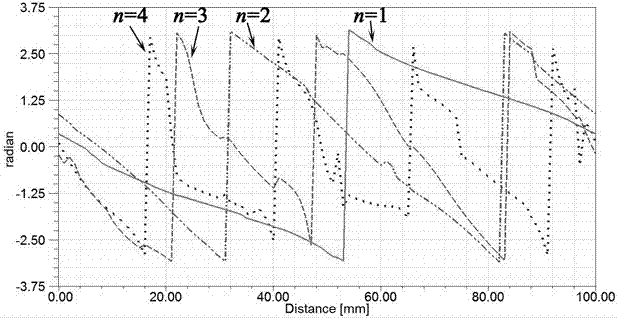
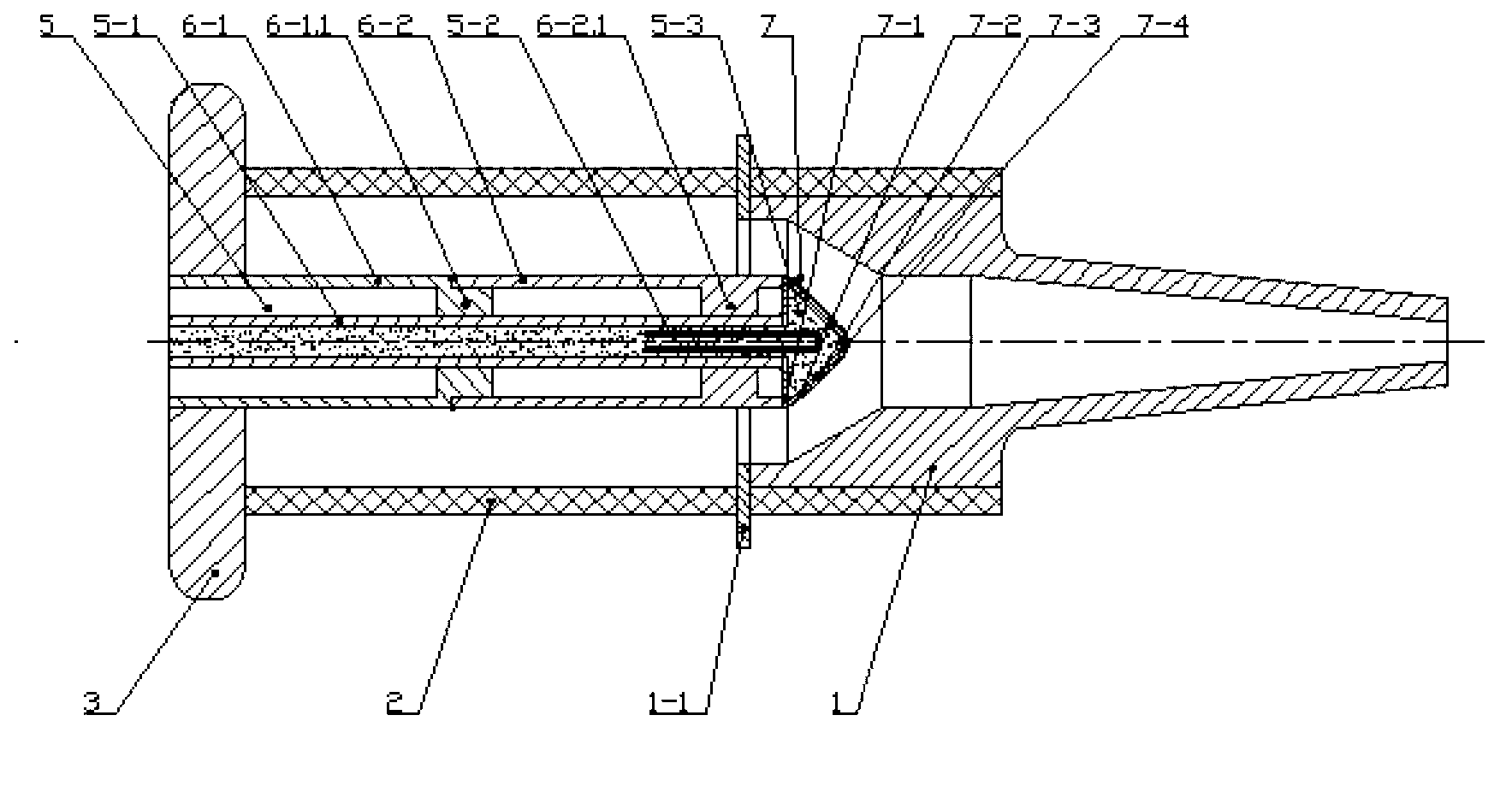
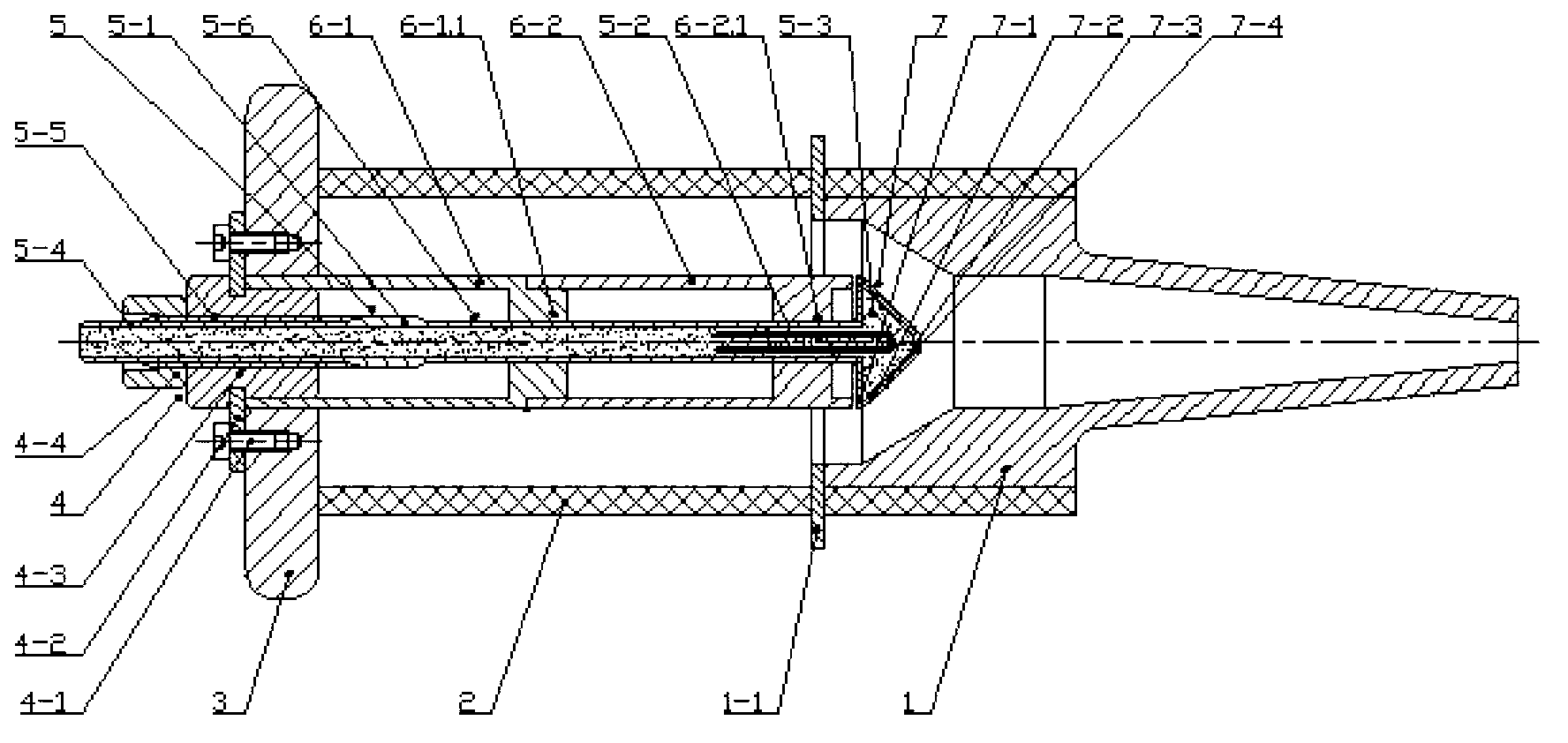
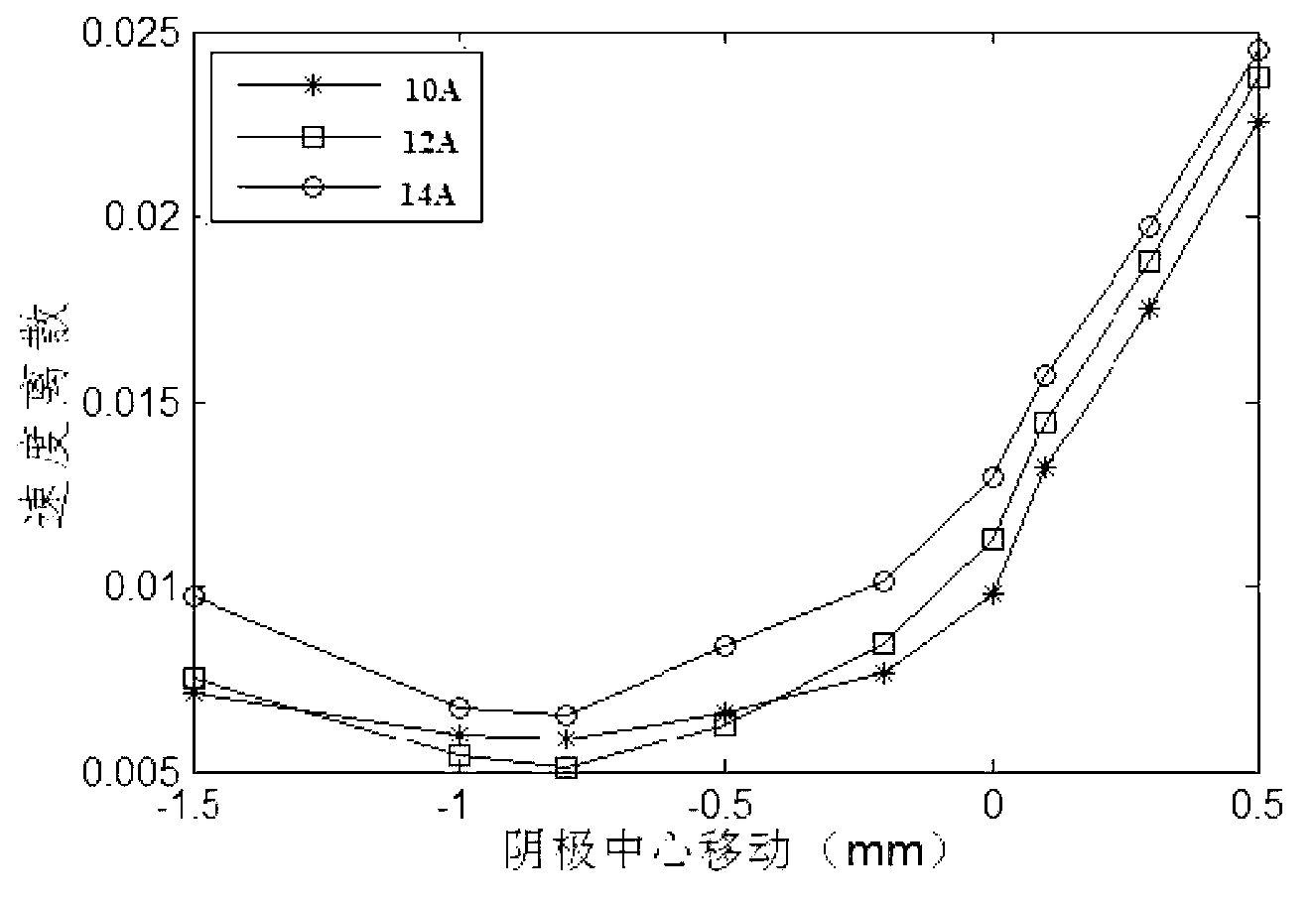
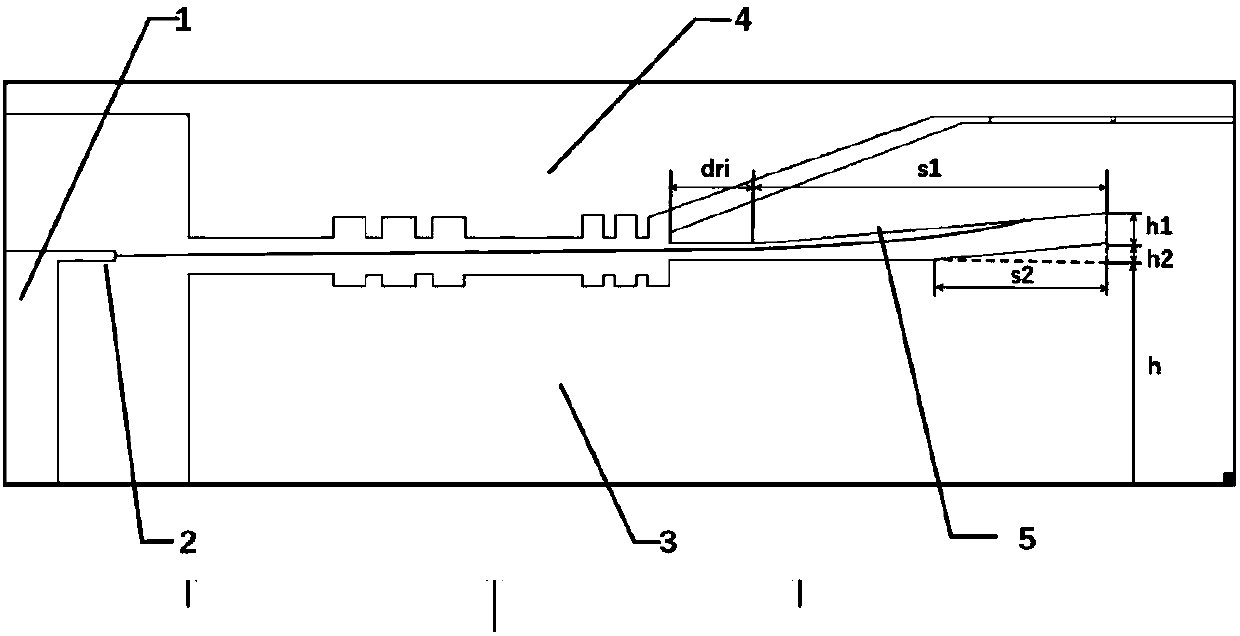
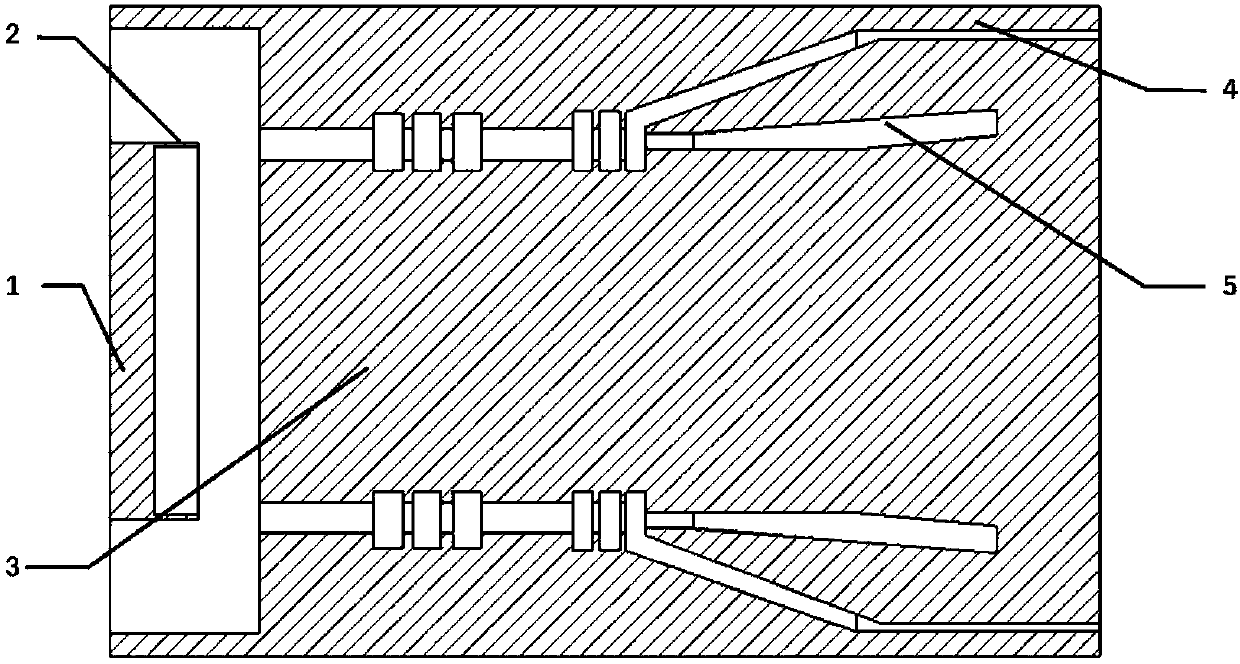
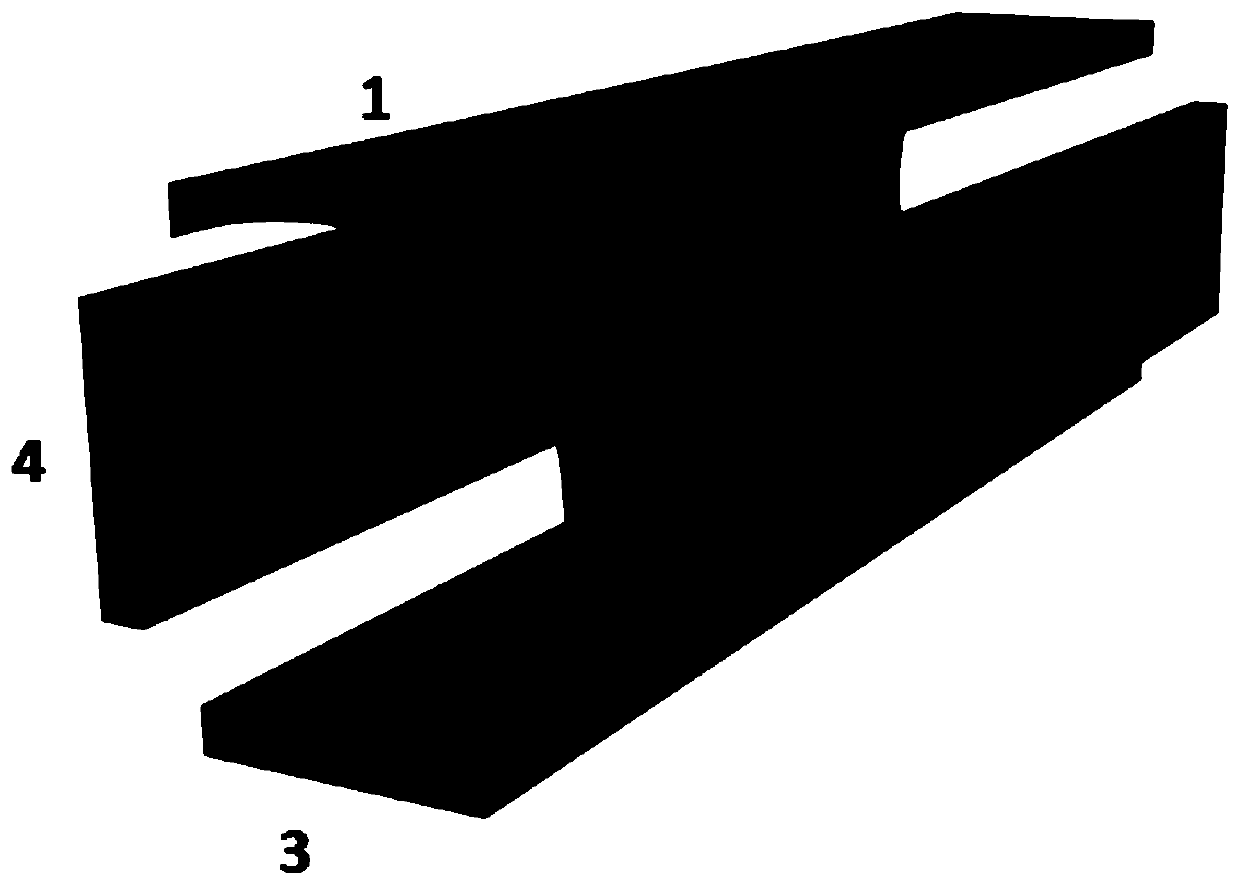
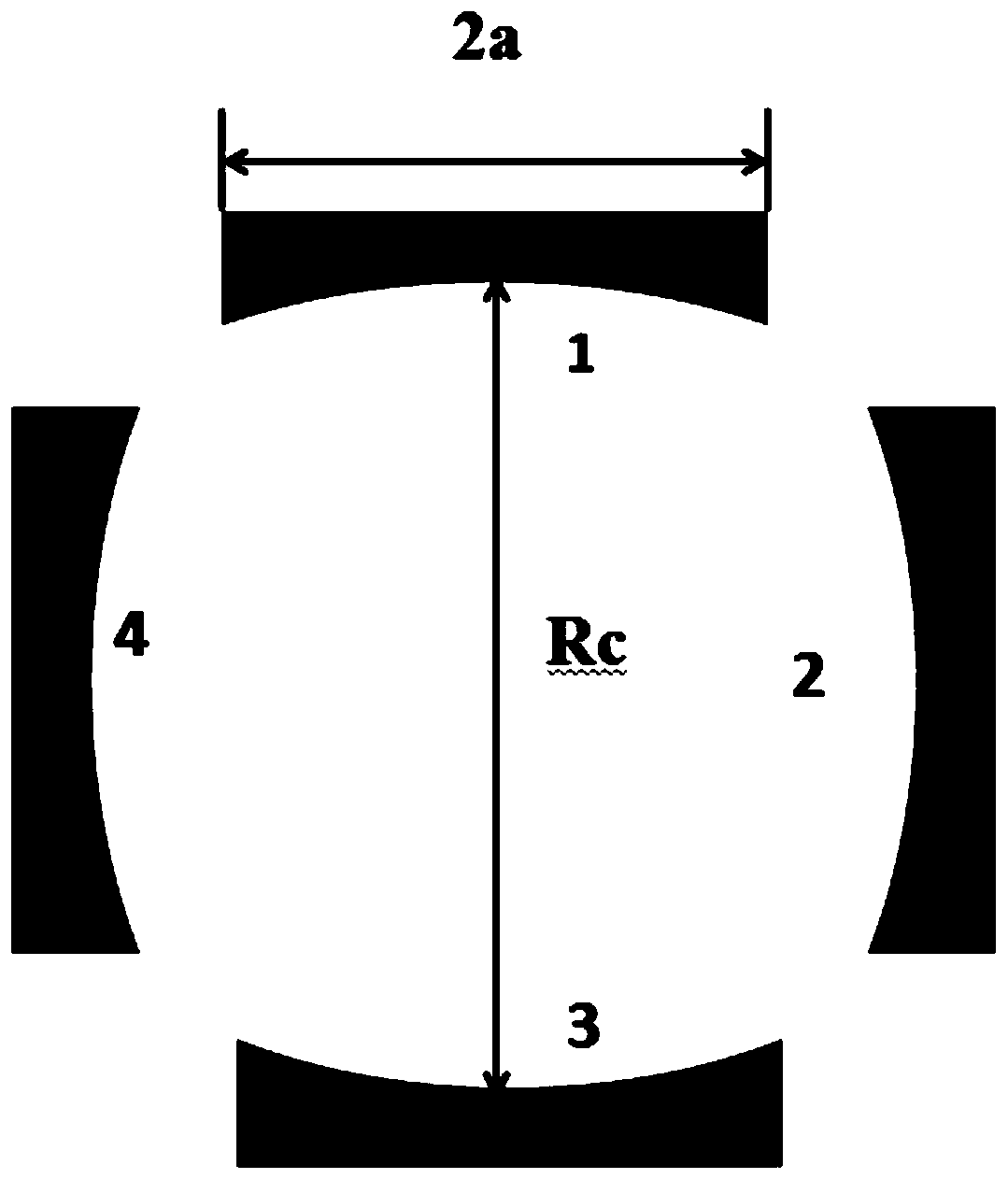
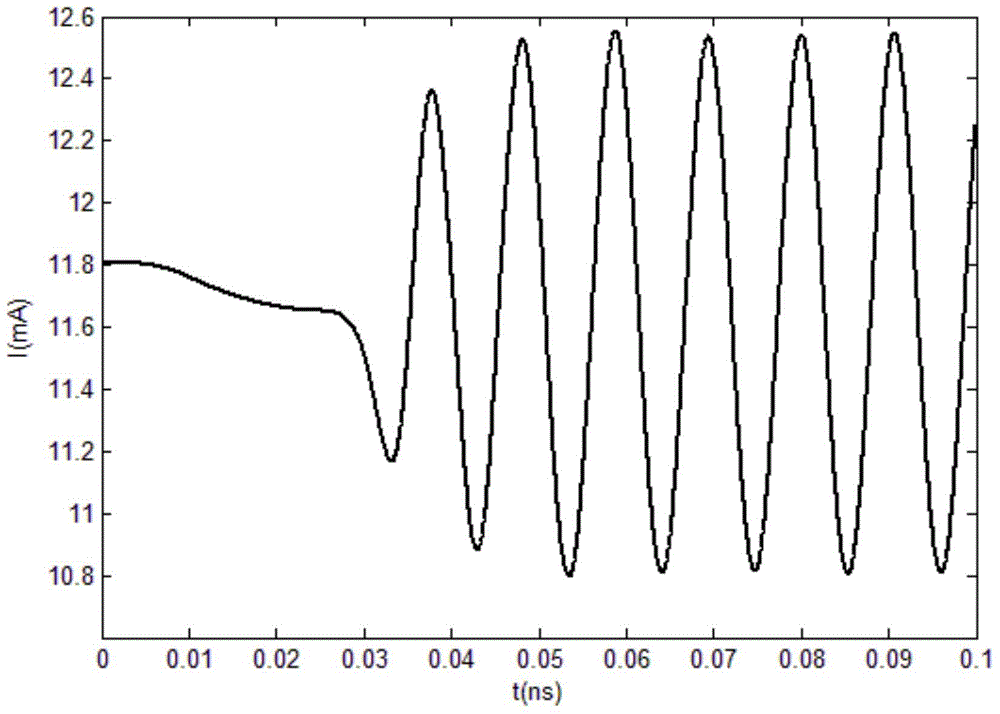
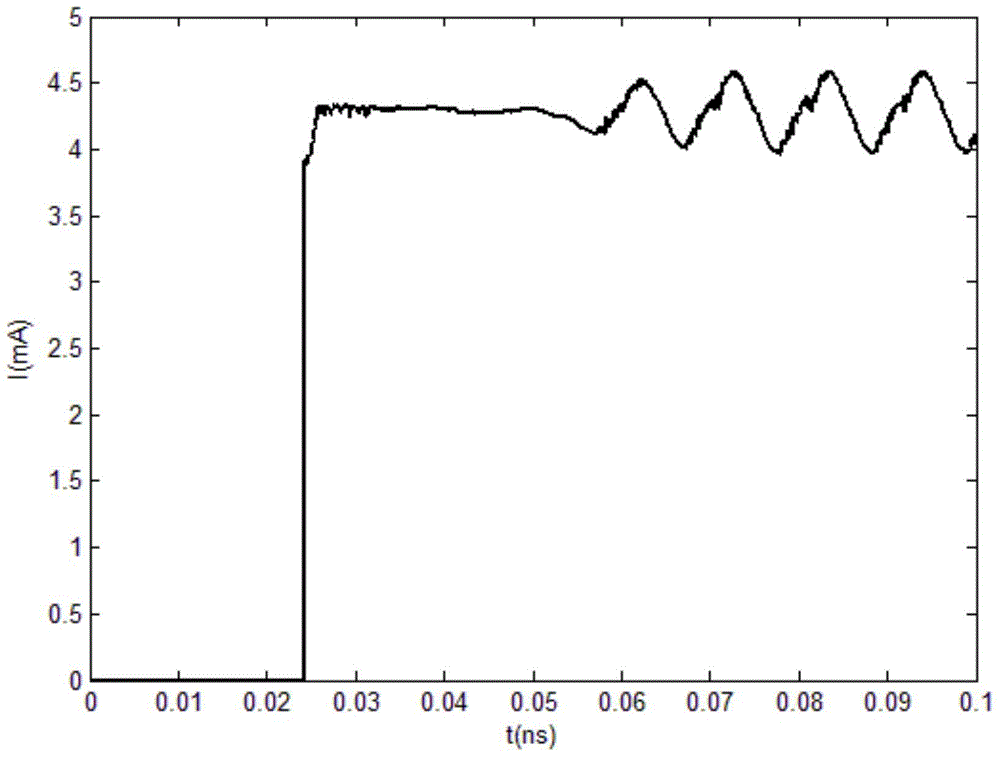
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
137 results about "Beam wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
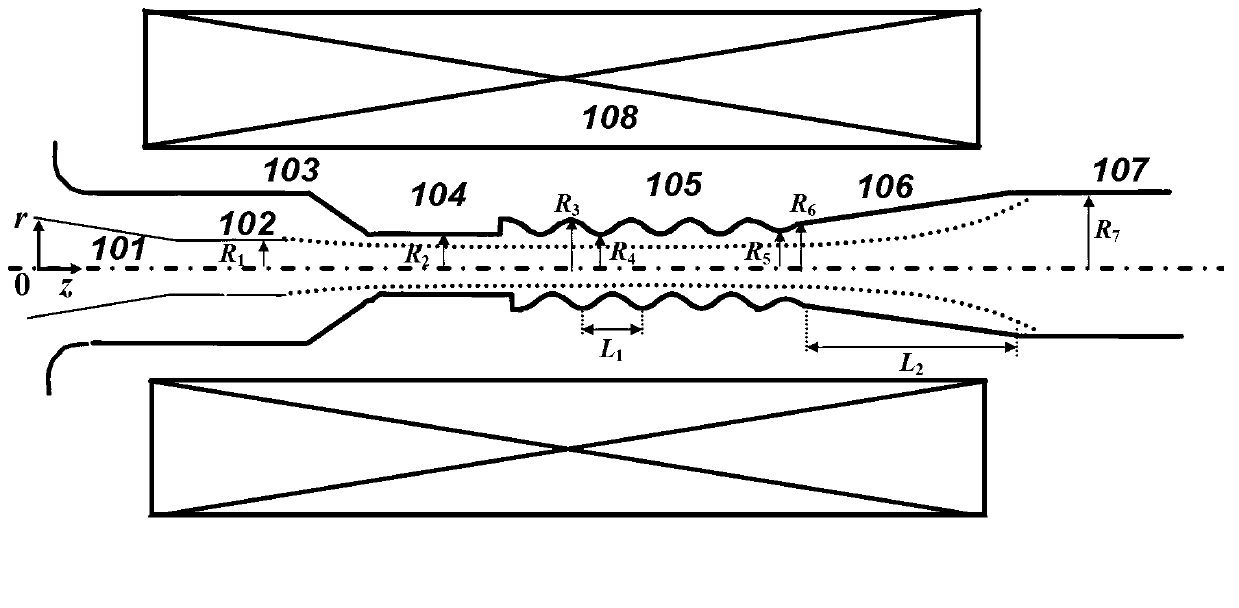
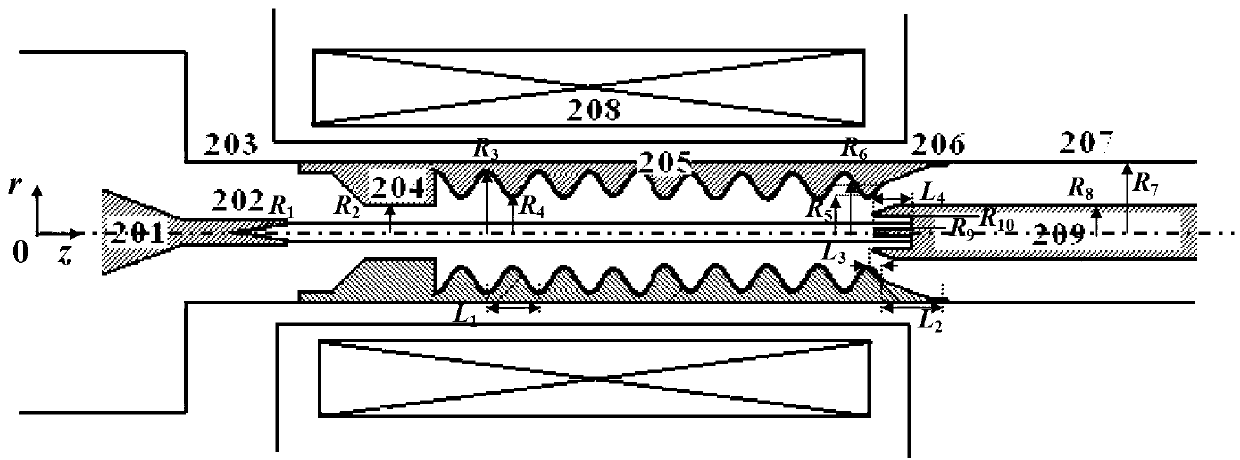
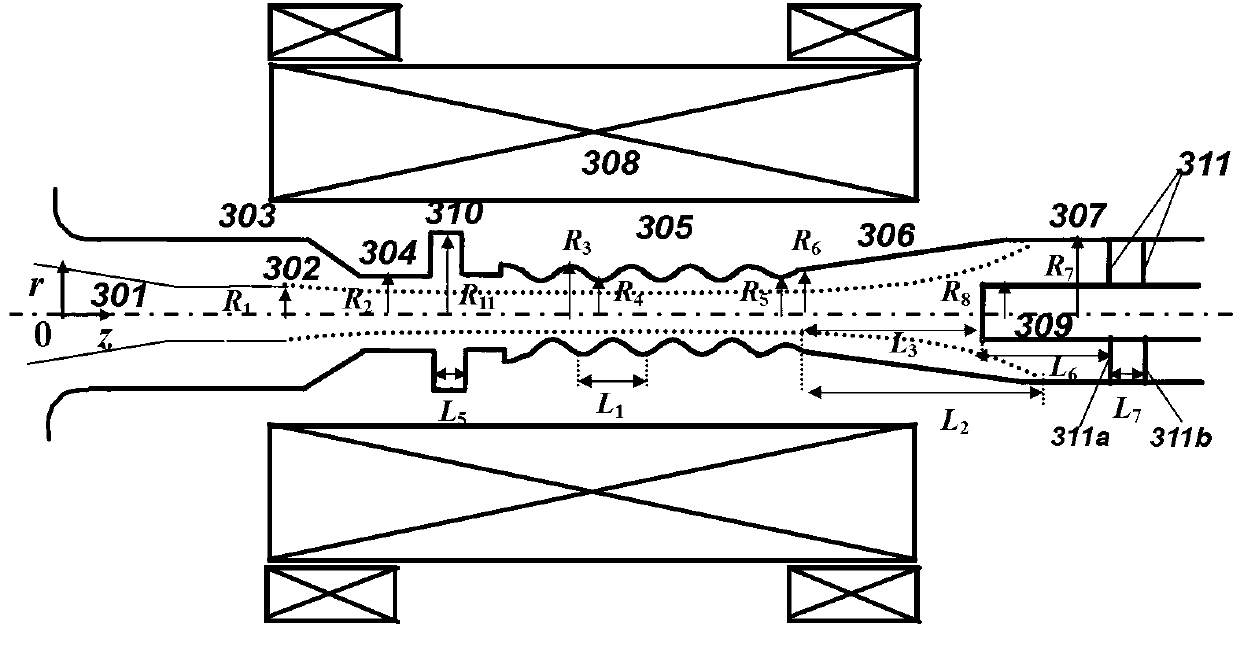
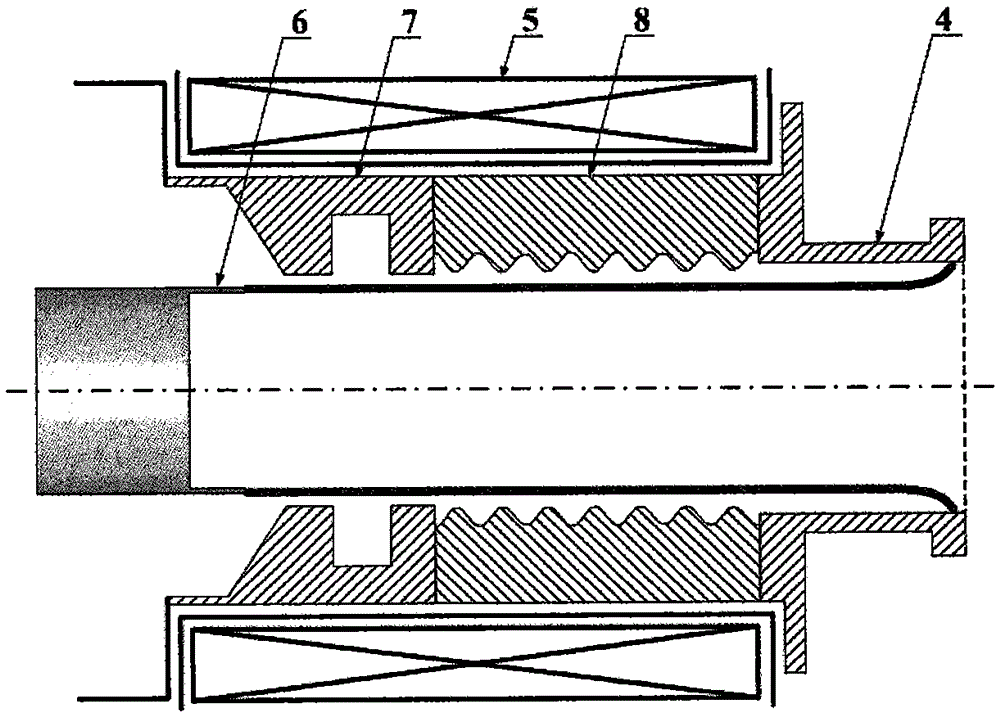
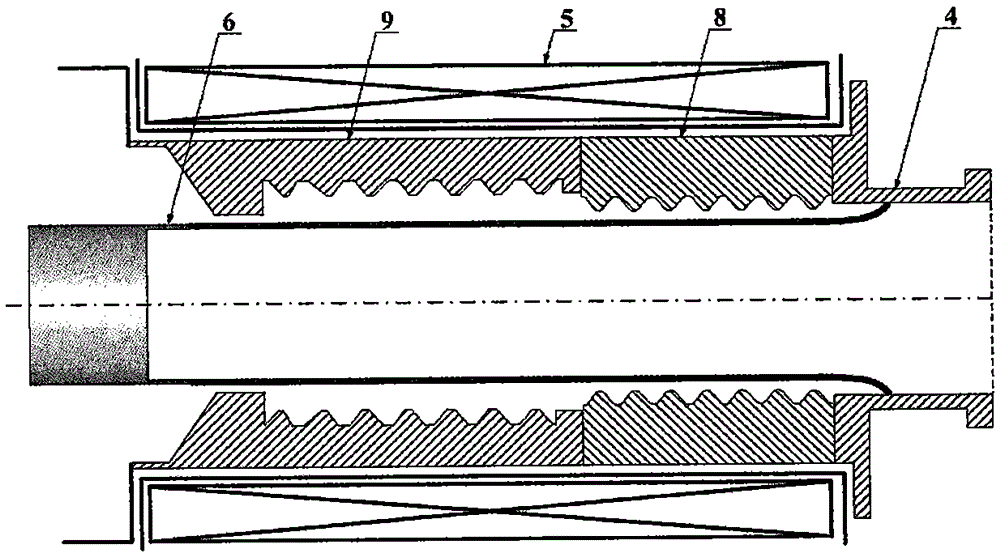
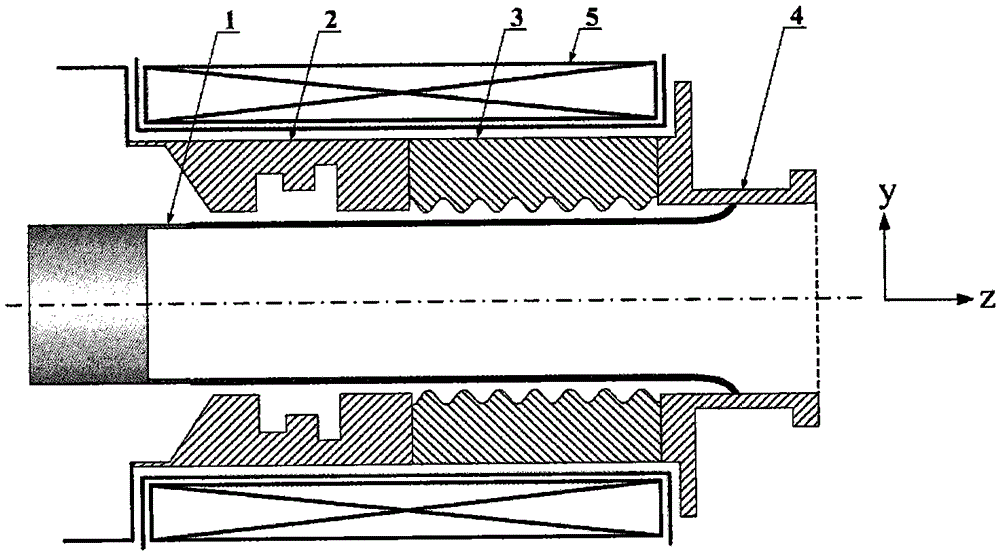
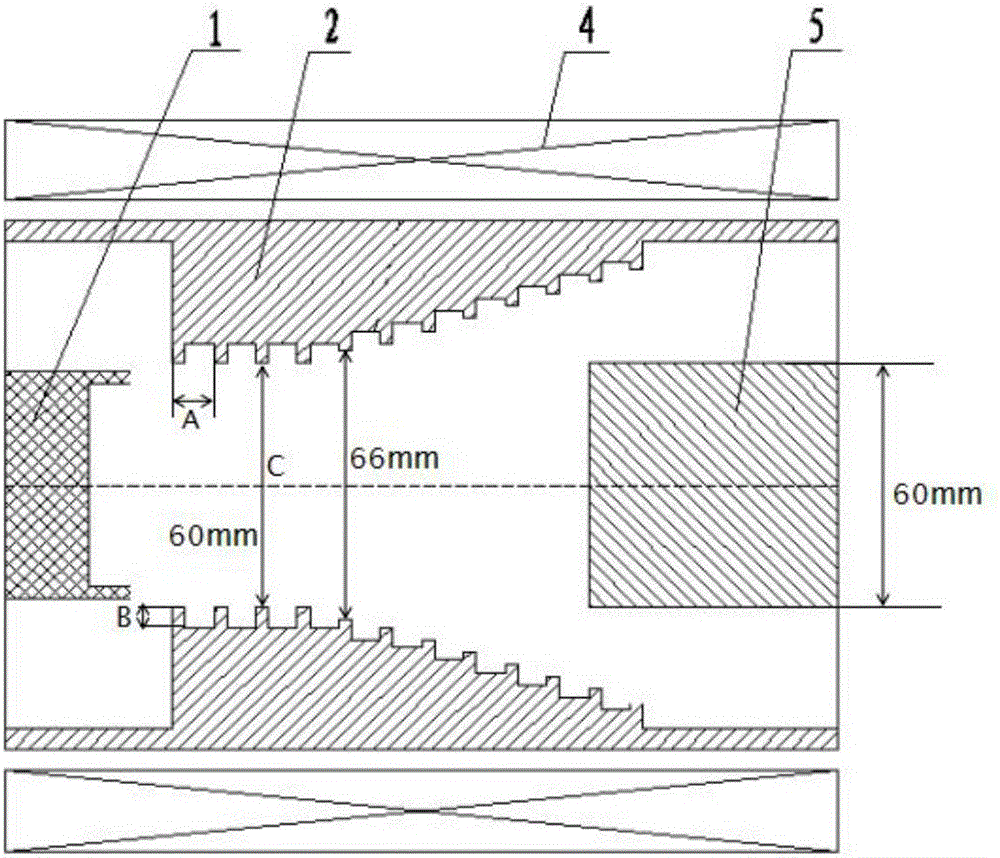
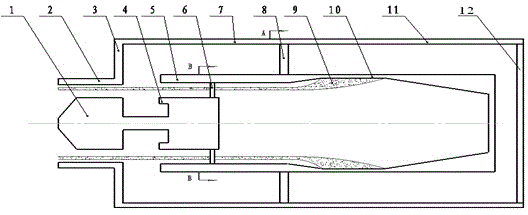
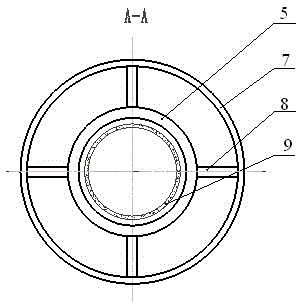
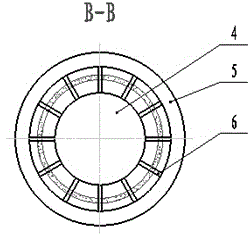
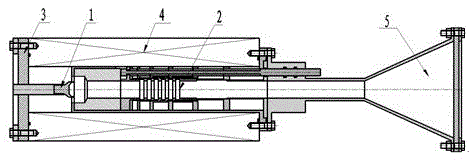
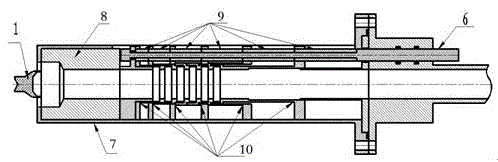
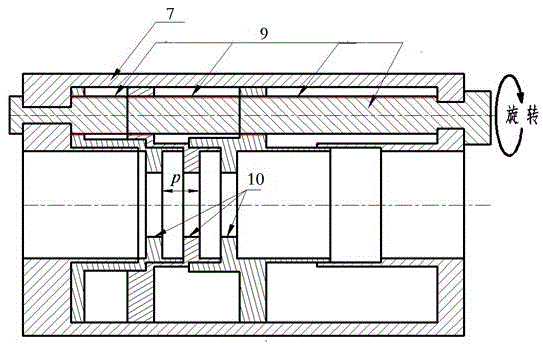
Coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator
ActiveCN103137399AHigh Q valueOvercome the impact on work efficiencyTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube collectorsWave structureMicrowave
The invention relates to a microwave component in the technical field of high power microwave and provides a coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator. The coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator comprises a cathode base, a cathode, an anode outer cylinder, a cut-off neck, a slow wave structure, a tapered waveguide, an output waveguide, a solenoidal field, a coaxial-extraction structure and a front-arranged reflection cavity. The coaxial-extraction structure is a cylinder. The front-arranged reflection cavity is disposed between the cut-off neck and the slow wave structure. According to the coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator, a cylinder is adopted as the coaxial-extraction structure, and therefore the defect that the coaxial-extraction structure with a groove generates plasma is overcome, and meanwhile in the electromagnetic wave mode, function transformation can be carried out and installation can be achieved conveniently. The front-arranged reflection cavity is utilized to replace the cut-off neck so that the resonance characteristic of the front-arranged reflection cavity can be utilized to achieve the effect of the cut-off neck, electron beam scraping or electron beam bombardment of the front-arranged reflection cavity can be avoided, and premodulation of electron beams emitted from the cathode also can be carried out. Therefore, the coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator is beneficial for subsequent beam wave interaction and improves power conversion efficiency of the component.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Relativistic backward wave oscillator for generating linearly polarized TE11 mode directly
ActiveCN105280462AEnhanced interactionImprove beam conversion efficiencyTransit-tube cathodesTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureMaser
The invention, which belongs to the maser field, directly relates to a relativistic backward wave oscillator for generating a linearly polarized TE11 mode directly. The relativistic backward wave oscillator comprises an arc cathode, a reflector, an angular partition slow wave structure, an output waveguide and a magnetic field coil. The arc cathode is arranged at the front end of the relativistic backward wave oscillator; the reflector, the angular partition slow wave structure, and the output waveguide are arranged at the rear side of the arc cathode successively; and the magnetic field coil is installed at the periphery. According to the invention, with the nonaxisymmetrical arc cathode and the angular partition slow wave structure, the TE11 mode is excited directly. The reflector employs the dual-premodulation-cavity unit preferably and is used for carrying out premodulation on an arc relativistic electron beam and leaking the part of TE11 mode to enter the arc cathode zone, so that certain premodulation of the electron beam at the arc cathode zone is realized and thus the beam wave conversion efficiency is improved. Moreover, the oscillator has advantages of simple structure and high conversion efficiency; and the linearly polarized TE11 mode can be generated directly.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Repetition-frequency low-magnetic-field axial C-waveband high-power microwave device
