Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1309 results about "Windmill" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A windmill is a structure that converts the energy of wind into rotational energy by means of vanes called sails or blades. Centuries ago, windmills usually were used to mill grain (gristmills), pump water (windpumps), or both. There are windmills that convert the rotational energy directly into heat. The majority of modern windmills take the form of wind turbines used to generate electricity, or windpumps used to pump water, either for land drainage or to extract groundwater. Windmills first appeared in Persia during the 9th century, and then later appeared across the Middle East, Central Asia, China, India, and Europe.
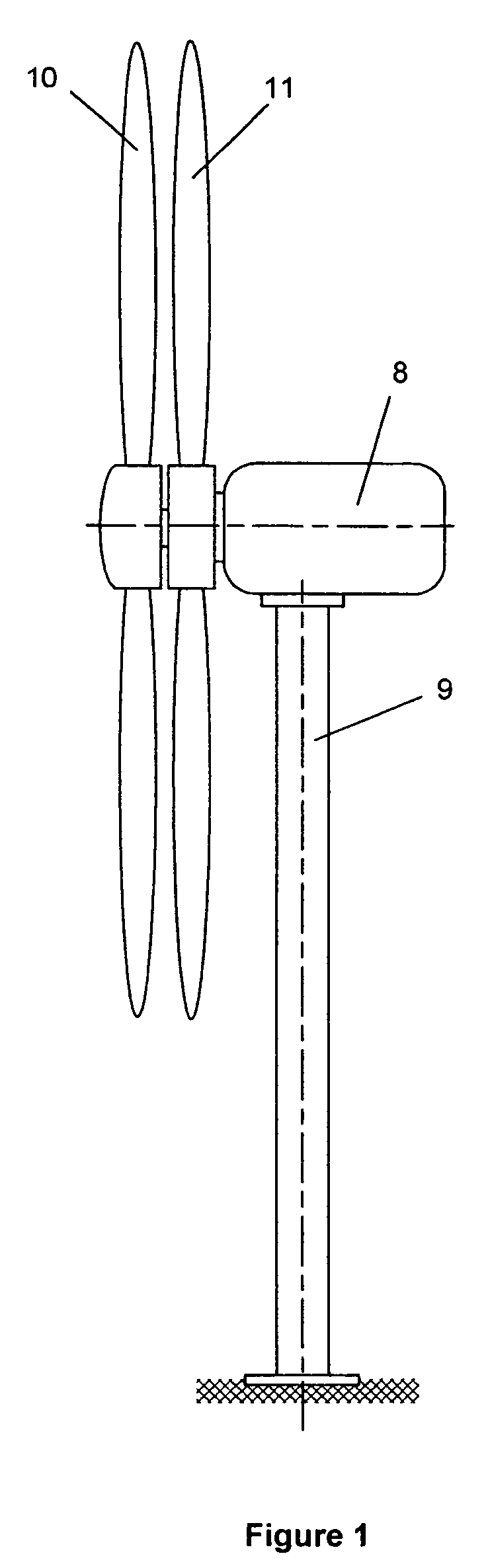
Wind dam electric generator and method
InactiveUS6984899B1Constant windmill shaft rotational speedWind motor controlEngine fuctionsAir volumeEngineering
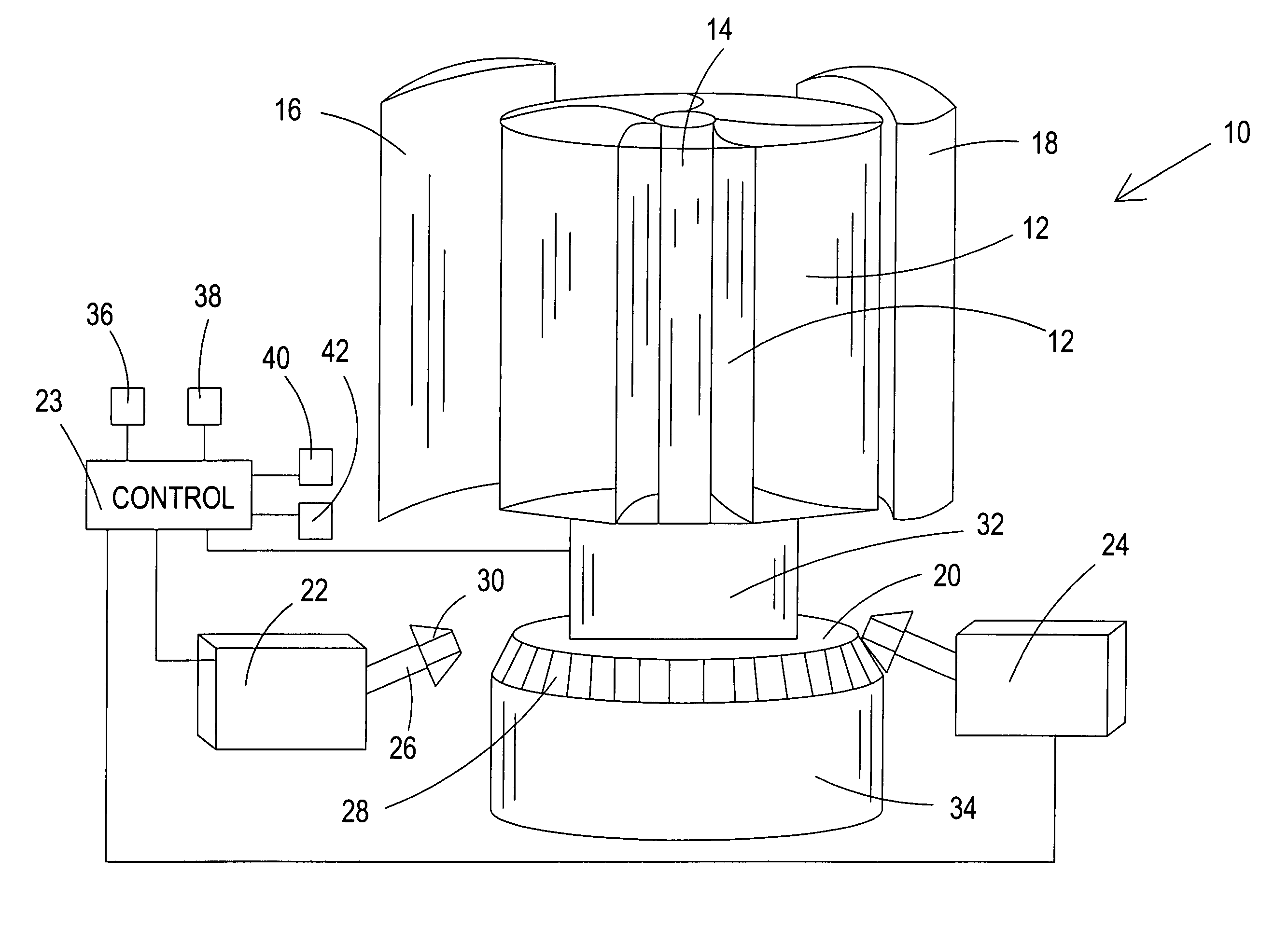
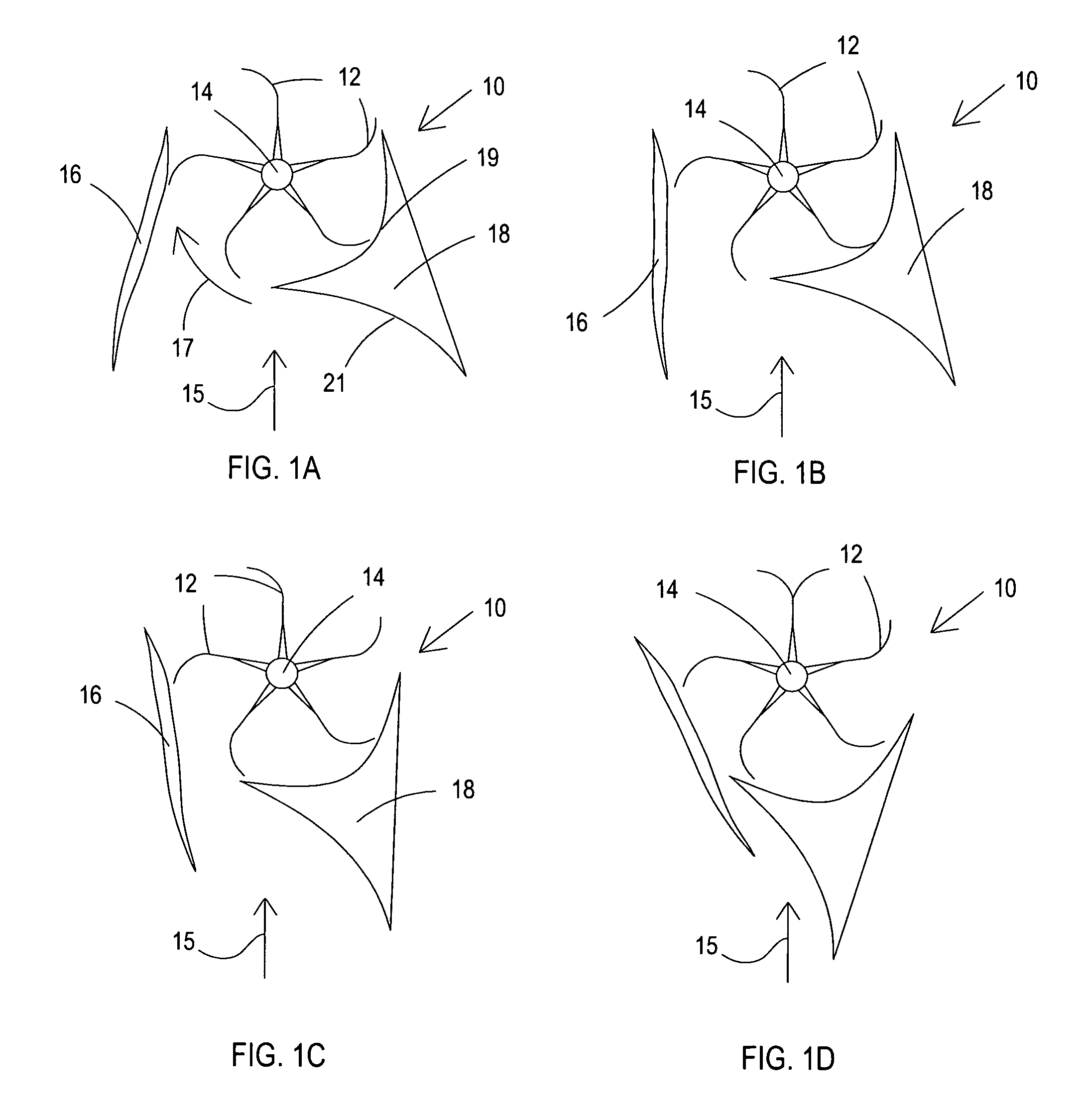
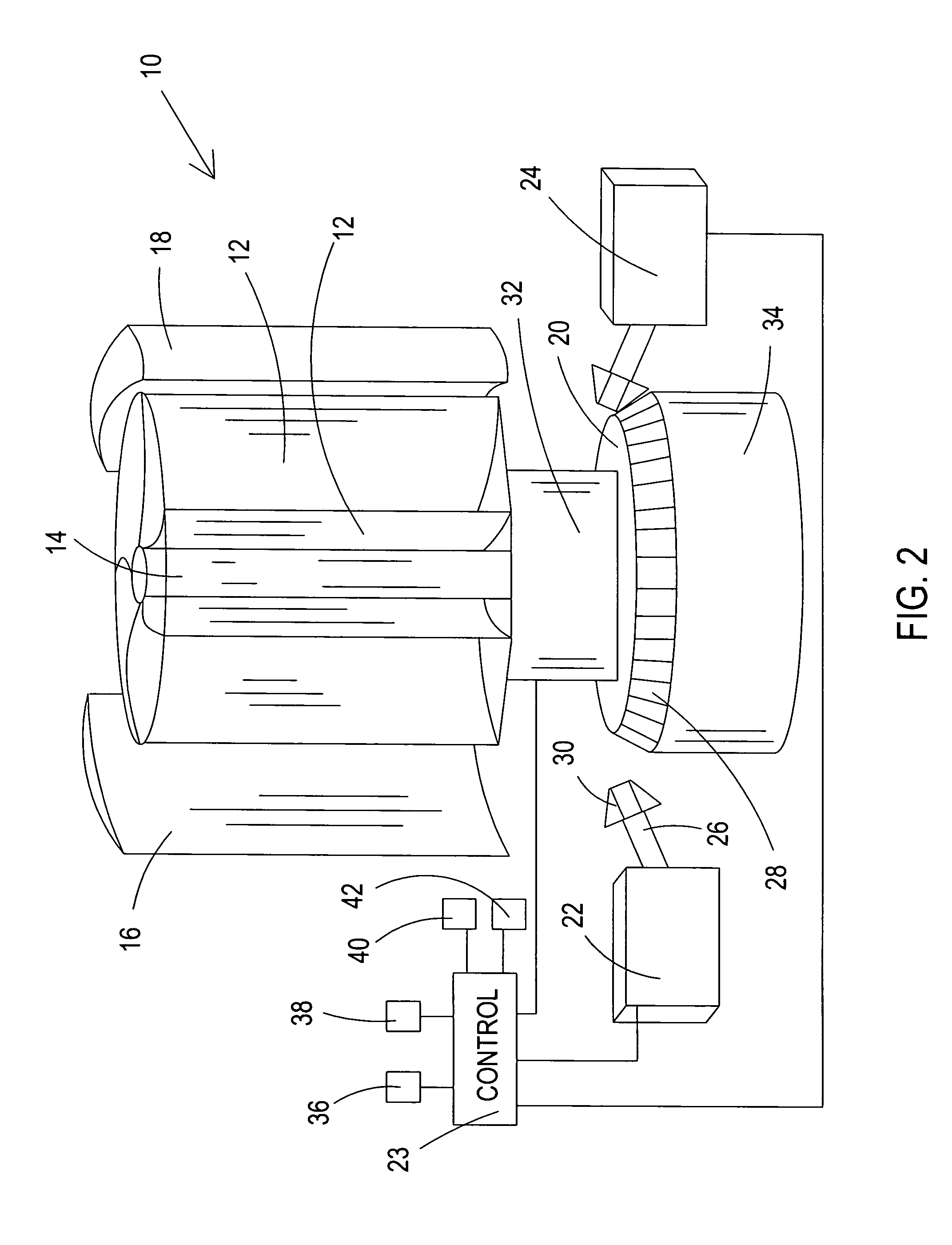
A vertical axis windmill is provided wherein the amount of wind directed to blades in the power producing part of rotation and the mechanical load of multiple generators is controlled by a feedback control to maintain a relatively constant rotational frequency of the shaft of the windmill. In a preferred embodiment, two wind foils extend radially outwardly from the blades to thereby provide a scoop capable of pulling in more air than would normally be received by the blades. The wind foils then direct the wind flow to the power producing part of rotation of the blades for maximum power output, when necessary. The wind foils can close to control the wind flow to the blades. The generating capacity of a plurality of generators is also controlled in response to shaft rotation to maintain substantially constant shaft rotation.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
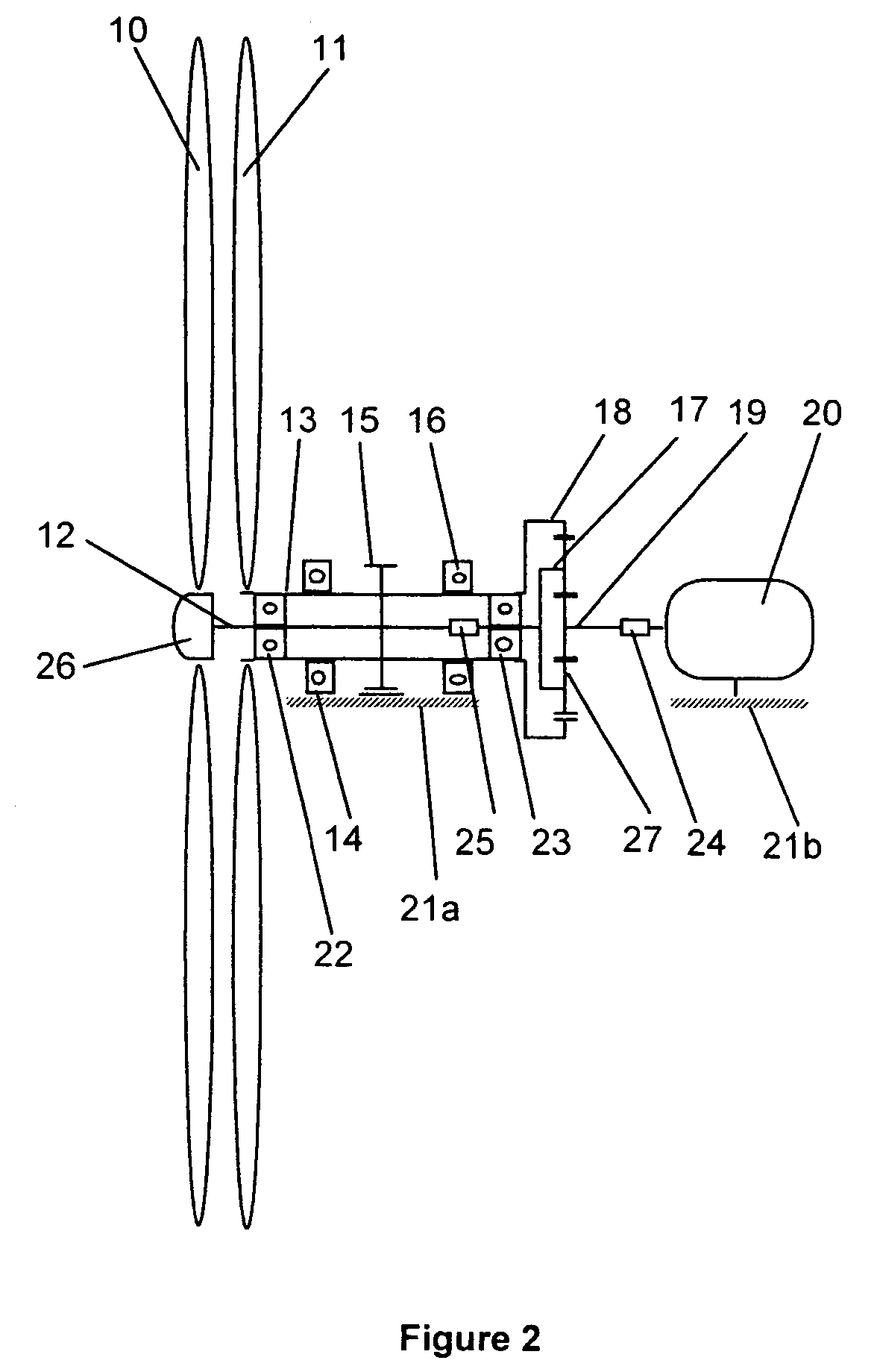
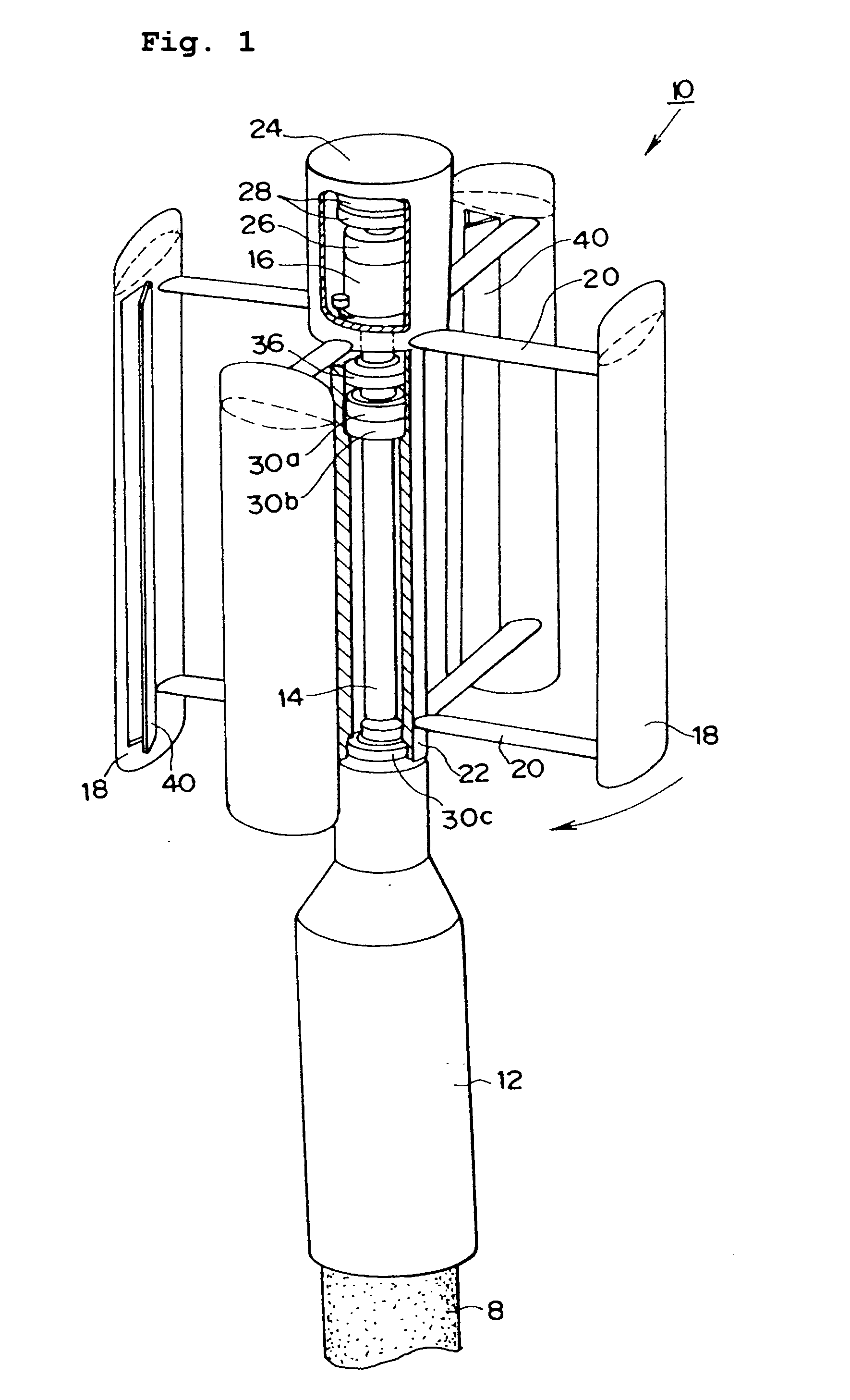
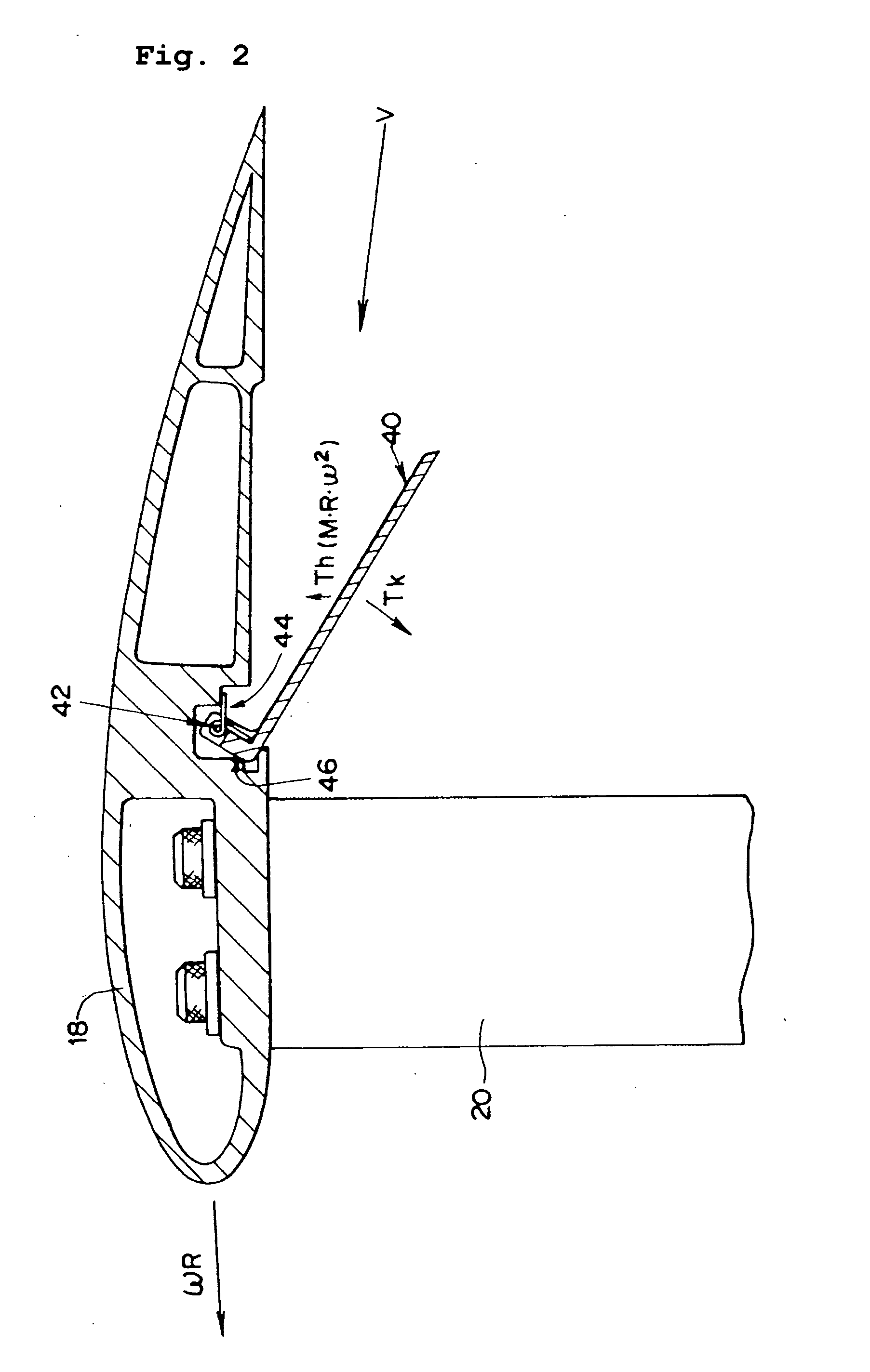
Windmill and windmill control method
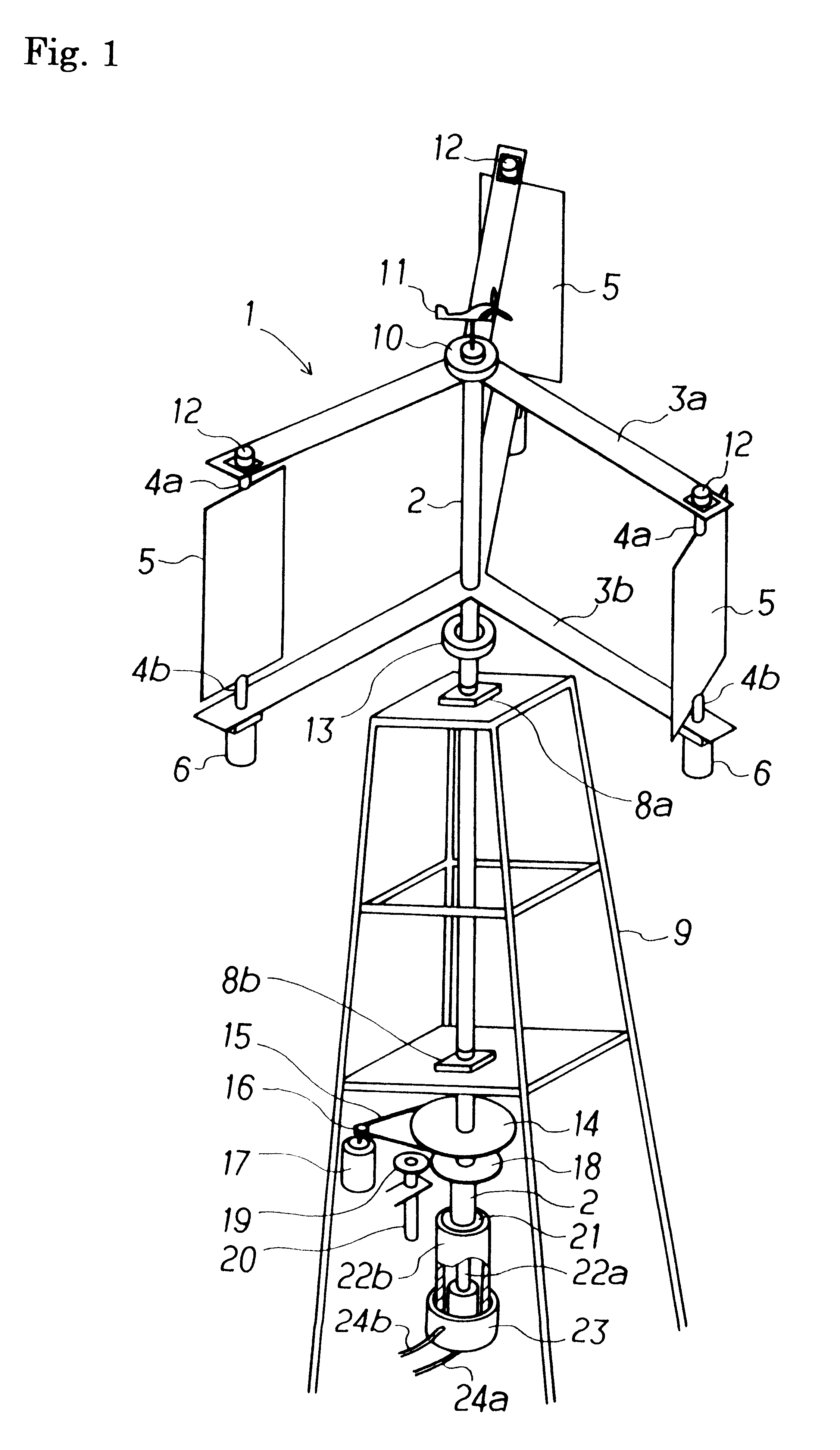
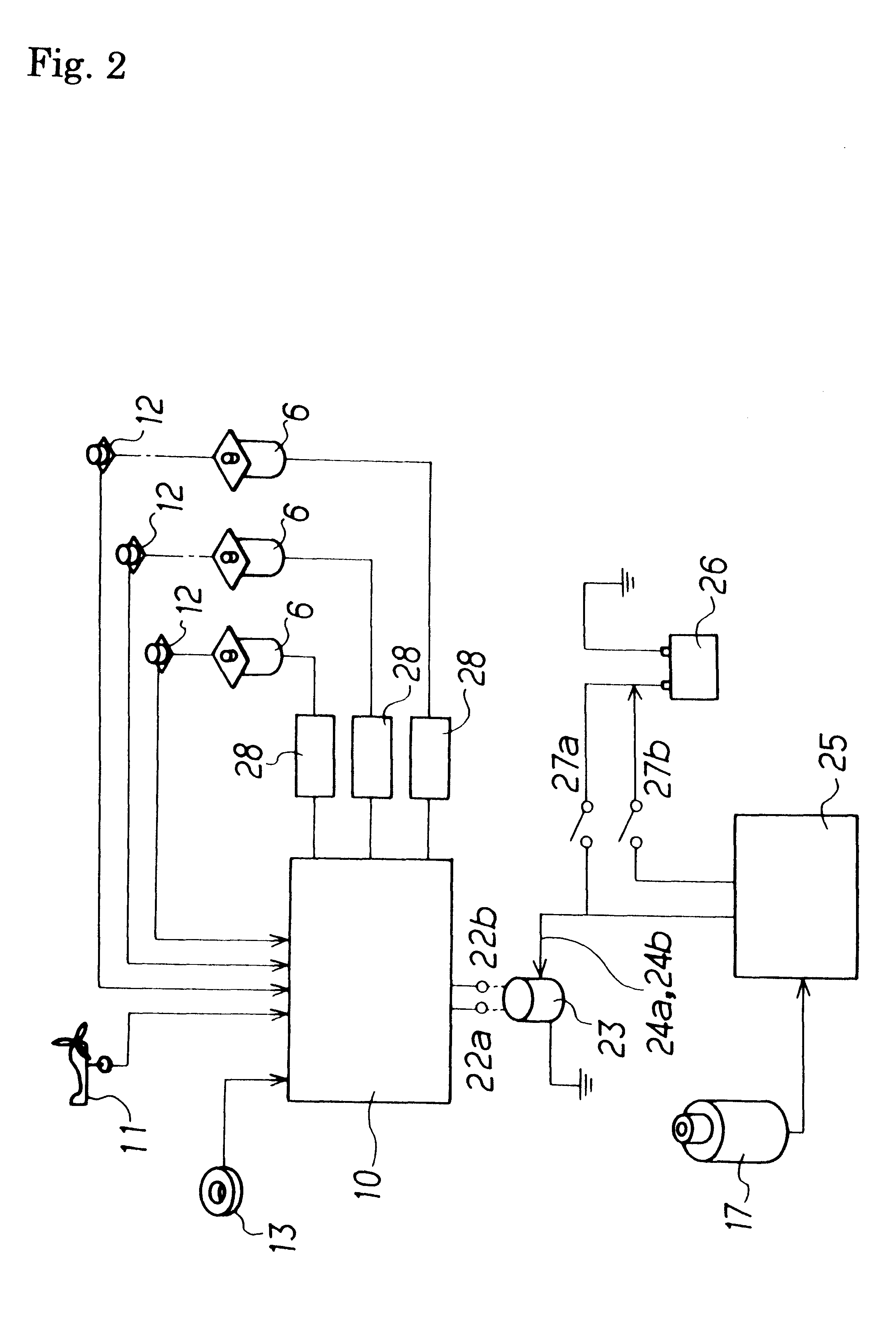
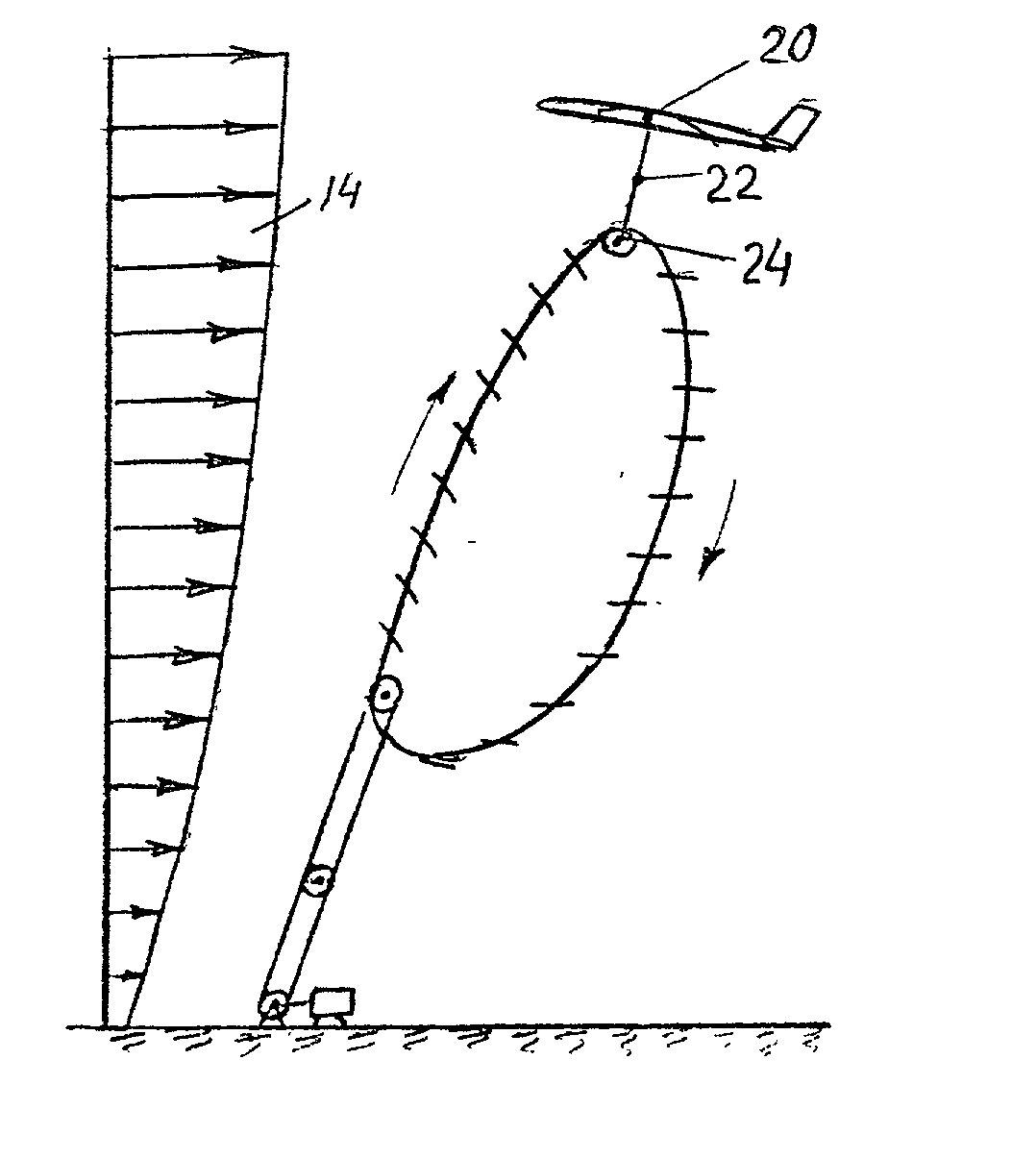
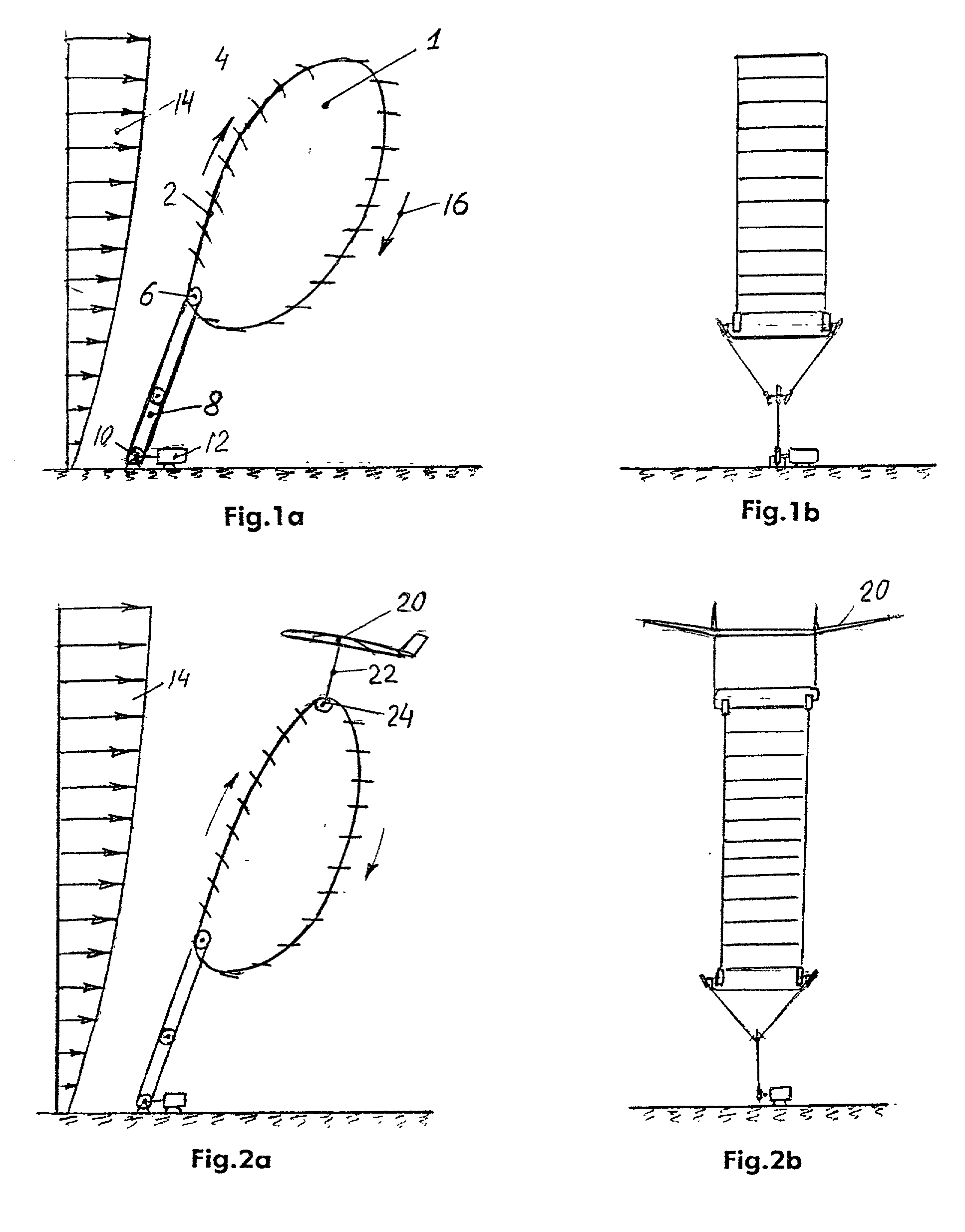
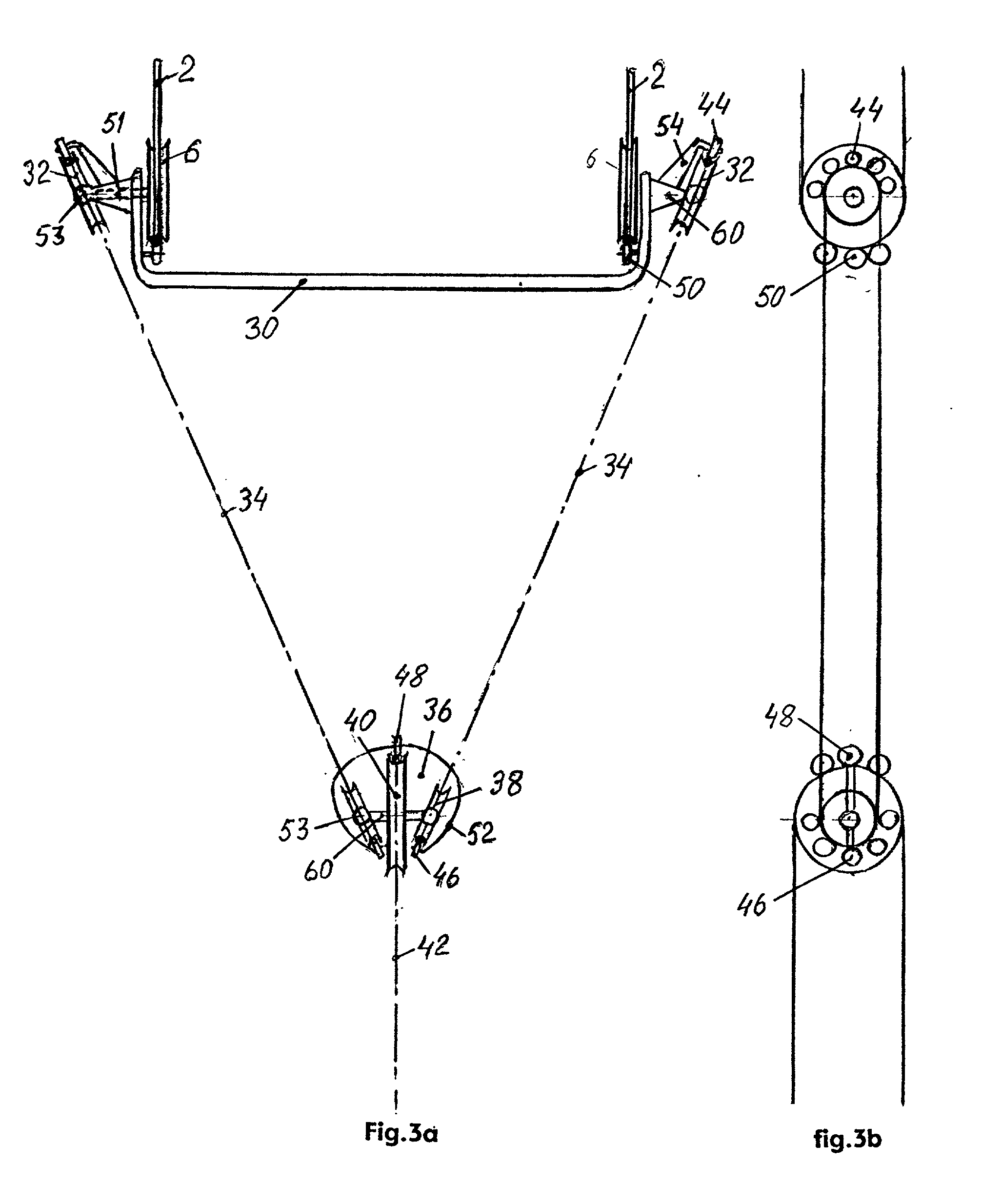
A windmill includes a freely rotatable revolution shaft, a plurality of pairs of pivotal support rods provided at the revolution shaft, and wind receiving blades respectively and rotatably set between the pivotal support rods with wind receiving blade shafts. The windmill is applied to the driving of a lifting pump, a generator and the like by employing revolution driving force. An anemometer / anemoscope measures wind velocity and direction. A servo motor controls the direction of the wind receiving blades based on the detected velocity and direction. Various methods of control are also provided.
