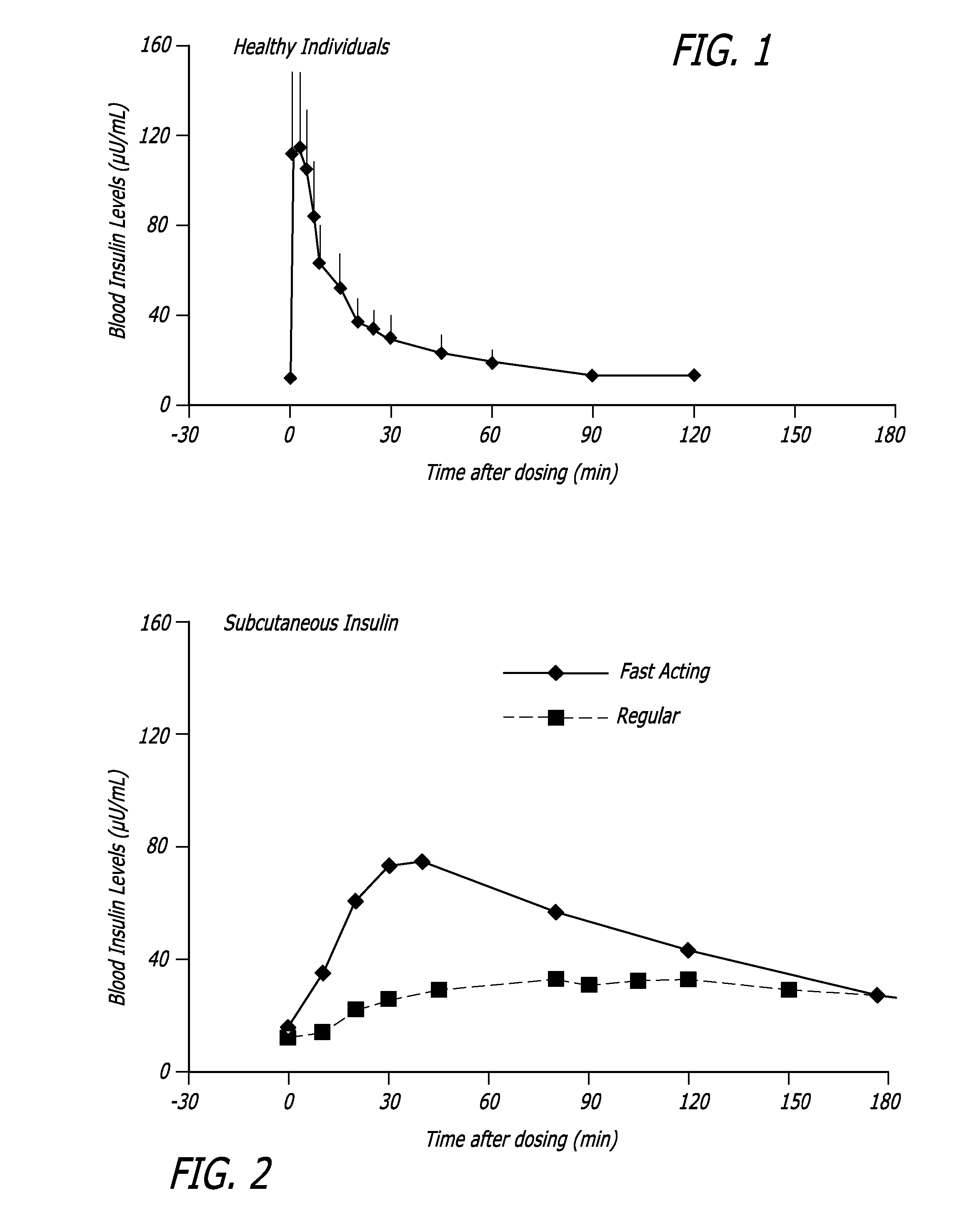
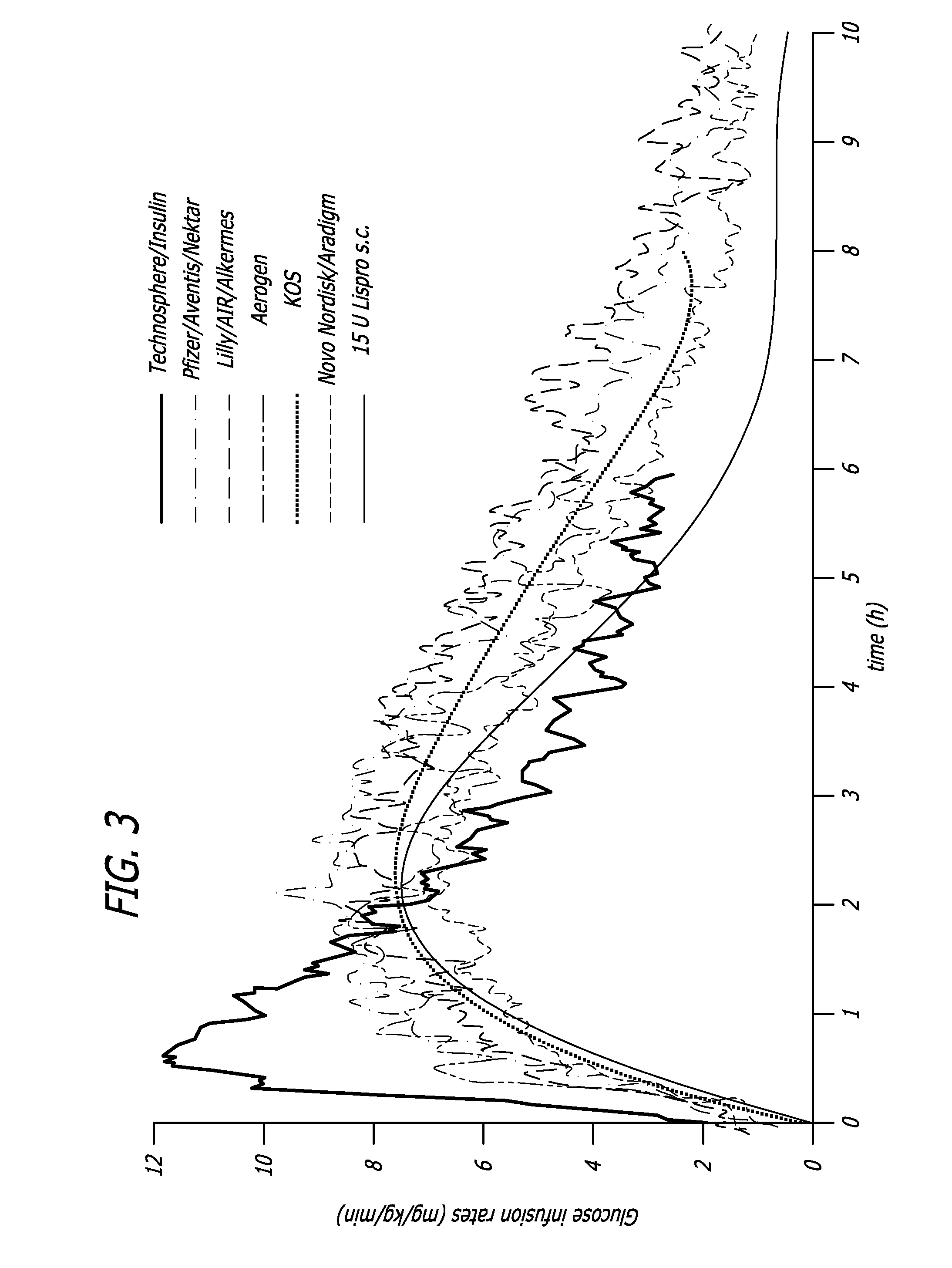
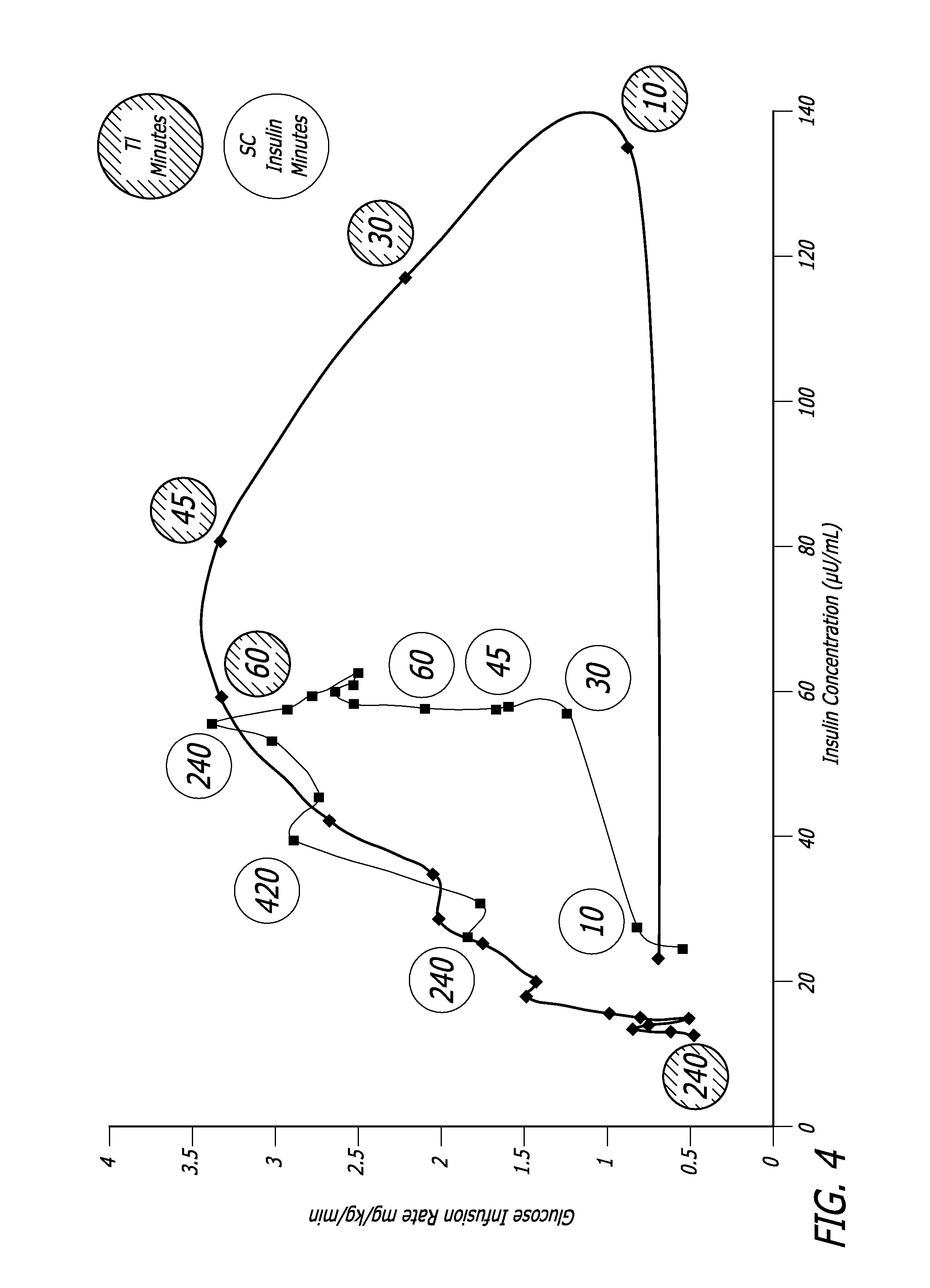
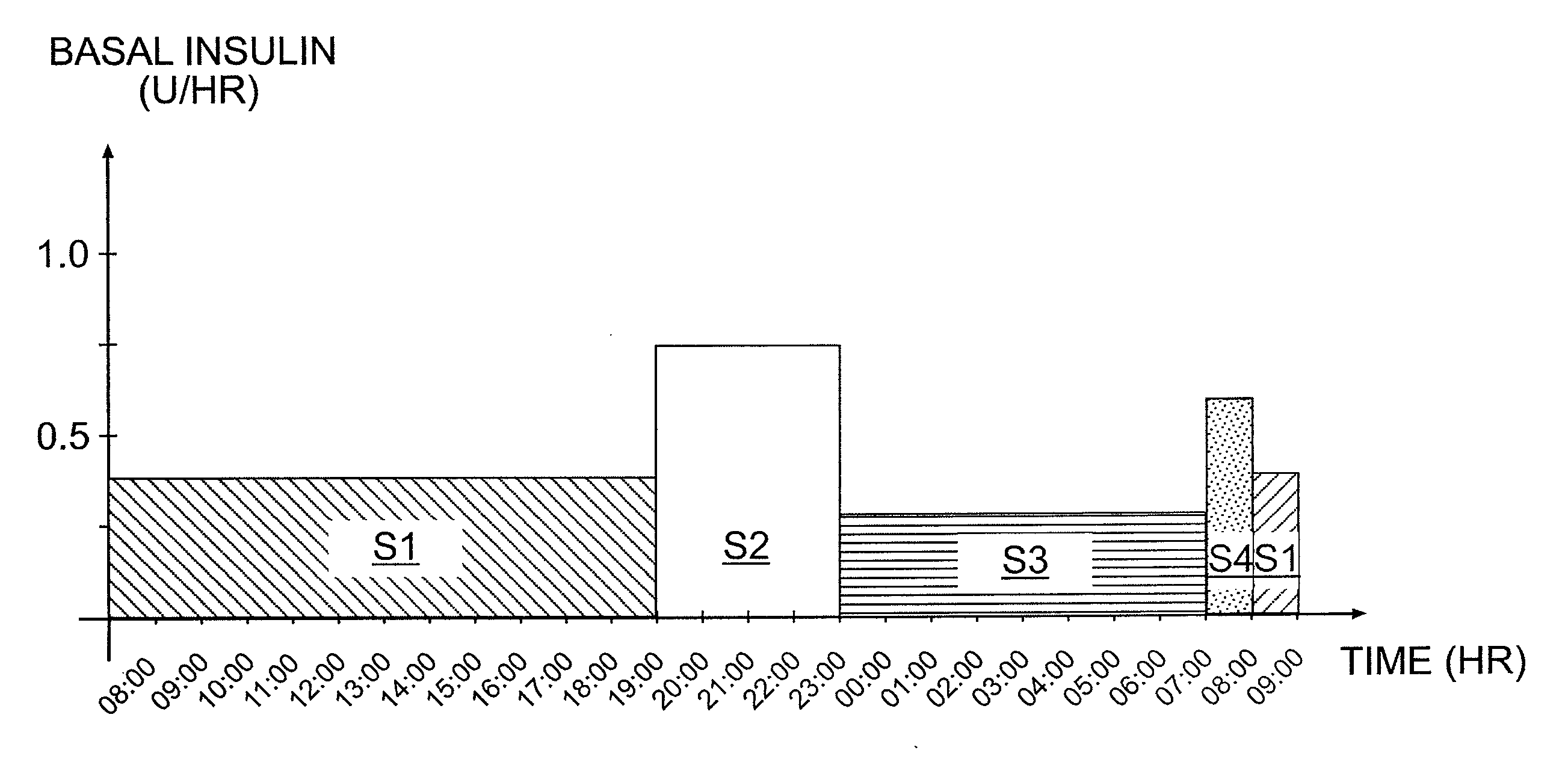
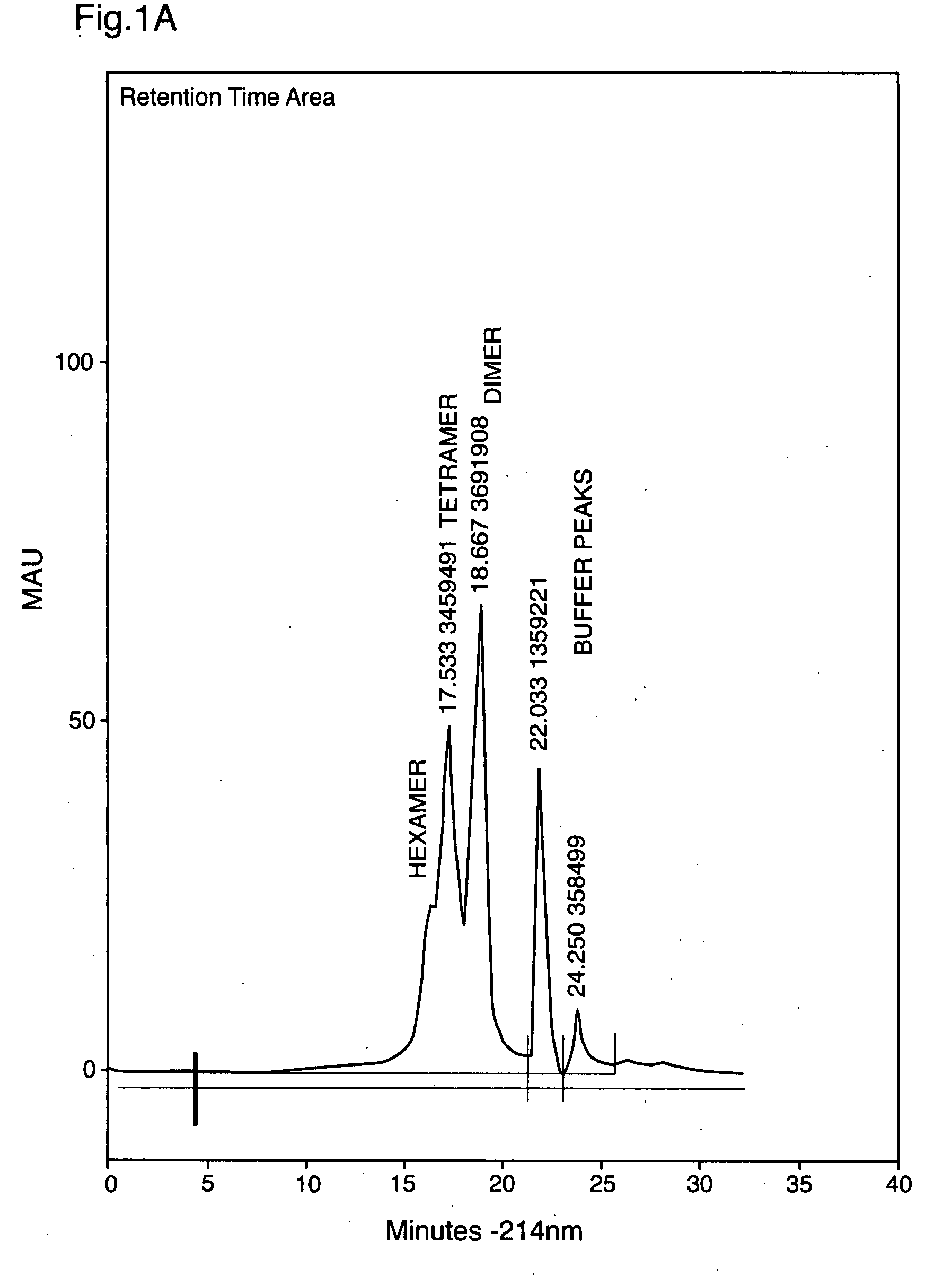
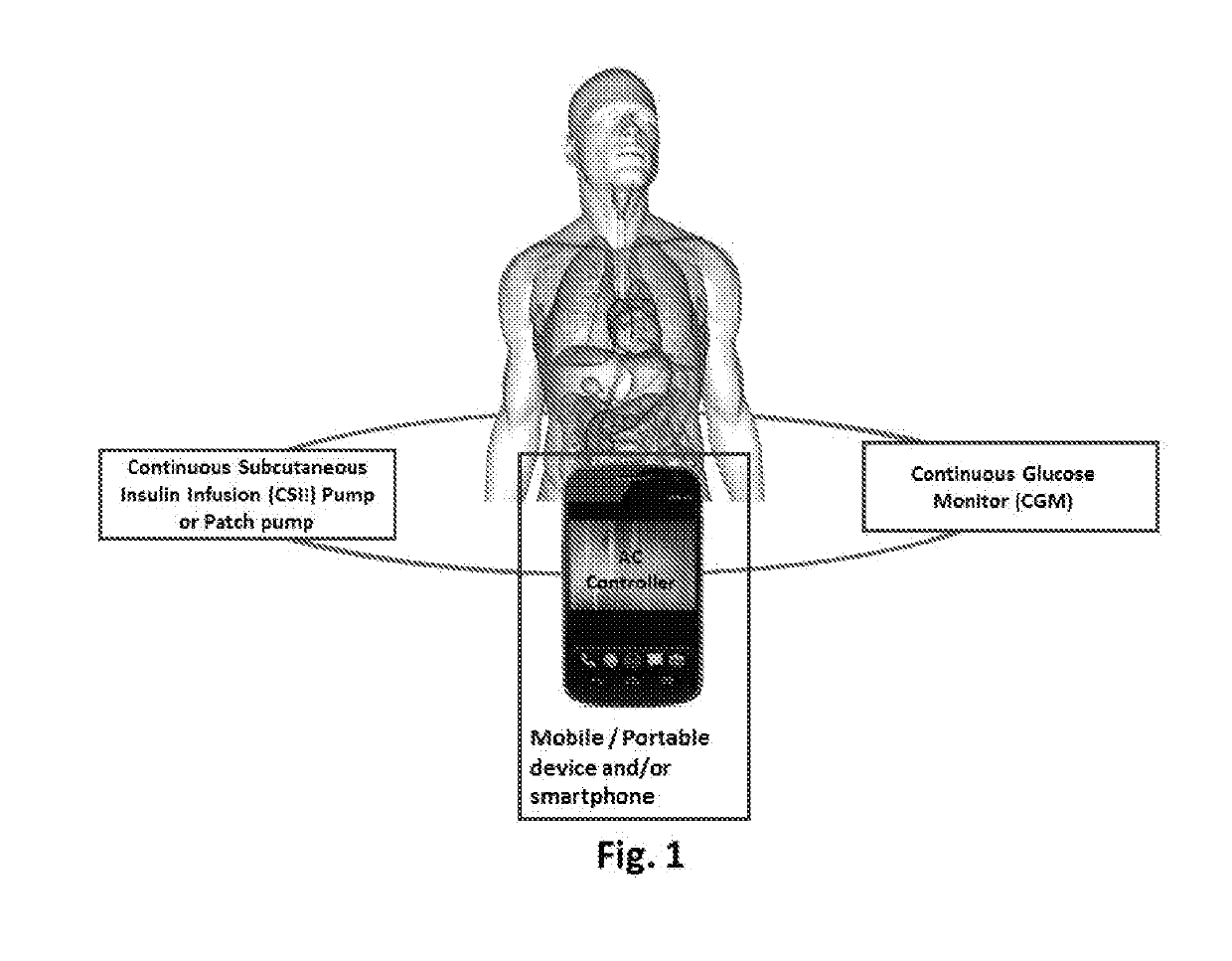
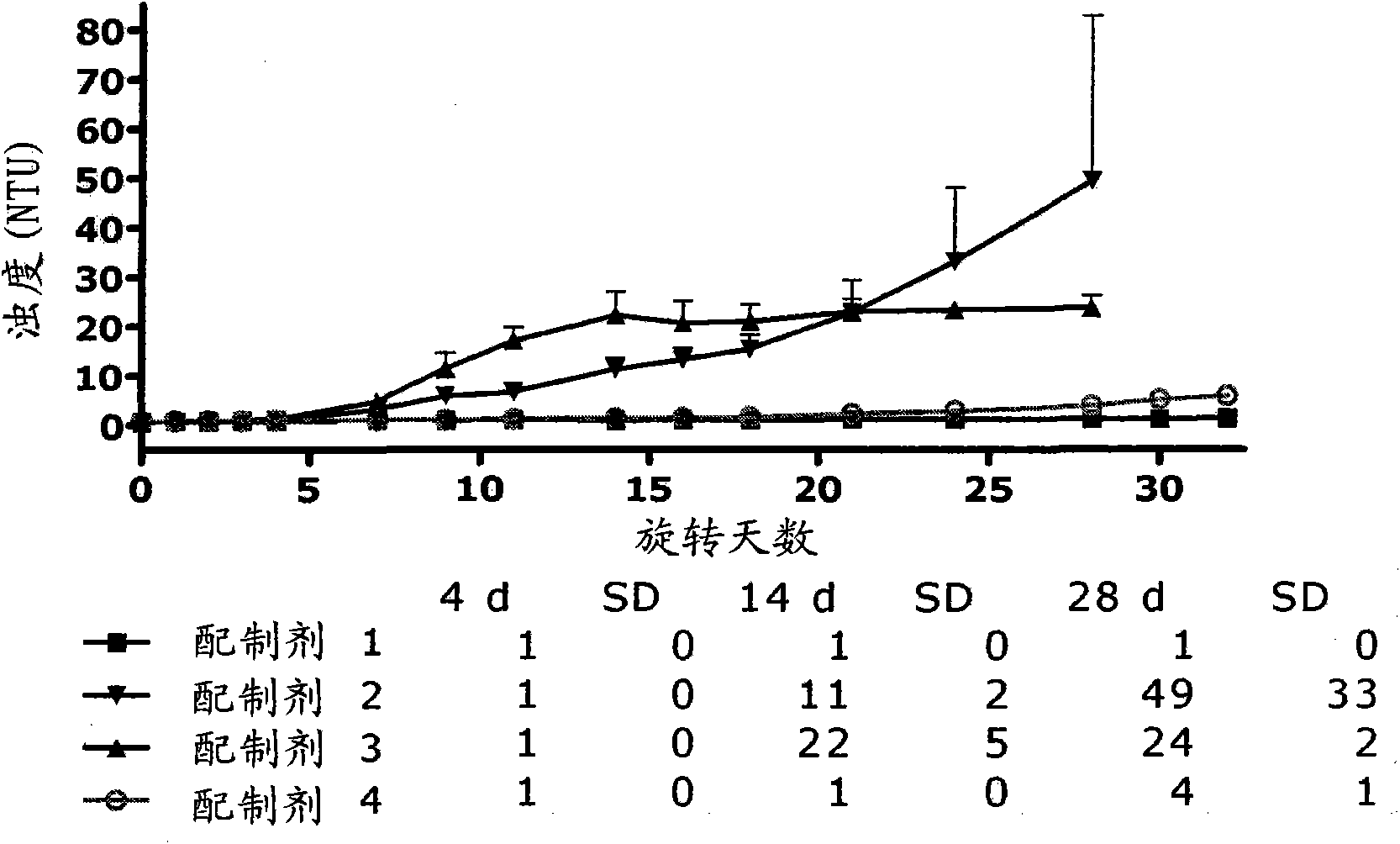
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Basal insulin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Basal insulin is a crucial component in your diabetes management. Work with your doctor or endocrinologist to determine which type is best for you and your needs.
