Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
236 results about "Spin current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
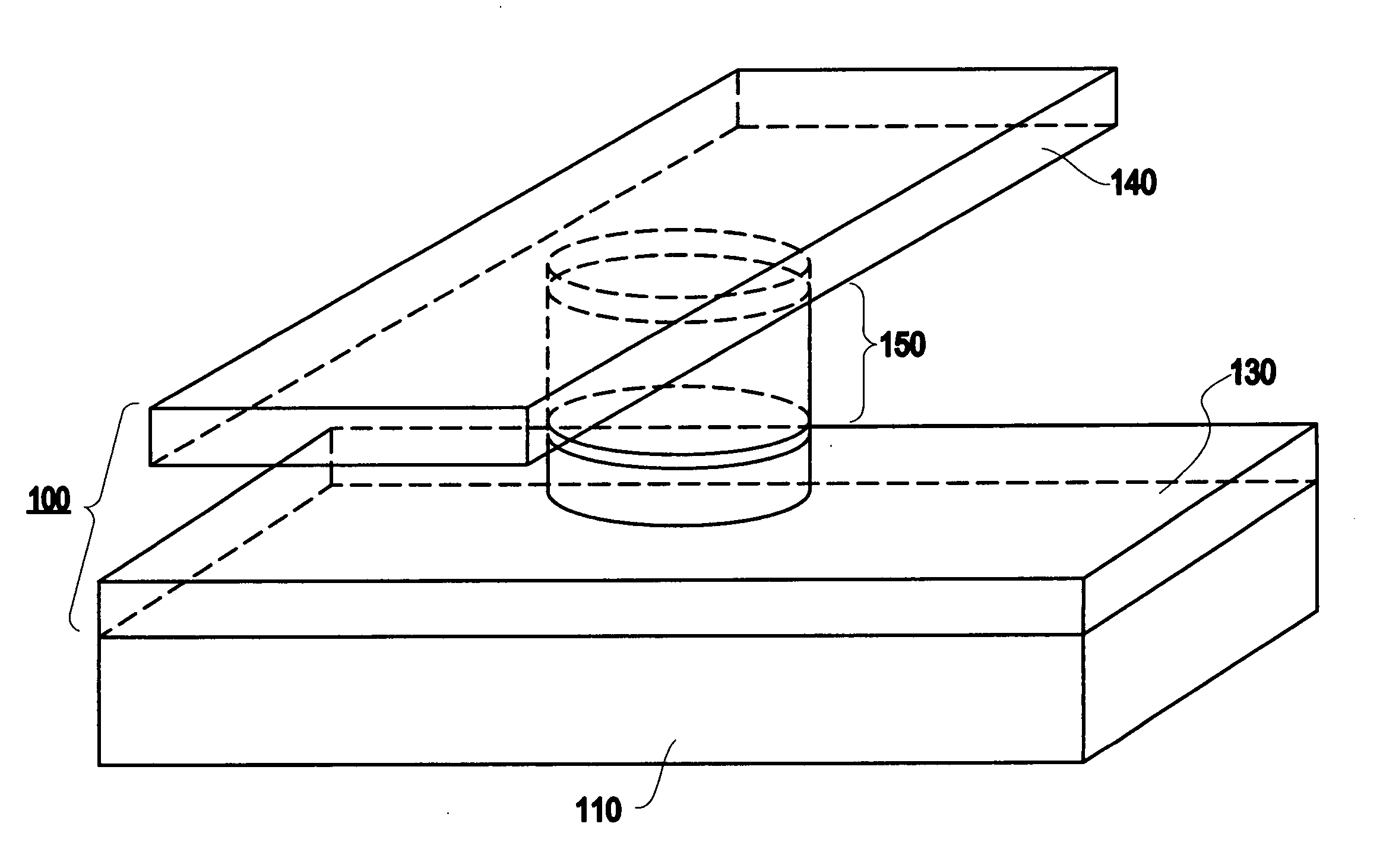
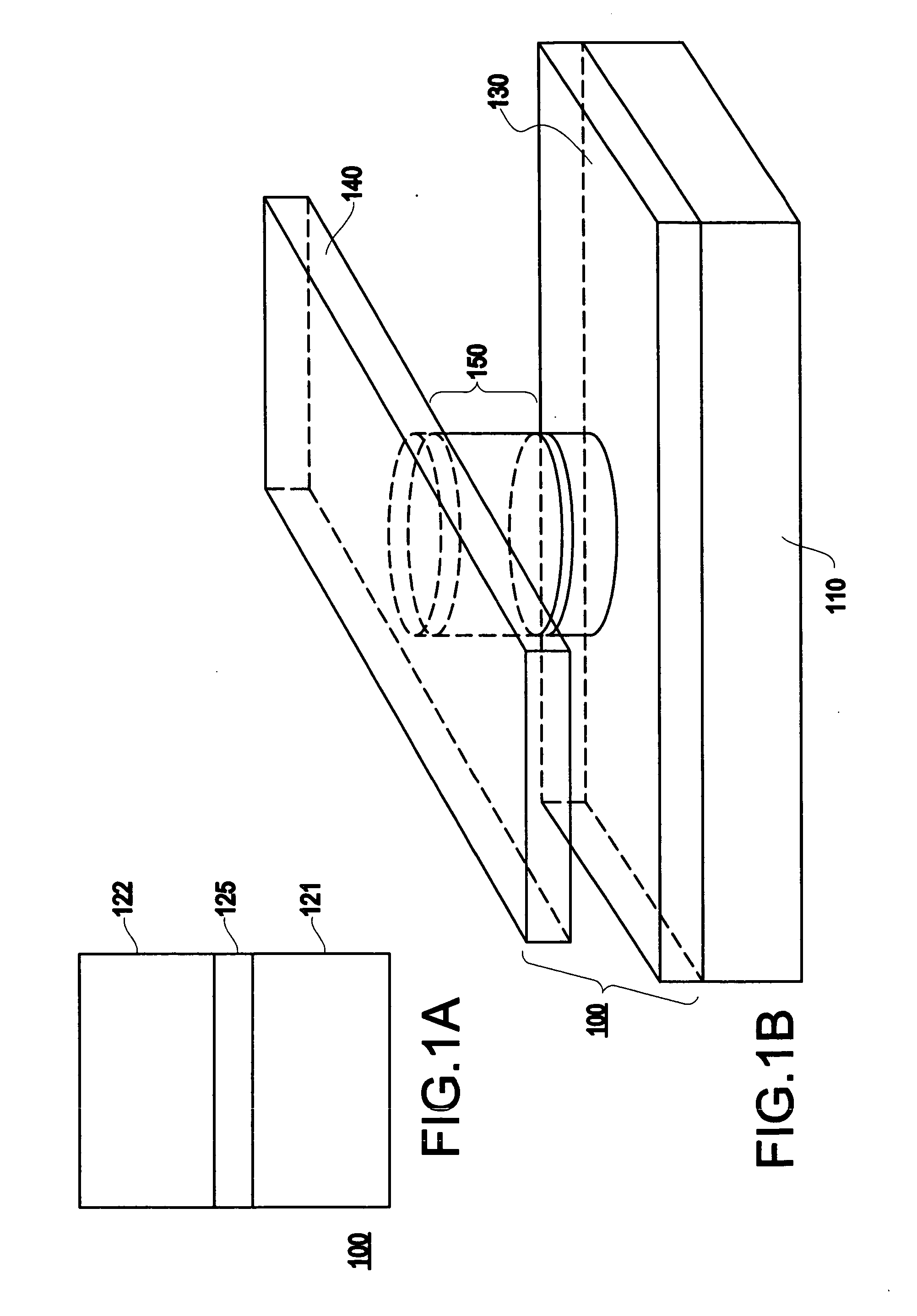
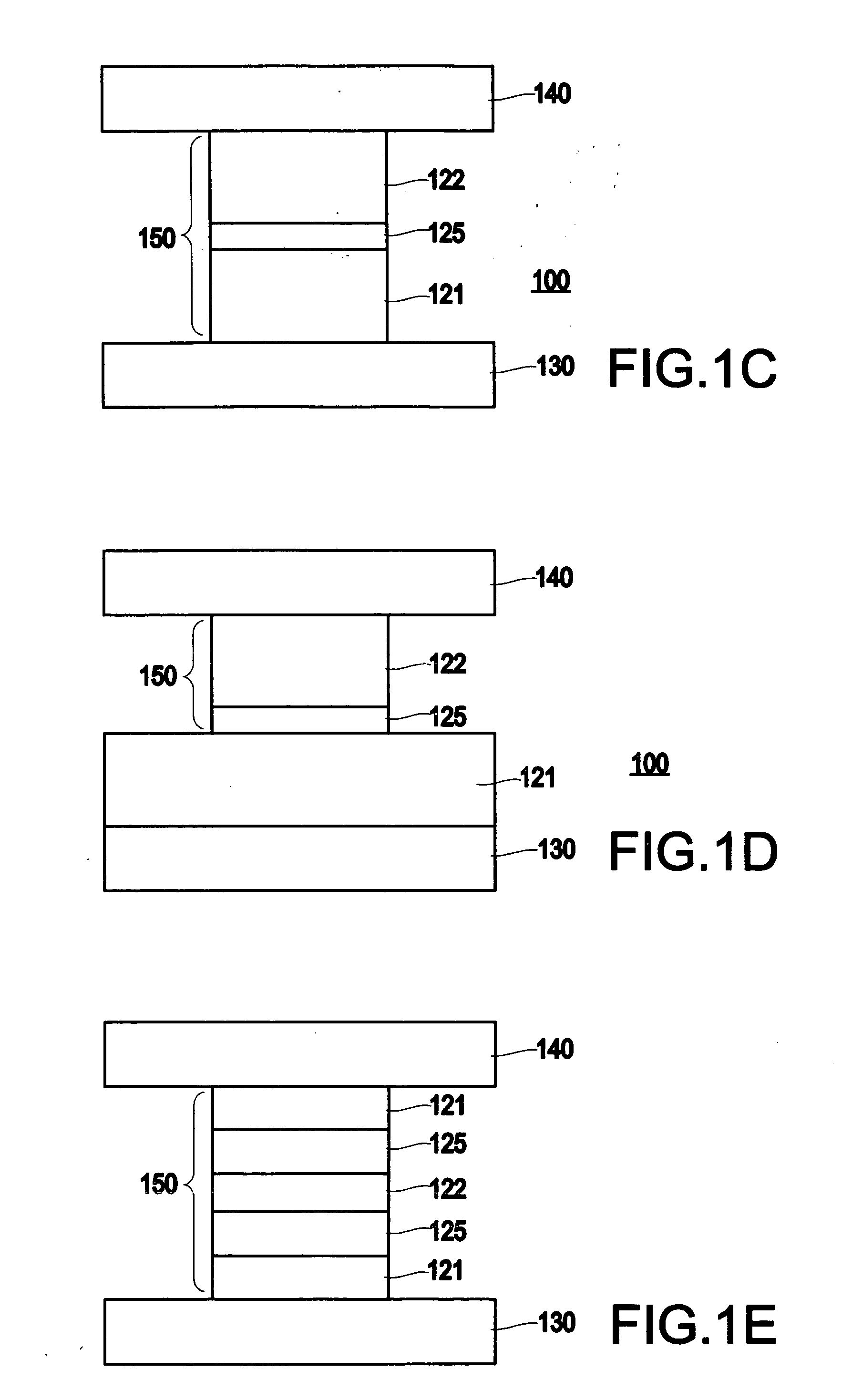
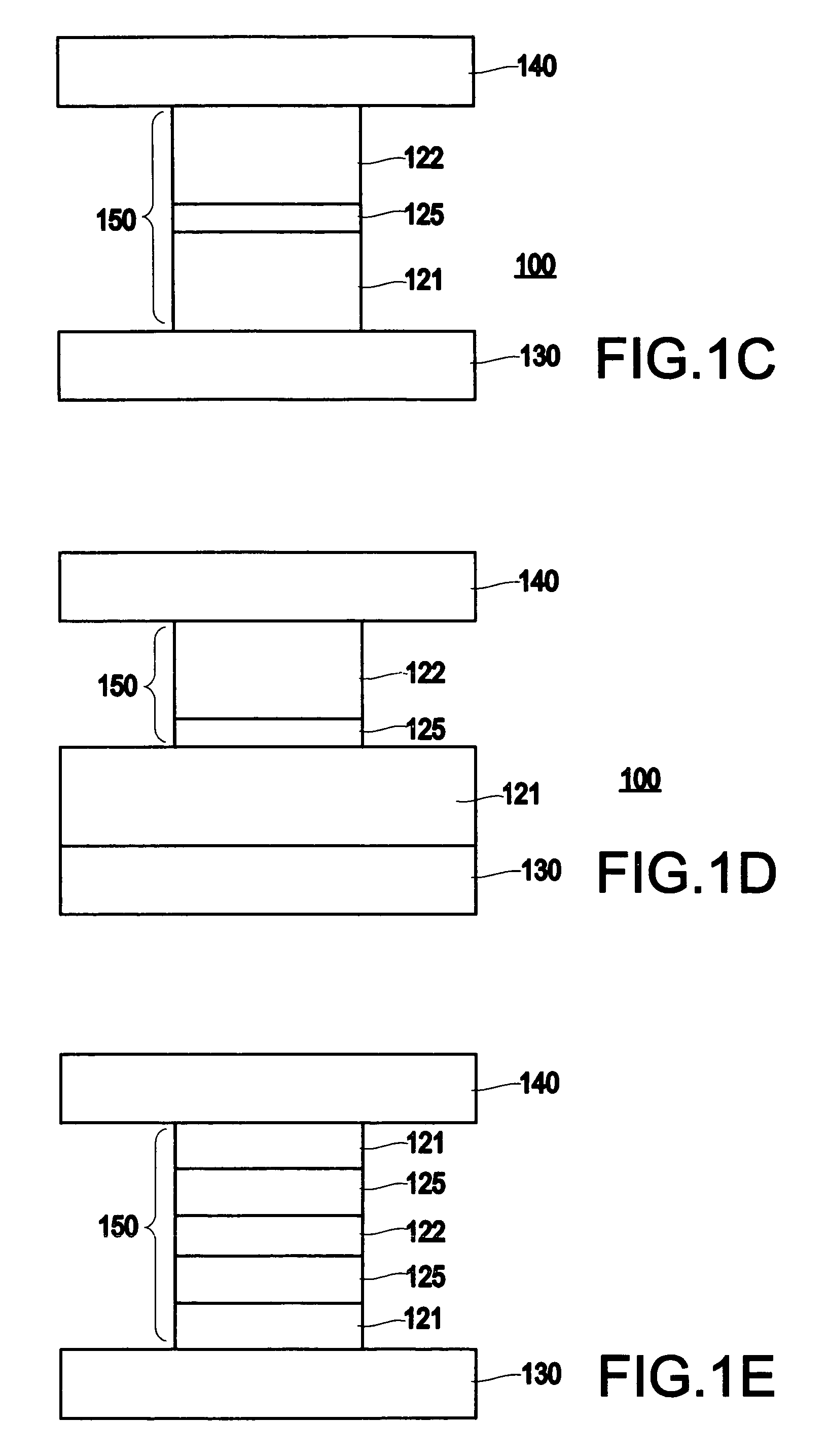
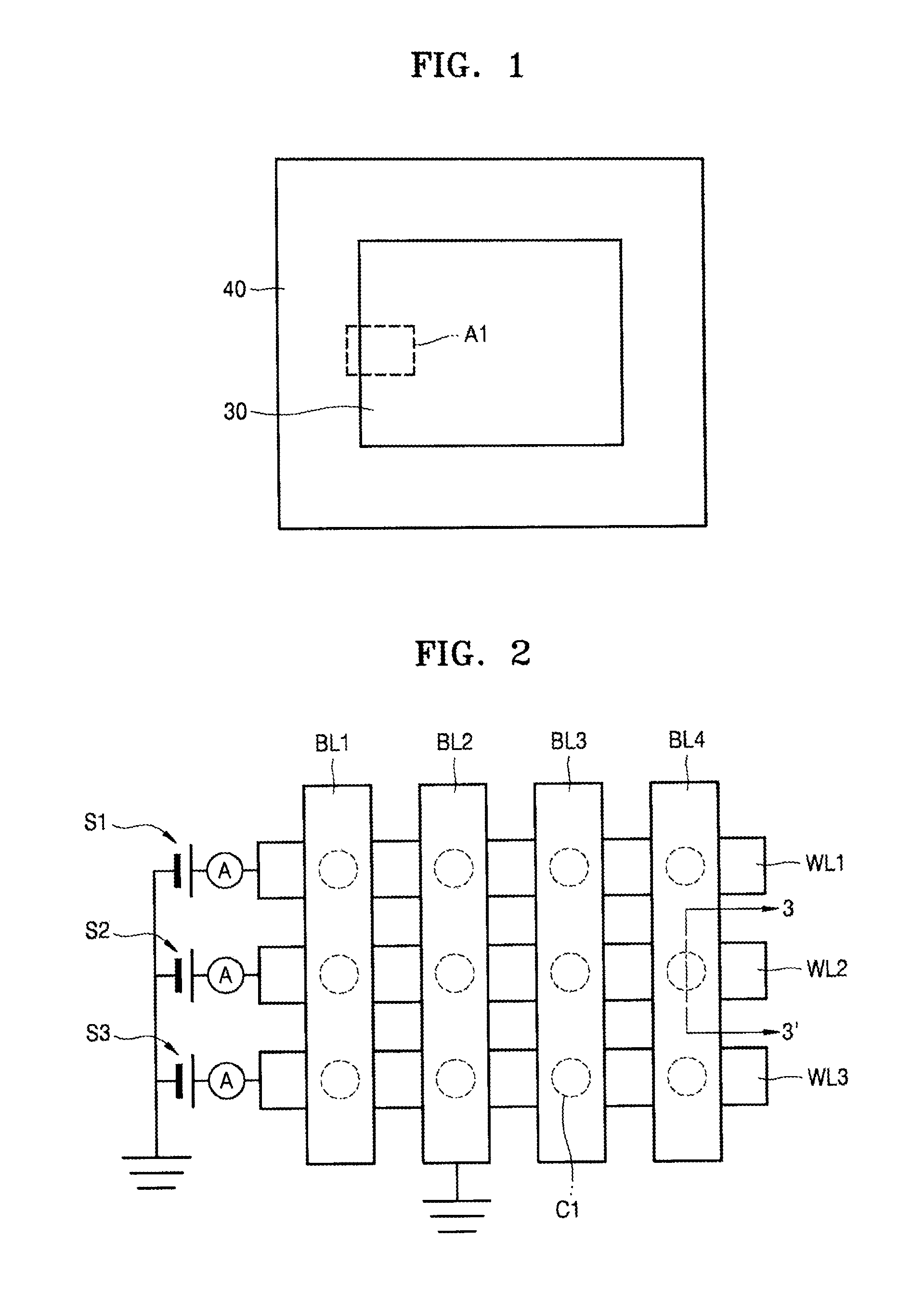
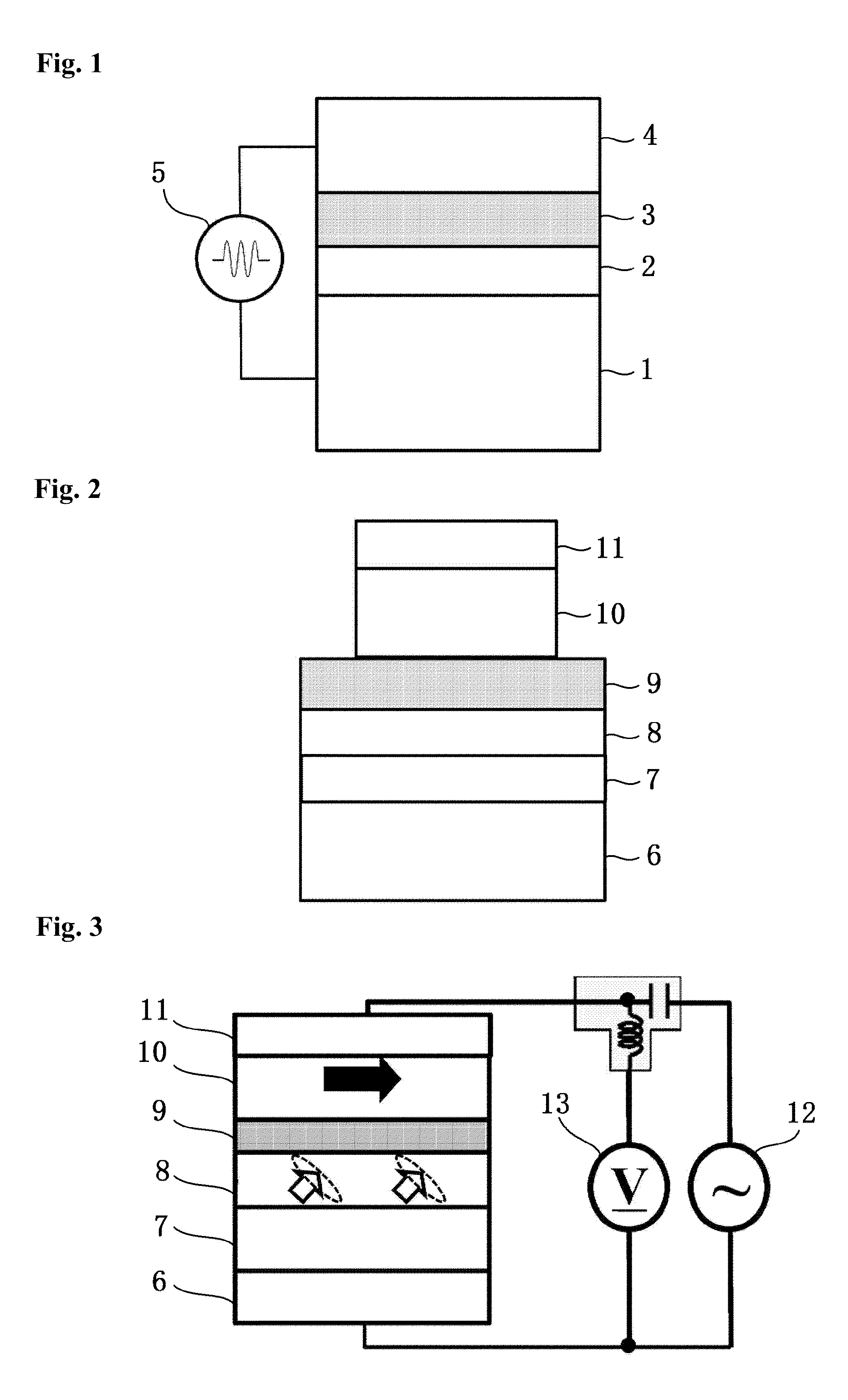
Spin-current switched magnetic memory element suitable for circuit integration and method of fabricating the memory element
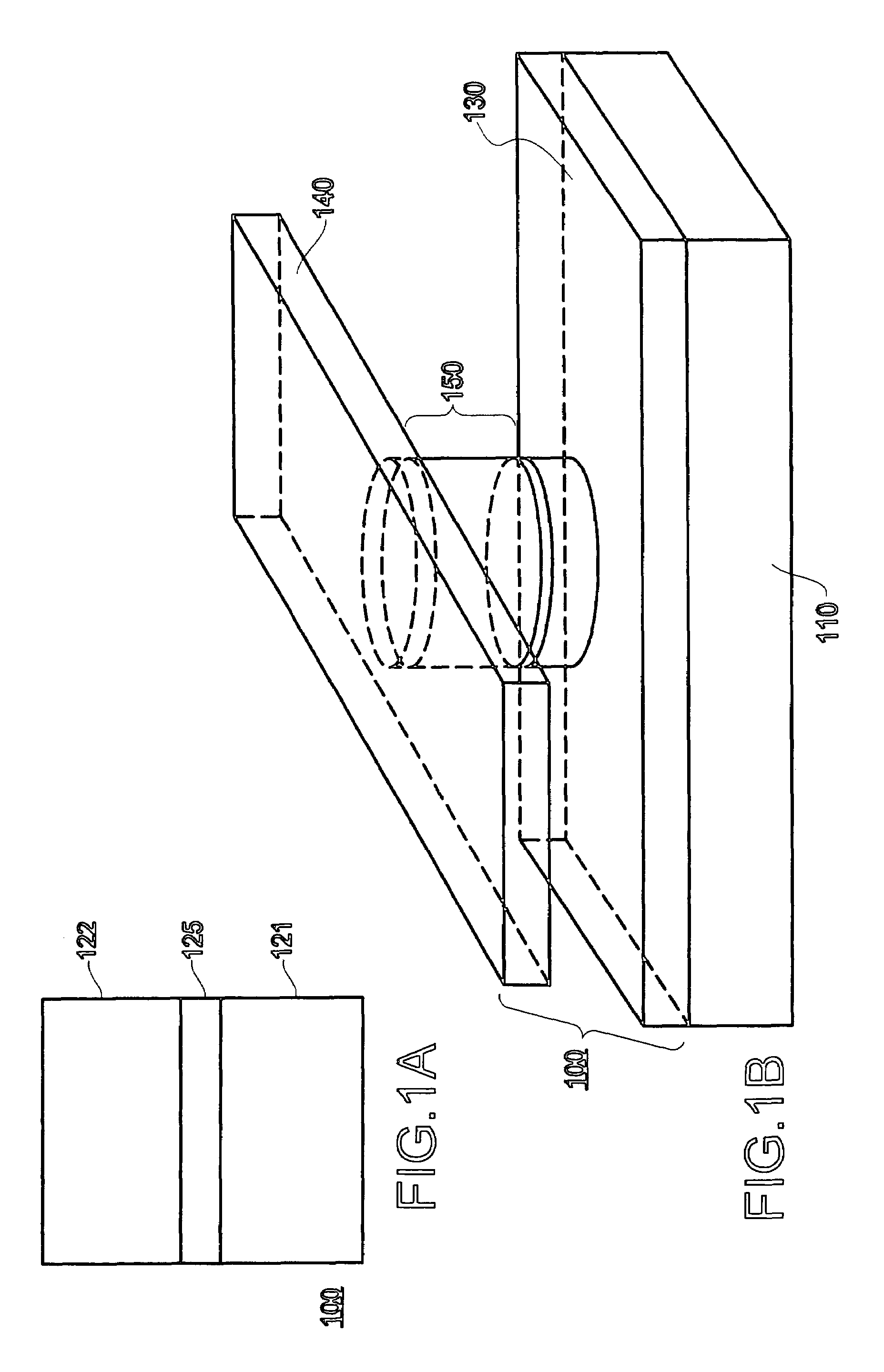
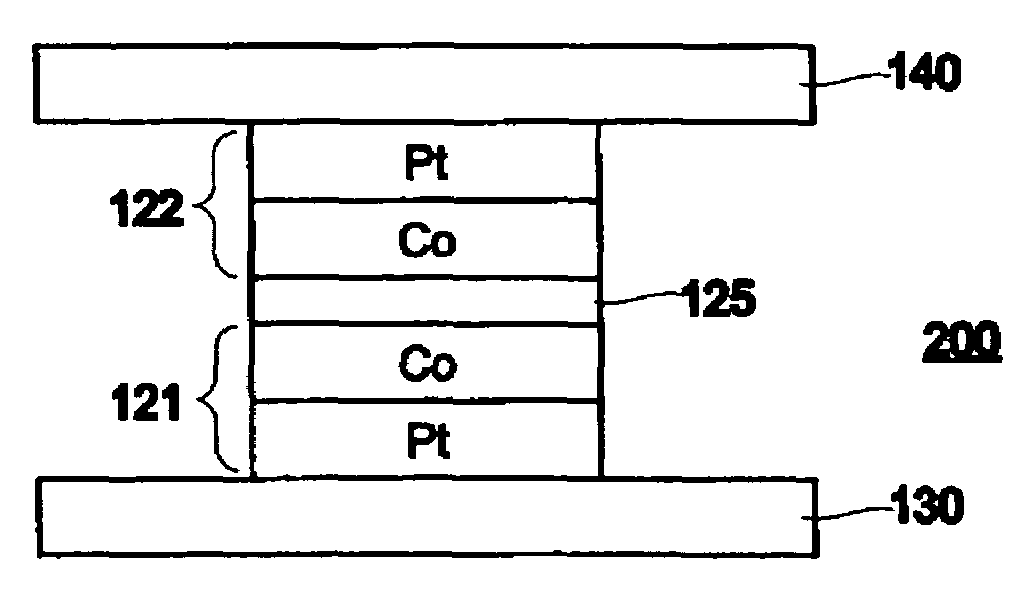
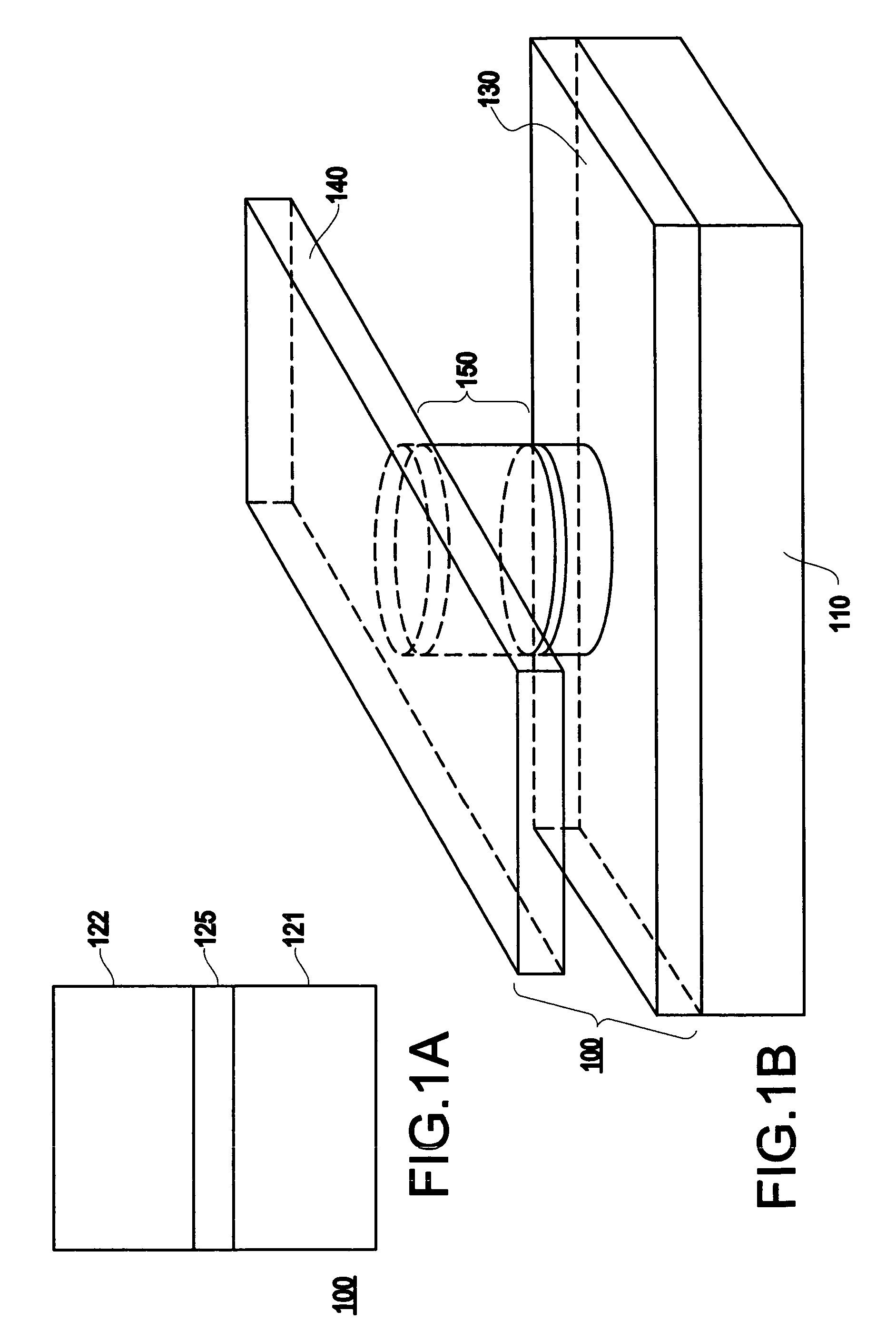
A magnetic memory element switchable by current injection includes a plurality of magnetic layers, at least one of the plurality of magnetic layers having a perpendicular magnetic anisotropy component and including a current-switchable magnetic moment, and at least one barrier layer formed adjacent to the plurality of magnetic layers (e.g., between two of the magnetic layers). The memory element has the switching threshold current and device impedance suitable for integration with complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) integrated circuits.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
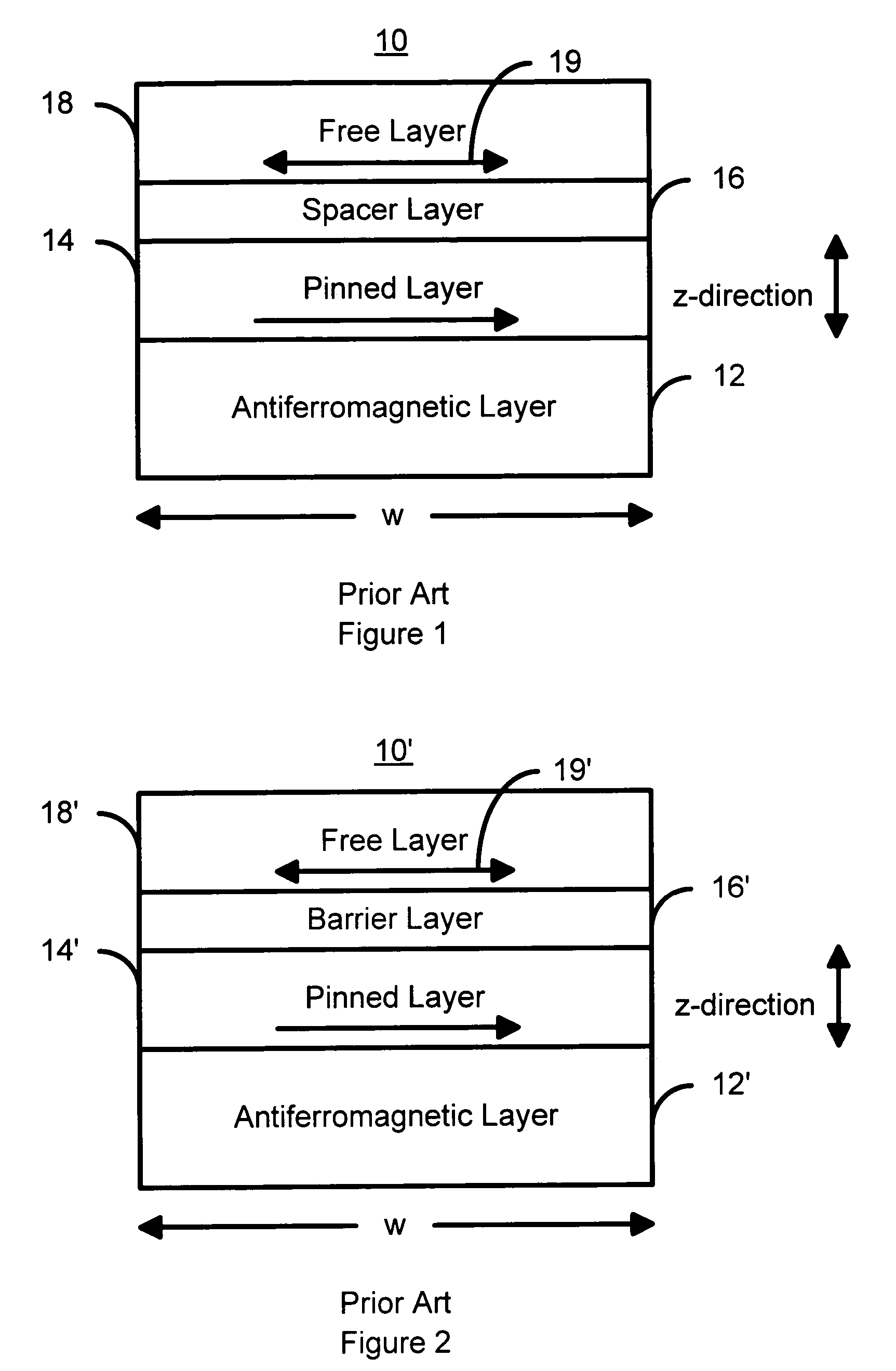
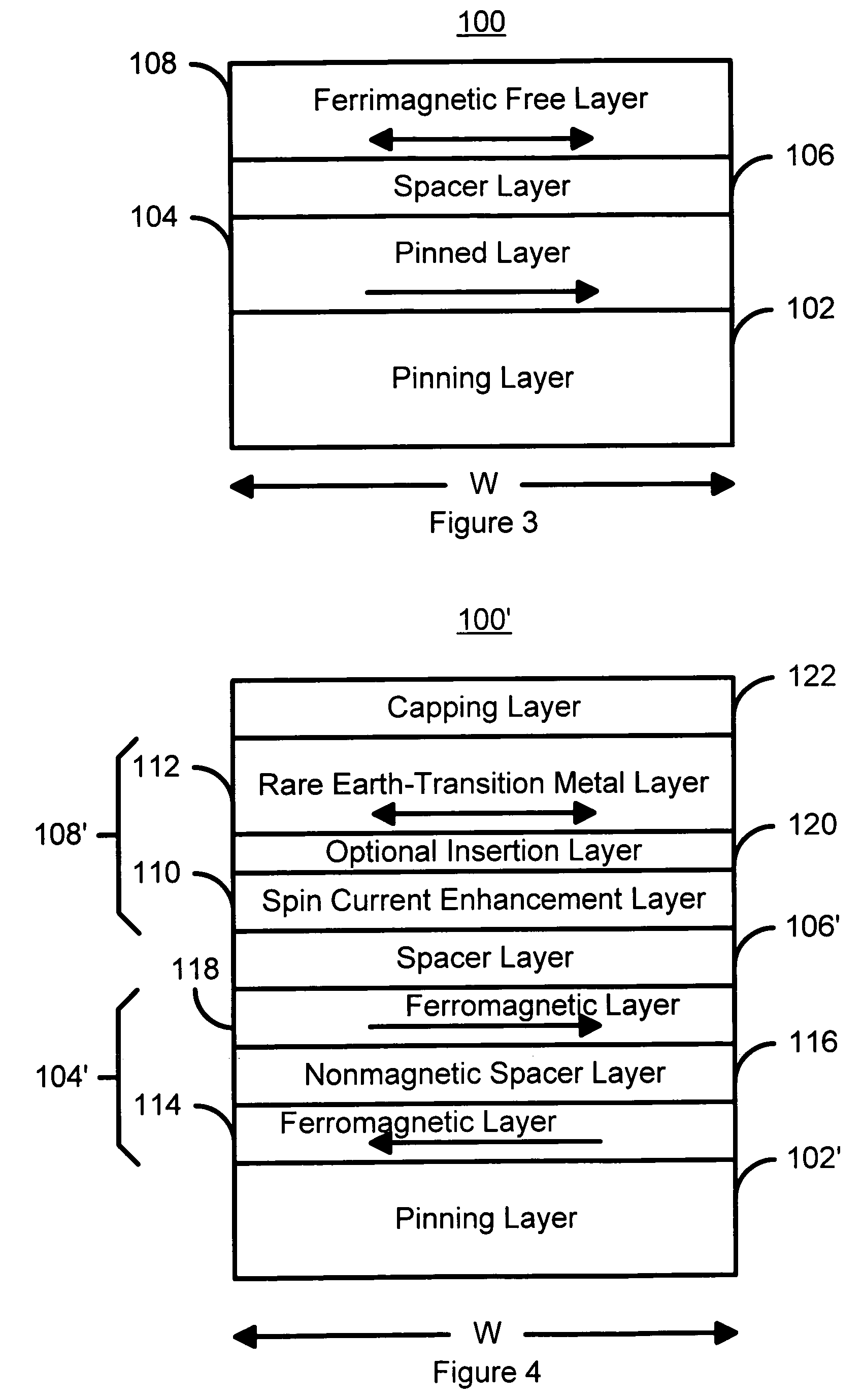
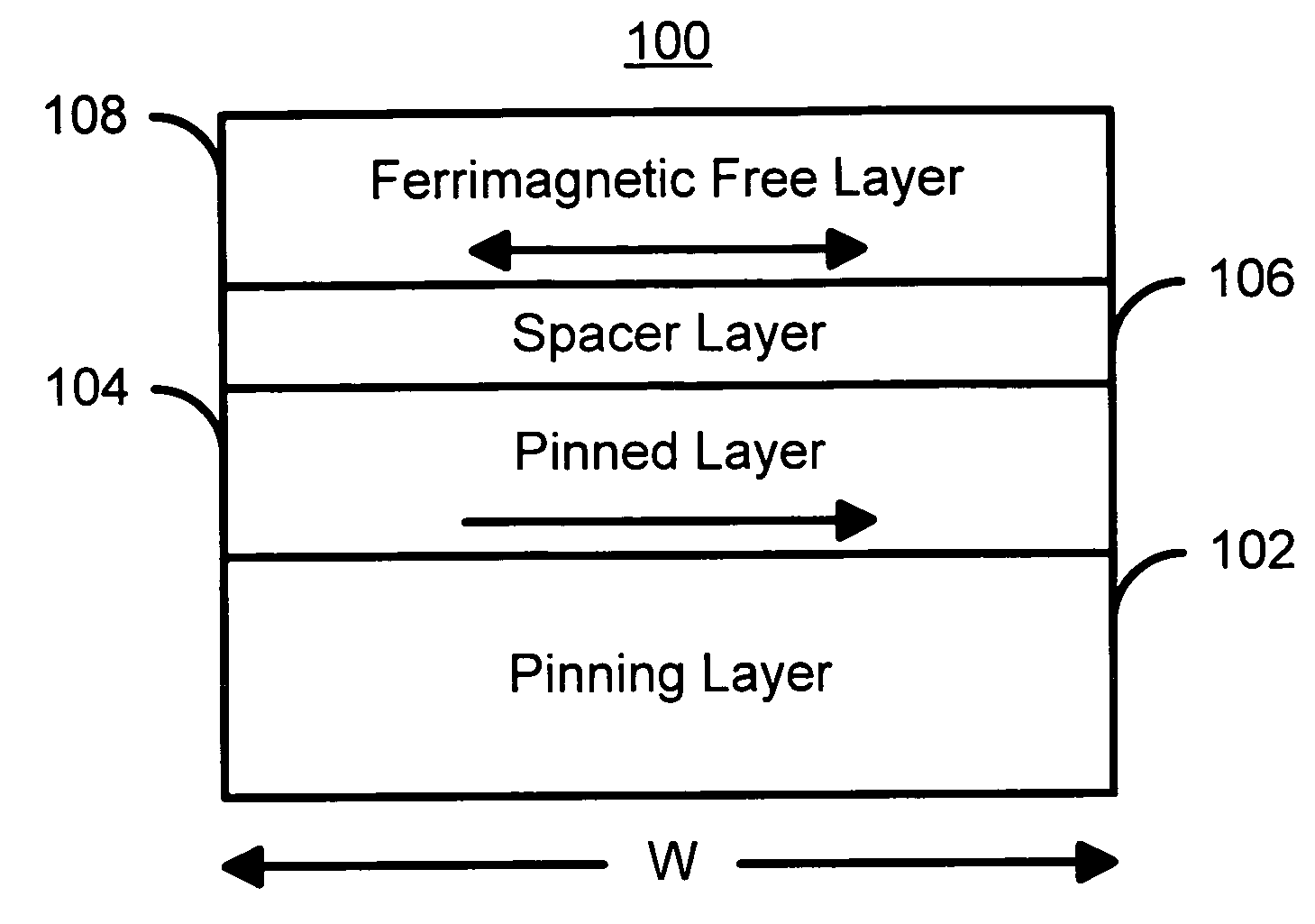
Spin-transfer switching magnetic elements using ferrimagnets and magnetic memories using the magnetic elements
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
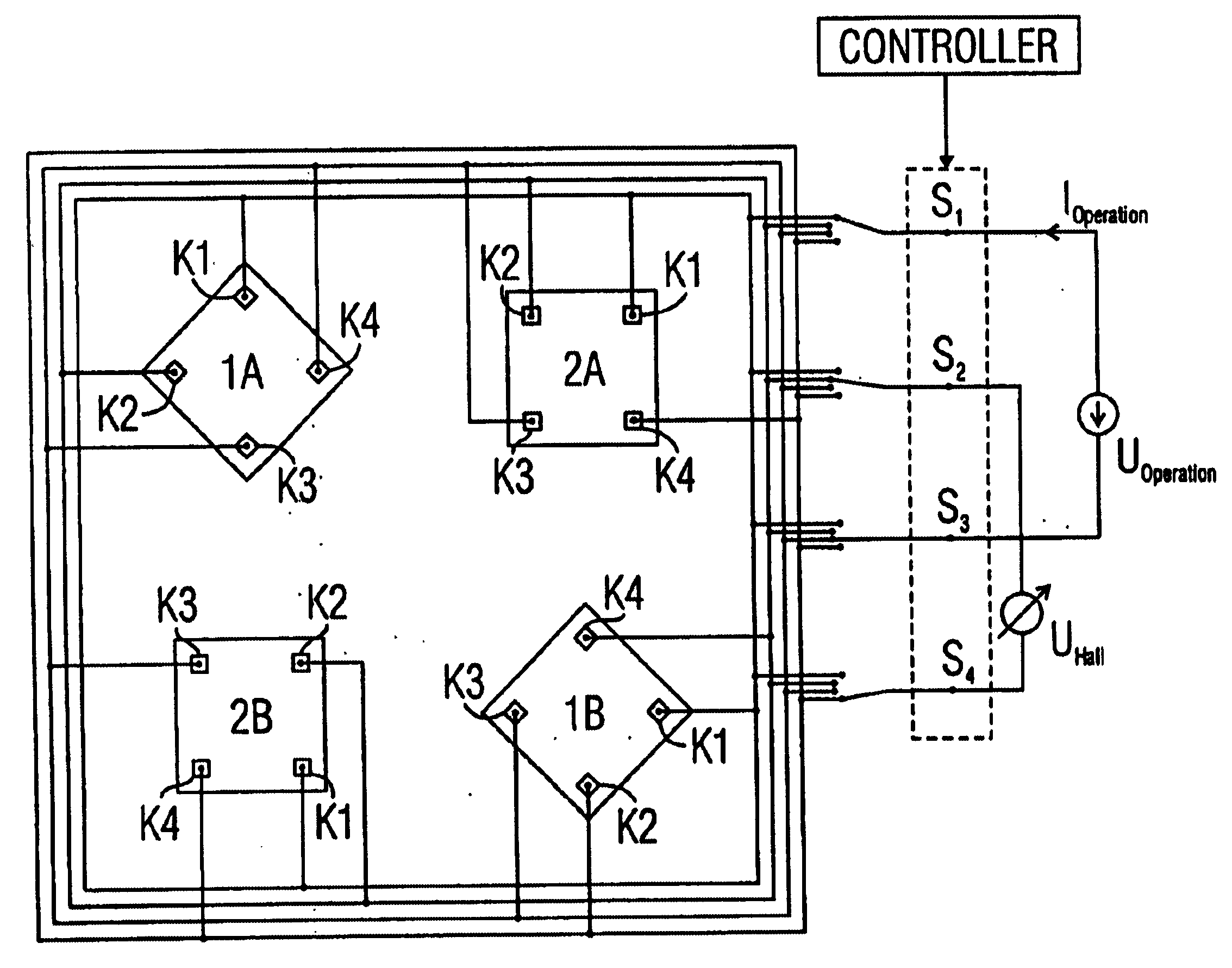
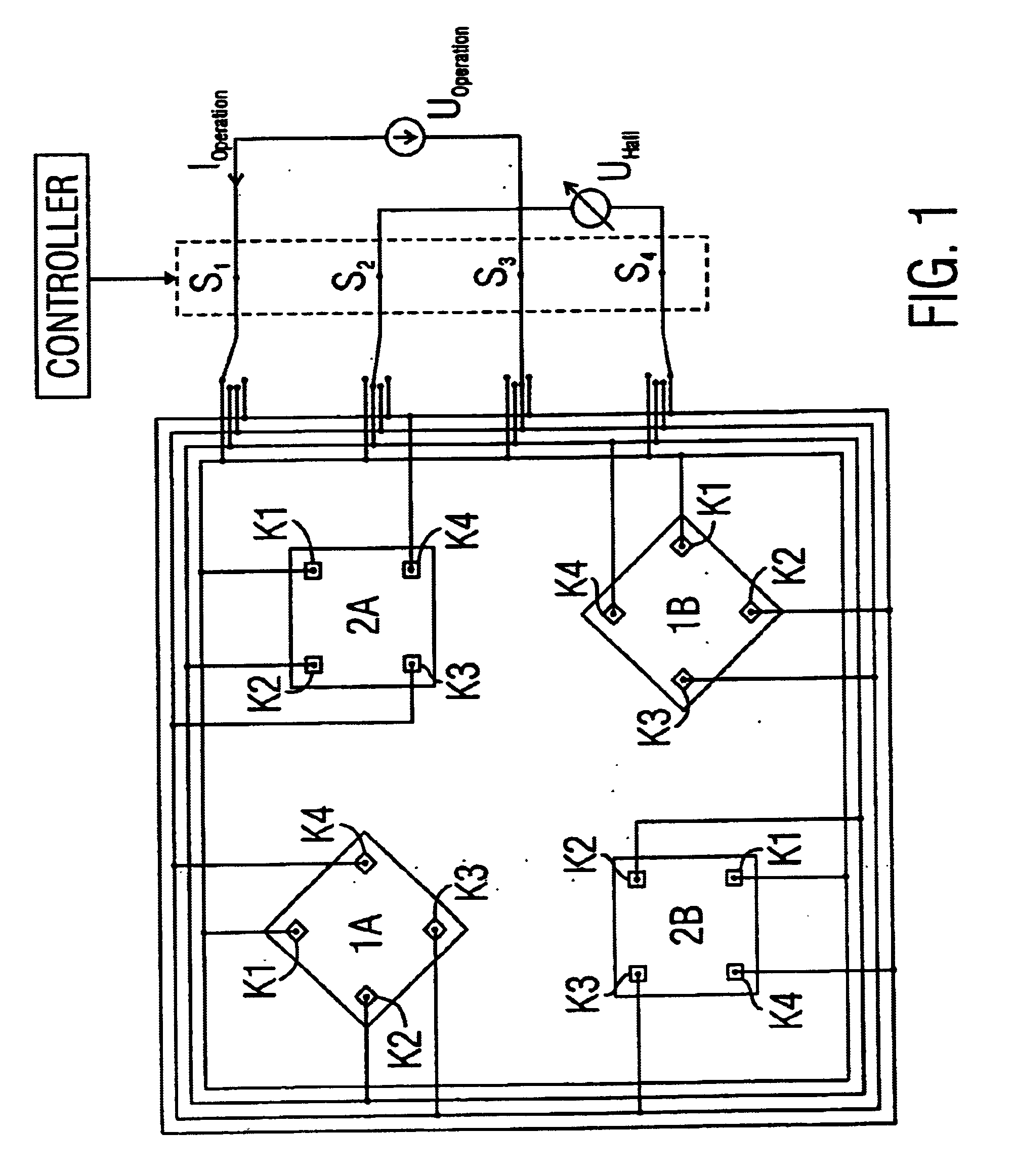
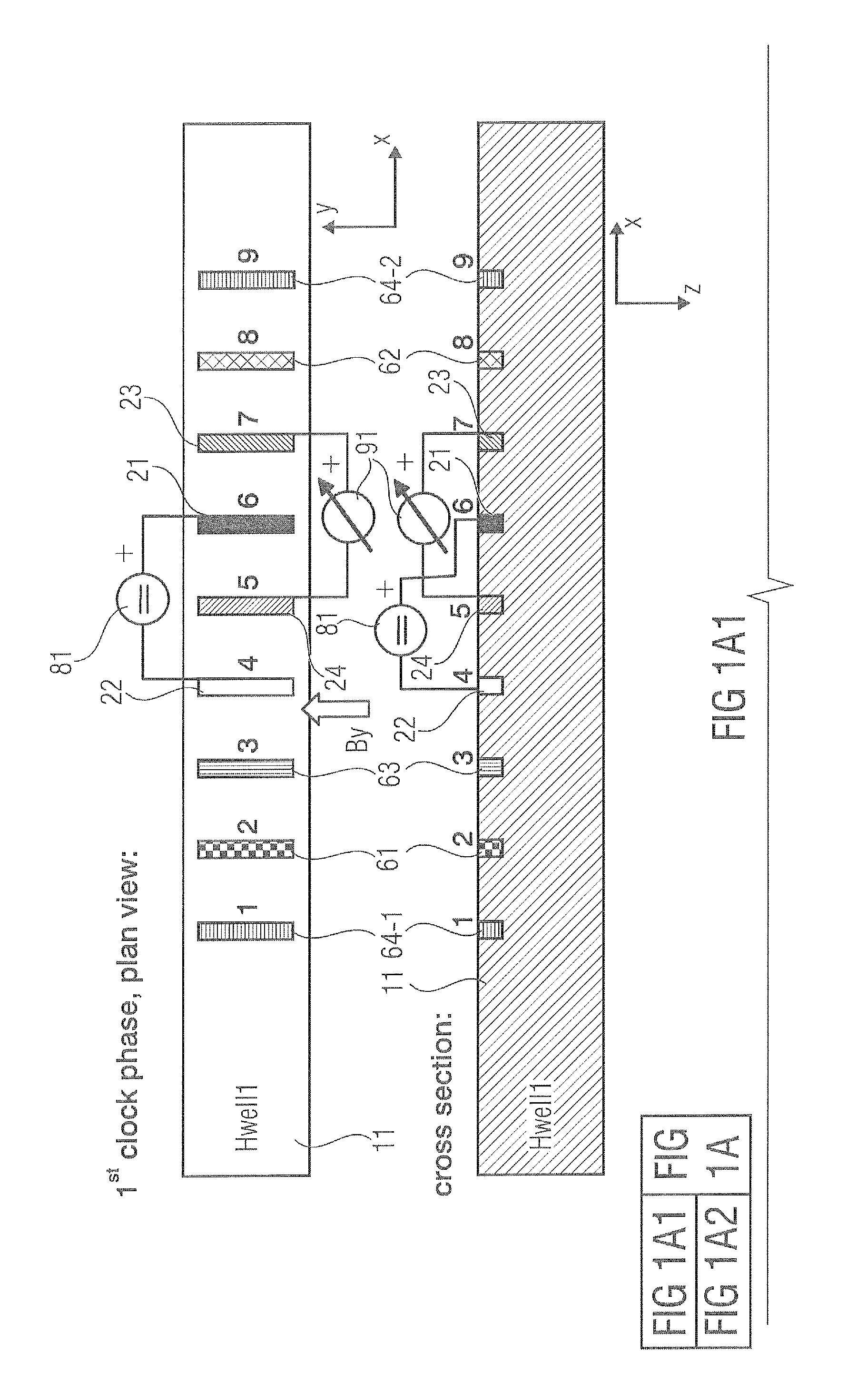
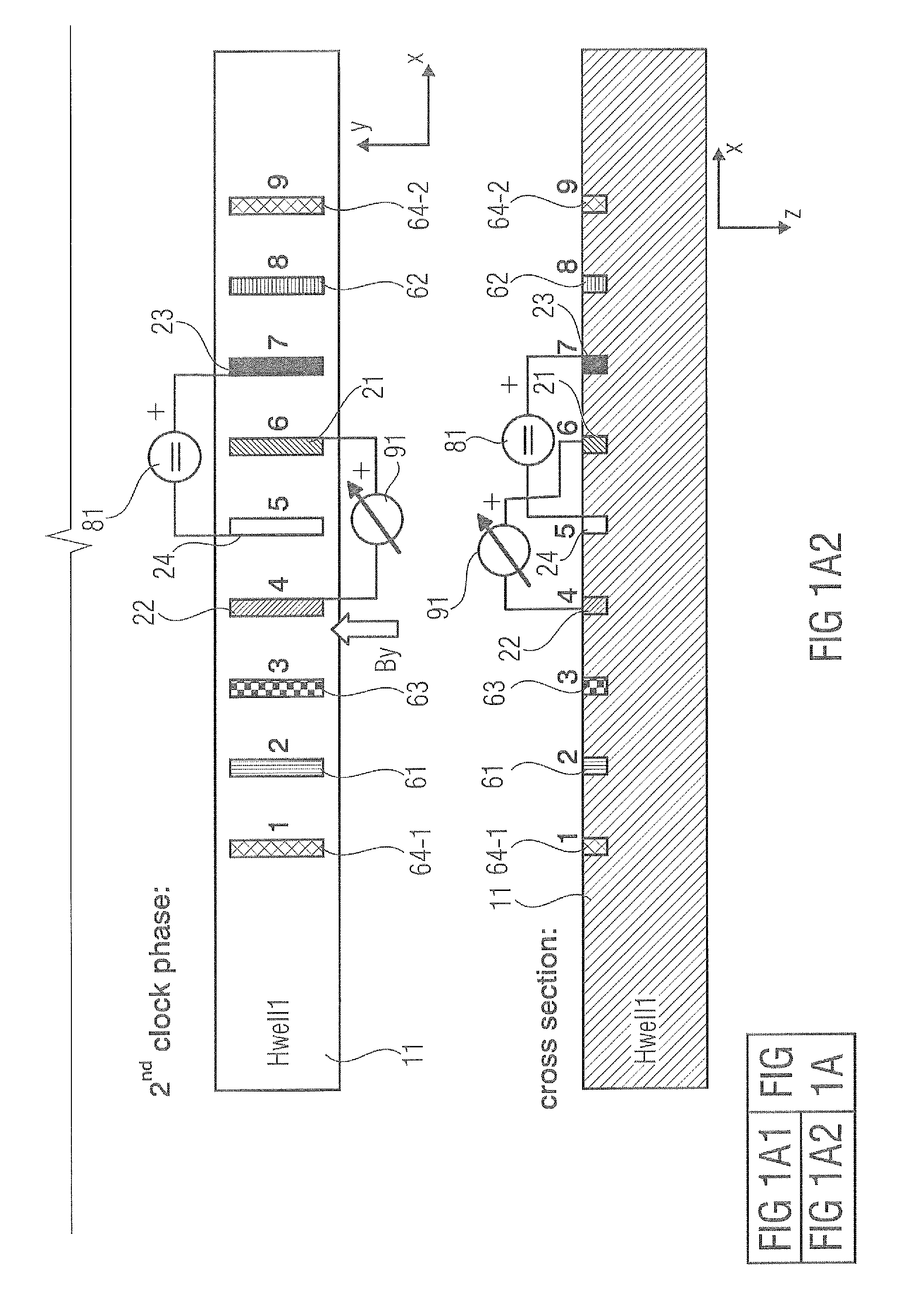
Hall sensor array for measuring a magnetic field with offset compensation
InactiveUS6768301B1Less complicated to manufactureReduce signalingSolid-state devicesMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesSensor arrayVoltage source
A Hall sensor array for offset-compensated magnetic field measurement comprises a first and at least one additional pair of Hall sensor elements. Each Hall sensor element has four terminals, of which two act as power supply terminals for supplying an operating current and two act as measurement terminals for measuring a Hall voltage. Respective first supply terminals of each Hall sensor element are connected together and to a first terminal of a common voltage source and respective second supply terminals of each Hall sensor element are connected together and to a second terminal of the common voltage source so that the common voltage source supplies an operating current for the Hall sensor elements. The Hall sensor elements are operated in the spinning current mode so that the offset voltages of the Hall sensor elements approximately cancel one another out in a revolution so that the Hall signal contributions which actually depend on the magnetic field remain.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Spin-current switchable magnetic memory element and method of fabricating the memory element
A spin-current switchable magnetic memory element (and method of fabricating the memory element) includes a plurality of magnetic layers having a perpendicular magnetic anisotropy component, at least one of the plurality of magnetic layers including an alloy of a rare-earth metal and a transition metal, and at least one barrier layer formed adjacent to at least one of the plurality of magnetic layers.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Spin-current switched magnetic memory element suitable for circuit integration and method of fabricating the memory element
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
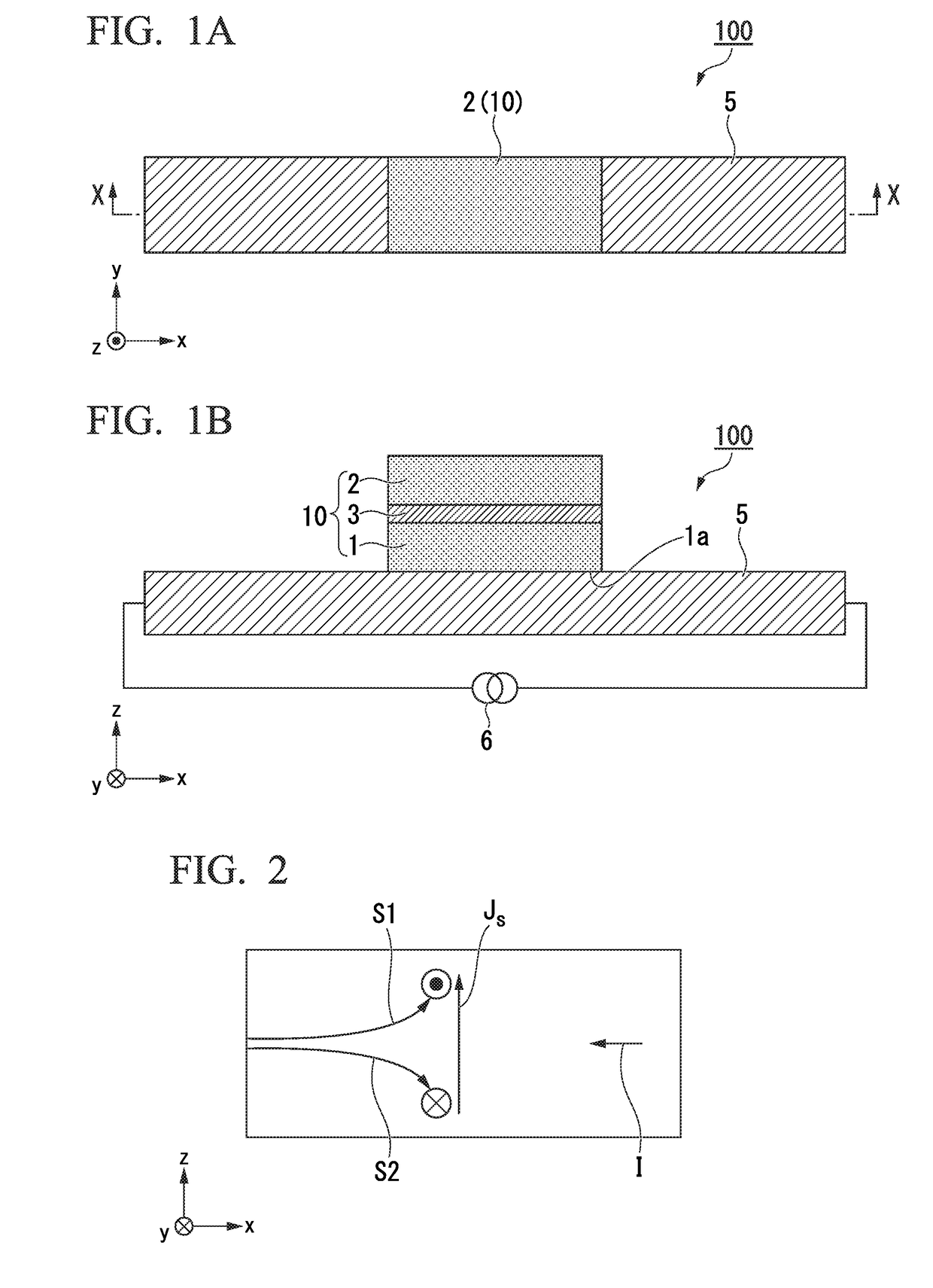
Magnetoresistive device, magnetoresistive random access memory and magnetic recording method
