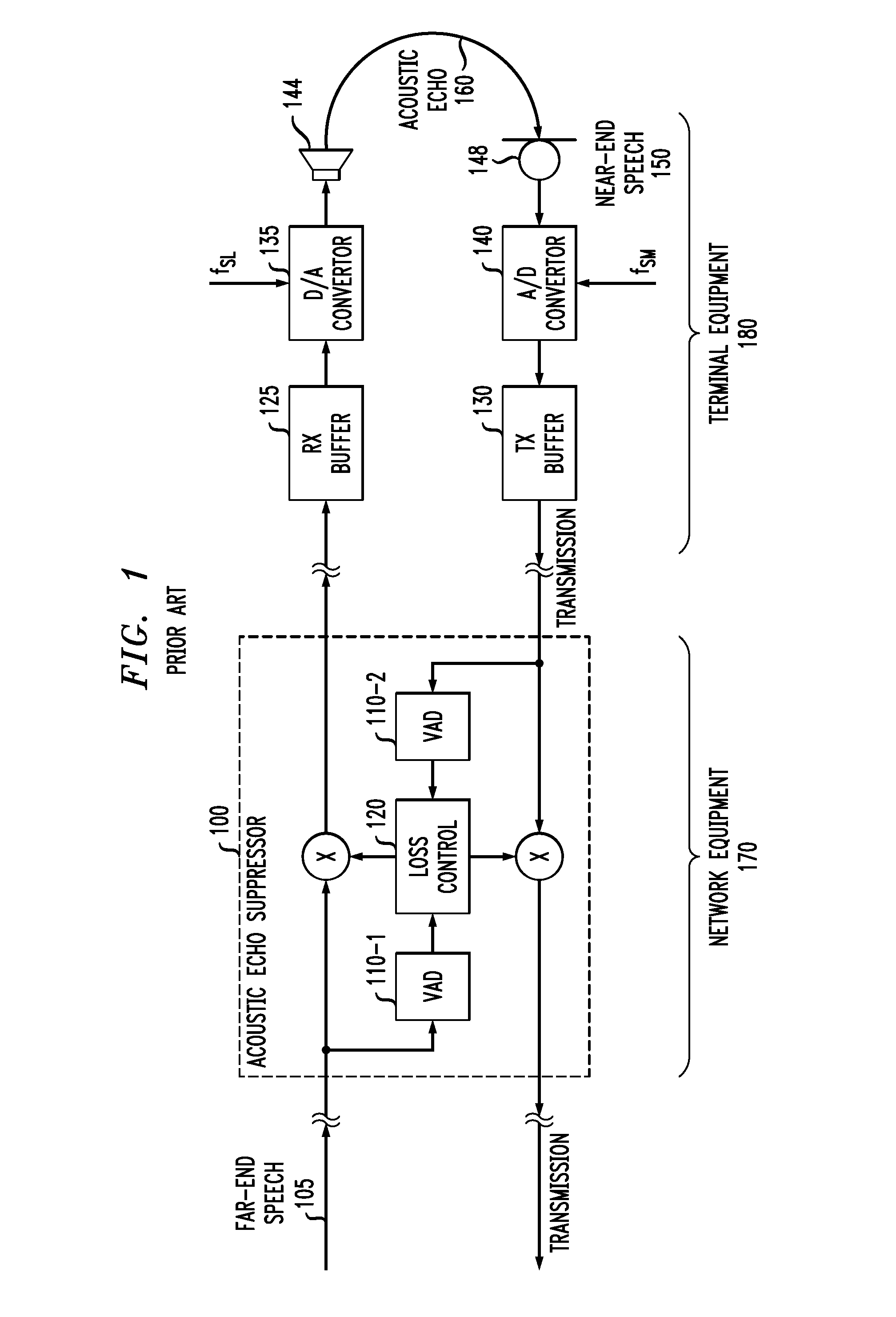
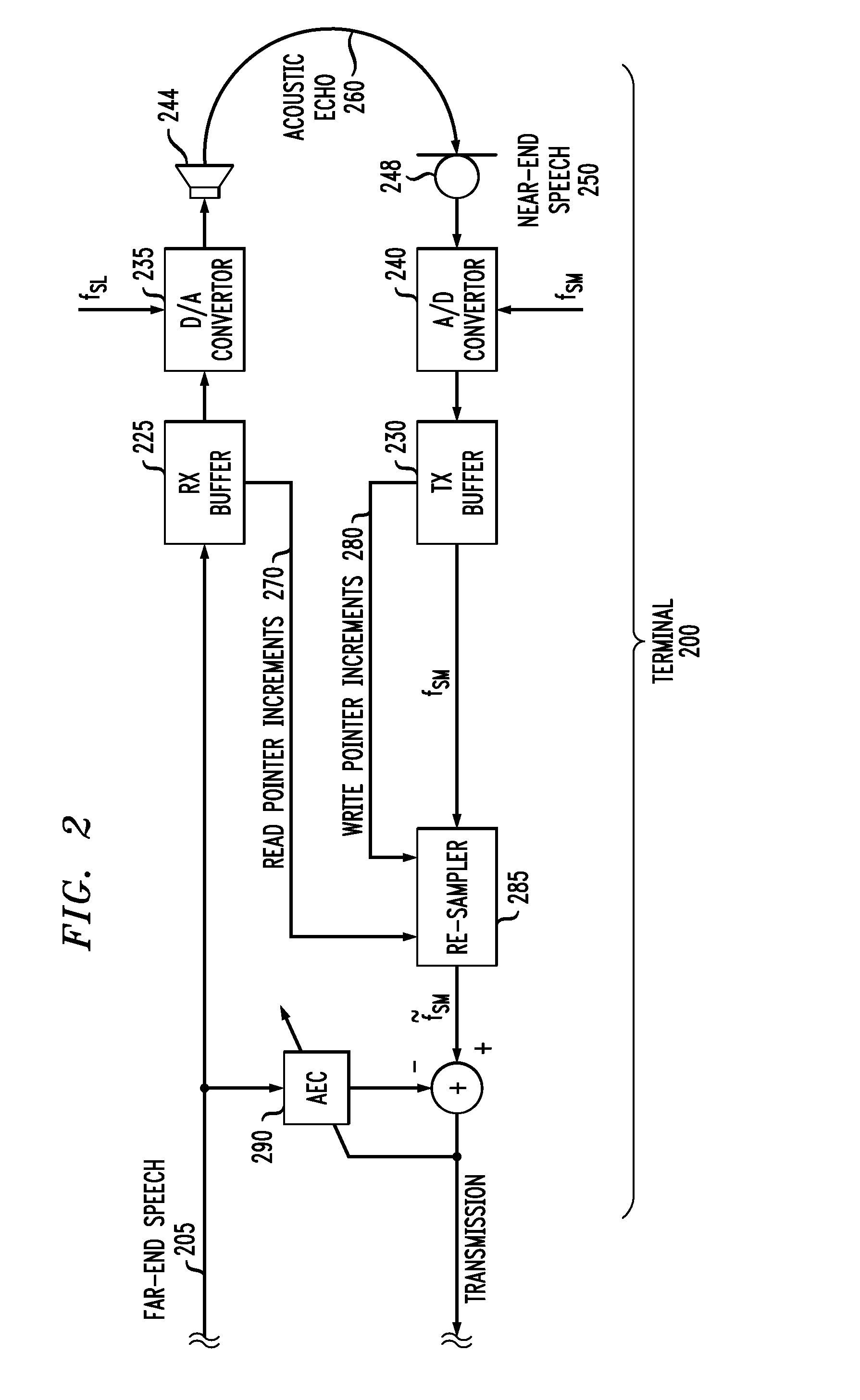
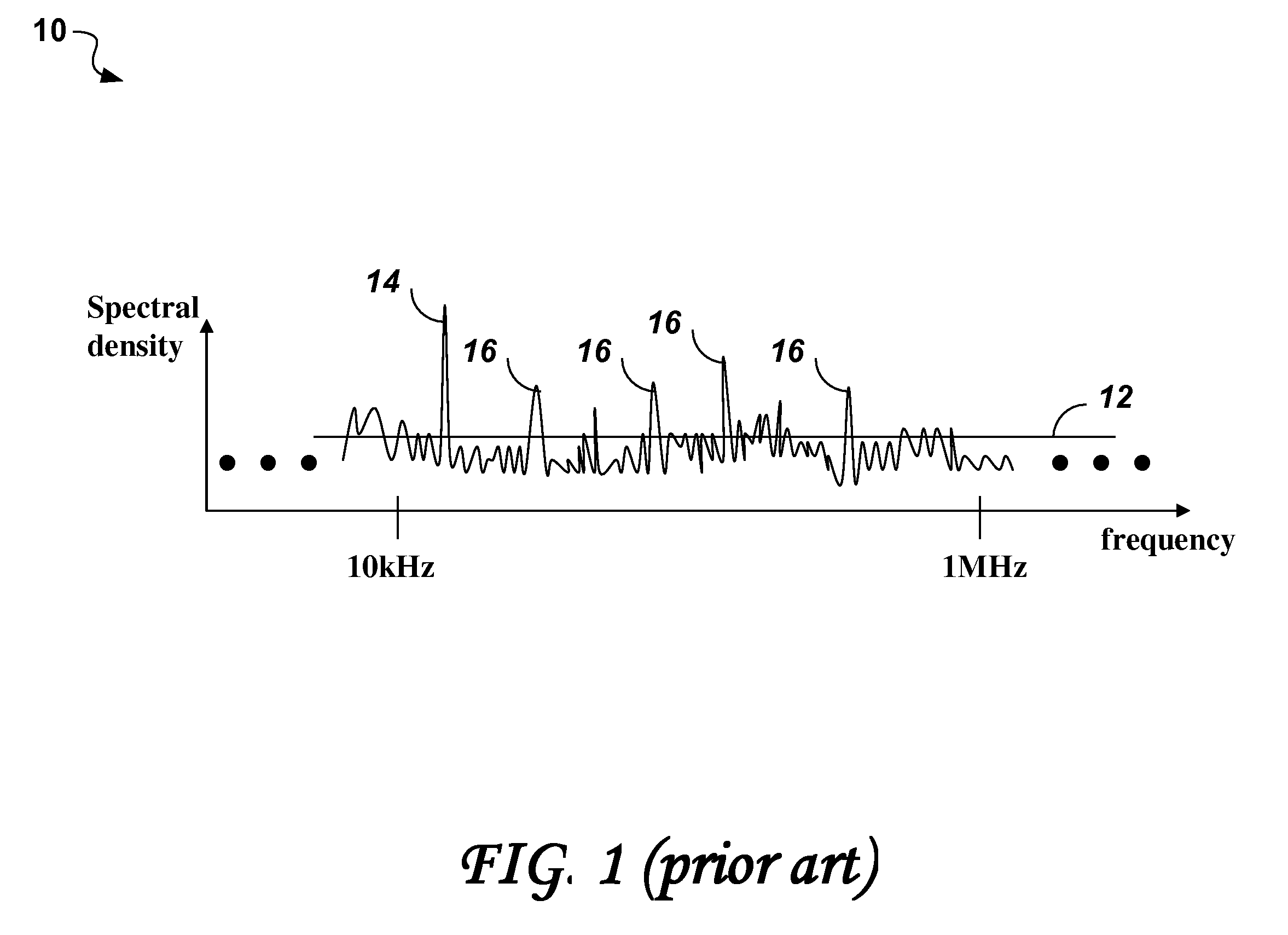
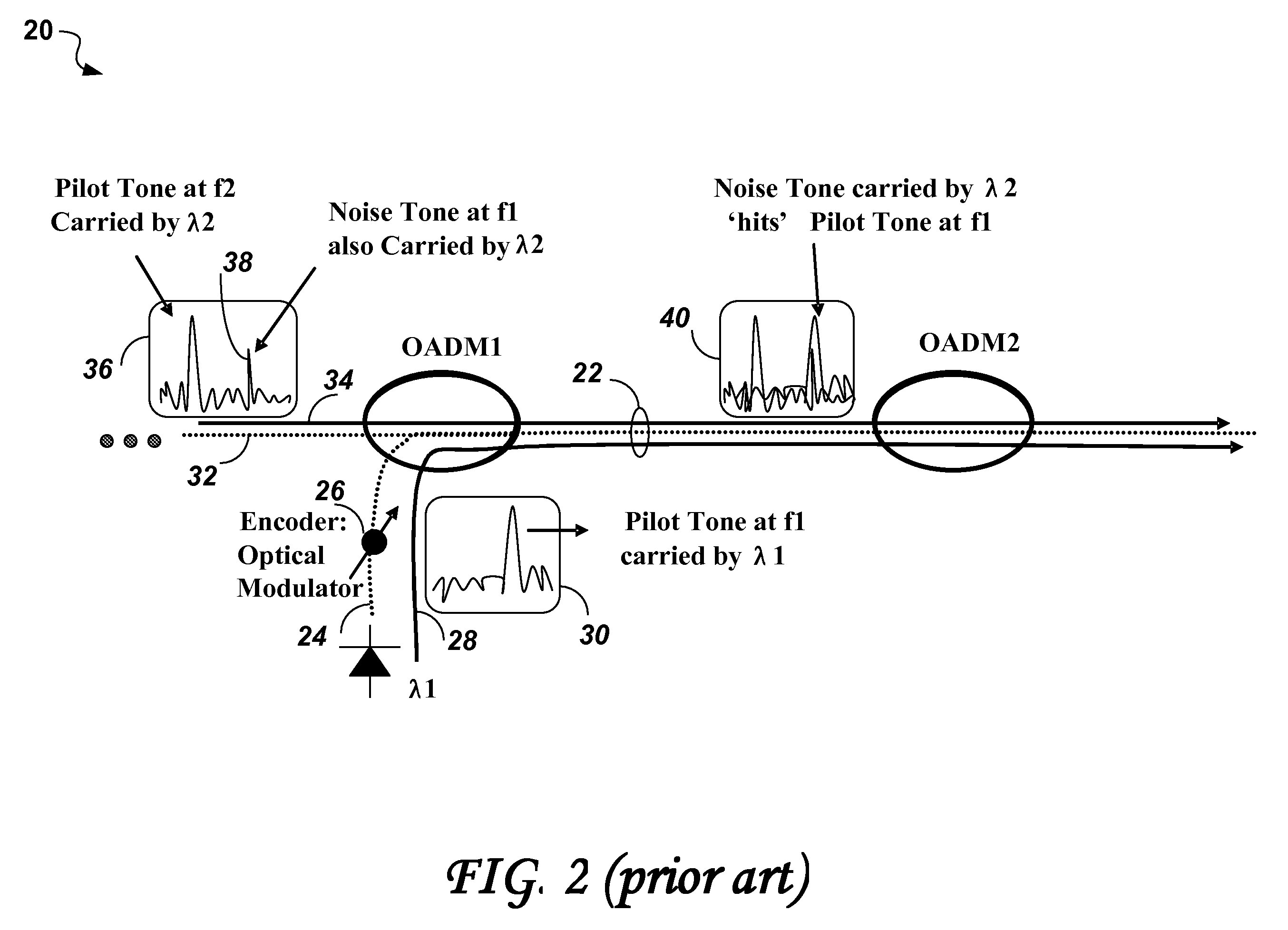
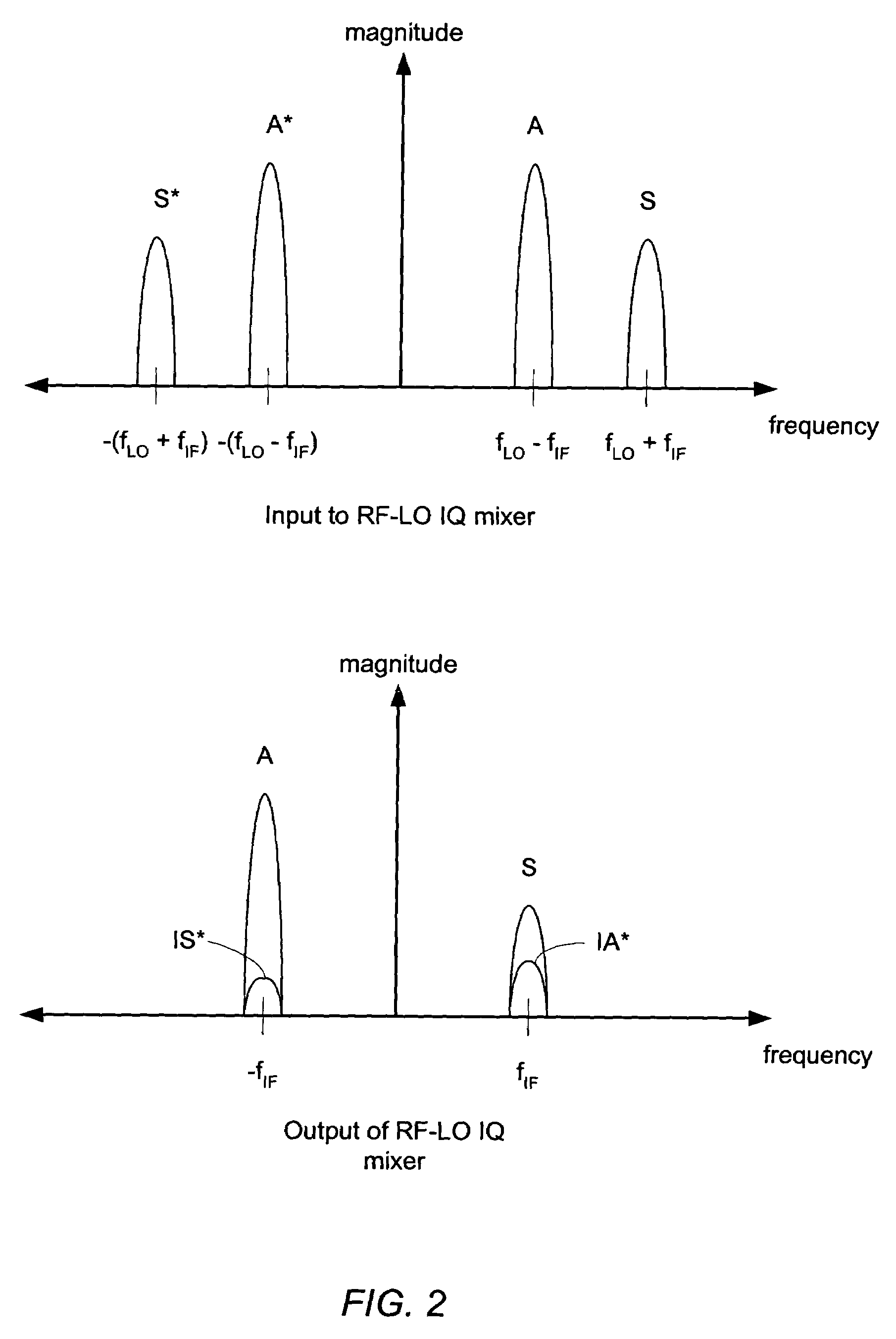Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
156 results about "Tone Frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tone, in acoustics, sound that can be recognized by its regularity of vibration. A simple tone has only one frequency, although its intensity may vary. A complex tone consists of two or more simple tones, called overtones. The tone of lowest frequency is called the fundamental; the others, overtones.
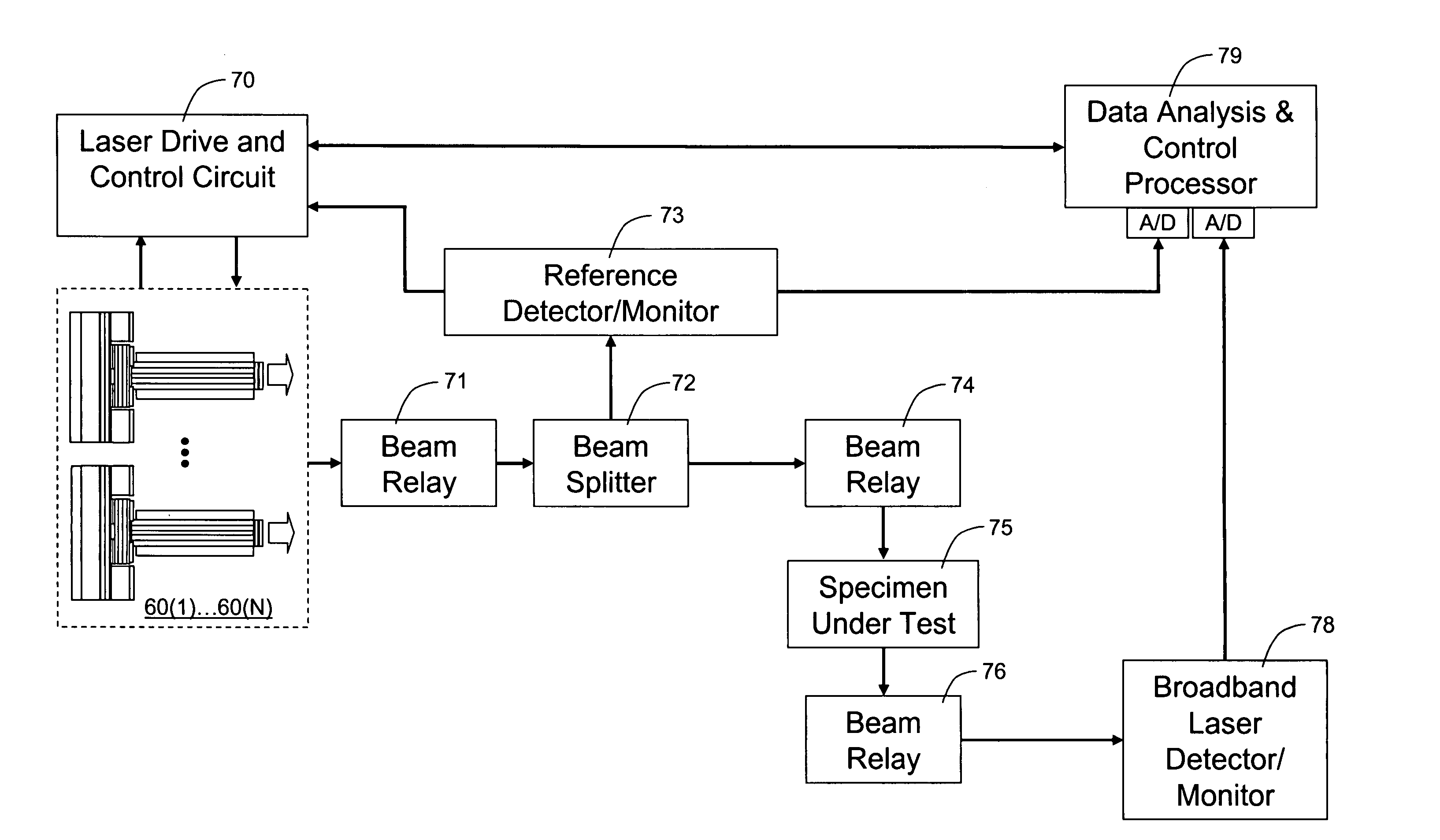
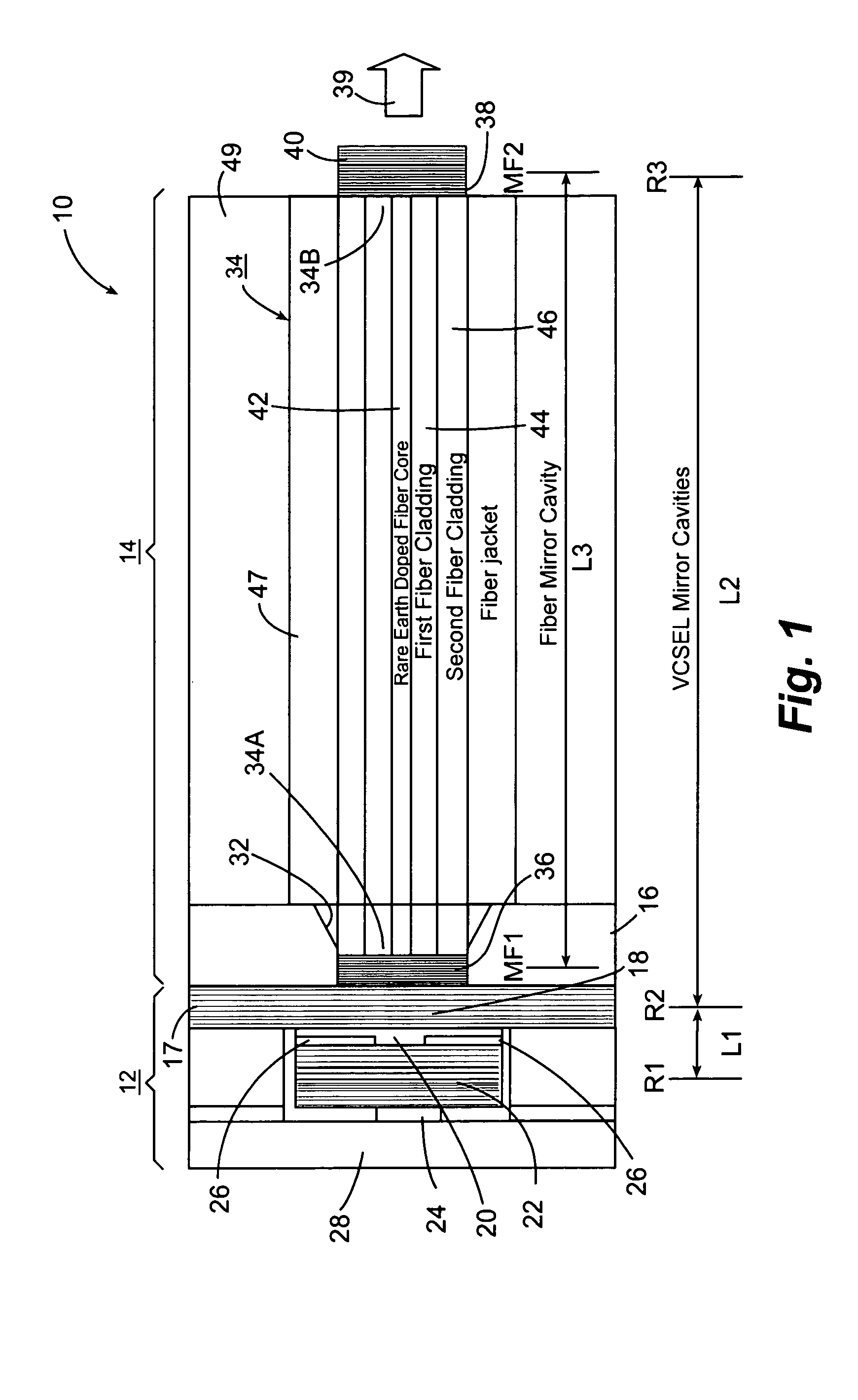
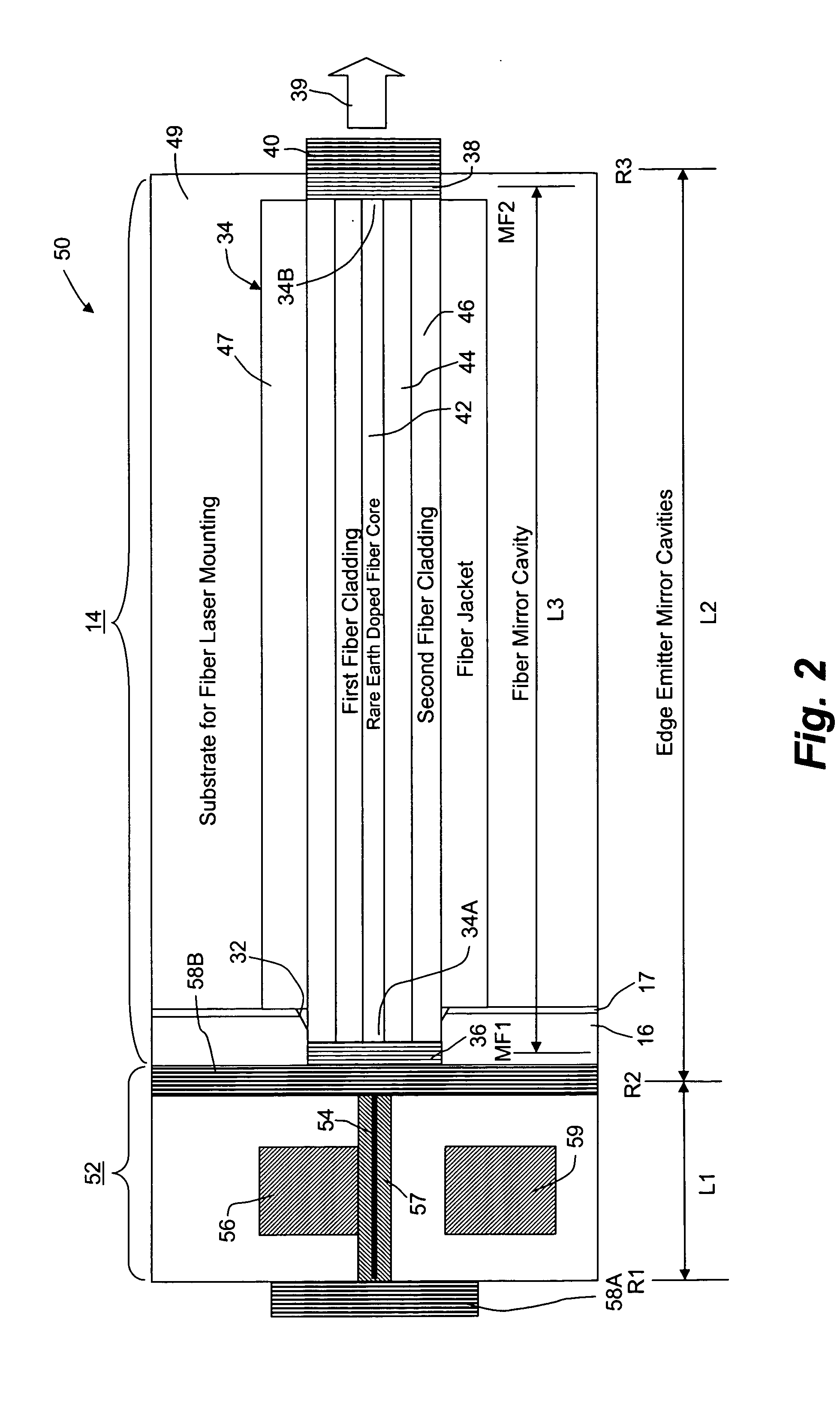
Optical spectroscopy apparatus and method for measurement of analyte concentrations or other such species in a specimen employing a semiconductor laser-pumped, small-cavity fiber laser
InactiveUS20050030540A1Improve absorption efficiencyShort physical path lengthMaterial analysis by optical meansLaser arrangementsSpectroscopyRare earth
An optical spectroscopy apparatus determines the concentration of analyte in a specimen that utilizes a single radiation source which is hybrid laser comprising a semiconductor pump laser and small-cavity rare earth fiber laser where laser cavities of both lasers are butt coupled or otherwise optically coupled to form a plurality of laser cavities that produce a plurality of emission wavelengths, one which may be the pump laser emission wavelength at the output of the fiber laser thereby forming a multi-wavelength combined output where the wavelengths substantially match distinguishing spectral characteristic features along at least a portion of a characteristic optical spectrum of the analyte under examination. In lieu of complex data analysis of these wavelengths to determine values representing the concentration of the analyte in an examined specimen, the semiconductor pump laser or lasers are modulated as a plurality of tone frequencies, where at least a first of the modulation frequencies is below the maximum frequency response of the fiber laser so that the first modulation effectively modulates the pump emission wavelength and a first emission wavelength of the fiber laser in the hybrid laser combined output, and at least a second of modulation frequencies is above the maximum frequency response of the fiber laser so that the second modulation effectively modulates the pump emission wavelength but not the first emission wavelength of the fiber laser in the hybrid laser combined output. Further, one or more additional modulation frequencies may be applied to the pump laser which are intermediate of the first and second modulation frequencies where it is at least responsive to at least one further emission wavelength of the fiber laser and also provided in the hybrid laser combined output.
