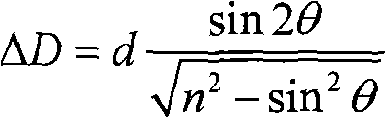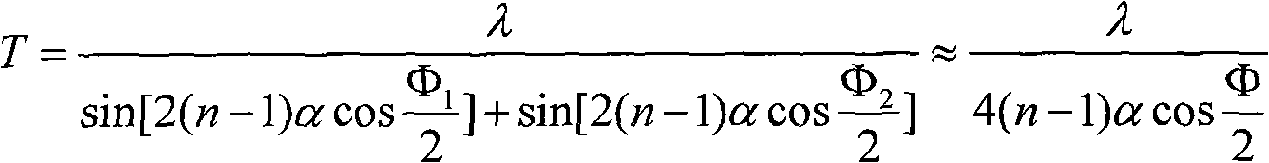Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
325 results about "Optical flat" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An optical flat is an optical-grade piece of glass lapped and polished to be extremely flat on one or both sides, usually within a few tens of nanometres (billionths of a meter). They are used with a monochromatic light to determine the flatness (surface accuracy) of other surfaces, whether optical, metallic, ceramic, or otherwise, by interference. When an optical flat is placed on another surface and illuminated, the light waves reflect off both the bottom surface of the flat and the surface it is resting on. This causes a phenomenon similar to thin-film interference. The reflected waves interfere, creating a pattern of interference fringes visible as light and dark bands. The spacing between the fringes is smaller where the gap is changing more rapidly, indicating a departure from flatness in one of the two surfaces. This is comparable to the contour lines one would find on a map. A flat surface is indicated by a pattern of straight, parallel fringes with equal spacing, while other patterns indicate uneven surfaces. Two adjacent fringes indicate a difference in elevation of one-half wavelength of the light used, so by counting the fringes, differences in elevation of the surface can be measured to better than one micrometre.
Enhancements to optical flat panel displays
InactiveUS7042618B2Good colorStatic indicating devicesColor television detailsEquipotential surfacePotential difference
A circuit for implementing a registration-free, contiguous conductive plane. A circuit may include a plurality of conductive structures in a first plane. The circuit may further include a contiguous conductive equipotential surface in a second plane parallel to the first plane. The circuit may further include activation means configured to adjust an electric field between the first and second planes thereby activating one or more structures in the first plane by increasing a potential difference between the first and second planes to a threshold level deemed to constitute an active state. The circuit may further include deactivation means configured to adjust the electric field between the first and second planes thereby deactivating one or more structures in the first plane by decreasing the potential difference between the first and second planes below a threshold level deemed to constitute a deactivation state.
Owner:RAMBUS DELAWARE
Self-adjusting lens mount for automated assembly of vehicle sensors
InactiveUS20060054802A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesCMOSAudio power amplifier
A two piece lens mount system for mounting a lens in correct focus and alignment relative to a CMOS imaging device such that the optical axis of the lens is coincident with and perpendicular to the center of the active area of the imager array. The lens is secured by the axial pressure of flexible ribs that are symmetrically spaced around the internal bore of a lens holder and act on a smooth surface on the outside of the lens. This arrangement eliminates translation of the lens across the imager array. Another portion of the body of the lens is threaded such that the lens, when rotated about its optical axis may be focused or axially aligned. When a focus or axial alignment point is reached, a staking fluid may be added to the lens thread, through a hole in the lens holder to prevent de-focusing. The second component of the lens mount system, the lens mount base, is fixedly secured to an imager board on which is mounted a CMOS imager. The upper wall of the lens mount base is in close, parallel proximity to the optical flat of the imager and has a rectangular opening which restricts light from the lens to the active area of the imager, and more specifically prevents light from falling on the column amplifiers of the imaging device. The design of both components is such that they may be moved relative to each other with external fixturing, in front of a known target, until it is decided that the lens is directly over the center of the imager array. The lens holder and the lens mount base are then fixed together permanently using a laser weld process or any other plastic bonding technique.
Owner:ITERIS INC +1
Enhancements to optical flat panel displays
InactiveUS20050063037A1Good colorStatic indicating devicesColor television detailsEquipotential surfacePotential difference
A circuit for implementing a registration-free, contiguous conductive plane. A circuit may include a plurality of conductive structures in a first plane. The circuit may further include a contiguous conductive equipotential surface in a second plane parallel to the first plane. The circuit may further include activation means configured to adjust an electric field between the first and second planes thereby activating one or more structures in the first plana by increasing a potential difference between the first and second planes to a threshold level deemed to constitute an active state. The circuit may further include deactivation means configured to adjust the electric field between the first and second planes thereby deactivating one or more structures in the first plane by decreasing the potential difference between the first and second planes below a threshold level deemed to constitute a deactivation state.
Owner:RAMBUS DELAWARE
Borderless display device and large screen displayer