ActiveUS20160247550A1Improve data storage capacitySmall write currentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsIn planePower flow
A magnetoresistive device includes a magnetic free layer having first and second surfaces, the magnetic free layer being comprised of a ferromagnetic material having a perpendicular magnetic anisotropy, a spin current generation layer contacting the first surface of the magnetic free layer, a tunnel barrier layer having one surface contacting the second surface of the magnetic free layer, a reference layer contacting another surface of the tunnel barrier layer, and a leakage field generation layer including first and second leakage field generation layers each of which is comprised of a ferromagnetic material and generates a leakage field, an in-plane component of the leakage field at an part of the magnetic free layer is formed generating a domain wall having an in-plane magnetization component in the magnetic free layer.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Thermoelectric conversion device
ActiveUS20110084349A1Improve efficiencyLow thermal conductivityGalvano-magnetic hall-effect devicesIron compoundsSpin Hall effectSpins
The thermoelectric conversion efficiency of a thermoelectric conversion device is increased by increasing the figure of merit of a spin-Seebeck effect element.An inverse spin-Hall effect material is provided to at least one end of a thermal spin-wave spin current generating material made of a magnetic dielectric material so that a thermal spin-wave spin current is converted to generate a voltage in the above described inverse spin-Hall effect material when there is a temperature gradient in the above described thermal spin-wave spin current generating material and a magnetic field is applied using a magnetic field applying means.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
Method for changing spin relaxation, method for detecting spin current and spintronics device using spin relaxation
InactiveUS20100097063A1Novel configurationShorten spin relaxation timeMagnetic measurementsNanoinformaticsSpin currentSpin relaxation time
The invention relates to a method for changing spin relaxation, a method for detecting a spin current, and a spintronic device using spin relaxation, and spin relaxation is changed through injection of a spin current.A spin current 4 is injected into a material 1 in a certain spin state, so that the spin relaxation time can be controlled.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Vertical hall sensor with high electrical symmetry
InactiveUS20130021027A1Reduce boundary effectsMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesGalvano-magnetic hall-effect devicesPower flowSpin current
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
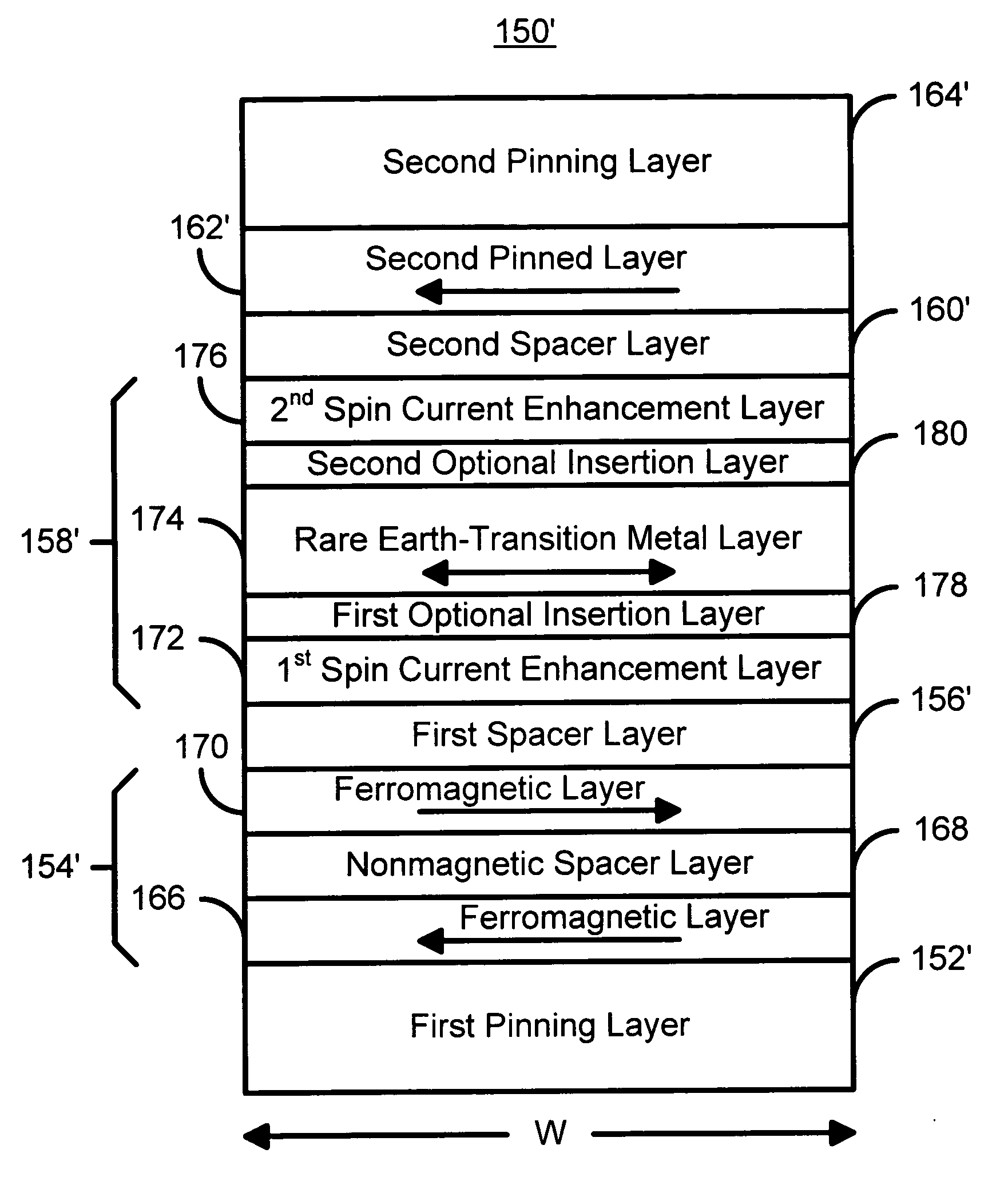
Spin-transfer switching magnetic elements using ferrimagnets and magnetic memories using the magnetic elements
A method and system for providing a magnetic element are disclosed. The method and system include providing a pinned layer, providing a spacer layer, and providing a free layer. The free layer is ferrimagnetic and includes at least one of a conductive ferrite, a garnet, a ferrimagnetic alloy excluding a rare earth, a heavy rare-earth-transition metal alloy, a half-metallic ferrimagnetic, and a bilayer. The bilayer includes a rare earth-transition metal alloy layer and a spin current enhancement layer. The magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
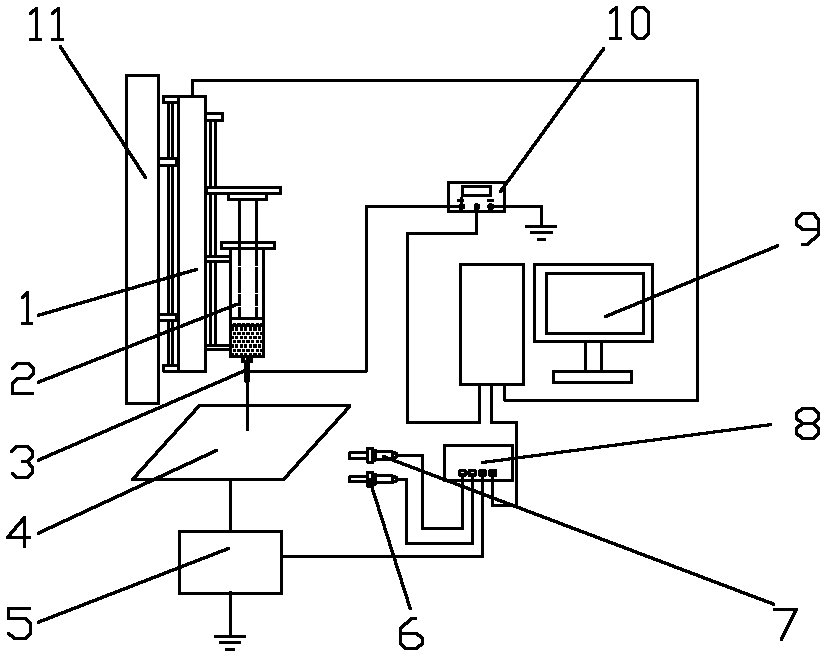
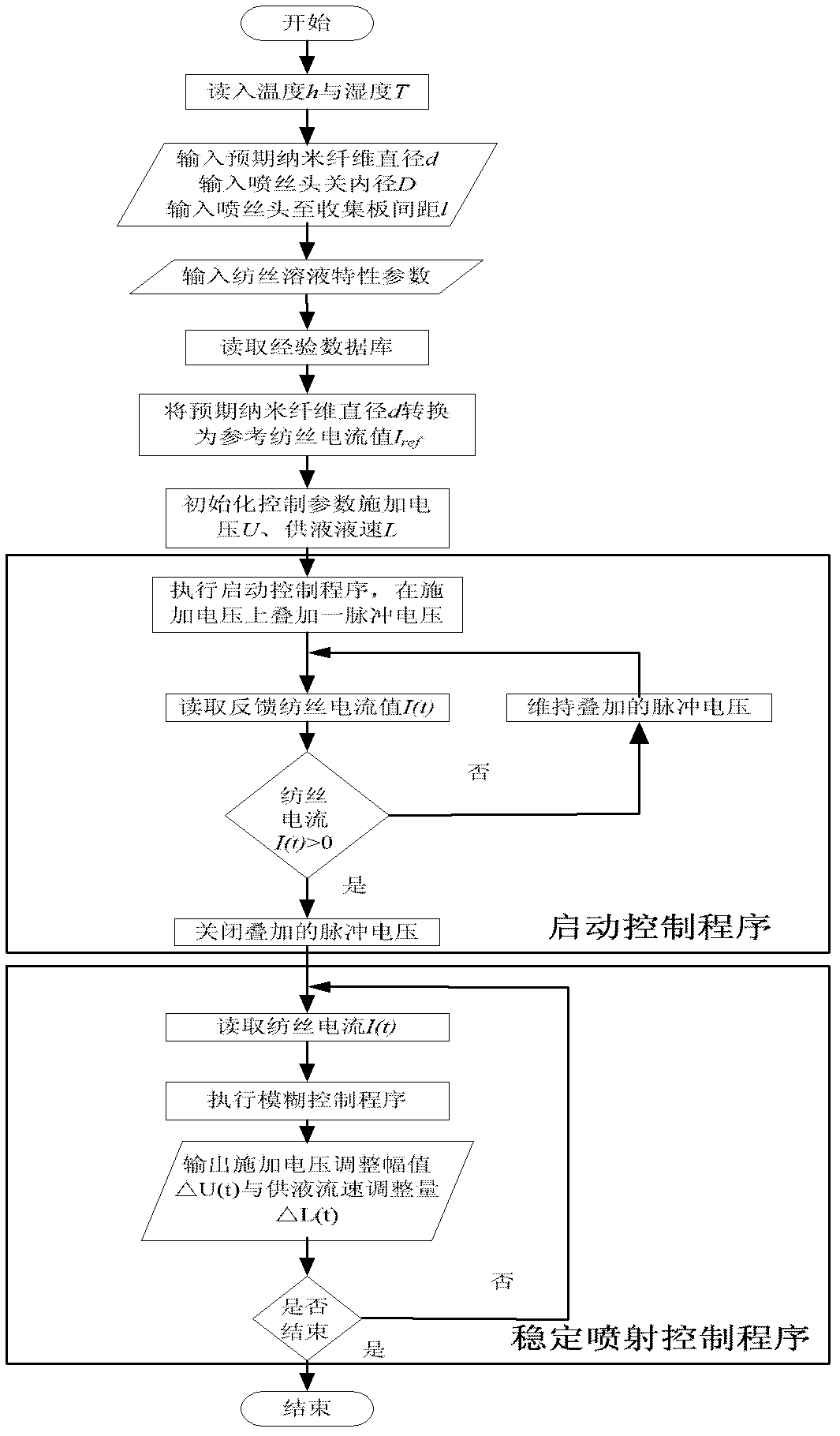
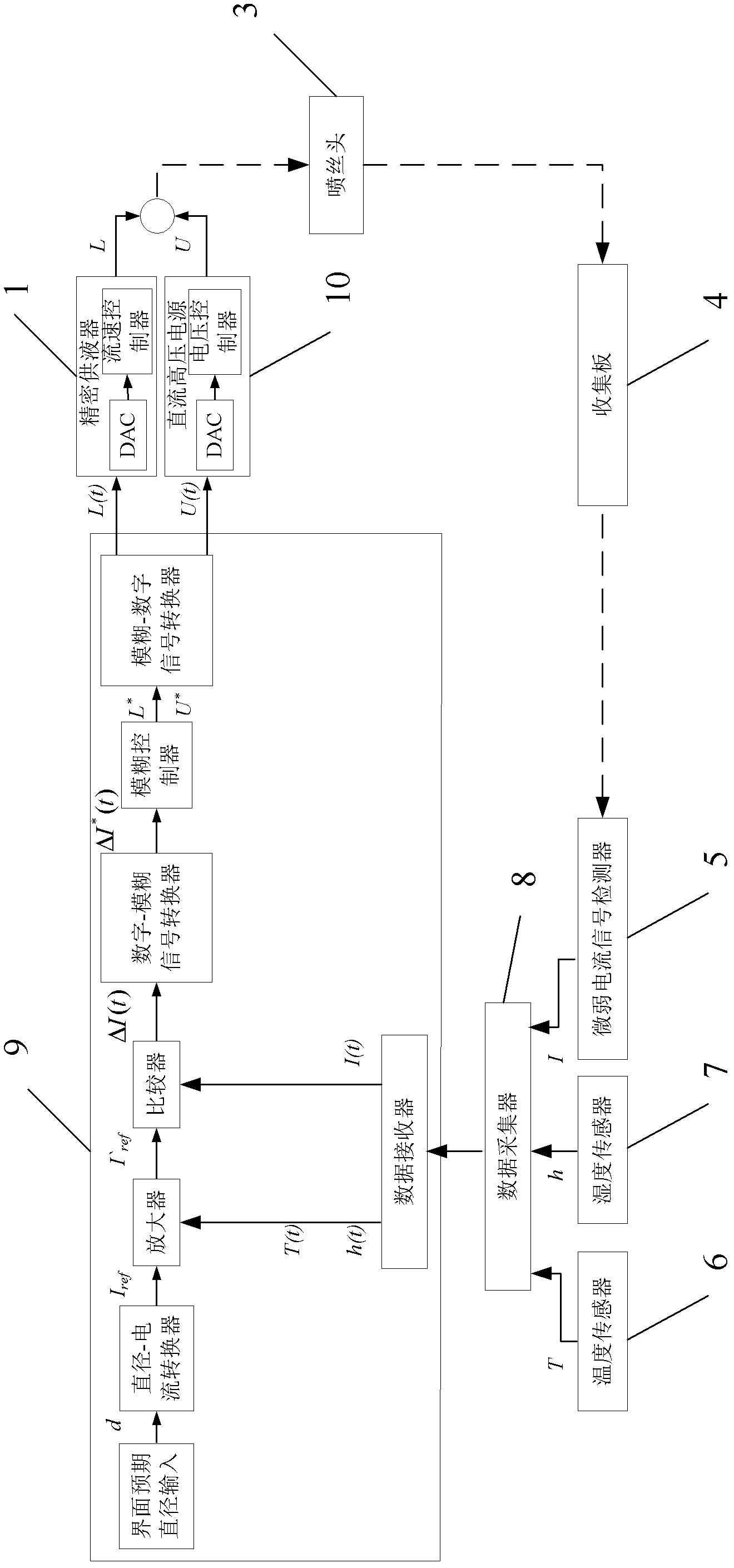
Electrospinning direct-writing closed-loop control system and control method
ActiveCN102582293ARealize controllable adjustmentImprove uniformityOther printing apparatusFiberLoop control
