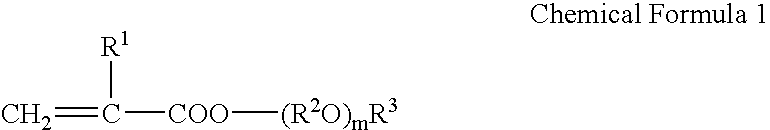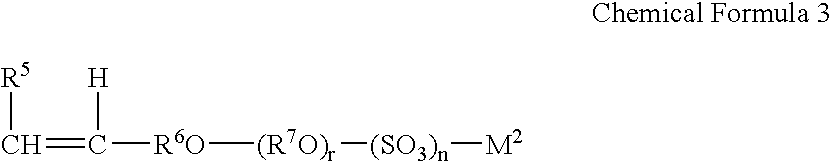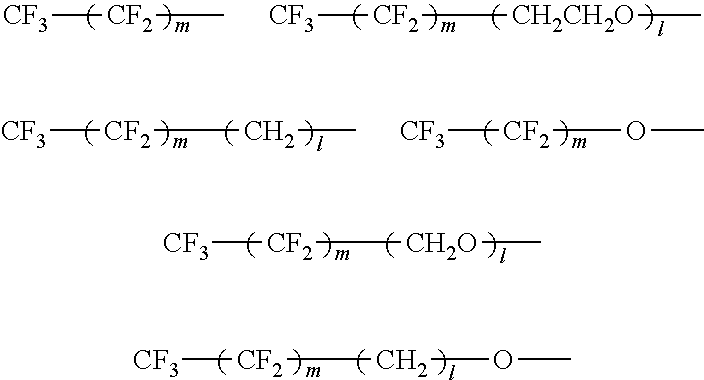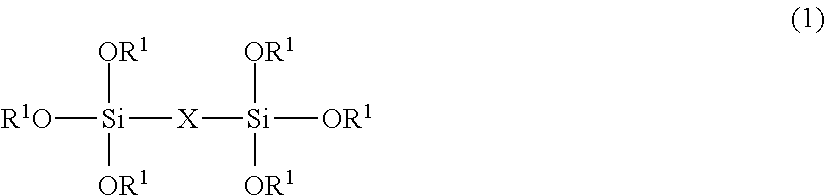Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47results about How to "Dispersion stability can be increased" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
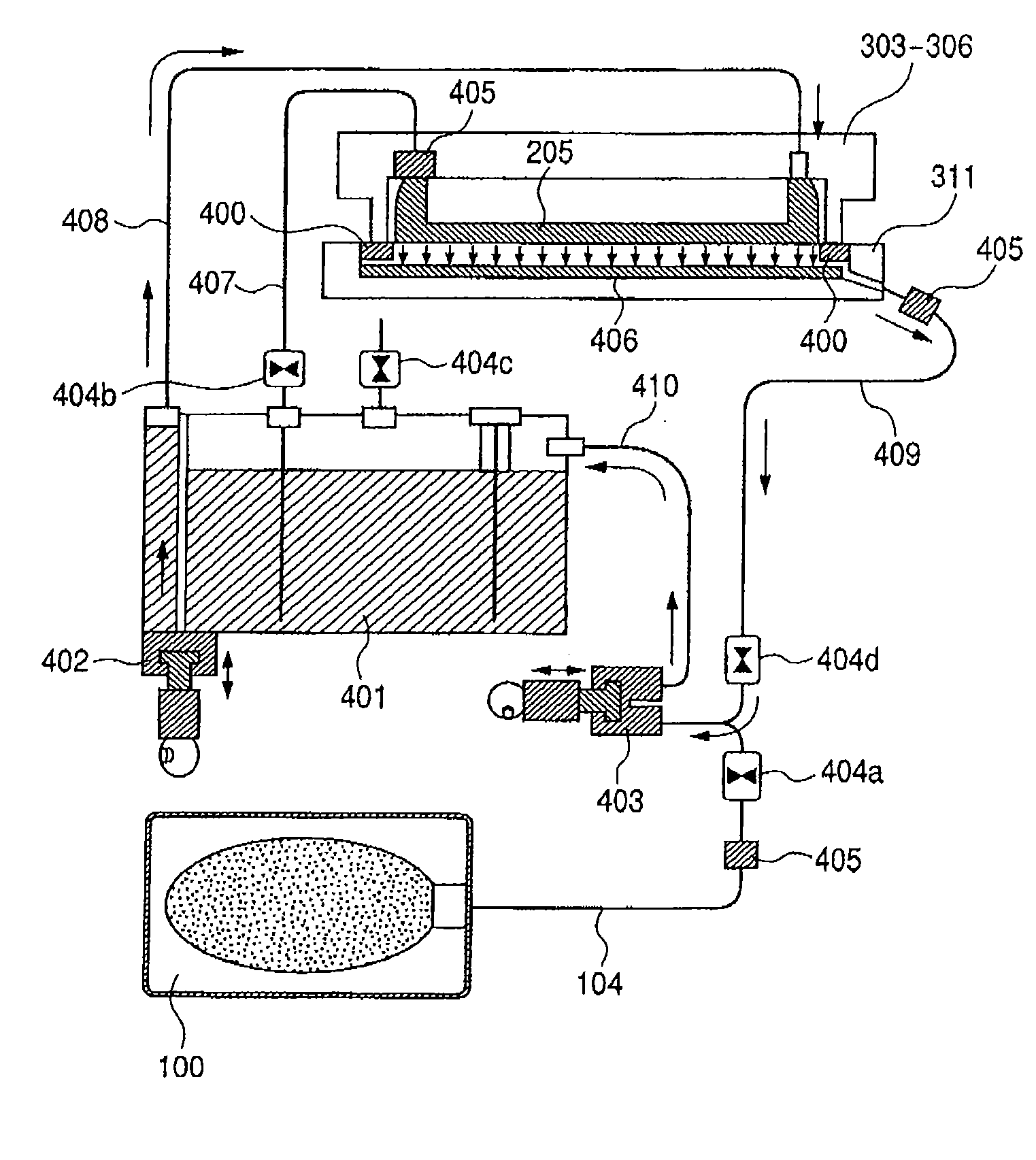
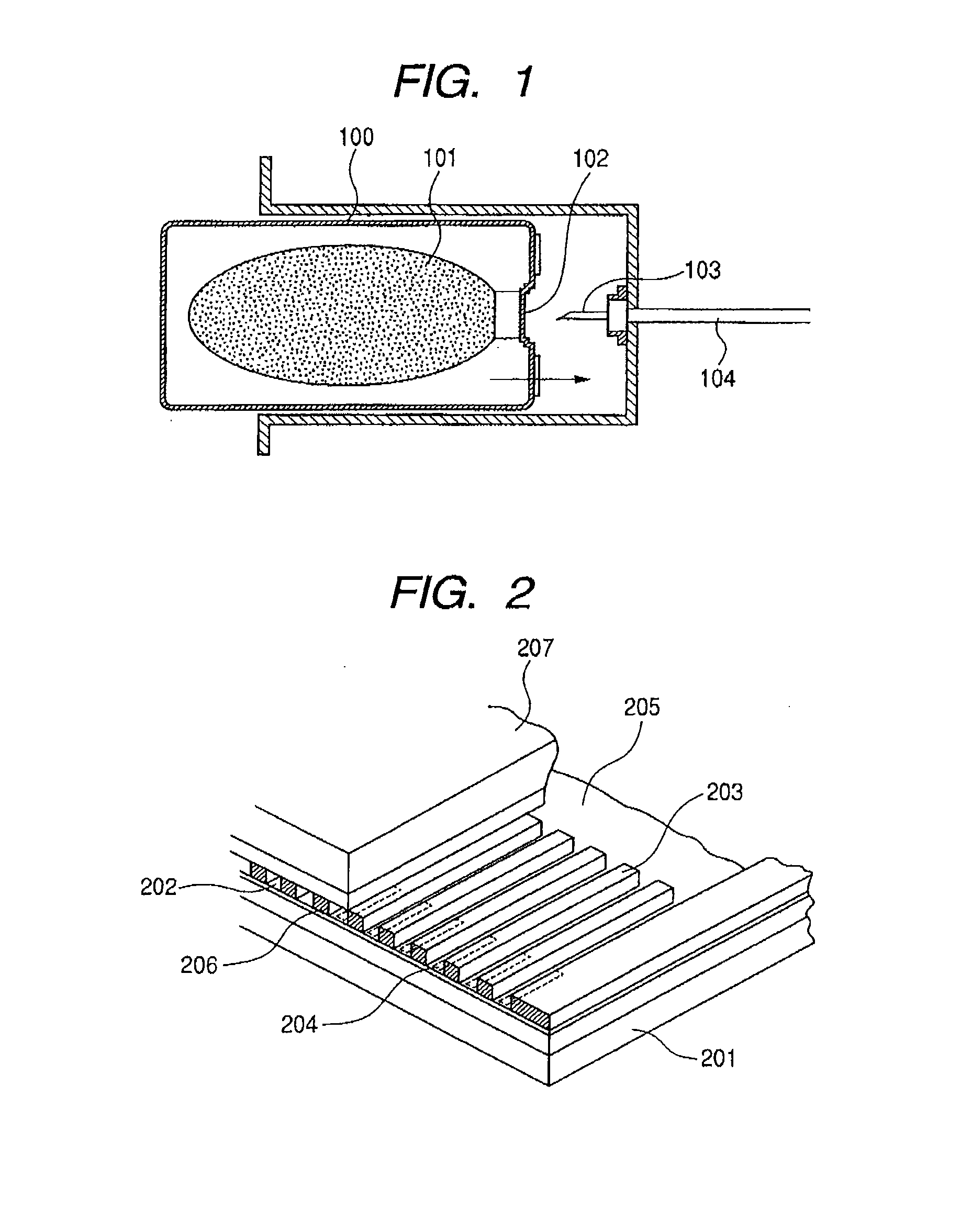
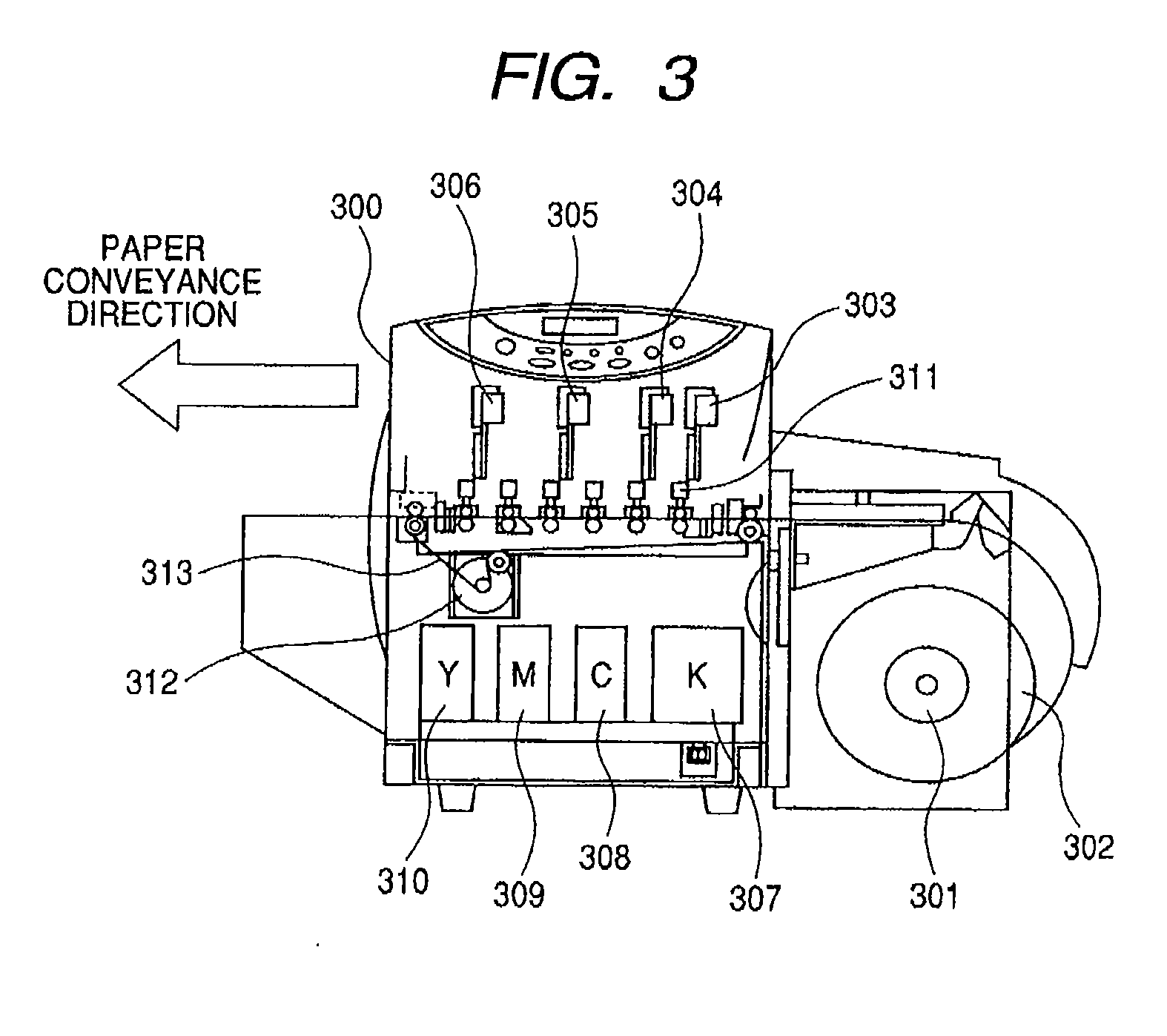
Pigment Dispersion, Recording Ink, Ink Cartridge, Ink-Jet Recording Method and Ink-Jet Recording Apparatus
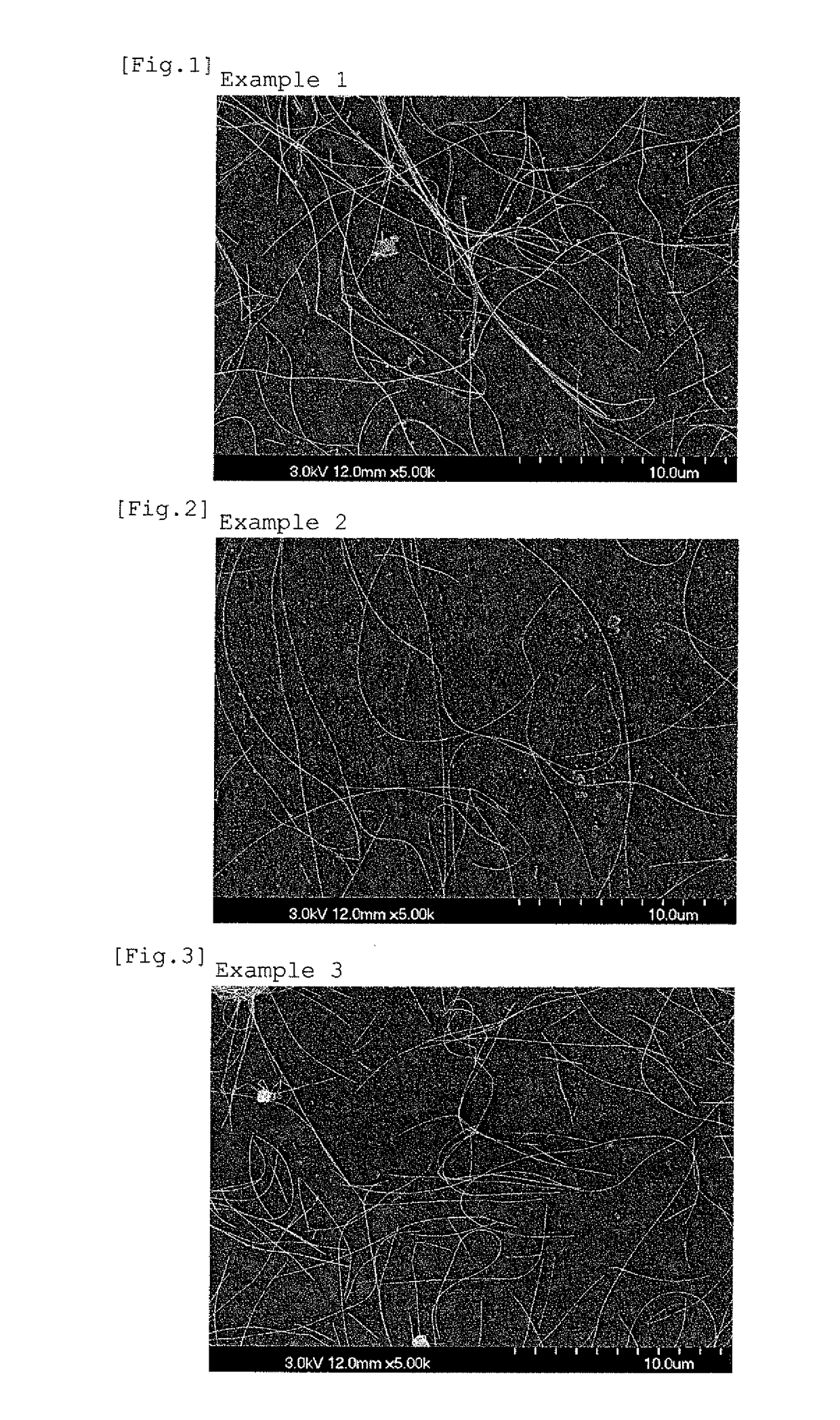
ActiveUS20090176070A1Dispersion stability can be increasedHigh image densityMeasurement apparatus componentsLayered productsPolymer scienceWater dispersible
A pigment dispersion is provided that includes a pigment, a pigment dispersant, a polymer dispersion stabilizer and water, wherein the polymer dispersion stabilizer is an alpha-olefin / maleic anhydride copolymer expressed by the formula (1) below. A recording ink is also provided that includes the pigment dispersion, a surfactant, a water-dispersible resin, a humectant and water.In the structural formula (1), R represents an alkyl group and n is an integer of 30 to 100.
Owner:RICOH KK
Pigment dispersion, recording ink, ink cartridge, ink-jet recording method and ink-jet recording apparatus
ActiveUS8242201B2Dispersion stability can be increasedHigh image densitySpecial tyresInksPolymer scienceWater dispersible
Owner:RICOH KK
Toner including compound having bisazo skeleton
An object of the present invention is to provide a toner having high dispersibility of an azo pigment in a binder resin and a good color tone, having suppressed image fogging and high transfer efficiency, and providing a stable image for a long time. The toner including toner base particles, each of which includes: at least a binder resin, a compound in which a specific bisazo skeleton unit bonds to a specific polymer resin unit, and an azo pigment as a colorant.
