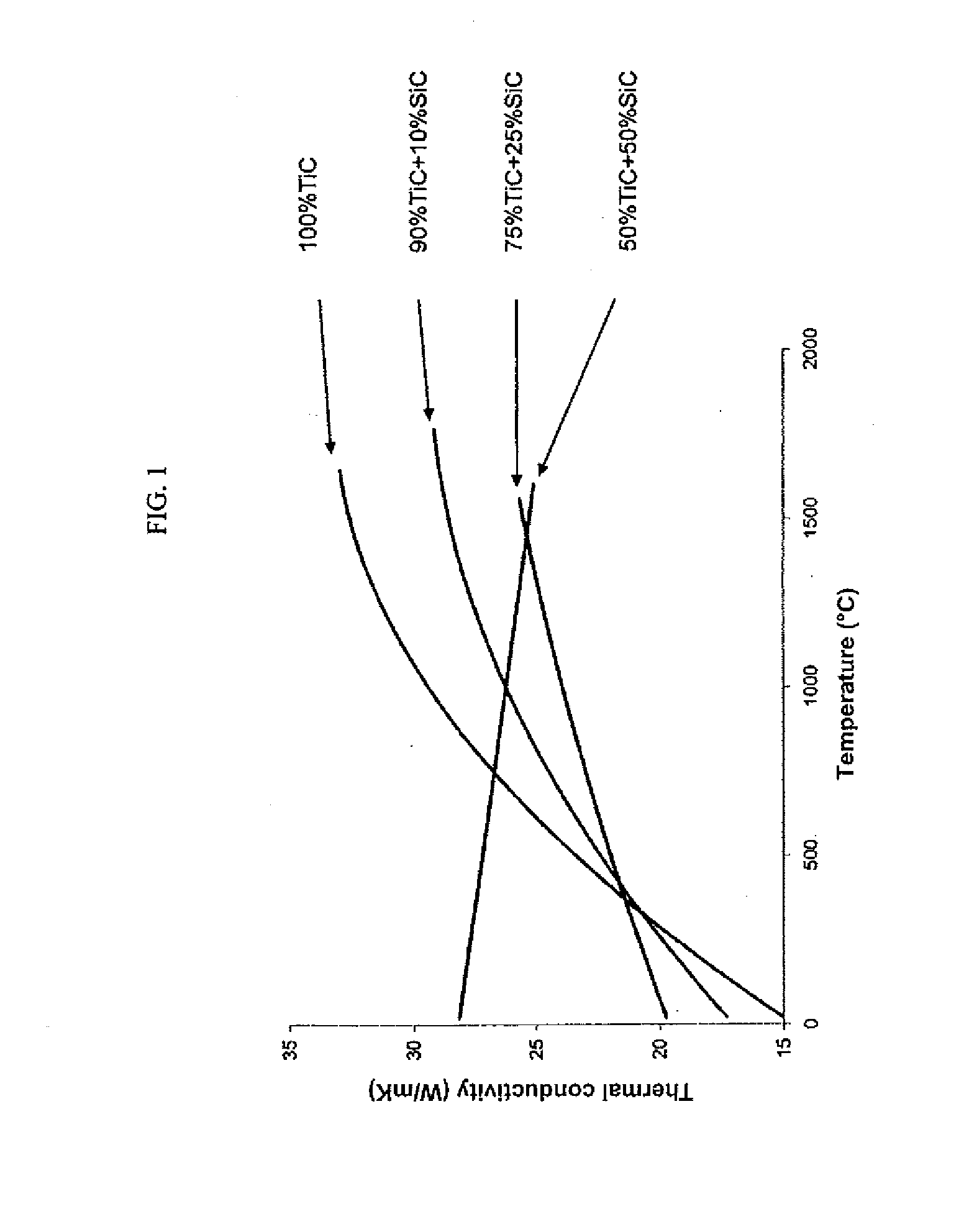
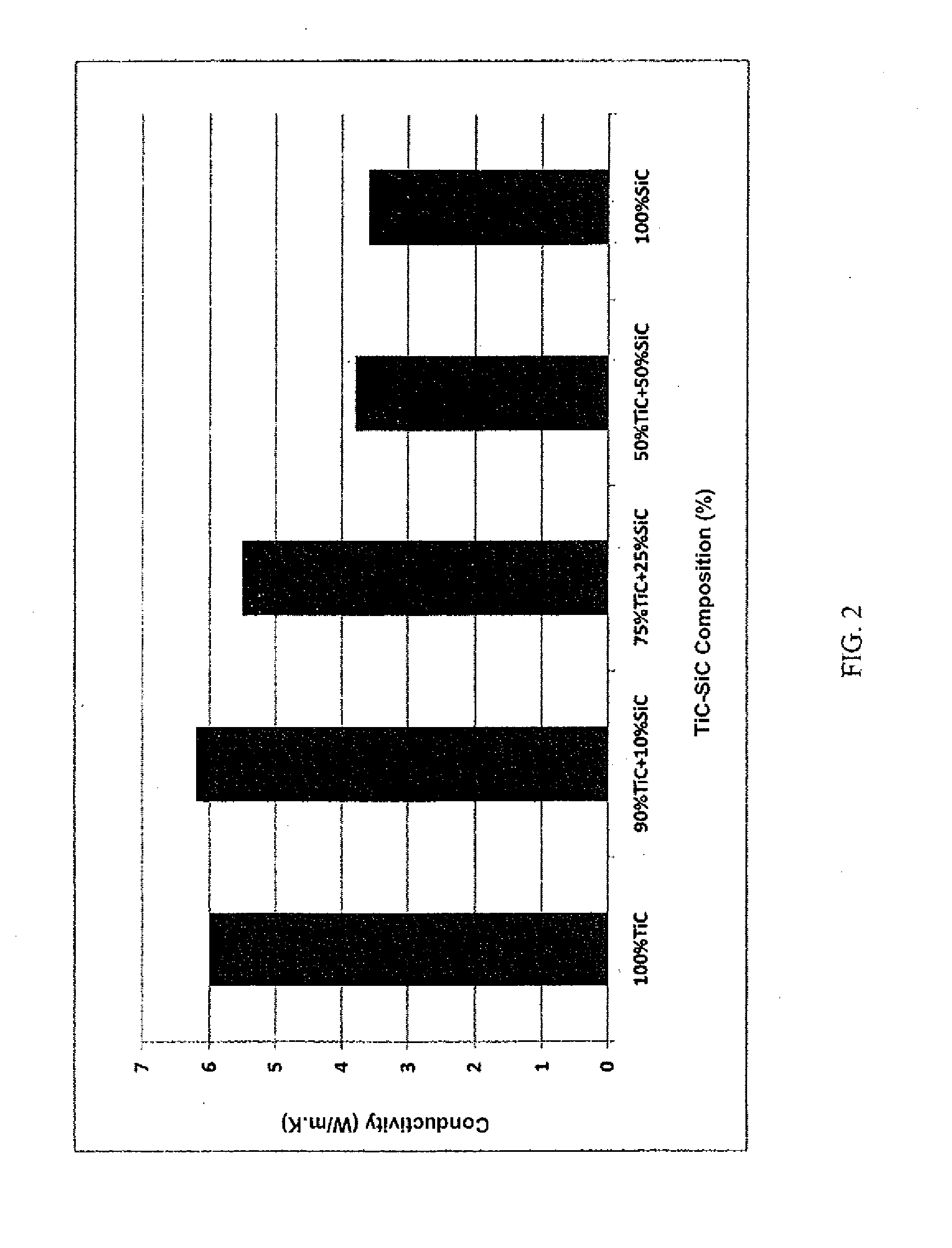
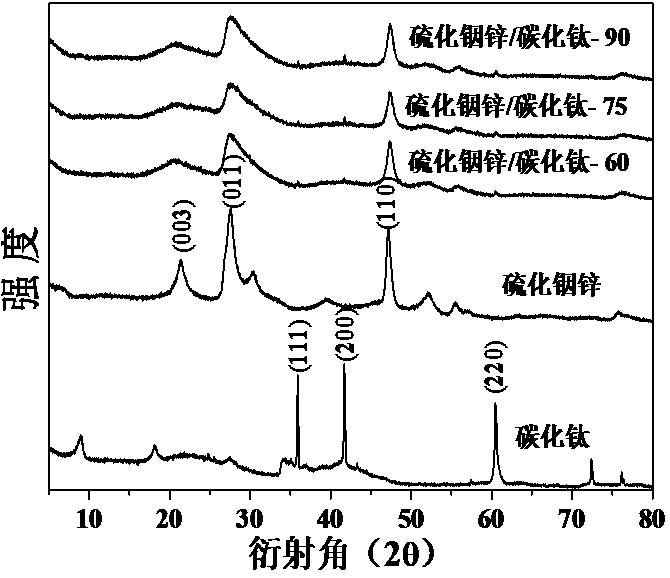
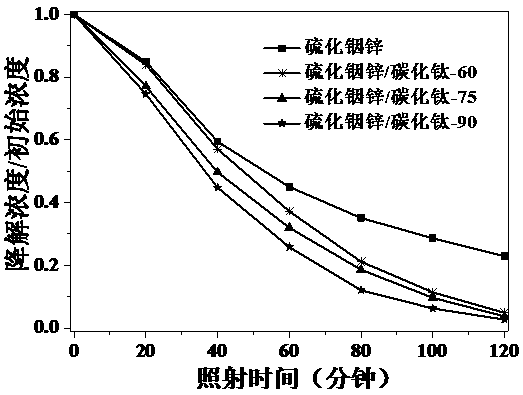
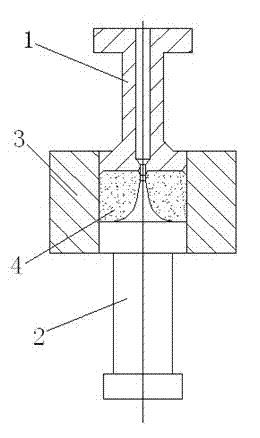
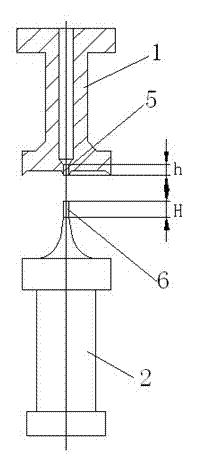
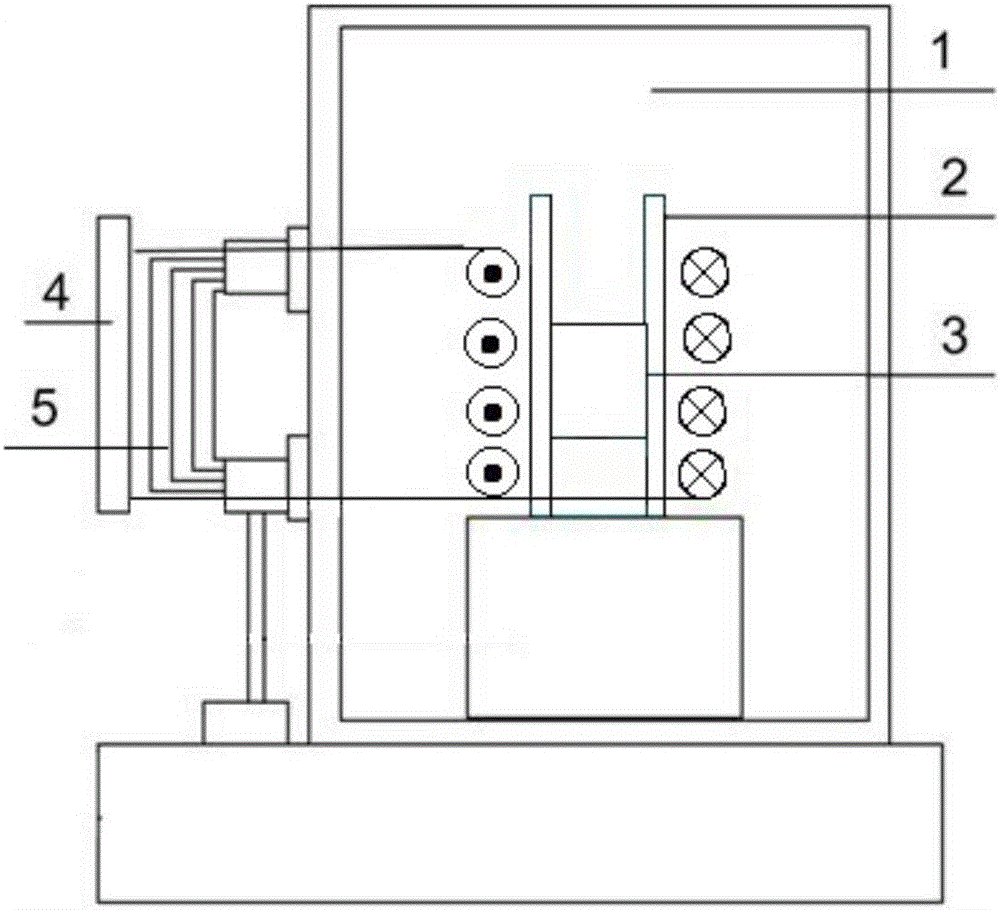
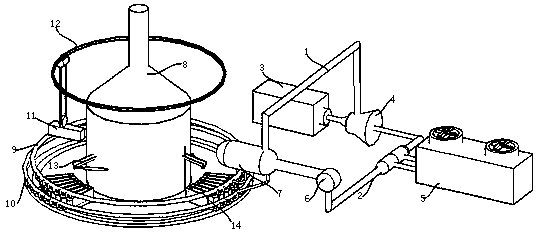
