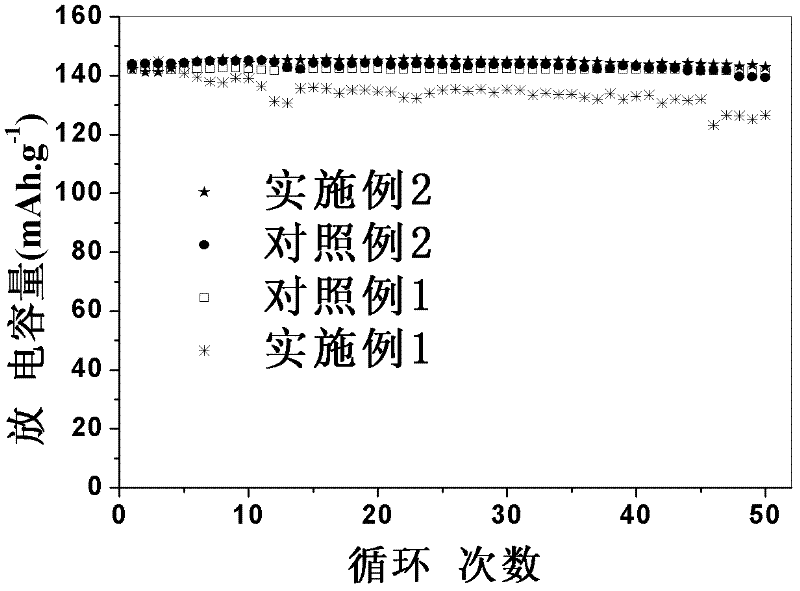
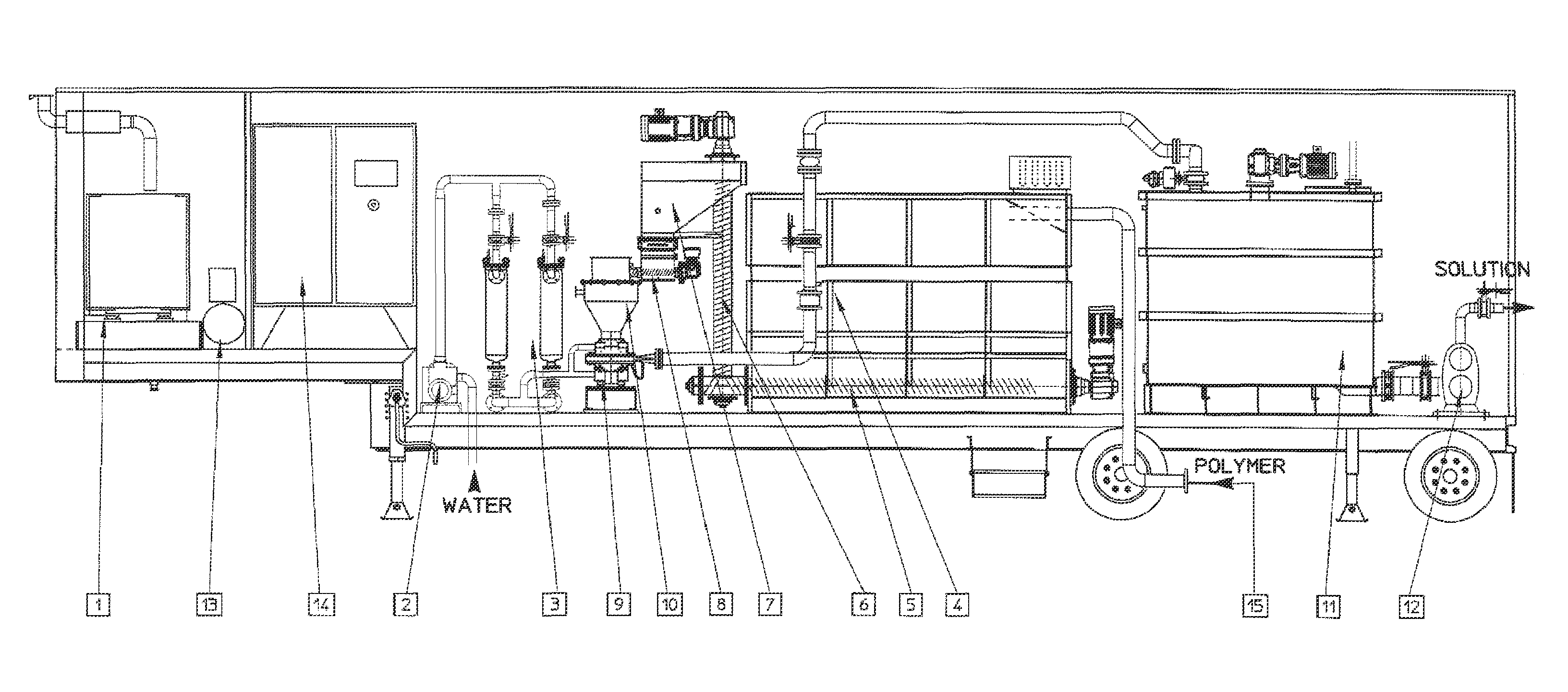
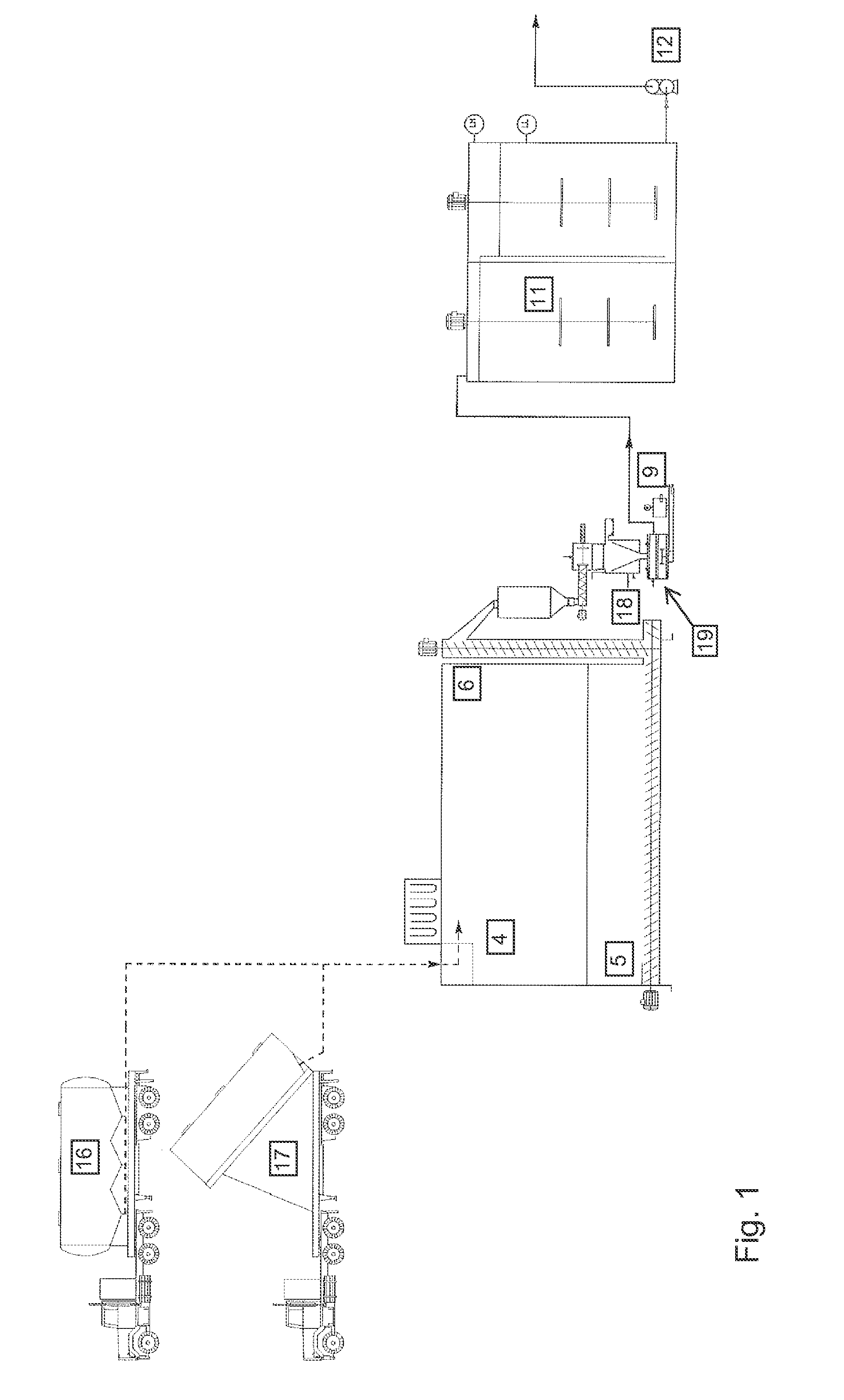
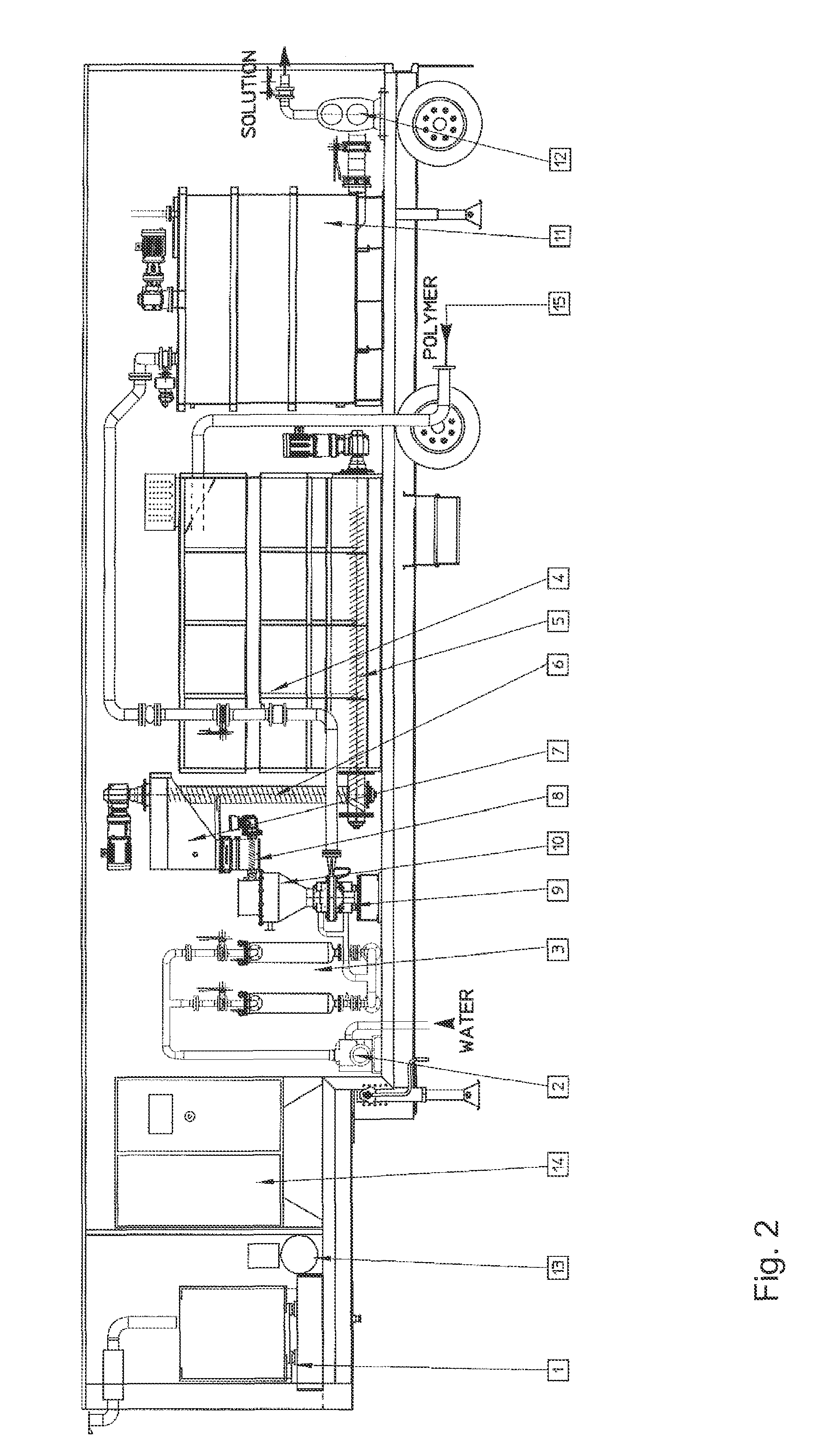
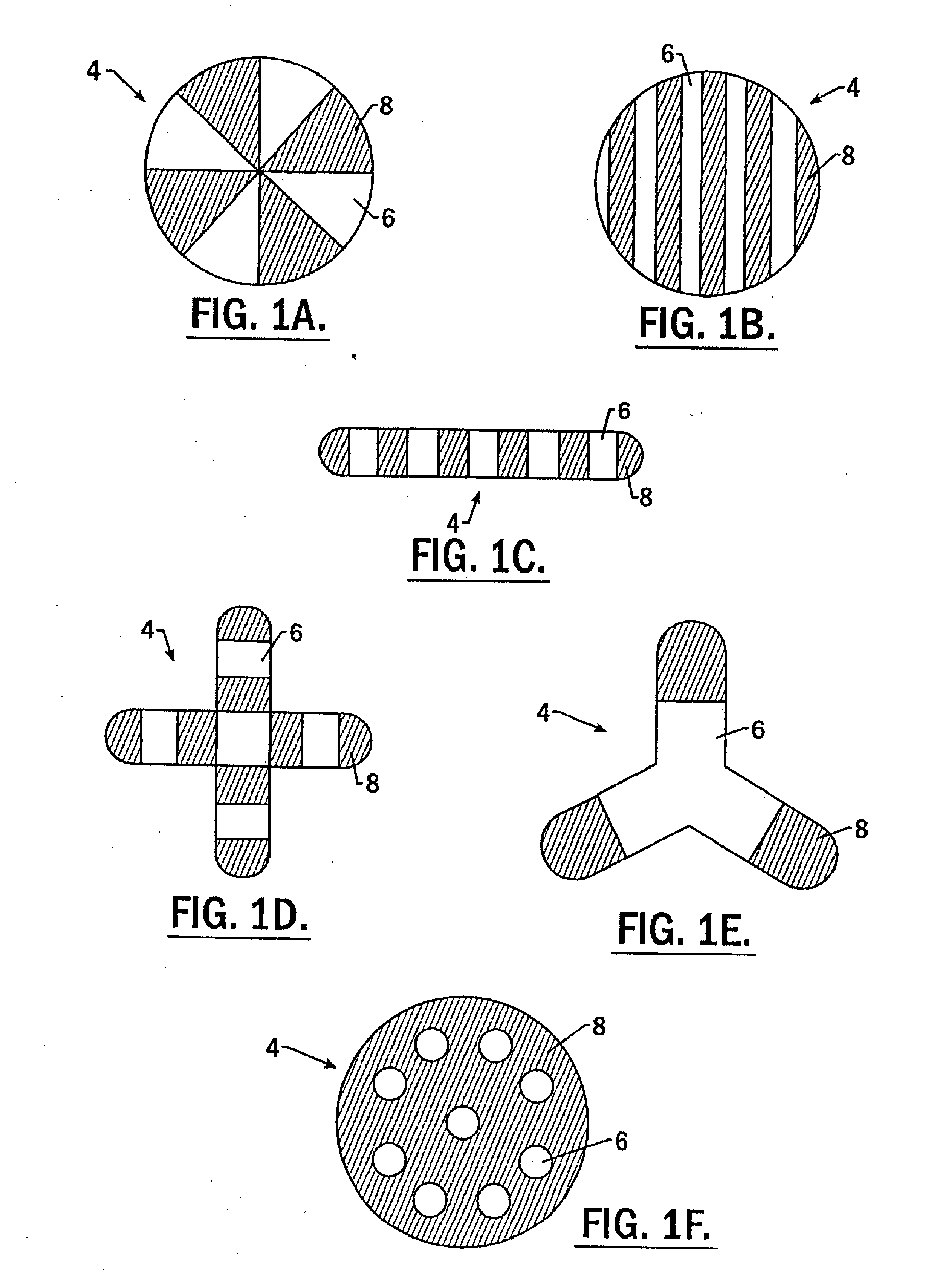
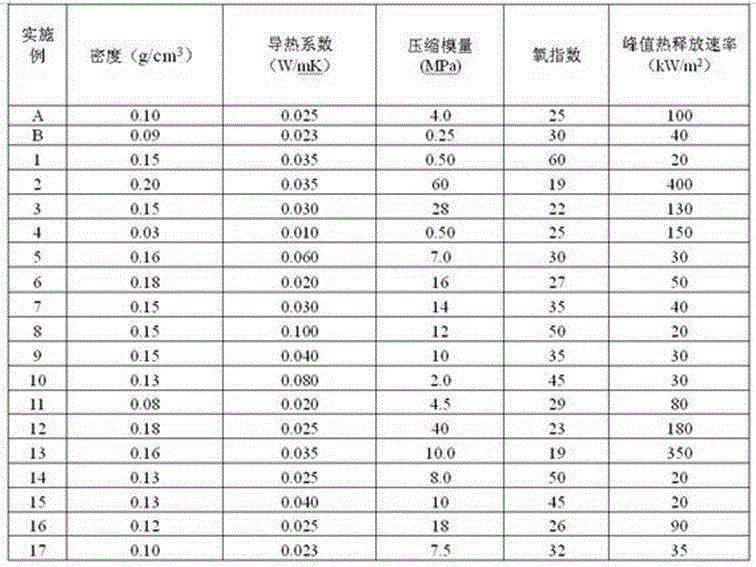
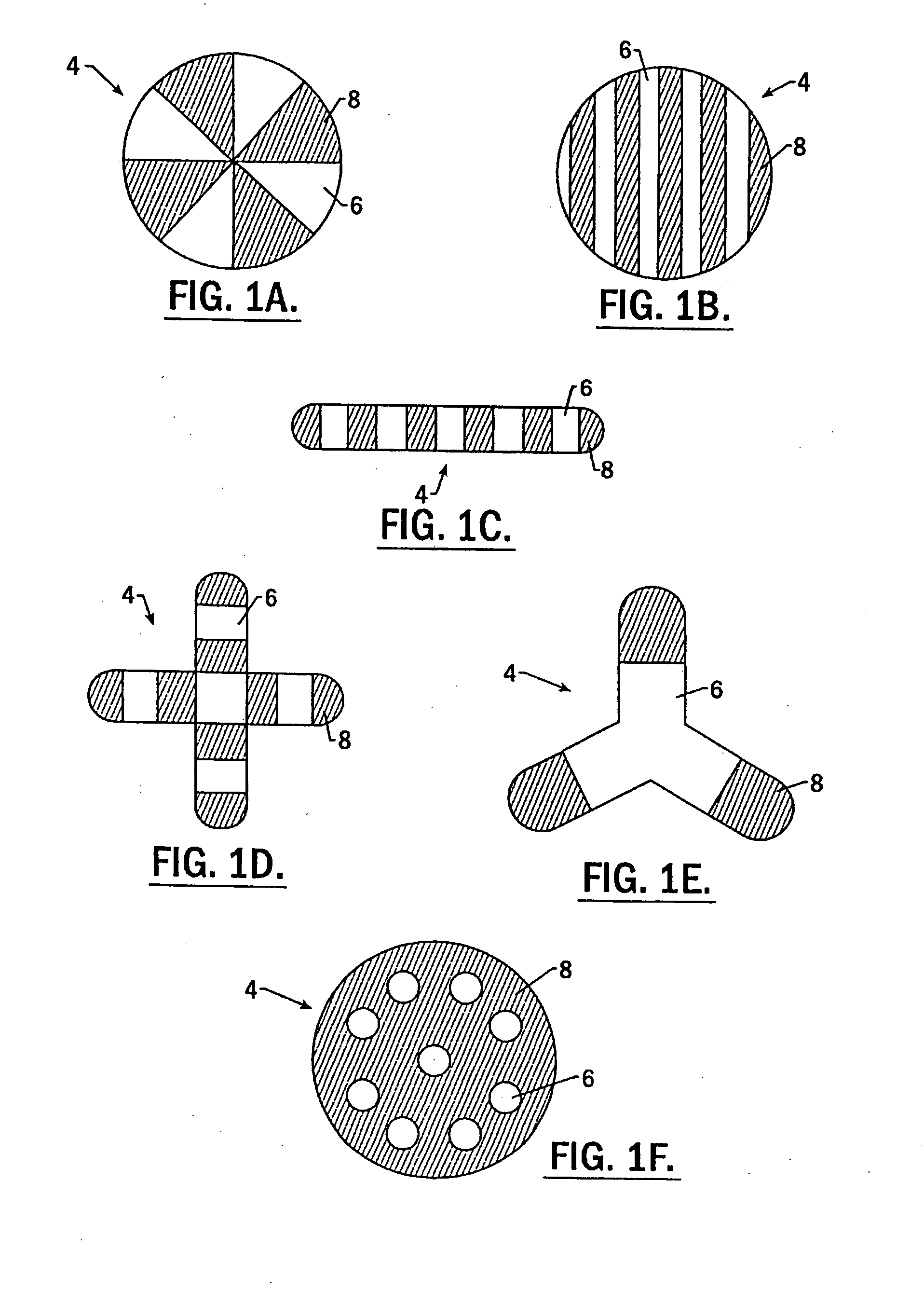
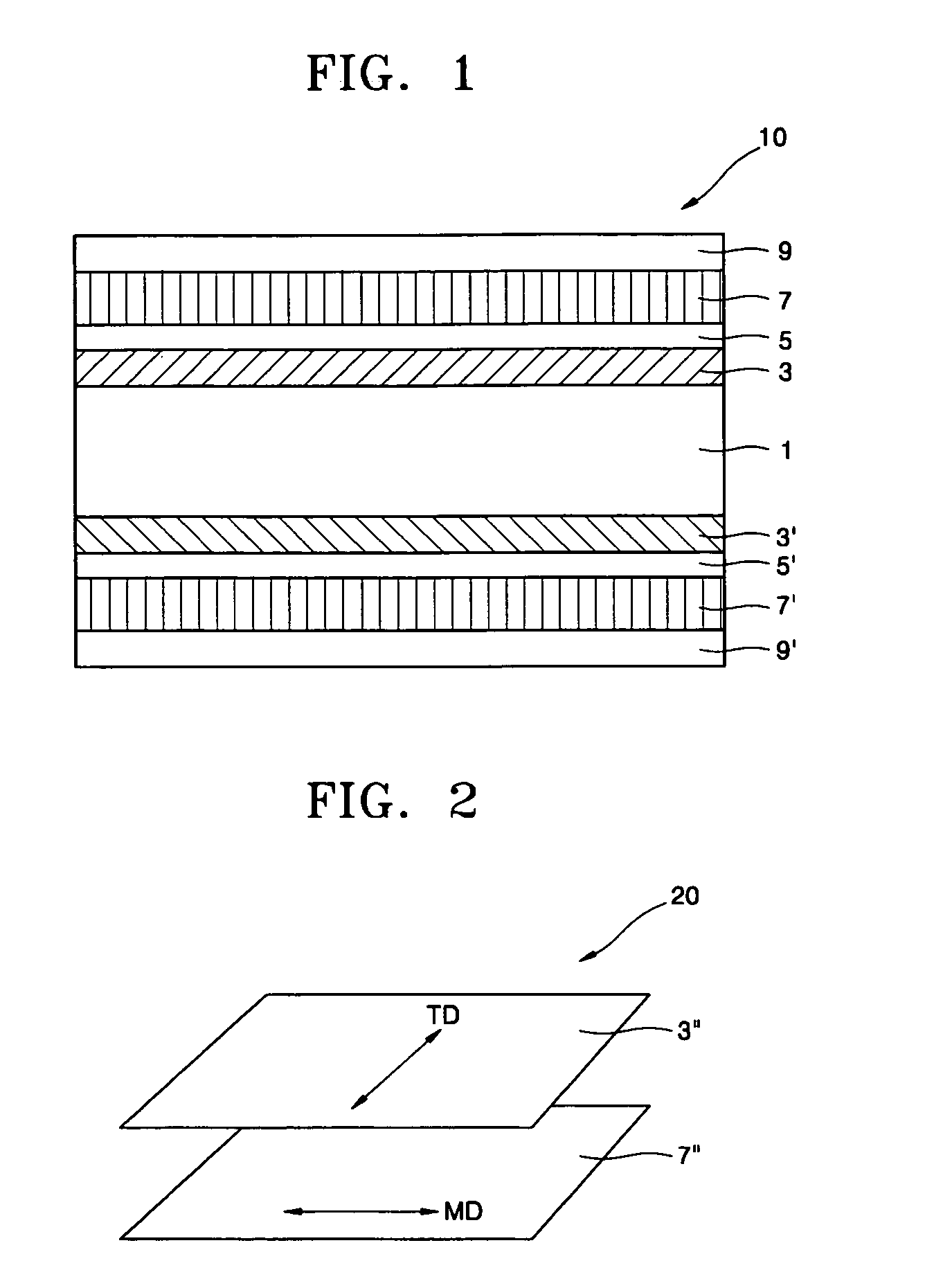
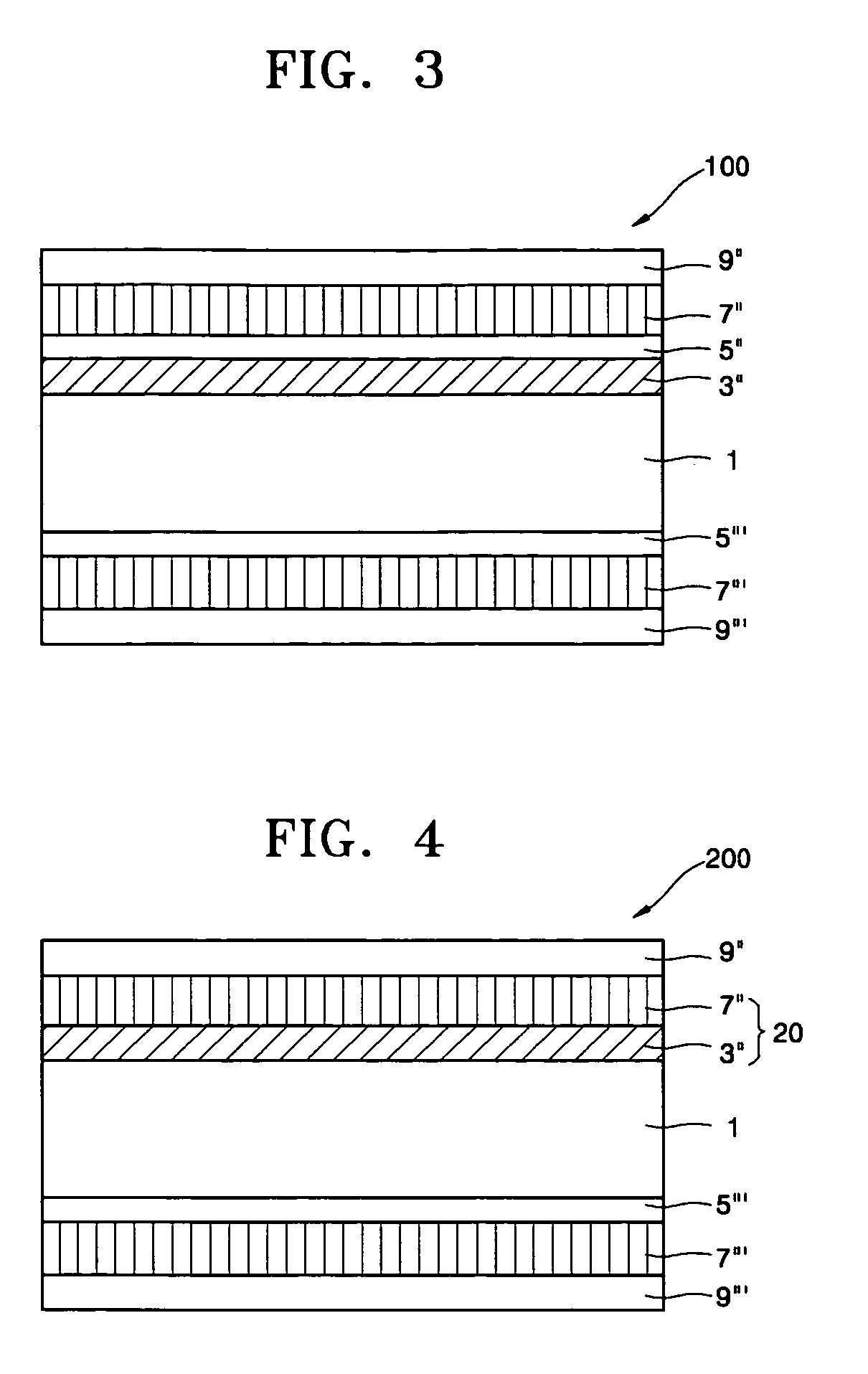
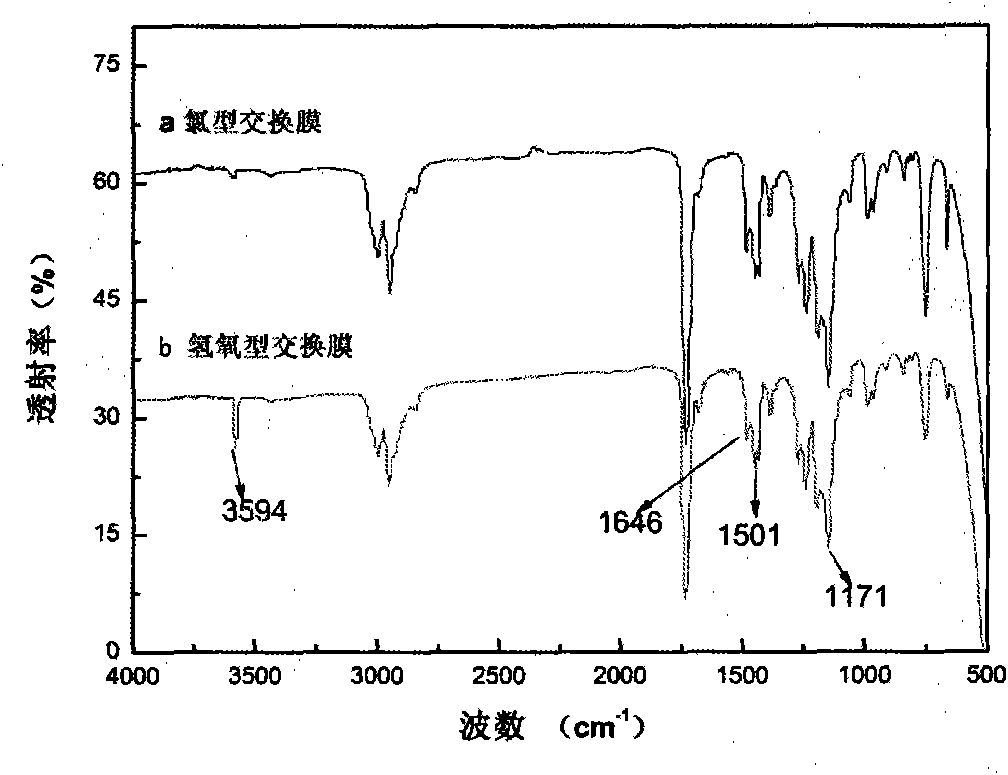
