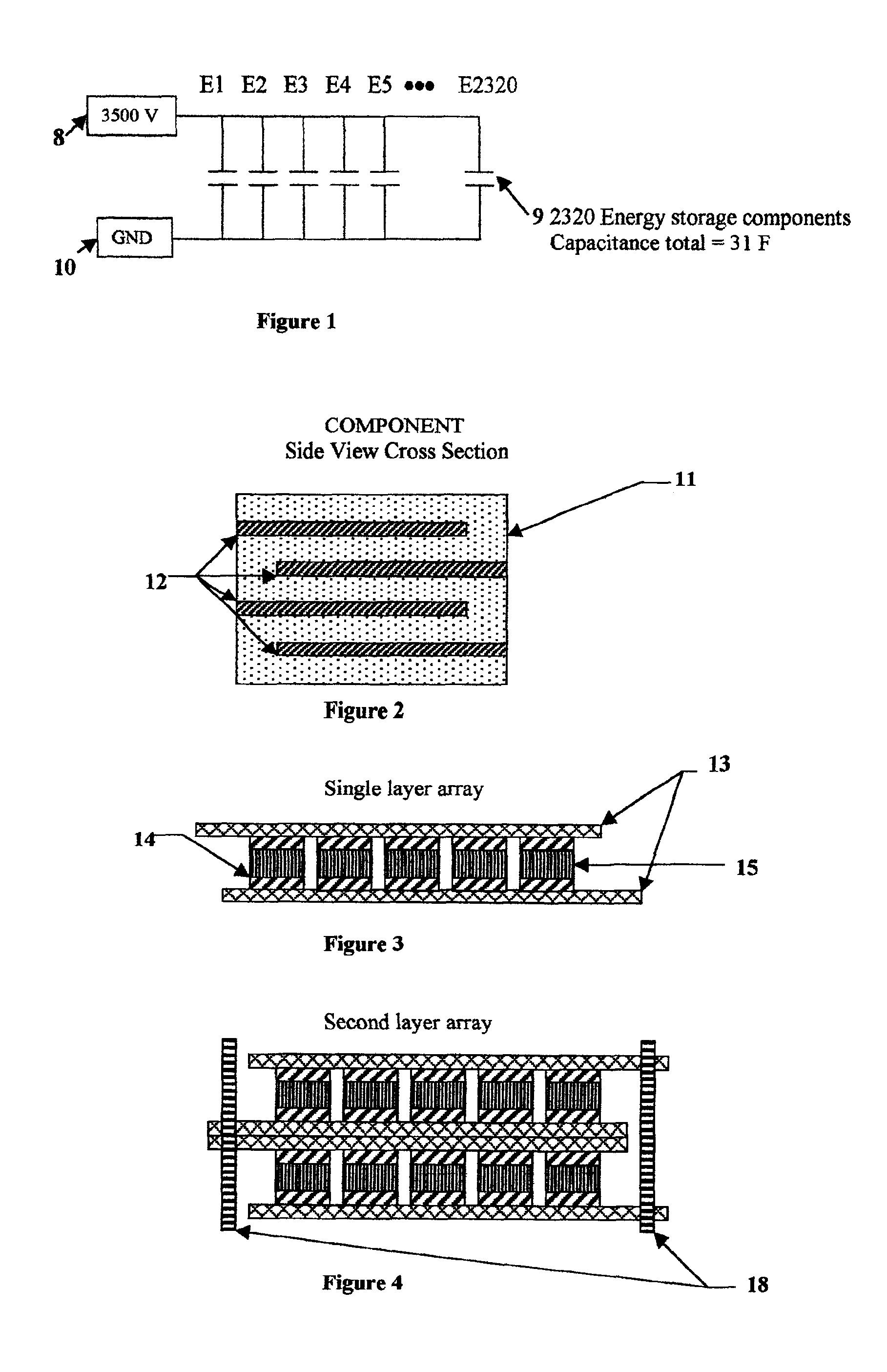
Utilization of poly(ethylene terephthalate) plastic and composition-modified barium titanate powders in a matrix that allows polarization and the use of integrated-circuit technologies for the production of lightweight ultrahigh electrical energy storage units (EESU)
InactiveUS7466536B1Low costLower sintering temperatureCell electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricManufacturing technologyBarium titanate
An electrical-energy-storage unit (EESU) has as a basis material a high-permittivity composition-modified barium titanate ceramic powder. This powder is single coated with aluminum oxide and then immersed in a matrix of poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) plastic for use in screen-printing systems. The ink that is used to process the powders via screen-printing is based on a nitrocellulose resin that provide a binder burnout, sintering, and hot isostatic pressing temperatures that are allowed by the PET plastic. These lower temperatures that are in the range of 40° C. to 150° C. also allows aluminum powder to be used for the electrode material. The components of the EESU are manufactured with the use of conventional ceramic and plastic fabrication techniques which include screen printing alternating multilayers of aluminum electrodes and high-permittivity composition-modified barium titanate powder, sintering to a closed-pore porous body, followed by hot-isostatic pressing to a void-free body. The 31,351 components