ActiveCN102087814ASimple structureEasy to implementDiffusing elementsOptical light guidesLight guideDisplay device
The invention relates to a borderless display device and a large screen displayer, wherein the borderless display device comprises a display screen and an optical element covering the display screen; the optical element comprises an optical flat and a light guide component arranged at periphery of the optical flat; the light guide component comprises a plurality of superposed light guide films which are arranged in a direction of being far away from the optical flat from a side of the optical flat; the light guide films are superposed in expanding form, and air gaps are formed among the light guide films; the light emitted from an edge display region of the display screen enters into the bottom surface of the light guide component and is output from a top surface of the light guide component after being guided by the light guide films of the light guide component, so as to form a light-emitting surface which is bigger than the bottom surface of the light guide component and is used for covering the border; and the large screen displayer is spliced by a plurality of borderless display devices. The borderless display device provided by the invention has the advantages of simple structure, excellent display effect and the like.
Owner:曹嘉灿
Combined interference device for aspheric surface measurement
InactiveCN101270975ARealize high-precision measurementRealize dynamic measurementUsing optical meansWedge angleGrating
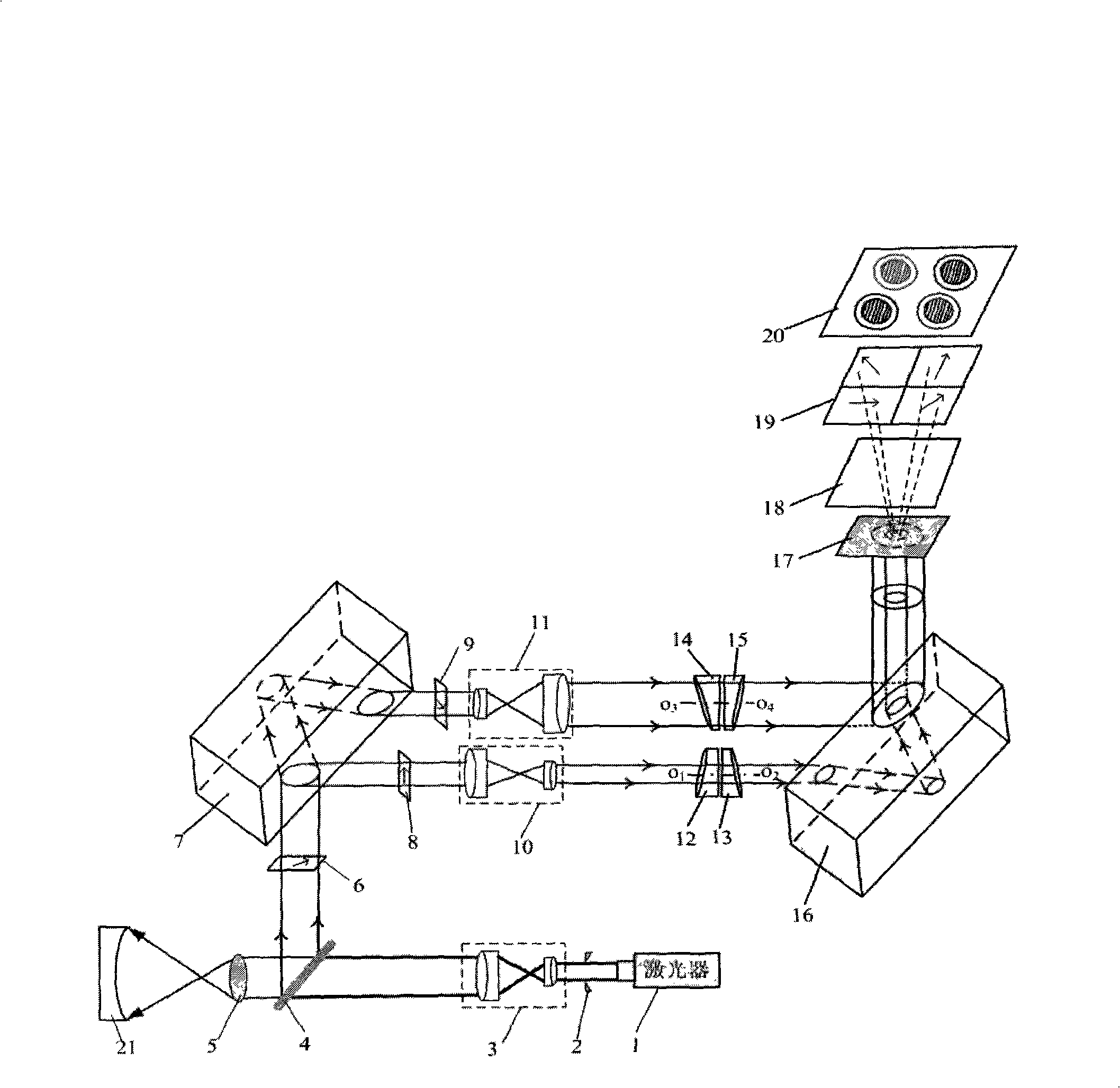
A combined interference device for measurement of aspheric surface includes a laser, a spatial filter, two beam expanding systems, a beam shrinking system, a spectroscope, a convertible lens, three polarizers, two optical plates, four circular optical wedges with small wedge angle, a beam-dividing grating, a 1 / 4 wave plate, a polarizer group and a CCD. In the device, real-time measurement is realized through simultaneous phase-shifting method, and frequency conversion function is realized through rotating two pairs of double optical wedges. The experimental device adopts common optical elements, so the cost is low, and the device can measure aspheric surfaces of different diameters and is suitable for the plane and the sphere. The real-time high precision measurement in conventional environment can be realized, and the invention has frequency conversion function, which is very effective for treating the mirror surface with discontinuous regions.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Modularized femtosecond time-resolved transient absorption and fluorescence depletion two-in-one spectrometer
ActiveCN104422519ASkilledEasy to moveEmission spectroscopyAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyNonlinear optical crystalFluorescence
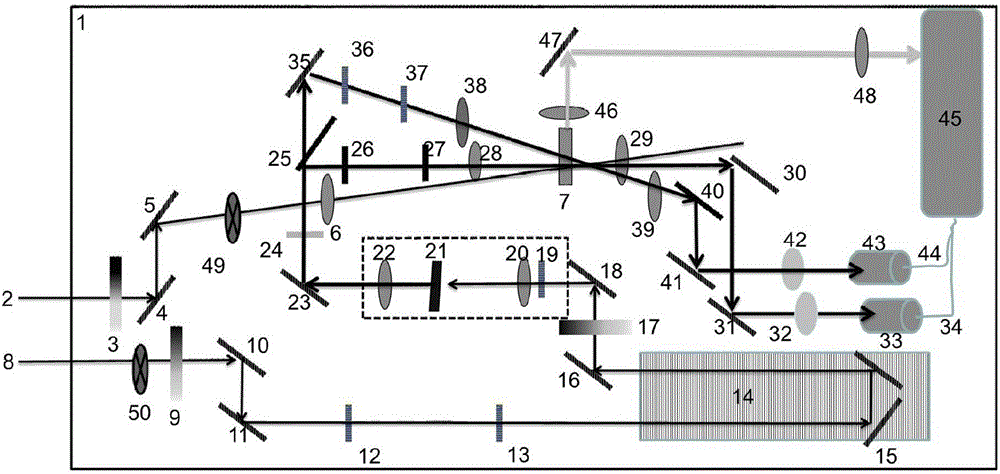
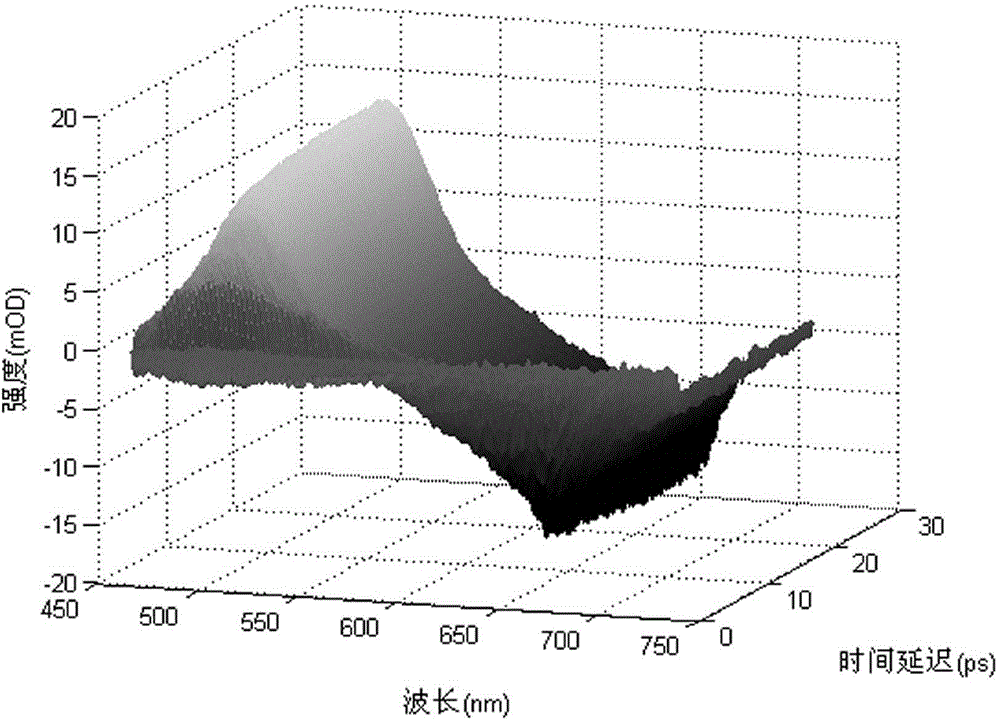
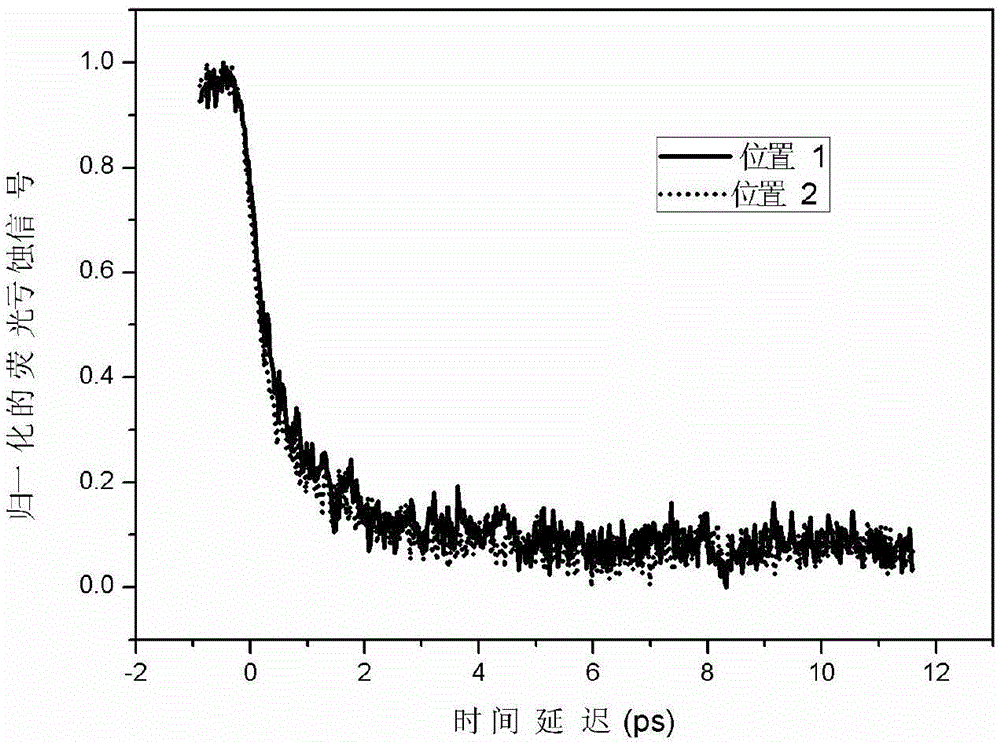
The invention relates to a time-resolved spectrum measurement instrument, in particular to a modularized femtosecond time-resolved transient absorption and fluorescence depletion two-in-one spectrometer. The modularized femtosecond time-resolved transient absorption and fluorescence depletion two-in-one spectrometer comprises an instrument optical flat, a pumping light path system and a probing light path system consisting of a plane mirror, a convex lens, a light diaphragm, a light filter, a time delay line, nonlinear optical crystals and a sample system, and also comprises a spectrum detection system. Since the spectrometer uses the optical flat as a bottom plate and various optical components, the modularization of the instrument is realized and the instrument can be moved on the whole; since a femtosecond time-resolved transient absorption spectrometer and a femtosecond time-resolved fluorescence depletion spectrometer are integrated into one, working personnel can conveniently conduct adjustment and the spectrometer can be widely popularized and used.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG IND TECH RES INST CO LTD DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Automated process and apparatus for planarization of topographical surfaces
InactiveUS20050056963A1Quickly and efficiently planarizingHigh planarization ratioPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringOptical flat
An improved apparatus (20) and method are provided for effective, high speed contact planarization of coated curable substrates such as microelectronic devices to achieve very high degrees of planarization. The apparatus (20) includes a planarizing unit (28) preferably having an optical flat flexible sheet (88) and a backup optical flat body (82), and a curing assembly (30). In operation, a substrate (78) having a planarizable coating (76) is placed within a vacuum chamber (26) beneath sheet (88) and body (82). A pressure differential is created across sheet (88) so as to deflect the sheet into contact with a central region C of the coating (76), whereupon the coating (76) is brought into full planarizing contact with sheet (88) and body (82) by means of a support (114) and vacuum chuck (120); at this point the coating (76) is cured using assembly (30). After curing, a pressure differential is established across sheet (88) for sequentially separating the sheet from the peripheral portion P of the coating, and then full separation of the sheet (88) and coating (76).
