Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2065 results about "Reflection coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics and electrical engineering the reflection coefficient is a parameter that describes how much of an electromagnetic wave is reflected by an impedance discontinuity in the transmission medium. It is equal to the ratio of the amplitude of the reflected wave to the incident wave, with each expressed as phasors. For example, it is used in optics to calculate the amount of light that is reflected from a surface with a different index of refraction, such as a glass surface, or in an electrical transmission line to calculate how much of the electromagnetic wave is reflected by an impedance. The reflection coefficient is closely related to the transmission coefficient. The reflectance of a system is also sometimes called a "reflection coefficient".
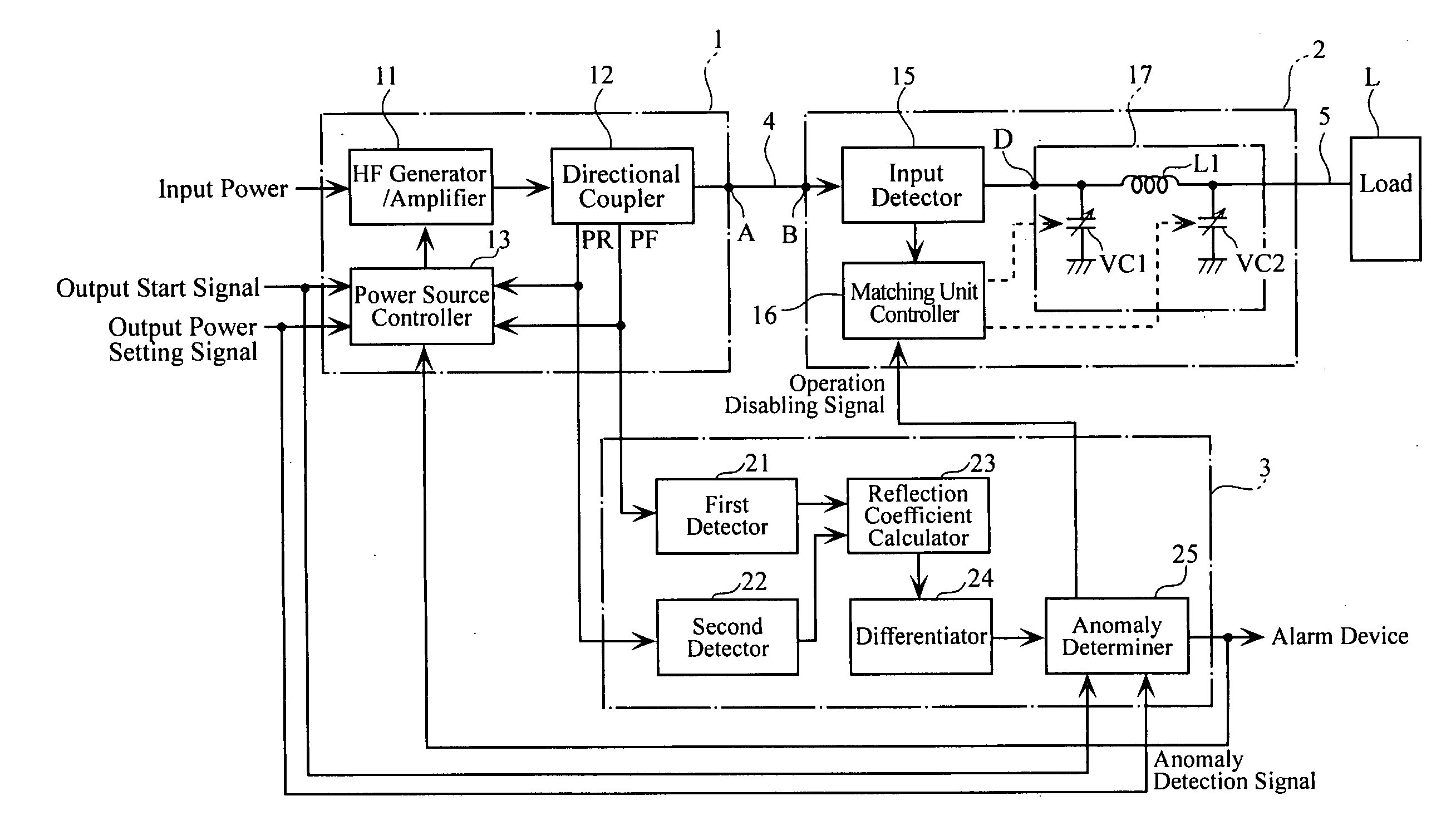
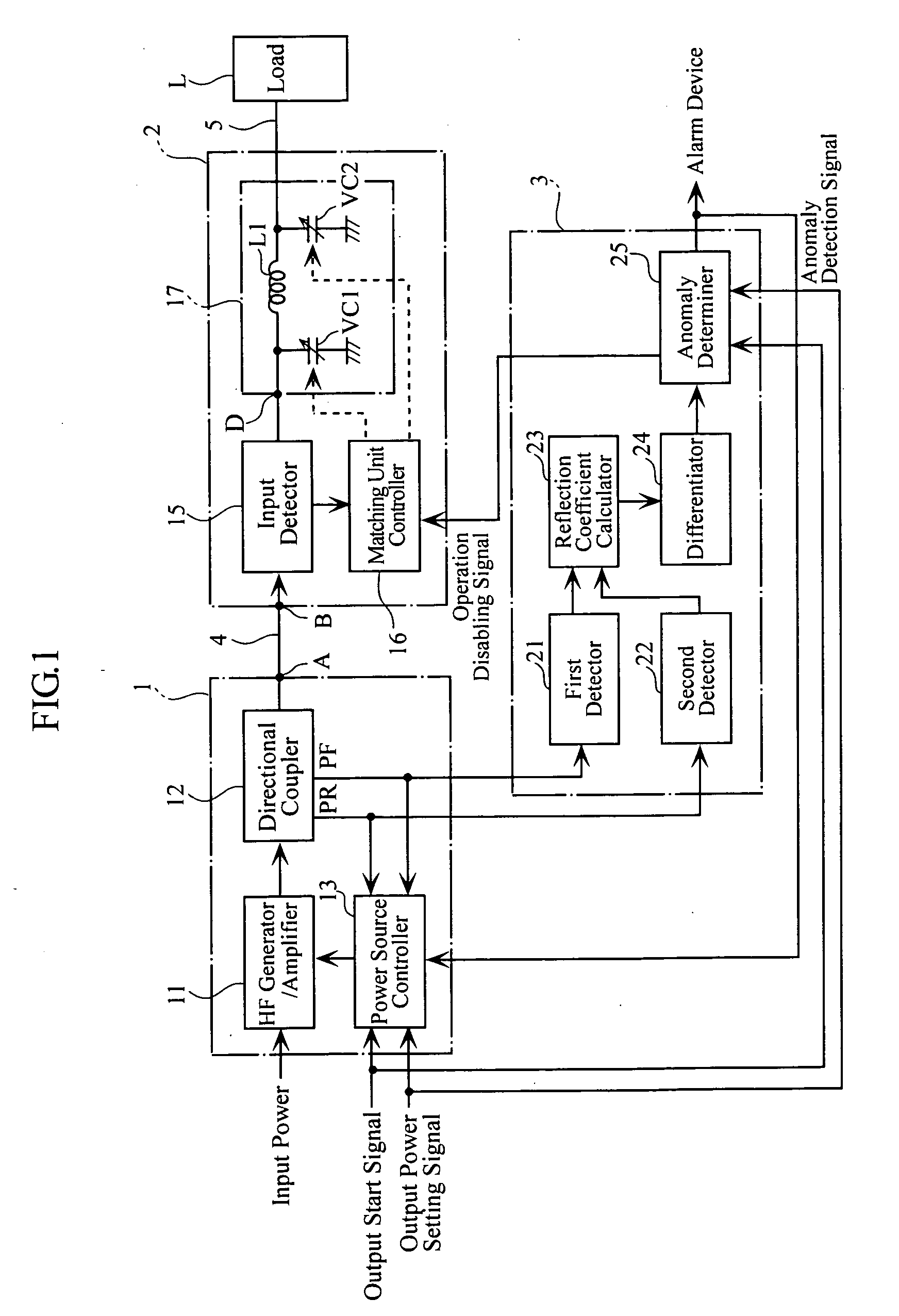
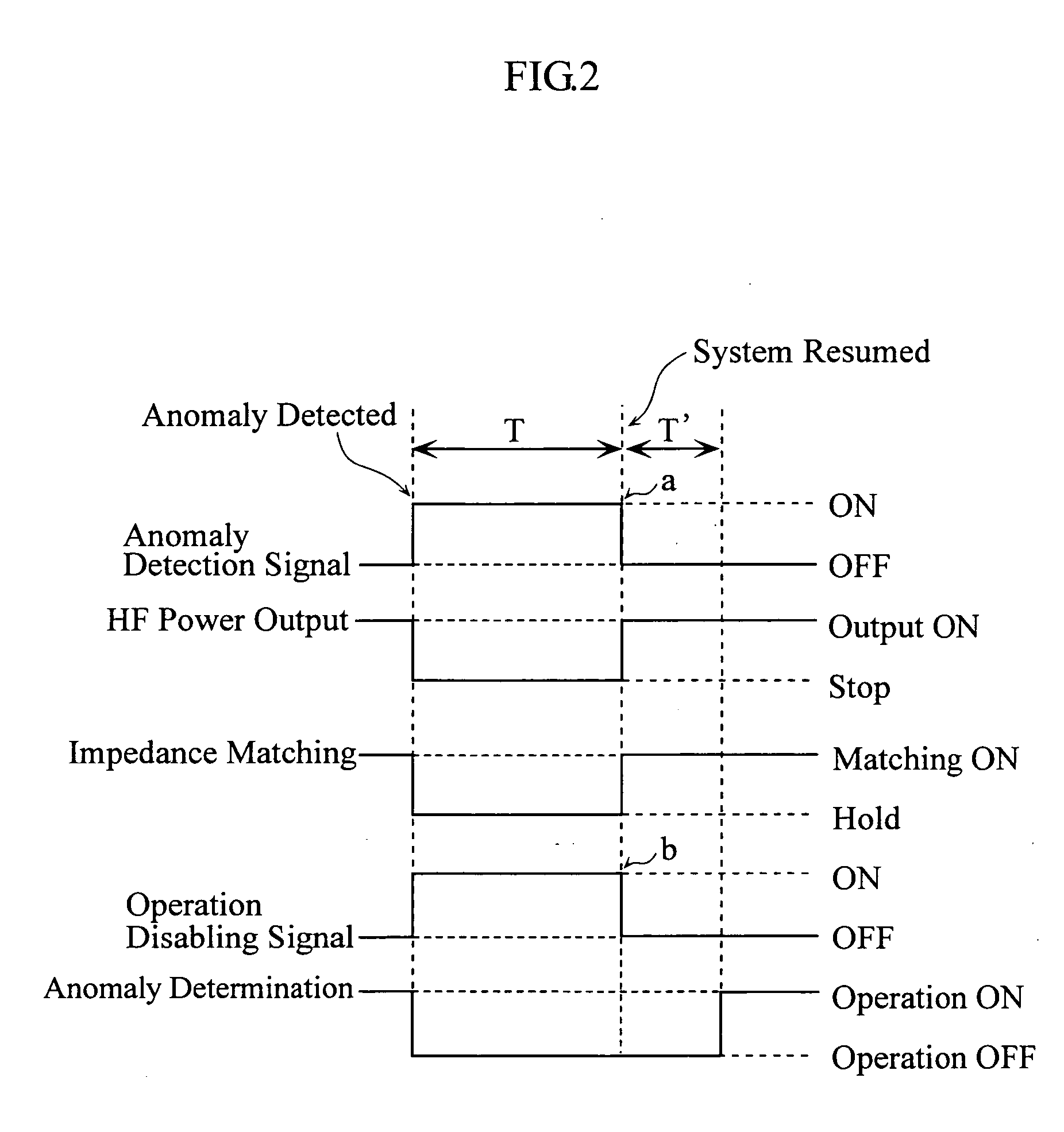
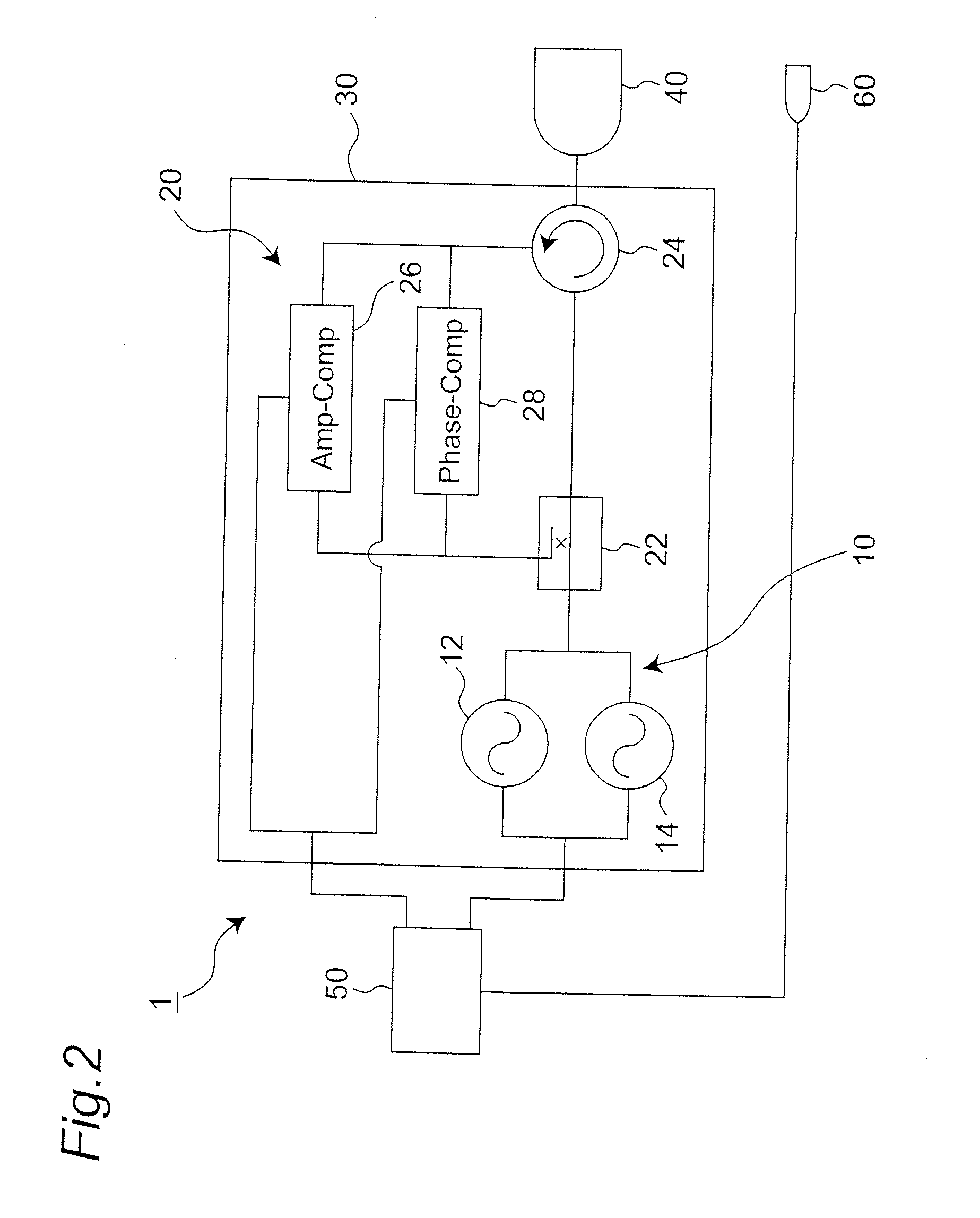
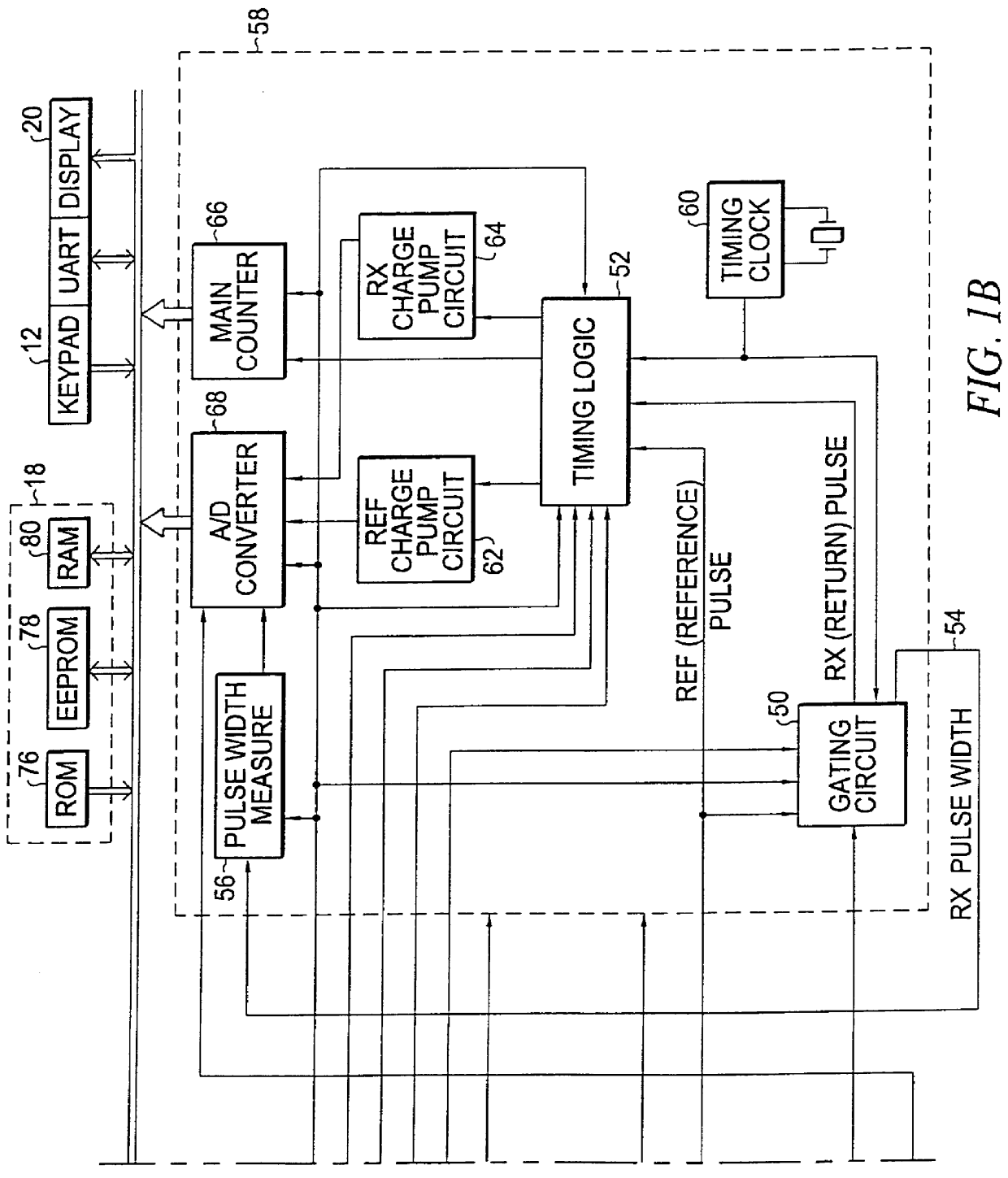
High-frequency power supply system
InactiveUS20070121267A1Multiple-port networksElectric discharge tubesDifferentiatorHigh frequency power
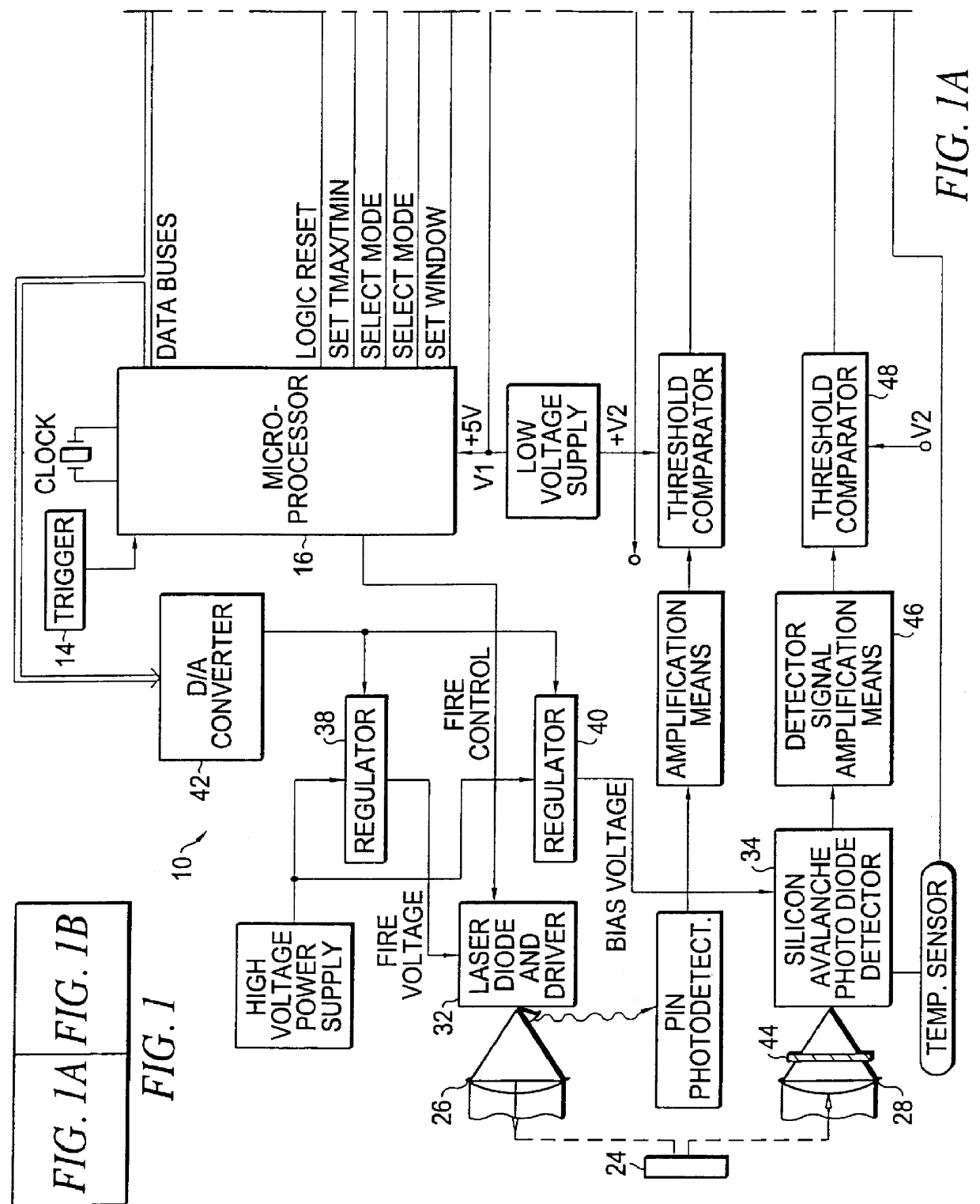
A high-frequency power supply system includes an anomaly detector 3 which detects an anomaly occurring in a circuit on the side of a load L as from an outputting end A of a high-frequency power source 1. The anomaly detector 3 includes a first detector 21 which detects a voltage value Vf of a high-frequency forward wave, a second detector 22 which detects a voltage value Vr of a high-frequency reflected wave, a reflection coefficient calculator 23 and a differentiator 24 which calculate a reflection coefficient differential value dΓ / dt from the forward wave voltage value Vf and the reflected wave voltage value Vr, and an anomaly determiner 25 which determines of an occurrence of an anomaly based on the reflection coefficient differential value dΓ / dt. When the anomaly detector 3 outputs an anomaly detection signal to the high-frequency power source 1, high-frequency power source 1 stops its power output operation.
