Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
278results about "Transuranic element compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
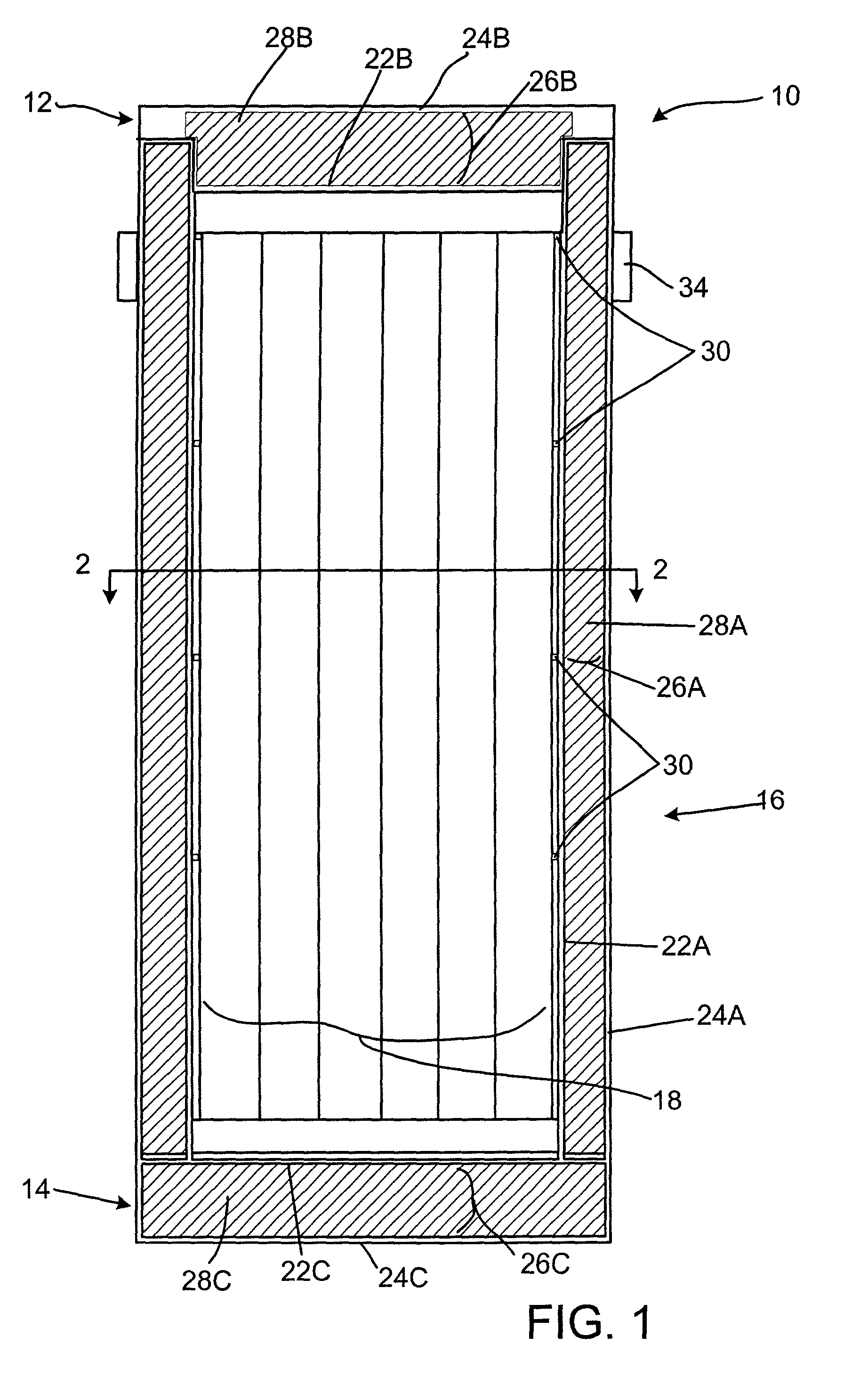
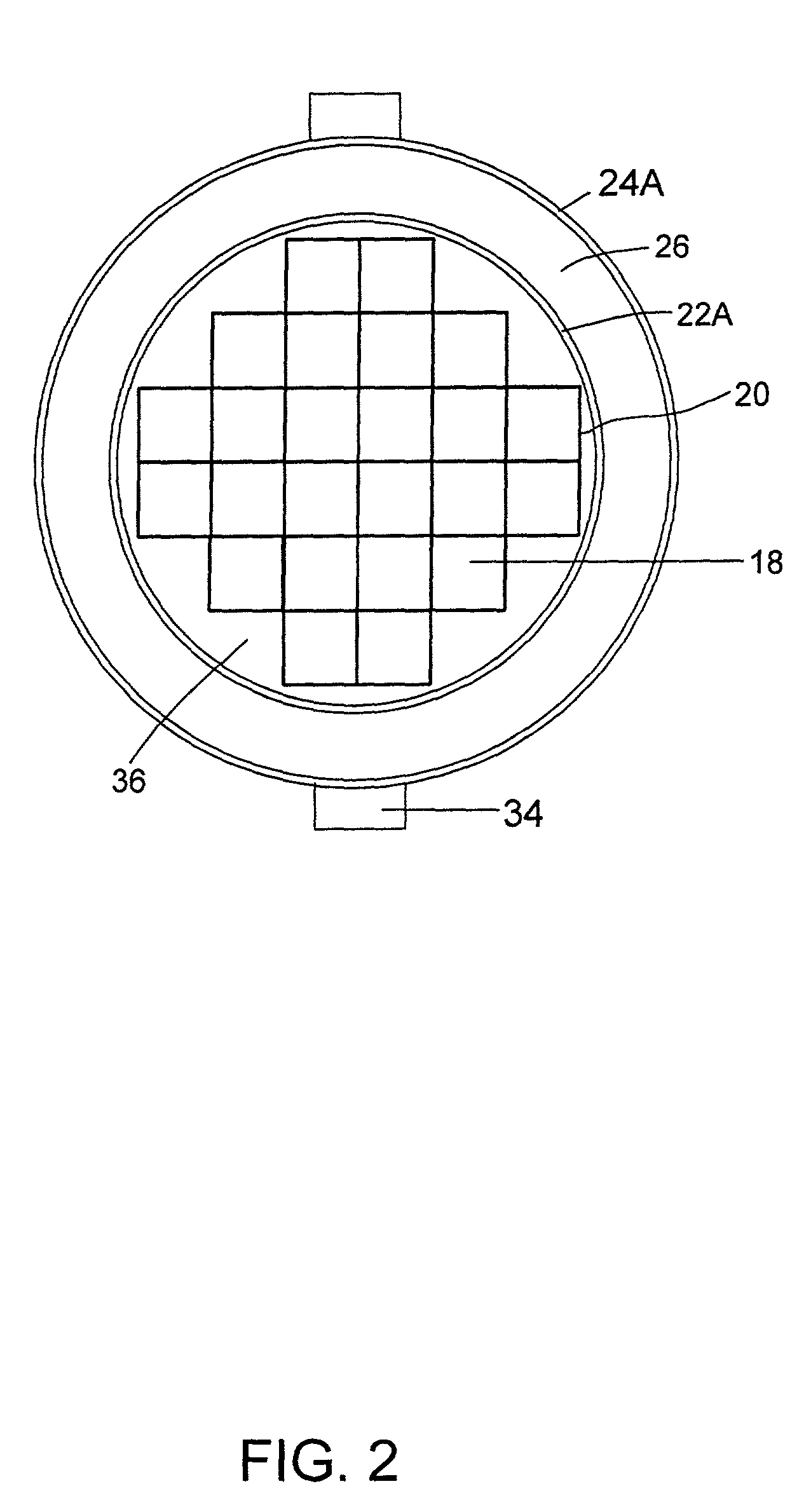
Process for radioisotope recovery and system for implementing same
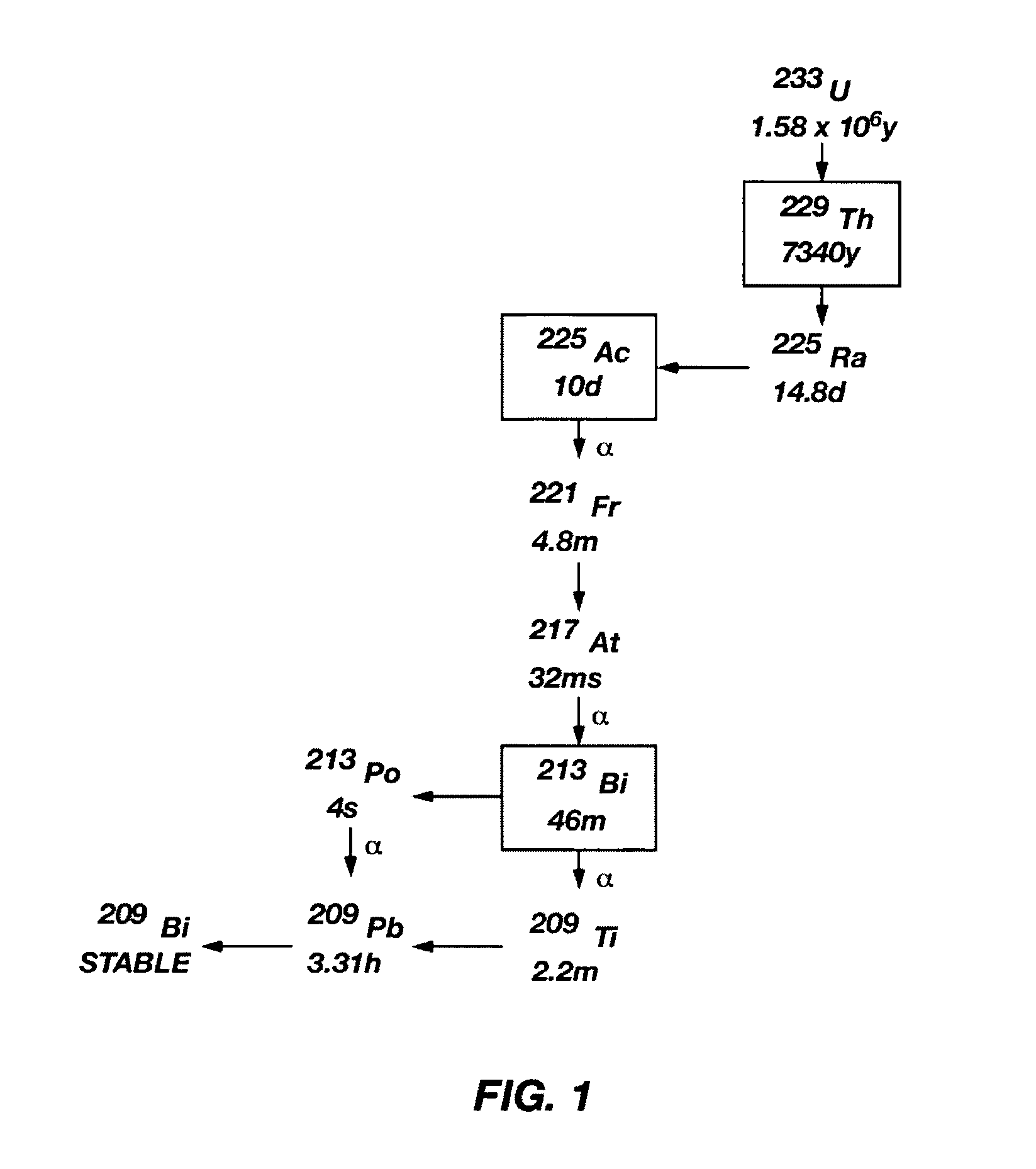
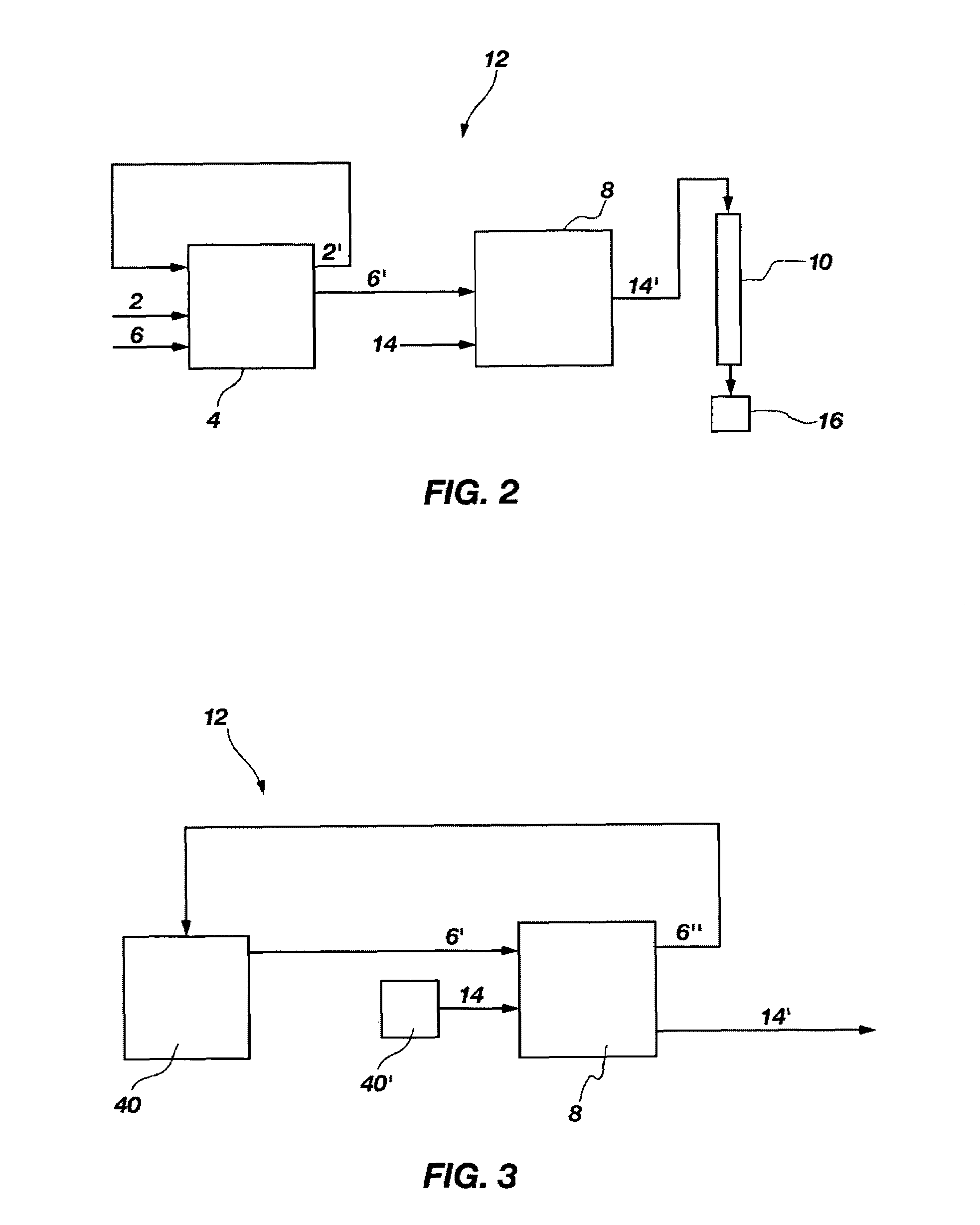
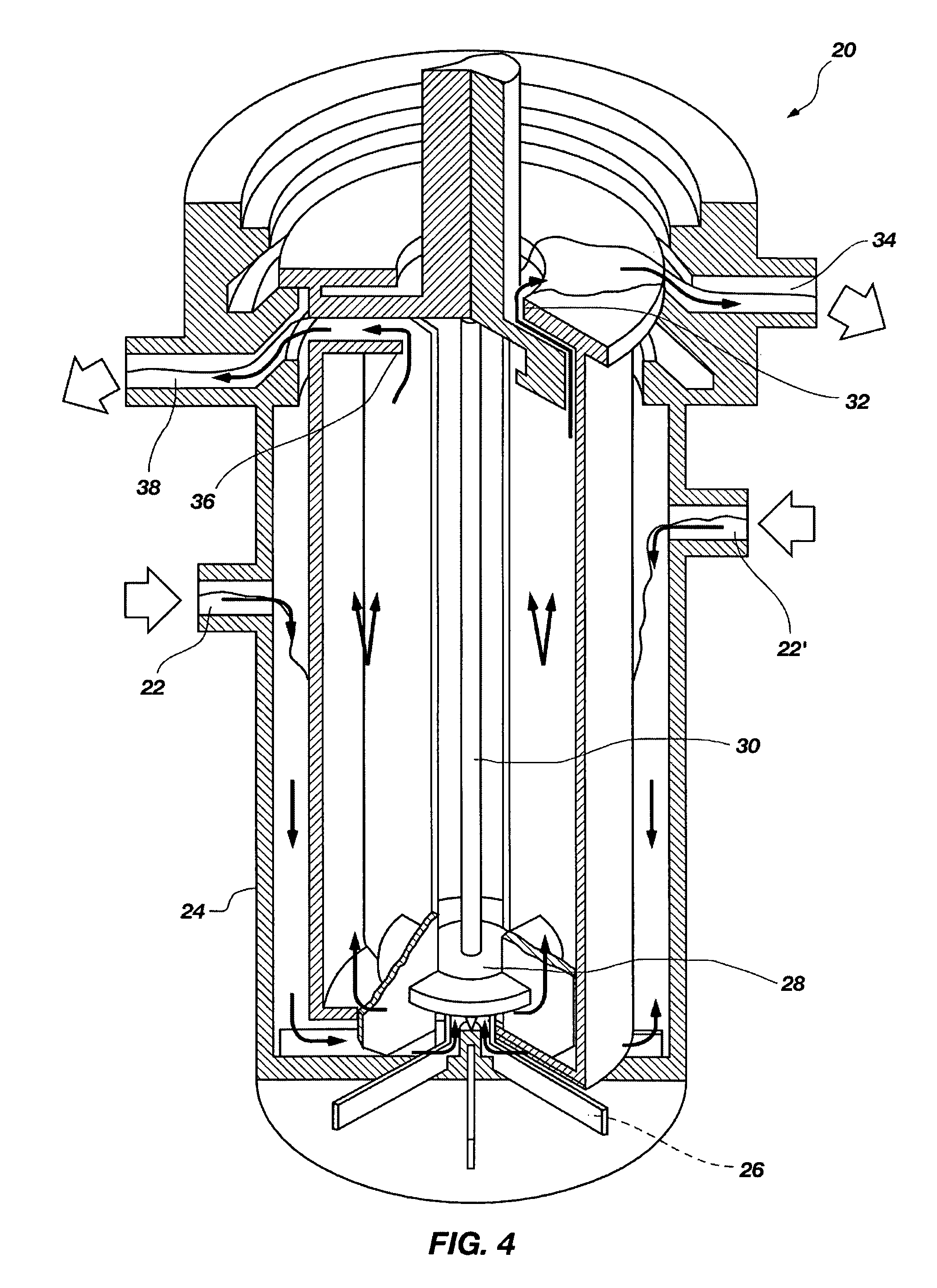
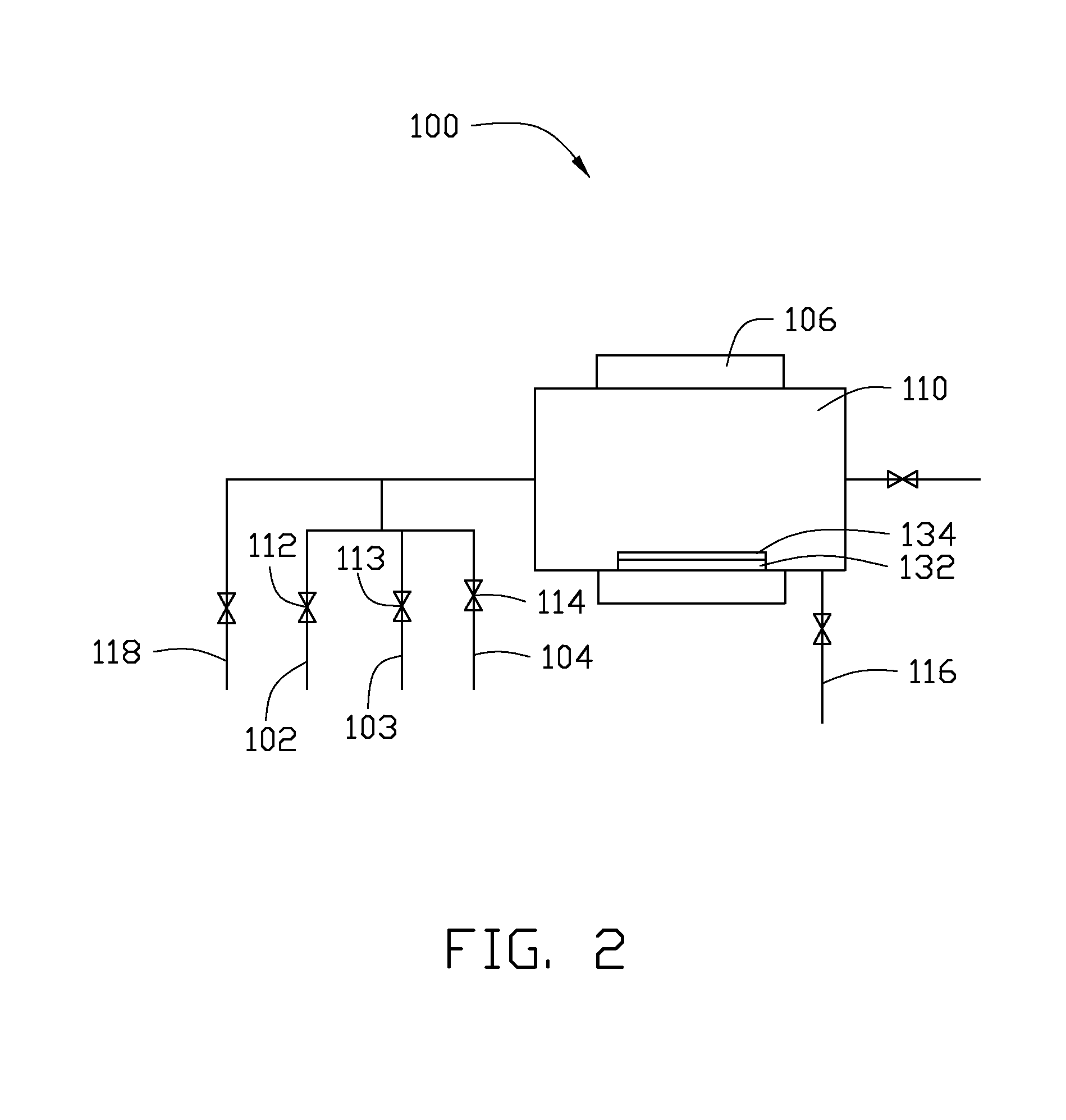
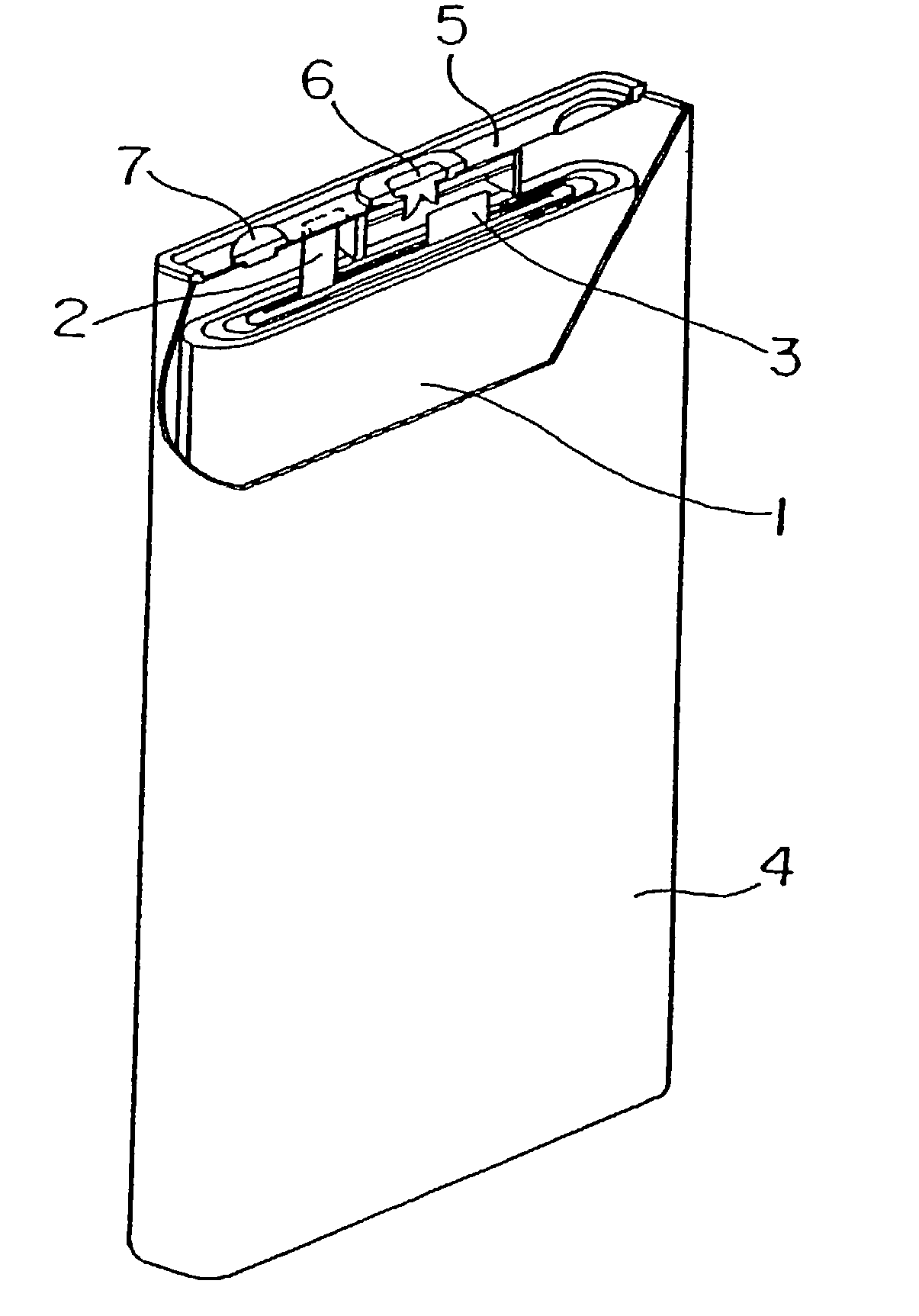
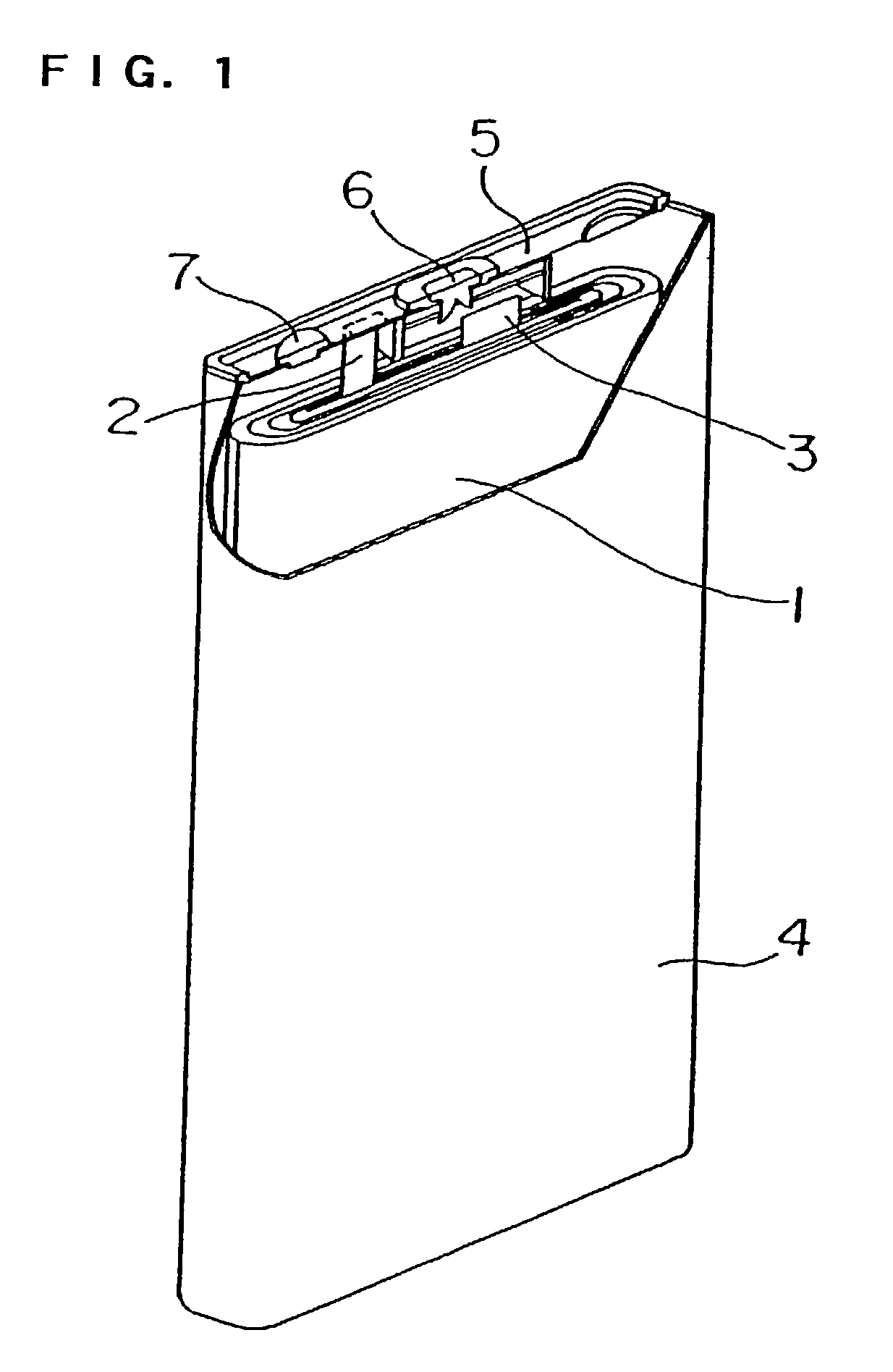
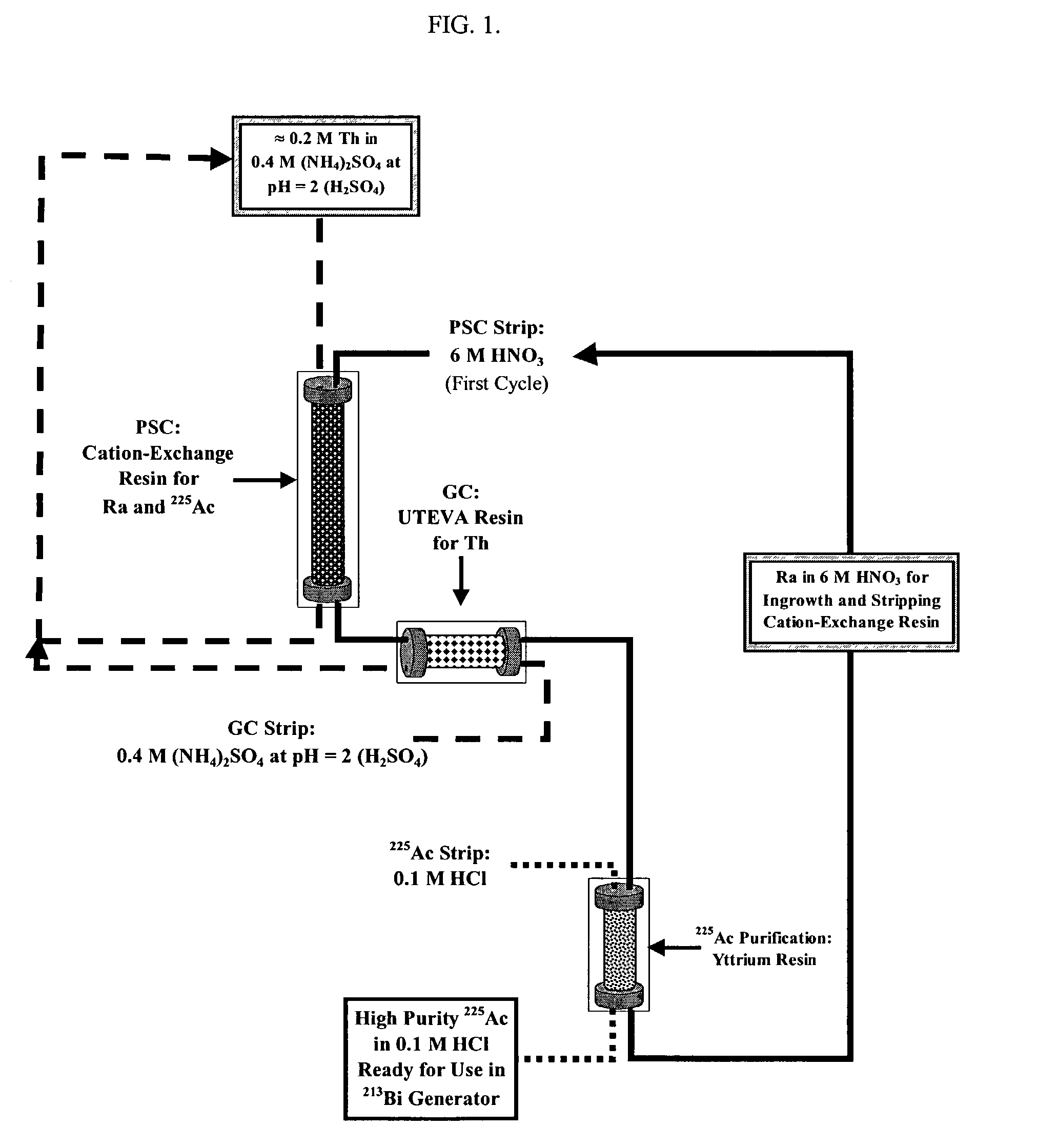
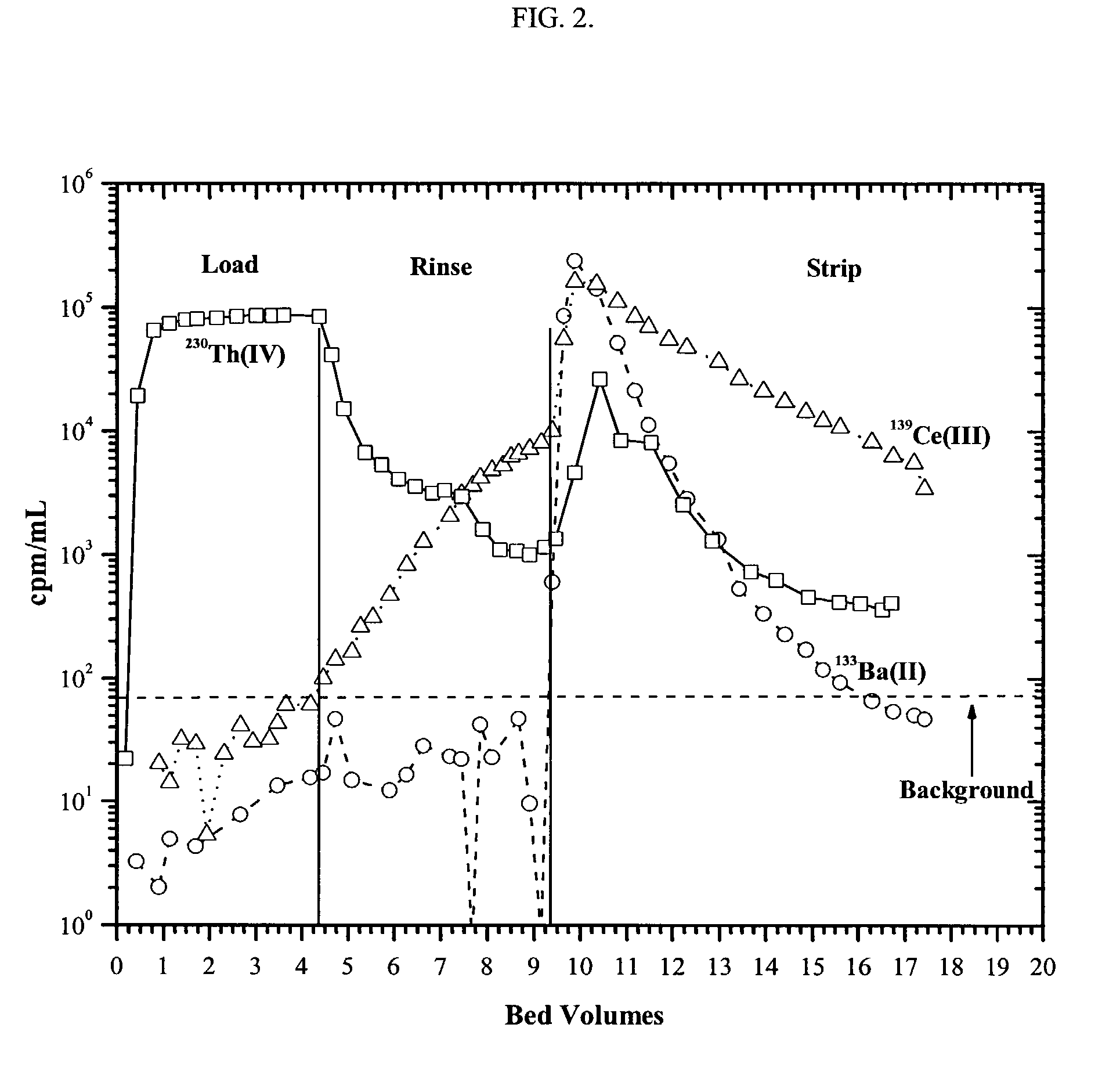
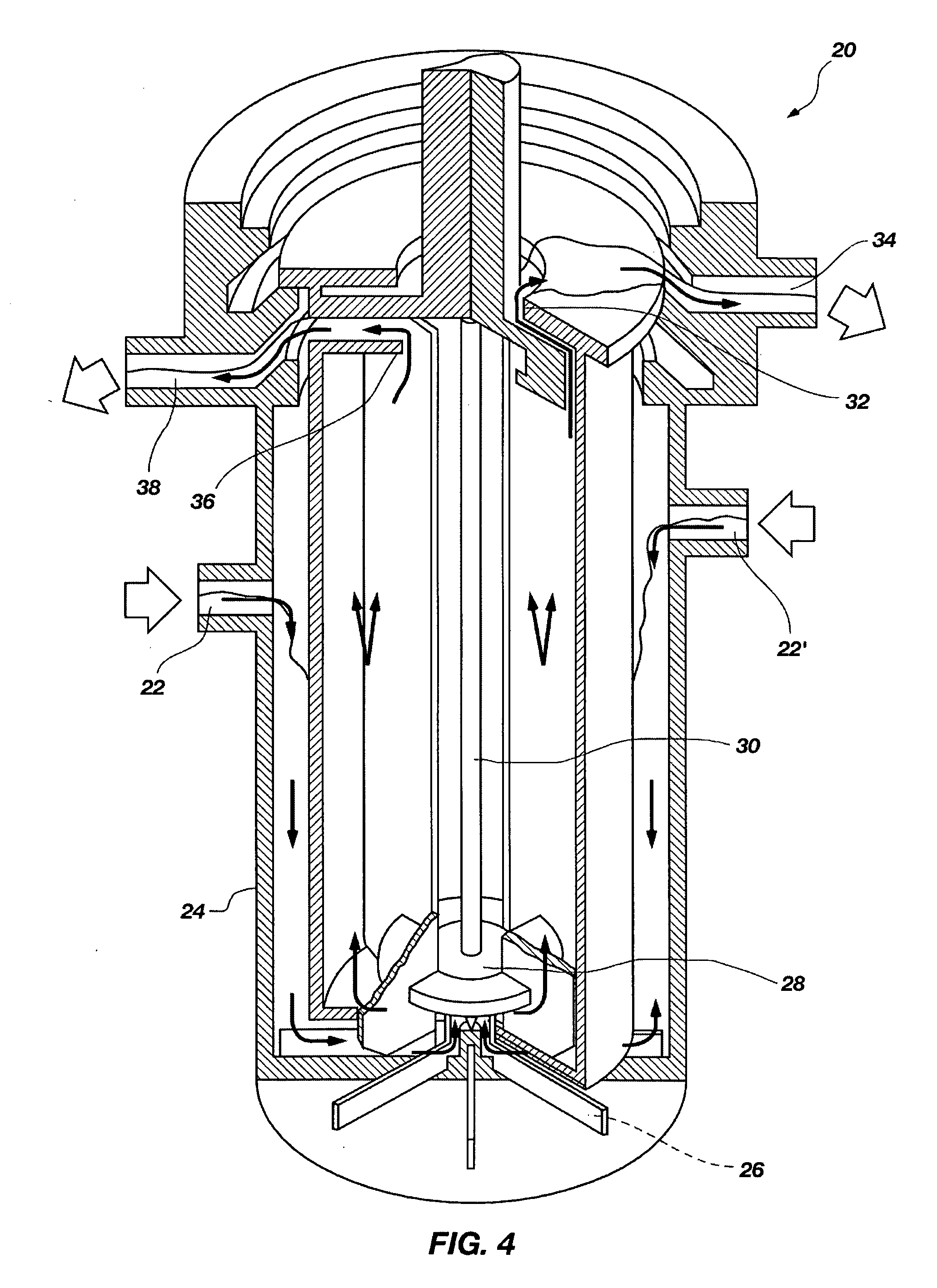
A method of recovering daughter isotopes from a radioisotope mixture. The method comprises providing a radioisotope mixture solution comprising at least one parent isotope. The at least one parent isotope is extracted into an organic phase, which comprises an extractant and a solvent. The organic phase is substantially continuously contacted with an aqueous phase to extract at least one daughter isotope into the aqueous phase. The aqueous phase is separated from the organic phase, such as by using an annular centrifugal contactor. The at least one daughter isotope is purified from the aqueous phase, such as by ion exchange chromatography or extraction chromatography. The at least one daughter isotope may include actinium-225, radium-225, bismuth-213, or mixtures thereof. A liquid-liquid extraction system for recovering at least one daughter isotope from a source material is also disclosed.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Method for Production of Radioisotope Preparations and Their Use in Life Science, Research, Medical Application and Industry
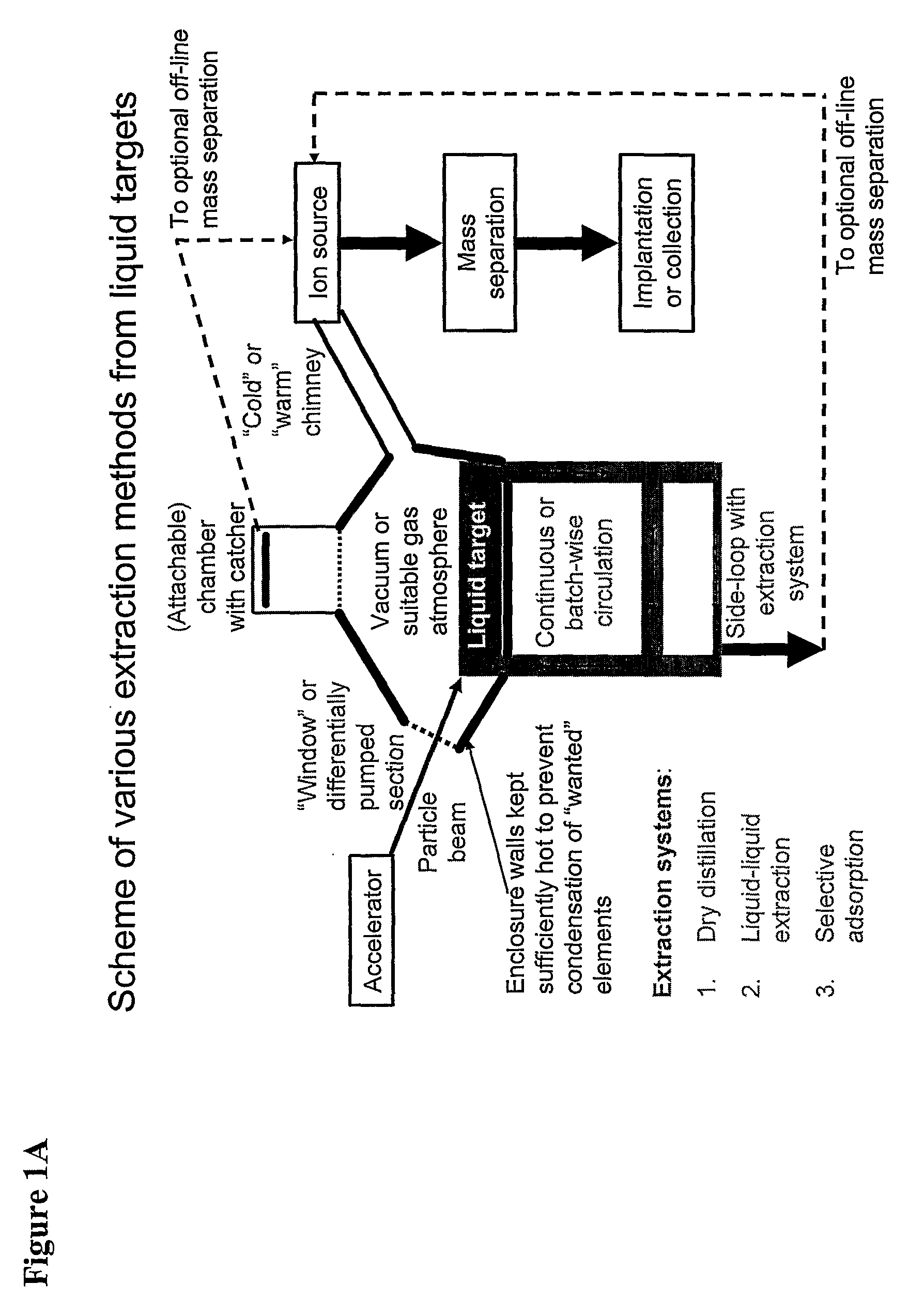
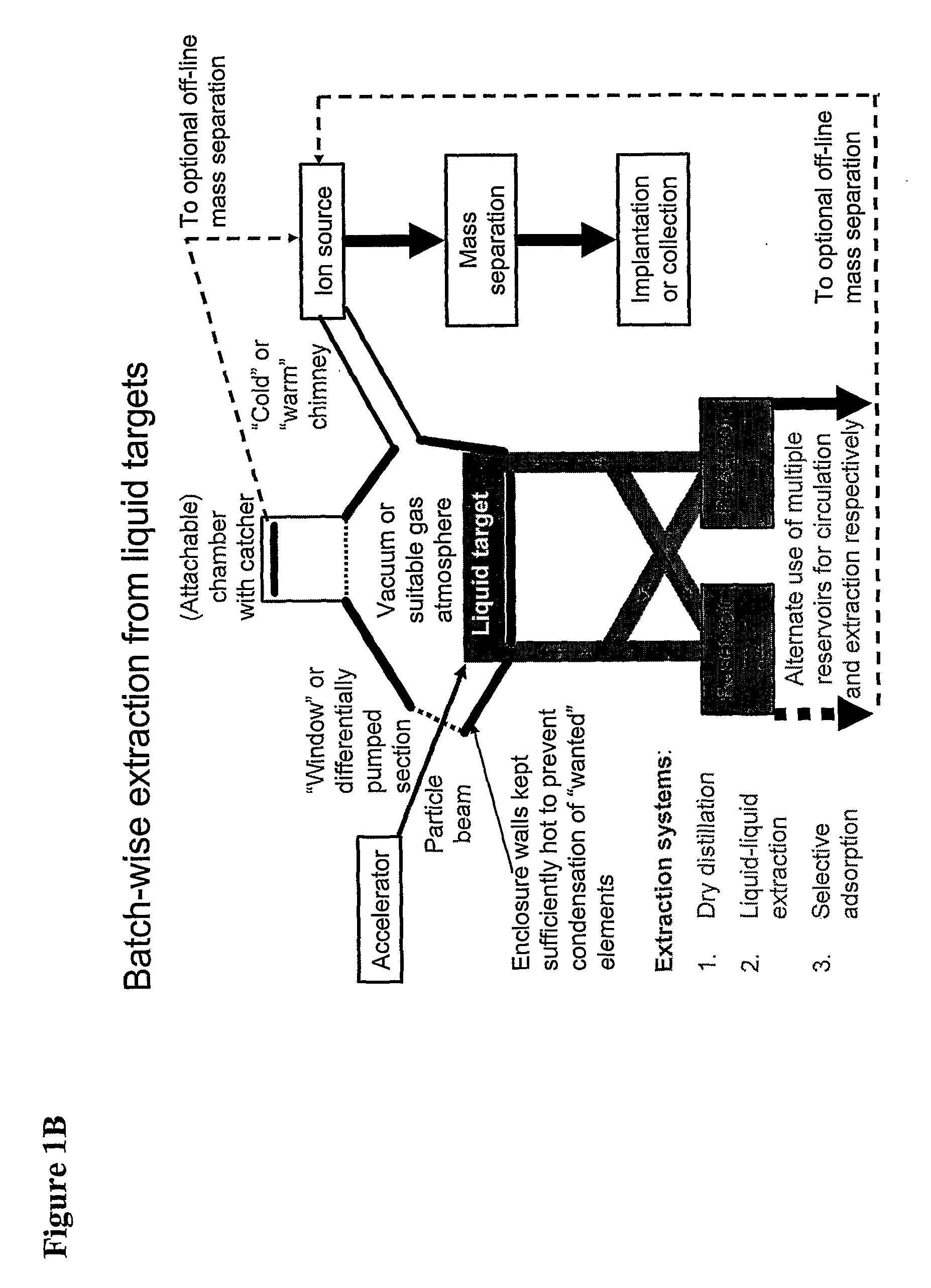
The present invention relates to an universal method for the large scale production of high-purity carrier free or non carrier added radioisotopes by applying a number of “unit operations” which are derived from physics and material science and hitherto not used for isotope production. A required number of said unit operations is combined, selected and optimised individually for each radioisotope production scheme. The use of said unit operations allows a batch wise operation or a fully automated continuous production scheme. The radioisotopes produced by the inventive method are especially suitable for producing radioisotope-labelled bioconjugates as well as particles, in particular nanoparticles and microparticles.
