Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
391 results about "Delay spread" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
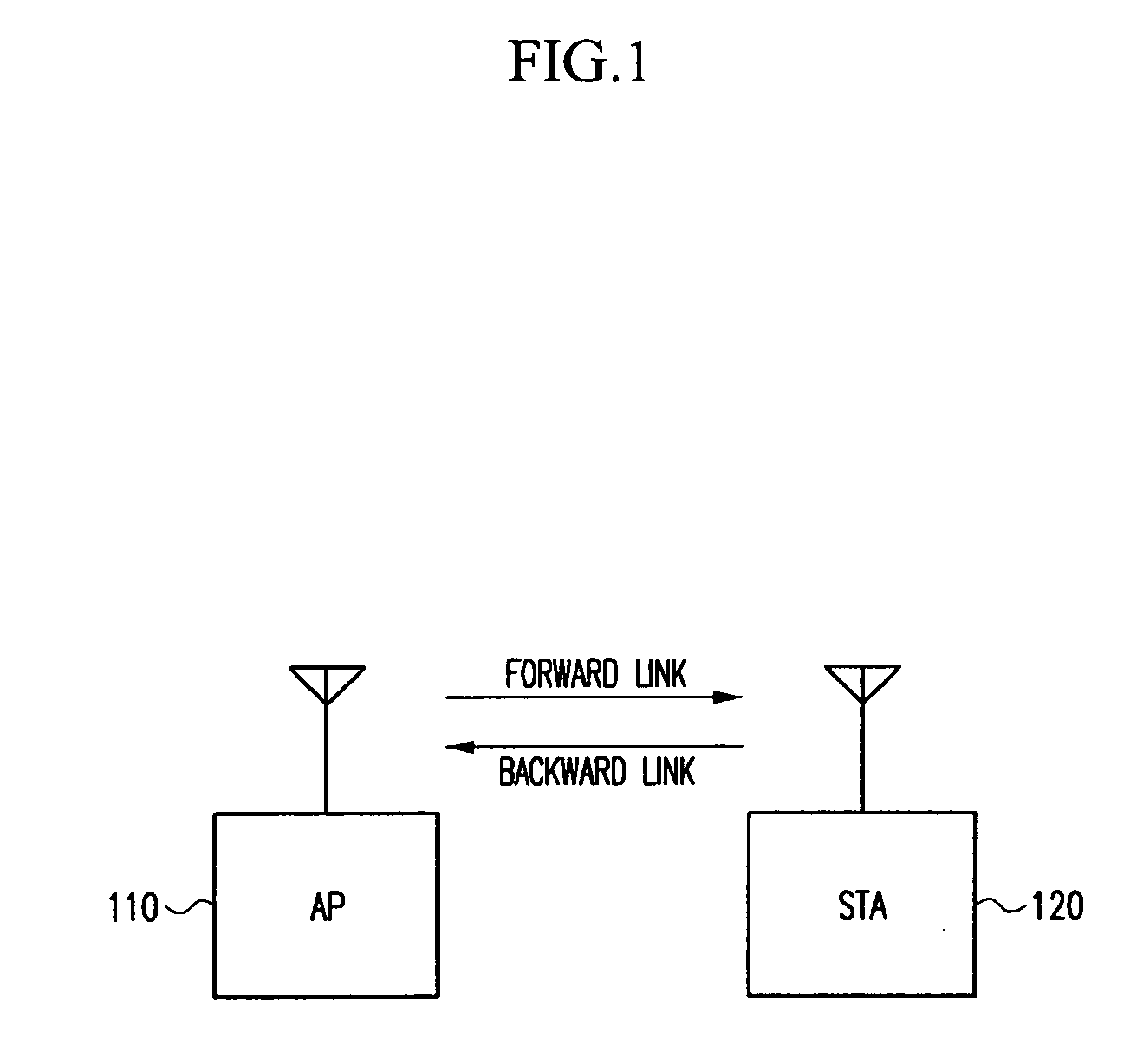
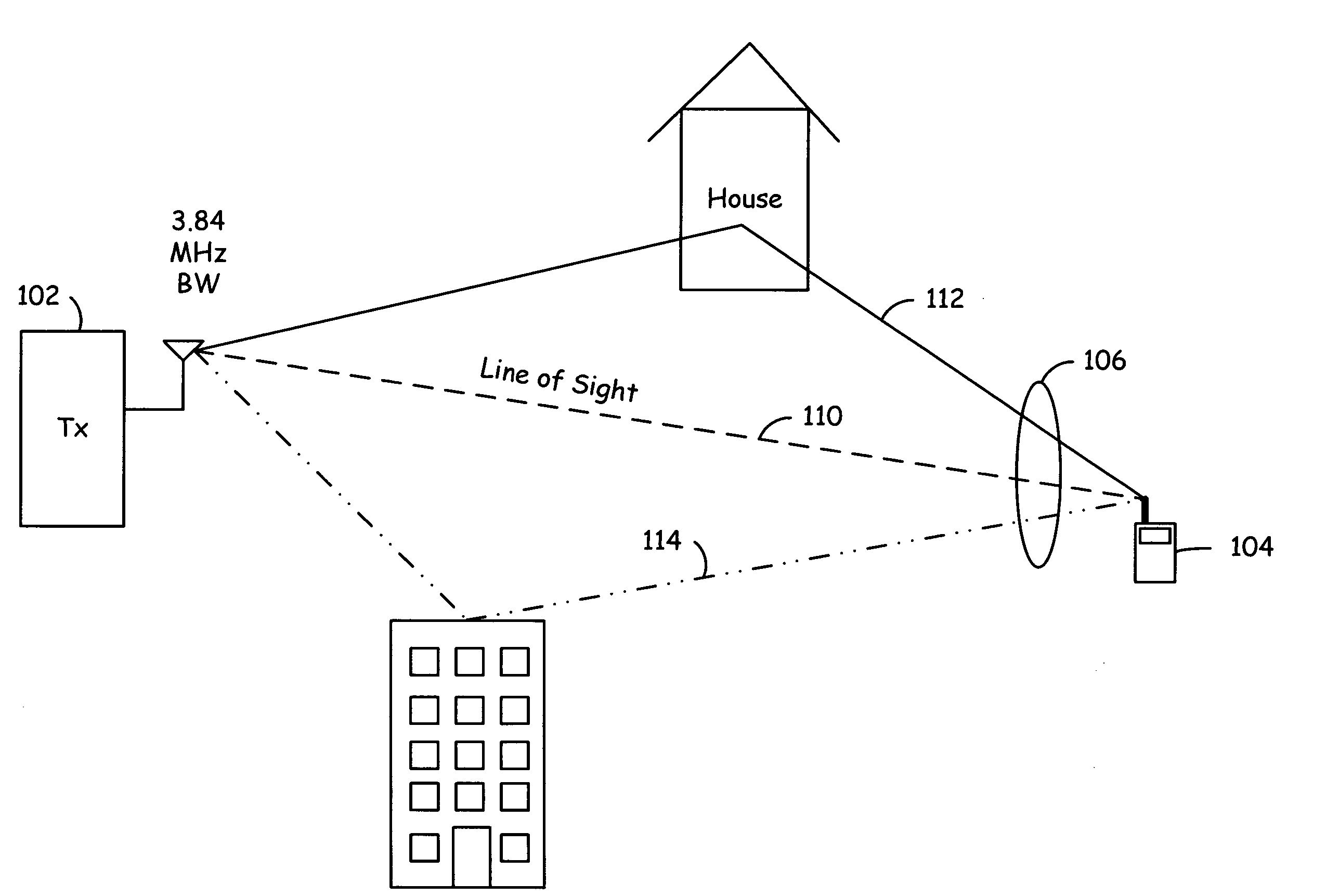
In telecommunications, the delay spread is a measure of the multipath richness of a communications channel. In general, it can be interpreted as the difference between the time of arrival of the earliest significant multipath component (typically the line-of-sight component) and the time of arrival of the last multipath components. The delay spread is mostly used in the characterization of wireless channels, but it also applies to any other multipath channel (e.g. multipath in optical fibers).
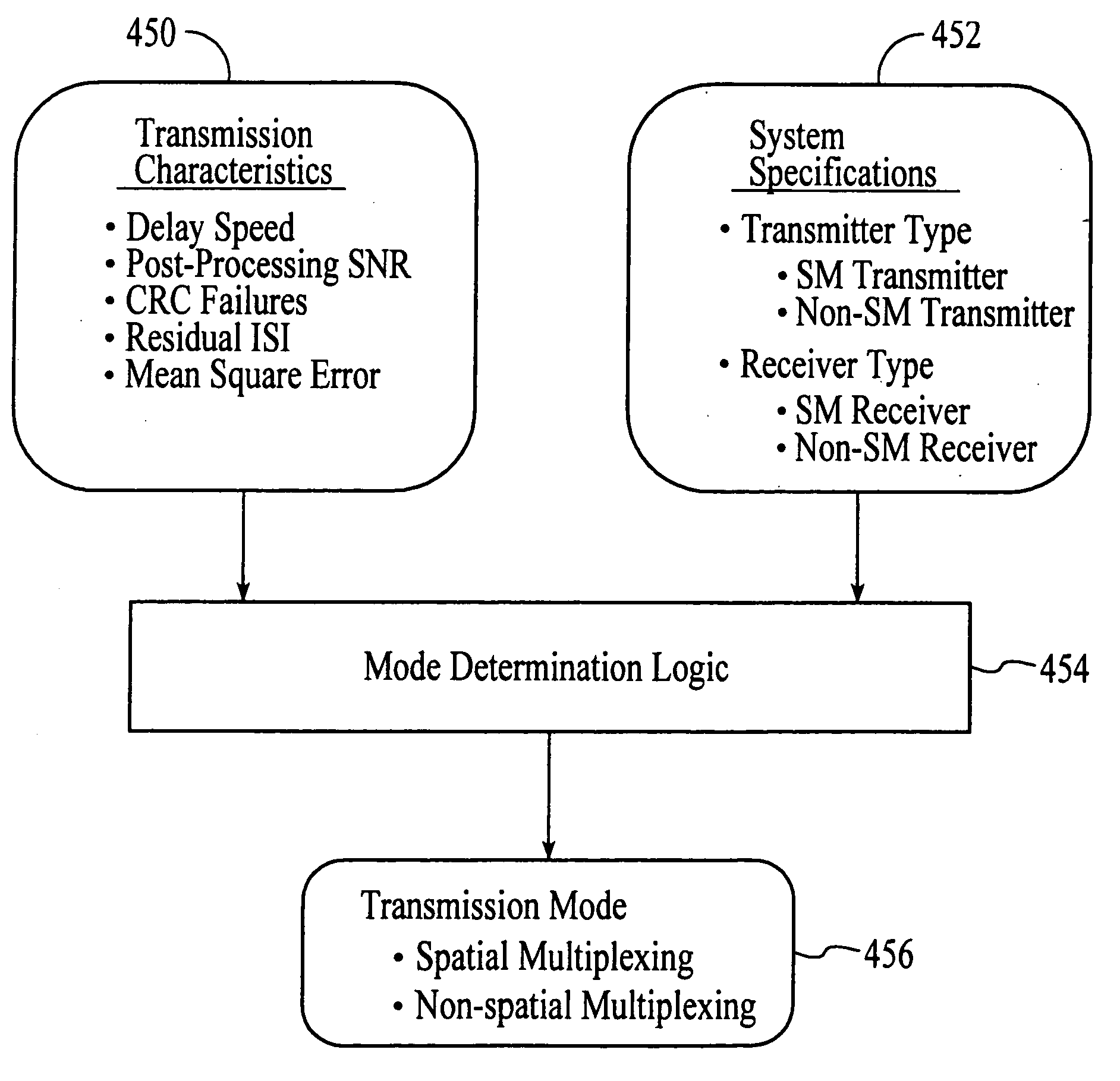
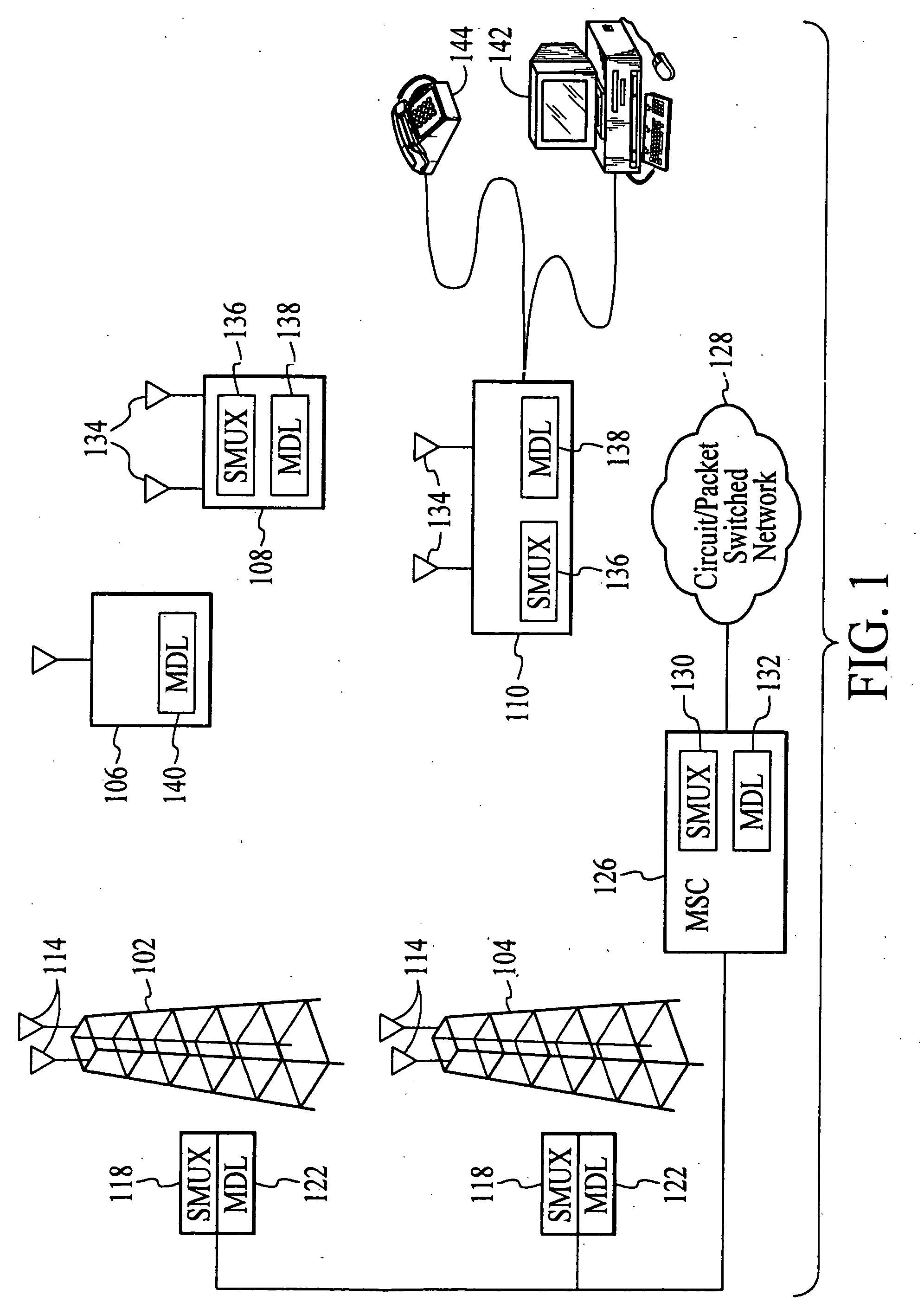
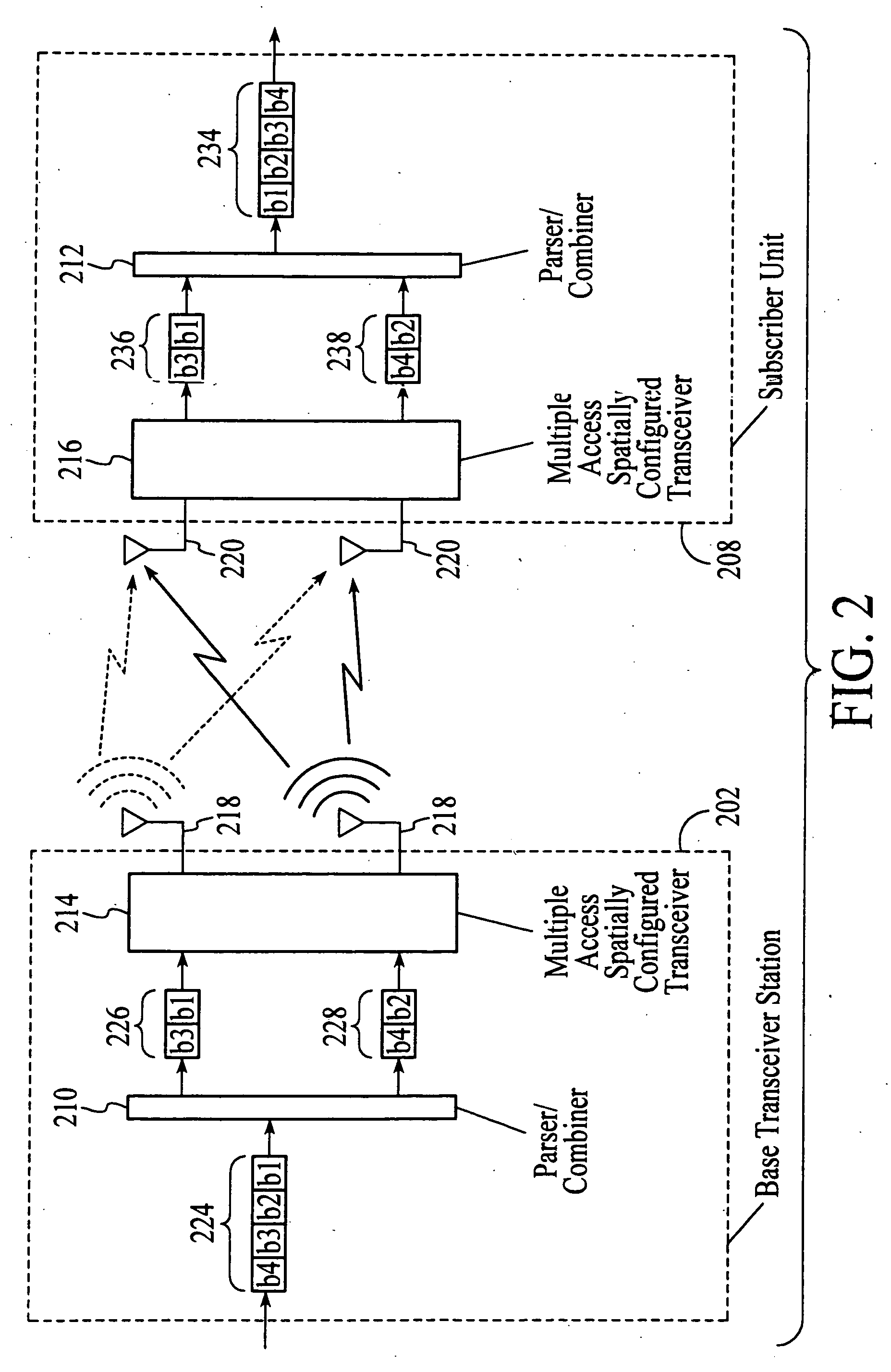
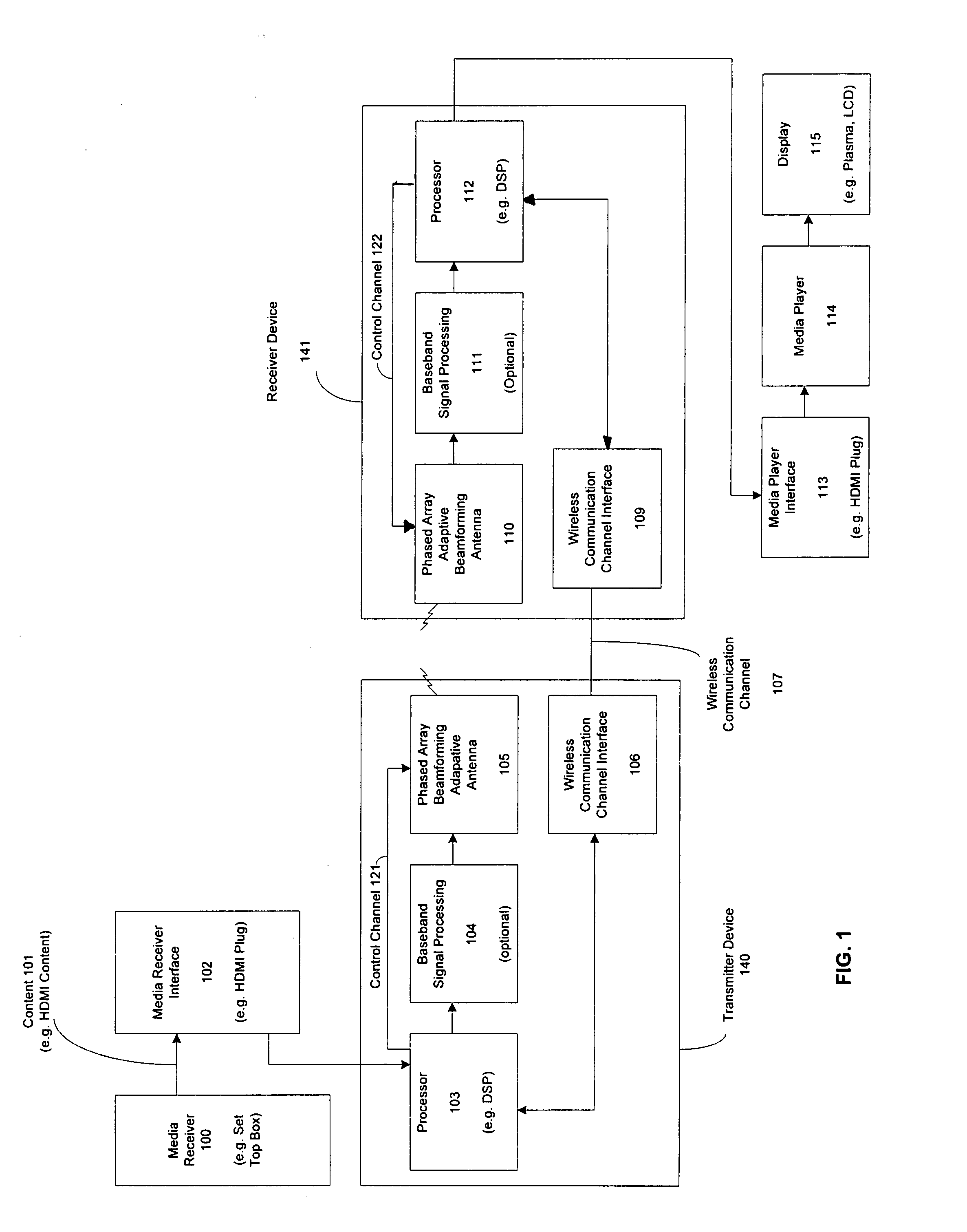
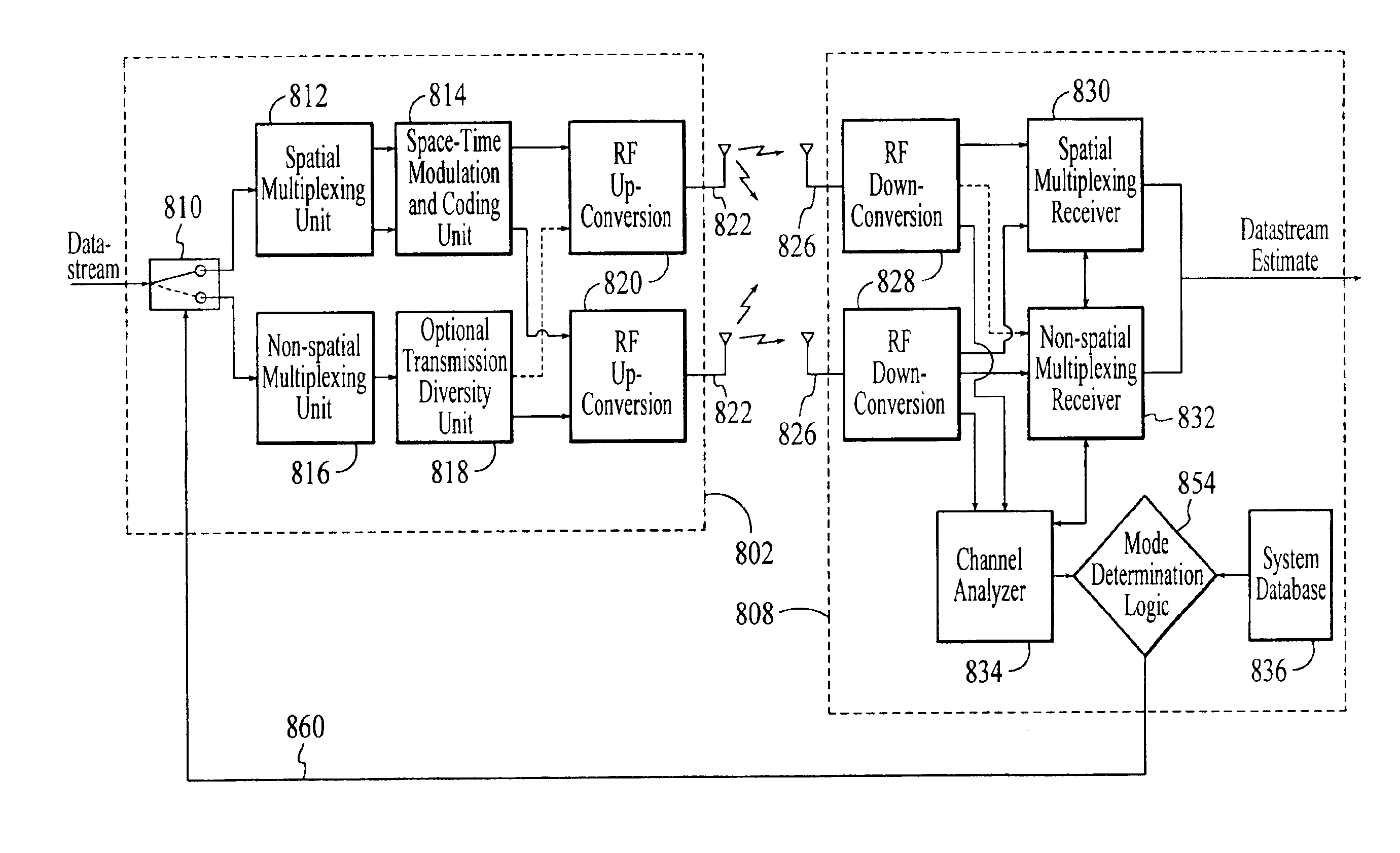
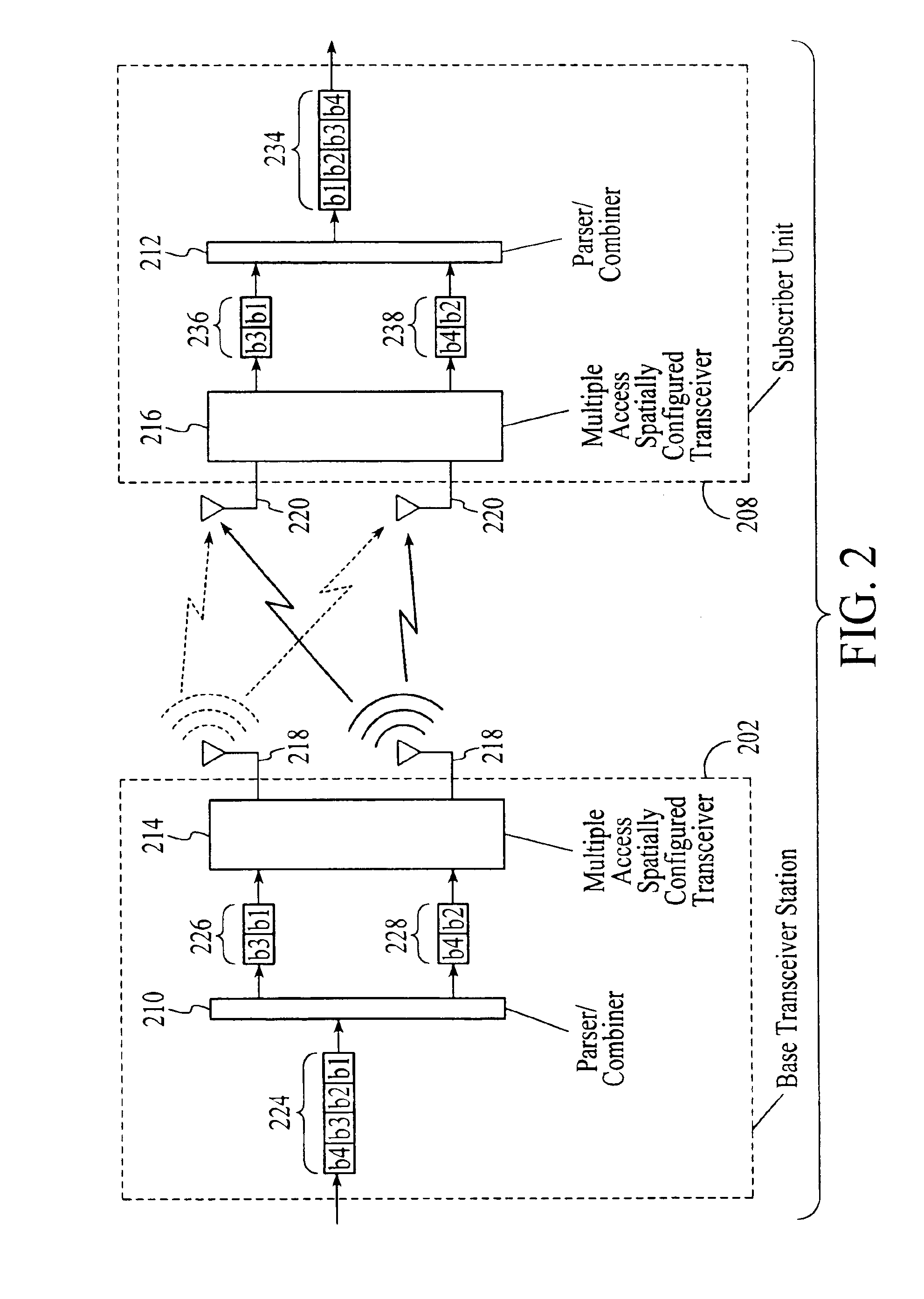
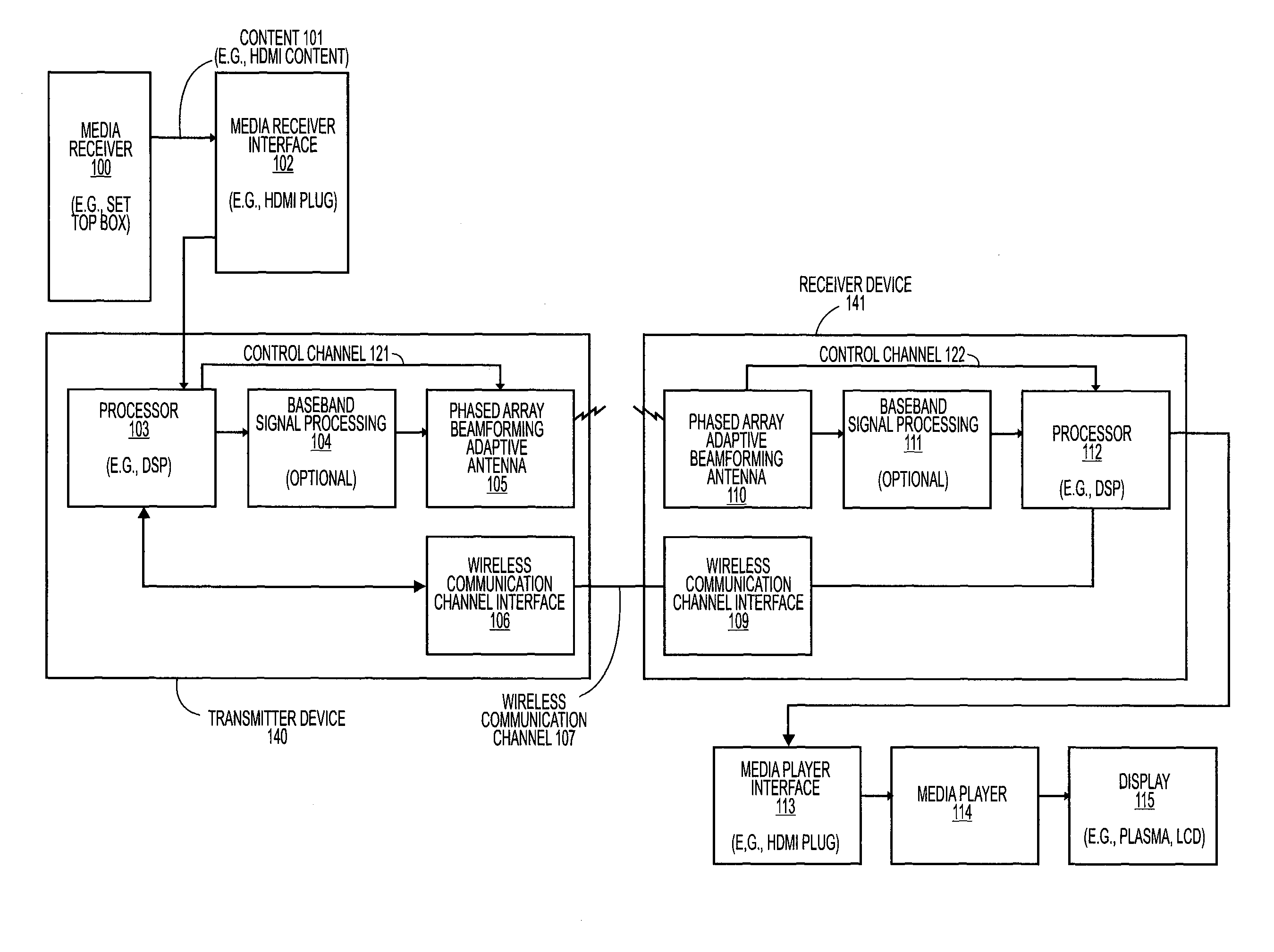
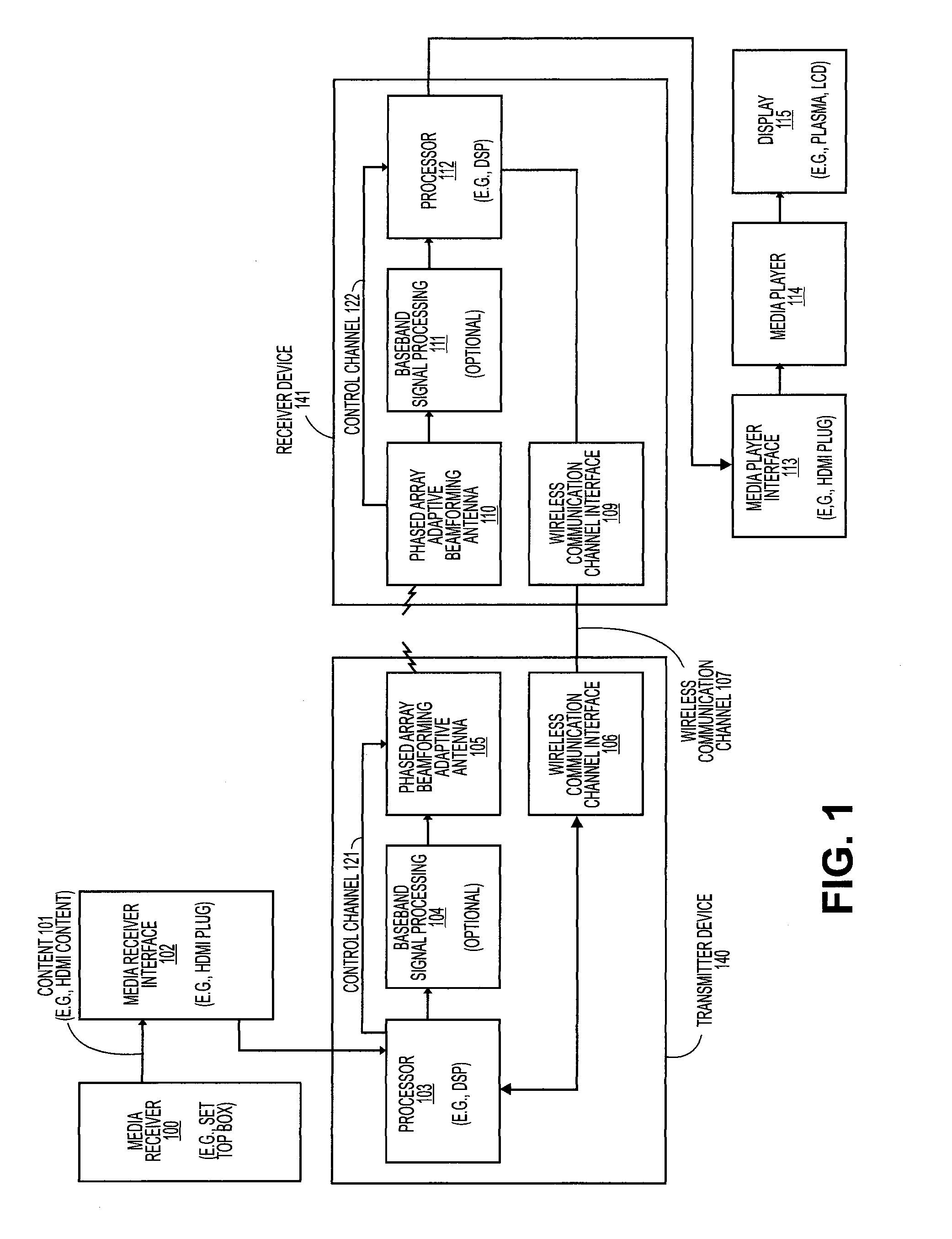
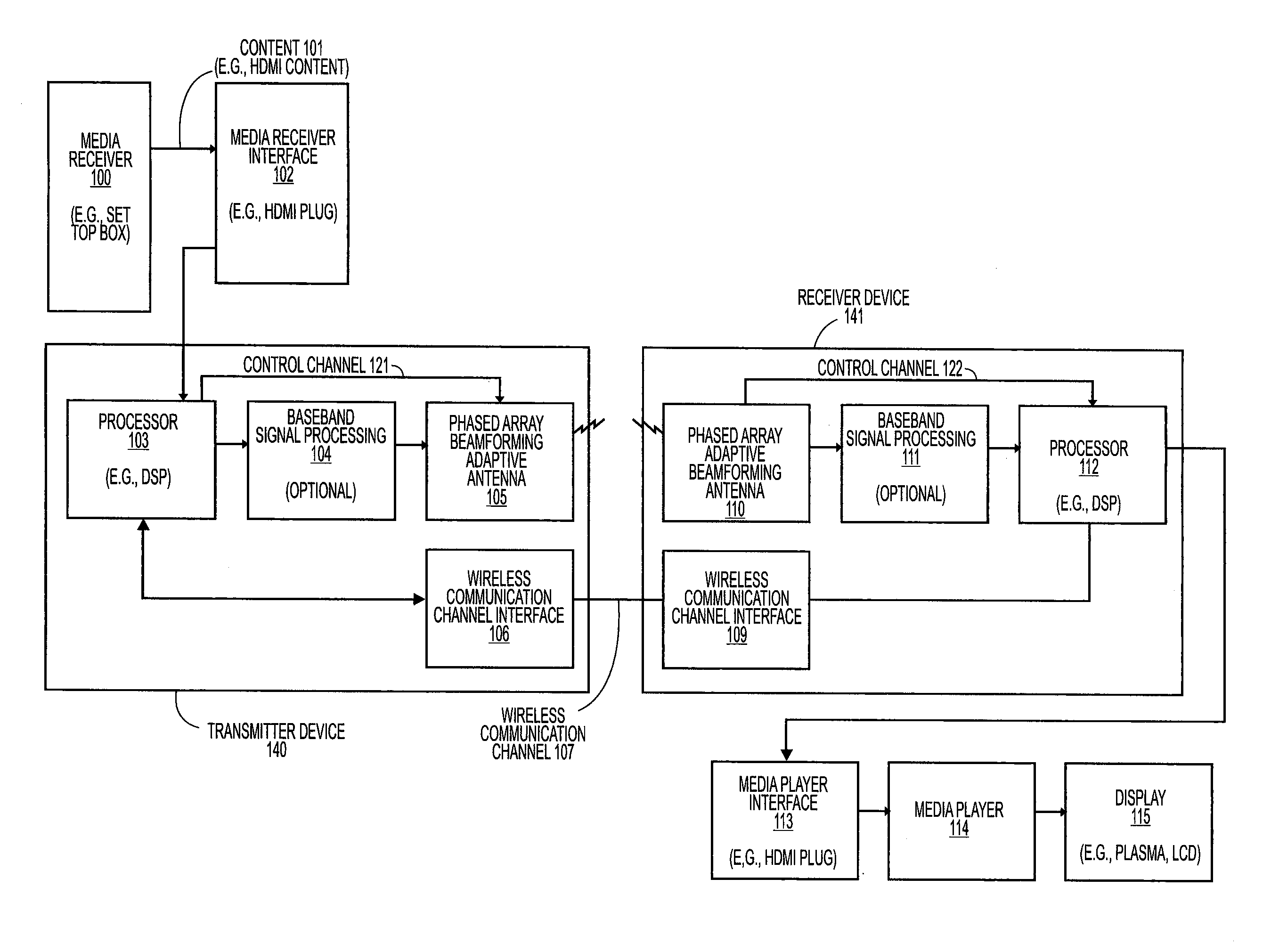
Wireless communications system that supports multiple modes of operation
InactiveUS20050174981A1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionTransceiverMultiple modes
A wireless communications adapts its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to transmission-specific variables. An embodiment of a wireless communications system for transmitting information between a base transceiver station and a subscriber unit includes mode determination logic. The mode determination logic is in communication with the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit. The mode determination logic determines, in response to a received signal, if a subscriber datastream should be transmitted between the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit utilizing spatial multiplexing or non-spatial multiplexing. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic has an input for receiving a measure of a transmission characteristic related to the received signal. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic includes logic for comparing the measured transmission characteristic to a transmission characteristic threshold and for selecting one of spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to the comparison of the measured transmission characteristic to the transmission characteristic threshold. In an embodiment, the transmission characteristic includes at least one of delay spread, post-processing signal-to-noise ratio, cyclical redundancy check (CRC) failure, residual inter-symbol interference, mean square error, coherence time, and path loss. By adapting the mode of operation in response to transmission-specific variables, the use of spatial multiplexing can be discontinued in unfavorable conditions. Additionally, because the wireless communications system can adapt its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing, the communications system is compatible with both subscriber units that support spatial multiplexing and subscriber units that do not support spatial multiplexing.