Owner:DAIHEN CORP
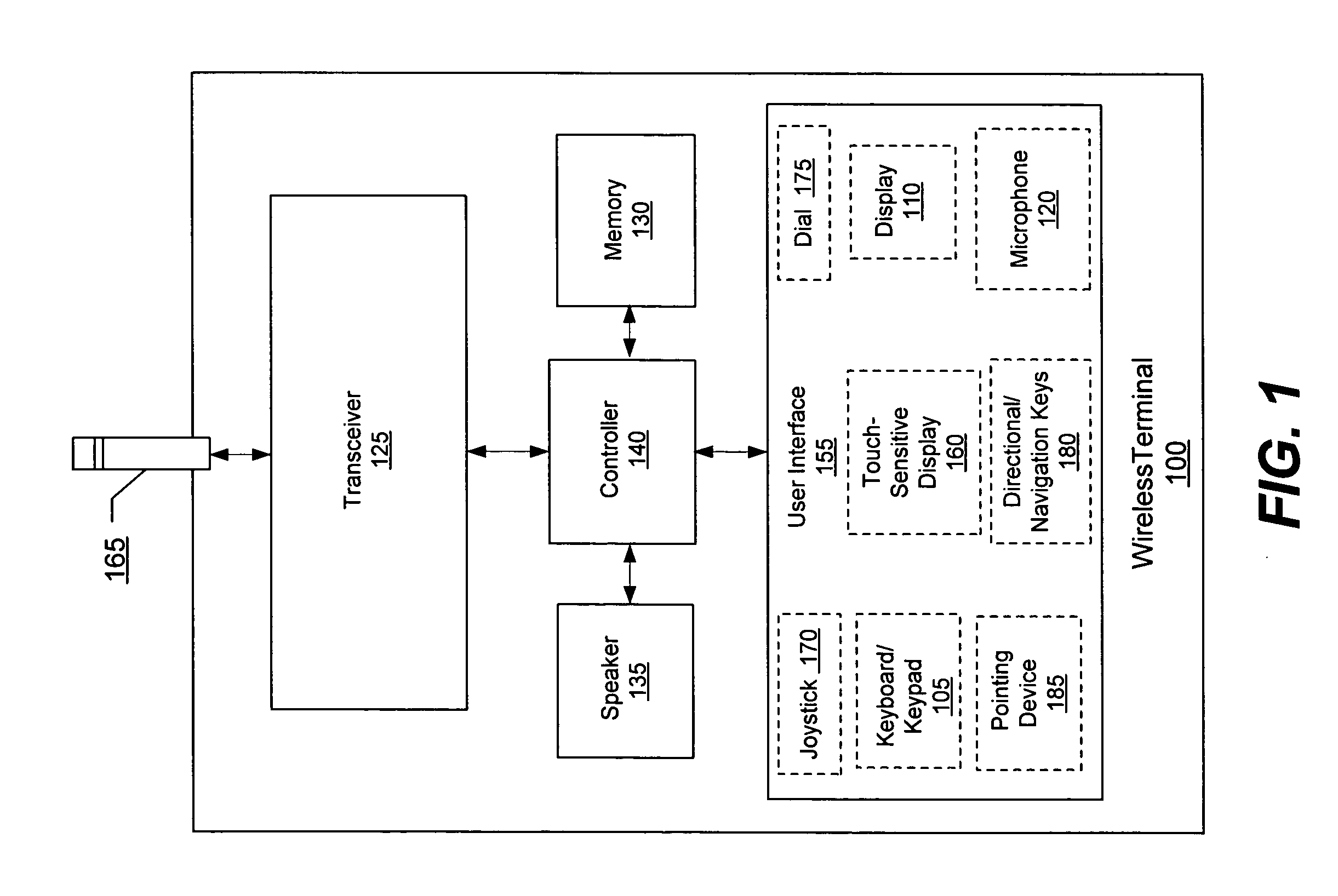
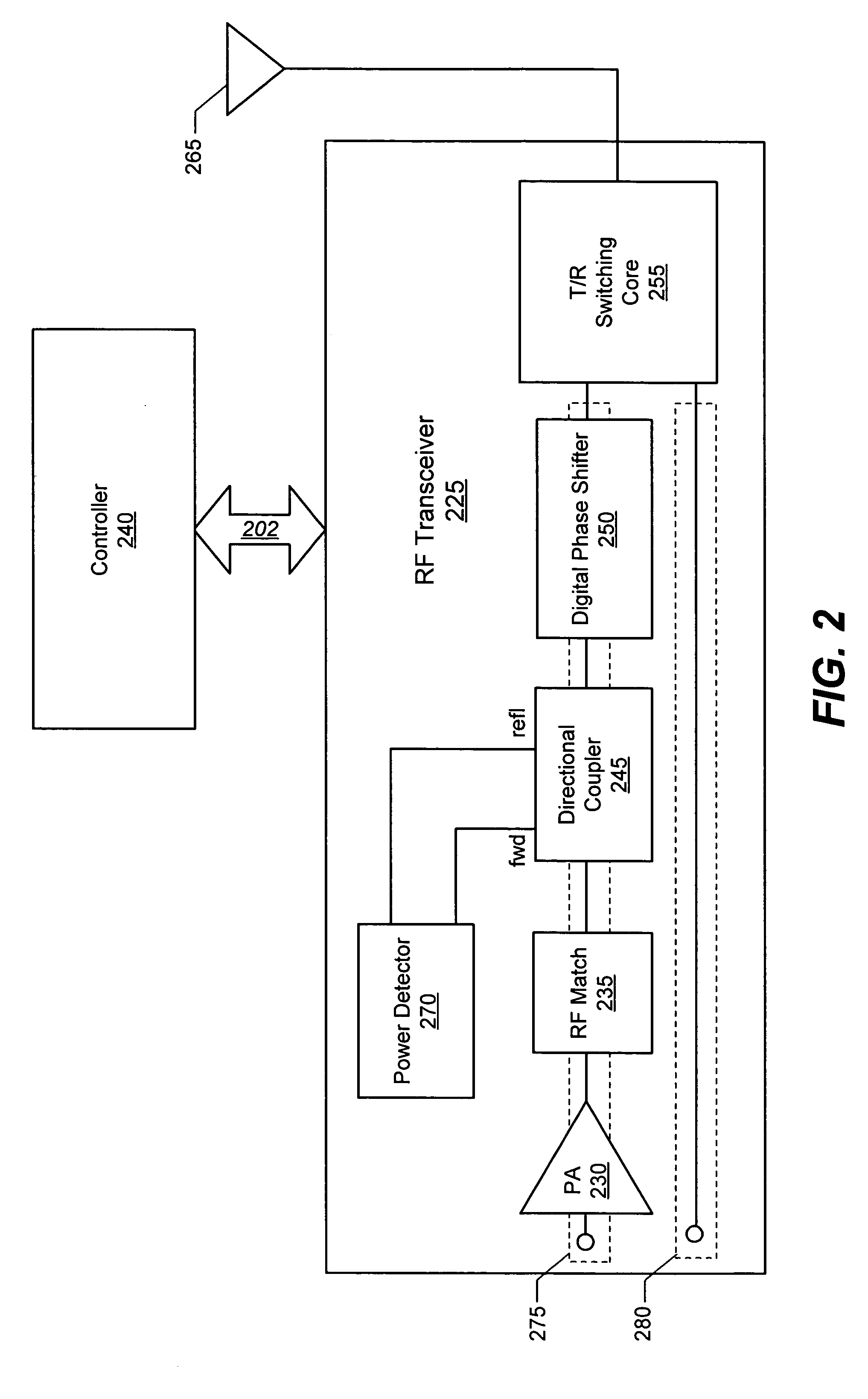
Devices, methods, and computer program products for controlling power transfer to an antenna in a wireless mobile terminal
InactiveUS20070142014A1Different electrical lengthResonant long antennasRadio relay systemsPower controllerAudio power amplifier
A wireless mobile terminal includes an antenna, a power amplifier coupled to the antenna, a power detector coupled to an output of the power amplifier, a phase shifter coupled between the output of the power amplifier and the antenna, and a controller coupled to the phase shifter. The power detector is configured to detect a power of a signal provided by the power amplifier. The controller is configured to adjust the phase shifter responsive to the detected signal power. More particularly, the controller may be configured to adjust the phase shifter to modify a phase component of a reflection coefficient of a load impedance at the power amplifier output without substantially altering a magnitude of the reflection coefficient. Related methods and computer program products are also discussed.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
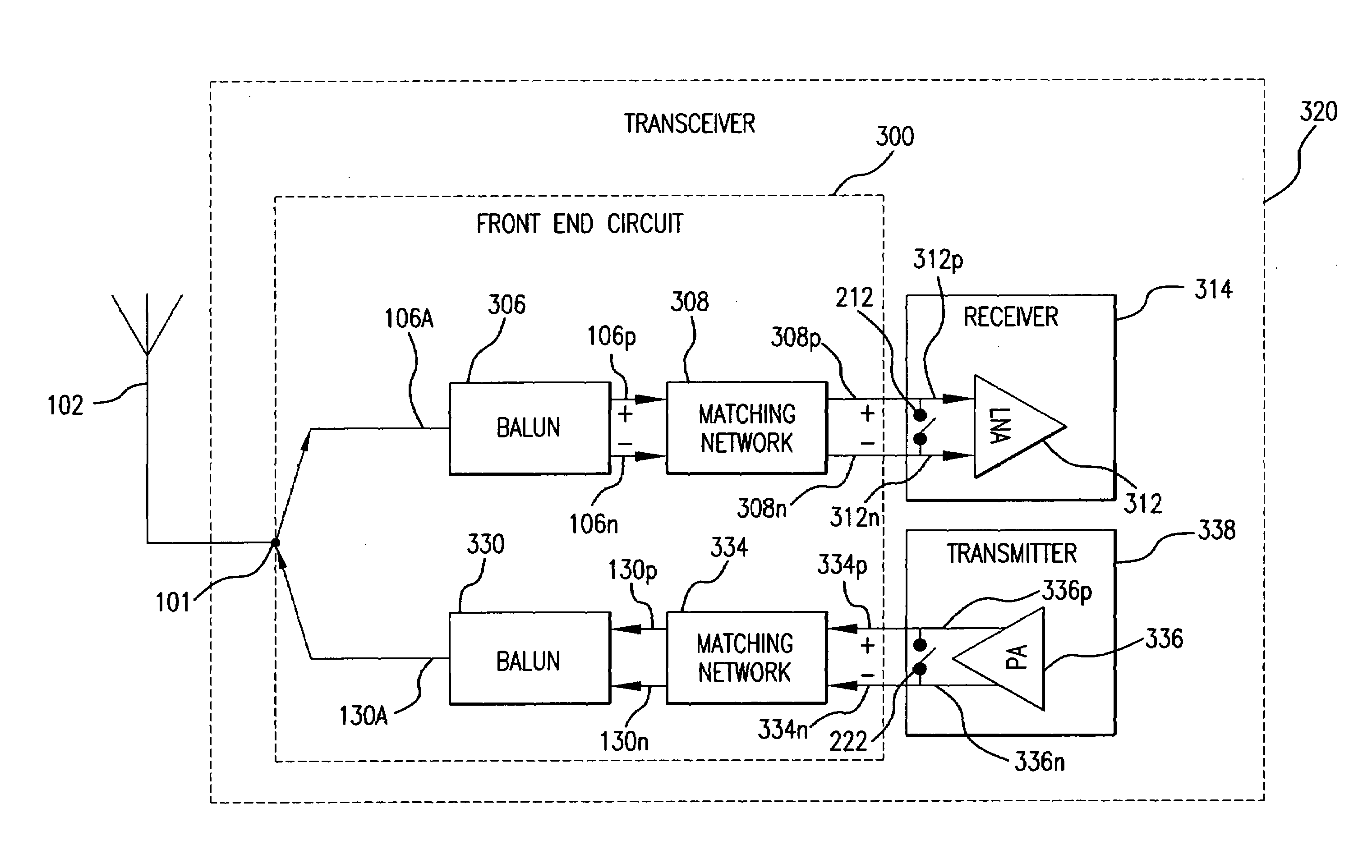
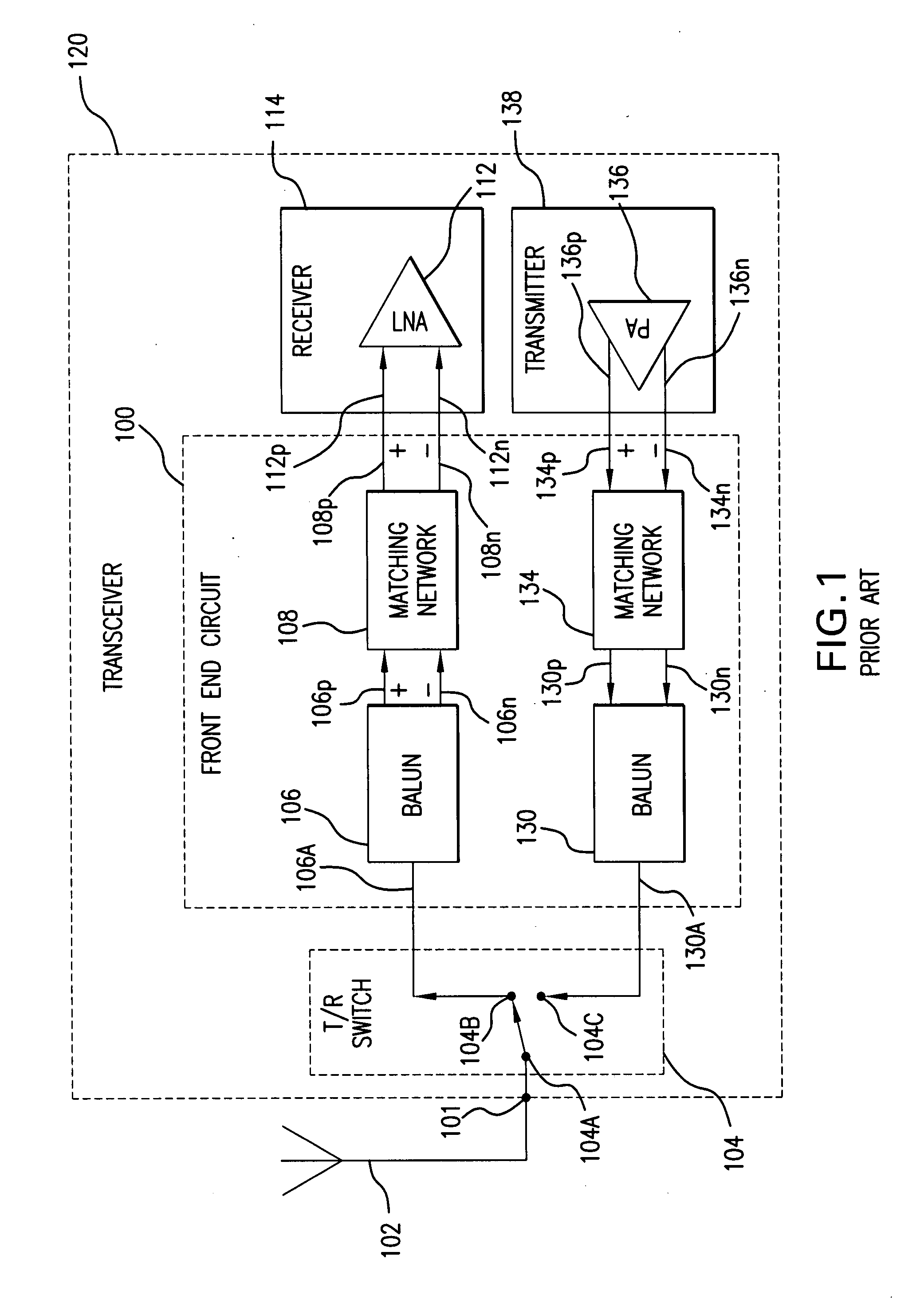
Package filter and combiner network
InactiveUS7283793B1Improve powerImprove efficiencyOne-port networksTransmissionPhase shiftedTransceiver
A transceiver front end circuit includes an antenna terminal capable of being coupled to an antenna. A first balun circuit has a single input that is coupled to the antenna terminal, and a pair of balanced outputs coupled to a corresponding pair of balanced receiver inputs. The first balun circuit matches an input impedance of the pair of balanced receiver inputs and substantially phase shifts the input reflection coefficient of the pair of balanced receiver inputs by about 180-degrees. A second balun circuit has a single output coupled to the antenna terminal and a pair of balanced inputs coupled to a corresponding pair of balanced transmitter outputs. The second balun circuit matches an output impedance of the pair of balanced transmitter outputs and substantially phase shifts the output reflection coefficient of the pair of balanced transmitter outputs by about 180-degrees. The first balun circuit and the second balun circuit can be contained within a single package. A first shunt switch can be coupled across the pair of receiver inputs. A second shunt switch can be coupled across the pair of transmitter outputs.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE +1
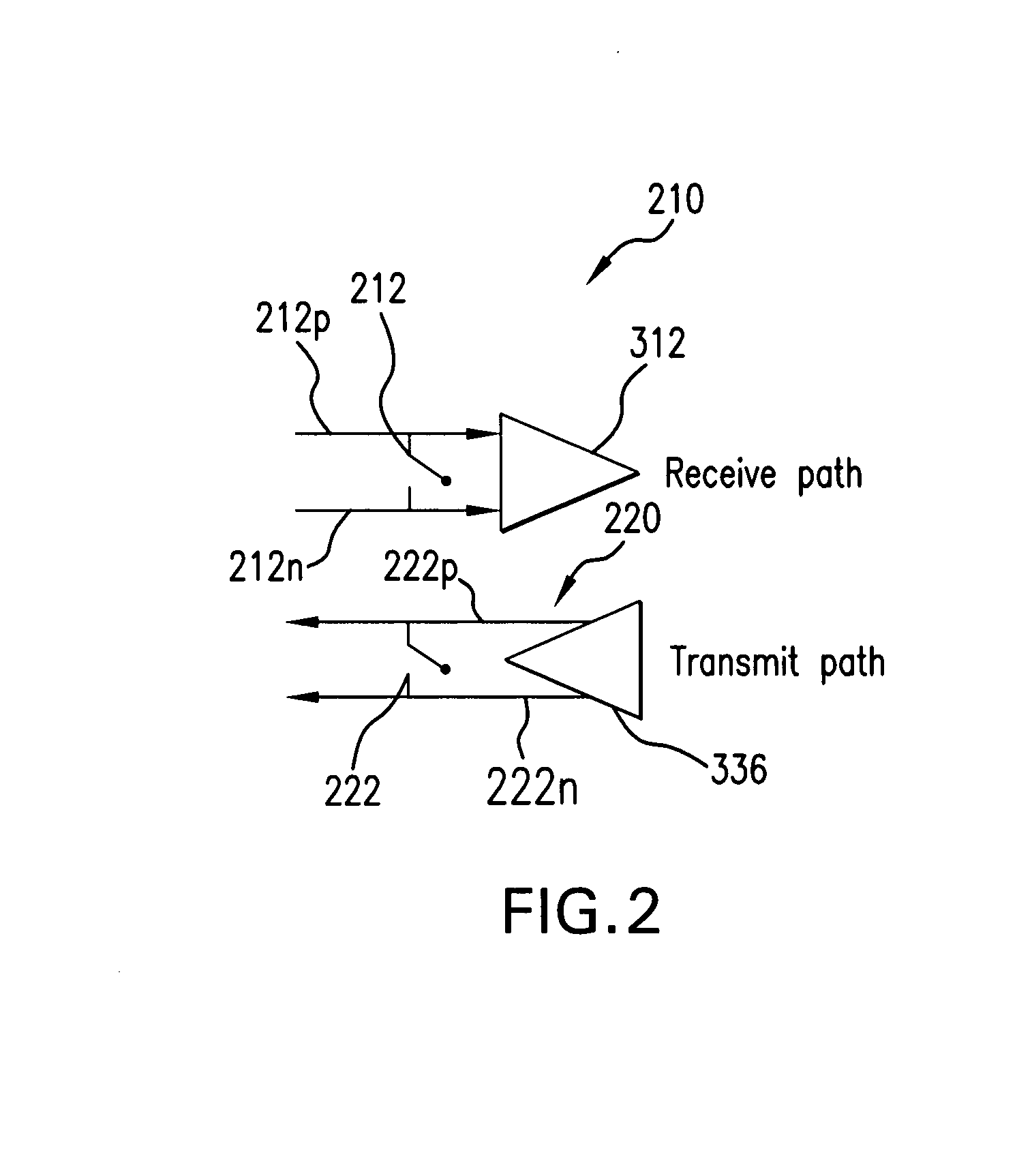
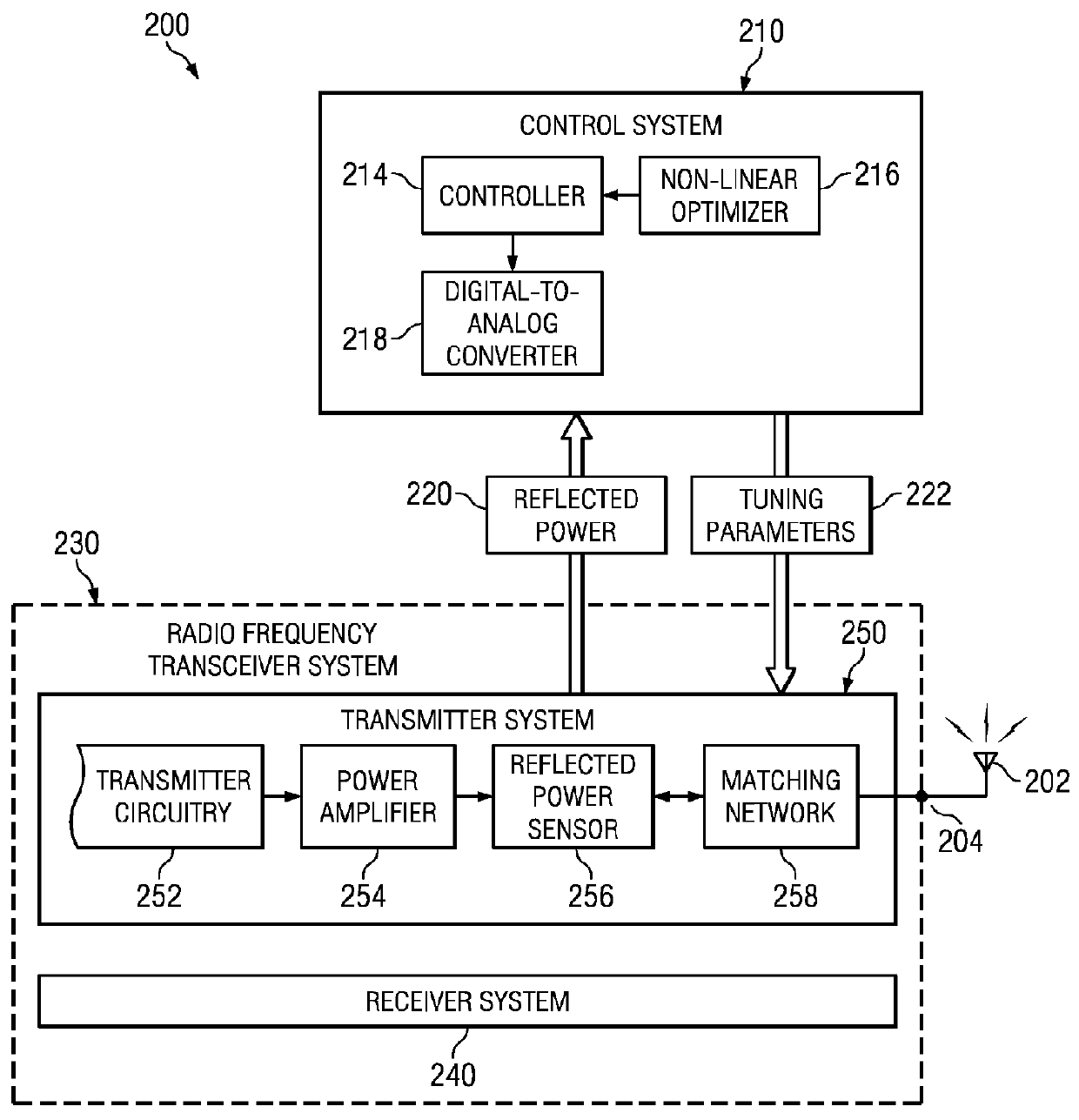
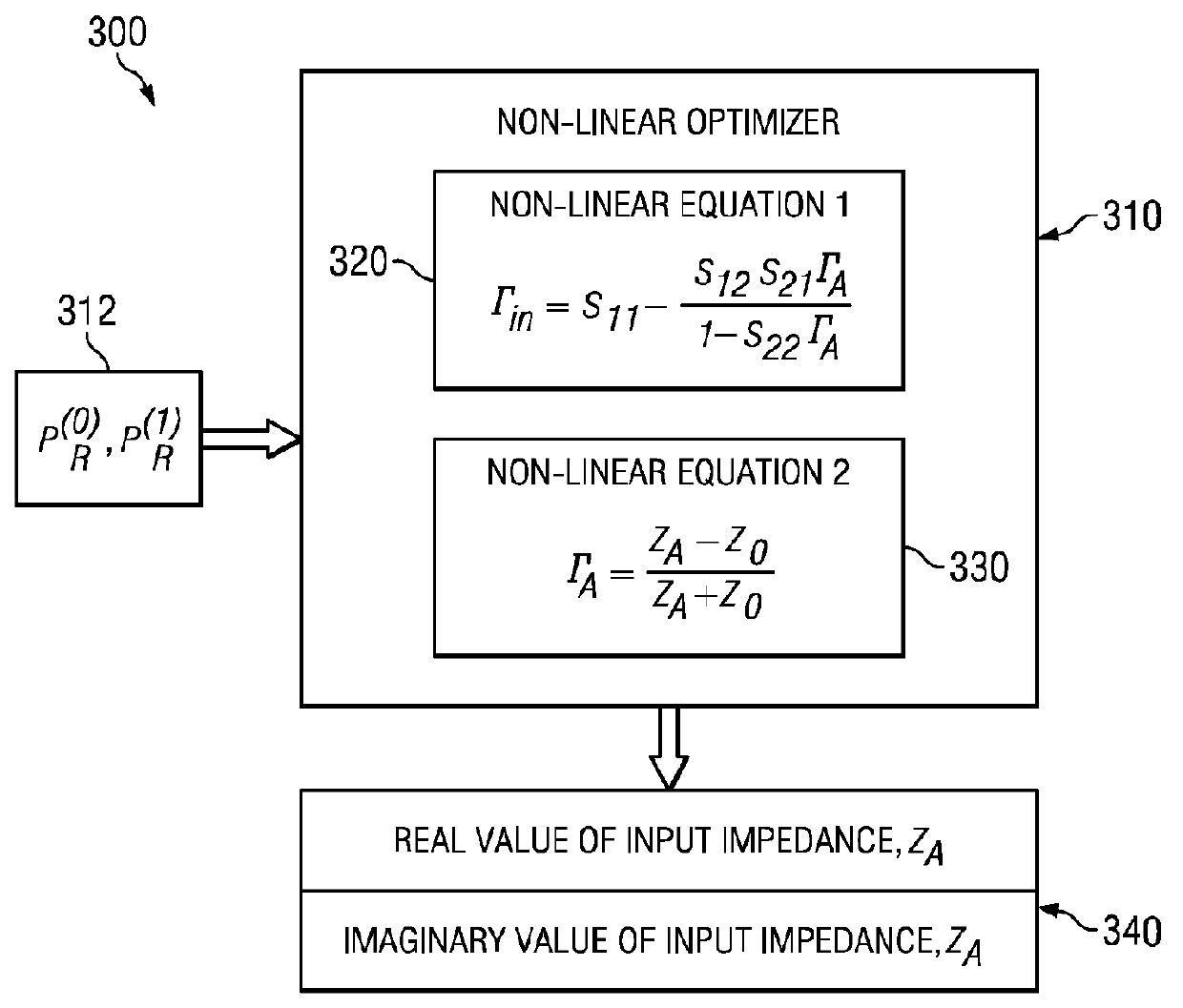
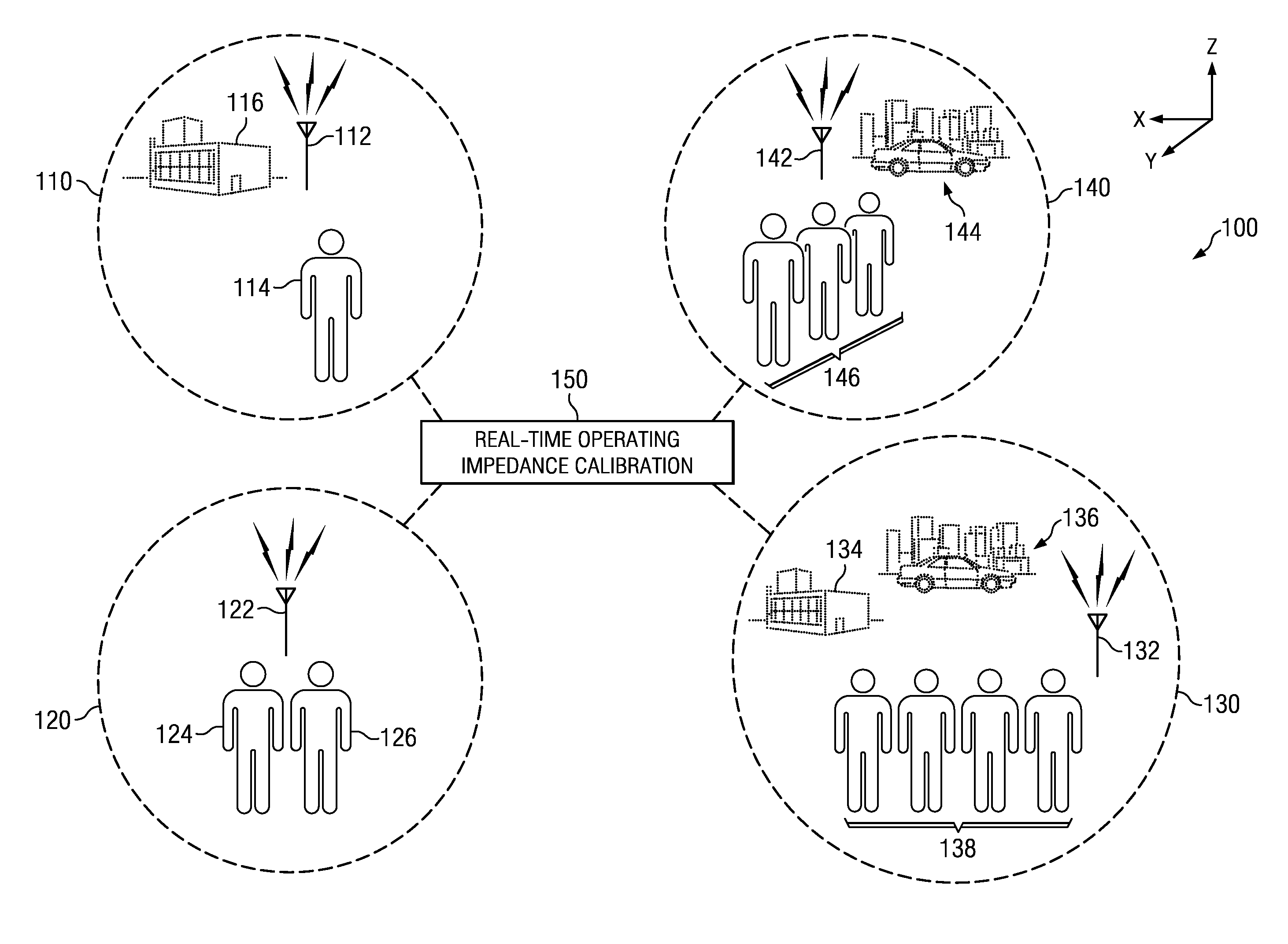
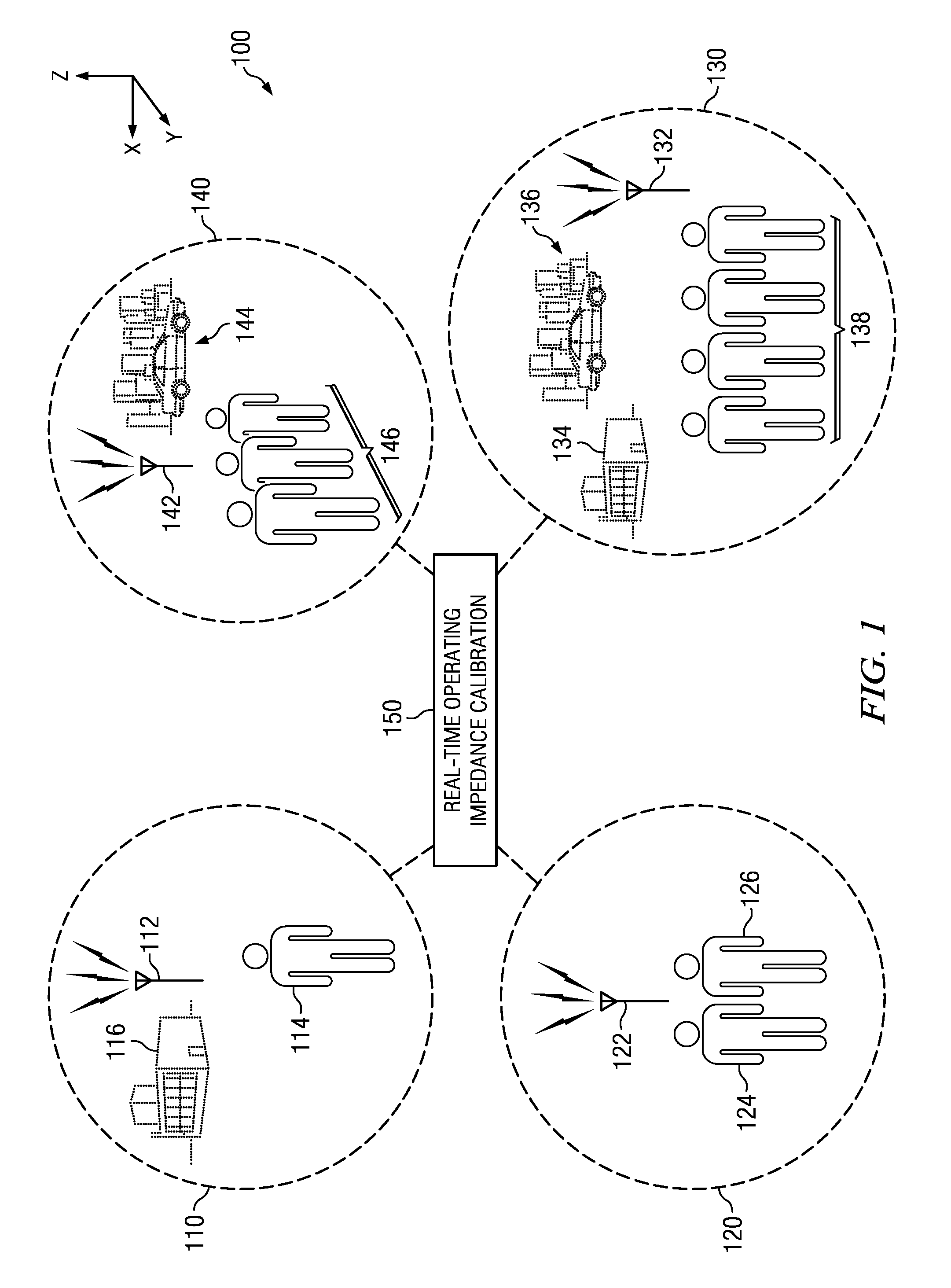
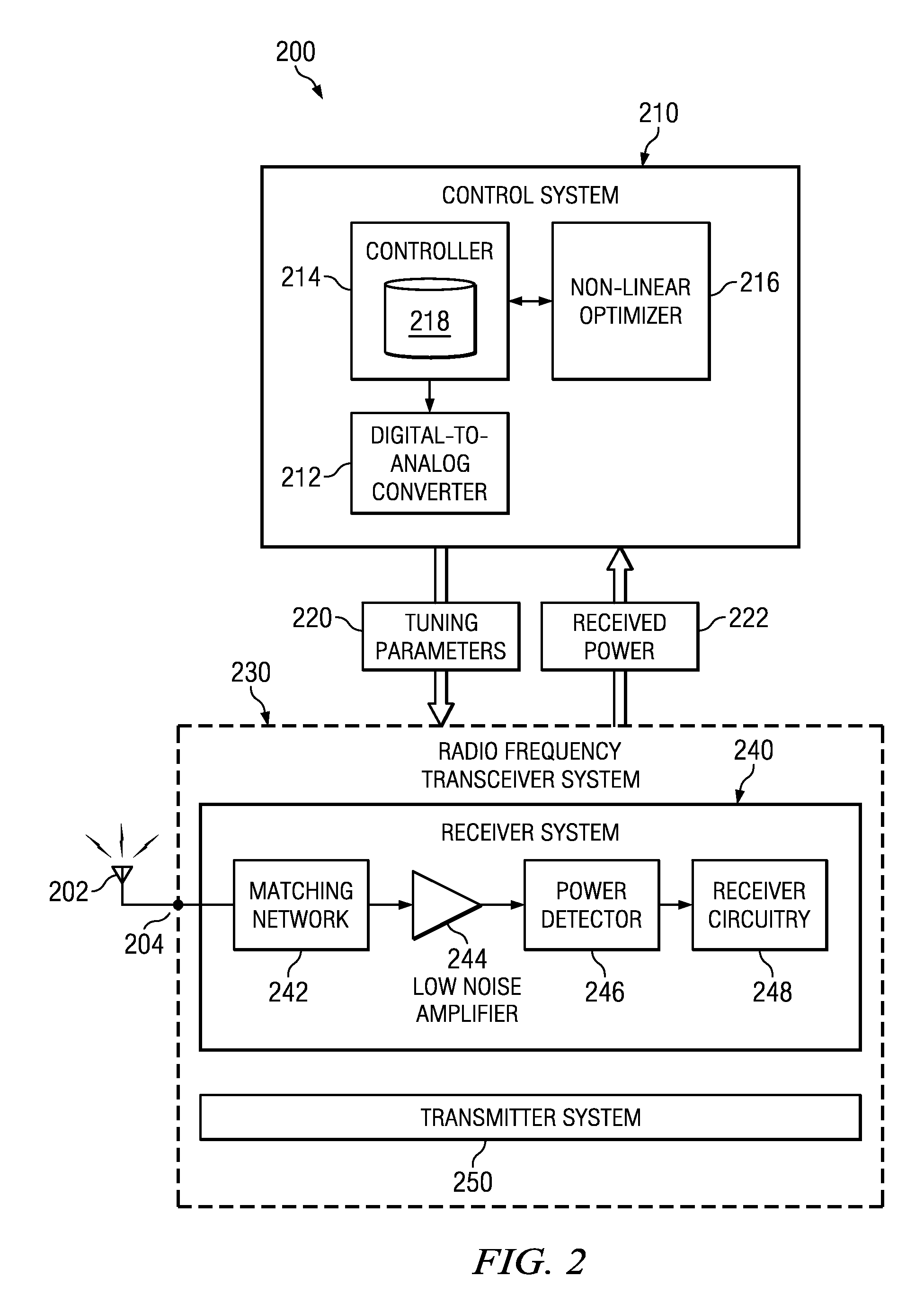
Dynamic real-time calibration for antenna matching in a radio frequency transmitter system
Real-time calibration of a tunable matching network that matches the dynamic impedance of an antenna in a radio frequency transmitter system. The radio frequency transmitter system includes two non-linear equations that may be solved to determine the reflection coefficient of the antenna. The tunable matching network is repeatedly perturbed and the power reflected by the antenna is measured after each perturbation at the same node within the tunable matching network. The power values are used by an optimizer in converging to a solution that provides input impedance of the antenna. The elements of the matching circuit are adjusted to match the input impedance of the antenna.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
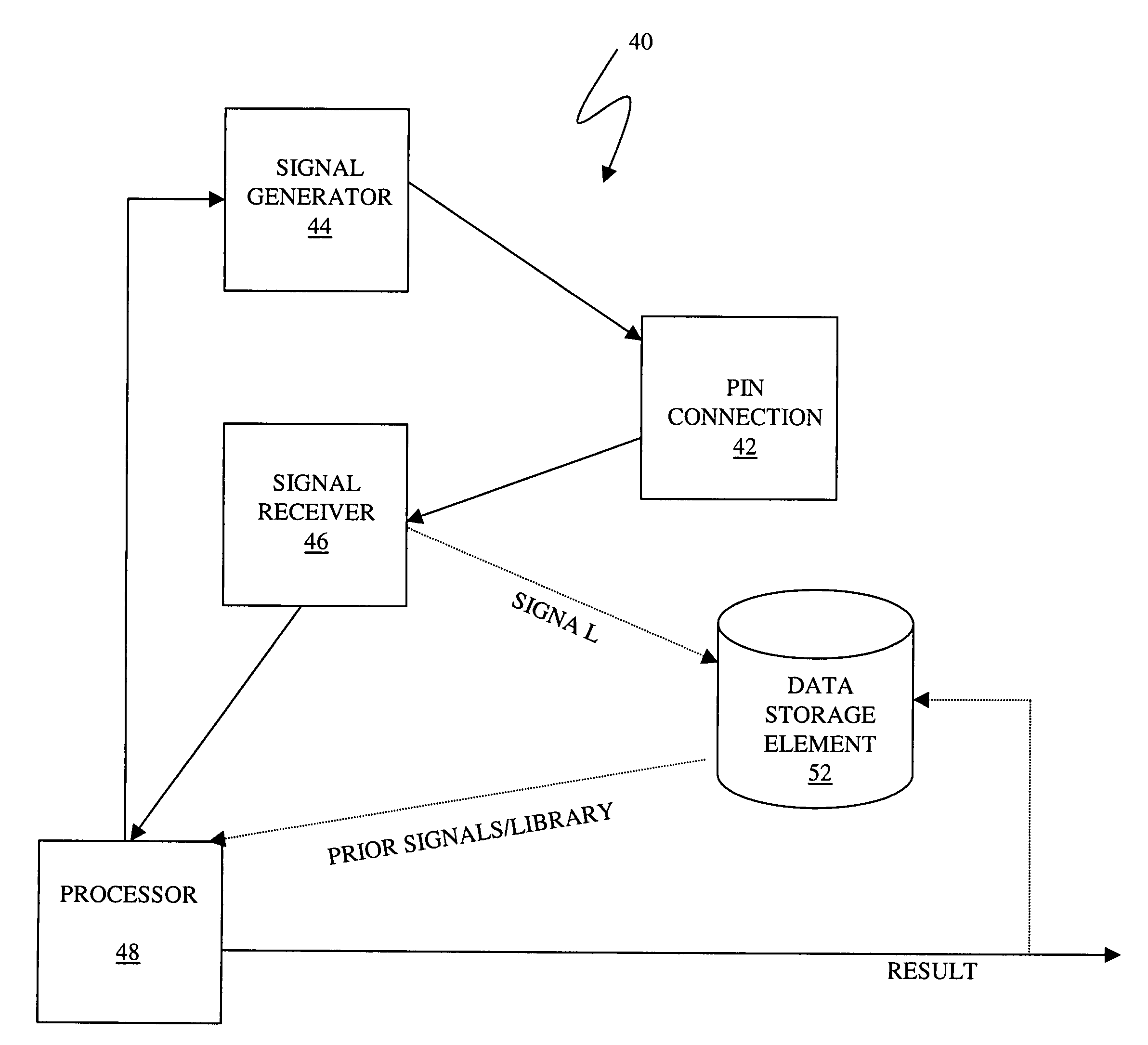
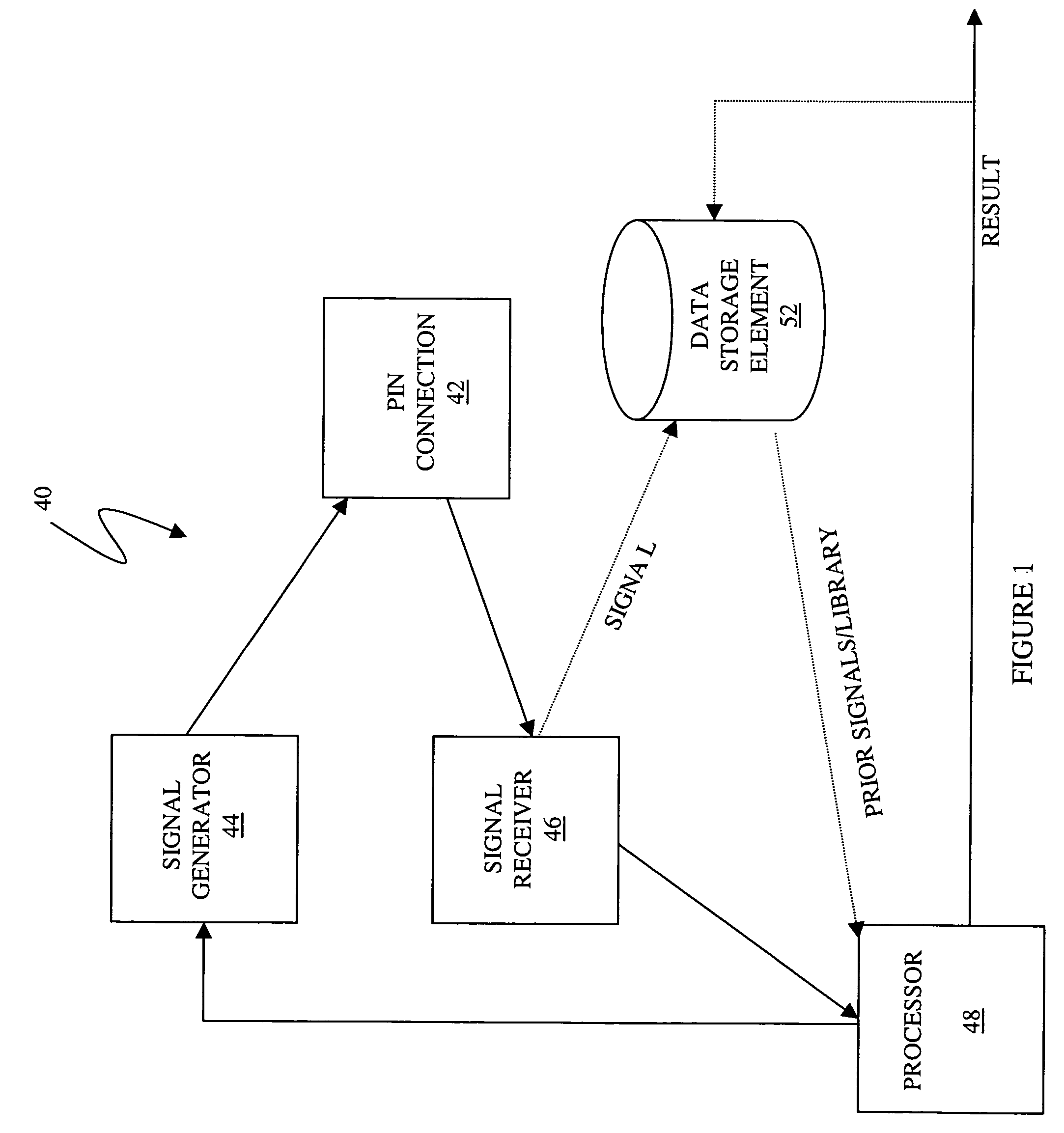
Wire event detection
Classifying a portion of an electrical signal propagating through a conductor includes digitizing the electrical signal to provide a digitized signal, providing a plurality of stored digitized signals, wherein each stored digitized signal corresponds to a type of fault for the conductor, comparing the digitized signal to each of the stored digitized signals to determine a score therefore, if the score is less than a predetermined value for a particular one of the stored digitized signals, classifying the portion of the electrical signal as a fault corresponding to the particular one of the stored digitized signals, and, if none of the scores are less than the predetermined value, classifying the portion of the electrical signal as having no fault. Classifying a portion of an electrical signal may also include converting the digitized electrical signal to reflection coefficients.
