Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
134results about How to "Good lattice matching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
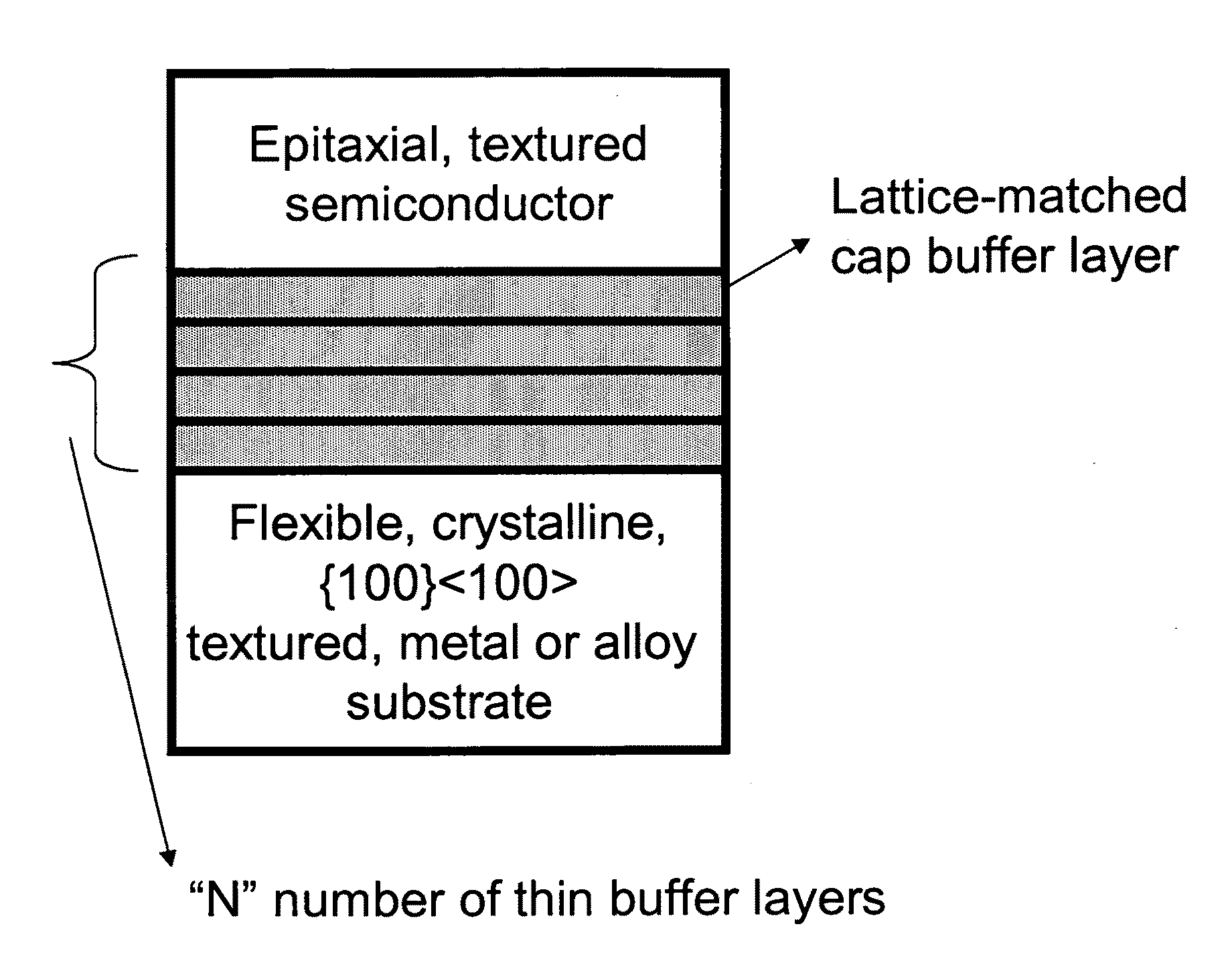
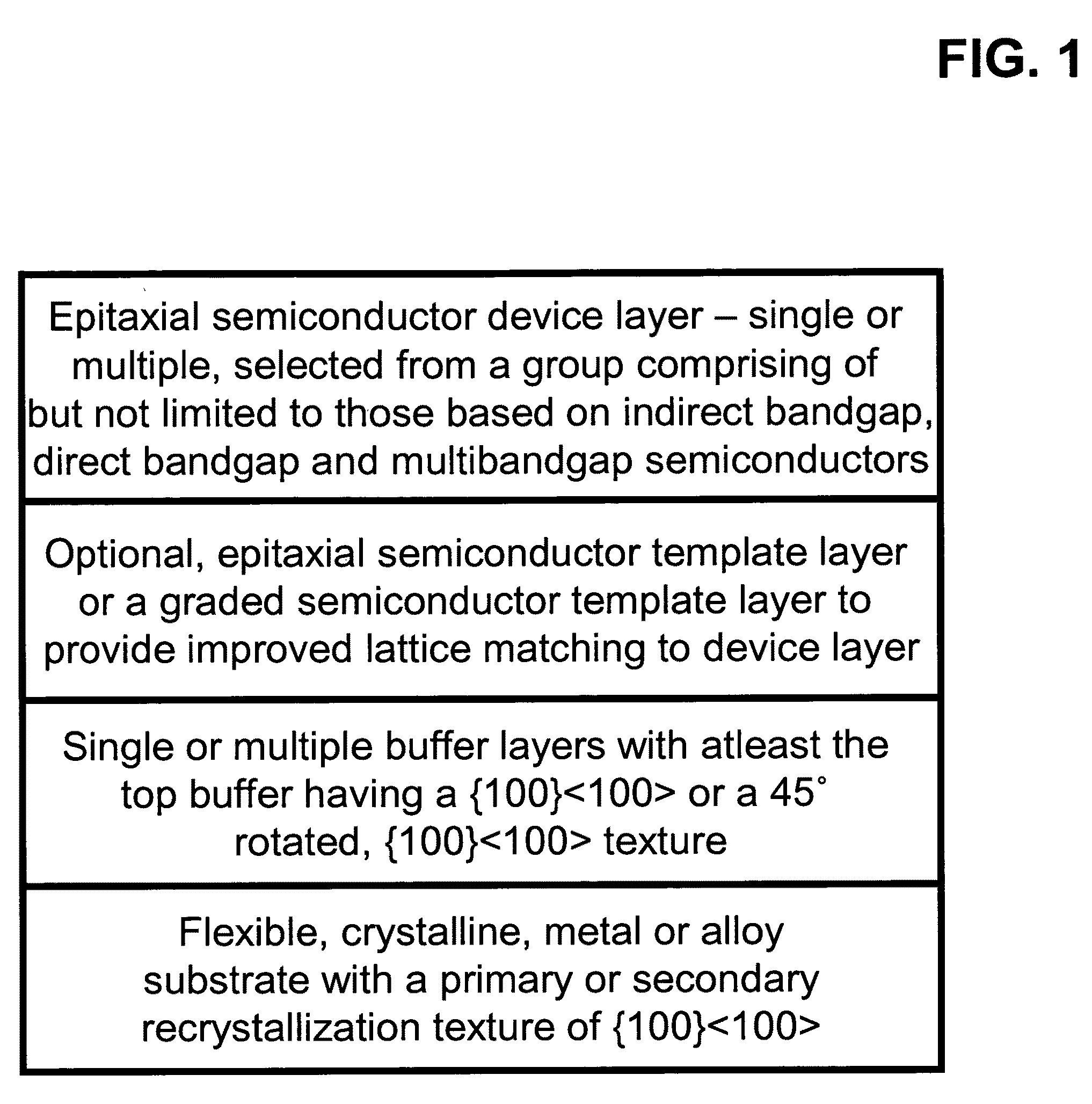
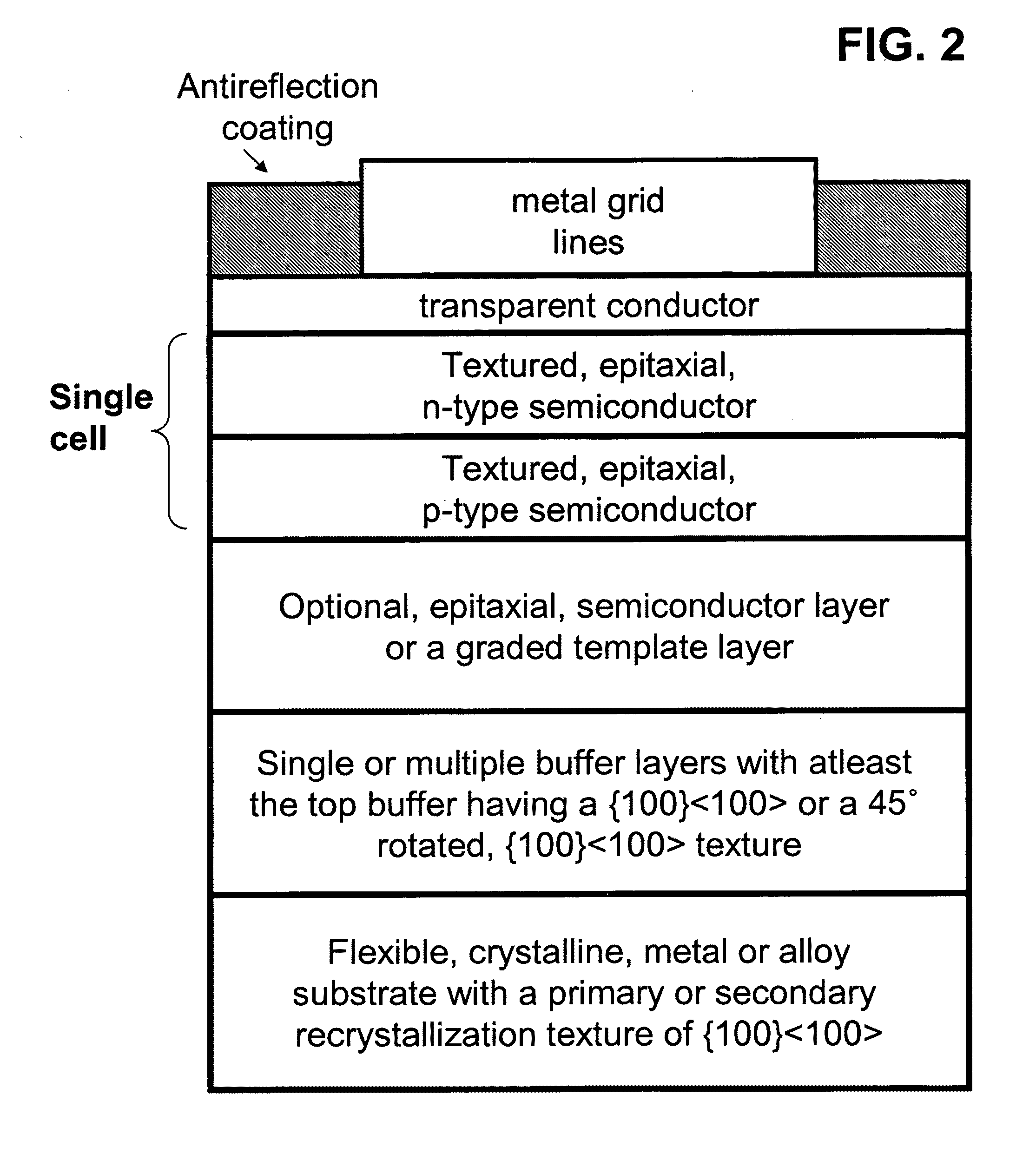
<100> or 45 degrees-rotated <100>, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices
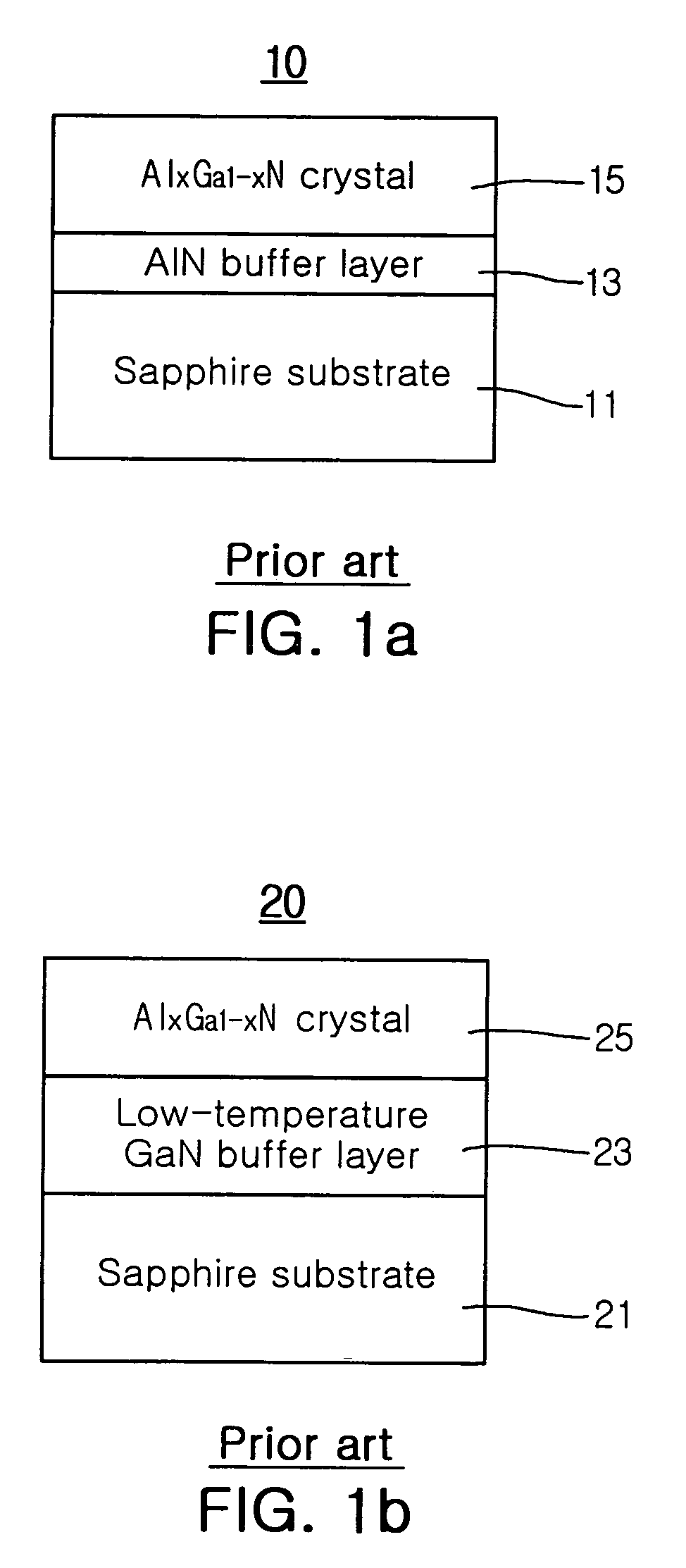
InactiveUS20110062446A1Good lattice matchingSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHard disc drivePhotoluminescence
Novel articles and methods to fabricate the same resulting in flexible, {100}<100> or 45°-rotated {100}<100> oriented, semiconductor-based, electronic devices are disclosed. Potential applications of resulting articles are in areas of photovoltaic devices, flat-panel displays, thermophotovoltaic devices, ferroelectric devices, light emitting diode devices, computer hard disc drive devices, magnetoresistance based devices, photoluminescence based devices, non-volatile memory devices, dielectric devices, thermoelectric devices and quantum dot laser devices.
Owner:GOYAL AMIT
Semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices on <100> oriented substrates
InactiveUS20080265255A1Improve performanceGood lattice matchingFinal product manufactureNanoinformaticsHard disc drivePhotoluminescence