Owner:APPLE INC
Adaptive beam-steering methods to maximize wireless link budget and reduce delay-spread using multiple transmit and receive antennas
A method and apparatus for adaptive beam-steering are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises performing adaptive beam steering using multiple transmit and receive antennas, including iteratively performing a pair of training sequences, wherein the pair of training sequences includes estimating a transmitter antenna-array weight vector and a receiver antenna-array weight vector.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Wireless communications system that supports multiple modes of operation
InactiveUS6937592B1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionOperation modeMultiple modes
A wireless communications adapts its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to transmission-specific variables. An embodiment of a wireless communications system for transmitting information between a base transceiver station and a subscriber unit includes mode determination logic. The mode determination logic is in communication with the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit. The mode determination logic determines, in response to a received signal, if a subscriber datastream should be transmitted between the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit utilizing spatial multiplexing or non-spatial multiplexing. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic has an input for receiving a measure of a transmission characteristic related to the received signal. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic includes logic for comparing the measured transmission characteristic to a transmission characteristic threshold and for selecting one of spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to the comparison of the measured transmission characteristic to the transmission characteristic threshold. In an embodiment, the transmission characteristic includes at least one of delay spread, post-processing signal-to-noise ratio, cyclical redundancy check (CRC) failure, residual inter-symbol interference, mean square error, coherence time, and path loss. By adapting the mode of operation in response to transmission-specific variables, the use of spatial multiplexing can be discontinued in unfavorable conditions. Additionally, because the wireless communications system can adapt its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing, the communications system is compatible with both subscriber units that support spatial multiplexing and subscriber units that do not support spatial multiplexing.