Owner:HIRAI TETSUO
Windmill
InactiveUS6911741B2Reduce bendabilityImprove bearing capacityEnergy storageWind motor combinationsVertical axisElectric generator
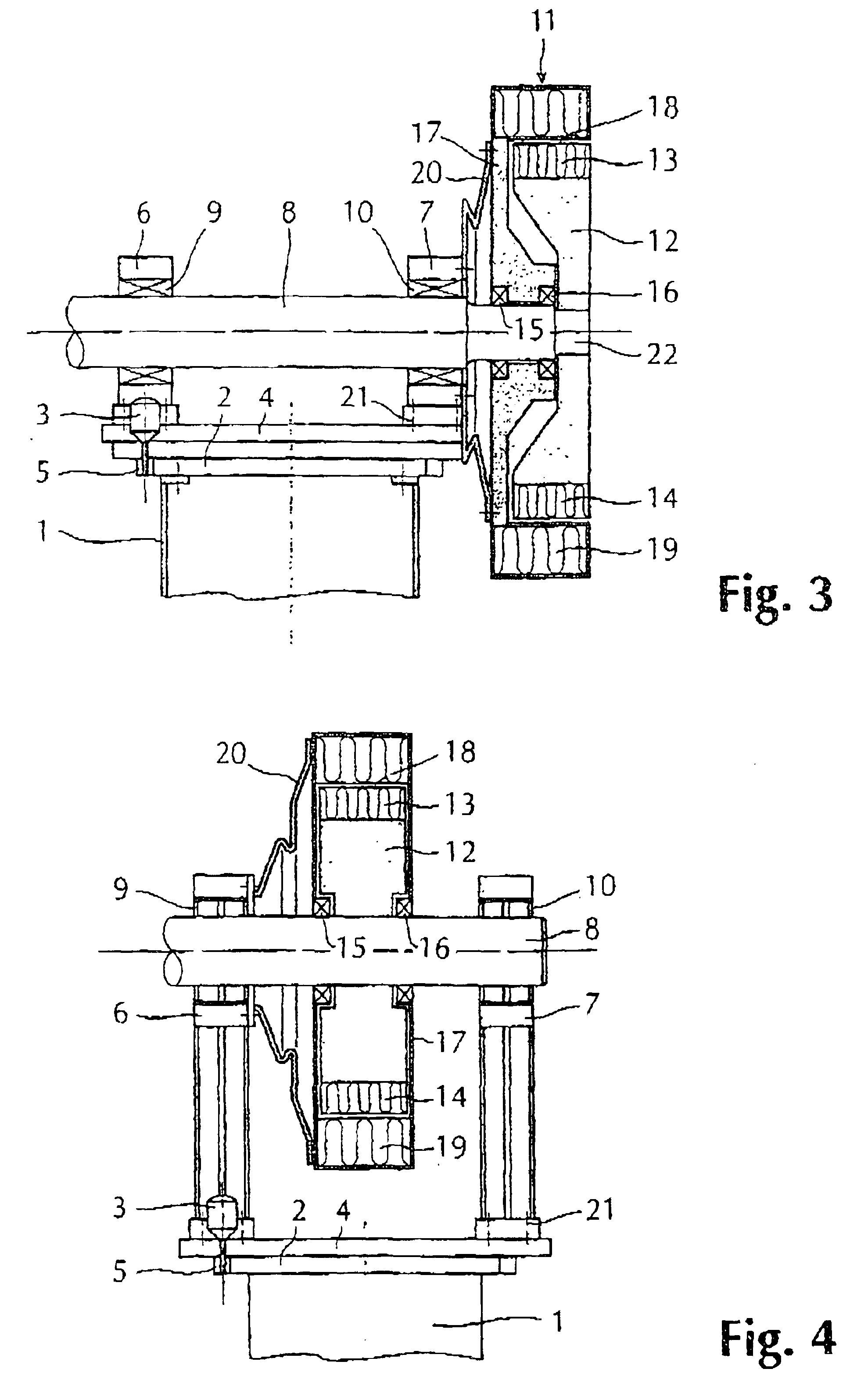
Wind power plant with a wind turbine with a turbine shaft with which a generator shaft, which can be an extension of the turbine shaft, is connected to the rotor (12) of an electric generator. The rotor is radially surrounded by a stator, the turbine shaft is journalled in two bearing housings with bearings arranged on a base at the top of a tower, the base is pivotable around a vertical axis, and a motor is provided to effect the pivoting. The generator shaft is integrated with or rigidly connected to a flexing turbine shaft, the stator and rotor are carried by the generator shaft, to allow the generator to follow the flexing movement of the turbine shaft and the stator is locked against turning by a non-rotatable coupling which transfers substantially no bending moment or axial force acting against the flexing of the turbine shaft due to the bending moment acting on the turbine shaft from its hub, the bearings being provided to allow flexing of the turbine shaft.
Owner:SCAN WIND GROUP
Method and apparatus for using wind turbines to generate and supply uninterrupted power to locations remote from the power grid
InactiveUS6927503B2Efficiently and continuouslyLittle orFrom solar energyWind energy with electric storagePower gridHigh pressure
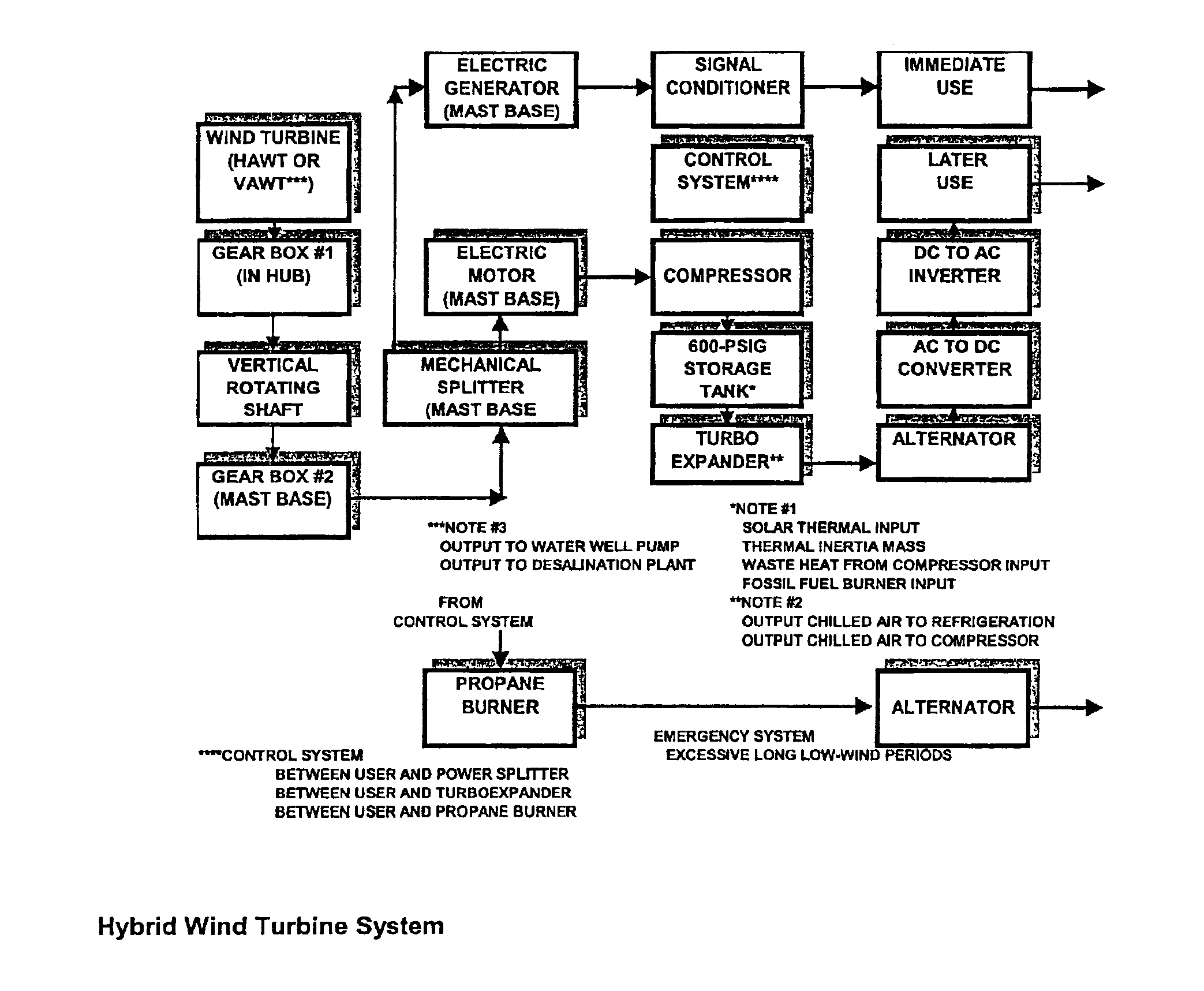
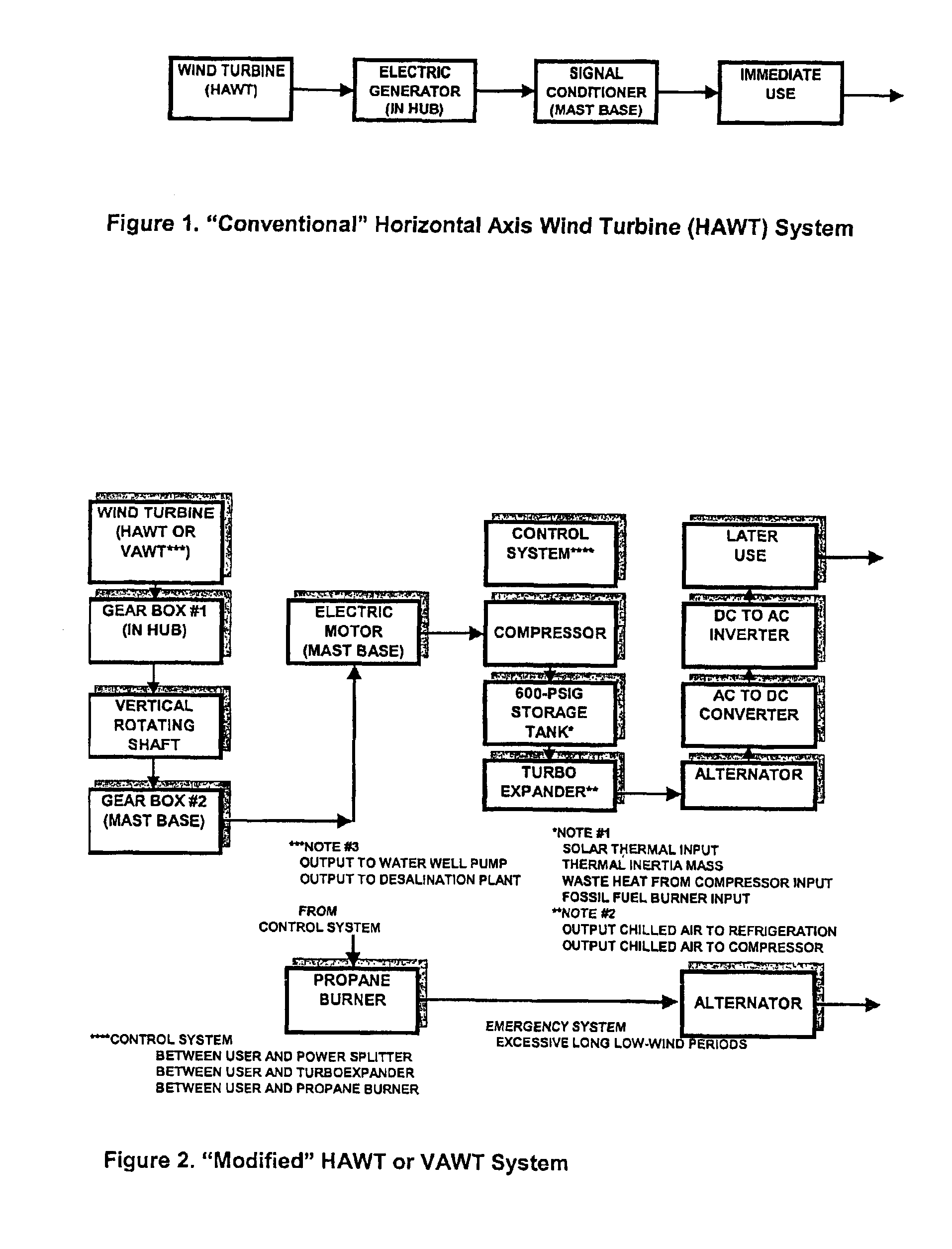
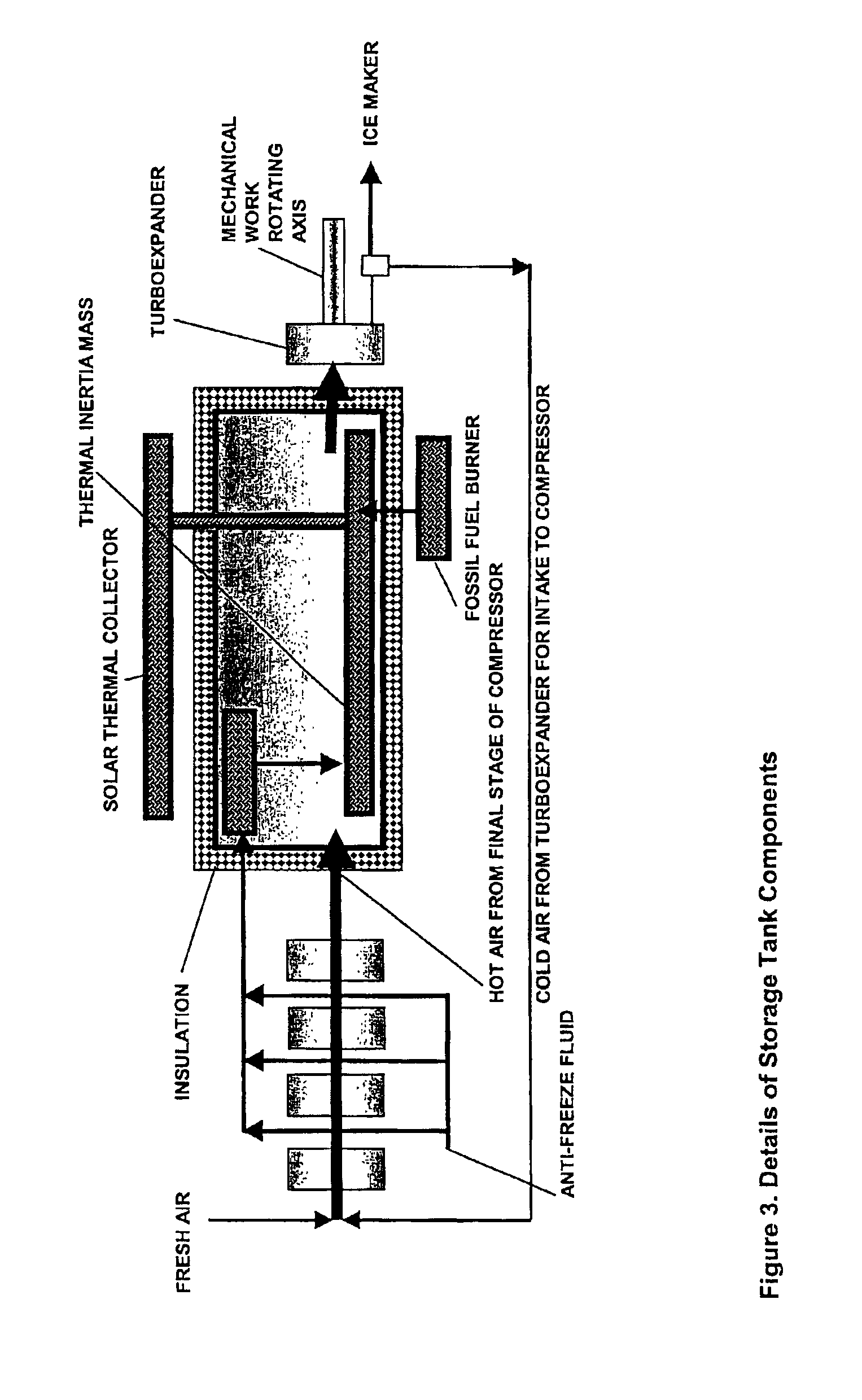
The present invention relates to a wind energy generating and storing system comprising methods and apparatuses for providing energy dedicated for immediate use and energy storage, to provide electrical power on an uninterrupted and continous basis, to locations remote from an electrical power grid. In a large application, the invention contemplates having a predetermined number of windmills dedicated for immediate use, and a predetermined number of windmills dedicated for energy storage, as compressed air energy in one or more high pressure tanks. A hybrid windmill having the ability to simultaneously switch between energy for immediate use and energy storage can also be provided.
Owner:ENIS BEN M +1
Up-wind type windmill and operating method therefor
InactiveUS7436083B2Avoid it happening againReduce weightWind motor controlWind energy with electric storageNacelleElectric power
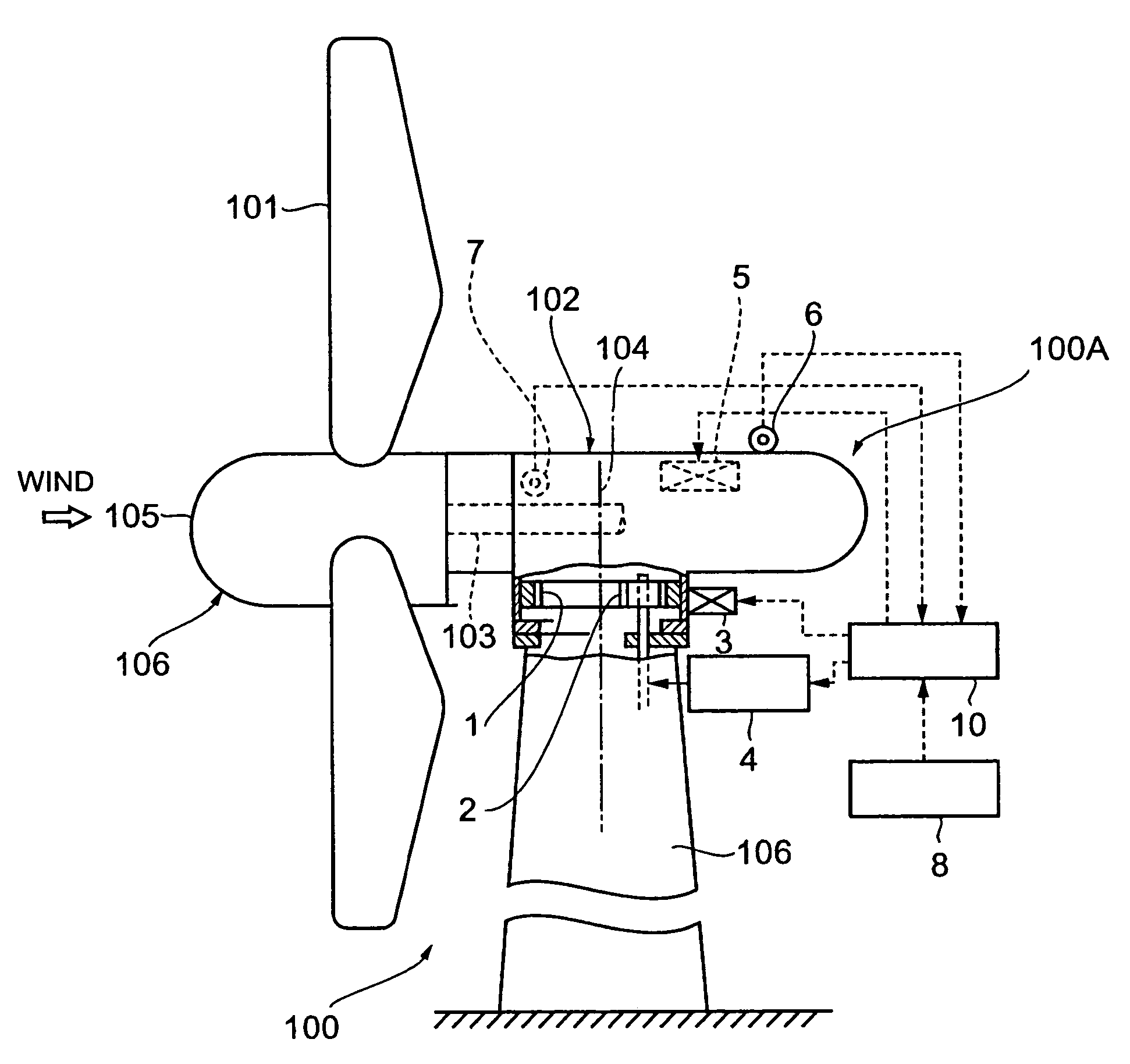
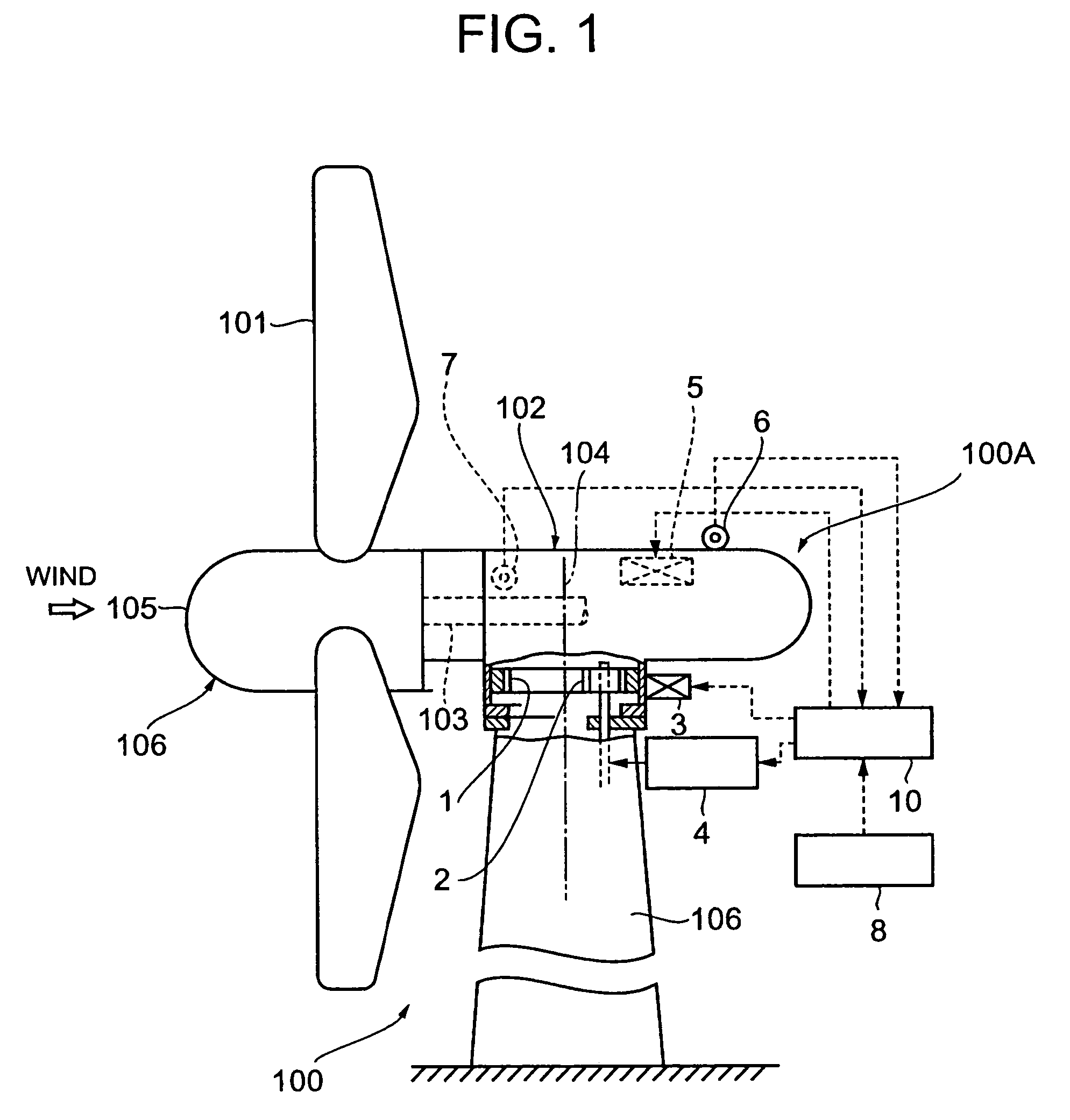
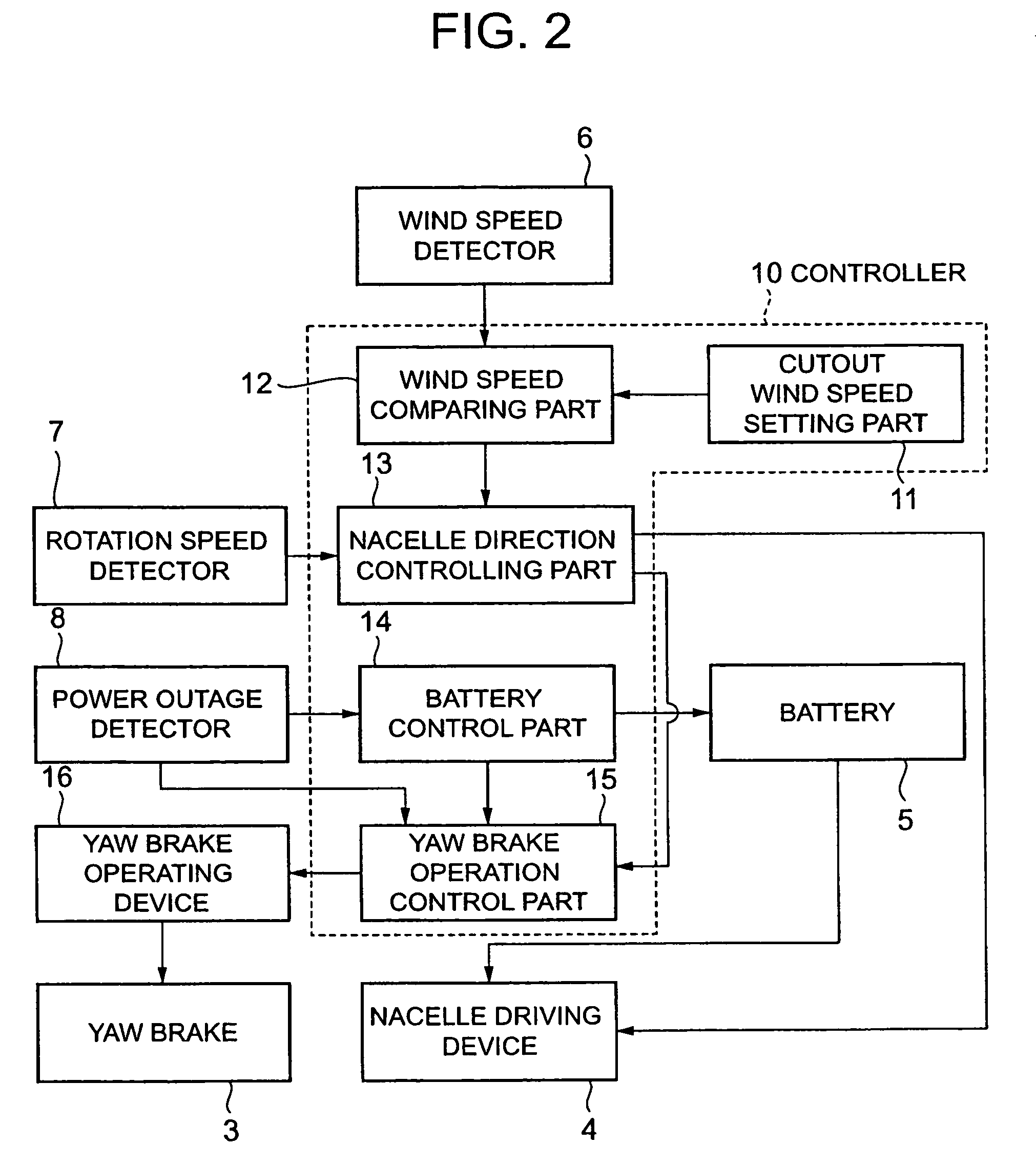
A structure of an upwind type wind turbine and the operating method thereof capable of preventing the occurrence of damage of the blades by evading excessive irregular loads from acting on the blades in the slanting direction in the event of power failure when strong wind blows, are provided.In the upwind type wind turbine having a nacelle supported for rotation on a support, the nacelle is rotated to a downwind position by rotating it by 180° from a normal upwind position and kept in stand-by condition at a downwind position when detected wind speed is higher than the predetermined cutout wind speed, which is the reference wind speed for shifting to an idle operation state. When the detected wind speed is higher than the DWSS wind speed determined based on the maximum permissible instantaneous wind speed, the nacelle is rotated from an upwind position to a downwind position and the yaw brake is released.