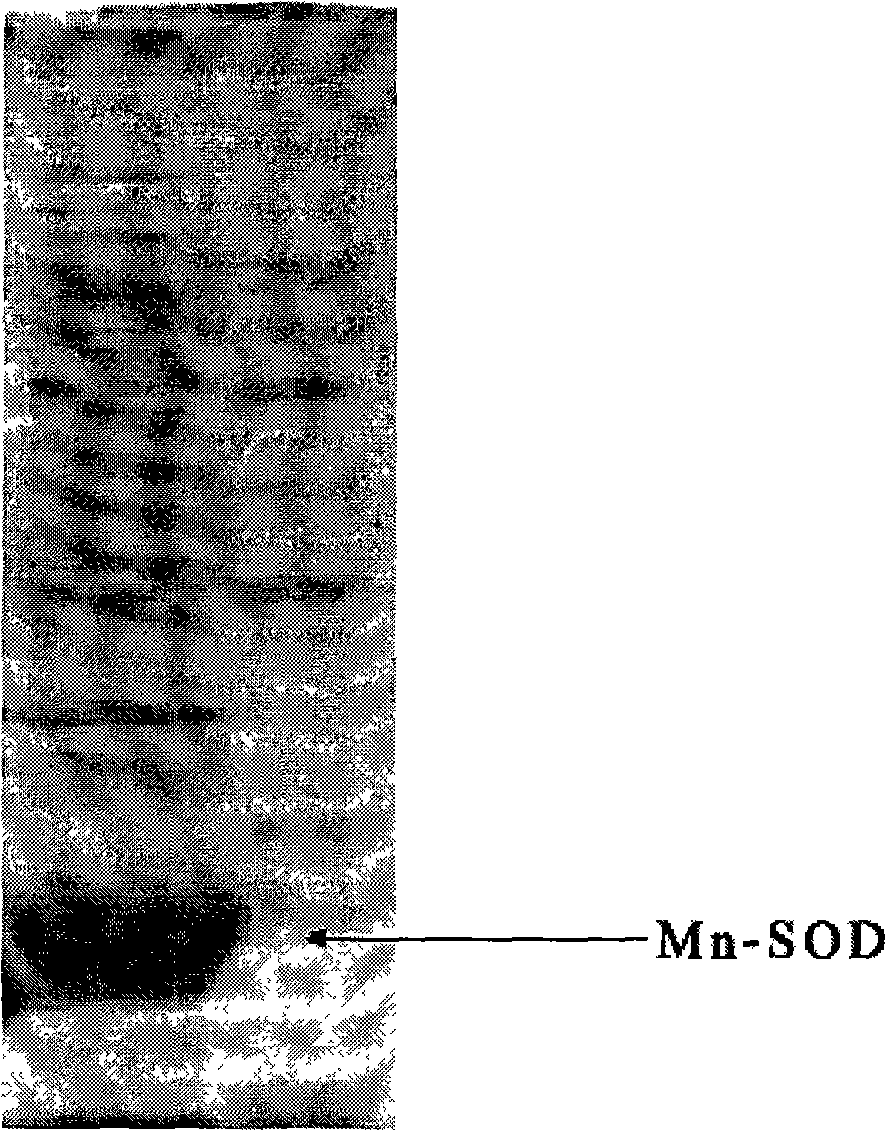Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
169 results about "Chemical transformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
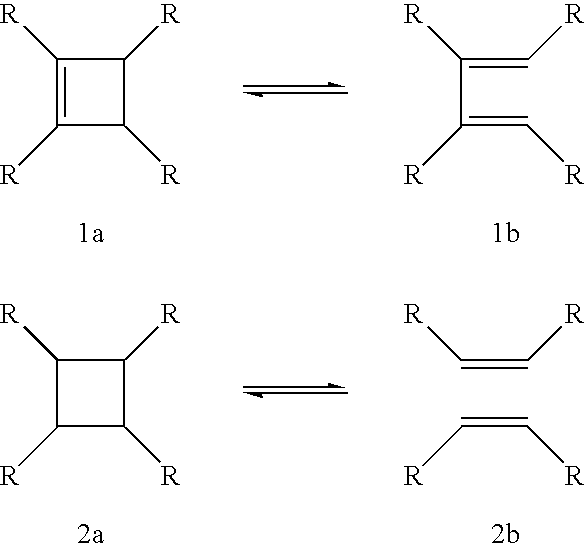
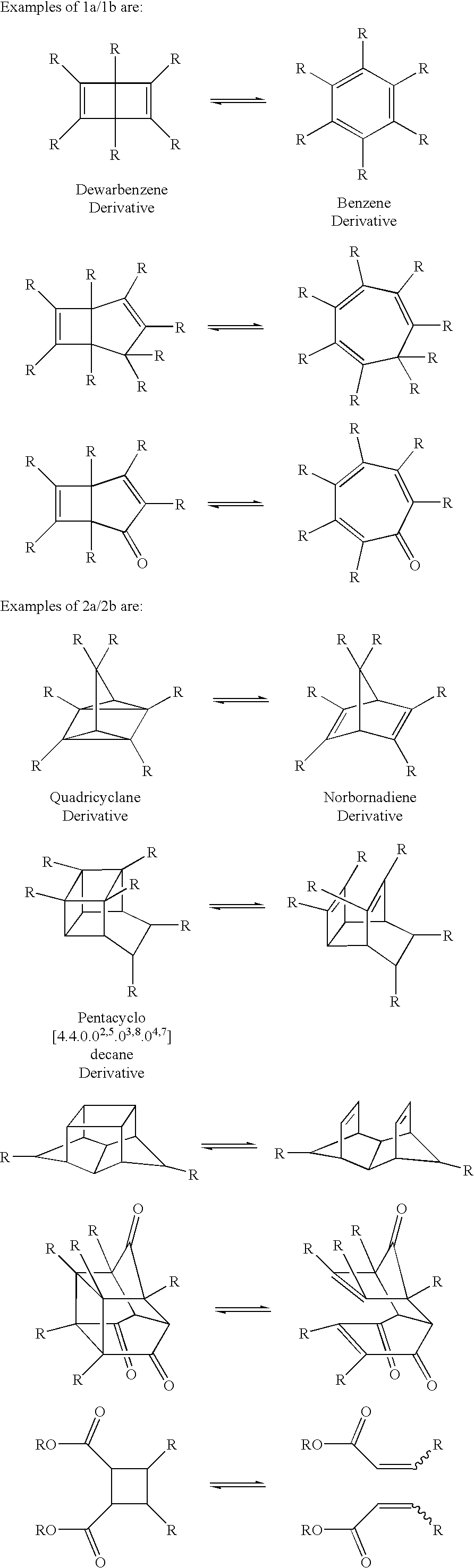
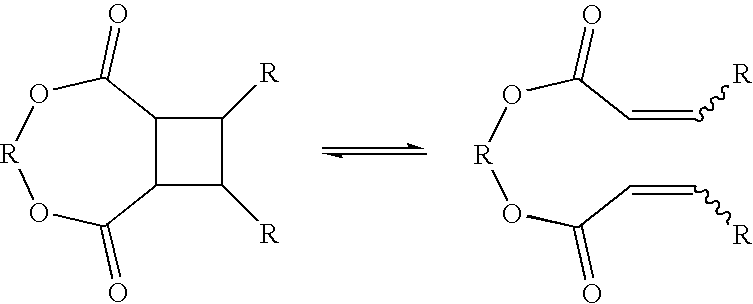
In chemistry a chemical transformation shows the conversion of a substrate to a product. The IUPAC Nomenclature for Transformations is based on this type of transformations.
Hybrid resist based on photo acid/photo base blending
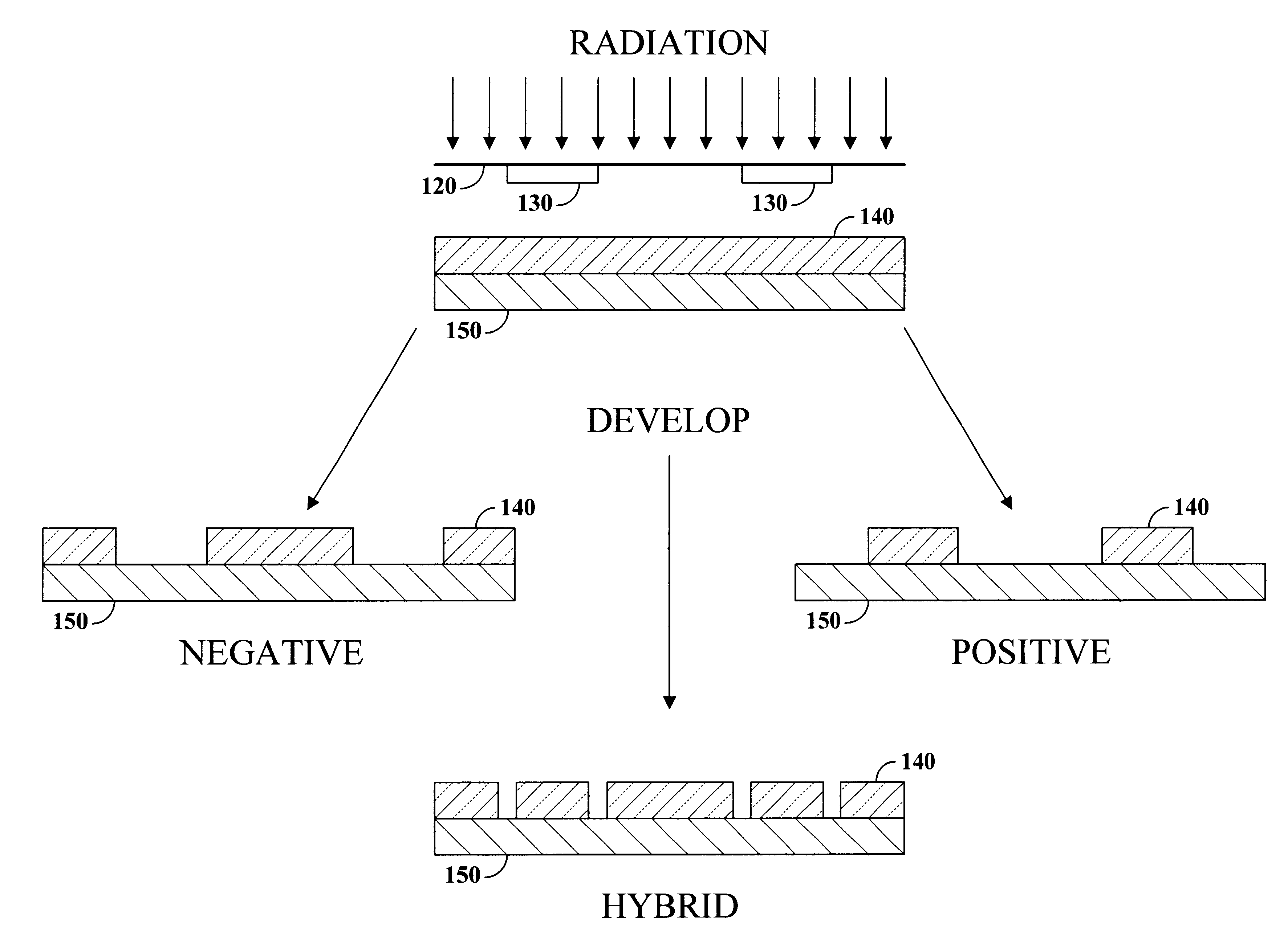
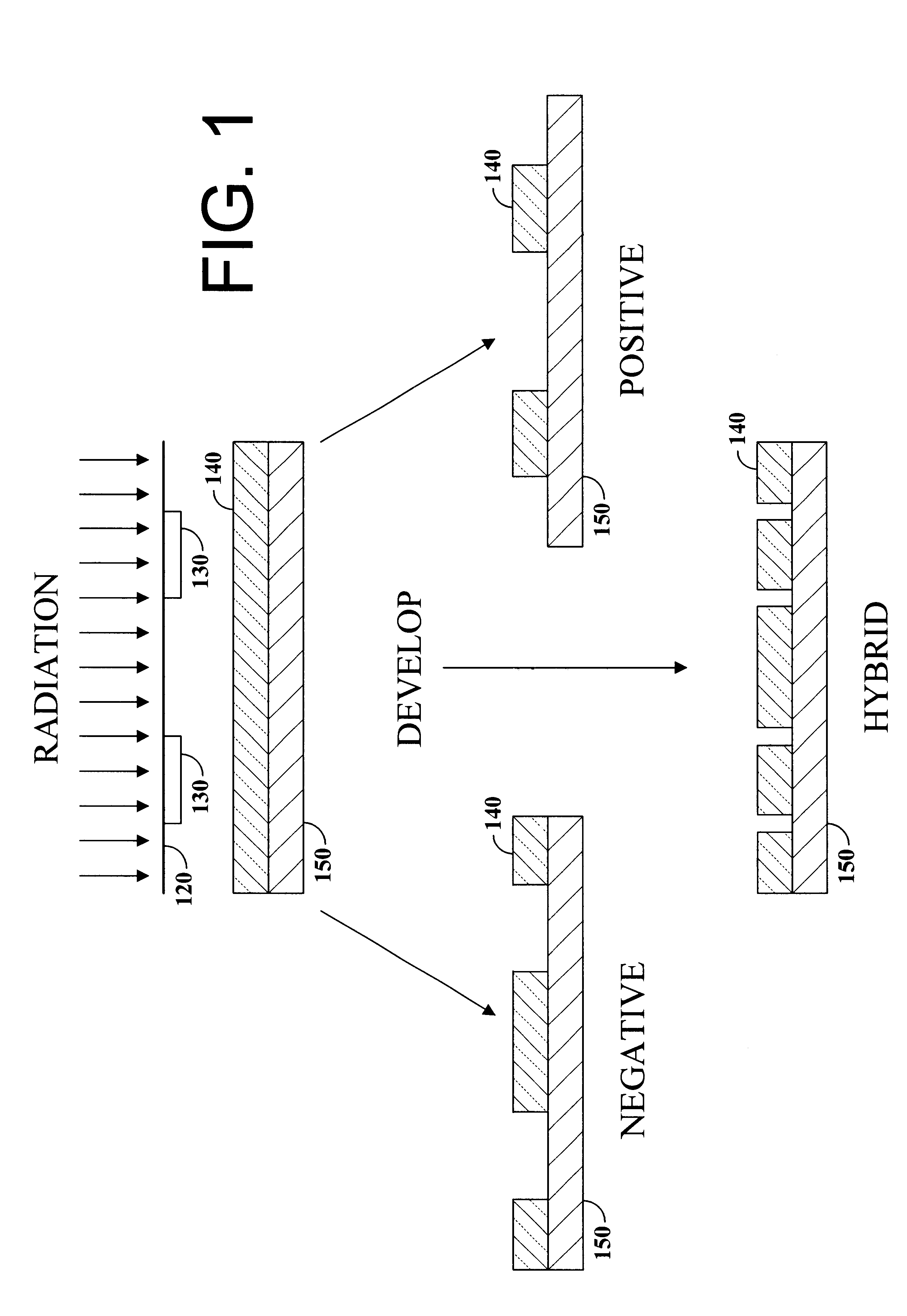
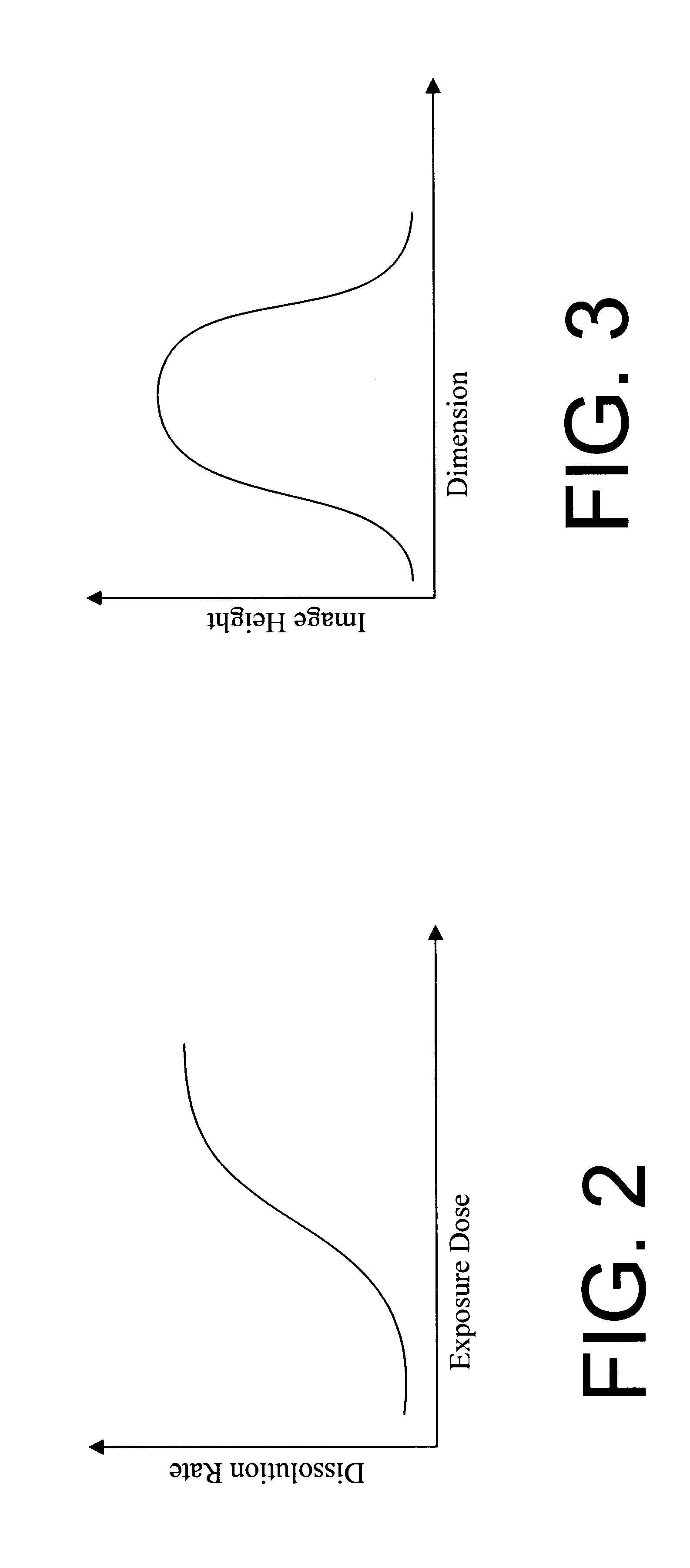
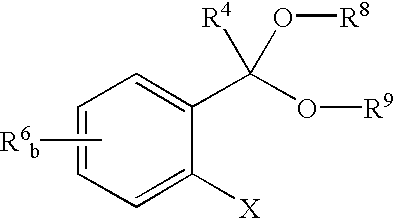
A photo resist composition contains a polymer resin, a first photo acid generator (PAG) requiring a first dose of actinic energy to generate a first photo acid, and a photo base generator (PBG) requiring a second dose of actinic energy, different from the first dose, to generate a photo base. The amounts and types of components in the photo resist are selected to produce a hybrid resist image. Either the first photo acid or photo base acts as a catalyst for a chemical transformation in the resist to induce a solubility change. The other compound is formulated in material type and loading in the resist such that it acts as a quenching agent. The catalyst is formed at low doses to induce the solubility change and the quenching agent is formed at higher doses to counterbalance the presence of the catalyst. Accordingly, the same frequency doubling effect of conventional hybrid resist compositions may be obtained, however, either a line or a space may be formed at the edge of an aerial image. Feature size may also be influenced by incorporating a quenching agent into the resist composition that does not require photo generation.
Owner:IBM CORP
Directed microwave chemistry
