Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
195 results about "Continuous glucose monitoring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
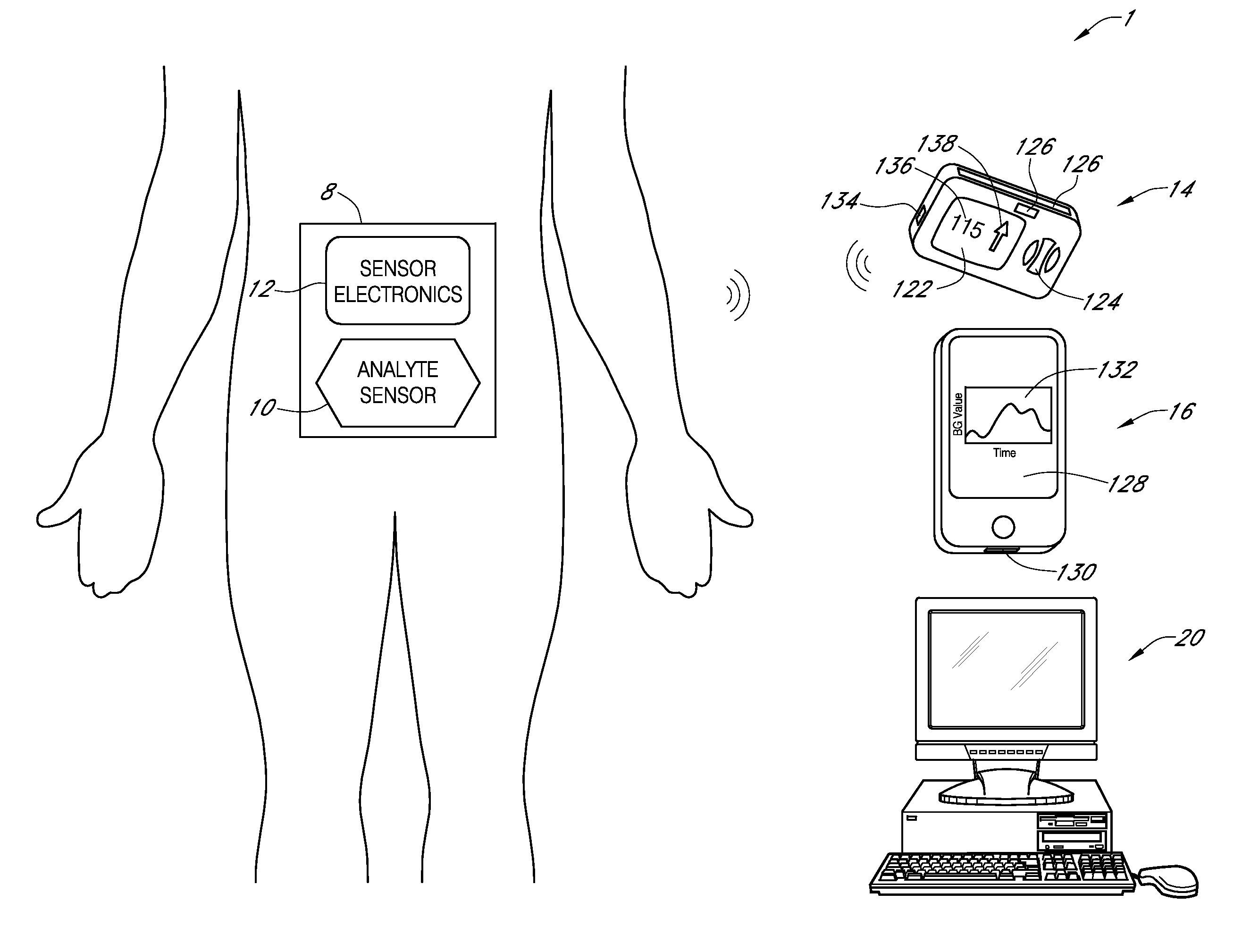
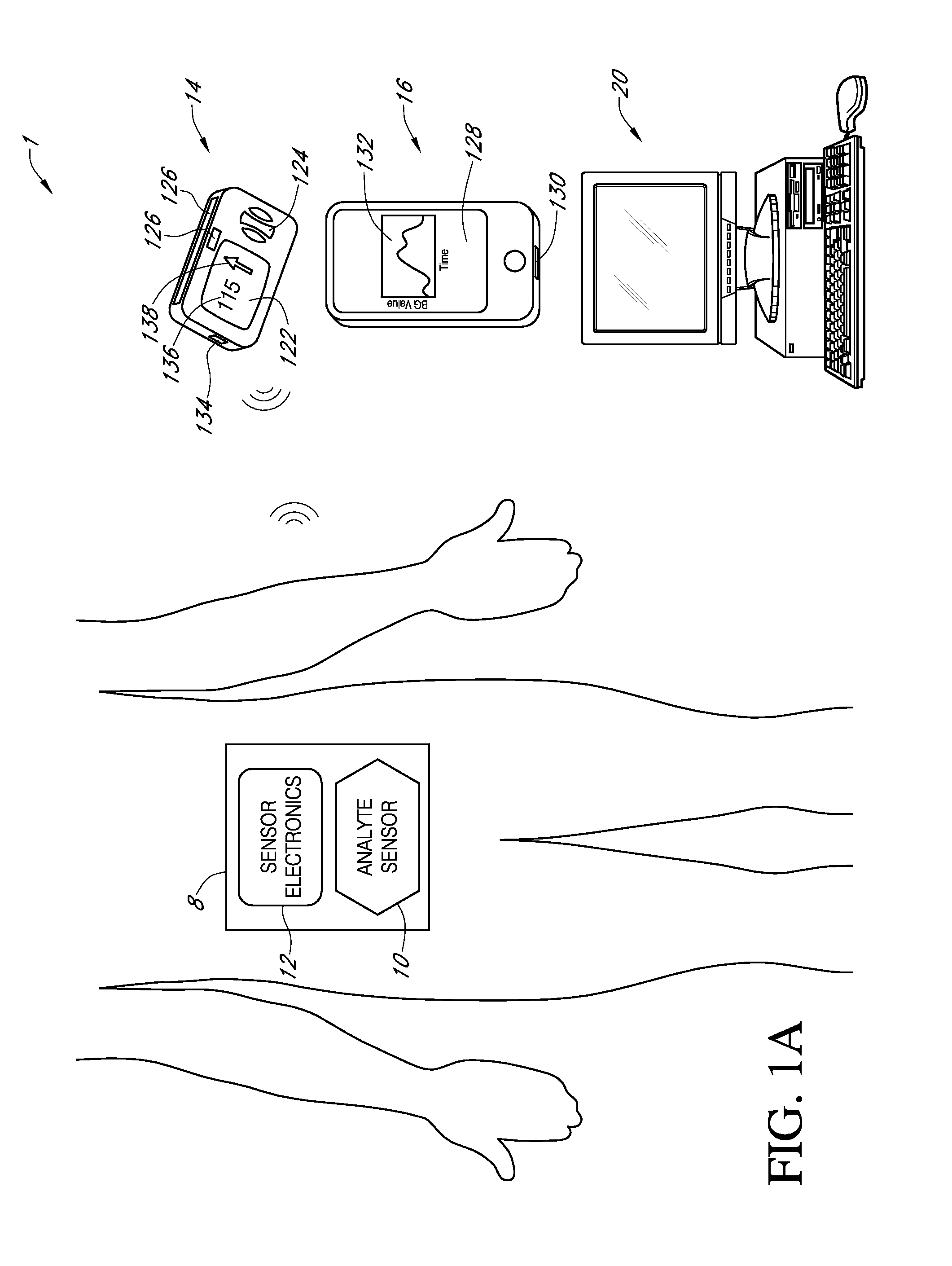
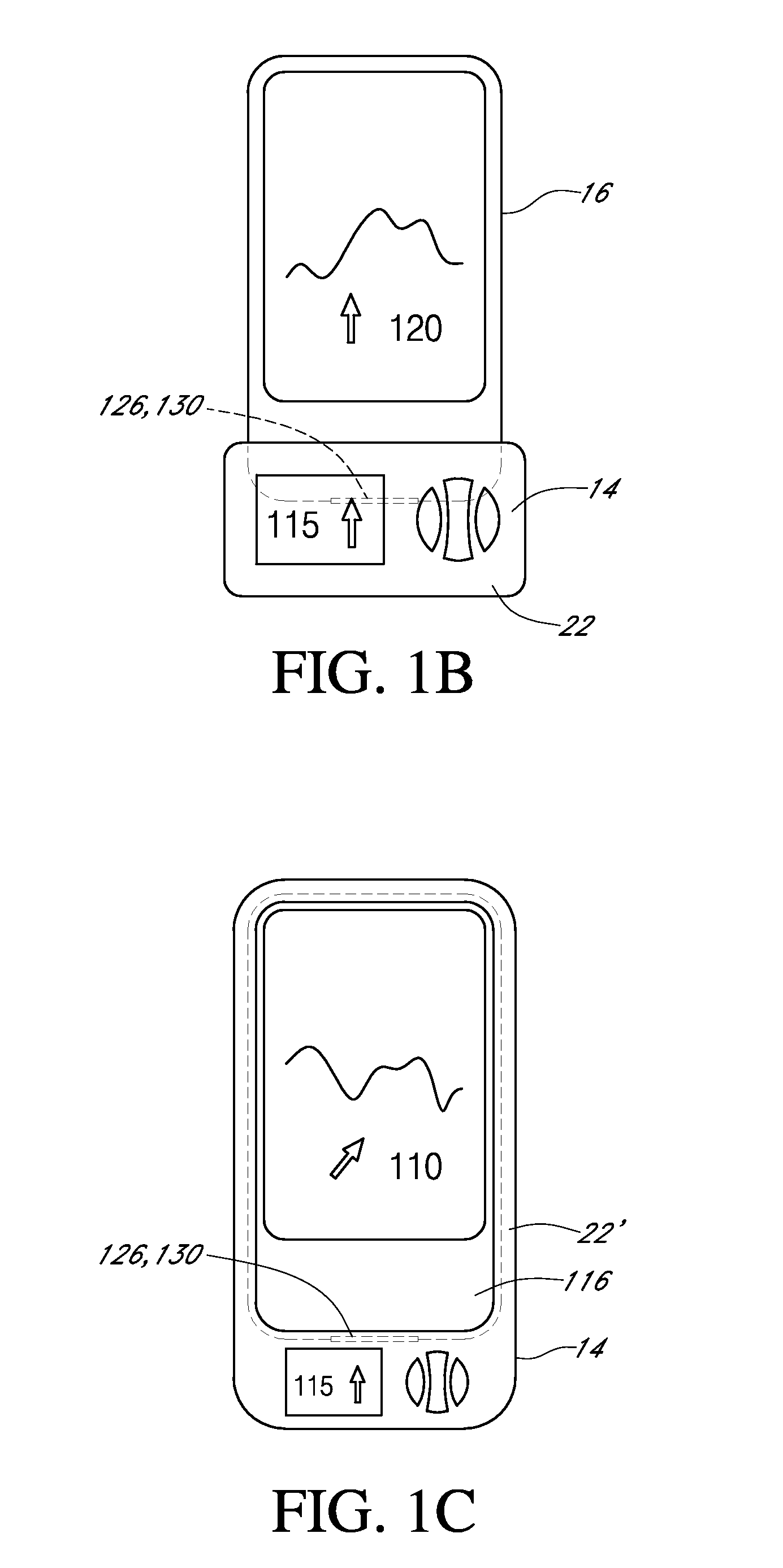
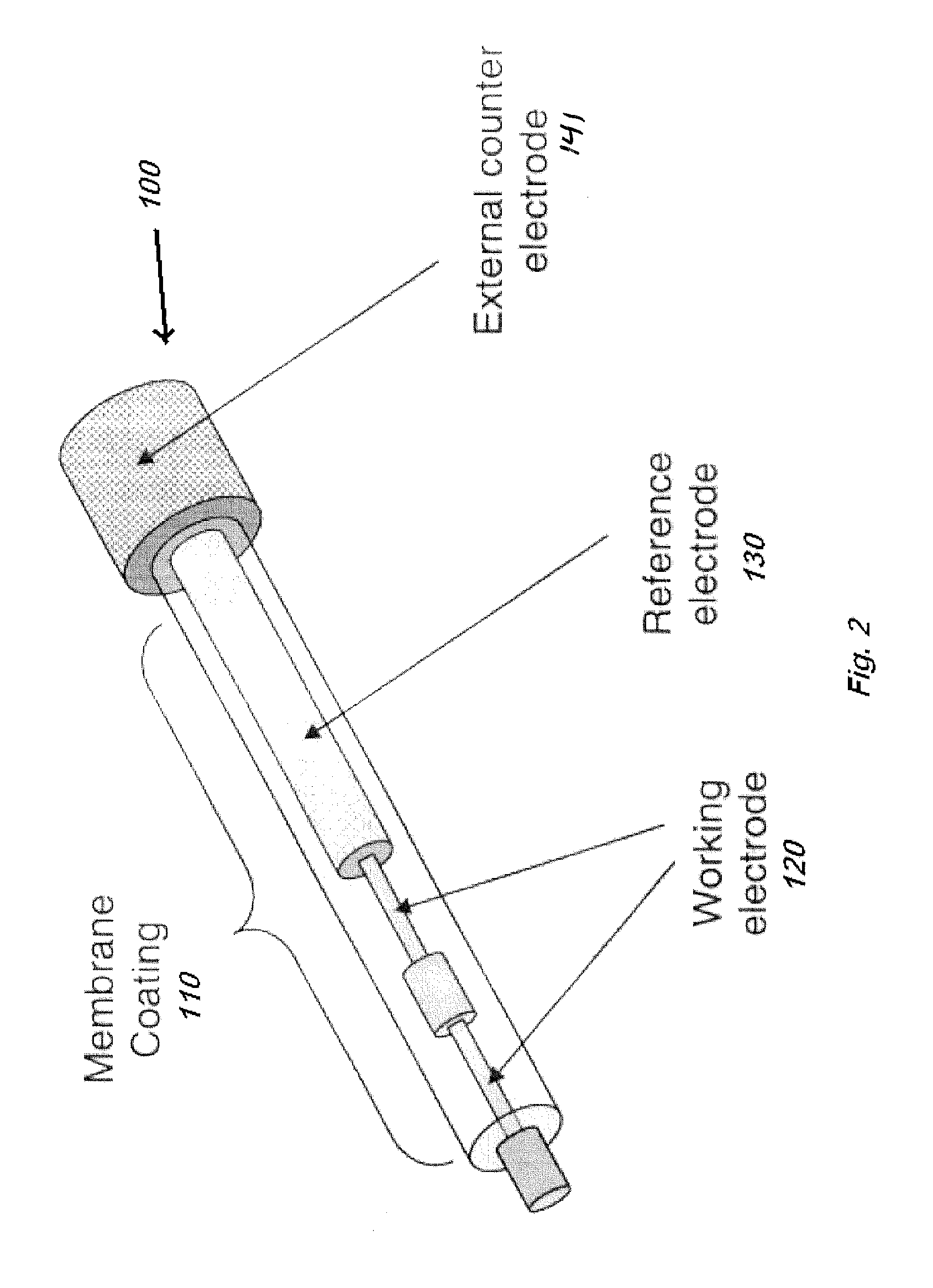
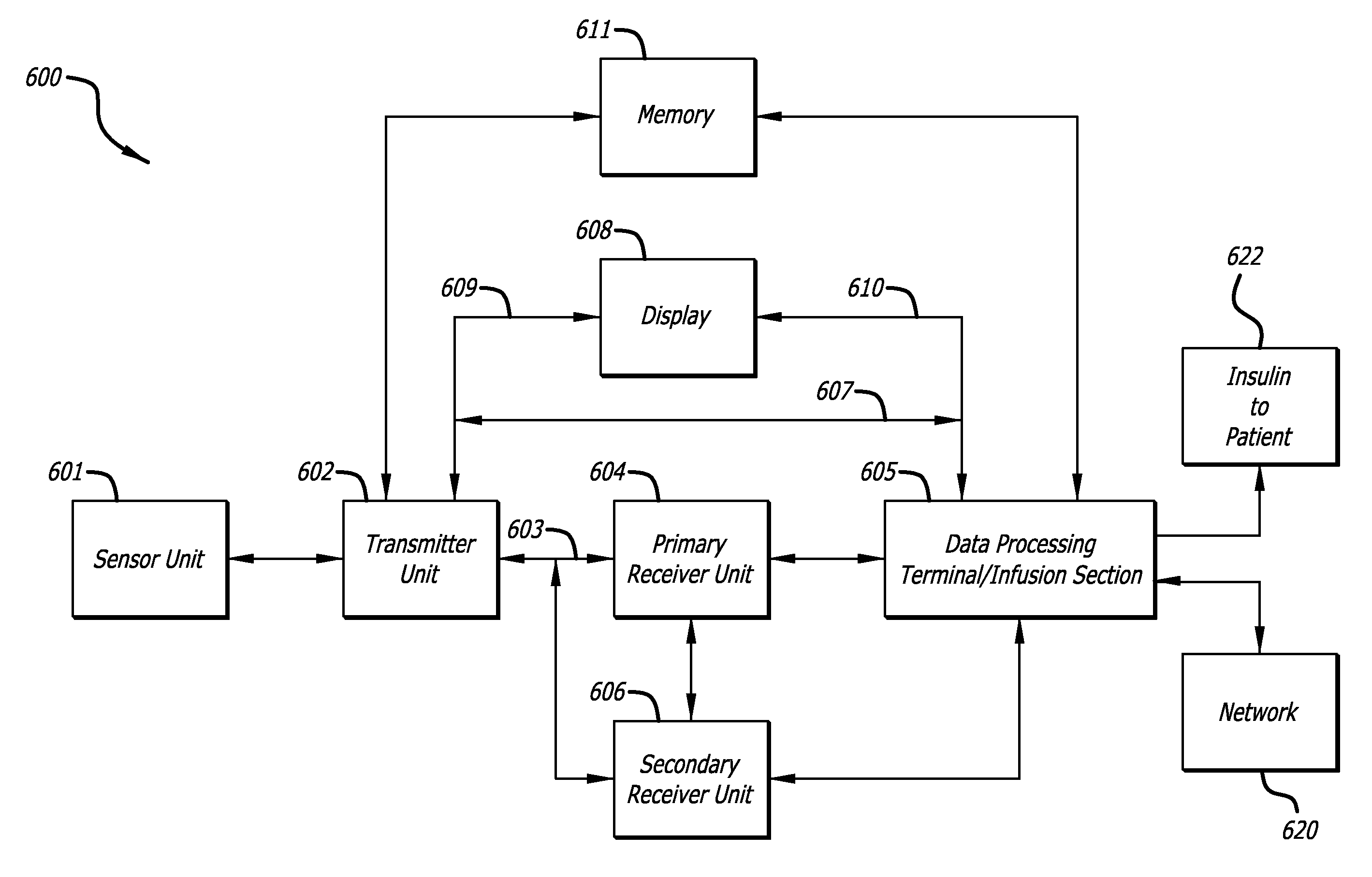
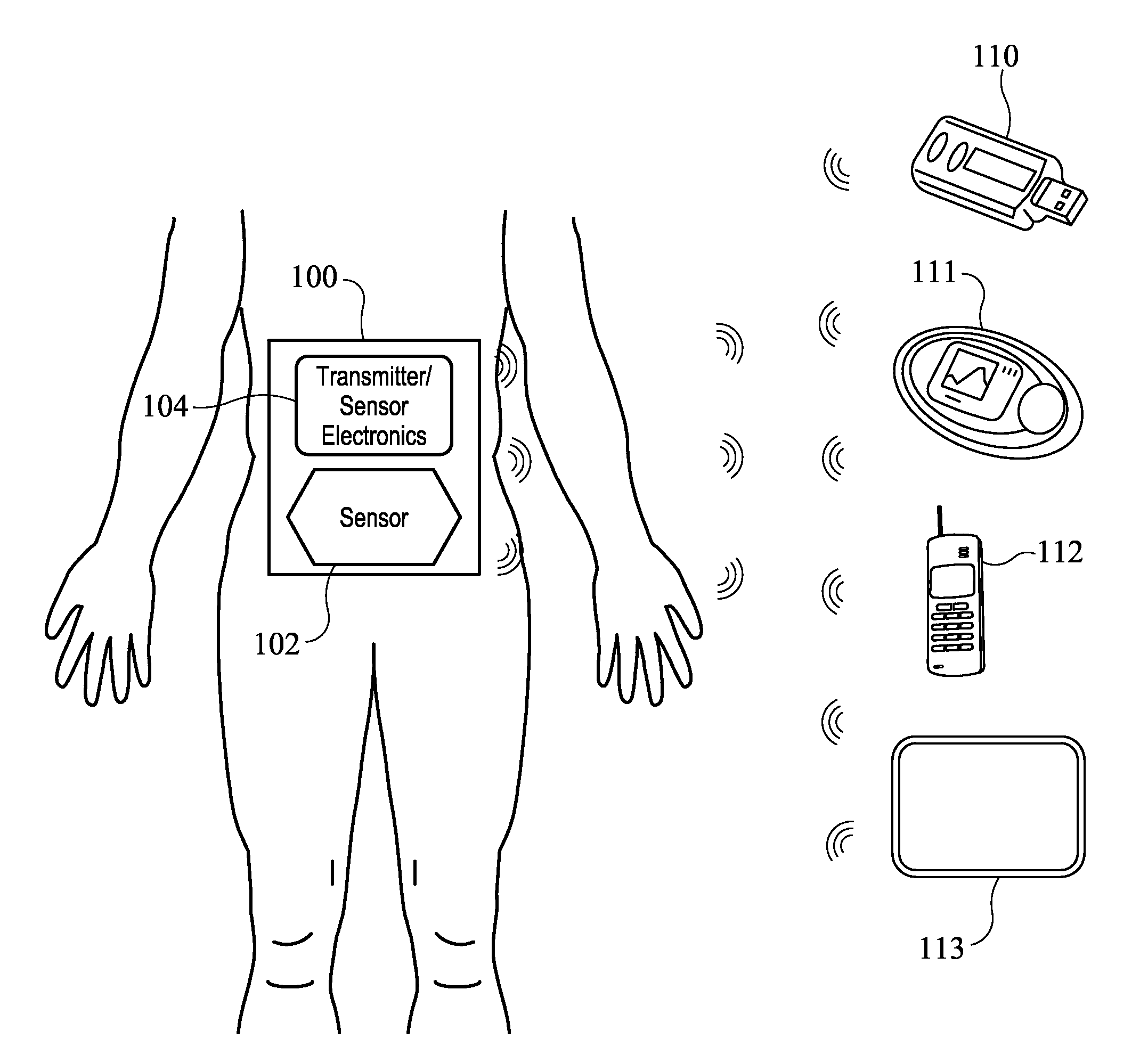
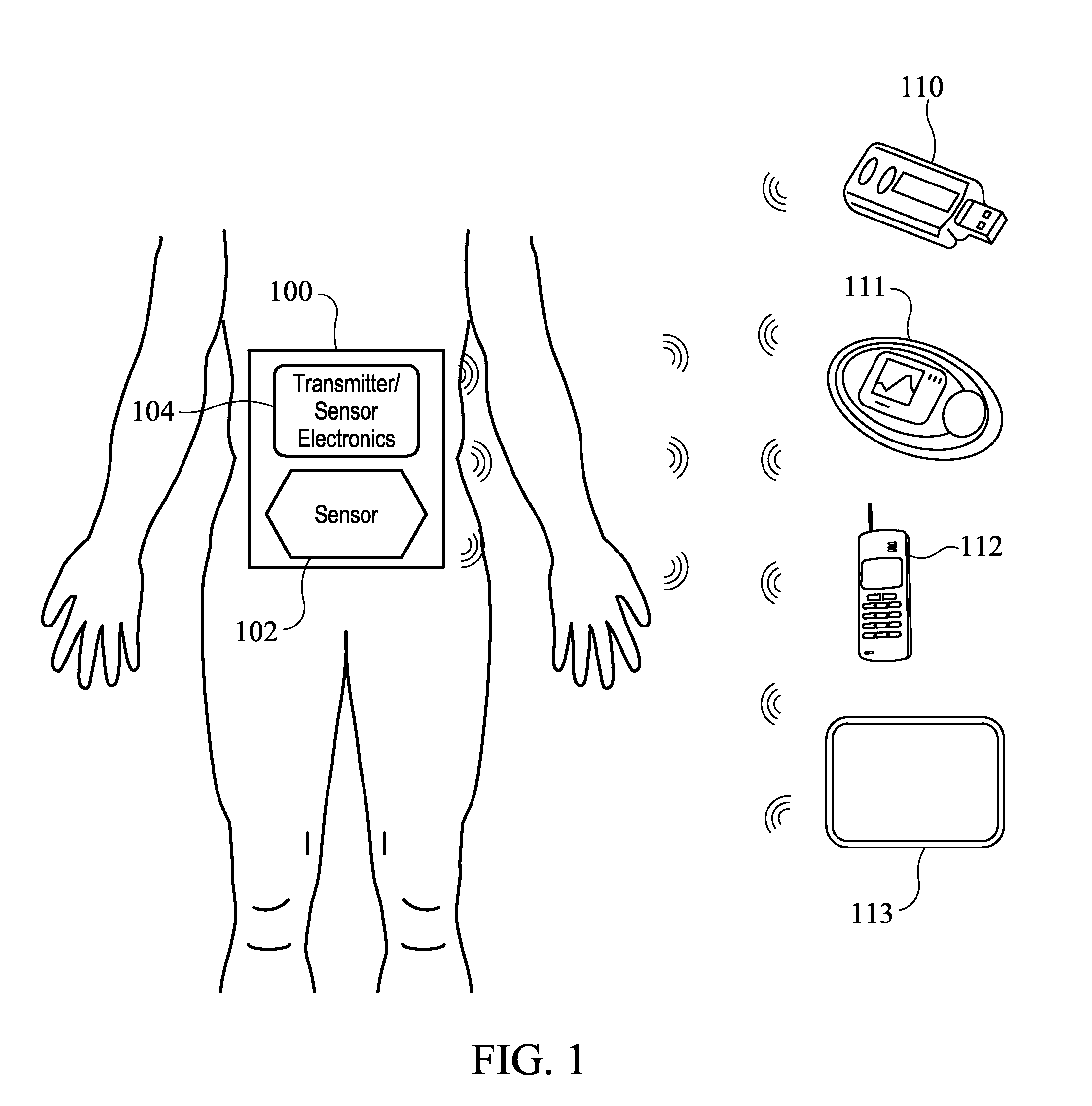
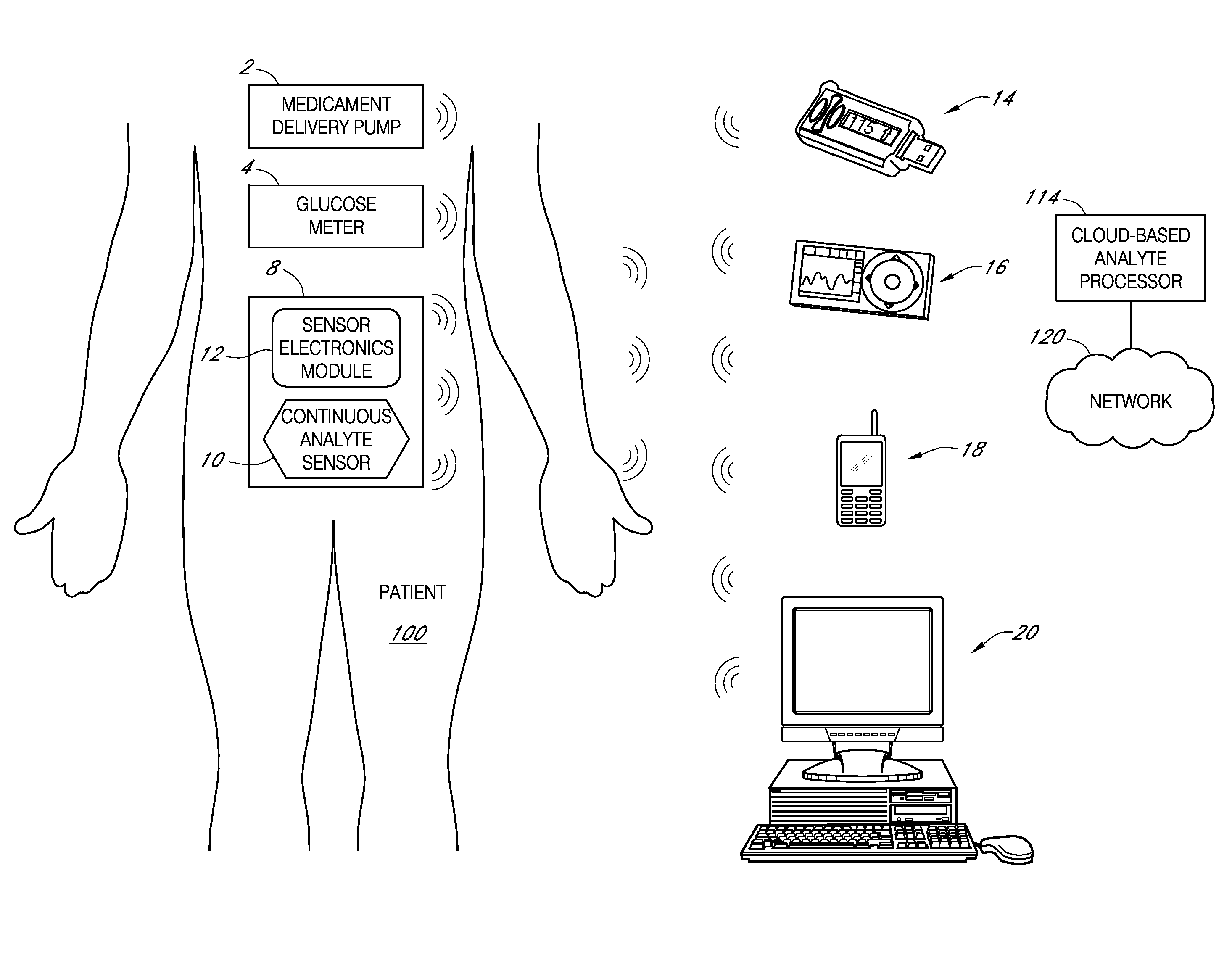
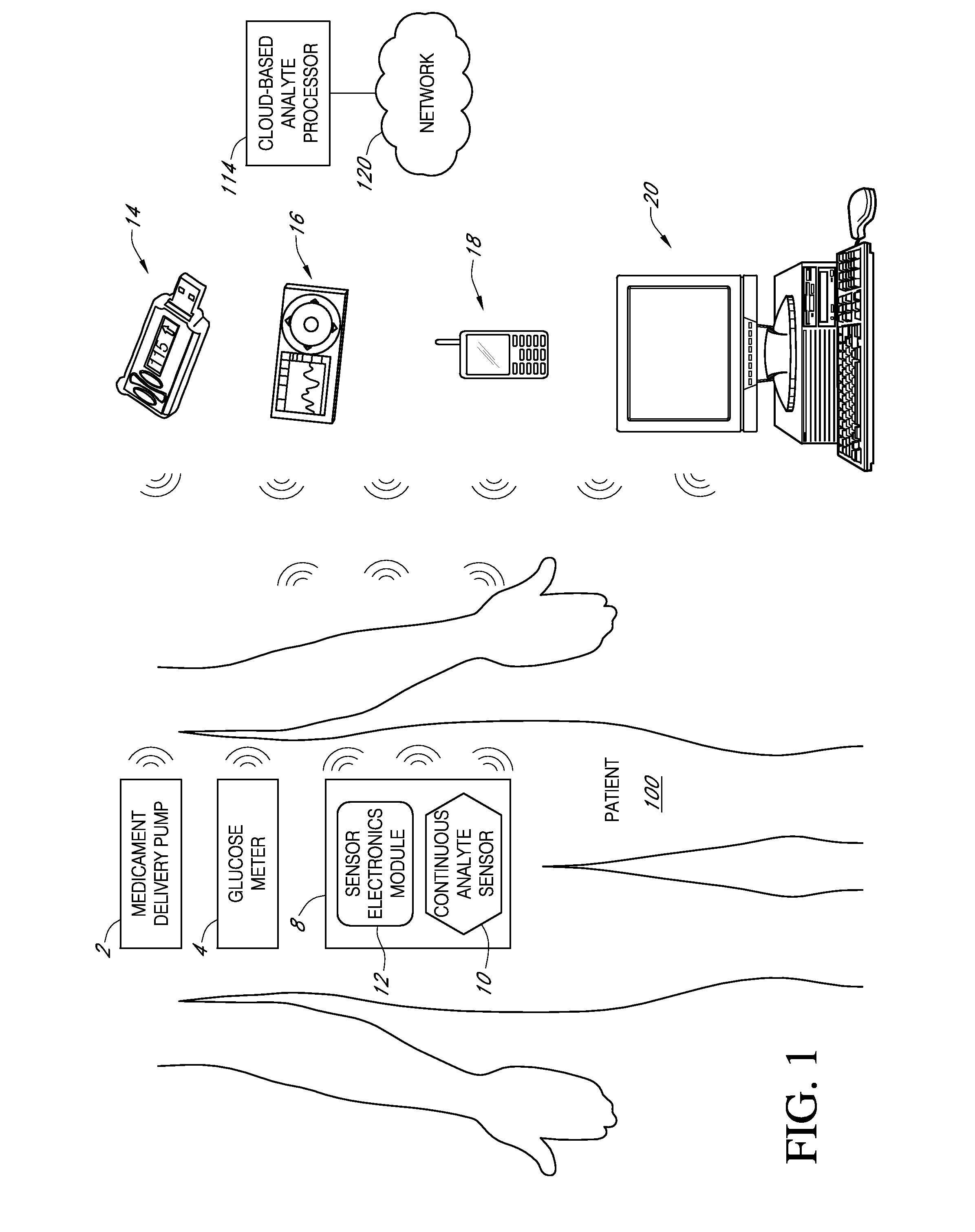
Systems and methods for communicating sensor data between communication devices
ActiveUS20110320130A1Local control/monitoringDrug and medicationsConcentrations glucoseDisplay device
System and method for communicating glucose concentration information between devices of a continuous glucose monitoring system is provided. The continuous glucose monitoring system can include a sensor module generates a glucose concentration measurement data and transmits the data to one or more further devices of the continuous glucose monitoring system. The further devices can include a receiver unit and one or more secondary display devices. The receiver unit can be configured to be a stand-alone device of or physically connect to a secondary display device. A user interface can also be provided that provides enhanced functionality for using the continuous glucose monitoring system.