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Wind powered hydroelectric power plant and method of operation thereof
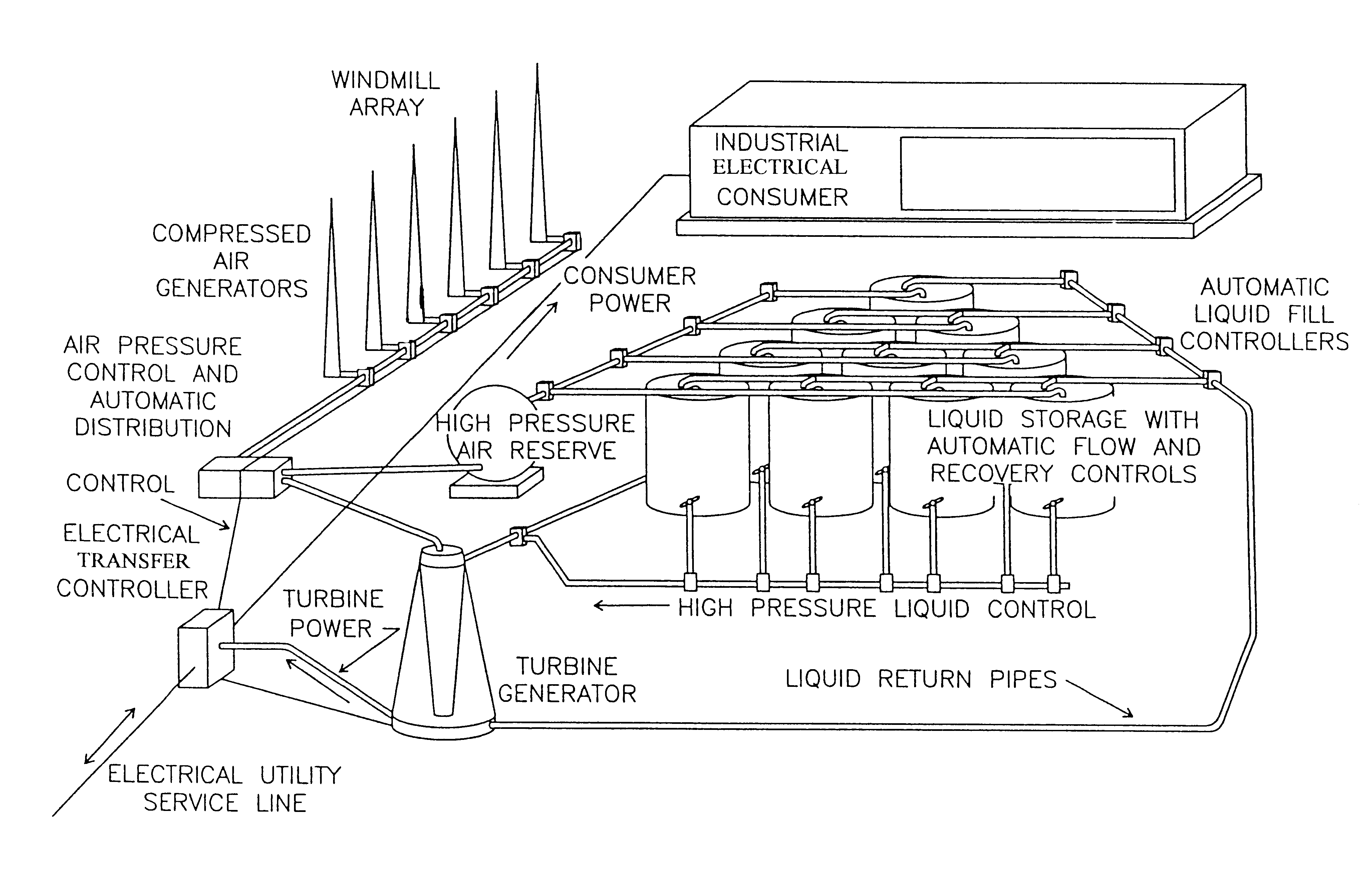
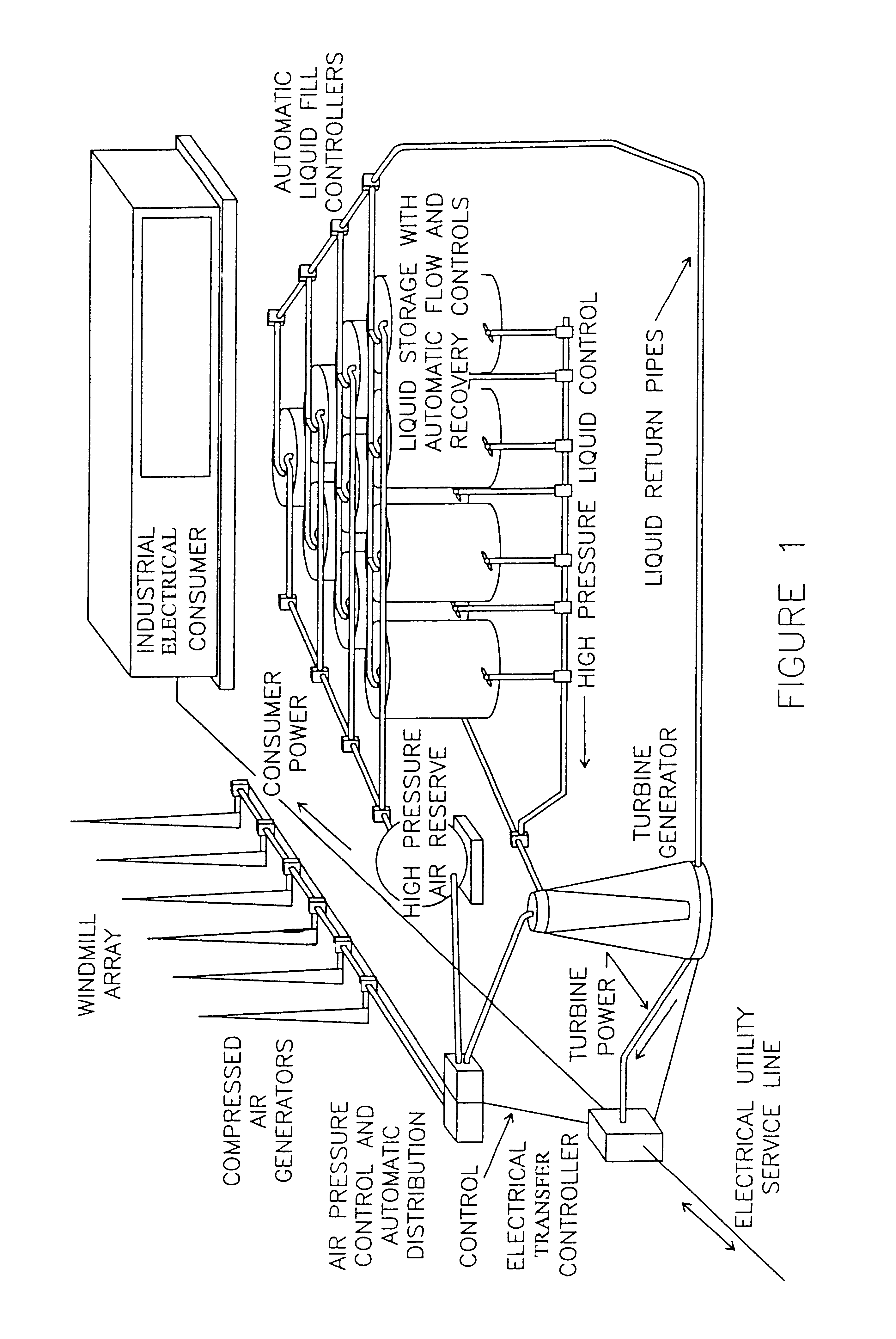
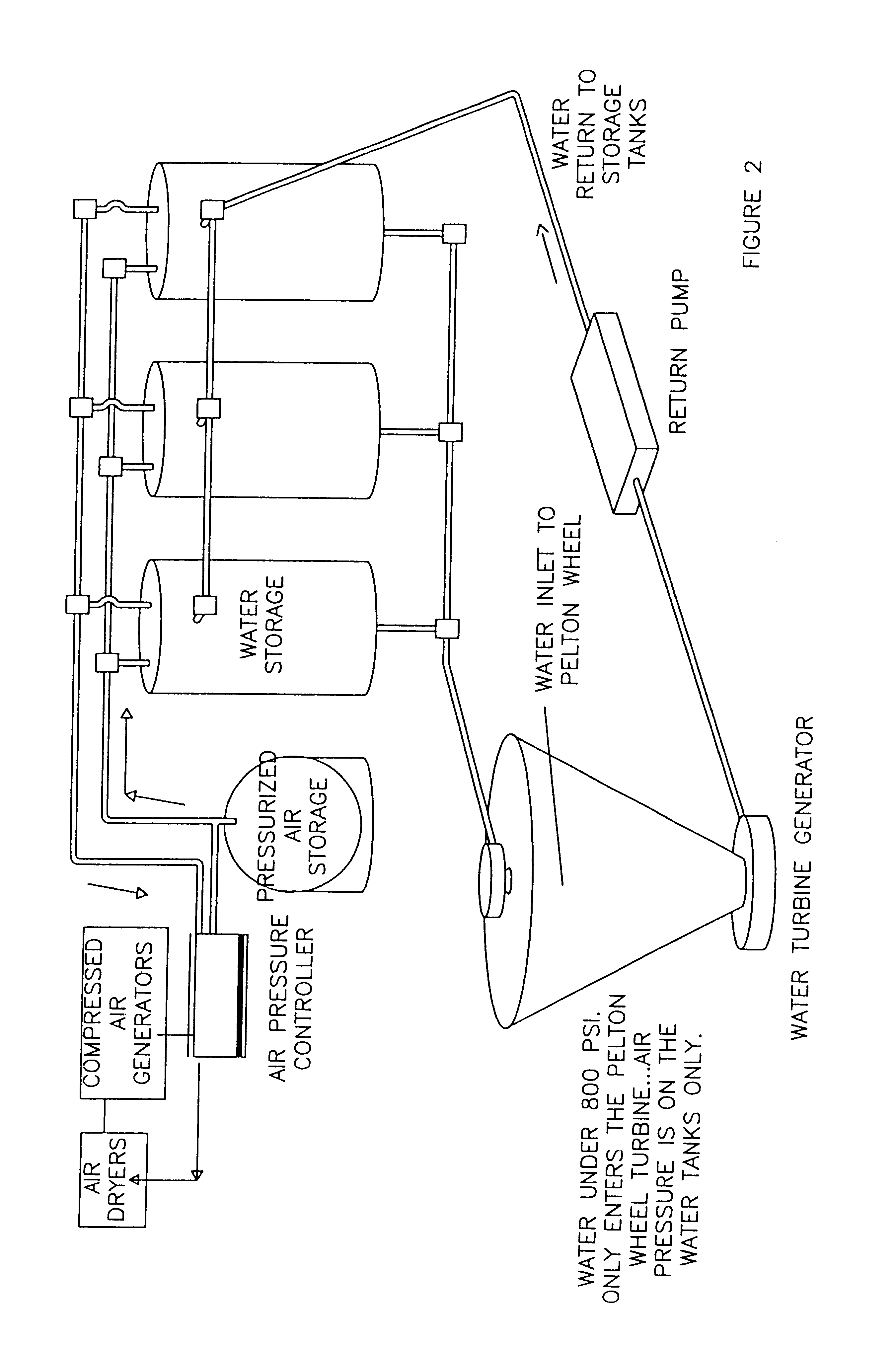
A hydroelectric power plant uses a plurality of windmills connected to compressed air generators to produce pressurized air. Pressurized air is used to drive water through a turbine to produce electrical power. The water is recycled and the power plant includes reserve pressurized air tanks to allow the plant to continue to operate when the wind levels are not sufficient to produce high pressure air. The power plant is designed to be operated on a continuous basis based on wind power. When the wind subsides and the reserve capacity has been exhausted, electricity can be drawn from the local utility supplier. When excess power is generated by the power plant, electricity from the power plant can be added to the grid of the local electricity supplier.
Owner:NEW WORLD GENERATION
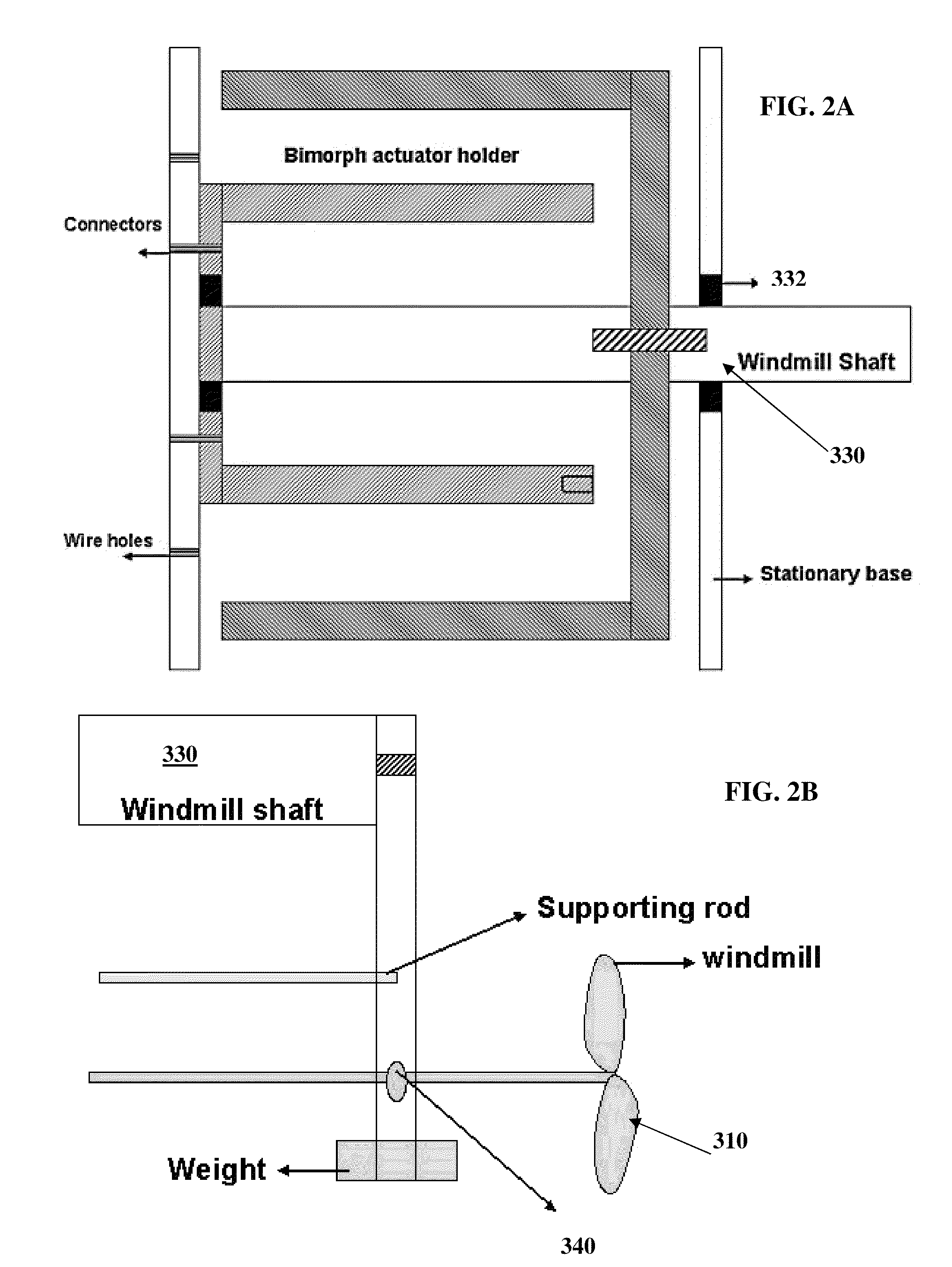
Piezoelectric windmill apparatus
InactiveUS20100052324A1Additive manufacturing apparatusPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityEngineering
A piezoelectric windmill configured to handle small scale wind flow. One embodiment the piezoelectric windmill solves problems associated with harvesting energy and generating electric energy or power using piezoelectric materials having significant advantages over previously available materials.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS
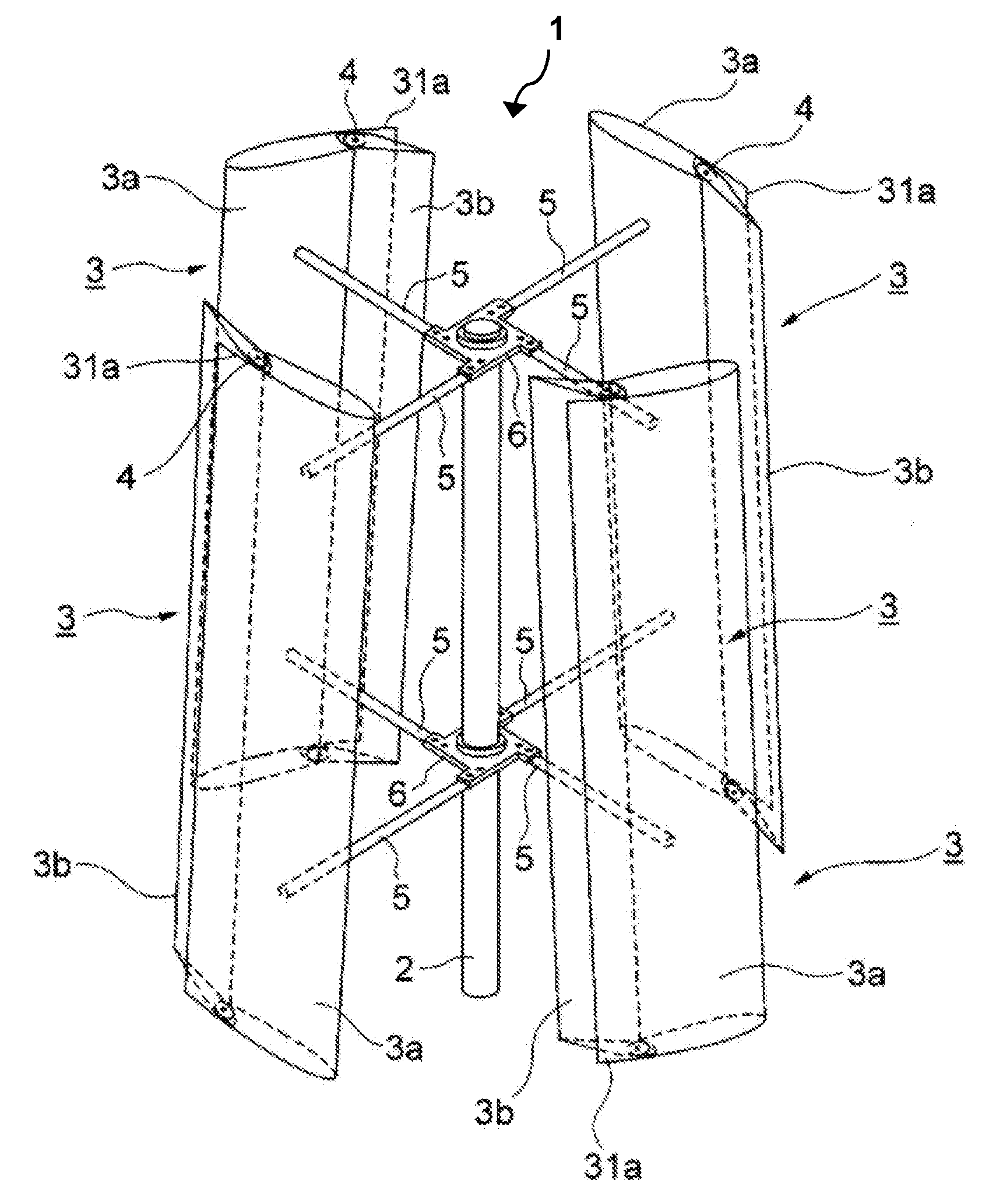
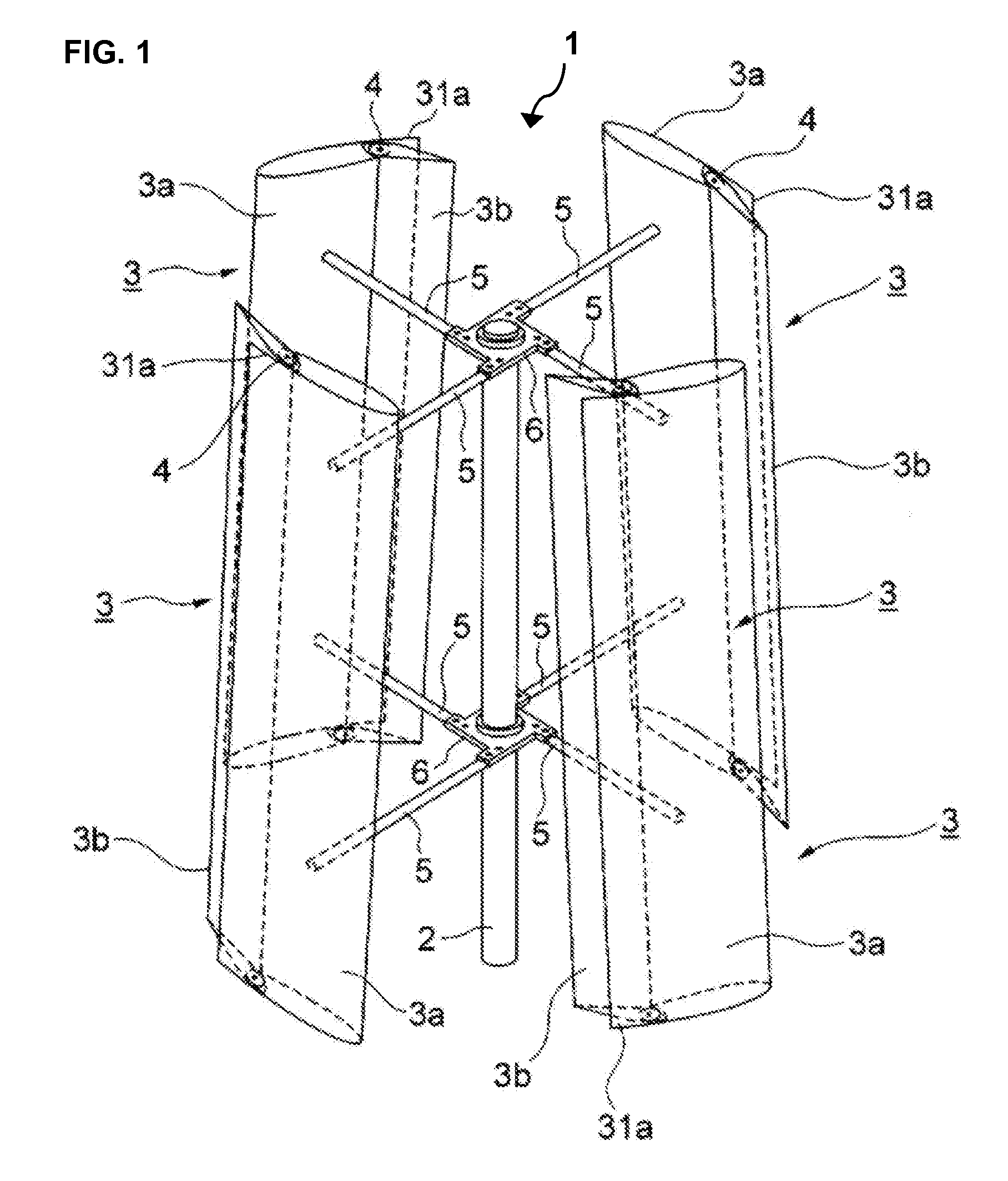
Stackable vertical axis windmill
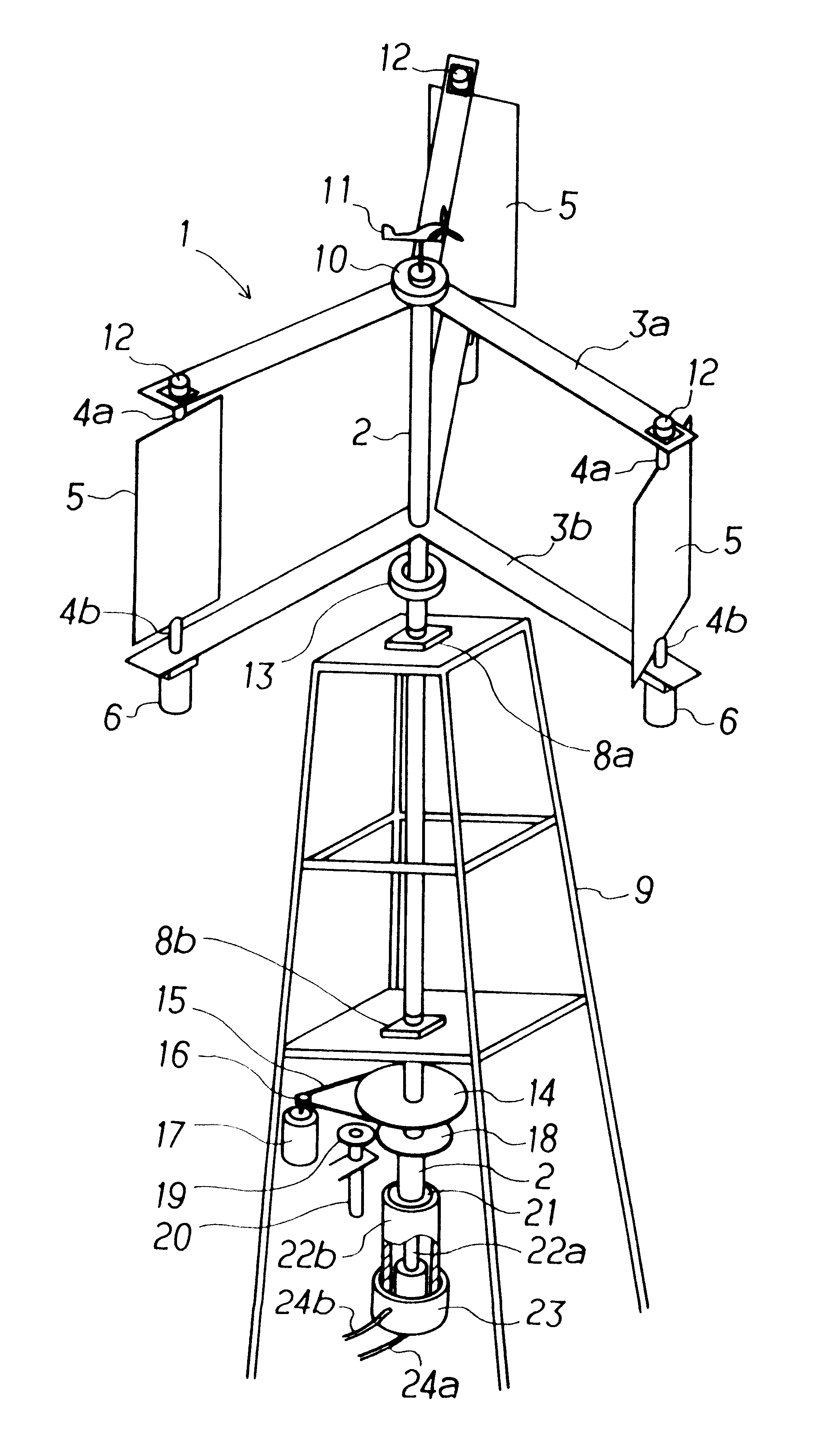
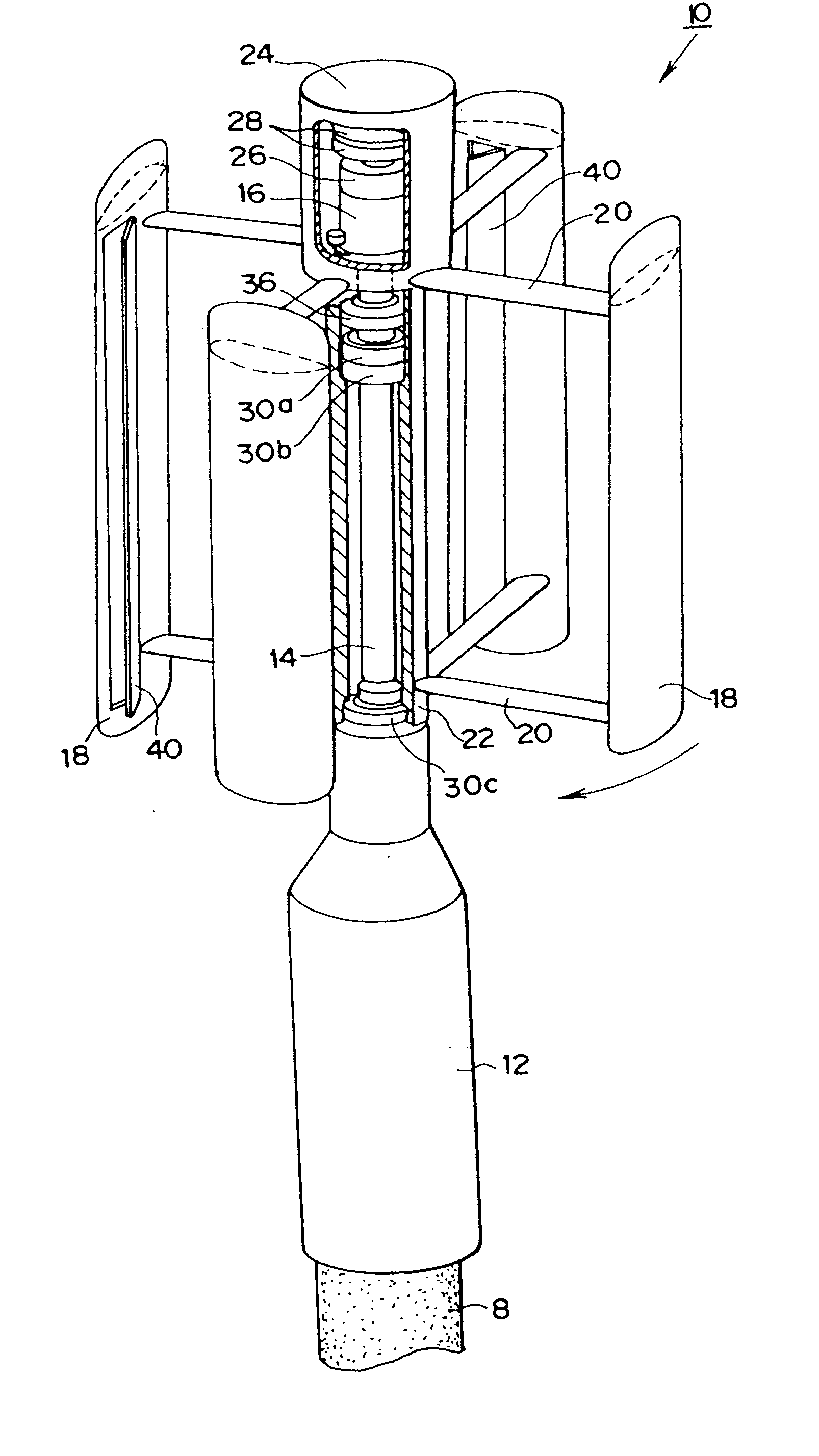
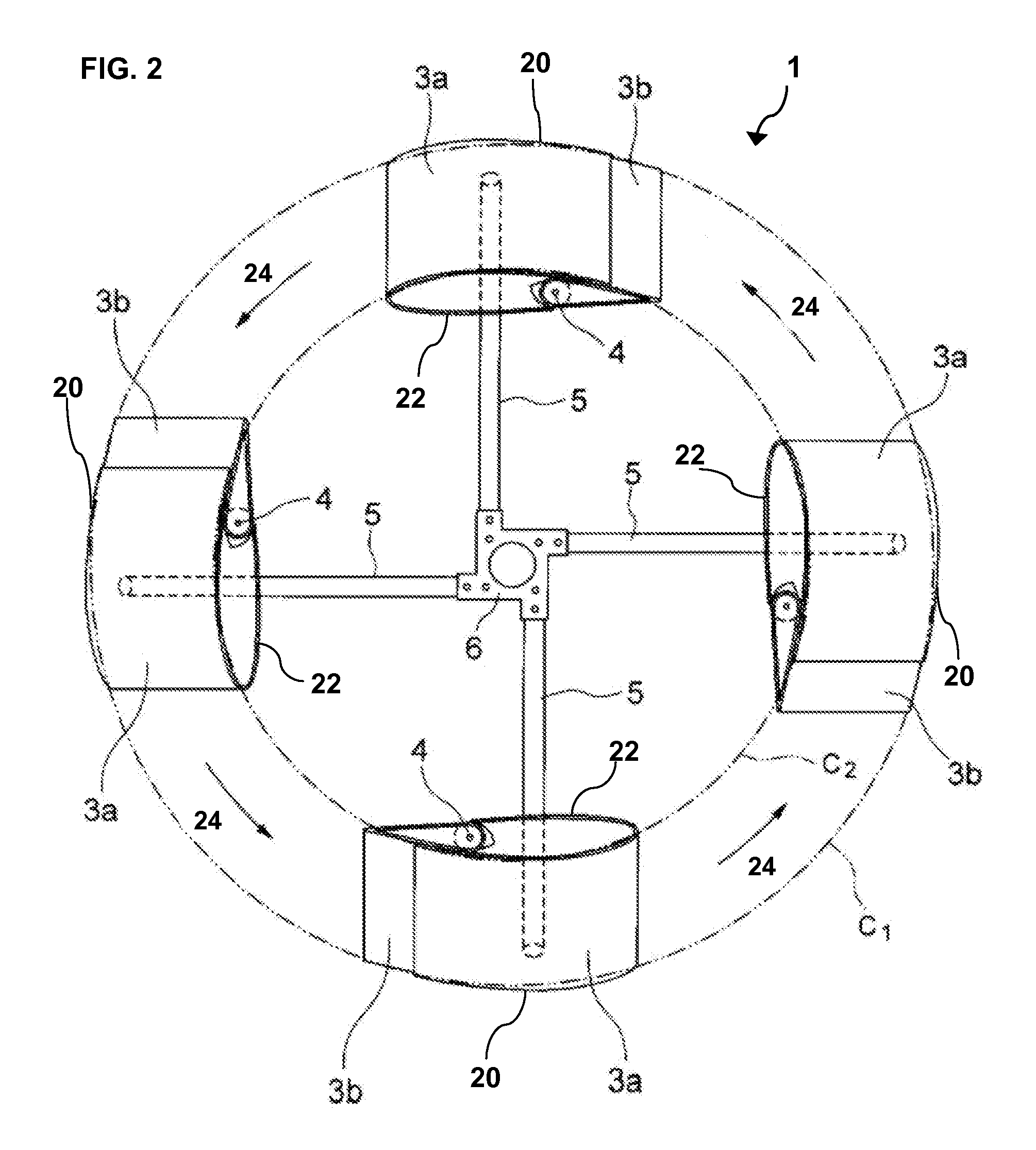
A stackable, vertical axis windmill comprised of a braced external frame that enables stacking of multiple windmill assemblies. Couplings are located on both ends of the vertical rotor shaft to enable stacking and the transmission of power, an internal wind flow cavity, and controlled wind guides is described. The external frame includes structural bracing that allows for two or more windmill to be stacked one upon another to optimize the use of land or rooftop space for the generation of electricity from wind power. The computer controlled wind guides automatically close partially in high wind conditions in order to prevent damage to the windmill. The internal wind flow cavity allows wind to transfer power to both the windward and leeward rotors blades. The rotor axis is constructed so that all bearings can be replaced without dismantling the structure.