The invention discloses a repetition-frequency low-magnetic-field axial C-waveband high-power microwave device. The device comprises an anode, a cathode, a guiding magnetic field generator, slow wave structures and a coaxial internal conductor, the anode is internally provided with an emission area and a beam wave interaction area, the cathode is arranged in the emission area, the slow wave structures and the coaxial internal conductor are arranged in the beam wave interaction area of the anode, the cathode is coaxial with the coaxial internal conductor, the slow wave structures are fixed to the inner side of the anode and arranged in the periphery of the coaxial internal conductor, a vacuum cavity is formed by vacuum pumping in the repetition-frequency low-magnetic-field axial C-waveband high-power microwave device, and the vacuum degree of the vacuum cavity does not exceed 10mPa. A baffle plate is arranged between the emission area and the beam wave interaction area. The baffle plate is provided with an annular inlet for guiding high-current electron beams generated by the cathode into the beam wave interaction area, and the diameter of the annular inlet is consistent with that of the cathode. The device is characterized by being capable of generating C-waveband high-power microwaves in repetition frequency and high in the beam wave conversion efficiency.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Cross-band dual-frequency relativistic backward-wave oscillator
The invention discloses a cross-band dual-frequency relativistic backward-wave oscillator. The cross-band dual-frequency relativistic backward-wave oscillator comprises a high-frequency microwave device and a low-frequency microwave device, which are coaxially arranged in sequence, wherein the high-frequency microwave device comprises a high-frequency relativistic backward-wave oscillator; a cathode and a high-frequency device beam wave interaction area are coaxially arranged in the high-frequency relativistic backward-wave oscillator in sequence; a first guide magnet is arranged outside the high-frequency relativistic backward-wave oscillator; the low-frequency microwave device comprises a low-frequency relativistic backward-wave oscillator; a low-frequency device beam wave interaction area is arranged in the low-frequency relativistic backward-wave oscillator; the low-frequency relativistic backward-wave oscillator is coaxially connected with the tail end of the high-frequency relativistic backward-wave oscillator; and a second guide magnet is arranged outside the low-frequency relativistic backward-wave oscillator. By the circular waveguide critical wavelength principle in the relativistic backward-wave oscillator, the same intense annular electron beam passes through magnetic field guide structures with different magnetic field intensity distributions, successively passes through the tandem high-frequency microwave device and low-frequency microwave device, and generates a high-frequency high-power microwave and a low-frequency high-power microwave respectively.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Comb-shaped slow-wave structure for multi-band electron beam channel
ActiveCN103077872ARealize pre-modulationThe main structure is simpleTransit-tube circuit elementsMulti bandWave structure
The invention discloses a comb-shaped slow-wave structure for a multi-band electron beam channel. The comb-shaped slow-wave structure for the multi-band electron beam channel comprises a rectangular wave guide wall of which the two ends are open; double rows of comb-shaped teeth are arranged on the inner walls of the upper end surface and the lower end surface of the rectangular wave guide wall in a staggered way; a plurality of insertion pieces are inserted into the rectangular wave guide wall at equal intervals; XYZ three-dimensional coordinates are established by taking the lower-left corner of the front end surface of the rectangular wave guide wall of which the two ends are open as an original point; the direction which is upwards vertical to the original point is the Z-axis; the direction which is leftwards horizontally is the Y-axis; the direction which is backwards horizontally is the X-axis; the teeth are at equal intervals and are parallel to the YZ plane; and the insertion pieces are parallel to the XZ plane. The comb-shaped slow-wave structure for the multi-band electron beam channel has a simple main structure, is easy to machine and is compatible with the modern micro electronic mechanical system (MEMS) technology; a transverse edge effect of the comb teeth can be ignored; the working frequency band is widened obviously; the beam-wave interaction efficiency is high; the working current is improved; the output power is increased; and the comb-shaped slow-wave structure is a novel slow-wave structure which extremely has application potential.