The invention relates to an electrospinning direct-writing closed-loop control system and a control method, which relate to electrospinning direct writing equipment. The invention provides the electrospinning direct-writing closed-loop control system which is capable of realizing the controllable adjustment of the electrospinning direct-writing nano fibre diameter and improves the jet injection stability of spinning and the uniformity of nano fibre diameter and the control method of the electrospinning direct-writing closed-loop control system. The system comprises a liquid storage tank, a liquid feeder, a spinning nozzle, a collecting plate, a weak current detector, a temperature sensor, a humidity sensor, a data collector, a control computer, a direct current high voltage power supply and an adjustable frame. The system establishes a fuzzy controller to obtain the jet injection state by detecting the spinning current, adjusts the applied voltage and the flow rate of the feeding liquid according to the change of the spinning current so as to avoid the influence of various interference factors and realize long time stable jet of the spinning jet flow. The set current of the fuzzy controller is adjusted to control the electrospinning direct-writing nano fibre diameter. The electrospinning direct-writing closed-loop control system is beneficial to improving the controllability of the electrospinning direct-writing nano fibre diameter and well promoting the industrialized application of the electrospinning direct-writing technology.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Spin accumulation device and magnetic sensor applied with spin current confined layer
InactiveUS20070253121A1Reduce electrical noiseHigh sensitivityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsLow noiseImage resolution
A spin accumulation device with high output, high resolution, and low noise. A spin current confined layer is located between a voltage-detection magnetic conductive material and a nonmagnetic conductive material. A spin current alone flows through the spin current confined layer. Due to the confinement of the spin current, since it is possible to prevent the spin current from flowing through excess portions other than the scatterer that exhibits resistance change, the detection efficiency of the spin accumulation device is dramatically increased.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
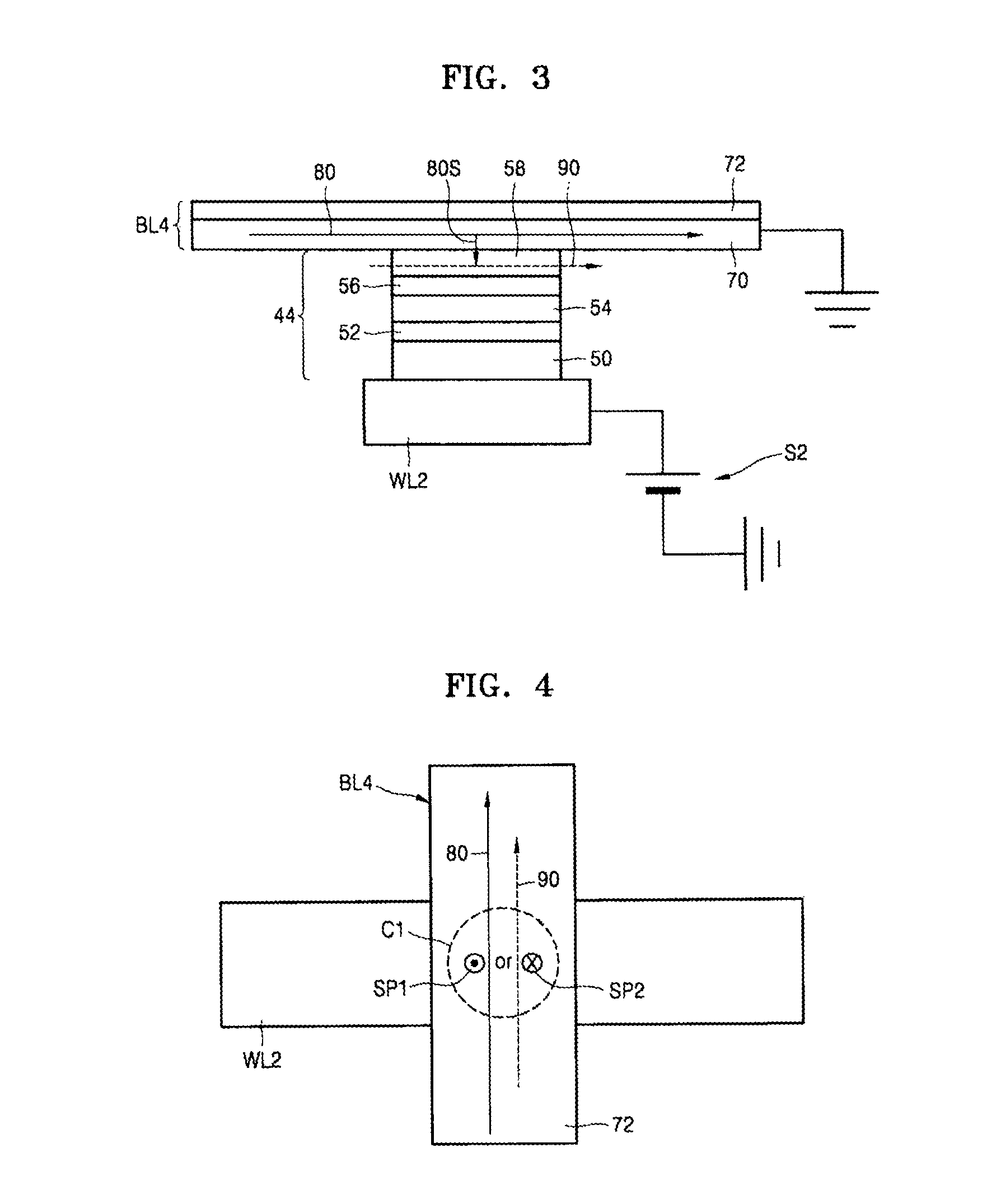
Memory device using spin hall effect and methods of manufacturing and operating the memory device
ActiveUS20140211552A1Small sizeGuaranteed uptimeMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesBit lineElectricity
A memory device using a spin hall effect, and methods of manufacturing and operating the memory device, include applying a first operational current to a bit line of the memory device such that a spin current is applied to a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) cell coupled to the bit line due to a material in the bit line, wherein the bit line is electrically connected to a word line via the MTJ cell, and the word line intersects the bit line.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
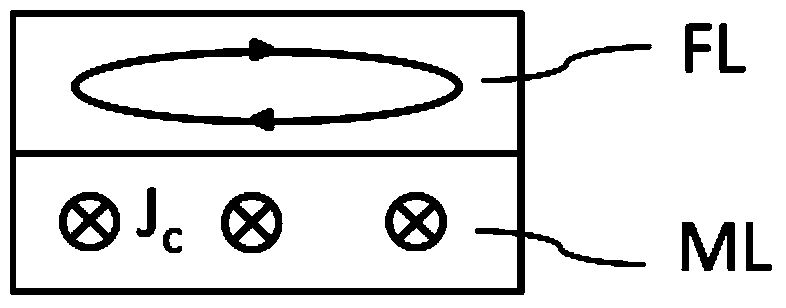
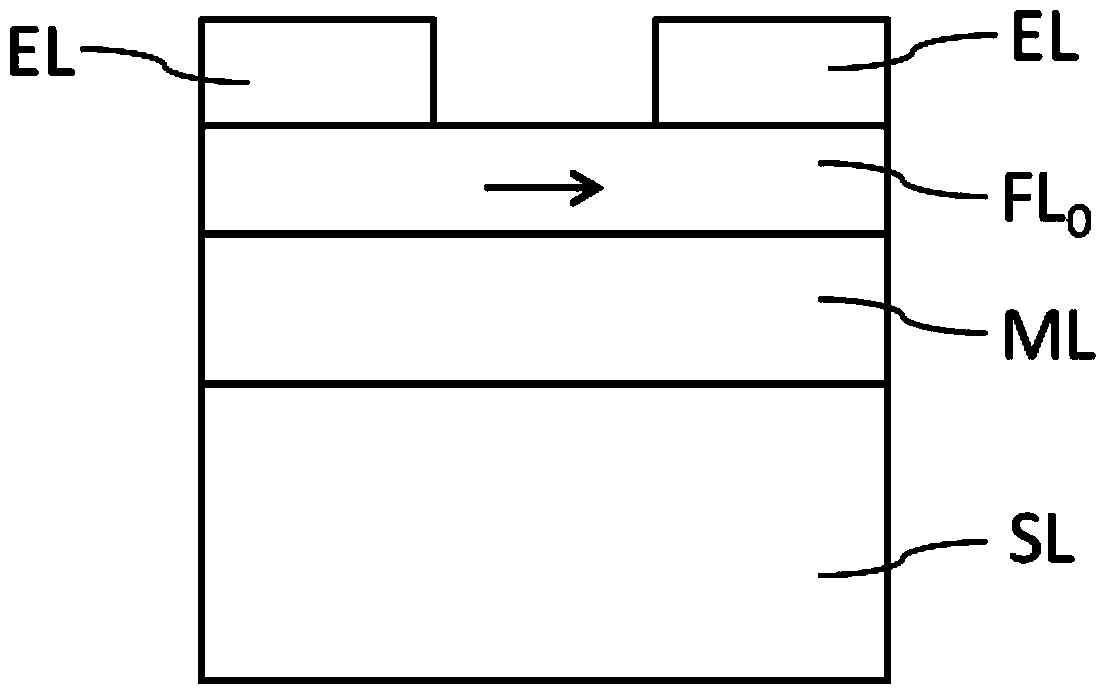
Magnetic element based on spin hall effect, microwave oscillator and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103779495AReduce noiseLarge adjustment rangeMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionManufacturing technologyMagnetization
