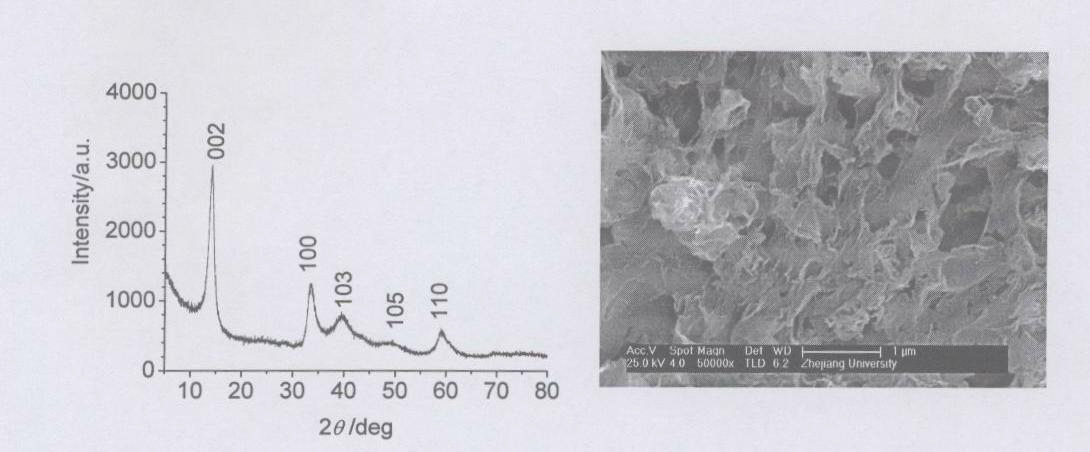
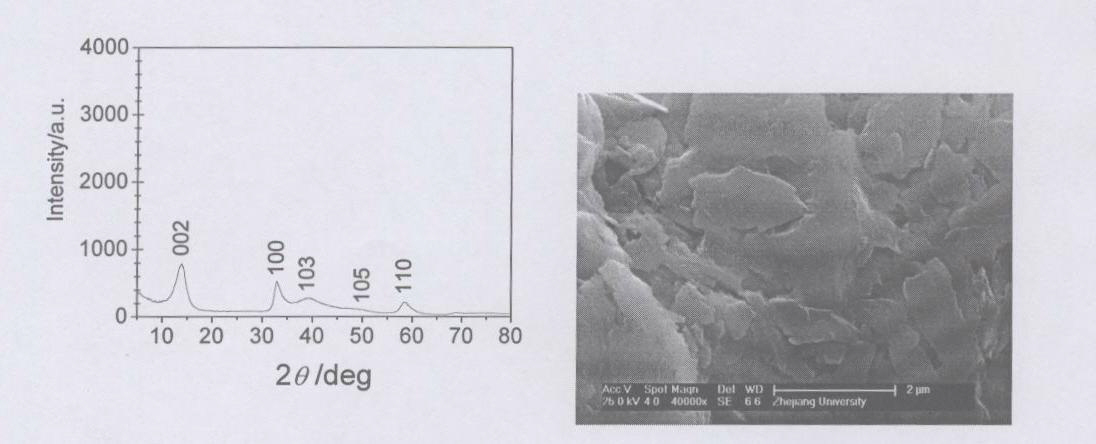
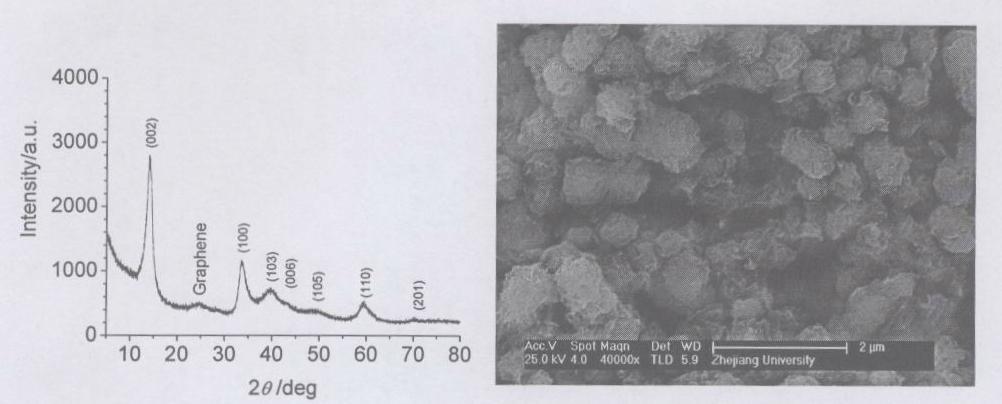
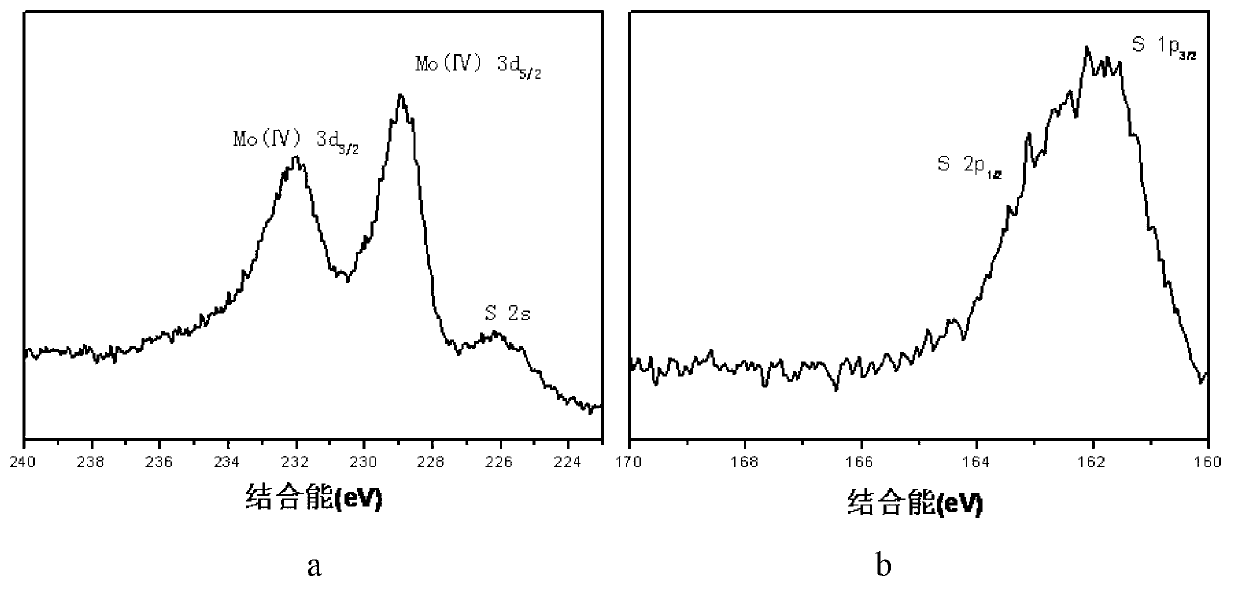
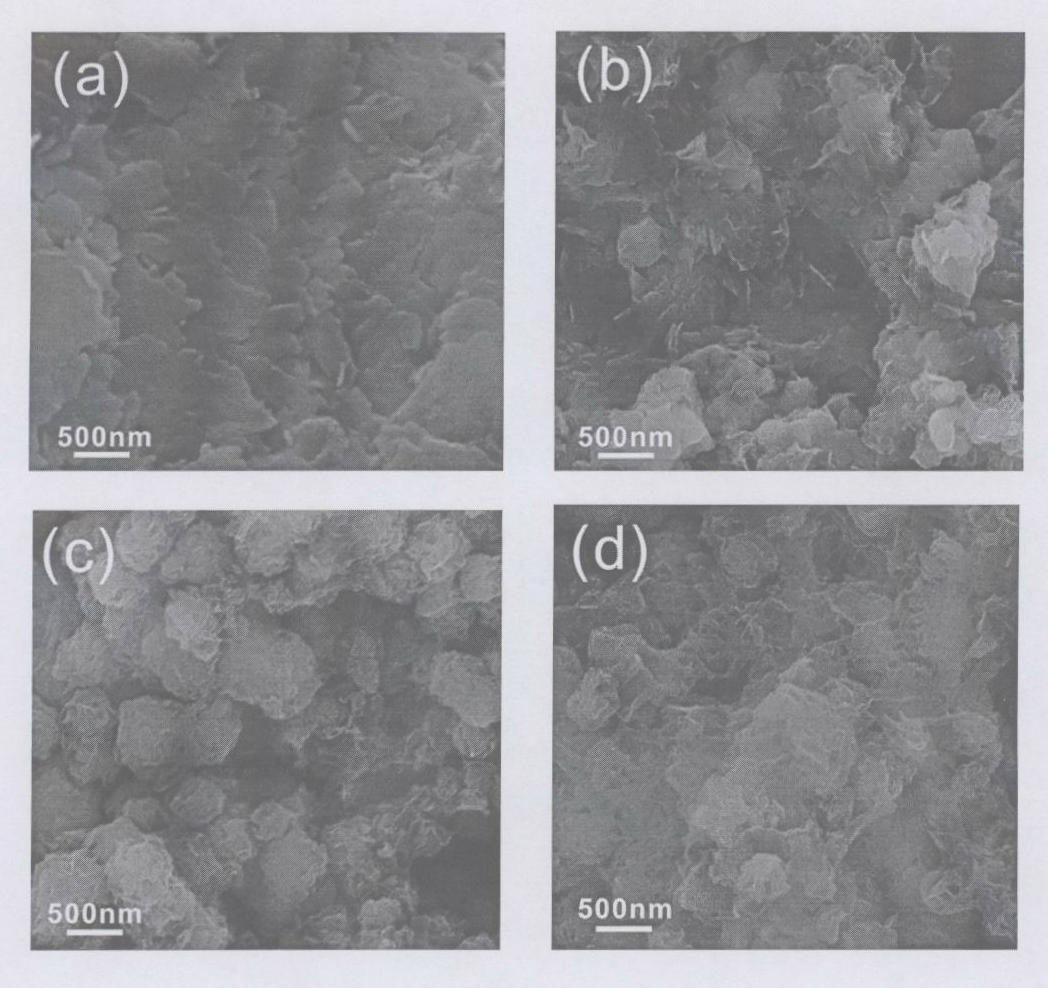
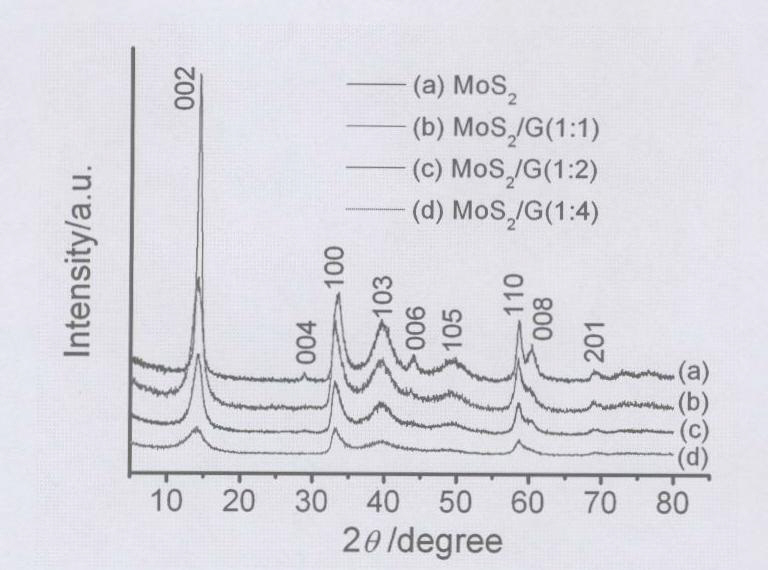
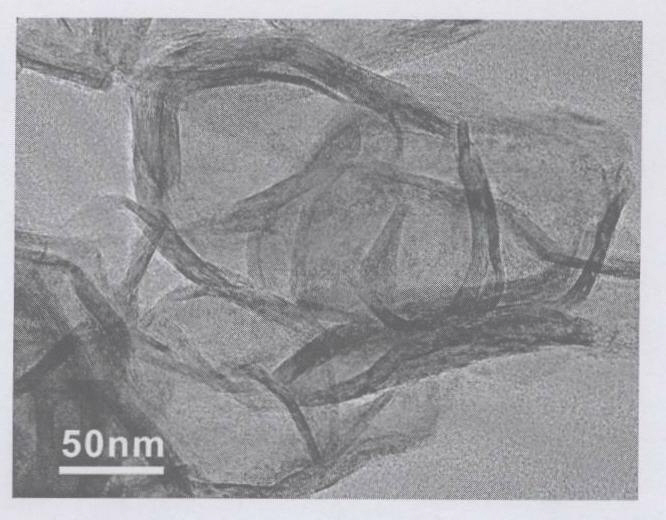
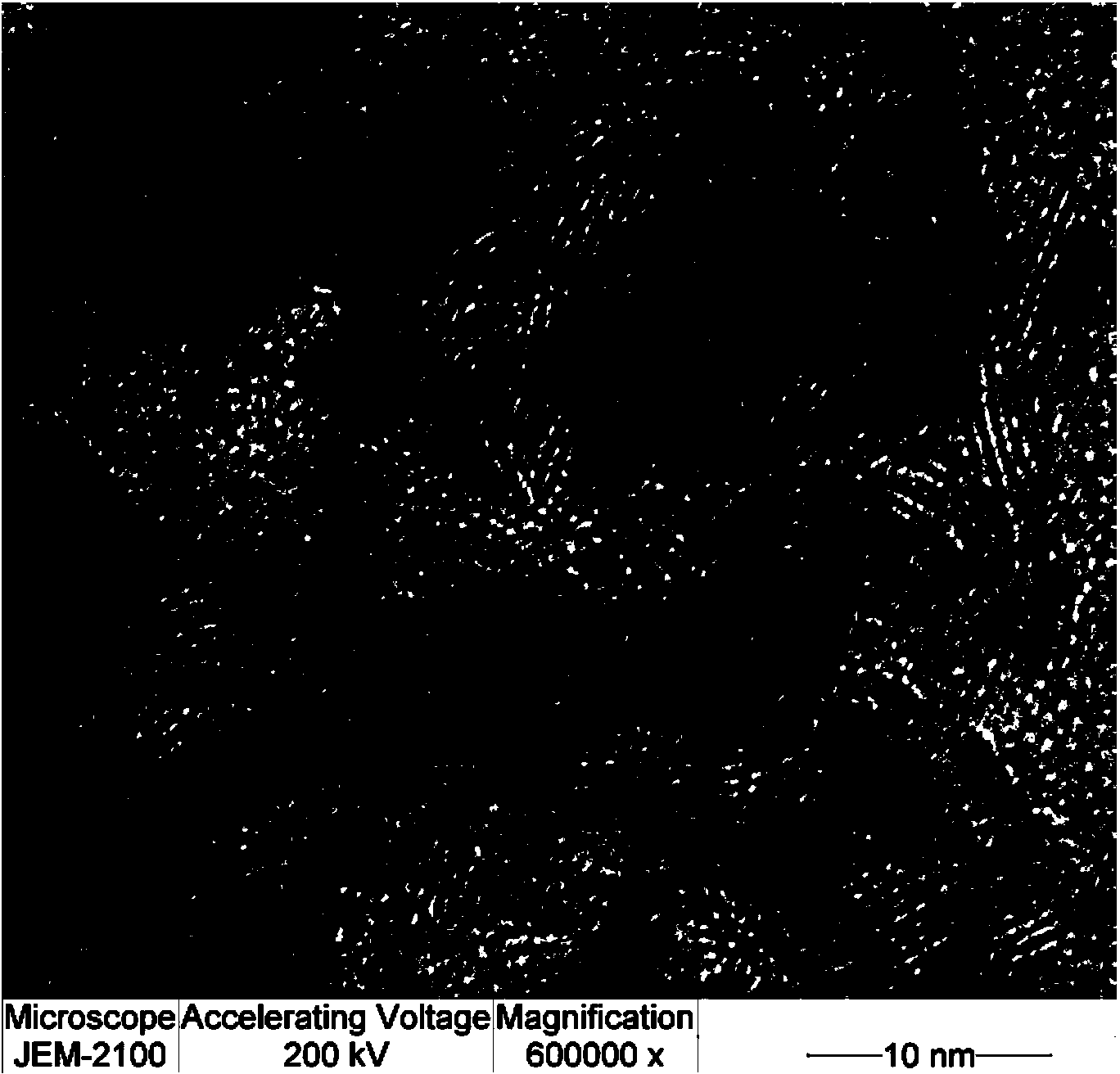
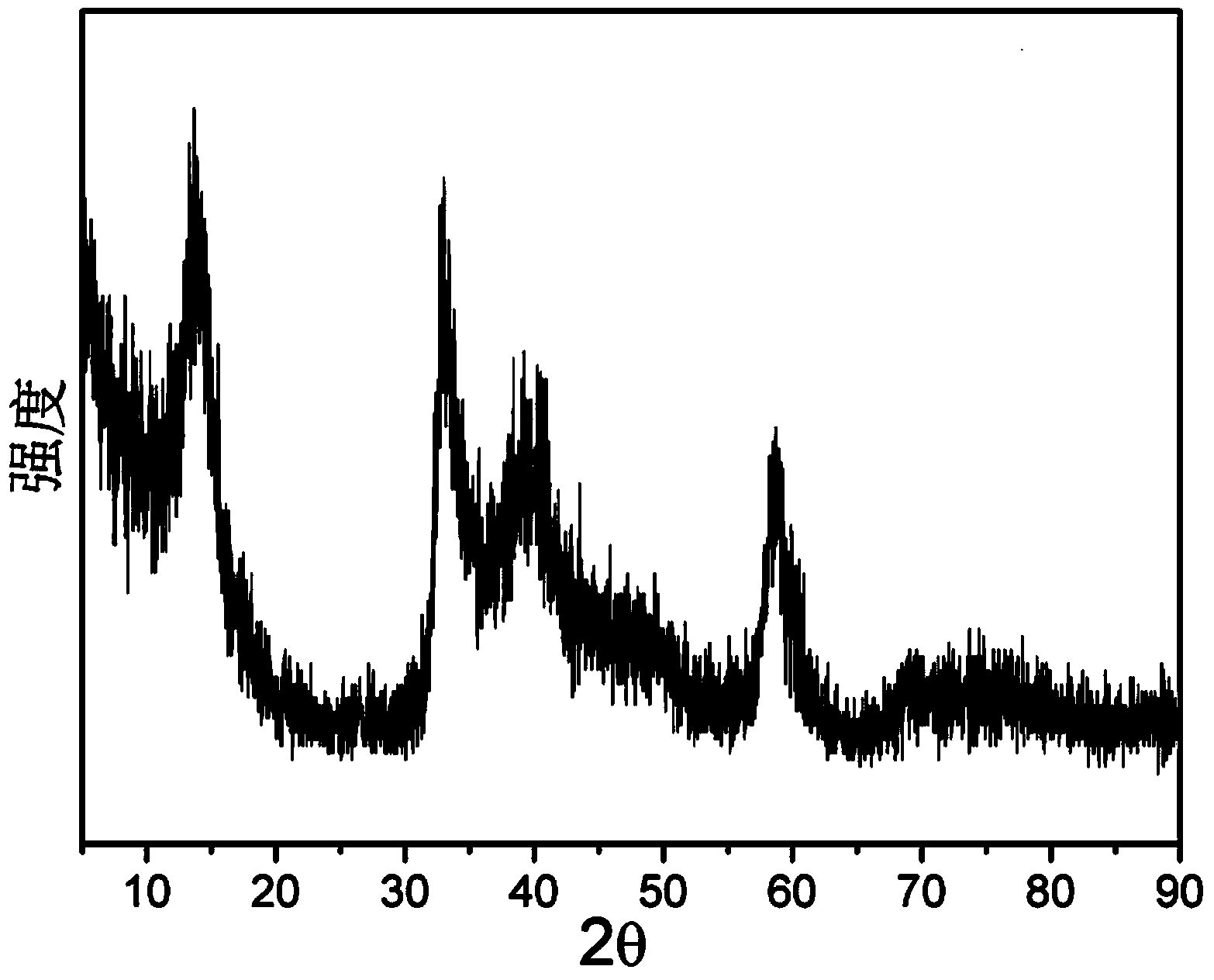
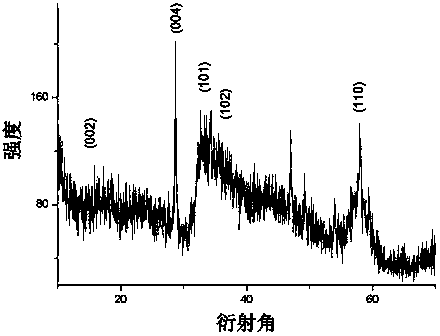
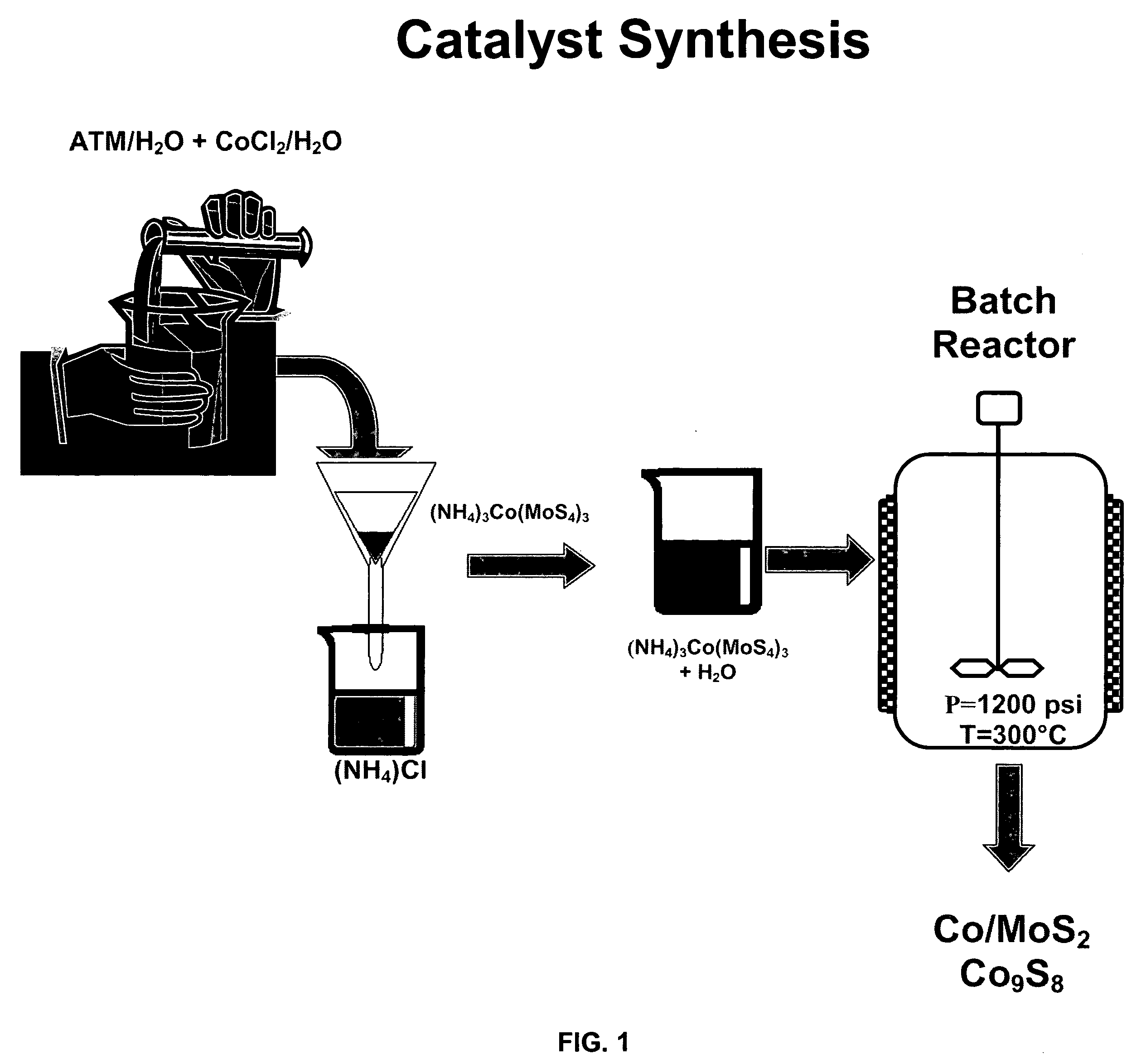
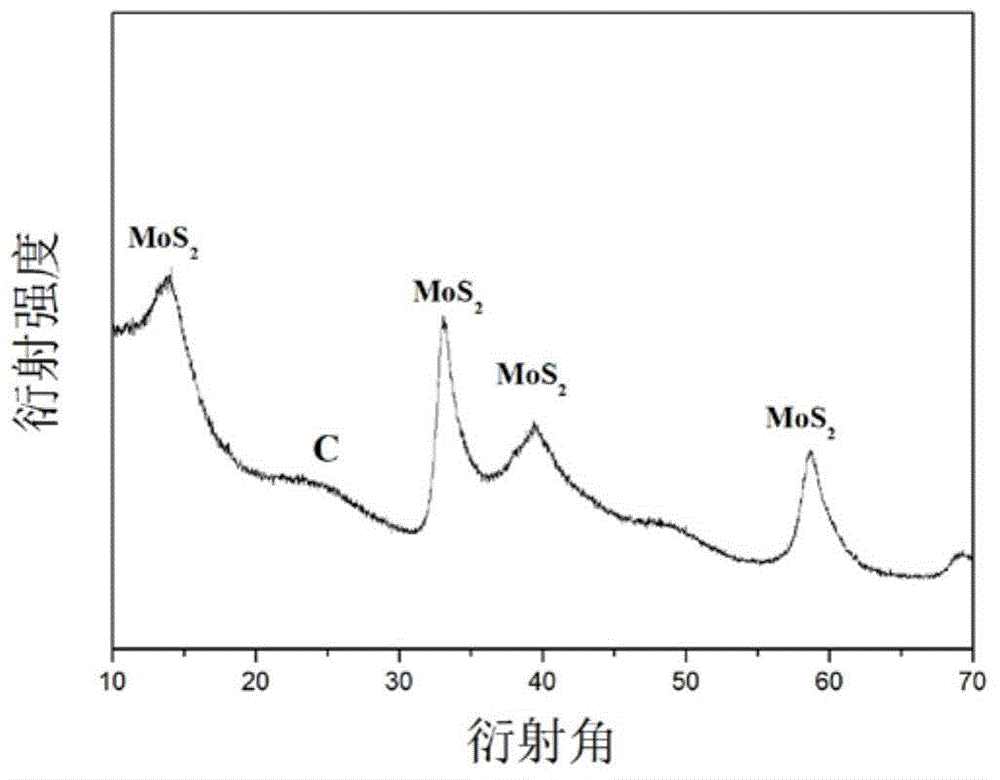
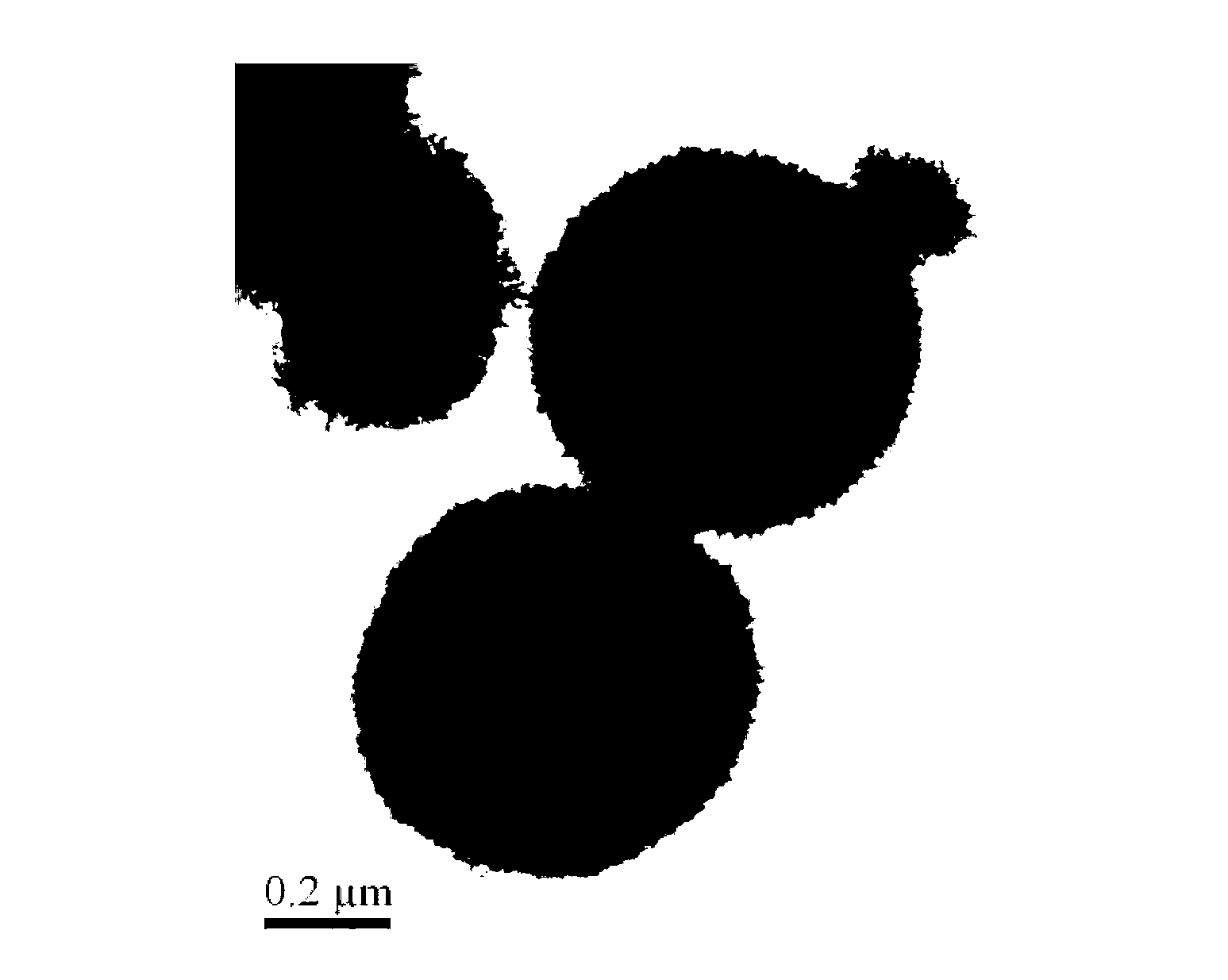Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5720 results about "Molybdenum disulfide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
