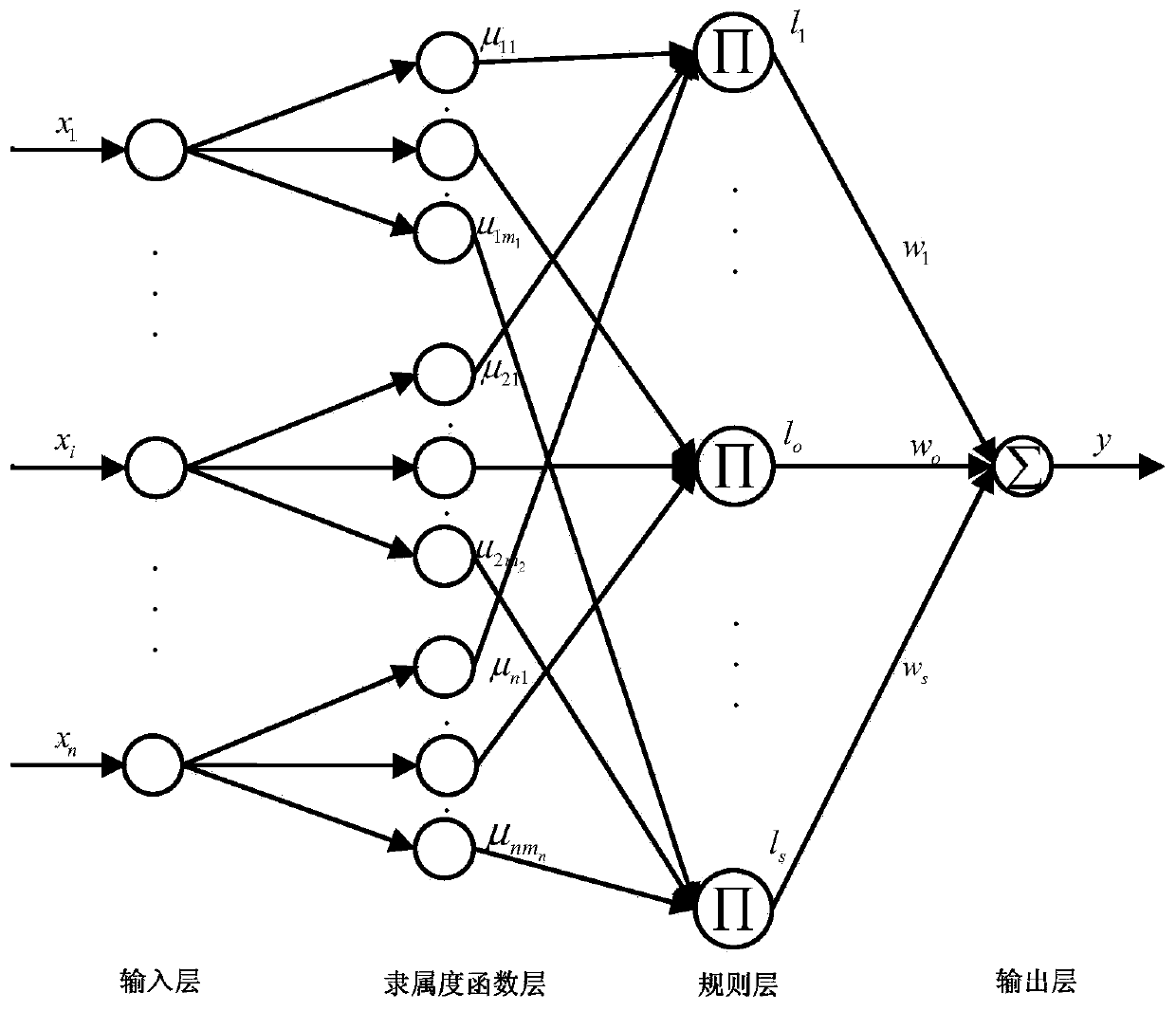
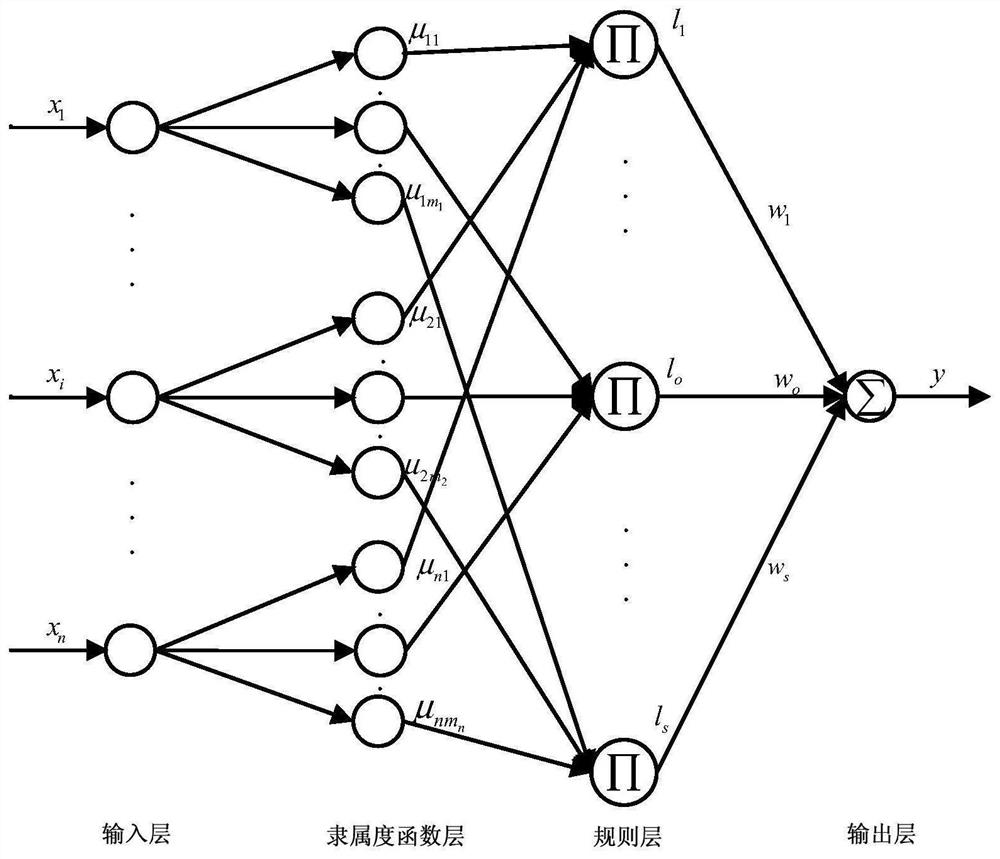
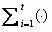Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Error surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
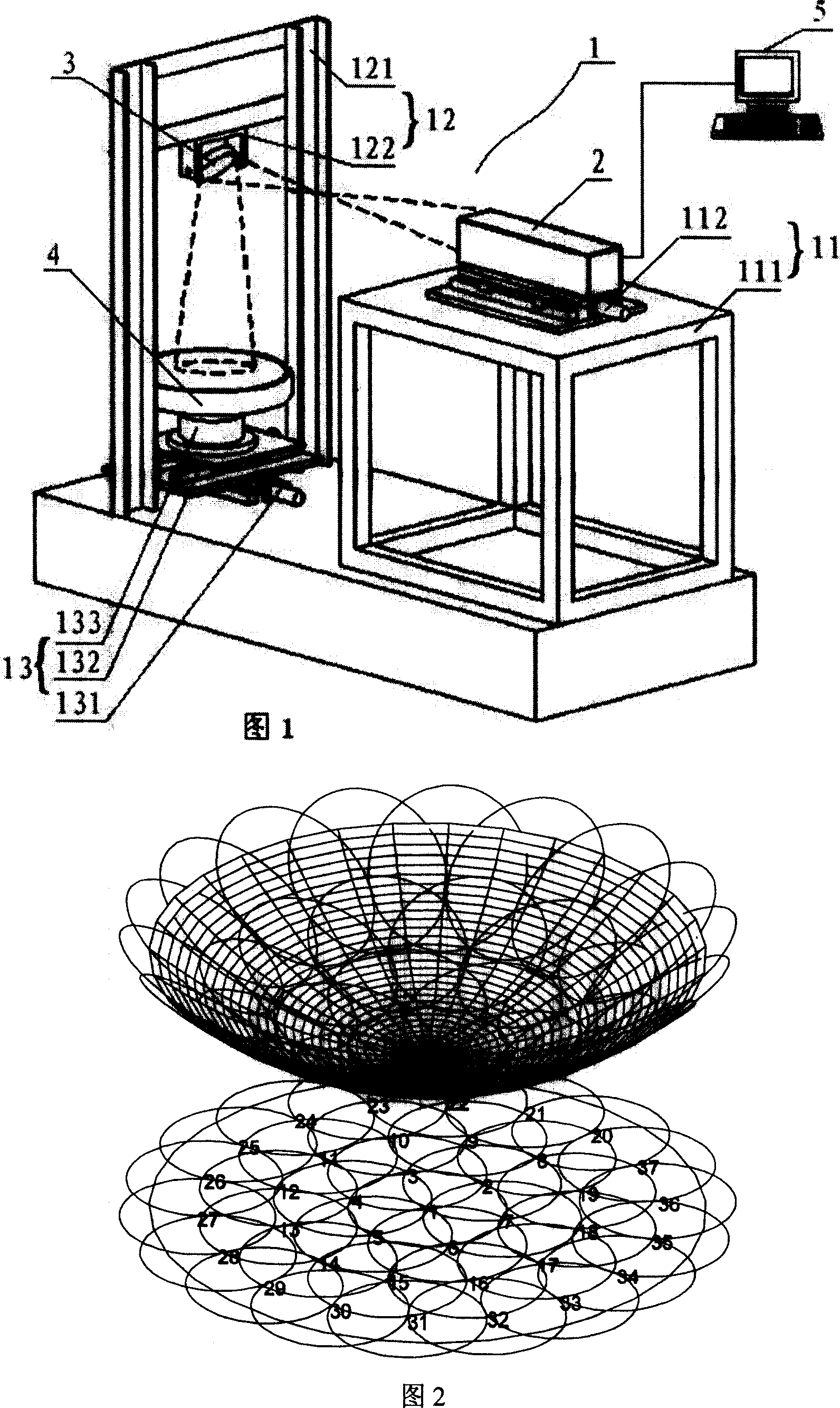
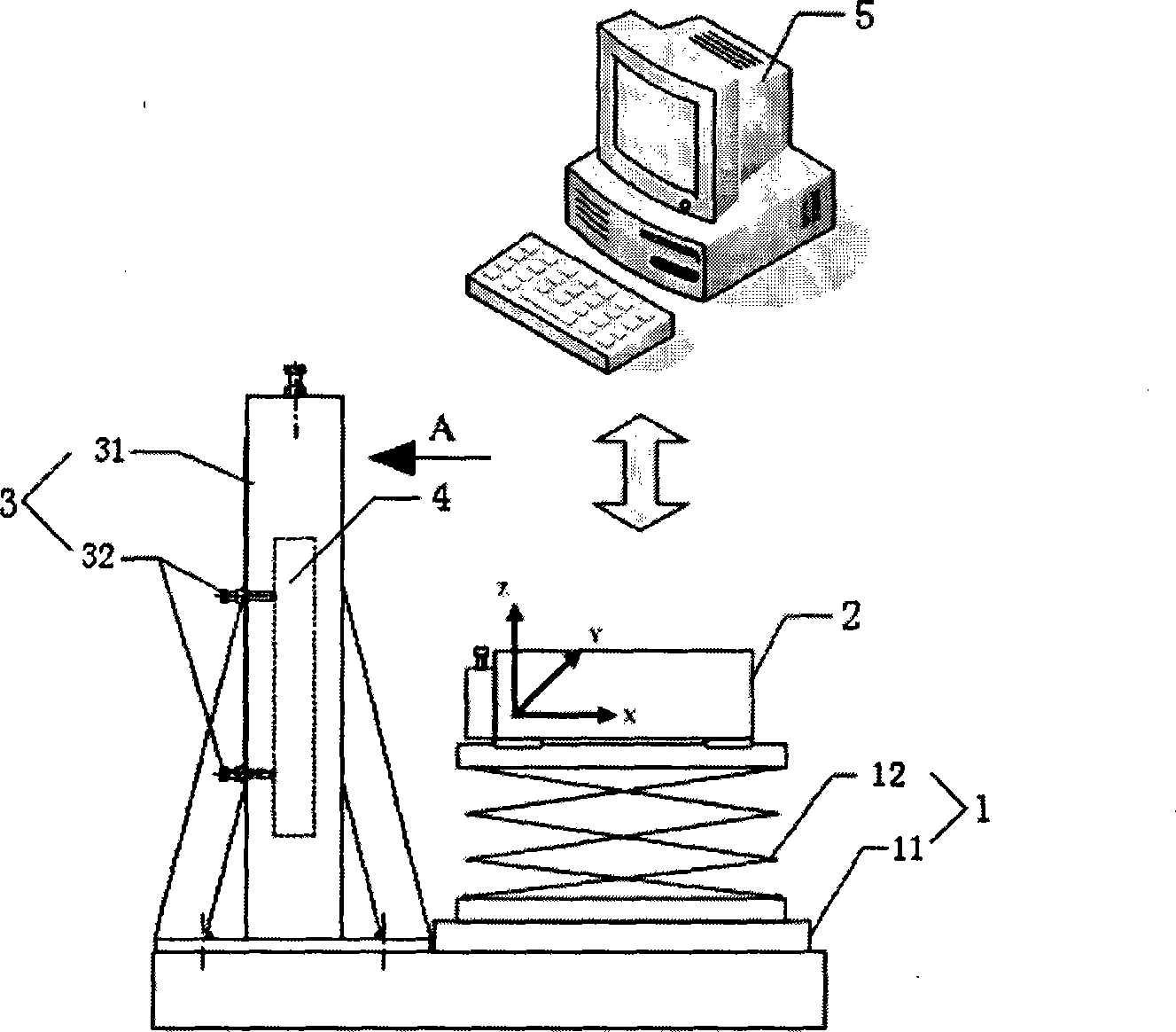
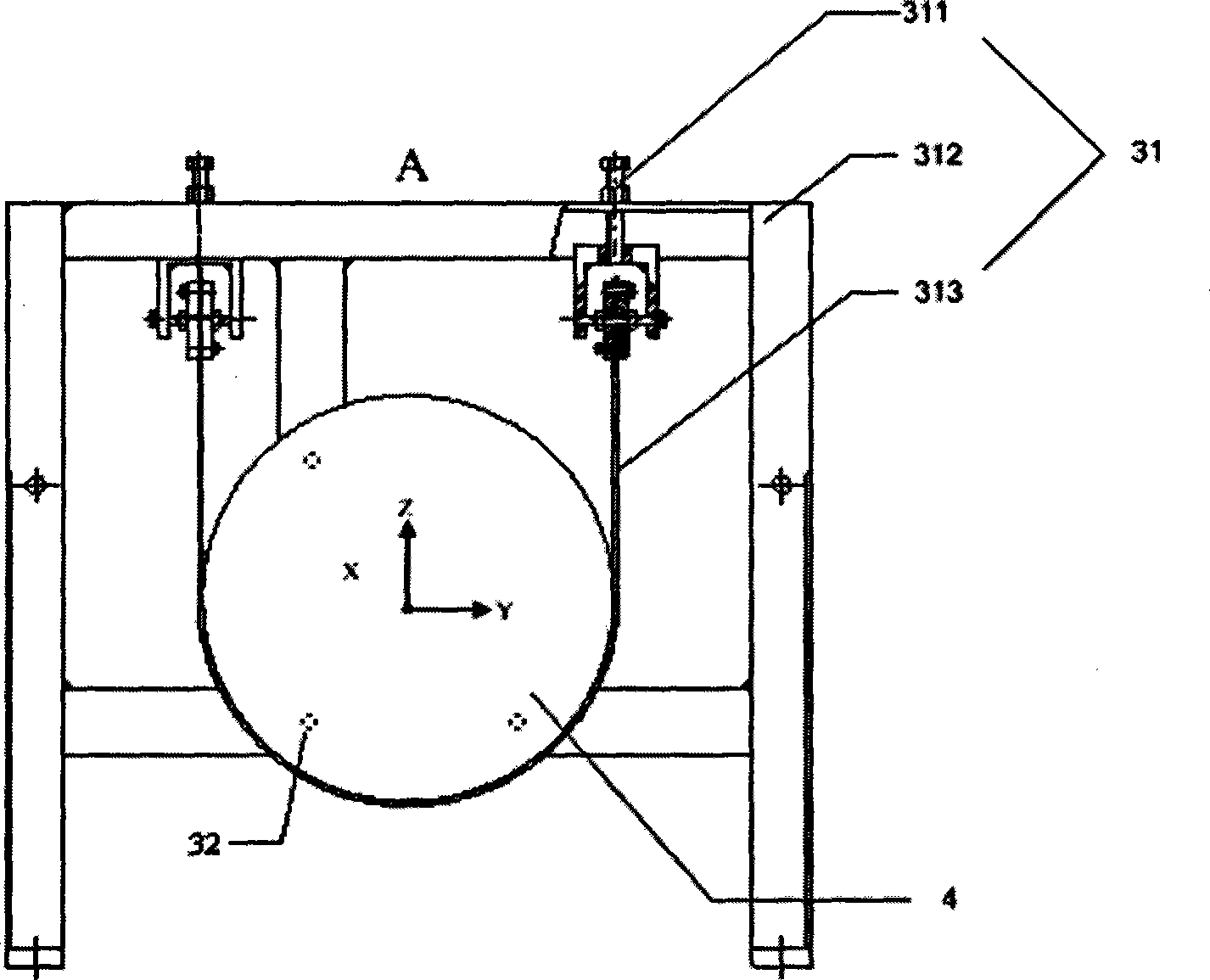
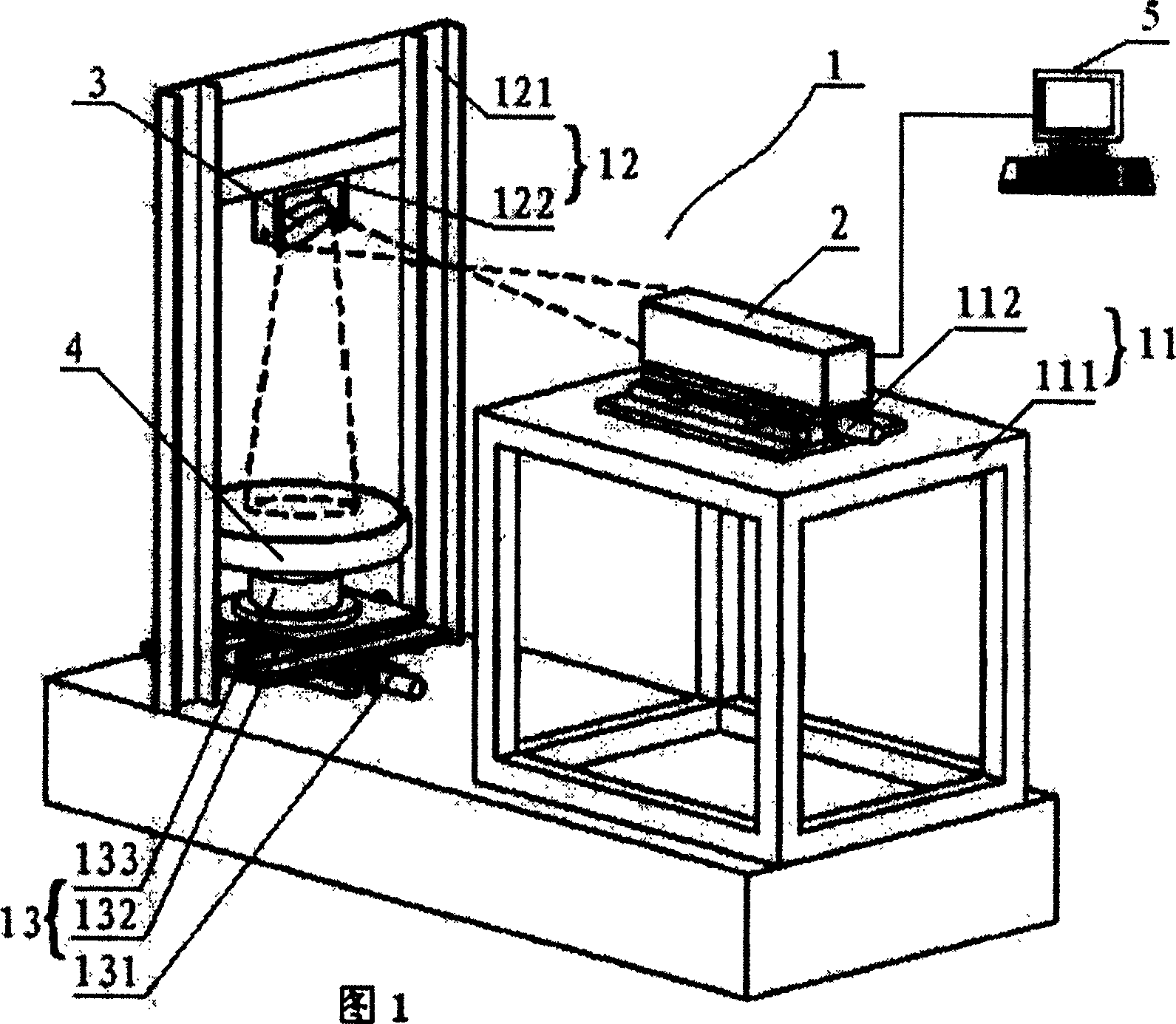
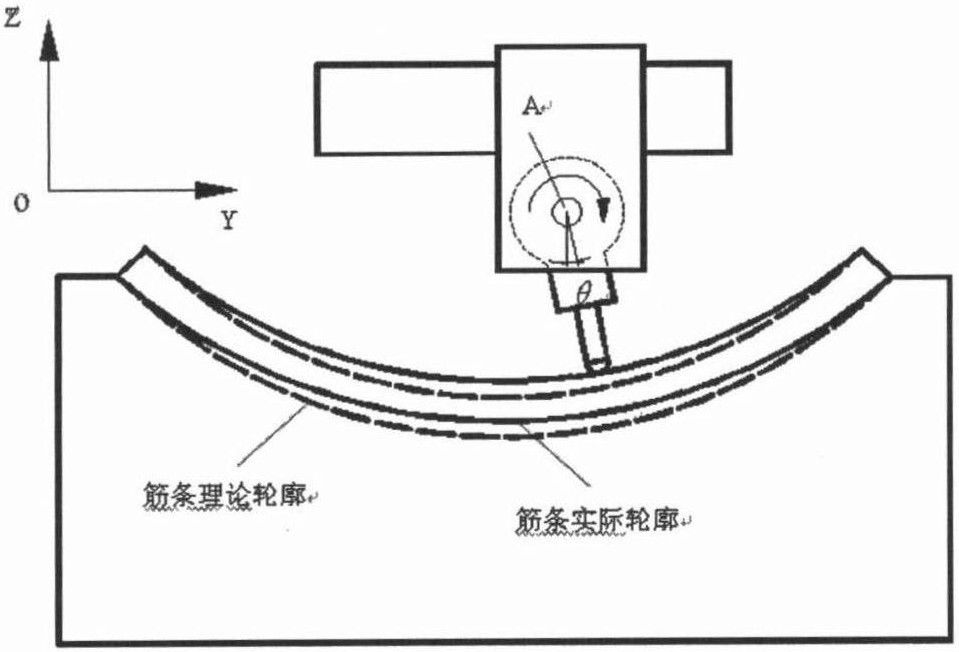
High-frequency error detecting apparatus and method for heavy caliber heavy relative aperture aspherical mirror
InactiveCN101013027AIncrease horizontal resolutionIncrease the vertical measurement rangeUsing optical meansTesting optical propertiesMultiple pointError surface
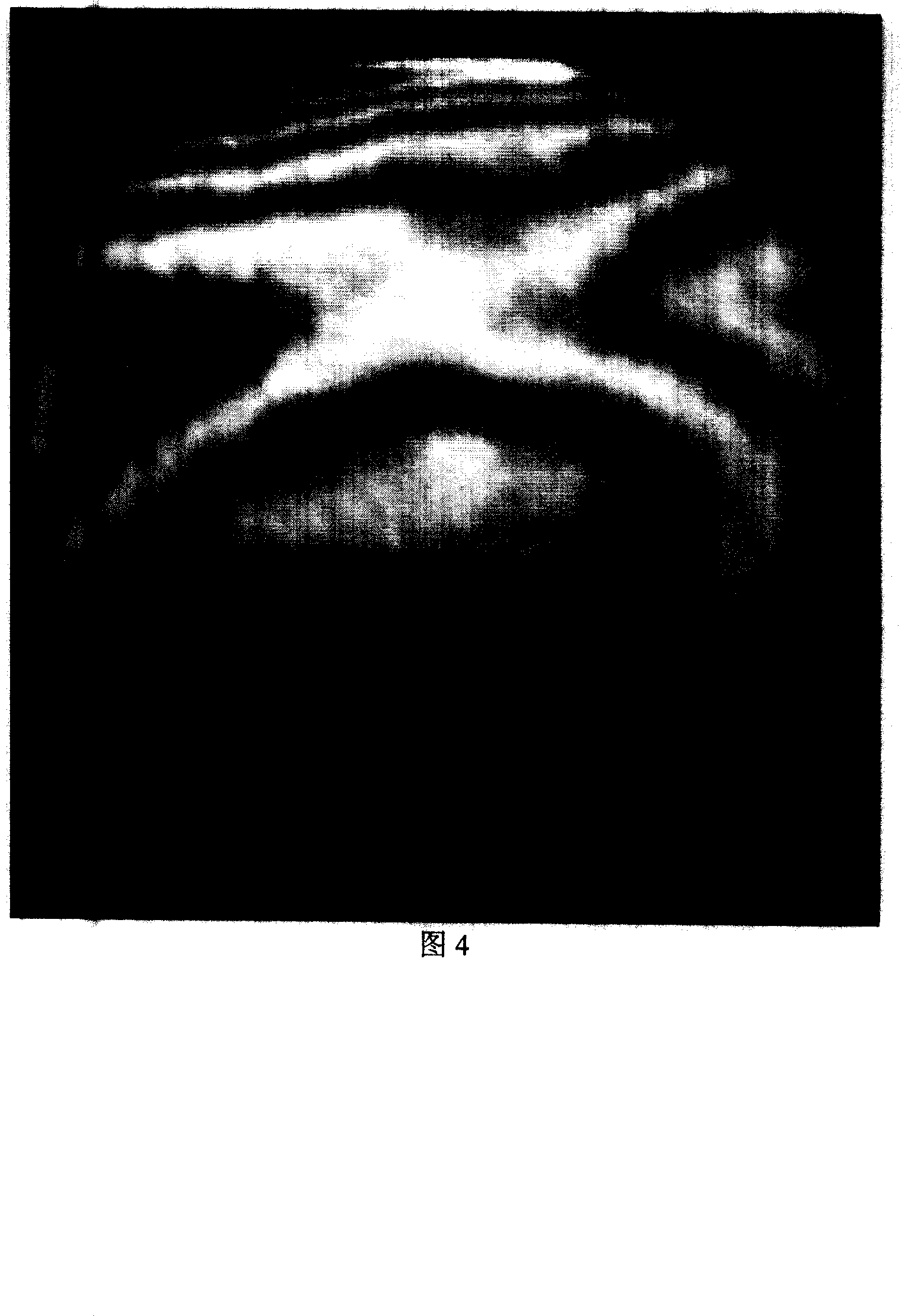
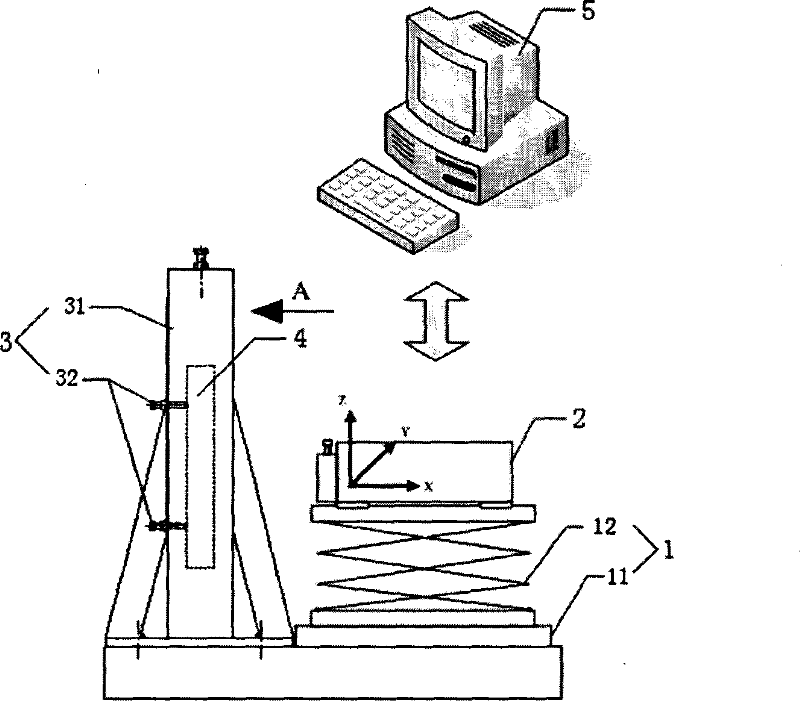
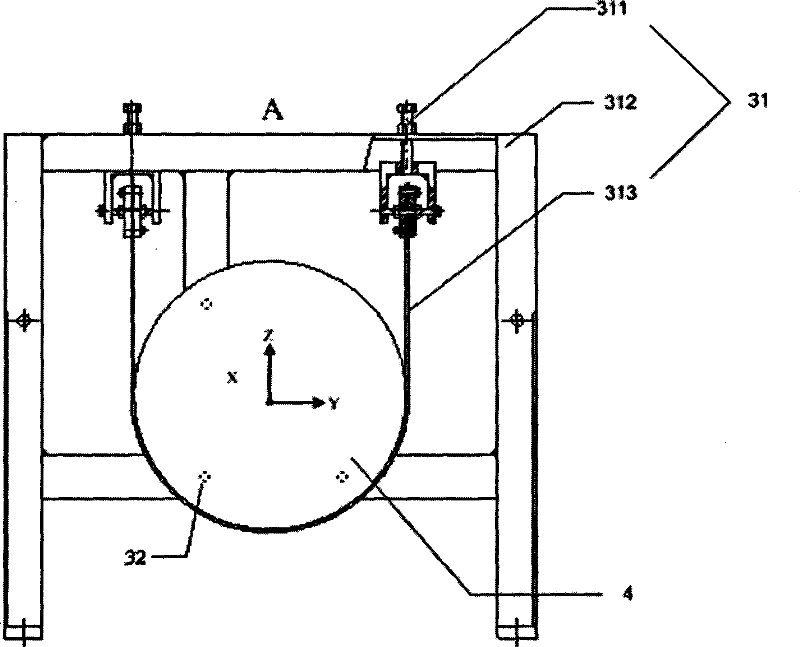
The invention discloses a high-frequency error detection device and method in the large caliber large relative aperture non-spherical mirror, the device including the five-axis movement adjustment platform with the interferometer focusing platform, the side swing reflecting mirror side swing platform located in front of the interferometer focusing platform, and the measured non-spherical mirror 3D movement adjustment platform located below the side swing reflection mirror side swing platform, and the multiple points supporting machine with the laser wave surface interferometer, the side swing reflection mirrors, and the measured non-spherical mirror installed on the corresponding platforms, and the main control computer with built-in detection data-processing algorithm program connecting with the laser wave surface interferometer. The device uses the main control computer to process the detection data-processing algorithm, which can combine the detected multiple part regions error surface maps into error surface map with medium or high frequency in full caliber, including the initial pose determining method, the overlapping regional data extraction algorithm and the regional data stitching algorithm. The invention is a high-frequency error detection device and method with low-cost, high-precision, high-efficiency in the large caliber large relative aperture non-spherical mirror.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
A correction method for electronic compass in underwater vehicle
ActiveCN102288170AEstimates are accurateEliminate the influence of external magnetic interferenceCompassesComputer scienceError surface
The invention discloses a correction method of an electronic compass in an underwater vehicle, which comprises the following steps of: inquiring magnetic declination, and carrying out corrected navigation on the water surface of the vehicle; recording navigation data by a navigation sensor; exporting correction navigation data from a communication module; searching a hard magnetic interference parameter, solving the error surface plot between a correction track and a reference track under the condition of (2N+1)<2> disperse hard magnetic interference parameters, wherein the minimum point corresponding to the surface plot is the search result; according to the set correction precision requirement, repeating and reducing the search range and grid, and re-searching to obtain a more precise hard magnetic interference parameter evaluation value; and finally, applying the searched magnetic parameter evaluation value in the navigation of the underwater vehicle. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the operation is simple, the influence of the outer magnetic interference to the electronic compass in the underwater vehicle can be effectively eliminated and thus, the corrected electronic compass can return back to the corrected attitude angle.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Large-sized optical flat interferometry device and method
InactiveCN101240999AGet medium and high frequency errorsIncrease horizontal resolutionUsing optical meansTesting optical propertiesLinear motionMeasurement device