Owner:EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH +1
Process for the preparation of metal carbides having a large specific surface from activated carbon foams
InactiveUS6217841B1Easy accessPhysical/chemical process catalystsTransuranic element compoundsActivated carbonCarbide
The invention relates to a silicon carbide or metal carbide foam to be used as a catalyst or catalyst support for the chemical or petrochemical industry or for silencers, as well as the process for producing the same.The foam is in the form of a three-dimensional network of interconnected cages, whose edge length is between 50 and 500 micrometres, whose density is between 0.03 and 0.1 g / cm3 and whose BET surface is between 20 and 100 m2 / g. The carbide foam contains no more than 0.1% by weight residual metal and the size of the carbide crystallites is between 40 and 400 Angstroms.The production process consists of starting with a carbon foam, increasing its specific surface by an activation treatment using carbon dioxide and then contacting the thus activated foam with a volatile compound of the metal, whose carbide it is wished to obtain.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
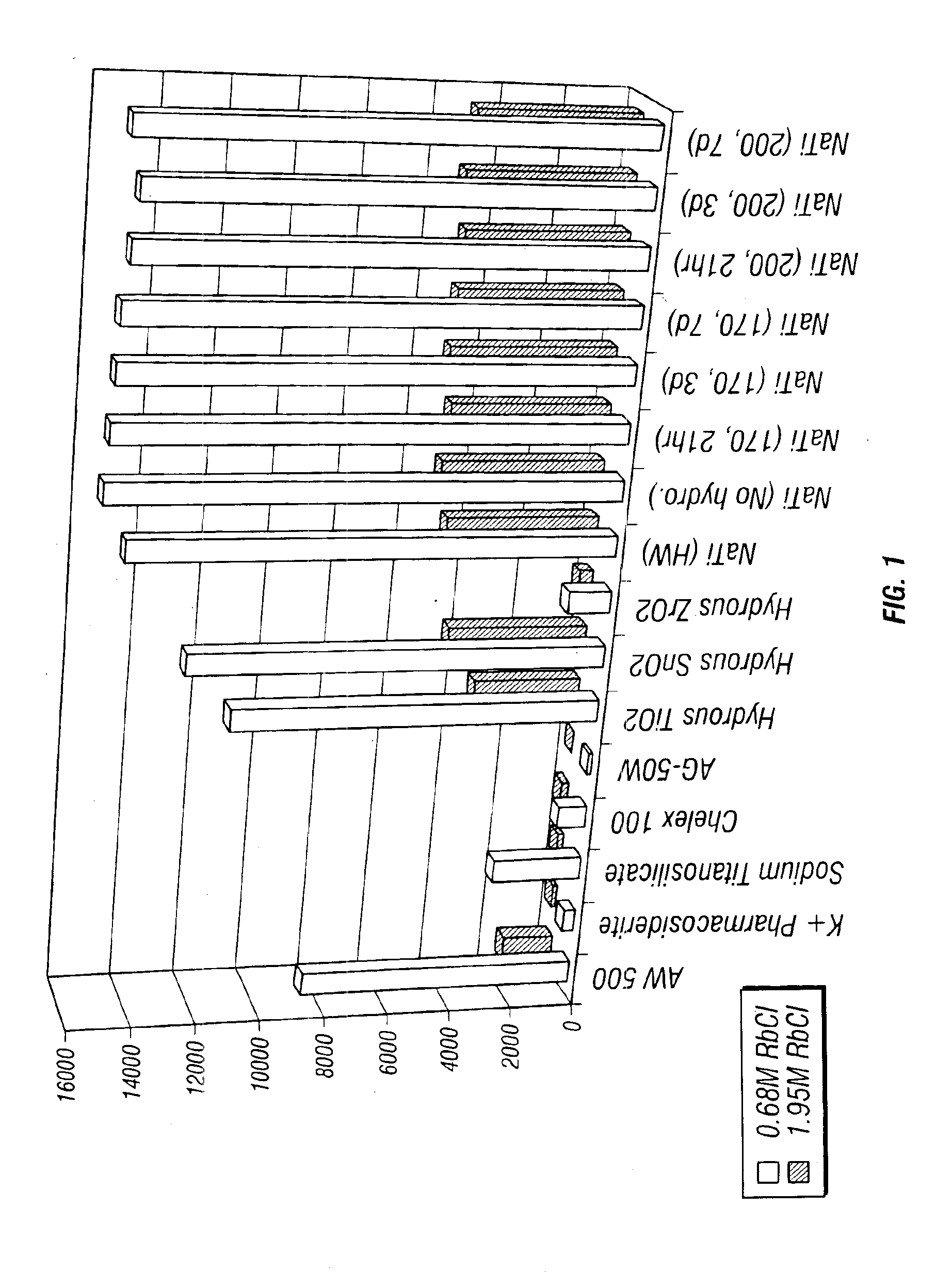
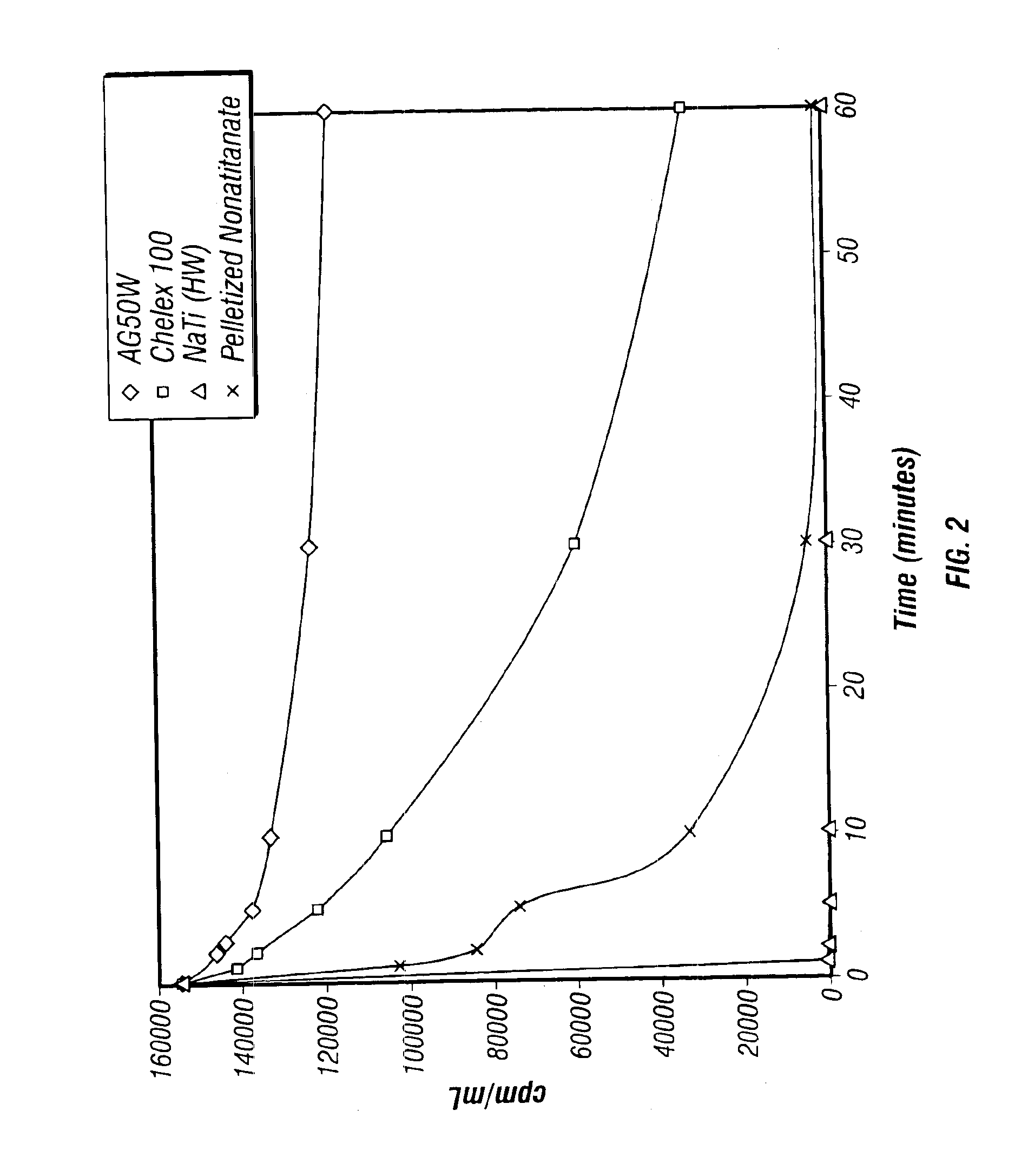
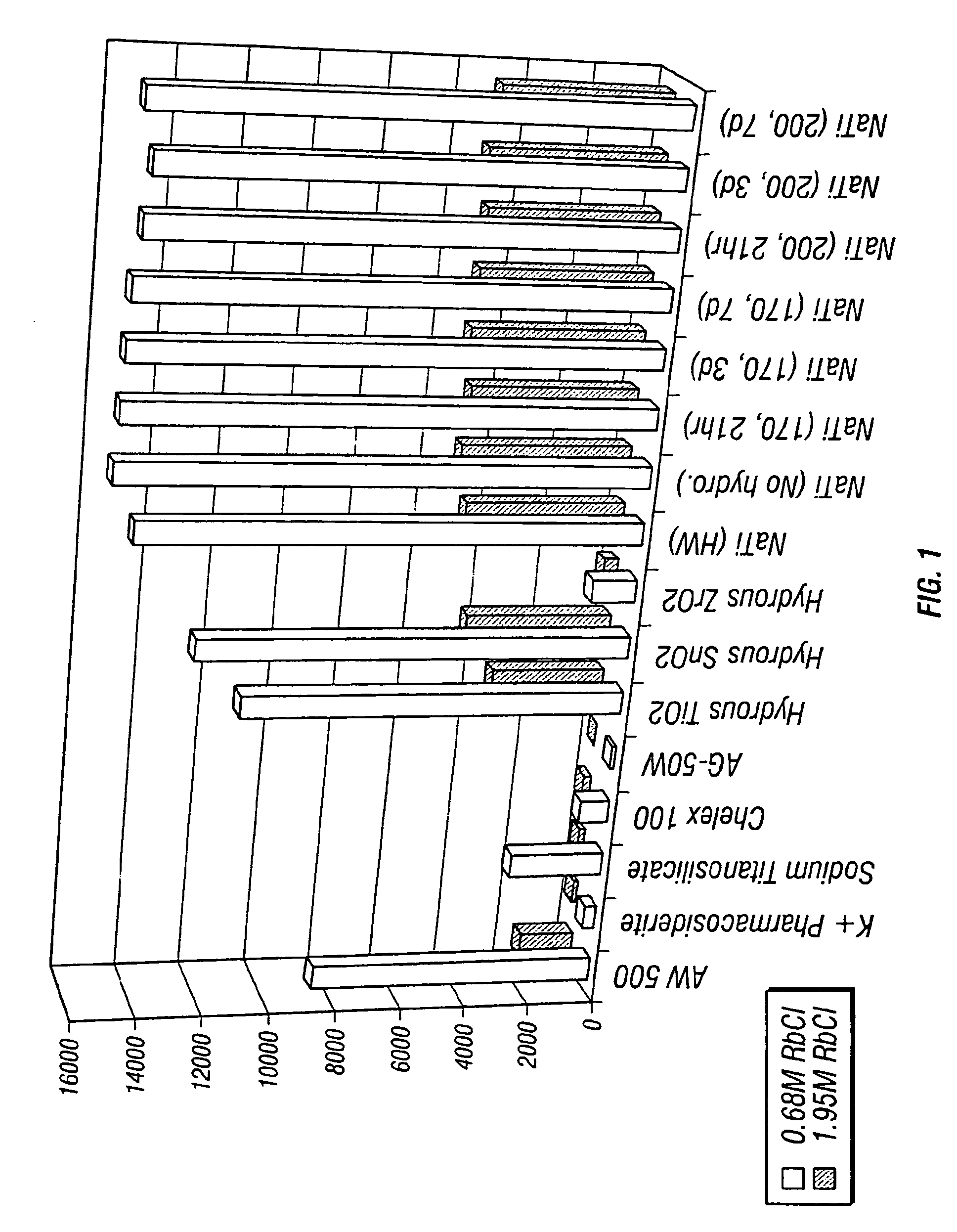
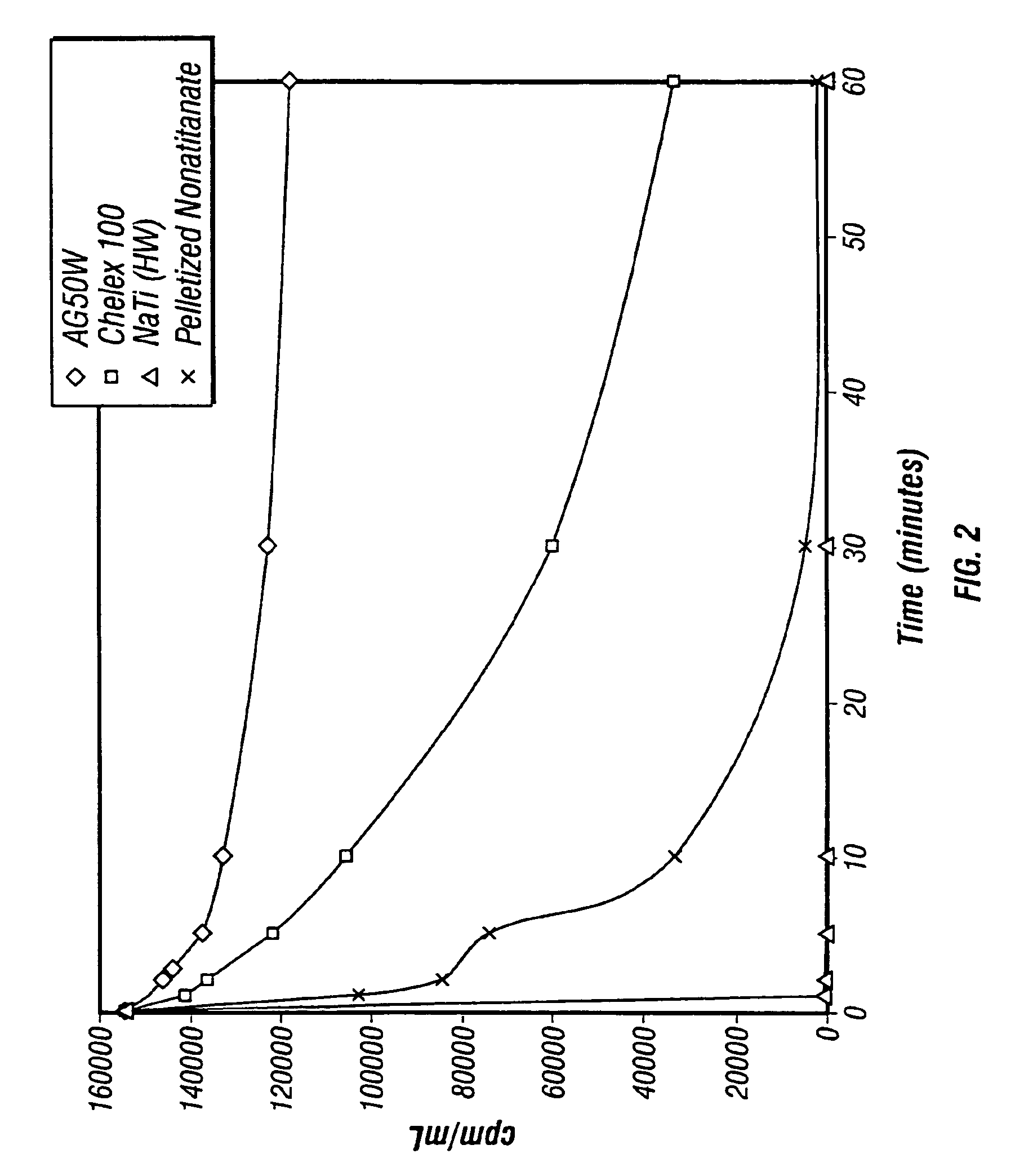
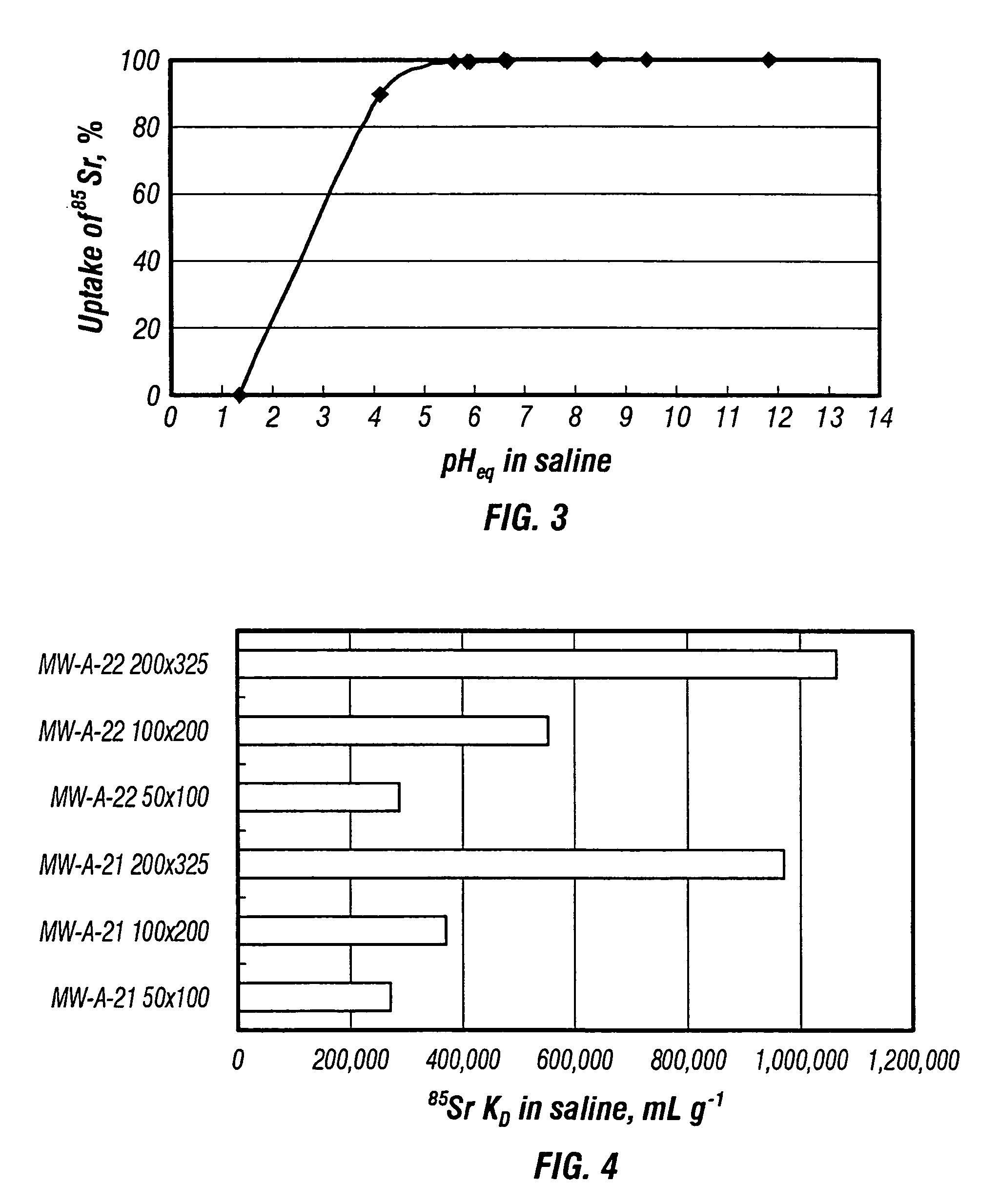
Rubidlum-82 generator based on sodium nonatitanate support, and improved separation methods for the recovery of strontium-82 from irradiated targets
InactiveUS6908598B2Effective recoveryOther chemical processesTransuranic element compoundsLow affinityRubidium
Sodium nonatitanate compositions, a method using the composition for recovery of 82Sr from irradiated targets, and a method using the composition for generating 82Rb. The sodium nonatitanate materials of the invention are highly selective at separating strontium from solutions derived from the dissolution of irradiated target materials, thus reducing target processing times. The compositions also have a very low affinity for rubidium, making it an ideal material for use as a 82Rb generator. Sodium nonatitanate materials of this type both improve the recovery of 82Sr and provide a safer, more effective 82Rb generator system.