Novel articles and methods to fabricate the same resulting in flexible, oriented, semiconductor-based, electronic devices on {110}<100> textured substrates are disclosed. Potential applications of resulting articles are in areas of photovoltaic devices, flat-panel displays, thermophotovoltaic devices, ferroelectric devices, light emitting diode devices, computer hard disc drive devices, magnetoresistance based devices, photoluminescence based devices, non-volatile memory devices, dielectric devices, thermoelectric devices and quantum dot laser devices.
Owner:GOYAL AMIT
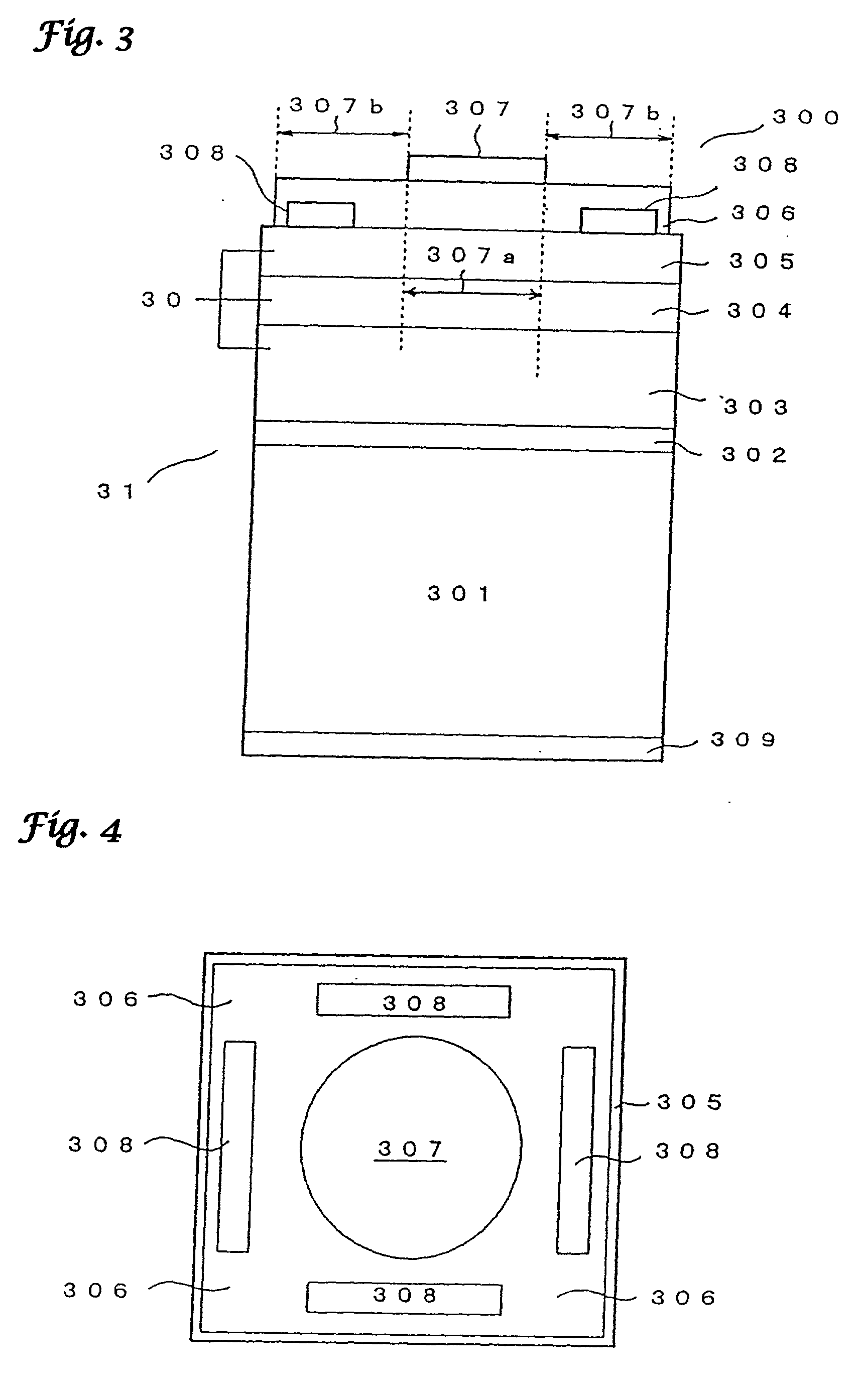
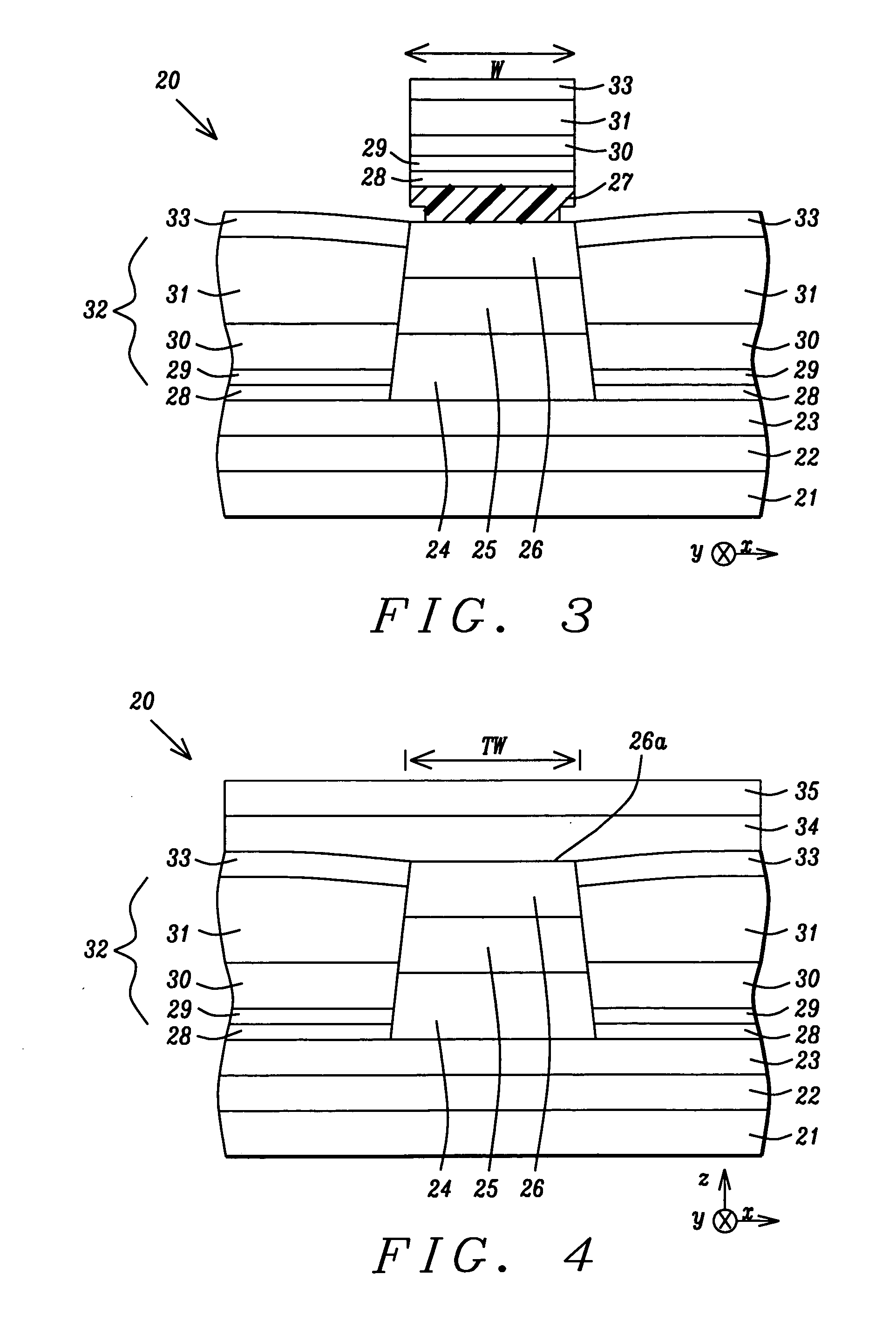
[100] Or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices
InactiveUS20080230779A1Good lattice matchingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHard disc drivePhotoluminescence
Novel articles and methods to fabricate the same resulting in flexible, large-area, [100] or [110] textured, semiconductor-based, electronic devices are disclosed. Potential applications of resulting articles are in areas of photovoltaic devices, flat-panel displays, thermophotovoltaic devices, ferroelectric devices, light emitting diode devices, computer hard disc drive devices, magnetoresistance based devices, photoluminescence based devices, non-volatile memory devices, dielectric devices, thermoelectric devices and quantum dot laser devices.