Owner:THORNTON ROBERT L
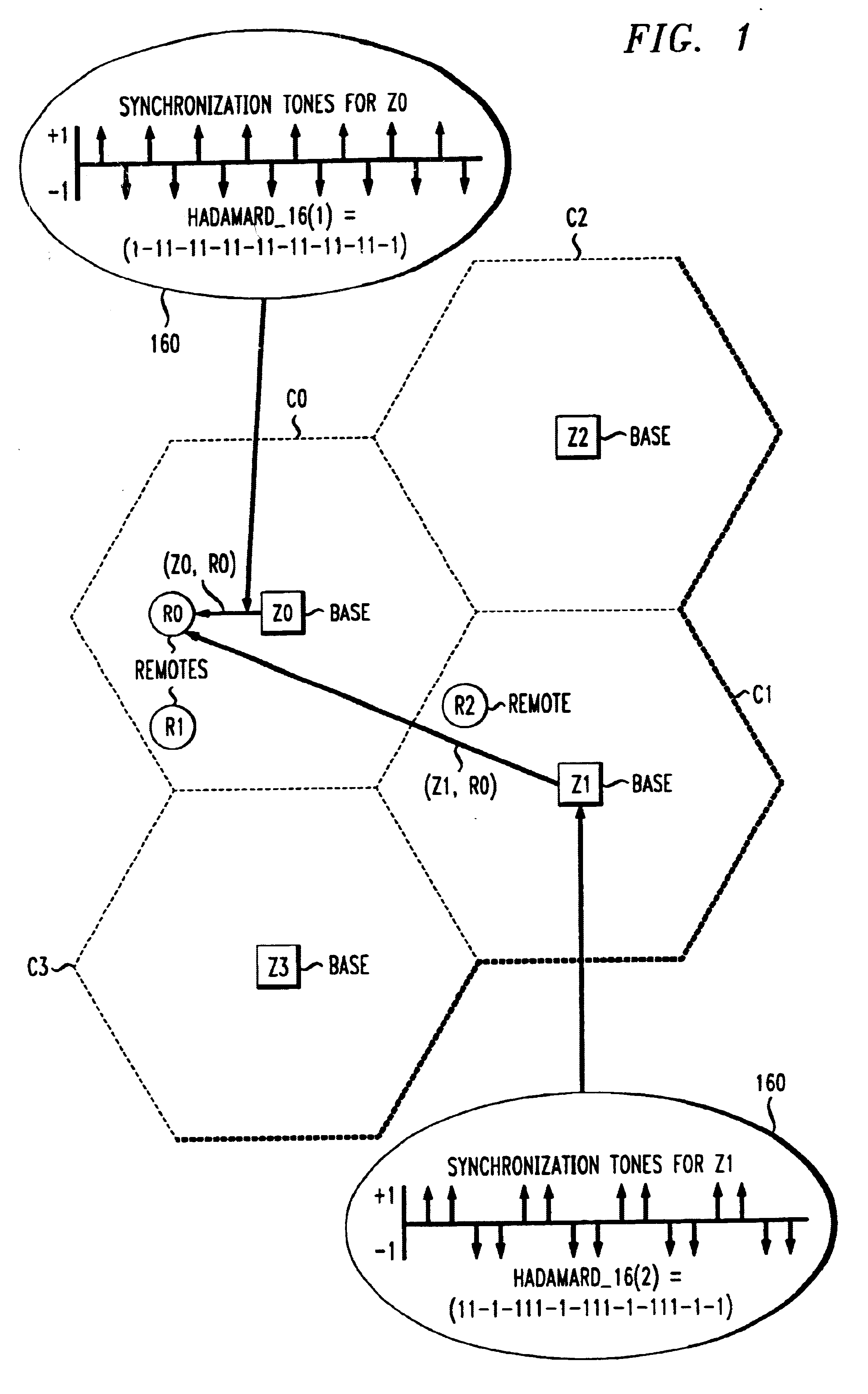
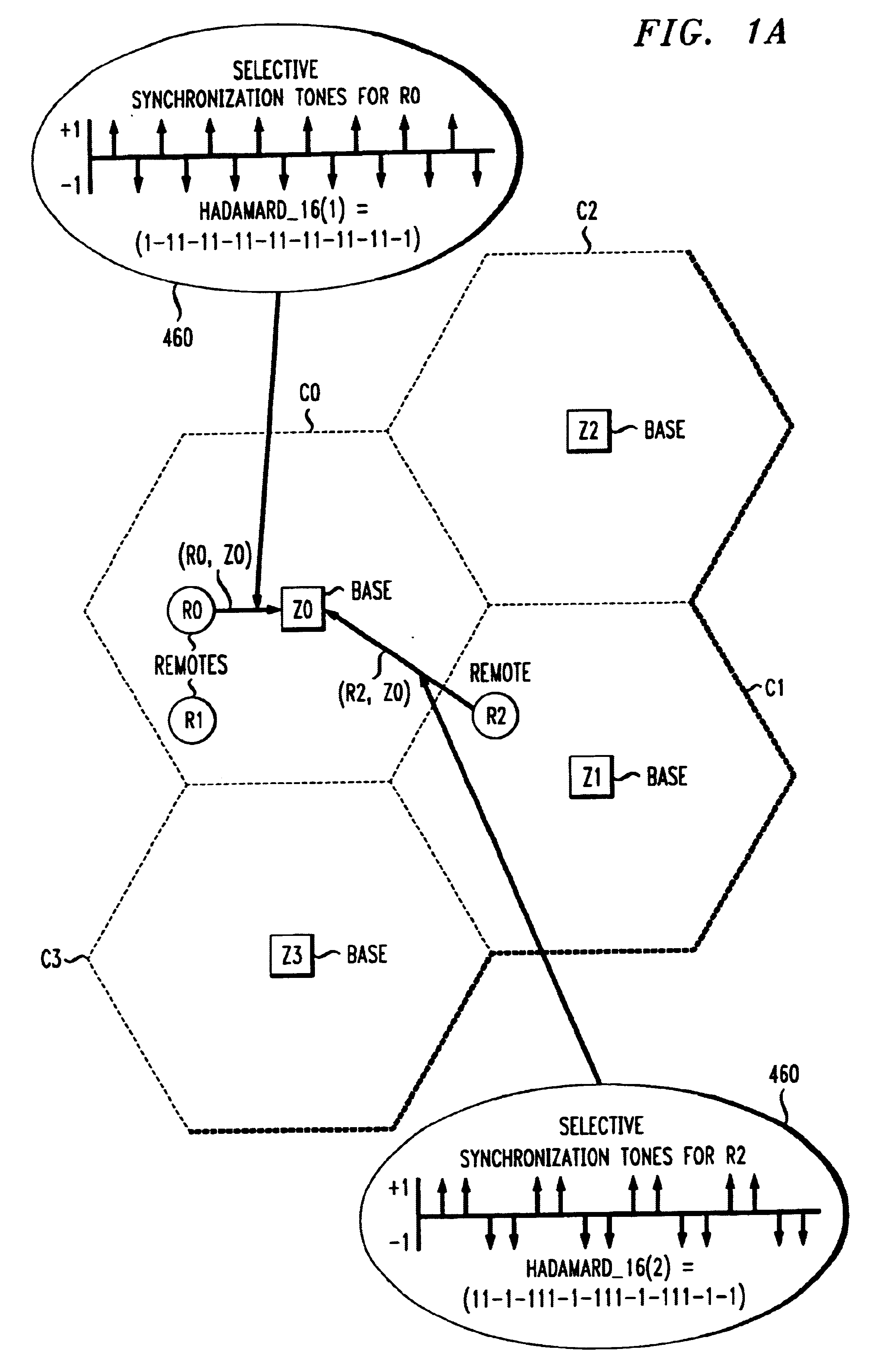
Synchronization preamble method for OFDM waveforms in a communications system
InactiveUS6643281B1Synchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexTraffic signalCommunications system
A highly bandwidth-efficient communications method is disclosed that enables remote stations to synchronize in time and frequency to their serving base station. The invention enables a base station and its remote stations in a cell to synchronize in a noisy environment where signals interfere from other base stations and remote stations in other cells. The base station forms a forward synchronization burst that includes a plurality of tone frequencies arranged in a distinctive orthogonal frequency division multiplexed pattern unique to the base station. The unique pattern enables a remote station to distinguish the base station's bursts from other signals present in a crowded area. The distinctive orthogonal frequency division multiplexed pattern can be a Hadamard code pattern, for example. When the a base station has received a signal on a reverse link from a remote station, having significant interference, the base station selectively forms a request signal requesting the remote station to respond with a reverse synchronization burst that includes a plurality of tone frequencies arranged in the same distinctive orthogonal frequency division multiplexed pattern. The base station then transmits the forward synchronization burst and the request signal at a base station reference instant of time to the remote station. The reverse synchronization signals selectively occupy time slots in the transmission frame from the remote station to the base station, that would otherwise be occupied by channel control or traffic signals. Only when the base station requests the remote station to respond with a reverse synchronization burst, does this burst preempt the time slot from its other uses.
Owner:CLEARWIRE COMM +2
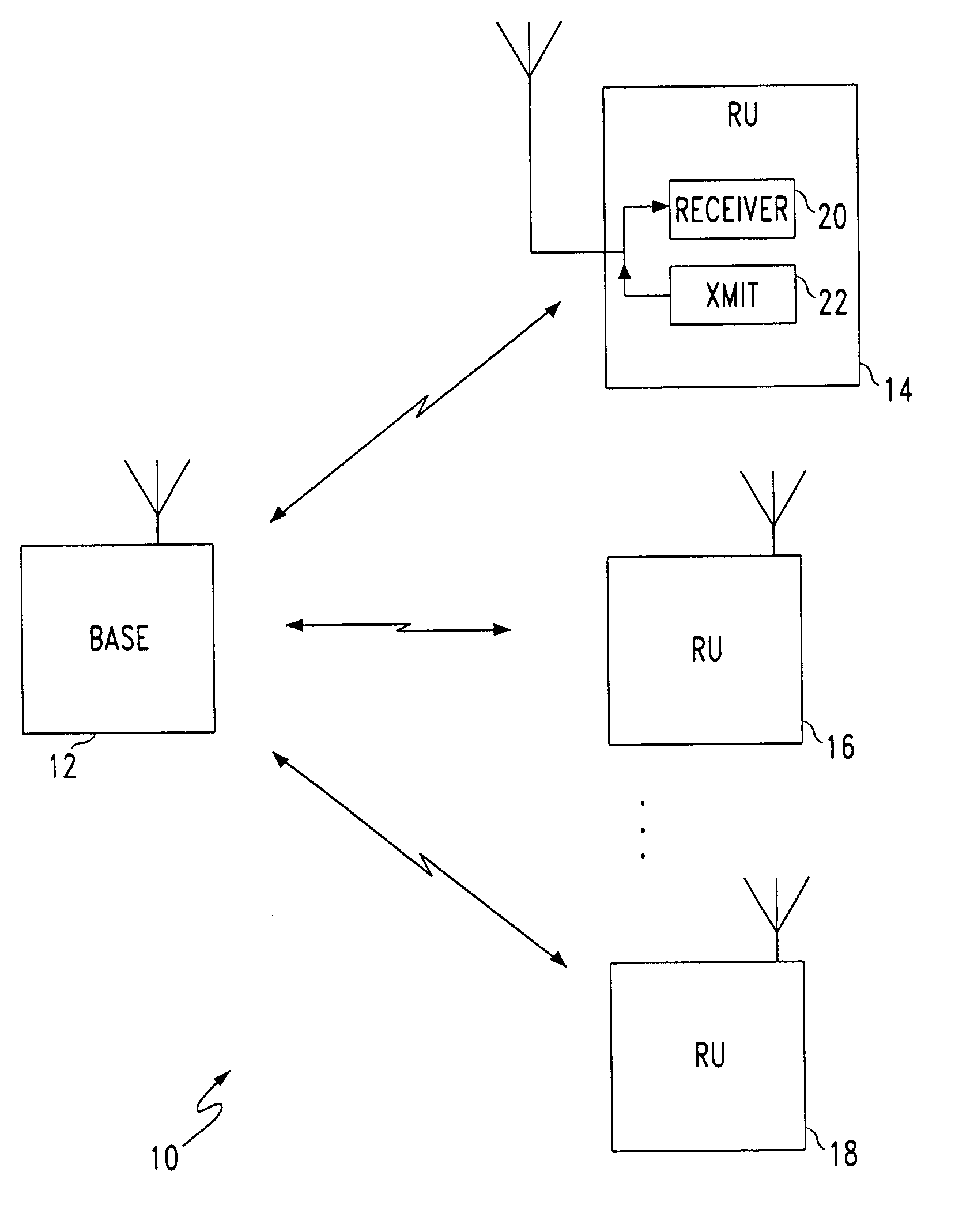
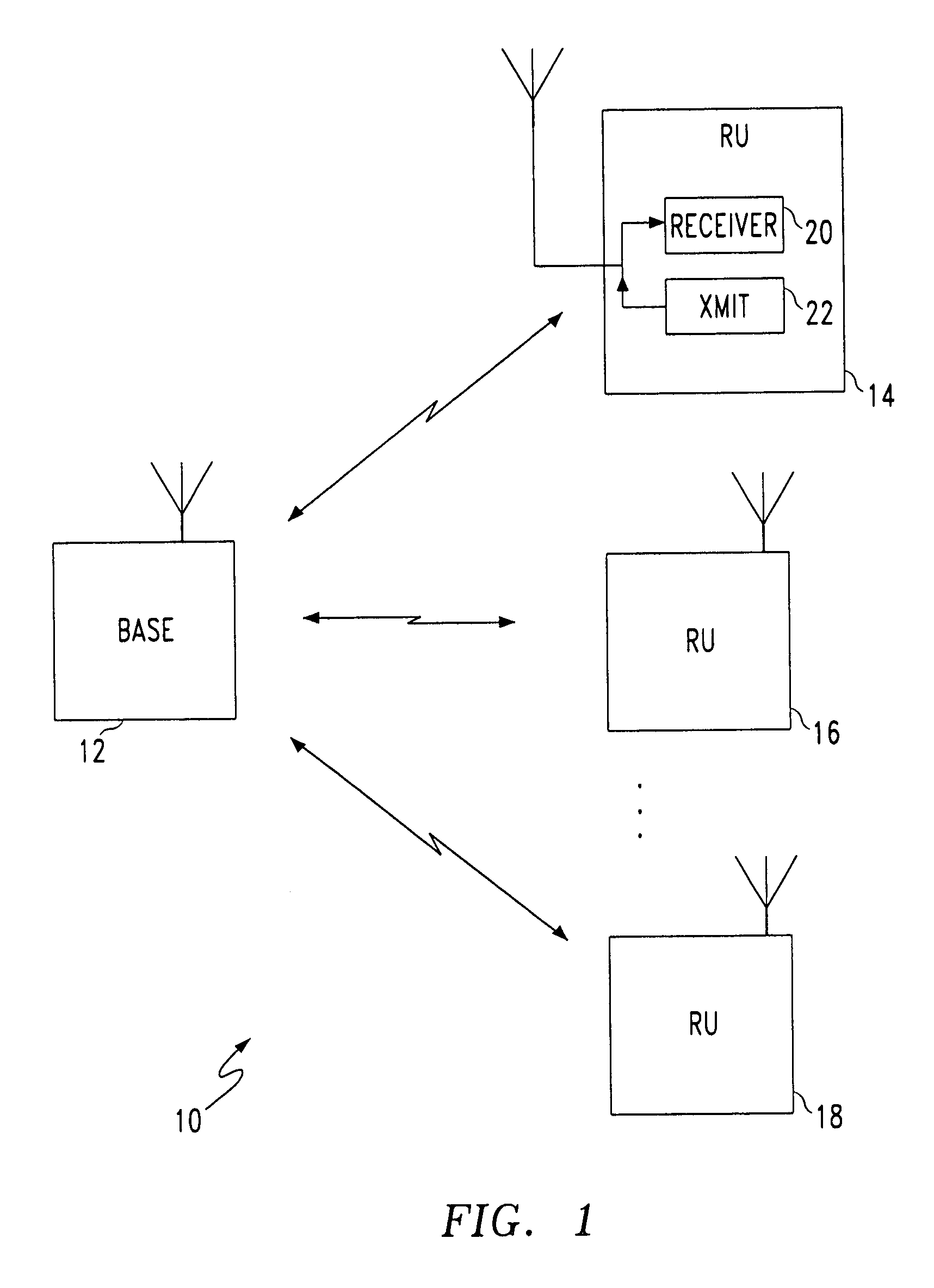
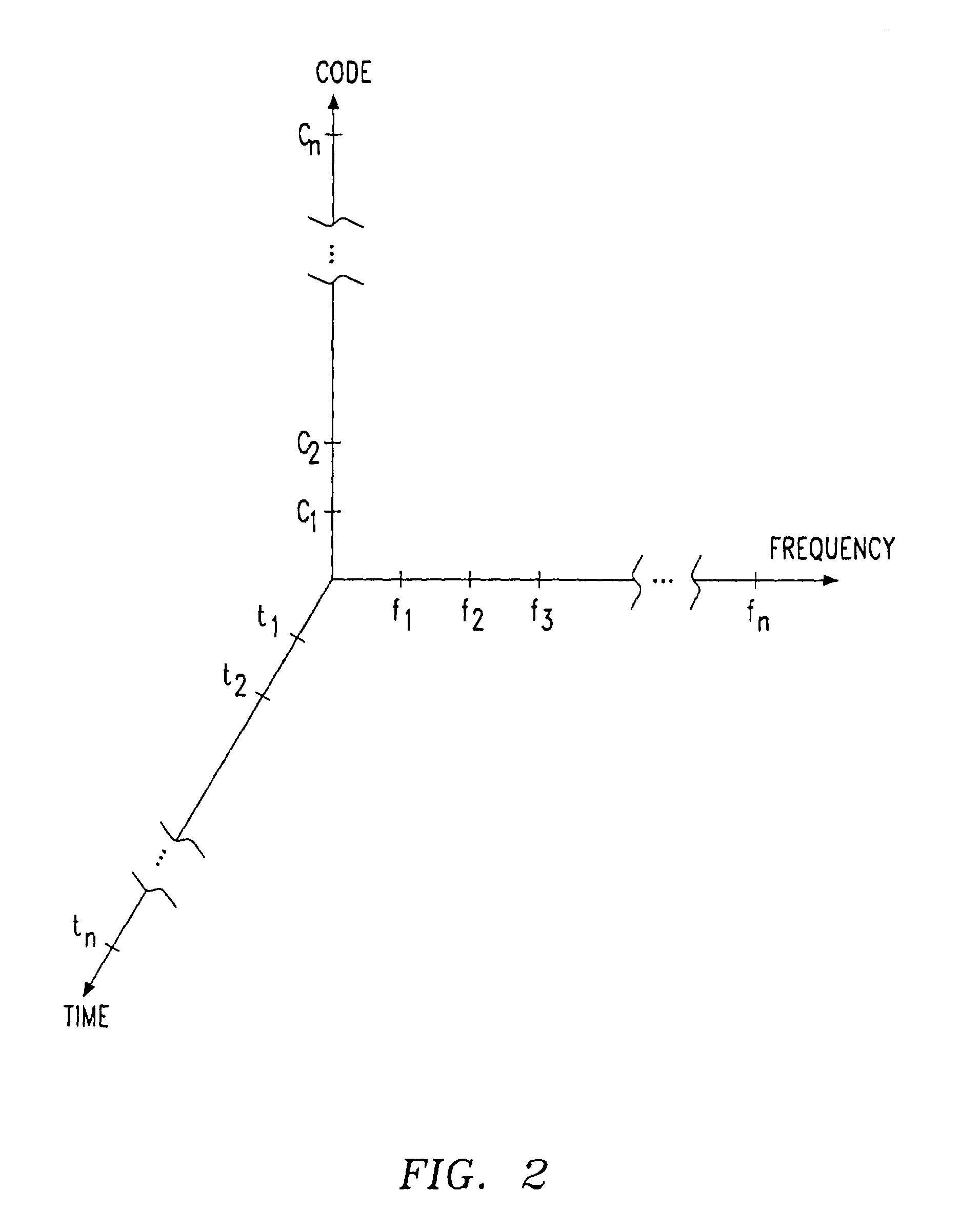
Collision-free multiple access reservation scheme for multi-tone modulation links
InactiveUS6967937B1Network traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionCommunications systemOfdm communication system
A method is provided for multiple remote units (RU)s to efficiently utilize resources on a shared OFDM high speed data channel without collisions. A collision occurs when two or more RUs transmit on the same frequency at the same time. The method defines two distinct states for accessing the channel. These are the Arbitration state and the Data Transfer state. A base station transmits a flag on the downlink to notify the RUs of which state is in effect. RUs having a data message notify the base station by transmitting a frequency tone, which acts as a request to transmit data, during the arbitration state. The tone frequencies are frequency spaced to be mutually orthogonal, so that the base station can receive all the uplink requests simultaneously. Upon receiving the uplink request signals, the base station establishes the data transfer state and orders the uplink data messages from the remote units is a non-interfering sequence. A system for preventing uplink data message collisions in an OFDM communications system is also provided.