Owner:LYNNTECH
Systems and Methods for Radioisotope Generation
ActiveUS20080093564A1Isotope delivery systemsTransuranic element compoundsEngineeringChromatographic column
Systems and methods are disclosed for producing customized, predictable and reproducible supplies of radioisotopes using, for example, a reactor housing that is fabricated from a radioactive shielding material and has both an internal volume and a surface that comprises an entry port and an exit port, a chromatographic column that is positioned within said internal volume such that a first end of said column is in fluid communication with said entry port and a second end of said column is in fluid communication with said exit port, and a changeable filter module that is disposed external to said reactor housing and in fluid communication with said exit port.
Owner:JUBILANT DRAXIMAGE
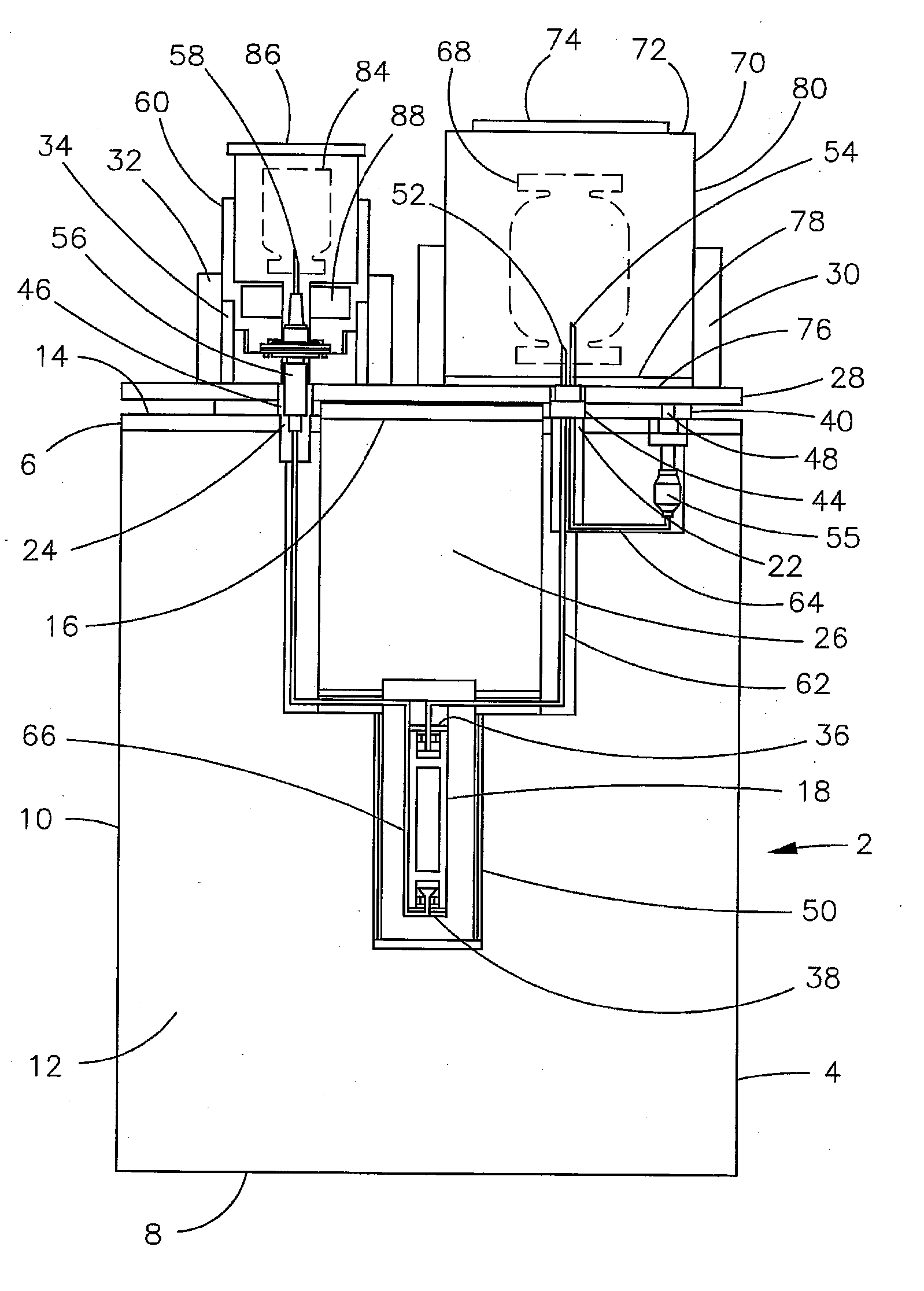
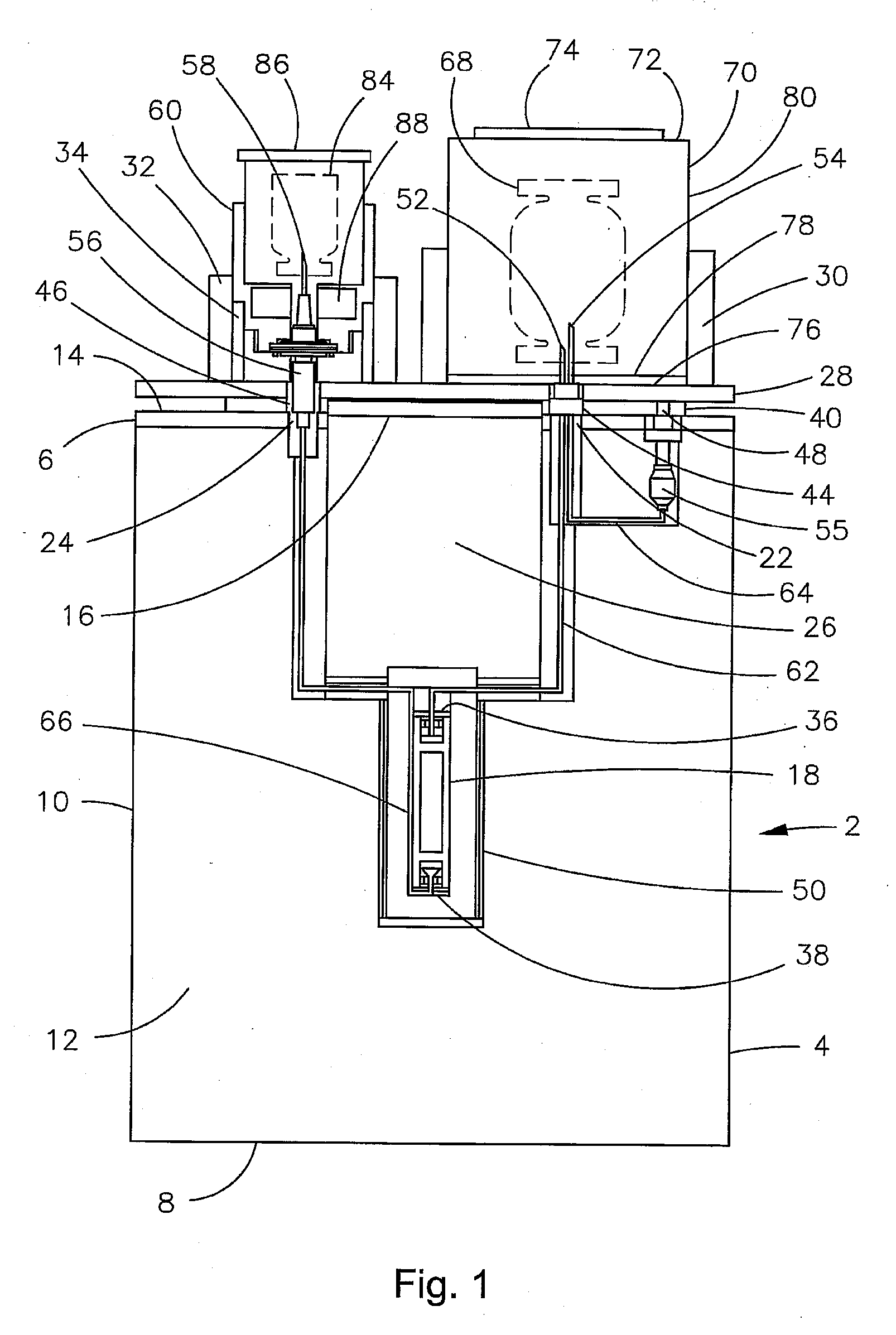
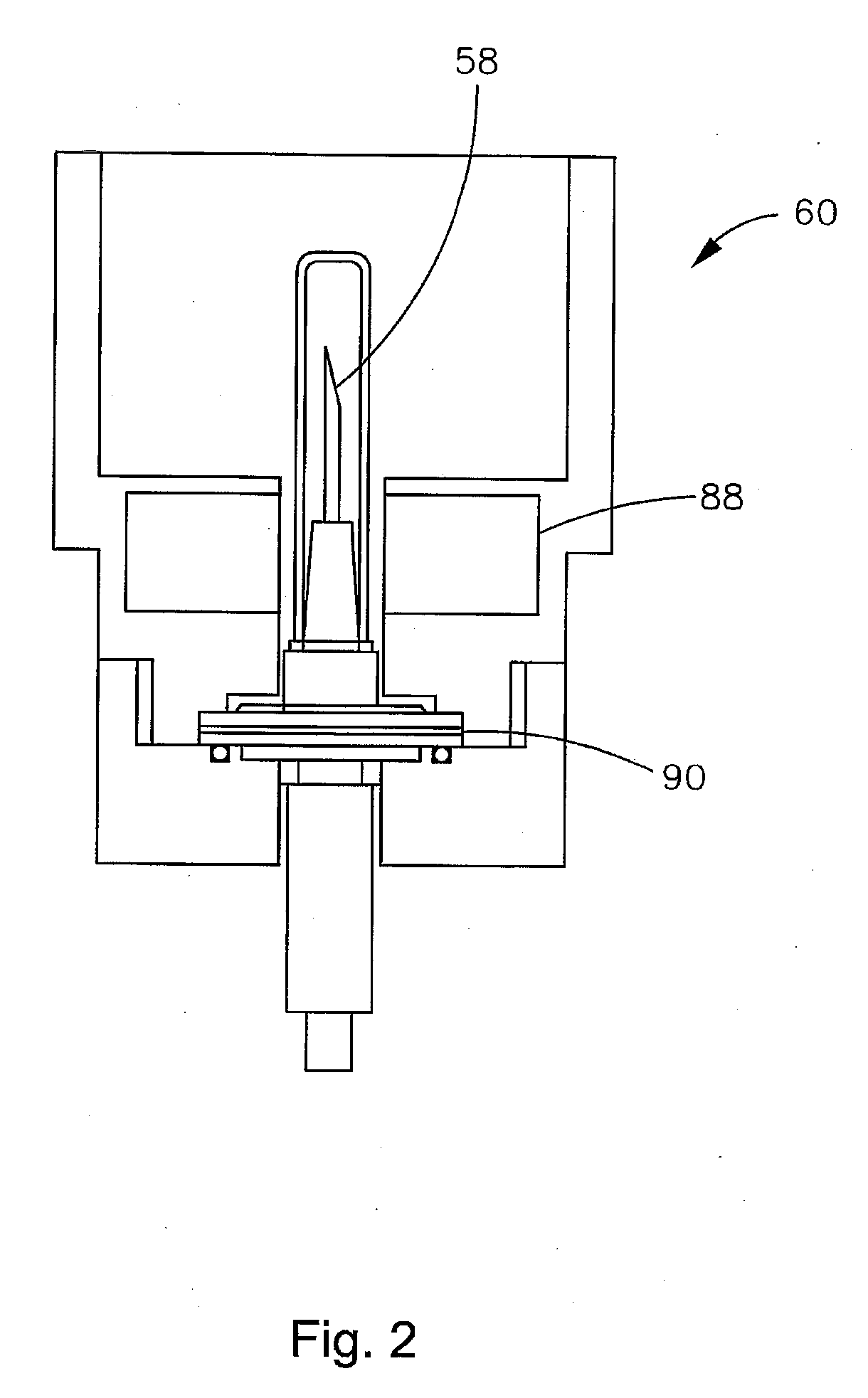
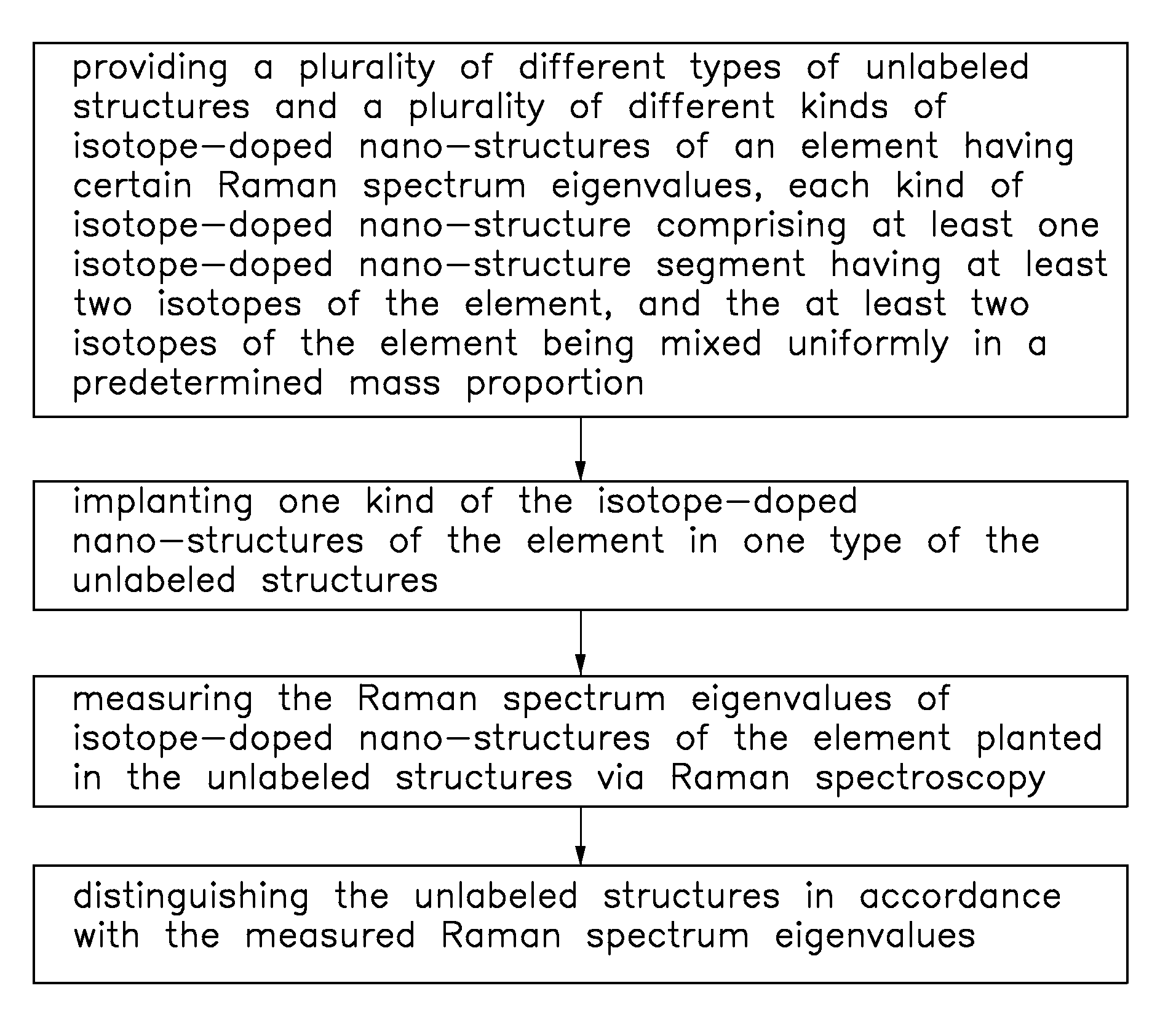
Isotope-doped nano-material, method for making the same, and labeling method using the same
An isotope-doped nano-structure of an element is provided. The isotope-doped nano-structure includes at least one isotope-doped nano-structure segment having at least two isotopes of the element, and the at least two isotopes of the element are mixed uniformly in a certain proportion. The present disclosure also provides a method for making the isotope-doped nano-structures, and a labeling method using the isotope-doped nano-structures.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Rubidium-82 generator based on sodium nonatitanate support, and improved separation methods for the recovery of strontium-82 from irradiated targets
InactiveUS7476377B2Effective recoveryTransuranic element compoundsOther chemical processesLow affinityRubidium
Sodium nonatitanate compositions, a method using the composition for recovery of 82Sr from irradiated targets, and a method using the composition for generating 82Rb. The sodium nonatitanate materials of the invention are highly selective at separating strontium from solutions derived from the dissolution of irradiated target materials, thus reducing target processing times. The compositions also have a very low affinity for rubidium, making it an ideal material for use as a 82Rb generator. Sodium nonatitanate materials of this type both improve the recovery of 82Sr and provide a safer, more effective 82Rb generator system.
Owner:LYNNTECH
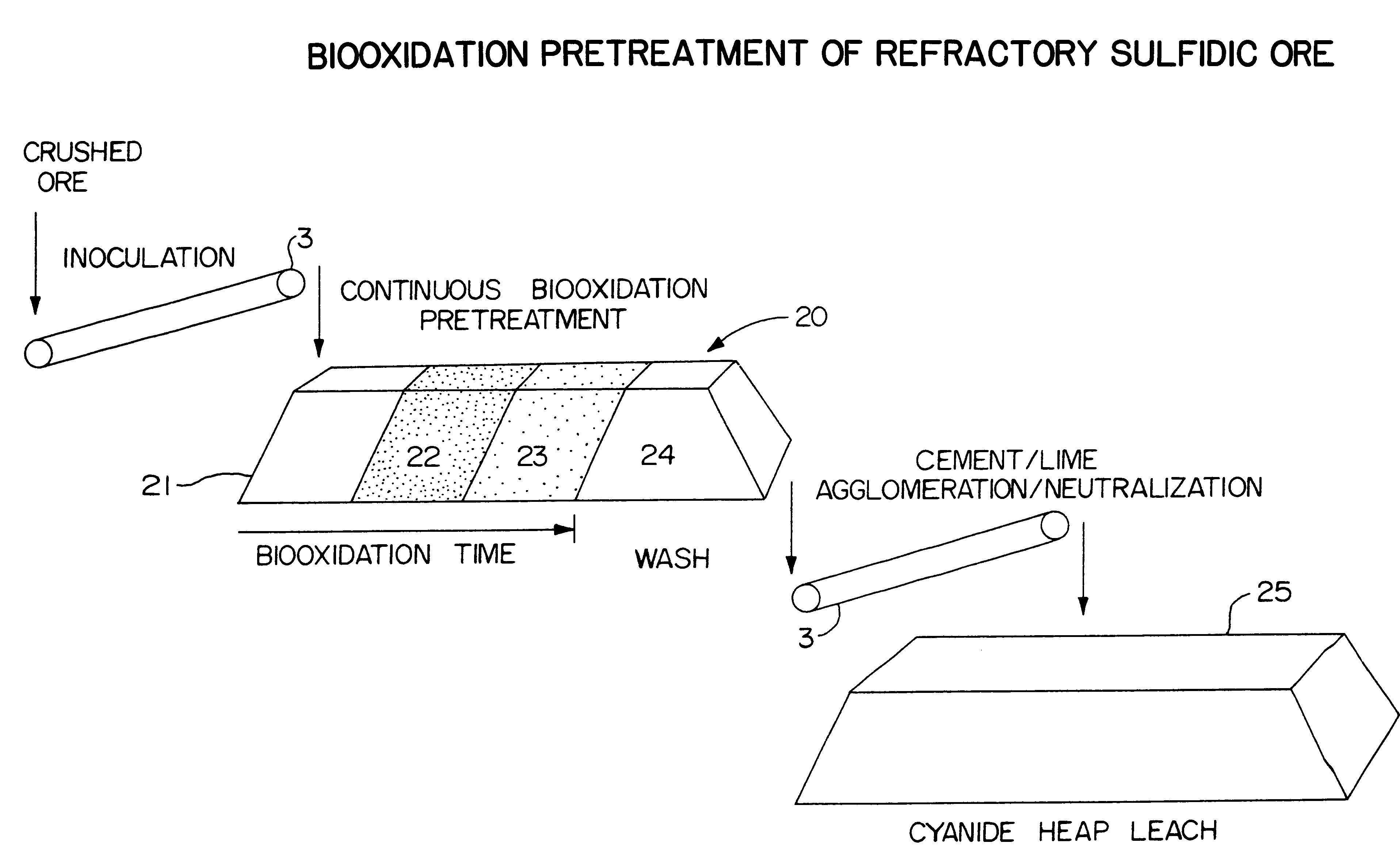
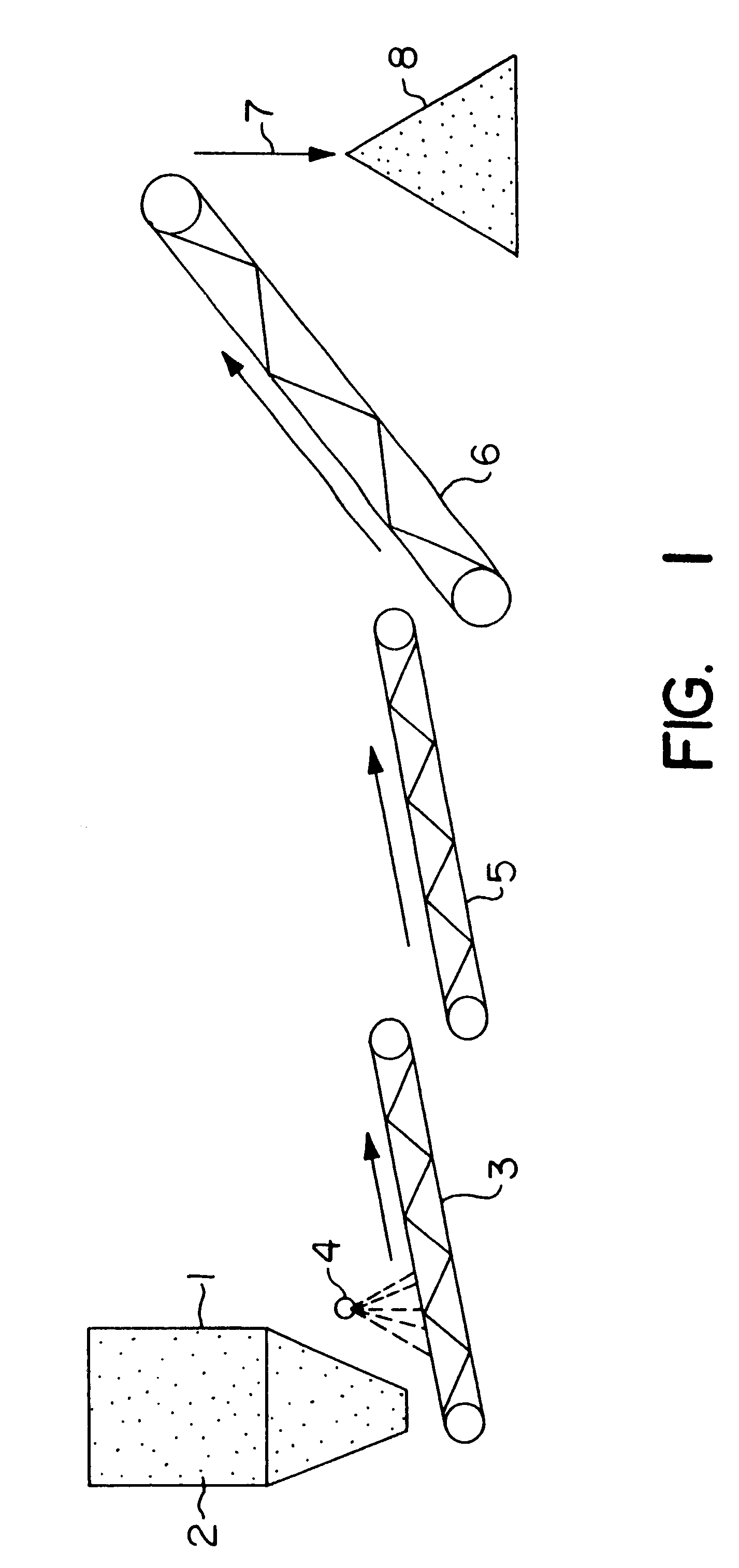
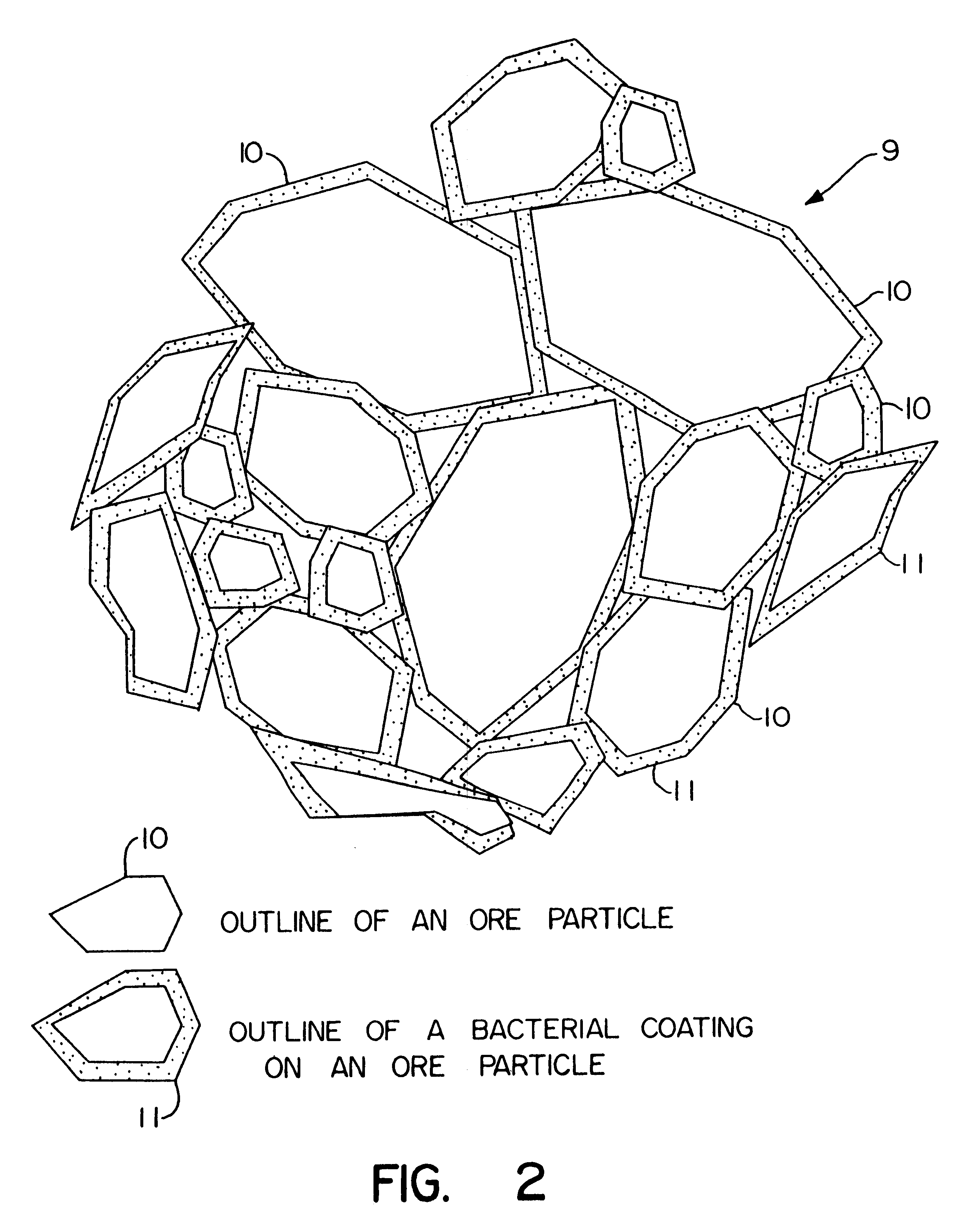
Biooxidation process for recovery of metal values from sulfur-containing ore materials
InactiveUS6383458B1Increase ratingsIncrease attractivenessTransuranic element compoundsSolvent extractionParticulatesPartial oxidation
A process for the recovery of one or more metal values from a metal ore material comprising those of one or more values and a matrix material having a sulfur content wherein the sulfur is present in an oxidation-reduction state of zero or less comprisinga. forming particulates from particles of said ore and an inoculate comprising bacteria capable of at least partially oxidizing the sulfur content;b. forming a heap of said particulates;c. biooxidizing the sulfur content andd. recovering those one or more metal values.