are configured into a multilayer array with the use of a solder-bump technique as the enabling technology so as to provide a parallel configuration of components that has the capability to store at least 52.22 kW·h of electrical energy. The total weight of an EESU with this amount of electrical energy storage is 281.56 pounds including the box, connectors, and associated hardware.
Owner:EESTOR
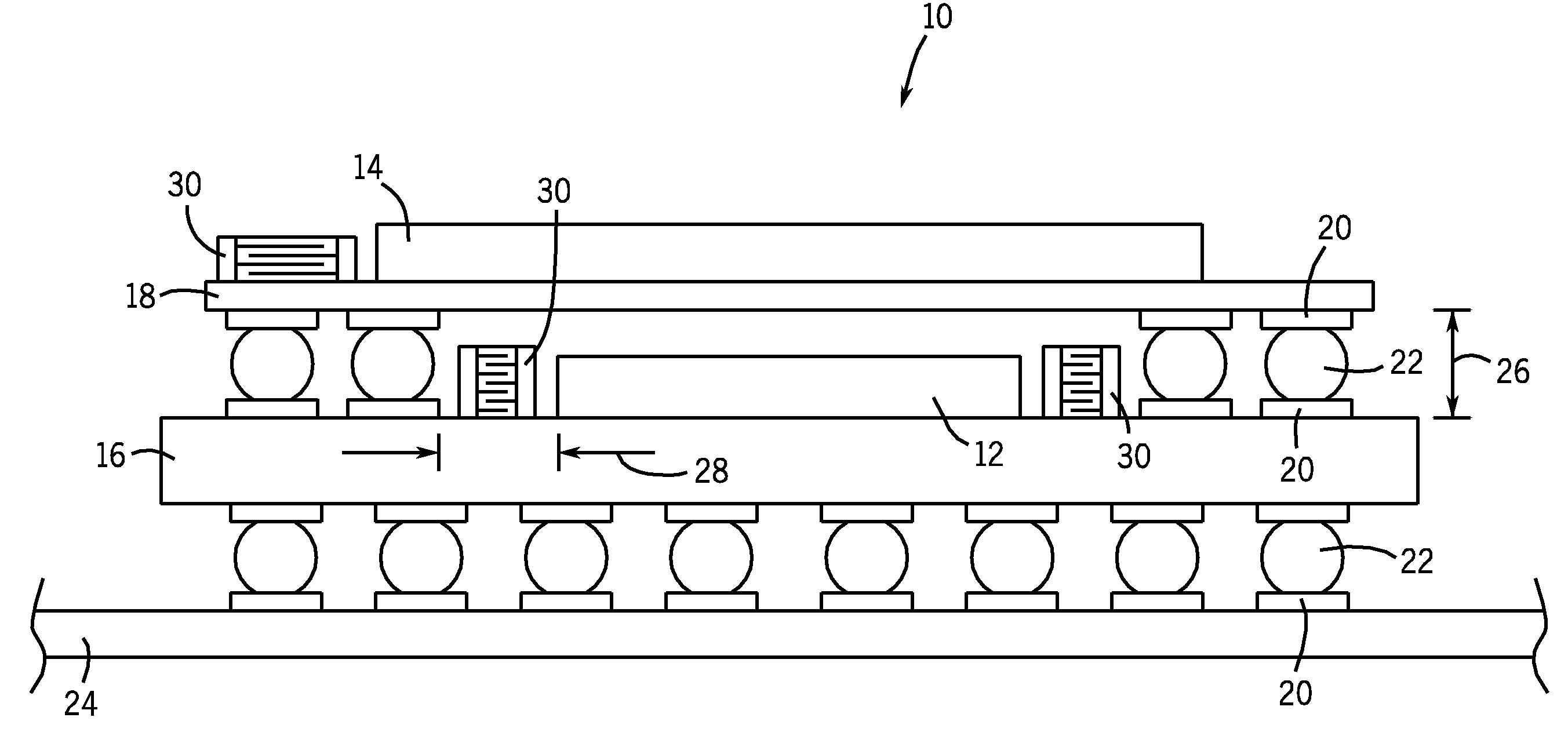
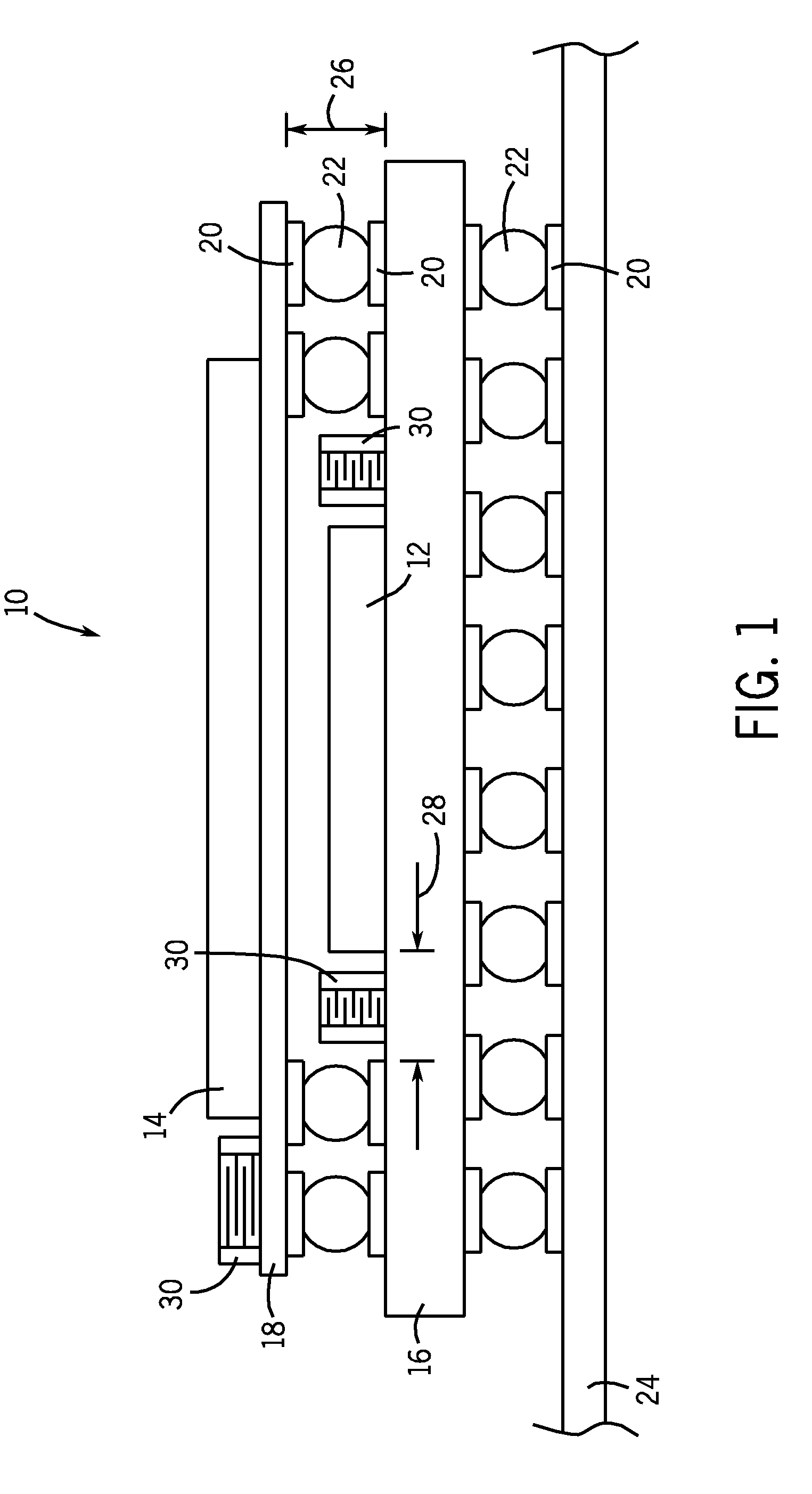
Universial energy conditioning interposer with circuit architecture
InactiveUS7110227B2Solve and reduce industry problemSolve and reduce and obstacleMagnetic/electric field screeningSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEnergy regulationInterposer
The present invention relates to an interposer substrate for interconnecting between active electronic componentry such as but not limited to a single or multiple integrated circuit chips in either a single or a combination and elements that could comprise of a mounting substrate, substrate module, a printed circuit board, integrated circuit chips or other substrates containing conductive energy pathways that service an energy utilizing load and leading to and from an energy source. The interposer will also possess a multi-layer, universal multi-functional, common conductive shield structure with conductive pathways for energy and EMI conditioning and protection that also comprise a commonly shared and centrally positioned conductive pathway or electrode of the