Owner:AT&T WIRELESS SERVICES
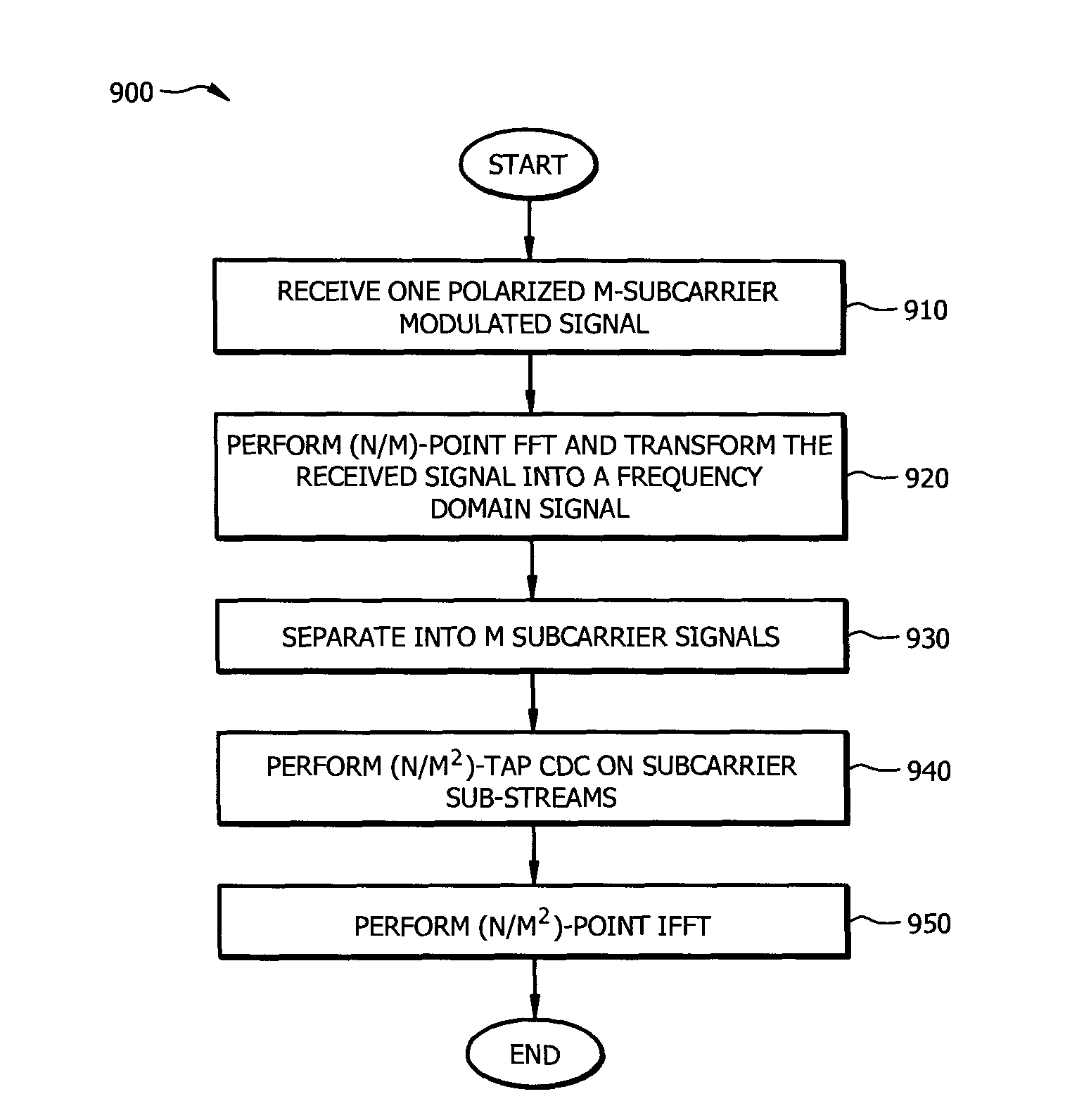
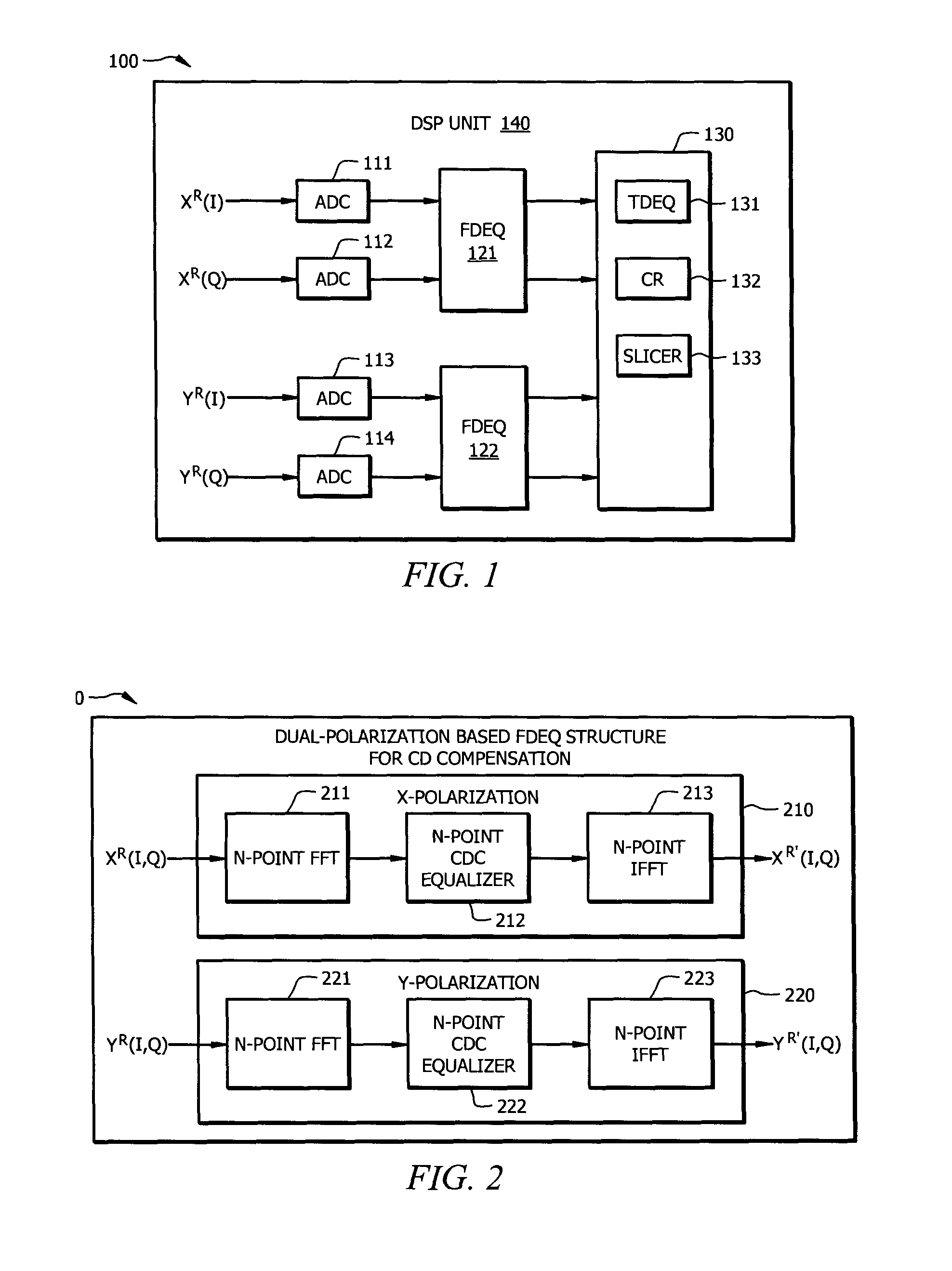
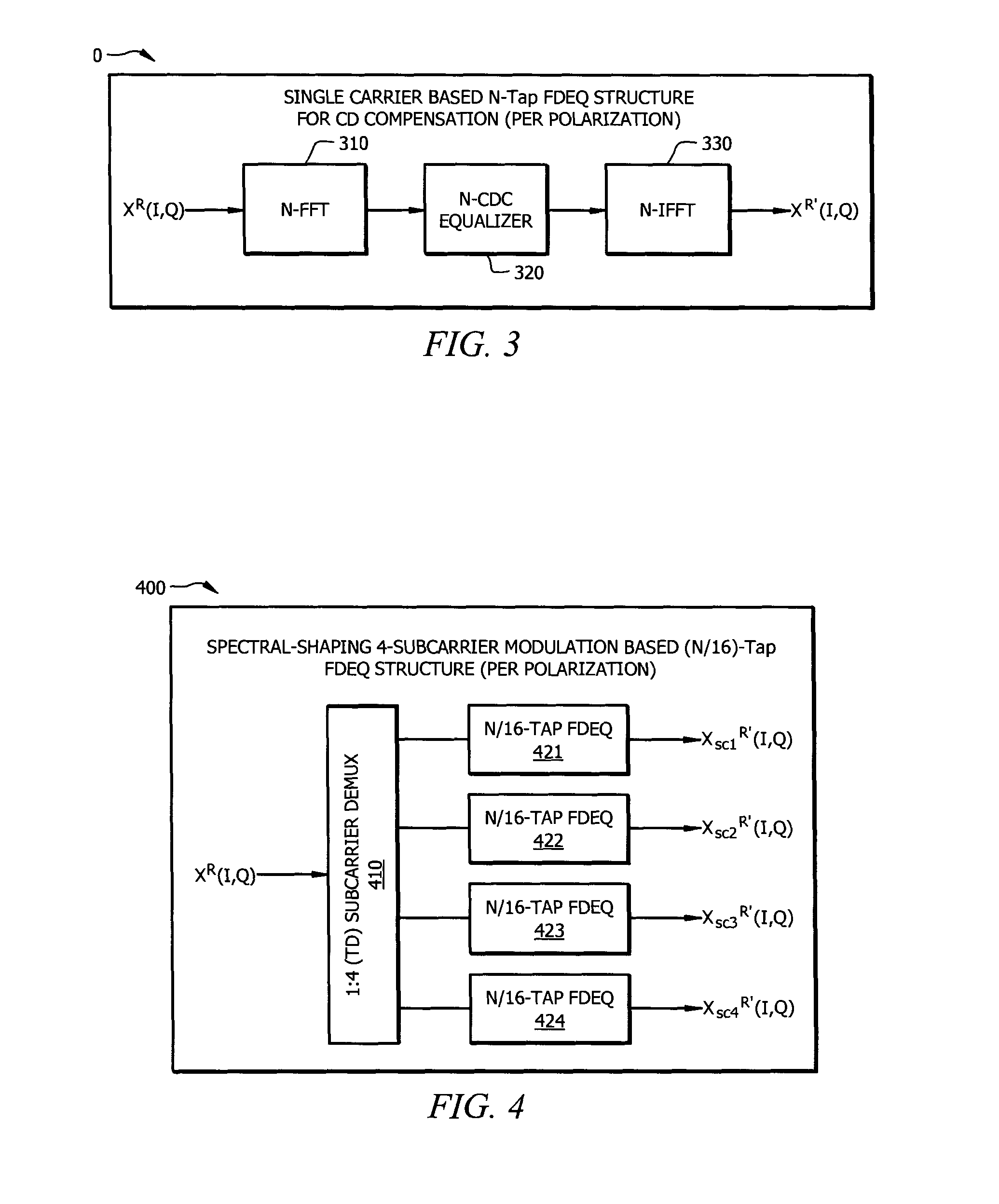
Resource-Efficient Digital Chromatic Dispersioin Compensation in Fiber Optical Communication Using Spectral-Shaping Subcarrier Modulation
ActiveUS20140099116A1Polarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberFrequency spectrum
An optical receiver comprising a frontend configured to receive an optical signal and convert the optical signal into a plurality of digital electrical signals comprising a plurality of spectrally shaped subcarrier signals carrying symbol mapped data information, and a digital signal processor (DSP) unit coupled to the frontend and configured to receive the digital signals from the frontend, demulitplex the digital signals into the subcarrier signals, and compensate chromatic dispersion (CD) for each of the subcarrier signals by applying an equalizer, wherein each of the subcarrier signals is associated with a unique tone frequency and a unique spectral shape. Also disclosed is an optical transmitter comprising a digital signal processor (DSP) unit configured to map data symbols onto a plurality of electrical subcarrier signals that are non-overlapping and spectrally shaped in a frequency domain.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
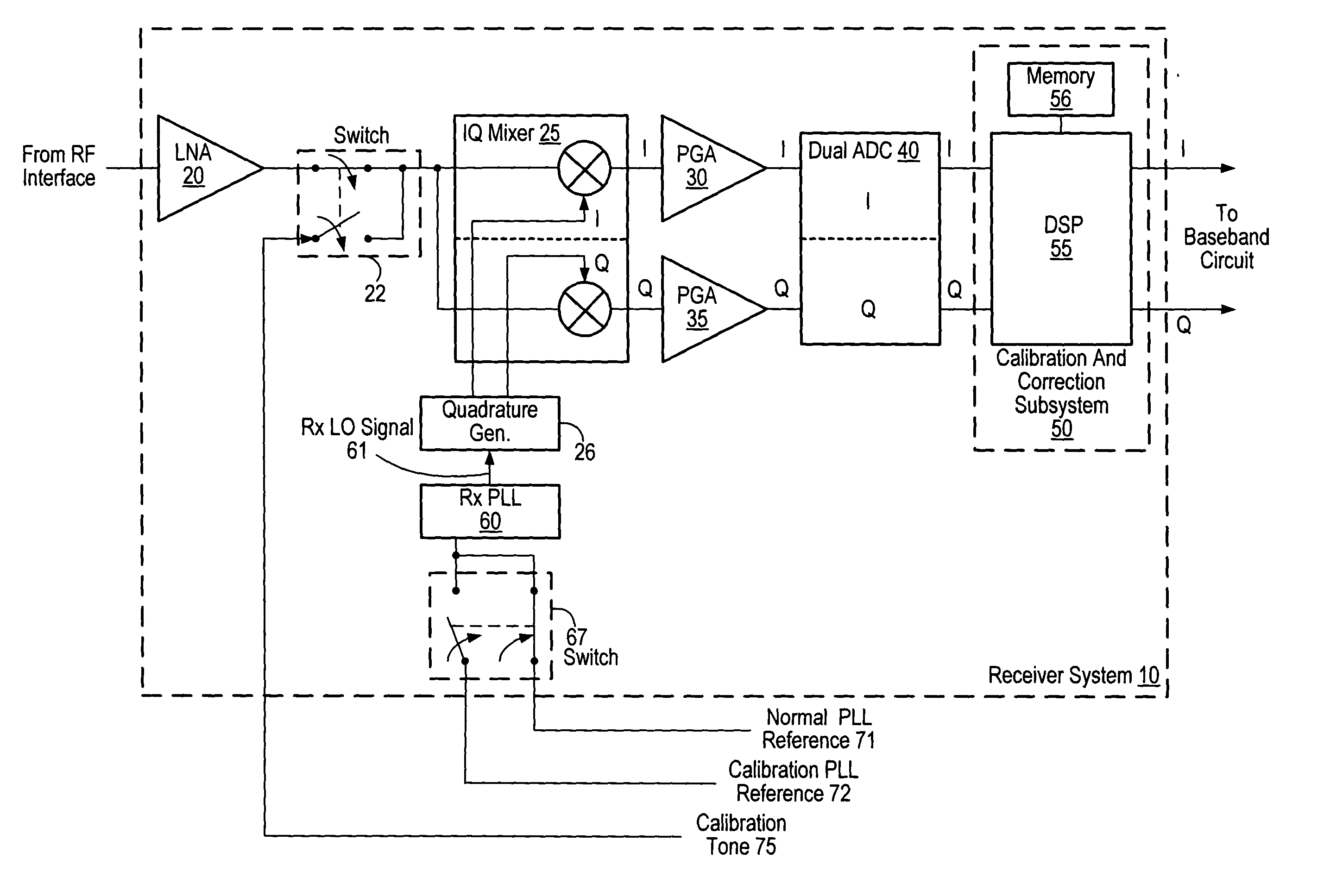
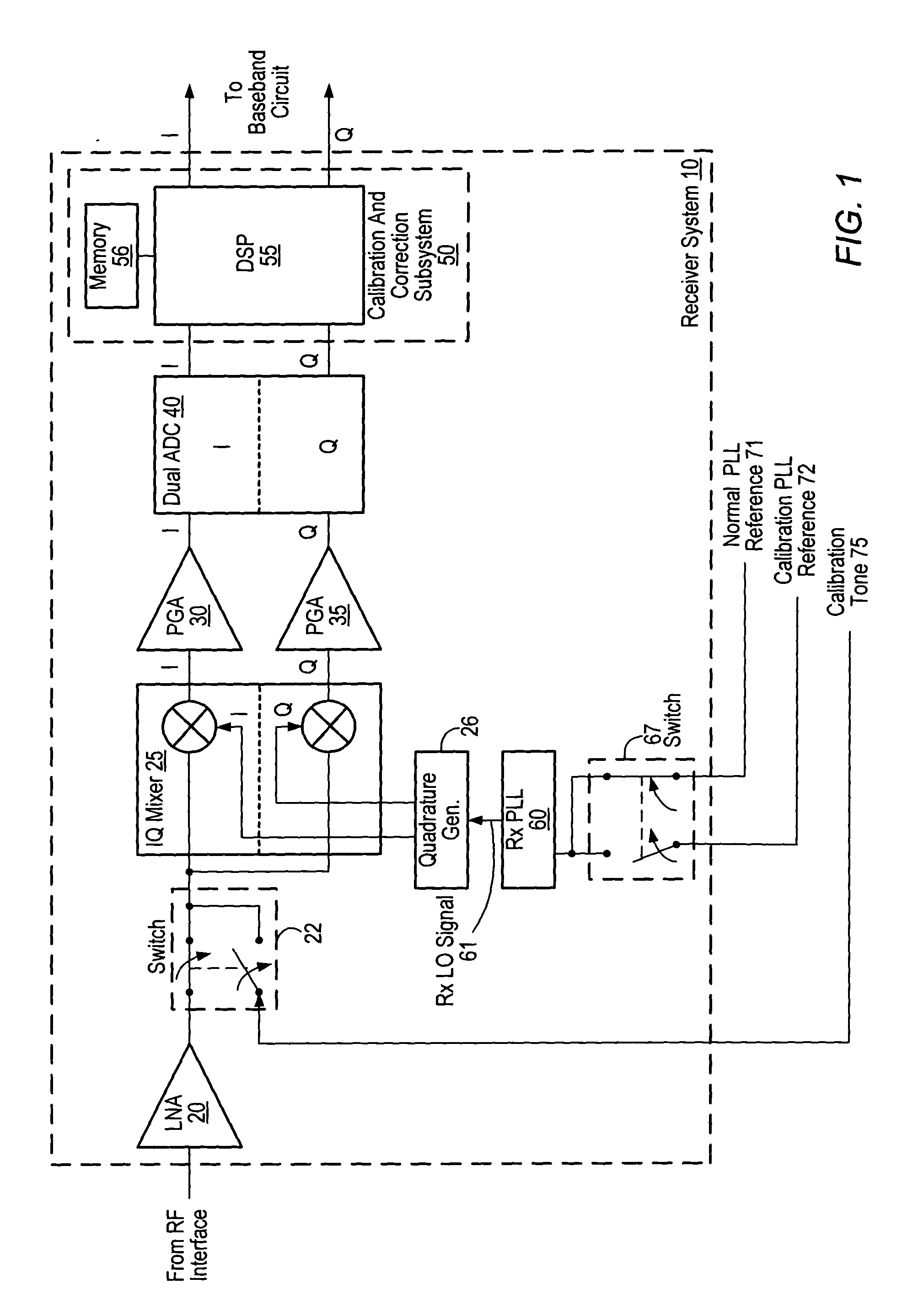
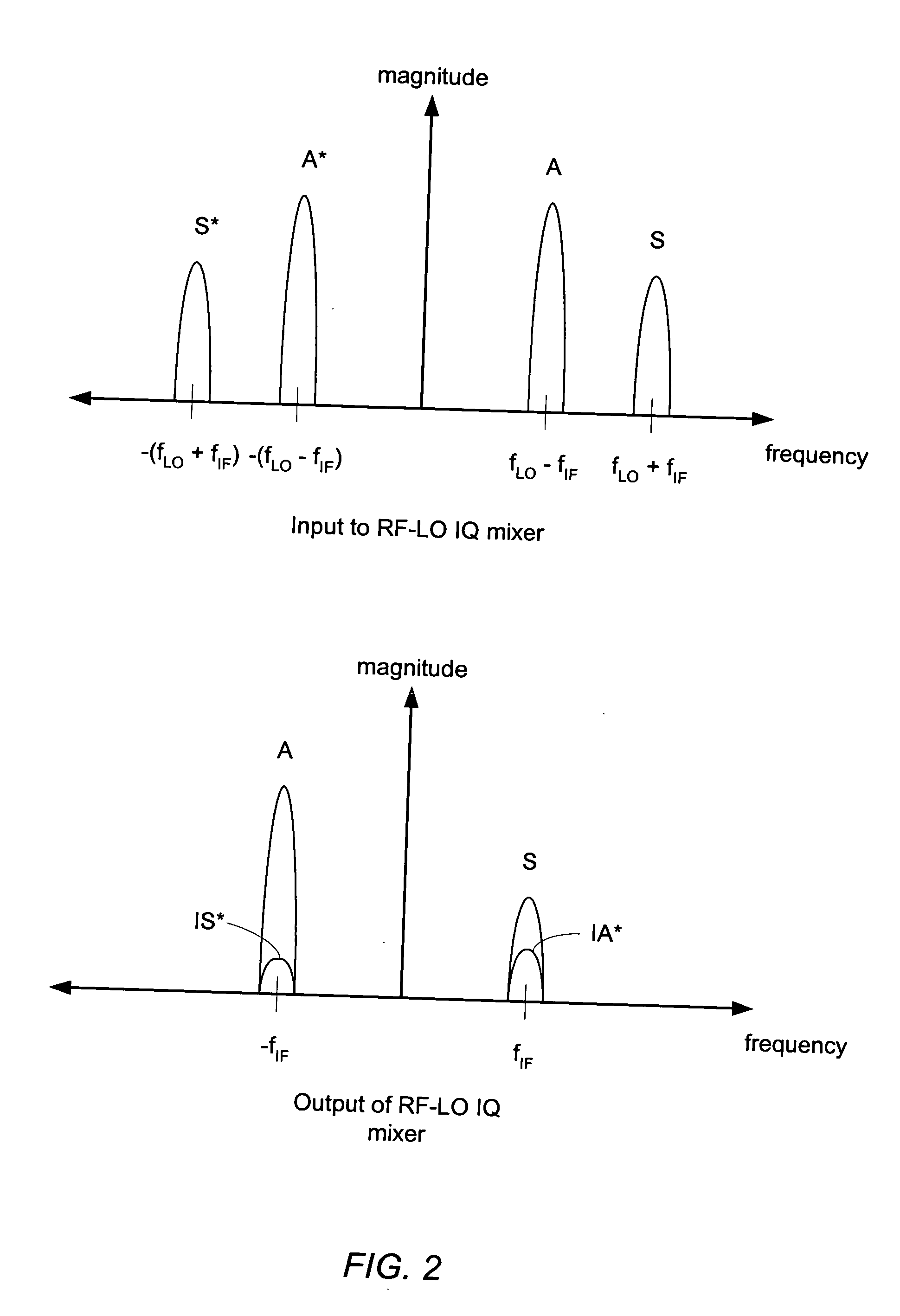
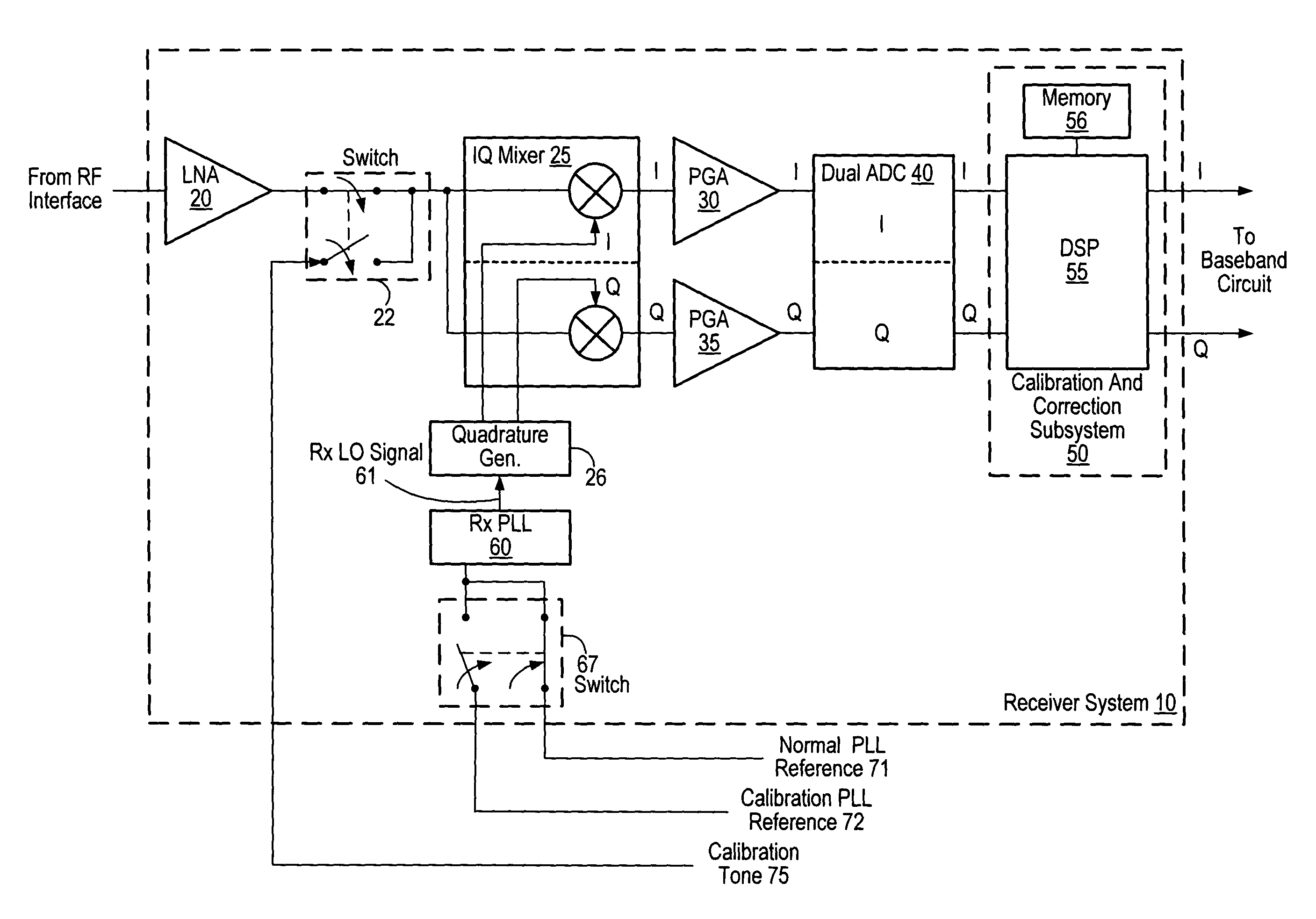
Receiver including an oscillation circuit for generating an image rejection calibration tone
ActiveUS20050069056A1Receivers monitoringPulse automatic controlLocal oscillator signalQuadrature mixer
A receiver circuit includes an oscillator circuit configured to generate a calibration tone and a phase locked loop (PLL) reference signal. An output frequency of the VCO may be divided by respective amounts to derive a desired calibration tone frequency and a desired PLL reference signal frequency. In addition to the oscillator circuit, the receiver circuit may further include a phase locked circuit configured to generate a PLL output signal that is phase locked in relation to the PLL reference signal. During a calibration mode, a quadrature generator may be used to generate quadrature mixer local oscillator signals dependent upon the PLL output signal, and an in-phase / quadrature mixer may be used to mix the calibration tone with the quadrature mixer LO signals.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Humming computer music searching method based on longest matching subsequence algorithm
ActiveCN102521281AImprove search efficiencyHigh speedSpeech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsHumTone Frequency
The invention discloses a humming computer music searching method based on longest matching subsequence algorithm, which comprises the following steps of (1) fundamental tone frequency extraction, (2) music characteristic database construction, (3) characteristic expression achieving and (4) searching matching. The method has the advantages of improving integral speed of similarity calculation, improving searching efficiency of a searching engine, constructing an accurate music searching platform for karaoke, a network engine based on content search and a multifunctional intelligent mobile terminal platform and being capable of being widely used in fields of relative plugs of the network searching engine and the like. The method for music characteristic extraction, music characteristic expression and similarity accurate calculation can conduct accurate calculation on a humming searching system, enables music search to be accurate, slight and happy, and has strong practical value and reality meaning.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
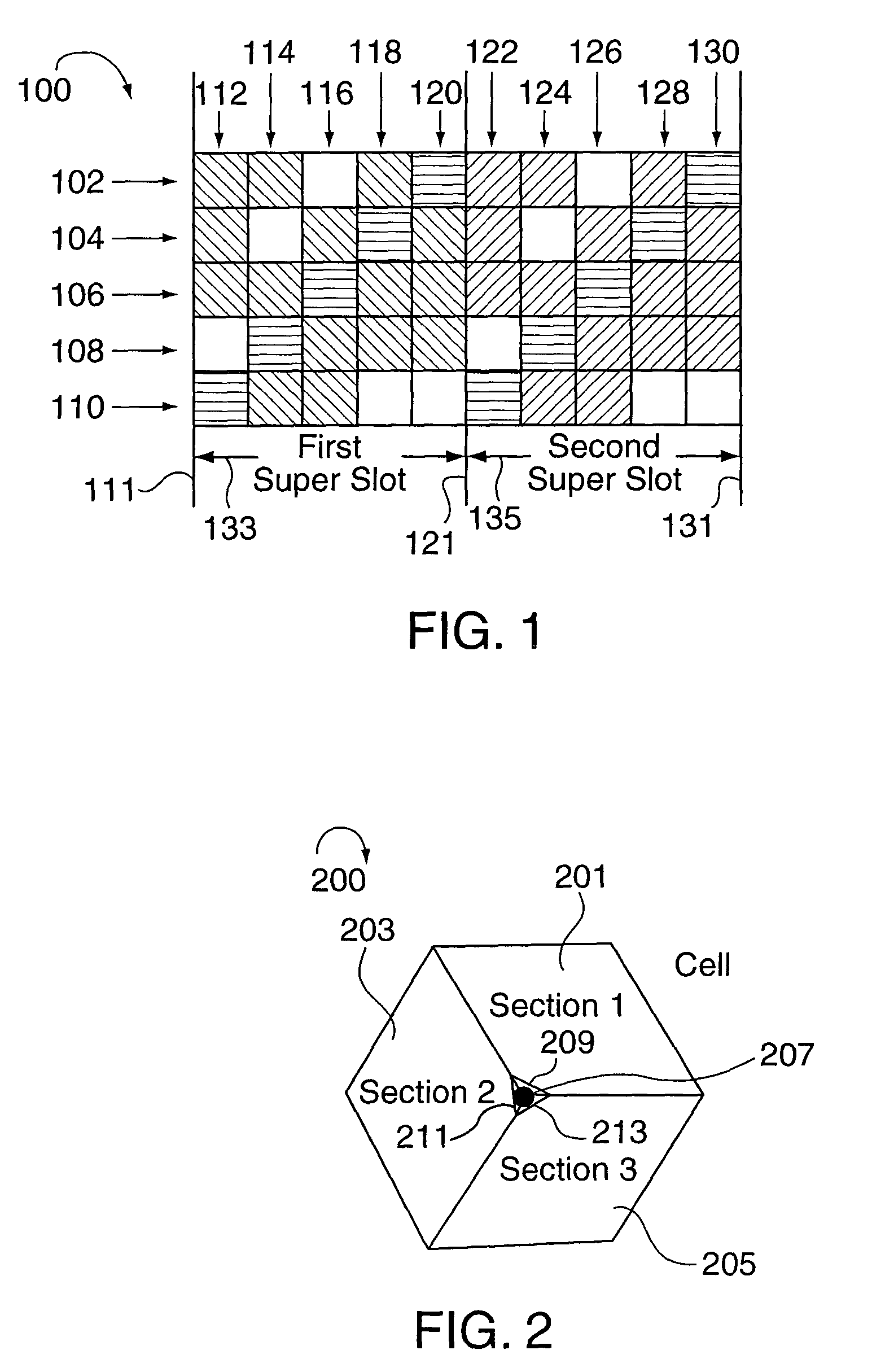
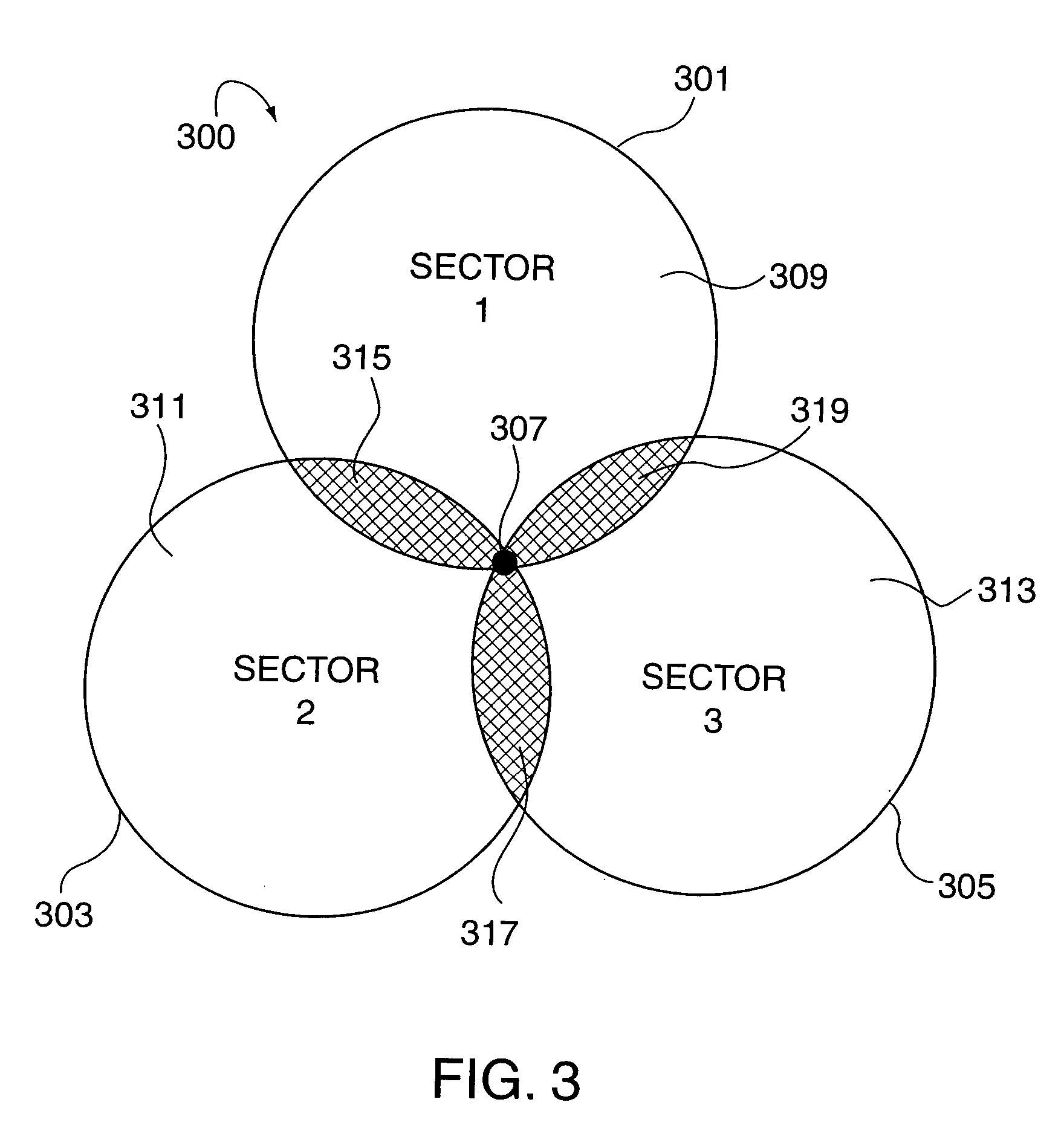
Multiple access wireless communications system using a multisector configuration
InactiveUS7388845B2Improve and optimize system performanceImprove throughputPower managementEnergy efficient ICTCommunications systemComputer terminal
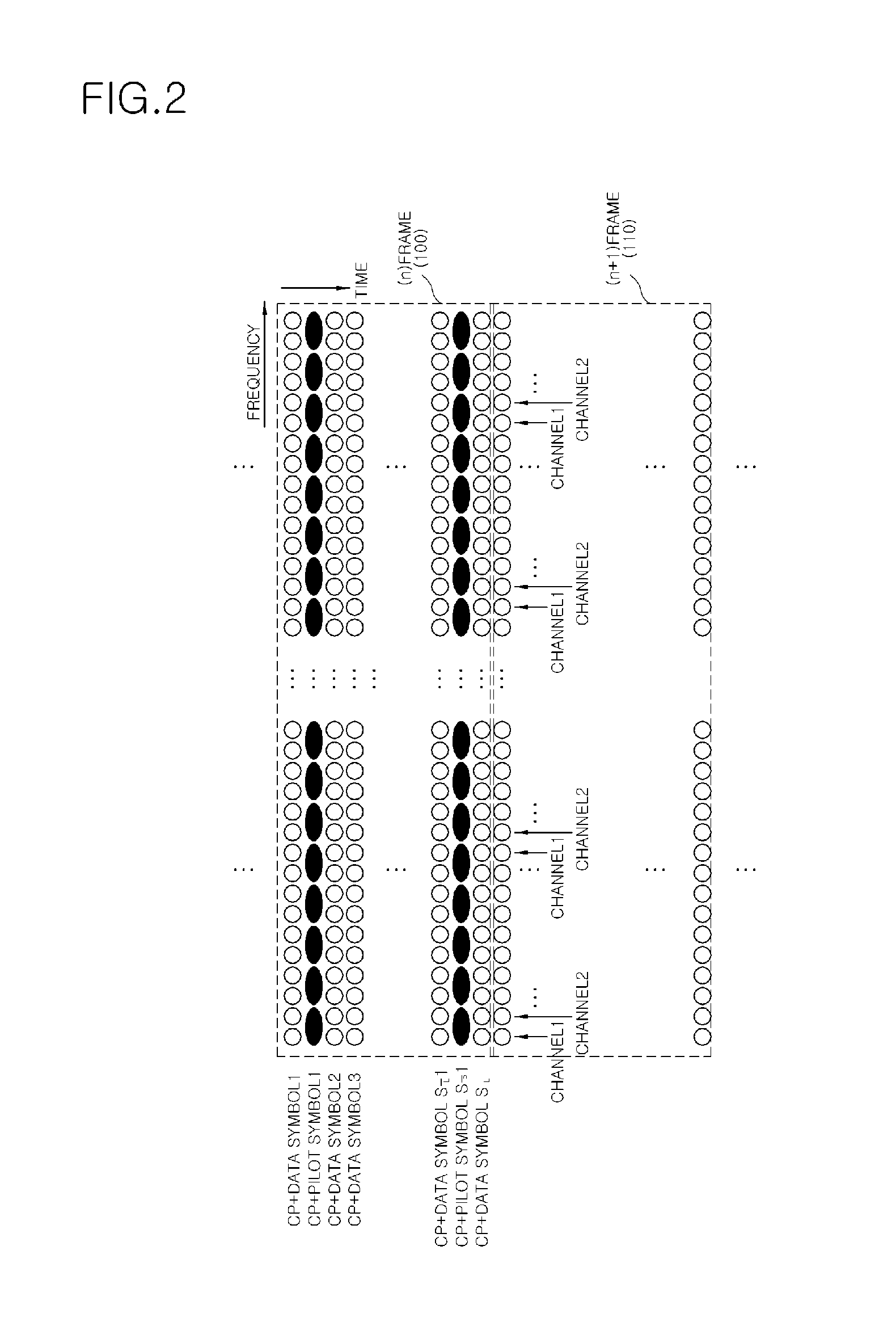
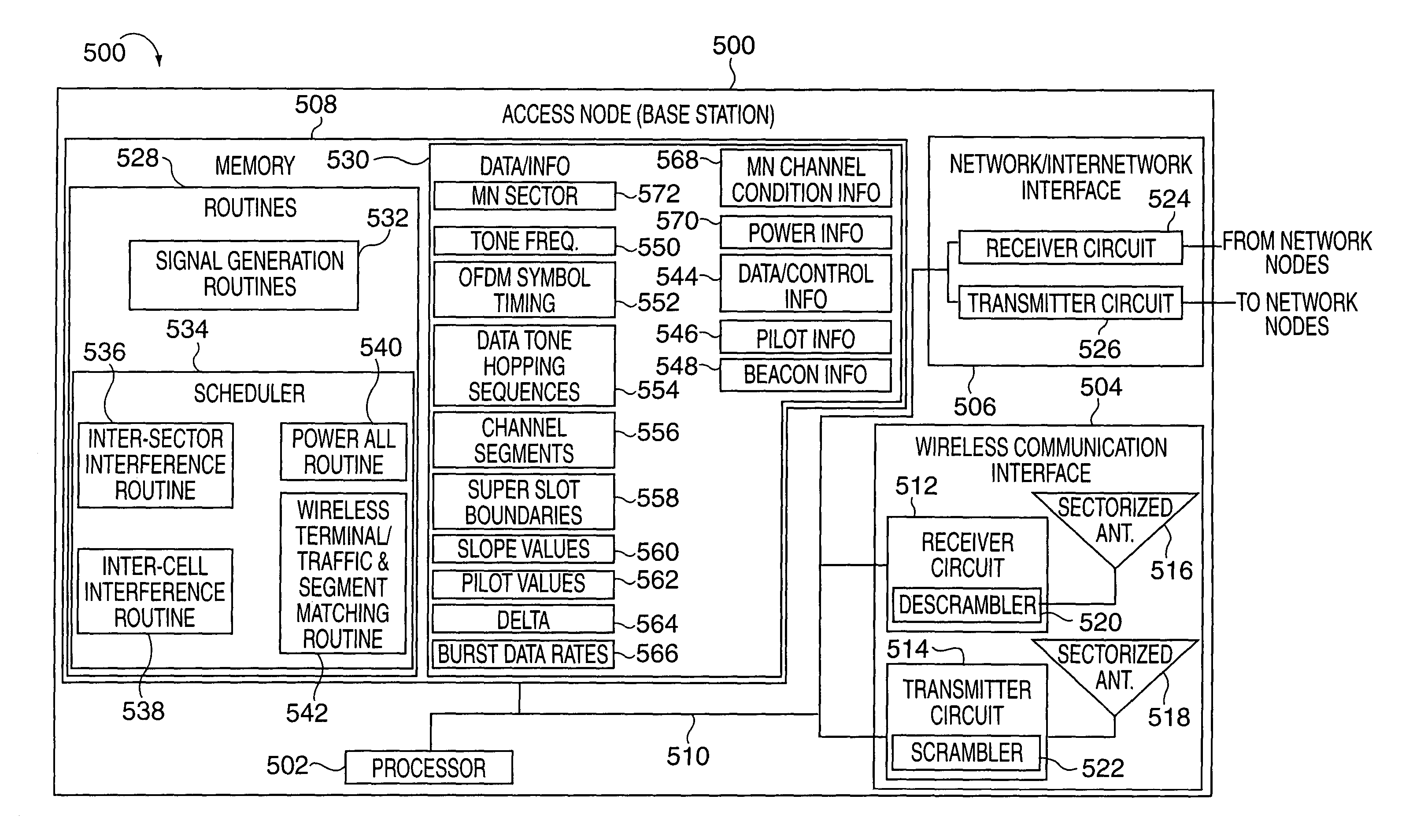
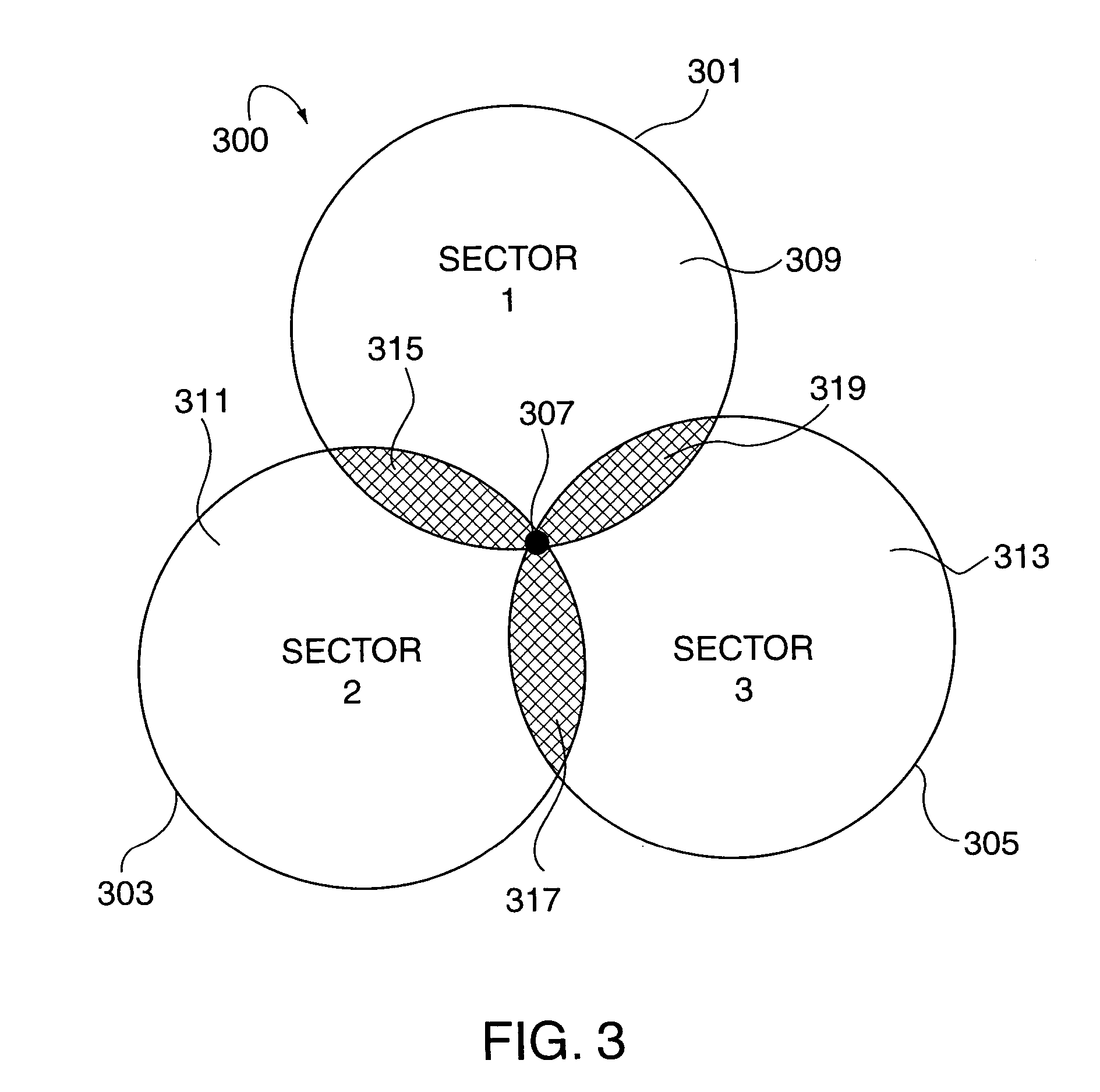
Power control methods and apparatus for use in a sectorized cell of an OFDM communications system are described. Each sector of a cell uses the same frequencies and transmission times and is synchronized with the other sectors in the cell in terms of tone frequencies used at any given time and symbol transmission times. Tones are allocated to channels in each cell in the same manner so that each channel in a sector has a corresponding channel in another sector. Power differences between channels in different sectors are maintained to be within a pre-selected power difference. Different channels in a cell are assigned different power levels. Wireless terminals are assigned to channels based on channel feedback information. Wireless terminals with poor channel conditions are allocated to higher power channels than wireless terminals with good channel conditions. Lower power channels often include more tones per symbol time than high power channels.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