Owner:MILLER LEWIS H
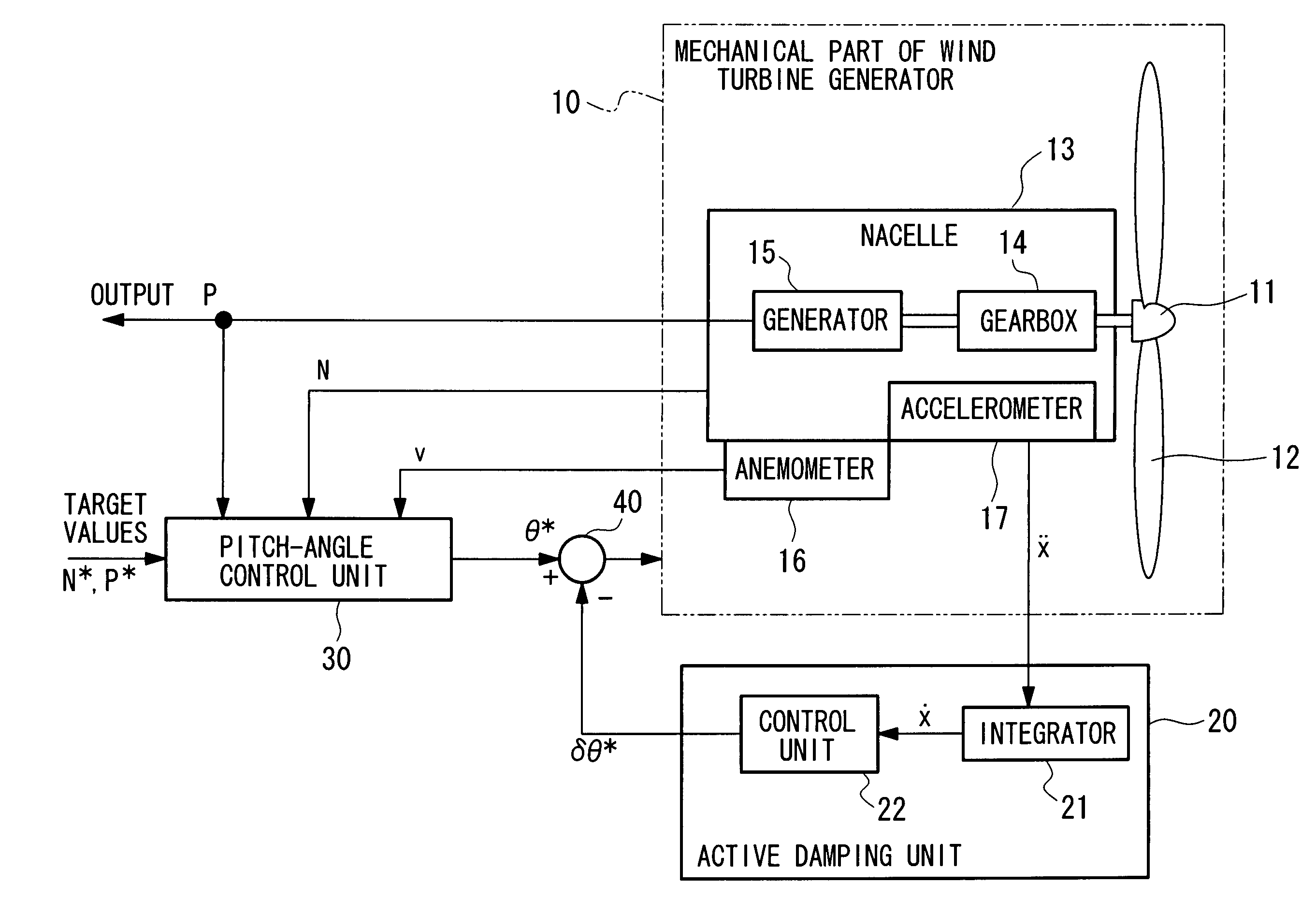
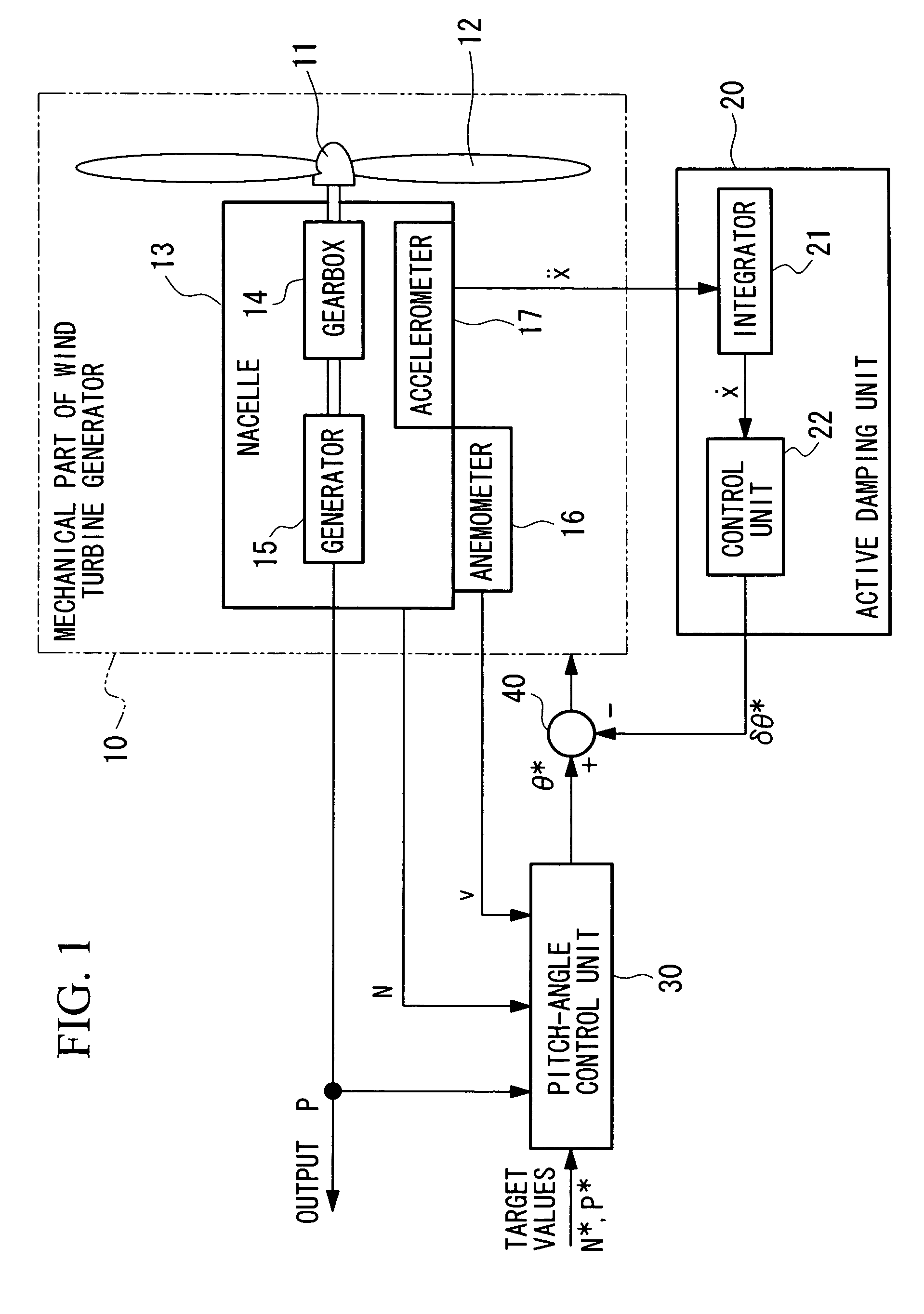
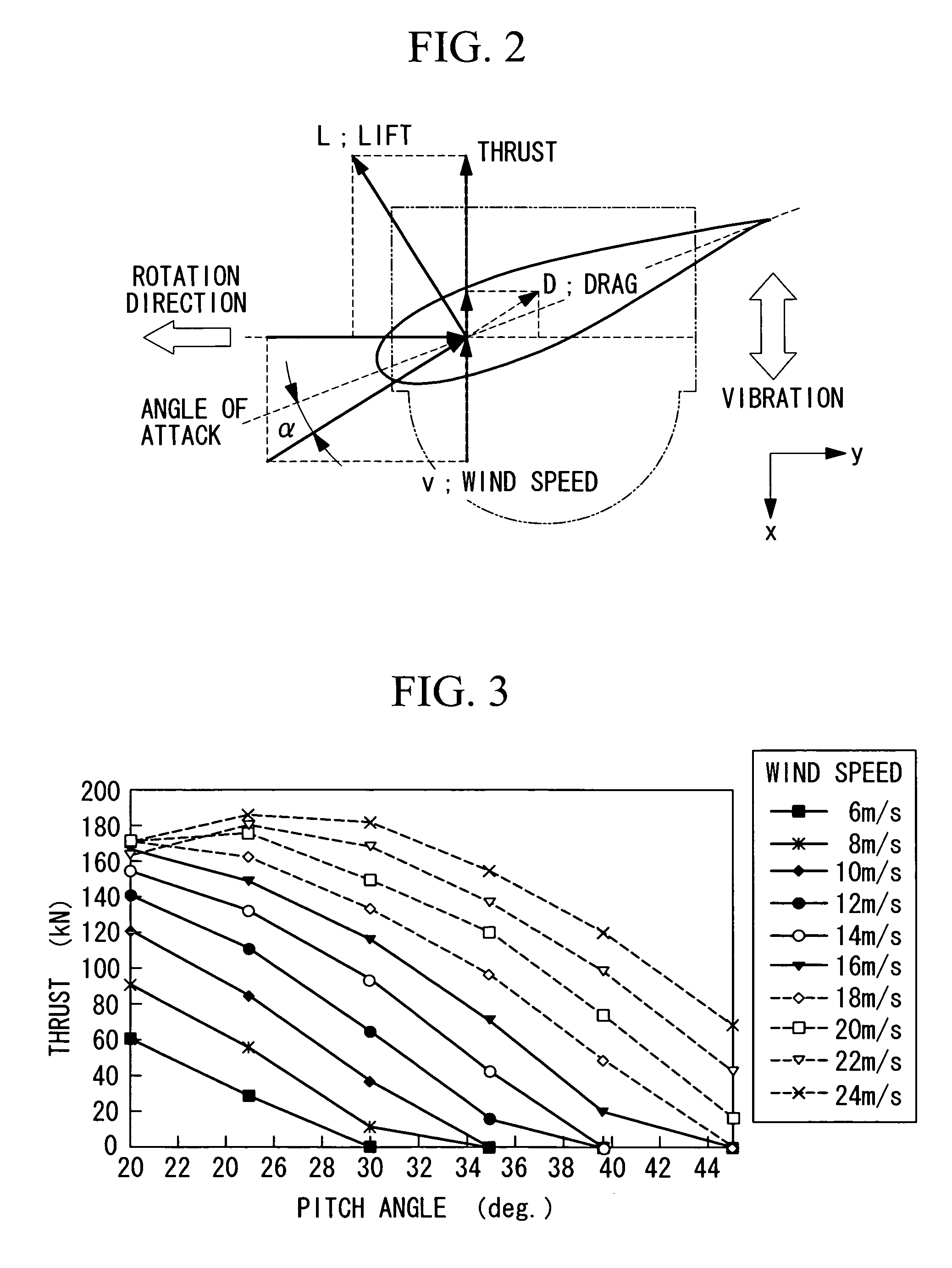
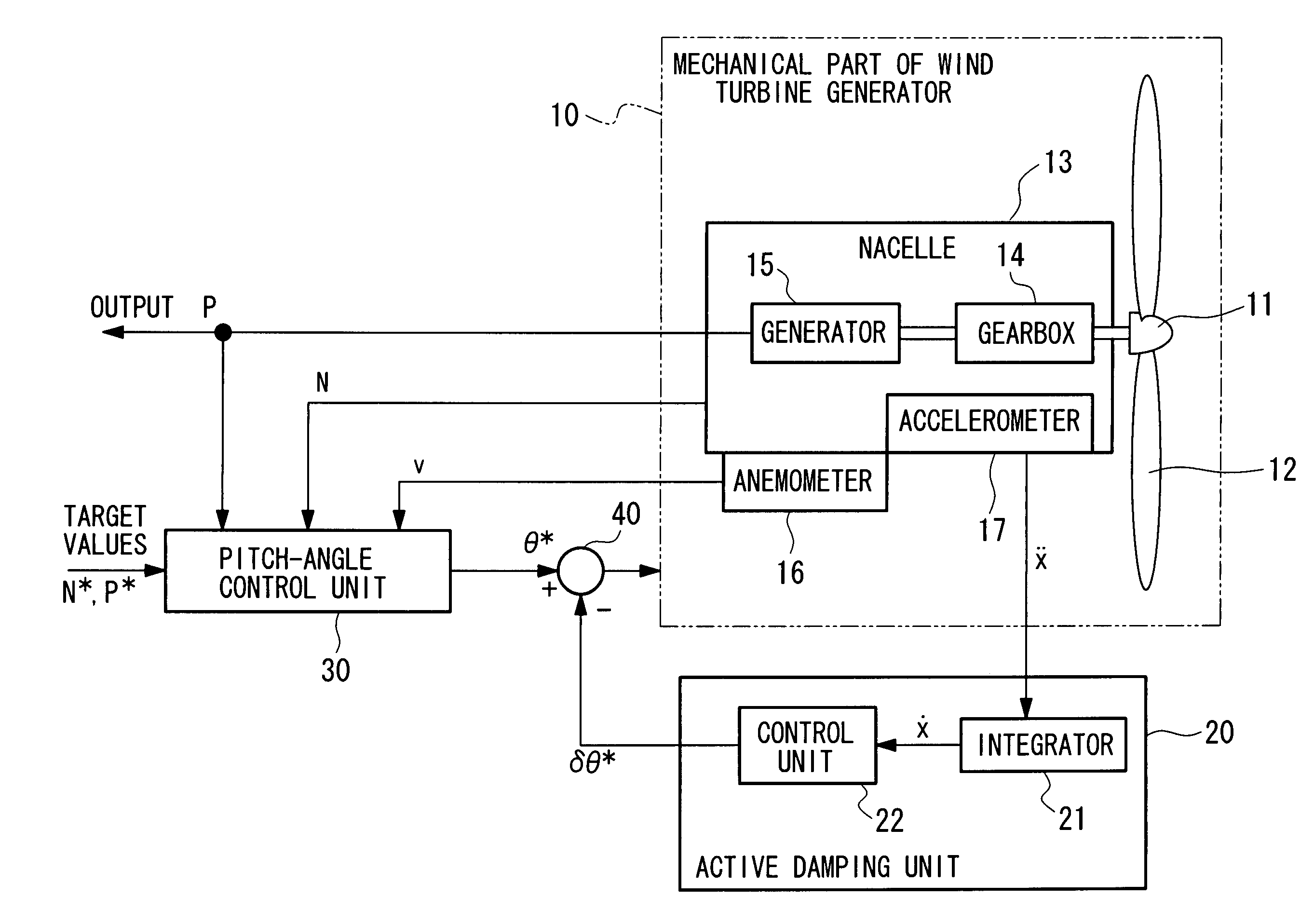
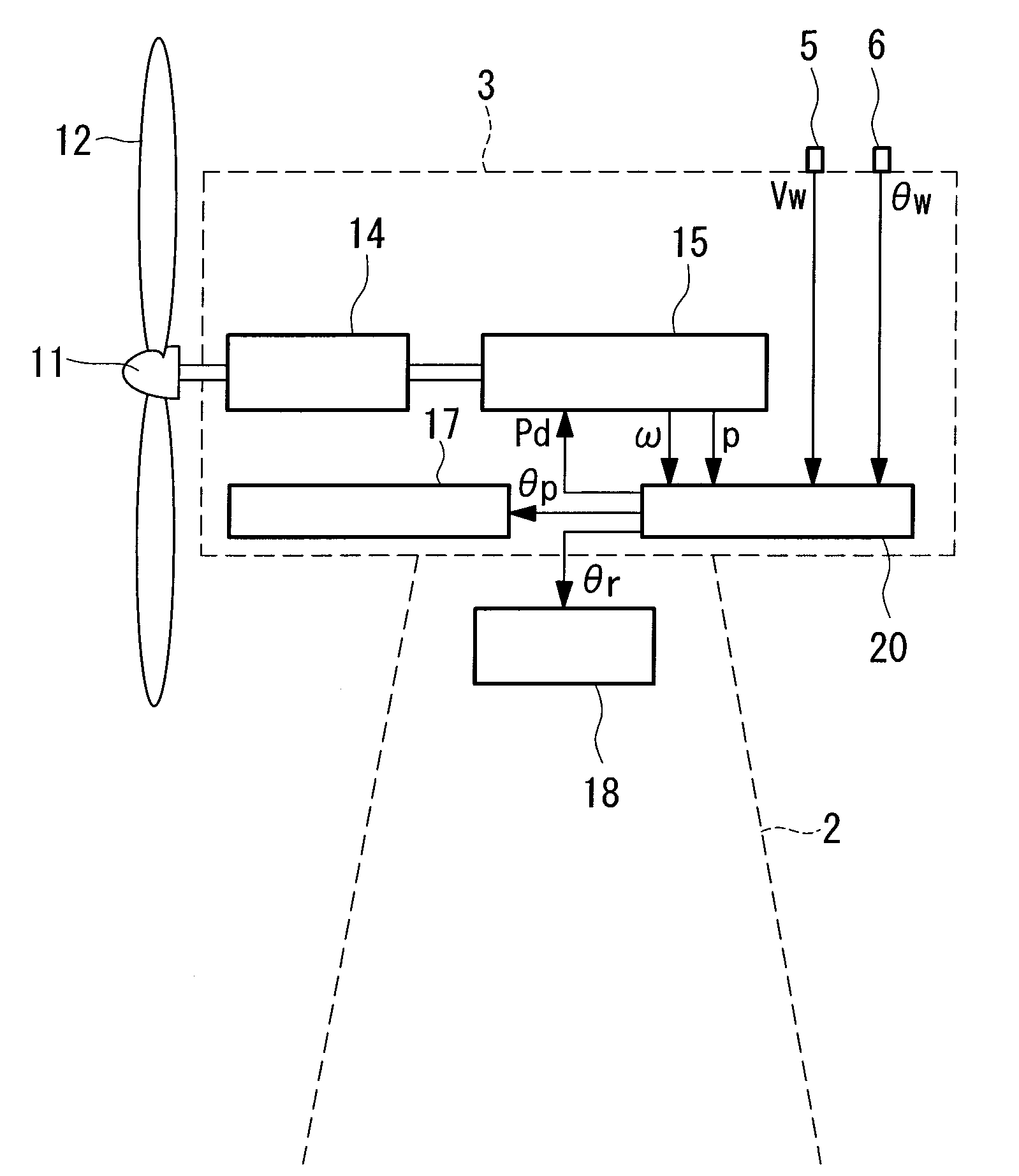
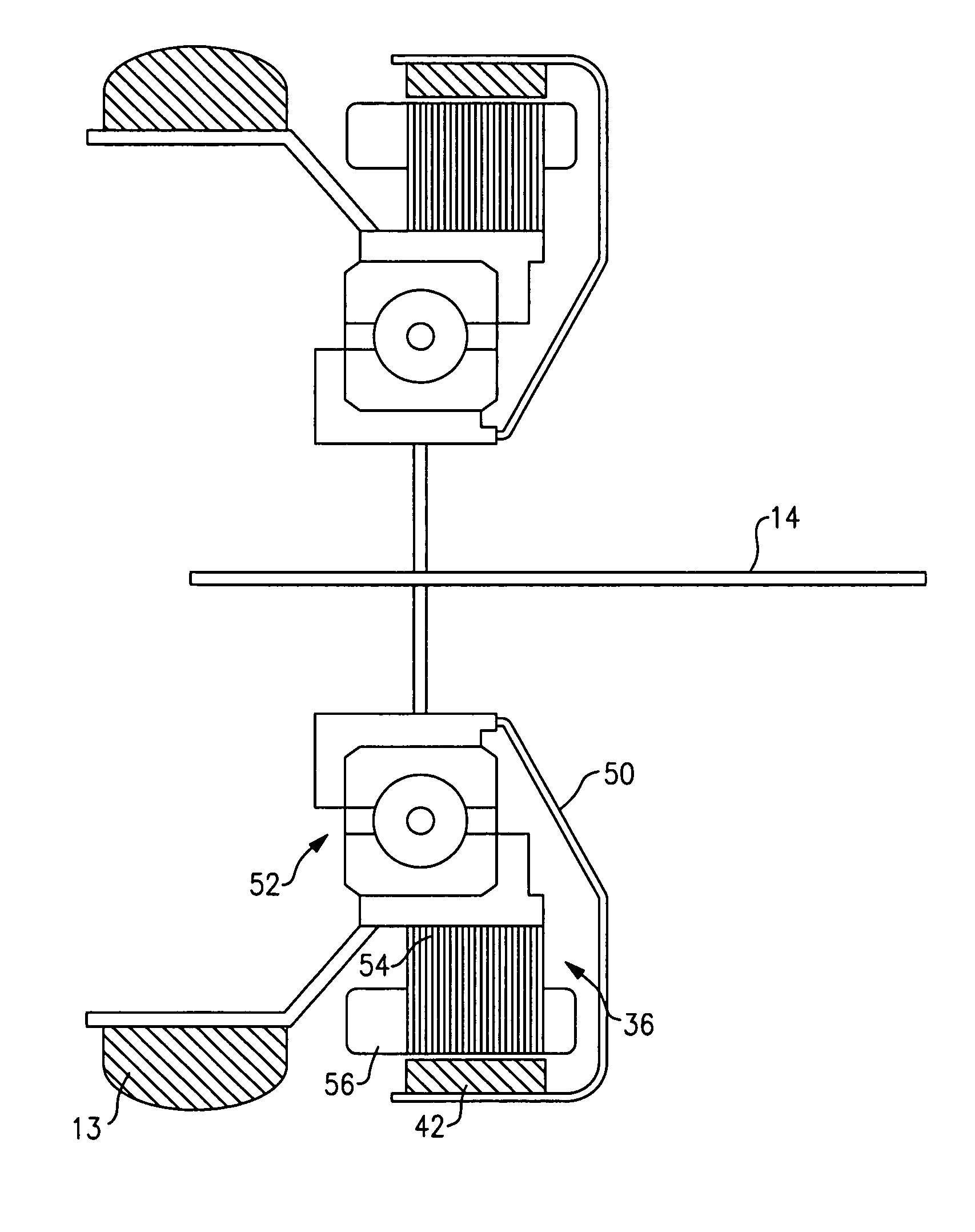
Wind Turbine Generator, Active Damping Method Thereof, and Windmill Tower
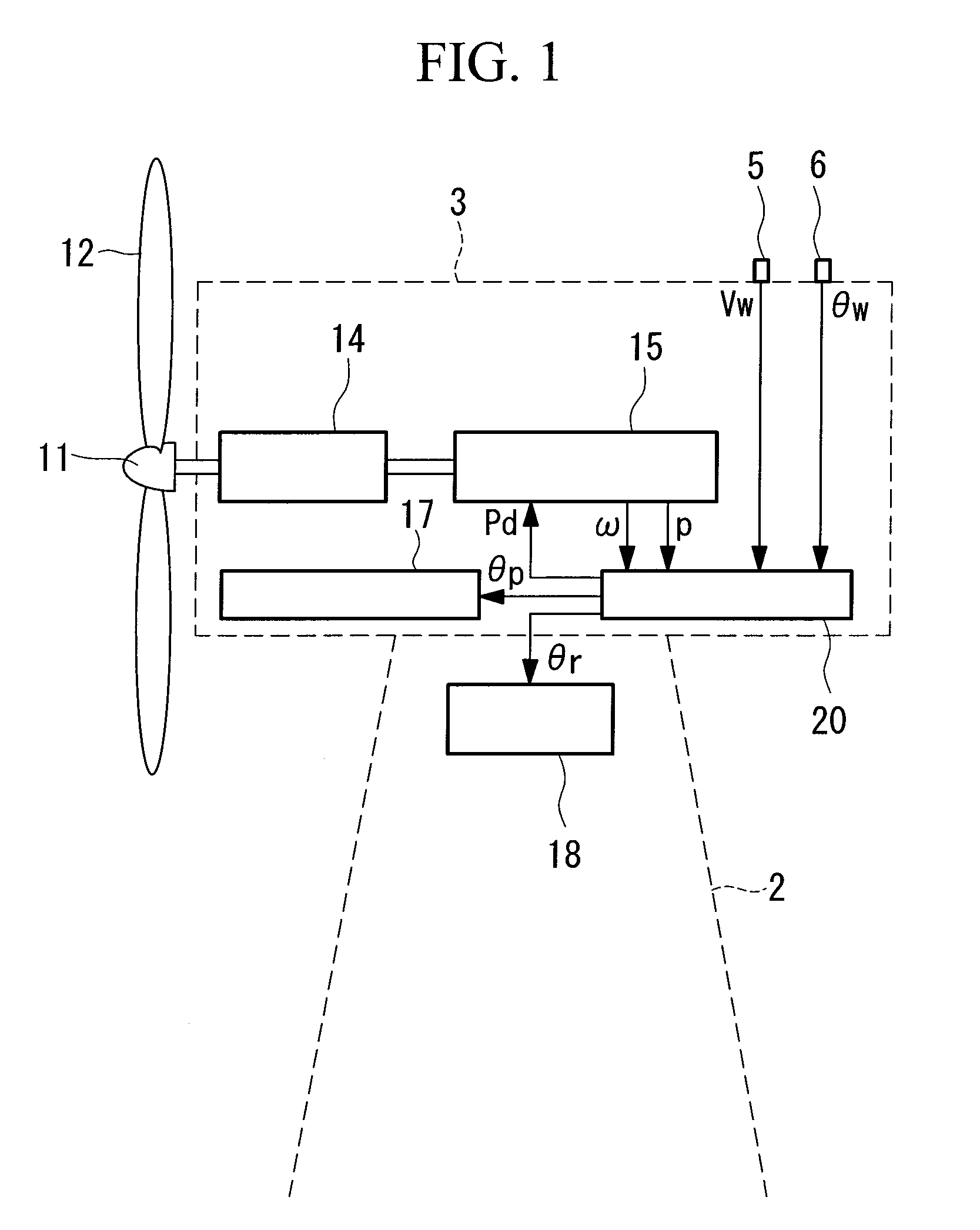
A wind turbine generator, an active damping method thereof, and a windmill tower in which vibrations of the wind turbine generator itself or the windmill tower can be reduced at low cost are provided. The acceleration due to vibrations of a nacelle (13) is detected with an accelerometer (17) attached to the nacelle (13). In an active damping unit (20), a pitch angle of windmill blades (12) for generating a thrust on the windmill blades (12) so as to cancel out the vibrations of the nacelle (13) is calculated on the basis of the acceleration, and the pitch angle is output as a blade-pitch-angle command δθ* for damping. On the other hand, in a pitch-angle control unit (30), a pitch angle of the windmill blades (12) for controlling the output to be a predetermined value is calculated, and the pitch angle is output as a blade-pitch-angle command θ* for output control. The blade-pitch-angle command δθ* for damping is combined with the blade-pitch-angle command θ* for output control using a subtracter (40). The pitch angle of the windmill blades is controlled on the basis of the resulting blade-pitch-angle command after combining.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Wind turbine generator, active damping method thereof, and windmill tower
A wind turbine generator, an active damping method thereof, and a windmill tower in which vibrations of the wind turbine generator itself or the windmill tower can be reduced at low cost are provided. The acceleration due to vibrations of a nacelle (13) is detected with an accelerometer (17) attached to the nacelle (13). In an active damping unit (20), a pitch angle of windmill blades (12) for generating a thrust on the windmill blades (12) so as to cancel out the vibrations of the nacelle (13) is calculated on the basis of the acceleration, and the pitch angle is output as a blade-pitch-angle command δθ* for damping. On the other hand, in a pitch-angle control unit (30), a pitch angle of the windmill blades (12) for controlling the output to be a predetermined value is calculated, and the pitch angle is output as a blade-pitch-angle command θ* for output control. The blade-pitch-angle command δθ* for damping is combined with the blade-pitch-angle command θ* for output control using a subtracter (40). The pitch angle of the windmill blades is controlled on the basis of the resulting blade-pitch-angle command after combining.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
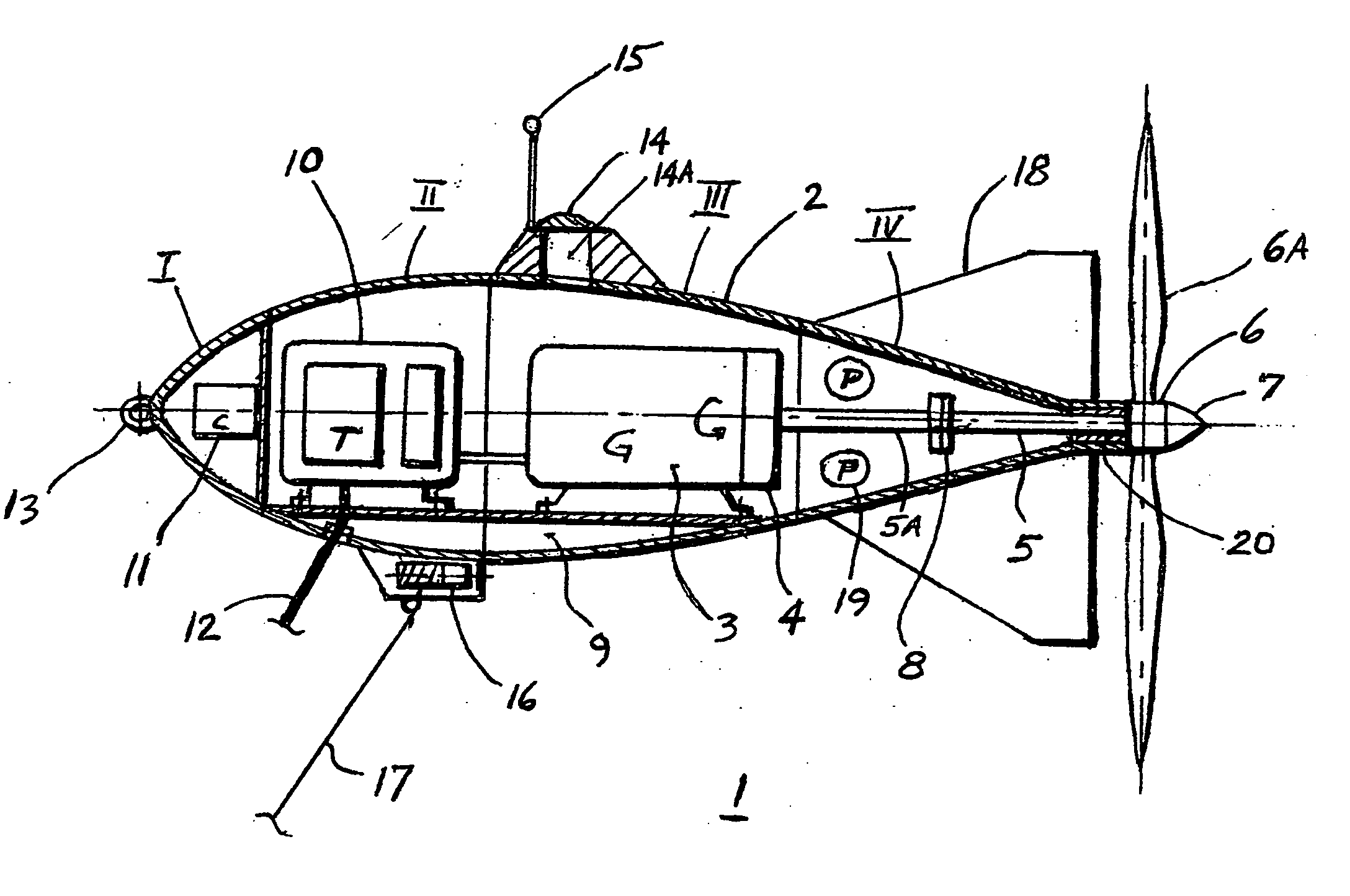
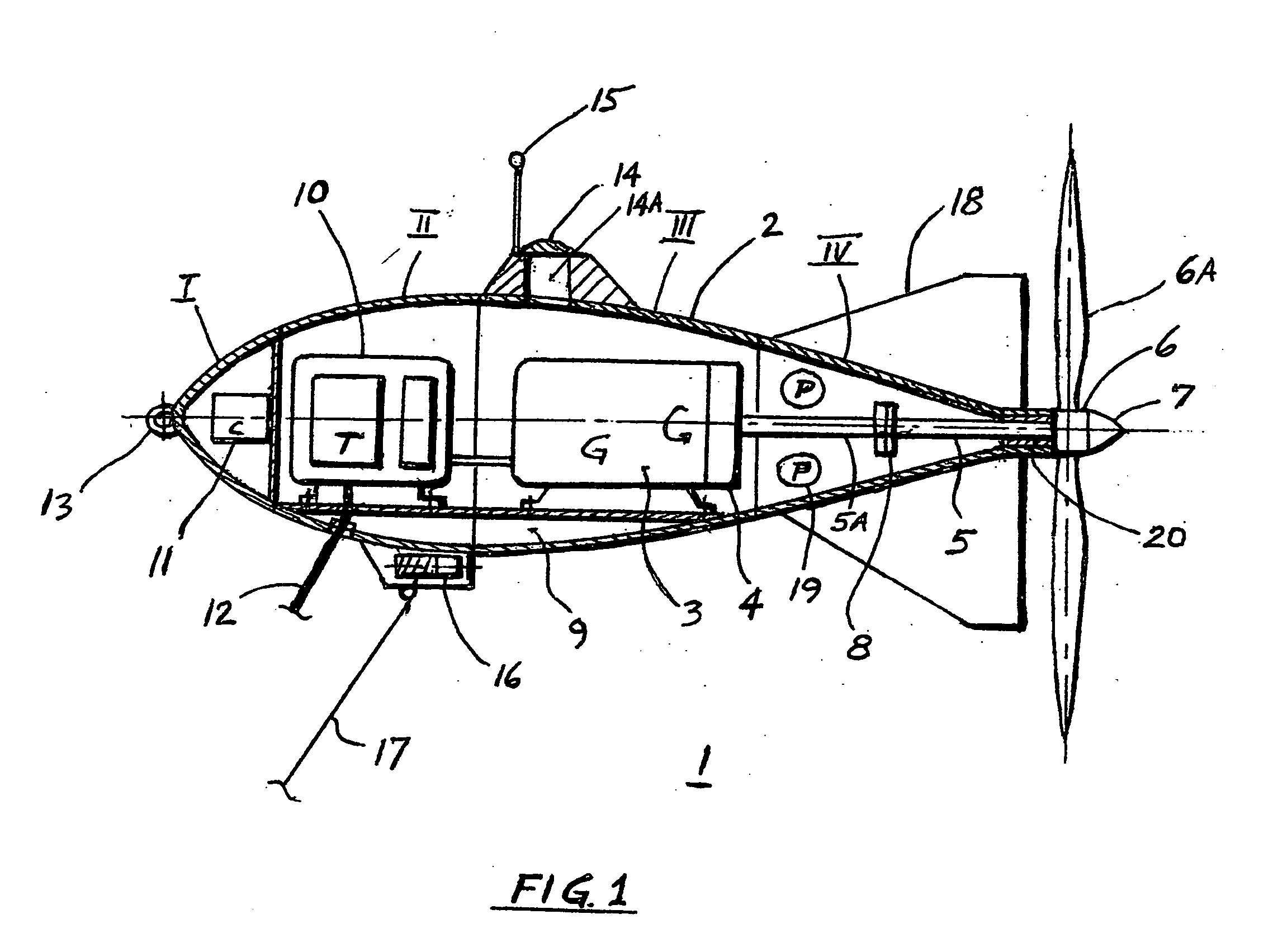
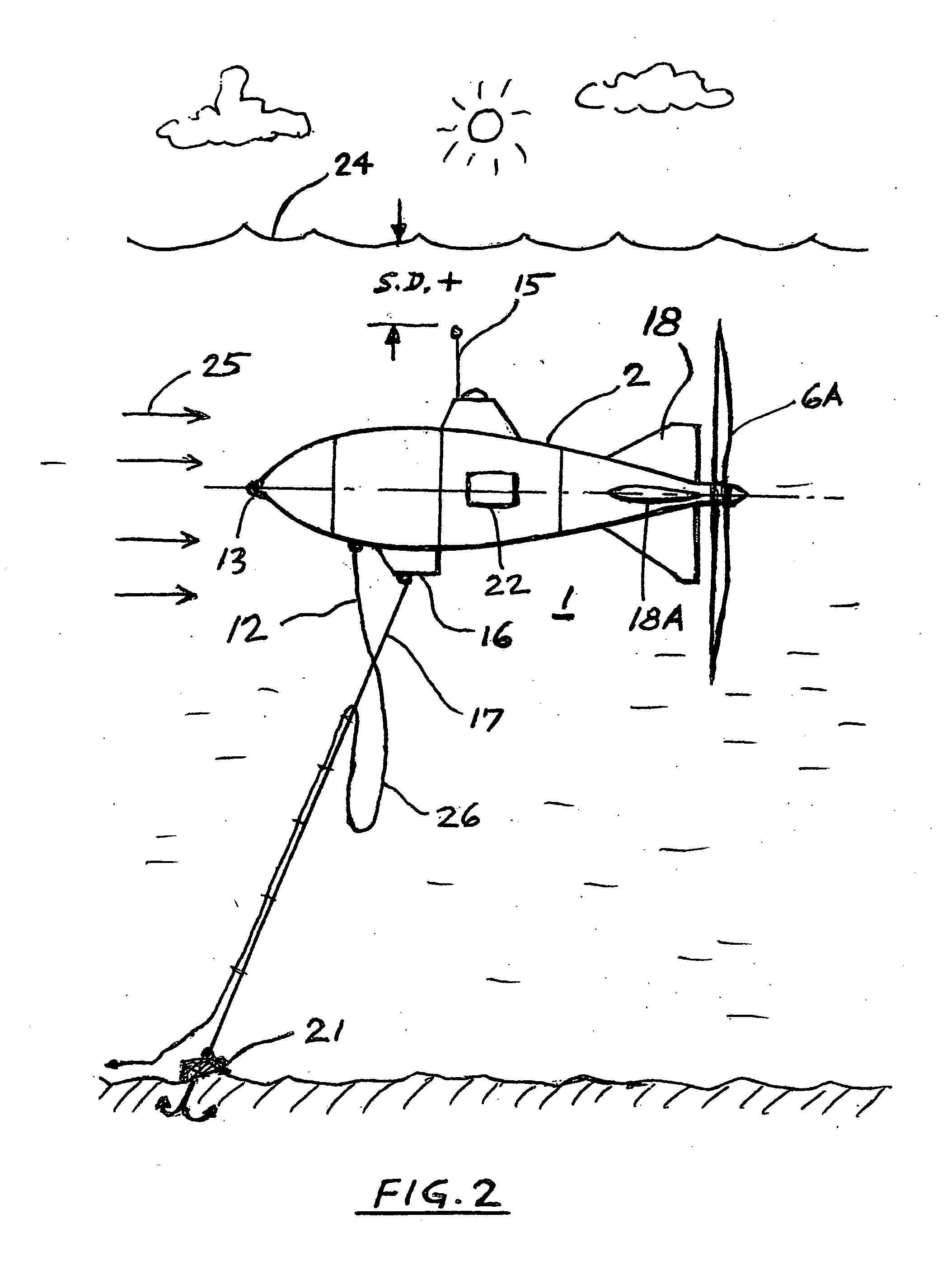
Method of utilization a flow energy and power installation for it
The author suggests a new method and a new inexpensive, large blade-rope type wind rotor, that will be suspended at high altitude and produce huge quantities of energy. The air installation embodiment includes (FIG. 25): propeller 220, wing 226, rope transmission 229, electric generator 12 located at ground. Water rotors can utilize energy of ocean and sea streams. The invention contains 11 projects: 6 for air, 1 for a river, 3 for the sea and ocean, and 1 for ships. They have a power capacity of up to 60 MgW (air), up to 200 MgW (water) for one unit. The suggested installations have the following advantages: 1. Huge power production capacity-up to 5000-10000 times more than conventional ground-based rotor designs. 2. The rotor operates at high altitude of 1-14 kilometers, where wind has high speed and high stability (permanent flows). 3. The installation is much less expensive compared to conventional currently-employed windmills, partly because no tower is necessary to fix the rotor in space. 4. Wind energy is free -environmentally friendly.