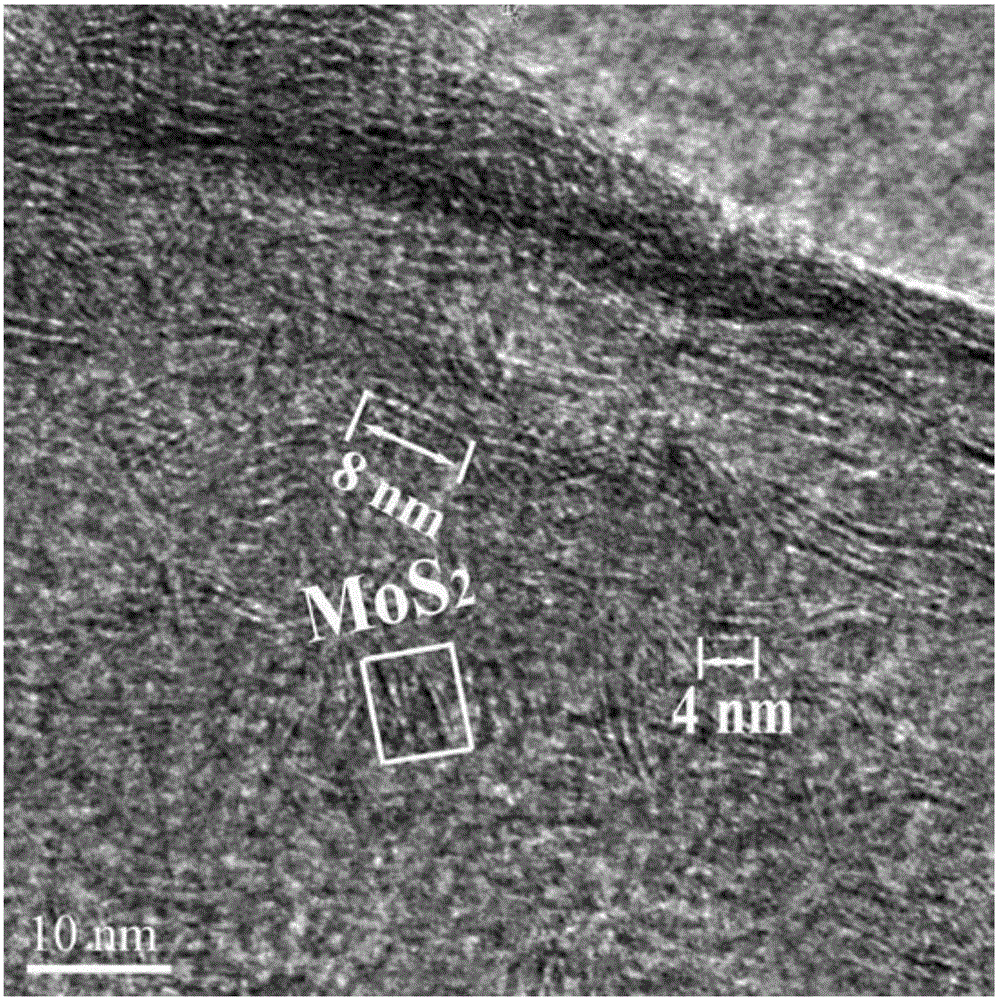
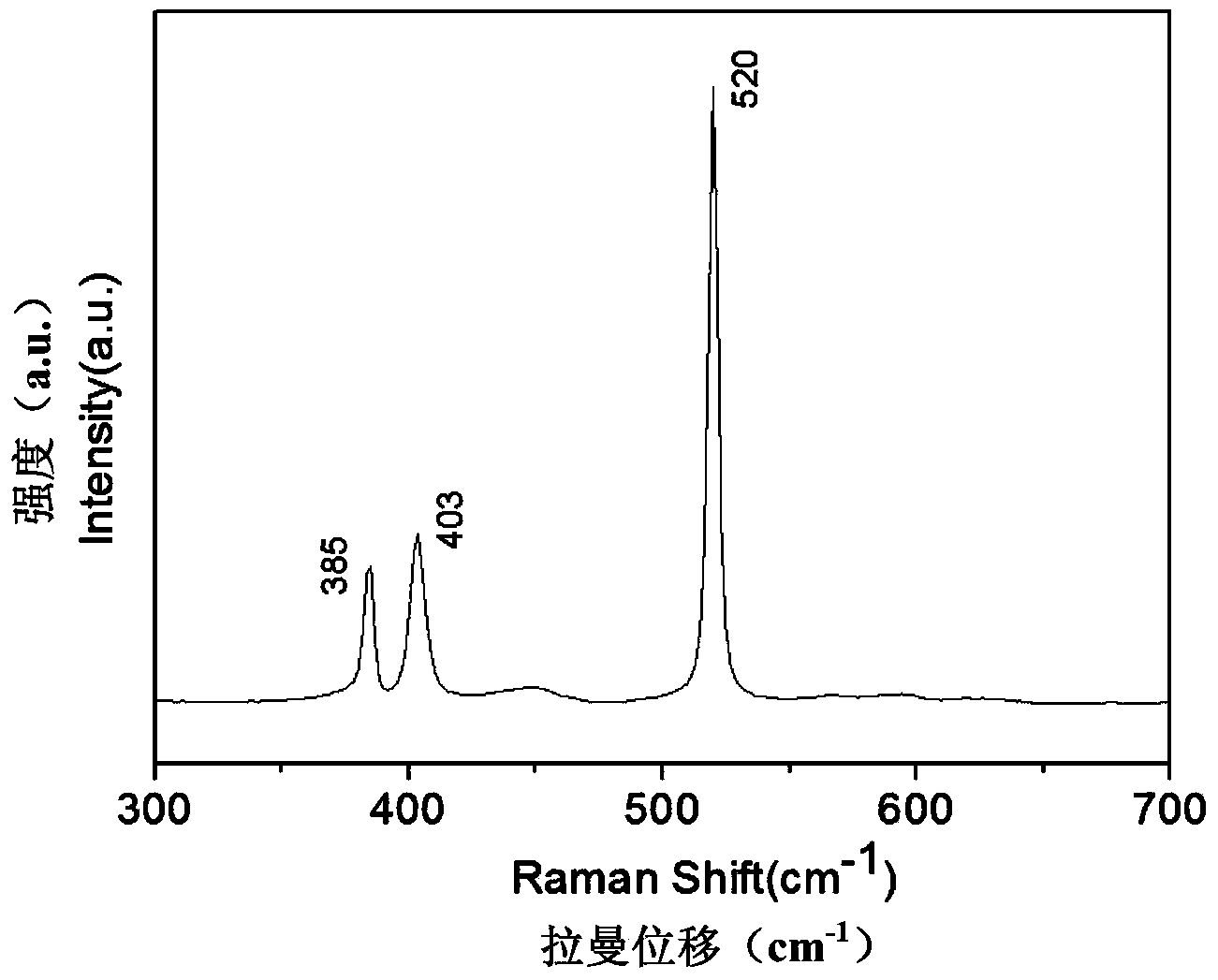
Molybdenum disulfide (or moly) is an inorganic compound composed of molybdenum and sulfur. Its chemical formula is MoS₂. The compound is classified as a transition metal dichalcogenide. It is a silvery black solid that occurs as the mineral molybdenite, the principal ore for molybdenum. MoS₂ is relatively unreactive. It is unaffected by dilute acids and oxygen. In appearance and feel, molybdenum disulfide is similar to graphite. It is widely used as a dry lubricant because of its low friction and robustness. Bulk MoS₂ is a diamagnetic, indirect bandgap semiconductor similar to silicon, with a bandgap of 1.23 eV.