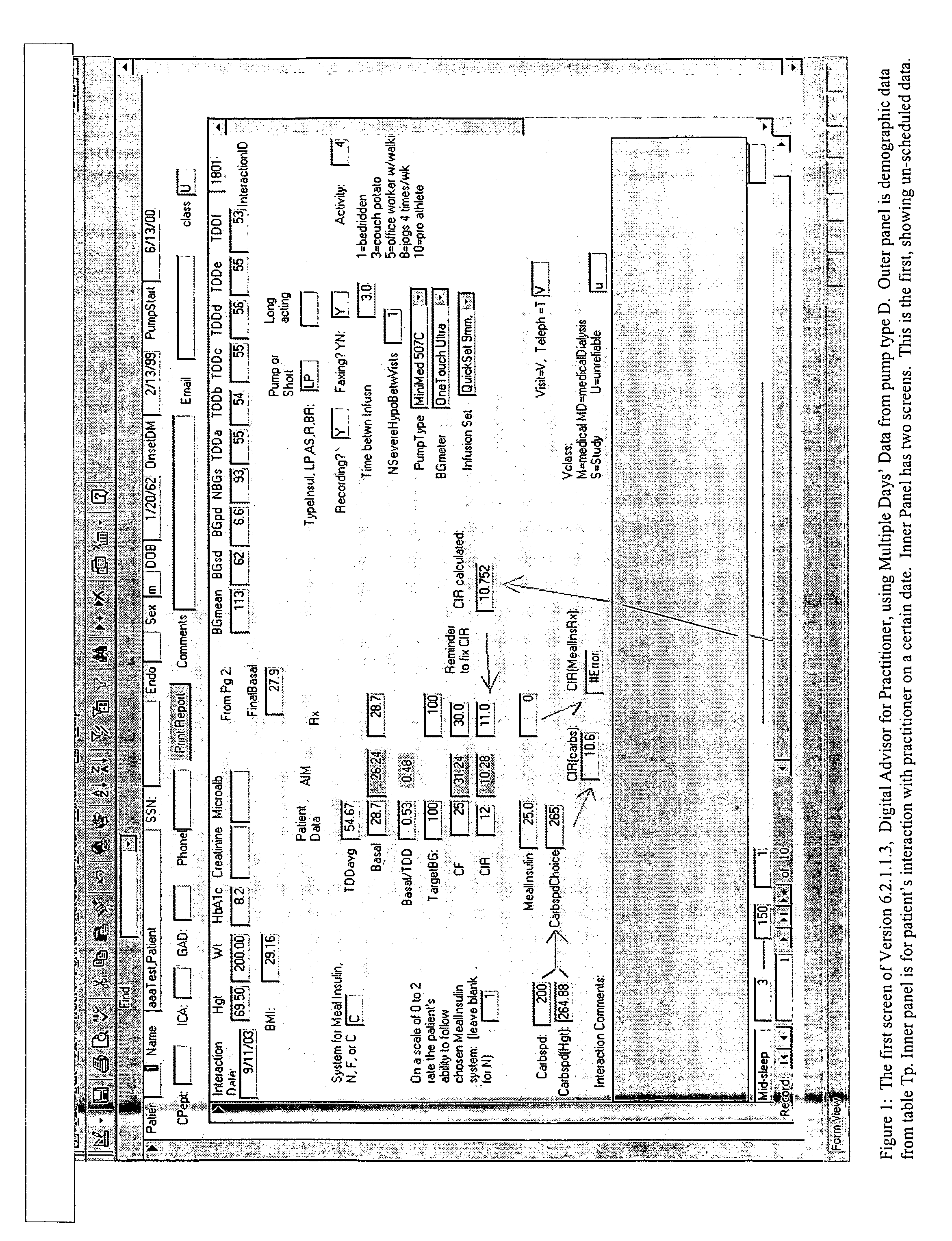
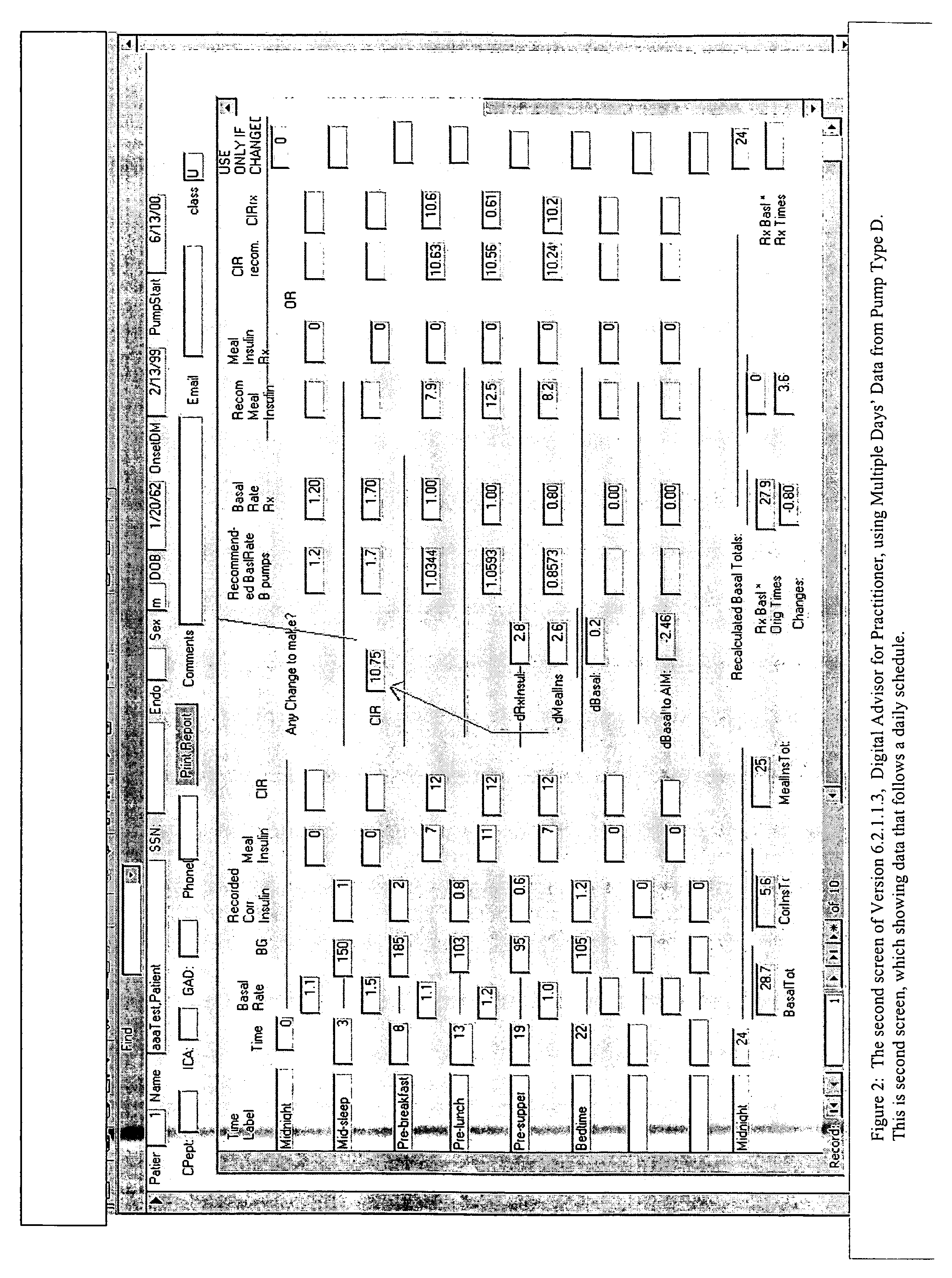
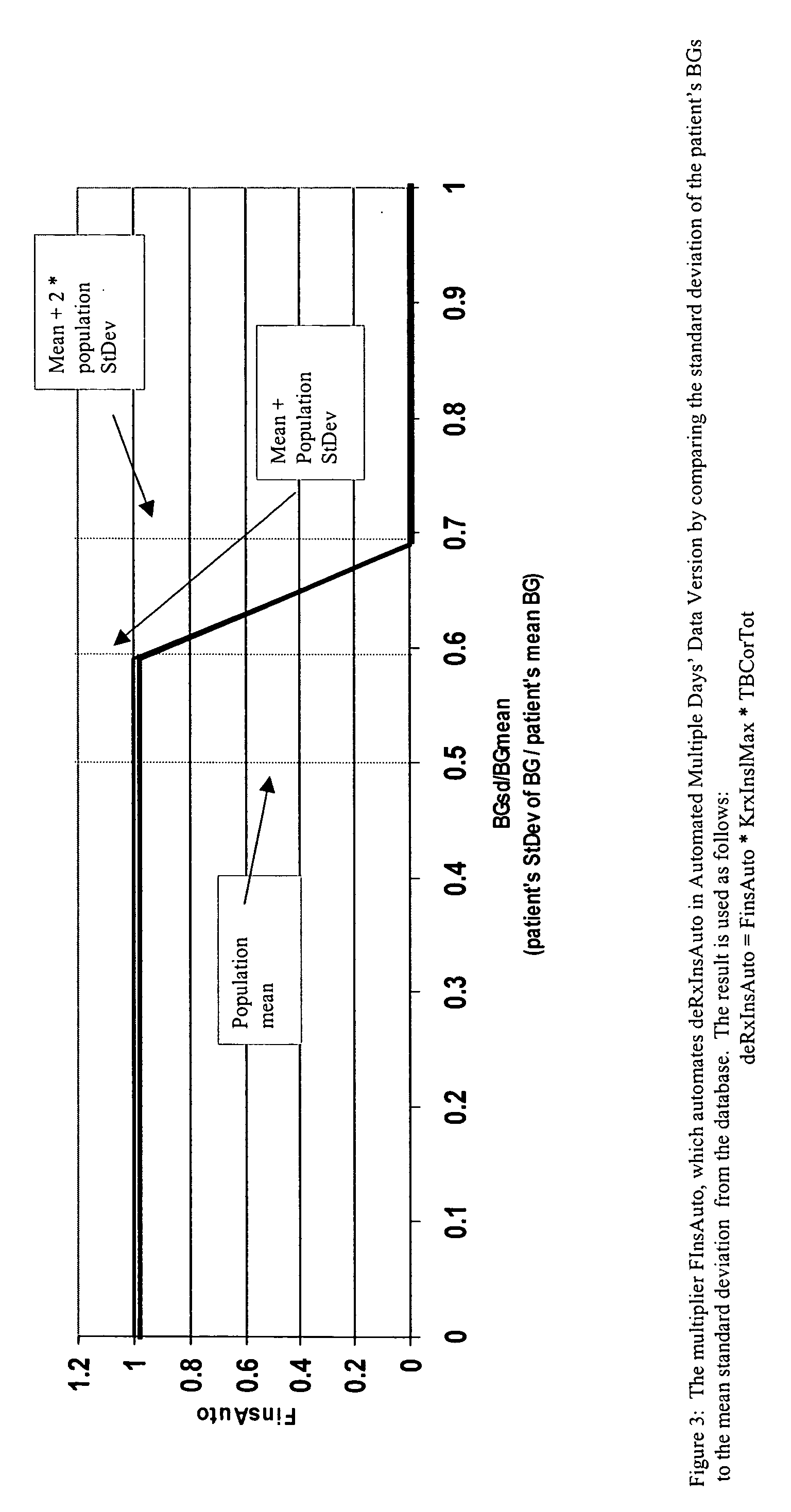
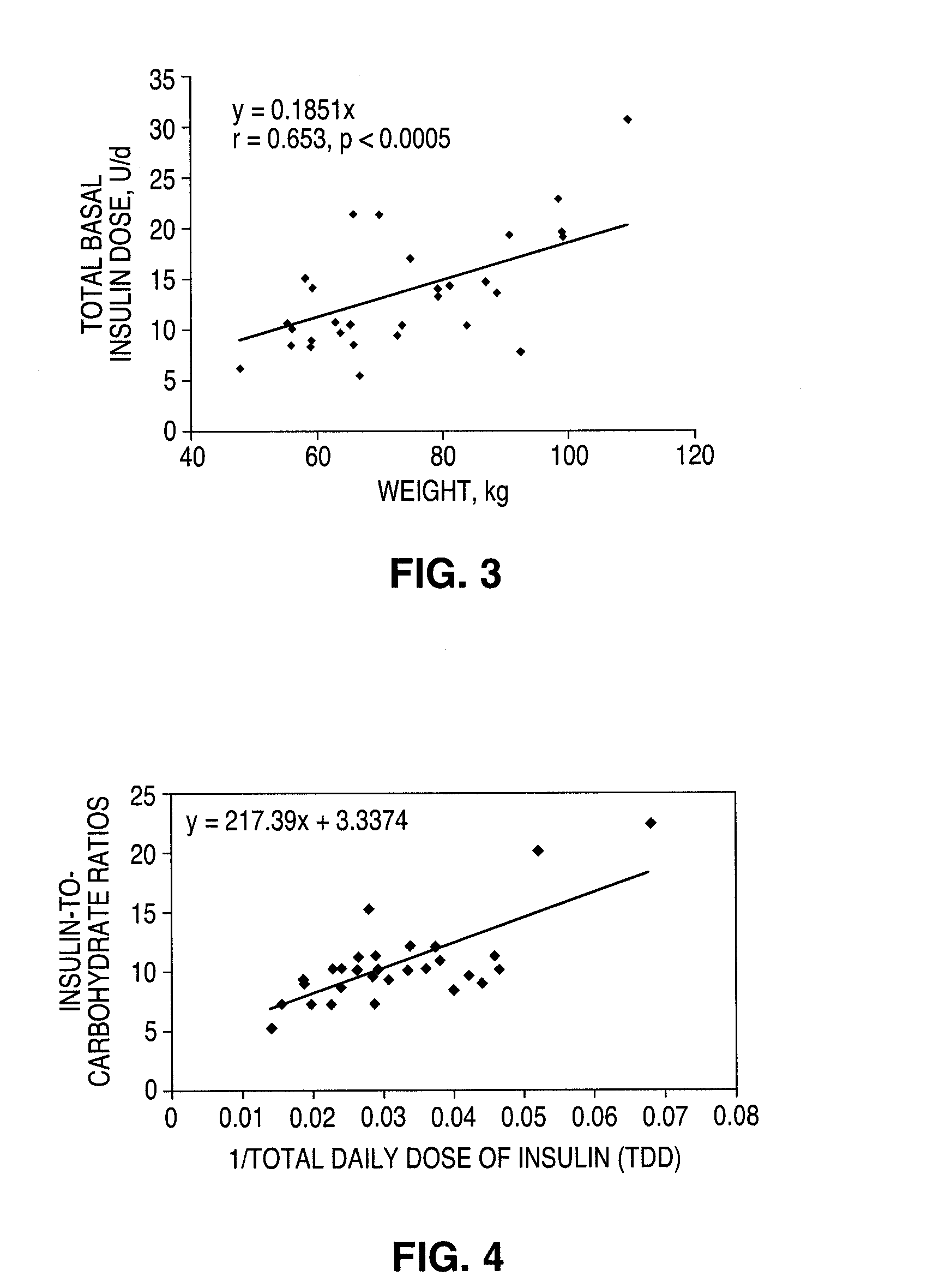
Method and system for determining insulin dosing schedules and carbohydrate-to-insulin ratios in diabetic patients
ActiveUS20050049179A1Prevent overshootPeptide/protein ingredientsAutomatic syringesInsulin regimenCompound (substance)
Method for digitally determining the daily insulin regimen for a diabetic patient. The invention divides the patient's day into adjustable time intervals containing basal insulin dosage rates and Carbohydrate-to-Insulin Ratio(s) (for determining meal insulin doses). The invention identifies the Corrective Insulin doses over a time interval as an “error” in the Prescription Insulin (Basal Insulin+Meal Insulin). Methods involve first estimating the change to one of these two components of Prescription Insulin, and then determining the change to the other by subtracting from the error. One method estimates Change in Meal Insulin distributed among intervals proportional to old Meal Insulin. Another method lumps After-Meal Corrective Insulin together with Meal Insulin. Another method splits the interval at the After-Meal Corrective Dose and determines Basal from Time-Boundary Corrective Dose. Data may be obtained from the previous day, and a small fraction of error applied, leading to asymptotic reduction of error. Data may be obtained from recent history, and a larger fraction of error applied by doctor or automatic method.
Owner:ASEKO
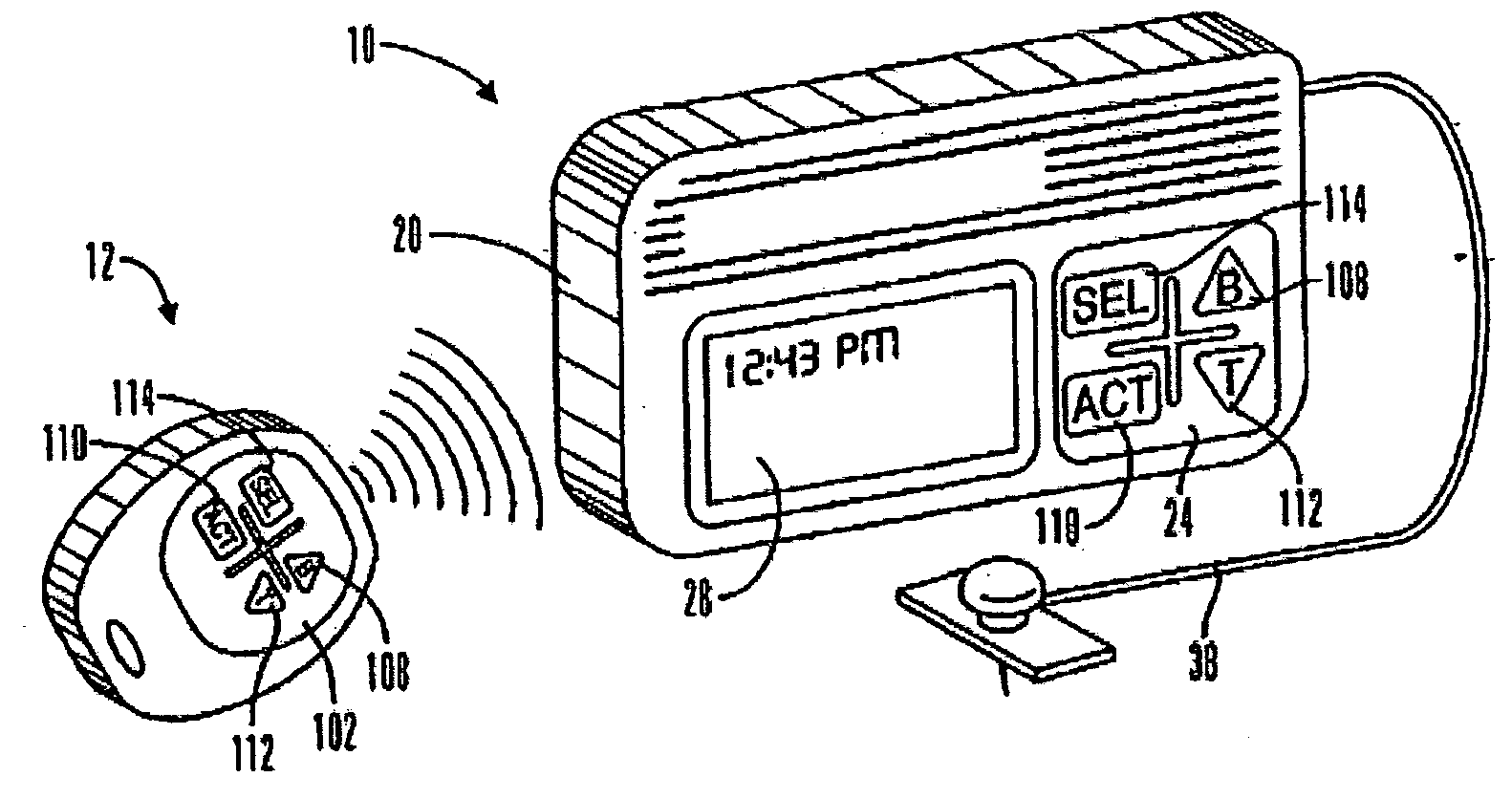
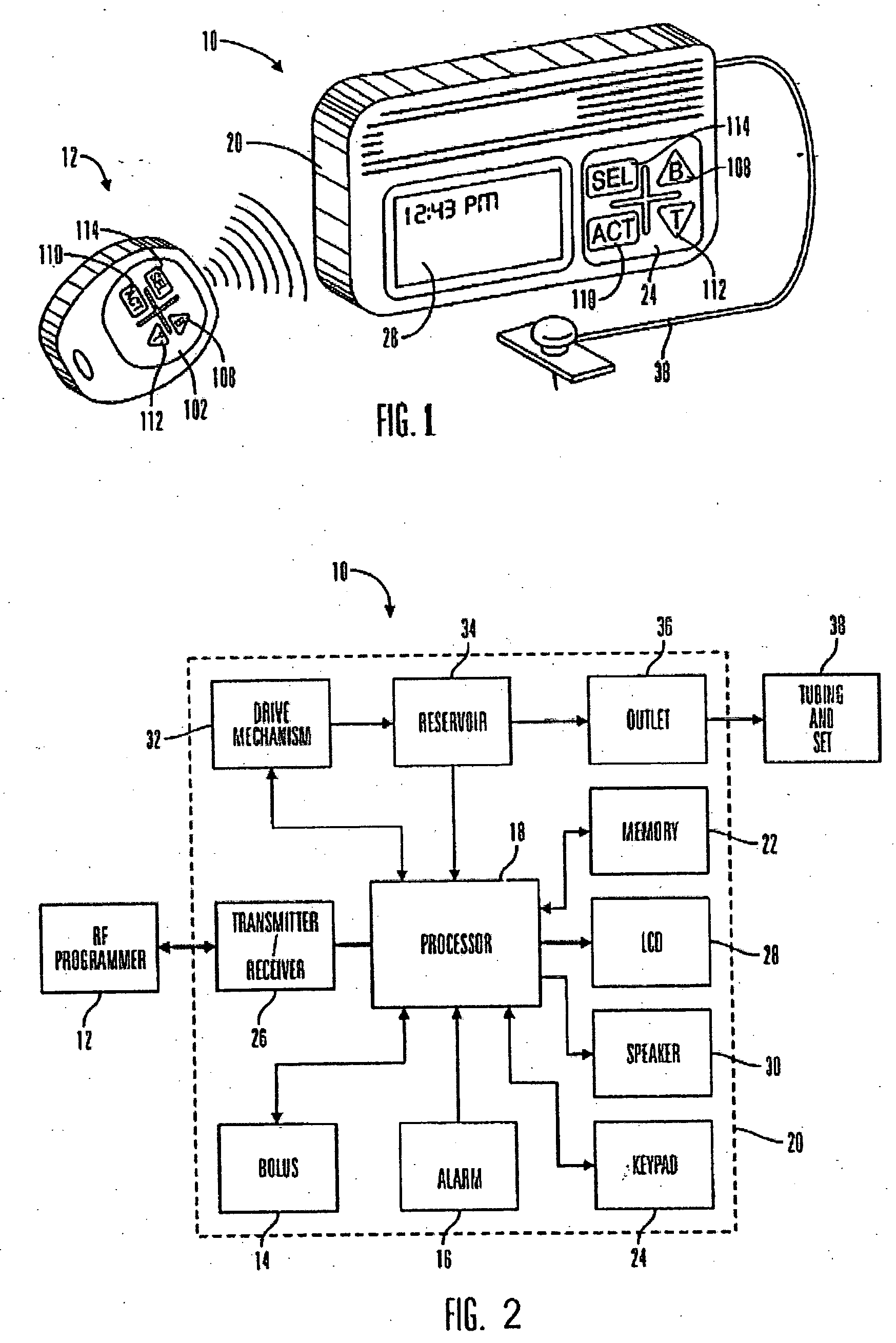
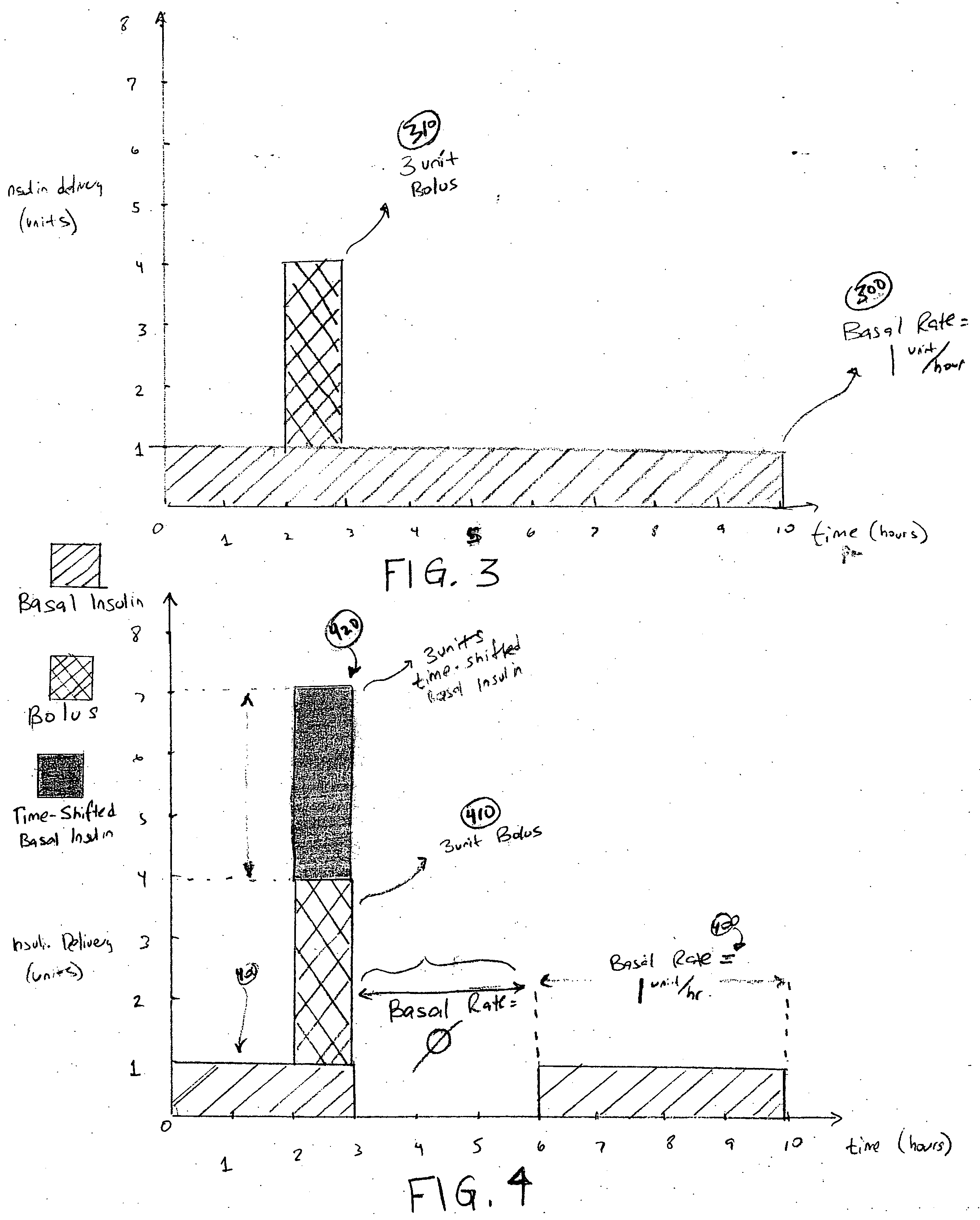
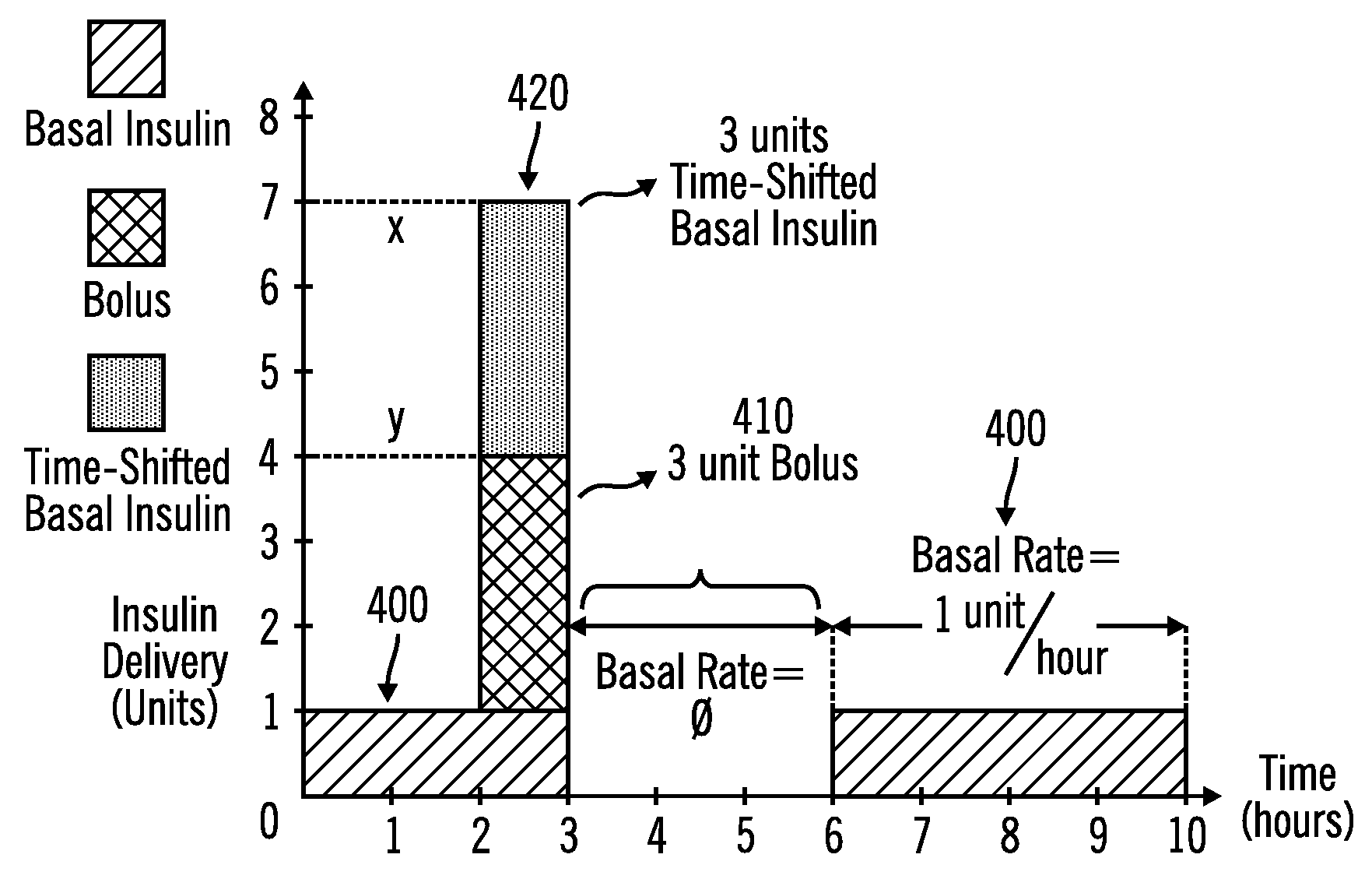
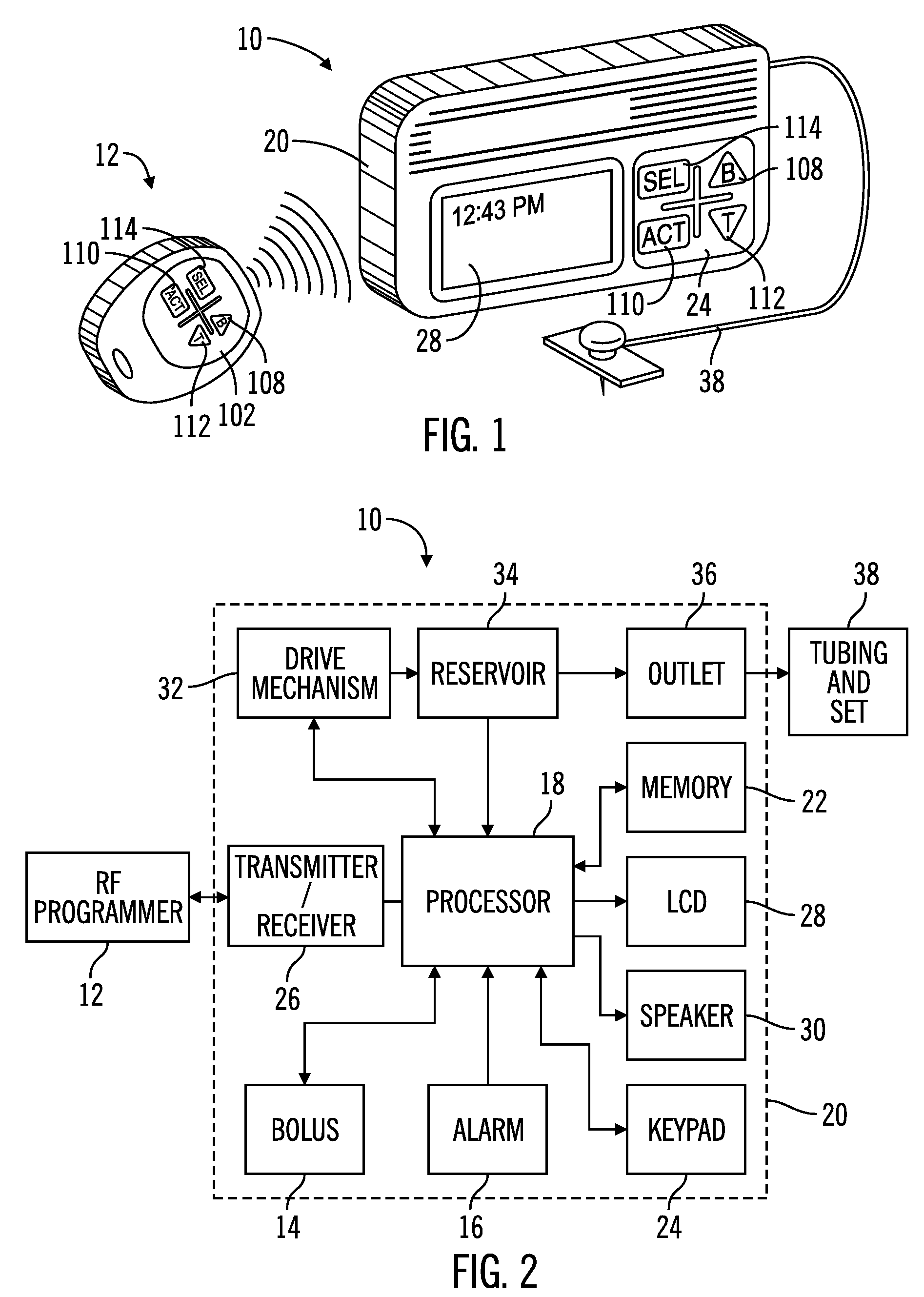
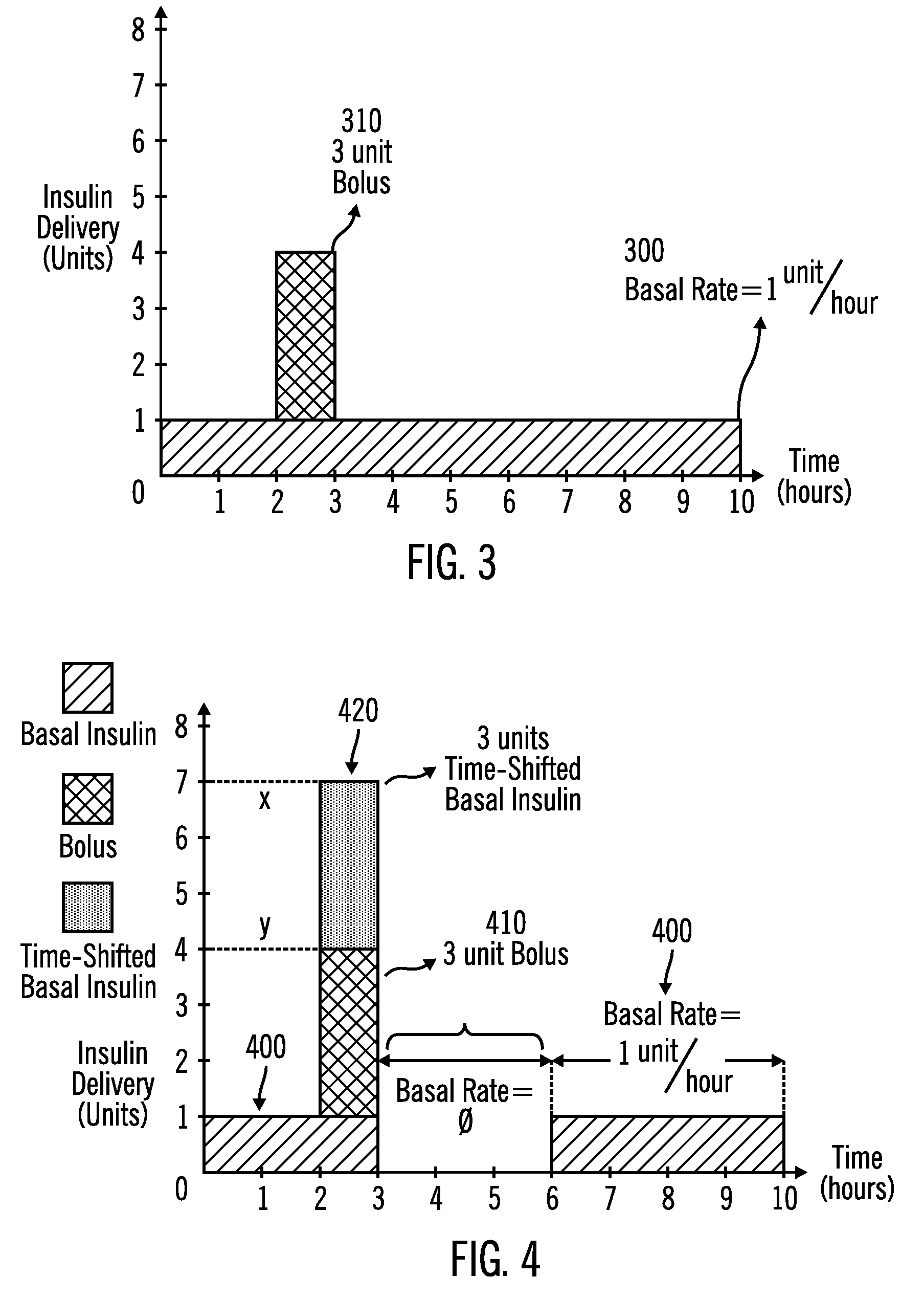
External infusion device with programmable capabilities to time-shift basal insulin and method of using the same
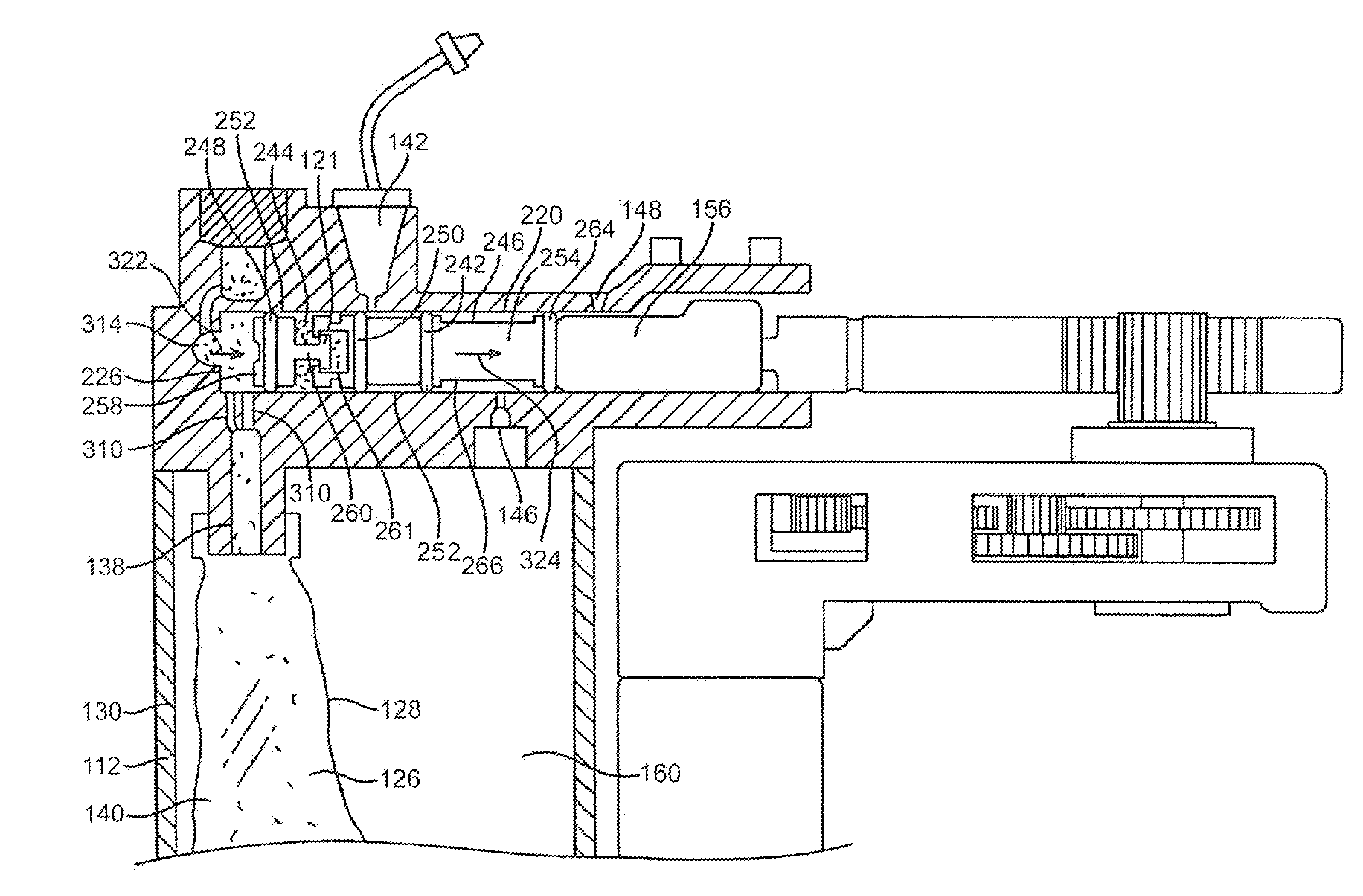
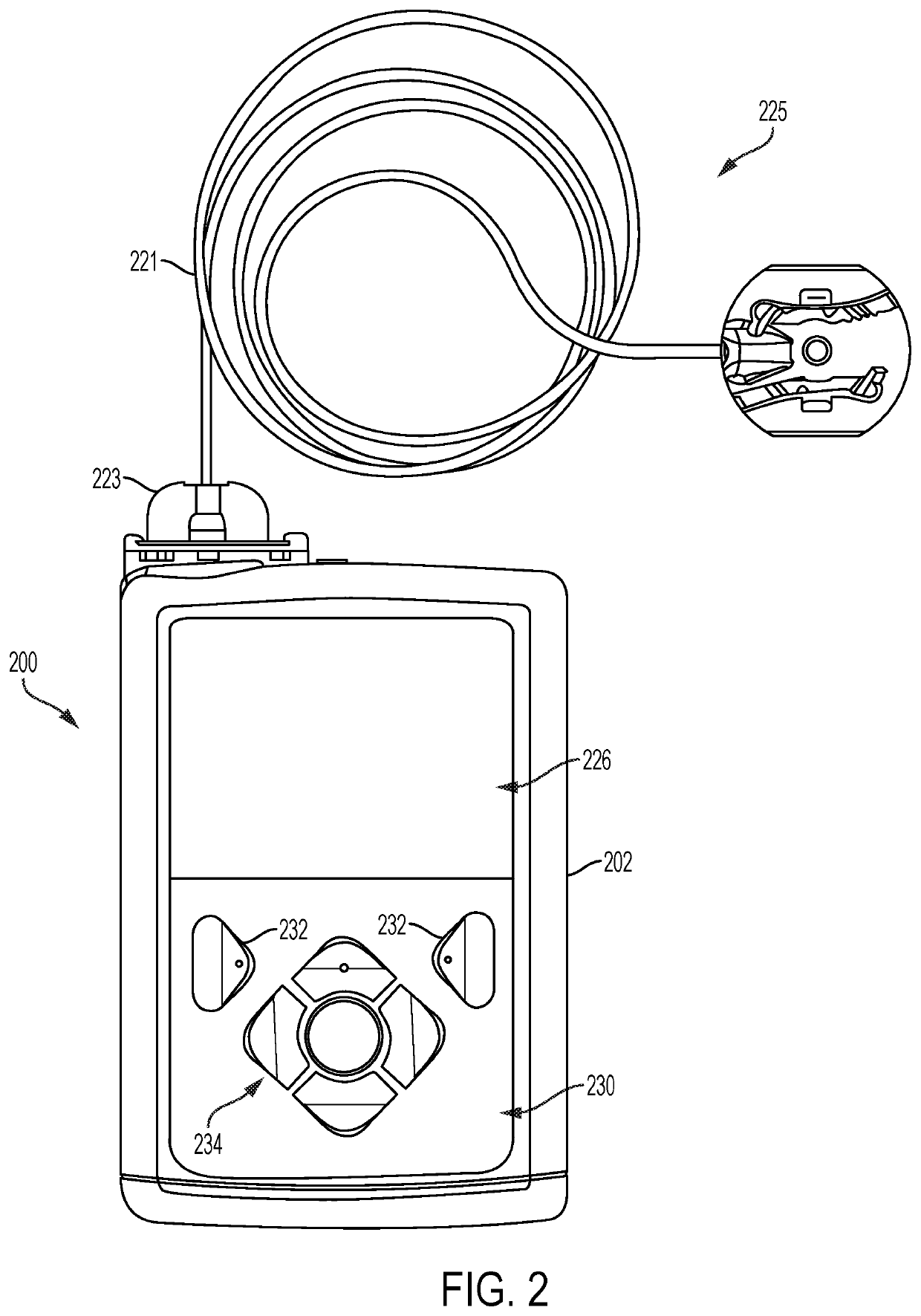
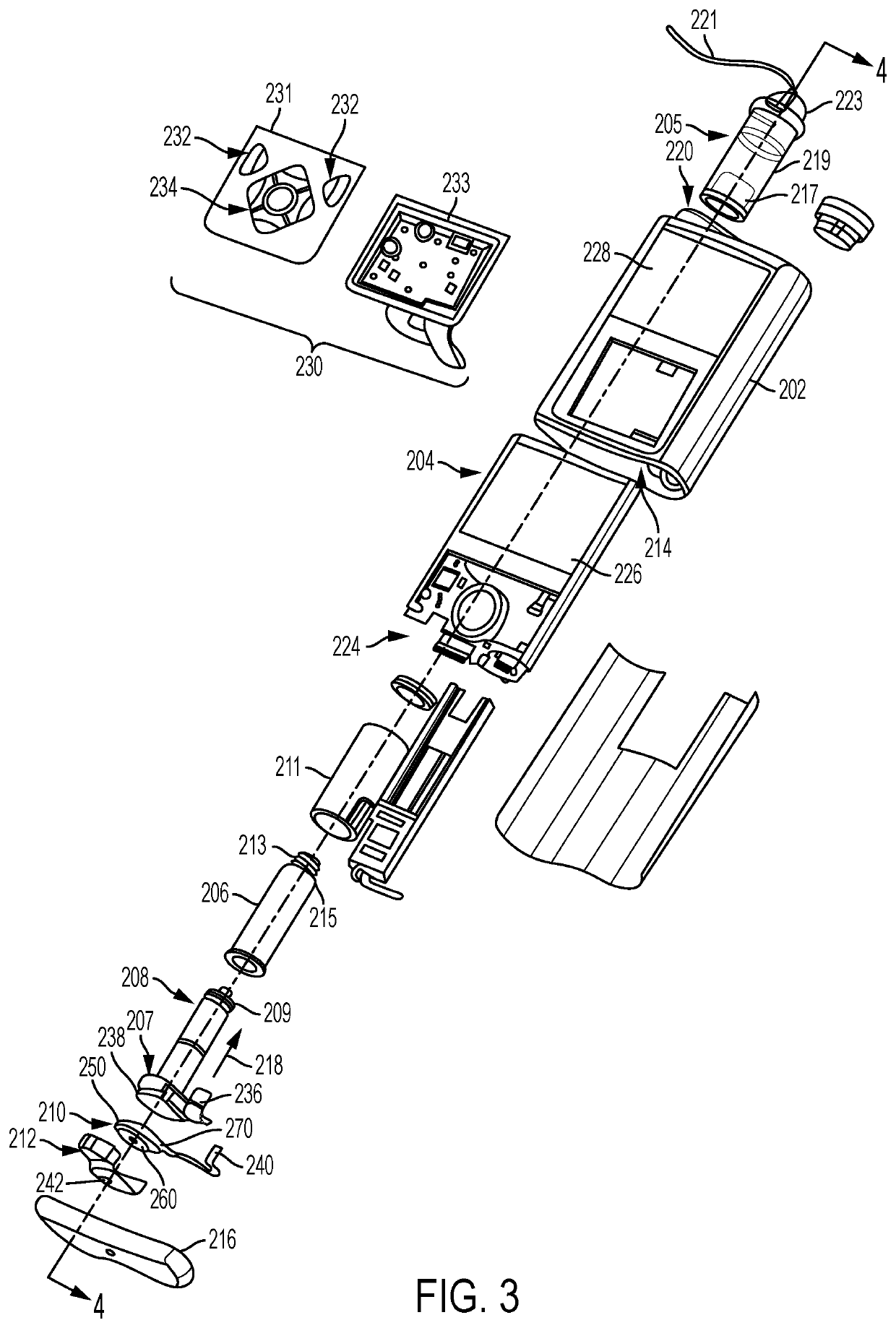