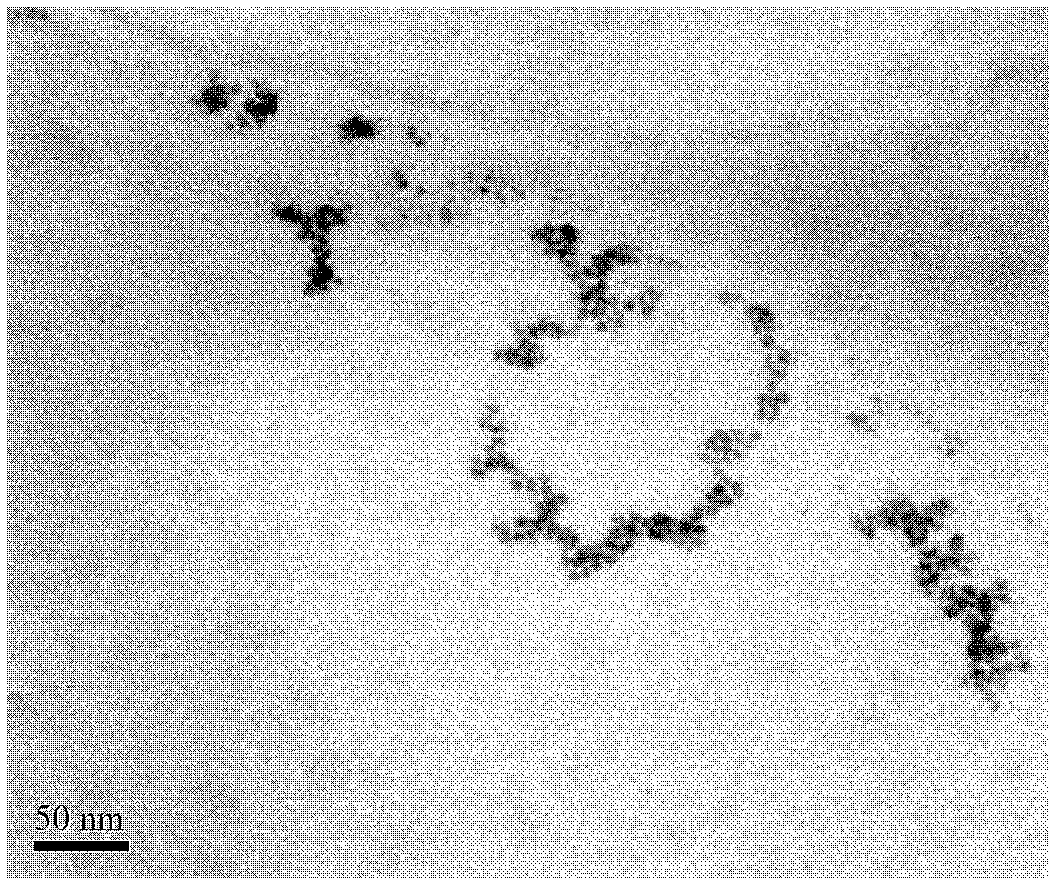
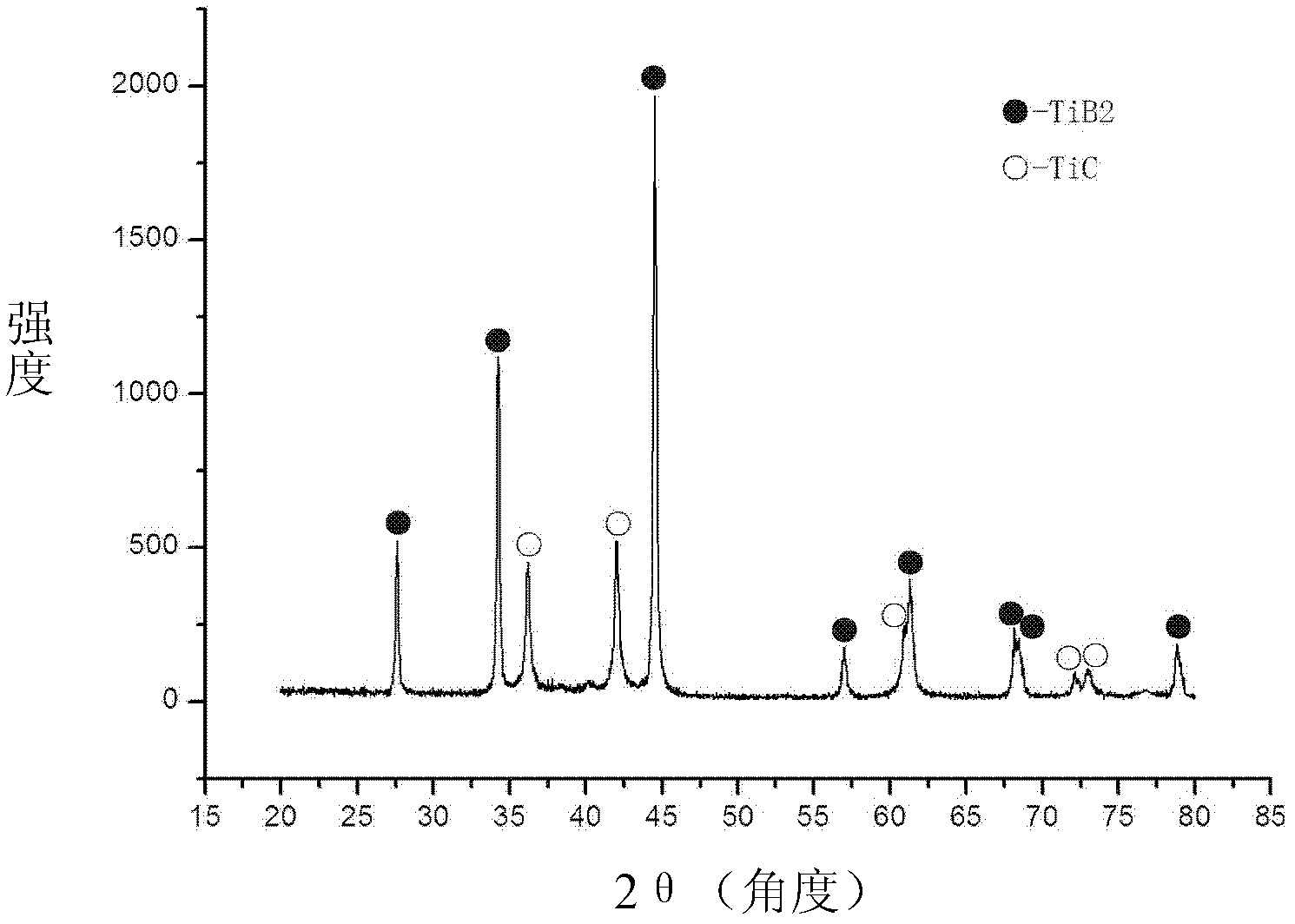
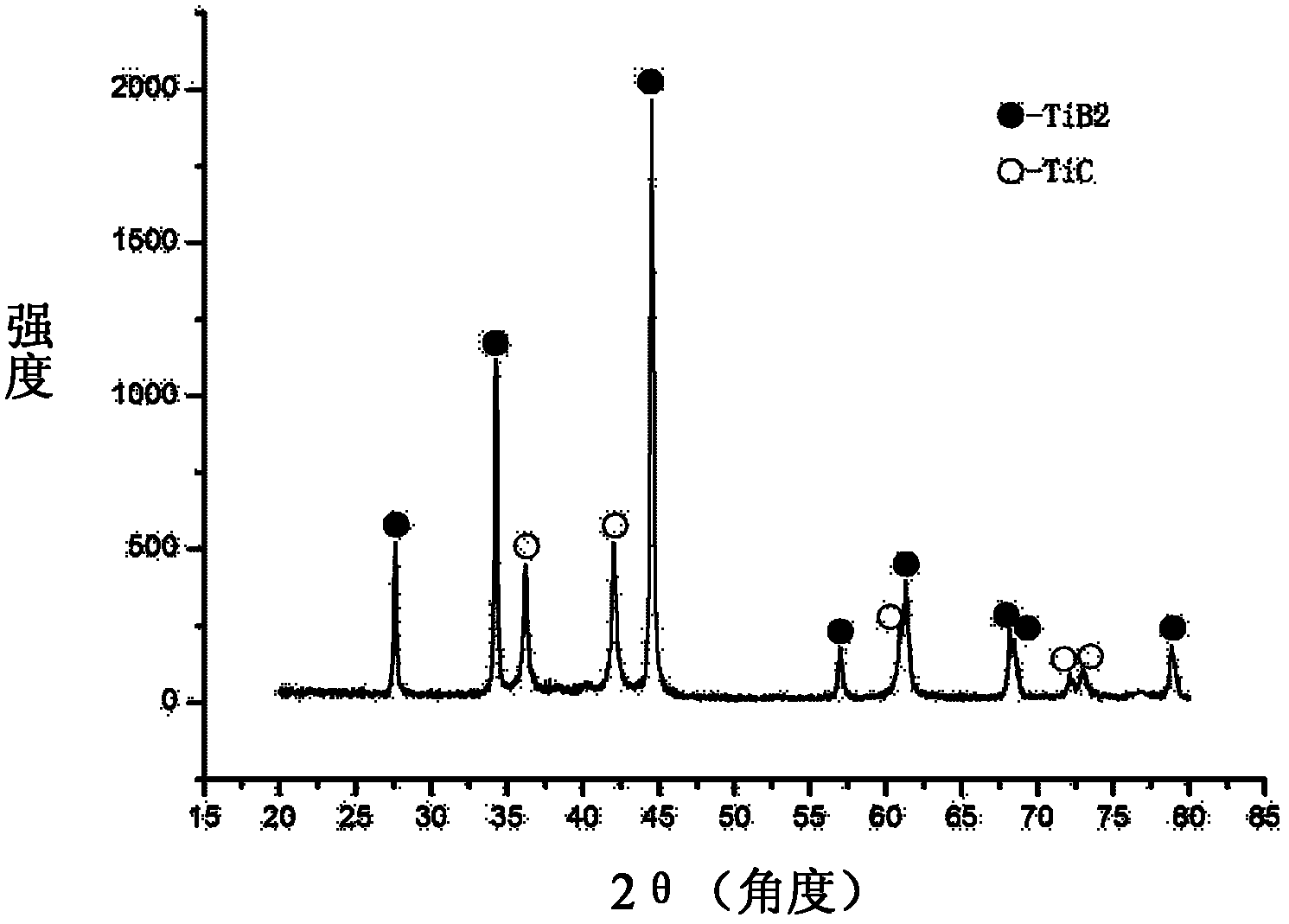
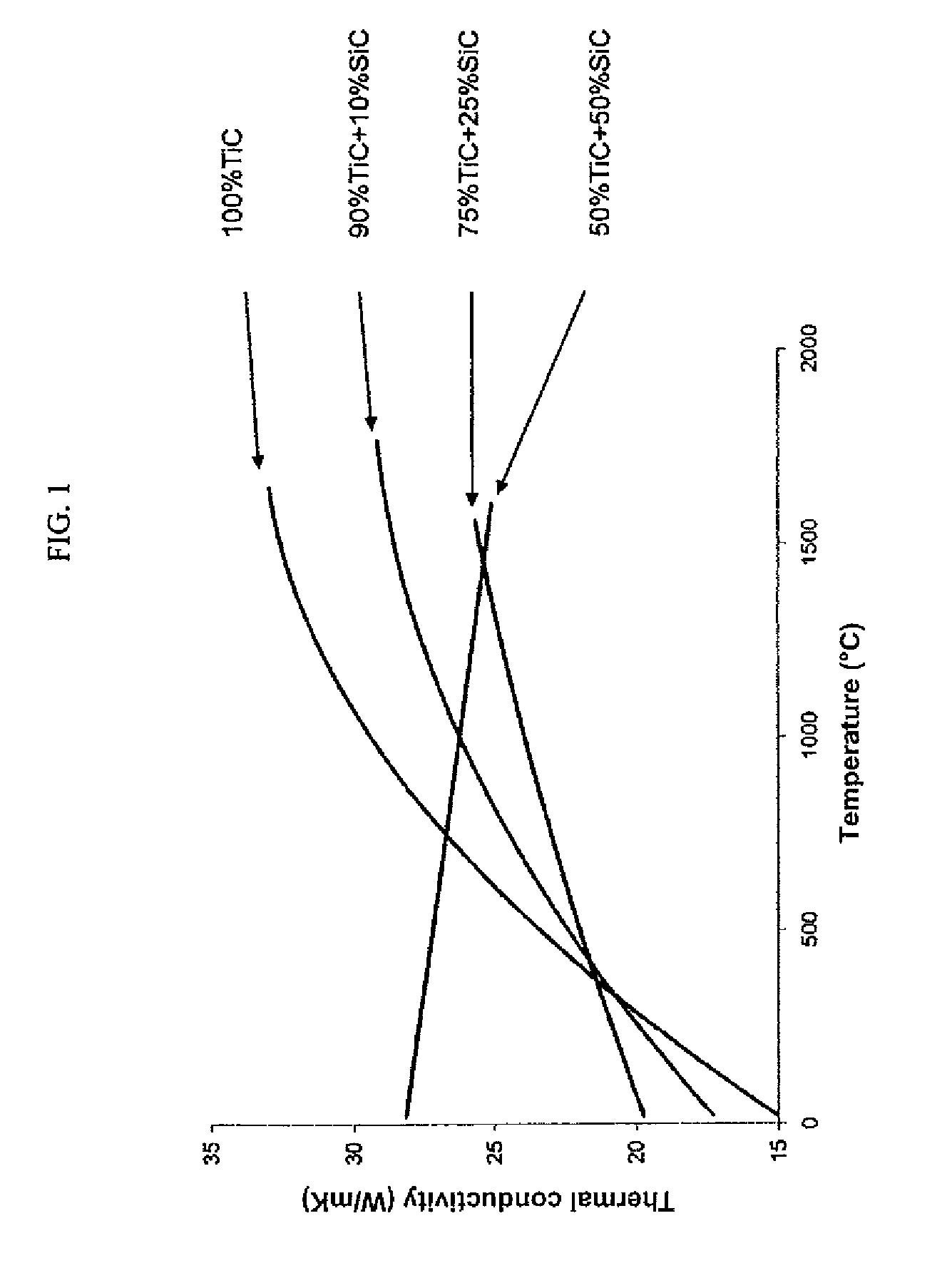
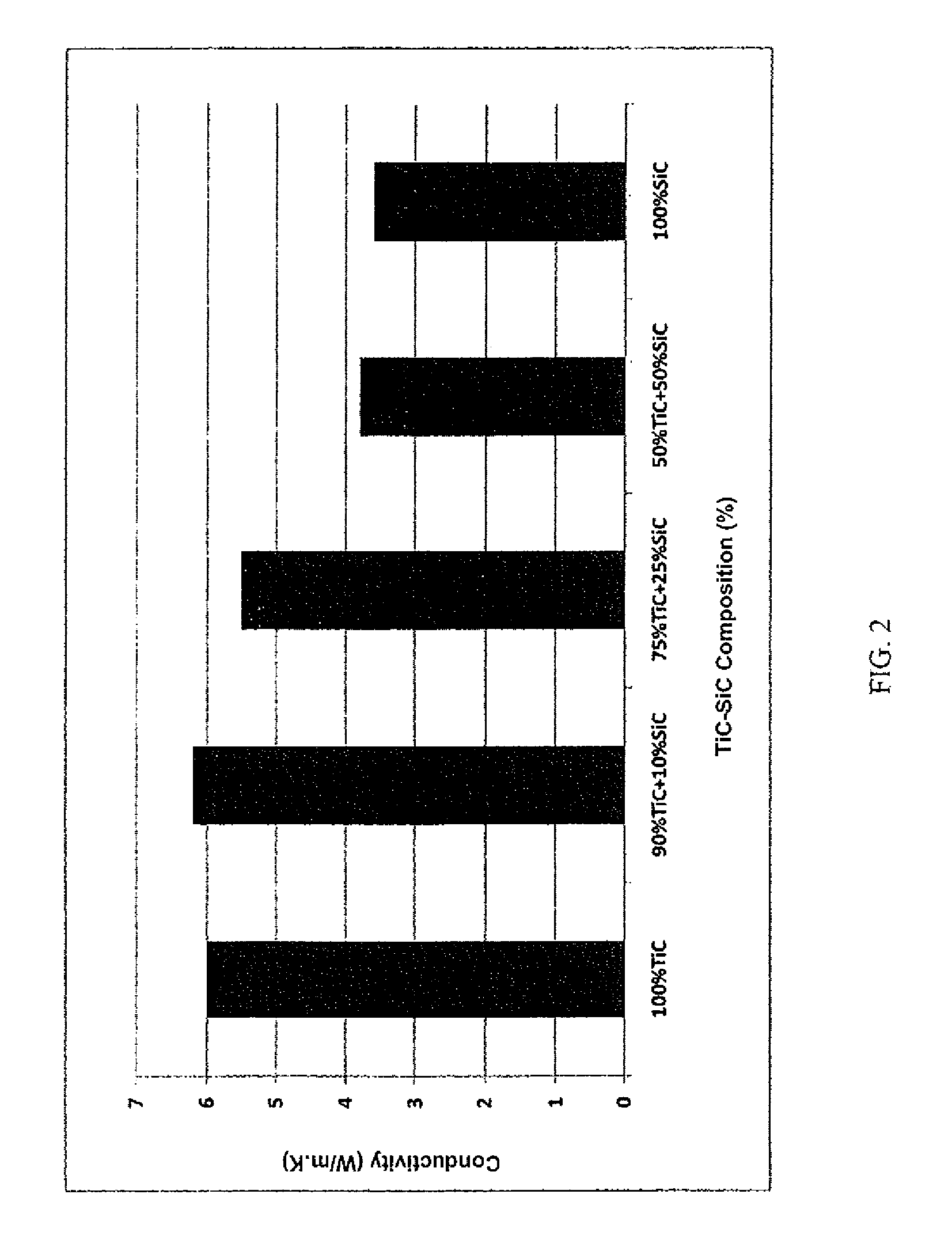
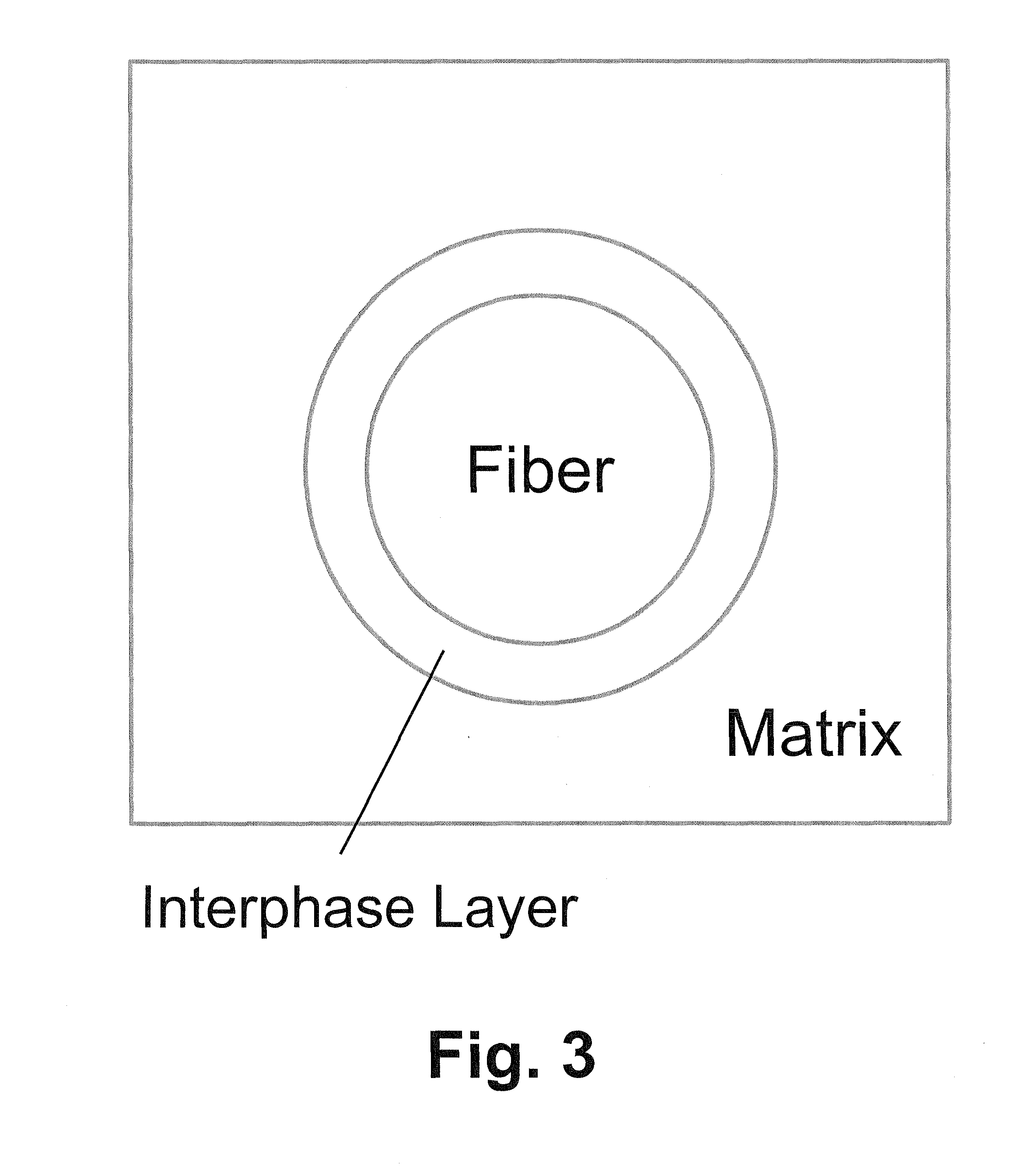
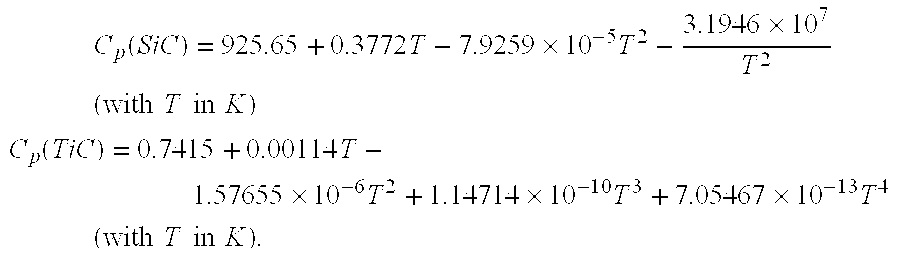Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
154 results about "Uranium carbide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Uranium carbide, a carbide of uranium, is a hard refractory ceramic material. It comes in several stoichiometries (UCₓ), such as uranium methanide (UC, CAS number 12070-09-6), uranium sesquicarbide (U₂C₃, CAS number 12076-62-9), and uranium acetylide (UC₂, CAS number 12071-33-9).