Owner:BREWER SCI
Laser scattering detecting system of optical flat surface blemishes
InactiveCN101135653AImprove signal-to-noise ratioHigh resolutionScattering properties measurementsPhotovoltaic detectorsImage resolution
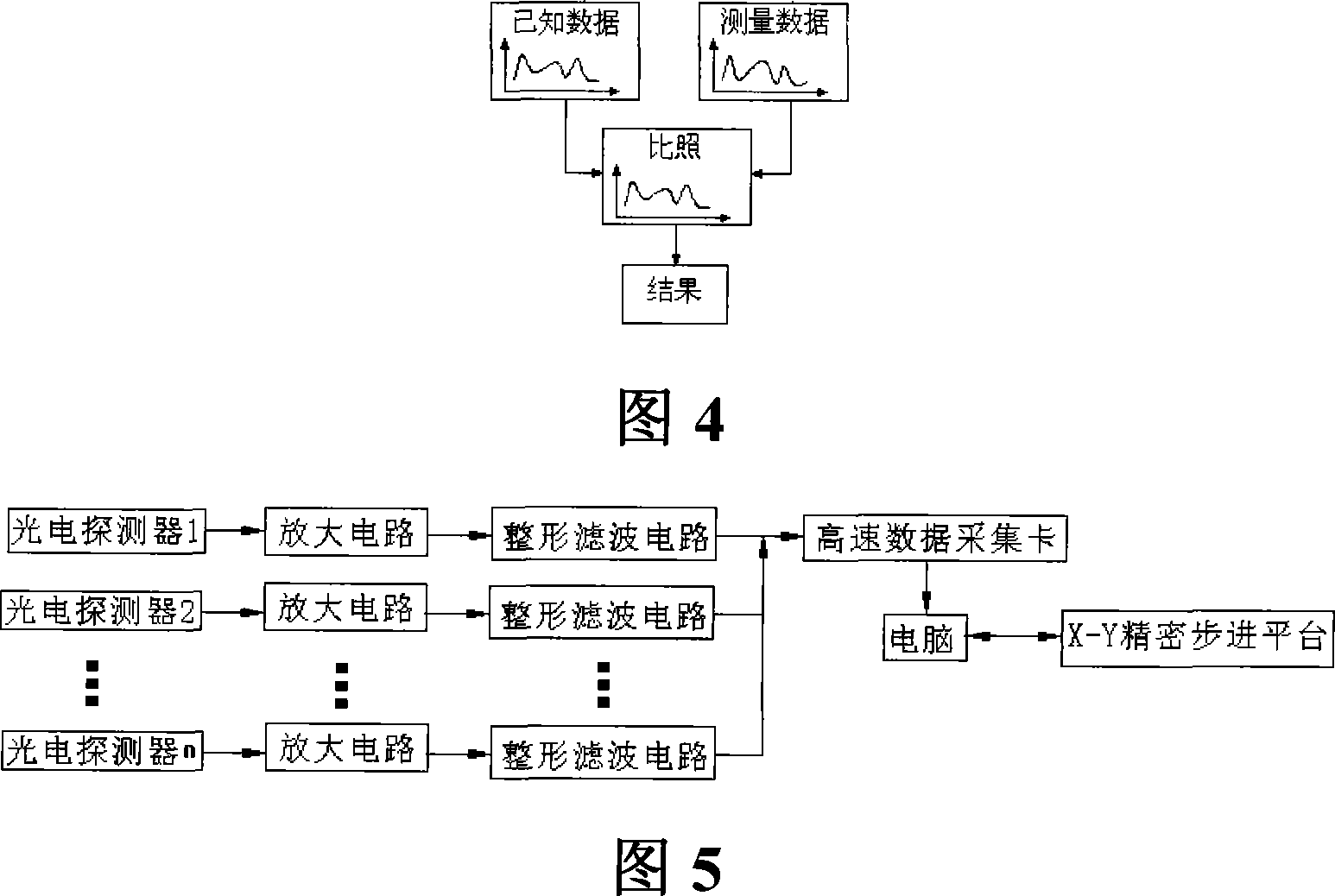
The system comprises: a X-Y precise stepping platform used for placing the optical component under test; using two laser beams to illuminate the surface of the optical component from both vertical and inclined directions; the generated scattered lights are collected by multi photoelectric detectors from different azimuth angles; converting the collected scattered lights into the electrical signals which are inputted into the computer; the computer controls the X-Y precise stepping platform to drive the optical component under test; making scan measurement, and comparing the scattered light signals with the scattered light signals used for showing the faults on the optical flat surface in order to realizing the location, classification and level of the faults on the optical flat surface.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Surface incidence graphene photoelectric detector based on one-dimensional optical grating
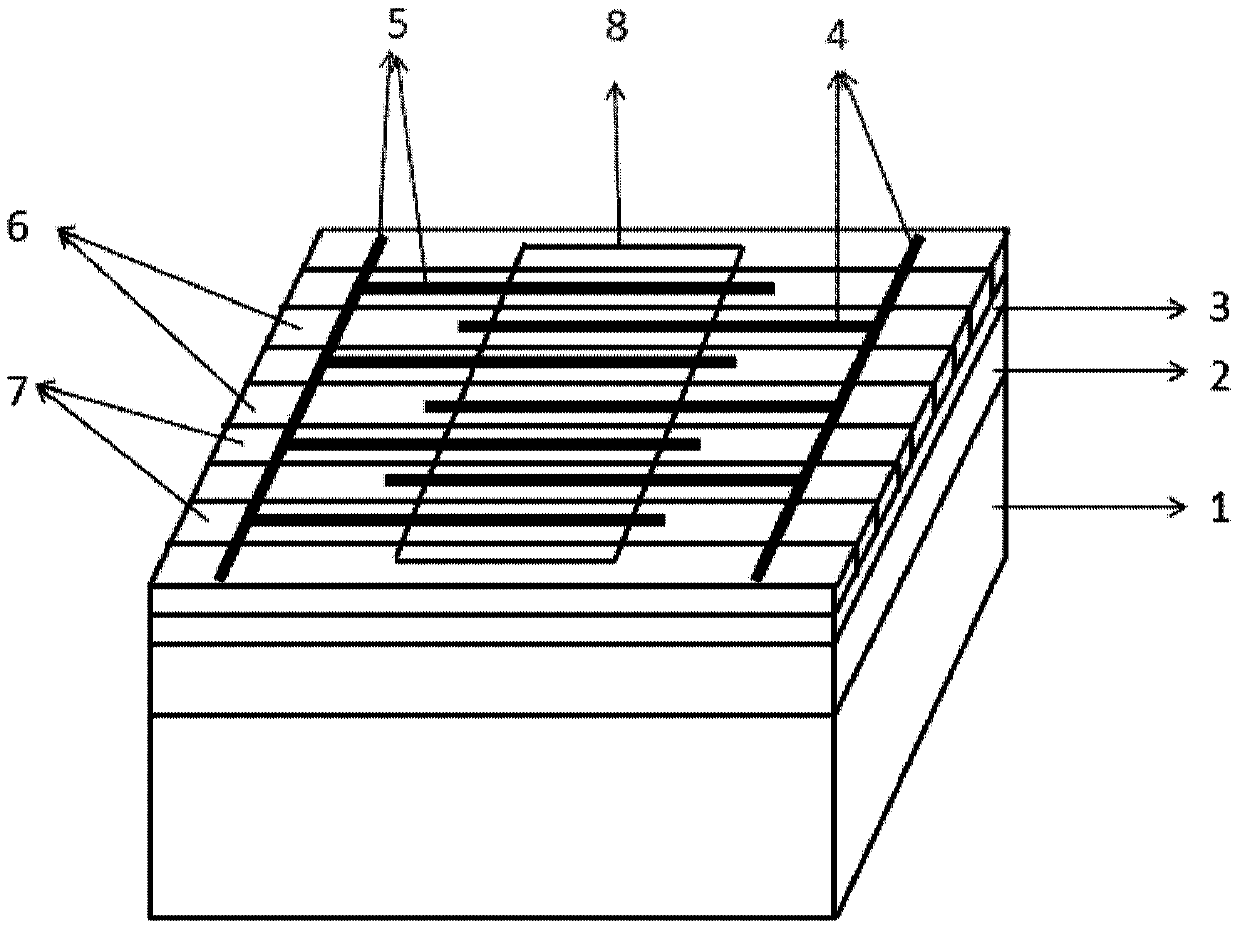
The invention discloses a surface incidence graphene photoelectric detector based on one-dimensional optical grating. The surface incidence graphene photoelectric detector based on the one-dimensional optical grating comprises a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) substrate, the one-dimensional optical grating, a graphene layer (8), a first interdigital electrode (4) and a second interdigital electrode (5), wherein the SOI substrate sequentially includes silicon, a buried oxide layer and top layer silicon from bottom to top; the top layer silicon is etched to form the one-dimensional optical grating, and the one-dimensional optical grating is formed by alternate distribution of a plurality of silicon dioxide strips (6) and a plurality of silicon strips (7) and used for modulating the space distribution of an optical field which acts with the graphene layer; the graphene layer (8) is formed on the one-dimensional optical grating and serves as an active layer to act with the surrounding optical field to generate an electron hole pair; the first interdigital electrode (4) and the second interdigital electrode (5) are formed on the graphene layer (8), the first interdigital electrode (4) and the second interdigital electrode (5) are both in contact with graphene so as to form a built-in electric field on a contact surface, and the built-in electric field is used for effectively collecting photon-generated carriers to form light current. By means of the surface incidence graphene photoelectric detector based on the one-dimensional optical grating, the optical field of incident light around the graphene is modulated through a grating structure, and thereby, high response degree and high bandwidth of infrared detection can be achieved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cascading coarse-fine data coupling optical scanning device
InactiveCN104793334ARealize coarse and fine scanningRealize fine scanningOptical elementsPlane mirrorOptical axis
The invention relates to a cascading coarse-fine data coupling optical scanning device. The cascading coarse-fine data coupling optical scanning device is formed by a rotation double-prism system and an orthogonal deflection optical panel system in the direction of an optical axis; the rotation double-prism system adopts two rotation stepping motors to respectively drive two wedge-shaped prisms to rotate surrounding a Z axis to achieve coarse scanning; the orthogonal deflection optical panel system adopts the two rotation stepping motors to respectively drive two optical panels to deflect surrounding a Y axis and a Z axis; displacement translation of light beams within local ranges through the displacement translation of refraction light beams and an exquisite scanning requirement is satisfied; two sets of prim systems of the rotation double-prism system are both formed by a base, a rotation stepping motor, an encoder, a wedge-shaped prism, an optical frame, a worm gear, a worm and a mirror bracket; the orthogonal deflection optical panel system is formed by a second base, a third mirror bracket, a third rotation stepping motor, a first plane mirror, a third mirror frame, a third encoder, a fourth encoder, a fourth mirror frame, a second plane mirror, a fourth rotation stepping motor and a fourth mirror frame. According to the cascading coarse-fine data coupling optical scanning device, the light beam propagation direction is easy to control and control is convenient.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Large-sized optical flat interferometry device and method
InactiveCN101240999AGet medium and high frequency errorsIncrease horizontal resolutionUsing optical meansTesting optical propertiesLinear motionMeasurement device