An external infusion device for delivering insulin from a reservoir into a body of a user includes the capability to deliver time-shifted basal insulin. The external infusion device includes at least one drive mechanism operatively couplable to the reservoir to deliver insulin into the body of the user, at least one processor to control the external infusion device, at least one power supply, at least one display device operatively coupled to the processor to provide visual information to the user, at least one input device operatively coupled to the processor to allow the user to command the processor, and a housing. Time-shifting of basal insulin occurs when a portion of basal insulin is added to a bolus, to a current basal rate, or to a bolus and a current basal rate.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Continuous glucose monitoring-directed adjustments in basal insulin rate and insulin bolus dosing formulas
InactiveUS20090036753A1Accurate estimateAppropriate confidence and self-sufficiencySurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringInsulin dependentHypoglycemic episodes
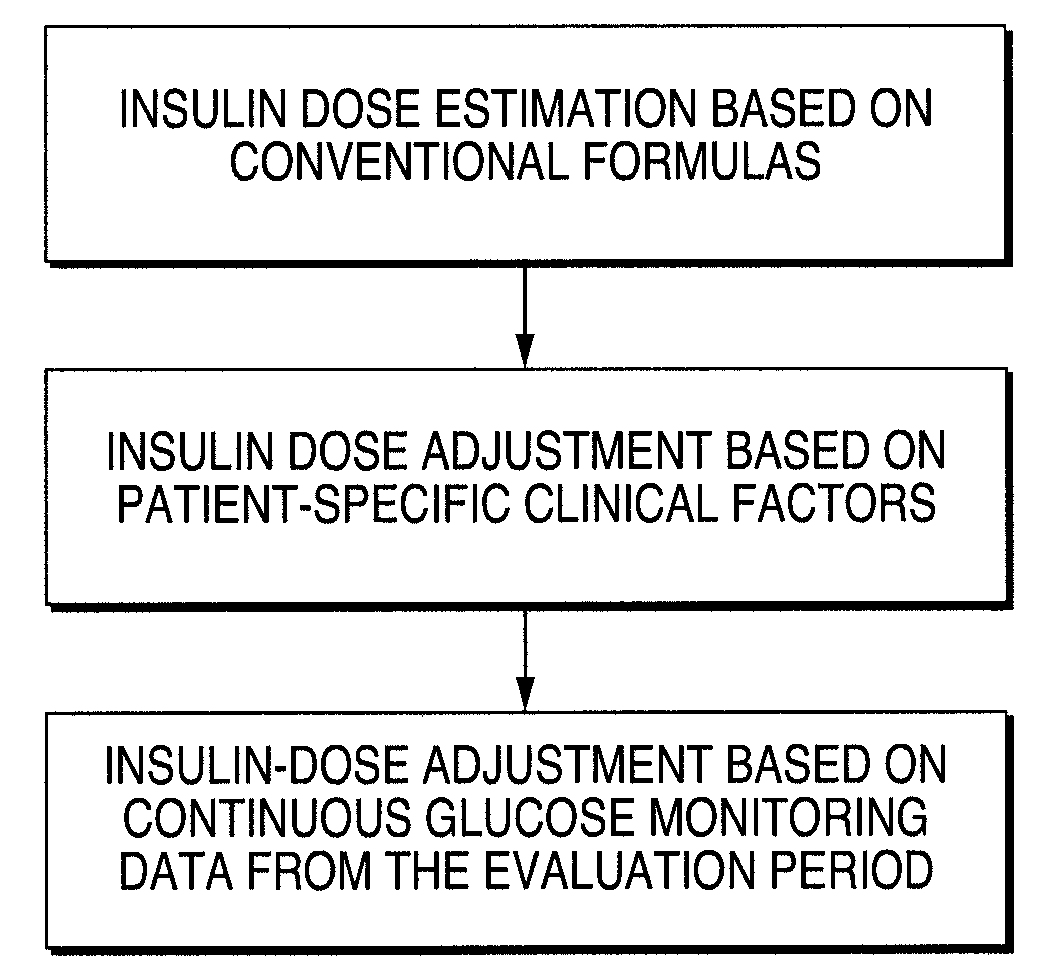
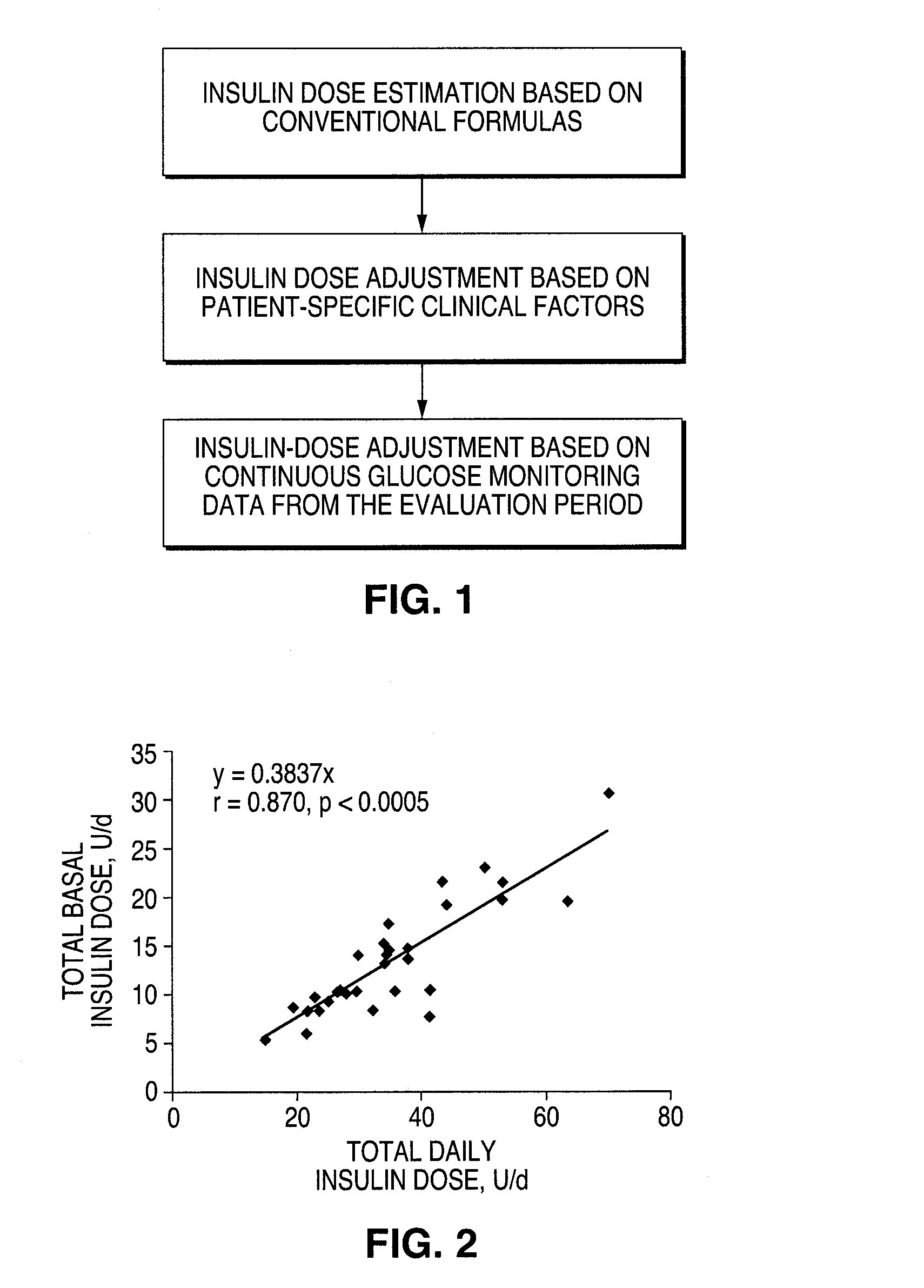
A method for individualized management of diabetes in insulin-dependent patients provides a period of evaluation as the patient adheres to a structured pattern of eating, sleeping, and physical activity. Glucose is monitored with a continuous glucose monitoring system, insulin doses are metered, carbohydrate consumption is quantified, and glucose, carbohydrate, and insulin data are collected and analyzed. Insulin dosage is adjusted in three steps: (1) an insulin dosage is estimated from conventional formulas, (2) adjustments are made according to the patient's clinical specifics, and (3) further insulin dose adjustments are made according to glucose data obtained during the evaluation period. By the end of the evaluation period, substantially normal glucose values are achieved, and quantitative relationships from data are calculated that are then applied to determine insulin dosages for an ensuing period of therapy. By this method, diabetic patients achieve a near normal glycemic profile, and without significant occurrence of hypoglycemic episodes.
Owner:DIABETES CARE CENT
External infusion device with programmable capabilities to time-shift basal insulin and method of using the same