The invention discloses a magnetic element based on a spin hall effect, a microwave oscillator and a manufacturing method thereof. The magnetic element comprises a non-magnetic metal film layer (ML) and a magnetic film layer (FL), wherein the non-magnetic metal film layer (ML) can induce electrons to generate spin currents, and the magnetic film layer (FL) is formed on the non-magnetic metal film layer (ML) and can balance magnetization. The microwave oscillator comprises the magnetic element, the magnetic element is formed on a substrate layer (SL), and metal electrodes (EL) are formed on the magnetic element. The microwave oscillator can be formed by using a thin film deposit technology, a photoetching and / or etching technology and the like. The structure of the magnetic element is beneficial to reducing the noise of the microwave oscillator, device microwave frequency is wide in adjustable range under the effect of impressed currents, and output microwave signals are excellent in performance. The microwave oscillator has the advantages of being small in size, simple in structure and the like, and is simple in manufacturing technology, compatible with traditional nano-meter processing technologies, easy to manufacture in a mass mode and capable of serving as a microwave source to be widely applied in the fields of electronics, communication and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Hall electromotive force signal detection circuit and current sensor thereof
ActiveUS20130193962A1Reduce generationShort timeMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesPower supply testingDriving currentSignal processing circuits
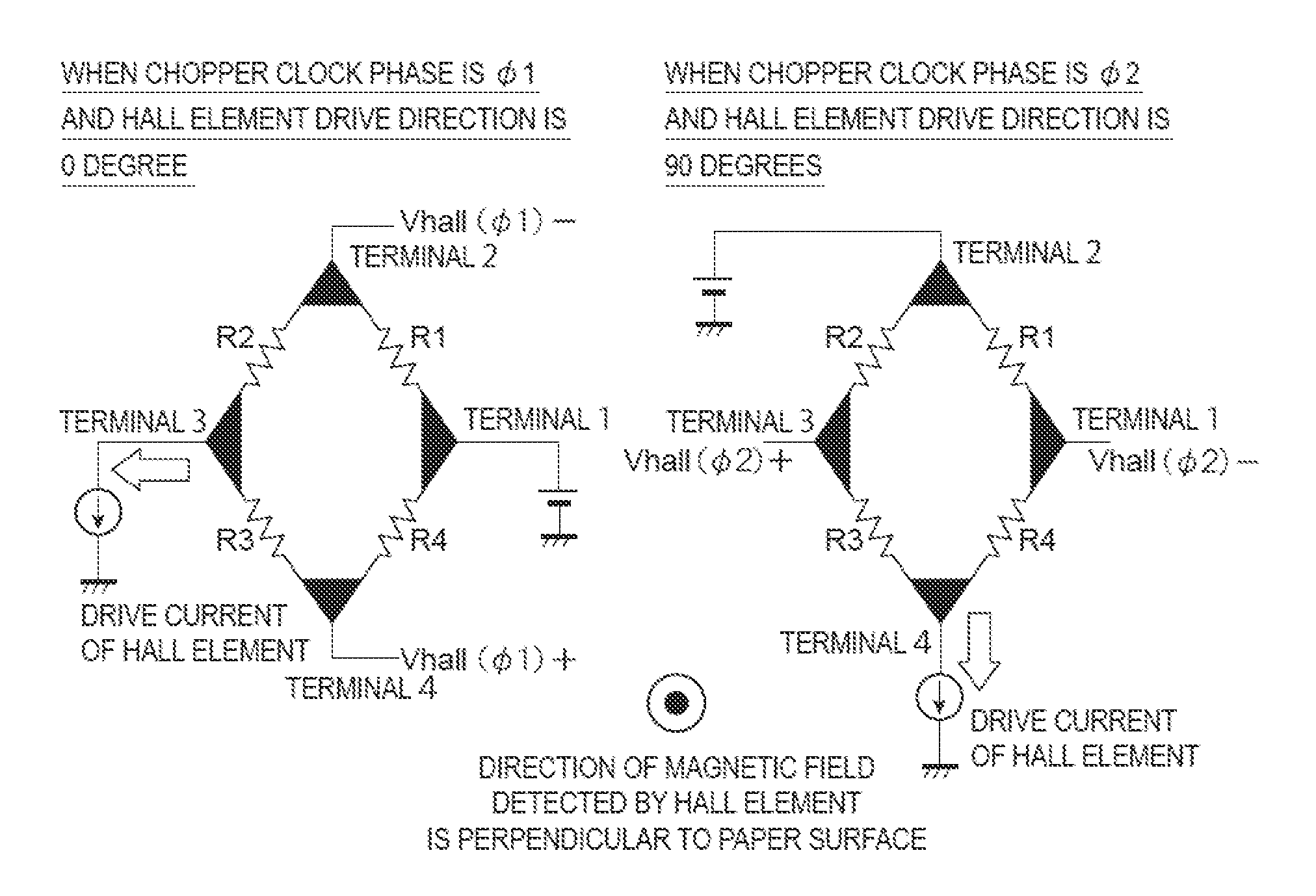
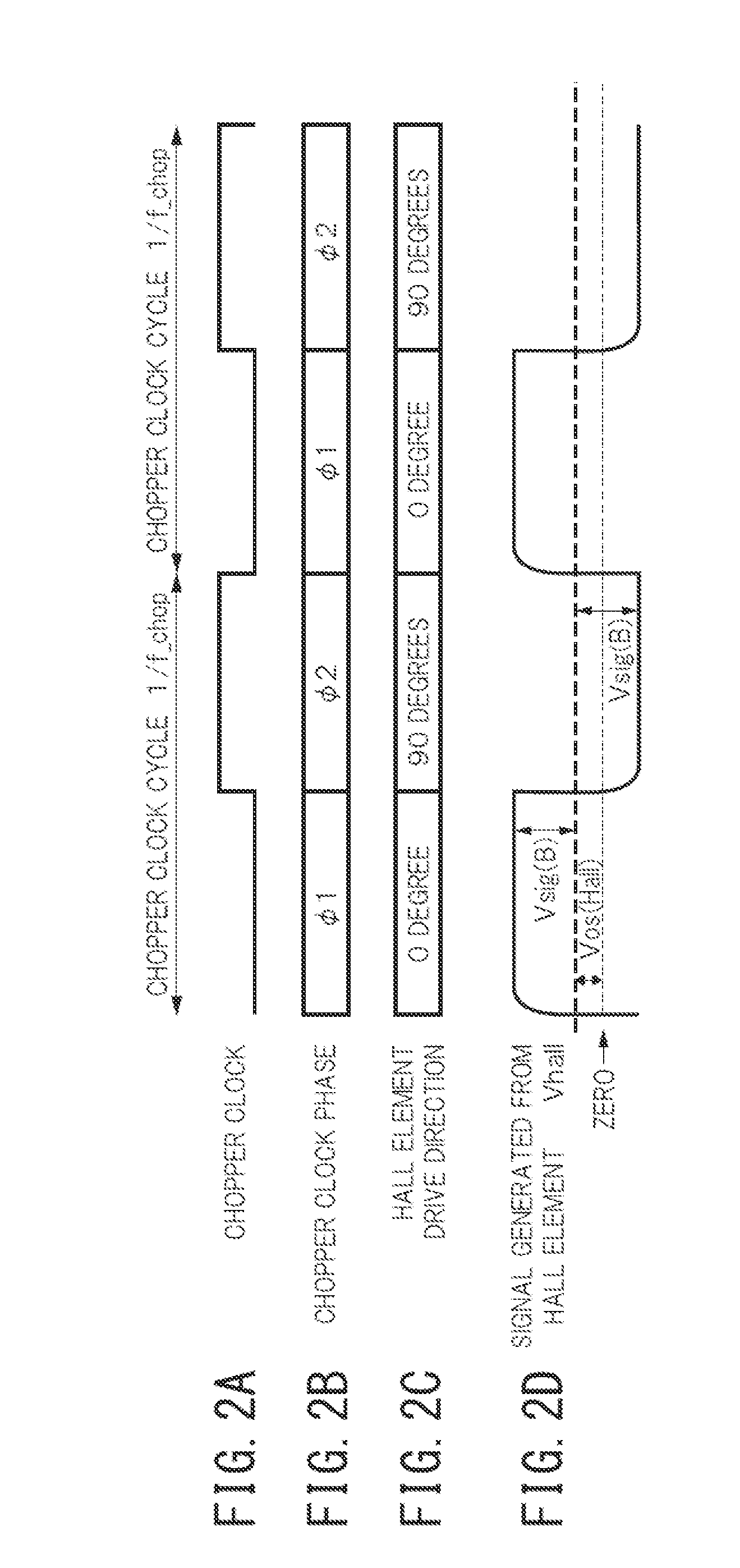
A Hall electromotive force signal detection circuit combines offset cancellation means by a spinning current method of a Hall element with a continuous-time signal processing circuit. A first Hall element includes first to fourth terminals, and generates a Hall electromotive force signal voltage Vhall1. A third Hall element generates an other Hall electromotive force signal voltage Vhall3. A first switching circuit selects a terminal position for applying a drive current from the four terminals of the first Hall element. A third switching circuit selects a terminal position for applying a drive current from the four terminals of the third Hall element, which is different from the terminal position selected by the first switching circuit. A chopper clock generation circuit supplies a chopper clock signal φ1, φ2 having two different phases to the switching circuit, and also supplies the chopper clock signal φ1, φ2 to the switching circuit.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Three-terminal design for spin accumulation magnetic sensor
ActiveUS20100296202A1Reduce technical difficultyReducing signal-to-noise degradationMagnetic measurementsRecord information storageElectricityTransport layer
A spin accumulation sensor having a three terminal design that allows the free layer to be located at the air bearing surface. A non-magnetic conductive spin transport layer extends from a free layer structure (located at the ABS) to a reference layer structure removed from the ABS. The sensor includes a current or voltage source for applying a current across a reference layer structure. The current or voltage source has a lead that is connected with the non-magnetic spin transport layer and also to electric ground. Circuitry for measuring a signal voltage measures a voltage between a shield that is electrically connected with the free layer structure and the ground. The free layer structure can include a spin diffusion layer that ensures that all spin current is completely dissipated before reaching the lead to the voltage source, thereby preventing shunting of the spin current to the voltage source.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Electric field ferromagnetic resonance excitation method and magnetic function element employing same
ActiveUS20150085569A1Efficient excitationLow powerNanotechnologyDigital storageControl layerMagnetic field magnitude