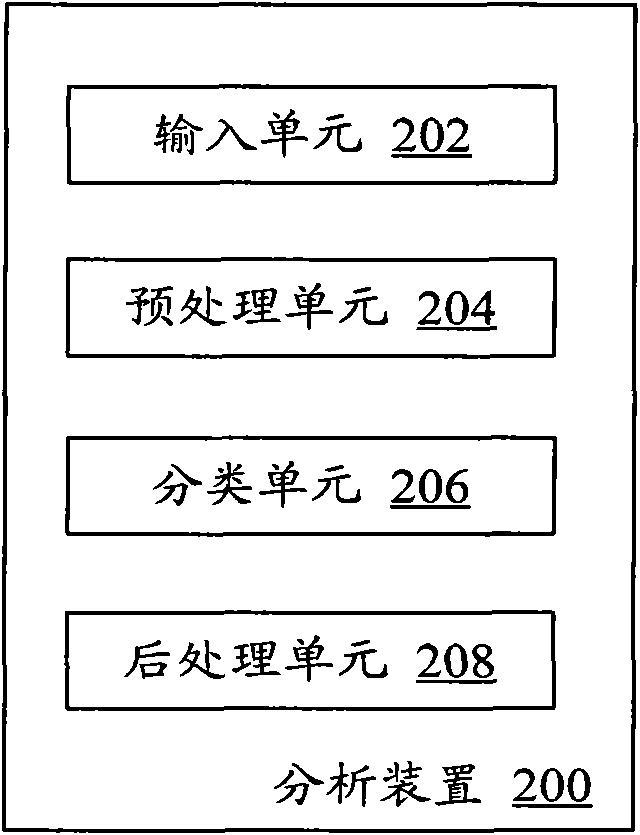
Device and method for analyzing audio data
InactiveCN101685446AQuick searchShorten the timeSpeech analysisSpecial data processing applicationsTone FrequencyZero-crossing rate
The invention provides a device for analyzing audio data by using an SVM method. The device is characterized by comprising an input unit, a preprocessing unit, a classifying unit and a post processingunit, wherein the input unit is used for inputting audio stream; the preprocessing unit is used for preprocessing the audio stream to obtain a characteristic parameter of each frame; the classifyingunit analyzes the category to which each frame belongs according to the characteristic parameter; and the post processing unit carries out post processing on the classifying result of the classifyingunit to obtain the final subsection result. The characteristic parameter comprises short time average energy, subband energy, zero-crossing rate, Mel frequency domain cepstrum coefficient, delta Mel frequency domain cepstrum coefficient, spectrum flux and fundamental tone frequency. The invention realizes quick retrieval of splendid contents, and can save the time of audiences and meet the watching demand of the audiences.
Owner:SONY CHINA
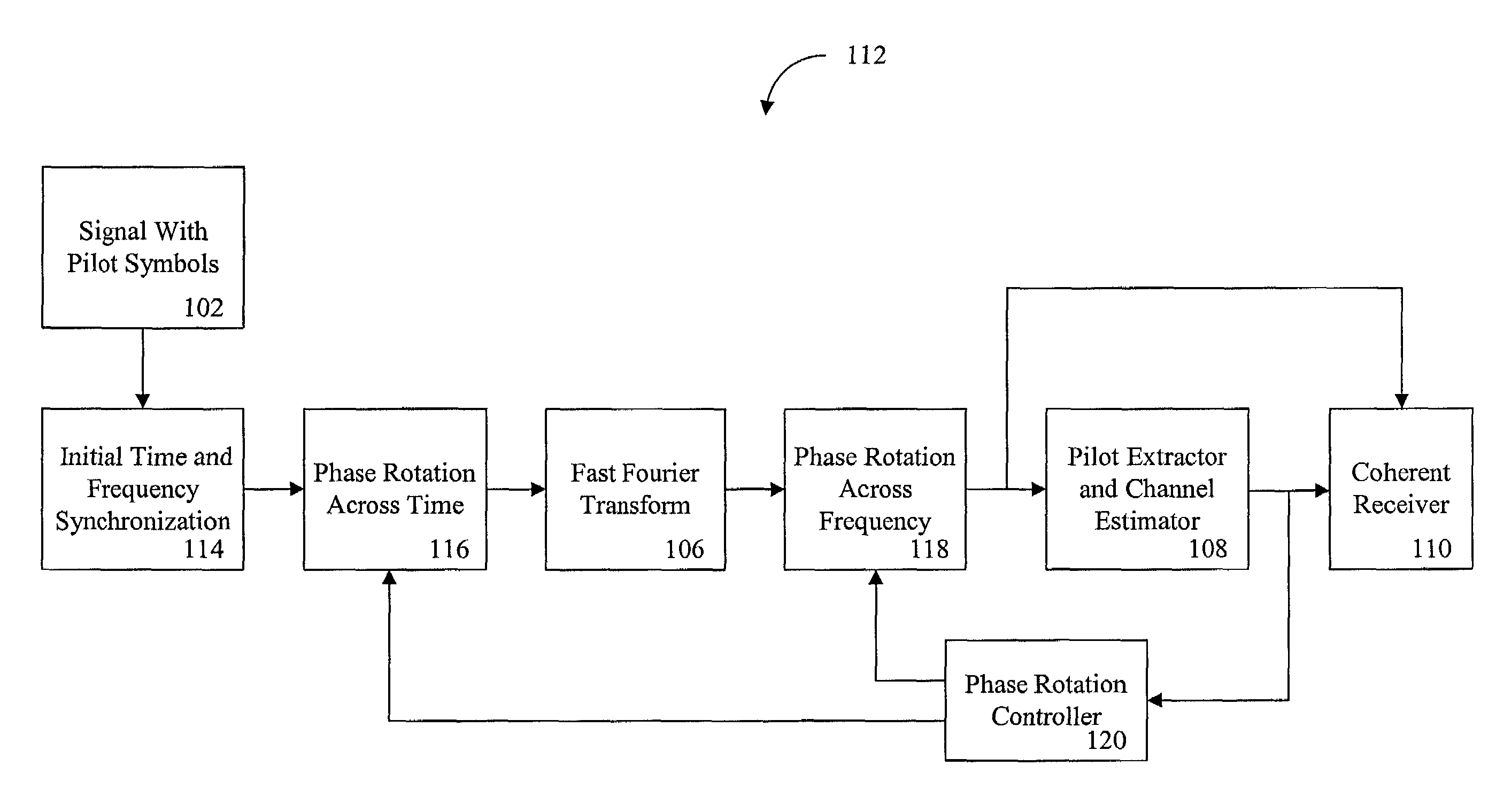
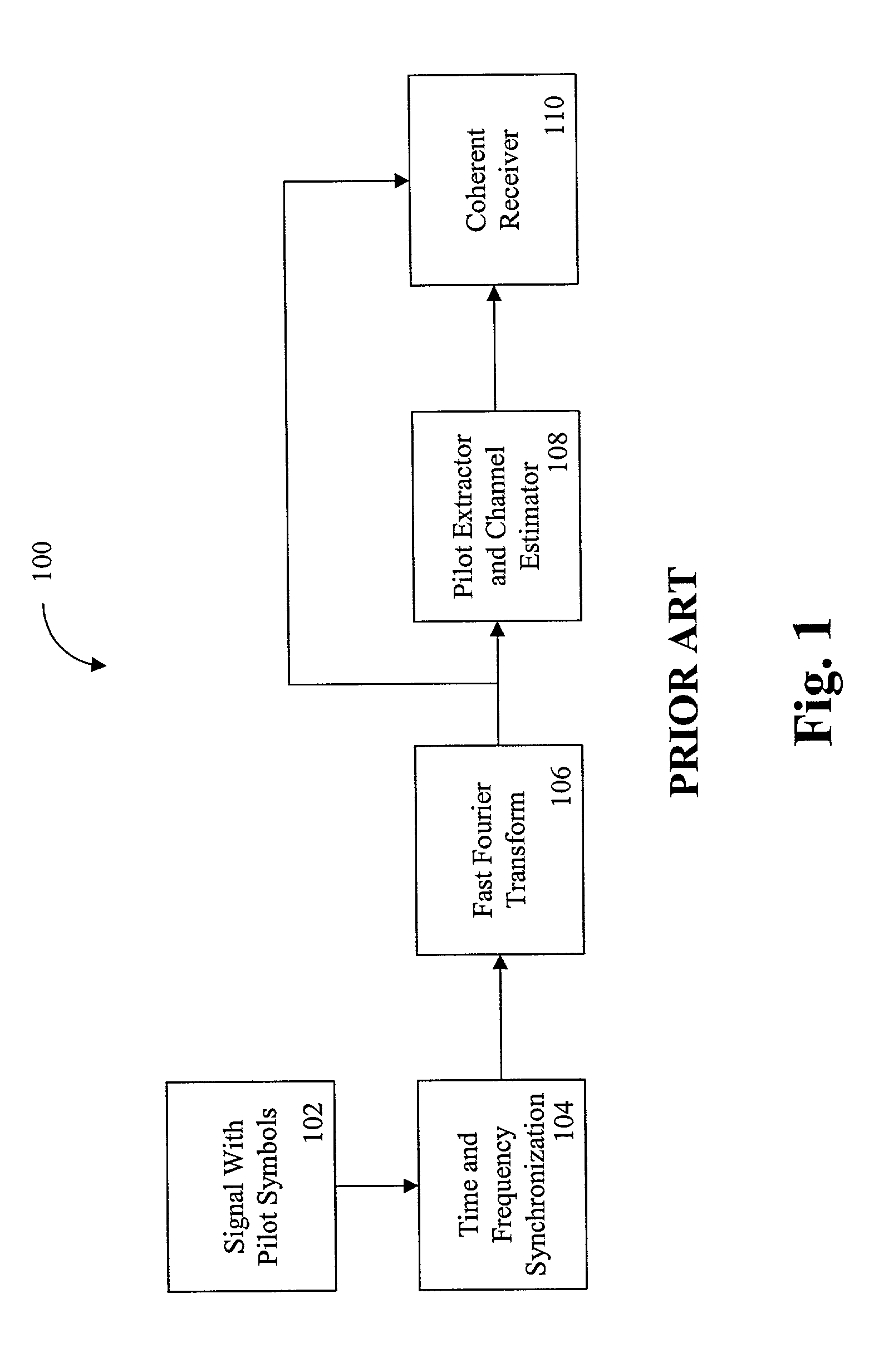
Synchronization of a pilot assisted channel estimation orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system
ActiveUS7023928B2Minimize estimated channel errorSensitive to frequencyBaseband system detailsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase differenceCarrier signal
A synchronization of a pilot assisted channel estimation orthogonal frequency division multiplexing can be achieved by receiving a signal containing pilot symbols, providing an initial time and frequency synchronization to the signal, phase rotating the signal across time, transforming the signal with a fast Fourier transformation, phase rotating the signal across frequency, extracting the pilot symbols and generating a channel estimator. The phase rotating across time and the phase rotating across frequency are controlled by a phase rotation controller in accordance with the channel estimator. The initial time and frequency synchronization synchronizes the signal such that intercarrier interference effects and intersymbol interference effects are negligible. The signal may include plural carrier frequencies each having an arrival timing offset and a frequency offset. The signal may also include delay spread or Doppler spread. The phase rotation controller measures a phase different between the channel estimator at times k and k+Δk, where k is time and Δk is a symbol period and measures a phase difference between the channel estimator at frequencies n and n+Δn, where n is tone frequency and Δn is a frequency spacing between adjacent tones.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
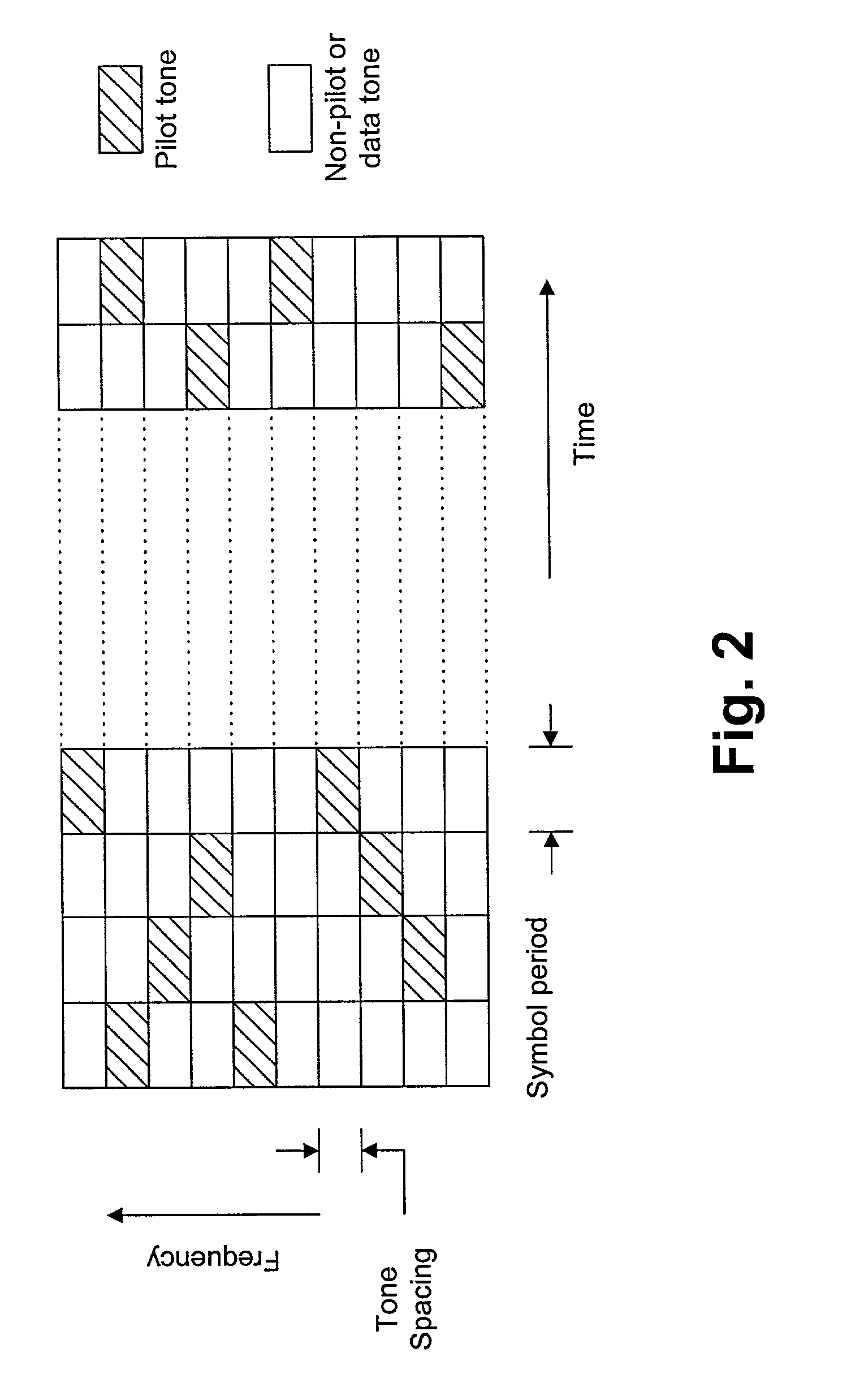
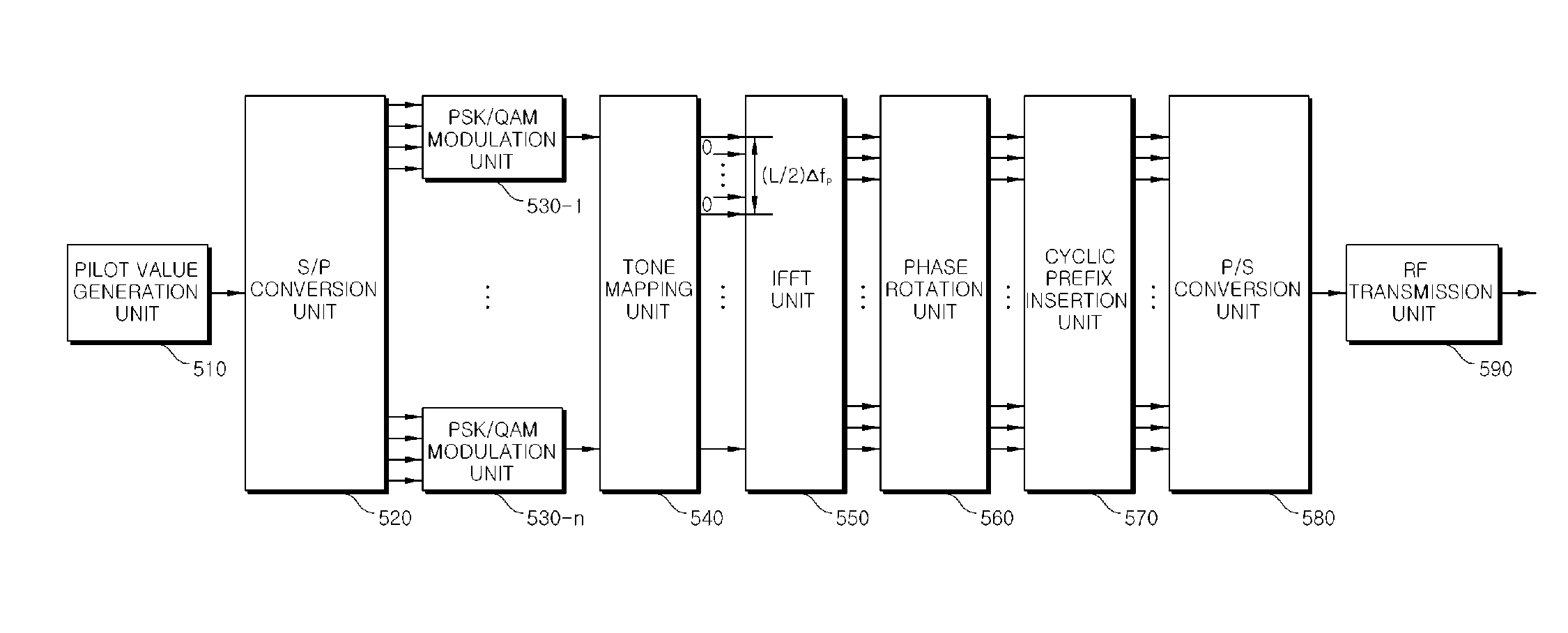
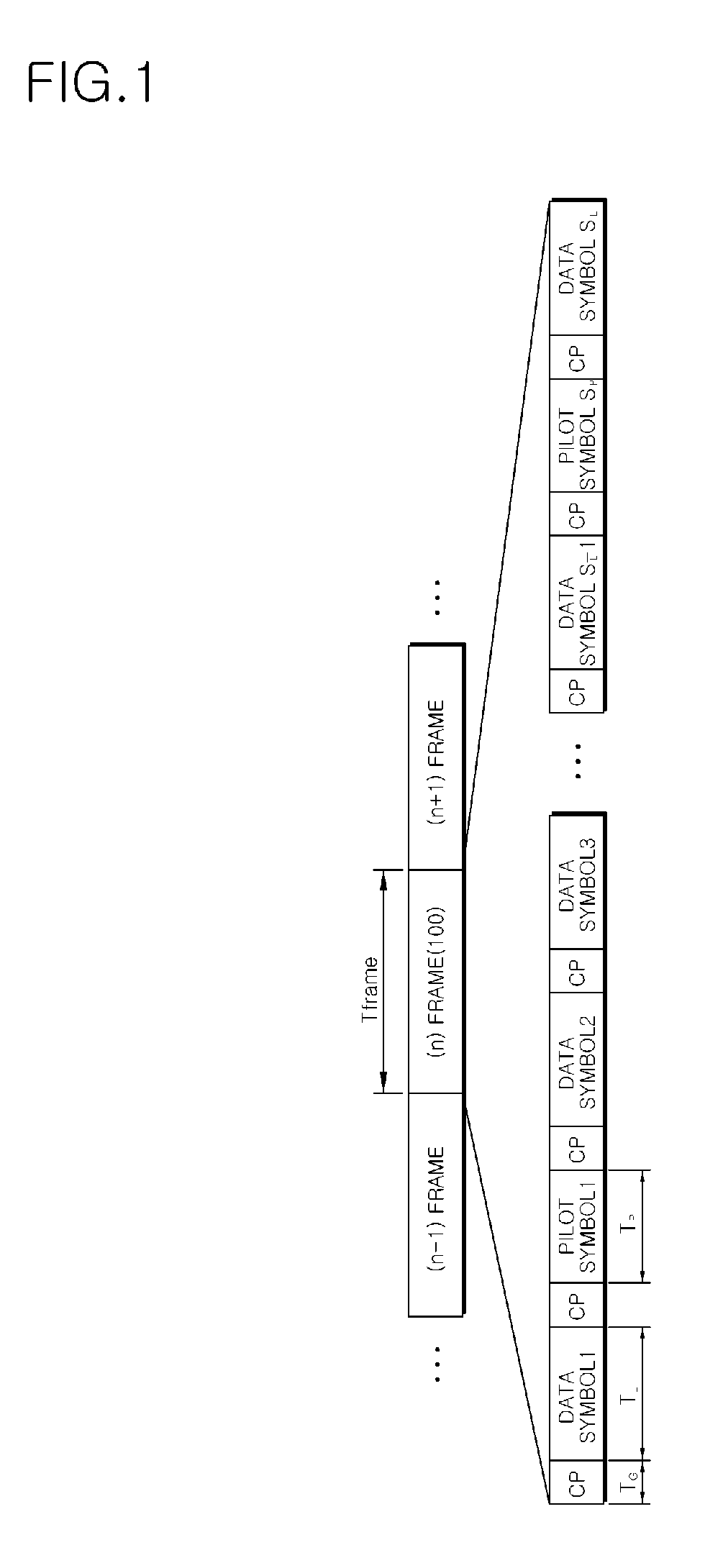
Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving pilot symbols in orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing based communication systems
InactiveUS20070189406A1Transmission path divisionSecret communicationTone mappingCommunications system
A method for transmitting and receiving pilot symbols in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM)-based communication system is provided. Pilot symbols are mapped to pilot tone frequencies assigned to terminals, and even-numbered or odd-numbered pilot symbols are phase-rotated to be orthogonal. An apparatus for transmitting pilot symbols in an OFDM-based communication system is provided. A tone mapping unit maps pilot tone frequencies assigned to terminals onto pilot symbols to be transmitted, and a phase rotation unit phase-rotates either even-numbered or odd-numbered pilot symbols. An apparatus for transmitting pilot symbols in an OFDM-based communication system is provided. A tone mapping unit maps pilot tone frequencies assigned to terminals onto pilot symbols to be transmitted, and a transmission unit stores a signal in a buffer and transmits a first portion of the signal in a first pilot symbol and a second portion of the signal in a second pilot symbol.