Owner:DEXCOM
Systems and Methods for Diabetes Management Using Consumer Electronic Devices
InactiveUS20080119705A1Facilitate communicationDrug and medicationsNutrition controlDiabetes managementContinuous glucose monitoring
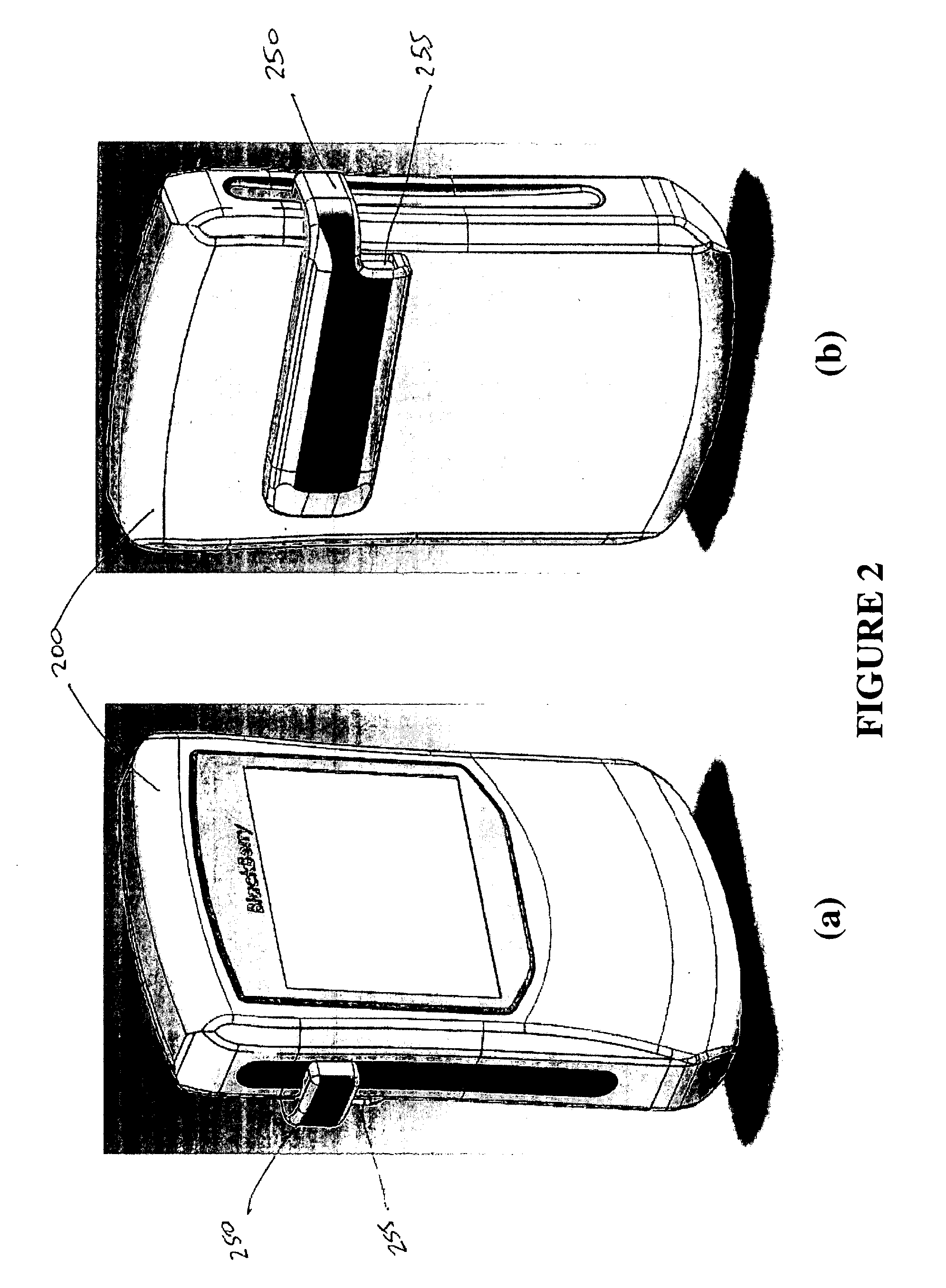
The invention is embodied in a system for diabetes management including a medical device (MD) and a consumer electronic device (CED). The CED may be used to monitor and / or control the MD. In particular embodiments, the system may include a connector that plugs into the CED to allow communication between the MD and the CED. The medical device may be an external infusion device, implantable pump, glucose meter, glucose monitor, continuous glucose monitoring system, or the like. The CED may be any type of consumer electronic device including, but not limited to, cellular phones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), BlackBerry, Smartphones, pocketpc phones, mp3 players, radios, CD players, and the like.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
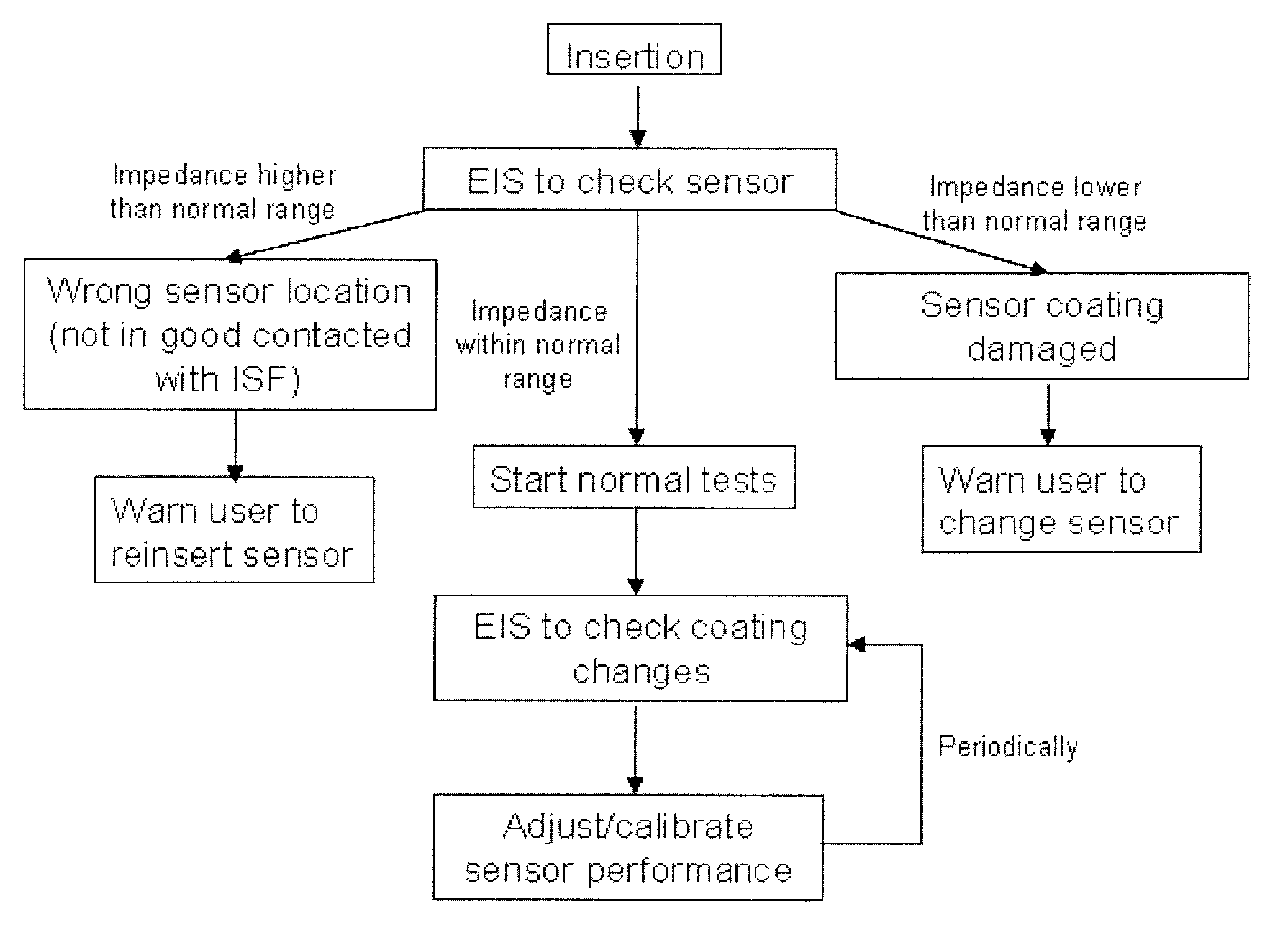
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy enabled continuous glucose monitoring sensor systems
ActiveUS20110040163A1CatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical impedance spectroscopy
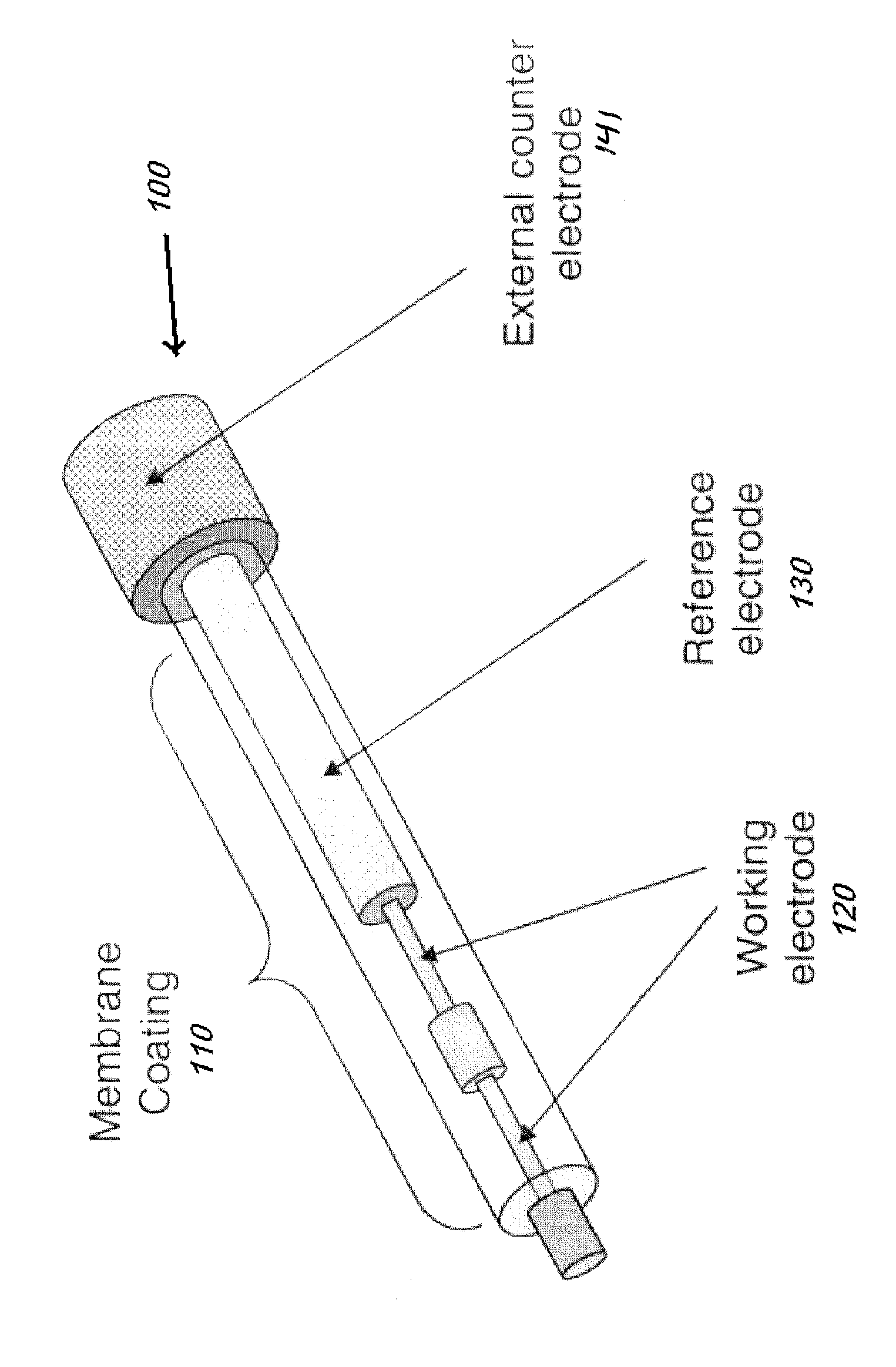
The use of electrical impedance spectroscopy to adjust calibration settings in an in vivo monitoring system, such as an in vivo continuous glucose monitoring sensor. The adjustments can compensate for the condition of the sensor membrane in vivo.
Owner:ASCENSIA DIABETES CARE HLDG AG
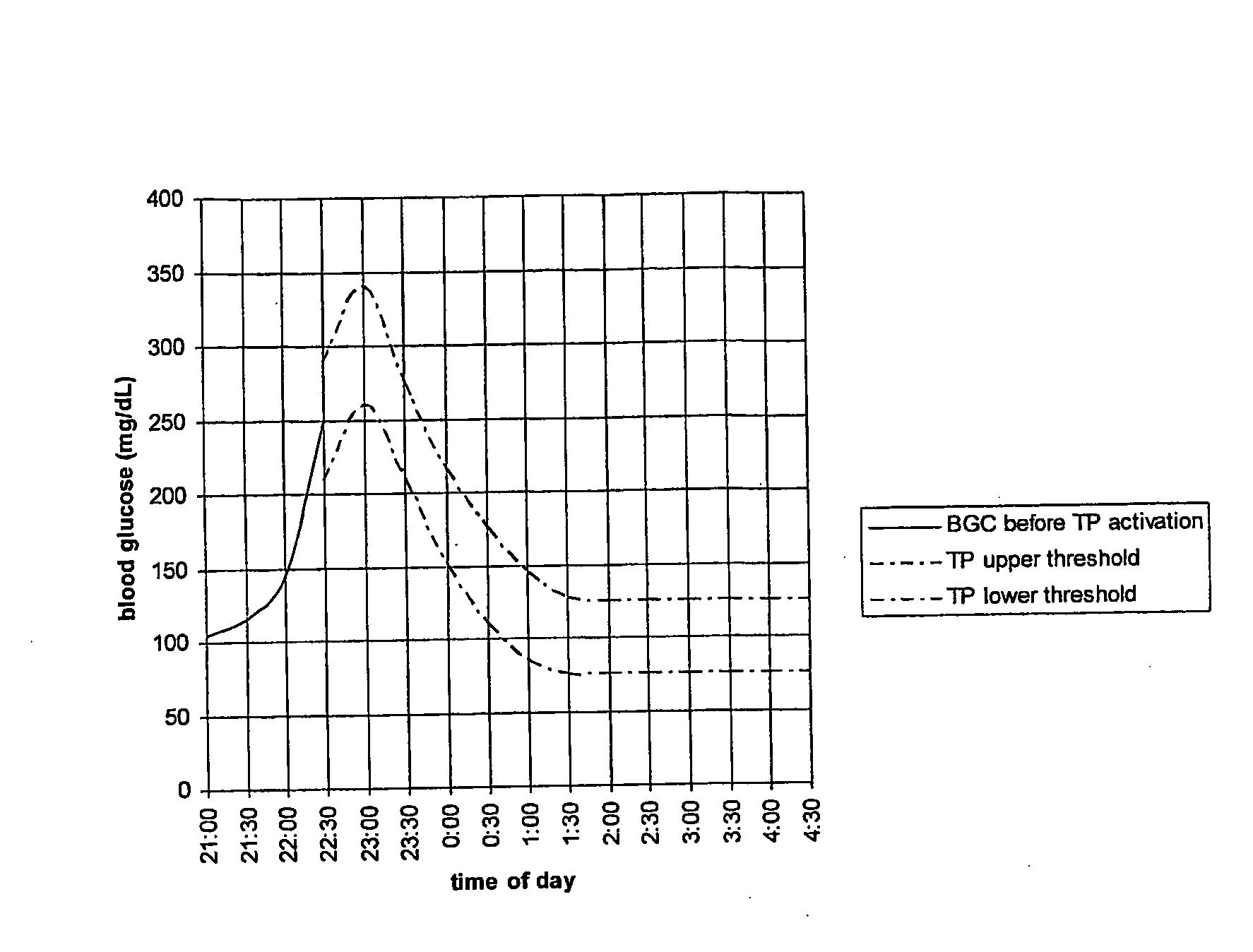
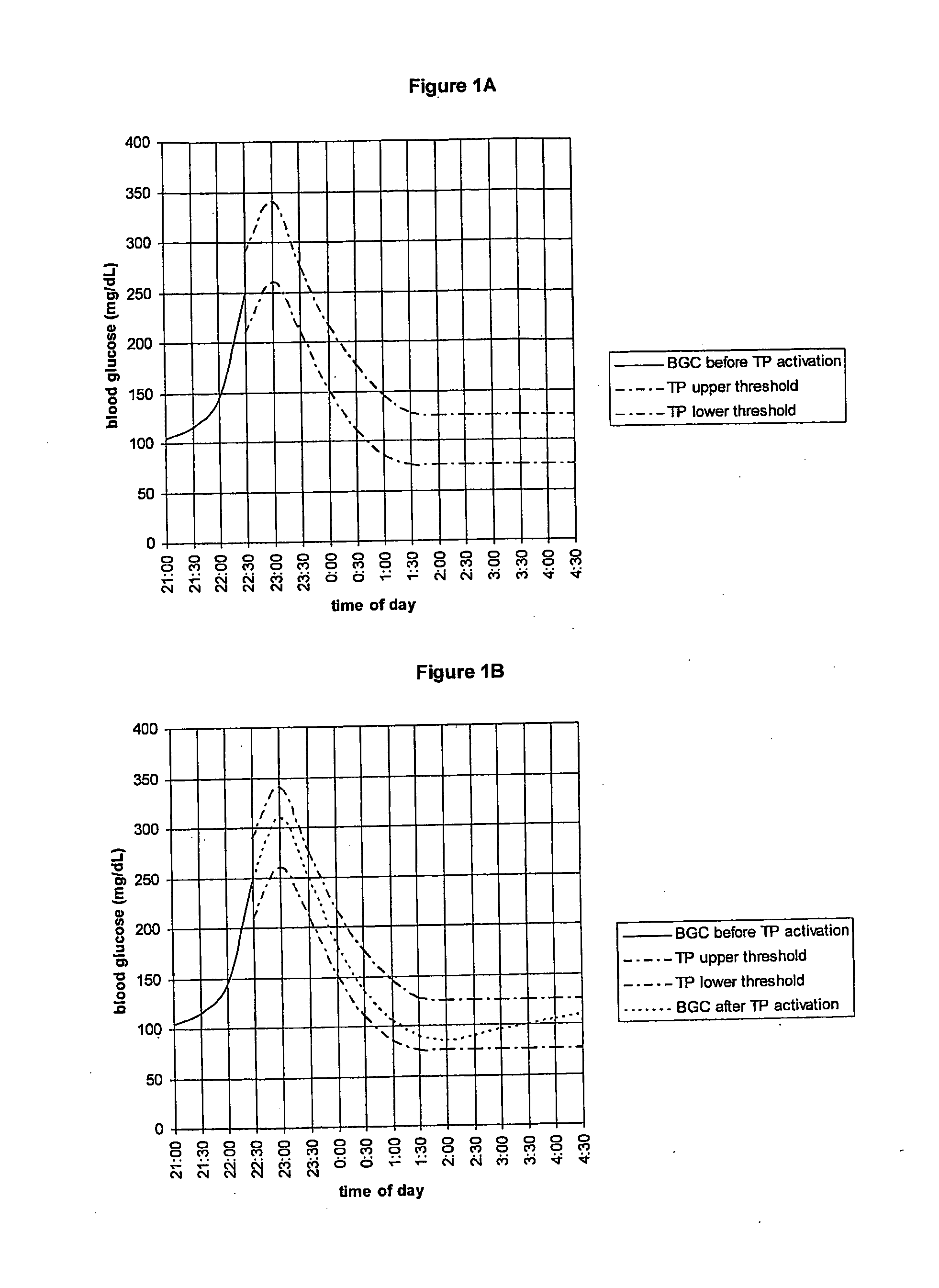
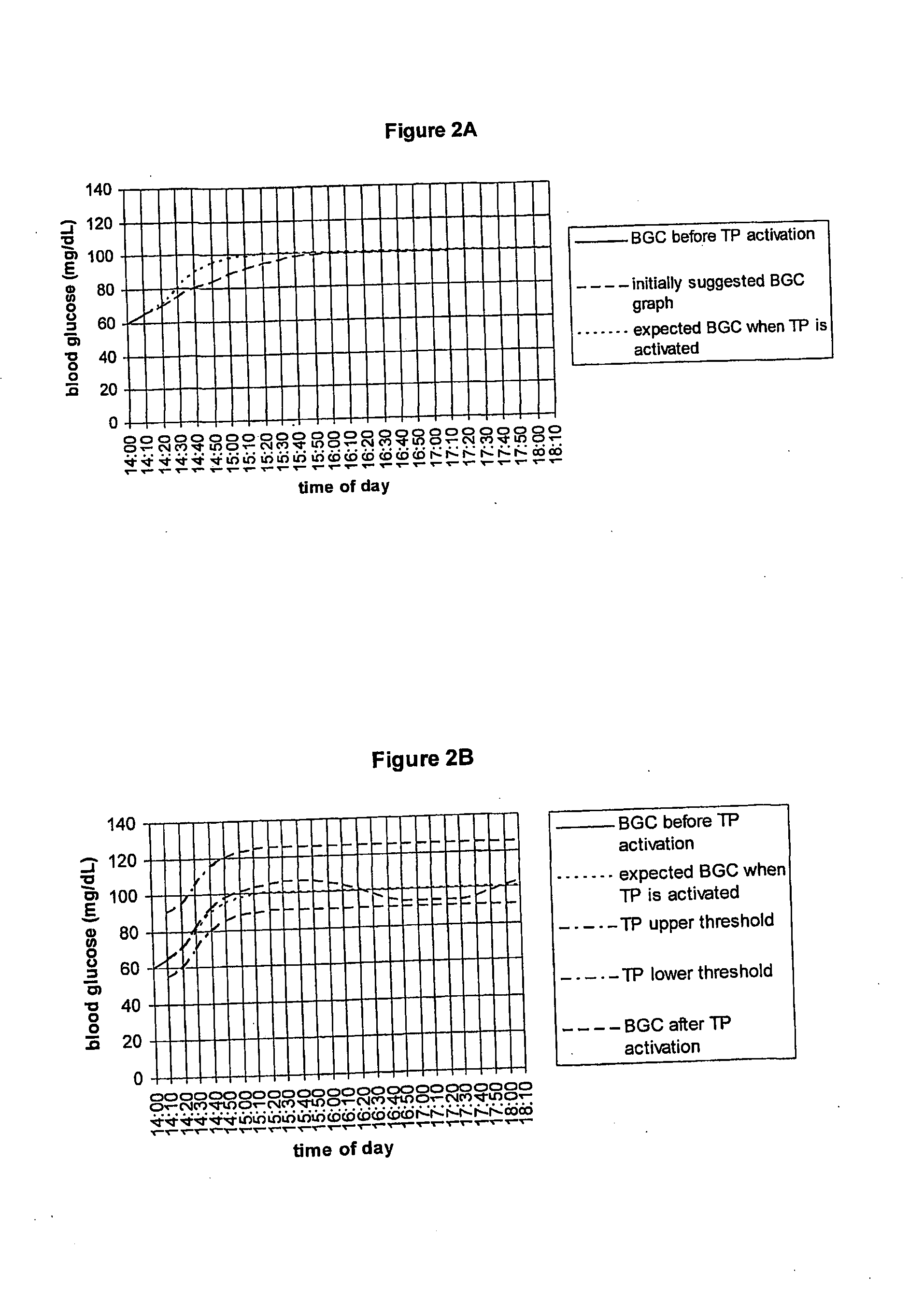
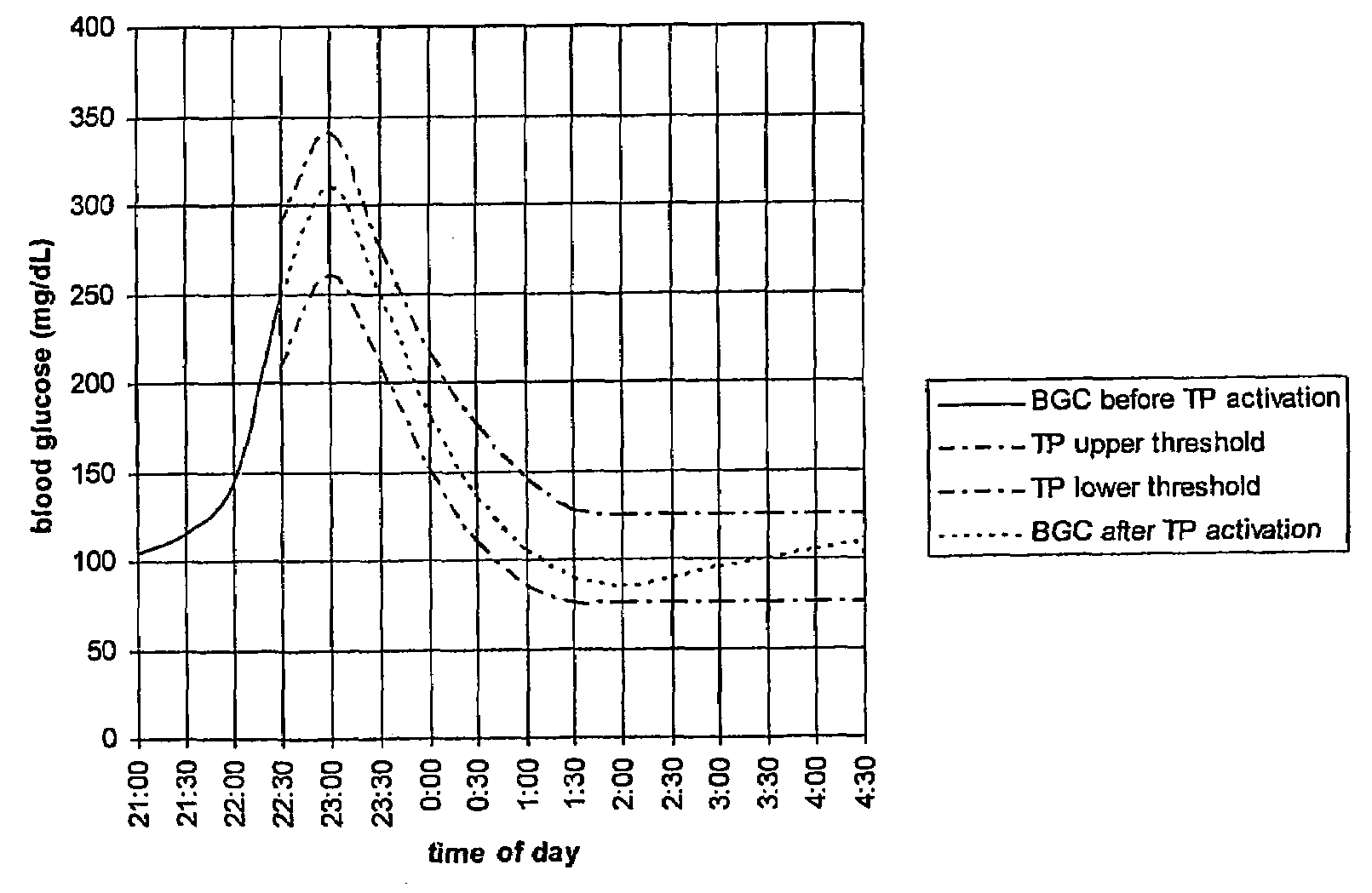
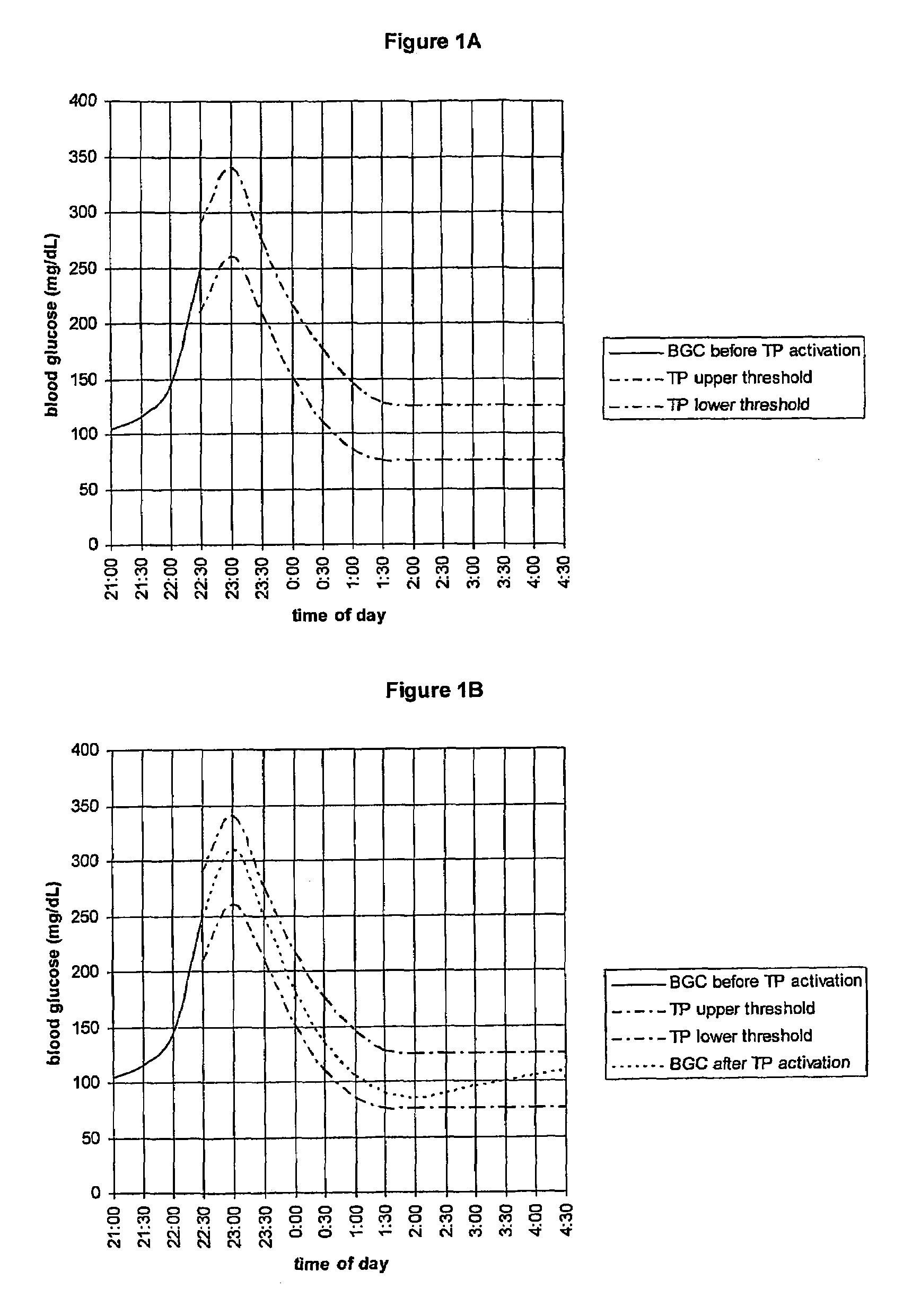
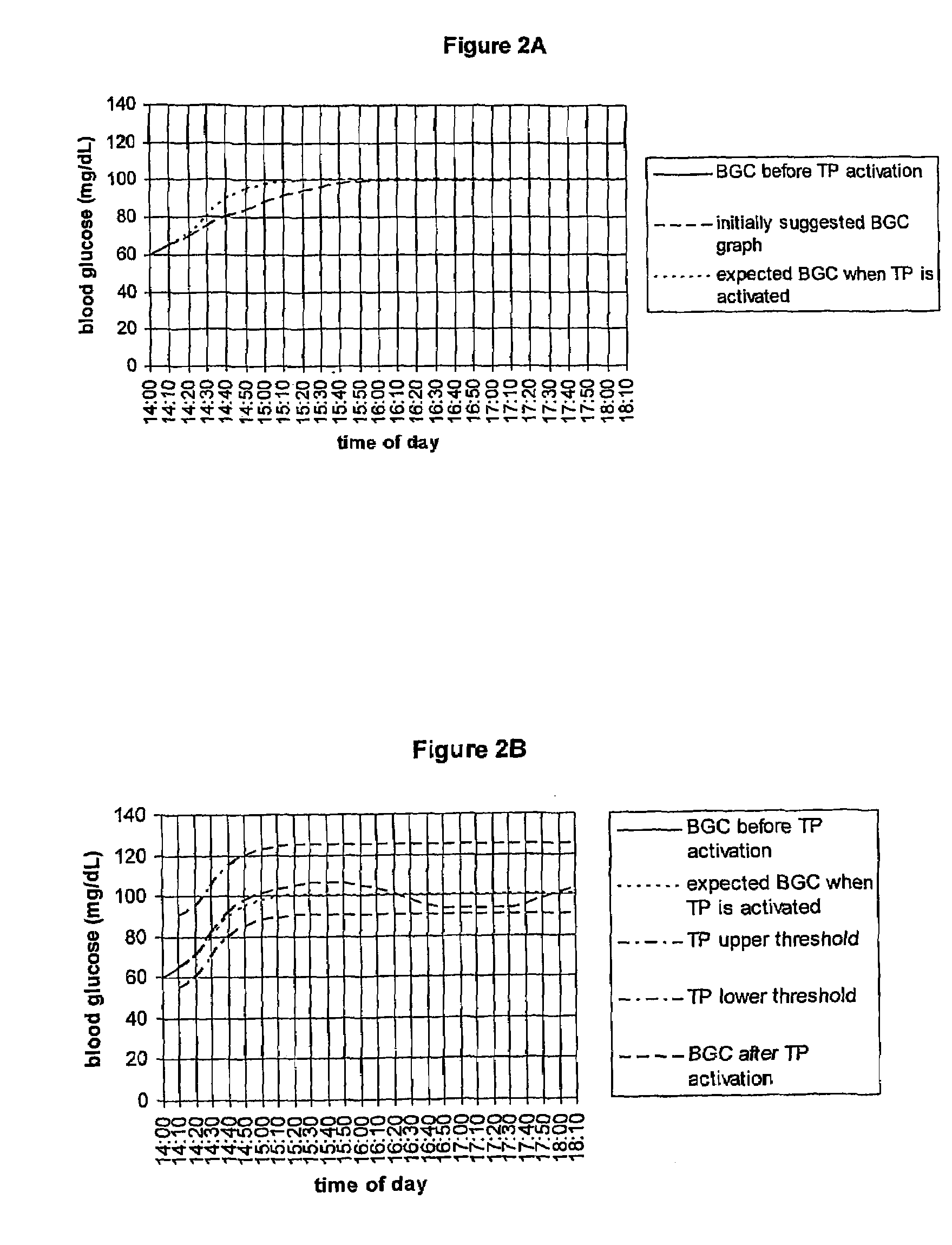
Fluctuating Blood Glucose Notification Threshold Profiles and Methods of Use
ActiveUS20080228055A1Improve visualizationHighly visualDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsContinuous glucose monitoringGlucose polymers
Embodiments of the present invention provide a new system and methods for monitoring blood glucose concentration. A user of a continuous glucose monitor may program upper and lower blood glucose notification thresholds to fluctuate over time in order to facilitate management of the short-term effects of food consumption, insulin delivery aberrations, physical activity, emotions, and unforeseen circumstances.
Owner:SHER PHILIP M
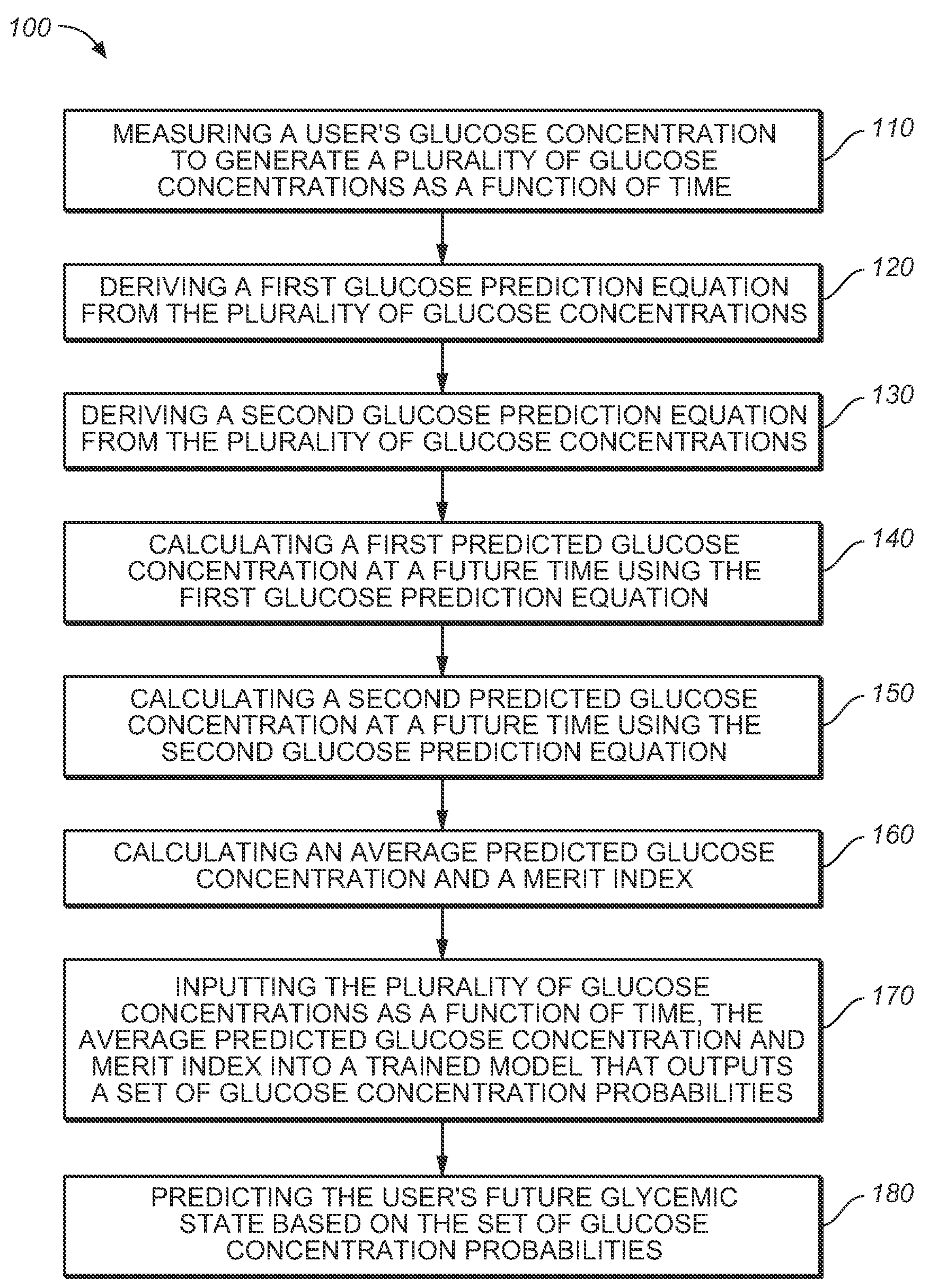
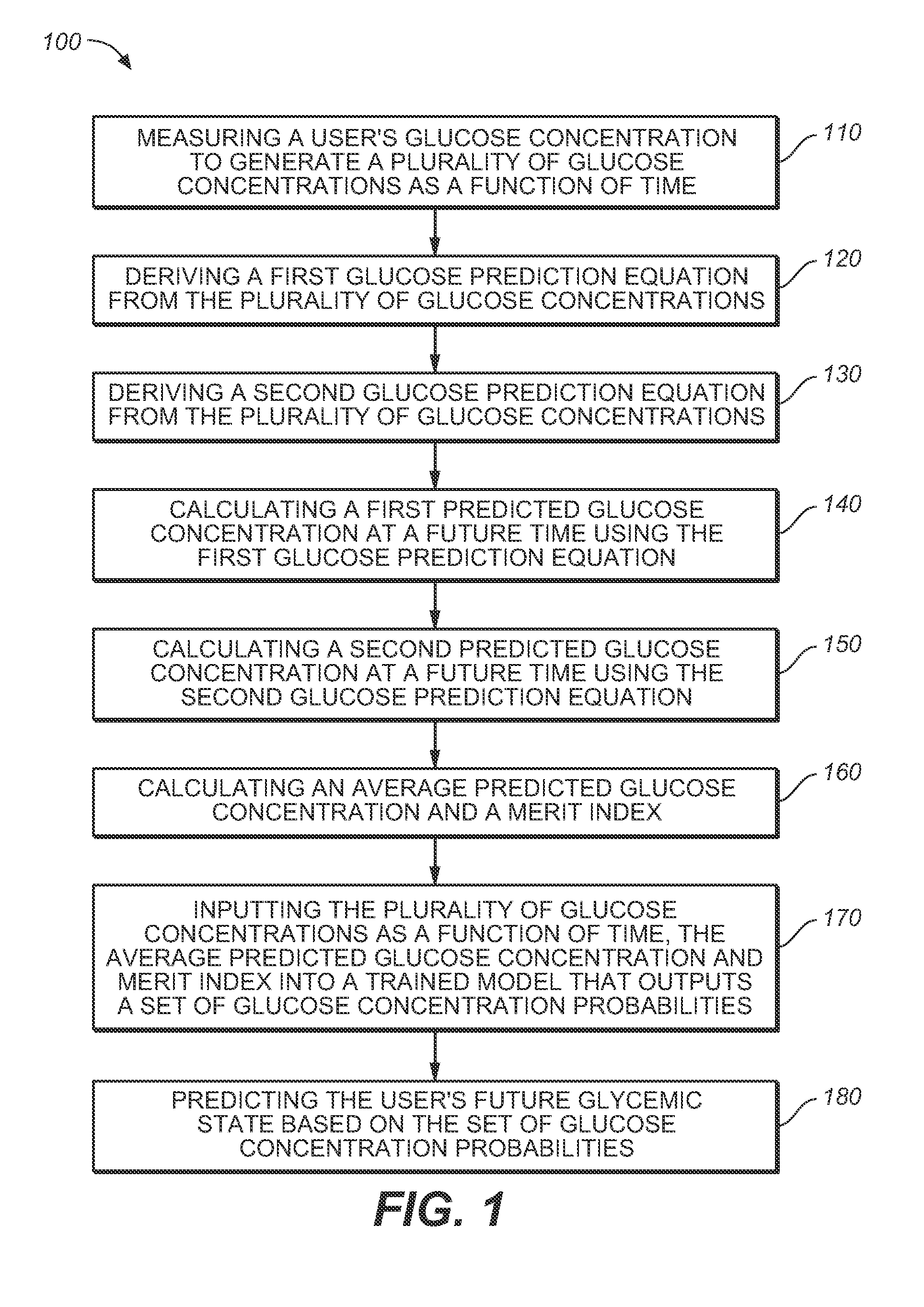
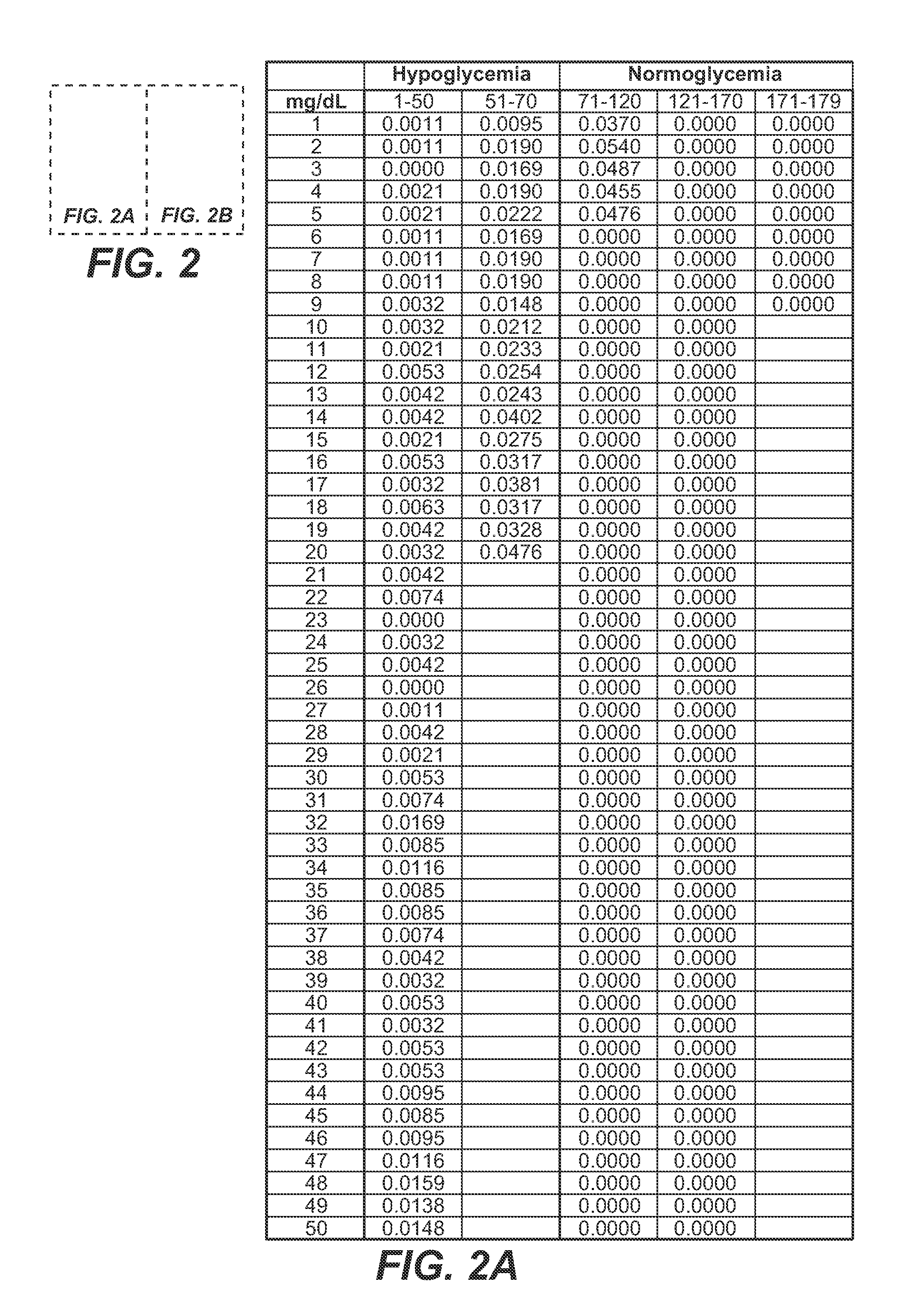
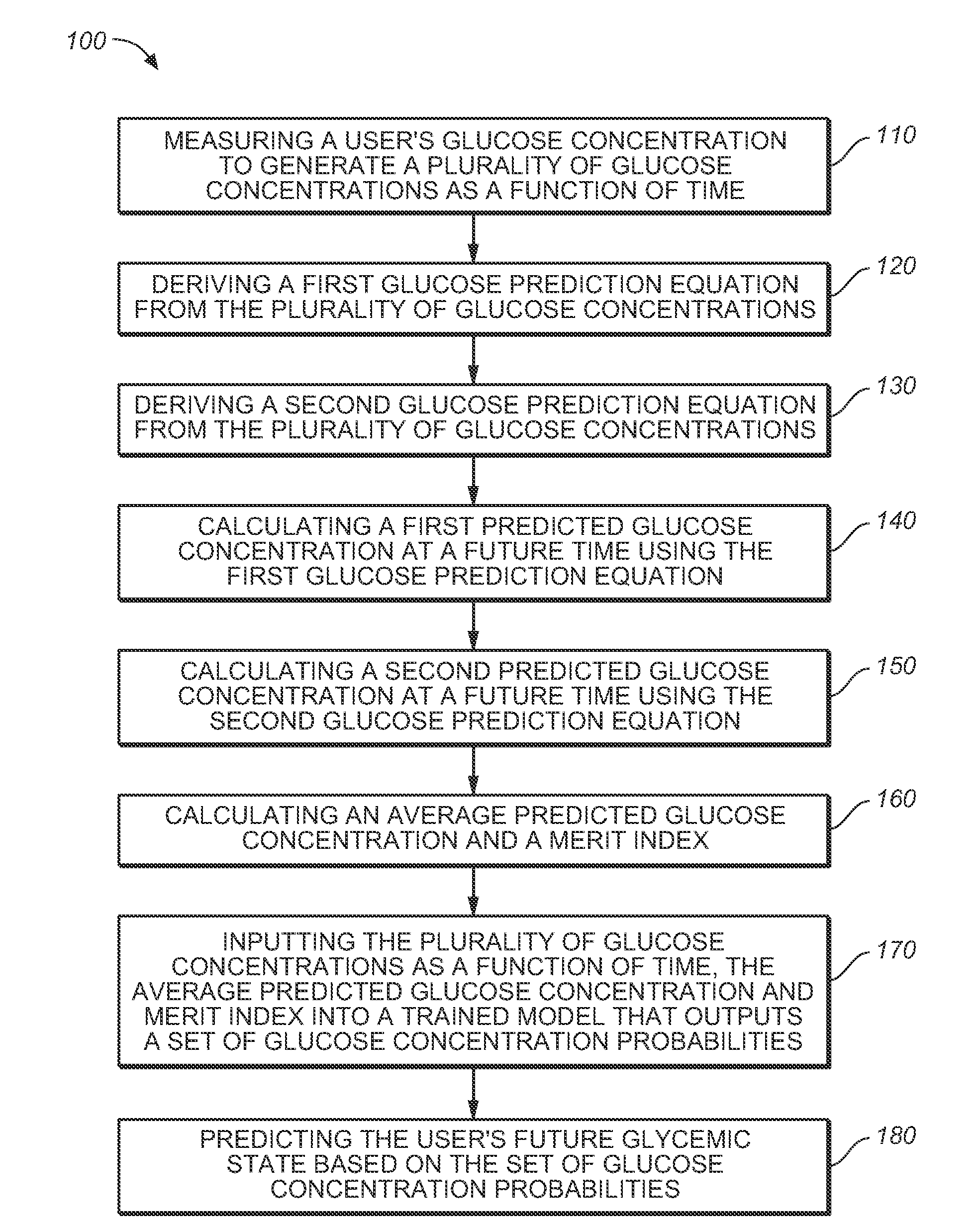
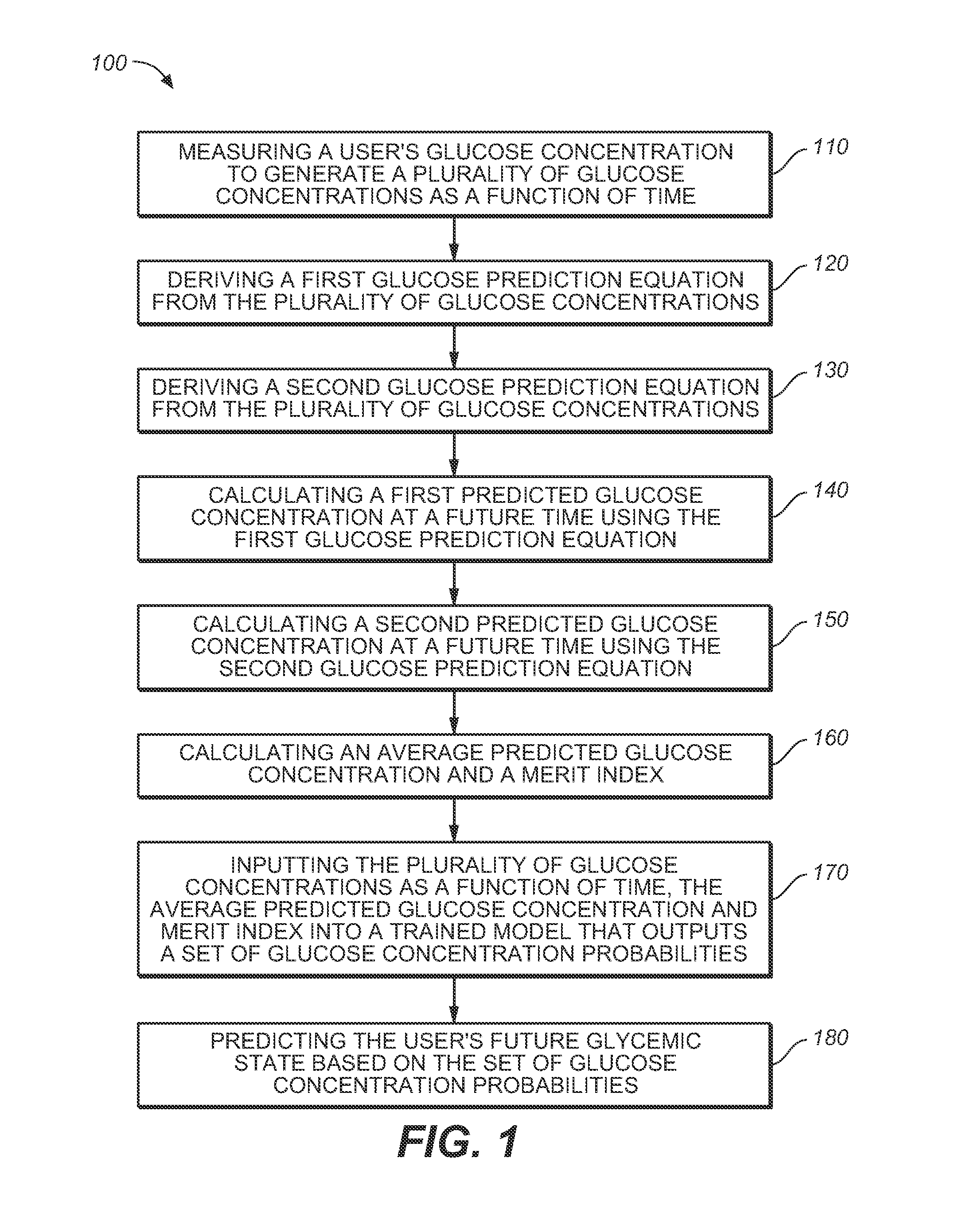
Medical device for predicting a user's future glycemic state