Owner:GOYAL AMIT
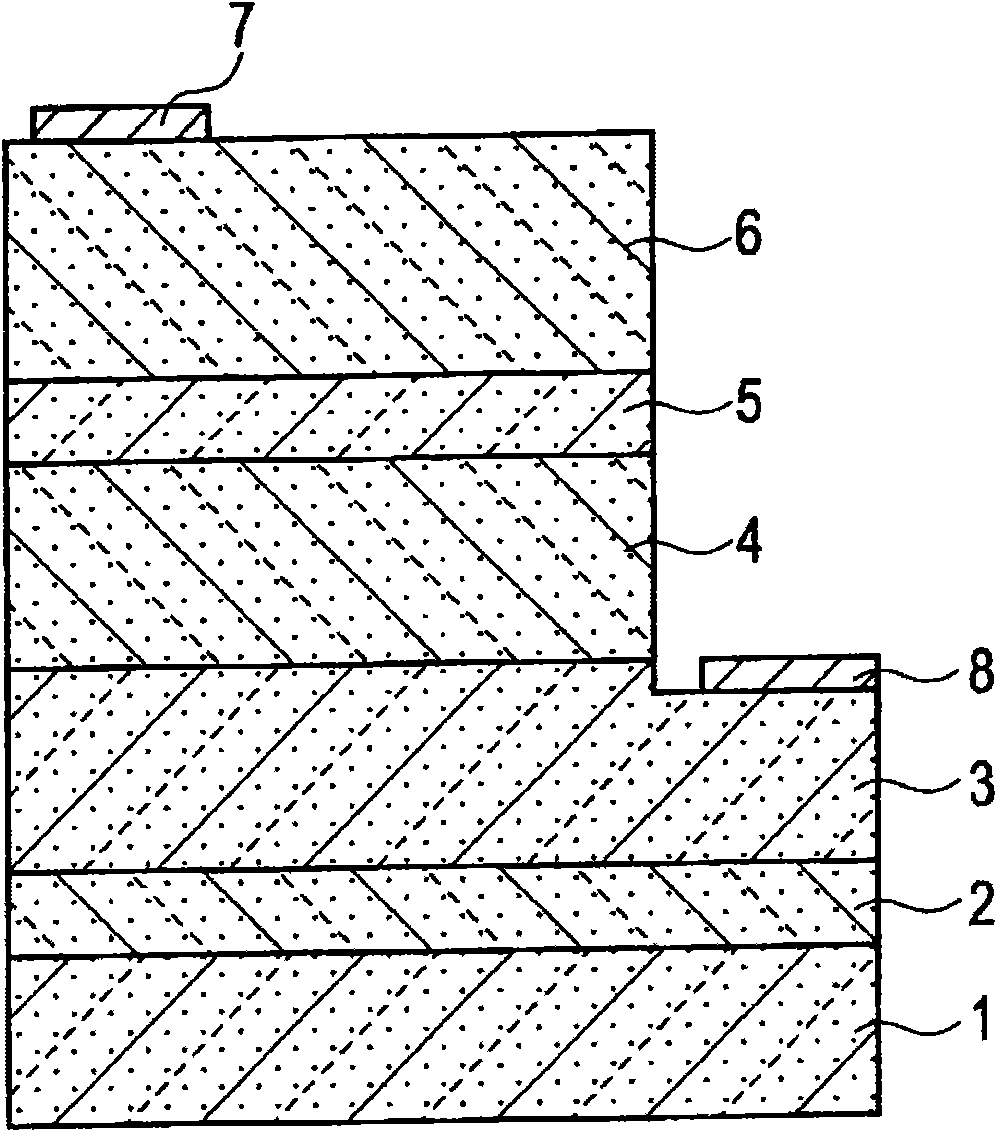
Group-III nitride semiconductor light-emitting diode, light-emitting diode lamp, light source, electrode for group-III nitride semiconductor light-emitting diode, and method for producing the electrode
InactiveUS20020000563A1Easy to displayHigh luminous intensitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDriving currentLight emission
The present invention solves the problem of conventional group-III nitride semiconductor LED in that, since the LED driving current is supplied only from a pad electrode serving also as an ohmic electrode, the driving current cannot diffuse over a wide range of the light-emitting region and a group-III nitride semiconductor LED having high light emission intensity cannot be successfully provided. A group-III nitride semiconductor LED having high light emission intensity, which is fabricated using a stacked layer structure obtained by providing a surface ohmic electrode, a window layer including an electrically conducting transparent oxide crystal layer and a pad electrode on an electrically conducting substrate through a boron phosphide (BP)-based buffer layer to allow the driving current to diffuse over a wide range of the light-emitting region is provided.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
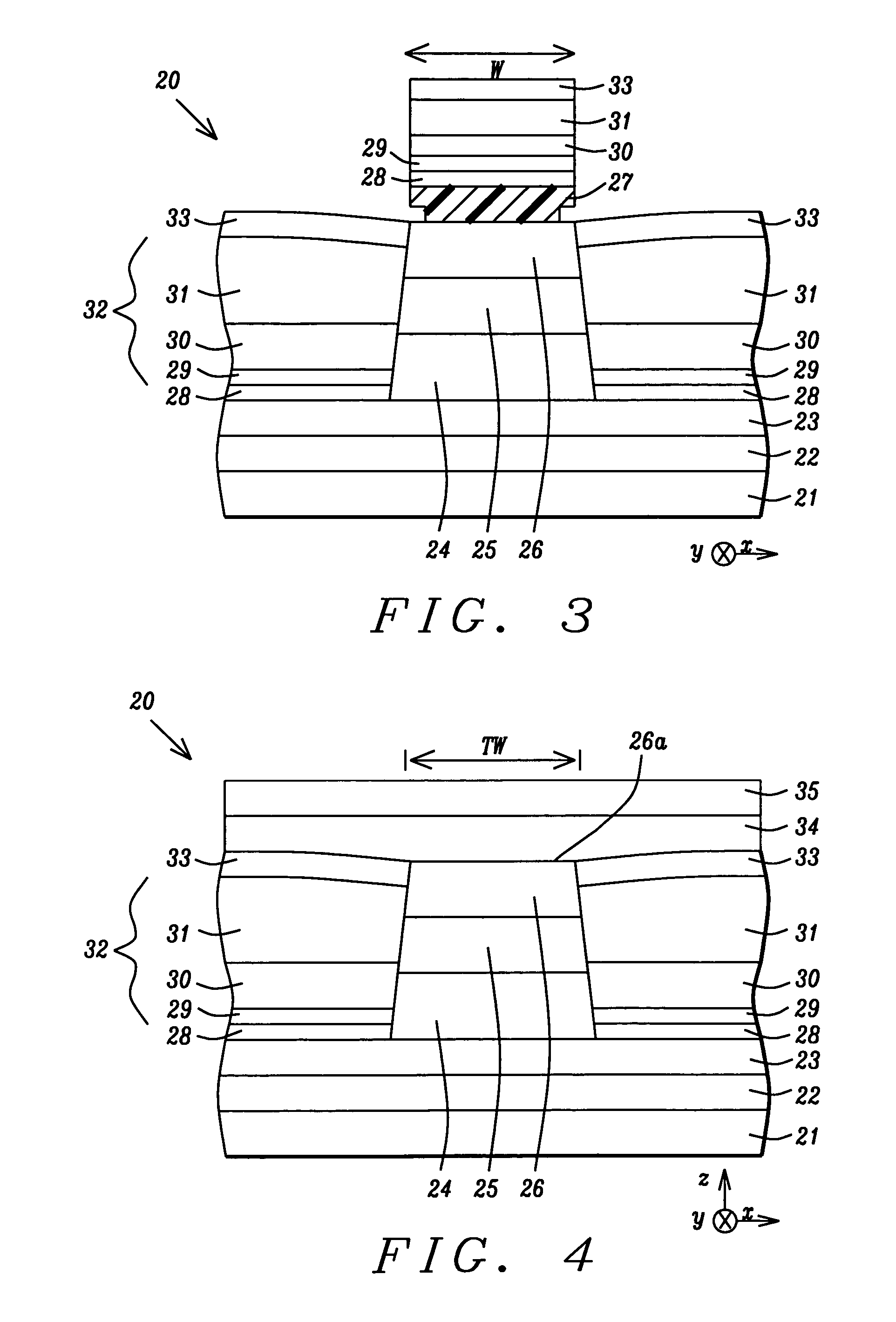
Novel hard bias design for extra high density recording
InactiveUS20050275975A1Enhance its moment contributionImprove coercive forceNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsHigh densityOptoelectronics
A hard bias structure for biasing a free layer in a MR element within a read head is comprised of a composite hard bias layer having a Co78.6Cr5.2Pt16.2 / Co65Cr15Pt20 configuration. The upper Co65Cr15Pt20 layer has a larger Hc value and a thickness about 2 to 10 times greater than that of the Co78.6Cr5.2Pt16.2 layer. The hard bias structure may also include a BCC underlayer such as FeCoMo which enhances the magnetic moment of the hard bias structure. Optionally, the thickness of the Co78.6Cr5.2Pt16.2 layer is zero and the Co65Cr15Pt20 layer is formed on the BCC underlayer. The present invention also encompasses a laminated hard bias structure. The Mrt value for the hard bias structure may be optimized by adjusting the thicknesses of the BCC underlayer and CoCrPt layers. As a result, a larger process window is realized and lower asymmetry output during a read operation is achieved.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Nitride semiconductor light emitting element and method for manufacturing nitride semiconductor
InactiveCN101689586AGood lattice matchingImprove crystal qualityNanoopticsSemiconductor devicesActive layerNitride semiconductors
Provided is a nitride semiconductor light emitting element having improved optical output with improved qualities, such as crystal qualities, of a nitride semiconductor laminated on an AlN buffer layer. An AlN buffer layer (2) is formed on a sapphire substrate (1), and on the buffer layer, nitride semiconductors of an n-type AlGaN layer (3), an InGaN / GaN active layer (4) and a p-type GaN layer (5)are laminated in sequence. On the surface of the n-type AlGaN layer (3), an n-electrode (7) is formed, and on the p-type GaN layer (5), a p-electrode (6) is formed. The n-type AlGaN layer (3) operates as a clad layer for confining light and carriers. The AlN buffer layer (2) is manufactured by alternately supplying an Al material and an N material at a growing temperature of 900 DEG C or higher.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
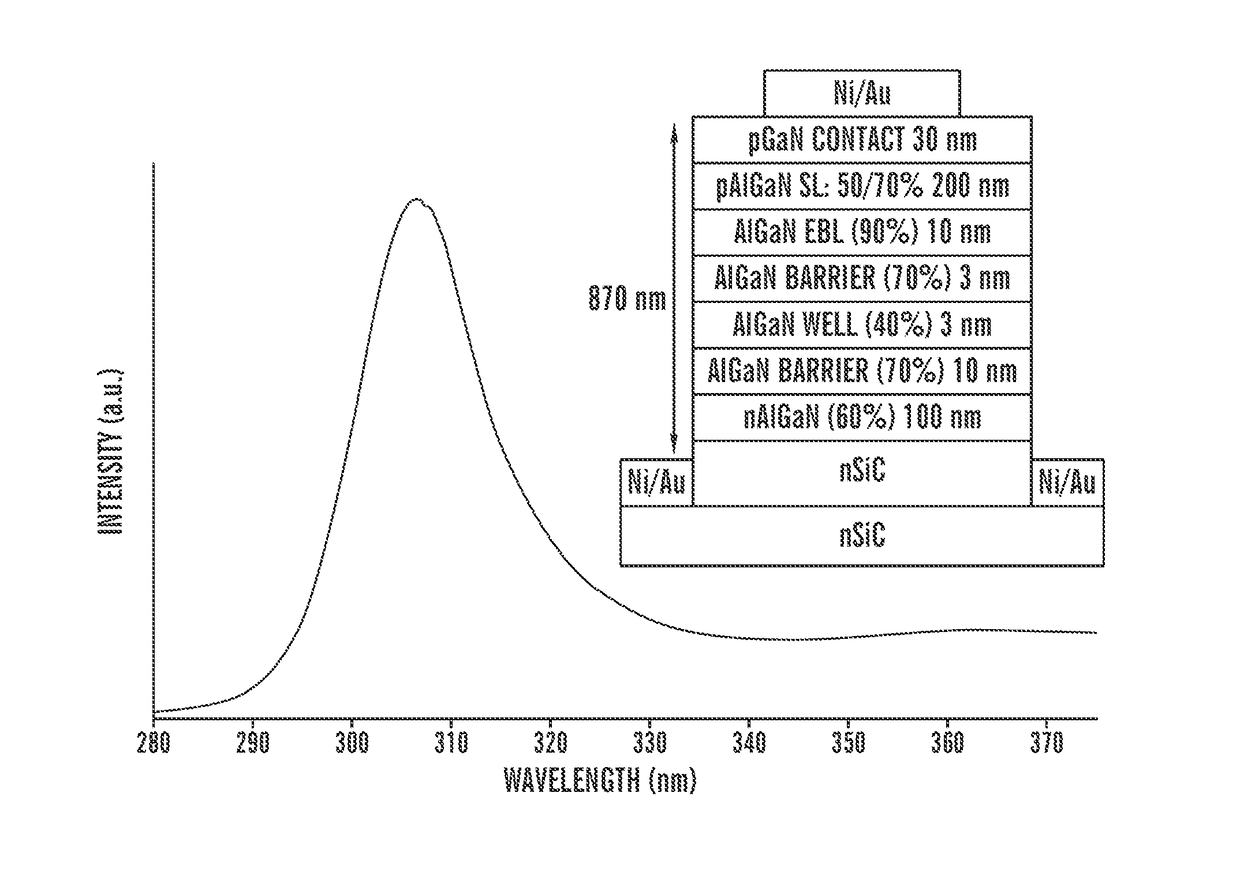
Ultraviolet light emitting diodes
ActiveUS20170200865A1Increasing EEReduce absorption lossSemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyDistributed Bragg reflector
The invention provides ultraviolet (UV) light-emitting diodes (LEDs). The UV LEDs can comprise abase layer including p-type SiC or p-type AlGaN, an active layer, and an n-AlGaN layer, wherein the active layer is disposed between the base layer and the n-AlGaN layer. In some embodiments, the absorption losses in p-SiC can be decreased or prevented by incorporating a conductive AlGaN Distributed Bragg Reflector (DBR) between the p-type SiC layer and the active layer. In some embodiments, the n-AlGaN layer can be textured to increase the extraction efficiency (EE). In some embodiments, the external quantum efficiency of the LEDs can be 20-30% or more.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Nitride semiconductor component layer structure on a group iv substrate surface
InactiveUS20100133658A1Good lattice matchingReduce the possibilityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrystal structureSingle crystal
The invention relates to nitride semiconductor component having a Group III nitride layer structure which is deposited on a substrate having a Group IV substrate surface made of a Group IV substrate material with a cubical crystal structure. The Group IV substrate surface has an elementary cell with C2 symmetry, but not with a higher rotational symmetry than C2 symmetry, when any surface reconstruction is ignored. The Group III nitride layer structure has a seeding layer of ternary or quaternary Al1-x-yInxGayN, where 0≦x, y<1 and x+y≦1, immediately adjacent to the Group IV substrate surface. High-quality monocrystalline growth is achieved as a result. The advantage of the invention consists in the high level of crystal quality that can be achieved, in the growth of c-, a- and m-plane GaN and above all in the ease with which the silicon substrate can be wholly or partially removed, since this is easier to do in a wet chemical process than on (111)-oriented substrates.