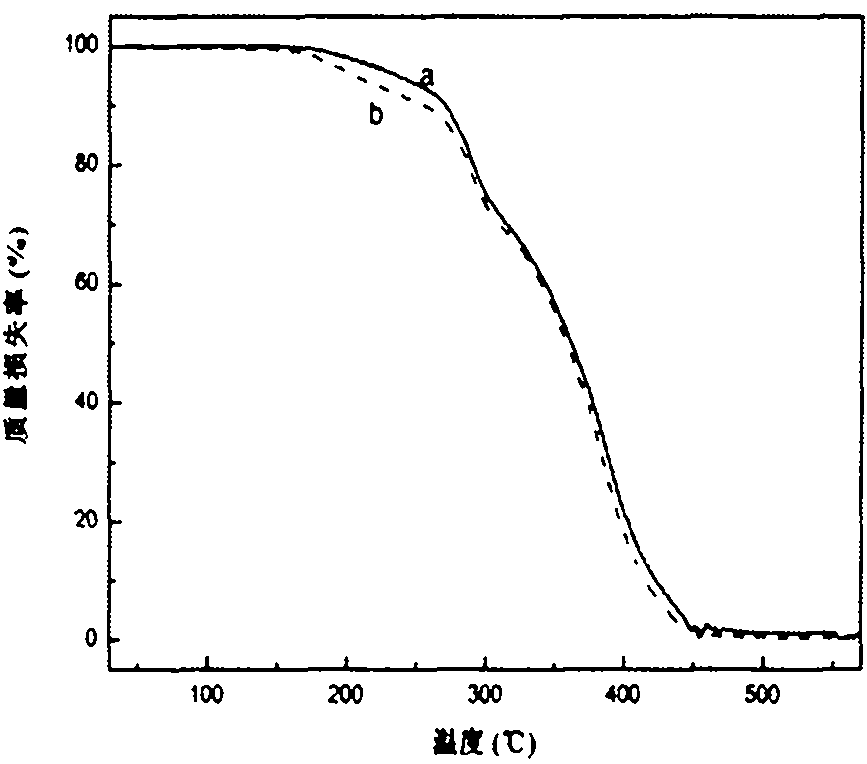
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
763 results about "Polymer dissolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
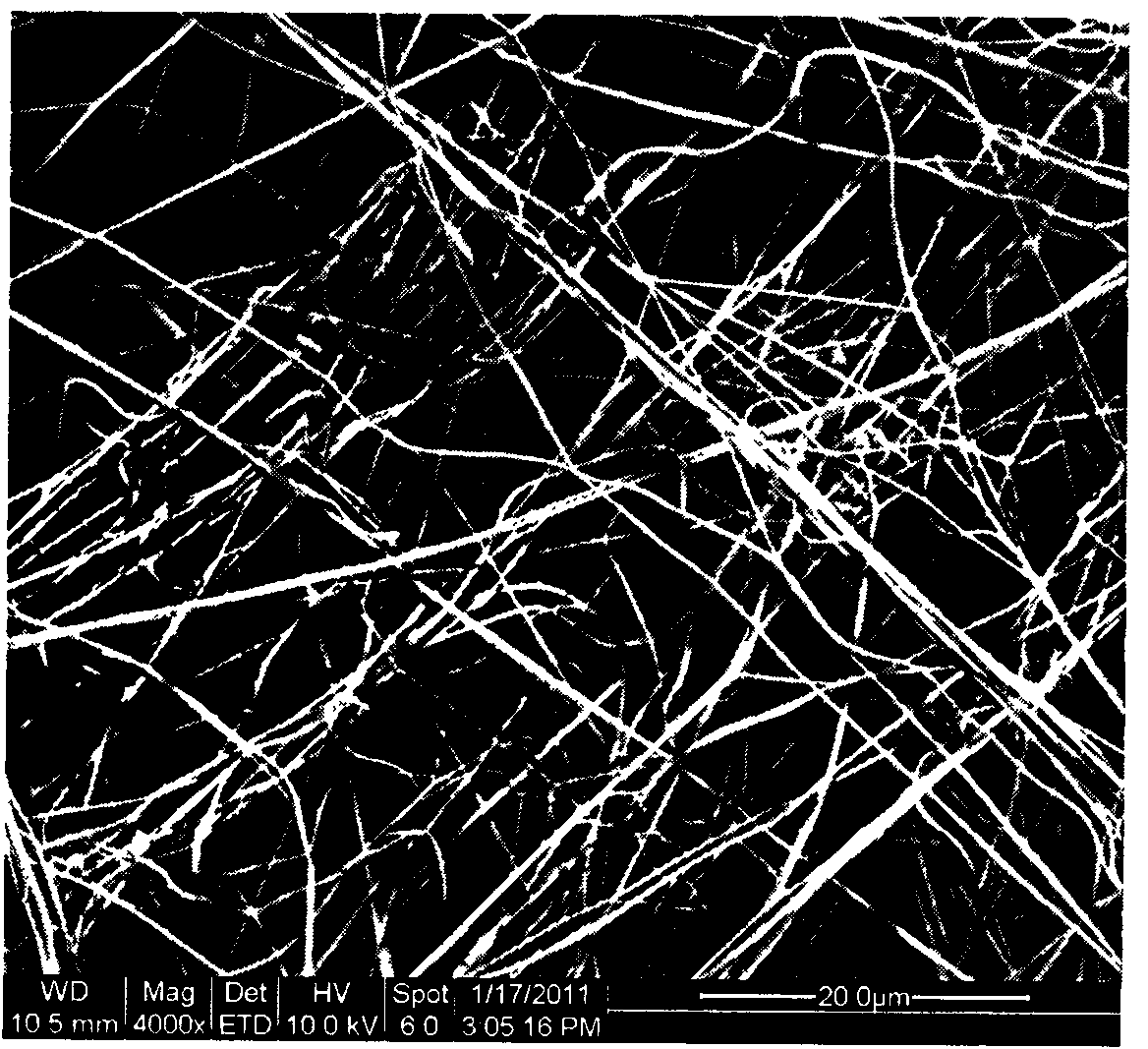
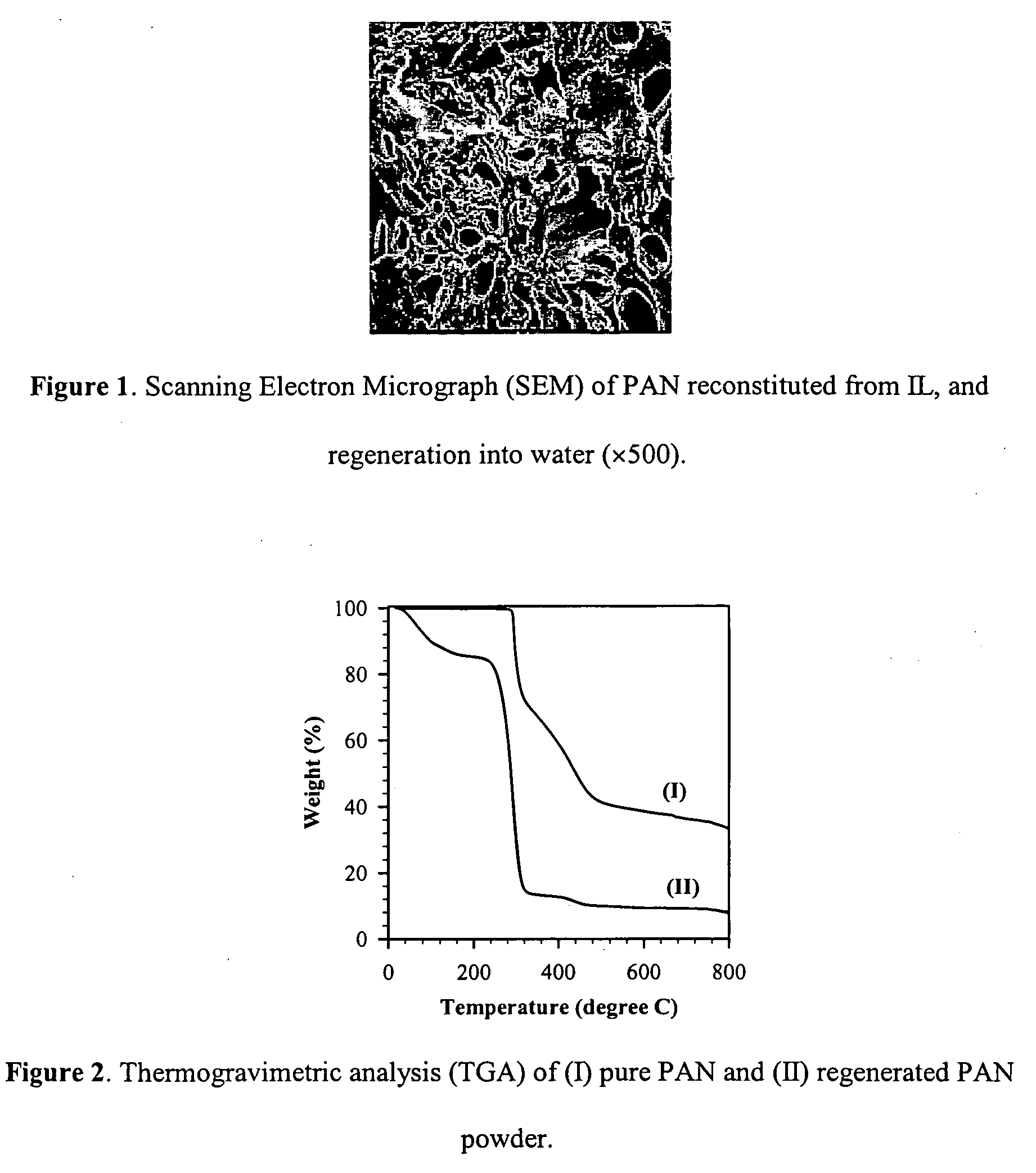
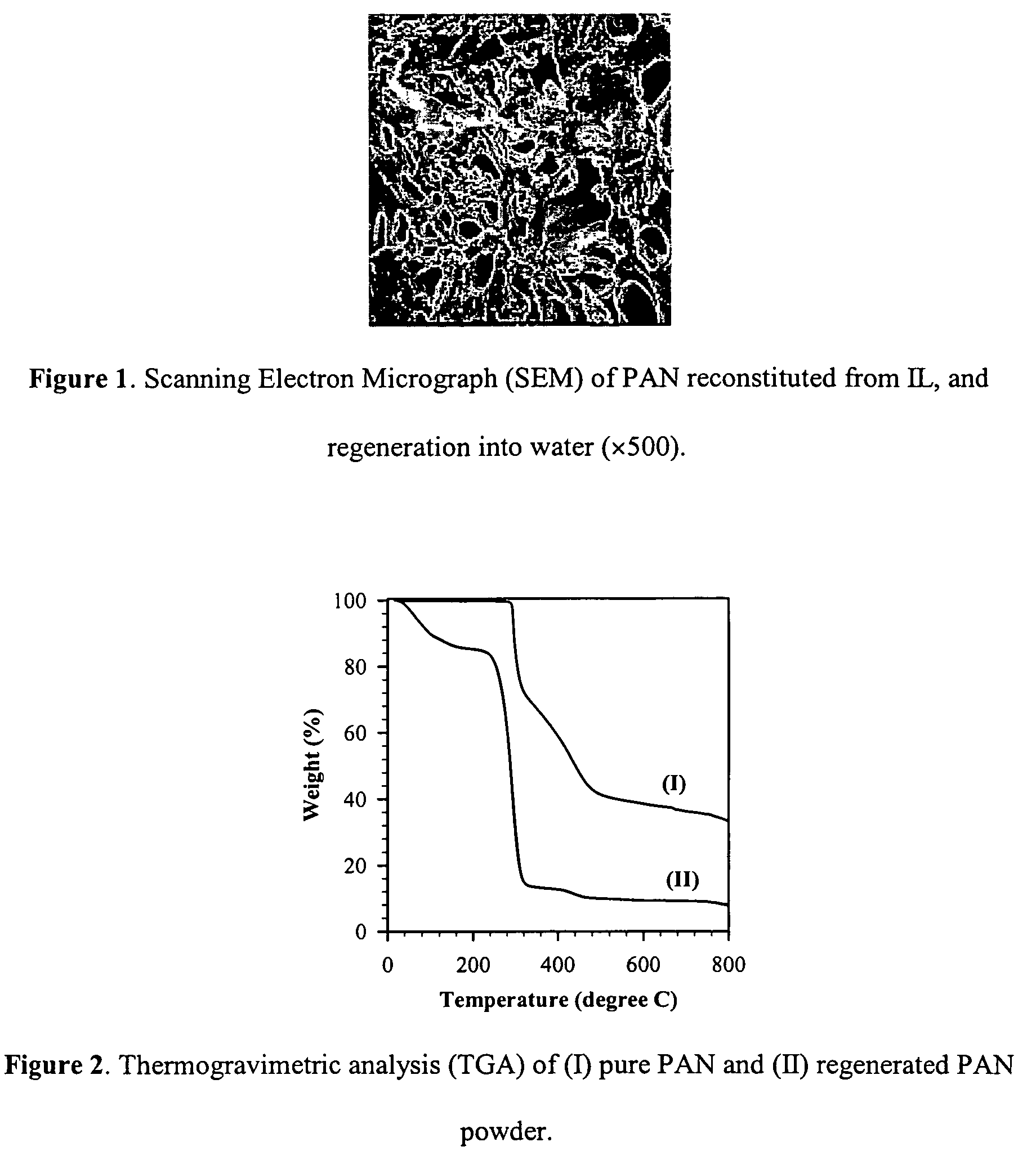
Polymer dissolution and blend formation in ionic liquids
InactiveUS20050288484A1Cosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPolymer dissolutionAdvanced composite materials
The present invention relates to processes utilizing ionic liquids for the dissolution of various polymers and / or copolymers, the formation of resins and blends, and the reconstitution of polymer and / or copolymer solutions, and the dissolution and blending of “functional additives” and / or various polymers and / or copolymers to form advanced composite materials.