InactiveUS20030082633A1Promote resultsImprove adsorption capacityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsChemical reactionChemical transformation
The present invention concerns a novel means by which chemical preparations can be made. Reactions can be accelerated on special chips using microwave energy. The chips contain materials that efficiently absorb microwave energy causing chemical reaction rate increases. The invention is important in many small scale chemical transformations including those used in protein chemistry and in combinatorial chemistry.
Owner:MIRARI BIOSCI
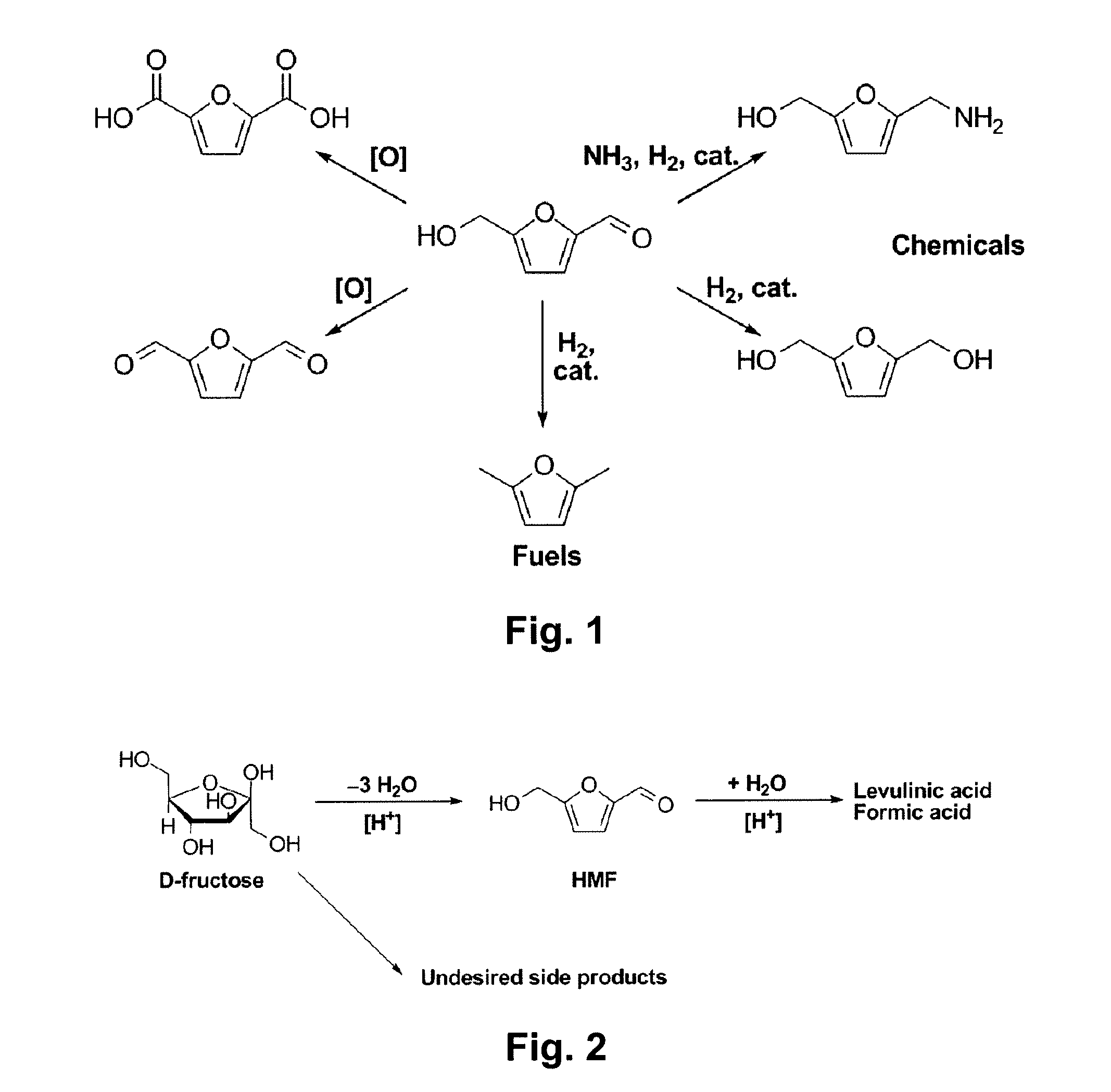
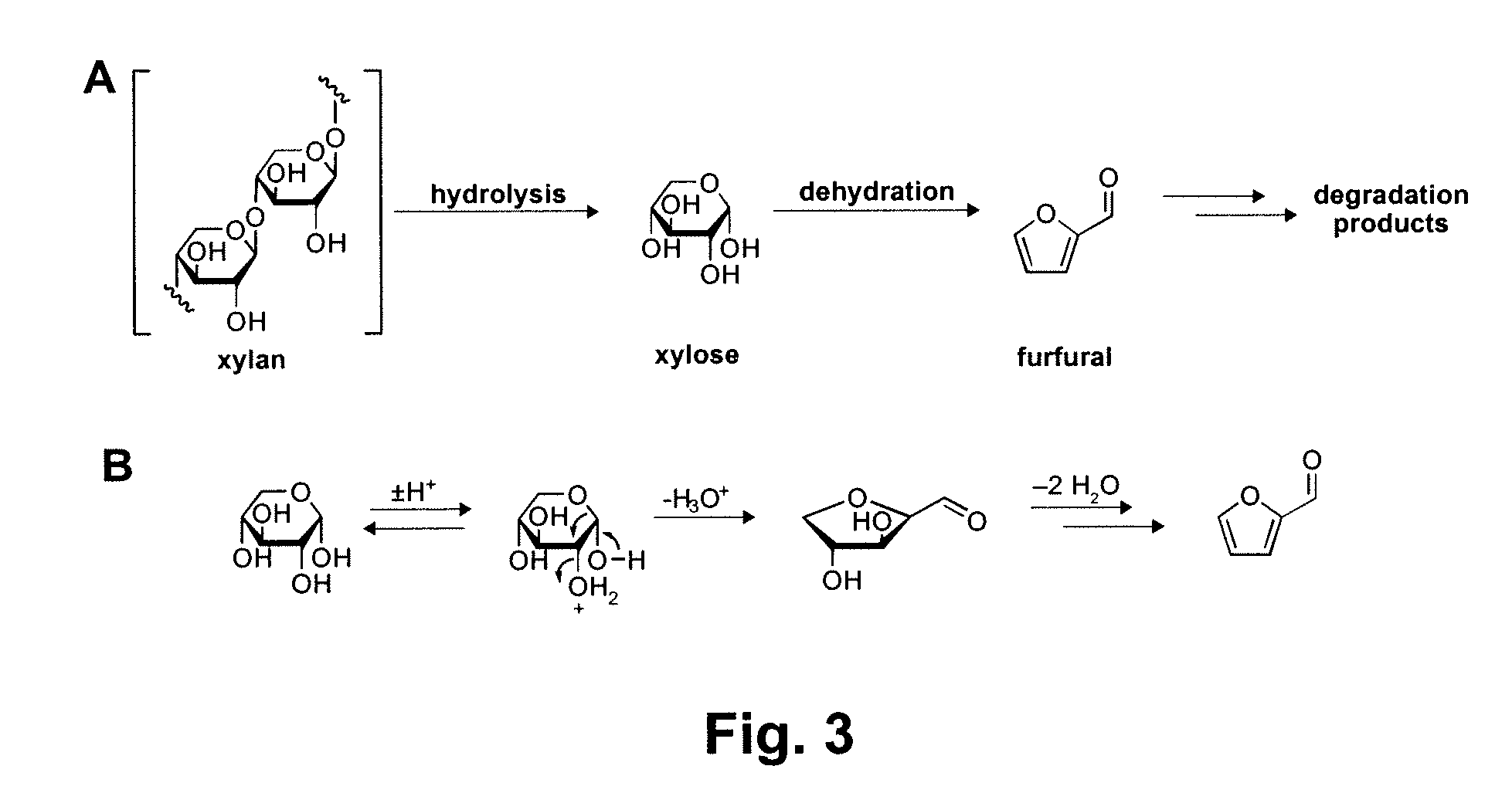
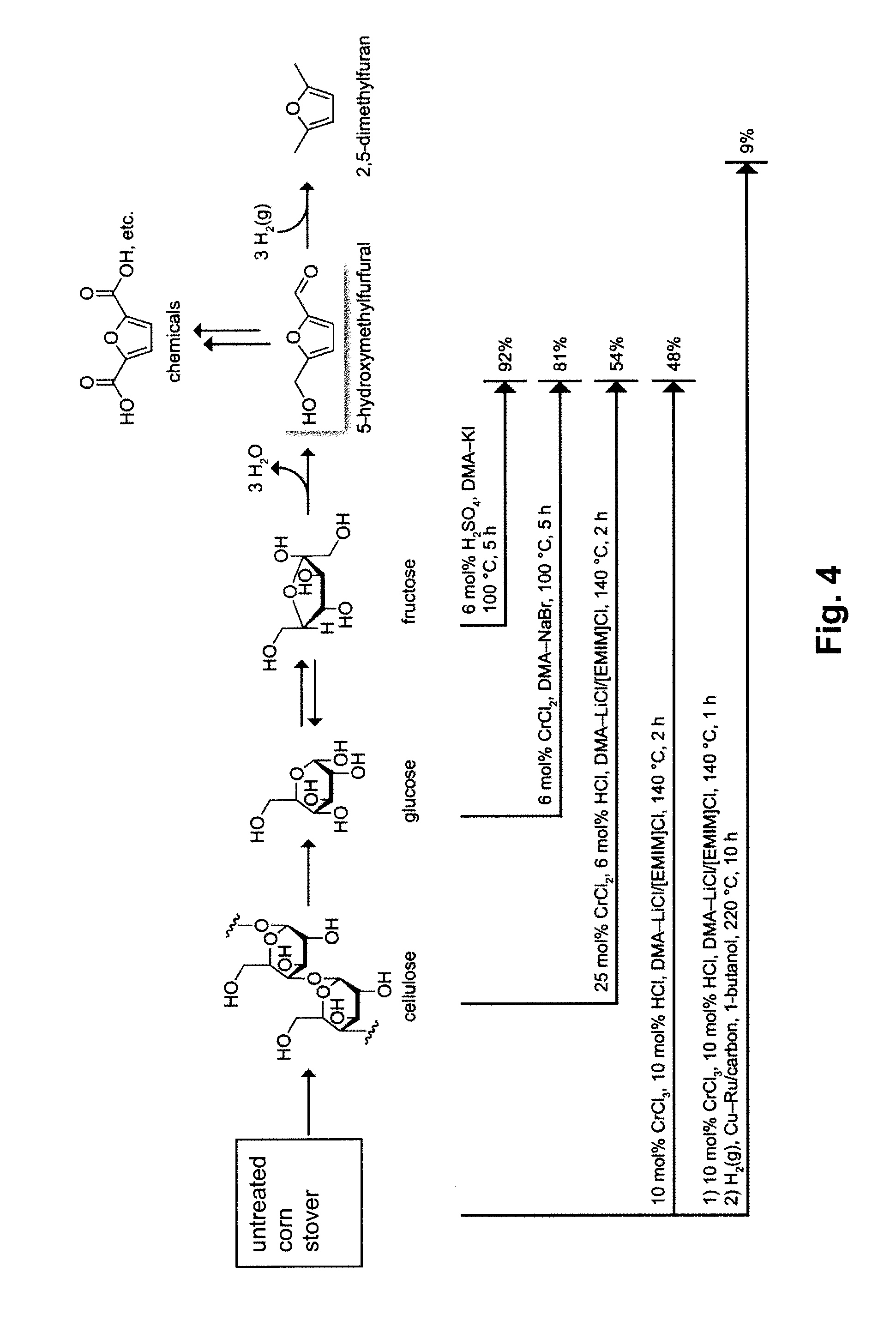
Chemical Transformation of Lignocellulosic Biomass into Fuels and Chemicals
A method for converting a carbohydrate to a furan in a polar aprotic solvent in the presence of a chloride, bromide, or iodide salt or a mixture thereof and optionally in the presence of an acid catalyst, a metal halide catalyst and / or an ionic liquid (up to 40 wt %). The method can be employed in particular to produce furfural or 5-hydroxymethylfurfural.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Methods and device for controlling pressure in reactive multilayer joining and resulting product
ActiveUS7441688B2ExplosivesWelding/cutting media/materialsChemical transformationMechanical engineering
The invention includes a method of joining two components. The method includes providing at least two components to be joined, a reactive multilayer foil, and a compliant element, placing the reactive multilayer foil between the at least two components, applying pressure on the two components in contact with the reactive multilayer foil via a compliant element, and initiating a chemical transformation of the reactive multilayer foil so as to physically join the at least two components. The invention also includes two components joined using the aforementioned method.