To realize an electric field-driven type ferromagnetic resonance excitation method of low power consumption using an electric field as drive power, and provide a spin wave signal generation element and a spin current signal generation element using the method, a logic element using the elements, and a magnetic function element such as a high-frequency detection element and a magnetic recording device using the method. A magnetic field having a specific magnetic field application angle and magnetic field strength is applied to a laminate structure in which an ultrathin ferromagnetic layer sufficiently thin so that an electric field shield effect by conduction electrons does not occur and a magnetic anisotropy control layer are directly stacked on each other and an insulation barrier layer and an electrode layer are arranged in order on an ultrathin ferromagnetic layer side. An electric field having a high-frequency component of a magnetic resonance frequency is then applied between the magnetic anisotropy control layer and the electrode layer, thereby efficiently exciting ferromagnetic resonance in the ultrathin ferromagnetic layer.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
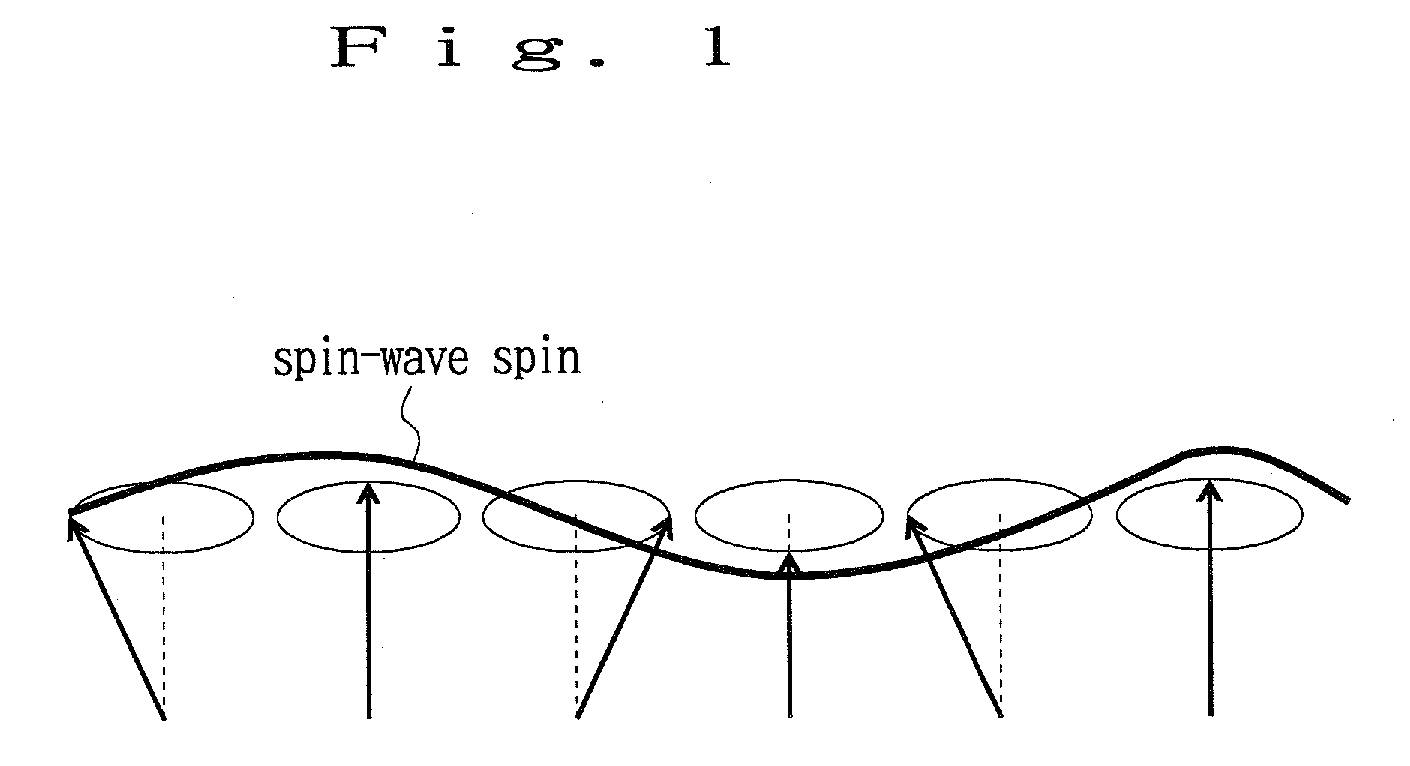
Spintronic device and information transmitting method
A concrete means for making transmission over long distances possible using a spin-wave spin current is provided in a spintronic device and an information transmitting method.At least one metal electrode made of any of Pt, Au, Pd, Ag, Bi, alloys of these, or elements having an f-orbital are provided on top of a magnetic dielectric layer and, so that spin-wave spin current—pure spin current exchange is carried out at the interface between the above described magnetic dielectric layer and the above described metal electrode.
Owner:NEC CORP
Spin transfer torque device with oxide layer beneath the seed layer
ActiveUS20190279666A1Reduce impactManufacture head surfaceRecord information storageMetal alloySpin-transfer torque
A spin transfer torque (STT) device is formed on an electrically conductive substrate and includes a ferromagnetic free layer near the substrate, a ferromagnetic polarizing layer and a nonmagnetic spacer layer between the free layer and the polarizing layer. A multilayer structure is located between the substrate and the free layer. The multilayer structure includes a metal or metal alloy seed layer for the free layer and an intermediate oxide layer below and in contact with the seed layer. The intermediate oxide layer reflects spin current from the free layer and thus reduces undesirable damping of the oscillation of the free layer's magnetization by the seed layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Voltage control magnetic random access memory unit, memory and logic device formed from memory unit
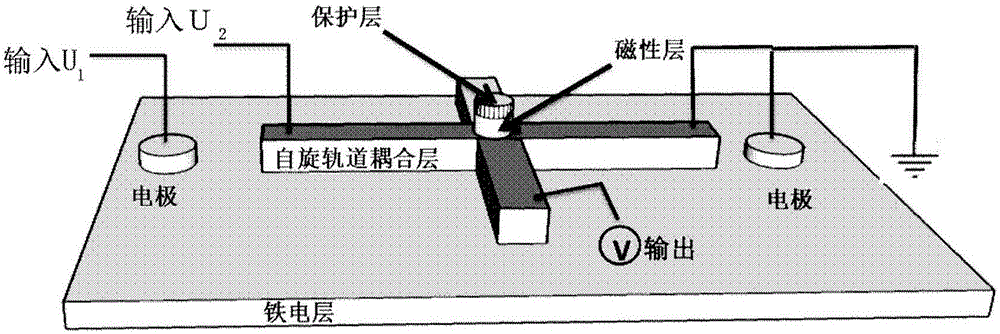
ActiveCN106531884ANo dependence on external magnetic fieldReduce power consumptionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsDigital storageDevice formRandom access memory
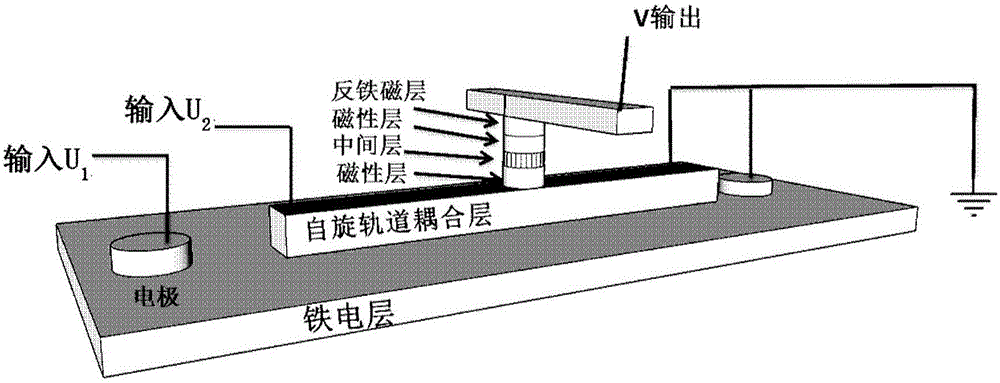
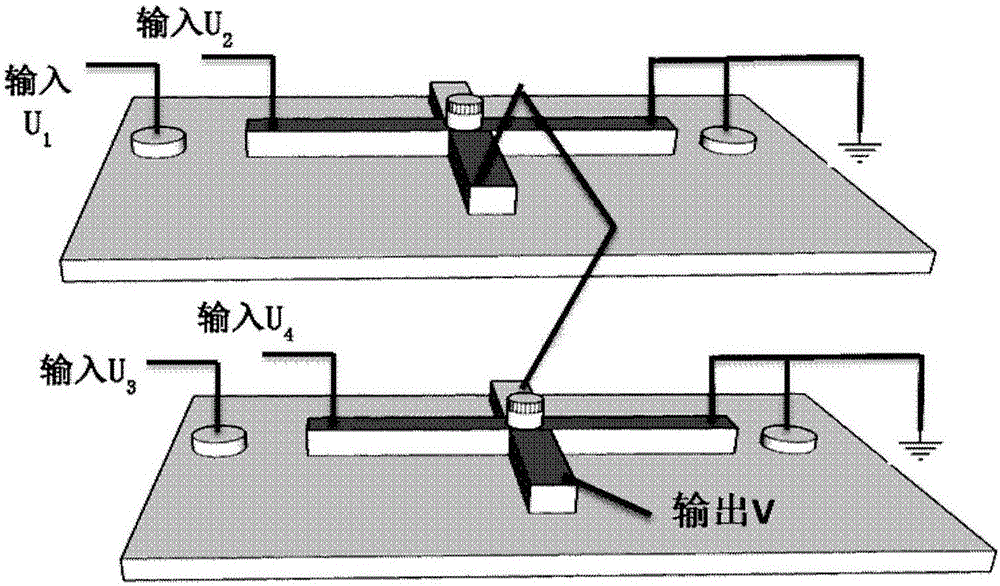
The invention proposes a voltage control magnetic random access memory unit, memory and logic device formed from the memory unit. The memory unit comprises a ferroelectric layer, a spin-orbit coupling layer and a first magnetic layer, wherein the a positive or negative first voltage can be applied onto the ferroelectric layer so as to control magnetized directional turnover, the spin-orbit coupling layer is arranged on the ferroelectric layer, a second voltage can be applied onto the spin-orbit coupling layer so as to generate a spinning current perpendicular to a direction of the layer, the first magnetic layer is arranged on the spin-orbit coupling layer, the spinning current can be used for inducing magnetism of the first magnetic layer to randomly and vertically turn over, and by combining the first voltage applied onto the ferroelectric layer, the spinning current can be used for inducing the first magnetic layer to directionally turn over. Ferroelectric polarization is generated by applying the voltages to two ends of the ferroelectric layers, a non-uniform spin-orbit coupling effect is generated, and the current can be modulated to induce the turnover direction of the magnetism of a magnetic thin film.