Owner:UNIVERSTIY OF ALABAMA THE
Method of producing morphologically uniform microcapsules and microcapsules produced by this method
InactiveUS6294204B1Readily water-miscibleSpeed up concentrationPowder deliveryBiocidePolymer dissolutionEmulsion
The invention relates to a process for the production of morphologically uniform microcapsules that contain peptides, proteins or other water-soluble biologically active substances as active ingredients as well as microcapsules that are produced according to this process with a degree of concentration of between 3 to 30% by weight and a diameter<=8 mum.According to the invention, biodegradable polymers are dissolved in a halogen-free solvent or solvent mixture, and the buffered active ingredient solution, which has a pH of between 6.0 to 8.0, is dispersed into this solution. Then, an aqueous solution that contains a surface-active substance (W / O / W-emulsion) is added to this W / O-emulsion, and the solvent is removed.The microcapsules that are produced with this process do not show any tendency toward agglomeration. The encapsulation efficiency of the process is approximately 90 to 95%.
Owner:ALRISE BIOSYST
Fluid loss reducer for high temperature and high pressure water-based mud application
ActiveUS7101829B2Improve high temperature stabilityImprove shear resistanceOther chemical processesMixing methodsPolymer dissolutionWater based
The present invention concerns a water-based drilling mud for utilization in the drilling of oil wells comprising an aqueous phase wherein the aqueous phase contains an oil soluble polymer in the form of a gel as fluid loss reducer. The subject invention further reveals a process for preparing an oil soluble polymer fluid loss control agent comprising the steps of dissolving at least one polymer in a hydrocarbon oil to form a clear solution or a gel, adding an emulsifier to the solution or the gel, and keeping the mixture under conditions of agitation until a clear creamy mixture is obtained.
Owner:ELIOKEM
Process for producing epoxidized diene polymer
InactiveUS6903165B2Improve thermal stabilityLow gel contentOrganic chemistrySpecial tyresPolymer dissolutionPolymer science
A process for producing an epoxidized diene polymer includes: dispersing or suspending a diene polymer (C) having a ball-reduced particle size of 0.05-20 mm in a medium (A) in the presence of powder particles (B) insoluble in the medium (A), or in an aqueous medium in the presence of a phenol-based stabilizer and / or a phosphorus-based stabilizer; and epoxidizing the diene polymer (C) by an epoxidizing agent, therefore, problems associated with epoxidation performed by dissolving diene polymer in a solvent are eliminated; an economical method for epoxidizing, producing, and purifying a diene polymer (C) in a solid form is provided; and the epoxidized diene polymer having an excellent heat stability can be obtained.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
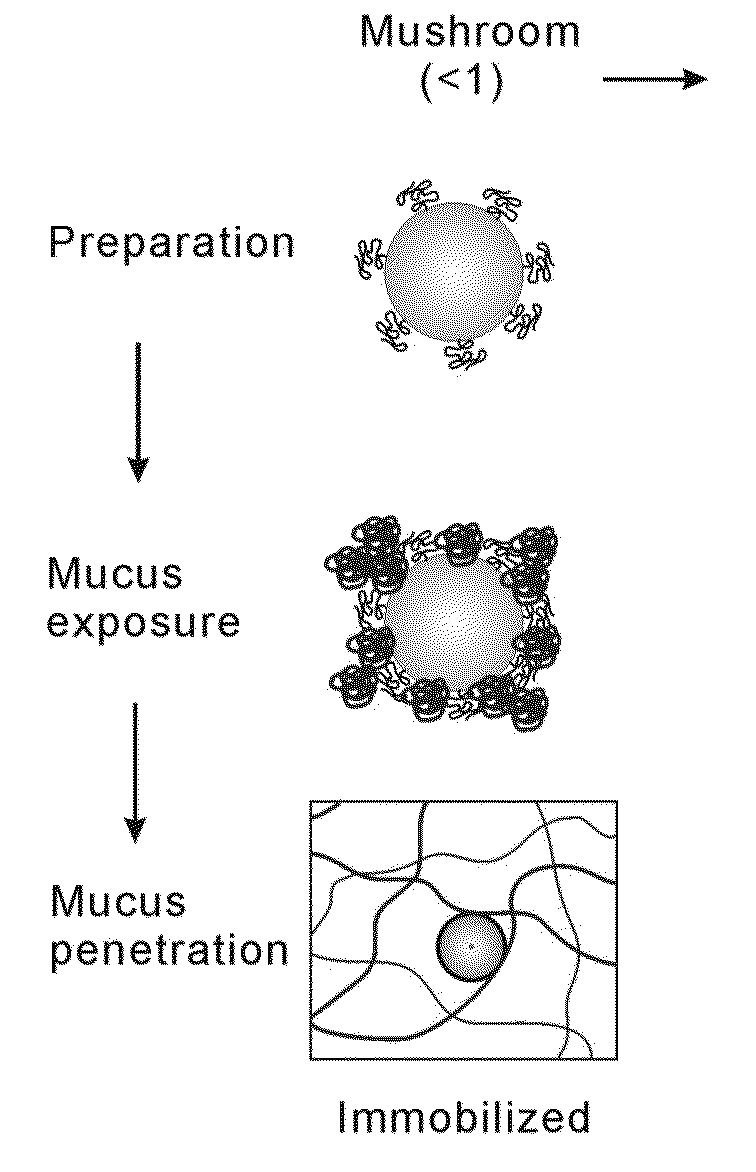
Nanoparticles with enhanced mucosal penetration or decreased inflammation
Nanoparticles formed by emulsion of one or more core polymers, one or more surface altering materials, and one or more low molecular weight emulsifiers have been developed. The particles are made by dissolving the one or more core polymers in an organic solvent, adding the solution of the one or more core polymers to an aqueous solution or suspension of the emulsifier to form an emulsion, and then adding the emulsion to a second solution or suspension of the emulsifier to effect formation of the nanoparticles. In the preferred embodiment, the molecular weight of the emulsifiers is less than 1500, 1300, 1200, 1000, 800, 600, or 500 amu. Preferred emulsifiers include cholic acid sodium salt, dioctyl sulfosuccinate sodium, hexadecyltrimethyl ammonium bromide, saponin, TWEEN® 20, TWEEN® 80, and sugar esters. The surface altering materials are present in an amount effective to make the surface charge of the particles neutral or essentially neutral when the one or more emulsifiers are charged. The emulsifiers have an emulsification capacity of at least about 50%, preferably at least 55, 60, 65, 70, 75, 80, 85, 90, or 95%.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Encapsulation method
InactiveUS6861064B1Easy to getImprove concentrationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsPolymer dissolutionEmulsion
A novel method of encapsulating an active substance in a biodegradable polymer, which comprises: a) dissolving said biodegradable polymer in an organic solvent therefor; b1) dispersing said active substance in the organic solution obtained in step a) to provide a dispersion with the active substance as the inner phase thereof; or alternatively b2) emulsifying said active substance, dissolved in water or other aqueous solvent therefor, in the organic solution obtained in step a) to provide an emulsion with the active substance as the inner aqueous phase thereof; and c) subjecting the dispersion obtained in step b1), or alternatively the emulsion obtained in step b2), to an encapsulation operation with an aqueous polyethylene glycol solution as a continuous phase to provide micro- or nanoparticles having the active substance encapsulated therein. Sustained release particles obtainable thereby.
Owner:PACIRA PHARMA INC
Polymer blends that swell in an acidic environment and deswell in a basic environment
InactiveUS6537584B1Improve propertiesControlling the swelling and/or deswelling behaviorBiocidePowder deliveryChemical structurePolymer dissolution
A polymer blend is prepared by dissolving chitosan and a second polymer in an acidic aqueous solution to form an aqueous polymer blend, dehydrating said aqueous polymer blend, and recovering said polymer blend. The second polymer may be selected from the group consisting of polyether glycols including polyethylene glycols; cellulose esters including cellulose acetate; poloxamers; polysaccharides including dextran and guar; polyvinylpyrrolidones; polyvinyl alcohols; and mixtures or copolymers thereof. These polymer blends swell in an acidic environment and deswell in a more neutral or basic environment. This technology is valuable for the dispensing of biologically active material or drugs into a surrounding environment, especially the environment as is found in the gastrointestinal tract. Since the various polymer blends of the present invention are not covalently or ionically crosslinked, but are physically combined, each polymer in the physical blend maintains its original chemical structure, and therefore, is safe for oral administration.
Owner:BTG INT LTD
Method for preparing polymeric nano-micro fiber non-woven fabric
ActiveCN102071542AOvercoming demandsUniversally applicableNon-woven fabricsDry spinning methodsFiberPolymer dissolution
The invention discloses a method for preparing a polymeric nano-micro fiber non-woven fabric. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, dissolving at least one polymer in at least one solvent to prepare spinning solution; then supplying the spinning solution to a spinneret plate with a series of spinneret orifices so as to make the spinning solution extruded from the spinneret orifices of the spinneret plate to form a trickle of the spinning solution; secondly, stretching and refining the trickle of the spinning solution by utilizing at least one high-speed jet airflow, and accelerating the volatilization of the solvent to form nano-micro fiber; and finally, collecting the nano-micro fiber on a web curtain by utilizing high-speed airflow and suction airflow. The polymer is a fiber-forming polymer; the solvent can dissolve the fiber-forming polymer and has the volatility; a jet angle of the high-speed airflow is between 15 and 60 degrees, and the jet velocity is at least 50 times higher than extrusion speed of the trickle of the spinning solution; the mass concentration of the polymer in the spinning solution is between 2 and 50 percent; and the viscosity of the spinning solution at a spinning temperature is between 10 and 100, 000mP.s.