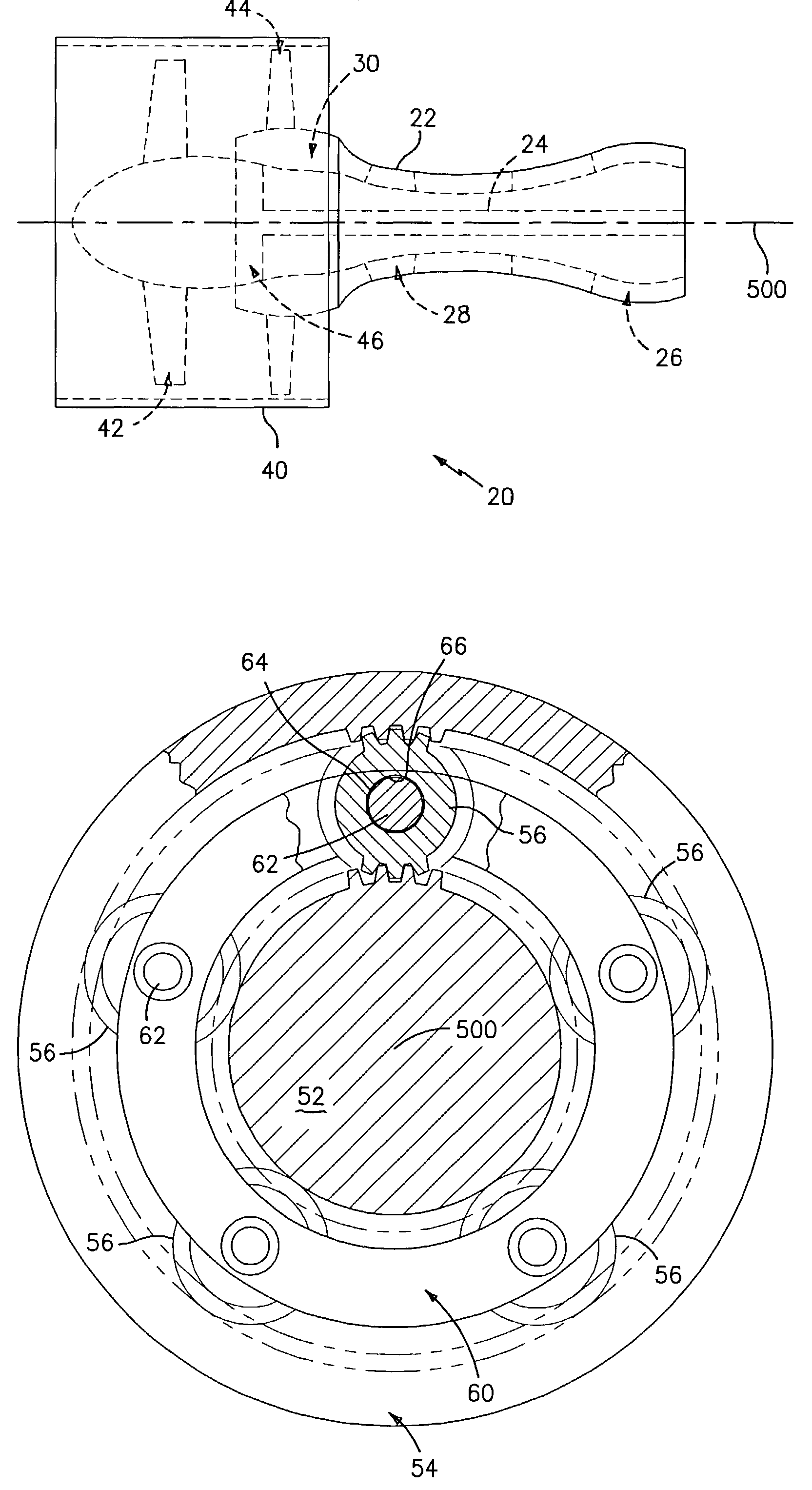
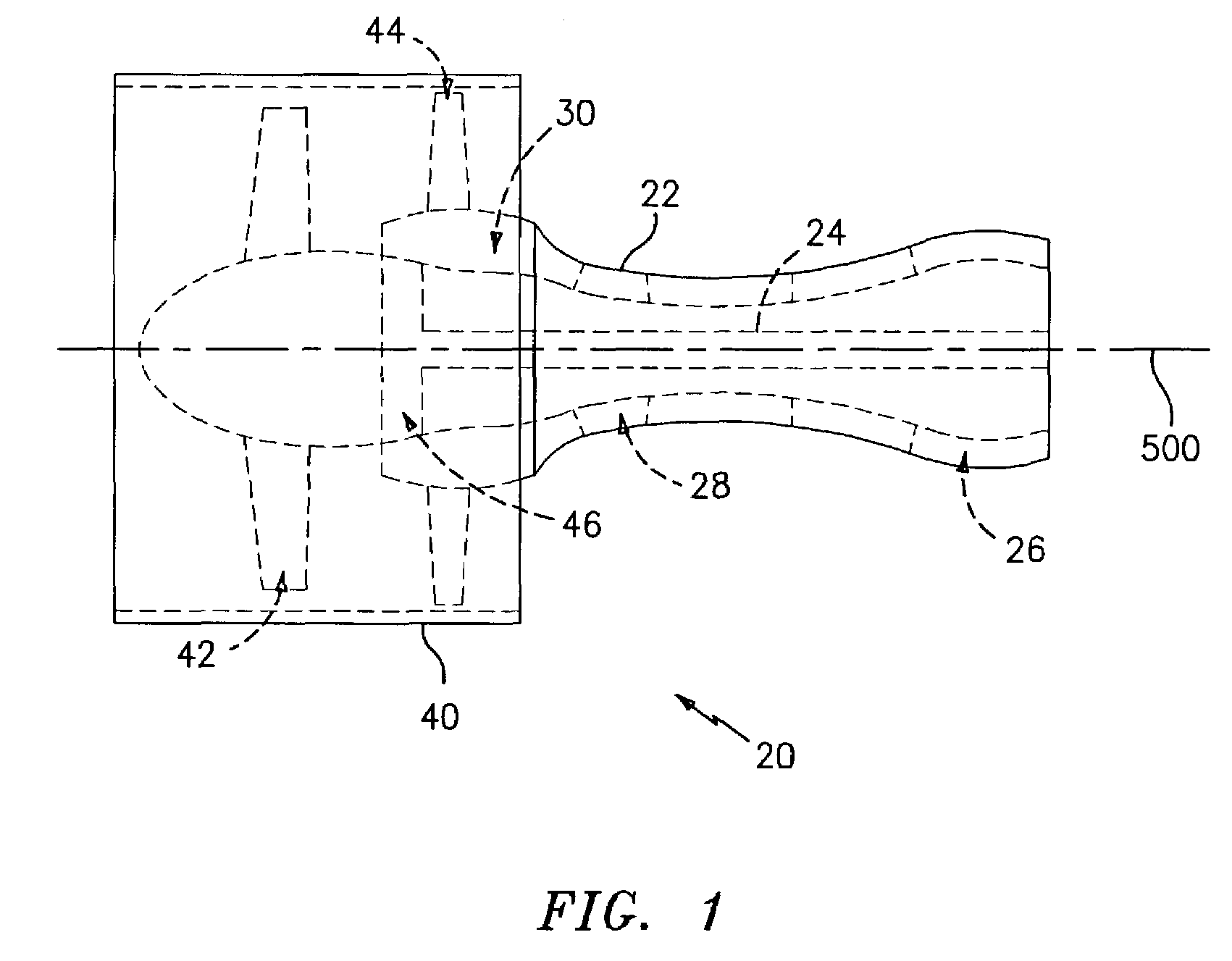
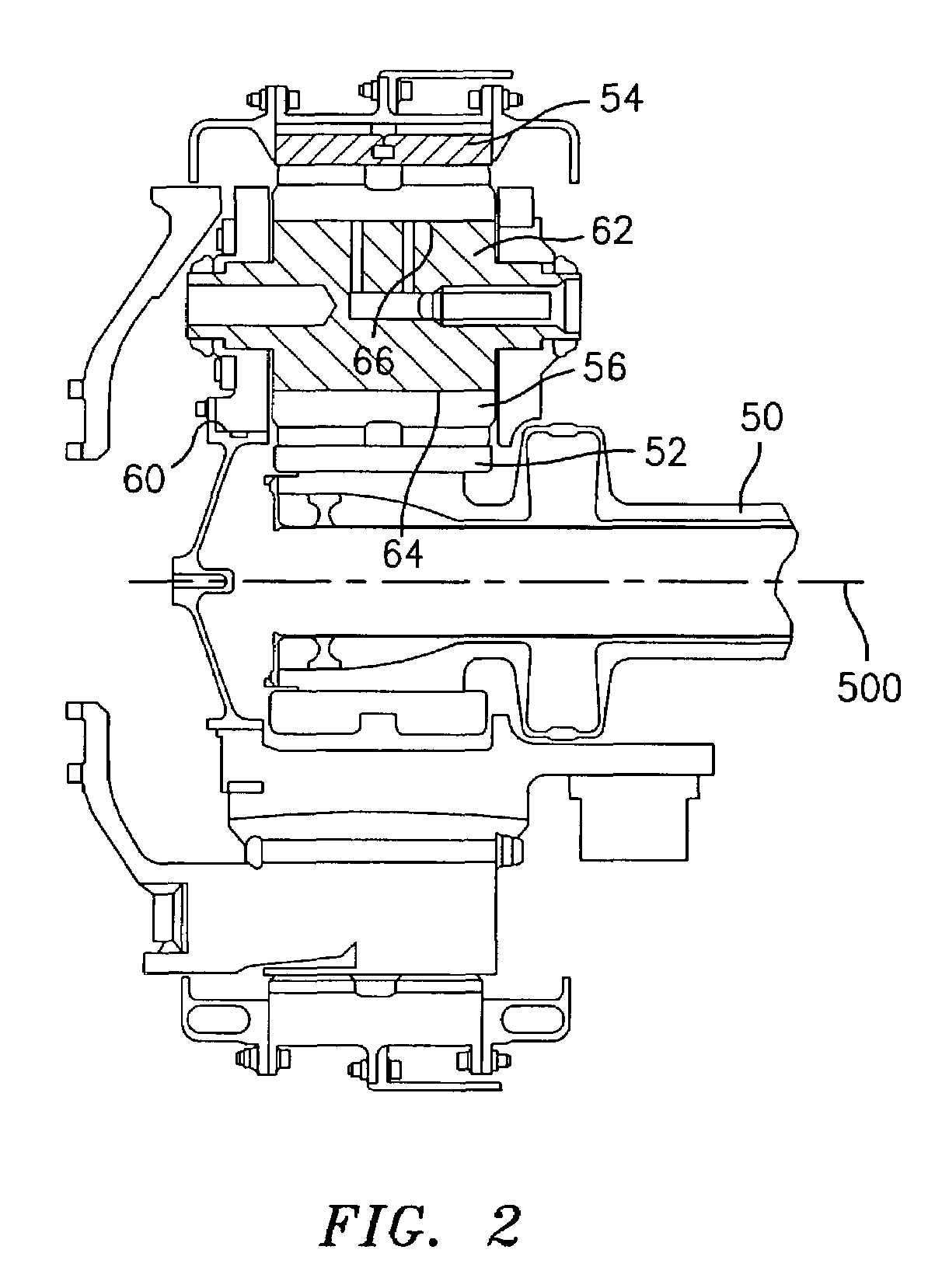
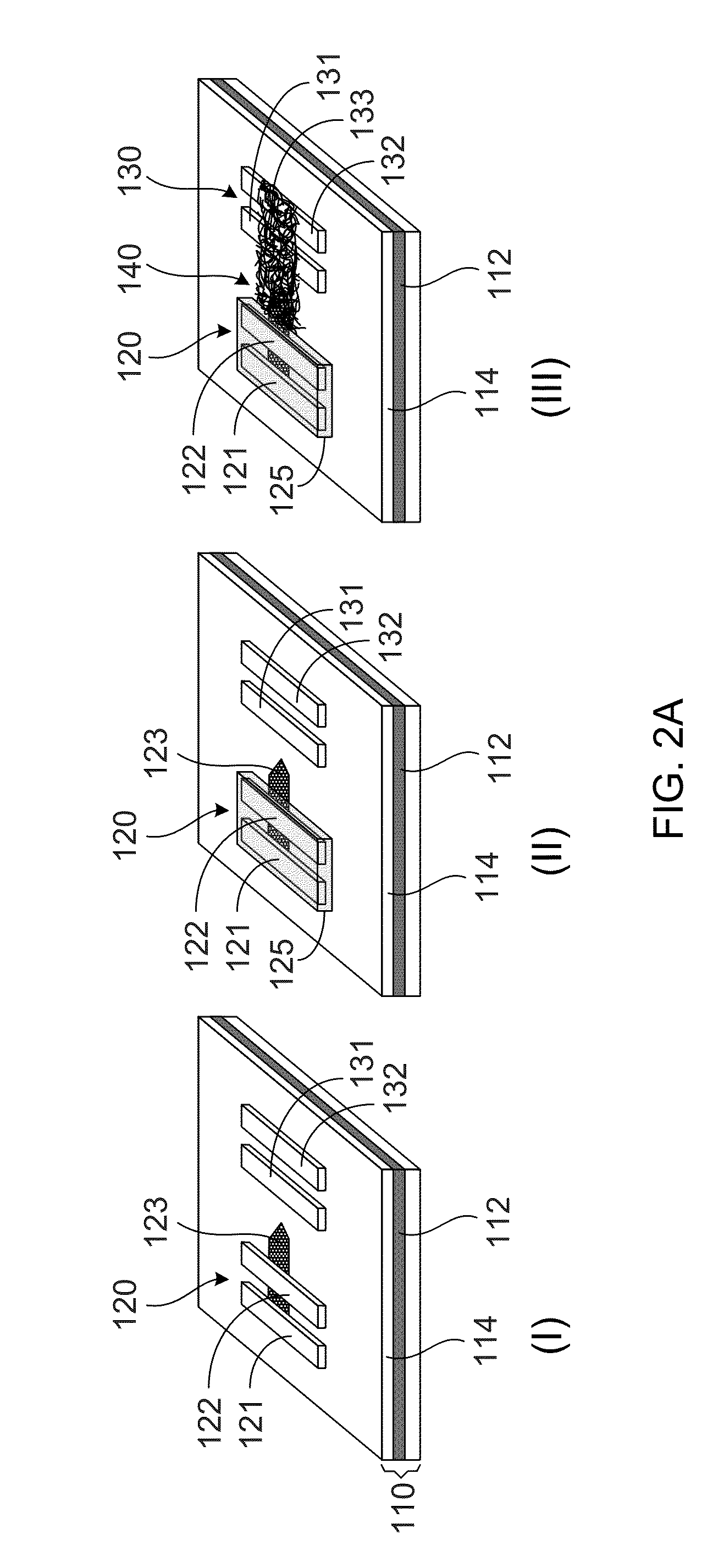
Geartrain coupling for a turbofan engine
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) is used as a journal coating for a gearing system. A particular application is the planetary gear system of a geared turbofan engine. Particularly advantageous coatings are deposited via physical vapor deposition (PVD) techniques.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
Joint for steel pipe having high galling resistance and surface treatment method thereof
InactiveUS6027145AShorten heating timeImprove the lubrication effectDrilling rodsPretreated surfacesEpoxyPolyamide
PCT No. PCT / JP95 / 02034 Sec. 371 Date May 23, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date May 23, 1997 PCT Filed Oct. 4, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 10710 PCT Pub. Date Apr. 11, 1996An object of the present invention is to provide galling resistance to a threaded joint used for an oil well pipe. On a thread portion and a metallic sealing portion of the joint, there is provided a manganese phosphate chemical formation coating layer, or alternatively there are provided a nitriding layer of 1 to 20 mu m thickness and a manganese phosphate chemical formation coating layer of 5 to 30 mu m thickness, and also there is coated a solid lubricant which contains powder of molybdenum disulfide or tungsten disulfide and also contains one of epoxy resin, furan resin and polyamide resin as an essential component, and a ratio of composition is maintained at a specific value, so that a solid lubricant coating layer of 10 to 45 mu m thickness can be formed by heating. Due to the above surface treatment, even when the frequency of repetition of fastening and unfastening of the joint is increased, the occurrence of galling can be prevented over a long period of time.