Owner:SIMMONDS PRECISION PRODS
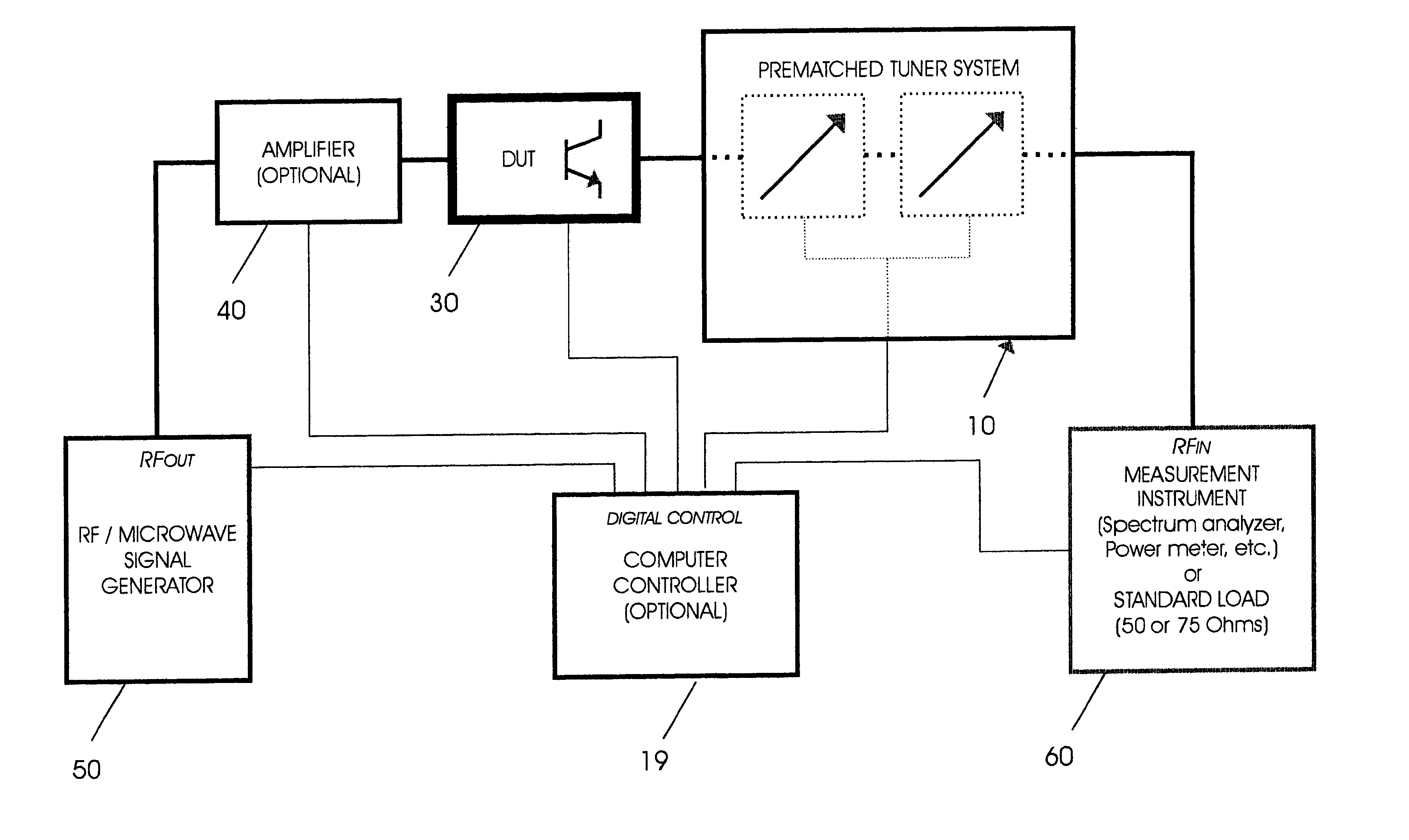
Adaptable pre-matched tuner system and method
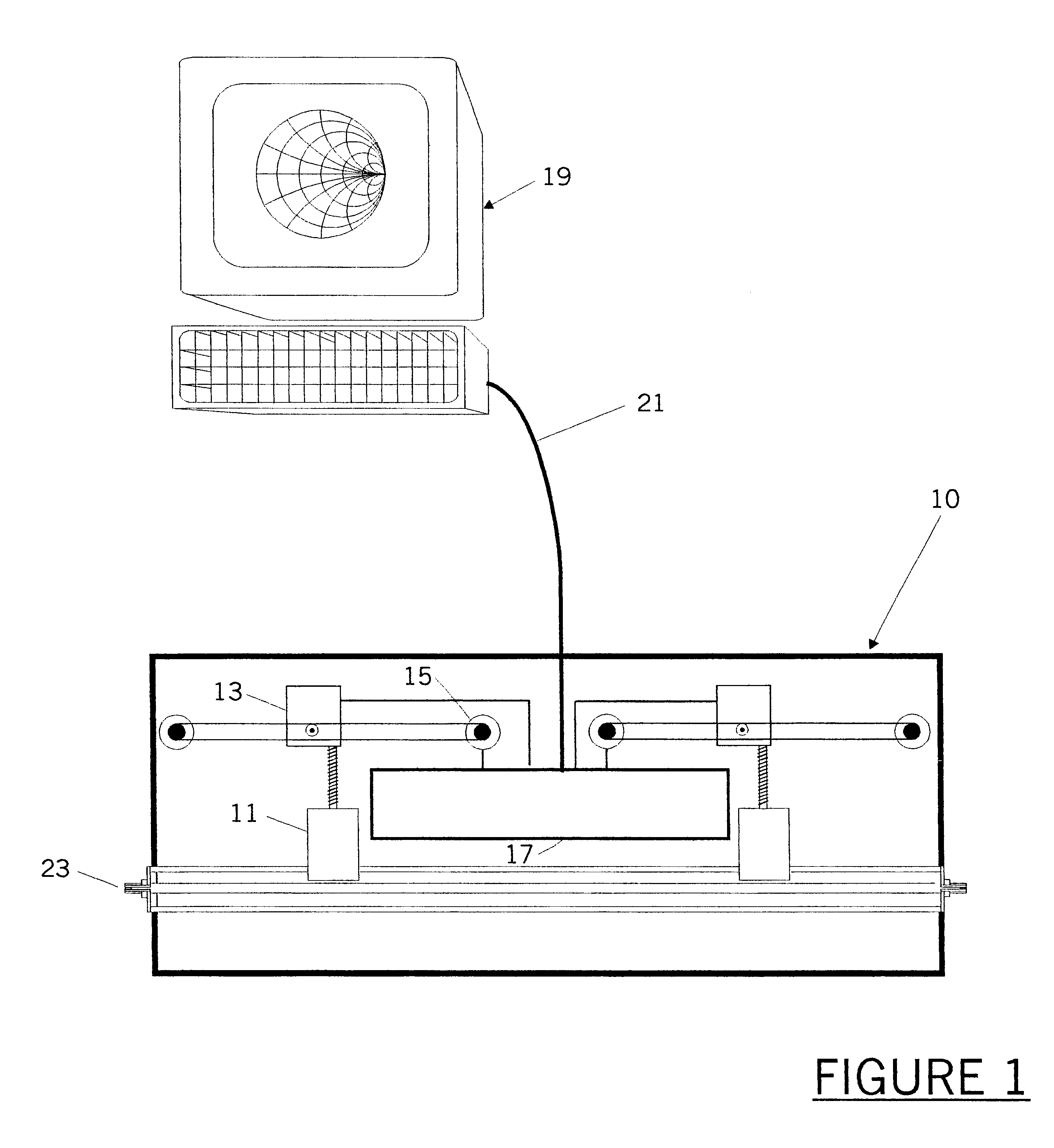
The present invention is an adaptable pre-matched tuner system and calibration method for measuring reflection factors above Gamma=0.85 for a DUT. The system includes a first and second large-band microwave tuners connected in series, the first and second large-band tuners being mechanically and electronically integrated; and a controller for controlling the two large-band tuners. The first tuner is adapted to act as a pre-matching tuner and the second tuner is adapted to investigate an area of a Smith Chart that is difficult to characterise with a single tuner, so that the combination of the first and second large-band tuners permits the measurement of reflection factors above Gamma=0.85. The pre-matched tuner system allows the generation of a very high reflection factor at any point of the reflection factor plane (Smith Chart). The pre-matched tuner must be properly calibrated, such as to be able to concentrate the search for optimum performance of the DUT in the exact location of the reflection factor plane where the DUT performs best, using a pre-search algorithm.
Owner:FOCUS MICROWAVES +1
System for attenuation of water bottom multiples in seismic data recorded by pressure sensors and particle motion sensors
ActiveUS20060050611A1Water resource assessmentSeismology for water-covered areasUltrasound attenuationWave field
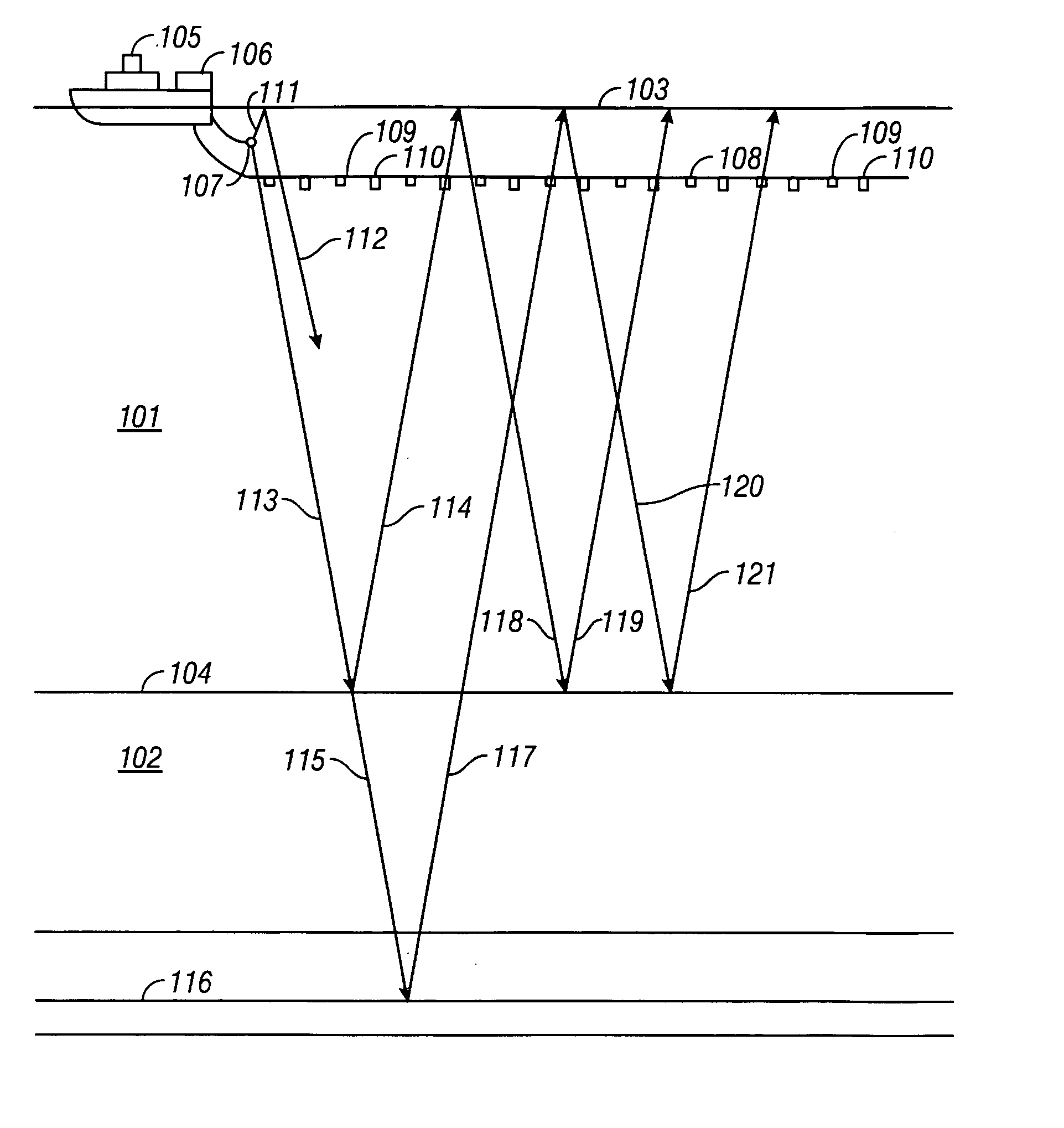
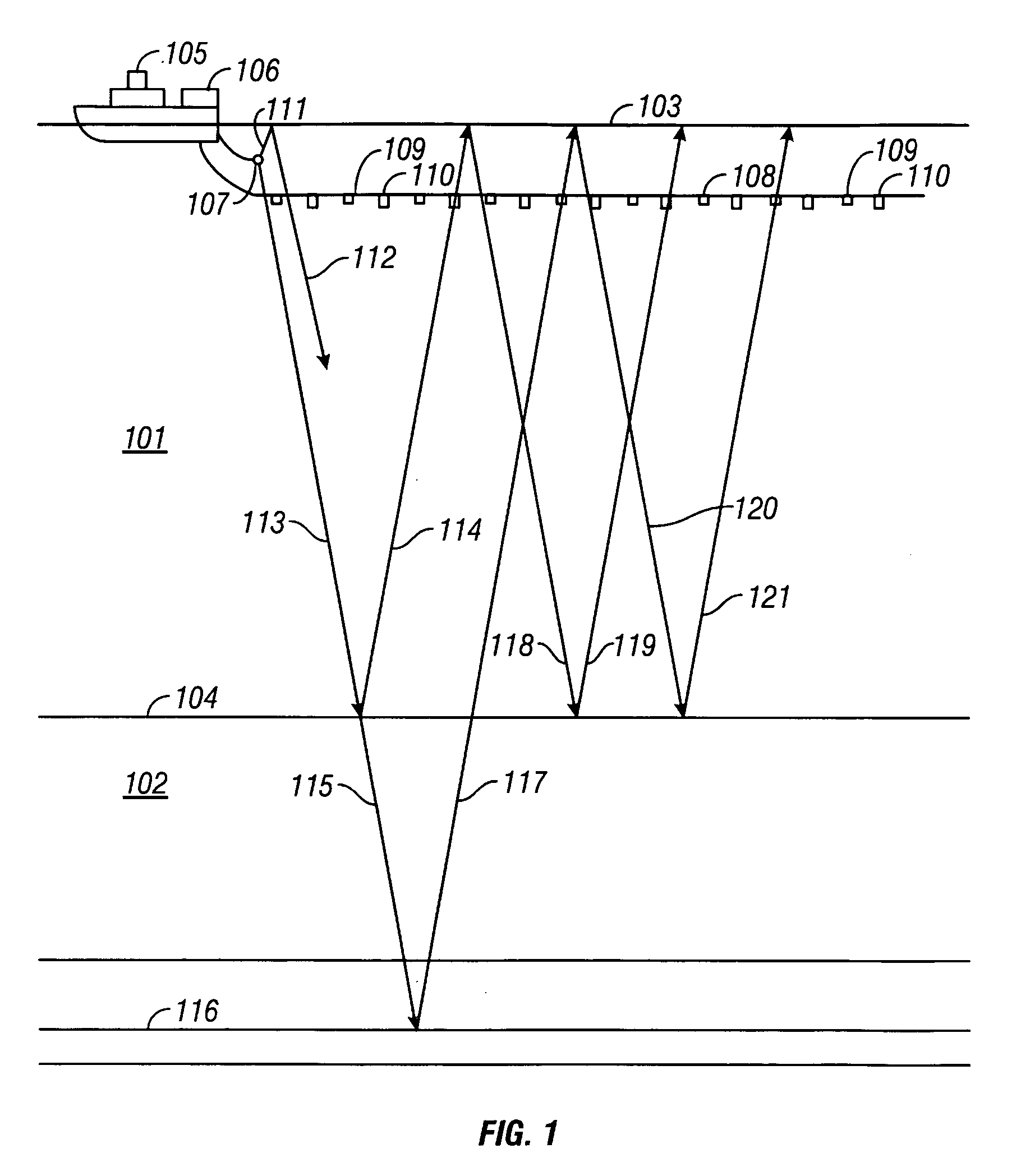
An up-going wavefield and a down-going wavefield are calculated at a sensor position from a pressure sensor signal and a particle motion sensor signal. Then, an up-going wavefield is calculated at a water bottom position substantially without water bottom multiples from the up-going and down-going wavefields at the sensor position. In one embodiment, the up-going wavefield at the sensor position is backward propagated to the water bottom, resulting in an up-going wavefield at the water bottom. The down-going wavefield at the sensor position is forward propagated to the water bottom, resulting in a down-going wavefield at the water bottom. The up-going wavefield at the water bottom without water bottom multiples is calculated from the backward propagated up-going wavefield at the water bottom, the forward propagated down-going wavefield at the water bottom, and a reflection coefficient of the water bottom.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
A standing wave ration detection device and method for time division duplex communication system
InactiveCN101146314AReduce volumeHigh precisionResistance/reactance/impedenceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMultiplexingDigital down conversion
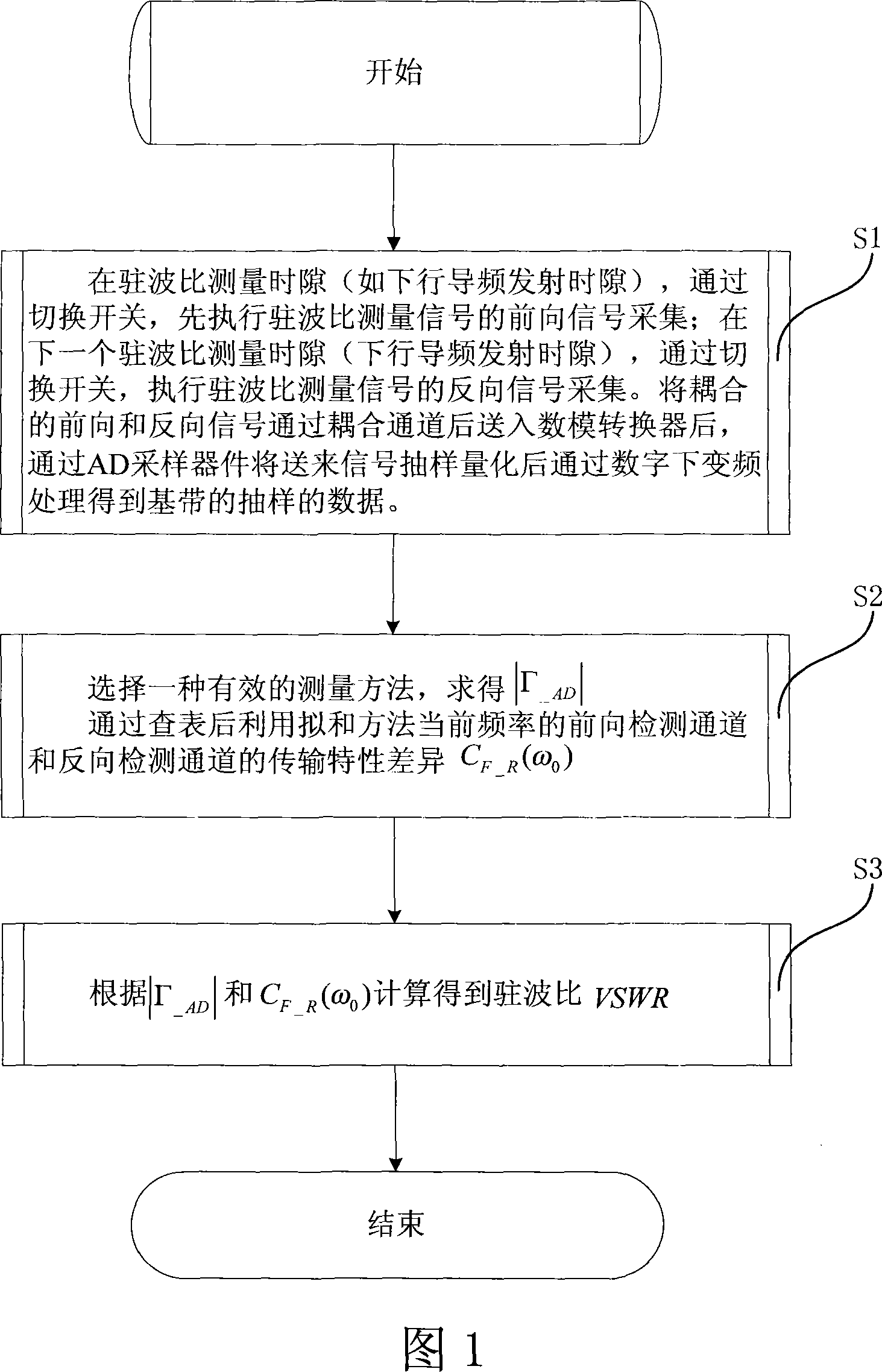
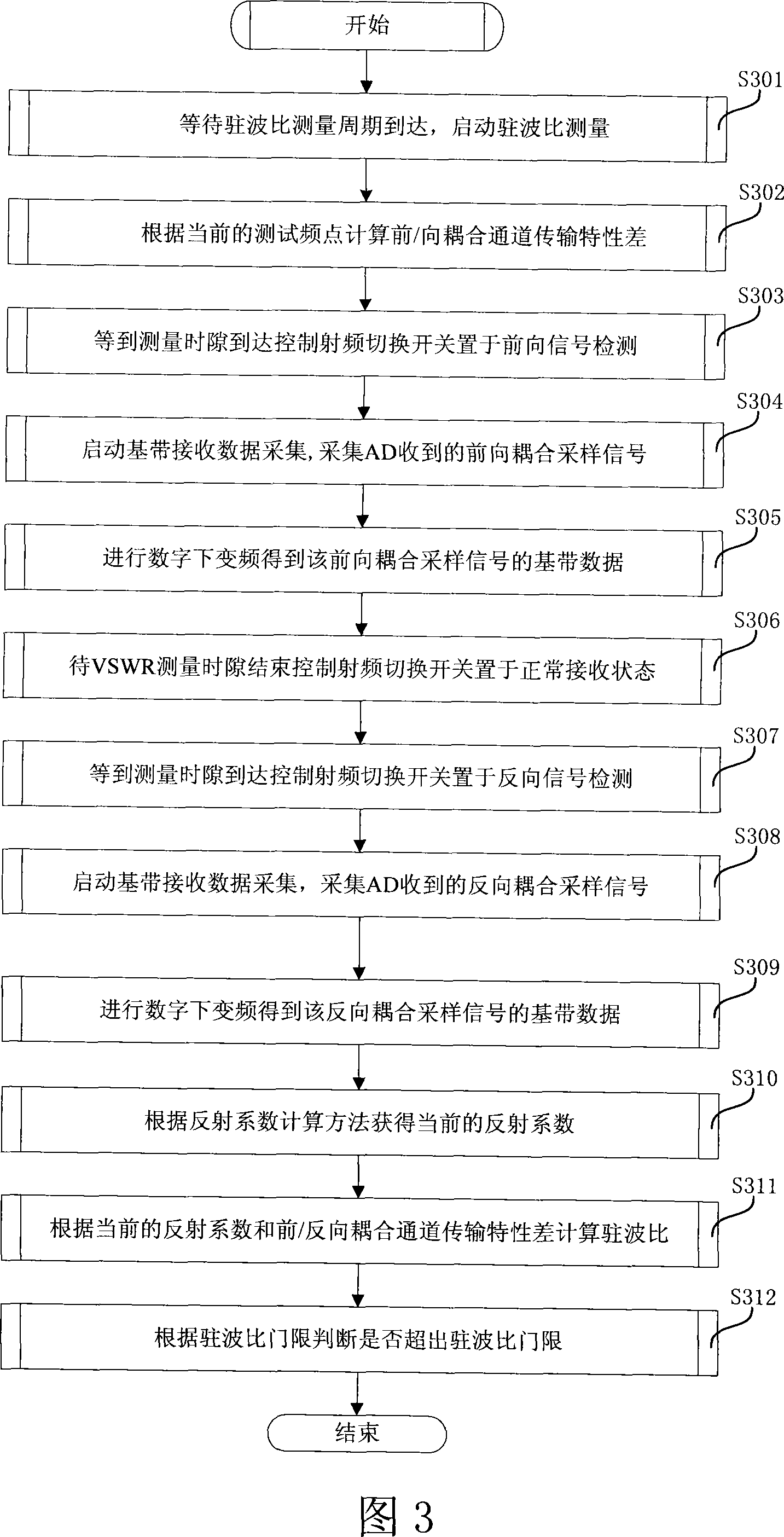
The invention relates to a detection method of standing-wave ratio of a time division duplex communication system, which comprises the following steps: a forward signal is sampled by switching a switch at a time interval of standing-wave ratio measurement; a reverse signal is sampled by switching the switch at the next time interval of standing-wave ratio measurement; the forward and the reverse signals is coupled and delivered to a digital-to-analog converter through a coupling passage, the delivered signal is sampled and quantized by using an AD sampler and processed by means of digital down-conversion to obtain a sampled data of baseband; a reflection coefficient |gamma_AD| is obtained by calculating, the transmission characteristic difference CF_R(Omega 0) between a forward detection channel and a reverse detection channel is obtained at the current frequency after table lookup process; and the standing-wave ratio VSWR is calculated based on the reflection coefficient |gamma_AD| and the transmission characteristic difference CF_R(Omega 0). Therefore, the invention realizes the multiplexing of a normal reception channel and the reverse and the forward standing-wave ratio channels, enables the normal reception channel to be used in standing-wave ratio detection, and ensures the equivalency of front / reverse power samplings by measuring the front and the reverse powers of the pilot frequency.
