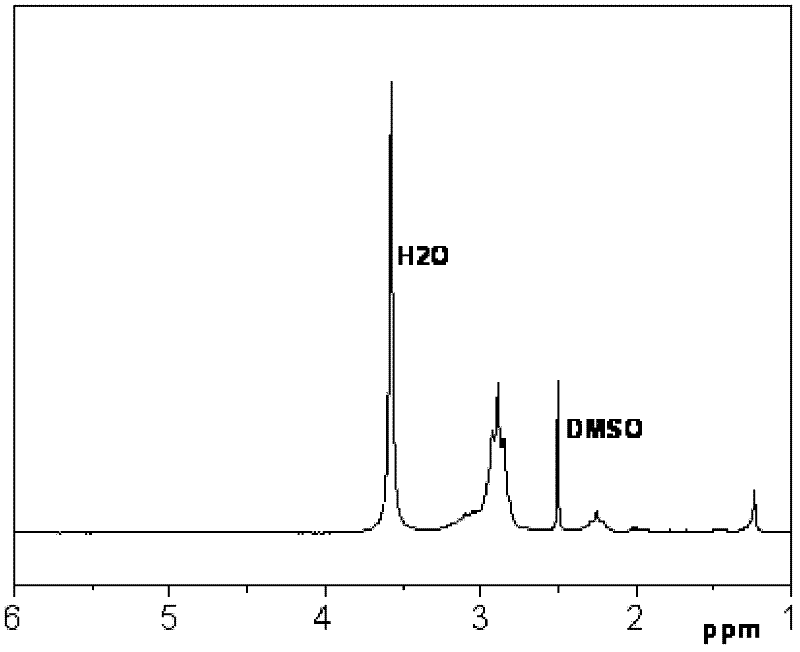
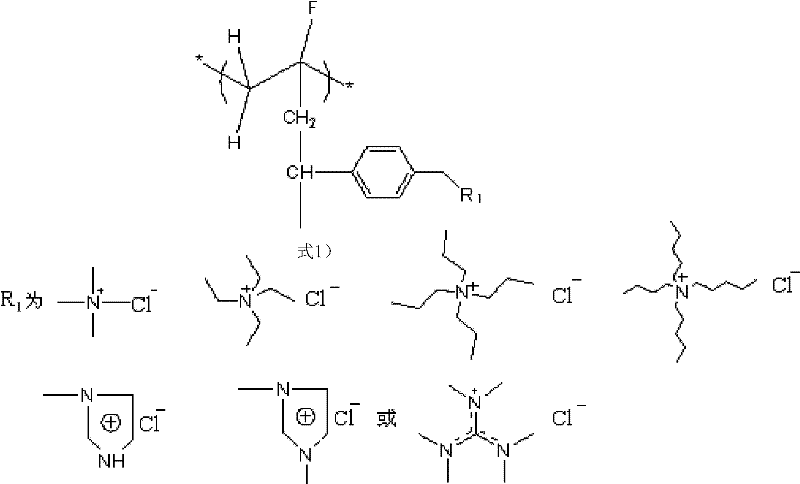
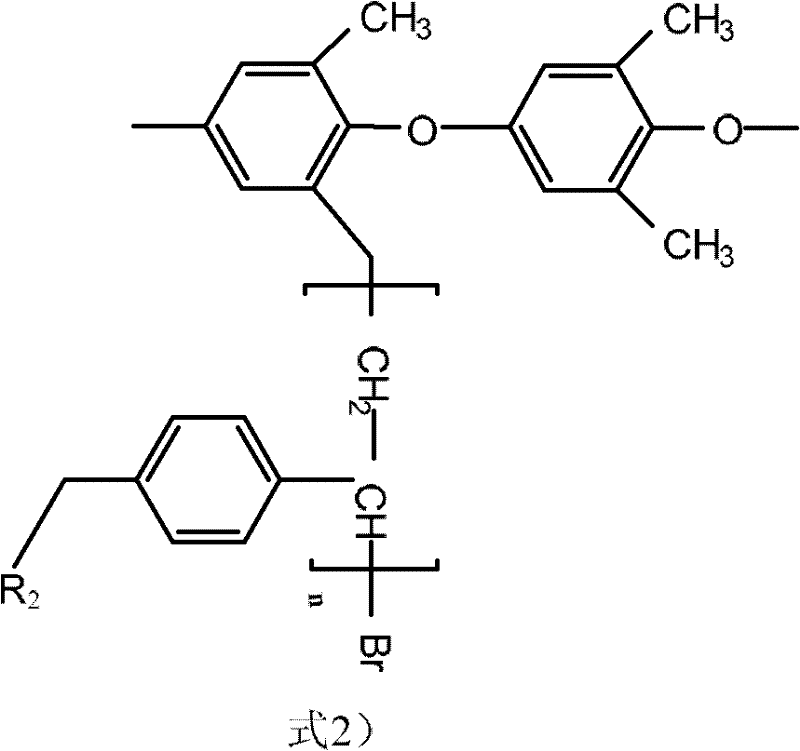
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
123results about How to "Facilitate phase separation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
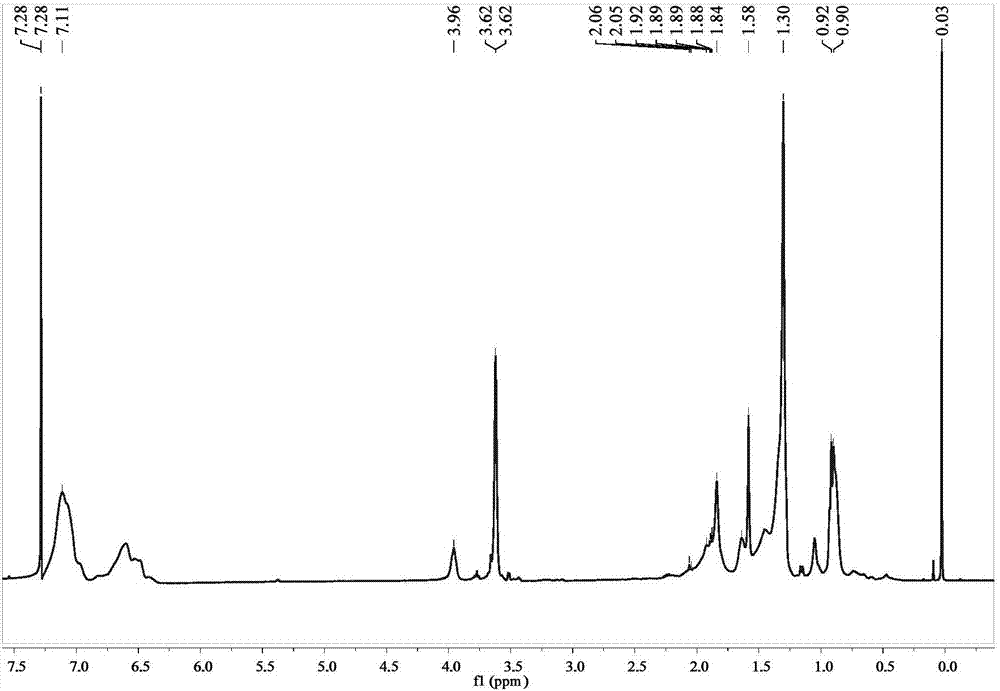
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS7208624B2Easy to separateFacilitate phase separationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionMethyl acetateFormate Esters
An improved process is disclosed for producing acetic acid, including the following steps: reacting a carbonylatable reactant such as methanol, methyl acetate, methyl formate or dimethyl ether with carbon monoxide in a reaction medium containing water, methyl iodide, and a catalyst to produce a reaction product that contains acetic acid; separating the reaction product to provide a volatile phase containing acetic acid, water, and methyl iodide and a less volatile phase; distilling the volatile phase to produce a purified acetic acid product and a first overhead containing water, methyl acetate, and methyl iodide; phase separating the first overhead to provide a first liquid phase containing water and a second liquid phase containing methyl iodide; and adding dimethyl ether to the process in an amount effective to enhance separation of the first overhead to form the first and second liquid phases.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
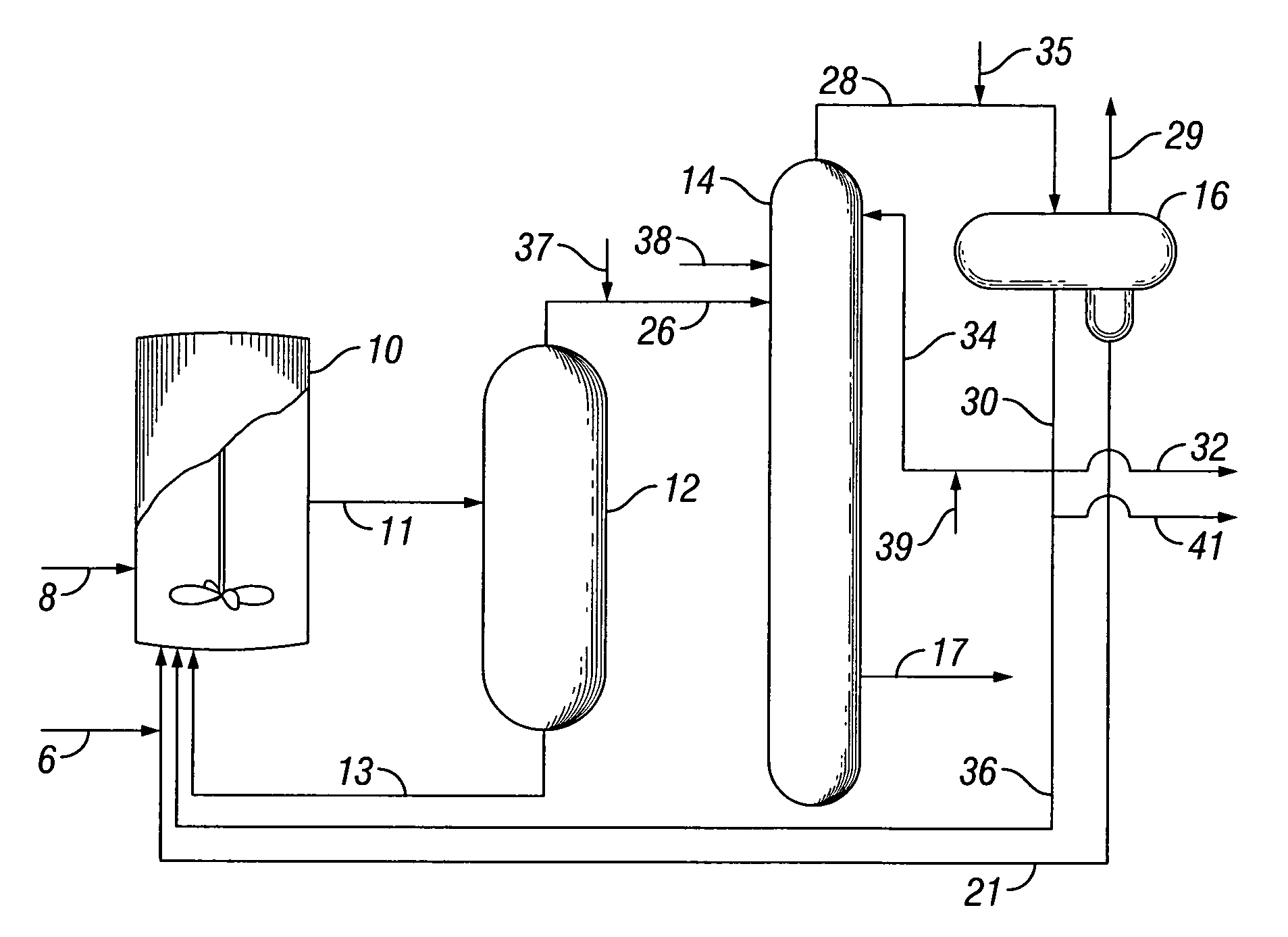
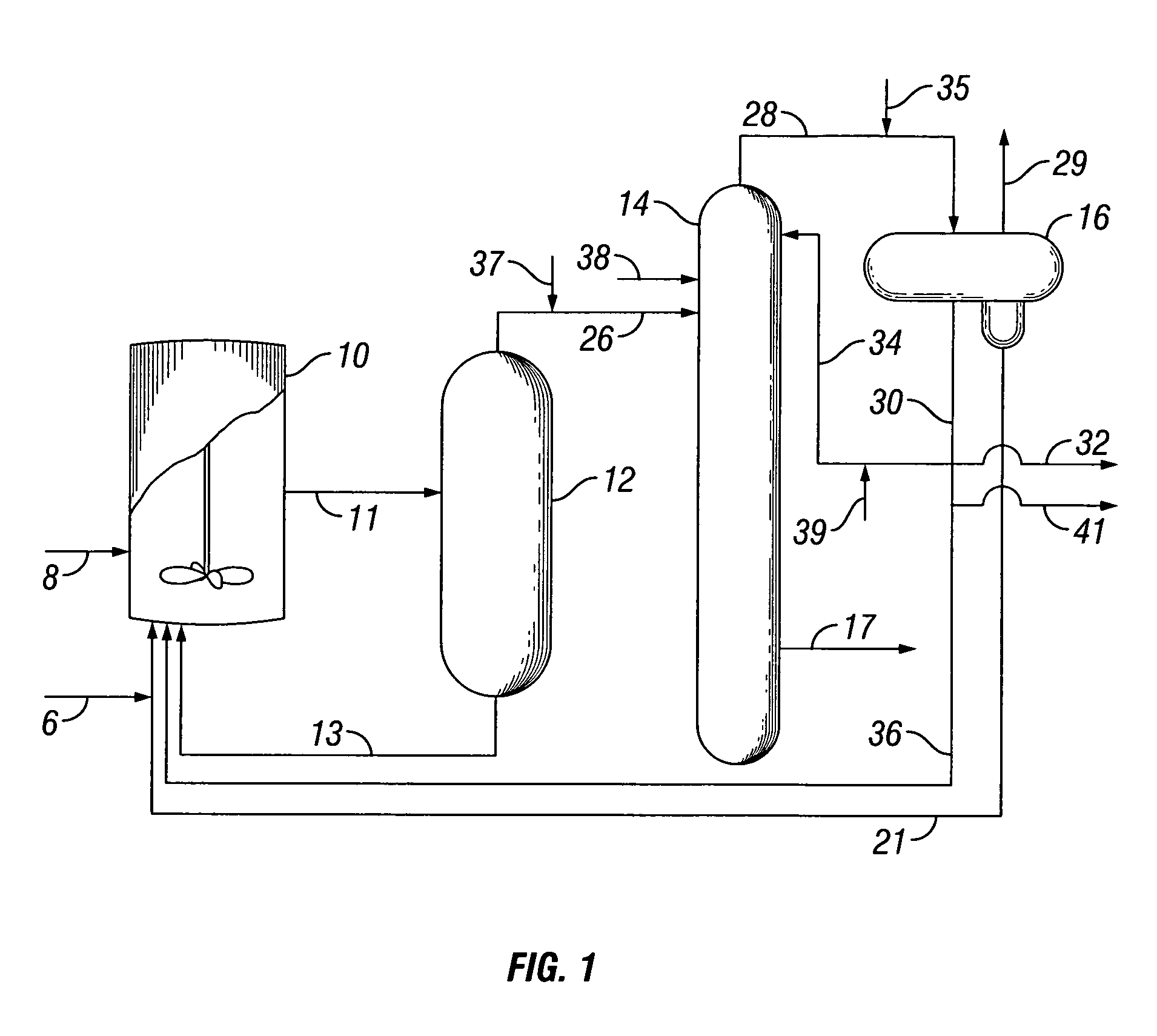
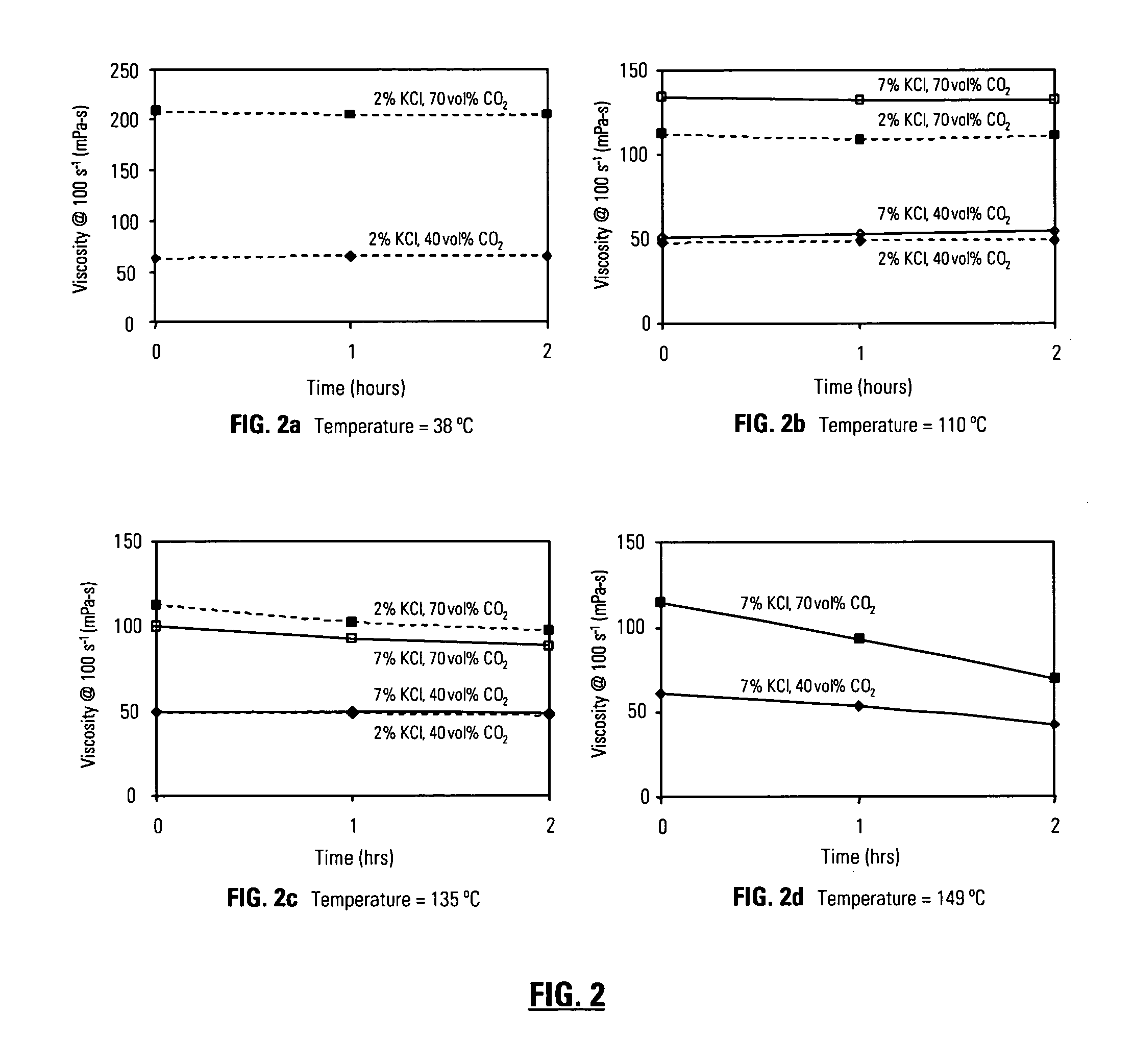
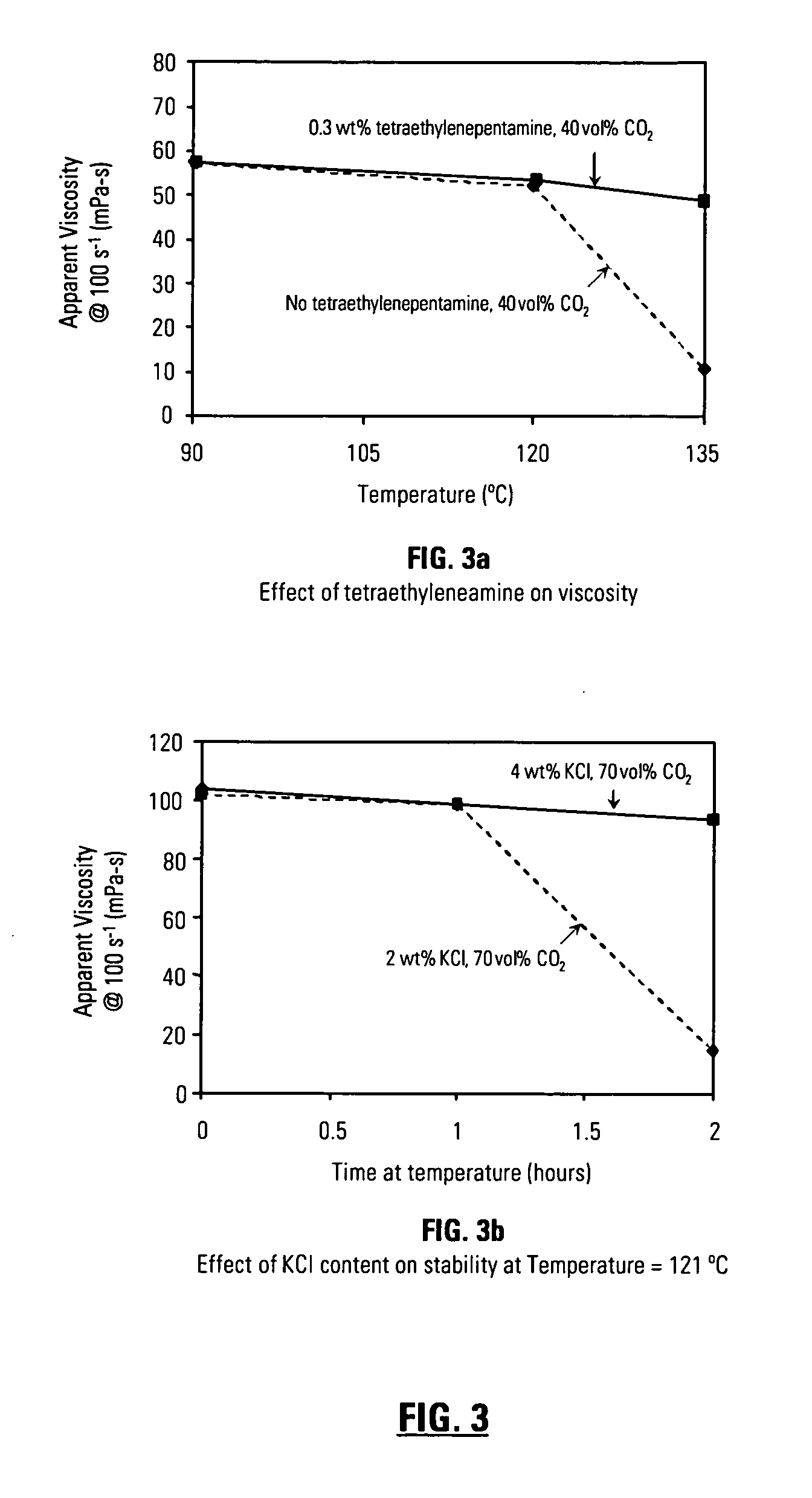
Methods of treating subterranean formations with heteropolysaccharides based fluids