Owner:APPLE INC
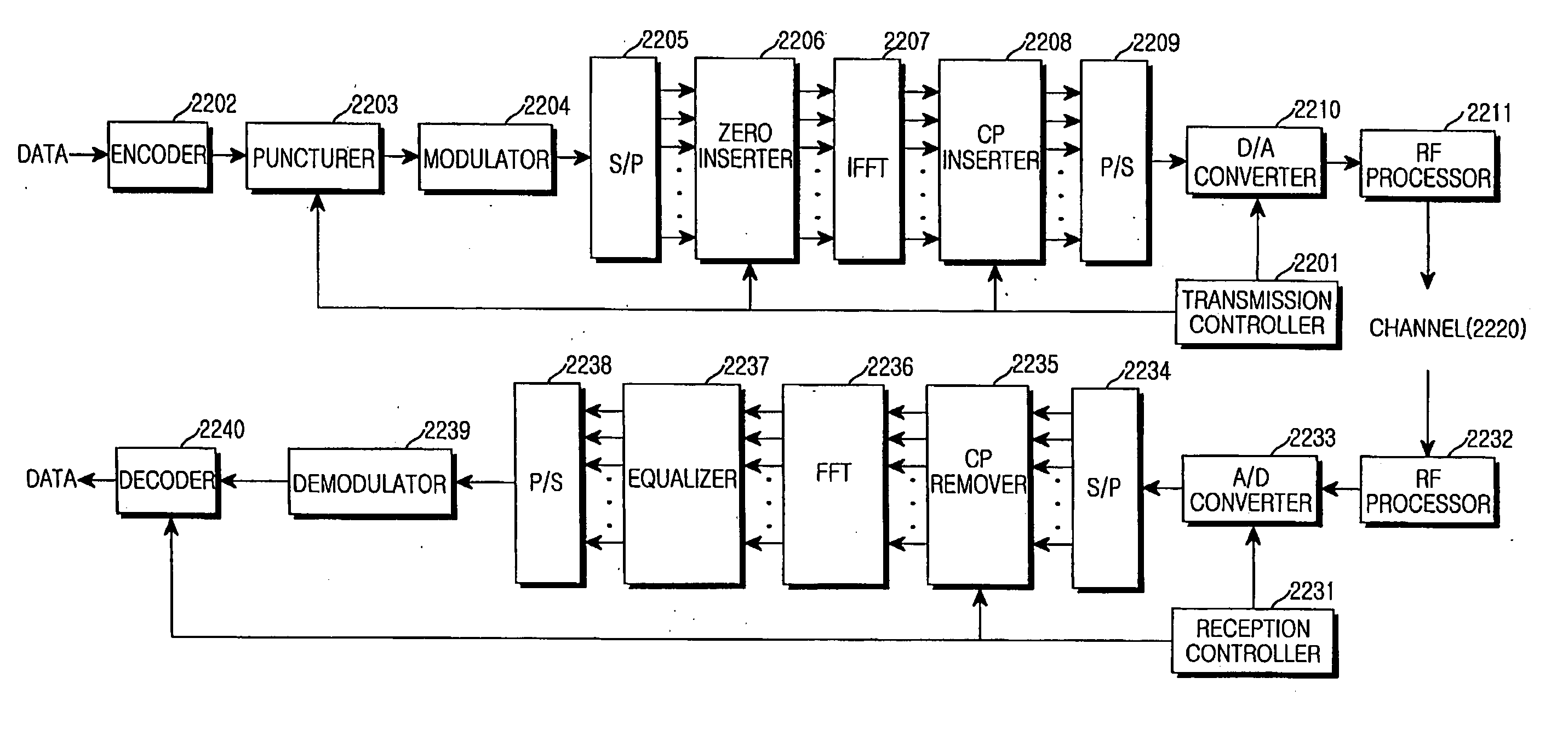
Apparatus and method for canceling inter-symbol interference in a broadband wireless communication system
ActiveUS20060087961A1Exclude dataSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsDelay spreadCommunications system
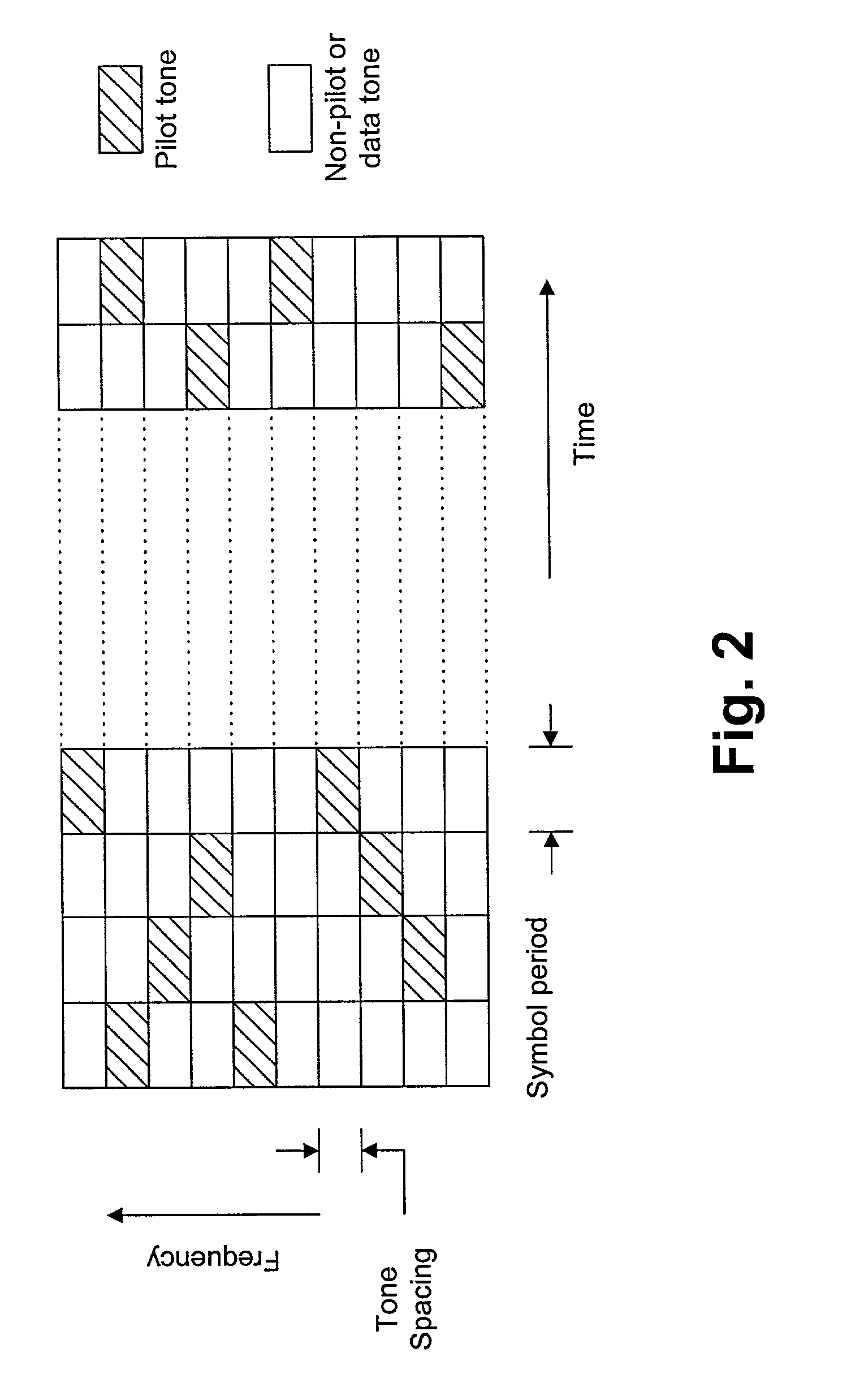
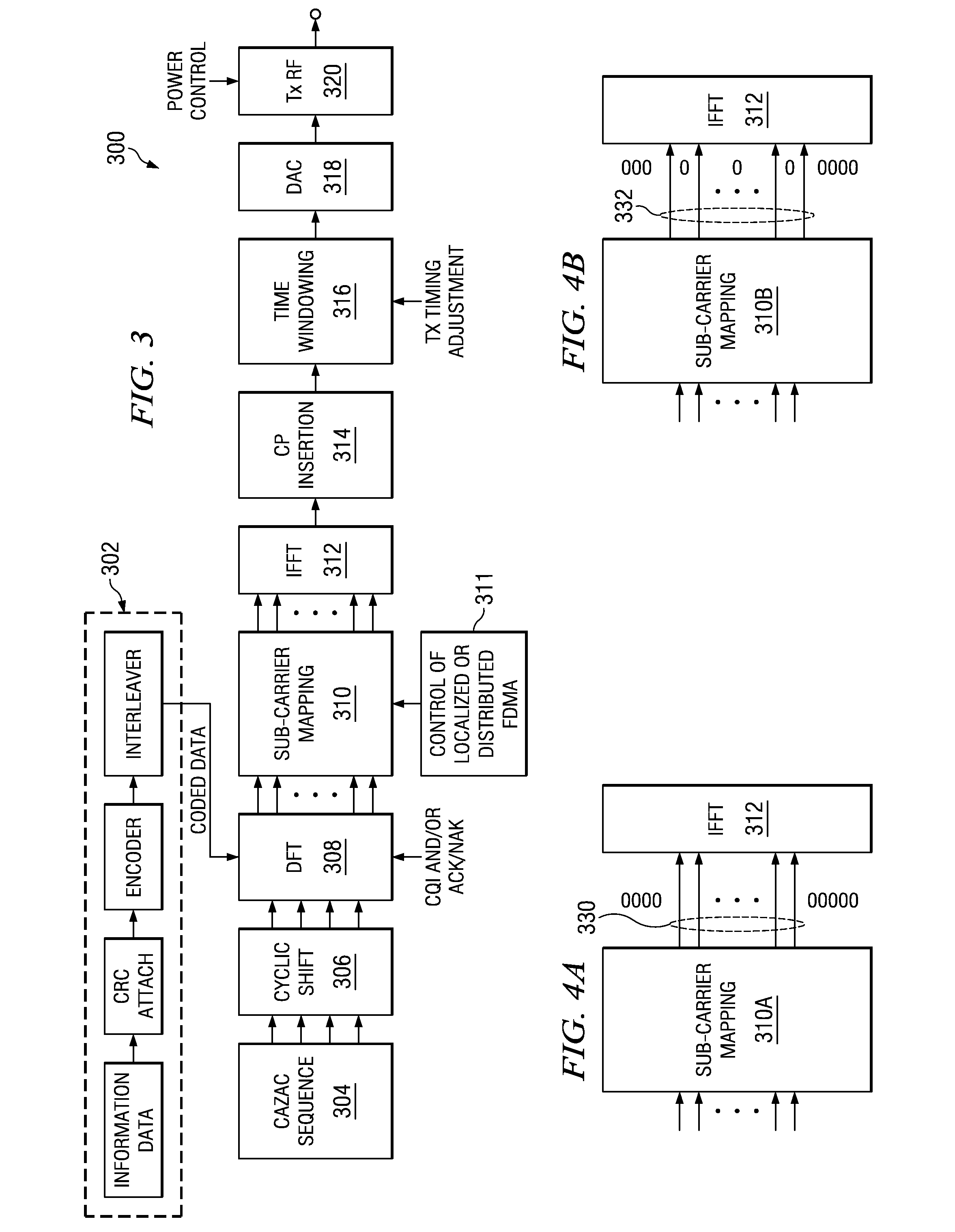
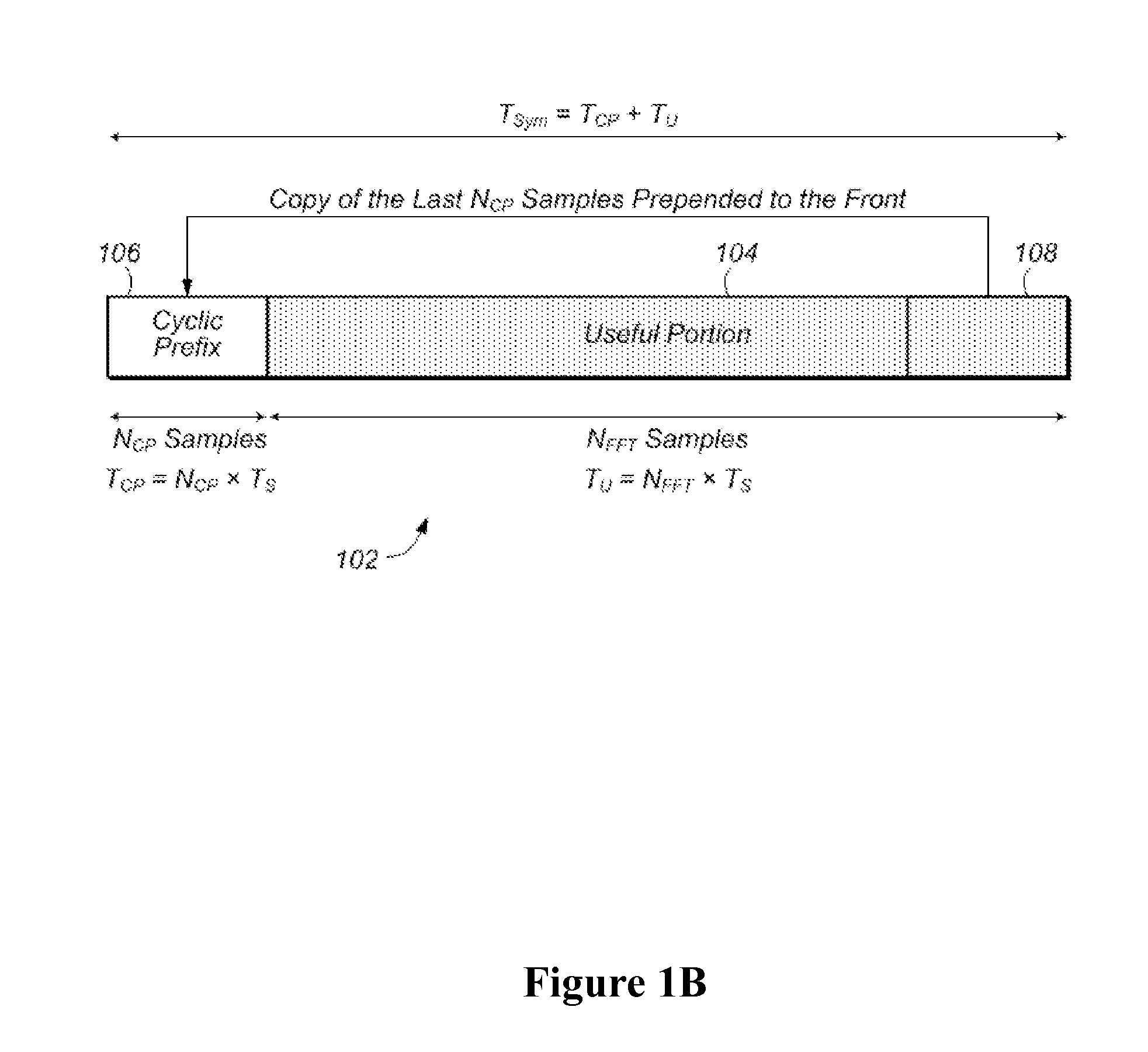
An apparatus and method for canceling ISI in a broadband wireless communication system are provided. In a transmitter of the broadband wireless communication system, a controller acquires a CP length, a puncturing pattern, and a time sample interval according to a delay spread. A puncturer punctures coded data in the puncturing pattern. An IFFT processor IFFT-processes the punctured coded data and outputs sample data. A CP inserter generates an OFDM symbol by inserting a copy of a last part of the sample data before the sample data. Here, the length of the last part of the sample data is equal to the CP length. A D / A converter converts the OFDM symbol to an analog signal at a sampling rate determined by the time sample interval.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method for setting a mobile node specific cyclic prefix in a mobile communication
ActiveUS20120281551A1Increase bitrateSpread the wordError preventionModulated-carrier systemsDelay spreadCyclic prefix
The invention concerns a method and an apparatus implementing the method. In the method is determined in a mobile node whether the mobile node supports mobile node specific cyclic prefixes. The mobile node transmits to a base station node an indication whether the mobile node supports mobile node specific cyclic prefixes. The base station node measures a delay spread of a radio resource transmitted by the mobile node. The mobile node receives an indication of an uplink direction cyclic prefix length from the base station node. The mobile node forms a cyclic prefix of the uplink direction cyclic prefix length selected from a useful symbol, adds the cyclic prefix in front of the useful symbol and transmits a signal comprising the cyclic prefix and the useful symbol to the base station.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
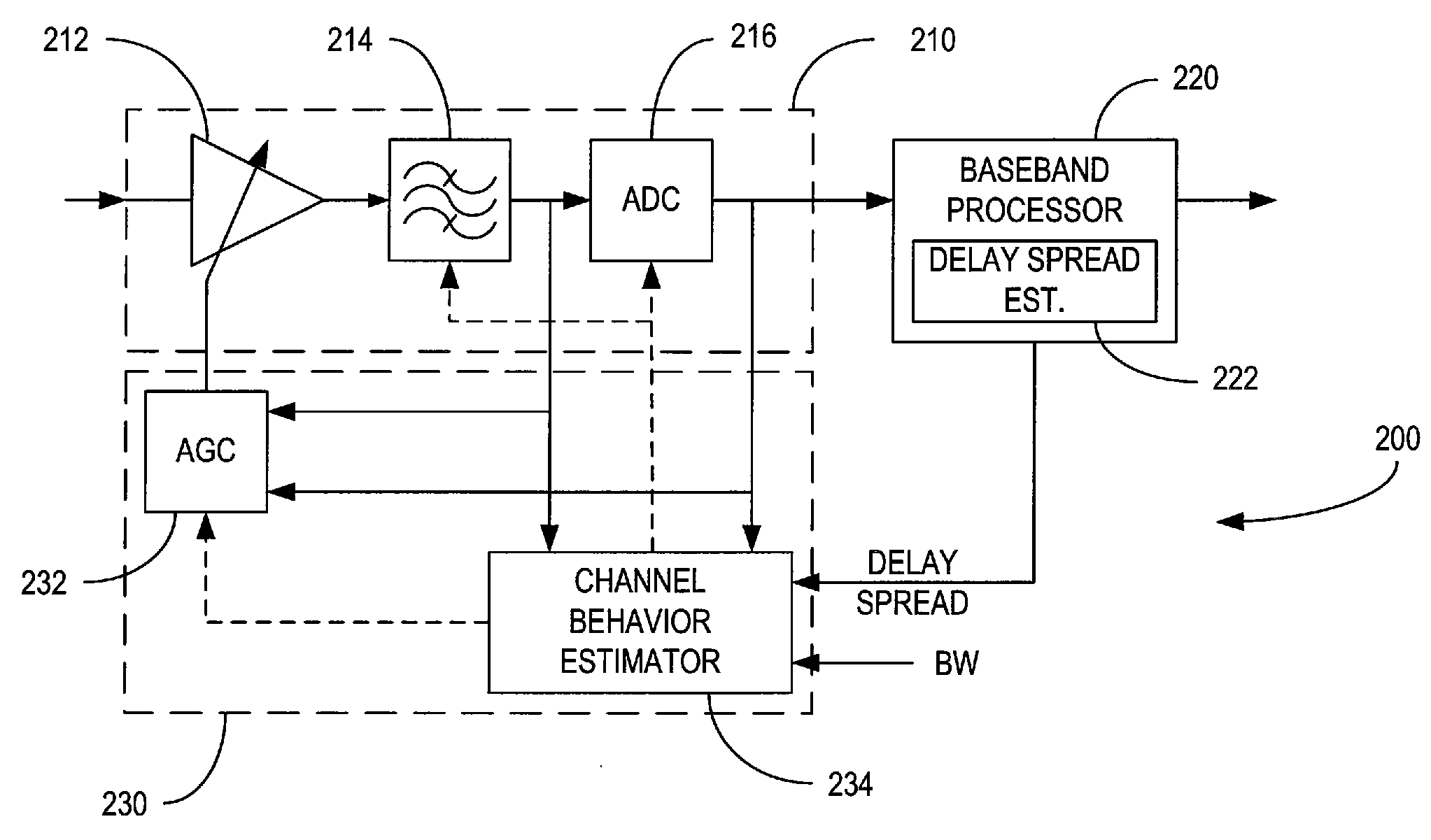
Automatic Gain Control Based on Bandwidth and Delay Spread
ActiveUS20100189203A1Dynamic range is efficientlyAmount of signal variationGain controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDelay spreadEngineering
A gain control circuit adjusts the signal level of a received signal responsive to the bandwidth a received signal and / or the delay spread of the channel in which the signal has propagated. The bandwidth and delay spread are evaluated to estimate the amount of signal variation that is expected due to fast fading. Adjustments to the signal level are then made to avoid clipping while at the same time ensuring that the dynamic range of a receiver component is efficiently utilized.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Adaptive beam-steering methods to maximize wireless link budget and reduce delay-spread using multiple transmit and receive antennas
A method and apparatus for adaptive beam-steering are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises performing adaptive beam steering using multiple transmit and receive antennas, including iteratively performing a pair of training sequences, wherein the pair of training sequences includes estimating a transmitter antenna-array weight vector and a receiver antenna-array weight vector.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
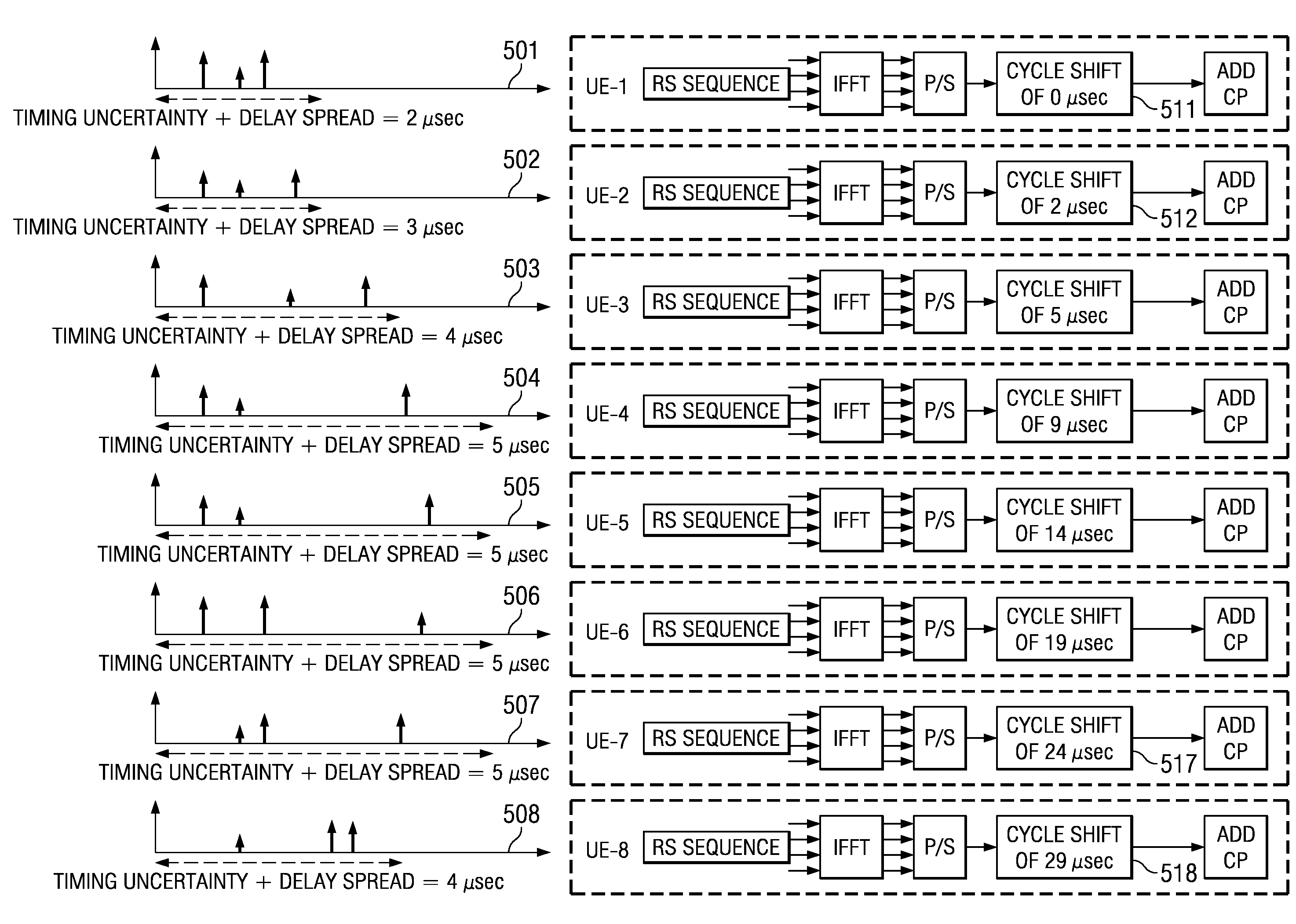
Adaptive Selection of Transmission Parameters for Reference Signals
ActiveUS20080051125A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionDelay spreadEngineering
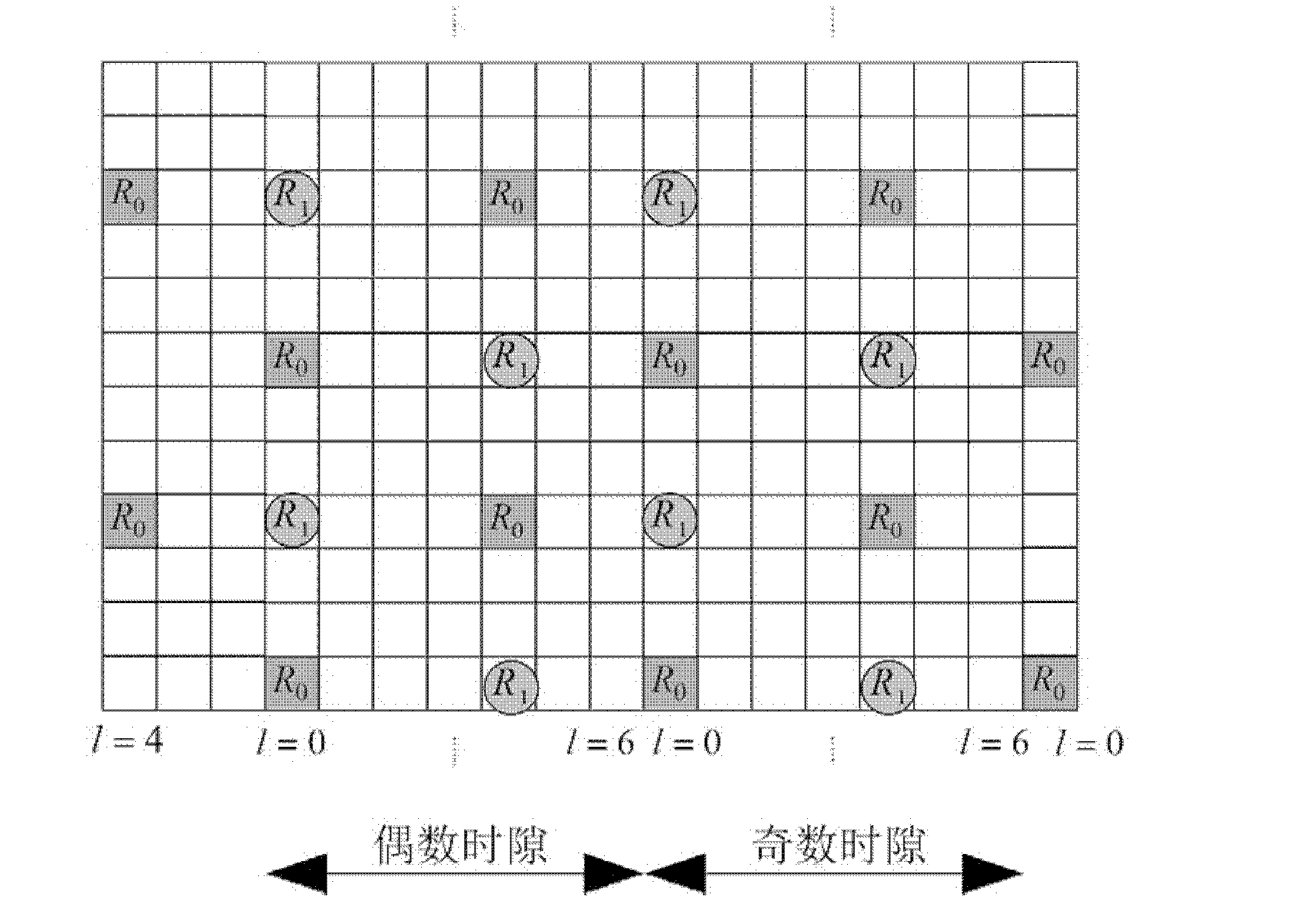
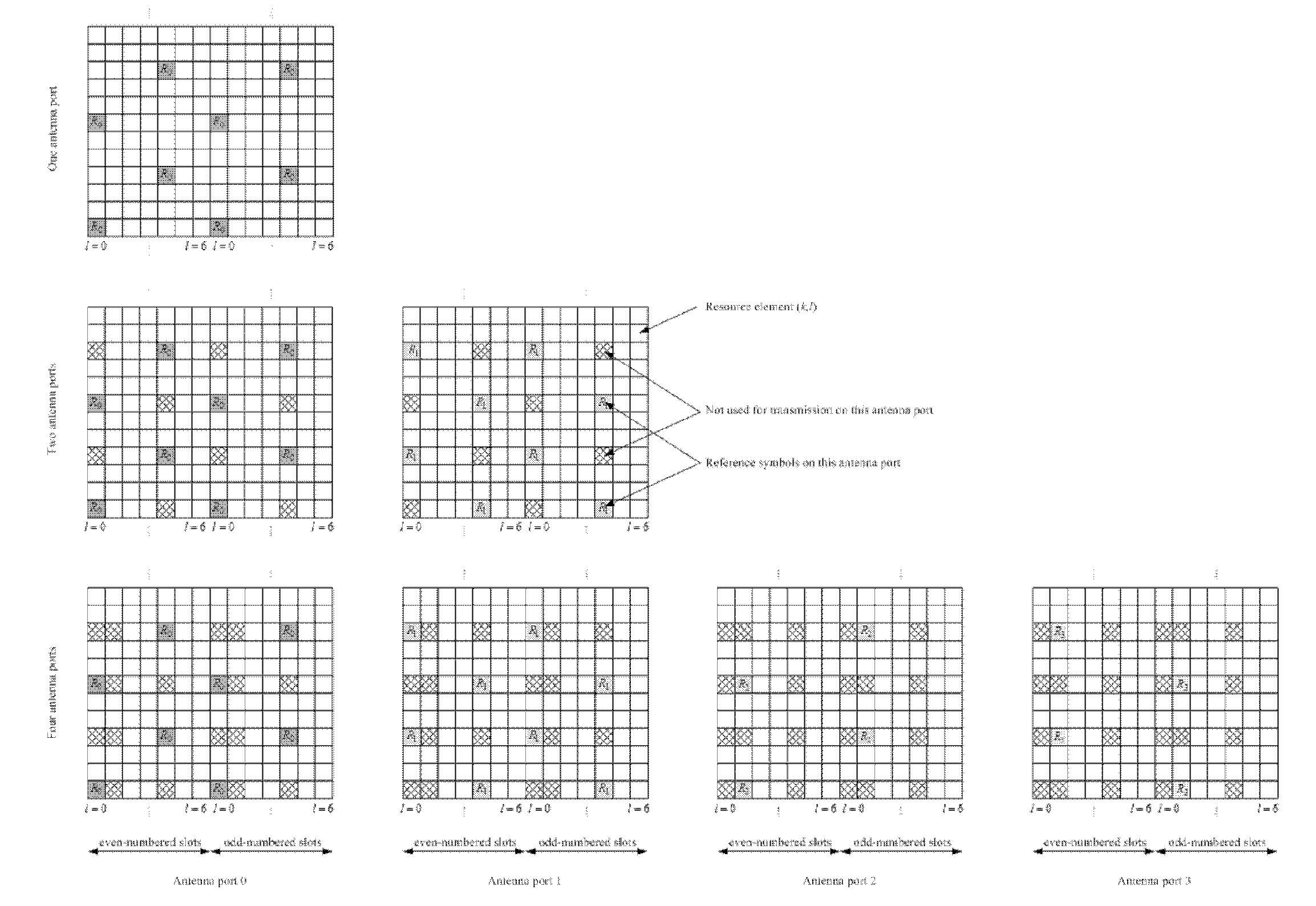
An embodiment of the present invention uses estimates of delay spreads of transmissions from user equipments (UEs) to a NodeB to determine a set of transmission parameters for the UEs reference signals. In an exemplary embodiment, the transmission parameters for reference signals include cyclic shifts. Thus, embodiments include a set of allocated cyclic shift values that are tailored to the delay spreads. The set of allocated cyclic shift values are used by a corresponding set of UE being served by a NodeB to form references signals. Each UE uses the allocated cyclic shift to form its reference signal by applying the cyclic shift to a modified reference sequence. The modified reference sequence can be generated from a Constant-Amplitude-Zero-Auto Correlation (CAZAC) sequence. The set of allocated cyclic shift values can be updated periodically to account for changes of delay spreads, which can be caused by physical movements of the set of UEs.