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Broadband and reconfigurable OAM antenna
PendingCN107104279AReduce complex structureUnlimited quantityRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsCoaxial probeElectricity
The invention relates to a broadband and reconfigurable OAM antenna. The antenna comprises metal spiral arms (1), a dielectric substrate (2), coaxial probes (3) and a floor (4). The metal spiral arms are arranged on the upper surface of the dielectric substrate, the spiral direction of the metal spiral arms is opposite to the rotation direction of an OAM beam wave finally generated by the antenna, and the quantity of the metal spiral arms can be flexibly set according to needs; the coaxial probes are used for feeding the metal spiral arms, the number of the coaxial probes are equivalent to that of the spiral arms, and the multiple coaxial probes are loaded with uniform-amplitude and in-phase feed signals; and the floor is arranged on the lower surface of the dielectric plate, and the radius of the floor is far smaller than that of the dielectric substrate. The antenna is simple in structure and easy to implement, has broadband operation and pattern reconfiguring capability, and can be expected to be applied to an OAM wireless communication technology, thereby improving spectrum effectiveness and system capacity of the wireless communication system.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
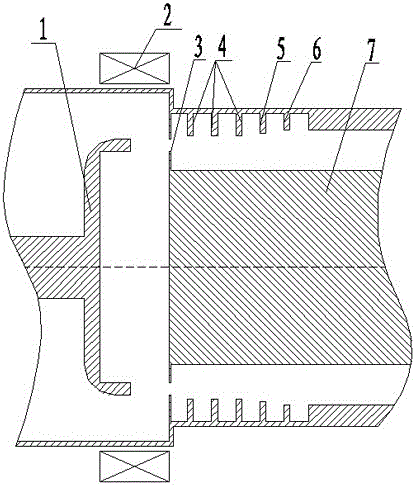
Cathode-adjustable single anode magnetic control electron gun
InactiveCN102800545AImprove performanceImprove adaptabilityTransit-tube electron/ion gunsBeam waveVoltage variation
A cathode-adjustable single anode magnetic control electron gun belongs to a single anode magnetic control electron gun that is used in conjunction with a vacuum gyrotron, and comprises an electron gun casing, a base, an electric heating wire component, a support cylinder, a regulating mechanism assembly, an electron gun cathode, a fixed annular plate, an anode and a retainer ring, wherein, the electric heating wire component comprises an electric heating wire, an electric heating wire sleeve and insulating fillers, and the electric heating wire sleeve is provided with a ring-shaped scale section, a threaded section and a guiding plane surface; the regulating mechanism assembly is arranged between the electric heating wire sleeve and the support cylinder thereof, and comprises an adjusting screw nut; in addition, the cathode-adjustable single anode magnetic control electron gun can adjust the distance between the cathode and anode according to the operating condition, the transverse to longitudinal velocity ratio of an obtained electron beam is greater than 1.0, and the longitudinal velocity spread is less than 2 percent. Therefore, the influence caused by assembly error and overheating deformation or great current and voltage variation of the electron gun can be overcome effectively, and the cathode-adjustable single anode magnetic control electron gun is characterized in that working current and voltage capable of adapting to wider range can be achieved, the discreteness of the electronic longitudinal velocity is low, the performance of the electron beam is excellent, and the power and the efficiency for later beam-wave interaction of the gyrotron can be improved and so on.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Fixed User Terminal for Inclined Orbit Satellite Operation
InactiveUS20110032143A1Easy to solveControl shapeRadio transmissionAntennasSystem requirementsInclined orbit