Owner:AZZURRO SEMICON
Method for manufacturing gallium nitride-based semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060246614A1Avoid it happening againImproving crystalinity of GaN-basedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialCompound (substance)
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a gallium nitride-based semiconductor device having low-density crystalline defects and high-quality crystalinity. In the manufacturing method according to the invention, first, a gallium oxide substrate is prepared. Then, a surface of the gallium oxide substrate is modified into a nitride via physical or chemical pretreatment to form a surface nitride layer having Ga—N bonding. Finally, gallium nitride-based semiconductor layer is formed on the surface nitride layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices
InactiveUS7906229B2Good lattice matchingFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHard disc drivePhotoluminescence
Novel articles and methods to fabricate the same resulting in flexible, large-area, triaxially textured, single-crystal or single-crystal-like, semiconductor-based, electronic devices are disclosed. Potential applications of resulting articles are in areas of photovoltaic devices, flat-panel displays, thermophotovoltaic devices, ferroelectric devices, light emitting diode devices, computer hard disc drive devices, magnetoresistance based devices, photoluminescence based devices, non-volatile memory devices, dielectric devices, thermoelectric devices and quantum dot laser devices.
Owner:GOYAL AMIT
Bismuth ferrite base film layer stacked structure capacitor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102222672AGood lattice matchingImprove insulation performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBarium strontium titanateLanthanide
The invention discloses a bismuth ferrite base film layer stacked structure capacitor and a preparation method thereof, wherein the capacitor comprises a bottom electrode, a substrate, a buffer layer, a ferroelectric film layer and a metal point electrode in sequence from the bottom to top; the buffer layer is a manganese-doped barium strontium titanate film, the chemical formula is Ba0.6Sr0.4Ti(1-x)MnxO3, x is the mole equivalent of element manganese, and x is equal to 0.005-0.05; and the ferroelectric film layer is a bismuth ferrite base film, the chemical formula is Bi(1-y)LnyFeO3, wherein Ln is one of lanthanide, y is the mole equivalent of lanthanide, and y is equal to 0.01-0.2. The preparation method is simple, and the obtained capacitor is a storage cell of a ferro-electric field effect transistor; and the capacitor overcomes the defects that the bismuth ferrite base film capacitor on ordinary silicon substrate has the defects of poor interface performance and high working voltage, and has good energy storage performance.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Nucleating agent for high-grade ductile iron and preparation method of nucleating agent
The invention discloses a nucleating agent for high-grade ductile iron and a preparation method of the nucleating agent. The nucleating agent for the high-grade ductile iron comprises the chemical components of 68-72% of Si, 3-5% of Ba, 1-3% of Ca, 0.15-0.6% of Sb and the balance Fe with the total weight of the nucleating agent for the high-grade ductile iron being 100%. By means of the nucleating agent for the high-grade ductile iron, the strength of the ductile iron can be increased, the elongation rate is increased, the hardness of the ductile iron is lowered, the cutting machinability is improved, and requirements for production and application are met.
Owner:ANHUI POLYTECHNIC UNIV MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL COLLEGE
Gallium oxide heterogeneous structure as well as growth method and special device thereof
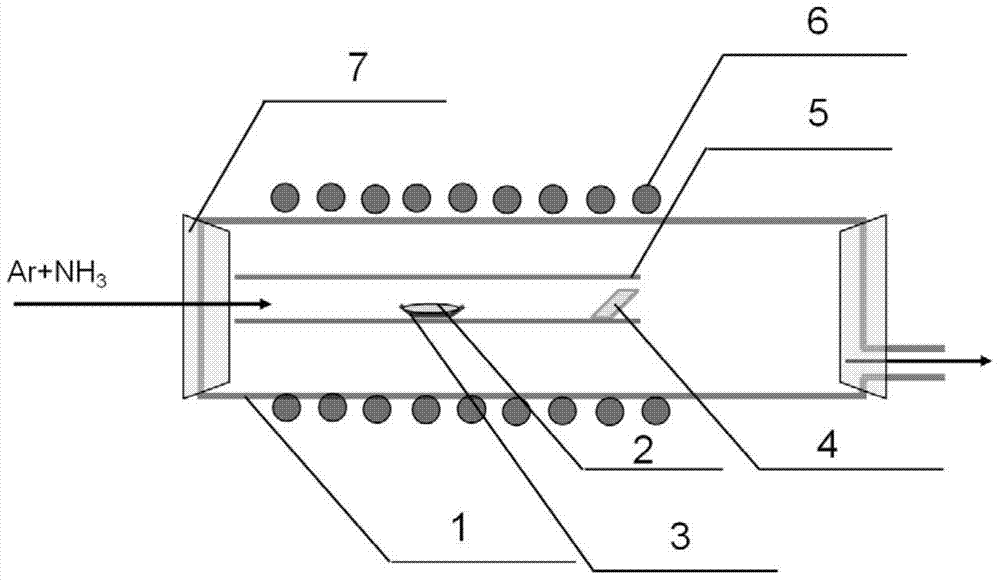
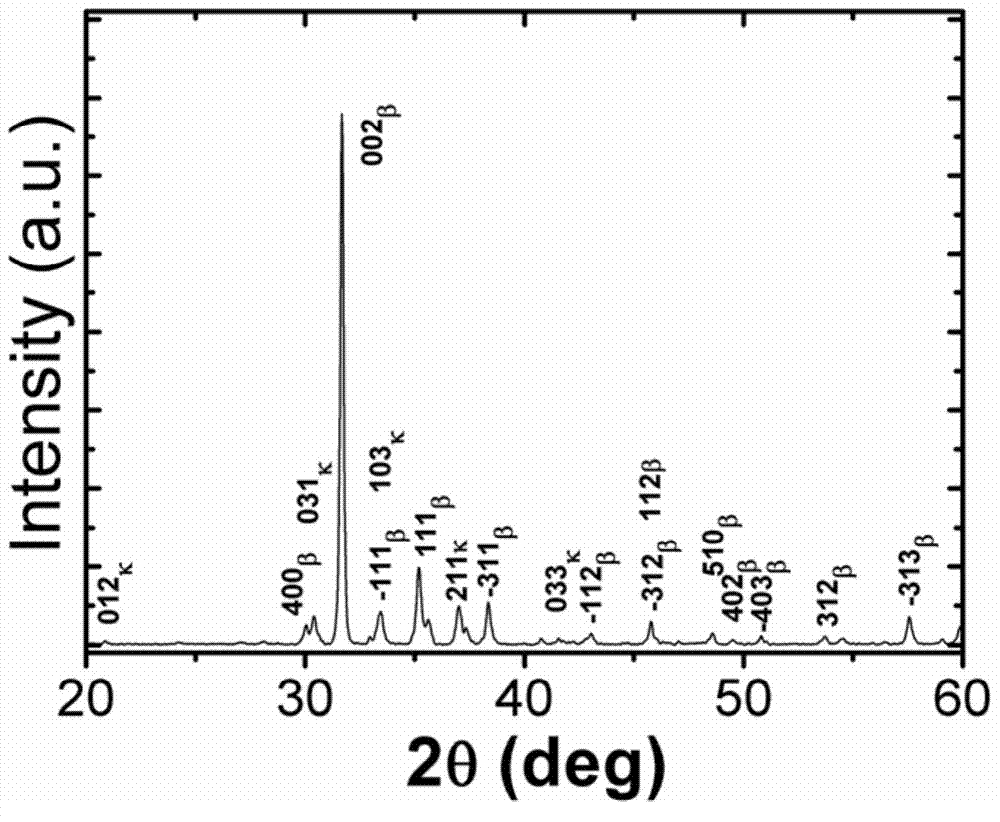
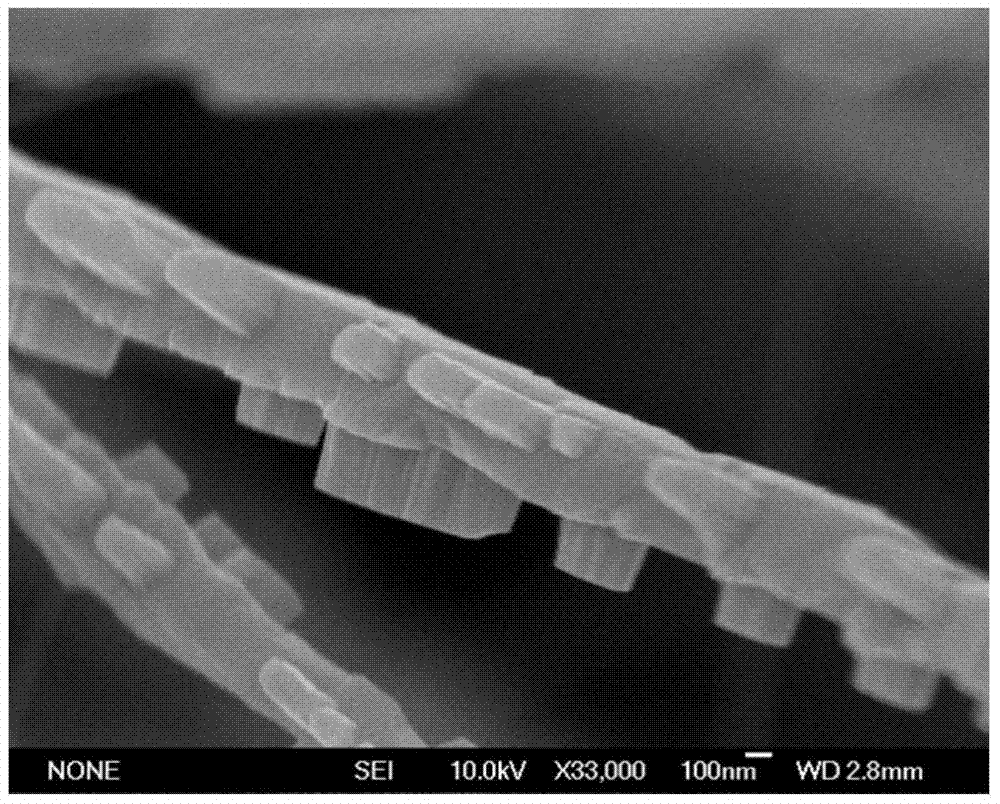
ActiveCN103924298AUniform sizeLarge specific surface areaMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthHeterojunctionSemiconductor materials
The invention belongs to the technical field of semiconductor materials and nanometer, specifically relates to a gallium oxide heterogeneous structure and a growth method thereof, and particularly relates to a method and a special device for a gallium oxide heterogeneous structure with a pseudo quartic symmetry nanometer size formed by beta-Ga2O3 and k-Ga2O3. The gallium oxide heterojunction comprises a beta-Ga2O3 nanowire trunk and a k-Ga2O3 nanorod on the surface of the beta-Ga2O3 nanometer linear trunk, wherein the length of the beta-Ga2O3 nanowire is 5-100 mu m and the diameter is 50-1000nm; the size of the k-Ga2O3 nanorod is 50-200nm and is distributed on the nanowire surface in a mode of pseudo quartic symmetry. The method adopted in the invention can be used for accurately controlling the temperature and ammonia gas flow in a deposition area in the process of chemical vapor deposition (CVD), so as to spontaneously form a k-Ga2O3 / beta-Ga2O3 heterogeneous structure, and the obtained k-Ga2O3 is a new crystal structure in a gallium oxide system and has rhombic symmetry. The prepared k-Ga2O3 / beta-Ga2O3 heterogeneous structure has extremely strong cathode ray fluorescence property in an ultraviolet region, has the discrete characteristic of luminescence and is suitable for serving as an ultraviolet light electricity detector and suitable for hydrogen production through photocatalytic water splitting.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for improving photoelectric conversion efficiency of solar cell panel