Owner:PANTECH & CURITEL COMM INC
Synchronization techniques for a wireless system
ActiveUS7133354B2Improve and optimize system performanceImprove throughputPower managementEnergy efficient ICTCommunications systemOfdm communication system
Power control methods and apparatus for use in a sectorized cell of an OFDM communications system are described. Each sector of a cell uses the same frequencies and transmission times and is synchronized with the other sectors in the cell in terms of tone frequencies used at any given time and symbol transmission times. Tones are allocated to channels in each cell in the same manner so that each channel in a sector has a corresponding channel in another sector. Power differences between channels in different sectors are maintained to be within a pre-selected power difference. Different channels in a cell are assigned different power levels. Wireless terminals are assigned to channels based on channel feedback information. Wireless terminals with poor channel conditions are allocated to higher power channels than wireless terminals with good channel conditions. Lower power channels often include more tones per symbol time than high power channels.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
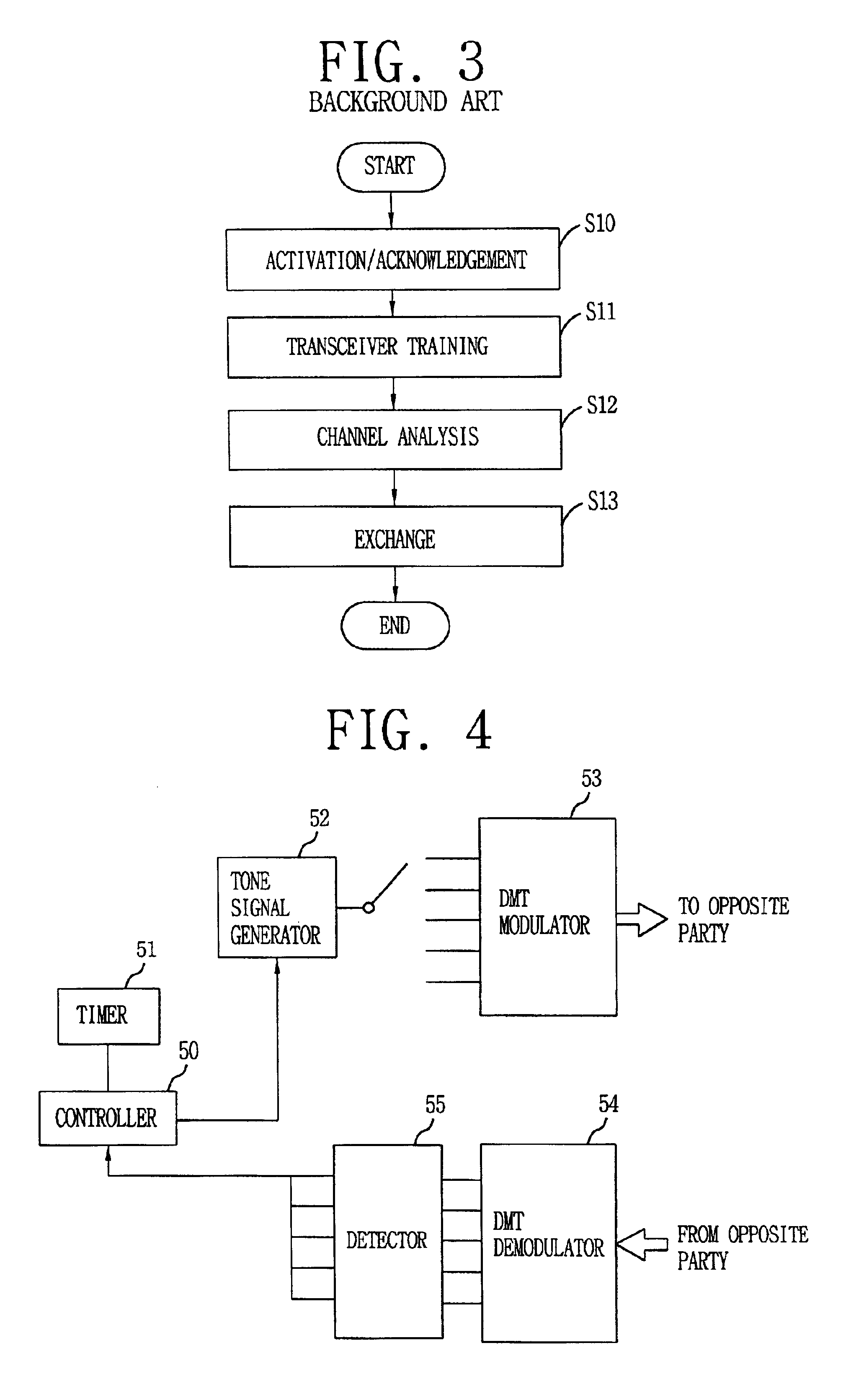
Method and apparatus for initializing modem communications
InactiveUS7035326B1Shorten the timeMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsModem deviceNetwork Communication Protocols
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for demodulating data received over a communication medium carrying a transmission having multiple pilot tones with pilot data modulated thereon and message tones with message data modulated thereon and with the pilot tones and message tones frequency division multiplexed with respect to one another. In an embodiment of the invention the communication protocol utilized for modulation and demodulation is discrete multi tone (DMT). The invention allows message processing and equalizer training to proceed in parallel before equalizer training tables have been completed thus reducing the time associated with modem initialization. The apparatus in one embodiment of the invention includes on the receive path of a DMT or other multi-tone modem, a fast Fourier transform engine (FFT), a message processor, and a decoder. The FFT converts the received data from a time domain to a frequency domain. The received data in the frequency domain includes successive sets of pilot tones together with message tones. The message processor selects pairs of message and pilot tones proximate to one another in the frequency domain in each set of pilot tones and message tones. The message tone in each pair is then equalized with the pilot tone in the pair to substantially remove frequency dependent phase shifts imparted by the communication medium to the message tone. The equalized message tone is then decoded in the decoder to the corresponding specific set of message data which it represents.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
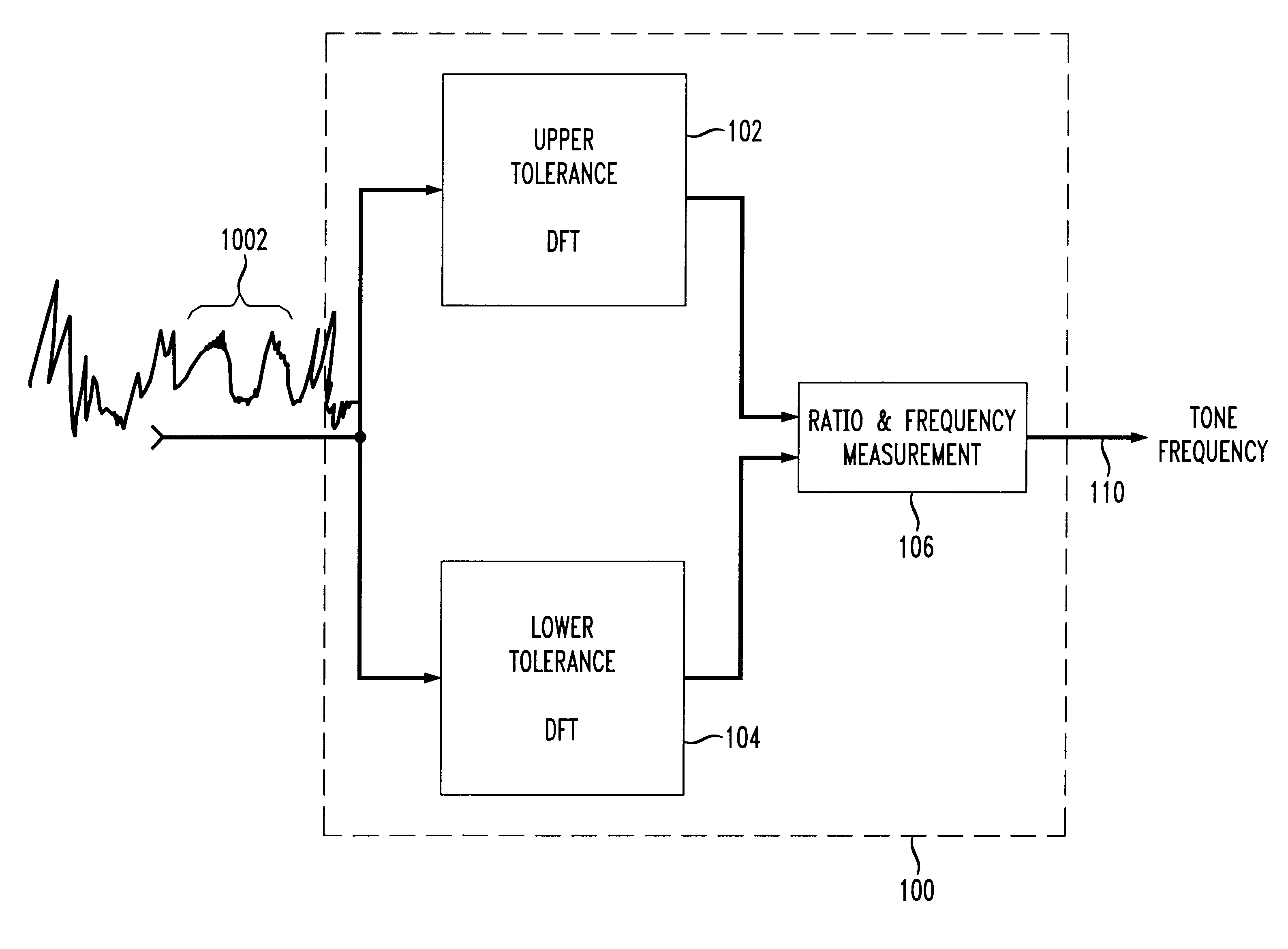
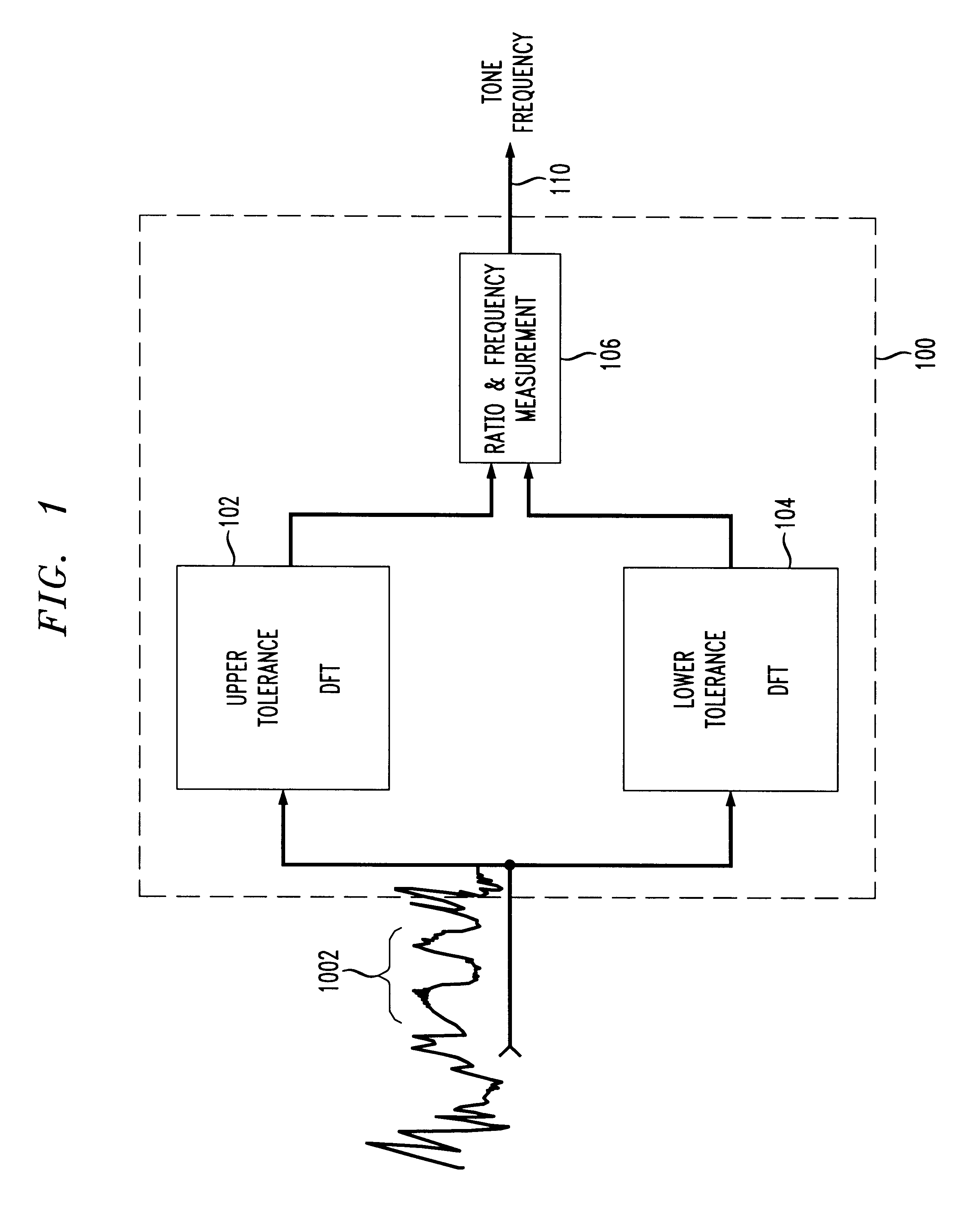
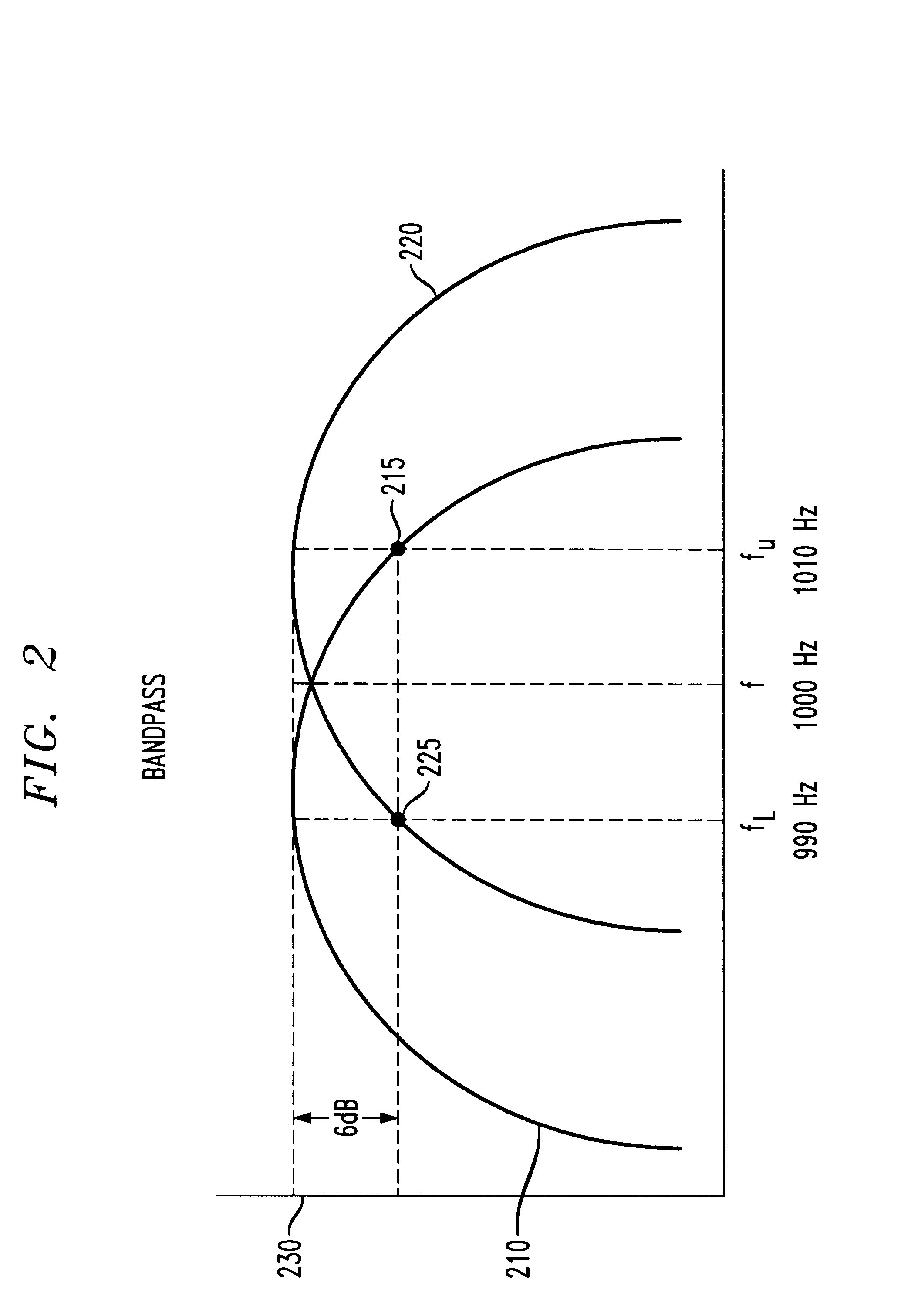
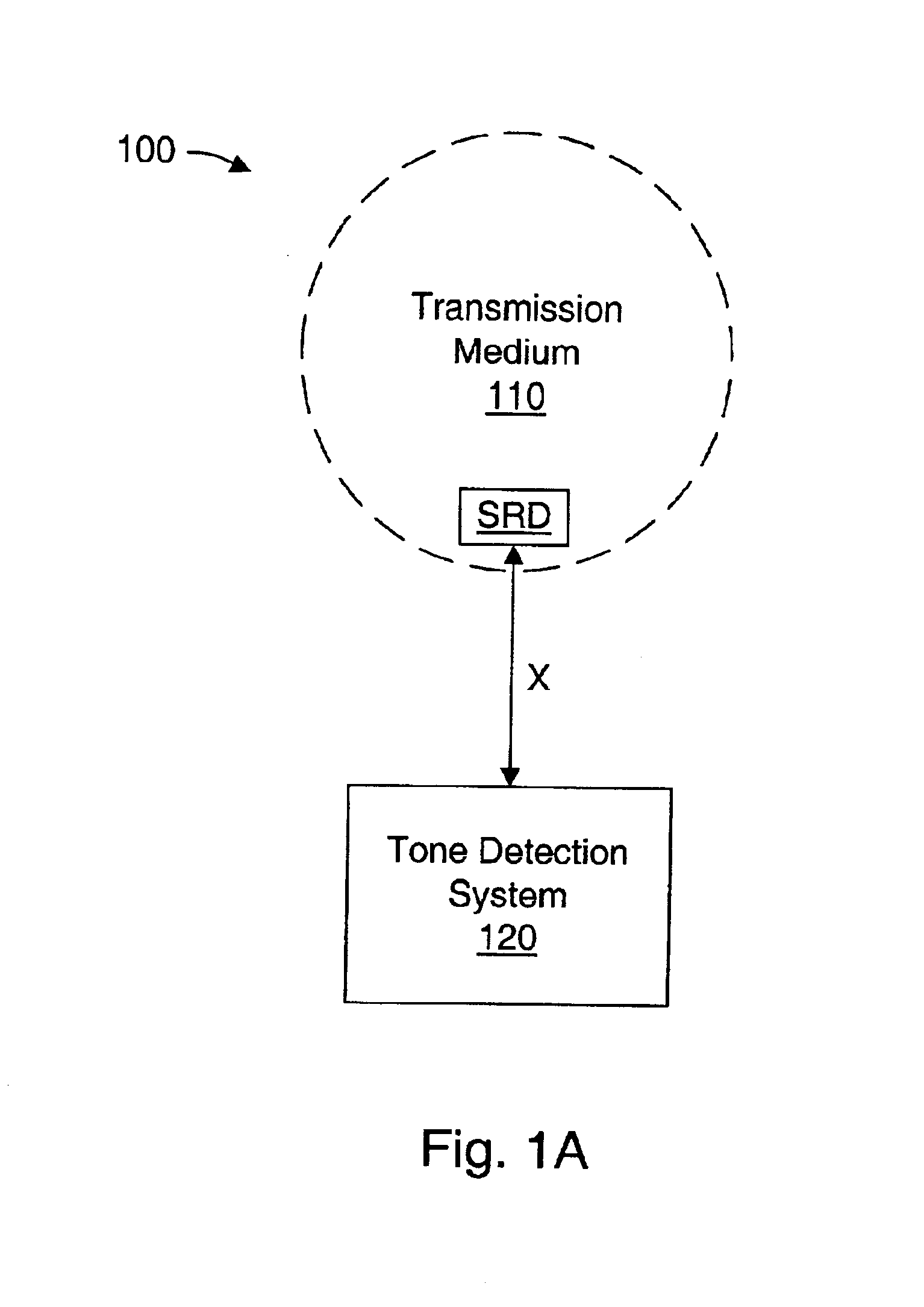
Robust signaling tone frequency measurement
InactiveUS6229889B1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexRelative energyTone Frequency
Apparatus and methods for adaptively, reliably, and accurately measuring the frequency of an alerting or other signaling tone. A tone detector measures the frequency of a tone (continuous or pulsed) with a high degree of accuracy (e.g., to within 1 part in 10,000). Two lower order or smaller DFTs measure the energy level in two separate but intersecting frequency ranges. A simple ratio is determined from the relative energy measured from discrete Fourier transforms relating to each of the two separate frequency ranges, and an actual measured frequency is determined.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
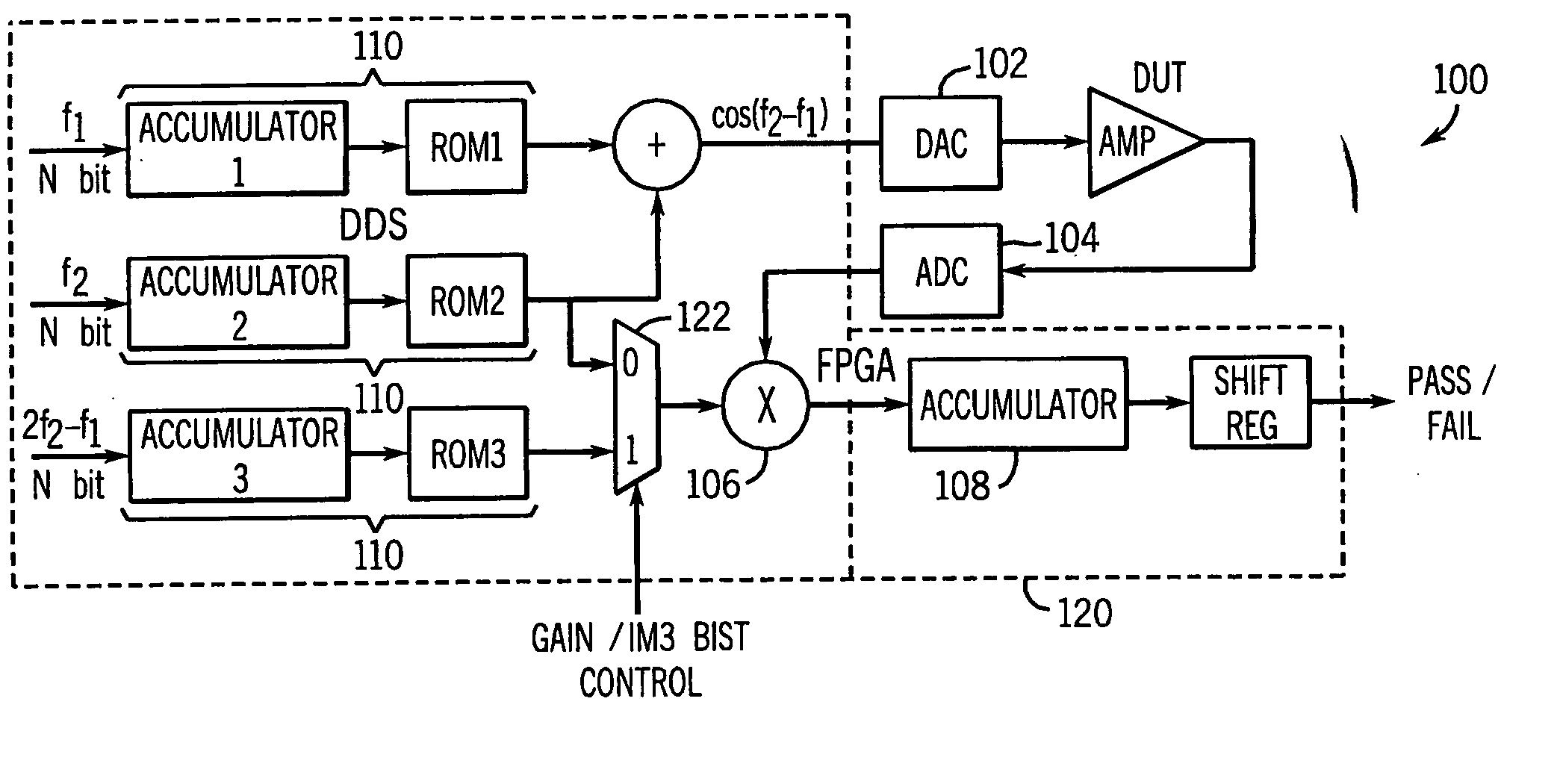
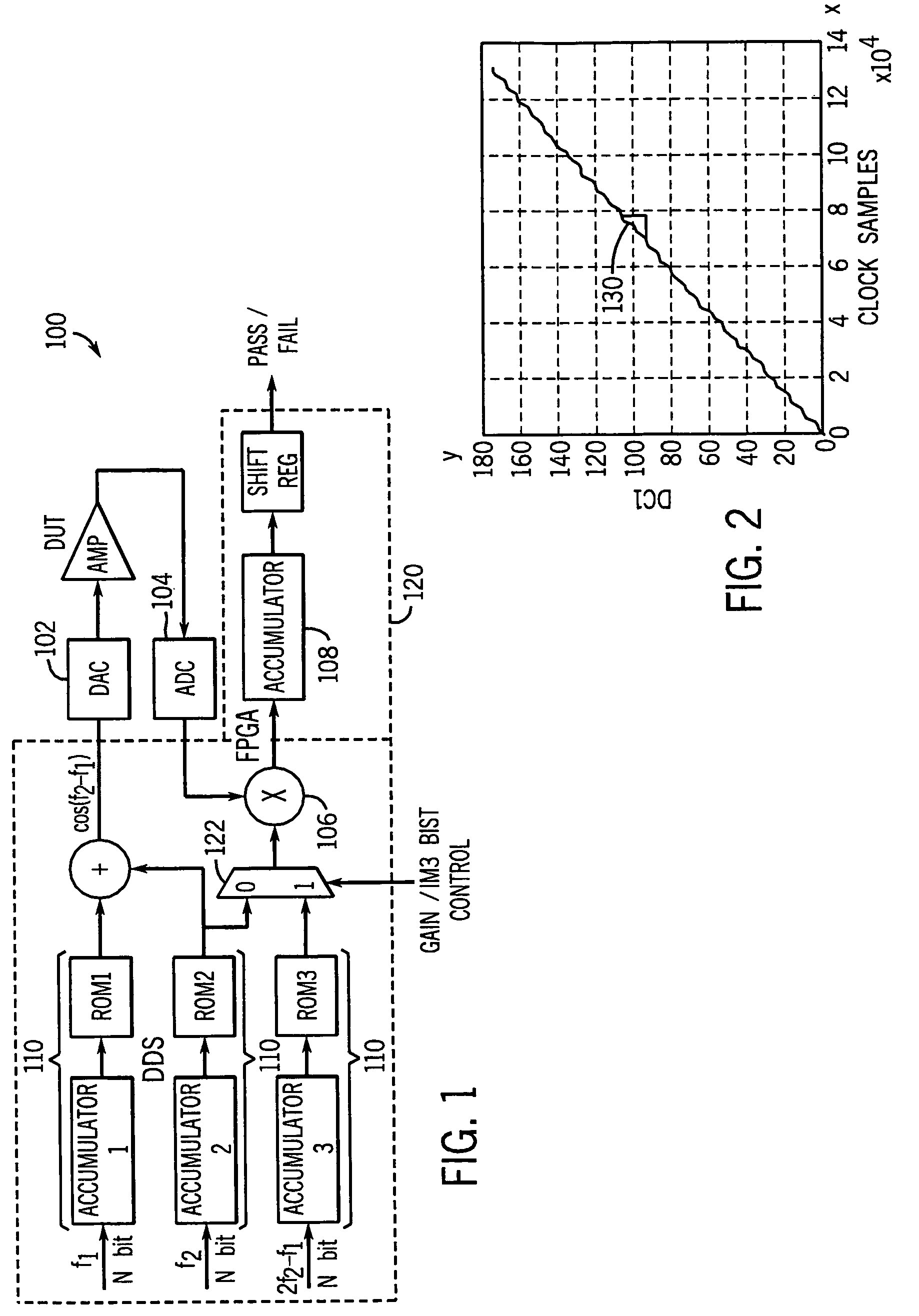
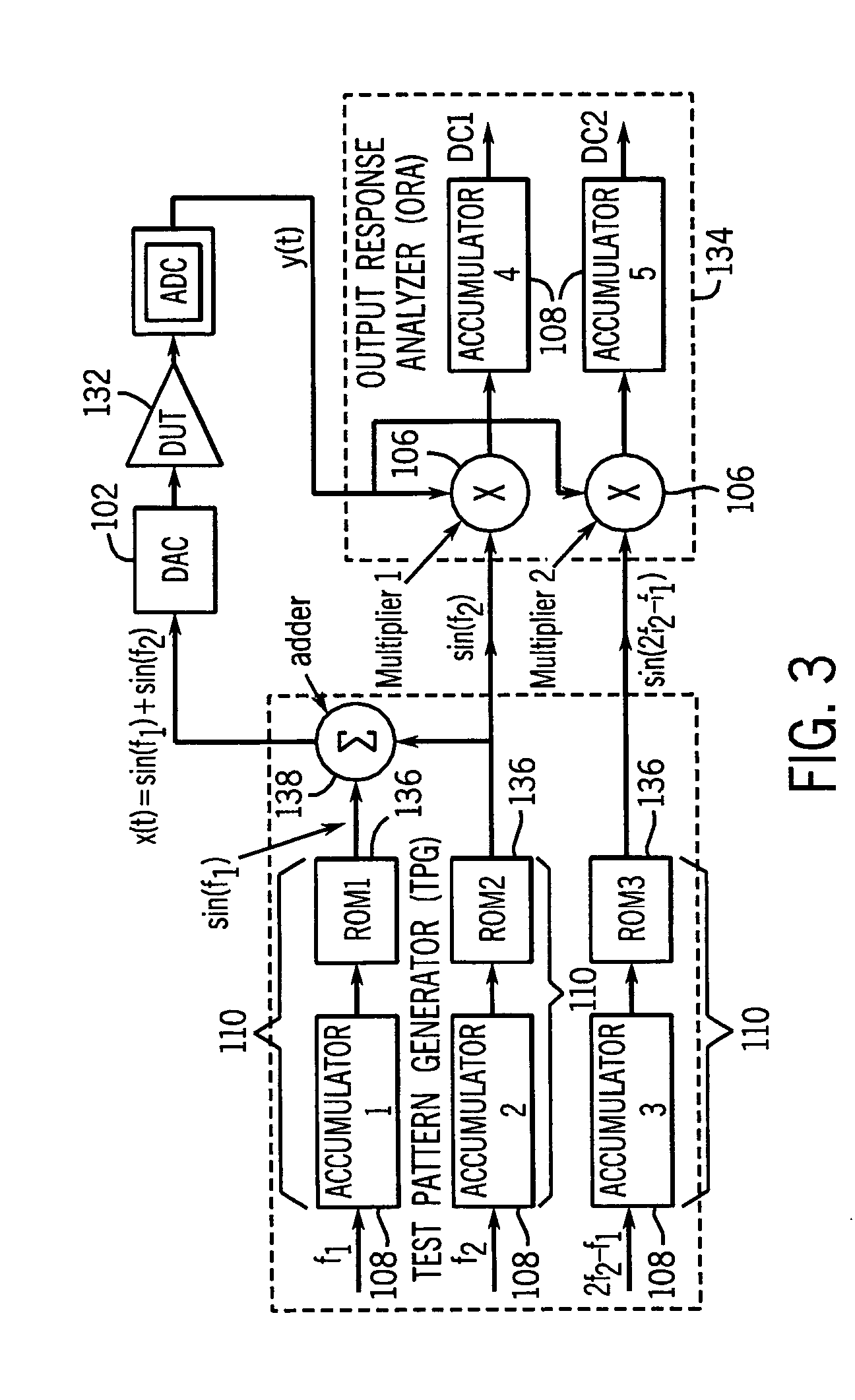
Automatic analog test & compensation with built-in pattern generator & analyzer
ActiveUS20060020865A1Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionFrequency spectrumEngineering