An advanced multiple-beam fixed ground terminal is achieved that is capable of simultaneously tracking multiple inclined orbit satellites, increasing and suppressing gain in multiple directions. The fixed user terminal equipped with digital beam-forming and null-forming technique can track and identify signals from multiple inclined orbit satellites at the same time. This technique enables a geostationary satellite drift to an inclined orbit without losing communication with ground terminals which not only increase the life span of an inclined orbit satellite, but also relieve the scarcity of geo-stationary orbit. In extreme cases, satellite can be placed in the same slot which further enhanced the usage of geosynchronous orbits. Another present invention is to from double nulls whose null width is much wider than a single null. A wider null increases the system robustness to frequency drift and change of signal direction, thus in turn reduce the system's complexity by lowering update beam wave vectors. To use the same beam wave vector on wider frequency spans, an FIR filter need to be designed according to system requirements.
Owner:SPATIAL DIGITAL SYST
Preparation method of crystalline silicon solar cell
InactiveCN102437246AReduce passivationReduce compoundingFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesBack reflectorConductive materials
The invention discloses a preparation method of a crystalline silicon solar cell. In the passivation process technology of the back surface of a silicon wafer, because aluminum oxide has constant negative charge, the composition of the back surface can be lowered, and the same time, because silicon nitride in rich in hydrogen, passivation can be realized effectively, and in addition, the passivation overlapping layers of aluminum oxide and silicon nitride act as a back reflector, the absorption of long beam waves can be improved greatly, the passivation overlapping layers are positioned between a back surface electrode and the silicon wafer, the warping degree of the crystalline silicon solar cell can be lowered greatly, and the influence on the lifetime of a minority carrier in the silicon wafer can be lowered effectively; and when the back surface electrode is manufactured, because the passivation overlapping layers for the corrosion depth in the corrosion region is just removed, the problem that the back surface electrode and the silicon wafer have less possibility of forming favorable ohmic contact due to the back surface passivation of the silicon wafer can be solved effectively, at the same time, a dense network structure is formed by connecting all the adjacent electric conducting materials by utilizing a silver wire, and the network structure is especially favorable for the collection and conduction of back surface current carriers of the silicon wafer.
Owner:苏元周
Coaxial cavity gyrotron with two electron beams
ActiveUS20100141143A1Increase output powerImprove mode competitionMagnetronsTubes with helical electron streamElectrical conductorLight beam
A coaxial cavity gyrotron with two electron beams includes an electron gun (magnetron injection gun, “MIG,” with two beams), a coaxial beam-wave interaction cavity and an outer magnetic field tube. The coaxial beam-wave interaction cavity consists of two parts: an outer conductor and an inner conductor. The two hollow electron beams produced by the MIG are located between the outer conductor and the inner conductor. The MIG includes inner and outer anodes, with a single cathode located between the anodes. The cathode further includes two emitter rings which produce the two hollow electron beams. The entire gyrotron is immersed in the magnetic field tube such that the magnetic field profile is the same or similar to that for a coaxial gyrotron with one electron beam.
Owner:LIU SHENGGANG +1
Positive-negative voltage conversion circuit
InactiveCN1925290ASmall output ripplePracticalDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
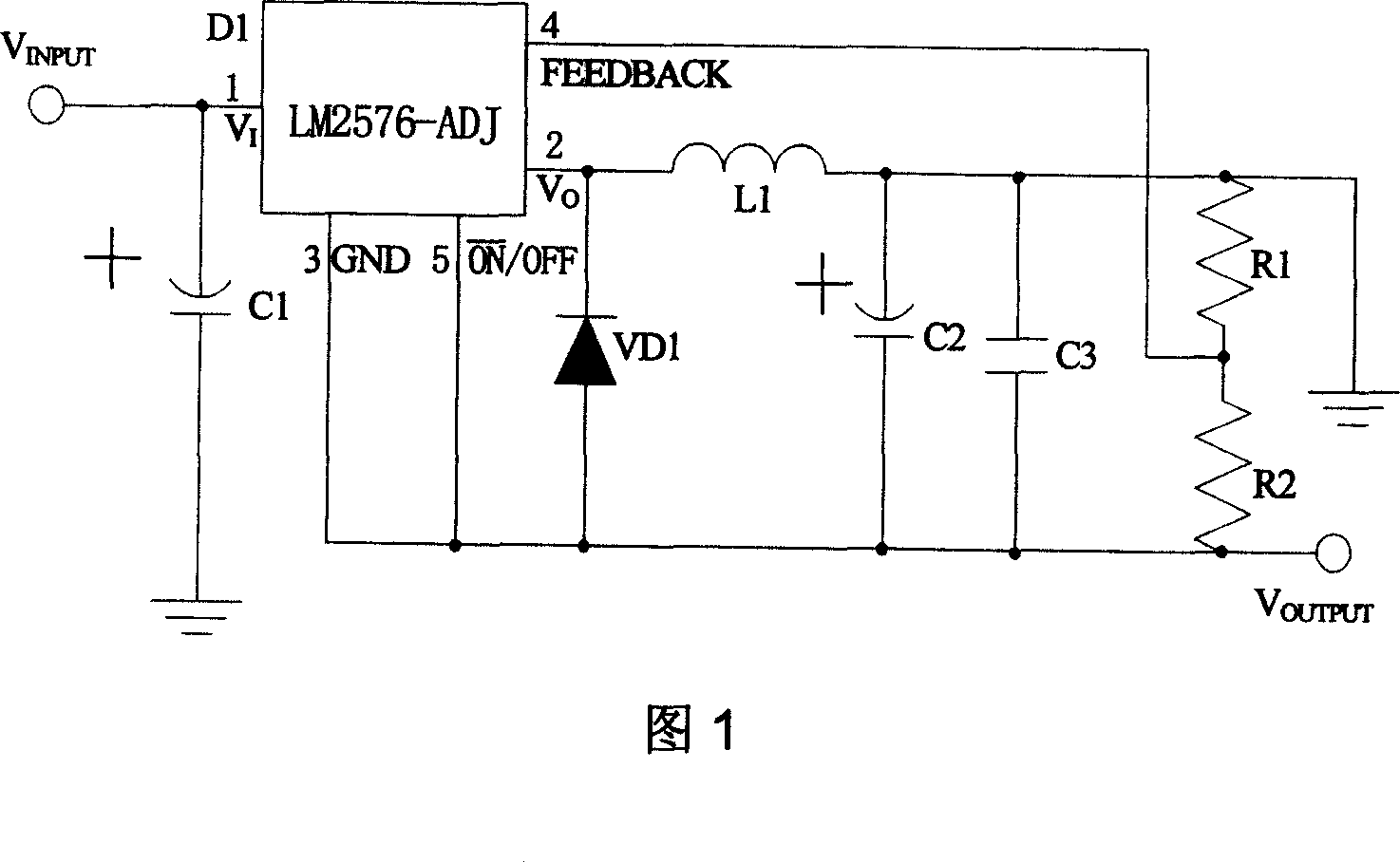
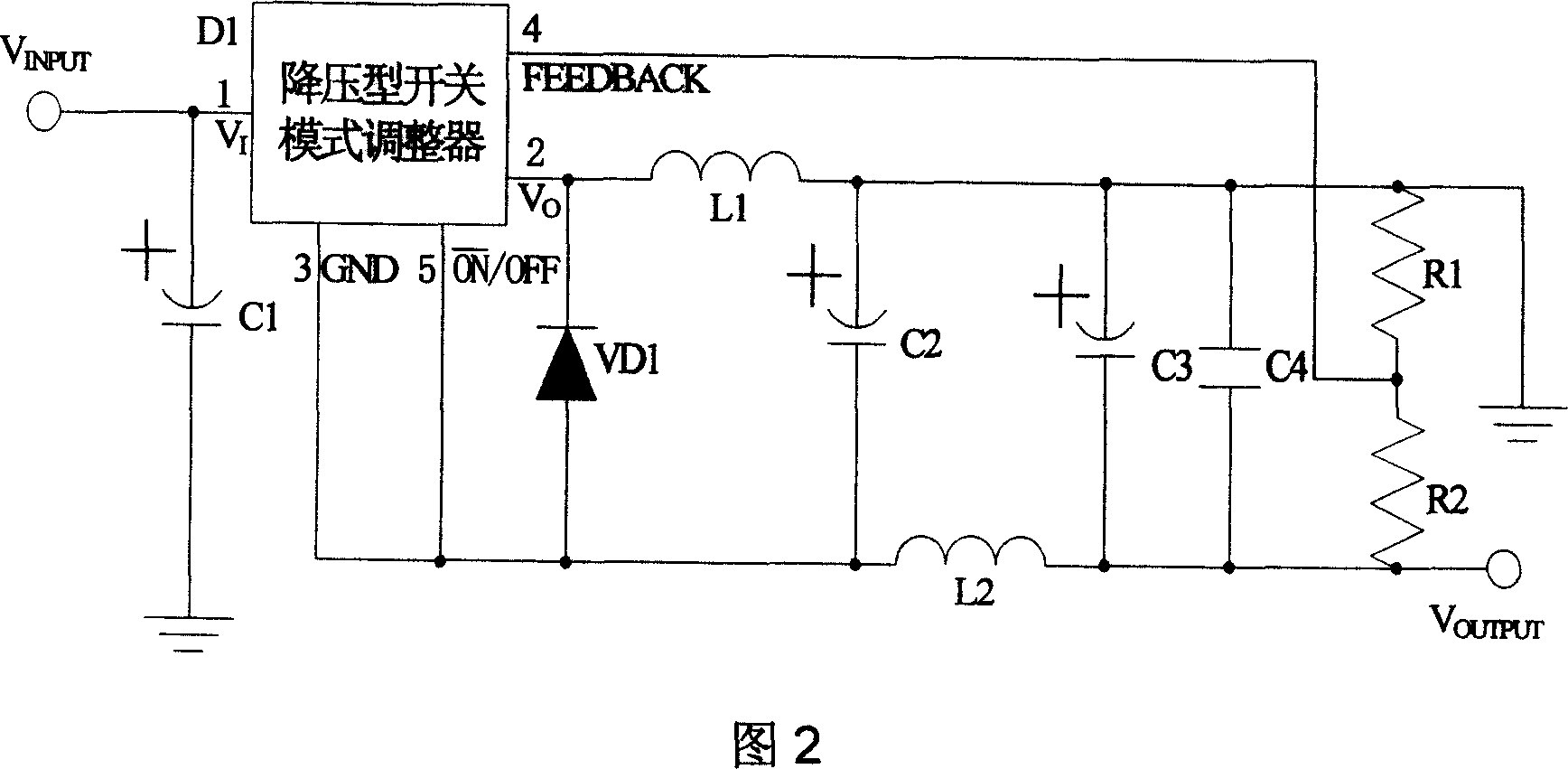
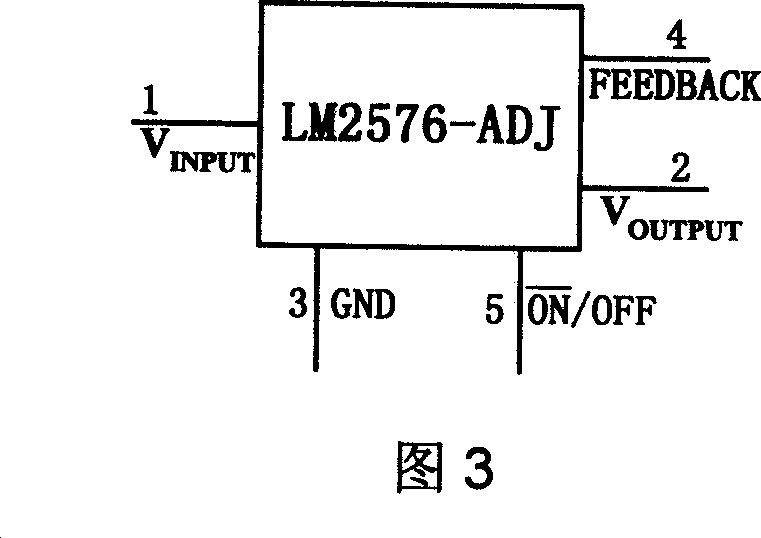
This invention provides one positive and negative voltage conversion circuit, which comprises the following parts: one dropping switch mode adjustor; electrolyte capacitor, diode, output memory induction, electrolyte capacity, high frequency filter capacitor, feedback resistance network, output filter induction and electrolyte capacity. This invention adopts filter induction to eliminate voltage beam wave and load ability resulted by Buck-Boost circuit and put filter induction on negative end.