ActiveCN102694066AHigh light transmittanceImprove conductivityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesCells panelComposite film
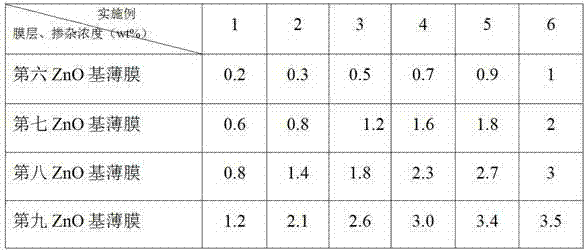
The invention discloses a method for improving photoelectric conversion efficiency of solar cell panels and solves the technical problem that photoelectric conversion efficiency is affected due to imperfect processes of interface matching between a ZnO base transparent conductive film and a film in a photoelectric conversion area in the prior art. The technical scheme adopted in the invention is a method for improving photoelectric conversion efficiency of solar cell panels based on improved TCO film layers. The method comprises the step of depositing TCO film layers of ZnO base on a glass sheet, wherein the TCO film layers form a ZnO base composite film with 2-4 layers deposited on the glass sheet by ZnO base target with sputtering technology and doping concentrations of each layer of the composite film are distributed in gradient. The key of the invention is to design the TCO film layers in a multi-layer composite structure, control the doping concentrations of each layer reasonably to make the doping concentrations form a gradient, thus greatly enhancing light transmittance and conductivity of cell panels and effectively improving photoelectric conversion efficiency of solar cell panels.
Owner:成都中浦科技有限公司
Thin film transistor, amorphous silicon flat detecting substrate and preparation method
ActiveCN103268891AReduce barriers to mobilityReduce obstaclesTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorOxide thin-film transistor
Owner:BEIJING BOE OPTOELECTRONCIS TECH CO LTD
Ga40Sb60/Sb superlattice phase transition film material for high-speed low-power-consumption phase change memory, and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN104900807AImprove thermal stabilityReduce volumeElectrical apparatusVacuum evaporation coatingPhase-change memoryThin membrane
The invention discloses a Ga40Sb60 / Sb superlattice phase transition film material for high-speed low-power-consumption phase change memory. The Ga40Sb60 / Sb superlattice phase transition film material has a multilayer composite film structure and is obtained through alternately depositing Ga40Sb60 layers and Sb layers. One Ga40Sb60 layer and one Sb layer are used as one alternating period, and the Ga40Sb60 layer of the next alternating period is deposited on the Sb layer of a previous alternating period. According to the Ga40Sb60 / Sb superlattice phase transition film material, a clamping effect of a multilayer interface in a superlattice structure is utilized for reducing dimensions of crystal particles, thereby shortening crystallization time, restraining crystallization, improving thermal conductivity of the material and furthermore increasing phase change speed. Furthermore the Ga40Sb60 / Sb superlattice phase transition film material has advantages of realizing small size change in the phase change process, ensuring good contact between a phase change layer and electrode material, and finally improving stability and reliability of a phase change memory device.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
Yttrium-iron-garnet single-crystal film and preparation method thereof
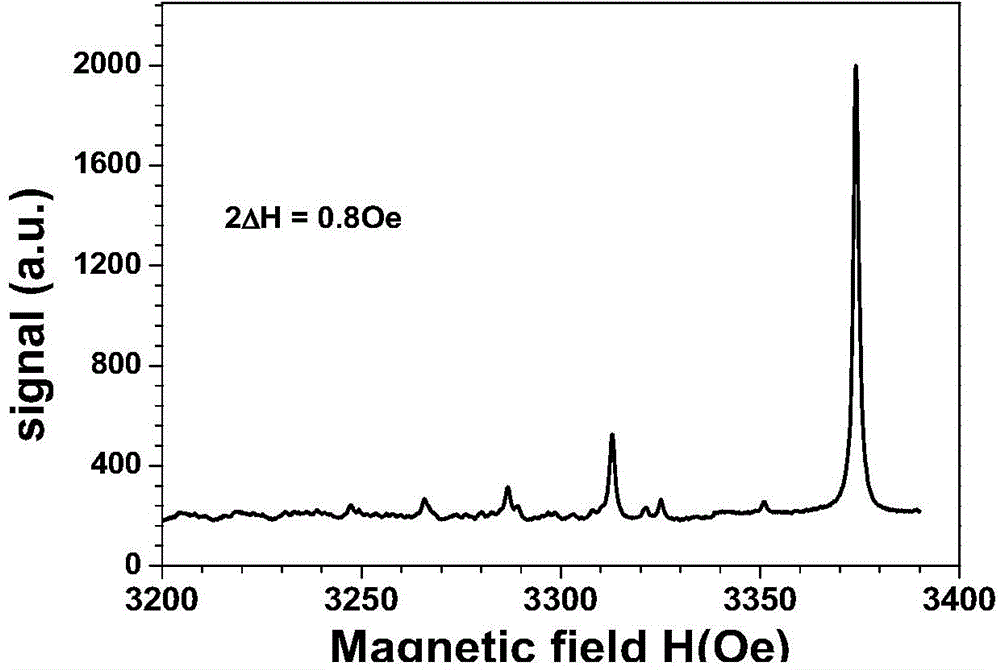
ActiveCN104831357AFerromagnetic resonance linewidthThe ferromagnetic resonance linewidth is very narrowPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthSingle crystalElectronic materials
The present invention provides an yttrium-iron-garnet single-crystal film and a liquid-phase epitaxy preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of electronic materials. According to the present invention, the component of the yttrium-iron-garnet single-crystal film is La[x]Y[3-x]Fe5O12, wherein x is 0.01-0.05; 0.44% by mass of Y2O3, 10.31% by mass of Fe2O3, 0.06% by mass of La2O3, 87.44% by mass of PbO and 1.75% by mass of B2O3 are adopted as raw materials; the liquid-phase epitaxy method is used to grow the single-crystal film; the ferromagnetic resonance line width of the obtained yttrium-iron-garnet single-crystal film is narrow and achieves less than or equal to 1 Oe; and the roughness, the lattice matching, the film stress, the lead content, the impure phase and the like of the film are improved.
Owner:成都威频科技有限公司
Red light quantum dot as well as synthesis method and quantum dot light emitting diode thereof
ActiveCN108841373AGood lattice matchingImprove optical qualityMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsSynthesis methodsQuantum dot
The invention provides a red light quantum dot as well as a synthesis method and a quantum dot light emitting diode thereof. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: S1, providing a solution with a CdSe quantium dot core; S2, carrying out epitaxial growth on the CdSe quantium dot core so as to obtain a plurality of ZnxCdl-xS single-layer shells, gradually increasing x of different ZnxCdl-xS single-layer shells from 0 till a maximum number within of 0.5-0.8 in a direction far away from the CdSe quantium dot core so as to obtain a system with CdSe / ZnxCd1-xS quantum dots; and optionalS3, continuously coating the CdSe / ZnxCd1-xS quantum dots of the step S2 with a ZnS shell layer. By controlling the components in the shell layers to be gradually transited to CdZnS or ZnS from CdZnS,a good lattice matching rate can be ensured, the quantum dots can be maintained at a single index dispersion level, and the quantum dots with high optical quality, high photobleaching resistance and high air stability can be finally prepared.