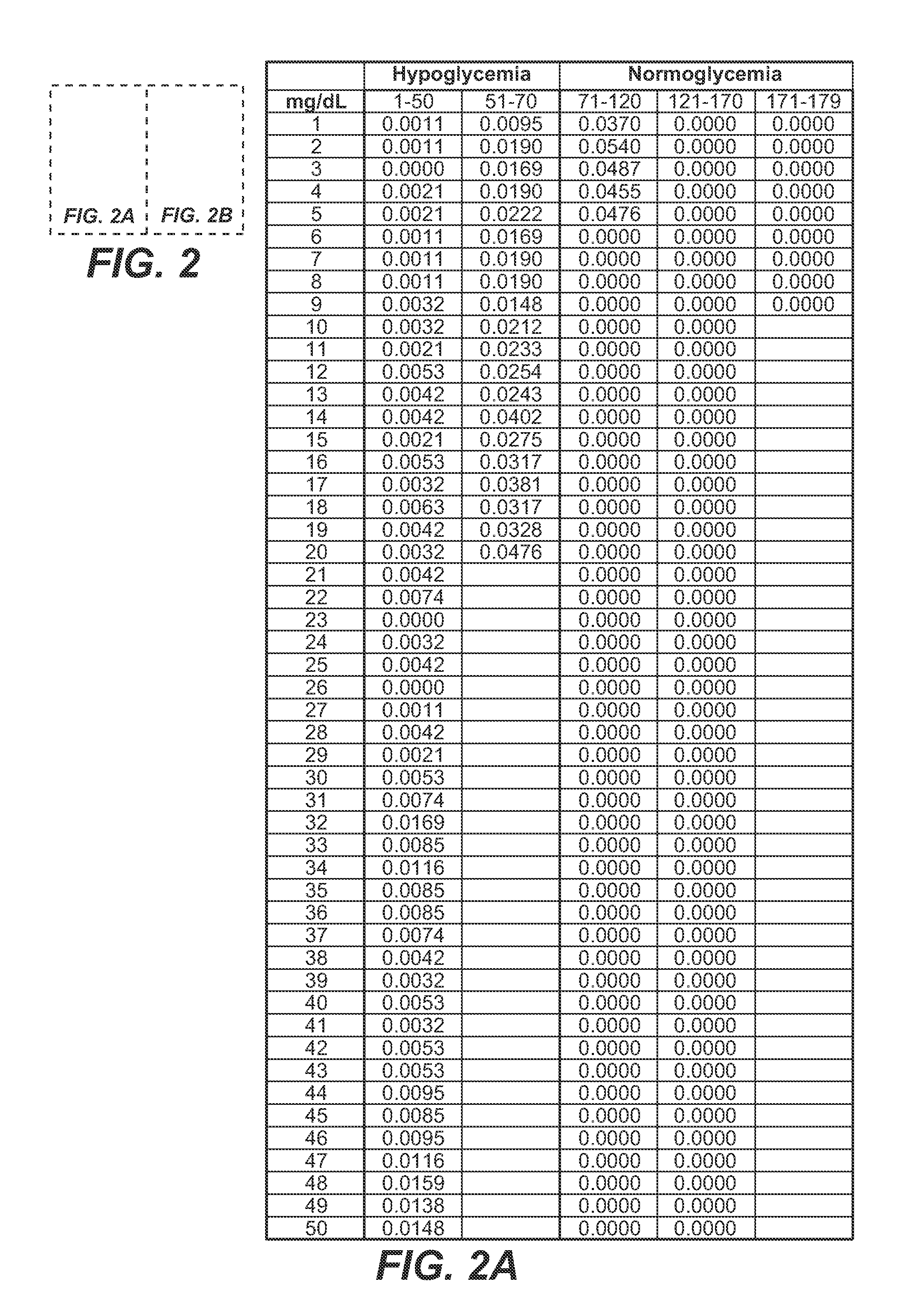
A medical device for predicting a user's future glycemic state includes a memory module, a processor module and a user alert module. The memory module is configured to receive and store a plurality of glucose concentrations as a function of time that were generated by a user's use of a continuous glucose monitor. The processor module is configured to derive first and second glucose prediction equations that are fits to the plurality of glucose concentrations stored in the memory module with the fits being based on first and second mathematical models, respectively. The processor module is also configured to calculate first and second predicted glucose concentrations at a future time using the first and second glucose prediction equations, respectively, and to also calculate an average predicted glucose concentration and a merit index based on the first and second predicted glucose calculations. The processor module is further configured to input the plurality of glucose concentrations as a function of time, the average predicted glucose concentration and the merit index into a trained model (e.g., a Hidden Markov Model) that outputs a set of glucose concentration probabilities for the future time and to then predict the user's future glycemic state based on the set of glucose concentration probabilities. The user alert module is configured to alert the user in a manner dependent on the predicted user's future glycemic state.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Medical device for predicting a user's future glycemic state
ActiveUS20090105573A1Medical simulationHealth-index calculationHide markov modelConcentrations glucose
A medical device for predicting a user's future glycemic state includes a memory module, a processor module and a user alert module. The memory module is configured to receive and store a plurality of glucose concentrations as a function of time that were generated by a user's use of a continuous glucose monitor. The processor module is configured to derive first and second glucose prediction equations that are fits to the plurality of glucose concentrations stored in the memory module with the fits being based on first and second mathematical models, respectively. The processor module is also configured to calculate first and second predicted glucose concentrations at a future time using the first and second glucose prediction equations, respectively, and to also calculate an average predicted glucose concentration and a merit index based on the first and second predicted glucose calculations. The processor module is further configured to input the plurality of glucose concentrations as a function of time, the average predicted glucose concentration and the merit index into a trained model (e.g., a Hidden Markov Model) that outputs a set of glucose concentration probabilities for the future time and to then predict the user's future glycemic state based on the set of glucose concentration probabilities. The user alert module is configured to alert the user in a manner dependent on the predicted user's future glycemic state.