A built-in-self test (BIST) scheme for analog circuitry functionality tests such as frequency response, gain, cut-off frequency, signal-to-noise ratio, and linearity measurement. The BIST scheme utilizes a built-in direct digital synthesizer (DDS) as the test pattern generator that can generate various test waveforms such as chirp, ramp, step frequency, two-tone frequencies, sweep frequencies, MSK, phase modulation, amplitude modulation, QAM and other hybrid modulations. The BIST scheme utilizes a multiplier followed by an accumulator as the output response analyzer (ORA). The multiplier extracts the spectrum information at the desired frequency without using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) and the accumulator picks up the DC component by averaging the multiplier output.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
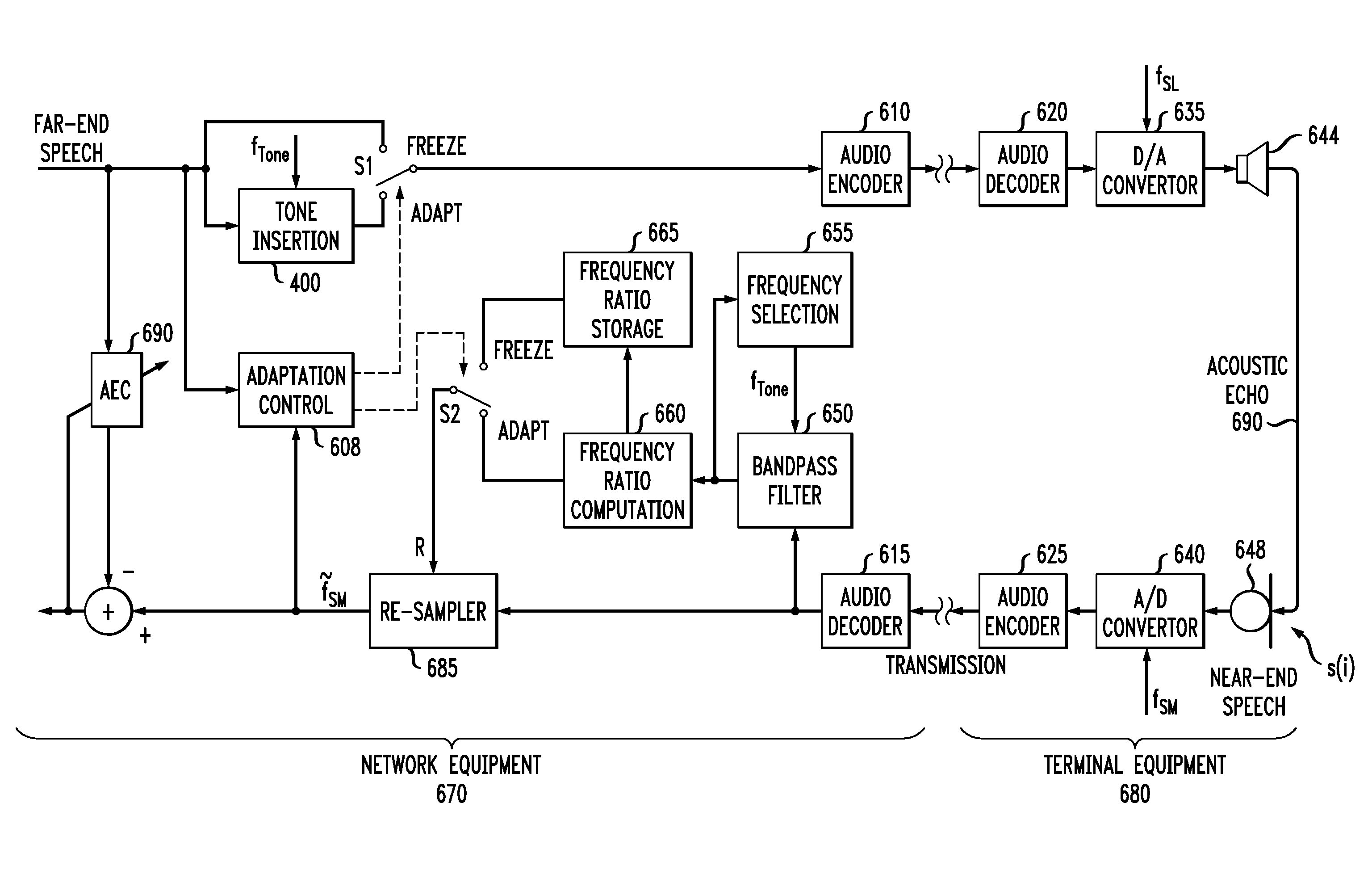
Clock Skew Compensation for Acoustic Echo Cancellers Using Inaudible Tones
InactiveUS20130044873A1Two-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpeech synthesisTone FrequencyFrequency shift
Methods and apparatus are provided for acoustic echo cancellation in a speech signal. Acoustic echo is cancelled by inserting at least one tone in the speech signal, wherein the at least one tone is substantially inaudible to a listener; determining a clock skew between two sampling clocks based on a frequency shift of the at least one tone; re-sampling the speech signal based on the determined clock skew; and performing the acoustic echo cancellation using the re-sampled speech signal. The provided acoustic echo cancellers can be implemented, for example, as terminal-based and / or network-based acoustic echo cancellers. The tone optionally comprises an inaudible tone or multiple tones. The tone generation can be limited to only when a speech power in the vicinity of the tone frequency is larger than a pre-determined threshold, or to the beginning of a call. A level of the tone can optionally be controlled so that the tone is masked by the speech signal.
Owner:PIECE FUTURE PTE LTD
Noise tone avoidance in optical networks
Identification of optical channels in wavelength division multiplex (WDM) optical networks may be confounded by unwanted noise tones interfering with pilot / dither tones used for identifying optical channels. The invention describes a method of selecting pilot / dither tones that are selectively restricted to avoid allocating dither / pilot tone frequencies that appear as noise tones along the path of an optical channel in the optical network.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
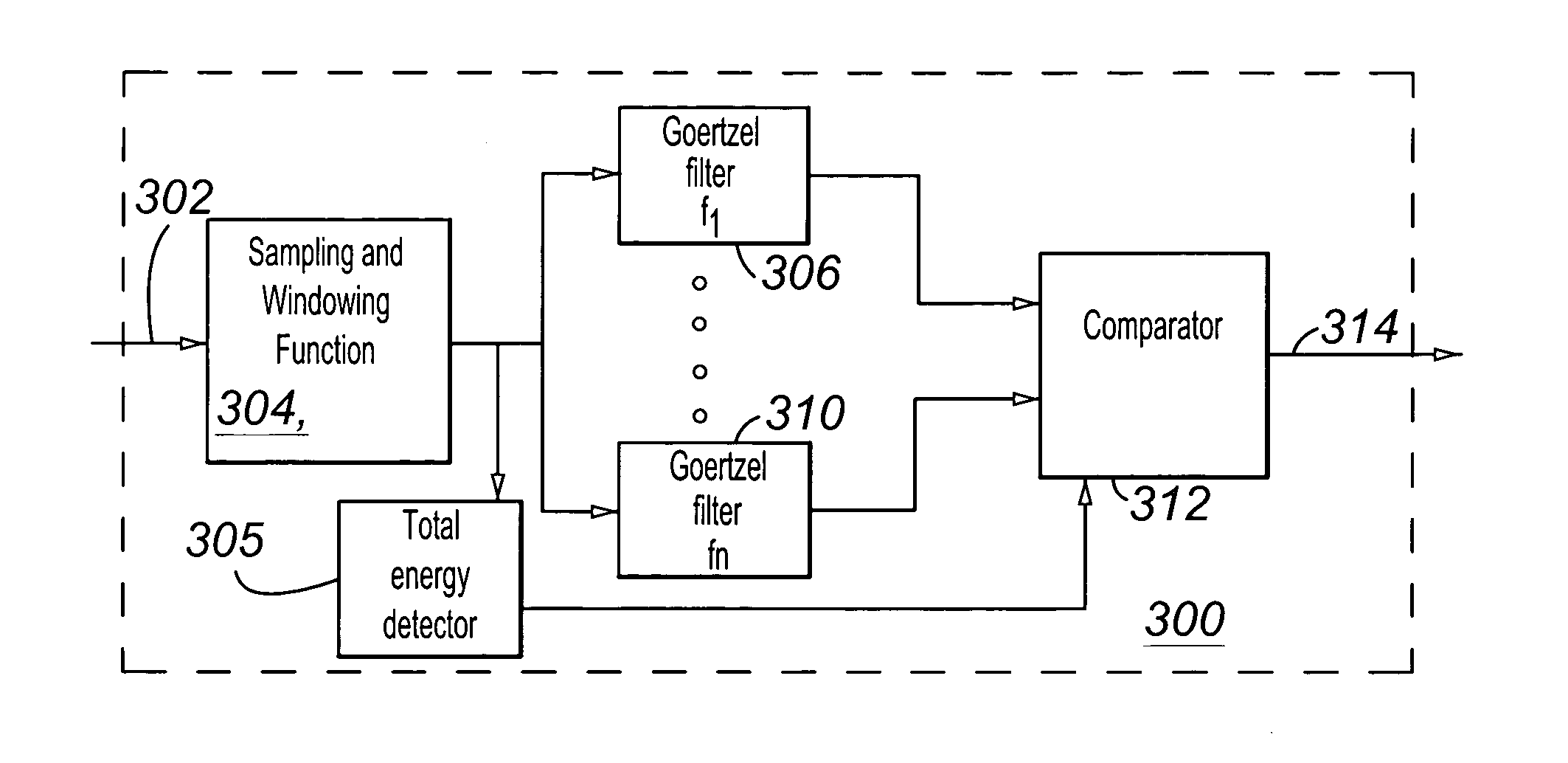
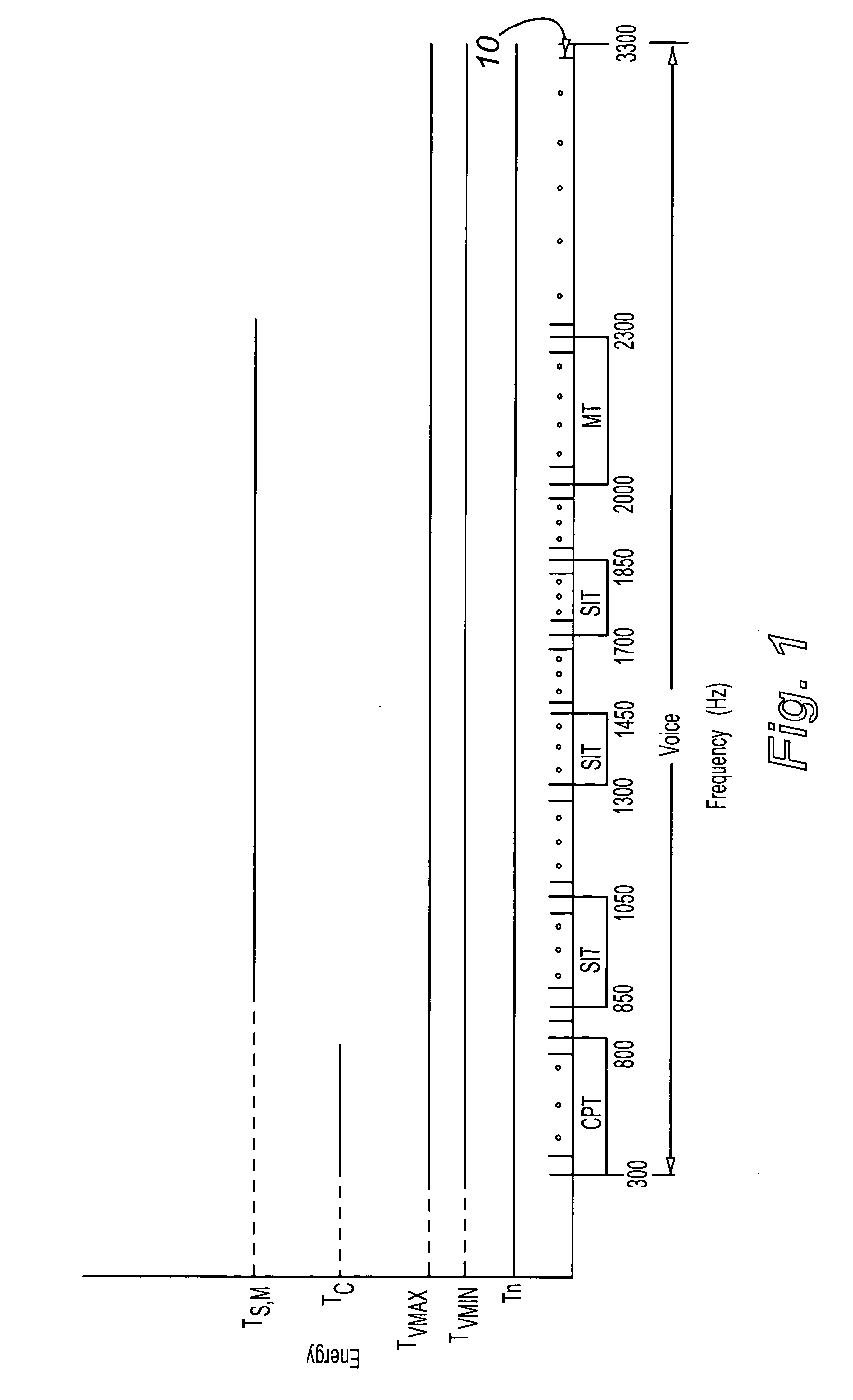
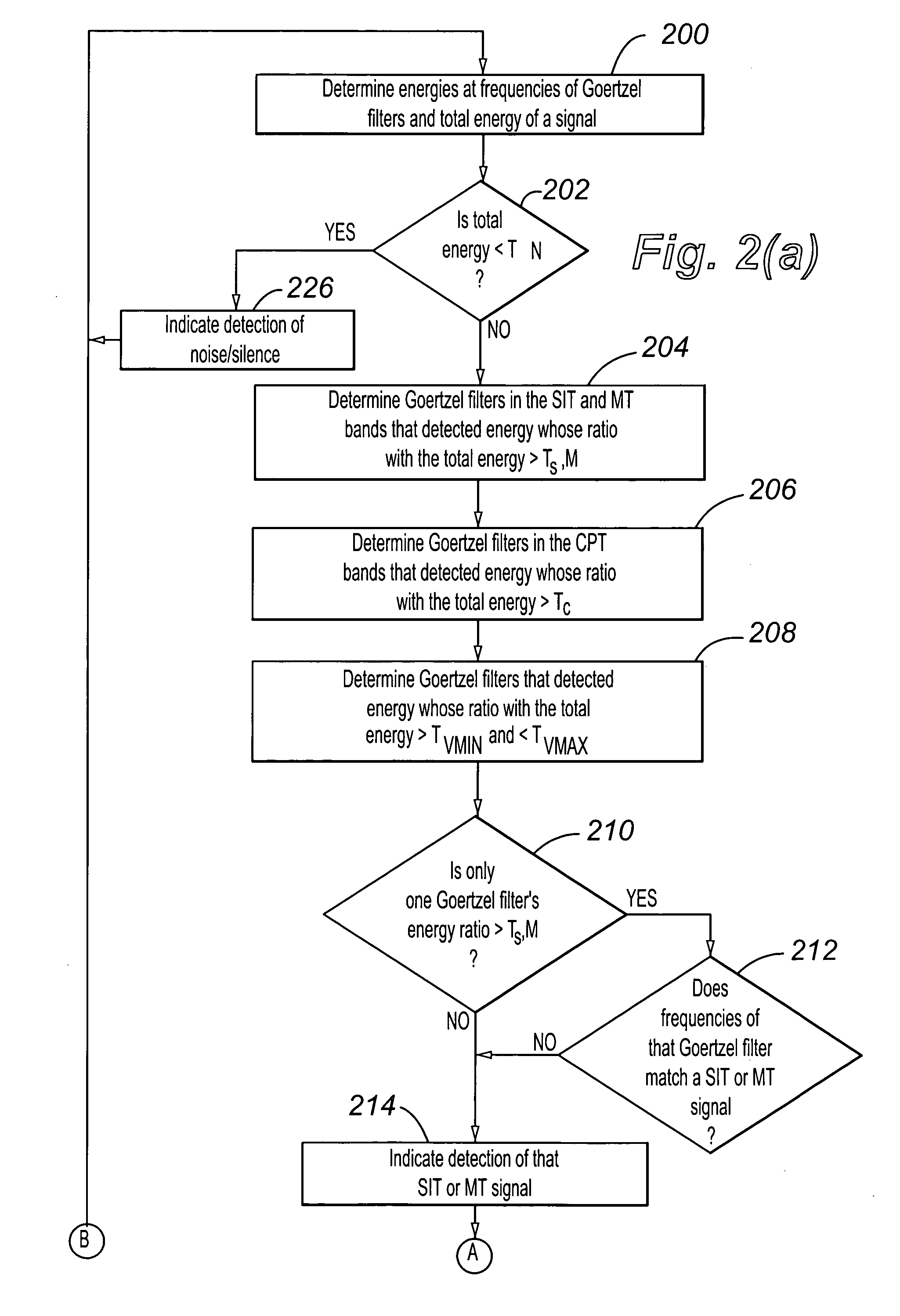
Detection of both voice and tones using Goertzel filters
ActiveUS20050105716A1Computationally efficientHigh-precision detectionInterconnection arrangementsSubstation equipmentControl signalEngineering
A plurality of Goertzel filters whose operating frequencies are distributed across the voice baseband are used to detect voice and control tones in a signal. Filters operating at frequencies of control tones and detecting that most of the signal energy occurs at those frequencies indicates presence of the control tones. At least three of the filters detecting that about 10% to 20% of the signal energy occurs at each of their operating frequencies indicate presence of voice. The total energy detected in the signal being below a noise threshold indicates presence of noise or silence.
Owner:AVAYA INC
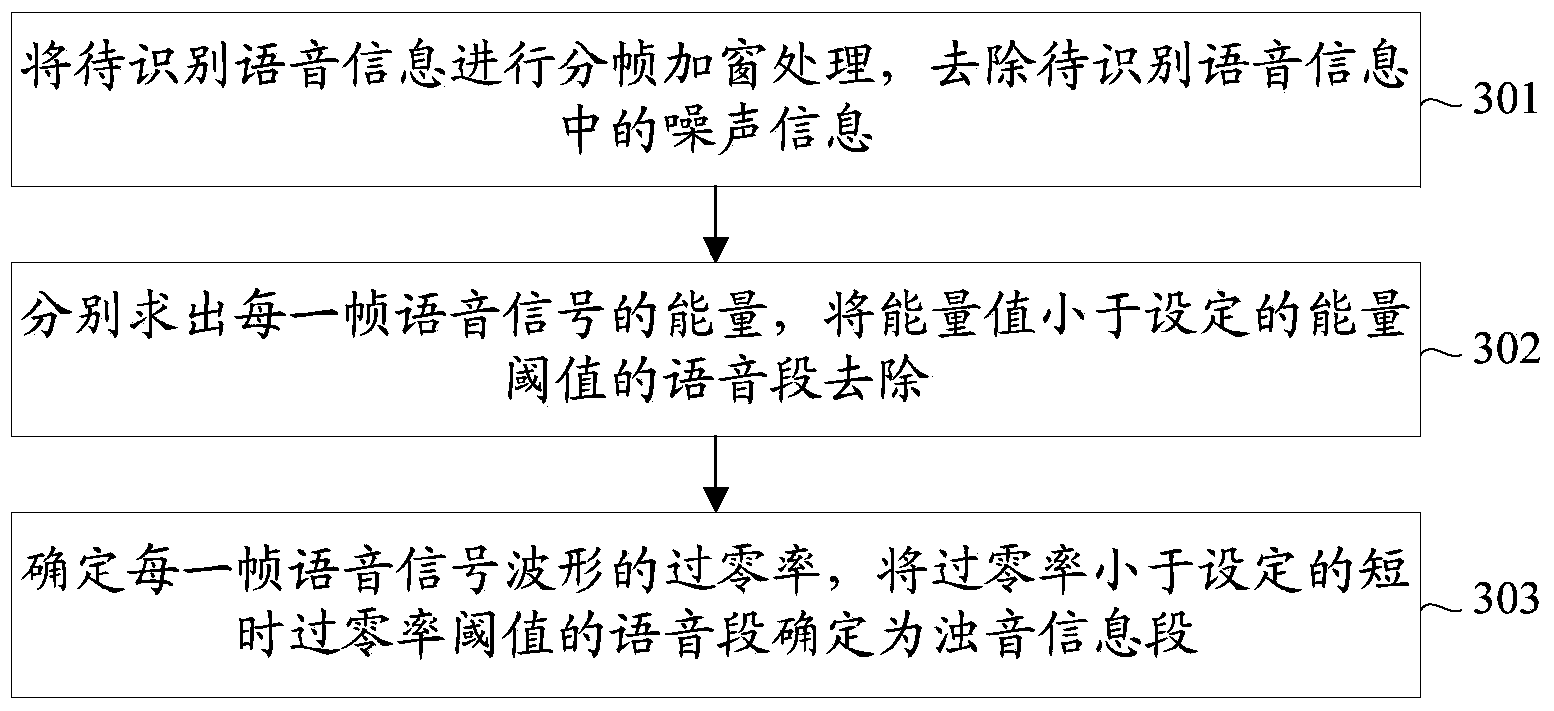
Voice information recognition method and terminal equipment
The invention relates to the field of information recognition, in particular to a voice information recognition method and terminal equipment. The voice information recognition method and the terminal equipment resolve the problem in the prior art that when a sound source of voice information to be recognized is not stable or sound transmission equipment generates interference, determined feature information has deviation easily. Voiced sound information is extracted from the voice information to be recognized, fundamental tone frequency parameters and an MFCC are extracted from the voiced sound information, the fundamental tone frequency parameters are processed to obtain a fundamental tone frequency parameter matching value, the MFCC is processed to obtain an MFCC parameter matching value, and the feature information of the voice information to be recognized is determined according to the fundamental tone frequency parameter matching value and the MFCC parameter matching value. Due to the facts that voiced sound in the voice information has the periodicity of a voice fundamental tone, the voiced sound information has a relatively fixed frequency in general, the characteristic of the voiced sound information can be treated as a quasi-steady-state process, and the probability that the feature information of the voice information determined according to the voiced sound information has mistakes is low.