Owner:NEWMONT USA LTD
Positive electrode active material for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary cell and cell using the same
InactiveUS20030013017A1Suppression of increase in battery thicknessImprove distortionTransuranic element compoundsConductive materialCrystal structureCobalt
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
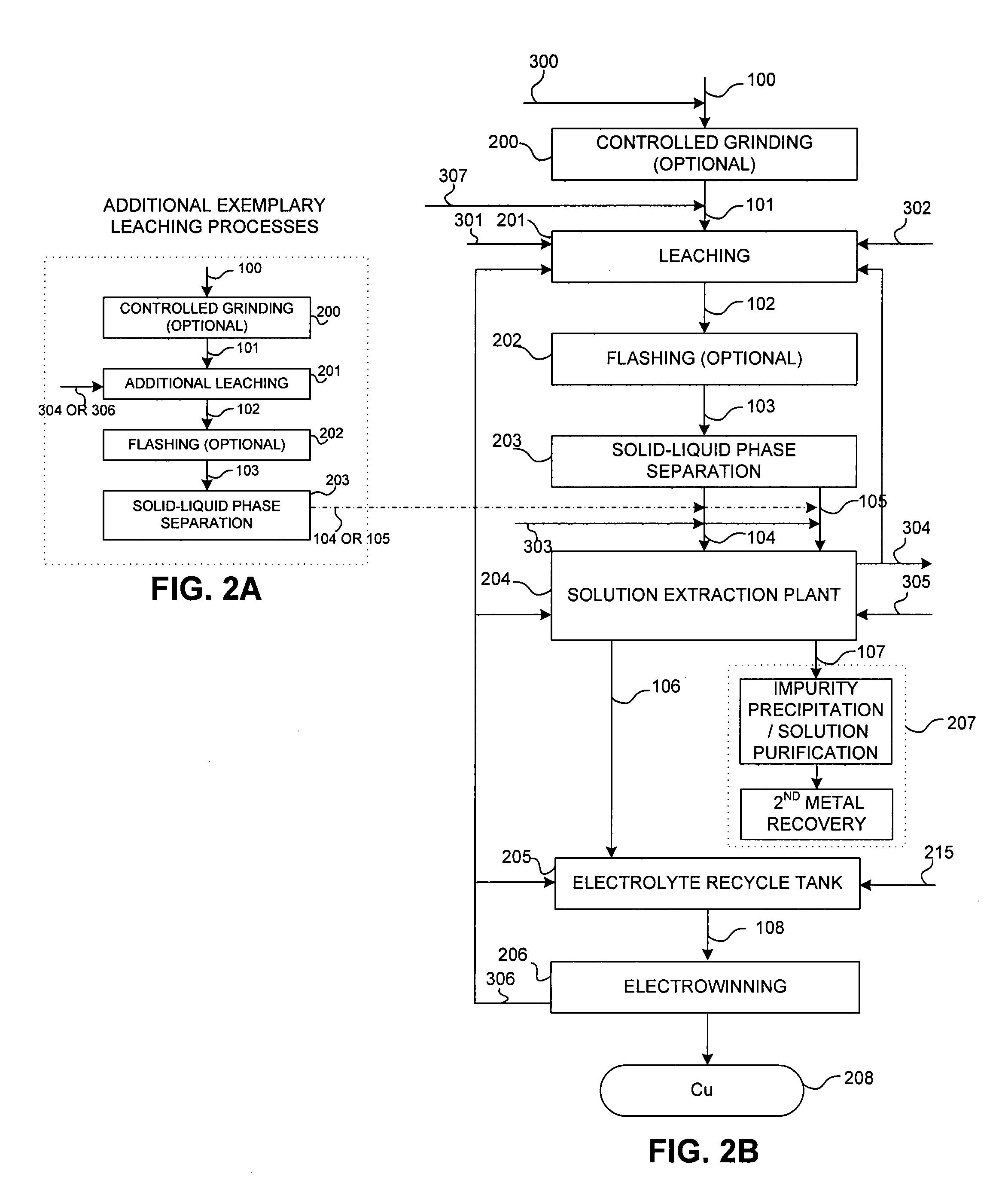
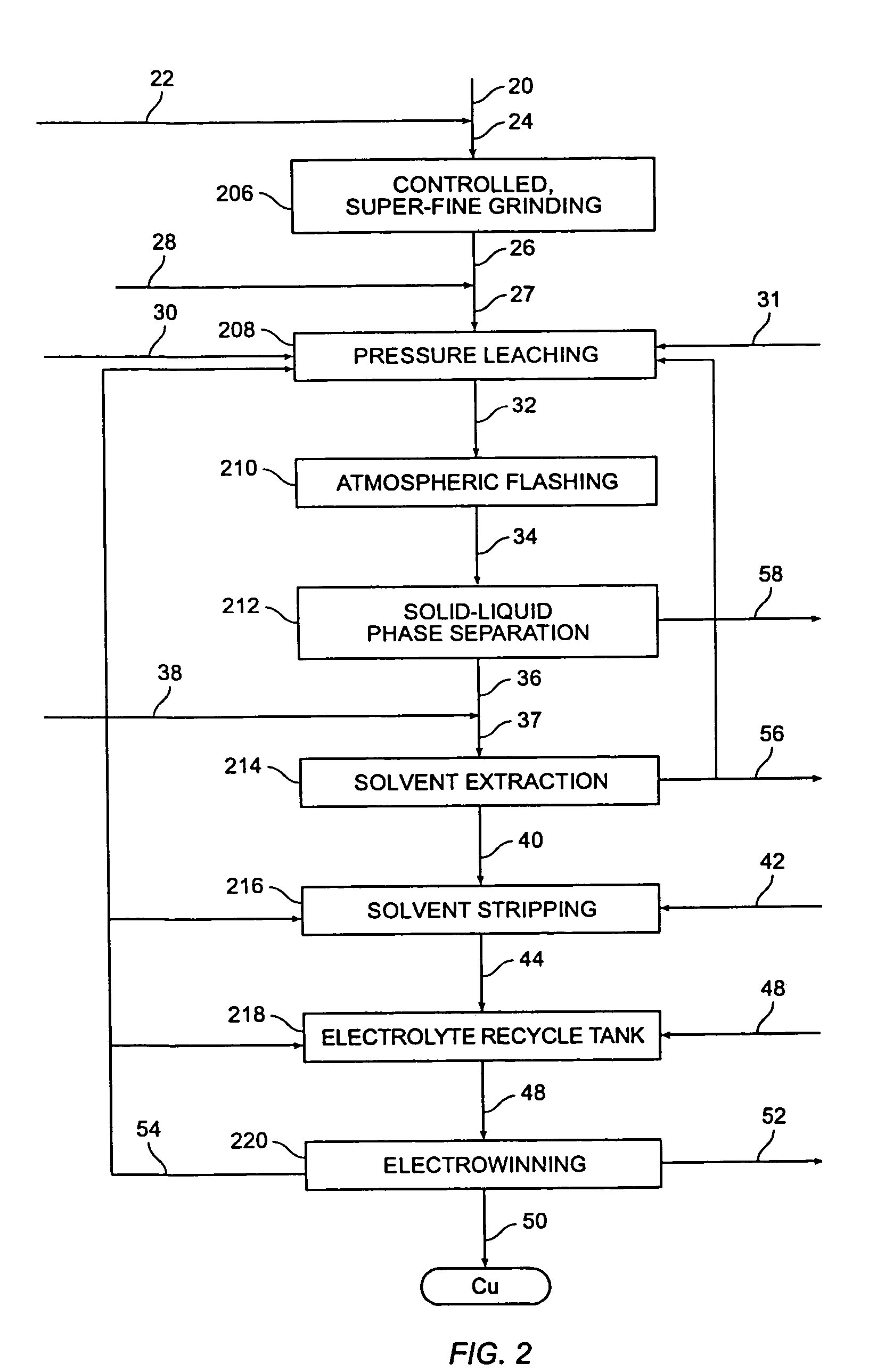
Controlled copper leach recovery circuit
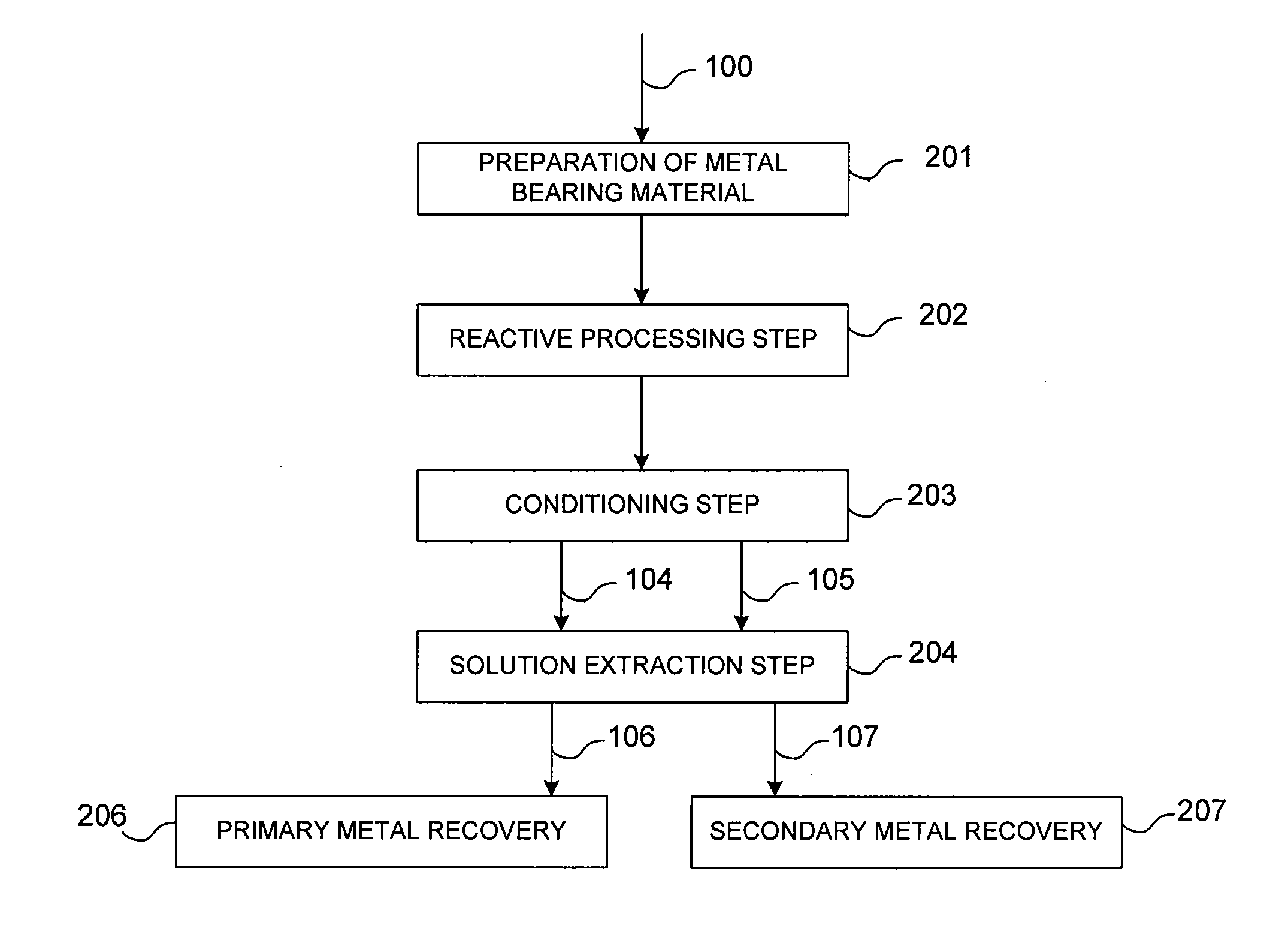
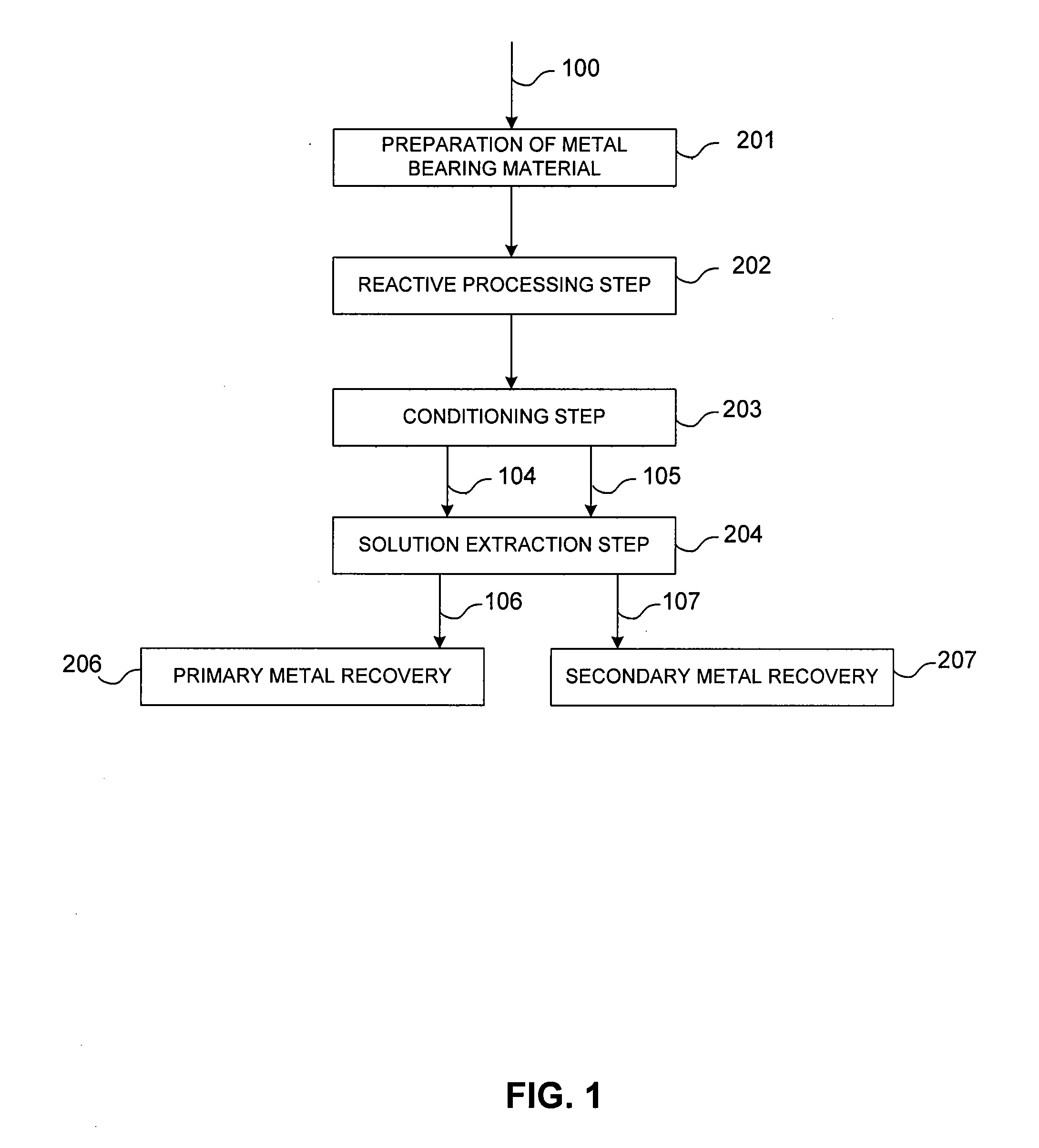
ActiveUS20090074639A1Effective recoveryLow constantPhotography auxillary processesTransuranic element compoundsPregnant leach solutionLower grade
The present invention relates generally to a process for controlled leaching and sequential recovery of two or more metals from metal-bearing materials. In one exemplary embodiment, recovery of metals from a leached metal-bearing material is controlled and improved by providing a high grade pregnant leach solution (“HGPLS”) and a low grade pregnant leach solution (“LGPLS”) to a single solution extraction plant comprising at least two solution extractor units, at least two stripping units, and, optionally, at least one wash stage.
Owner:FREEPORT MCMORAN COPPER & GOLD INC
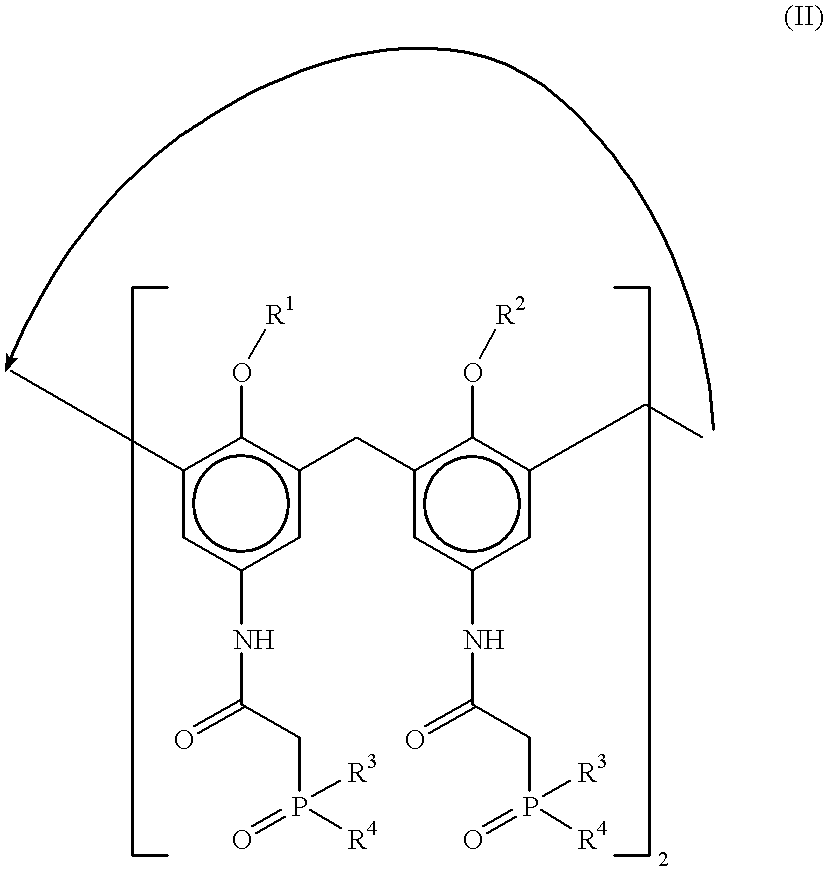
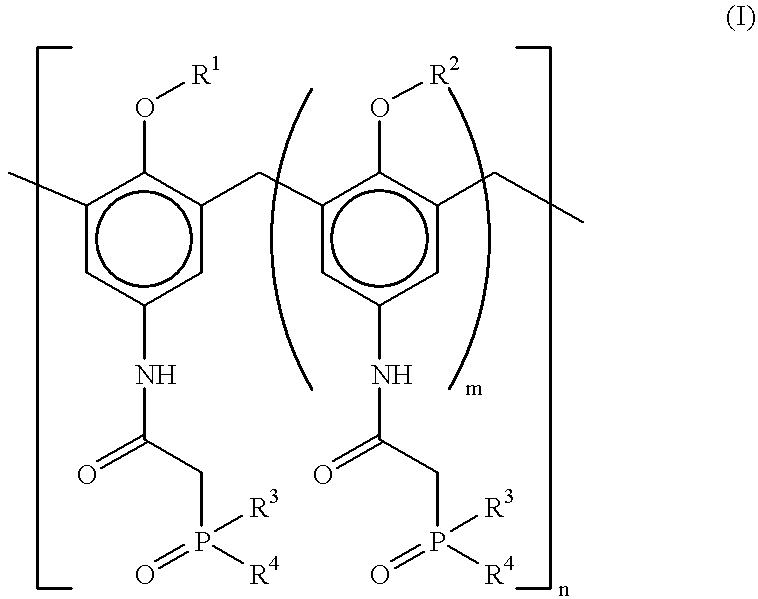
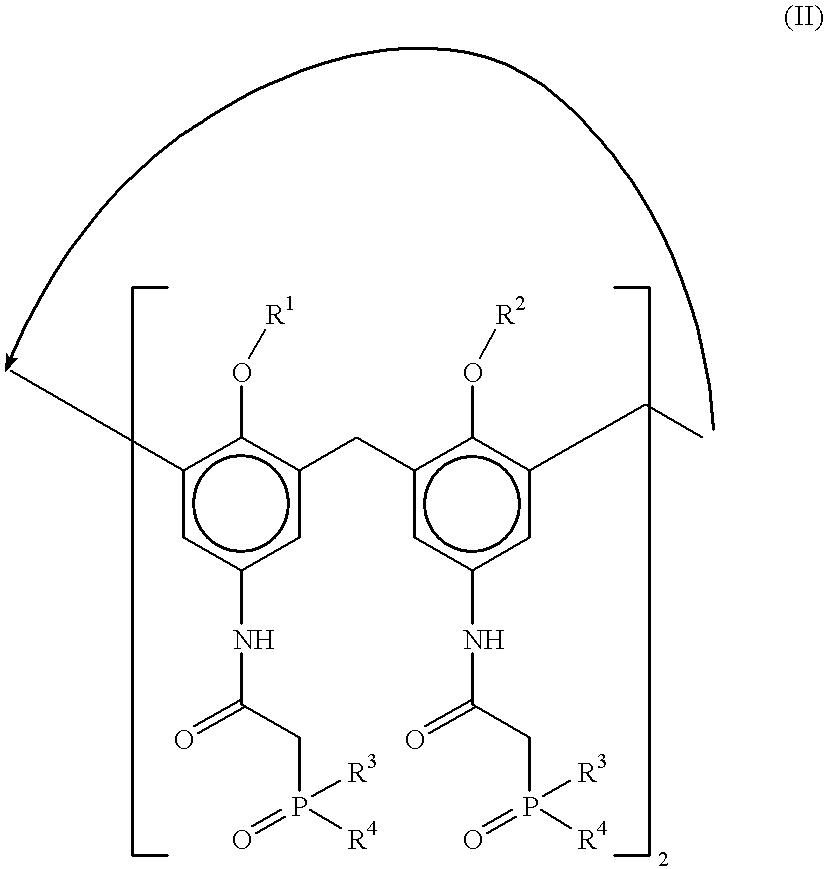
Method for separating actinides and lanthanides by liquid-liquid extraction using calixarenes
The invention involves a process for separating actinides and lanthanides by liquid-liquid extraction by means of calixarenes.These calixarenes have the formula:with R1 and R2 being alkyl groups or o-nitrophenoxy alkyl groups and R3 and R4 being aryl groups,and they are used in an organic liquid phase containing an organic diluent. The diluent and the calixarene concentration of the organic phase are chosen so as to ensure an enrichment of the organic phase with the actinide(s) and / or lanthanide(s) to be separated from an aqueous acid or saline solution.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
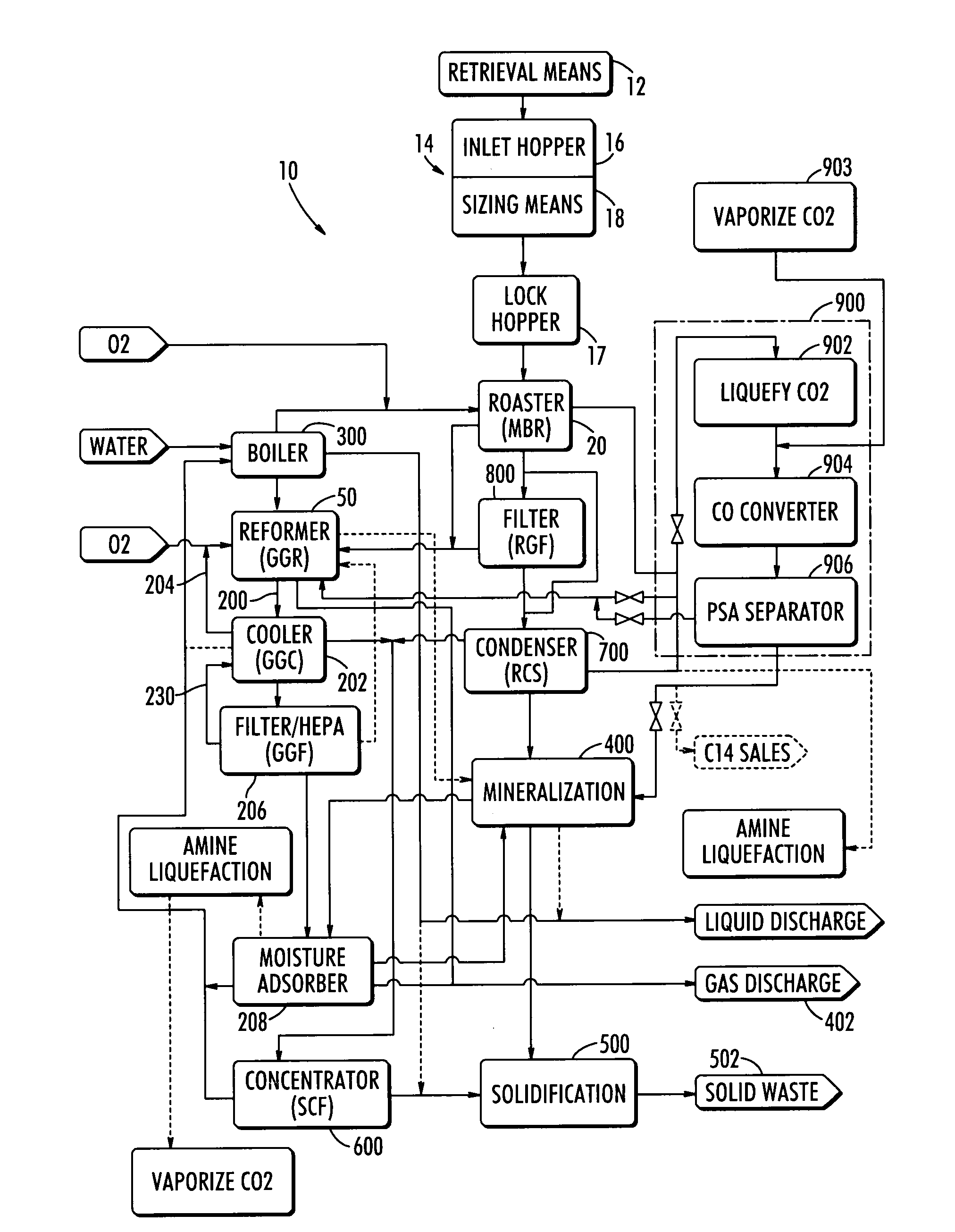
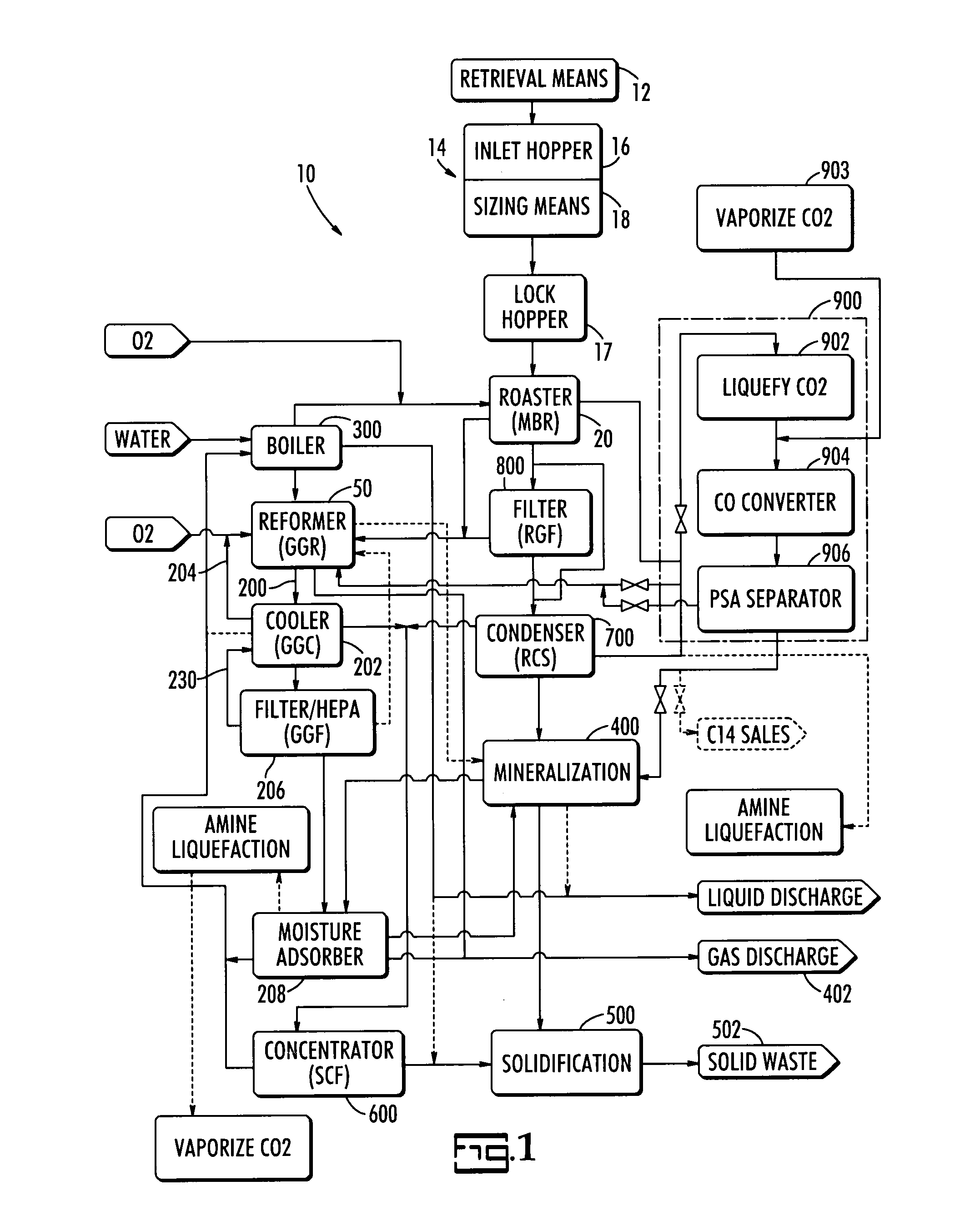
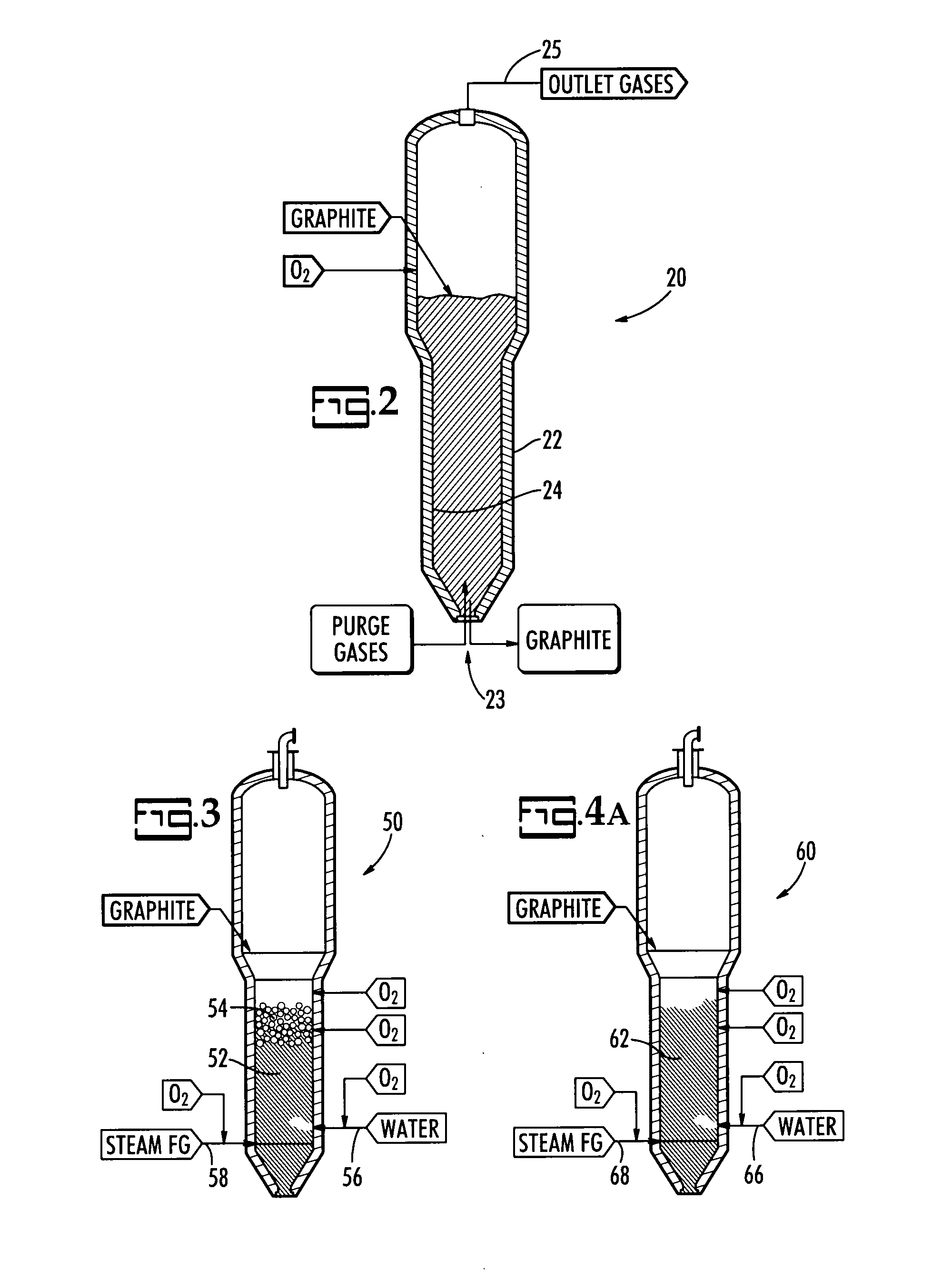
Steam reforming process system for graphite destruction and capture of radionuclides
InactiveUS20080181835A1Step is made and efficientAvoid excessive dischargeTransuranic element compoundsRadium compoundsProcess systemsSteam reforming
A system for the treatment and recycling of graphite containing radionuclides including a two stage method that employes a thermal roaster that is operatively connected to a steam reformer. In the first stage, radioactive graphite is roasted or heated to volatize a first amount of radionuclides contained in the graphite. In the second stage, the roasted graphite is reacted with steam or gases containing water vapor so that a second amount of radionuclides is removed. Optionally, the present system also processes the radionuclides to enable their disposal.