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Predictive control based system and method for control of insulin delivery in diabetes using glucose sensing
A system and method for providing optimal insulin injections to a subject, using a controller, a continuous glucose monitor, and an insulin delivery unit is disclosed. The controller possesses a discrete-time, linear model predictive control law, means for sending information to the insulin delivery unit, and means for receiving information from the CGM. The control law implemented is derived from a discrete-time model of glucose insulin dynamics and an aggressiveness parameter. The result is that using only glucose measurements obtained from sensor readings and, prior values of external insulin infusion and meal and exercise announcement the optimal insulin injection necessary to safely regulate blood glucose can be calculated.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
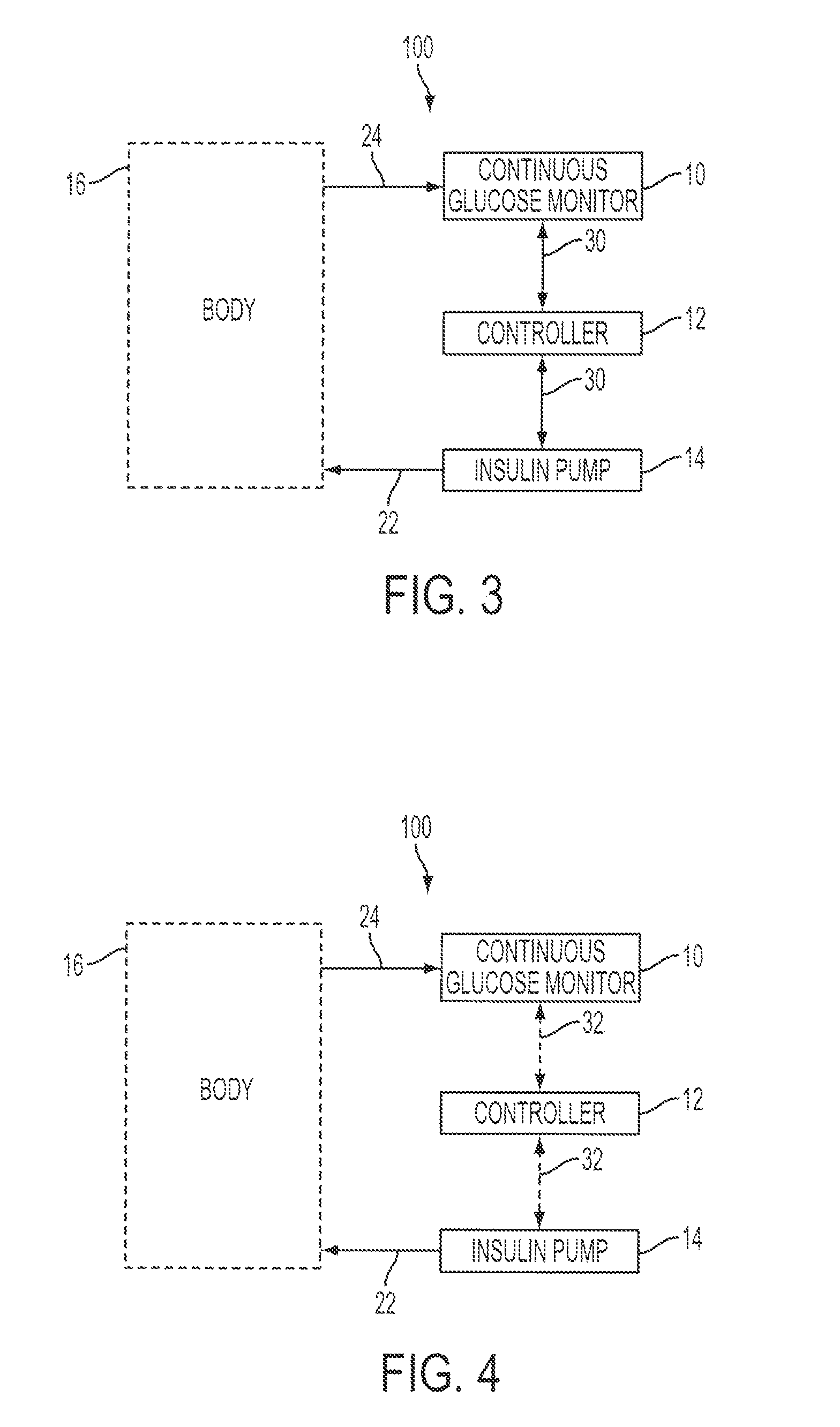
Continuous glucose monitoring-directed adjustments in basal insulin rate and insulin bolus dosing formulas
InactiveUS20090036753A1Accurate estimateAppropriate confidence and self-sufficiencySurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringInsulin dependentHypoglycemic episodes
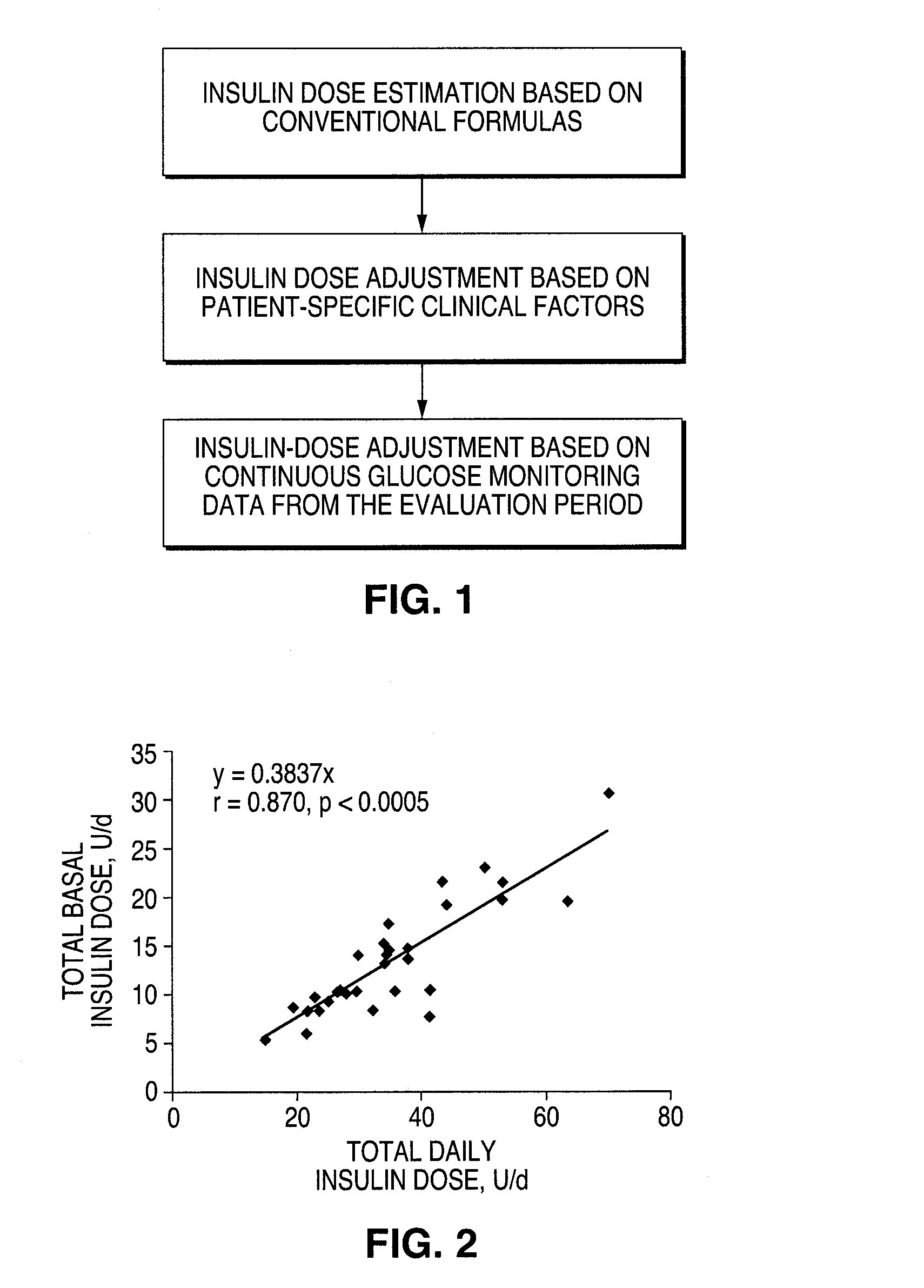
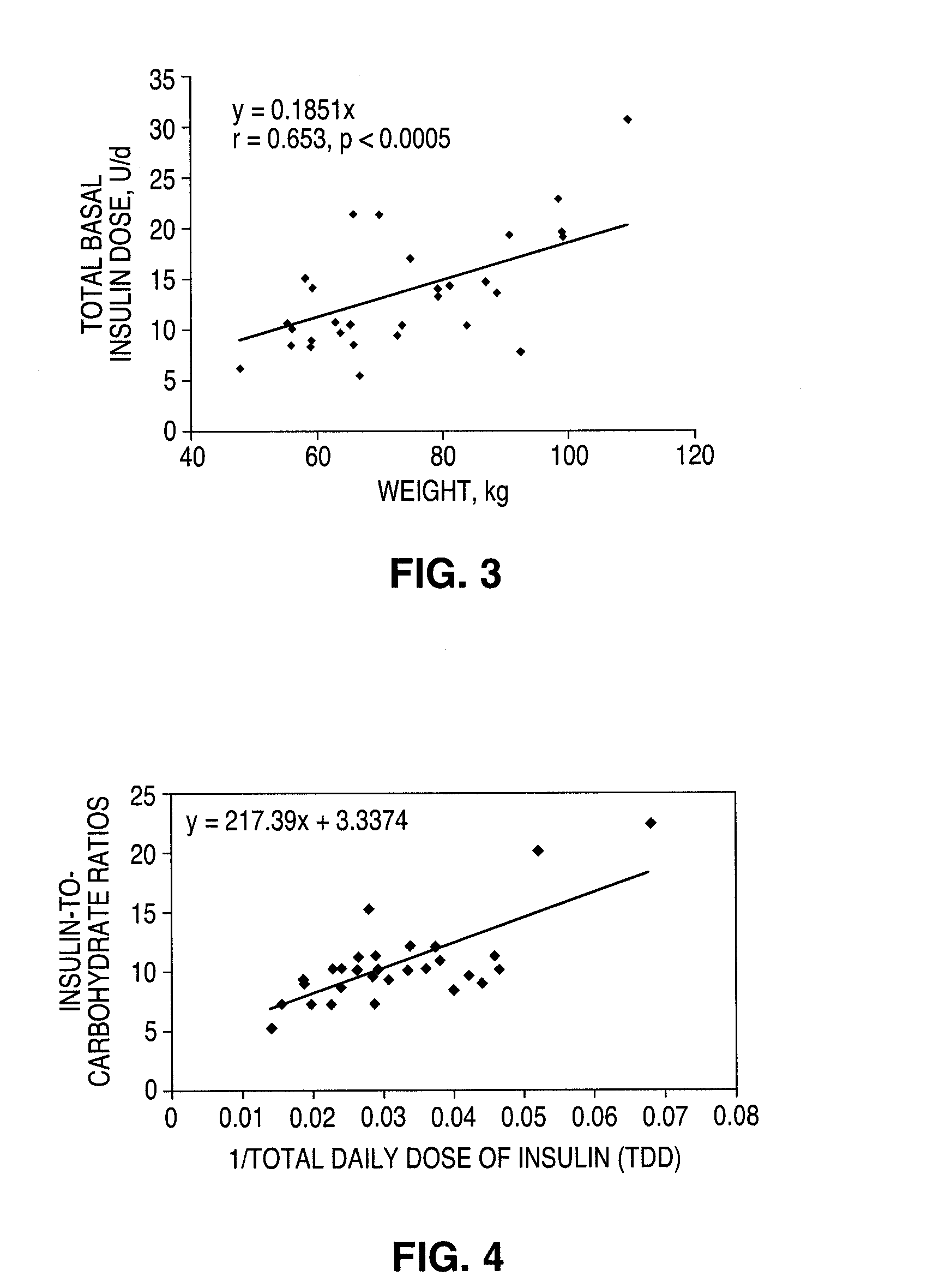
A method for individualized management of diabetes in insulin-dependent patients provides a period of evaluation as the patient adheres to a structured pattern of eating, sleeping, and physical activity. Glucose is monitored with a continuous glucose monitoring system, insulin doses are metered, carbohydrate consumption is quantified, and glucose, carbohydrate, and insulin data are collected and analyzed. Insulin dosage is adjusted in three steps: (1) an insulin dosage is estimated from conventional formulas, (2) adjustments are made according to the patient's clinical specifics, and (3) further insulin dose adjustments are made according to glucose data obtained during the evaluation period. By the end of the evaluation period, substantially normal glucose values are achieved, and quantitative relationships from data are calculated that are then applied to determine insulin dosages for an ensuing period of therapy. By this method, diabetic patients achieve a near normal glycemic profile, and without significant occurrence of hypoglycemic episodes.