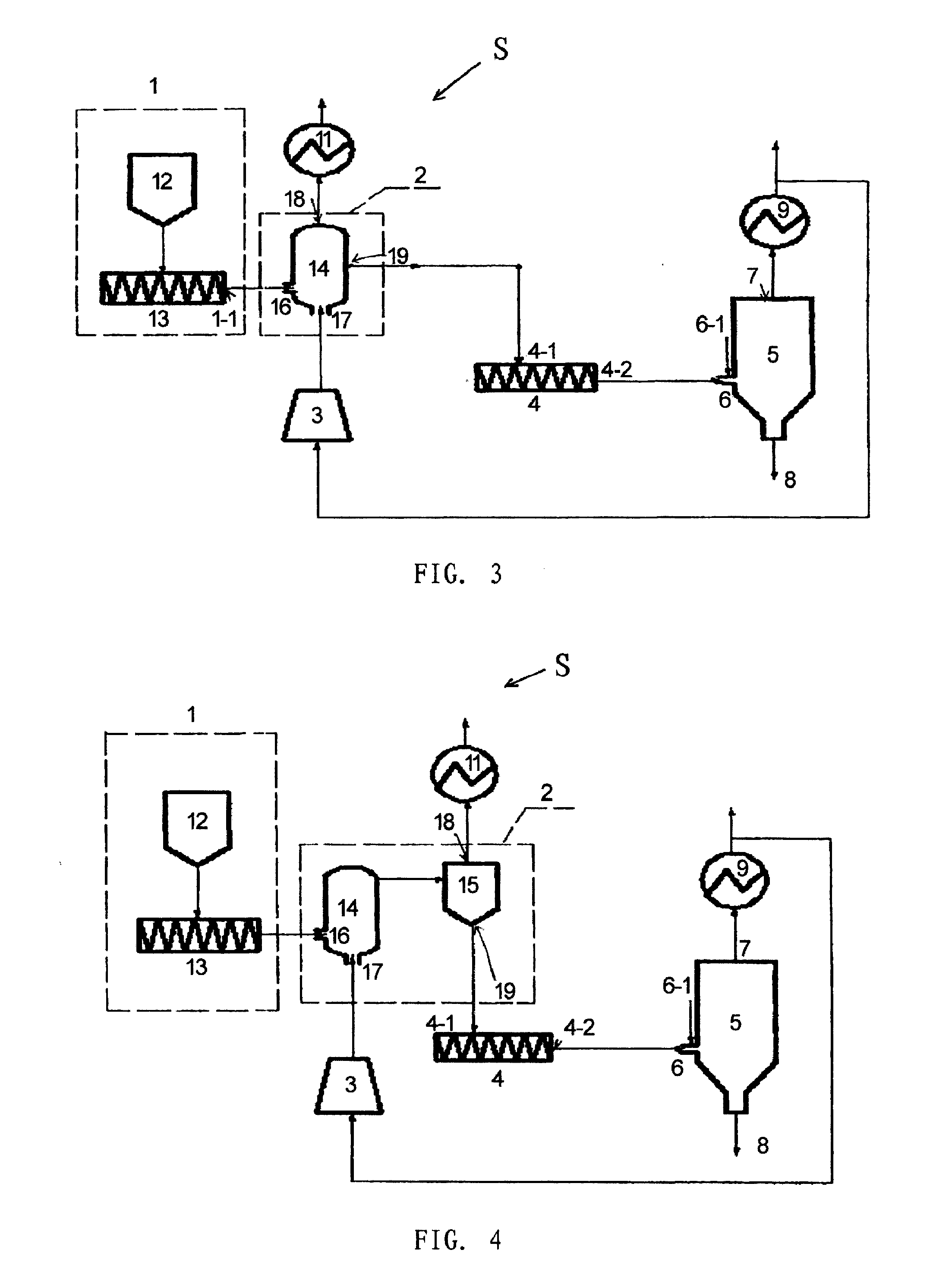
Nuclear fuel cladding with high heat conductivity and method for making same
ActiveUS20110170653A1Optimal transfer of thermal energyEasy transferFuel elementsNuclear energy generationThermal energyFiber
The invention relates to a nuclear fuel cladding totally or partially made of a composite material with a ceramic matrix containing silicon carbide (SiC) fibers as a matrix reinforcement and an interphase layer provided between said matrix and said fibers, the matrix including at least one carbide selected from titanium carbide (TiC), zirconium carbide (ZrC), or ternary titanium silicon carbide (Ti3SiC2).When irradiated and at temperatures of between 800° C. and 1200° C., said cladding can mechanically maintain the nuclear fuel within the cladding while enabling optimal thermal-energy transfer towards the coolant.The invention also relates to a method for making the nuclear fuel cladding.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Methods for manufacturing porous nuclear fuel elements for high-temperature gas-cooled nuclear reactors
Methods for manufacturing porous nuclear fuel elements for use in advanced high temperature gas-cooled nuclear reactors (HTGR's). Advanced uranium bi-carbide, uranium tri-carbide and uranium carbonitride nuclear fuels can be used. These fuels have high melting temperatures, high thermal conductivity, and high resistance to erosion by hot hydrogen gas. Tri-carbide fuels, such as (U,Zr,Nb)C, can be fabricated using chemical vapor infiltration (CVI) to simultaneously deposit each of the three separate carbides, e.g., UC, ZrC, and NbC in a single CVI step. By using CVI, a thin coating of nuclear fuel may be deposited inside of a highly porous skeletal structure made, for example, of reticulated vitreous carbon foam.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Castings of metallic alloys with improved surface quality, structural integrity and mechanical properties fabricated in titanium carbide coated graphite molds under vacuum
Molds are fabricated having a substrate of high density, high strength ultrafine grained isotropic graphite, and having a mold cavity coated with titanium carbide. The molds may be made by making the substrate (main body) of high density, high strength ultrafine grained isotropic graphite, by, for example, isostatic or vibrational molding, machining the substrate to form the mold cavity, and coating the mold cavity with titanium carbide via either chemical deposition or plasma assisted chemical vapor deposition, magnetron sputtering or sputtering. The molds may be used to make various metallic alloys such as nickel, cobalt and iron based superalloys, stainless steel alloys, titanium alloys and titanium aluminide alloys into engineering components by melting the alloys in a vacuum or under a low partial pressure of inert gas and subsequently casting the melt in the graphite molds under vacuum or low partial pressure of inert gas.
Owner:SANTOKU CORP
Castings of metallic alloys with improved surface quality, structural integrity and mechanical properties fabricated in titanium carbide coated graphite molds under vacuum
InactiveUS20040055725A1Cheap constructionImprove performanceFoundry mouldsPretreated surfacesUranium carbideSuperalloy
Molds are fabricated having a substrate of high density, high strength ultrafine grained isotropic graphite, and having a mold cavity coated with titanium carbide. The molds may be made by making the substrate (main body) of high density, high strength ultrafine grained isotropic graphite, by, for example, isostatic or vibrational molding, machining the substrate to form the mold cavity, and coating the mold cavity with titanium carbide via either chemical deposition or plasma assisted chemical vapor deposition, magnetron sputtering or sputtering. The molds may be used to make various metallic alloys such as nickel, cobalt and iron based superalloys, stainless steel alloys, titanium alloys and titanium aluminide alloys into engineering components by melting the alloys in a vacuum or under a low partial pressure of inert gas and subsequently casting the melt in the graphite molds under vacuum or low partial pressure of inert gas.
Owner:SANTOKU CORP
Radiation shielding materials and containers incorporating same
InactiveUS6960311B1Improve shielding effectMaximum flexibilityOther chemical processesTransuranic element compoundsMicrosphereUranium carbide
An improved radiation shielding material and storage systems for radioactive materials incorporating the same. The PYRolytic Uranium Compound (“PYRUC”) shielding material is preferably formed by heat and / or pressure treatment of a precursor material comprising microspheres of a uranium compound, such as uranium dioxide or uranium carbide, and a suitable binder. The PYRUC shielding material provides improved radiation shielding, thermal characteristic, cost and ease of use in comparison with other shielding materials. The shielding material can be used to form containment systems, container vessels, shielding structures, and containment storage areas, all of which can be used to house radioactive waste. The preferred shielding system is in the form of a container for storage, transportation, and disposal of radioactive waste. In addition, improved methods for preparing uranium dioxide and uranium carbide microspheres for use in the radiation shielding materials are also provided.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
A method for prepare a nitrogen doped carbon nanotube three-dimensional composite material by in-situ growth of a small lay of titanium carbide
InactiveCN109167066AImprove conductivityAchieve controlled growthCell electrodesTetramethylammonium hydroxideFreeze-drying
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of nano-functional materials, in particular to a method for preparing a nitrogen doped carbon nanotube three-dimensional composite materialby in-situ growth of a few layers of titanium carbide, immersing ternary layered Ti3AlC2 ceramic powder in hydrofluoric acid solution, heating and stirring, centrifugally cleaning with ultrapure waterand absolute ethanol, drying to obtain two-dimensional layered titanium carbide nano-powder, adding it into tetramethylammonium hydroxide solution, heating and stirring, centrifuging with deionized water to obtain a few layers of titanium carbide nano-sheet dispersion; Adding cobalt salt into a dispersion of a few layers of titanium carbide nano-sheets for reaction, adding dicyandiamide, heatingand stirring until dicyandiamide is completely dissolved, freezing, and freeze-drying to obtain precursor powder; Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes (CNTs) three-dimensional composites were prepared by in-situ growth of a few layers of titanium carbide after grinding the precursor powder and heat treatment. A three-dimensional composite material is prepared by a simple pyrolysis method using a few layers of titanium carbide as a carrier, cobalt as a catalyst, dicyandiamide as a carbon and nitrogen source, and the electrochemical performance of the few layers of titanium carbide can be improved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Method and system for producing calcium carbide
InactiveUS20110123428A1Increase response rateLow reaction temperatureEnergy inputCalcium carbideSlagUranium carbide
A method and a system for producing calcium carbide, the method including mixing powdery carbon-containing raw material with powdery calcium-containing raw material, and directly heating the mixture by combusting a part of carbon-containing raw material in an oxygen-containing atmosphere to produce calcium carbide. The carbon-containing raw material can be coal, semi-coke or coke, the calcium-containing raw material can be calcium carbonate, calcium oxide, calcium hydroxide or carbide slag. The system includes a raw material preheating unit, such as a fluidized bed or an entrained flow bed, and a reaction unit such as an entrained flow bed. By combustion of the by-product CO produced during the production of calcium carbide or auxiliary fuel in the air to preheat the raw materials to 500-1500° C., the carbon consumption and the oxygen consumption for the calcium carbide production can be reduced, and thus process energy consumption is further reduced.