Owner:STATE GRID TIANJIN ELECTRIC POWER
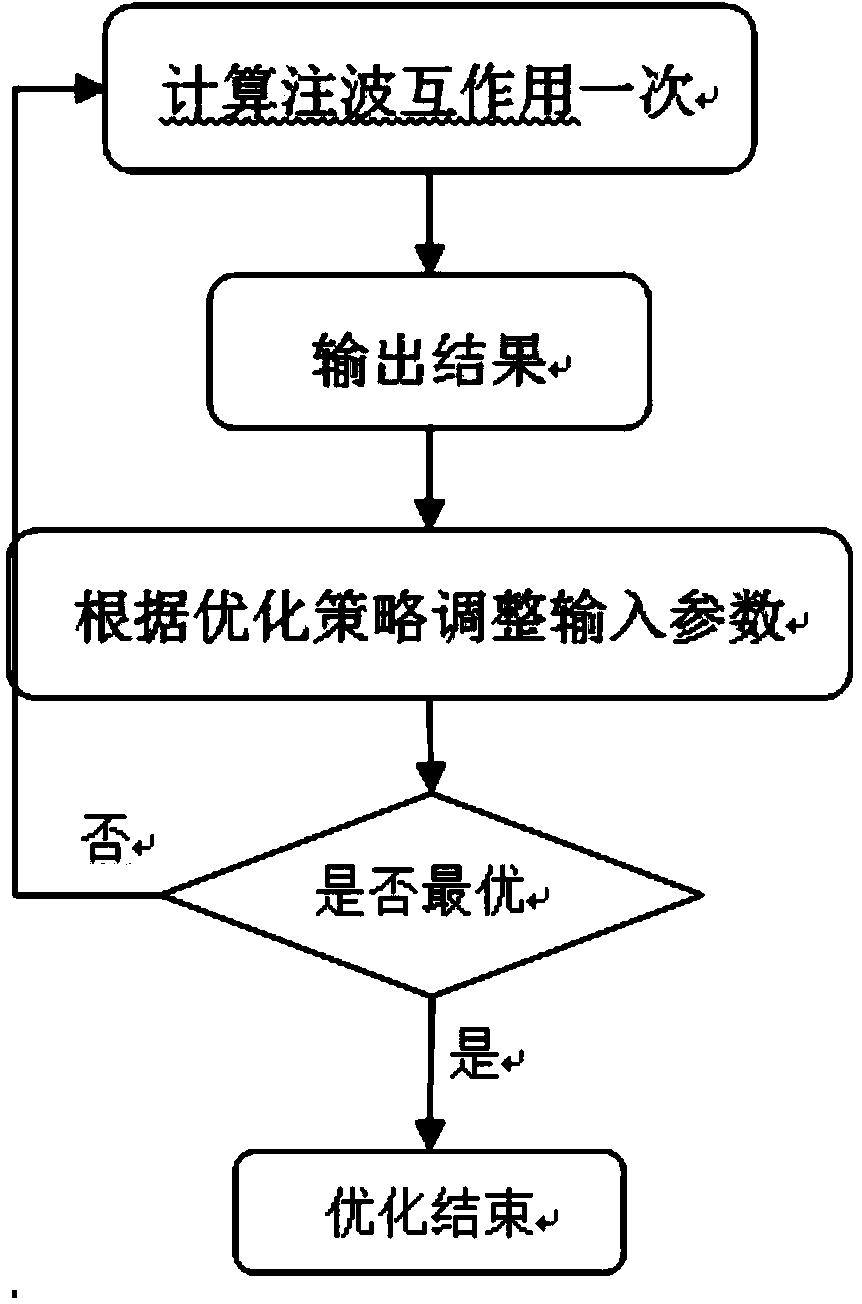
Optimization method of traveling-wave tube beam wave interaction distribution structure
The invention discloses an optimization method of a traveling-wave tube beam wave interaction distribution structure. The optimization method of the traveling-wave tube beam wave interaction distribution structure aims to improve the optimization efficiency of a traveling-wave tube beam wave interaction optimization algorithm. The optimization method combines the optimization algorithm with the internal mechanism of beam wave interaction and relates to a nest algorithm, through the beam wave interaction process sequencing computation characteristic and whether the relative phase angle phi meets the condition that phi > pi / 2 or phi < -pi / 2, computation is ended in advance. For an ordinary high-efficiency screw pitch distribution structure, the efficiency of the optimization method is improved by three to four times compared with an ordinary optimization method.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
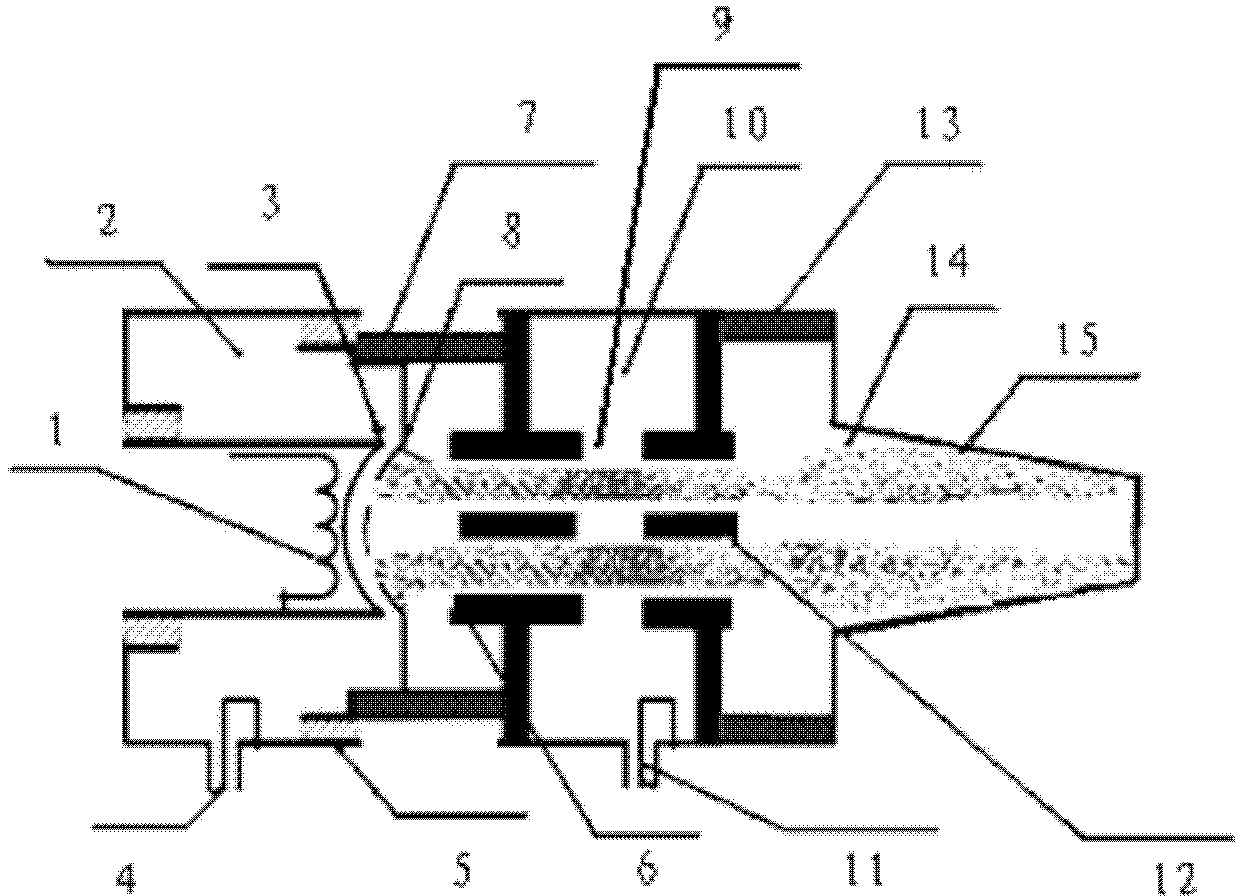
Multi-electron-beam inductive output tube
InactiveCN104134598ALow working voltageLarge conductivityTransit-tube coupling devicesResonant cavityEngineering
A multi-electron-beam inductive output tube is composed of three portions, wherein the first portion is an input system composed of a grid-control multi-electron-beam electronic gun and an input cavity, and feed-in microwave signals are fed into the input cavity through a coaxial input cable; the second portion is an output cavity, a reentry-type cylindrical resonant cavity is adopted in the output cavity, a clearance of the output cavity is composed of a gap between two machining drifting channels in the axial direction of cylindrical metal, direct-current energy of multiple electron beams is interchanged with energy generated by a high-frequency field at the clearance of the output cavity, and transformational high-frequency microwaves are output through a coaxial output cable; the third portion is a collector which is used for collecting energy of the electron beams finishing beam-wave interaction. The multi-electron-beam inductive output tube is simple and practical, has the advantages of being easy to machine, low in technology processing difficulty and the like, and also has the advantages of being low in working voltage, high in efficiency, wide in frequency band, high in gain, long in service life, low in operating and maintaining cost and the like at the same power level compared with a traditional inductive output tube.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
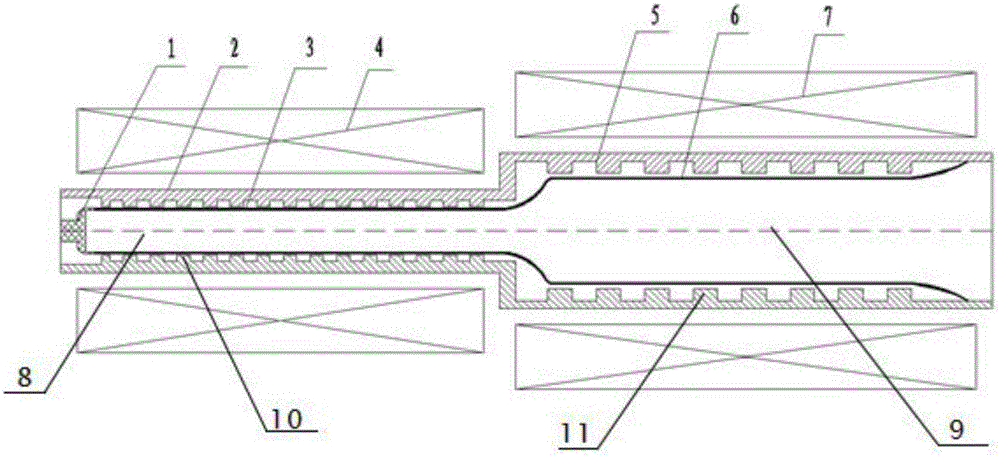
L-waveband low-guide magnetic field compact high-power microwave device
ActiveCN109616393AReduce volumeReduce weightTransit-tube circuit elementsResonant cavityElectrical conductor
The invention provides an L-waveband low-guide magnetic field compact high-power microwave device; according to the scheme, the microwave device comprises a circular waveguide outer cylinder, a coaxial inner conductor and a cathode; the circular waveguide outer cylinder is arranged outside the coaxial inner conductor in a sleeved mode, and the cathode is arranged at the front end of the coaxial inner conductor to transmit an annular electron beam; a microwave reflection cavity, a beam-wave interaction cavity, a first microwave extraction cavity and a second microwave extraction cavity are sequentially arranged in the circular waveguide outer cylinder along the electron beam transmission direction; and the annular electron beam emitted by the cathode can be radiated to generate high-power microwaves with the frequency of 1.56 GHz after passing through the four-resonant cavity structure in the primary pulse. According to the device, the size and the weight of a high-power microwave source system are greatly reduced, and the energy requirement of the magnetic field on the power supply can be greatly reduced.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Speed-modulated relativistic backward wave tube which operates in a locally inhomogeneous magnetic field
ActiveCN109243943AIncrease kinetic energyHigh Output Microwave PowerKlystronsWave structureMicrowave
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Radial shearing interference wave front detection device based on micro-optical device
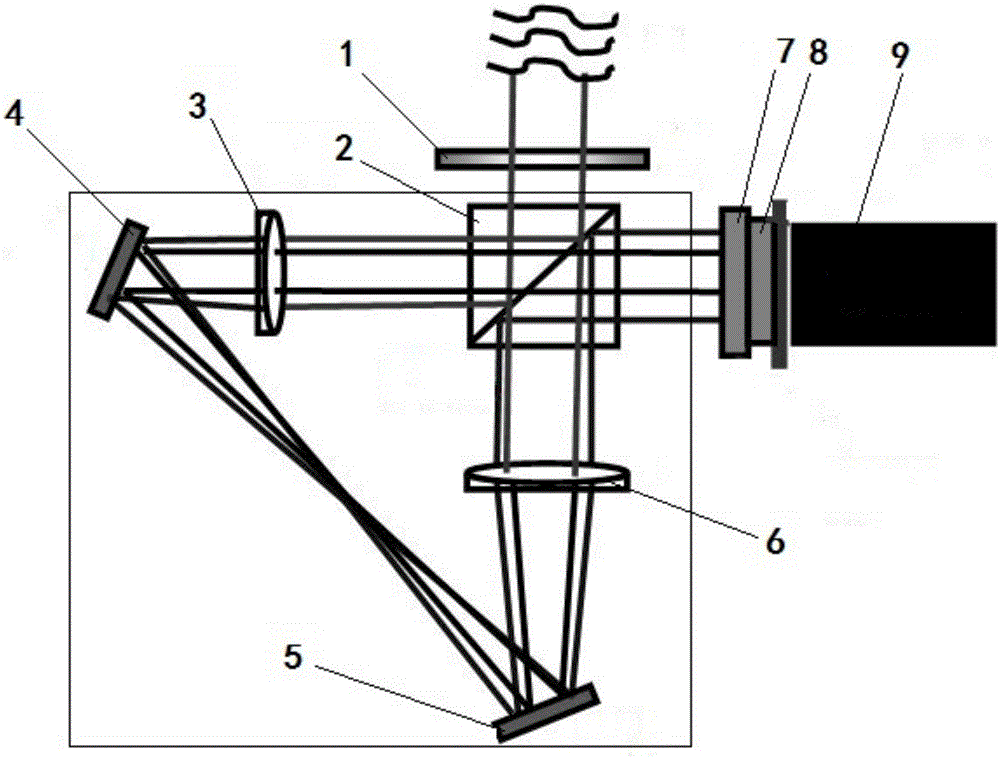
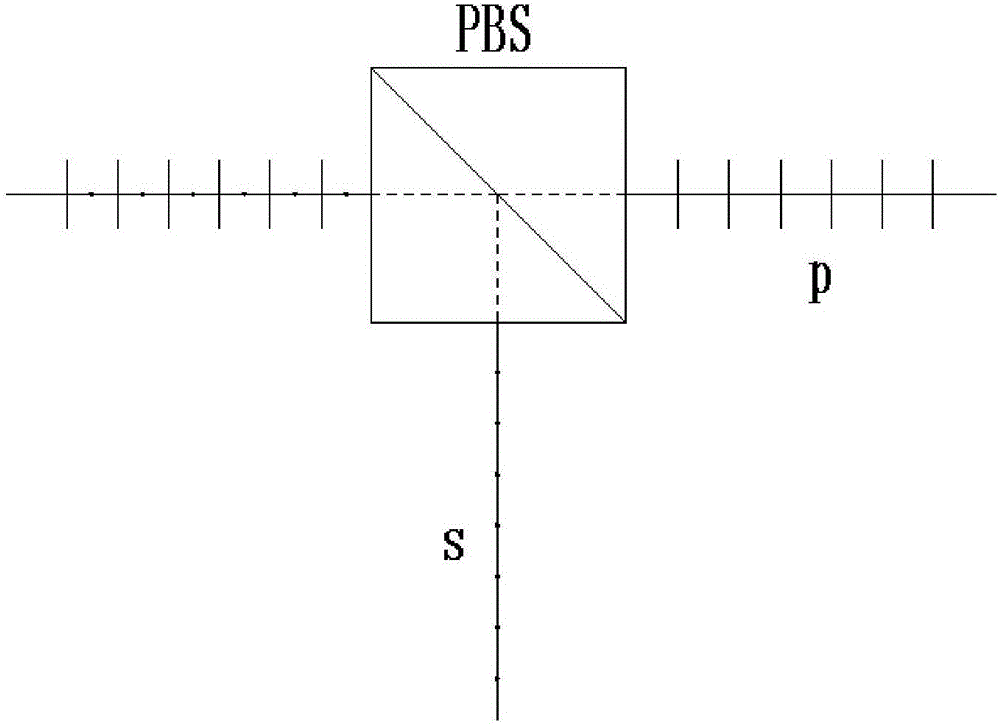
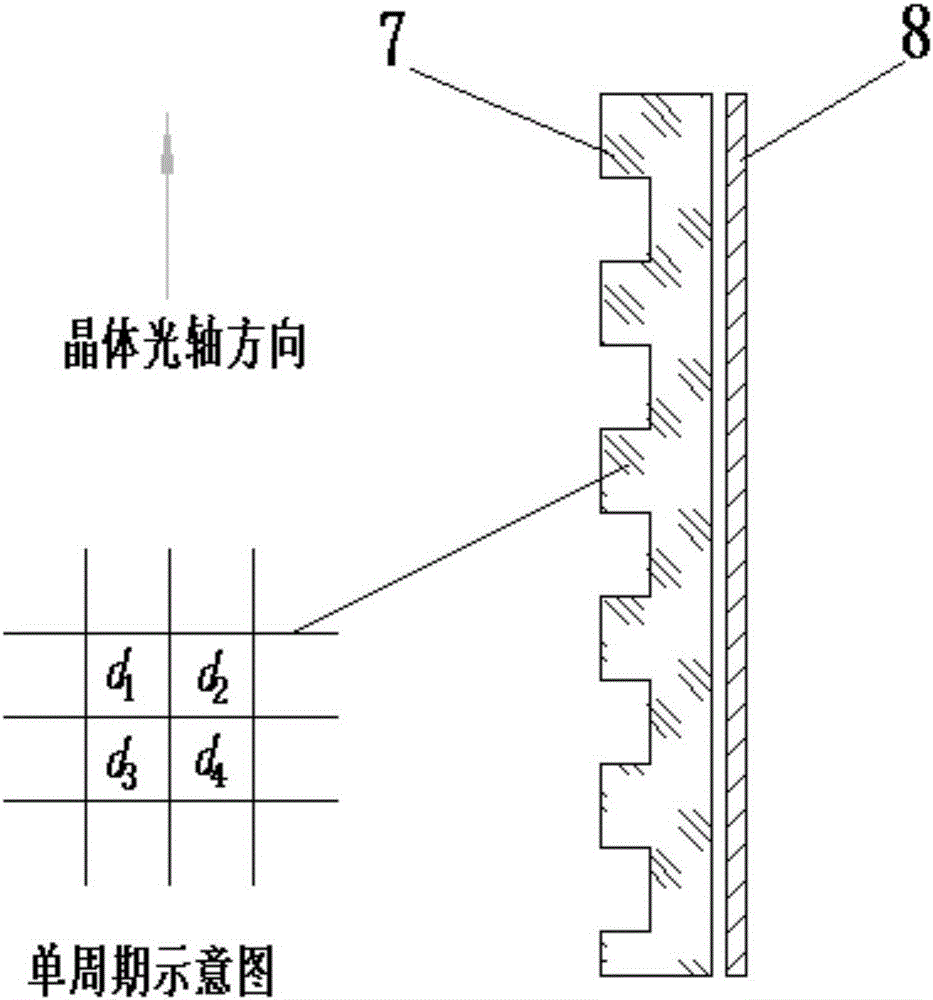
InactiveCN106813778ASuppress disturbanceLower requirementRadiation pyrometryPolarisation spectroscopyBirefringent crystalOptical processing
The invention discloses a radial shear interference wavefront detection device based on a micro-optical device, comprising a polarization direction modulator (1), a polarization ring path direction shear system CRSS, a micro phase modulation array MPA and a photodetector (9 ), the micro-phase modulation array MPA is composed of a microwave chip array (7) and a polarizer (8). Using the birefringence effect of a birefringent crystal, the micro-phase modulation array is fabricated by a micro-optical processing method to realize the space phase of the radially sheared beam. The wavefront phase distribution of the beam to be measured is inverted by a random phase shift algorithm. The invention adopts an all-common optical path structure, which can be immune to environmental vibration and has a stable interferogram; the structure is compact and easy to transplant; the micro-optical device has a large scale, low precision requirements, low cost, and is convenient for mass production; it has a wide spectral range and is insensitive to chromatic aberration. The invention can be applied to the fields of adaptive optics, optical detection, thermal imaging and the like.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
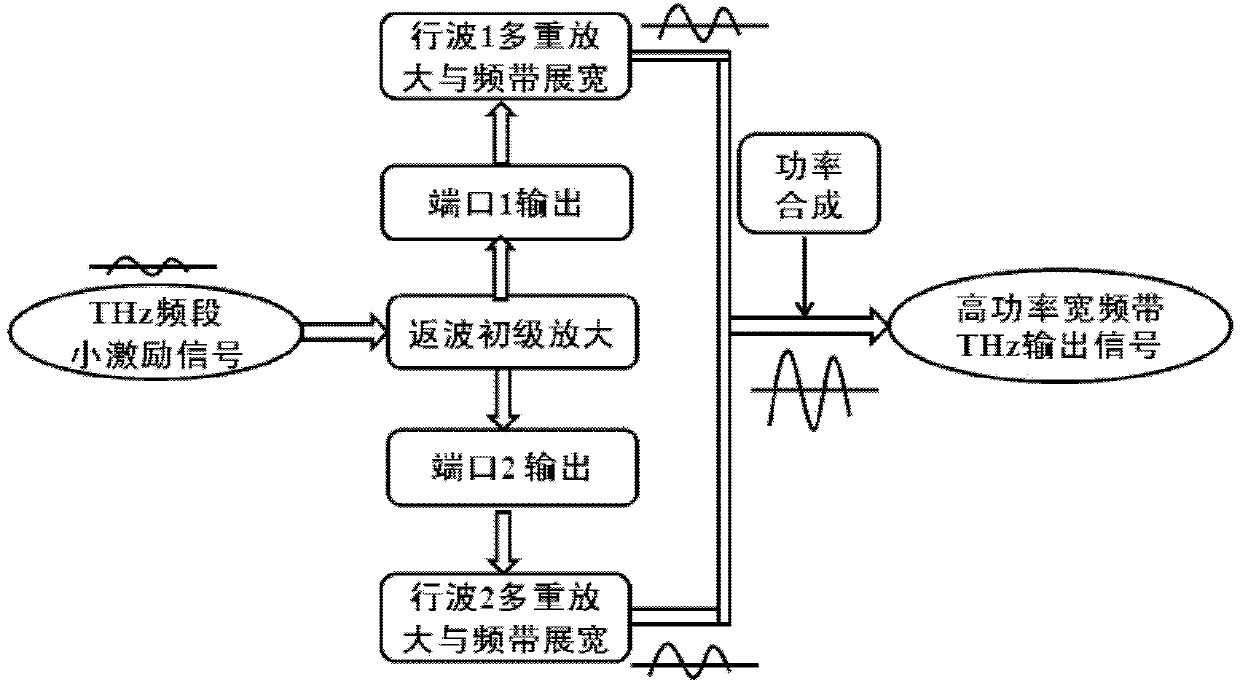
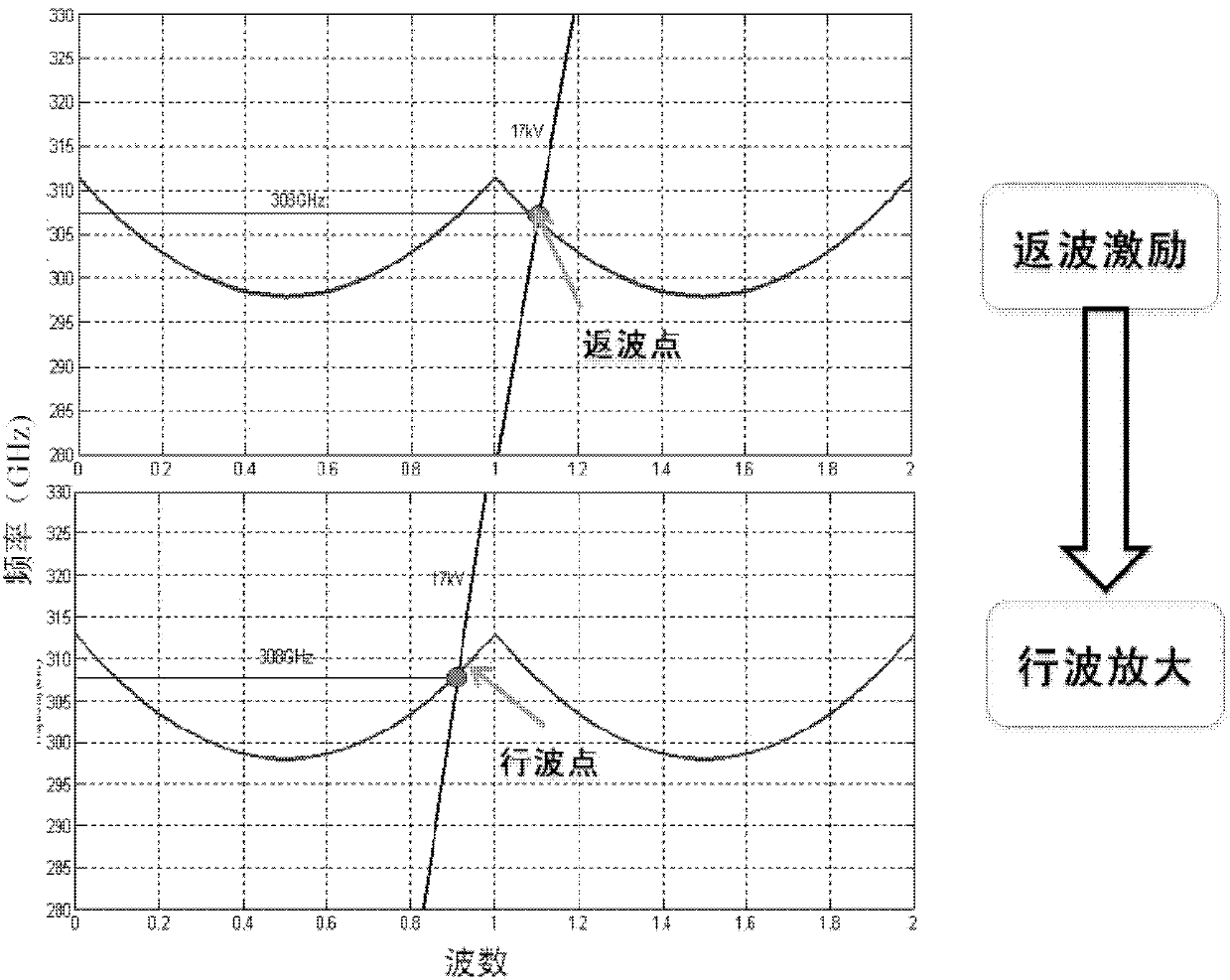
Terahertz source amplifying device based on multiple-cascade high-frequency structure
ActiveCN103632910AIncrease powerHigh gainTransit-tube electron/ion gunsTravelling-wave tubesTerahertz radiationElectron
The invention provides a terahertz source amplifying device based on a multiple-cascade high-frequency structure. The terahertz source amplifying device is a cascaded multi-electron-beam terahertz radiation source combining a backward wave amplifier and a traveling wave amplifier. A THz excitation signal is input to the backward wave amplifier and is amplified through backward wave electron beam-wave interaction, a backward wave signal is output to a traveling wave high-frequency structure through dual ports, multistage amplification and band broadening are realized through multiple beam-wave interaction at a traveling wave section, and power synthesis is carried out on signals output by the multiple-cascade structure. The terahertz source amplifying device based on multiple-cascade high-frequency structure has the characteristics of high power, high gain and wide band, has absolute advantages in implementing a THz integrated vacuum electronic device and has important application prospects in aspects such as THz radar, communication, danger detection and imaging.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Double-frequency relativistic backward-wave oscillator capable of directly outputting TE11-mode electromagnetic waves