Owner:NSCT PREMIUM TUBULARS
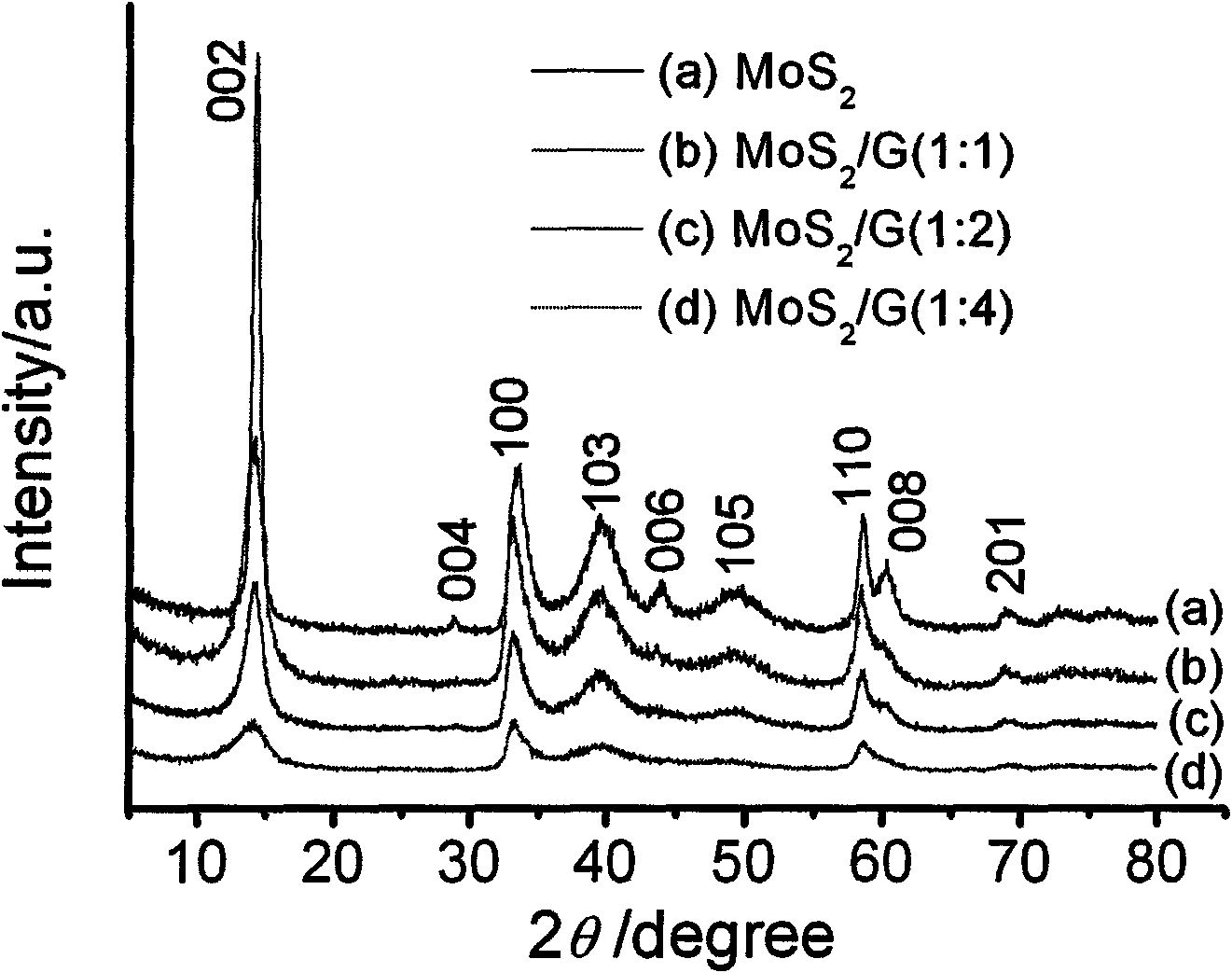
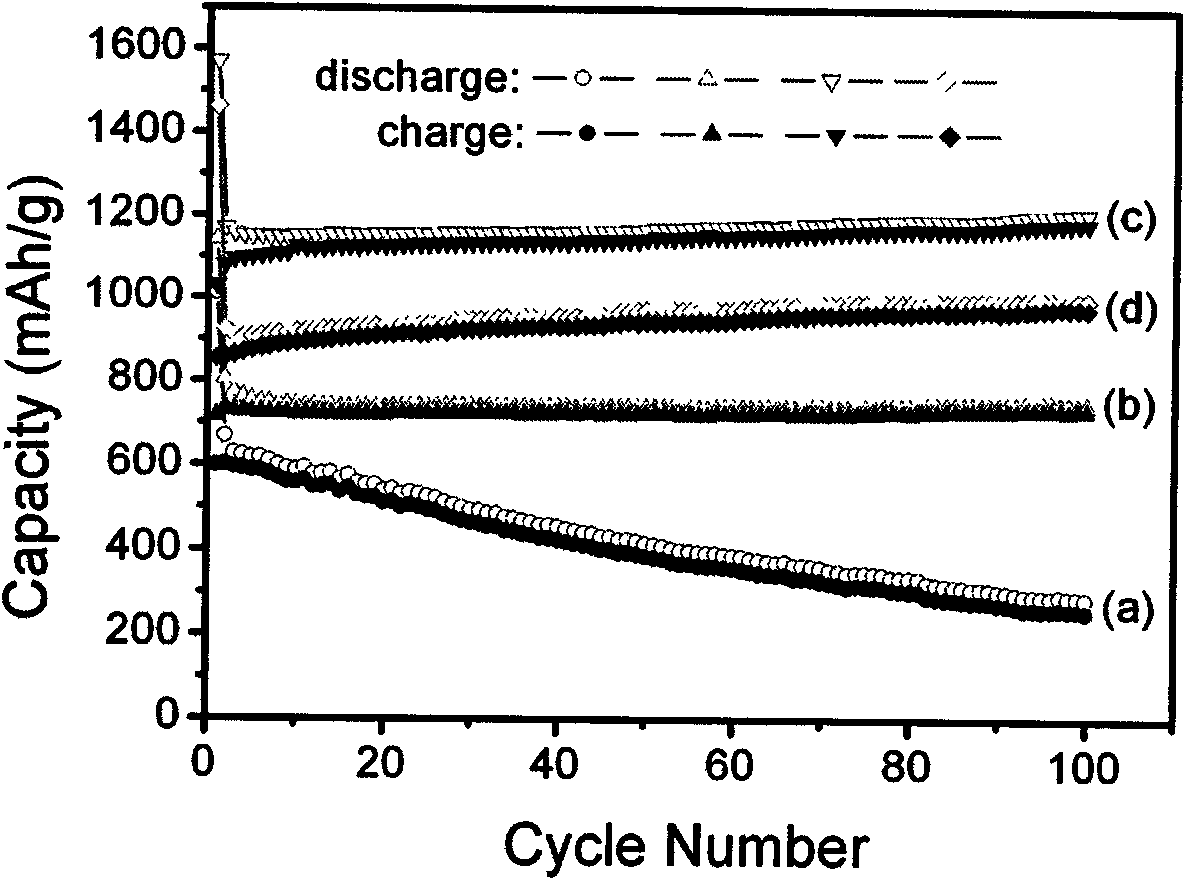
Graphene/MoS2 compound nano material lithium ion battery electrode and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102142537ALarge specific surface areaImprove mechanical propertiesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesLithium-ion batteryMaterials science
The invention discloses a graphene / molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) compound nano material lithium ion battery electrode and a preparation method thereof. The electrode comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 75 to 85 percent of compound nano material serving as an active substance, of a graphene nano slice and MoS2, and 5 to 10 percent of acetylene black and 10 percent of polyvinylidene fluoride; and the mass ratio of the graphene nano slice to the MoS2 nano material in the compound nano material active substance is (1 to 1)-(4 to 1). The preparation method of the electrode comprises the following steps of: preparing an oxidized graphite nano slice by using graphite as a raw material by a chemical oxidization method; synthesizing by a one-step hydrothermal in-situ reduction method in the presence of the oxidized graphite nano slice to obtain a graphene nano slice / MoS2 compound nano material; and finally, preparing the electrode by using the graphene nano slice / MoS2 compound nano material as the active substance. The electrode has high electrochemical lithium storage reversible capacity and cyclic stabilization performance, and can be widely applied to new generation lithium ion batteries.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Graphene nano sheet/MoS2 composite nano material and synthesis method thereof
InactiveCN102142551AMild reaction conditionsSimple processMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesSynthesis methodsThiourea
The invention discloses a graphene nano sheet / MoS2 composite nano material and a synthesis method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a graphite oxide nano sheet from graphite by using a chemical oxidation method, then dissolving molybdate into deionized water to form a solution of 0.02 to 0.07M, and adding thioacetamide or thiourea serving as a sulfur source and a reducer, wherein the mass ratio of the thioacetamide or the thiourea to the molybdate is 5:1-12:1; and adding the graphite oxide nano sheet into the solution, performing ultrasonic treatment for 1 to 2 hours so that the graphite oxide nano sheet is fully dispersed in a hydrothermal reaction solution, transferring the mixture into a hydrothermal reaction kettle, sealing, reacting for 20 to 36 hours at the temperature of between 220 and 260 DEG C, and obtaining the graphene nano sheet / molybdenum disulfide composite nano material by one-step hydrothermal synthesis, wherein the mass ratio of the graphene nano sheet to the molybdenum disulfide in the composite material is 1:2-4:1. The method has the characteristics of mild reaction condition and simple process. The synthesized graphene nano sheet / molybdenum disulfide composite nano material serving as an electrochemical lithium storage and electrochemical magnesium storage electrode material has wide application.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Molybdenum disulfide nano-sheet film material and its preparation methods
ActiveCN102849798AImprove hydrogen evolution performanceShape is easy to controlMaterial nanotechnologyCable/conductor manufactureThioureaFilm material
The invention discloses a molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nano-sheet film material and its preparation methods. The film material is characterized in that MoS2 nano-sheets vertically and sequentially grow on a conductive substrate, and the diameters and the thicknesses of the MoS2 nano-sheets are 0.05-2mum and 2-30nm respectively. There are two preparation methods of the film material. One preparation method comprises the following steps: a substrate which can be a copper sheet, a silver sheet, a titanium sheet, a tungsten sheet, a molybdenum sheet or carbon is placed in a solution comprising a molybdate and sulfur-containing compounds (comprising thiourea, thioacetamide and L-cysteine); and the sulfur-containing compounds undergo a hydrothermal reaction to grow the compactly-grown and uniformly-sequential MoS2 nano-sheet films on the substrate. Another method comprises the following steps: the molybdenum sheet is directly placed in a solution of the sulfur-containing compounds (comprising thiourea, thioacetamide and L-cysteine); and the sulfur-containing compounds undergo a sulfuration reaction under a hydrothermal condition to form the compact and uniform MoS2 nano-sheet ordered films. The film has a low hydrogen evolution overpotential (-30mv), a small Tafel slope (52mV / dec) and a high electrochemical stability, and is a hydrogen evolution electrode material extremely having an application prospect.
Owner:深圳海氢科技有限公司
Polytetrafluoroethylene composite material and product preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101775186AImprove thermal conductivityImproved ball compressive strengthFiberTetrafluoroethylene
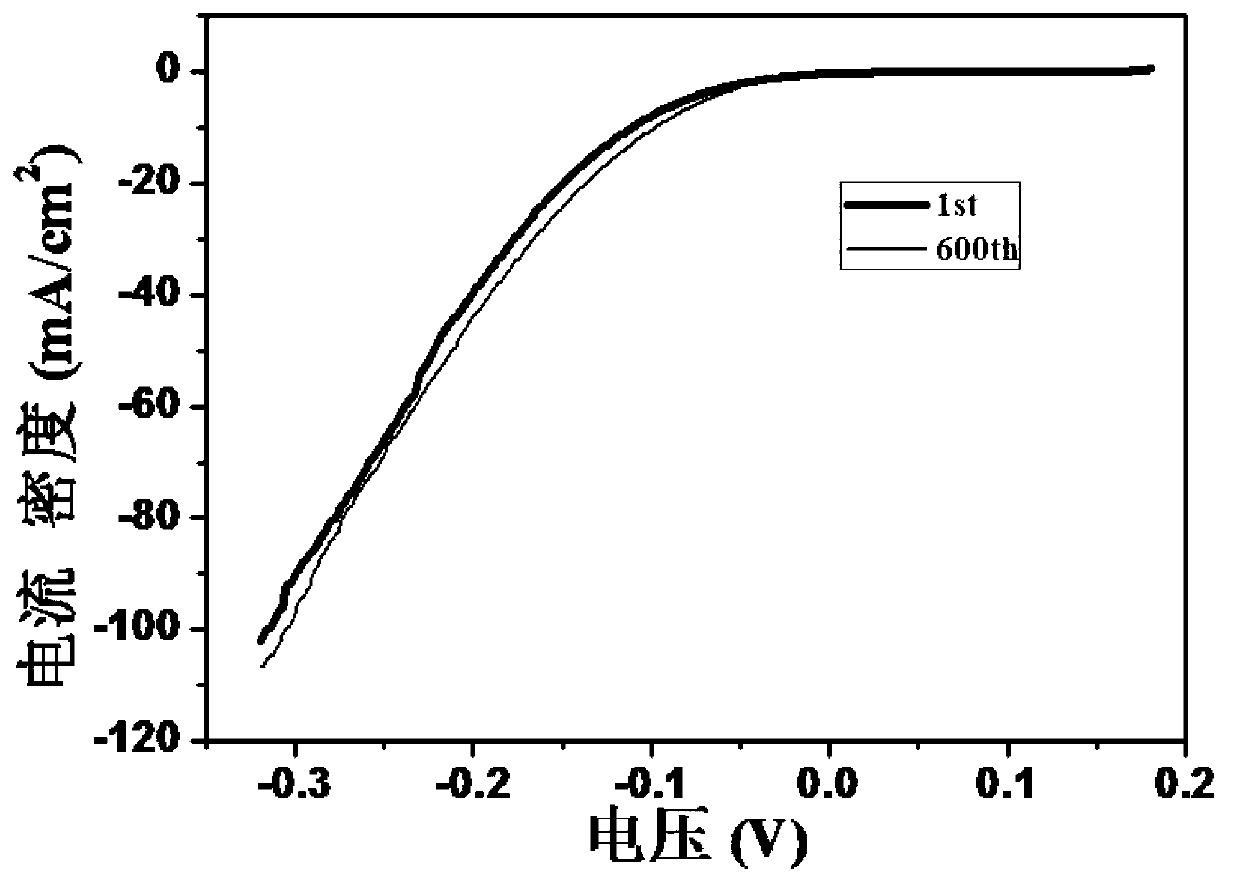
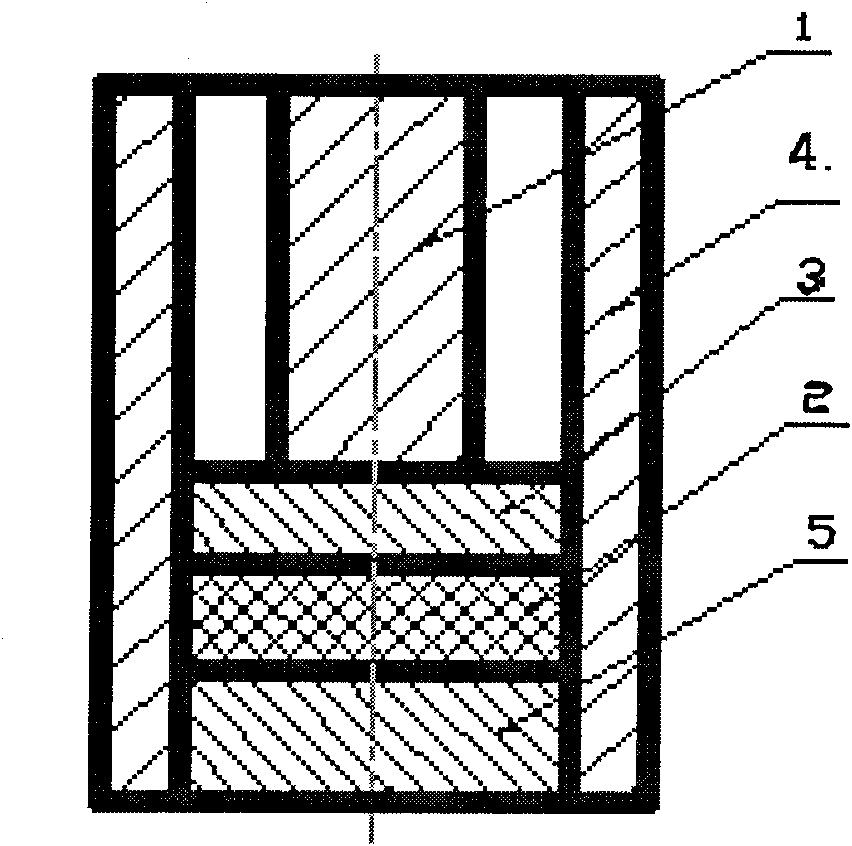
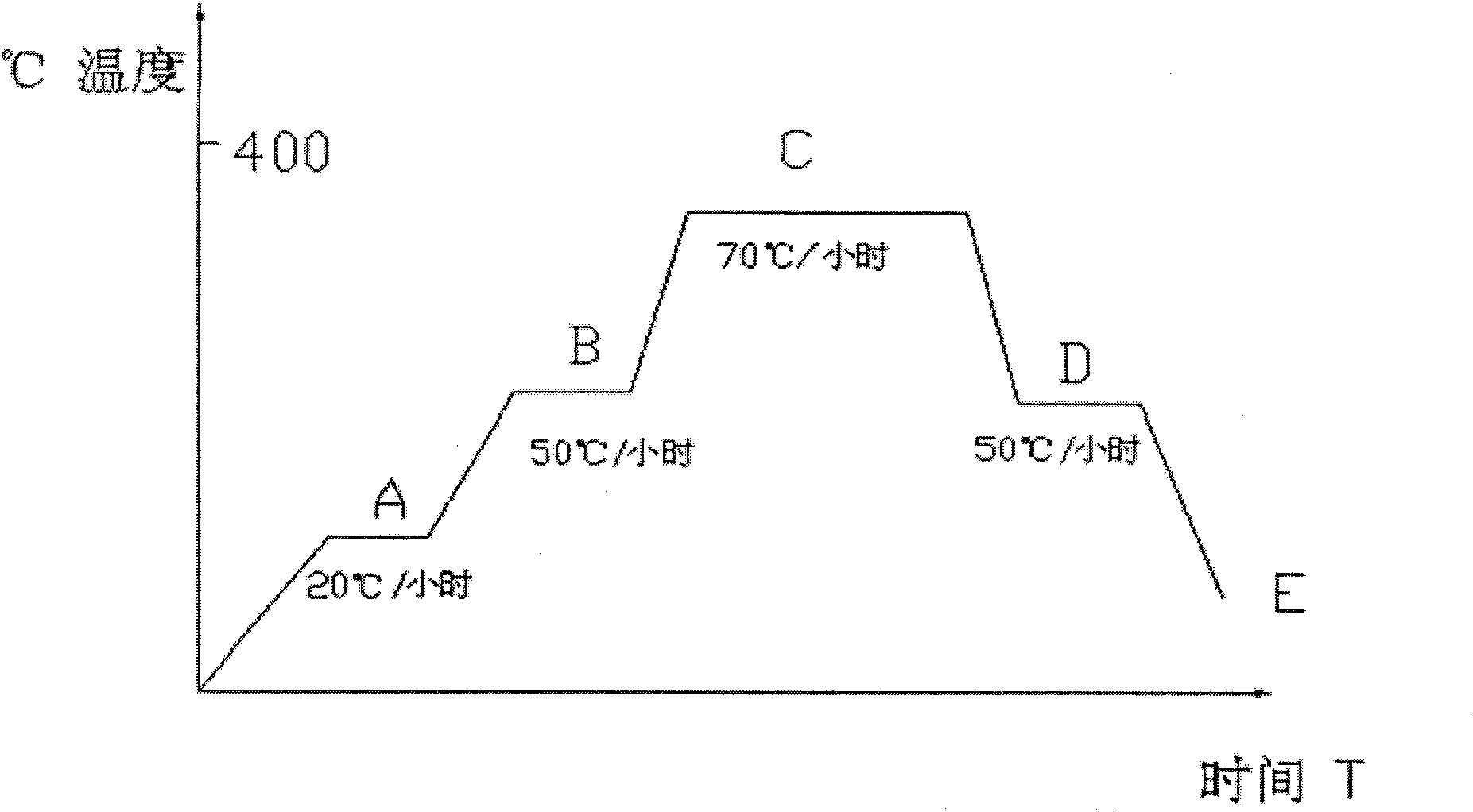
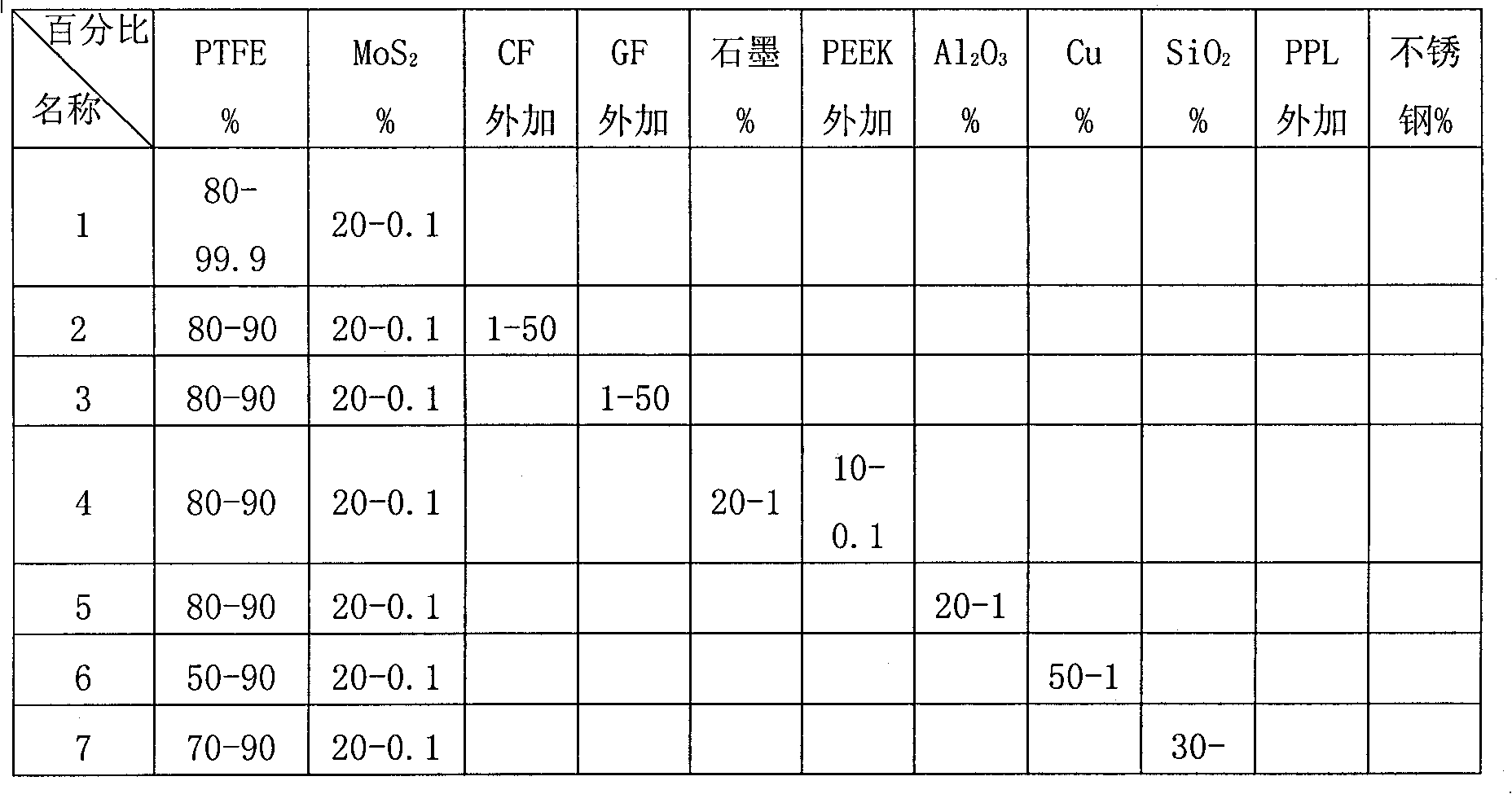
The invention discloses a polytetrafluoroethylene composite material, which comprises one or more of molybdenum disulfide, aluminum sesquioxide, copper powder, graphite, silicon dioxide and stainless steel powder and polytetrafluoroethylene, wherein the polytetrafluoroethylene composite material is a binary polytetrafluoroethylene composite material, which comprises 80 to 99.9 weight percent of the polytetrafluoroethylene, and the balance of other components. A product preparation method for the material comprises the following steps: compounding the materials of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), aluminium oxide (Al2O3), Cu powder, silicon dioxide (SiO2), polyphenylester (PPL), stainless steel powder, carbon fiber (CF), glass fiber (GF) and the like, molding the materials by a mold pressing sintering method, and then mechanically machining the materials to form an L-shaped sealing element.