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magnetic memory using single domain switching by direct current
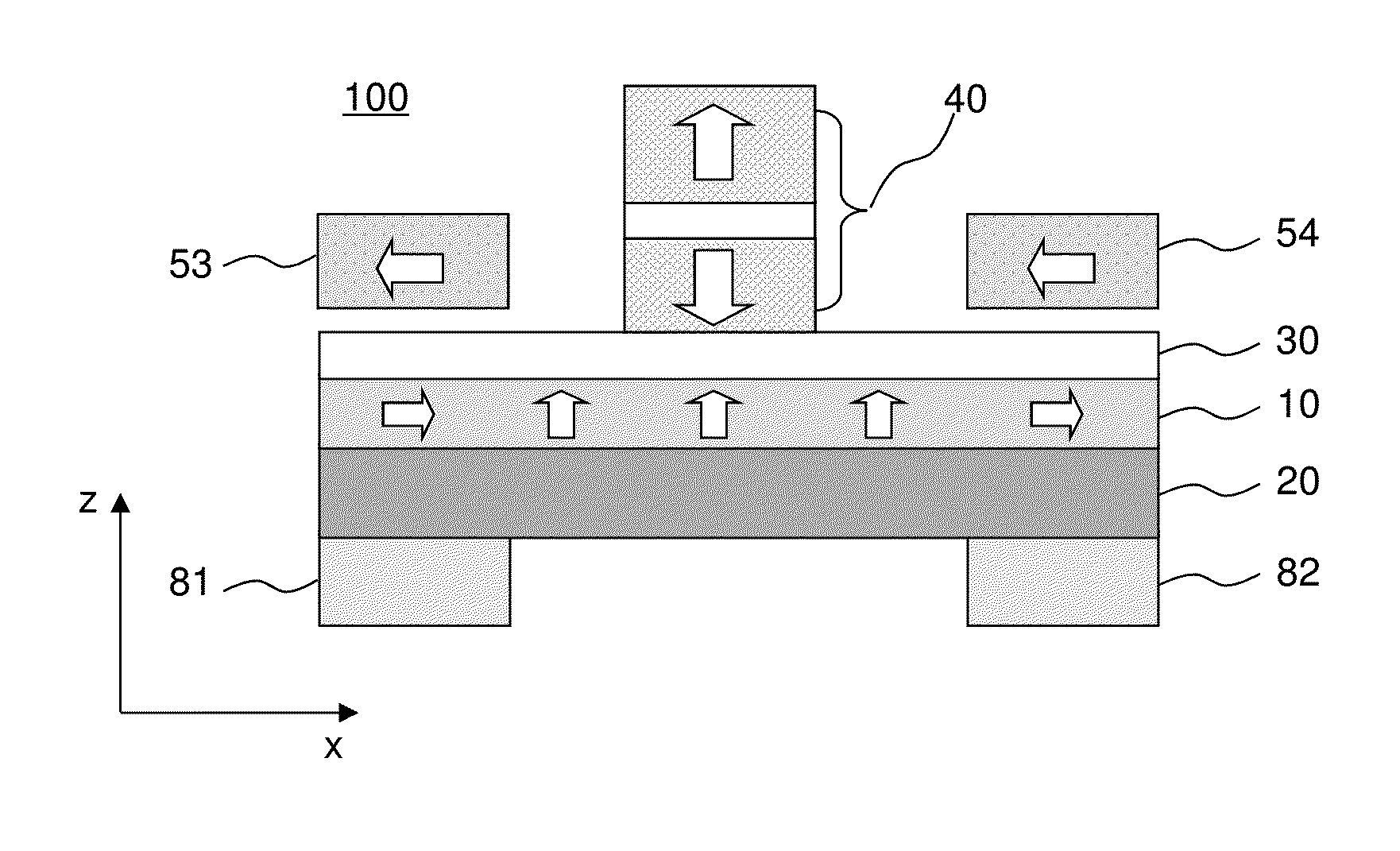
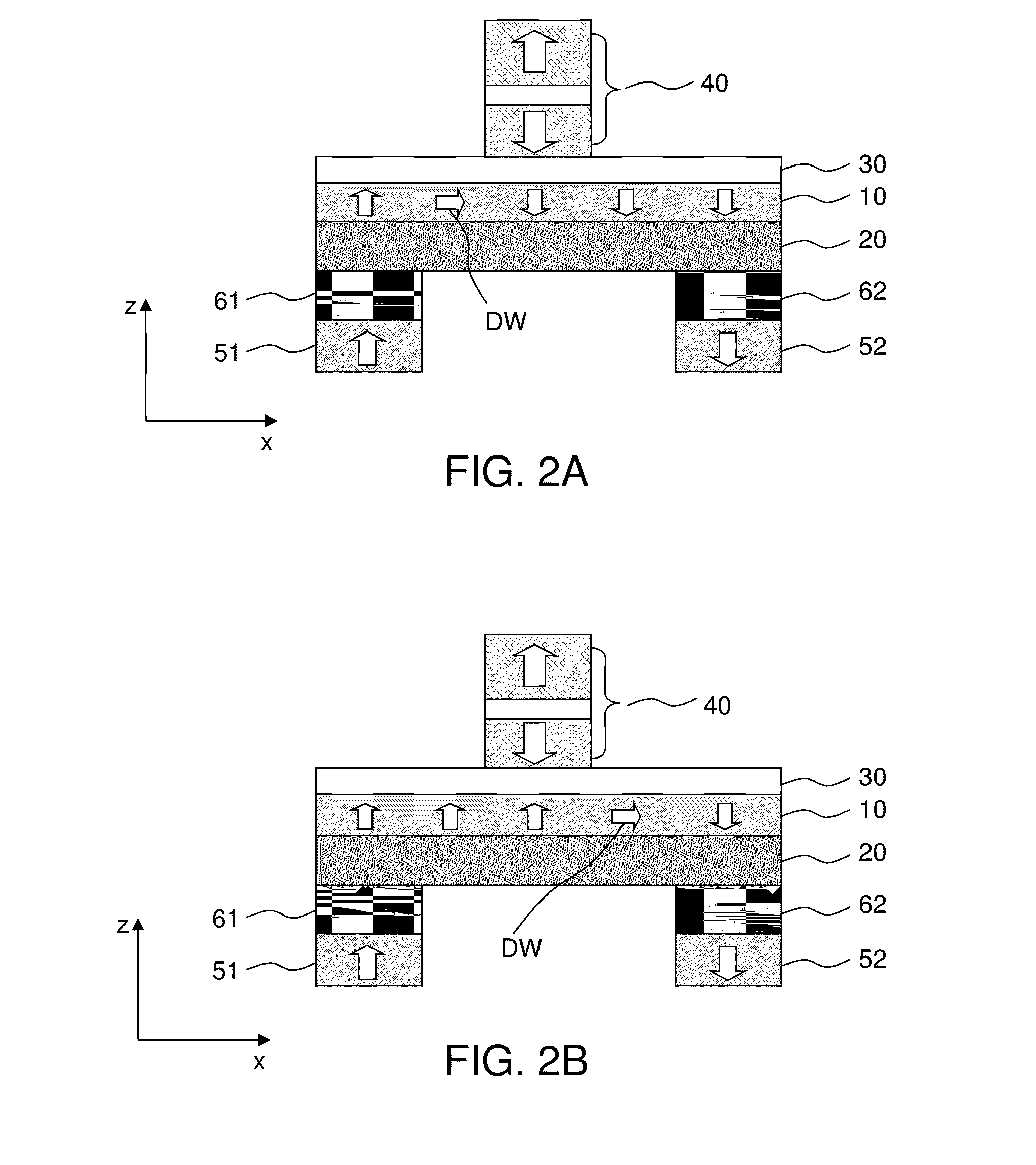
InactiveUS20060028863A1Eliminate crosstalkMinimize magnetostatic interactionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsDigital storageStatic random-access memoryMagnetic memory
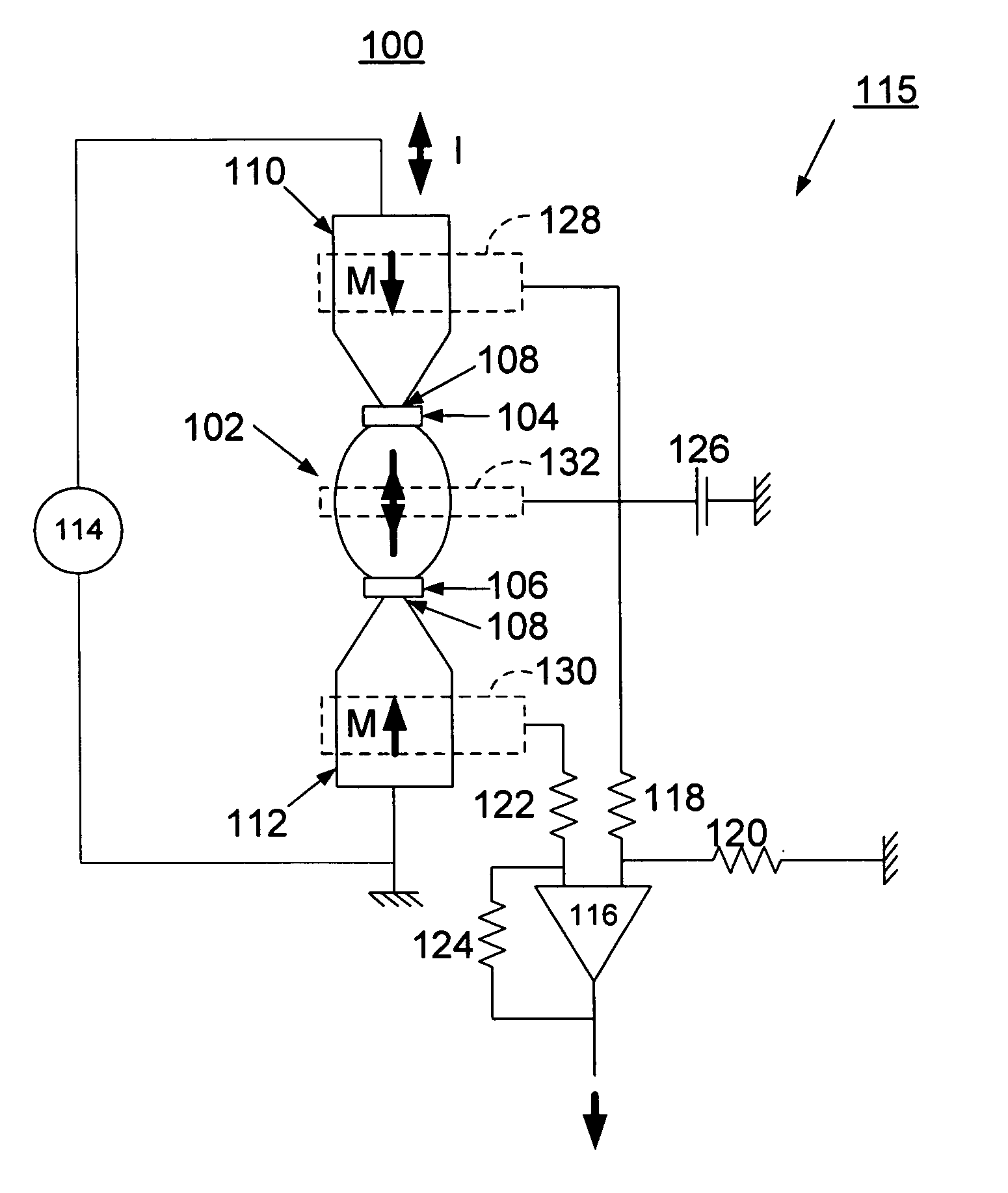
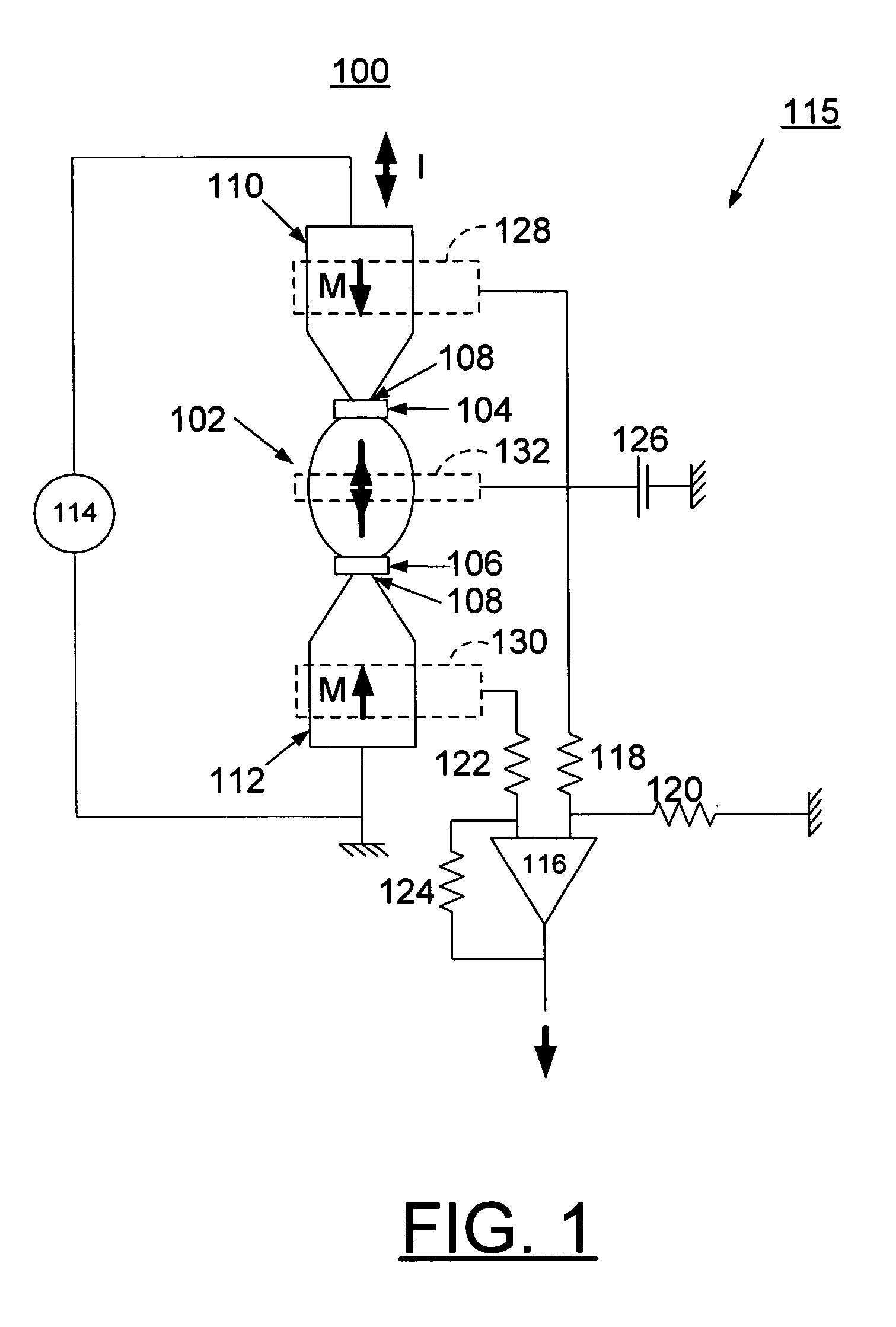
A method for implementing miniaturization of magnetic random access memory (MRAM) and a magnetic memory using single domain switching by direct current are provided. The magnetic memory preferably includes a half-circle or U-shaped architecture with an exchange biasing pad, such as a FeMn exchange biasing pad that effectively generates a head-to-head magnetization configuration. The magnetic memory also includes nanometer scale notches in order to minimize magnetostatic interaction between a single domain memory element and the spin current sources and to effectively trap the magnetic domain wall. Reading the bit can be carried out by anisotropic magnetoresistance, or by other means of determining the magnetization orientation through resistance measurements, such as a spin valve or a magnetic tunneling junction.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Spin current generator for stt-mram or other spintronics applications
Spin current generators and systems and methods for employing spin current generators. A spin current generator may be configured to generate a spin current polarized in one direction, or a spin current selectively polarized in two directions. The spin current generator may by employed in spintronics applications, wherein a spin current is desired.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
Spin current assisted magnetoresistance effect device
ActiveUS20190147929A1Increase write speedSolid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic device detailsSpin orbit torqueOrbit
A spin current assisted magnetoresistance effect device includes: a spin current assisted magnetoresistance effect element including a magnetoresistance effect element part and a spin-orbit torque wiring; and a controller electrically connected to the spin current assisted magnetoresistance effect element. In a portion in which the magnetoresistance effect element part and the spin-orbit torque wiring are bonded, an STT inversion current flowing through the magnetoresistance effect element part and an SOT inversion current flowing through the spin-orbit torque wiring merge or are divided, and the controller is configured to be capable of performing control for applying the STT inversion current to the spin current assisted magnetoresistance effect element at the same time as an application of the SOT inversion current or a time application of the SOT inversion current.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Self-excited spinning single-electron electromagnetic field effect transistor, preparation method and application
ActiveCN104779275ASmall blocking voltageReflect the entanglement effectGalvano-magnetic hall-effect devicesSemiconductor devicesNanowireSelf excited