The invention discloses a device and method of interferometry for a large-scale optical plane. Wherein, the interferometry device comprises an adjustment platform for the two-axis linear motion of an interferometer, a two-dimensional tilt adjustment platform for the measured plane mirror located at the front of the adjustment platform, a laser wave-front interferometer installed in the adjustment platform for the two-axis linear motion of an interferometer and a control computer contained the program of measured data processing algorithm, which is connected to the laser wave-front interferometer. With the device, a plurality of obtained error surface maps of partial region can be spliced to an error surface map containing medium-high frequency (MHF) band on the whole caliber according to the measured data processing algorithm through the control computer, which includes a method for determining the initial position, an algorithm for extracting data from the overlap region and an algorithm for splicing the area data. The invention is a device and method of interferometry for a large-scale optical plane with low cost, high precision and high efficiency.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
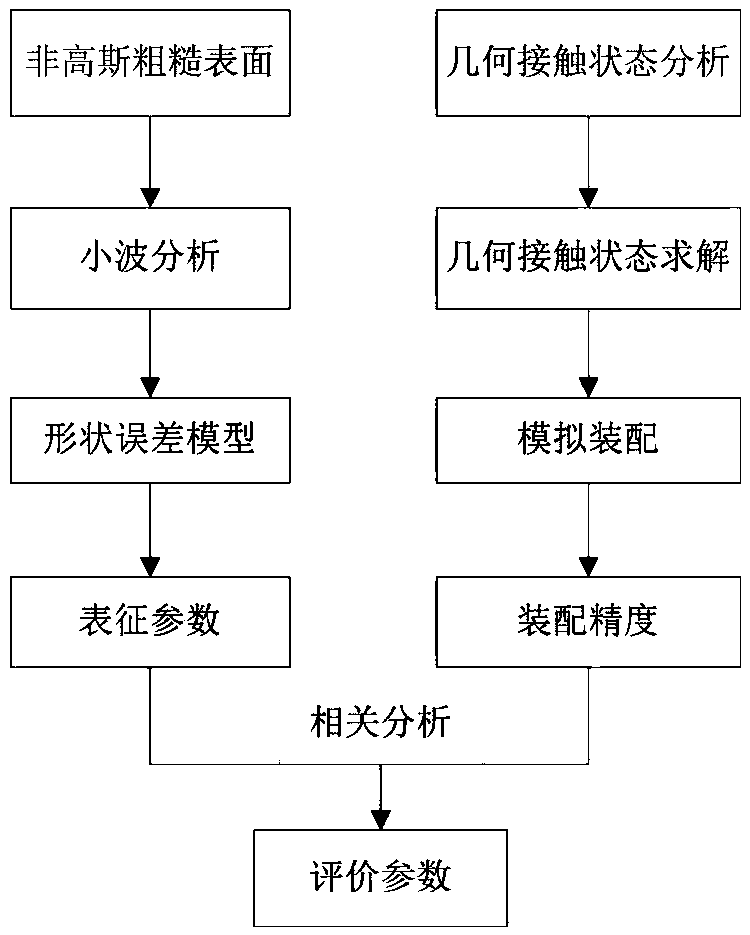
Method for determining assembly-oriented rectangular plane shape error evaluation parameters
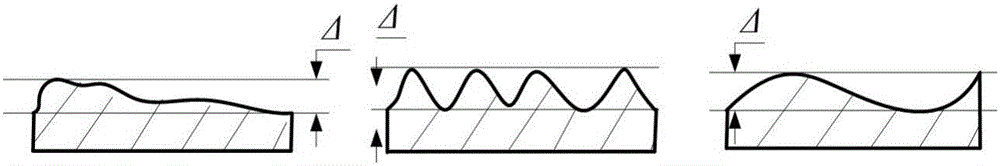
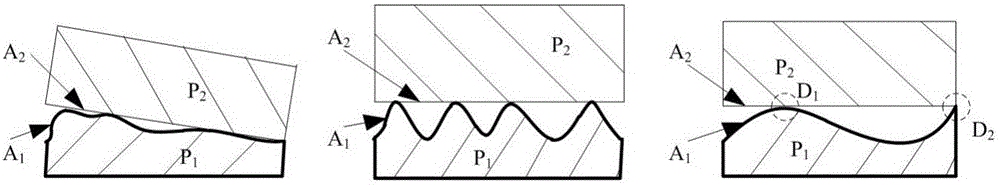
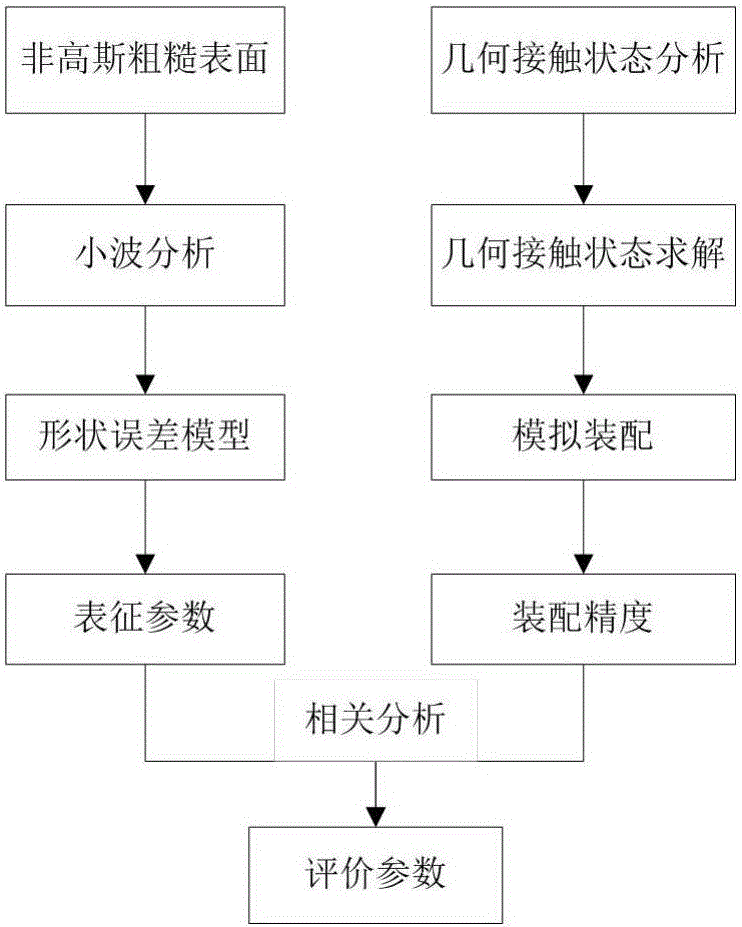
InactiveCN105868496AImprove processing qualityImprove assembly accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationSpatial OrientationsSimulation
The invention relates to a method for determining assembly-oriented rectangular plane shape error evaluation parameters and belongs to the field of error evaluation. The method comprises: generating a cutting surface by non-Gaussian plane simulation method, acquiring a shape error surface via wavelet filtering, and extracting characterization parameters of surface shape error distribution; subjecting the shape error surface to simulation assembly through contact algorithm, calculating assembly precision of spatial orientation changes of a second part after assembly, determining a relation between surface characterization parameters and post-assembly part assembly precision through correlation analysis, thereby determining shape error evaluation parameters and enabling quantitative description for the relation between the surface distribution characterization parameters and assembly precision. Plane characteristic parameters having important impact on assembly precision are obtained, and scientific basis is provided for improving machining quality of mating planes and optimizing assembly process to improve assembly precision.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
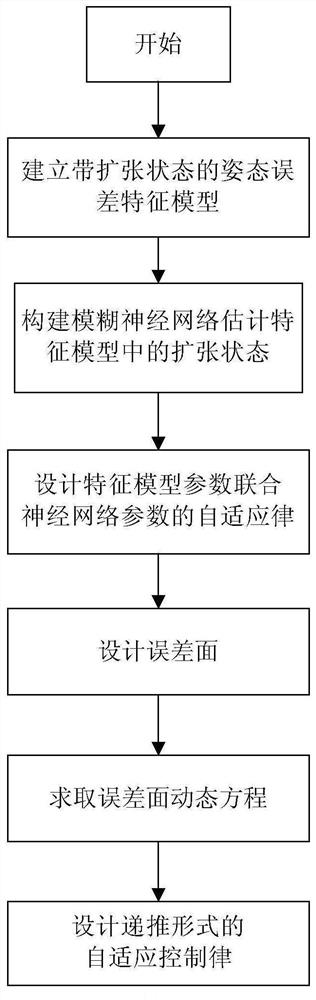
Adaptive recursive control method and system for posture of hypersonic aircraft
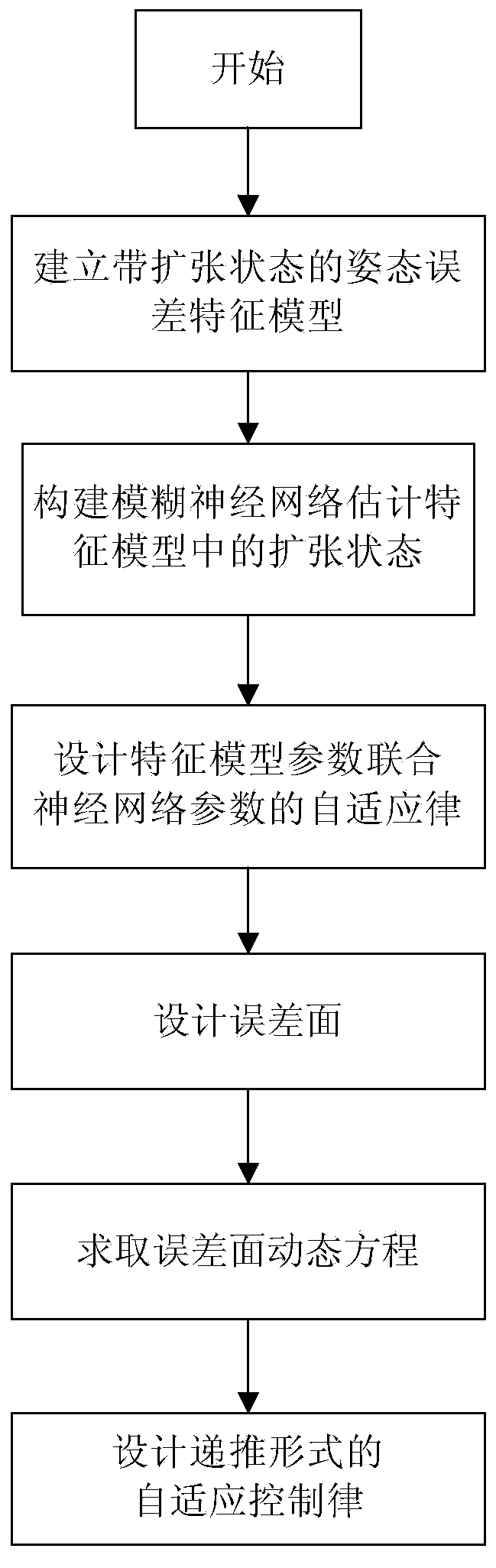
ActiveCN110244751AAvoid uncertaintyImprove modeling accuracyAttitude controlAdaptive controlRobustificationError surface
The invention discloses an adaptive recursive control method and system for the posture of a hypersonic aircraft. The method comprises the following steps of 1, building a posture error feature model with an expansion state through combining a control target, aircraft reentry attitude kinetic analysis and unmodelled dynamics and interference analysis, wherein the expansion state is used for describing the unmodelled dynamics and interference of the system; 2, building a fuzzy neural network estimator to estimate the expansion state in the feature mode, and combining with the structure of the feature model to jointly design an adaptive law of feature mode parameters and neural network parameters; and 3, based on an error surface, designing an adaptive control law in a recursive form to further improve the robustness of the control system. The method provided by the invention has better adaptive capacity to nondeterminacy, has the advantages of relatively strong robustness and relatively high control accuracy, and is applicable to accurately tracking the posture of the hypersonic aircraft under the complex unmodelled dynamics and strong interference environments.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Sample-based texture synthesis method
InactiveCN107767411AConform to the visual experiencePrecise Least Error PathImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionComputer science
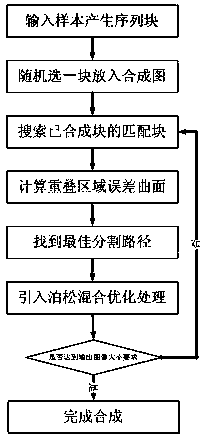