An external infusion device for delivering insulin from a reservoir into a body of a user includes the capability to deliver time-shifted basal insulin. The external infusion device includes at least one drive mechanism operatively couplable to the reservoir to deliver insulin into the body of the user, at least one processor to control the external infusion device, at least one power supply, at least one display device operatively coupled to the processor to provide visual information to the user, at least one input device operatively coupled to the processor to allow the user to command the processor, and a housing. Time-shifting of basal insulin occurs when a portion of basal insulin is added to a bolus, to a current basal rate, or to a bolus and a current basal rate.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
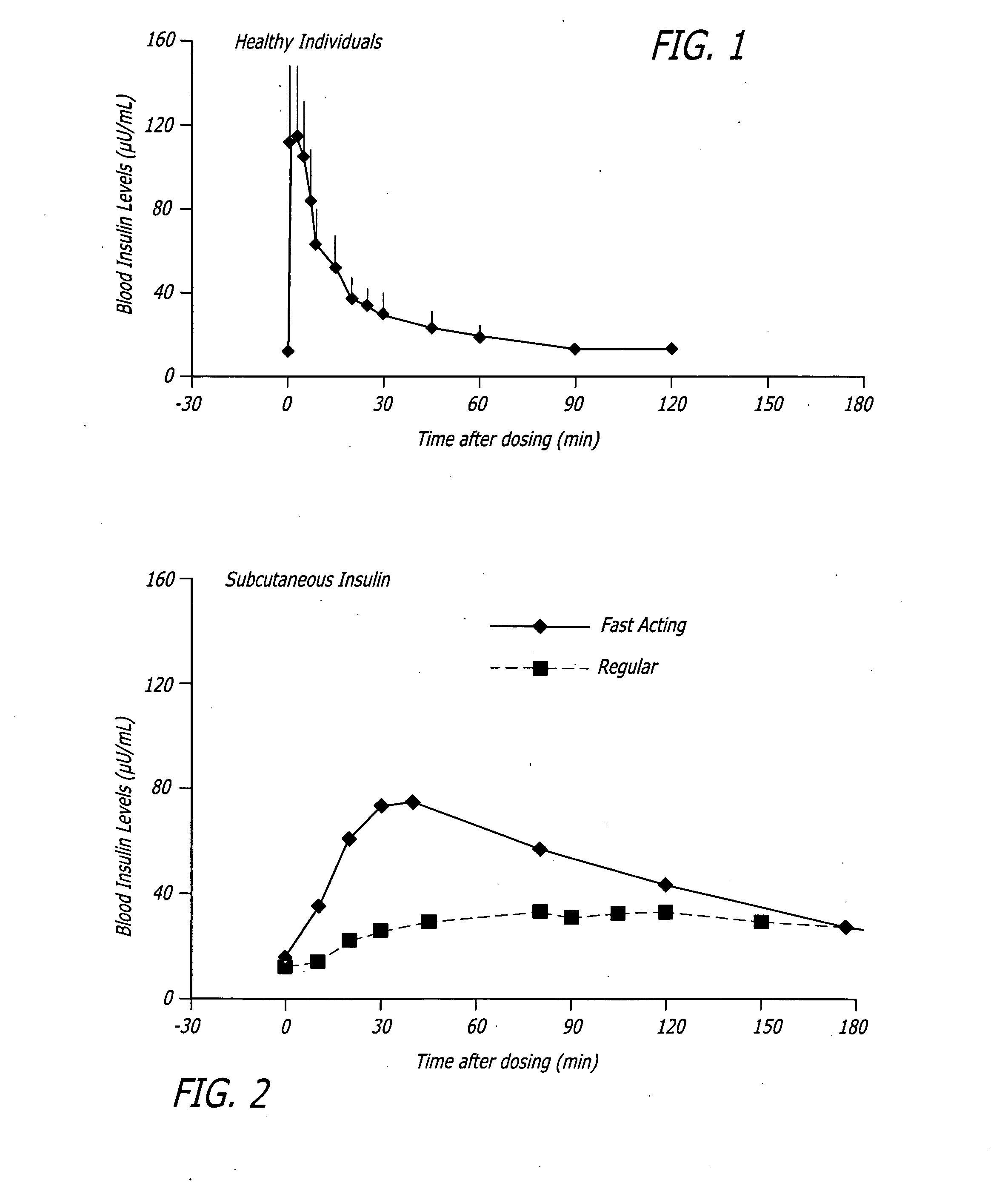
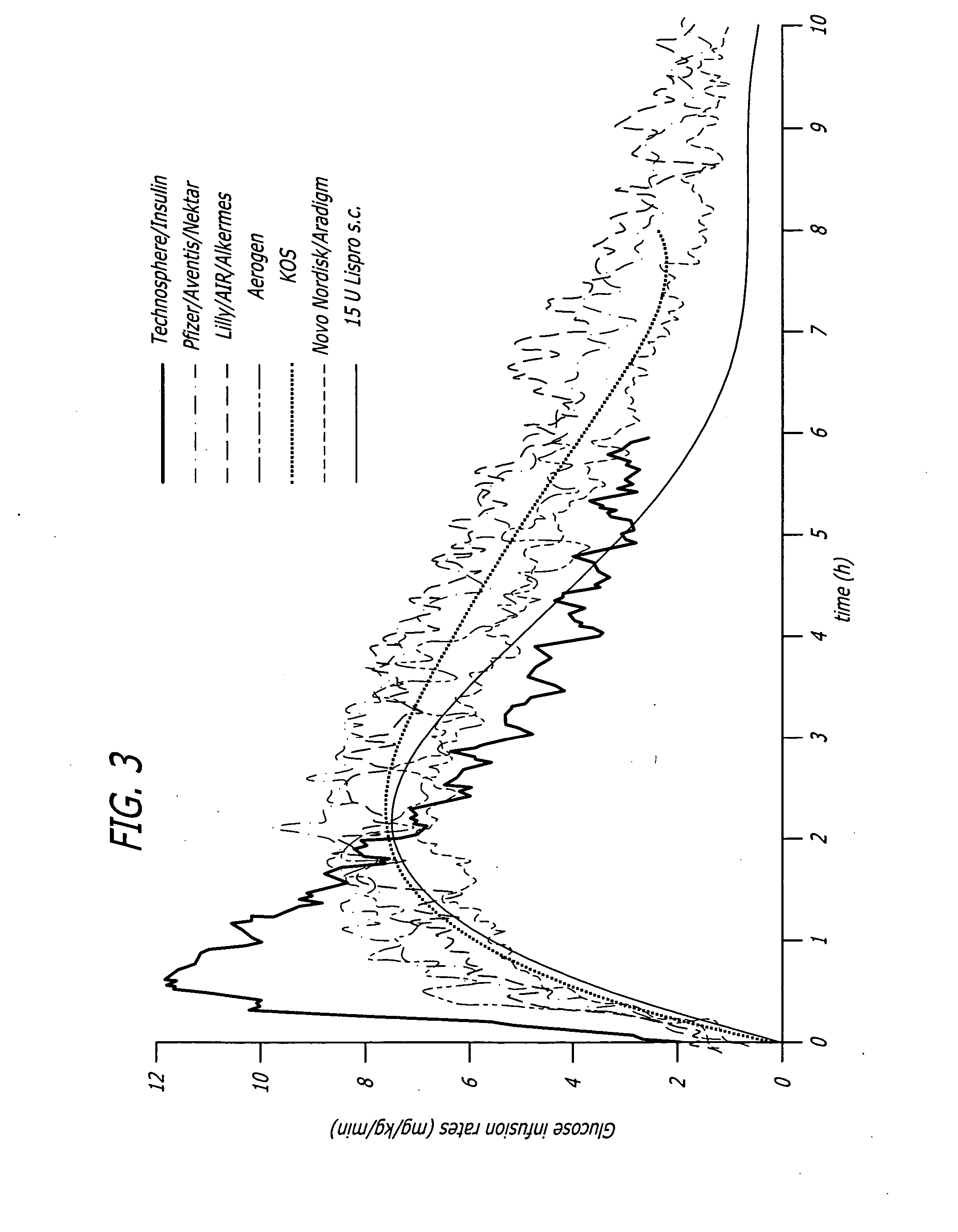
Superior control of blood glucose in diabetes treatment
InactiveUS20060239934A1Easy to controlReduce riskOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryPostprandial HypoglycemiaGlucose fluctuations
Methods related to the treatment of diabetes and improving the control of blood glucose levels are provided. In particular, methods are provided for effectively reducing postprandial glucose excursions while reducing the incidence of clinically significant late postprandial hypoglycemia by administered an insulin composition in a form suitable for pulmonary administration. Additionally, methods for effectively reducing post-prandial glucose excursions while reducing the incidence of clinically significant late postprandial hypoglycemia by administered an insulin composition in a form suitable for pulmonary administration along with a long-acting basal insulin.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
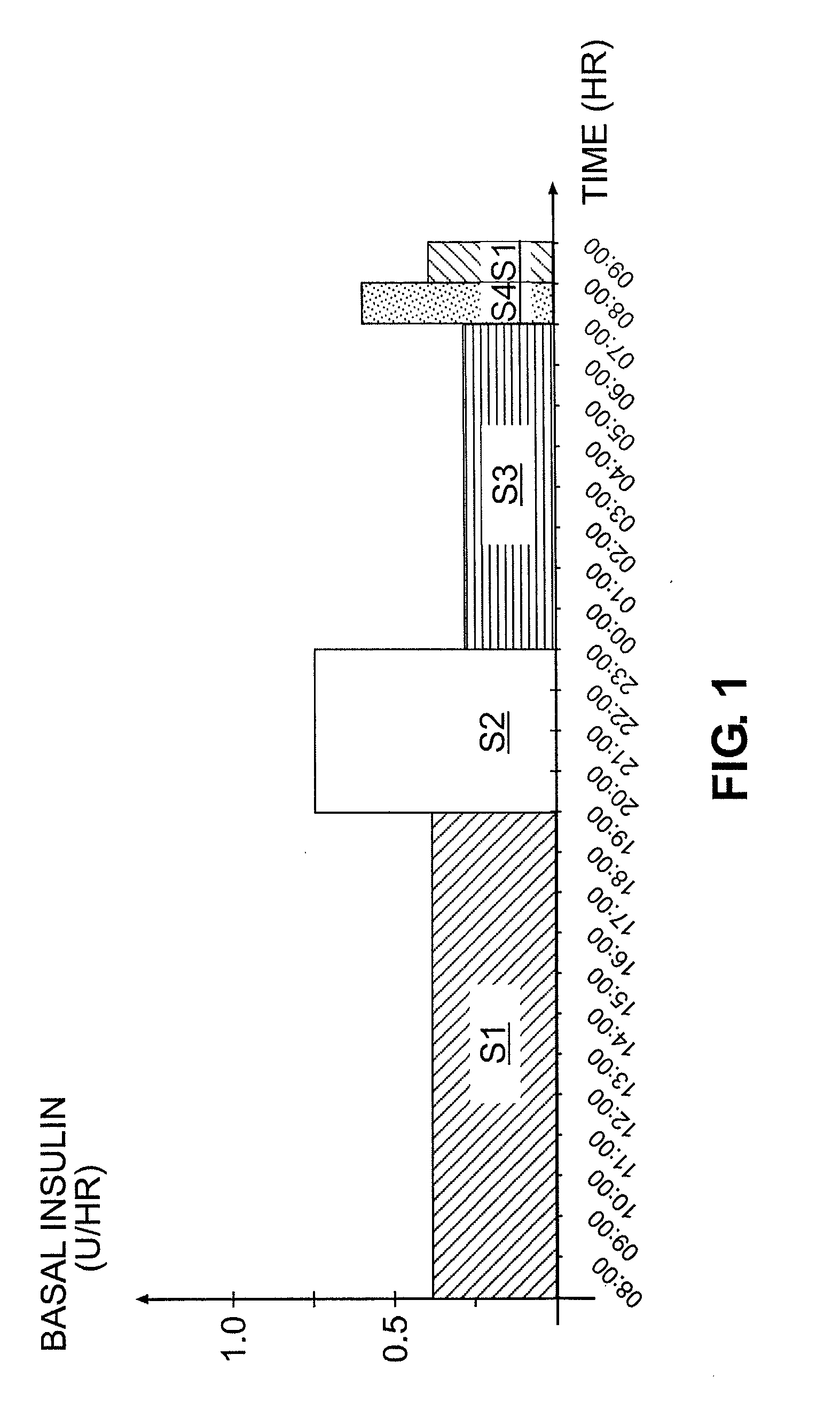
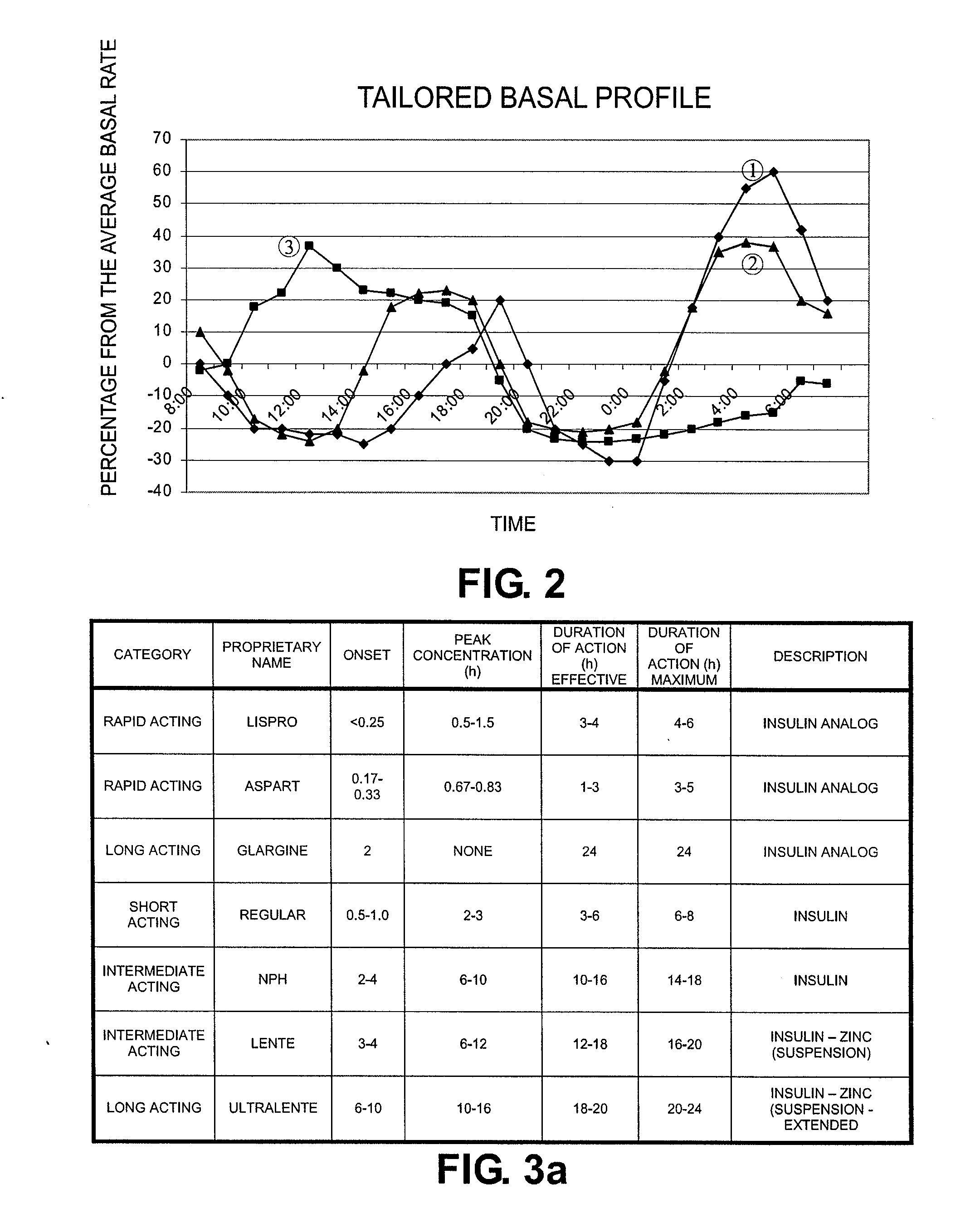
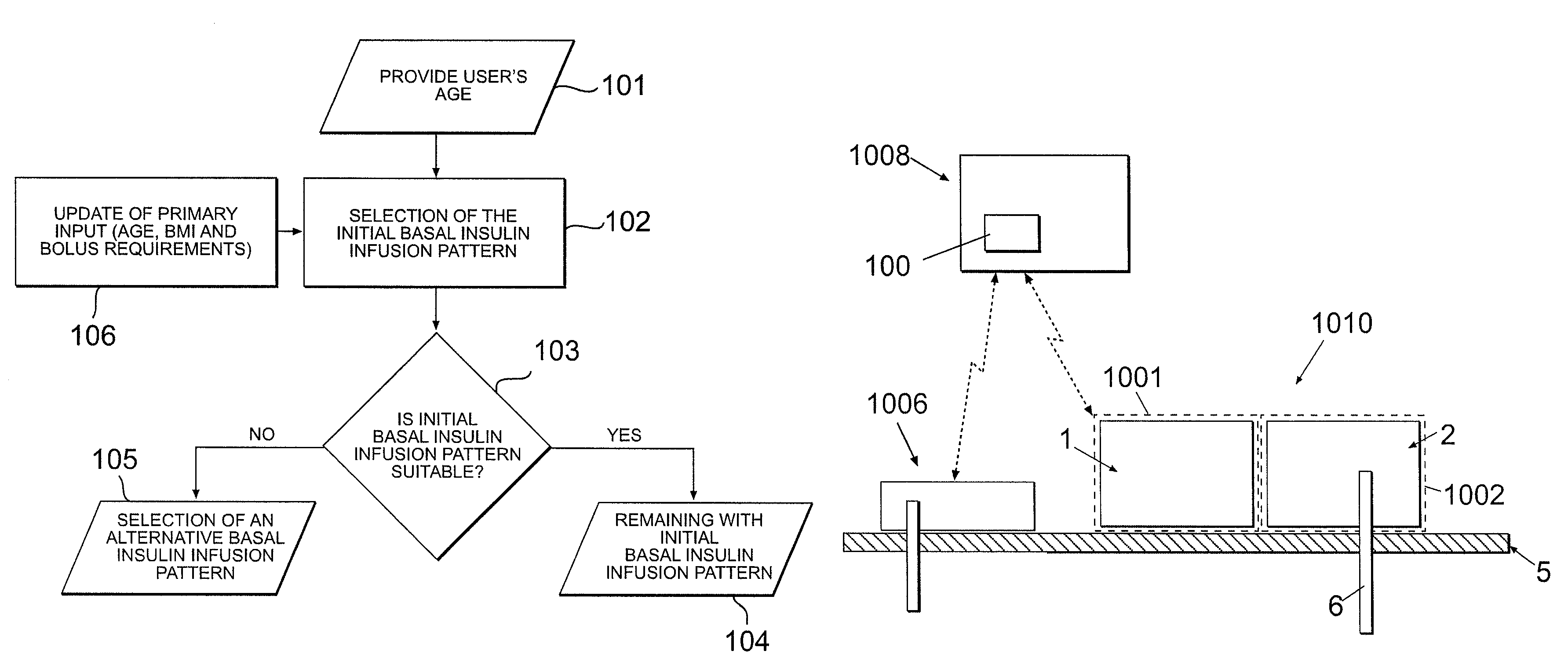
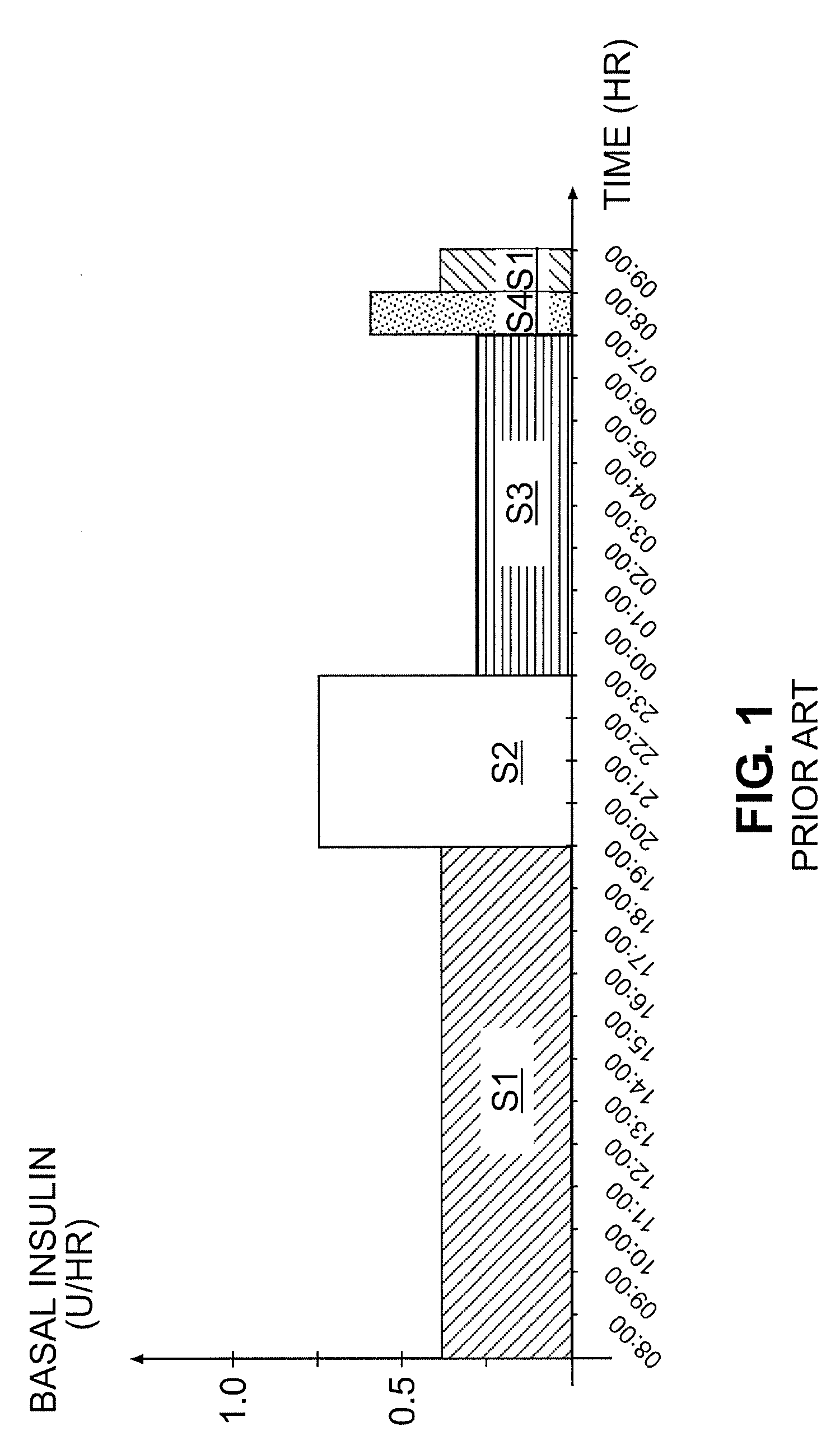
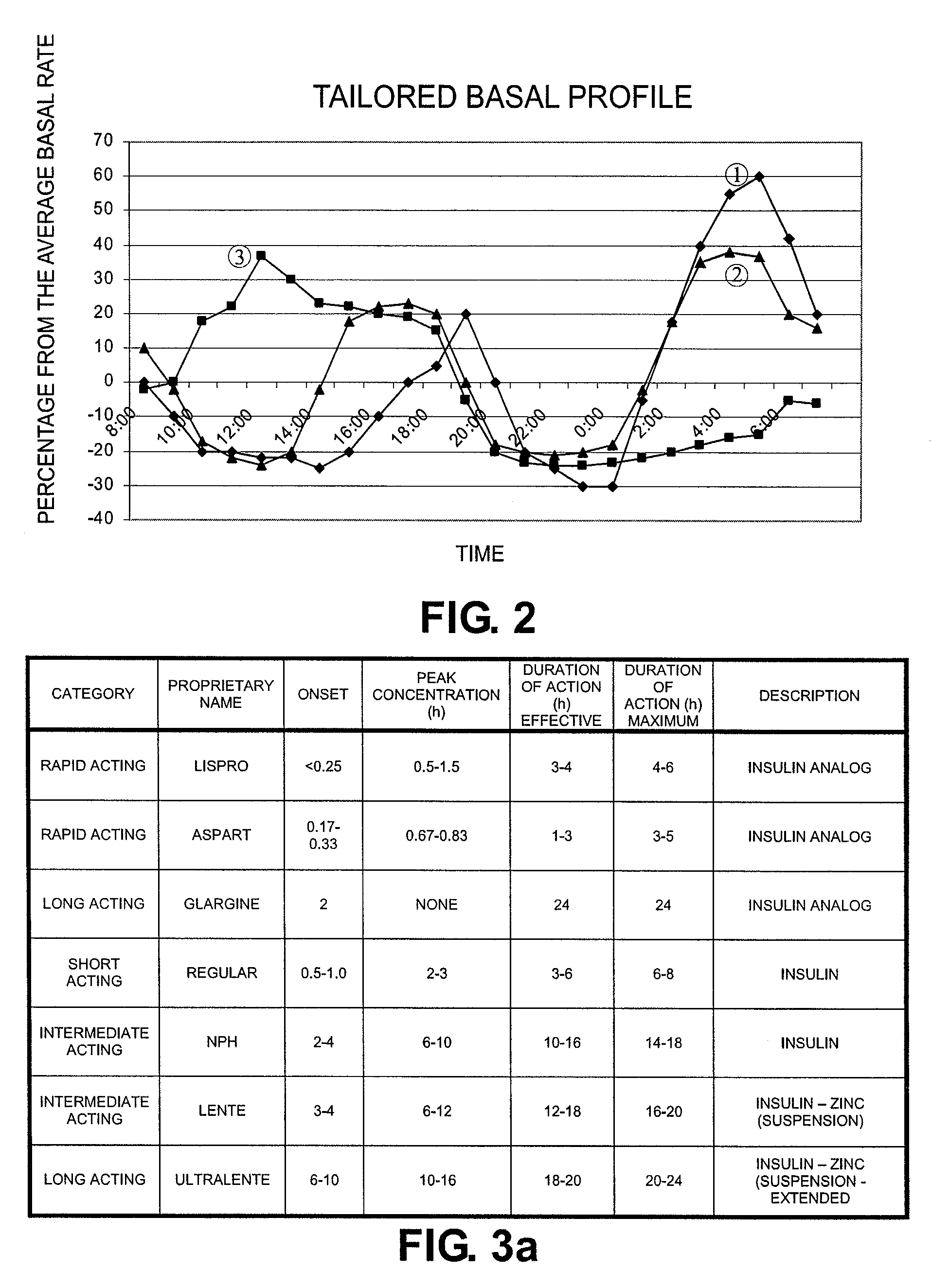
Tailored Basal Insulin Delivery System and Method
ActiveUS20080319384A1Monitor body glucose levelEconomical and cost-effectiveMetabolism disorderHealth-index calculationDelivery systemControlled delivery
