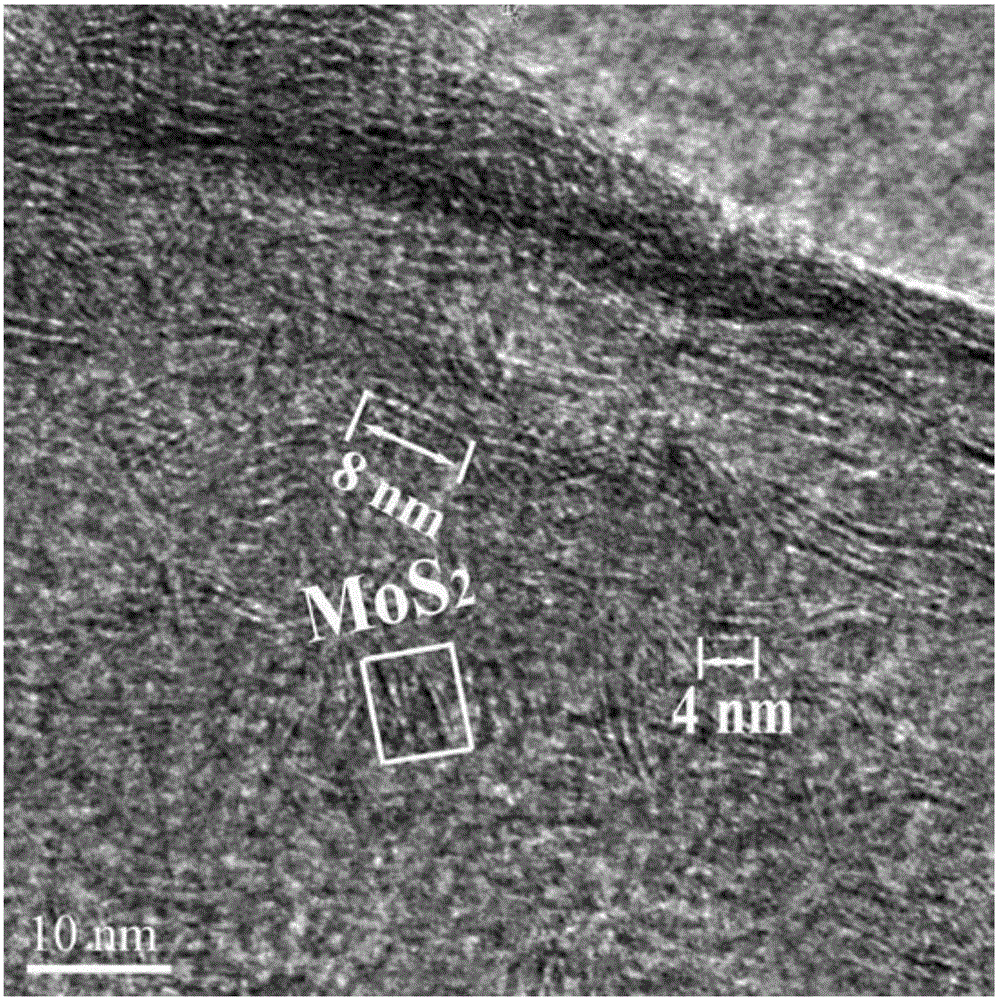
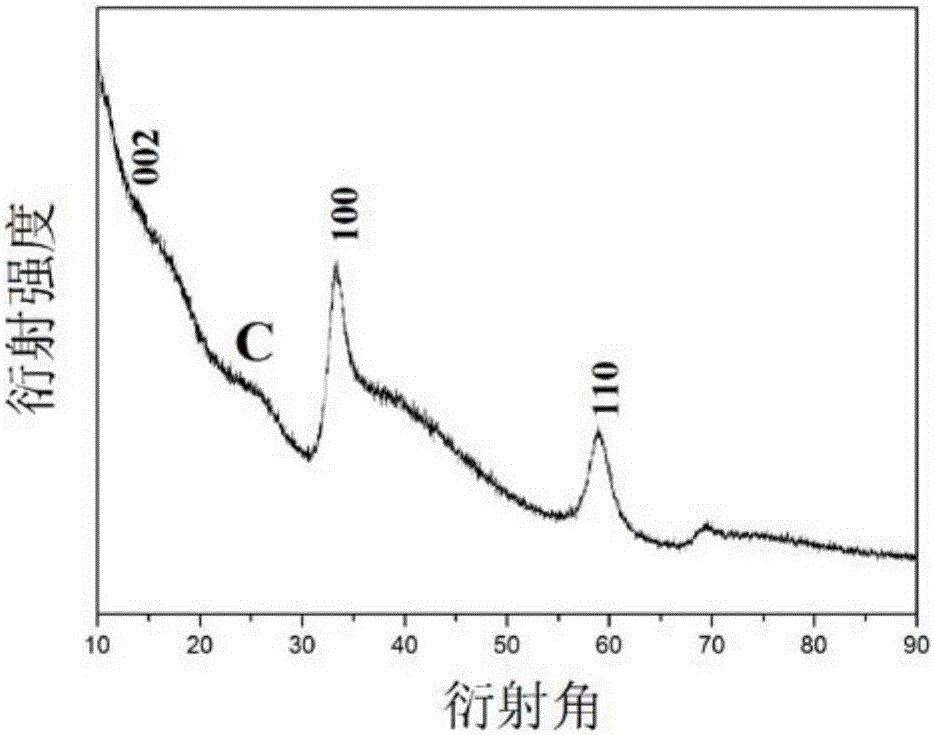
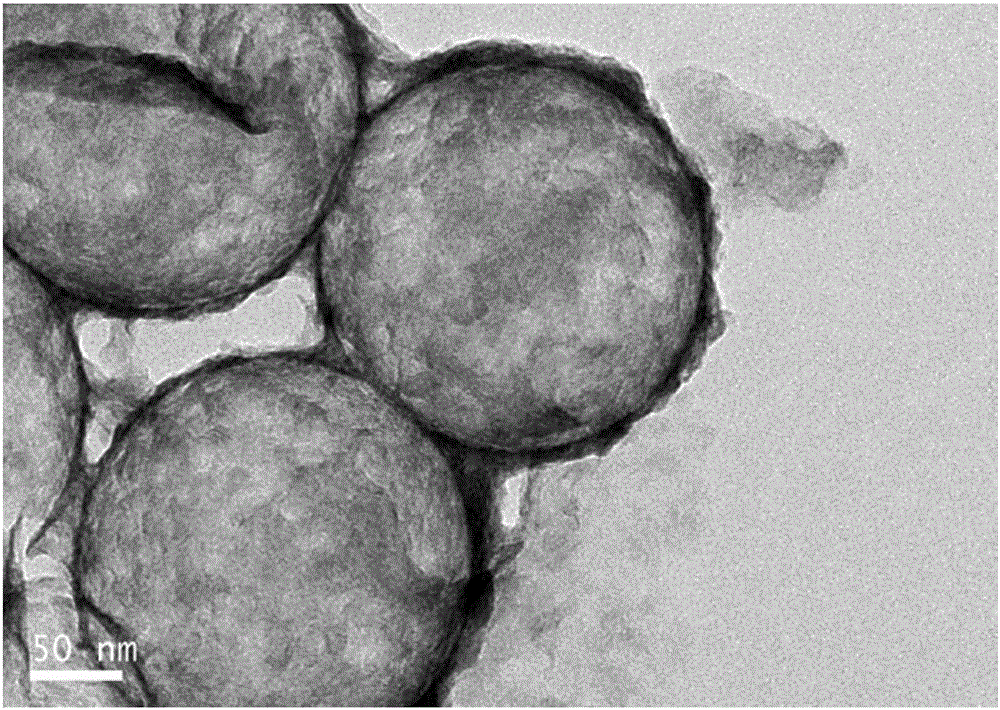
Molybdenum disulfide-carbon hollow ball hybrid material and preparation method thereof
A technology of molybdenum disulfide and hybrid materials, which is applied in the field of energy storage materials, can solve the problems of cumbersome preparation process, long synthesis cycle, loss of single/few layers of molybdenum disulfide, etc., and achieve simple process, improved rate performance, and easy The effect of industrial production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] (1) Preparation of negative electrode material (molybdenum disulfide-carbon hollow sphere hybrid material):
[0031] Step 1. At room temperature, add 1g of silica nanospheres (particle size about 100nm) to 10ml of absolute ethanol, after ultrasonic treatment, then add 8ml of triaminopropyltriethoxysilane, and magnetically stir for 2 hours to form a suspension liquid; after the suspension is centrifuged to obtain the first reaction product, the first reaction product is washed with ethanol, and then the first reaction product is dried, and the dried first reaction product is Amino-modified silica particles.
[0032] Step 2: Add 1g of ammonium tetrathiomolybdate, 4g of glucose and 2g of the amino-modified silica particles obtained in step 1 into 30ml of N,N-dimethylformamide, stir vigorously for 2h and then pour it into a 50ml reaction kettle. Then the reaction kettle was heated from room temperature to 220°C, and the reaction kettle was kept at 220°C for 4h, and then th...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Preparation of negative electrode material (molybdenum disulfide-carbon hollow sphere hybrid material):