Owner:CANON KK
Pigment dispersion liquid, inkjet recording ink, inkjet recording method, ink cartridge and inkjet recording apparatus
InactiveUS20100021635A1Dispersion stability can be increasedEnhanced ejectionDuplicating/marking methodsInksPolymer sciencePigment
To provide a pigment dispersion liquid which provides an ink capable of recording an image having high fixability and fastness such as scratch resistance and excellent quality stably for a long time in any conditions. A pigment dispersion liquid mainly containing a polymer dispersant, a coloring material and water, in which the polymer dispersant is formed of at least a hydrophobic unit and a hydrophilic unit, the hydrophobic unit having a block portion formed of at least one hydrophobic monomer, the coloring material is formed of a pigment having on its surface an acid form anionic group, and the pigment dispersion liquid further contains a basic compound capable of forming a complex with an alkaline metal.
Owner:CANON KK
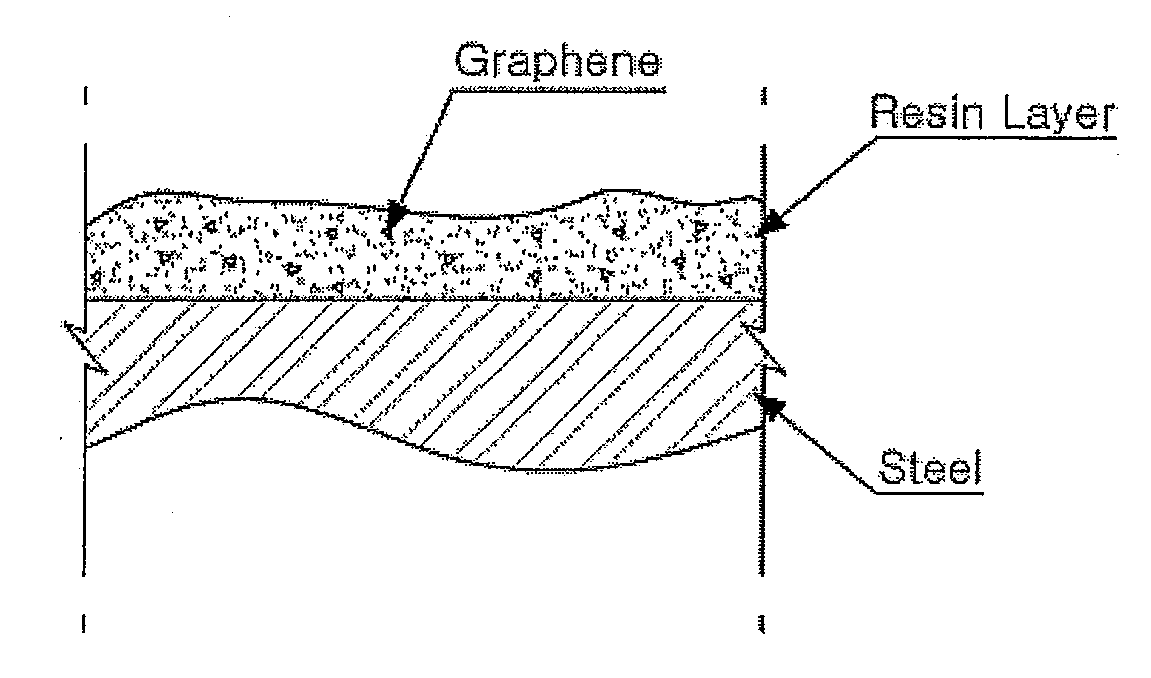
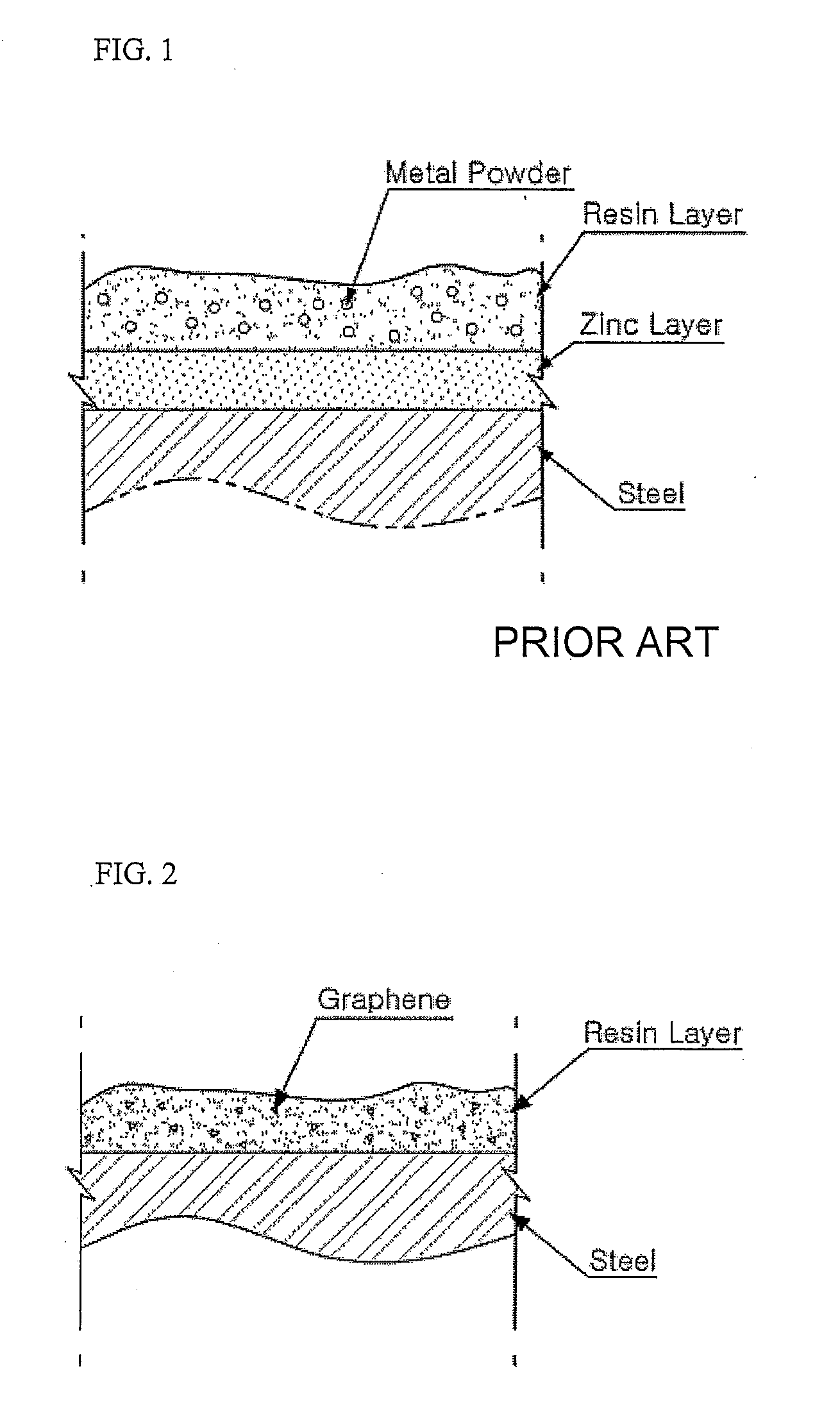
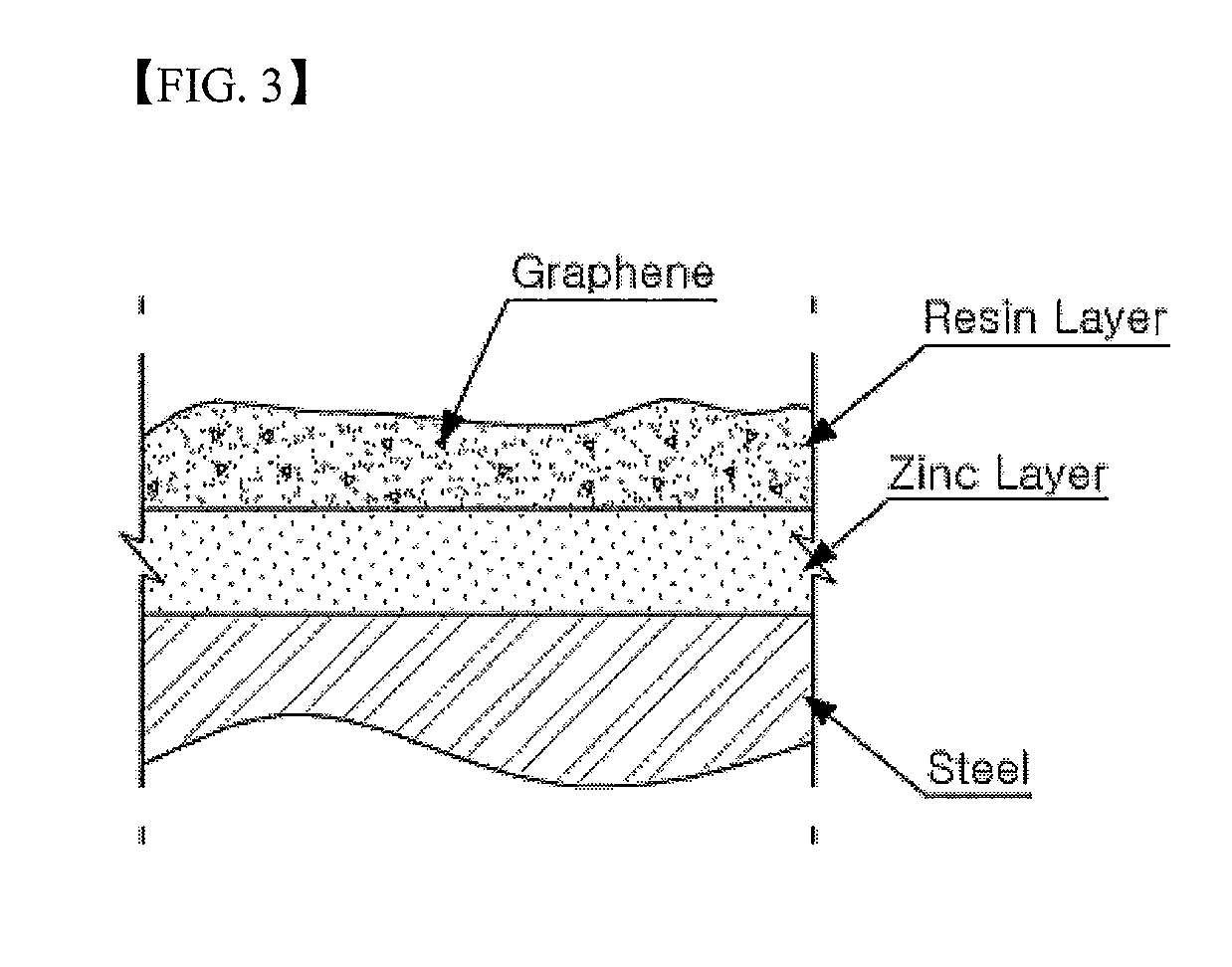
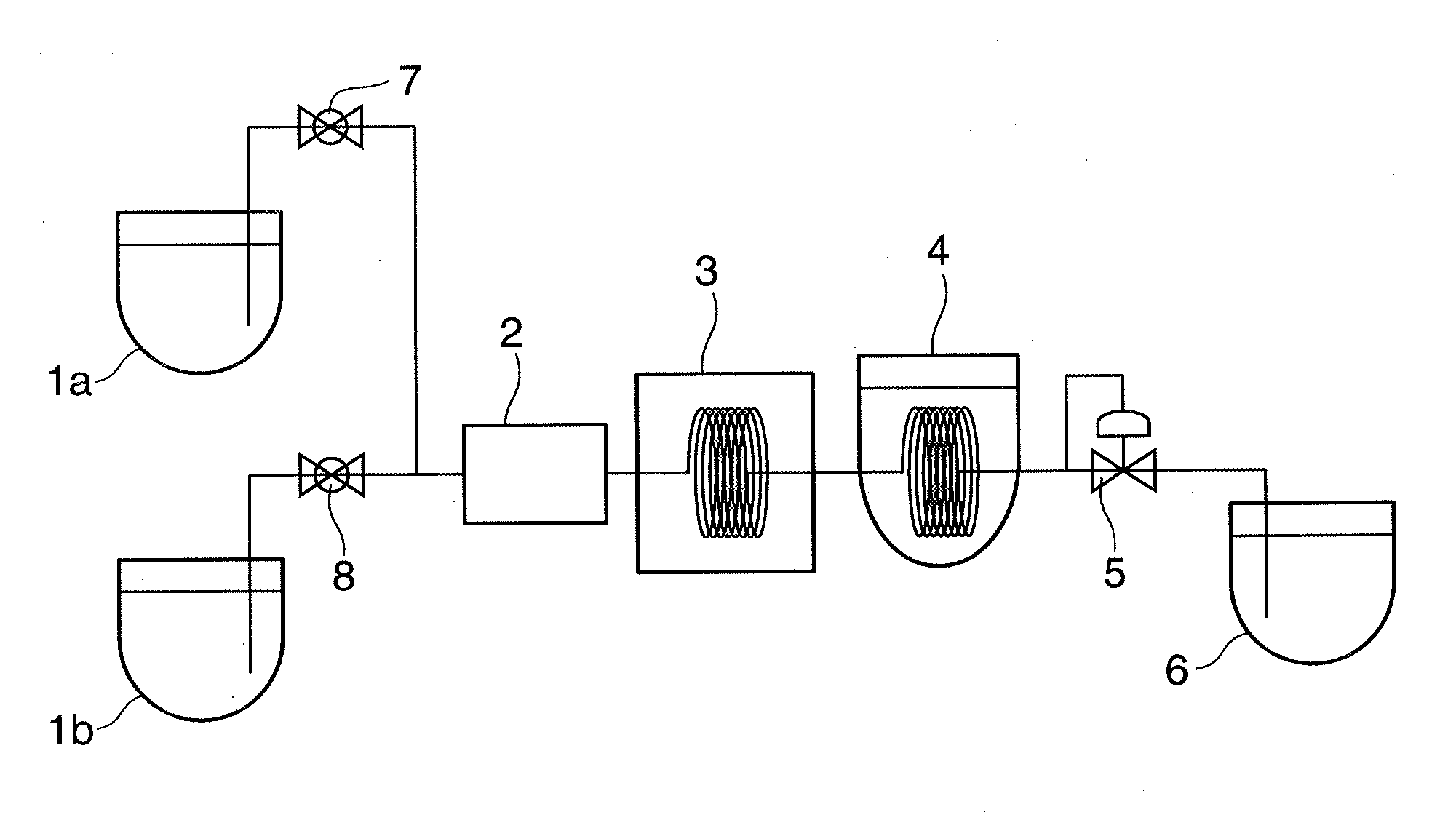
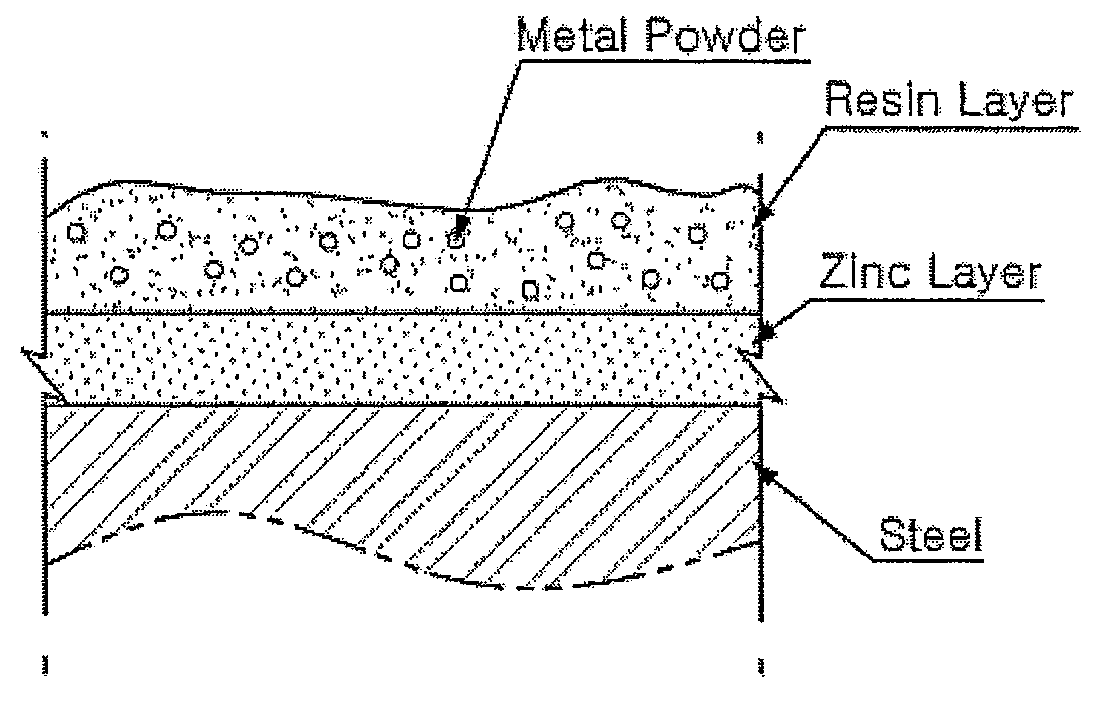
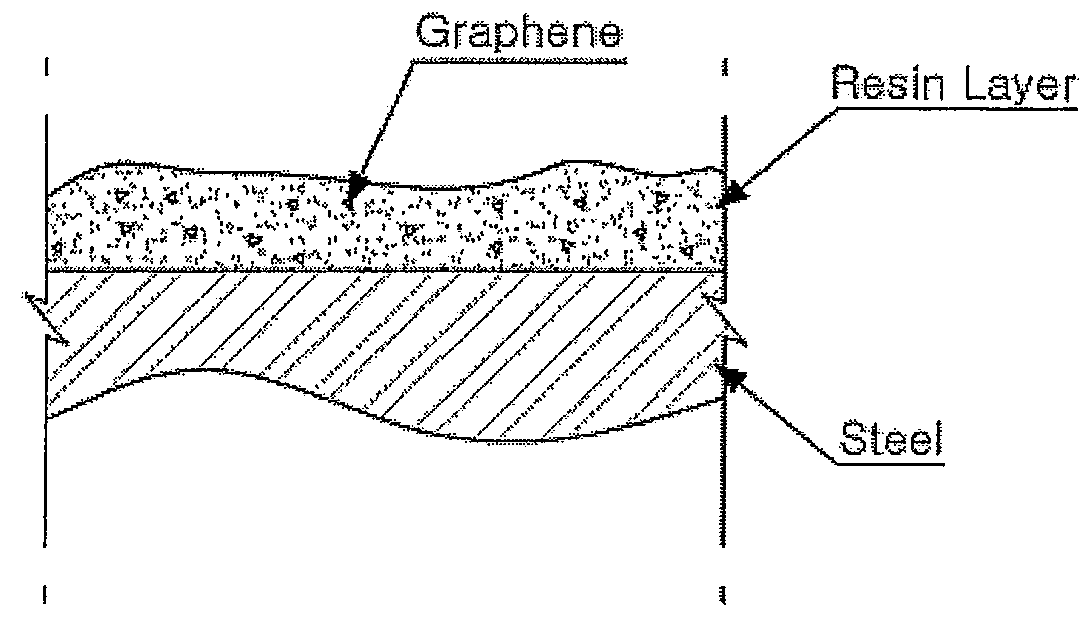
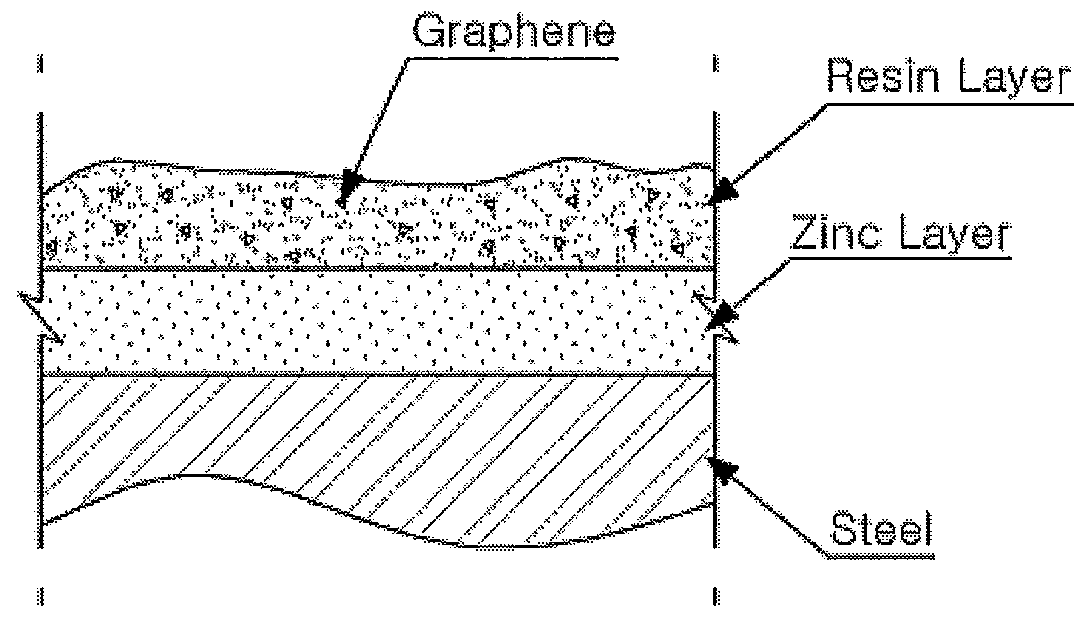
Resin Composition for Surface Treatment of Steel Sheet and Surface-Treated Steel Sheet Using the Same
ActiveUS20110256387A1Dispersion stability can be increasedMaterial nanotechnologyConductive materialSheet steelSolvent
Provided is a resin composition for surface treatment of a steel sheet including a binder resin, graphene and a solvent. More particularly, as only a small amount of the graphene is included in the resin composition used for surface treatment of a steel sheet, a user-required electrical conductivity can be provided to the steel sheet.
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Conductive film-forming composition and conductive film producing method
ActiveUS20160024316A1Dispersion stability can be increasedFew voidRadiation applicationsConductive materialVolume averageCopper oxide