Owner:NANJING COMPTECH MATERIALS
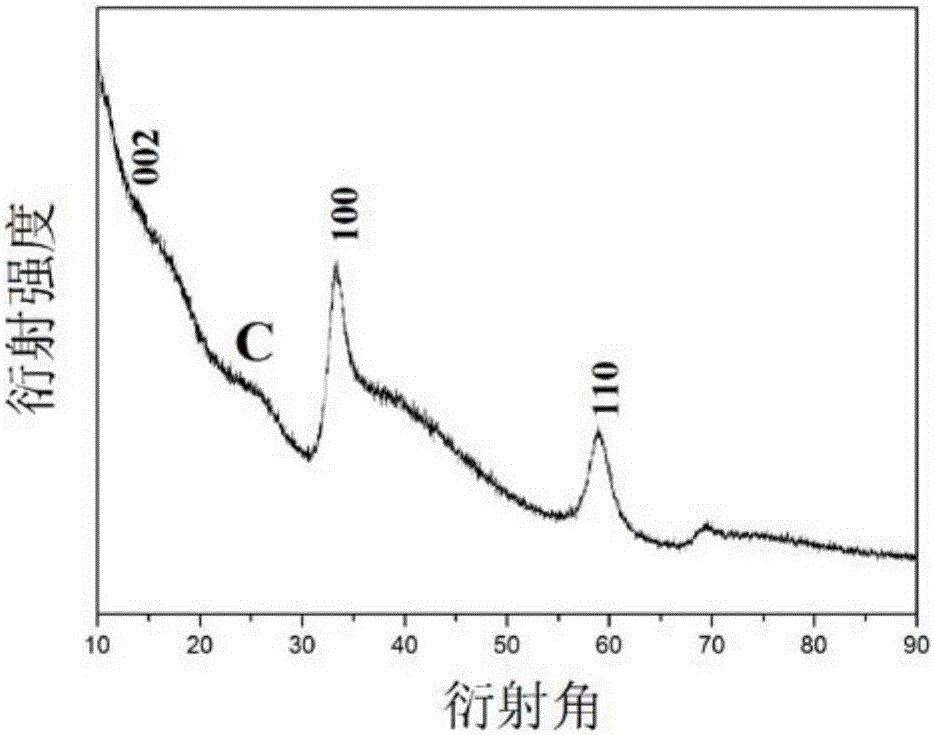
Preparation method of one-step hydrothermal synthesis of carbon/molybdenum disulfide composite microsphere
InactiveCN1994896AUniform particle sizeSimple methodVanadium oxidesMolybdenum sulfidesSucroseMicrosphere
The invention discloses a making method of carbon / molybdenum disulfide composite microball through water heat method, which comprises the following steps: dissolving molybdate in the deionized water to form 0.02-0.1m solution; adding thioacetamide or sulfourea as sulfur source with molar rate of thioacetamide or sulfourea and molybdate at 31-51; stirring evenly; adding glucose or sucrose as carbon source with the molar rate of glucose or sucrose and molybdate at 51-251; stirring completely; transmitting solution into water heat reacting autoclave to react under 200-240 deg. c for 20-24h; cooling naturally; separating; washing; drying to obtain the product.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Compound nano material of graphene and MoS2 and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102142548AMild reaction conditionsSimple preparation processMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesCysteine thiolateNew energy
The invention discloses a compound nano material of graphene and molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) and a preparation method thereof. The compound material is formed by mixing graphene and a MoS2 nano material in a mass ratio of (1 to 1)-(4 to 1). The preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparing an oxidized graphite nano slice from graphite by a chemical oxidization method; then dissolving molybdate into deionized water so as to form 0.02 to 0.07M of solution; adding L-cysteine serving as a sulfur source and a reduction agent, wherein the mass ratio of the L-cysteine to the molybdate is (5 to 1)-(12 to 1); adding the oxidized graphite nano slice into the solution, and ultrasonically treating so that the oxidized graphite nano slice can be fully dispersed in the hydrothermal reaction solution; transferring the mixture into a hydrothermal reaction kettle and sealing; and synthesizing by a one-step hydrothermal method to obtain the compound nano material of graphene and MoS2, wherein the mass ratio of the graphene nano slice to the MoS2 is (1 to 1)-(4 to 1). The method has the characteristics of mild reaction condition and simple process. The compound nano material of graphene and MoS2 synthesized by the method can be widely used as electrode materials of new energy batteries, high-performance national lubricants, catalyst carriers and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Graphene/molybdenum disulfide composite electrode material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the fields of a novel chemical electric power source and a new energy material, and particularly discloses a graphene / molybdenum disulfide composite electrode material and a preparation method of the composite electrode material. The preparation method comprises the steps of: (1) preparing graphite oxide from graphite as a raw material by an oxidation and intercalation method; (2) dissolving prepared graphite oxide with deionized water, carrying out ultrasonic stripping to obtain a graphene oxide solution, then adding DMF (dimethyl formamide) and molybdate, finally adding a reducing agent, and dispersing uniformly to obtain a mixed solution; and (3) transferring the mixed solution to a reaction kettle, keeping the temperature in the temperature condition of greater than or equal to 180 DEG C for 5-10h, centrifuging and washing the product to remove DMF, and drying to obtain the graphene / molybdenum disulfide composite electrode material product. The preparation method of the graphene / molybdenum disulfide composite electrode material is simple, uniform in reaction system and low in production cost, and is particularly suitable for requirements of industrial large scale production; and the prepared product graphene / molybdenum disulfide composite electrode material has better electrochemical performances.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biodegradable penetrating lubricant
InactiveUS20030040444A1Easy to moveEnhanced inhibitory effectAdditivesBase-materialsOrganic solventAntioxidant
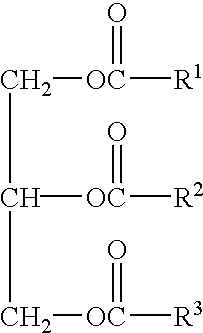
A biodegradable penetrating lubricant, comprised of: (A) at least one triglyceride oil of the formula: wherein R1, R2, and R3 are aliphatic hydrocarbyl groups containing from about 7 to about 23 carbon atoms; (B) an organic solvent selected from the group comprising: (1) ethyl lactate, (2) soy methyl ester, (3) at least one mineral spirit, and (4) combinations of 1, 2, and 3; and, (C) an antioxidant. Optionally, the lubricant may further include an additive selected from the group comprising: (D) an anti-wear inhibitor; (E) a corrosion inhibitor; (F) a pour point depressant; and, (G) a component chosen from the group comprising: (1) a food grade tackifier; (2) molybdenum disulfide; and (3) a combination of 1 and 2.
Owner:RENEWABLE LUBRICANTS INC
Steel-based copper alloy dual-metal sliding bearing and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101649858ALow costImprove carrying capacityBearing componentsReflex reflectorsStearic acidLubrication
The invention discloses a dual-metal sliding bearing and a preparation method thereof. Carbon steel or stainless steel is taken as an outer layer material, and a powder metallurgy material taking a copper alloy as a basal body is taken as an inner layer material; the inner surface of the outer layer material is electroplated to form an electroplated copper layer with the thickness of 4-8 micrometres; the inner layer material comprises the following components by weight percent: 1%-20% of aluminum, 1%-8% of titanium, 1%-15% of stannum, 0.1%-5% of ferrum, 0.1%-2% of phosphorus, 0.1%-5% of nickel, at least one of 0.1%-2% of graphite and 0.1%-2% of molybdenum disulfide or 0.1%-2% of zinc stearate, and the balance of copper; and the bearing is impregnated with lubricating oil. The dual-metal sliding bearing has the advantages of low cost, high carrying capability, self-lubrication, excellent abrasion resisting capability, and the like, and can be widely applied to reciprocating swing positions of a swing arm, a bucket rod, a bucket, and the like of a large-tonnage and high-power excavator.
Owner:COB PRECISION PARTS
Nitrogen-doped graphene/molybdenum disulfide composite material, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104393254AHigh activityImprove conductivityCell electrodesSecondary cellsSolventNitrogen doped graphene
The invention discloses a nitrogen-doped graphene / molybdenum disulfide composite material, and a preparation method and application thereof. The nitrogen-doped graphene / molybdenum disulfide composite material is obtained by mixing a graphite oxide solution, a nitrogen-containing precursor, a sulfur-containing precursor and a molybdenum-containing precursor in a solution, removing the solvent or hetero-ion to obtain a precursor material, performing heat treatment on the precursor material under the protection of an inert gas, and performing nitrogen doping and crystallization. The nitrogen-doped graphene / molybdenum disulfide composite material is applicable to lithium ion batteries, sodium cells, magnesium cells, hydrogen generation under electrocatalysis, hydrogen generation under photocatalysis and super capacitors, and is capable of improving the capacity of an anode material and also enhancing the cycling performance and the rate performance of the anode material when being used as a lithium ion battery anode material.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Hydrothermal synthesis method of molybdenum disulfide nano flowers