Owner:LIU ZHENYU +2
Hard alloy, hard alloy cutter bar and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a hard alloy, a hard alloy cutter bar and a manufacturing method thereof. The hard alloy comprises 80-90 parts by mass of tungsten carbide, 10-20 parts by mass of cobalt, 0.15-0.5 part by mass of tantalum carbide, 0.2-0.4 part by mass of chromium carbide and 0.1-0.3 part by mass of vanadium carbide. A cutter bar body (2) of a cutter bar made by the hard alloy is provided with a threaded hole (3) used for mounting a cutting tool (4). The manufacturing method of the cutter bar comprises the following steps of: adding the tungsten carbide, cobalt, chromium carbide, tantalum carbide and vanadium carbide into a ball mill according to the proportions of the ingredients, adding alcohol, mixing and grinding the ingredients, discharging, drying and sieving; adding a forming agent; pressing the ingredients to a blank; sintering the blank at a temperature of 1360-1450 DEG C to form the hard alloy cutter bar; conventionally polishing the surface of the hard alloy cutter bar; and electrosparking the tool bar and burning out the threaded hole.
Owner:CHANGSHA KENBEI TECH
High capacity lithium ion battery containing metal conductive substances
ActiveCN102751530AImprove corrosion resistanceImprove antioxidant capacityCell electrodesSecondary cellsTitanium nitrideUranium carbide
The present invention discloses a high capacity lithium ion battery containing metal conductive substances. The battery comprises a positive electrode sheet, a negative electrode sheet, separation membranes, an electrolyte, a binder and a sealing material. A conductive substance of the positive electrode sheet comprises a metal carbide, a metal boride or a metal nitride. A conductive substance of the negative electrode sheet comprises a metal carbide, a metal boride or a metal nitride. The metal carbide is titanium carbonitride, tungsten carbide or titanium carbide, vanadium carbide, tantalum carbide, or a co-melting body of tungsten carbide and titanium carbide. The metal boride is a molybdenum boride, tungsten boride or vanadium boride. The metal nitride is titanium nitride, tungsten nitride or tantalum nitride. The conductive material of the positive electrode sheet further can contain powder metal, and the conductive material of the negative electrode sheet further can contain powdered metal, wherein the powdered metal is nickel powder, copper powder or chromium powder.
Owner:SHIHLIEN APEX HUAIAN TECH CO LTD
Preparation method for promoting to sinter zirconium boride or zirconium carbide ceramics by using reaction aids
The invention provides a preparation method for promoting to sinter zirconium boride or zirconium carbide ceramics by using reaction aids. Two-phase sintering aids capable of being reacted, namely Zr powder and C powder, or Zr powder and B4C powder, are added, and a material is promoted to be compact and crystals of a matrix are inhibited from growing by zirconium carbide / zirconium boride second phase particles with higher sintering activity, which are generated through in-situ reaction between the sintering aids. The ZrB2 or ZrC-based bulk material prepared by the method has the relative density of over 97 percent, the room temperature bending strength of 500-800MPa, the fracture toughness of 3.5-6.5MPa.ml / 2, and the hardness of 14-20GPa. The second phase generated through the in-situ reaction has the same melting point as the matrix, and the sintering acids cannot bring adverse effect to the high temperature mechanical properties of the material.
Owner:江苏先进无机材料研究院
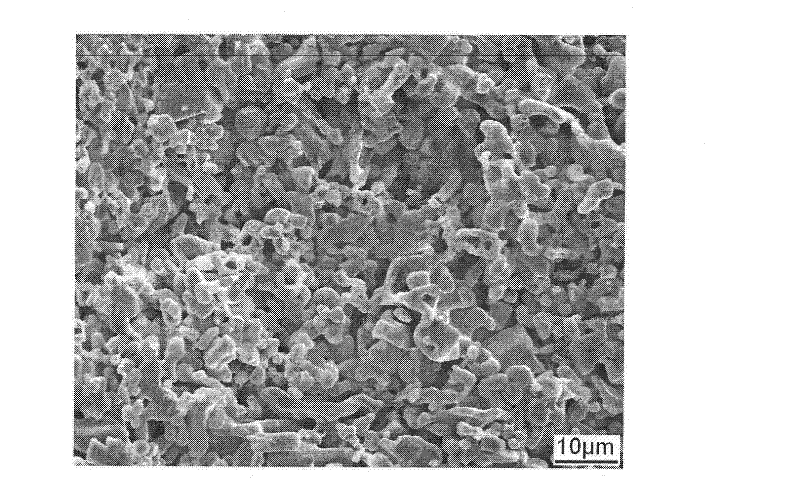
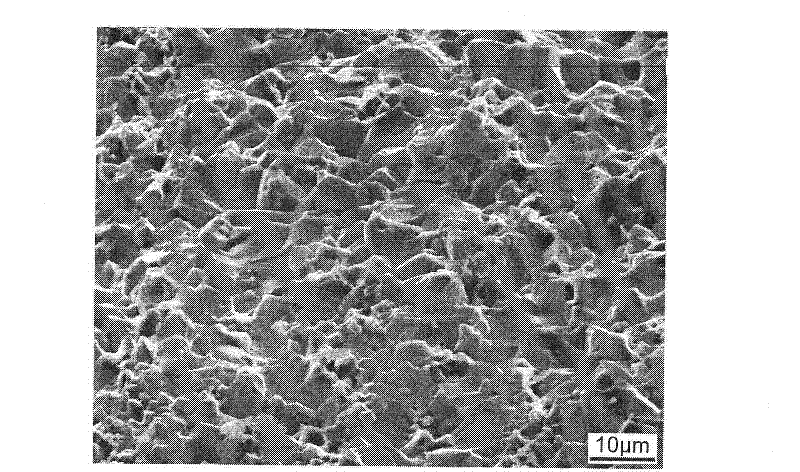
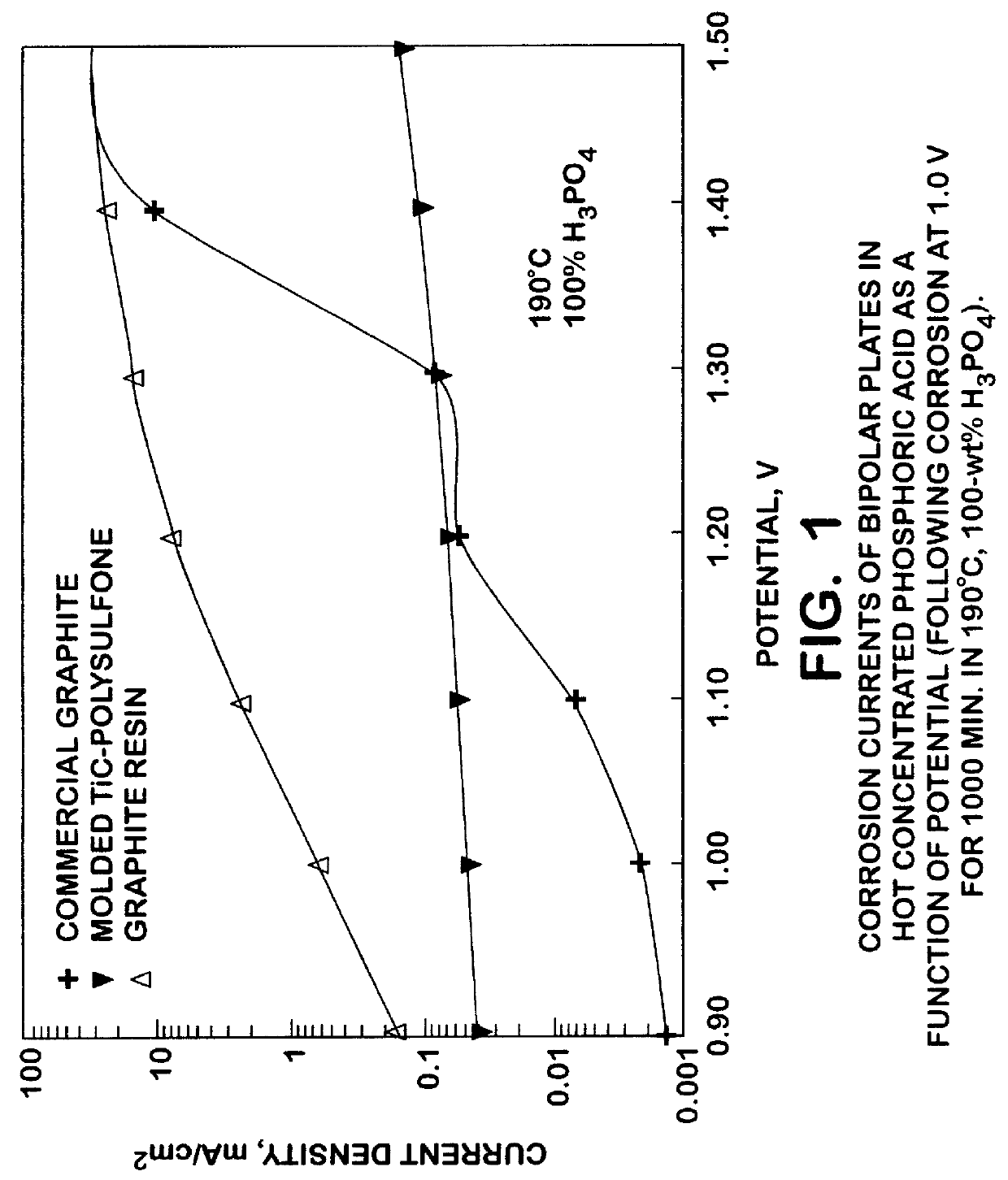
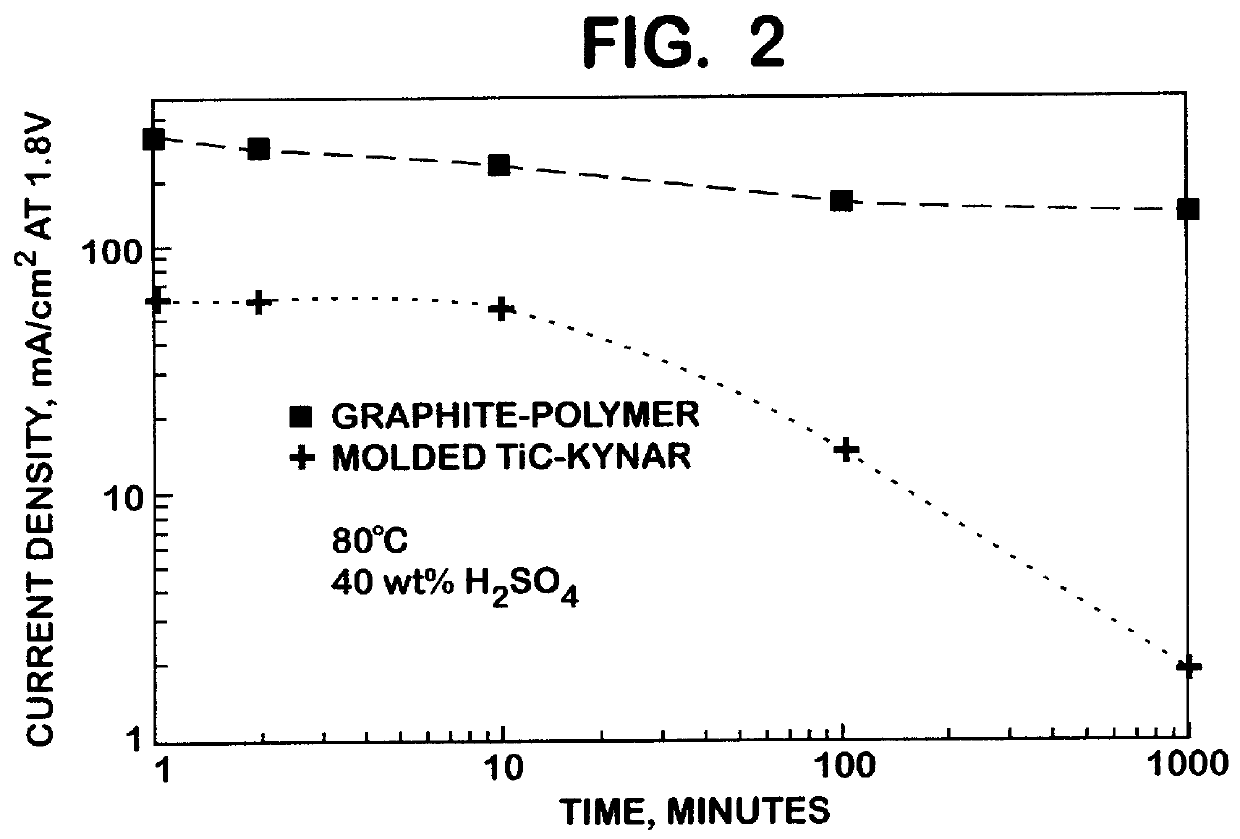
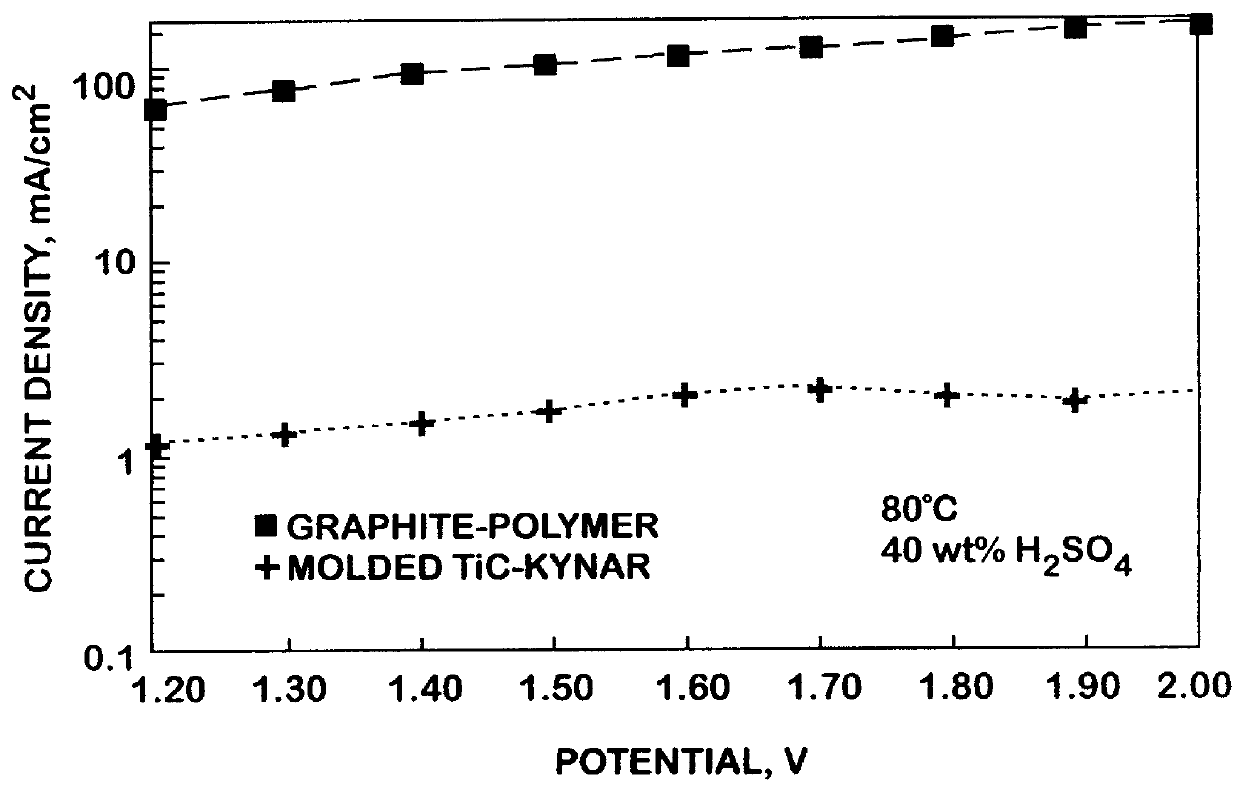
Titanium carbide bipolar plate for electrochemical devices
InactiveUS6083641ALow costEasy to makeSolid electrolytesElectrode carriers/collectorsMetallurgyShell molding
A corrosion resistant, electrically conductive, non-porous bipolar plate is made from titanium carbide for use in an eletrochemical device. The process involves blending titanium carbide powder with a suitable binder material, and molding the mixture, at an elevated temperature and pressure.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Cubic Boron Nitride Compact
InactiveUS20080302023A1Poor EDM-cuttabilityImprove conductivityPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesBorideAluminium carbide
A polycrystalline cubic boron nitride compact which comprises greater than 75 volume % and not greater than 90 volume % cubic boron nitride particles, the cubic boron nitride particles comprising particles of at least two average particle sizes, and a binder phase constituting the balance of the compact and comprising at least one titanium compound selected from titanium boride, titanium nitride, titanium carbide and titanium carbonitride and at least one aluminium compound selected from aluminium oxide, aluminium boride, aluminium nitride, aluminium carbide and aluminium carbonitride.
Owner:GOUDEMOND IAIN PATRICK +2
Preparation method and application of uranium-based ternary carbide
ActiveCN107010960AHigh melting pointImprove thermal conductivityNuclear energy generationReactor fuel susbtancesFault toleranceNuclear power
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of uranium-based ternary carbide, and is used for overcoming the shortcomings of the uranium monocarbidc (UC) and uranium dioxide (UO2) nuclear fuels in the prior art on the aspects of melting point, heat conduction, irradiance resistance, and the like. The preparation method comprises the steps of processing mixing uranium carbide powder and transition metal carbide powder or mixing uranium dioxide powder and transition metal carbide powder and carbon powder, placing in a designed graphite jig, and allowing reactive sintering to obtain high-stability uranium-based ternary carbide. The uranium-based ternary carbide prepared by the preparation method of the invention has the characteristics of high melting point, high heat conductivity and good irradiation resistance, and can be used as an accident fault-tolerance nuclear fuel of a nuclear power station, or a nuclear fuel of a nuclear-powered rocket.
Owner:MATERIAL INST OF CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
Paint for laser nanometer cermet alloying of metallurgical hot roller
InactiveCN1931790AHigh hardnessHigh strengthMetallic material coating processesLaser beam welding apparatusUranium carbideNanoceramic
The paint for laser nanometer cermet alloying of metallurgical hot roller is compounded with boron carbide 40-70 wt%, tungsten carbide 15-30 wt%, titanium carbide 0-15 wt%, and chromium carbide 5-20 wt%. The optimized technological parameters of the present invention result in obviously solid solution strengthening effect and dispersion strengthening effect; the structure fining generates obvious alloy layer strengthening effect, raised toughness and plasticity; and the dispersion of the carbide can arrest the growth of crystalline grain to ensure the high heat stability of the alloy structure. Therefore, the roller will not be annealed and softened during high temperature rolling.