The invention discloses a device and method of interferometry for a large-scale optical plane. Wherein, the interferometry device comprises an adjustment platform for the two-axis linear motion of an interferometer, a two-dimensional tilt adjustment platform for the measured plane mirror located at the front of the adjustment platform, a laser wave-front interferometer installed in the adjustment platform for the two-axis linear motion of an interferometer and a control computer contained the program of measured data processing algorithm, which is connected to the laser wave-front interferometer. With the device, a plurality of obtained error surface maps of partial region can be spliced to an error surface map containing medium-high frequency (MHF) band on the whole caliber according to the measured data processing algorithm through the control computer, which includes a method for determining the initial position, an algorithm for extracting data from the overlap region and an algorithm for splicing the area data. The invention is a device and method of interferometry for a large-scale optical plane with low cost, high precision and high efficiency.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Polarization phase shifting double shearing interference wave face measuring apparatus and inspect method thereof
InactiveCN101140186AFully restoredComplete measurementOptical measurementsPolarising elementsPhase shiftedParallel plate
The invention relates to a polarization phase-shifting double-shear interference wave surface measuring instrument and a detection method, wherein the measuring instrument orderly comprises a first Yamin parallel plate, a left lower wedge-shaped optical plate, a left upper wedge-shaped optical plate, a right lower wedge-shaped optical plate, a right upper wedge-shaped optical plate, a second Yamin parallel plate, a polarization phase shifter, an imaging mirror group and an image sensor along the forward direction of light beam, and the output end of the image sensor is connected with a computer. The invention not only keeps all characteristics of the double-shear interference wave surface measuring instrument, but also has the advantages of the high sensitivity, the accurate measurement of random symmetrical wave surfaces and the supply of complete wave surface profile.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for manufacturing multi-wavelength volume bragg gratings
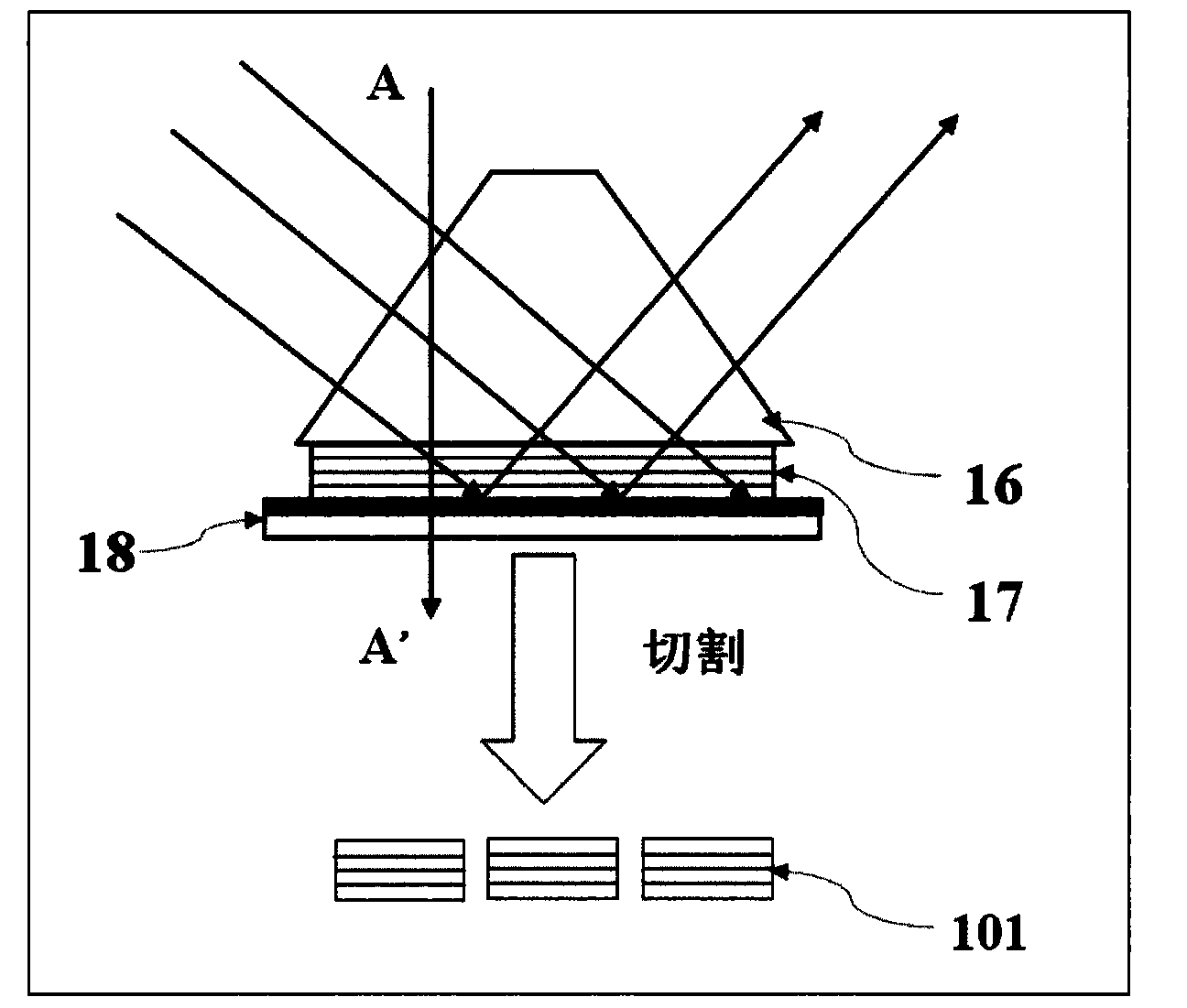
ActiveCN104133267AEasy to fixThe production process is simple and practicalCladded optical fibrePhotomechanical apparatusGratingUltraviolet lights
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing multi-wavelength VBGs. The method particularly includes the steps that an ultraviolet light passes through a trapezoid prism to irradiate photosensitive dielectric PTR glass; incoming recording light is reflected through an auxiliary optical flat or the PTR glass, the reflected recording light and the incoming recording light are intervened in the PTR glass to form standing waves; the wavelength of a tuning laser source or a rotary laser reflection element enables the incoming angle of the recording light to be changed, and exposure in different periods is achieved; heat processing and cutting are carried out on the PTR glass obtained after exposure, and the multi-wavelength VBGs are finally obtained. The method for manufacturing the multi-wavelength VBGs is concise and practical, continuous tuning of the VBG working wavelength can be achieved under the condition that a recording device is kept unchanged; the clear aperture of the manufactured VBGs is not limited by sample absorption or other kinds of performance of materials; incoming of only one beam of recording light is needed, so that the recoding device is greatly simplified, and the large-amount efficient manufacturing of the VBGs is facilitated.
Owner:林安英 +1
Suspended 360-degree optical field three-dimension display device and method based on flat plane display
ActiveCN103048866AHigh image resolutionHigh viewing angle resolutionProjectorsStereoscopic photographyParallaxOptical axis
The invention discloses a suspended 360-degree optical field three-dimension display device and method based on a flat plane display. The device comprises a flat plane display array, a first lens group array, a second lens and a scattering screen which are arranged in sequence, wherein the flat plane display array is formed by splicing a plurality of flat plane displays; each flat plane display is used for displaying one part of various 360-degree sub-images around one circle of a three-dimension object, namely a sub-image sequence; various sub-images in the image sequences displayed by the flat plane display array, each first lens group in the first lens group arrays and various view points of an observation area correspond to one another. One observer can only see one sub-image at one view point. Through controlling the parameters such as the number of the sub-images displayed by the flat plane display array, an optical axis inclined angle of the overall system and the scattering angle of the scattering screen, the eyes of the observer in the observation area can be located in different view points, so that the two different sub-images displayed on the flat plane display array can be observed, and binocular parallax can be produced, thereby reaching the effect of watching three-dimension scenes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
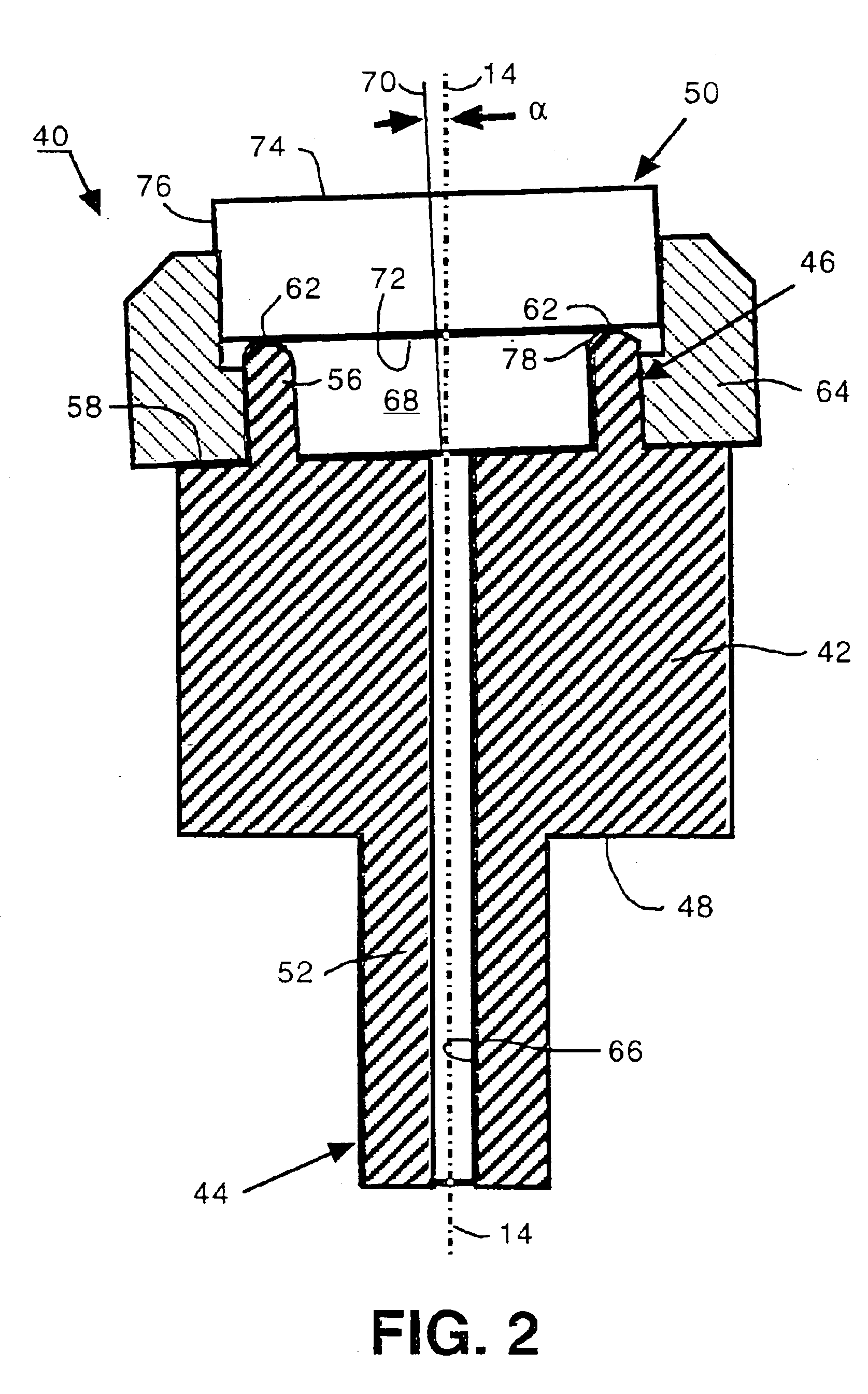
Part-holding fixture for grinding wedged optical flats
InactiveUS6855036B1Low costAvoid interfering with grinding processEdge grinding machinesOptical surface grinding machinesWedge angleOptical flat
A part-holding fixture is adapted for rotation about a work spindle axis and includes a mounting land that seals a back surface of an optical flat for securing the optical flat to the part-holding fixture and that inclines the back surface of the optical flat through a wedge angle for grinding wedged optical flats at repeatable wedge angles.