Owner:APPLE INC
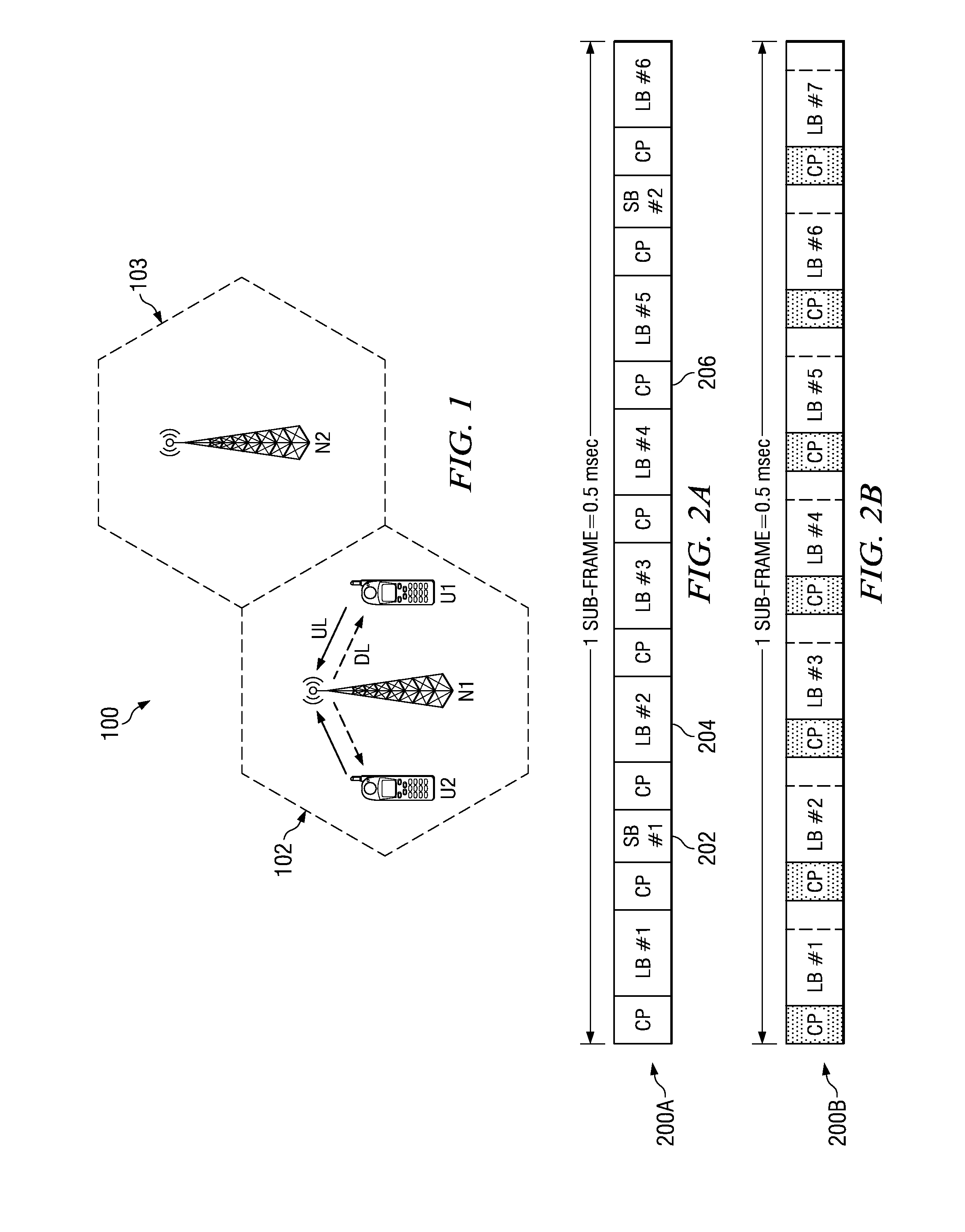
Frame structure for support of large delay spread deployment scenarios
ActiveUS20110103494A1Network traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionDelay spreadLow frequency band
A frame structure for support of large delay spread deployment scenarios (e.g., cellular system operation in large cell sizes or low frequency bands) is generally presented. In this regard a method is introduced comprising partitioning a radio frame into a plurality of equal-sized (or non-equal-sized) sub-frames to simplify system implementation. Other embodiments are also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:APPLE INC
Frequency division multiplexing system with selectable rate
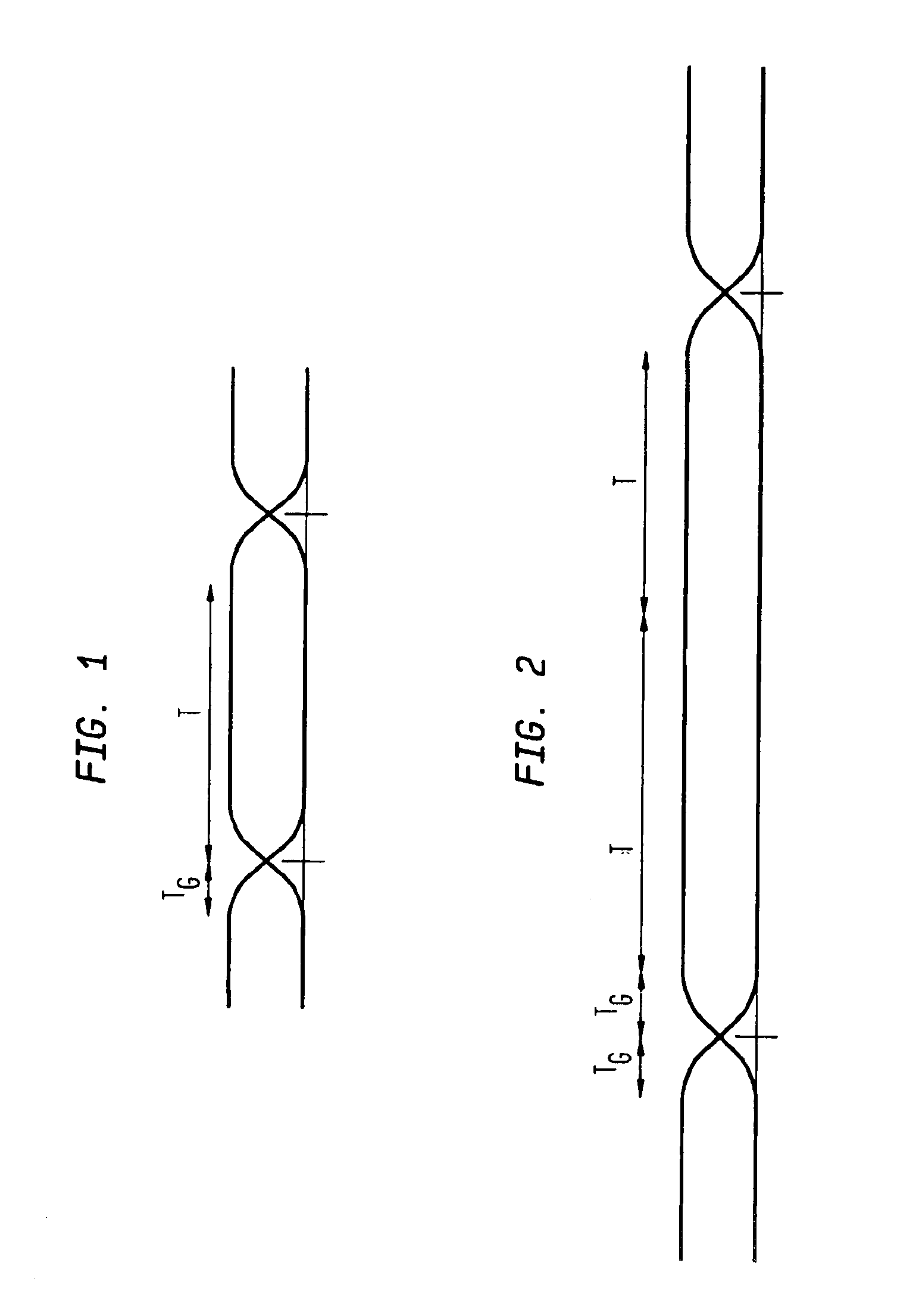
InactiveUS6992972B2Increase delayIncrease rangeLine-faulsts/interference reductionMulti-frequency code systemsFourier transform on finite groupsCarrier signal
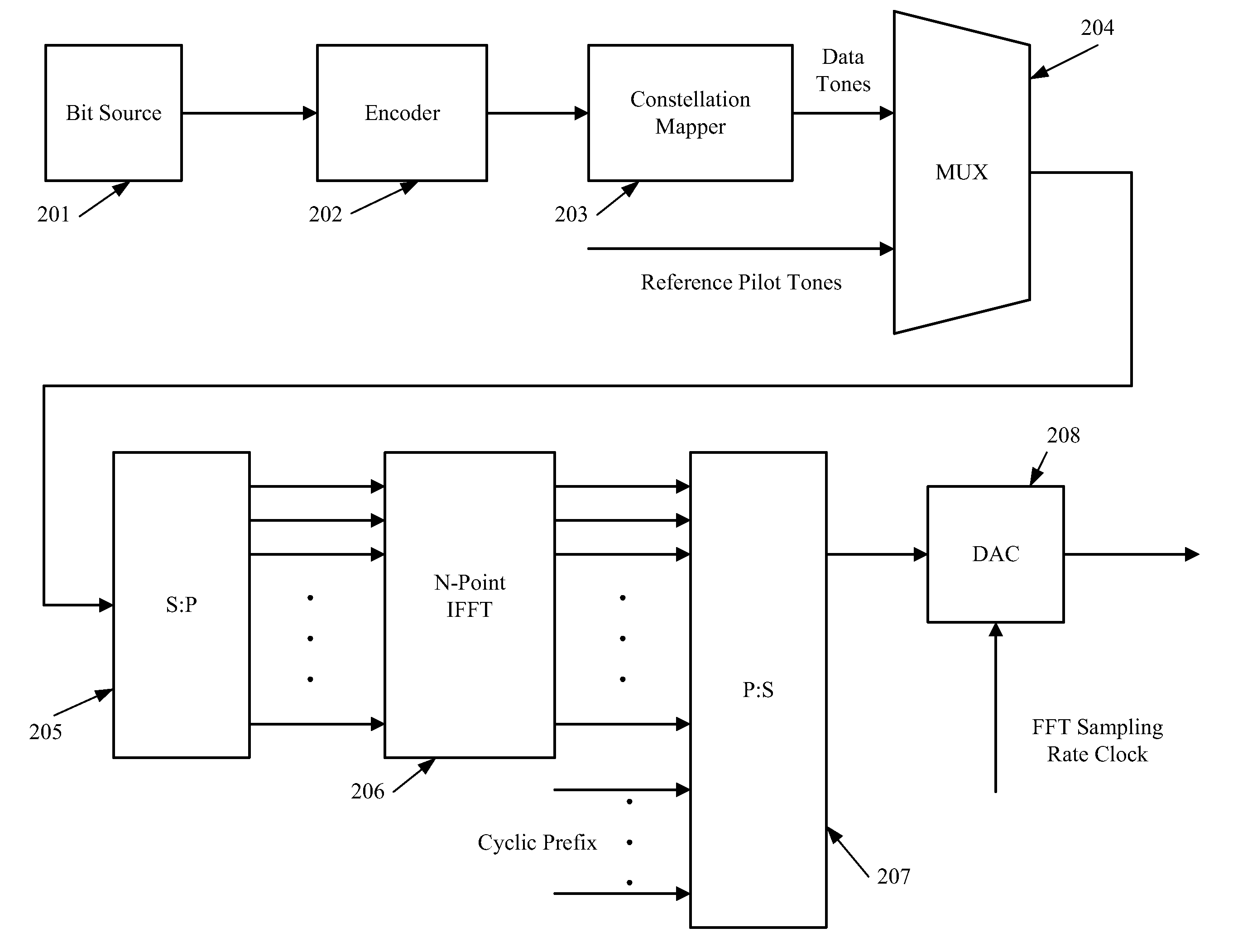
An OFDM system uses a normal mode which has a symbol length T, a guard time TG and a set of N sub-carriers, which are orthogonal over the time T, and one or more fallback modes which have symbol lengths KT and guard times KTG where K is an integer greater than unity. The same set of N sub-carriers is used for the fallback modes as for the normal mode. Since the same set of sub-carriers is used, the overall bandwidth is substantially constant, so alias filtering does not need to be adaptive. The Fourier transform operations are the same as for the normal mode. Thus fallback modes are provided with little hardware cost. In the fallback modes the increased guard time provides better delay spread tolerance and the increased symbol length provides improved signal to noise performance, and thus increased range, at the cost of reduced data rate.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
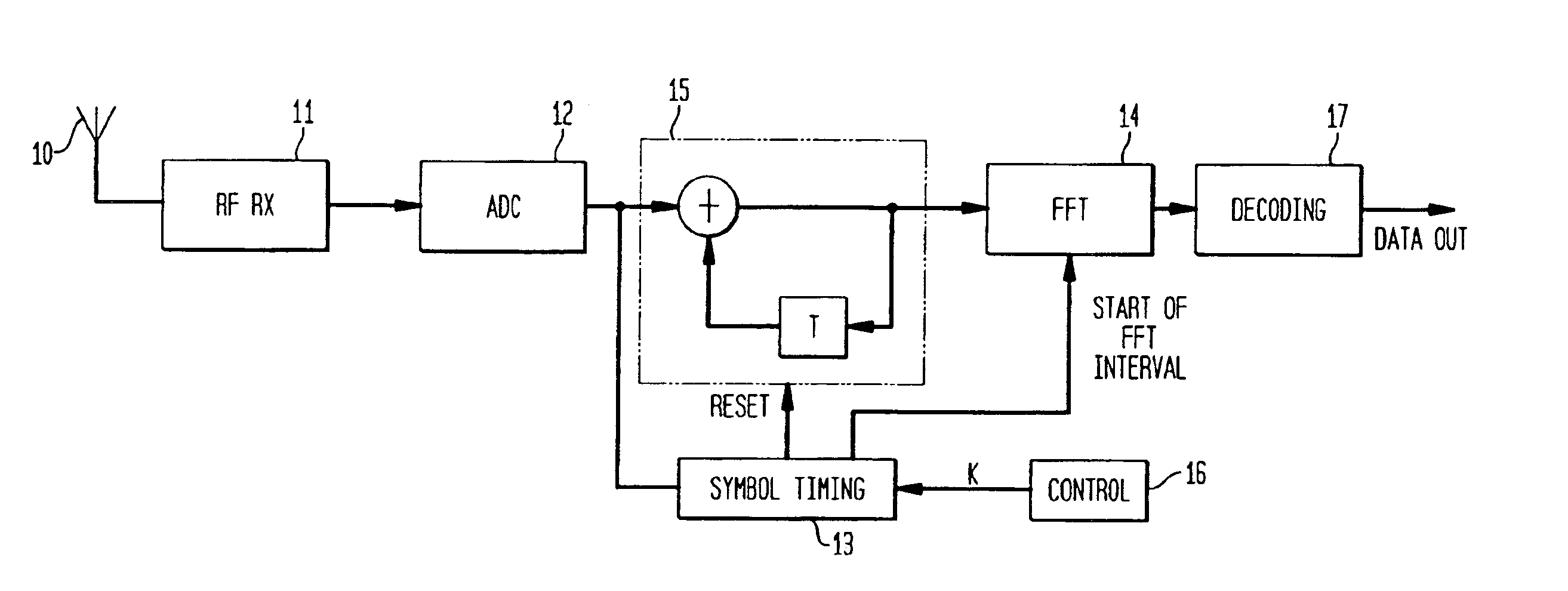
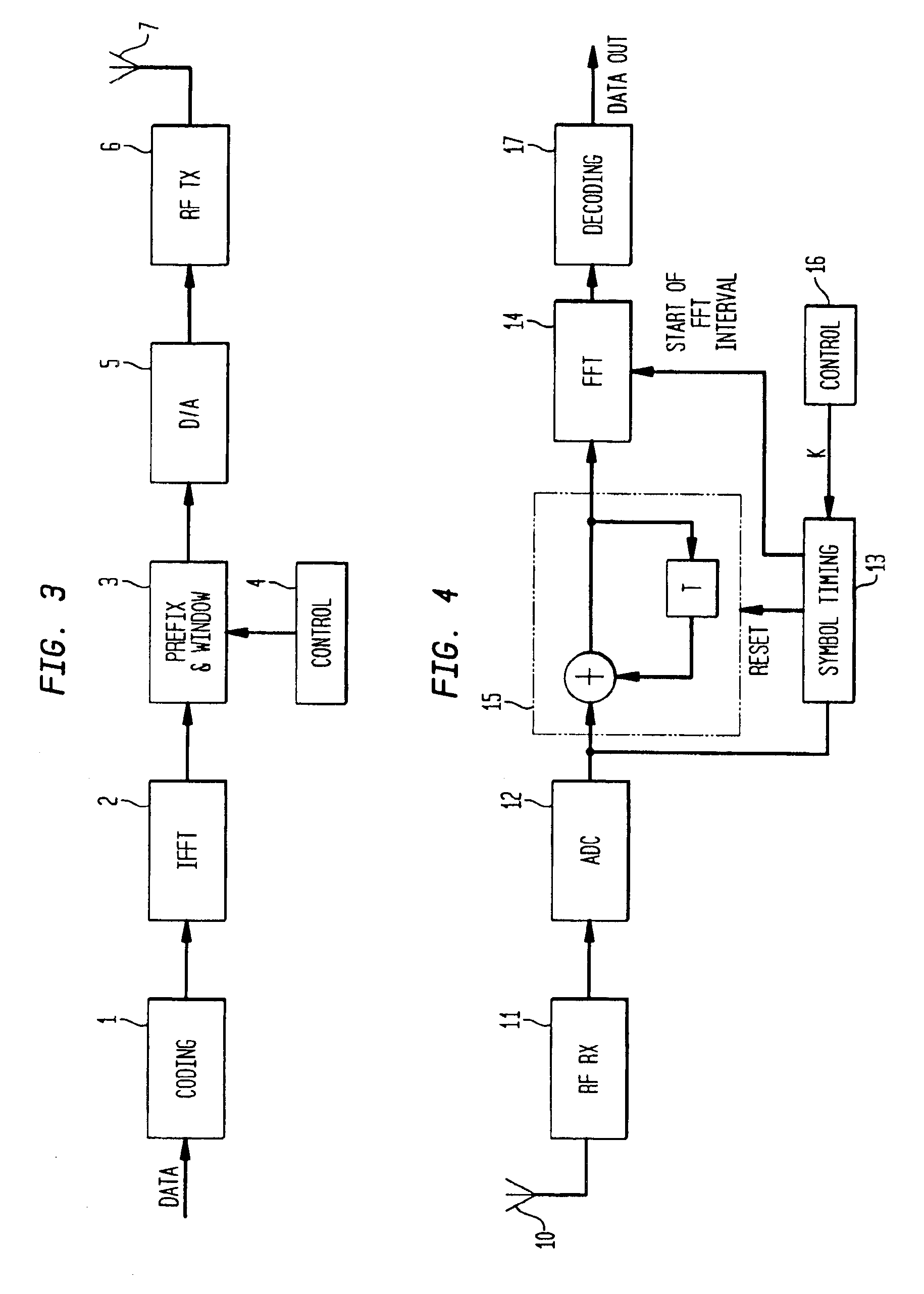
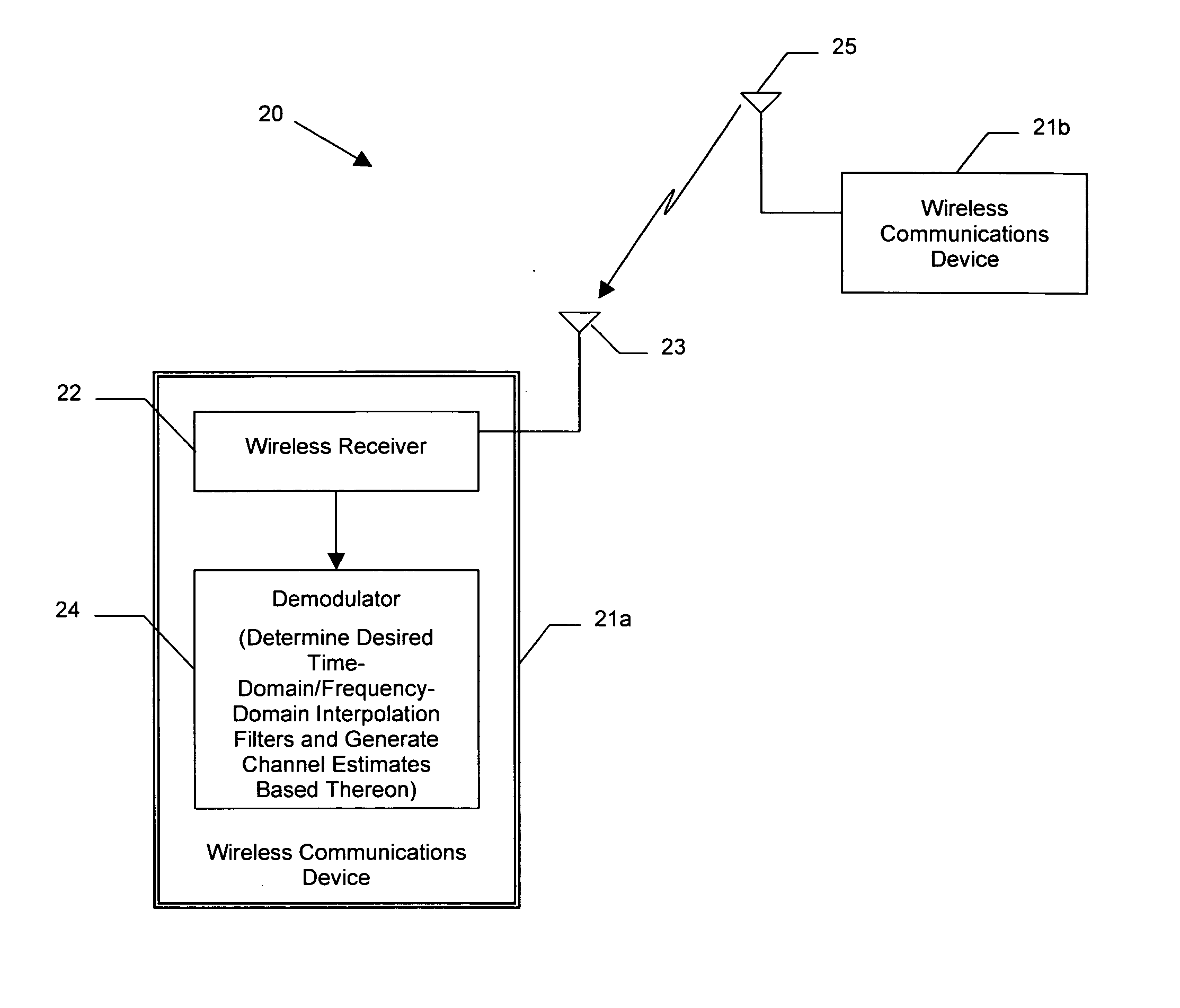
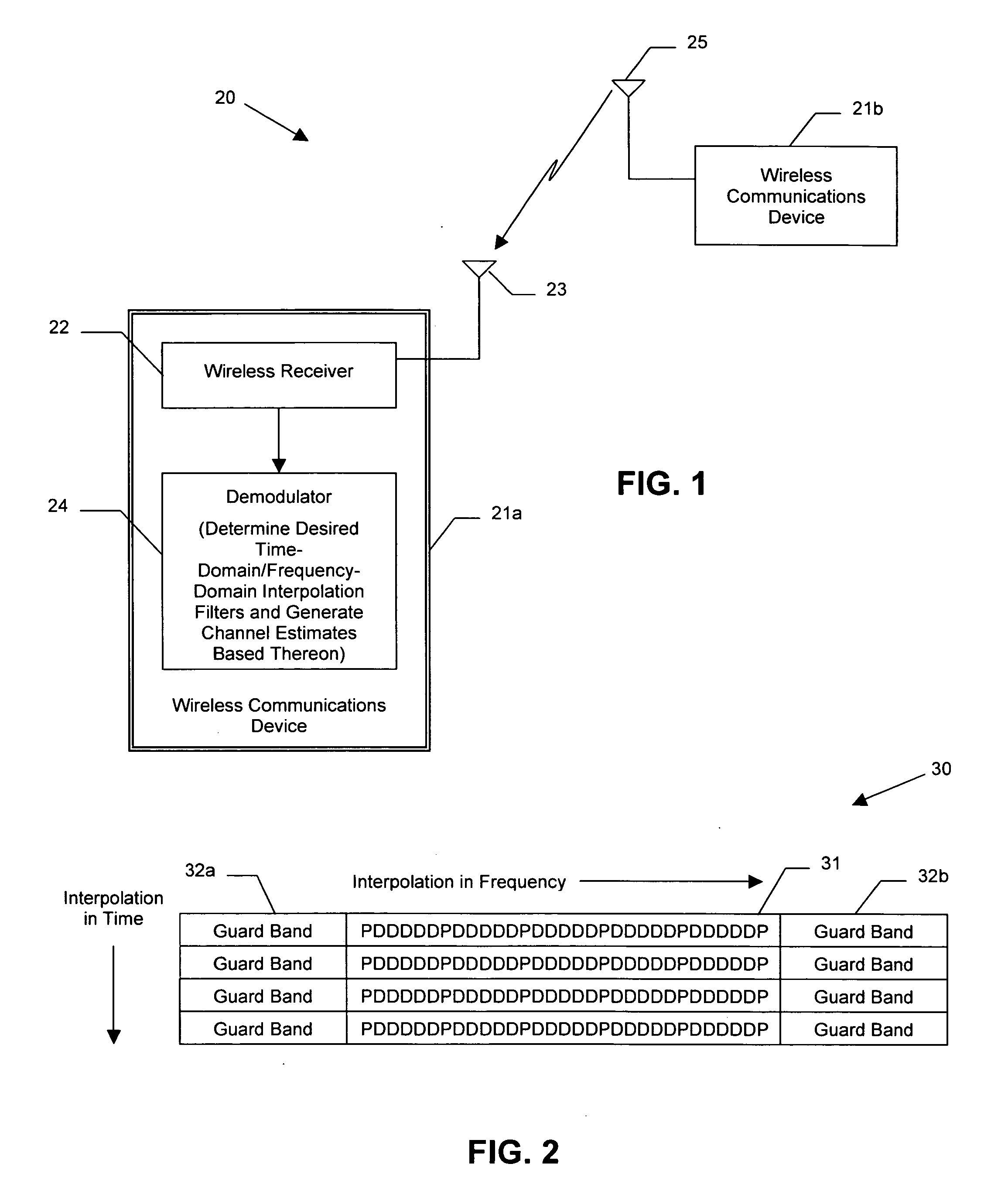
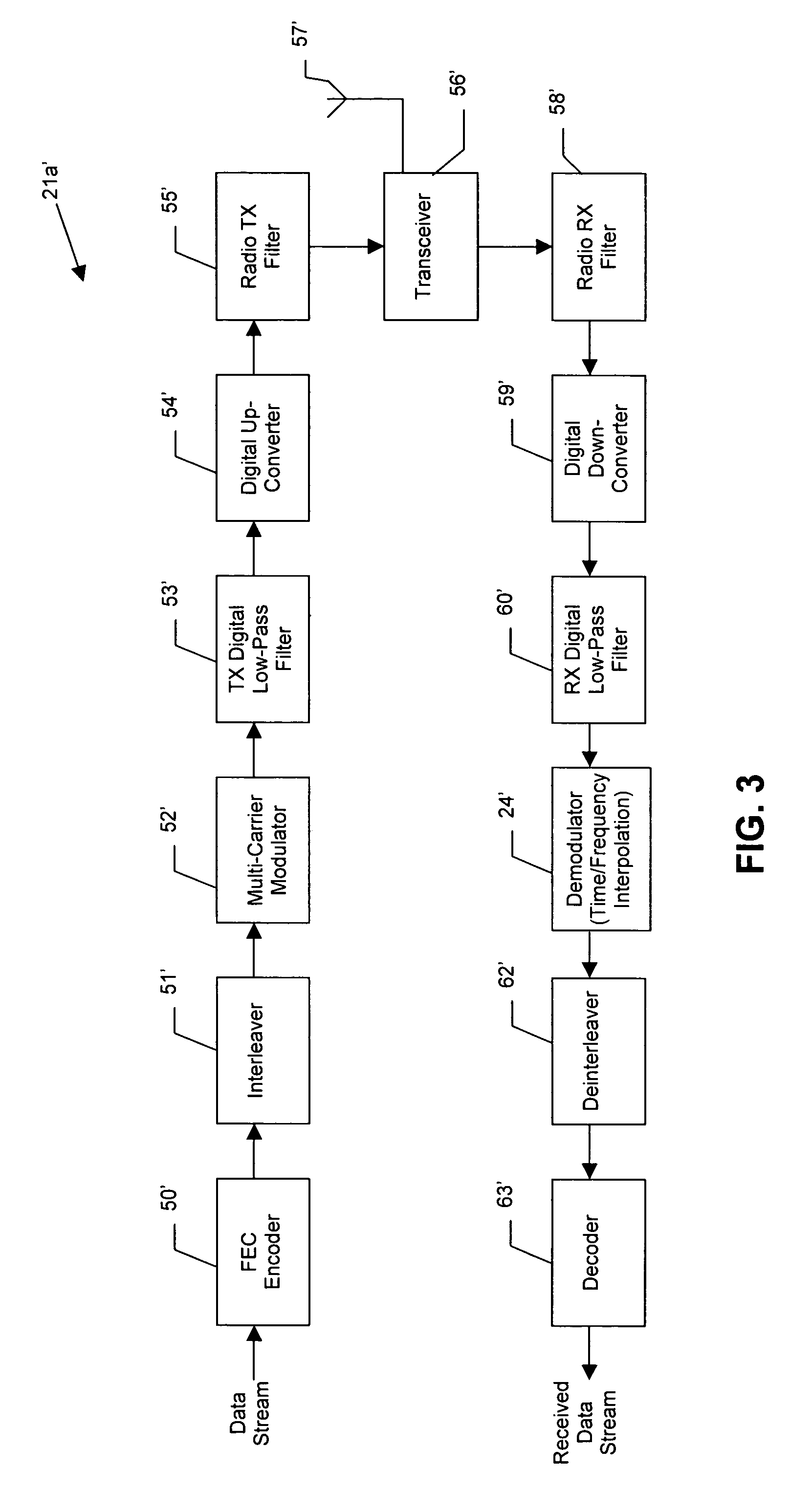
Wireless communications device providing time and frequency-domain channel estimates interpolation and related methods
ActiveUS20060109919A1Improved channel estimationImprove methodError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionDelay spreadTime domain
A wireless communications device which may include a wireless receiver for receiving wireless signals comprising unknown data portions over a channel, and a demodulator connected to the wireless receiver. The demodulator may be for estimating a delay spread and a fade rate associated with the channel, determining a desired time-domain interpolation filter based upon the estimated fade rate, and determining a desired frequency-domain interpolation filter based upon the estimated delay spread. The demodulator may further generate channel estimates for the unknown data portions based upon the desired time-domain interpolation filter and the desired frequency-domain interpolation filter, and determine the unknown data portions based upon the channel estimates.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMMUNICATIONS INC
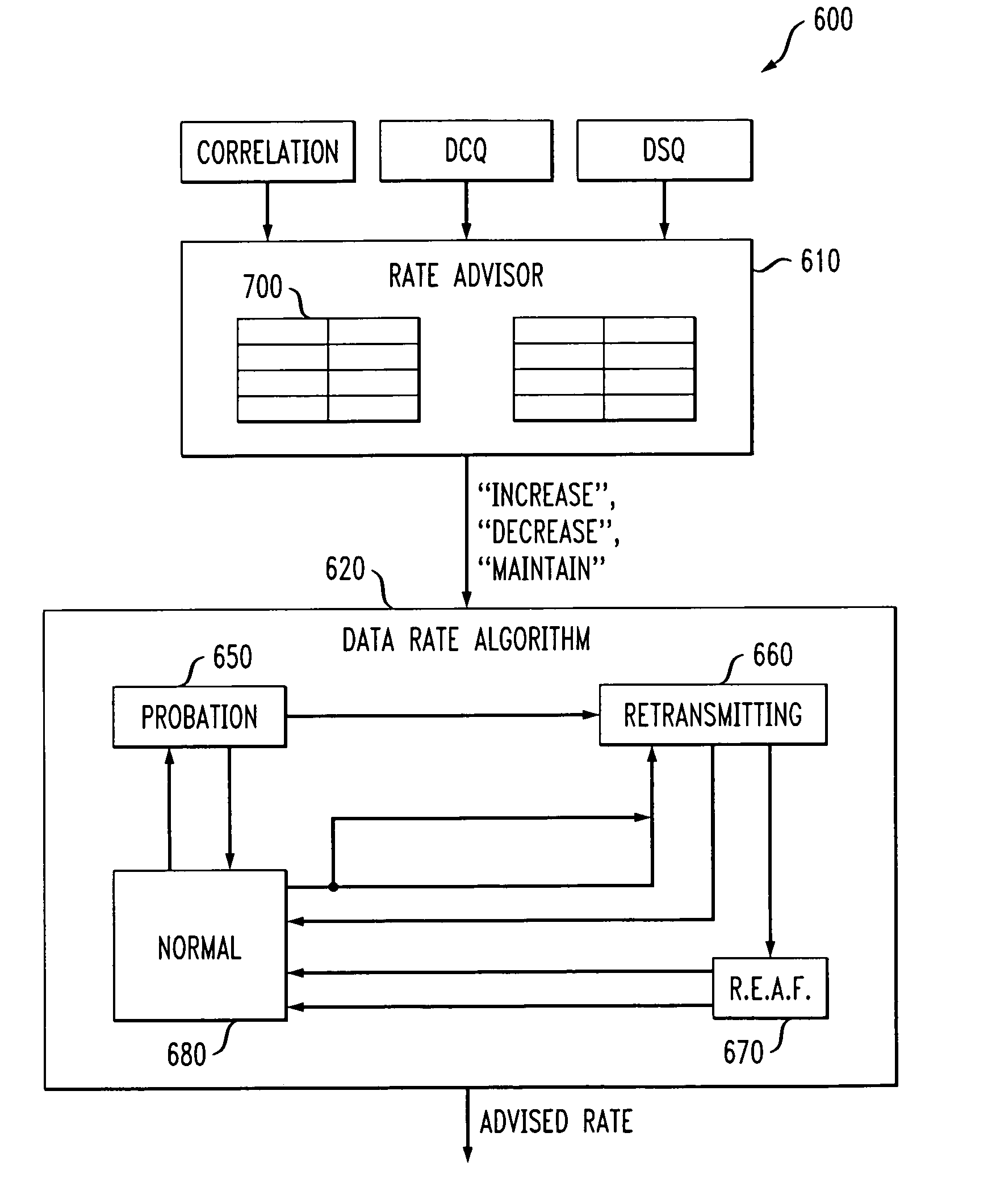
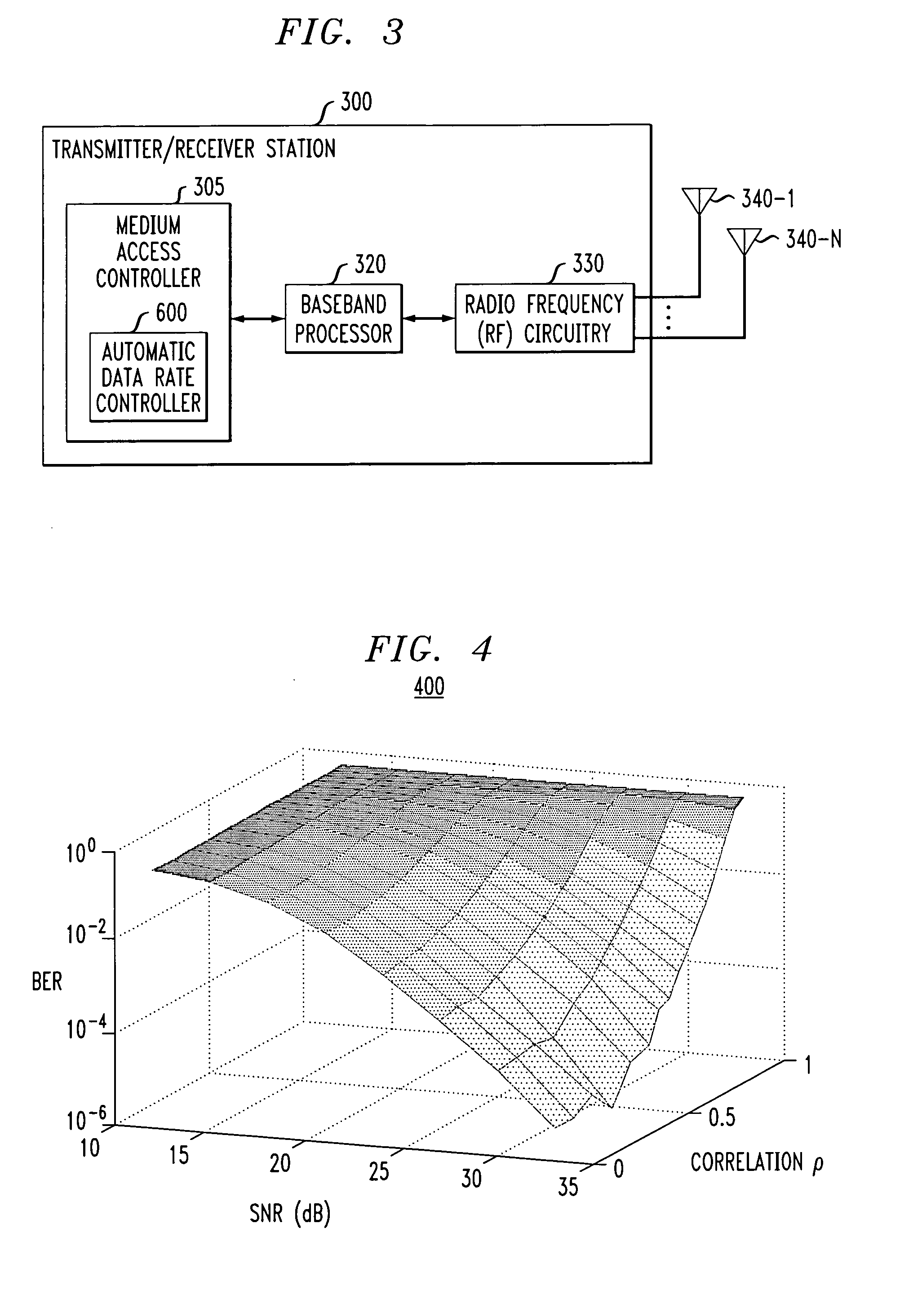
Method and apparatus for automatic data rate control using channel correlation in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS20050136844A1Special service provision for substationNetwork traffic/resource managementDelay spreadSignal quality
A method and apparatus are provided for automatic data rate control in wireless communication systems, such as wireless LANs. A wireless communication device according to the present invention includes a data rate controller that adapts a transmission rate based on a channel correlation measure. The channel correlation measure may be, for example, eigenvalues or singular values of a channel matrix. The data rate controller may also consider the signal quality, channel delay spread or both in determining a data rate.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
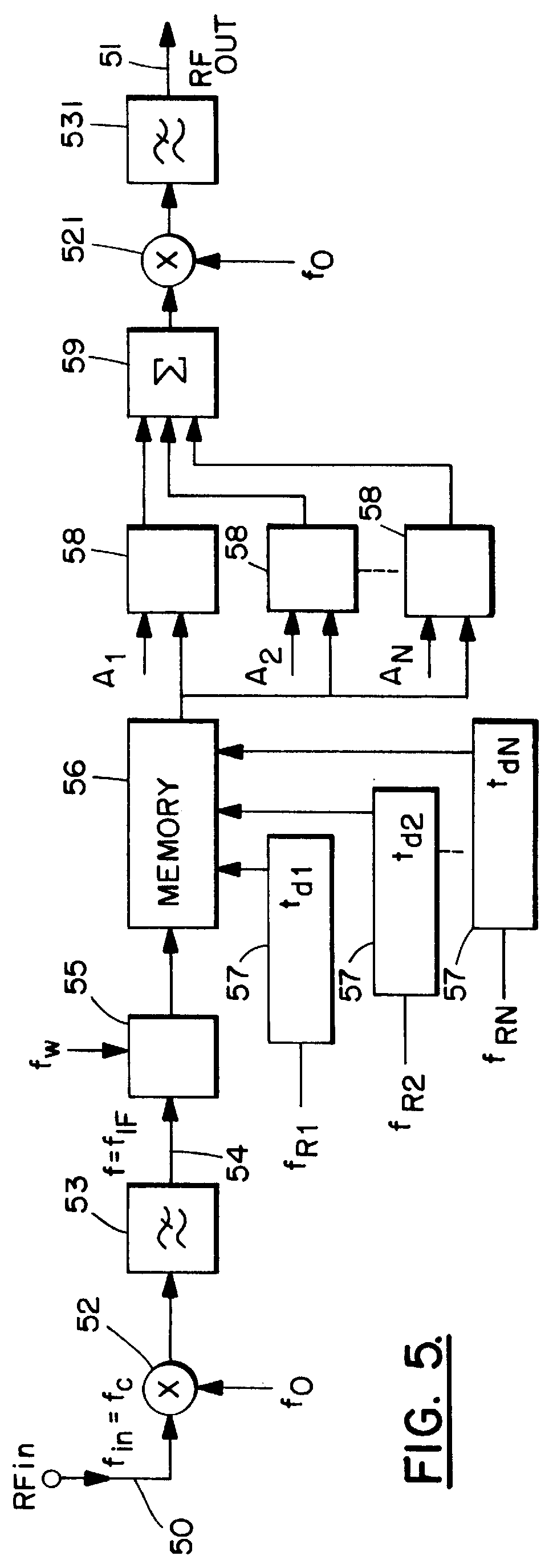
RF channel simulator
InactiveUS6058261AComputation using non-denominational number representationTransmission monitoringFar distanceRadio reception
The present invention relates to a method and a simulator for simulating an RF channel between a radio transmitter and a radio receiver located at a far distance from one another, in which radio channel multipath propagation occurs, and with which simulation at least part of the phenomena caused by the multipath propagation to the radio signal, such as delay spread, attenuation and Doppler shift are implemented. As taught by the method, an RF signal (fin) is moved to a lower frequency (fIF), and from said lower frequency signal (fIF) thus produced samples are taken and written in a memory at a predetermined write frequency (fw). The stored samples are read from the memory after a period of time of the length of the propagation delay (tDi) of each propagation path (i) to be simulated from the storage in the memory at a read frequency (fPi) predetermined for each propagation path (i) to be simulated, said read frequency differing from the write frequency (fw), when the frequency difference ( DELTA f01) of said write frequency (fw) and the propagation-specific read frequency (fRi) represent the Doppler shift of the frequency occurring in each propagation path (i).