The invention relates to a sample-based texture synthesis method, which comprises the following steps: 1) randomly selecting size-specific sample blocks from input texture to form a sample block sequence; 2) randomly selecting a block B1 from the sample block sequence and placing the block to an output image; 3) at the place of each block to be synthesized, searching a texture block B2 meeting matching conditions from the input sample block sequence and placing the texture block B2 to a synthesis image to enable the B2 to have a certain overlap region with the B1; 4) calculating multi-order error surface of the overlap region of the B1 and B2; 5) finding an optimum segmentation path from the error surface calculated in the step 4) as the boundary of the new texture block B2, and splicing the B2 to the synthesis image; 6) after splicing, introducing Poisson fusion to optimize boundary un-matched regions around the segmentation path; and 7) carrying out the steps 1)-6) until finishing texture synthesis.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
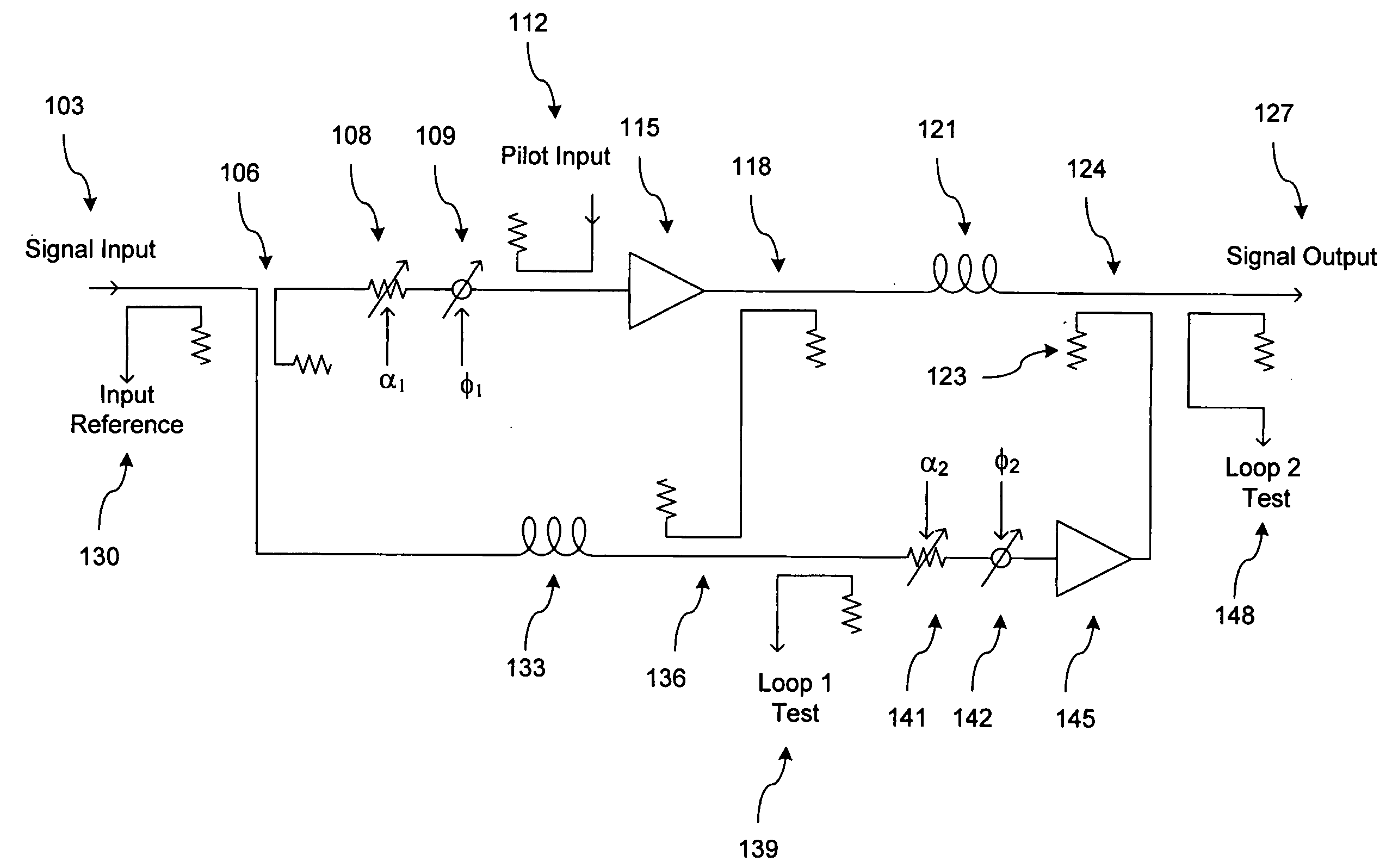
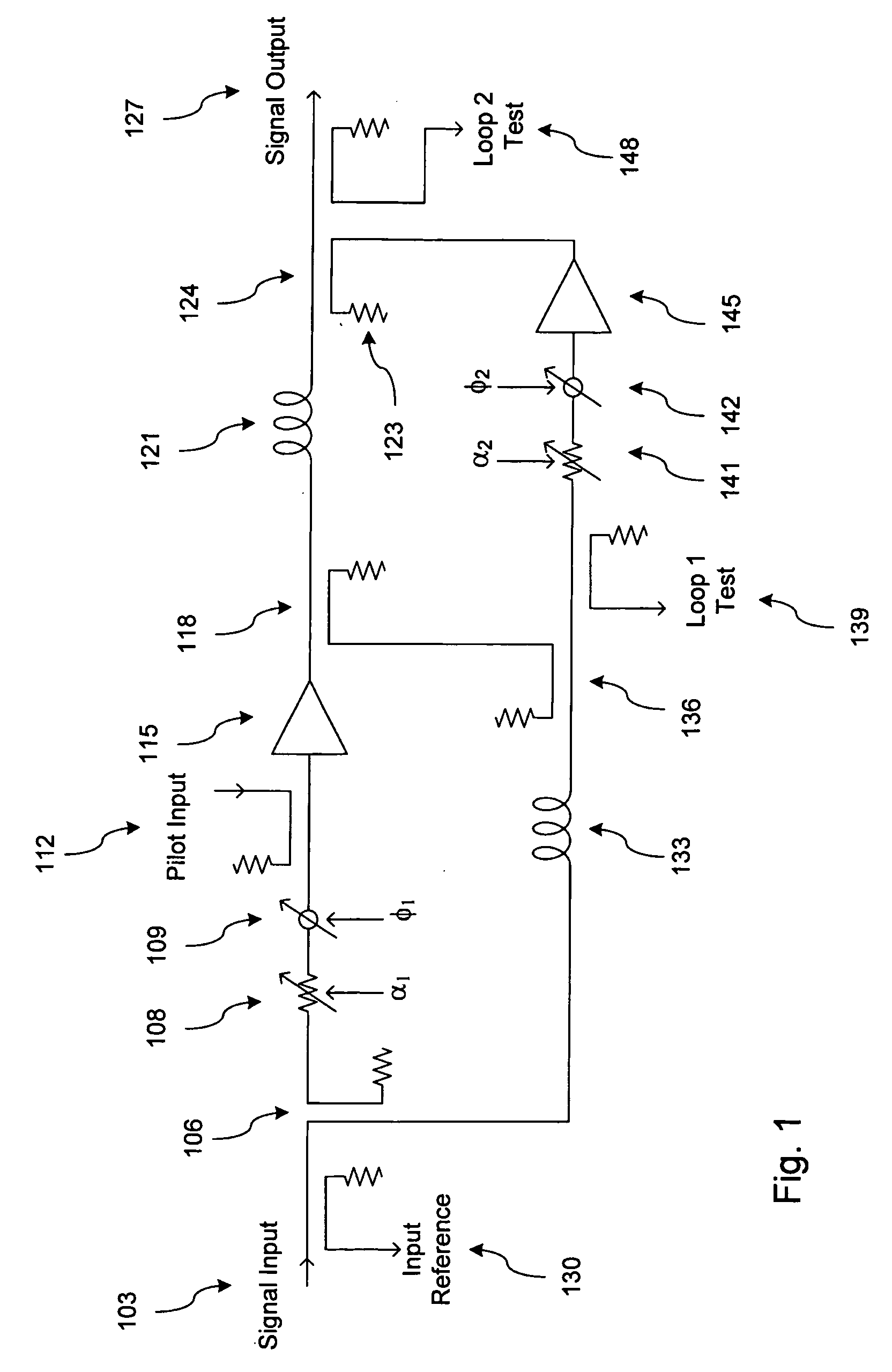
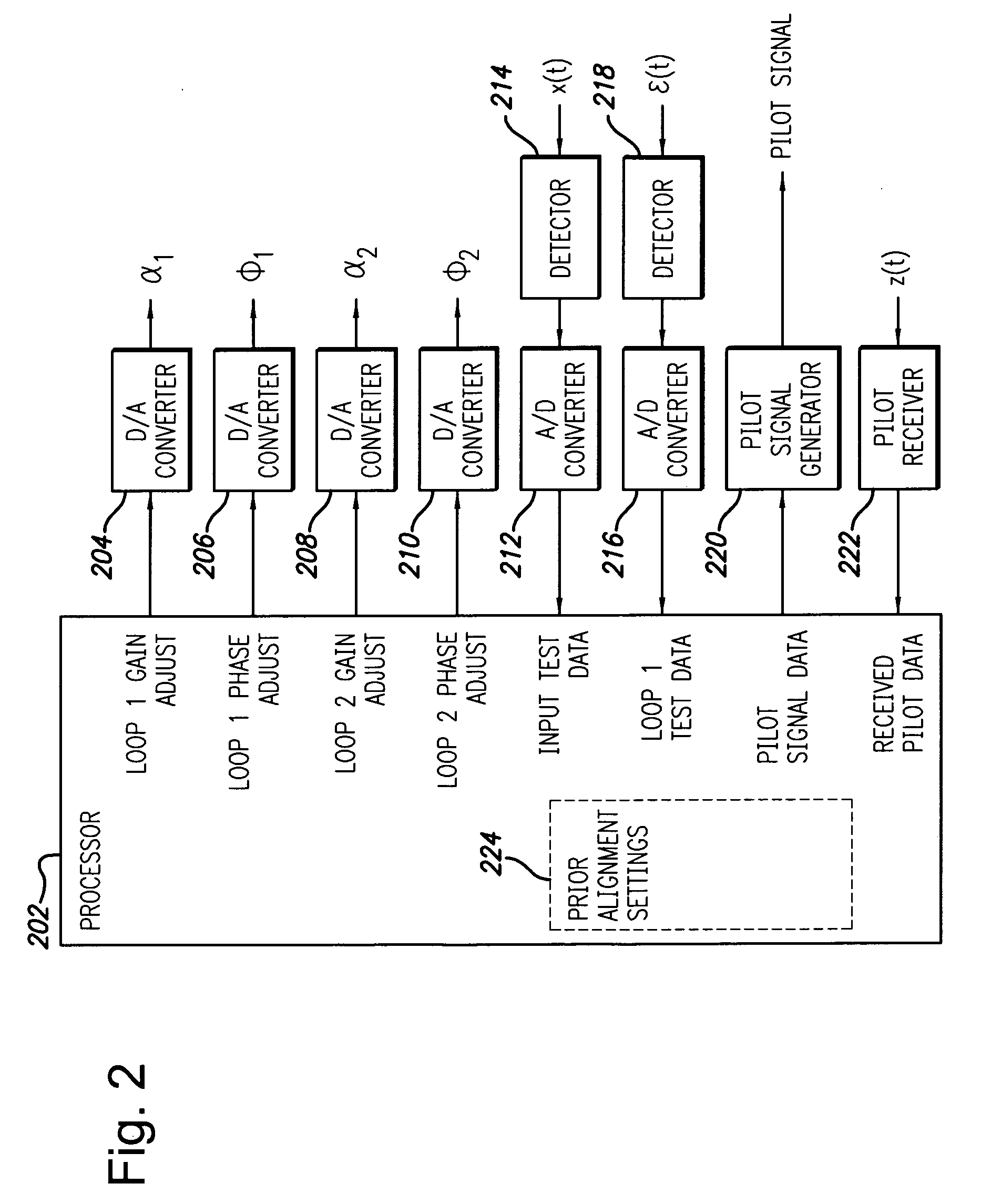
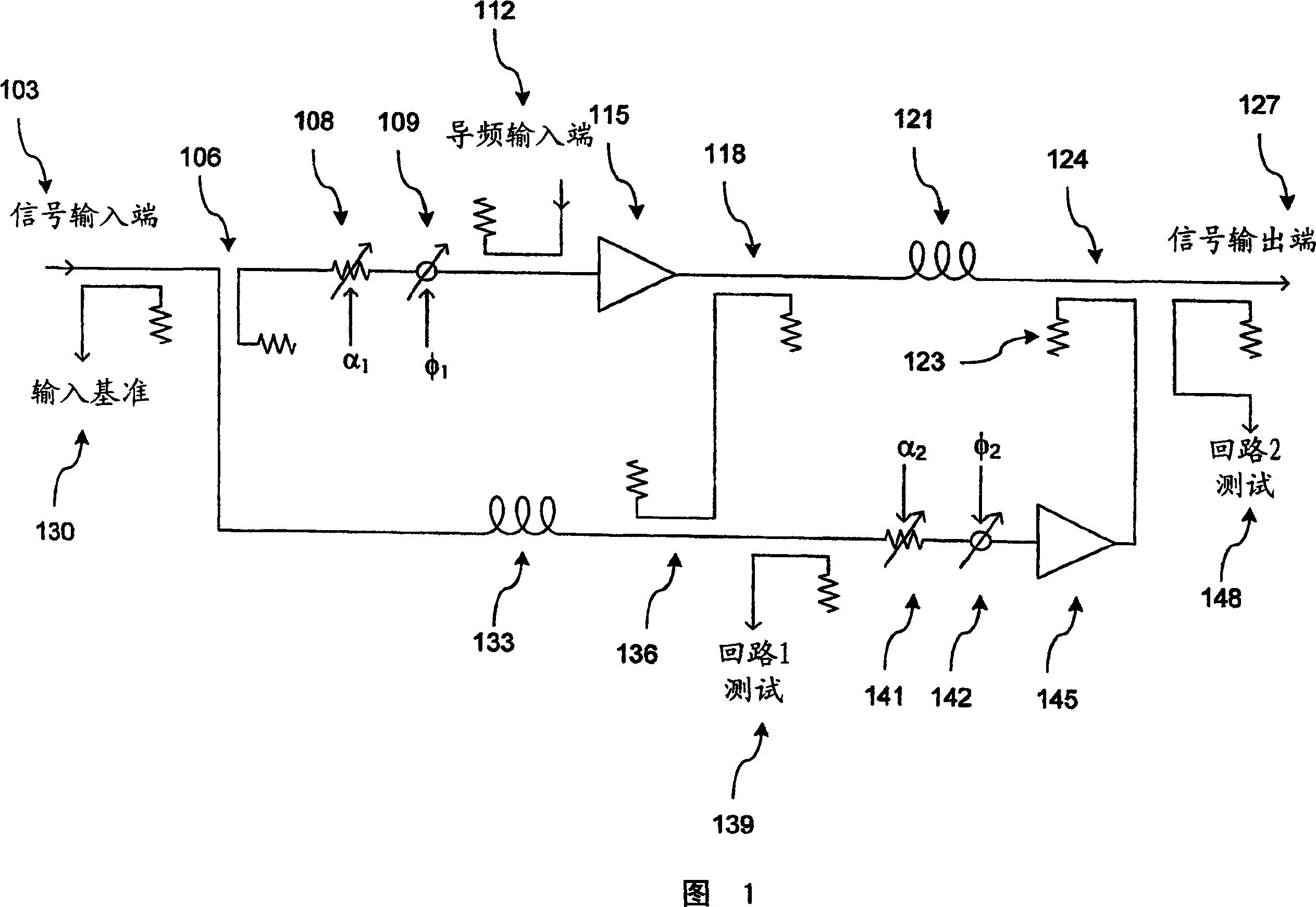
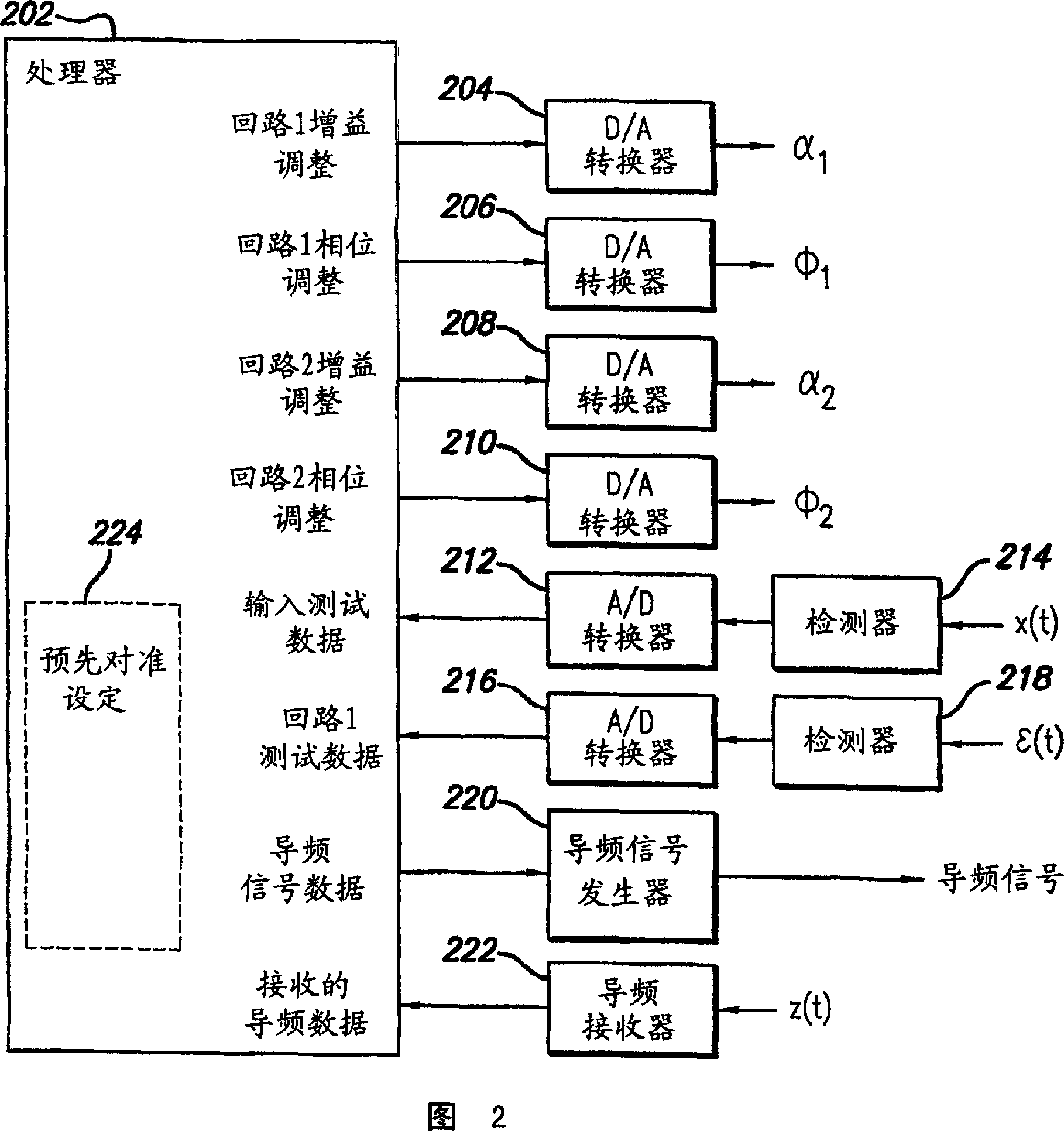
System and method for control of loop alignment in adaptive feed forward amplifiers
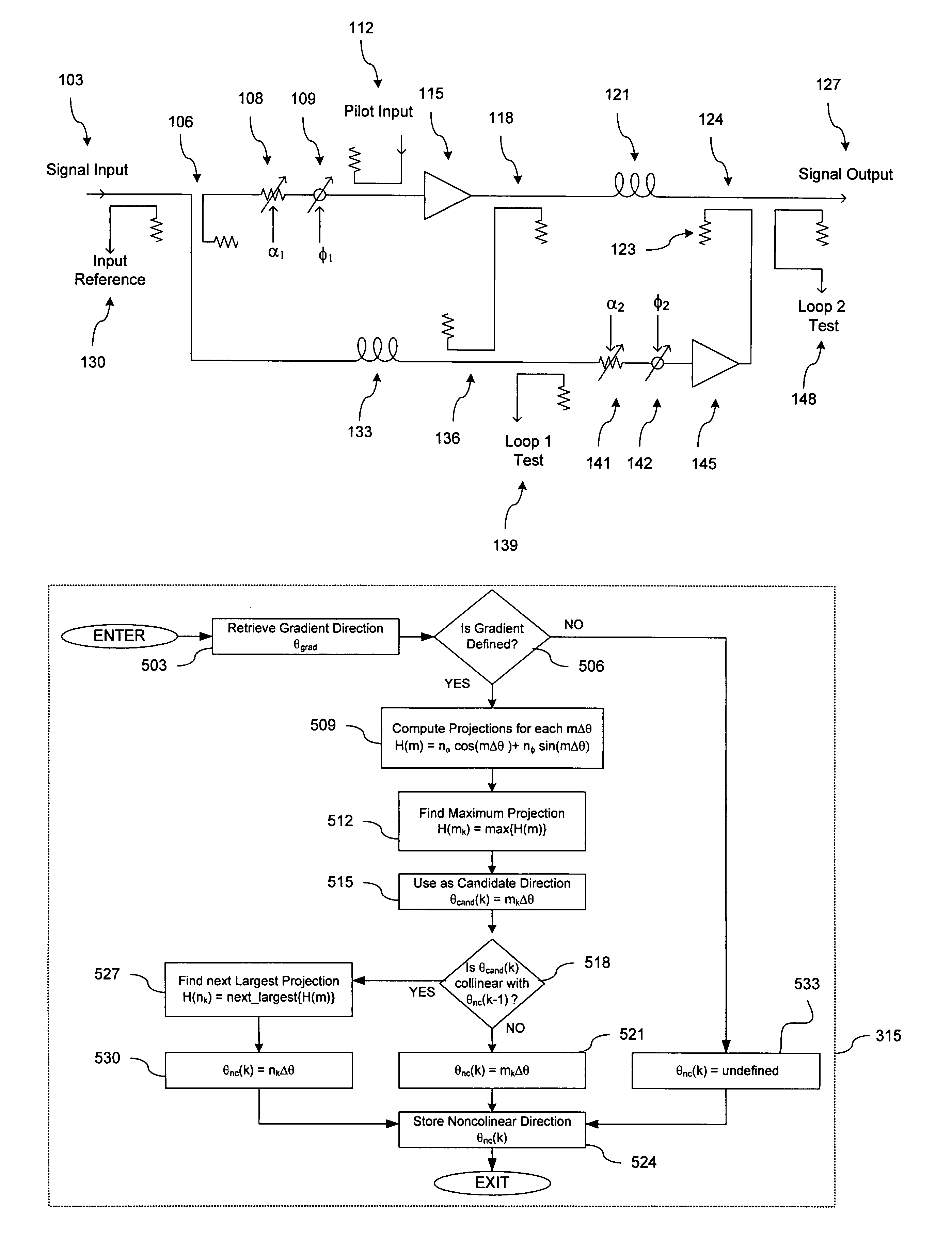
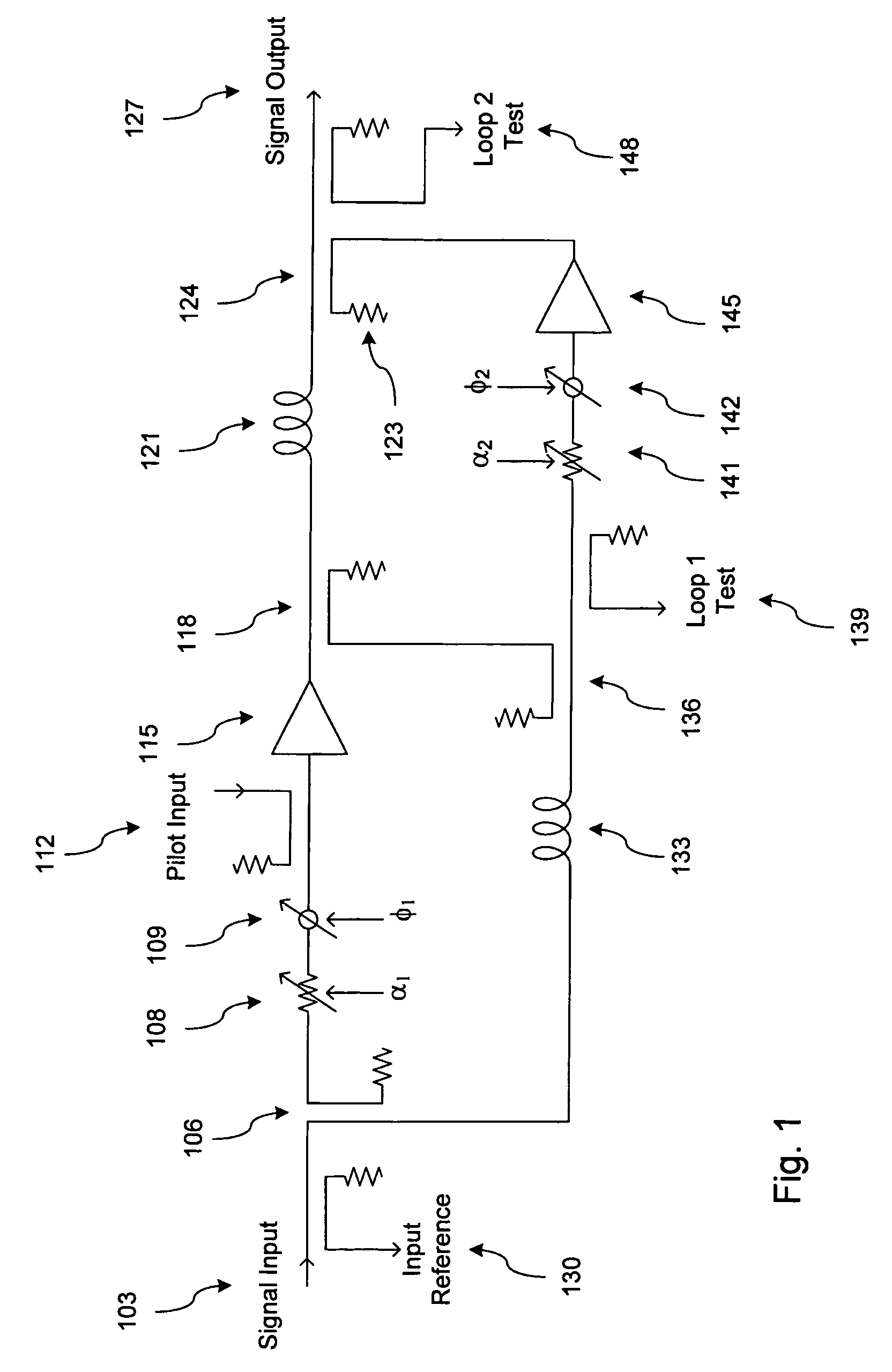
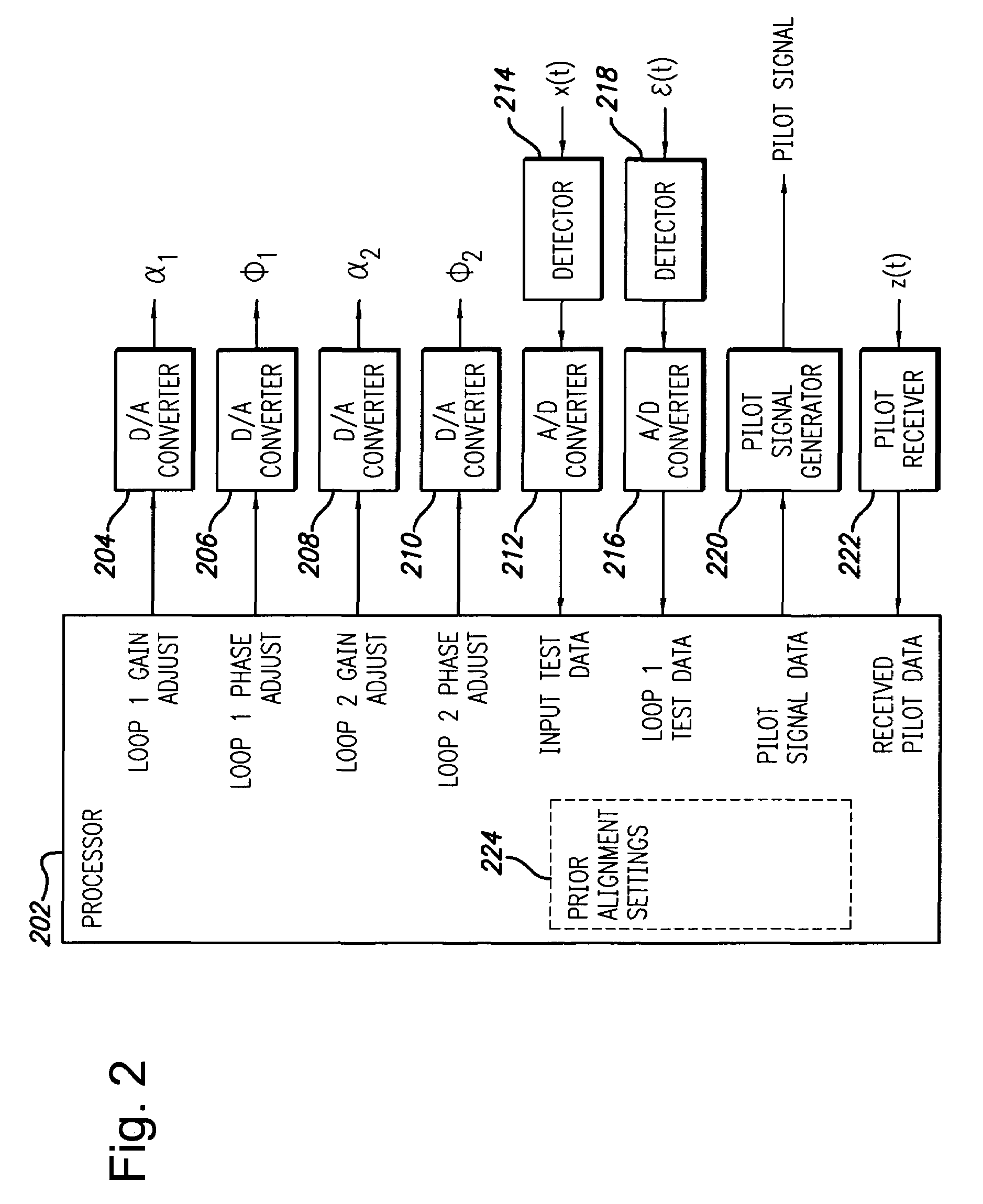
InactiveUS20050200409A1Quick alignmentAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDescent directionAudio power amplifier
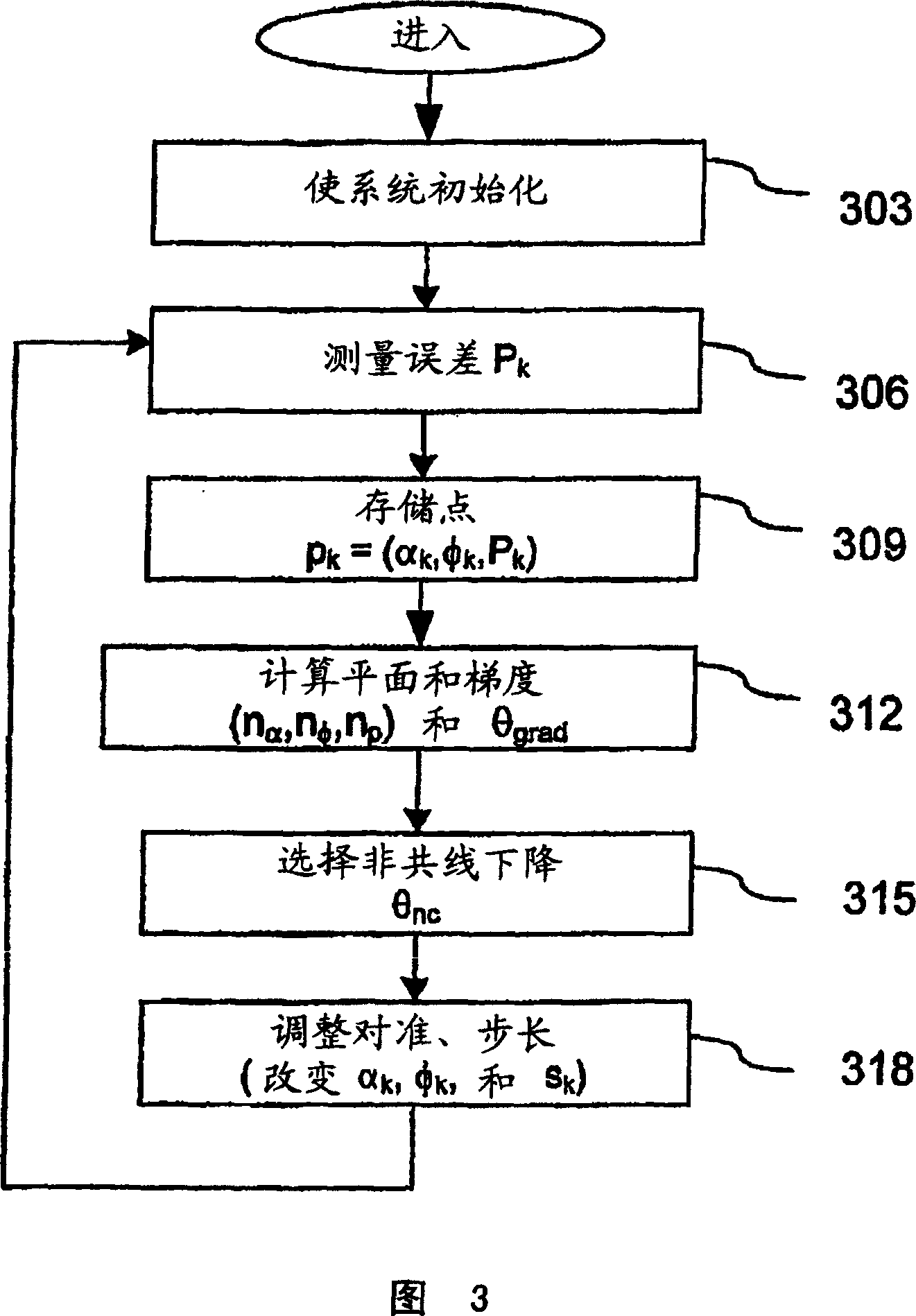
A fast search algorithm for loop alignment of a feed forward amplifier is disclosed. The algorithm controls a processor that adjusts, digitally, the gain and phase of the loop alignment based on power measurements at the input and output of cancellation combiners, to find the optimal setting. A “non-collinear descent” algorithm is used to search, iteratively, for the minimum within an error surface. For loop alignment, the error surface is defined by the set of measurement points comprising the alignment settings and the associated cancellation residuals. For the case of first loop alignment, the cancellation residual is measured using the ratio of two power detectors located at the input and after the cancellation (error) combiner. For second loop alignment, cancellation is estimated using the residual pilot power detected at the output of the amplifier. The preferred alignment method uses three successive measurements to estimate the gradient direction with respect to gain and phase shifter settings. The actual descent direction is selected to be close to the gradient direction without being collinear with the most recent alignment adjustments. Quantization of the descent direction simplifies the implementation as well as the enforcement of the non-collinearity constraint on successive alignment settings. Two different step size selection approaches are disclosed, however, any standard step size selection approach may be employed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
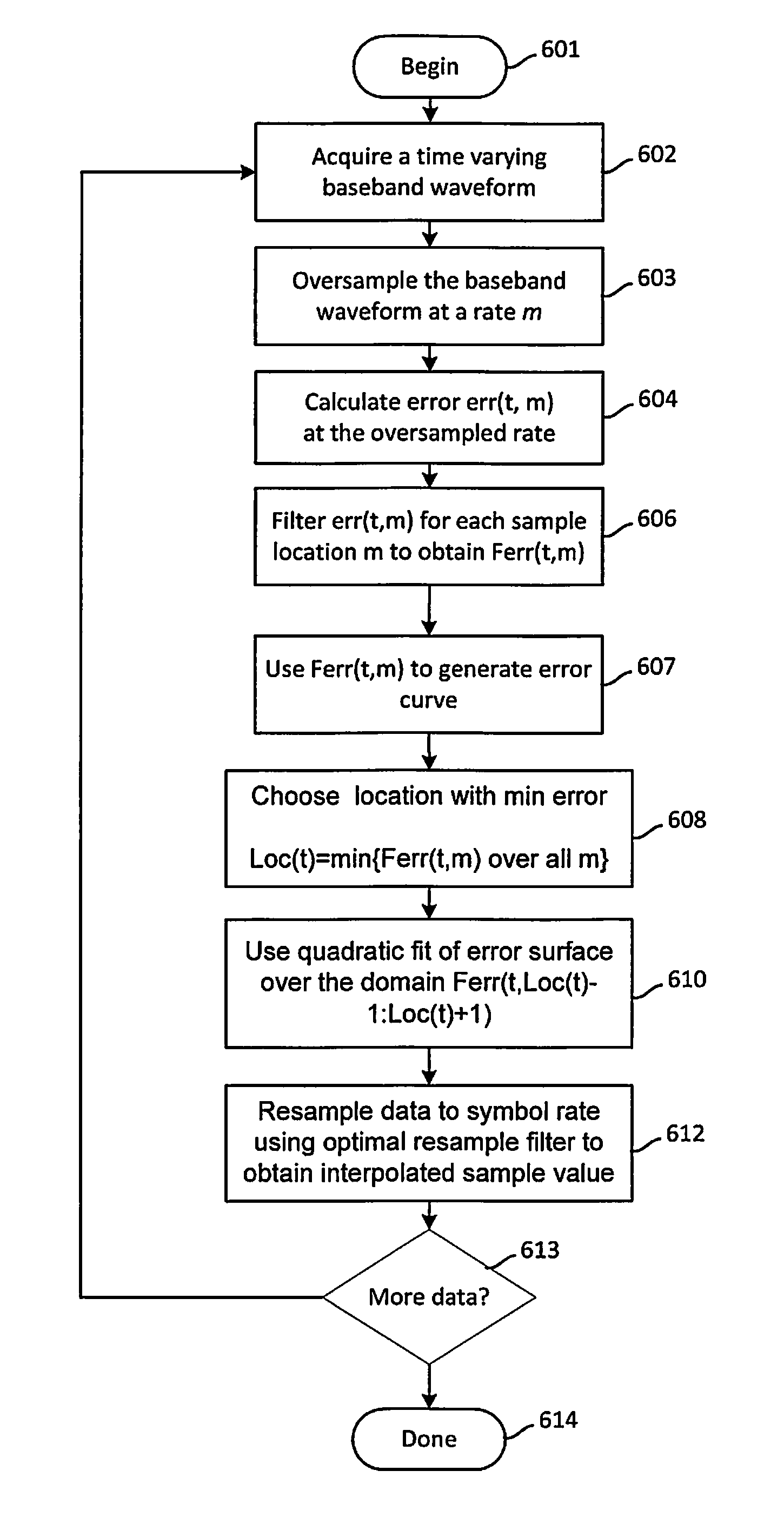
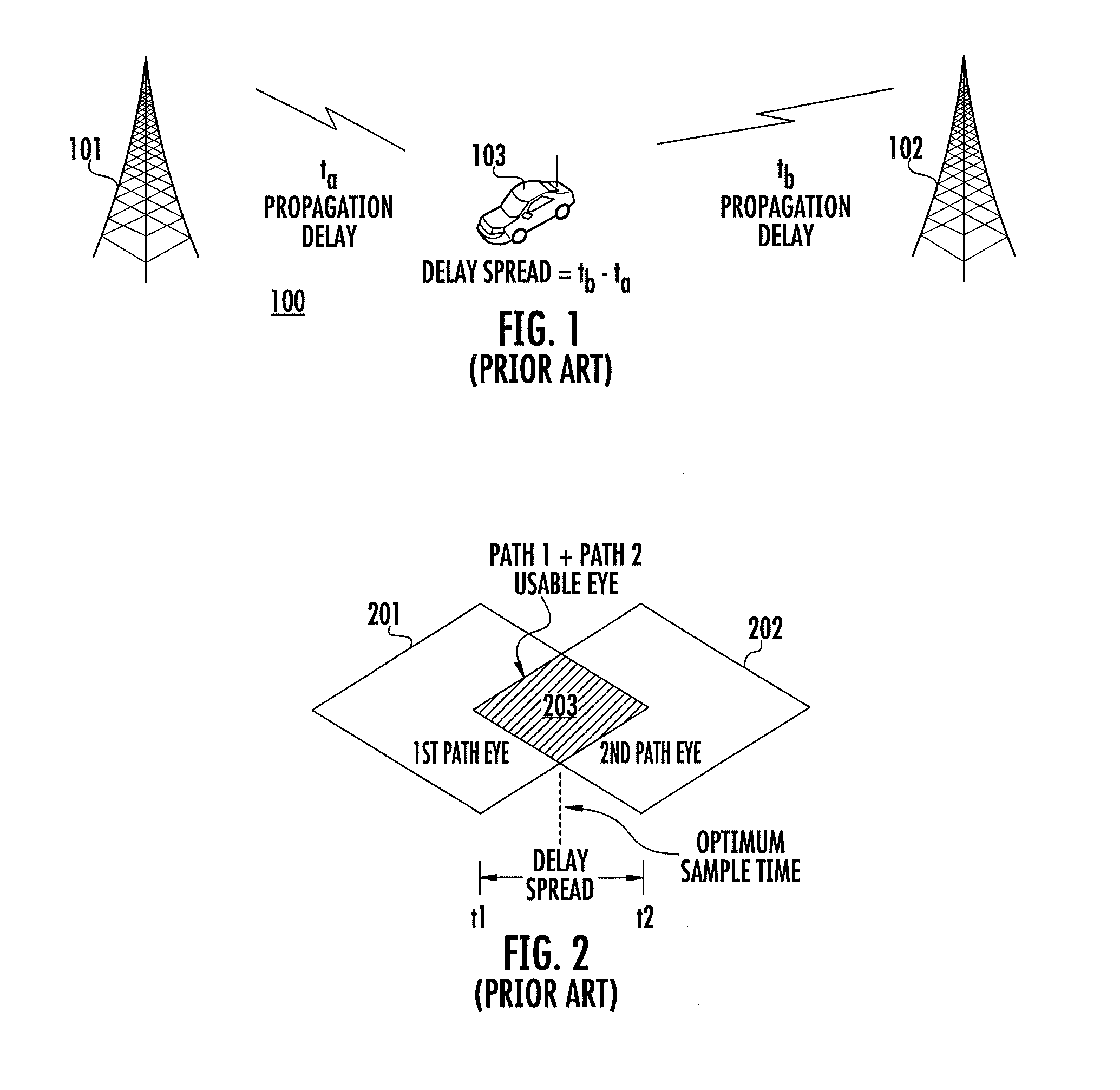
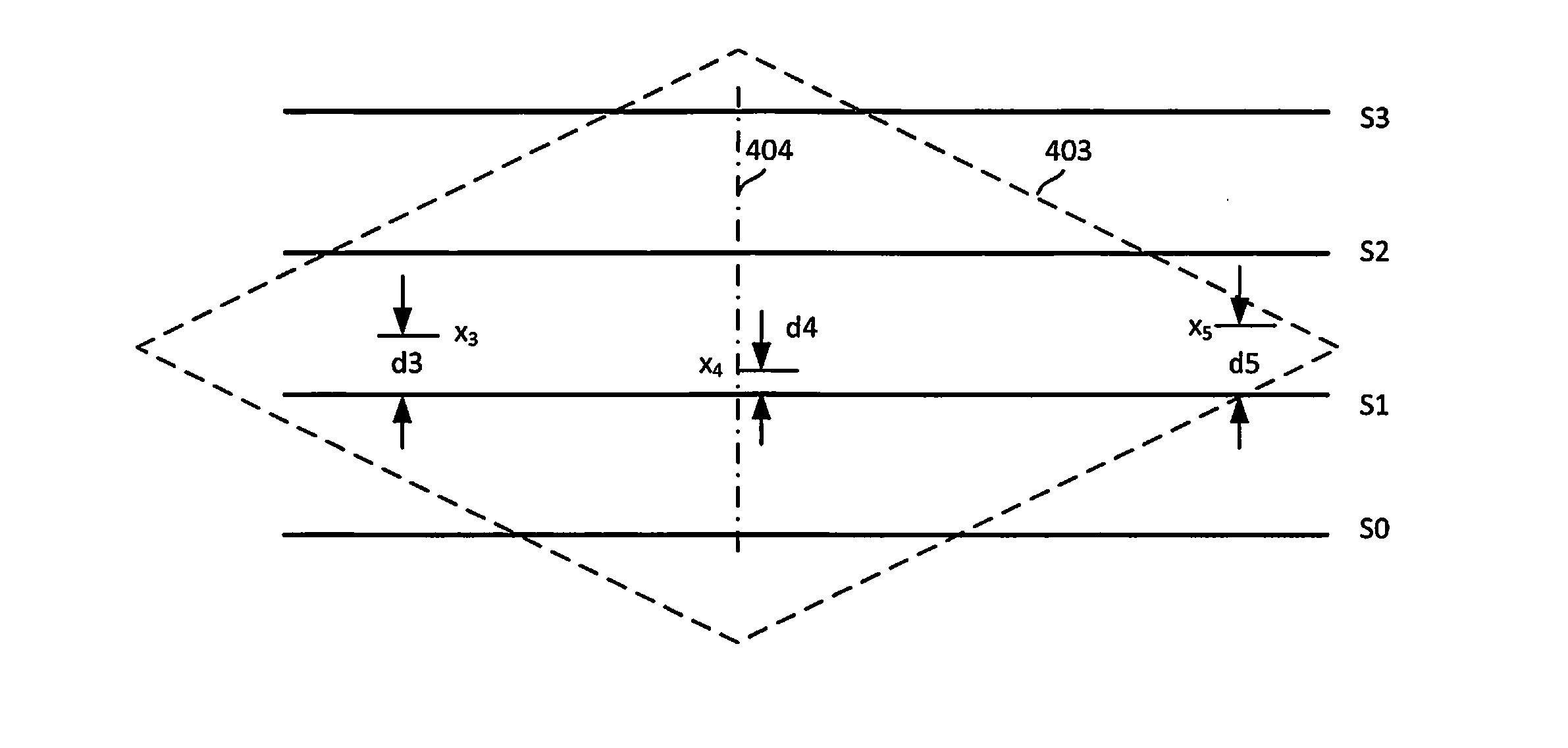
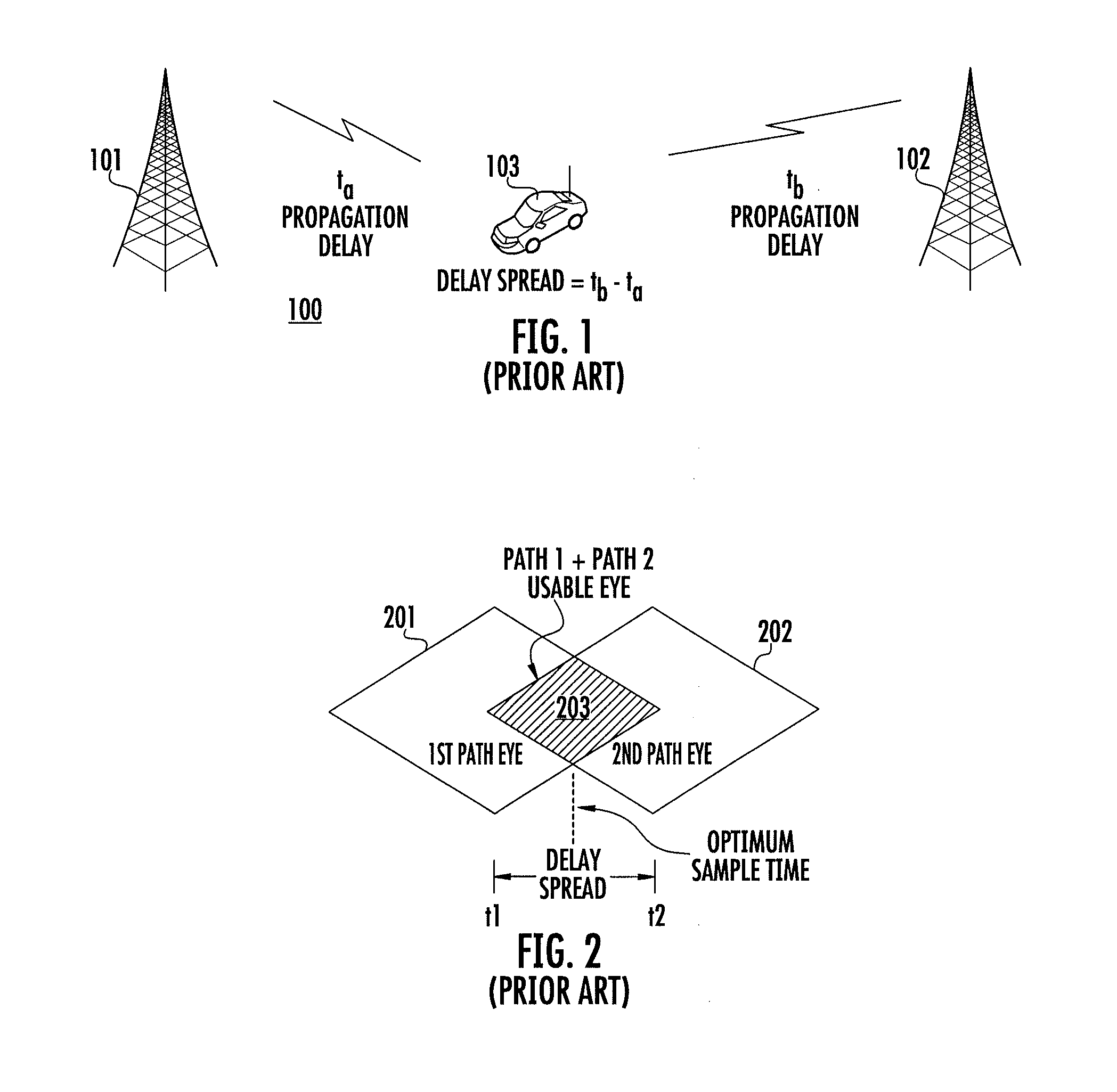
Method for symbol sampling in a high time delay spread interference environment
Symbol sampling in a high time delay spread interference environment includes acquiring (602) a time varying baseband waveform. The waveform has a signal amplitude that varies between one of a plurality of symbol states. The waveform is sampled (603) at a rate of m times the symbol rate. During an evaluation time, an error value is calculated (604, 606) for each of m data sample positions. Each of the error values comprises an average distance between the measured value of the waveform as indicated by the data sample and a closest known symbol value. The error values are used to create an error surface. Thereafter, the error surface is modeled as a quadratic and an optimal sample time is determined (608, 610, 612) based on finding the time location where the quadratic surface is minimum. A sinc interpolator is then used to resample the data.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Solid modeling method and device for joint surface error
ActiveCN109446539ASimple methodEasy to useGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationEngineeringJoint surface
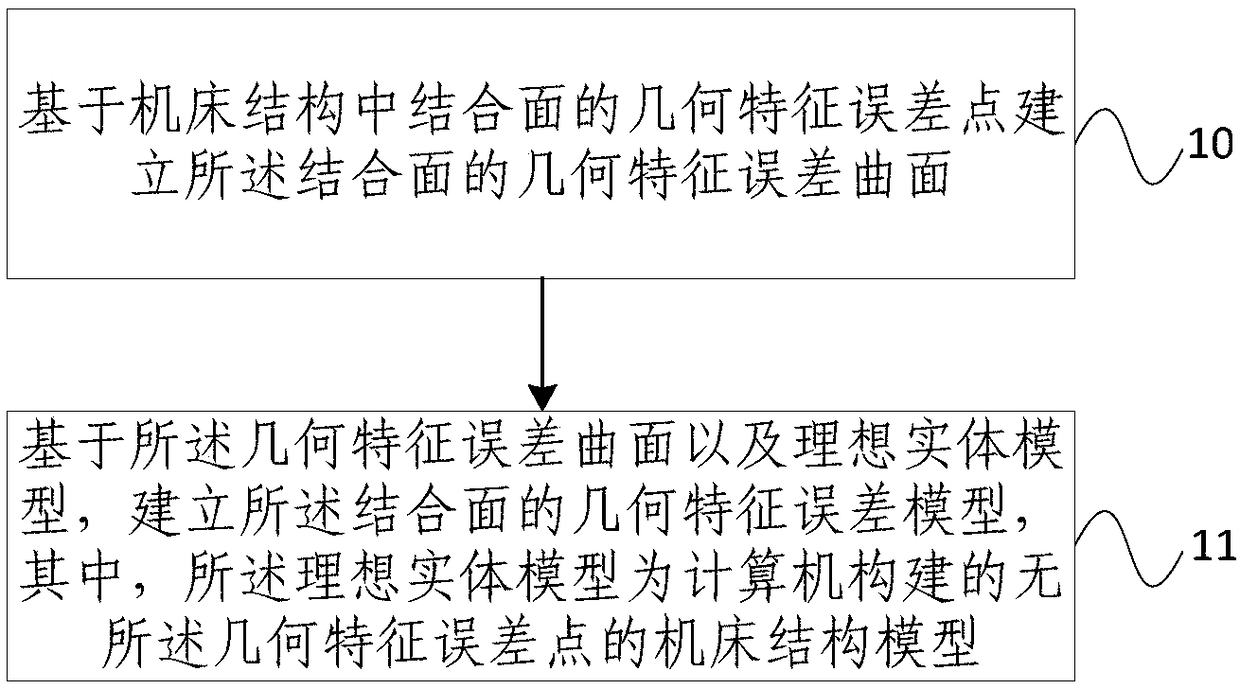
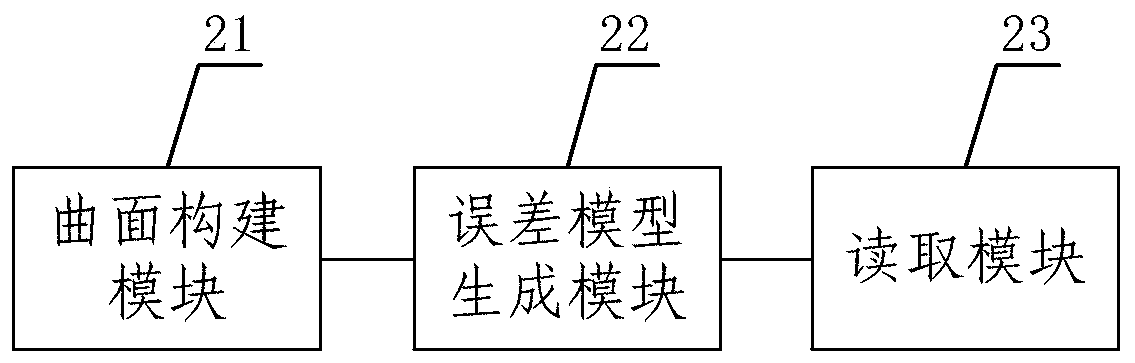