Owner:RUGAO CHANGJIANG SCI & TECHCAL IND CO LTD
Seismic exploration position calibration method based on prestack wave field simulation
InactiveCN101013161AImprove consistencyHigh precisionSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingWave fieldReflected waves
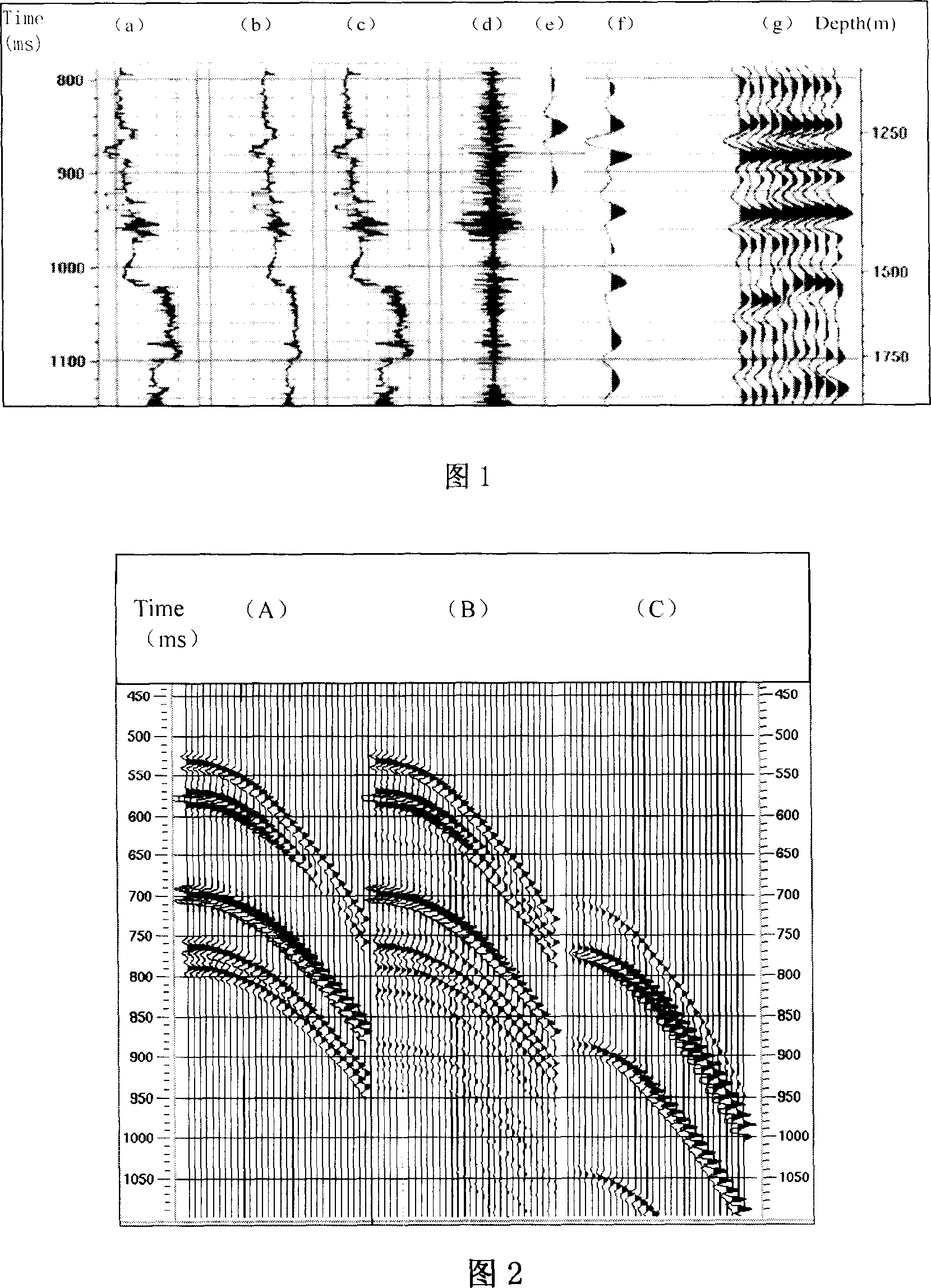
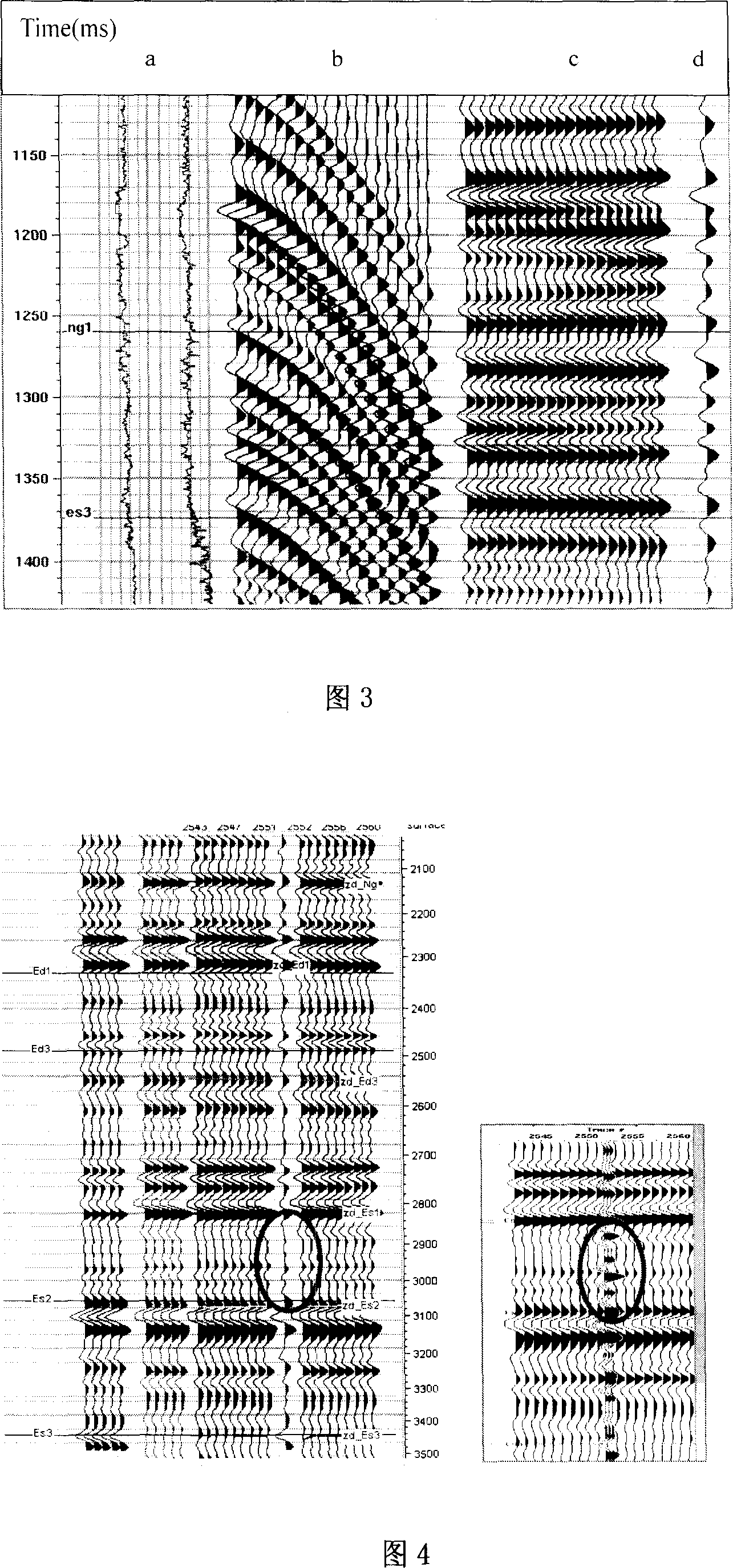
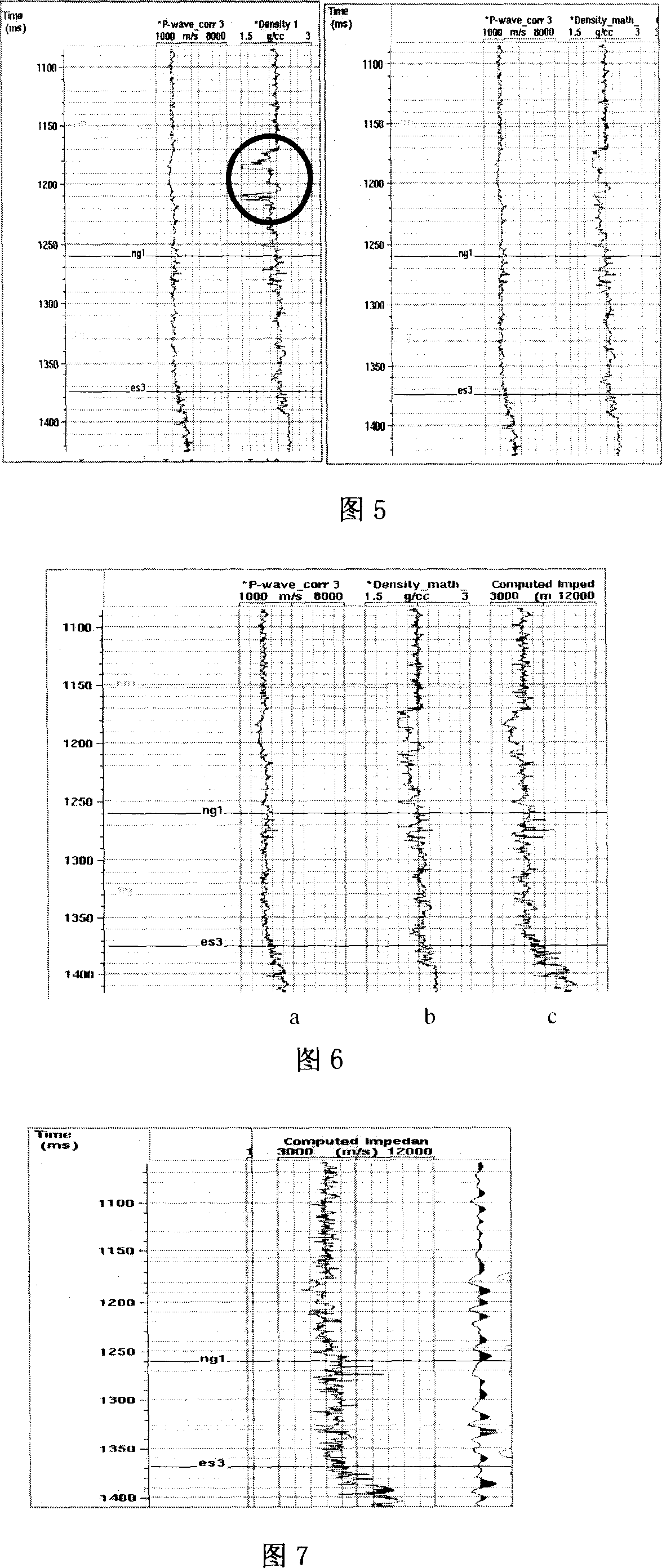
The invention relates to the earthquake exploration position calibration technology based on the pre-stack wave field simulation, belonging to the seismic data processing and interpretation technology field in oil exploration. The invention considers the seismic information acquisition and processing impact, considers multiple waves and conversion waves action in the reflection waves, enhances the accuracy of integrated seismic records, and enhances the consistency of integrated seismic records and real seismic records, this approach including the following eight steps: filtering and editing of density and acoustic logging well curve; using density and acoustic logging well curve to calculate the wave impedance curve; using statistics sub wave to integrate the seismic records; comparing the integrated seismic records and well-side seismic road, properly stretching the logging well curve; using well-side seismic road and logging well reflection coefficient curve to extract certainty sub wave; using the reflection rate method to simulate the pre-stack common reflection points roads set; simulating the real seismic data processing, and obtaining the final integrated seismic records; using the final integrated seismic records and comparing with the well-side seismic road, to process seismic exploration position calibration.
Owner:DAGANG OIL FIELD OF CNPC
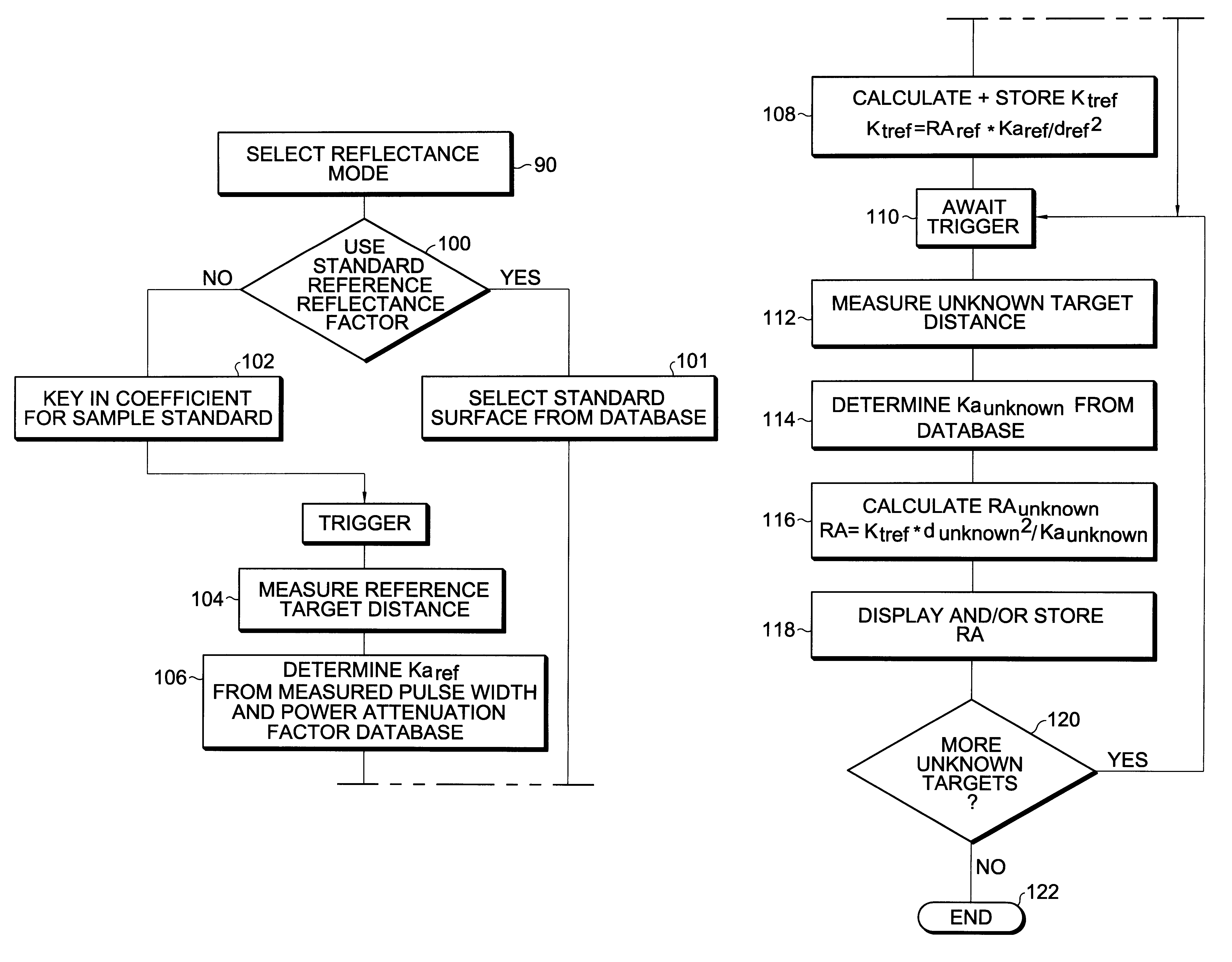
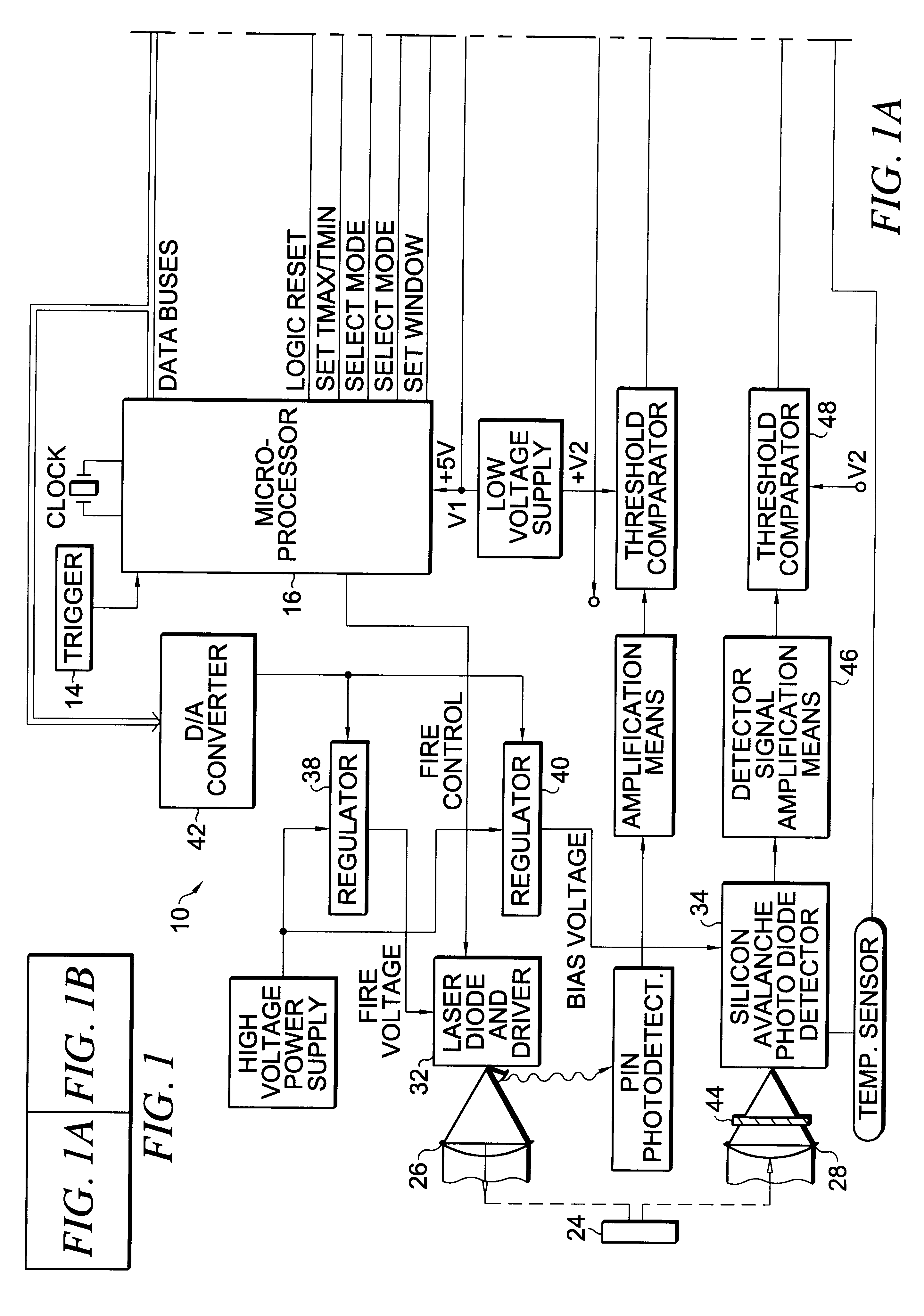
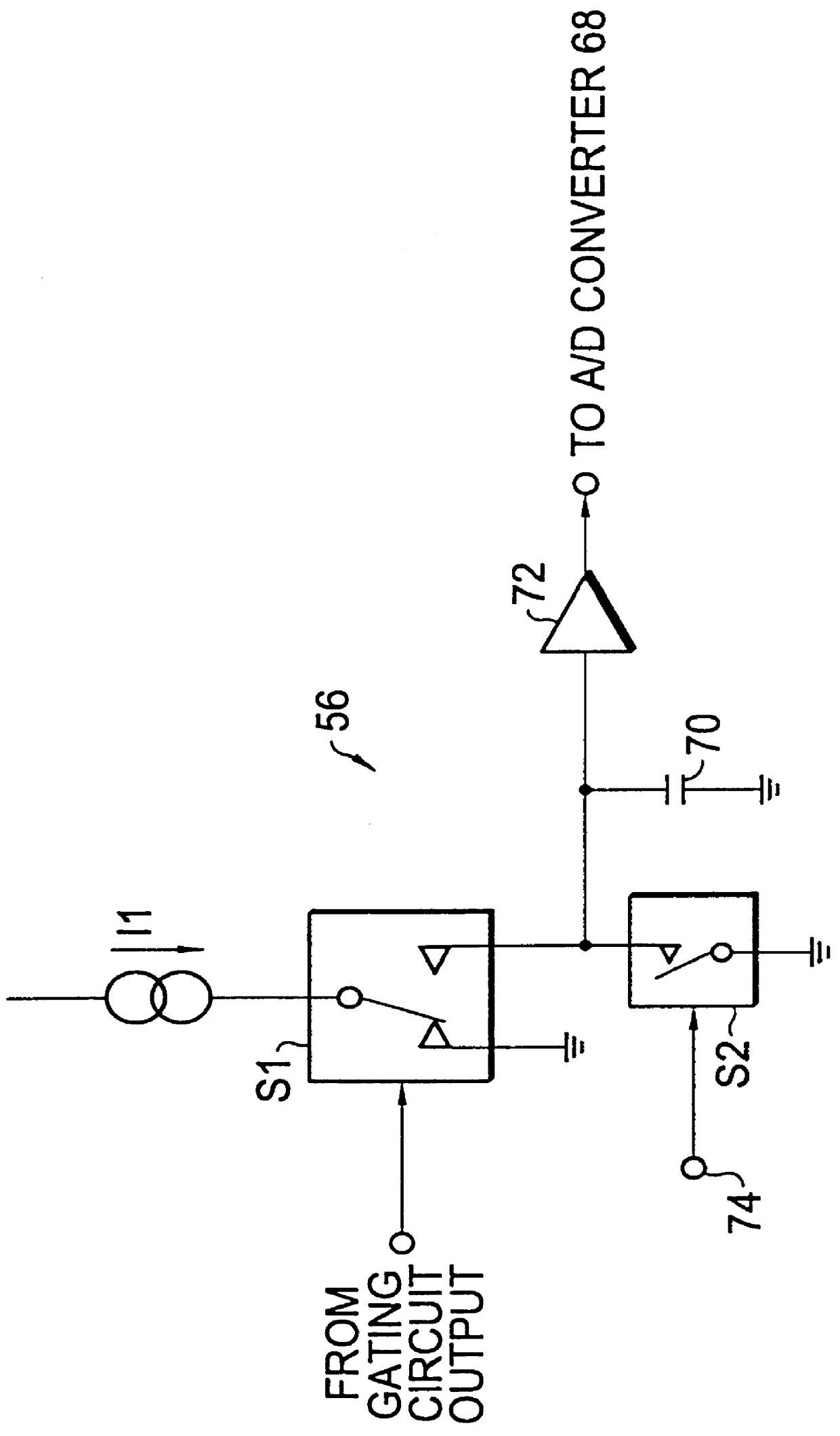
Apparatus and method for determining precision reflectivity of highway signs and other reflective objects utilizing an optical range finder instrument
An apparatus and method for measuring coefficients of retroreflectance of retroreflective surfaces such as road signs involves use of a modified light based range finder. The apparatus includes a power attenuation factor data base which relates pulse width of received pulses to power attenuation of the transmitted pulses. The range finder calculates target range based on time of flight of light pulses. The apparatus automatically calculates the absolute coefficient of retroreflectance for an unknown reflective surface being measured by comparison of the measurement to a reading with the same instrument of a known reflectance standard. The method involves either recalling a stored standard reference reflectance factor or determining a reflectance factor via the range finder for a sample of retroreflective material with a predetermined coefficient of retroreflectance, and then measuring the distance to an unknown target, determining a power attenuation factor from the received pulse width from the unknown target and then calculating the absolute coefficient of retroreflectance based upon these determined values of power attenuation factor, distance and the reference reflectance factor.