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Hybrid domain block equalizer
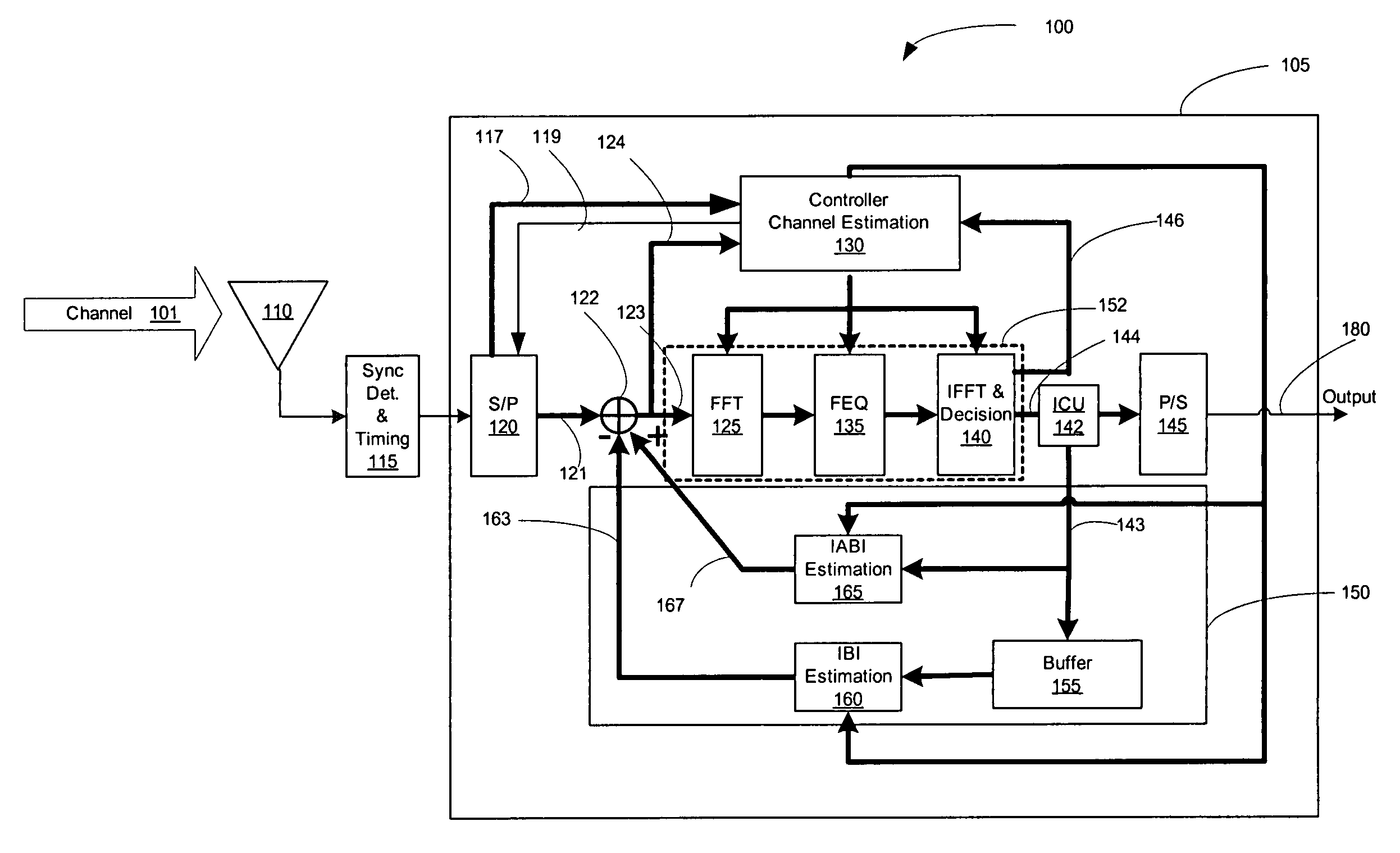
The invention provides a method and device for iterative hybrid time-frequency domain block equalization of signals received via a communication channel subject to multipath interference. The equalization method includes frequency-domain equalization of blocks of received signals in a forward path, and time-domain inter-block echo correction and intra-block cyclic echo addition in the feedback path. The invention can be used for equalizing signals transmitted without cyclic prefix and subjected to multi-path interference with long delay spread.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
Self-adapting channel estimating method applied to 3GPP LTE system
InactiveCN102571650AEasy to useSimplified Computational ComplexityBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsOccupancy rateDelay spread
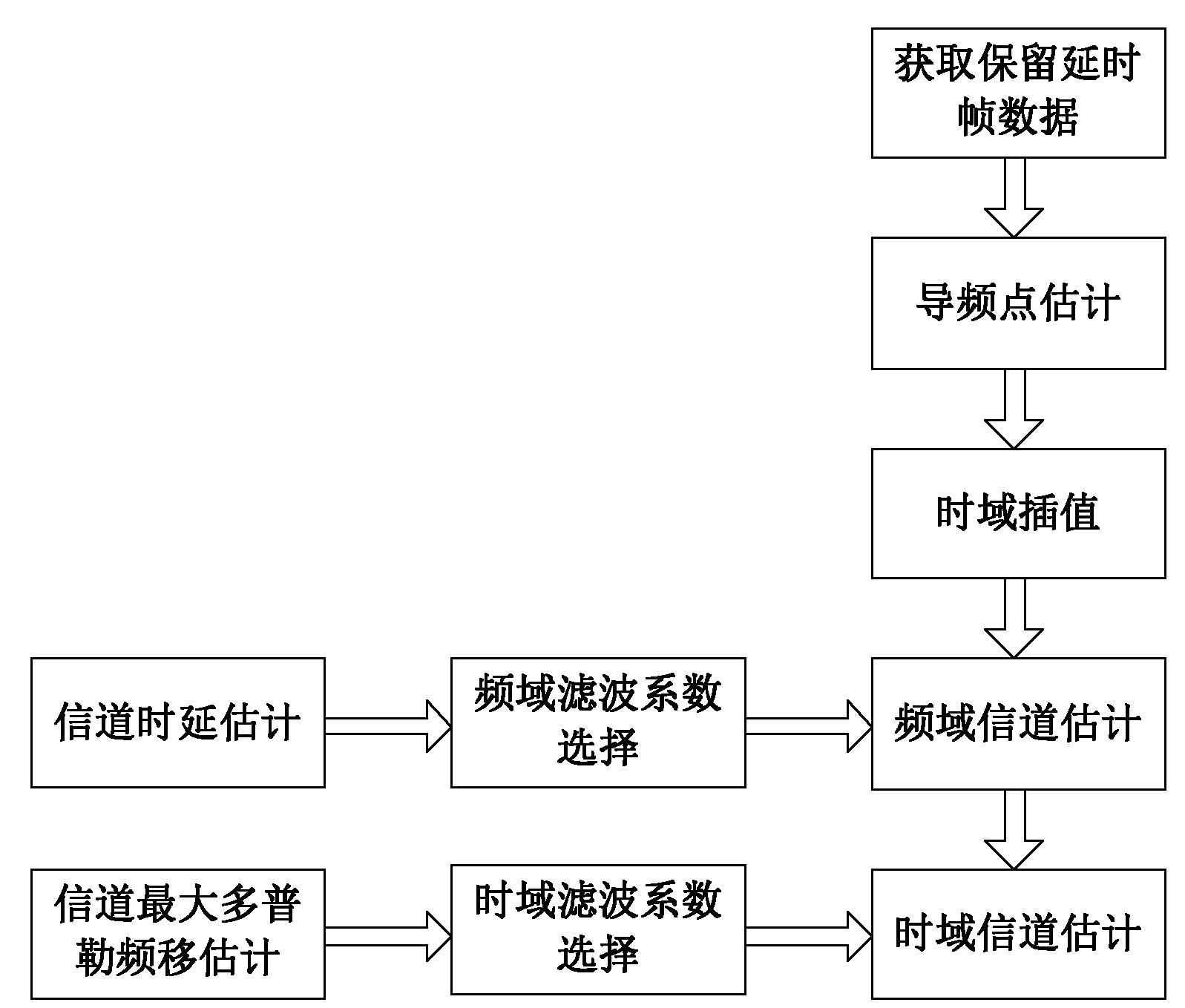
The invention discloses a self-adapting channel estimating method applied to 3GPP LTE system. The method comprises the following steps: (1) the LS (least square) channel estimating value at a pilot tone is computed according to reference signals in a receiving data field; (2) interpolation in the time domain is performed according to current frame pilot tone channel estimated value data and reserved delay frame pilot tone channel estimated value data, and a pilot matrix encrypted is obtained through computing; (3) channel delay spread is estimated according to LS estimation value at the pilot tone, then radio frequency channel filtering coefficient is selected according to the delay spread, and the frequency domain estimation value is computed; and (4) channel Doppler spread is estimated according to the LS estimation value at the pilot tone, then time domain filtering coefficient is selected according to the Doppler spread, and the time domain channel estimation value is computed. The self-adapting channel estimating method provided by the invention has a self-adapting capability to channel characteristics, reduces the occupancy rate and working consumption of hardware resource, improves the estimating speed and reduces computation delay of an estimator.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for setting cyclic shift considering frequency offset
ActiveUS20080168114A1Prevent sequenceDeteriorate whole sequenceDigital data processing detailsSecret communicationDelay spreadPropagation delay
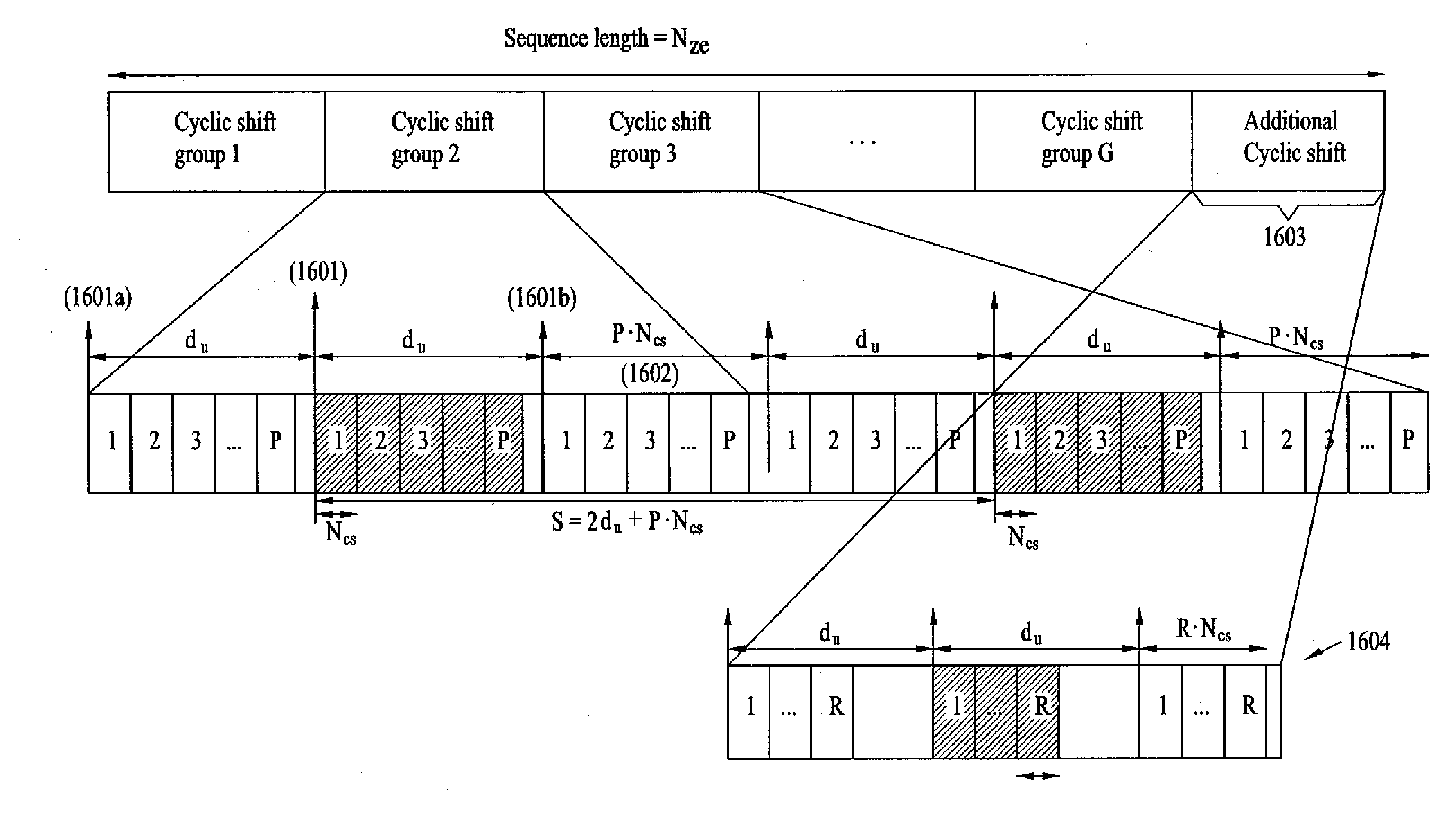
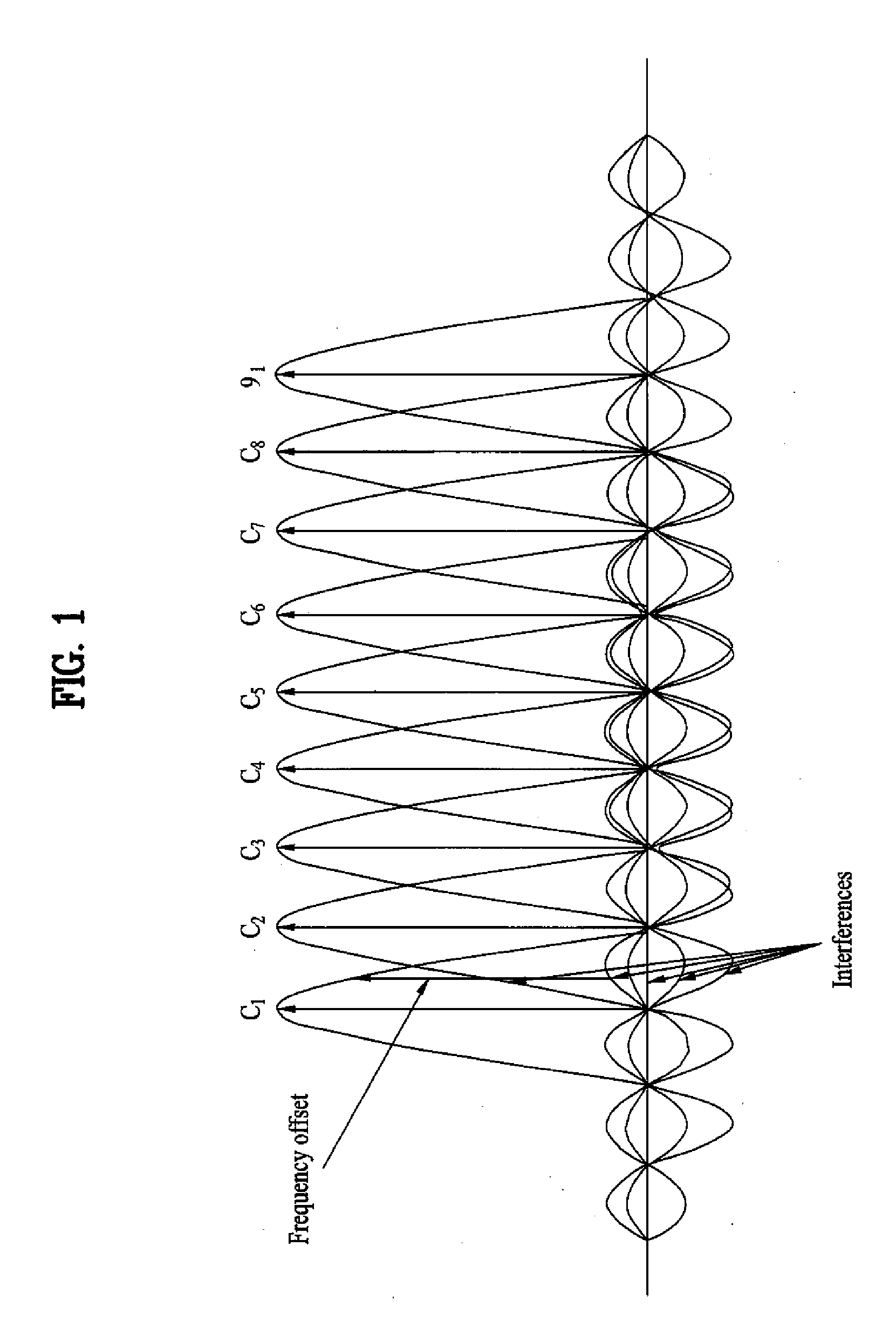
A method for establishing a cyclic shift sequence to provide against the frequency offset is disclosed. The method calculates a distance between a channel response position of the sequence and an alias channel response position caused by a frequency offset, calculates the number of cyclic shifts per group according to the calculated distance, and establishes the cyclic shift (CS)-applying interval. This method easily establishes a cyclic shift (CS) interval at a specific location having no overlapping by considering a channel response of a reception (Rx) sequence and an alias location of this reception (Rx) sequence, although a reception (Rx) signal is shifted by a channel delay spreading or a propagation delay irrespective of categories of a domain generating a sequence, so that it can greatly reduce the number of the detection errors and the false alarm rate. And, if a sequence of the cyclic shift (CS) is allocated to a cell having a frequency offset of more than a predetermined level, the present invention can minimize the influence of a frequency offset on a high-mobility cell.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
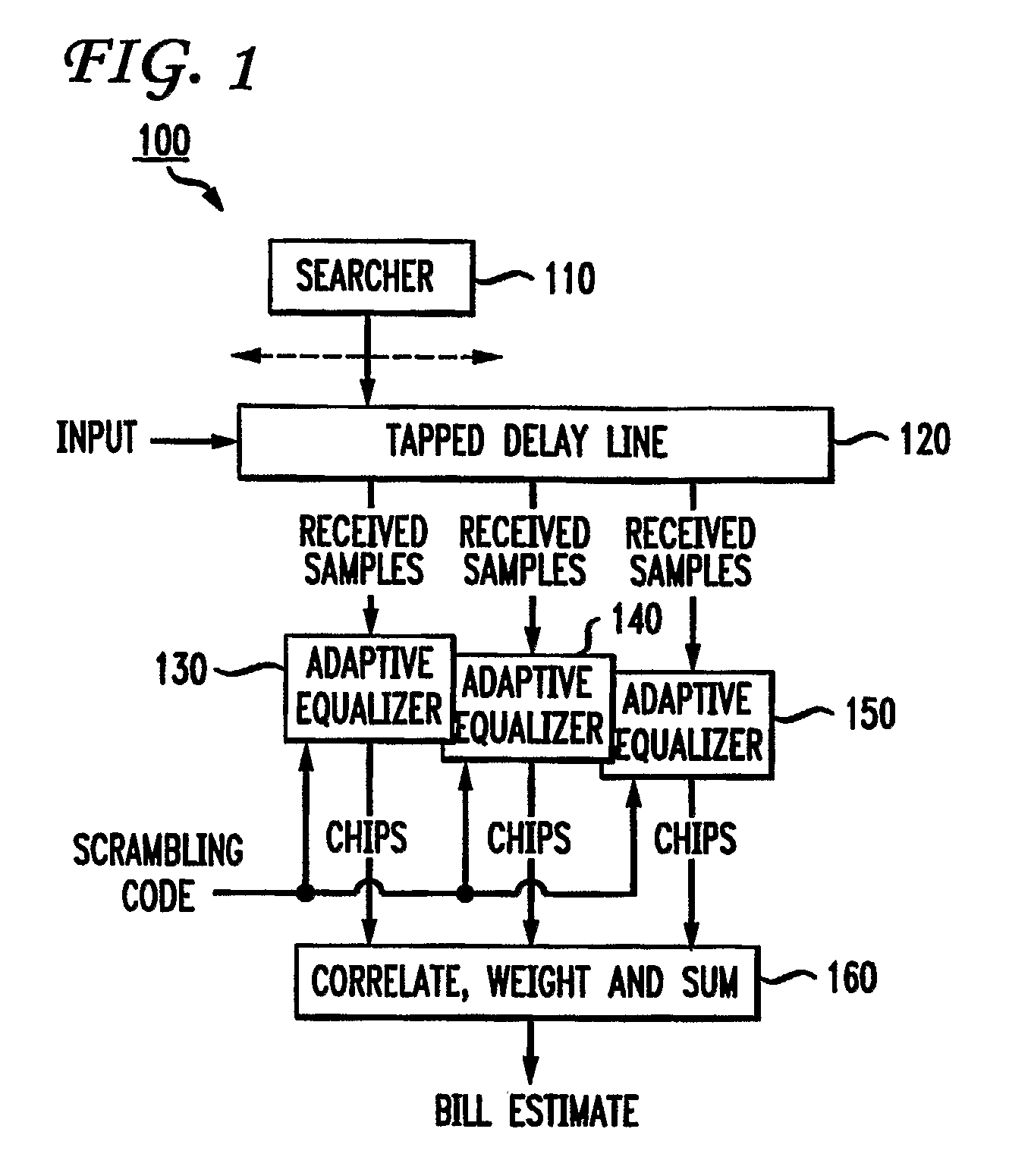
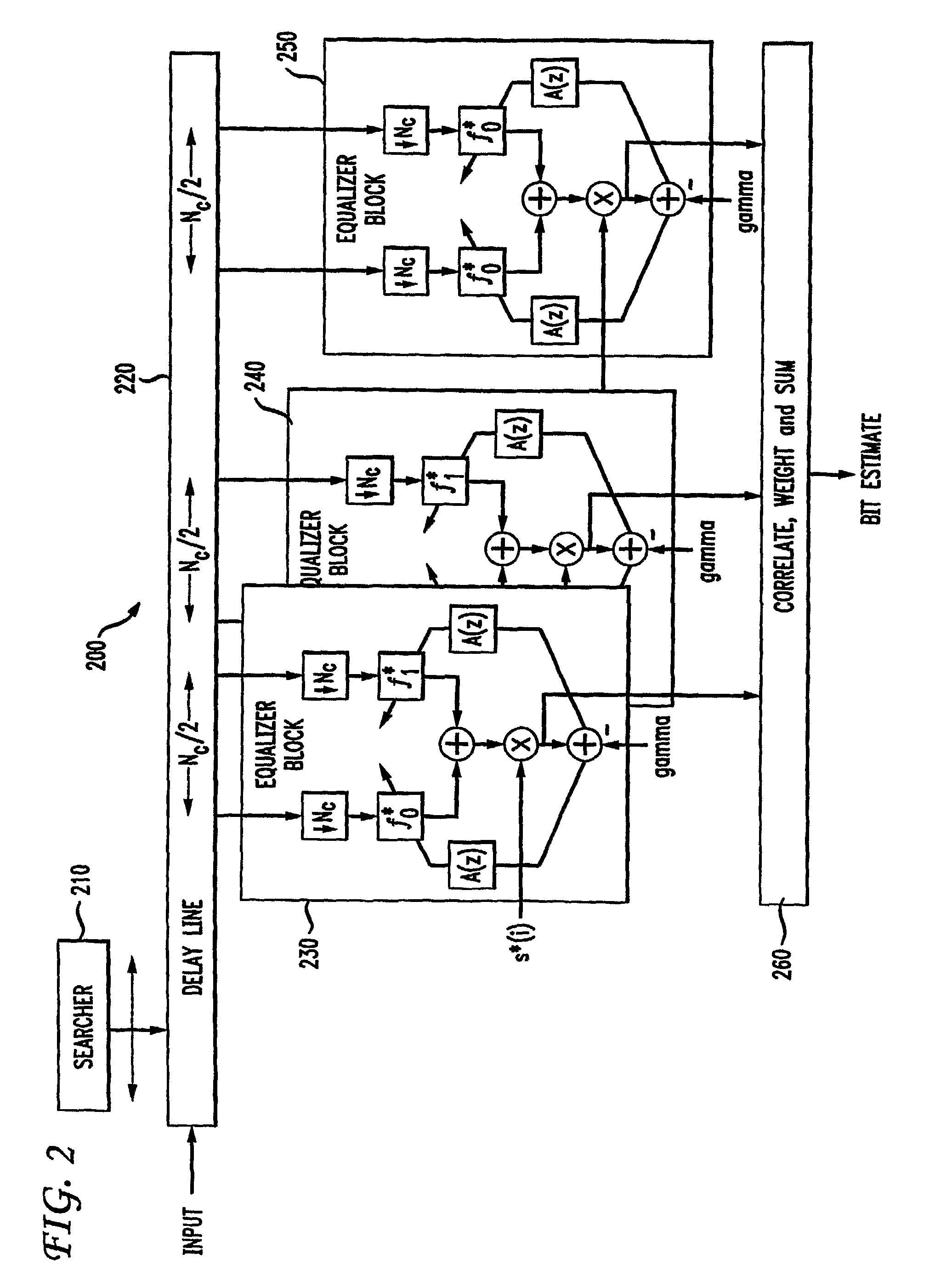
Hybrid rake/equalizer receiver for spread spectrum systems
There is provided a hybrid rake / equalizer receiver for correlating a delay spread in a spread spectrum system. The hybrid rake / equalizer receiver includes a plurality of adaptive equalizers, each for filtering different regions of the delay spread that have an energy level above a pre-specified threshold to respectively provide equalized-descrambled chip sequences for correlation. Equalizer coefficients respectively corresponding to the plurality of adaptive equalizers are updated individually.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
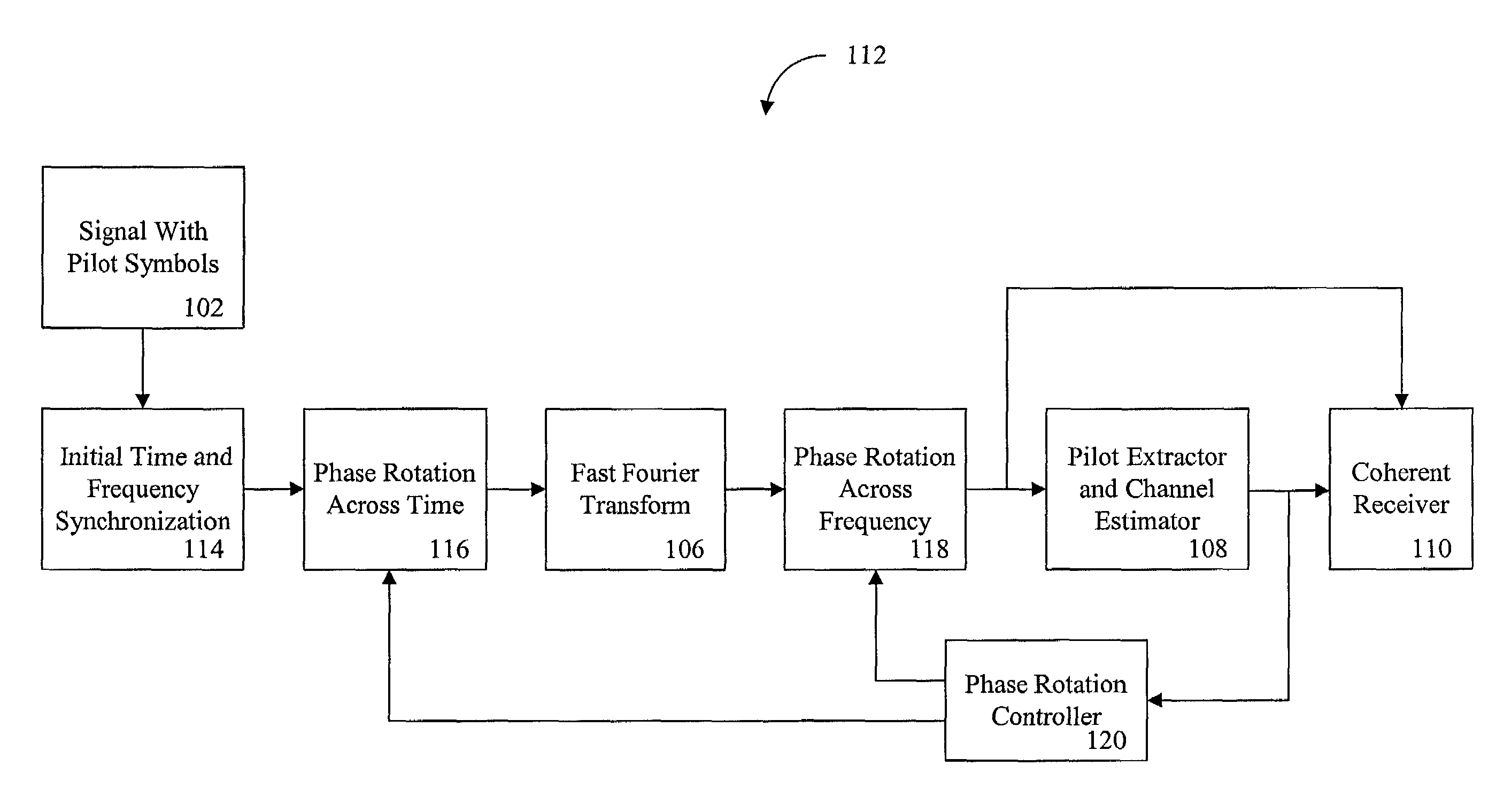
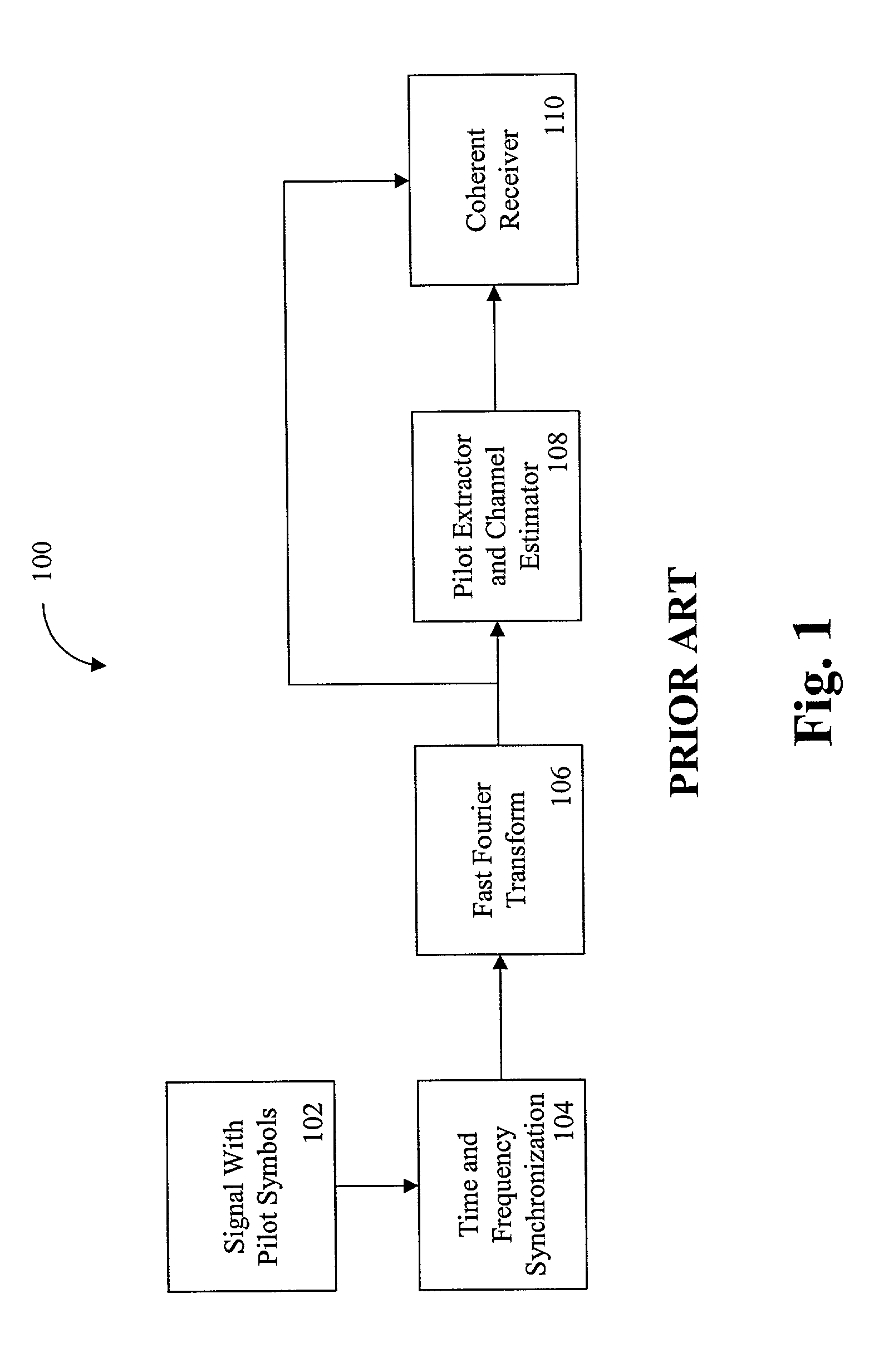
Synchronization of a pilot assisted channel estimation orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system
ActiveUS7023928B2Minimize estimated channel errorSensitive to frequencyBaseband system detailsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase differenceCarrier signal