Owner:NANJING TECH CORP LTD
Nitride semiconductor light emitting diode
InactiveUS20080042161A1Good lattice matchingMaximize light efficiencySemiconductor devicesElectron blocking layerActive layer
A nitride semiconductor light emitting diode includes: an n-type clad layer; an active layer formed on the n-type clad layer; an electron blocking layer formed on the active layer, the electron blocking layer being composed of a p-type nitride semiconductor including a transition element of group III; and a p-type clad layer formed on the electron blocking layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG LED CO LTD
{100}<100> or 45°-rotated {100}<100>, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices
InactiveUS8178221B2Good lattice matchingSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHard disc drivePhotoluminescence
Owner:GOYAL AMIT
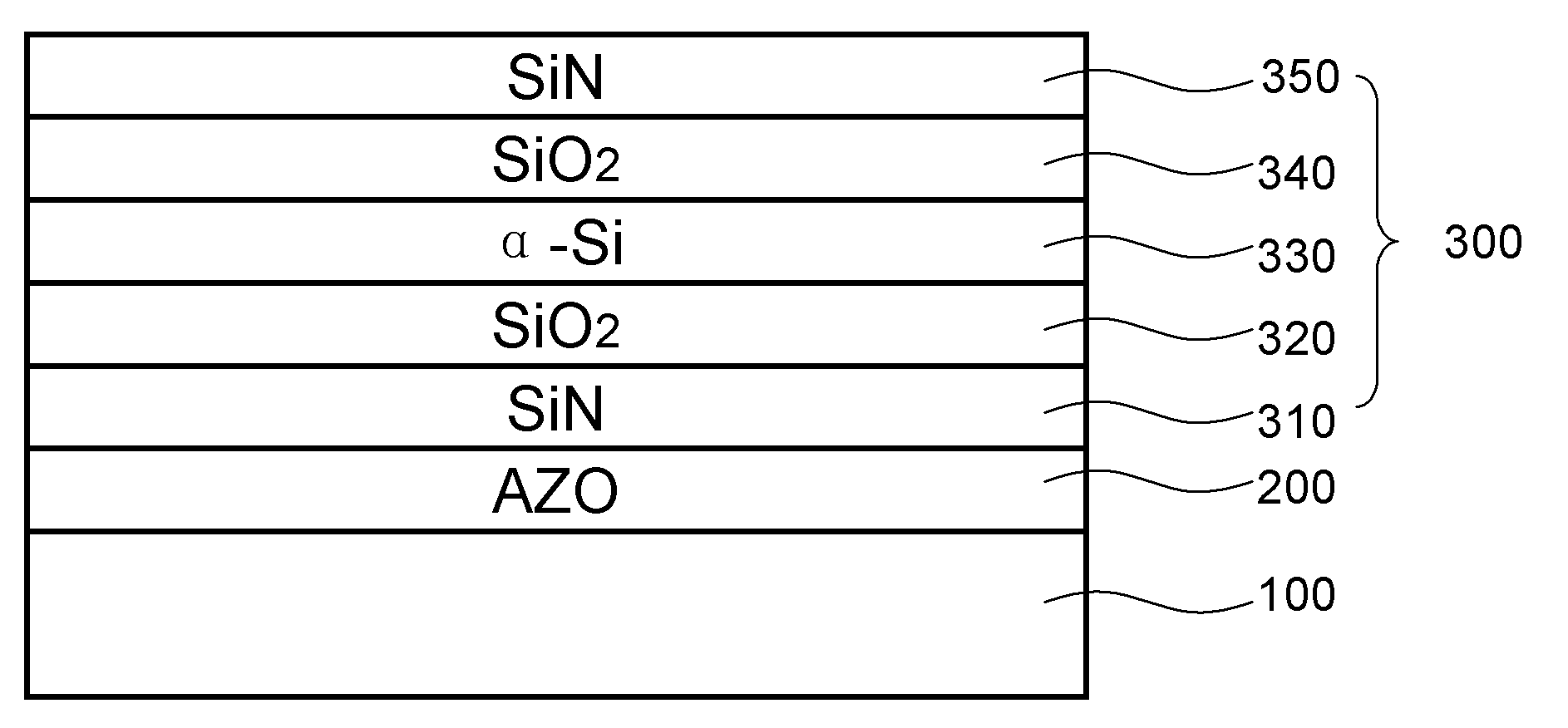
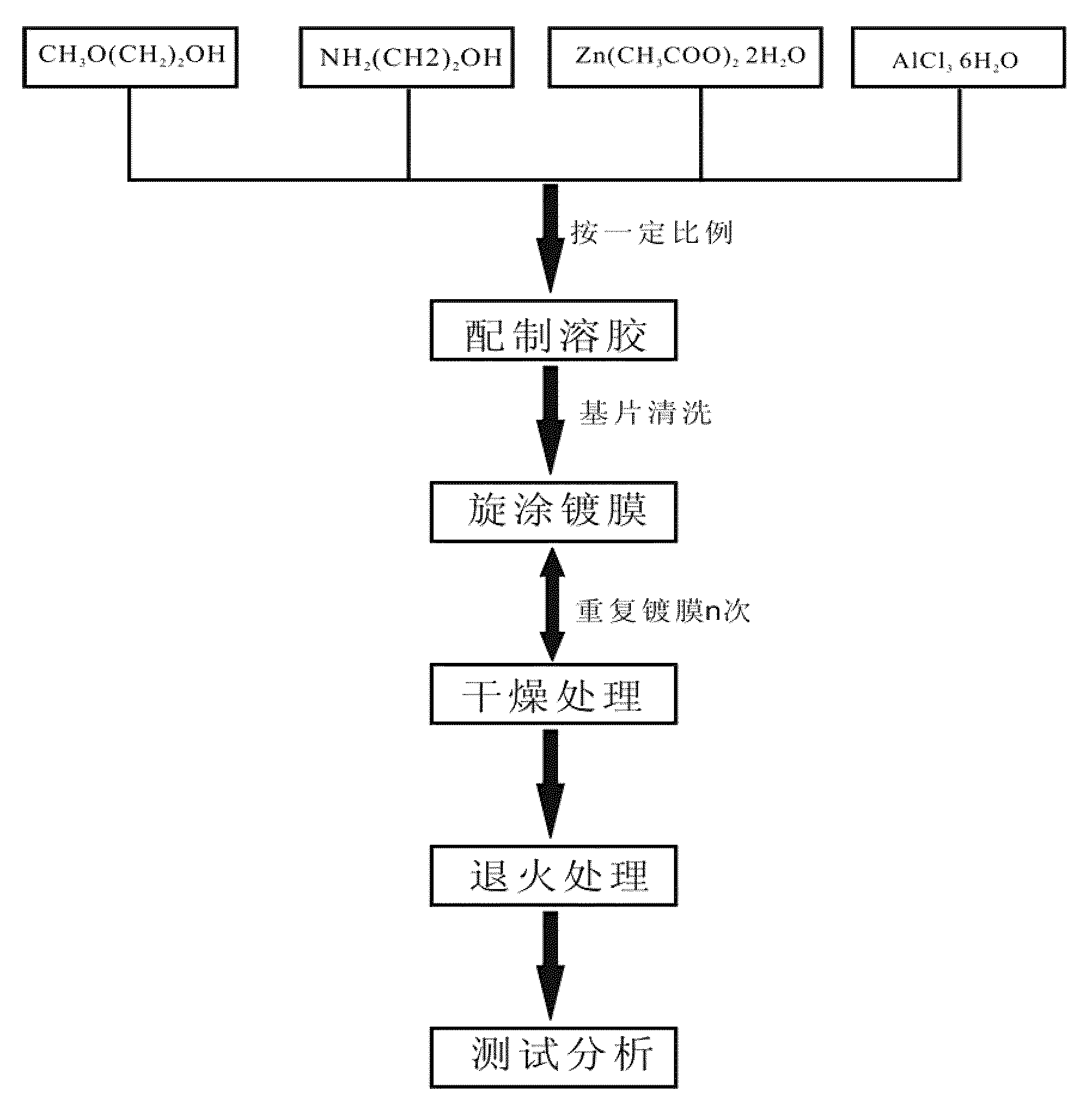
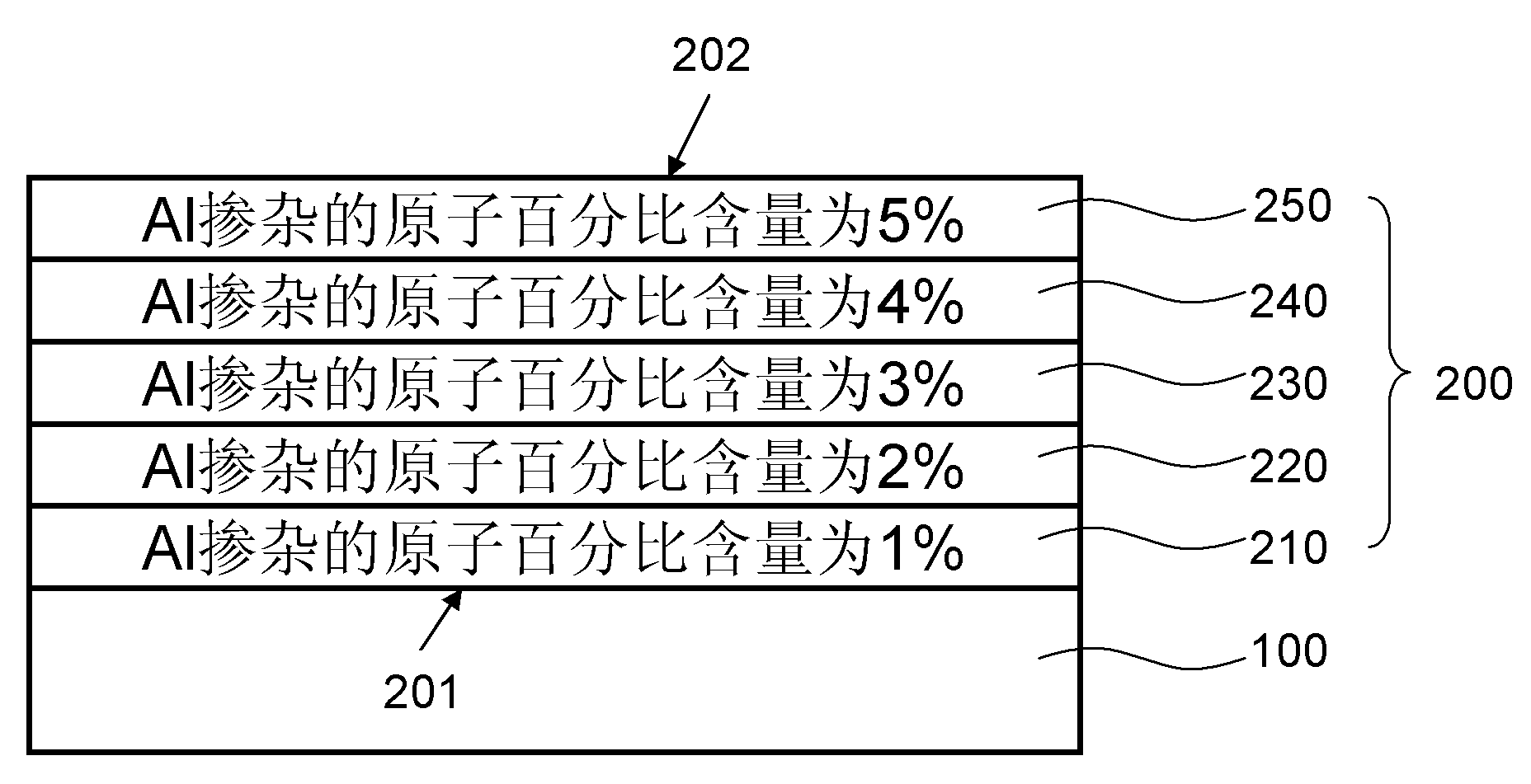
AZO thin film, preparing method and MEMS device comprising AZO thin film
ActiveCN103508406AImprove conductivityLow costDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesComposite filmAluminum doped zinc oxide
An aluminum-doped zinc oxide (AZO) thin film (200), a preparation method thereof, and a micro electro mechanical system (MEMS) device comprising same. The AZO thin film (200) is formed on a substrate (100), the aluminum dosage concentration of the AZO thin film (200) being increased gradually in the thin film thickness direction; in the preparation method, the AZO thin film (200) is prepared by using a sol-gel method; the MEMS device uses the AZO thin film (200) and form a composite thin film layer (300) on the AZO thin film (200) through chemical vapor deposition filming. The AZO thin film (200) has desirable conductivity, has good lattice matching with the composite thin film layer (300), has matched thermal expansion and low cost, and is nontoxic, pollution free, and simple in preparation.