ActiveCN107527781ADirect output implementationTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureMicrowave
The invention relates to the technical field of high-power microwave devices, and discloses a double-frequency relativistic backward-wave oscillator capable of directly outputting TE11-mode electromagnetic waves. The oscillator comprises a Bragg reflector, a first slow wave structure and a second slow wave structure, wherein the Bragg reflector, the first slow wave structure and the second slow wave structure are sequentially set in a coaxial manner. The interior of the Bragg reflector is sequentially provided with an electron beam emission gun and a reflection work cavity. The first slow wave structure comprises a slow wave structure employing a periodic ripple design, and the interior of the slow wave structure is provided with a slow wave structure beam-wave interaction cavity. The second slow wave structure comprises a slow wave structure employing a periodic ripple design, and the interior of the slow wave structure is provided with a slow wave structure beam-wave interaction cavity. According to the invention, an electron beam sequentially passes through two coaxial slow wave structures, and performs the beam-wave interaction with the slow wave structures to generate a double-frequency TE11-mode electromagnetic wave traveling in an opposite direction. The double-frequency TE11-mode electromagnetic wave traveling in the opposite direction is converted into a TE11-mode electromagnetic wave propagating forwards through the Bragg reflector, and the electromagnetic wave with the beat effect is outputted at a radiation end.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Gradually-amplified slow-wave-structure microwave oscillator outputting high power microwave
ActiveCN105845531AImprove output efficiencyHigh microwave output efficiencyTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureElectrical conductor
The invention discloses a gradually-amplified slow-wave-structure microwave oscillator outputting high power microwaves. A slow-wave structure of the microwave oscillator is distributed in a conical shape. The microwave oscillator comprises a guide magnet, wherein the guide magnet comprises a cylinder hollow cavity, and a cathode, the slow-wave structure and a coaxial inner conductor are arranged inside the guide magnet coaxially. The slow-wave structure of the microwave oscillator disclosed by the invention is gradually amplified and distributed in a conical shape, an electron beam is guided into an interaction chamber of the slow-wave structure gradually-amplified high power microwave oscillator from the cathode through axial and radial distribution of a guide magnetic field; an intense electron beam is closely adhered to the surface of the slow-wave structure for transmission under the constraint of the guide magnetic field; and the coaxial inner conductor in a microwave output cavity enhances beam-wave interaction and increases microwave output efficiency, and can be used for adjusting size of an output window, thereby ensuring compactness of the microwave output structure, adjusting size structure of the coaxial inner conductor properly, and achieving high-efficiency microwave output under low magnetic field guidance.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
RKA (relativistic klystron amplifier) output cavity with inner conductor arranged inside
InactiveCN104952676AGuaranteed uptimeEasy to collectTransit-tube coupling devicesKlystronElectrical conductor
The invention provides a technical scheme of an RKA (relativistic klystron amplifier) output cavity with an inner conductor arranged inside. According to the scheme, the output cavity comprises a drift tube, an output cavity body, an output cavity end cover, an output coaxial outer conductor, a collector, the inner conductor, inner support rods and outer support rods, wherein the drift tube is connected with the output cavity end cover; the output coaxial outer conductor is arranged on the outer wall of the output cavity body; the collector is fixed in the output coaxial outer conductor through the outer support rods; an outer nose cone is arranged on the collector; the inner conductor is arranged at one end, close to the outer nose cone, in the collector and connected with the outer nose cone on the collector through the inner support rods. The structure of the RKA output cavity is improved, the minimum energy required when electrons arrive at an output cavity gap can be reduced, and the output microwave power and the beam wave conversion efficiency of an RKA can be improved.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Far-field detection method for near-field evanescent beam wave filed transmittance transmission characteristic function aiming at ultra-diffraction structural material
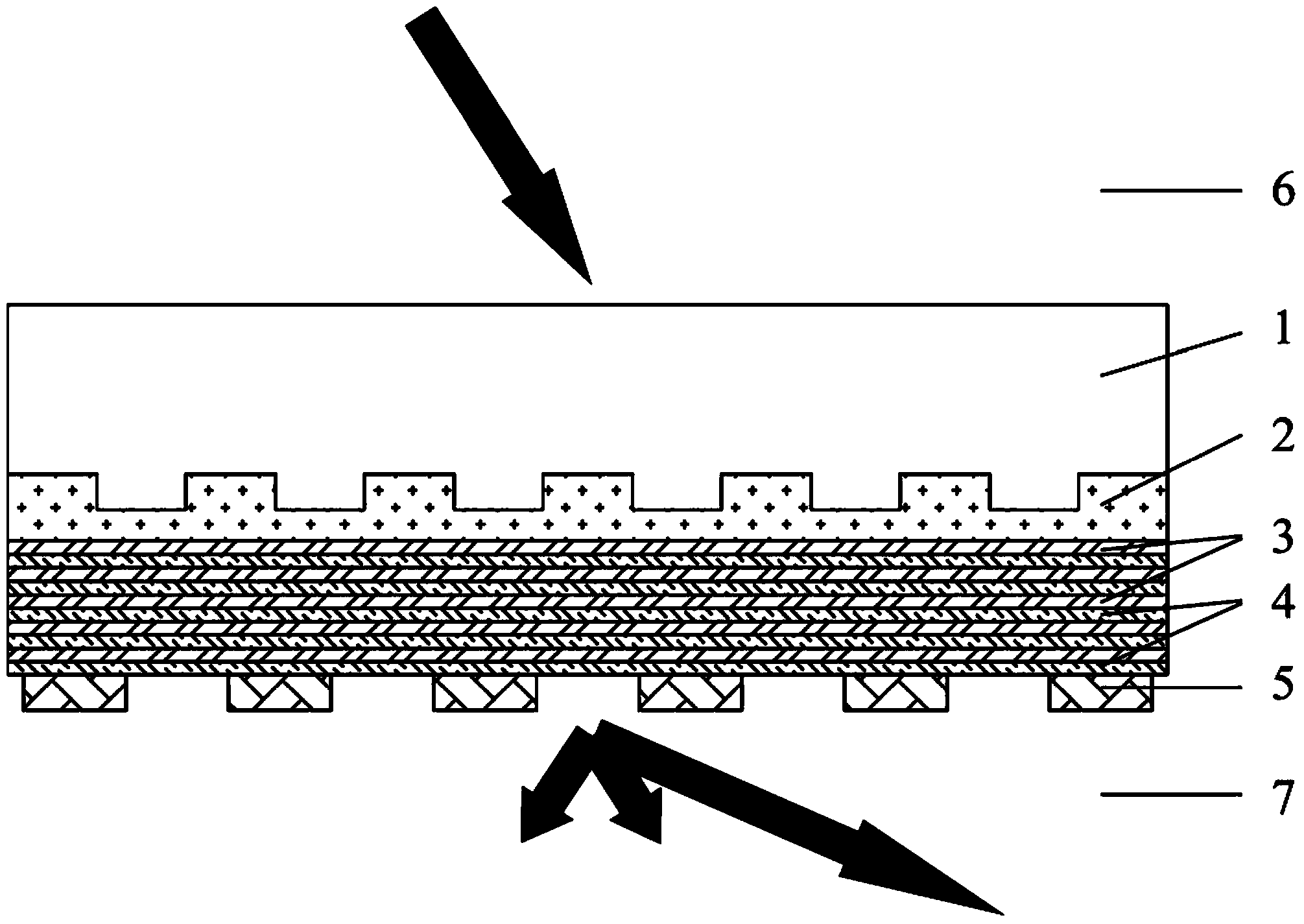
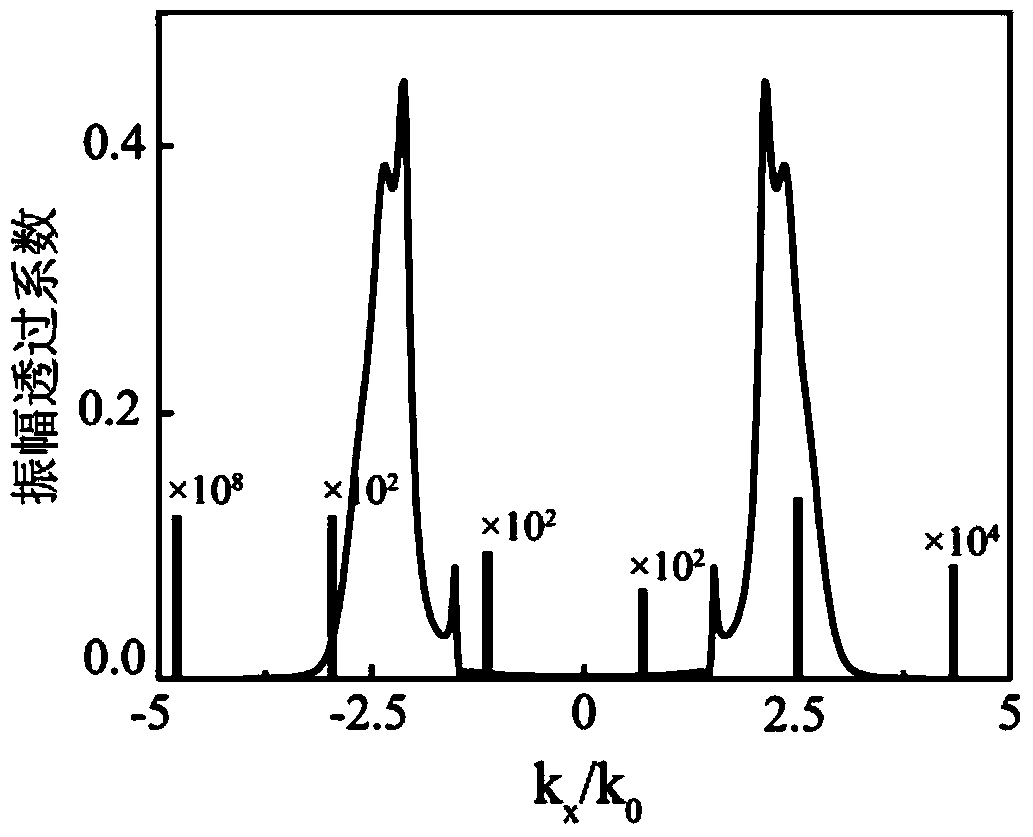
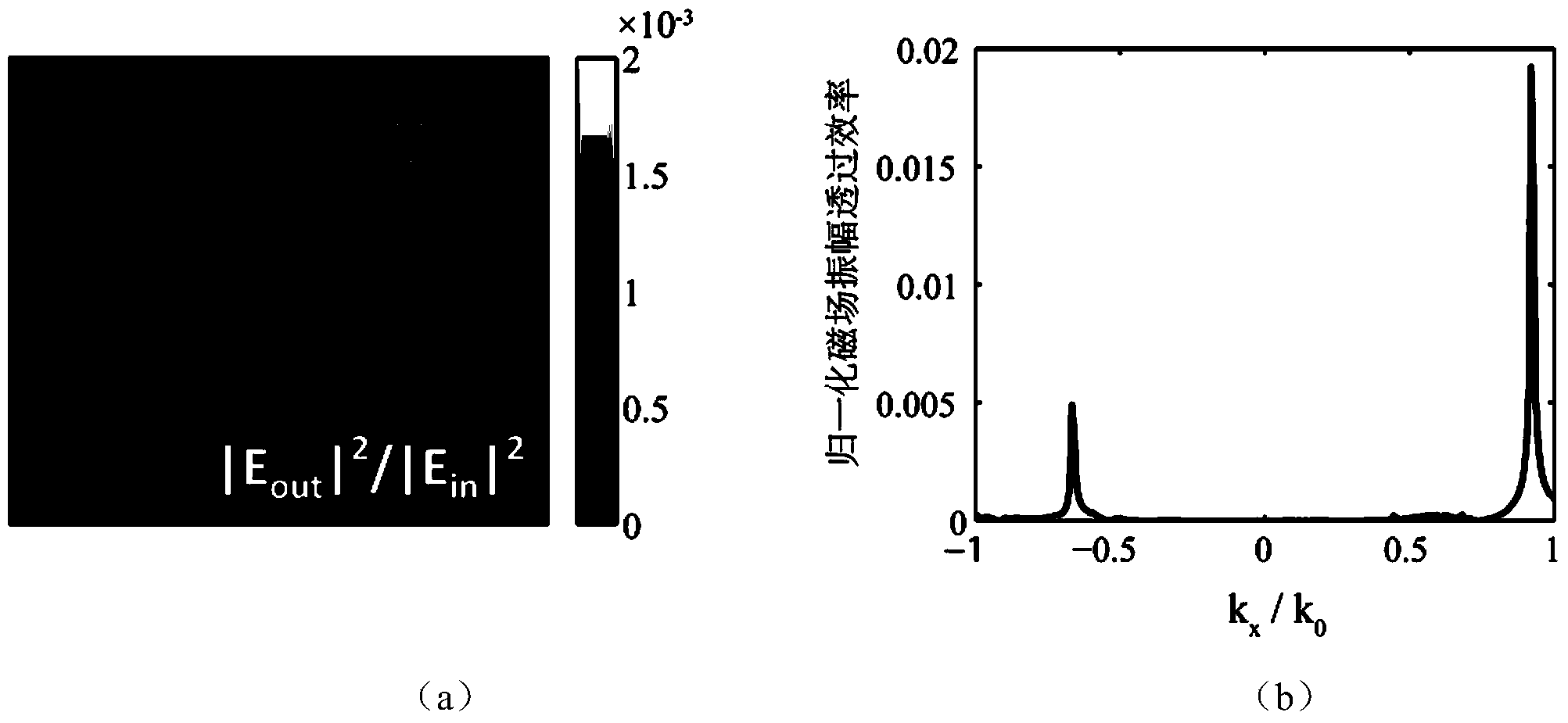
ActiveCN103969225AAchieve qualitativeEasy to detectTransmissivity measurementsTesting optical propertiesGratingTransmittance
The invention provides a far-field detection method for a near-field evanescent beam wave filed transmittance transmission characteristic function aiming at an ultra-diffraction structural material. According to the method, adopted devices comprise a transparent substrate layer, an exciting grating layer, ultra-diffraction structural material layers and a detecting grating layer from top to bottom, wherein incident lights from the back surface of the transparent substrate layer are excited with evanescent wave levels after passing the exciting grating layer, the ultra-diffraction structural material layers can perform spatial frequency high-pass filtering of a horizontal wave vector on the evanescent wave levels so as to form an evanescent beam wave filed with the specific near-field transmission of the horizontal wave vector, the detecting grating layer can convert the evanescent wave levels to be transmitted wave levels to be transmitted to a far field, and detection light corresponding to evanescent wave components one by one can be received at the far field finally. The method can be used in the far-field detection of the near-field evanescent beam wave filed transmittance transmission characteristic function of the ultra-diffraction structural material, so as to realize the horizontal wave vector near-field distribution of the evanescent wave filed as well as the qualitative analysis and quantitative detection of the corresponding wave vector energy transmittance of the evanescent wave filed.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