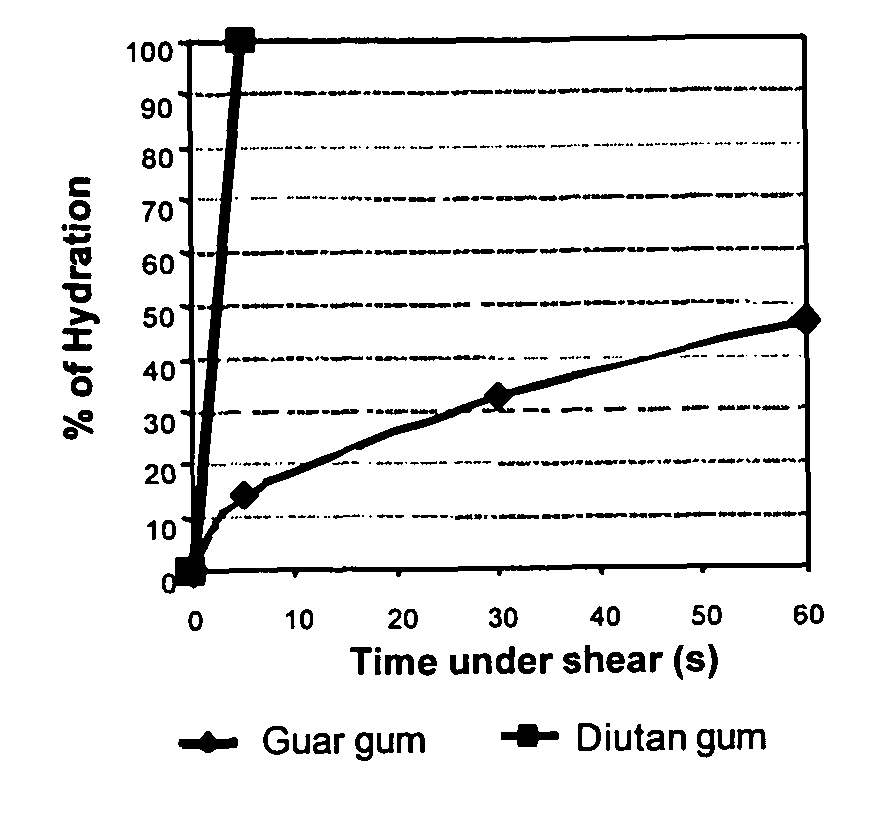
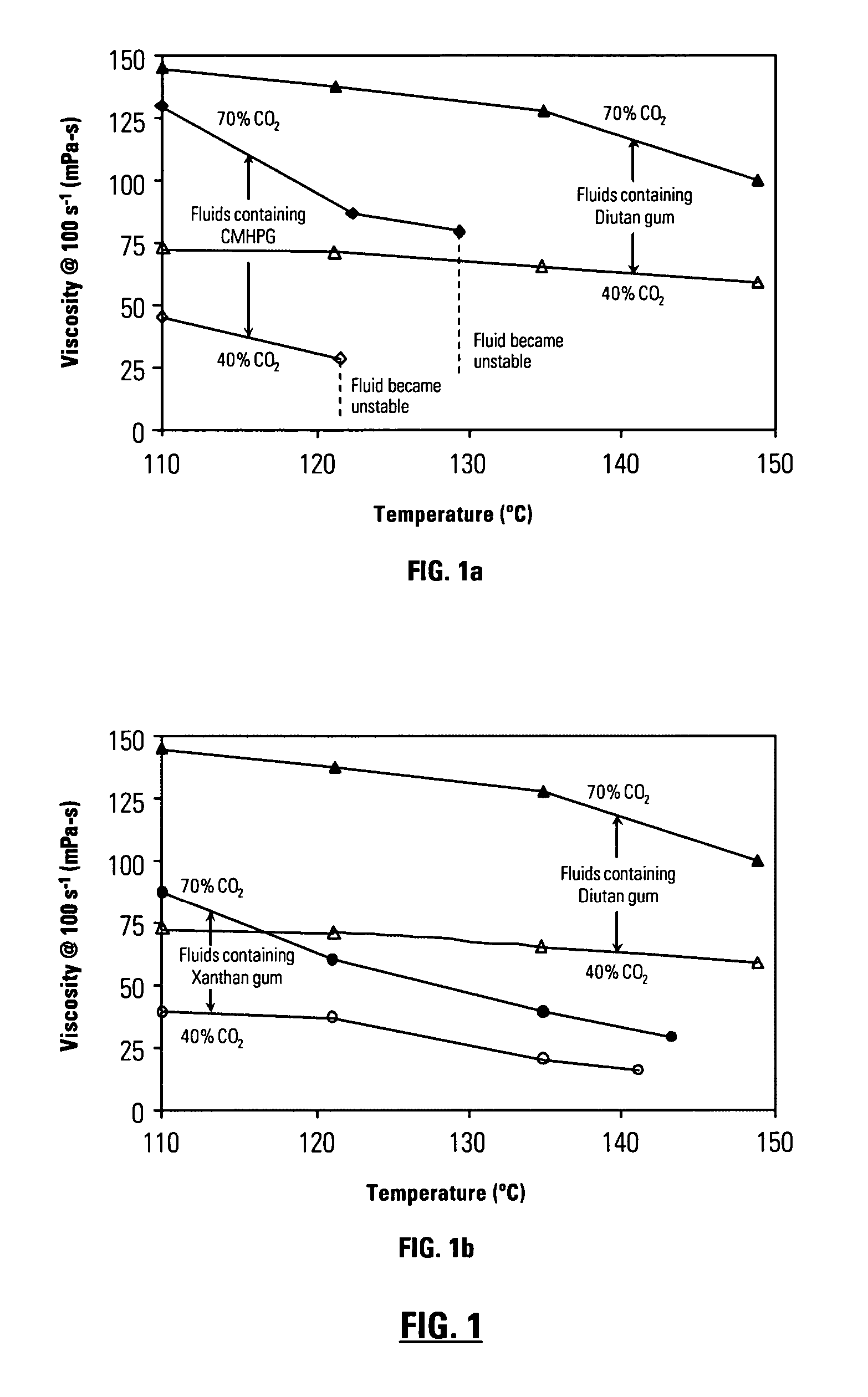
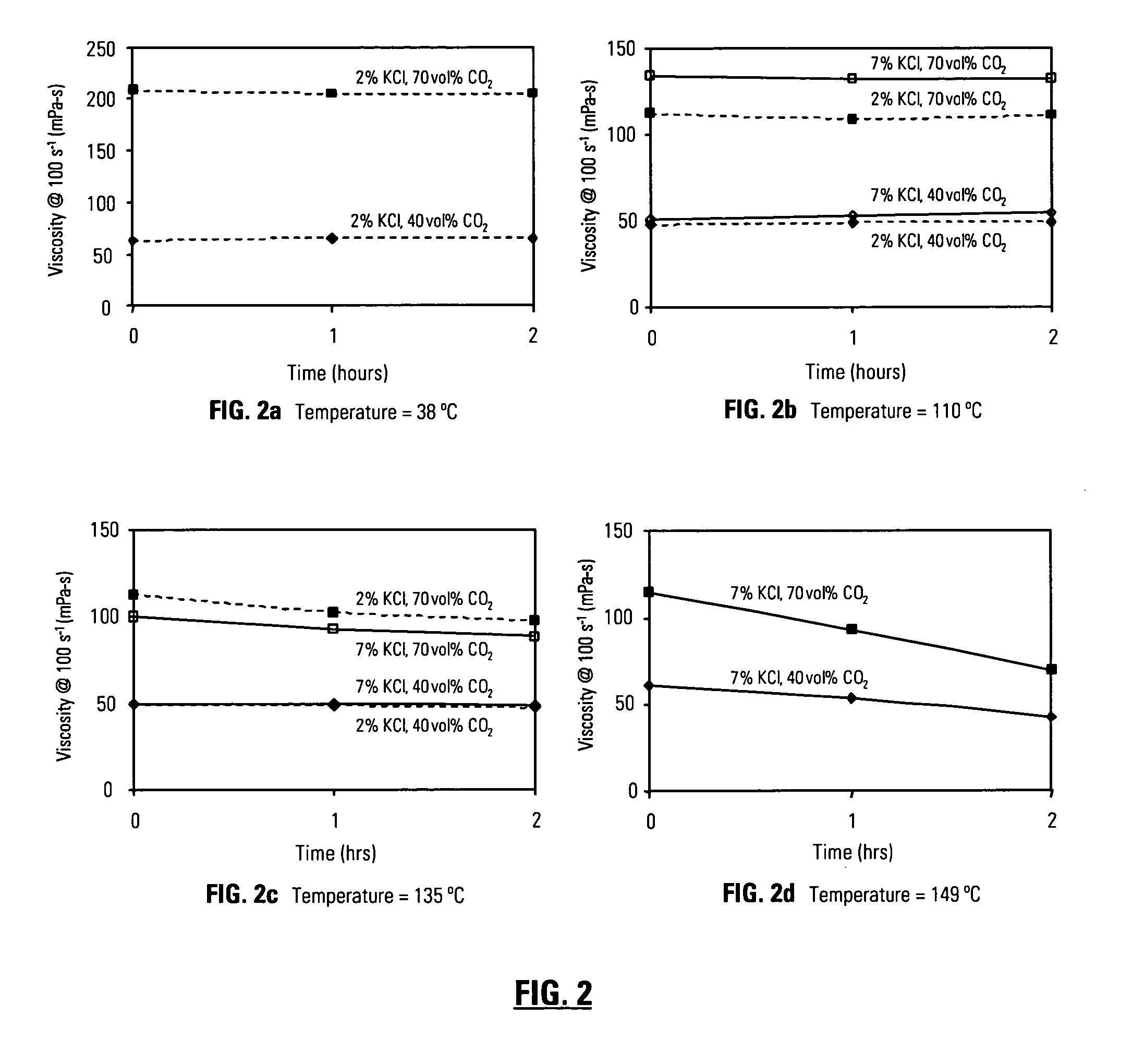
InactiveUS20060166837A1Rapidly hydratableAdequate rheologyCleaning apparatusFluid removalAqueous mediumSURFACTANT BLEND
Disclosed are methods of treating subterranean formations with rapidly hydratable treatment fluids based upon heteropolysaccharides. In particular, the invention relates to treatment methods with fluids containing a heteropolysaccharide, aqueous medium, and an electrolyte, wherein the fluids may further include a gas component, a surfactant and / or an organoamino compound. The fluids exhibit good rheological properties at elevated temperatures, and unusually rapid hydration rates which allows utilizing such fluids without the need of hydration tanks.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Membrane post treatment
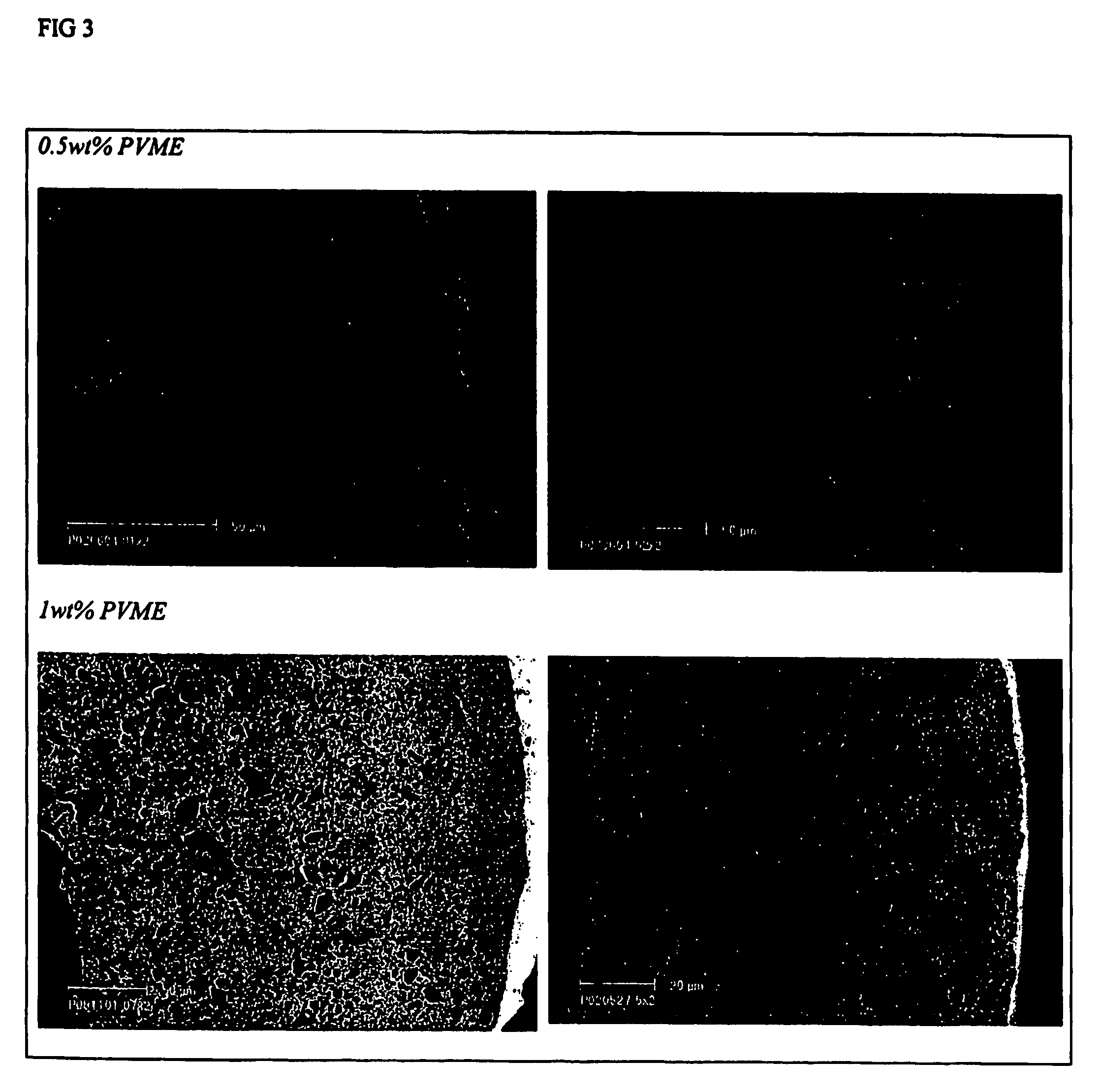
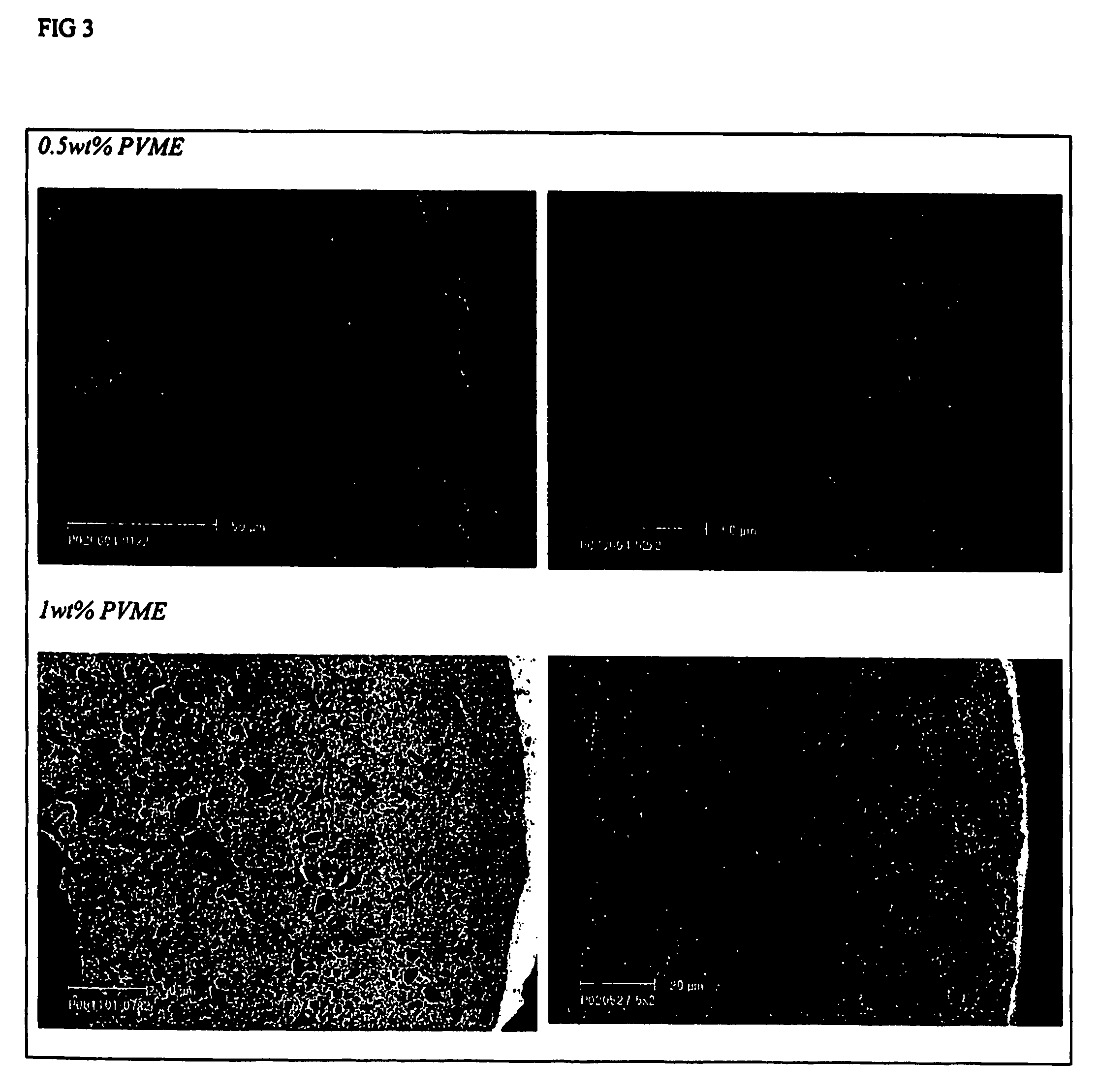
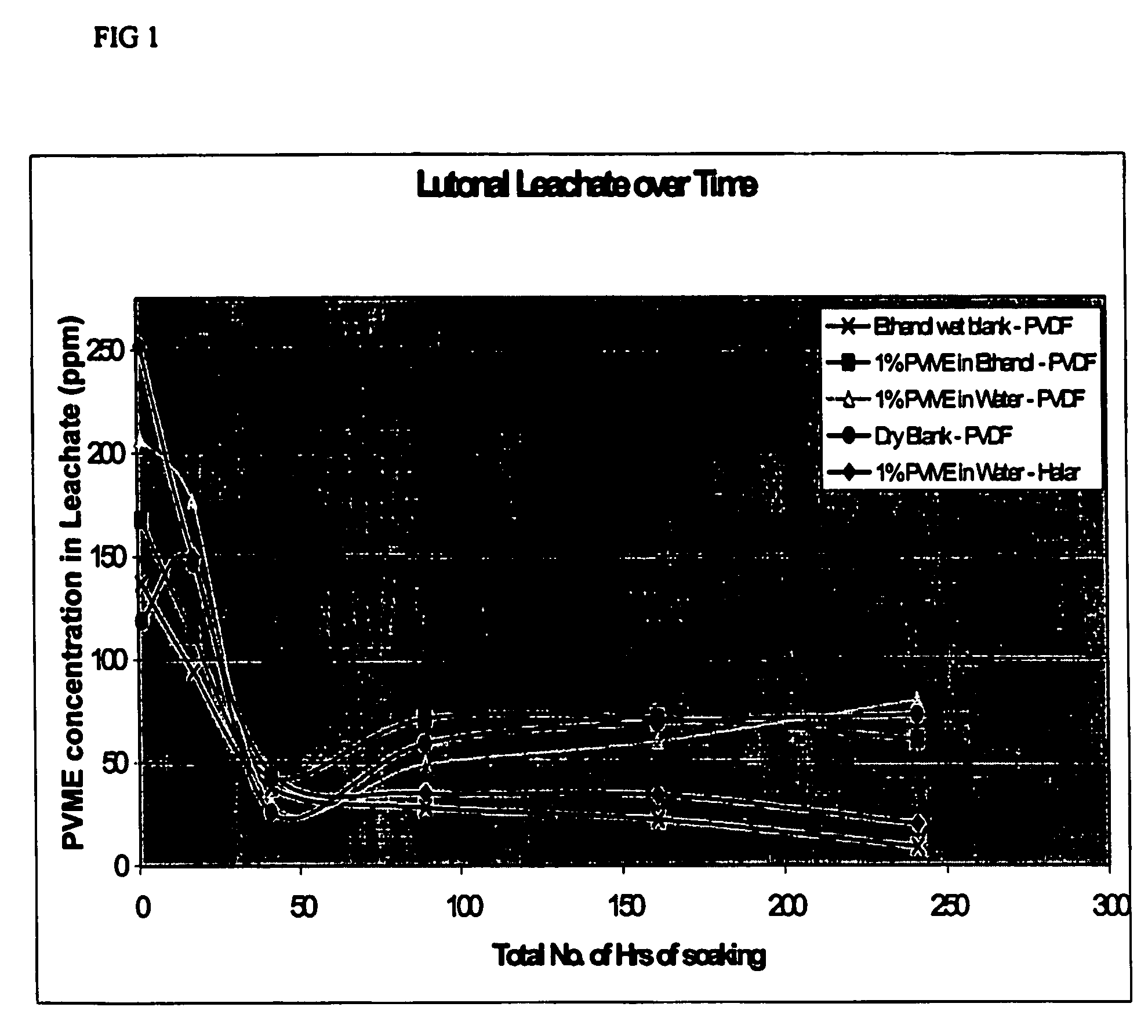
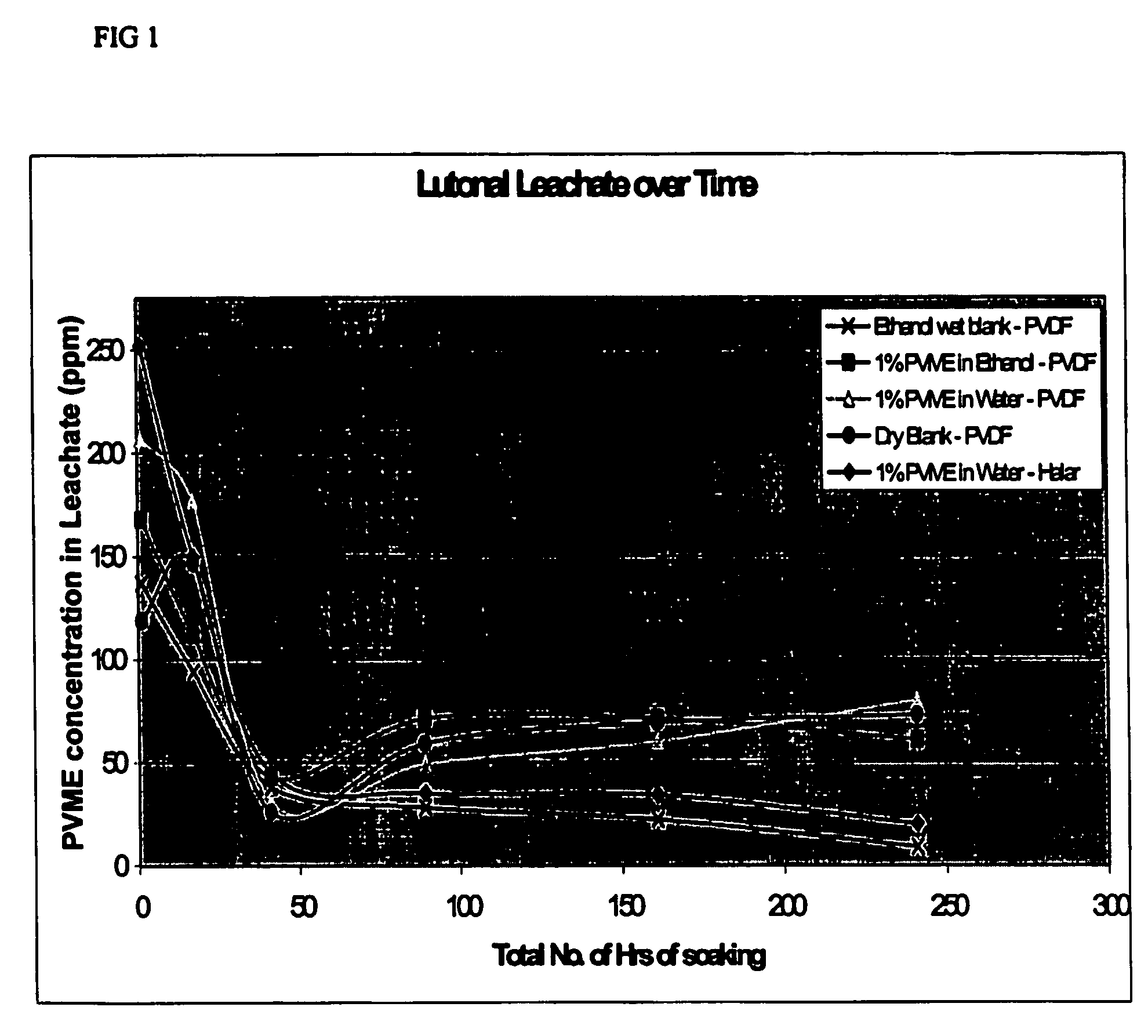
InactiveUS7662212B2Low toxicityReduce riskSolid sorbent liquid separationPretreated surfacesHydrophilizationMicrofiltration membrane
The invention relates to polymeric ultrafiltration or microfiltration membranes of, for instance, Halar, PVDF or PP, incorporating PVME or vinyl methyl ether monomers. The PVME may be present as a coating on the membrane or dispersed throughout the membrane or both. The membranes are preferably hydrophilic with a highly asymmetric structure with a reduced pore size and / or absence of macrovoids as a result of the addition of PVME. The PVME maybe cross-linked. The invention also relates to methods of hydrophilising membranes and / or preparing hydrophilic membranes via thermal or diffusion induced phase separation processed.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