The invention discloses a self-excited spinning single-electron electromagnetic field effect transistor, a preparation method and the application. The electromagnetic field effect transistor comprises a base plate, a source electrode, a drain electrode, a gate electrode and a nanowire active area. The source electrode, the drain electrode and the gate electrode are arranged on the base plate. The nanowire active area is a current channel between the source electrode and the drain electrode, and the nanowire active area is polymorphic silicon carbide nanowires mingling with magnetic metals. According to the self-excited spinning single-electron electromagnetic field effect transistor, the preparation method and the application, and the indoor temperature can realize a single-electron coulomb block effect and a single-electron tunneling effect; at the same time, when the single-electron coulomb block effect and the single-electron tunneling effect are achieved, the single electron oscillation generates a variable electric field, and the variable electric field generates a magnetic field; under the condition that drain voltage replenishes energy, multi-structure electromagnetic oscillation can be presented, and pA-grade single-electron spinning current is generated. The self-excited spinning single-electron electromagnetic field effect transistor can be used as component for generating, converting, transferring and storing of quantum information.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Electric-current-generated magnetic field assist type spin-current-induced magnetization reversal element, magnetoresistance effect element, magnetic memory and high-frequency filter
ActiveUS20180123026A1High currentProlong lifeMultiple-port networksMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
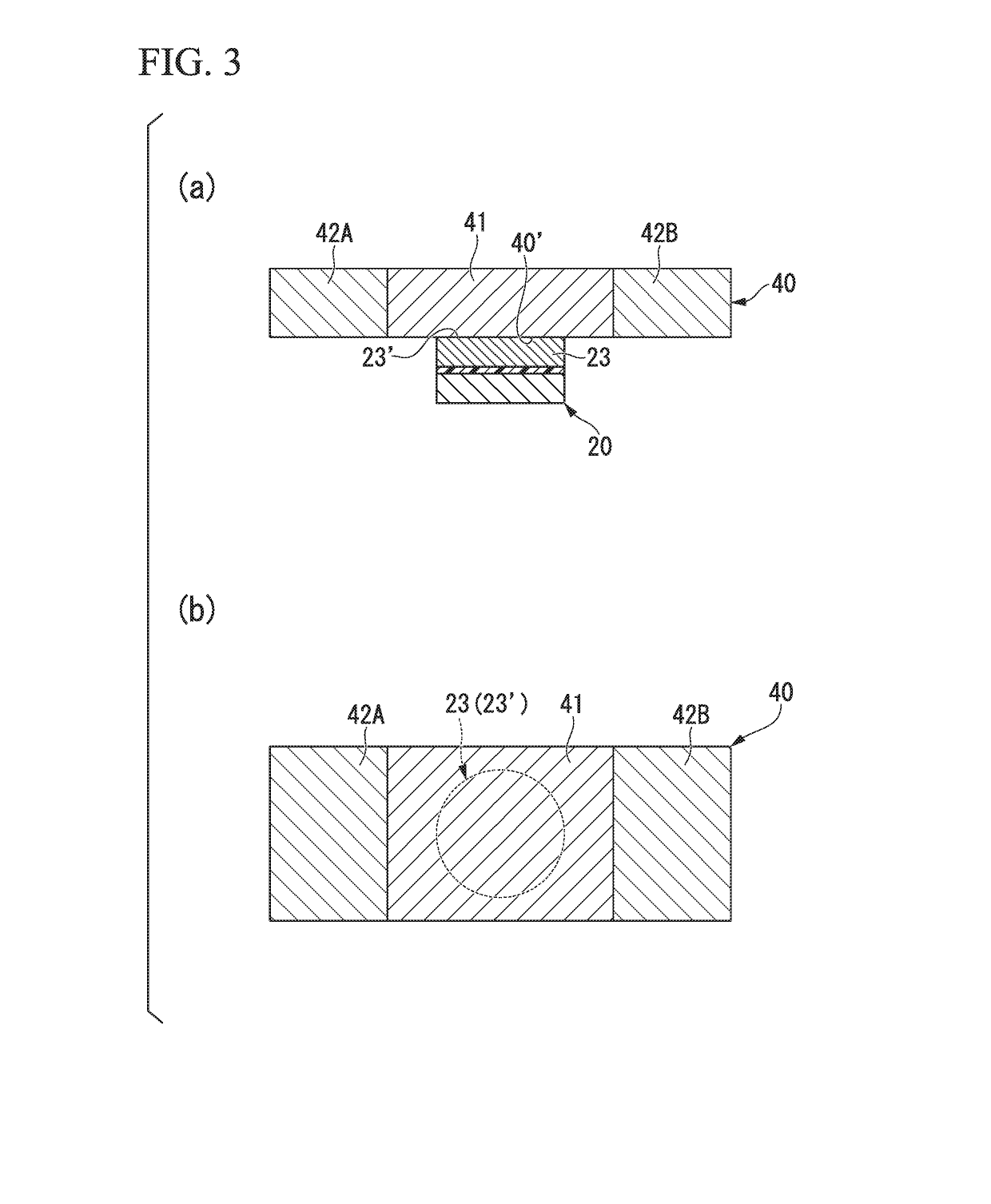
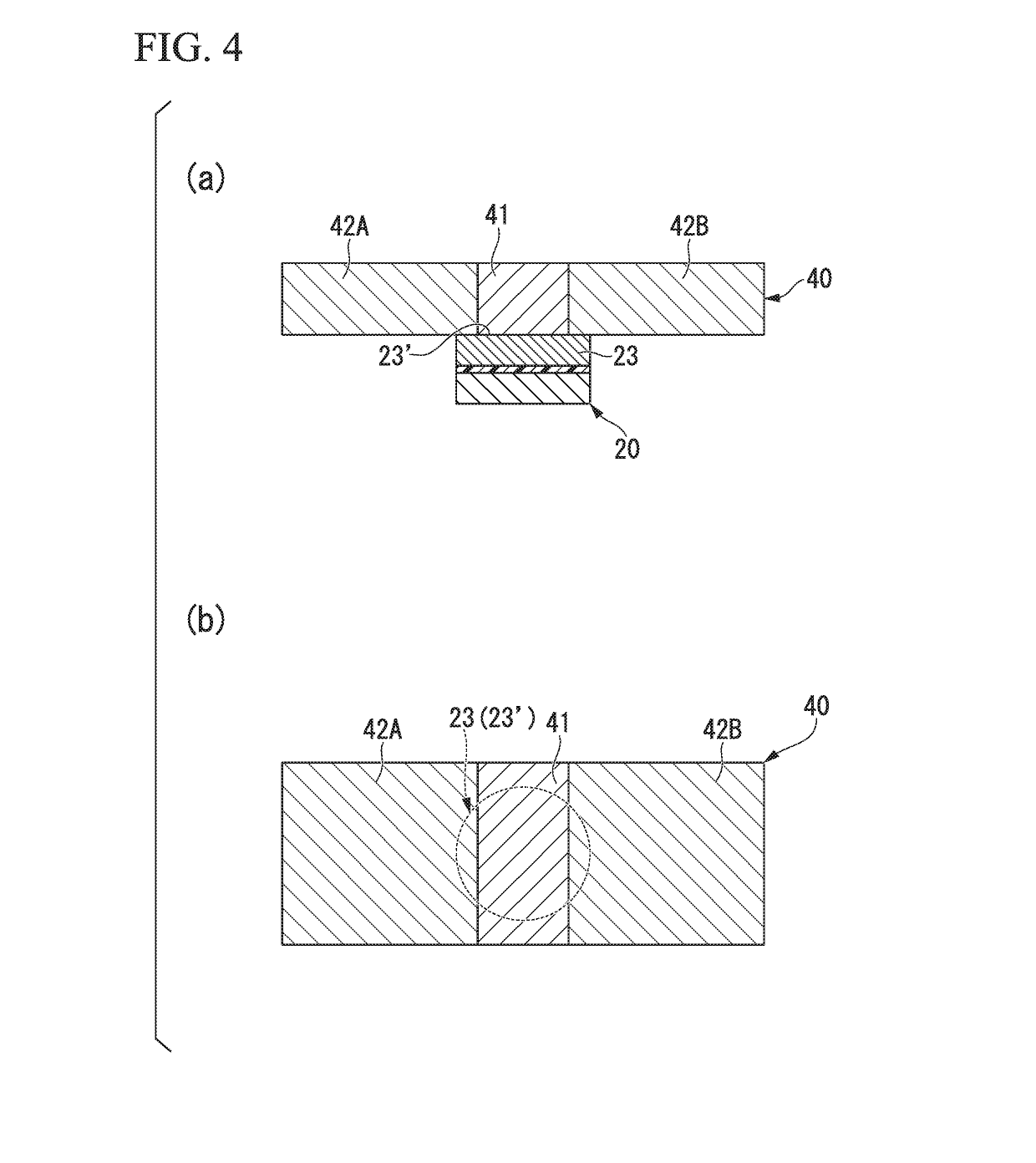
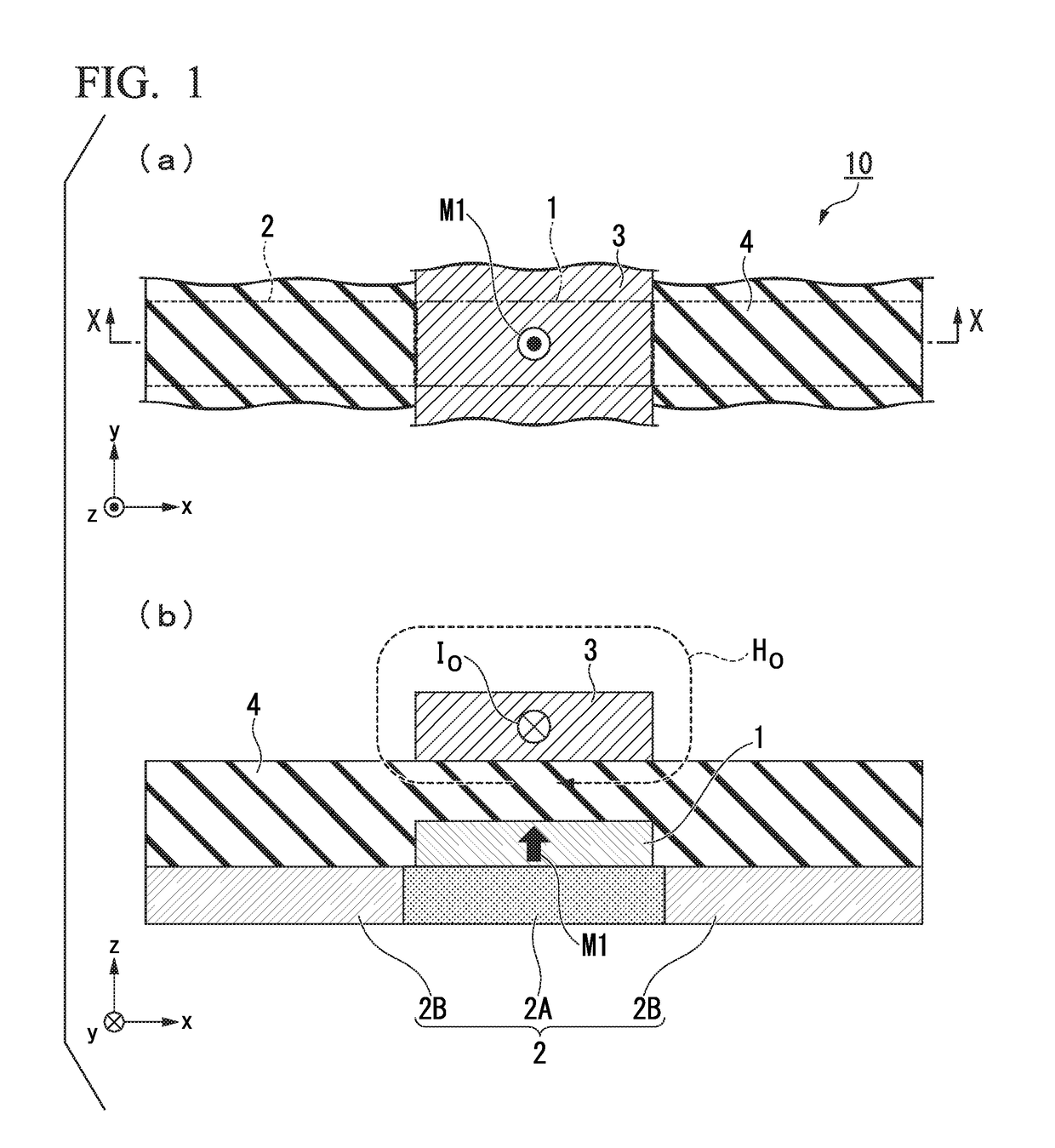
The present invention has the purpose of providing an electric-current-generated magnetic field assist type spin-current-induced magnetization reversal element that utilizes magnetization reversal based on pure spin current. The electric-current-generated magnetic field assist type spin-current-induced magnetization reversal element of the present invention includes a first ferromagnetic metal layer with a varying magnetization direction; spin-orbit torque wiring that adjoins the first ferromagnetic metal layer and that extends in a second direction in a plane orthogonal to a first direction normal to the first ferromagnetic metal layer; and electric-current-generated magnetic field assist wiring that is arranged so as to be electrically insulated from the first ferromagnetic metal layer by an insulating layer and in which flows an electric current I0 for forming a magnetic field H0 that assists magnetization reversal of the first ferromagnetic metal layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Electric current-spin current conversion device
InactiveUS20130154633A1Improve conversion efficiencyAc-dc conversionMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesSpin Hall effectSpins
An electric current-spin current conversion device according to the invention performs conversion between electric current and spin current utilizing the spin Hall effect or the inverse spin Hall effect of a 5d transition metal. A spin accumulation apparatus according to the invention includes a non-magnetic body in which injected spins are accumulated and an injection unit that injects spins into the non-magnetic body, wherein said injection unit comprises said electric current-spin current conversion device provided on said non-magnetic body, and an electric power source that supplies an electric current to said electric current-spin current conversion device in such a way that a spin current flowing toward said non-magnetic body is generated by the spin Hall effect.