In a conductive film-forming composition including copper oxide particles, water and a dispersant selected from the group consisting of a water-soluble polymer and a surfactant, the copper oxide particles have a volume average secondary particle size of 20 to 240 nm, and the copper oxide particles are contained in an amount of 10 to 70 wt % with respect to a total weight of the conductive film-forming composition.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Cement admixture having superior water-reducing properties and method for preparing the same
InactiveUS6939402B2Dispersion stability can be increasedImprove machinabilityPolymer scienceCarboxylic acid
The present invention provides a cement admixture that comprises at least one of a carboxylic acid based copolymer comprising a reactive surfactant as a monomer or a copolymer salt obtained by neutralizing the copolymer with an alkaline substance, a method for preparing the same, and a cement composition comprising the same. The cement admixture of the present invention increases composition fluidity even at a high water-reducing formulation by improving dispersibility of cement particles, prevents a decrease of fluidity as the function of time, and offers good workability by supplying an adequate amount of air flow continuously.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Visible light-responsive photocatalytic nanoparticle dispersion liquid, method for producing same, and member having photocatalytic thin film on surface
ActiveUS20150273440A1Dispersion stability can be increasedPromote formationGas treatmentDispersed particle separationWater basedDispersion stability
It is possible to obtain a visible light-responsive photocatalytic nanoparticle dispersion liquid containing copper-containing titanium oxide nanoparticles by subjecting an aqueous peroxotitanic acid solution containing a copper compound to hydrothermal reaction for crystallizing the aqueous solution by means of heat under high pressure. The visible light-responsive photocatalytic nanoparticle dispersion liquid thus obtained exhibits excellent dispersion stability of