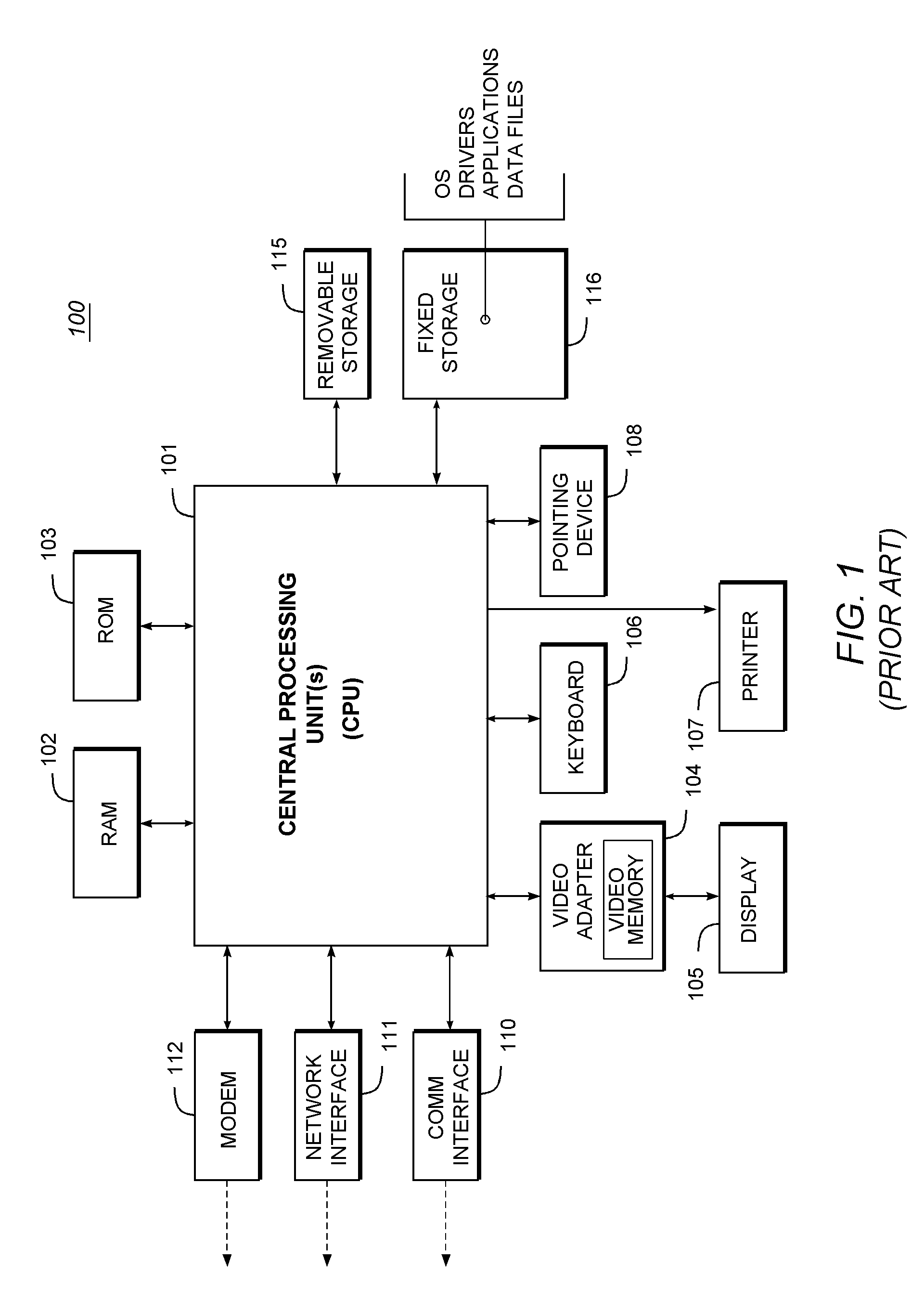
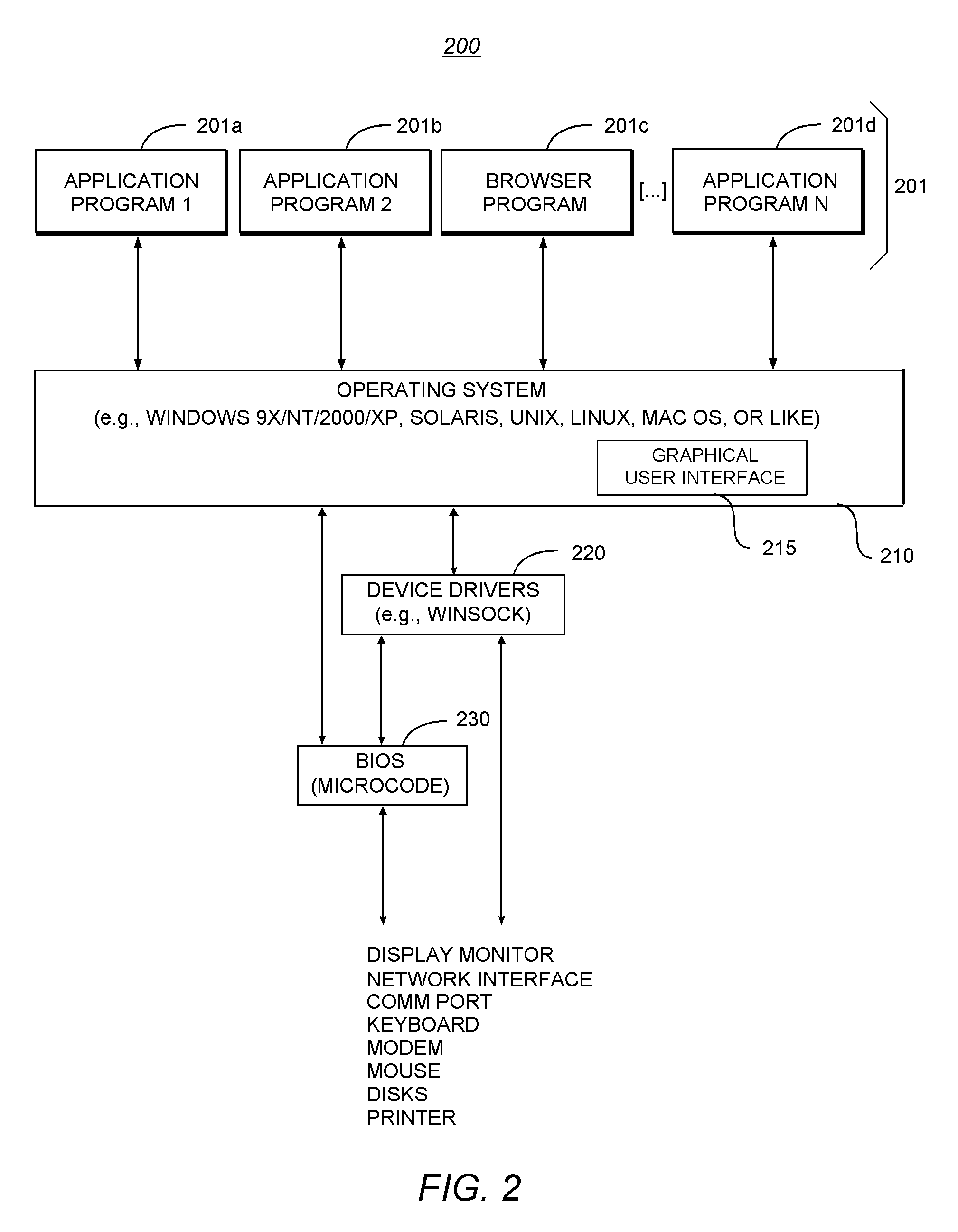
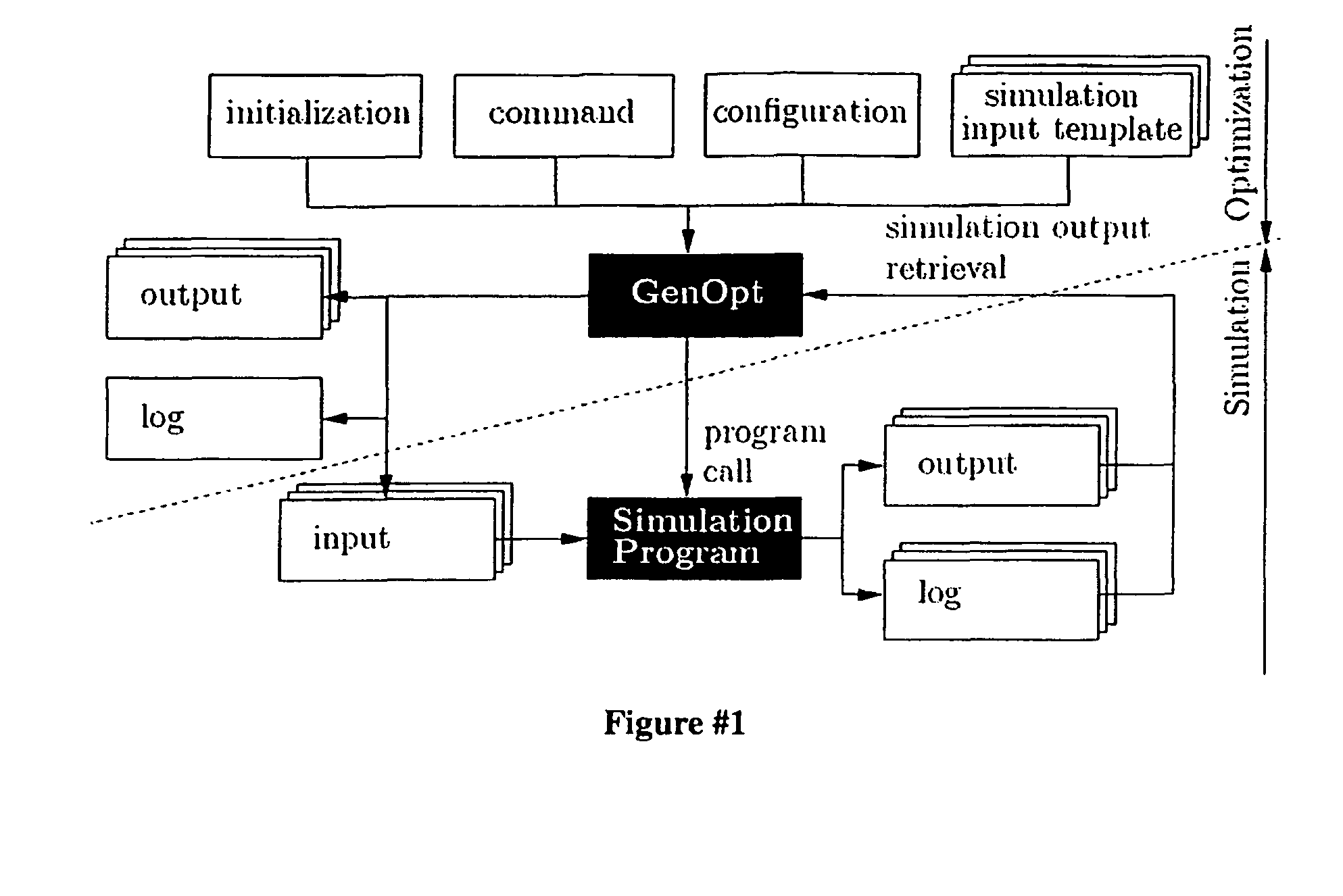
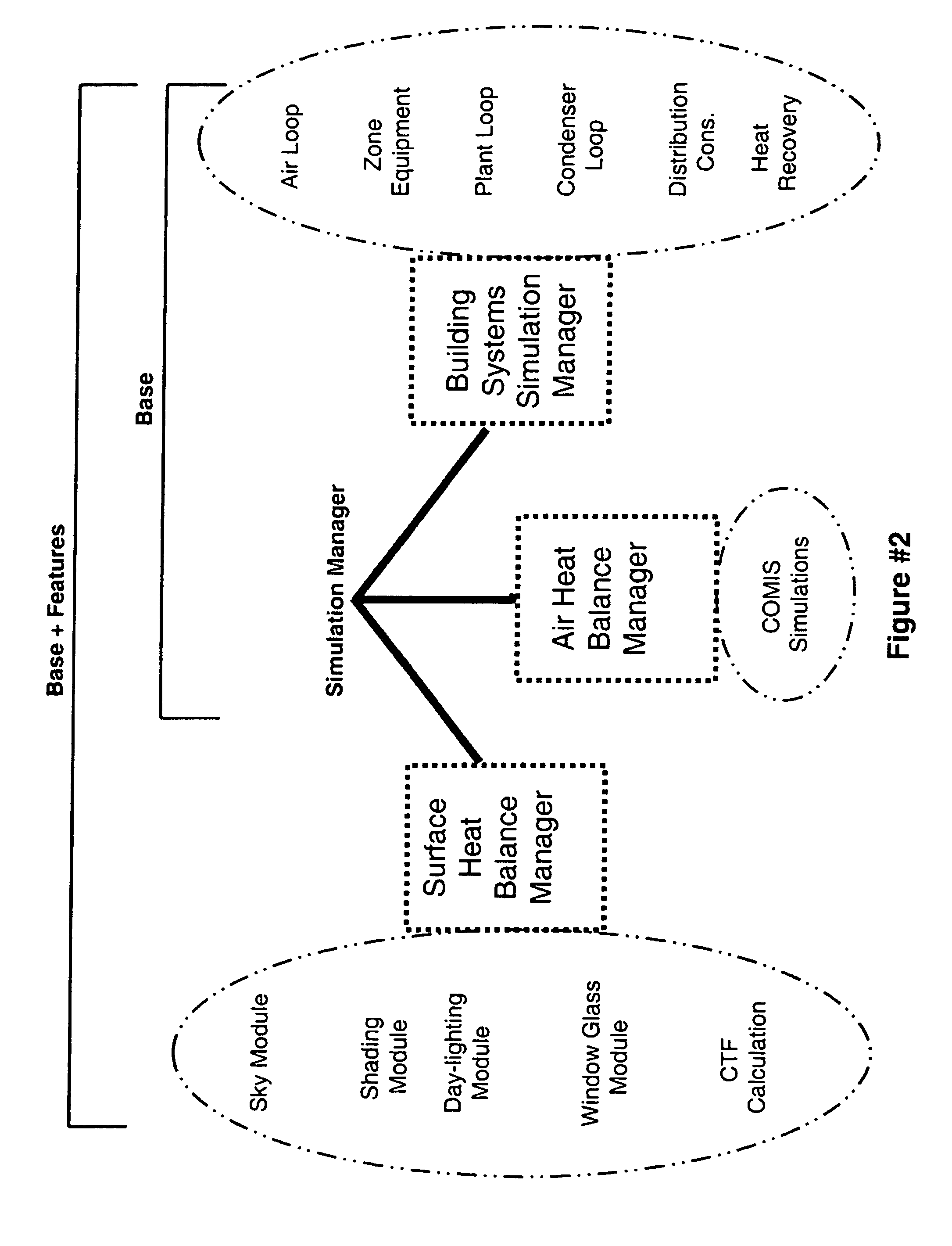
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2298 results about "Optimization system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optimization is the process of making a trading system more effective by adjusting the variables used for technical analysis.
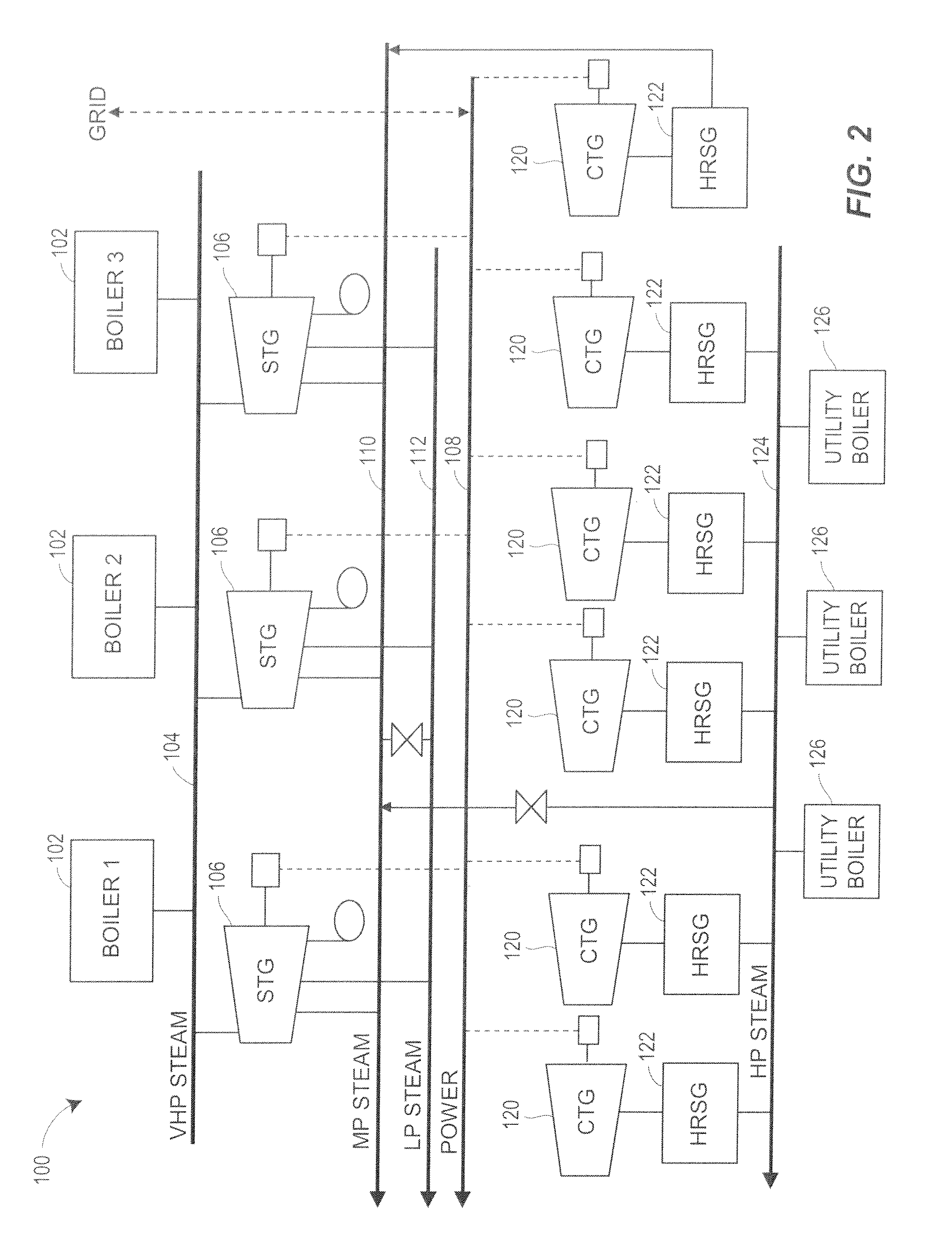
Multifactorial optimization system and method
A method for providing unequal allocation of rights among agents while operating according to fair principles, comprising assigning a hierarchal rank to each agent; providing a synthetic economic value to a first set of agents at the a high level of the hierarchy; allocating portions of the synthetic economic value by the first set of agents to a second set of agents at respectively different hierarchal rank than the first set of agents; and conducting an auction amongst agents using the synthetic economic value as the currency. A method for allocation among agents, comprising assigning a wealth generation function for generating future wealth to each of a plurality of agents, communicating subjective market information between agents, and transferring wealth generated by the secure wealth generation function between agents in consideration of a market transaction. The method may further comprise the step of transferring at least a portion of the wealth generation function between agents.
Owner:MEADWESTVACO CORP
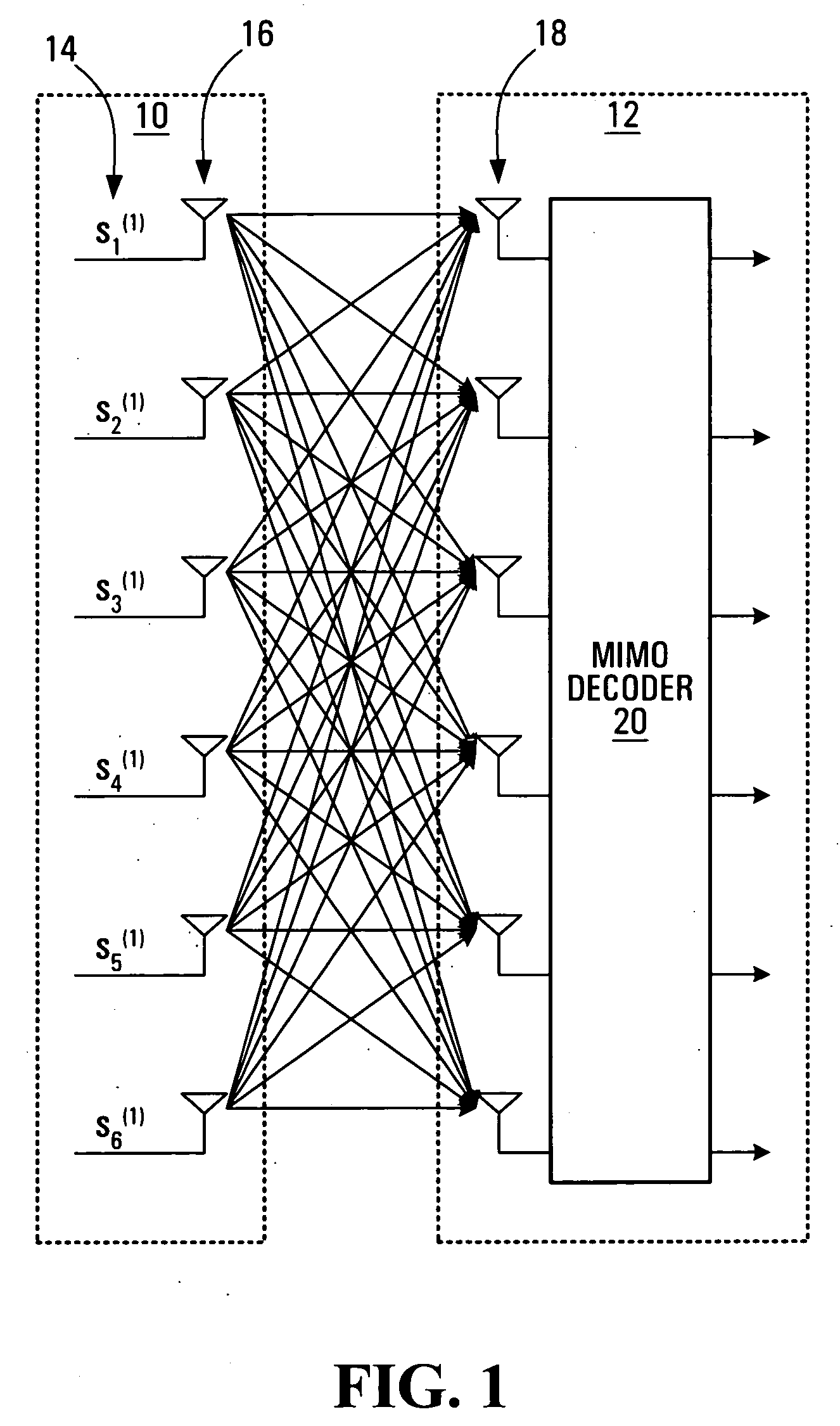
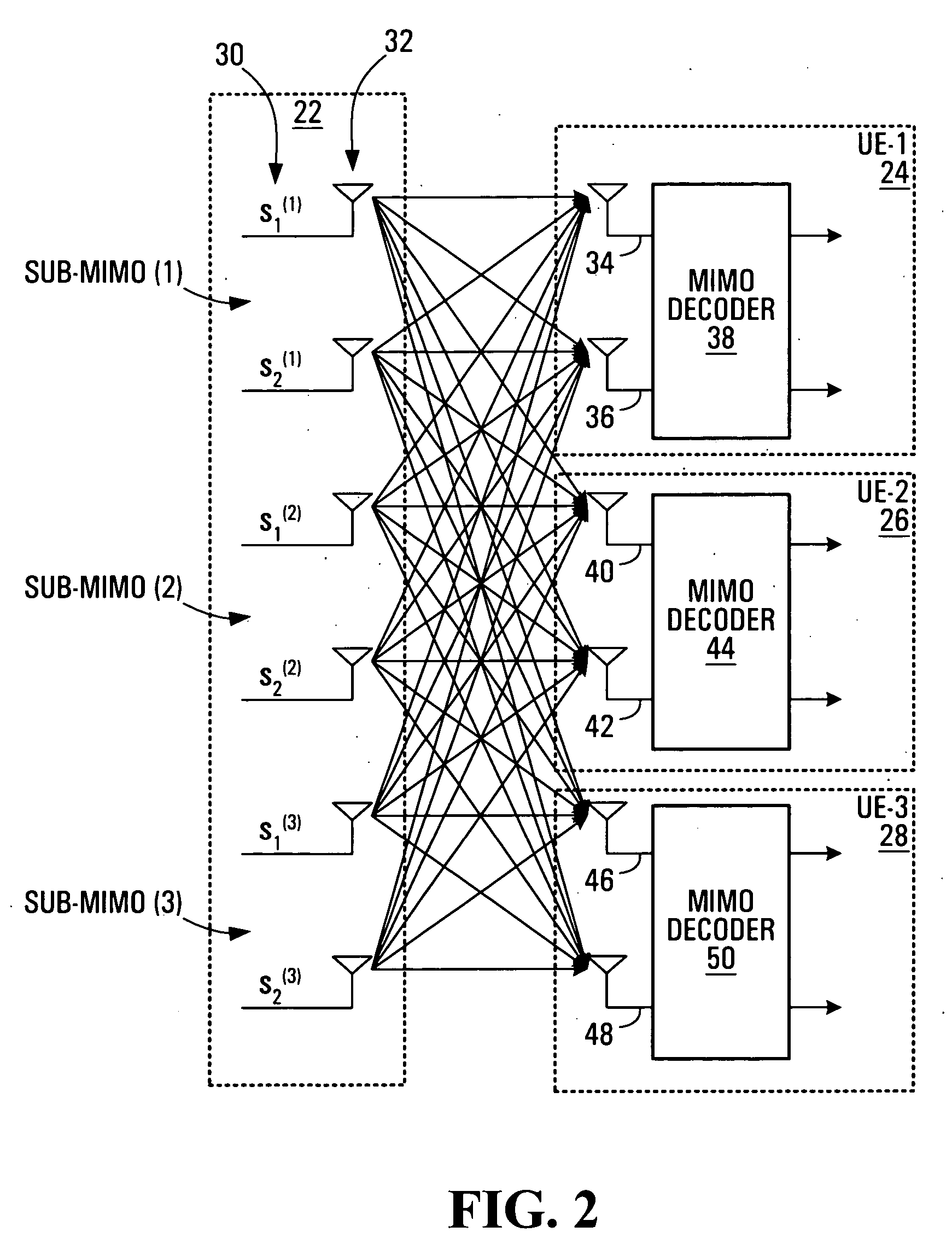
Communication channel optimization systems and methods in multi-user communication systems
ActiveUS20050101259A1Spatial transmit diversityBaseband system detailsChannel state informationCommunications system
Systems and methods of optimizing communication channels in multi-user communication systems are provided. Coding weights are determined based on communication channel state information for communication channels between a transmitter and multiple receivers. The coding weights are applied to communication signals to be transmitted from the transmitter to the receivers. Each receiver decodes received signals using inverses of the coding weights. Embodiments of the invention support multi-user MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) where each receiver has fewer antennas than the transmitter, and enhance system performance if the total number of antennas at all of the receivers exceeds the number of antennas at the transmitter.