Owner:DIABETES CARE CENT
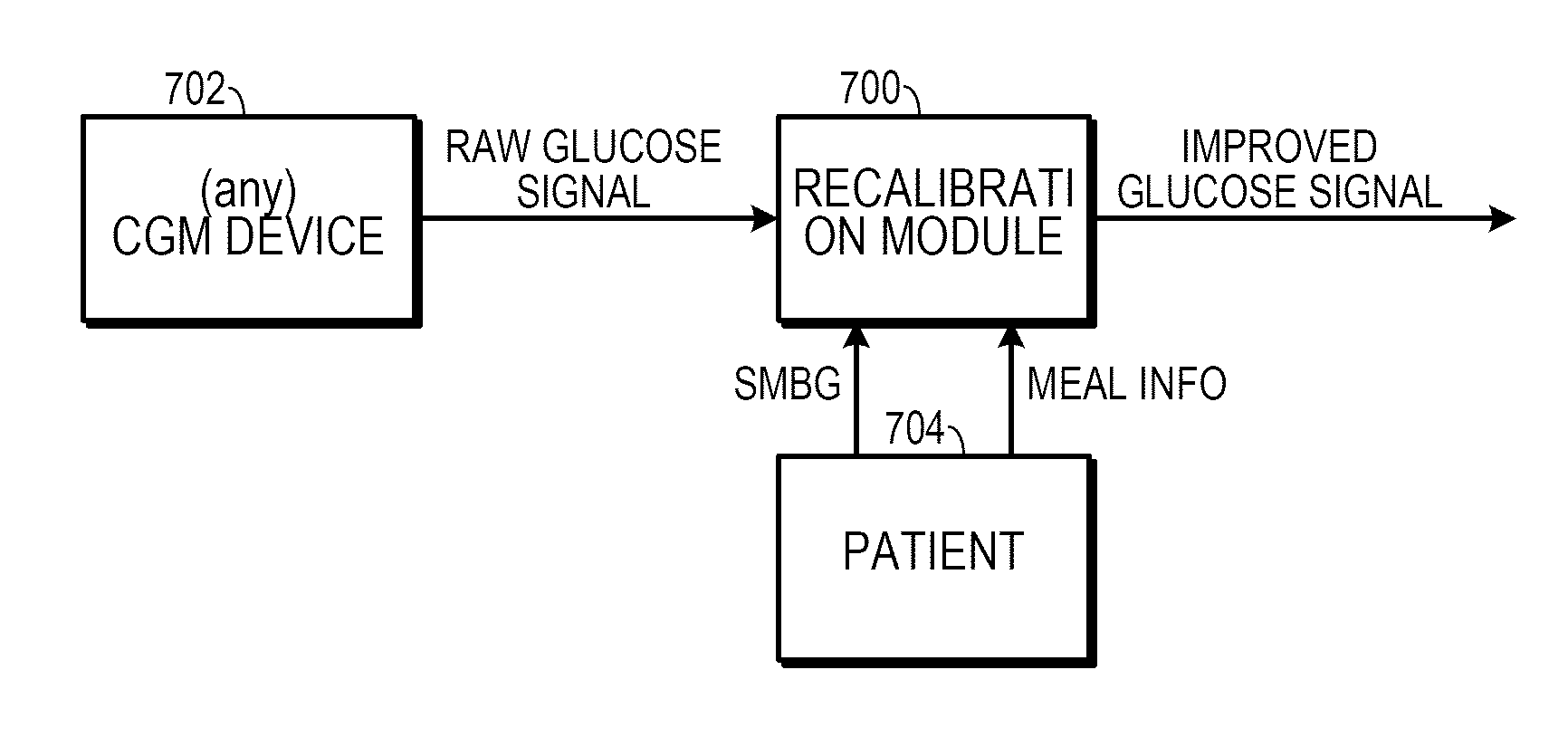
Method to recalibrate continuous glucose monitoring data on-line
ActiveUS20120215087A1Improve CGM recalibration algorithmMore physiology-awareLocal control/monitoringDiagnostic recording/measuringContinuous glucose monitoringLinear regression
In a method of recalibrating continuous glucose monitoring data from a user, operable on a digital processor, an indication from the user that the user has taken a meal is received (806). A self-monitored of blood glucose levels from the user (810) at two separate times during a day corresponding to when the user has taken a meal. A glucose signal is received from a continuous glucose monitoring sensor (818) at times corresponding to the two separate times that the user has taken a meal. Two reconstructed blood glucose values based on the glucose signal from the continuous monitoring sensor at times when the at least two self-monitored of blood glucose levels are received from the user. A linear regression is performed (822) using y=ax+b, wherein x corresponds to the two reconstructed blood glucose values and y corresponds to the two self-monitored of blood glucose levels thereby generating an estimation of a and b. A recalibration signal, including the estimation of a and b, is transmitted to the continuous glucose monitoring sensor (824) based on the linear regression.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI PADOVA
Real time management of data relating to physiological control of glucose levels
ActiveUS20110021898A1Physical therapies and activitiesMedical simulationInsulin on boardPatient specific
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data and insulin delivery data are used to generate more reliable projected alarms related to a projected glucose levels. A memory stores endogenous data related to measurements of glucose level in a patient, and also stores exogenous data, such as insulin on board, both of which are used by a processor to create projected alarms. Profiles of CGM data are created for use in tuning patient-specific insulin data, such at basal rate, carb ratio, and insulin sensitivity. A processor searches for patterns in the data profiles and if found, recommended changes to patient-specific insulin data are provided to permit more accurate control over a patient's glucose levels.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Methods for reducing false hypoglycemia alarm occurrence
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC +1
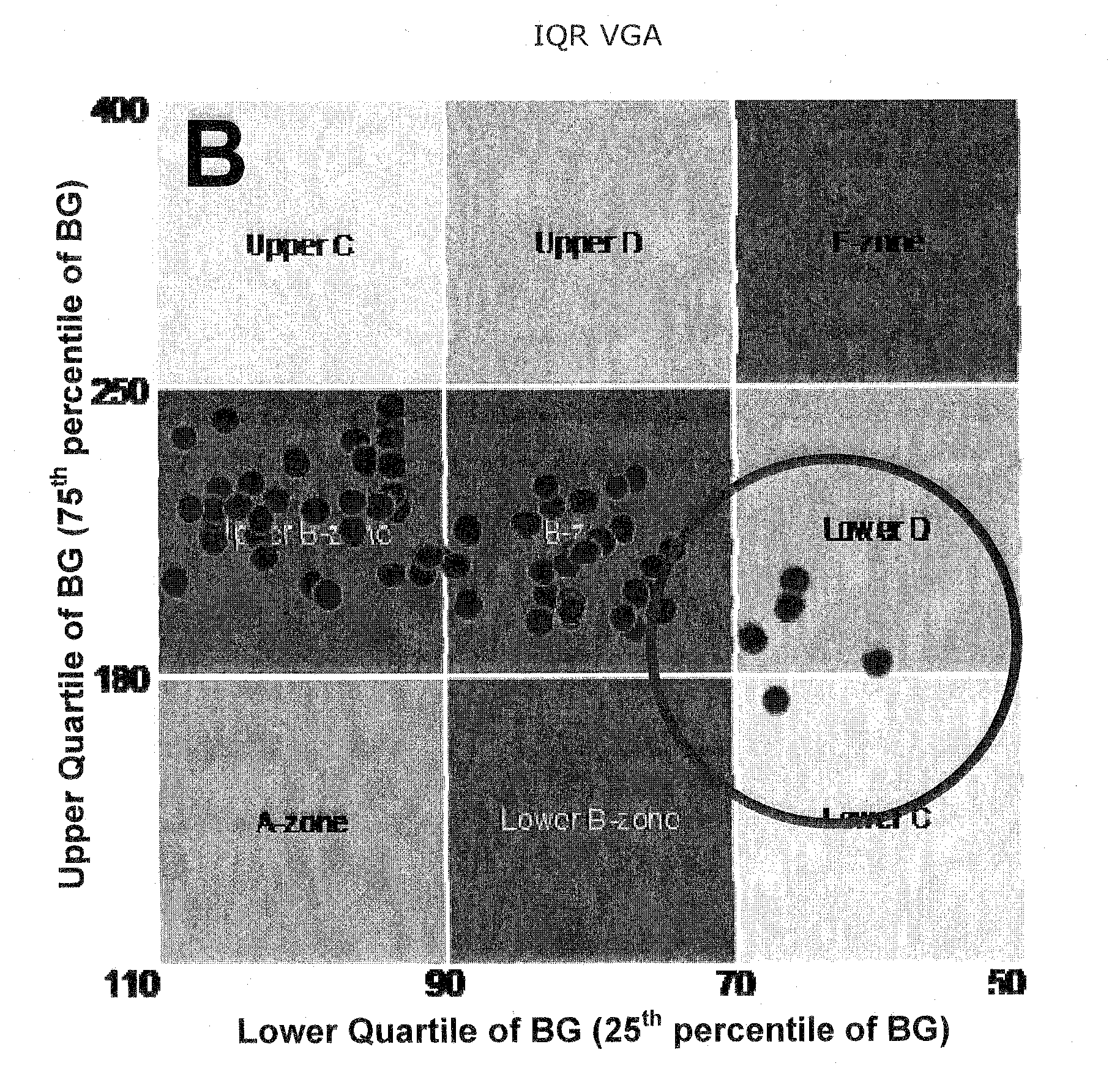
Method, System, and Computer Program Product For Tracking of Blood Glucose Variability in Diabetes
ActiveUS20110264378A1Optimal glucose controlAudibly trackingLocal control/monitoringComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionMedicineContinuous glucose monitoring
An embodiment may be in the field of glycemic analysis and control. More specifically, an embodiment or approach may provide a novel method, system, and computer program for the visual and quantitative tracking of blood glucose variability in diabetes from self-monitoring blood glucose (SMBG) data and / or continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data. More particularly, an embodiment or aspects thereof may use glucose measurements obtained from self-monitoring data and / or CGM data of an individual or a group of individuals to track and analyze blood glucose variability.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
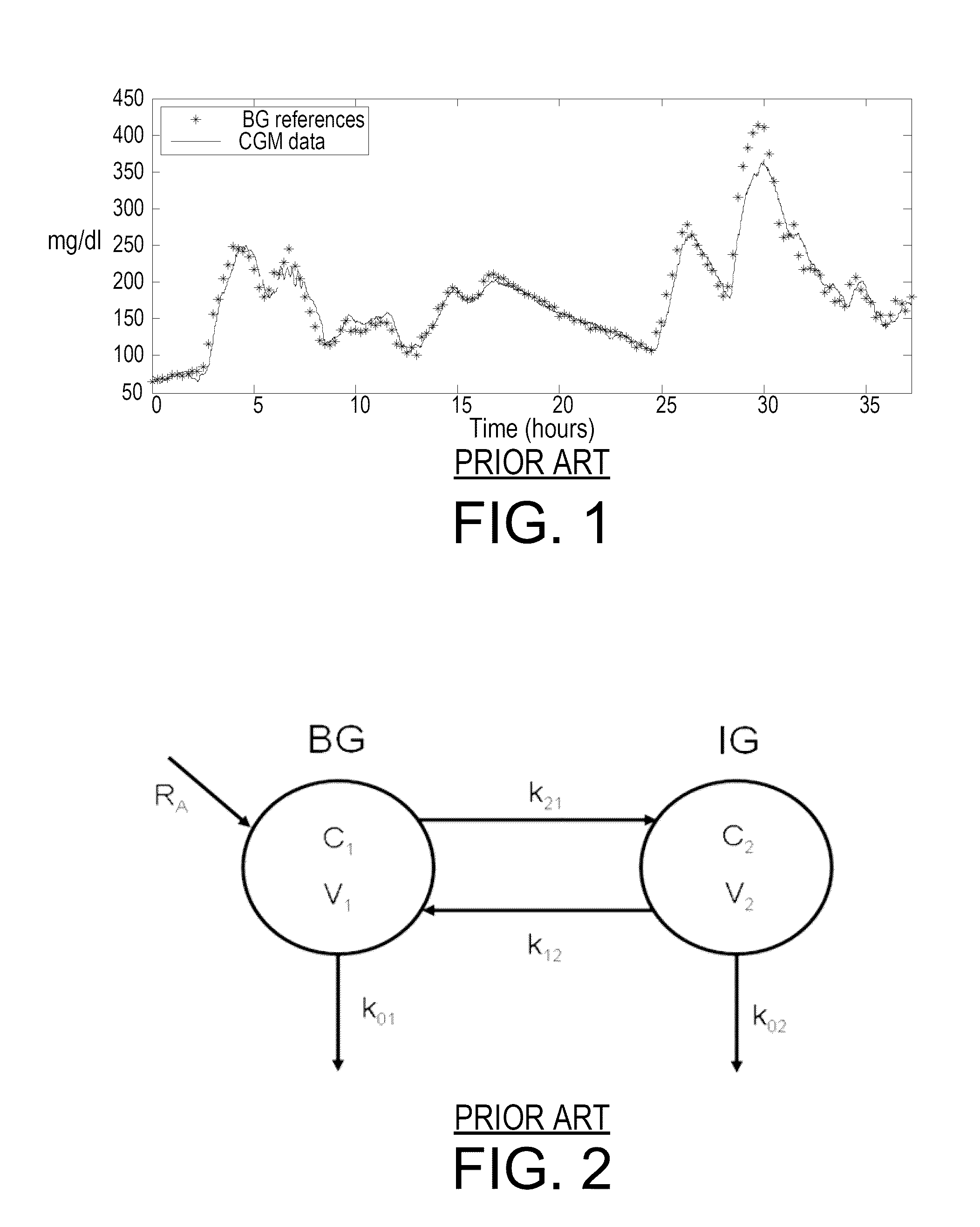
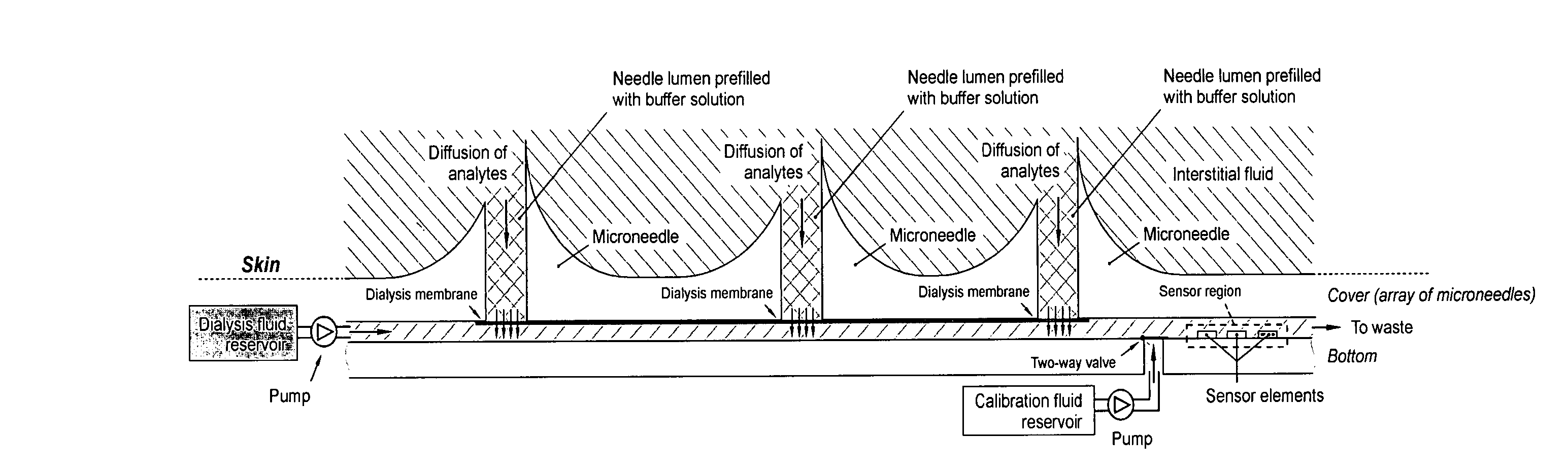
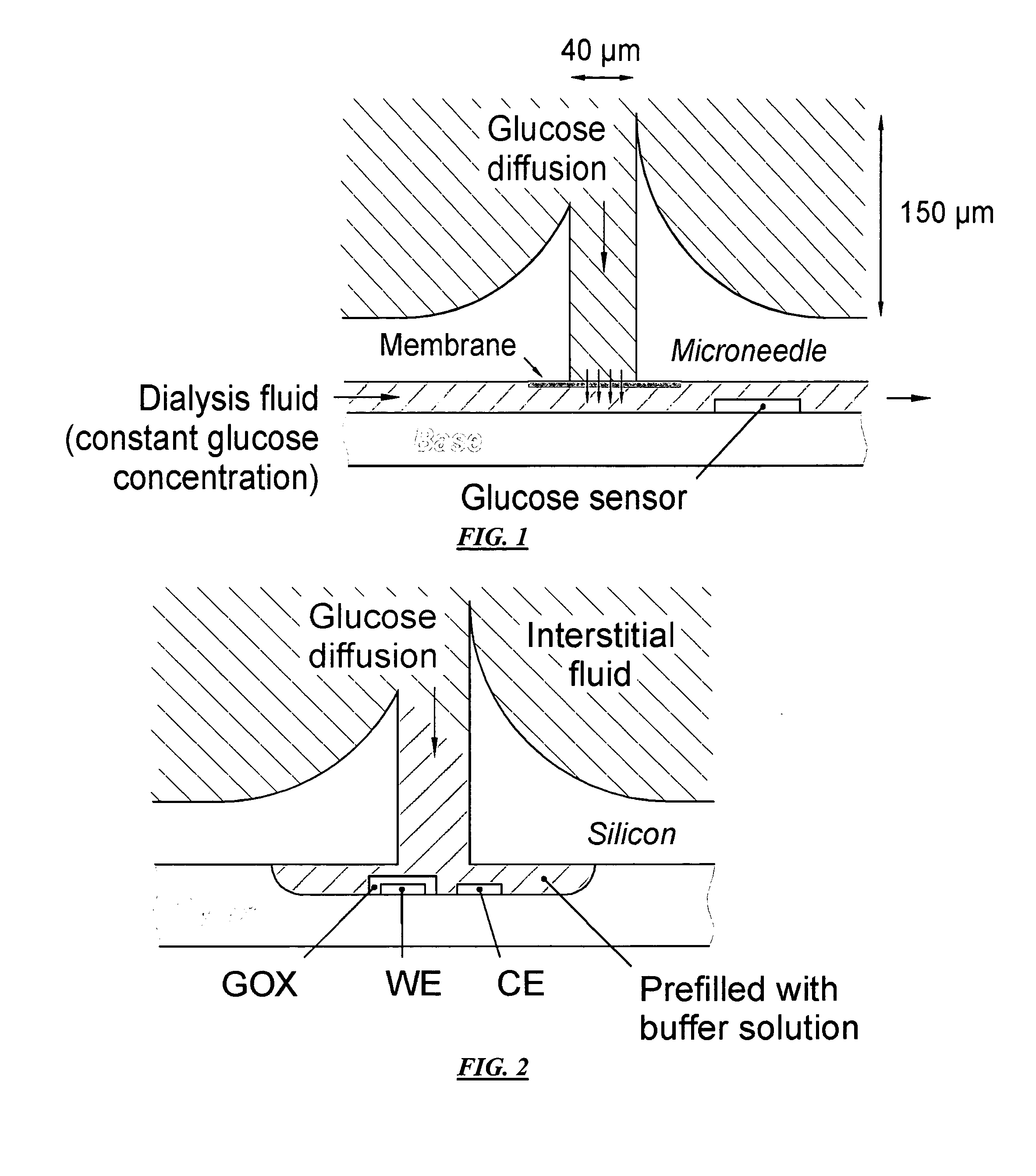
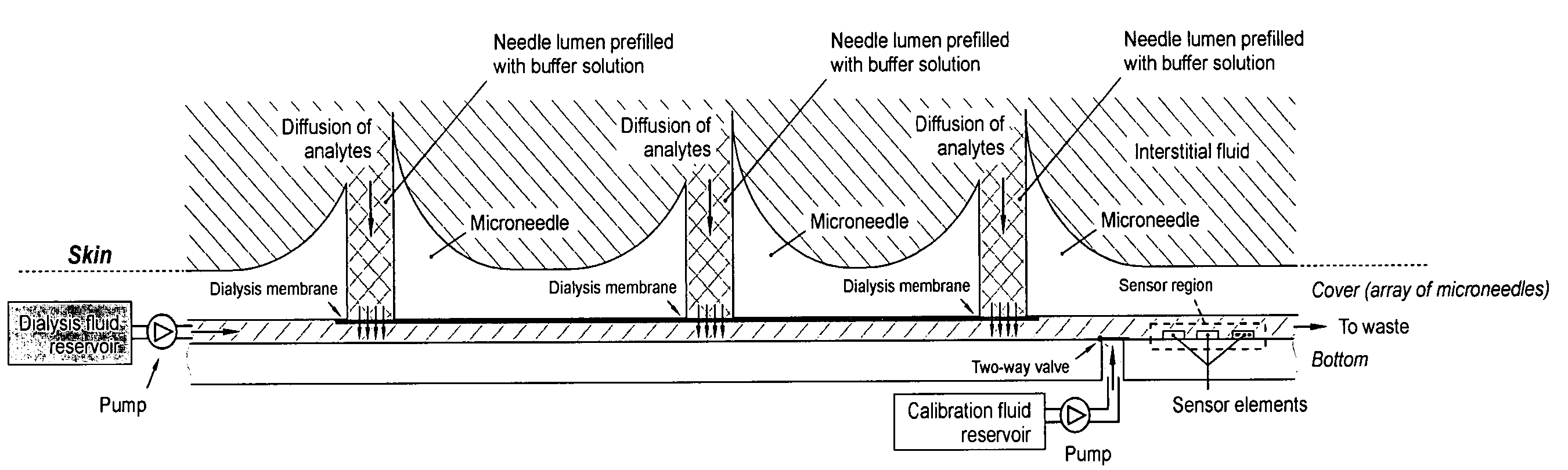
Monitoring method and/or apparatus
ActiveUS20060211933A1Easy recalibrationMinimally invasiveSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisDialysis membranesContinuous glucose monitoring
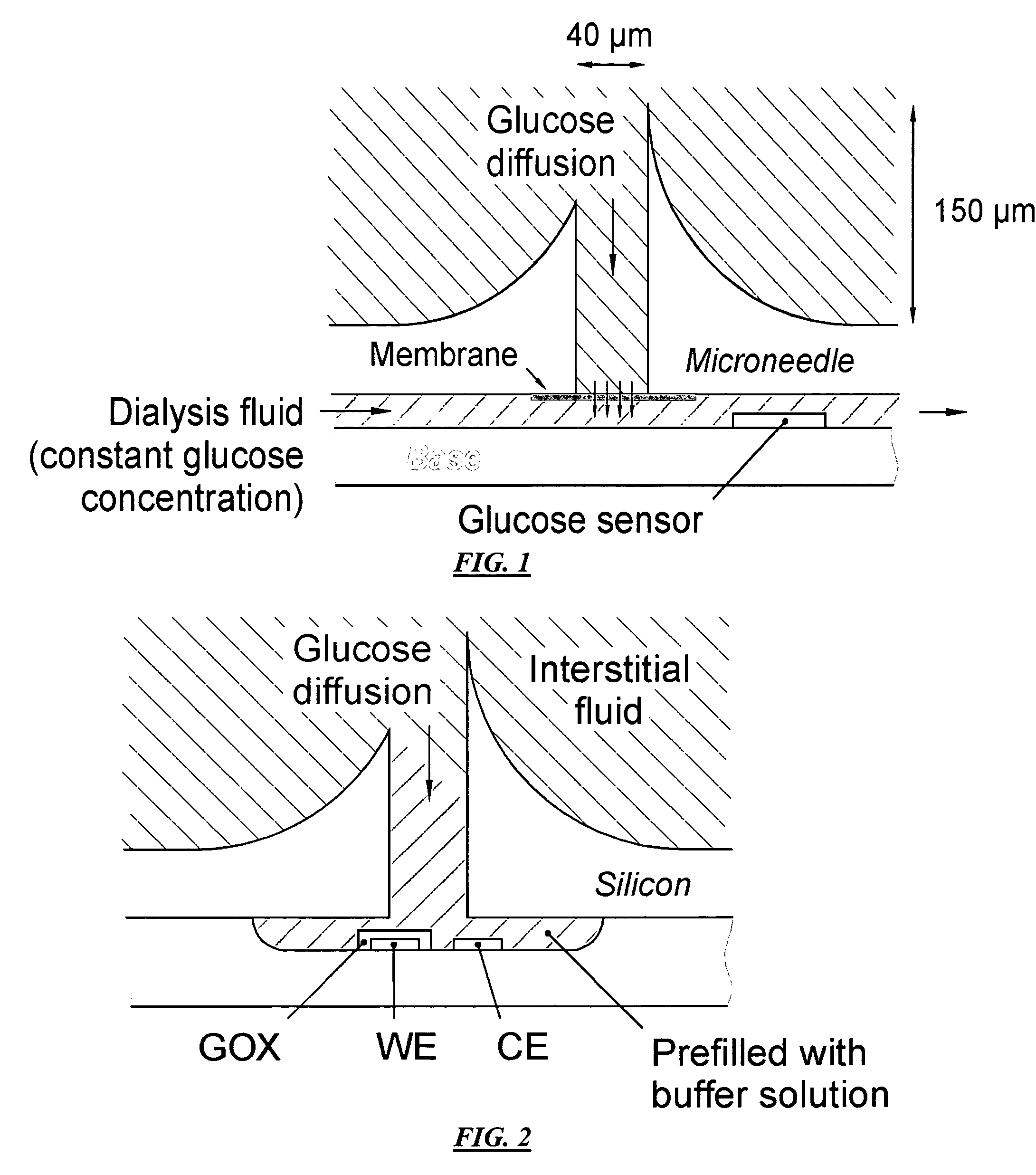
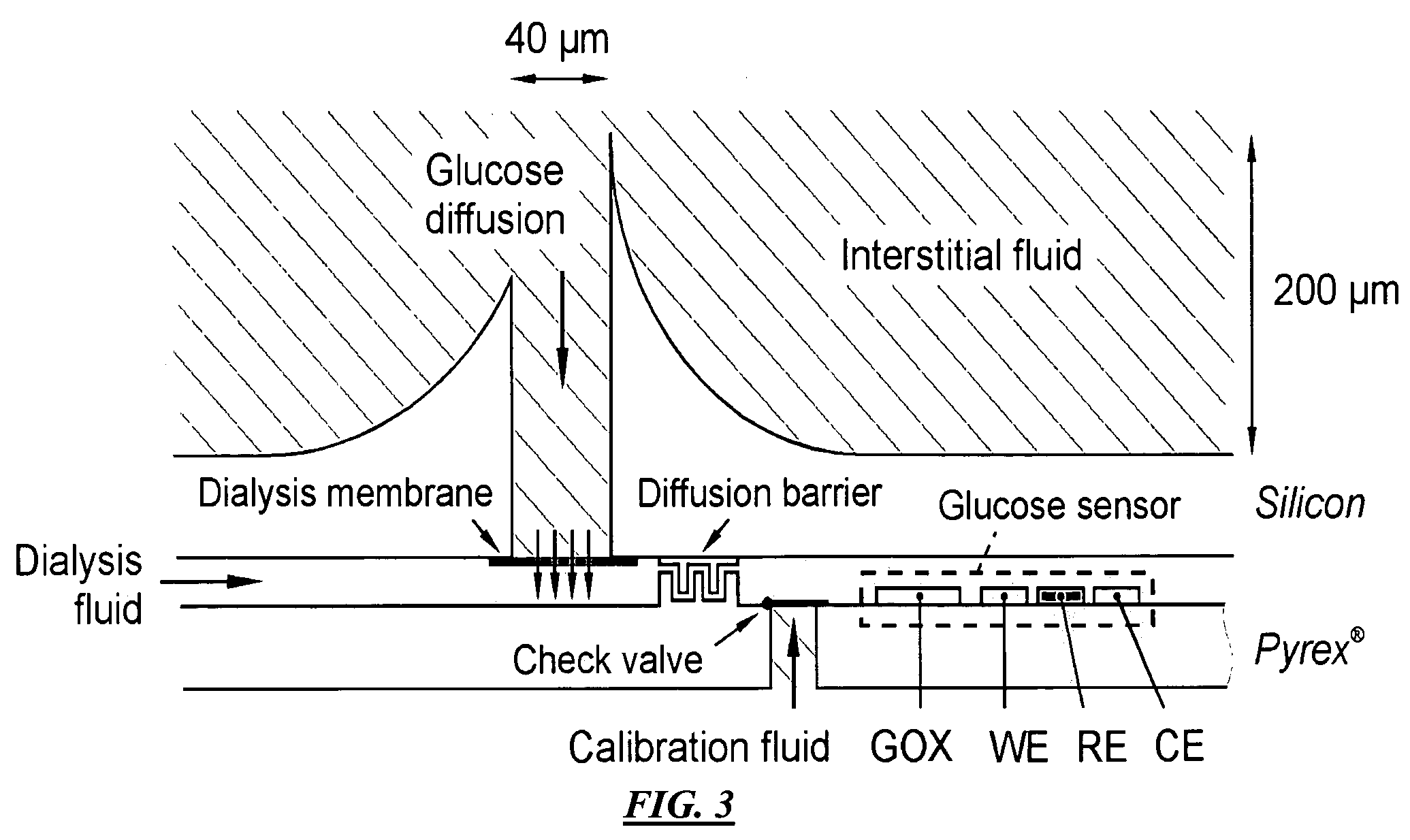
A method and apparatus for substance monitoring. One application is an easy to handle continuous glucose monitor using a group of hollow out-of-plane silicon microneedles to sample substances in interstitial fluid from the epidermal skin layer. The glucose of the interstitial fluid permeates a dialysis membrane and reaches a sensor. Using MEMS technology, for example, allows well-established batch fabrication at low cost.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
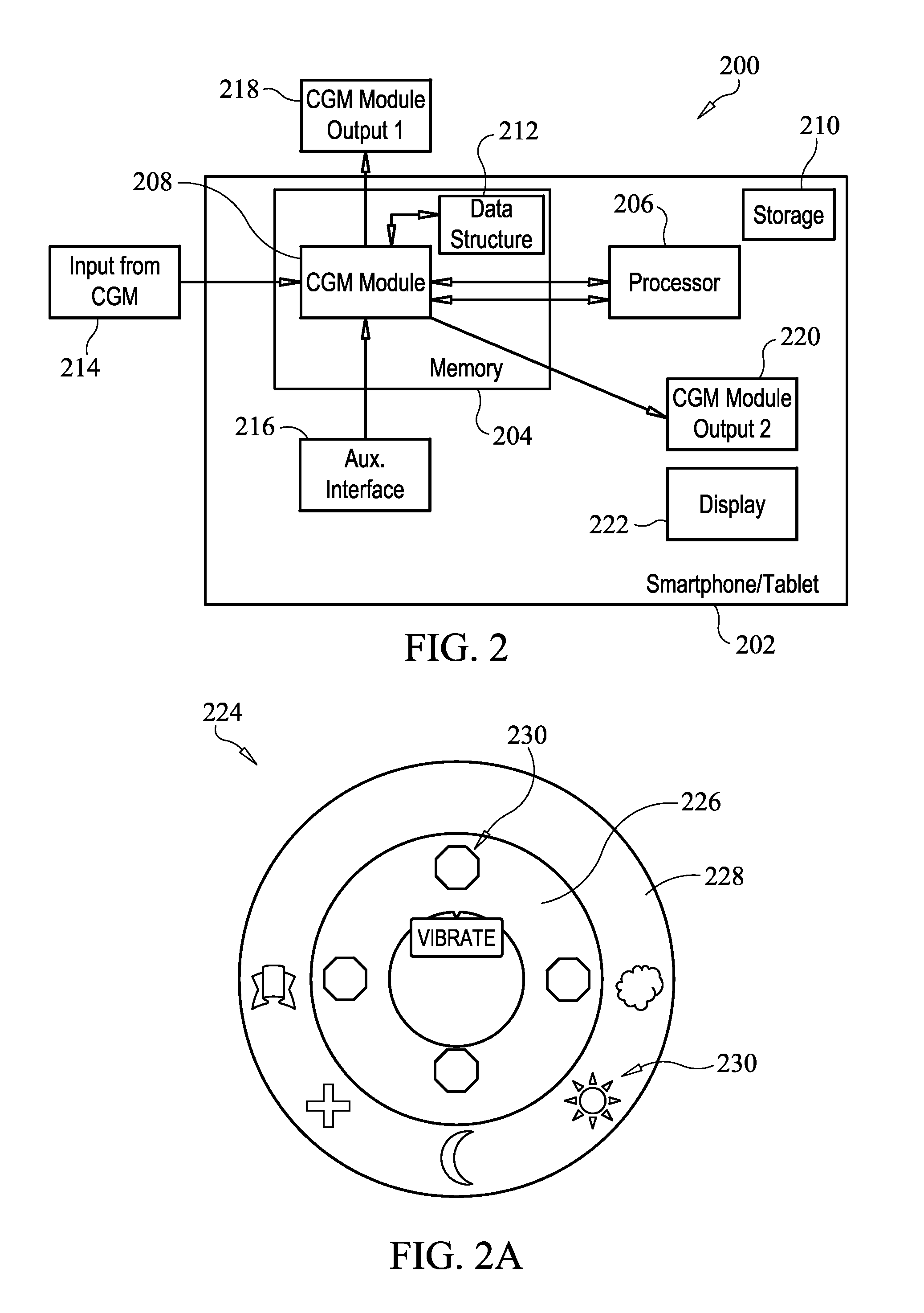
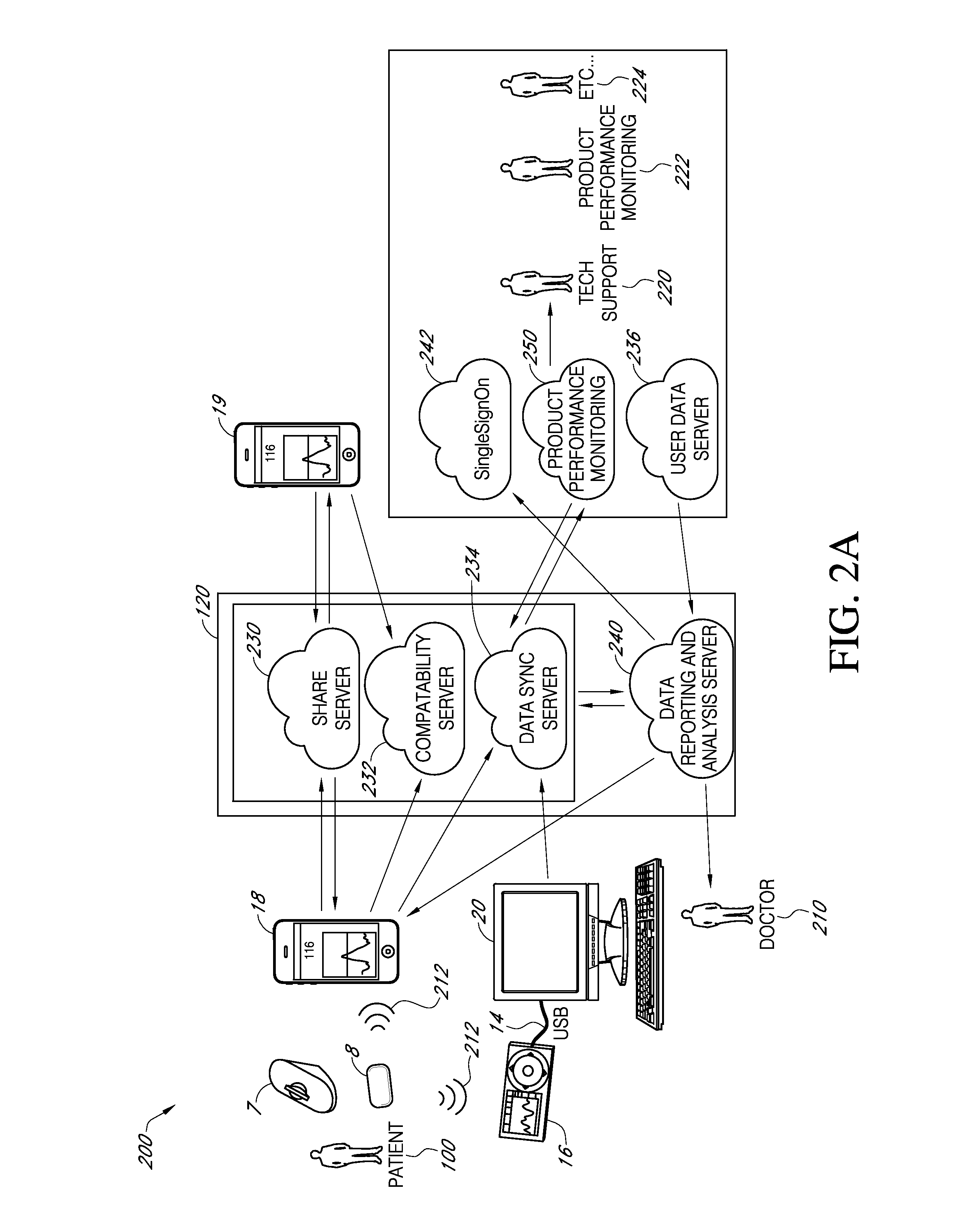
Systems and methods for leveraging smartphone features in continuous glucose monitoring
InactiveUS20140012118A1Strong alarmDiagnostic signal processingDrug and medicationsInternet privacyDiabetes management
The present embodiments harness a wide variety of capabilities of modern smartphones, and combine these capabilities with information from a continuous glucose monitor to provide diabetics and related people with more information than the continuous glucose monitor can provide by itself. The increased information provides the diabetic with an increased likelihood of good diabetes management for better health.