Owner:HISENSE
Receiver including an oscillation circuit for generating an image rejection calibration tone
A receiver circuit includes an oscillator circuit configured to generate a calibration tone and a phase locked loop (PLL) reference signal. An output frequency of the VCO may be divided by respective amounts to derive a desired calibration tone frequency and a desired PLL reference signal frequency. In addition to the oscillator circuit, the receiver circuit may further include a phase locked circuit configured to generate a PLL output signal that is phase locked in relation to the PLL reference signal. During a calibration mode, a quadrature generator may be used to generate quadrature mixer local oscillator signals dependent upon the PLL output signal, and an in-phase / quadrature mixer may be used to mix the calibration tone with the quadrature mixer LO signals.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
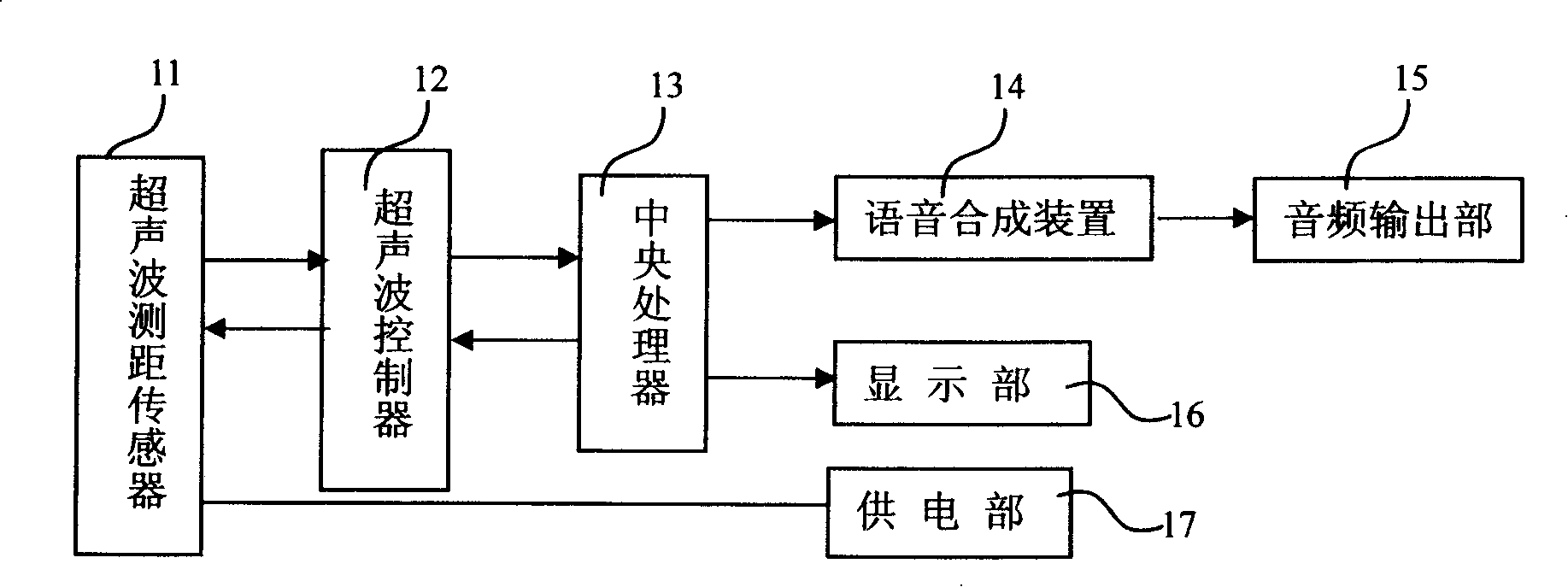
Radar type obstruction warning mobile phone
InactiveCN101207645AGood travel guaranteeImprove playbackRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelephone set constructionsRadarEngineering
The invention discloses a radar obstruction warning handset, the handset comprises a handset casing, a central processor, a keyboard, a display part, a tone frequency output part, and a power supply part. The handset is characterized in that the handset also comprises an ultrasonic controller and an ultrasonic ranging sensor; wherein, the ultrasonic controller is respectively connected with the central processor and the ultrasonic ranging sensor, and is used to trigger and control the sensor ultrasonic detection; the ultrasonic ranging sensor has an ultrasonic probe, the probe sends ultrasonic to a measuring-awaited obstruction, the ranging sensor sends a received echo signal to the central processor through analog-digital converting, and the display part displays the ranging.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS (CHINA) R&D CENT CO LTD
Automatic analog test and compensation with built-in pattern generator and analyzer
A built-in-self test (BIST) scheme for analog circuitry functionality tests such as frequency response, gain, cut-off frequency, signal-to-noise ratio, and linearity measurement. The BIST scheme utilizes a built-in direct digital synthesizer (DDS) as the test pattern generator that can generate various test waveforms such as chirp, ramp, step frequency, two-tone frequencies, sweep frequencies, MSK, phase modulation, amplitude modulation, QAM and other hybrid modulations. The BIST scheme utilizes a multiplier followed by an accumulator as the output response analyzer (ORA). The multiplier extracts the spectrum information at the desired frequency without using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) and the accumulator picks up the DC component by averaging the multiplier output.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
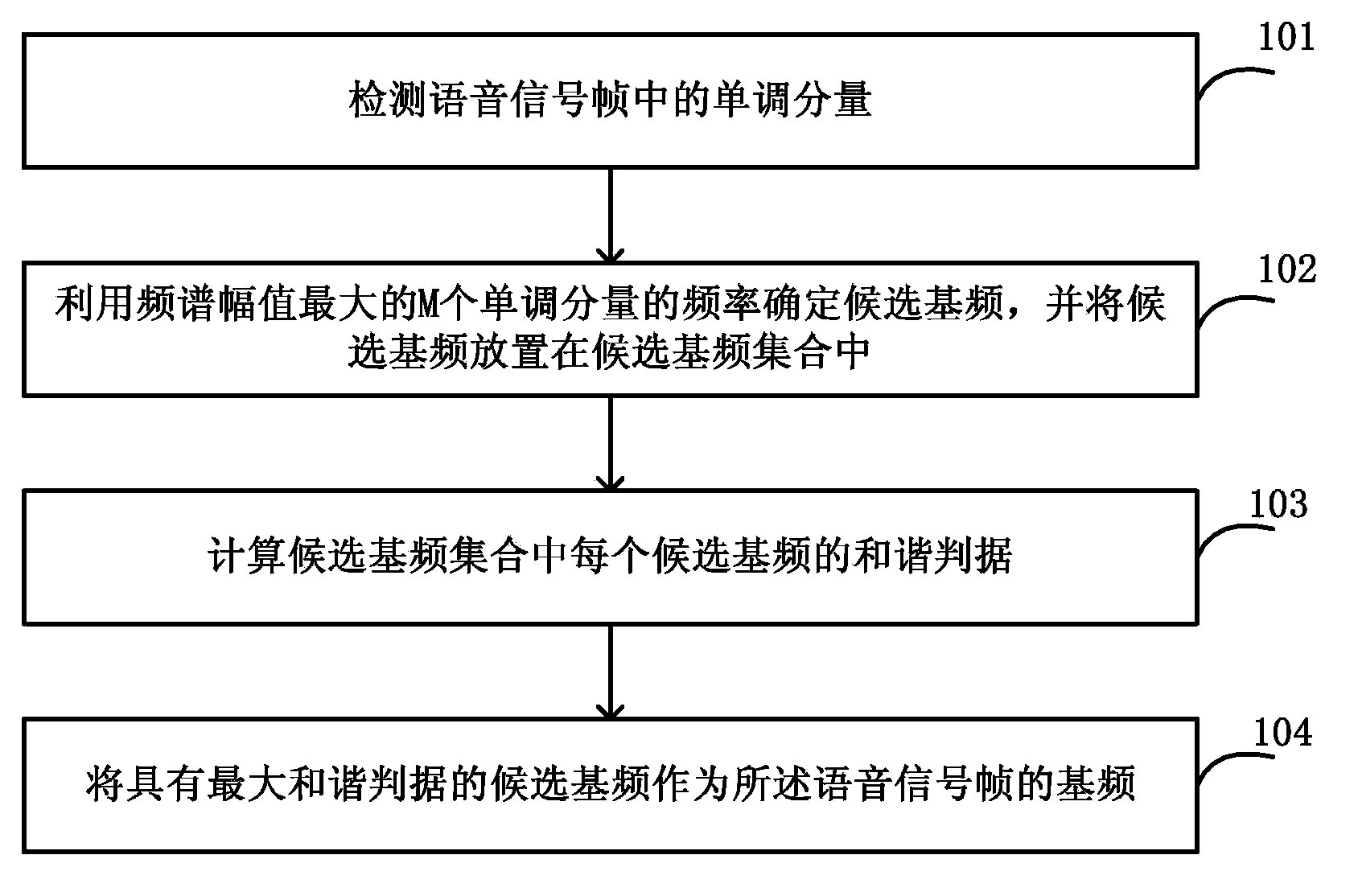
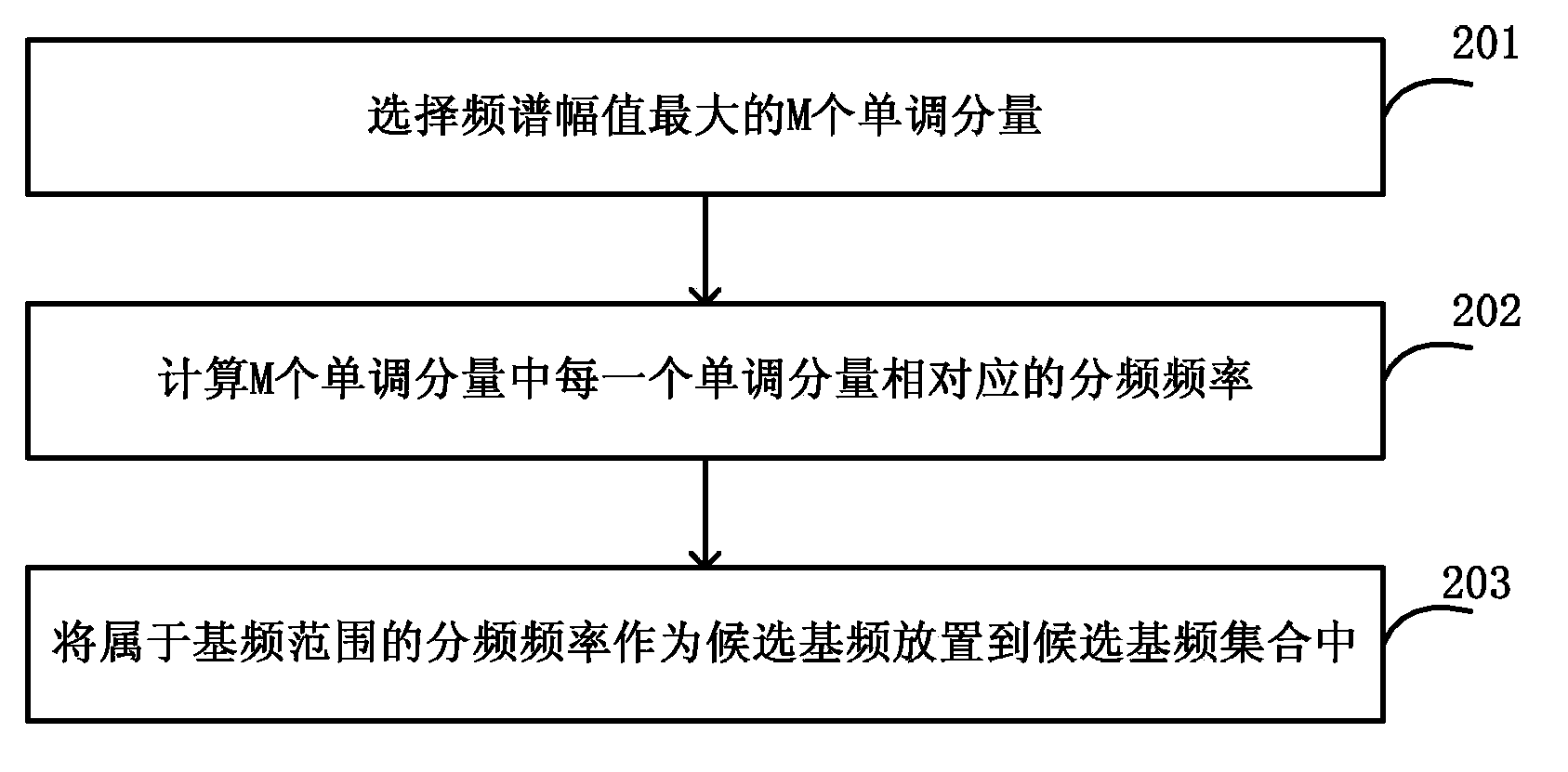
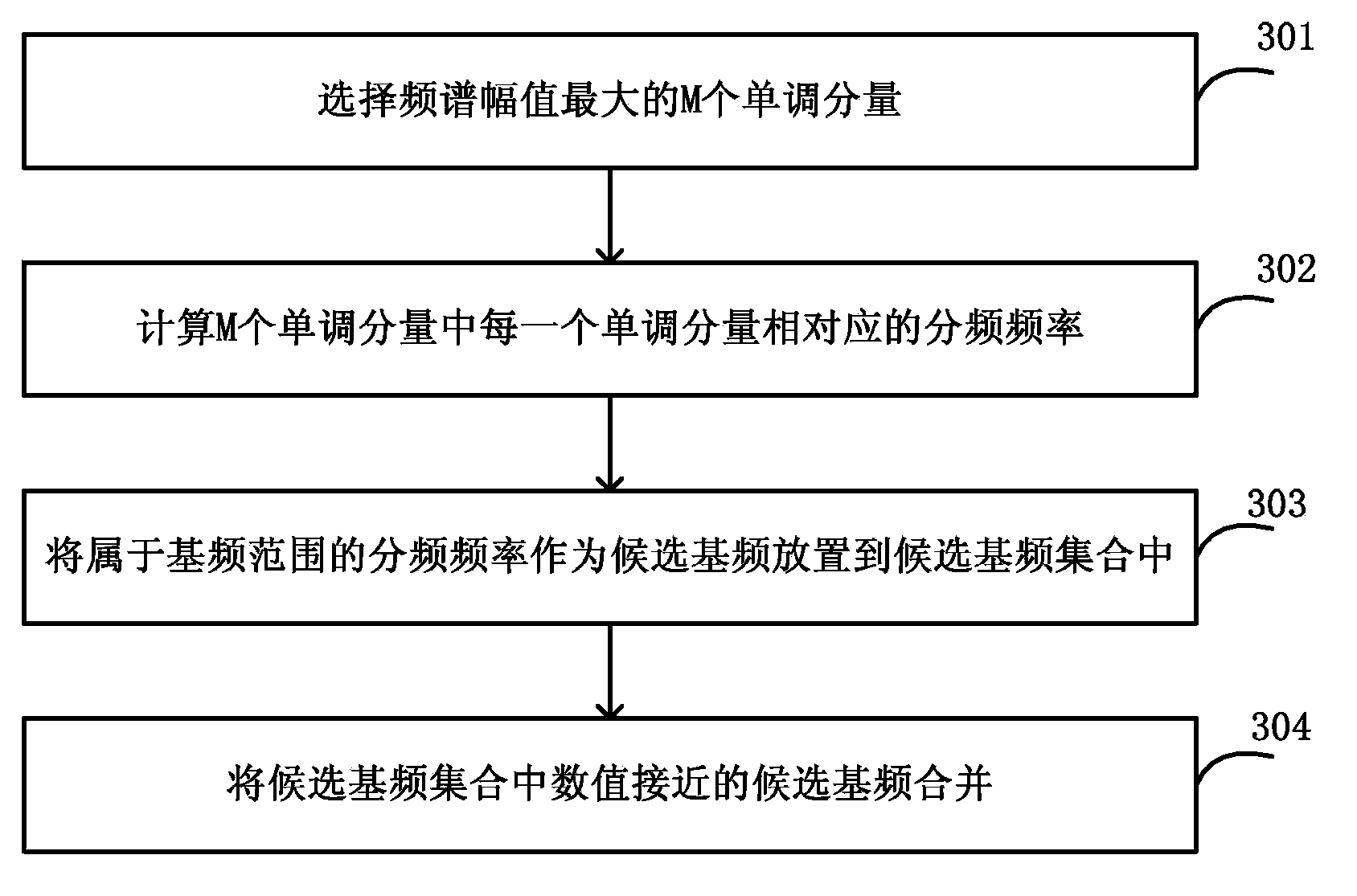
Method and apparatus for detecting voice fundamental tone frequency
The invention discloses a method and apparatus for detecting voice fundamental tone frequency. The method for detecting voice fundamental tone frequency comprises detecting monotone components in a voice signal frame; determining a candidate fundamental frequency by means of the frequencies of M monotone components with maximum frequency spectrum amplitudes; placing the candidate fundamental frequency in a candidate fundamental frequency set; calculating the harmonious criterion of each candidate fundamental frequency in the candidate fundamental frequency set; and using the candidate fundamental frequency with the maximum harmonious criterion as the fundamental frequency of the voice signal frame. The monotone component with large energy is used as the basis of fundamental tone detection such that the accuracy of fundamental tone detection in noise environment is increased.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Pure Tone and Beat Generator
InactiveUS20060249004A1Easy to tuneUnwanted overtones are minimizedPercussion musical instrumentsMusic aidsMedicineTone Frequency
This invention is for a percussion instrument that when struck produces a sustained tone. The instrument is shaped to produce a harmonious tone by tuning the appropriate overtones. The fundamental tone generated by the instruments disclosed herein are controllably tunable to within fractions of a hertz (Hz). Also disclosed are instruments that minimize and dampen unwanted overtones to generate a substantially pure tone. Also provided are related methods for generating a sustained tone as well as methods and devices for generating a beat, wherein a pair of the percussion instruments of the present invention having different tone frequencies provide the beat.
Owner:BUNKER ROBERT M +1
Portable device and method of providing user with information on operation of portable device
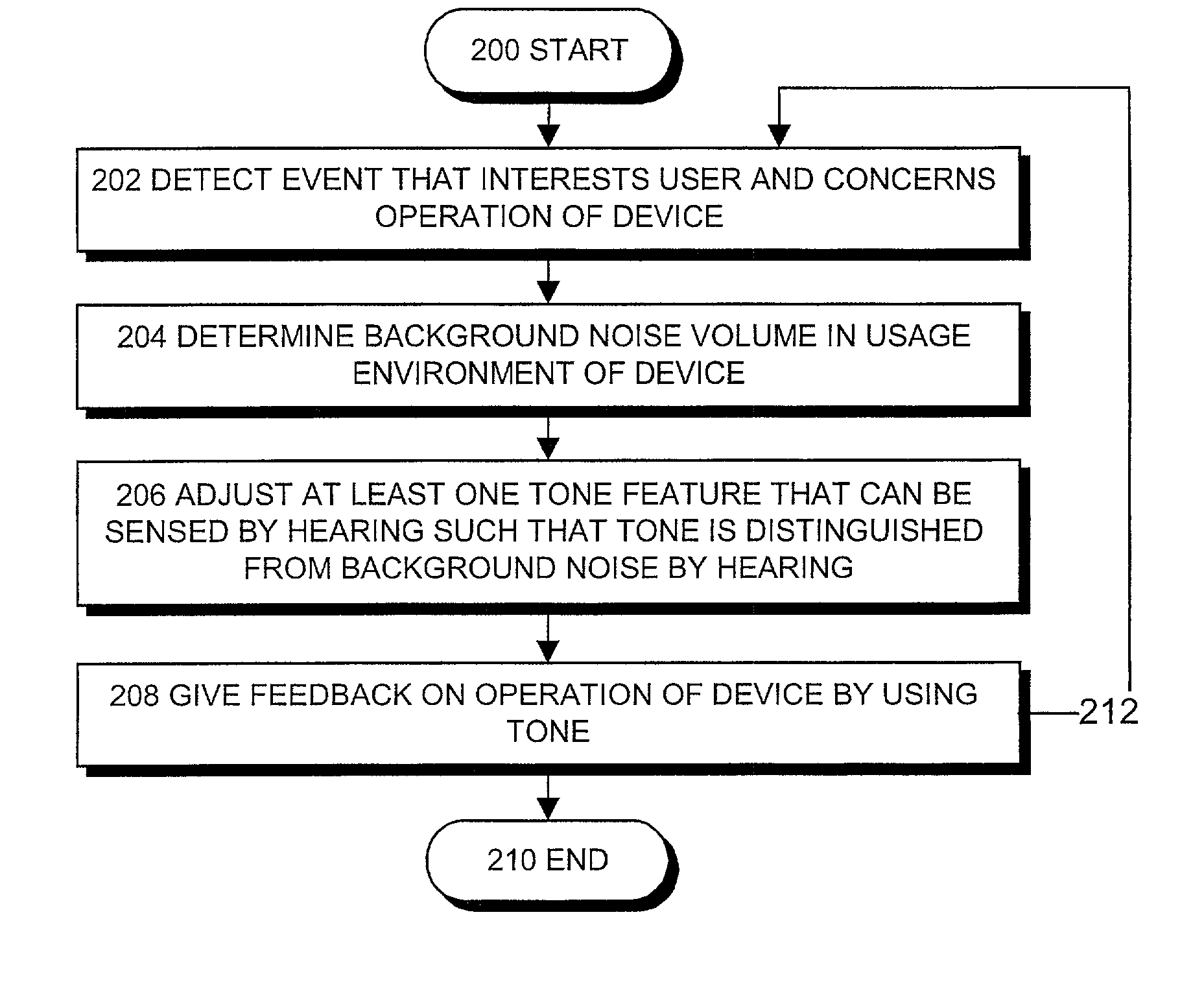
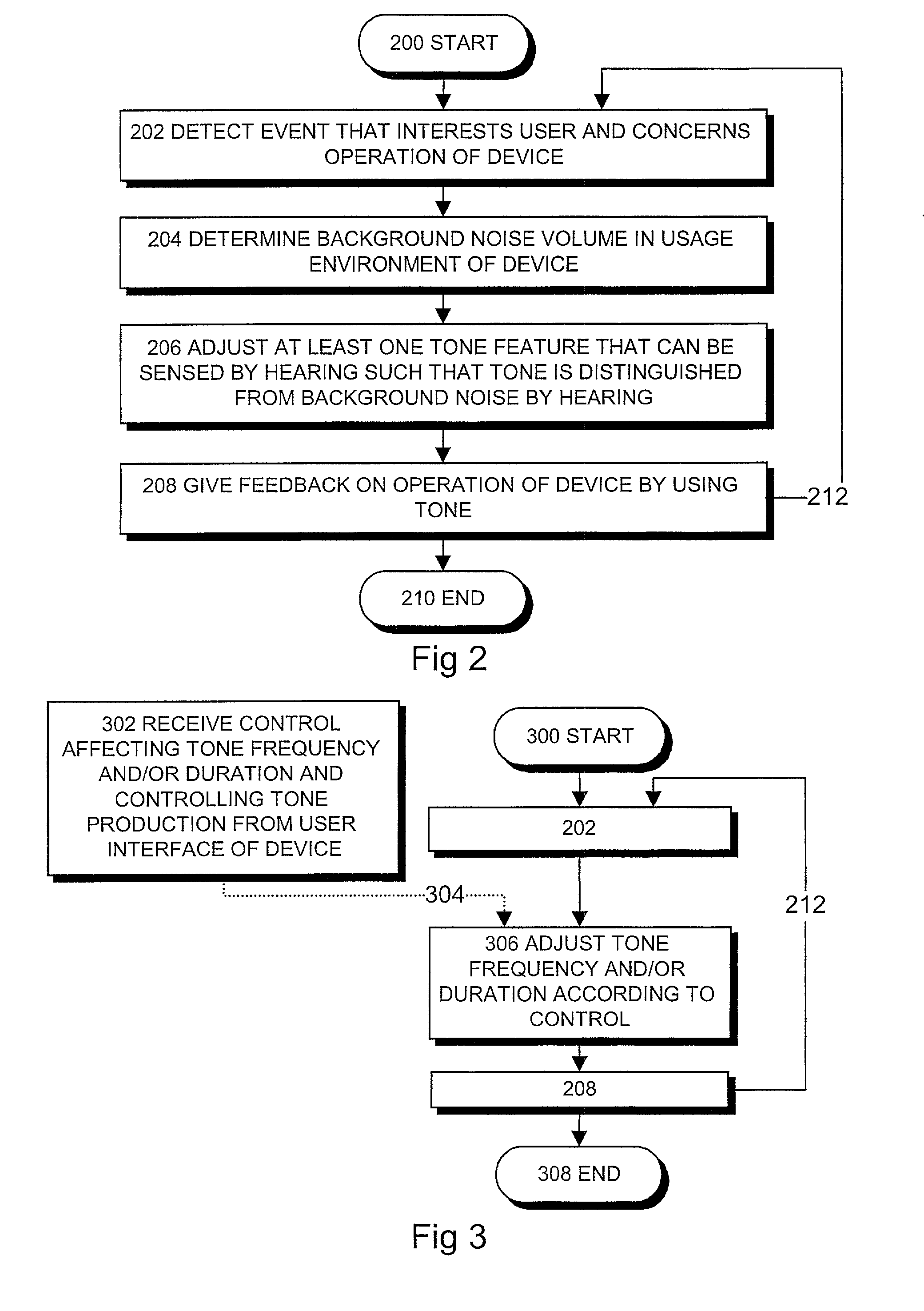
InactiveUS20020006207A1Excessive “background noise”Distinguish clearlyEar treatmentGain controlTone FrequencyBackground noise
The invention relates to a method of providing a user with information on the operation of the portable device and to a portable device. In the device, such a tone is produced that, due to a tone feature, can be distinguished from background noise. This feature can be tone frequency, duration, volume or moment of time. The device can analyse background noise automatically, and based on this, it adjusts at least one feature of the tone automatically such that the tone can be distinguished from background noise, and the background noise does not mask out the tone. Alternatively, the user himself can adjust the tone frequency or duration in a desired way so that it would be distinguished from background noise more clearly.
Owner:NOKIA MOBILE PHONES LTD
Method and Device for Creating a Control Channel in an Optical Transmission Signal and Method and Device for Extracting the Information Included Therein
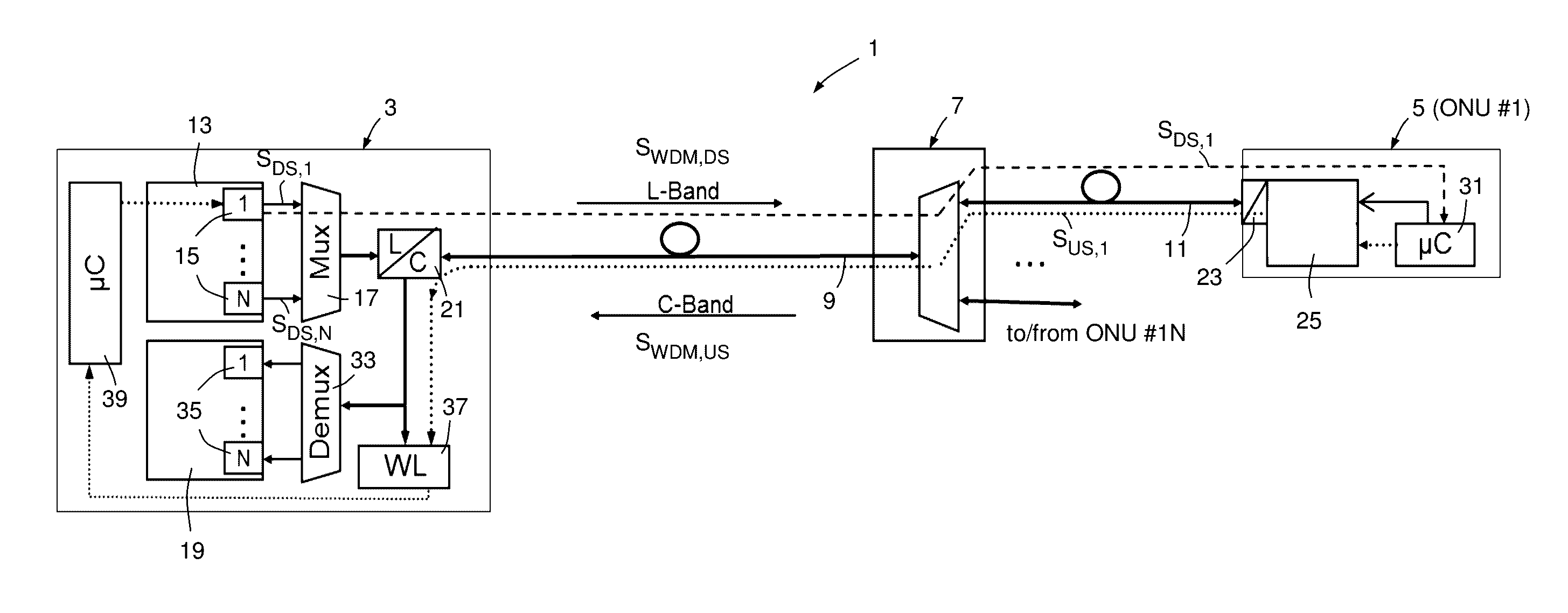
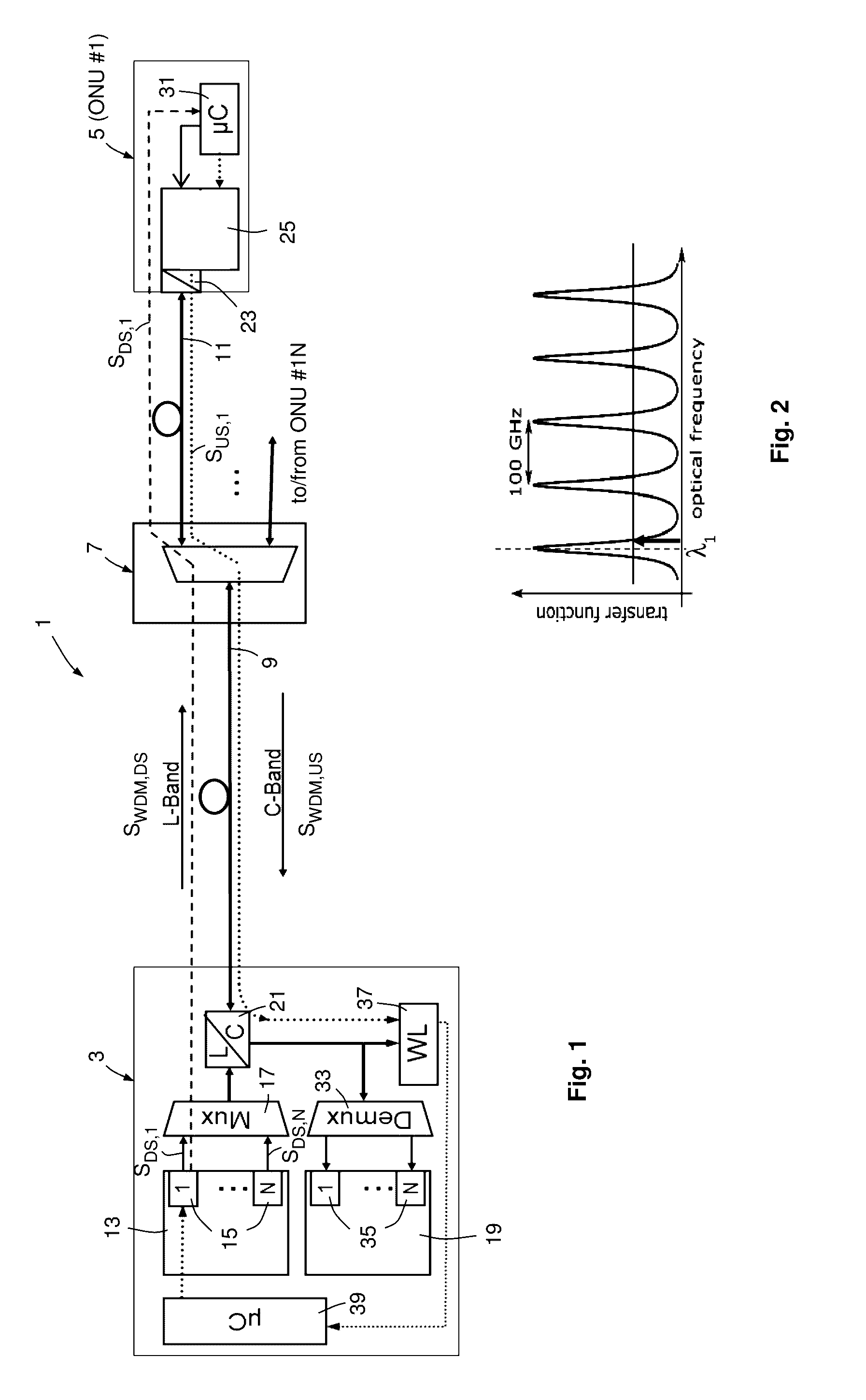
ActiveUS20160301496A1Low costEasy to createWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic network arrangementsHigh frequency modulationCarrier signal
The invention relates to a method for creating a control channel in an optical transmission signal, wherein the optical transmission signal (SDS,i, SUS,i) includes an optical carrier frequency component, a higher frequency modulation component carrying user information to be transported from a first end to a second end of an optical transmission link and a lower frequency modulation component carrying control information, the higher frequency modulation component realizing a user channel and the lower frequency modulation component realizing the control channel, and wherein the lower frequency modulation component is created by amplitude modulation. According to the invention, the lower frequency modulation component includes a binary digital pilot tone signal component which corresponds to a pilot tone signal having a predetermined pilot tone frequency (fi).