Owner:KAMA TECH CORP +1
CD metrology analysis using green's function
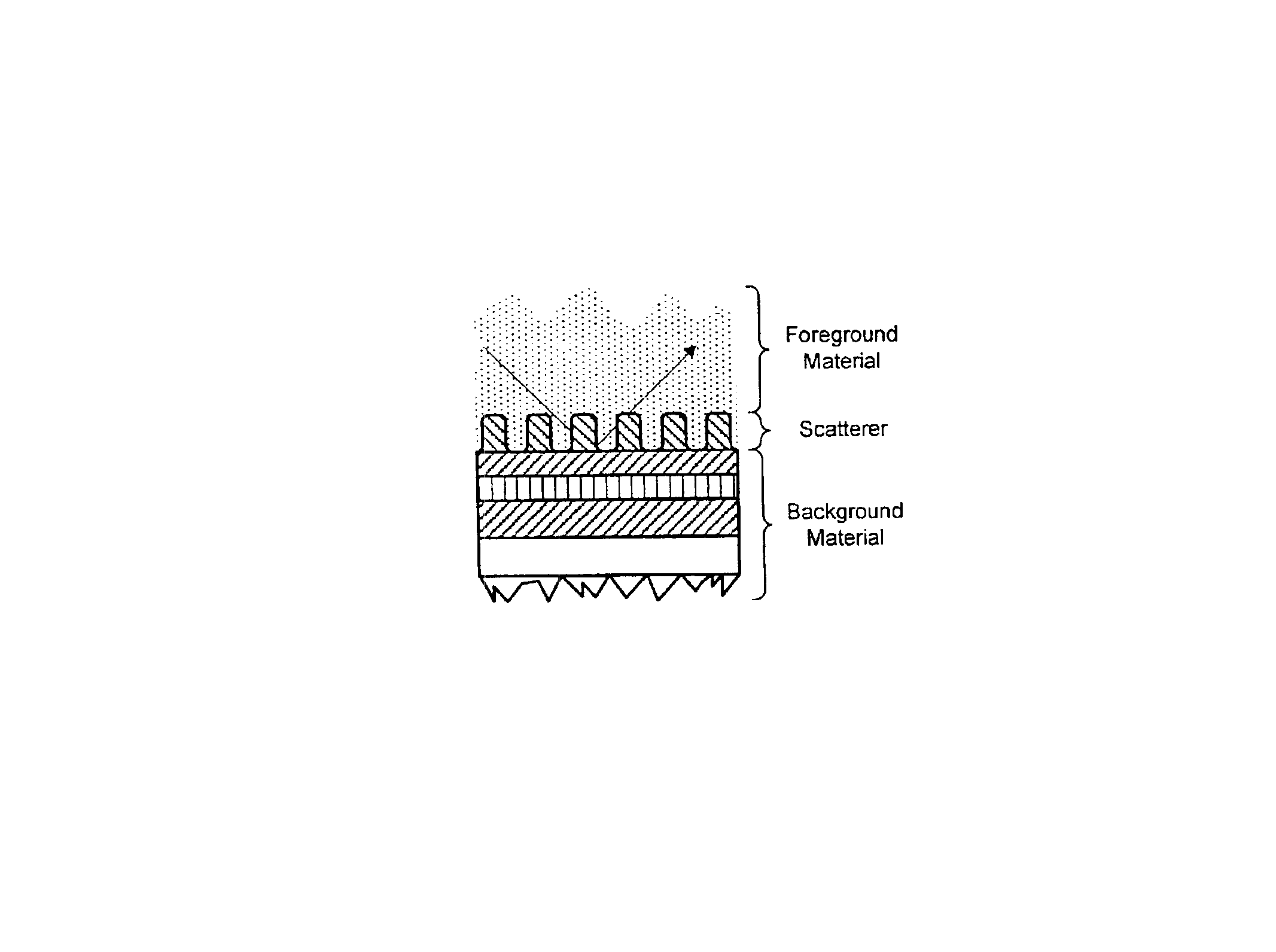
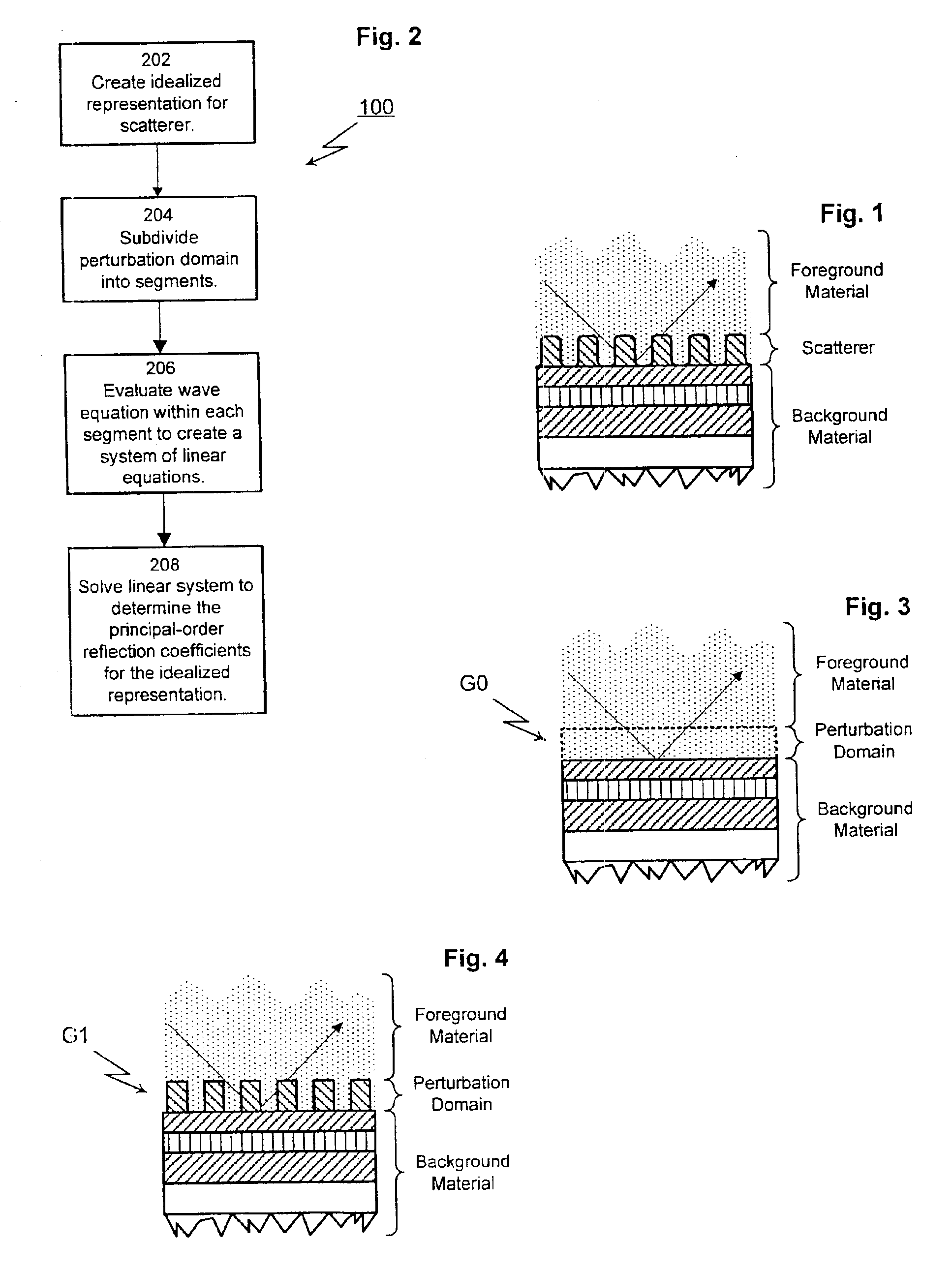
InactiveUS6867866B1Efficient methodImprove efficiencyScattering properties measurementsDigital computer detailsMetrologyRigorous coupled-wave analysis
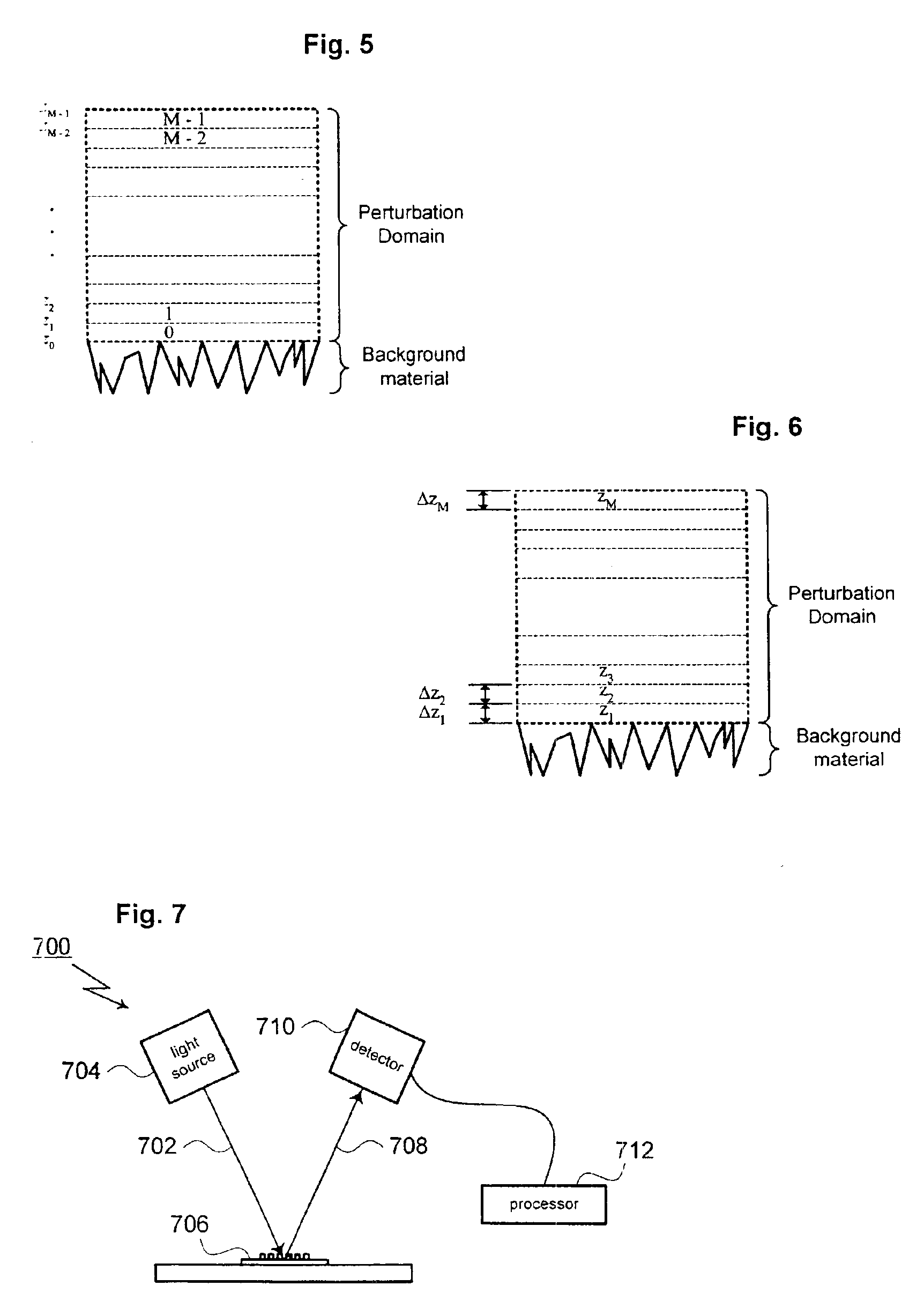
A method for modeling optical scattering includes an initial step of defining a zero-th order structure (an idealized representation) for a subject including a perturbation domain and a background material. A Green's function and a zero-th order wave function are obtained for the zero-th order structure using rigorous coupled wave analysis (RCWA). A Lippmann-Schwinger equation is constructed including the Green's function, zero-th order wave function and a perturbation function. The Lippmann-Schwinger equation is then evaluated over a selected set of mesh points within the perturbation domain. The resulting linear equations are solved to compute one or more reflection coefficients for the subject.
Owner:THERMA WAVE INC
Apparatus and method for manufacturing optical disks, apparatus and method for recording data on optical disks, apparatus and method for reproducing data from optical disks, and optical disk
InactiveUS6665240B1Television system detailsAccessories for auxillary signalsDigital dataCompact Disc manufacturing
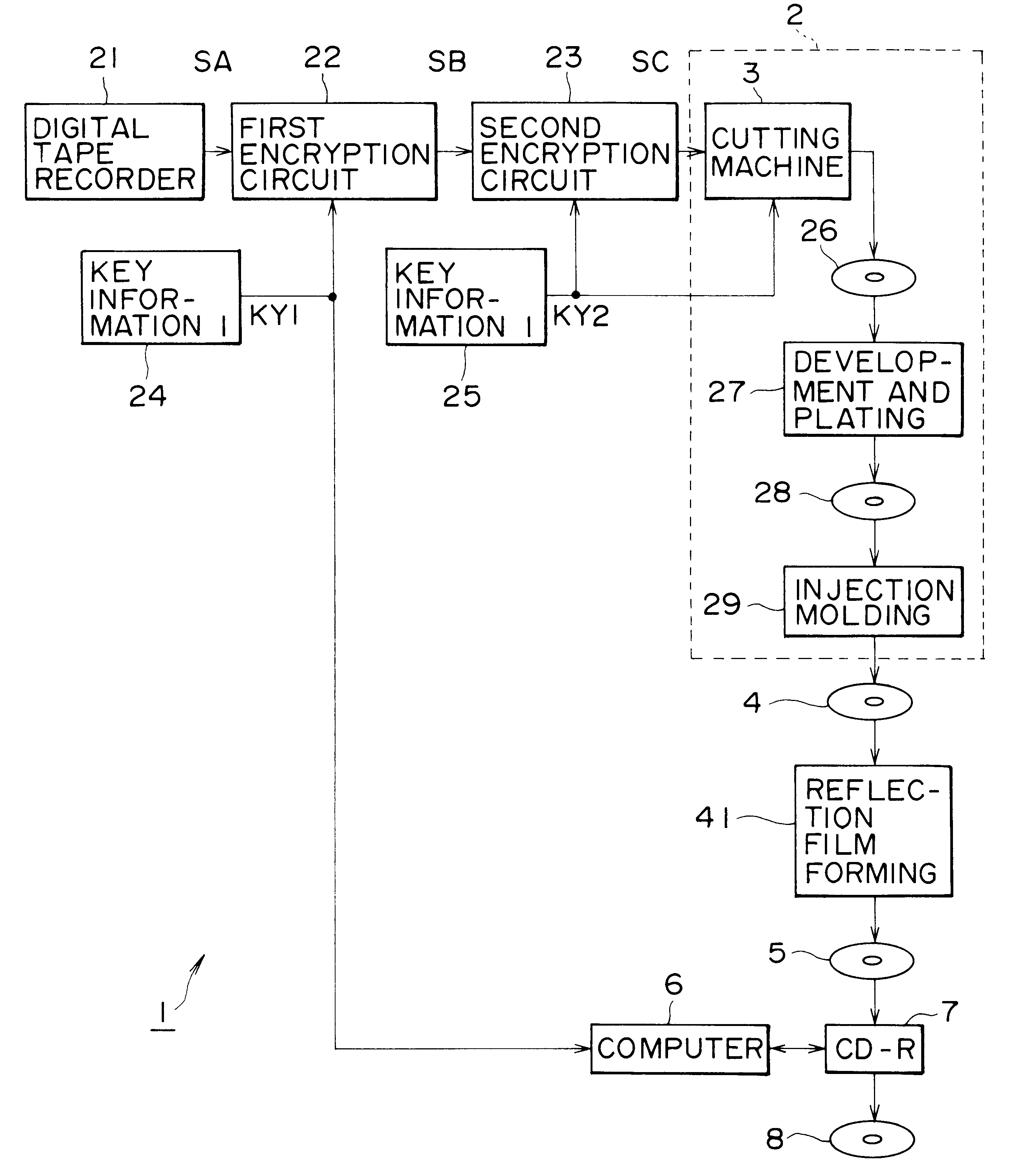
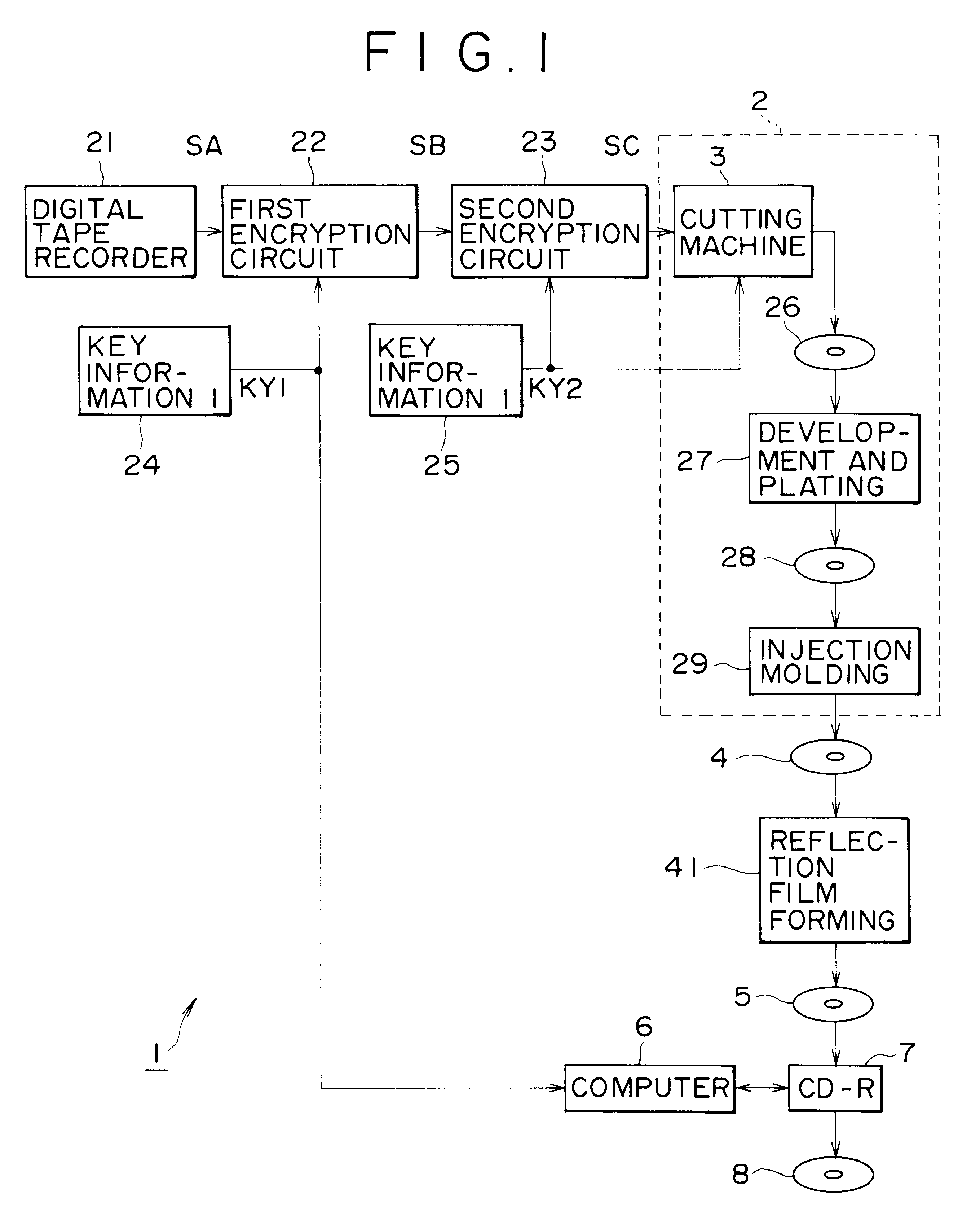
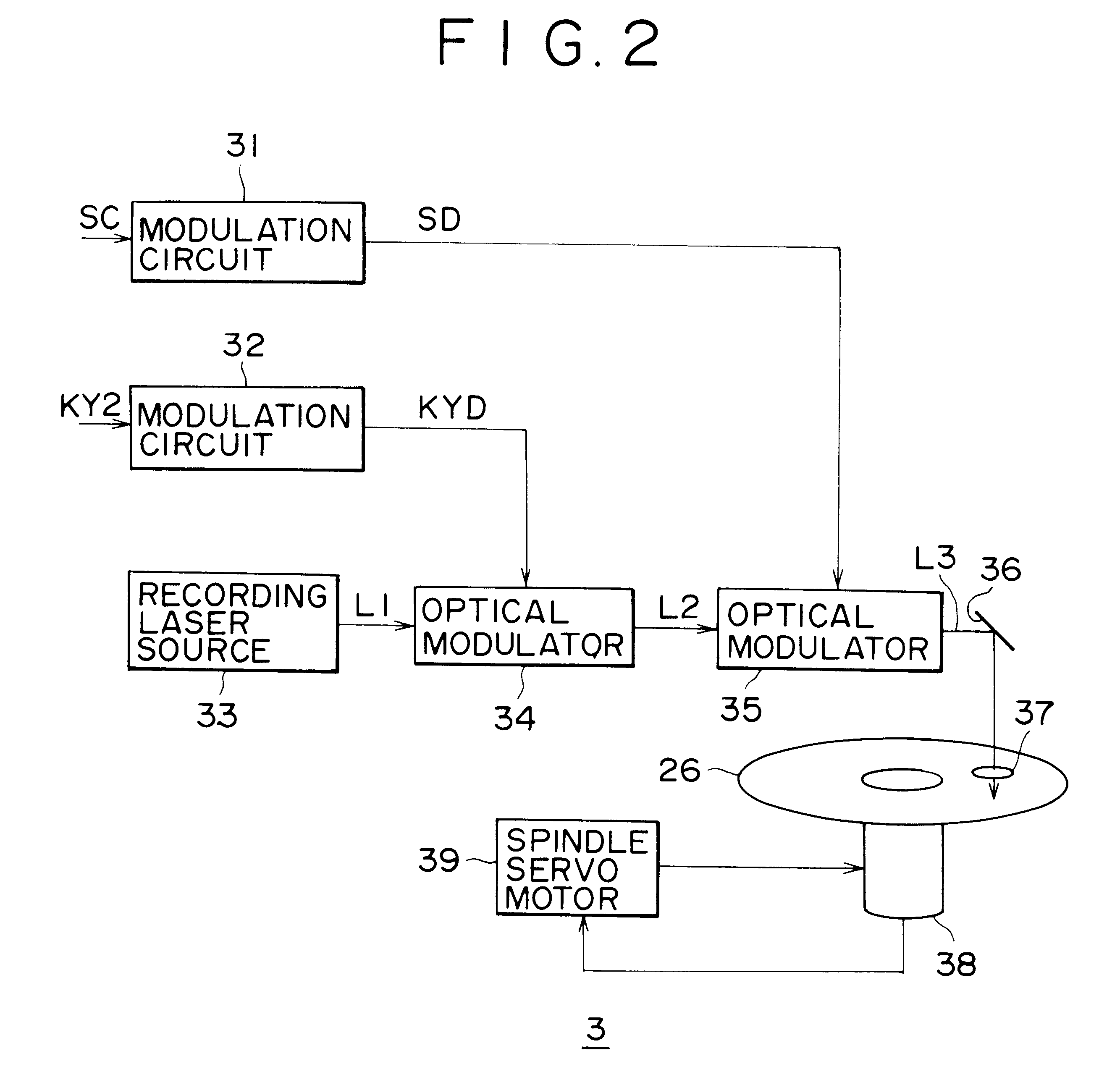
Described herewith is an optical disk manufacturing apparatus for reading recorded digital data from an optical disk, comprising an encryption unit (22, 23) for encrypting entered digital data according to a plurality of key information; an optical disk substrate manufacturing unit 2 for manufacturing an optical disk substrate 4 on which the encrypted digital data and key information are recorded in the form of physical form changes; a reflection film forming unit 41 for forming a reflection film on the optical disk substrate 4; and a key information recording unit 7 for recording key information on the optical disk substrate on which the reflection film is formed. The reflection factor of the optical disk is changed locally, thereby giving a jitter to the position information of each pit edge, and desired data is recorded additionally according to this jitter. Pits, etc. are disposed so as to be deviated from the track center towards the inner / outer region of the optical disk 2, thereby recording such subdata as key information KY, etc.