Owner:DEXCOM
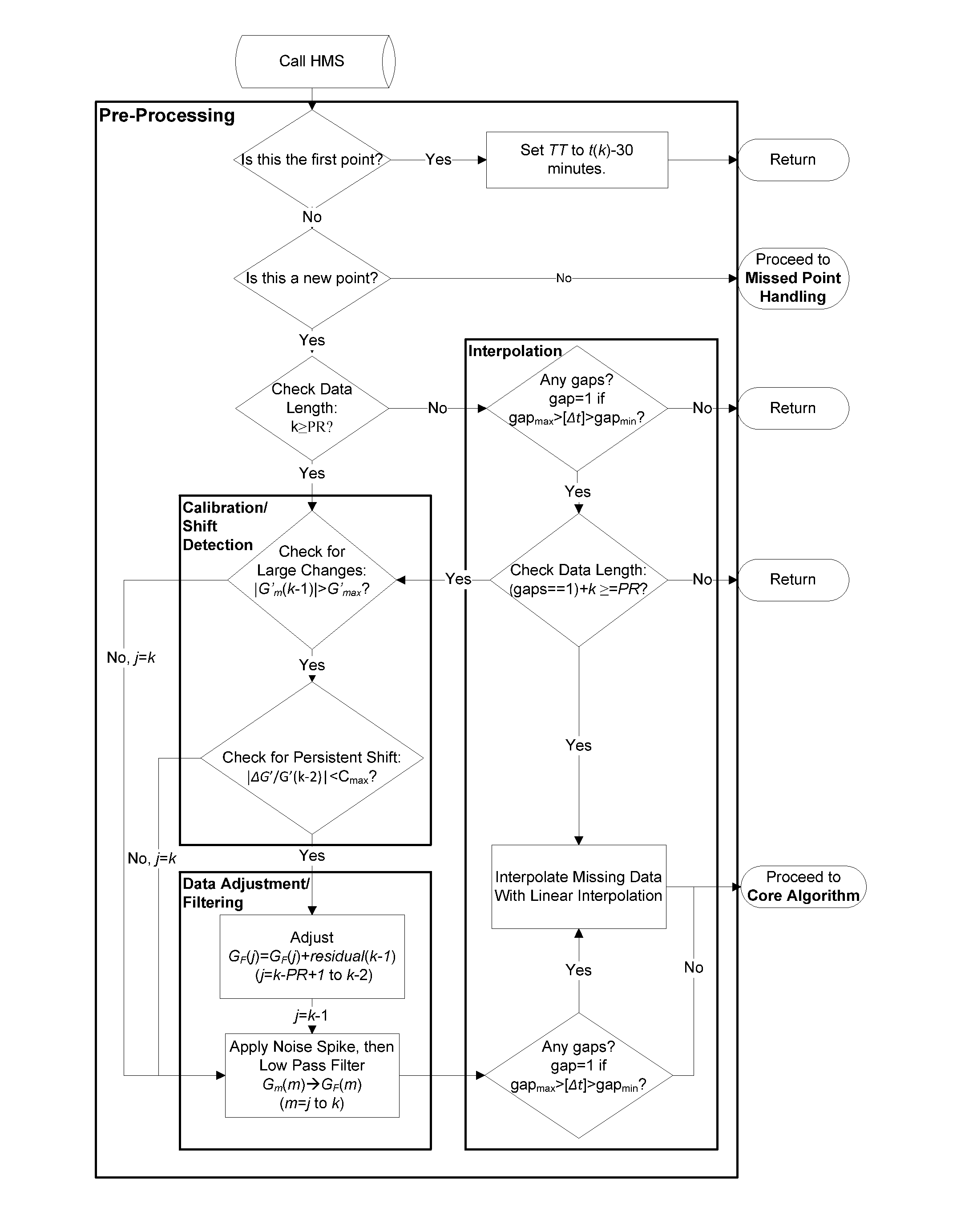
Health Monitoring System
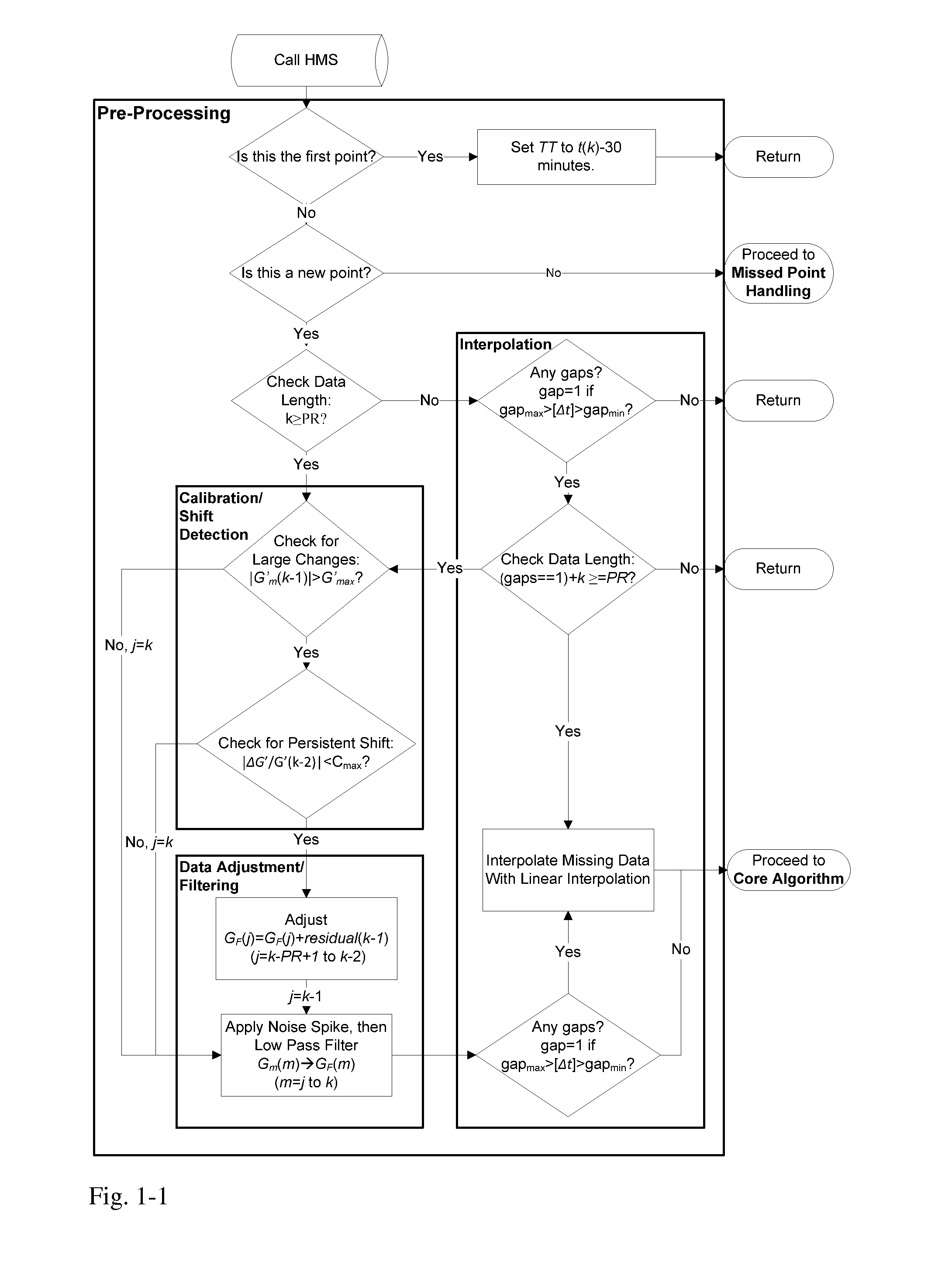
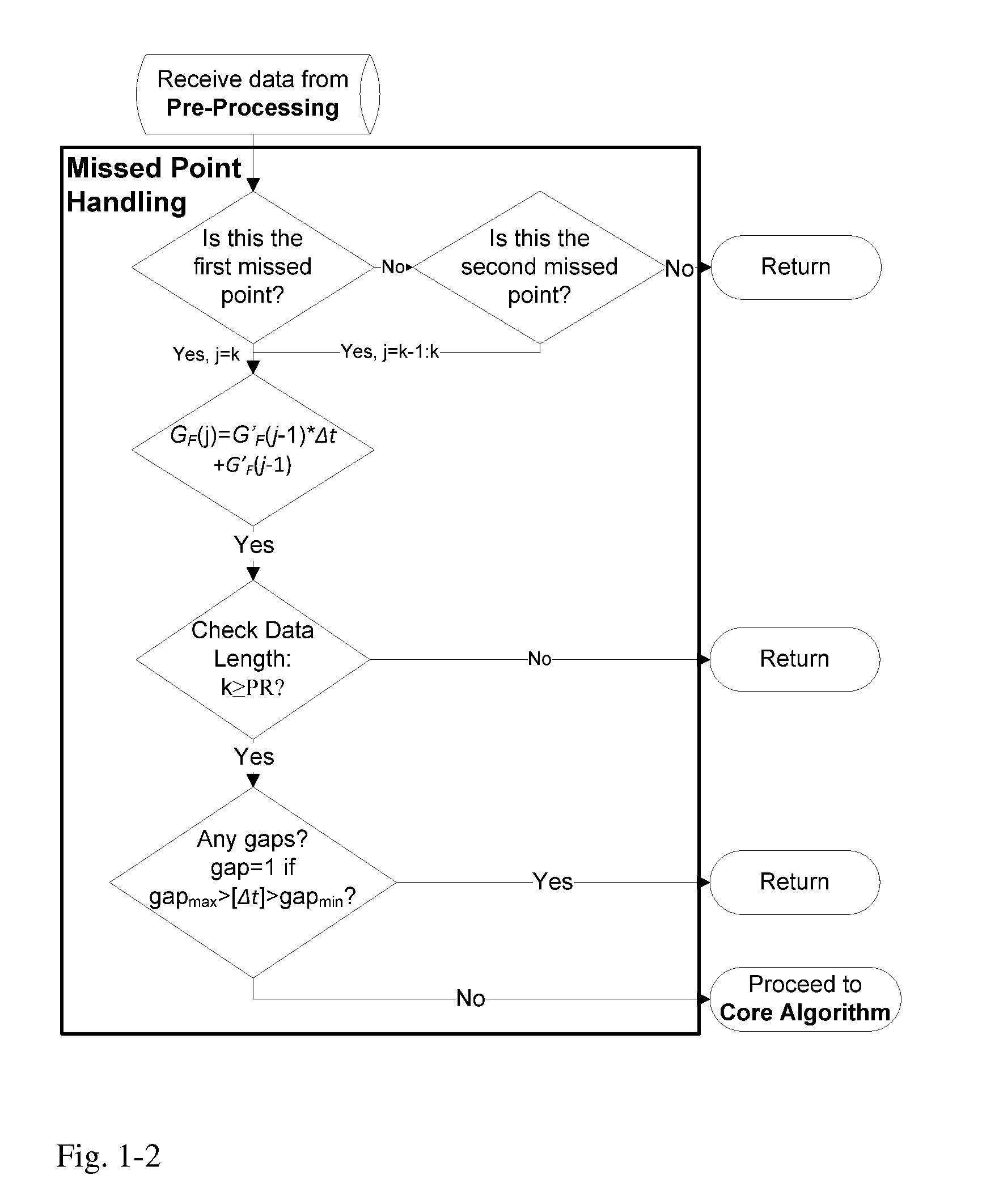
InactiveUS20110313680A1Reduce noisePoint was missedTelemedicineNutrition controlNegative feedbackMissing data
A machine for processing continuous glucose monitoring data and issuing an alert if hypoglycemia is imminent has three modules: (a) a pre-processing module that receives and modulates continuous glucose monitoring data by reducing noise and adjusting for missed data points and shifts due to calibration; (b) a core algorithm module that receives data from the pre-processing module and calculates a rate of change to make a hypoglycemia prediction, and determine if hypoglycemia is imminent; and (c) an alarm mode module that receives data from the core algorithm and issues an audio or visual alert or warning message or a negative feedback signal to an insulin delivery device if hypoglycemia is imminent.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Fluctuating blood glucose notification threshold profiles and methods of use
Embodiments of the present invention provide a new system and methods for monitoring blood glucose concentration. A user of a continuous glucose monitor may program upper and lower blood glucose notification thresholds to fluctuate over time in order to facilitate management of the short-term effects of food consumption, insulin delivery aberrations, physical activity, emotions, and unforeseen circumstances.
Owner:SHER PHILIP M
Subcutaneous sensor inserter and method
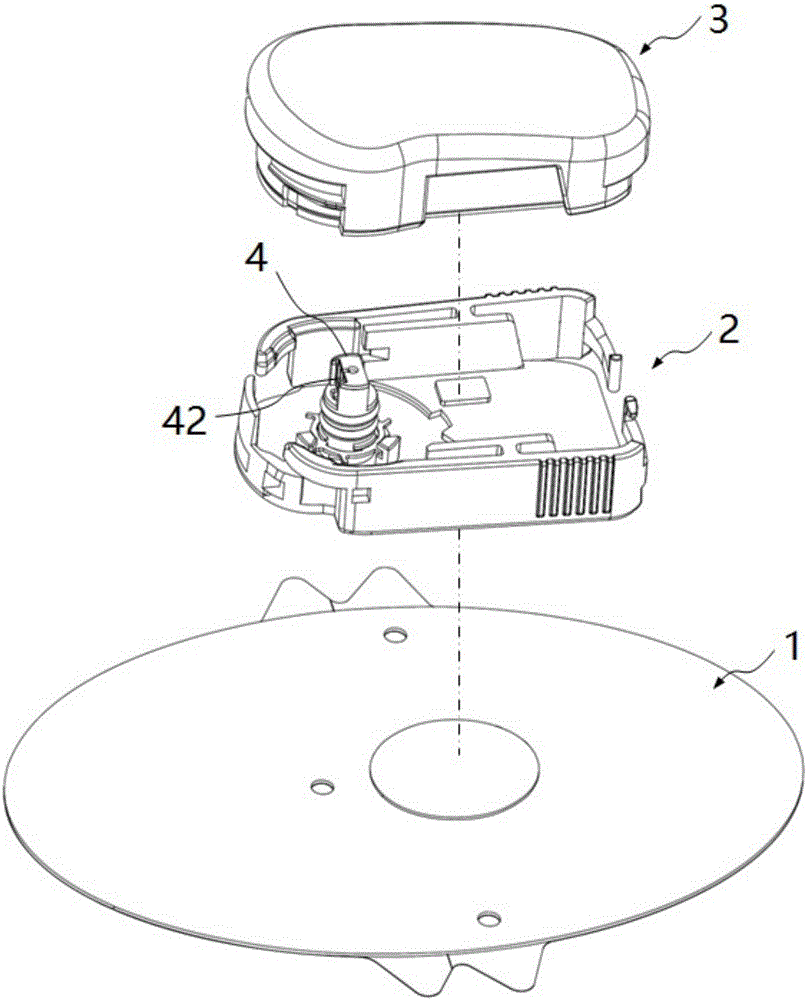
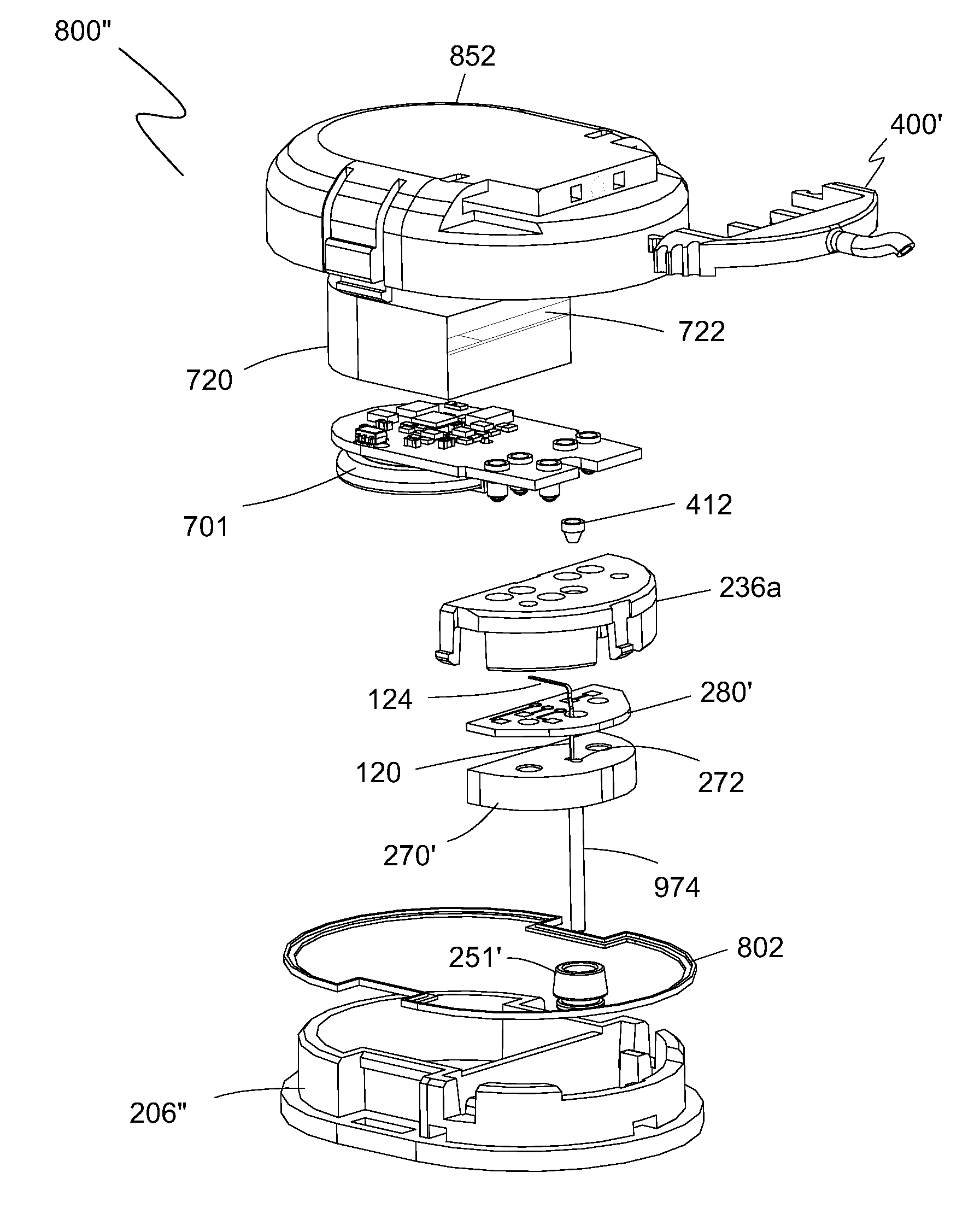
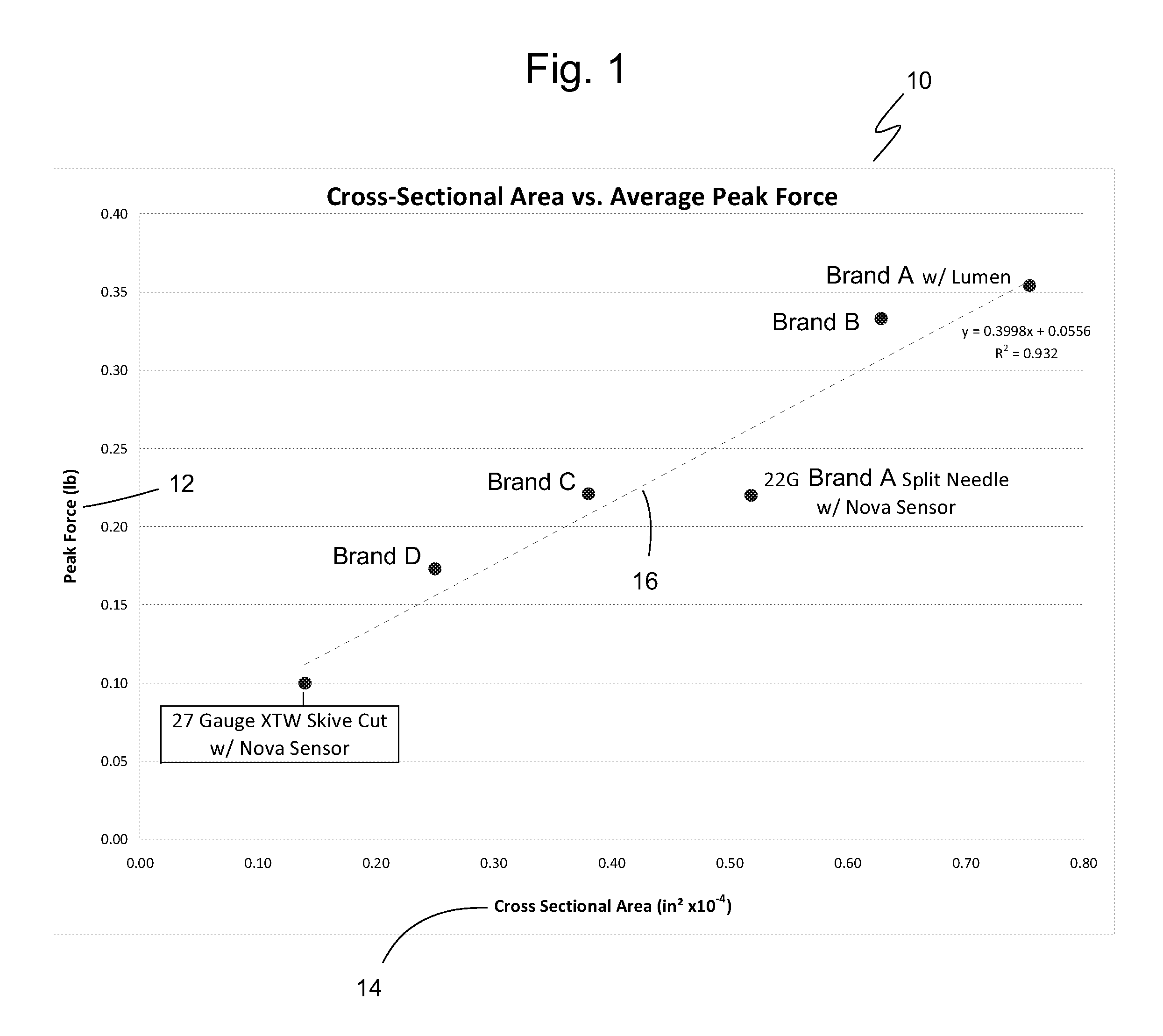
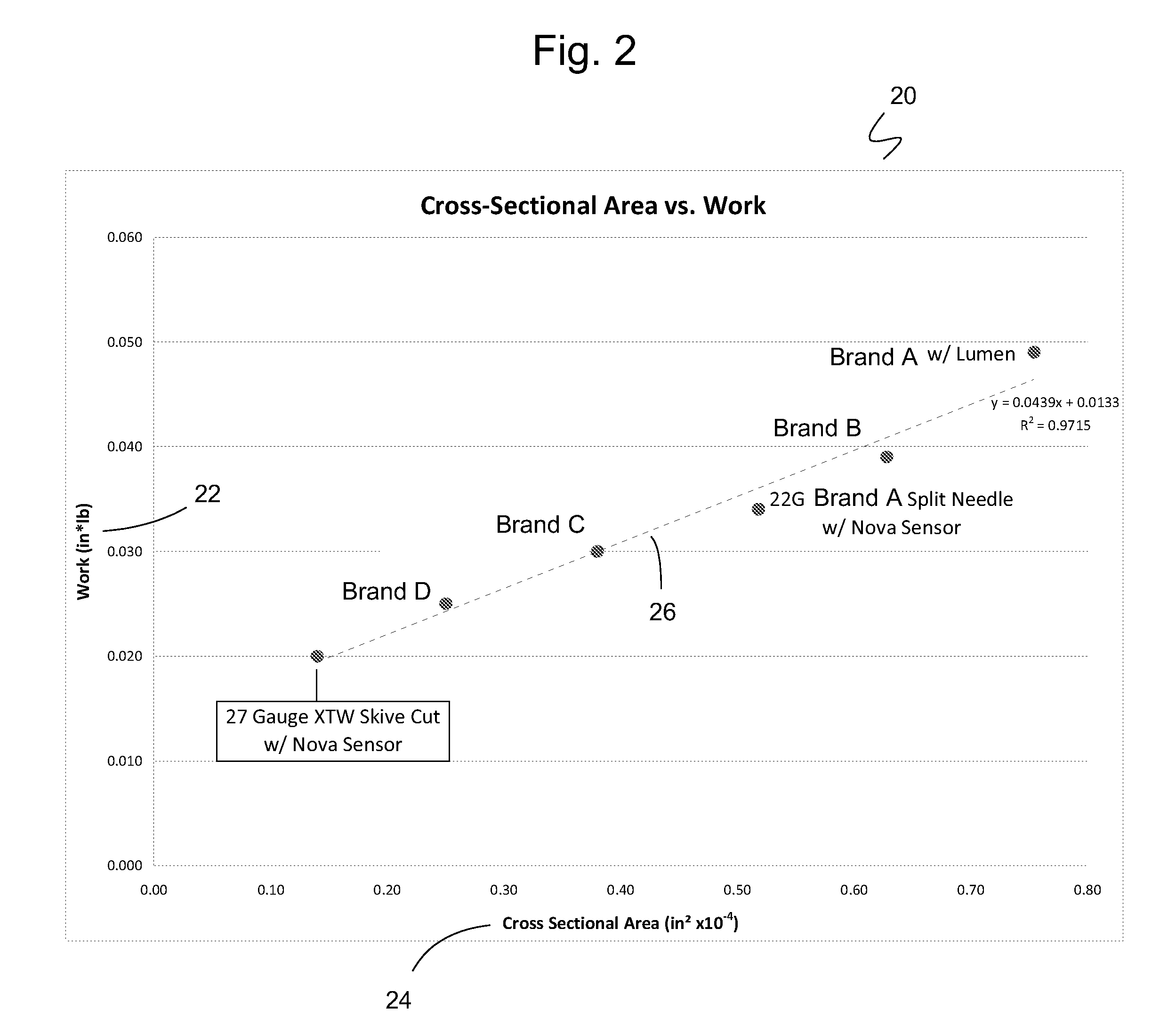
ActiveUS20160058344A1Relieve painMinimizes peak forceSurgical needlesCatheterContinuous glucose monitoringBiomedical engineering
An inserter assembly for continuous glucose monitoring with medication delivery capability where the assembly has a deployment button containing a needle deployment mechanism having a sharp held in a pre-release position, a housing body in which the deployment button is movably received within a top end of the housing body, the housing body having a sensor deployment assembly containing a lumen and a sensor disposed within the lumen and extending out of the lumen to a circuit board that is part of the sensor deployment assembly, the sensor deployment assembly matingly connected to the sharp where the sharp extends beyond the sensor deployment assembly and contains the sensor not fixedly attached to the sharp, and a sensor housing releasably received within a lower end of the housing body, the sharp extending into a sensor deployment assembly recess within the sensor housing and directly above a sensor opening in a bottom of the sensor housing.