The embodiment of the invention provides a solid modeling method and device for a joint surface error. The method comprises the following steps of establishing a geometrical characteristic error surface of the joint surface based on the geometrical characteristic error points of the joint surface in a machine tool structure; based on geometrical feature error surface and ideal solid model, establishing the geometrical feature error model of joint surface, in which the ideal solid model is machine tool structure model without geometrical feature error points constructed by computer. The invention provides the solid modeling method and device for the joint surface error, which adopts the geometric characteristic error points of the joint surface of a machine tool structure to construct a geometric characteristic error surface, by combining the geometric feature error surface with the ideal solid model, the geometrical feature error model is established, and the geometrical feature errormodel can truly reflect the joint surface feature error between the actual parts and the ideal solid model constructed by computer, which provides a basis for the machine tool structure optimization design and the accurate calculation and analysis of assembly characteristics prediction.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Correction method of electronic compass in underwater vehicle
ActiveCN102288170BEliminate the influence of external magnetic interferenceEasy to operateCompassesError surfaceCorrection method
The invention discloses a correction method of an electronic compass in an underwater vehicle, which comprises the following steps of: inquiring magnetic declination, and carrying out corrected navigation on the water surface of the vehicle; recording navigation data by a navigation sensor; exporting correction navigation data from a communication module; searching a hard magnetic interference parameter, solving the error surface plot between a correction track and a reference track under the condition of (2N+1)<2> disperse hard magnetic interference parameters, wherein the minimum point corresponding to the surface plot is the search result; according to the set correction precision requirement, repeating and reducing the search range and grid, and re-searching to obtain a more precise hard magnetic interference parameter evaluation value; and finally, applying the searched magnetic parameter evaluation value in the navigation of the underwater vehicle. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the operation is simple, the influence of the outer magnetic interference to the electronic compass in the underwater vehicle can be effectively eliminated and thus, the corrected electronic compass can return back to the corrected attitude angle.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
System and method for control of loop alignment in adaptive feed forward amplifiers
InactiveUS7157967B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDescent directionMeasurement point
A fast search algorithm for loop alignment of a feed forward amplifier is disclosed. The algorithm controls a processor that adjusts, digitally, the gain and phase of the loop alignment based on power measurements at the input and output of cancellation combiners, to find the optimal setting. A “non-collinear descent” algorithm is used to search, iteratively, for the minimum within an error surface. For loop alignment, the error surface is defined by the set of measurement points comprising the alignment settings and the associated cancellation residuals. For the case of first loop alignment, the cancellation residual is measured using the ratio of two power detectors located at the input and after the cancellation (error) combiner. For second loop alignment, cancellation is estimated using the residual pilot power detected at the output of the amplifier. The preferred alignment method uses three successive measurements to estimate the gradient direction with respect to gain and phase shifter settings. The actual descent direction is selected to be close to the gradient direction without being collinear with the most recent alignment adjustments. Quantization of the descent direction simplifies the implementation as well as the enforcement of the non-collinearity constraint on successive alignment settings. Two different step size selection approaches are disclosed, however, any standard step size selection approach may be employed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
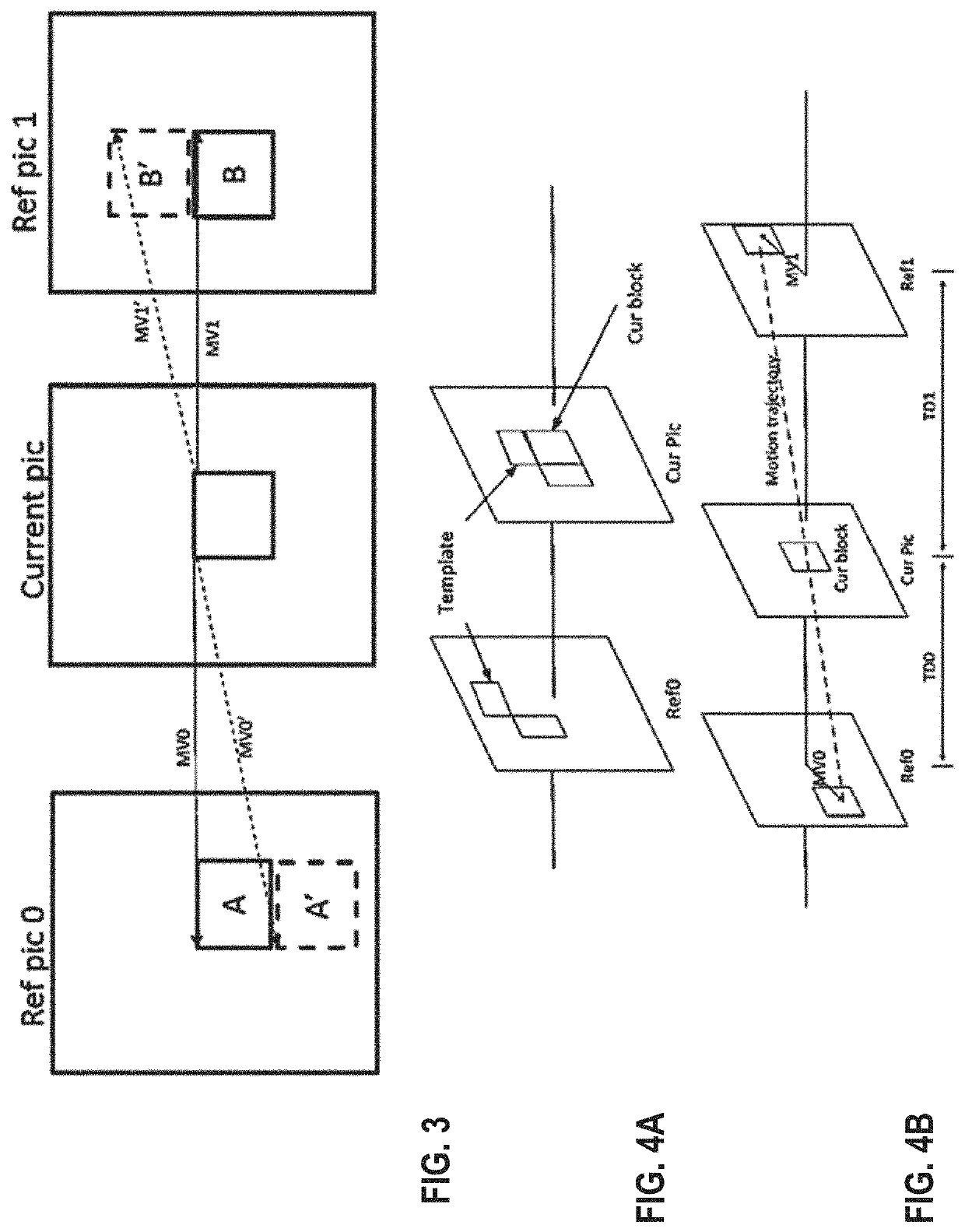
Error surface based sub-pixel accurate refinement method for decoder side motion vector refinement
ActiveUS20210076059A1Unnecessary computation can be reduced and eliminatedDigital video signal modificationMotion vectorTemplate match