Disclosed is a system to deliver insulin to a user's body. The system includes a dispensing unit to deliver the insulin to the body, and a control mechanism to control delivery of basal insulin according to a predetermined basal infusion pattern, the basal infusion pattern selected from a plurality of predetermined basal infusion patterns. In some embodiments, selection of the basal infusion pattern may be based on one or more personal characteristics of the user.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Potentiation of glucose elimination
InactiveUS20070020191A1Improve efficiencyEffective controlPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsInsulin activityPostprandial Hypoglycemia
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Amylin formulations
InactiveUS20080248999A1Reduce in quantityAct quicklyPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderGLP-1 MimeticsBefore Breakfast
A combined insulin and amylin and / or GLP-1 mimetic formulation has been developed wherein the pH of the insulin is decreased so that the amylin and / or GLP-1 remains soluble when mixed together with the insulin. In the preferred embodiment, a bolus insulin is administered by injection before breakfast, providing adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, without producing hypoglycemia after the meal. This can be combined with an adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of the insulin and amylin and / or GLP-1 mimetic combination. A GLP-1 mimetic may be combined with either rapid acting or basal insulin formulations. As a result, a patient using the combination formulation therapy may only need to inject half as many times per day.
Owner:BIODEL INC
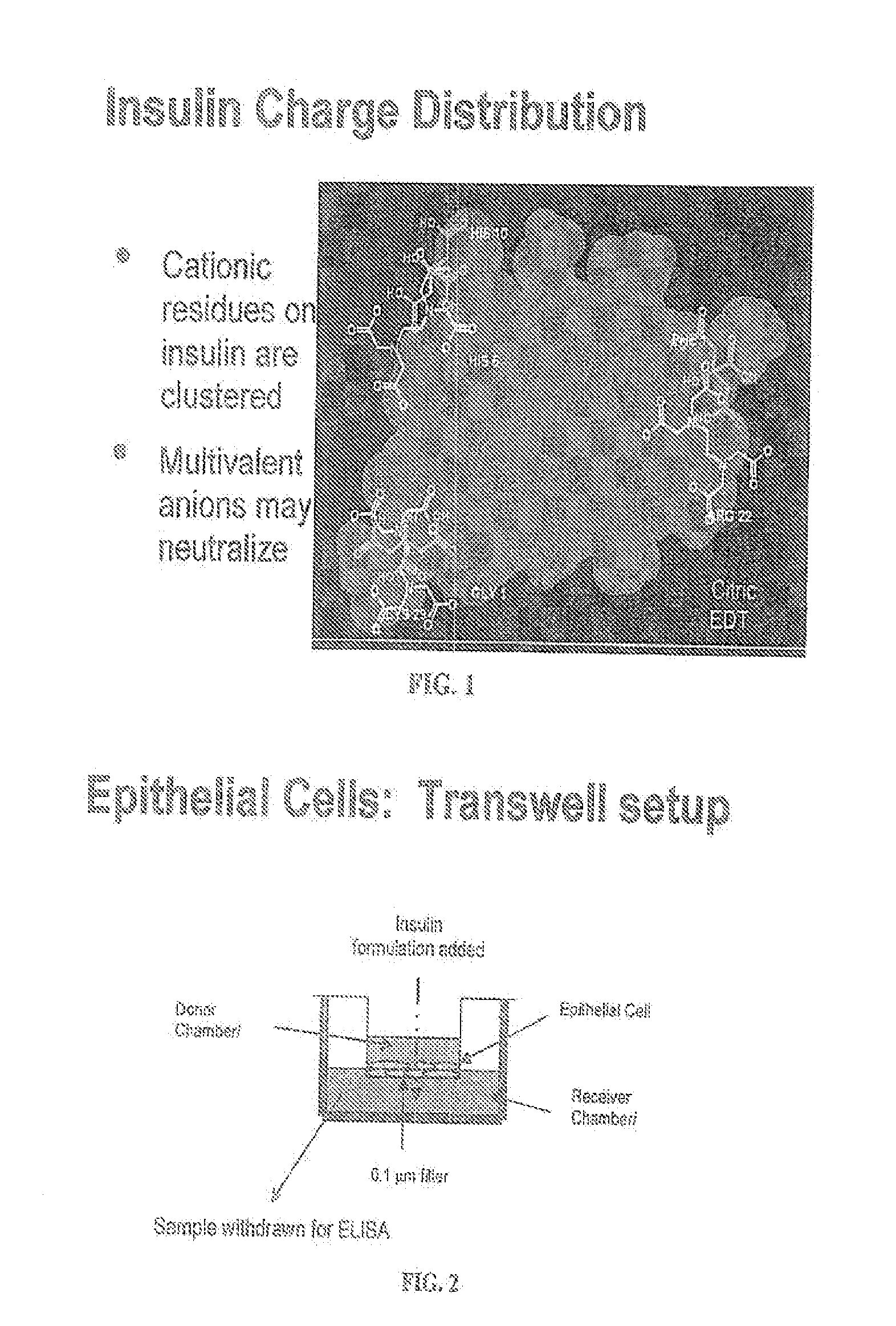
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
ActiveUS20080039368A1Increase speedReduce the amount of solutionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
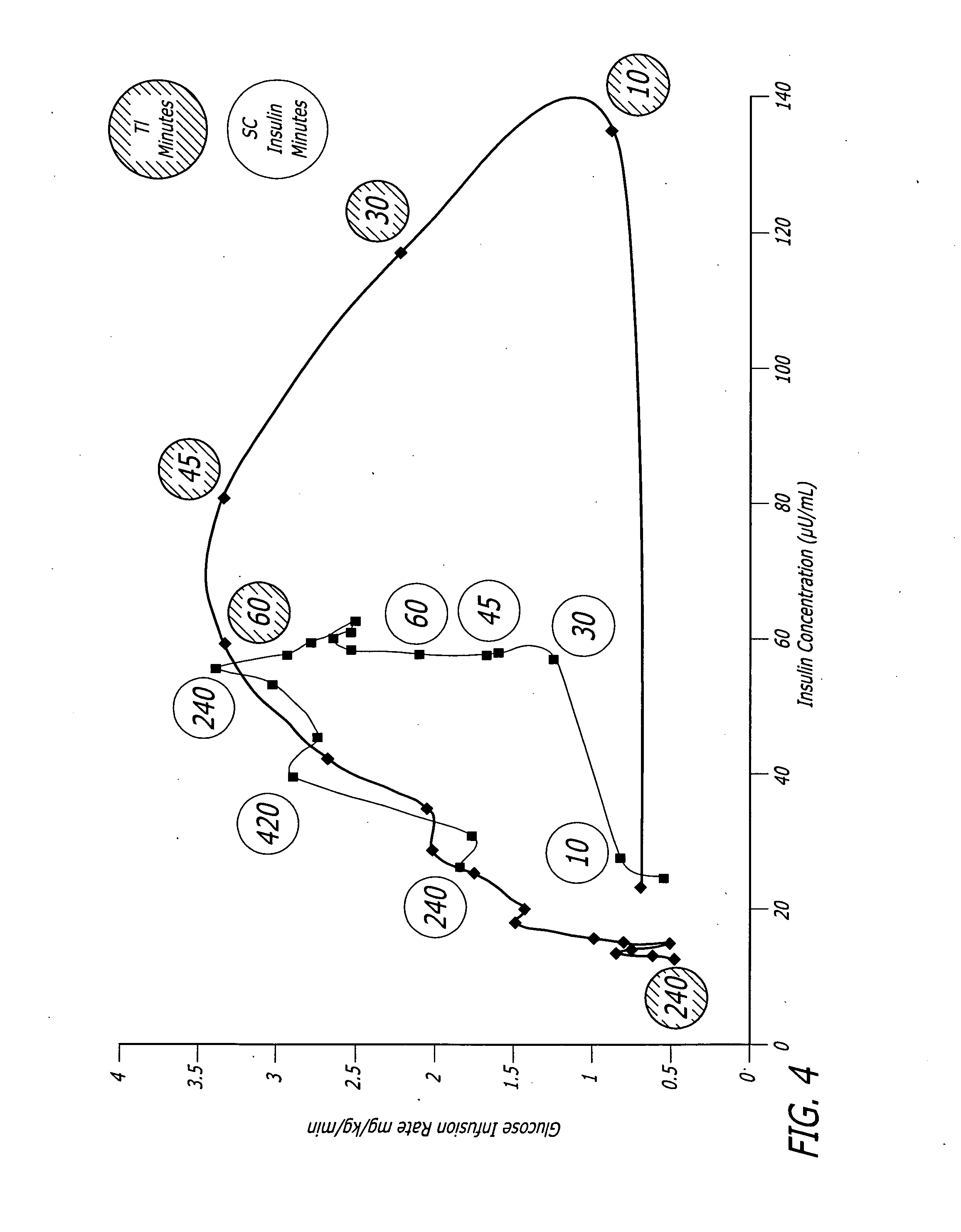
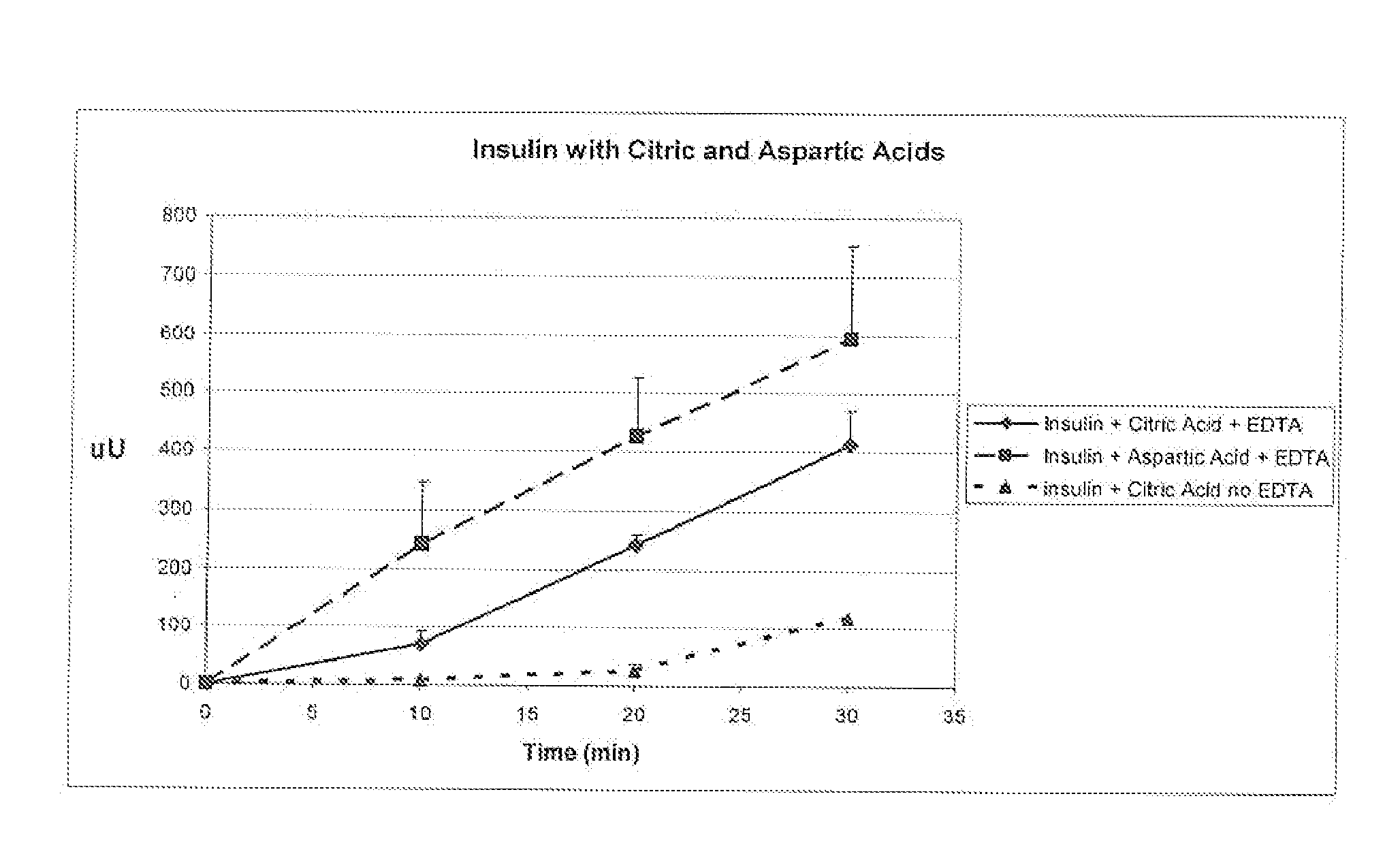
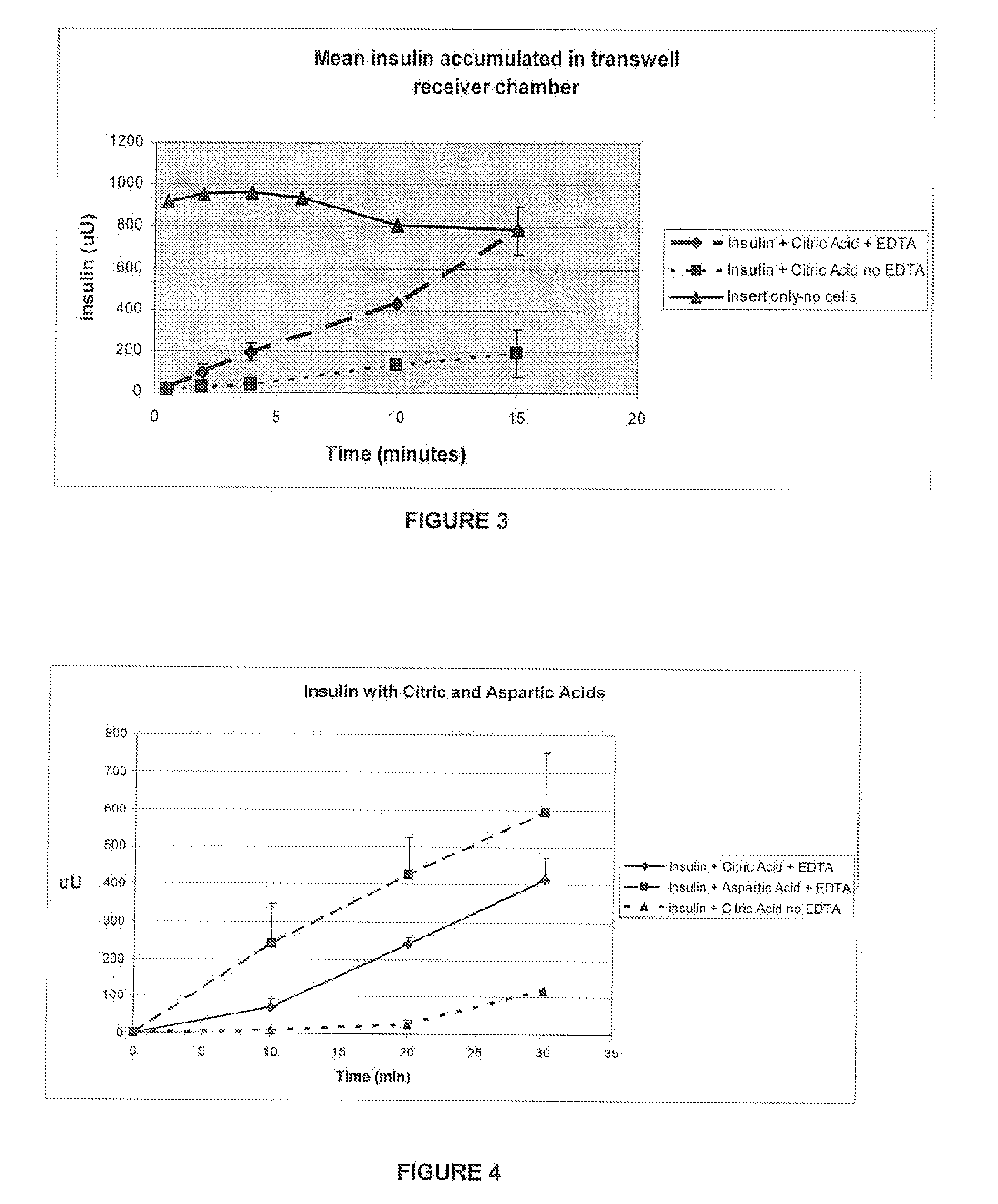
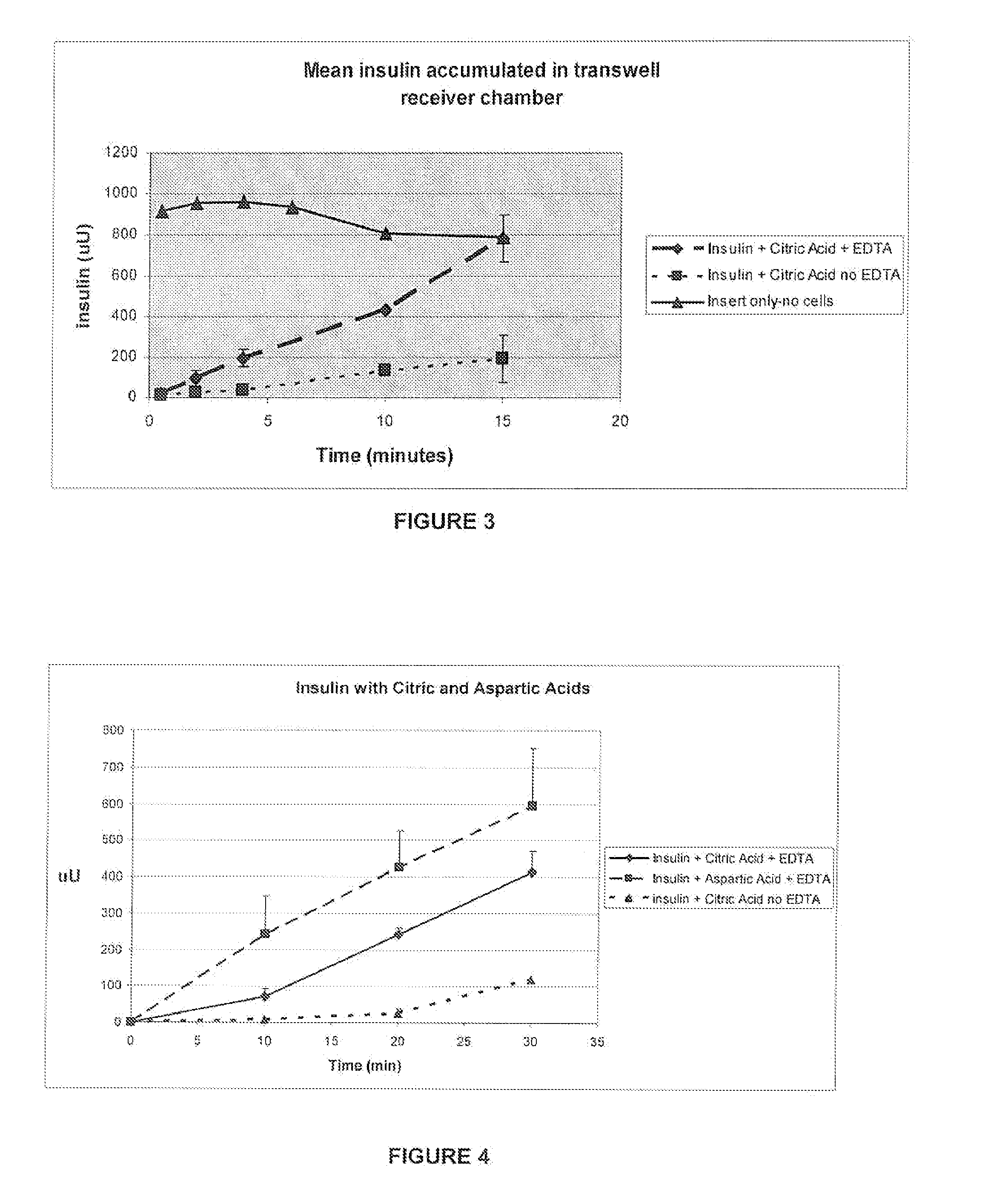
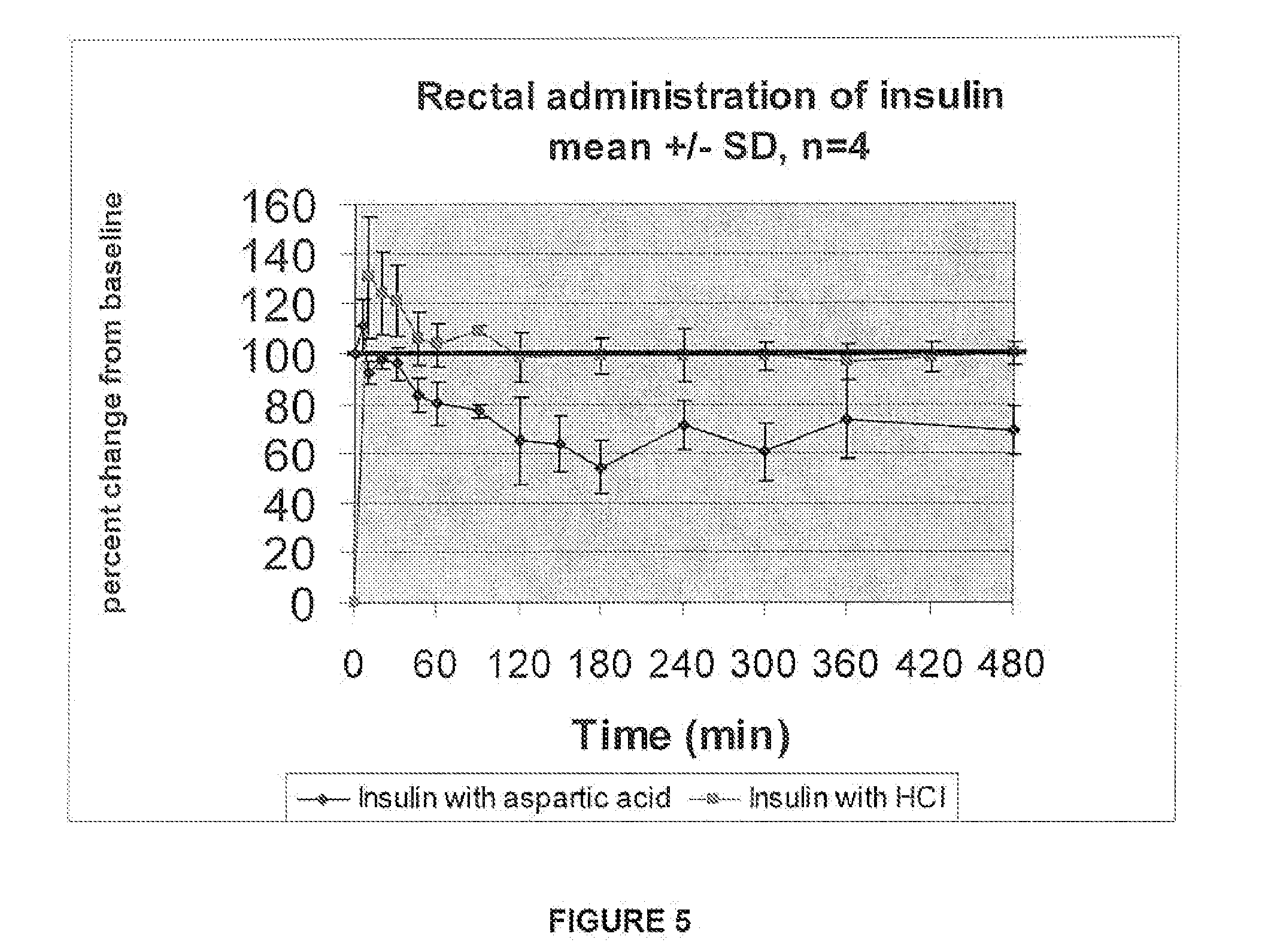
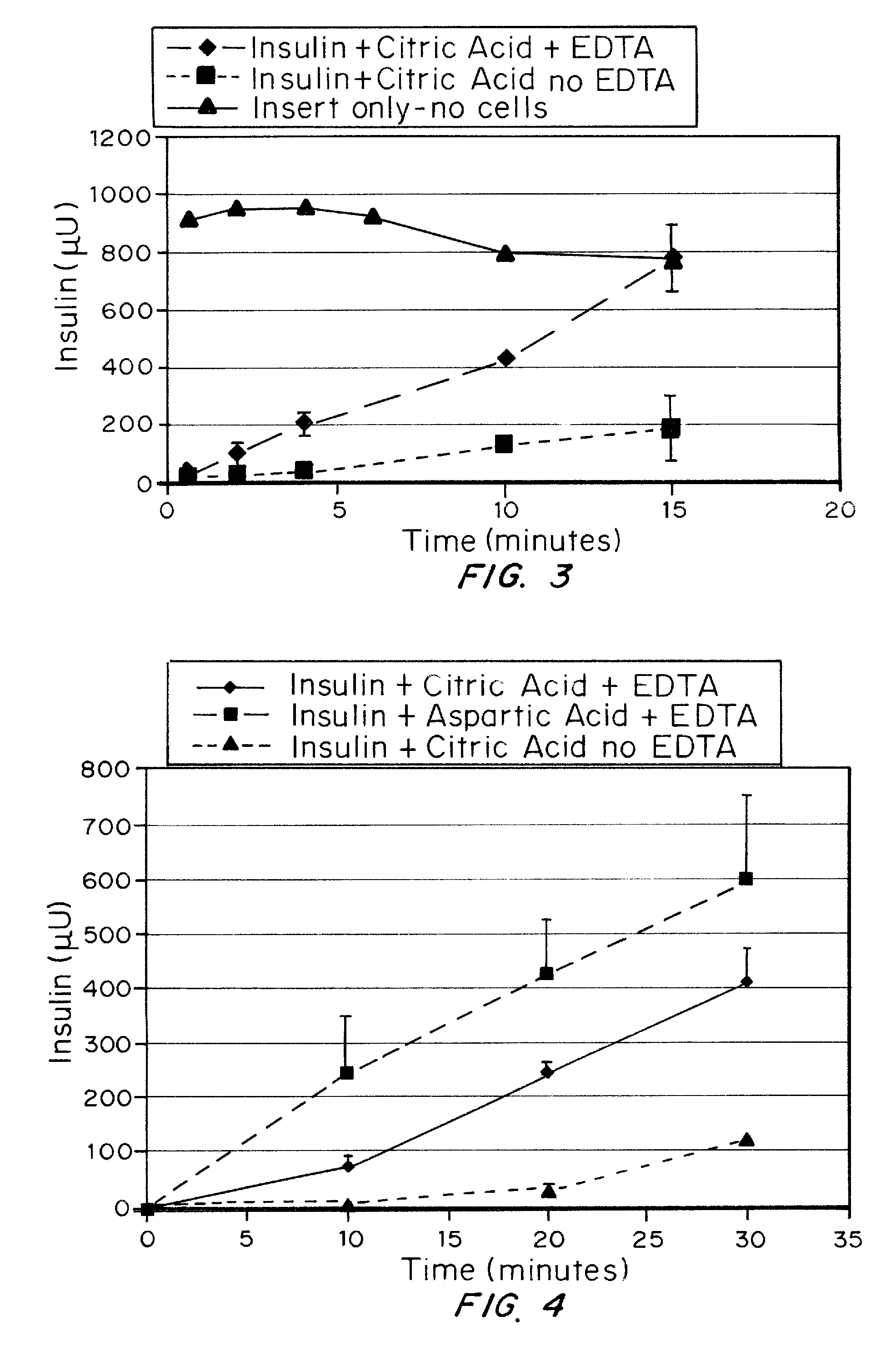
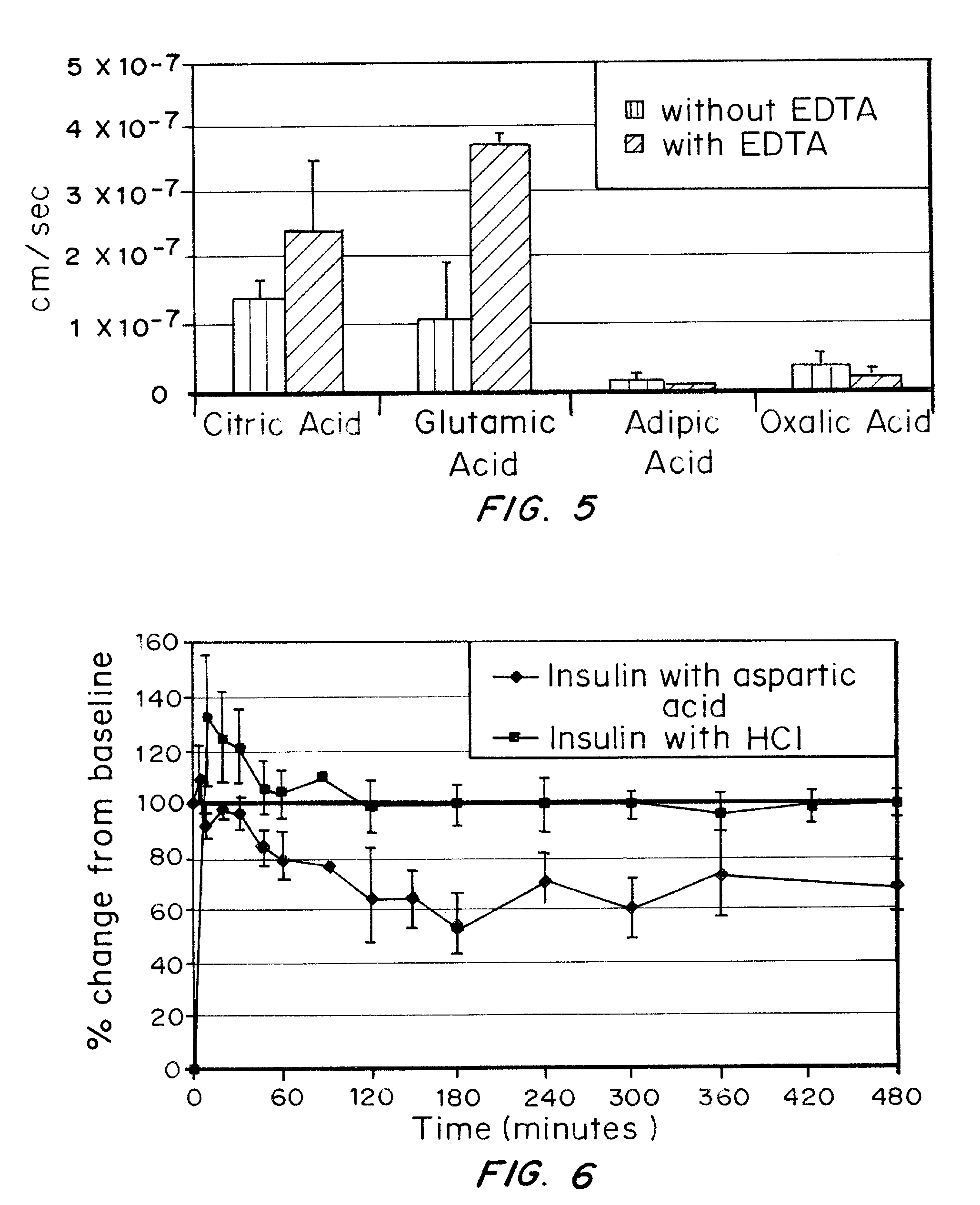
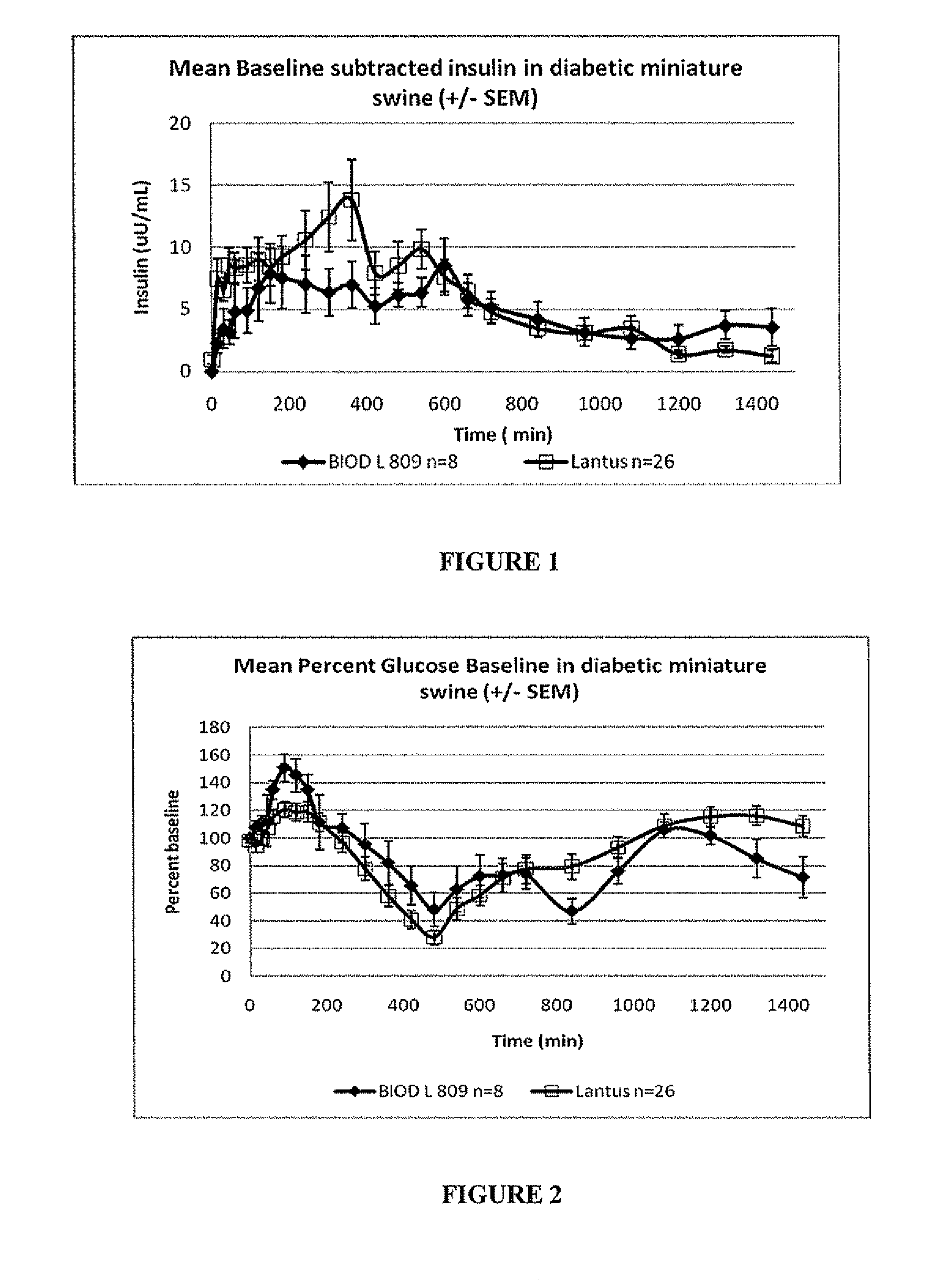
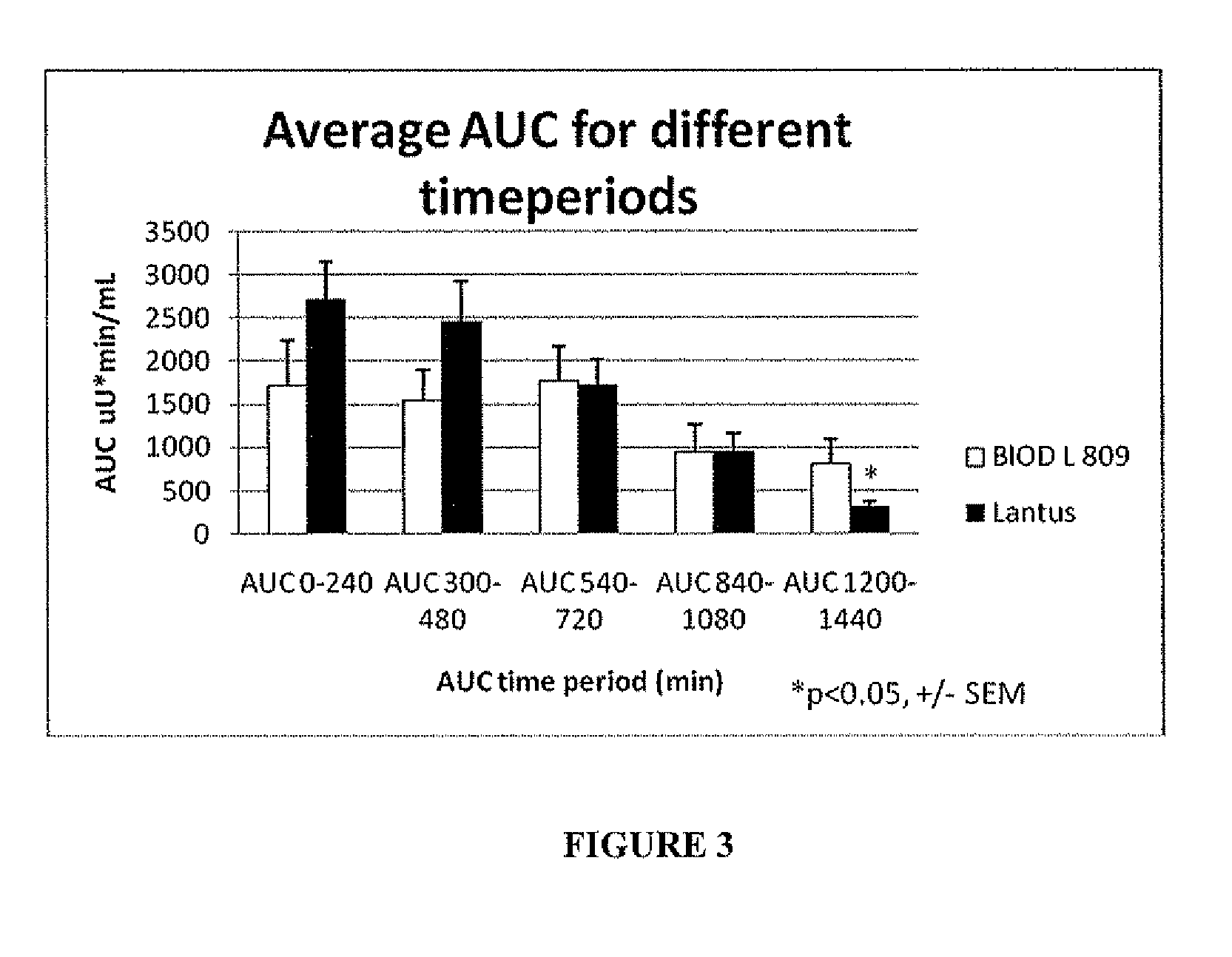
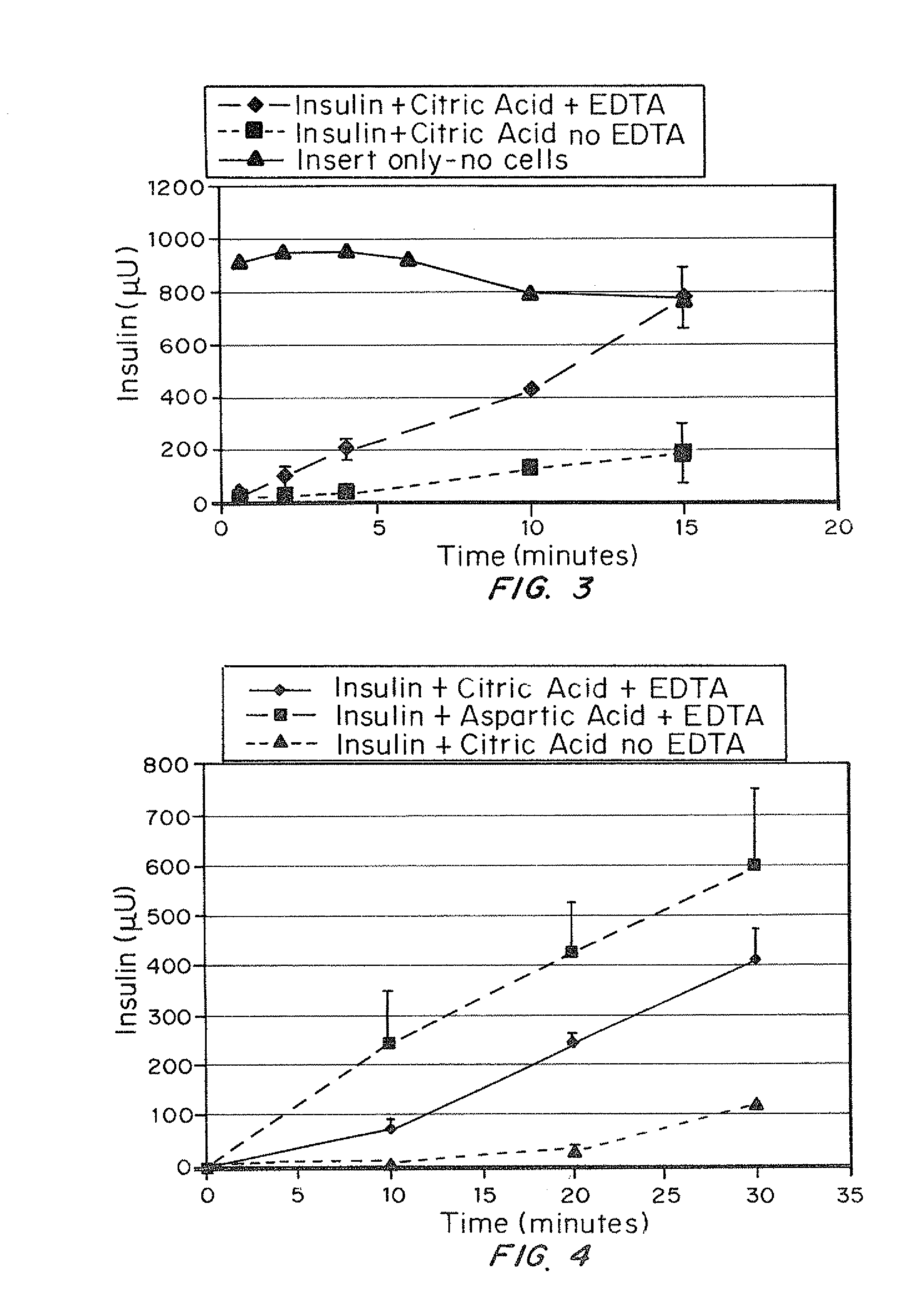