InactiveCN103613137AAvoid direct exposureGuaranteed purityNanotechnologyMolybdenum sulfidesAir exposureSulfur
The invention discloses a hydrothermal synthesis method of molybdenum disulfide nano flowers. The hydrothermal synthesis method mainly comprises the following steps: adding an inorganic molybdenum source, an organic sulfur source and a proper amount of reducing agent into deionized water, uniformly mixing the ingredients, transferring the mixture into a high pressure reaction kettle, and then heating the mixture at a high temperature for 24 hours; washing and centrifugally separating the obtained solution for multiple times, and finally drying the solution to obtain black solid powder, namely, the molybdenum disulfide nano flowers. The hydrothermal synthesis method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the whole reaction and drying process is carried out in a sealed environment to avoid direct air exposure so as to ensure the product purity; since the reducing agent adopted by the hydrothermal synthesis method disclosed by the invention can be both used as the sulfur source and as a catalyst, no impurity is generated, and thus, the product purity is further improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Molybdenum sulfide/carbide catalysts
InactiveUS7223713B2High activityImprove stabilityCell electrodesCatalyst activation/preparationMolybdateNitrogen
The present invention provides methods of synthesizing molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) and carbon-containing molybdenum disulfide (MoS2-xCx) catalysts that exhibit improved catalytic activity for hydrotreating reactions involving hydrodesulfurization, hydrodenitrogenation, and hydrogenation. The present invention also concerns the resulting catalysts. Furthermore, the invention concerns the promotion of these catalysts with Co, Ni, Fe, and / or Ru sulfides to create catalysts with greater activity, for hydrotreating reactions, than conventional catalysts such as cobalt molybdate on alumina support.
Owner:GABRIEL ALONSO +2
Gate-tunable p-n heterojunction diode, and fabrication method and application of same
ActiveUS20150034907A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCarbon nanotubeRectifier diodes
One aspect of the invention relates to a gate-tunable p-n heterojunction diode including a vertical stacked heterojunction of two ultrathin semiconductors. In one embodiment, single-layer molybdenum disulphide of an n-type semiconductor are stacked below semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes of a p-type semiconductor with each of them connected to a gold electrodes to form a p-n heterojunction. The electrical properties of the p-n heterojunction can be modulated by a gate voltage applied to a gate electrode and range from an insulator to a linear-response resistor to a highly rectifying diode. The gate tunability of the p-n heterojunction also allows spectral control over the photoresponse.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
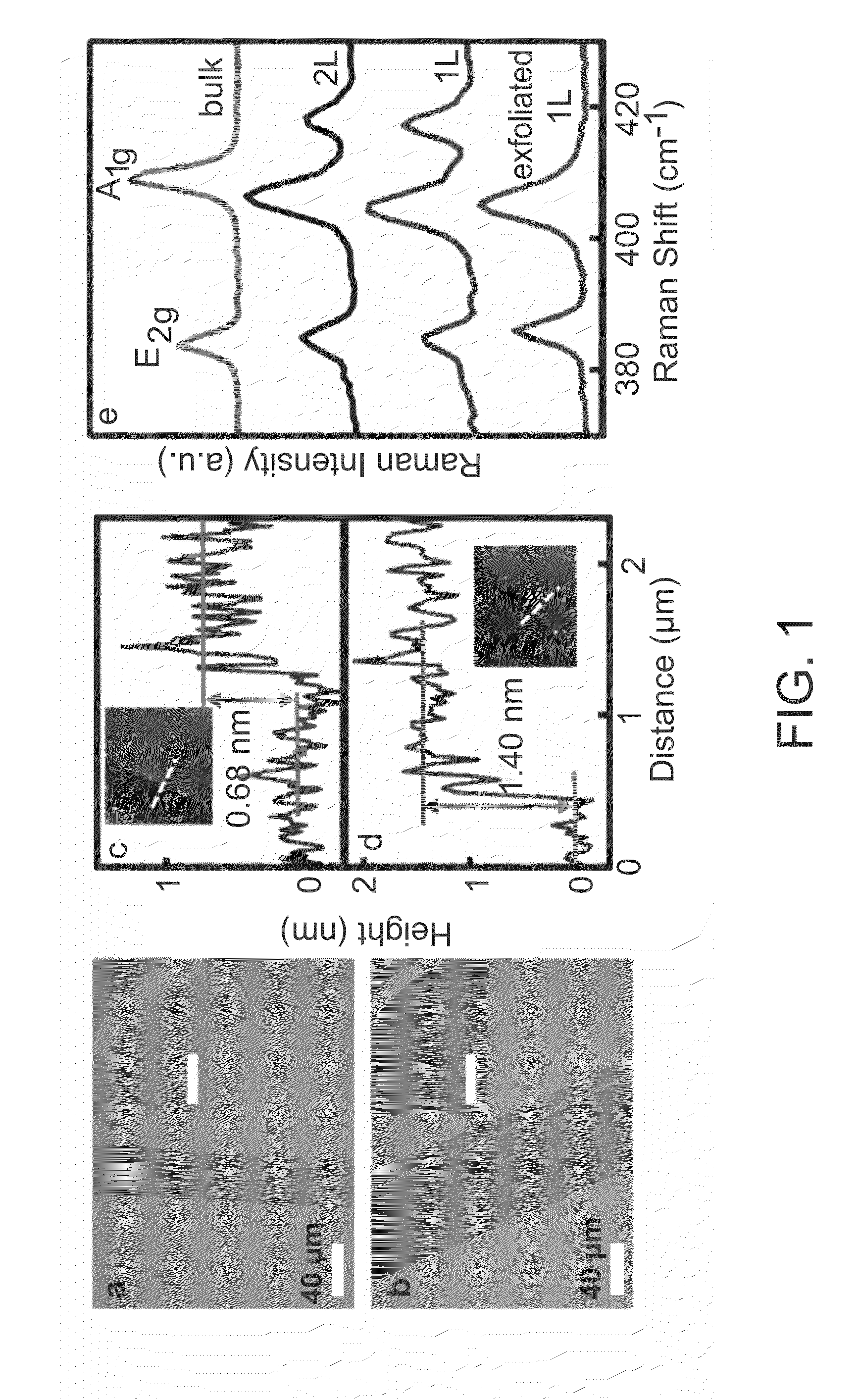
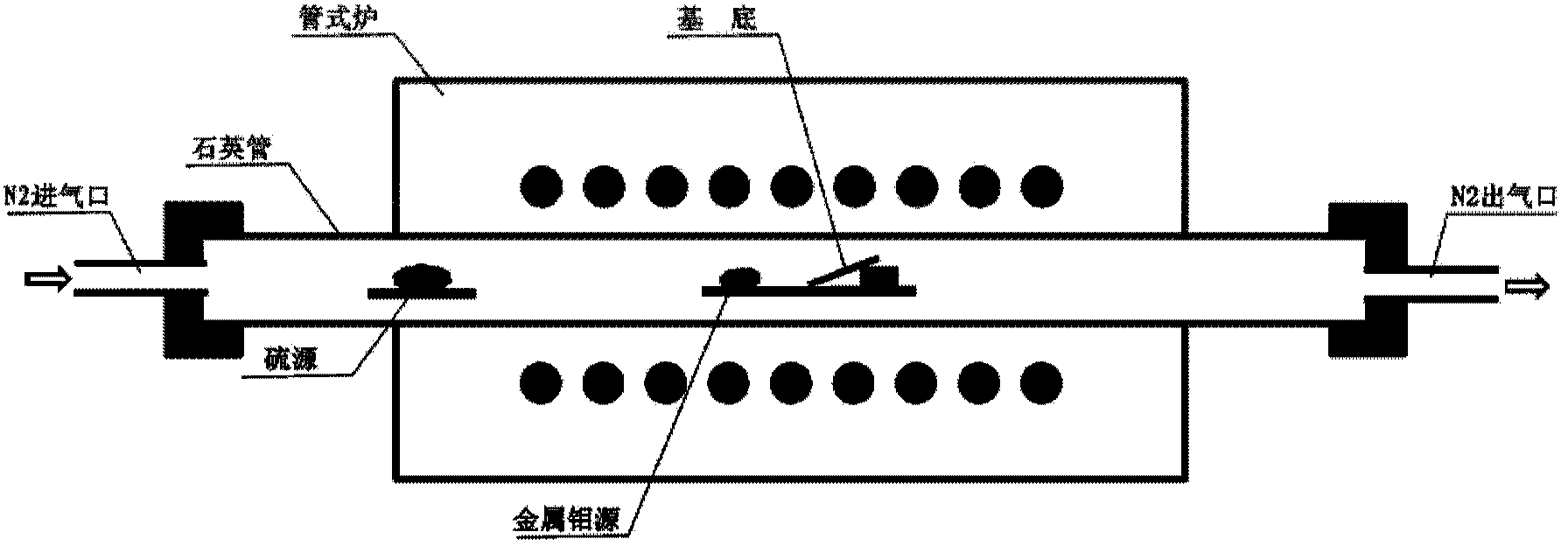
Novel process for scalable synthesis of molybdenum disulfide monolayer and few-layer films
The present disclosure relates to nanosheet synthesis. More particularly, the present disclosure relates to molybdenum sulfide (MoS2) atomic thin films and hydrogen evolution reactions. In one or more embodiments, a synthesis process may include sublimation of sulfur and MoCl5, reaction of MoCl5 and S to produce gaseous MoS2 species, transfer of the MoS2 species by carrier gas, diffusion of MoS2 species from the gas phase onto receiving substrates, and precipitation of MoS2 on the substrates.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
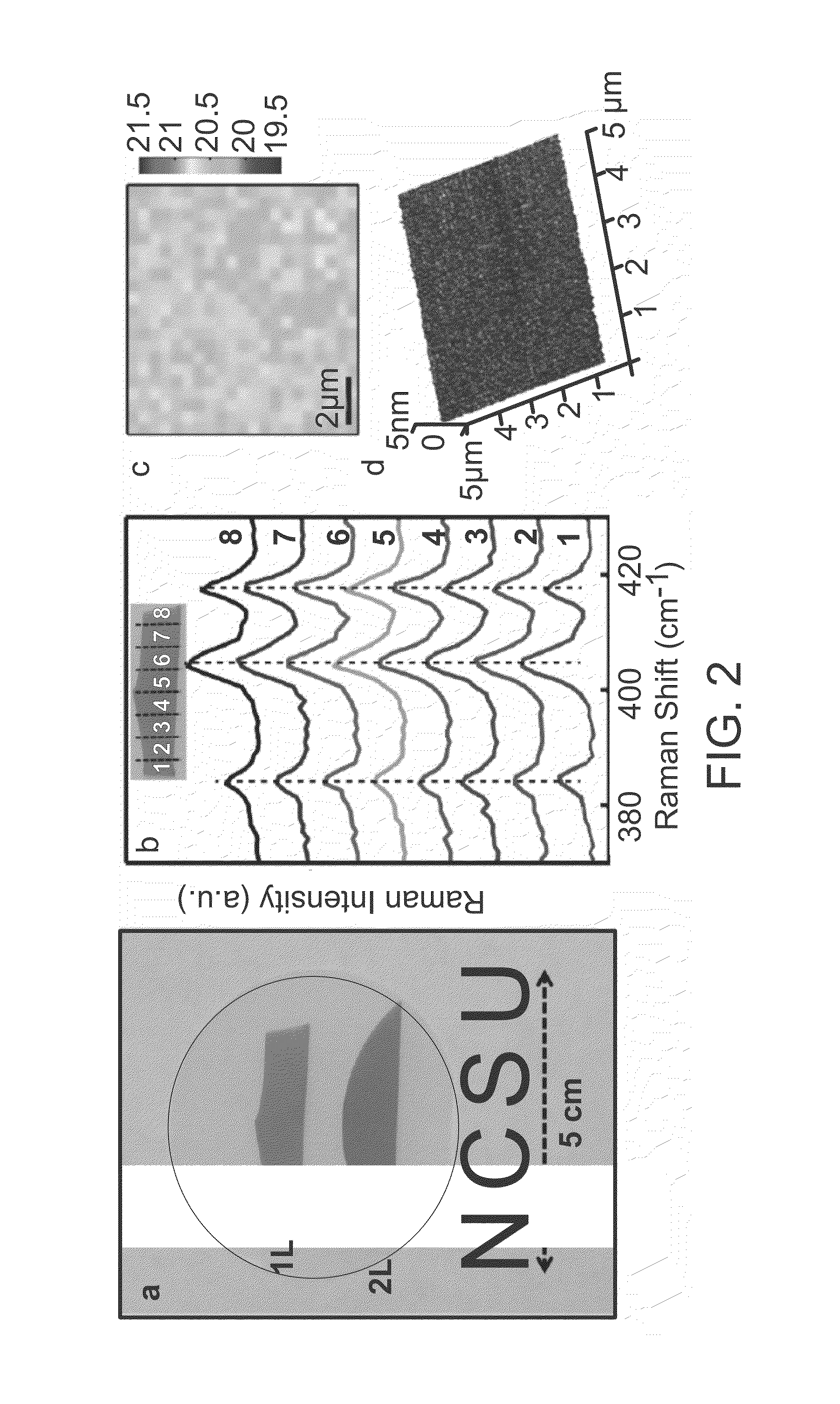
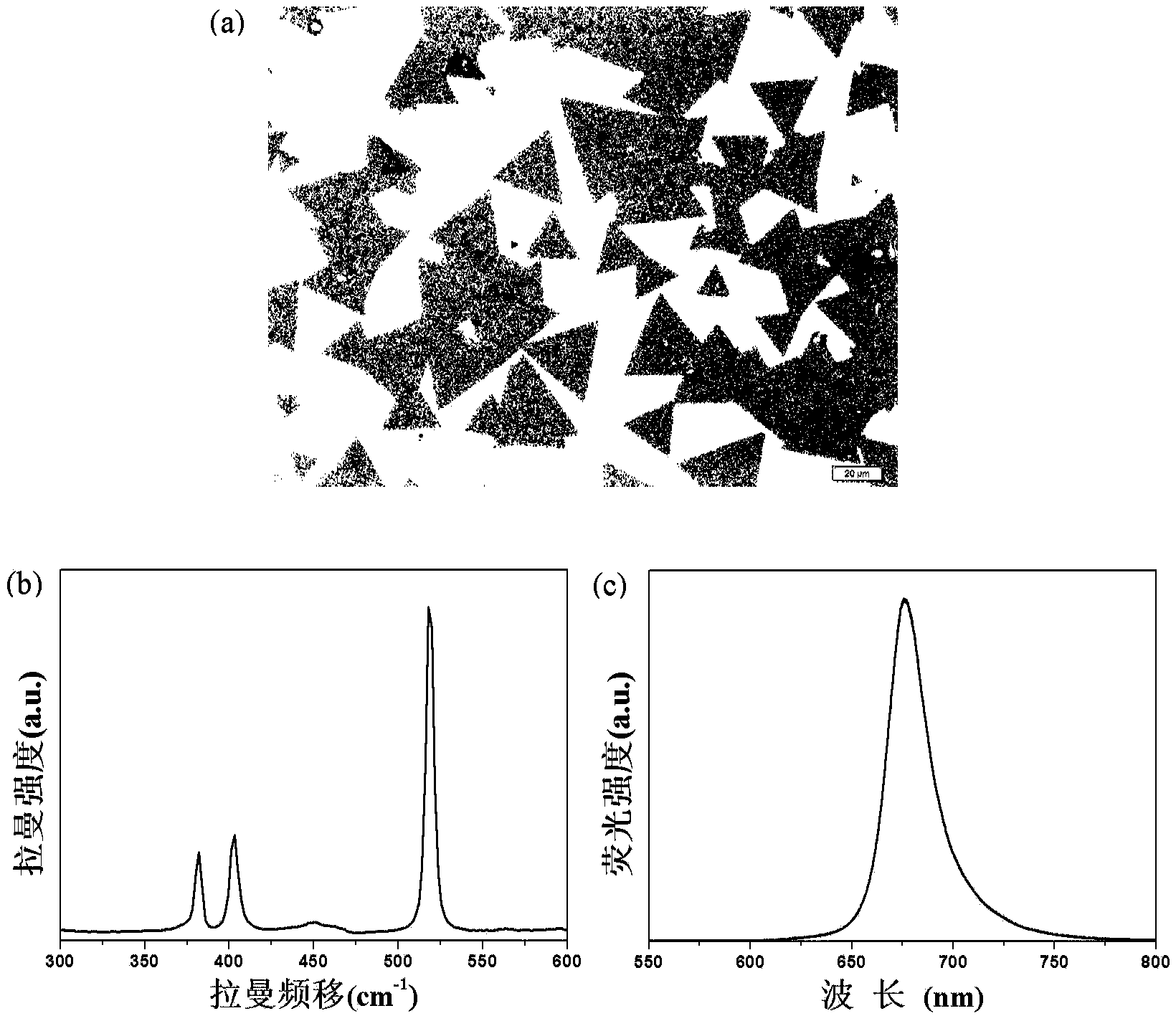
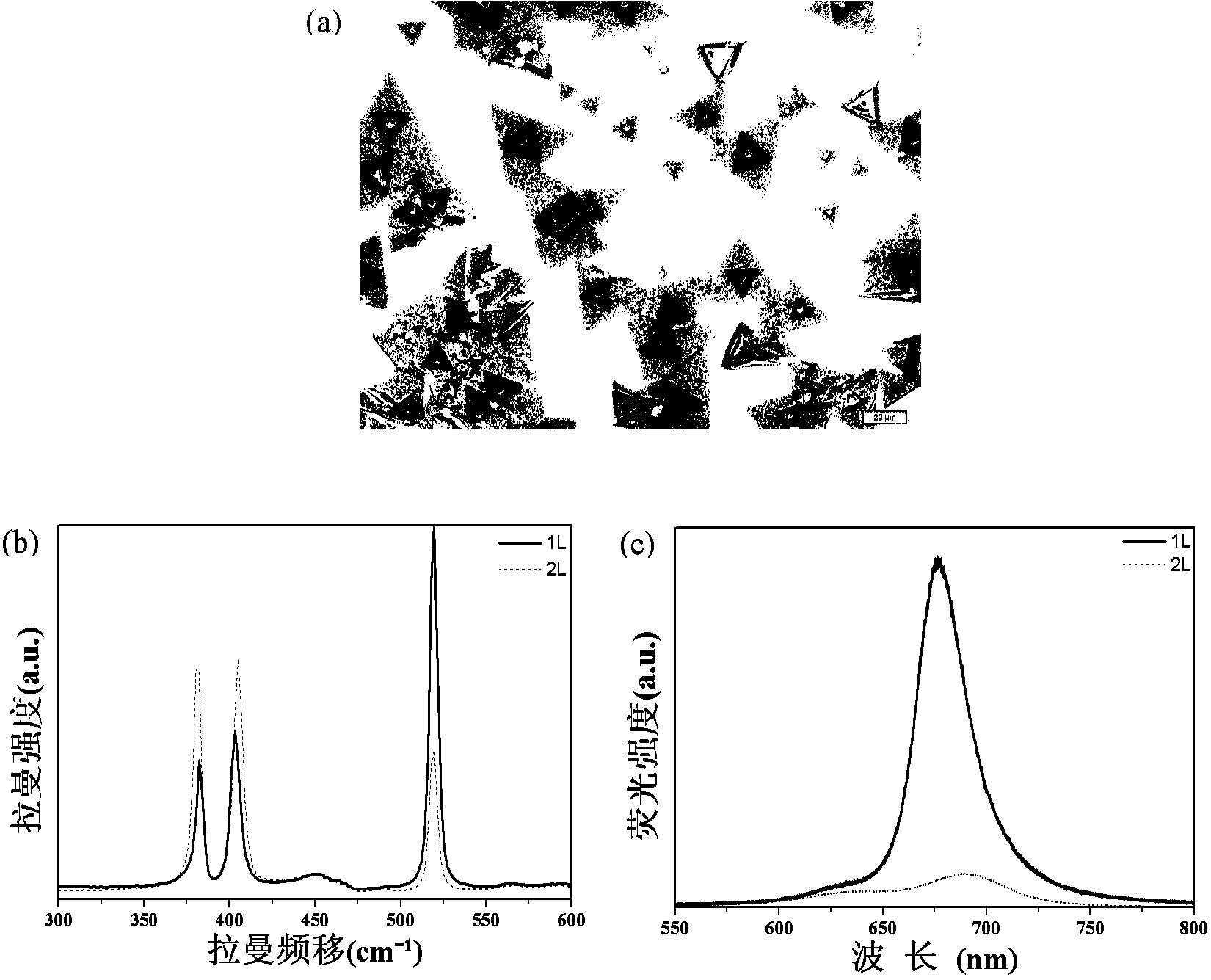
Method for preparing high-quality single/double-layer controllable molybdenum disulfide
ActiveCN104058458AQuality improvementLow equipment requirementsMolybdenum sulfidesDeposition temperatureSulfur
The invention relates to a method for preparing layered molybdenum disulfide. The layered molybdenum disulfide is in a single-layer or double-layer structure, wherein a chemical vapor deposition method is adopted, elemental molybdenum metal and powdered sulfur is taken as a source, two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide is deposited on the surface of a substrate, the preparation parameters such as deposition temperature and growth time are optimized, and controllable growth of the single-layer or double-layer structure of the high-quality molybdenum disulfide is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Copper-free ceramic friction material with little falling ash and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101823856AAvoid secondary pollutionMeet the requirements of environmental protectionBraking membersFriction liningAdhesiveAramid
The invention discloses a copper-free ceramic friction material with little falling ash and a preparation method thereof. The copper-free ceramic friction material with little falling ash is prepared by mixing, shaping and thermally processing the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 5 to 14 percent of adhesive, 20 to 45 percent of reinforcing material, 10 to 40 percent of ceramic material, 10 to 18 percent of lubricant and the balance of filler, wherein nitrile rubber modified phenolic resin and nitrile rubber powder are used as the adhesive; the reinforcing material is one or a mixture of more of aramid fiber, carbon fiber, steel fiber, foam iron powder and aluminum oxide fiber; the ceramic material is one or a combination of more of molybdenum disulfide, magnesium oxide andferrous disulphide; the lubricant is the mixture of graphite and mica; and the filler is the mixture of composite filler, barite, friction powder and aluminum powder. The material has high friction performance, low brake noise and high heat fading resistance, and particularly shows high performance in aspects of wear resistance, long life and great reduction in the falling ash of a wheel hub; therefore, the material can meet both the requirement of a modern automobile braking system on operating conditions and the requirement on economy and environment friendliness when an automobile is used.
Owner:HUNAN BOYUN AUTOMOBILE BRAKE MATERIALS +1
Preparation method of molybdenum disulfide nanosheet in stripping manner
ActiveCN104495935AReduce energy consumptionNo pollution in the processMaterial nanotechnologyMolybdenum sulfidesRoom temperatureSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method of a molybdenum disulfide nanosheet in a stripping manner. Stirring or ultrasonic treatment is carried out in a mixed solvent containing an oxidizing agent, and a raw material, namely molybdenum disulfide, is stripped, so that the molybdenum disulfide nanosheet is formed. The preparation method of the molybdenum disulfide nanosheet has the advantages that a cheap reagent is adopted, operation is carried out at room temperature, energy consumption is low, no pollution is caused, efficiency is high, and the prepared molybdenum disulfide nanosheet can be widely applied to the fields of energy storage and conversion, catalysis, lubrication, various composite materials and the like.