Owner:APPLE INC
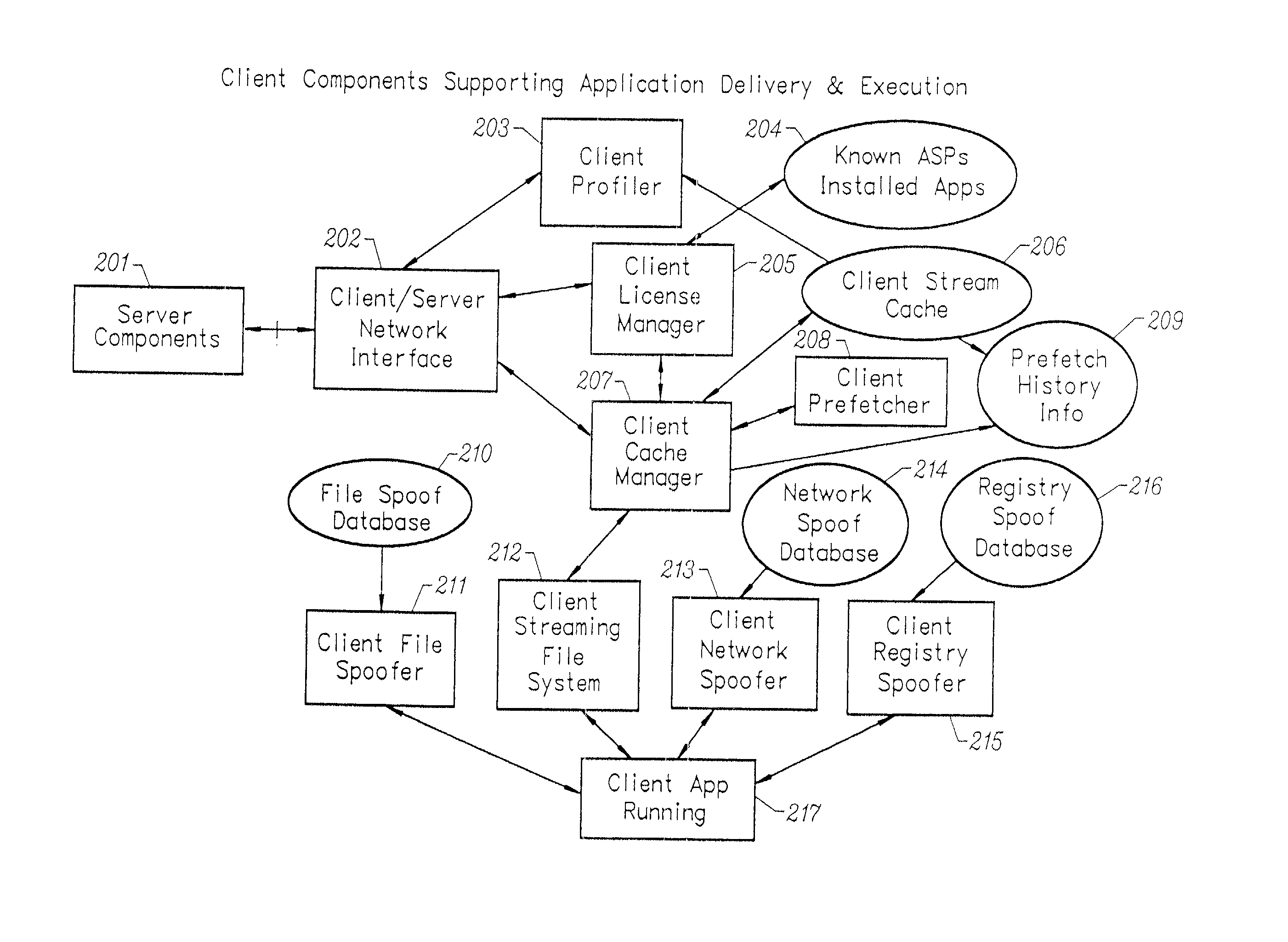
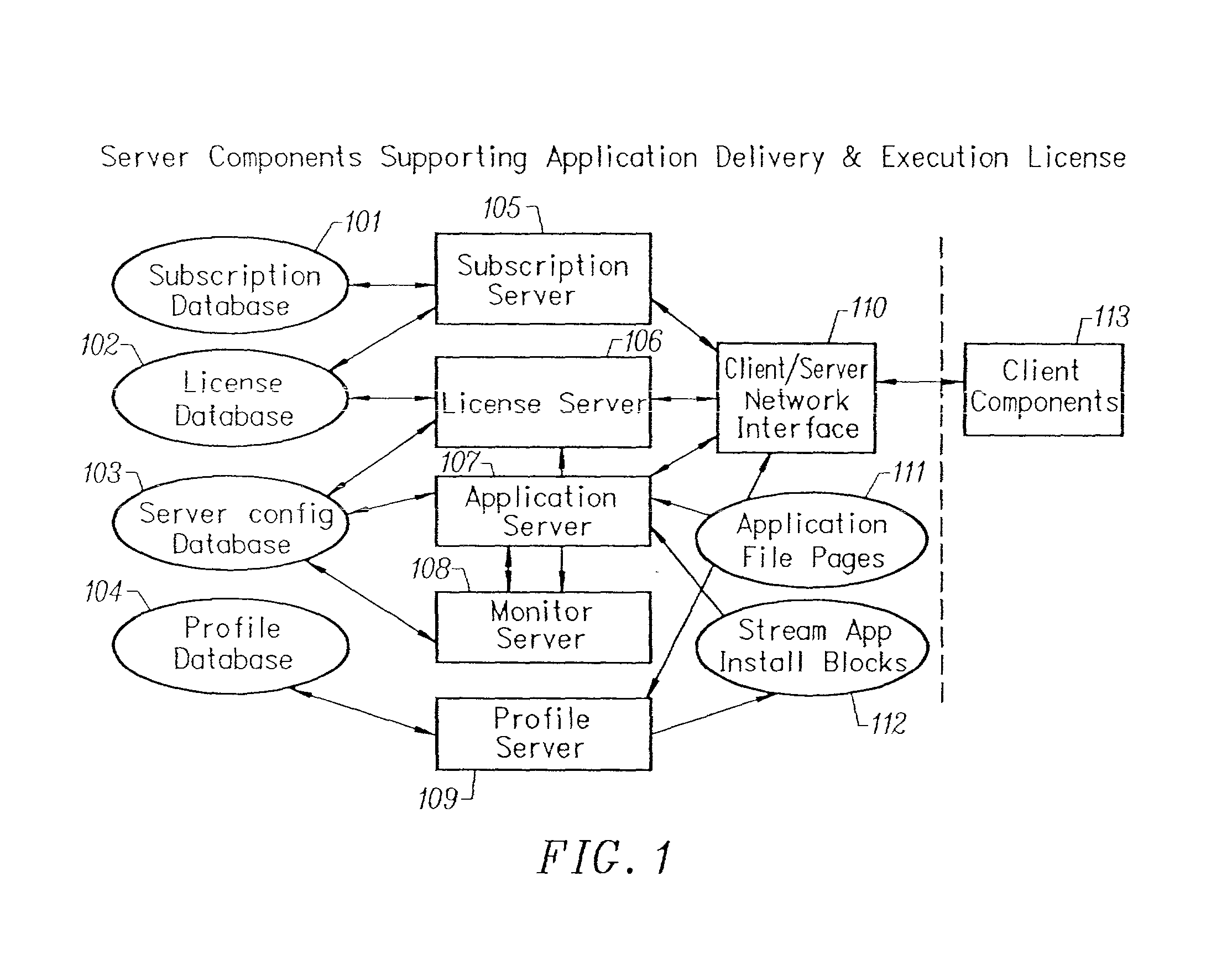
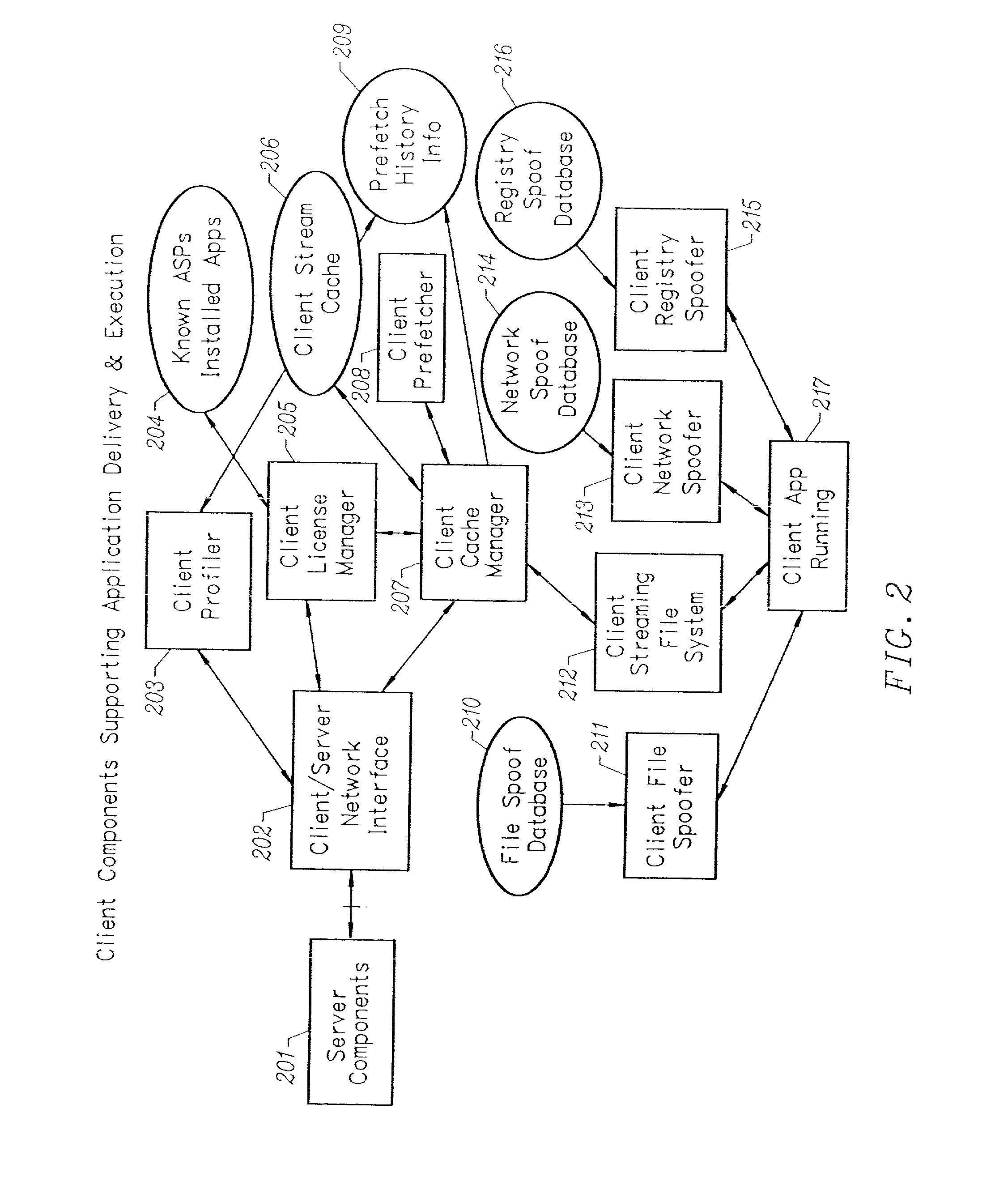
Client-side performance optimization system for streamed applications
InactiveUS20020091763A1Improve application performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram loading/initiatingData fileApplication software
An client-side performance optimization system for streamed applications provides several approaches for fulfilling client-side application code and data file requests for streamed applications. A streaming file system or file driver is installed on the client system that receives and fulfills application code and data requests from a persistent cache or the streaming application server. The client or the server can initiate the prefetching of application code and data to improve interactive application performance. A client-to-client communication mechanism allows local application customization to travel from one client machine to another without involving server communication. Applications are patched or upgraded via a change in the root directory for that application. The client can be notified of application upgrades by the server which can be marked as mandatory, in which case the client will force the application to be upgraded. The server broadcasts an application program's code and data and any client that is interested in that particular application program stores the broadcasted code and data for later use.
Owner:NUMECENT HLDG
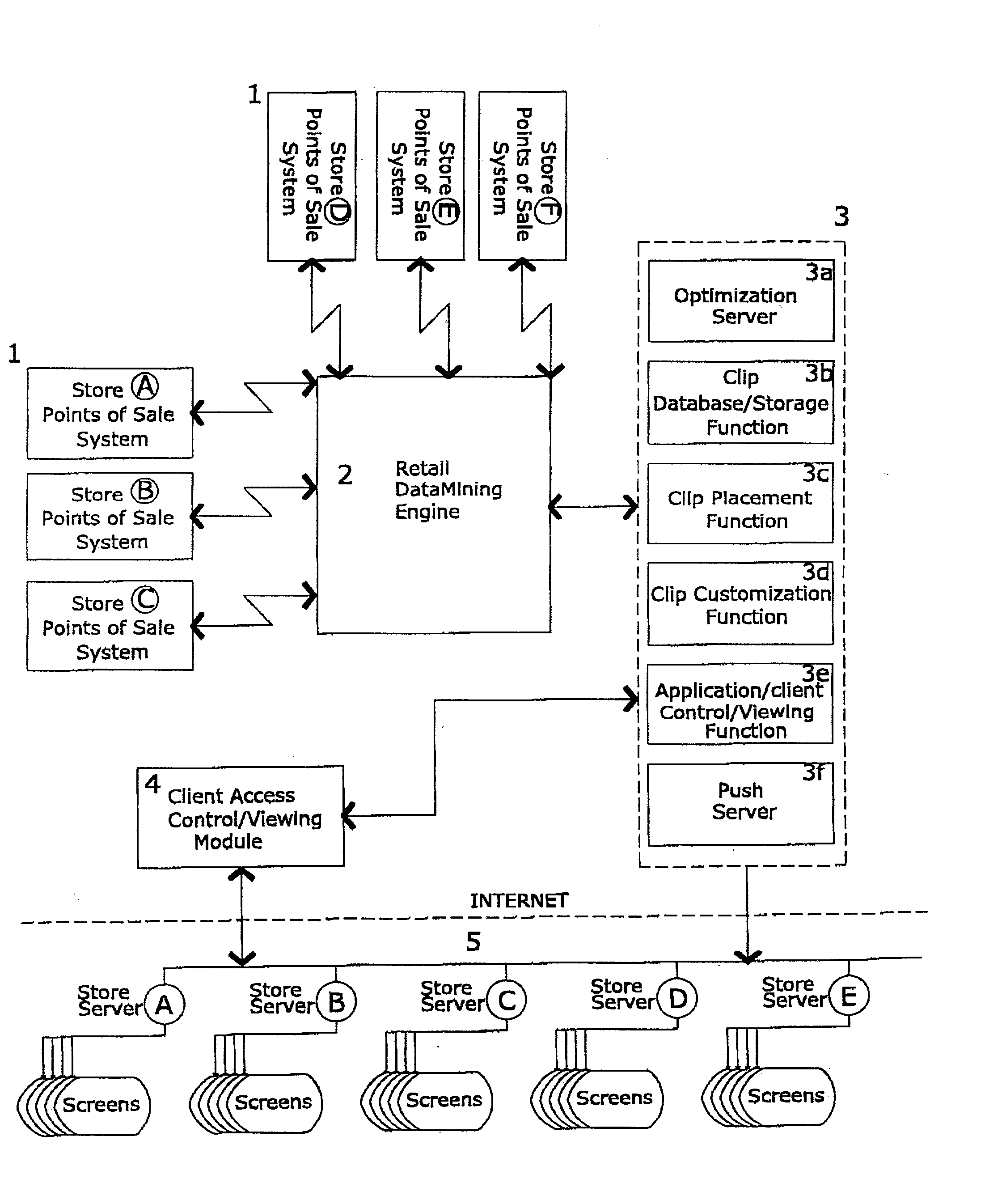
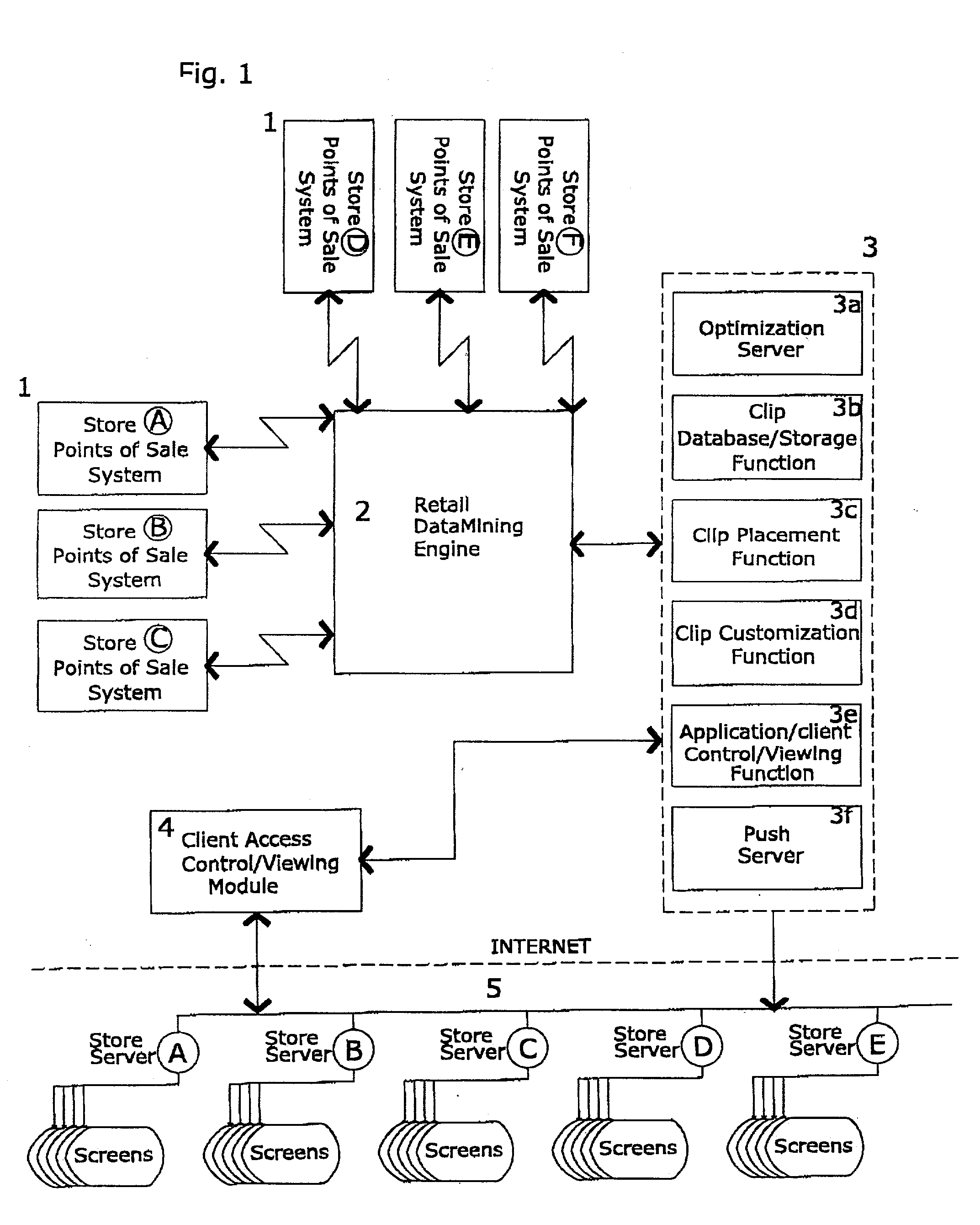
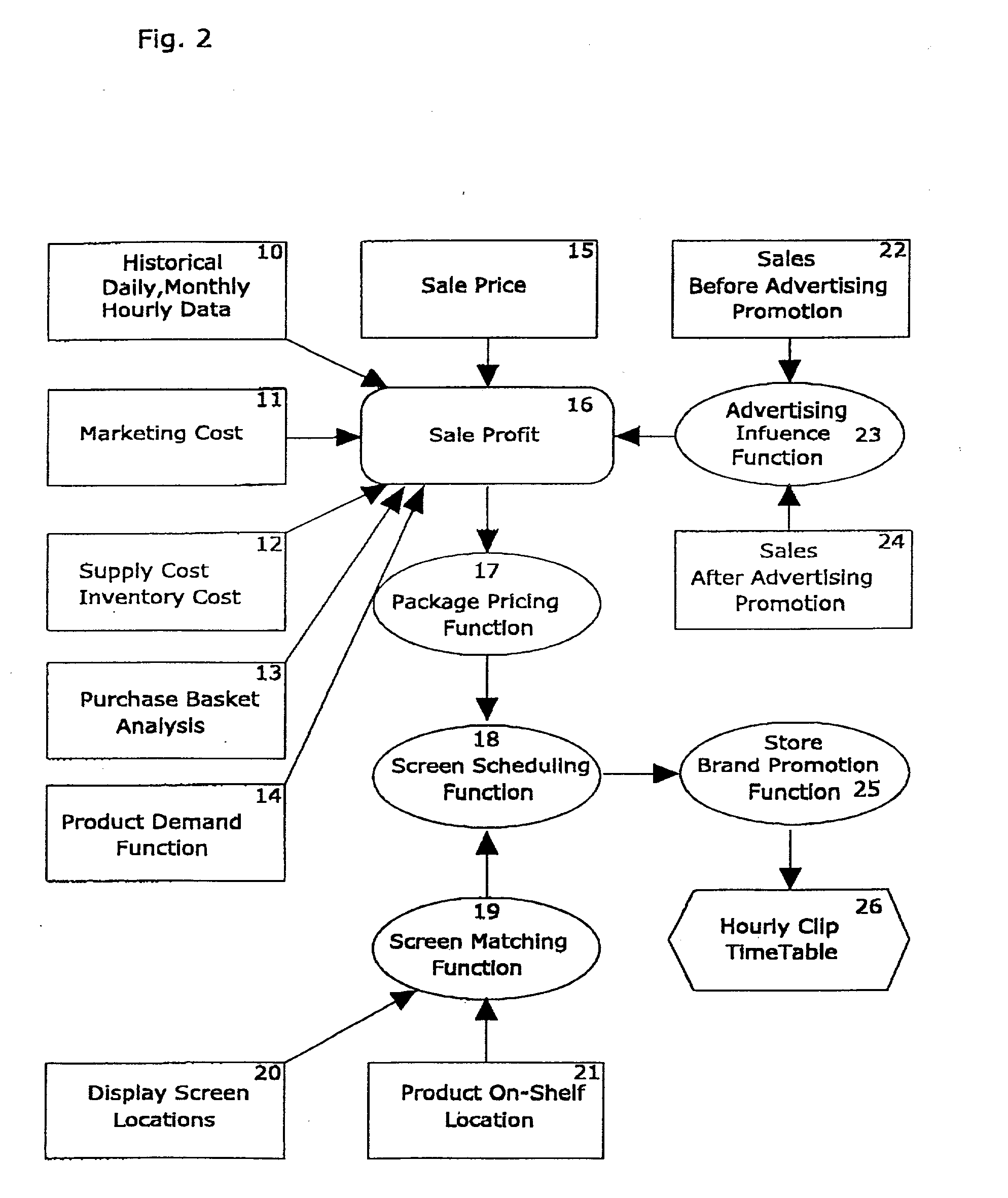
Method and system for maximizing sales profits by automatic display promotion optimization
The present invention is remotely controlled automatic optimization system for maximizing in-store net profits by customized script-generated clip promotions to thousands of individually networked retail display-nodes from central server (OptiRetailChain). The computer-based and machine-learning display system includes: an advertising optimization function for display nodes, point of sale (POS) data input, retail database mining engine (RDME), client access and management control module, and in-store networked electronic clip display apparatus. The optimization function obtains data from chain-store database, combines product bundling data, which describe the associative relationships of various product sales in stores with recorded times of sale, inventory costs, margin profits etc. Physical location of purchased products on the store floor-areas are correlated with relevant display-nodes to create optimal clip display program (playlist) configurations for that specific display location and time. Most preferred product advertising combinations will be displayed in the best time slots for each node automatically. OptiRetailChain uses two methods of promotion optimization: real time scheduling and longer-term statistical optimization. Utilizing the machine learning capabilities, actual video-clip playlists will be dynamically updated for every display-node and respond to daily sales fluctuations for that store display location. This enables the optimization system to effectively control and automatically feature target advertising to large number of display-nodes in supermarket chain networks optimizing advertising capital without necessitating outside intervention.
Owner:MAKOR ISSUES & RIGHTS
Managing power consumption based on utilization statistics
InactiveUS6996728B2Save powerEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementService-level agreementResource depletion
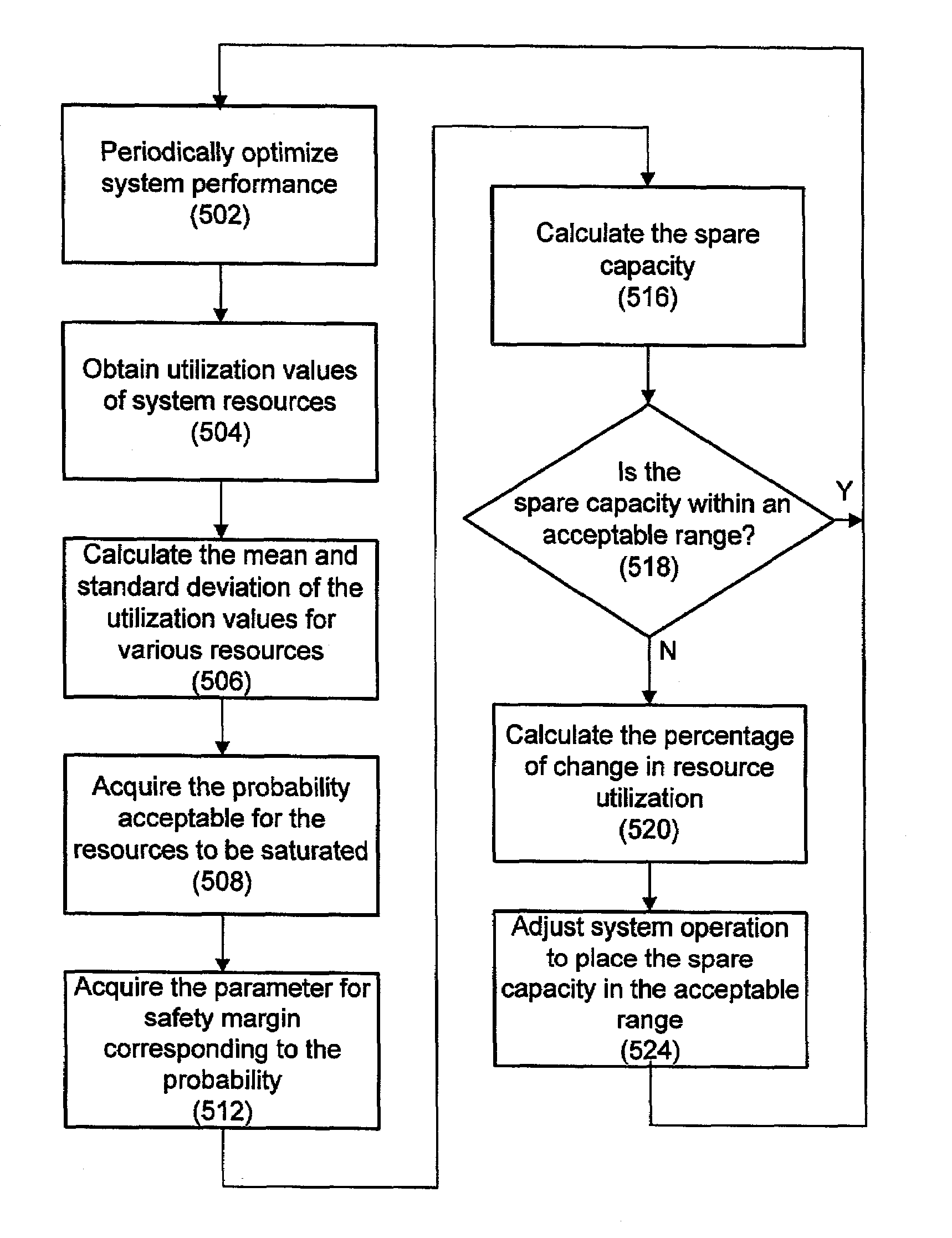
The present invention, in various embodiments, provides techniques for managing system power. In one embodiment, system compute loads and / or system resources invoked by services running on the system consume power. To better manage power consumption, the spare capacity of a system resource is periodically measured, and if this spare capacity is outside a predefined range, then the resource operation is adjusted, e.g., the CPU speed is increased or decreased, so that the spare capacity is within the range. Further, the spare capacity is kept as close to zero as practical, and this spare capacity is determined based on the statistical distribution of a number of utilization values of the resources, which is also taken periodically. The spare capacity is also calculated based on considerations of the probability that the system resources are saturated. In one embodiment, to maintain the services required by a Service Level Agreement (SLA), a correlation between an SLA parameter and a resource utilization is determined. In addition to other factors and the correlation of the parameters, the spare capacity of the resource utilization is adjusted based on the spare capacity of the SLA parameter. Various embodiments include optimizing system performance before calculating system spare capacity, saving power for system groups or clusters, saving power for special conditions such as brown-out, high temperature, etc.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
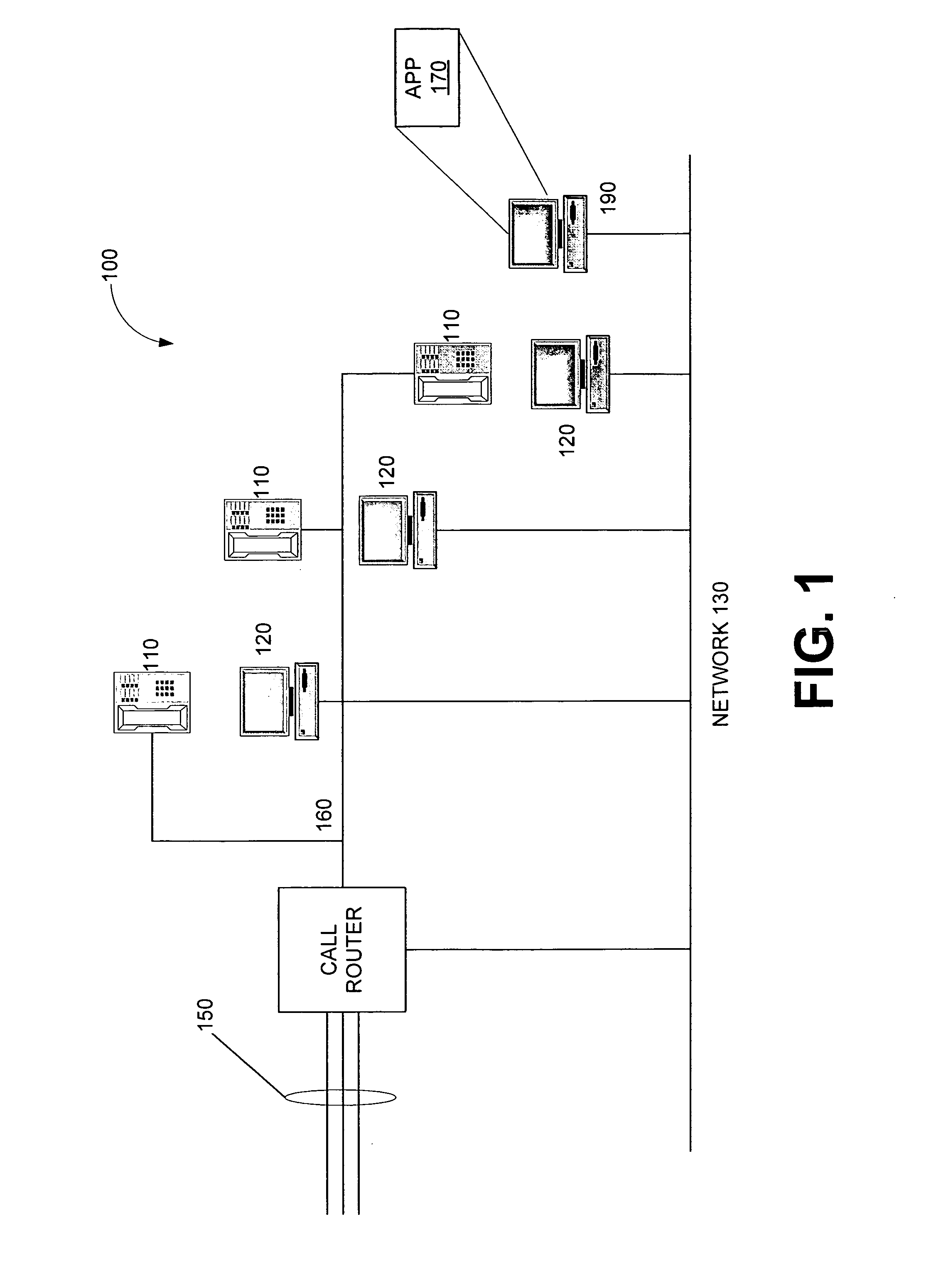
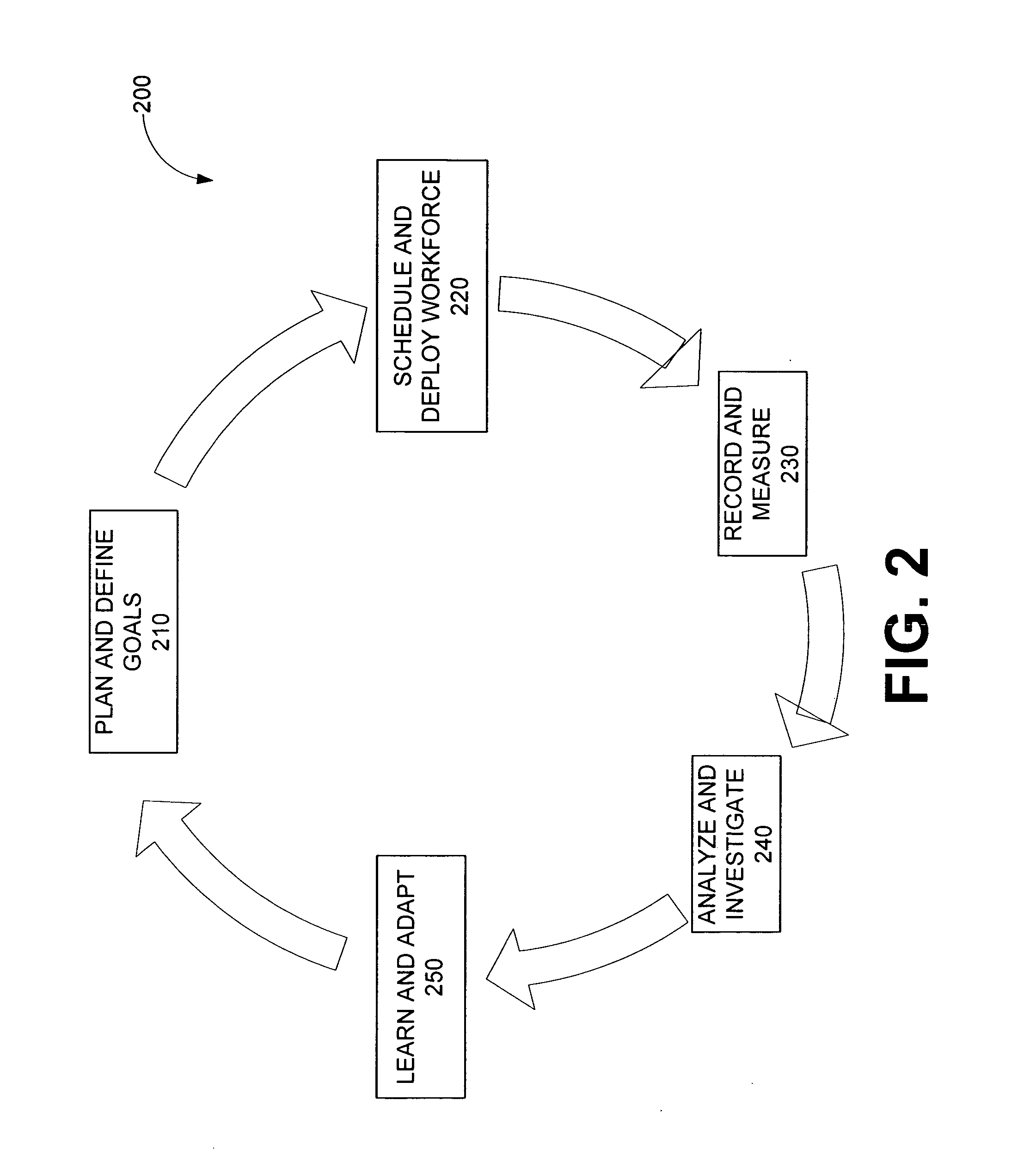
Systems and methods for workforce optimization
ActiveUS20070198322A1Easy to operateResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsContact centerPerformance index
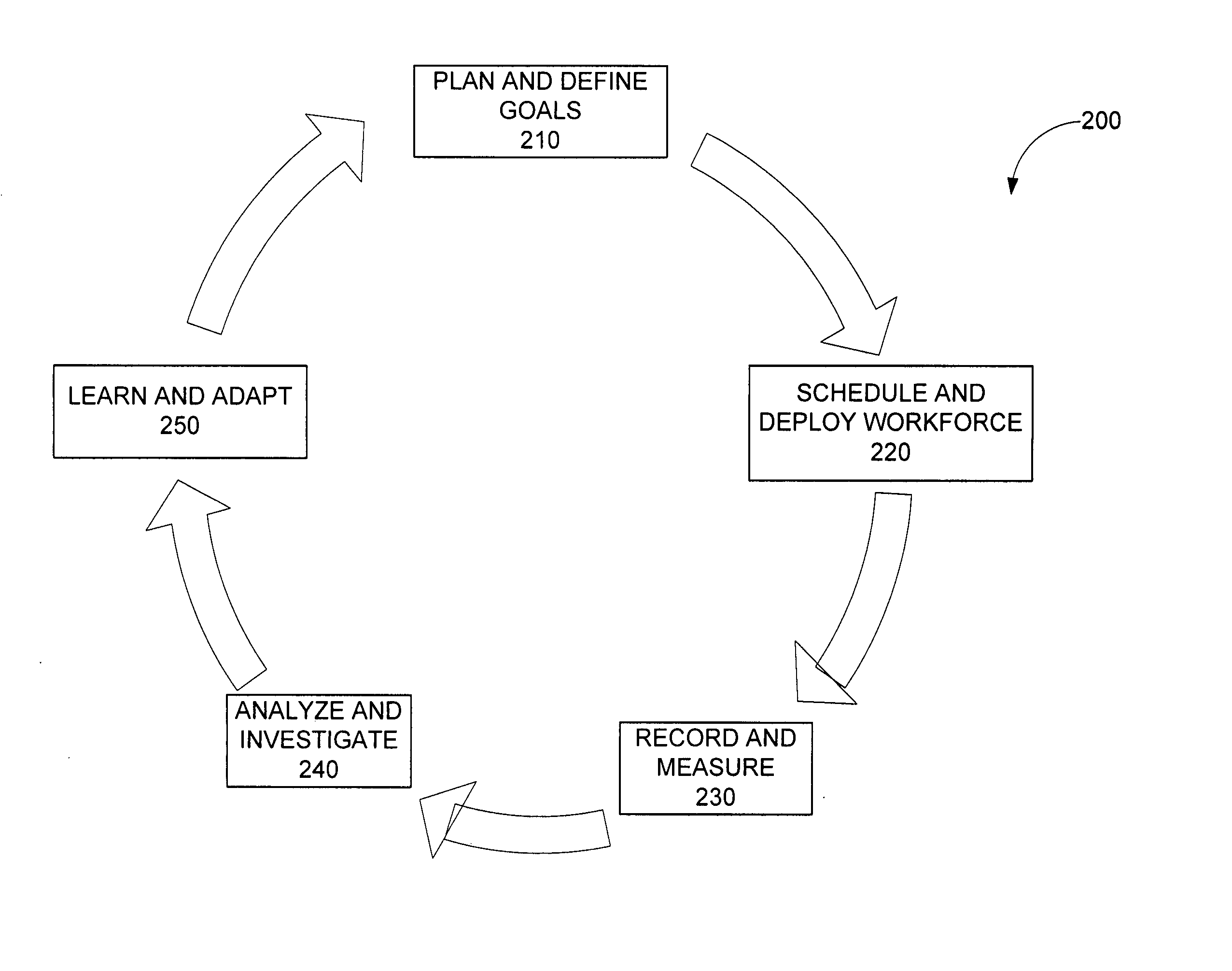
Systems and methods are disclosed for an integrated process for optimizing operations at a contact center. In one embodiment, the method comprises: defining contact center business goals; planning at least one campaign to implement the goals; scheduling and deploying a workforce in accordance with the campaign to produce agent-customer interactions; measuring agent performance on the interactions to produce quality metrics; analyzing the metrics to produce a rating; combining quality metrics to produce performance indicators; and using the performance indicators in the planning step of a second campaign or another iteration of the first campaign.