Owner:NANOFOIL CORP
Process for the conversion of renewable oils to liquid transportation fuels
InactiveUS20120157734A1Efficient reductionEfficient processingBiofuelsSolid fuelsIsomerizationKerosene
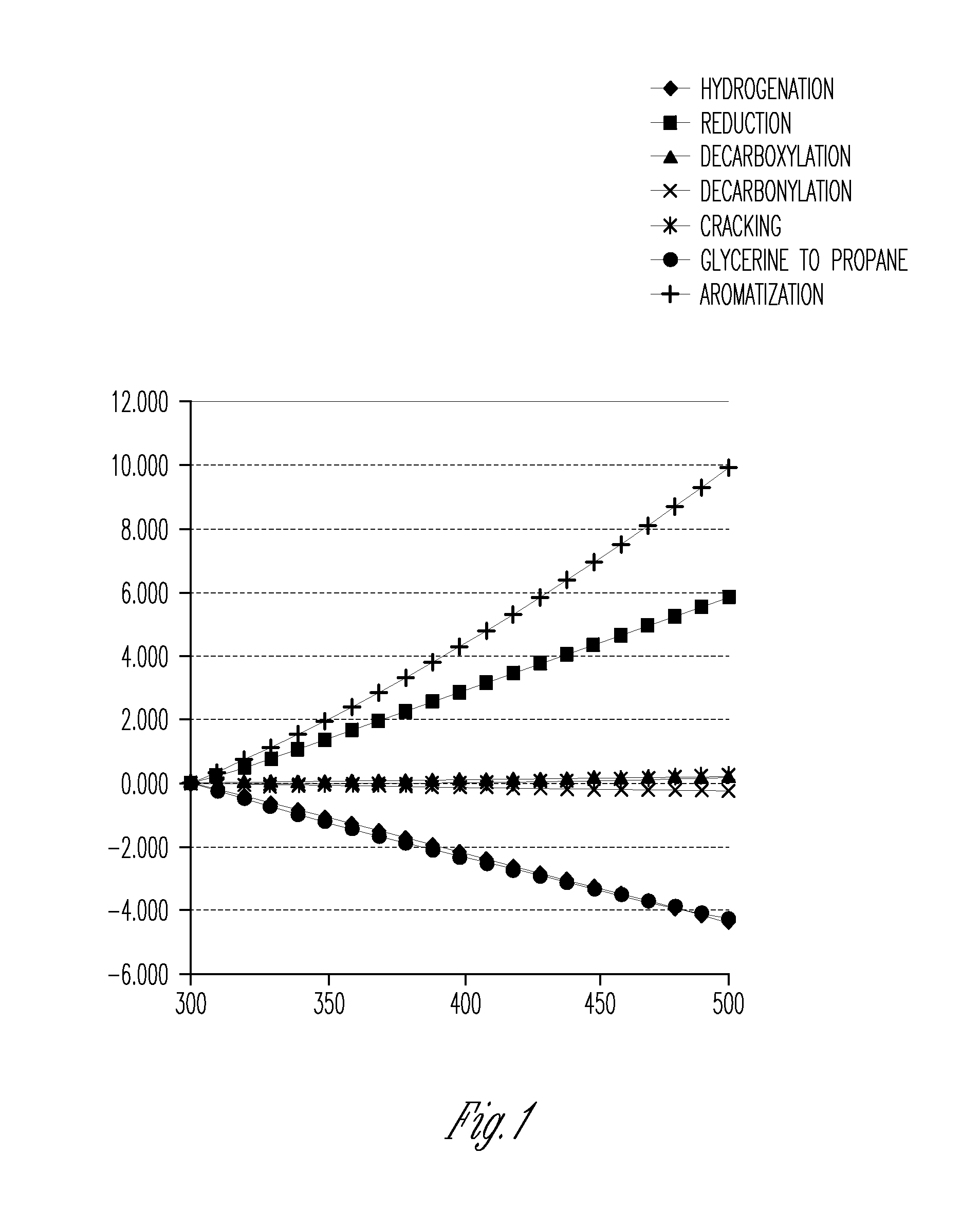
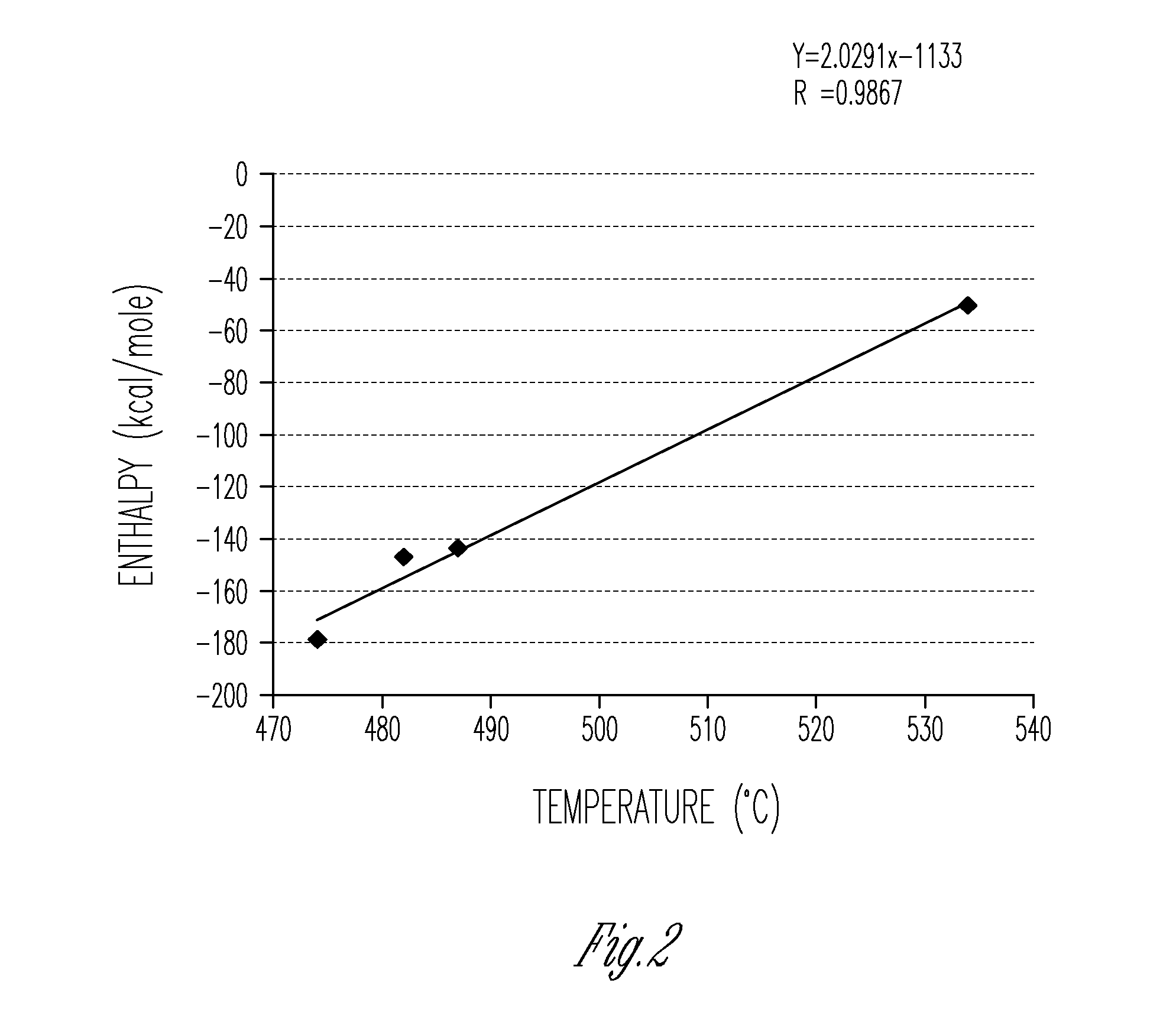
The present invention relates to production of fuels or fuel blendstocks from renewable sources. Various embodiments provide a method of producing a hydrocarbon product by hydrotreating a feedstock including at least one of a renewable triacylglyceride (TAG), renewable free fatty acid (FFA), and renewable fatty acid C1-C5 alkyl ester (C1-C5 FAE) in the presence of a nonsulfided hydrotreating catalyst to produce a first product including hydrocarbons. In some examples, the first product can be subjected to further chemical transformations such as aromatization, cracking, or isomerization to produce a second product including hydrocarbons. In various embodiments, the first or second hydrocarbon product with minimal or substantially no further processing can be suitable as a liquid transportation fuel or fuel blendstock, including fuels such as gasoline, naptha, kerosene, jet fuel, and diesel fuels.
Owner:ENERGY & ENVIRONMENTAL RES CENT FOUNDATIO
Laser irradiation of metal nanoparticle/polymer composite materials for chemical and physical transformations
InactiveUS20080004364A1Material nanotechnologyLamination ancillary operationsChemical transformationPolymer composites
A metal nanoparticle supported on or dispersed in a polymer is irradiated with photons from a laser source to address the nanoparticles. The polymer is transmissive to the photons and addressed nanoparticles transform the energy of the photon to heat which is transferred to a material in the vicinity of the nanoparticle. The locally heated material undergoes a physical or chemical transformation upon heating. The transformed material can be a material in the proximity of the metal nanoparticle supported polymer or metal nanoparticle / polymer composite. In this manner thermally induced physical or chemical transformations can be carried out in very small volumes of material without significant heating to the bulk of the material.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Therapeutic agents—I
InactiveUS7449492B2Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsChemical fractionChemical synthesis
The present invention relates generally to chemical agents useful in the treatment and prophylaxis of infection by pathogenic or potentially pathogenic entities, or entities capable of opportunistic infection in mammals, including humans and primates, non-mammalian animals and avian species. More particularly, the present invention provides a chemical agent of the macrocyclic diterpene family obtainable from a member of the Euphorbiaceae family of plants or botanical or horticultural relatives thereof or derivatives or chemical analogues or chemically synthetic forms of the agents for use in the treatment or prophylaxis of infection by pathogenic entities in mammalian, animal and avian subjects. The present invention further contemplates a method for the prophylaxis and / or treatment in mammalian, animal or avian subjects of infection or potential infection by pathogenic entities by the topical or systemic administration of a macrocyclic diterpene obtainable from a member of the Euphorbiaceae family of plants or their botanical or horticultural derivatives or a derivative, chemical analogue or chemically synthetic form of the agent. The chemical agent of the present invention may be in the form of a purified compound, mixture of compounds, a precursor form of one or more of the compounds capable of chemical transformation into a therapeutically active agent or in the form of a chemical fraction, sub-fraction, preparation or extract of the plant.
Owner:AF 30 APRIL 2003 +1
Methods and device for controlling pressure in reactive multilayer joining and resulting product
The invention includes a method of joining two components. The method includes providing at least two components to be joined, a reactive multilayer foil, and a compliant element, placing the reactive multilayer foil between the at least two components, applying pressure on the two components in contact with the reactive multilayer foil via a compliant element, and initiating a chemical transformation of the reactive multilayer foil so as to physically join the at least two components. The invention also includes two components joined using the aforementioned method.