Owner:上海榕融新材料技术有限公司
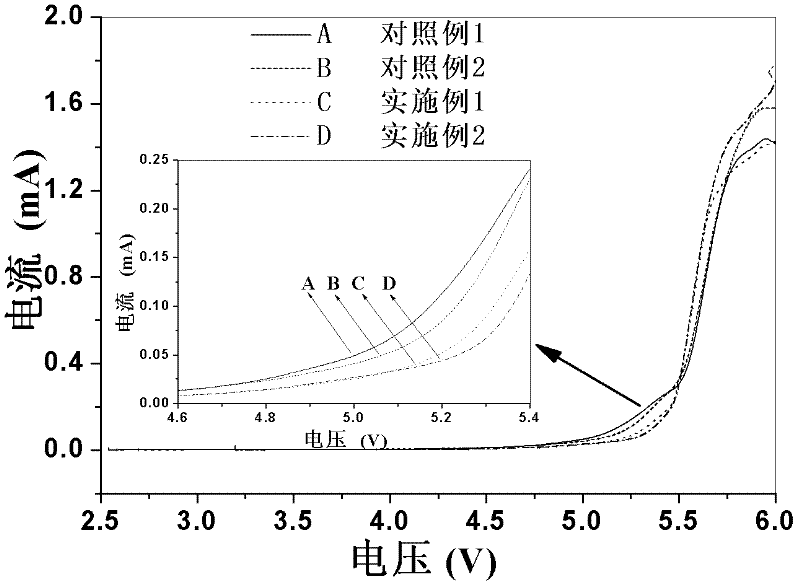
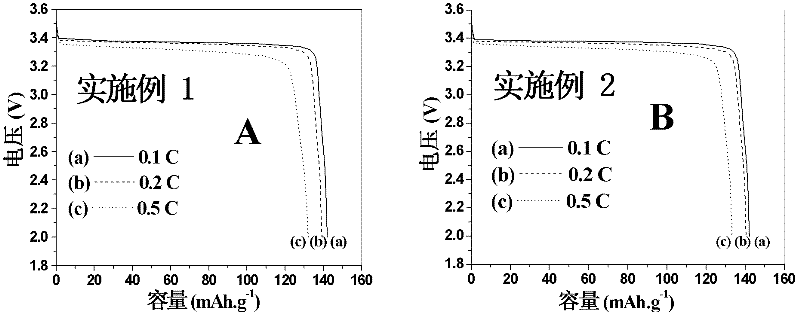
Lithium ion battery ionic liquid based gel polymer electrolyte as well as preparation and applications thereof
InactiveCN102244292AFix security issuesHigh mechanical strengthSecondary cellsPolymer dissolutionPolymer electrolytes
The invention discloses a lithium ion battery ionic liquid based gel polymer electrolyte as well as a preparation method and applications thereof. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving a polymer into an organic solvent; then adding deionized water and an inorganic ceramic material, thus obtaining a gel liquid; soaking an non-activated supporting body in the gel liquid; taking out and airing, thus a heat-resistant contracted lithium ion battery polymer diaphragm doped with the inorganic ceramic materials is obtained; dissolving lithium salt in an ion liquid, and adding a film formation addition agent, thus an ion liquid based electrolyte capable of gelating the polymer diaphragm is obtained; and soaking the dried heat-resistant contracted lithium ion battery polymer diaphragm doped with the inorganic ceramic material in the ion liquid based electrolyte, thus the heat-resistant contracted lithium ion battery ionic liquid based gel polymer electrolyte doped with the inorganic ceramic material is obtained. The preparation method is simple, and the safety performance, mechanical intensity and electromechanical performance of the lithium ion battery ionic liquid based gel polymer electrolyte are improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
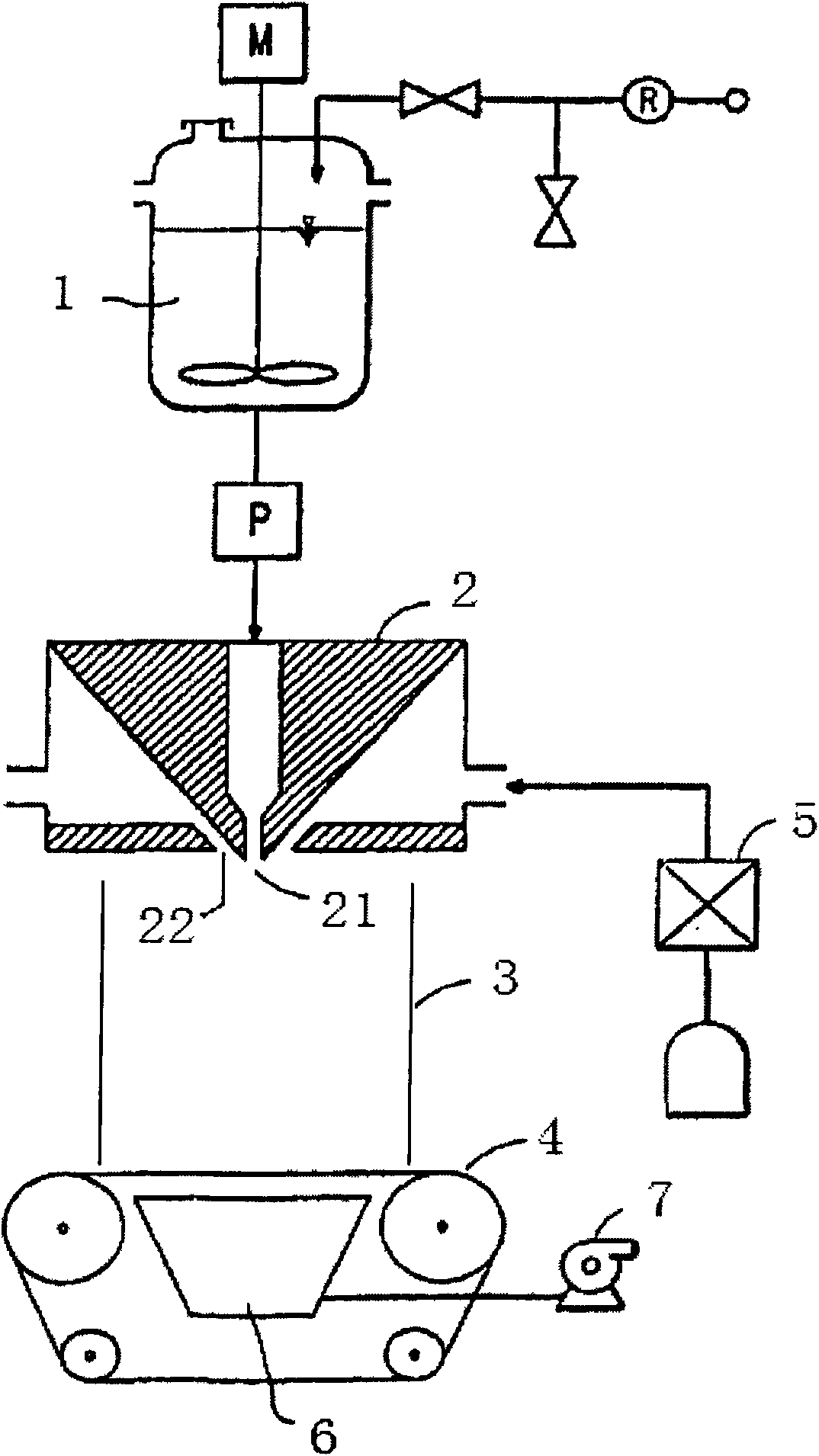
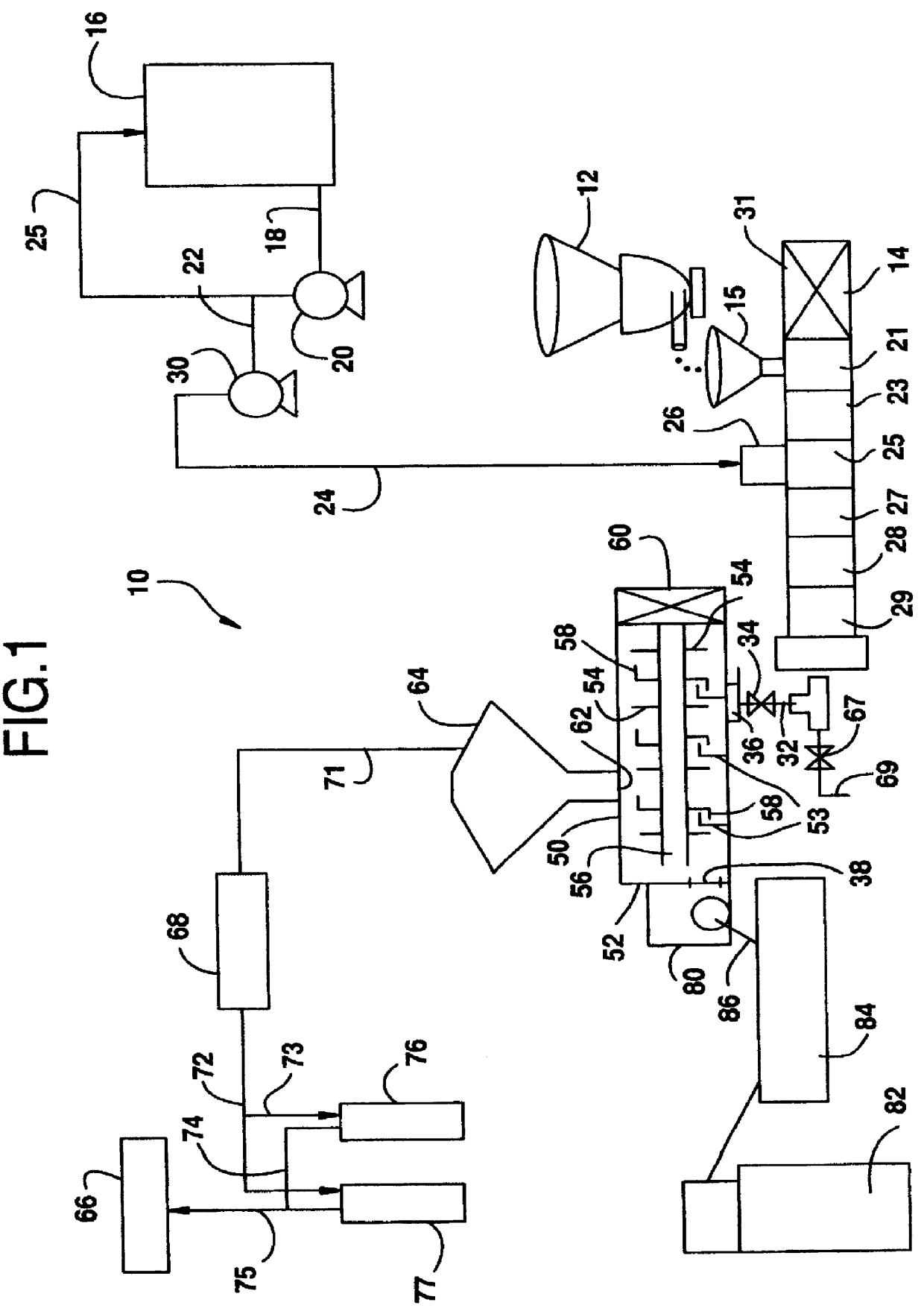
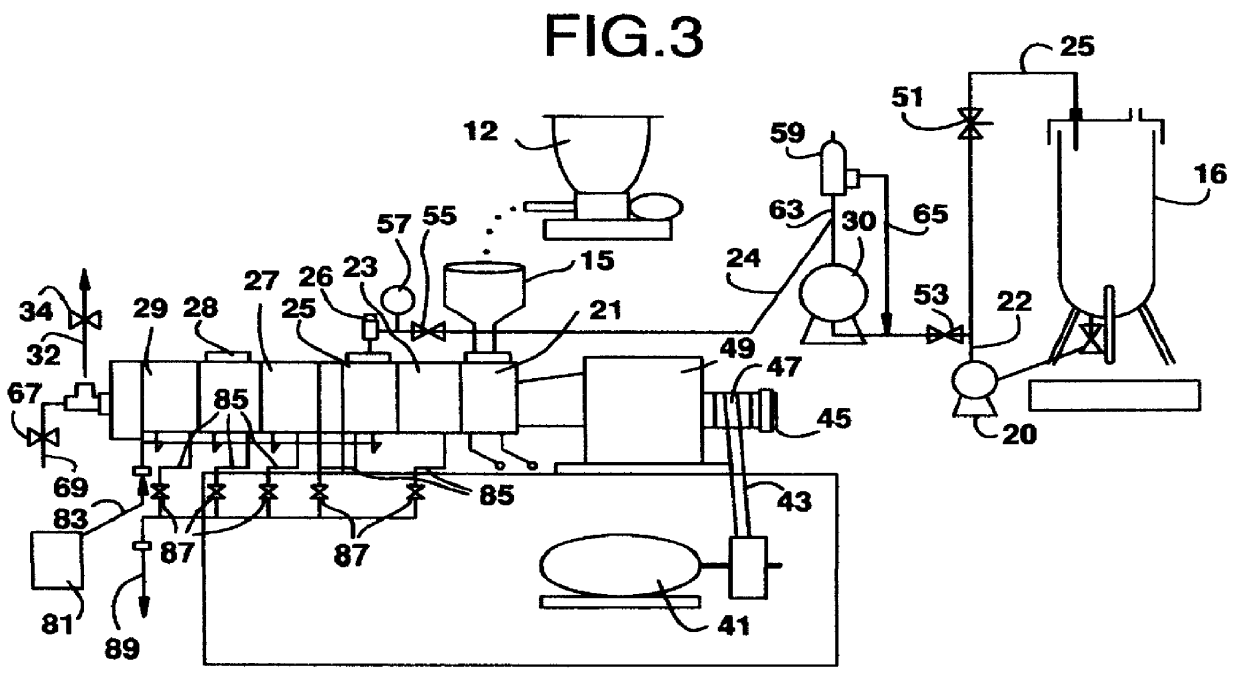
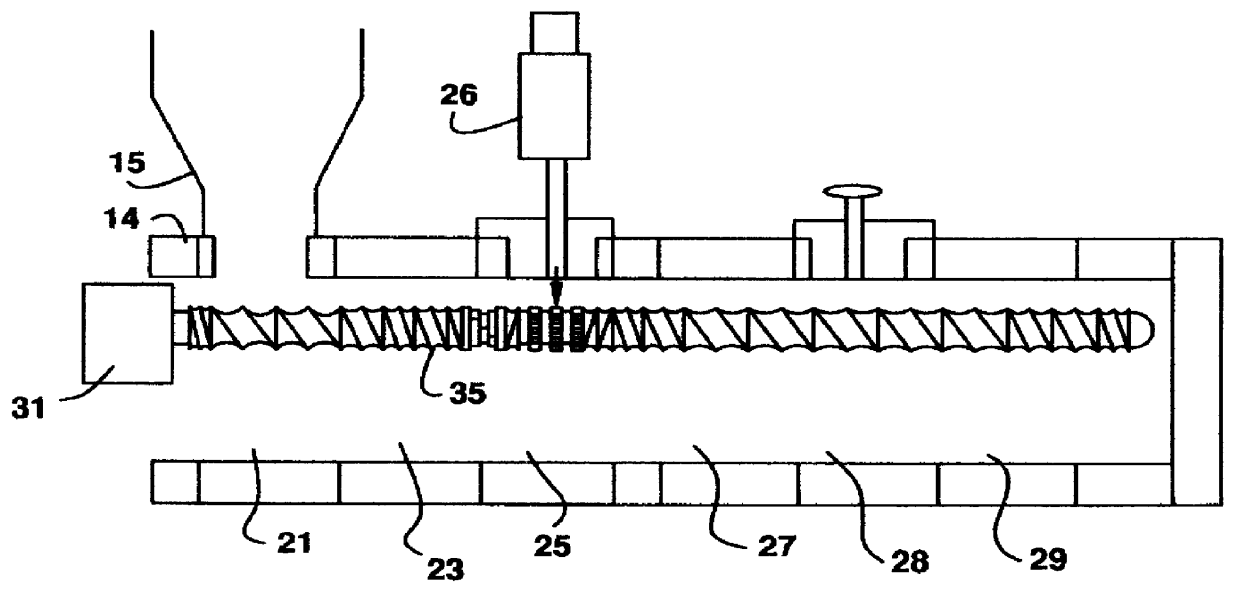
Polymer dissolution equipment suitable for large fracturing operations
ActiveUS9067182B2Improve performanceSmall sizeRotary stirring mixersTransportation and packagingPolymer dissolutionEngineering
Compact and transportable equipment that can be used for fracturing operations on gas or oil fields, includes, successively, a silo for storing polymer in powder form, a feed hopper of a polymer metering device, a device for metering out the powder polymer, a device for dispersing and grinding the polymer, and at least two volumetric pumps enabling the injection and metering of the polymer solution obtained in the mixer used for supplying at least one high-pressure fracturing pump.
Owner:S P C M SA
Polymer recovery
InactiveUS6150498ALow solvent contentImprove cooling effectDrying using combination processesEvaporationRecovery methodPolymer dissolution
Methods for devolatilizing polymer solutions have been invented which include, in certain aspects, dissolving a viscous polymer in a solvent forming a polymer-solvent solution, introducing the polymer-solvent solution into a thermal dryer, heating or cooling the polymer-solvent solution in the thermal dryer forming product polymer with solvent removed and separated solvent (which may include other residuals), the separated solvent with other residuals if present vaporizing in the thermal dryer forming a vapor, removing the vapor from the thermal dryer, and discharging product polymer from the thermal dryer.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
Soluble Microfilament-Generating Multicomponent Fibers
InactiveUS20070077427A1Improve solubilityFilament/thread formingConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsFiberPolymer dissolution
Owner:FIBER INNOVATION TECH
Aerogel material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103599734AThe preparation process is environmentally friendlyIncrease productivityColloidal chemistry detailsPolymer dissolutionHigh energy
The invention provides an aerogel material and a preparation method thereof. The material is prepared from a polymer and clay by the steps of aqueous solution blending, irradiation crosslinking and freeze drying, wherein the polymer accounts for 5-95% of the aerogel weight, the clay accounts for 95-5% of the aerogel weight, and the aerogel density is 0.03-0.20g / cm<3>. The preparation method of the aerogel material provided by the invention sequentially comprises the following steps: (a) dissolving the polymer in deionized water, adding the clay and stirring to obtain turbid liquid in uniform distribution; (b) performing irradiation crosslinking of the turbid liquid obtained by the step (a) under high-energy rays, wherein the irradiation dosage of the high-energy rays is 1-200kGy; and (c) freezing the irradiation product obtained by the step (b), and drying to obtain the aerogel material. Since water is used as a solvent only in the preparation process and a chemical crosslinking agent is not required by the irradiation crosslinking, the crosslinking is efficient and controllable, the crosslinking density is uniform, the preparation process is green and environment-friendly, and the production efficiency is high.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
Soluble microfilament-generating multicomponent fibers
InactiveUS20060083917A1Improve solubilityConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsYarnFiberPolymer dissolution
Microfilament-generating multicomponent fibers are provided that include a first polymer component and a second polymer component extruded together in separate contiguous polymer segments extending along the length of the fiber. The first polymer component comprises a synthetic melt-processable polymer that is substantially soluble in a first relatively benign solvent selected from water, aqueous caustic solution, and non-halogenated organic solvents. The second polymer component is formed from a second synthetic melt-processable polymer dimensioned to produce one or more microfilaments upon dissolution of the first polymer, and that is substantially soluble in an aqueous solvent selected from water and aqueous caustic solution. The two polymer components are dissolvable in different solvents.
Owner:FIBER INNOVATION TECH
Polymer and method for using the polymer for solubilizing nanotubes
A new, non-wrapping approach to solubilize nanotubes, such as carbon nanotubes, in organic and inorganic solvents is provided. In accordance with certain embodiments, carbon nanotube surfaces are functionalized in a non-wrapping fashion by functional conjugated polymers that include functional groups for solubilizing such nanotubes. Various embodiments provide polymers that noncovalently bond with carbon nanotubes in a non-wrapping fashion. For example, various embodiments of polymers are provided that comprise a relatively rigid backbone that is suitable for noncovalently bonding with a carbon nanotube substantially along the nanotube's length, as opposed to about its diameter. In preferred polymers, the major interaction between the polymer backbone and the nanotube surface is parallel π-stacking. The polymers further comprise at least one functional extension from the backbone that are any of various desired functional groups that are suitable for solubilizing a carbon nanotube.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH +1
Polymer dissolution and blend formation in ionic liquids
InactiveUS7888412B2Cosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPolymer dissolutionAdvanced composite materials
The present invention relates to processes utilizing ionic liquids for the dissolution of various polymers and / or copolymers, the formation of resins and blends, and the reconstitution of polymer and / or copolymer solutions, and the dissolution and blending of “functional additives” and / or various polymers and / or copolymers to form advanced composite materials.