Owner:BOLONKIN ALEXANDER ALEXANDROVICH
Wind turbine generator, wind turbine generator system, and power generation control method of wind turbine generator
ActiveUS20100066087A1Accurate wind directionIncrease costElectric motor controlWind motor controlNacellePeak value
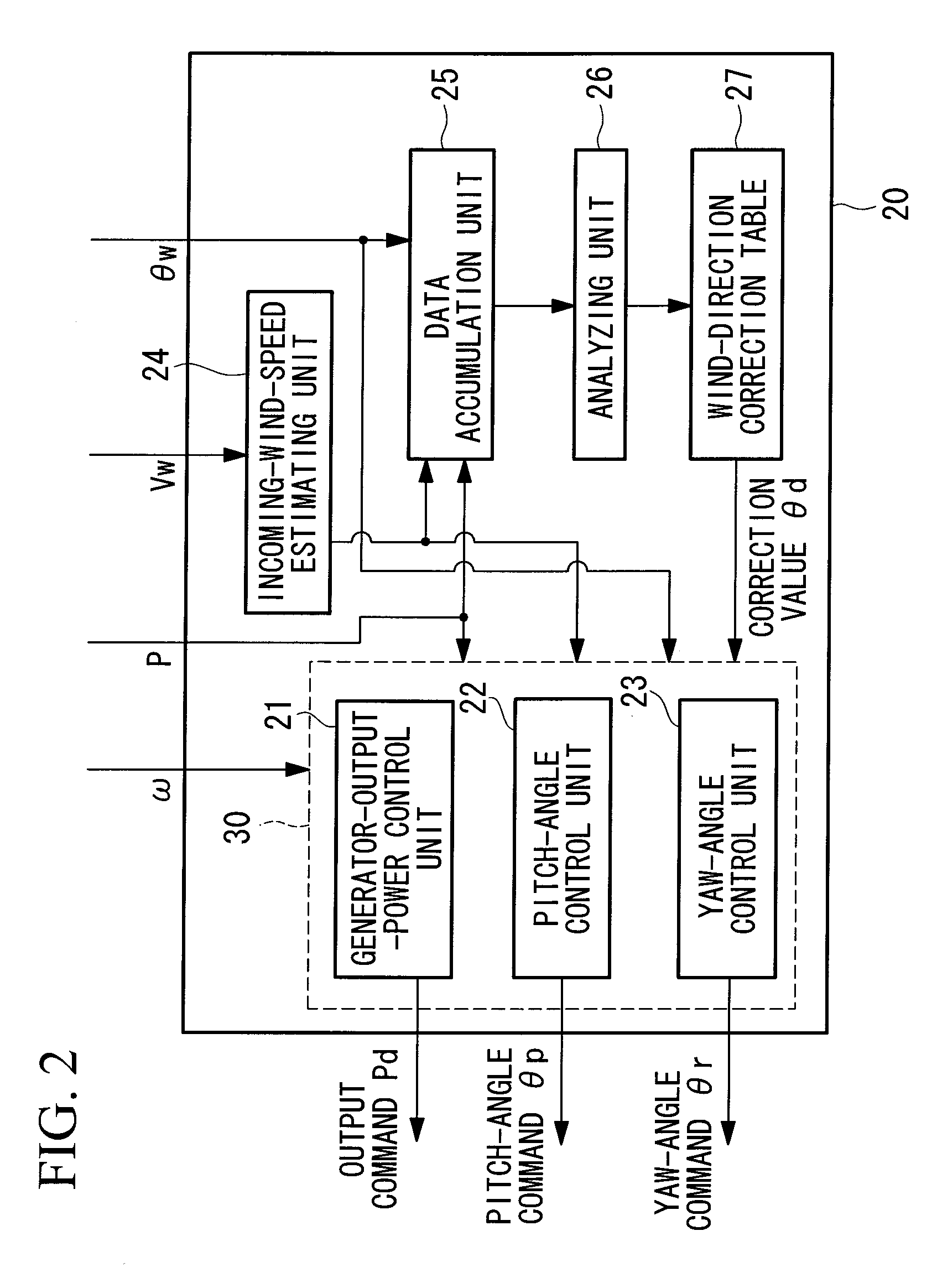
To provide a wind turbine generator, a wind turbine generator system, and a power-generation control method of a wind turbine generator that are capable of improving the power-generation capability and reducing the fatigue load on the windmill. A data accumulation unit 25 sequentially accumulates data sets of a generated output power P during operation of the wind turbine generator, an incoming wind speed Ws estimated on the basis of a wind speed measured at the anemometer, and a wind direction deviation, which is the difference between a wind direction θw measured at the anemoscope and the orientation of the nacelle; statistical analysis of the data accumulated is carried out by an analyzing unit 26; a distribution curve corresponding to the wind direction deviation of the generated output power at each incoming wind speed is determined; the wind direction deviation corresponding to the peak of the distribution curve is set as a correction value θd of the anemoscope; the correction value of the anemoscope for each incoming wind speed is stored in the wind-direction correction table 27; the wind direction Vw measured at the anemoscope is corrected with the correction value θd of the anemoscope for each incoming wind speed Ws; and power-generation control is carried out using the corrected wind direction as a control parameter.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Method and apparatus for treatment of a rotor blade on a windmill
ActiveUS20050042102A1High degree of automationLow costPropellersPretreated surfacesMechanical engineeringWindmill
Method and apparatus for treatment of a surface of a rotor blade of a windmill, the apparatus being placed in such a manner to be moveable in relation to the surface of a rotor blade, and the apparatus being caused to move depending on a form of treatment determined by means for treatment mounted on, in or next to the apparatus. In this manner, various forms of treatment of a rotor blade may be carried out such as for instance washing, finishing, sealing, etc.
Owner:PP ENERGY APS
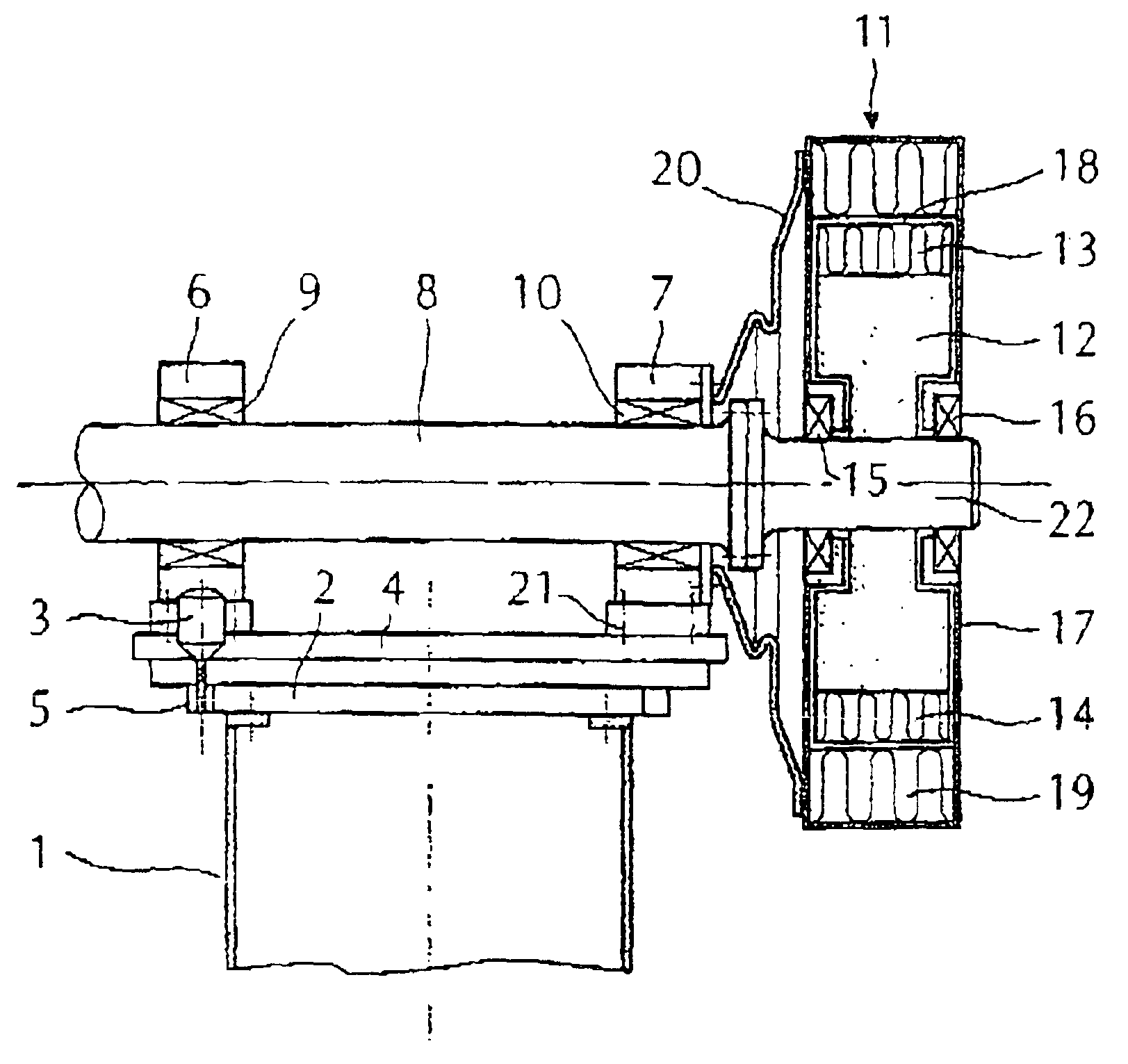
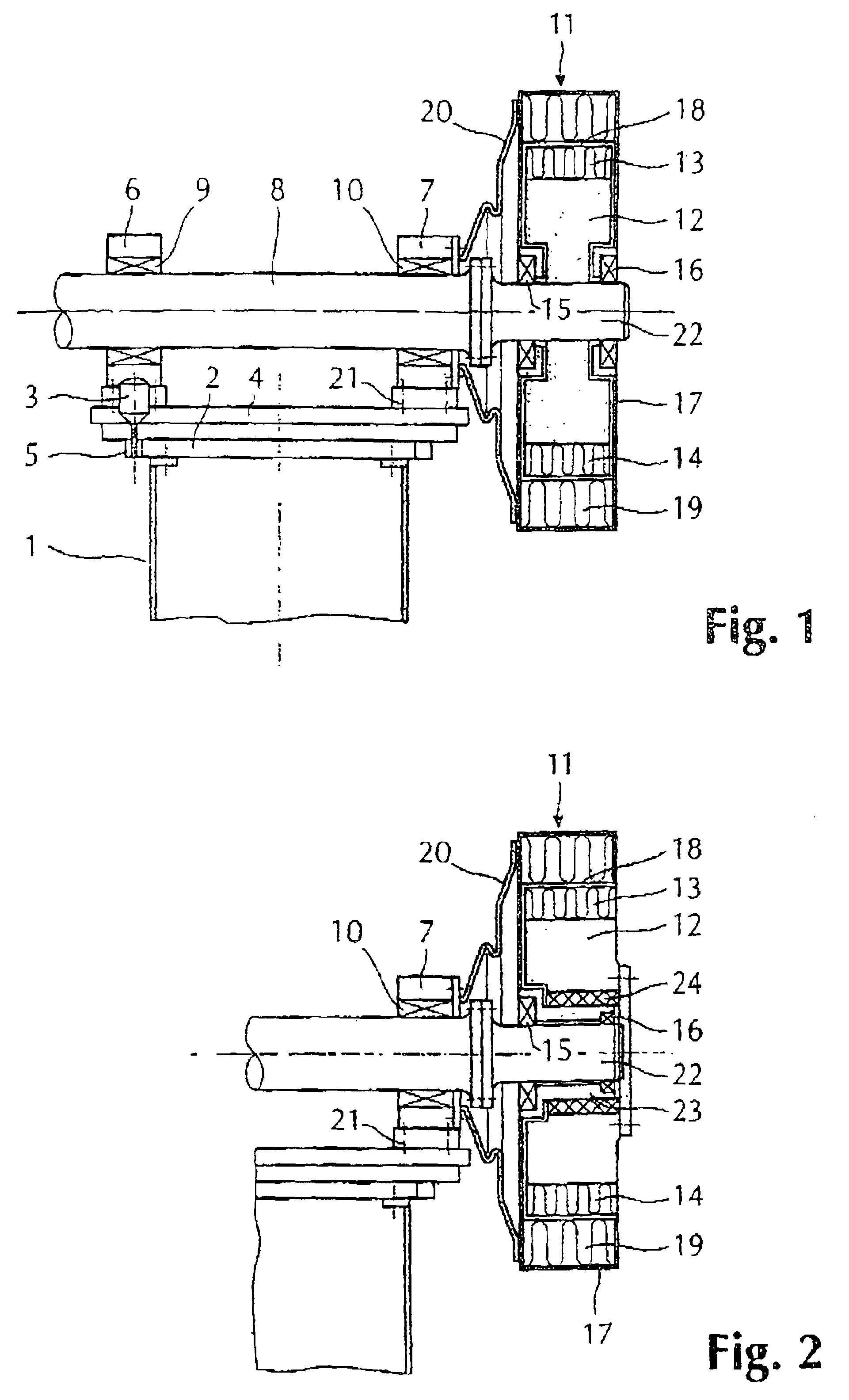
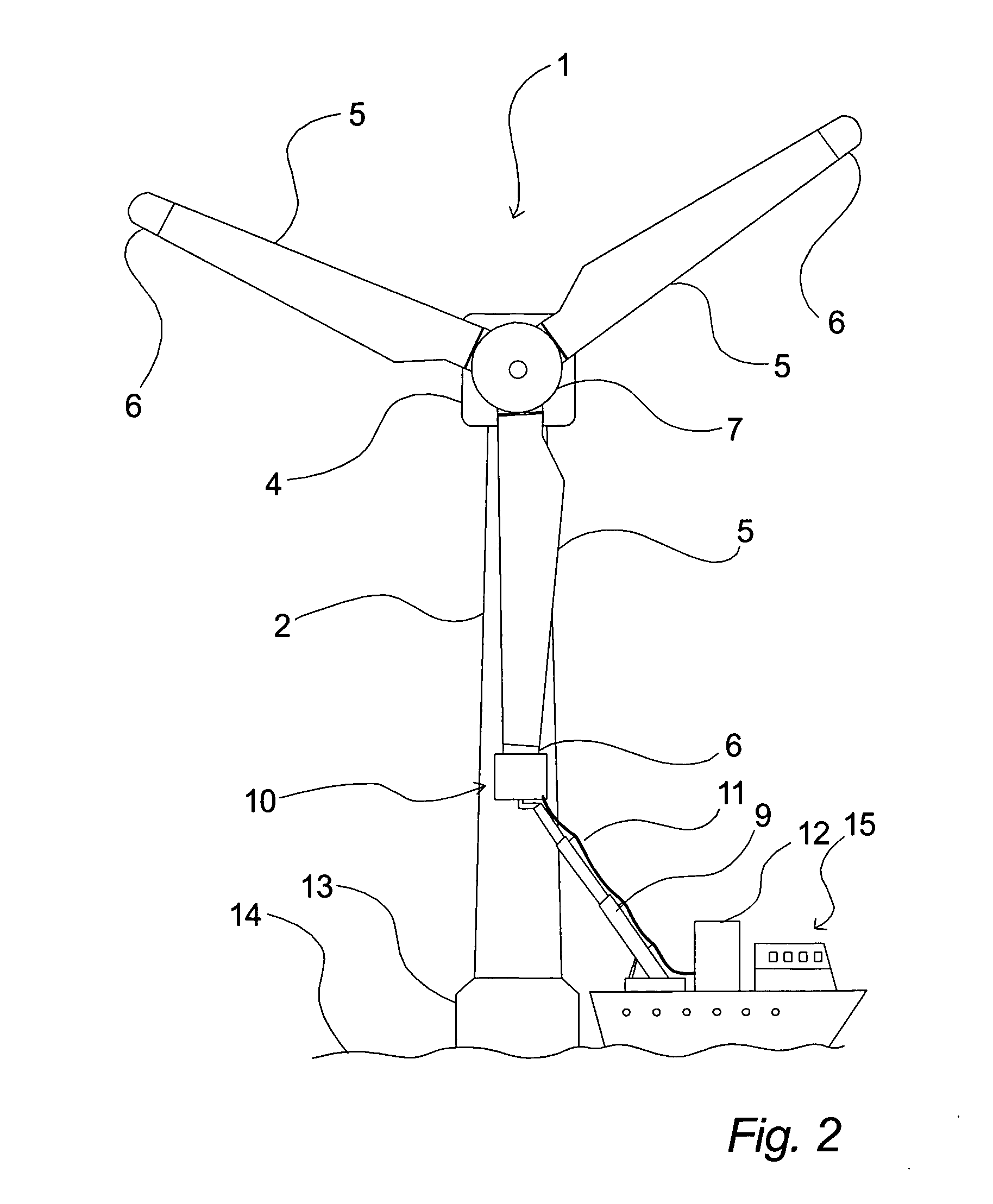
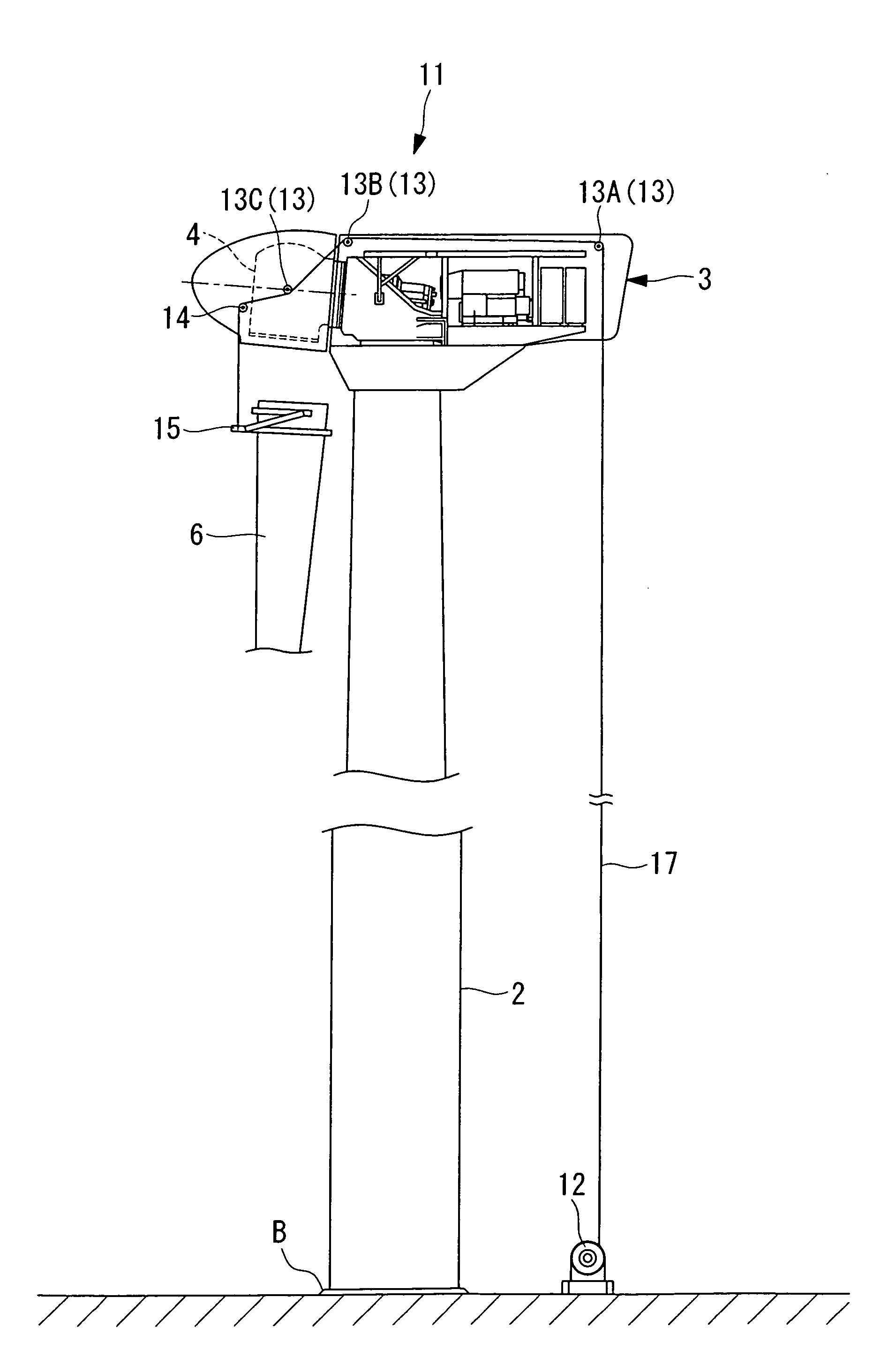
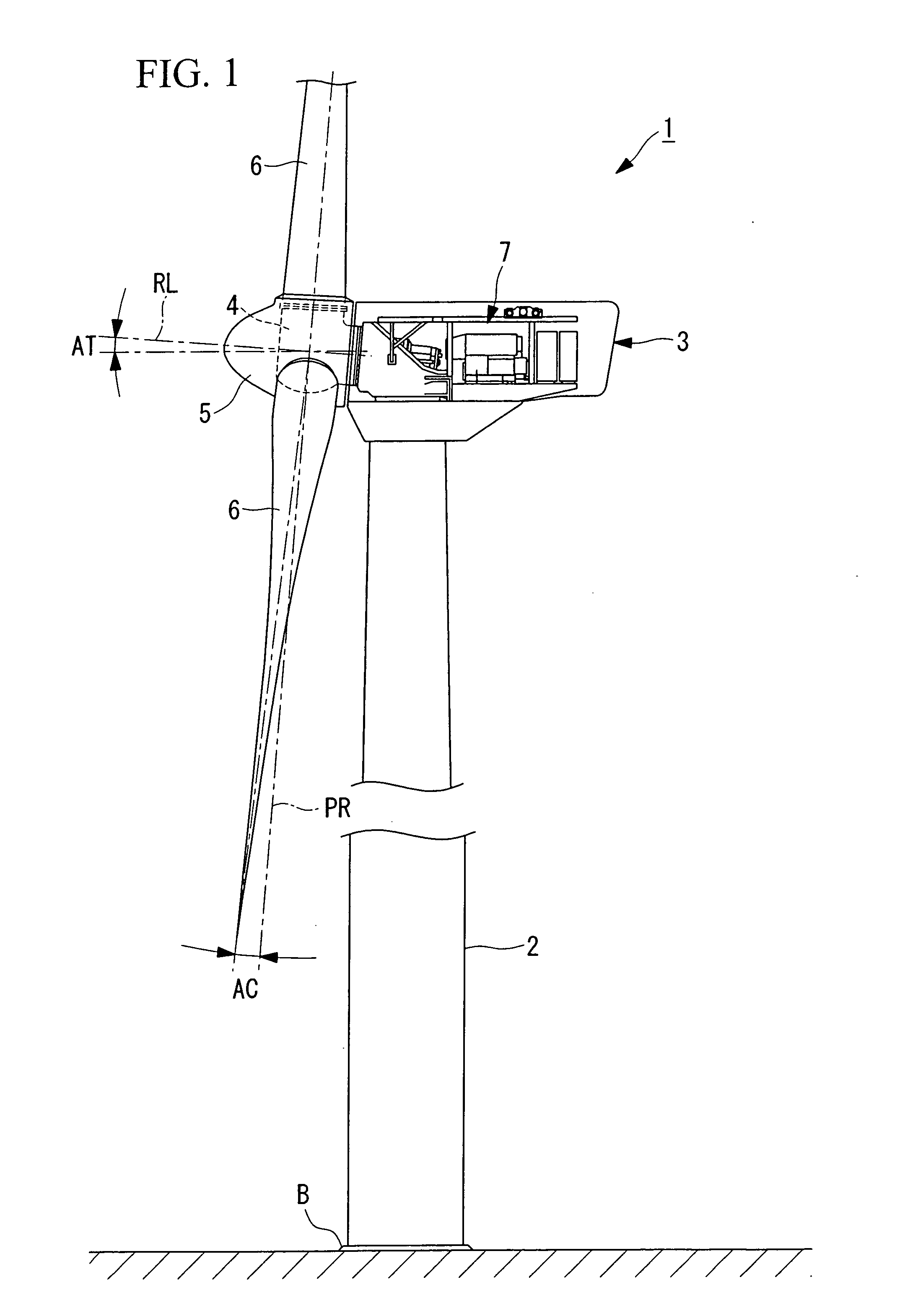
Wind-turbine rotor-blade hoisting apparatus, method for attaching wind-turbine rotor blade, and method for constructing wind power generator
The present invention provides a wind-turbine rotor-blade hoisting apparatus that enables attachment and removal of wind-turbine rotor blades without using a plurality of heavy machines and that enables attachment and removal of wind-turbine rotor blades on a site having a complex land shape with little flat land, a method for attaching a wind-turbine rotor blade, and a method for constructing a wind power generator. The present invention is characterized in that it includes a sheave (14) that guides a hoisting wire (17) from a rotor head (4), to which a wind-turbine rotor blade (6) is to be attached, toward the wind-turbine rotor blade (6) and that is arranged so as to be movable in a direction along the rotation axis of the rotor head (4); a retaining portion (15) that retains an attaching end of the wind-turbine rotor blade (6) such that a line connecting the center of gravity of the wind-turbine rotor blade (6) and a connecting portion, to which the hoisting wire (17) is connected, crosses the longitudinal axis of the wind-turbine rotor blade (6); and a winch (12) that is disposed on the ground and that draws the hoisting wire (17) to wind up or let out the retaining portion (15).
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Device and method to measure inhalation and exhalation air flows
InactiveUS6126613AMore to inhalationSimple recalibrationRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsInhalationAir filter
A spirometer is provided which has an air flow path comprising a mouthpiece, filter (such as an air filter or biostatic filter), and an air pathway in which a multiblade transparent windmill rotor rotates when air travels through same. Tips of the rotor are used to detect the rate of rotation providing a train of pulses linearly proportional to the volume of air flowing through the cylindrical air path.
Owner:EDWARDS RAYMOND A +1
Windmill blade and apparatus for generating power using the blade
InactiveUS6984110B2Improve efficiencyEasy windingPropellersWind motor controlRotational axisEngineering
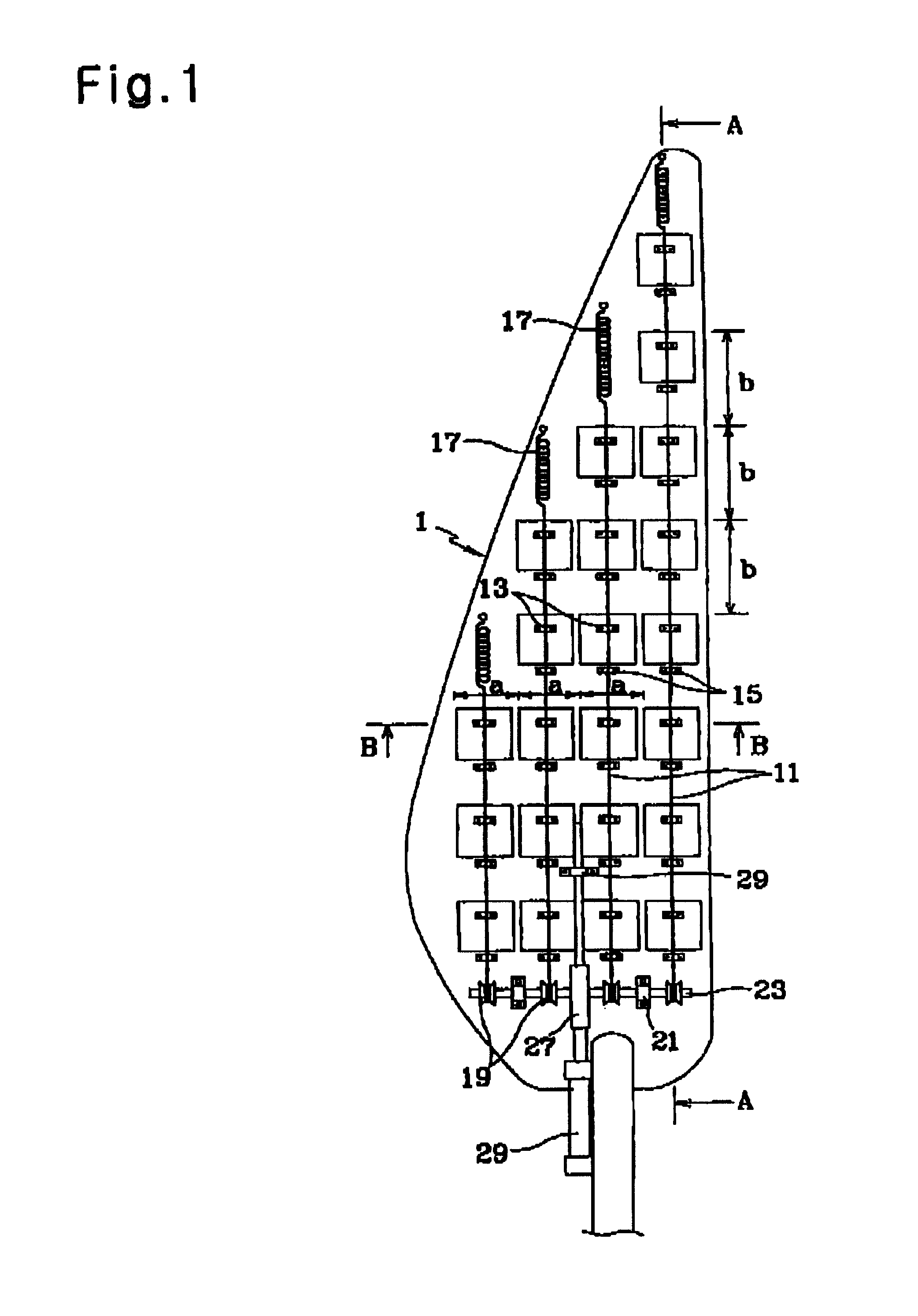
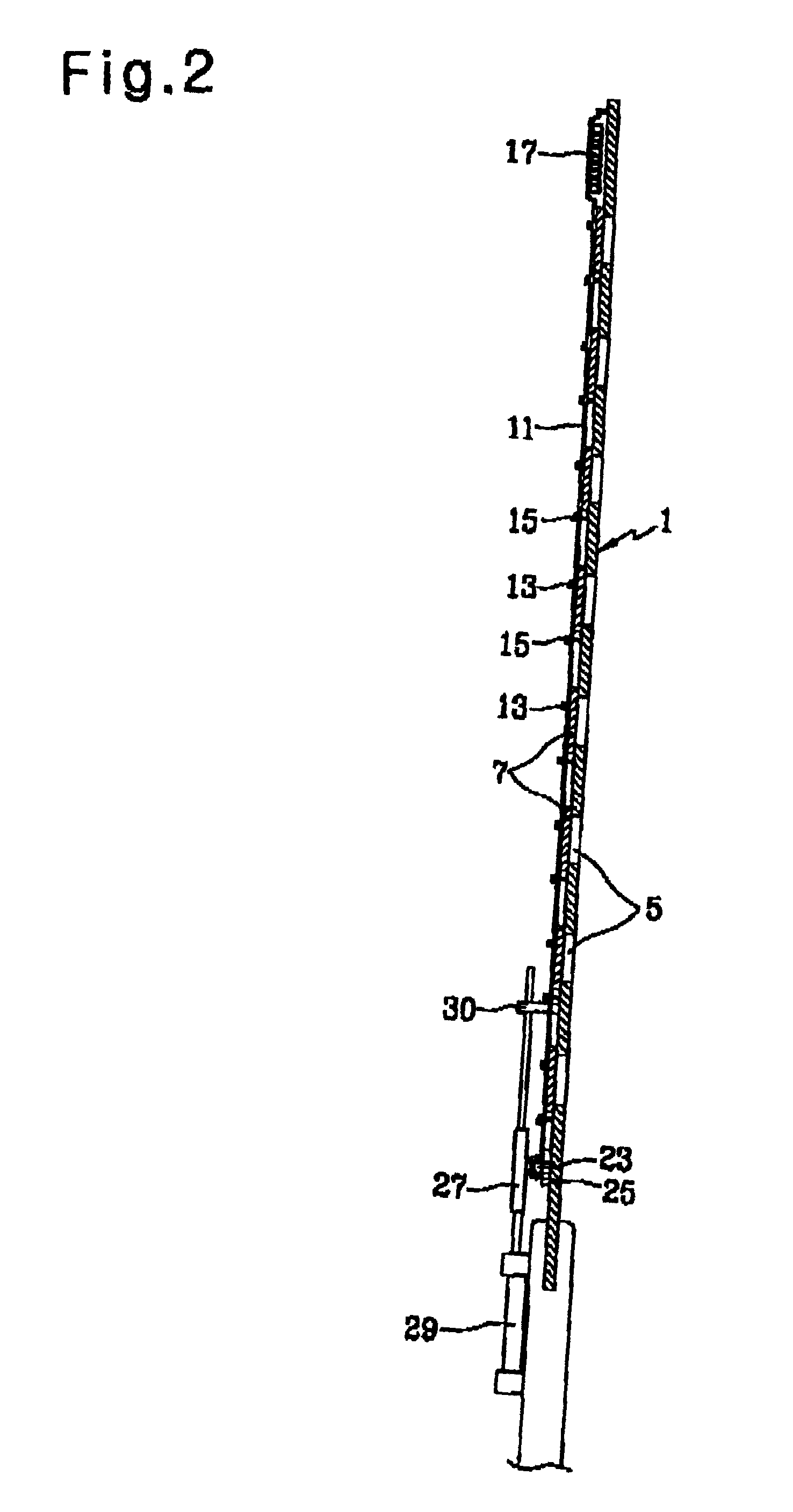
Disclosed is a wind power generating apparatus in which windmill blades are mounted in a multi-stage fashion to a rotating shaft while being spaced apart from one another to efficiently generate wind power. Each windmill blade includes blade bodies mounted to the rotating shaft, and provided with wind pressure adjusting holes, wind pressure adjusting plates coupled to each blade body, and connected together to a wire, each wind pressure adjusting plate being slidable along guides respectively arranged at opposite sides of the associated wind pressure adjusting hole to adjust an opening degree of the wind pressure adjusting hole, elastic members each adapted to connect one end of the associated wire to the associated blade body, and winches each adapted to connect the other end of the associated blade body, the winches being mounted to a single shaft to simultaneously wind or unwind all wire.
Owner:JANG KEUN SUK
Deployable submarine-hydroelectric generator for sea currents energy harvesting
InactiveUS20090140524A1Easy to harvestReduce global warmingFinal product manufactureGas turbine plantsOcean bottomElectrolysis
Deployable submarine hydroelectric generator for conversion of kinetic energy of deep ocean currents into electricity by having an electric generator mounted in a sealed hydrodynamic, buoyant vessel with tail fins, and connected by a shaft to a rotary turbine blades at the tail end of the submarine vessel, which vessel is anchored at desired depth to the bottom of the ocean by a cable. The drag of the turbine blades causes the vessel to self-steer against the direction of the ocean current. An electric cable is also provided, connecting said electric generator with electric grid on the land. Such generator is out of sight, unlike windmills, and is environmentally friendly to the sea life, due to slow rotating blades. This clean electricity can also be used for production of low cost hydrogen by electrolysis of sea water.