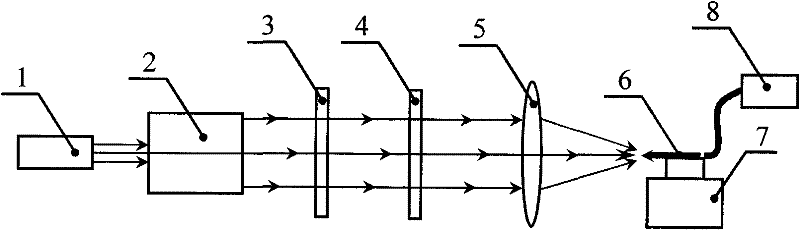
Lagrange Gaussian beam Gouy phase parameter measuring method
The invention relates to a Lagrange Gaussian beam Gouy phase parameter measuring method. In the prior art, an optical path structure is complicated, restriction from optical beam coherence is obtained and the measurement in an optical system with high sensitivity and high numerical aperture cannot be realized. According to the invention, the method comprises the following steps of: carrying out sector light shielding modulation on beam wave front by using wave front amplitude modulation technology of the Lagrange Gaussian beam; and selecting beam radial parameters as zero, wherein a circular ring shaped light spot with a gap is formed after beams are gathered; detecting the circular ring shaped light spot with the gap by using a near field optical technology, wherein azimuth angle parameter corresponding to the center of the gap is fundamental mode beam Gouy phase; and obtaining the Gouy phase of any Lagrange Gaussian beam in different spreading positions through simple calculation. The Lagrange Gaussian beam Gouy phase parameter measuring method provided by the invention has the characteristics of simplicity for realization, low requirement on structure positioning, high reliability, strong anti-interference performance, capability of realizing direct measurement with high sensitivity, capability of measuring the Gouy phase in the optical system with high numerical aperture, wide application range and the like.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Broadband high-gain slow wave structure
ActiveCN110060911ASmall sizeAchieving High Gain AmplificationTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureWave slowing
The invention discloses a broadband high-gain slow wave structure. The broadband high-gain slow wave structure comprises a first traveling wave type slow wave structure, a second traveling wave type slow wave structure and a standing wave type slow wave structure between the first traveling wave type slow wave structure and the second traveling wave type slow wave structure, a traditional standingwave type slow wave structure is combined with a traveling slow wave structure so as to create a novel interaction slow wave structure. In the first traveling wave type slow wave structure, premodulation is carried out on an input electromagnetic signal, an electron beam is carried with information in the electromagnetic signal, then the electron beam is fed into the standing wave type slow wavestructure for further modulation, the carried information is further amplified, and finally the electron beam is used for stimulating the electromagnetic signal in the second traveling wave type slowwave structure and further carrying out beam-wave interaction, so that the amplified electromagnetic signal is output by the second traveling wave slow wave structure. The standing wave type slow wavestructure is introduced in a traditional wave slow wave structure, and the size of an original slow wave structure interaction circuit part is shortened effectively, so that the purposes of the invention such as broad band and high gain are realized by using the advantages that the size of a standing wave type slow wave structure interaction circuit is short, the gain is high and the frequency band of the traveling wave type slow wave structure is wide.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A staggered grid slow wave structure with sinusoidal function profile
InactiveCN109273336AIncrease working frequencyHigh coupling impedanceTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureBand shape
The invention discloses a staggered grid slow wave structure with sinusoidal function profile, which is composed of a rectangular shell, upper / lower grid teeth, upper / lower cavities and strip injection channels. The wide-edge profile of the band-shaped electron beam channel has changed from the traditional straight-line profile to the sinusoidal profile. The distribution of the longitudinal electric field along the broad side of the slow wave structure is in good agreement with the shape of the strip channel, and the distribution is sinusoidal function. The slow-wave structure can not only increase the operating frequency but also the coupling impedance, which can compensate for the non-uniformity of the coupling impedance in the wide-side direction, thus increasing the intensity of the beam-wave interaction, and further improving the electronic efficiency and output power of the traveling wave tube / backward wave tube based on the slow-wave structure. When applied to band-beam TWT, thegain of the whole TWT can also be increased. Millimeter-wave terahertz traveling-wave tubes / backward-wave tubes based on this slow-wave structure have been widely used in many military and civil applications such as communications radar electronic countermeasures imaging and so on.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Coaxial transit time oscillator electron collector capable of working in long-pulse state
InactiveCN107946156AIncrease the interaction areaLow densityTransit-tube collectorsSecondary electronsLong pulse
The invention relates to a coaxial transit time oscillator electron collector capable of working in a long-pulse state. The coaxial transit time oscillator electron collector is characterized in thatmagnetic induction lines on the edge of a magnetic field of a solenoid bend obliquely upwards, and an electron collection surface is of an obliquely-upward electron collector structure, so that the current density at a collection position is lowered; energy deposit is reduced; and reflected and scattered electrons are reduced. Generated plasma and secondary electrons return to a beam wave interaction area, so that microwave output is prevented from being influenced.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Novel high-frequency structure of double-confocal waveguide gyro traveling wave tube
InactiveCN109950115ASparse pattern densityGood mode selection characteristicsTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube coupling devicesClassical mechanicsBeam wave