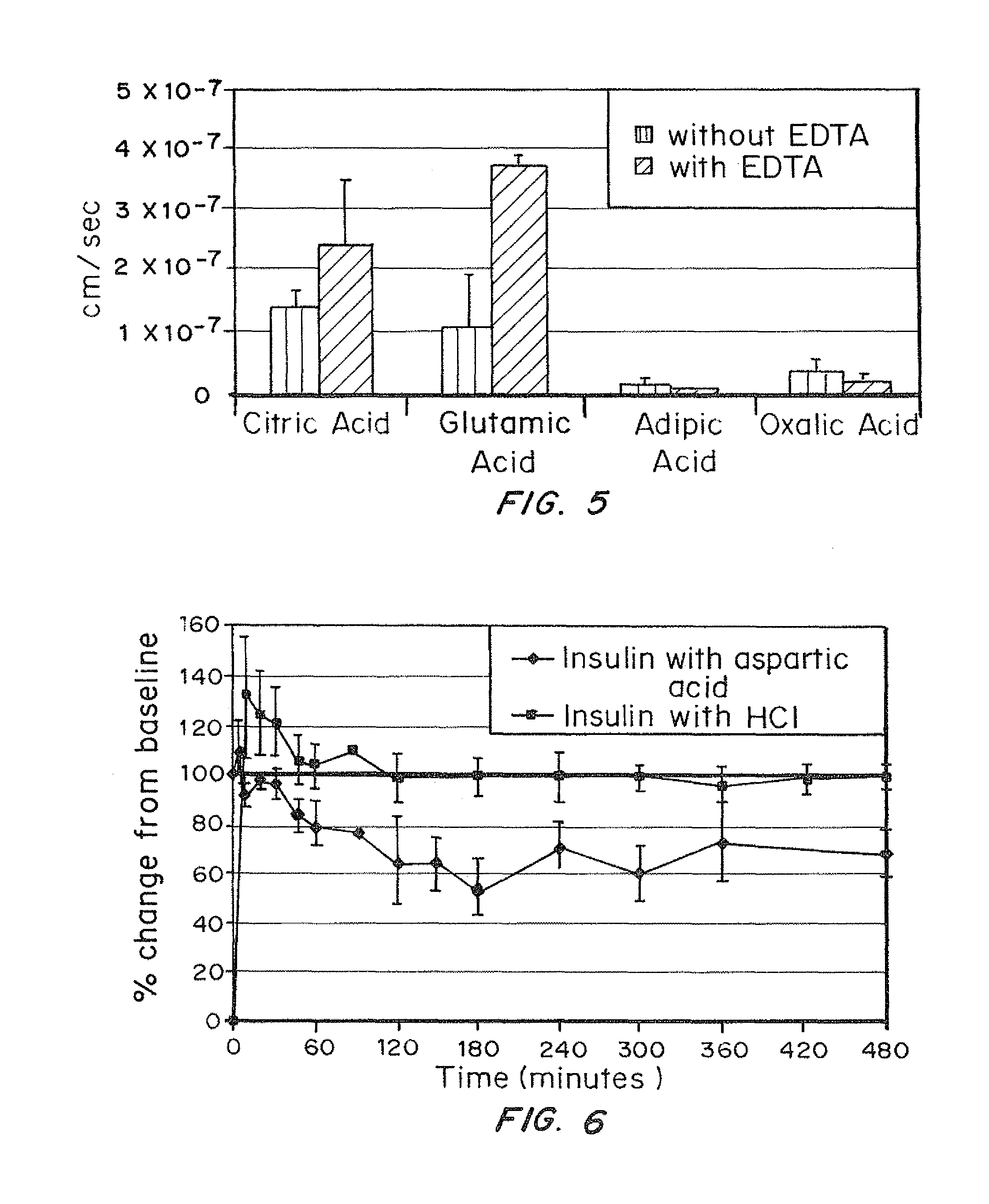
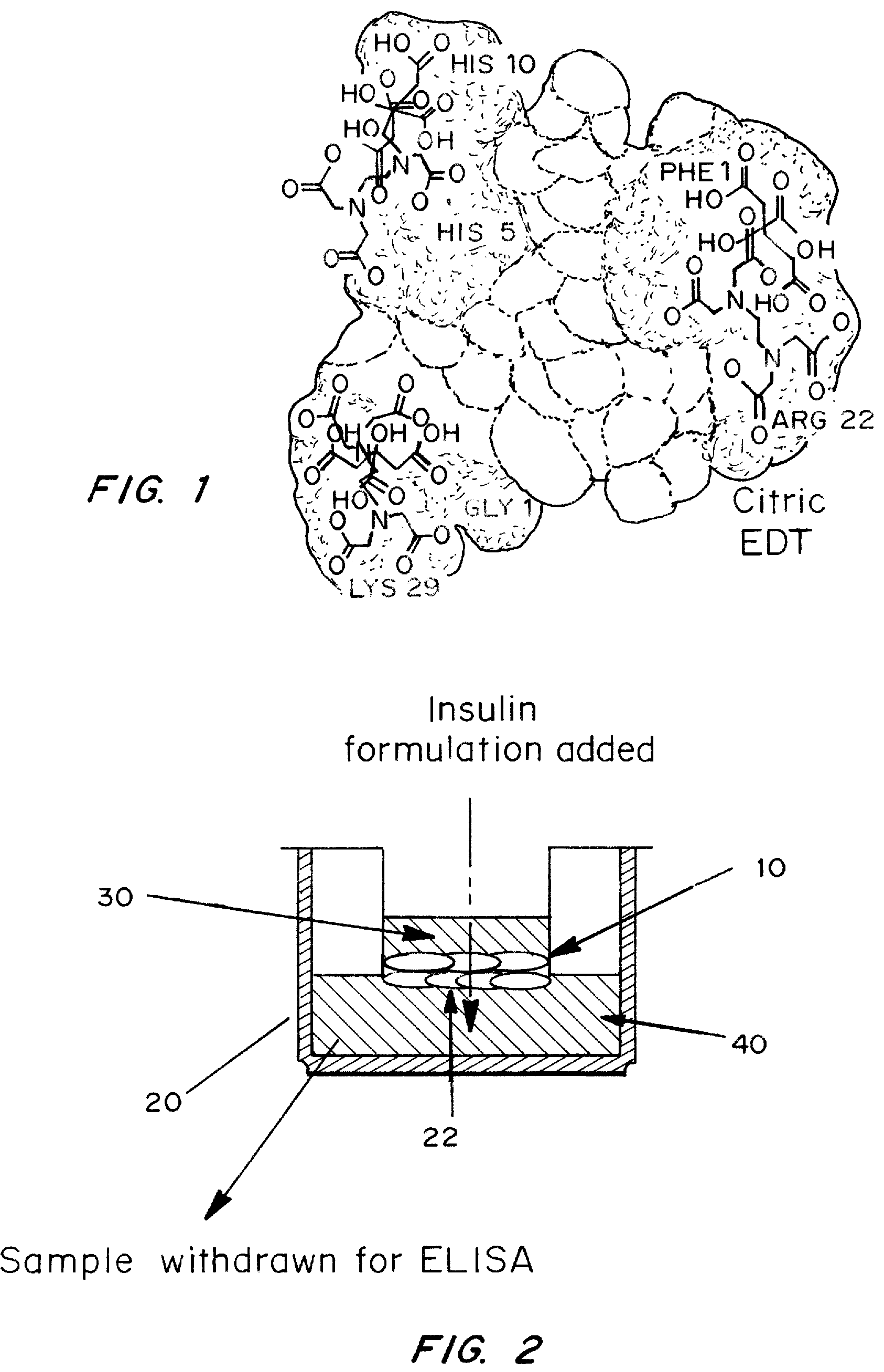
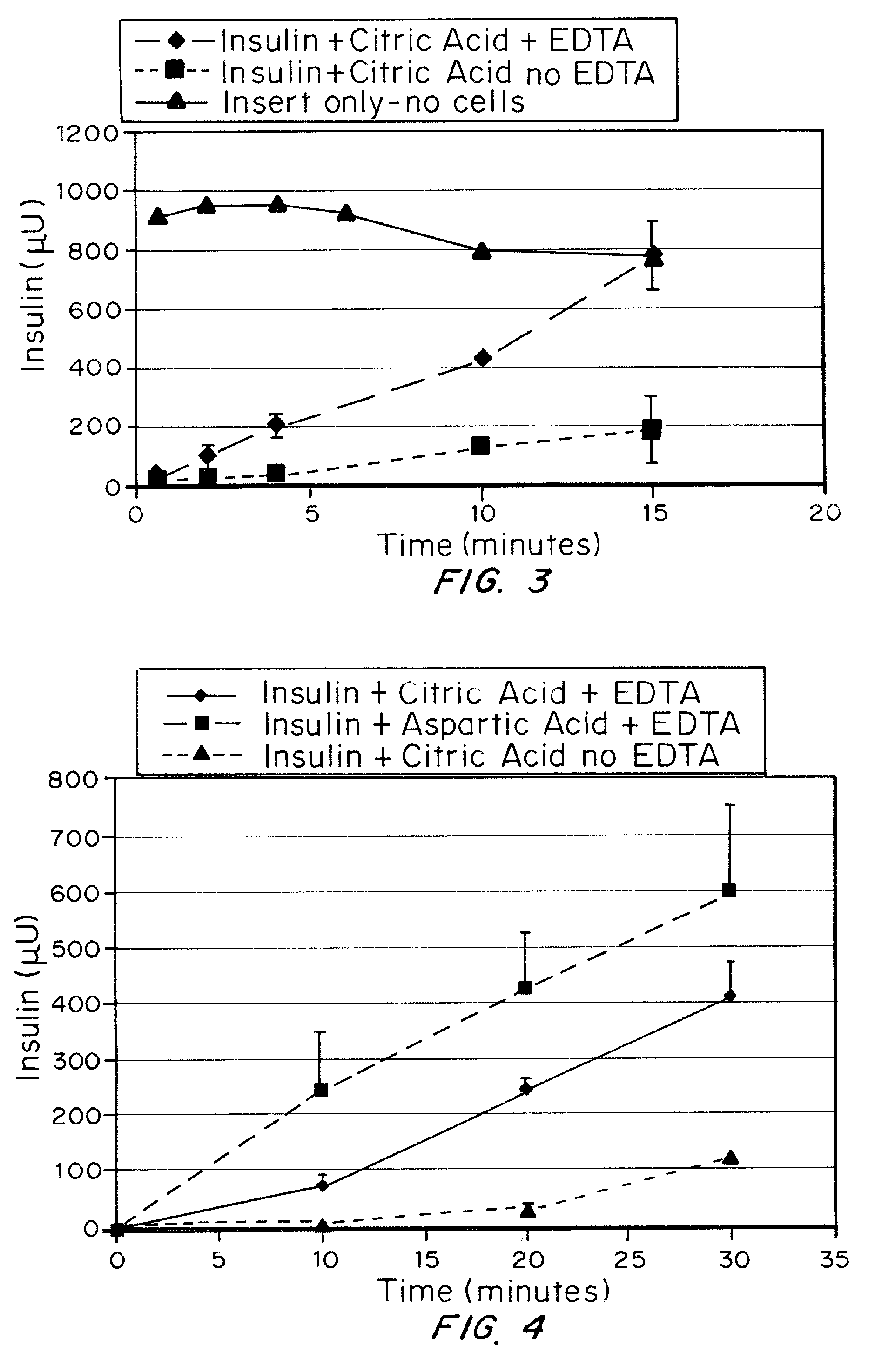
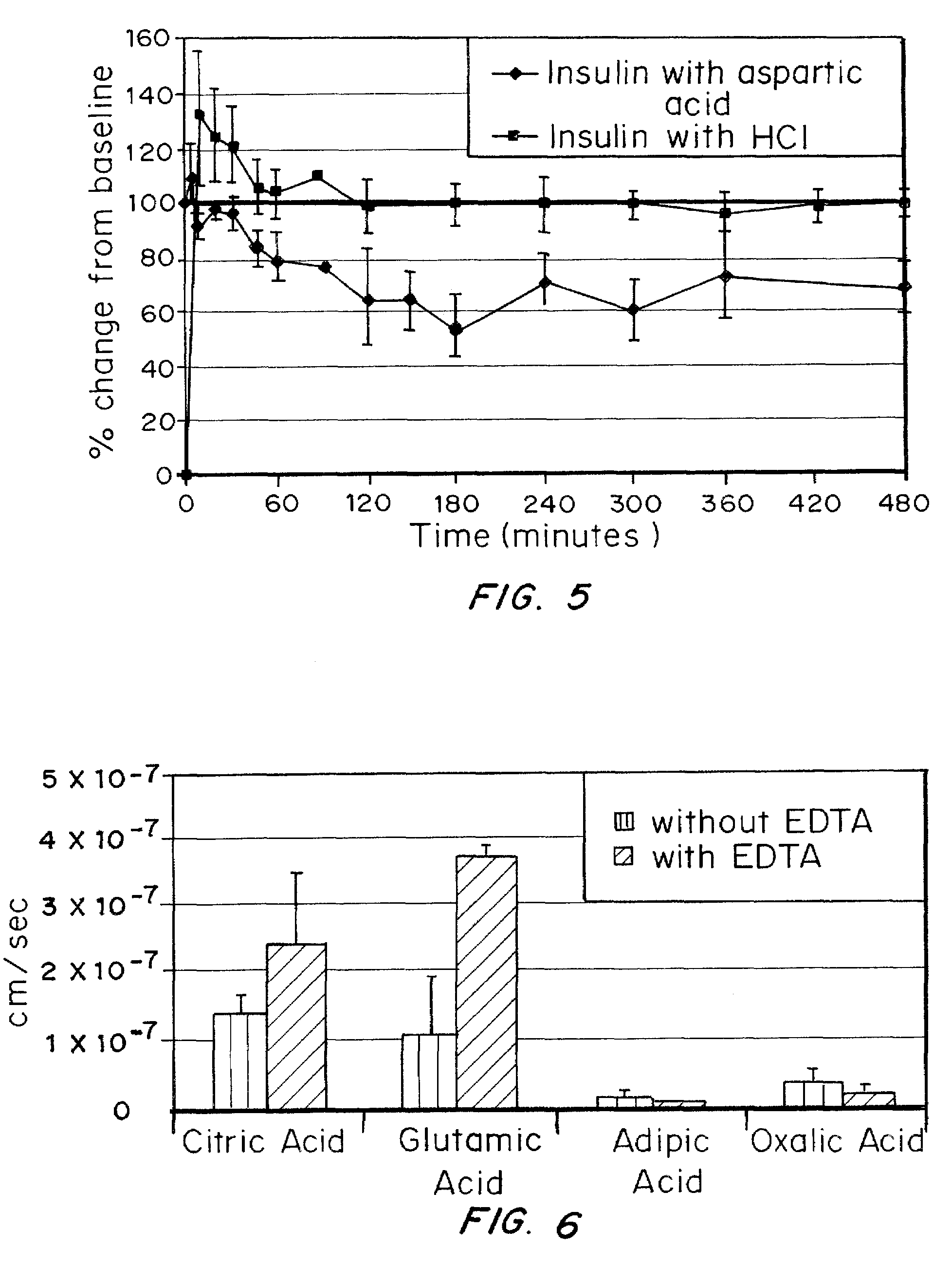
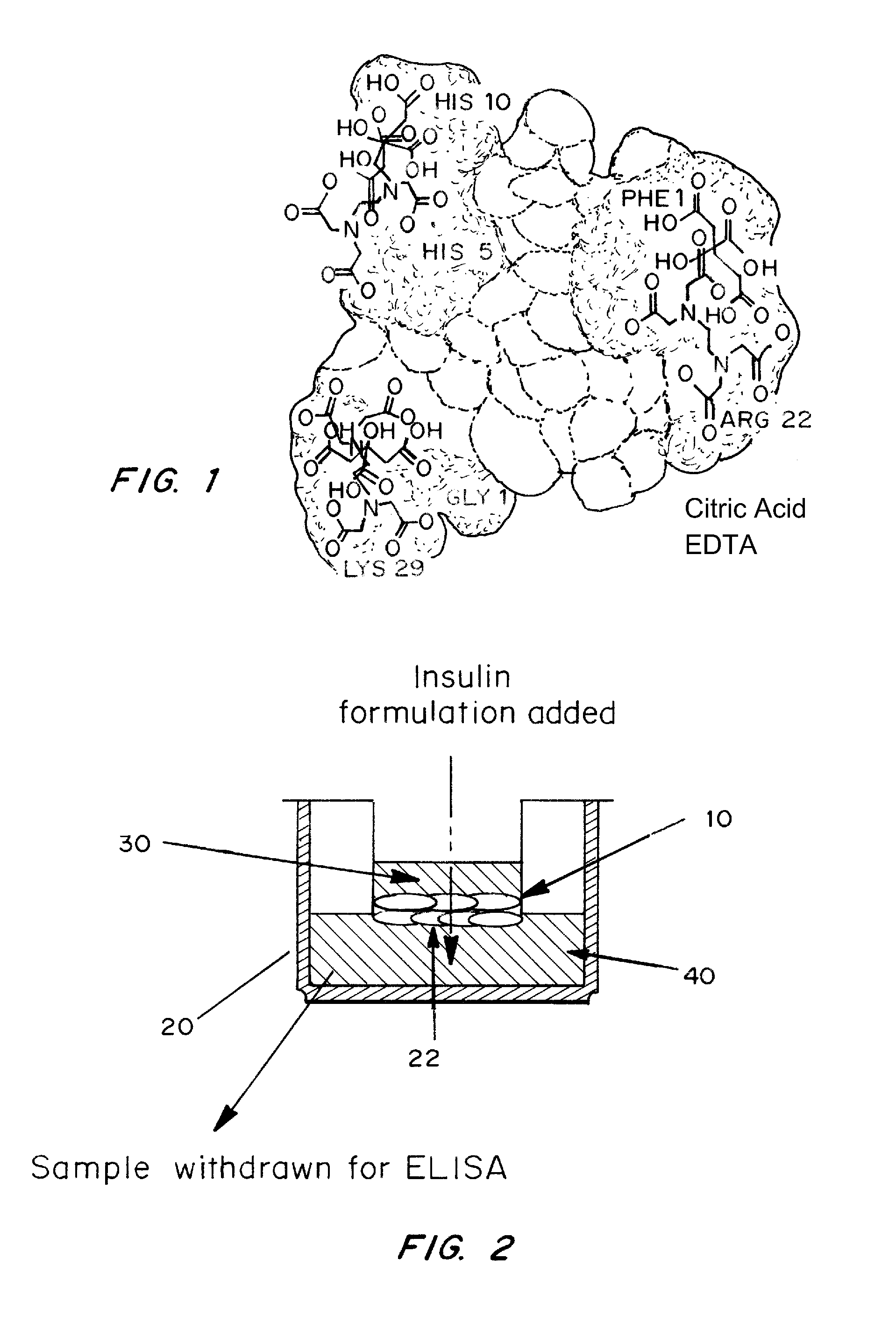
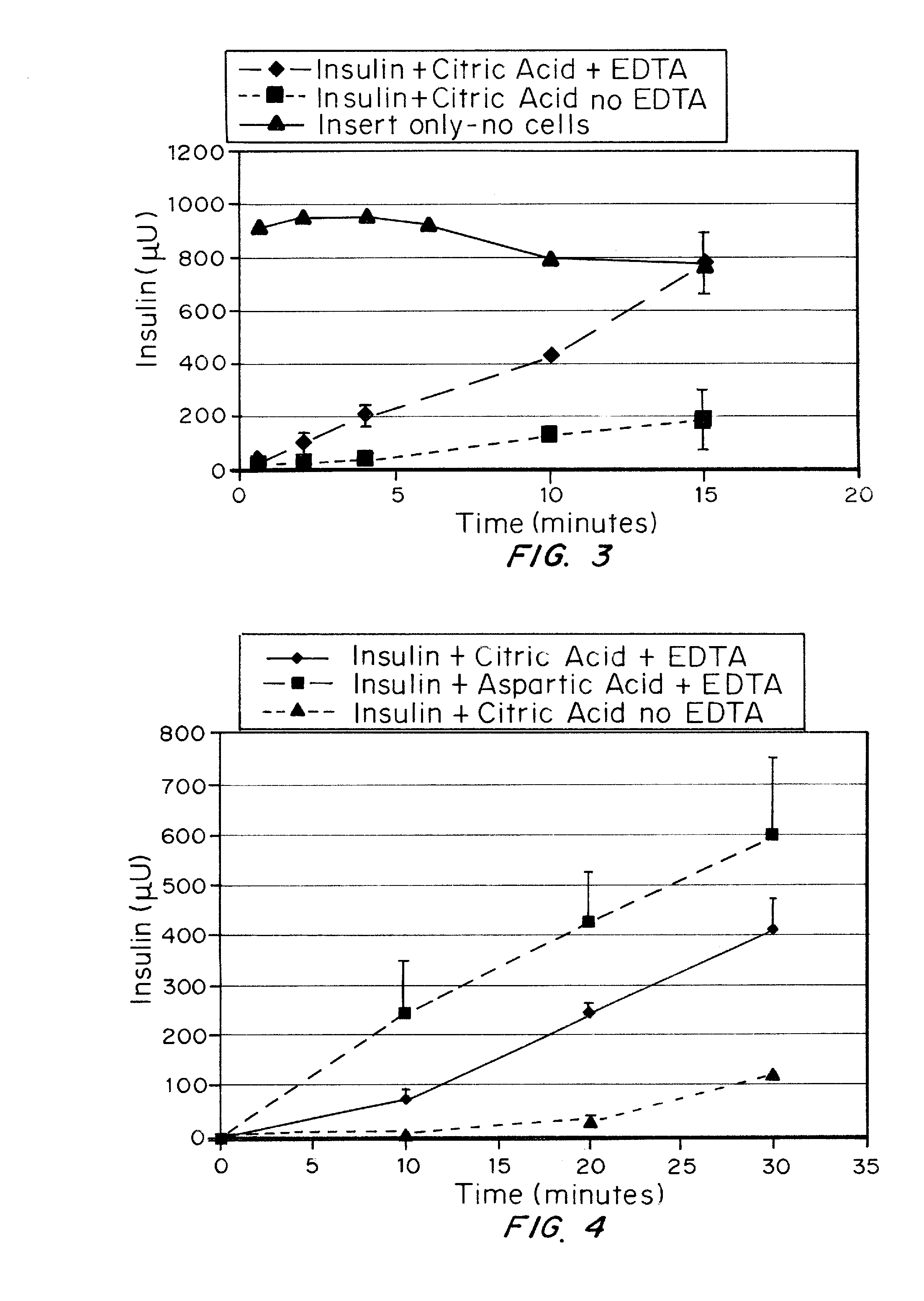
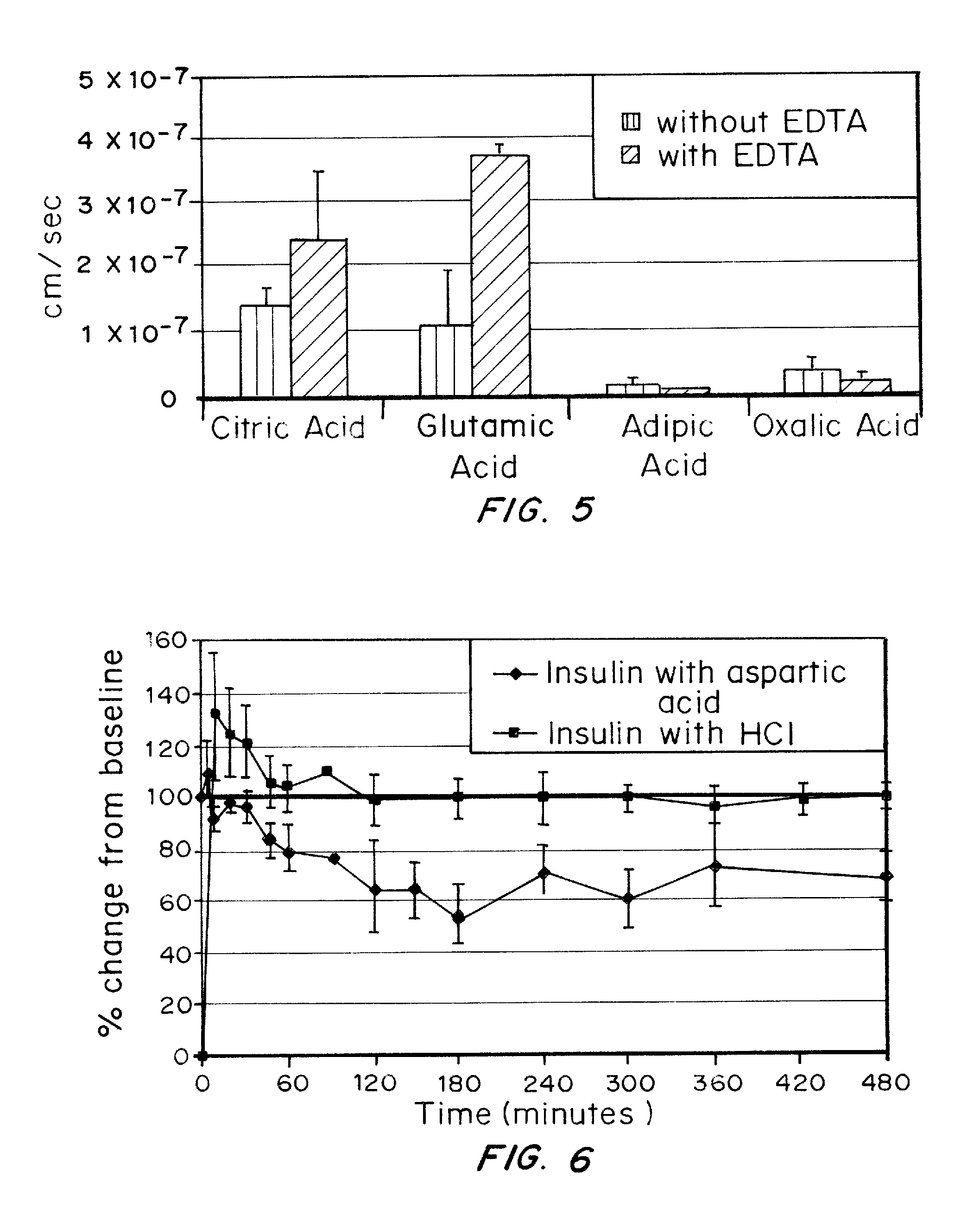
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed wherein the pH of the rapid acting insulin is adjusted so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day. Experiments have been performed to demonstrate, the importance of the addition of specific acids to hexameric insulin to enhance speed and amount of absorption and preserve bioactivity following dissociation into the monomeric form by addition of a chelator such as EDTA. As shown by the examples, the preferred acids are aspartic, maleic, succinic, glutamic and citric acid. These are added in addition to a chelator, preferably ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). The results show that the citric acid formulation was more effective at dropping the blood glucose rapidly than the identical rapid acting formulation prepared with HCl in swine. Charge masking by the polyacid appears to be responsible for rapid insulin absorption. EDTA was not effective when used with adipic acid, oxalic acid or HCl at hastening the absorption of insulin. These results confirm the results seen in clinical subjects and patients with diabetes treated with the rapid acting insulin in combination with citric acid and EDTA.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Tailored basal insulin delivery system and method
ActiveUS8088098B2Easy to operateIncreased and decreasedMetabolism disorderHealth-index calculationDelivery systemInsulin delivery
Disclosed is a system to deliver insulin to a user's body. The system includes a dispensing unit to deliver the insulin to the body, and a control mechanism to control delivery of basal insulin according to a predetermined basal infusion pattern, the basal infusion pattern selected from a plurality of predetermined basal infusion patterns. In some embodiments, selection of the basal infusion pattern may be based on one or more personal characteristics of the user.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Rapid Acting and Long Acting Insulin Combination Formulations