Owner:NANOFOIL CORP
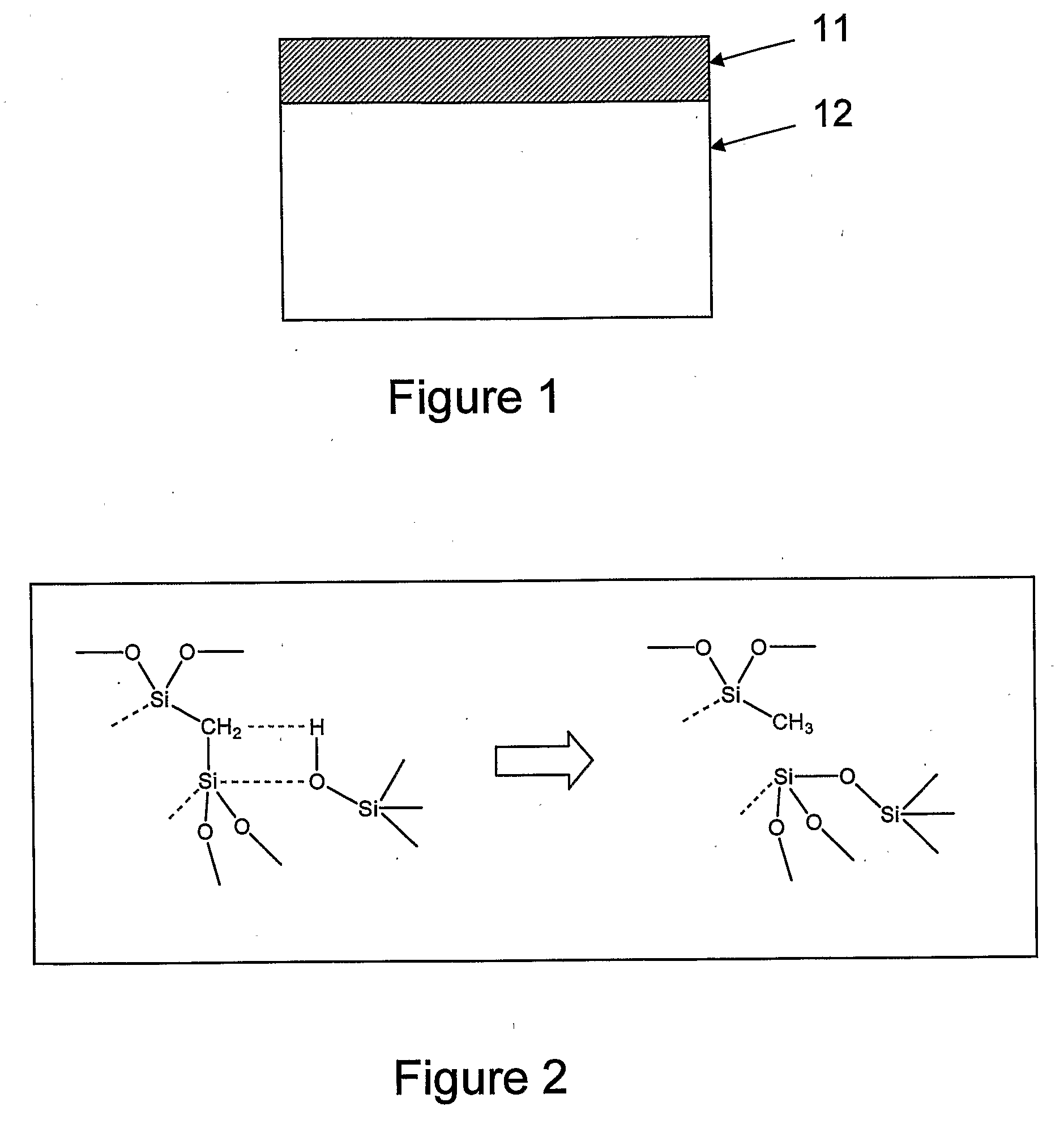
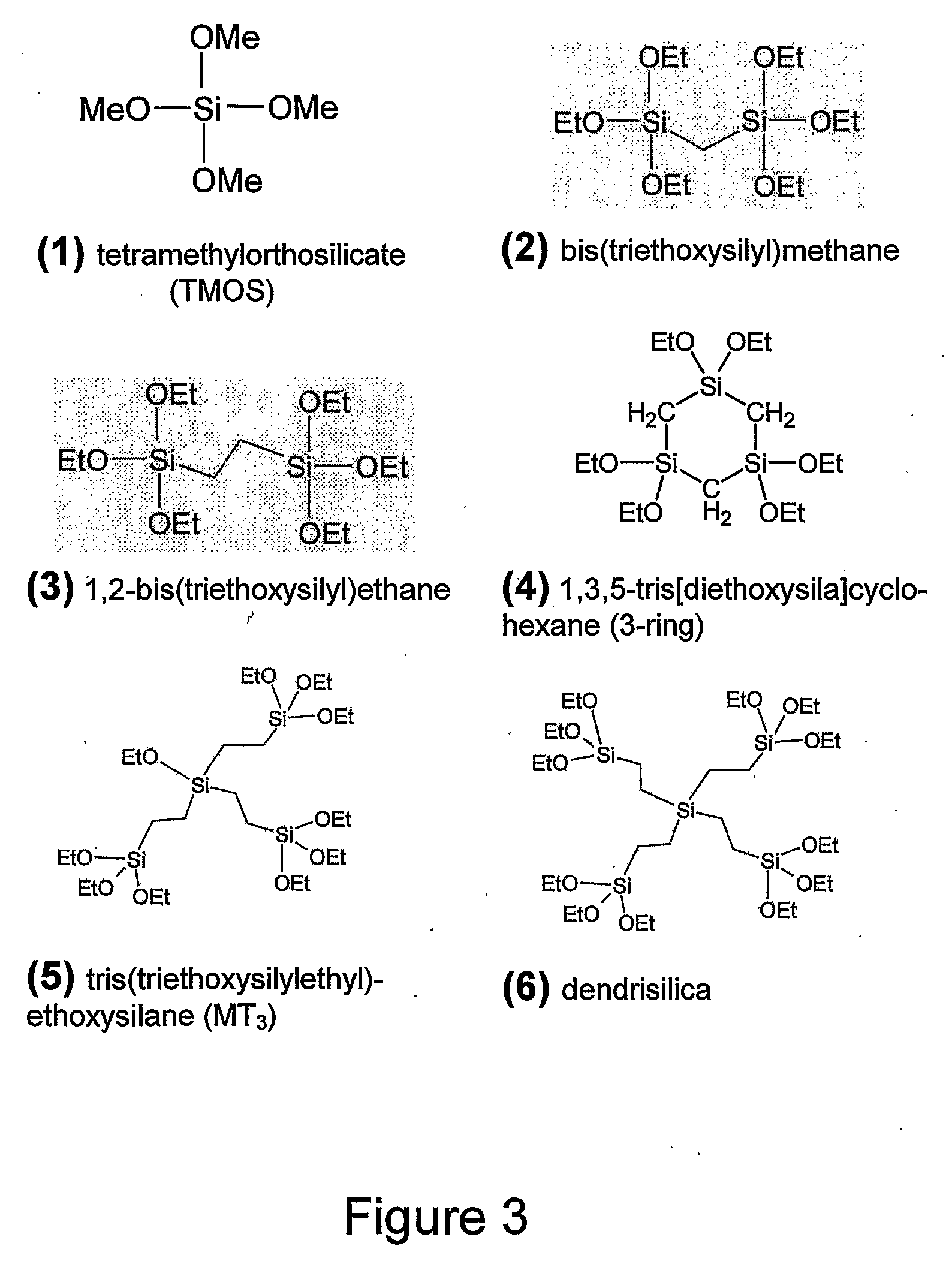
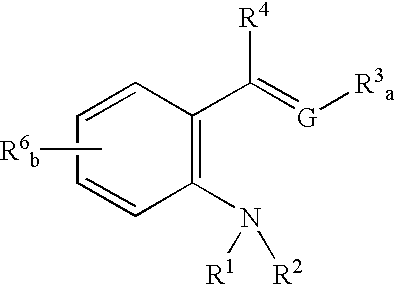
Method of transformation of bridging organic groups in organosilica materials
InactiveUS20090130412A1Improve hydrophobicityLow dielectric constantSilicon organic compoundsMolecular sieve catalystsChemical transformationOrganic group
This invention relates to a chemical transformation of the bridging organic groups in metal oxide materials containing bridging organic groups, such as bridged organosilicas, wherein such a transformation greatly benefits properties for low dielectric constant (k) applications. A thermal treatment at specific temperatures is shown to cause a transformation of the organic groups from a bridging to a terminal configuration, which consumes polar hydroxyl groups. The transformation causes k to decrease, and the hydrophobicity to increase (through ‘self-hydrophobization’). As a result of the bridge-terminal transformation, porous organosilica films are shown to have k<2.0, E>6 GPa, do not require additional chemical surface treatment for dehydroxylation (hydrophobicity).
Owner:HATTON BENJAMIN DAVID +3
Catalyst ligands, catalytic metal complexes and processes using same
InactiveUS6974878B2Silicon organic compoundsIsocyanic acid derivatives preparationChemical transformationCatalytic metal
A new ligands that include a benzene ring in the backbone can be combined with a metal or metal precursor compound or formed into a metal-ligand complex catalyze a number of different chemical transformations, including olefin polymerization reactions. The ligands, complexes formed with the ligands and compositions including the ligands are useful catalysts, depending on the reaction.
Owner:FREESLATE
Foam and gel methods for the decontamination of metallic surfaces
InactiveUS20060217584A1Effective dissolutionStrong chelating abilitySolid waste disposalHollow article cleaningChemical solutionHydroxamic acid
Decontamination of nuclear facilities is necessary to reduce the radiation field during normal operations and decommissioning of complex equipment. In this invention, we discuss gel and foam based diphosphonic acid (HEDPA) chemical solutions that are unique in that these solutions can be applied at room temperature; provide protection to the base metal for continued applications of the equipment; and reduce the final waste form production to one step. The HEDPA gels and foams are formulated with benign chemicals, including various solvents, such as ionic liquids and reducing and complexing agents such as hydroxamic acids, and formaldehyde sulfoxylate. Gel and foam based HEDPA processes allow for decontamination of difficult to reach surfaces that are unmanageable with traditional aqueous process methods. Also, the gel and foam components are optimized to maximize the dissolution rate and assist in the chemical transformation of the gel and foam to a stable waste form.
Owner:NUNEZ LUIS +1
Catalytic filter based on silicon carbide (beta-SiC) for combustion of soot derived from exhaust gases from an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20050159292A1Reduce manufacturing costIncrease surface areaGas treatmentOther chemical processesPorosityChemical transformation
This invention relates to β-SiC foam parts with a specific surface area preferably equal to at least 5 m2 / g and with at least two zones A and B with a different cellular porosity distribution, wherein the parts were made by chemical transformation of a porous precursor medium comprising at least two blocks A′ and B′, each having a different cellular porosity distribution, and in that the at least two zones A and B are derived from the chemical transformation of the two blocks A′ and B′. This foam, optionally after deposition of an active layer, may be used as a filter medium in cartridges designed for the purification of exhaust gases. The invention also relates to manufacturing processes for preparing such a filter medium.