[0046] Step 1. At room temperature, add 0.5g of silica nanospheres (particle size about 250nm) to 25ml of absolute ethanol. After ultrasonic treatment, add 0.5ml of triaminopropyltriethoxysilane and stir magnetically for 0.5h Finally, a suspension is formed; the suspension is centrifuged to obtain a first reaction product, and the first reaction product is washed with ethanol, and then the first reaction product is dried, and the first reaction product after drying is The product is amino-modified silica particles.
[0047] Step 2. Add 0.2g ammonium tetrathiomolybdate, 2.5g glucose and 0.5g amino-modified silica particles obtained in step 1 into 10ml N,N-dimethylformamide, stir vigorously for 1h and pour into 20ml reaction Then, the reaction kettle was heated from room temperature to 180°C, and the reaction kettle was kept at 180°C for 10h, and then the product in ...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Preparation of negative electrode material (molybdenum disulfide-carbon hollow sphere hybrid material):
[0052] Step 1. At room temperature, add 5g of silica nanospheres (particle size about 50nm) to 70ml of absolute ethanol, after ultrasonic treatment, then add 30ml of triaminopropyltriethoxysilane, and magnetically stir for 1 hour to form a suspension liquid; after the suspension is centrifuged to obtain the first reaction product, the first reaction product is washed with ethanol, and then the first reaction product is dried, and the dried first reaction product is Amino-modified silica particles.
[0053] Step 2. Add 6g of ammonium tetrathiomolybdate, 25g of glucose and 3g of the amino-modified silica particles obtained in step 1 into 50ml of N, N-dimethylformamide, stir vigorously for 2 hours and then pour it into a 100ml reaction kettle. Then, the reaction kettle was heated from room temperature to 200°C, and the reaction kettle was kept at 200°C for 6h, and the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Outer diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com