Owner:SANVITA MEDICAL CORPORATION
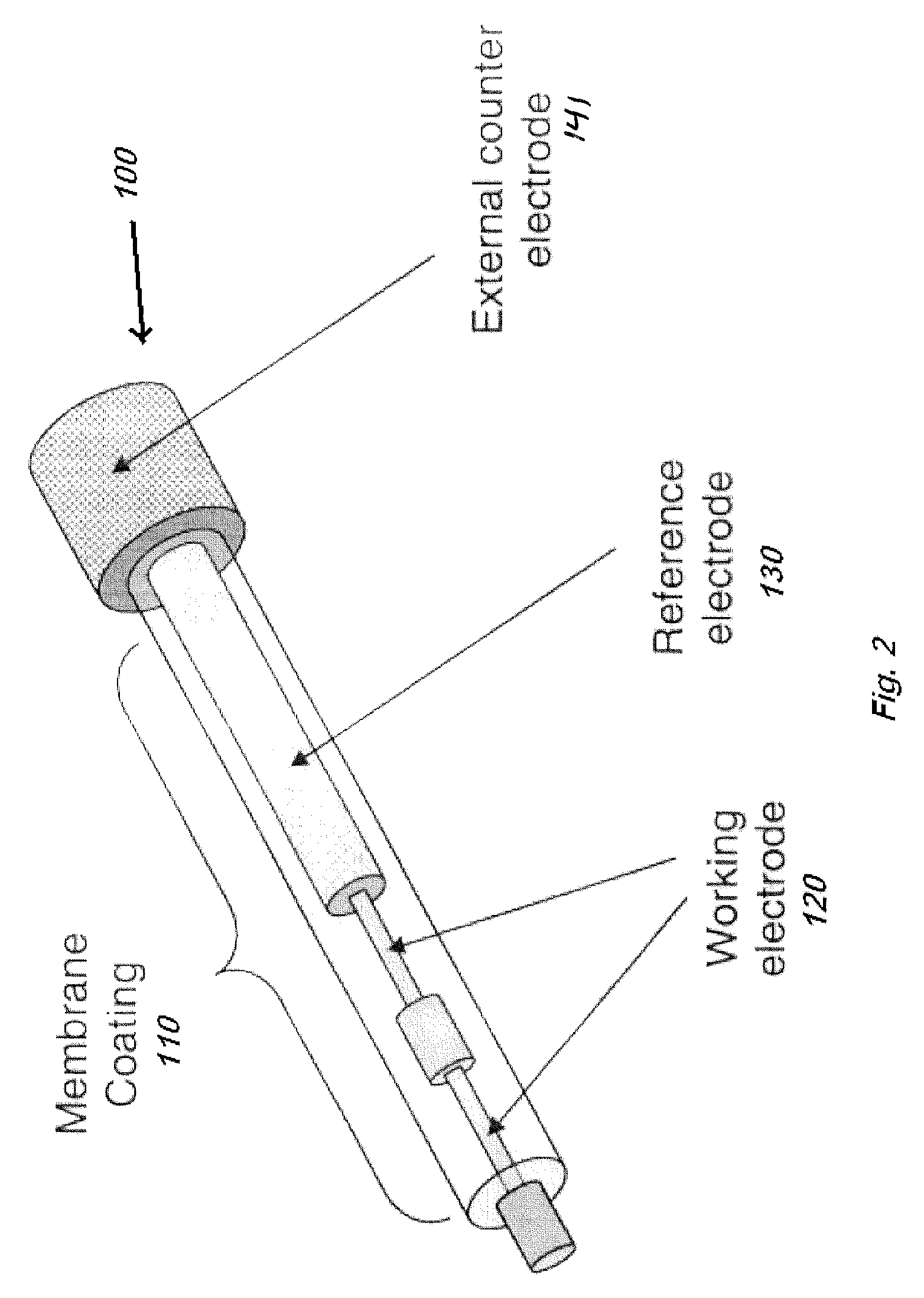
Percutaneous analyte sensing device and installing method thereof
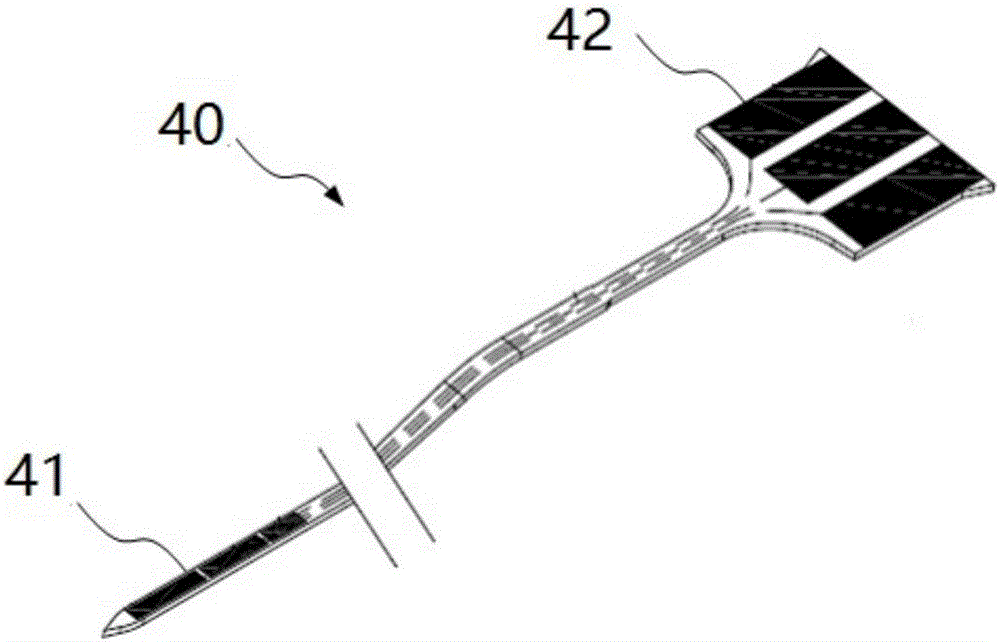
The invention provides a transdermal analyte sensing device and an installation method thereof. The percutaneous analyte sensing device includes a medical adhesive plaster, a probe base with first, second and third installation structures on it; used for combining the probe body, the probe installer and the emitter. The probe installer includes an instant ejection-recovery mechanism and a release button, which can instantly complete the ejection and recovery actions of the guide needle without manual operation. After the probe body of the present invention is installed, the probe installer can be easily removed, and the transmitter can be easily installed and removed. The transdermal analyte sensing device of the present invention is also provided with a protective cover that can be combined with the probe base and the probe mount. The transdermal analyte sensing device of the present invention is small in size, easy to wear, simple and safe to install and operate, and provides a perfect solution for users to realize continuous blood sugar monitoring by themselves.
Owner:MEDTRUM TECH
Continuous blood glucose monitor
A device may be implanted subcutaneously with an attached catheter inserted within, e.g., the peritoneal cavity of a subject. The catheter and / or device may also be inserted into another space, e.g., subcutaneous, vascular, peritoneal, cerebrospinal, pleural spaces, etc. The peritoneal fluid which normally collects and / or flows through the peritoneal cavity may be detected by the catheter and analyzed via the device to detect the concentration of glucose within the fluid.
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
Hypoglycemia prediction and control
InactiveUS20100174228A1Severe hypoglycemia can be preventedDrug and medicationsMedical devicesMedicineInsulin pump
A system for predicting hypoglycemia based on continuous blood glucose monitor values is provided. The hypoglycemia detection algorithm is a set of individual alarms that are combined through a voting system into one combined alarm. The system could have five components and an overall voting algorithm that produces a binary alarm outcome depending on the number of constituent algorithms that report an alarm. A controller system automatically shuts off the insulin pump when pending or real hypoglycemia has been reached. The algorithms operate in a closed loop and automatically take action when the subject is asleep.
Owner:BUCKINGHAM BRUCE +8
Subcutaneous sensor inserter and method
ActiveUS20160058474A1Reduce and minimize painRelieve painSurgical needlesCatheterContinuous glucose monitoringBiomedical engineering
An inserter assembly for continuous glucose monitoring with medication delivery capability where the assembly has a deployment button containing a needle deployment mechanism having a sharp held in a pre-release position, a housing body in which the deployment button is movably received within a top end of the housing body, the housing body having a sensor deployment assembly containing a lumen and a sensor disposed within the lumen and extending out of the lumen to a circuit board that is part of the sensor deployment assembly, the sensor deployment assembly matingly connected to the sharp where the sharp extends beyond the sensor deployment assembly and contains the sensor not fixedly attached to the sharp, and a sensor housing releasably received within a lower end of the housing body, the sharp extending into a sensor deployment assembly recess within the sensor housing and directly above a sensor opening in a bottom of the sensor housing.
Owner:SANVITA MEDICAL CORPORATION
Monitoring method and/or apparatus
ActiveUS7415299B2Easy recalibrationMinimally invasiveSemi-permeable membranesMedical devicesDialysis membranesContinuous glucose monitoring
A method and apparatus for substance monitoring. One application is an easy to handle continuous glucose monitor using a group of hollow out-of-plane silicon microneedles to sample substances in interstitial fluid from the epidermal skin layer. The glucose of the interstitial fluid permeates a dialysis membrane and reaches a sensor. Using MEMS technology, for example, allows well-established batch fabrication at low cost.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
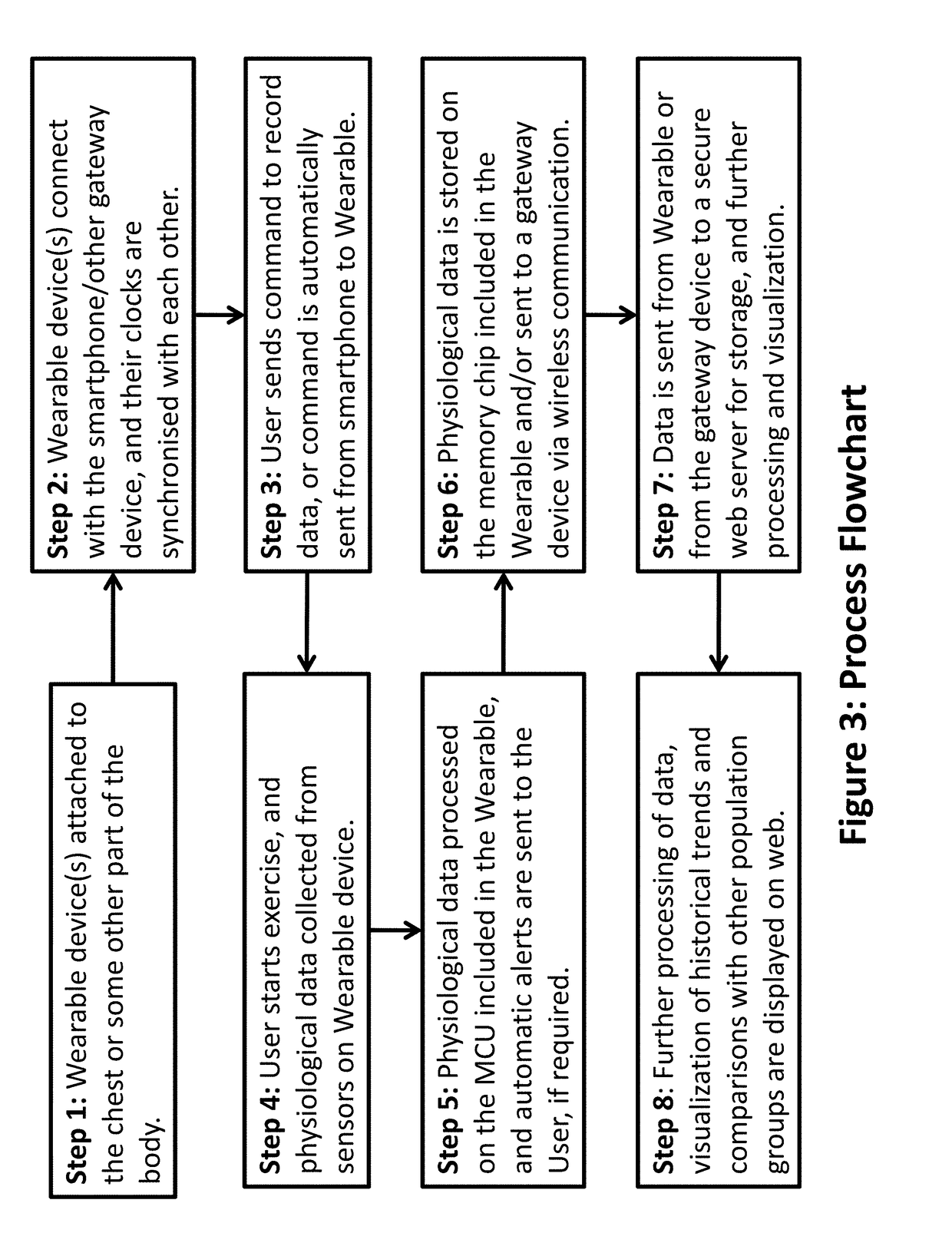
Method and system for continuous monitoring of health parameters during exercise
PendingUS20180358119A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPhysical therapies and activitiesEngineeringNon invasive
The various embodiments of the present invention provide a system and method for a fully mobile, non-invasive, continuous system for monitoring the cardiovascular and musculoskeletal health of an individual during exercise. The system includes one or more wearable devices affixed on the User with a chest strap or adhesive sticker, coupled with an application running on a computing device (smartphone / smartwatch), which performs various computations on the wearable device, or a smart phone / smart watch, or the cloud, and provides the user or the concerned personnel with various insights about the general health of the user. The exercise health monitoring system further enables the Users to get real time alerts during exercise or running, by way of vibrations or audio messages or notifications on the gateway device when they have an event of arrhythmia or cardiac fatigue, or they cross prescribed ranges of one or more of the following parameters: PEP, LVET, CO, HR, Shock, Braking Force, Sway.
Owner:FOURTH FRONTIER TECH PVT LTD
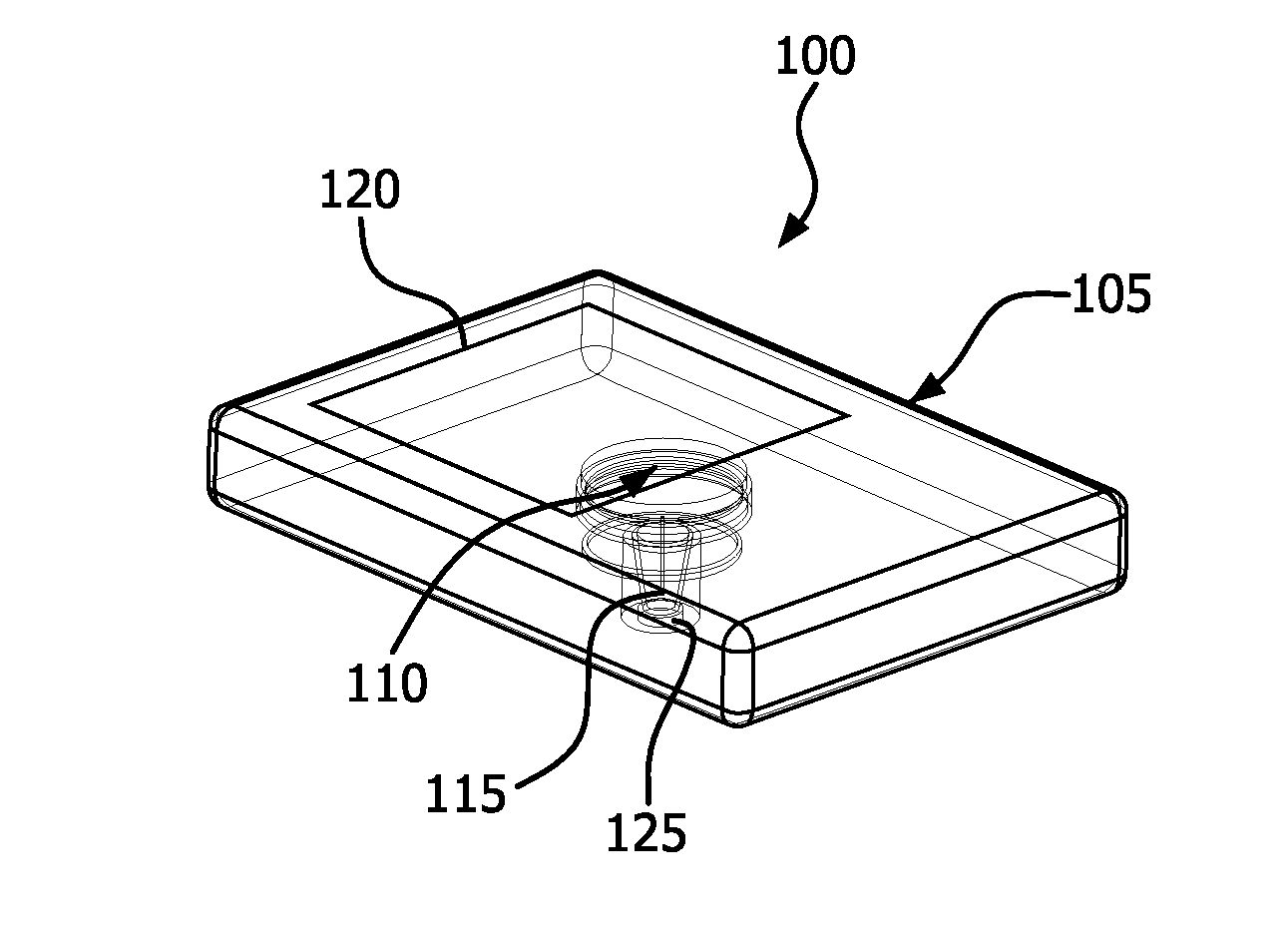
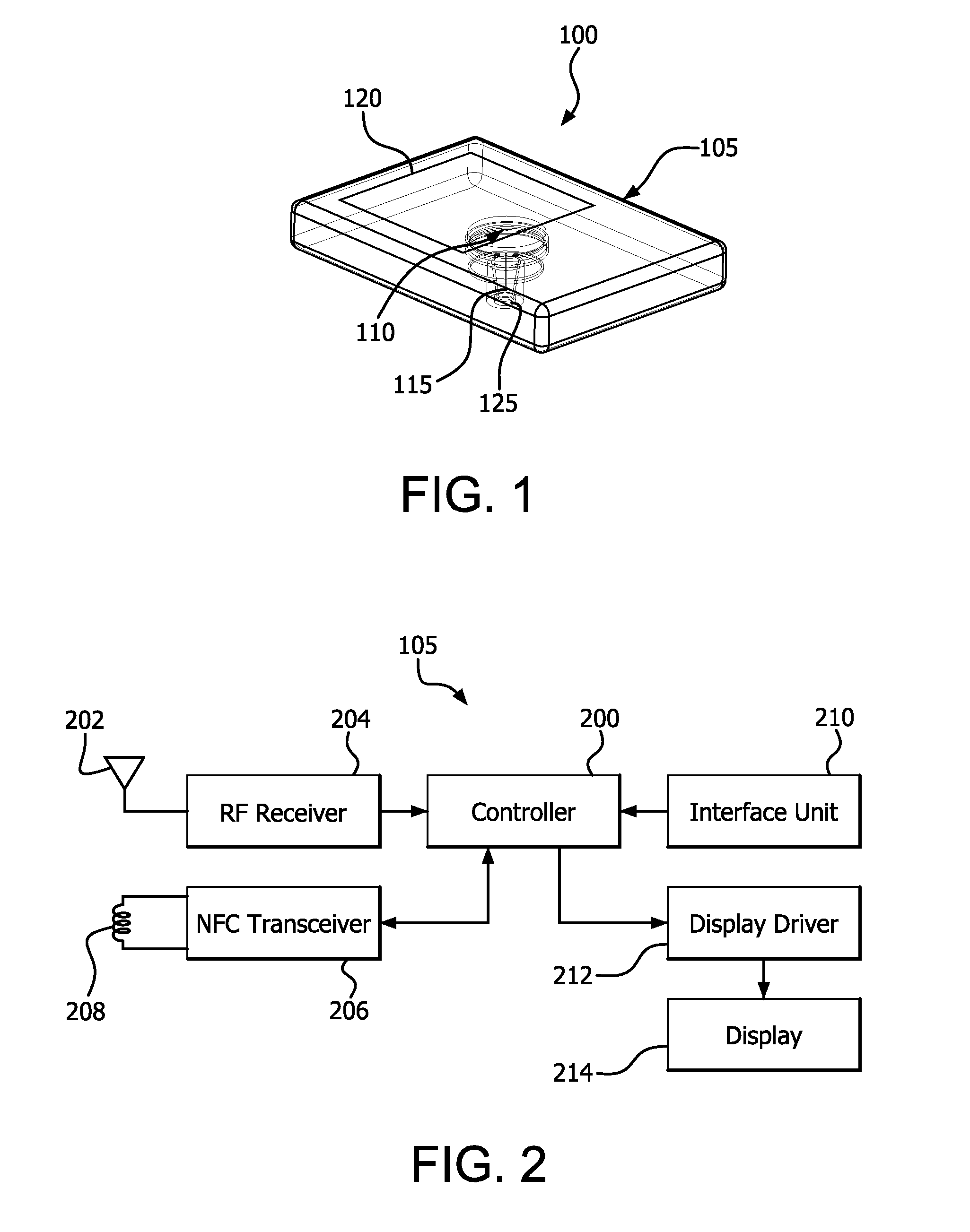
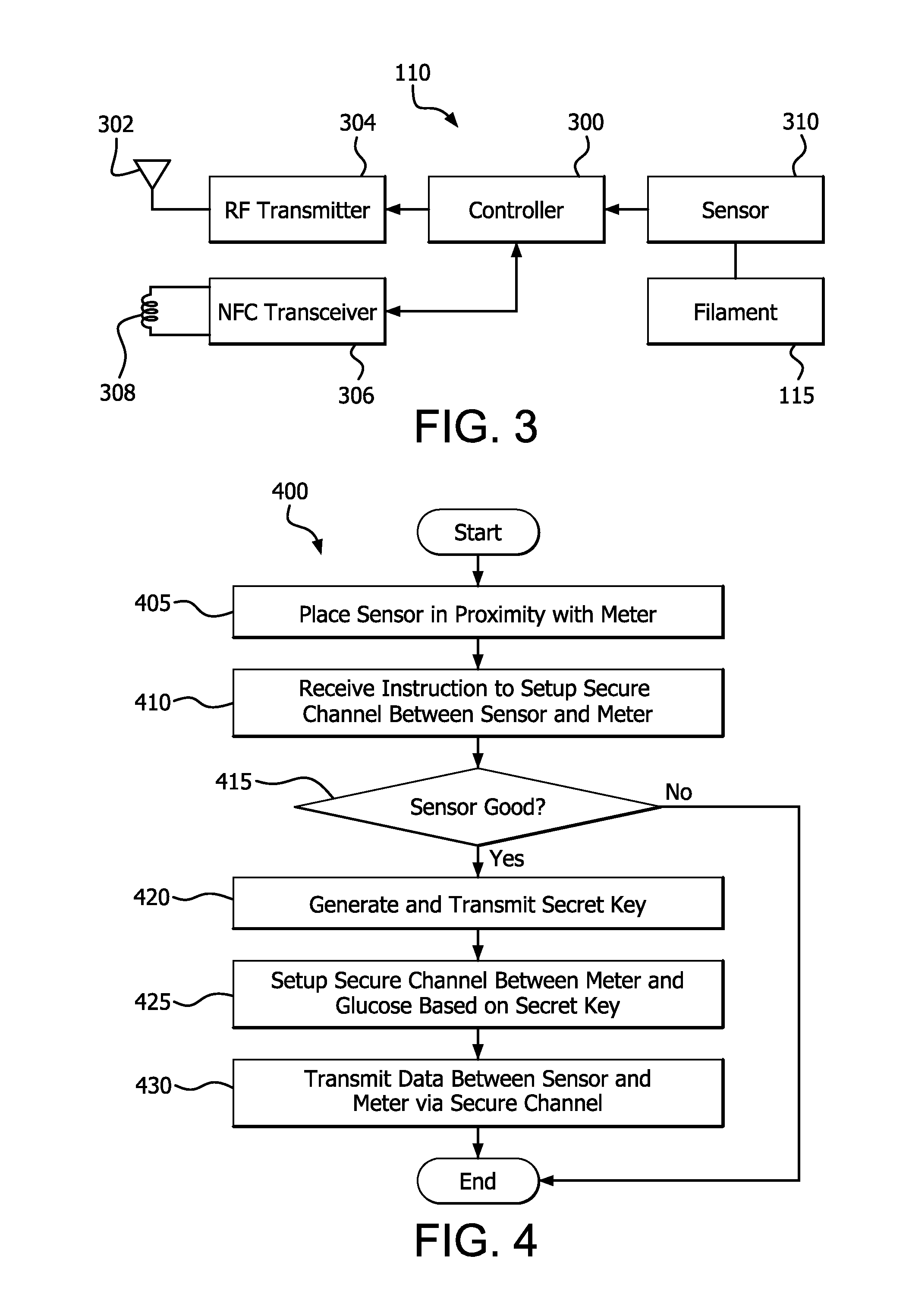
Near Field Telemetry Link for Passing a Shared Secret to Establish a Secure Radio Frequency Communication Link in a Physiological Condition Monitoring System
A physiological condition monitoring system (e.g., a continuous glucose monitoring system) includes a physiological condition meter and a physiological condition sensor. The physiological condition meter and the physiological condition sensor are be placed in proximity to exchange a secret key using a near field wireless link, which is used to encrypt data to secure a radio frequency (RF) wireless channel.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy enabled continuous glucose monitoring sensor system
ActiveUS8868151B2Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansSensorsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical impedance spectroscopy
The use of electrical impedance spectroscopy to adjust calibration settings in an in vivo monitoring system, such as an in vivo continuous glucose monitoring sensor. The adjustments can compensate for the condition of the sensor membrane in vivo.