Owner:UNIVERSTIY OF ALABAMA THE
PVDF microporous membrane and method
Methods for making microporous polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes from vinylidene fluoride polymers and the products produced. The PVDF microporous membranes have a significantly faster flow rate at a given pore size as compared to equally-sized microporous membranes made by conventional procedures. The PVDF microporous membranes also have significantly smaller pore sizes than conventional microporous PVDF membranes. The present membranes have unique macrostructural features responsible, in part, for their unique functional properties. The process includes dissolving the polymer in a liquid that includes a solvent and a co-solvent for the polymer. The dissolution of the polymer can be at temperatures ranging from about 20 DEG C. to about 50 DEG C. while the formation of the microporous membrane can be at temperatures ranging from about -10 DEG C. to 50 DEG C. Selection of appropriate operating parameters of temperature and solvent / co-solvent concentration can optimize the membrane at a given nominal pore size, flow rate, and polymer distribution.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Preparation method of conductive high-strength graphene-reinforced polymer fiber
ActiveCN102828267ARaw materials are easy to getLow costElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureFiberPolymer dissolution
The invention discloses a preparation method of conductive high-strength graphene-reinforced polymer fiber, which comprises the following steps of: (1) dissolving a graphene oxide raw material in solvent, and carrying out ultrasonic treatment to obtain graphene oxide dispersion; (2) dissolving a polymer in solvent to obtain a polymer solution; and (3) adding the graphene oxide dispersion obtained in the step (1) to the polymer solution obtained in the step (2) under stirring, continuing stirring after complete addition, adding a reducing agent, centrifuging or carrying out rotary evaporation treatment, concentrating, transferring to a spinning device, continuously extruding from a spinning head at uniform speed, forming after entering a solidifying solution, and collecting to a roller to obtain continuous graphene-reinforced polymer fiber. The preparation method is simple and convenient, low in cost and multiple in used polymer variety, and is suitable for large-scale industrialized production; and the produced fiber has excellent mechanical property and better conductivity, and can be used for power transmission, antistatic textile, engineering material engineering material and other fields.
Owner:杭州德烯科技集团有限公司
Method of producing quantum-dot powder and film via templating by a 2-d ordered array of air bubbles in a polymer
InactiveUS20030129311A1Improve productivityMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingPolymer dissolutionQuantum dot
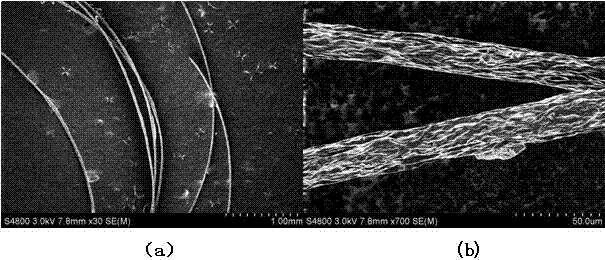
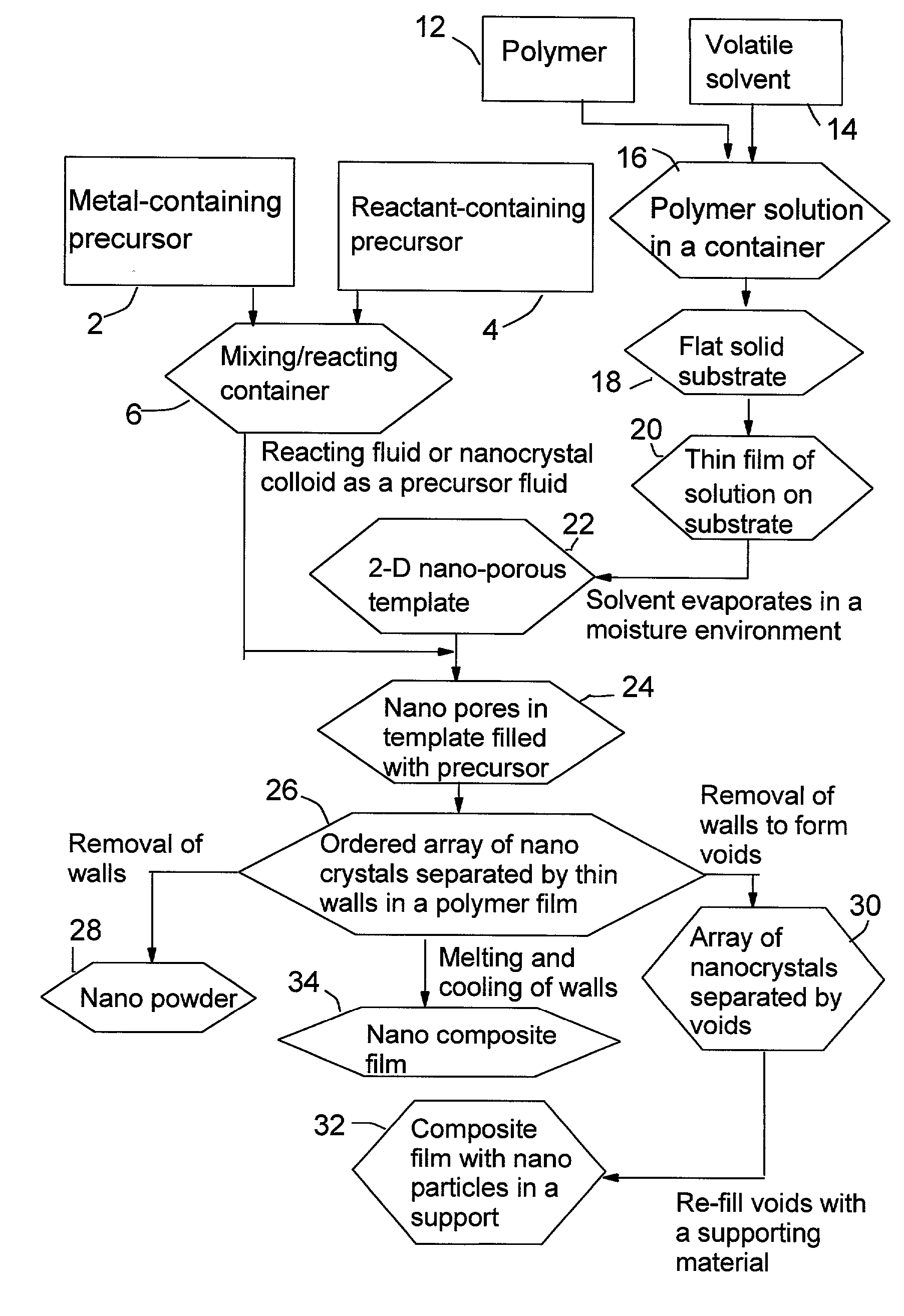
A quantum-sized material and a method for producing such a material according to a predetermined nano-porous polymer template. The method includes the steps of: (a) preparing a nano-porous polymer template, wherein the preparation step includes the sub-steps of (i) dissolving a polymer in a volatile solvent to form an evaporative solution, (ii) depositing a thin film of this solution onto a substrate, and (iii) directing a moisture-containing gas to flow over the spread-up solution film while allowing the solvent in the solution to evaporate for forming a template, which is constituted of an ordered array of nanometer-scaled air bubbles with polymeric walls dispersed in a polymer film; (b) filling the air bubbles with a precursor fluid; and (c) converting the precursor fluid in such bubbles to obtain a quantum-sized material in the form of an array of dots supported in the template. At least one of the dot dimensions is on the 100 nm scale or smaller, preferably smaller than 20 nm.
Owner:HUANG WEN CHIANG
Biaxial-optical polynorbornene-based film and method of manufacturing the same, integrated optical compensation polarizer having the film and method of manufacturing the polarizer, and liquid crystal display panel containing the film and/or polarizer
ActiveUS20060105117A1High light transmittanceUniform in-plane retardation valueLiquid crystal compositionsOptical articlesIn planePolymer dissolution
A method of manufacturing a biaxial-optical polynorbornene-based film is provided, including: preparing a polynorbornene-based polymer containing composition by dissolving a polynorbornene-based polymer in a mixed solvent containing a high-boiling solvent and a low-boiling solvent, with a difference in boiling points of the two solvents of 20° C. or greater and an amount of the high-boiling solvent being 0.1 to 15 wt % based on a weight of the polynorbornene-based polymer; casting and partially drying the composition to obtain a polynorbornene-based film containing 1 to 6 wt % of the mixed solvent based on a total weight of the polynorbornene-based film; and uniaxially stretching the partially dried film in one direction parallel with the surface of the film at a stretching temperature less than or equal to the boiling point of the high-boiling solvent +20° C. and drying the stretched film at a temperature greater than or equal to the boiling point of the high-boiling solvent. According to the method of manufacturing a biaxial polynorbornene-based film, a compensation film which has good light transmittance and a uniform in-plane retardation value and can function as both a negative C-plate and an A-plate can be obtained.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Preparation method of anion-exchange membranes based on ionic liquid
InactiveCN101844042AImprove conductivityImprove thermal stabilitySemi-permeable membranesBulk chemical productionPolymer dissolutionPolymer solution
The invention provides a preparation method of anion-exchange membranes based on ionic liquid, which relates to an ion exchange membrane. The invention provides an anion-exchange membrane based on ionic liquid with the advantages of environment-friendly effect, high electric conductivity, good chemical stability, good thermostability and good mechanical performance and a preparation method thereof. The free radical copolymerization reaction is carried out for preparing imidazolium type polymers according to the following steps: adding imidazole type ionic liquid monomers, acrylic ester monomers, solvents and triggering agents into a reaction vessel for carrying out back flowing reaction under the protection of inert gas; carrying out precipitation, washing and drying on obtained products to obtain the imidazolium type polymers. The membrane forming is carried out according to the following steps: dissolving the imidazolium type polymers obtained in the first step into organic solvents to be prepared into polymer solution, forming the membranes through a phase conversation method, and obtaining the anion-exchange membranes based on the ionic liquid.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Sheets including fibrous aerogel and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20120171488A1High mechanical strengthImprove cooling effectElectro-spinningHeat proofingElectrospinningPolymer dissolution
Disclosed herein is a method for producing a sheet including a silica aerogel, the method including (S1) gelling a water glass solution in a mixture of an alcohol and water to prepare a wet gel, (S2) hydrophobically modifying the surface of the wet gel with a non-polar organic solvent, an organosilane compound and an alcohol, (S3) dissolving the hydrophobically modified silica gel and a polymer in an aprotic organic solvent to prepare an electrospinning solution, and (S4) electrospinning the electrospinning solution to produce a fiber web including a silica aerogel, and a sheet in which a polymer and a silica aerogel coexist in the form of a fiber.