Owner:VERINT AMERICAS
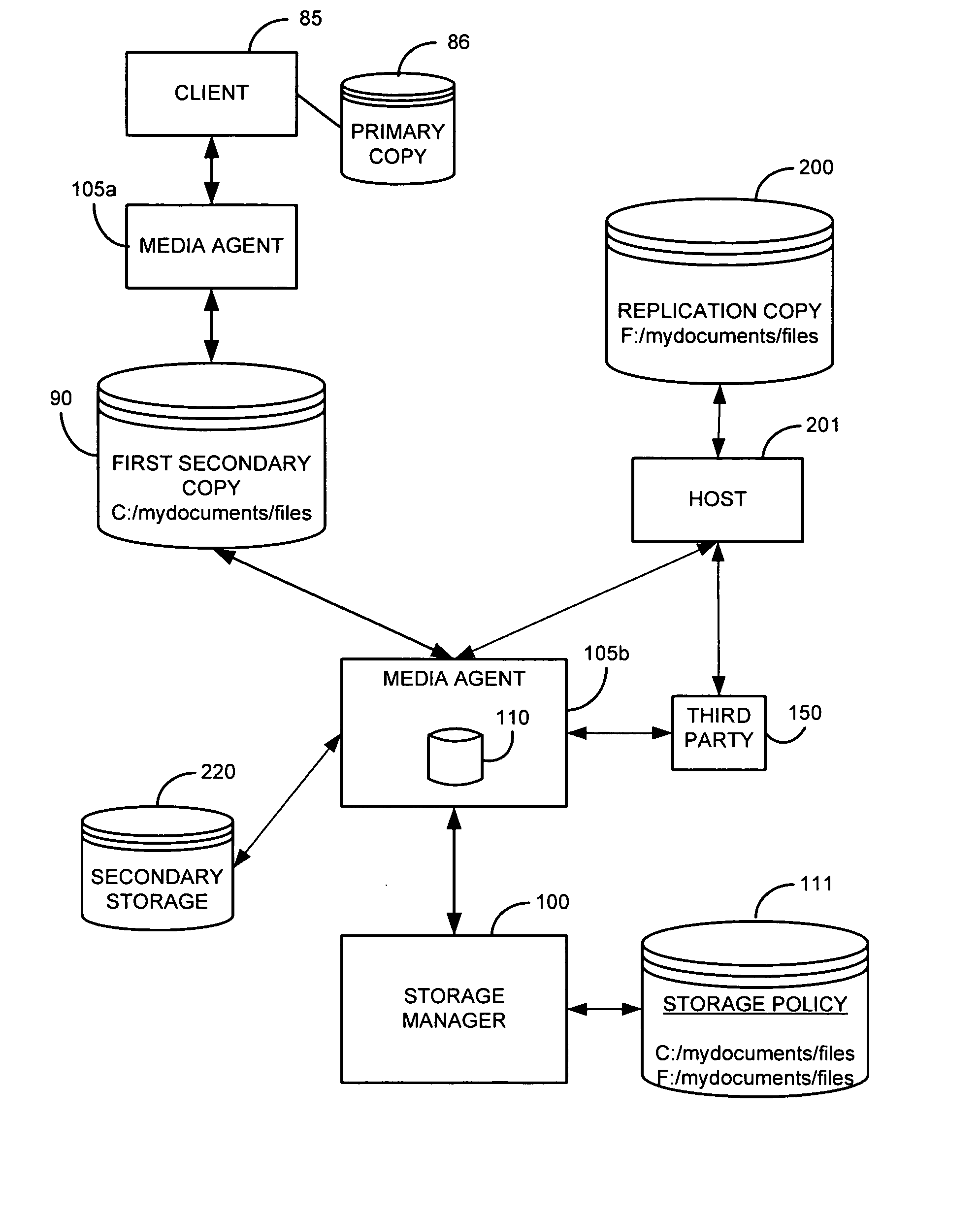
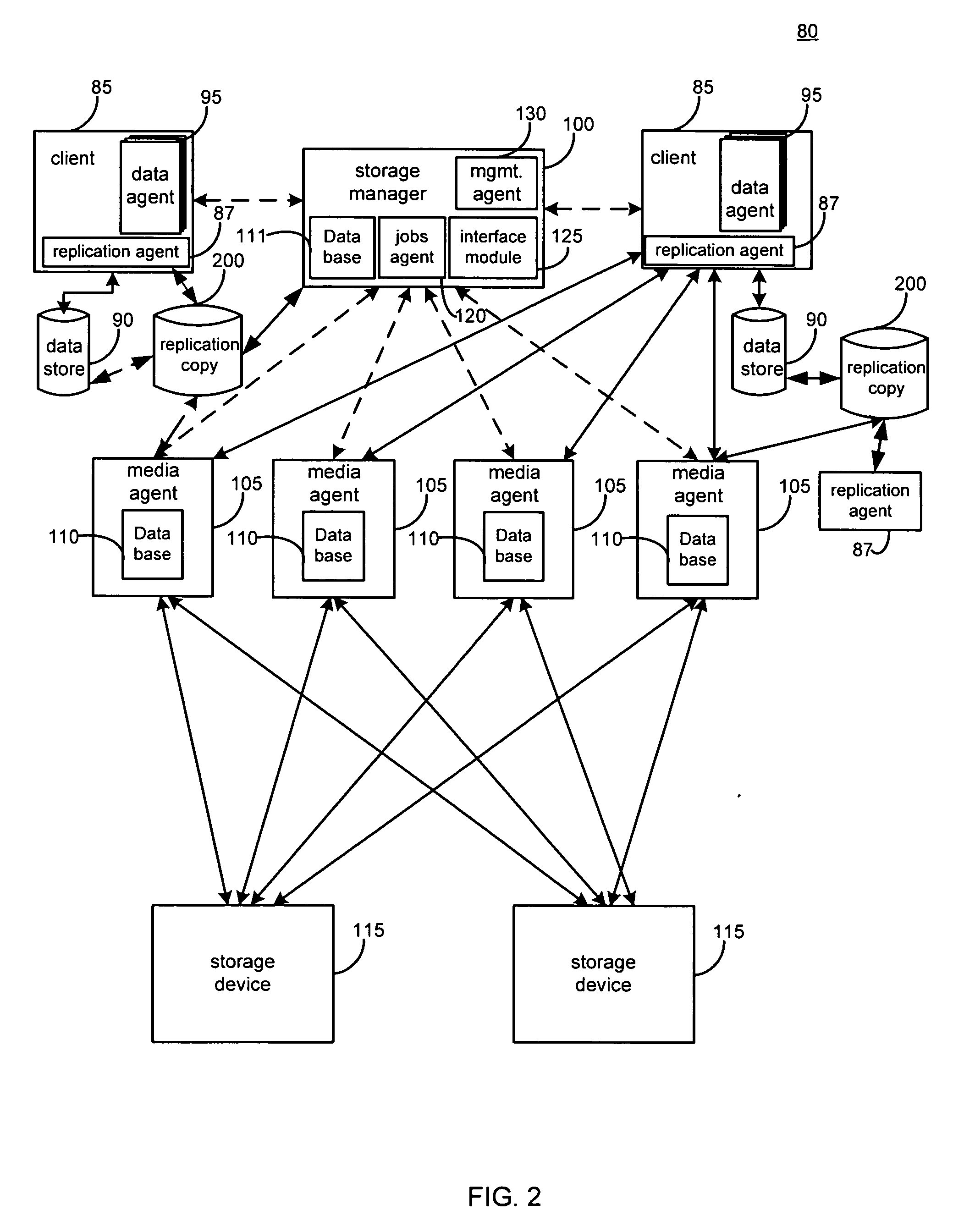
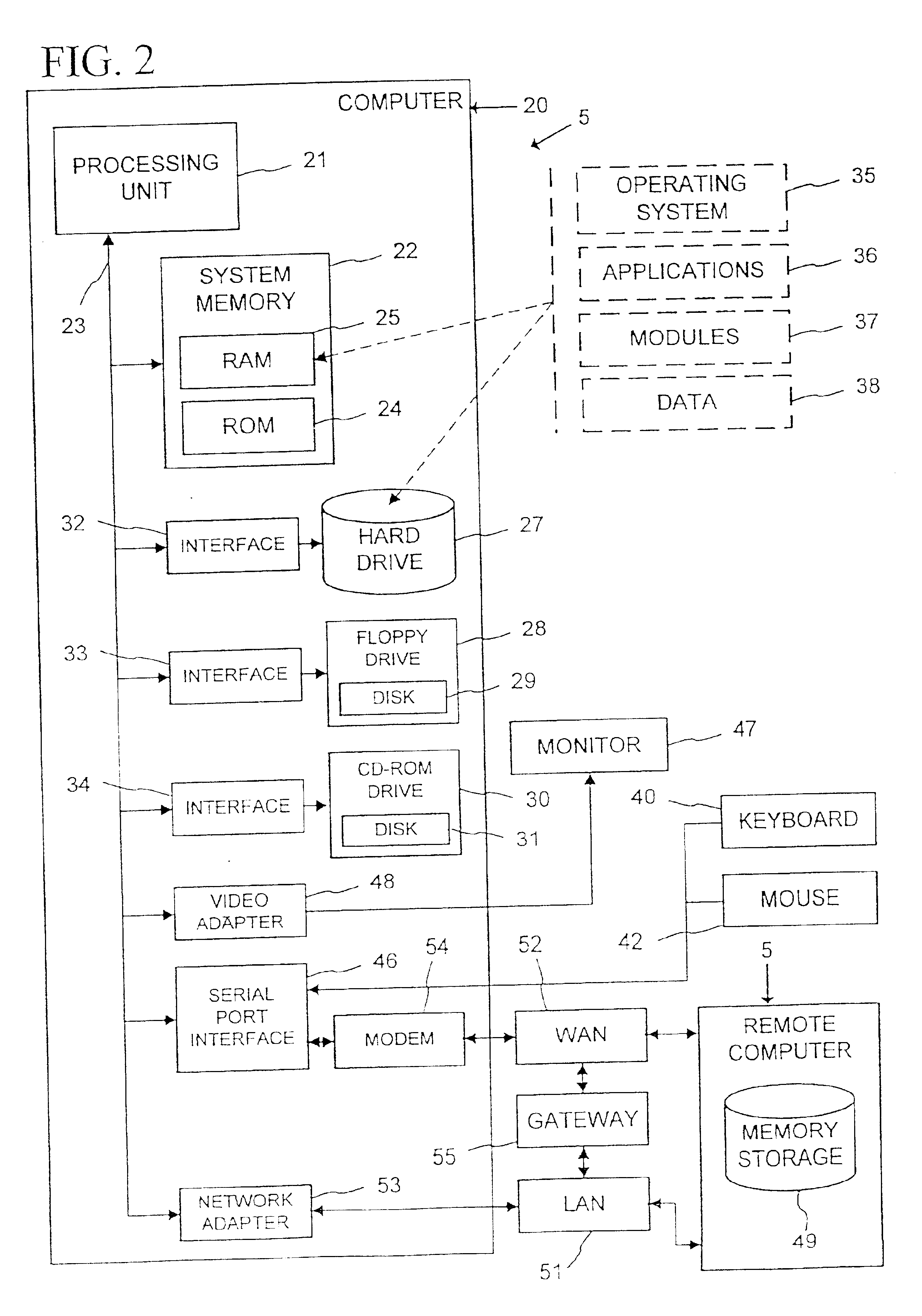
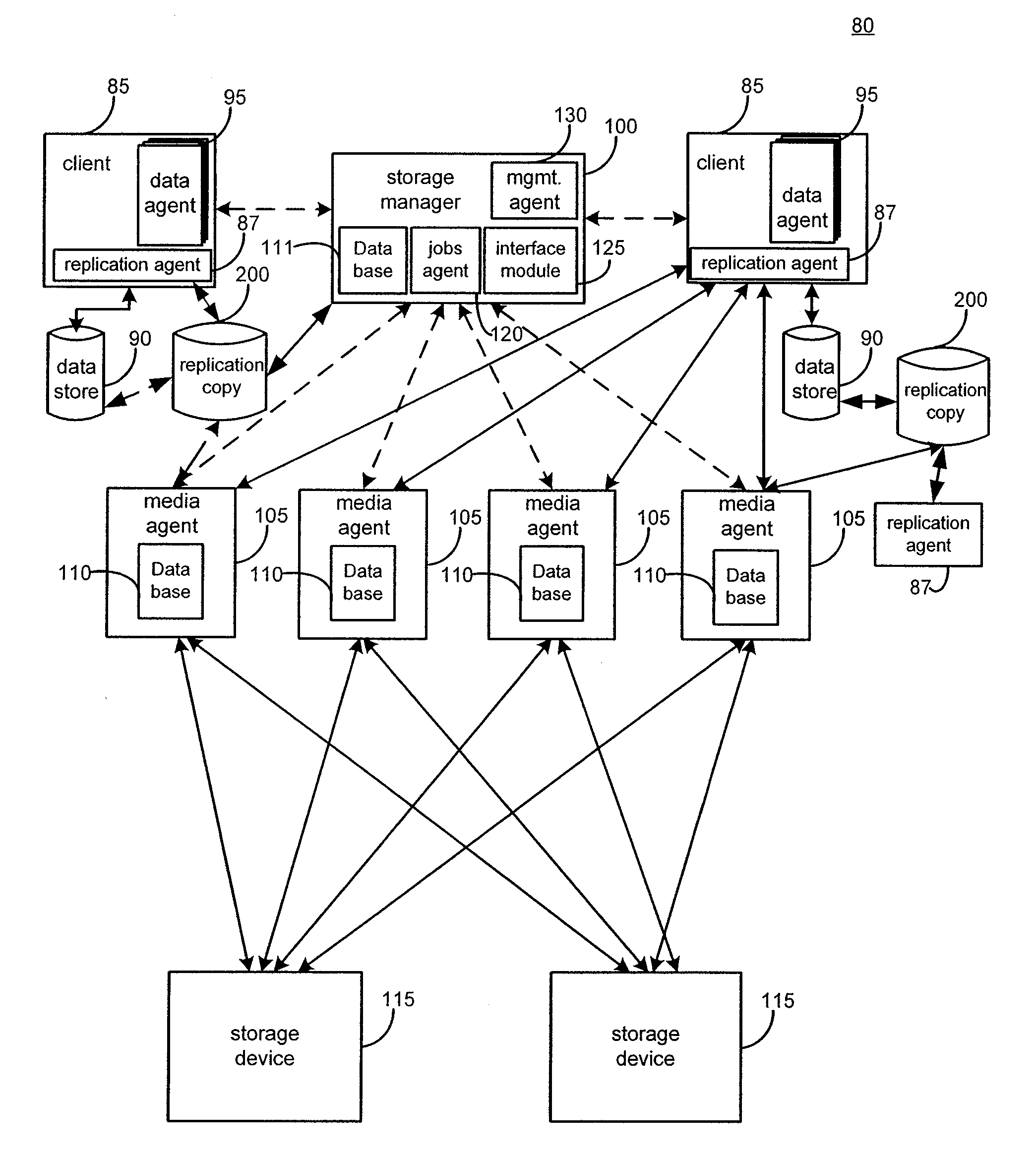
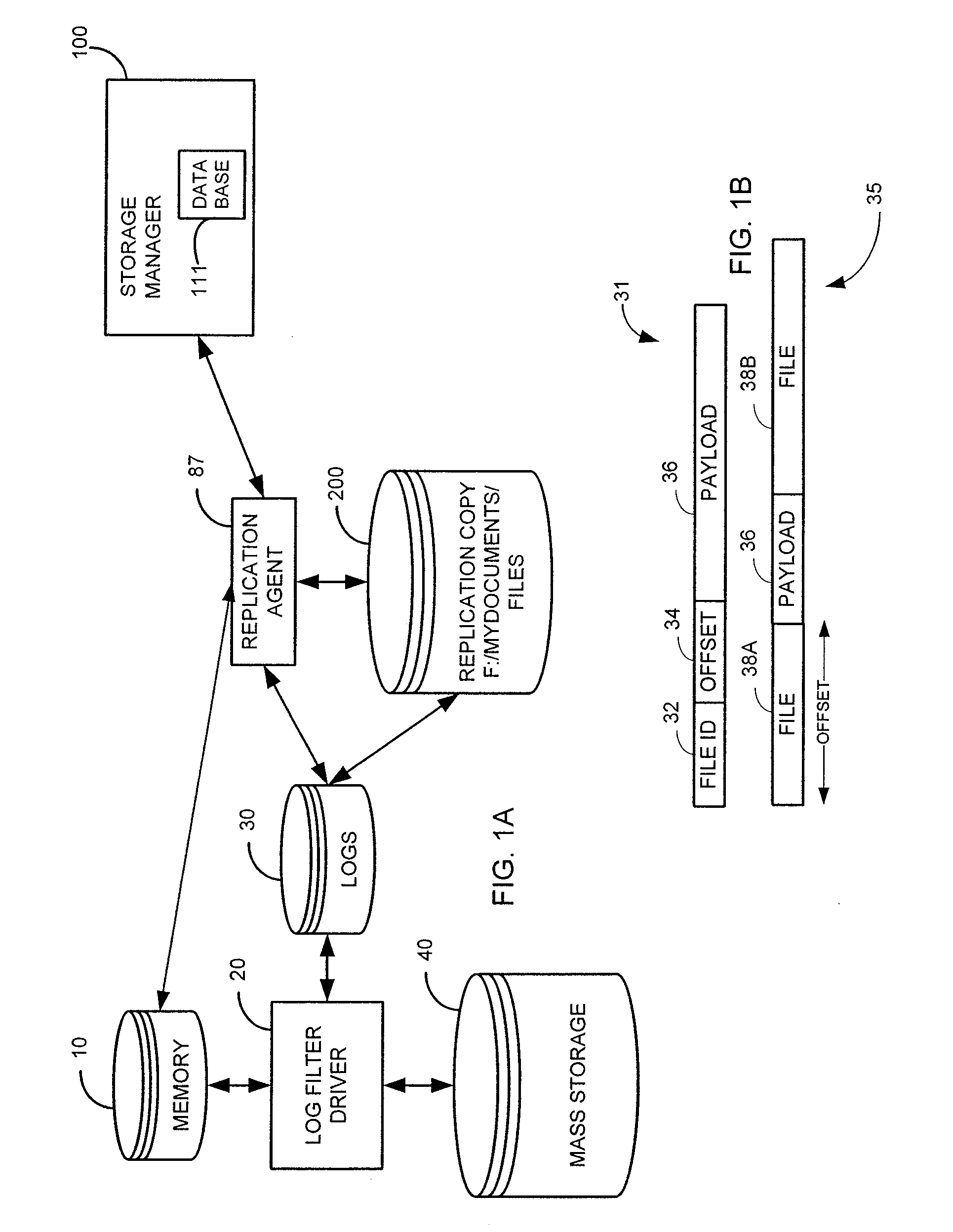
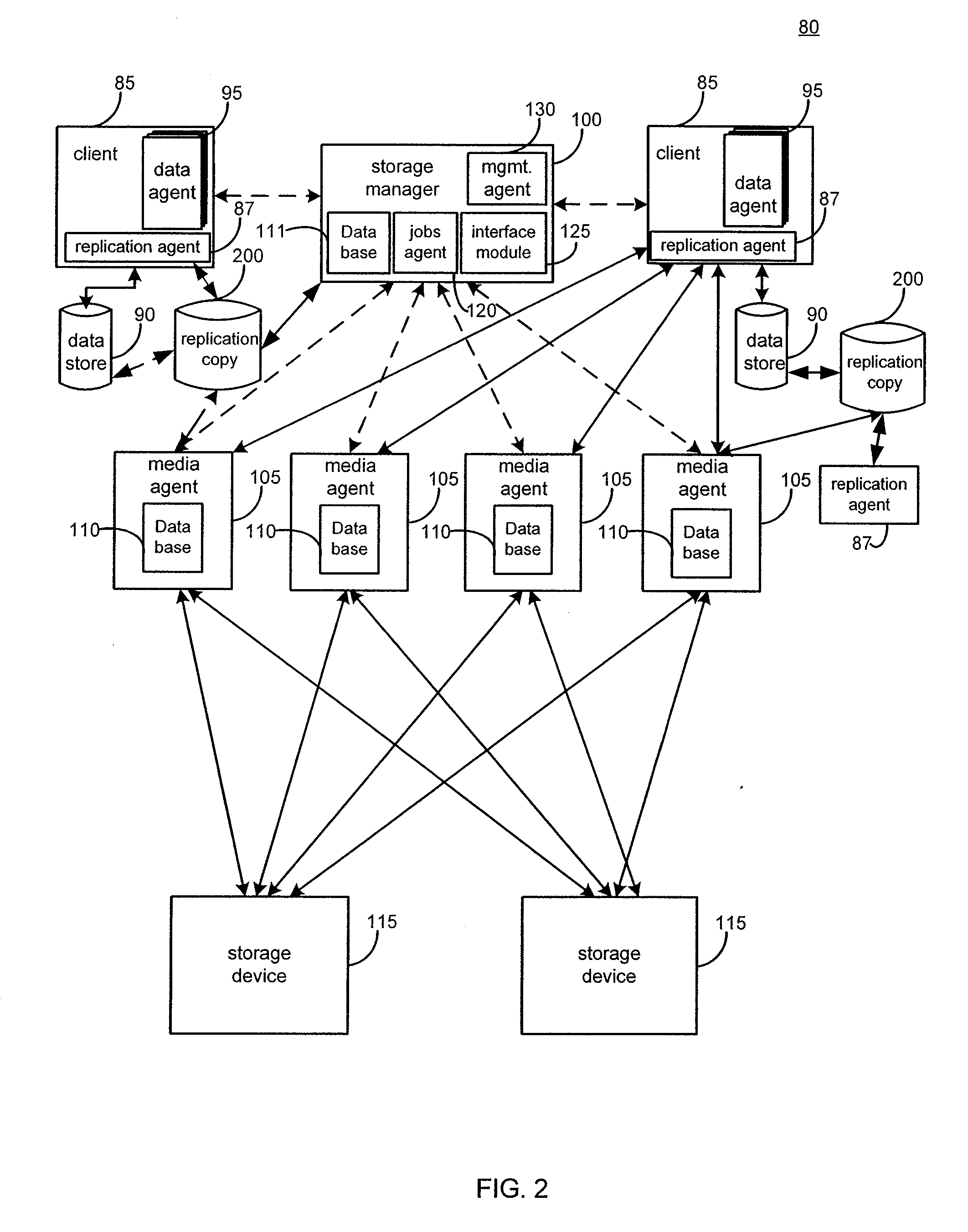
System and method for performing replication copy storage operations
InactiveUS20070143371A1Data processing applicationsDatabase distribution/replicationThird partyStorage management
A system and method are provided for performing storage operations relating to a first secondary copy of electronic data. A storage policy or storage preferences may dictate that a replication copy should be used in storage operations performed to a particular client, sub-client, data, media or other item. Based on the storage policy, when a new client, sub-client, data, media or other item is received, a media agent determines whether there is a replication copy of the item. In the absence of a replication copy, one may be created. The replication copy may be provided by a third party application, or created by the client or a storage management system component. Information regarding the replication copy and its corresponding first secondary copy may be stored in a database. To optimize use of system resources, storage operations relating to the first secondary copy may be performed using the replication copy instead of the first secondary copy.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
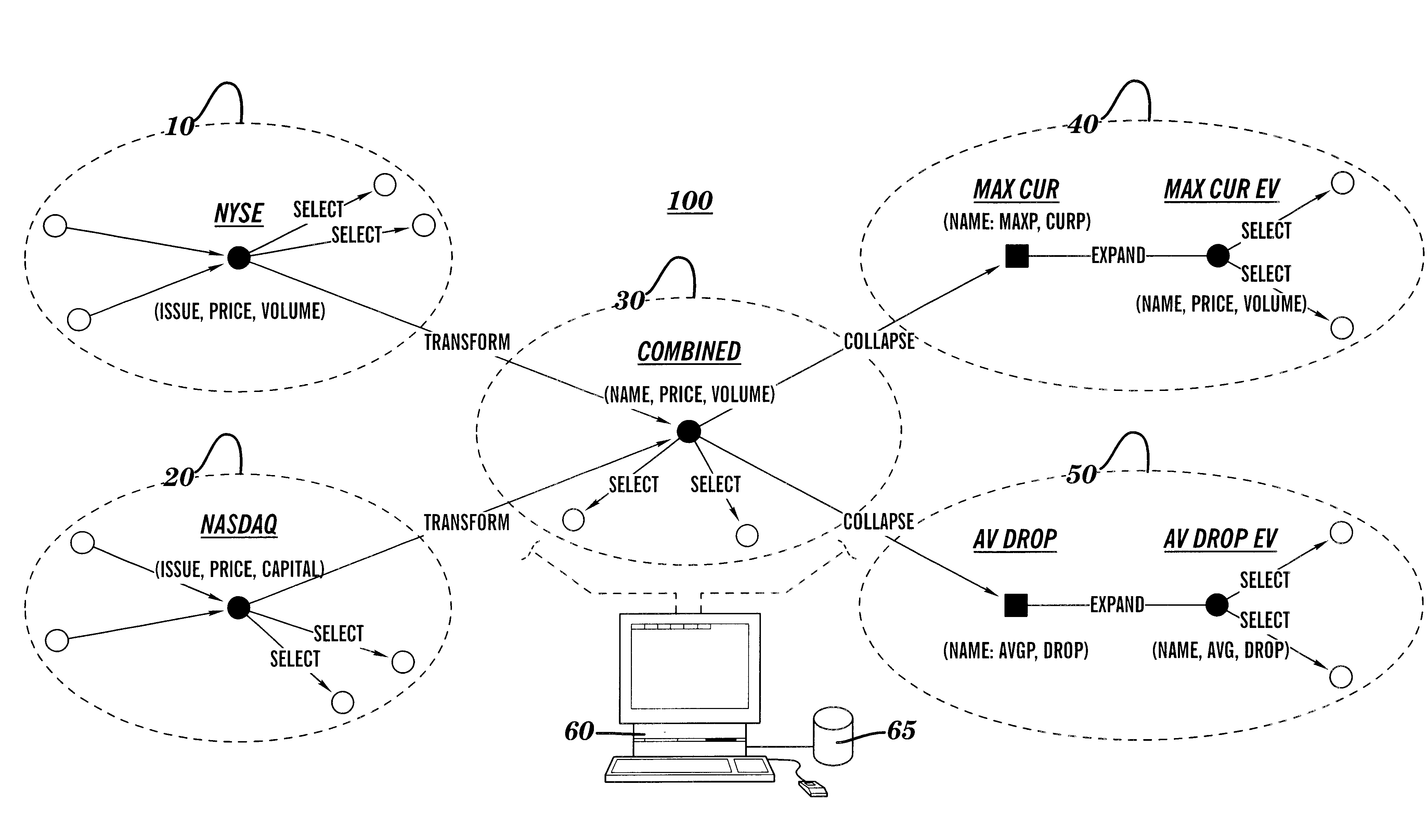
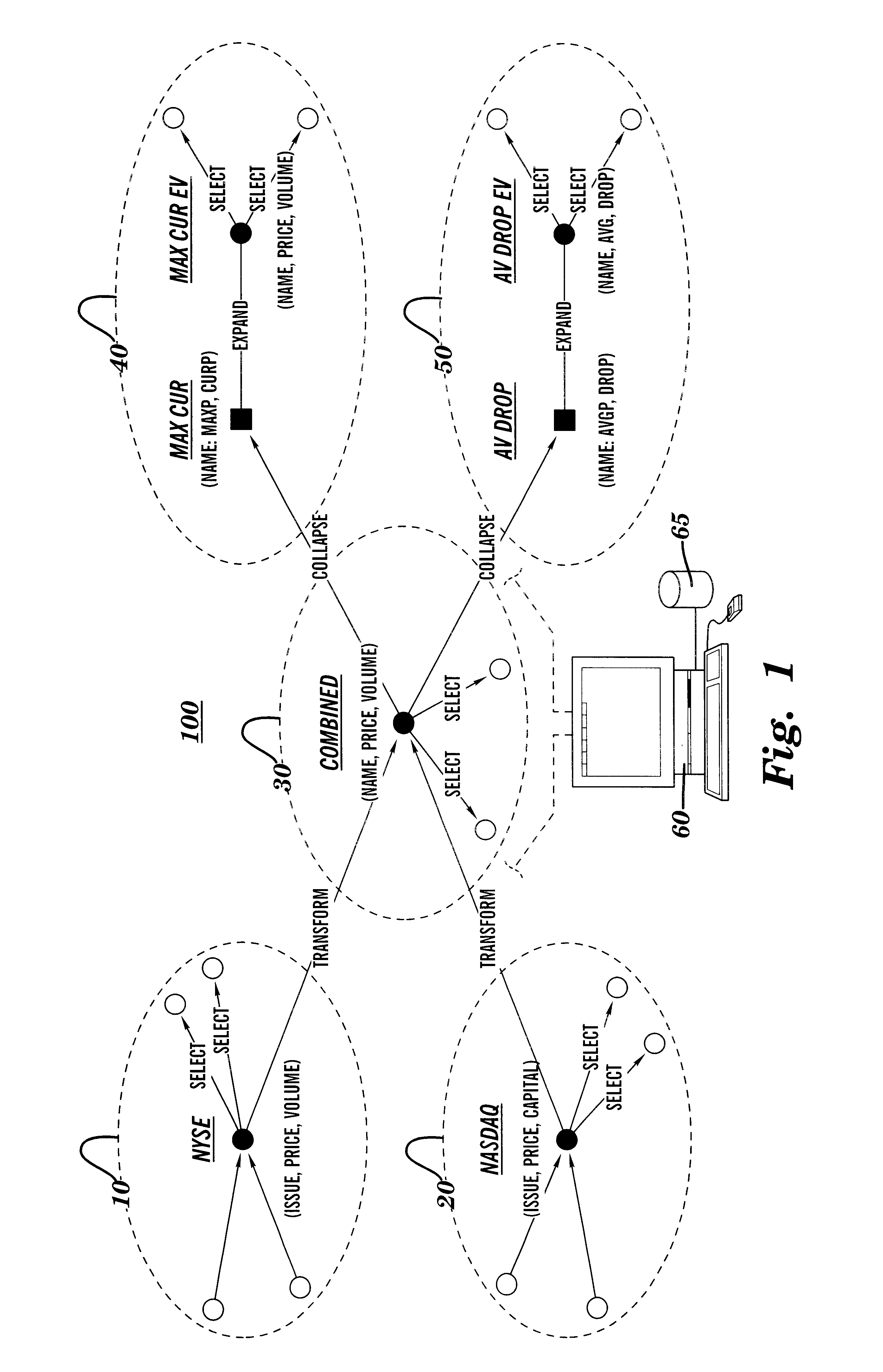
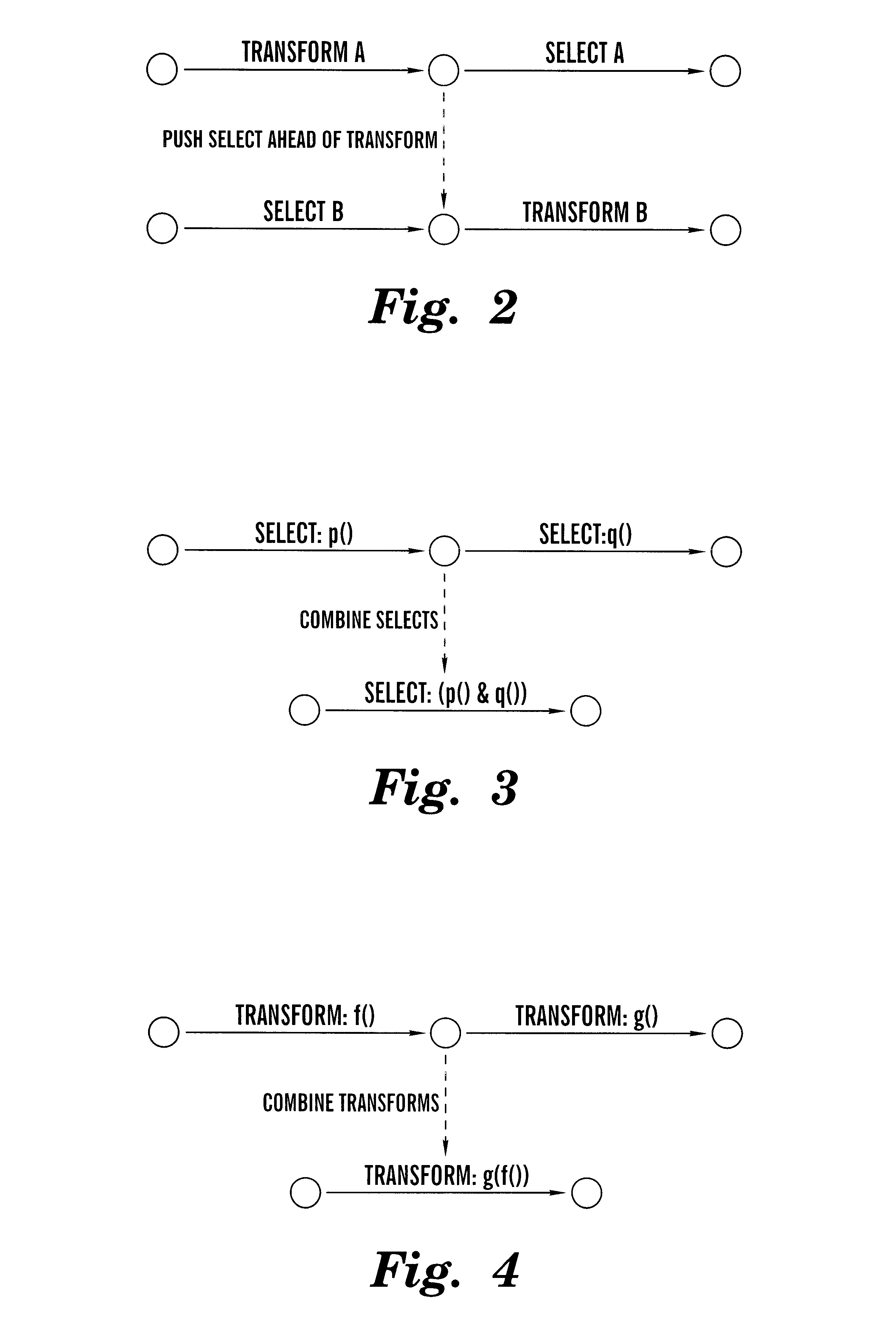
Reduction and optimization of operational expressions applied to information spaces between nodes in a publish/subscribe system
InactiveUS6681220B1Advanced technologyEfficient implementationData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsInformation processingInformation space
Techniques for arranging operations performable on information in an information processing system are provided. In a system having a plurality of information producers and a plurality of information subscribers, paths are identified over which information traverses, and within which the information is subject to select and / or transform operations. The present invention optimizes the system by reorganizing the sequence of select and transform operations so that transforms follow select operations; and by combining multiple select and transform operations into single select and transform operations, respectively. Using these optimizations, the processing resources of the system can be reorganized, and / or information flow graphs describing the system can be designed, so that the select operations are "pushed" toward the producers, and transform operations are "pushed" toward the subscribers. Efficient content-based routing systems can then be used to implement the select operations.