structure that can simultaneously shield and allow smooth energy interaction between grouped and energized conductive pathway electrodes containing a circuit architecture for energy conditioning as it relates to integrated circuit device packaging. The invention can be employed between an active electronic component and a multilayer circuit card. A method for making the interposer is not presented and can be varied to the individual or proprietary construction methodologies that exist or will be developed.
Owner:X2Y ATTENUATORS L L C
Capacitor for incorporation in wiring board, wiring board, method of manufacturing wiring board, and ceramic chip for embedment
InactiveUS20070030628A1High bonding strengthImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectric layerCapacitor
A capacitor comprising: a capacitor body including a plurality of laminated dielectric layers, a plurality of inner electrode layers which are respectively disposed between mutually adjacent ones of the dielectric layers, a first main surface located in a laminated direction of the dielectric layers, and a second main surface opposite to the first main surface; a first outer electrode formed on the first main surface of the capacitor body and electrically connected to the inner electrode layers; a second outer electrode formed on the second main surface of the capacitor body and electrically connected to the inner electrode layers; a first dummy electrode formed on the first main surface of the capacitor body; and a second dummy electrode formed on the second main surface of the capacitor body.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
Controlled esr low inductance capacitor
InactiveUS20100188799A1Improve current cancellationIncrease path lengthFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricElectrical resistance and conductancePath length
Multilayer capacitors incorporate both low inductance (ESL) and controlled Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) features into a cost-effective unitary device. Internal electrode patterns generally include one or more pairs of mother electrodes adapted for external connection (e.g., to a circuit, another electrical component, circuit board, or other mounting environment), and multiple pairs of daughter electrodes adapted only for internal connection to other electrodes (e.g., other daughter electrodes and / or selected mother electrodes) without direct connection to an external circuit. Mother and daughter electrodes are interdigitated with electrode tab features, where daughter electrodes have internal-connection tabs, and mother electrodes have both internal-connection tabs and circuit-connection tabs, all of which are connected to respective internal-connection or circuit-connection terminals. ESR is increased by the parallel connection between mother and daughter electrodes as well as other optional features such as but not limited to resistive terminations, resistive connectors, serpentine terminations and increased current path lengths.