Owner:SHENYANG DALU LASER COMPLETE EQUIP
Method of utilizing microwave energy to prepare calcium carbide at low temperature
The invention discloses a method of utilizing microwave energy to prepare calcium carbide at low temperature. The method comprises the following steps of using coal as a carbon source, using limestone or lime as a calcium source, heating by the microwave energy, and reacting and synthesizing to form the calcium carbide, wherein the reaction temperature of the synthesized calcium carbide is 1300-2000 DEG C, the reaction pressure is 0.3-1.1atm, and the reaction time is 3-120min; primarily grinding the carbon source and the calcium source, mixing according to a ratio, and performing ultrafine treatment to obtain an ultrafine mixed material; heating to react and synthesizing to form the calcium carbide by utilizing the microwave energy. The method has the advantages that the coal and the limestone are directly used as the raw materials, are subjected to ultrafine crushing, and are heated and synthesized to form the calcium carbide by the microwave energy; by utilizing various coal types, two steps of the coking of raw coal and the high-temperature decomposing of the calcium carbonate to prepare the limestone are not needed, the synthesizing temperature of the calcium carbide is lowered, the production efficiency and mechanical degree of the calcium carbide are improved, and a byproduct of carbon monoxide can be used as a chemical raw material to produce other chemical products.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Preparation method of molybdenum disulfide/titanium carbide composite material
InactiveCN108735984AAvoid high temperature conditionsGood repeatabilityCell electrodesSecondary cellsMass ratioUranium carbide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a molybdenum disulfide / titanium carbide composite material. The preparation method mainly comprises the following steps: adding a molybdenum source, a sulfur source and titanium carbide into a stainless steel reaction kettle in sequence according to a certain mass ratio, then stirring the molybdenum source, the sulfur source and the titanium carbidefor 10 to 30 min according to a filling volume of 60 percent, putting the mixture into the stainless steel reaction kettle, sealing the reaction kettle, placing the reaction kettle into a crucible furnace, heating the crucible furnace at 180 to 220 DEG C for 16 to 24 h, naturally cooling the reaction kettle to room temperature, and taking out the mixture; and washing the mixture with anhydrous ethanol, diluted hydrochloric acid and distilled water in sequence for three to six times, filtering the mixture, putting the obtained powder into a vacuum drying oven for vacuum drying at 60 DEG C for 12 h. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the process is simple, and reaction conditions are mild; no surfactant is added; the repetitiveness is high, and the cost is low; the prepared molybdenum disulfide / titanium carbide composite material is excellent in electrochemical performance and excellent in rate performance and high in cycle stability and has important significance in the field of lithium ion batteries.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
High capacity lithium ion battery containing metallic conducting materials
InactiveUS20140113175A1High capacity densityEasy dischargeElectrode carriers/collectorsOrganic electrolyte cellsAdhesiveElectrical battery
A lithium ion battery containing conducting materials comprises a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a separator, an electrolyte, adhesives and sealing materials. The conducting materials in the positive electrode comprise metal carbides, metal borides or metal nitrides. The conducting materials in the negative electrode comprise metal carbides, metal borides or metal nitrides. The metal carbide is titanium carbonitride, tungsten carbide or titanium carbide, vanadium carbide, tantalum carbide, and eutectic of tungsten carbide and titanium carbide. The metal boride is molybdenum boride, tungsten boride or vanadium boride. The metal nitride is titanium nitride, tungsten nitride or tantalum nitride. The conducting materials in the positive electrode may also comprise powdered metals. The conducting materials in the negative electrode comprise powdered metals. The powdered metal is nickel powder, copper powder or chromium powder.
Owner:ZHANG PANYI
Bicrystal gradient hard alloy cutter material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105945291ALess investmentEasy to operateTurbinesOther manufacturing equipments/toolsHigh resistanceUranium carbide
The invention belongs to the field of manufacturing of hard alloys, in particular to a bicrystal gradient hard alloy cutter material and a preparation method thereof. The bicrystal gradient hard alloy cutter material adopts tungsten carbide, titanium carbide, cobalt, vanadium carbide, chromium carbide and polyvinylpyrrolidone as raw materials; five symmetric gradient layers are provided; each layer contains coarse-grain tungsten carbide and fine-grain tungsten carbide from surface to inside; the ratio of coarse-grain tungsten carbide to fine-grain tungsten carbide is increased; the ratio of titanium carbide is reduced; and the ratio of a binding phase is increased. The preparation method comprises the steps of: ball milling of a mixture-drying and screening-molding by pressing-vacuum hot press sintering. The preparation method is low in equipment investment, convenient for operation, high in material utilization rate and suitable for industrial production; and the prepared product has a surface for satisfying the requirements of double high (high wear resistance and high toughness), and in particular, is suitable for interrupted metal turning and milling.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Composite impactor for percussion crushers
The present invention discloses a composite impactor for percussion crushers, said impactor comprising a ferrous alloy at least partially reinforced with titanium carbide according to a defined geometry, in which said reinforced portion comprises an alternating macro-microstructure of millimetric areas concentrated with micrometric globular particles of titanium carbide separated by millimetric areas essentially free of micrometric globular particles of titanium carbide, said areas concentrated with micrometric globular particles of titanium carbide forming a microstructure in which the micrometric interstices between said globular particles are also filled by said ferrous alloy.