Owner:CORNING TROPEL
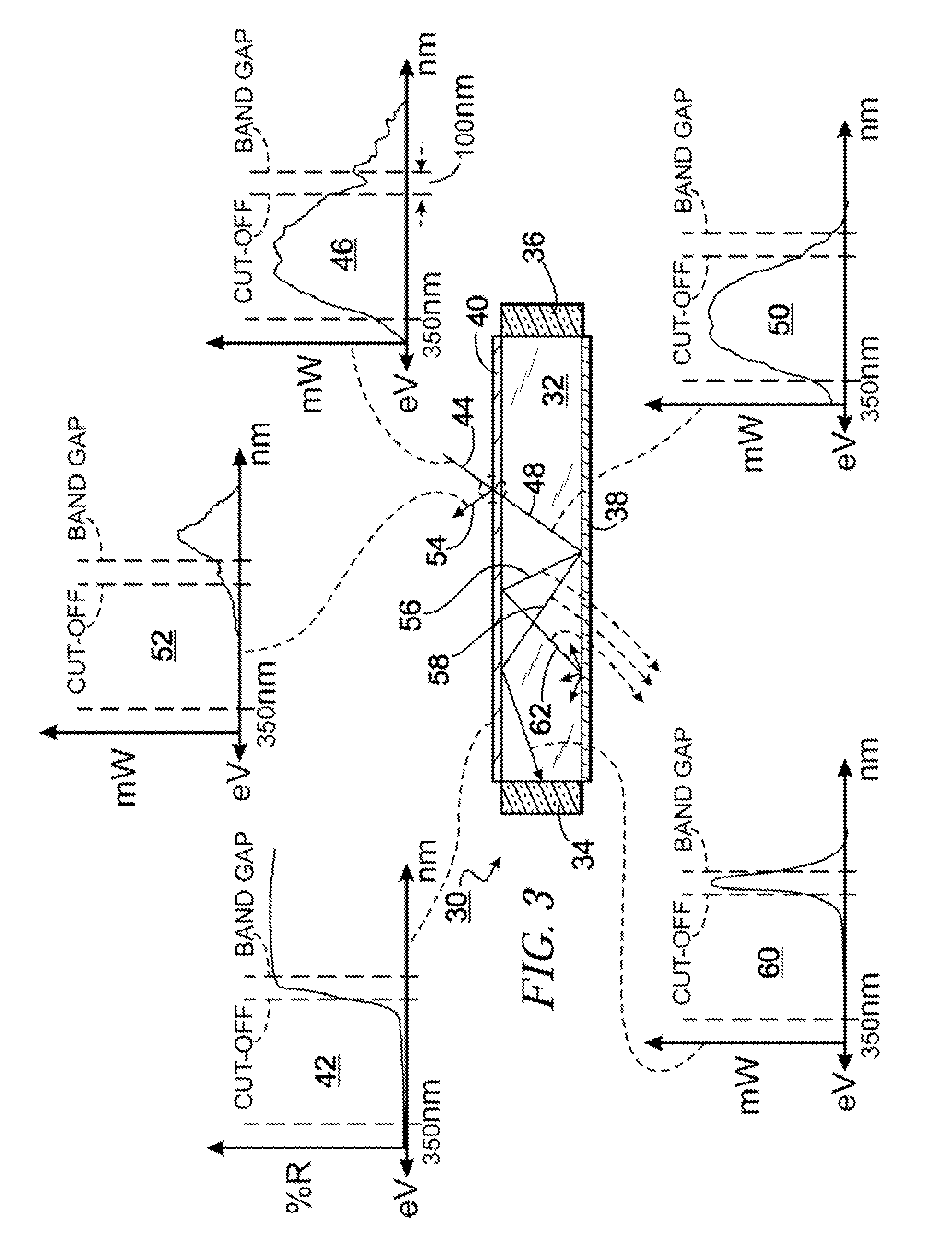
Photovoltaic Conversion Assembly with Concentrating Optics
InactiveUS20100275999A1Spread the wordPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesLight energyOptical flat
A photovoltaic conversion assembly comprises an optical slab with first and second major surfaces and an intermediate surface therebetween. Light energy to be collected impinges as incoming photons on the first major surface. At least one PV cell is mounted to receive light energy from the intermediate surface of the optical slab and convert such light energy to electrical energy. The PV cell has a highest band gap E. A down-converting structure is located on the second major surface of the slab for converting to lower energy light received through the slab, with at least about 75 percent of the converted light having an energy level above the band gap E. A two-way spectrally selective reflector, located proximate the first major surface, cooperates with the down-converting structure for preventing high angle light from undesirably exiting the optical slab via the first major surface.
Owner:ENERGY FOCUS INC
Phase-controllable birefringence space light bridge
InactiveCN101561554AOvercome the difficult problem of optical path transmission assemblyOvercoming uncontrollable difficultiesPolarising elementsFree-space transmissionPhase differenceOptical flat
The invention relates to a phase-controllable birefringence space light bridge, which uses a combined birefringence optical flat to achieve light splitting synthesis of two input light beams, wherein a quarter-wave plate performs phase-shift control and is used for space compounding of a laser communication signal light beam and a local oscillation laser beam in a coherent optical communication receiver and outputting four paths of synthesized light beams with a required phase-shift relation so as to achieve 2*4 space light bridging. The quarter-wave plate makes two perpendicular polarized components generate 90-degree phase shift, and the phase difference between the two components can be changed by rotating the optical axis direction so as to compensate phase errors generated by errors of processing, assembling, calibration and the like, thus the phase-controllable birefringence space light bridge has the advantages of simple structure, stable performance and controllable phase. The phase-controllable birefringence space light bridge is applicable in the field of free space laser coherent communication and laser radar.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Production method for sensitivity enhanced extrinsic F-P optical fiber temperature sensor
InactiveCN101476949AImprove reliabilityHigh temperature sensitivityThermometers using physical/chemical changesCoupling light guidesStress concentrationTemperature response
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a sensitized extrinsic F-P optical fiber temperature sensor, which belongs to the technical field of a sensor. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps that: deficiency is generated by carving, and a flat end surface of an optical fiber is formed by tensing carved deficiency and using the characteristic that stress on the carved deficiency is concentrated; and a metal capillary tube and a bare optical fiber of an extrinsic F-P interface cavity are bonded together by a bonding agent, and the sensitized extrinsic F-P optical fiber temperature sensor is formed by two optical flat end surfaces and the metal capillary tube which has thermal expansion coefficients more than those of a glass capillary tube. The method has the advantages that the sensitized extrinsic F-P optical fiber temperature sensor which has excellent optical end surface and has no impurities in the interference cavity can be obtained, has fast temperature response, high temperature sensitivity, small volume, simple structure, high reliability, flexible manufacture, and the like, and can be used for high accuracy temperature measurement in strong electromagnetic radiating, inflammable and explosive and other situations.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Laser mark printing device for section steel
InactiveCN101121349ADoes not change mechanical propertiesCausing mechanical deformationAblative recordingLaser beam welding apparatusGraphicsOptical flat
The invention relates to the field of laser marking. The invention discloses a laser marking device for section steel, which includes a computer system, a laser, and an optical flat-field mirror located below the light-emitting part of the laser. It is characterized in that it also includes a main workbench trolley , workpiece, laser X-direction precision sliding table, laser Y-direction precision lifting mechanism, guide rail, driven work trolley, among which, the main workbench trolley and the slave work trolley are on the guide rail, and the workpiece is placed on the main workbench trolley and the slave work trolley The upper surface of the trolley is located below the optical flat field mirror. The invention has high efficiency, does not affect the performance of workpieces, can realize laser marking on large workpieces, changes the operation mode of manual painting on section steel for model marking, and can mark permanent pictures and texts on section steel.
Owner:武汉楚天激光(集团)股份有限公司
Mode converter having multi-layer structure and optical branching device
ActiveCN102156324AImprove coupling efficiencyReduce one etching processOptical waveguide light guideRidge waveguidesOptical flat
The invention discloses a mode converter having a multi-layer structure and an optical branching device. The mode converter comprises flat waveguides and at least three layers of ridge waveguides which are arranged on the flat waveguide, wherein the width of each layer of ridge waveguides is gradually decreased from an input end to an output end; when the width is decreased to a certain value, the layer of ridge waveguides is cut off, namely one layer of the at least three layers of ridge waveguides is reduced, so that the height of the ridge waveguides is reduced gradually; the input end is farther away from a cut-off position of the ridge waveguides of the optical flat waveguides; and the output end of the mode converter consists of the single-layer flat waveguides and the single-layer ridge waveguides. A transverse free propagation area of the optical branching device consists of the flat waveguides without transverse limitation. Compared with the prior art, a technology provided by the invention has the advantages that: the efficiency of coupling from optical fibres to an optical device can be improved, a one-step etching process is reduced, and the stability of mode transmission in the optical device is improved at the same time.