Owner:安徽百特新材料科技有限公司
Molybdenum disulfide/carbon composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104934602AImprove poor conductivityNot easy to reuniteCell electrodesSecondary cellsCarbon compositesCarbonization
The invention discloses a molybdenum disulfide / carbon composite material. The molybdenum disulfide / carbon composite material comprises a molybdenum disulfide layer and a carbon hollow ball, wherein the molybdenum disulfide layer is positioned outside the carbon hollow ball; and the carbon hollow ball has a hollow structure. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the molybdenum disulfide / carbon composite material. The preparation method comprises the following steps of using amino modified silica spheres as a template; wrapping the template by pyrolyzation of an organic carbon source; performing thermal reaction on the template and ammonium tetrathiomolybdate through solvent; performing high-temperature carbonization in an inert atmosphere; and removing the silicon oxide template to obtain the molybdenum disulfide / carbon composite material. The lithium-intercalation capacity of the molybdenum disulfide / carbon composite material is 1467mAh / g for the first time, and the specific capacity of the molybdenum disulfide / carbon composite material can be kept at 733mAh / g after 30 times of repeated charging and discharging cycles.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
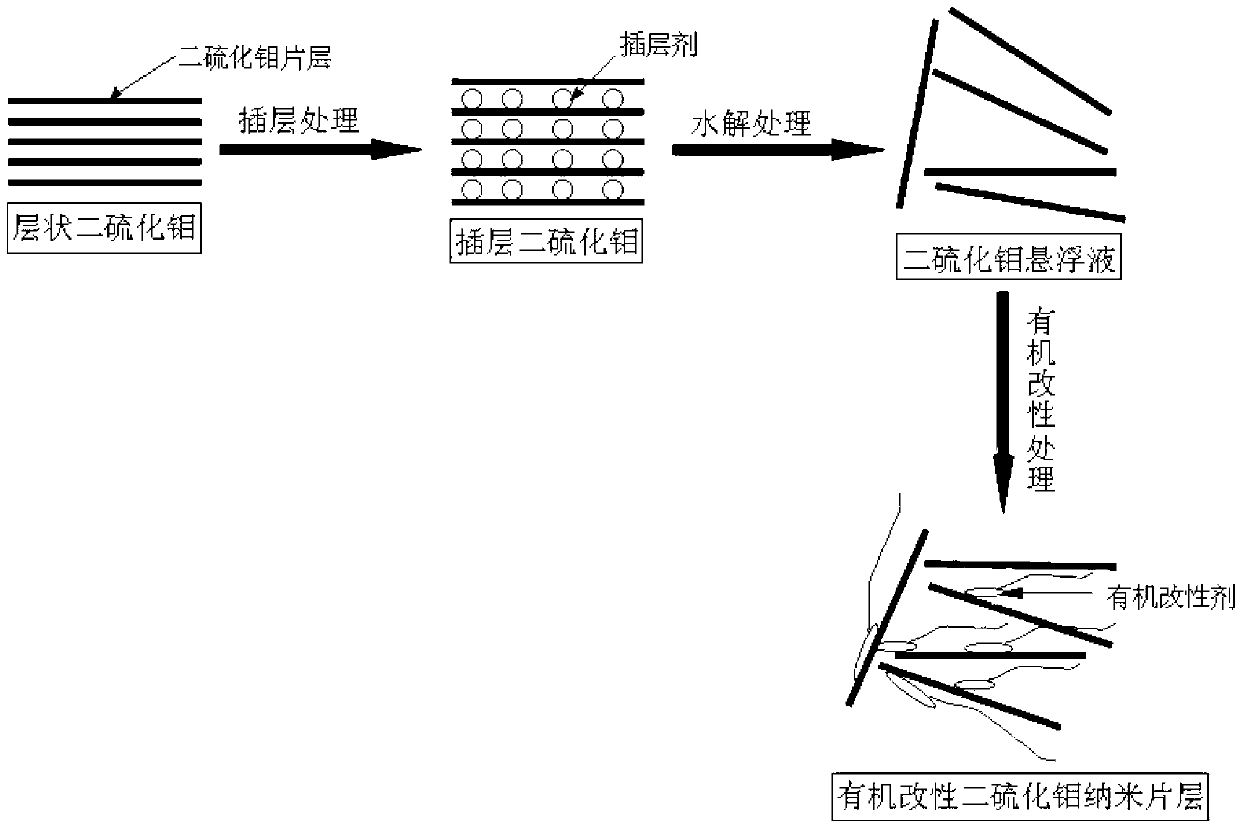
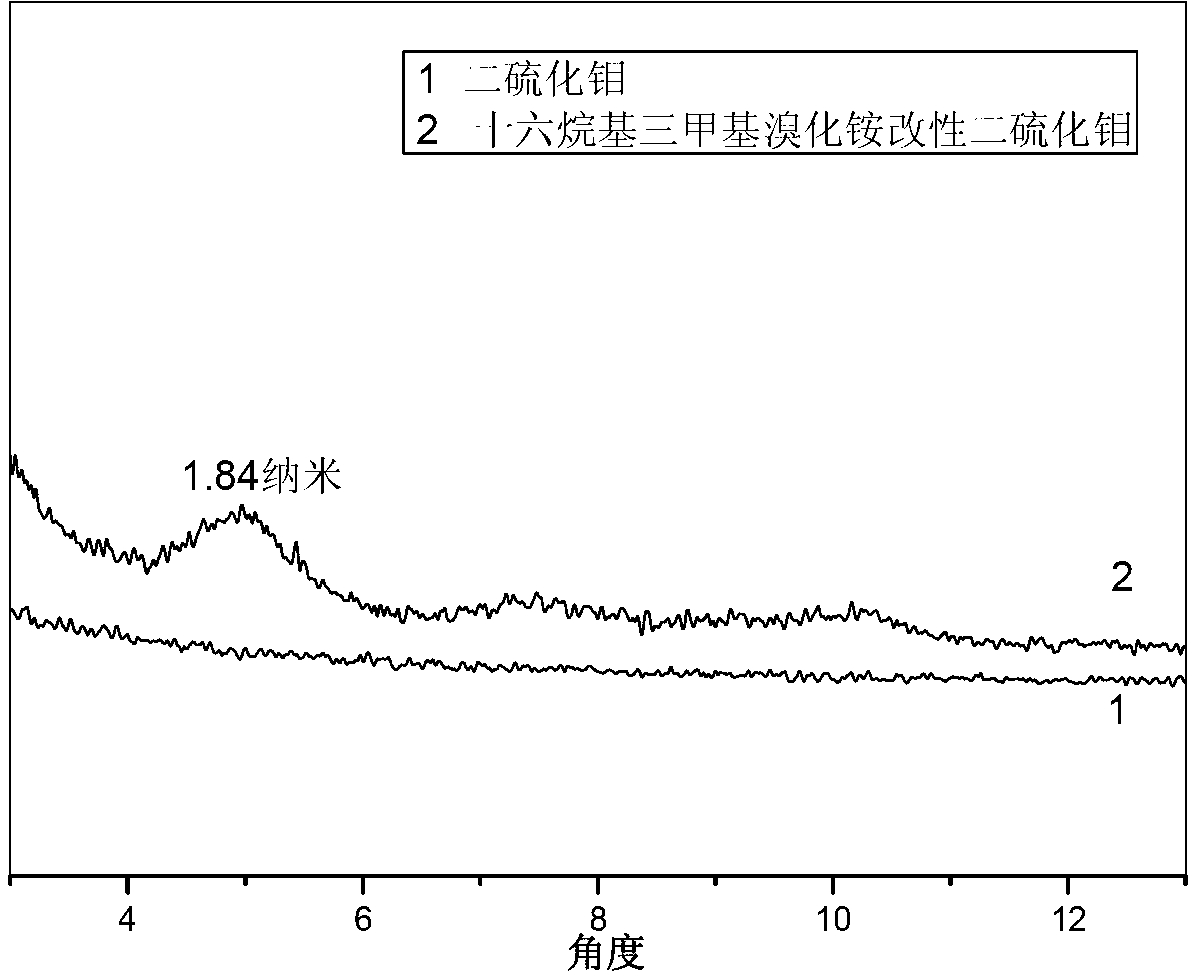
Organic modified molybdenum disulfide nanosheet layer and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a preparation method of an organic modified molybdenum disulfide nanosheet layer. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: carrying out intercalation treatment on layered molybdenum disulfide by using an intercalator through a solvothermal method, centrifuging, washing and drying to obtain the intercalated molybdenum disulfide; hydrolyzing the intercalated molybdenum disulfide to obtain molybdenum disulfide suspension liquid, adding an organic modifying agent to the molybdenum disulfide suspension liquid, reacting for 3-10 hours at 25-90 DEG C, centrifuging, washing and drying an obtained product to obtain the organic modified molybdenum disulfide nanosheet layer. The preparation method of the organic modified molybdenum disulfide nanosheet layer is simple and low in cost; the interlayer spacing of the prepared organic modified molybdenum disulfide nanosheet layer is large; and the organic modified molybdenum disulfide nanosheet layer can be better dispersed in an organic solvent, is not easy to agglomerate and has wide application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Preparation method of polyaniline and molybdenum disulfide intercalated composite material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a polyaniline and molybdenum disulfide intercalated composite material. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing suspension of graphene molybdenum disulfide from molybdenum disulfide powder through a chemical intercalation process, adding an aniline monomer, an oxidizing agent and organic acid dopants, and implementing in-situ emulsion polymerization to prepare the polyaniline / molybdenum disulfide intercalated composite material. The preparation method is simple and convenient, controllable and environment-friendly; the material is in emulsion or solid powder, and can be formed by coating, deposition, or pressing powder thereof, and other methods; the material is uniform in texture, stable in performance, and excellent in both photoelectrical performance and thermal stability; and the composite material is applicable to the fields of photoelectronic devices such as a secondary battery, a super-capacitor, an electromagnetic shielding device, an antistatic device, a field effect transistor, a sensor, an organic electroluminescence device and the like.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
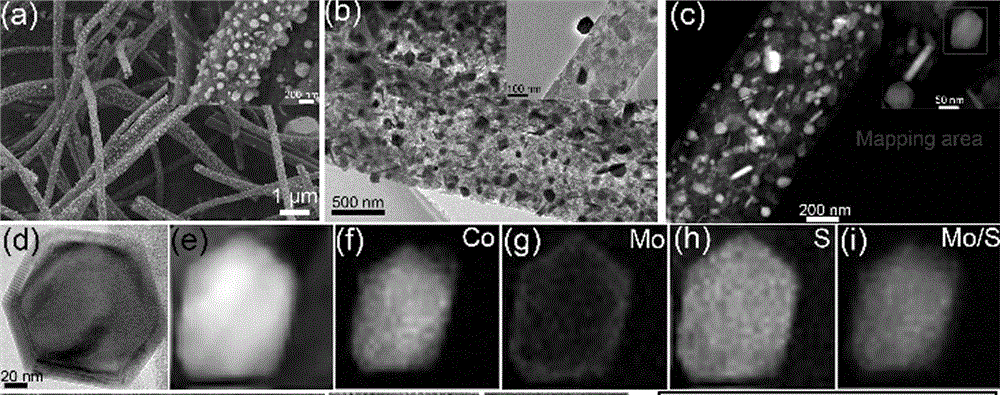
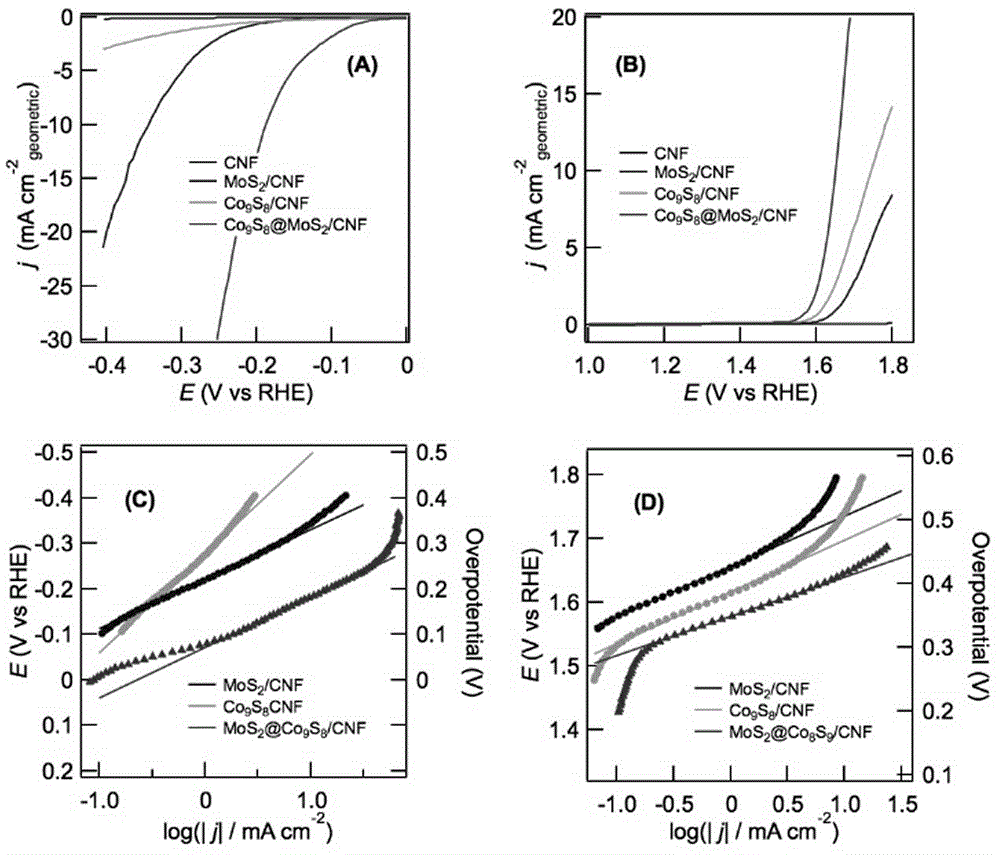
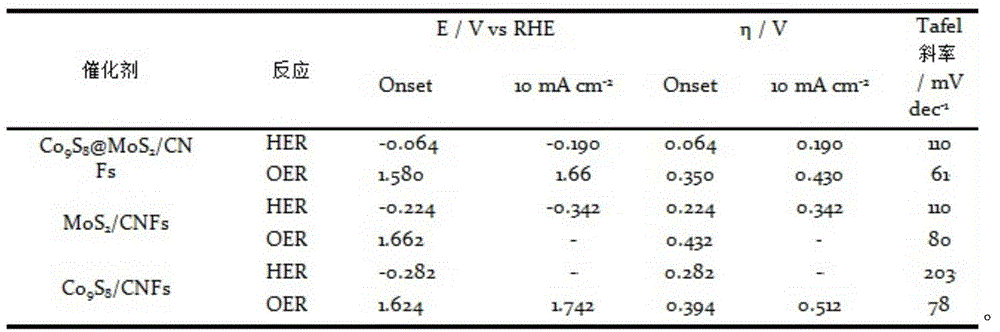
Electrolyzed-water catalytic material with nanometer core-shell structure of cobalt sulfide and molybdenum disulfide
ActiveCN104971744AIncrease the areaHigh porosityPhysical/chemical process catalystsElectrolysis componentsFiberPorosity
The invention discloses an electrolyzed-water catalytic material with a nanometer core-shell structure of cobalt sulfide and molybdenum disulfide. The electrolyzed-water catalytic material is composed of a catalytic active material and a carrier, wherein the catalytic active material is a material with the nanometer core-shell structure of cobalt sulfide and molybdenum disulfide; molybdenum disulfide is a shell; cobalt sulfide is a core; and the carrier is ultrafine carbon fiber. The electrolyzed-water catalytic material provided by the invention has high specific surface area and porosity, is favorable for diffusion and gas desorption of electrolyte, has the characteristics of dual functions of hydrogen evolution and oxygen evolution at the same time, and can be directly used as an electrode for electrocatalytic hydrogen preparation without the need of loading onto the electrode.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
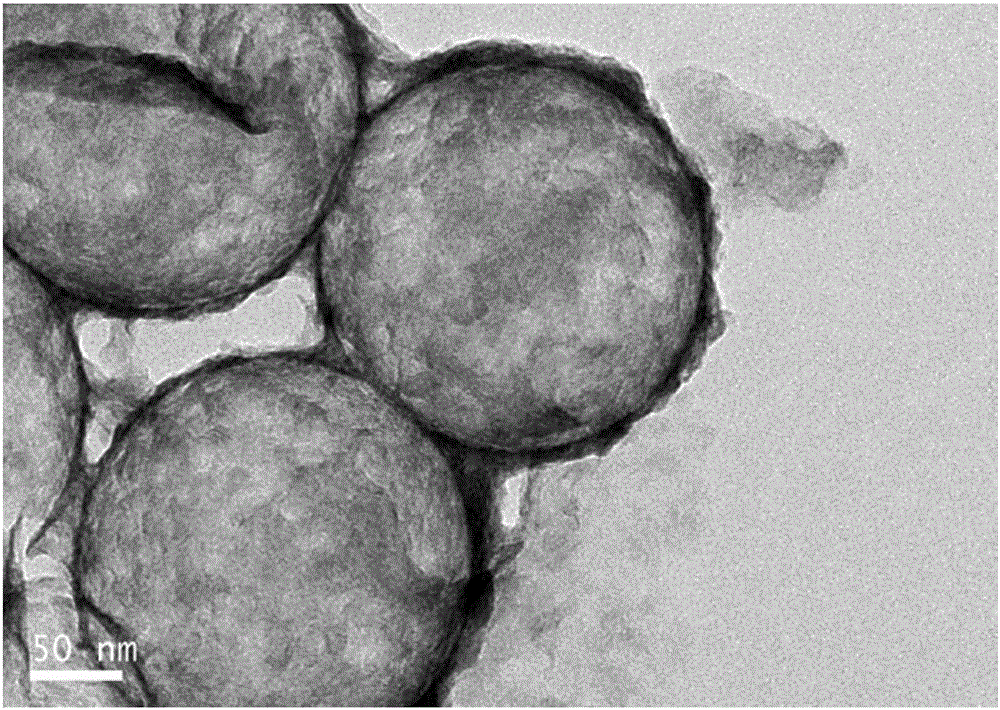
Preparation method of flower-shaped hollow molybdenum disulfide microspheres
InactiveCN102701281ASimple processLow costNanotechnologyMolybdenum sulfidesMaterials preparationMicrosphere
The invention relates to a preparation method of flower-shaped hollow molybdenum disulfide microspheres, belonging to the technical field of nanometer material preparation. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: (1) solution preparation: dissolving (NH4)2MoO4, CS(NH2)2, NH2OH.HCl and a surfactant into water, dissolving to obtain the solution, and then adjusting the pH value to 5-6.5 by acid; (2) agitating the solution obtained in step (1), and then transferring to a reaction kettle, sealing and reacting at a constant temperature, and then cooling to the room temperature to obtain the reaction product; (3) separating the reaction product, washing and drying to obtain the flower-shaped hollow molybdenum disulfide microspheres. The shape of the flower-shaped hollow molybdenum disulfide microspheres prepared by the method provided by the invention is controllable. The method provided by the invention is simple in process and low in cost; the prepared product is high in purity and high in yield, has an important application in the field of tribology and photochemistry, and is expected to be applied to large-scale industrial production.
Owner:无锡润鹏复合新材料有限公司
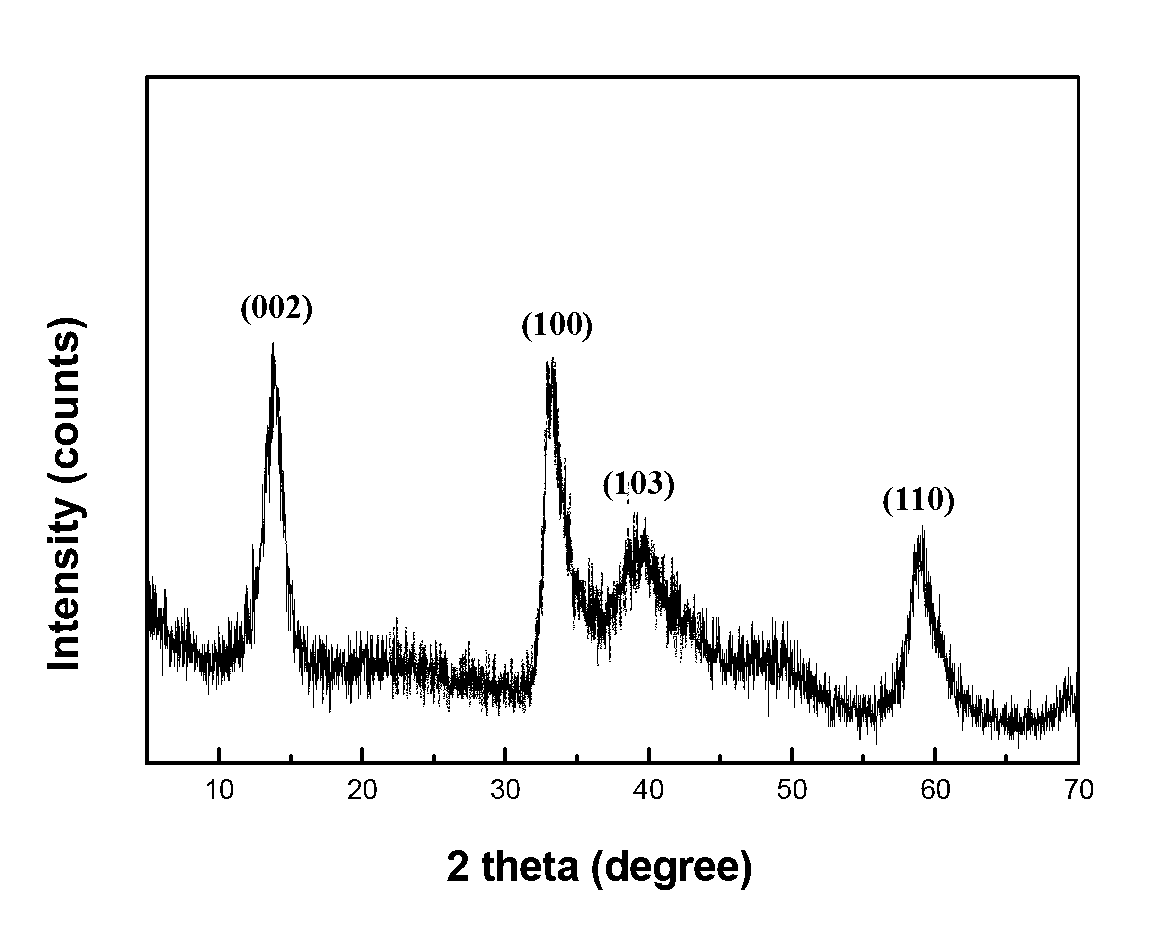
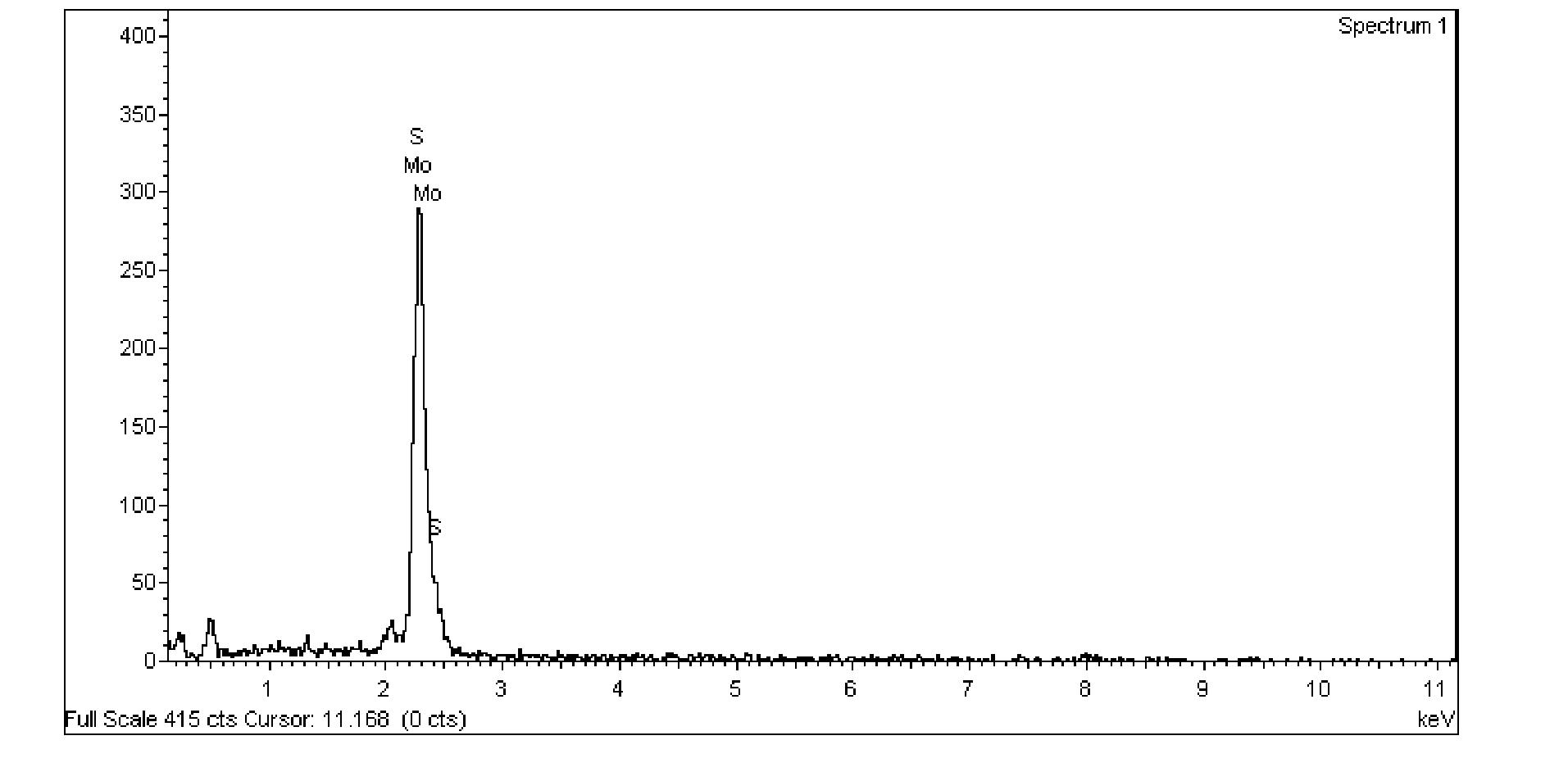
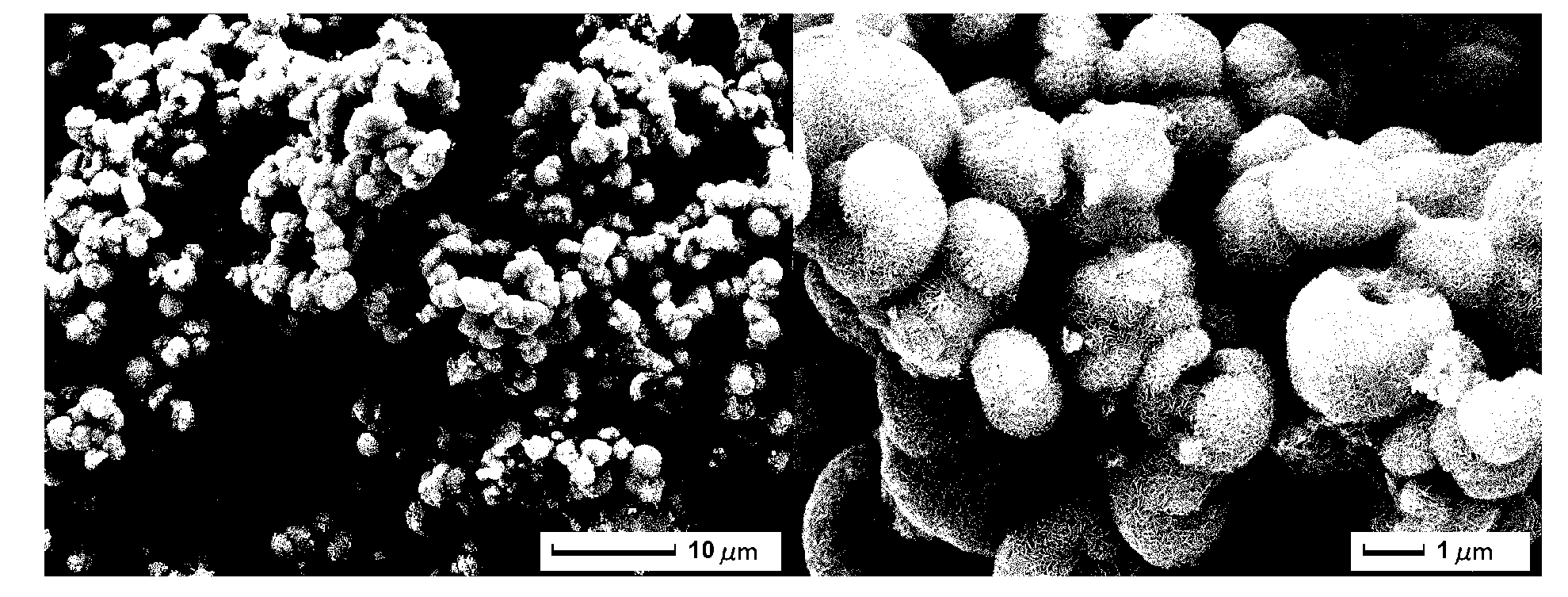
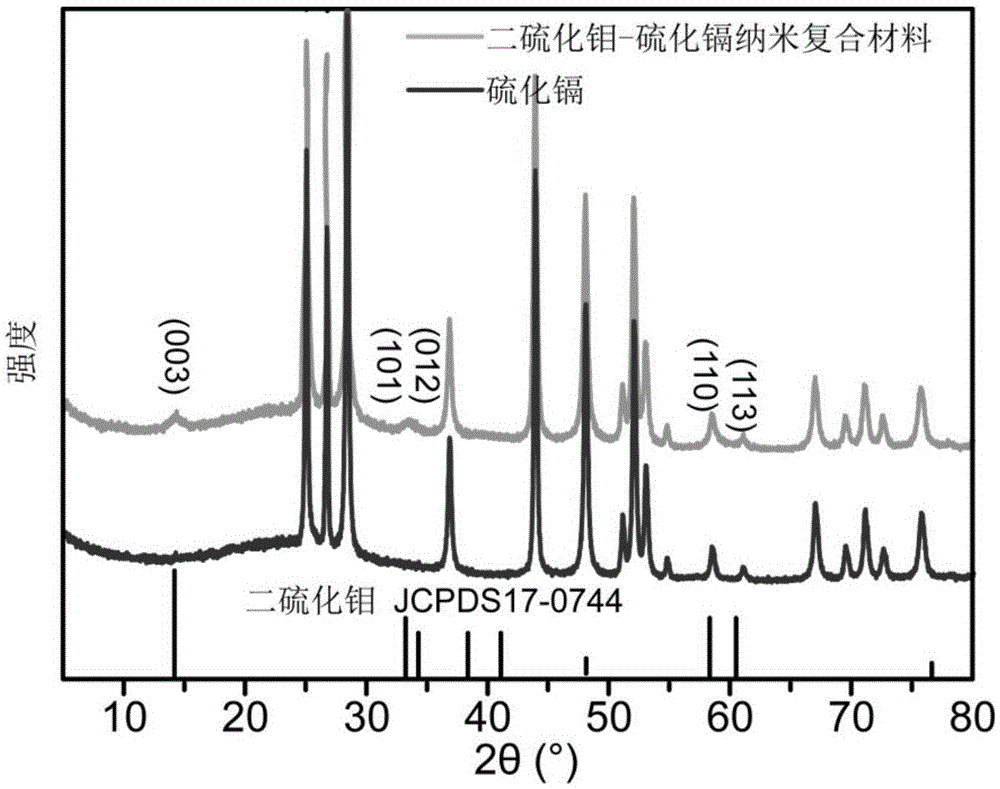
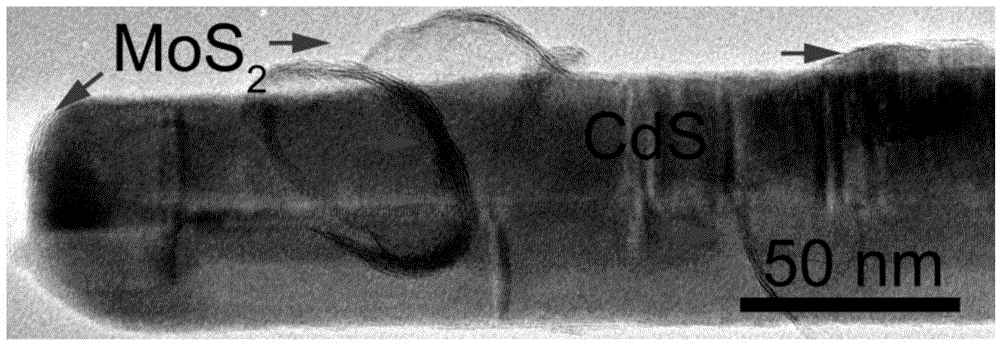
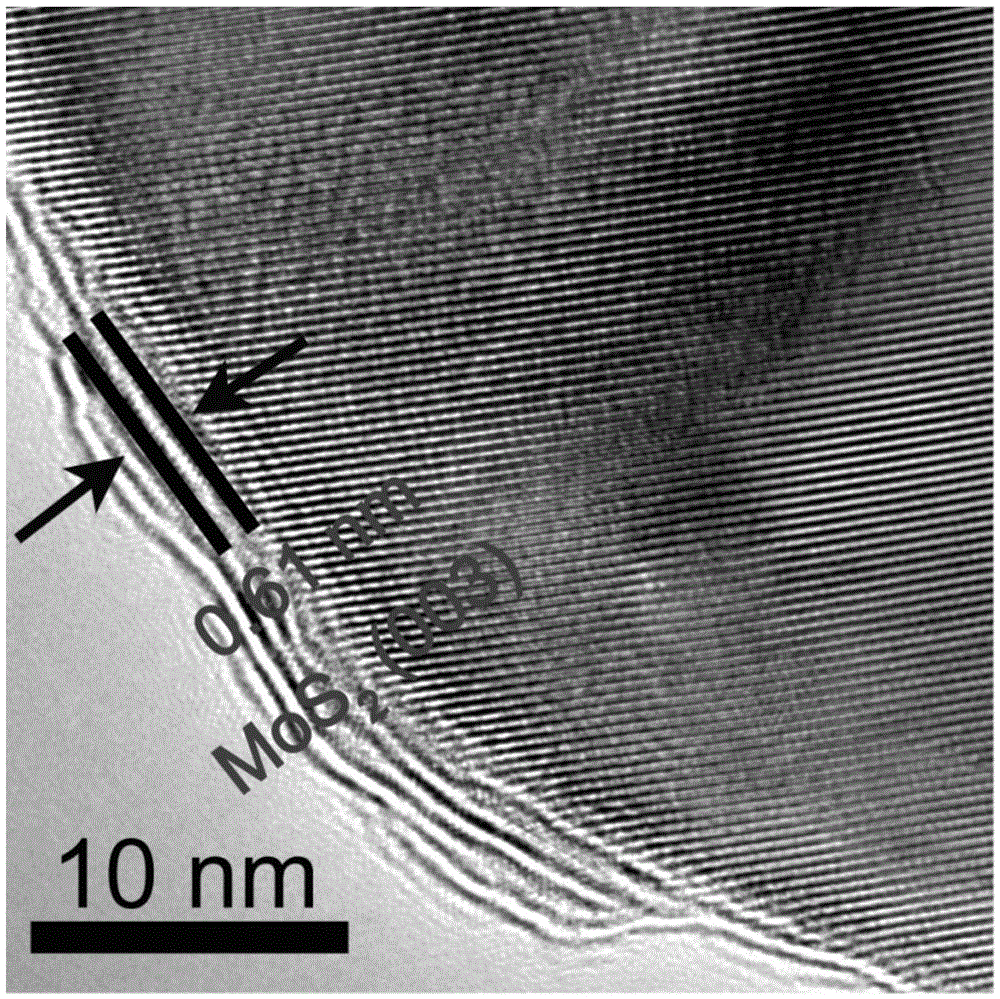
Molybdenum disulfide-cadmium sulfide nanometer composite material and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN105664977AThe load is easy to controlHigh catalytic activityPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionElectron holeNano composites