Owner:STUDSVIK INC
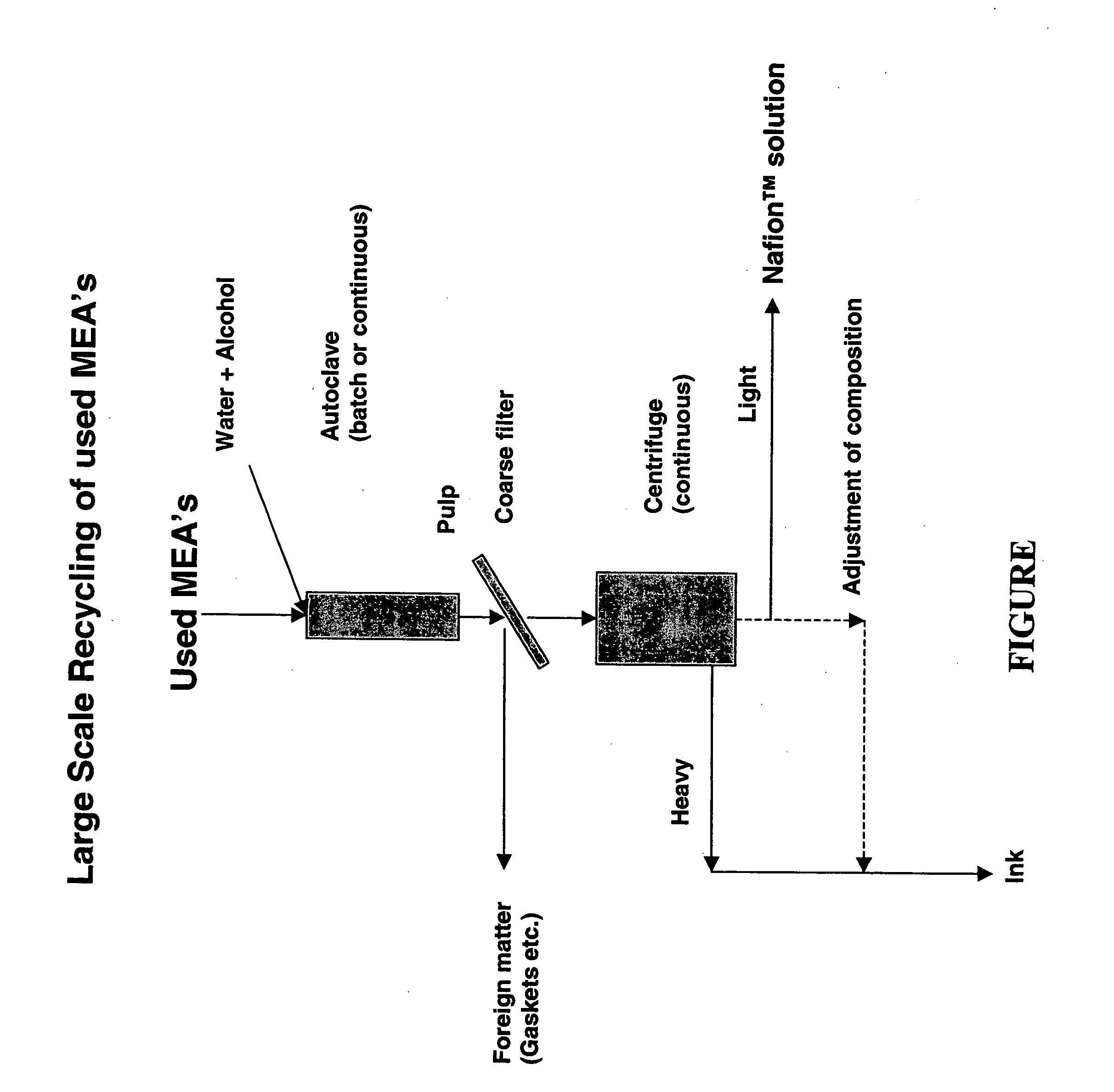
Recycling of used perfluorosulfonic acid membranes
InactiveUS20050211630A1Guaranteed long-term availabilityIncrease consumptionTransuranic element compoundsActive material electrodesSolventMembrane configuration
Owner:ION POWER
Method for synthesizing extremely high-temperature melting materials
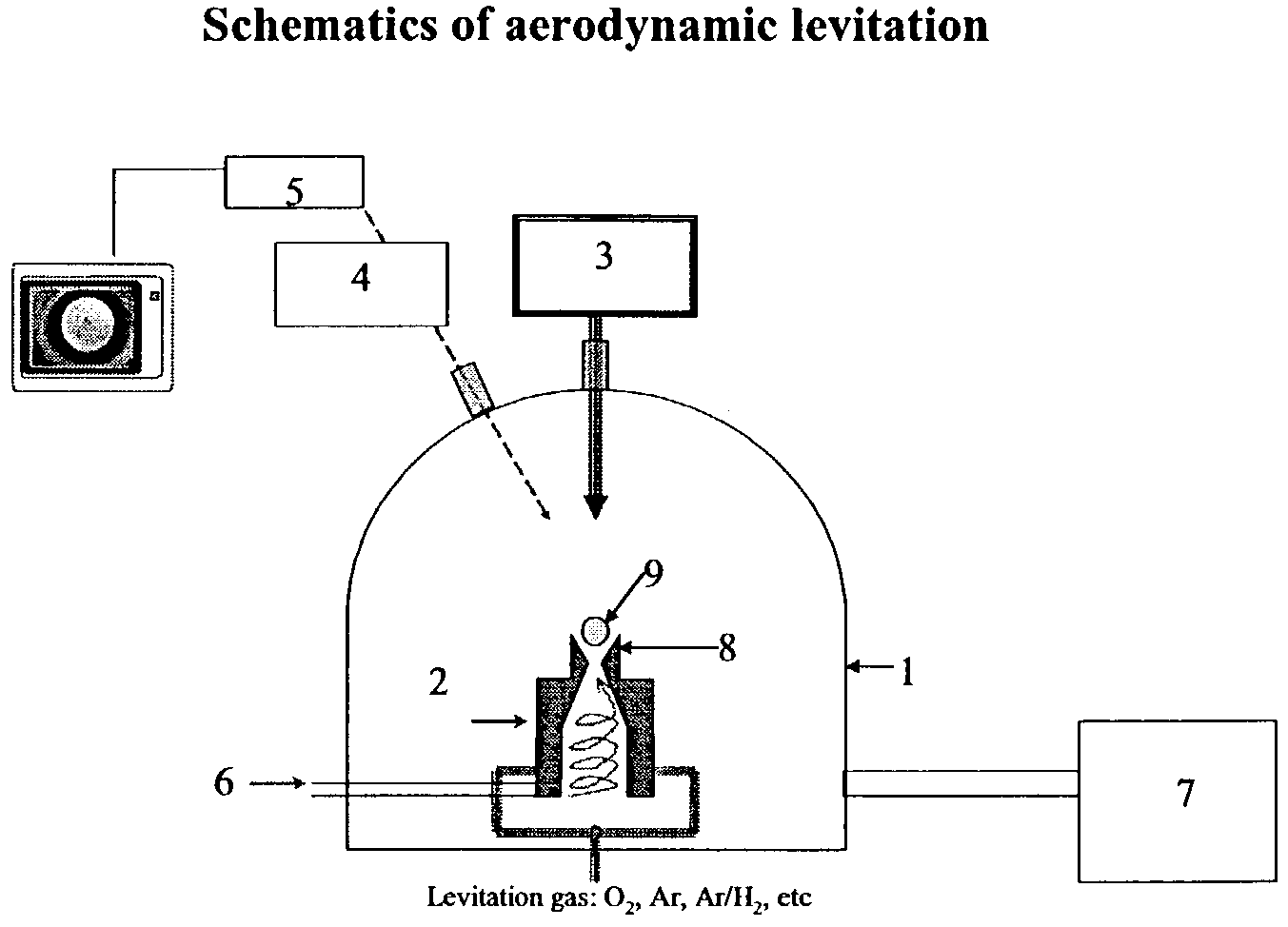
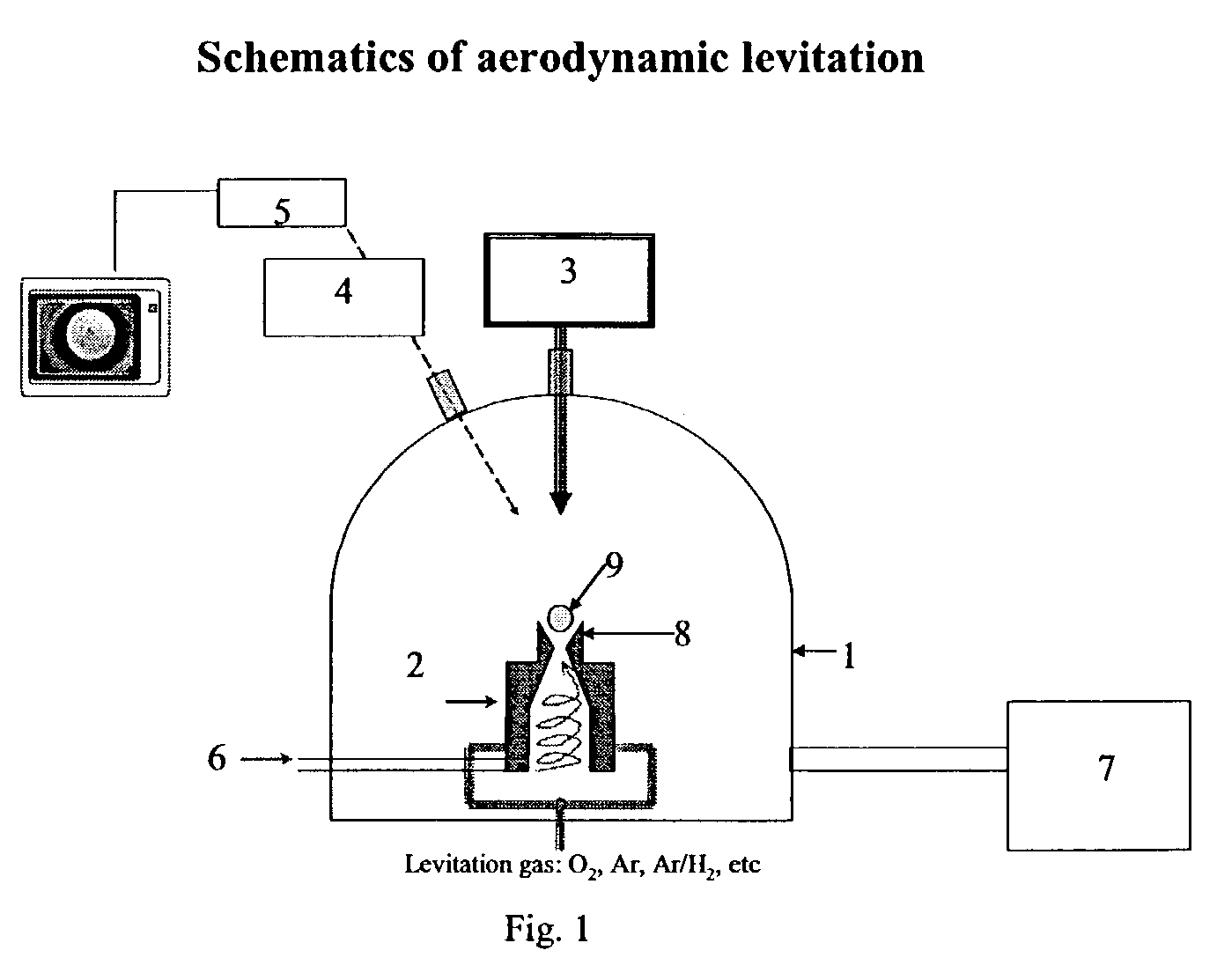
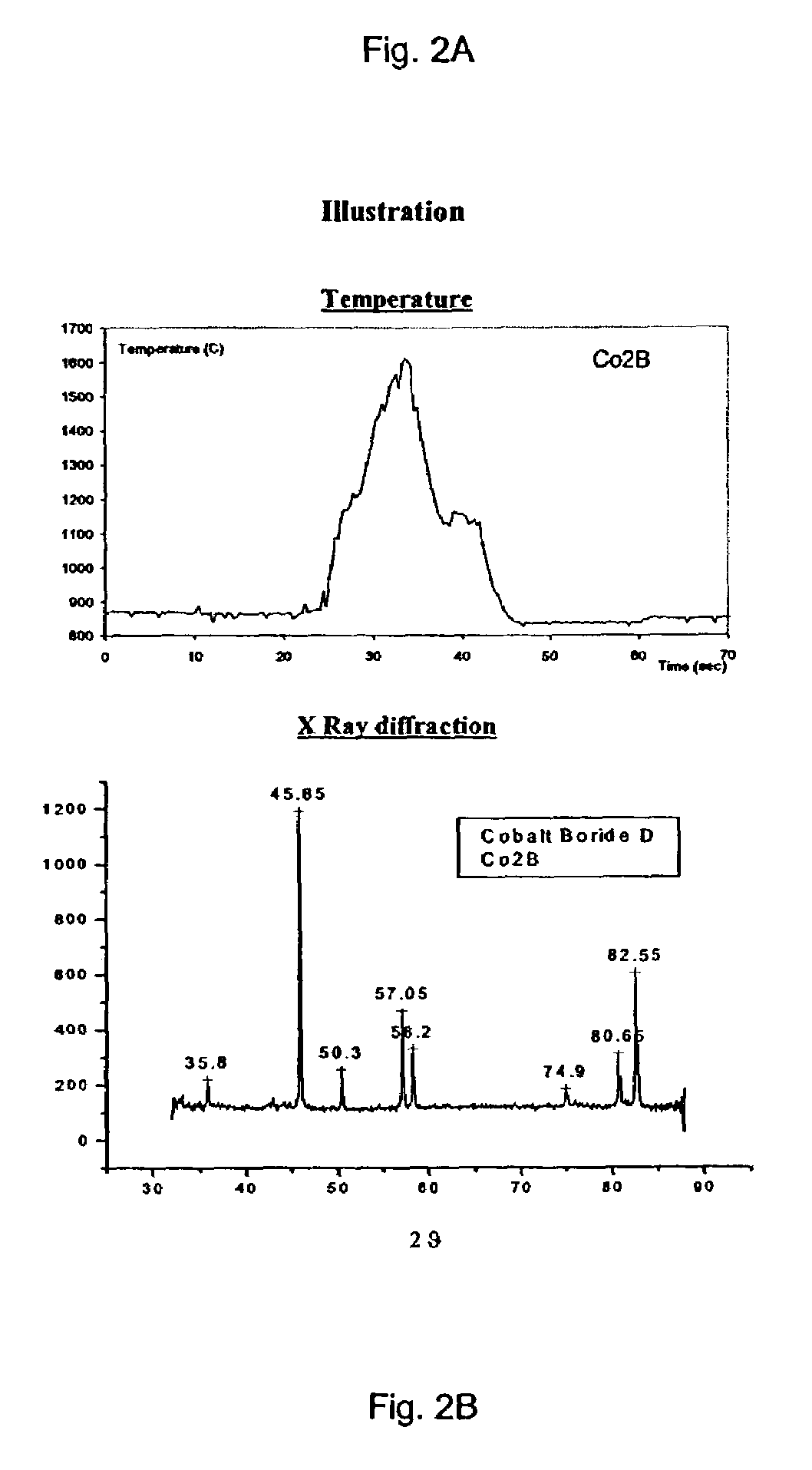
The invention relates to a method of synthesizing high-temperature melting materials. More specifically the invention relates to a containerless method of synthesizing very high temperature melting materials such as borides, carbides and transition-metal, lanthanide and actinide oxides, using an Aerodynamic Levitator and a laser. The object of the invention is to provide a method for synthesizing extremely high-temperature melting materials that are otherwise difficult to produce, without the use of containers, allowing the manipulation of the phase (amorphous / crystalline / metastable) and permitting changes of the environment such as different gaseous compositions.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
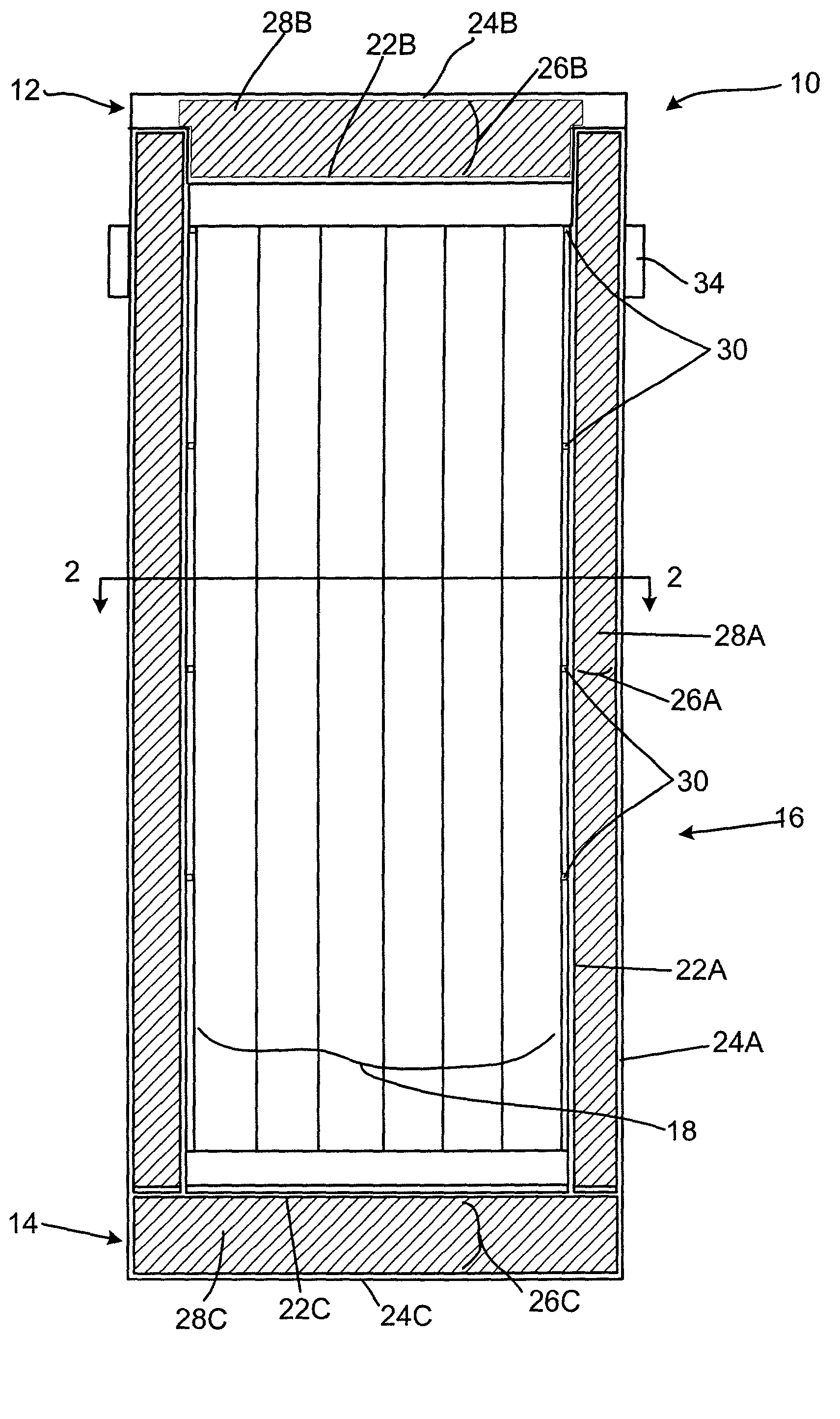
Radiation shielding materials and containers incorporating same
InactiveUS6960311B1Improve shielding effectMaximum flexibilityOther chemical processesTransuranic element compoundsMicrosphereUranium carbide
An improved radiation shielding material and storage systems for radioactive materials incorporating the same. The PYRolytic Uranium Compound (“PYRUC”) shielding material is preferably formed by heat and / or pressure treatment of a precursor material comprising microspheres of a uranium compound, such as uranium dioxide or uranium carbide, and a suitable binder. The PYRUC shielding material provides improved radiation shielding, thermal characteristic, cost and ease of use in comparison with other shielding materials. The shielding material can be used to form containment systems, container vessels, shielding structures, and containment storage areas, all of which can be used to house radioactive waste. The preferred shielding system is in the form of a container for storage, transportation, and disposal of radioactive waste. In addition, improved methods for preparing uranium dioxide and uranium carbide microspheres for use in the radiation shielding materials are also provided.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Methods for making and processing metal targets for producing Cu-67 radioisotope for medical applications
ActiveUS20100028234A1Improve productivitySimple methodBacterial antigen ingredientsTransuranic element compoundsHigh energyCompound (substance)
The present invention provides a method for producing Cu67 radioisotope suitable for use in medical applications. The method comprises irradiating a metallic zinc-68 (Zn68) target with a high energy gamma ray beam. After irradiation, the Cu67 is isolated from the Zn68 by any suitable method (e.g., chemical and / or physical separation). In a preferred embodiment, the Cu67 is isolated by sublimation of the zinc (e.g., at about 500-700° C. under reduced pressure) to afford a copper residue containing Cu67. The Cu67 can be further purified by chemical means (i.e., dissolution in acid, followed by ion exchange).
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
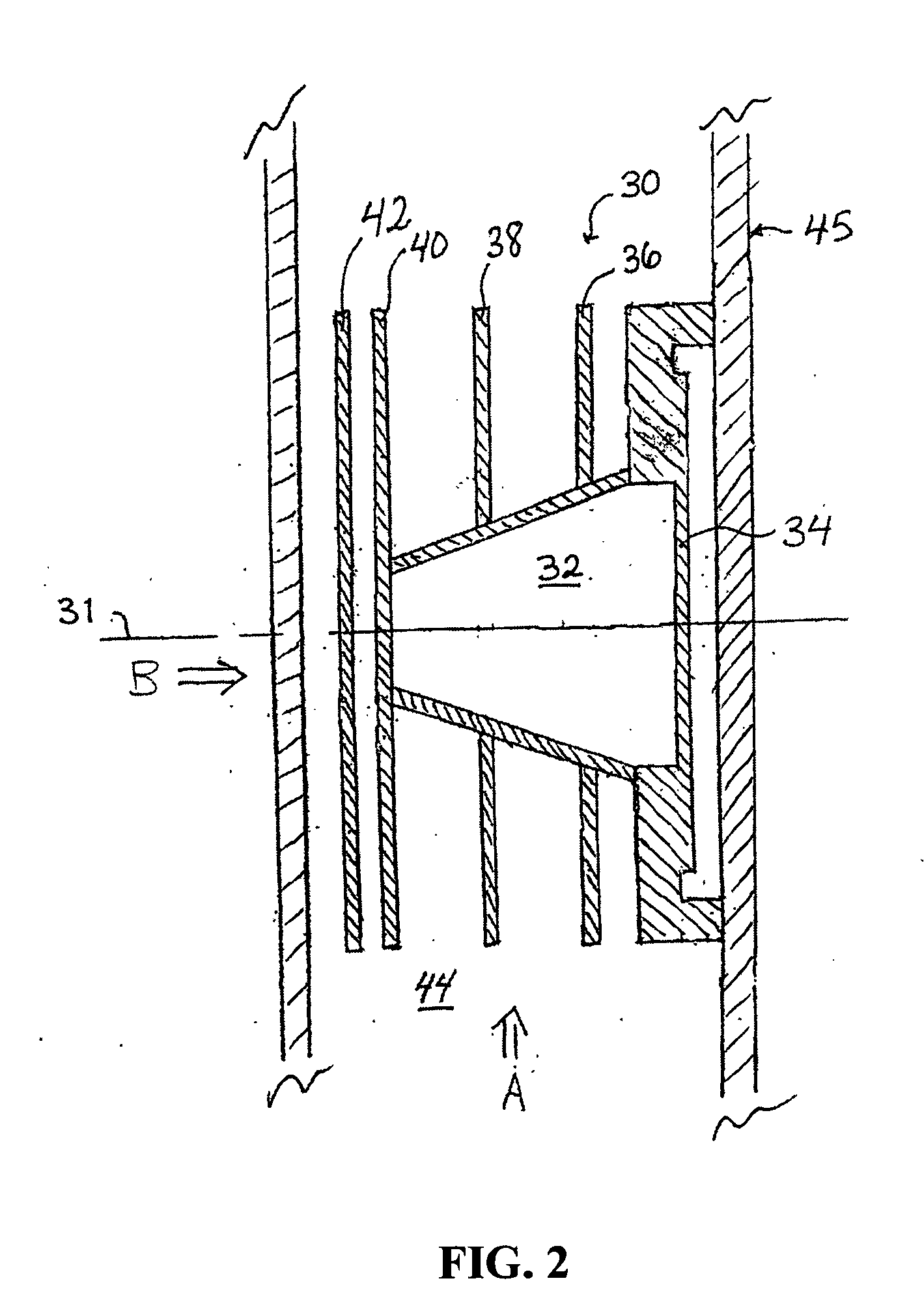
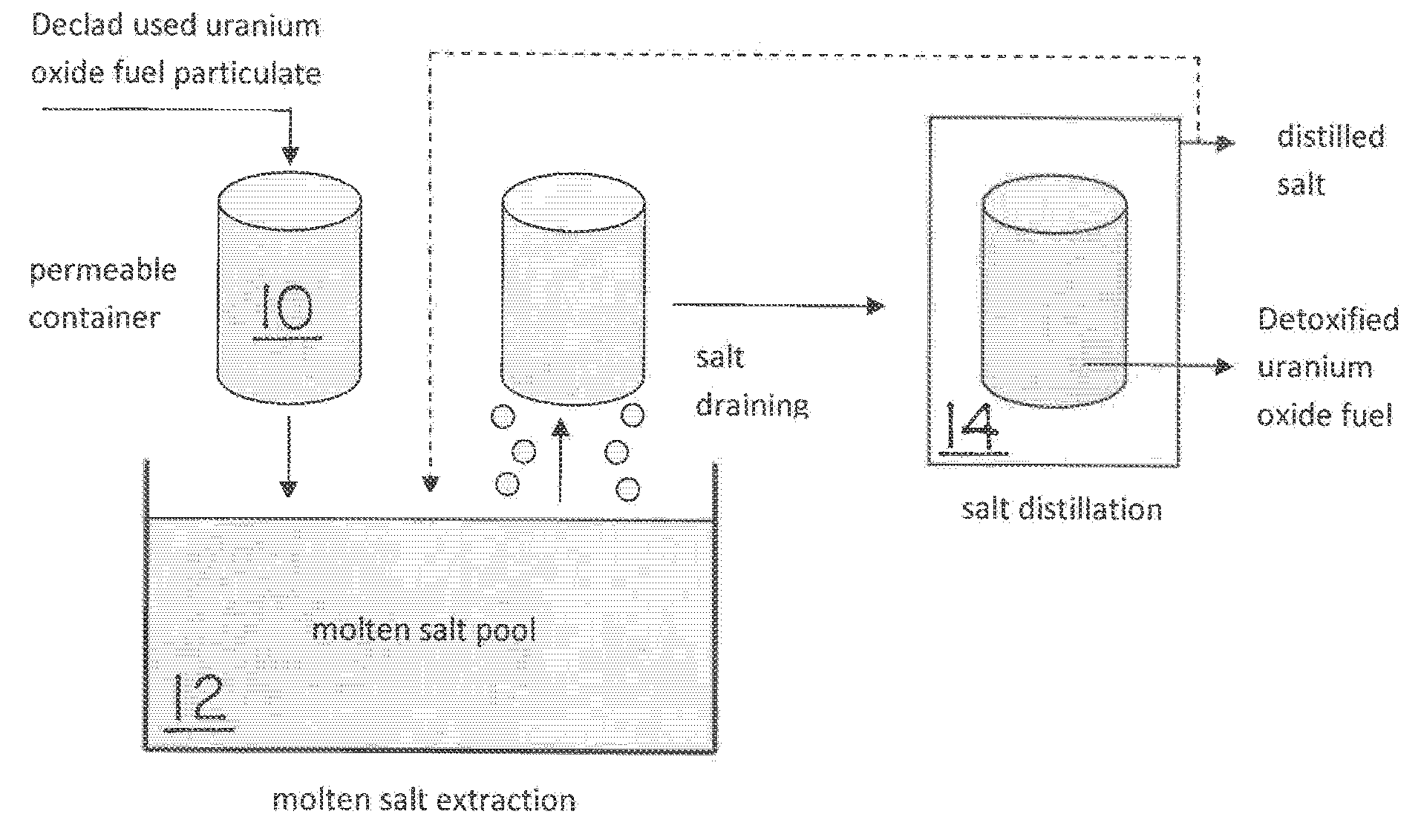
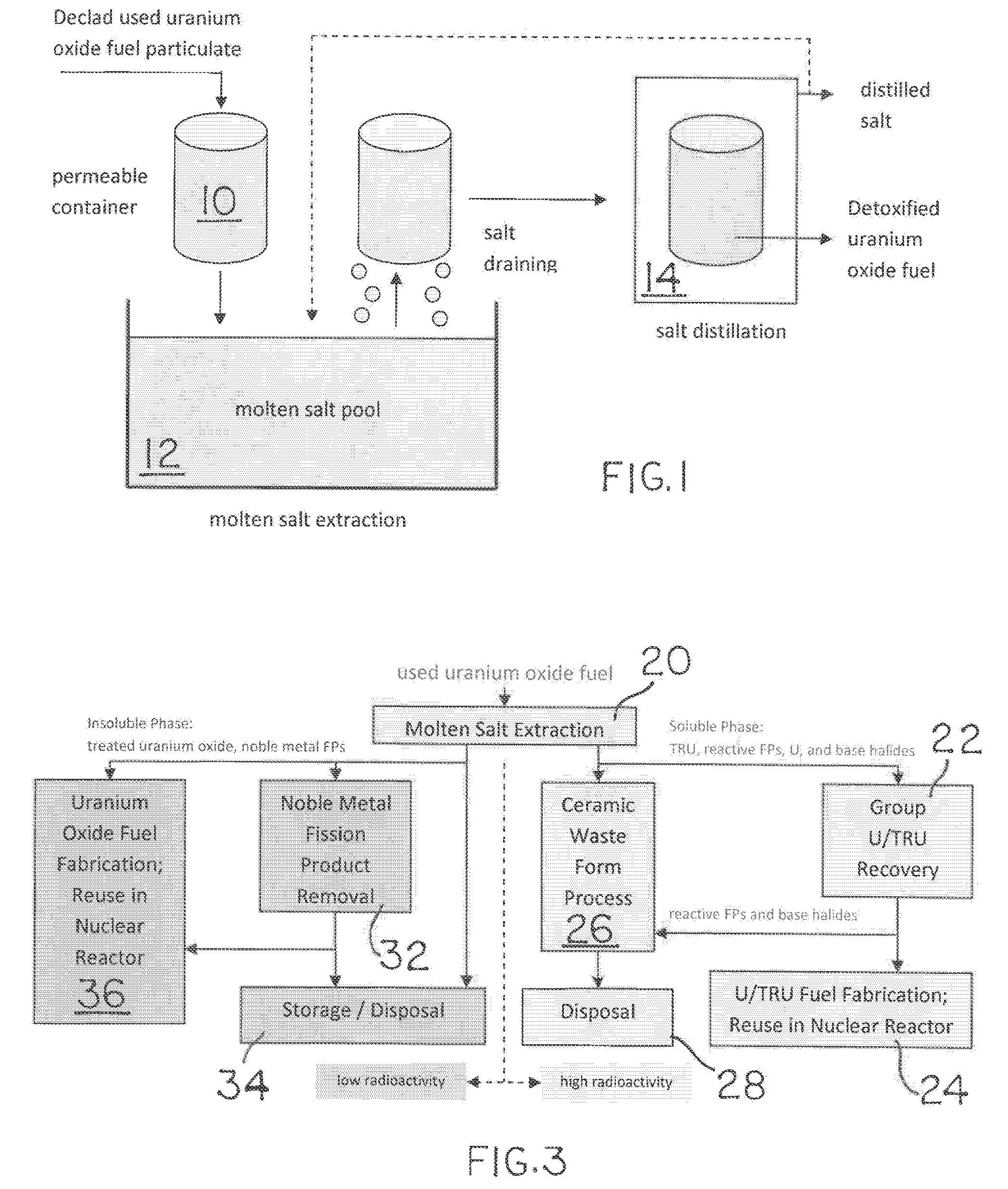
Molten salt extraction of transuranic and reactive fission products from used uranium oxide fuel
Used uranium oxide fuel is detoxified by extracting transuranic and reactive fission products into molten salt. By contacting declad and crushed used uranium oxide fuel with a molten halide salt containing a minor fraction of the respective uranium trihalide, transuranic and reactive fission products partition from the fuel to the molten salt phase, while uranium oxide and non-reactive, or noble metal, fission products remain in an insoluble solid phase. The salt is then separated from the fuel via draining and distillation. By this method, the bulk of the decay heat, fission poisoning capacity, and radiotoxicity are removed from the used fuel. The remaining radioactivity from the noble metal fission products in the detoxified fuel is primarily limited to soft beta emitters. The extracted transuranic and reactive fission products are amenable to existing technologies for group uranium / transuranic product recovery and fission product immobilization in engineered waste forms.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Systems and methods for radioisotope generation