Owner:SONY CORP
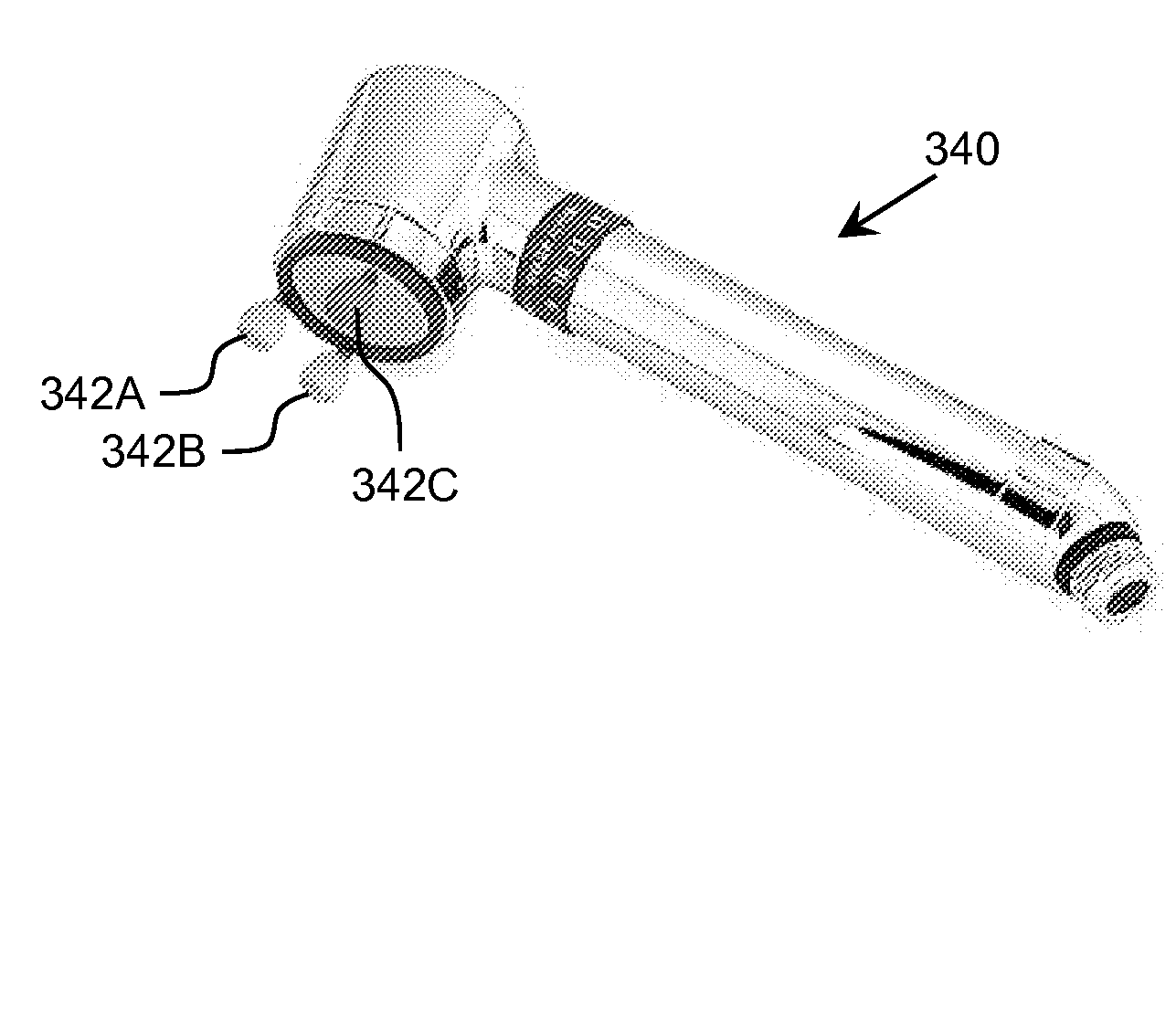
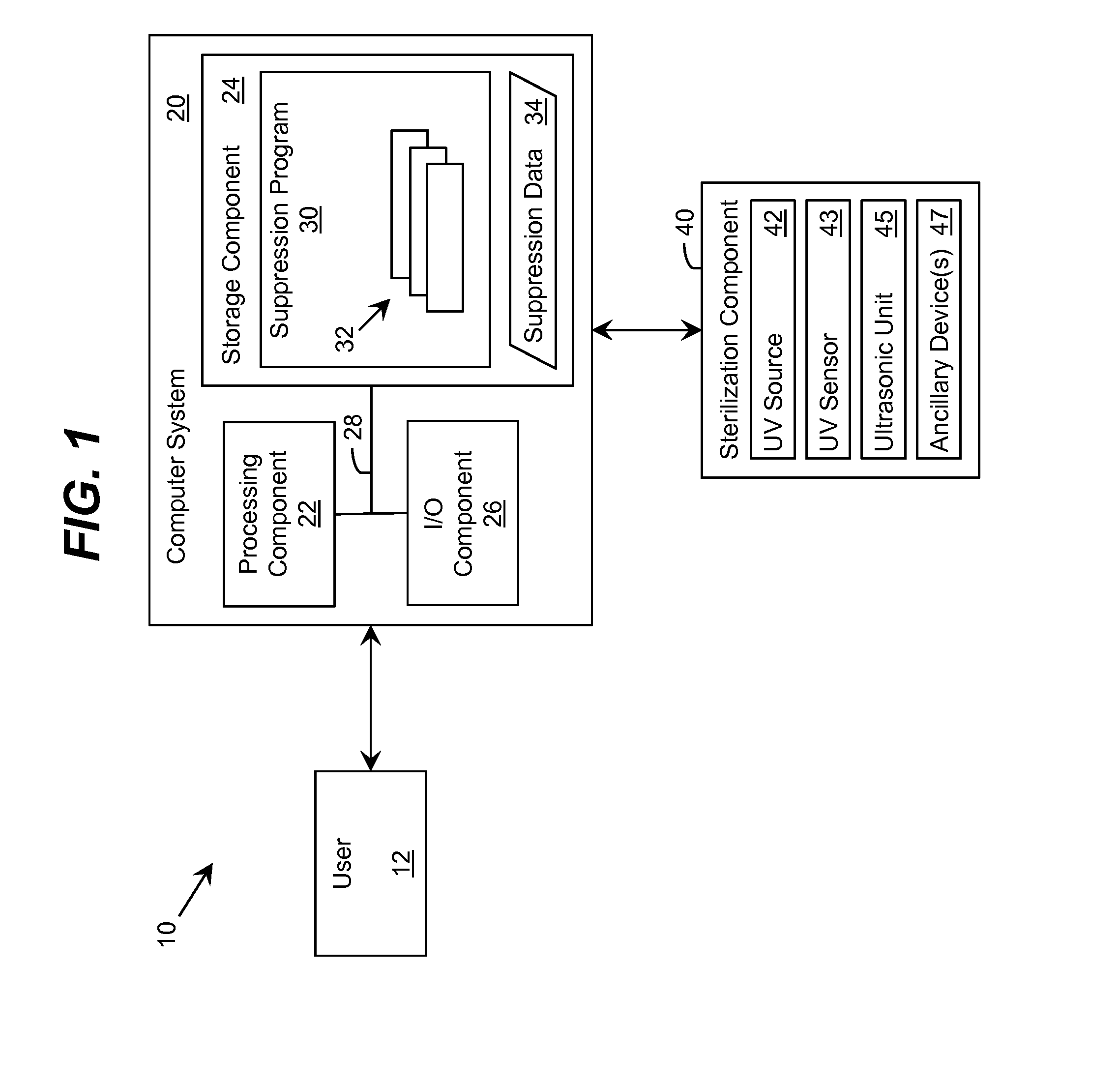
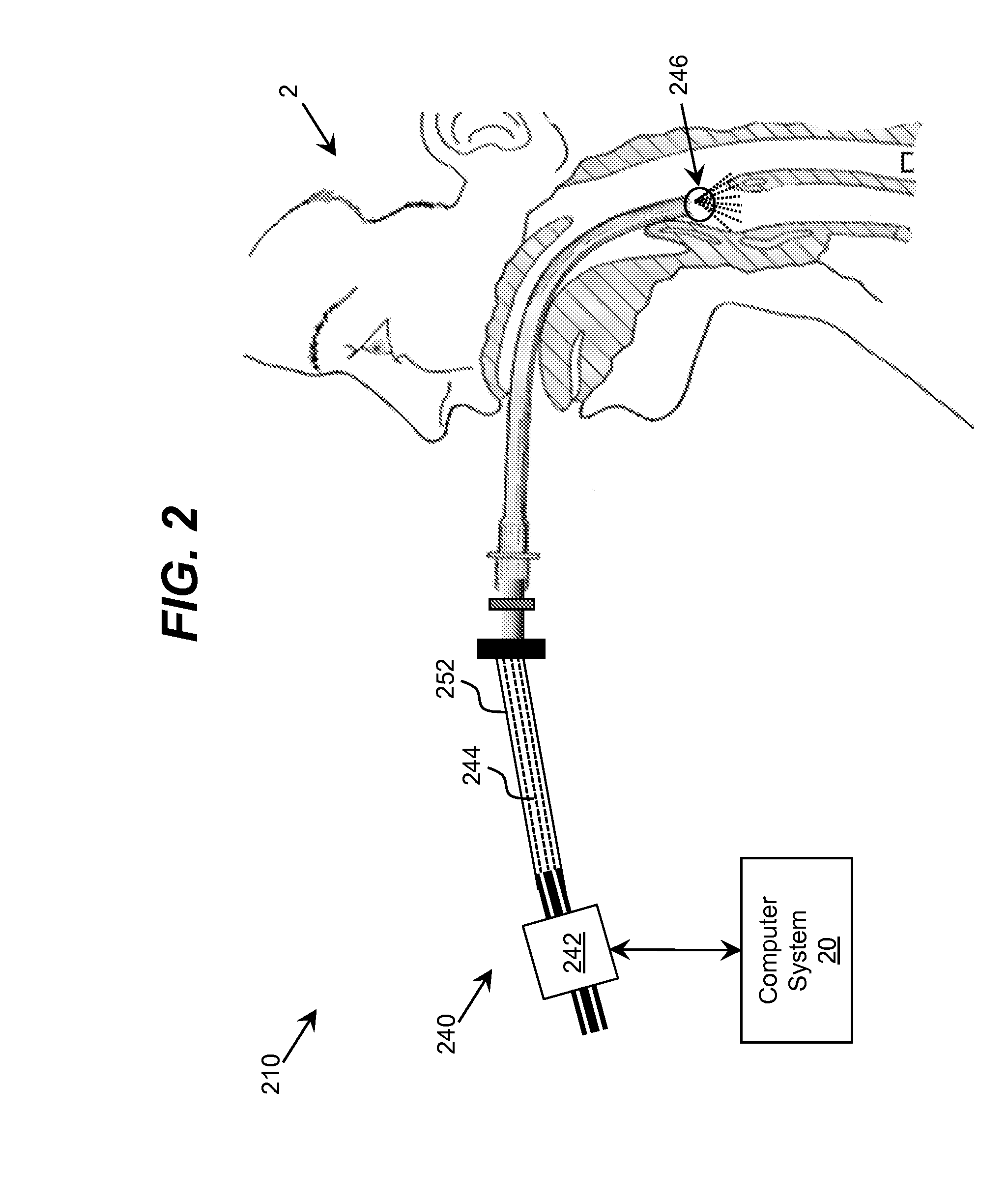
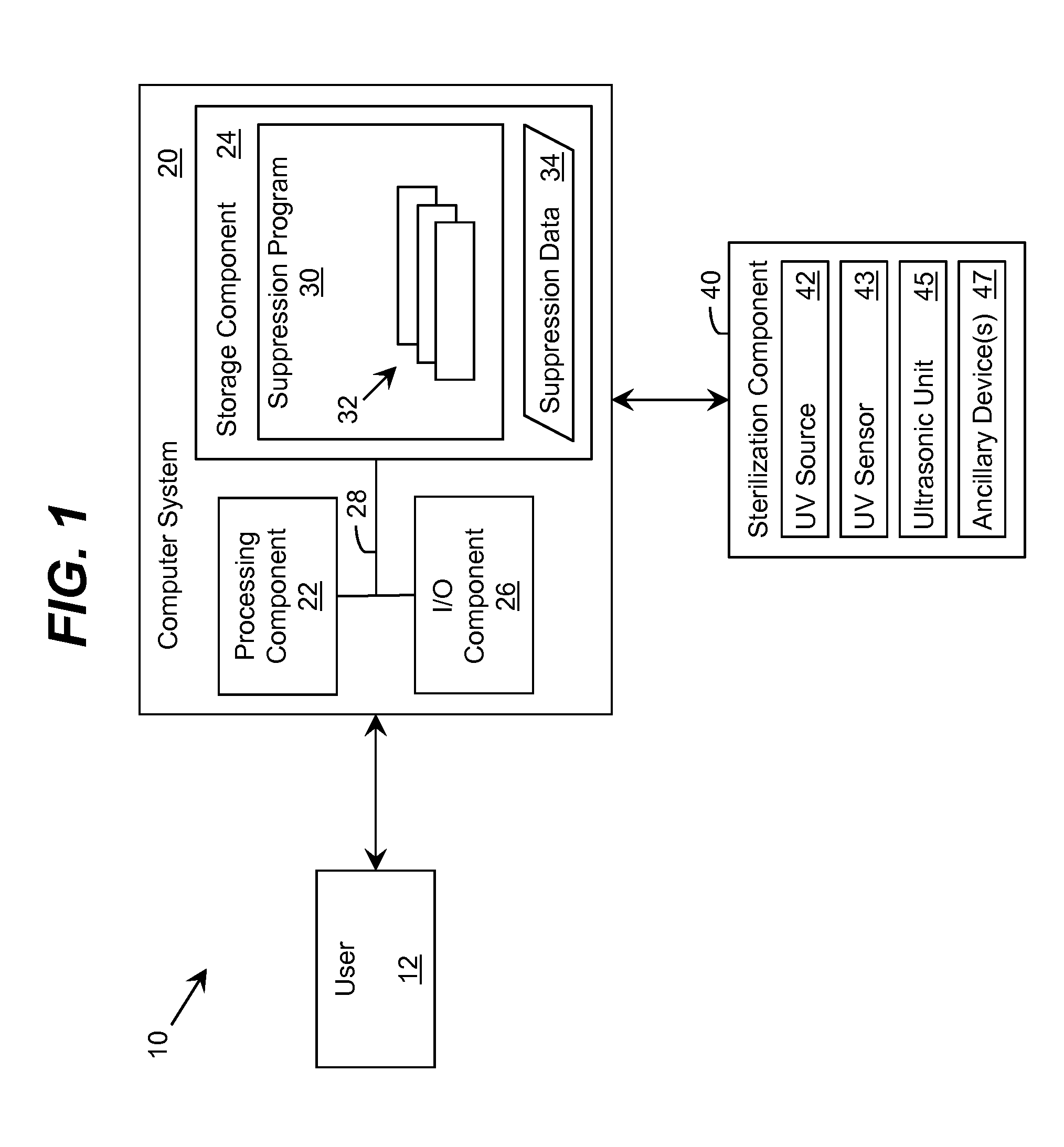
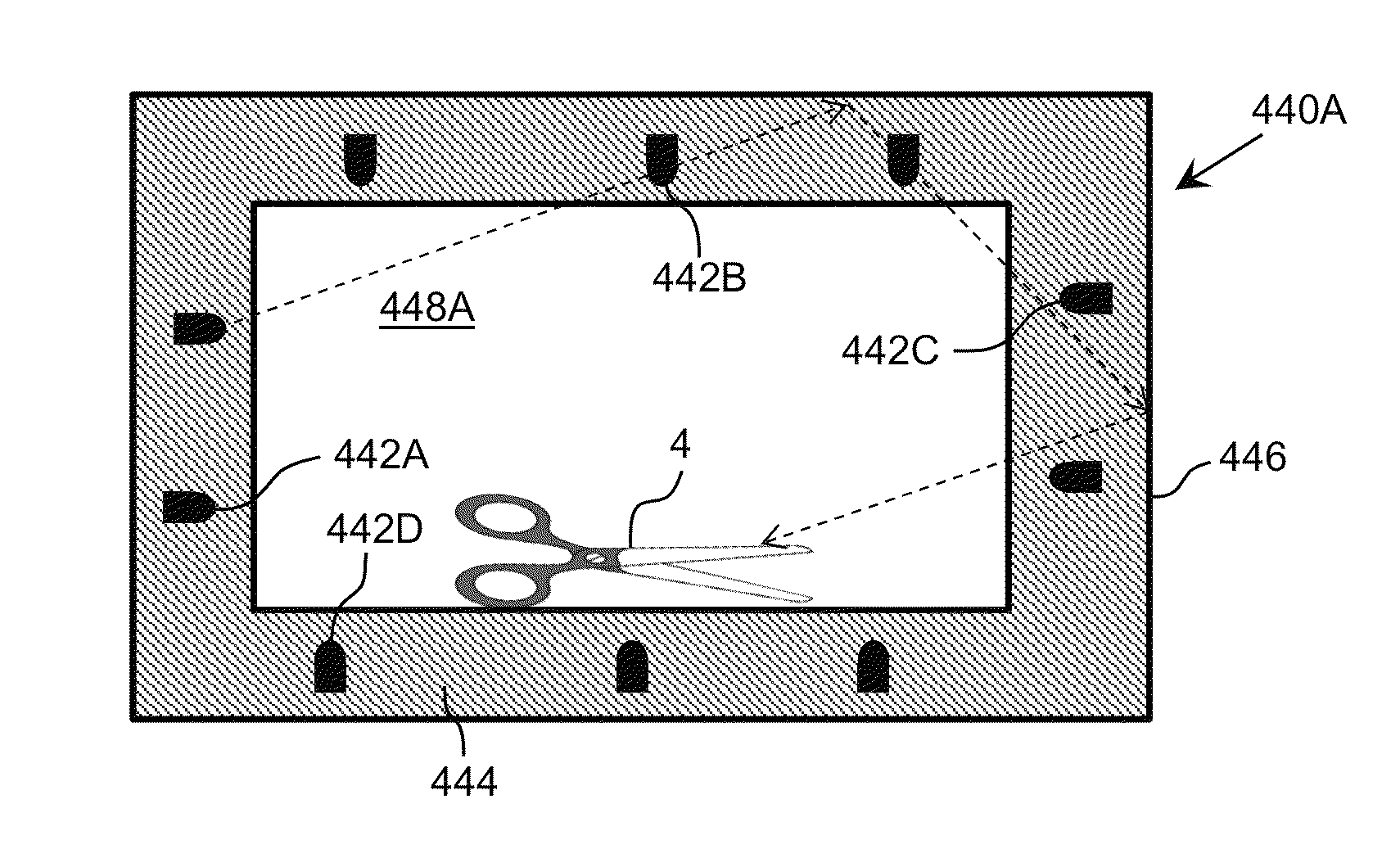
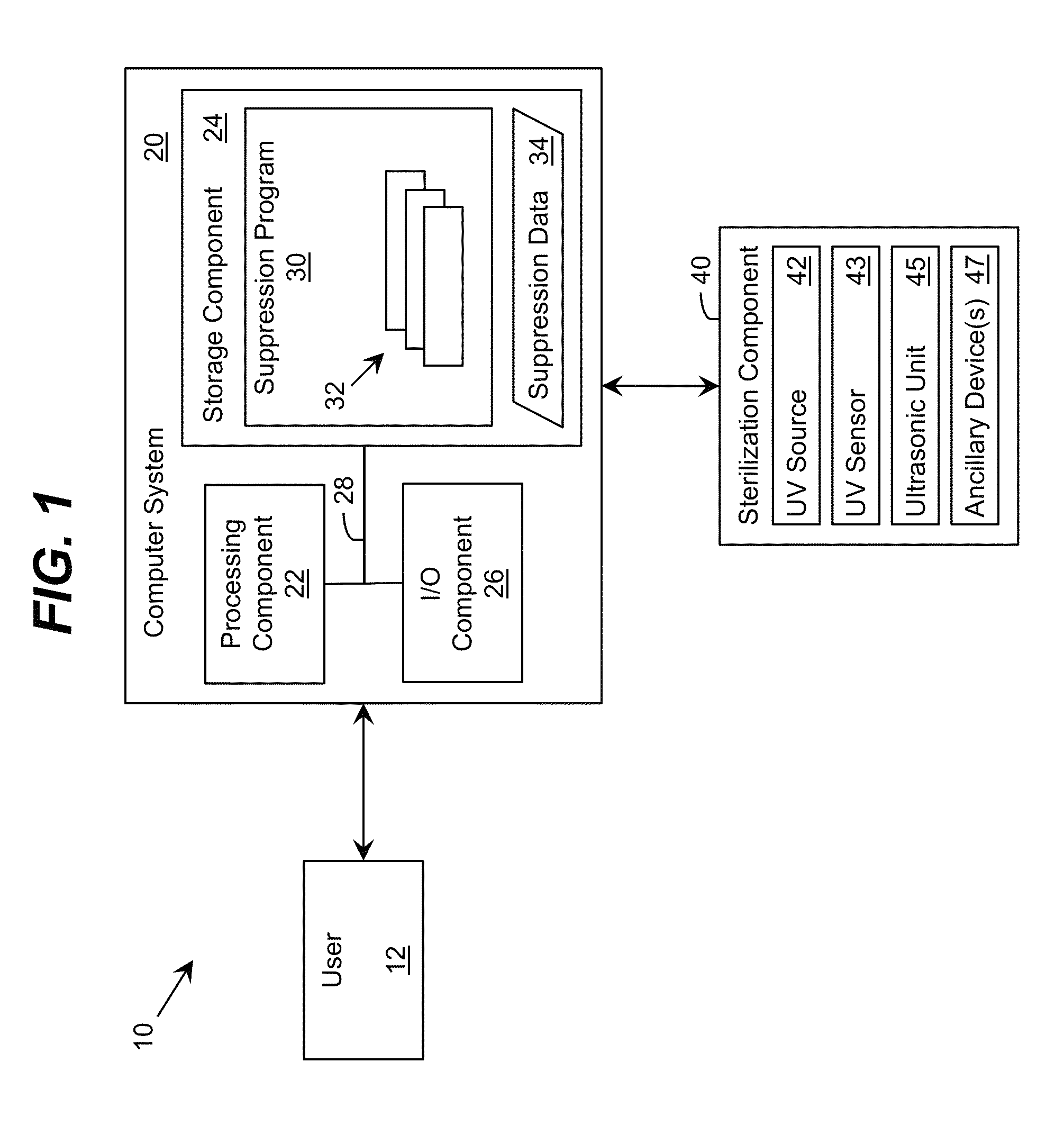
Ultraviolet-Based Sterilization
ActiveUS20130270445A1Scattering properties measurementsLight therapyTarget surfaceUltraviolet radiation
A system for sterilizing at least one surface of an object is provided. The system includes a set of ultraviolet radiation sources and a set of wave guiding structures configured to direct ultraviolet radiation having a set of target attributes to a desired location on at least one surface of the object. The set of wave guiding structures can include at least one ultraviolet reflective surface having an ultraviolet reflection coefficient of at least thirty percent. Furthermore, the system can include a computer system for operating the ultraviolet radiation sources to deliver a target dose of ultraviolet radiation to the at least one target surface of the object.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
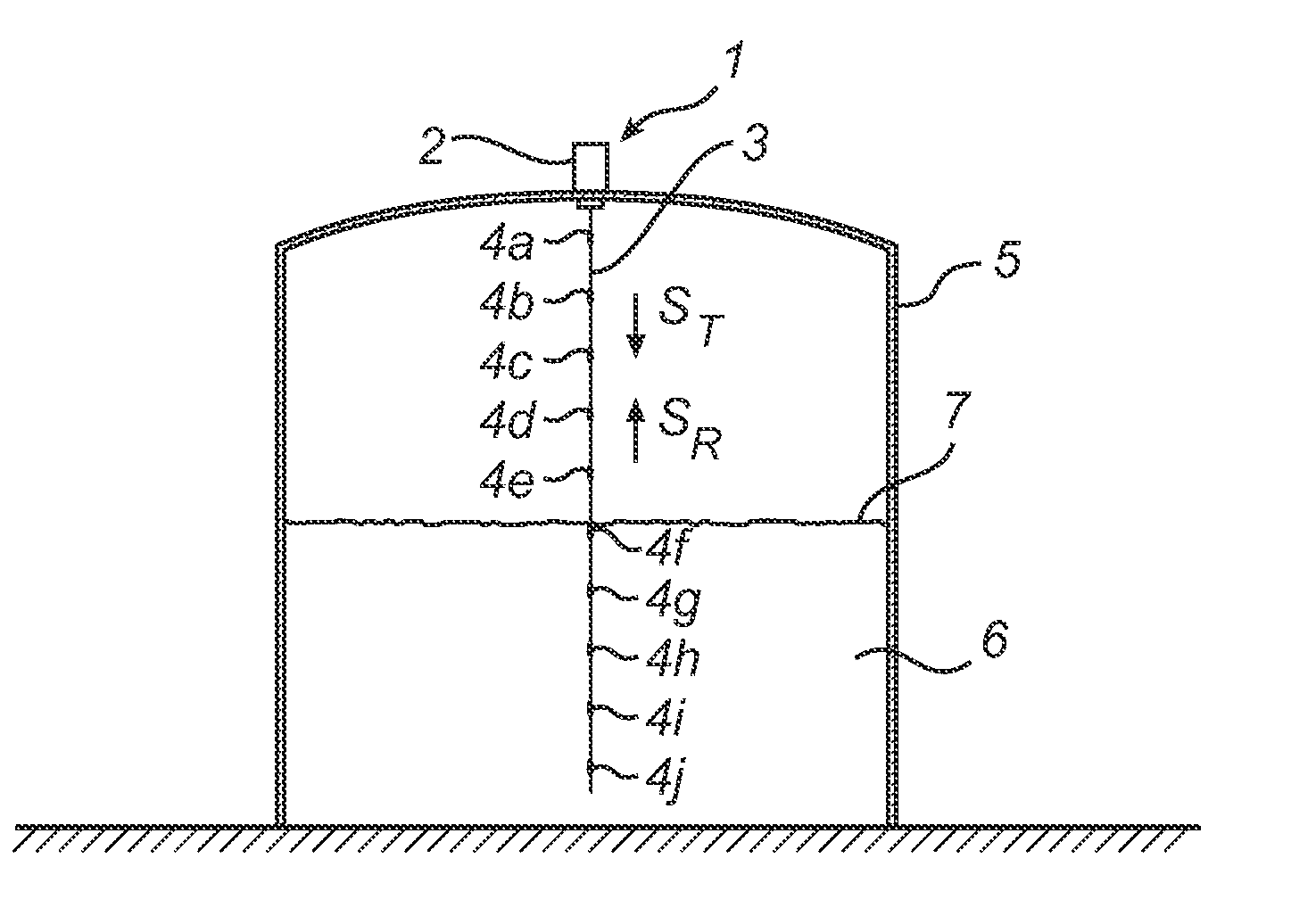
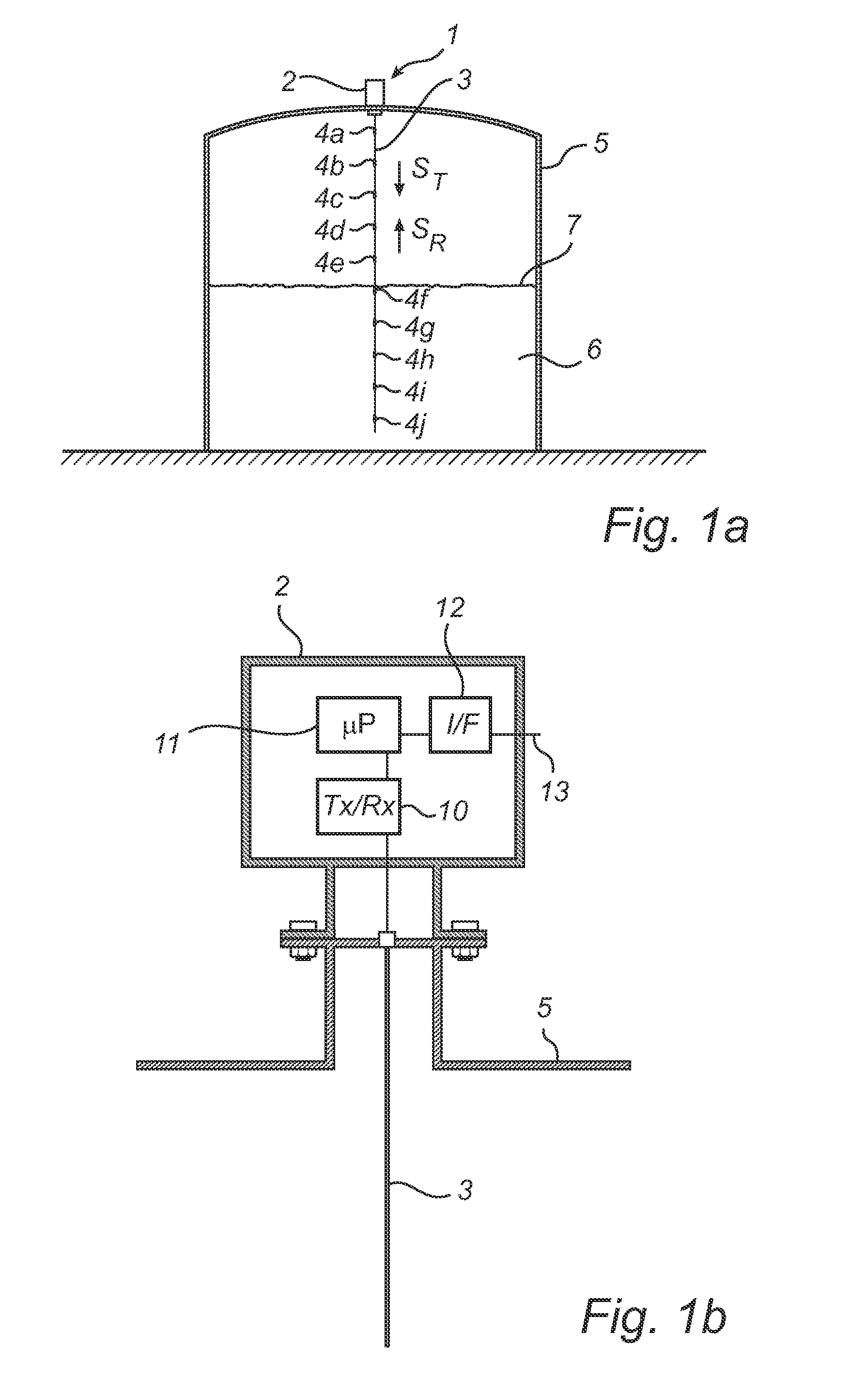
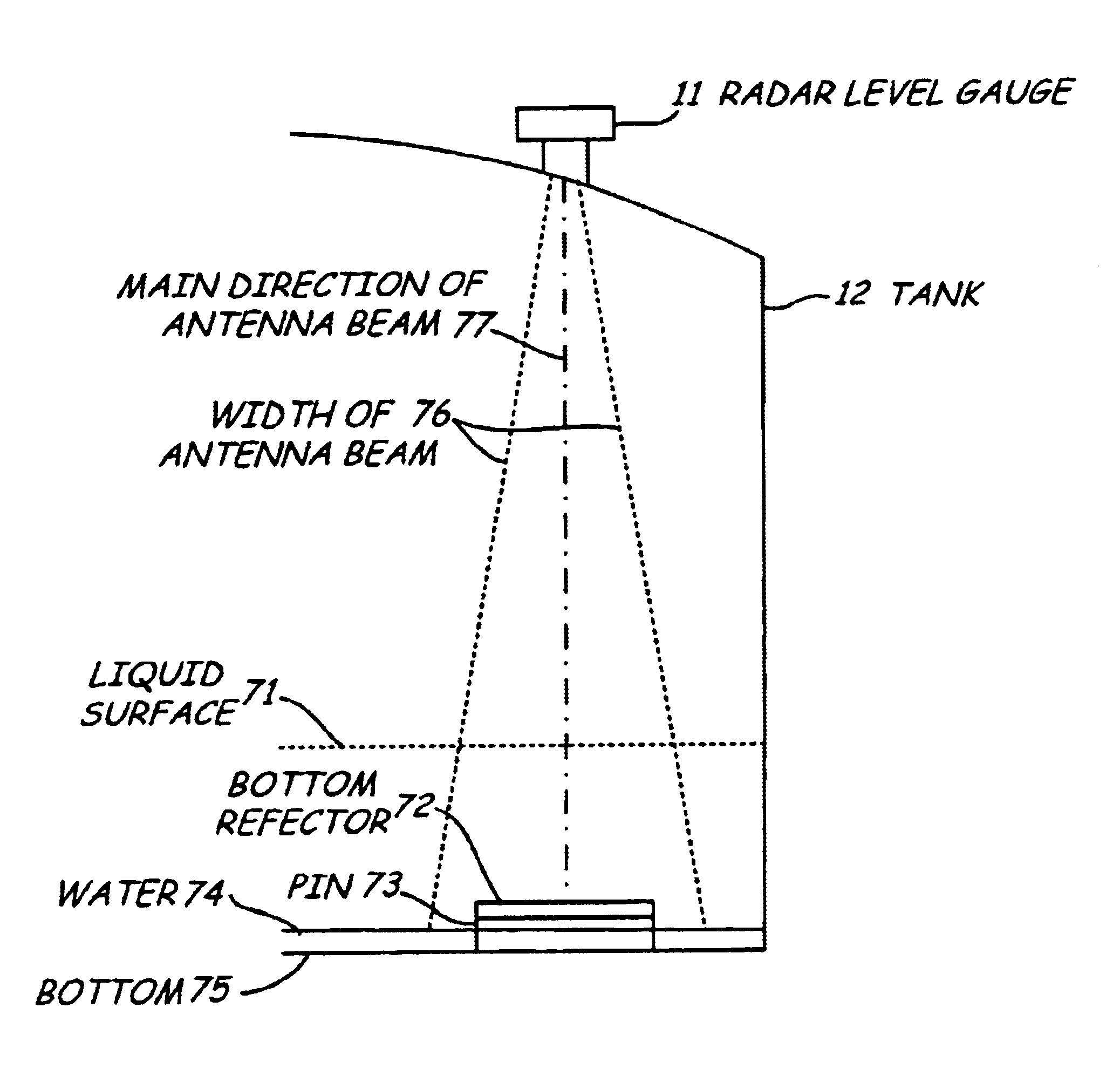
System and method for filling level determination
ActiveUS20100156702A1High accuracy filling level determinationWaveguide hornsLevel indicatorsMicrowaveTransceiver
A radar level gauge system using microwaves for measuring a level of a surface of a product in a container, comprising a waveguide arranged to extend into the product contained in the container, wherein a plurality of reference impedance transitions are arranged at known position along the waveguide and being configured to reflect a portion of transmitted electromagnetic signals back towards the transceiver. Preferably, each of the reference impedance transitions has a first reflection coefficient for the electromagnetic signals when the level of the surface is above the reference impedance transition and a second reflection coefficient for the electromagnetic signal when the level of the surface is below the reference reflector, the first reflection coefficient being substantially lower than the second reflection coefficient. According to this design, a higher accuracy of filling level measurements can be achieved.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
System and method for measuring constituent concentration
InactiveUS20090275814A1Accurate measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAcousticsDielectric permittivity
A system and method for measuring concentration of a constituent of a specimen are provided. The system includes an oscillator for outputting, towards the specimen, electromagnetic waves having respective different frequencies between 5 GHz and 300 GHz; a detector for detecting the electromagnetic waves that are reflected from the specimen; and a processor measuring at least one of reflection coefficient and complex permittivity of the electromagnetic waves detected and calculating the concentration of the constituent of the specimen based upon at least one of the reflection coefficient measured and the complex permittivity measured.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP +1
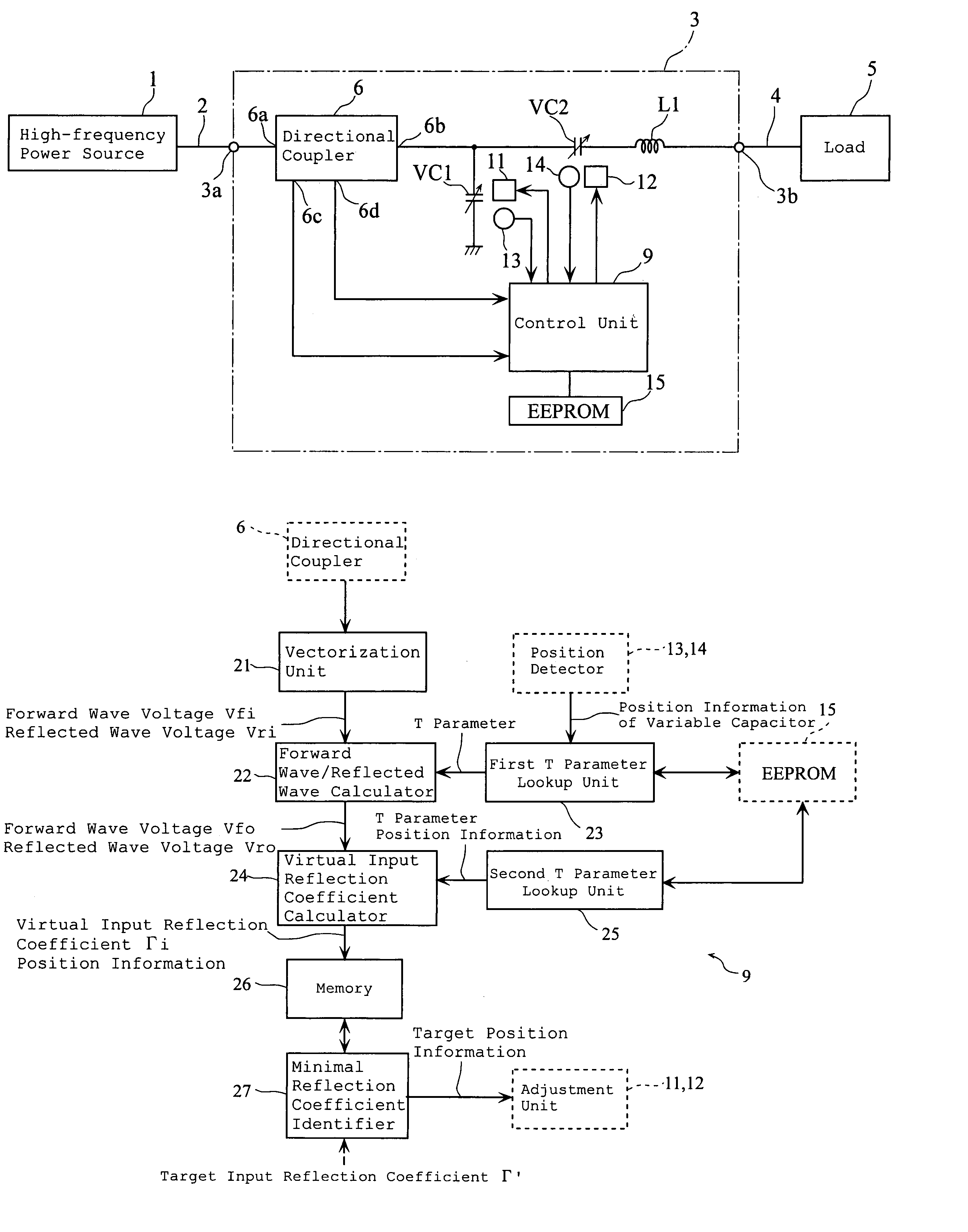
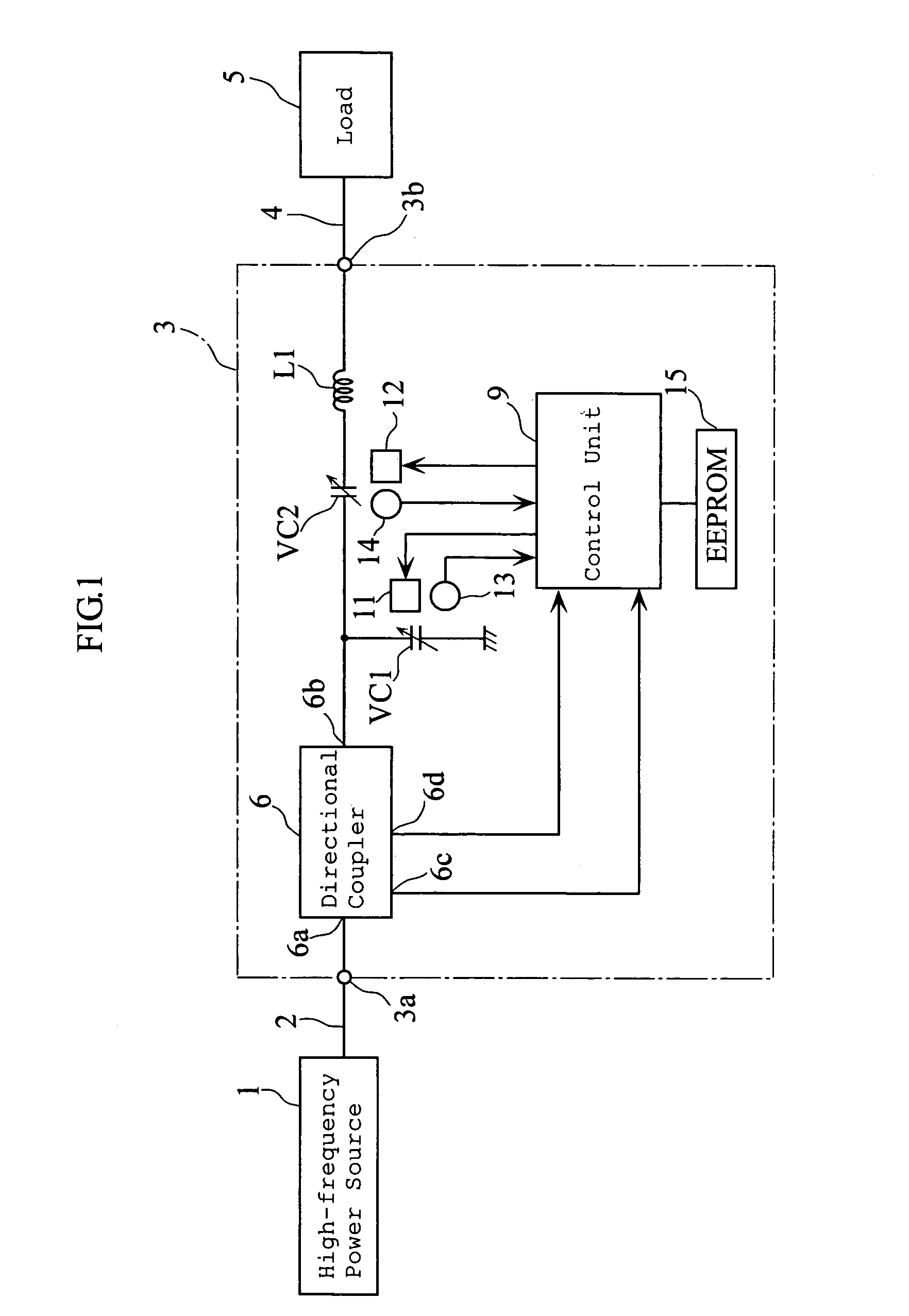
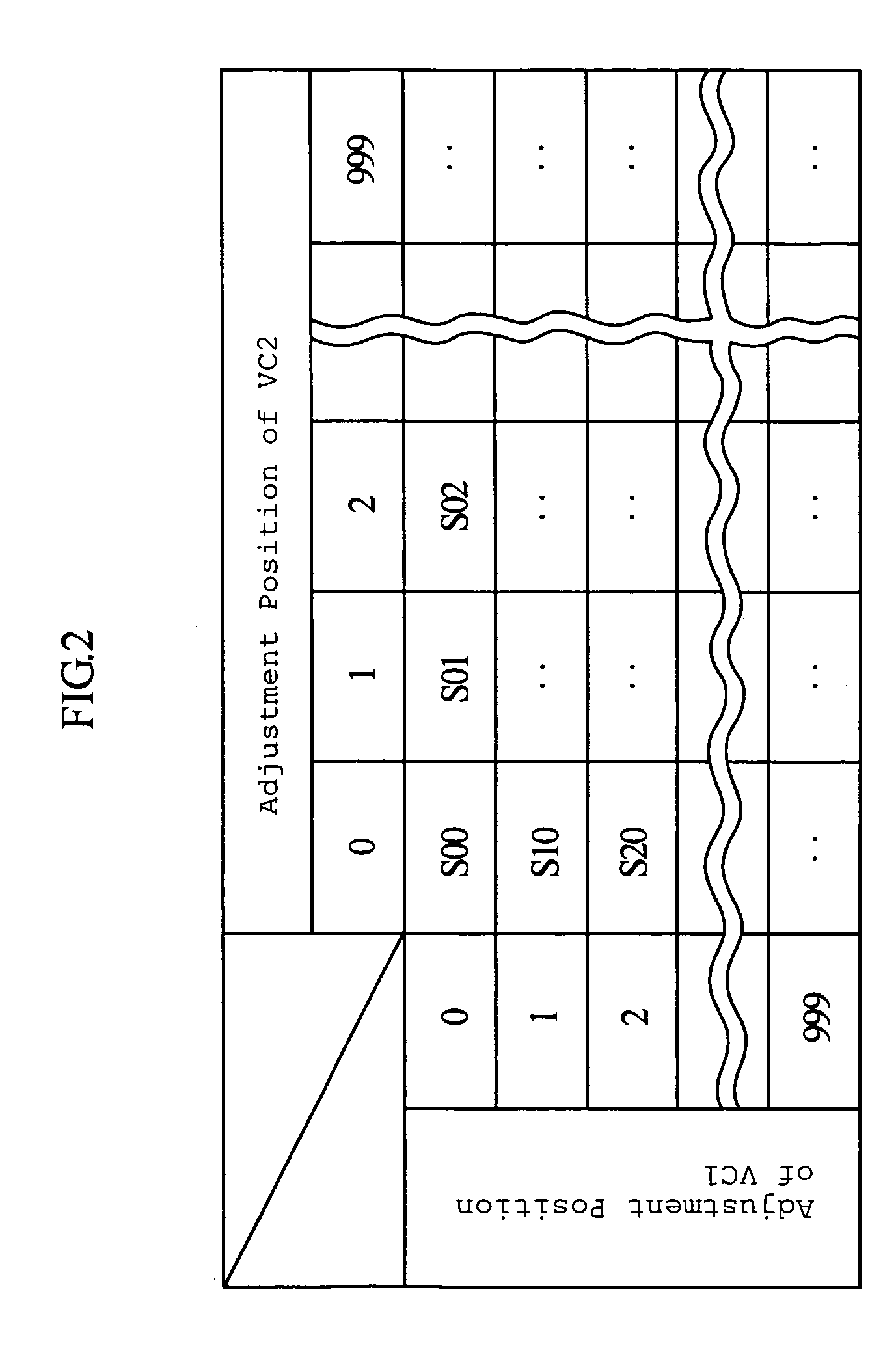
Impedance matching apparatus for a plasma chamber comprising two separate storage units and calculators
An impedance matching apparatus 3 calculates a forward wave voltage Vfo and a reflected wave voltage Vro at an output terminal 3b, based on a forward wave voltage Vfi and a reflected wave voltage Vri at an input terminal 3a, on information on variable values of variable capacitors VC1, VC2 acquired in advance through measurement, and on a T parameter of the impedance matching apparatus 3 corresponding to the information on the variable values of variable capacitors VC1, VC2. The impedance matching apparatus 3 calculates an input reflection coefficient Γi at the input terminal 3a corresponding to the information on the variable values of the variable capacitors VC1, VC2, based on the forward wave voltage Vfo, the reflected wave voltage Vro and the T parameter. The impedance matching apparatus 3 selects the lowest absolute value out of absolute values |Γi| of the input reflection coefficients corresponding to the variable values of the variable capacitors VC1, VC2, and adjusts the impedance of the variable capacitors VC1, VC2 based on the lowest value.
Owner:DAIHEN CORP
Physics Modeling for Radar and Ultrasonic Sensors
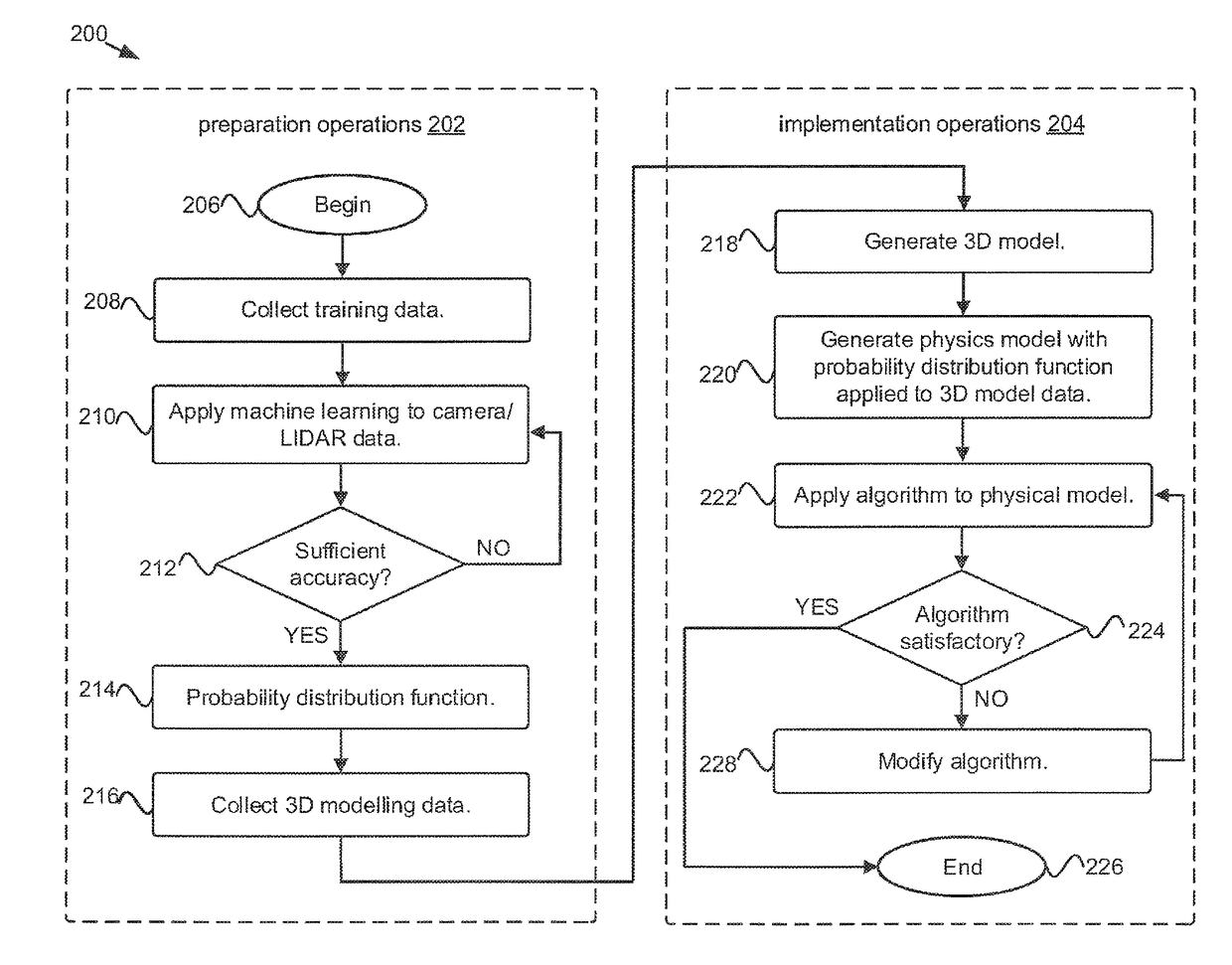
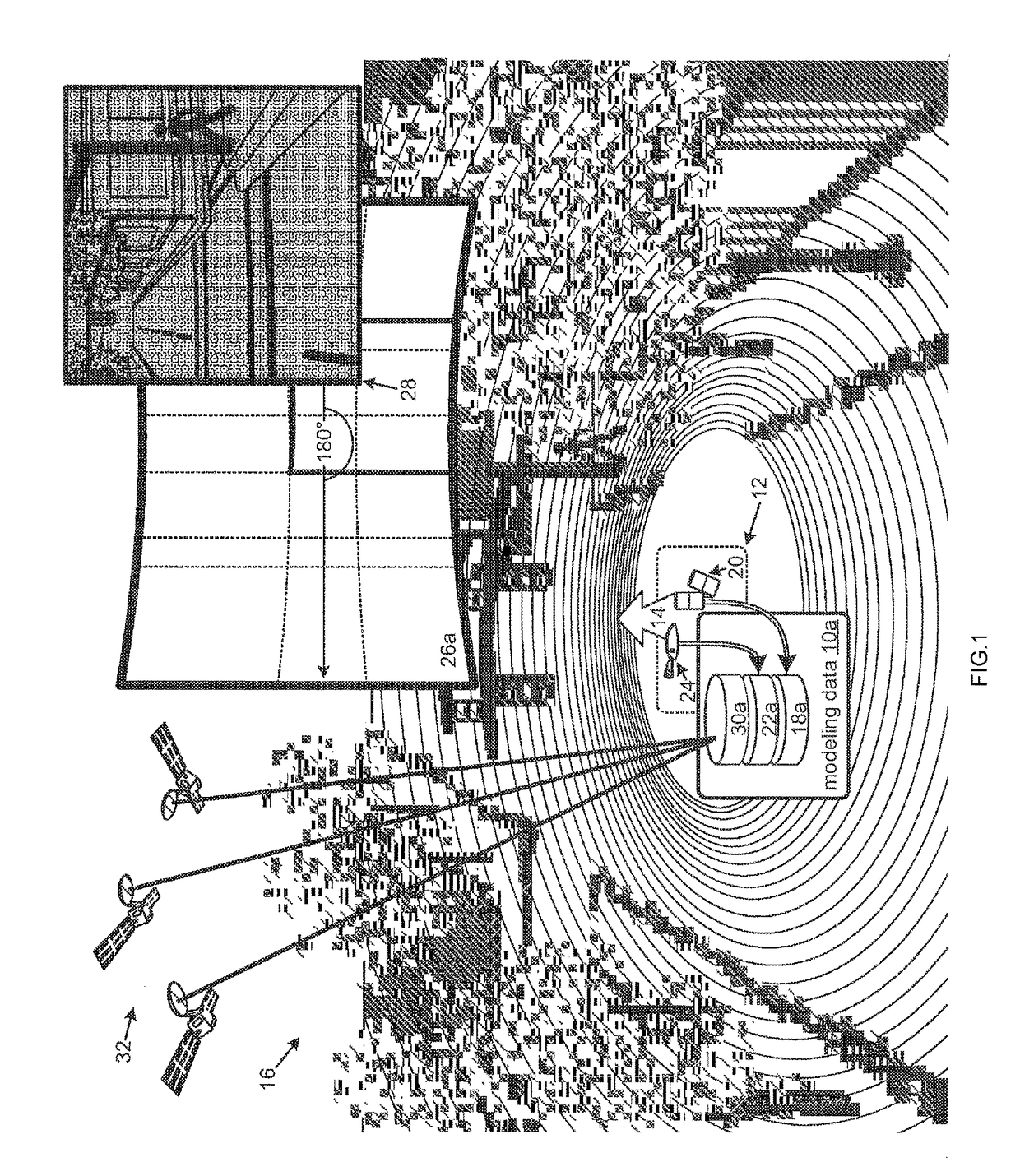
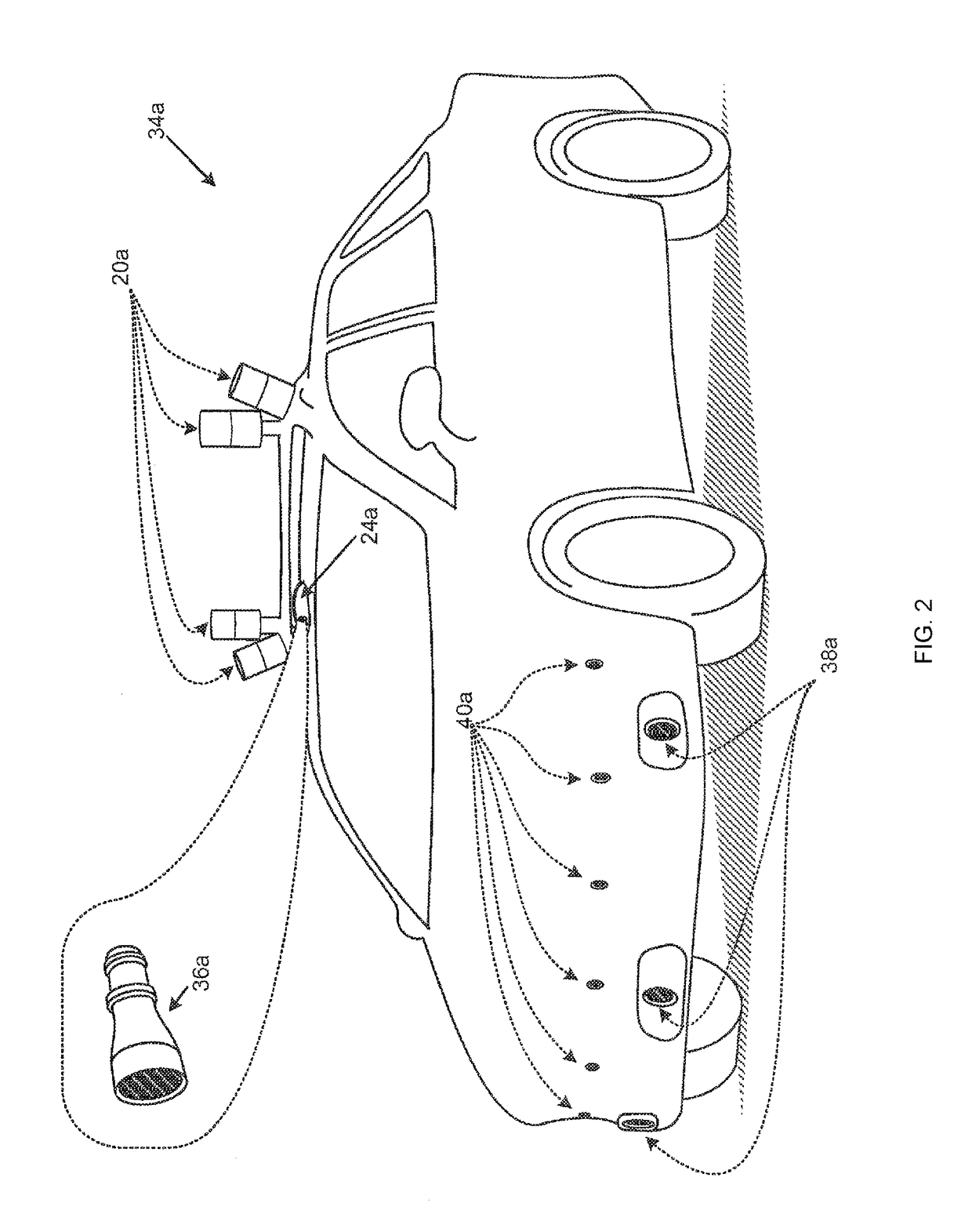
A machine learning module may generate a probability distribution from training data including labeled modeling data correlated with reflection data. Modeling data may include data from a LIDAR system, camera, and / or a GPS for a target environment / object. Reflection data may be collected from the same environment / object by a radar and / or an ultrasonic system. The probability distribution may assign reflection coefficients for radar and / or ultrasonic systems conditioned on values for modeling data. A mapping module may create a reflection model to overlay a virtual environment assembled from a second set of modeling data by applying the second set to the probability distribution to assign reflection values to surfaces within the virtual environment. Additionally, a test bench may evaluate an algorithm, for processing reflection data to generate control signals to an autonomous vehicle, with simulated reflection data from a virtual sensor engaging reflection values assigned within the virtual environment.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Ultraviolet-Based Sterilization
ActiveUS20150297767A1Material analysis by optical meansLight therapyTarget surfaceUltraviolet radiation
A system for sterilizing at least one surface of an object is provided. The system includes a set of ultraviolet radiation sources and a set of wave guiding structures configured to direct ultraviolet radiation having a set of target attributes to a desired location on at least one surface of the object. The set of wave guiding structures can include at least one ultraviolet reflective surface having an ultraviolet reflection coefficient of at least thirty percent. Furthermore, the system can include a computer system for operating the ultraviolet radiation sources to deliver a target dose of ultraviolet radiation to the at least one target surface of the object.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
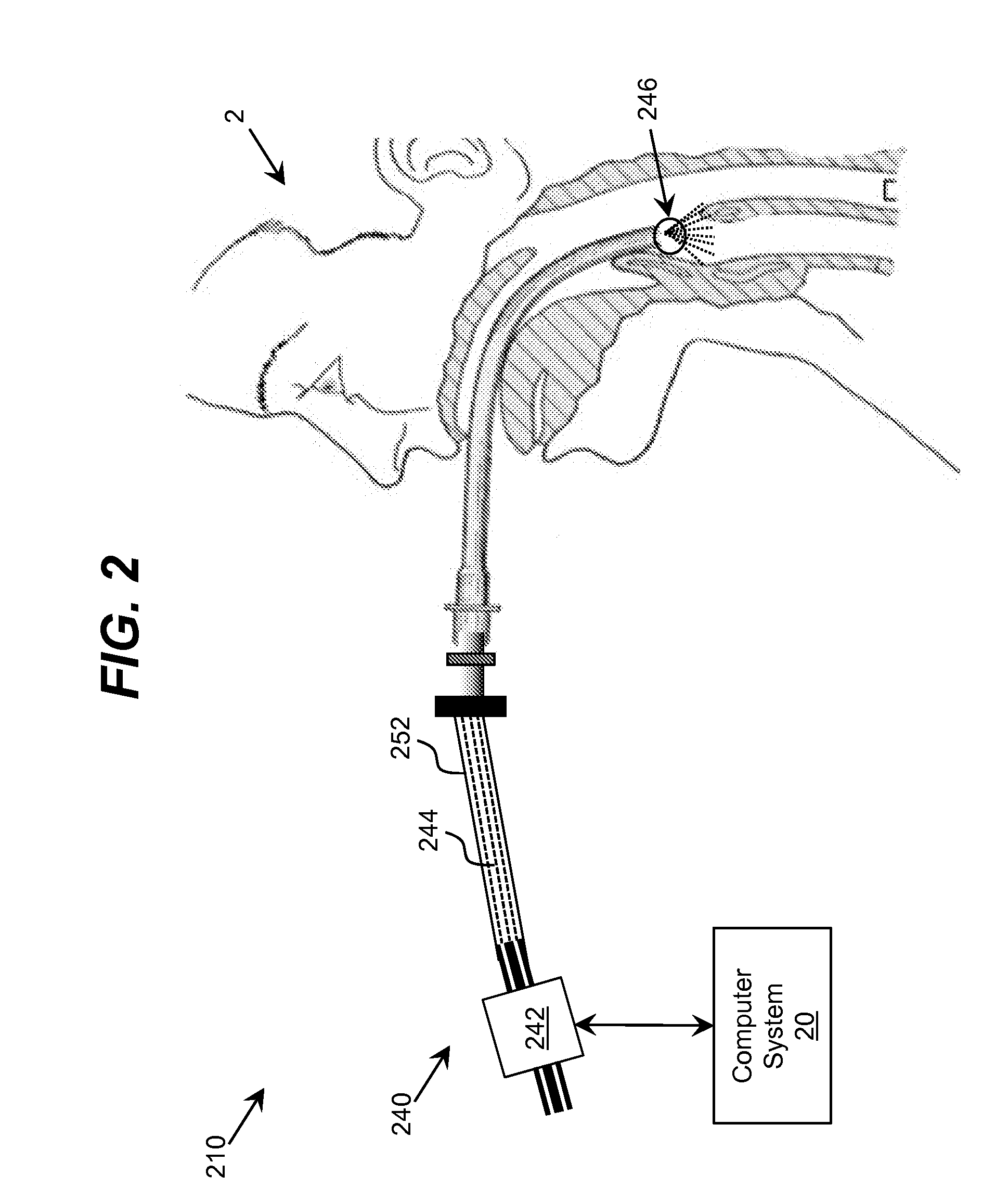