The invention relates to a molybdenum disulfide-cadmium sulfide nanometer composite material and a preparing method thereof and an application of the molybdenum disulfide-cadmium sulfide nanometer composite material to water-photocatalytic-decomposition hydrogen production. The nanometer composite material comprises nanometer cadmium sulfide, and undefined-structure layered nanometer molybdenum disulfide growing on the nanometer cadmium sulfide in an in-situ mode. According to the nanometer composite material, the nanometer cadmium sulfide serves as a carrier; as the nanometer cadmium sulfide is of a nanometer structure, on one hand, the transmission path of electron holes can be shortened; on the other hand, as the specific surface area of the nanometer cadmium sulfide is large, the loading capacity of the molybdenum disulfide can be controlled. The molybdenum disulfide is in a layered shape and is of the undefined structure; when the molybdenum disulfide is used as a catalyst of water-photocatalytic-decomposition hydrogen production, a large number of active sites are provided for photoelectron and hydrogen ions in water reacting, and therefore the catalytic activity is improved. The molybdenum disulfide-cadmium sulfide nanometer composite material is used as the catalyst, and has the multiple advantages of being simple in method, low in cost, high in catalytic activity and the like.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Molybdenum disulfide-carbon hollow ball hybrid material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105098151AShorten the transmission distanceImproved magnification performanceCell electrodesSecondary cellsSolventSilicon dioxide
The invention discloses a molybdenum disulfide-carbon hollow ball hybrid material. The molybdenum disulfide-carbon hollow ball hybrid material has a hollow ball structure; and the hybrid material formed by embedding a single layer of molybdenum disulfide nanosheet or a few of layers of molybdenum disulfide nanosheets into a carbon material is a shell layer of the hollow ball. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the molybdenum disulfide-carbon hollow ball hybrid material. The method comprises the following steps: with amino-modified silica particles as a template, coating the template with an organic pyrolytic carbon material and ammonium tetrathiomolybdate through solvothermal reaction; carrying out high-temperature treatment in an inert atmosphere; and finally removing a silicon dioxide template, so as to obtain the molybdenum disulfide-carbon hollow ball hybrid material disclosed by the invention. The initial lithium insertion capacity of the molybdenum disulfide-carbon hollow ball hybrid material disclosed by the invention is close to 1010mAh / g; and the specific capacity can still be kept at 662mAh / g after 40 repeated charge and discharge cycles.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
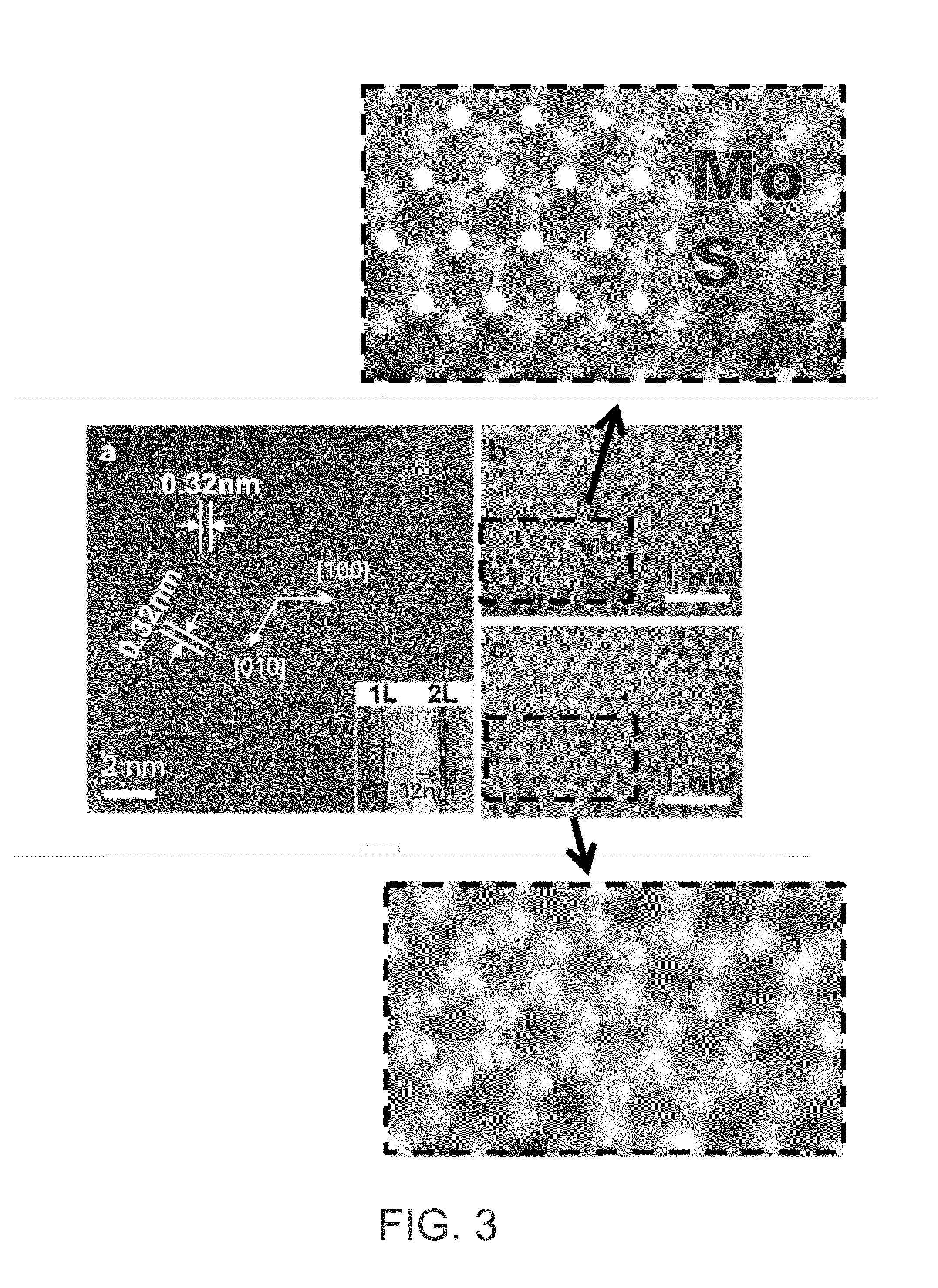
Method for preparing single-layer molybdenum disulfide film
ActiveCN103757602AThe number of layers is controllableChemical vapor deposition coatingSulfurMolybdenum trioxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing a single-layer molybdenum disulfide film. The method comprises the following steps: providing powdered sulfur and heating and transferring the powdered sulfur to sulfur vapor; blowing the sulfur vapor into a reaction cavity filled with a substrate and molybdenum trioxide powder by utilizing carrier gas; heating the temperature of the reaction cavity to a first preset temperature, and keeping the temperature for a first preset time, so that the molybdenum trioxide and the sulfur vapor are reacted to generate MoO3-x in a gas state to be deposited on the substrate, and x is more than 0 and less than or equal to 1; heating the temperature of the reaction cavity to a second preset temperature, keeping the temperature for a second preset time, continuously introducing the sulfur vapor, so that the sulfur vapor is reacted with the MoO3-x, and forming the single-layer molybdenum disulfide film on the surface of the substrate, wherein the first preset temperature is lower than the second preset temperature. According to the method, the large-area single-layer molybdenum disulfide film with controllable layers can be obtained through a two-step reaction method.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Thermal spray compositions for abradable seals
Owner:SULZER METCO CANADA INC
Graphene-supported layered MoS2 (molybdenum disulfide) nanocomposite and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104226337AImprove catalytic performanceHigh crystallinityPhysical/chemical process catalystsThioureaCrystallinity
The invention relates to a graphene-supported layered MoS2 (molybdenum disulfide) nanocomposite and a preparation method thereof, belongs to the technical field of preparation of nano materials, and is used for solving the problem that graphene-supported MoS2 nanoparticles prepared in the prior art are poorer in catalytic performance due to small composite areas between the nanoparticles and graphene. Ammonium molybdate and thiourea are taken as initiators, and layered nano MoS2 can be supported on the surface of graphene oxide under the hydrothermal condition; after roasting treatment, the graphene-supported layered MoS2 has the higher crystallinity, and the photocatalytic efficiency is more than 1.7 times that of commercial nano titanium oxide. The method is simple and easy to operate; MoS2 nanosheets are uniformly distributed on the surface of the graphene and have larger contact areas with the graphene, so that the nanocomposite has the high catalytic performance and is widely applied to fields of electro-catalysis, photo-catalysis, hydrogen evolution catalysis and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
High friction composite brake shoe for railway freight car and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN101391611AHigh compressive strengthHigh impact strengthBraking membersBrake arrangement with braking memberFiberEngineering
The invention discloses a high friction composite brake shoe for a railway wagon and a manufacturing method thereof. The composite brake shoe comprises: a steel back and a brake shoe body which is fixed on the steel back, wherein, the brake shoe body is prepared by materials which are synthesized by various components with the following weight ratio: 8 to13 parts of nitrile butadiene rubber, 2 to10 parts of styrene butasiene rubber, 5 to10 parts of cresol modified A-stage phenolic resin, 15 to 30 parts of steel fiber, 10 to 15 parts of magnesium oxide, 5 to 10 parts of calcined petroleum coke, 2 to 5 parts of silicon carbide, 10 to25 parts of mineral fiber, 5 to 10 parts of calcium hydride, 10 to 20 parts of barium sulfate, 5 to 10 parts of graphite, 1 to 5 parts of molybdenum disulfide, 1 to 5 parts of carbon black, 1 to 3 parts of sulfur and 1 to 3 parts of enhancer. The brake shoe can be used in the railway heavy-duty high-speed wagon and has stable friction performance and better wear resistance; the brake shoe can effectively inhibit the phenomena of metal inlay, cracks, dropping blocks and the like and reduce the damages on wheels; and the brake shoe is characterized by better impact resistance performance and good weatherability.
Owner:BEIJING RAILWAY STAR FORTUNE HIGH TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com