Owner:IBM CORP
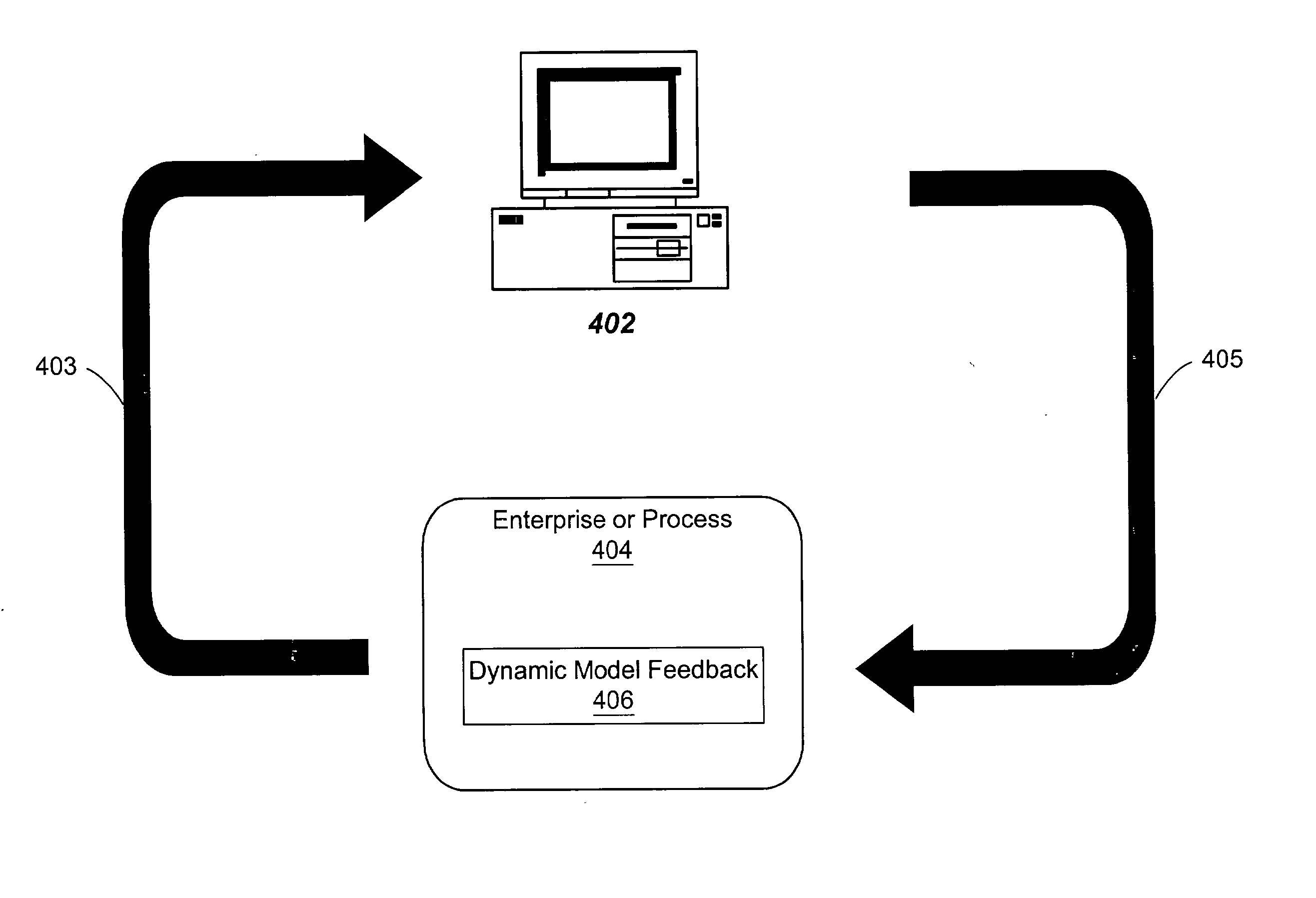
System and method for real-time enterprise optimization
System and method for asynchronous distributed optimization of an enterprise. The system includes multiple computer systems coupled over a network, which store and implement multiple models, including one or more dynamic models representing respective sub-systems or processes of the enterprise. At least two of the models are interdependent. The system also includes an optimizing system that includes multiple optimizers, at least two of which are interdependent, and constraints and / or objectives, and is operable to receive information related to the enterprise from multiple information sources, and use one or more of the plurality of models to generate a solution subject to the one or more constraints and / or objectives, which is usable in managing the enterprise. Some or all of the system operates in an asynchronous manner. Various portions of the system, e.g., the models, data sources, optimizers, constraints and / or objectives, etc., may be updated, e.g., asynchronously, as desired.
Owner:PAVILION TECHNOLOGIES INC
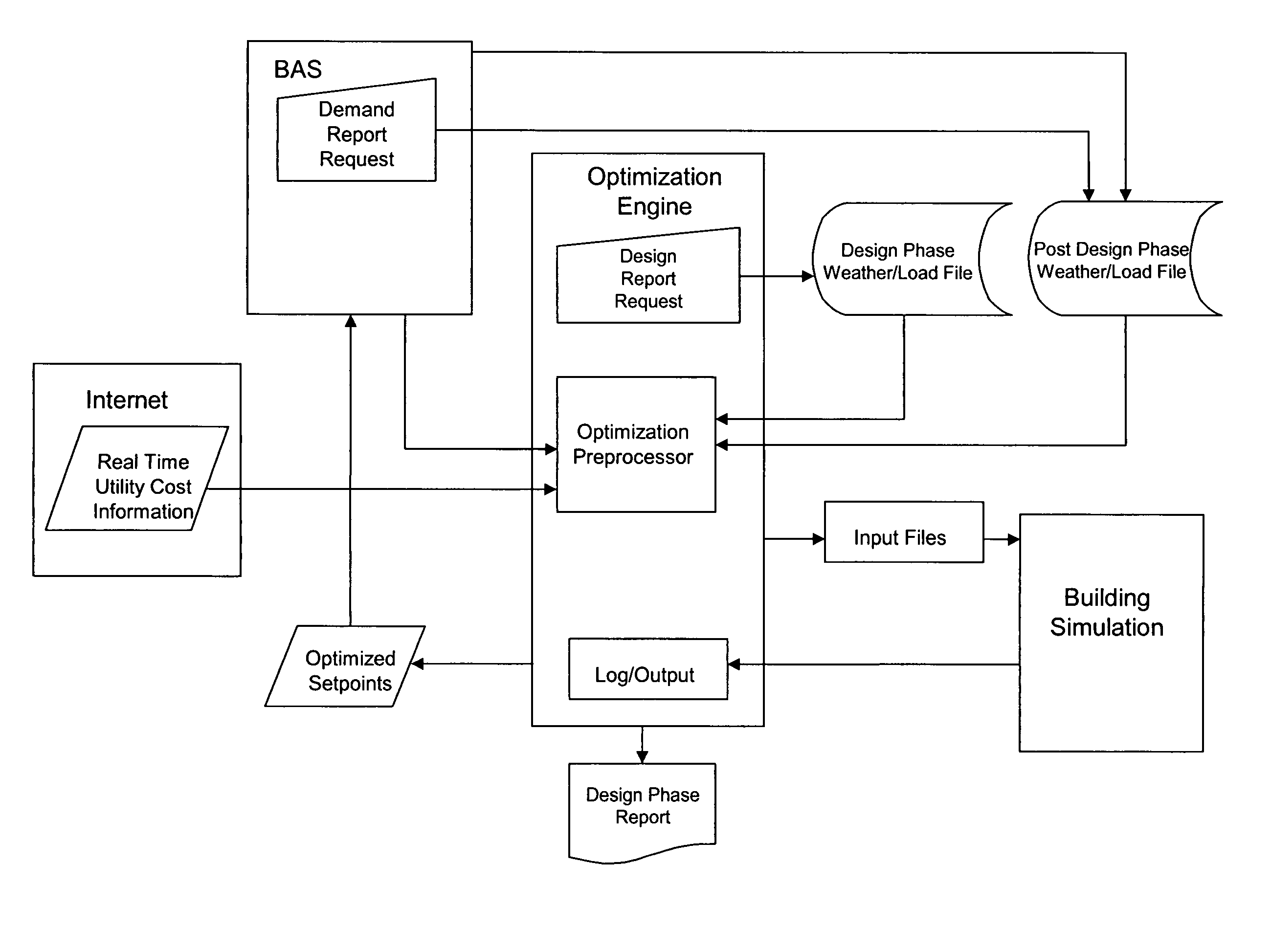
Real-time global optimization of building setpoints and sequence of operation
ActiveUS20070005191A1Operation efficiency can be improvedSimple and straightforward in implementationSampled-variable control systemsComputer controlReal-time dataMathematical model
A building heating / cooling system energy optimization method for a building having a heating / cooling system includes the steps of providing a mathematical model of the heating / cooling system, obtaining real-time weather information, reading the input water temperature (IWT), the output water temperature (OWT) and the supply air temperature (SA) output to the building, periodically transferring the IWT, the OWT and the SA to an optimization system which is operative to analyze the real-time data in coordination with the mathematical model by assigning at least three selected values in a range surrounding and including the current values of each of the IWT, the OWT and the SA and calculating the efficiency profile of the components of the heating / cooling system for each of the selected values, then cooperatively optimizing and selecting those values calculated to provide the highest efficiency profile, then periodically resetting the system values to those selected by the optimization system.
Owner:SLOUP CHARLES J +2
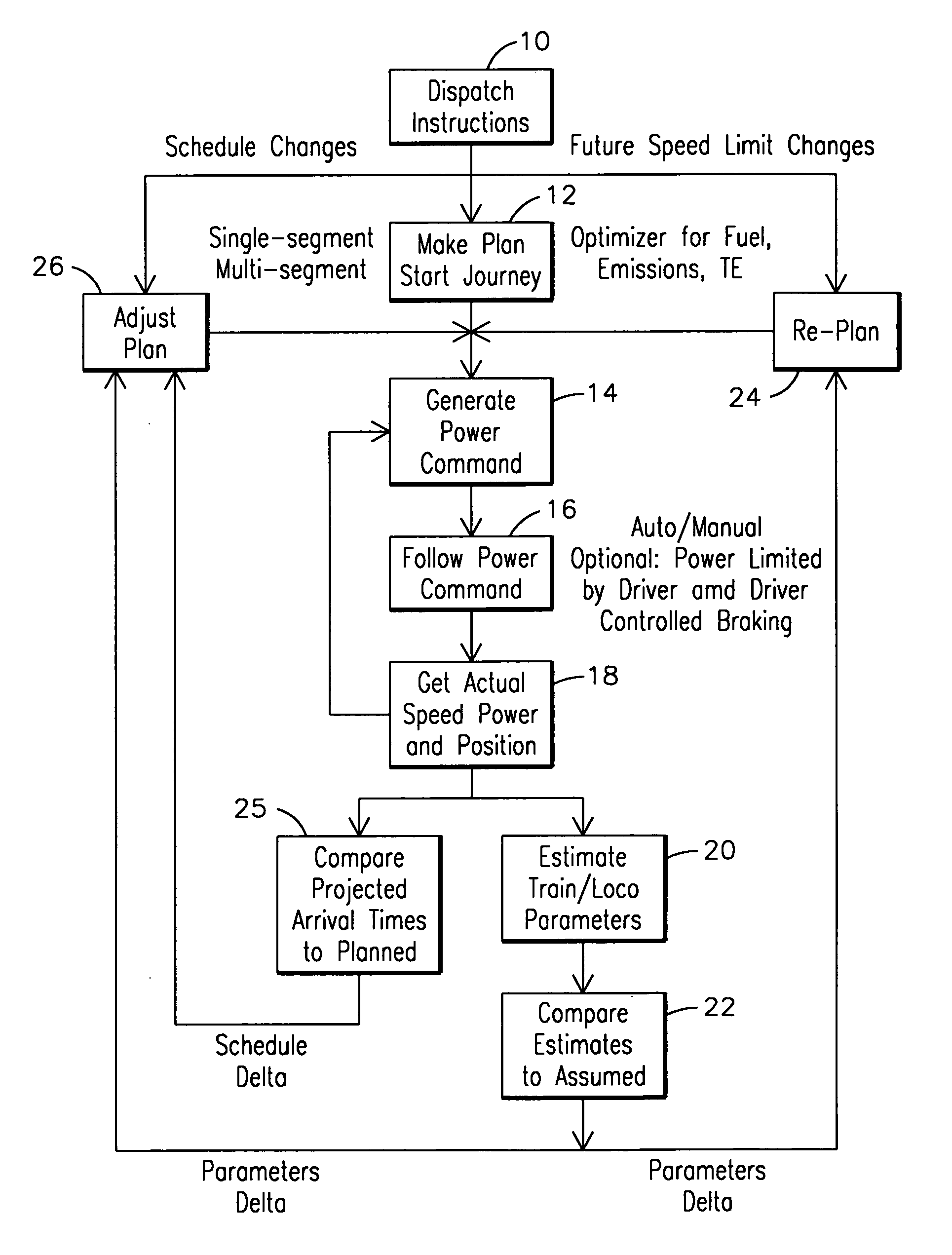
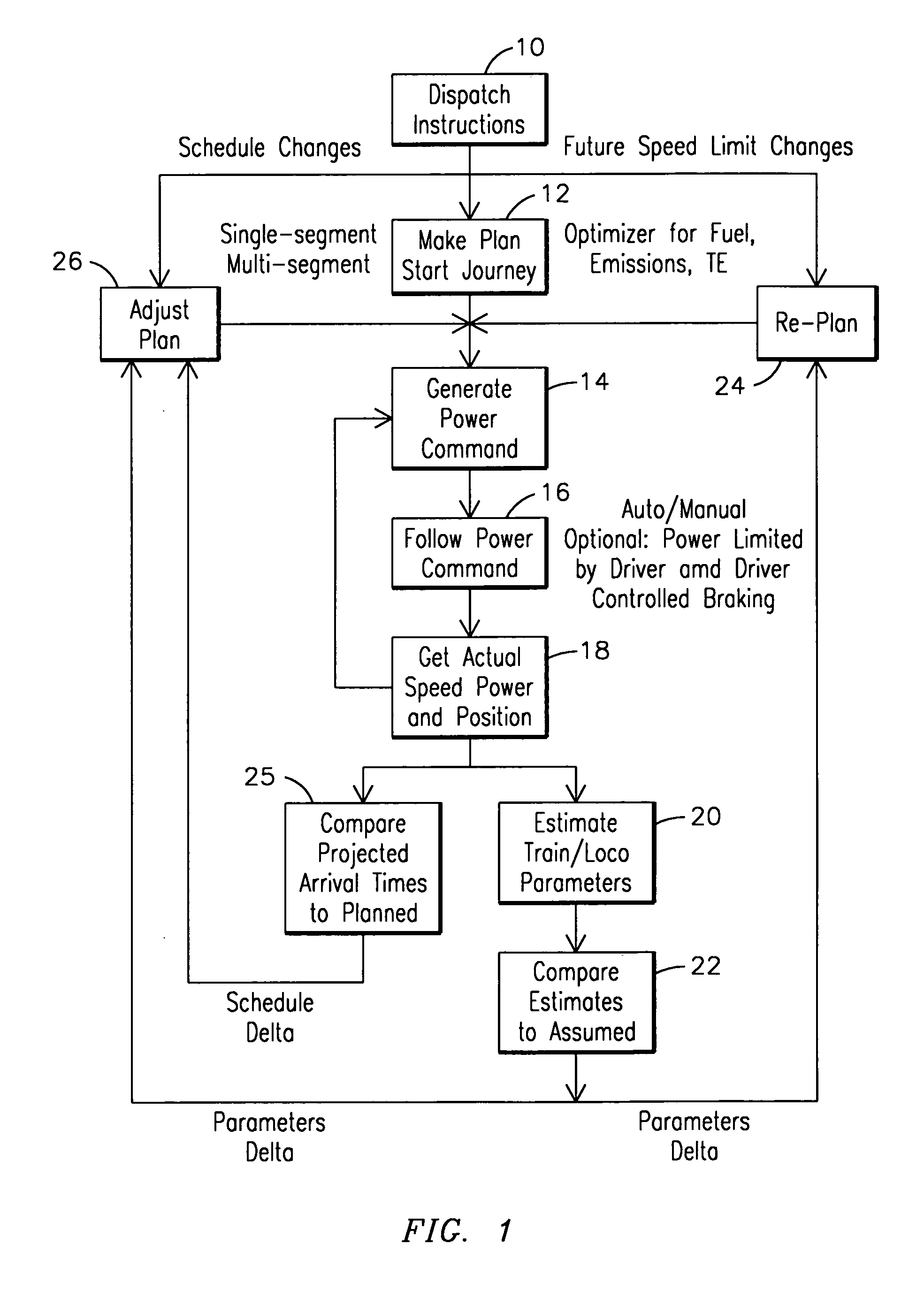
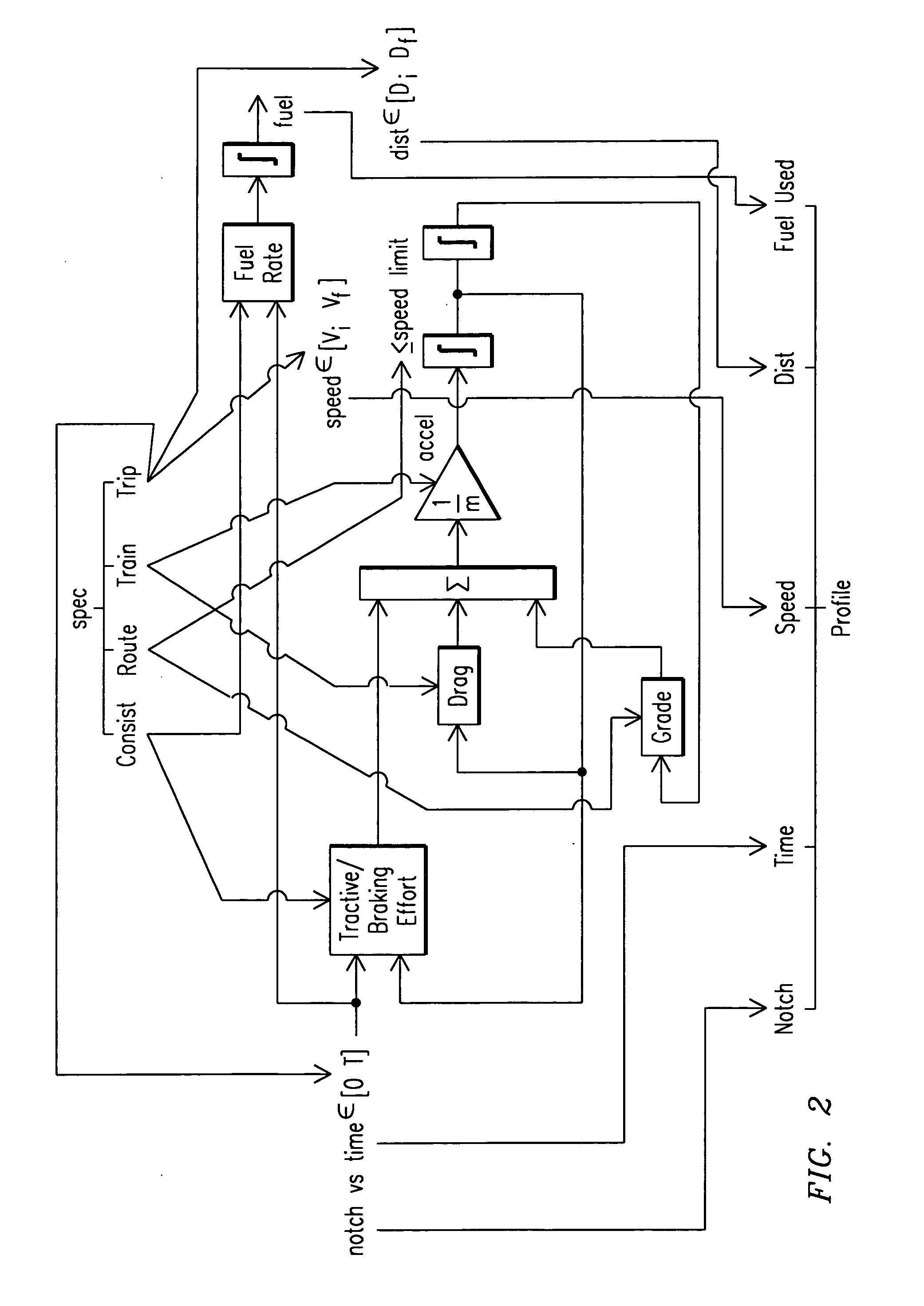
Trip optimization system and method for a train
ActiveUS20070219680A1Minimize consumptionDigital data processing detailsTraffic regulationEngineeringOptimization system
A system for operating a train having one or more locomotive consists with each locomotive consist comprising one or more locomotives, the system including a locator element to determine a location of the train, a track characterization element to provide information about a track, a sensor for measuring an operating condition of the locomotive consist, a processor operable to receive information from the locator element, the track characterizing element, and the sensor, and an algorithm embodied within the processor having access to the information to create a trip plan that optimizes performance of the locomotive consist in accordance with one or more operational criteria for the train.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
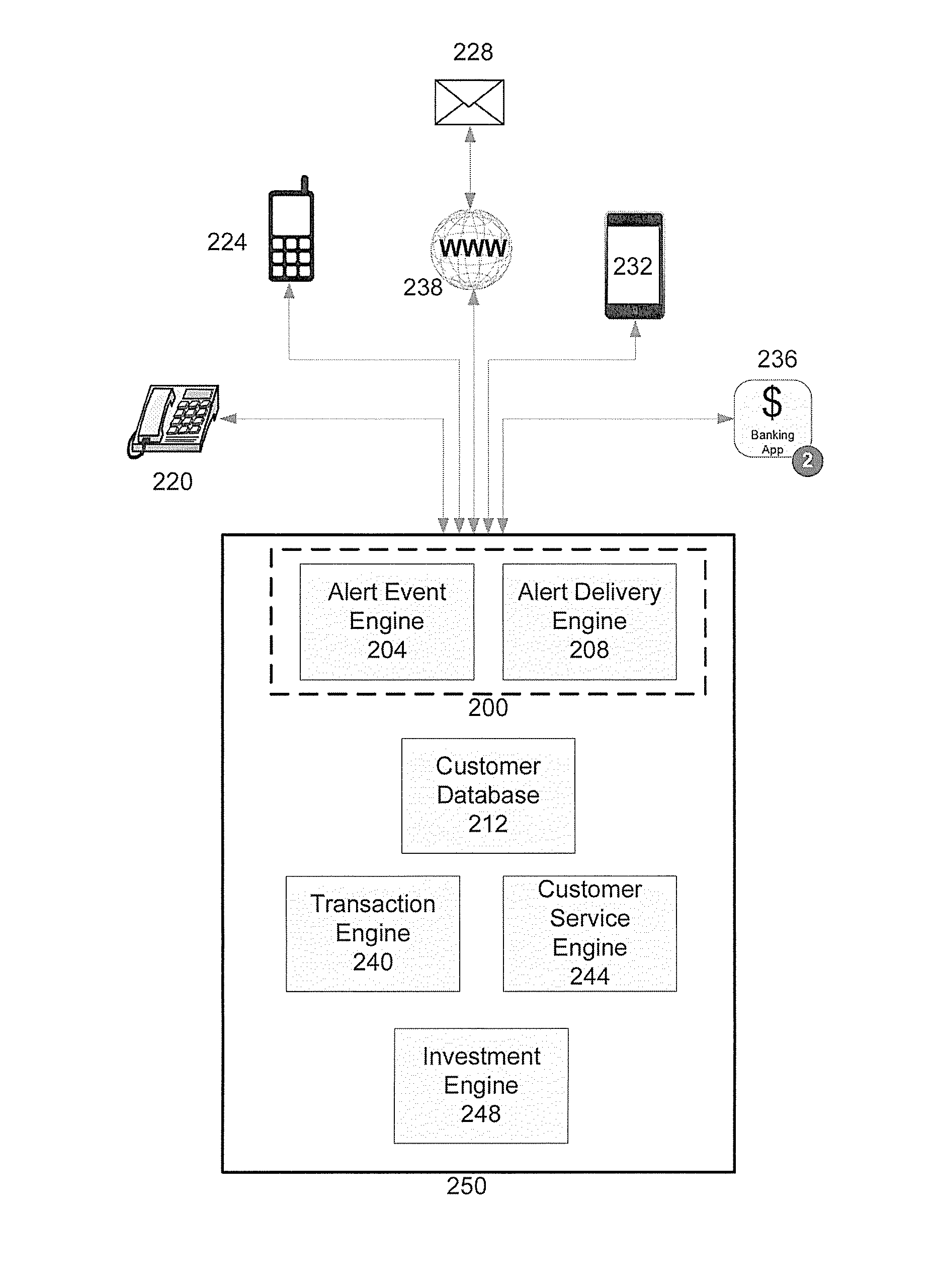
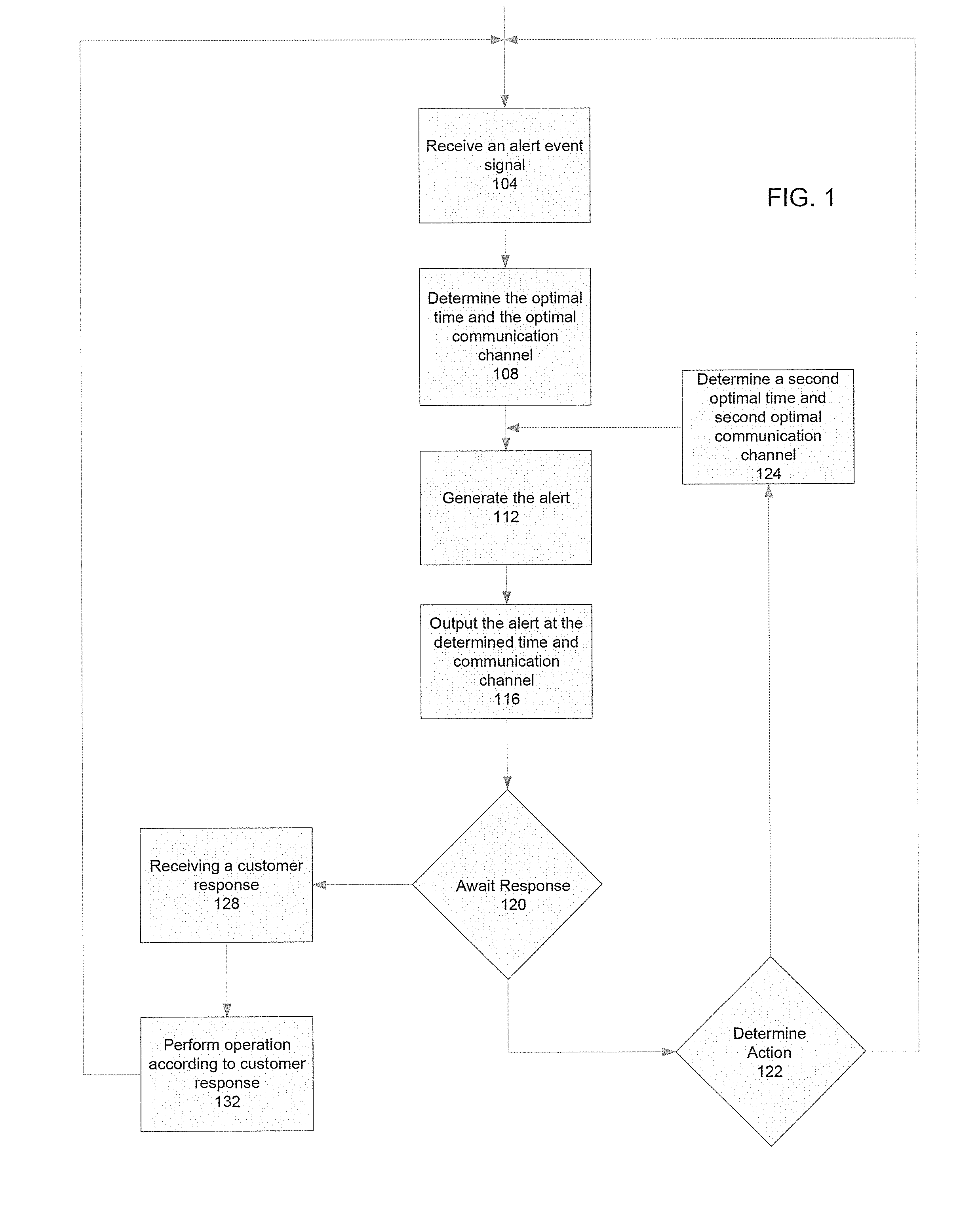
Alert Optimization System and Method
ActiveUS20130293363A1Optimize timingSignalling system detailsTransmissionDirect responseOptimization system
Systems and methods are disclosed for providing alerts to one or more customers at an optimized time and communication channel based on at least customer preferences, transactions, activities, usage patterns, and other information; and for allowing customers to directly respond and communicate feedback to alerts that are provided to complete various account actions, including to “snooze” one or more alerts.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
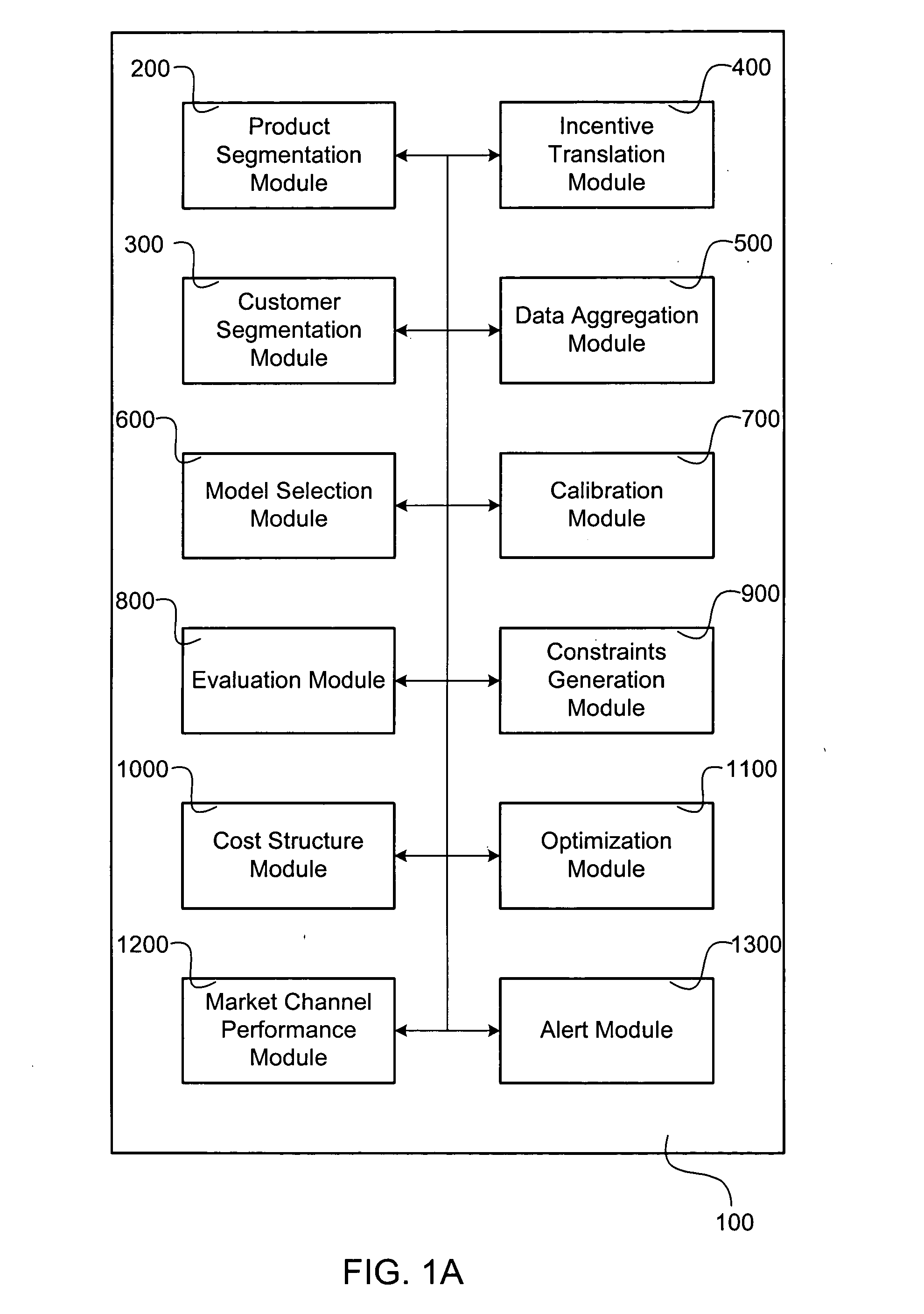
Configurable pricing optimization system
InactiveUS20050256778A1OptimizationEasy to deployMarket predictionsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsGraphicsGraphical user interface
The present invention provides a configurable pricing system that allows users to define or modify data used to analyze, evaluate, improve, and design pricing changes according to the user's need. A Graphical user interface or some other type of user interface allows the user to access and review various data to be used during pricing optimization. The user may then modify this data as needed to improve the pricing evaluation, such as defining sales or pricing trends, or relationships between the product of interest and other competing items. The user interface may further display changes in pricing and the effects of the pricing changes, as caused by the user's changes. The interface may also allow the user to modify the mathematical model to be used during price optimization, as well as define variables, constraints, and boundaries to be considered during the price optimization.