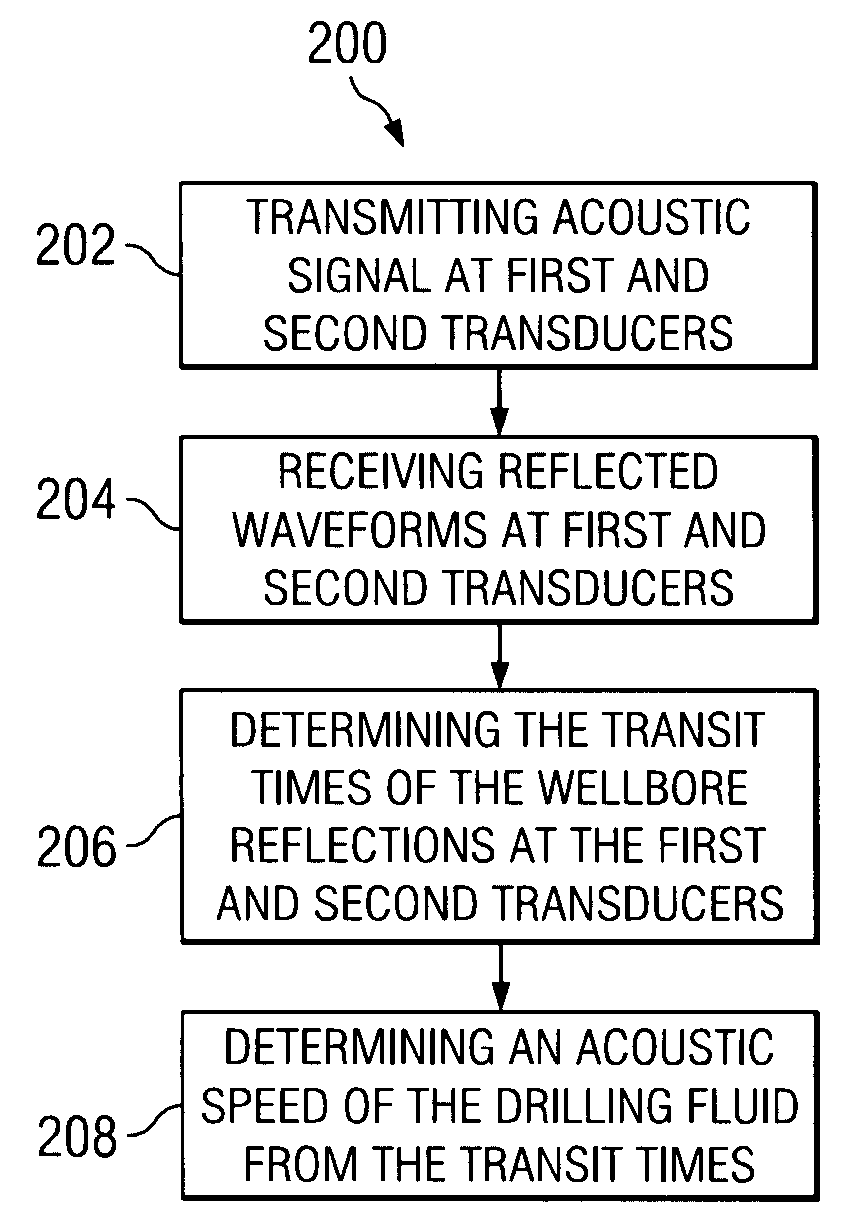
Apparatus and method for determining drilling fluid acoustic properties
ActiveUS20080186805A1Improve accuracyProvide goodAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSurveyReflection coefficientAttenuation coefficient
Aspects of this invention include a downhole tool having first and second radially offset ultrasonic standoff sensors and a controller including instructions to determine at least one of a drilling fluid acoustic velocity and a drilling fluid attenuation coefficient from the reflected waveforms received at the standoff sensors. The drilling fluid acoustic velocity may be determined via processing the time delay between arrivals of a predetermined wellbore reflection component at the first and second sensors. The drilling fluid attenuation coefficient may be determined via processing amplitudes of the predetermined wellbore reflection coefficients. The invention advantageously enables the acoustic velocity and attenuation coefficient of drilling fluid in the borehole annulus to be determined in substantially real-time.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Granule graininess, concentration and density measuring method and device
InactiveCN101169363AImprove versatilityGuaranteed accuracyAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesParticle size analysisParticulatesSonification
The invention discloses a measuring method and device for measuring the particle granularity, consistency and density, which relates to the technical field of ultrasonic measurement. The invention aims at solving the technical problem of increasing the commonality and the precision of the ultrasonic measurement. The measuring device includes a computer, a signal process circuit, a pulse wave launch / receive circuit and a broadband transducer, which are orderly connected together; the broadband transducer is arranged at the external side of a baffle plate. The process procedures of the computer are as follows: ultrasonic amplitude phase spectrum is obtained after the rapid Fourier transformation of the signal, and then the phase spectrum is converted to obtain a reflection coefficient, the acoustic characteristic impedance, the acoustic attenuation coefficient and the sound velocity; the compound density can be calculated by the measuring value, and the consistency can be calculated through the known particle and the density of the continuous medium; the frequency analysis of the direct reflection wave and the transmission echo is carried out to obtain difference between the acoustic attenuation spectrum and the theoretical acoustic attenuation spectrum, and the difference is then regarded as the objective function, and then is optimized with optimization method to calculate the distribution of the particle granularity. The invention has the advantages of measuring and analysis basing on the reflecting ultrasonic, great commonality and precise measuring result.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Ultraviolet-based sterilization
ActiveUS9061082B2Scattering properties measurementsLavatory sanitoryTarget surfaceUltraviolet radiation
A system for sterilizing at least one surface of an object is provided. The system includes a set of ultraviolet radiation sources and a set of wave guiding structures configured to direct ultraviolet radiation having a set of target attributes to a desired location on at least one surface of the object. The set of wave guiding structures can include at least one ultraviolet reflective surface having an ultraviolet reflection coefficient of at least thirty percent. Furthermore, the system can include a computer system for operating the ultraviolet radiation sources to deliver a target dose of ultraviolet radiation to the at least one target surface of the object.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
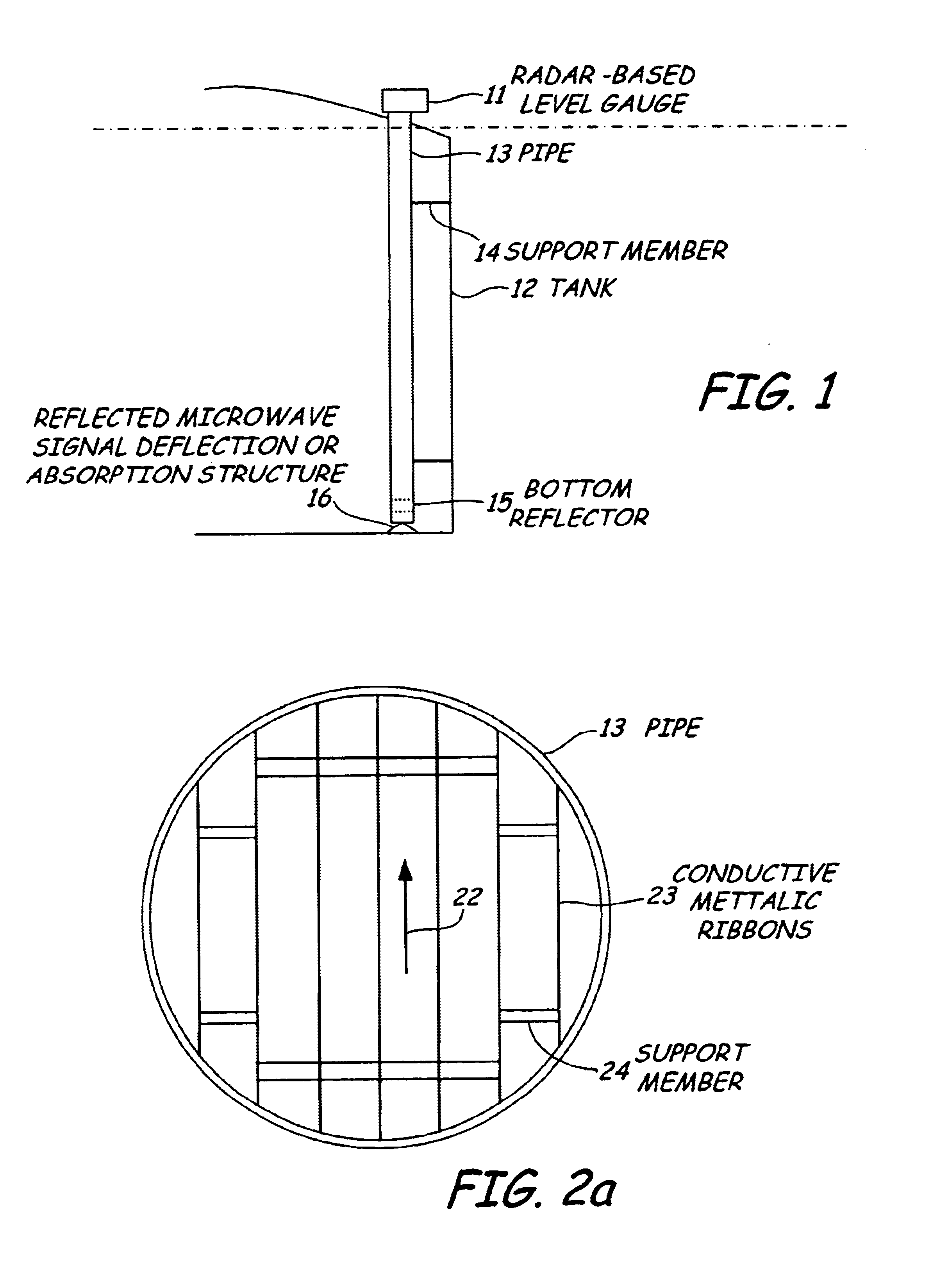
Bottom reflector for a radar-based level gauge
InactiveUS6795015B2Simple and reliable processEasy to installMachines/enginesLubrication indication devicesRadarPropagation time
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
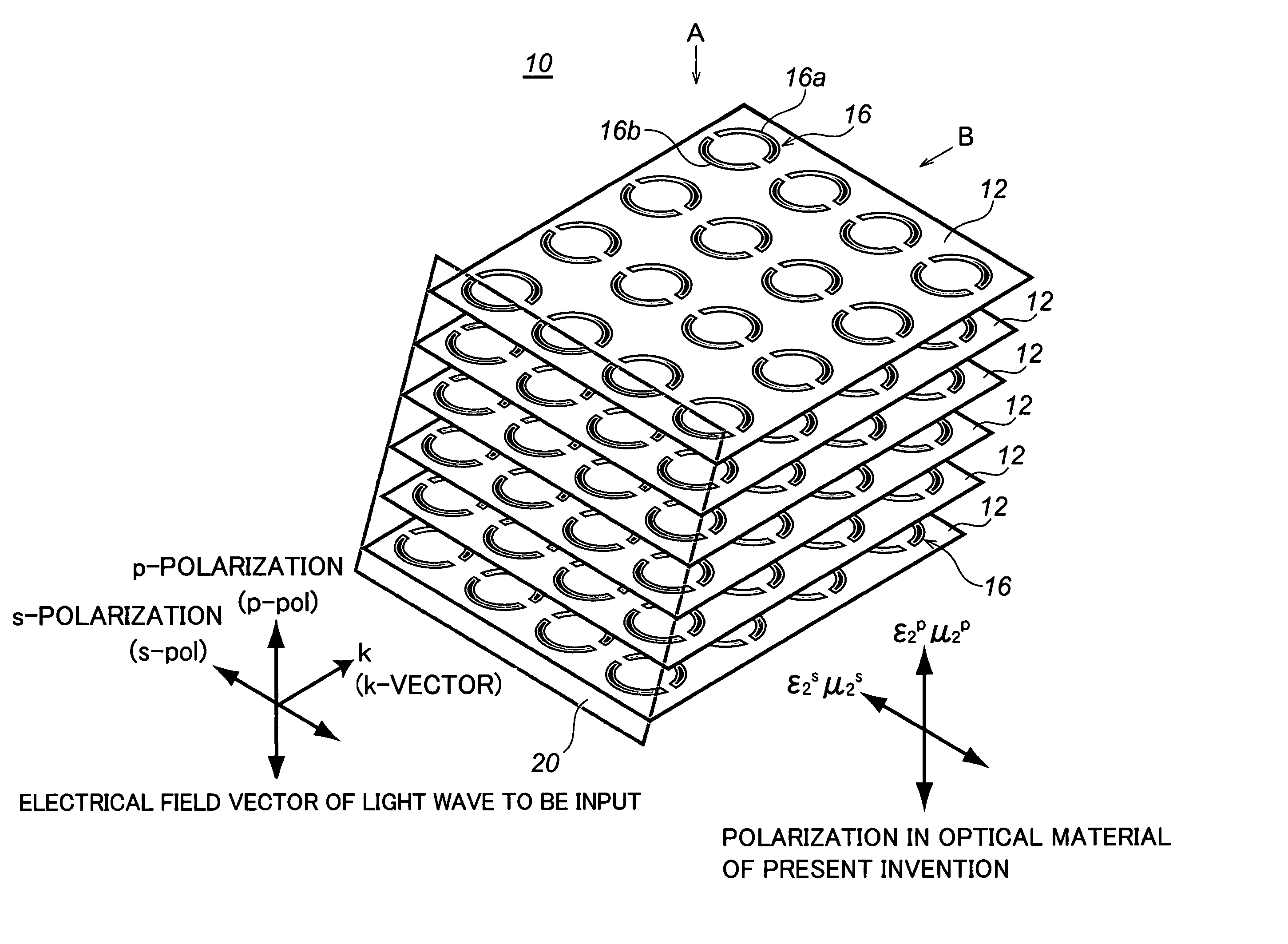
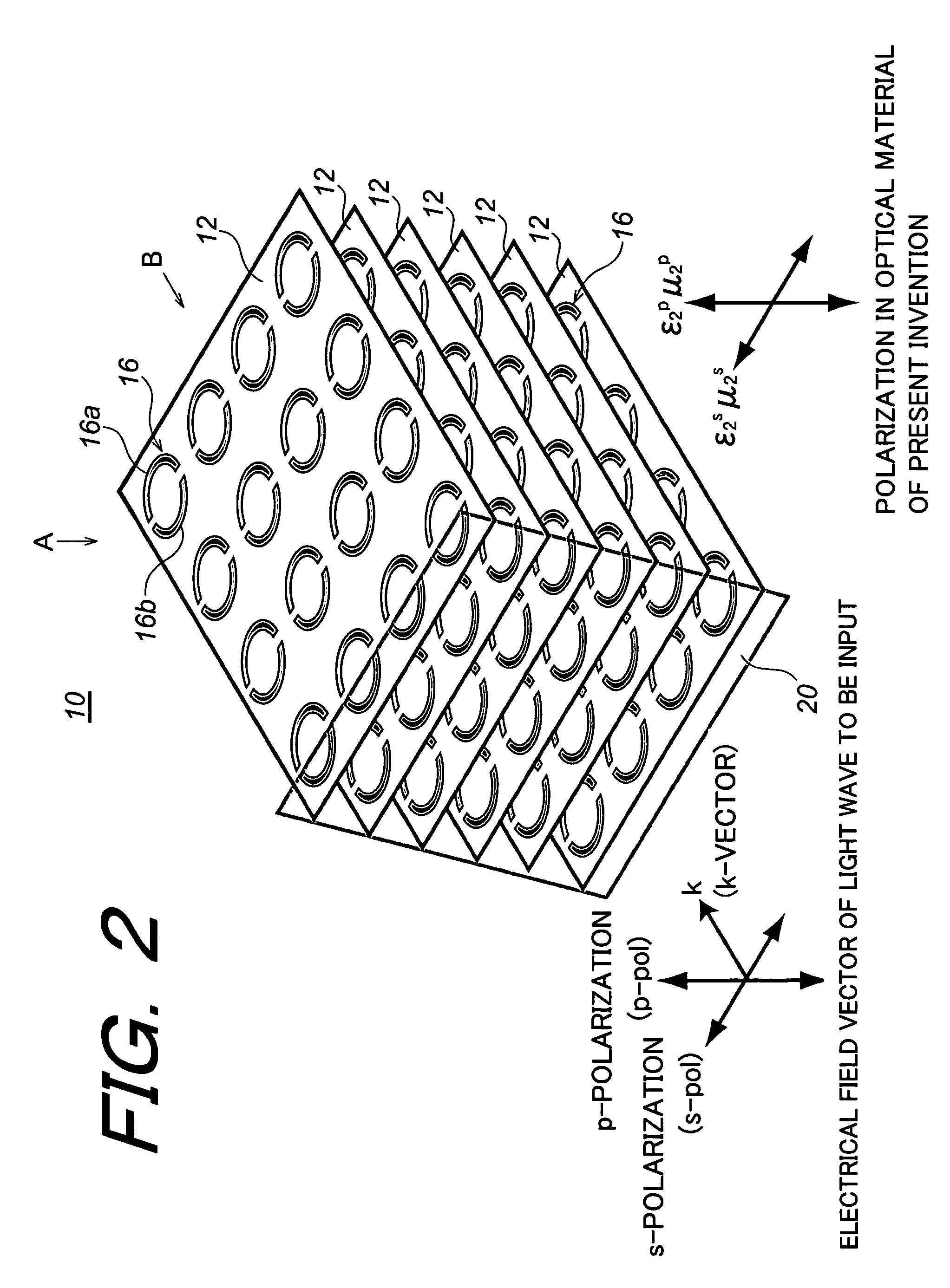
Optical material, optical device fabricated therefrom, and method for fabricating the same
In order to make a reflection coefficient in boundary surface between materials to be zero and permeate 100% of a light independent of a polarization direction, an optical device made of an optical material composed of a metamaterial prepared by arranging a plurality of at least either of electrical resonators or magnetic resonators each being smaller than a wavelength of a light wave in only a predetermined plane, and at least either of the electrical resonators and the magnetic resonators arranged functioning with respect to s-polarization, whereby at least either of the dielectric constant or the magnetic permeability is controlled in response to the function to induce a Brewster phenomenon in the s-polarization wherein the incident plane of a light wave being set out at a Brewster's angle with respect to the p-polarization and further at least either of the dielectric constant and the magnetic permeability of the optical material being controlled with respect to the s-polarization of the optical material, whereby the Brewster condition is independently satisfied in both the p-polarization and the s-polarization at the same time.
Owner:RIKEN
Dynamic real-time calibration for antenna matching in a radio frequency receiver system
ActiveUS20110086598A1Multiple-port networksResonant long antennasRadio frequencyReflection coefficient
Real-time calibration of a tunable matching network that matches the dynamic impedance of an antenna in a radio frequency receiver system. The radio frequency receiver system includes two non-linear equations that may be solved to determine the reflection coefficient of the antenna. The tunable matching network is repeatedly perturbed and the power received by the antenna is measured after each perturbation at the same node in the matching network. The measured power values are used by an optimizer in converging to a solution that provides the reflection coefficient of the antenna. The reflection coefficient of the antenna may be used to determine the input impedance of the antenna. The elements of the matching circuit are then adjusted to match the input impedance of the antenna.
Owner:RES IN MOTION LTD
Frequency selective load pull tuner and method
ActiveUS7248866B1Easy to manufactureReadily available for frequency rangeResistance/reactance/impedenceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsDiscriminatorMicrowave