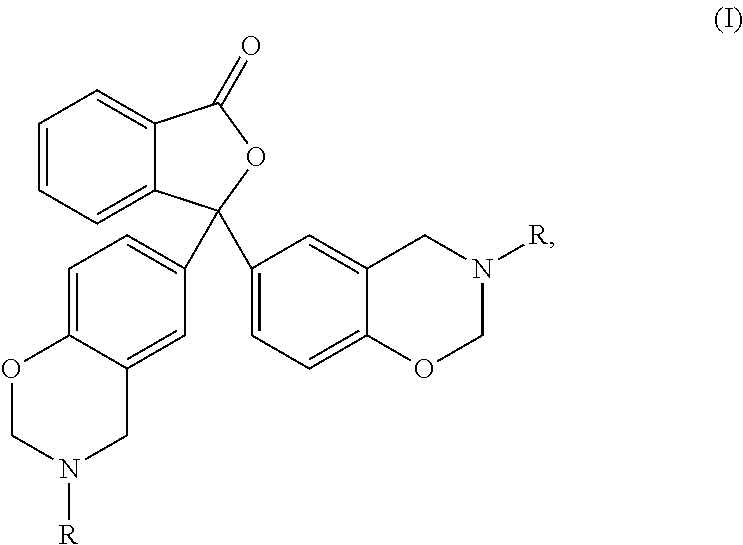
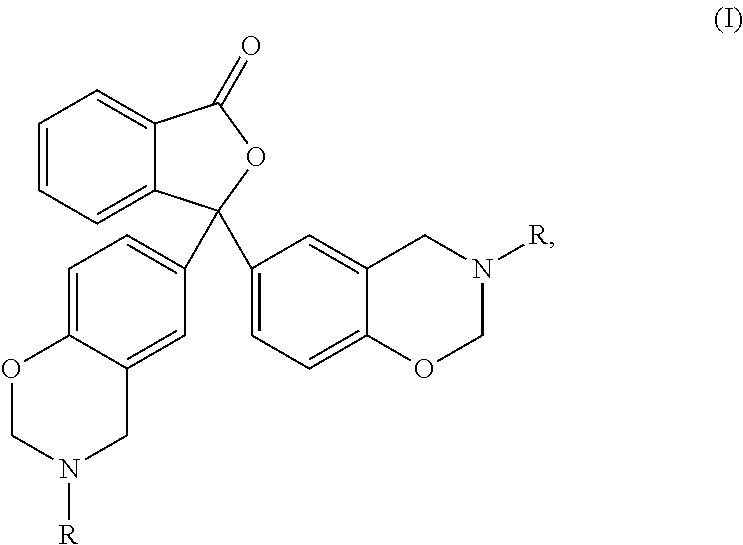
Processes for preparing of glucopyranosyl-substituted benzyl-benzene derivatives
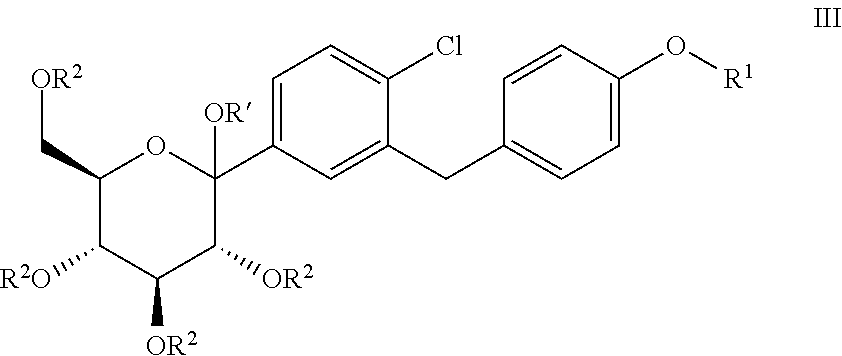
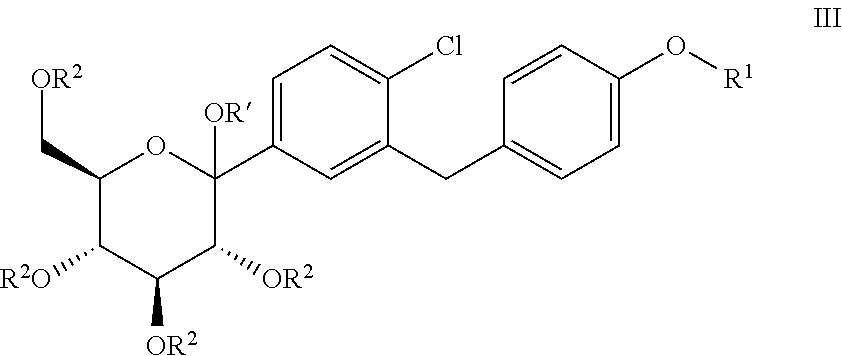
ActiveUS20110237789A1High yieldHigh puritySaccharide with carbocyclic radicalsSugar derivativesCombinatorial chemistryPerylene derivatives
The present invention relates to processes for preparing a glucopyranosyl-substituted benzyl-benzene derivative of general formula III,wherein R1 is defined according to claim 1.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
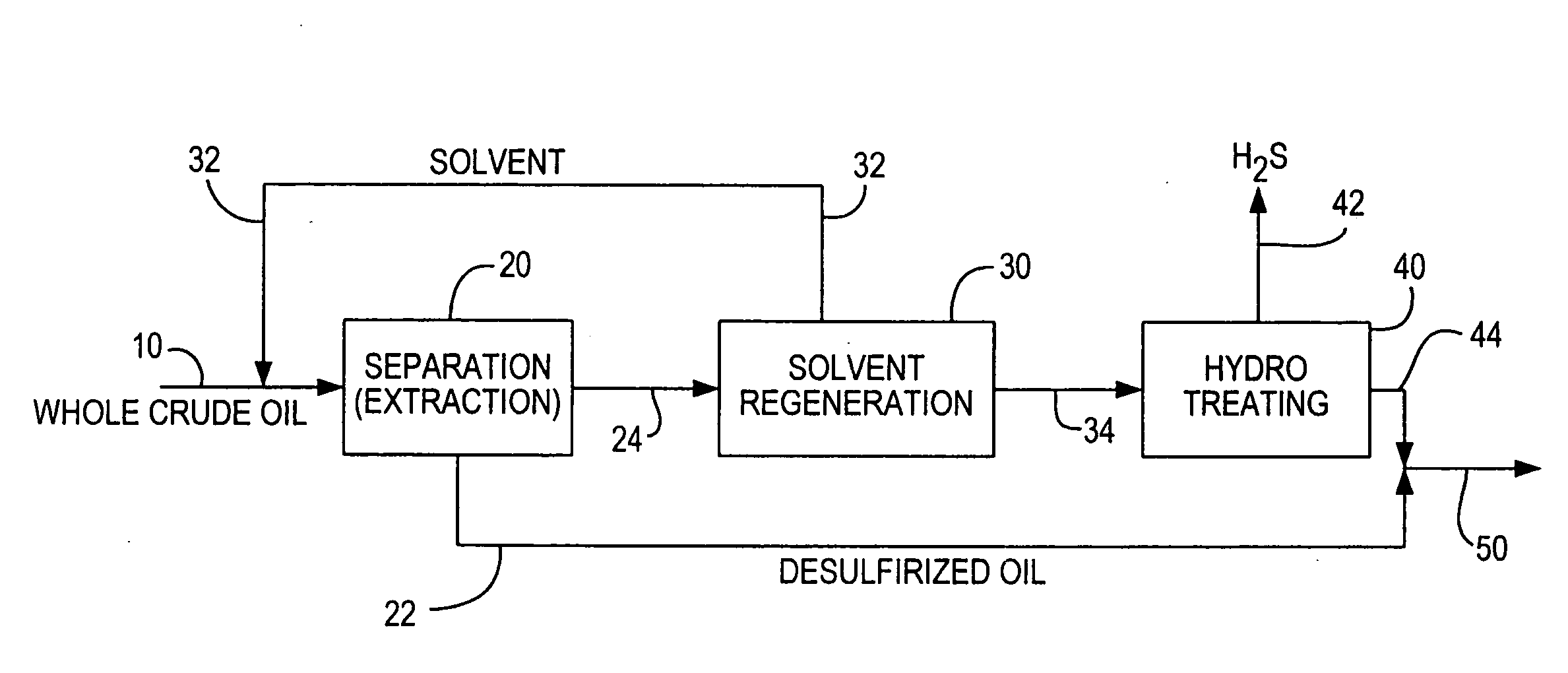
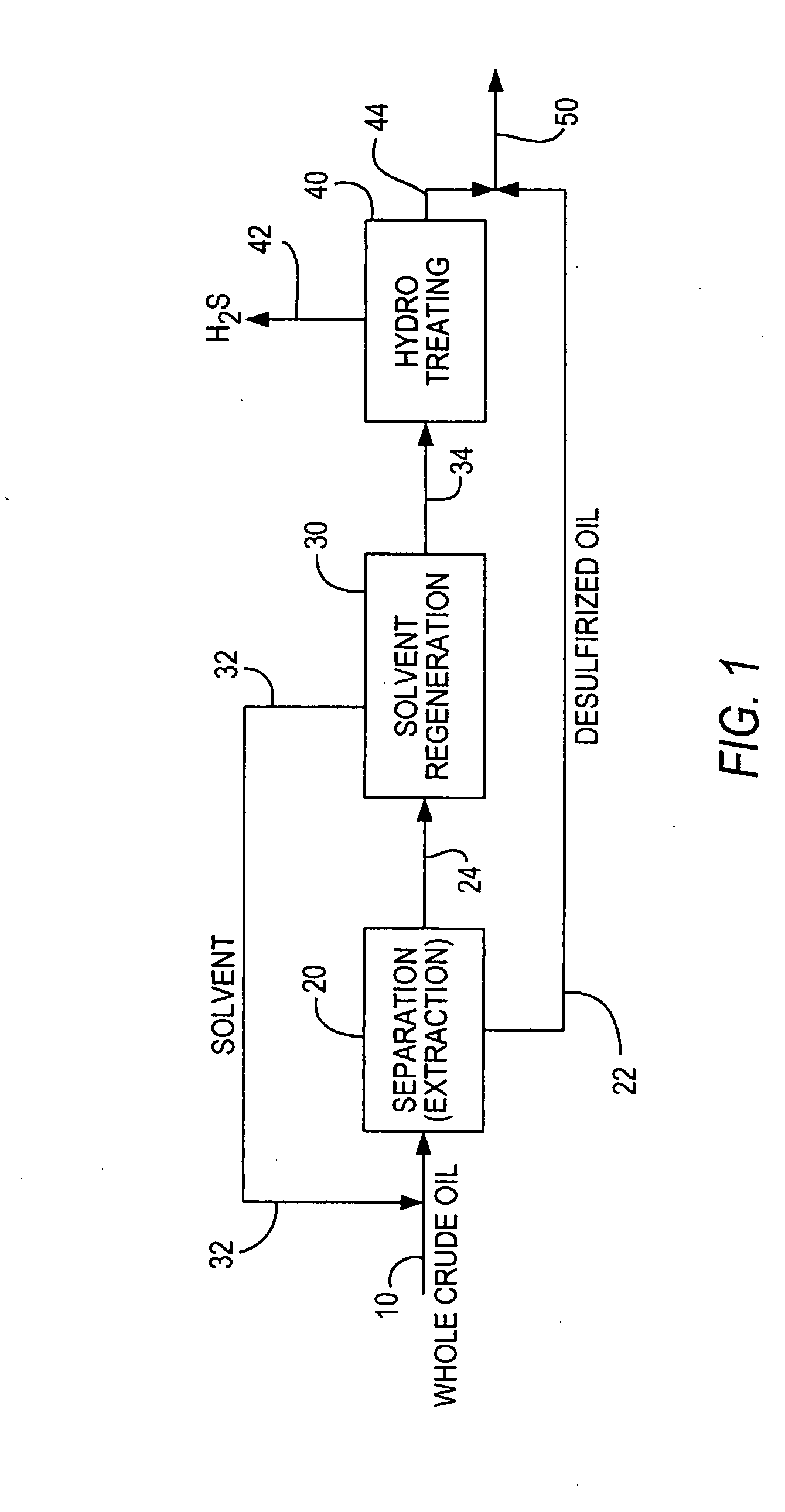
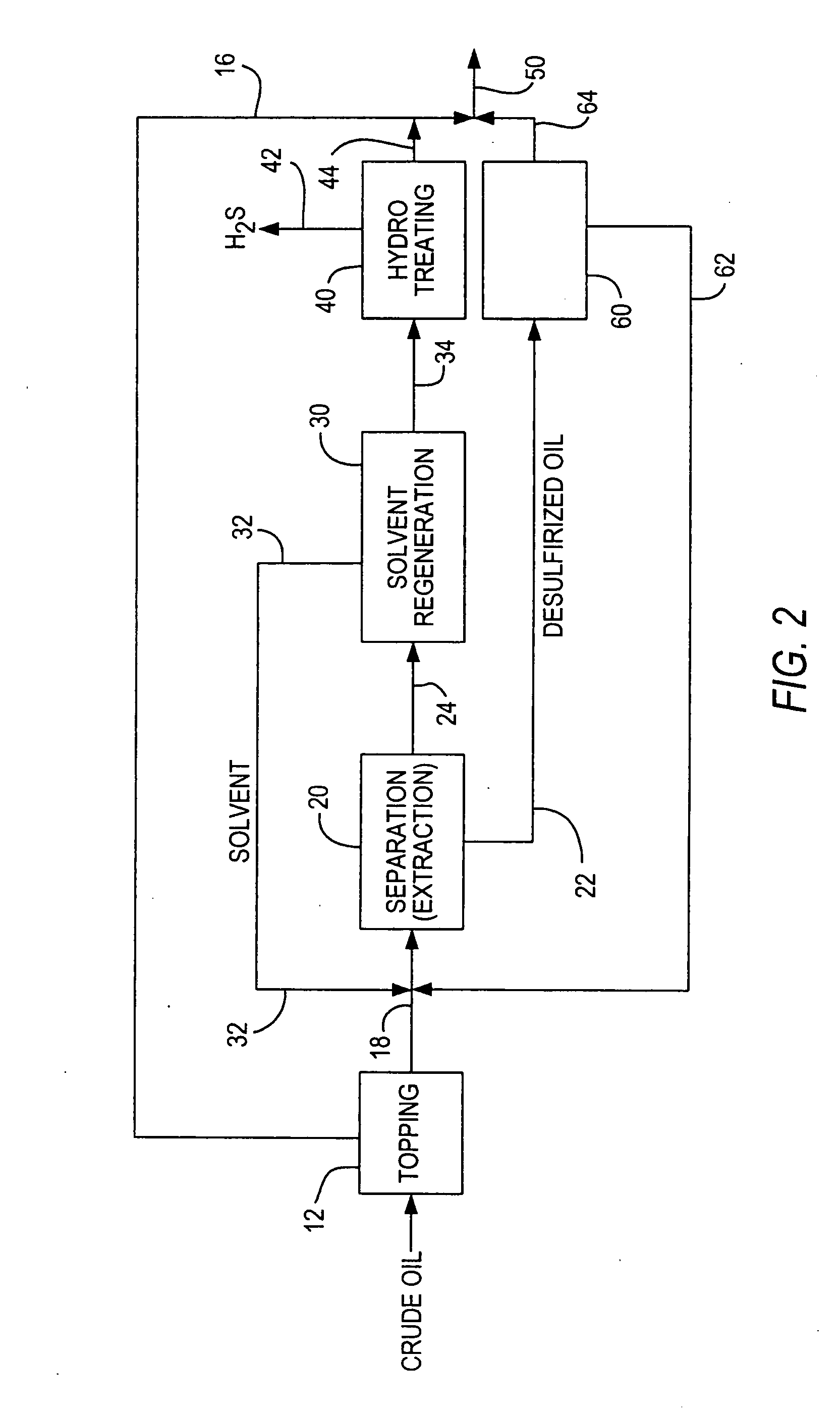
Desulfurization of whole crude oil by solvent extraction and hydrotreating
ActiveUS20090107890A1Eliminate and linimize needReduce and break emulsionTreatment with hydrotreatment processesHydrocarbon oils refiningSolventSulfur containing
A high sulfur content crude oil feedstream is treated by mixing one or more selected solvents with a sulfur-containing crude oil feedstream for a predetermined period of time, allowing the mixture to separate and form a sulfur-rich solvent-containing liquid phase and a crude oil phase of substantially lowered sulfur content, withdrawing the sulfur-rich stream and regenerating the solvent, hydrotreating the remaining sulfur-rich stream to remove or substantially reduce the sulfur-containing compounds to provide a hydrotreated low sulfur content stream, and mixing the hydrotreated stream with the separated crude oil phase to thereby provide a treated crude oil product stream of substantially reduced sulfur content and without significant volume loss.