Owner:CSMC TECH FAB2 CO LTD
Double-layer transparent electrode on P type GaN (gallium nitride)
InactiveCN102142496AImprove thermal stabilityIncrease contactSemiconductor devicesPower flowIndium tin oxide
The invention discloses a double-layer transparent electrode on P type GaN (gallium nitride) in GaN based LED (Light-Emitting Diode). The transparent electrode is composed of a double-layer structure of an ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) film and a ZnO (Zinc Oxide) based film. The process steps are that: 1, the ITO film is deposited on the P type GaN to be used as a first transparent conducting layer, and the thickness is 1-1000 microns; and 2, the low-resistance ZnO based film is deposited on the first transparent conducting layer to be used as a second transparent conducting layer, and the resistivity is 10-4 to 10-5 ohm cm. The double-layer transparent electrode has the advantages of low resistivity, high light transmittance and good stability, the current is uniformly deposited, and the double-layer electrode can improve the luminous efficiency of the GaN based LED and prolong the service life.
Owner:HANGZHOU SILAN AZURE
Hard bias design for extra high density recording
InactiveUS7688555B2Increase contributionImprove coercive forceNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsHigh densityOptoelectronics
A hard bias structure for biasing a free layer in a MR element within a read head is comprised of a composite hard bias layer having a Co78.6Cr5.2Pt16.2 / Co65Cr15Pt20 configuration. The upper Co65Cr15Pt20 layer has a larger Hc value and a thickness about 2 to 10 times greater than that of the Co78.6Cr5.2Pt16.2 layer. The hard bias structure may also include a BCC underlayer such as FeCoMo which enhances the magnetic moment of the hard bias structure. Optionally, the thickness of the Co78.6Cr5.2Pt16.2 layer is zero and the Co65Cr15Pt20 layer is formed on the BCC underlayer. The present invention also encompasses a laminated hard bias structure. The Mrt value for the hard bias structure may be optimized by adjusting the thicknesses of the BCC underlayer and CoCrPt layers. As a result, a larger process window is realized and lower asymmetry output during a read operation is achieved.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Double face high-temperature superconducting film multi-layer structures and method for producing the same
InactiveCN101162626AImprove textureGood lattice matchingSuperconductors/hyperconductorsLayered productsHigh temperature superconductingSingle crystal
The invention discloses a double-sided high temperature super-conductive film multiple-layer structure and the preparation method. The double-sided high temperature super-conductive film multiple-layer structure comprises a non-monomorph oxide uropatagia of low cost, both sides of the non-monomorph oxide uropatagia of low cost are provided with a metal film layer, an oxide film layer of biaxial texture and a super-conductive film layer. At first, the metal film with a good surface is arranged on the non-monomorph oxide uropatagia of low cost and then the ion beam ancillary deposition technology is adopted to prepare the oxide film material of biaxial texture on the metal film, saving the expensive oxide monomorph material as the material of the uropatagia of large area of double-sided high temperature super-conductive film but choosing the Si monomorph of low cost and the like. The double-sided high temperature super-conductive film that is prepared is of low cost.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
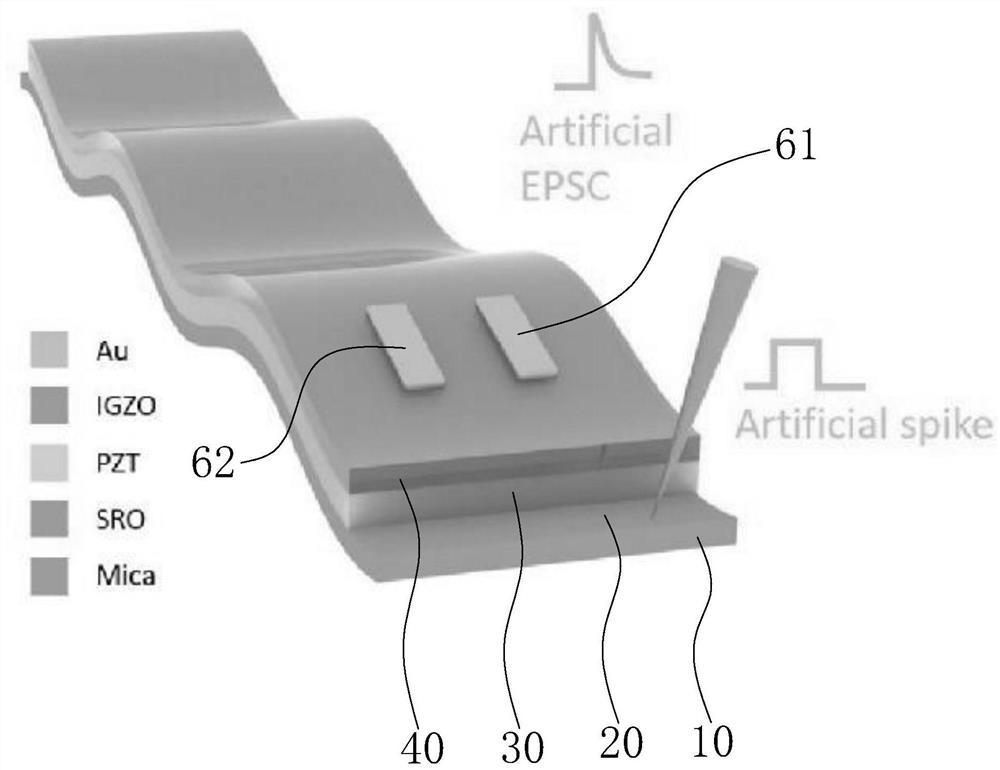
Inorganic synaptic transistor structure and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN111739935AImproved leakage current resistanceEasy to operateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysical realisationGate dielectricBottom gate
The invention relates to an inorganic synaptic transistor structure and a manufacturing method thereof. The structure comprises a flexible substrate; a buffer layer formed on the substrate; a bottom gate electrode formed on the buffer layer; an epitaxial gate dielectric layer formed on the bottom gate electrode; a channel layer formed on the epitaxial gate dielectric layer; and a source electrodeand a drain electrode which are disposed on the channel layer. The manufactured synaptic transistor effectively overcomes the defects that the miniaturization and integration of the synaptic transistor adopting ionic liquid or solid electrolyte as a gate medium are difficult to achieve, the linearity and symmetry of a device are worse, and the synaptic transistor is not resistant to high temperature. The synaptic transistor prepared by the method has flexibility, bending resistance and high temperature resistance, the performance can still be kept basically unchanged under the bending condition or at 100 DEG C, and the energy consumption of each device in the learning process is only 10-30 pJ, which is beneficial to the practical application of the synaptic transistor in the field of high-precision artificial neuromorphic calculation.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
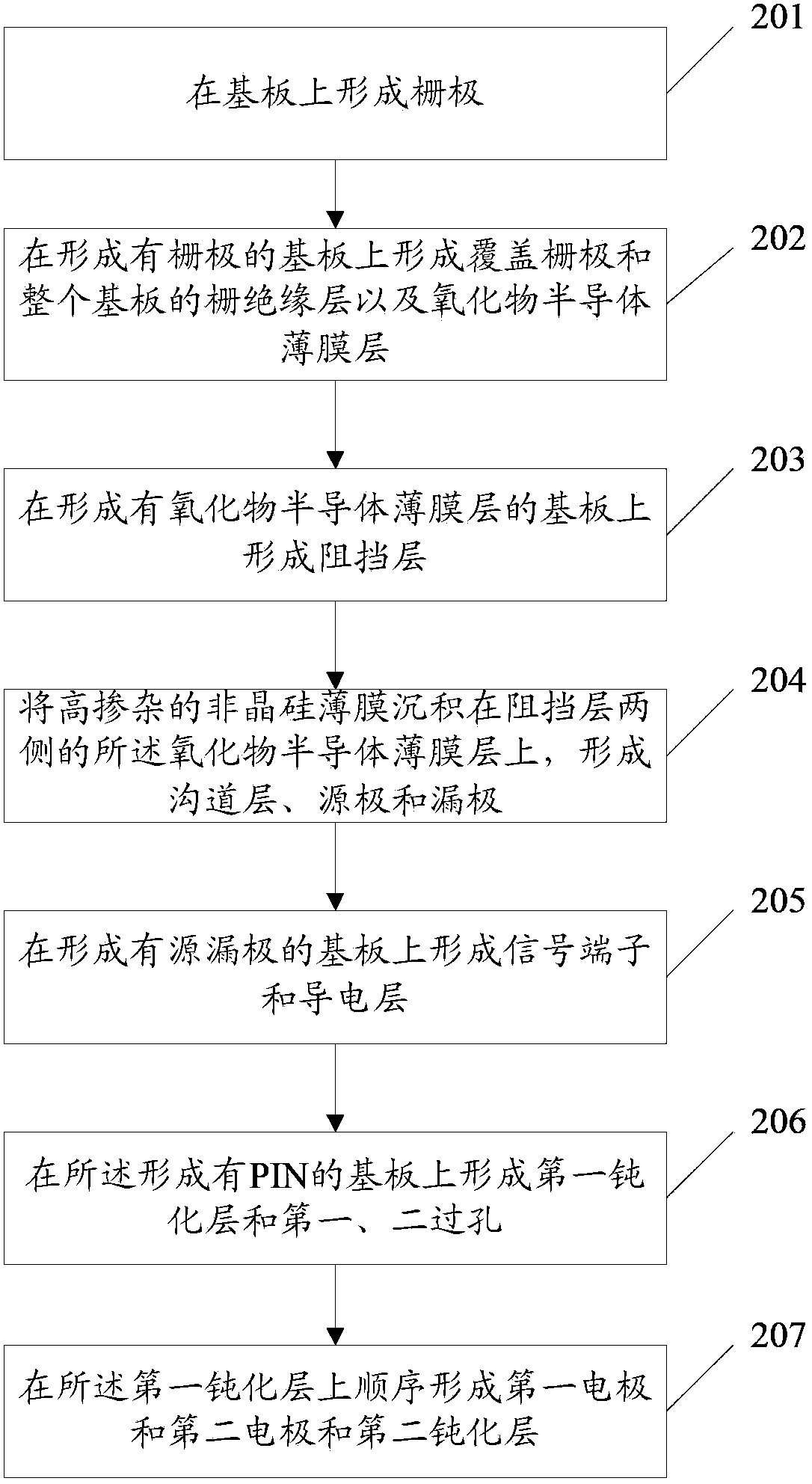
Thin film transistor and production method thereof and array substrate
ActiveCN104124277AExcellent electrical propertiesReduce the impactTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDoped oxideSemiconductor
Provided are a thin film transistor, a method for manufactur thereof and an array substrate. The thin film transistor comprises: a gate electrode (102) formed on a substrate (101), a gate insulating layer (103) formed on the gate electrode (102) and covering at least a part of the substrate (101), and a semiconductor layer (105'), a source electrode (107a) and a drain electrode (107b) formed on the gate insulating layer (103). The material of the semiconductor layer (105') is an oxide semiconductor, and the material of the source electrode (107a) and the drain electrode (107b) is a doped oxide semiconductor. The source electrode (107a), the drain electrode (107b) and the semiconductor layer (105') are disposed in the same layer.