titanium oxide nanoparticles within a water-based dispersion medium even when left in a cold and dark indoor area for a long period of time, expresses photocatalytic activity even in visible light (400 to 800 nm) alone, and can easily create a photocatalytic thin film which is extremely transparent and exhibits excellent durability, and in which the state of copper coordination when exposed to heat or ultraviolet rays is stable and cannot be easily modified.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Binder for nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery electrode, manufacturing method therefor and use therefor
ActiveUS20170352886A1Improve bending resistanceUniform layersSecondary cellsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesPolymer scienceCrosslinked polymers
Provided is a binder for a nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery electrode. The binder contains a crosslinked polymer having a carboxyl group, or salt thereof, a use therefor, and a method for manufacturing a carboxyl group-containing crosslinked polymer or salt thereof for use in the binder. The crosslinked polymer contains a structural unit derived from an ethylenically unsaturated carboxylic acid monomer in the amount of 50 to 100 mass % of total structural units, and after the crosslinked polymer neutralized to a degree of a neutralization of 80 to 100 mol % has been subjected to water swelling in water and then dispersed in a 1 mass % NaCl aqueous solution, the particle diameter thereof is 0.1 to 7.0 μm in a volume-based median diameter.
Owner:TOAGOSEI CO LTD
Conjugate of fine porous particles with polymer molecules and the utilization thereof
InactiveUS20060159715A1Dispersion stability can be increasedControl releaseCosmetic preparationsBiocideWater solublePorous particle
A conjugate which comprises fine porous particles (on which functional substance may be adhered) and a polymer based on water-soluble high molecular chain segment, and the use of the conjugate (for the purpose of stably supporting, or slowly releasing, a physiologically active substance, or the like).