Owner:KOREA INST OF ENERGY RES
Preparation method for polymer-grafted graphene laminated fiber with electrical conductivity and high-strength
InactiveCN102926020ARaw materials are easy to getLow costElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentFiberPolymer dissolution
The invention discloses a preparation method for a polymer-grafted graphene laminated fiber with electrical conductivity and high-strength. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: (1) dissolving graphene oxide raw materials into a solvent, and ultrasonically processing to obtain graphene oxide dispersing liquid; 2) dissolving the polymer into the solvent to obtain the polymer solution; 3) slowly adding the graphene oxide dispersing liquid into the polymer solution, and adding a reducing agent to reduce the graphene oxide into graphene; and 4) centrifugally processing to wash away free polymer to obtain polymer-grafted graphene sol, transferring the polymer-grafted graphene sol into a spinning device, continuously extruding the polymer-grafted graphene sol from a spinning head at a constant speed, forming in solidifying liquid, and then collecting the formed polymer-grafted graphene sol on a roller shaft, so as to obtain the continuous polymer-grafted graphene laminated fiber. The preparation method is simple and convenient, low in cost, rich in variety of used polymers, and suitable for massive industrial production; the produced fiber is excellent in mechanical performance, and higher in conductivity; and the produced fiber can be applied to fields of power transmission, anti-static textile, engineering material, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Passive radiation refrigeration composite material layer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111393915AImprove Radiation PerformanceImprove mechanical propertiesLiquid surface applicatorsChemical industryPolymer dissolutionNanoparticle
The invention discloses a passive radiation refrigeration composite material layer which coats a substrate to form a composite layer structure of the substrate and a passive radiation refrigeration layer, and the passive radiation refrigeration layer reflects visible light and near-infrared light in sunlight and dissipates heat through an atmospheric window in an infrared radiation form. The invention discloses a preparation method of the passive radiation refrigeration composite material layer, and the method comprises the following steps: dissolving resin in a volatile solvent, dispersing nanoparticles in the volatile solvent, and mixing at normal temperature to form a suspension; dissolving a functional polymer in the suspension, and uniformly mixing to form a coating solution; and coating the substrate with the coating solution to volatilize the solvent so as to form the passive radiation refrigeration layer on the surface of the substrate. The material disclosed by the invention has a simple single-layer structure, can simply coat the surfaces of various substrates like a coating, can reduce the incompatibility among multi-layer structures and reduce the cost, and is simple and convenient in preparation method, easy to operate and low in cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for preparing porous hollow nano-alumina fiber by static spinning
InactiveCN102776603ALow equipment requirementsImprove environmental friendlinessFilament/thread formingArtificial filament chemical after-treatmentPolymer dissolutionFiber
The invention relates to a method for preparing porous hollow nano-alumina fiber by static spinning. The method comprises the steps of: (1) dissolving metal salt and polymer into a cosolvent to obtain uniform or stably diffused spinning liquid, wherein the decomposing temperature of the metal salt is lower than that of the polymer, the vitrification transformation temperature of the polymer is lower than the decomposing temperature of the metal salt, and the diffusing rate of the oxide produced by decomposing the metal salt is less than the diffusing rate of the metal salt; (2) carrying out static spinning on the spinning liquid to obtain hybridized nanometer fiber; and (3) drying the hybridized nanometer fiber, and thermally processing to obtain the porous hollow nano-alumina fiber. According to the static spinning preparation method, the preparation technology is simple, and a special spinning needle head with an internal inserting pipe is not needed, and the requirement on equipment is low; and the obtained alumina fiber has the characteristics of high specific surface area, porous performance, and hollow performance and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Slow release fertilizer applicable to water-fertilizer integration and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103910586ATo achieve the purpose of slow release and controlled releaseSuitable for integrationFertilizer mixturesPolymer dissolutionOrganic solvent
Owner:广西田阳县创新农业综合开发有限公司
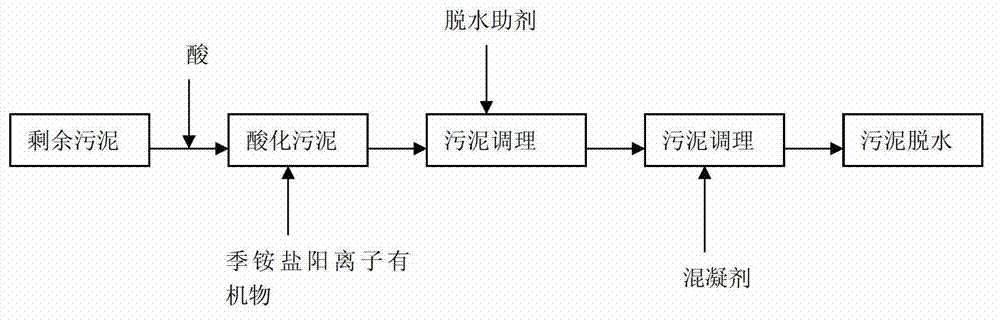
Method for conditioning and dehydrating residual sludge
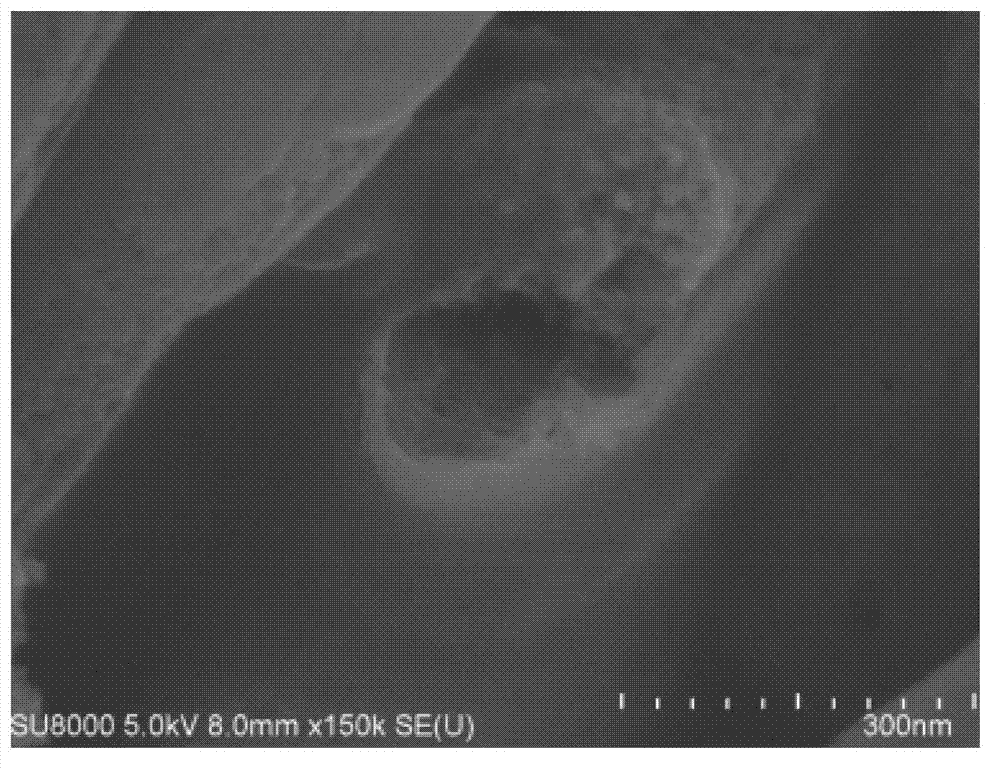
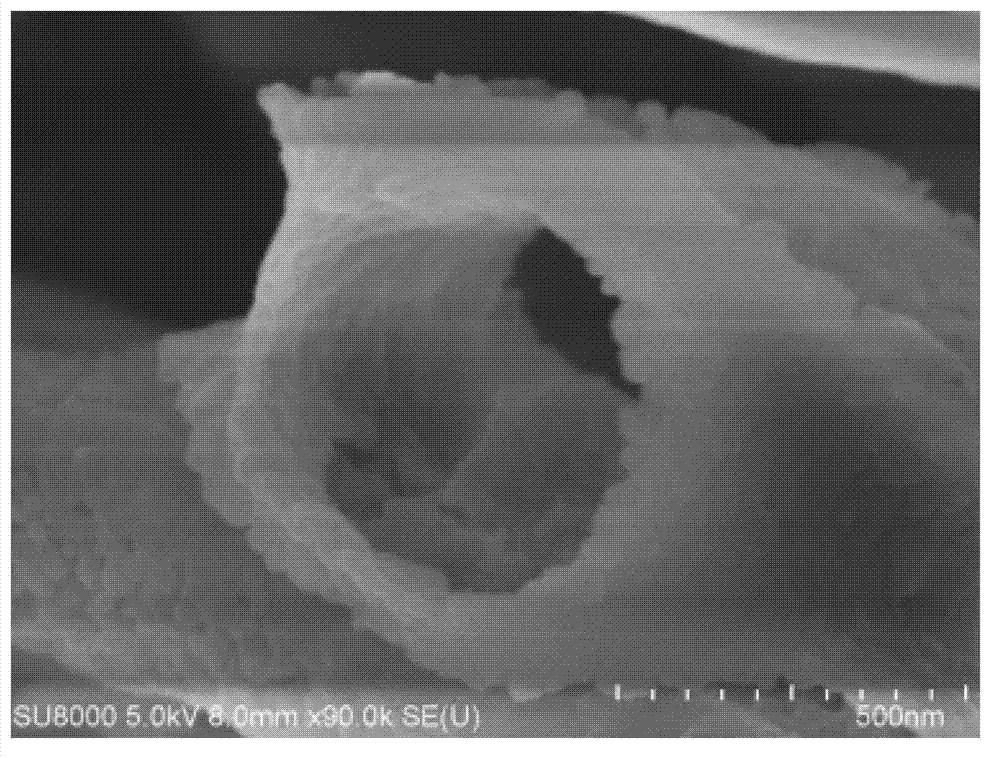
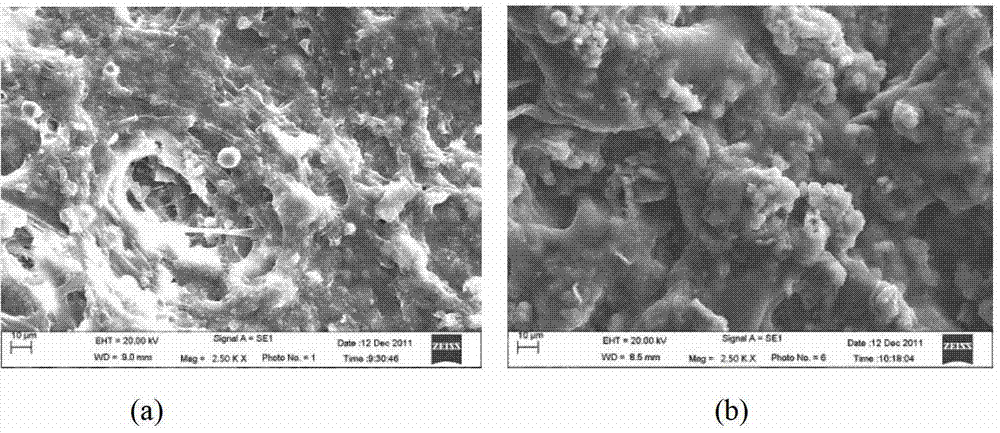
ActiveCN103030259APromote moisture penetrationImprove dehydration effectSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningPolymer dissolutionBiological cell
The invention relates to the technical field of residual sludge treatment, in particular to a process method for conditioning and dehydrating residual sludge. The method particularly comprises the following steps: (1) adding acid into the residual sludge to be treated and with the water content of 90 to 95 percent and adjusting until the pH value is between 4.0 and 6.0; (2) adding quaternary ammonium salt cationic organic matters into the conditioned sludge in the step (1) and performing hybrid reaction; (3) adding a dehydration aid into the conditioned sludge in the step (2) and stirring uniformly; and (4) adding coagulant into the conditioned sludge in the step (3) and mechanically dehydrating after mixing and stirring. The extracellular polymers on sludge flocs are stripped and partially hydrolyzed by a chemical conditioning mode, microbial cells are dissolved, a large amount of bound water is released, and the water permeability of the sludge is improved by utilizing the aid, so that the dehydration performance of the sludge is integrally improved, the water content of the sludge is reduced, the dehydration time is shortened and the dehydration cost is reduced.
Owner:北京方兴科创环境科技有限公司
Radiation sensitive resin composition
InactiveUSRE37179E1Improve accuracyIncrease resistanceRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolymer dissolutionPolymer science
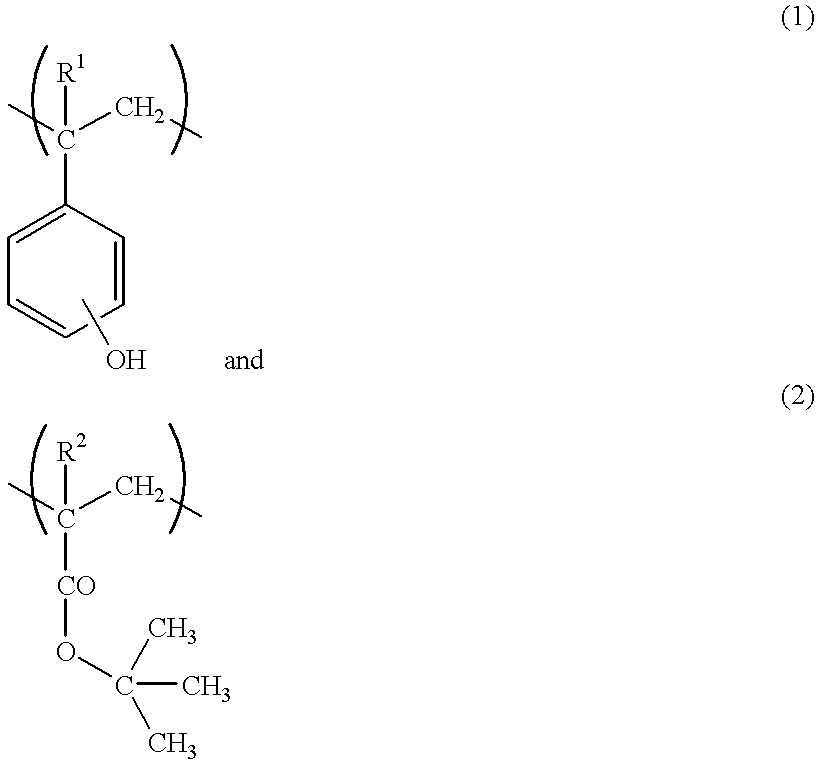
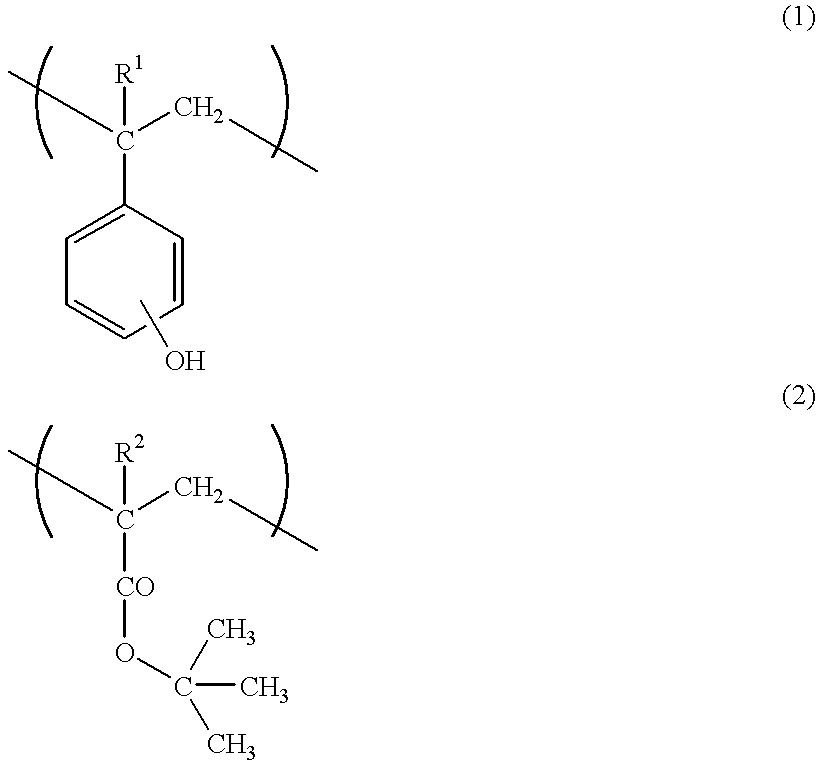
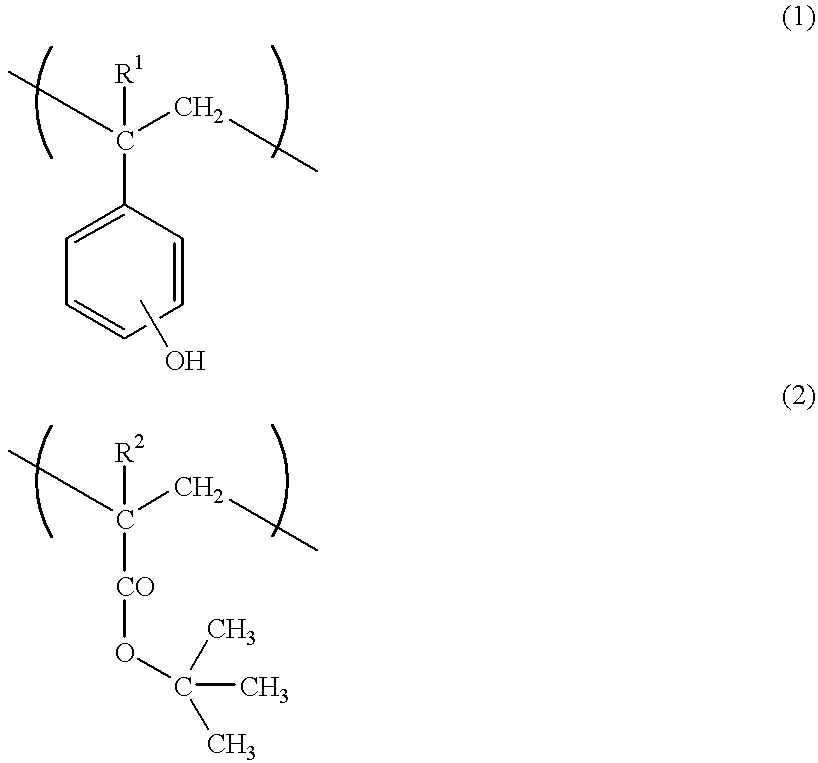
A radiation sensitive resin composition which comprises (A) a polymer which becomes alkali-soluble in the presence of an acid and (B) a radiation sensitive acid generator which generates an acid upon irradiation with a radiation, said polymer (A) comprising two recurring units represented by the general formulas (1) and (2) and a recurring unit which acts to reduce the solubility of the polymer is an alkali developer after the irradiation:wherein R1 represents a hydrogen atom or a methyl group and R2 represents a hydrogen atom or a methyl group. Said composition provides a chemically amplified positive resist which can give a fine pattern with a good pattern shape, and said resist is freed from volume shrinkage, peeling failure and adhesive failure, is excellent in dry etching resistance and effectively reacts with various radiations to give a good pattern shape which is excellent in photolithographic process stability, said pattern shape having no thinned portion at the upper part.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Waterproof membrane with good adhesion to concrete
ActiveUS20150231863A1Without diminishing adhesive capacityReduce adhesionFilm/foil adhesivesSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer dissolutionPremature aging
A waterproof membrane is described that includes a barrier layer and a functional layer. The functional layer can include a thermoplastic polymer that changes consistency under the influence of highly alkaline media, and an adhesive. The production and use of the membrane are also described. The functional layer of the membrane can be designed in the form of a film, a coating, or a nonwoven fabric. The fibers in the fabric can include a hard core that is surrounded by a polymer layer, is inert prior to coming into contact with liquid concrete and acts as a protective layer. Thus, the membrane is protected from premature aging and allows work to be performed with the seal in place. During the concreting process, i.e. when the functional layer comes into contact with liquid concrete, the polymer dissolves and thus allows the adhesive to bond to the concrete. The functional layer thus acts as an adhesive sealing compound and the seal is leakproof.