Owner:KEJHA JOSEPH B
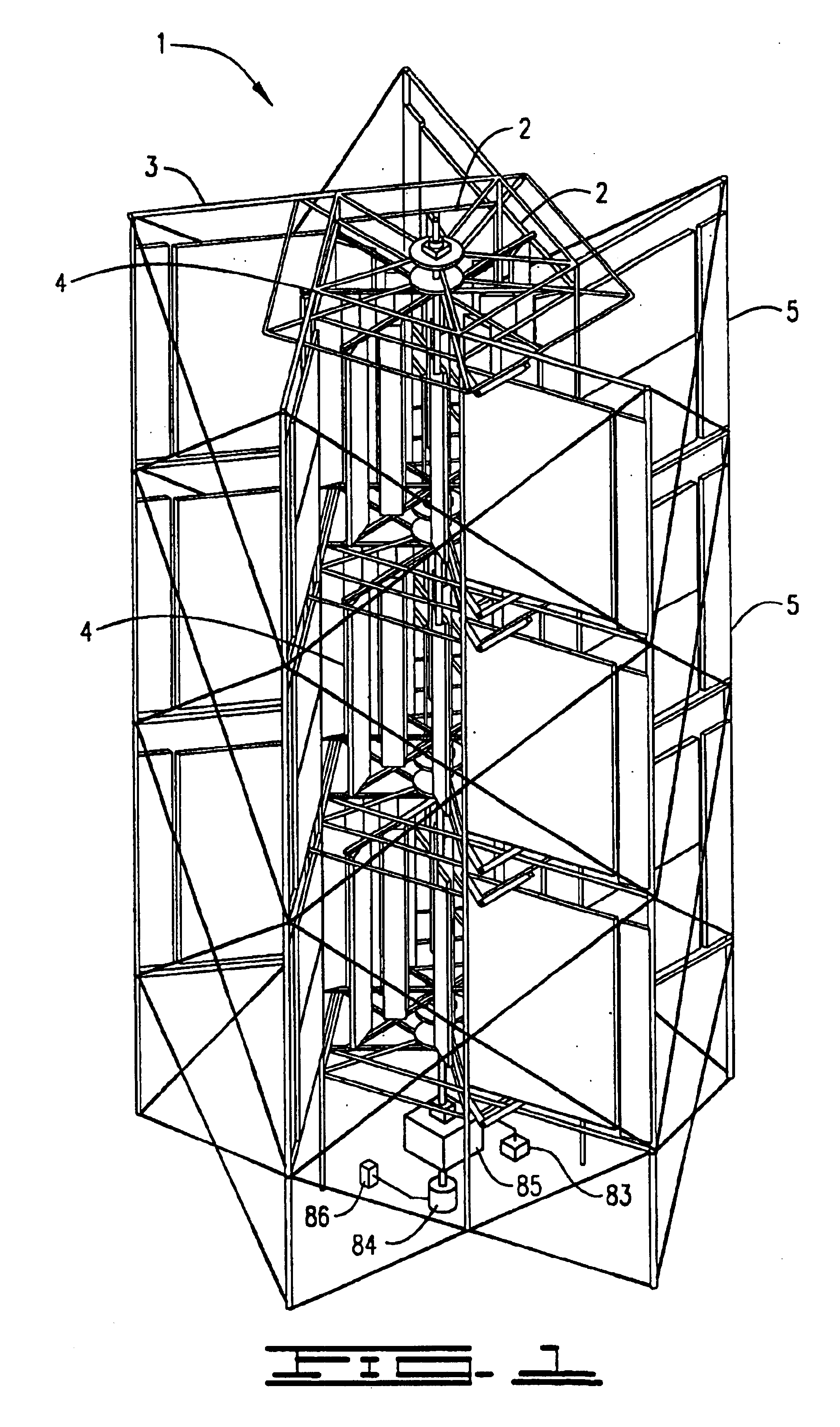
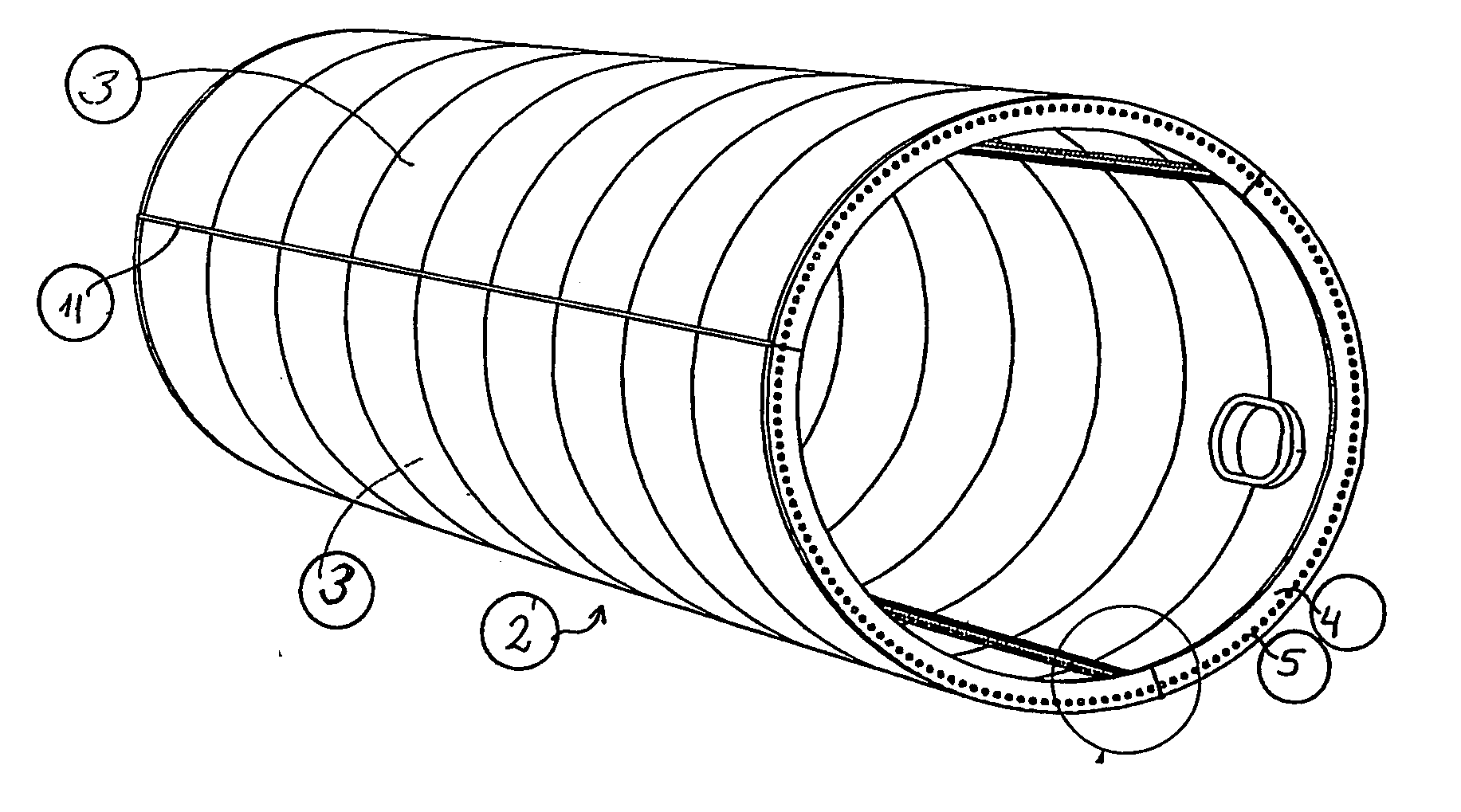
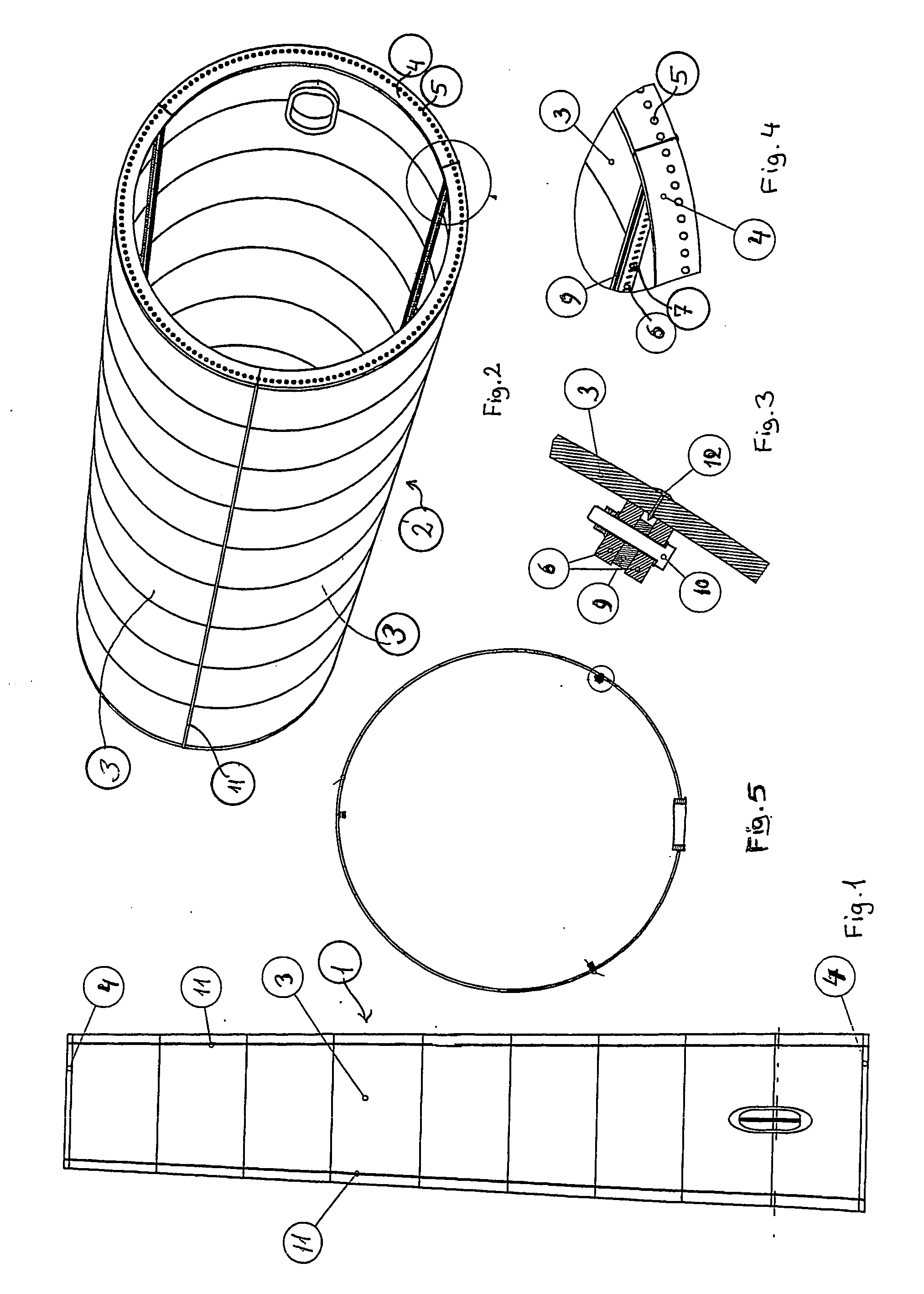
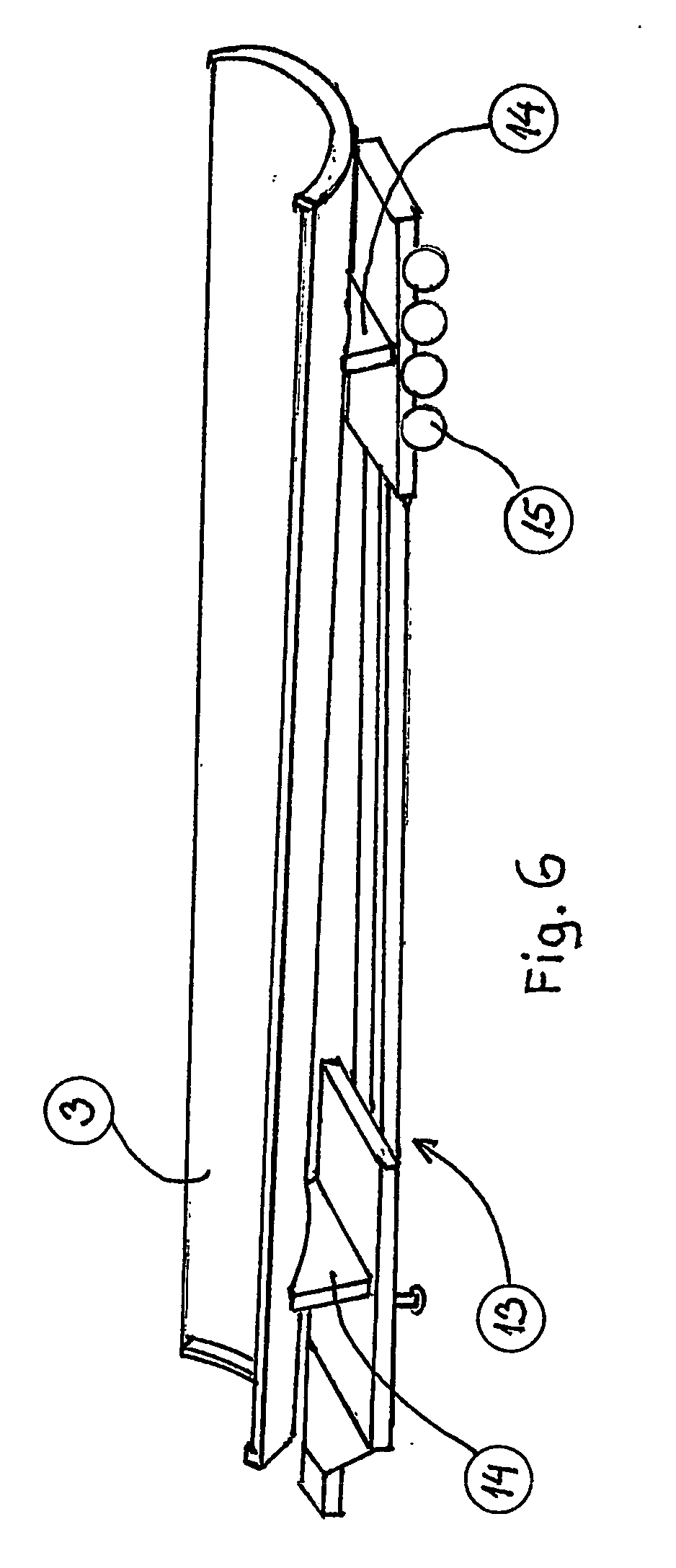
Method of contructing large towers for wind turbines
ActiveUS20060272244A1Large lengthSmooth outer surfaceWind motor assemblyWind motor supports/mountsInterconnectionTower
In order to transport large size windmill towers, the invention suggests a steel tower (1) for a windmill, comprising a number of cylindrical or tapered tower sections (2), at least the wider sections (2) of which being subdivided into two or more elongated shell segments (3), which combine into a complete tower section (2) by means of vertical flanges (6) tightened together, e.g., by bolts (10), said shells being also provided with upper and lower horizontal flanges (4), respectively, to allow interconnection of tower sections (2) one on top of the other.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
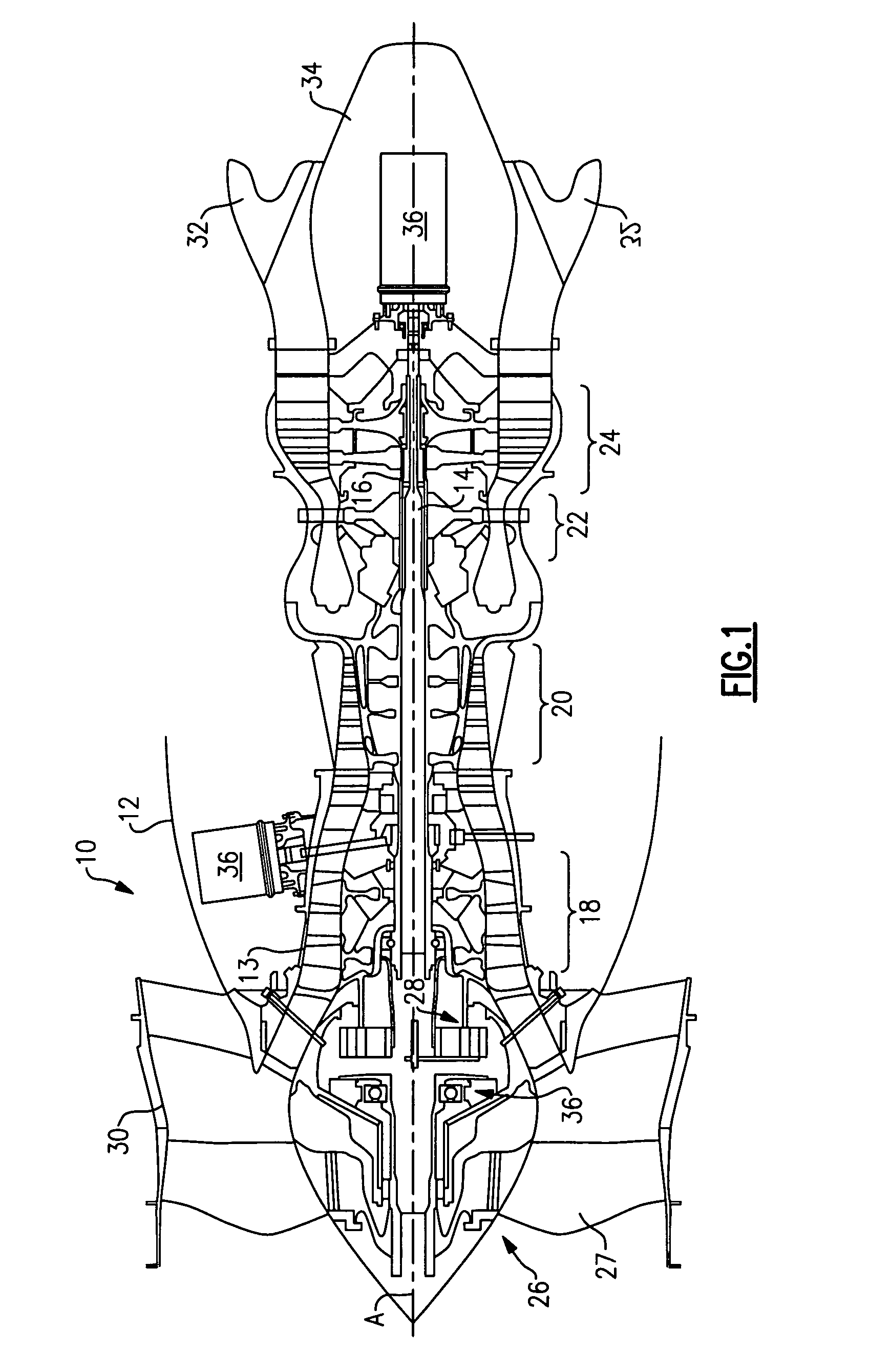
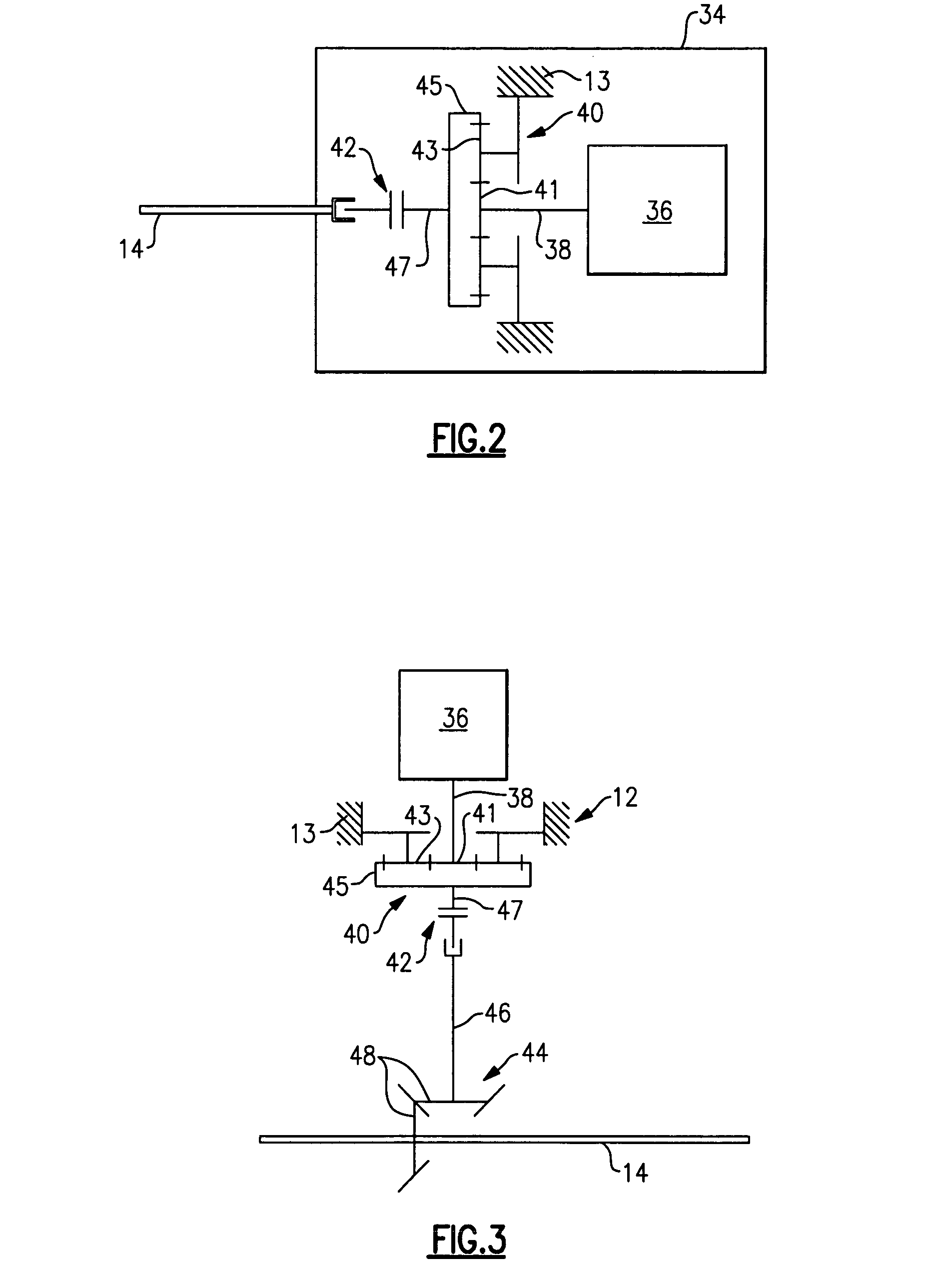
Turbofan emergency generator
A turbine engine emergency power system includes low and high pressure spools, the lower pressure spool including a low pressure compressor. A turbofan is coupled to the low pressure spool. The turbofan drives the low pressure spool in a windmill condition in which the low pressure turbine fails to provide rotational drive to the turbofan. A generator is rotationally driven by the low pressure spool in the windmill condition. A gear train is used to increase the speed of the generator in one example. In one example embodiment, a centrifugal clutch is used to selectively decouple the generator from the low pressure spool at a predetermined engine speed, which corresponds to normal operating speeds when the turbine engine is under power.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP +1
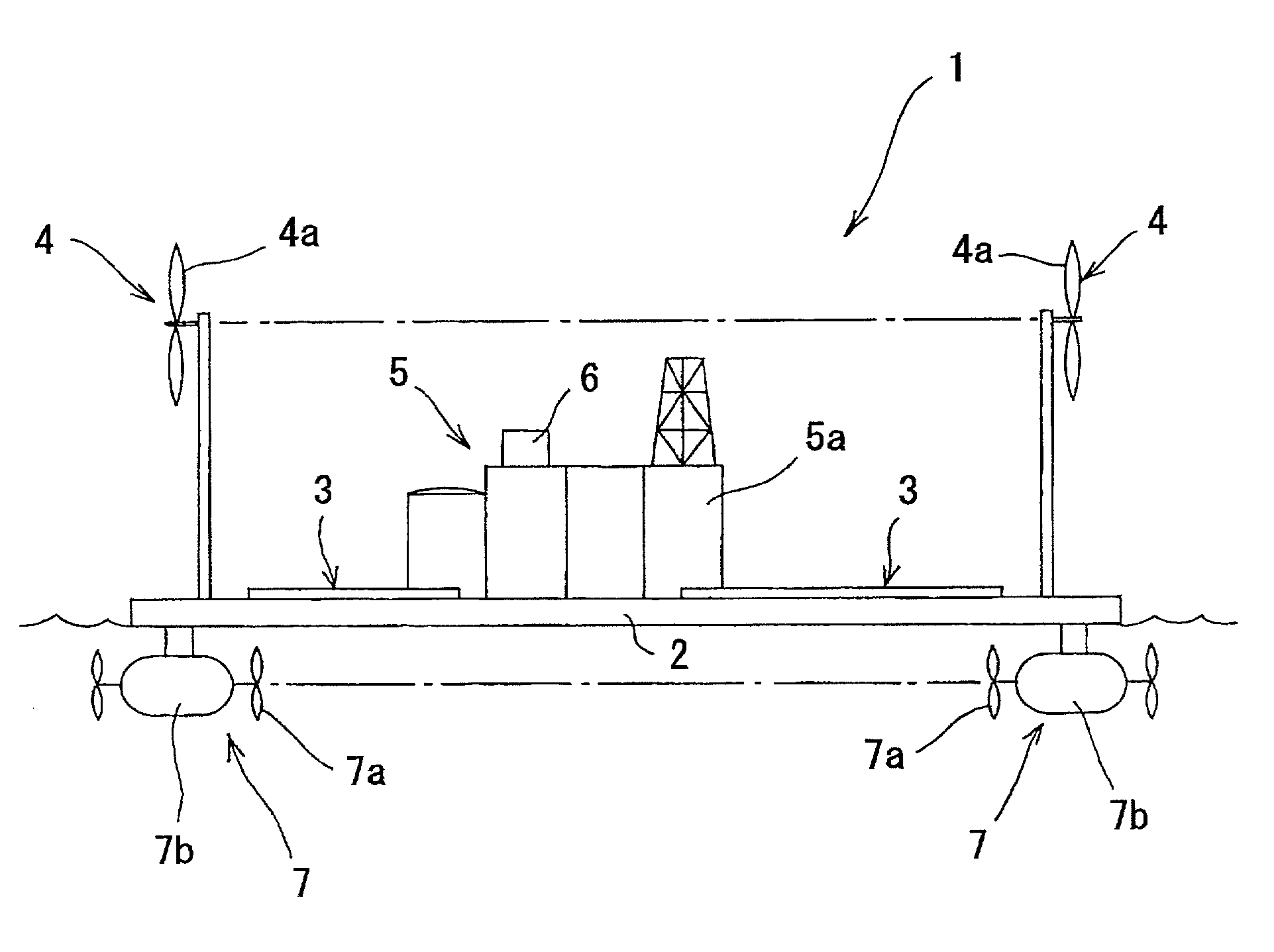
Power generation plant ship
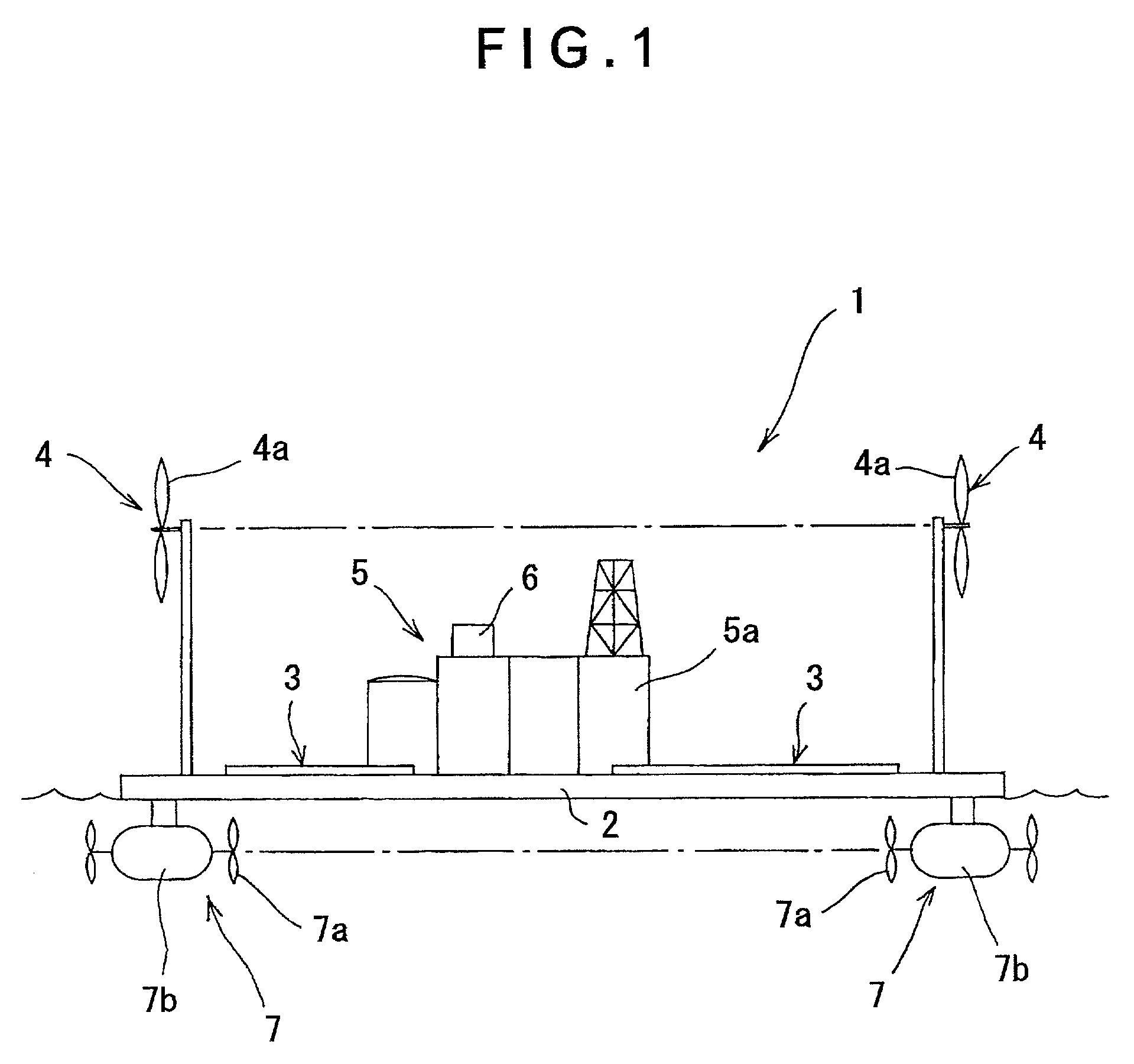
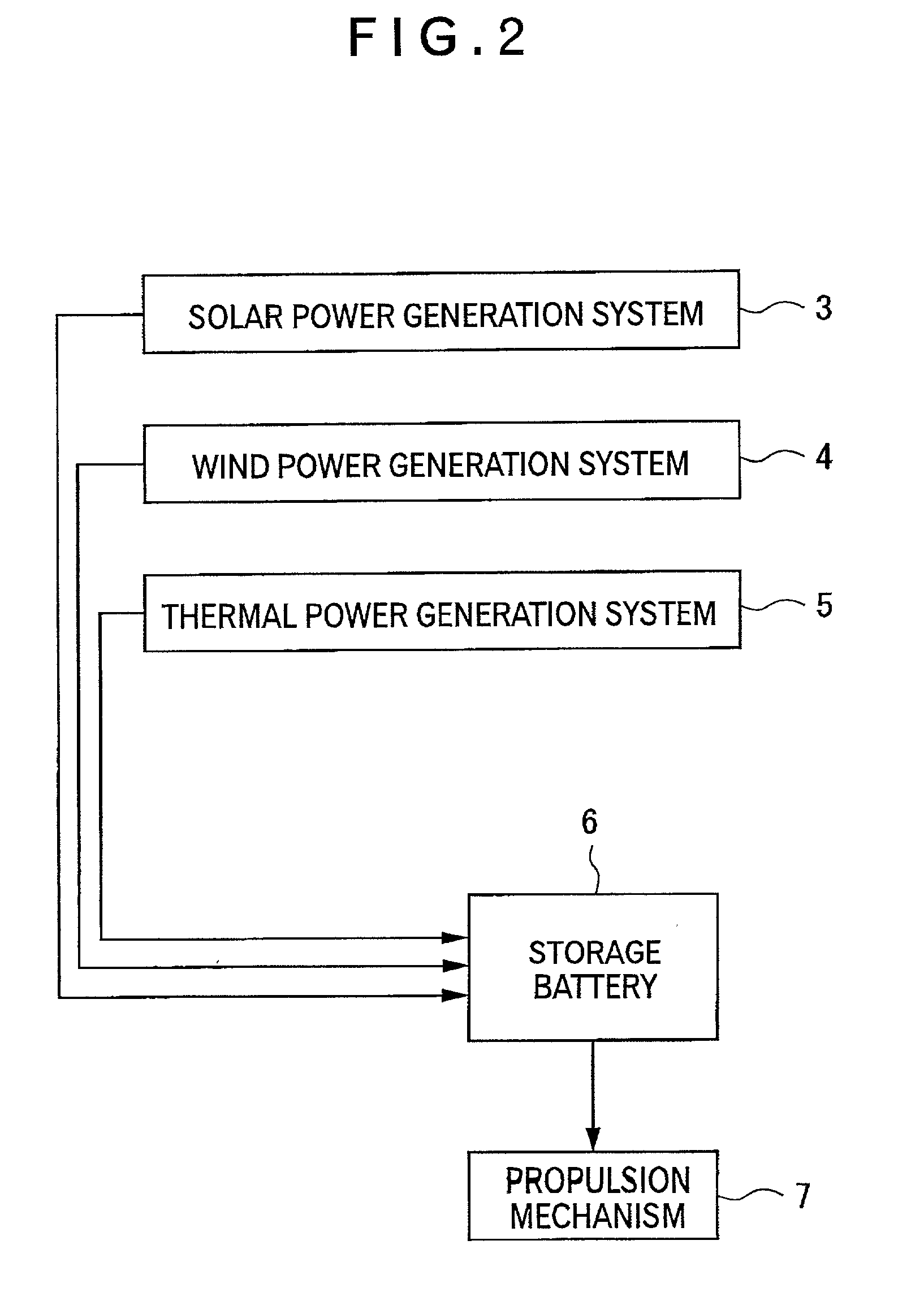
A power generation plant ship (1) of the present invention having a body (2) with a propulsion mechanism (7) includes a solar power generation system (3), a wind power generation system (4) for obtaining electric energy by driving a generator by rotating a windmill (4a) by receiving wind power, and a storage battery (6) for storing the electric energy generated by the respective power generation systems (3, 4).