Owner:SHANGHAI SILIGHT TECH
Light projection device used for three-dimensional measurement of object surface
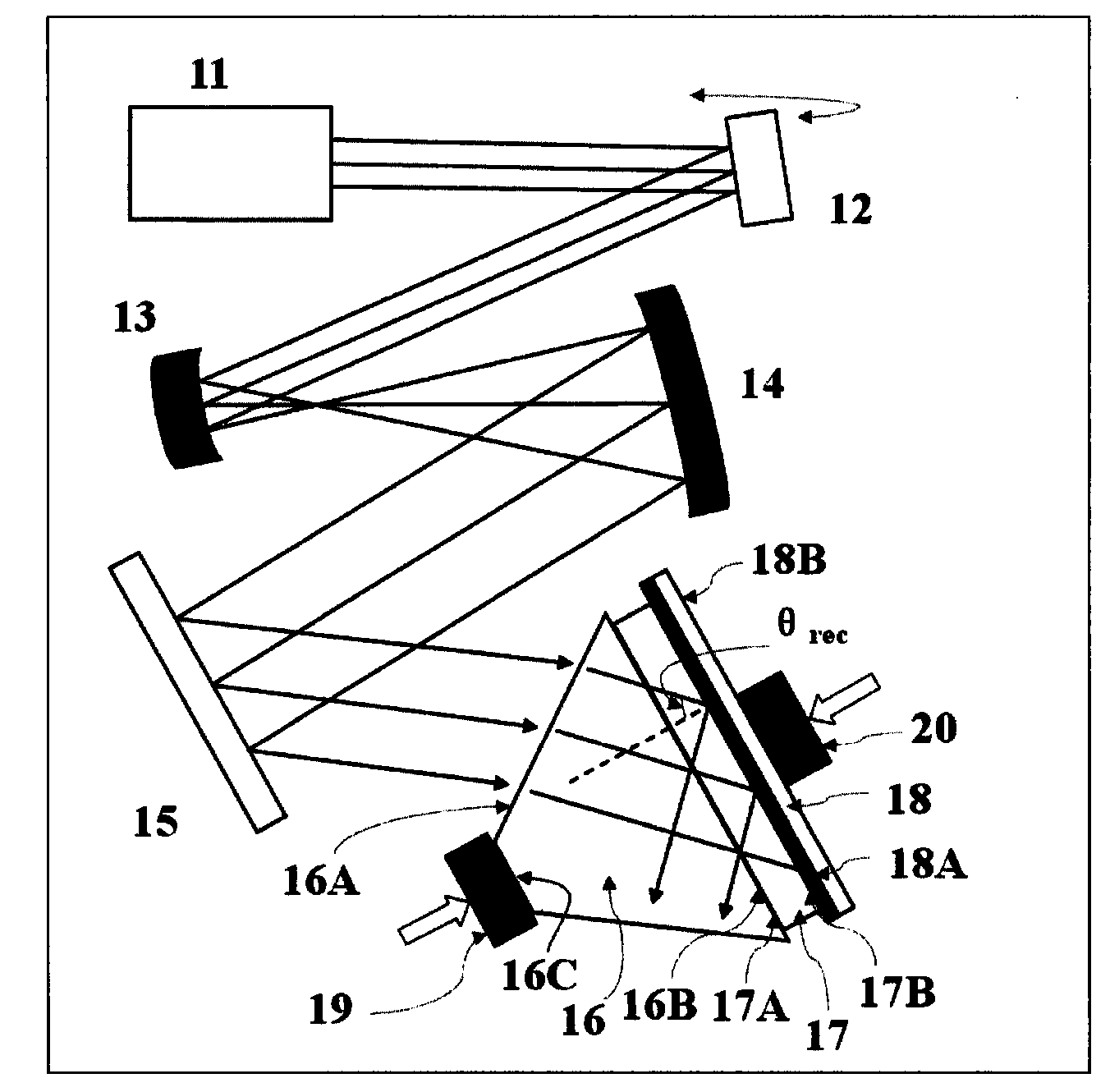
ActiveCN106403846AReduce processing difficultyIncrease brightnessUsing optical meansPhase shiftedThree dimensional measurement
The invention discloses a light projection device used for the three-dimensional measurement of an object surface. Laser generated by a laser generates polarized light through an optical expansion unit, a mirror and a first polarizing piece. The polarized light is projected to front and back surfaces of a first sensitive optical flat plate, and forms two light paths through the sensitive optical flat plate. The first light path forms vertical polarized light through a second polarizing piece, and the vertical polarized light is projected onto a second sensitive optical flat plate through a first optical wedge pair. The second light path forms vertical polarized light through a third polarizing piece, and the vertical polarized light is projected onto the second sensitive optical flat plate through a second optical wedge pair. Two light paths form combined beam through the second sensitive optical flat plate, and the combined beam is enlarged sequentially through a 1 / 4 wave piece, an adjustable polarizing piece and a projection objective, and is projected onto the measured object surface. According to the invention, a polarization technology and a phase shift stripe technology are combined; the three-dimensional topography of the surface of various objects of different structures is measured by a machine / off-machine; and the light projection device has strong abilities of vibration resistance and noise dynamic, and especially has strong robustness for the surface measurement of molds with complex structures.
Owner:深圳中科岹科技有限公司
Method and apparatus rapidly regulating lidar transmit-receive system light path coaxial
InactiveCN101251598ASimple structureLow machining accuracy requirementsSurveying instrumentsElectromagnetic wave reradiationTransceiverLight beam
The invention discloses a method and a device capable of realizing fast coaxial adjustment of a lidar transceiver system light path. The device comprises a receiving telescope, a laser, a first wedge-shaped optic flat plate, a second wedge-shaped optic flat plate and a drive step motor thereof and a computer, etc. The two wedge-shaped optic flat plates are driven to rotate by the motor under the control of the computer, thereby ensuring that the direction of an emergent light beam changes continuously within a certain tapered space angular range. The method and the device can realize convenient and fast coaxial adjustment of the lasing beam of a lidar and a receiving telescope system.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for measuring light beam orbit angular momentum spectrum
InactiveCN101334315AImprove parallelismImprove coaxialityOptical measurementsPhotometryBeam splittingPower detector
The invention relates to a method for realizing beam orbital angular momentum spectrometry, which belongs to the technical field of laser application. The invention consists of a light source to be tested, two polarization dispersion prisms, 1 / 2 wave plate, two parallel optical flats, two pieces of 1 / 4 wave plates, a total reflector, a rectangular prism, a Porro prism, a Pi / 2 phase delay piece and a power detector. The invention adopts the two parallel optical flats and the rectangular prism to realize the beam splitting and the beam combining of the beams, ensure the good parallelism of beam splitting light and the coaxiality of beam combining light, and realize the complete identical optical paths and attenuation of the two bunches of light. The invention adopts the polarization dispersion prism, the total reflector, the Porro prism and the two 1 / 4 wave plates to realize the beam splitting, and the two bunches of light obtained by the beam splitting rotate coaxially to further realize the coaxial superimposition of the beam and a rotating mirror image thereof. The orbital angular momentum spectrum of an incident beam can be analyzed by measuring the relation between the power of the beam combining light and the rotation of the Porro prism. The method of the invention has application value in the laser intelligence processing field.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Tuning method for optic tunable filter