Owner:AVX CORP
Multilayer ceramic capacitor
ActiveUS20150340155A1Reduce moistureImprove moisture resistanceFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricMetallurgyCeramic capacitor
A multilayer ceramic capacitor includes a ceramic body and external electrodes provided on opposite end surfaces of the ceramic body. The ceramic body includes an inner layer portion including a plurality of ceramic layers defining inner layers and a plurality of first and second internal electrodes each disposed at an interface of adjacent ones of the ceramic layers defining the inner layers, outer layer portions sandwiching the inner layer portion in a direction in which the layers are stacked, and side margin portions sandwiching the inner layer portion and the outer layer portions in a widthwise direction. The side margin portion includes pores that decrease in number along a direction from inside to outside of the ceramic body.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
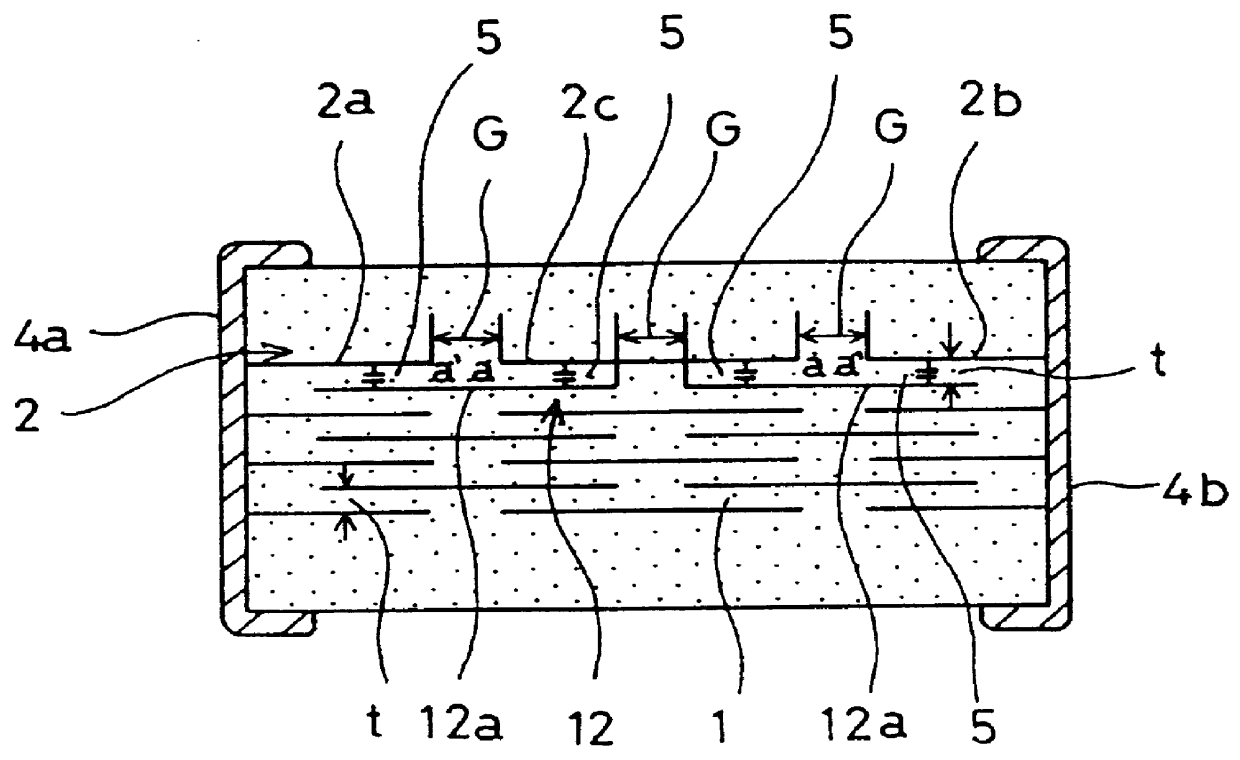
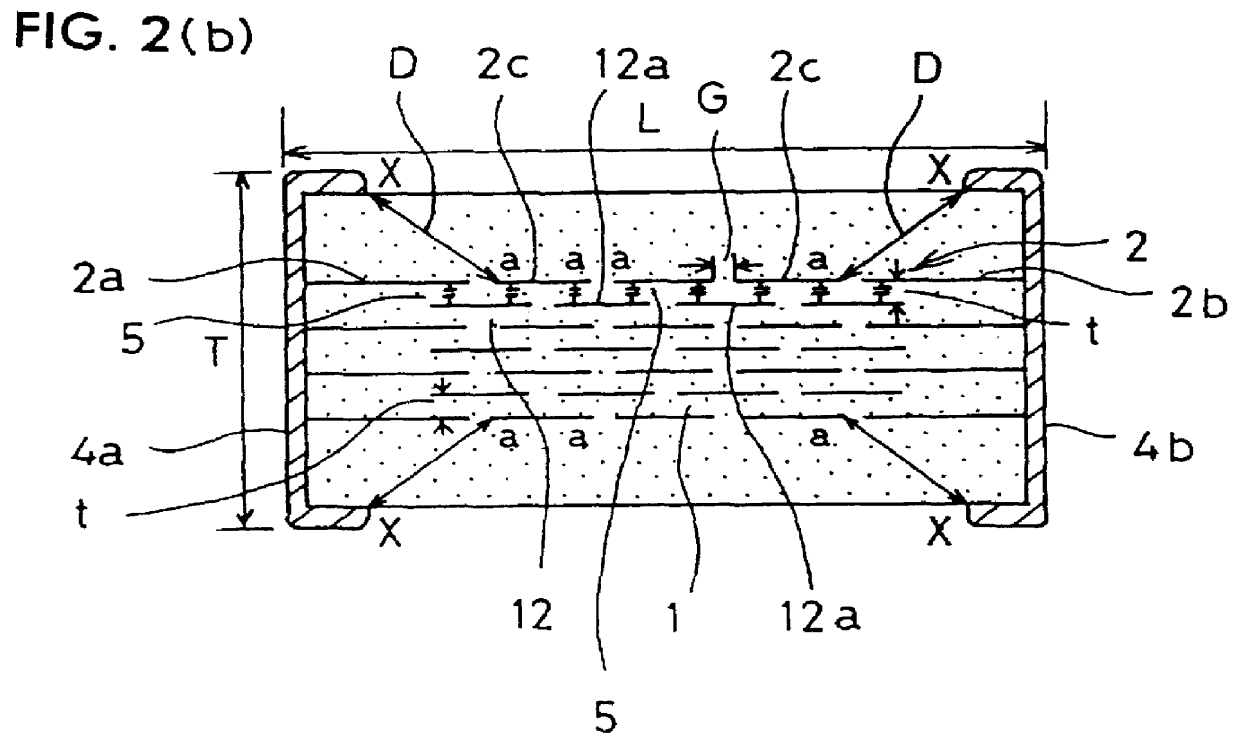
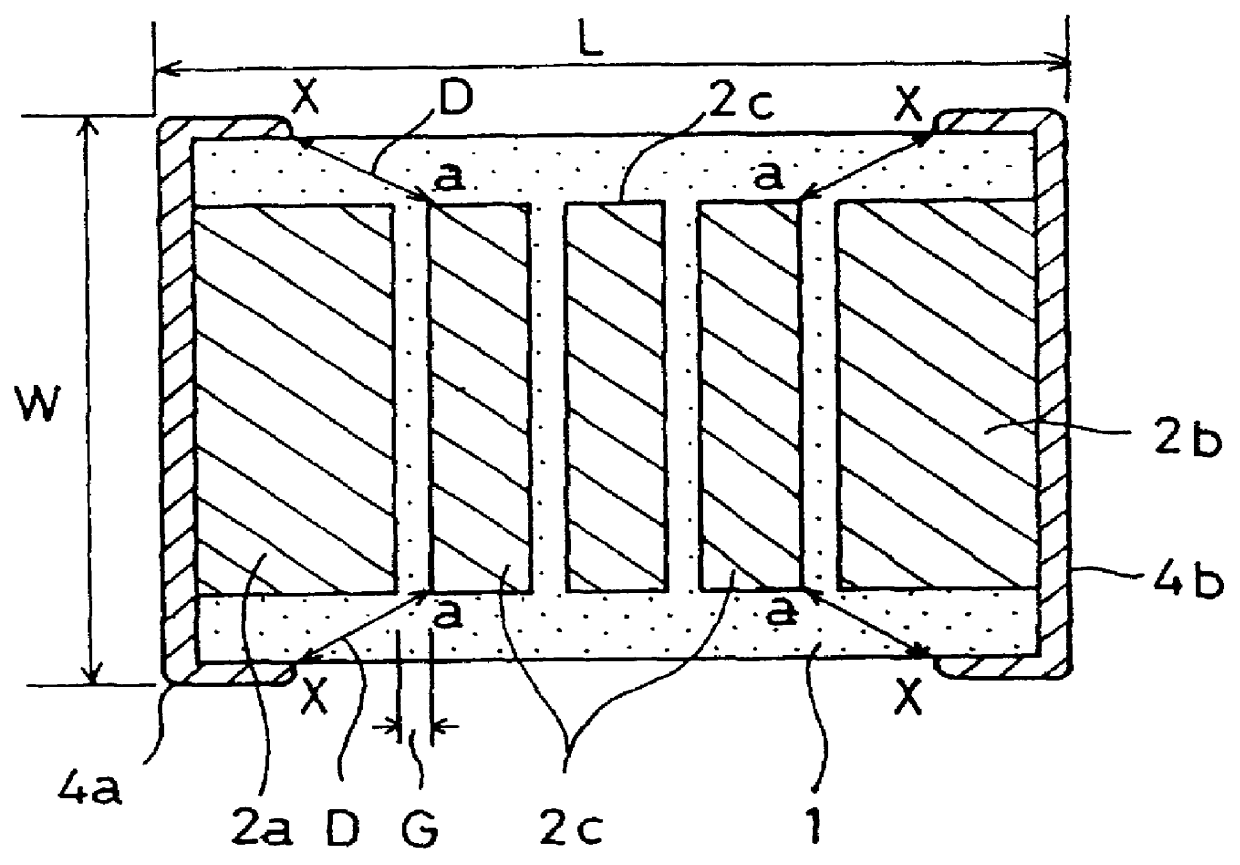
Laminated capacitor
A laminated capacitor that can be made small in size, that can prevent flashover, has excellent dielectric strength performance and a large capacitance is disclosed. Each gap between internal electrodes in the same plane is set