Owner:MAGOTTEAUX INT SA
Titanium carbide in-situ-growth CNTs three-dimensional composite material with carbon microspheres being transition layers and preparing method thereof
The invention relates to a titanium carbide in-situ-growth CNTs three-dimensional composite material with carbon microspheres being transition layers and a preparing method thereof. The method comprises the steps of dispersing Ti3C2 nano powder into ultrapure water, then adding glucose after uniformly dispersing Ti3C2 nano powder, stirring the mixture for 5-30 min, and afterwards conducting a hydrothermal reaction to obtain a Ti3C2 @C composite material; adding the Ti3C2 @C composite material into the ultrapure water, then adding Co(NO3)2.6H2O into the ultrapure water after uniformly dispersing the Ti3C2 @C composite material, and stirring the mixture for a reaction for 2-6 h; then adding urea after the reaction is over, and conducting continuous stirring at a constant temperature to evaporate moisture to obtain precursor powder; conducting thermal treatment on the precursor powder to obtain the titanium carbide in-situ-growth CNTs three-dimensional composite material with the carbon microspheres being the transition layers. According to the titanium carbide in-situ-growth CNTs three-dimensional composite material with the carbon microspheres being the transition layers and the preparing method thereof, carbon nano tubes are grown on the surface of Ti3C2, the carbon nano tubes are utilized to provide an electron transferring channel, and thus the electric conductivity of the material is increased.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of titanium carbide/zinc indium sulfide composite visible light photocatalyst
ActiveCN110124706AHigh catalytic efficiencyEasy to preparePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationIndiumUranium carbide
The invention relates to a preparation method of a titanium carbide / zinc indium sulfide composite visible light photocatalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparation of a novel two-dimensional layered material titanium carbide, and preparation of the titanium carbide / zinc indium sulfide composite photocatalyst. The preparation method has the advantages of simplicity, easiness in operation, and easiness in control of the preparation conditions; and the prepared titanium carbide / zinc indium sulfide composite visible light photocatalyst is a green and pollution-free high-performance catalyst, has a high photocatalytic degradation efficiency, and has a certain application prospect.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Manufacture method for micropore wiredrawing die and manufacture mould
ActiveCN102896319AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed smoothnessDrawing diesUranium carbideMixed materials
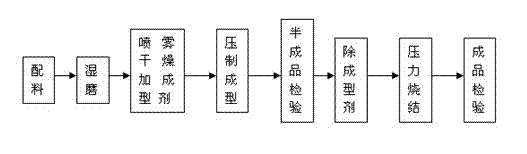
The invention discloses a manufacture method for a micropore wiredrawing die, which is characterized in that tungsten carbide (WC) is taken as a main material, an appropriate amount of titanium carbide (TaC) and cobalt (Co) are added, the weight percentage of tungsten carbide (WC), titanium carbide (TaC) and cobalt (Co) is (93-95 percent) : (1.5-1.8 percent) : (3.5-4.5 percent); and after mixing up the raw materials according to a proportion, wet grinding is carried out to enable the overall particle size of the ground mixed materials to be smaller than 2-3mu.m, then a spray drying formation agent is added to carry out spraying and drying, the materials are delivered into a compressive formation mould to be compressed and formed, a semi-finished product is manufactured, the formation agent is removed after the semi-finished product is inspected to be qualified, and finally the semi-finished product is sent to a sintering furnace to be sintered and formed, and the finish product of the micropore metal wiredrawing die is manufactured.
Owner:株洲美特优硬质合金有限公司
Preparation method of calcium carbide formed coke
ActiveCN101774569AIncrease ashIncrease productionDirect heating destructive distillationIndirect heating destructive distillationCalcium hydroxideAdhesive
The invention discloses a preparation method of calcium carbide formed coke, which takes a plasma coal cracking solid product as a raw material and comprises the following steps of: (1) preprocessing: firstly, deashing the plasma coal cracking solid product and then carrying out devolatilization and carbonization to obtain coke powder with the ash content of no more than 9% and the volatile constituent of no more than 2%; (2) proportioning: taking powdery calcium hydroxide as an adhesive and mixing the coke powder and the powdery calcium hydroxide evenly to obtain a mixture; then, mixing the mixture and water to obtain a material; (3) forming: pressing and forming the material at room temperature to obtain a green-ball; and (4) solidifying the green-ball: stacking the green-ball into a solidification tank, introducing CO2 and solidifying; taking out of the tank and drying or airing to obtain the formed coke. The formed coke prepared by adopting the method can be used as a special carbon material for producing calcium carbide.
Owner:XINJIANG YUEHETAI CHEM TECH CO LTD
Iron oxide/titanium carbide composite cathode material and preparation method thereof
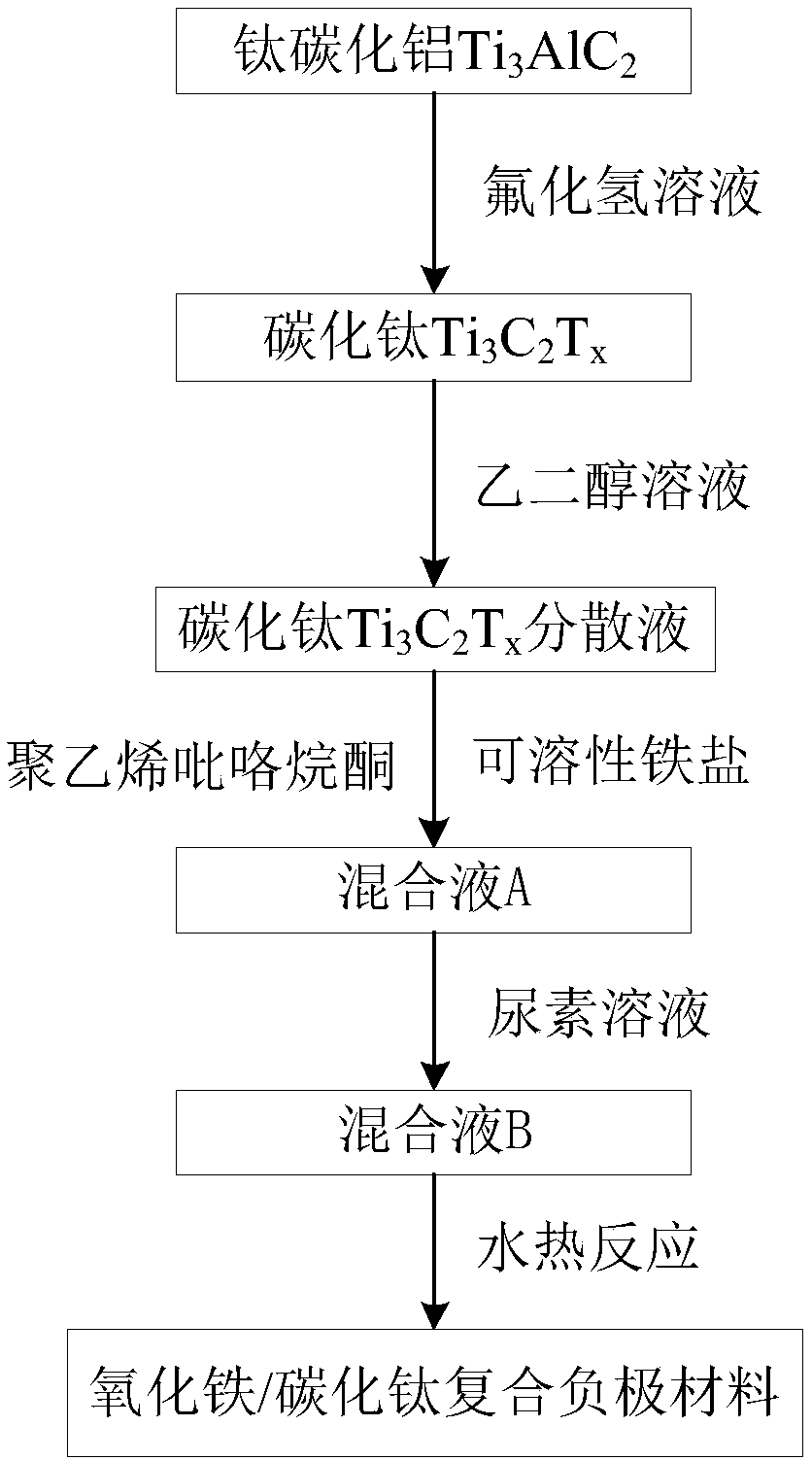
InactiveCN108365190AReduce energy consumptionSimple processCell electrodesIron(II) oxideUranium carbide
The invention relates to an iron oxide / titanium carbide composite cathode material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: dispersing titanium carbide in an organicsolution to form uniform titanium carbide dispersion liquid; then adding soluble ferric salt and polyvinylpyrrolidone in the titanium carbide dispersion liquid and stirring the materials to obtain mixed liquor A; dropping an urea solution in the mixed liquor A while stirring to obtain mixed liquor B; placing the mixed liquor B at the temperature of 80-200 DEG C and performing a hydrothermal reaction for 1-24 h, and performing steps of centrifugation, washing and drying on a reaction product to obtain the iron oxide / titanium carbide composite cathode material. The preparation technology is simple, a high temperature process is not required, energy consumption is low, the cycle performance of the iron oxide / titanium carbide composite cathode material is greatly increased, and the conductivity and capacity conservation rate are good.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FOREVER NEW ENERGY TECH CO LTD +1
Process and system of preparing calcium carbide and ethylene through oxygen/coal injection
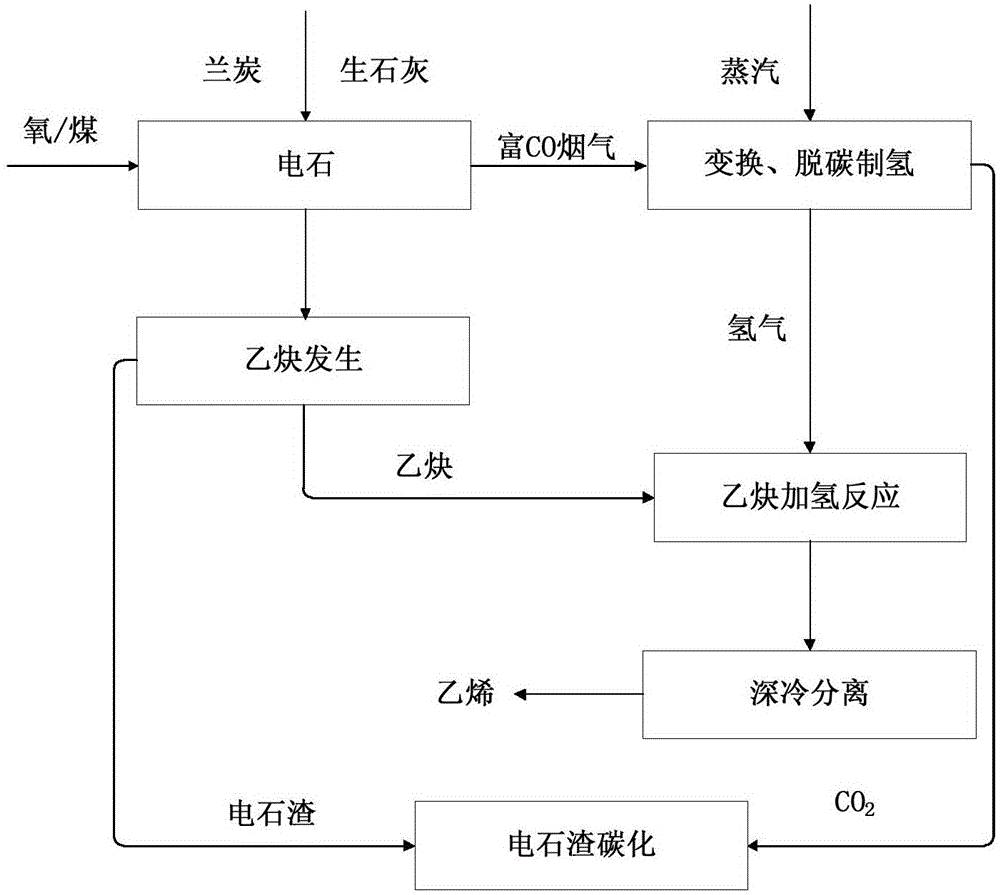
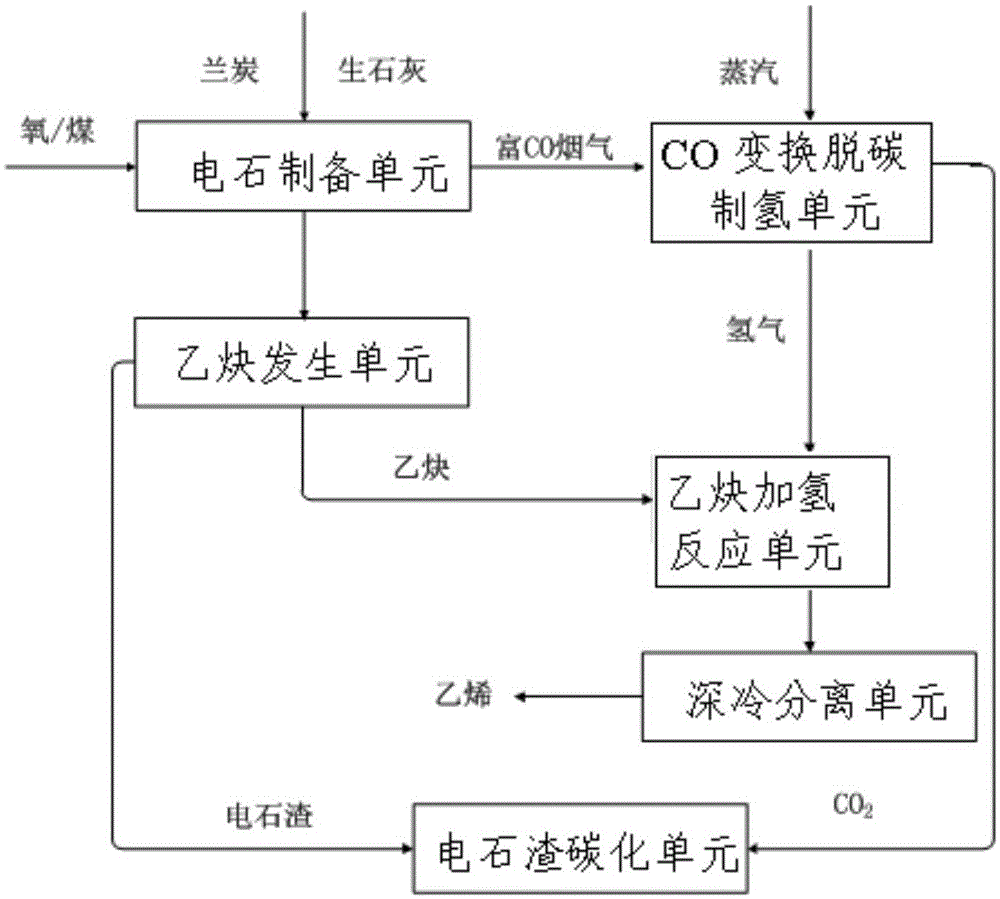
ActiveCN105129800AImprove uniformityReduce usageHydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrocarbon purification/separationUranium carbideElectric consumption