The invention discloses a tuning method for an optic tunable filter, wherein the optic tunable filter is a thin or ultrathin optic parallel plate and the tuning of the optic tunable filter is realized by changing the optical path difference of lights in the optic plate. The ultrathin optic parallel plate is a micron-level ultrathin plate, which is made of materials having a certain optical band and the refractive index or thickness of which can change following the change of temperature field, electric field or magnetic field; a better filtering property also can be achieved under the condition of being free from plating a high-reflectance coating, by utilizing the characteristics that the reflectance is high when the light enters into a natural optical surface in grazing incidence manner (theta is more than 80 degrees); and the ultrathin optic parallel plate also can be made of common materials, through which a certain optical band can permeate, and the tuning of the optic tunable filter can be realized by changing the incident angle of the light by rotating the plate. The invention designs a grazing incidence optic filter, aiming at the difficulty of plating film on the ultrathin plate, thereby solving the difficulty of plating film as well as realizing filtering the optical wave of full-transmission light.
Owner:FUZHOU PHOTOP QPTICS CO LTD
Absolute measurement method of homogeneity of optical flat
ActiveCN106501216AFew stepsEasy to operatePhase-affecting property measurementsFlat glassRefractive index
The invention discloses an absolute measurement method of homogeneity of an optical flat, belonging to the field of optical interferometry. The method comprises the following steps: 1. putting detected optical flat into a measurement light path, and measuring the wave surface deviation of interference cavities formed by the front and back surfaces of the optical flat; 2. putting the optical flat into an interferometry cavity formed by reference optical flat working surfaces and reflection optical flat working surfaces, and measuring the aberration of waves reflected by the optical flat; 3. removing the detected optical flat from the interferometry cavity, and measuring the wave surface deviation of the interferometry cavity formed by the reference optical flat working surfaces and reflection optical flat working surfaces; and calculating the homogeneity distribution of the detected optical flat according to the three measurement results. The method has the advantages of fewer steps and high accuracy, is simple to operate, and can be used for high-precision measurement of refractivity homogeneity distribution of the optical flat for laser working materials and spacecraft window glass.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Optical flat structure achieving air imaging
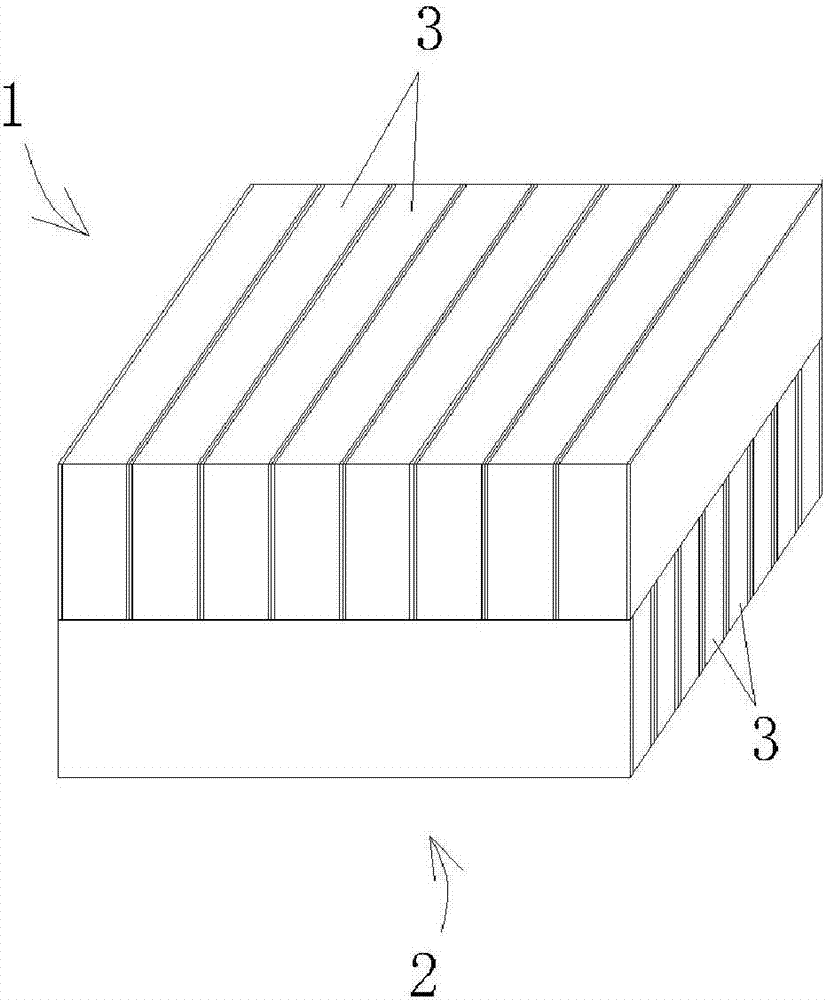
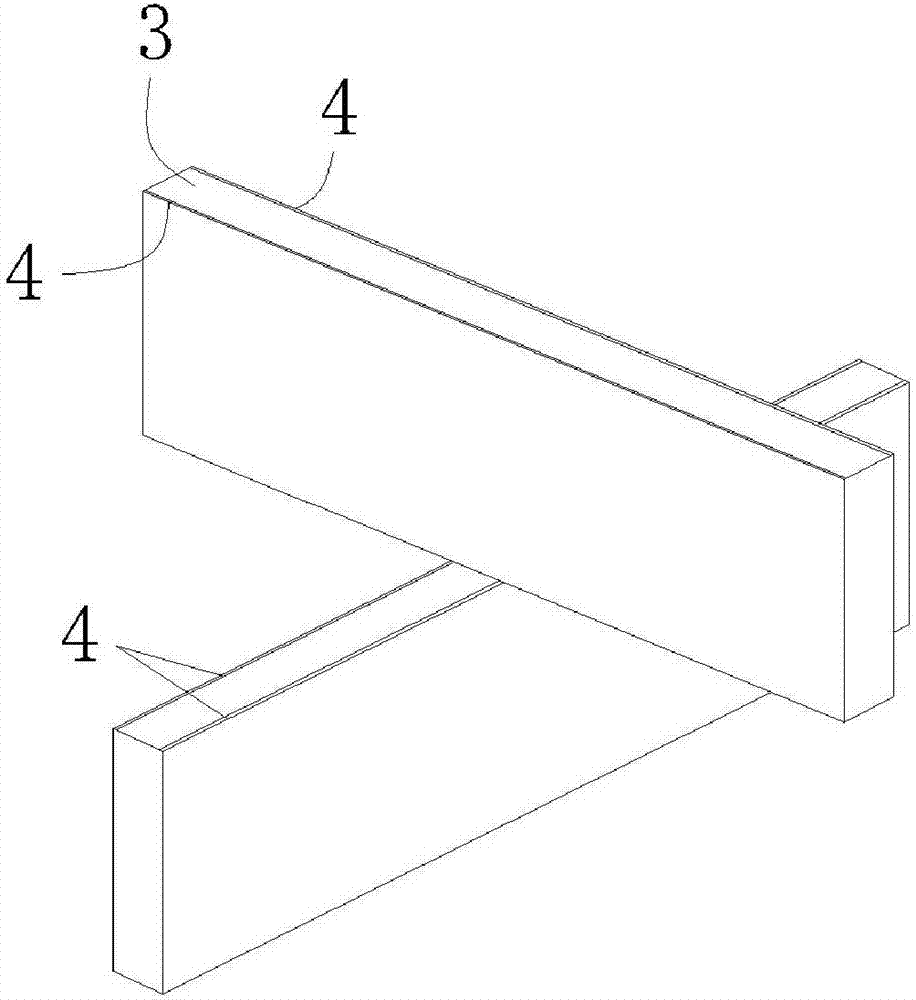
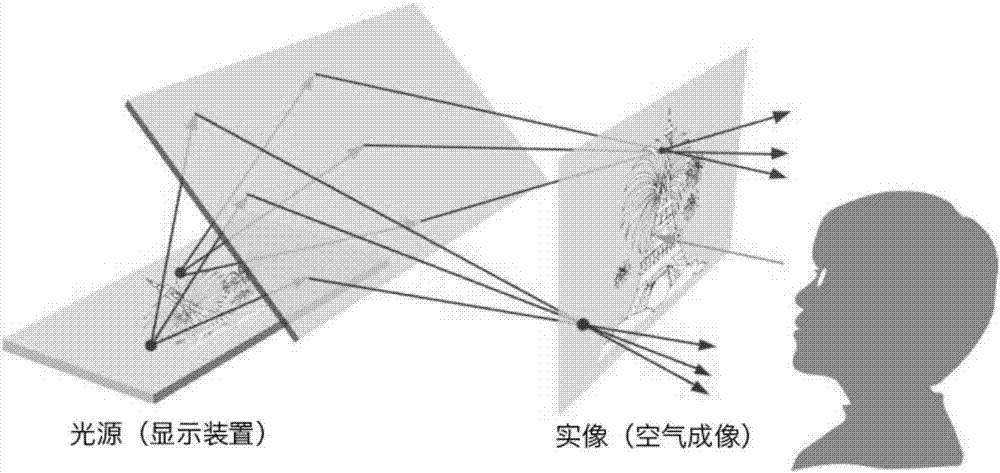
PendingCN107193125ARealize Holographic ImageTrue hologramOptical elementsSystem integrationOptical flat
The invention provides an optical flat structure achieving air imaging. The optical flat structure is characterized by comprising an upper lens and a lower lens which are overlaid in a closely attached mode; the upper lens and the lower lens are both formed by multiple reflecting bars which are perpendicular to the lens surface and arranged in parallel, reflecting films are arranged on the two side faces of each reflecting bar respectively, and the reflecting bars of the upper lens and the reflecting bars of the lower lens are arranged in an orthogonal mode. According to the optical flat structure, through an optical panel reconstructed through a special precise microstructure, a two-dimensional or three-dimensional light source can form a real image in air directly to realize a real holographic image; the structure is simple, a real image can be directly formed before a user's eyes, and real holographic interaction can be achieved through system integration in the later stage.
Owner:ANHUI EASPEED TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Reflection cavity type confocal measuring method of super-large radius of curvature
InactiveCN103673926AReduce the impactImprove focus accuracyUsing optical meansOptical flatFocal position