Owner:MAPLE VISION TECH +3
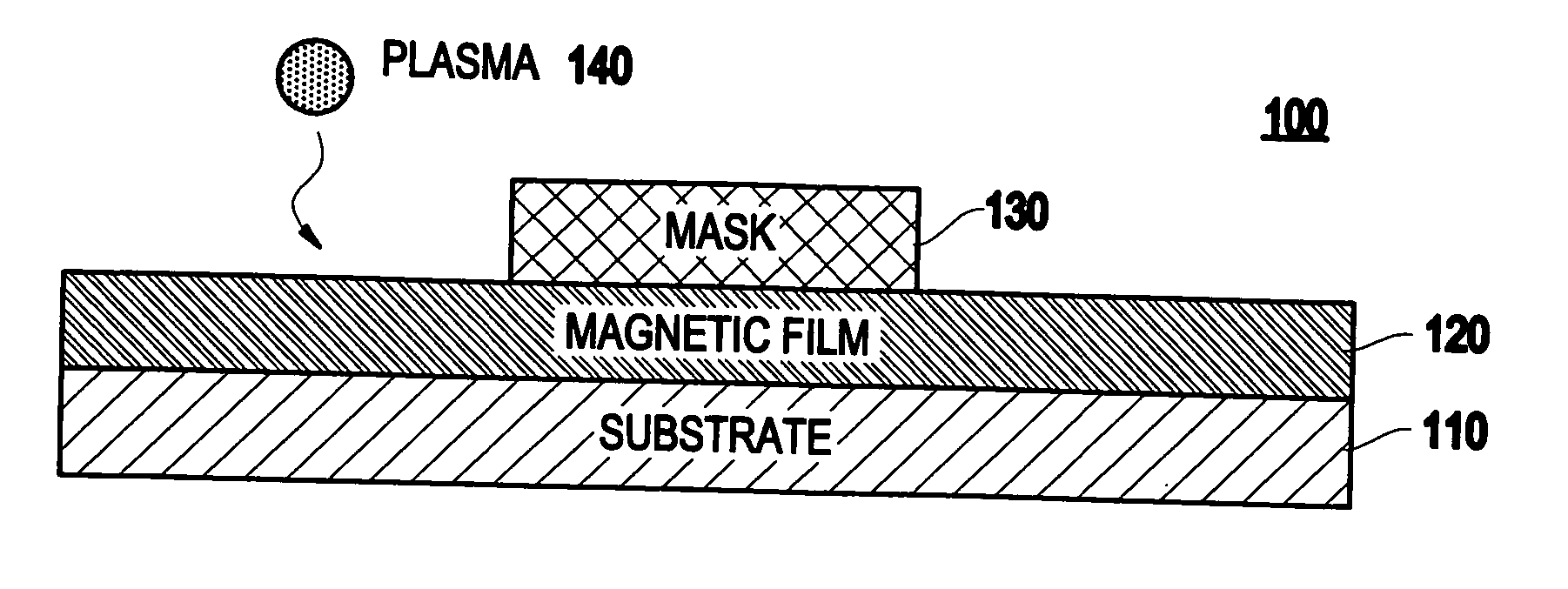
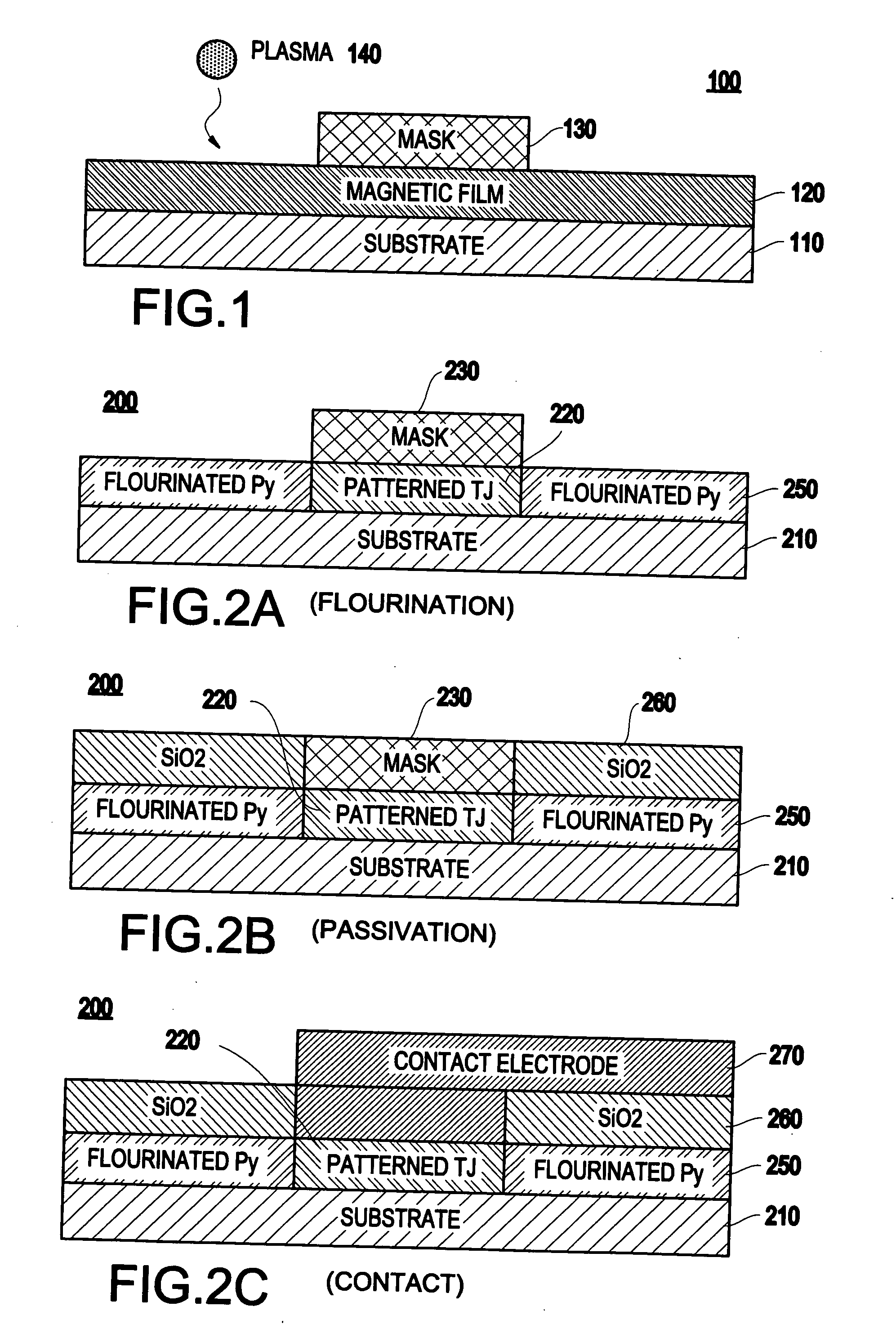
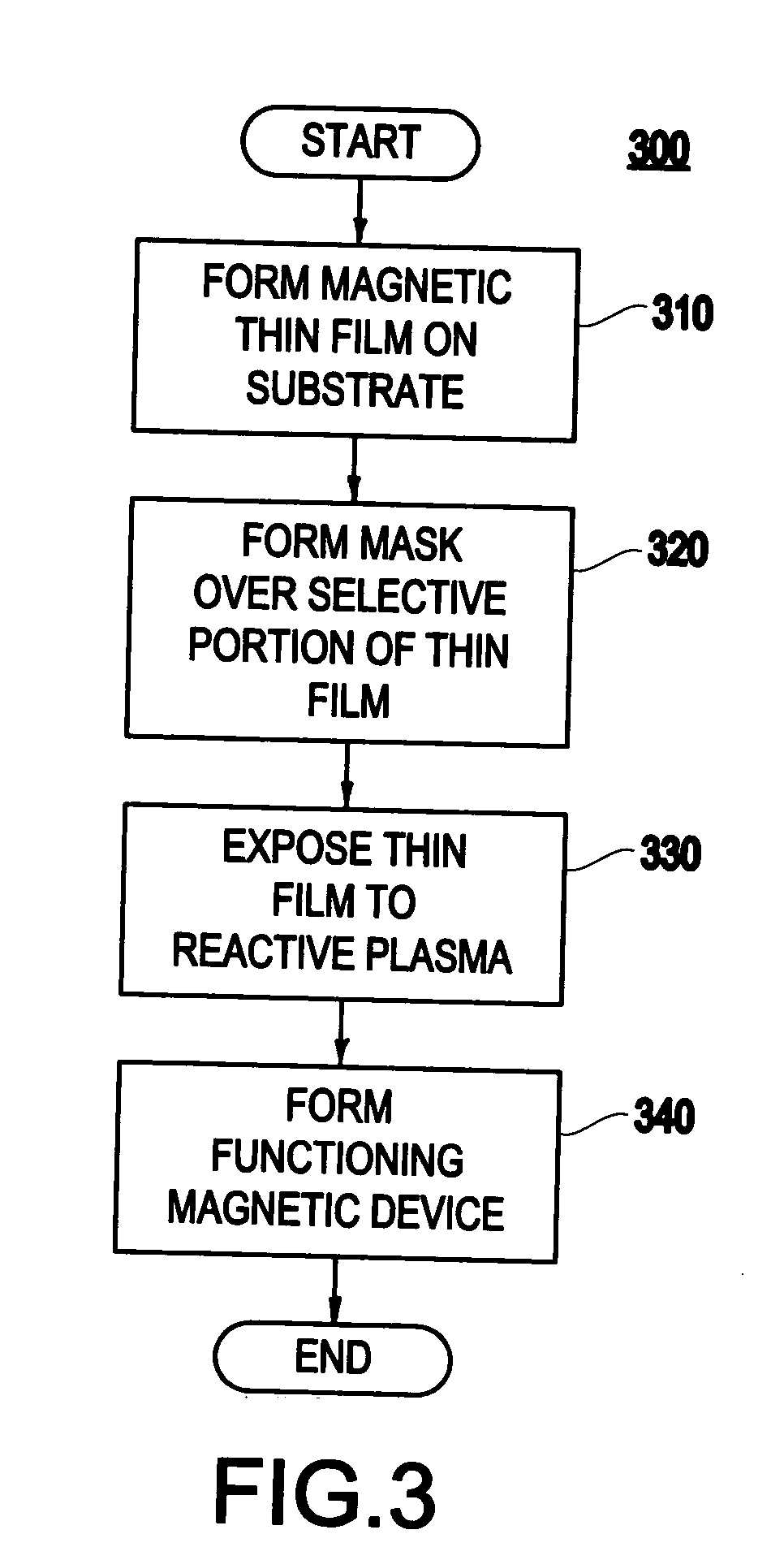
Method and system for patterning of magnetic thin films using gaseous transformation
A method (and resulting structure) of patterning a magnetic thin film, includes using a chemical transformation of a portion of the magnetic thin film to transform the portion to be non-magnetic and electrically insulating.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for manufacturing plastic optical transmission medium
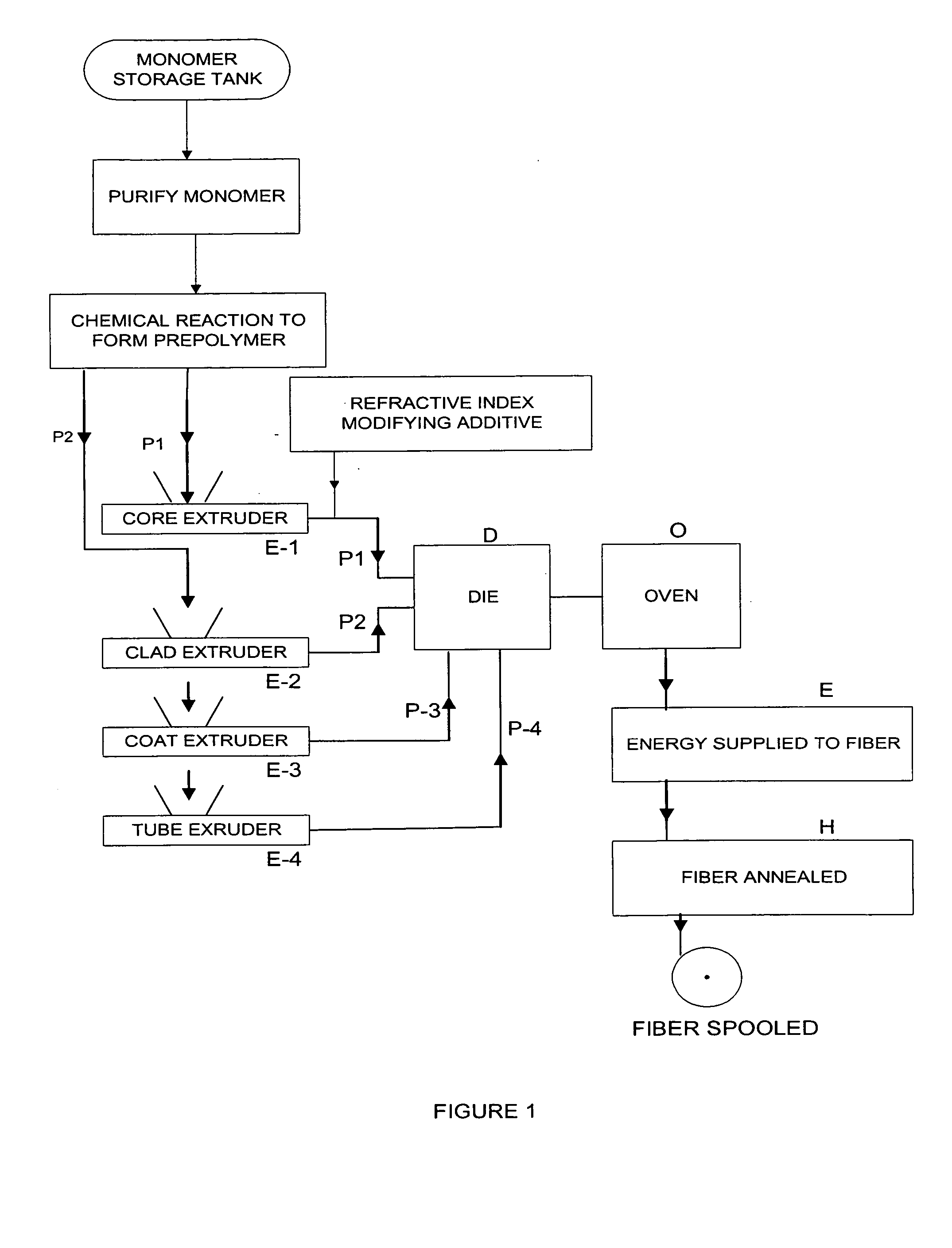
InactiveUS20050062181A1Reduce light transmittanceHigh light transmittanceOptical articlesFibre mechanical structuresFiberPolymer science
The subject invention pertains to a method for high speed, continuous manufacture of graded refractive index polymer optical fiber. The subject fiber material may be organic or perfluorinated. The subject method can include first forming energy activatable prepolymer compositions containing additives. The prepolymer compositions can be extruded at low temperature through a multi-annular die and surrounded by a co-extruded concentric melt stream which forms a tube with good structural integrity. The prepolymer compositions contained in the tube can be maintained at a temperature for a time sufficient to form the desired graded index profile. Energy can be delivered to the prepolymer compositions which can cause an irreversible chemical transformation and forms a mechanically and thermally stable polymer. A continuous process of thermal annealing of the fiber can be used to minimize residual stress. Multiple fibers may be produced simultaneously in a variety of physical configurations.
Owner:NANOPTICS
Optical recording material
InactiveUS6969578B2Higher effective concentrationImprove performancePhotosensitive materialsMechanical record carriersOptical propertyChemical transformation
An optical recording material which when exposed to actinic radiation produces a change in optical properties in the exposed regions, thereby providing a pattern of intelligence for storing and retrieving information, the recording material having: a) a polymer containing a covalently bound reactant moiety which is capable of undergoing a chemical transformation upon a one electron oxidation, thus causing the change in optical properties in the exposed regions; and b) a sensitizer capable of absorbing actinic radiation to cause an initial one electron oxidation of the reactant.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
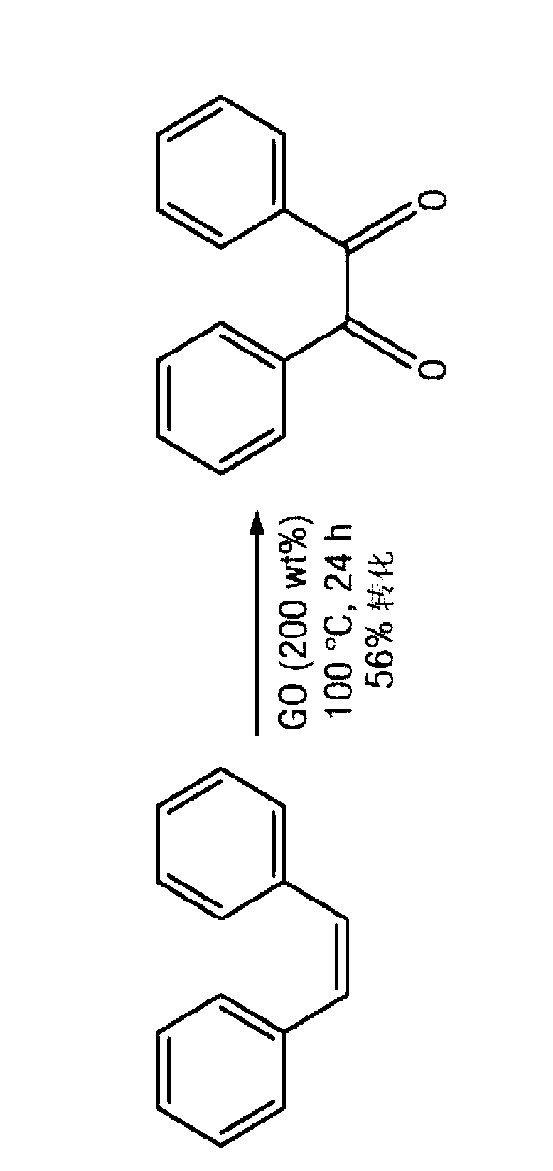
Carbocatalysts for chemical transformations
InactiveCN103025685AMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic compound preparationHydration reactionChemical reaction
The disclosure relates to catalytically active carbocatalysts, e.g., a graphene oxide or graphite oxide catalyst suitable for use in a variety of chemical transformations. In one embodiment, it relates to a method of catalyzing a chemical reaction of an organic molecule by reacting the organic molecule in the presence of a sufficient amount of graphene oxide or graphite oxide for a time and at a temperature sufficient to allow catalysis of a chemical reaction. According to other embodiments, the reaction may be an oxidation reaction, a hydration reaction, a dehydrogenation reaction, a condensation reaction, or a polymerization reaction. Some reactions may include auto-tandem reactions. The disclosure further provides reaction mixtures containing an organic molecule and graphene oxide or graphite oxide in an amount sufficient to catalyze a reaction of the organic molecule.