Owner:BLUE YONDER GRP INC
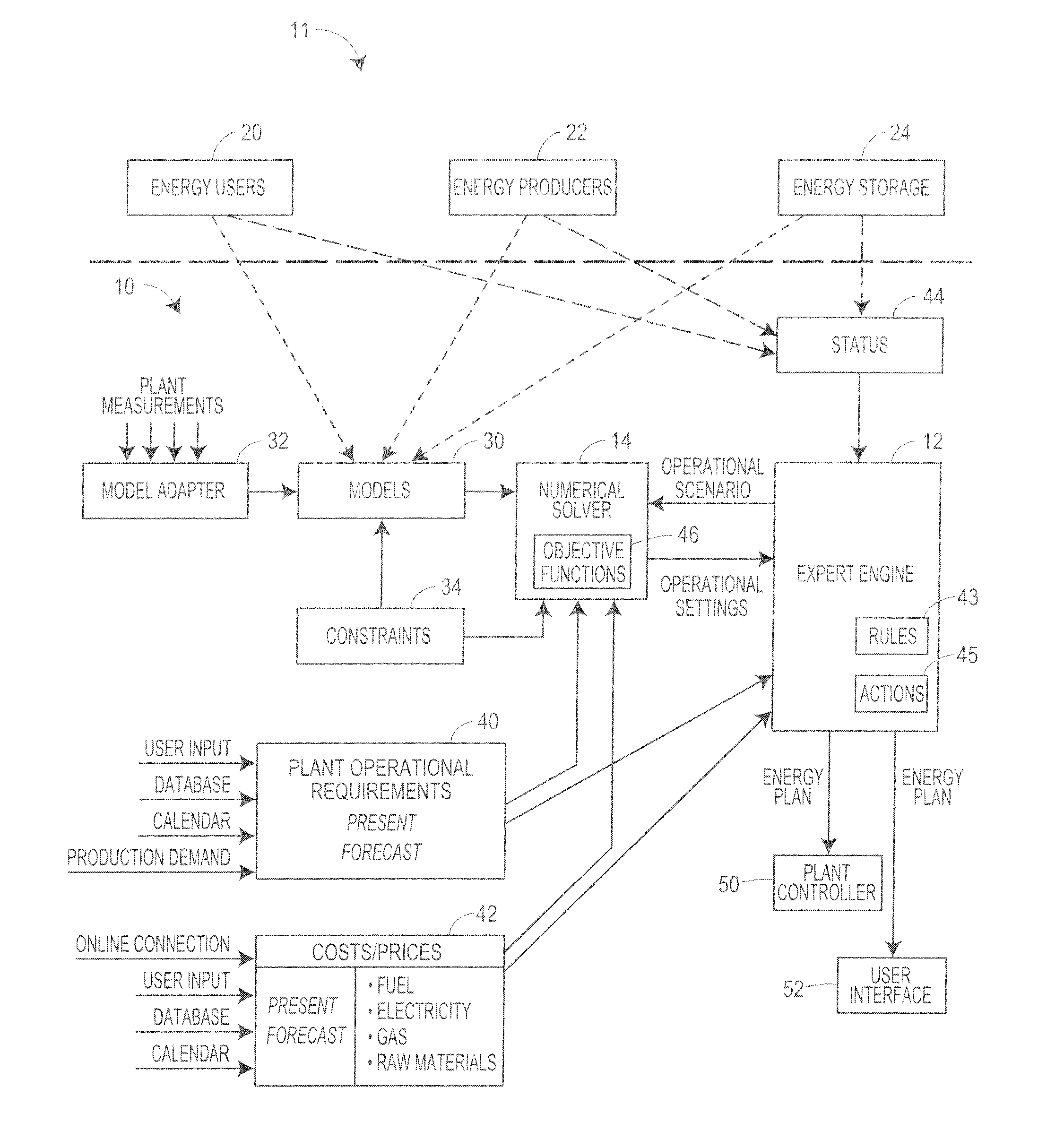
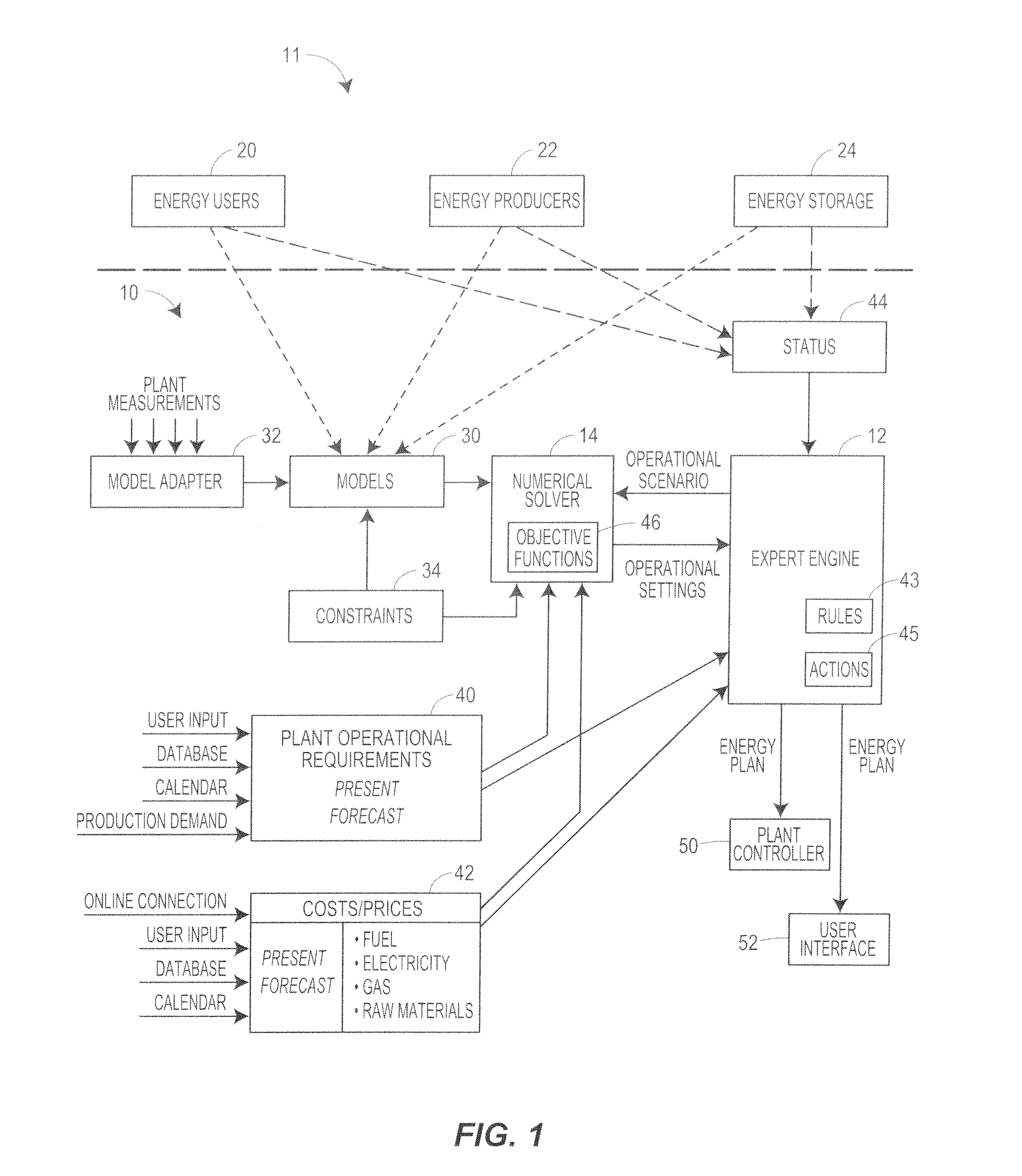
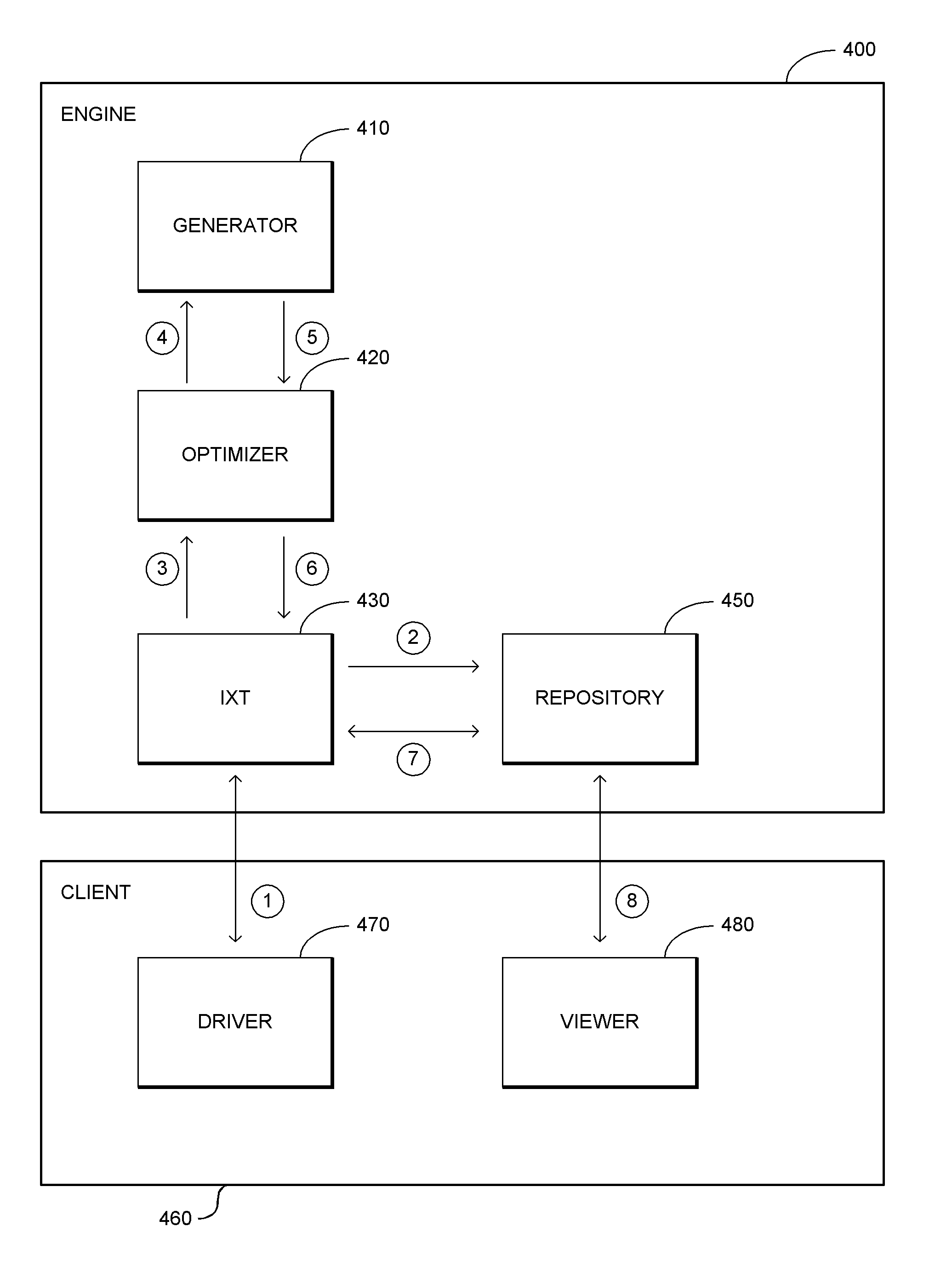
Optimization system using an iteratively coupled expert engine
ActiveUS20120010758A1Minimizes and maximizes objective functionEasy to operateProgramme controlMechanical power/torque controlOperational systemProcess engineering
An energy management system uses an expert engine and a numerical solver to determine an optimal manner of using and controlling the various energy consumption, producing and storage equipment in a plant / communities in order to for example reduce energy costs within the plant, and is especially applicable to plants that require or that are capable of using and / or producing different types of energy at different times. The energy management system operates the various energy manufacturing and energy usage components of the plant to minimize the cost of energy over time, or at various different times, while still meeting certain constraints or requirements within the operational system, such as producing a certain amount of heat or cooling, a certain power level, a certain level of production, etc. In some cases, the energy management system may cause the operational equipment of the plant to produce unneeded energy that can be stored until a later time and then used, or that can be sold back to a public utility, for example, so as to reduce the overall cost of energy within the plant.
Owner:EMERSON PROCESS MANAGEMENT POWER & WATER SOLUTIONS
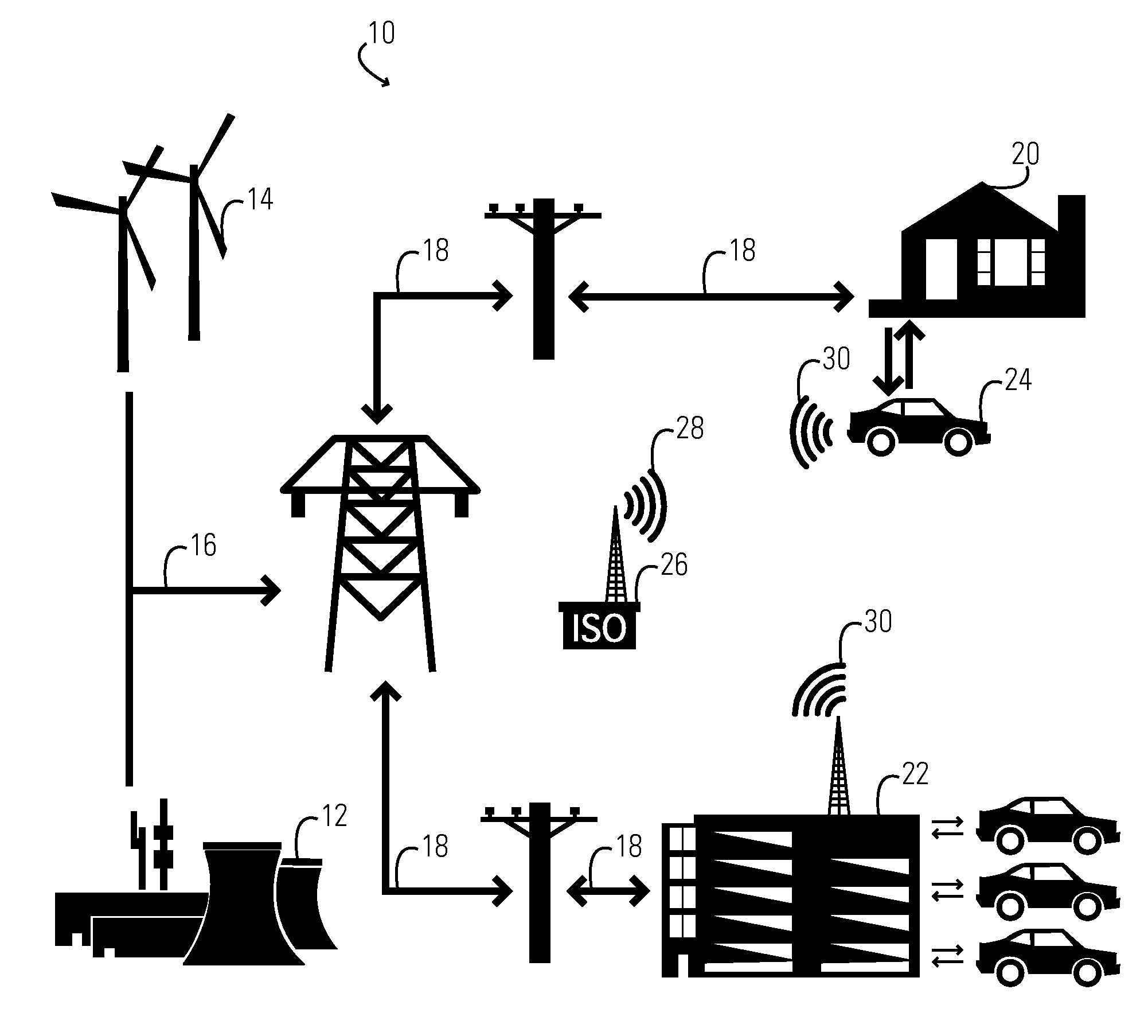
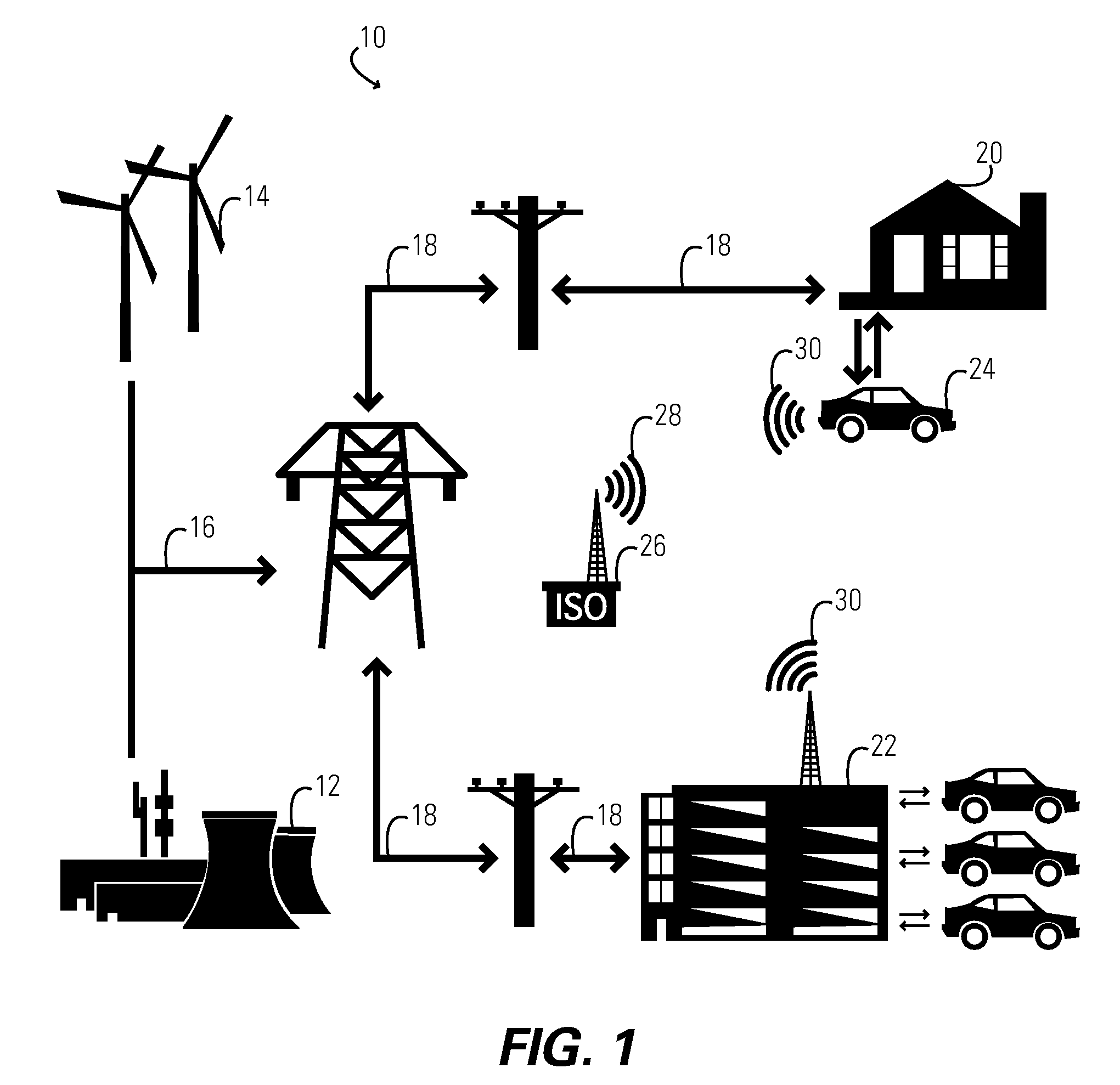
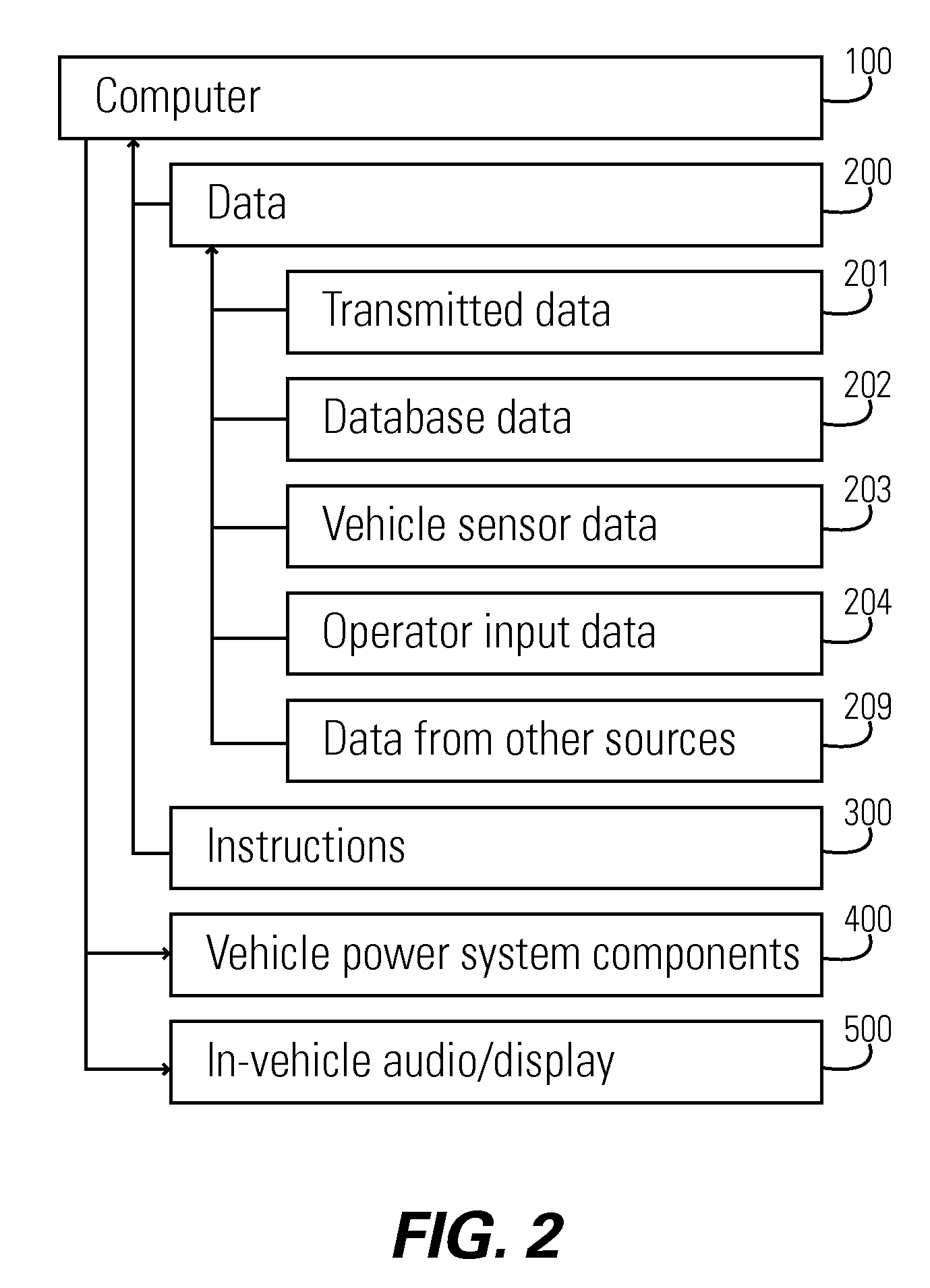
Plugin hybrid electric vehicle with v2g optimization system
In one aspect of the present invention, a vehicle comprises: a consumable fuel powered engine, a battery and an electric motor powered by the battery. The battery is rechargeable both from an external electric power source (such as an electric power grid) and from the consumable fuel powered engine. A computer receives data as inputs and providing outputs, wherein the input data includes an expected state of the electric power source at a time when the vehicle is expected to be coupled to the electric power source. The outputs include control signals to control the state of charge of the battery during the time the vehicle is expected to be coupled to the electric power source.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
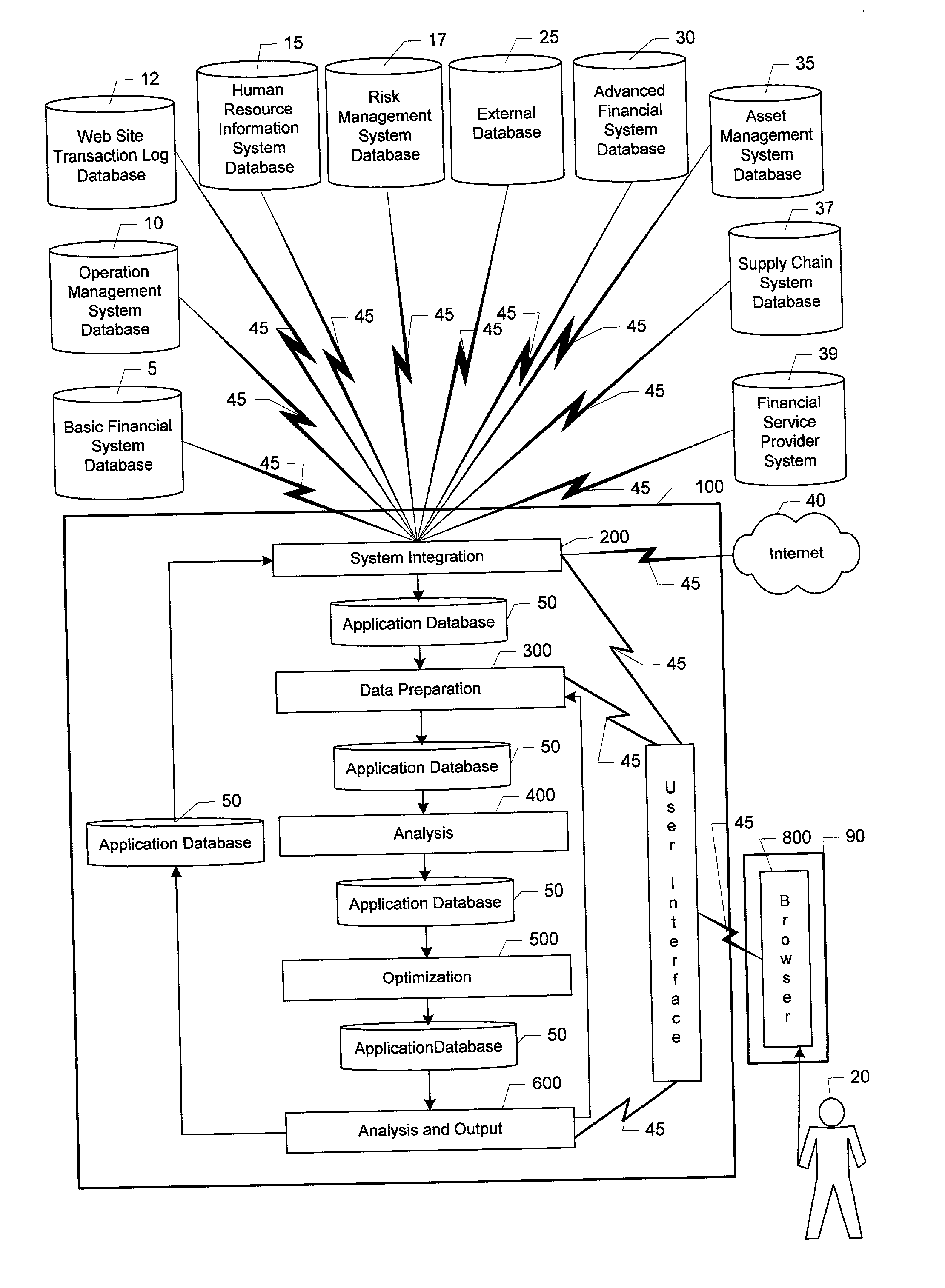
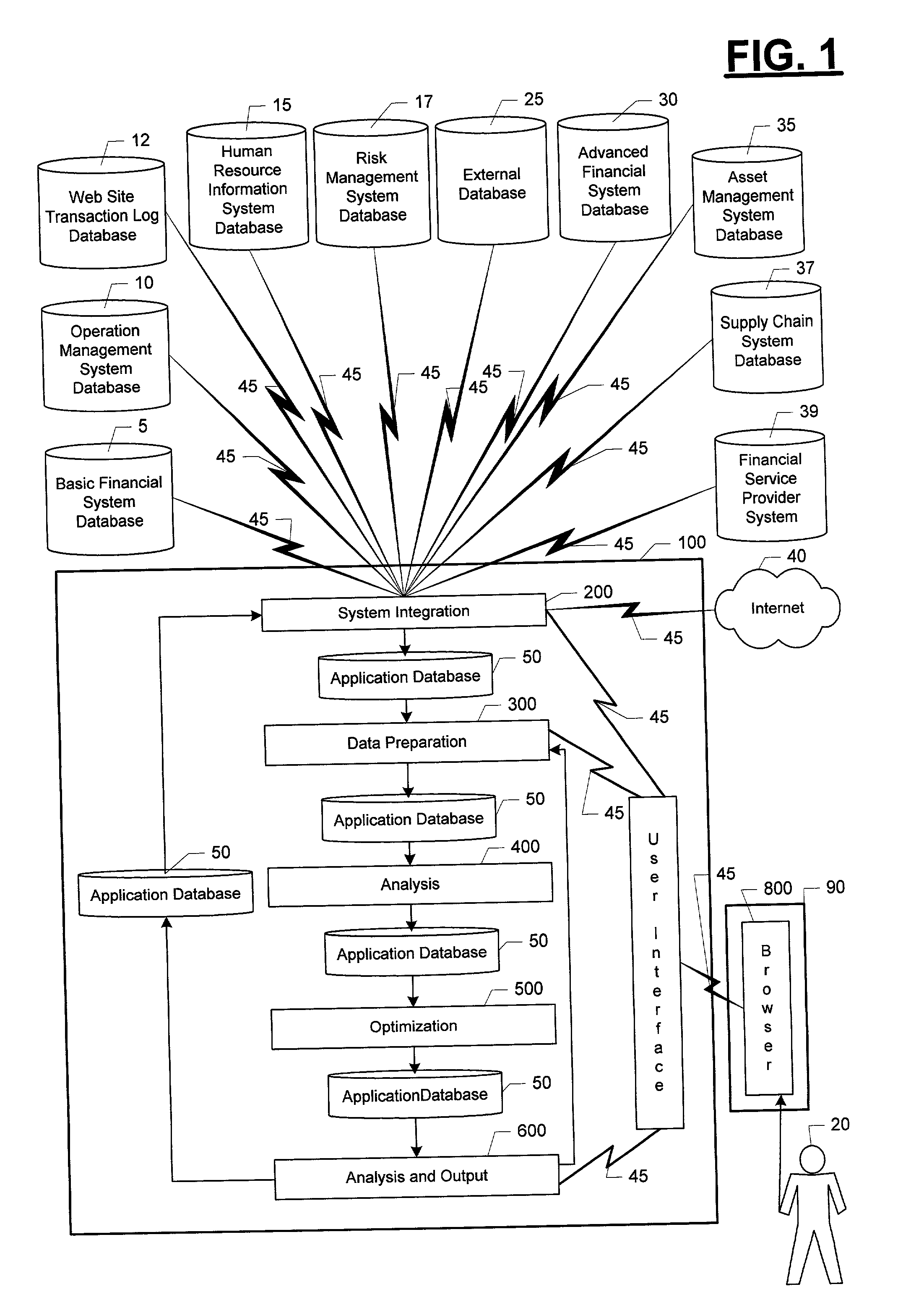
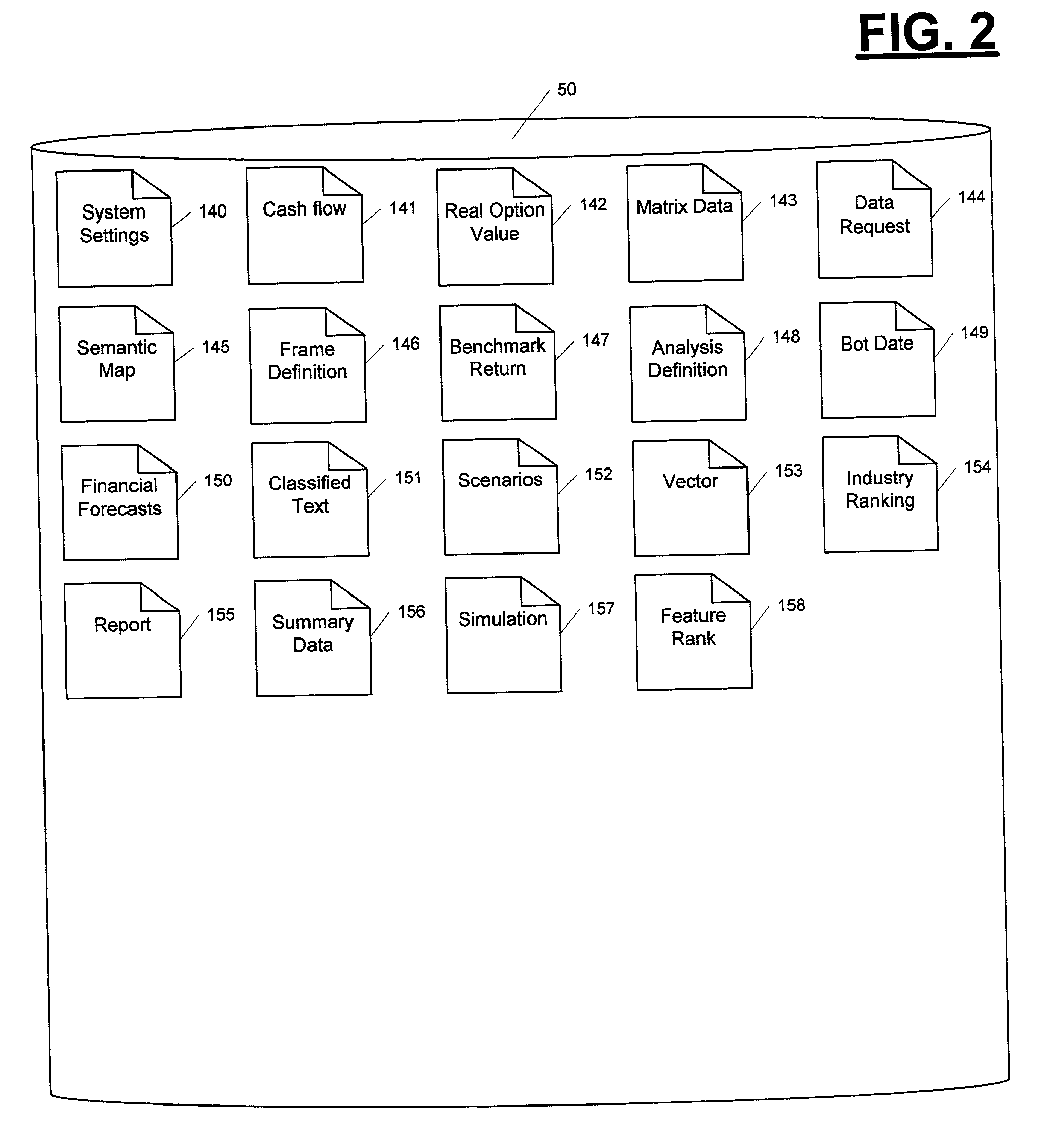
System for integrating enterprise performance management
An automated system (100) for integrating narrowly focused management systems in to a financial measurement and optimization system for a multi-enterprise commercial organization. A matrix of market value is developed for each enterprise in the organization. The matrices of market value are then used to guide the integration of narrow systems in to the organization's financial system. Value and risk are analyzed by element of value on the system date as required to complete and display the matrix of market value for the organization by enterprise. A series of scenarios under both normal and extreme conditions are then developed. The information from these scenarios is then combined with market value matrix information to determine the optimal mode for financial management. The information on the optimal mode of organization operation is then communicated to the integrated narrow systems for implementation. The efficient frontier for organization financial performance is also calculated, displayed and optionally printed.