at 2.7 to 20 times a thickness (element thickness) of a dielectric layer positioned between first and second internal electrode groups which face each other and a distance between an edge of the external terminal and an edge of the floating internal electrode closest to the external terminal among floating internal electrodes of the internal electrode group of the outermost layer is set at 0.4 mm to 1.4 mm.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Structure for a thin film multilayer capacitor
An electronic component structure is proposed, wherein an interposer thin film capacitor structure is employed between an active electronic component and a multilayer circuit card. A method for making the interposer thin film capacitor is also proposed. In order to eliminate fatal electrical shorts in the overlying thin film regions that arise from pits, voids, or undulations on the substrate surface, a thick first metal layer, on the order of 0.5-10 mu m thick, is deposited on the substrate upon which the remaining thin films, including a dielectric film and second metal layer, are then applied. The first metal layer includes of Pt or other electrode metal, or a combination of Pt, Cr, and Cu metals, and a diffusion barrier layer. Additional Ti layers may be employed for adhesion enhancement. The thickness of the first metal layers are approximately: 200 A for the Cr layer; 0.5-10 mu m for the Cu layer; 1000 A-5000 A for the diffusion barrier; and 100 A-2500 A for a Pt layer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods of forming hafnium-containing materials, methods of forming hafnium oxide, and constructions comprising hafnium oxide
The invention includes methods of forming hafnium-containing materials, such as, for example, hafnium oxide. In one aspect, a semiconductor substrate is provided, and first reaction conditions are utilized to form hafnium-containing seed material in a desired crystalline phase and orientation over the substrate. Subsequently, second reaction conditions are utilized to grow second hafnium-containing material over the seed material. The second hafnium-containing material is in a crystalline phase and / or orientation different from the crystalline phase and orientation of the hafnium-containing seed material. The second hafnium-containing material can be, for example, in an amorphous phase. The seed material is then utilized to induce a desired crystalline phase and orientation in the second hafnium-containing material. The invention also includes capacitor constructions utilizing hafnium-containing materials, and circuit assemblies comprising the capacitor constructions.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com