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Method For Manufacturing Separator, Separator Manufactured By The Method And Method For Manufacturing Electrochemical Device Including The Separator
ActiveUS20120115036A1Enhances bindabilityFacilitating laminationCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersFinal product manufacturePolymer dissolutionPorous substrate
Disclosed is a method for manufacturing a separator. The method includes (S1) preparing a porous planar substrate having a plurality of pores, (S2) preparing a slurry containing inorganic particles dispersed therein and a polymer solution including a first binder polymer and a second binder polymer in a solvent, and coating the slurry on at least one surface of the porous substrate, (S3) spraying a non-solvent incapable of dissolving the second binder polymer on the slurry, and (S4) simultaneously removing the solvent and the non-solvent by drying. According to the method, a separator with good bindability to electrodes can be manufactured in an easy manner. In addition, problems associated with the separation of inorganic particles in the course of manufacturing an electrochemical device can be avoided.
Owner:TORAY BATTERY SEPARATOR FILM +1
Membrane post treatment
InactiveUS20060157404A1Low toxicityReduce riskSolid sorbent liquid separationPretreated surfacesCross-linkPhase separation process
The invention relates to polymeric ultrafiltration or microfiltration membranes of, for instance, Halar, PVDF or PP, incorporating PVME or vinyl methyl ether monomers. The PVME may be present as a coating on the membrane or dispersed throughout the membrane or both. The membranes are preferably hydrophilic with a highly asymmetric structure with a reduced pore size and / or absence of macrovoids as a result of the addition of PVME. The PVME maybe cross-linked. The invention also relates to methods of hydrophilising membranes and / or preparing hydrophilic membranes via thermal or diffusion induced phase separation processed.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Porous molecularly imprinted polymer membranes
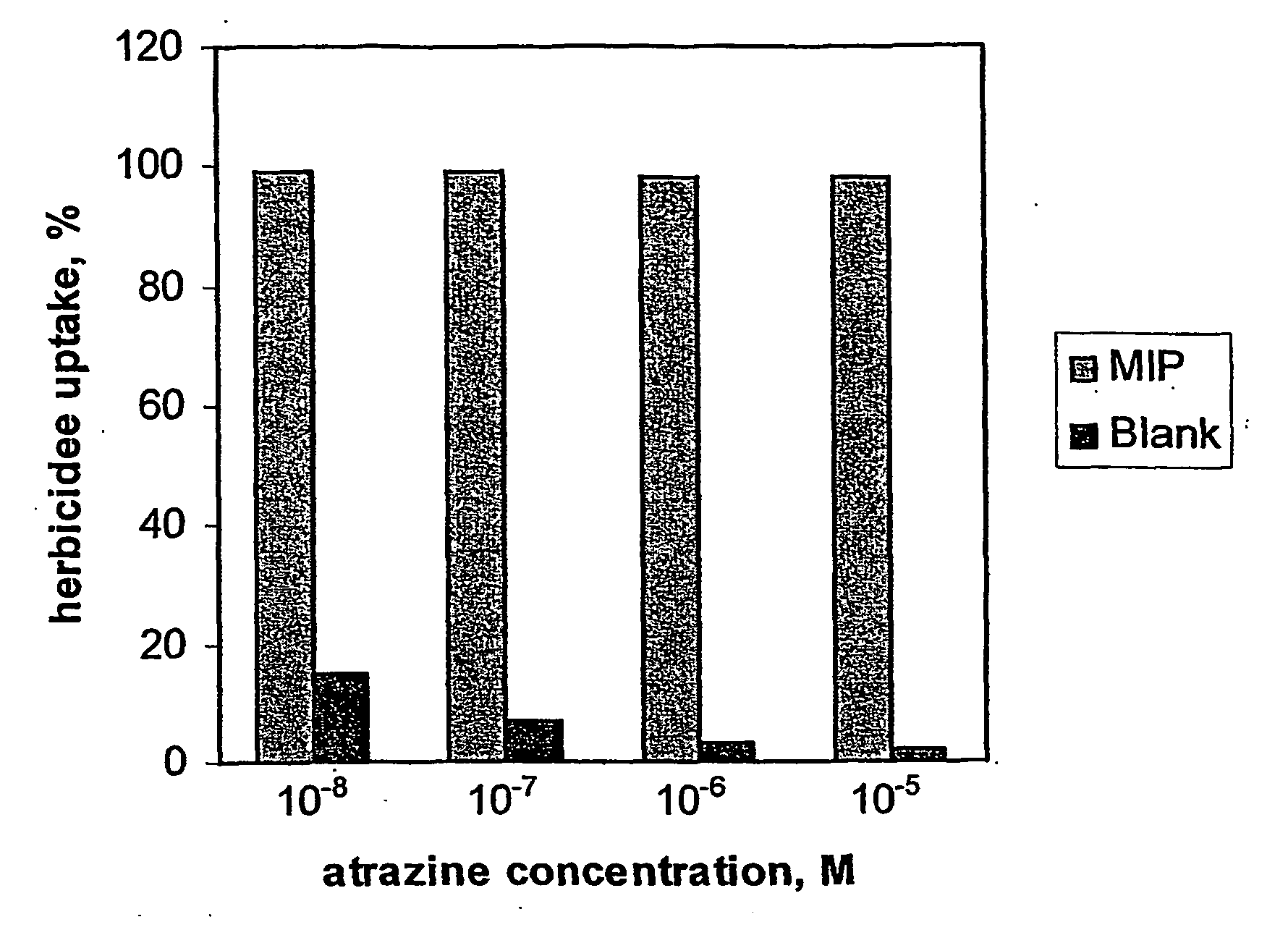
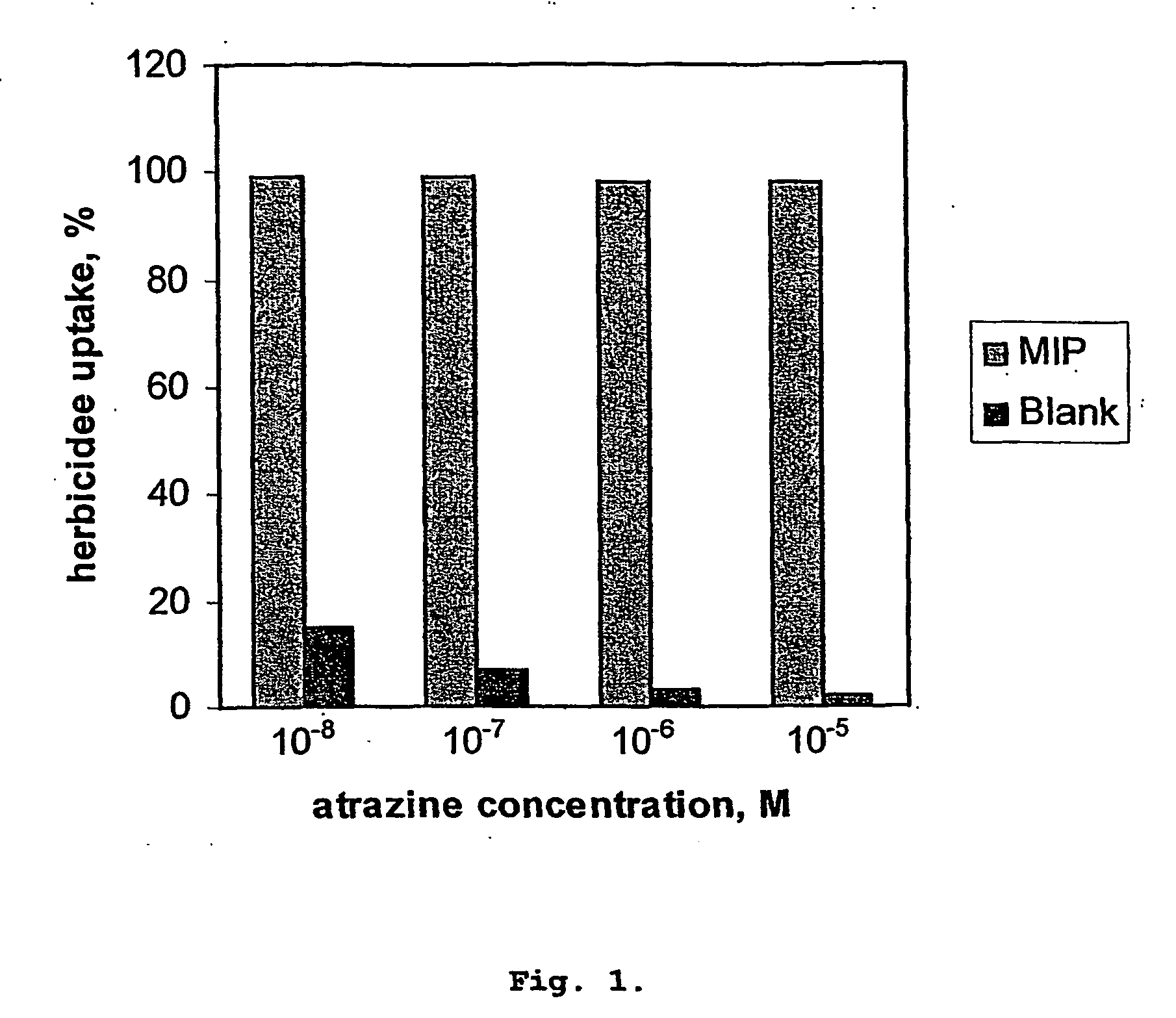
InactiveUS20060102556A1Facilitate phase separationIncrease levelMembranesSemi-permeable membranesFunctional monomerChemistry
Highly porous substance-selective polymeric membranes are produced by co-polymerisation of functional monomers and cross-linker in the presence of template, plasticiser (non-extractable component), and pore-forming component (extractable component). Extraction of the template and porogen molecules leads to the formation of small (<100 nm) and large (>500 nm) pores, including small pores having a shape and arrangement of functional groups complementary to the template molecule. The membranes possess enhanced affinity towards the template and its analogues and also have high flexibility and porosity. Such membranes can be used in analytical chemistry (as sensor elements and for solid-phase extraction materials) for applications in pharmacology, medicine, the food industry, water purification and environmental clean up.