Given that decoder side motion vector refinement / derivation is a normative aspect of a coding system, the encoder will also have to perform the same error surface technique in order to not have any drift between the encoder's reconstruction and the decoder's reconstruction. Hence, all aspects of all embodiments are applicable to both encoding and decoding systems. In template matching, the refinement movement occurs only in the reference starting from the sub-pixel accurate center that is derived based on the explicitly signaled merge index or implicitly through cost evaluations. In bilateral matching (with or without averaged template), the refinements start in the reference lists L0 and L1 starting from the respective sub-pixel accurate centers that are derived based on the explicitly signaled merge index or implicitly through cost evaluations.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
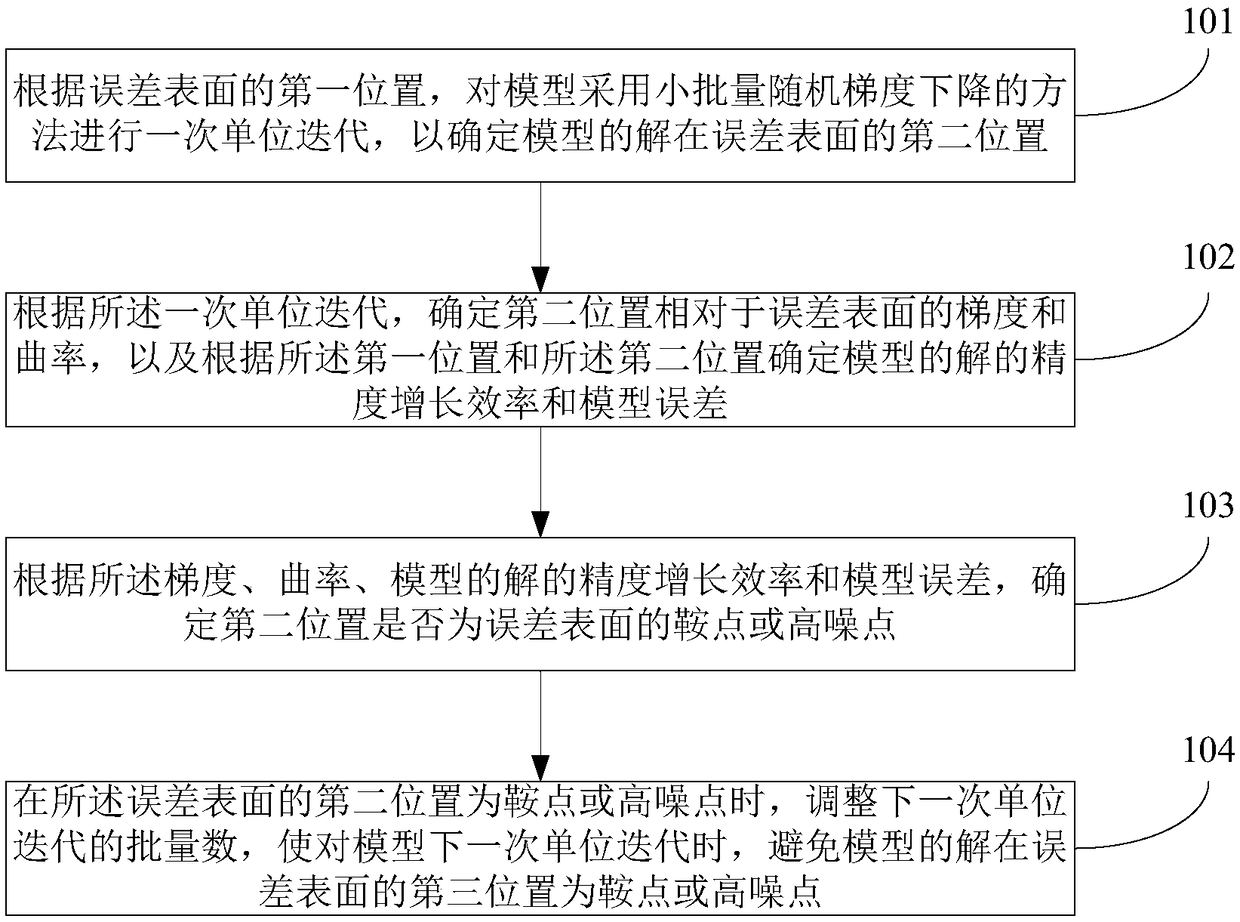
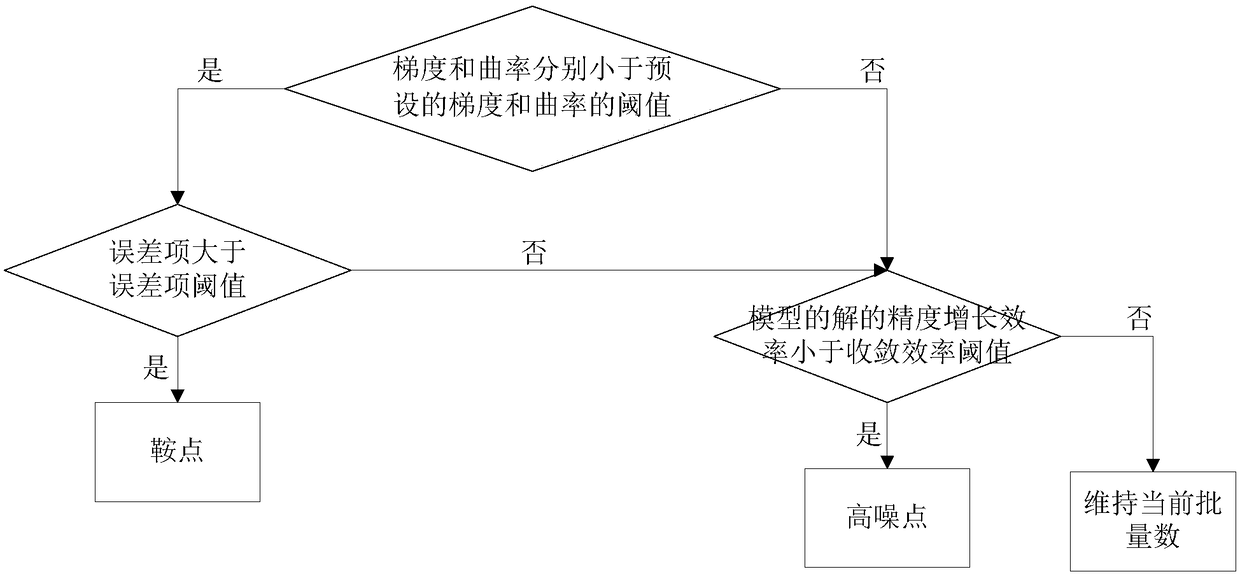
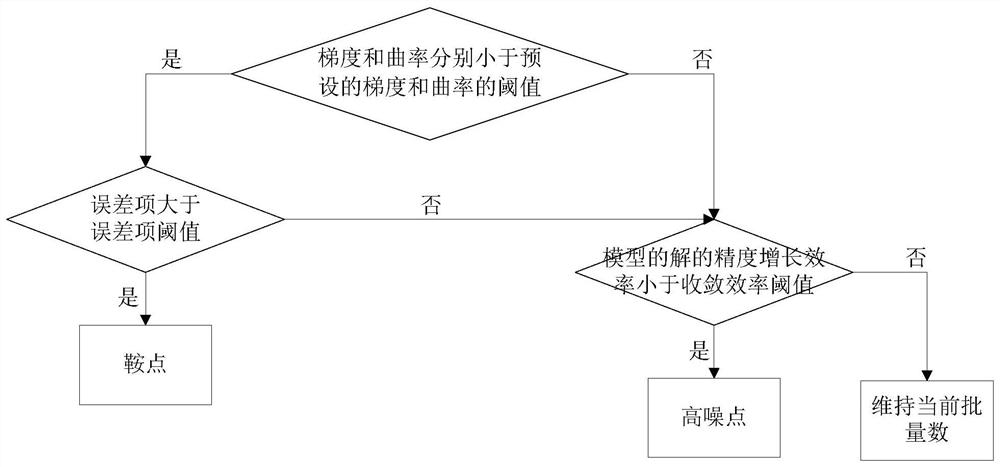
Convergence method of high-dimensional depth learning model and device
The embodiment of the invention discloses a convergence method of a high-dimensional depth learning model and a device. The method includes the steps of performing one unit iteration on a model according to a first position of the error surface to determine a solution of the model at a second position of the error surface; determining a gradient and a curvature of the second position relative to the error surface according to one unit iteration, and determining an accuracy increasing efficiency and a model error of the solution of the model according to the first position and the second position; determining whether the second position is a saddle point or a high noise point of the error surface based on the gradient, the curvature, the accuracy increasing efficiency and the model error; and when the second position of the error surface is a saddle point or a high noise point, adjusting the batch number of the next unit iteration. Embodiments of the present invention determine the batch number of the model at the next batch iteration based on the saddle point or high noise. Therefore, it is possible to optimize the accuracy increasing efficiency and the escape saddle point of the model by adjusting the gradient and stochastic noise estimation in the iteration process.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
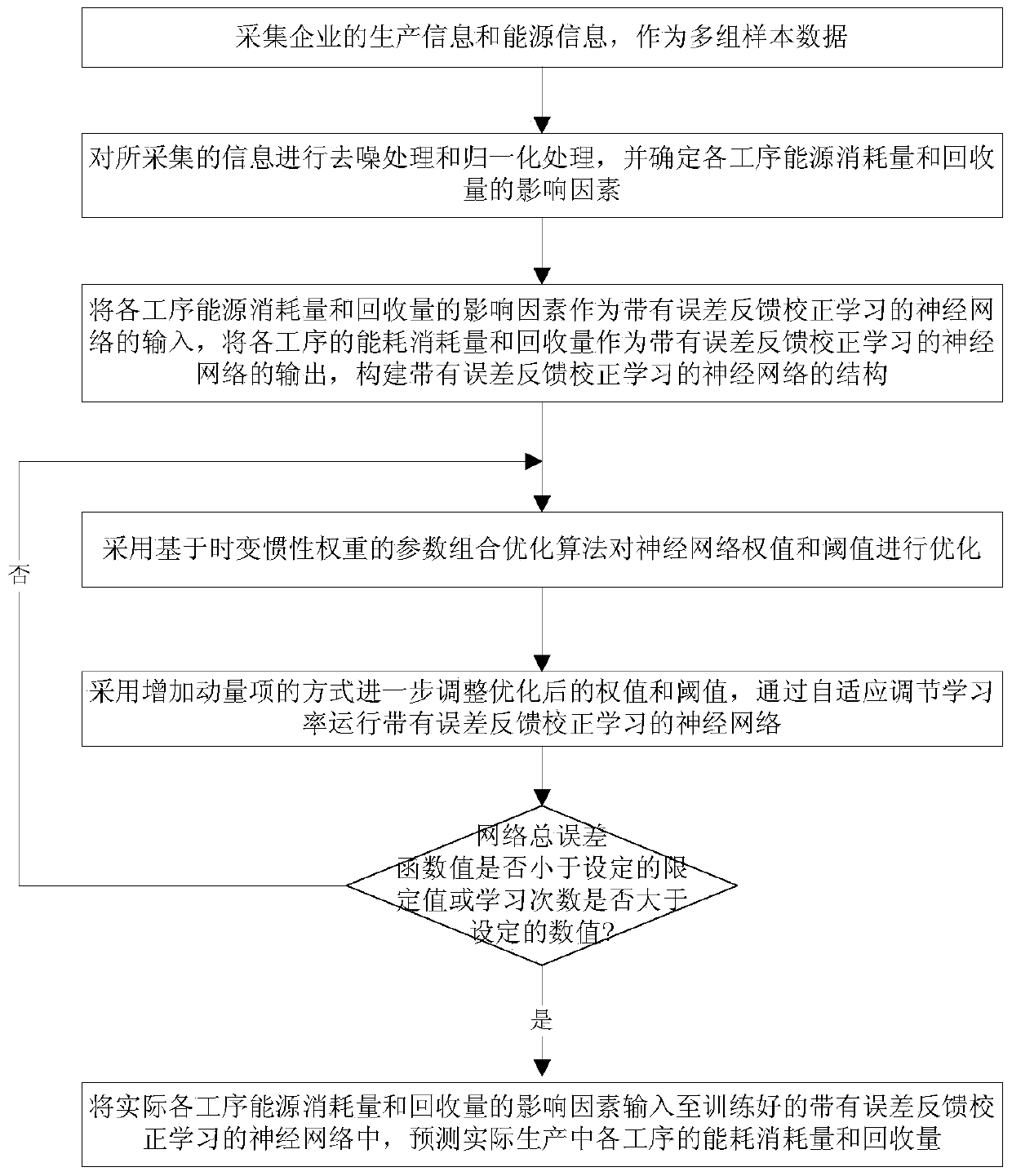
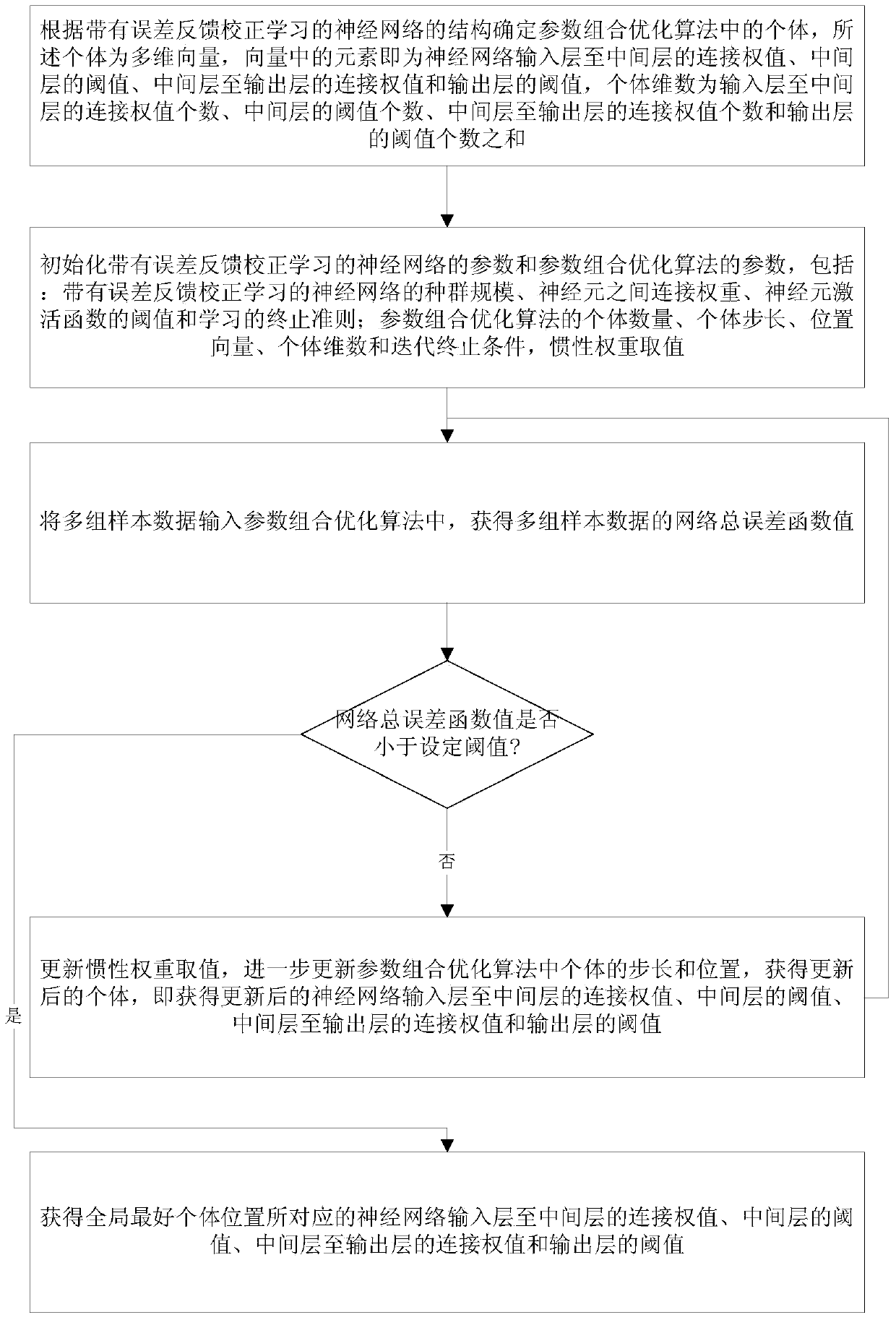
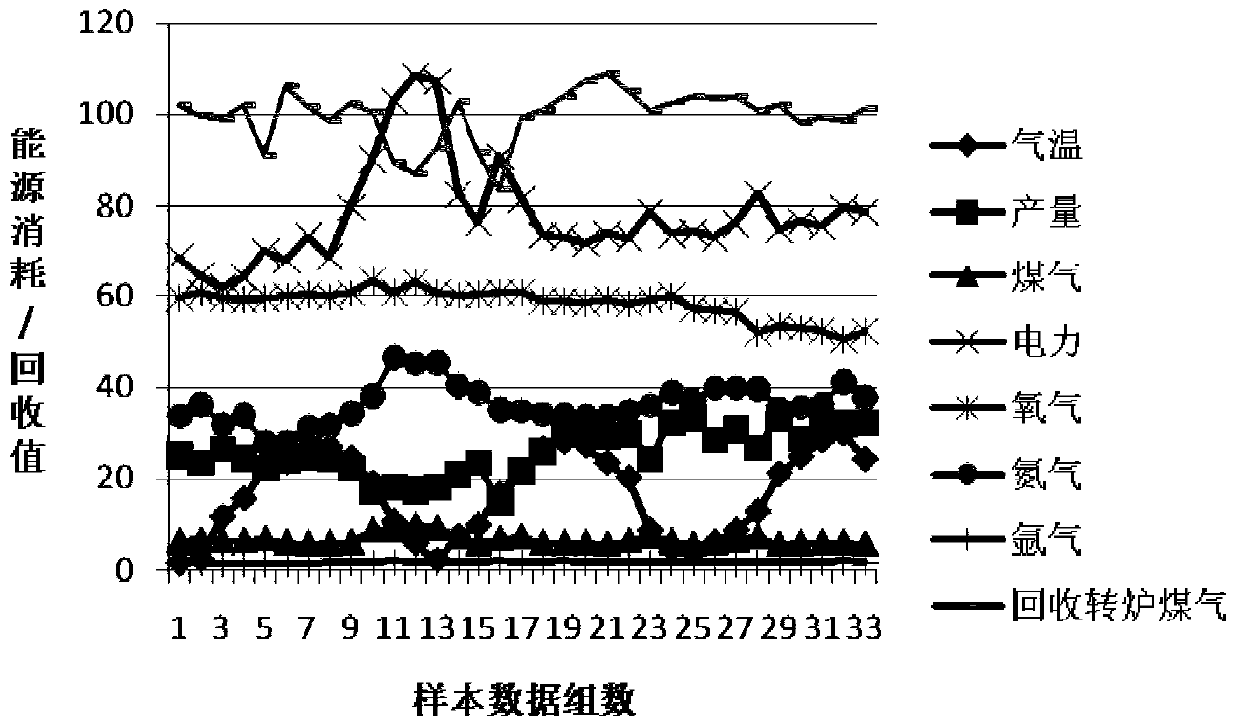
An Energy Consumption Prediction Method for Improving Energy Utilization Rate of Iron and Steel Enterprises
ActiveCN105204333BIncrease training speedImprove efficiencyAdaptive controlPower usage effectivenessStudy methods
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
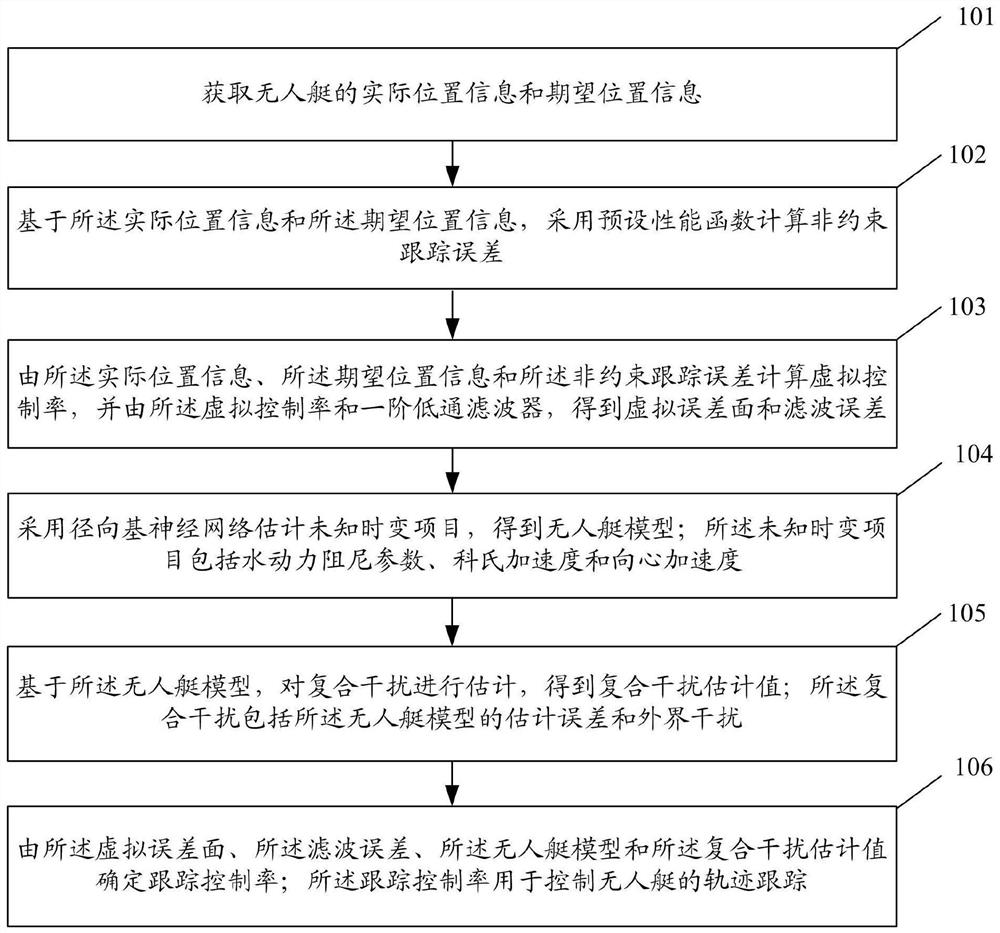
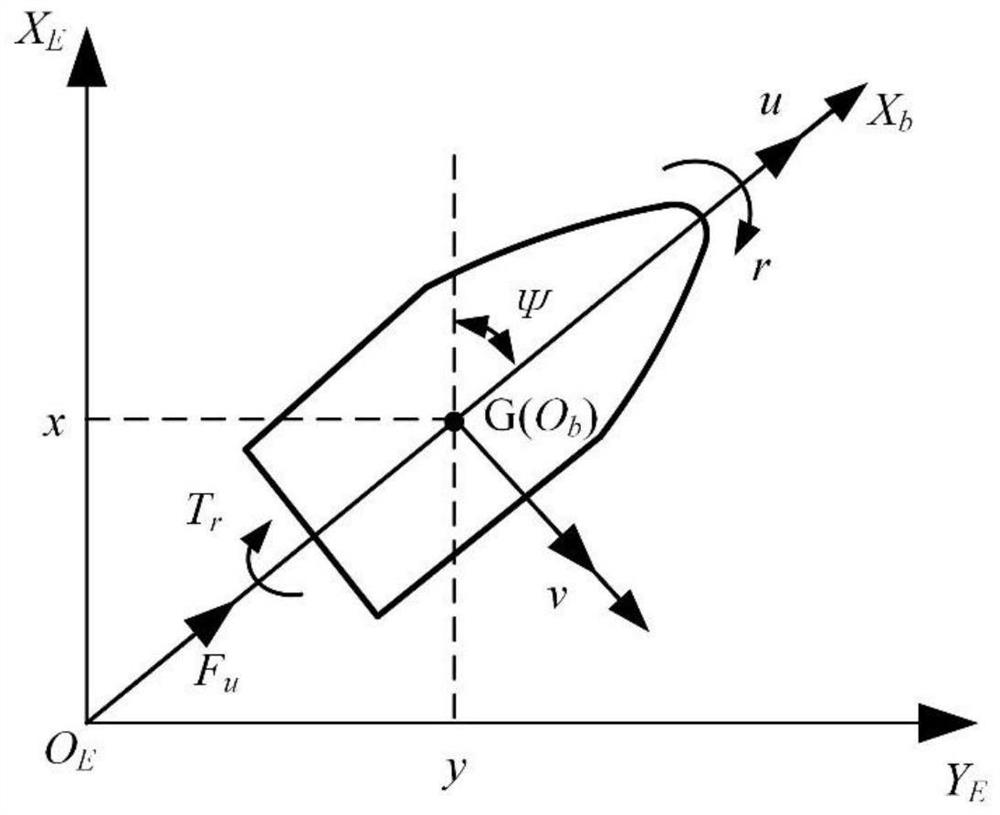
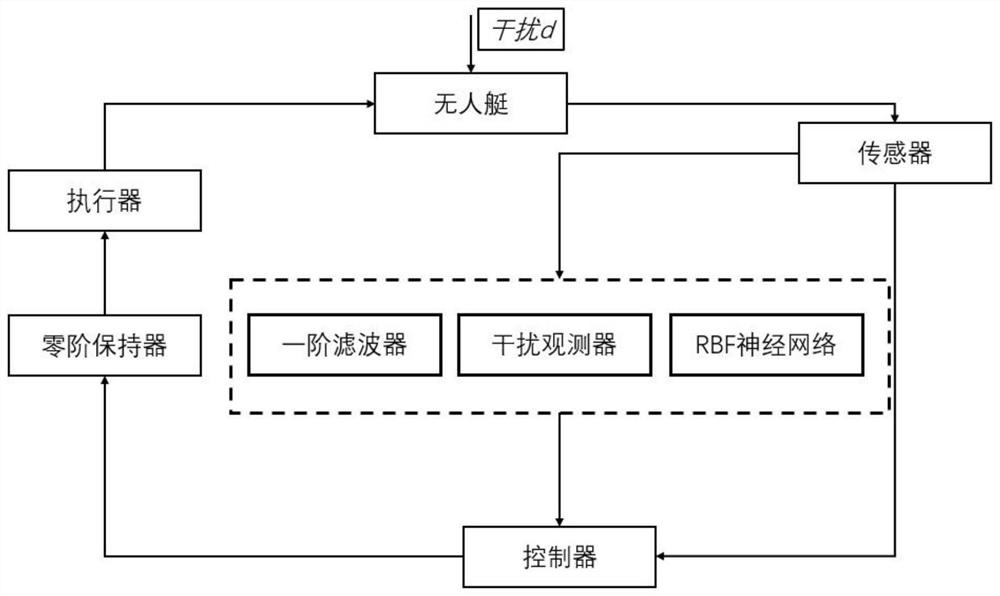
Unmanned ship tracking control method and system
PendingCN113608534ATracking Accuracy LimitsHigh precisionPosition/course control in two dimensionsPerformance functionRadial basis function neural
The invention discloses an unmanned ship tracking control method and system. The method comprises the following steps of calculating an unconstrained tracking error by adopting a preset performance function based on actual position information and expected position information, calculating a virtual control rate according to the actual position information, the expected position information and the unconstrained tracking error, and obtaining a virtual error surface and a filtering error according to the virtual control rate and a first-order low-pass filter, estimating an unknown time-varying item by adopting a radial basis function neural network to obtain an unmanned ship model, estimating the composite interference based on the unmanned ship model to obtain a composite interference estimated value, and determining a tracking control rate according to the virtual error surface, the filtering error, the unmanned ship model and the composite interference estimated value. The control rate is used for controlling trajectory tracking of the unmanned ship. The precision of tracking control of the unmanned ship can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
System and method for control of loop alignment in adaptive feed forward amplifiers