Owner:JUBILANT DRAXIMAGE
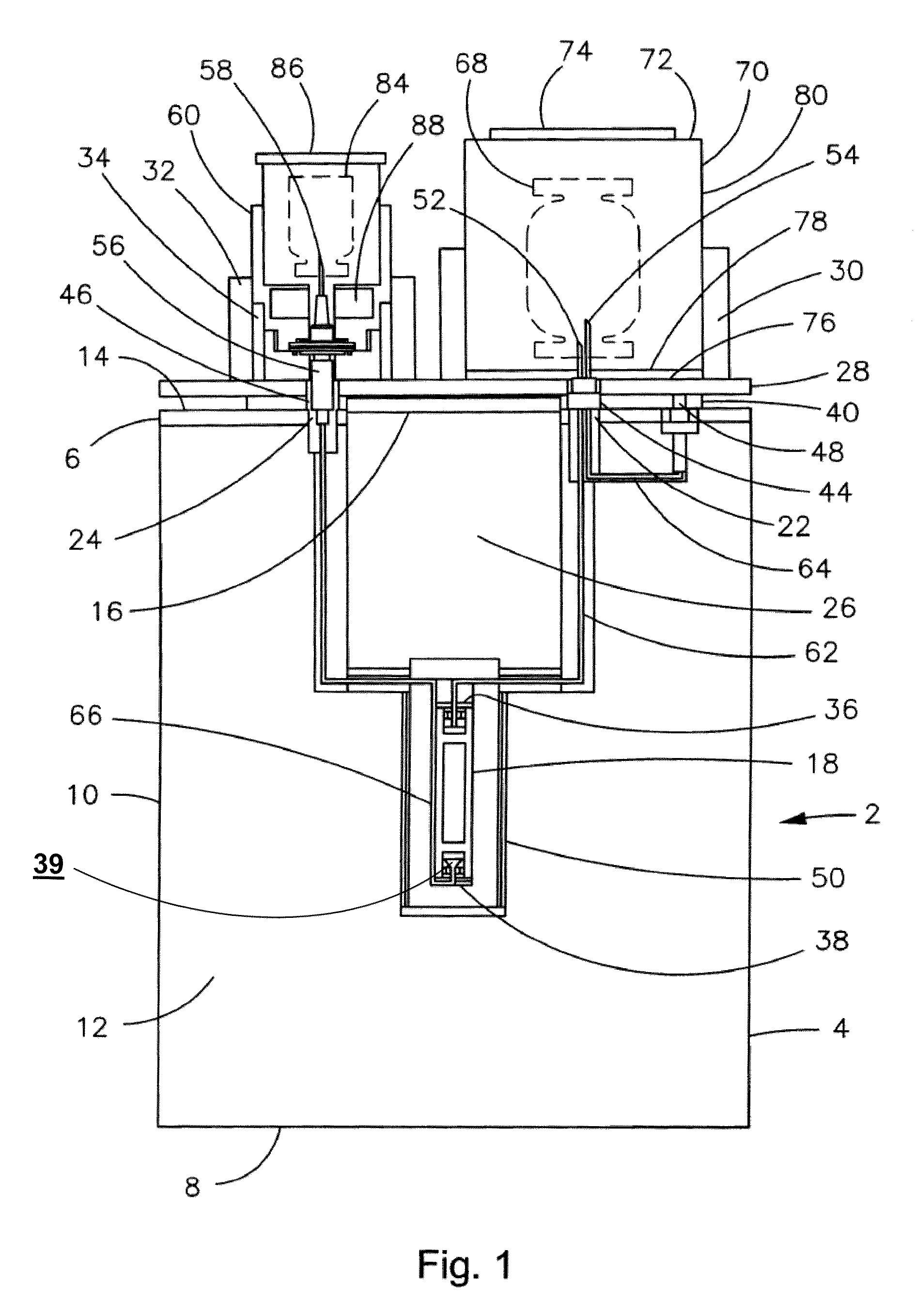
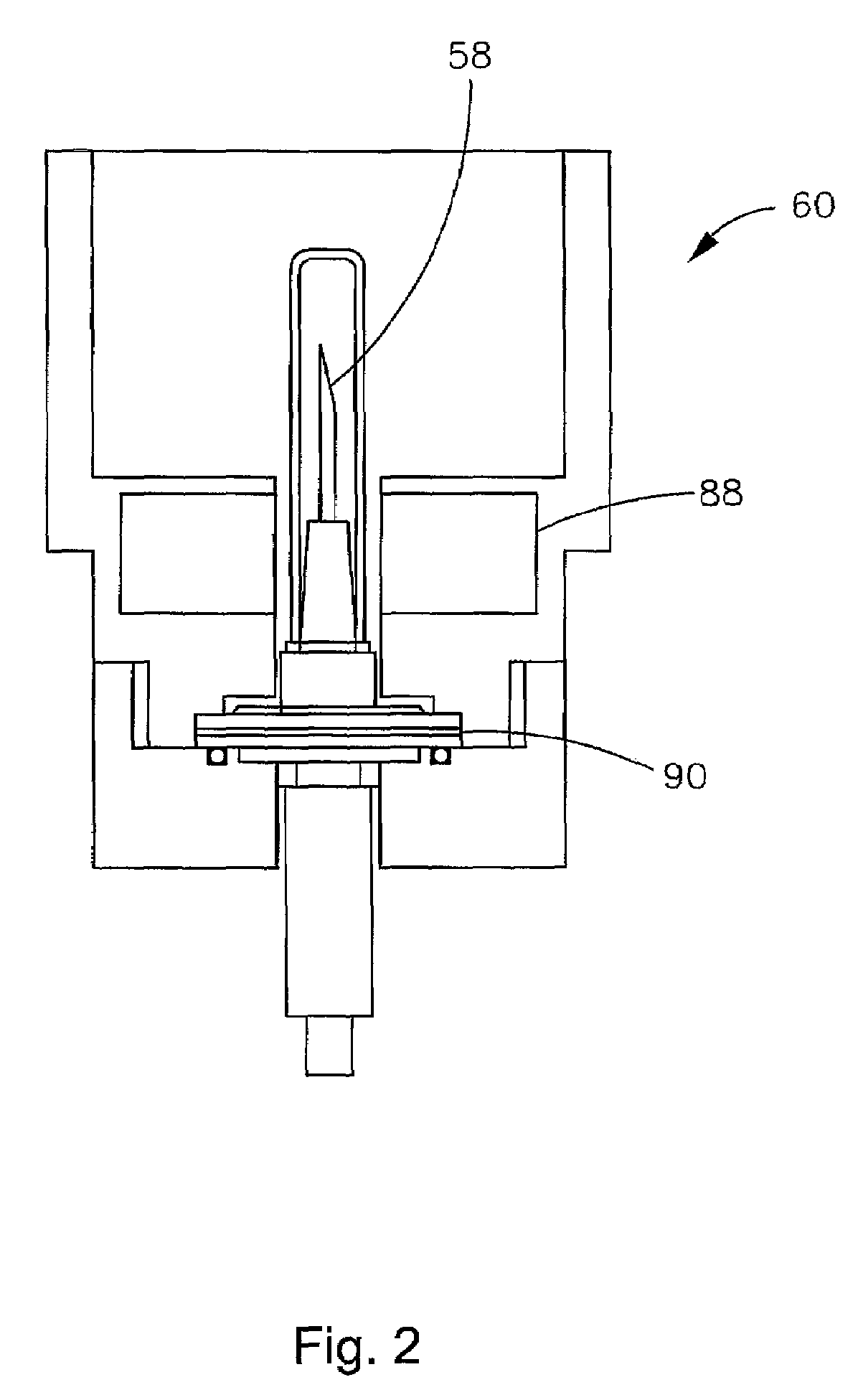
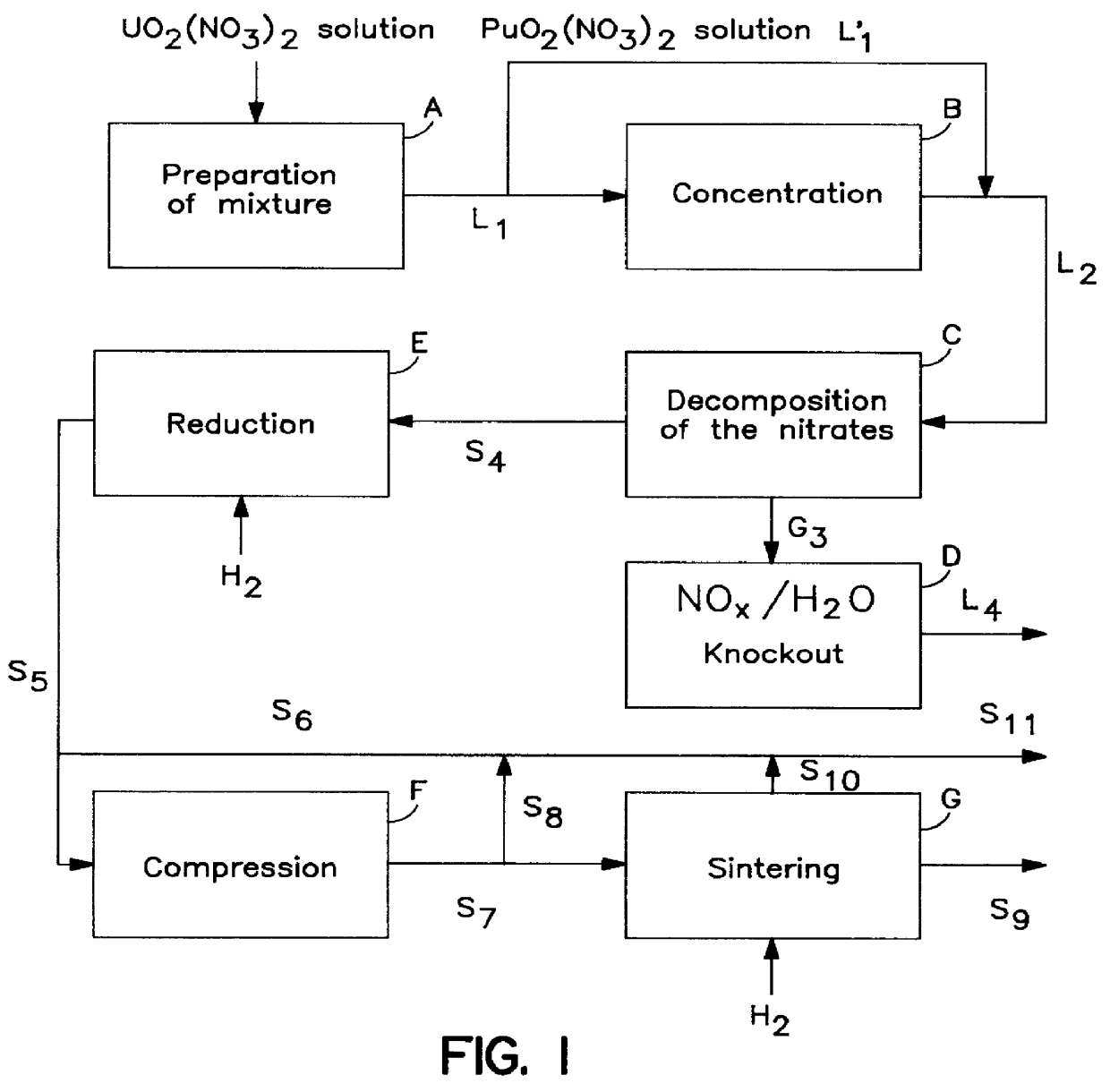
Method for preparing a mixture of powdered metal oxides from nitrates thereof in the nuclear industry
InactiveUS6110437AEasy to recycleImprove responseOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideTransuranic element compoundsPowder mixtureNitrate
PCT No. PCT / FR96 / 01993 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 2, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 2, 1999 PCT Filed Dec. 12, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 21629 PCT Pub. Date Jun. 19, 1997A thermal decomposition method useful in the nuclear industry for preparing a powdered mixture of metal oxides having suitable reactivity from nitrates thereof in the form of an aqueous solution or a mixture of solids. According to the method, the solution or the mixture of solids is thermomechanically contacted with a gaseous fluid in the contact area of a reaction chamber, said gaseous fluid being fed into the reaction chamber at the same time as the solution or mixture at a temperature no lower than the decomposition temperature of the nitrates, and having a mechanical energy high enough to generate a fine spray of the solution or a fine dispersion of the solid mixture, and instantly decompose the nitrates. The resulting oxide mixtures may be used to prepare nuclear fuels.
Owner:COMURHEX
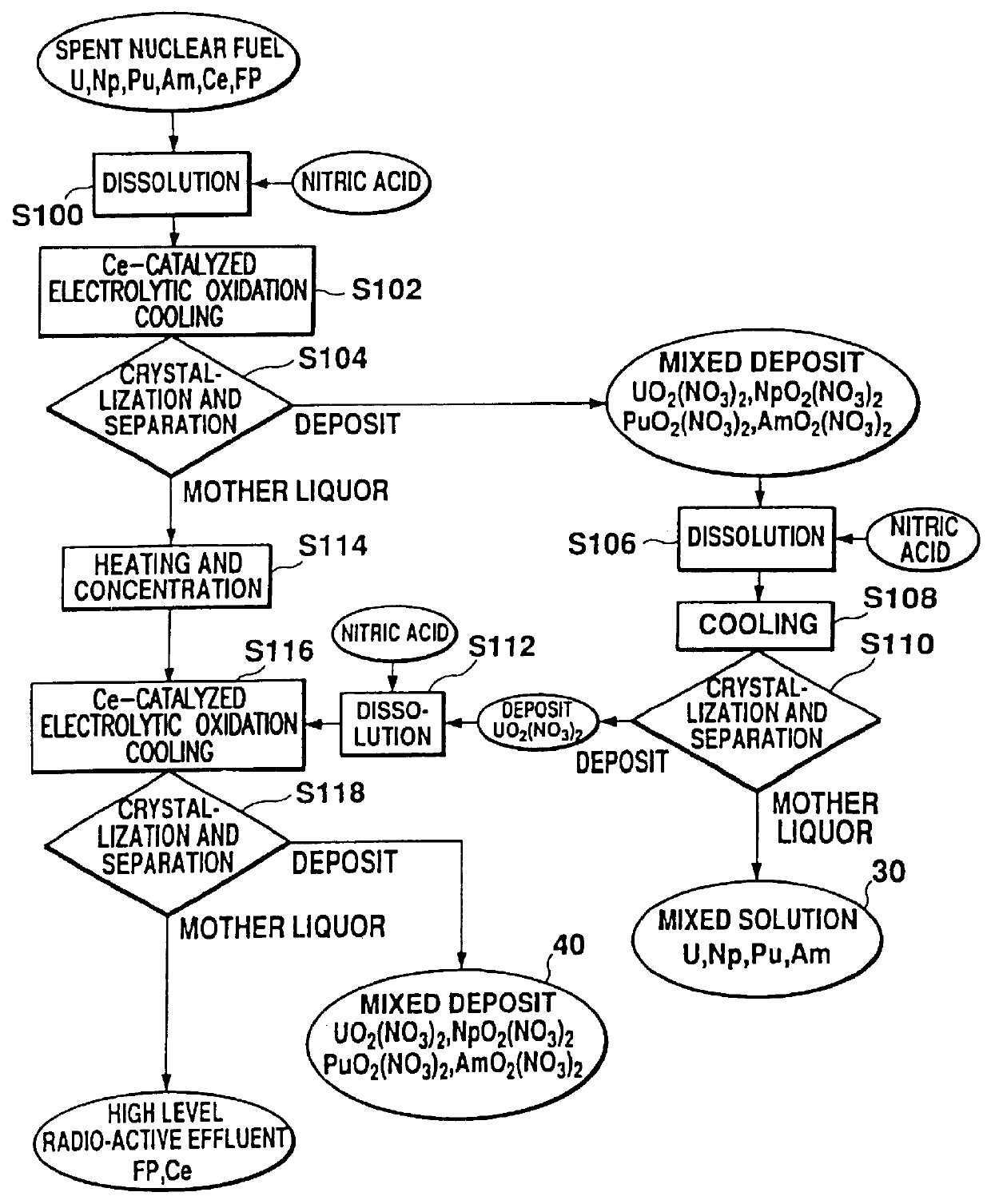
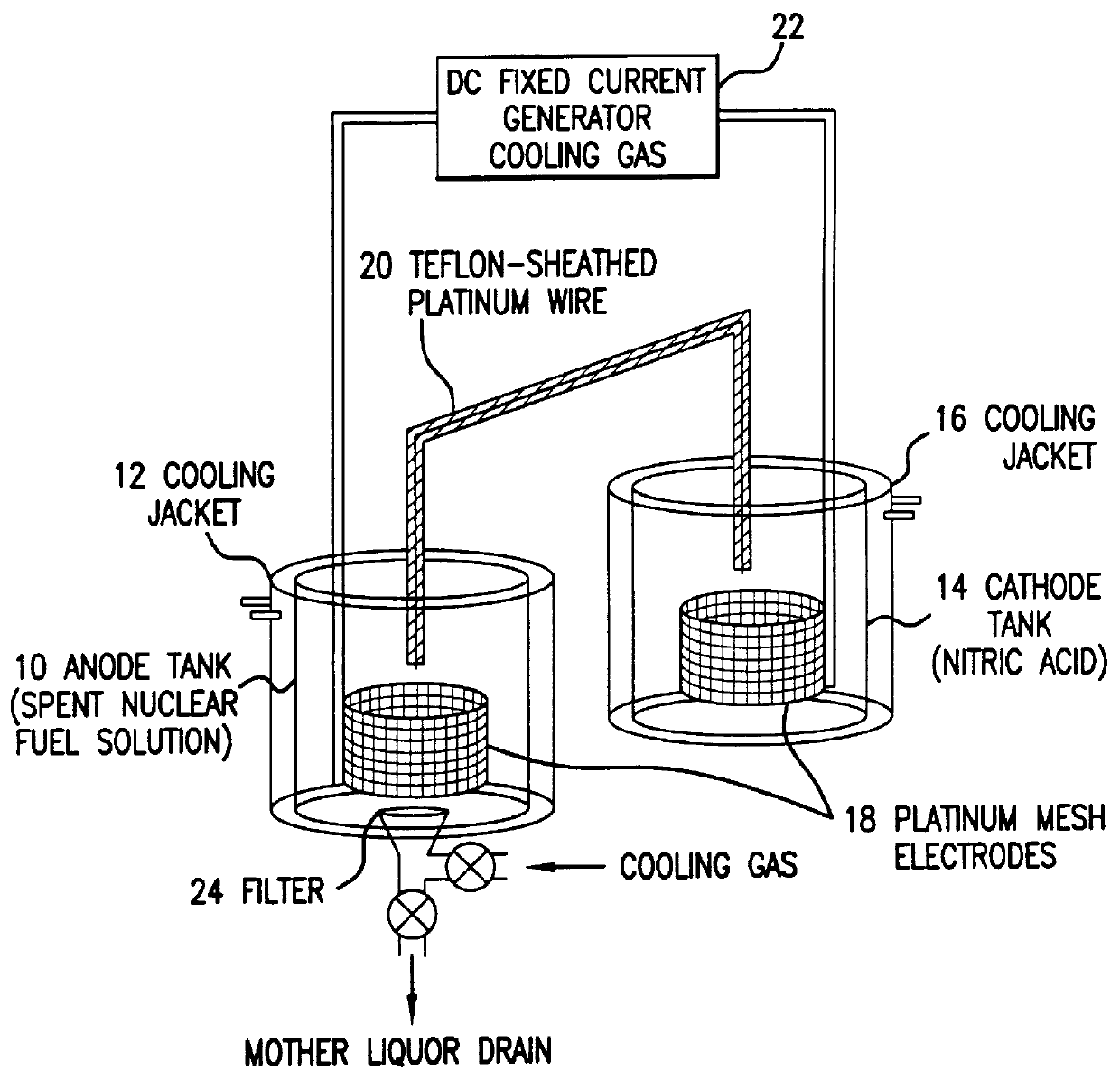
Method of recovering uranium and transuranic elements from spent nuclear fuel
InactiveUS6033636AReduce solubilityPromote recoveryElectrolysis componentsSolvent extractionSolventWaste material
The steps for recovering uranium and transuranic elements are simplified, and the generation of waste solvent and waste materials is suppressed. Spent nuclear fuel is dissolved in nitric acid (S100) and the resulting solution is subjected to electrolytic oxidation so that U, Np, Pu, Am is oxidized to VI using Ce as oxidation catalyst. The solution is cooled, and nitrates of valence VI thereby deposit as crystals and are separated from the mother liquor (S104). The mother liquor is heated and concentrated (S114). The mixed crystalline deposit is dissolved in nitric acid (S106), uranyl nitrate is deposited alone by cooling (S108), and the crystals are separated from the U, Np, Pu, Am mixed solution (S110). The uranyl nitrate is dissolved in nitric acid (S112), and the heated and concentrated mother liquor is added to it to prepare another mixed solution. This mixed solution is then subjected to electrolytic oxidation to oxidize the remaining U, Np, Pu, Am to valence VI, and the solution is cooled so that U, Np, Pu, Am are coprecipitated with uranyl nitrate as crystals, and can be separated from high level radioactive effluent (S118).
Owner:DORYOKURO KAKUNENRYO KAIHATSU JIGYODAN
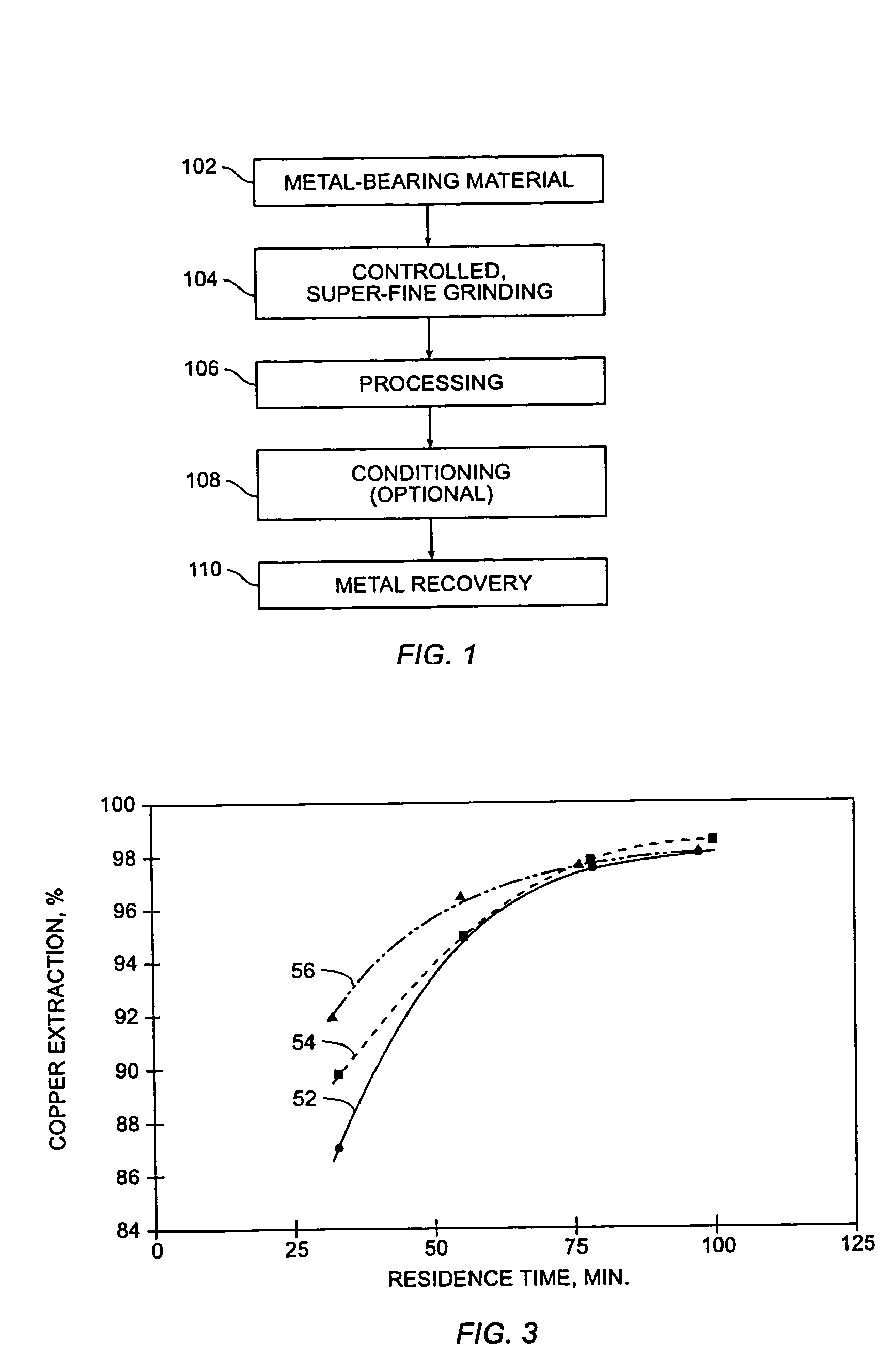
Method for recovery of metals from metal-containing materials using medium temperature pressure leaching
InactiveUS7341700B2Promote recoveryEnhanced metal value recoveryBiocideChromium compoundsRheniumMetallic materials
The present invention relates generally to a process for recovering copper and other metal values from metal-containing materials using controlled, super-fine grinding and medium temperature pressure leaching. Processes embodying aspects of the present invention may be beneficial for recovering a variety of metals such as copper, gold, silver, nickel, cobalt, molybdenum, rhenium, zinc, uranium, and platinum group metals, from metal-bearing materials, and find particular utility in connection with the extraction of copper from copper sulfide ores and concentrates.