Owner:CRANFIELD UNIVERSITY
Method For Manufacturing Separator, Separator Manufactured By The Method And Method For Manufacturing Electrochemical Device Including The Separator
ActiveUS20120090758A1Facilitate laminationEnhance bindabilityFinal product manufactureLaminationPolymer dissolutionPlanar substrate
Disclosed is a method for manufacturing a separator. The method includes (S1) preparing a porous planar substrate having a plurality of pores, (S2) preparing a slurry containing inorganic particles dispersed therein and a polymer solution including a first binder polymer and a second binder polymer in a solvent, and sequentially coating the slurry on the porous substrate through a first discharge hole and a non-solvent incapable of dissolving the second binder polymer on the slurry through a second discharge hole adjacent to the first discharge hole, and (S3) simultaneously removing the solvent and the non-solvent by drying. According to the method, a separator with good bindability to electrodes can be manufactured in an easy manner. In addition, problems associated with the separation of inorganic particles in the course of manufacturing an electrochemical device can be avoided.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD +1
Styrene-butadiene copolymer as well as preparation and applications thereof
ActiveCN103030756AImprove physical and mechanical propertiesHigh glossButadiene-styrene rubberPolystyrene
The invention relates to a styrene-butadiene copolymer as well as a preparation method and applications thereof. The styrene-butadiene copolymer is obtained by regulating an arrangement mode of a polystyrene chain segment and a polybutadiene chain segment, wherein the polybutadiene chain segment can freely move. The copolymer is mainly used for preparing high-gloss and high-impact-resistance polystyrene. According to the styrene-butadiene copolymer provided by the invention, the viscosity of 5 % styrene solution of the styrene-butadiene copolymer is low, the styrene-butadiene copolymer exists in a polystyrene polymer molecular chain mainly in a block mode when being added into the polystyrene, can also freely flow in the polystyrene, can be used for improving the physical and mechanical properties of the polystyrene and is particularly used for keeping high gloss of the polystyrene when the properties are impacted.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Homogeneous anion exchange membrane and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a method for preparing a homogeneous anion exchange membrane. In the method, a graft high polymer is synthesized by an atom transfer radical polymerization process, wherein the hydrophobic-main-chain and hydrophilic-side-chain structure of the graft high polymer is favorable for the phase separation of hydrophilic groups from hydrophobic groups; meanwhile, the graft high polymer has an ion exchange group and can dissolve in a solvent to form a homogenous membrane casting liquid. In a membrane forming process, the phase separation caused by the coexistence of the hydrophilic groups and the hydrophobic groups in the graft high polymer leas to the formation of an ion transfer channel; therefore, the conductivity of the prepared homogeneous anion exchange membrane is high. In the invention, an alkaline functional monomer is also prepared by using an alkaline functional reagent and p-chloromethylstyrene as reaction raw materials, wherein the preparation process of the alkaline functional monomer is easy to control, the reaction conditions are mild, the need of using a large amount of alkaline functional reagent is obviated, and thus the waste of the alkaline functional reagent is avoided.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Acrylic organosilicone water-emulsion coating as well as preparation method and application for same
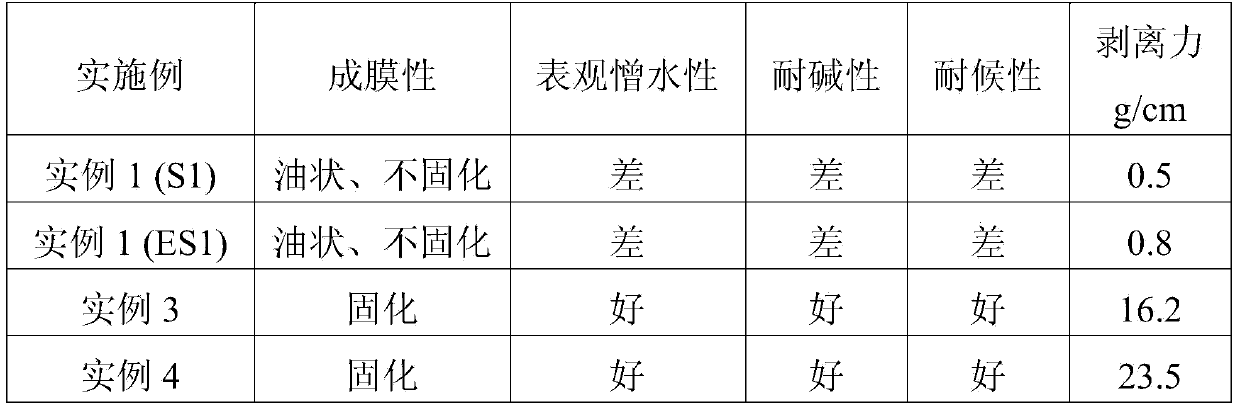
The invention belongs to the technical field of acrylic coatings, and discloses an acrylic organosilicone water-emulsion coating as well as a preparation method and an application for the same. The acrylic organosilicone water-emulsion coating comprises the following components in the following parts by weight: 100 parts of water, 0.1-4 parts of an emulsifier, 5-20 parts of liquid hydrogen-containing polymethyl siloxane, and 5-50 parts of acrylic polymers. The organosilicone content of the acrylic organosilicone water-emulsion coating disclosed by the invention is up to more than 10% in the polymers, organosilicone and the acrylic polymers are compounded in a wide range, and curing film-forming is performed at a room temperature. The preparation process disclosed by the invention is simple, and the obtained emulsion is good in stability; and after curing film-forming, the acrylic organosilicone water-emulsion coating is good in mechanical performance (wherein the hardness can be up to 3 H), excellent in waterproof and hydrophobic performances, acid-base resistance, weather resistance, and adhesive force (which can be up to 2.5 MPa), and proper in peel strength (which can be up to 23 g / cm).
Owner:GUANGZHOU CHEM CO LTD CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Photocurable compositions for preparing abs-like articles
ActiveUS20110293891A1Improve performanceMechanical property and thermal resistanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusOrganic chemistryPolyolRapid prototyping
The present invention provides a clear, low viscosity photocurable composition including (i) a cationically curable compound (ii) an acrylate-containing compound (iii) a polyol-containing mixture (iv) a cationic photoinitiator and (v) a free radical photoinitiator. The photocurable composition can be cured using rapid prototyping techniques to form opaque-white three-dimensional articles having ABS-like properties.
Owner:3D SYST INC
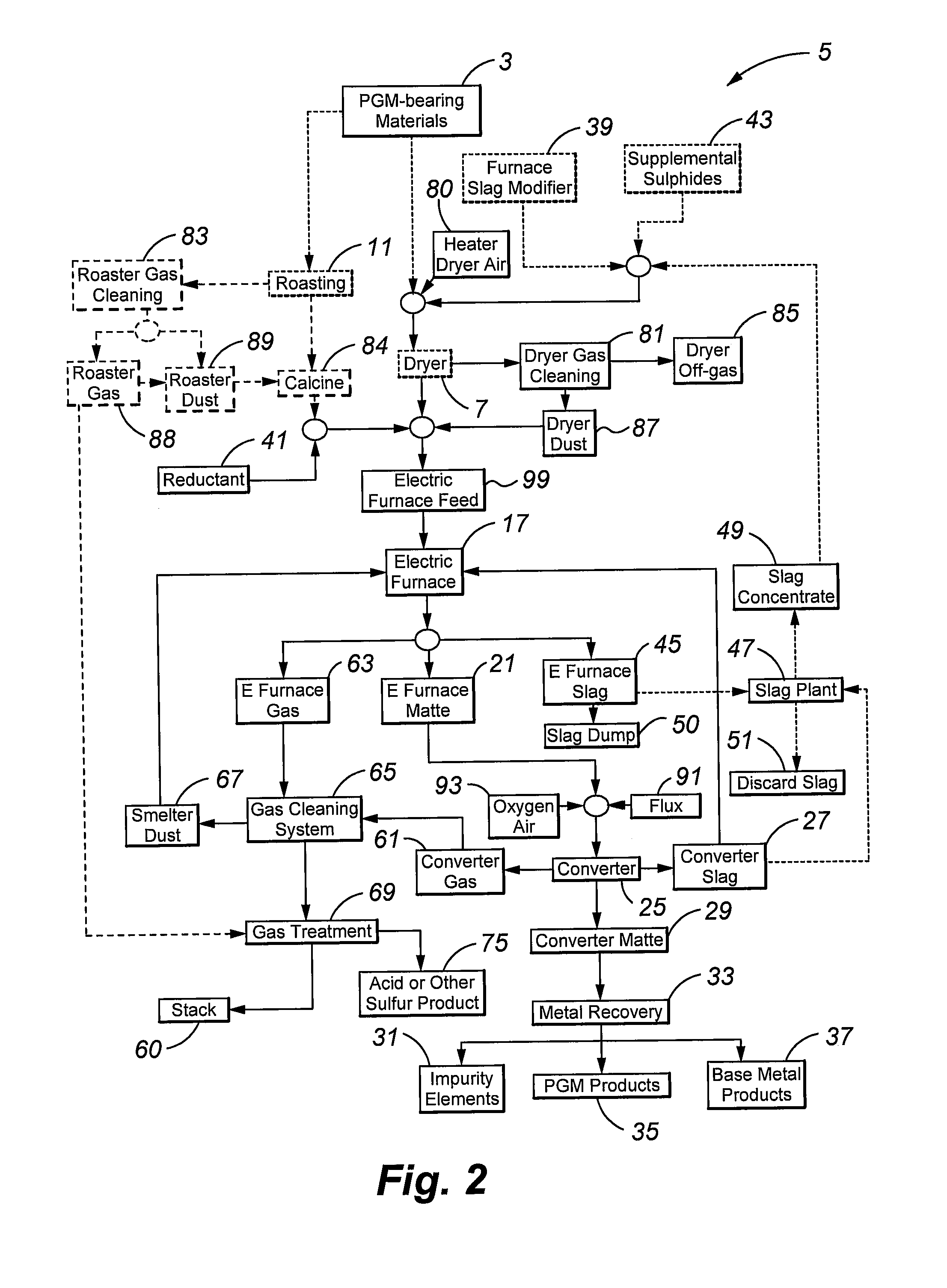
Process for recovering platinum group metals using reductants
InactiveUS20090071289A1Increases liquidus temperatureHigh melting temperatureProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceSulfurSlag
In the process of recovering platinum group metals from platinum group metal- and base metal-containing materials, the present invention uses reductants and a sulfur-deficient matte to aide the separation of the furnace matte from the furnace slag and therefore improve recovery of platinum group metals.
Owner:BARRICK GOLD
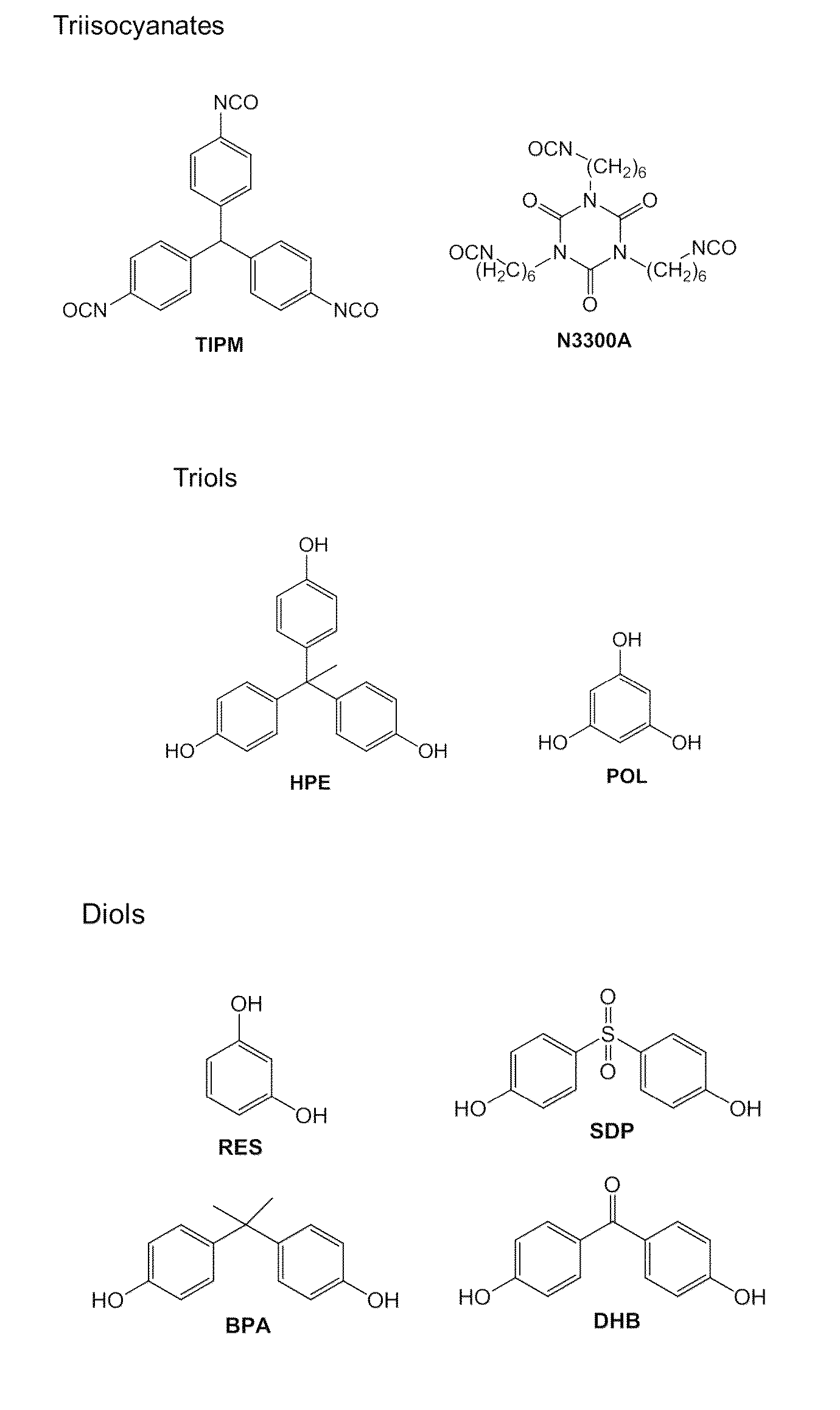
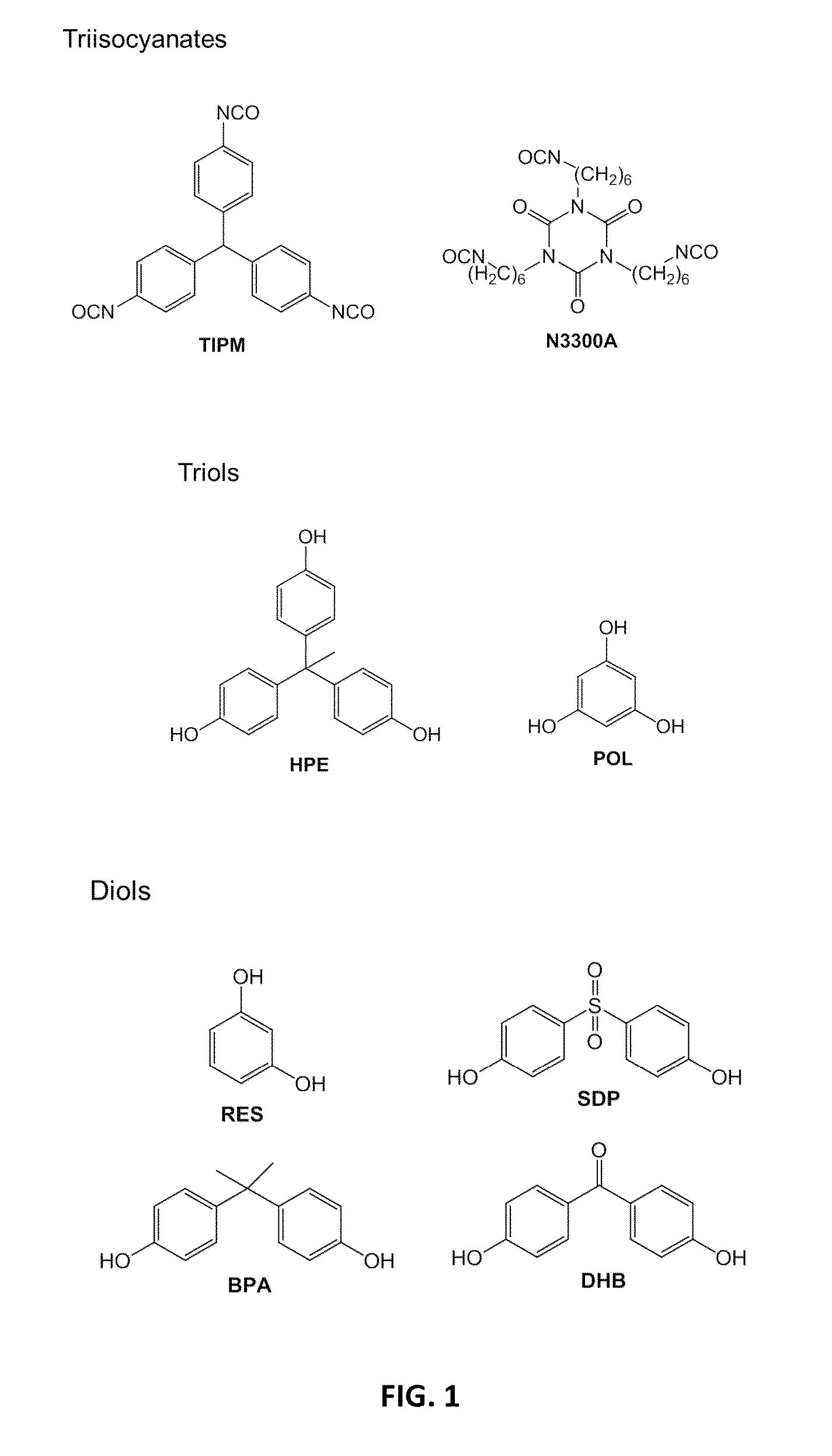
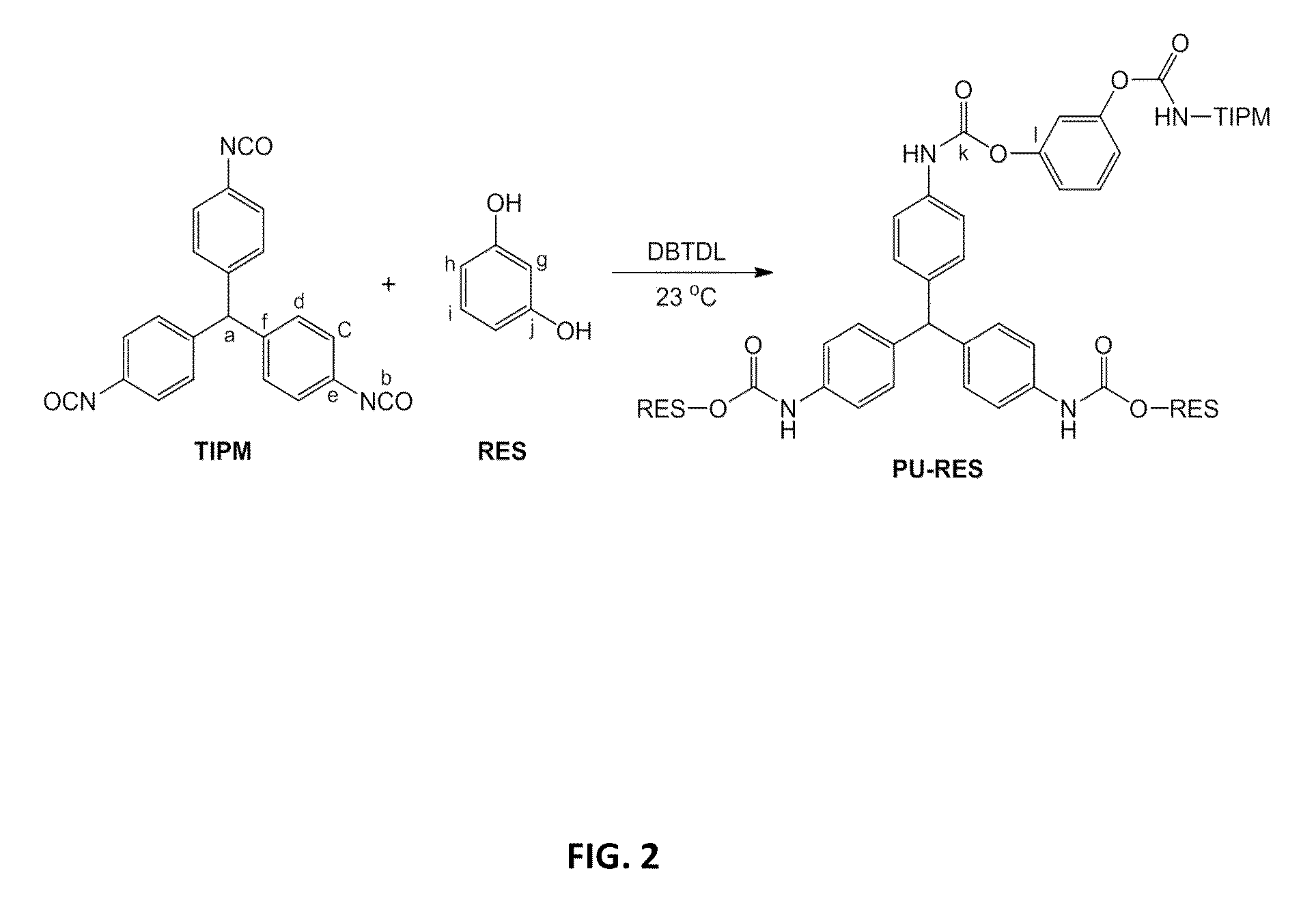
Porous polyurethane networks and methods of preparation
ActiveUS8927079B2Facilitate phase separationCarbon preparation/purificationGlass/slag layered productsPolyolSolvent
Nanoporous three-dimensional networks of polyurethane particles, e.g., polyurethane aerogels, and methods of preparation are presented herein. Such nanoporous networks may include polyurethane particles made up of linked polyisocyanate and polyol monomers. In some cases, greater than about 95% of the linkages between the polyisocyanate monomers and the polyol monomers are urethane linkages. To prepare such networks, a mixture including polyisocyanate monomers (e.g., diisocyanates, triisocyanates), polyol monomers (diols, triols), and a solvent is provided. The polyisocyanate and polyol monomers may be aliphatic or aromatic. A polyurethane catalyst is added to the mixture causing formation of linkages between the polyisocyanate monomers and the polyol monomers. Phase separation of particles from the reaction medium can be controlled to enable formation of polyurethane networks with desirable nanomorphologies, specific surface area, and mechanical properties. Various properties of such networks of polyurethane particles (e.g., strength, stiffness, flexibility, thermal conductivity) may be tailored depending on which monomers are provided in the reaction.