The invention belongs to the field of optical precision measurement technology and relates to a reflection cavity type confocal measuring method of super-large radius of curvature. According to the method, by a confocal focusing theory in cooperation with parallel optical flat, a focal position of a measured surface is positioned accurately so as to further realize high-precision measurement of super-large radius of curvature. The method combining the confocal focusing theory and a reflection cavity type folded optical path theory has advantages as follows: displacement distance of a measured piece is small; optical path is simple; measurement precision is high; measuring speed is fast; environmental disturbance resistance is strong; and the measured surface is not damaged. The method provided by the invention can be used in high-precision non-contact measurement of super-large radius of curvature.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Polarizing beam-splitting birefringence space light bridge
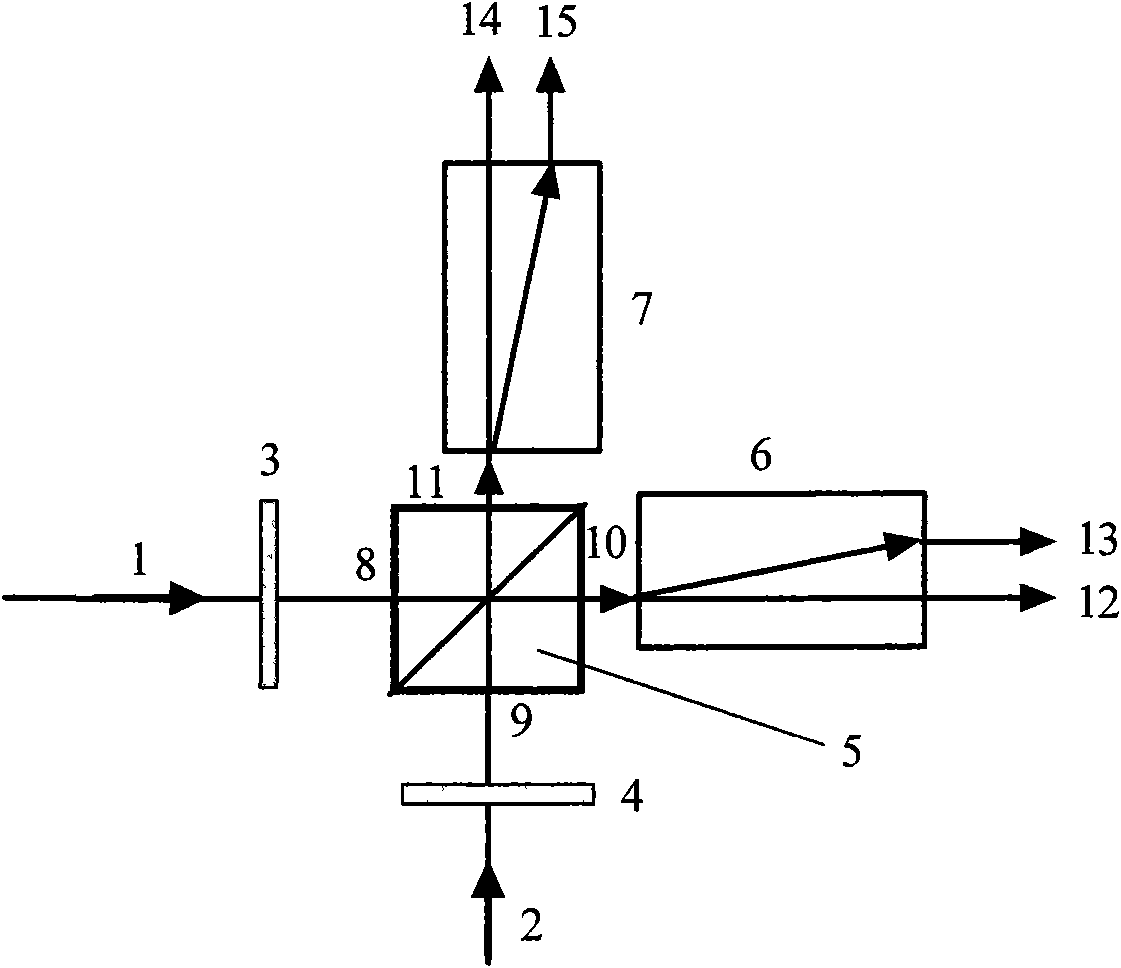
InactiveCN101561560ACompact structureImprove performancePolarising elementsFree-space transmissionBeam splitterCommunications system
The invention relates to a polarizing beam-splitting birefringence space light bridge, which is characterized by consisting of a first 1 / 8 wave plate, a second 1 / 8 wave plate, a polarizing beam splitter, a first birefringence optical flat and a second birefringence optical flat, wherein the first 1 / 8 wave plate, a first incident face of the polarizing beam splitter, a first emergent face and the first birefringence optical flat are arranged in turn along the advancing direction of a first light beam; the second 1 / 8 wave plate, a second incident face of the polarizing beam splitter, a second emergent face and the second birefringence optical flat are arranged in turn along the advancing direction of a second light beam; and the main cross section of the first birefringence optical flat is parallel to the main cross section of the first 1 / 8 wave plate, and the main cross section of the second birefringence optical flat is parallel to the main cross section of the second 1 / 8 wave plate. The polarizing beam-splitting birefringence space light bridge has the advantages of compact structure, stable performance, adjustable phase and the like, and is applicable to a coherent laser communication system with free space transmission.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Vertical shape measuring device capable of compensating shaft system errors of wafer
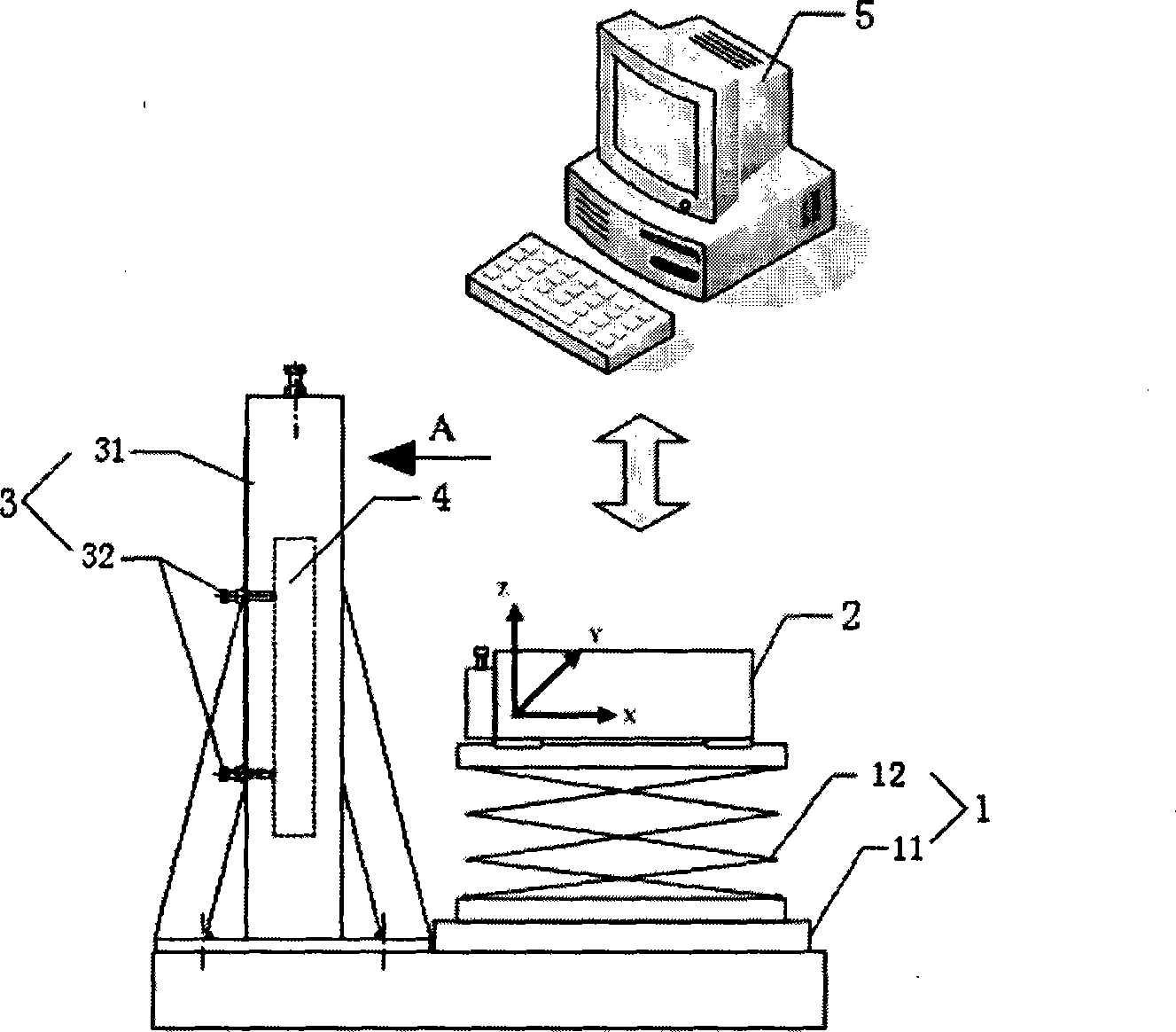
InactiveCN103389052ASolve functionSolve the problem that the measurement force is difficult to controlUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceOptical flat
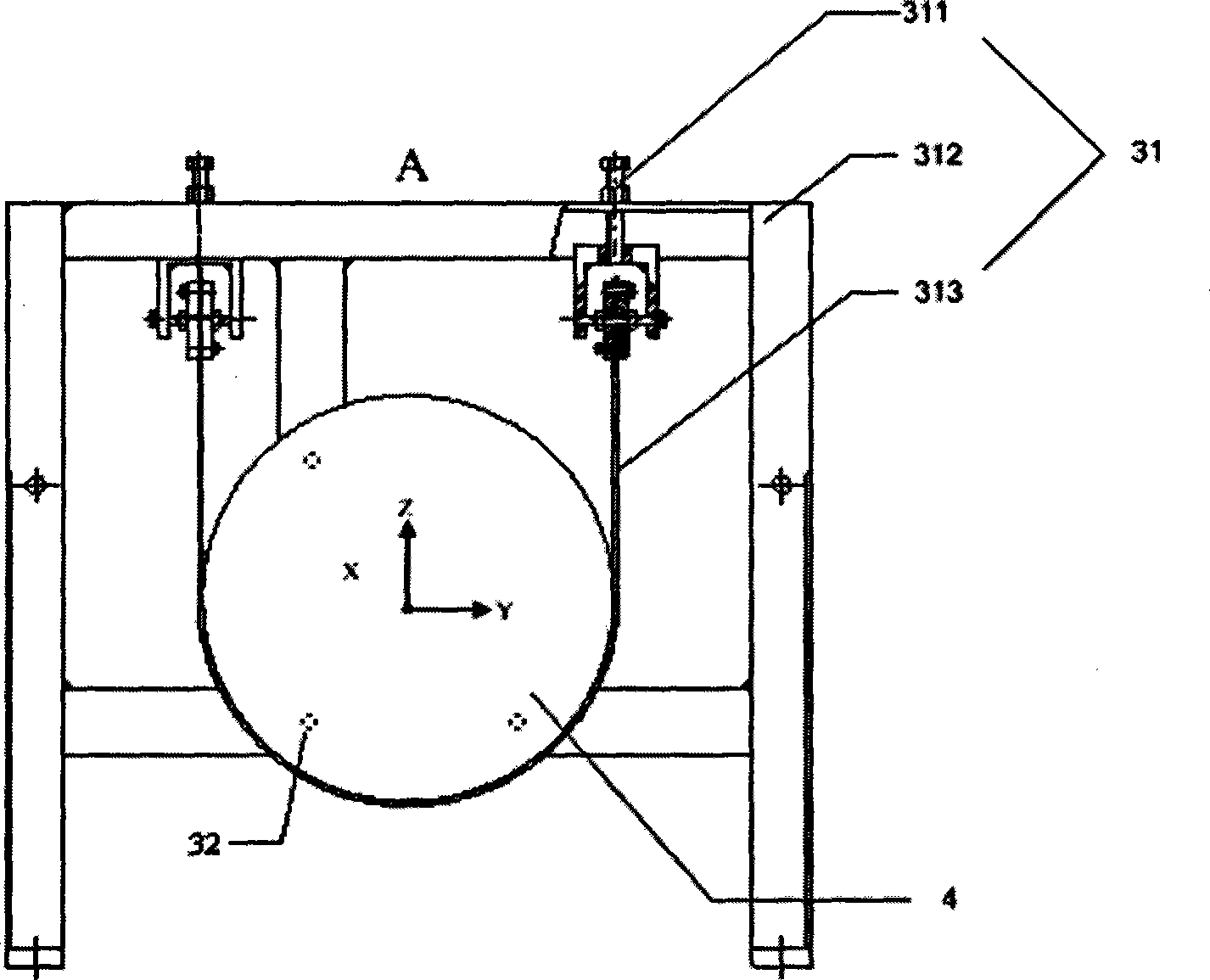
A vertical shape measuring device capable of compensating shaft system errors of a wafer, which comprises a steel frame base, a platform, a support seat, a beam, a shaft system, a wafer bearing table, a contact-type length measuring device, and an optical flat, wherein the platform is arranged on the steel frame base; the support seat is arranged on the platform; the beam is arranged on the support seat; the shaft system comprises an X shaft, a Y shaft, a Z shaft, and a rotating shaft, the X shaft is arranged on the beam, the Y shaft is arranged on the platform and is perpendicular to the X shaft mutually, the Z shaft is fixed on an X shaft movable plate and is perpendicular to the motion direction of the X shaft mutually, the motion direction of the Z shaft is perpendicular to the measuring platform, and the rotating shaft is fixed on a Y shaft movable plate; the wafer bearing table is fixed on the rotating shaft; the contact-type length measuring device is fixed on a Z shaft movable plate; the optical flat is fixed on the beam parallel to the motion direction of the X shaft. The shape measuring device has simple structure, high integrated level, and full functions, and provides a solution for the measuring of wafer shape parameters.
Owner:KUNSHAN YUNCO PRECISION IND TECH
Method for correcting system error during splicing sub-aperture
The invention discloses a method for correcting a system error during splicing sub-aperture. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a two-dimensional profile curve of a reference optical flat on a splicing shaft by utilizing absolute plane inspection participated by an auxiliary optical flat; constructing a surface shape error correction wave surface of the reference optical flat by utilizing data of the profile curve; and performing real-time correction during measurement of the sub-aperture. By the method, the influence of a surface shape error of the reference optical flat on the solving of an inclined coefficient during splicing the sub-aperture can be reduced to the greatest extent, and the precision of a splicing wave surface is effectively improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com