Owner:TOKYO UNIV OF SCI EDUCATIONAL FOUND
Inkjet recording ink and recorded matter
InactiveUS20150353752A1Good storage stabilityExcellent ejection stabilityLayered productsInksSolubilityDisperse dye
An inkjet recording ink is used for an inkjet recording device that includes a silicone rubber having a solubility parameter at 25° C. of 6 to 8 as a member with which an ink comes in contact, the inkjet recording ink including water, a disperse dye, and an anionic surfactant, the content X (mass %) of the disperse dye and the content Y (mass %) of the anionic surfactant in the inkjet recording ink satisfying the relationship “Y / X≧0.7”.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Visible light-responsive photocatalytic nanoparticle dispersion liquid, method for producing same, and member having photocatalytic thin film on surface
ActiveUS9604198B2Dispersion stability can be increasedFormation of thinGas treatmentDispersed particle separationTitanium oxidePhoto catalysis
It is possible to obtain a visible light-responsive photocatalytic nanoparticle dispersion liquid containing copper-containing titanium oxide nanoparticles by subjecting an aqueous peroxotitanic acid solution containing a copper compound to hydrothermal reaction for crystallizing the aqueous solution by means of heat under high pressure. The visible light-responsive photocatalytic nanoparticle dispersion liquid thus obtained exhibits excellent dispersion stability of titanium oxide nanoparticles within a water-based dispersion medium even when left in a cold and dark indoor area for a long period of time, expresses photocatalytic activity even in visible light (400 to 800 nm) alone, and can easily create a photocatalytic thin film which is extremely transparent and exhibits excellent durability, and in which the state of copper coordination when exposed to heat or ultraviolet rays is stable and cannot be easily modified.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Hydrophobic metal and metal oxide particles with unique optical properties
InactiveUS20080214718A1Dispersion stability can be increasedHigh optical clarityMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic dyesOptical transparencyOptical property
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
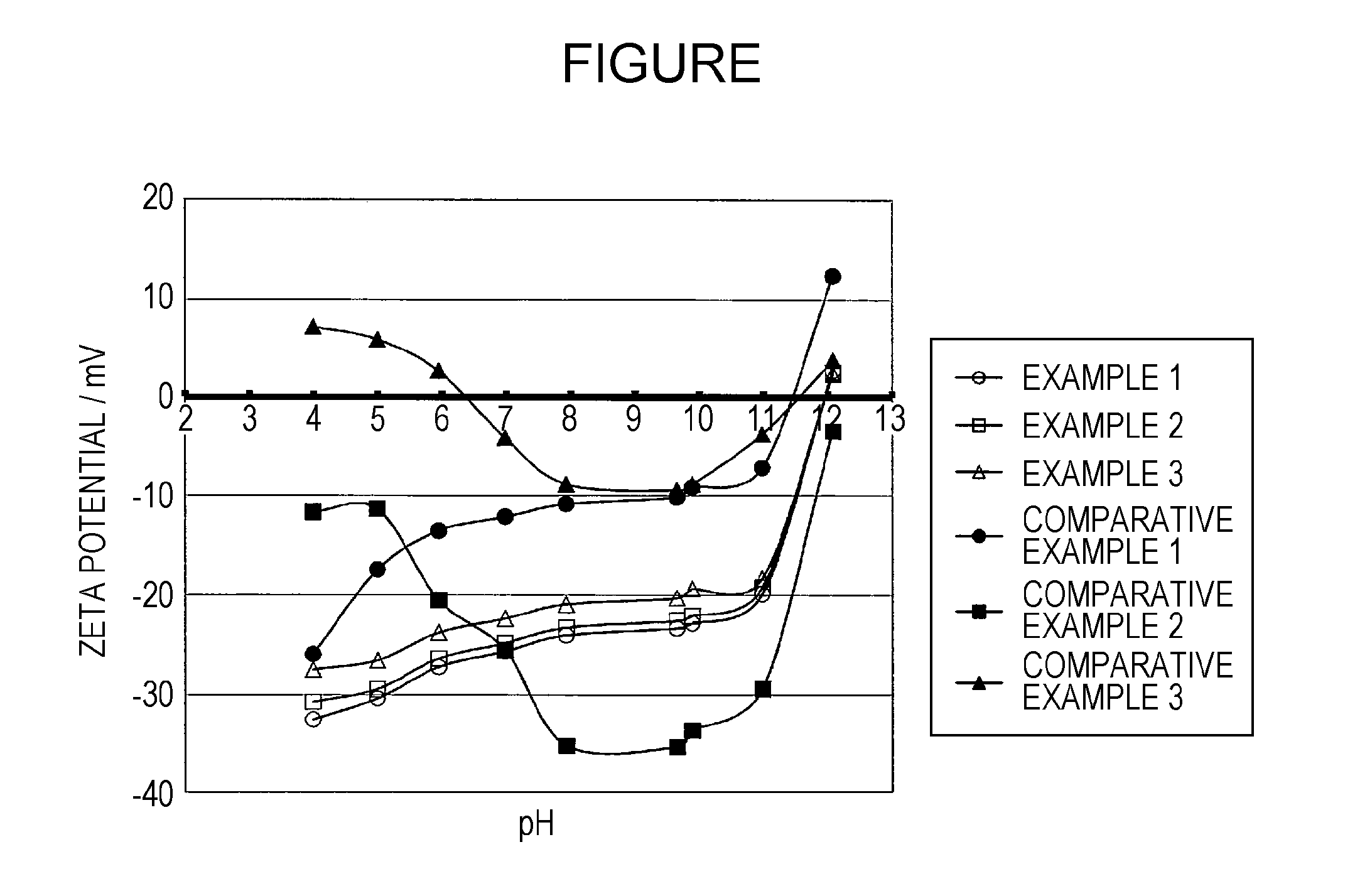
Base metal pigment, aqueous base metal pigment dispersion liquid, and aqueous ink composition
ActiveUS20150210859A1Dispersion stability can be increasedEasily detachedPigmenting treatmentInksSolventChemistry
Disclosed herein is a base metal pigment, which is used for an aqueous ink composition containing water as a part of a solvent, in which the base metal pigment is surface-treated with a fluorine-based compound, and has a zeta potential of greater than or equal to −50 mV and less than or equal to −15 mV, as measured by an ultrasonic zeta potential measurement device, in a pH range of greater than or equal to 5 and less than or equal to 10.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Rapid method for production of cerium-containing oxide organic colloids
InactiveUS20130192122A1Simple and rapid and low temperature processDispersion stability can be increasedLiquid carbonaceous fuelsIron compoundsOctanoic AcidsEmulsion
Improved methods for producing colloidal dispersions of cerium-containing oxide nanoparticles in substantially non-polar solvents is disclosed. The cerium-containing oxide nanoparticles of an aqueous colloid are transferred to a substantially non-polar liquid comprising one or more amphiphilic materials, one or more low-polarity solvents, and, optionally, one or more glycol ether promoter materials. The transfer is achieved by mixing the aqueous and substantially non-polar materials, forming an emulsion, followed by a phase separation into a remnant polar solution phase and a substantially non-polar organic colloid phase. The organic colloid phase is then collected. The promoter functions to speed the transfer of nanoparticles to the low-polarity phase. The promoter accelerates the phase separation, and also provides improved colloidal stability of the final substantially non-polar colloidal dispersion. The glycol ether promoter reduces the temperature necessary to achieve the phase separation, while providing high extraction yield of nanoparticles into the low-polarity organic phase. In addition, use of particular amphiphilic materials, such as heptanoic acid or octanoic acid, enable efficient extractions at ambient temperatures without the use of a glycol ether promoter.
Owner:CERION
Solid electrolyte composition, electrode sheet for all-solid state secondary battery, all-solid state secondary battery, and methods for manufacturing electrode sheet for all-solid state secondary battery and all-solid state secondary battery
ActiveUS20180090787A1Improve bindingImprove ionic conductivityNon-metal conductorsSolid electrolytesAll solid statePhysical chemistry
Provided are a solid electrolyte composition containing at least one dendritic polymer selected from the group consisting of dendrons, dendrimers, and hyperbranched polymers and a specific inorganic solid electrolyte, in which the dendritic polymer has at least one specific functional group, an electrode sheet for an all-solid state secondary battery and an all-solid state secondary battery for which the solid electrolyte composition is used, a method for manufacturing an electrode sheet for an all-solid state secondary battery, and a method for manufacturing an all-solid state secondary battery.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Visible-light-responsive titanium oxide microparticle dispersion, method for manufacturing same, and member having surficial photocatalyst thin film formed using same dispersion
ActiveUS20140309103A1Dispersion stability can be increasedEasy to produceCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsDispersion stabilityMicroparticle
Provided is a visible-light-responsive titanium oxide microparticle dispersion or the like readily enabling manufacture of a highly transparent photocatalyst thin film demonstrating photocatalyst activity even using visible light alone, and having exceptional titanium oxide microparticle dispersion stability even after storage for prolonged periods of time in cold and dark interior locations. The present invention makes it possible to: produce a peroxotitanic acid solution containing vanadium and a tin compound from a titanium compound, a vanadium compound, a tin compound, a basic substance, hydrogen peroxide, and an aqueous dispersion medium as starting materials; subject the peroxotitanic acid solution to a hydrothermal reaction under high pressure; subsequently admix a copper compound into the acid solution; and obtain a visible-light-responsive titanium oxide microparticle dispersion or the like.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Coating composition and optical article having a coat layer made of the coating composition
ActiveUS20170240769A1Good effectImprove adhesionSpectales/gogglesCoatingsWeather resistanceMicroparticle
A coating composition comprising inorganic oxide fine particles containing at least one element selected from the group consisting of Ti, Zr, Sn and Sb, a hydrolysable group-containing organic silicon compound, and (C1) a surfactant having an HLB value of 8 or less and (C2) a surfactant having an HLB value of more than 8, for forming a coat layer having little white turbidity, a good appearance and excellent scratch resistance, chemical resistance, hot water resistance and weather resistance on the surface of a plastic optical substrate.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP
Electrophotographic photoreceptor and image forming apparatus including the same
ActiveUS20150017580A1Good dispersionImprove wear resistanceElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeX-rayComposition analysis
An electrophotographic photoreceptor having a photosensitive layer formed on a conductive substrate, wherein the photosensitive layer contains oxygen-containing fluorinated fine particles in a surface layer thereof, and the oxygen-containing fluorinated fine particles have an oxygen composition ratio of 0.9 to 3.0% by atom based on the whole composition of the fine particles according to an X-ray fluorescence composition analysis.
Owner:SHARP KK
Dispersion of metal fine particles
PendingUS20220204798A1Good storage stabilityDispersion stability can be increasedMaterial nanotechnologyFixed capacitor electrodesPhysical chemistryPropylene glycol
The present invention relates to [1] a dispersion of metal fine particles containing hydroxyacetone and propylene glycol, in which a cumulant average particle size of the metal fine particles is not less than 0.01 μm and not more than 0.1 μm, and [2] an ink containing the dispersion of metal fine particles as described in the above [1].