Owner:GRAPHEA
High-density fermentation and purification process for recombination high temperature-resistant hyperoxide dismutase
InactiveCN101275144AAvoid pollutionSimple purification processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliDismutase
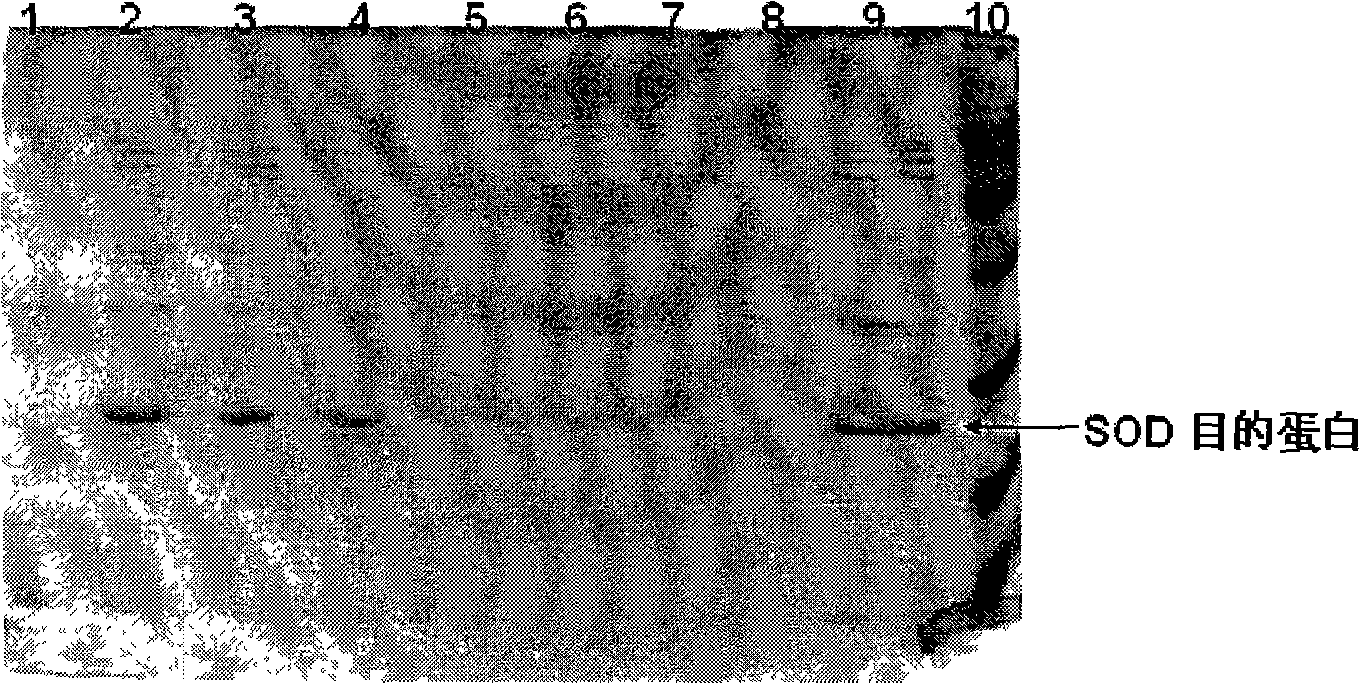
The present invention provides a high density fermentation and a purification process of a recombination high temperature resistance superoxide dismutase, the construction method of the invention includes: using gene coded for SOD in a thermophilic bacteria as a template, designing specific primer amplification target gene having restriction enzyme sites, after double digestion, connecting to plasmid vector pET28a after the same double digestion, constructing a recombinant plasmid, named for pSOD, transforming plasmid pSOD to competence escherichia coli BL21(DE3) by chemical transformation method, obtaining strain having high SOD yield after screening, completing the construction of SOD engineering bacteria; the fermentation process includes four steps of first order seed culture, secondary order feed culture, batch fermentation and induced expression, fermentation product SOD is finally obtained; the fermentation process realizes high level expression of SOD, the expression of the target protein is more than 60% of the bacterial protein total; SOD has excellent thermal stability and heat resistance, the expression product accounts for more than 60% of the whole proteins, and fully soluble protein, avoiding any trouble in the course of inclusion body renaturation; the purification process is simple, having high yield, lower cost, the final product SOD has high purification, high activity and strength stability.
Owner:YANGTZE DELTA REGION INST OF TSINGHUA UNIV ZHEJIANG +1
Method for manufacturing high performance components
InactiveUS6355211B1Promote resultsEliminate contaminating gasesAdditive manufacturing apparatusOther chemical processesChemical transformationReactive material
A method for producing high performance components by the consolidation of powdered materials under conditions of hot isostatic pressure. The method uses the inclusion of reactive materials mixed into pressure-transmitting mold materials and into the powder to be consolidated to contribute to in-situ materials modification including purification, chemical transformation, and reinforcement. The method also uses encapsulation of the mold in a sealed container to retain the mold material in position, and to exclude air and contaminants.
Owner:HUANG XIAODI
Self-Heating Chemical System for Sustained Modulation of Temperature
InactiveUS20070289720A1Easy to adjustBiofuelsWaste based fuelElectrical conductorChemical transformation
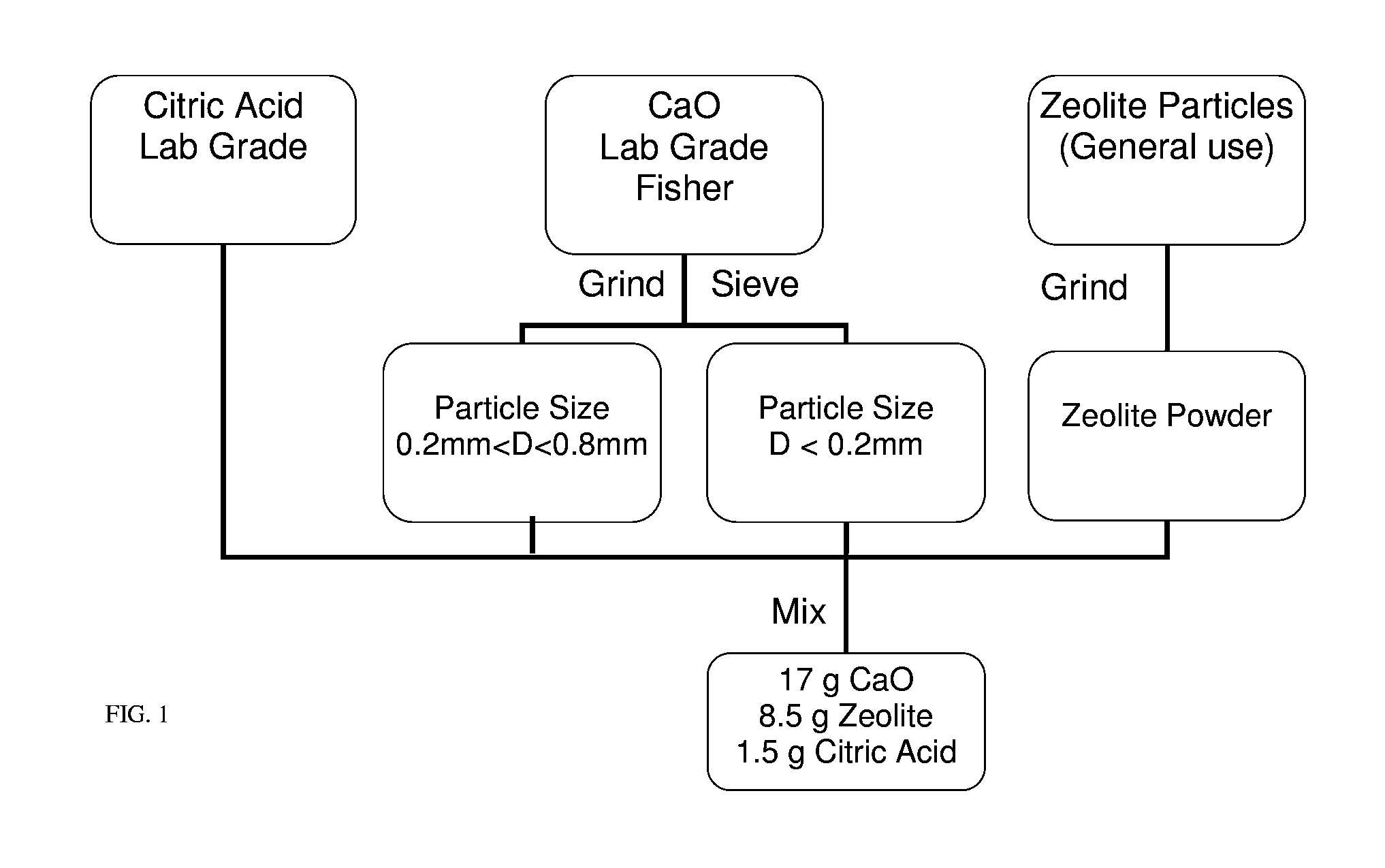
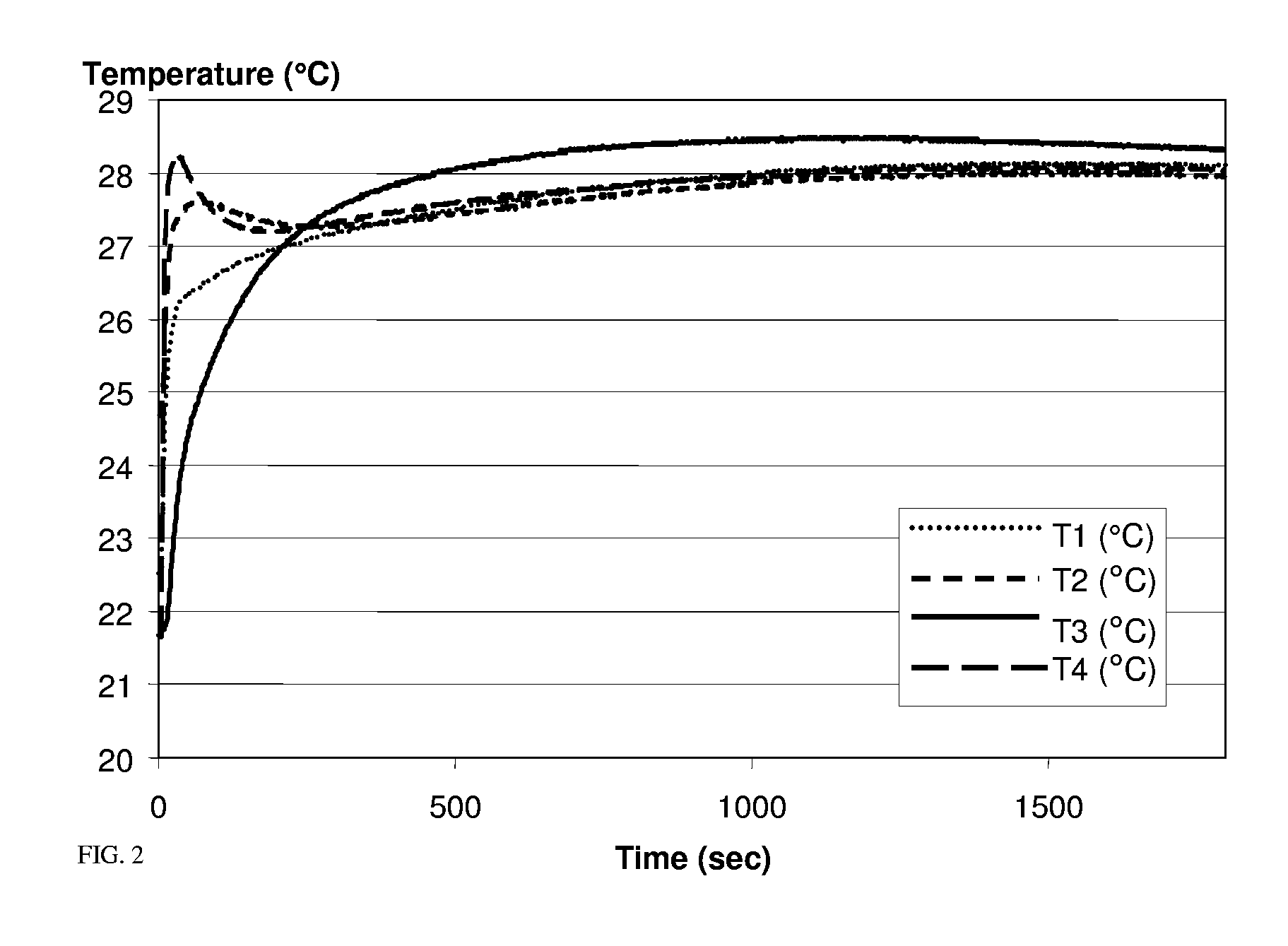
A self-heating chemical system using one or more primary components for exothermic reactions (such as calcium oxide), one or more porous components that can serve as a heat sink and conductor of heat as well as under going chemical transformations that release heat (zeolite), a weak acid (citric acid) for sustained modulation of temperature and pH. Exothermic reactions, mixing of some chemicals, sorption of certain chemicals, phase changes in chemicals, and dissolution of some chemicals in solvents release heat during these operations. The rate of heat generation coupled with mass and energy transfer rates to or from system(s) allows modulation of the temperature of systems. The modulation can be further enhanced by controlled release and availability of some of the components. This method provides with a class of self-heating product applications and focuses on the modulation of temperature through sequestering of reactions with different rates, heat release through dissolution, heat release through mixing, heat release through sorption, heat release through phase change as well as controlling mass and heat transfer rates.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Method of treating magnesium alloy work-piece surface
InactiveCN101016627AProtectiveDecorativeMetallic material coating processesElectrolysisChemical transformation
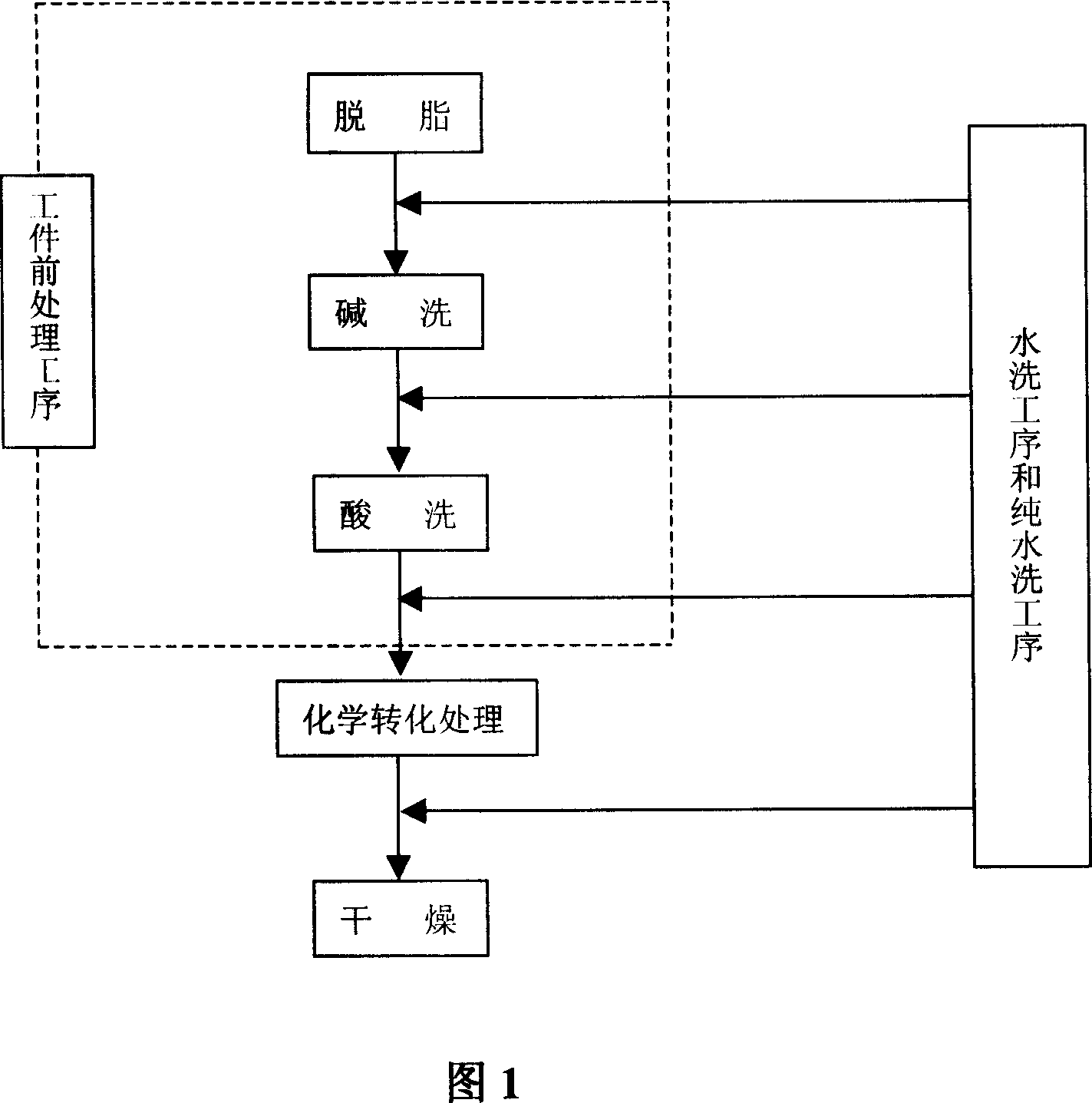
The invention discloses a surface disposing method of electron alloys work piece, which is characterized by the following: including work piece fore treatment, chemical transformation treatment, drying treatment and washing treatment of each interprocess; dipping electron alloys work piece into inverting liquid of main filming matter and assistance filming matter as chemical transformation treatment; setting main filming matter as one or several zircon salt, manganic salt, molybdate and tungstate and so on transient metal salt; converting to Na2MoO4.2H2O content with density at 5-150g / L; setting the assistance filming matter as one or several nitrate and sulfate of lithium, sodium and potassium alkali metal; converting to LiNO3 content with density at 0.5-20g / L and pH value of inverting liquid at 2-6; controlling the disposing temperature at 10-90 deg.c and disposing time at 5-30 min. This surface film possesses properties of protection and decoration.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Macro preparation method for mesoporous ordered graphene
The invention relates to a macro preparation method for mesoporous ordered graphene, and belongs to the technical field of nanometer materials. The method is characterized in that graphene is prepared by chemical transformation of carbon dioxide gas and in-situ quenching method. The method comprises the following steps of: igniting magnesium in a container filled with carbon dioxide to perform reaction of magnesium and carbon dioxide, and quenching the reaction product in different media; then, removing magnesium and magnesium oxide in the mixture; and washing and drying to obtain graphene. The method has the advantages that mesoporous ordered graphene is self-grown without a template, the method is simple to operate, low in cost and environment-friendly, and prepared graphene is high in quality and yield.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Halosilane Assisted PVT Growth of SiC
ActiveUS20120225004A1Reduce lossesReduce chemical attackPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesHalogenGas phase
In a physical vapor transport growth technique for silicon carbide a silicon carbide powder and a silicon carbide seed crystal are introduced into a physical vapor transport growth system and halosilane gas is introduced separately into the system. The source powder, the halosilane gas, and the seed crystal are heated in a manner that encourages physical vapor transport growth of silicon carbide on the seed crystal, as well as chemical transformations in the gas phase leading to reactions between halogen and chemical elements present in the growth system.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Therapeutic agents - II