Owner:ASSET RELIANCE INC
Database System with Methodology for Automated Determination and Selection of Optimal Indexes
ActiveUS20050203940A1Superior cost benefitImprove performanceData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsDatabase queryCost effectiveness
A database system with methodology for automated determination and selection of optimal indexes is described. In one embodiment, for example, in a database system, a method of the present invention is described for recommending database indexes to be created for optimizing system performance, the method comprises steps of: capturing a workload representative of database queries employed during system use; creating virtual indexes for optimizing system performance during execution of the database queries captured in the workload; computing cost benefits for different combinations of the virtual indexes; and recommending physical indexes to be created based on virtual indexes that have favorable cost benefits for the captured workload.
Owner:IANYWHERE SOLUTIONS
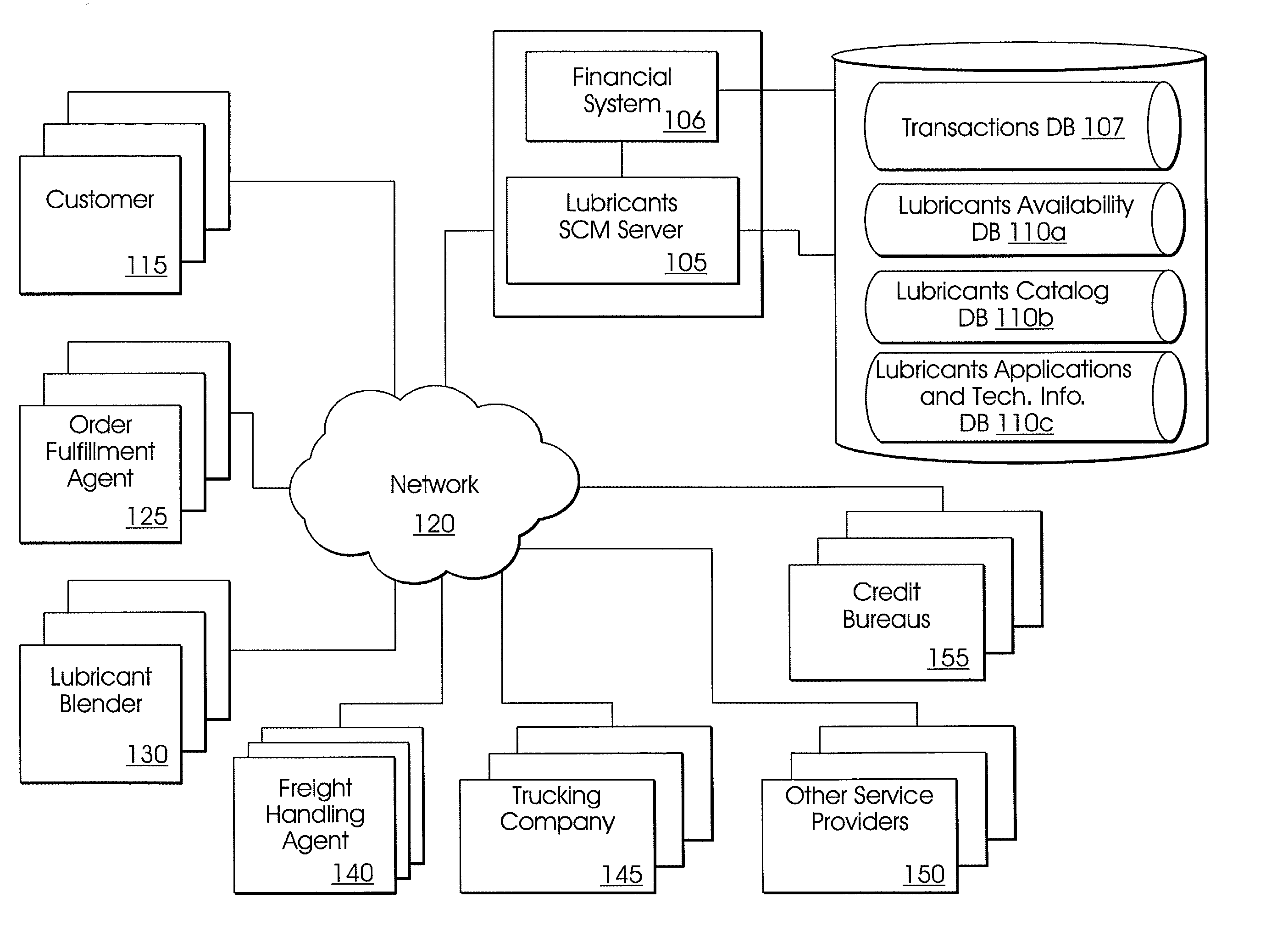
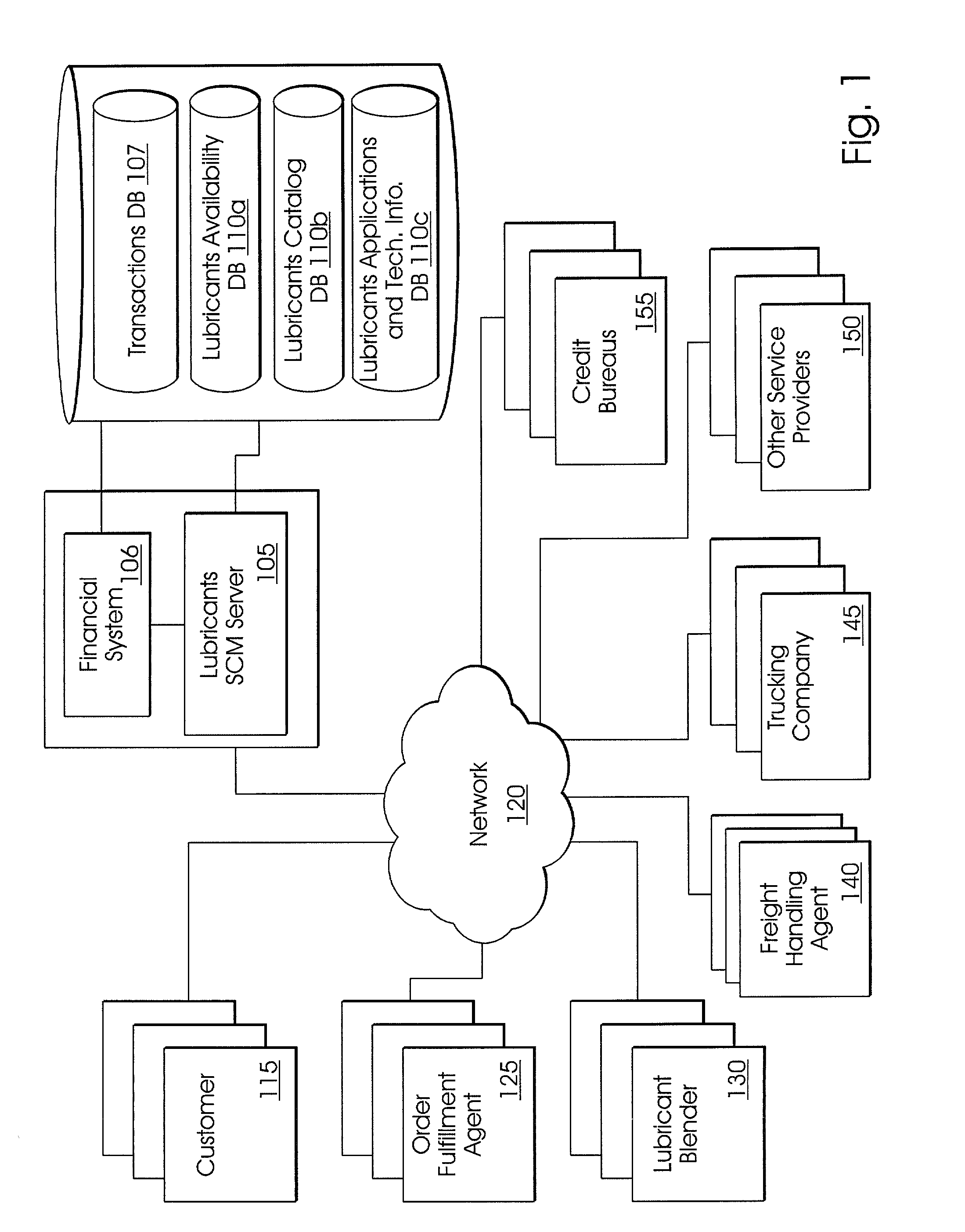
System and method for lubricants supply chain management
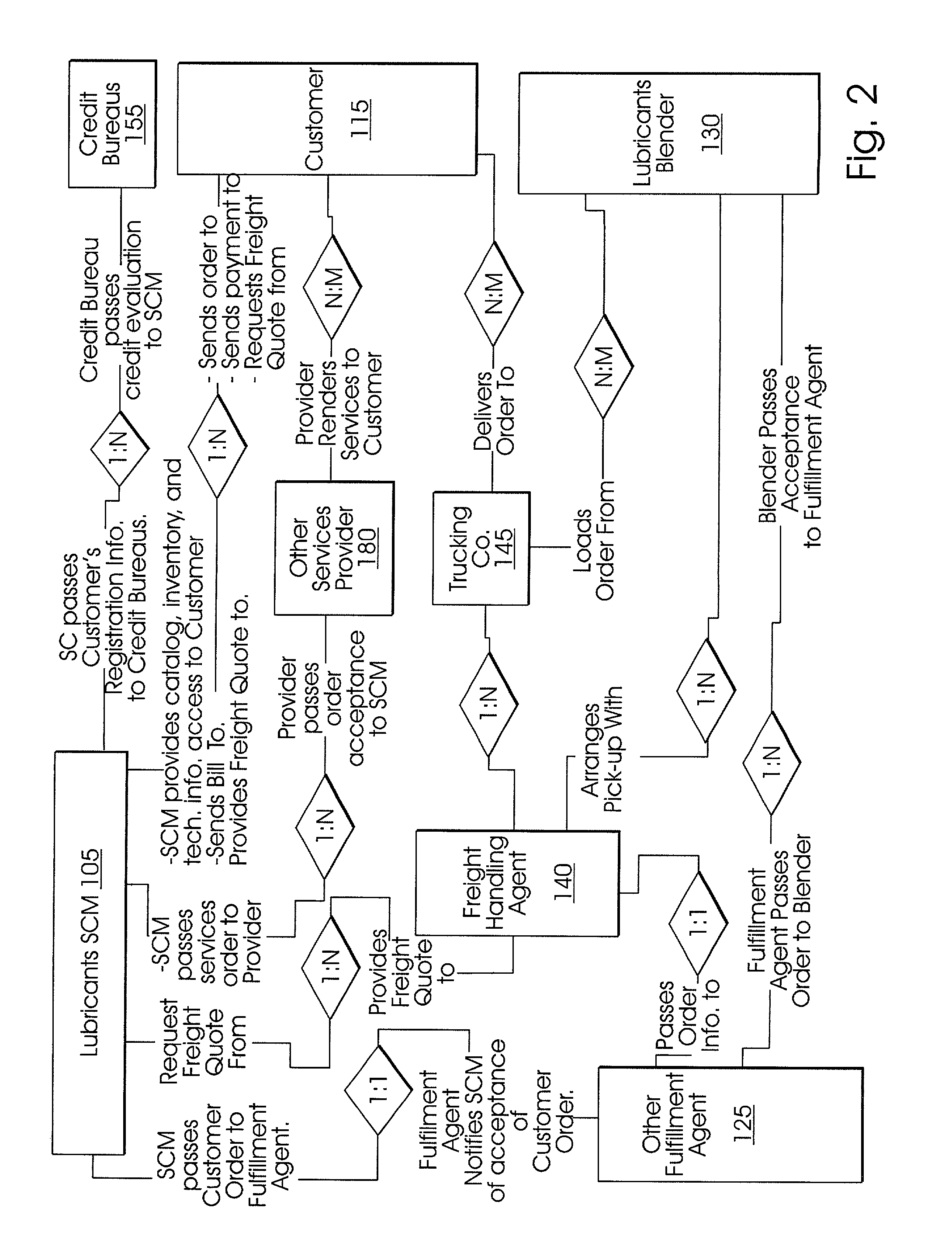
The invention includes a method of lubricants supply chain management including: storing in a web-accessible database a catalog of lubricants and prices-per-unit for same which prices-per-unit optionally decrease based on certain pre-determined cumulative volume purchases; upon receiving at a web server a request from a web-browser client, querying the database and serving the results of the query to the requesting web-browser client for display; serving an order form to the web-browser client which is configured to contain fields for order quantity and type for lubricants, delivery type preferences and delivery address entered in the web-browser client, and determining and displaying on the web-browser client a delivery price quote; receiving an order from the web-browser client for a specific type and quantity of lubricants and having a specific delivery type selected; electronically transmitting over a network the order to an order fulfillment agent; where the order fulfillment agent electronically transmits over a network the order to at least one lubricant blender; electronically transmitting over a network the order and the delivery information to a freight-handling agent; where the freight-handling agent inputs the information into a delivery optimization system which outputs a delivery schedule which includes the order, and electronically transmits over a network the order and the delivery information to at least one trucking company; and maintaining the status and all actions and communications for the order in a second web-accessible database.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
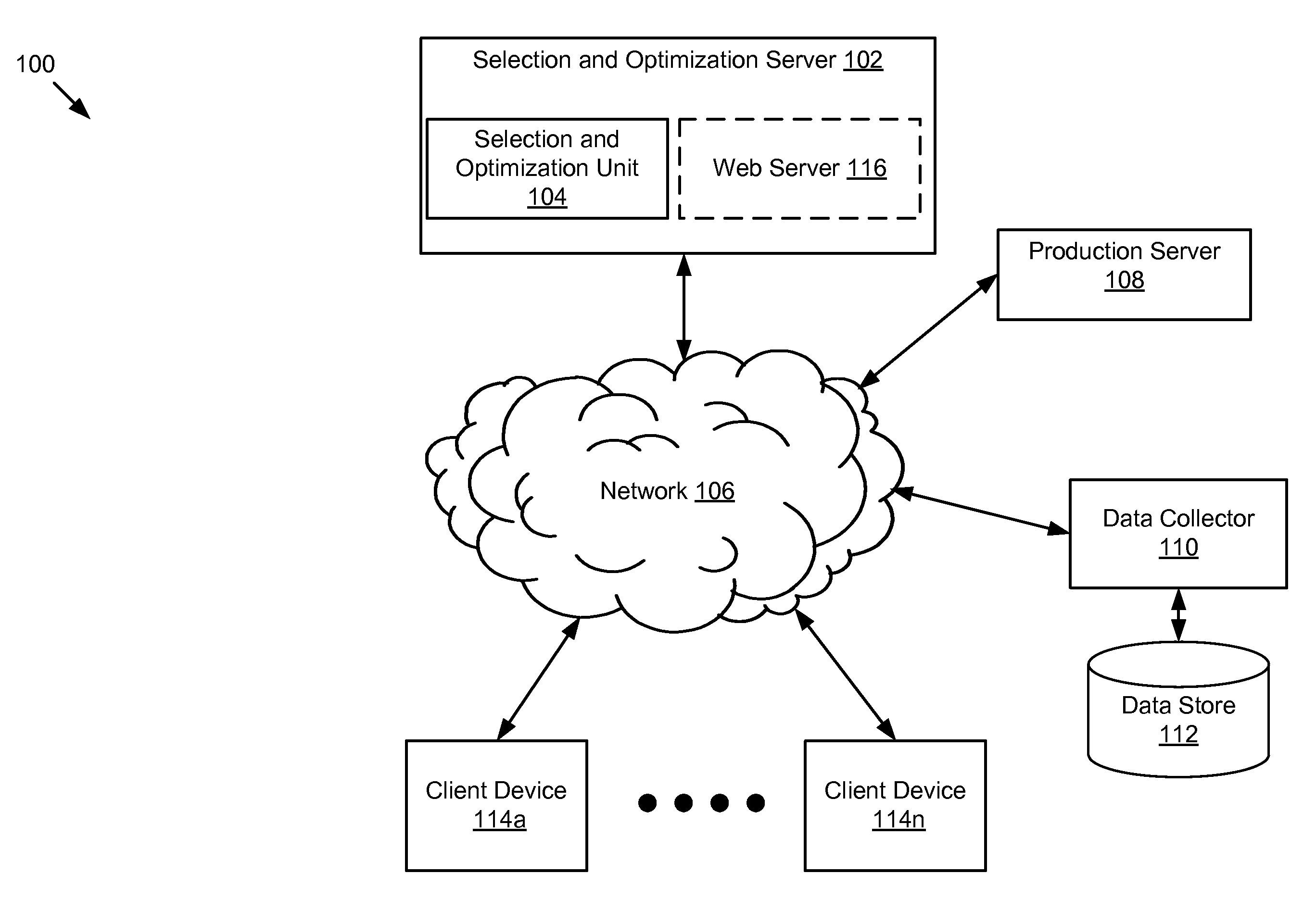
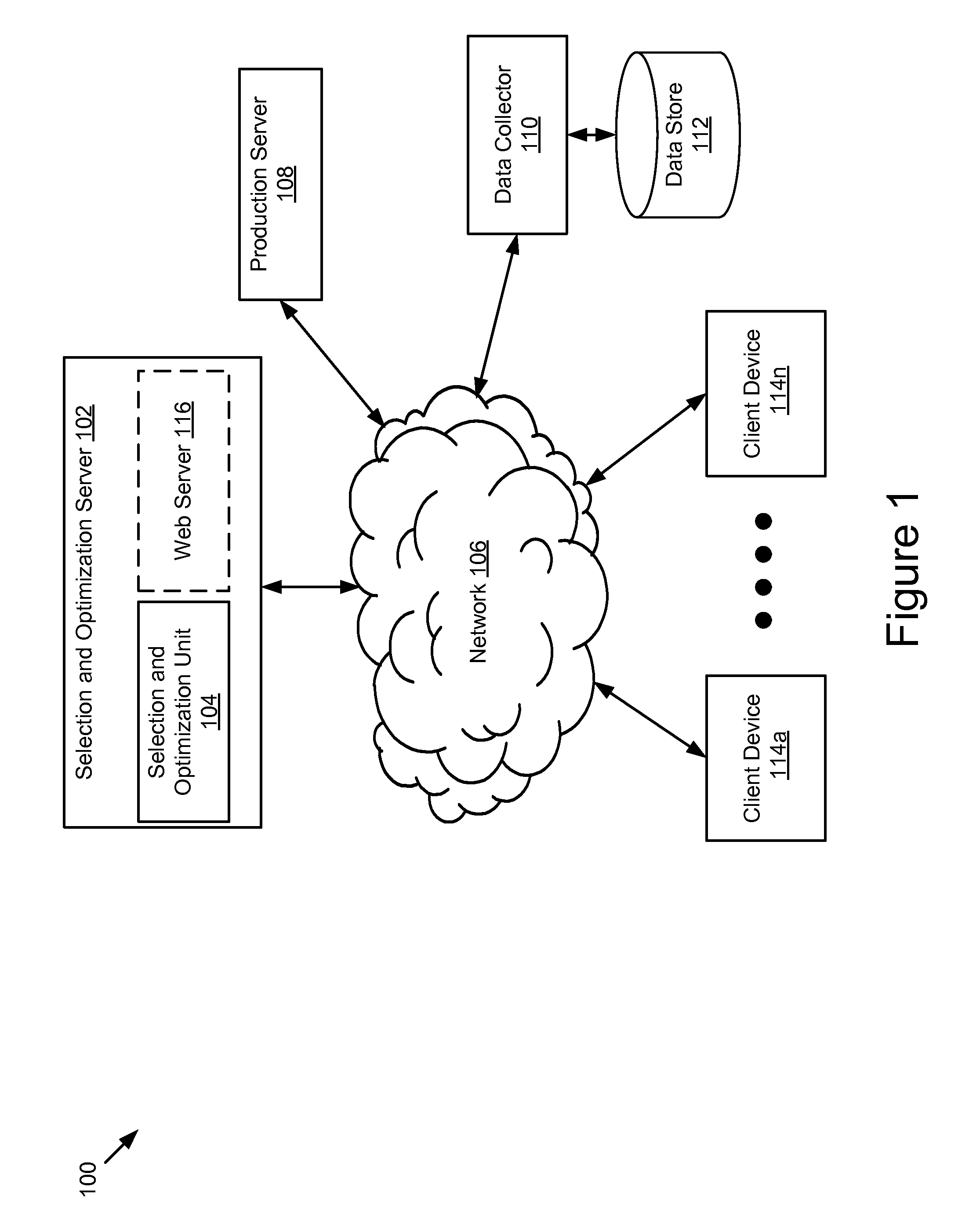
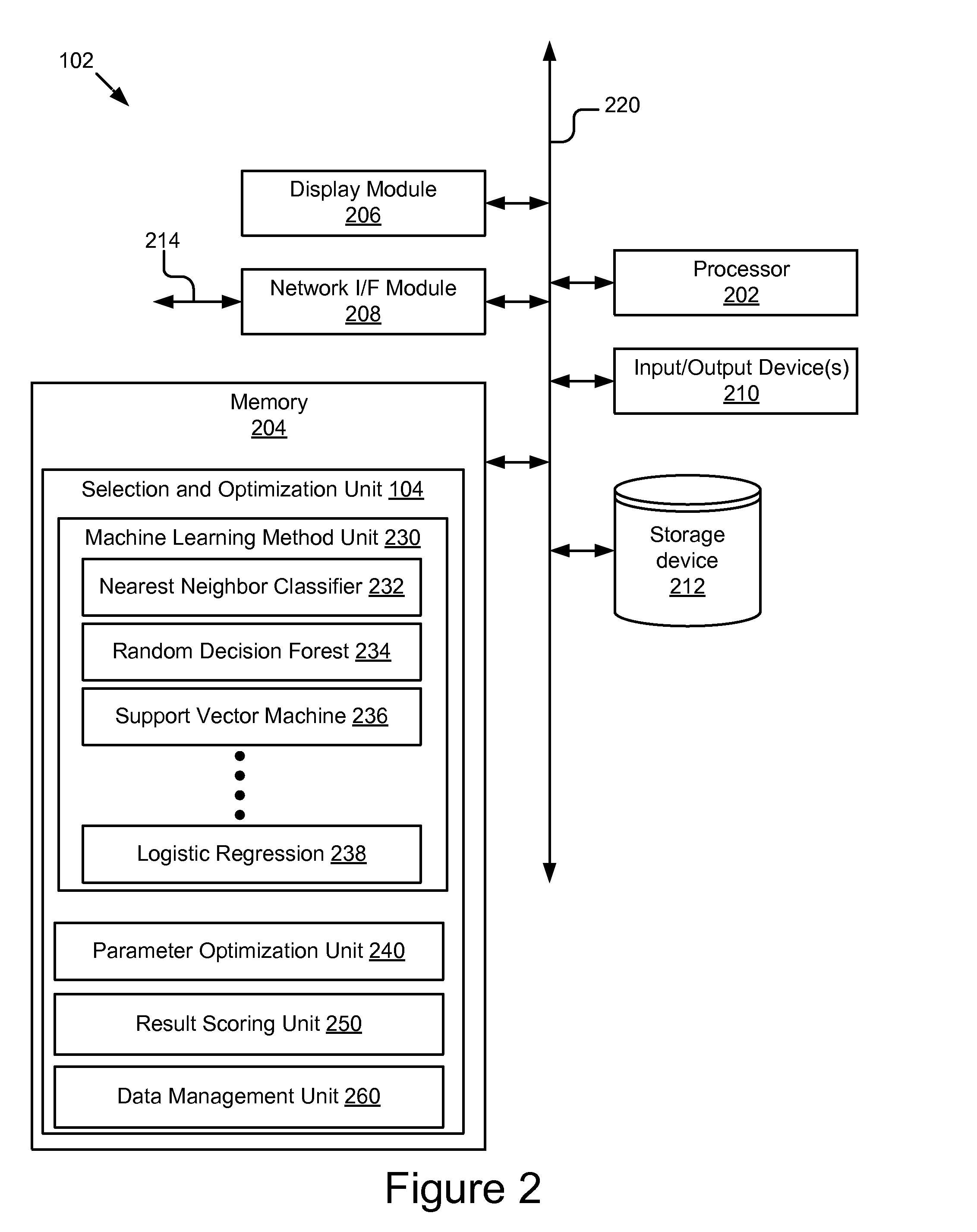
Configurable Machine Learning Method Selection and Parameter Optimization System and Method
InactiveUS20160110657A1Improve performanceDigital computer detailsMachine learningMethod selectionLearning methods
A system and method for selecting a machine learning method and optimizing the parameters that control its behavior including receiving data; determining, using one or more processors, a first candidate machine learning method; tuning, using one or more processors, one or more parameters of the first candidate machine learning method; determining, using one or more processors, that the first candidate machine learning method and a first parameter configuration for the first candidate machine learning method are the best based on a measure of fitness subsequent to satisfaction of a stop condition; and outputting, using one or more processors, the first candidate machine learning method and the first parameter configuration for the first candidate machine learning method.