Owner:RIKEN
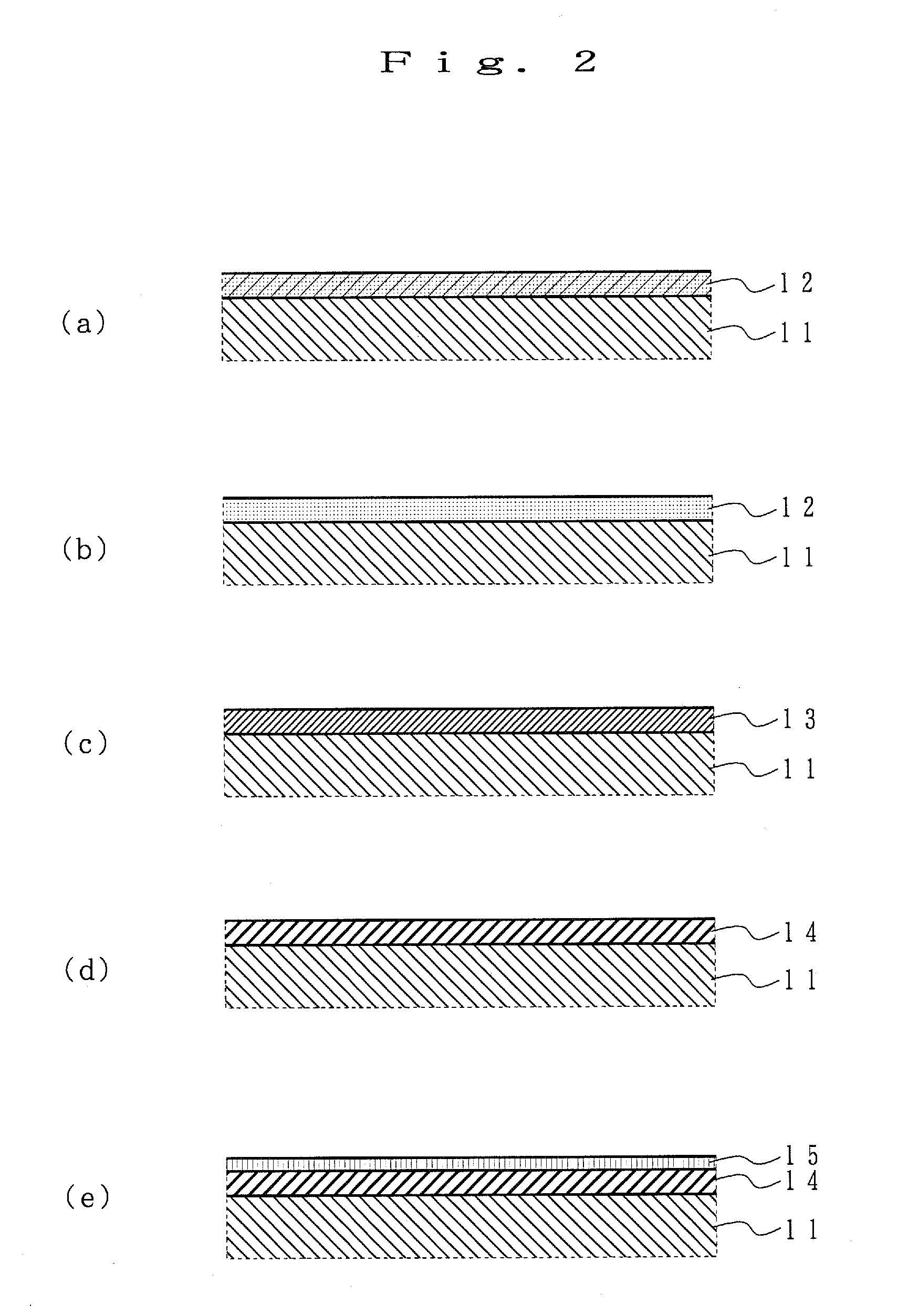
Storage nodes, magnetic memory devices, and methods of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20120139069A1Reduce generationReduce standby powerMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesMagnetizationMagnetic memory
A storage node of a magnetic memory device includes: a lower magnetic layer, a tunnel barrier layer formed on the lower magnetic layer, and a free magnetic layer formed on the tunnel barrier. The free magnetic layer has a magnetization direction that is switchable in response to a spin current. The free magnetic layer has a cap structure surrounding at least one material layer on which the free magnetic layer is formed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electric field regulation and control-based two-dimensional spinning electronic device and preparation method thereof
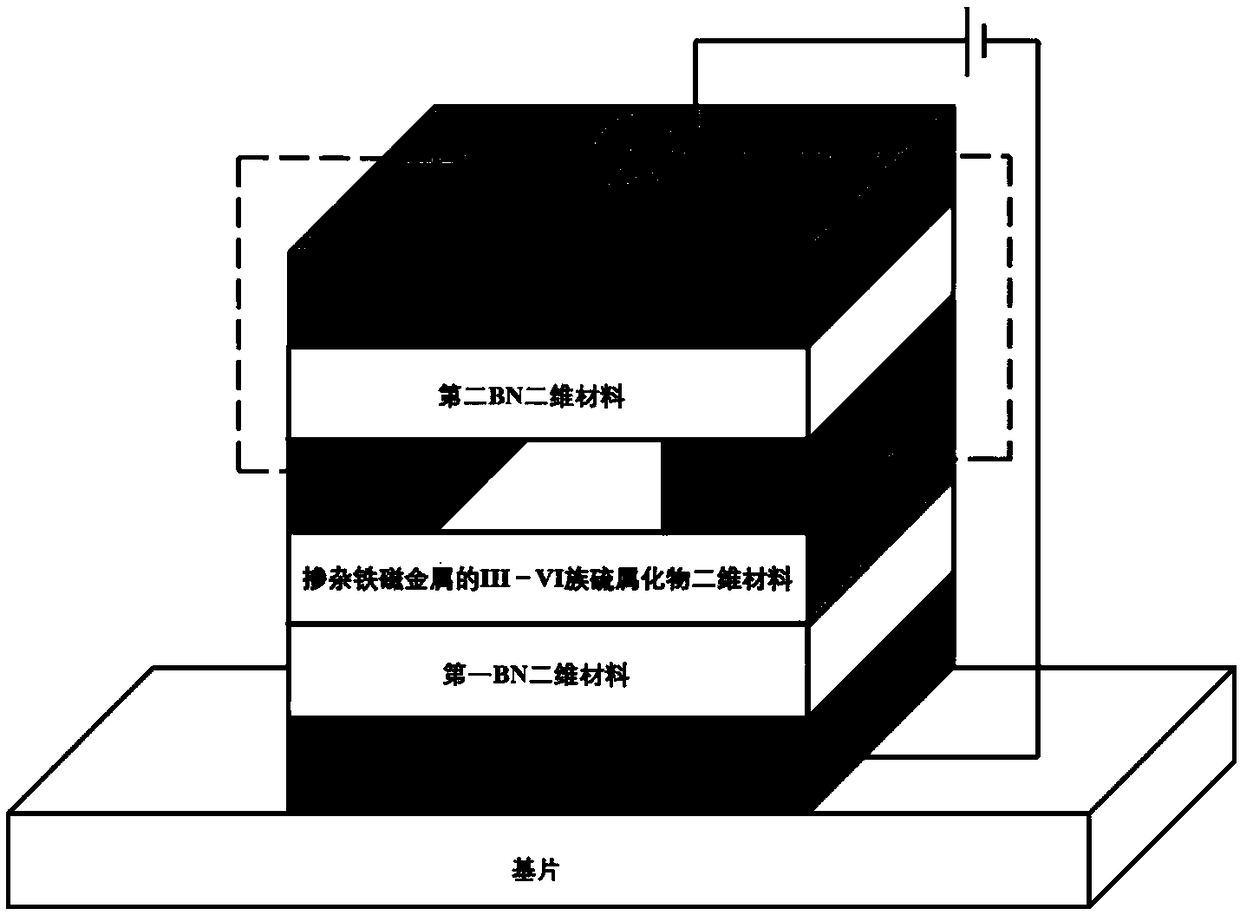
ActiveCN108767107ARegulating polarizabilitySolve the need in a strong magnetic fieldGalvano-magnetic material selectionGalvano-magnetic device detailsElectricityAntiferromagnetic coupling
The invention discloses an electric field regulation and control-based two-dimensional spinning electronic device and a preparation method thereof, and relates to electric field regulation and controlfor generation and polarization rates of spinning currents. The device structure comprises a sandwich structure of a first BN two-dimensional material / ferromagnetic metal-doped III-VI group chalcogenide two-dimensional material / second BN two-dimensional material, a transparent electrode connected with the first BN two-dimensional material and the second BN two-dimensional material, and a channelelectrode connected with the III-VI group chalcogenide two-dimensional material; the ferromagnetic metal is doped in crystal lattice displacement position or gap position of the III-VI group chalcogenide two-dimensional material, so that the electrons of the III-VI group chalcogenide two-dimensional material are subjected to spinning polarization; the spin-polarized electrons generate a spin current through a channel loop under excitation of the incident laser, and the magnetic structure of the ferromagnetic metal-doped III-VI group chalcogenide two-dimensional material is regulated to be converted between ferromagnetic coupling and anti-ferromagnetic coupling through an externally applied perpendicular electric field, so that the polarization rate of the spin current can be regulated within the range of 0-100%, and the two-dimensional spinning electronic device with controllable polarization rate is formed.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Spin current magnetization rotational element, magnetoresistance effect element, and magnetic memory
ActiveUS20180159026A1Improve thermal stabilityMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesSpin orbit torqueMagnetic memory
A spin current magnetization rotational element includes: a magnetization free layer including a synthetic structure consisting of a first ferromagnetic metal layer, a second ferromagnetic metal layer and a first non-magnetic layer sandwiched by the first ferromagnetic metal layer and the second ferromagnetic metal layer; and an antiferromagnetic spin-orbit torque wiring that extends in a second direction intersecting with a first direction that is a lamination direction of the synthetic structure and is joined to the first ferromagnetic metal layer, wherein the spin current magnetization rotational element is configured to change a magnetization direction of the magnetization free layer by applying current to the antiferromagnetic spin-orbit torque wiring.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
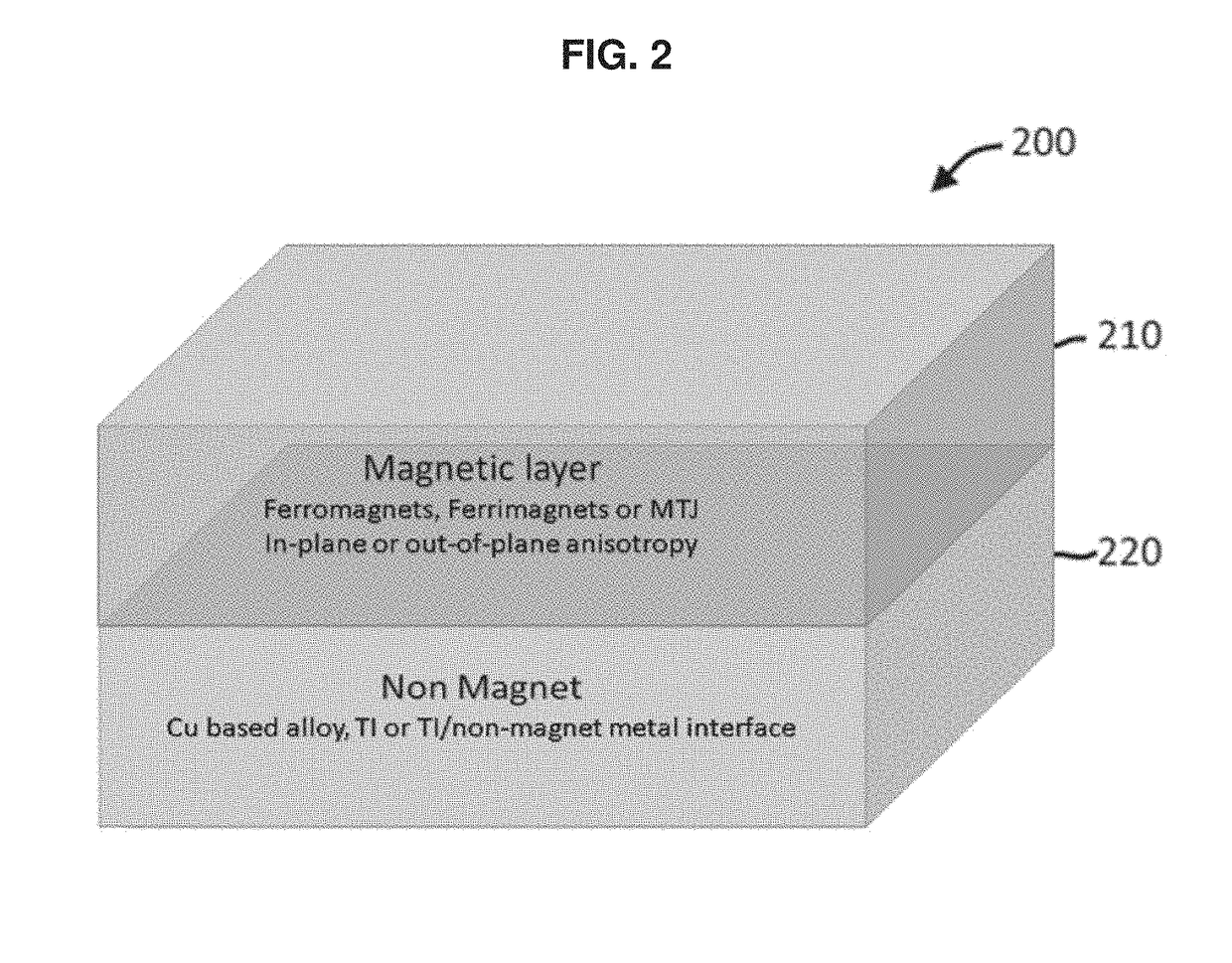
Spin orbit materials for efficient spin current generation
ActiveUS20190058113A1Current generatedEasy to integrateSolid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic material selectionCMOSSpins
In one embodiment, a SOT device is provided that replaces a traditional NM layer adjacent to a magnetic layer with a NM layer that is compatible with CMOS technology. The NM layer may include a CMOS-compatible composite (e.g., CuPt) alloy, a TI (e.g., Bi2Se3, BixSe1-x, Bi1-xSbx, etc.) or a TI / non-magnetic metal (e.g., Bi2Se3 / Ag, BixSe1-x / Ag, Bi1-xSbx / Ag, etc.) interface, that provides efficient spin current generation. Spin current may be generated in various manners, including extrinsic SHE, TSS or Rashba effect.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com