InactiveUS20050209192A1Symptoms improvedEnsure adequate treatmentAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsChemical fractionChemical synthesis
The present invention relates generally to chemical agents useful in the treatment and prophylaxis of inflammatory conditions or in the amelioration of symptoms resulting from or facilitated by an inflammatory condition in a mammalian animal including human and primate, non-mammalian animal and avian species. More particularly, the present invention provides a chemical agent of the macrocyclic diterpene family obtaining from a member of the Euphorbiaceae family of plants or botanical or horticultural relatives thereof or derivatives or chemical analogues or chemically synthetic forms of the agents for use in the treatment or prophylaxis of an inflammatory condition or in the amelioration of symptoms resulting from or facilitated by an inflammatory condition in a mammal, animal or avian species. The present invention further contemplates a method for the prophylaxis or treatment of mammalian, animal or avian subjects for inflammatory conditions including chronic or transitory inflammatory conditions or for ameliorating. the symptoms of an inflammatory condition by the topical or systemic administration of a macrocyclic diterpene obtainable from a member of the Euphorbiaceae family or botanical or horticultural relatives thereof or a derivative, chemical analogue or chemically synthetic form of the agent. The chemical agent of the present invention may be in the form of a purified compound, mixture of compounds, a precursor form of one or more of the compounds capable of chemical transformation into a therapeutically active agent or be in the form of a chemical fraction, sub-fraction or preparation or extract of the plant.
Owner:PEPLIN RES
Pulping method for plant fibre raw material combined with biology
InactiveCN101158126AGood permeation and diffusion performancePromote dissolutionCellulose material pulpingChemical transformationDrug biotransformation
A method of making refined plant fiber raw material pulping combined with biomass is to extract sugar material such as hemicelluloses by water extractives before digesting pulping by plant fiber raw material or processing wastes of plant fiber raw material. When the products of extraction are separated, the liquid part are used for producing fuel ethanol and / or other products by adopting a biotransformation process or a chemical transformation process; the extraction residue can be made into paper pulp by conventional method or used for extracting lignin or processed into fertilizer. By adopting method of the invention, the extracted sugar material such as hemicelluloses can be recycled. When the solid residue left after extraction is used for making pulp by a traditional chemical method, the black liquid pollution can be alleviated and the treatment load of alkali recovery can be reduced; when the solid residue is used for making pulp by organic solvent method, the proportion of sugar material such as hemicelluloses degraded in the cooking residual liquid can be greatly reduced and the difficulty of separation of sugar material and organic solvent in the cooking residual liquid can be reduced, at the same time, by products---lignin can be obtained.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Carbocatalysts for chemical transformations
InactiveUS20130123514A1Promote oxidationPromote hydrationMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesHydration reactionChemical reaction
The disclosure relates to catalytically active carbocatalysts, e.g., a graphene oxide or graphite oxide catalyst suitable for use in a variety of chemical transformations. In one embodiment, it relates to a method of catalyzing a chemical reaction of an organic molecule by reacting the organic molecule in the presence of a sufficient amount of graphene oxide or graphite oxide for a time and at a temperature sufficient to allow catalysis of a chemical reaction. According to other embodiments, the reaction may be an oxidation reaction, a hydration reaction, a dehydrogenation reaction, a condensation reaction, or a polymerization reaction. Some reactions may include auto-tandem reactions. The disclosure further provides reaction mixtures containing an organic molecule and graphene oxide or graphite oxide in an amount sufficient to catalyze a reaction of the organic molecule.
Owner:MOSELEY SAMUEL G +8
Precoated coil coating for adhering polyester film and using method thereof
ActiveCN101602914AImprove adhesionFirmly attachedLiquid surface applicatorsPolyester coatingsPolyester resinSolvent
The invention relates to precoated coil coating for adhering a polyester film and a using method thereof. The precoated coil coating comprises the following compositions in percentage by mass: 20 to 35 percent of film-forming resin in solid, 0.5 to 5 percent of an auxiliary agent, 20 to 35 percent of pigment and filling, and 25 to 50 percent of solvent, wherein the film-forming resin consists of 70 to 95 percent of polyester resin which is provided with hydroxy functional group and has number average molecular weight of between 3,500 and 20,000 and a hydroxyl value of between 6 and 35, and 5 to 30 percent of crosslinked resin. The using method is to directly coat the precoated coil coating for adhering the polyester film on a steel plate which is treated by chemical transforming solution and laminate and adhere the polyester film on site, or directly coat the precoated coil coating on a precoated coil which is precoated with priming coat, bake and cure the coil, and laminate and adhere the polyester film on site. The polyester film laminated precoated coil prepared by the precoated coil coating has excellent adhesive force, cup drawing and water boiling resistance.
Owner:CNOOC CHANGZHOU PAINT & COATINGS IND RES INST +1
Device for performing a chemical transformation in fluidic media
ActiveUS20110203995A1Eliminate the problemImprove good performanceShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersRotary stirring mixersChemical transformationEngineering
A device is provided for performing chemical transformation in a fluid, with a flow distributor having at least one fluid medium inlet, at least one fluid medium outlet, and at least one confinement wherein the chemical transformation is performed; and a means for rotating, rocking, wagging, or oscillating the device. At least one confinement may be equipped with a provision for providing heat, cooling, sound, light or other types of radiation, such provision being contacted to an external source through an actuator shaft. The flow distributor may be provided with sectors connected with the centrally located fluid medium inlet and a designated peripheral fluid medium outlet. The means for rotating, rocking, wagging, or oscillating the device may be an element producing magnetic fields or a shaft mechanically connected to an external actuating device.