Owner:TANAKA EITARO
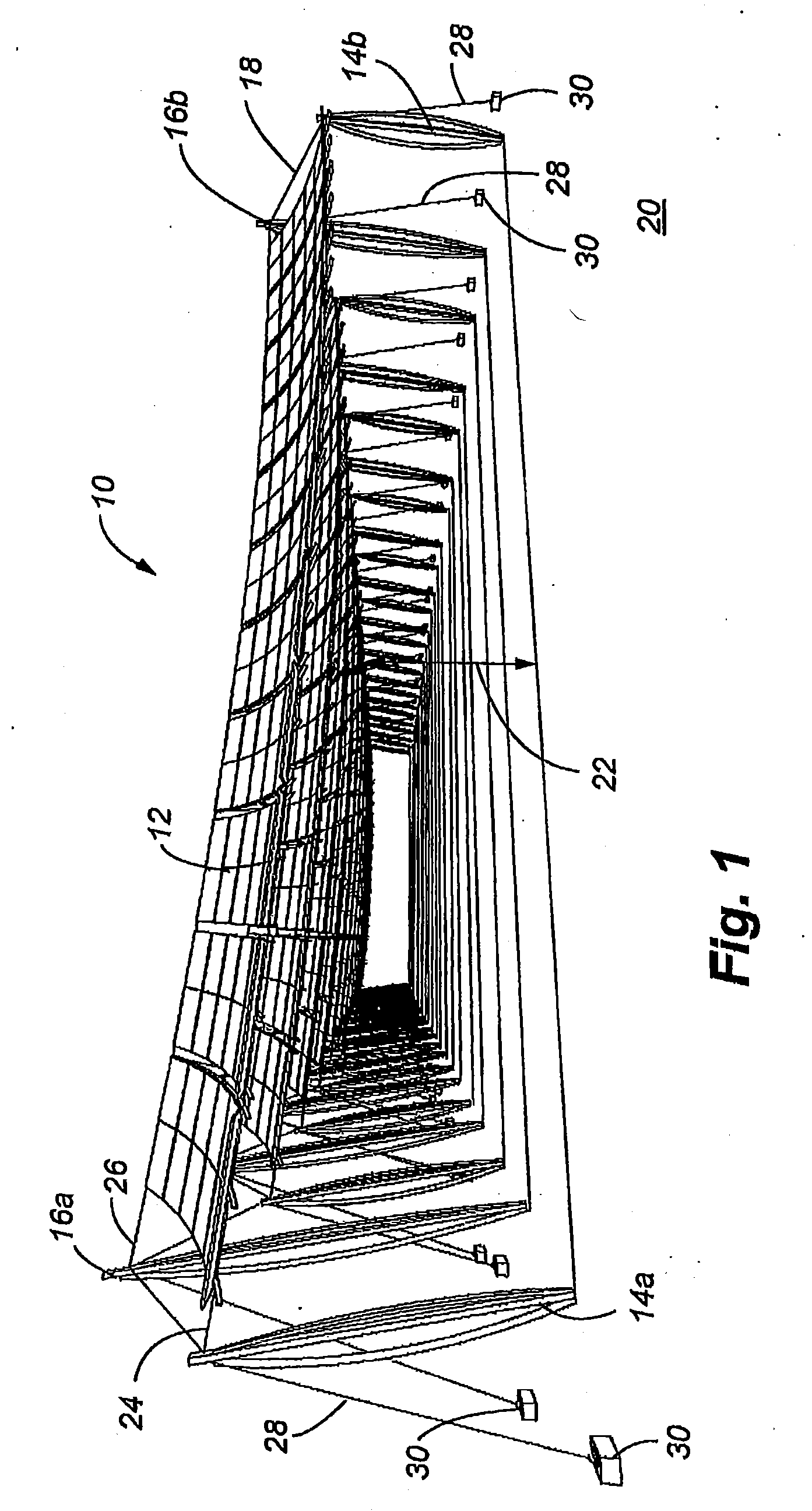
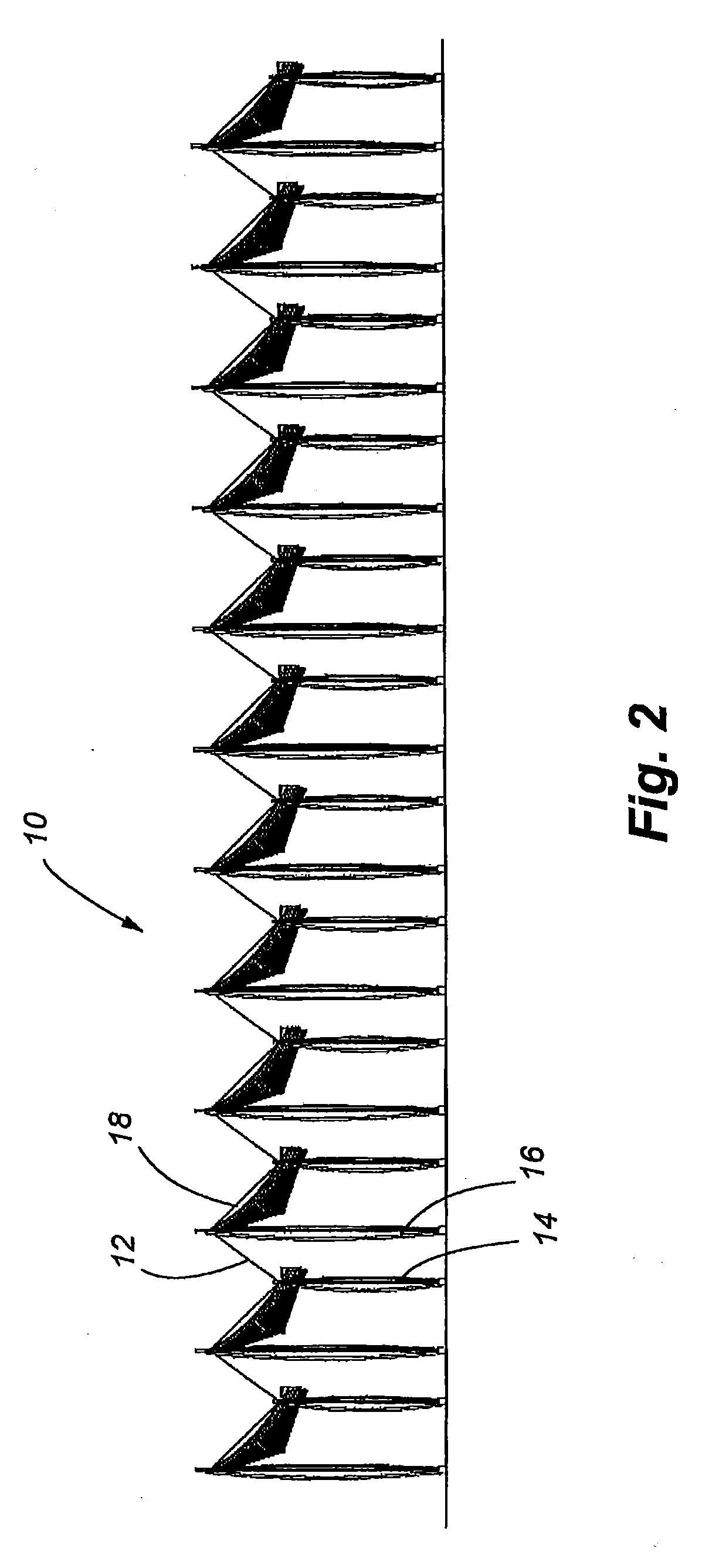
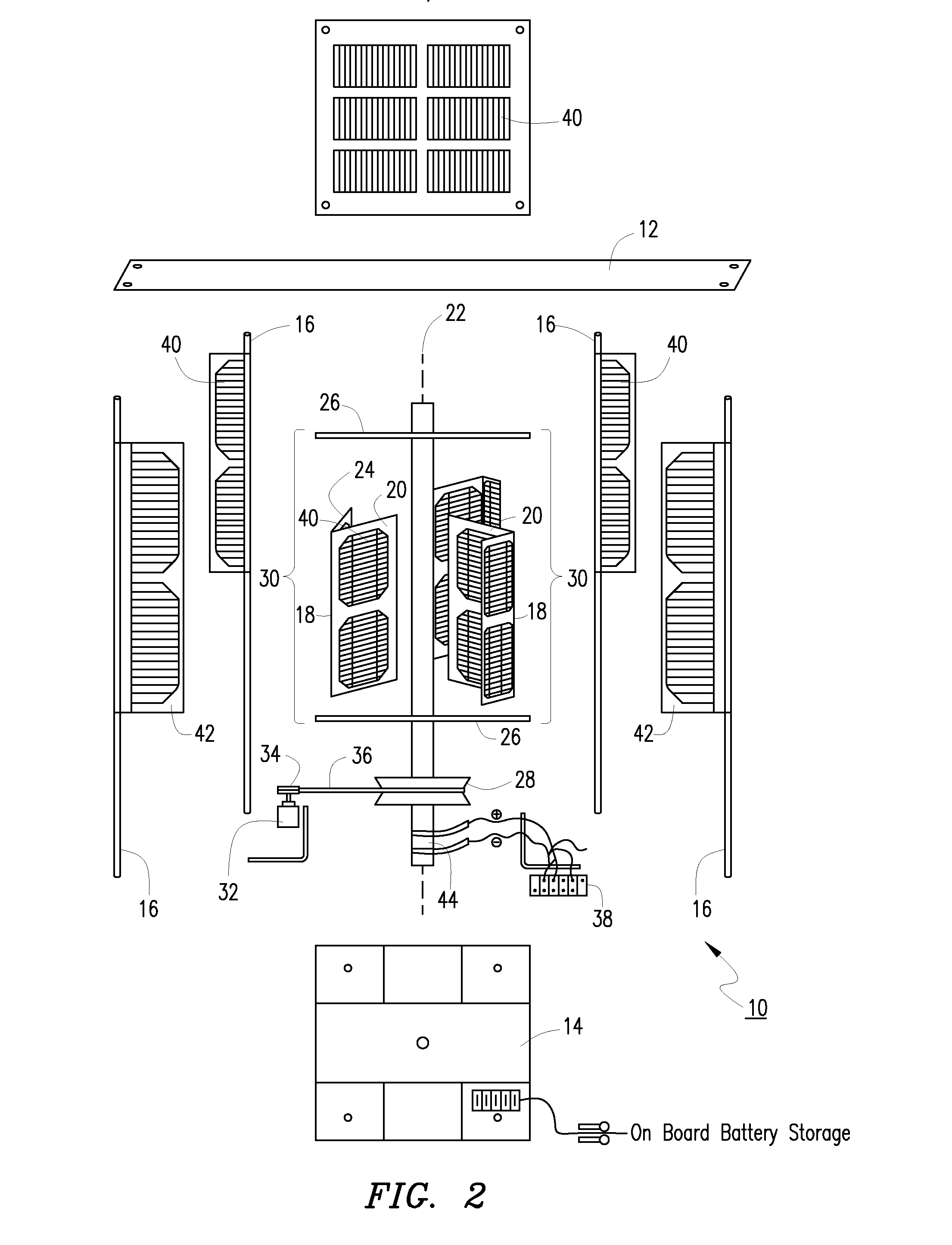
Solar array support methods and systems
InactiveUS20100314509A1Minimizes construction effortMinimizes maintenance needPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyEngineeringLand use
Systems and methods for disposing and supporting a solar panel array are disclosed. The embodiments comprise various combinations of cables, support columns, and pod constructions in which to support solar panels. The solar panels can incorporate single or dual tracking capabilities to enhance sunlight capture. The embodiments encourage dual land use in which installation of the systems minimizes disruption of the underlying ground. Supplemental power may be provided by vertical axis windmills integrated with the columns. Special installations of the system can include systems mounted over structures such as parking lots, roads and aqueducts. Simplified support systems with a minimum number of structural elements can be used to create effective support for solar panel arrays of varying size and shapes. These simplified systems minimize material requirements and labor for installation of the systems.
Owner:P4P HLDG
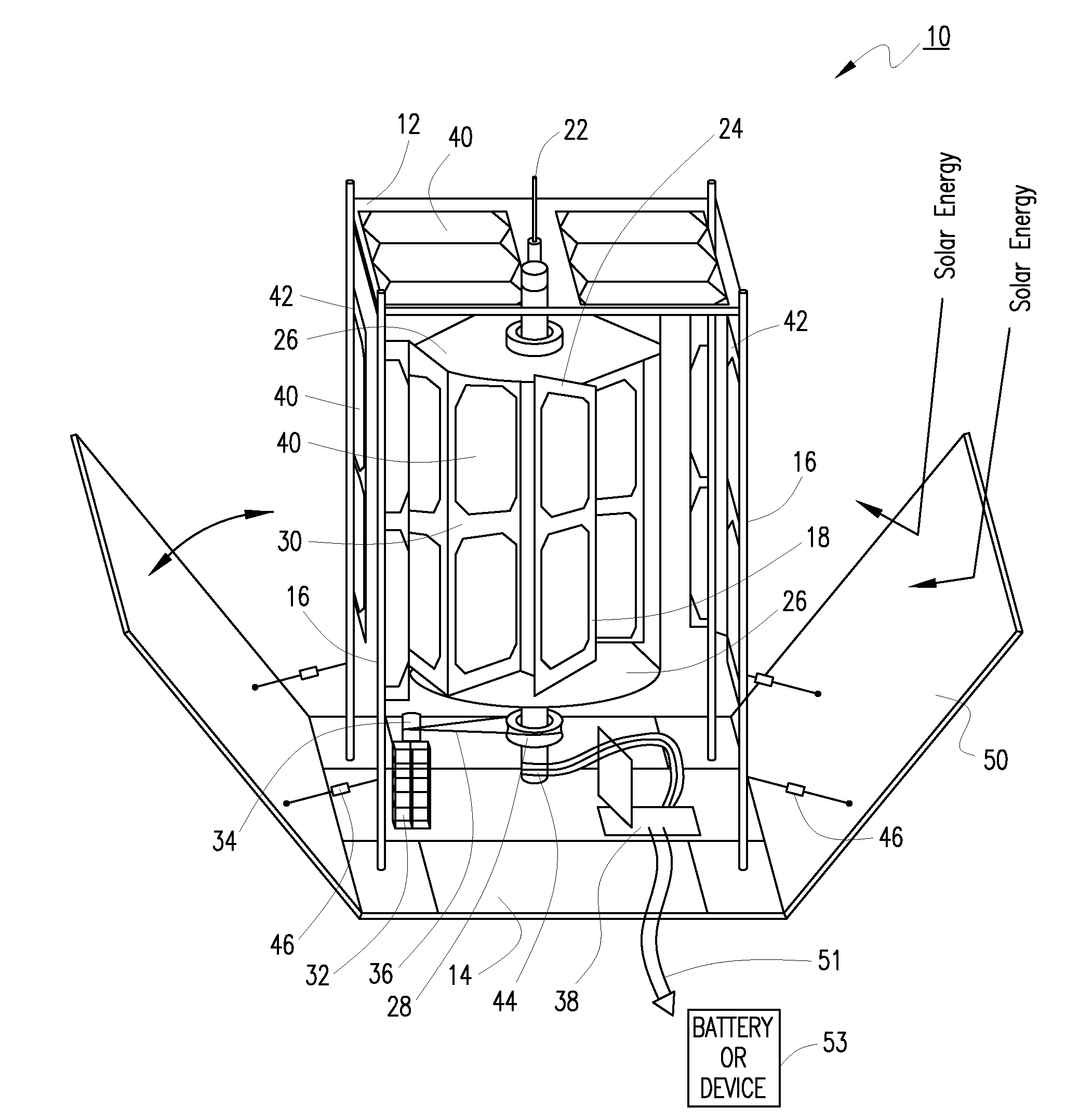
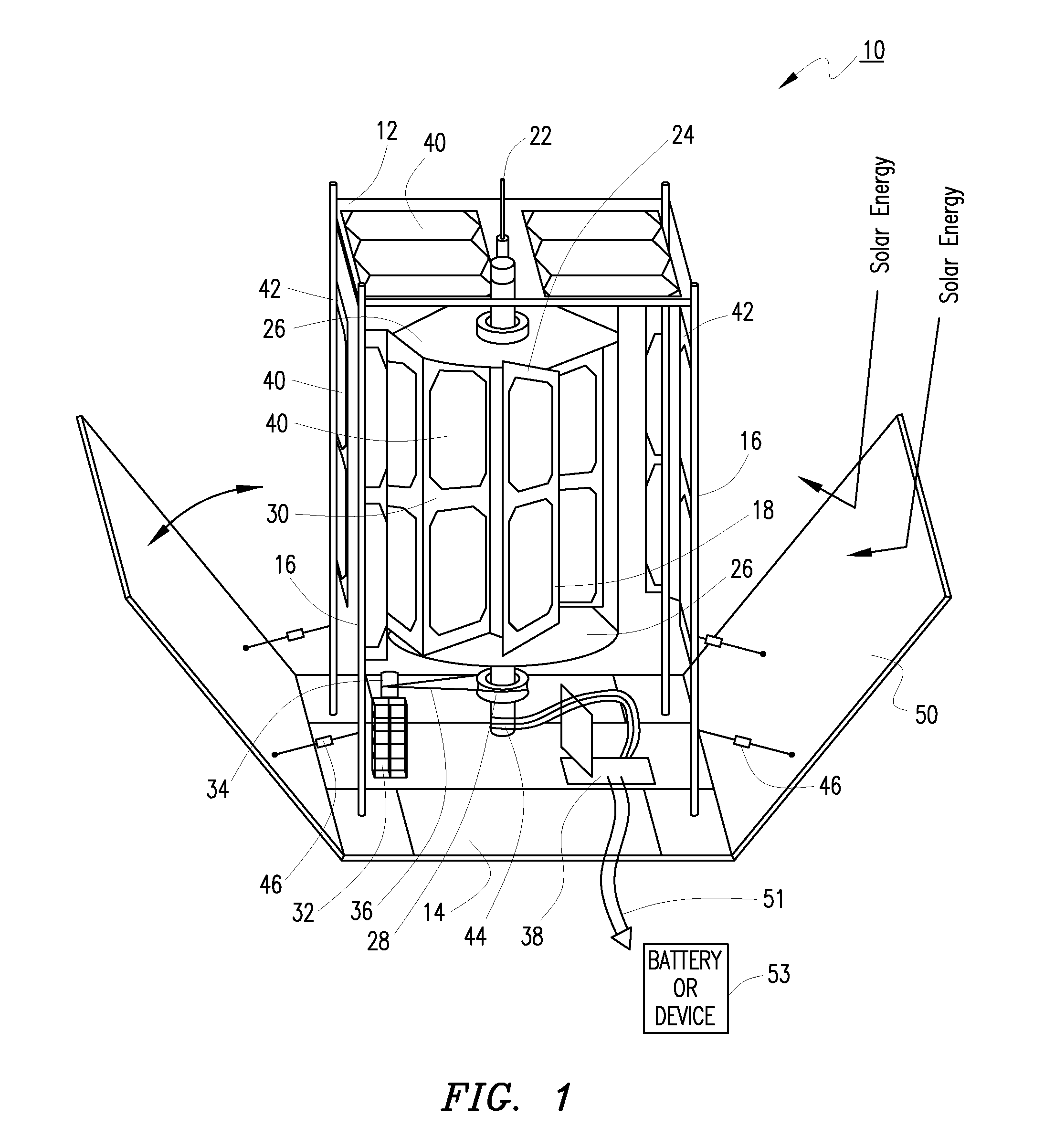
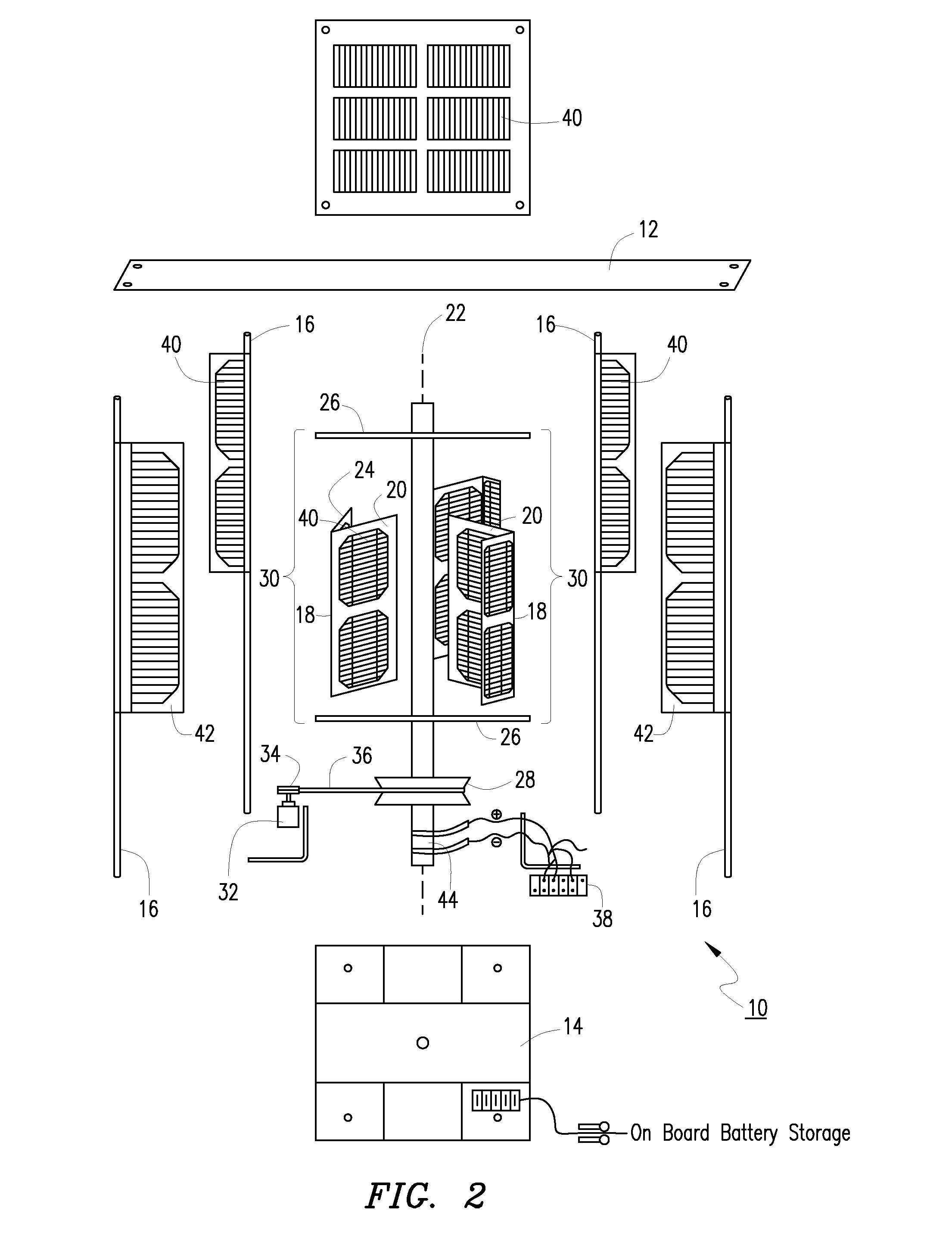
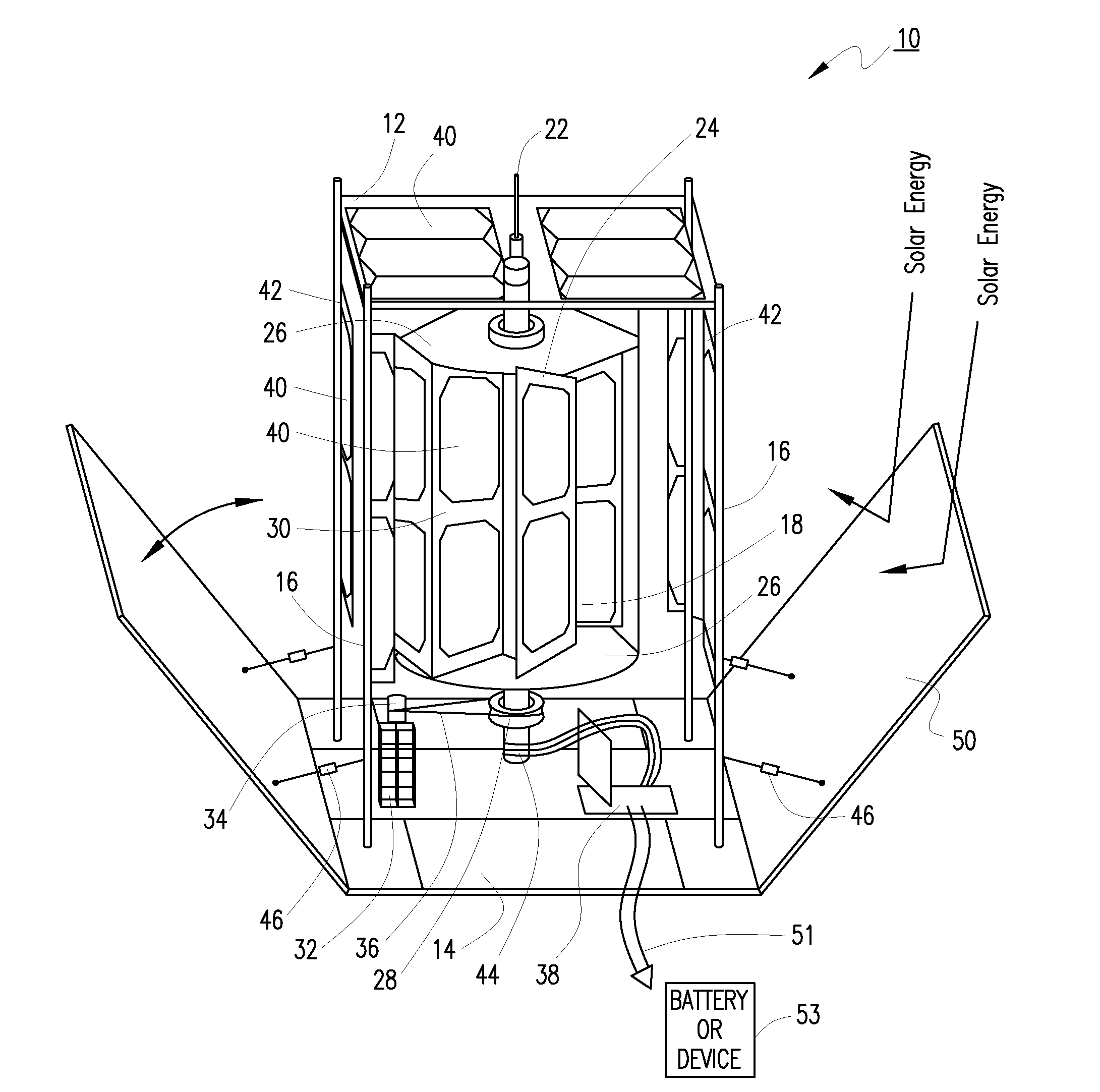
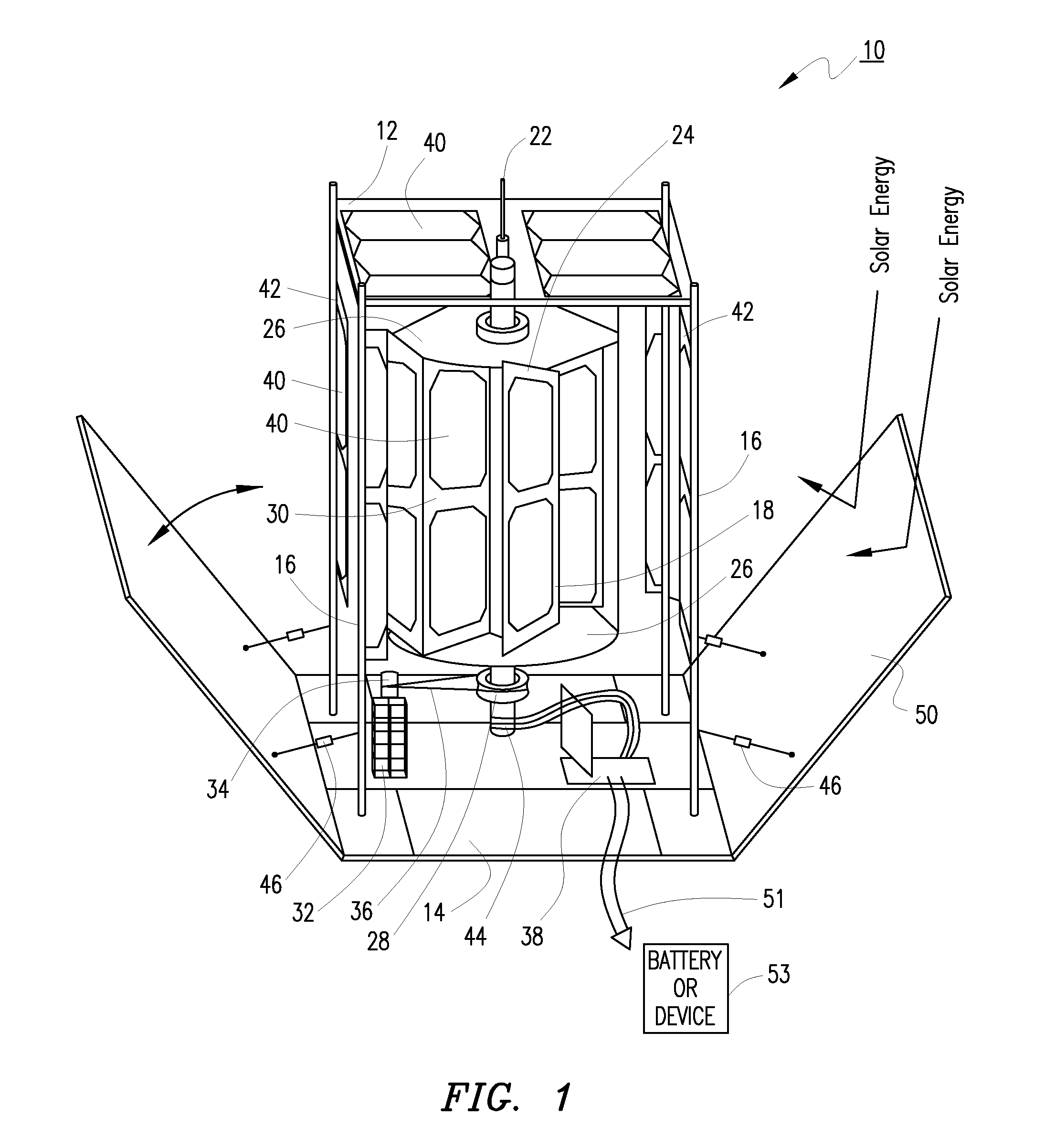
Solar windmill
An environmentally friendly combination wind turbine and solar energy collector is provided. Solar panels are mounted on the surfaces of a wind turbine such that the combined energy from the wind turbine and the solar panels are provided as an output.
Owner:GILBERT MICAH
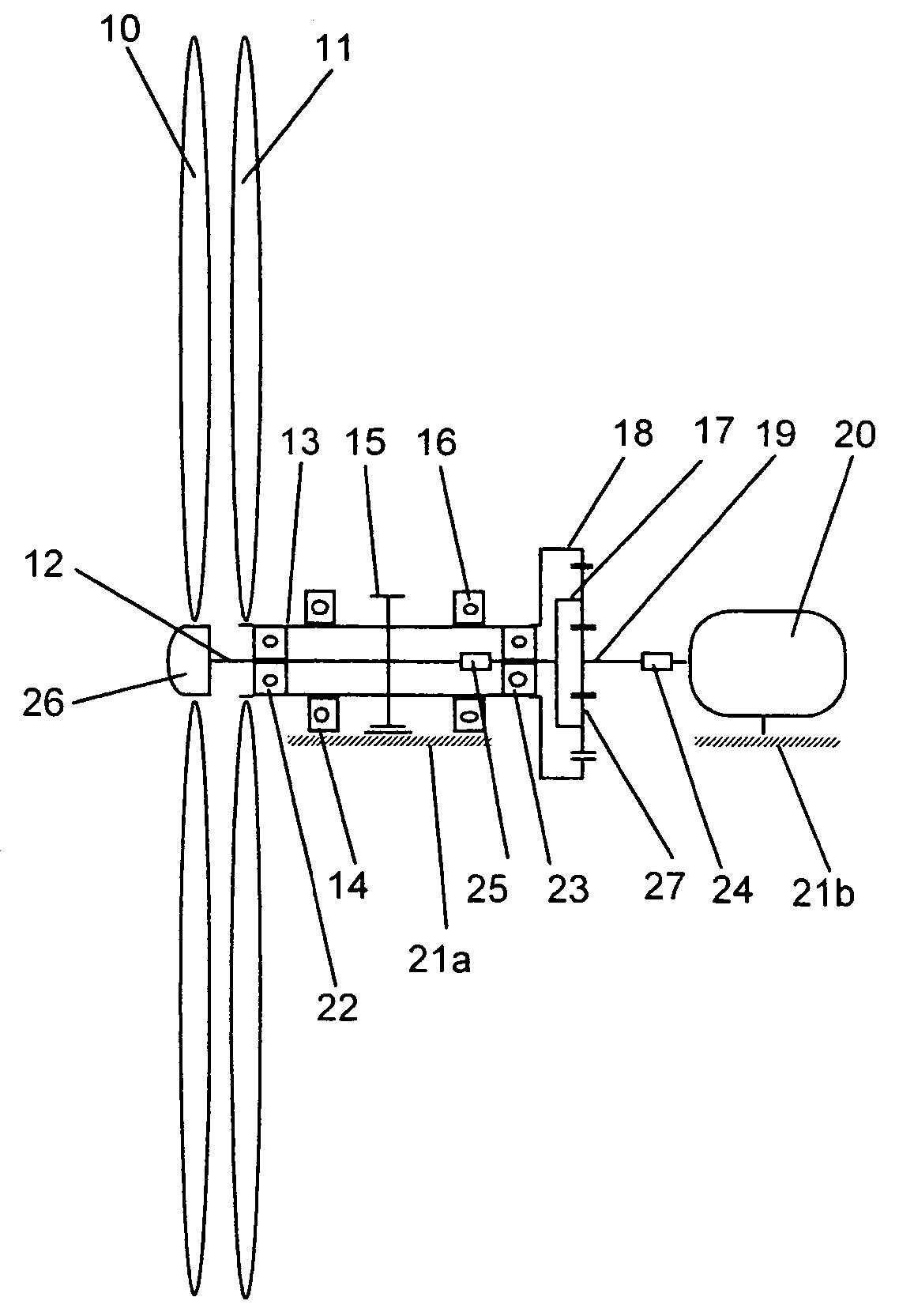
Drive device for a windmill provided with two counter-rotative propellers
The drive device is provided for inclusion in a windmill with two counter-rotating screws. The shafts of the screws are each connected to a spindle of an epicyclical gearbox, the third spindle providing the energy for the user. The device further comprises a brake device simultaneously acting on the two shafts of the screws. In particular, said device permits the installation of a second screw on a windmill mast designed for a single screw on a windmill mast designed for a single screw, thus greatly increasing the power supplied.
Owner:EOTHEME
Solar windmill
InactiveUS20080047270A1Wind motor with solar radiationFrom solar energyTurbineSolar energy harvesting
An environmentally friendly combination wind turbine and solar energy collector is provided. Solar panels are mounted on the surfaces of a wind turbine such that the combined energy from the wind turbine and the solar panels are provided as an output.