A fast search algorithm for loop alignment of a feed forward amplifier is disclosed. The algorithm controls a processor (202) that adjusts, digitally, the gain and phase of the loop alignment based on power measurements at the input and output of cancellation combiners, to find the optimal setting. A ''non-collinear descent'' algorithm is used to search, iteratively, for the minimum within an error surface. For loop alignment, the error surface is defined by the set of measurement points comprising the alignment settings and the associated cancellation residuals. For the case of first loop alignment, the cancellation residual is measured using the ratio of two power detectors (214, 218) located at the input and after the cancellation (error) combiner. For second loop alignment, cancellation is estimated using the residual pilot power detected at the output of the amplifier. The preferred alignment method uses three successive measurements to estimate the gradient direction with respect to gain and phase shifter settings. The actual descent direction is selected to be close to the gradient direction without being collinear with the most recent alignment adjustments. Quantization of the descent direction simplifies the implementation as well as the enforcement of the non-collinearity constraint on successive alignment settings. Two different step size selection approaches are disclosed, however, any standard step size selection approach may be employed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
A Method of Automatically Compensating the Variation Error of Network Analyzer's Measuring Surface
ActiveCN103543425BImprove measurement efficiencySimple calculationElectrical measurementsCurve fittingCalibration curve
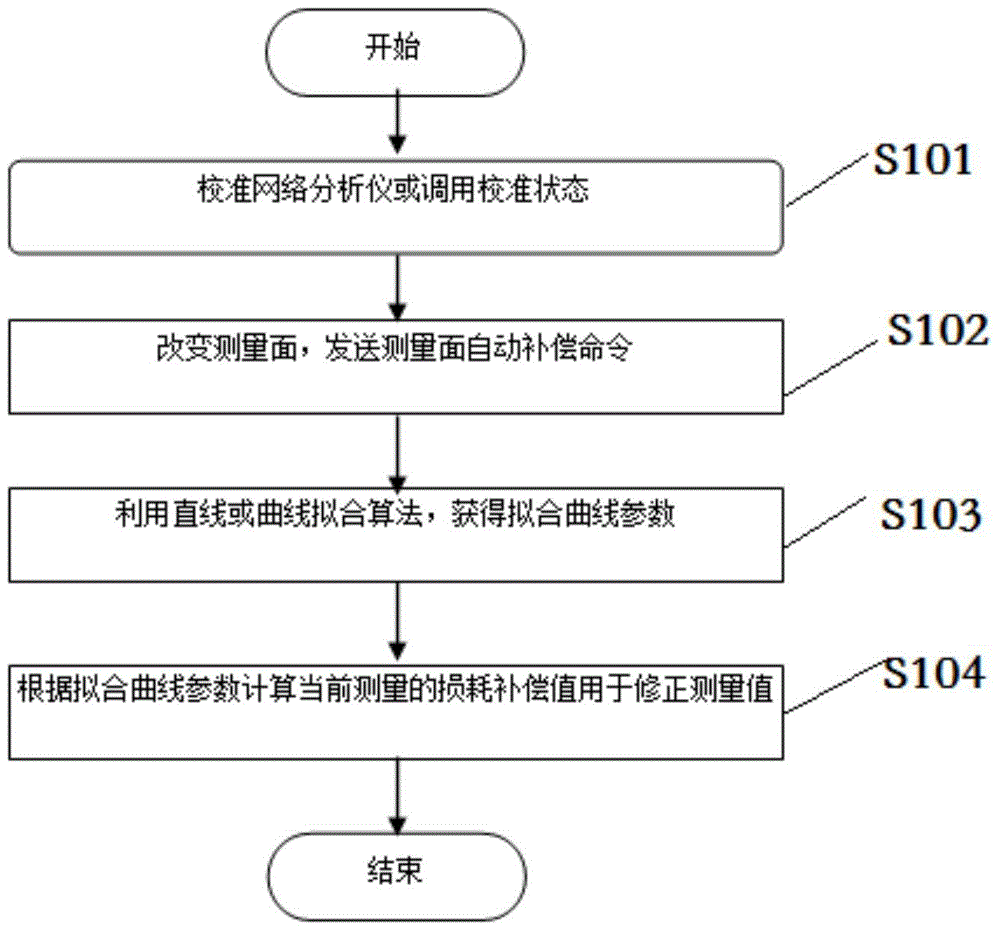
The invention provides a method for automatically compensating the error of the measurement surface change of a network analyzer, step 1: calibrate the network analyzer or call the calibration state; step 2: change the measurement surface, and send a measurement surface automatic compensation command; step 3: call the measurement surface to automatically Compensation fitting algorithm, obtain fitting curve parameters and calculate compensation data; Step 4: store parameters and compensation data. Using the above scheme, the calibration compensation algorithm is realized by using the curve fitting method, and the error introduced by the change of the measurement reference surface can be removed without user intervention. The obtained compensation data is simple to calculate and fast to run, improving the user's measurement efficiency.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIS TECH INSTR CO LTD
An Assembly-Oriented Method for Determining Evaluation Parameters of Rectangular Planar Shape Errors
InactiveCN105868496BImprove processing qualityImprove assembly accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationSpatial OrientationsSimulation
The invention relates to a method for determining assembly-oriented rectangular plane shape error evaluation parameters and belongs to the field of error evaluation. The method comprises: generating a cutting surface by non-Gaussian plane simulation method, acquiring a shape error surface via wavelet filtering, and extracting characterization parameters of surface shape error distribution; subjecting the shape error surface to simulation assembly through contact algorithm, calculating assembly precision of spatial orientation changes of a second part after assembly, determining a relation between surface characterization parameters and post-assembly part assembly precision through correlation analysis, thereby determining shape error evaluation parameters and enabling quantitative description for the relation between the surface distribution characterization parameters and assembly precision. Plane characteristic parameters having important impact on assembly precision are obtained, and scientific basis is provided for improving machining quality of mating planes and optimizing assembly process to improve assembly precision.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
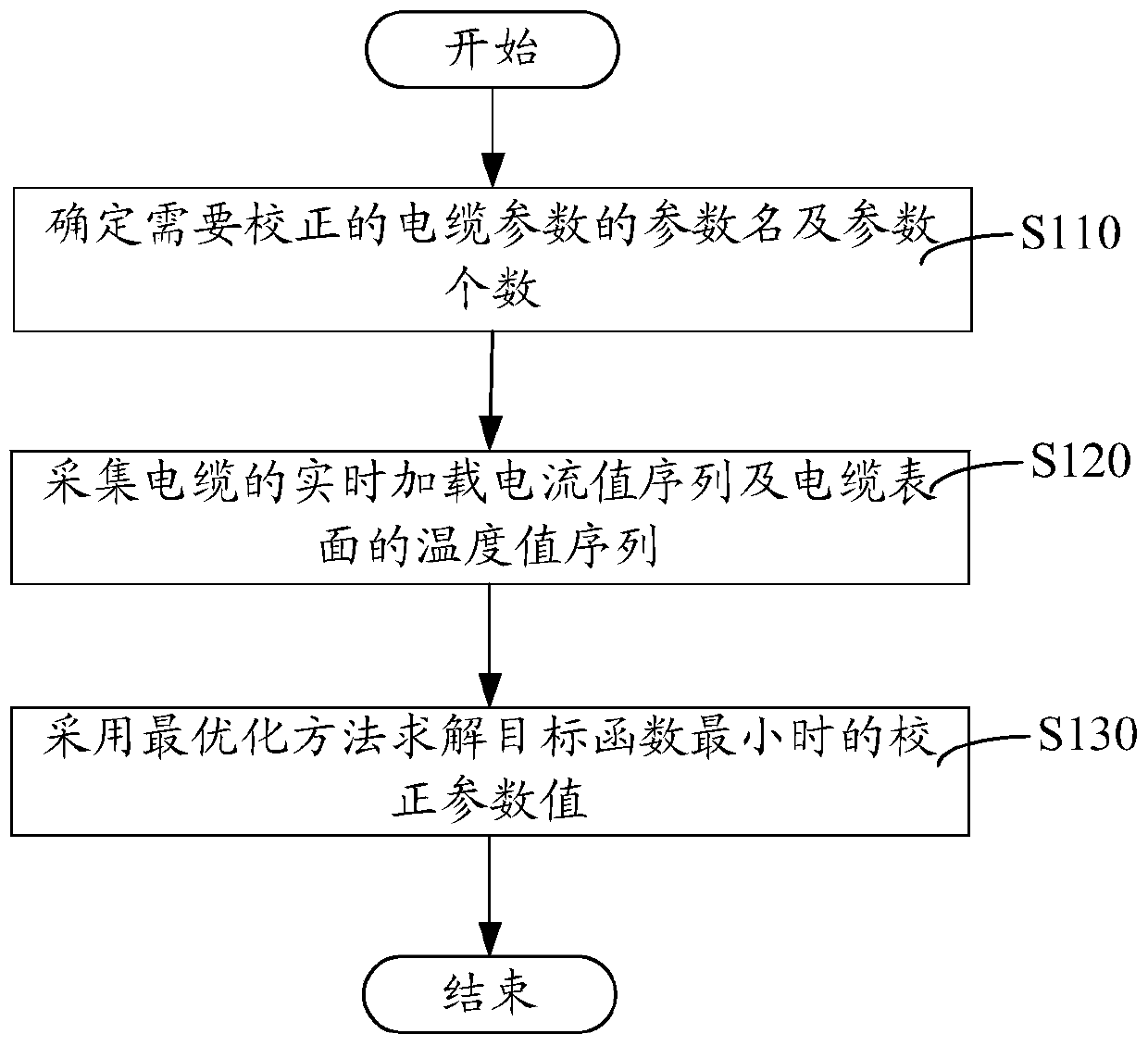
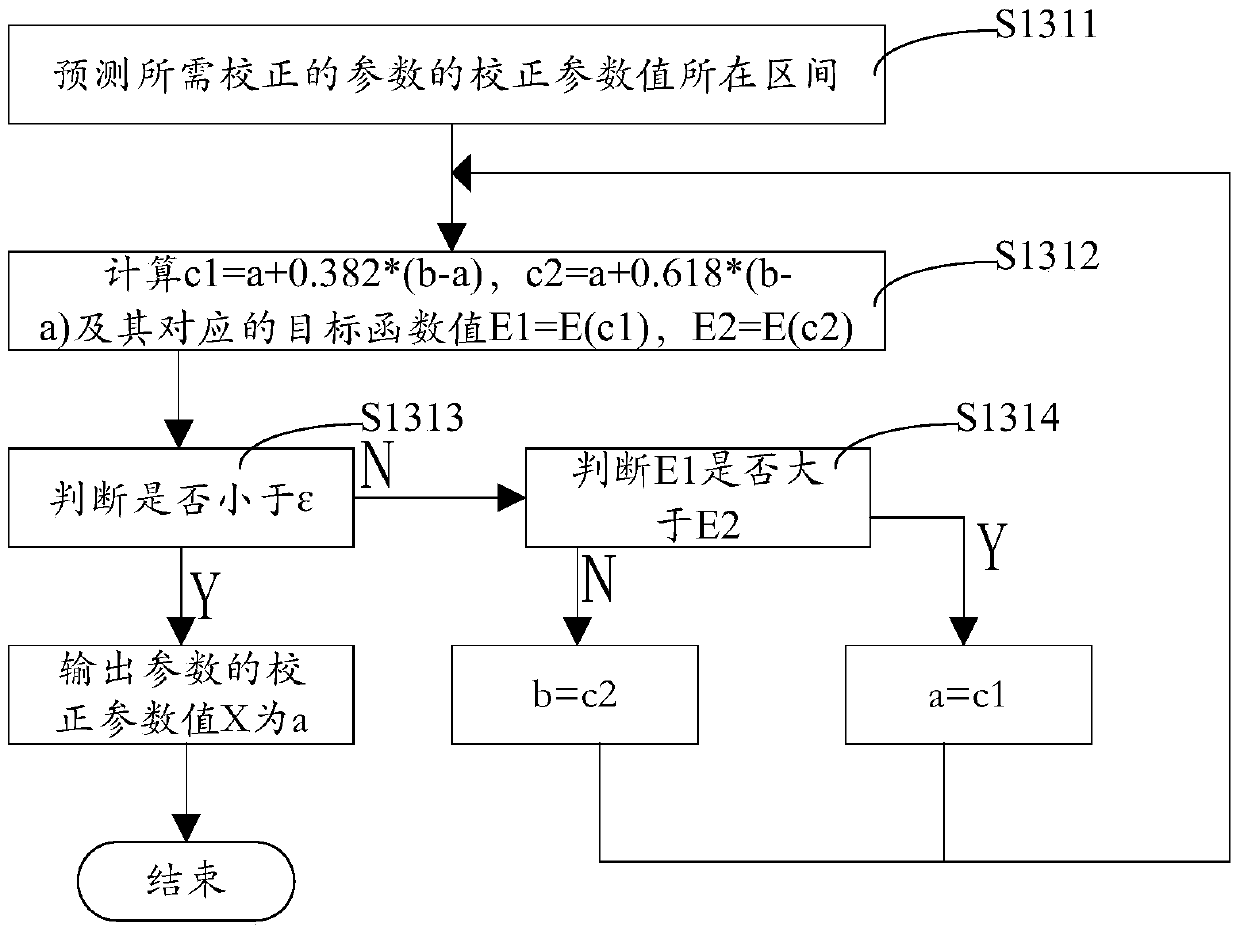
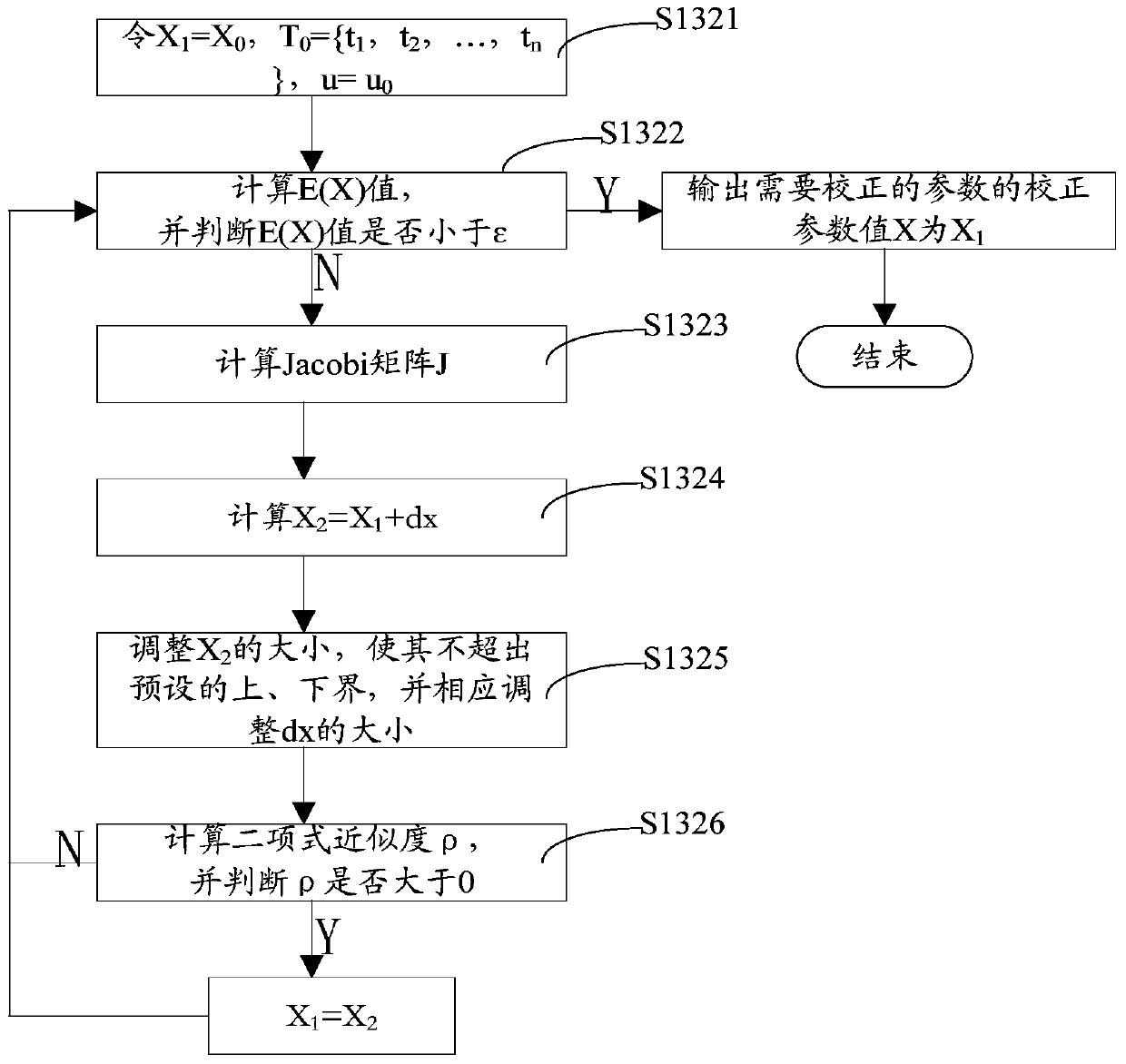
Calculation method of inverse problem of ampacity
ActiveCN104778149BImprove reliabilityImprove accuracyComplex mathematical operationsCarrying capacityEngineering
The invention relates to a calculation method for the inverse problem of ampacity. By comparing the cable surface temperature monitored in real time and the cable surface temperature data in the dynamic ampacity analysis, the error of the parameters in the cable and the laying environment is corrected to obtain the corrected parameter values. The calculation result is accurate, which effectively improves the reliability and accuracy of the ampacity analysis software.