Owner:FREEPORT MCMORAN COPPER & GOLD INC
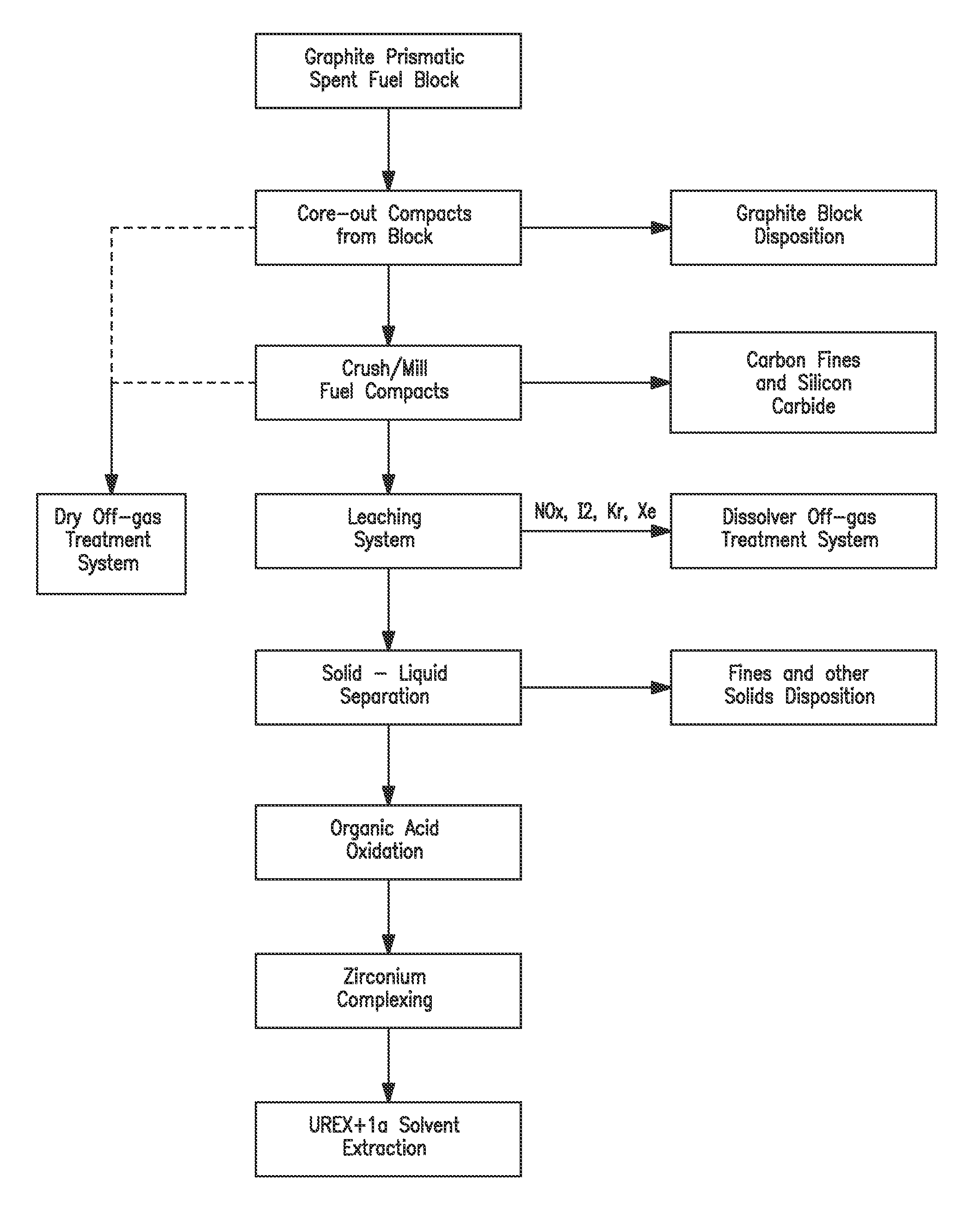
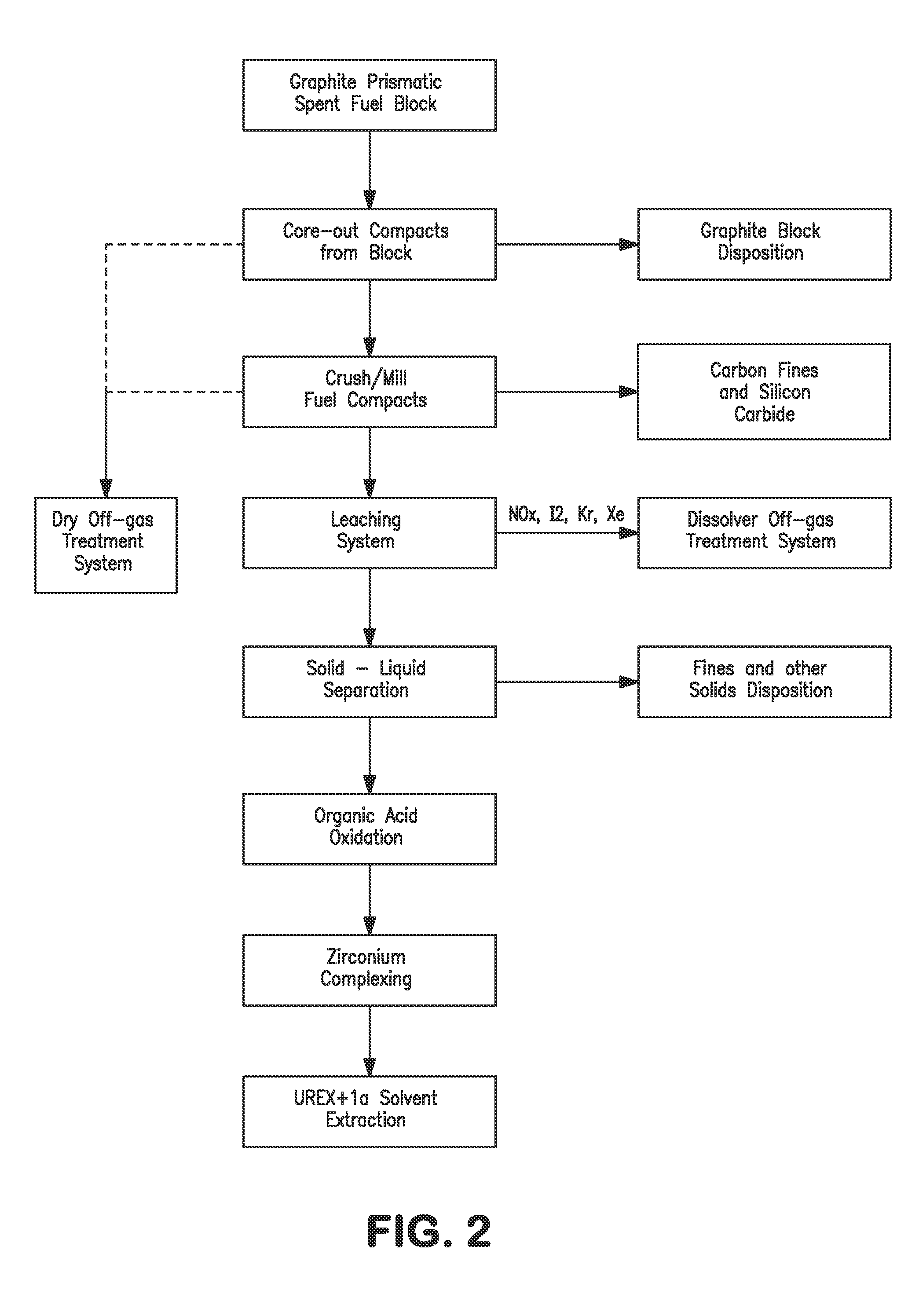
Processing fissile material mixtures containing zirconium and/or carbon
A method of processing spent TRIZO-coated nuclear fuel may include adding fluoride to complex zirconium present in a dissolved TRIZO-coated fuel. Complexing the zirconium with fluoride may reduce or eliminate the potential for zirconium to interfere with the extraction of uranium and / or transuranics from fission materials in the spent nuclear fuel.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
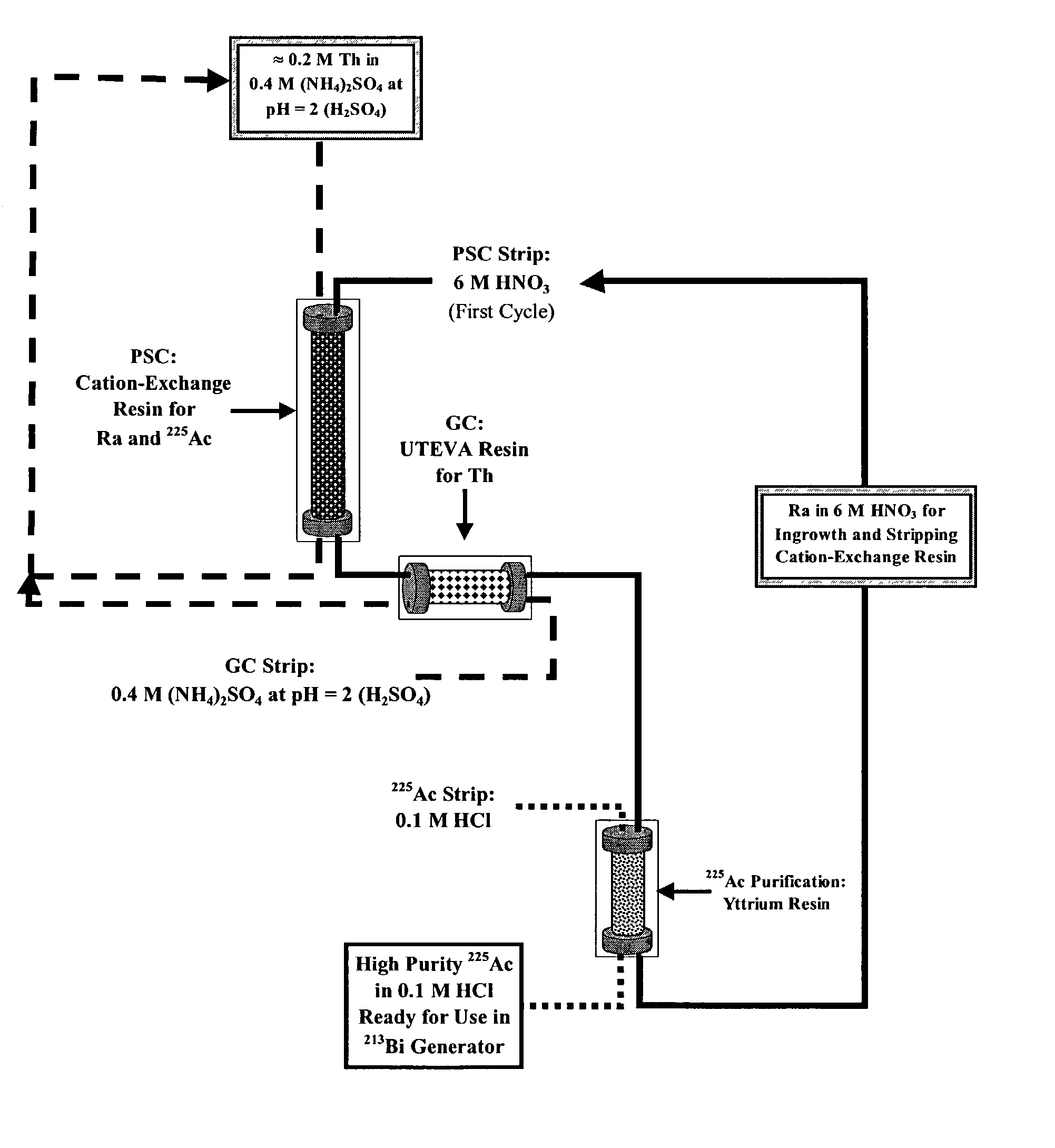
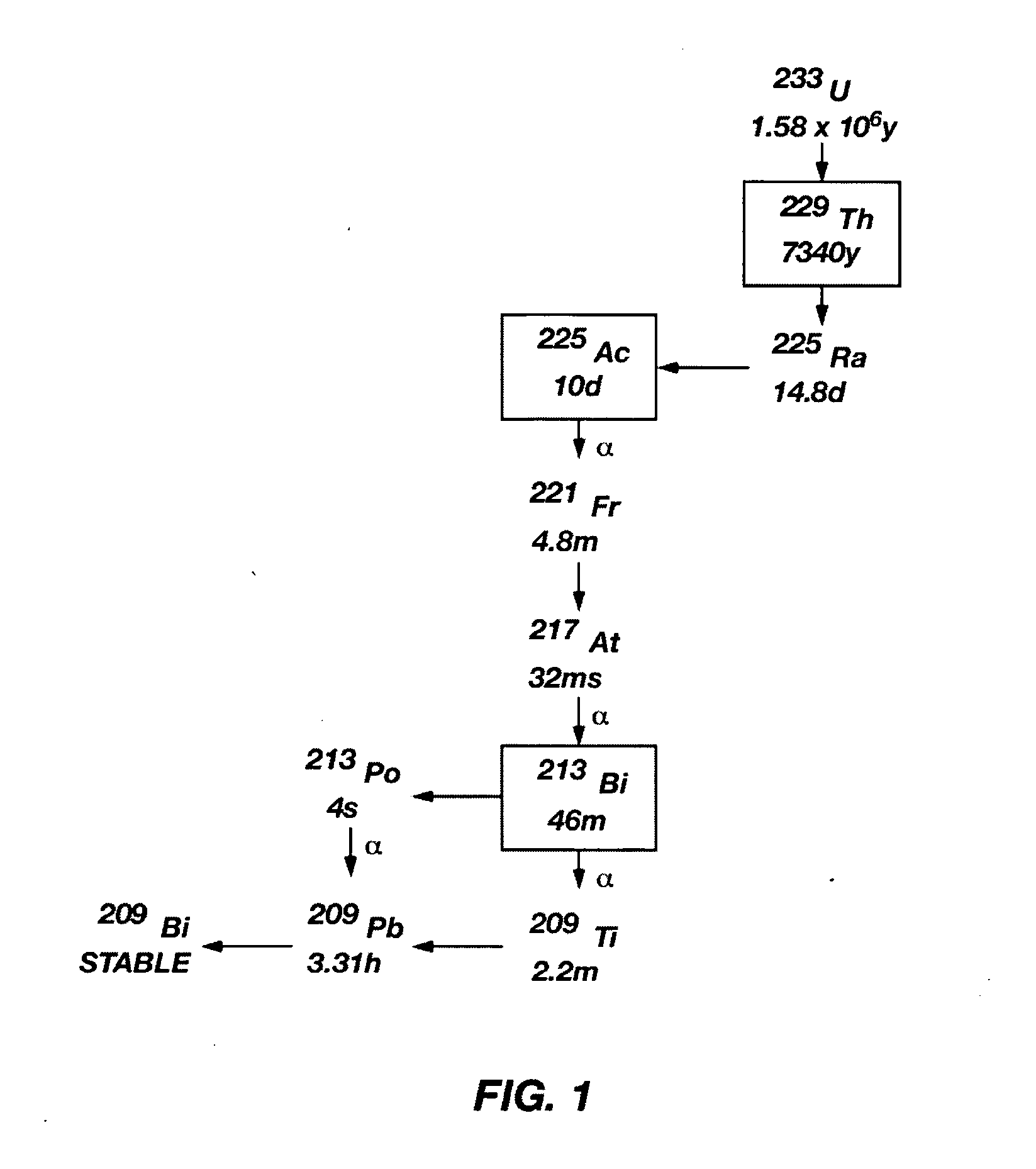
Multicolumn selectivity inversion generator for production of high purity actinium for use in therapeutic nuclear medicine
InactiveUS7087206B2Separation efficiency is highSmall volumeIsotope delivery systemsTransuranic element compoundsActiniumRadiation damage
A multicolumn selectivity inversion generator separation method has been developed in which actinium ions, a desired daughter radionuclide, are selectively extracted from a solution of the thorium parent and daughter radionuclides by a primary separation column, stripped, and passed through a second guard column that retains any parent or other daughter interferents, while the desired daughter actinium ions and radium ions elute. This separation method minimizes the effects of radiation damage to the separation material and permits the reliable production of radionuclides of high chemical and radionuclidic purity for use in diagnostic or therapeutic nuclear medicine.
Owner:PG RES FOUND
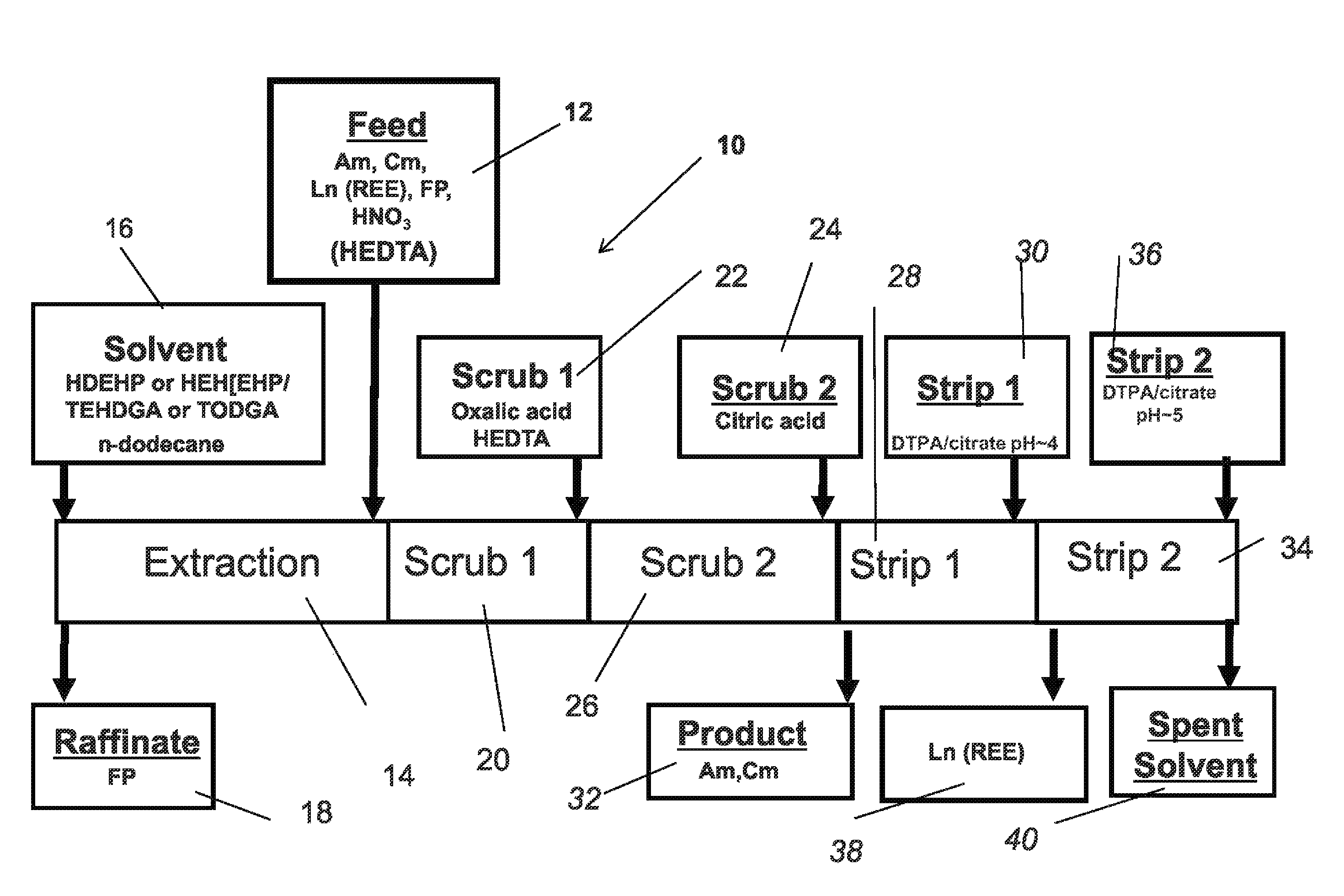
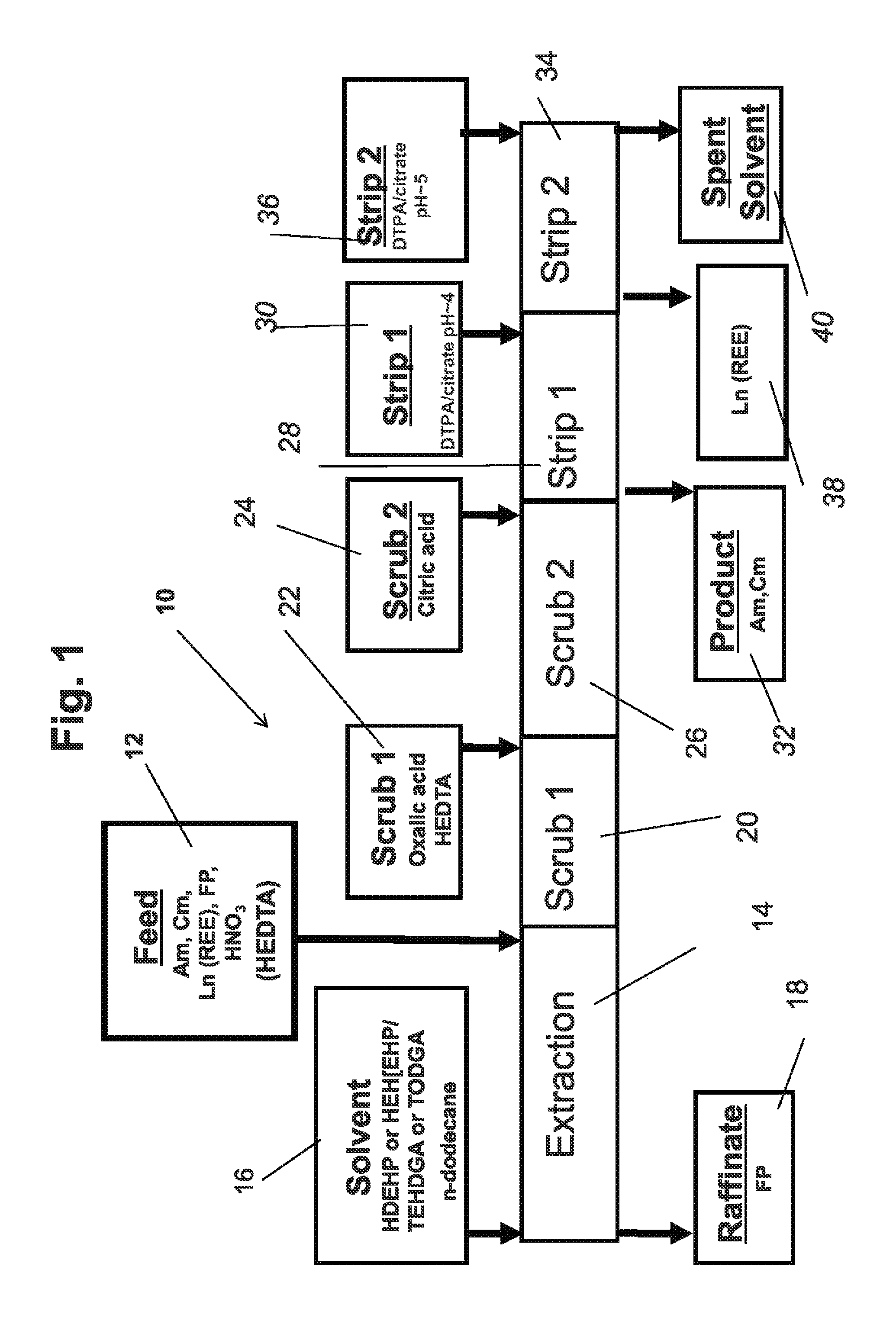
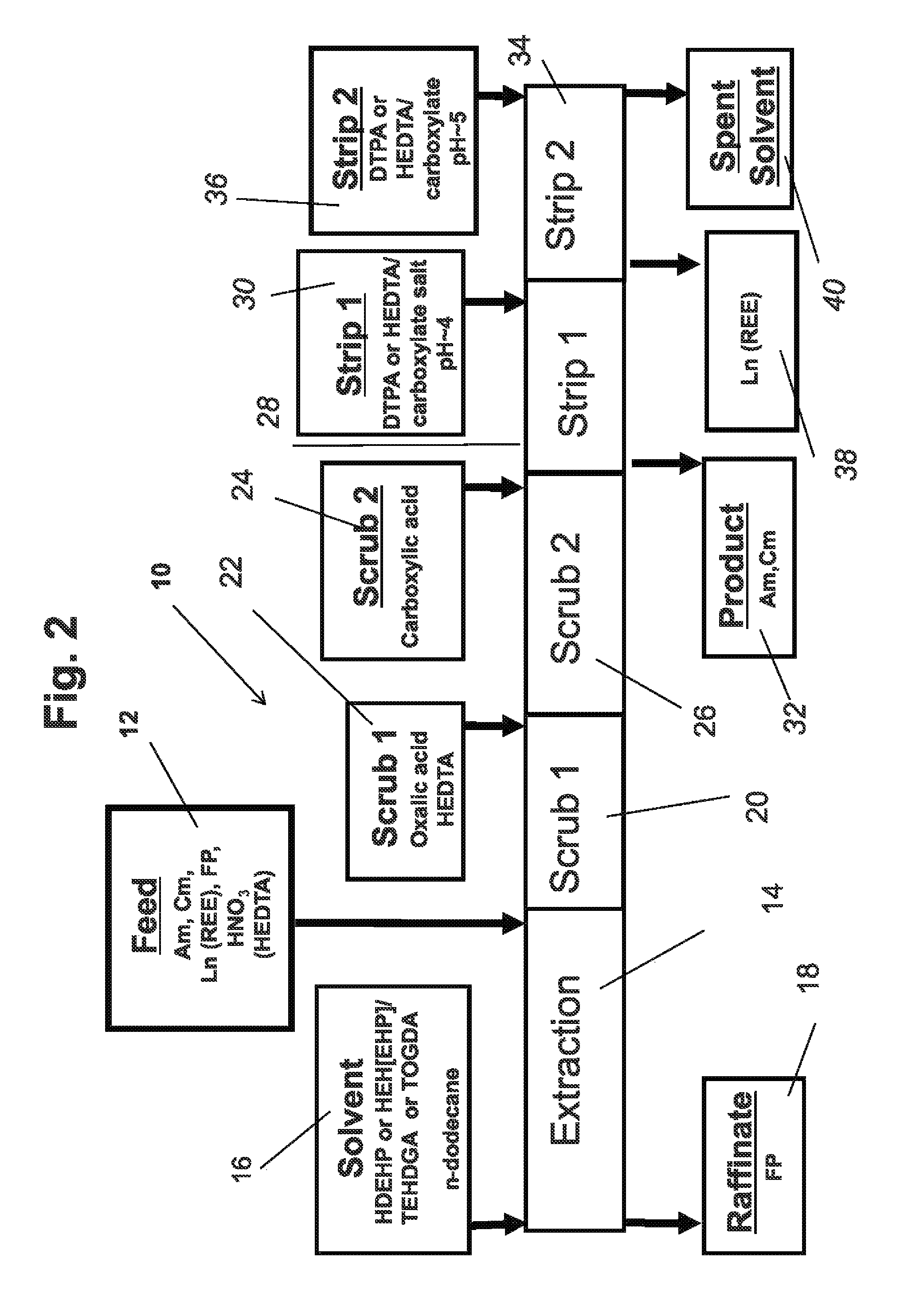
Actinide and lanthanide separation process (ALSEP)
InactiveUS8354085B1Permit separationSolvent extractionTransuranic element compoundsRare-earth elementLanthanide
The process of the invention is the separation of minor actinides from lanthanides in a fluid mixture comprising, fission products, lanthanides, minor actinides, rare earth elements, nitric acid and water by addition of an organic chelating aid to the fluid; extracting the fluid with a solvent comprising a first extractant, a second extractant and an organic diluent to form an organic extractant stream and an aqueous raffinate. Scrubbing the organic stream with a dicarboxylic acid and a chelating agent to form a scrubber discharge. The scrubber discharge is stripped with a simple buffering agent and a second chelating agent in the pH range of 2.5 to 6.1 to produce actinide and lanthanide streams and spent organic diluents. The first extractant is selected from bis(2-ethylhexyl)hydrogen phosphate (HDEHP) and mono(2-ethylhexyl)2-ethylhexyl phosphonate (HEH(EHP)) and the second extractant is selected from N,N,N,N-tetra-2-ethylhexyl diglycol amide (TEHDGA) and N,N,N′,N′-tetraoctyl-3-oxapentanediamide (TODGA).
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents comprising zinc-containing magnetic metal oxide nanoparticles
ActiveUS20100143263A1Improve magnetic propertiesLow cytotoxicityBiocideNanomagnetismMRI contrast agentMetal oxide nanoparticles
The present invention relates to an MRI contrast agent that includes zinc-containing water-soluble metal oxide nanoparticles and has an improved contrast effect. The zinc-containing water-soluble metal oxide nanoparticles are characterized by addition of zinc to a matrix comprising the metal oxide nanoparticles or by substitution of metal in the matrix, resulting in the improved contrast effect of MRI. In addition, the zinc-containing metal oxide nanoparticles of the present invention include the MRI contrast agent t having hybrid structures of “zinc-containing metal oxide nanoparticle—biologically / chemically active material” in which the nanoparticle is conjugated with a bioactive material such as proteins, antibodies, and chemical materials.
Owner:INVENTERA PHARM INC
Preparation of chitosan-based microporous composite material and its applications
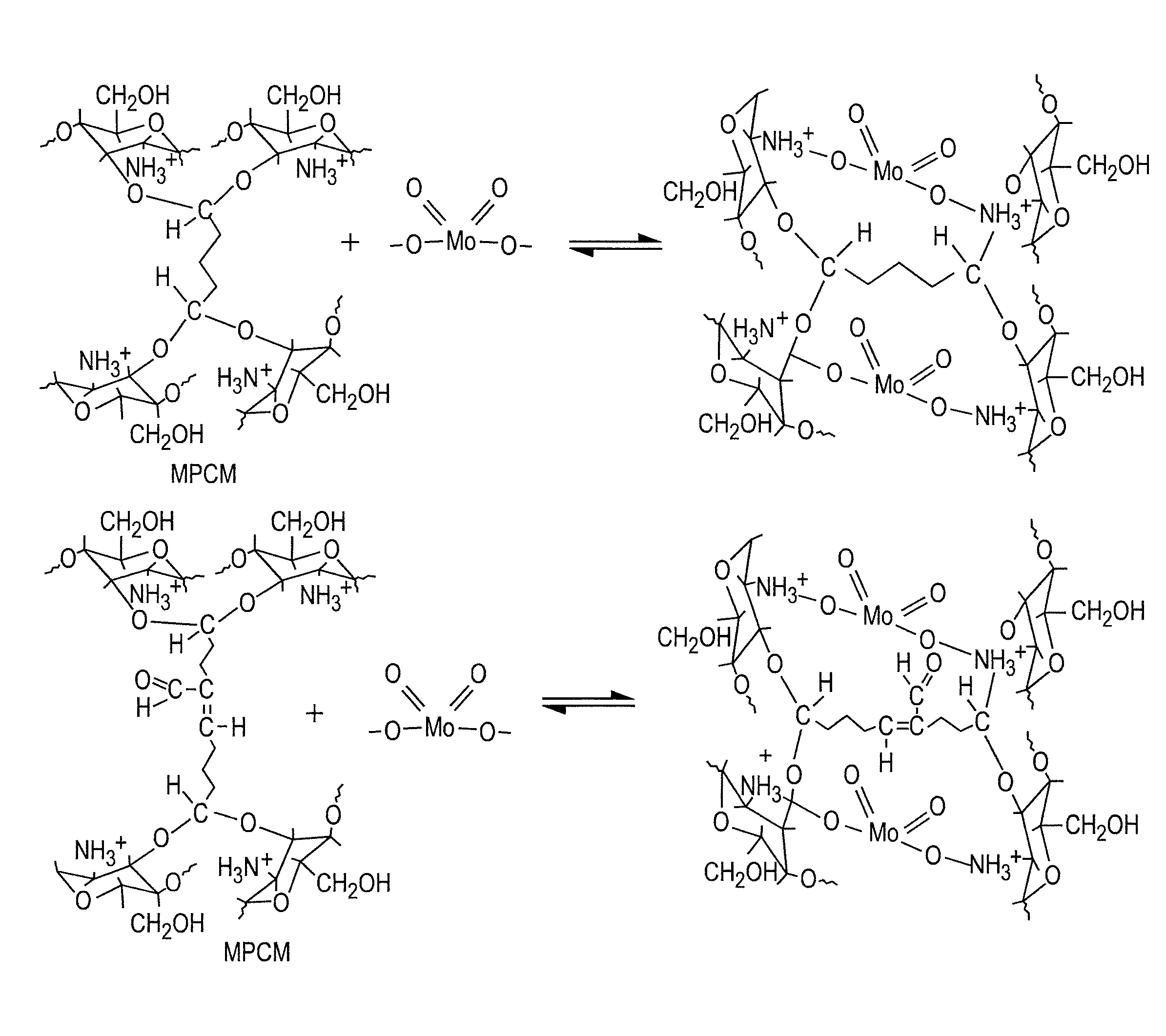
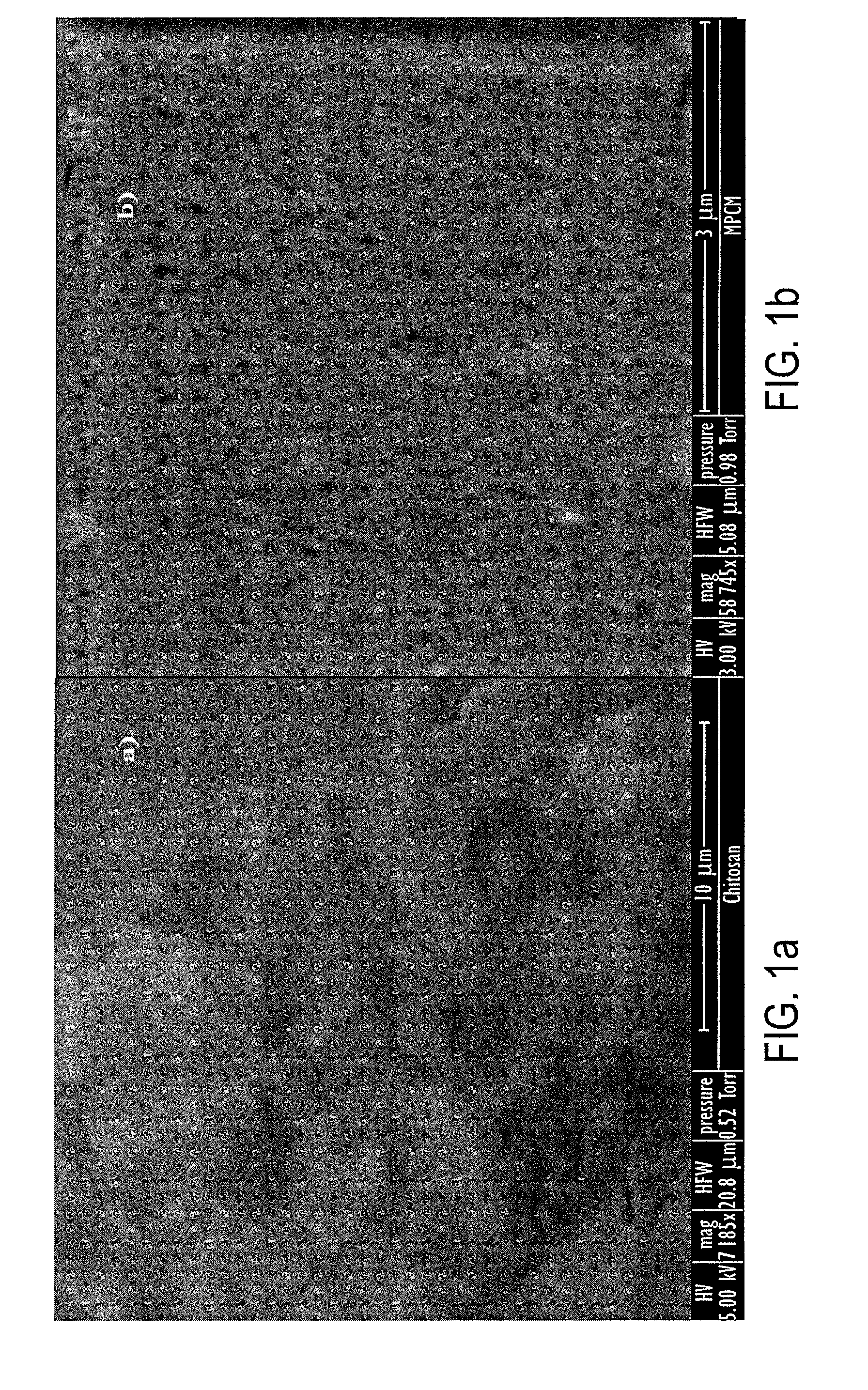
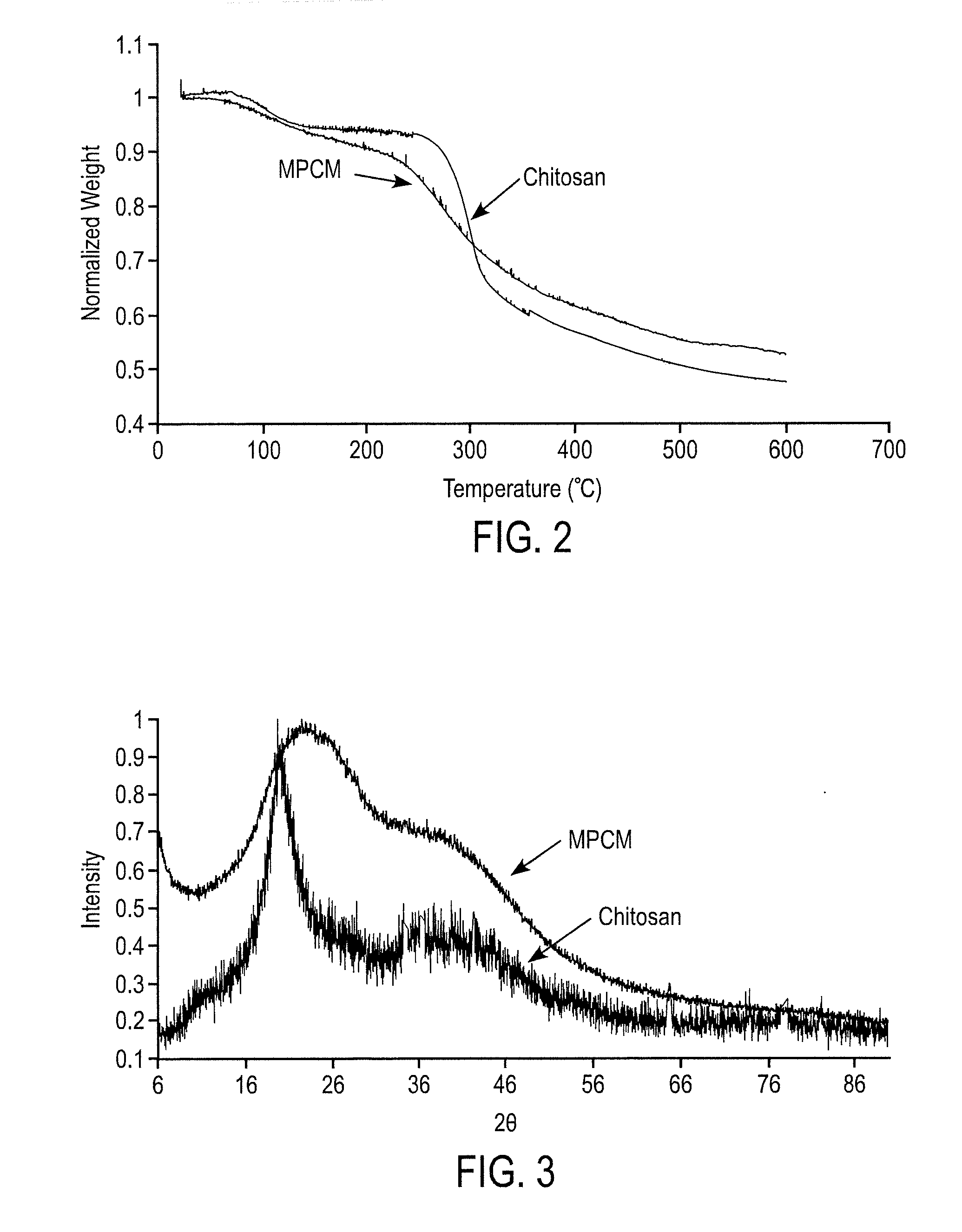
ActiveUS20130039822A1The material is lowCostTransuranic element compoundsRadium compoundsCrosslinked chitosanSorbent
Microporous glutaraldehyde-crosslinked chitosan sorbents, methods of making and using them, and a generator for the radioisotope 99Mo containing the sorbents.