Owner:BEIJING BOE OPTOELECTRONCIS TECH CO LTD
Method for thinning Mg-RE-Mn-Sc series magnesium alloy crystalline grains by adding Zr
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
GaN device with mixed polarity
ActiveCN105789281AQuality improvementReduce defectsSemiconductor devicesOhmic contactElectrical polarity
The invention discloses a GaN device with the mixed polarity. The GaN device relates to the technical field of field effect transistors with two-dimensional carrier gas channels. The GaN device comprises a substrate layer, an N-polar GaN buffer layer, a first N-polar Alx GaN layer with a gradually increased Al component x, a second N-polar AlxGaN layer with a constant Al component x, a third N-polar AlxGaN layer with a gradually reduced Al component x, and a Ga-polar GaN channel layer. By virtue of the structure, a GaN based material with higher quality can grow epitaxially and the surface density and migration rate of 2DEG in a channel can be increased; and meanwhile a device with smaller ohmic contact resistance can be fabricated on a material with the mixed polarity by adopting a conventional Ga-polar GaN based device fabrication process.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of topology insulator/ferromagnet heterostructure film
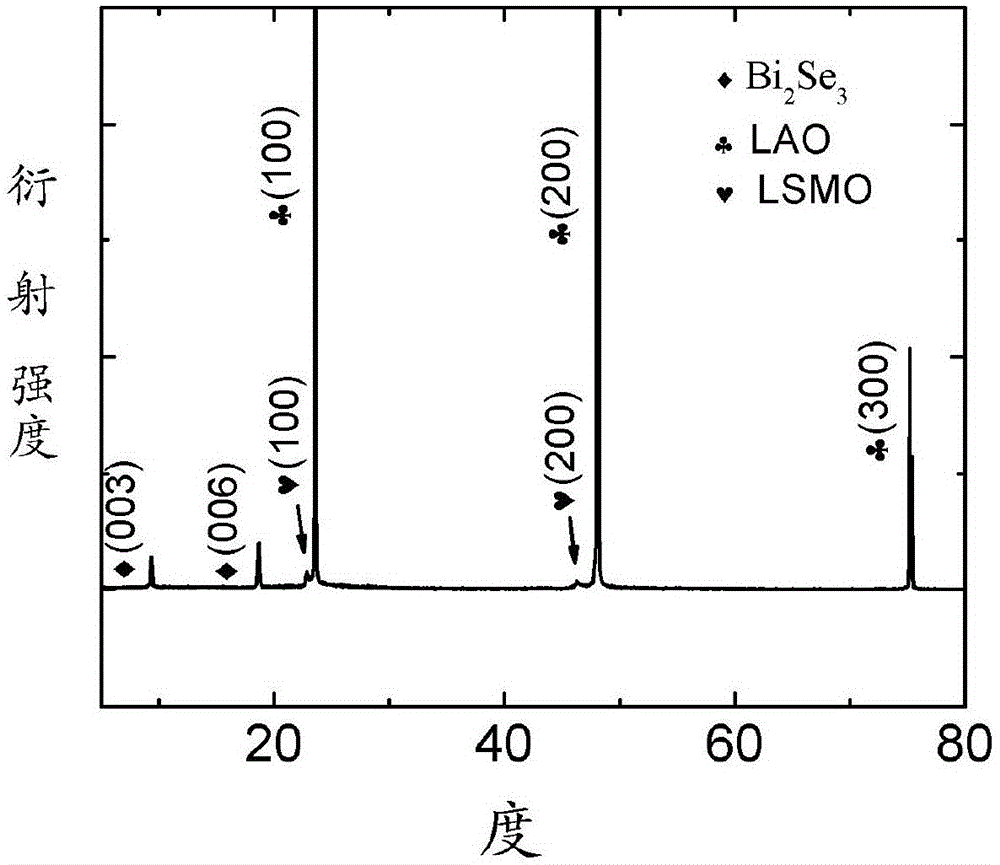
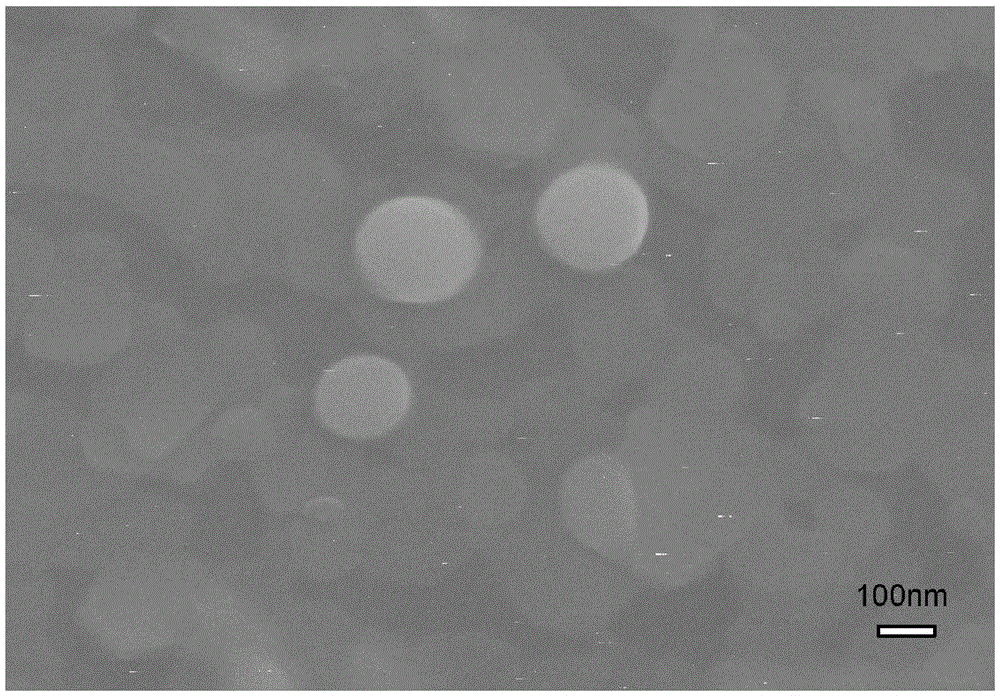
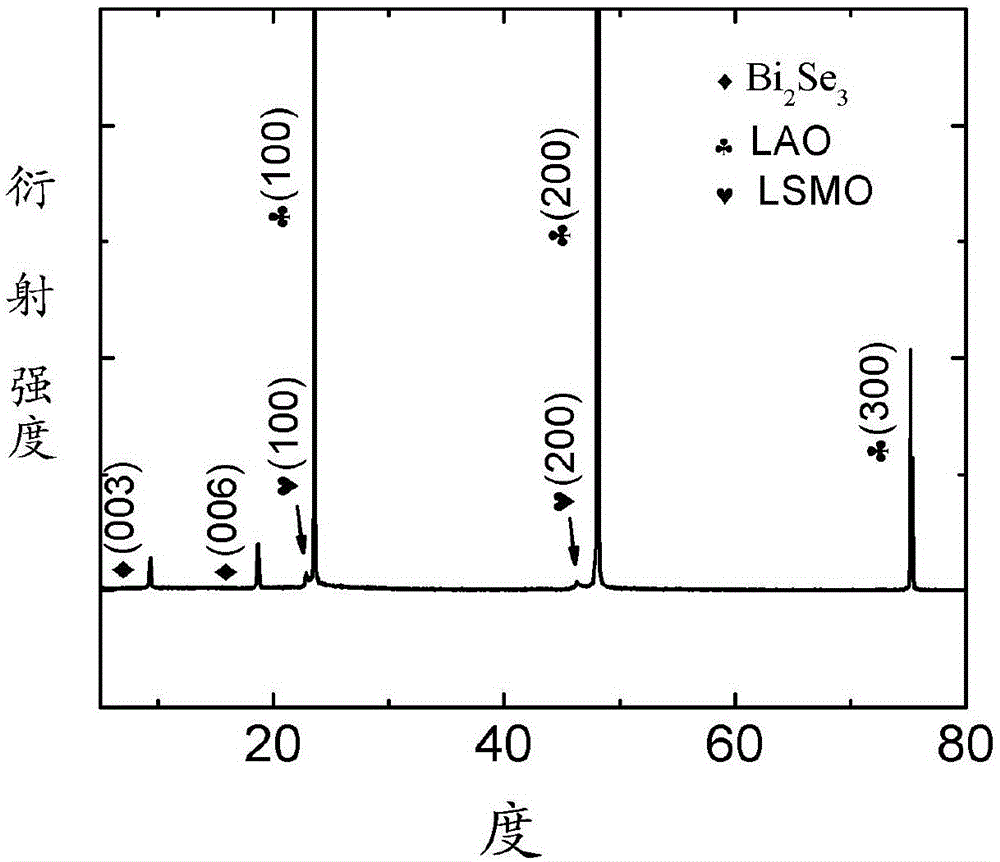
InactiveCN105112868AImprove diffusion abilityGood adhesionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingN dimethylformamideTube furnace
The invention discloses a preparation method of a topology insulator / ferromagnet heterostructure film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (a) N, N-dimethylformamide solution of La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 is prepared; polyvinylpyrrolidone is added in the solution to form a colloid; and the colloid is coated on a substrate for drying, and is put in a tube furnace for insulation annealing treatment to obtain a La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 film; (b) the La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 film is put in a magnetron sputtering instrument; a Bi2Se3 film is deposited on the La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 film through a magnetron sputtering method to obtain a Bi2Se3 / La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 heterostructure film; and (c) the Bi2Se3 / La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 heterostructure film and selenium particles are sealed in a vacuum quartz tube for post-annealing treatment. The method is simple in operation and low in cost; and the prepared heterostructure film is excellent in performance.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Epitaxial wafer of light emitting diode and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN109786520AGood lattice matchingRelieve compressive stressSemiconductor devicesLight-emitting diodeLuminescence
The invention discloses an epitaxial wafer of a light emitting diode and a manufacturing method thereof, belonging to the technical field of semiconductors. A quantum well layer of the epitaxial waferof the light emitting diode is a BInGaN layer; a quantum barrier layer includes a first sub-layer, a second sub-layer, and a third sub-layer sequentially stacked on the quantum well layer; the firstsub-layer and the third sub-layer are both GaN layers; and the second sub-layer is a BAlGaN layer. By adjusting the molar ratio of B to In in the BInGaN well layer, better lattice matching between theBInGaN material and the GaN material can be achieved; therefore, the compressive stress between the quantum well layer and the quantum barrier layer can be alleviated, the piezoelectric polarizationeffect generated in the quantum well layer can be reduced, the overlap of the wave functions of electrons and holes in spatial distribution can be increased, and the luminous efficiency of the LED canbe improved. Meanwhile, a heterojunction interface is formed between the GaN layer and the BAlGaN layer of the quantum barrier layer, which can improve the luminous efficiency of radiant composite luminescence performed by the electrons and holes in a multiple quantum well layer.
Owner:HC SEMITEK ZHEJIANG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



![[100] Or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices [100] Or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/05ef1fe0-6ace-42a2-8058-990b1467d89a/US20080230779A1-20080925-D00000.png)
![[100] Or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices [100] Or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/05ef1fe0-6ace-42a2-8058-990b1467d89a/US20080230779A1-20080925-D00001.png)
![[100] Or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices [100] Or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/05ef1fe0-6ace-42a2-8058-990b1467d89a/US20080230779A1-20080925-D00002.png)