InactiveUS20080039365A1Promote absorptionAct quicklyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed wherein the pH of the rapid acting insulin is decreased so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day. Experiments have been performed to demonstrate the importance of the addition of specific acids to hexameric insulin to enhance speed and amount of absorption and preserve bioactivity following dissociation into the monomeric form by addition of a chelator such as EDTA. As shown by the examples, the preferred acids are aspartic, glutamic and citric acid. These are added in addition to a chelator, preferably ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). The results show that the citric acid formulation was more effective at dropping the blood glucose rapidly than the identical rapid acting formulation prepared with HCl in swine. Charge masking by the polyacid appears to be responsible for rapid insulin absorption. EDTA was not effective when used with adipic acid, oxalic acid or HCl at hastening the absorption of insulin. These results confirm the results seen in clinical subjects and patients with diabetes treated with the rapid acting insulin in combination with citric acid and EDTA.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Amylin Formulations
InactiveUS20090192075A1Reduce in quantityAct quicklyPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderGLP-1 MimeticsBefore Breakfast
A combined insulin and amylin and / or GLP-1 mimetic formulation has been developed wherein the pH of the insulin is decreased so that the amylin and / or GLP-1 remains soluble when mixed together with the insulin. In the preferred embodiment, a bolus insulin is administered by injection before breakfast, providing adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, without producing hypoglycemia after the meal. This can be combined with an adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of the insulin and amylin and / or GLP-1 mimetic combination. A GLP-1 mimetic may be combined with either rapid acting or basal insulin formulations. As a result, a patient using the combination formulation therapy may only need to inject half as many times per day.