Owner:PERMA FIX ENVIRONMENTAL SERVICES
Process for radioisotope recovery and system for implementing same
InactiveUS20060153760A1Sure easySolvent extractionTransuranic element compoundsSource materialIon exchange
A method of recovering daughter isotopes from a radioisotope mixture. The method comprises providing a radioisotope mixture solution comprising at least one parent isotope. The at least one parent isotope is extracted into an organic phase, which comprises an extractant and a solvent. The organic phase is substantially continuously contacted with an aqueous phase to extract at least one daughter isotope into the aqueous phase. The aqueous phase is separated from the organic phase, such as by using an annular centrifugal contactor. The at least one daughter isotope is purified from the aqueous phase, such as by ion exchange chromatography or extraction chromatography. The at least one daughter isotope may include actinium-225, radium-225, bismuth-213, or mixtures thereof. A liquid-liquid extraction system for recovering at least one daughter isotope from a source material is also disclosed.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
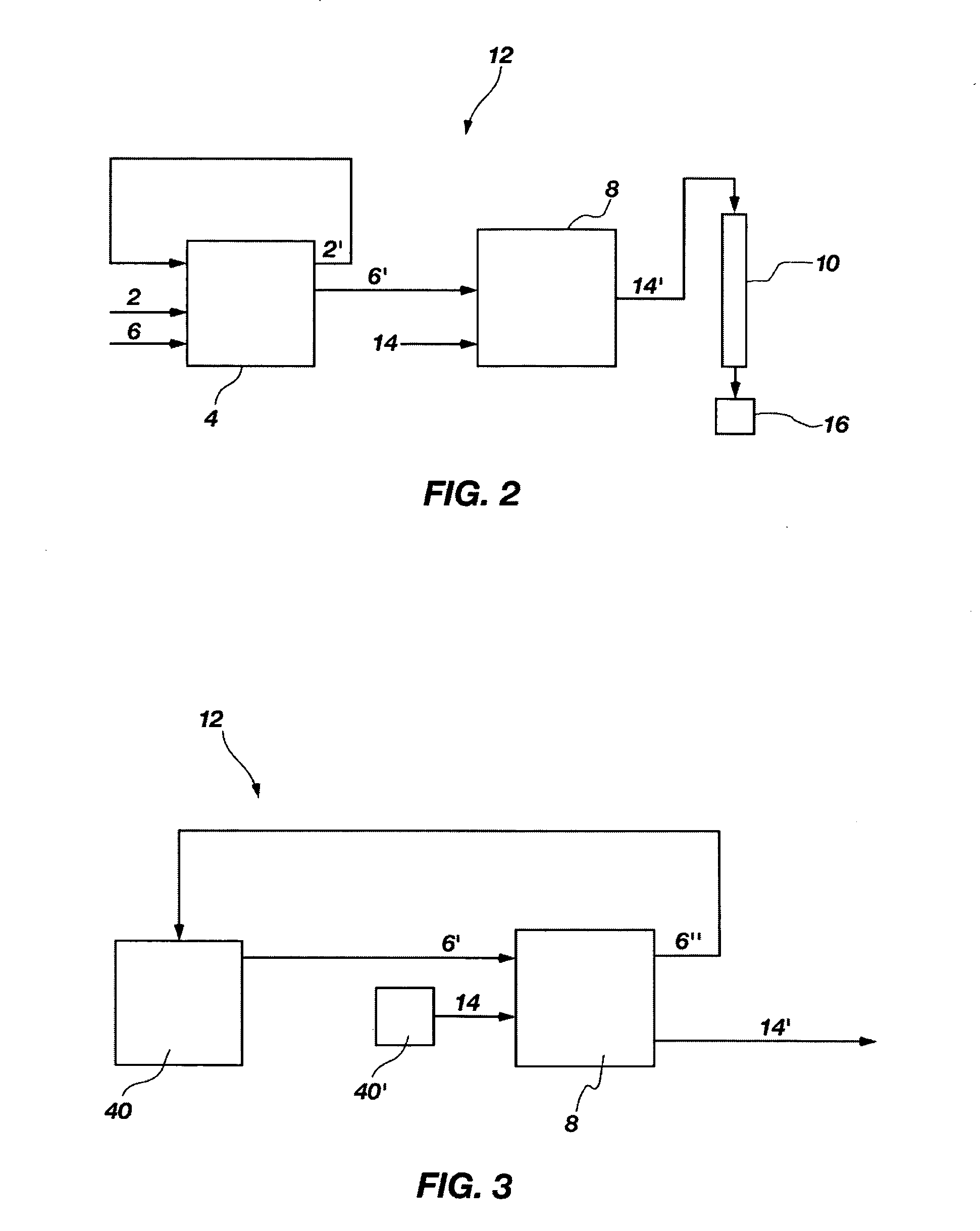
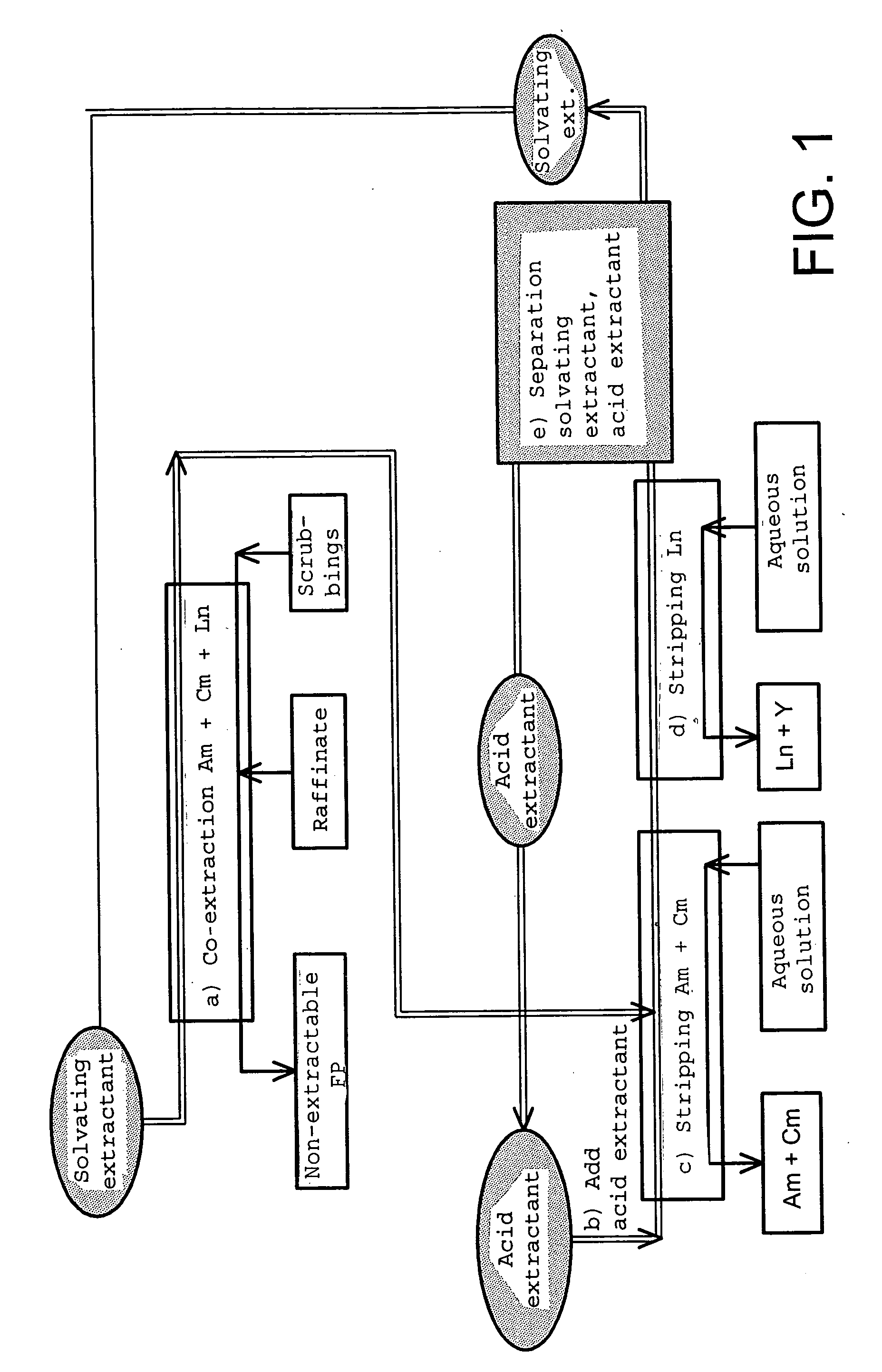
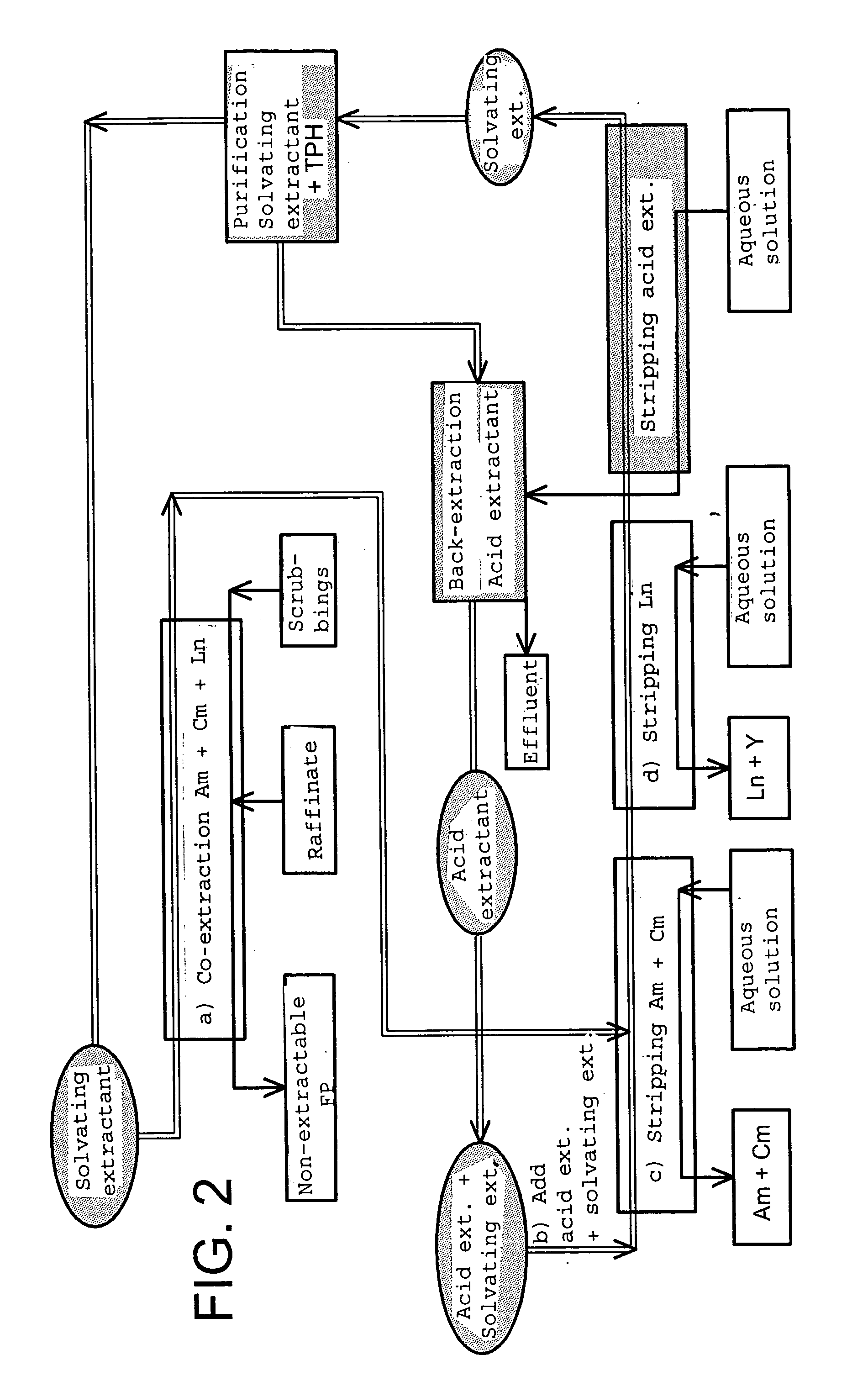
Cyclic method for separating chemcial elements present in an aqueous solution
ActiveUS20040124141A1Easy to deal withConstant compositionTransuranic element compoundsSolid sorbent liquid separationChemical elementCompound (substance)
The invention concerns a cyclic method for separating at least one chemical element E1 from at least one chemical element E2 from an aqueous solution containing said elements, which employs a mixture of two extractants operating in non-overlapping chemical fields. Each cycle of said method comprises: a) co-extracting elements E1 and E2 by means of an organic phase containing a first extractant suited to causing the migration of said elements into said organic phase; b) adding to the organic phase a second extractant suited to selectively retaining the element(s) E2 in said organic phase during step c): c) selectively stripping the element(s) E1 from the organic phase; d) selectively stripping the element(s) E2 from the organic phase; e) separating the first and second extractants present in said organic phase at the end of step d).
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
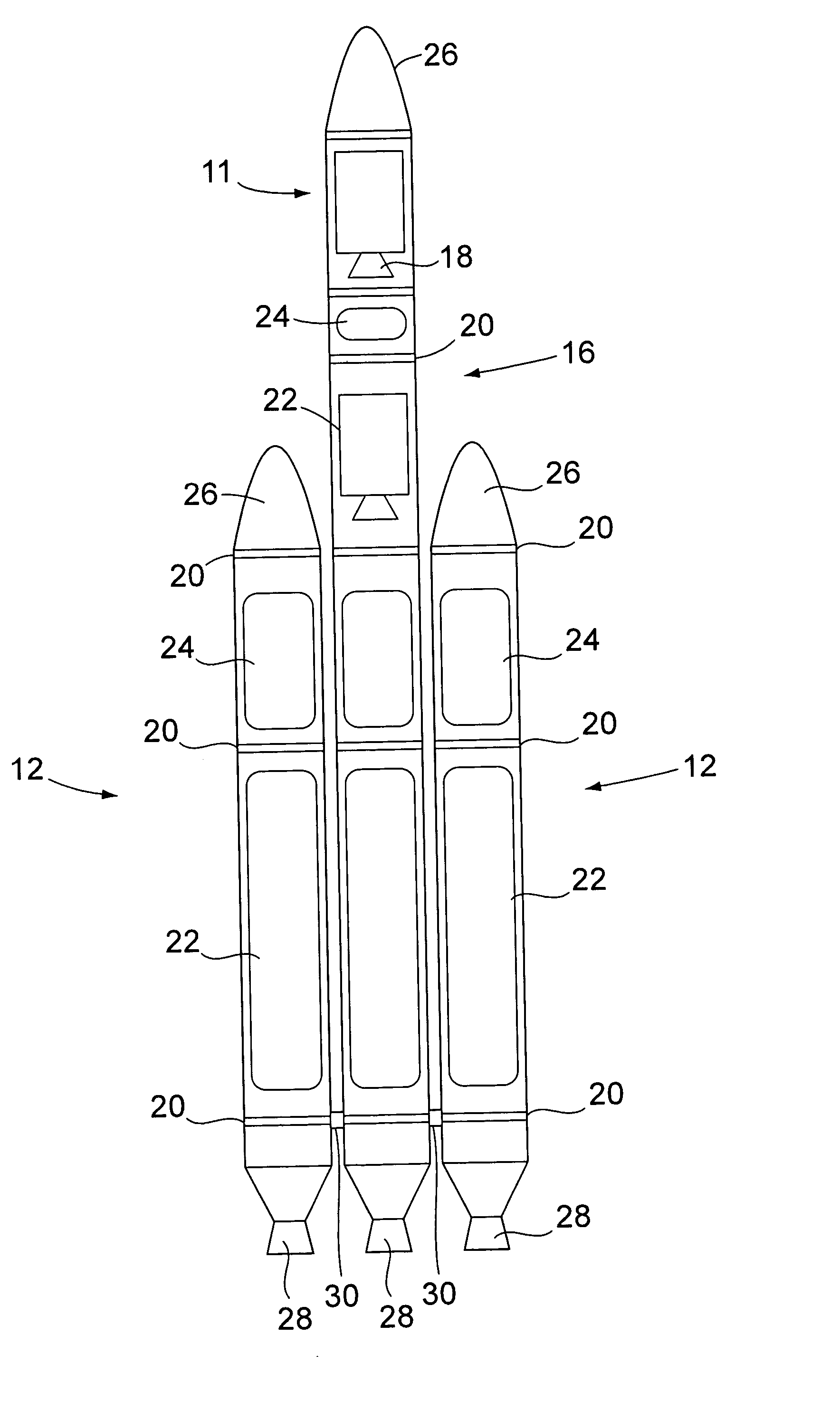
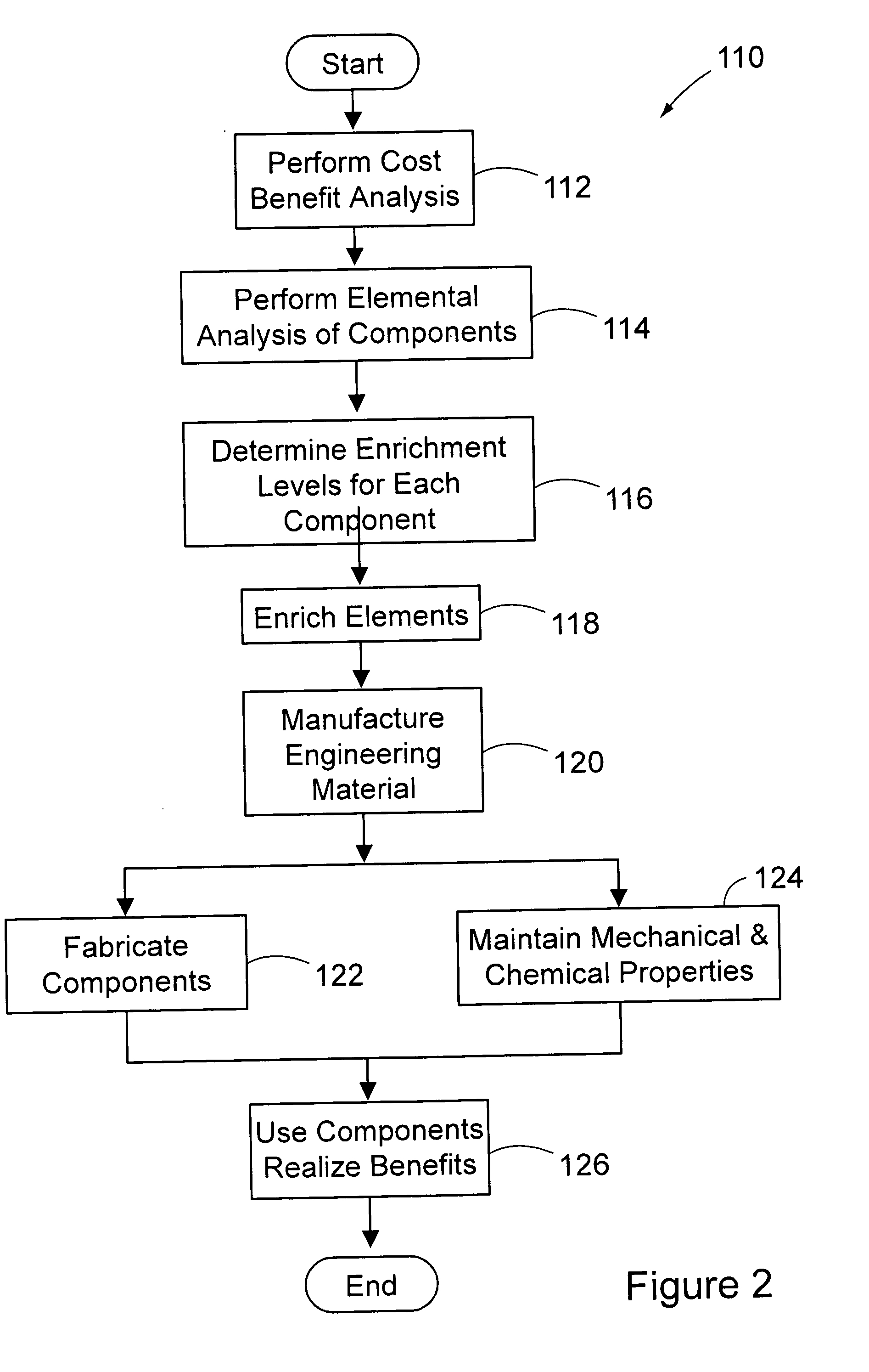
Isotopic lightening
ActiveUS20060102464A1Low densityLight weightTransuranic element compoundsLaunch systemsLithiumHydrogen
A method of manufacturing a component. In a preferred embodiment, the method includes enriching an element with an isotope and using the enriched element as a material of the component. A property of the first isotope being the same as a property of a second isotope and is preferably a mechanical, chemical, or electrical property. A second element can also be used as a material of the component, for instance, where the material is an alloy or a composite material. Further, the first isotope can be a lighter isotope of the element. Lightweight components may be manufactured using the method such that mobile platforms (e.g. spacecraft) can be assembled from the component(s). In other exemplary embodiments, the element can be hydrogen, lithium, boron, magnesium, titanium, or iron. Additionally, the component may carry a load. Components including isotopically enriched elements are also provided.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
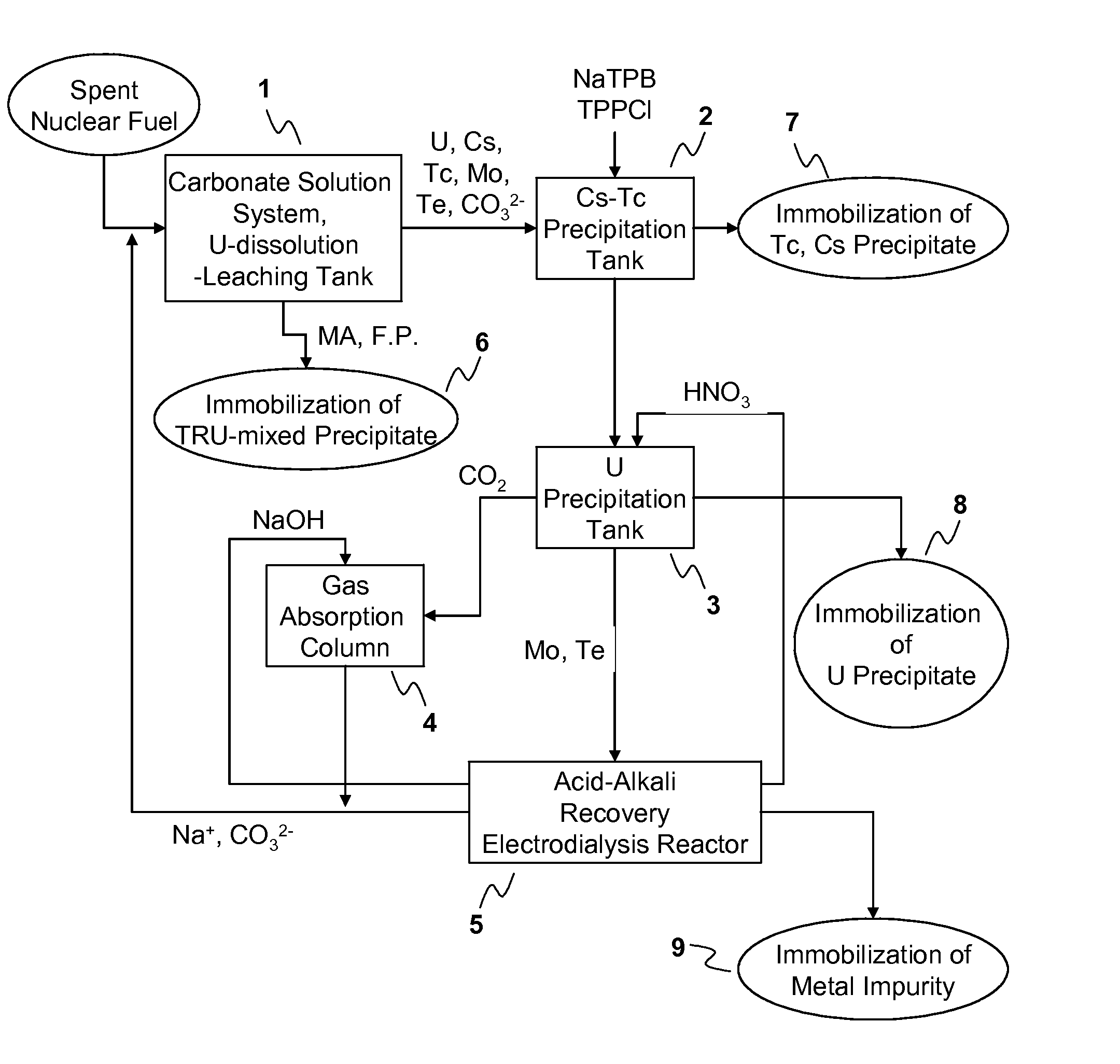
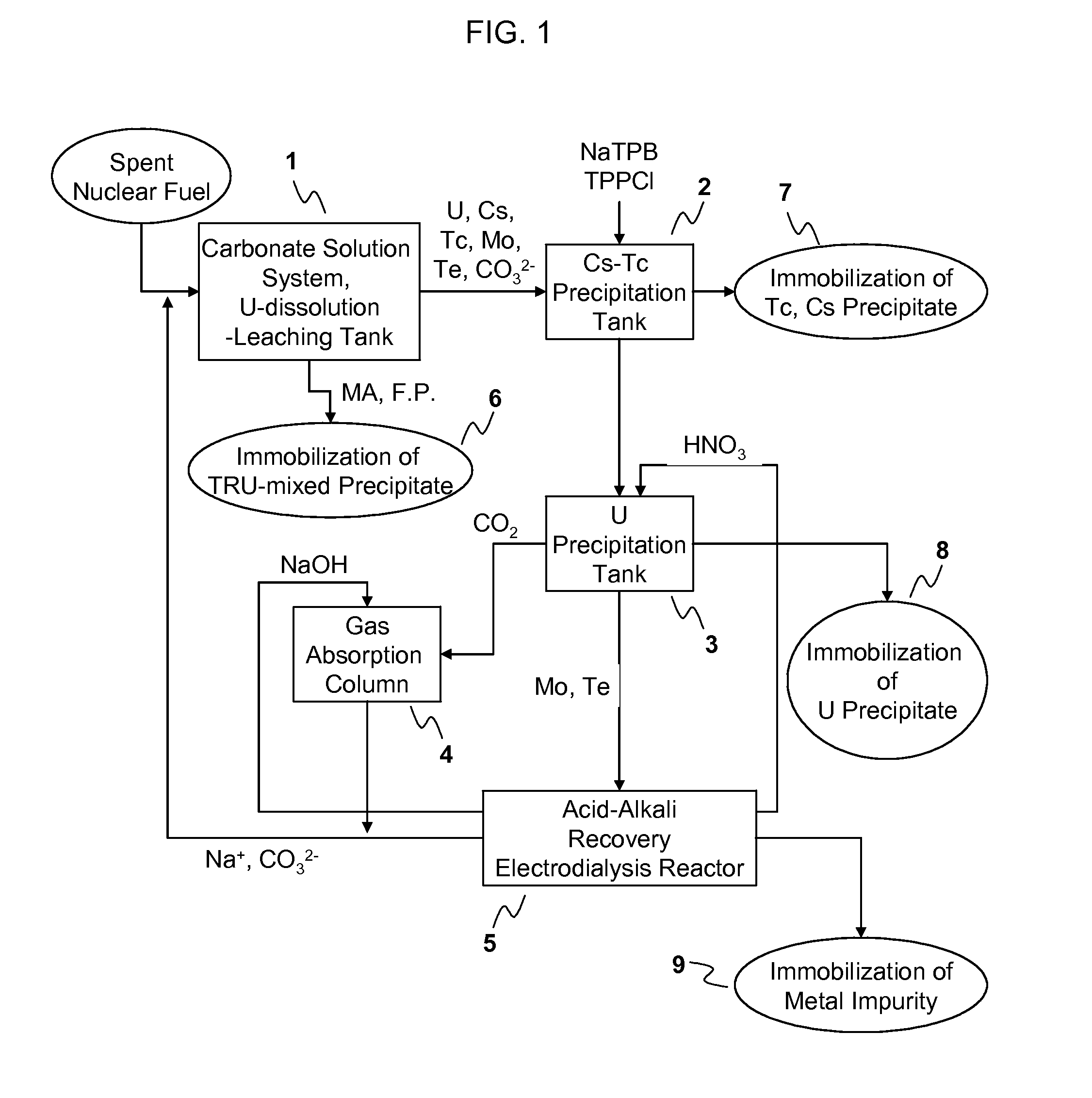
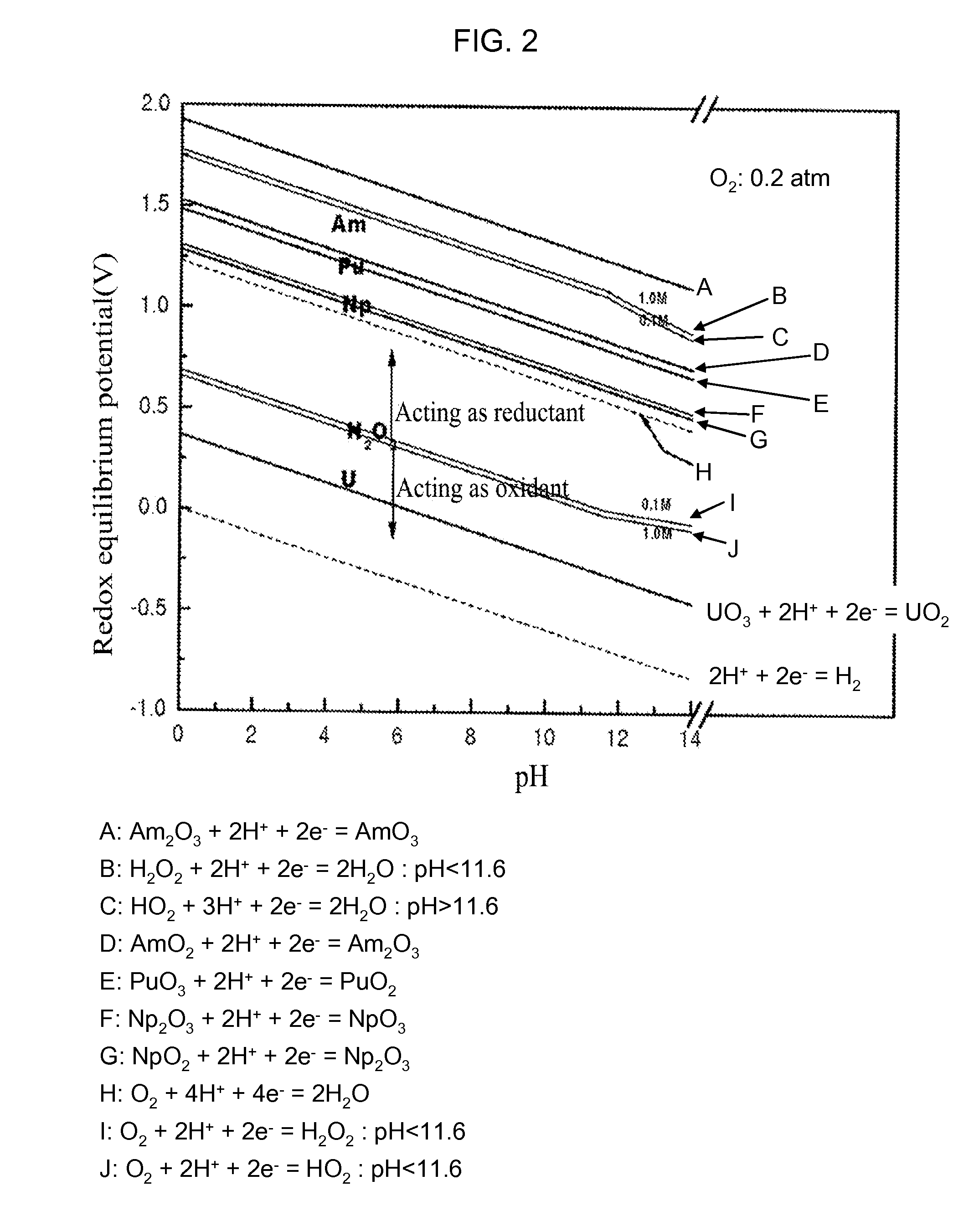
Process for Recovering Isolated Uranium From Spent Nuclear Fuel Using a Highly Alkaline Carbonate Solution
InactiveUS20090269261A1Easy to separateEnhance proliferation resistanceElectrolysis componentsPhotography auxillary processesTransuranium elementCarbonate
Disclosed is a process for recovery of uranium from a spent nuclear fuel using a carbonate solution, characterized by excellent proliferation resistance of preventing leaching of transuranium element (TRU) nuclides such as Pu, Np, Am, Cm, etc. from the spent nuclear fuel as well as environmental friendliness of minimizing waste generation, wherein a highly alkaline carbonate solution is used to separate uranium alone from the spent nuclear fuel.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com