Owner:SUZHOU GUANGGE EQUIP
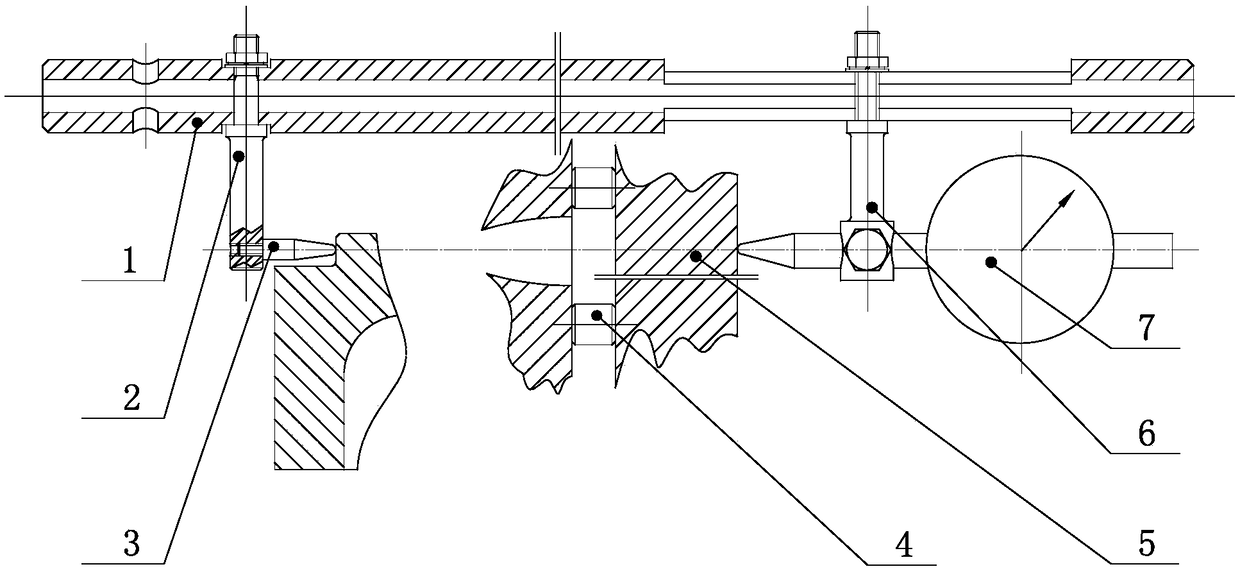
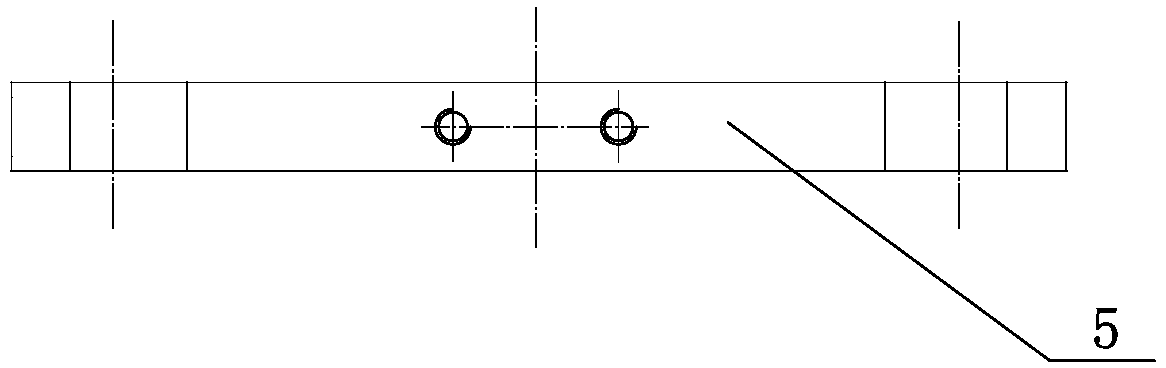
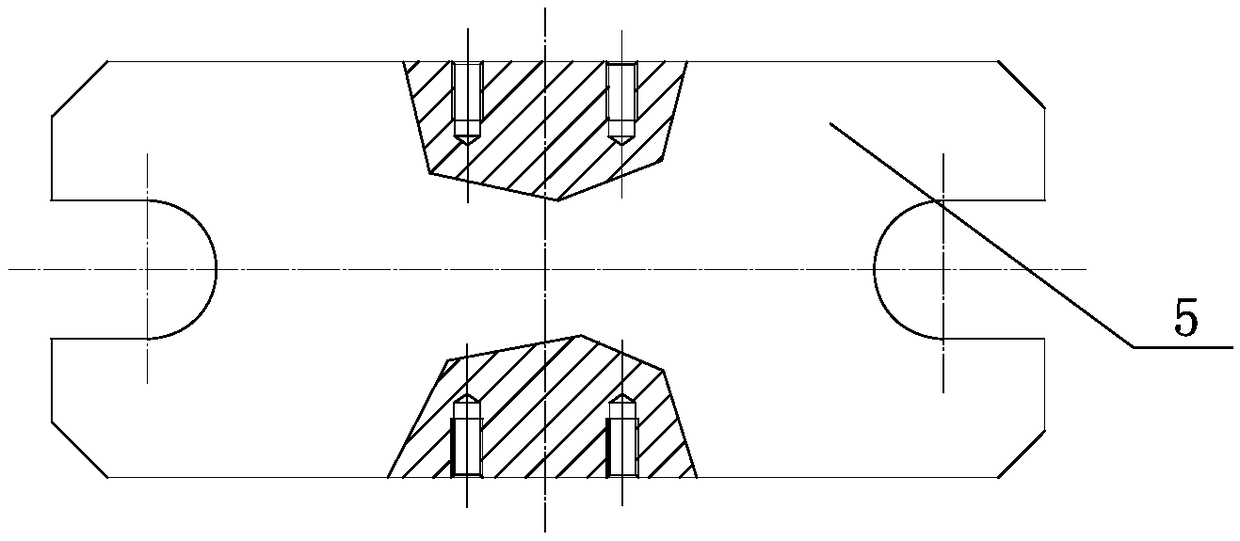
Machine body error surface size measurement device and method
PendingCN109029204AQuick checkHigh measurement accuracyMechanical measuring arrangementsSize measurementMeasurement device
The invention is mainly applied to the field of diesel engine part detection and particularly relates to a machine body error surface size measurement device and method. The machine body error surfacesize measurement device comprises a measurement staff, a parallel plate and an equal-height gauge block; the measurement staff comprises a measurement rod; a fixed gauge frame and a movable gauge frame are respectively mounted at both ends of the measurement rod; corresponding to the movable gauge frame, a slideway is formed on the measurement rod; a gauge measurement head is mounted on the fixedgauge frame; a dial gauge is mounted on the movable gauge frame; the equal-height gauge block is set as a cylindrical measurement block; and the measurement rod, the gauge measurement rod and the dial gauge are all arranged in parallel. The machine body error surface size measurement device adopts a relative measurement detection method, follows the Abbe principle which is one of four basic measurement principles, can be directly used in inspection field, fills in one gap in the aspect of the measurement technology, is tried out in a machining workshop and is relatively ideal in effect.
Owner:ZICHAI POWER CO LTD
High-frequency error detecting apparatus and method for heavy caliber heavy relative aperture aspherical mirror
InactiveCN100462673CIncrease horizontal resolutionIncrease the vertical measurement rangeUsing optical meansTesting optical propertiesMultiple pointError surface
The invention discloses a high-frequency error detection device and method in the large caliber large relative aperture non-spherical mirror, the device including the five-axis movement adjustment platform with the interferometer focusing platform, the side swing reflecting mirror side swing platform located in front of the interferometer focusing platform, and the measured non-spherical mirror 3D movement adjustment platform located below the side swing reflection mirror side swing platform, and the multiple points supporting machine with the laser wave surface interferometer, the side swing reflection mirrors, and the measured non-spherical mirror installed on the corresponding platforms, and the main control computer with built-in detection data-processing algorithm program connecting with the laser wave surface interferometer. The device uses the main control computer to process the detection data-processing algorithm, which can combine the detected multiple part regions error surface maps into error surface map with medium or high frequency in full caliber, including the initial pose determining method, the overlapping regional data extraction algorithm and the regional data stitching algorithm. The invention is a high-frequency error detection device and method with low-cost, high-precision, high-efficiency in the large caliber large relative aperture non-spherical mirror.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method for symbol sampling in a high time delay spread interference environment
Symbol sampling in a high time delay spread interference environment includes acquiring (602) a time varying baseband waveform. The waveform has a signal amplitude that varies between one of a plurality of symbol states. The waveform is sampled (603) at a rate of m times the symbol rate. During an evaluation time, an error value is calculated (604, 606) for each of m data sample positions. Each of the error values comprises an average distance between the measured value of the waveform as indicated by the data sample and a closest known symbol value. The error values are used to create an error surface. Thereafter, the error surface is modeled as a quadratic and an optimal sample time is determined (608, 610, 612) based on finding the time location where the quadratic surface is minimum. A sinc interpolator is then used to resample the data.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
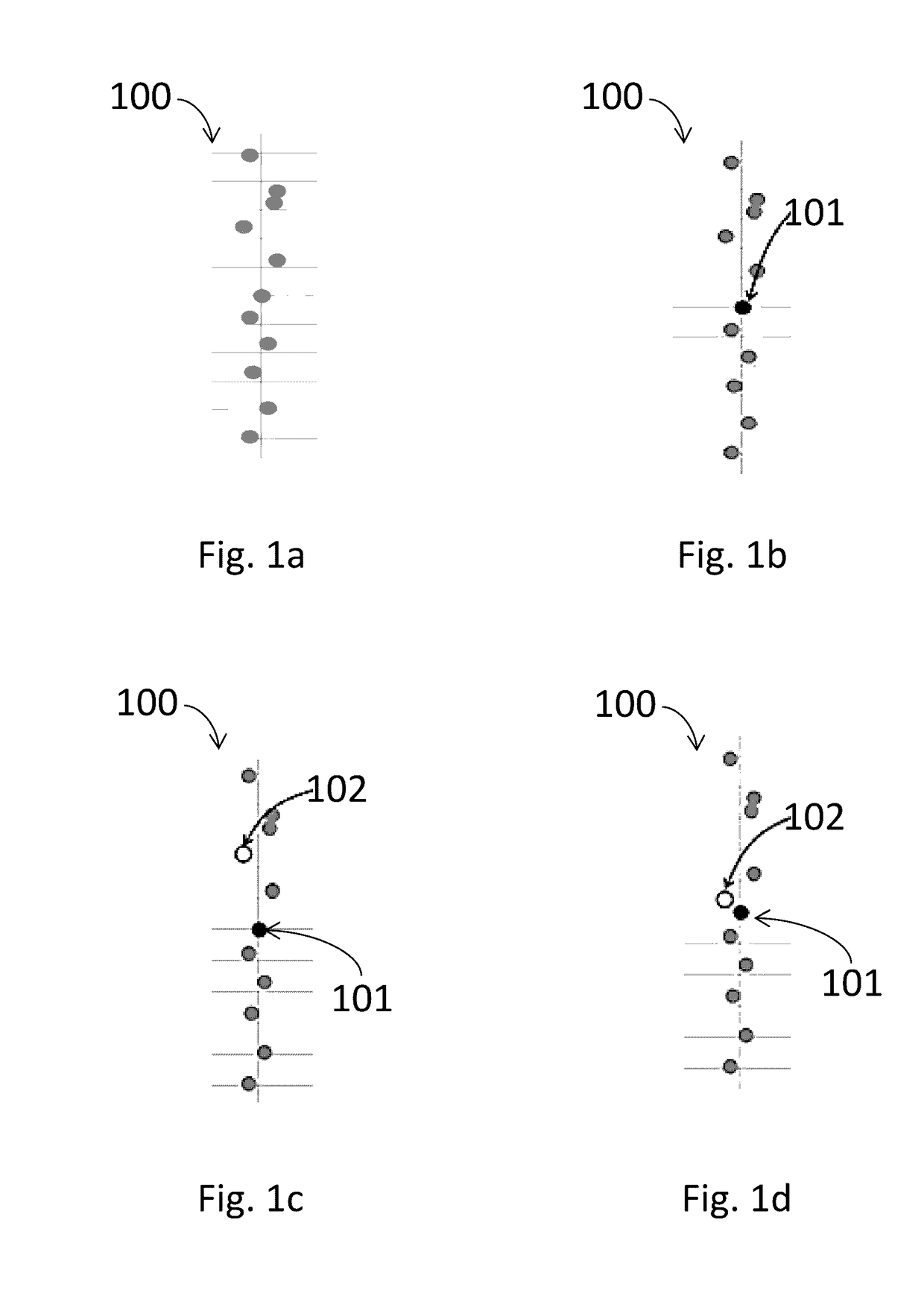
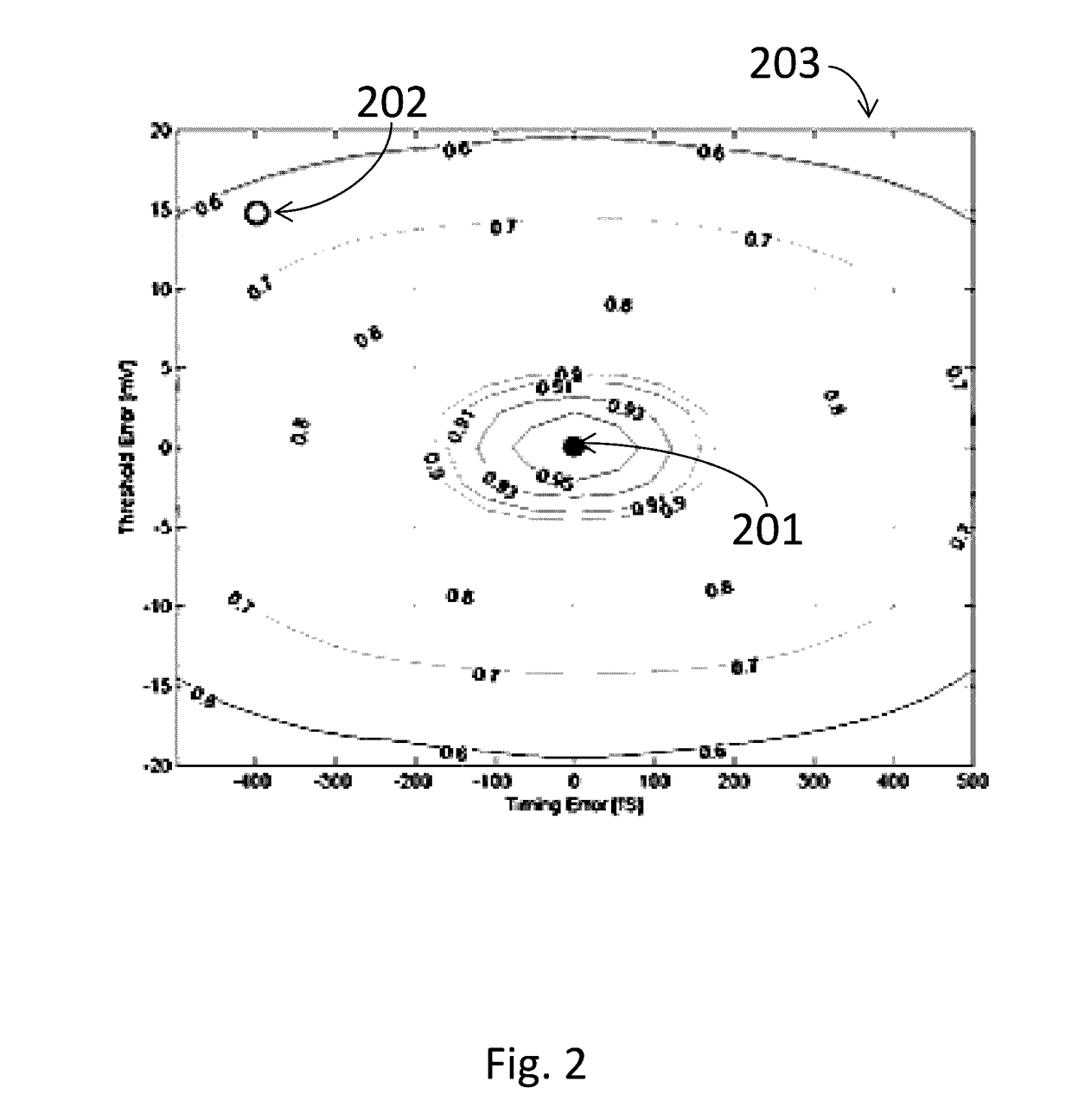
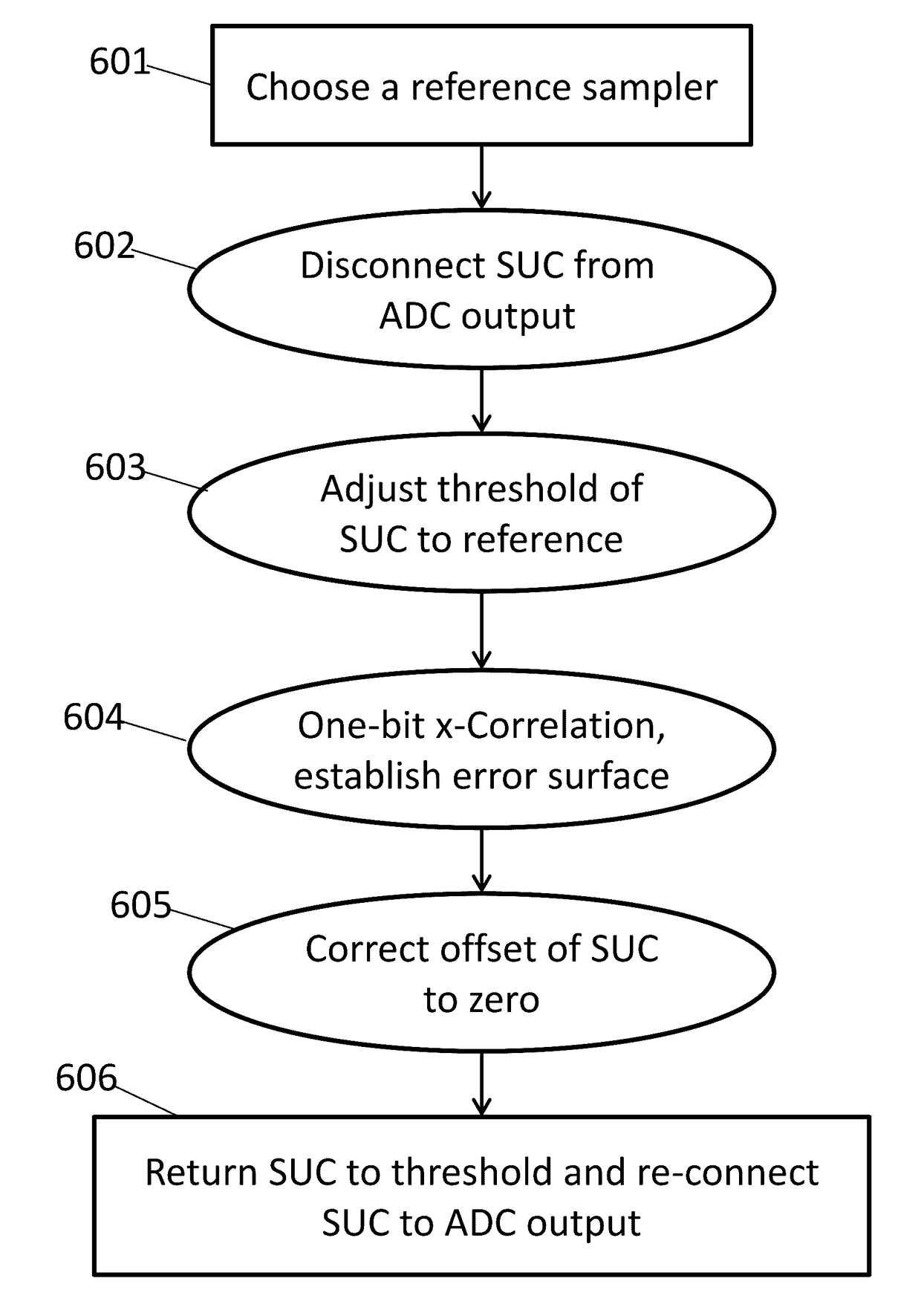
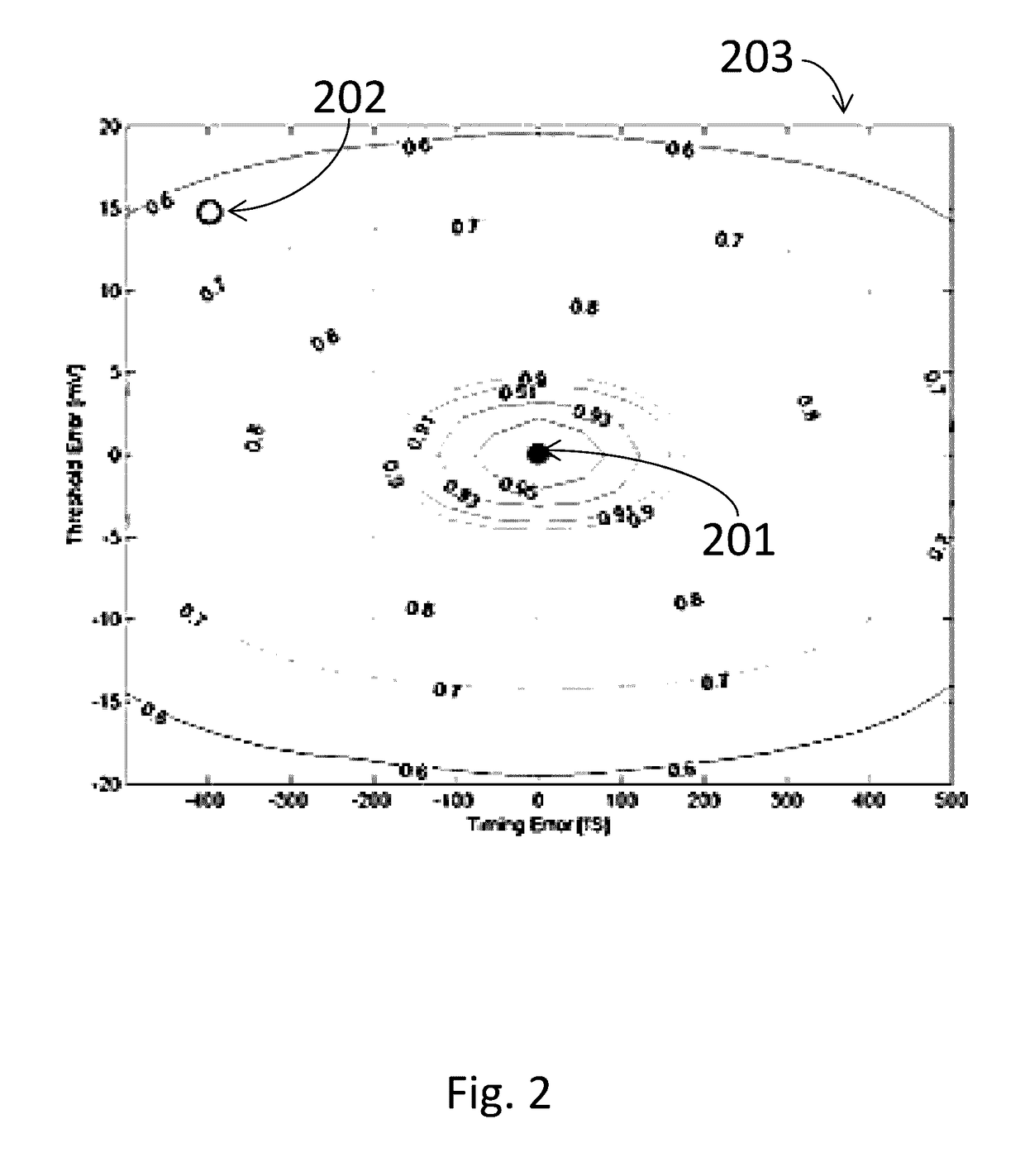
Background calibration of sampler offsets in analog to digital converters
ActiveUS20170099061A1Analogue-digital convertersAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingDigital down converterA d converter
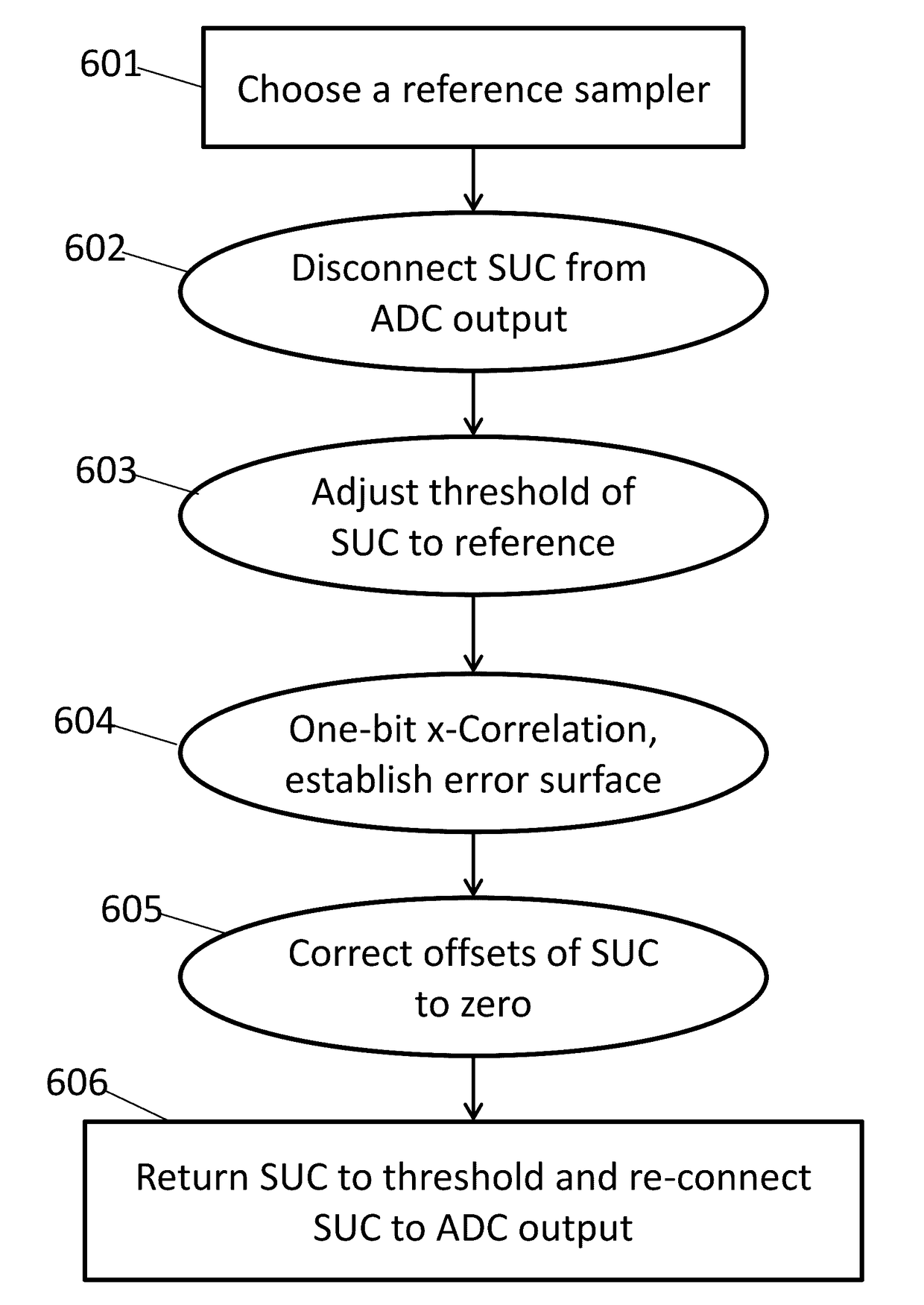
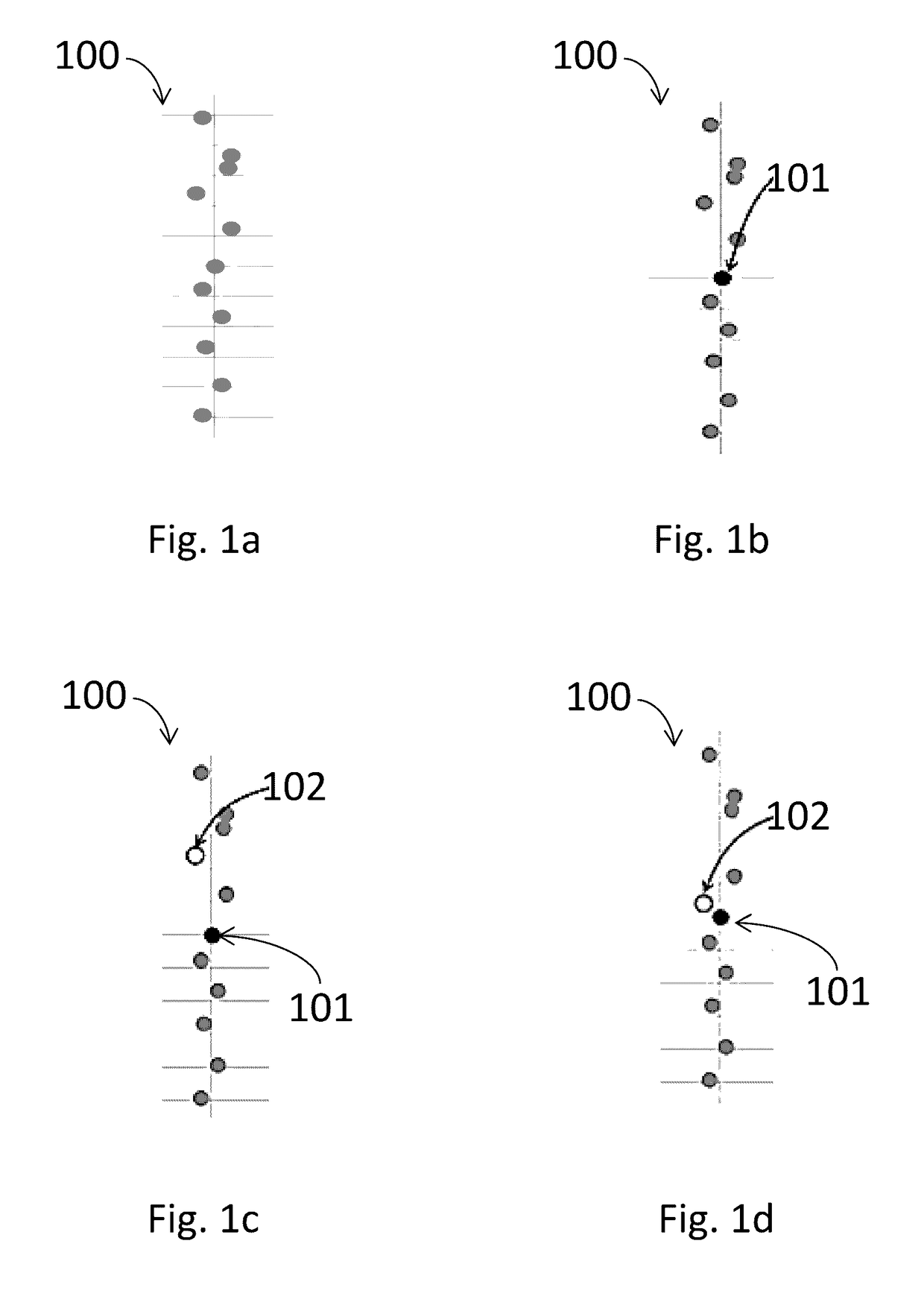
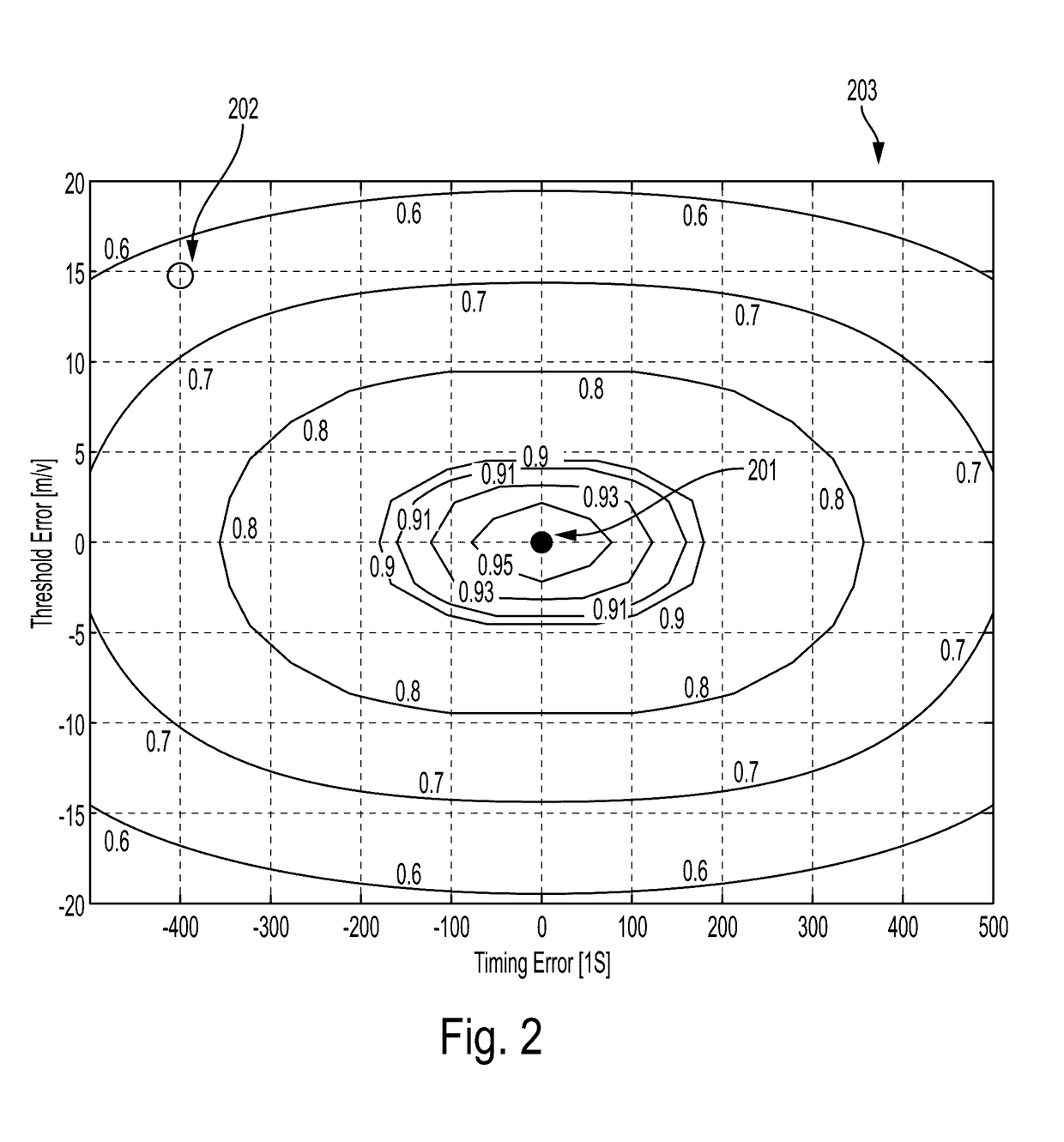
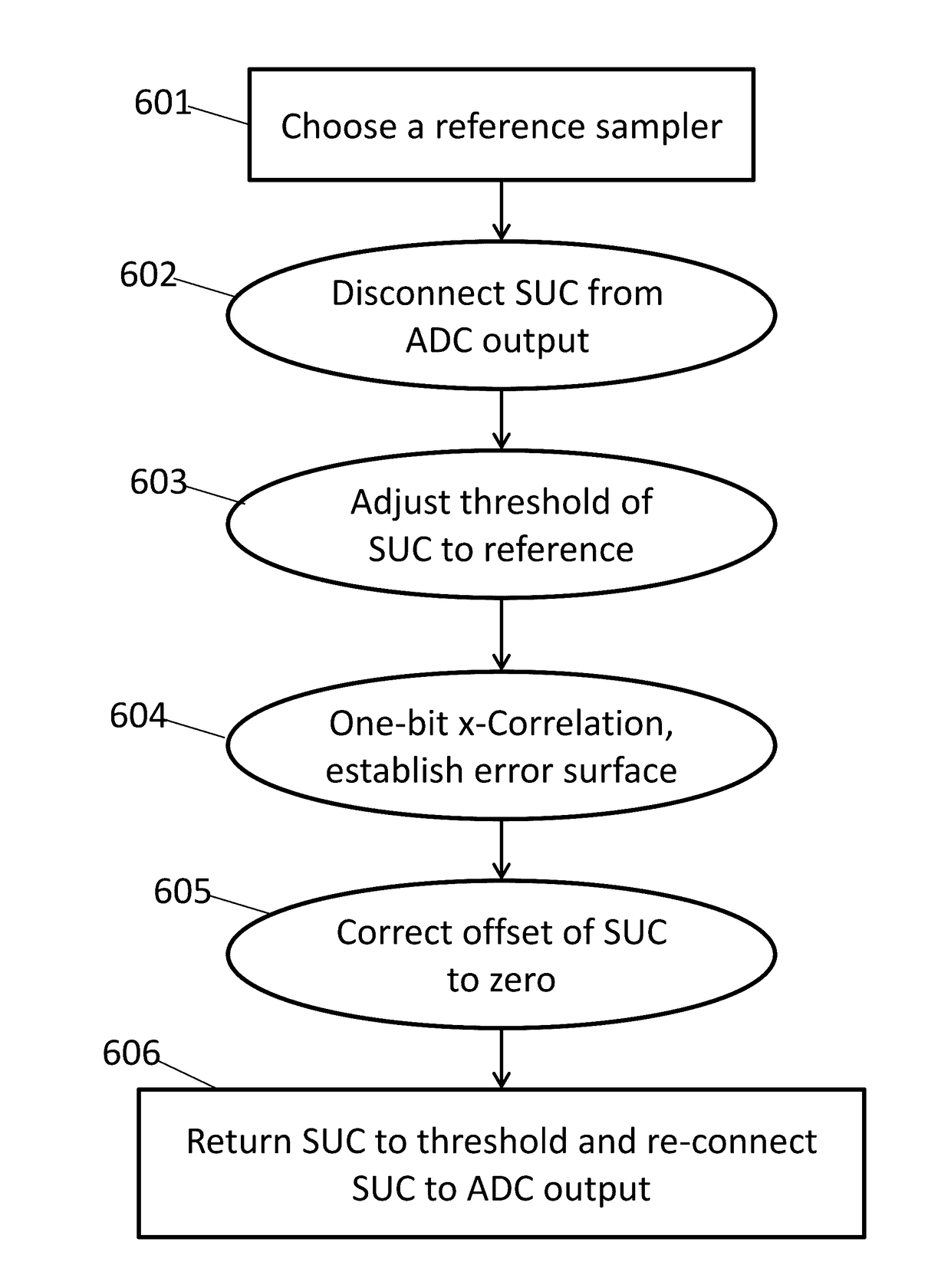
A method for background calibration of sampler offsets in an Analog to Digital Converter (ADC), according to which one of the samplers of the ADC is established as a reference sampler, whose threshold and timing offsets will be the criterion for adjusting threshold offsets and timing offsets of all other samplers. Then each of the other samplers of the ADC, one at a time, is calibrated by selecting an uncalibrated sampler and establishing it as the current Sampler Under Calibration (SUC); disregarding contribution of the SUC to the output of the ADC; adjusting the threshold of the SUC to be identical to the threshold of the reference sampler; performing one-bit cross-correlation between the reference sampler and the SUC; establishing an error surface representing the threshold offset and timing offset of the SUC with respect to the reference sampler; adjusting the threshold and the timing of the SUC to be equal to the threshold and timing of the reference sampler; restoring level of the SUC to its original threshold with respect to the overall ADC and restoring contribution of the SUC to the output of the ADC.
Owner:MULTIPHY
Background calibration of sampler timing errors in flash analog to digital converters
ActiveUS20170117915A1Analogue-digital convertersAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingDigital down converterDigital converter
A method for background calibration of sampler offsets in an Analog to Digital Converter (ADC), according to which one of the samplers of the ADC is established as a reference sampler, whose threshold and timing offsets will be the criterion for adjusting threshold offsets and timing offsets of all other samplers. Then each of the other samplers of the ADC, one at a time, is calibrated by selecting an uncalibrated sampler and establishing it as the current Sampler Under Calibration (SUC); disregarding contribution of the SUC to the output of the ADC; adjusting the threshold of the SUC to be identical to the threshold of the reference sampler; performing one-bit cross-correlation between the reference sampler and the SUC; establishing an error surface representing the threshold offset and timing offset of the SUC with respect to the reference sampler; adjusting the threshold and the timing of the SUC to be equal to the threshold and timing of the reference sampler; restoring level of the SUC to its original threshold with respect to the overall ADC and restoring contribution of the SUC to the output of the ADC.
Owner:MULTIPHY
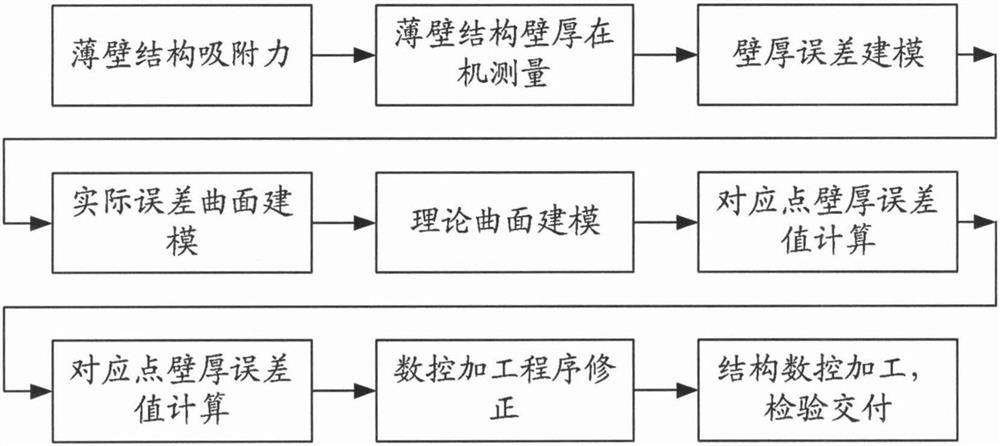