Owner:SKYTREE INC
Method and apparatus for mobile station management and system
ActiveUS20060128371A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringAccess networkCommunications system
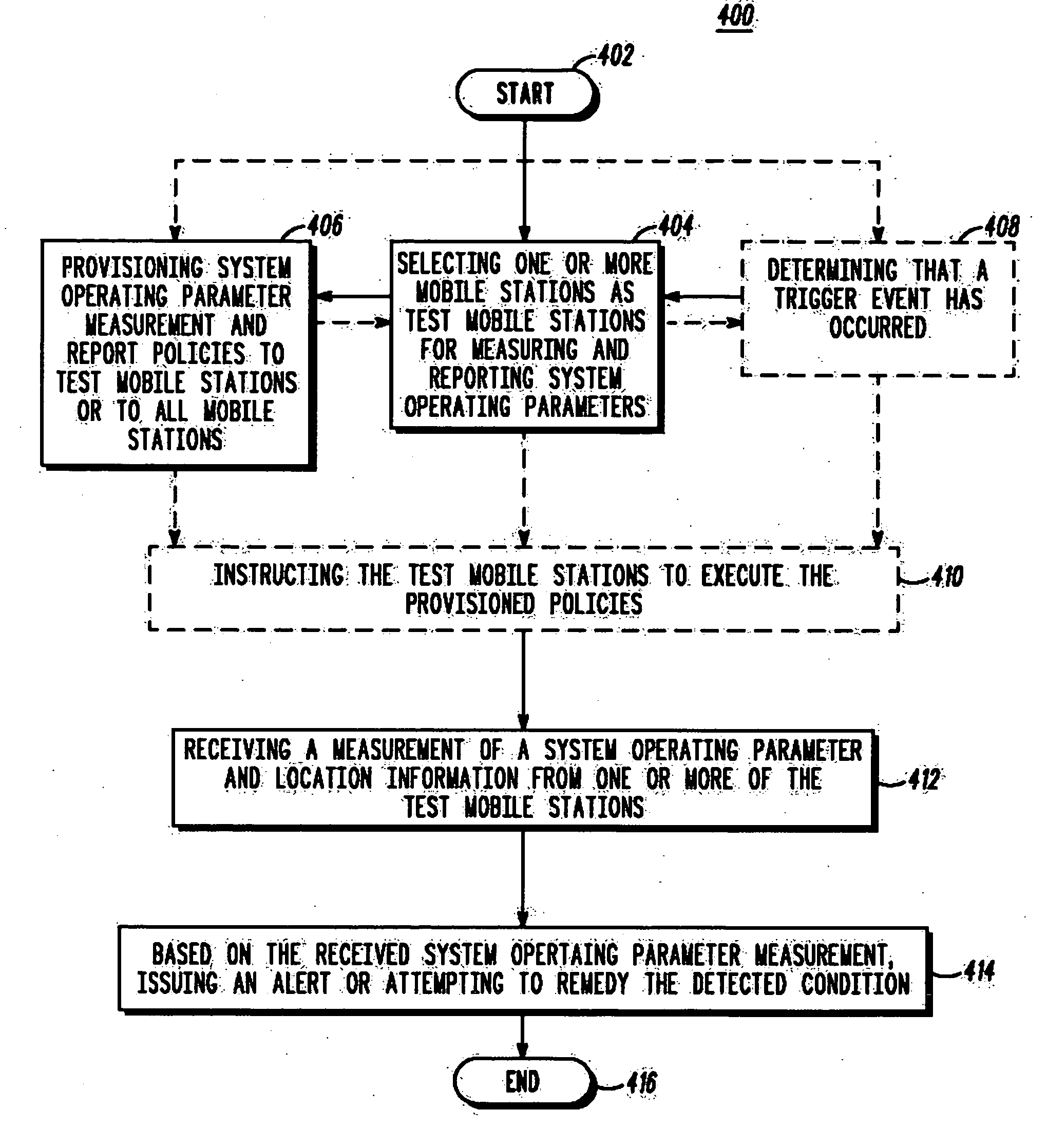
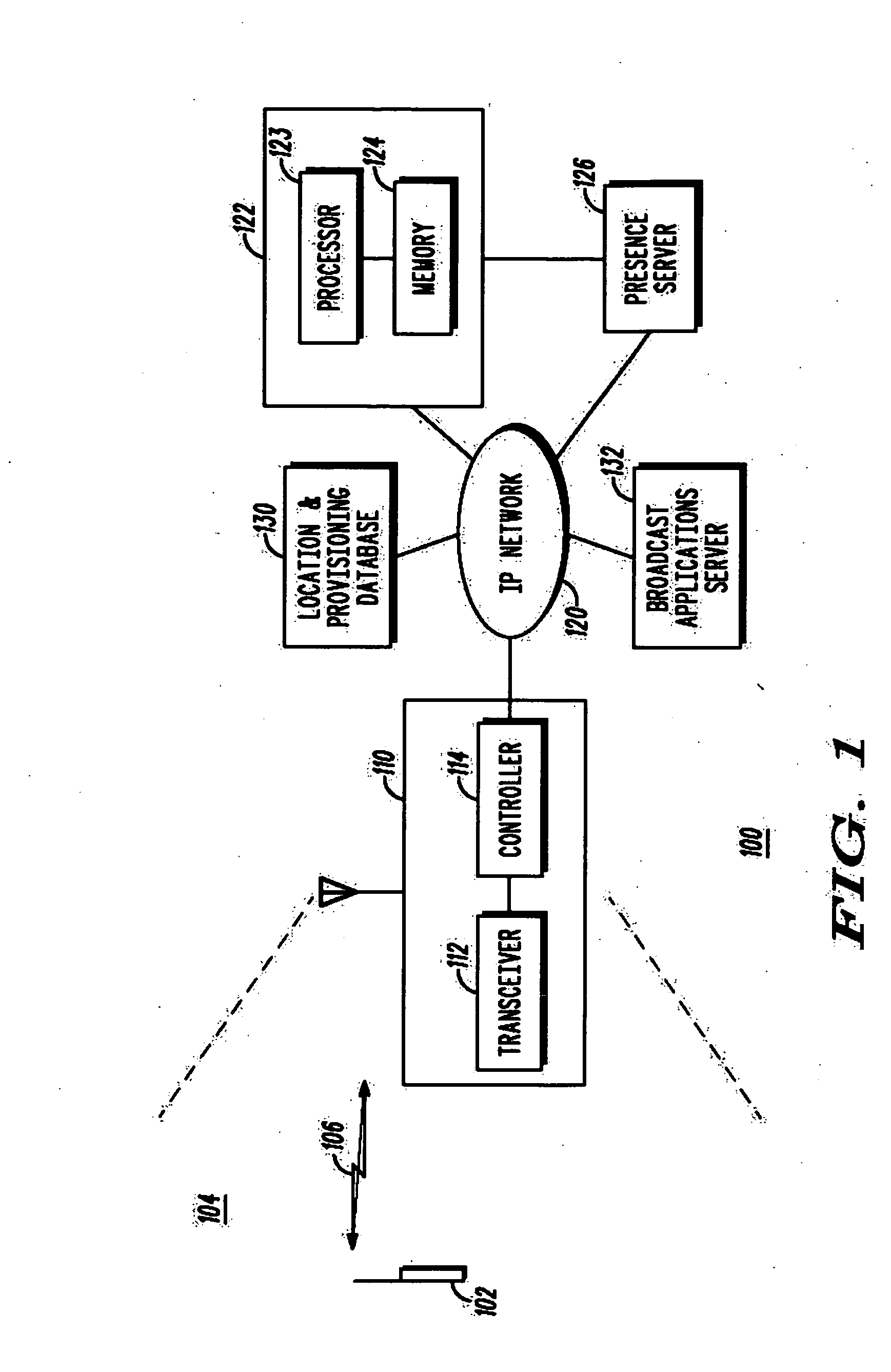
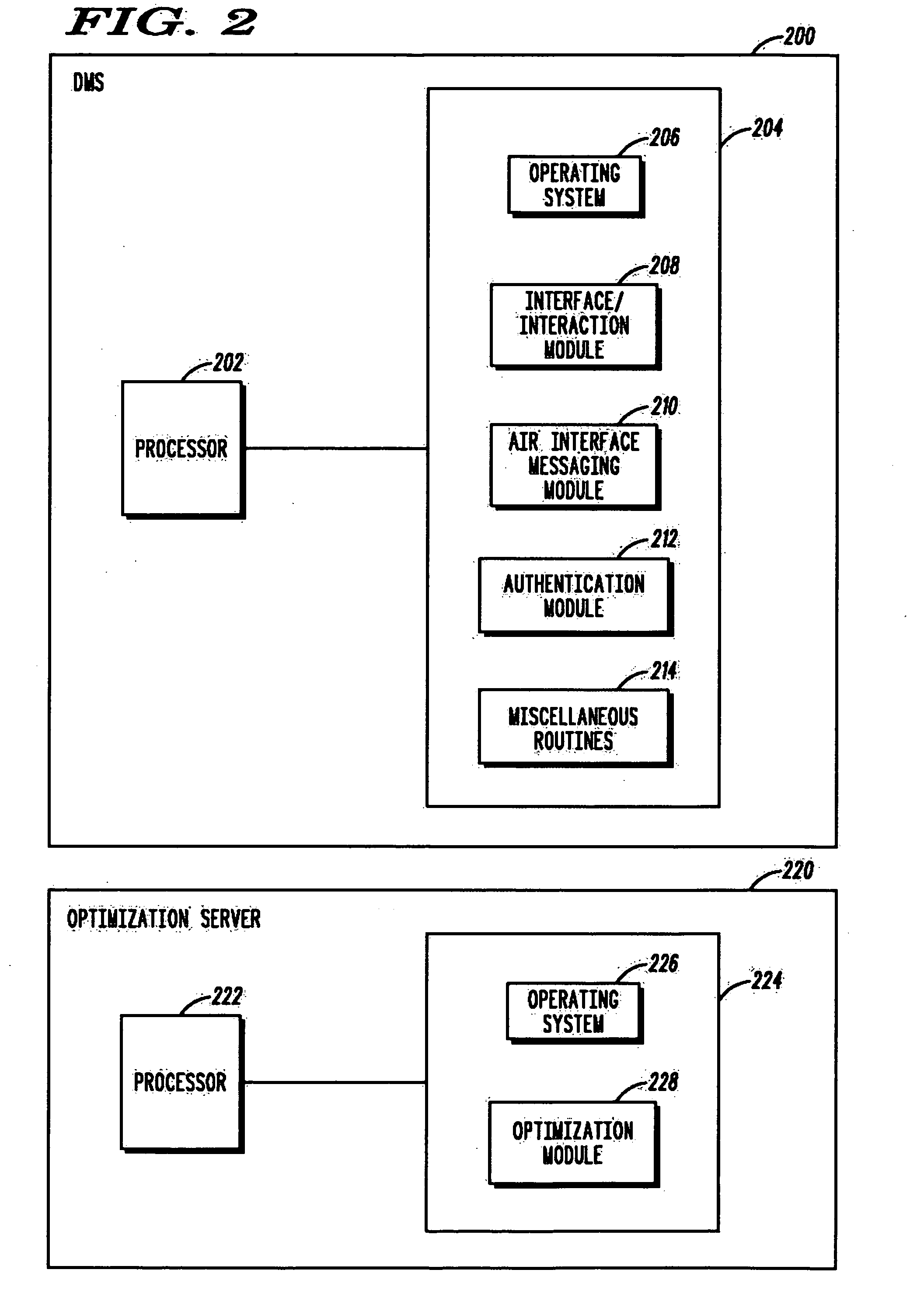
A communication system optimizes system performance by selectively managing which mobile stations (MSs) are to serve as test MSs. The test MSs report system operating parameters in order to detect sleeping cells, coverage holes, or other flaws in system coverage or in order to determine an impact of a change in an access network configuration. The communication system further provides for end-to-end messaging between the test MSs and network servers via an access network and a core network, thereby permitting network elements that are best able to perform system optimization to control the monitoring, measuring, and reporting by the MSs. To minimize system and user inconvenience, reporting by a test MS further may be based on one or more of whether the MS is in an area of low mobility, has an acceptable power source output level, and is operating in a cell with an acceptable load level.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Dynamic classification of sections of software
InactiveUS6957422B2Improve performanceResource allocationDigital data processing detailsSoftware engineeringSoftware
Dynamic classification of sections of software using a profile-based optimization system optimizes management of the sections of software. Software executes under expected usage conditions. After execution, a set of usage profiles describes the dynamic properties of sections of the software. Each usage profile includes information identifying a section of software. Each usage profile maps to an outcome meant to optimize management of the sections of the software during later execution. During such later execution, a usage background describes the dynamic properties of a section of the software. The usage background includes information identifying the section of software. By matching the usage background to a usage profile in the set of usage profiles, the section is dynamically classified during later execution. Based on this dynamic classification, the section maps to the outcome meant to optimize management of the sections of software.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
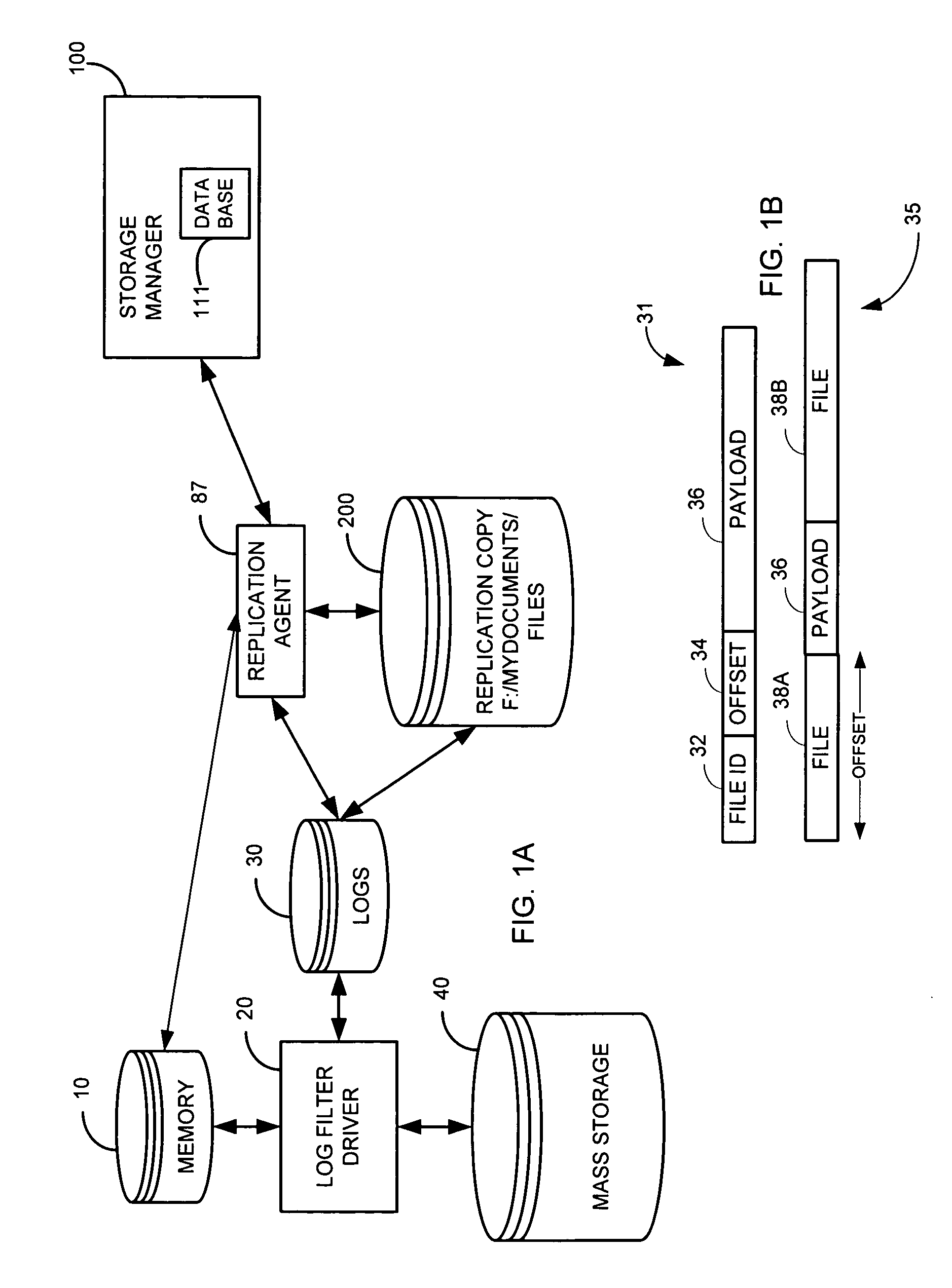
Systems and methods for performing replication copy storage operations
InactiveUS20100082541A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsThird partyStorage management
A system and method are provided for performing storage operations relating to a first secondary copy of electronic data. A storage policy or storage preferences may dictate that a replication copy should be used in storage operations performed to a particular client, sub-client, data, media or other item. Based on the storage policy, when a new client, sub-client, data, media or other item is received, a media agent determines whether there is a replication copy of the item. In the absence of a replication copy, one may be created. The replication copy may be provided by a third party application, or created by the client or a storage management system component. Information regarding the replication copy and its corresponding first secondary copy may be stored in a database. To optimize use of system resources, storage operations relating to the first secondary copy may be performed using the replication copy instead of the first secondary copy.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
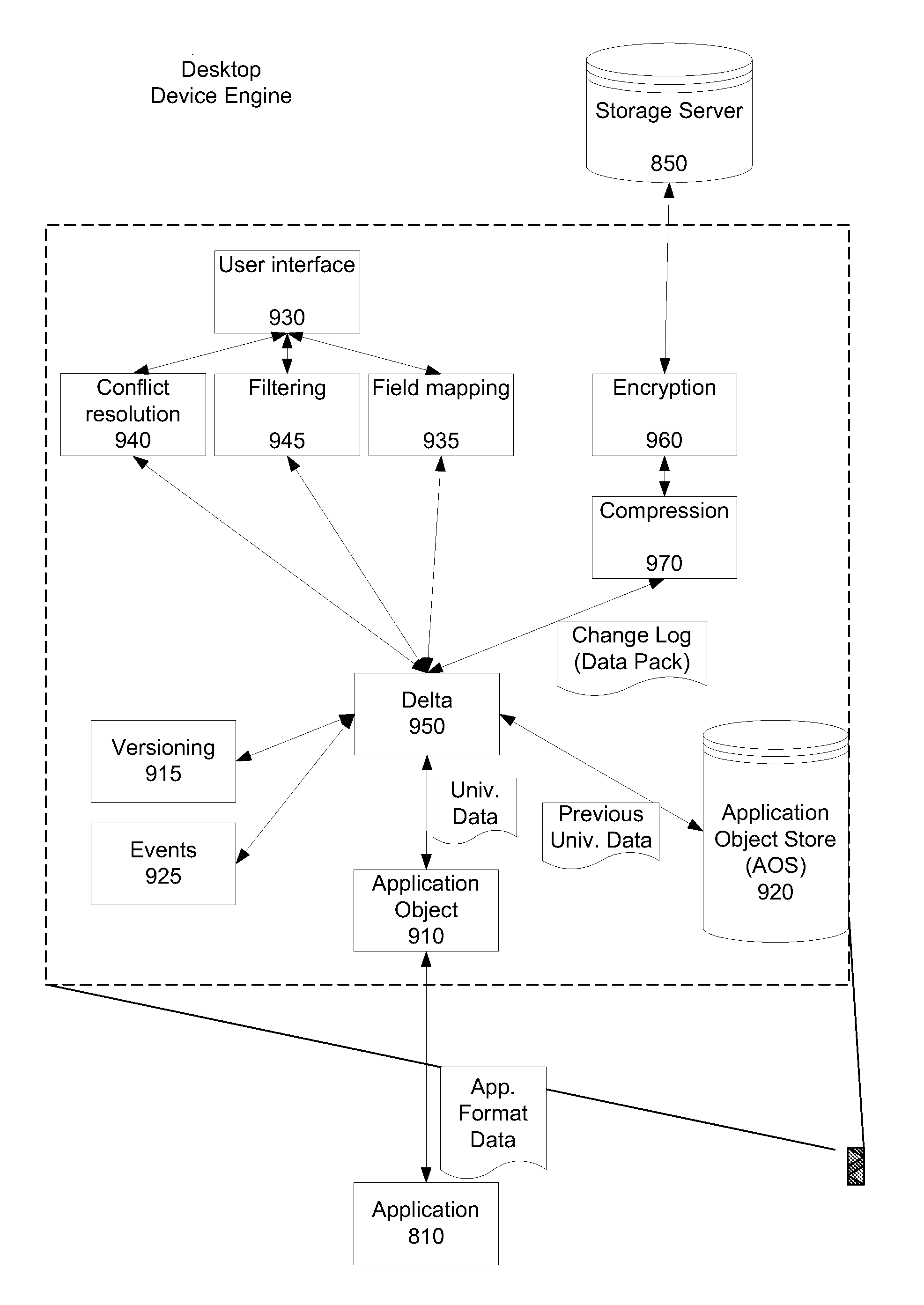
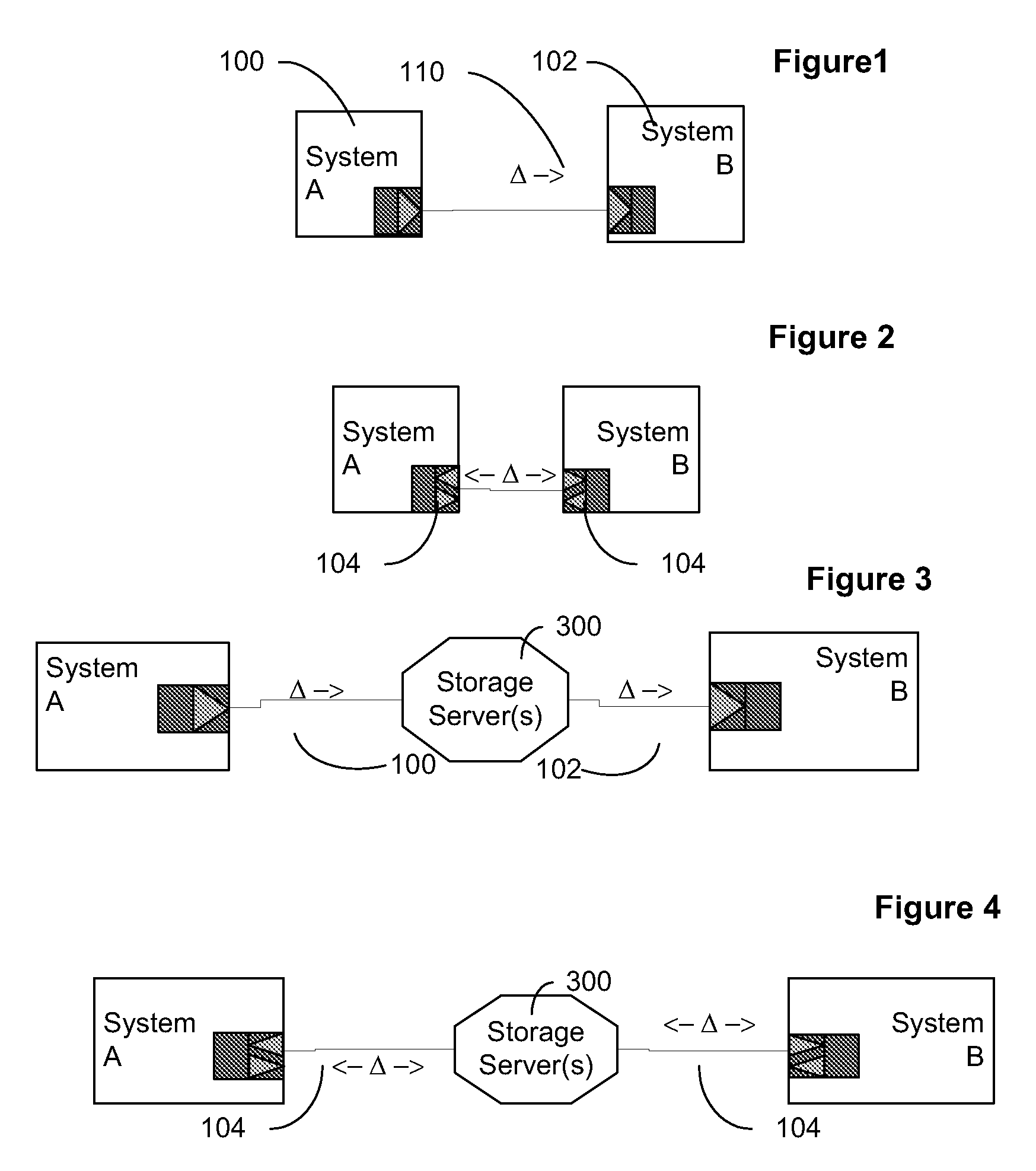
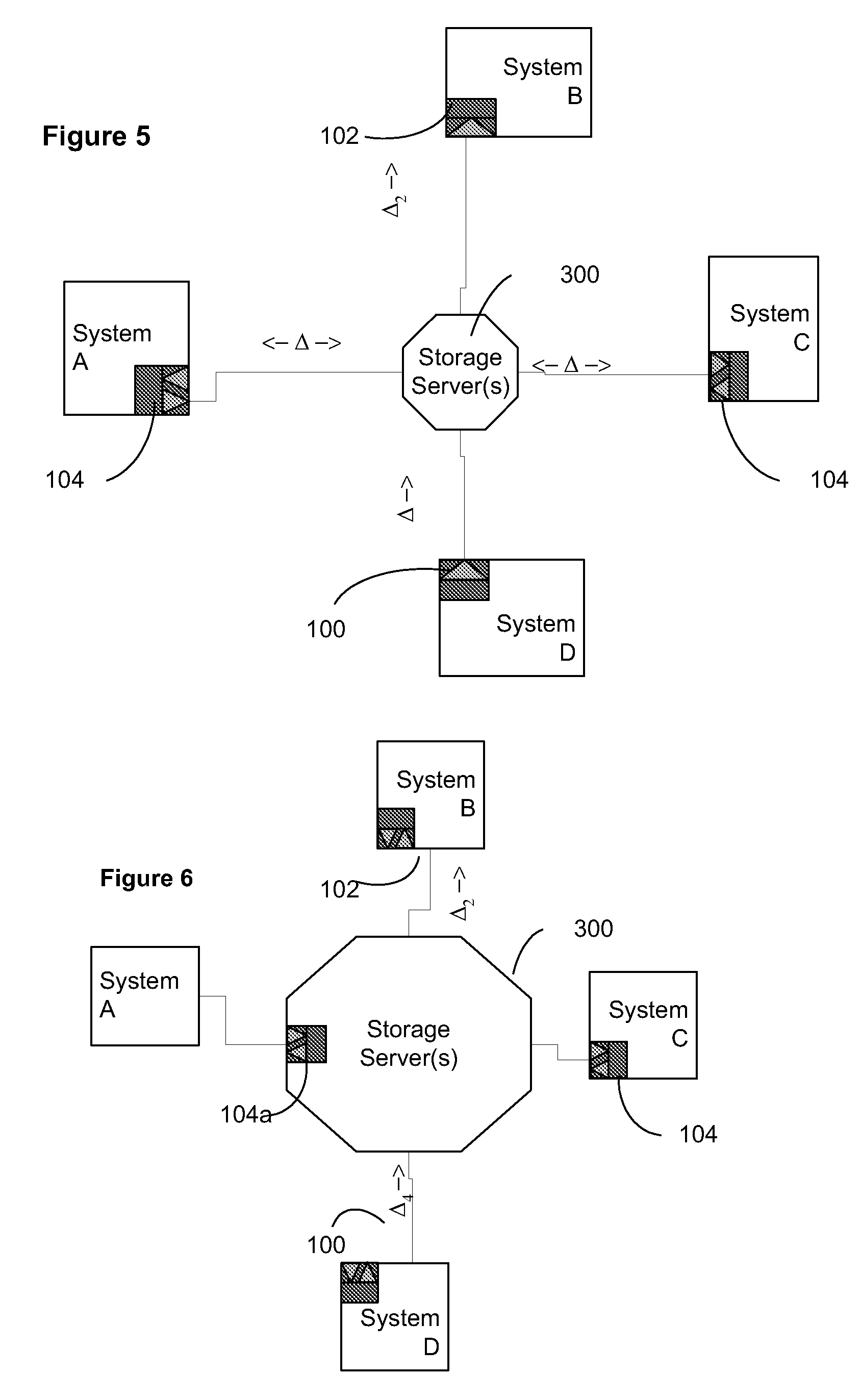
Data transfer and synchronization system
InactiveUS20080201362A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData packTransfer system
A data transmission system is disclosed which optimizes transfer and updates of information between systems by providing difference information between the systems. The system transmits data packages having instructions for manipulating user data. The data packages include a header identifying the respective packages, as well as transaction objects for effecting a change to user data on a device having object instructions.
Owner:SYNCHRONOSS TECH
Real-time global optimization of building setpoints and sequence of operation
ActiveUS7894943B2High efficiency profileEfficiency profileSampled-variable control systemsAir-treating devicesReal-time dataMathematical model
Owner:SLOUP CHARLES J +2
Network optimisation systems
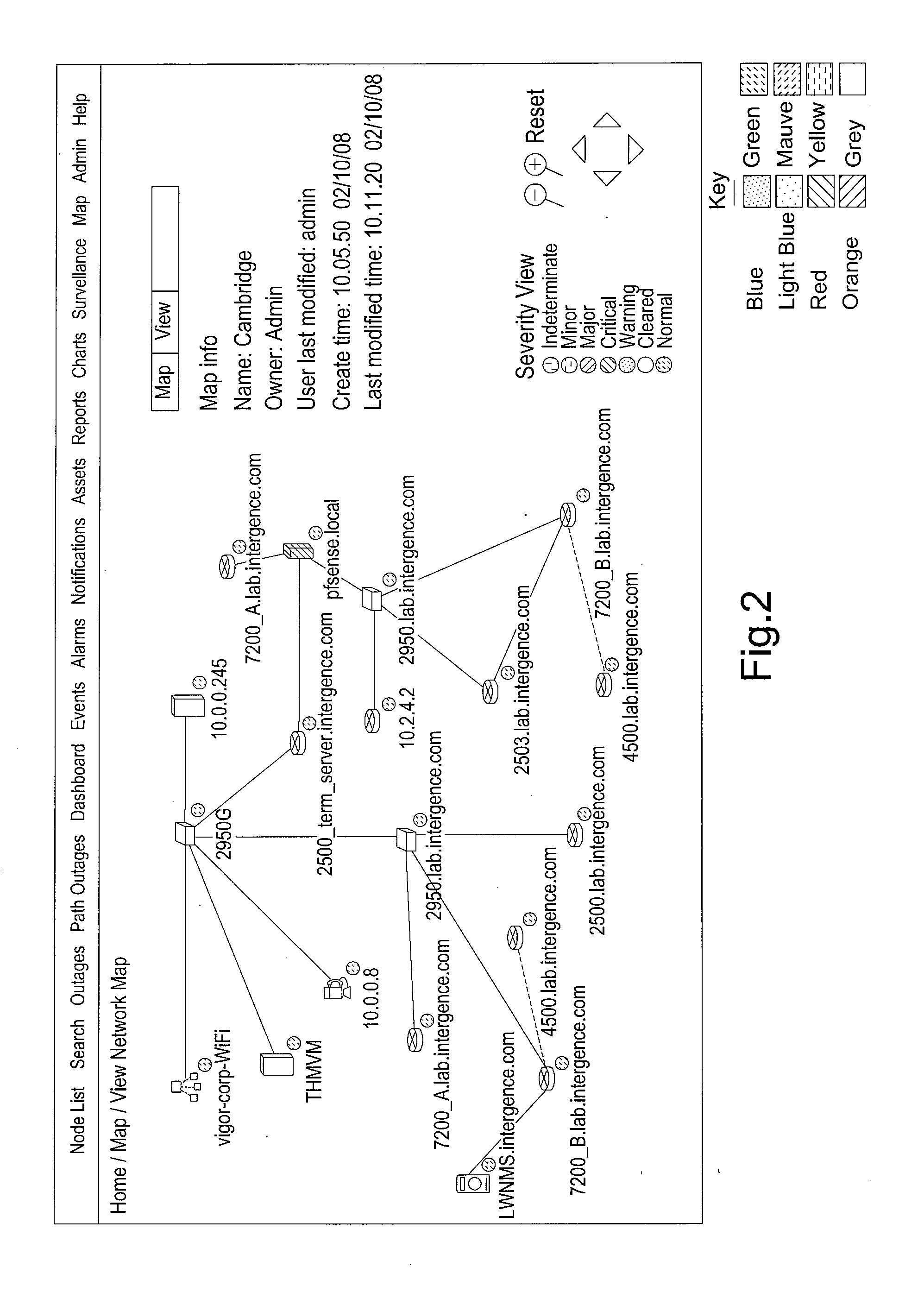
InactiveUS20100110932A1Easy to troubleshootEnhances capacity managementData switching by path configurationOperational systemNetwork management
We describe a 3D computer network optimisation tool using network management data including one or more of: network device data including hardware identification data, interface data characterising one or more interfaces of a said network device, firmware identification data for a said network device, operating system identification data for a said network device; information flow data relating to information flow within the network including network device information flow load data and link bandwidth data / statistical information flow data; as well as environmental data for a network device such as temperature or power consumption data and / or physical network device location data. The tool also uses captured network data and sniffer data from communication links; and connectivity of the network devices. A three-dimensional (3D) visualisation module constructs a 3D representation of said network including 3D representations of said network devices in conjunction with a representation of said connectivity in three dimensions.