Owner:BIODEL INC
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
ActiveUS7718609B2Increase speedReduce the amount of solutionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed in which the pH of the rapid acting insulin is adjusted so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Insulin with a stable basal release profile
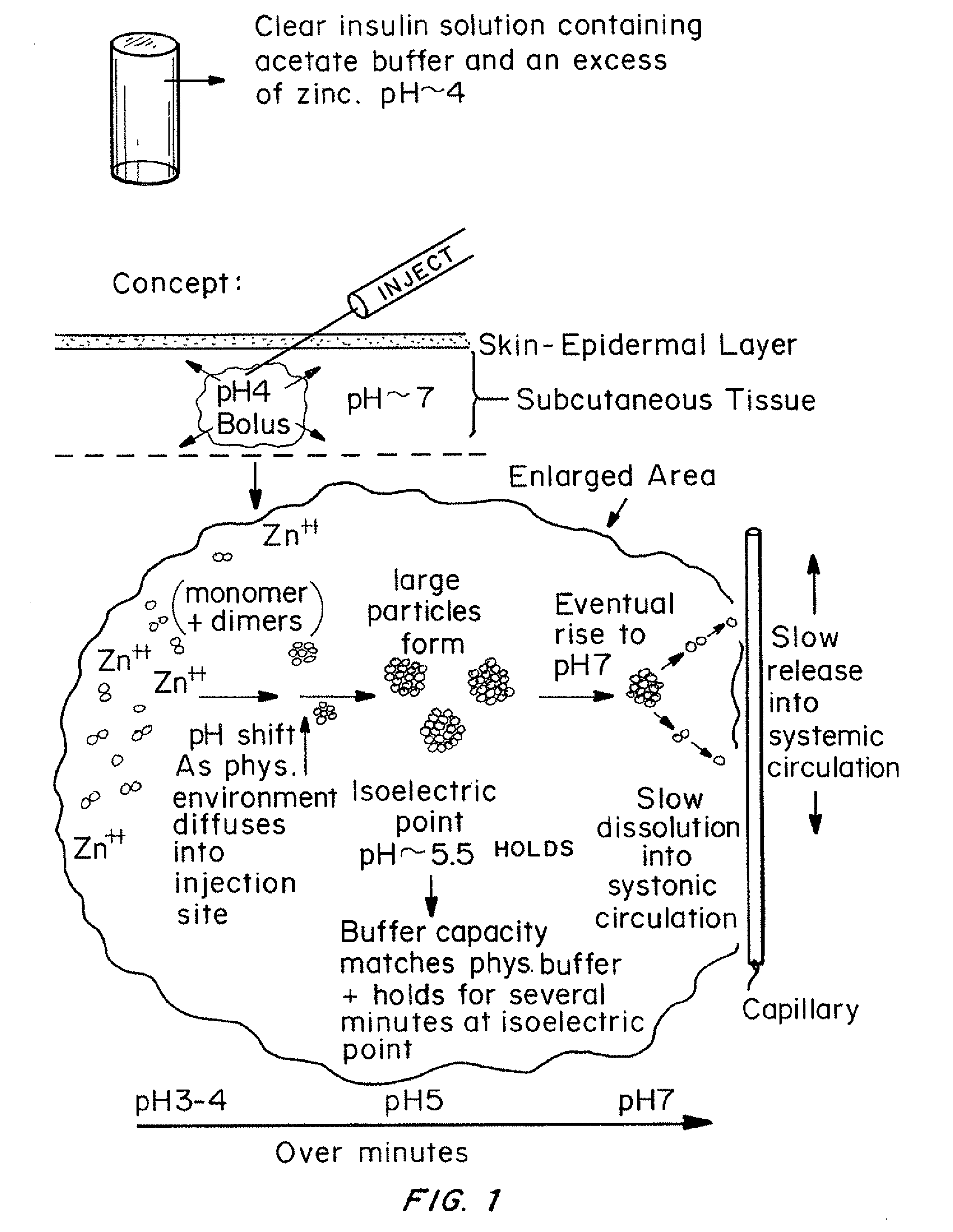
ActiveUS20110281790A1Accelerated precipitationLess solublePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin glargineZinc
A basal insulin formulation composed of insulin, preferably insulin glargine, injectable zinc and injectable iron compounds as precipitating and / or stabilizing agents has been developed for subcutaneous, intradermal or intramuscular administration. The formulation is designed to form a precipitate of insulin following injection, creating a slow releasing “basal insulin” over a period of 12 to 24 hours.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
ActiveUS8084420B2Short durationImprove blood sugar controlPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBefore BreakfastInsulin injection
An injectable formulation containing a rapid acting insulin and a long acting insulin has been developed. The pH of the rapid acting insulin is adjusted so that the long acting insulin, remains soluble when they are mixed together. Preferably, the formulation is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal and basal insulin for up to 24 hours, and does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast, rapid, or very rapid acting insulin. Alternatively, by adjusting the ratio of rapid to long acting insulin, the long acting insulin may be shortened to a 12 hour formulation, and re-administered to the patient at dinner time, providing a safe and effective basal insulin level until morning. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three times a day.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
InactiveUS7713929B2Rapid acting insulin isPromote absorptionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed in which the pH of the rapid acting insulin is decreased so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Insulin with a basal release profile
InactiveUS20100069292A1Not possibleAvoid the needPeptide/protein ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsBuffering agentINSULIN PREPARATIONS
A clear basal insulin formulation composed of insulin (preferably human recombinant insulin), buffering agents, precipitating agents, and / or stabilizing agents for subcutaneous, intradermal or intramuscular administration. The formulation is designed to form a precipitate of insulin following injection, creating a slow releasing “basal insulin” over a period of 12 to 24 hours, which can be varied by compositional changes to tailor the release profile to the needs of the individual diabetic patient
Owner:BIODEL
System and method for detecting occlusions in an infusion pump
ActiveUS20140276409A1Minimize impactMedical devicesPressure infusionLine tubingDifferential pressure
Occlusions in a delivery line of an infusion pump can be detected by measuring pressure differentials in the pump over short periods of time in order to minimize the effects of long term systematic sensor changes. In a delivery mode such as basal insulin delivery where a small portion of a volume of fluid is delivered, pressure readings can be obtained before and after the motor move to deliver each portion and compared. The differentials after one or more motor moves can be compared to determine whether an occlusion is present. In a delivery mode such as bolus insulin delivery in which an entire volume of fluid is delivered, pressure differentials can be obtained for consecutive deliveries at a common point in the delivery cycle of each delivery. Comparison of these pressure values can be used to determine whether an occlusion is present.
Owner:TANDEM DIABETES CARE INC
System and method for detecting occlusions in an infusion pump
ActiveUS9173998B2Minimize impactMedical devicesPressure infusionPressure differenceIntensive care medicine
Occlusions in a delivery line of an infusion pump can be detected by measuring pressure differentials in the pump over short periods of time in order to minimize the effects of long term systematic sensor changes. In a delivery mode such as basal insulin delivery where a small portion of a volume of fluid is delivered, pressure readings can be obtained before and after the motor move to deliver each portion and compared. The differentials after one or more motor moves can be compared to determine whether an occlusion is present. In a delivery mode such as bolus insulin delivery in which an entire volume of fluid is delivered, pressure differentials can be obtained for consecutive deliveries at a common point in the delivery cycle of each delivery. Comparison of these pressure values can be used to determine whether an occlusion is present.
Owner:TANDEM DIABETES CARE INC
Fluid infusion system that automatically determines and delivers a correction bolus
A method of controlling an insulin infusion device involves controlling the device to operate in an automatic basal insulin delivery mode, obtaining a blood glucose measurement for the user, and initiating a correction bolus procedure when: the measurement exceeds a correction bolus threshold value; and a maximum basal insulin infusion rate is reached during the automatic basal insulin delivery mode. The correction bolus procedure calculates an initial correction bolus amount, and scales the initial amount to obtain a final correction bolus amount, such that a predicted future blood glucose level resulting from simulated delivery of the final correction bolus amount exceeds a low blood glucose threshold level. The final amount is delivered to the user during operation in the automatic basal insulin delivery mode.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Adaptive System for Optimizing a Drug Dosage Regimen Over Time
ActiveUS20140371682A1Reducing “ aggressiveness ”Ampoule syringesDrug and medicationsTemporal changeRegimen
A system for optimizing a patient's basal insulin dosage regimen over time, adapted to determine from blood glucose values whether and by how much to vary a patient's present recommended amount of the insulin-containing drug in order to maintain the patient's future blood glucose level measurements within a predefined range, and wherein a given blood glucose value is disregarded if no patient-actuated operation being indicative of the administration of a dose of an insulin containing drug has been detected in a pre-defined amount of time prior to the determination of the given blood glucose value.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
ActiveUS20090137455A1Short durationImprove blood sugar controlPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
An injectable formulation containing a combination of a rapid acting insulin and a long acting insulin has been developed wherein the pH of the rapid acting insulin is adjusted so that the long acting insulin, e.g. insulin glargine, remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for up to 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. Alternatively, through adjustment of the ratio of rapid acting insulin to long acting insulin, the long acting insulin may be shortened to a 12 hour formulation. This rapid and long acting blend is re-administered to the patient at dinner time, providing a safe and effective basal insulin level until morning. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
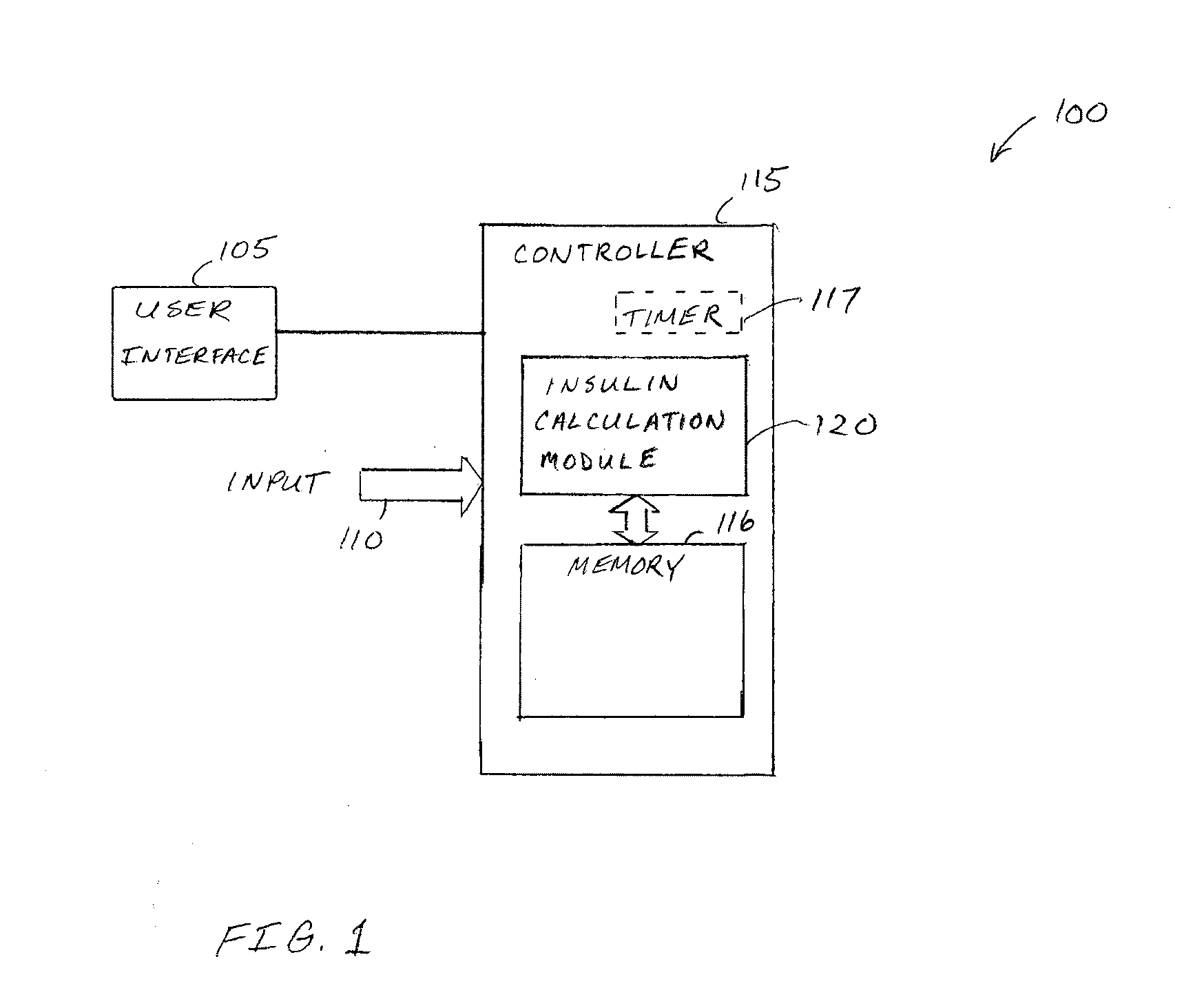
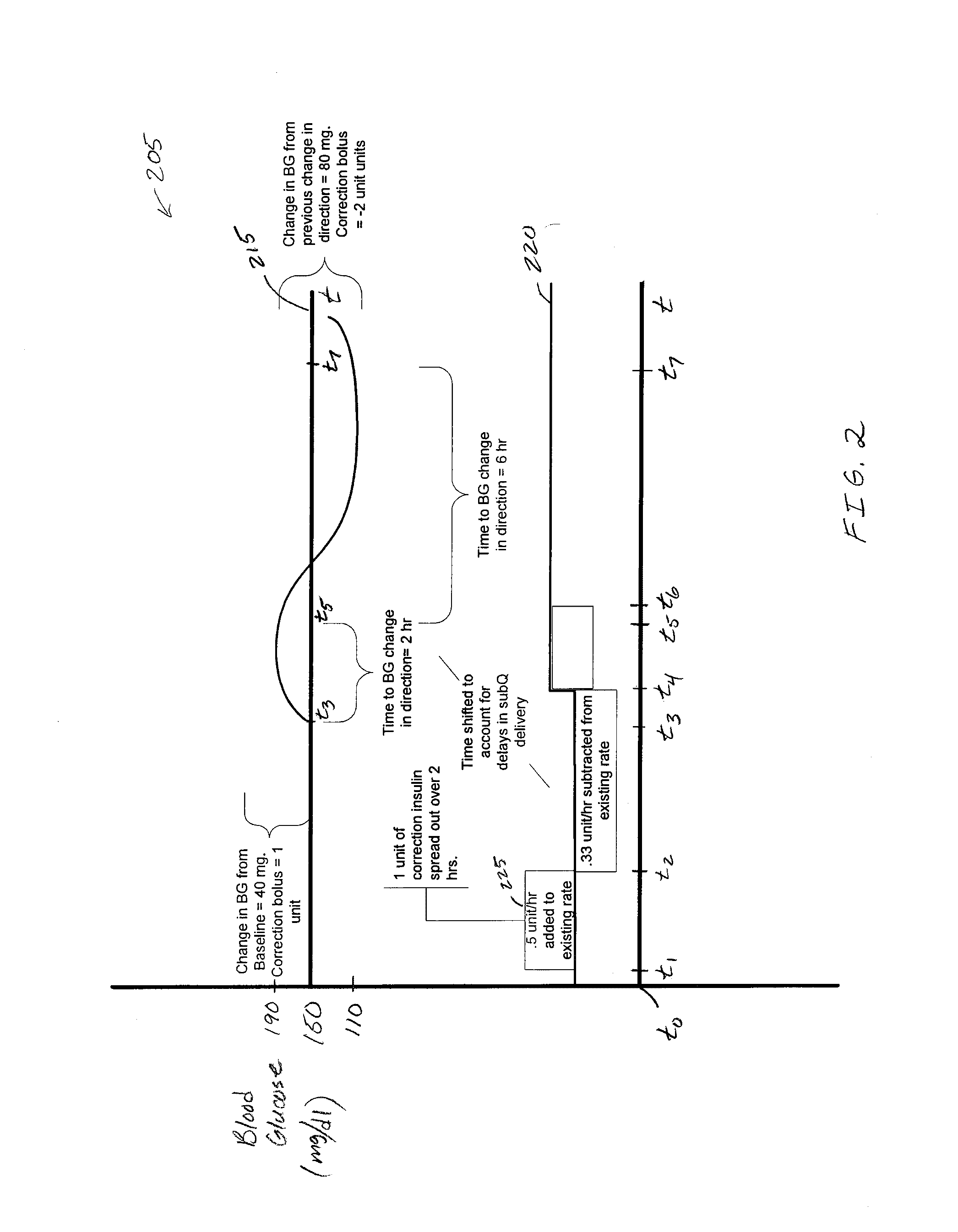
Basal rate testing using frequent blood glucose input
An apparatus comprising a user interface configured to generate an electrical signal to start a basal insulin rate test when prompted by a user, an input configured to receive sampled blood glucose data of a patient that is obtained during a specified time duration, including a time duration during delivery of insulin according to a specified basal insulin rate pattern, and a controller communicatively coupled to the input and the user interface. The controller includes an insulin calculation module configured for determining at least one of an amount of basal insulin over-delivered and an amount of basal insulin under-delivered during the basal insulin rate test in trying to meet a target blood glucose baseline. Other devices and methods are disclosed.
Owner:TANDEM DIABETES CARE INC
System for Optimizing a Patient's Drug Dosage Regimen Over Time
ActiveUS20140094743A1Simple and cost-effectiveEffective calculationAmpoule syringesDrug and medicationsRegimenLevel measurement
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Derivatized insulin oligomers
InactiveUS20090099064A1Quality improvementImprove actionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderPhosphorylationLower risk
The present invention provides oligomers of phosphorylated insulin and formulations thereof. The oligomeric derivatives of the invention exhibit pharmacodynamic properties that are significantly improved over native insulin or other intermediate-acting or basal insulins, for example NPH, Lantus or Detemir, in that they demonstrate a 4-fold higher therapeutic index and a 4-fold lower risk of hypoglycemia. The invention provides the advantage of protracted glycemic lowering and combines it with the advantage of reduced hypoglycaemic risk. The above is not a property of any presently-known or available basal or intermediate-acting insulin. In a further embodiment of the invention, formulations of oligomeric phosphorylated insulin are suitable for all routes of administration including inhalation, buccal absorption, subcutaneous injection, infusion or other technically proven routes for insulin administration. The invention additionally provides the advantage of a longer-acting formulation for inhalation between meals and at bedtime. Such longer-acting inhalable formulations are not presently available.
Owner:DIABECORE MEDICAL
Estimation of insulin based on reinforcement learning
ActiveUS20190214124A1Improve performanceReduce deliveryMedical simulationMathematical modelsPersonalizationReinforcement learning algorithm
The optimal insulin to be delivered by an insulin infusion pump is determined by using a reinforcement learning algorithm aiming to the personalized glucose regulation. The algorithm optimizes the daily basal insulin rate and insulin: carbohydrate ratio for each patient, on the basis of his / her measured glucose profile. The proposed algorithm is able to learn in real-time patient-specific characteristics captured in the daily glucose profile and provide individualised insulin treatment. An automatic and personalised tuning method contributes in the optimisation of the algorithm's performance.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BERN
System for optimizing a patient's drug dosage regimen over time
ActiveUS9619625B2Simple and cost-effectiveEffective calculationAmpoule syringesDrug and medicationsRegimenLevel measurement
A system for optimizing a patient's basal insulin dosage regimen over time, adapted to (a) determine from blood glucose values whether and by how much to vary a patient's present recommended amount of the insulin-containing drug in order to maintain the patient's future blood glucose level measurements within a predefined range, and (b) at the same time display blood glucose value data and the recommended amount data as a function of time.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Transdermal administration kit
ActiveCN102039000AMeet supply needsEasy accessPeptide/protein ingredientsMedical devicesHypodermoclysisProtamine zinc insulin
The present invention provides a transdermal administration kit, wherein the transdermal administration kit comprises a microneedle array and a transdermal administration patch; the penetration depth of the microneedle array into the skin is about 20 to 150 um; the transdermal administration patch comprises a medicament holder and insulin as active medicament components; the medicament holder is made from inert substances capable of adsorbing and holding the adsorbed liquid. The transdermal administration kit provided by the invention enables the blood sugar value of a rat suffering from diabetes mellitus to be kept constant during a period of from 2 to 24 hours after the rat is administered the formulation. So the transdermal administration kit provided by the invention can replace the hypodermic injection of protamine zinc insulin and other similar ways to maintain the stabilization of the basic insulin level in the human body blood.
Owner:SUZHOU NANOMED BIOMED CO LTD
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising GLP-1 peptides or exendin-4 and a basal insulin peptide
Pharmaceutical composition for parenteral administration comprising a basal insulin peptide and an insulinotropic GLP-1 peptide comprising at least 6 zinc atoms per 6 insulin molecules.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
System for optimizing a patient's drug dosage regimen over time
InactiveCN103443798AHas blood sugar control effectAmpoule syringesDrug and medicationsTemporal changeRegimen
A system for optimizing a patient's basal insulin dosage regimen over time, adapted to (a) determine from blood glucose values whether and by how much to vary a patient's present recommended amount of the insulin-containing drug in order to maintain the patient's future blood glucose level measurements within a predefined range, and (b) at the same time display blood glucose value data and the recommended amount data as a function of time.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com