Owner:KAO CORP
Method for manufacturing microparticulate anatase or rutile titanium oxide dispersion and component having photocatalytic thin film on surface
ActiveUS9463436B2Dispersion stability can be increasedWell formedAntifouling/underwater paintsCatalyst activation/preparationMicroparticleTitanium oxide
A method for manufacturing a microparticulate anatase or rutile titanium oxide dispersion from a peroxotitanic acid solution optionally containing tin, wherein the method for manufacturing an anatase or rutile titanium oxide dispersion is characterized in that the peroxotitanic acid solution is fed continuously to a flow reactor and subjected to hydrothermal treatment at 150 to 250° C. and 0.5 to 10 MPa. The invention makes it possible to provide a method for manufacturing a microparticulate anatase or rutile titanium oxide dispersion having excellent stability in regard to the titanium oxide microparticles and enabling a high-transparency photocatalytic thin film to be produced, and to provide a member having a photocatalytic thin film formed on the surface using this dispersion.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Ink composition and recording method
ActiveUS20180265722A1Improved pigment dispersionHigh ejecting stabilityInksChemistrySURFACTANT BLEND
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Resin composition for surface treatment of steel sheet and surface-treated steel sheet using the same
ActiveUS9228111B2Good dispersionDispersion stability can be increasedConductive materialRecord information storageSheet steelSolvent
Provided is a resin composition for surface treatment of a steel sheet including a binder resin, graphene and a solvent. More particularly, as only a small amount of the graphene is included in the resin composition used for surface treatment of a steel sheet, a user-required electrical conductivity can be provided to the steel sheet.
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Method for preparing a polishing slurry having high dispersion stability
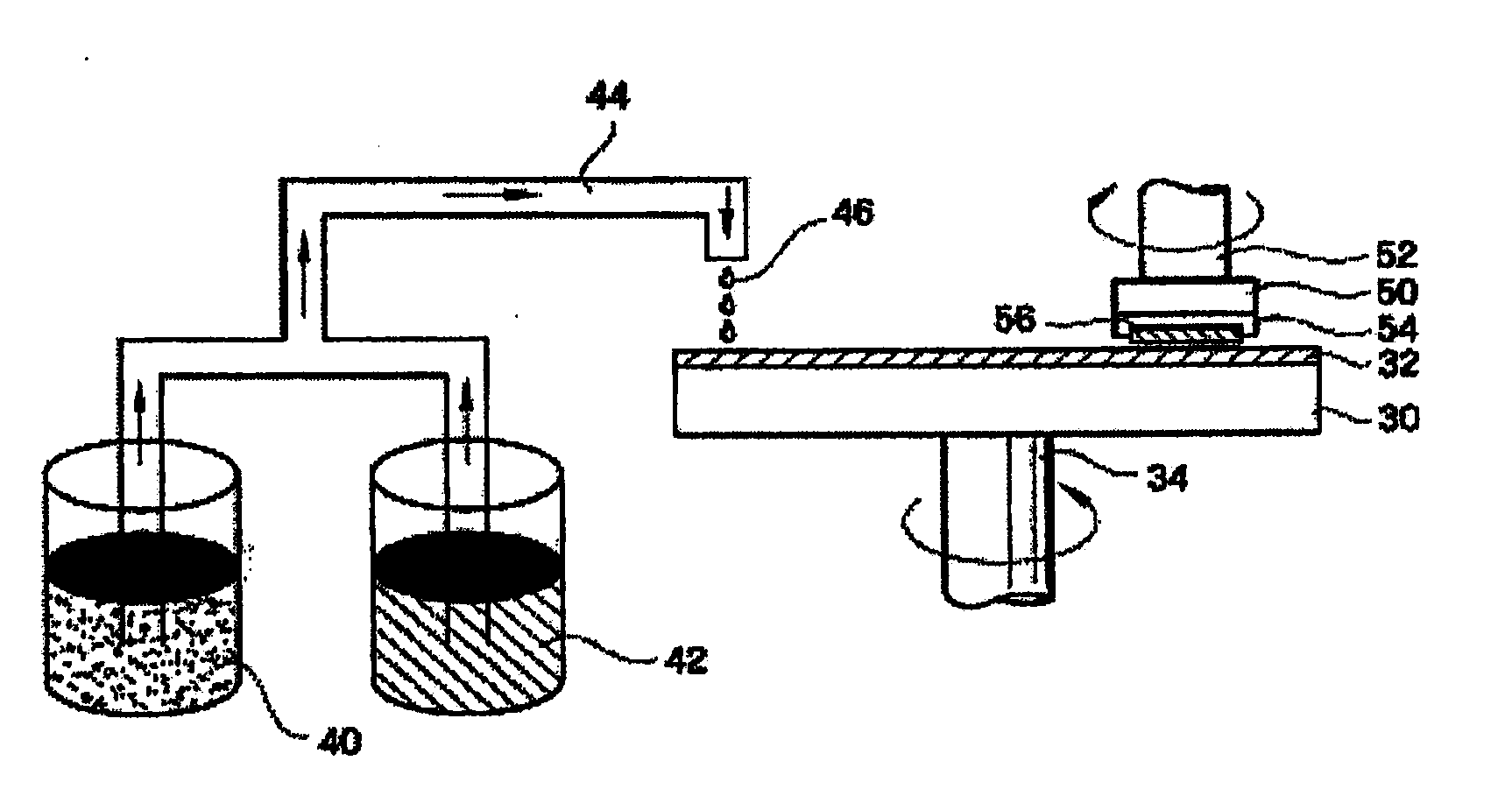
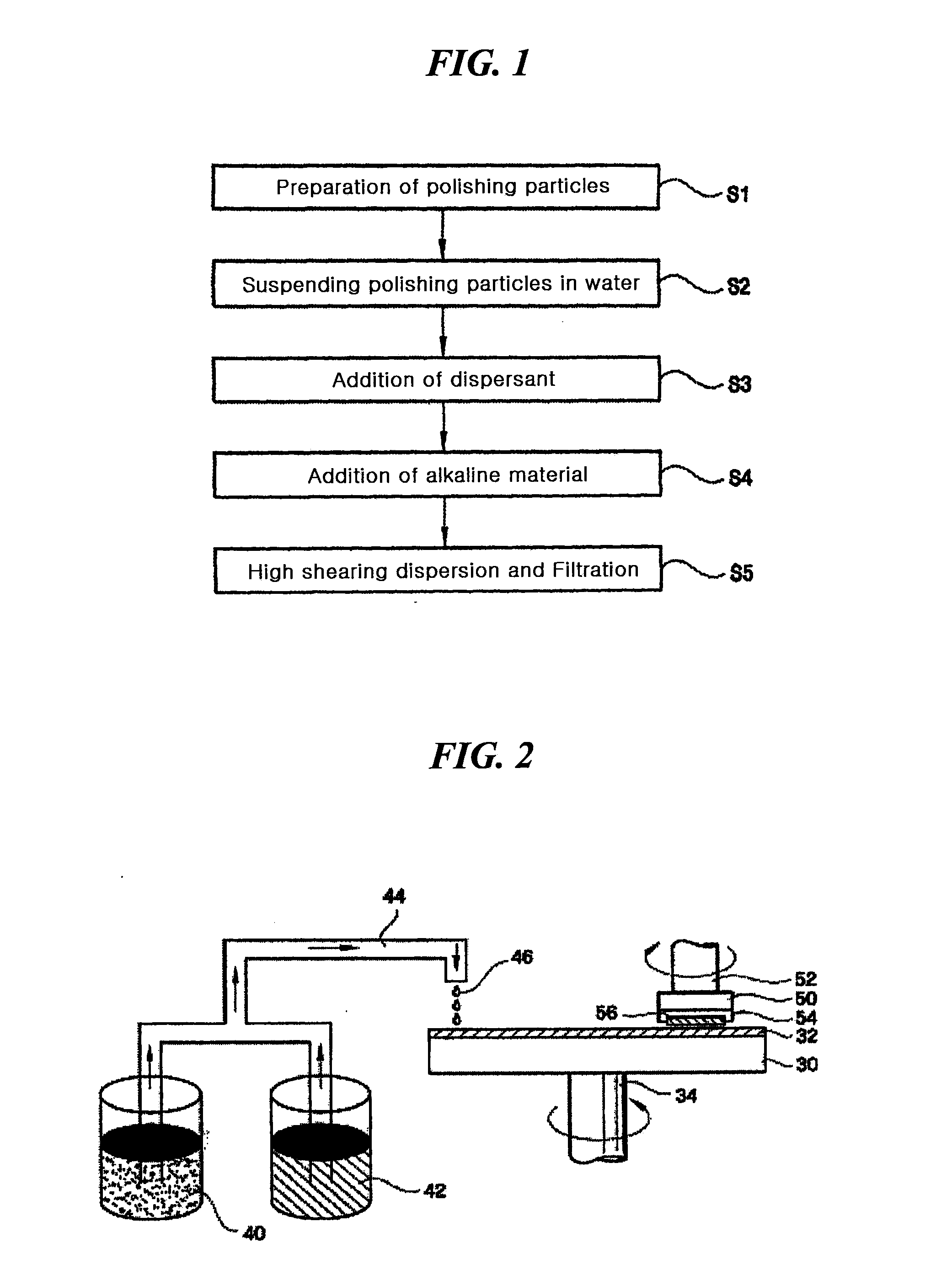
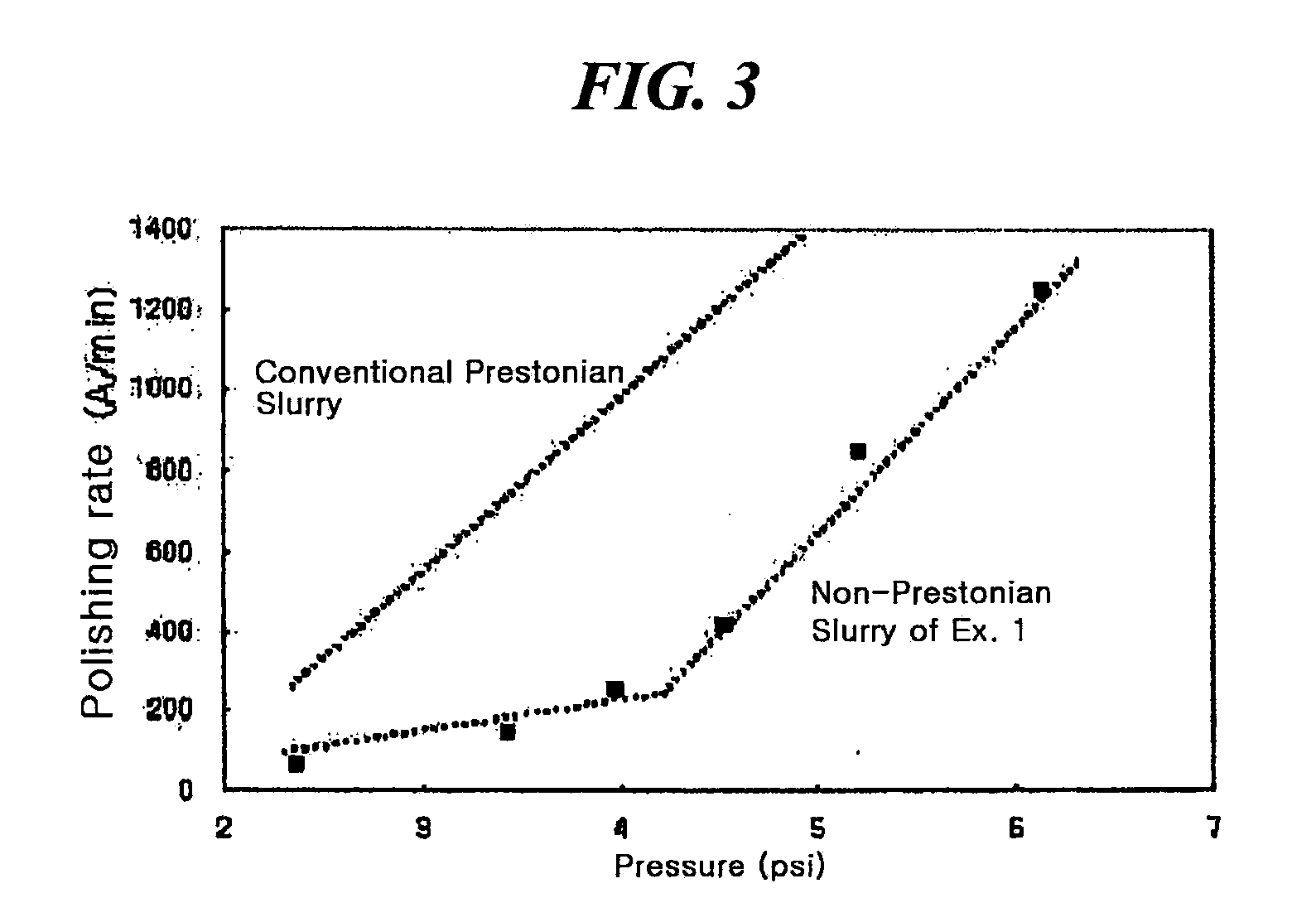
InactiveUS20090229189A1Dispersion stability can be increasedGood dispersionOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDispersion stabilitySlurry
The present invention relates to an improved method for preparing a polishing slurry, comprising dispersing polishing particles and an anionic polymeric acid in water and then adding to the resulting dispersion an alkaline material in an amount of 0.1 to 8 weight parts based on 100 weight parts of the polishing particles. The polishing slurry obtained by the inventive method exhibits good dispersion stability and non-Prestonian polishing performance, which can be beneficially employed in chemical mechanical polishing of various precision electronic devices.
Owner:SAMSUNG CORNING PRECISION MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for production of stable cerium oxide organic colloids
ActiveUS9669375B2Simple and rapid and low temperature processDispersion stability can be increasedSol preparationColloidal chemistry detailsEmulsionCerium
An improved process for producing substantially non-polar doped or un-doped cerium oxide nanoparticle dispersions is disclosed. The cerium-containing oxide nanoparticles of an aqueous colloid are transferred to a substantially non-polar liquid comprising one or more amphiphilic materials, one or more low-polarity solvents, and one or more glycol ether promoter materials. The transfer is achieved by mixing the aqueous and substantially non-polar materials, forming an emulsion, followed by a phase separation into a remnant polar solution phase and a substantially non-polar organic colloid phase. The organic colloid phase is then collected. The promoter functions to speed the transfer of nanoparticles to the low-polarity phase. The promoter accelerates the phase separation, and also provides improved colloidal stability of the final substantially non-polar colloidal dispersion. Importantly, the glycol ether promoter reduces the temperature necessary to achieve the phase separation, while providing high extraction yield of nanoparticles into the low-polarity organic phase.
Owner:CERION
Aqueous dispersion polymerization process for ethylene/tetrafluoroethylene copolymer
InactiveUS20110092644A1Improve dispersion stabilityDispersion stability can be increasedFibre treatmentNanotechnologyTetrafluoroethylenePolymer science