A synchronization of a pilot assisted channel estimation orthogonal frequency division multiplexing can be achieved by receiving a signal containing pilot symbols, providing an initial time and frequency synchronization to the signal, phase rotating the signal across time, transforming the signal with a fast Fourier transformation, phase rotating the signal across frequency, extracting the pilot symbols and generating a channel estimator. The phase rotating across time and the phase rotating across frequency are controlled by a phase rotation controller in accordance with the channel estimator. The initial time and frequency synchronization synchronizes the signal such that intercarrier interference effects and intersymbol interference effects are negligible. The signal may include plural carrier frequencies each having an arrival timing offset and a frequency offset. The signal may also include delay spread or Doppler spread. The phase rotation controller measures a phase different between the channel estimator at times k and k+Δk, where k is time and Δk is a symbol period and measures a phase difference between the channel estimator at frequencies n and n+Δn, where n is tone frequency and Δn is a frequency spacing between adjacent tones.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
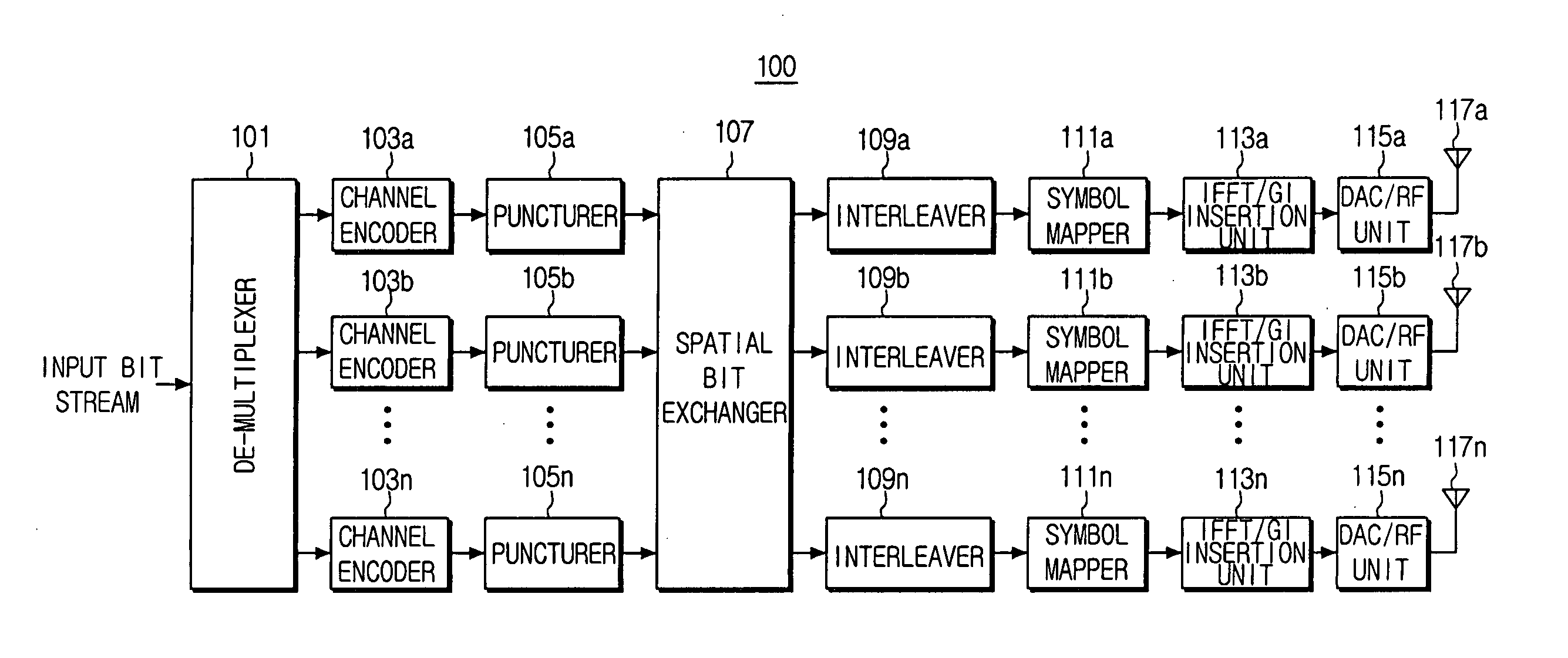
MIMO transmission system and method of OFDM-based wireless LAN systems
InactiveUS20060013330A1Enhance effect of diversityDiversity/multi-antenna systemsMulti-frequency code systemsDelay spreadTelecommunications
A MIMO transmission system and method of an OFDM-based wireless LAN system. The MIMO transmission system includes multiple transmission paths to channel antennas and receives and encodes plural rows of bit streams. The MIMO transmission system does not transmit the plural rows of bit streams through the same paths and channel antennas, but sequentially switches, OFDM-modulates, and sends bits of each bit stream to the plural paths such that the bit streams are not transmitted through the same paths and channel antennas. Through the bit exchange among the channel antennas, the MIMO transmission system can enhance diversity gains by the channel encoding in flat-fading environments having a small RMS delay spread.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Adaptive beam-steering methods to maximize wireless link budget and reduce delay-spread using multiple transmit and receive antennas
ActiveUS20100178884A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsElectromagnetic wave modulationDelay spreadBeam steering
A method and apparatus for adaptive beam-steering are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises performing adaptive beam steering using multiple transmit and receive antennas, including iteratively performing a pair of training sequences, wherein the pair of training sequences includes estimating a transmitter antenna-array weight vector and a receiver antenna-array weight vector.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
System and method for dynamic overlap compensation in a simulcast network
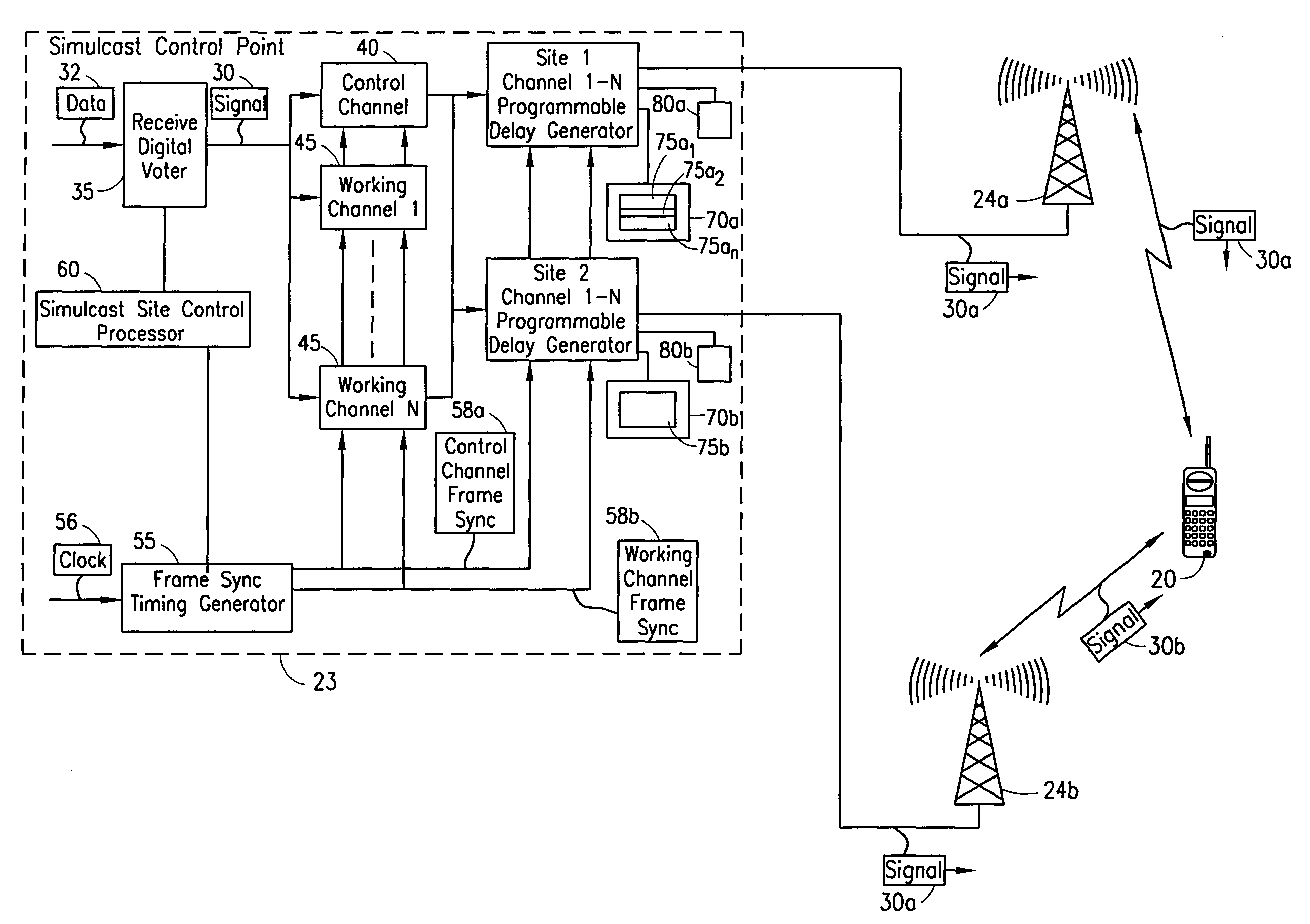
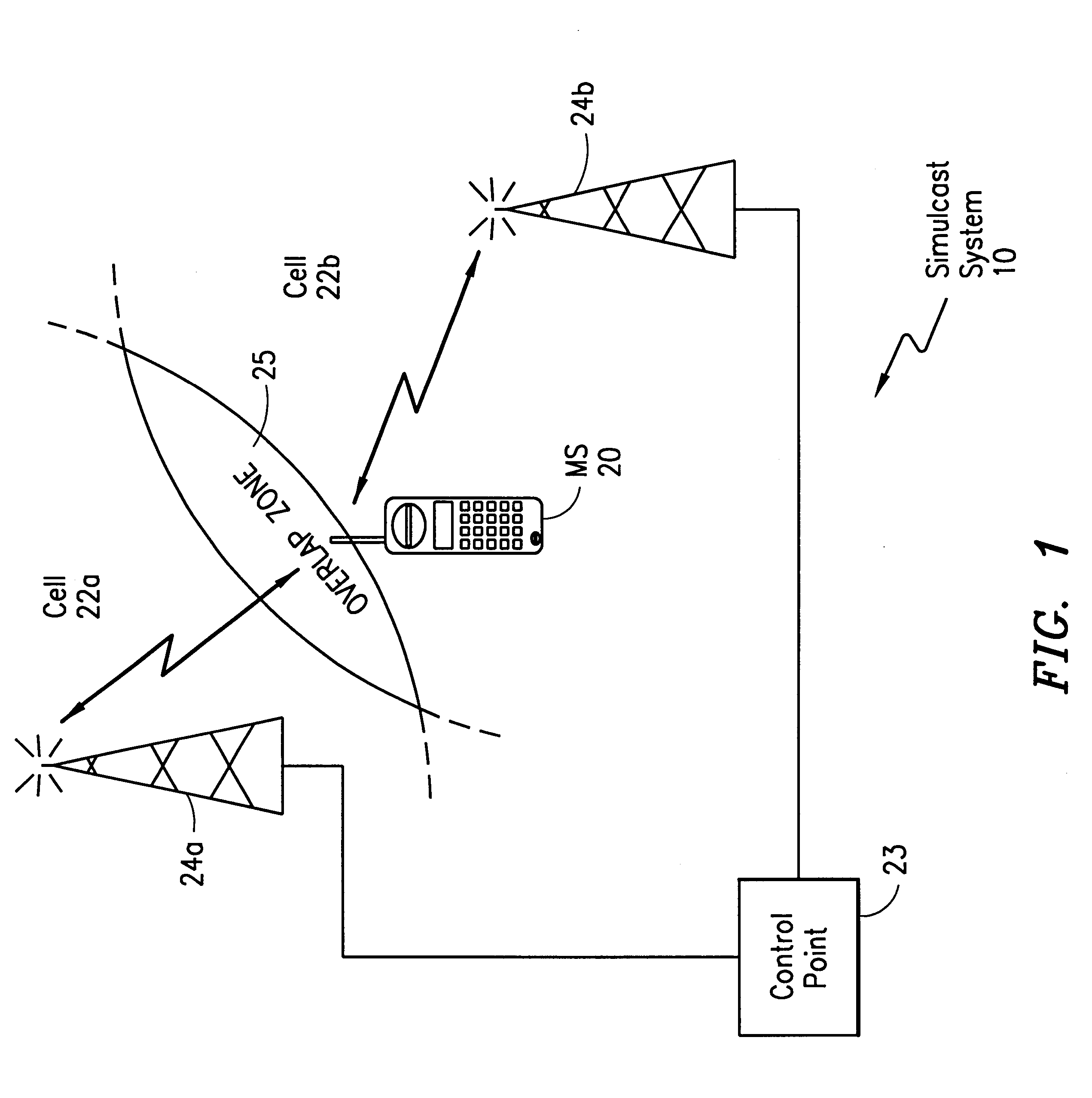
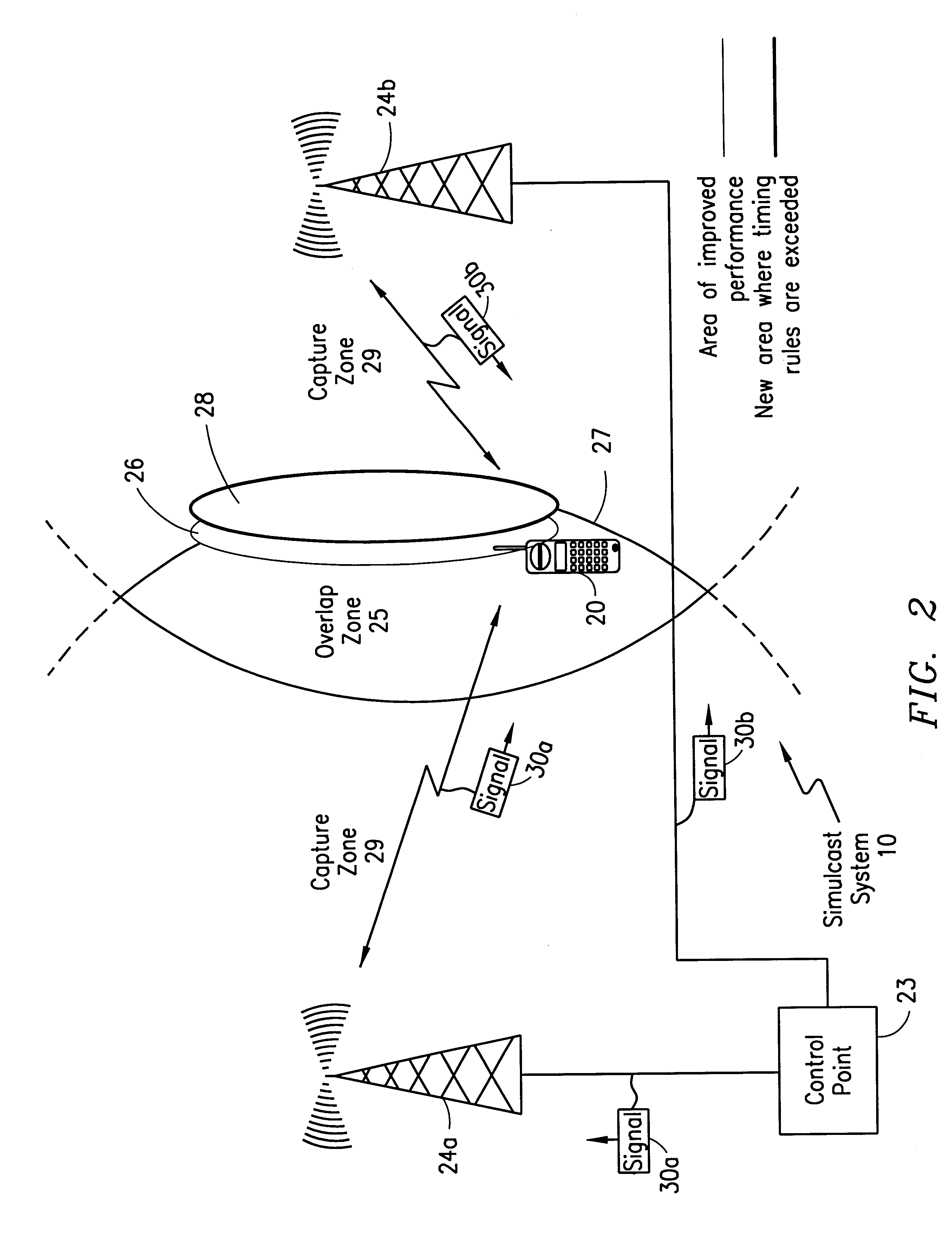
InactiveUS6266536B1Easy to useImproved in-building coverageBroadcast transmission systemsRadio transmission for post communicationOverlap zoneDelay spread
A telecommunications system and method is disclosed for deliberately producing synchronous timing jitters in order to dynamically shift the delay spread within the overlap zone in a simulcast system. At a synchronous periodic rate, the timing differential between transmission of the signal from the control point to each of the transmitters can be continuously adjusted to continuously change the relative timing between multiple received signals in the overlap zone. Alternatively, the timing adjustments can be performed only upon reception of a retransmission request. In either case, the timing adjustments are performed so as to not be noticed by the mobile subscriber.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
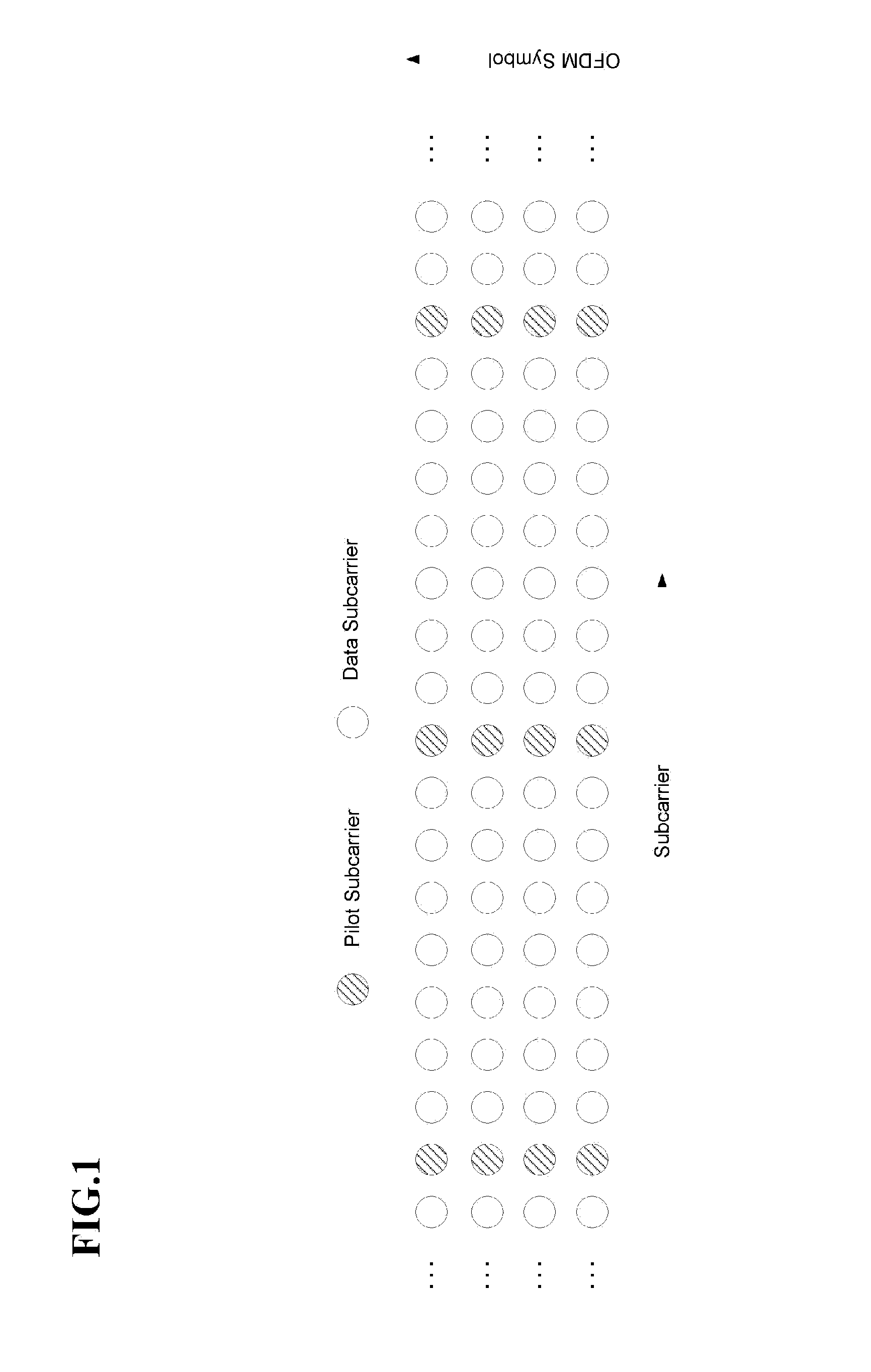
Apparatus and method of estimating channel based on channel delay spread in mobile communication system
ActiveUS20080137788A1Reduce the amount of calculationAccurately estimating a channelMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsDelay spreadFinite impulse response
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method of estimating a channel based on a channel delay spread in a mobile communication system. Pilot subcarriers are inserted between data subcarriers at predetermined intervals to estimate a channel at locations of the pilot subcarriers. An approximate channel delay spread value is estimated by using an autocorrelation value of a pilot signal. Then, a channel for data subcarriers between the pilot subcarriers is estimated by using a Wiener finite impulse response (FIR) filter that has a separate coefficient according to the estimated delay spread value. Accordingly, by changing the Wiener FIR filter coefficient according to the delay spread value of the channel, it is possible to estimate the channel so as to be adaptive for a change of the channel over time. Since the filter coefficients, which are calculated in advance, are used, it is possible to reduce the amount of calculation required when calculating the filter coefficients. As a result, an apparatus for estimating a channel can be easily achieved.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