Owner:ASCENSIA DIABETES CARE HLDG AG
Fully automatic intelligent infusion method and device based on model predictive control for large doses of insulin
The invention provides an intelligent method based on model predictive control for automatic infusion of large doses of insulin, which is characterized in that: a continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) and an insulin pump are used as the basis of hardware; online detection of food is carried out based on a strong tracking filter; when the food is detected, large doses of insulin is transfused immediately, and the amount of insulin depends on historical food; whether the dosage is needed to be increased is judged every 30 minutes based on the model predictive control, and the dosage is designed; when the blood glucose concentration decreases, whether the basic amount of insulin is needed to be maintained is determined according to the predicted blood glucose value; and finally the blood glucose concentration is controlled to be within the safe range. Compared with the existing corresponding technology, the invention has the advantages of high degree of intelligence and fully automatic operation, and the blood glucose control effects can be improved significantly in case that self-management cannot be carried out by patients.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
User interfaces for continuous glucose monitoring
ActiveUS20160119210A1Reduce riskReduce the chance of changeError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsSubject matterContinuous glucose monitoring
The subject matter disclosed herein provides methods for presenting glucose level data. Glucose data for a patient may be received. A current glucose level and a rate of change of the current glucose level may be determined based on the received glucose data. A first interface may be displayed on a screen of a device. The first interface may include a unitary icon. The unitary icon may display the current glucose level and a visualization of the rate of change. Related apparatus, systems, techniques, and articles are also described.
Owner:DEXCOM
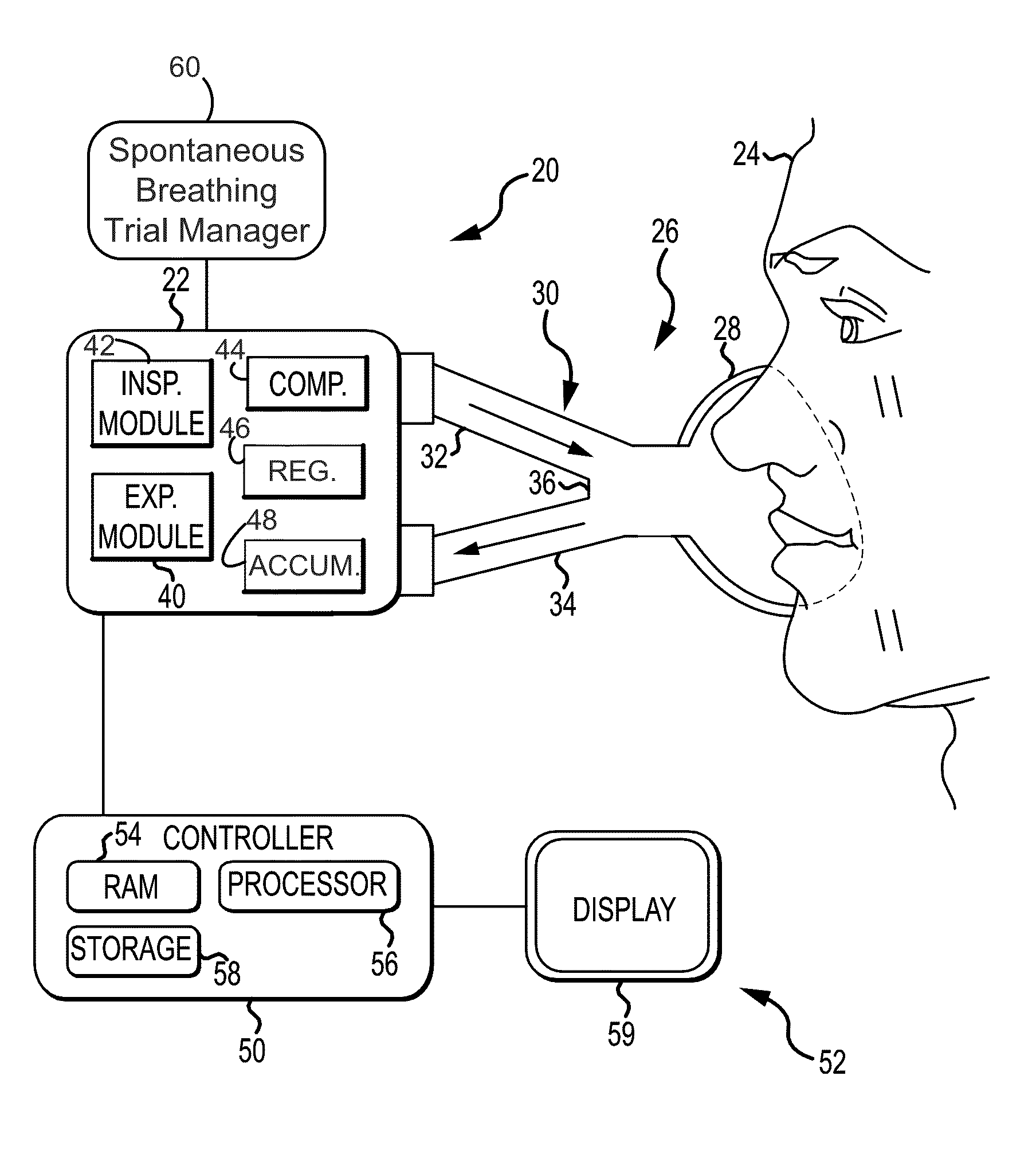
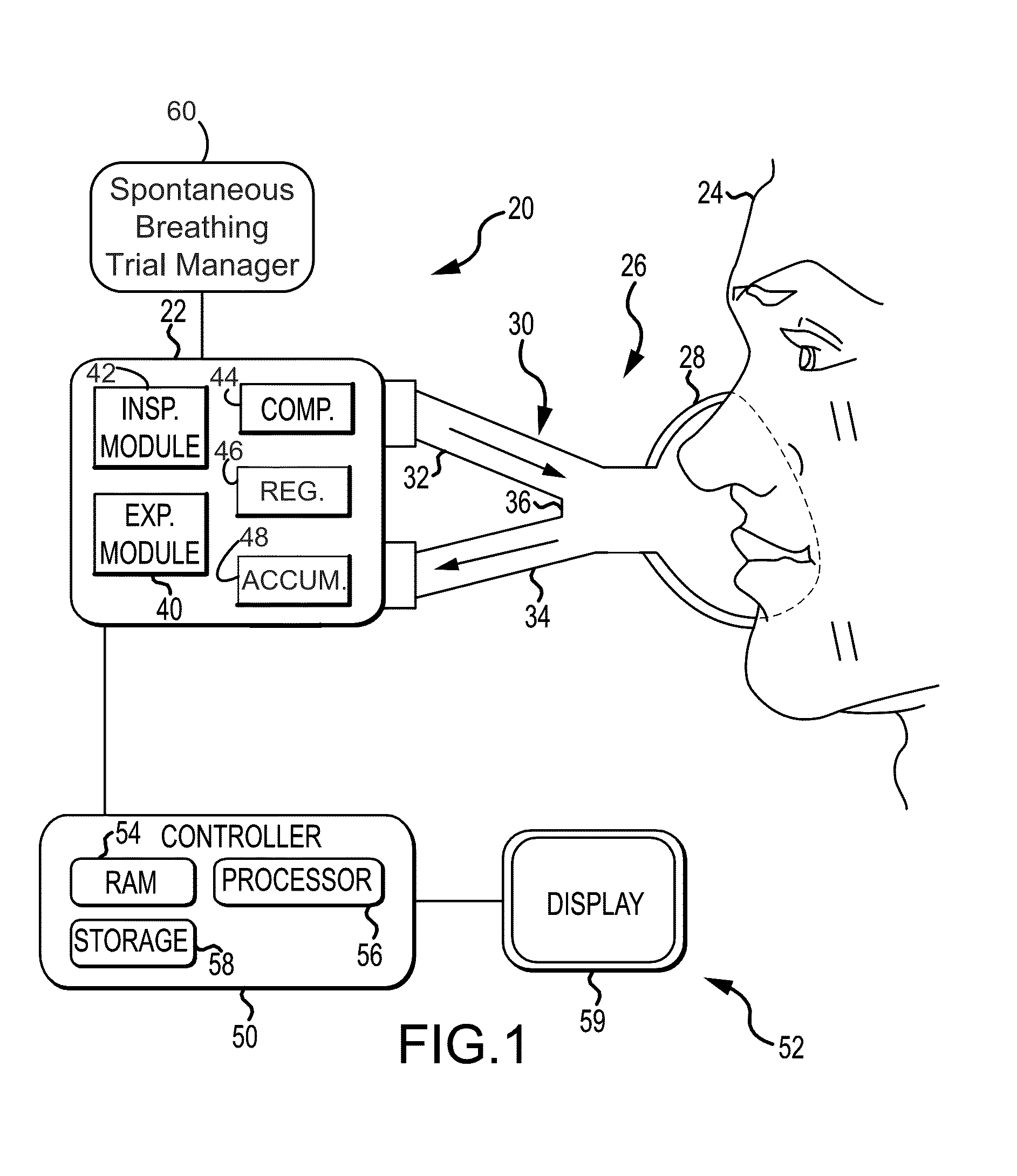
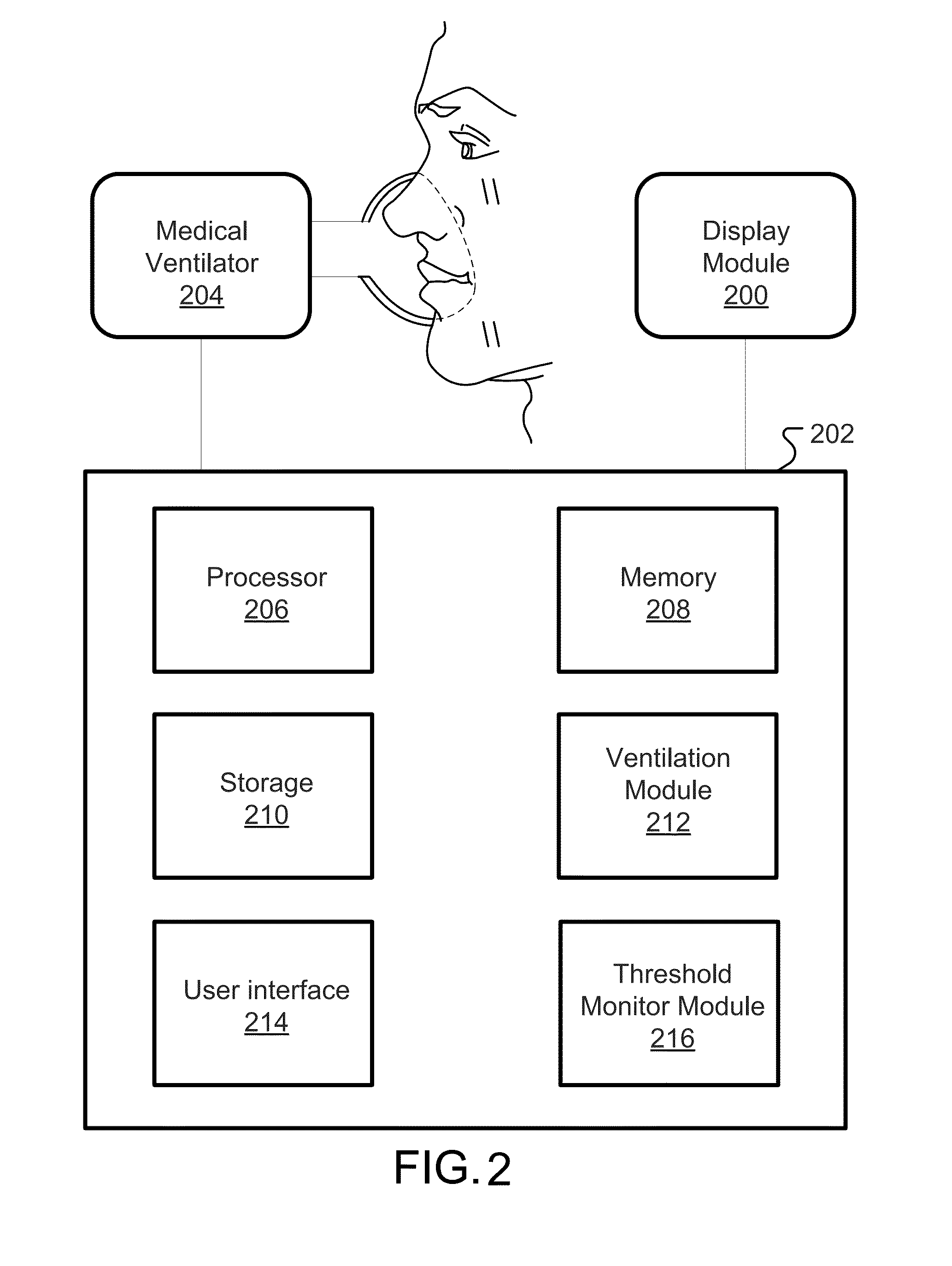
Spontaneous breathing trial manager
InactiveUS20130158370A1RespiratorsElectrocardiographyContinuous glucose monitoringIntensive care medicine
This disclosure describes systems and methods for conducting and terminating spontaneous breathing trials on patients receiving mechanical ventilation. The disclosure describes a novel spontaneous breathing trial manager for a medical ventilator with rapid initiation and continuous monitoring of a patient's tolerance of the spontaneous breathing trial and displaying of that tolerance as a function of time, which provides for bedside adjustment of the spontaneous breathing trial parameters and automatic termination of a spontaneous breathing trial based on a time interval expiration or poor patient tolerance of the SBT.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Methods for reducing false hypoglycemia alarm occurrence
InactiveUS9579456B2Minimizing false alarmsDrug and medicationsMedical devicesContinuous glucose monitoringHypoglycemia
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC +1
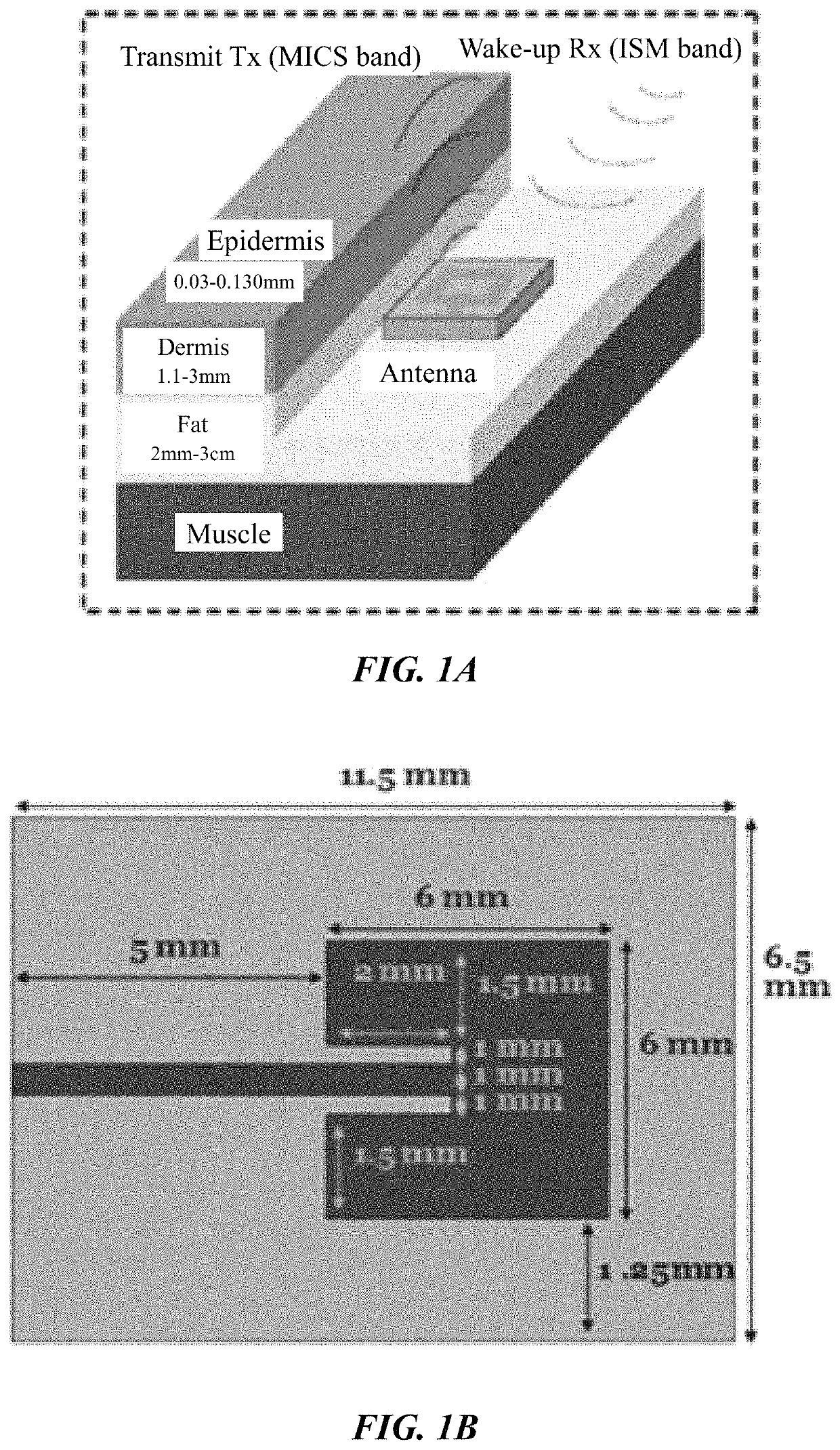
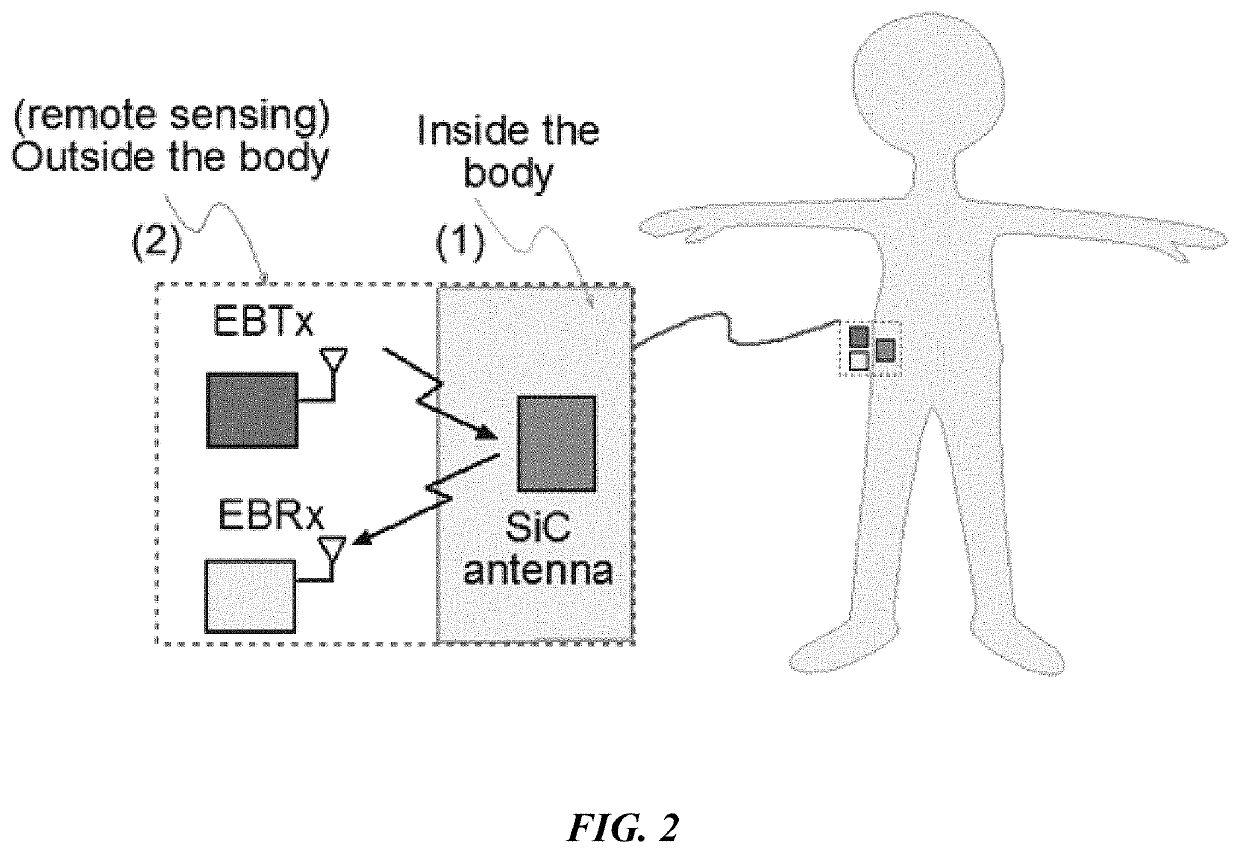
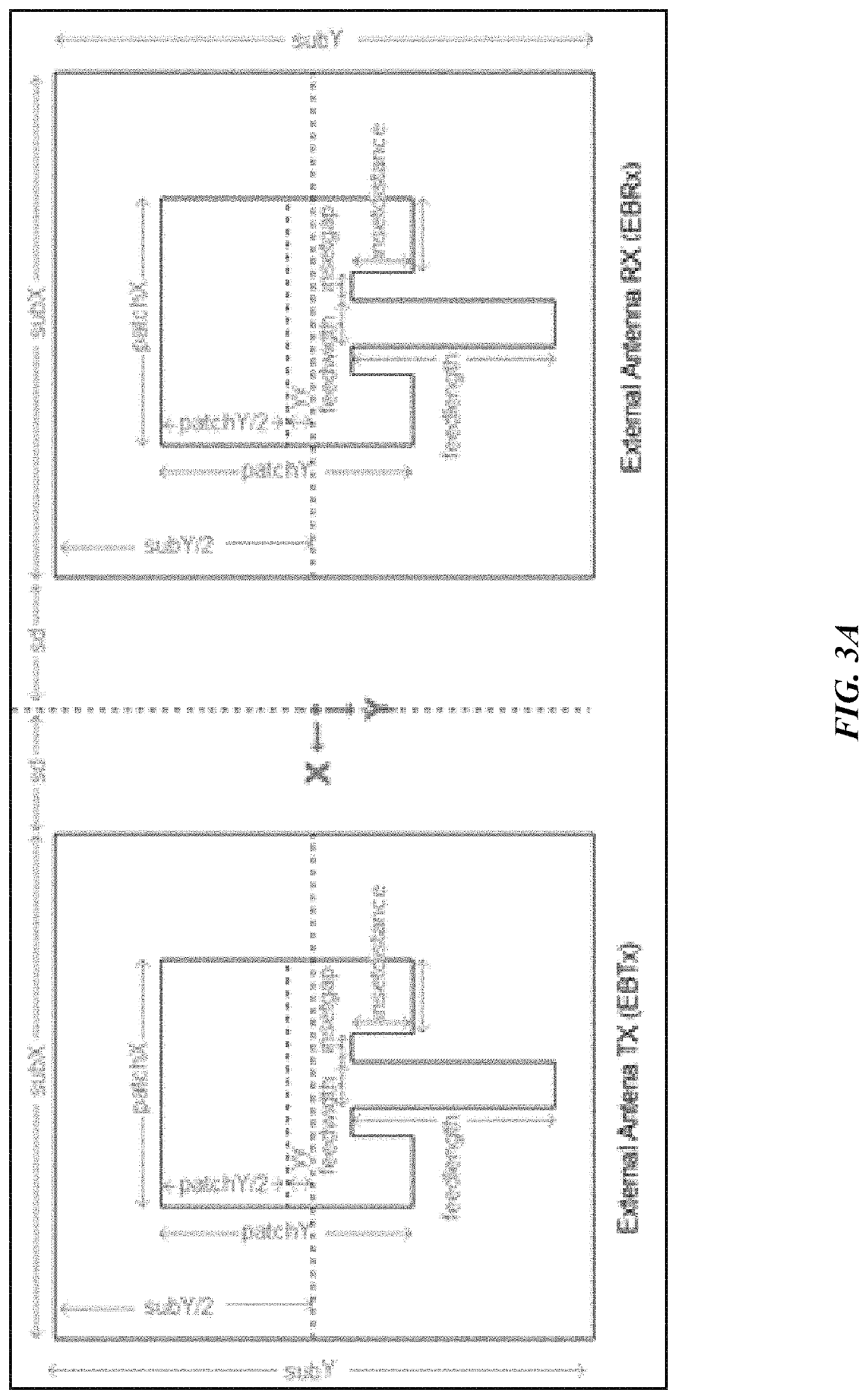
Continuous glucose monitoring based on remote sensing of variations of parameters of a SiC implanted antenna
A passive sensing continuous glucose monitoring system and method of use thereof. The system includes a passive antenna formed of biocompatible silicon carbide (SiC), modeled to a desired frequency, which is permanently implanted subcutaneously. The system further includes an external-to-the-body transmitting antenna to detect changes in the blood glucose level by sending a radio signal at the frequency of the implanted passive antenna into the body. This signal is received and reflected by the passive antenna, and the reflected signal is then received at an external-to-the-body receiving antenna. Changes in the glucose level lead to modifications in the signal and can be used to determine the blood glucose level externally.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com