Owner:AEROGEL TECH
Method for extracting and separating molybdenum (VI) in aqueous solution
ActiveCN106591604AWide concentration rangeFast extraction rateProcess efficiency improvementPhase ratioSaline solutions
The invention discloses a method for extracting and separating molybdenum (VI) in an aqueous solution. The method is mainly characterized in that a non-ionic surface active agent, the molybdenum-containing aqueous solution, a saline solution and deionized water are mixed and stirred evenly, the concentration of the non-ionic surface active agent is 50-300 g / L, the concentration of molybdenum is 1-40 g / L, and the salt concentration is 50-300 g / L; the pH value is adjusted to 1-4, the mixture is subjected to still standing and phase separation after being stirred for 10-60 min at 25-80 DEG C, phase separation is conducted for 10-60 min, an aqueous two-phase system with the upper phase being a non-ionic surface active agent phase loading the molybdenum and the lower phase being an aqueous phase, and the concentration of the molybdenum in the non-ionic surface active agent phase loading the molybdenum is 2-80 g / L; the reextraction temperature is 25-80 DEG C, the time is 10-60 min, phase separation is conducted for 10-60 min, the phase ratio of the non-ionic surface active agent phase loading the molybdenum to an ammonium sulfate aqueous solution is 1 to 5, and the reextraction product is ammonium molybdate. According to the method, the extraction rate is high, good phase separation is achieved, the molybdenum extraction rate reaches 95% or above, and the molybdenum reextraction rate reaches 95% or above.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Photonic Bandgap Structures for Multispectral Imaging Devices
InactiveUS20140313342A1Facilitate phase separationHigh degree of polymerizationTelevision system detailsSpectrum investigationPhotonic bandgapPrism
The invention discloses methods for making photonic bandgap structures and photonic bandgap structures made by those processes. In one embodiment, the photonic bandgap structure is flexible. In another photonic bandgap structure, the structure has a graded, periodic grating. One embodiment of a method according to the present invention comprises the steps of preparing a pre-polymer mixture, positioning that mixture between two slides, exposing the mixture to electromagnetic radiation, curing the mixture, and discarding at least one of the slides. In another embodiment of the method, the pre-polymer mixture is exposed to the electromagnetic radiation through a prism. In one embodiment of the method, the pre-polymer mixture is exposed to the electromagnetic radiation through a lens.In one embodiment of the invention, the photonic bandgap structure is used as a filter in a multispectral imaging device comprising a imaging device, the filter, a processor, and an electronic image storage device.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
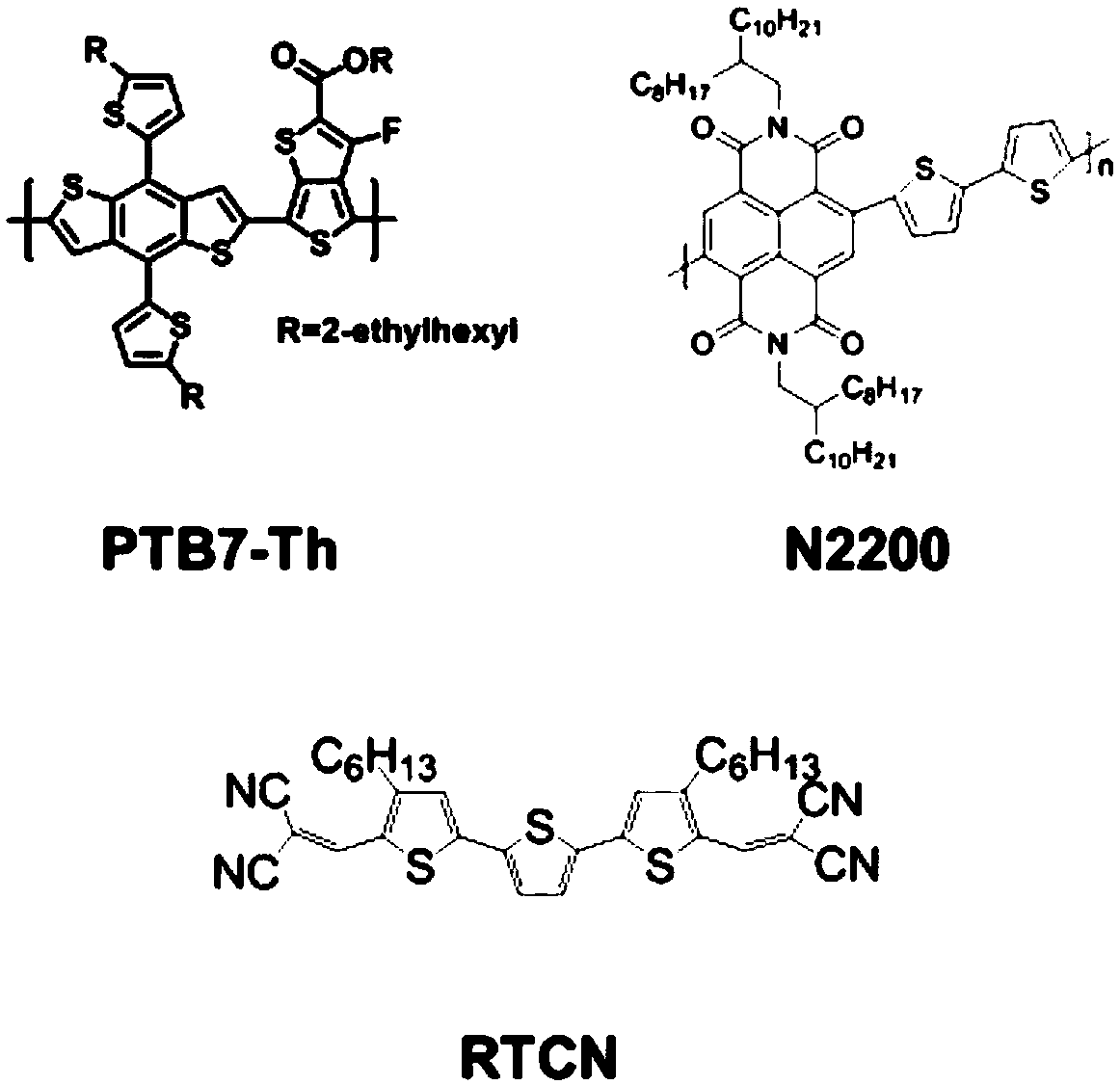
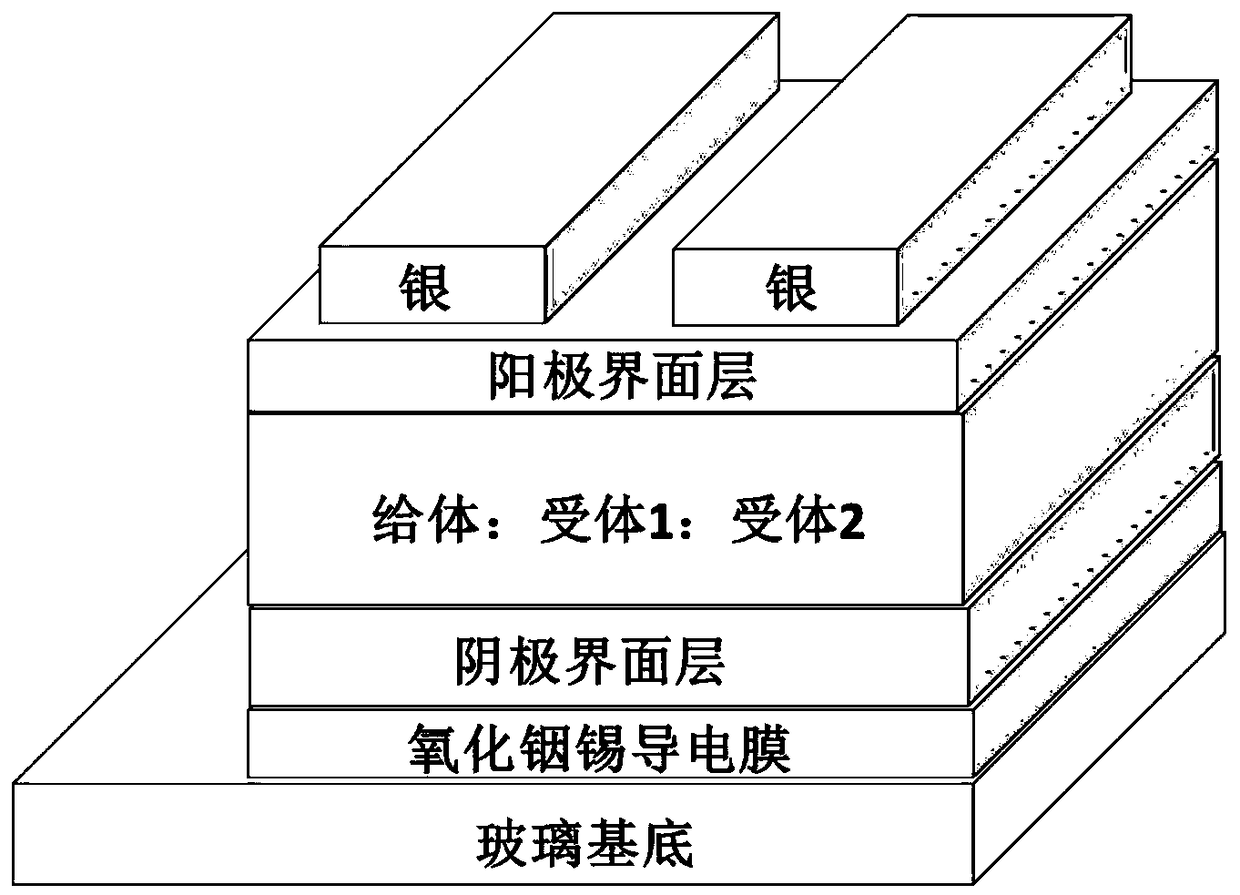
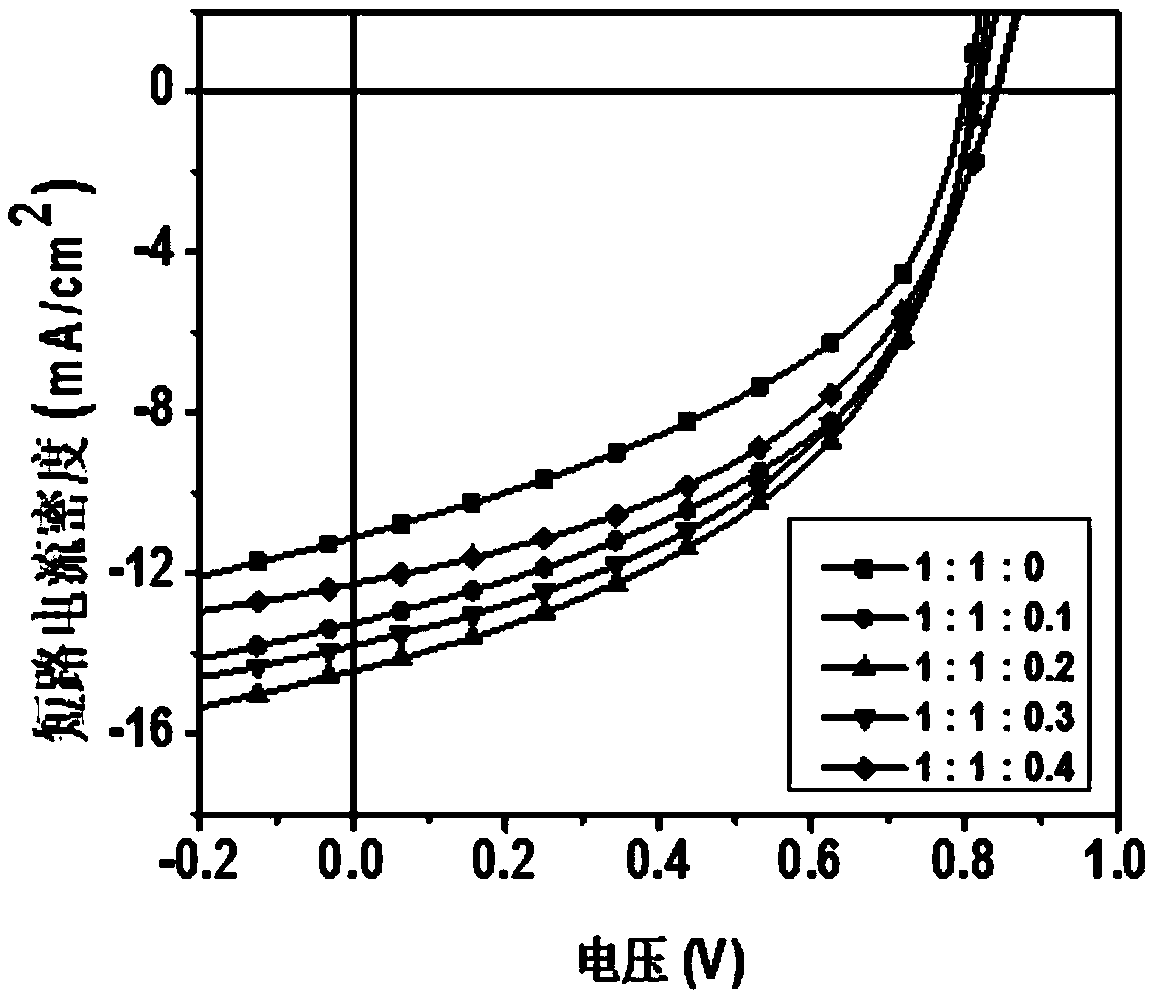
Ternary all-polymer solar cell
ActiveCN108767118AAvoid recombinationGuaranteed normal transmissionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron donorCrystallinity
The invention discloses a ternary all-polymer solar cell and belongs to the technical field of photovoltaics. A non-fullerene small molecule receptor with strong crystallinity is added to an optical active layer of a binary all-polymer solar cell as a third component. An inversion structure is adopted by the cell; and the optical active layer is prepared from the following components in percentages by weight: 41.6-50% of an electron donor, 41.6-50% of an electron receptor and 0-16.6% of the non-fullerene small molecule receptor with the strong crystallinity. A non-fullerene small molecule receptor material with strong crystallinity is added to the optical active layer, so that spectral absorption is widened, phase separation is improved and bimolecular charge recombination can be inhibited, thereby causing more effective charge generation and transportation, improving the short-circuit current density of a device and finally improving the photoelectric conversion property of the device. The ternary all-polymer solar cell disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being high in photoelectric conversion property, simple in preparation process, short in process and low in cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Process for the production of aromatic amines
InactiveUS20100324336A1Good miscibilityEasily separated offAmino compound purification/separationOrganic compound preparationAqueous solutionCyclic amines
Aromatic amines produced by hydrogenation of the corresponding nitroaromatic compounds are purified in a specified manner. In the purification procedure, the particular amine is initially mixed with an aqueous solution of a base. The organic and aqueous phases are then separated by adding excess water.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
Method for manufacturing separator, separator manufactured by the method and method for manufacturing electrochemical device including the separator
ActiveCN102754243AFacilitate phase separationImprove adhesionLiquid surface applicatorsFinal product manufactureNon solventPorous substrate
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD +1
Process for improving phase separations in solvent extraction circuits
InactiveUS20070292325A1Facilitate phase separationFacilitates removal of contaminantSolvent extractionTransuranic element compoundsEmulsionElectrolysis
The addition of a compatible metal salt crystal to the organic solution entering the mixer(s) in the solvent extraction stage(s) and / or the stripping stage(s), or to the emulsion mixture of the organic solution and the aqueous solution in the mixer(s), or to the mixture of the organic solution and the aqueous solution in a settler tank(s) following the mixer(s) in the solvent extraction and / or stripping stage(s) following the leaching of metal values from the ore containing that / those value(s) into an aqueous solution, and prior to the further refining of those values in processes, such as electrowinning, during mining operations for those metal values in order to improve the phase separation of the organic phase and the aqueous phase, and to promote the removal of contaminants from the organic phase.
Owner:COGNIS IP MANAGEMENT GMBH
Carbon nanotube-metal particle composite and catalyst comprising the same
ActiveUS20140011671A1Good dispersionFacilitate phase separationMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCarbon nanotubeMetal particle
A carbon nanotube-metal particle composite includes: carbon nanotubes, polymer layer, and metal particles. The polymer layer is coated on a surface of the carbon nanotubes and defines a number of uniformly distributed pores. the metal particles are located in the pores. A catalyst including the carbon nanotube-metal particle composite is also disclosed.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Liquid-liquid-liquid three-phase continuous countercurrent extraction device and use thereof
InactiveUS20130315803A1Guaranteed uptimeEasy to controlOrganic chemistryZirconium compoundsPhase mixingThree-phase