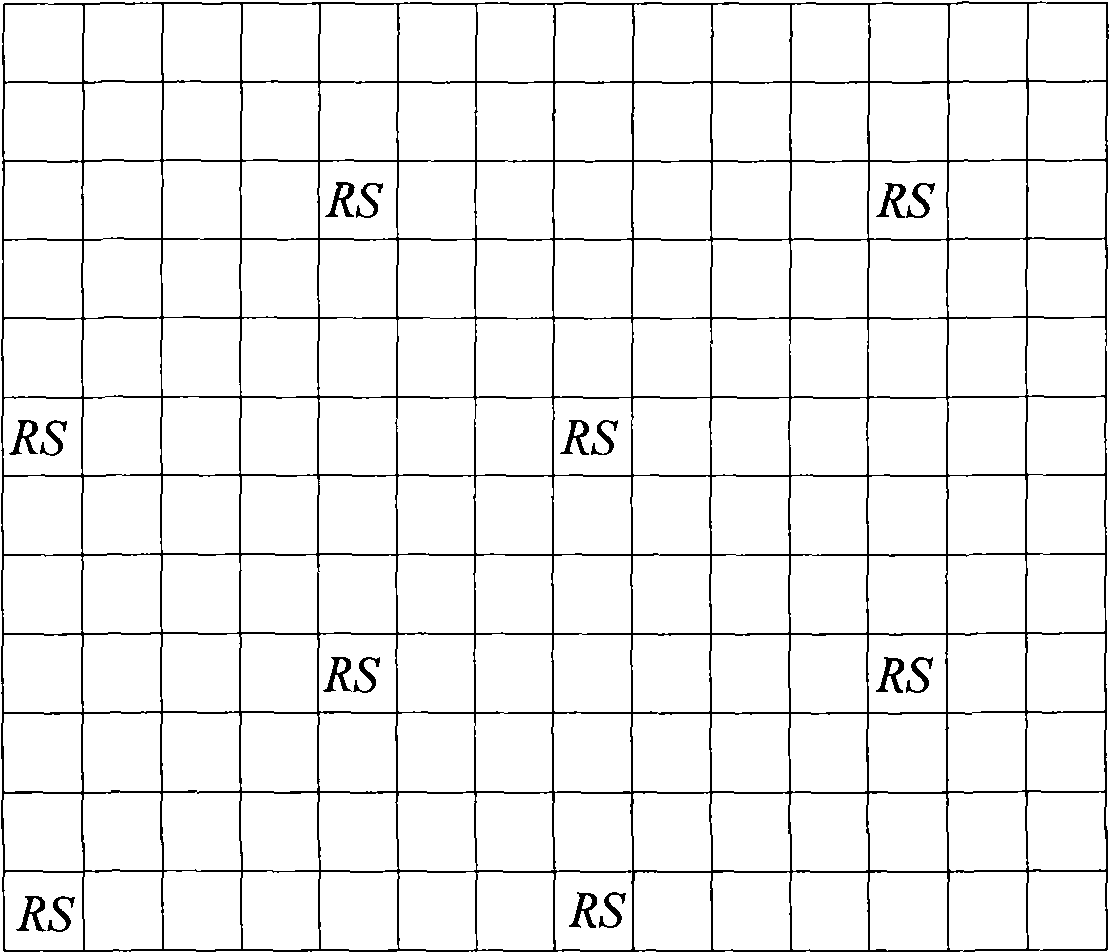
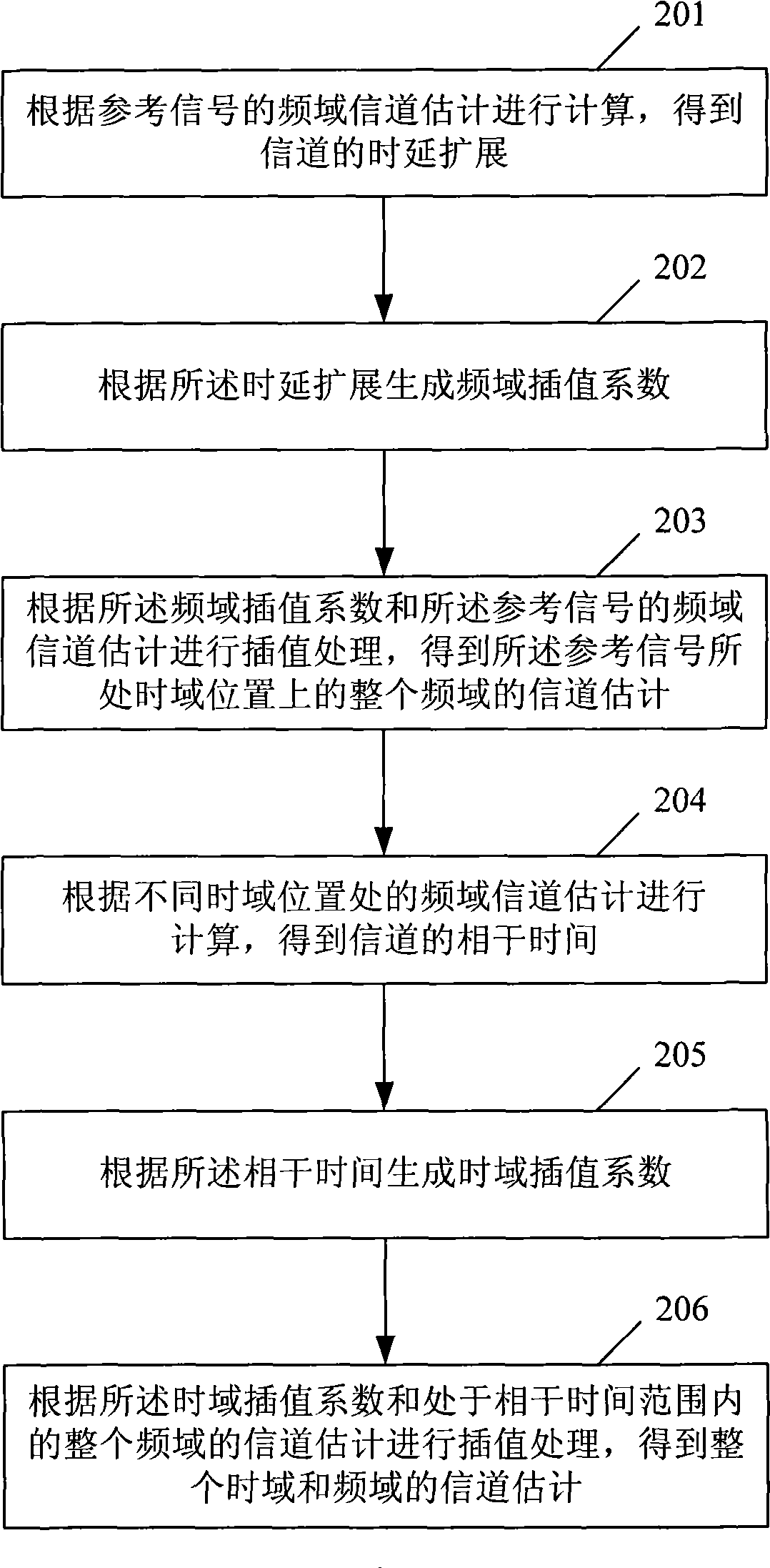
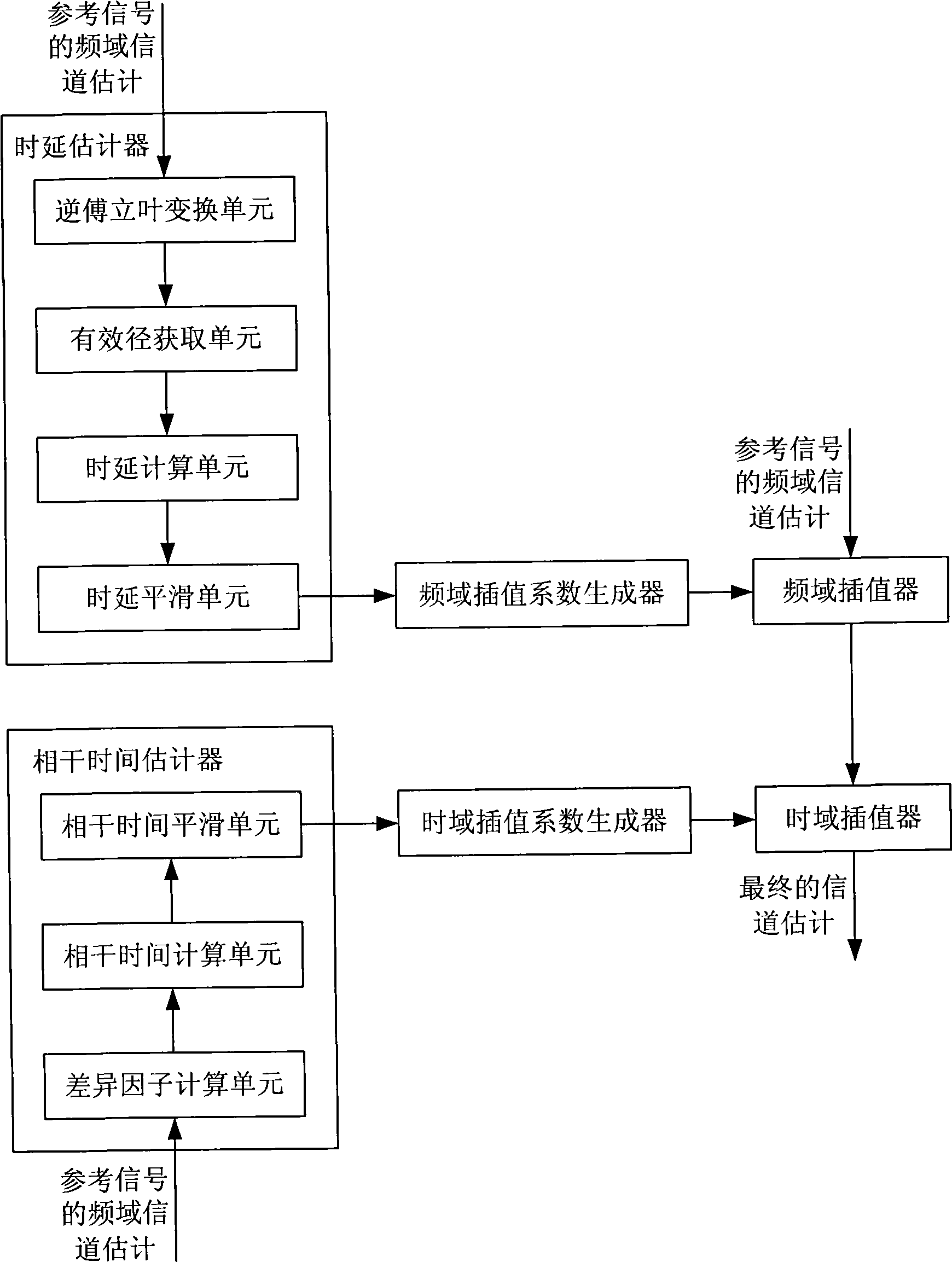
Channel estimation method for Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing system and device thereof
The invention provides a channel estimation method for Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing system and a device thereof. The channel estimation method comprises the following steps: A. calculating according to the frequency domain channel estimation of a reference signal to obtain the delay spread of the channel; B. generating a frequency domain interpolation coefficient according to the delay spread; C. carrying out interpolation according to the frequency domain interpolation coefficient and the frequency domain channel estimation of the reference signal to obtain the channel estimation of the whole frequency of the position where the reference signal is located; D. calculating according to the frequency domain channel estimation at different time domain positions to obtain the coherence time of the channel; E. generating a time domain interpolation coefficient according to the coherence time; and F. carrying out interpolation according to the time domain interpolation coefficient and the channel estimation of the whole frequency located with the range of the coherence time to obtain the whole channel estimation of the time domain and the frequency domain. In light of the invention, the channel estimation result can self-adaptively change with the change of the channel.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SEMICON BEIJING
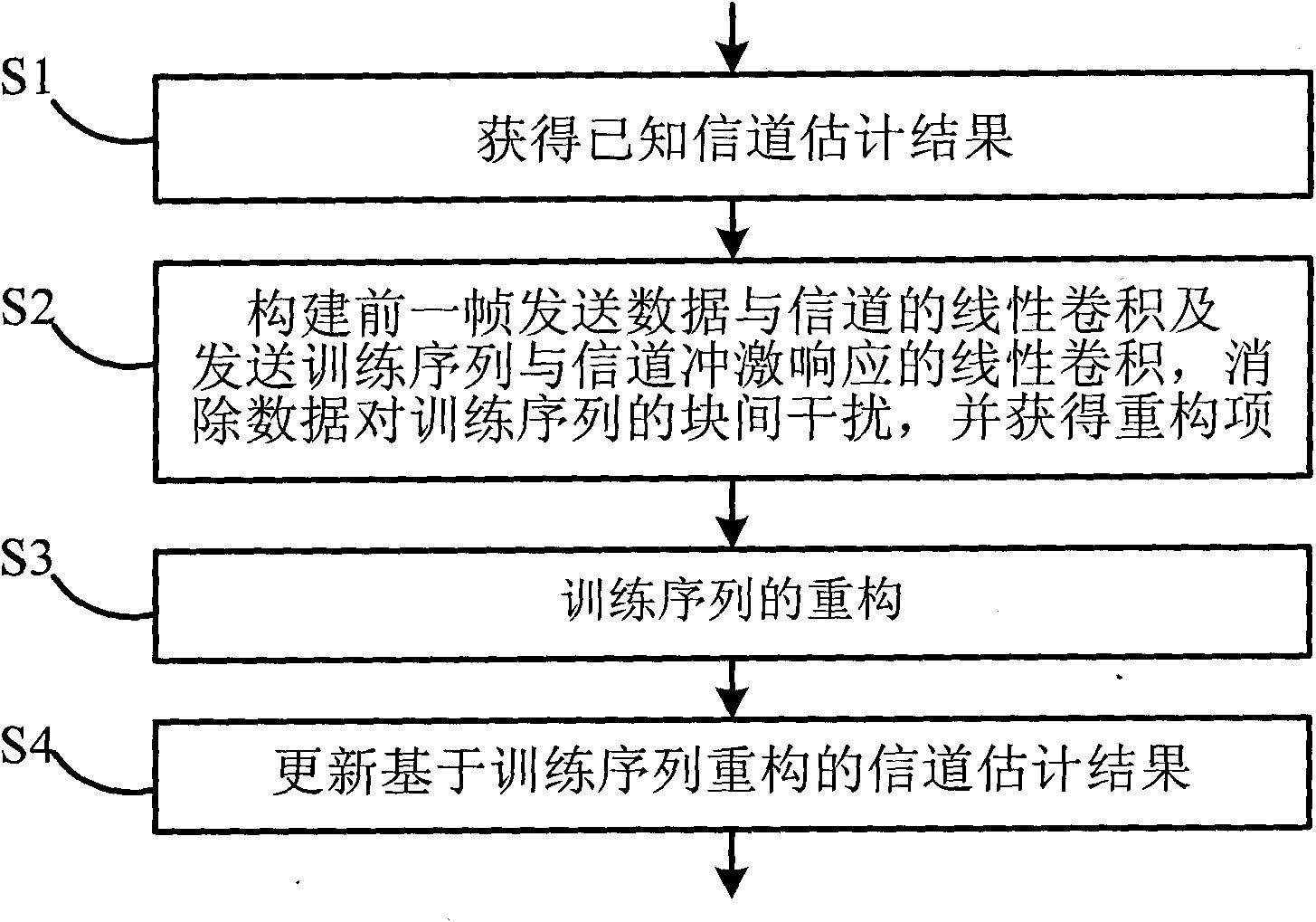
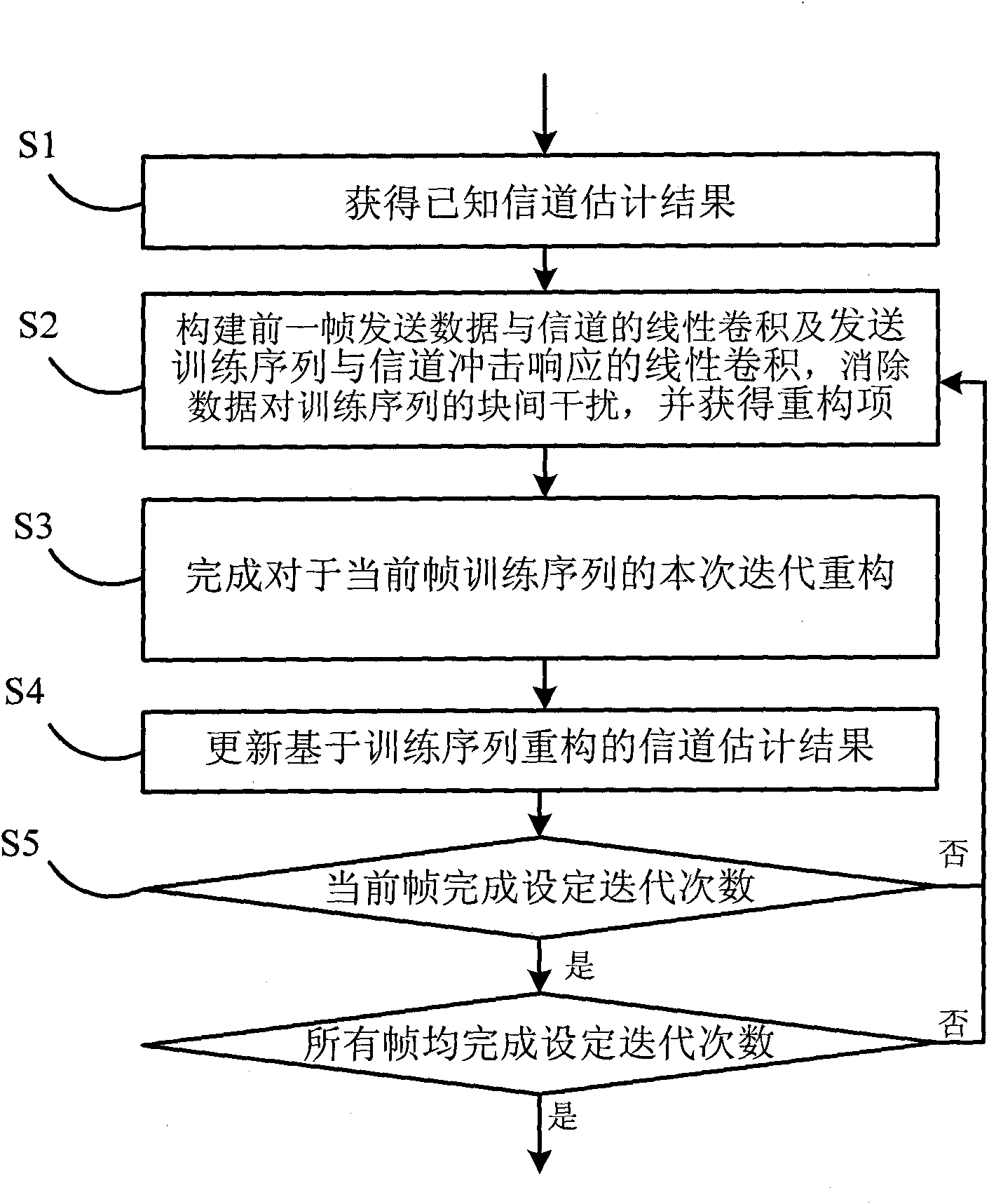
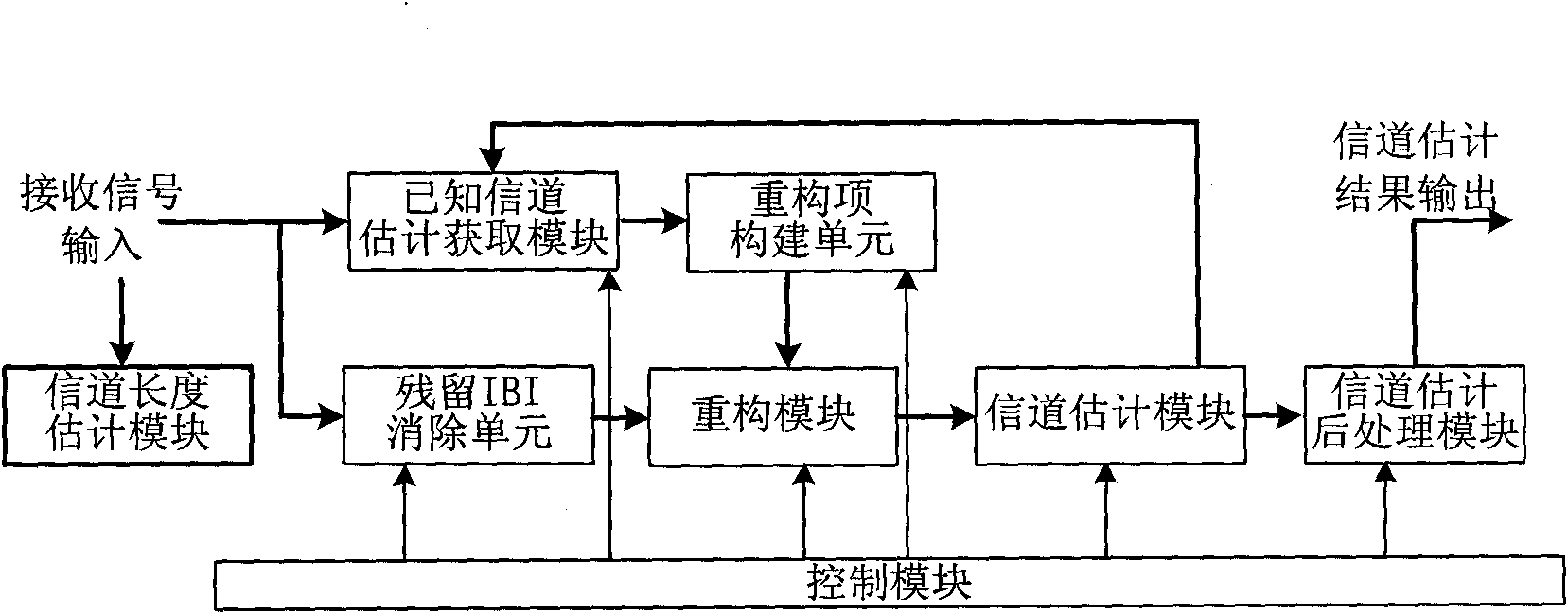
Training sequence reconstruction-based channel estimation method and system
ActiveCN101808056AAccurate estimateImprove estimation accuracyMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksSequence reconstructionDelay spread
The invention discloses a training sequence reconstruction-based channel estimation method and a training sequence reconstruction-based channel estimation system. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a known channel estimation result; according to the known channel estimation result, constructing linear convolution of former frame transmitted data and a channel and the linear convolution of a transmitted training sequence and a channel impulse response; eliminating inter-block interference of data on a training sequence; obtaining a cyclic convolution, of the training sequence and the channel impulse response, serving as a reconstruction item; according to the reconstruction item, reconstructing the training sequence; and performing channel estimation by utilizing the reconstructed training sequence, and updating a channel estimation result. The method and the system of the invention can ensure that a TDS-OFDM system can also obtain relatively accurate channel estimation when maximum delay extension of the channel exceeds the guard space length of the training sequence, simultaneously improves the accuracy of the channel estimation and improves the spectrum utilization ratio and the mobility performance of the system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Link adaptation method using feedback information for wireless communication system
ActiveUS20050122912A1Reduce data transmission delay timeImprove transmission performancePower managementTransmission systemsDelay spreadCommunications system
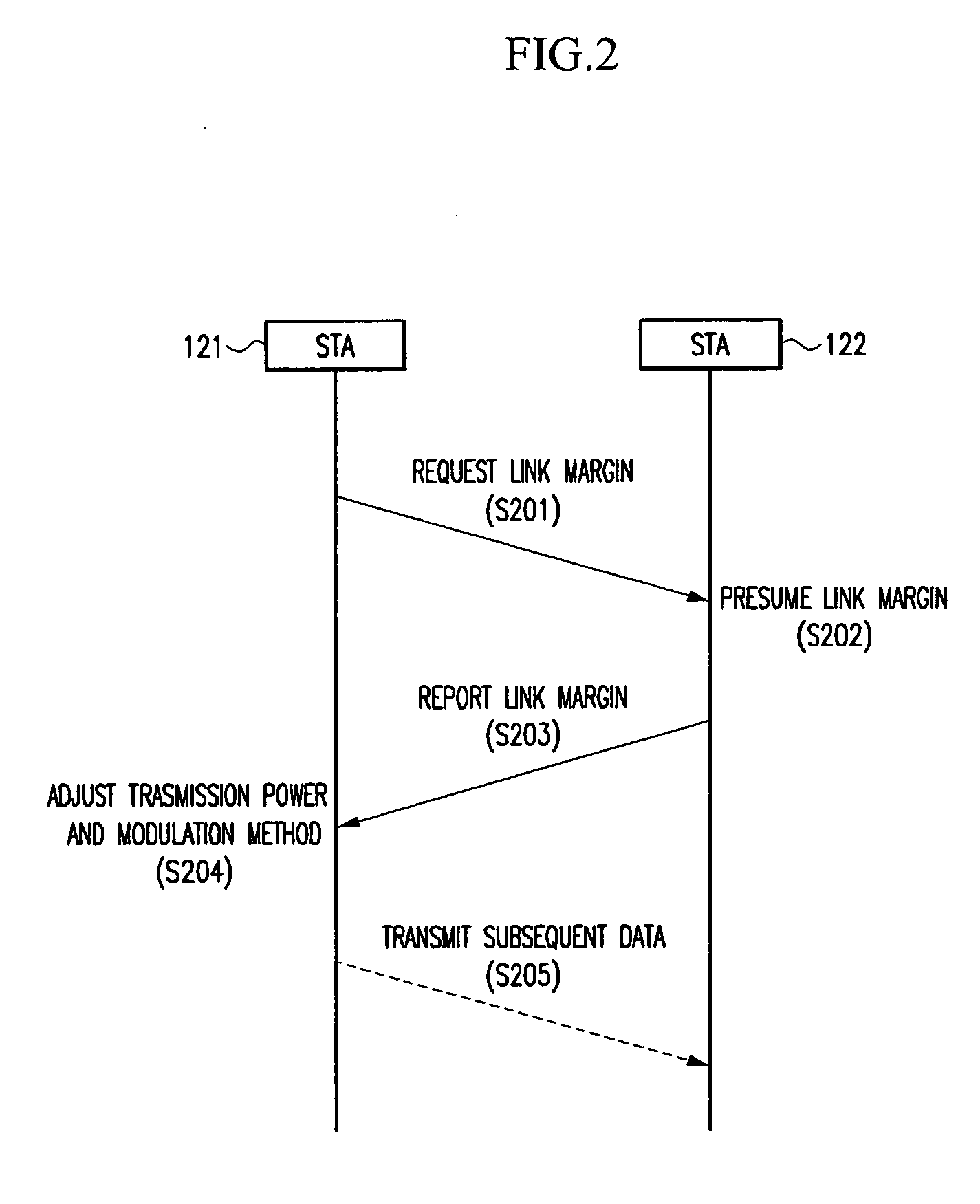
Disclosed is a link margin adaptation method using feedback information of a wireless communication system. For transmission and reception of data between two nodes of the wireless communication system, a transmission node requests a receiving node to transmit a link margin. The transmission node receives the link margin, and selects one of a white noise table or a delay spread table according to a delay spread value between the two nodes. Then, the transmission node adapts a link between the two nodes to a transmission mode and decides a transmission rate to transmit data at the decided transmission rate, thereby improving transmission capacity of the wireless communication system, obtaining the optimum link state, extending power utilization time of stations, and reducing interference between stations.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method and apparatus for synchronization of the OFDM systems
ActiveUS20050105659A1Overcome disadvantagesReduce the impact of noiseError preventionBroadcast transmission systemsDelay spreadGuard interval