The invention relates to a process and a system of preparing calcium carbide and ethylene through oxygen / coal injection, wherein the process includes following steps: (1) preparation of calcium carbide; (2) CO conversion and decarburization and hydrogen production; (3) acetylene generation; (4) acetylene hydrogenation reaction; and (5) cryogenic separation. In the invention, oxygen and coal powder are injected during a calcium carbide smelting process. Because that heat generated from incomplete combustion of oxygen and coal can radiate to a position which is difficult to reach by arc light, the process, compared with a conventional calcium carbide furnace method, is more uniform in heat distribution in furnace, thereby reducing electric consumption in the calcium carbide furnace and calcium carbide production period. The injected coal powder can replace a part of coke, so that the process can reduce production cost of the calcium carbide. Meanwhile, the process fully utilizes calcium carbide smelting tail gas being rich in CO, which is used for preparing hydrogen through the CO conversion to prepare the hydrogen source in the acetylene hydrogenation reaction, so that not only is environment pollution reduced but also economic benefit is improved greatly.
Owner:SHENWU TECH GRP CO LTD
Zirconium carbide-zirconium diboride complex-phase ceramic powder synthesized through thermal explosion and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to zirconium carbide-zirconium diboride complex-phase ceramic powder synthesized through thermal explosion and a preparation method thereof. The ceramic powder is prepared from, by mass, 0%-30% of Al powder and 70%-100% of Zr powder and B4C powder, wherein the molar ratio of Zr to B4C is 3:1, and the sum of the mass percent of the components is 100%. The preparation method comprises the steps that the Al powder, the Zr powder and the B4C powder which are dried are fully mixed and then pressed into green blank blocks, a thermal explosion chemical reaction is conducted in an induction furnace which is vacuumized and then is full of Ar gas, and the ceramic powder is obtained. The ceramic powder and the preparation method thereof have the advantages that reacting is rapid, energy saving and cleanliness are achieved, and the product compounding degree is high; the product is a ceramic compound mainly containing ZrC powder and ZrB2 powder and can be directly applied as a zirconium carbide-zirconium diboride complex-phase ceramic powder material, the zirconium carbide-zirconium diboride complex-phase ceramic powder can be separated after other impurities in the compound are washed off through extraction, and then the single pure zirconium carbide or pure zirconium diboride ceramic powder can be obtained for application.
Owner:TONGREN UNIV
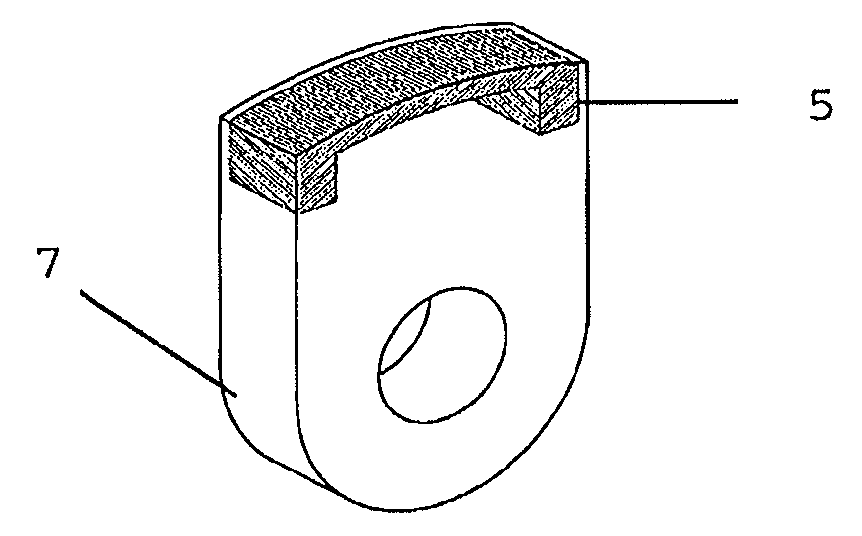
Calcium carbide furnace based calcium carbide sensible heat power generation system and implementation method thereof
ActiveCN104006670AReasonable structural designEasy to implementIncreasing energy efficiencyHandling discharged materialUranium carbideSteam drum
The invention discloses a calcium carbide furnace based calcium carbide sensible heat power generation system and an implementation method thereof. The calcium carbide sensible heat power generation system comprises an annular heat exchange system, a steam drum (7), a steam turbine (4), a power generator (3) and a return-flow system; the annular heat exchange system surrounds the periphery of a calcium carbide furnace; the steam drum (7) is communicated with the annular heat exchange system; the steam turbine (4) is connected with the steam drum (7) through a steam inlet pipe (1); the power generator (3) is connected with the steam turbine (4); the return-flow system is connected with a steam outlet of the steam turbine (4) and the steam drum (7) and used for recycling steam exhaust to the steam drum (7). According to the calcium carbide furnace based calcium carbide sensible heat power generation system and the implementation method thereof, the structural design is reasonable, the implementation is convenient, the calcium carbide sensible heat can be effectively recycled, the environment temperature is reduced, the manual operation links are greatly reduced, the risk of work of workers is effectively reduced, and the problem that the sensible heat of calcium carbide discharged out of the furnace cannot be recycled in the prior art is solved.
Owner:CHINA MCC5 GROUP CORP
Method for preparing TiB2/TiC (titanium diboride/titanium carbide) ultrafine powder for surface spraying of engine piston ring by means of high energy ball milling
InactiveCN102430757AReaction raw materials are cheapSimplify the process of evacuating and filling with argonMolten spray coatingHigh energyUranium carbide
The invention discloses a method for preparing TiB2 / TiC (titanium diboride / titanium carbide) ultrafine powder for surface spraying of an engine piston ring by means of high energy ball milling. The method includes the steps: (1) weighing Ti (titanium) powder and B4C (boron carbide) powder as powder materials, (2) weighing grinding balls, (3) placing the powder materials into a ball milling tank and then covering the powder materials with the grinding balls so as to press the upper surfaces of all the powder materials, (4) leading inert gas into the ball milling tank so as to exhaust air, and (5) performing ball milling. The method for mechanical alloying by means of high energy ball milling is used for in-situ synthesis of nanoscale metal ceramic composite TiB2 / TiC powder, vacuum pumping and argon filling during in-situ synthesis do not need to be performed in a vacuum glove box, accordingly, operation procedures are simplified, production efficiency is improved, and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Nuclear fuel cladding with high heat conductivity and method for making same
ActiveUS9031184B2Easy transferImprove heat transfer performanceOptical rangefindersFuel elementsFiberThermal energy
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Stirring head for friction stir welding and fabrication method of stirring head
ActiveCN110576255AExtended service lifeInhibit growthNon-electric welding apparatusRheniumFriction welding
The invention provides a stirring head for friction stir welding and a fabrication method of the stirring head. The stirring head for friction stir welding comprises the following raw materials basedon percent by mass: 55-85% of tungsten powder, 5-15% of rhenium powder and 10-30% of zirconium carbide and / or hafnium carbide powder. The fabrication method of the stirring head for friction stir welding comprises the following steps of A, preparing matrix alloy powder; B conducting pressing and forming, specifically conducting pressing and forming on the matrix alloy powder obtained in the step Ato obtain a formed blank; C, performing high-temperature sintering, specifically sintering the formed blank in the step B to obtain a sintered blank; and D, performing hot isostatic pressure processing. By introducing elements such as rhenium, zirconium carbide and / or hafnium carbide into a tungsten matrix, the plasticity and the processability can be remarkably improved, and the zirconium carbide and / or hafnium carbide is distributed in the tungsten matrix in a diffusion way so as to achieve an effect of fine-grain strengthening; and meanwhile, a W-C chemical bond can be formed at an interface bonding position, so that the enhancement effect can be further improved.
Owner:安泰天龙钨钼科技有限公司 +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com