Owner:SIKA TECH AG
Method for manufacturing separator, separator manufactured therefrom, and electrochemical device comprising the same
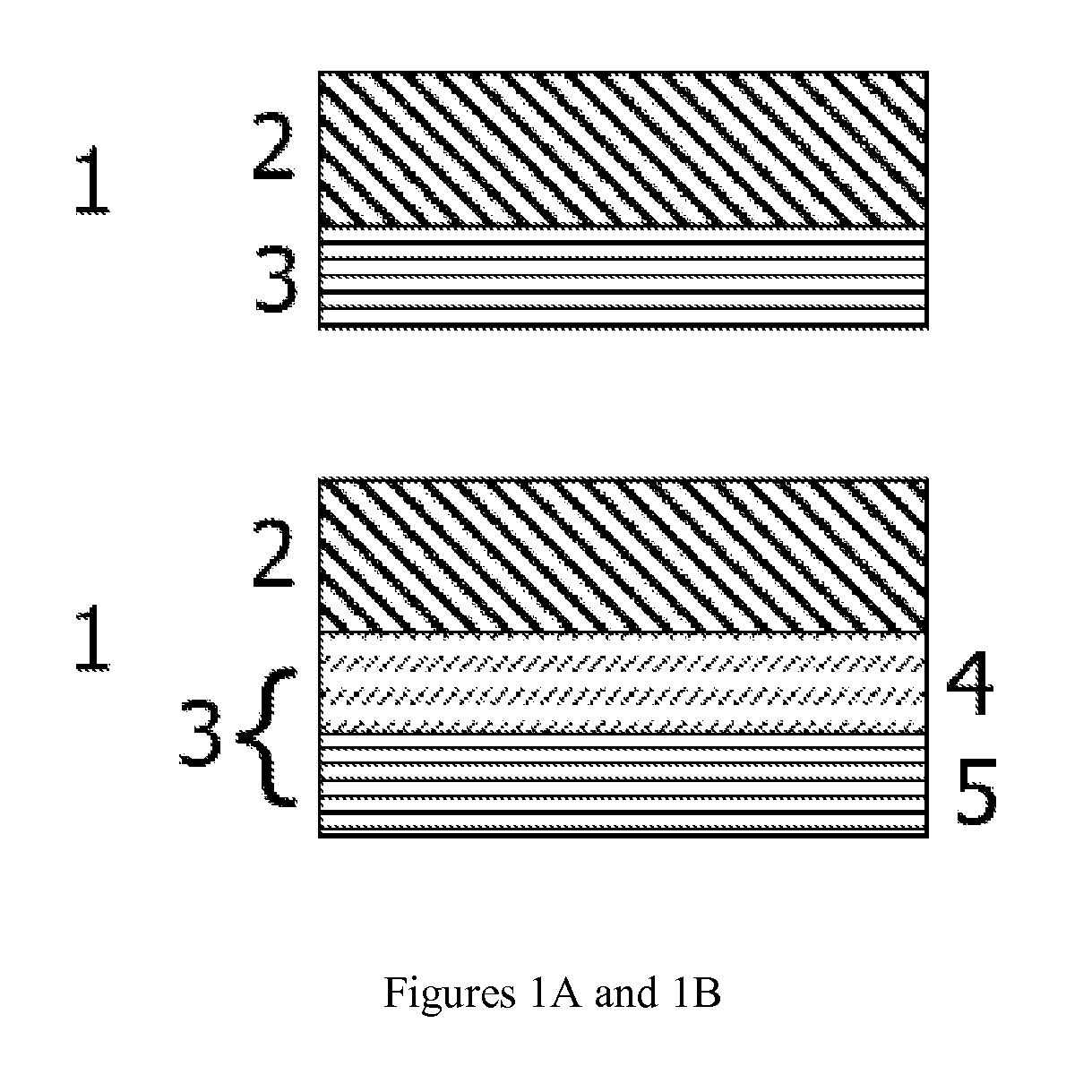
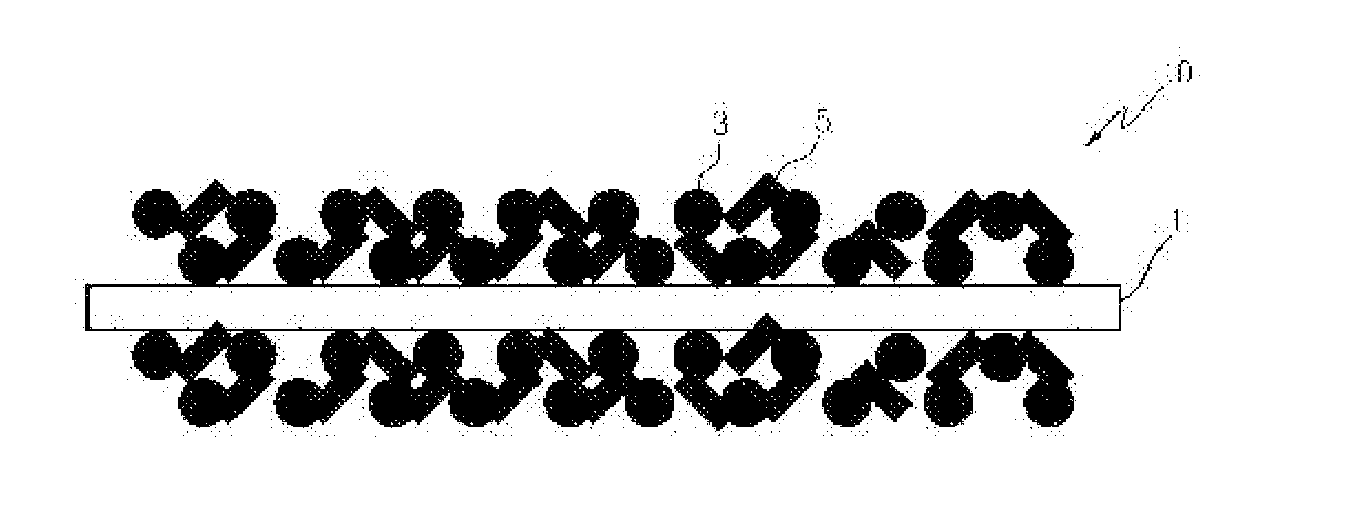
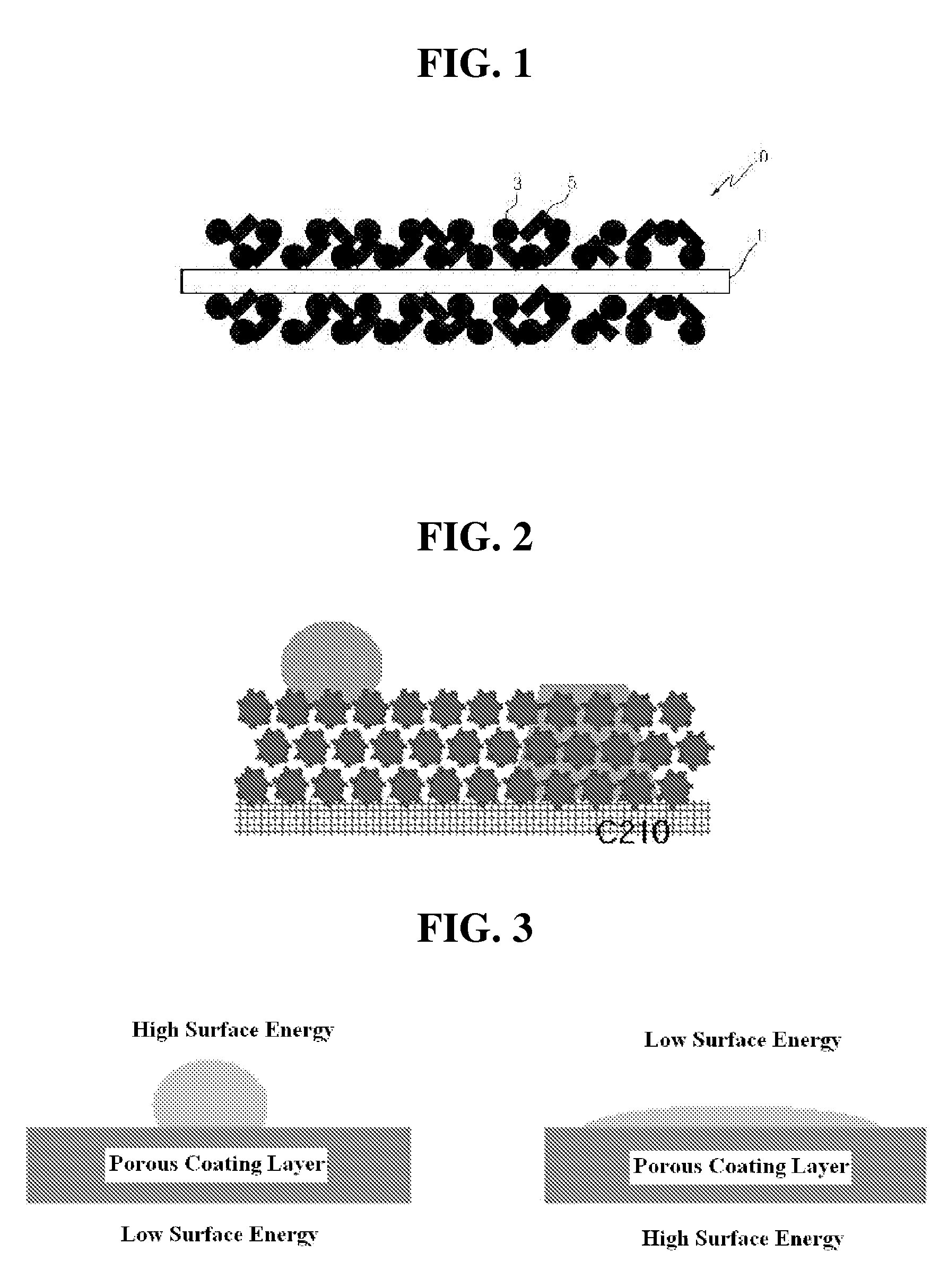
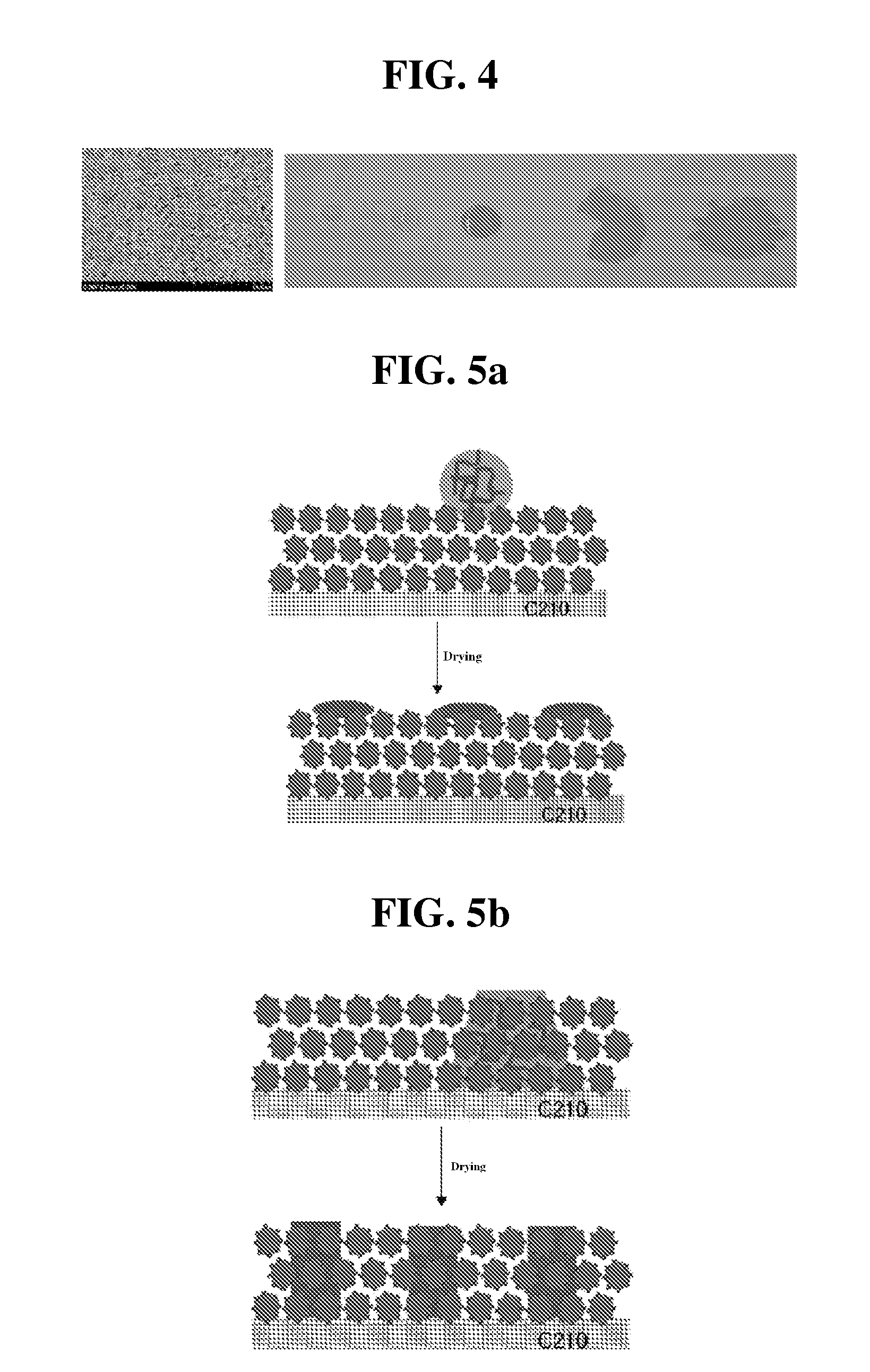
ActiveUS20130316219A1Minimize blockingImprove adhesionElectric discharge heatingFinal product manufacturePorous substratePolymer dissolution
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing a separator, comprising the steps of (S1) preparing a porous planar substrate having multiple pores; (S2) coating a coating solution obtained by dissolving a binder polymer in a solvent and dispersing inoganic particles therein on the porous substrate to form a porous coating layer and drying the porous coating layer; and (S3) applying a binder solution on the surface of the dried porous coating layer to form an adhesive layer, wherein the binder solution has a surface energy of at least 10 mN / m higher than that of the porous coating layer and a contact angle of the binder solution to the surface of the porous coating layer maintained at 80° or more for 30 seconds. In accordance with the present invention, a separator capable of obtaining sufficient adhesion force with minimizing the amount of an adhesive used for the adhesion with an electrode, and minimizing the deterioration of battery performances can be easily manufactured.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com