The invention relates to a novel high-frequency structure for a gyro traveling wave tube, which is called as a double-confocal waveguide. The structure is characterized in that the structure consistsof two groups of single confocal waveguides, wherein each group of single confocal waveguides consists of confocal mirrors, the curvature radiuses of which are equal to the distance between the mirrors. Therefore, the double-confocal waveguides are totally composed of four same and symmetrically distributed confocal mirrors. The double-confocal waveguides have sparse mode density and good mode selection characteristics, so that the high-order mode work of the gyro traveling wave tube is realized, and the working frequency of the gyro traveling wave tube is expanded to be above the W wave band(94 GHz). Compared with the traditional single confocal waveguide, the novel double confocal waveguides have the advantage that the beam-wave interaction efficiency of the gyro traveling wave tube isobviously improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Multi-frequency controllable high-power microwave device
Disclosed in the invention is a multi-frequency controllable high-power microwave device comprising a vacuum cavity formed by vacuum and sealed connection of a high-power microwave device, a device slow-wave-structure period adjusting mechanism, an insulator, a microwave radiation antenna and a guide magnet. The high-power microwave device consists of a cathode, a drift cavity, a beam wave interaction cavity, and a microwave output cavity; the beam wave interaction cavity is characterized in that a plurality of disk-loaded waveguide plates with central holes form a uniform periodic slow-wave structure; and the disk-loaded waveguide plates with central holes are connected in series with the device slow-wave-structure period adjusting mechanism by a threaded hole to form a uniform disk-loaded waveguide period adjusting device. With the uniform disk-loaded waveguide period adjusting device, the on-line, remote, and adjustable effect for the frequency of the high-power microwave device is realized; and high-power microwave outputs with different frequencies for the single device can be realized successively.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Cold cathode electronic gun modulated by microwave
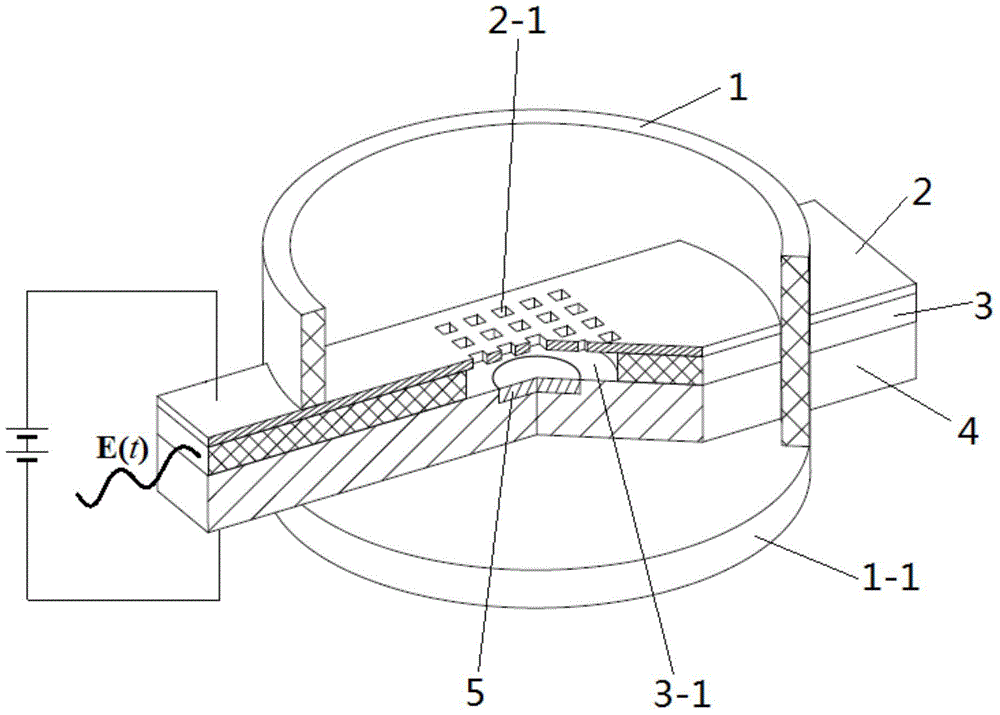
InactiveCN103606505ADoes not affect transmissionThe influence of small electric field distributionElectrode and associated part arrangementsElectricityMicrowave
The invention relates to a cold cathode electronic gun used in cooperation with a vacuum radiation source device. The cold cathode electronic gun comprises an electronic gun shell and a base of the electronic gun shell. The cold cathode electronic gun is provided with an upper electrode plate with array-type electron beam output holes, a lower electrode plate and a cold cathode, and further provided with a microwave input layer which is provided with an interaction cavity and arranged between the upper electrode plate and the lower electrode plate. Due to the fact that the microwave input layer is additionally arranged between the upper electrode plate and the lower electrode plate of a traditional cold cathode electronic gun, a cavity formed above the cold cathode in the middle section of the microwave input layer is used as the interaction cavity, the cold cathode is embedded in the bottom of the interaction cavity, the array-type electron beam output holes which are smaller than the microwave length in size are formed in the position, right opposite to the interaction cavity, of the upper electrode plate, and therefore the cold cathode electronic gun has the advantages of being small in space of the beam wave interaction cavity, low in power consumption, capable of being integrated, small in size, high in response speed and capable of feeding in microwaves with different frequencies as needed to modulate the current transmitted by the cold cathode so as to generate electron beams with different frequencies and strengths, providing an electron transmitting source for the mini-type electron vacuum device, effectively expanding the application range and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for manufacturing optical flat plate with beam converging function
InactiveCN101907781AReduce weightHighly integratedPhotomechanical apparatusOptical elementsSolid massEtching
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing an optical flat plate with beam converging function. In the prior art, a solid lens has large volume and cannot realize super resolution, and meanwhile a liquid lens has high liquidity, has no fixed shape and needs encapsulation for use. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a scattering plate with multi-stage scattering based on the beam focusing principle of a multi-stage scattering layer, then constructing an incident beam wave front phase optimization system, obtaining incident beam optimized wave front phase distribution required by focusing of the multi-stage scattering layer by using a beam wave front phase optimization method focused by the multi-stage scattering layer, preparing a phase plate with the incident beam optimized wave front phase distribution by using a photo-etching method, and finally sticking the phase plate and the scattering plate together by using optical cement to obtain the optical flat plate with beam converging function. The manufacturing method is simple; and the manufactured focusing component has the characteristics of small device volume, light weight, high integration, remarkable focusing effect and the like.
Owner:杭州帝泓科技有限公司
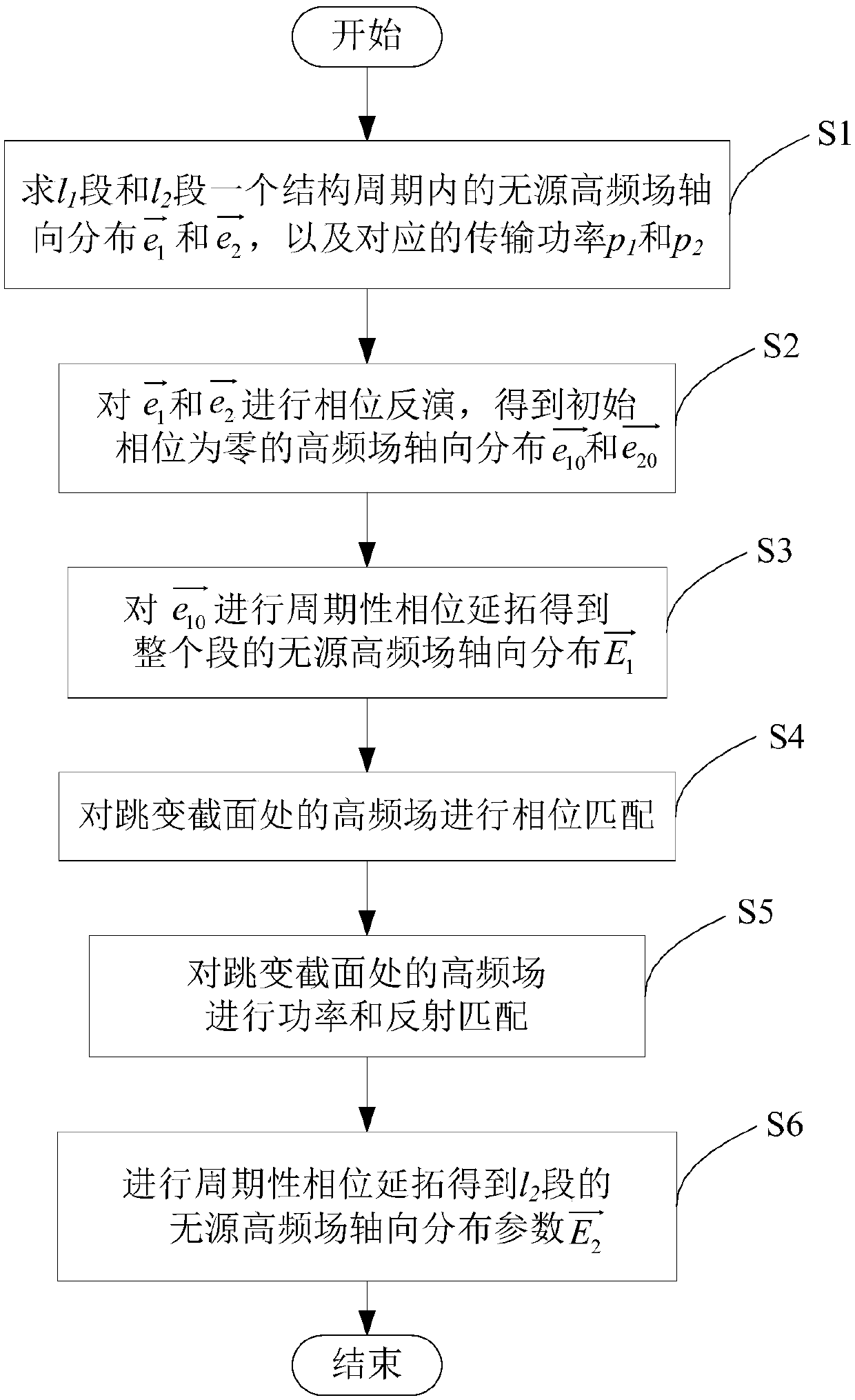
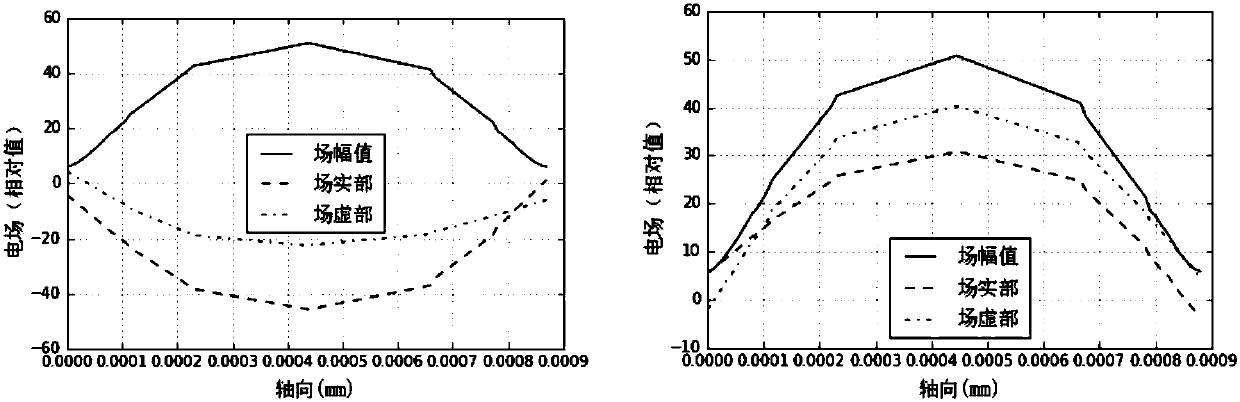
Discontinuous field matching method for general beam-wave interaction model of traveling wave tube
ActiveCN107609233AImprove practicalityEfficientSpecial data processing applicationsPhase retrievalInteraction model
The invention discloses a discontinuous field matching method for a general beam-wave interaction model of a traveling wave tube. The method comprises the following steps of S1, solving passive high-frequency field axial distribution e1 and e2 and transmission power p1 and p2 in a structural cycle; S2, performing phase retrieval on e1 and e2 to obtain e10 and e20; S3, performing periodic phase extension on e10 to obtain passive high-frequency field axial distribution E1 of an l1 section; S4, performing phase matching on a field at a jump cross section to obtain a field distribution parameter,with a continuous phase, of a high-frequency field axial component at the jump cross section; S5, performing power and reflection matching on the field at the jump cross section to obtain a passive high-frequency field axial distribution parameter of an l2 section in one structural cycle; and S6, performing periodic phase extension on the parameter obtained in the step S5 to obtain field distribution E2. Through the phase, power and reflection matching and phase extension methods, the field distribution of a whole interaction region is obtained, so that the general beam-wave interaction theoretical model can simulate the beam-wave interaction problem of the traveling wave tube adopting a high-frequency structure with dynamic phase velocity jump.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com