Owner:GILBERT MICAH
High-power permanent-magnet motor rotor, installation method of rotor and method for magnetizing rotor permanent magnet
ActiveCN102005838AEasy to producePlay a supporting roleMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesPermanent magnet motorMagnetic isolation
Owner:东元总合科技(杭州)有限公司
Laminar air turbine
InactiveUS7214029B2Low costMaximize rotational forcePump componentsWind motor controlWind drivenTurbine wheel
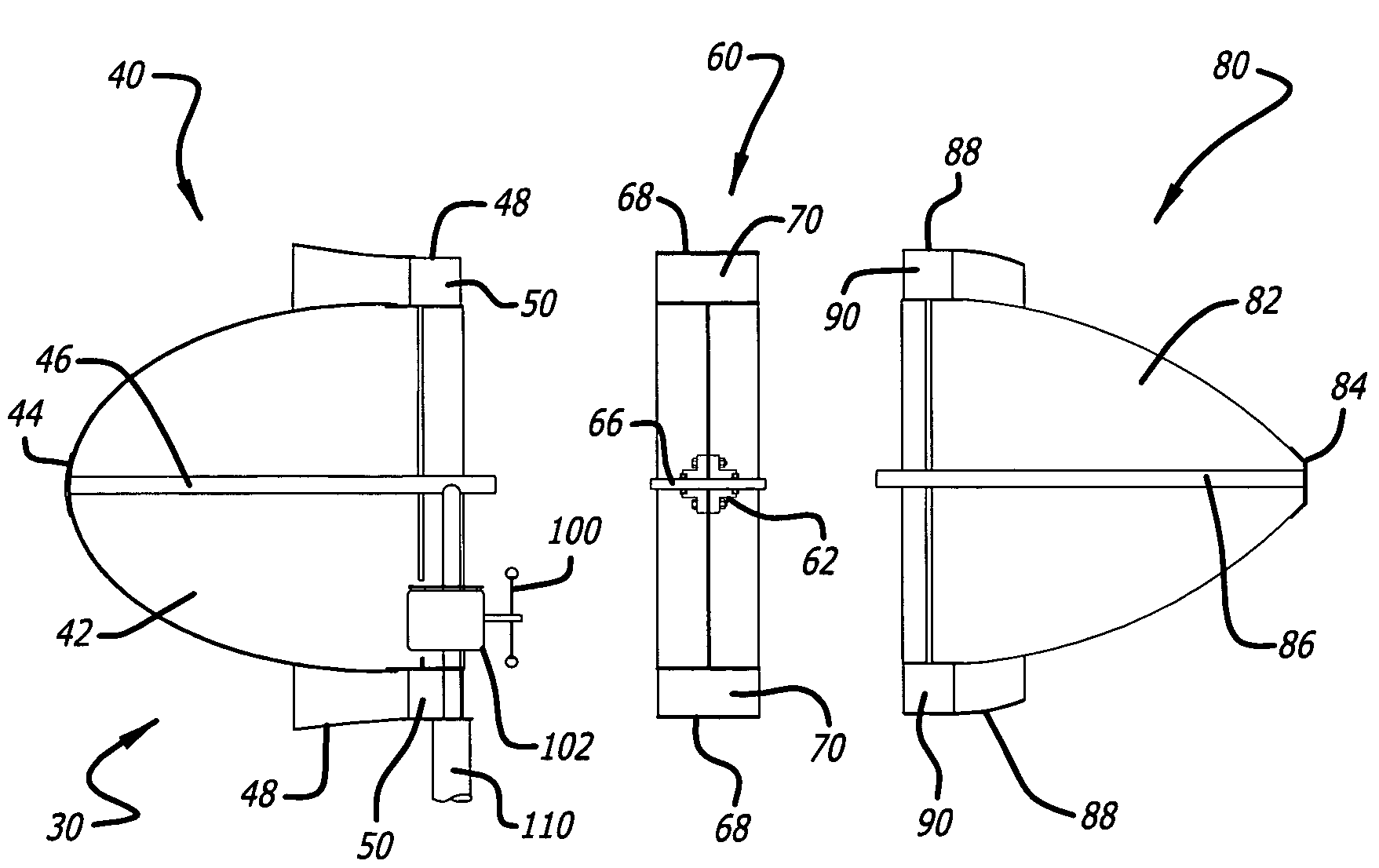
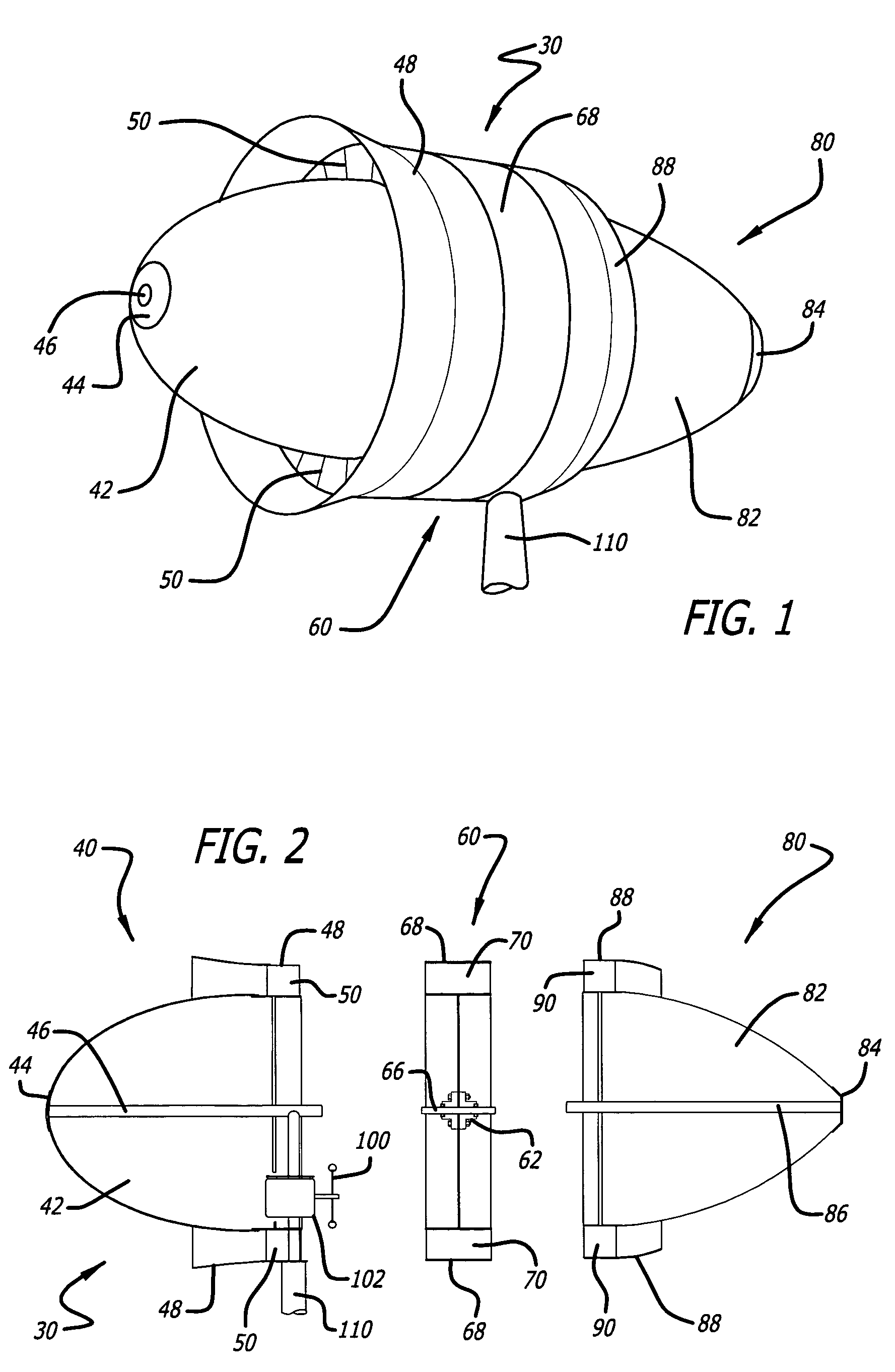
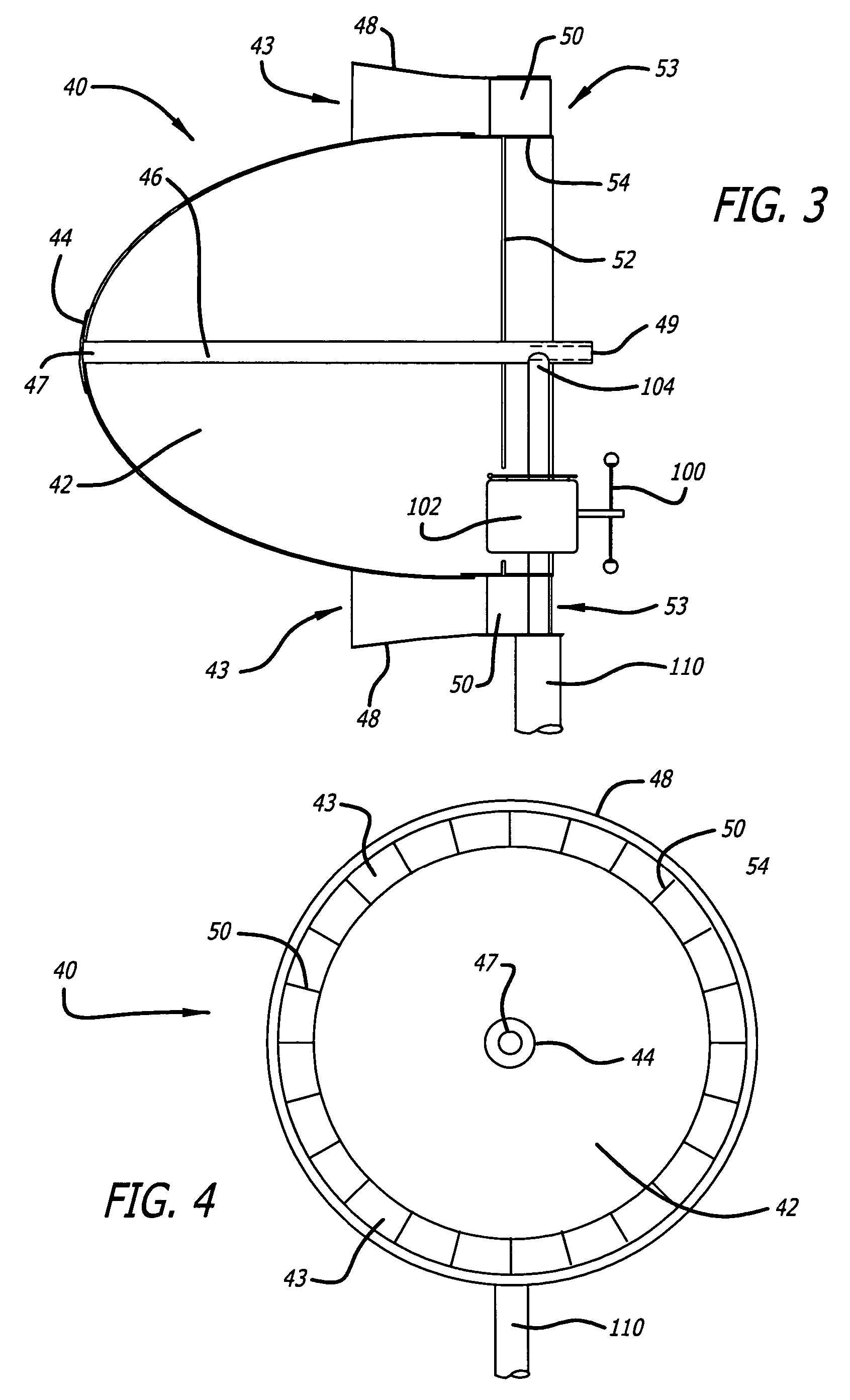
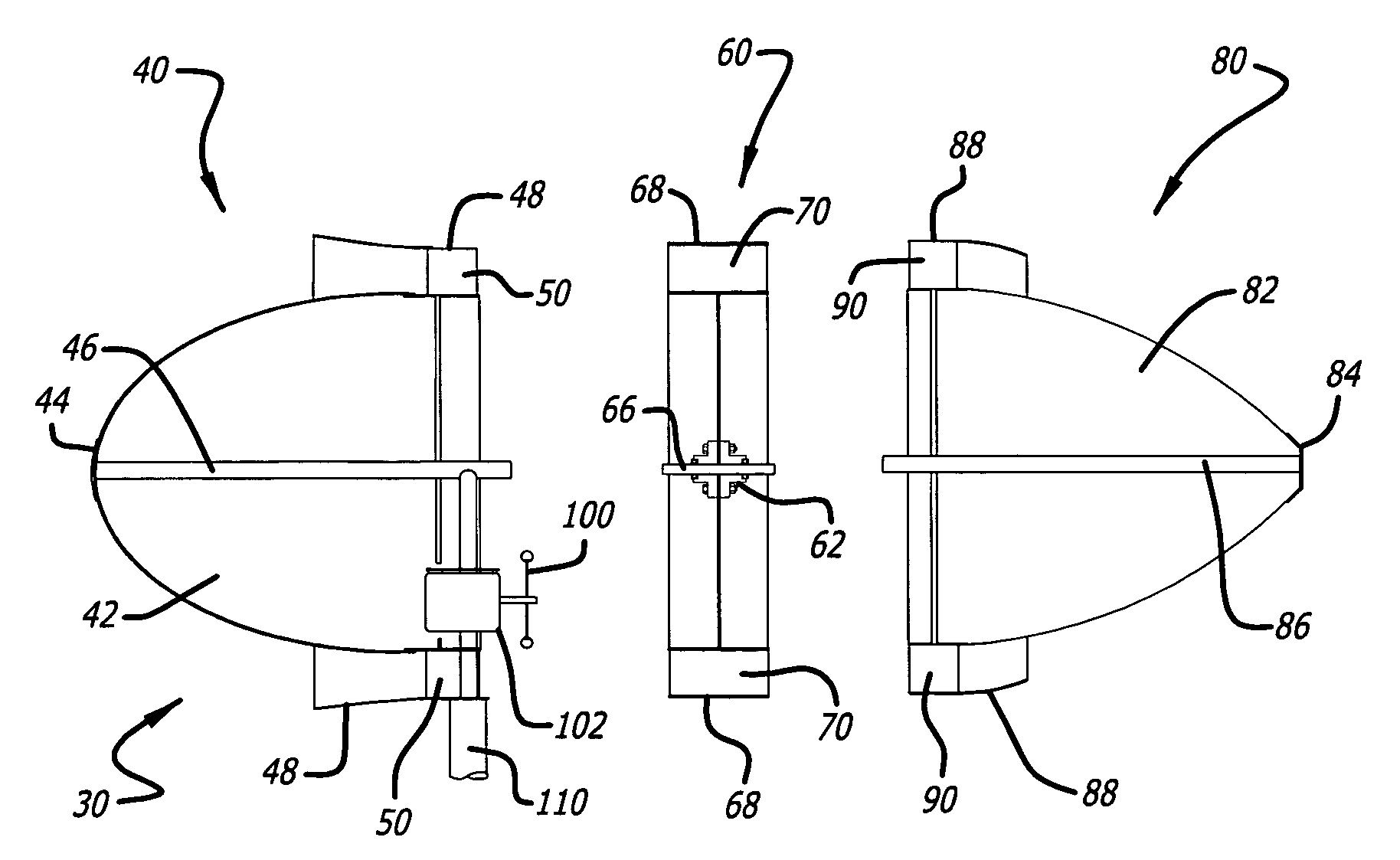
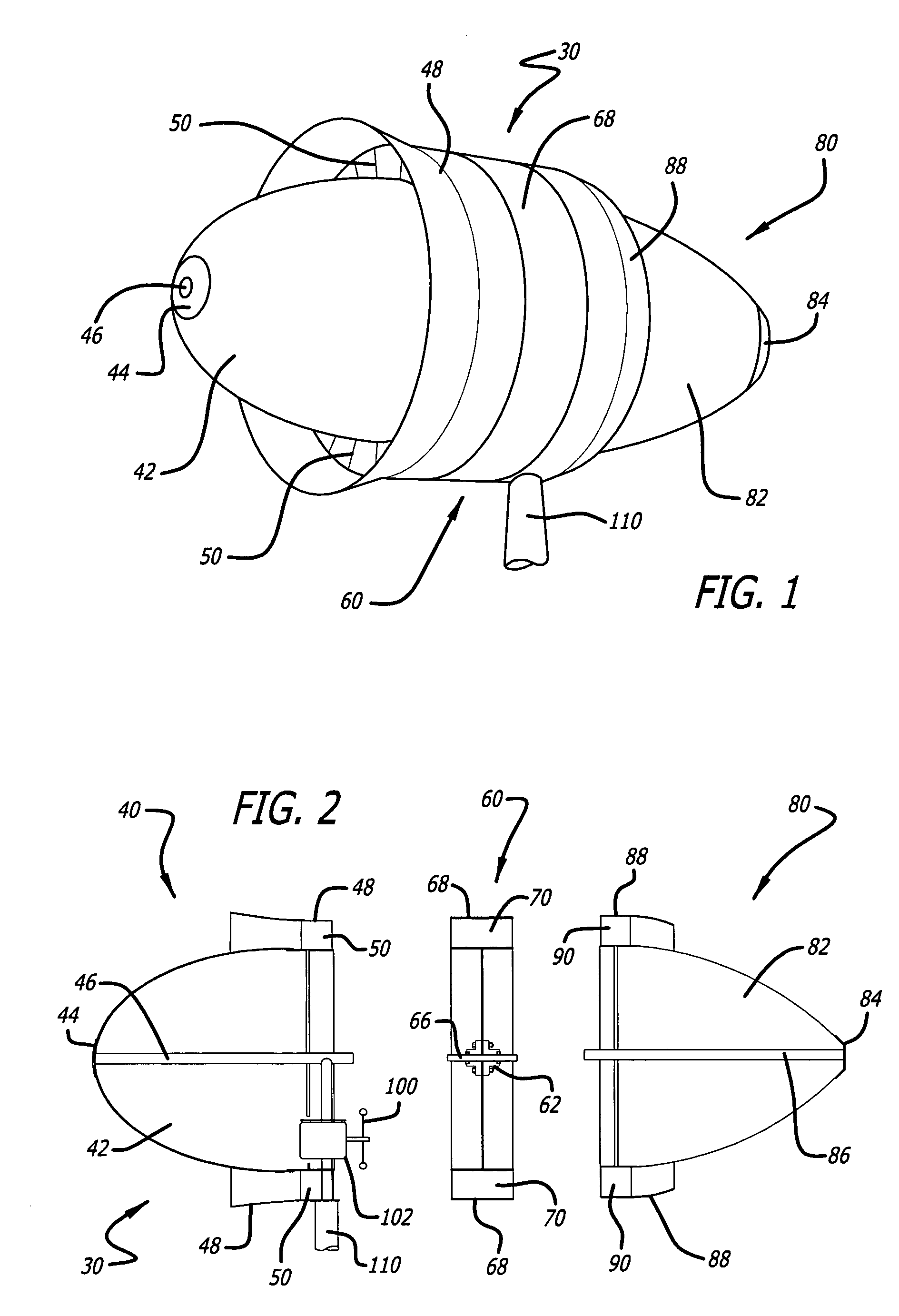
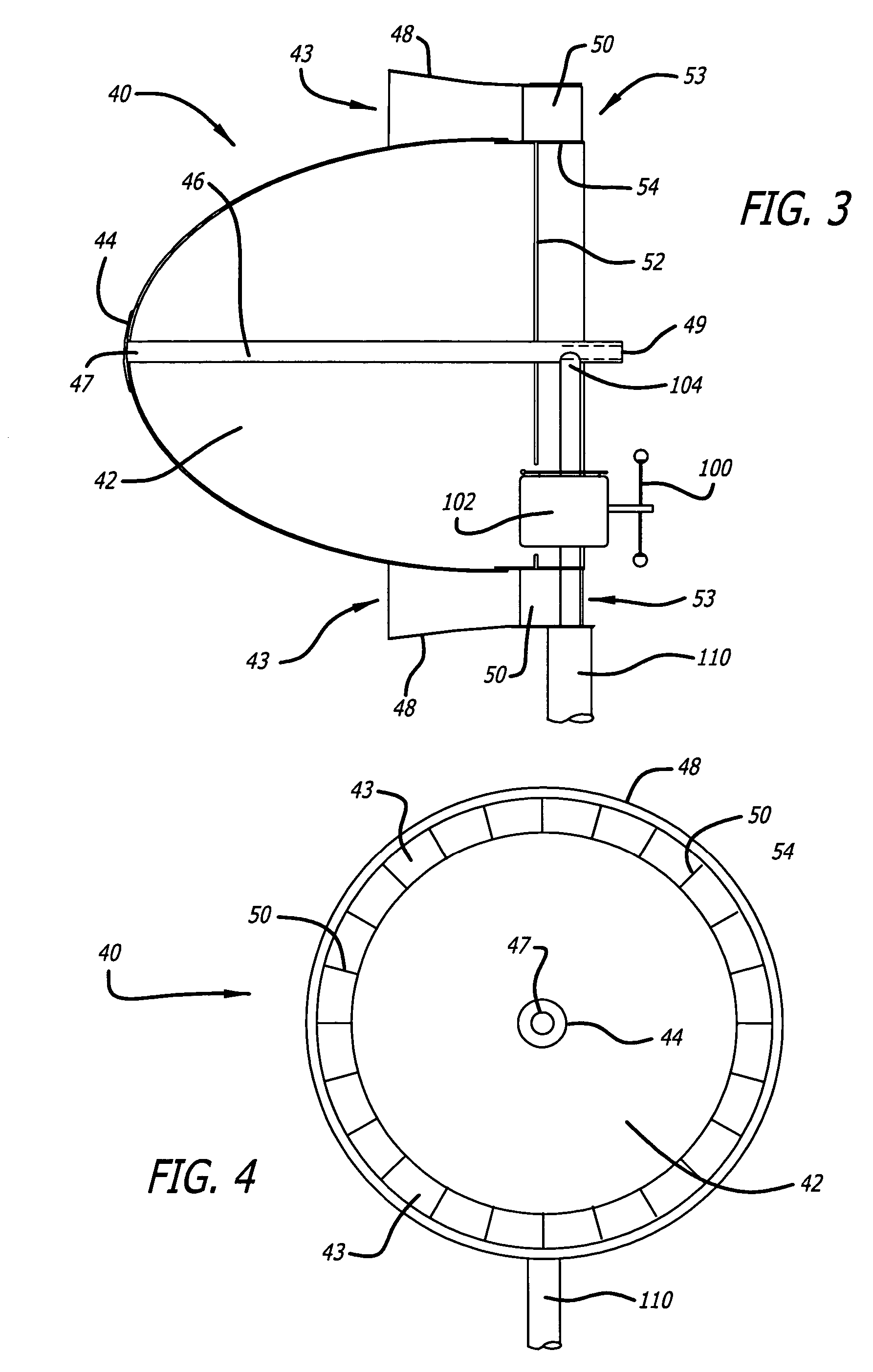
The windmill assembly is a low drag, streamlined body of revolution that captures the kinetic energy content of the accelerated laminar air surrounding the body. The assembly includes a power-generating, wind-driven turbine that is compact, lightweight and capable of producing a substantially greater output than a conventional windmill with a comparable size rotor. The turbine includes a protruding aerodynamic nose and outer cowling that provide a streamlined, wind-collecting inlet section that constricts the incoming air stream and increases its velocity through the turbine blades. The turbine further includes an exit section designed to exhaust the air stream with a minimum of turbulence. One or more generators are coupled to a turbine wheel, and are electrically switched on and off to maximize the energy capture over the full range of ambient winds. The wind turbine assembly may be configured around a blimp-type body having counter-rotating turbine assemblies.
Owner:RICHTER DONALD L
Vertical axis wind turbine and wind turbine blade
InactiveUS20070177970A1Improve lifting performanceImprove startup performanceWind motor controlMachines/enginesTurbine bladeVertical axis wind turbine
It is an object of the invention is to provide a vertical axis wind turbine and a wind turbine blade, which are excellent in self-starting performance and have a high torque constant. Since the present invention comprises a wind receiving plate 40 having a wind receiving surface and an openable and closable pivot 42, which wind receiving plate 40 is operated to close in the direction in which the centrifugal force is produced in proportion to the revolution of a blade 18 generating a lifting power, and an energizing means (such as spring 44) for energizing an opening force to open the wind receiving plate to the wind receiving side, the starting performance of the lift type wind turbine can be improved by means of the wind receiving plate 40, which opens at a low revolution of the blade 18 so as to function as a drag type wind turbine, and automatically closes at a high revolution of the blade 18 so as to function as a lift type wind turbine.
Owner:INTPROP BANK CORP (JP)
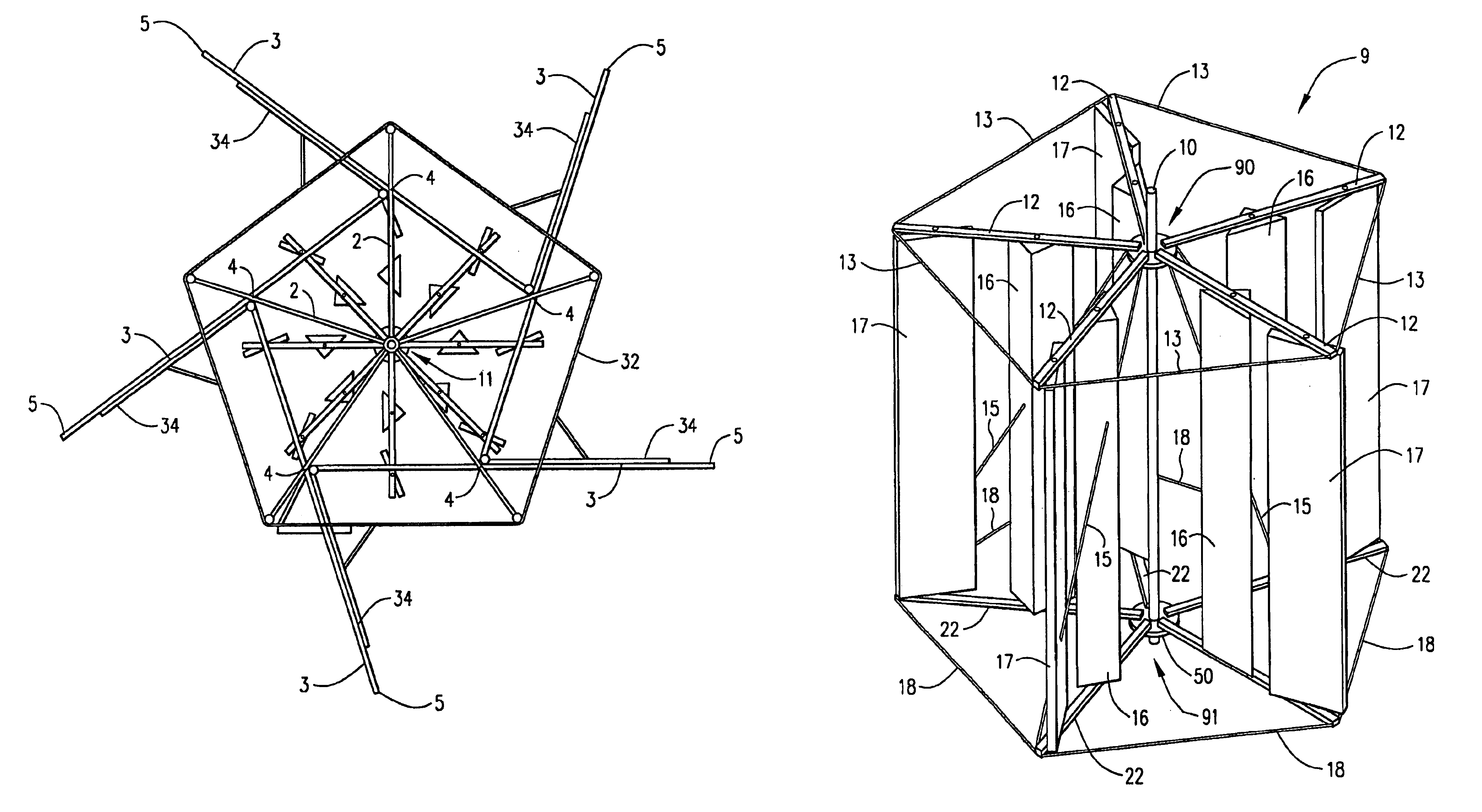
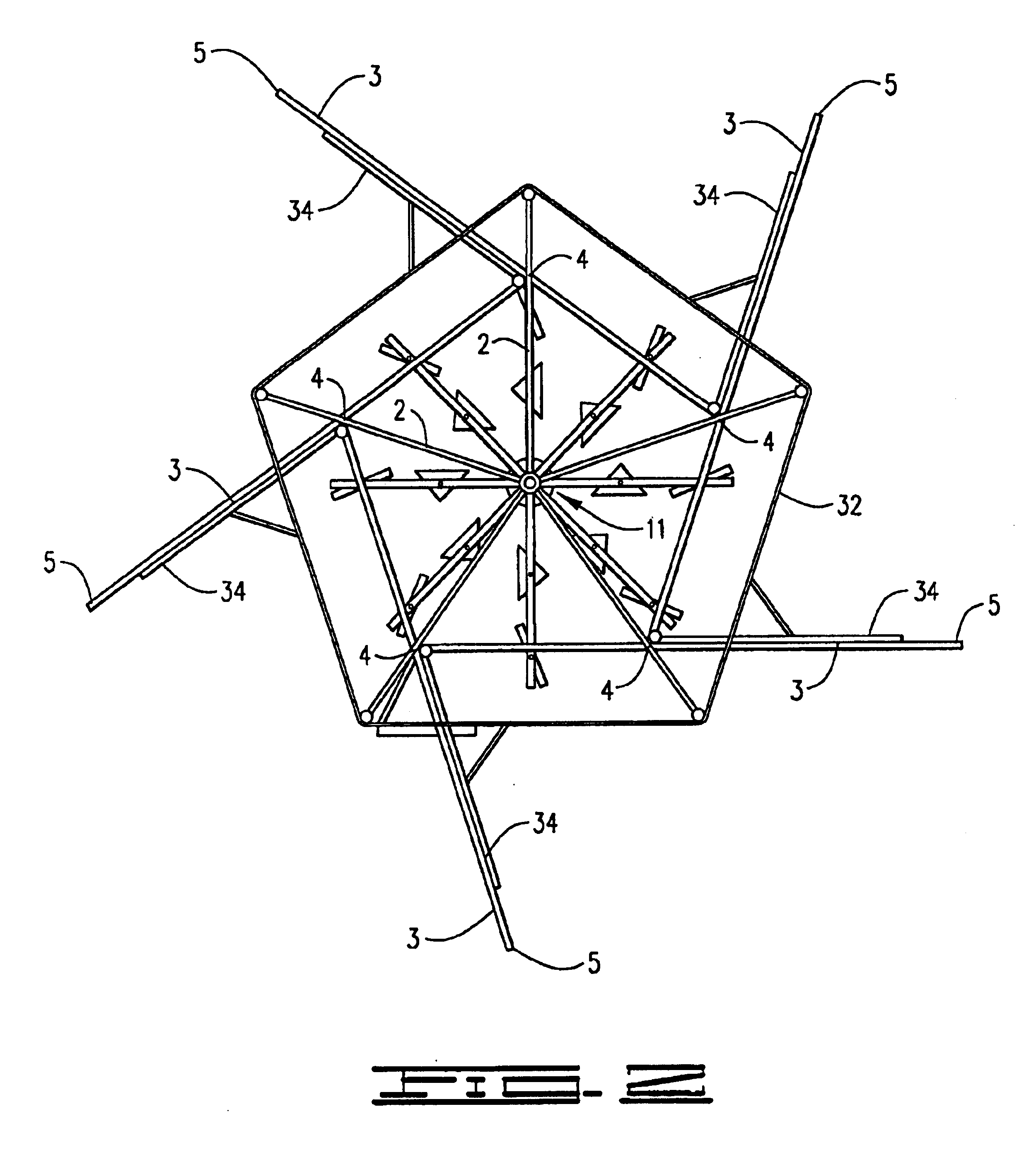
Vertical Axis Windmill And Wind Turbine System For Generating Electricity From Wind Energy
InactiveUS20080213083A1Dampen pivoting movementContinuous rotationPropellersWind motor controlElectricityTurbine
A lift-type wind turbine having a substantially vertical rotating shaft and a plurality of substantially vertical blades secured to the shaft. Each blade includes a front portion, a rear portion, and a pivot axis pivotally securing the rear and front portions. The rear portion pivots relative the front portion. The blades additionally include bottom and top edges positioned on each of the front portions. Each bottom edge is arranged substantially equidistant from the shaft proximate a first circumference extending substantially horizontally about the shaft, whereas each top edge is arranged substantially equidistant from the shaft proximate a second circumference extending substantially horizontally about the shaft. The blades are angled relative to the rotating shaft. The blades have an open, drag means position as well as a closed, lift means position, and passively switch between the positions based on wind speed for efficient rotation.
Owner:SEABELL INT CO LTD
Laminar air turbine
InactiveUS20060002786A1Low costMaximize rotational forceWind motor controlPump componentsWind drivenTurbine wheel
The windmill assembly is a low drag, streamlined body of revolution that captures the kinetic energy content of the accelerated laminar air surrounding the body. The assembly includes a power-generating, wind-driven turbine that is compact, lightweight and capable of producing a substantially greater output than a conventional windmill with a comparable size rotor. The turbine includes a protruding aerodynamic nose and outer cowling that provide a streamlined, wind-collecting inlet section that constricts the incoming air stream and increases its velocity through the turbine blades. The turbine further includes an exit section designed to exhaust the air stream with a minimum of turbulence. One or more generators are coupled to a turbine wheel, and are electrically switched on and off to maximize the energy capture over the full range of ambient winds. The wind turbine assembly may be configured around a blimp-type body having counter-rotating turbine assemblies.
Owner:RICHTER DONALD L
Interface for renewable energy system
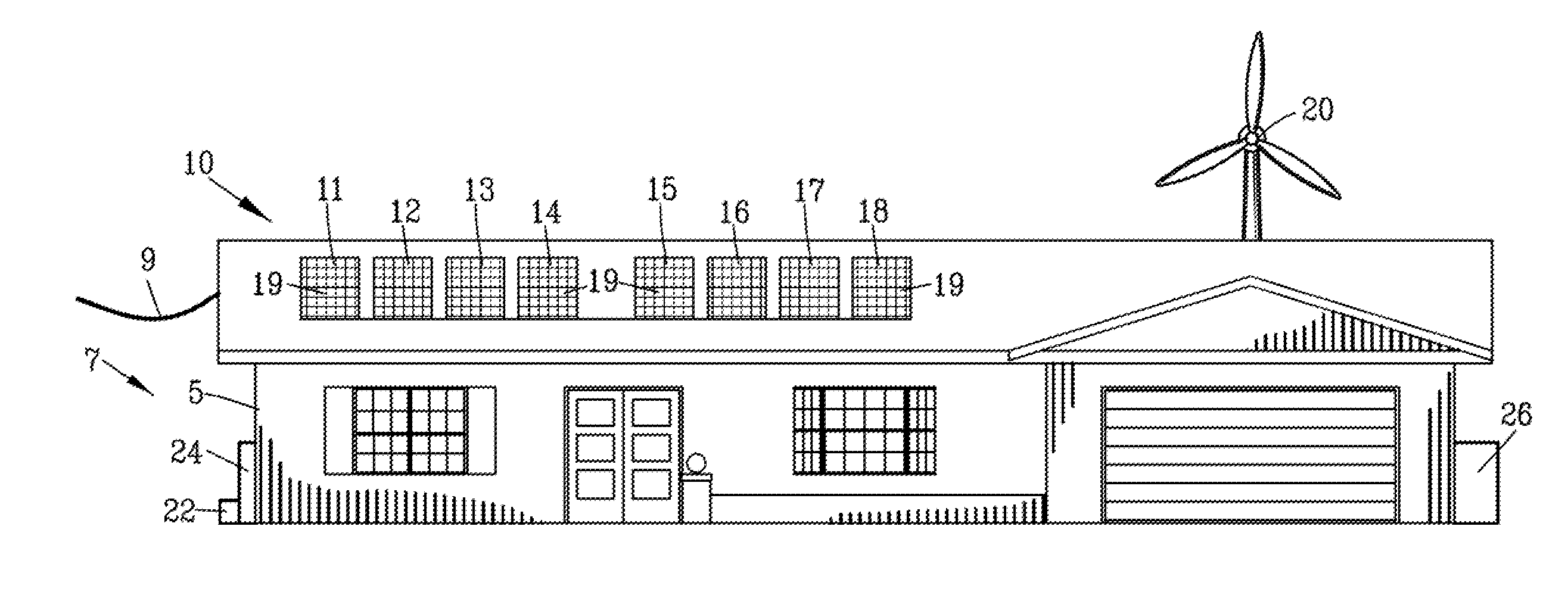
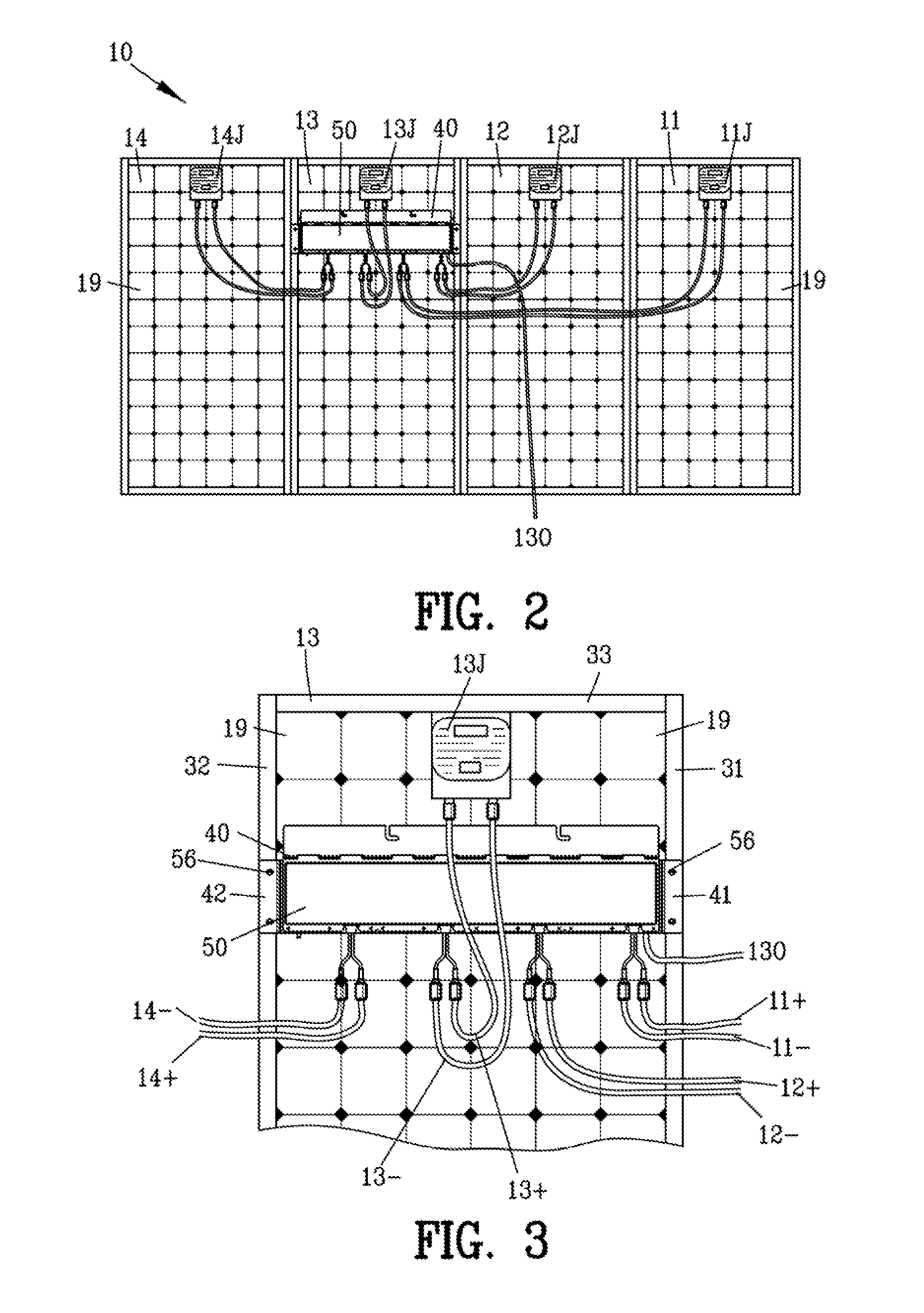
ActiveUS20140266289A1Maximizing elevationPhotovoltaic monitoringSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsRenewable energy systemElectric power
An improved interface for renewable energy systems is disclosed for interconnecting a plurality of power sources such as photovoltaic solar panels, windmills, standby generators and the like. The improved interface for renewable energy systems includes a multi-channel micro-inverter having novel heat dissipation, novel mountings, electronic redundancy and remote communication systems. The improved interface for renewable energy systems is capable of automatic switching between a grid-tied operation, an off grid operation or an emergency power operation. The interface provides for monitoring and for detecting performance and / or faults in power sources such as photovoltaic solar panels.
Owner:TECH RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com