Owner:SPINCHEM AB
Chemical transformation of lignocellulosic biomass into fuels and chemicals
A method for converting a carbohydrate to a furan in a polar aprotic solvent in the presence of a chloride, bromide, or iodide salt or a mixture thereof and optionally in the presence of an acid catalyst, a metal halide catalyst and / or an ionic liquid (up to 40 wt %). The method can be employed in particular to produce furfural or 5-hydroxymethylfurfural.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
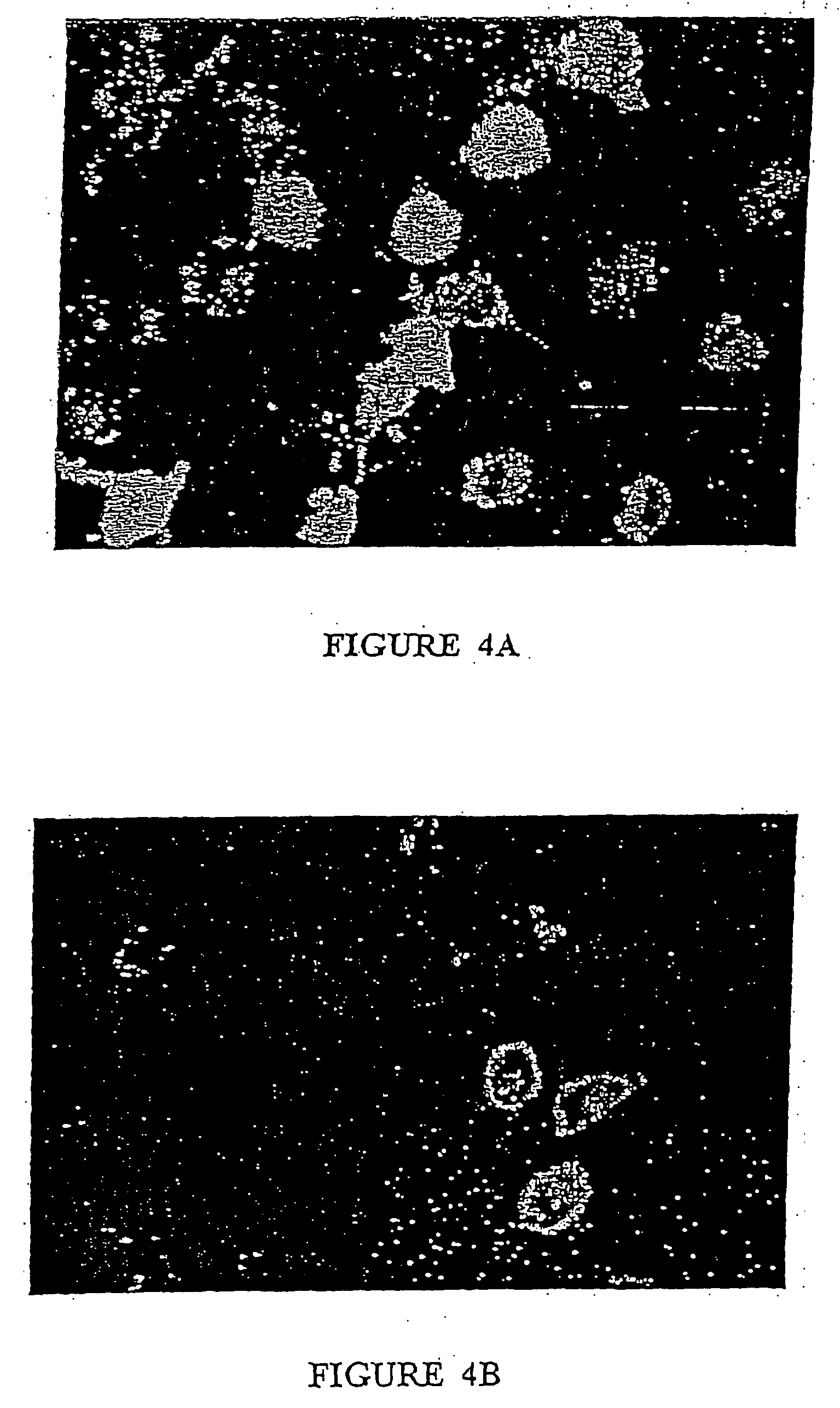
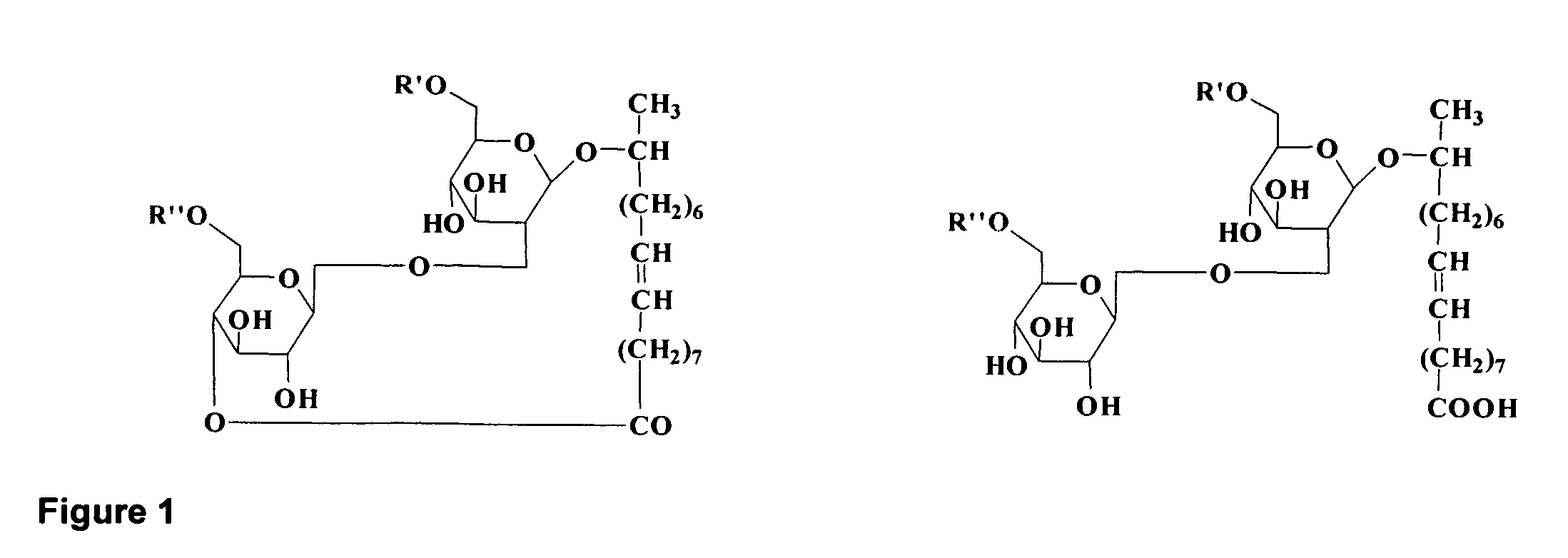
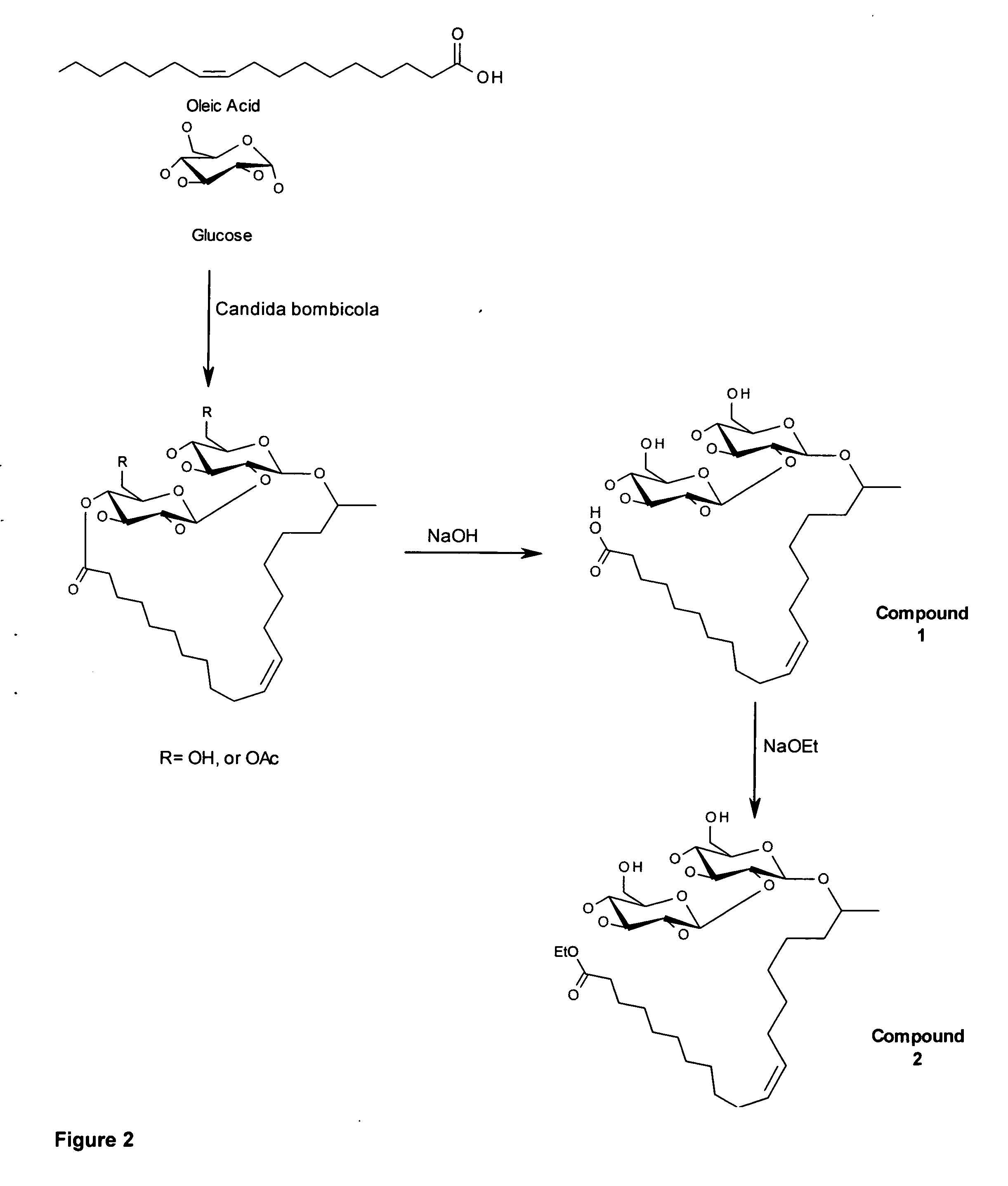
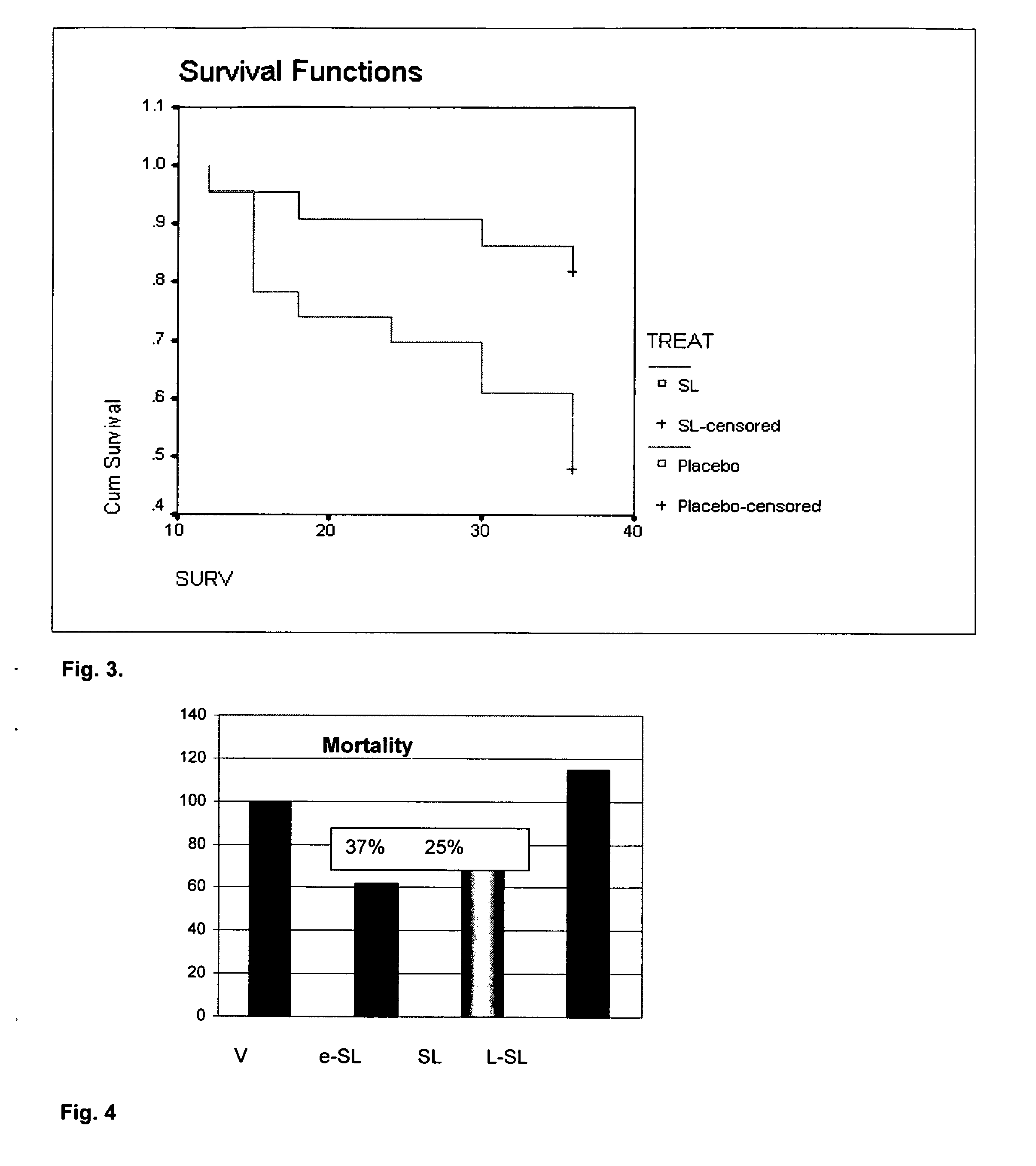
Purified Ethyl Ester Sophorolipid for the Treatment of Sepsis
InactiveUS20120142621A1High purityEfficient productionBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredients[Candida] apicolaChemical transformation
A microbial ethyl esther sophorolipid derivative with no acetylated groups produced by Candida species, for treating and preventing sepsis / septic shock. The method of producing sophorolipids is through microbial resting cells of Candida bombicola. The sophorolipids obtained from resting state cultures are isolated as a complex mixture of compounds and then decanted as a dense oil from the culture broth, subsequently washed to remove free fatty acids. Secondary chemical transformation via base catalyzed hydrolysis is used to reduce the 8 possible structural sophorolipid species to a single moiety, the 17-L-[(2′-O-b-D-glucopyranosyl-b-D-glucopyranosyl)-oxy]-cis-9-octadecenoate de-acetylated free acid. The compound acts primarily through decreasing inflammatory cytokines and eliciting other synergistic anti-inflammatory mechanisms by blocking TLR4-CD14 upstream of the inflammatory signaling cascade. The compound can be administered either intraperitoneally or intravenously at single or multiple doses of 5-30 mg / kg of weight in solvent media or in capped nanoparticles, preferably within 48 hours of sepsis inception.
Owner:STREETCAREC SLOAN
Deposition of uniform layer of desired material
InactiveUS20060275542A1High depositionIncrease speedMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsVitrificationChemical transformation
A process for the deposition of a thin film of a desired material on a surface comprising: (i) providing a continuous stream of amorphous solid particles of desired material suspended in at least one carrier gas, the solid particles having a volume-weighted mean particle diameter of less than 500 nm, at an average stream temperature below the glass transition temperature of the solid particles of desired material, (ii) passing the stream provided in (i) into a heating zone, and heating the stream in the heating zone to elevate the average stream temperature to above the glass transition temperature of the solid particles of desired material, wherein no substantial chemical transformation of the desired material occurs due to heating of the desired material, (iii) exhausting the heated stream from the heating zone through at least one distributing passage, at a rate substantially equal to its rate of addition to the heating zone in step (ii), wherein the carrier gas does not undergo a thermodynamic phase change upon passage through heating zone and distribution passage, and (iv) exposing a receiver surface that is at a temperature below the temperature of the heated stream to the exhausted flow of the heated stream, and depositing particles of the desired material to form a thin uniform layer of the desired material on the receiver surface.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com