Owner:ADVA OPTICAL NETWORKING SE
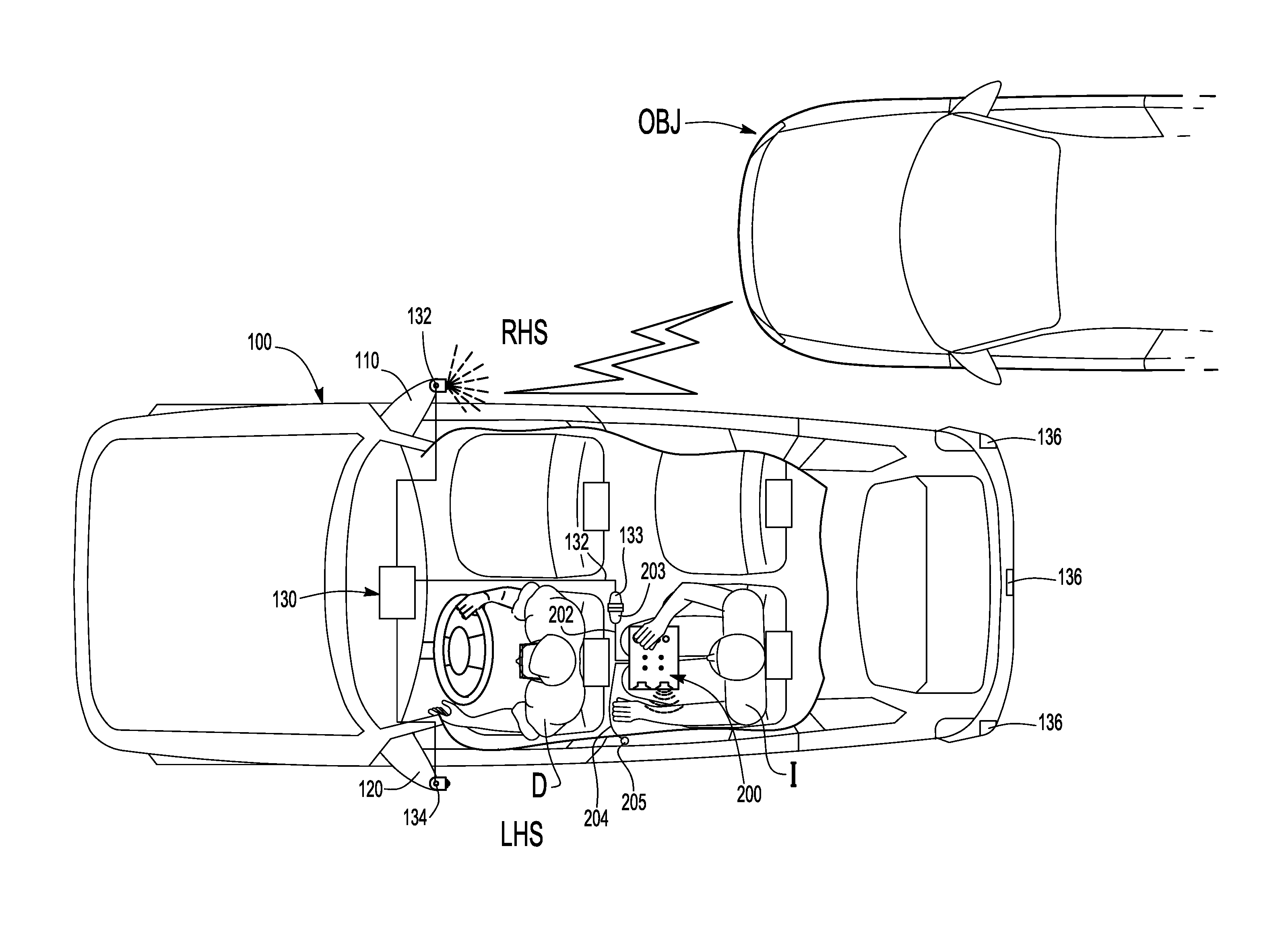
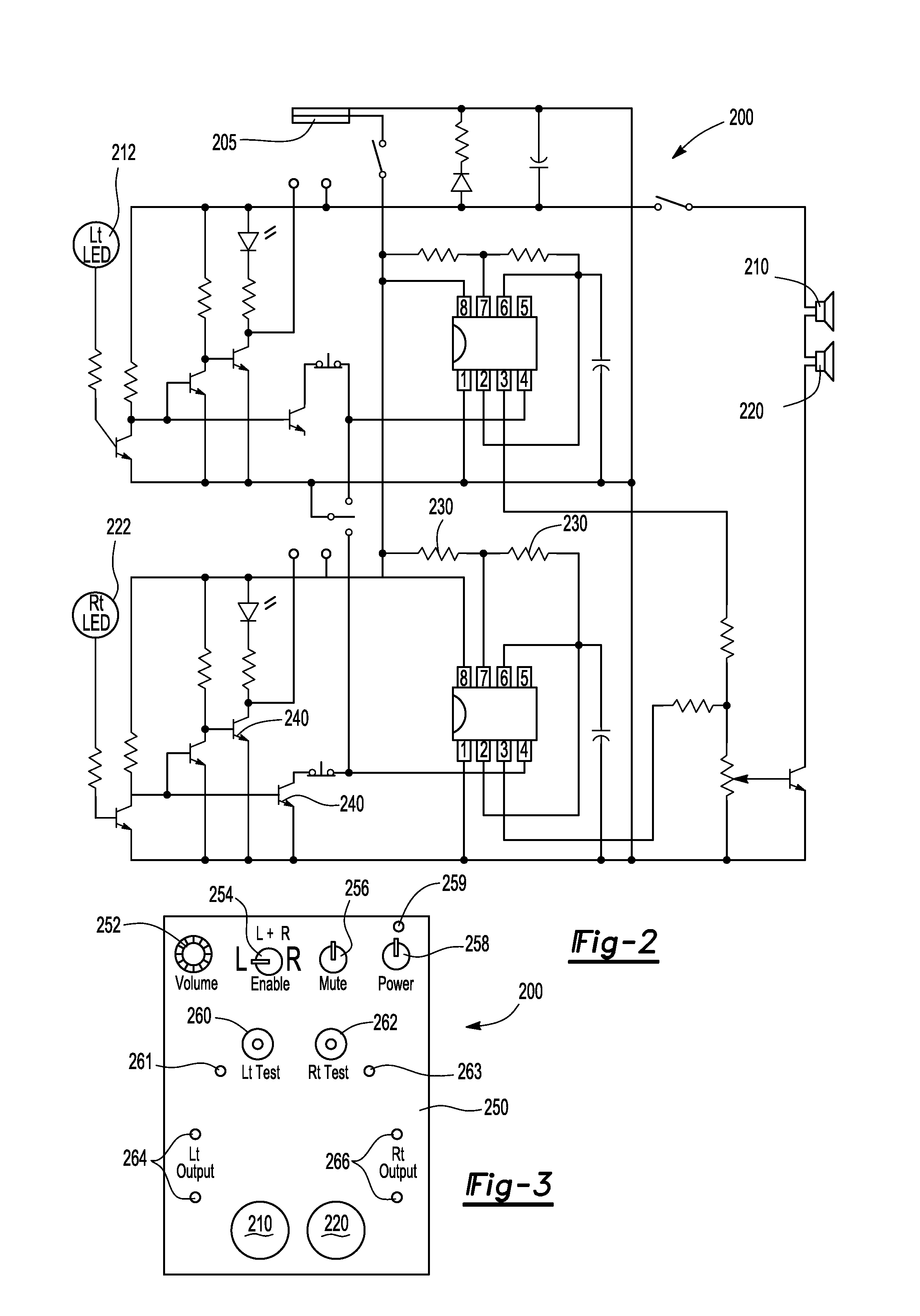
Audible blind spot indicator
An audible blind spot indicator for a motor vehicle having a blind spot detection system is provided. The audible blind spot indicator can include an audible module that has a first tone generator operable to generate a first tone frequency and a second tone generator operable to generate a second tone frequency that is different than the first tone frequency.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD
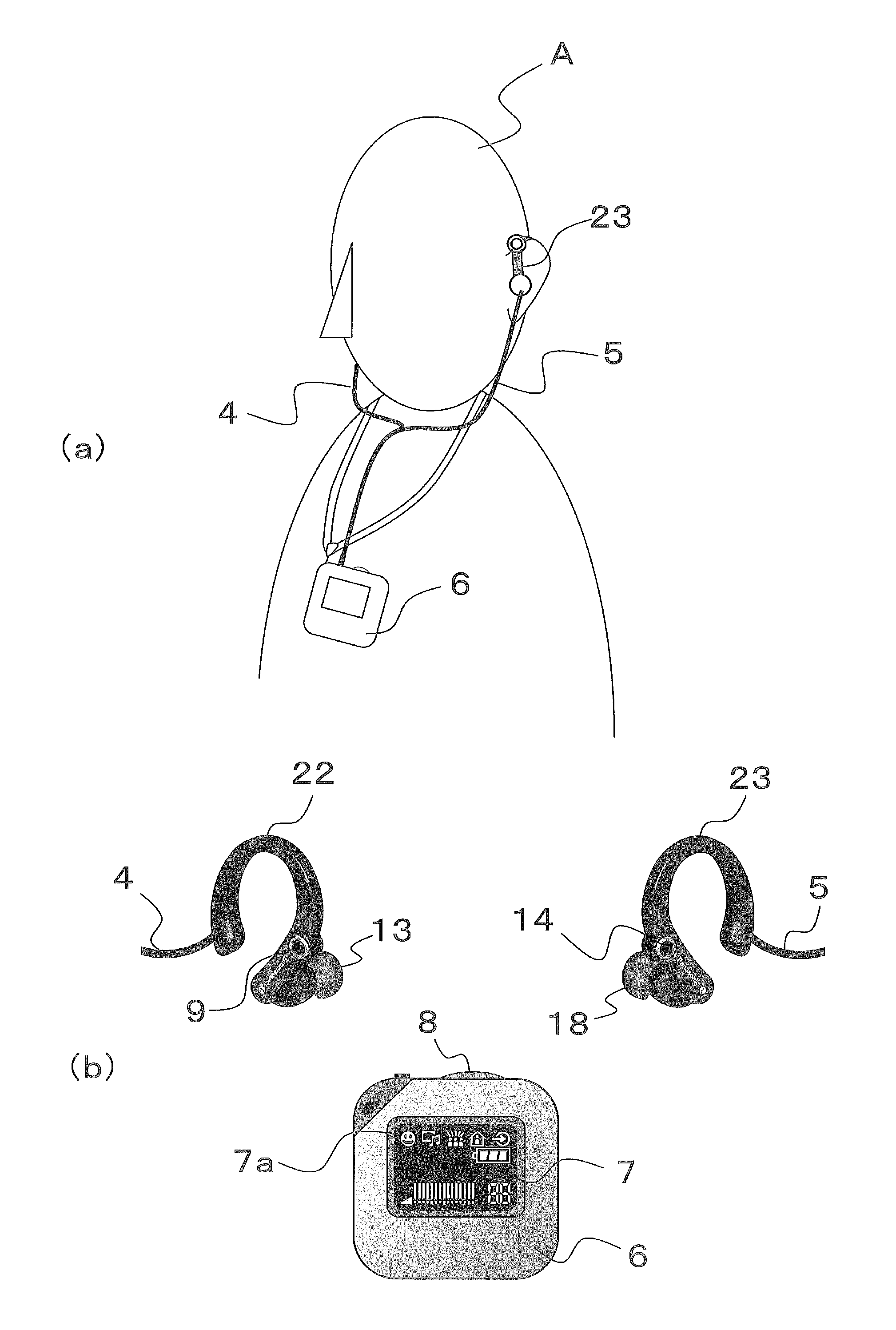
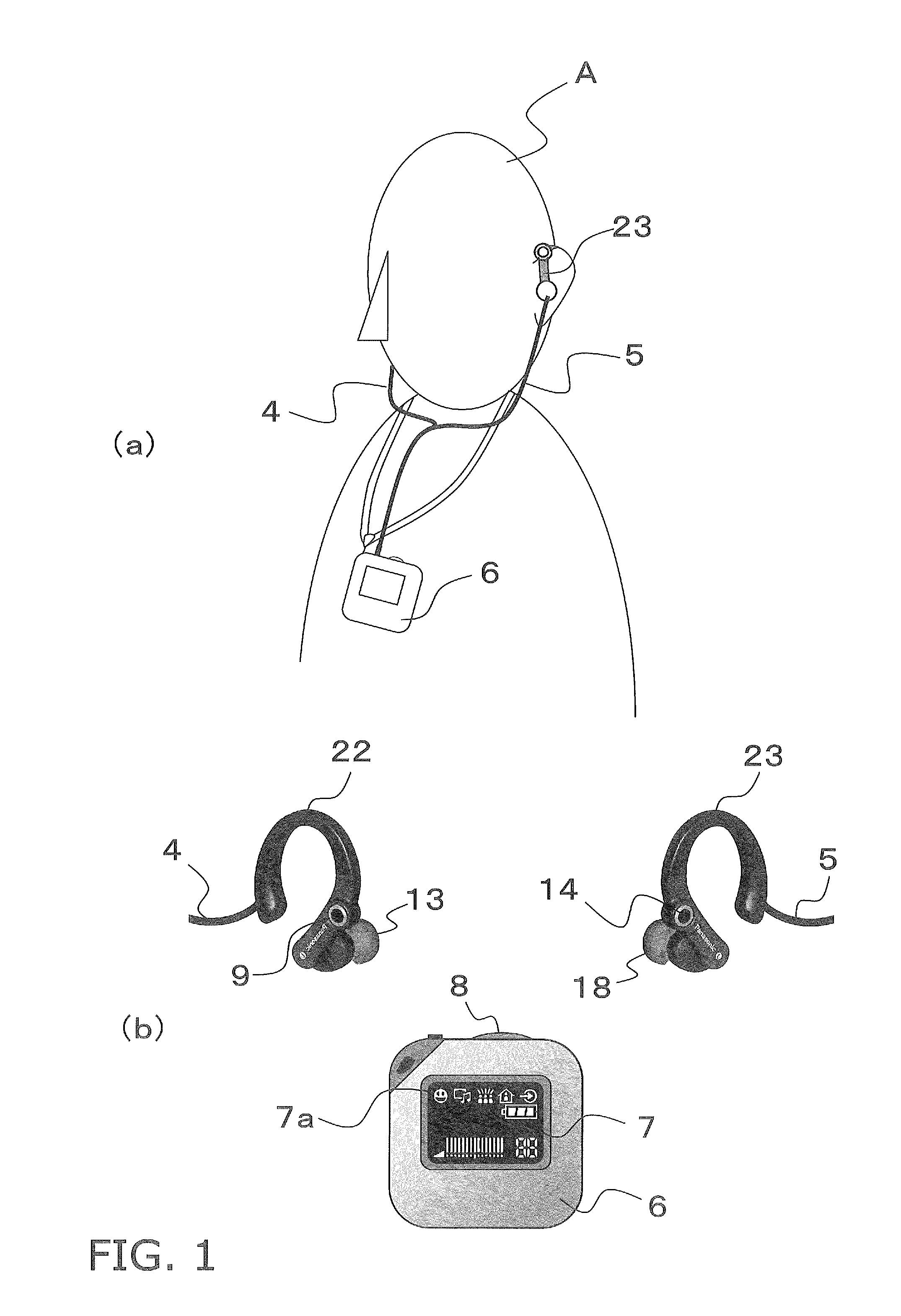
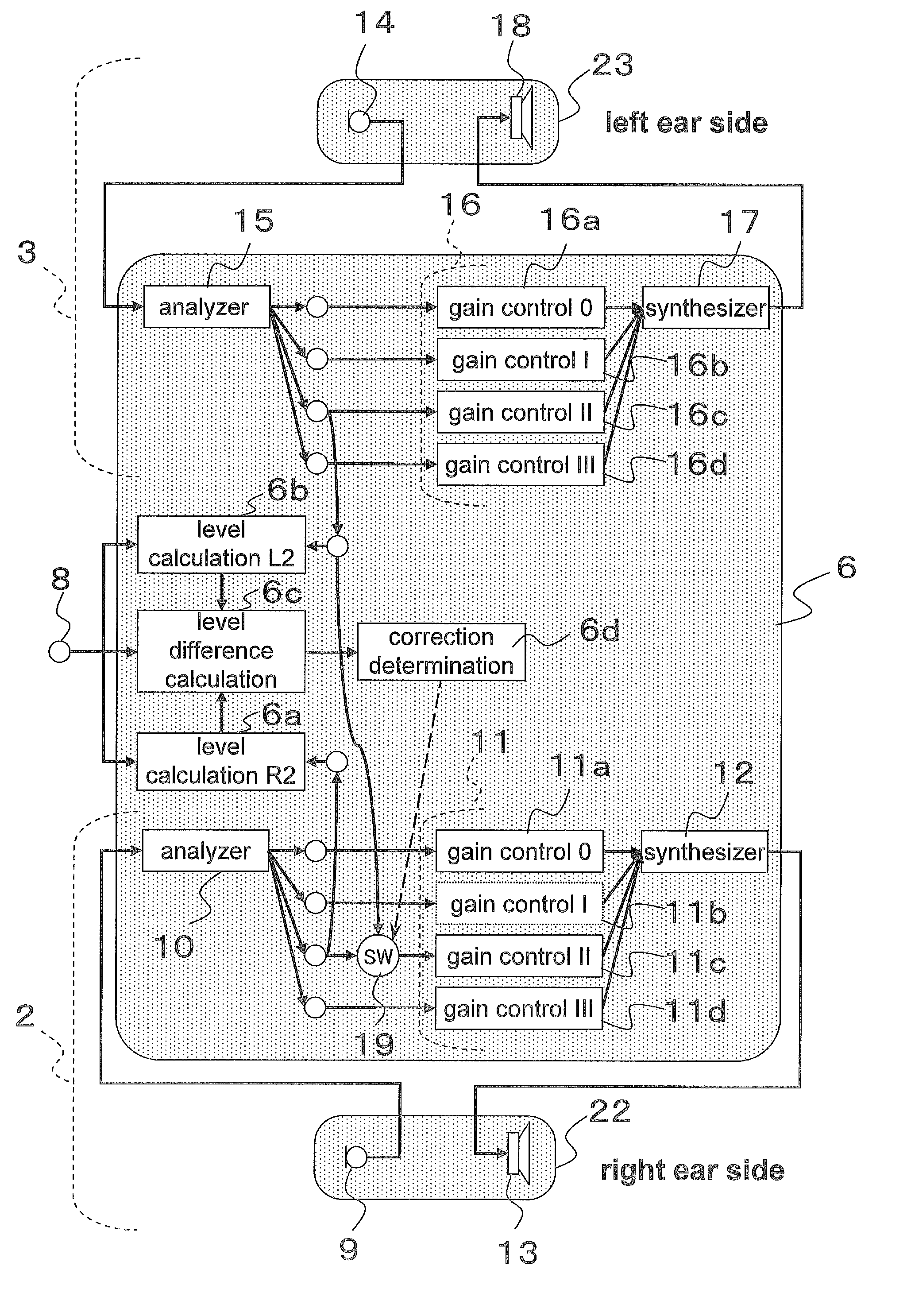
Hearing aid device
A hearing aid is used for a low tone frequency band, a hearing aid is used for a high tone frequency band, and a controller that compares sound pressure of the high tone frequency band split by a frequency band analyzer of the hearing aid used for the high tone frequency band with sound pressure of the high tone frequency band split by a frequency band analyzer of the hearing aid used for the low tone frequency band. If the sound pressure of the high tone frequency band of the hearing aid used for the low tone frequency band is higher by at least a specific amount than the sound pressure of the high tone frequency band of the hearing aid used for the high tone frequency band, the sound pressure of the high tone frequency band of the hearing aid used for the high tone frequency band is raised.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
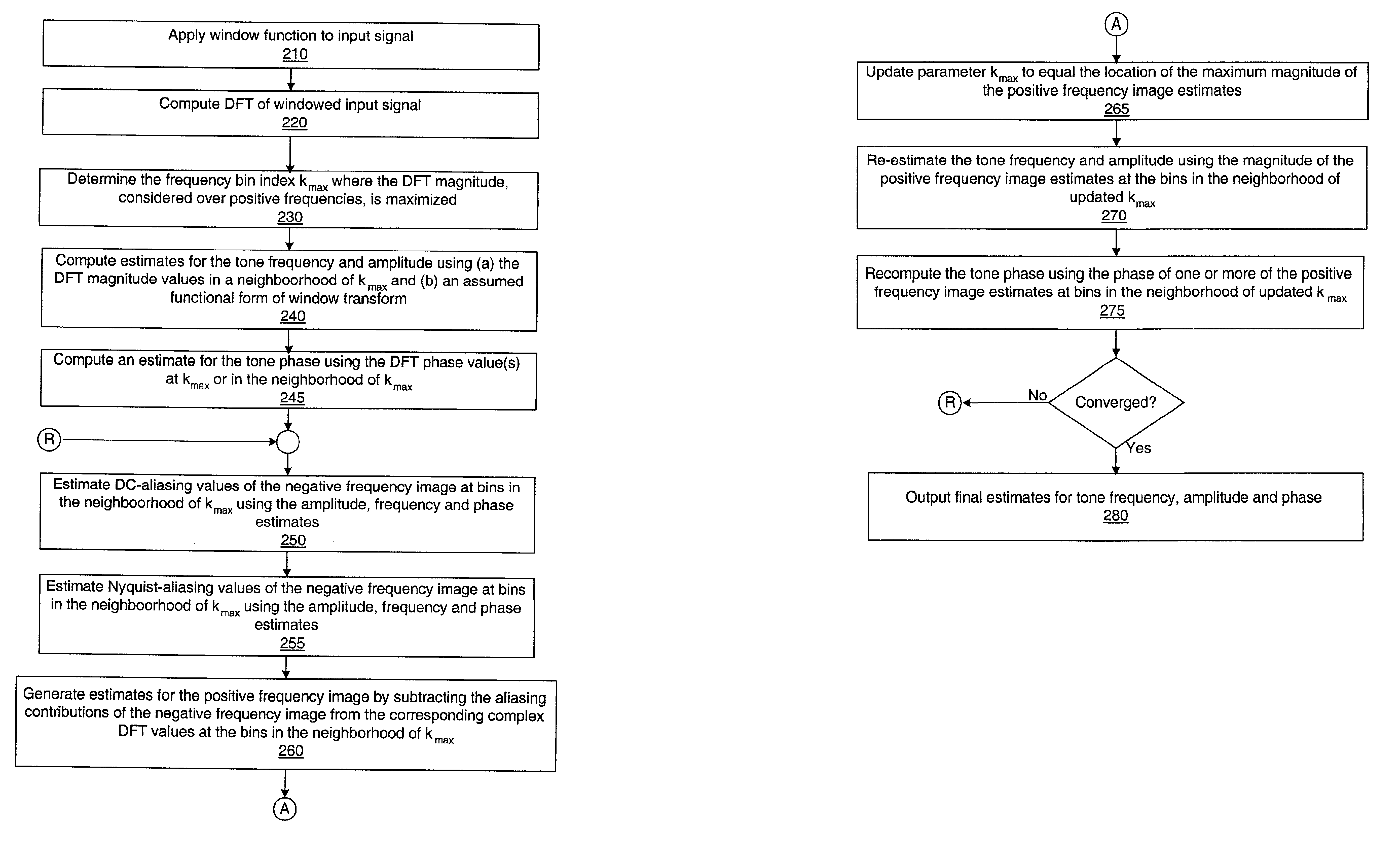
System and method for estimating tones in an input signal
ActiveUS6965068B2Improve approximationAccurate valueElectrophonic musical instrumentsComplex mathematical operationsComplex amplitudePeak value
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Hearing aid device
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Apparatus and method for controlling initialization of a DMT system
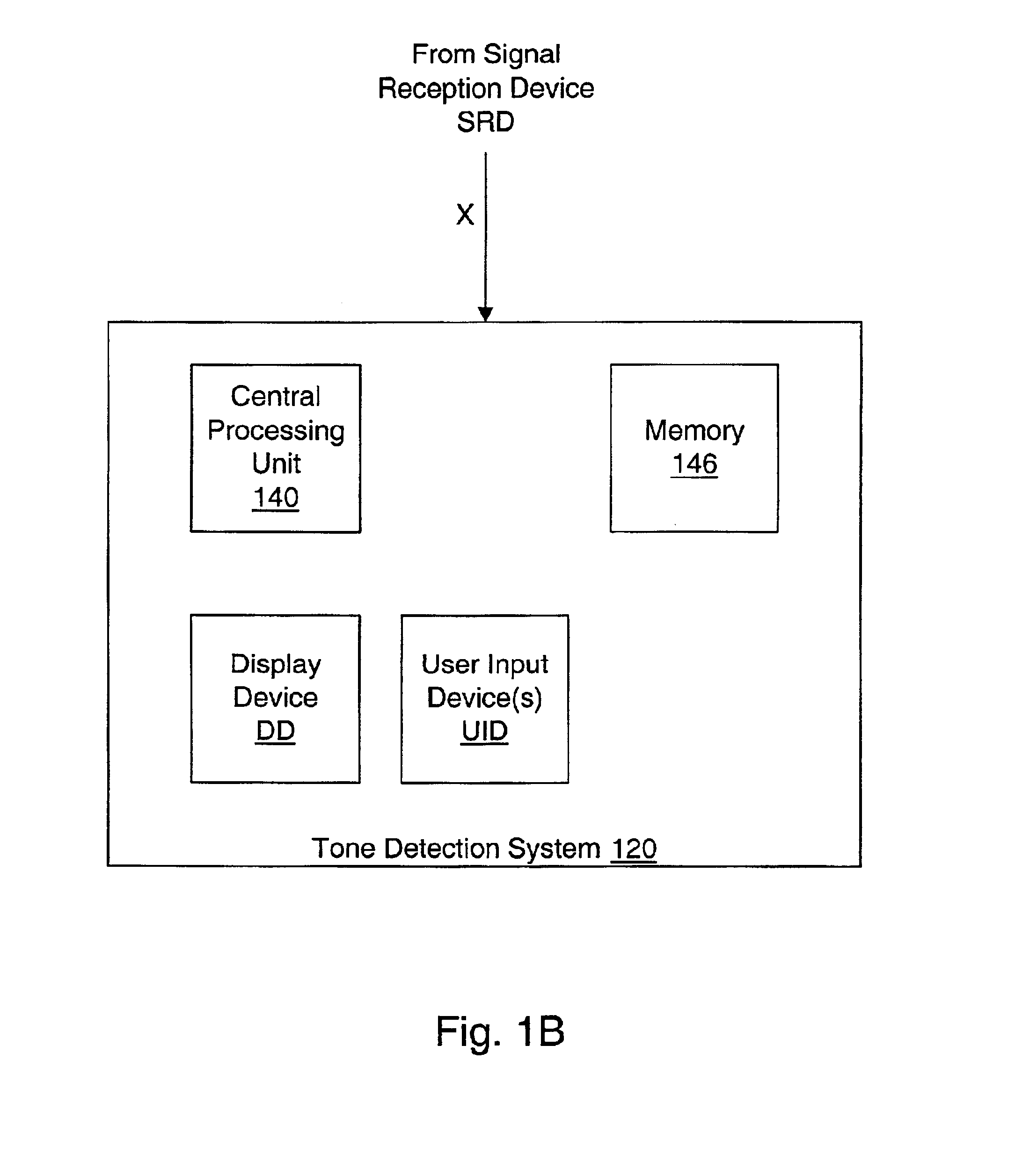
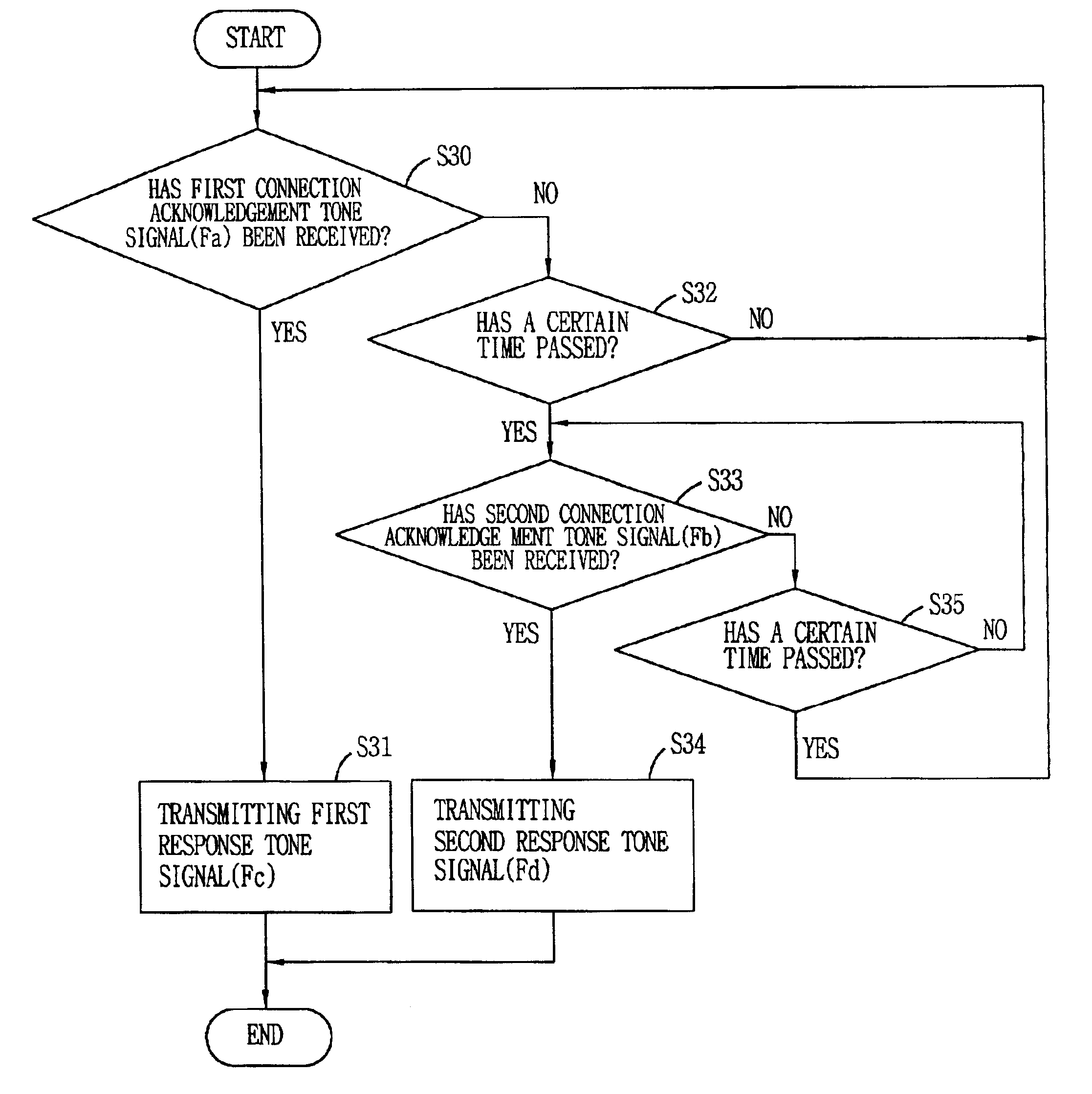
InactiveUS6845103B1Guaranteed reliabilityError preventionTransmission systemsBiological activationTone Frequency
An apparatus for controlling initialization of a discrete multi-tone (DMT) system is provided in which a connection between first and second devices is acknowledged by using a plurality of connection acknowledgment tone frequencies to thereby improve the reliability of the activation / acknowledgment procedure. The method includes transmitting a first connection acknowledgment tone signal at a predetermined frequency from the first device to the second device; detecting a first response tone signal transmitted from the second device; transmitting a second connection acknowledgment tone signal to the second device if the first response tone signal is not detected for a predetermined time; and detecting a second response tone signal inputted from the second device to thereby acknowledge a connection to the second device.
Owner:LG ERICSSON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com