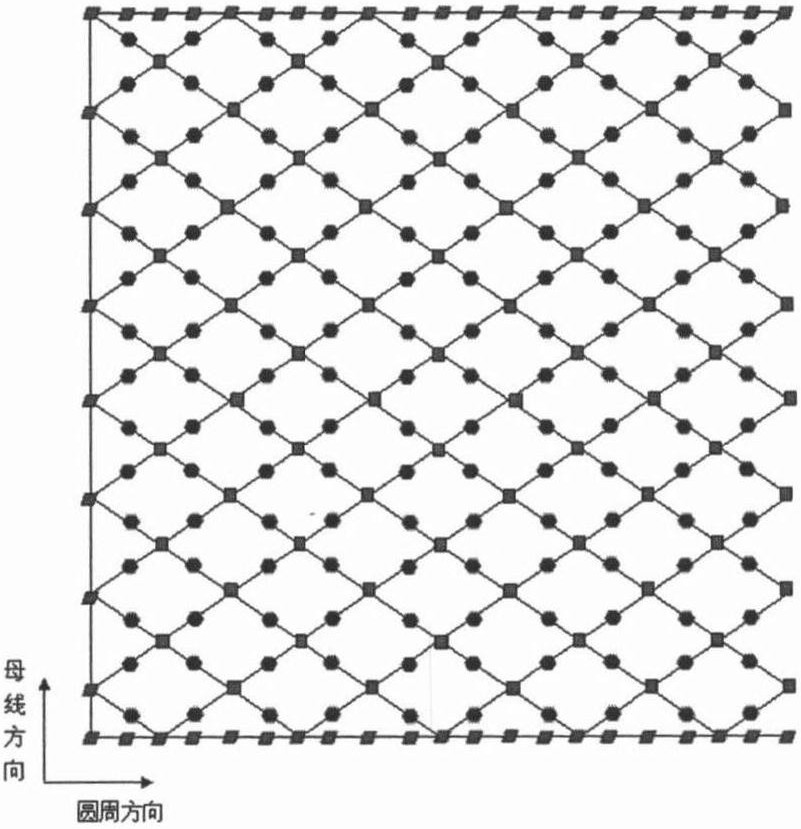
A Machining Error Compensation Method for Complicated Thin-walled Structures
The invention discloses a processing error compensation method for a complex thin-walled structure, which comprises the following steps: (1) Firstly, the adsorption force of the thin-walled structure is obtained based on theoretical calculations to realize high-precision clamping. (2) Plan the measurement points and use the on-machine measurement software to measure the wall thickness. (3) Carry out wall thickness error modeling and calculate the thickness error value. (4) Establish the actual error surface model based on the error value and inverse technique. (5) Establish the theoretical surface model of the thin-walled structure. (6) Based on the theoretical surface model and the actual error surface model, calculate the wall thickness error value of the corresponding point. (7) Research on NC program correction algorithm and generate new NC machining program after error compensation. (8) Structural CNC machining, product inspection and delivery. The invention solves the problems of low processing precision and excessive wall thickness of existing complex thin-walled structures, and achieves beneficial effects such as improving product quality and reducing processing costs.
Owner:SHANGHAI SPACE PRECISION MACHINERY RES INST
Convergence method and device for a high-dimensional deep learning model
The embodiment of the invention discloses a convergence method and device for a high-dimensional deep learning model. The method includes performing a unit iteration on the model according to the first position of the error surface to determine a second position of the solution of the model on the error surface; according to a unit iteration, determining the gradient and curvature of the second position relative to the error surface, And determine the precision growth efficiency and model error of the solution of the model according to the first position and the second position; According to the gradient, curvature, precision growth efficiency and model error, determine whether the second position is a saddle point or a high noise point on the error surface; When the second position of the error surface is a saddle point or a high noise point, the batch number of the next unit iteration is adjusted. In the embodiment of the present invention, the batch number of the model in the next batch of iterations is determined according to the saddle point or high noise. In this way, by adjusting the gradient and random estimation noise in the iterative process, the accuracy growth efficiency of the solution of the model can be optimized and the saddle point can be escaped.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
A hypersonic vehicle attitude adaptive recursive control method and system
ActiveCN110244751BAvoid uncertaintyImprove modeling accuracyAttitude controlAdaptive controlFlight vehicleControl objective
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Background calibration of sampler timing errors in flash analog to digital converters
ActiveUS9692436B2Analogue-digital convertersAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingDigital down converterDigital converter
A method for background calibration of sampler offsets in an Analog to Digital Converter (ADC), according to which one of the samplers of the ADC is established as a reference sampler, whose threshold and timing offsets will be the criterion for adjusting threshold offsets and timing offsets of all other samplers. Then each of the other samplers of the ADC, one at a time, is calibrated by selecting an uncalibrated sampler and establishing it as the current Sampler Under Calibration (SUC); disregarding contribution of the SUC to the output of the ADC; adjusting the threshold of the SUC to be identical to the threshold of the reference sampler; performing one-bit cross-correlation between the reference sampler and the SUC; establishing an error surface representing the threshold offset and timing offset of the SUC with respect to the reference sampler; adjusting the threshold and the timing of the SUC to be equal to the threshold and timing of the reference sampler; restoring level of the SUC to its original threshold with respect to the overall ADC and restoring contribution of the SUC to the output of the ADC.
Owner:MULTIPHY
Method and device for solid modeling of joint surface error
ActiveCN109446539BSimple methodEasy to useGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationAlgorithmEngineering
The embodiment of the invention provides a solid modeling method and device for a joint surface error. The method comprises the following steps of establishing a geometrical characteristic error surface of the joint surface based on the geometrical characteristic error points of the joint surface in a machine tool structure; based on geometrical feature error surface and ideal solid model, establishing the geometrical feature error model of joint surface, in which the ideal solid model is machine tool structure model without geometrical feature error points constructed by computer. The invention provides the solid modeling method and device for the joint surface error, which adopts the geometric characteristic error points of the joint surface of a machine tool structure to construct a geometric characteristic error surface, by combining the geometric feature error surface with the ideal solid model, the geometrical feature error model is established, and the geometrical feature errormodel can truly reflect the joint surface feature error between the actual parts and the ideal solid model constructed by computer, which provides a basis for the machine tool structure optimization design and the accurate calculation and analysis of assembly characteristics prediction.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Large-sized optical flat interferometry device and method
InactiveCN101240999BGet medium and high frequency errorsIncrease horizontal resolutionUsing optical meansTesting optical propertiesLinear motionMeasurement device
The invention discloses a device and method of interferometry for a large-scale optical plane. Wherein, the interferometry device comprises an adjustment platform for the two-axis linear motion of an interferometer, a two-dimensional tilt adjustment platform for the measured plane mirror located at the front of the adjustment platform, a laser wave-front interferometer installed in the adjustmentplatform for the two-axis linear motion of an interferometer and a control computer contained the program of measured data processing algorithm, which is connected to the laser wave-front interferometer. With the device, a plurality of obtained error surface maps of partial region can be spliced to an error surface map containing medium-high frequency (MHF) band on the whole caliber according to the measured data processing algorithm through the control computer, which includes a method for determining the initial position, an algorithm for extracting data from the overlap region and an algorithm for splicing the area data. The invention is a device and method of interferometry for a large-scale optical plane with low cost, high precision and high efficiency.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com