A liquid-liquid-liquid three-phase continuous and countercurrent extraction apparatus comprises a three-phase-mixing chamber, a three-liquid-flow settler, and a two-phase-mixing chamber; a liquid-flow control separator placed in the three-liquid-flow settler aims to flexibly regulate the directions of three liquid flows in the three-phase system by different control separator combinations to achieve either a countercurrent operation of the top-layered phase with the middle-bottom two-layered mixtures, or a countercurrent operation of the top-middle two-layered mixtures with the bottom-layered phase; and a method of using the same, relating to extraction and separation field of chemical technology.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polymers and Their Use as Coatings
InactiveUS20080026154A1More cost-effectivelyGood physical propertiesNon-macromolecular organic additionPretreated surfacesPolymer sciencePolyol
Owner:BAXENDEN CHEM
Methods of treating subterranean formations with heteropolysaccharides based fluids
InactiveUS7781380B2Rapidly hydratableAdequate rheologyCleaning apparatusFluid removalAqueous mediumSURFACTANT BLEND
Disclosed are methods of treating subterranean formations with rapidly hydratable treatment fluids based upon heteropolysaccharides. In particular, the invention relates to treatment methods with fluids containing a heteropolysaccharide, aqueous medium, and an electrolyte, wherein the fluids may further include a gas component, a surfactant and / or an organoamino compound. The fluids exhibit good rheological properties at elevated temperatures, and unusually rapid hydration rates which allows utilizing such fluids without the need of hydration tanks.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Process and apparatus for production of halogenated butyl rubber with reduced emissions
ActiveUS9644041B2Mitigate issueReduction tendencyChemical/physical/physico-chemical reactor detailsChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsPolymer scienceOrganic solvent
The present invention relates to a process for the production of halogenated butyl rubber and an apparatus for the production of rubber cement for use in the production of halogenated butyl rubber. The process and apparatus permit direct mixing of aqueous rubber slurry with a non-halogenated organic solvent to make a rubber cement solution. The water layer is then separated from the partially dissolved rubber cement and the cement phase is sent for halogenation. The apparatus is an enclosed vessel comprised of at least one dissolving zone and at least one separator zone. The process and apparatus advantageously employ recycle of rubber cement in order to disrupt an interface layer that forms between the water and rubber cement, to thereby improve continuously operation of the process.
Owner:ARLANXEO DEUT GMBH
Small-size block polymer material rapidly assembled at low quenching temperature as well as preparation and application of small-size block polymer material
ActiveCN107245133ALow annealing temperatureShort annealing timeMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic chemistryVitrificationPolymer science
The invention relates to a small-size block polymer material assembled at a low quenching temperature as well as preparation and application of the small-size block polymer material. Particularly, the invention discloses a block copolymer which has a glass transition temperature below 120 DEG C. The invention also discloses a preparation method and the application of the block copolymer. The block copolymer can realize excellent phase separation and rapid patterning at a relatively low annealing temperature (e.g., 80 DEG C) and relatively short annealing time (e.g., 30 seconds), and is etched to obtain a photoetch pattern with extremely high resolution (e.g., 5 nm half-pitch), thereby providing a new photoetch means for the further extension of Moore's Law and photoetching semiconductors smaller than 10 nm, even 5 nm (half-pitch).
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Rapid method for production of cerium-containing oxide organic colloids
InactiveUS20130192122A1Simple and rapid and low temperature processDispersion stability can be increasedLiquid carbonaceous fuelsIron compoundsOctanoic AcidsEmulsion
Improved methods for producing colloidal dispersions of cerium-containing oxide nanoparticles in substantially non-polar solvents is disclosed. The cerium-containing oxide nanoparticles of an aqueous colloid are transferred to a substantially non-polar liquid comprising one or more amphiphilic materials, one or more low-polarity solvents, and, optionally, one or more glycol ether promoter materials. The transfer is achieved by mixing the aqueous and substantially non-polar materials, forming an emulsion, followed by a phase separation into a remnant polar solution phase and a substantially non-polar organic colloid phase. The organic colloid phase is then collected. The promoter functions to speed the transfer of nanoparticles to the low-polarity phase. The promoter accelerates the phase separation, and also provides improved colloidal stability of the final substantially non-polar colloidal dispersion. The glycol ether promoter reduces the temperature necessary to achieve the phase separation, while providing high extraction yield of nanoparticles into the low-polarity organic phase. In addition, use of particular amphiphilic materials, such as heptanoic acid or octanoic acid, enable efficient extractions at ambient temperatures without the use of a glycol ether promoter.
Owner:CERION
Method for treating chemical nickel plating concentrated waste liquid by solvent extraction method and ion exchange method
ActiveCN104962888AFast extractionImprove extraction efficiencyLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingLiquid solutions solvent extractionLiquid wasteIon exchange
The invention discloses a method for treating a chemical nickel plating concentrated waste liquid by a solvent extraction method and an ion exchange method. The method comprises adjusting a chemical nickel plating concentrated waste liquid concentration to 6-7 by NaOH, fully mixing the waste liquid subjected to pH adjustment and an extractant, carrying out standing for two phase layering, separating the two phases to obtain organic and water phases, wherein the water phase is a nickel-free solution and the organic phase is a loading organic phase, fully mixing sulfuric acid and the above organic phase, carrying out standing for two phase layering, separating the two phases to obtain a water phase and an organic phase, wherein the water phase is a nickel sulfate solution and the organic phase is an extractant, treating the nickel-free solution by an alkalescent anion exchange resin column to remove hypophosphite, carrying out cooling to precipitate sodium sulfate crystals, and adding nickel sulfate and hypophosphite into the sodium sulfate crystals to obtain a regenerated chemical nickel plating liquid for direct chemical nickel plating. The method has the advantages of high extraction efficiency, environmental friendliness, simple operation, low cost and high economic value.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Device and Method For Particle Separation
InactiveUS20110120303A1Increasing centrifugal pressureEasy to separateCombination devicesGas treatmentParticle separationChemistry
A separation device with a gas inlet port that accepts an inlet gas. The inlet gas is composed of a mixture of at least two separable particle components with each component having a different mass. A rotating separation rotor accepts the inlet gas and uses a separator to substantially separate the gas according to mass into two fractions, a heavier and a lighter fraction. One of the fractions is passed to a second separator that further separates that fraction into another two fractions consisting of heavier and lighter fractions. The desired fractions are collected and exhausted from the separation device for use.
Owner:TENOROC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com