Owner:INTERGENCE SYST
Extensible Authentication Protocol Authentication and Key Agreement (EAP-AKA) Optimization
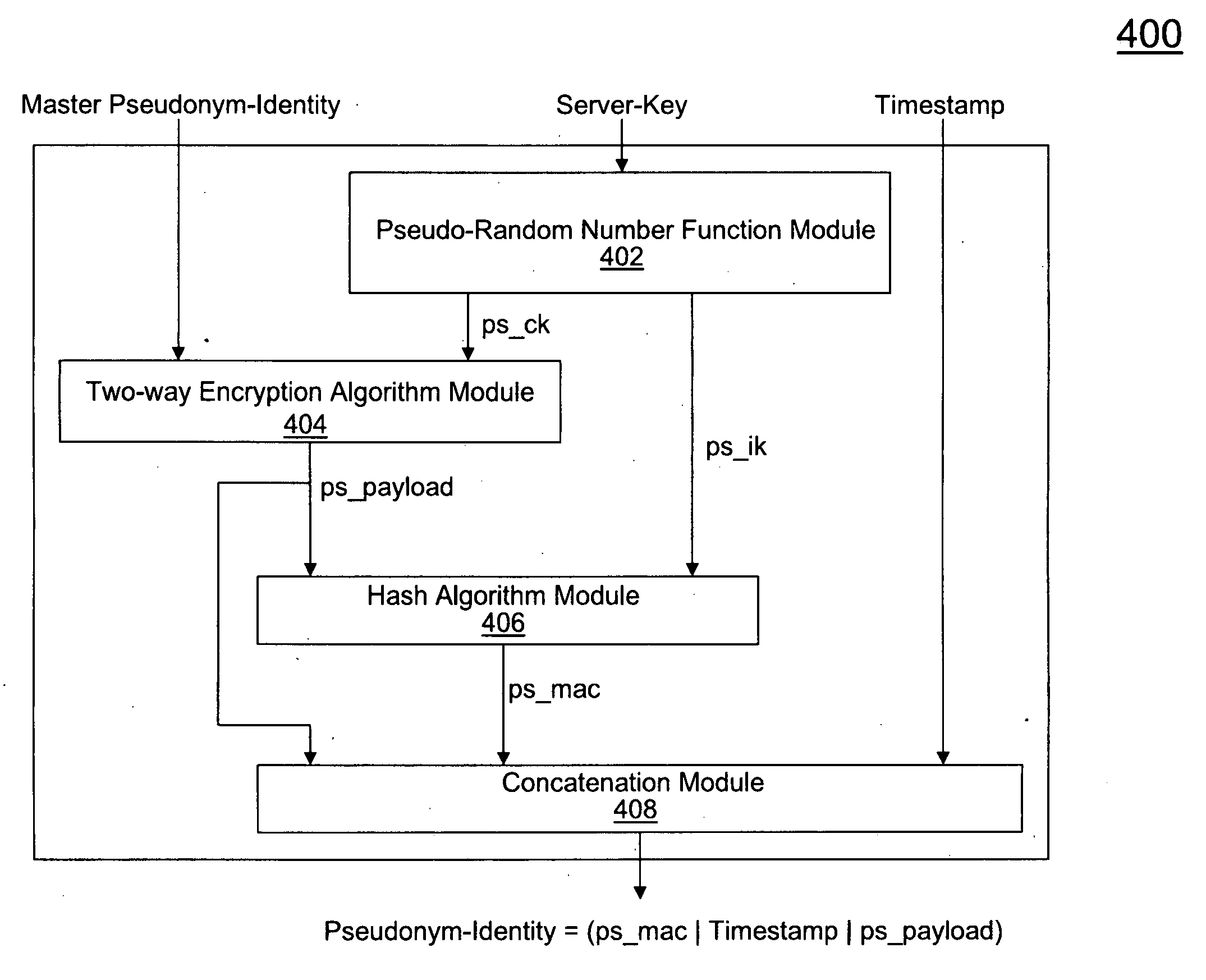
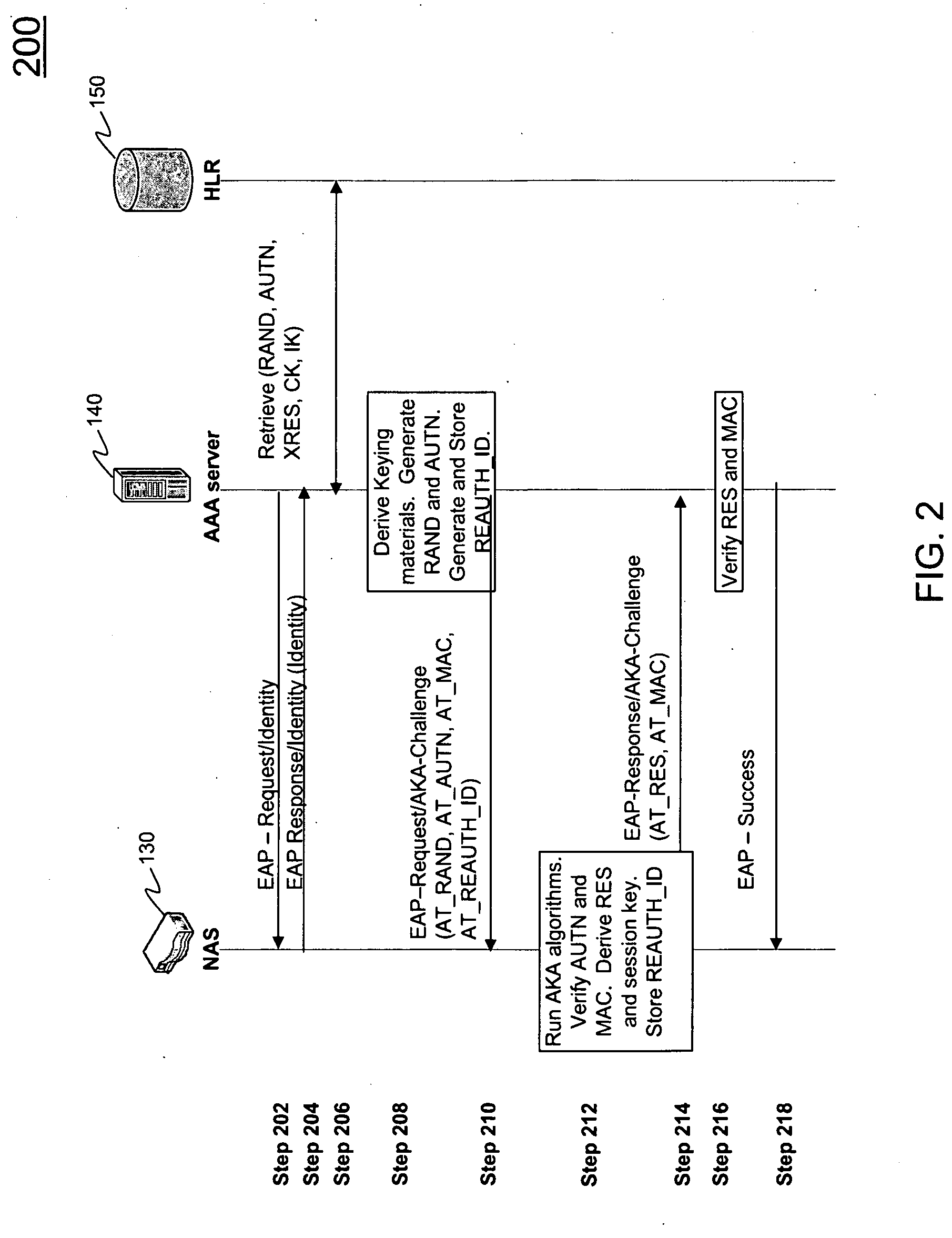
ActiveUS20100017603A1Low costEliminate needUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesClient-sideProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
Systems and methods are described for improved authentication of subscribers wishing to connect to a wireless network using the EAP-AKA protocol. Embodiments exploit the requirement that the client store and transmit the Pseudonym and Fast Re-authentication Identities upon request. By using the Fast Re-authentication Identity to store session state key information, the need for the AAA server to store and replicate the EAP-AKA key information for every session is eliminated.
Owner:AMDOCS CANADIAN MANAGED SERVICES INC +1
Method and system for adaptive offer determination
ActiveUS20110029362A1Improve efficiencyIncrease ratingsDiscounts/incentivesSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionEngineeringSelf adaptive
The optimization system monitors a mobile phone user's behavior in response to an offer for a reward and determines a good level for a product promotion. The determination may be made based upon the user's current response, past response patterns to various reward levels or a correlation between a user's behavior and the behavior corresponding to a class of users. The system can determine an offer level that maximizes the return on the profit or revenue from a potential purchase for which the offer applies.
Owner:SHOPKICK
Knowledge driven composite design optimization process and system therefor
InactiveUS7010472B1Easy to understandFacilitates later update of knowledge baseConstraint-based CADSpecial data processing applicationsGeneral purpose computerInterconnection
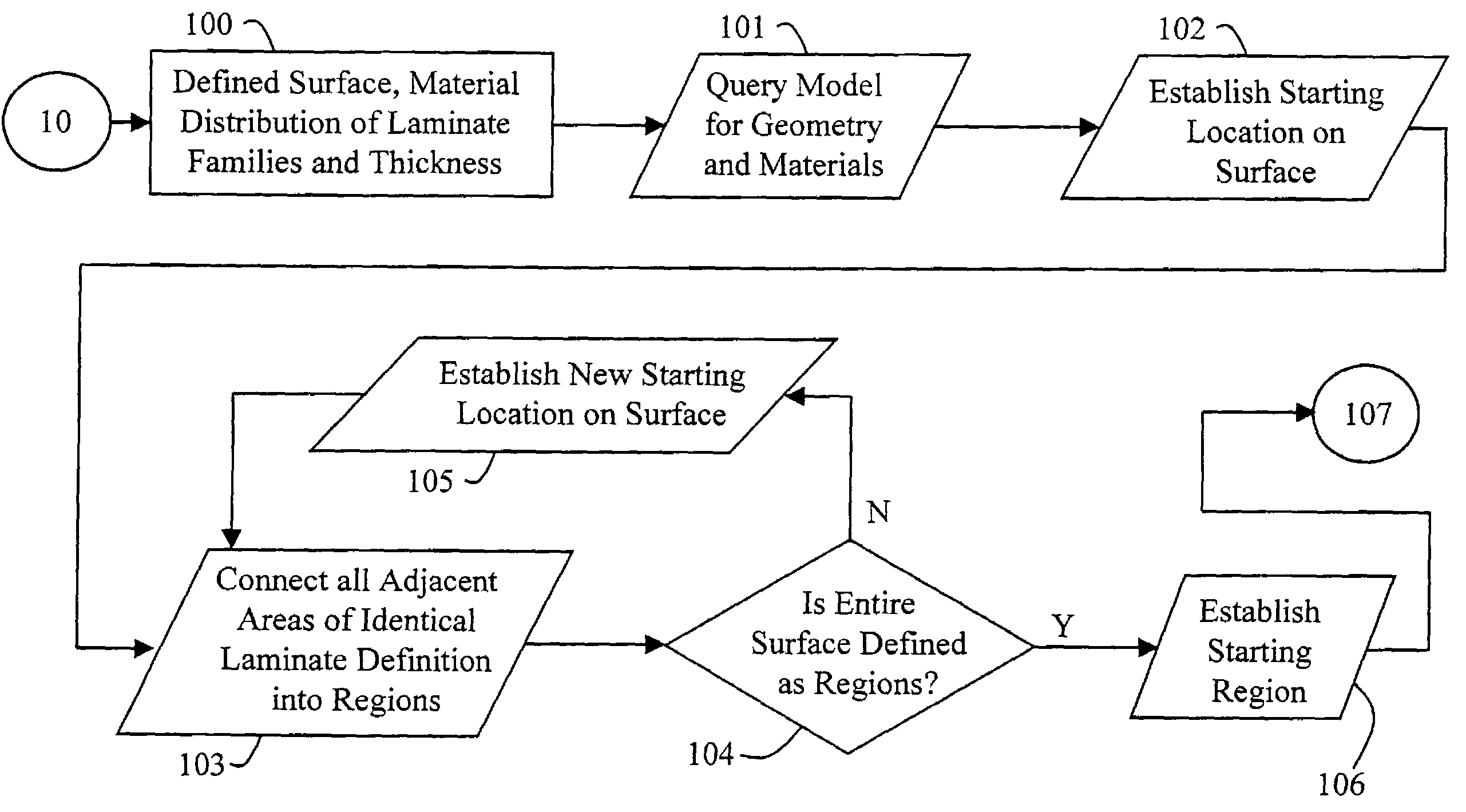
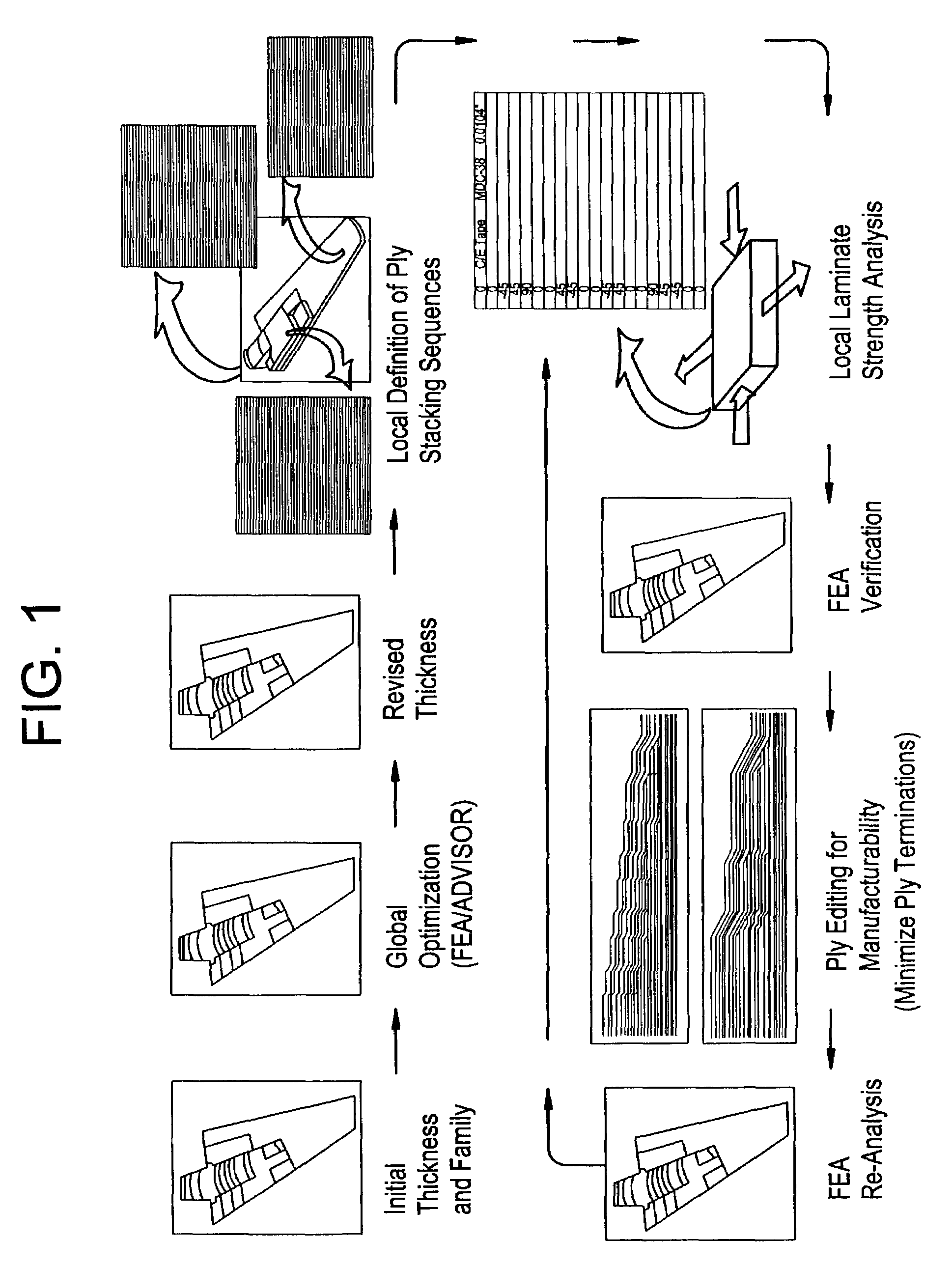
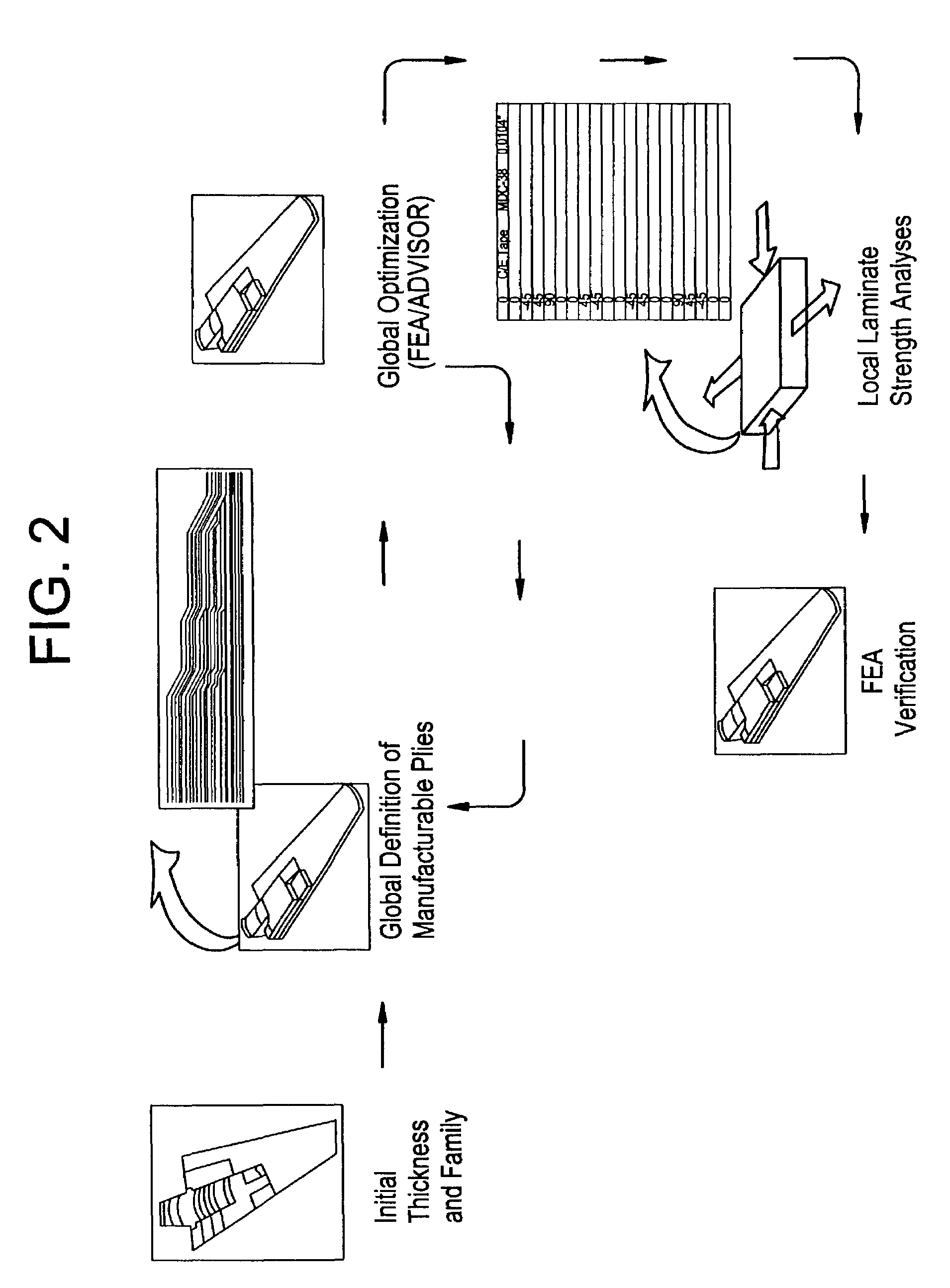
A knowledge driven composite design optimization process for designing a laminate part includes steps for generating a globally optimized 3-D ply definition for a laminate part, and modifying the 3-D ply definition to include features of the laminate part, where the generating and modifying steps are parametrically linked to one another and are performed in the recited order. Preferably, the generating step includes substeps for determining connectivity between a plurality of regions defining the laminate part, subsequently generating ramp features detailing interconnection of the regions defining the laminate part, and displaying views and corresponding tabular data describing the laminate part and illustrating both inter-region connectivity and the ramp features as specified by a user. A knowledge driven composite design optimization system and associated computer memory for operating a general purpose computer as a knowledge driven composite design optimization system are also described.
Owner:MCDONNELL DOUGLAS
Service-oriented architecture
InactiveUS20070011126A1ModificationEasy to adaptData processing applicationsKnowledge representationService implementationReusability
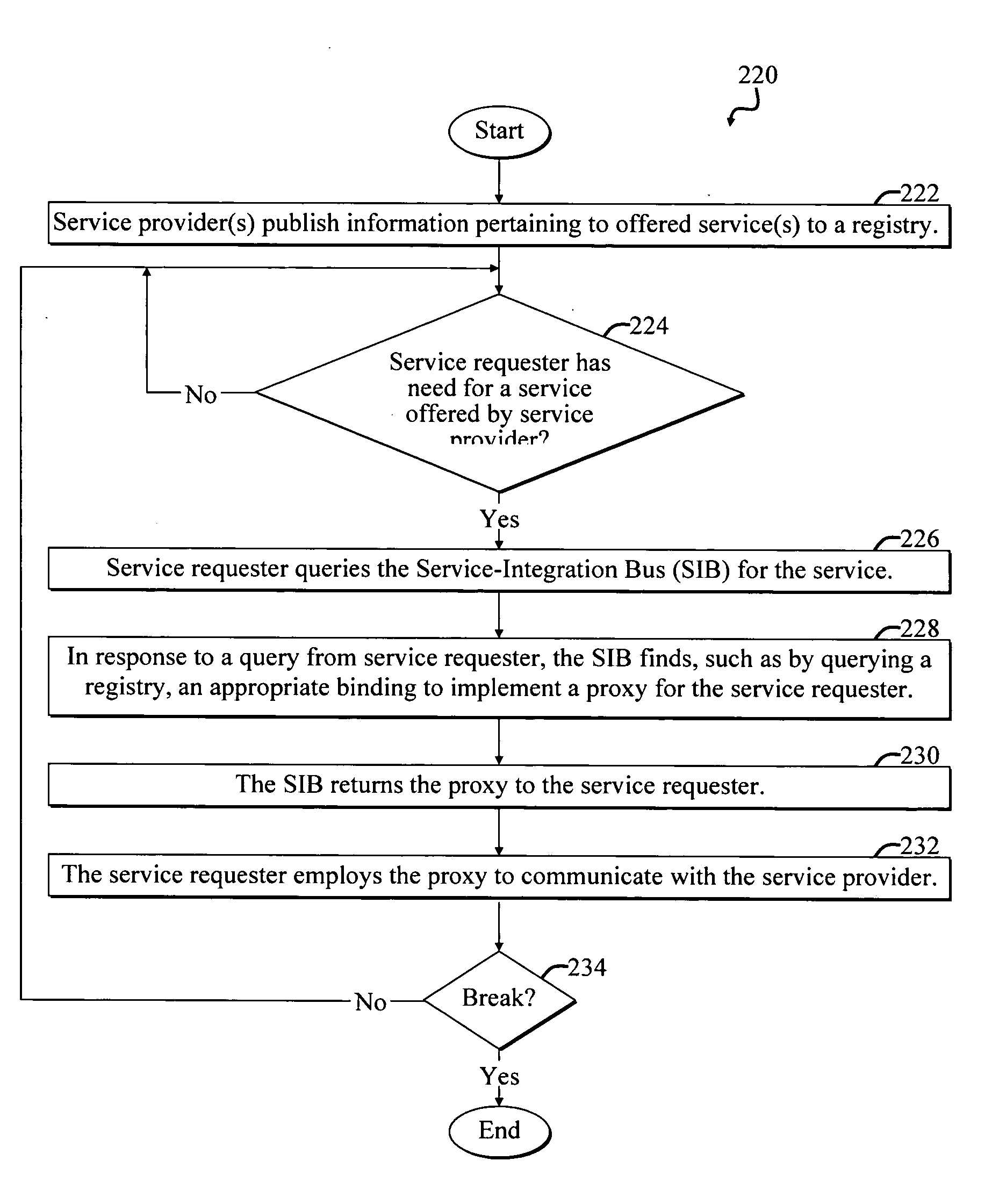
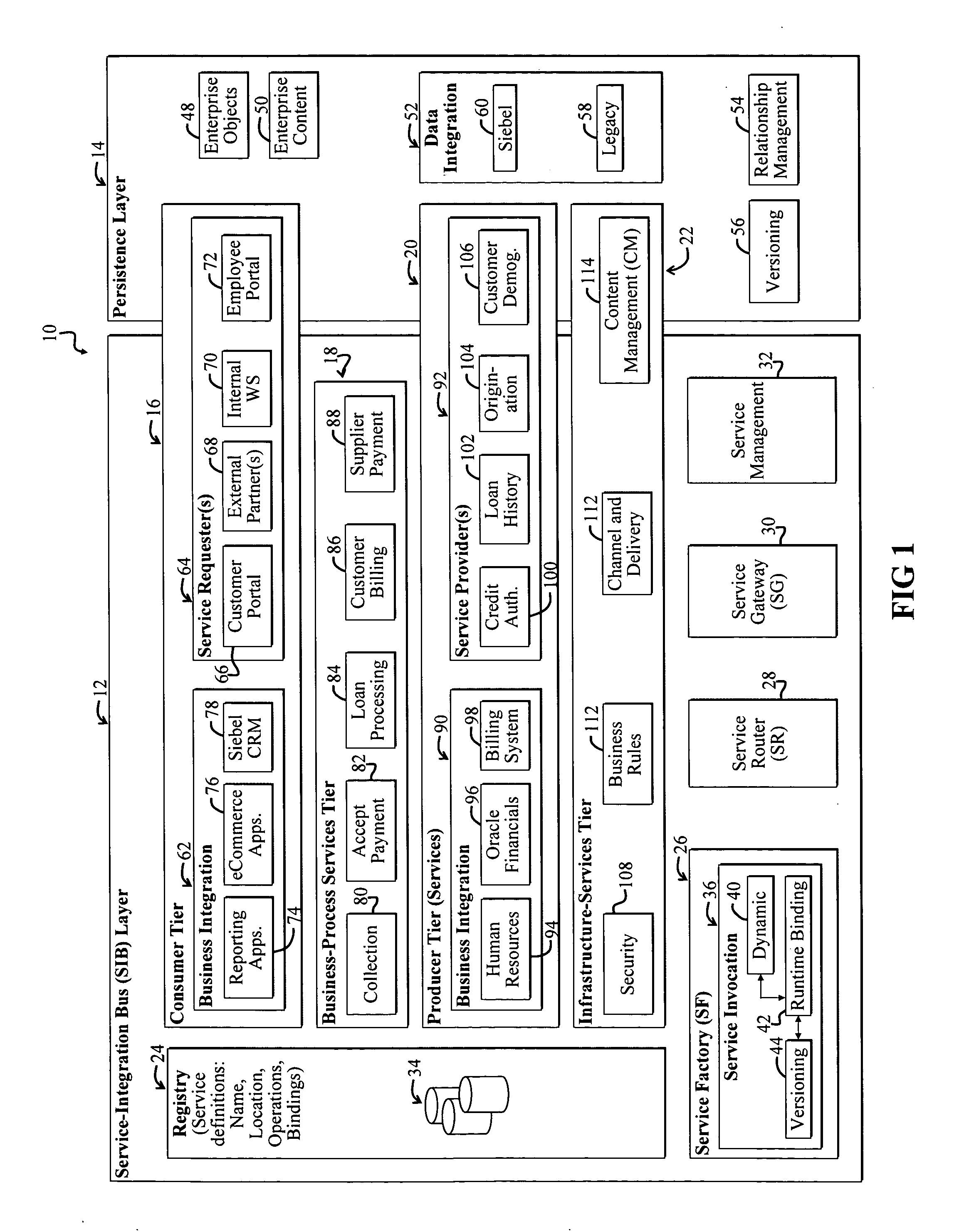
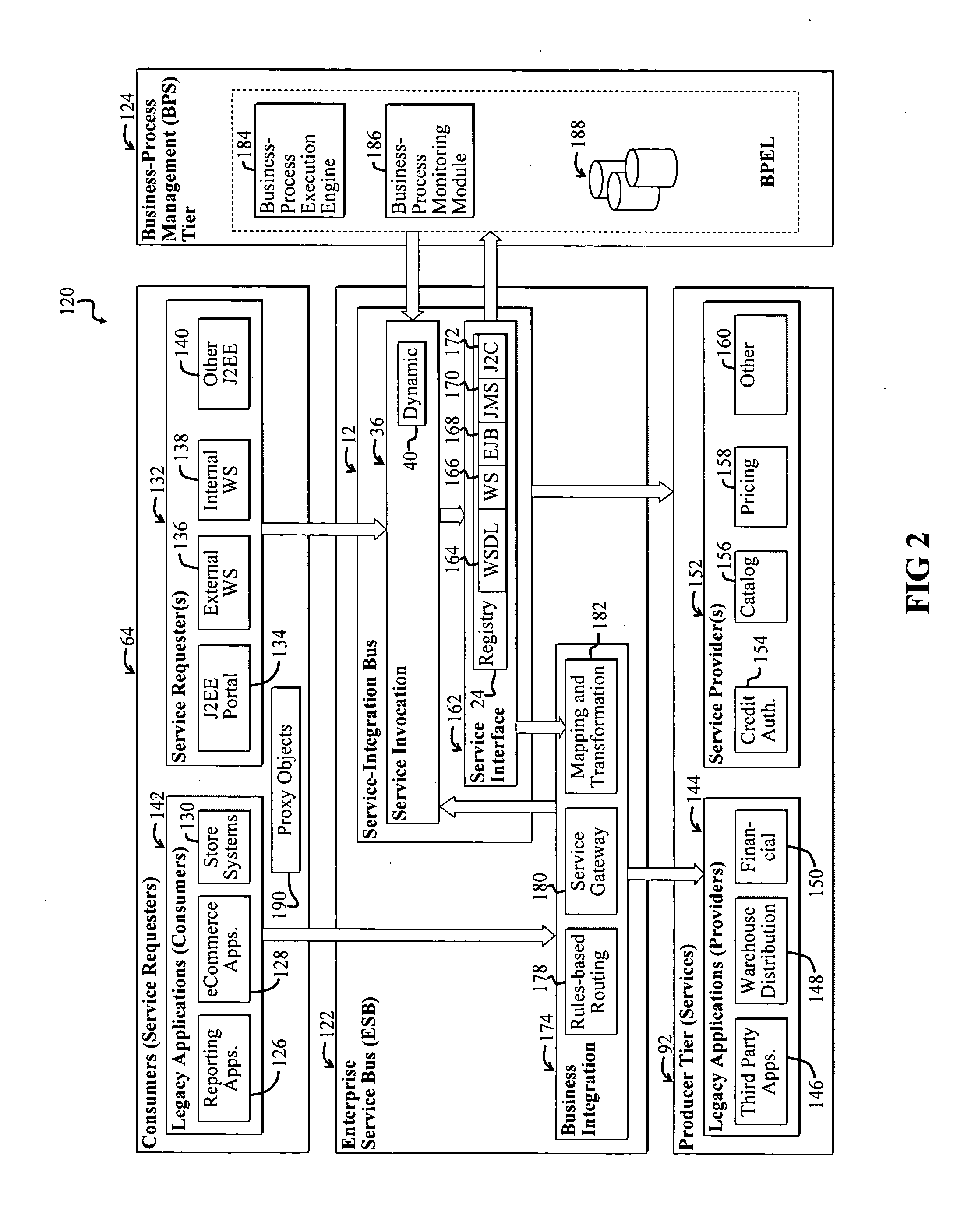
A Service-oriented architecture (SOA) and accompanying method. In one embodiment, the SOA includes one or more service requesters coupled to one or more service providers via a bus. The bus includes runtime-binding functionality to facilitate interaction between the one or more service requesters and the one or more service providers. A registry, which stores information pertaining to a service provided by the one or more service providers, communicates with one or more service providers and / or requesters and the bus. In a more specific embodiment, bus includes a Service-Integration Bus (SIB) that includes a Service-Factory (SF) module for facilitating implementing the runtime binding functionality and for selectively invoking the service. Functionality of the SOA is strategically organized into various tiers and layers, including a requester tier, a provider tier, a business-process services tier, an infrastructure-services tier, an SIB layer, a persistence layer, and so on, to optimize system reusability, adaptability, and other desirable properties. A service interface pattern is described whereby a change in service implementation does not require modification to the manner in which the service is invoked by a requester
Owner:PRIMITIVE LOGIC
Configurable pricing optimization system
InactiveUS7287000B2Increase valueImprove forecast accuracyMarket predictionsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsGraphicsGraphical user interface
The present invention provides a configurable pricing system that allows users to define or modify data used to analyze, evaluate, improve, and design pricing changes according to the user's need. A Graphical user interface or some other type of user interface allows the user to access and review various data to be used during pricing optimization. The user may then modify this data as needed to improve the pricing evaluation, such as defining sales or pricing trends, or relationships between the product of interest and other competing items. The user interface may further display changes in pricing and the effects of the pricing changes, as caused by the user's changes. The interface may also allow the user to modify the mathematical model to be used during price optimization, as well as define variables, constraints, and boundaries to be considered during the price optimization.
Owner:BLUE YONDER GRP INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com