A method and apparatus for the signal synchronization of an OFDM system are proposed including a delay conjugate multiplication module, a phase processor and an edge detector. It provides estimates for the boundaries of ISI-free region by utilizing the characteristics of the guard interval and combining the techniques of the delay conjugate multiplication module, phase differential operation, symbol-by-symbol average operation, and edge detection. This method provides an improved performance in a multi-path fading channel with large delay spread, and can be utilized in a broadcasting system, such as the DAB and DVB-T systems. This invention is easy to determine a fixed optimal threshold that can directly separate the ISI region in any mobile environment, thereby most symbol information with ISI-free version can be obtained.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Cluster path processor time alignment for signal suppression/separation in a wireless device
ActiveUS20080075216A1Polarisation/directional diversitySynchronisation error detectionDelay spreadSignal Repression
A system for processing radio frequency (RF) signals includes a searcher and a plurality of Cluster Path Processor (CPPs). The searcher detects a maximum signal energy level and position of at least one of a plurality of individual distinct path signals in a signal cluster of a first information signal, wherein at least a portion of the plurality of individual distinct path signals is received within a duration of a corresponding delay spread. The sampling position is used as a starting sampling location by the plurality of CPPs, including a first information signal CPP and a second information signal CPP. Fine sampling positions of the plurality of CPPs are based upon channel energy estimates for the plurality of individual distinct path signals. CPP outputs are employed to produce channel estimates, which are themselves used in subsequent equalization operations. Sampling positions may change over time in order to satisfy alignment criteria.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Fft numerology for an OFDM transmission system
An exemplary fast Fourier transform (FFT) numerology for an orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) downlink transmission system is described. The exemplary FFT numerology reduces the FFT sampling rate for a given transmission bandwidth, thereby increasing the battery life of a UE. The FFT numerology increases robustness against Doppler spread, phase noise, and frequency offset, enabling operation in channels with high delay spread, such as occurs in mountainous regions. The described numerology might provide the following without altering standard sub-frame duration: increased intercarrier spacing; reduced FFT sampling frequency across the transmission bandwidths; reduced FFT size across all transmission bandwidths; increased number of OFDM symbols per sub-frame; and / or increased cyclic prefix length choices.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Adaptive selection of transmission parameters for reference signals
An embodiment of the present invention uses estimates of delay spreads of transmissions from user equipments (UEs) to a NodeB to determine a set of transmission parameters for the UEs reference signals. In an exemplary embodiment, the transmission parameters for reference signals include cyclic shifts. Thus, embodiments include a set of allocated cyclic shift values that are tailored to the delay spreads. The set of allocated cyclic shift values are used by a corresponding set of UE being served by a NodeB to form references signals. Each UE uses the allocated cyclic shift to form its reference signal by applying the cyclic shift to a modified reference sequence. The modified reference sequence can be generated from a Constant-Amplitude-Zero-Auto Correlation (CAZAC) sequence. The set of allocated cyclic shift values can be updated periodically to account for changes of delay spreads, which can be caused by physical movements of the set of UEs.
Owner:APPLE INC
Dynamic Configuration of a Flexible Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing PHY Transport Data Frame
ActiveUS20160043830A1Increase flexibilityIncrease data rateError preventionModulated-carrier systemsDelay spreadUser device
A base station may generate and transmit a transport stream including a sequence of frames. A frame may include a plurality of partitions, where each partition includes a corresponding set of OFDM symbols. For each partition, the OFDM symbols in that partition may have a corresponding cyclic prefix size and a corresponding FFT size, allowing different partitions to be targeted for different collections of user devices, e.g., user devices having different expected values of maximum delay spread and / or different ranges of mobility. The base station may also dynamically re-configure the sample rate of each frame, allowing further resolution in control of subcarrier spacing. By allowing the cyclic prefixes of different OFDM symbols to have different lengths, it is feasible to construct a frame that conforms to a set payload duration and has arbitrary values of cyclic prefix size per partition and FFT size per partition. The partitions may be multiplexed in time and / or frequency.
Owner:ONE MEDIA LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com