A polymerization process is provided to form a copolymer of ethylene with tetrafluoroethylene and a modifying monomer having a side chain containing at least two carbon atoms by initiating the polymerization in an aqueous medium with a fluoromonomer that forms a stable dispersion of polymer particles from the fluoromonomer in the aqueous medium, which forms polymerization sites for further polymerization, and carrying the further polymerization by copolymerizing the ethylene, tetrafluoroethylene, and modifying monomer as a dispersion in at least said aqueous medium to a polymer solids content of at least 15 wt %, said copolymer comprising at least 60 wt % of the total polymer content of the polymer solids.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Aqueous pigment dispersion
ActiveUS20190338152A1Good dispersionImprove spraying effectDuplicating/marking methodsInksDispersion stabilityWater based
The present invention provides a pigment water dispersion that is excellent in dispersion stability, and also excellent in ejection properties even when used as an ink for ink-jet printing. The present invention relates to [1] a pigment water dispersion containing (A) a pigment, (B) a carboxy group-containing crosslinked polymer and (C) an alkyl group-containing ethanolamine having a pKa of not less than 8.7, [2] a water-based ink containing the pigment water dispersion, an organic solvent and a surfactant, and [3] a process for producing a pigment water dispersion, including step (I) of subjecting a mixture containing the pigment (A), a crosslinkable polymer, the aforementioned ethanolamine (C), an organic solvent and water to dispersion treatment, thereby obtaining a dispersion of pigment-containing polymer particles containing the pigment (A) and the crosslinkable polymer that is adhered onto the pigment (A); step (II) of removing the organic solvent from the obtained dispersion, thereby obtaining a water dispersion of the pigment-containing polymer particles; and step (III) of further subjecting the polymer to crosslinking reaction with a crosslinking agent, thereby obtaining the pigment water dispersion containing pigment-containing crosslinked polymer (B) particles.
Owner:KAO CORP
Method for producing silver nanowires, silver nanowires, and ink using same
ActiveUS10220441B2High transparencyImprove conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAlcoholChloride
A method for producing silver nanowires, containing reduction-precipitating silver in the form of wire in an alcohol solvent having dissolved therein a silver compound, the deposition being performed in the alcohol solvent having dissolved therein a chloride, a bromide, an alkali metal hydroxide, an aluminum salt, and an organic protective agent, the molar ratio Al / OH of the total Al amount of the aluminum salt dissolved in the solvent and the total hydroxide ion amount of the alkali metal hydroxide dissolved therein being from 0.01 to 0.40, the molar ratio OH / Ag of the total hydroxide ion amount of the alkali metal hydroxide dissolved in the solvent and the total Ag amount of the silver compound dissolved therein being from 0.005 to 0.50.
Owner:DOWA HLDG CO LTD
Base metal pigment, aqueous base metal pigment dispersion liquid, and aqueous ink composition
ActiveUS9512320B2Easy to manufactureGood effectPigmenting treatmentInksZeta potentialMeasurement device
Disclosed herein is a base metal pigment, which is used for an aqueous ink composition containing water as a part of a solvent, in which the base metal pigment is surface-treated with a fluorine-based compound, and has a zeta potential of greater than or equal to −50 mV and less than or equal to −15 mV, as measured by an ultrasonic zeta potential measurement device, in a pH range of greater than or equal to 5 and less than or equal to 10.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Visible light absorbing film, structural member having this visible light absorbing film and visible light absorbing ink which forms visible light absorbing film
InactiveUS7927696B2Glare suppressionMaintain propertiesDiffusing elementsInksLight reflectanceVisible spectrum
The visible light absorbing film according to the present invention is formed by a visible light absorbing ink having been coated on one side or both sides of a substrate which has solar radiation reflecting properties and whose visible light reflectance is 10% or more, and is characterized in that the degree of reduction of visible light reflectance is 0.9 or less as defined by degree of reduction of visible light reflectance=[visible light reflectance (%) after coating of the ink] / [visible light reflectance (%) before coating of the ink], and the degree of reduction of solar radiation reflectance is 0.25 or more as defined by degree of reduction of solar radiation reflectance=[solar radiation reflectance (%) after coating of the ink] / [solar radiation reflectance (%) before coating of the ink].
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com