An automatic, frequency selective microwave tuner, used for load pull transistor testing, is capable of generating independently controllable reflection factors, both in amplitude and phase, at several, harmonic or not, frequencies simultaneously. The tuner employs horizontally and vertically adjustable high Q resonant probes and replaces, when used in harmonic load pull set-ups, otherwise required combinations of wide-band tuners with harmonic rejection tuners or wide-band tuners and frequency discriminators (diplexers or triplexers).
Owner:TSIRONIS CHRISTOS
Strain sensitive coax cable sensors for monitoring structures
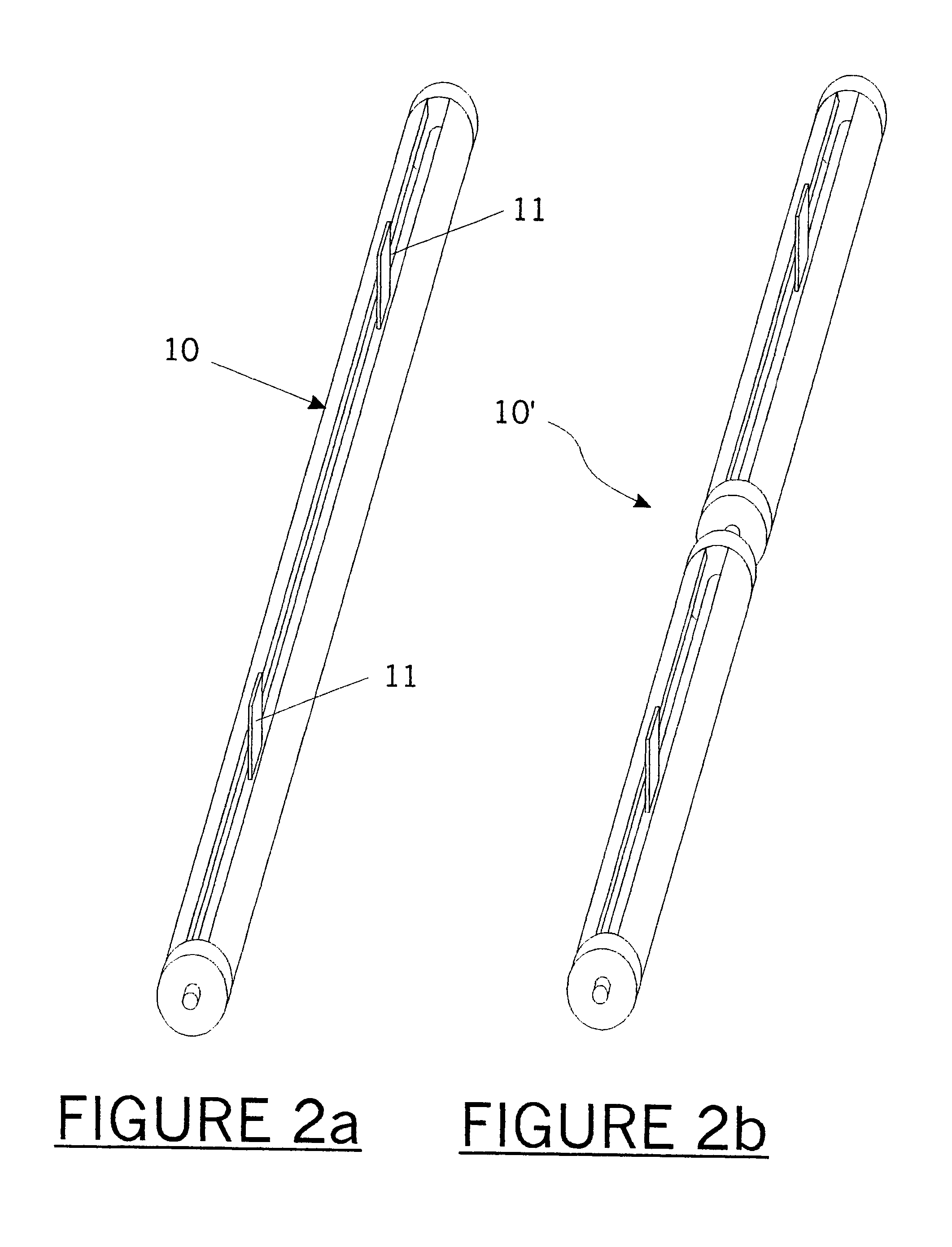
The invention provides increased structural monitoring systems that have sensitive continuous coaxial cable sensors. A preferred embodiment sensor cable of the invention includes an inner conductor, a dielectric jacket, and an outer conductor that is configured to passively deform responsively to strain in an associated structure. The deformation can be aided by the physical structure of the dielectric jacket, the outer conductor, or a combination of both. The deformation translates strain into a measurable change in a reflection coefficient associated with the outer conductor.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Apparatus and method for determining drilling fluid acoustic properties
ActiveUS7587936B2Improve accuracyImprove the accuracy of standoff measurementsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSurveyAttenuation coefficientTime delays
Aspects of this invention include a downhole tool having first and second radially offset ultrasonic standoff sensors and a controller including instructions to determine at least one of a drilling fluid acoustic velocity and a drilling fluid attenuation coefficient from the reflected waveforms received at the standoff sensors. The drilling fluid acoustic velocity may be determined via processing the time delay between arrivals of a predetermined wellbore reflection component at the first and second sensors. The drilling fluid attenuation coefficient may be determined via processing amplitudes of the predetermined wellbore reflection coefficients. The invention advantageously enables the acoustic velocity and attenuation coefficient of drilling fluid in the borehole annulus to be determined in substantially real-time.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for calibrating a frequency domain reflectometer
InactiveUS20050234662A1Accurate estimateAccurate modelingElectric devicesResistance/reactance/impedenceEngineeringReflectometry
A calibration system is provided for calibrating frequency domain reflectometers in the field by using both the scattering parameters of the multi-port junction determined at the factory and changing the offset and gain terms used in generating a complex reflection coefficient by using internal calibrated loads so that heavy, cumbersome external calibrated transmission lines are not required. In one embodiment the internal calibrated loads include RLC circuits and in another embodiment the internal calibrated loads include attenuators. Further, retesting or recalibration does not necessitate reconnecting the cable under test, which may remain connected to the reflectometer's test port throughout the procedure.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Method for designing ultra wideband impedance matching network
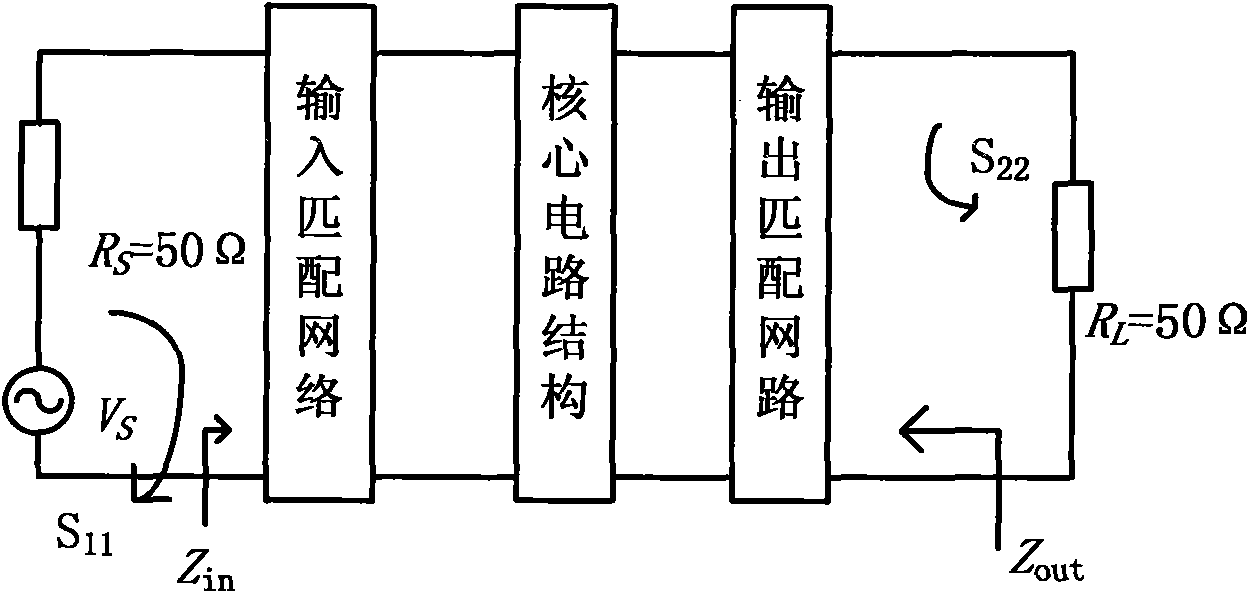
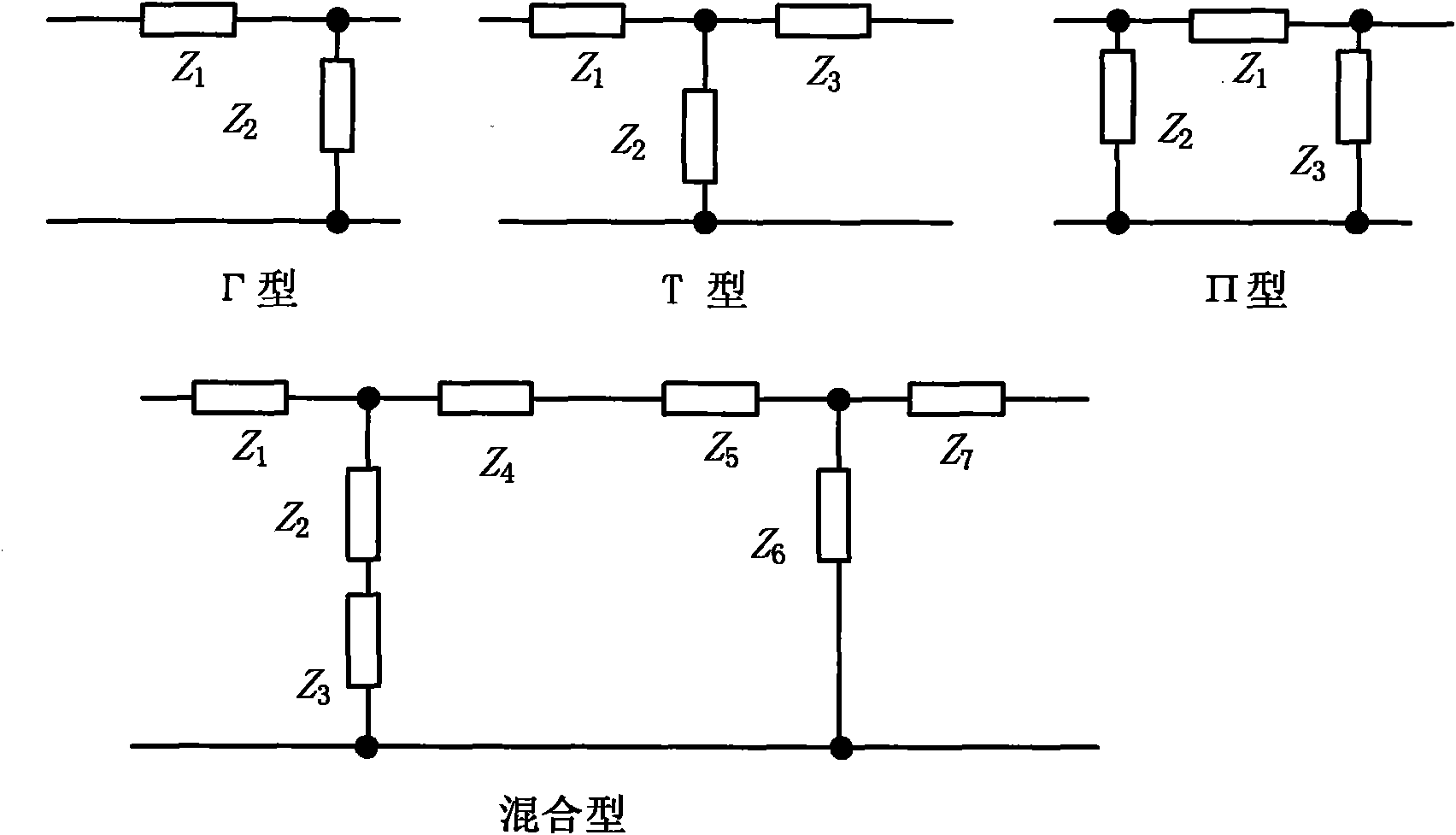
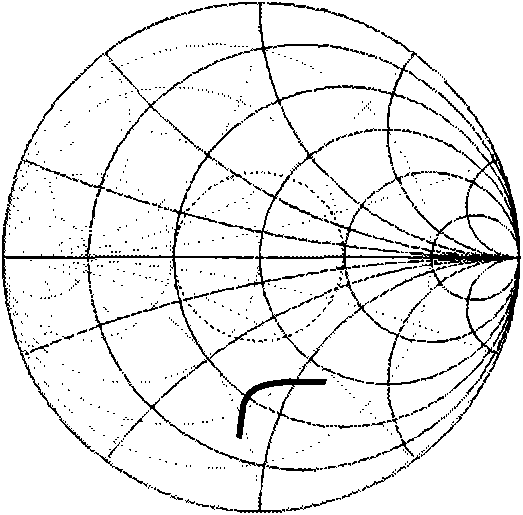
The invention discloses a method for designing a universal ultra wideband impedance matching network. A wideband matching network is added at the radio frequency input end or the radio frequency output end of a radio frequency circuit, and can be one of a T-type matching network, a Pi-type matching network and a hybrid matching network; elements in the matching network can be inductors or capacitors; the input reflection coefficient S11 or the output reflection coefficient S22 of the designed radio frequency circuit is shown in a Smith chart; an S11 curve or an S22 curve changes in the Smith chart by serially or parallelly connecting the inductors or the capacitors in the matching network; and the two curves finally completely fall into a -10dB impedance matching circle, so that the radio frequency circuit realizes impedance matching within an ultra wideband frequency band. An optimal ultra wideband impedance matching network can be conveniently designed by the method; and taking a low noise amplifier (LNA) as an example, for an optionally given LNA structure, an optimized matching network can be acquired by inserting one or more inductors or capacitors into an input and output matching network. In the process of designing the matching network, the positions of the reflection coefficient curves in the Smith chart are adjusted by adjusting the connecting mode and the sizes of the elements, and the reflection coefficient curves can move into reflection coefficient circles such as -10dB and the like in the range of an overall designing frequency band, so that the aim of accomplishing the good impedance matching in a wide frequency band range is fulfilled.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Apparatus and method for determining precision reflectivity of highway signs and other reflective objects utilizing an optical range finder instrument
An apparatus and method for measuring coefficients of retroreflectance of retroreflective surfaces such as road signs involves use of a modified light based range finder. The apparatus includes a power attenuation factor data base which relates pulse width of received pulses to power attenuation of the transmitted pulses. The range finder calculates target range based on time of flight of light pulses. The apparatus automatically calculates the absolute coefficient of retroreflectance for an unknown reflective surface being measured by comparison of the measurement to a reading with the same instrument of a known reflectance standard. The method involves either recalling a stored standard reference reflectance factor or determining a reflectance factor via the range finder for a sample of retroreflective material with a predetermined coefficient of retroreflectance, and then measuring the distance to an unknown target, determining a power attenuation factor from the received pulse width from the unknown target and then calculating the absolute coefficient of retroreflectance based upon these determined values of power attenuation factor, distance and the reference reflectance factor.
Owner:KAMA TECH (HK) LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com